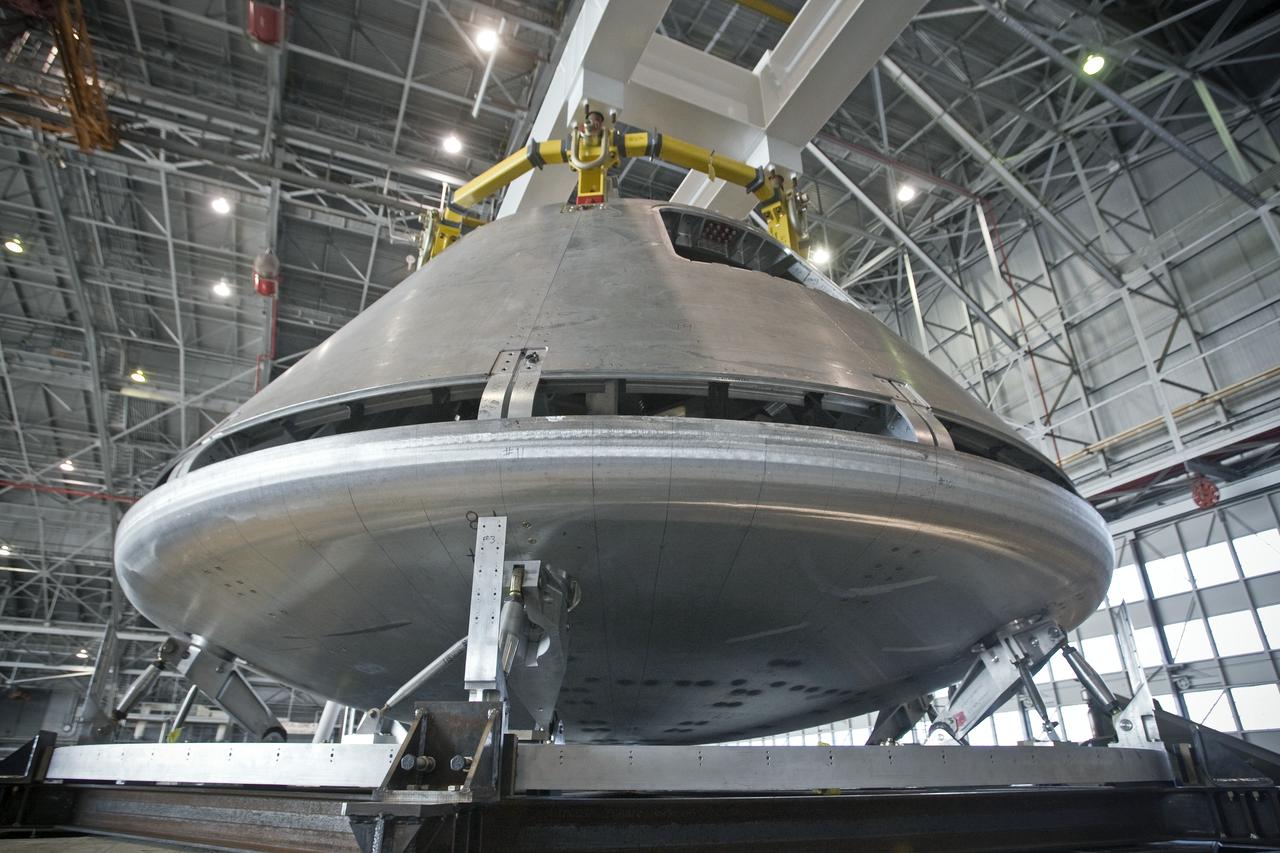

CM SepRing Integration work being done in NASA's Langley Hanger
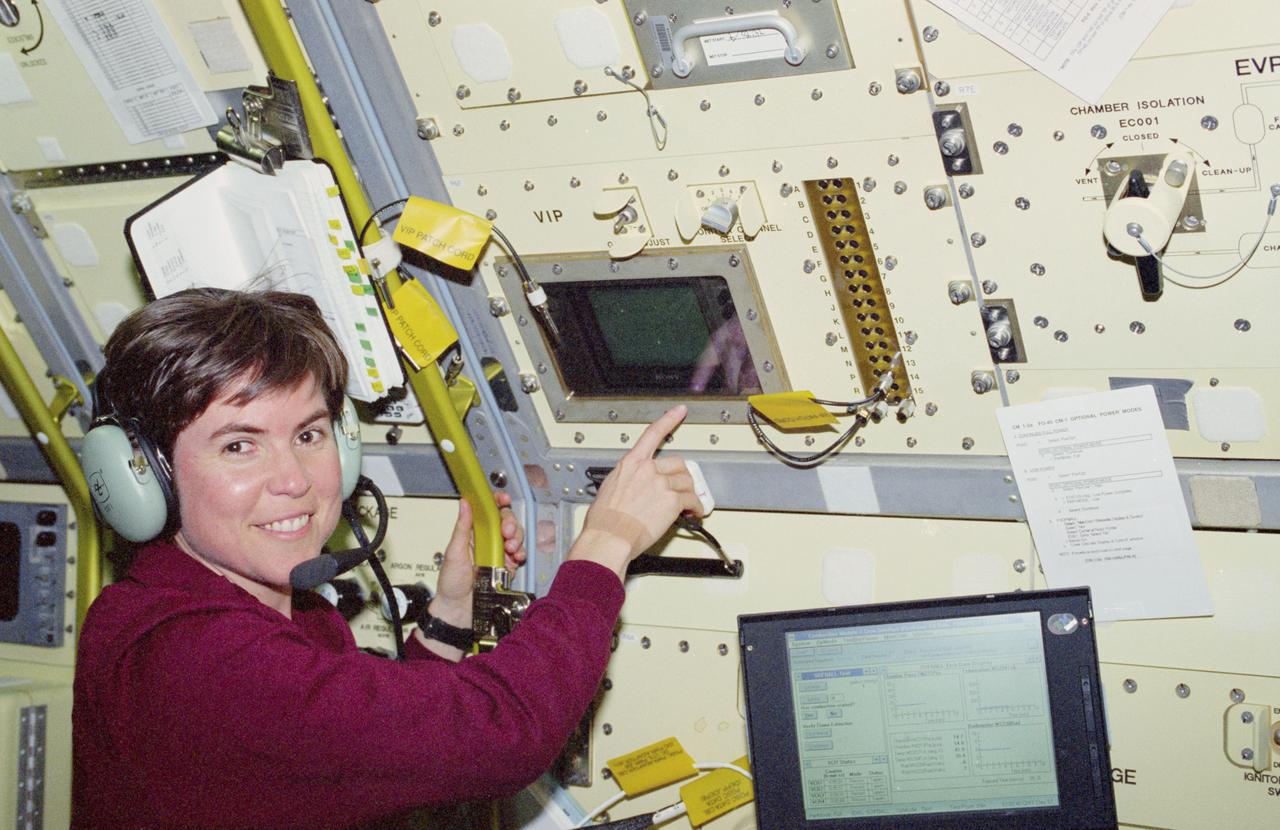

STS083-305-017 (4-8 April 1997) --- Astronaut Janice E. Voss, payload commander, displays a pleasant countenance following a successful test at the Combustion Module-1 (CM-1). The test was designed to study the Structures of Flame Balls at Low Lewis (SOFBALL) numbers. The CM-1 facility accommodates a number of experiments using different chamber inserts.
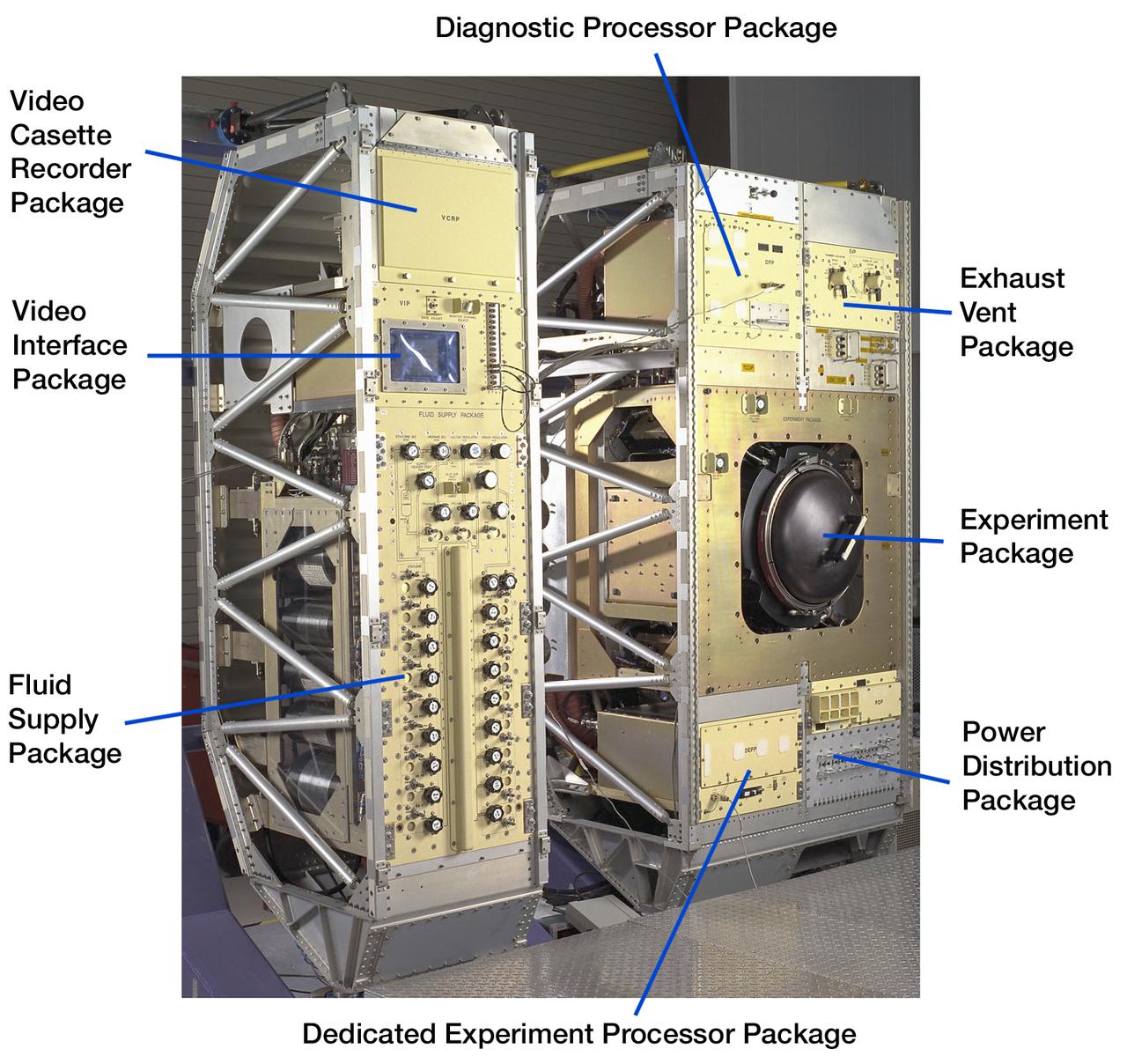
Exterior view of Combustion Module-2 with callouts to identify key sections. The original CM flew on the Microgravity Sciences Lab-1 and 1R in 1997. It has been refurbished and placed in new racks for flight on the STS-107 Research 1 mission in 2001. Glenn Research in Cleveland, OH, manages the project.
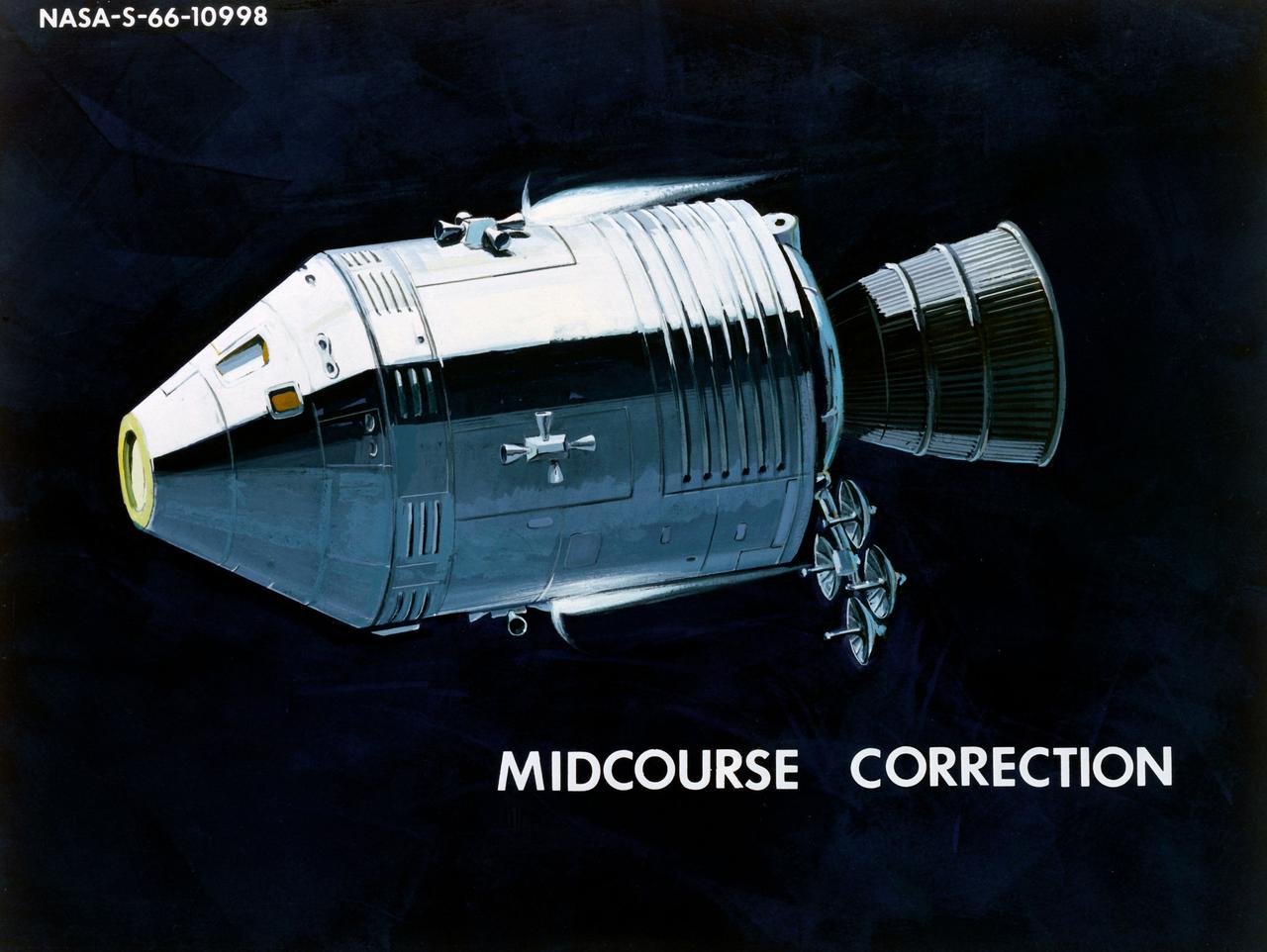
Apollo CM, Mid-Course Correction. MSC, HOUSTON, TX CN/BW 12/01/1966 - 06/01/1966

Apollo CM, Transfer to Lunar Module (LM). MSC, HOUSTON, TX CN/BW 12/01/1966 - 06/01/1966
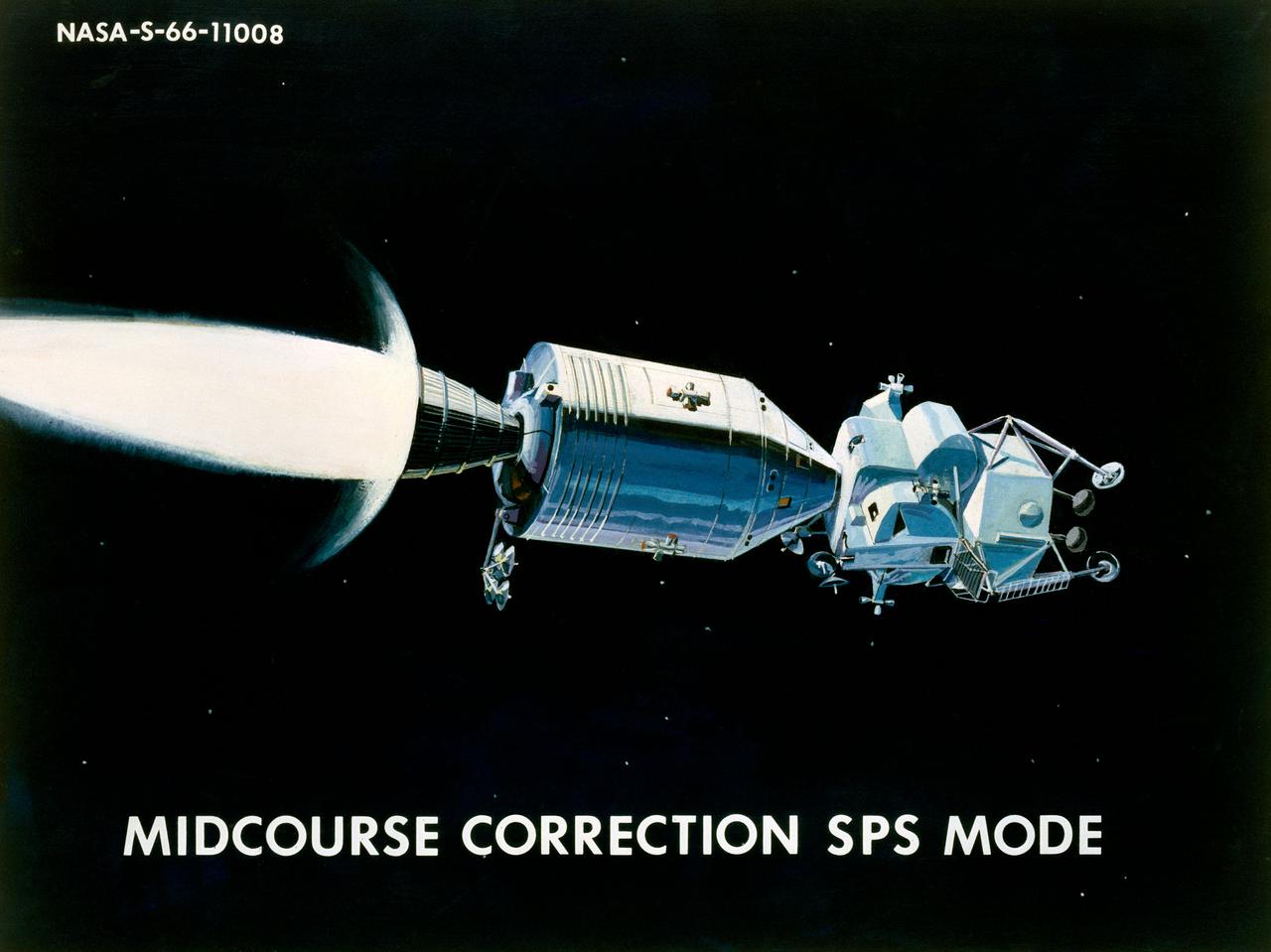
Apollo CM, Mid-Course correction, SPS Mode. MSC, HOUSTON, TX CN/BW 12/01/1966 - 06/01/1966
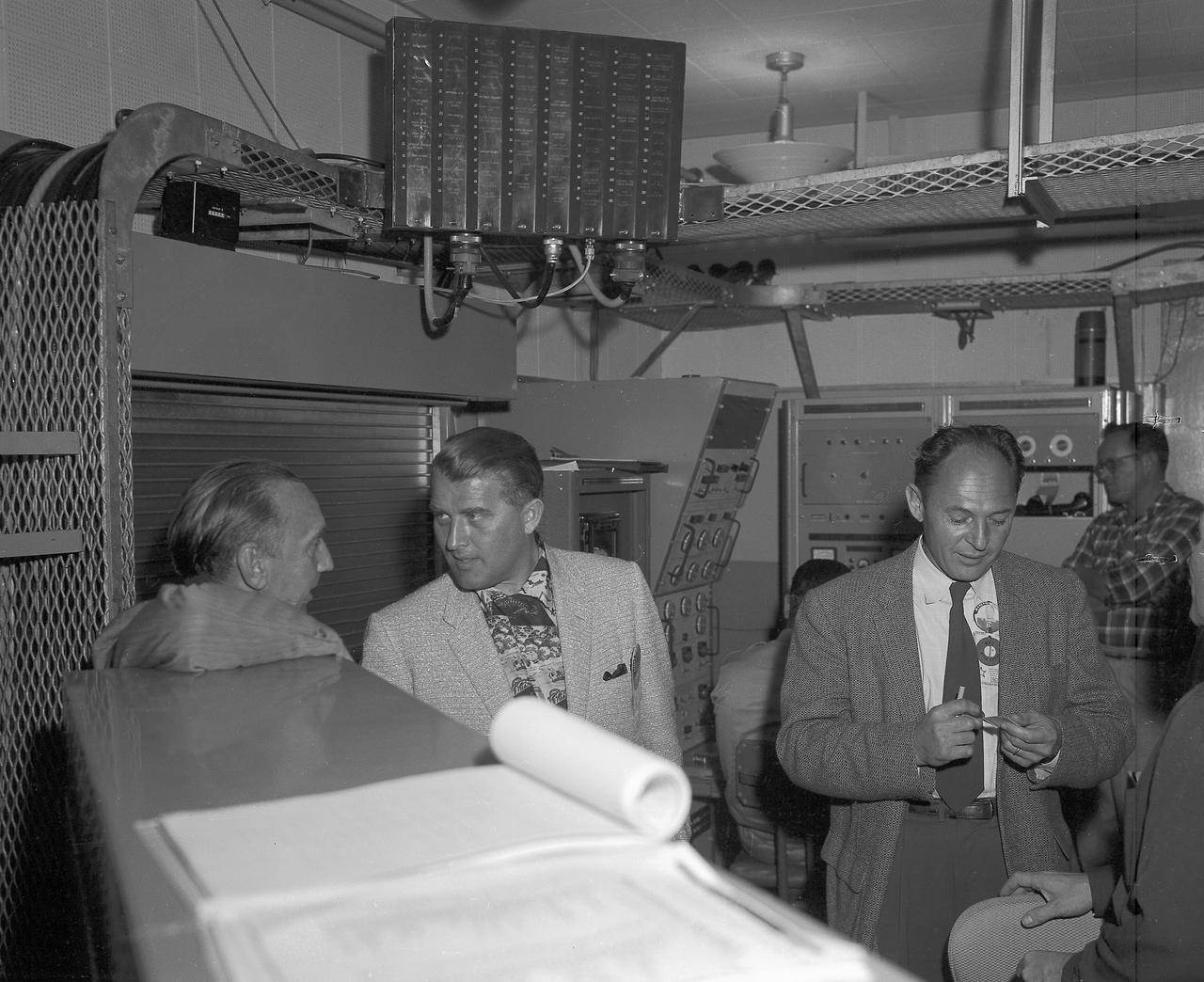

In this photo, (left to right) Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA) Missile Firing Laboratory Chief Dr. Kurt Debus, Director of the ABMA Development Operations Division, Dr. von Braun and an unidentified individual in blockhouse during the CM-21 (Jupiter) firing. The Jupiter missile CM-21 became the first Chrysler production qualification missile to be fired and in March 1959 launched the Pioneer IV.

Exterior view of Combustion Module-2 with an Experiment Module partially extracted during a crew training session. The original CM flew on the Microgravity Sciences Lab-1 and 1R in 1997. It has been refurbished and placed in new racks for flight on the STS-107 Research 1 mission in 2001. See MSFC 0100158 for a view with callouts. Glenn Research in Cleveland, OH, manages the project.
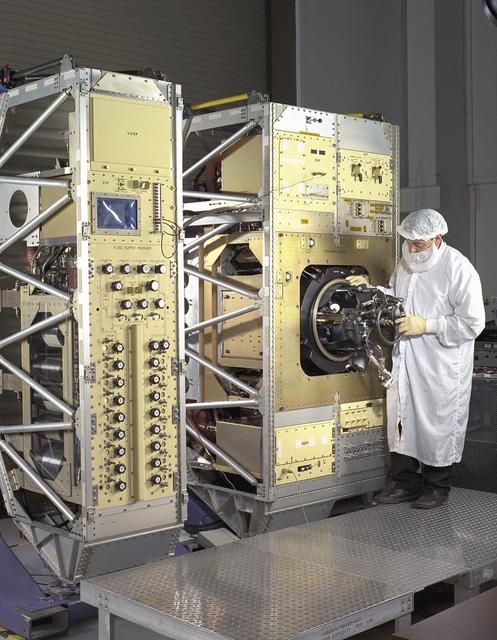

Exterior view of Combustion Module-2 with an Experiment Module partially extracted during a crew training session. The original CM flew on the Microgravity Sciences Lab-1 and 1R in 1997. It has been refurbished and placed in new racks for flight on the STS-107 Research 1 mission in 2001. See MSFC 0100158 for a view with callouts. Glenn Research in Cleveland, OH, manages the project.
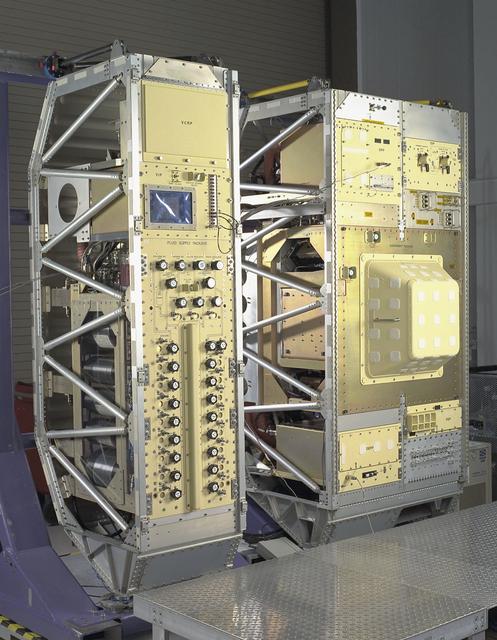

Exterior view of Combustion Module-2 with the Experiment Module covered. The original CM flew on the Microgravity Sciences Lab-1 and 1R in 1997. It has been refurbished and placed in new racks for flight on the STS-107 Research 1 mission in 2001. See MSFC 0100158 for a view with callouts. Glenn Research in Cleveland, OH, manages the project.
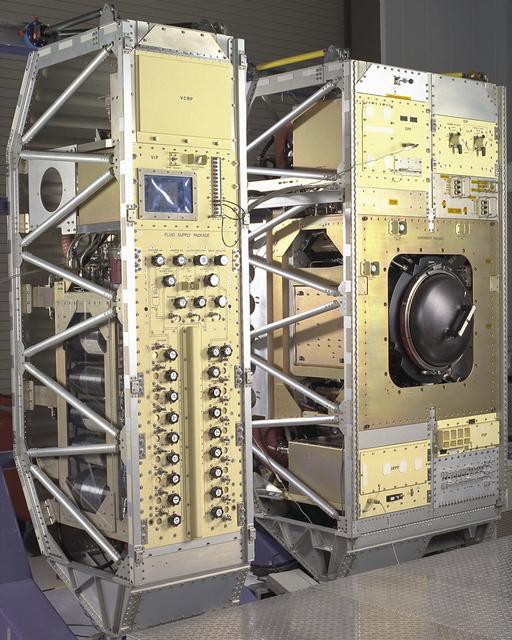

Exterior view of Combustion Module-2 with the Experiment Module cover (black dome) exposed. The original CM flew on the Microgravity Sciences Lab-1 and 1R in 1997. It has been refurbished and placed in new racks for flight on the STS-107 Research 1 mission in 2001. See MSFC 0100158 for a view with callouts. Glenn Research in Cleveland, OH, manages the project.
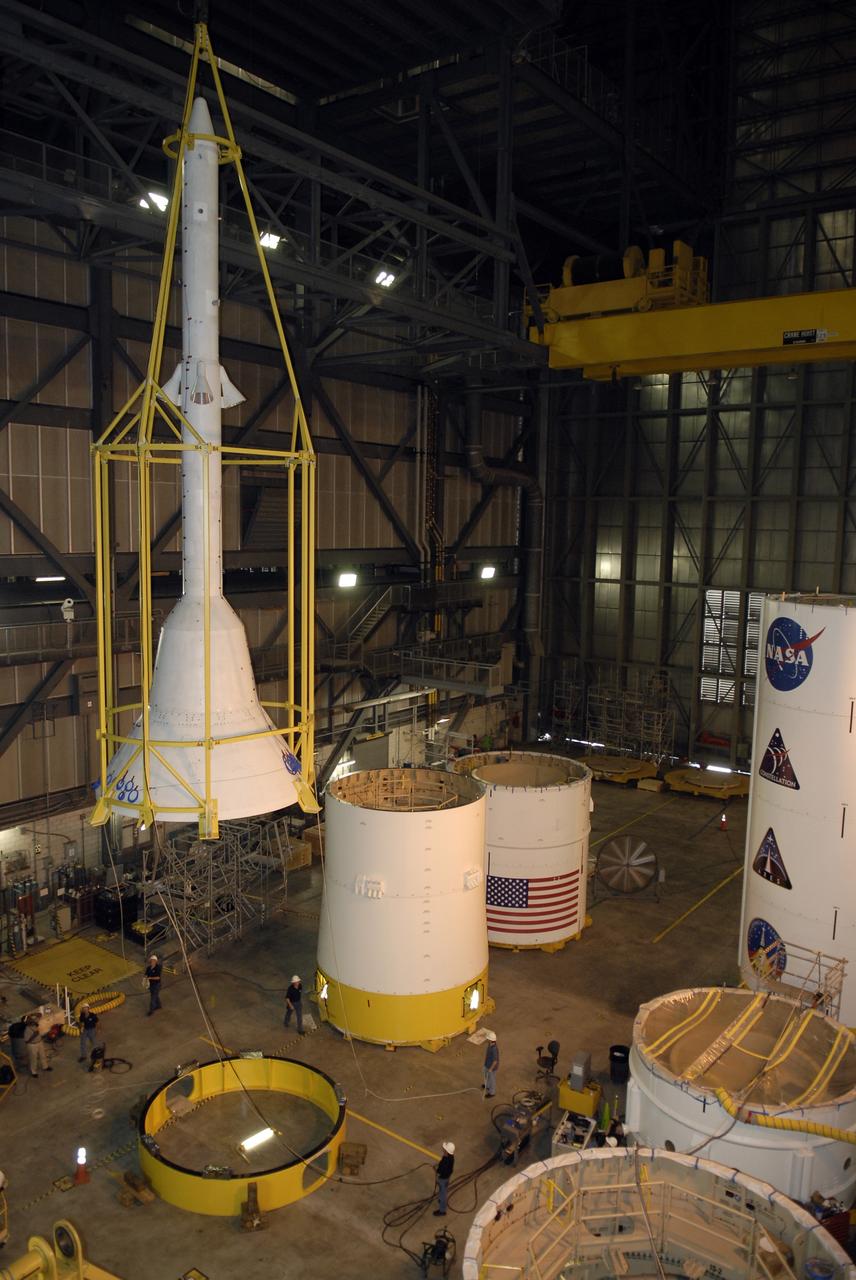

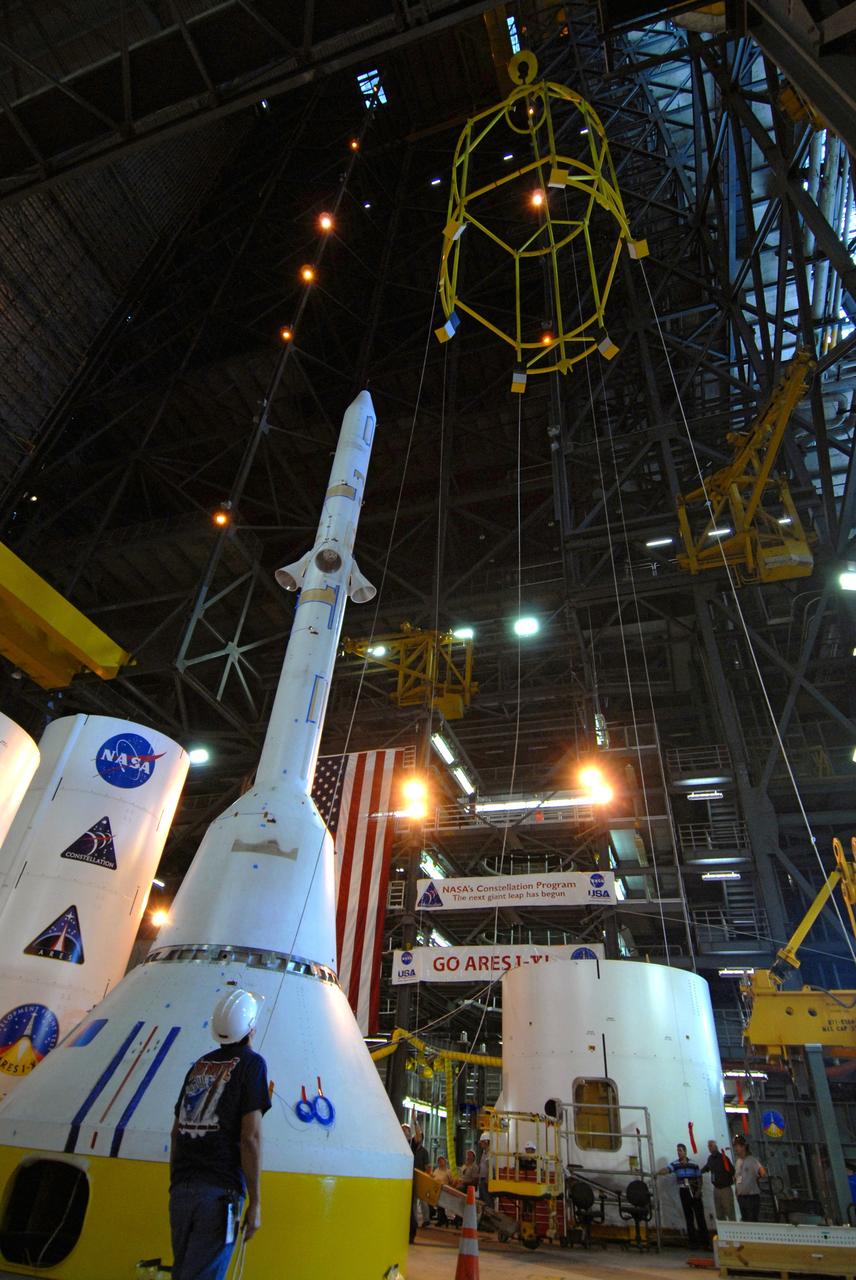
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In high bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the framework known as the "birdcage" lifts the Ares I-X simulator crew module-launch abort system, or CM-LAS. The CM-LAS stack will be mated with the simulator service module-service adapter stack. Ares I-X is the flight test for the Ares I. The I-X flight will provide NASA an early opportunity to test and prove hardware, facilities and ground operations associated with Ares I. The launch of the 327-foot-tall, full-scale Ares I-X is targeted for August 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
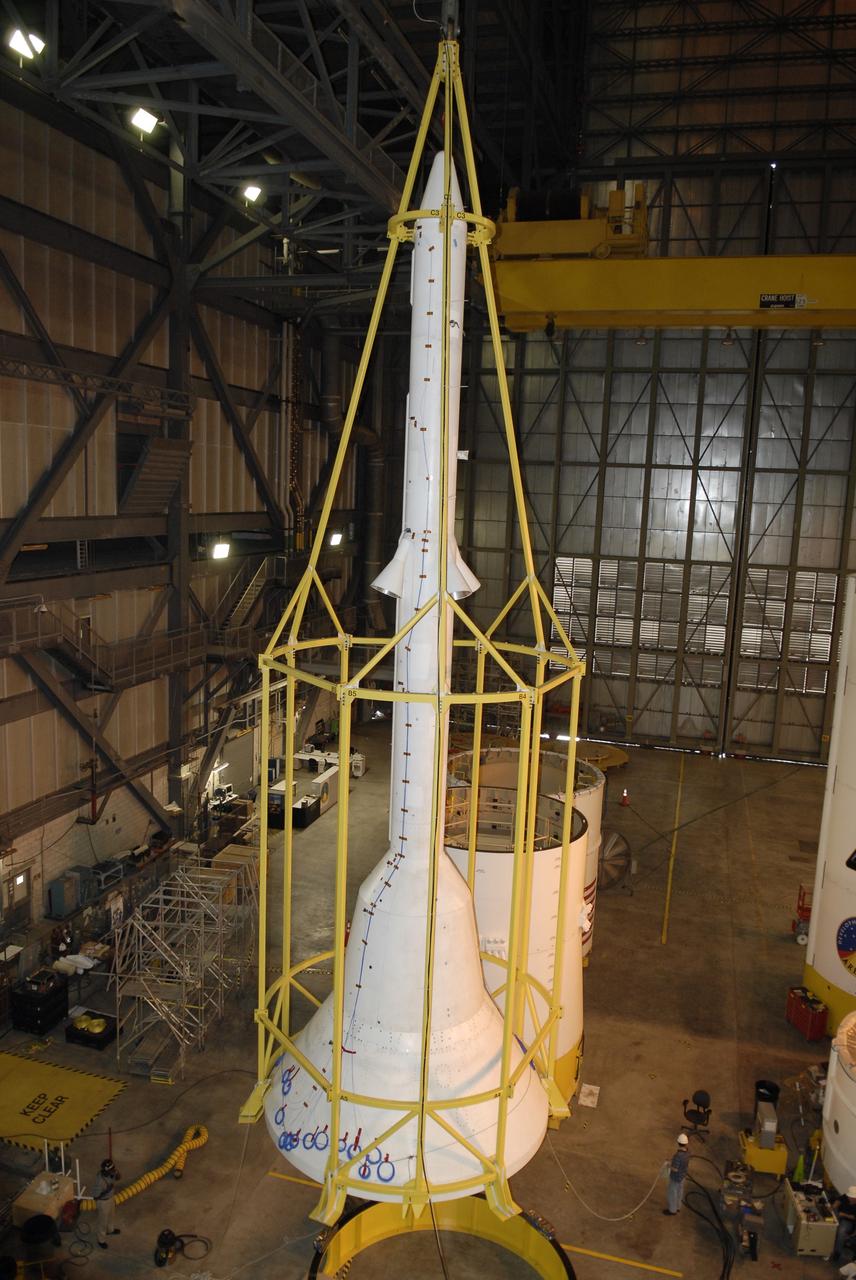

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In high bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the framework known as the "birdcage" is placed over the Ares I-X simulator crew module-launch abort system, or CM-LAS. The birdcage will be used to lift the CM-LAS to mate the stack with the simulator service module-service adapter stack. Ares I-X is the flight test for the Ares I. The I-X flight will provide NASA an early opportunity to test and prove hardware, facilities and ground operations associated with Ares I. The launch of the 327-foot-tall, full-scale Ares I-X is targeted for August 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
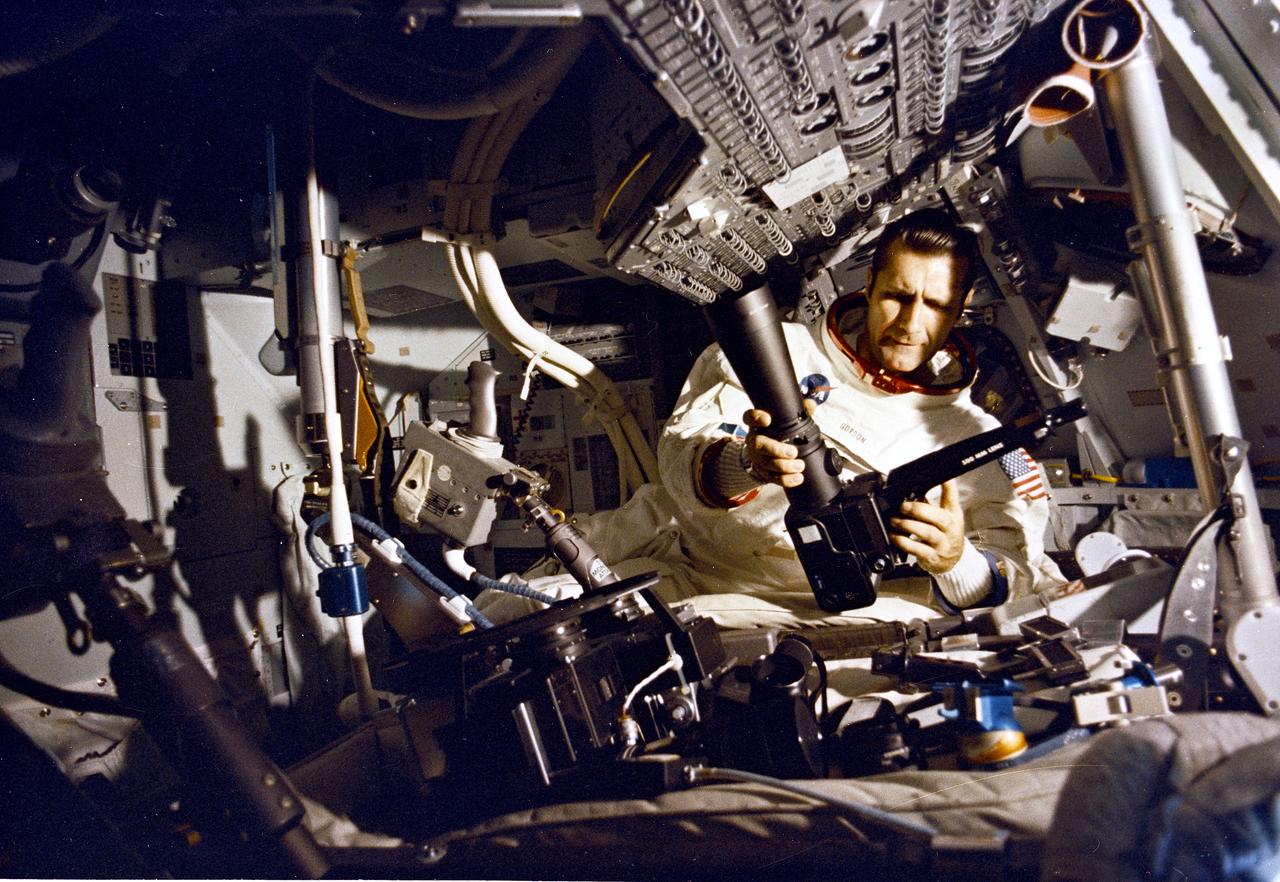

This is a view of astronaut Richard F. Gordon attaching a high resolution telephoto lens to a camera aboard the Apollo 12 Command Module (CM) Yankee Clipper. The second manned lunar landing mission, Apollo 12 launched from launch pad 39-A at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on November 14, 1969 via a Saturn V launch vehicle. The Saturn V vehicle was developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) under the direction of Dr. Wernher von Braun. Aboard Apollo 12 was a crew of three astronauts: Alan L. Bean, pilot of the Lunar Module (LM), Intrepid; Richard Gordon, pilot of the Command Module (CM), Yankee Clipper; and Spacecraft Commander Charles Conrad. The LM, Intrepid, landed astronauts Conrad and Bean on the lunar surface in what’s known as the Ocean of Storms. Their lunar soil activities included the deployment of the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package (ALSEP), finding the unmanned Surveyor 3 that landed on the Moon on April 19, 1967, and collecting 75 pounds (34 kilograms) of rock samples. Astronaut Richard Gordon piloted the CM, Yankee Clipper, in a parking orbit around the Moon. Apollo 12 safely returned to Earth on November 24, 1969.
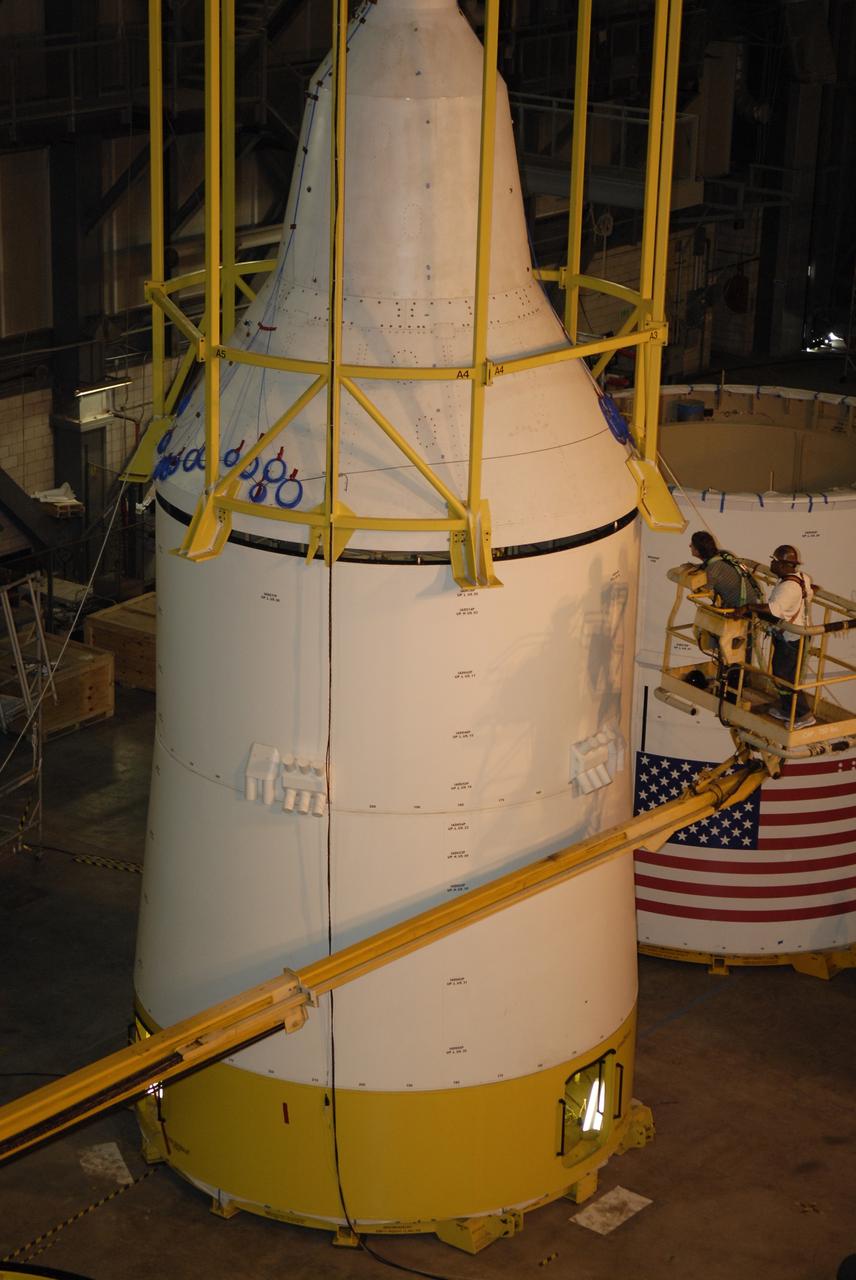

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In high bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the framework known as the "birdcage" lowers the Ares I-X simulator crew module-launch abort system, or CM-LAS, onto the simulator service module-service adapter stack. Ares I-X is the flight test for the Ares I. The I-X flight will provide NASA an early opportunity to test and prove hardware, facilities and ground operations associated with Ares I. The launch of the 327-foot-tall, full-scale Ares I-X is targeted for August 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
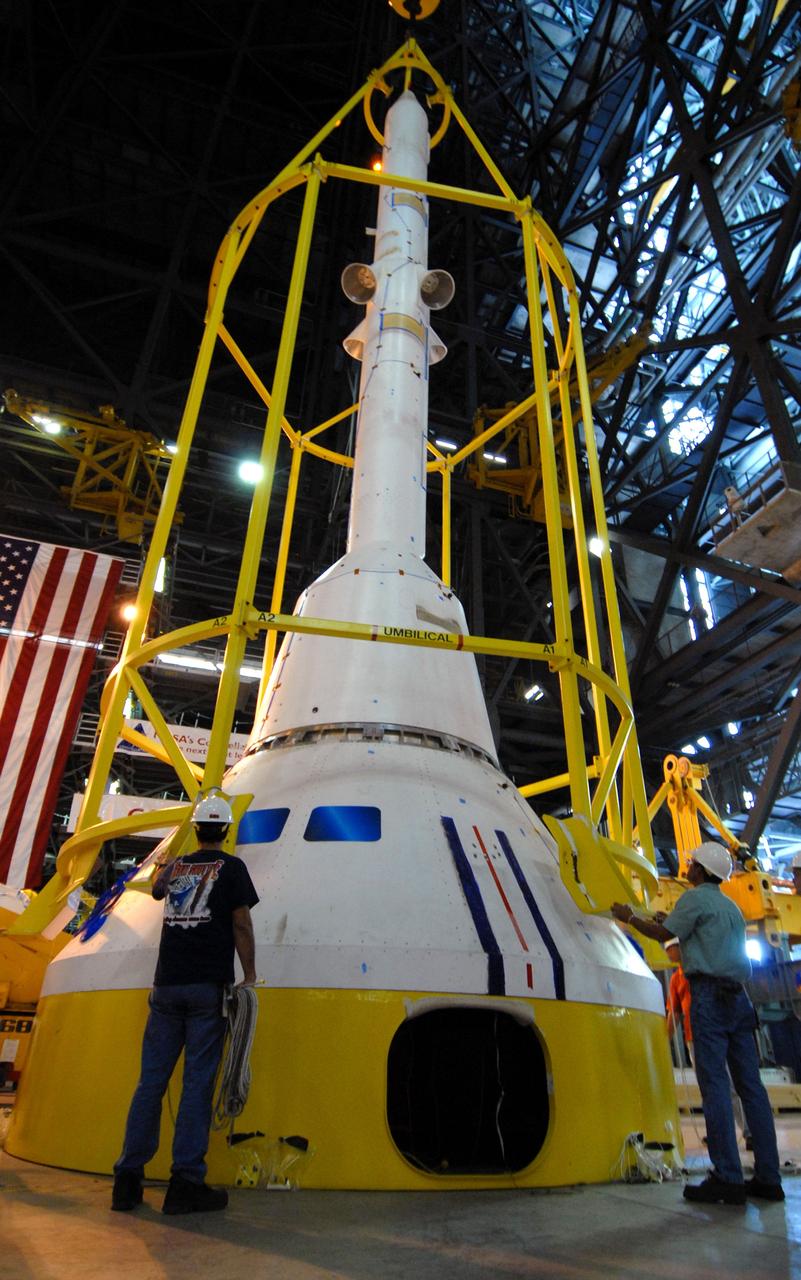

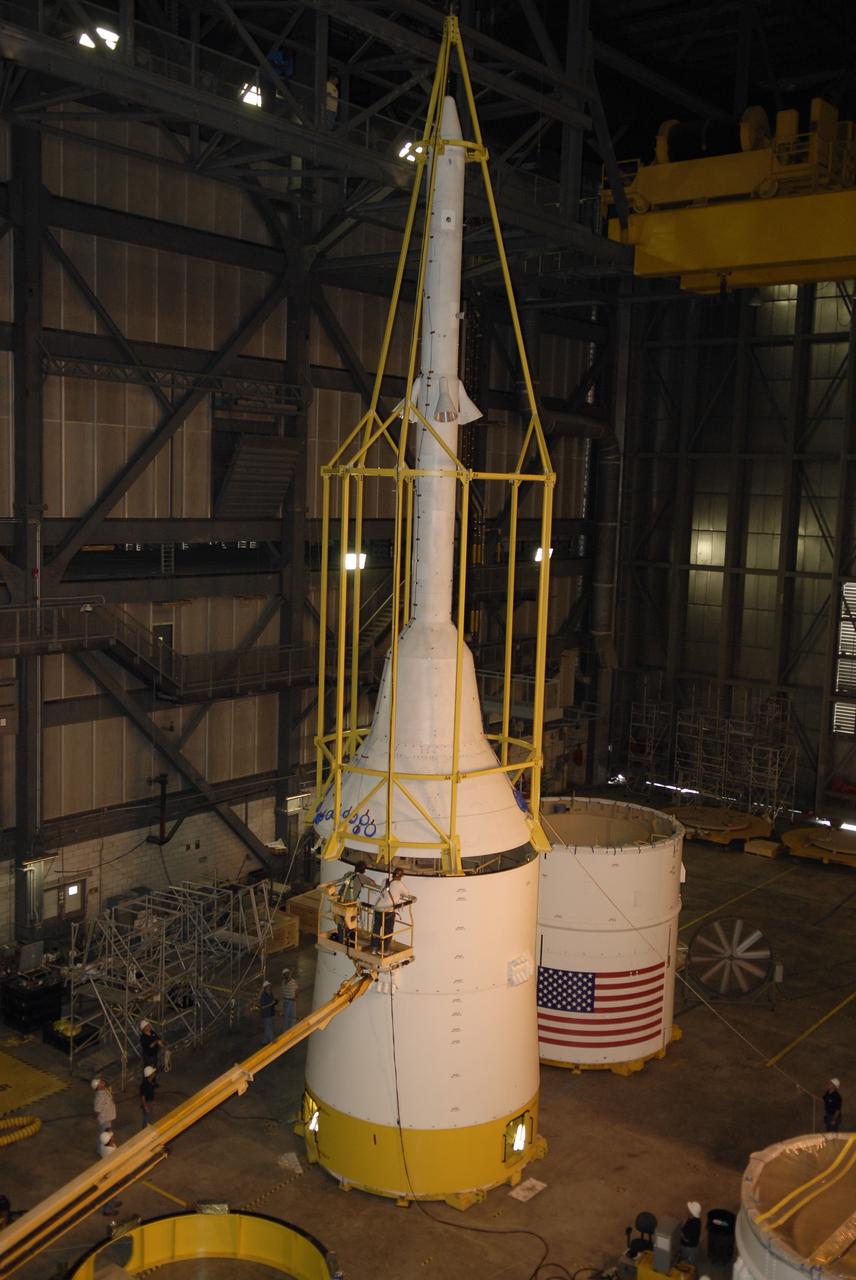
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –– In High Bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the yellow framework , nicknamed the "birdcage," is lowered over the Crew Module, or CM, and Launch Abort System, or LAS, assembly for a fit check. Ares I-X is the flight test for the Ares I. The I-X flight will provide NASA an early opportunity to test and prove hardware, facilities and ground operations associated with Ares I. The launch of the 327-foot-tall, full-scale Ares I-X is targeted for July 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –– In High Bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the yellow framework , nicknamed the "birdcage," is lowered over the Crew Module, or CM, and Launch Abort System, or LAS, assembly for a fit check. Ares I-X is the flight test for the Ares I. The I-X flight will provide NASA an early opportunity to test and prove hardware, facilities and ground operations associated with Ares I. The launch of the 327-foot-tall, full-scale Ares I-X is targeted for July 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
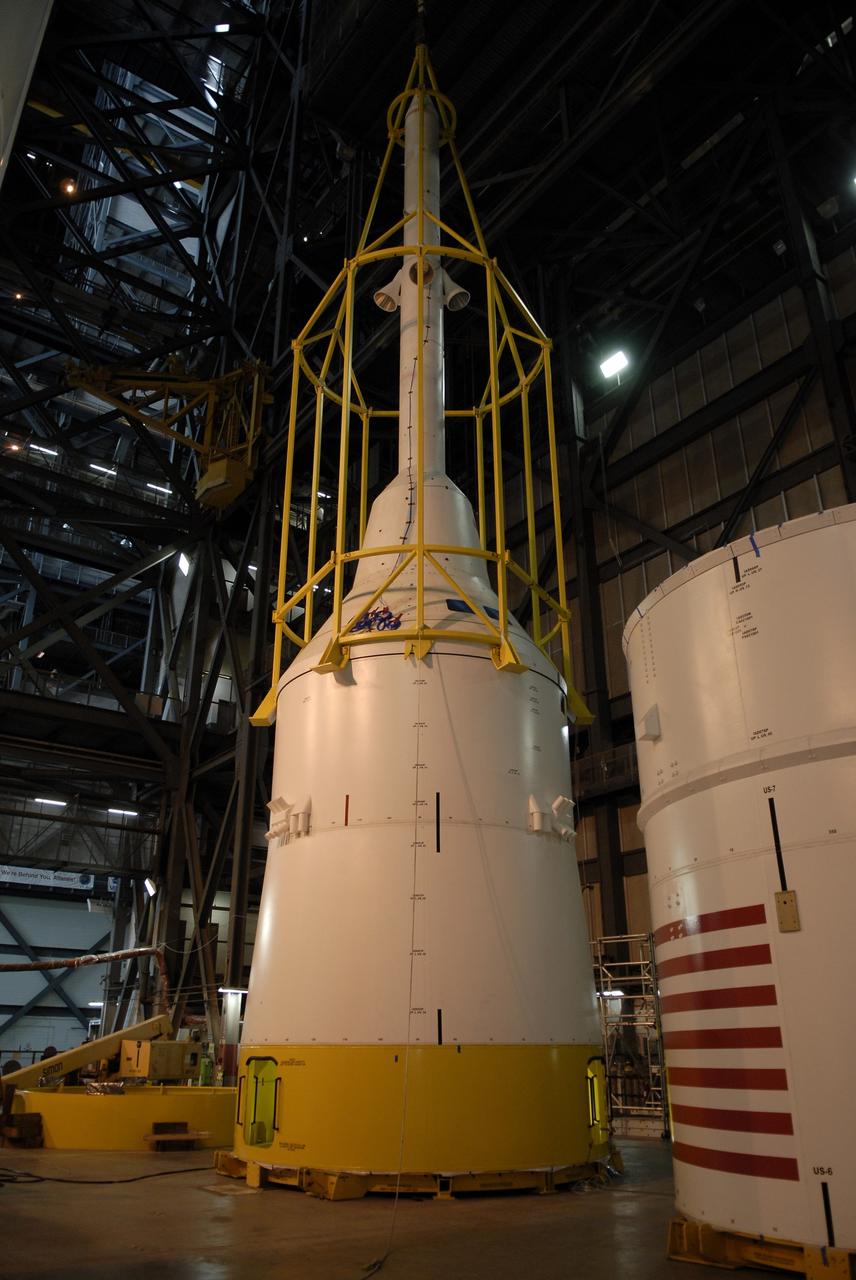

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In high bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the framework known as the "birdcage" lowers the Ares I-X simulator crew module-launch abort system, or CM-LAS, onto the simulator service module-service adapter stack. Ares I-X is the flight test for the Ares I. The I-X flight will provide NASA an early opportunity to test and prove hardware, facilities and ground operations associated with Ares I. The launch of the 327-foot-tall, full-scale Ares I-X is targeted for August 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

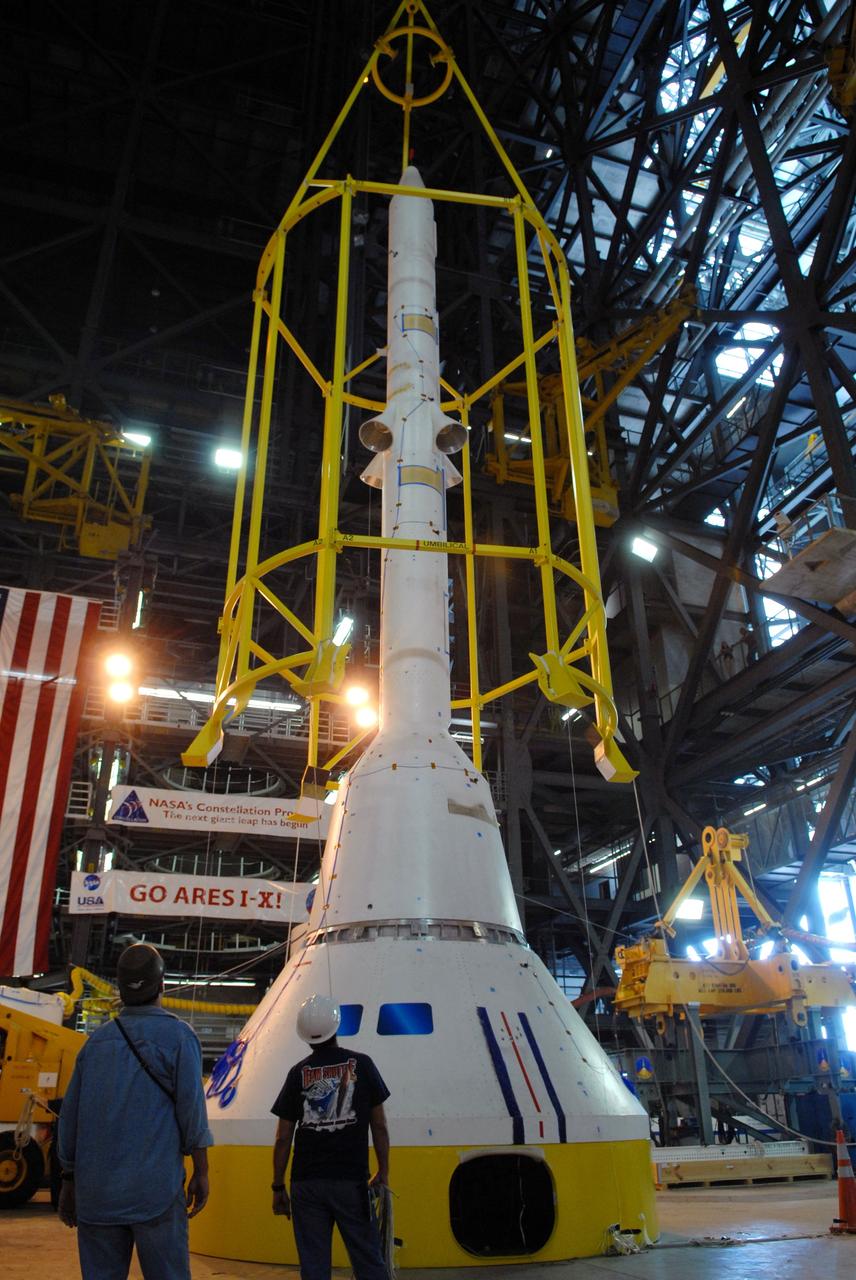
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –– In High Bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the yellow framework at center will undergo a fit check. Nicknamed the "birdcage," it is the lifting fixture that will have the ability to lift the Crew Module, or CM, and Launch Abort System, or LAS, assembly for the Ares I-X rocket. Ares I-X is the flight test for the Ares I. The I-X flight will provide NASA an early opportunity to test and prove hardware, facilities and ground operations associated with Ares I. The launch of the 327-foot-tall, full-scale Ares I-X is targeted for July 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In high bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the framework known as the "birdcage" lowers the Ares I-X simulator crew module-launch abort system, or CM-LAS, onto the simulator service module-service adapter stack. Ares I-X is the flight test for the Ares I. The I-X flight will provide NASA an early opportunity to test and prove hardware, facilities and ground operations associated with Ares I. The launch of the 327-foot-tall, full-scale Ares I-X is targeted for August 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In high bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a technician checks the mating from the inside of the Ares I-X simulator crew module-launch abort system, or CM-LAS, with the simulator service module-service adapter stack. Ares I-X is the flight test for the Ares I. The I-X flight will provide NASA an early opportunity to test and prove hardware, facilities and ground operations associated with Ares I. The launch of the 327-foot-tall, full-scale Ares I-X is targeted for August 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

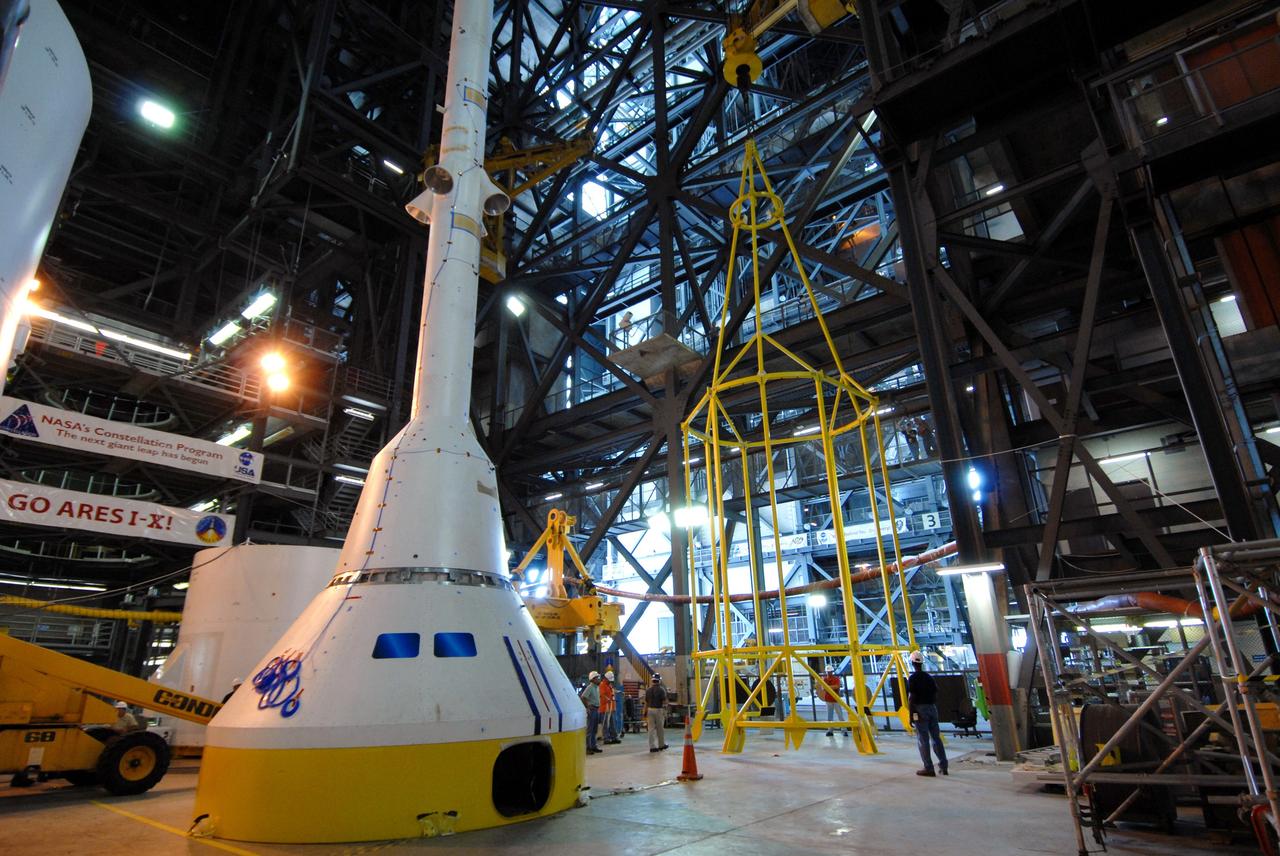
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –– In High Bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the yellow framework at top, nicknamed the "birdcage," is lifted high above the floor for a fit check with the Crew Module, or CM, and Launch Abort System, or LAS, assembly at lower left for the Ares I-X rocket. Ares I-X is the flight test for the Ares I. The I-X flight will provide NASA an early opportunity to test and prove hardware, facilities and ground operations associated with Ares I. The launch of the 327-foot-tall, full-scale Ares I-X is targeted for July 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In high bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the framework known as the "birdcage" lowers the Ares I-X simulator crew module-launch abort system, or CM-LAS, onto the simulator service module-service adapter stack. Ares I-X is the flight test for the Ares I. The I-X flight will provide NASA an early opportunity to test and prove hardware, facilities and ground operations associated with Ares I. The launch of the 327-foot-tall, full-scale Ares I-X is targeted for August 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –– In High Bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the yellow framework , nicknamed the "birdcage," is lowered over the Crew Module, or CM, and Launch Abort System, or LAS, assembly for a fit check. Ares I-X is the flight test for the Ares I. The I-X flight will provide NASA an early opportunity to test and prove hardware, facilities and ground operations associated with Ares I. The launch of the 327-foot-tall, full-scale Ares I-X is targeted for July 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
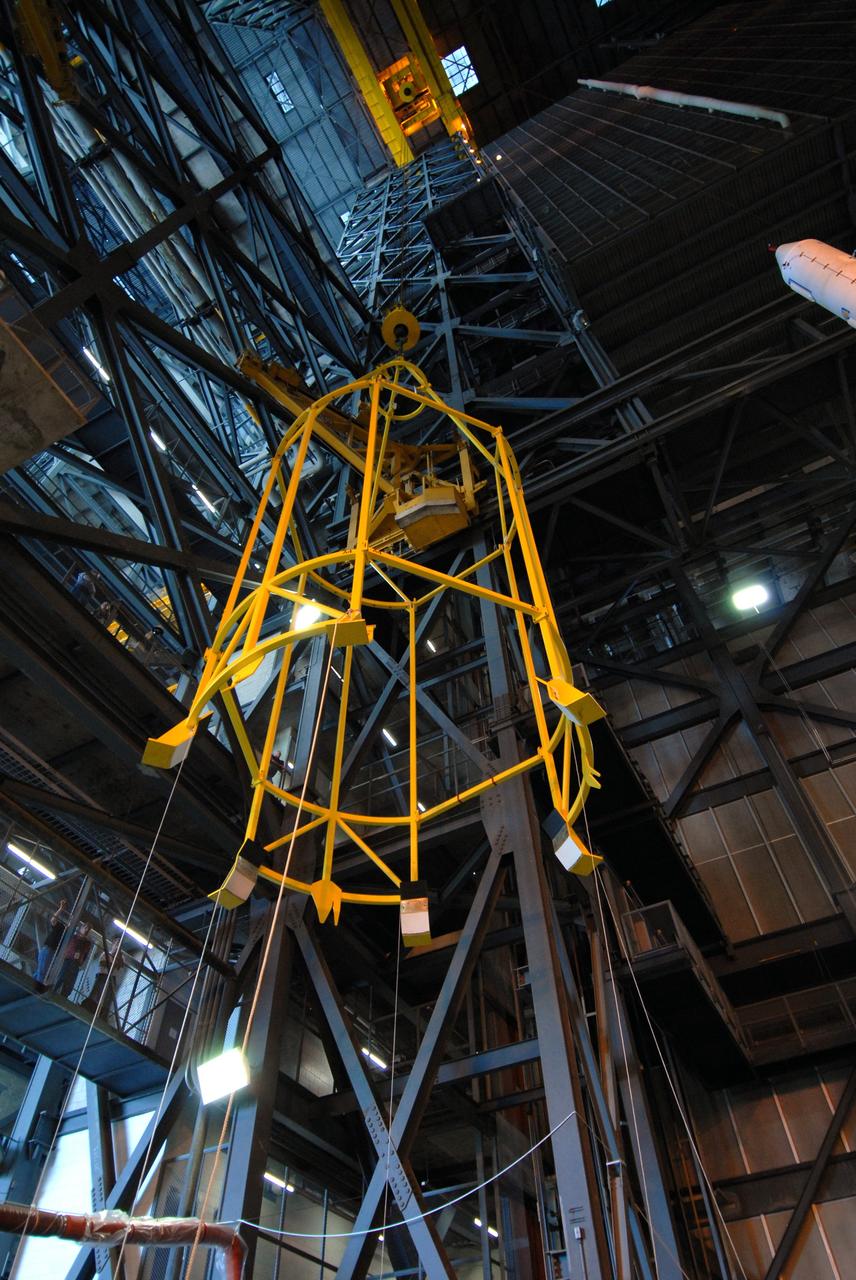

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –– In High Bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the yellow framework at left, nicknamed the "birdcage," is lifted high above the floor for a fit check with the Crew Module, or CM, and Launch Abort System, or LAS, assembly nearby for the Ares I-X rocket. Ares I-X is the flight test for the Ares I. The I-X flight will provide NASA an early opportunity to test and prove hardware, facilities and ground operations associated with Ares I. The launch of the 327-foot-tall, full-scale Ares I-X is targeted for July 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
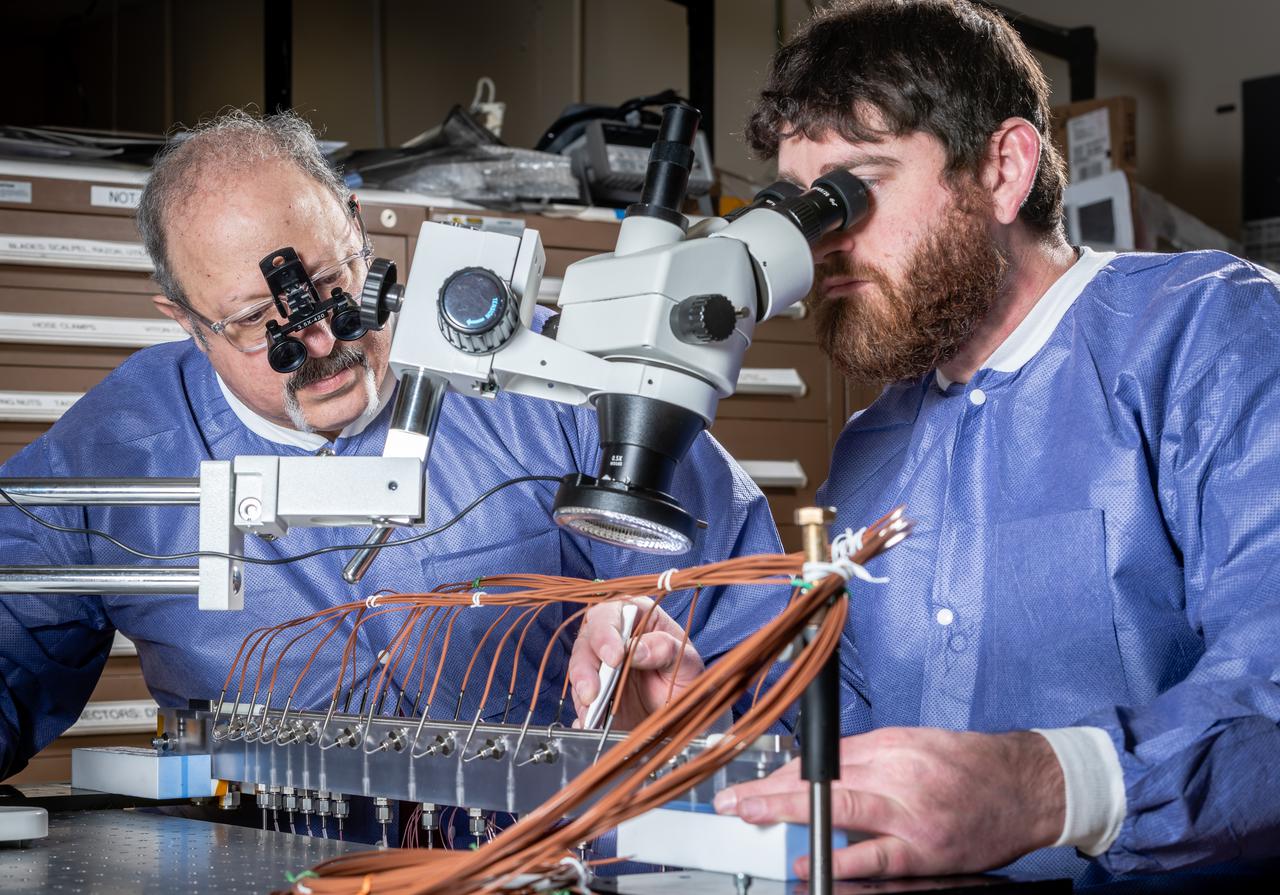

Flow Boiling Condensation Experiment, FBCE Micro Gravity Payload, Condensation Module – Heat Transfer (CM-HT) Test Section Hardware Fabrication
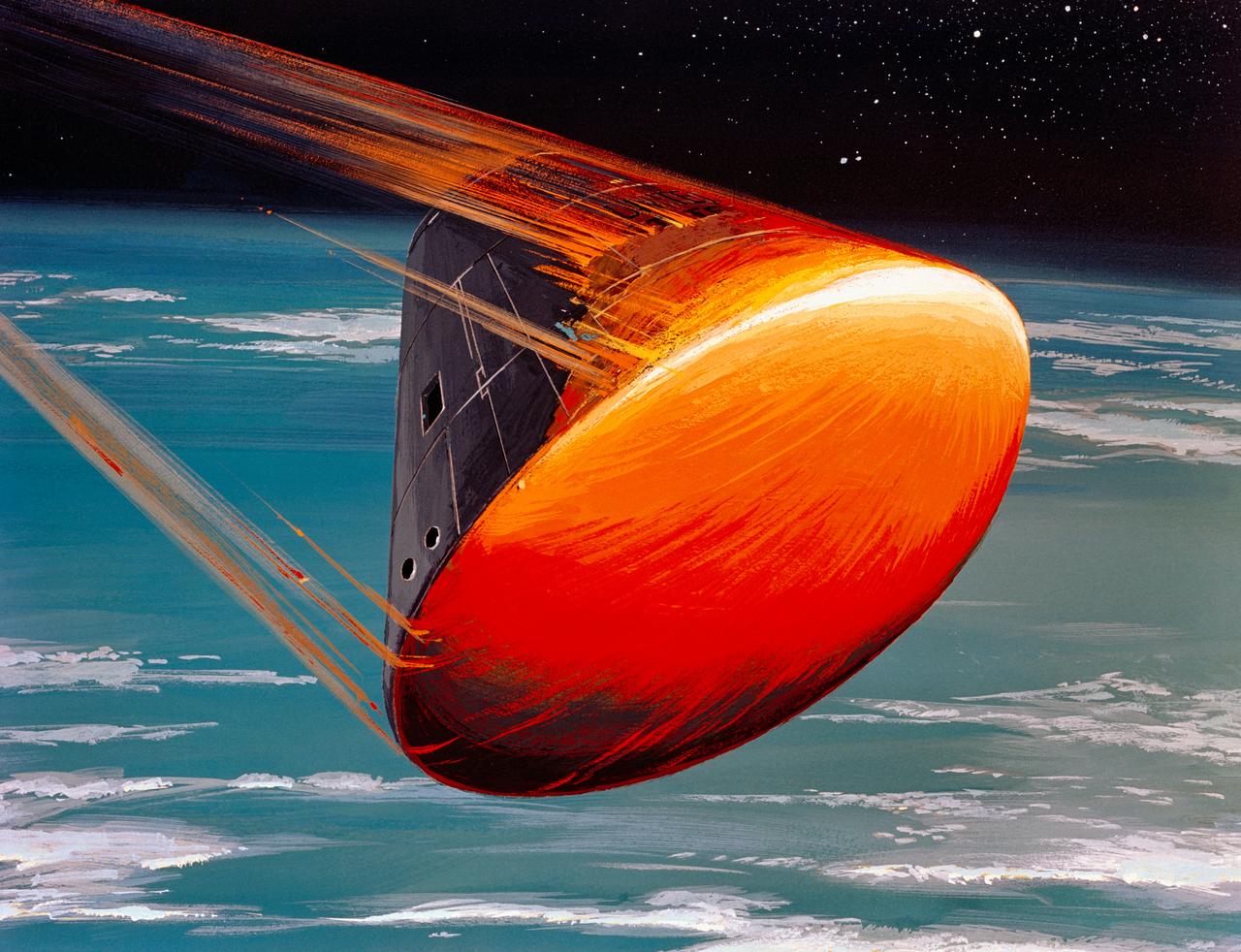

S68-55292 (August 1968) --- A North American Rockwell Corporation artist's concept depicting the Apollo Command Module (CM), oriented in a blunt-end-forward attitude, re-entering Earth's atmosphere after returning from a lunar landing mission. Note the change in color caused by the extremely high temperatures encountered upon re-entry.
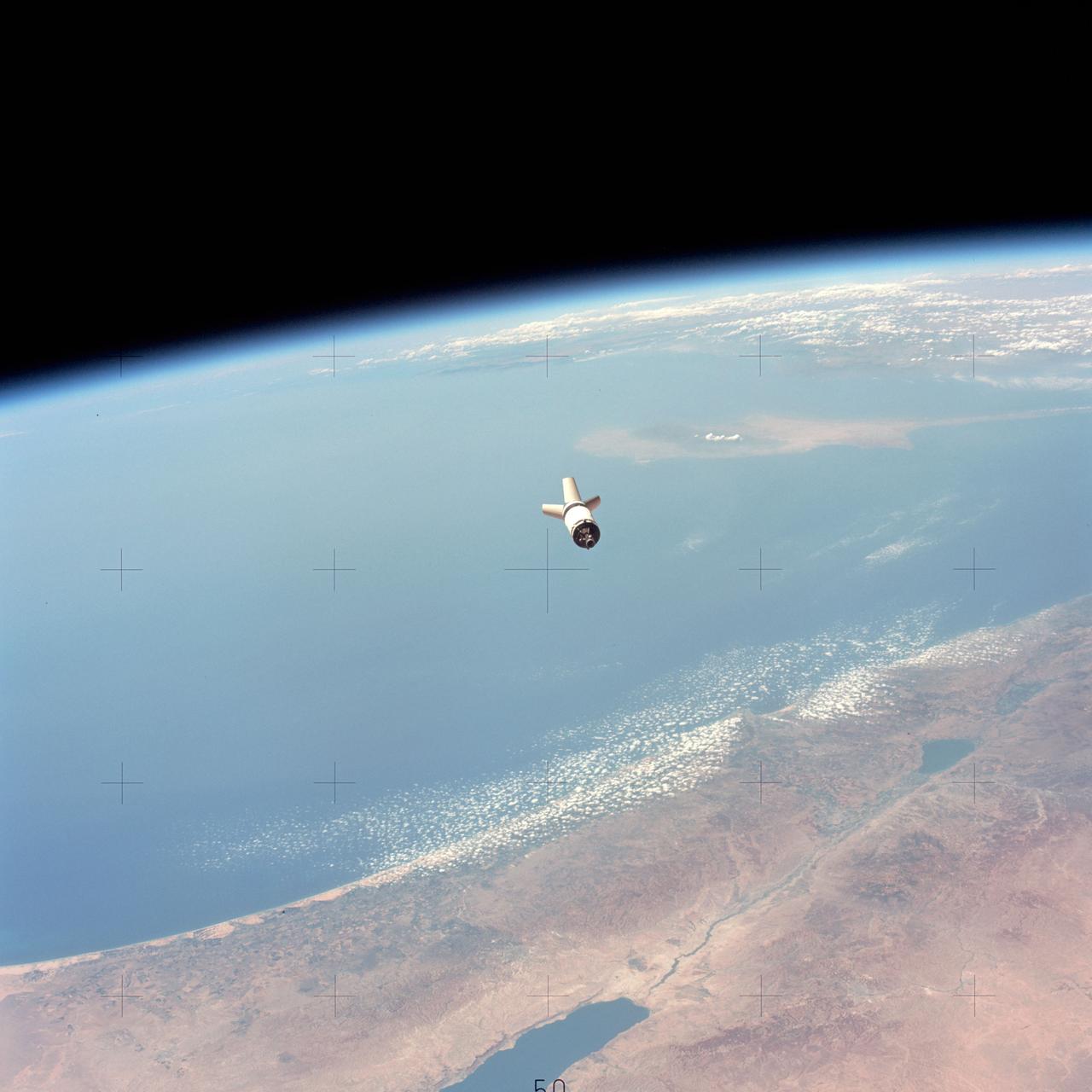

SL3-114-1634 (July-September 1973) --- Skylab 3, Saturn S-4B (S-IVB) stage falls away from the Command Module (CM) after separation. Earth limb in background, pass over Israel, the Dead Sea and the Mediterranean Sea. Photo credit: NASA
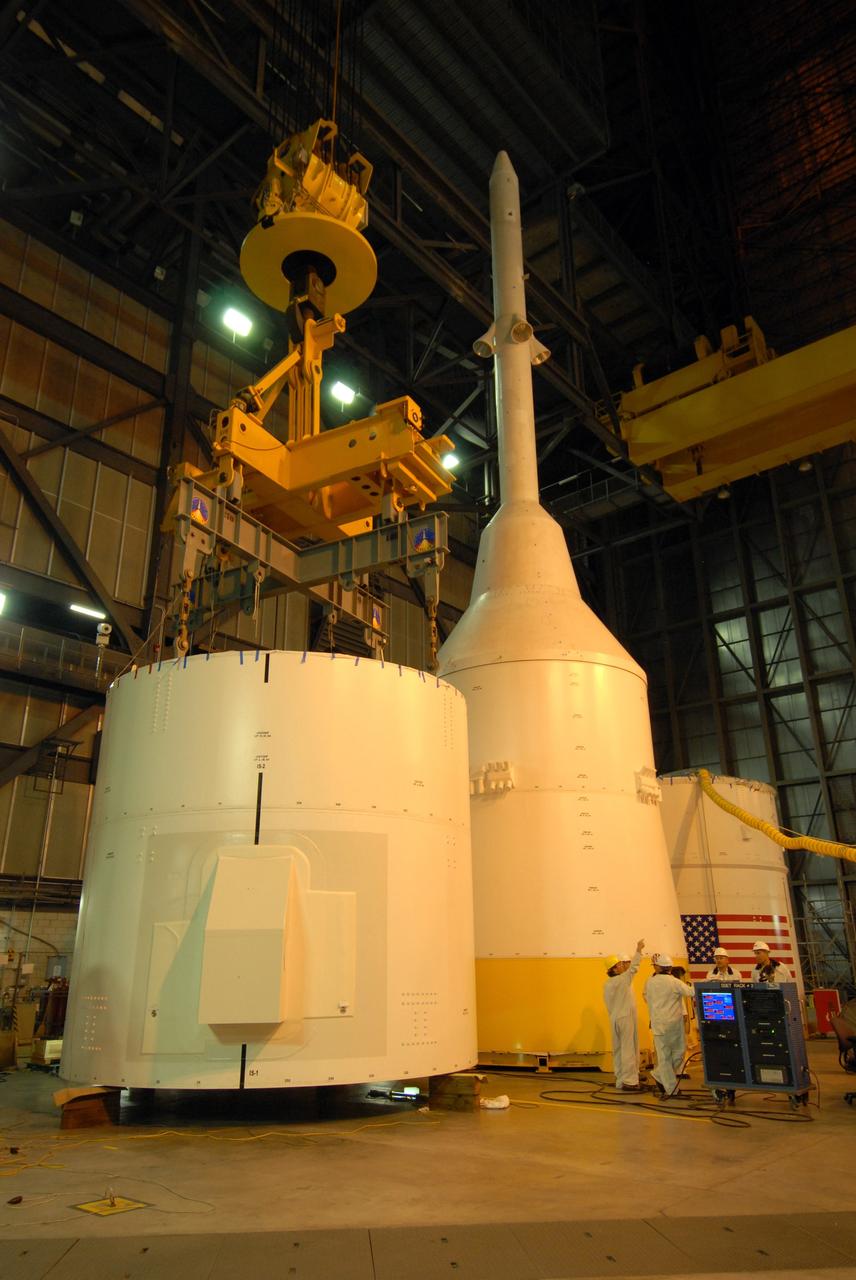

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 4 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Ares I-X interstage 1 for the upper stage simulator is lifted to move it to the forward assembly. The interstage will be mated with the frustum on the forward assembly. To the right is the crew module-launch abort system, or CM-LAS, and simulator service module-service adapter stack. Ares I-X is the flight test vehicle for the Ares I, a component of the Constellation Program. Ares I is the essential core of a safe, reliable, cost-effective space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system. Ares I-X is targeted for launch in August 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
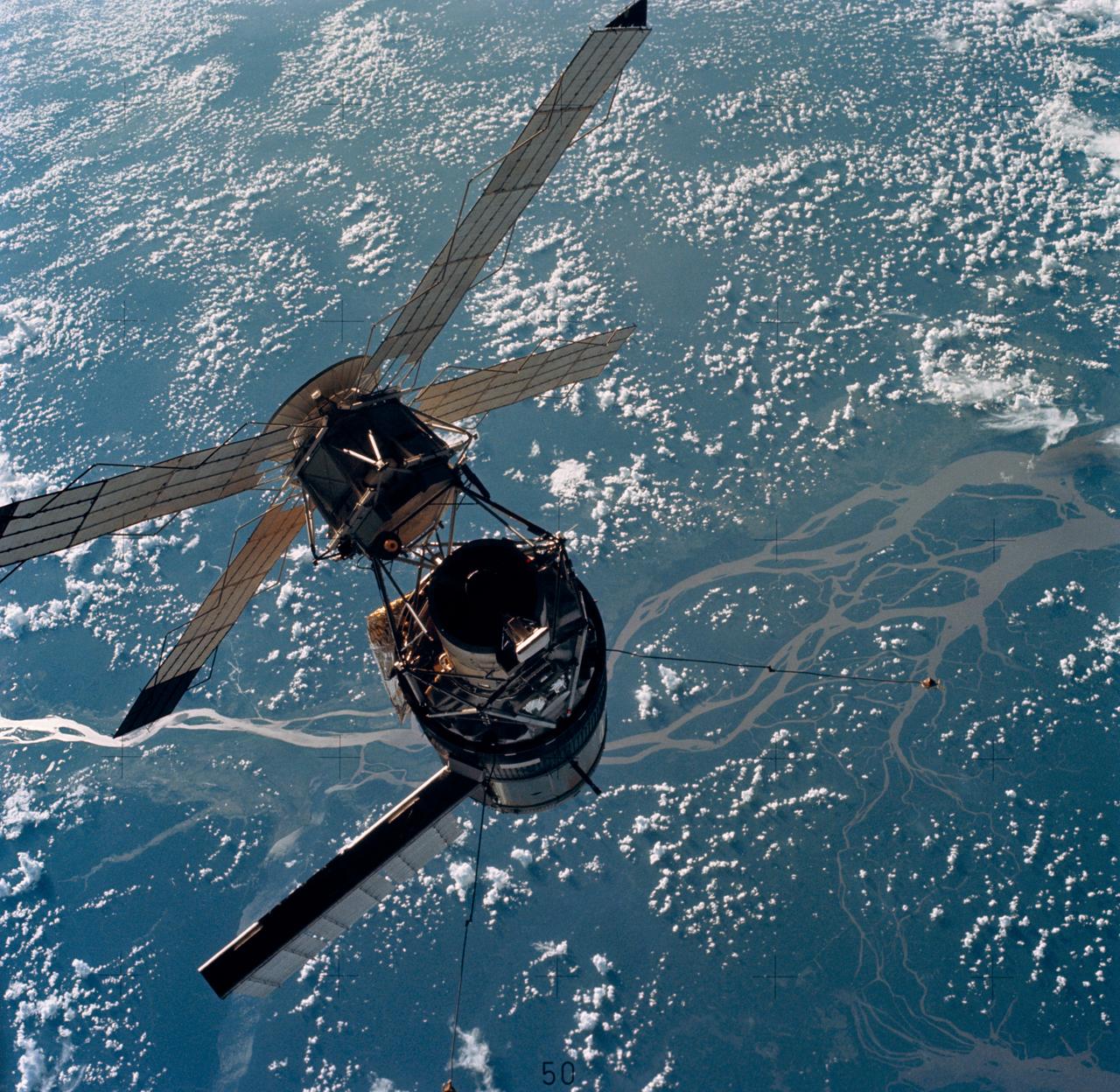

SL3-114-1683 (28 July 1973) --- A close-up view of the Skylab space station photographed against an Earth background from the Skylab 3 Command and Service Modules (CSM) during station-keeping maneuvers prior to docking. Aboard the Command Module (CM) were astronauts Alan L. Bean, Owen K. Garriott and Jack R. Lousma, who remained with the Skylab Space Station in Earth orbit for 59 days. This picture was taken with a hand-held 70mm Hasselblad camera using a 100mm lens and SO-368 medium speed Ektachrome film. Note the one solar array system wing on the Orbital Workshop (OWS) which was successfully deployed during extravehicular activity (EVA) on the first manned Skylab flight. The parasol solar shield which was deployed by the Skylab 2 crew can be seen through the support struts of the Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM). Photo credit: NASA
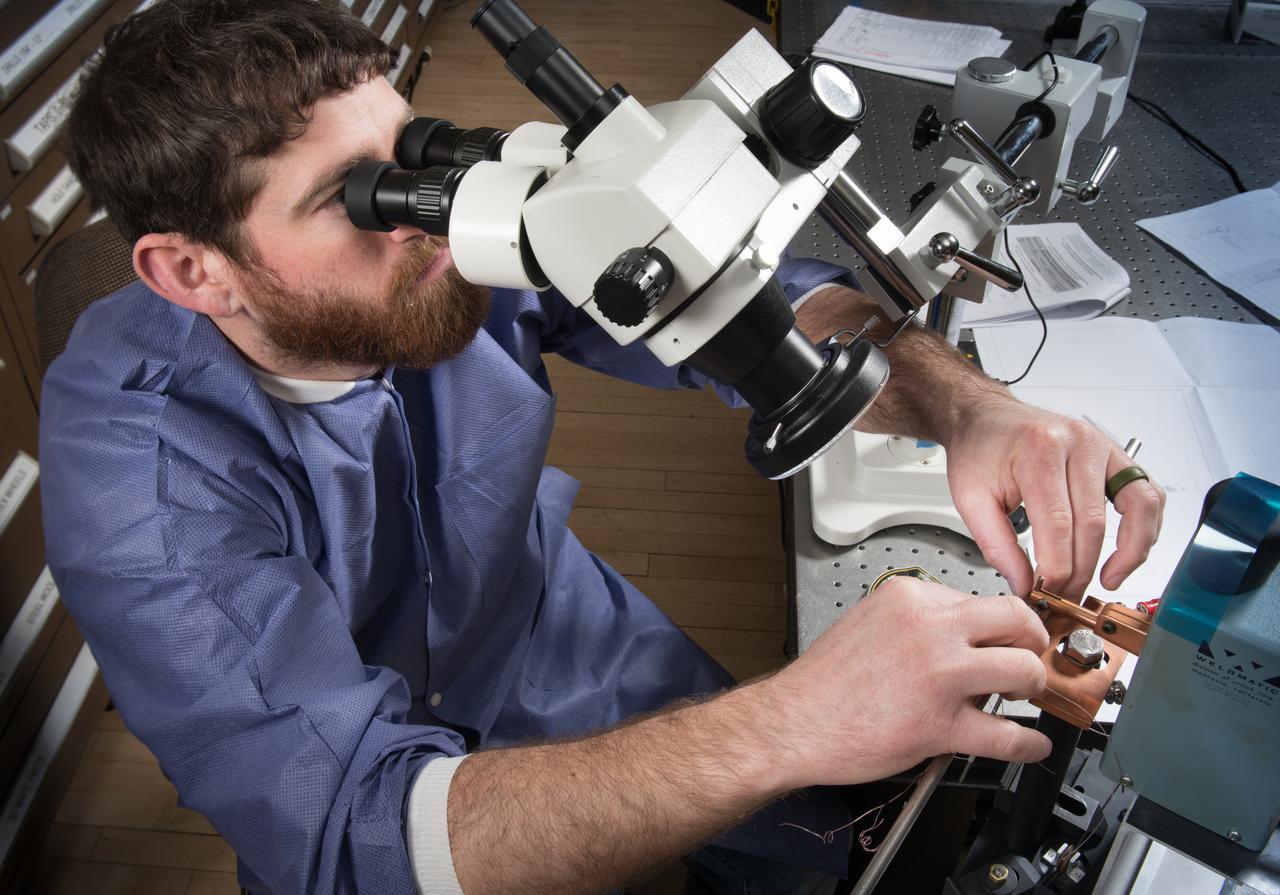

A technician in the Instrumentation Shop during the buildup of Flow Boiling Condensation Experiment, FBCE Micro Gravity Payload, Condensation Module – Heat Transfer, CM-HT, Test Section Hardware Fabrication
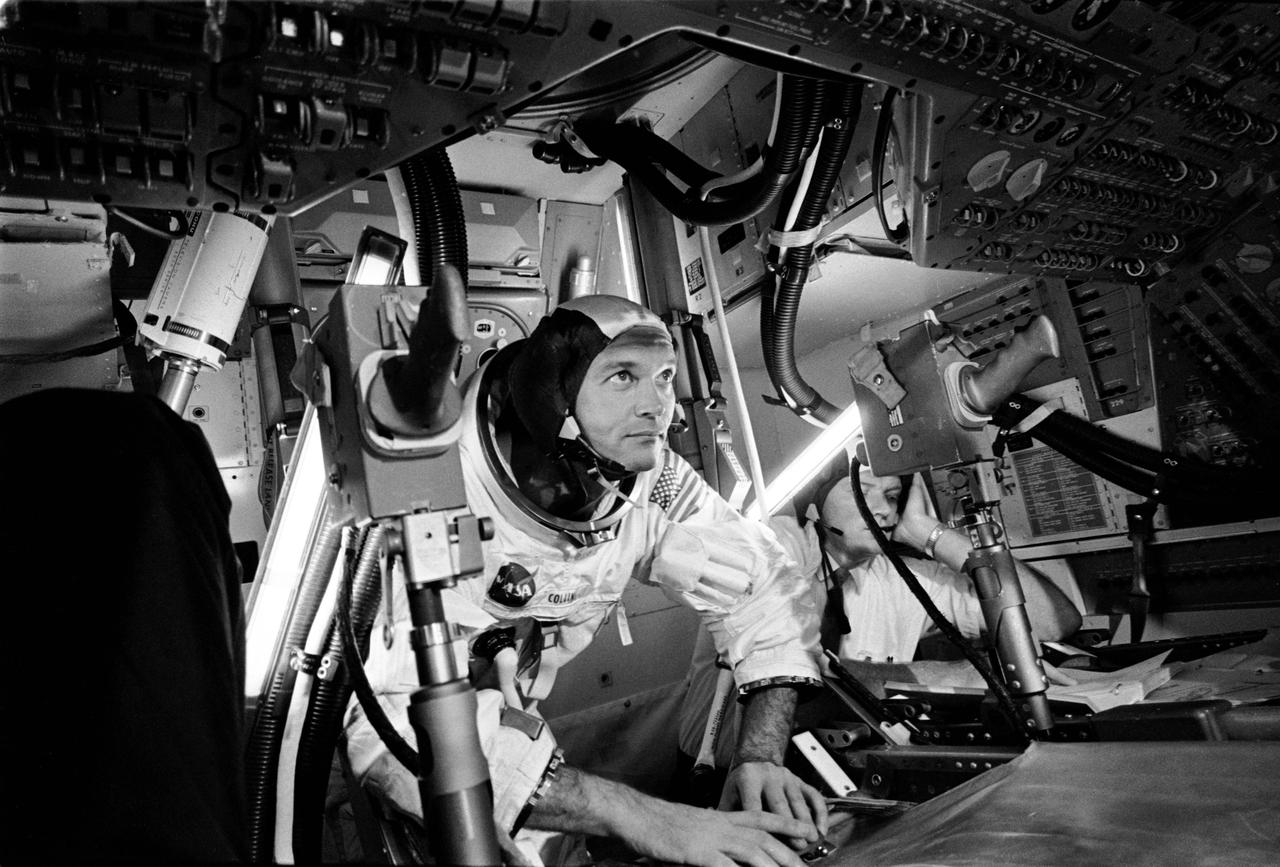

Apollo 11 Command Module (CM) pilot Mike Collins practicing docking hatch removal from CM turned in simulator.
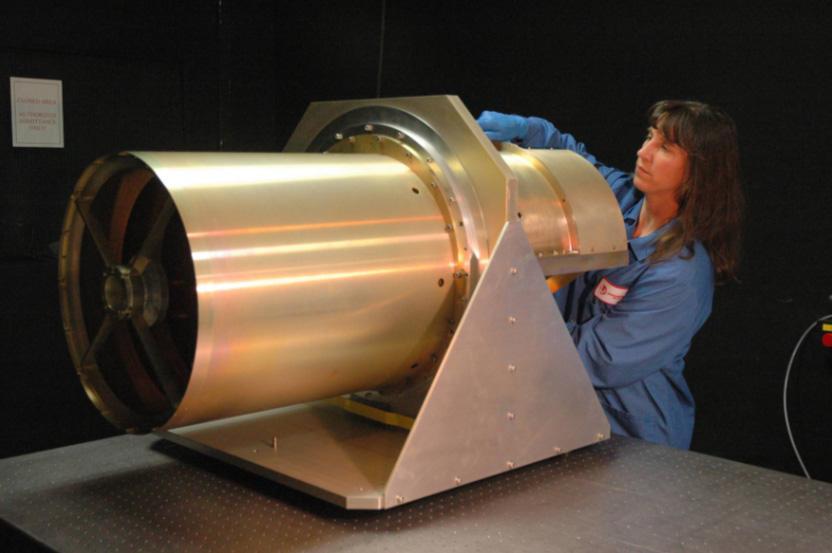
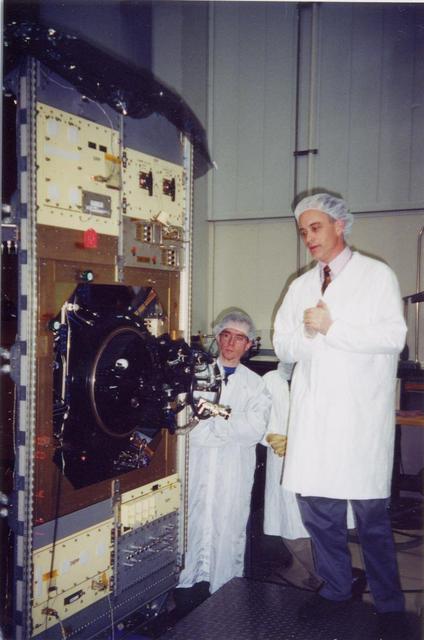
This image shows NASA 40 cm diameter Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer telescope. Here the lead optical test engineer attaches the back-end imager optics to the afocal.
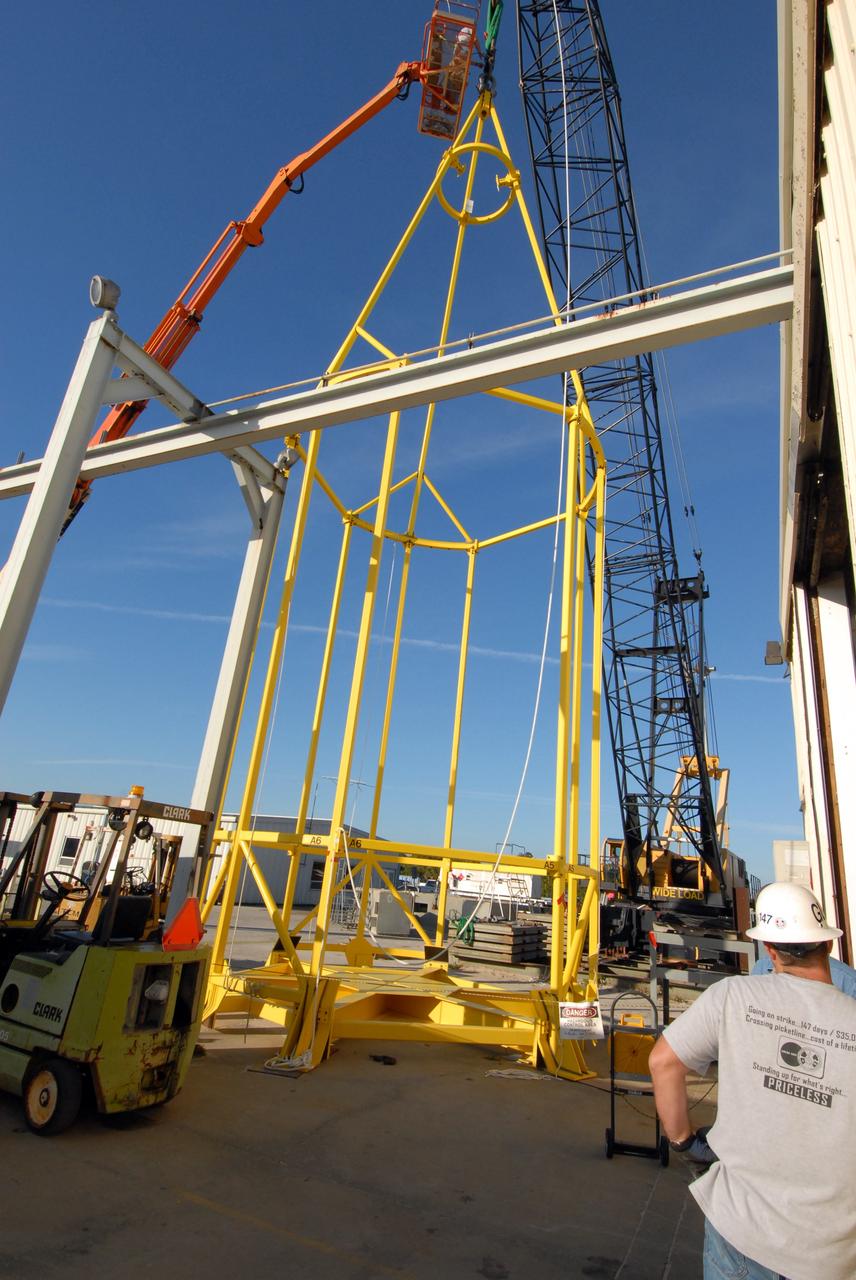

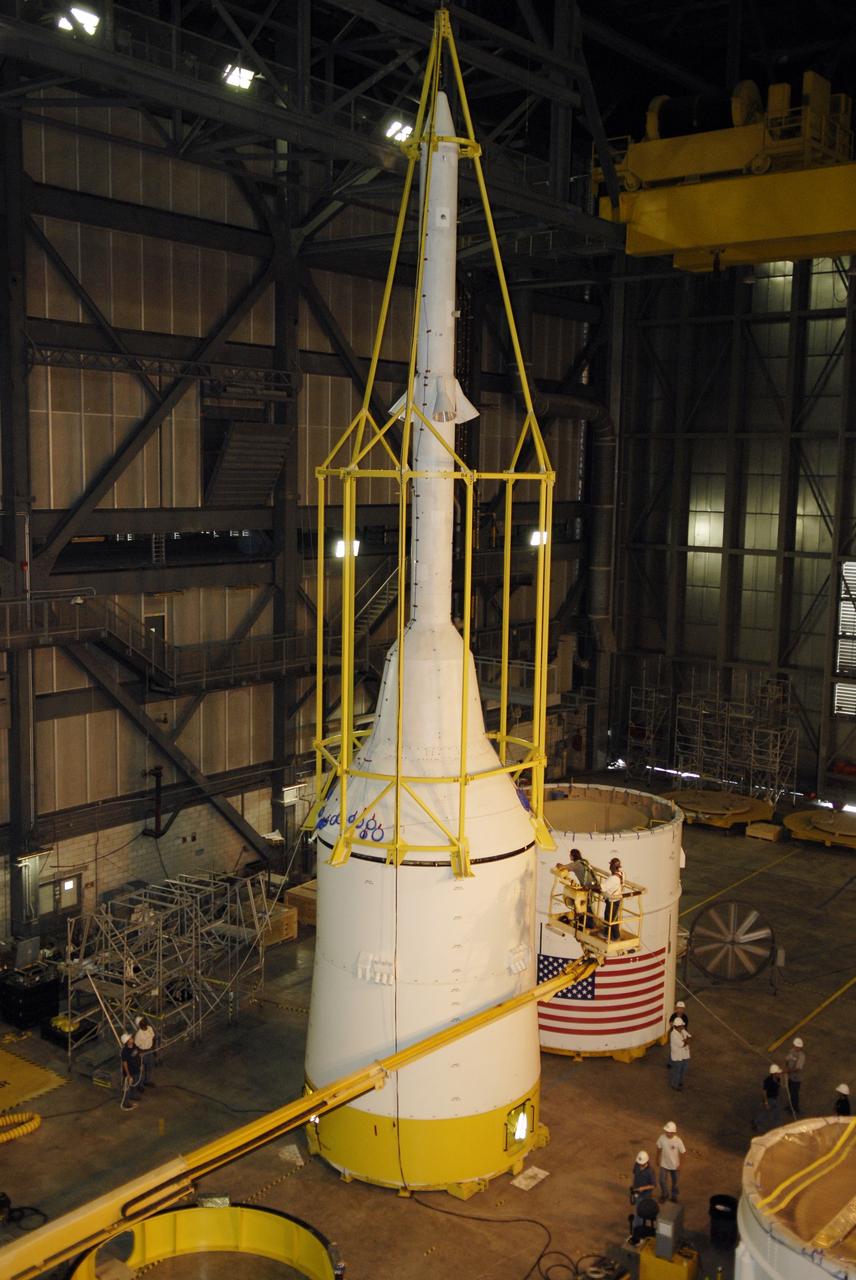
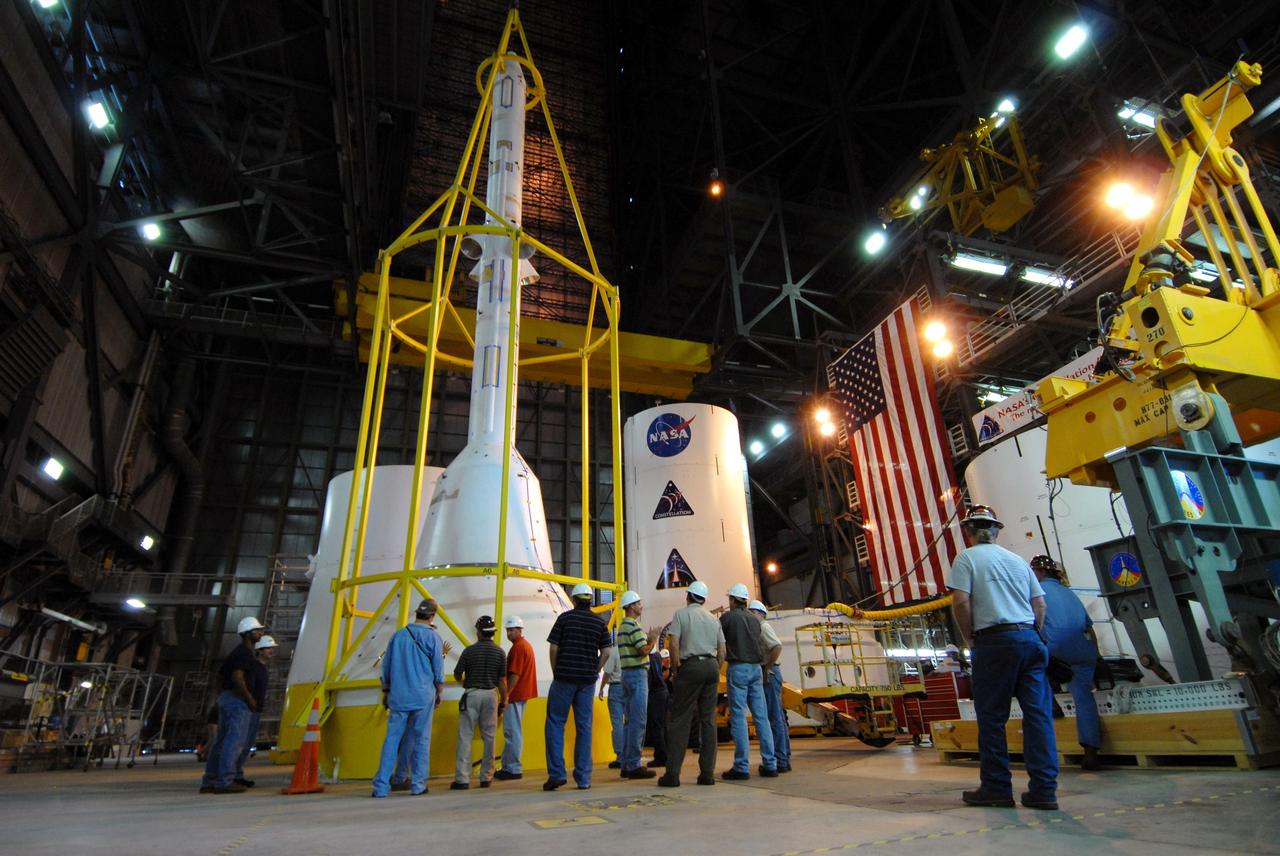
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The yellow framework seen here is the lifting fixture nicknamed the "Birdcage" that will have the ability to lift the Crew Module, or CM, and Launch Abort System, or LAS, assembly for the Ares I-X rocket and to stack and de-stack the assembly from the Service Module/Spacecraft Adapter assembly. It will also have the ability to lift and to stack and de-stack Stack-5 (all of the above components) from the Ares I-X in the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Ares I-X is the test flight for the Ares I. The I-X flight will provide NASA an early opportunity to test and prove hardware, facilities and ground operations associated with Ares I. The launch of the 321-foot-tall, full-scale Ares I-X, targeted for July 2009, will be the first in a series of unpiloted rocket launches from Kennedy. When fully developed, the 16-foot diameter crew module will furnish living space and reentry protection for the astronauts, while their launch abort system will provide safe evacuation if a launch vehicle failure occurs. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
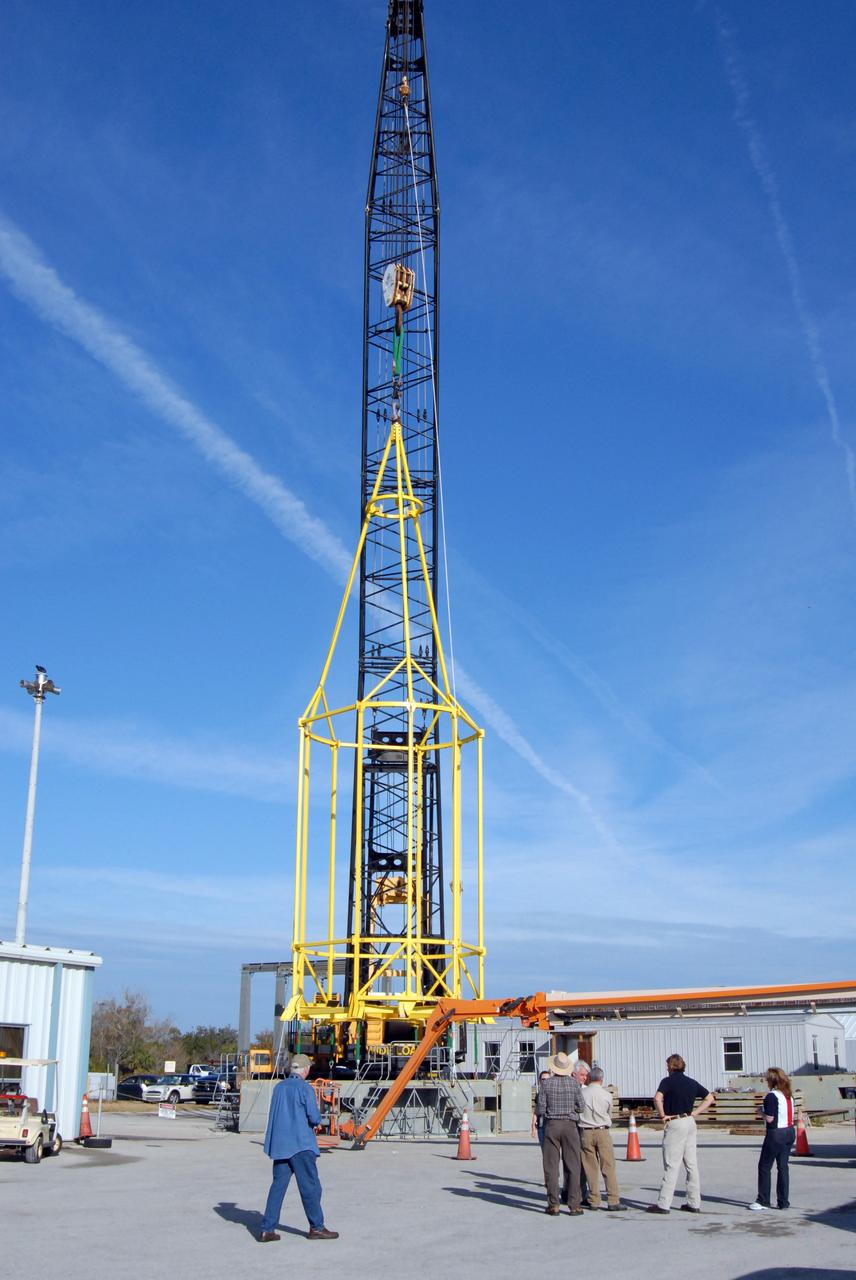

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The lifting fixture nicknamed the "Birdcage" is lifted by a crane to test the load capability. The Birdcage will be used to lift the Crew Module, or CM, and Launch Abort System, or LAS, assembly for the Ares I-X rocket and to stack and de-stack the assembly from the Service Module/Spacecraft Adapter assembly. It will also have the ability to lift and to stack and de-stack Stack-5 (all of the above components) from the Ares I-X in the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Ares I-X is the test flight for the Ares I. The I-X flight will provide NASA an early opportunity to test and prove hardware, facilities and ground operations associated with Ares I. The launch of the 321-foot-tall, full-scale Ares I-X, targeted for July 2009, will be the first in a series of unpiloted rocket launches from Kennedy. When fully developed, the 16-foot diameter crew module will furnish living space and reentry protection for the astronauts, while their launch abort system will provide safe evacuation if a launch vehicle failure occurs. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
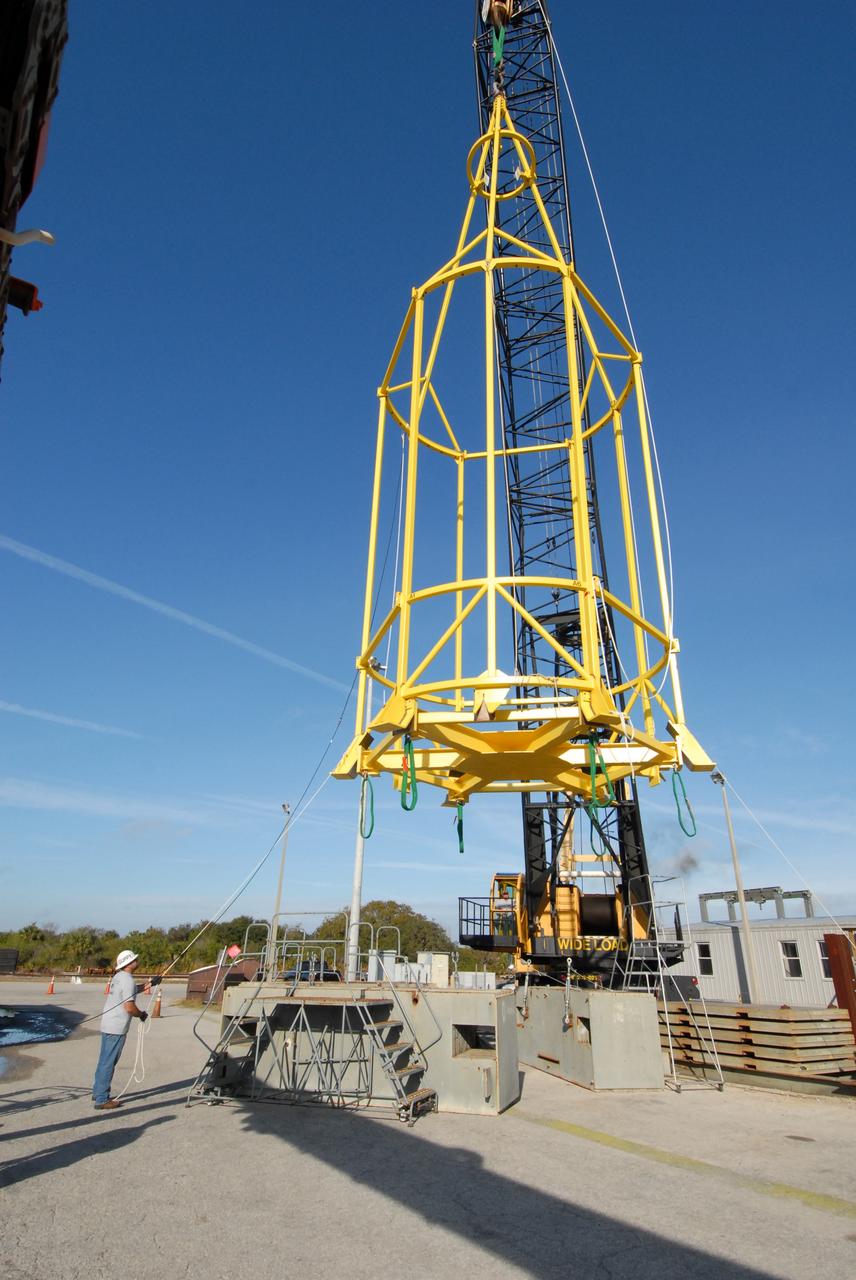

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The lifting fixture nicknamed the "Birdcage" is lifted by a crane to test the load capability. The Birdcage will be used to lift the Crew Module, or CM, and Launch Abort System, or LAS, assembly for the Ares I-X rocket and to stack and de-stack the assembly from the Service Module/Spacecraft Adapter assembly. It will also have the ability to lift and to stack and de-stack Stack-5 (all of the above components) from the Ares I-X in the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Ares I-X is the test flight for the Ares I. The I-X flight will provide NASA an early opportunity to test and prove hardware, facilities and ground operations associated with Ares I. The launch of the 321-foot-tall, full-scale Ares I-X, targeted for July 2009, will be the first in a series of unpiloted rocket launches from Kennedy. When fully developed, the 16-foot diameter crew module will furnish living space and reentry protection for the astronauts, while their launch abort system will provide safe evacuation if a launch vehicle failure occurs. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
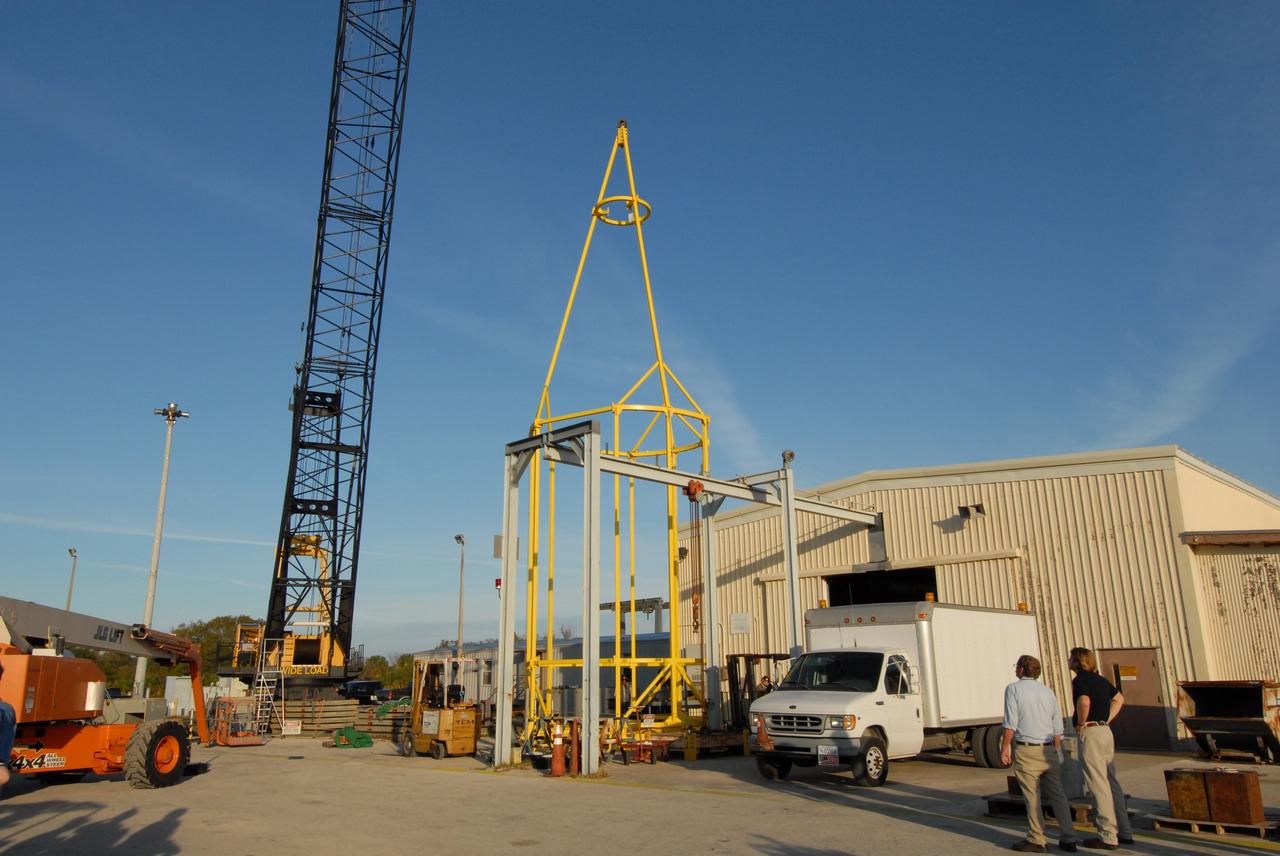

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The yellow framework at center is the lifting fixture nicknamed the "Birdcage" that will have the ability to lift the Crew Module, or CM, and Launch Abort System, or LAS, assembly for the Ares I-X rocket and to stack and de-stack the assembly from the Service Module/Spacecraft Adapter assembly. It will also have the ability to lift and to stack and de-stack Stack-5 (all of the above components) from the Ares I-X flight test vehicle in the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Ares I-X is the test flight for the Ares I. The I-X flight will provide NASA an early opportunity to test and prove hardware, facilities and ground operations associated with Ares I. The launch of the 321-foot-tall, full-scale Ares I-X, targeted for July 2009, will be the first in a series of unpiloted rocket launches from Kennedy. When fully developed, the 16-foot diameter crew module will furnish living space and reentry protection for the astronauts, while their launch abort system will provide safe evacuation if a launch vehicle failure occurs. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

A close-up view of the Orion crew module for NASA’s Artemis III mission enclosed on a work stand inside the high bay of the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 20, 2022. Lockheed Martin technicians are processing and preparing the crew module for its launch atop the Space Launch System rocket. Launched atop the Space Launch System rocket, Artemis missions will aim to send astronauts, including the first woman and first person of color, on a mission to the surface of the Moon.
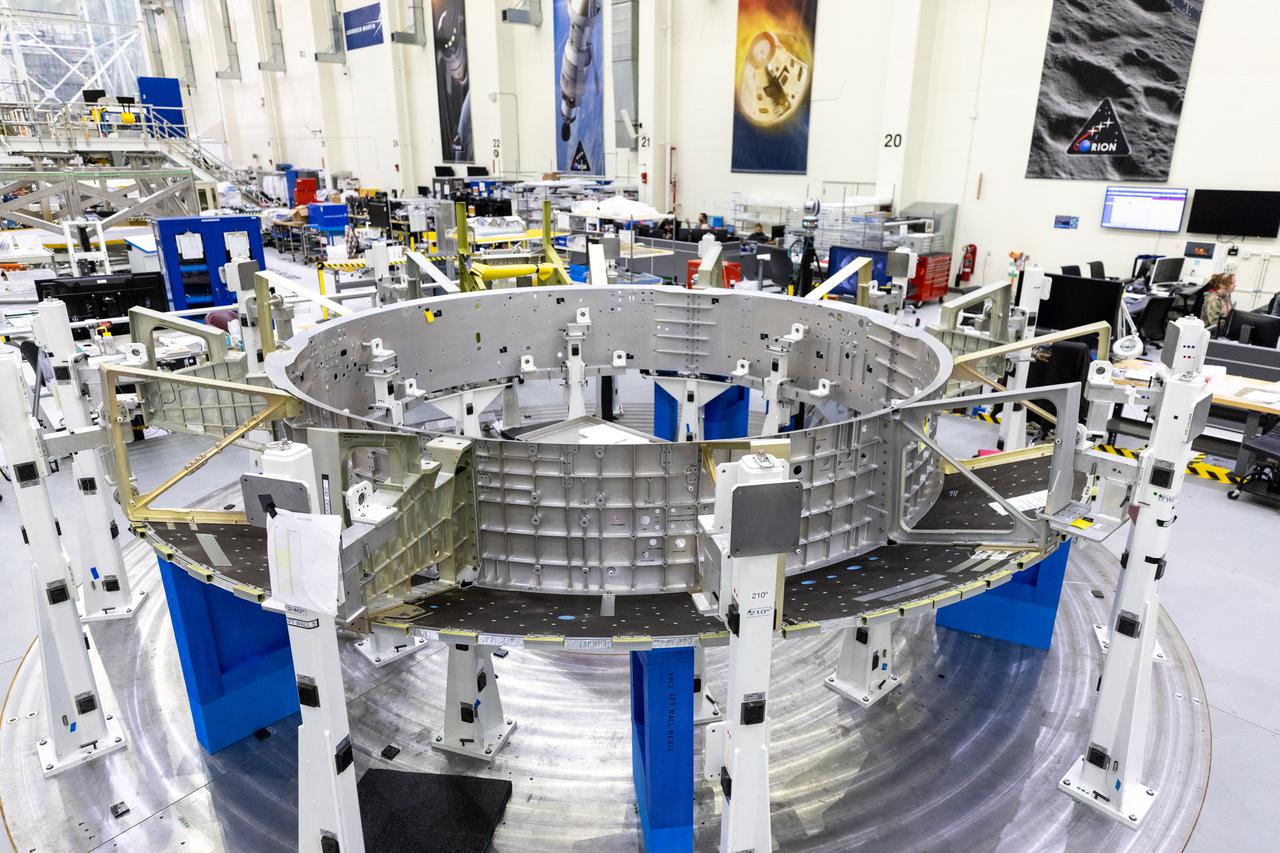

The Orion crew module adapter for NASA’s Artemis III mission is on a work stand inside the high bay of the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 20, 2022. Lockheed Martin technicians continue working to install the aft walls as the ring-shaped structure is prepared to ultimately be attached to the European-built service module. Launched atop the Space Launch System rocket, Artemis missions will aim to send astronauts, including the first woman and first person of color, on a mission to the surface of the Moon.

The Orion crew module for NASA’s Artemis III mission is enclosed on a work stand inside the high bay of the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 20, 2022. Lockheed Martin technicians are processing and preparing the crew module for its launch atop the Space Launch System rocket. Launched atop the Space Launch System rocket, Artemis missions will aim to send astronauts, including the first woman and first person of color, on a mission to the surface of the Moon.

The Orion crew module adapter for NASA’s Artemis III mission is on a work stand inside the high bay of the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 20, 2022. Lockheed Martin technicians continue working to install the aft walls as the ring-shaped structure is prepared to ultimately be attached to the European-built service module. Launched atop the Space Launch System rocket, Artemis missions will aim to send astronauts, including the first woman and first person of color, on a mission to the surface of the Moon.
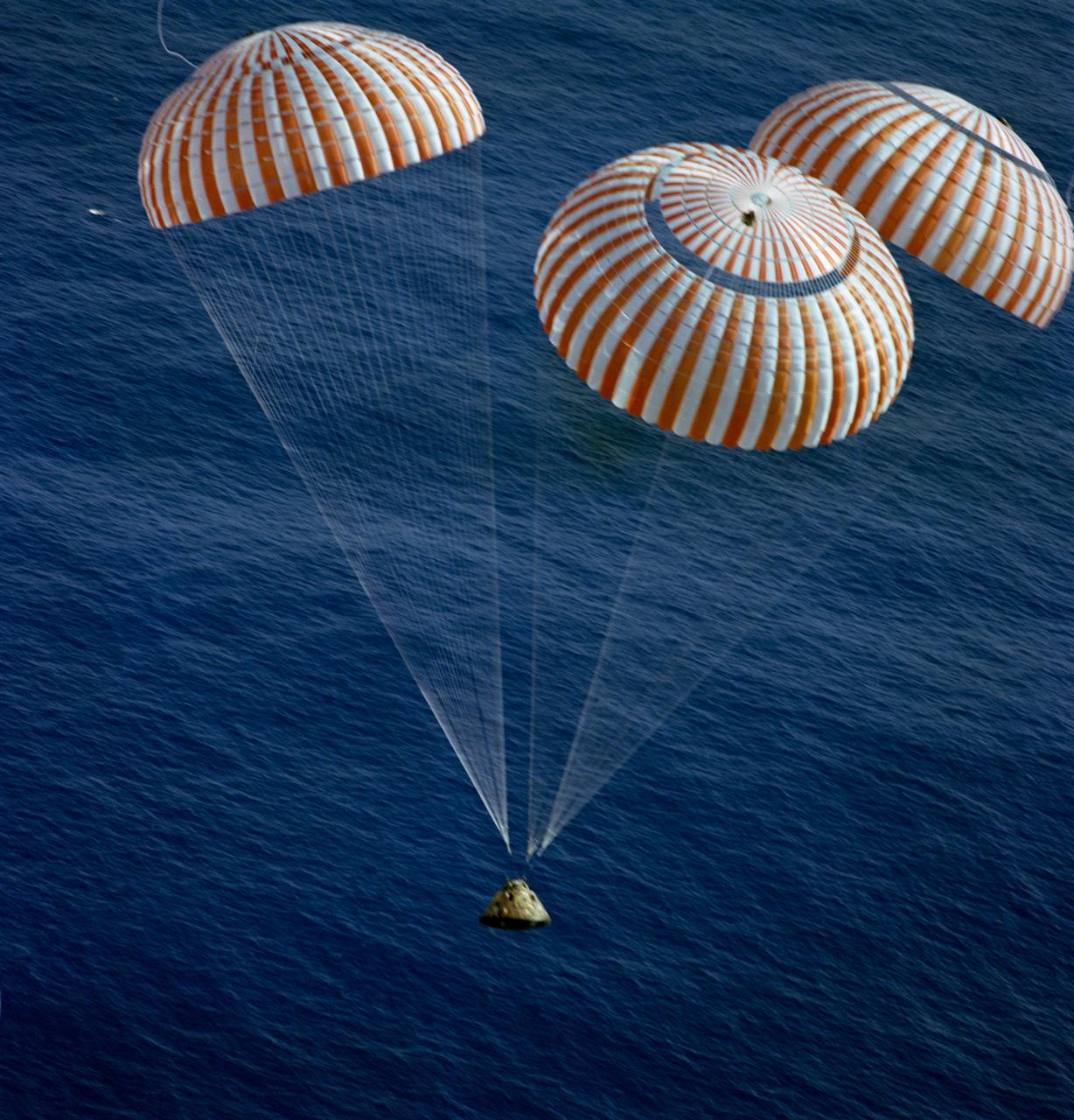

S72-55834 (19 Dec. 1972) --- The Apollo 17 Command Module (CM), with astronauts Eugene A. Cernan, Ronald E. Evans and Harrison H. Schmitt aboard, nears splashdown in the South Pacific Ocean to successfully concludes the final lunar landing mission in NASA's Apollo program. This overhead view was taken from a recovery aircraft seconds before the spacecraft hit the water. The splashdown occurred at 304:31:59 ground elapsed time, 1:24:59 p.m. (CST) Dec. 19, 1972, at coordinates of 166 degrees 8 minutes west longitude and 27 degrees 53 minutes south latitude, about 350 nautical miles southeast of the Samoan Islands. The splashdown was only .8 miles from the target point. Later, the three crewmen were picked up by a helicopter from the prime recovery ship, USS Ticonderoga.
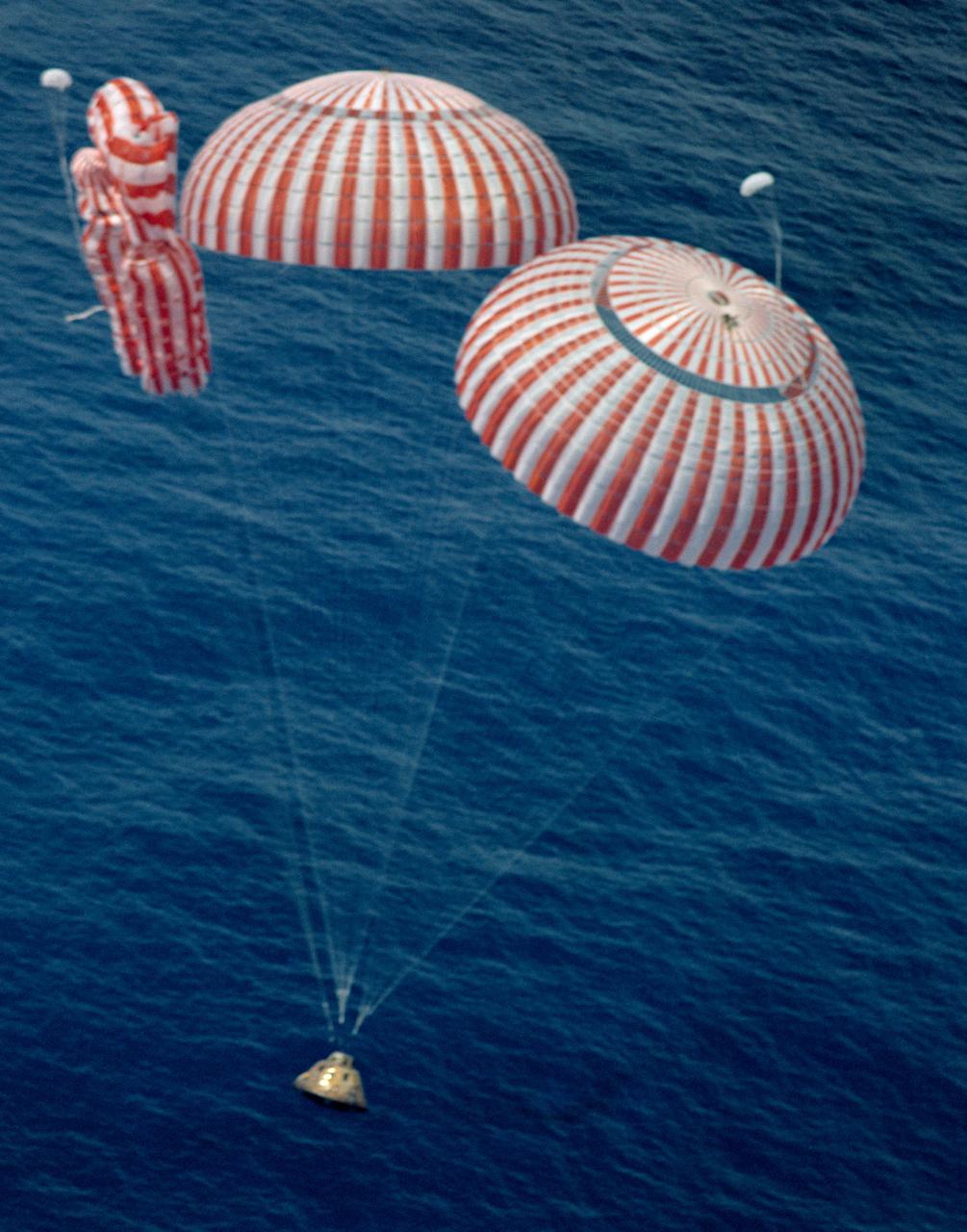

S71-41999 (7 Aug. 1971) --- The Apollo 15 Command Module (CM), with astronauts David R. Scott, commander; Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot; and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, aboard, nears a safe touchdown in the mid-Pacific Ocean to conclude a highly successful lunar landing mission. Although causing no harm to the crewmen, one of the three main parachutes failed to function properly. The splashdown occurred at 3:45:53 p.m. (CDT), Aug. 7, 1971, some 330 miles north of Honolulu, Hawaii. The three astronauts were picked up by helicopter and flown to the prime recovery ship USS Okinawa, which was only 6 1/2 miles away.
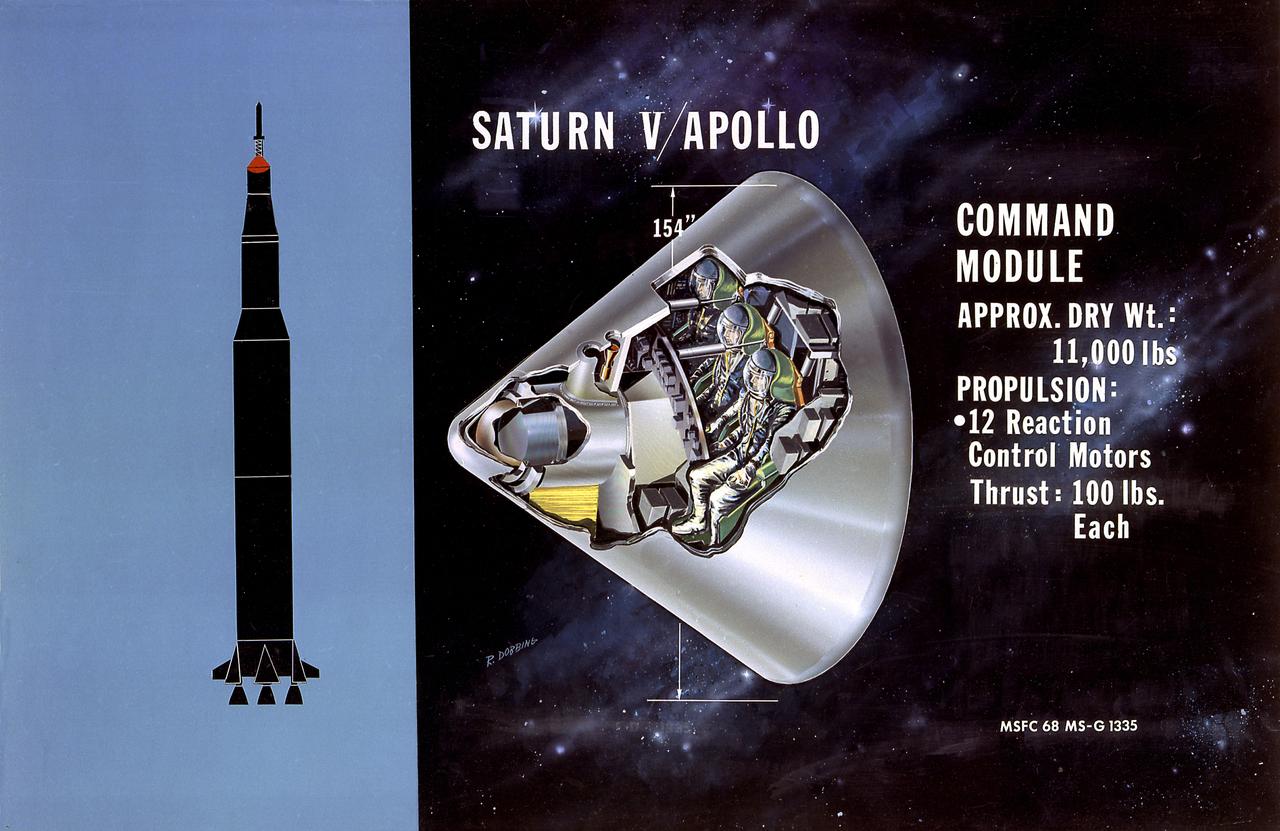
This is a cutaway illustration of the Saturn V command module (CM) configuration. The CM was crammed with some of the most complex equipment ever sent into space at the time. The three astronaut couches were surrounded by instrument panels, navigation gear, radios, life-support systems, and small engines to keep it stable during reentry. The entire cone, 11 feet long and 13 feet in diameter, was protected by a charring heat shield. The 6.5 ton CM was all that was finally left of the 3,000-ton Saturn V vehicle that lifted off on the journey to the Moon.

40 CM Engineering Model 1 Engine - Ion Thruster

S72-56147 (19 Dec. 1972) --- A water-level view of the Apollo 17 Command Module (CM) floating in the Pacific Ocean following splashdown and prior to recovery. The prime recovery ship, the USS Ticonderoga, is in the background. When this picture was taken, the three-man crew of astronauts Eugene A. Cernan, Ronald E. Evans and Harrison H. Schmitt, had already been picked up by helicopter and flown to the deck of the recovery ship. The spacecraft was later hoisted aboard the USS Ticonderoga. A United States Navy UDT swimmer stands on the flotation collar. Apollo 17 splashdown occurred at 1:24:59 p.m. (CST), Dec. 19, 1972, about 350 nautical miles southeast of Samoa.

The Orion crew module test article begins acoustical testing in the Reverberant Acoustics Laboratory (RAL) at the Lockheed Martin facility in Waterton, Colorado on July 7, 2011. The testing of approximately 150dB simulated sound pressure levels that the vehicle will encounter during launch, ascent, and if required, abort. The facility’s high ceilings also accommodate the launch abort system test article, which was attached to the crew module for subsequent acoustic tests. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.

S70-35622 (17 April 1970) --- United States Navy underwater demolition team swimmers assist in the recovery operations of the Apollo 13 crewmembers, shortly after splashdown. The divers prepare to assist the astronauts out of their crippled Command Module (CM), into an awaiting life raft. Astronaut John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot, is preparing to exit the CM. A Navy helicopter is waiting to take the astronauts to the prime recovery ship, the USS Iwo Jima. Apollo 13 splashed down at 12:07:44 p.m. (CST), April 17, 1970. Still aboard the CM are astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., commander; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot.

Test hardware for Orion crew capsule from the Artemis 1 flight arrives in the SEC (Space Experiments Complex) at ATF (Armstrong Test Facility), The LAS (Launch Abort System) arrived in four separate shipments from locations in Florida and Colorado. It is now being integrated with the Orion CM (crew module) for critical testing before the flight of Artemis II.

Seeing small areas of the Moon at 50 cm per pixel often presents unexpected views, and sometimes it is hard to interpret the geology at first glance, much less what is up and what is down, as evidenced by NASA Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter.
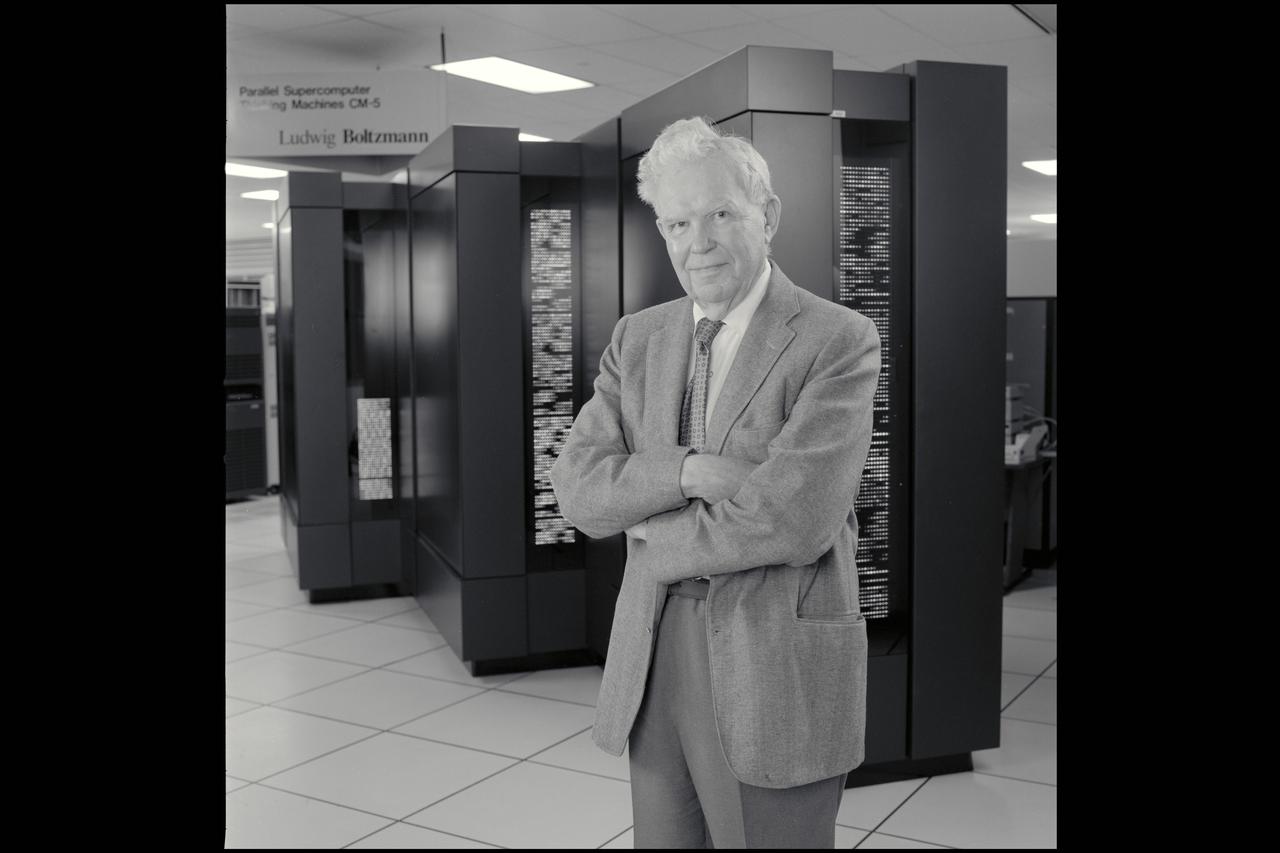

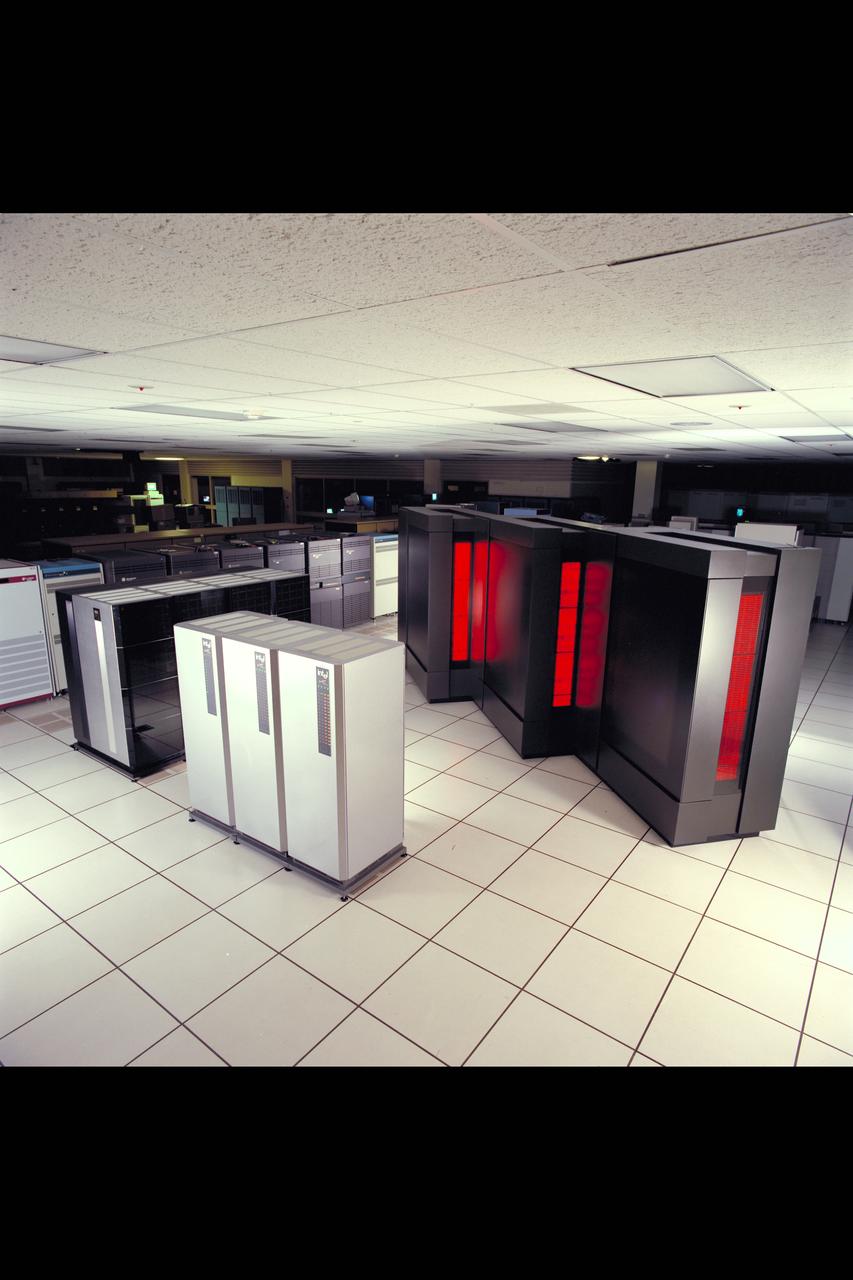
Harvey Lomax in front of the Cm-5 Parallel computer in the NAS Facility N-258 in honor of 50yrs of service
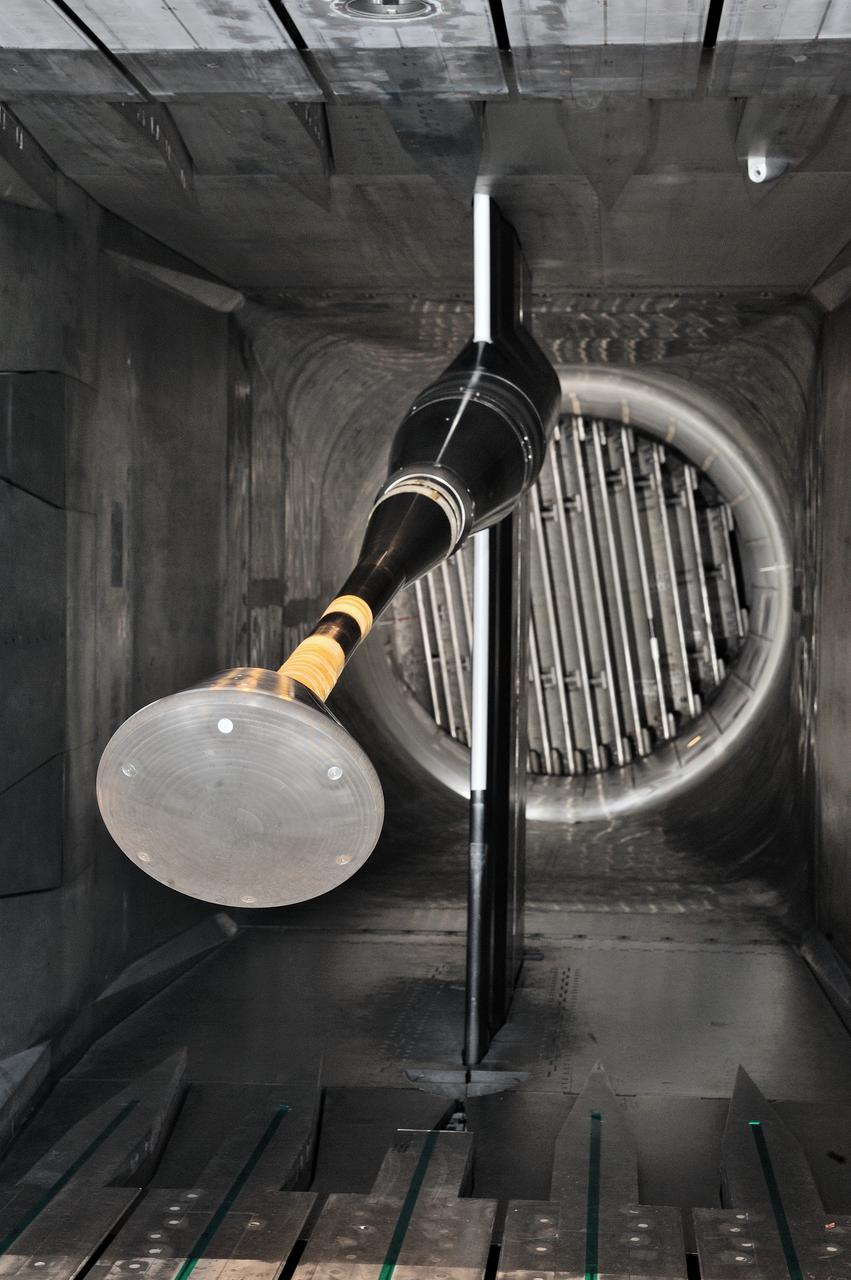

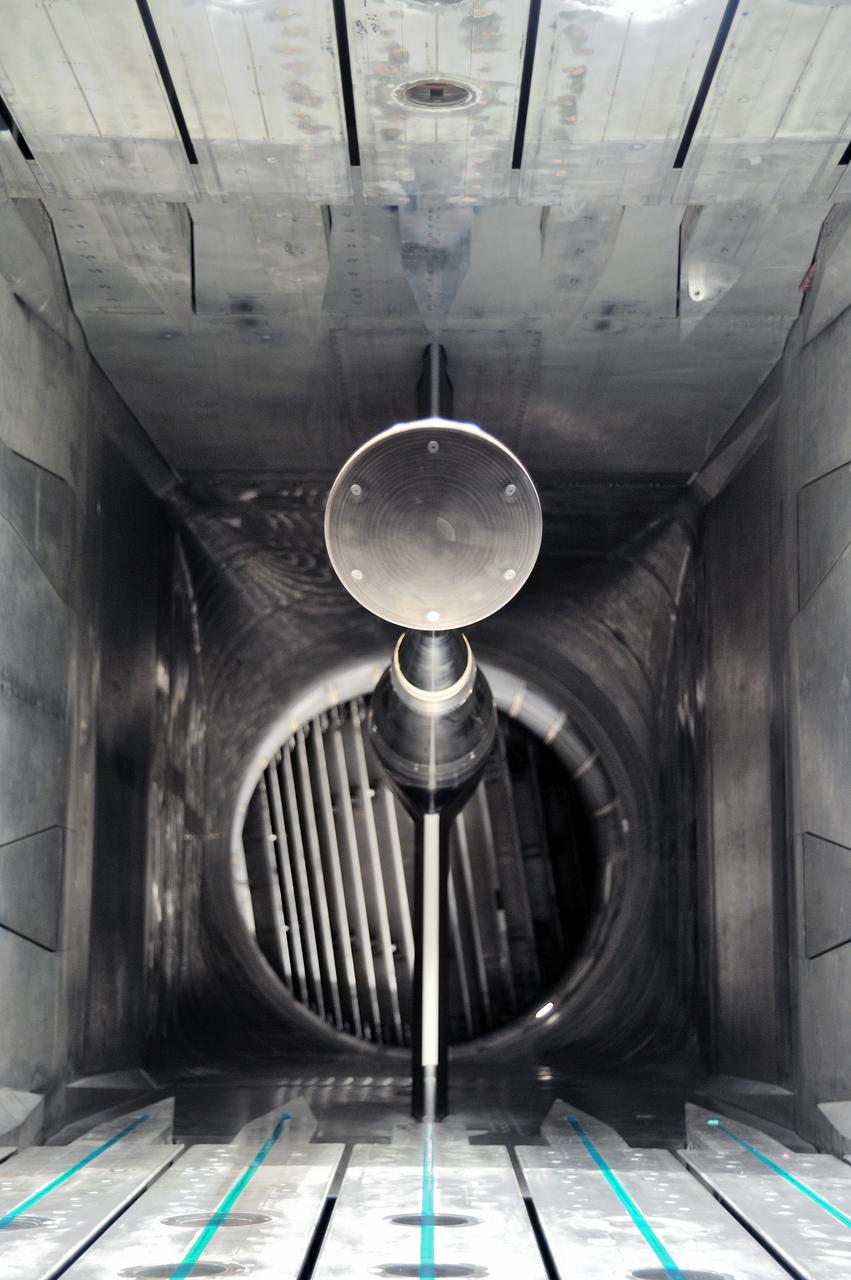
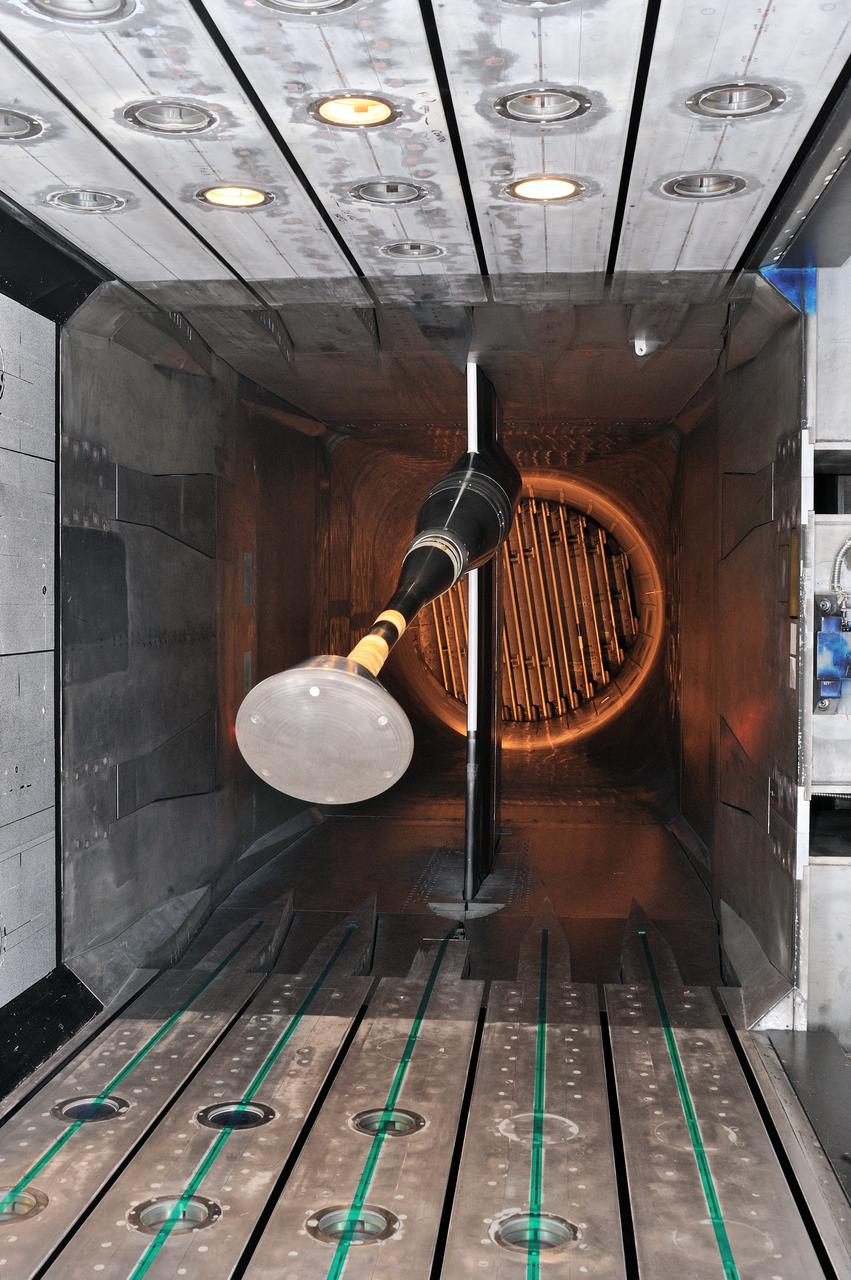
MPCV Orion 7% Crew Module in (NTF) National Transonic Facility, Test team for T211, 7% Orion CM in NTF
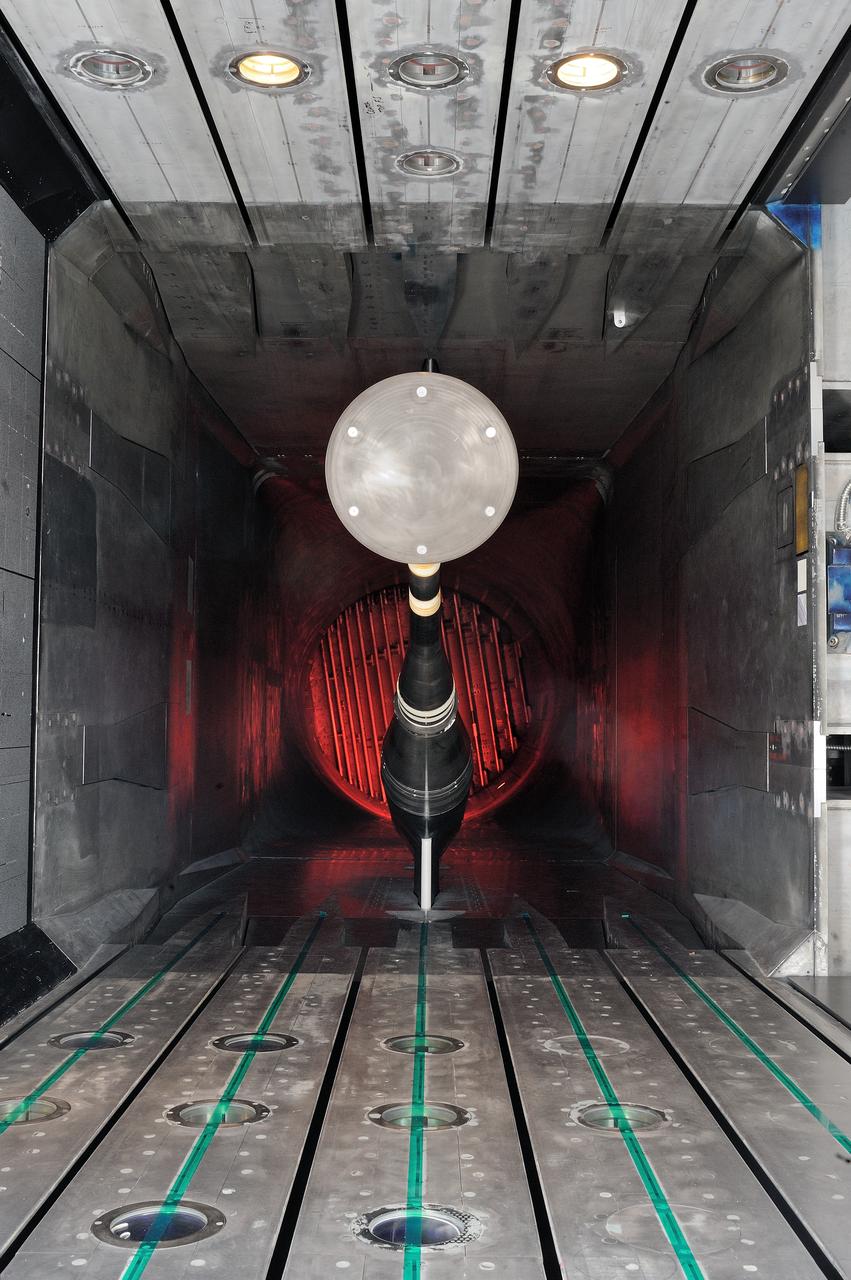

MPCV Orion 7% Crew Module in (NTF) National Transonic Facility, Test team for T211, 7% Orion CM in NTF
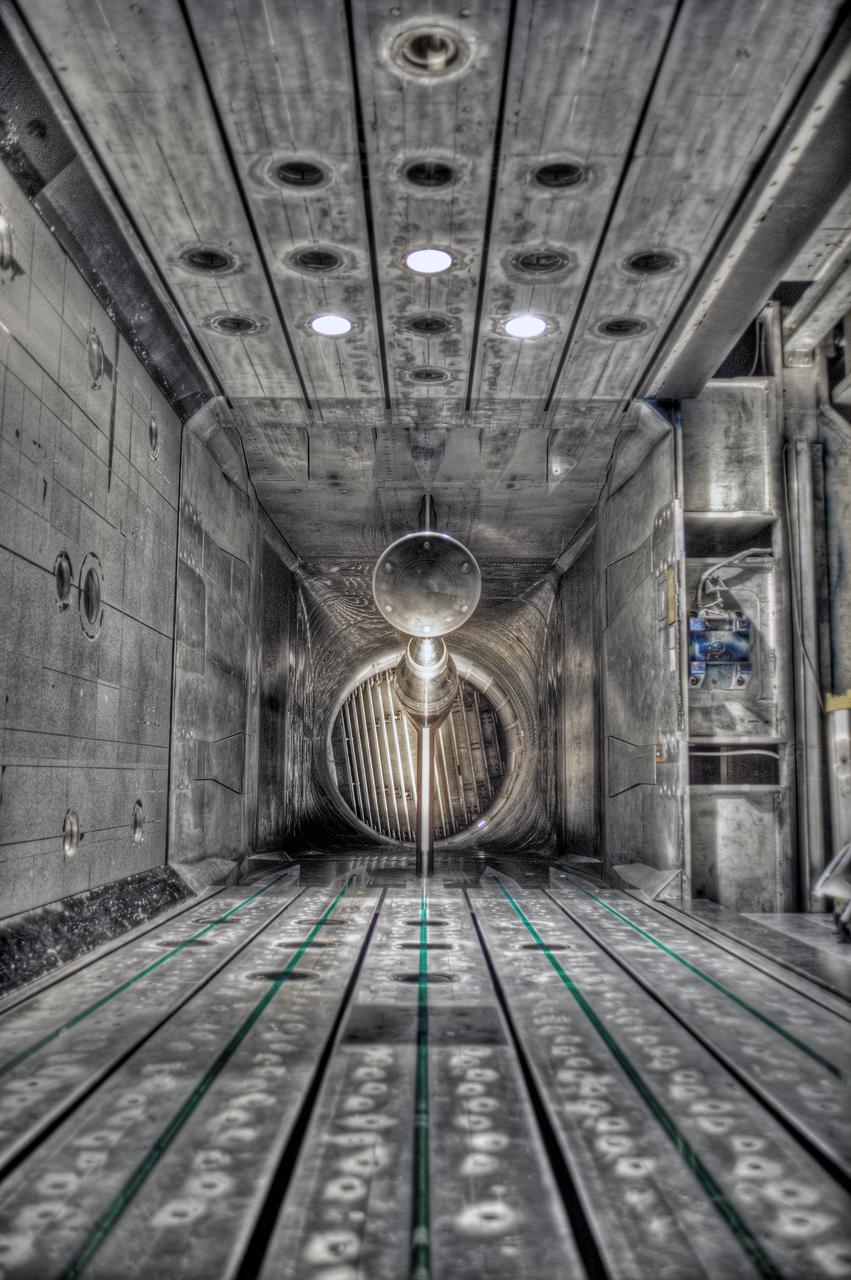

MPCV Orion 7% Crew Module in (NTF) National Transonic Facility, Test team for T211, 7% Orion CM in NTF
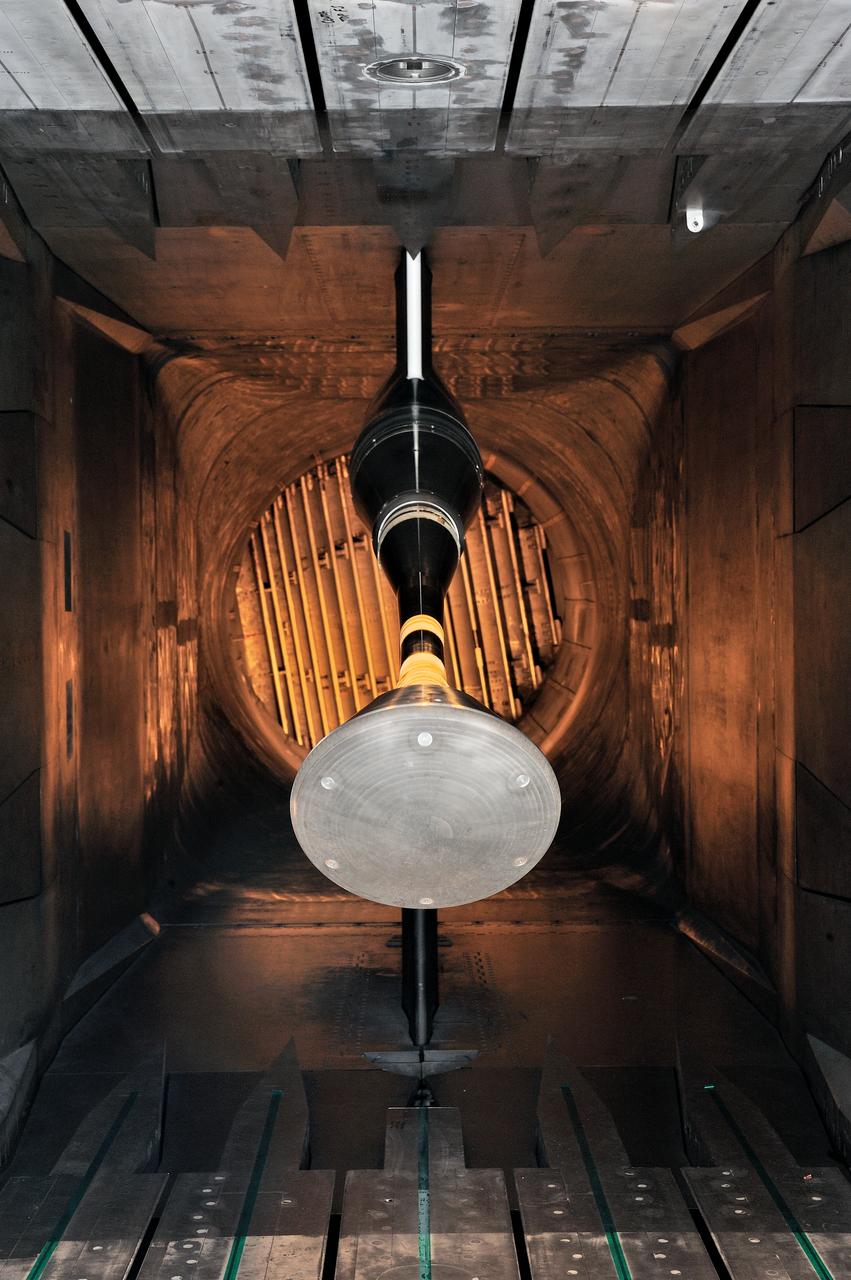

MPCV Orion 7% Crew Module in (NTF) National Transonic Facility, Test team for T211, 7% Orion CM in NTF
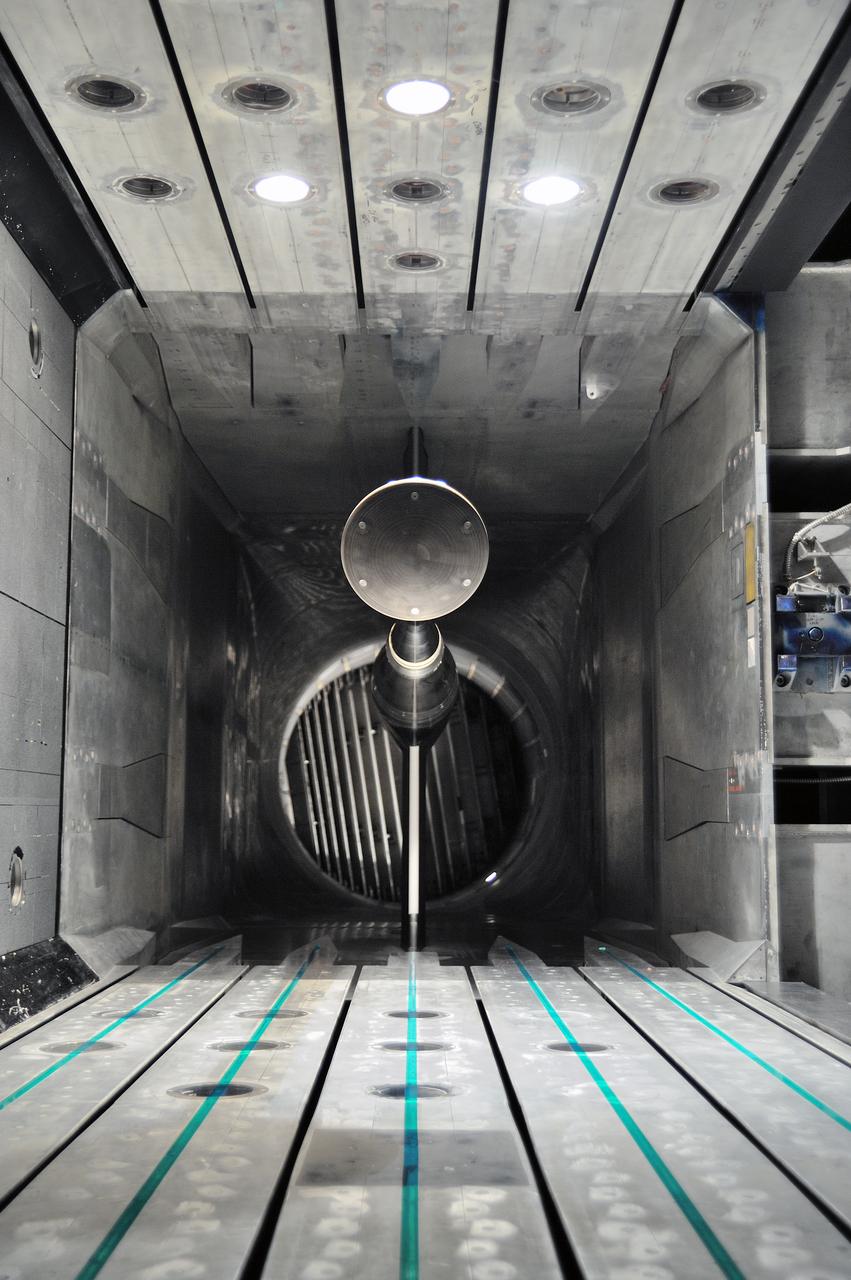
MPCV Orion 7% Crew Module in (NTF) National Transonic Facility, Test team for T211, 7% Orion CM in NTF
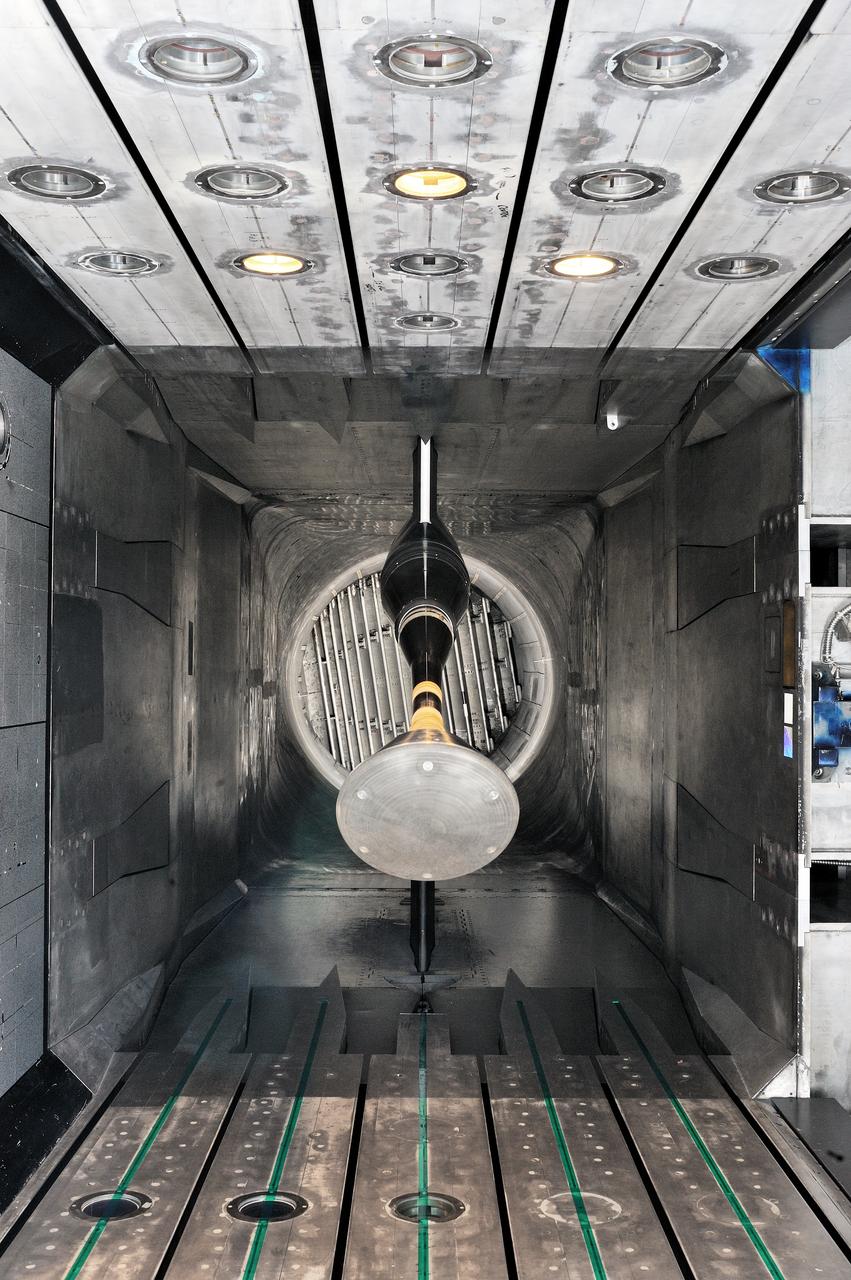

MPCV Orion 7% Crew Module in (NTF) National Transonic Facility, Test team for T211, 7% Orion CM in NTF
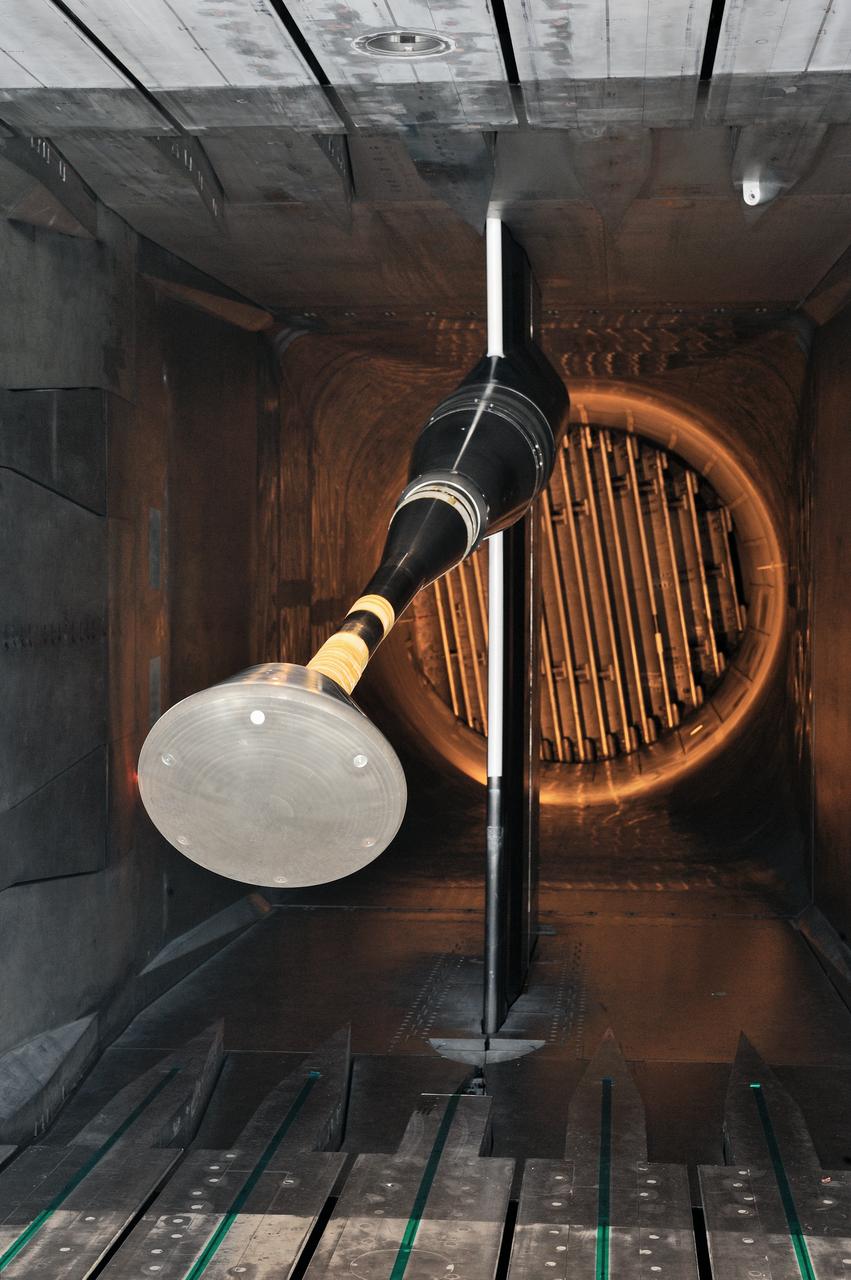

MPCV Orion 7% Crew Module in (NTF) National Transonic Facility, Test team for T211, 7% Orion CM in NTF

Perseid Meteor flight on Google's Gulfstream Aircraft. P.I. Peter Jenniskens, SETI Group with D.K. Holman, CMS/IMO

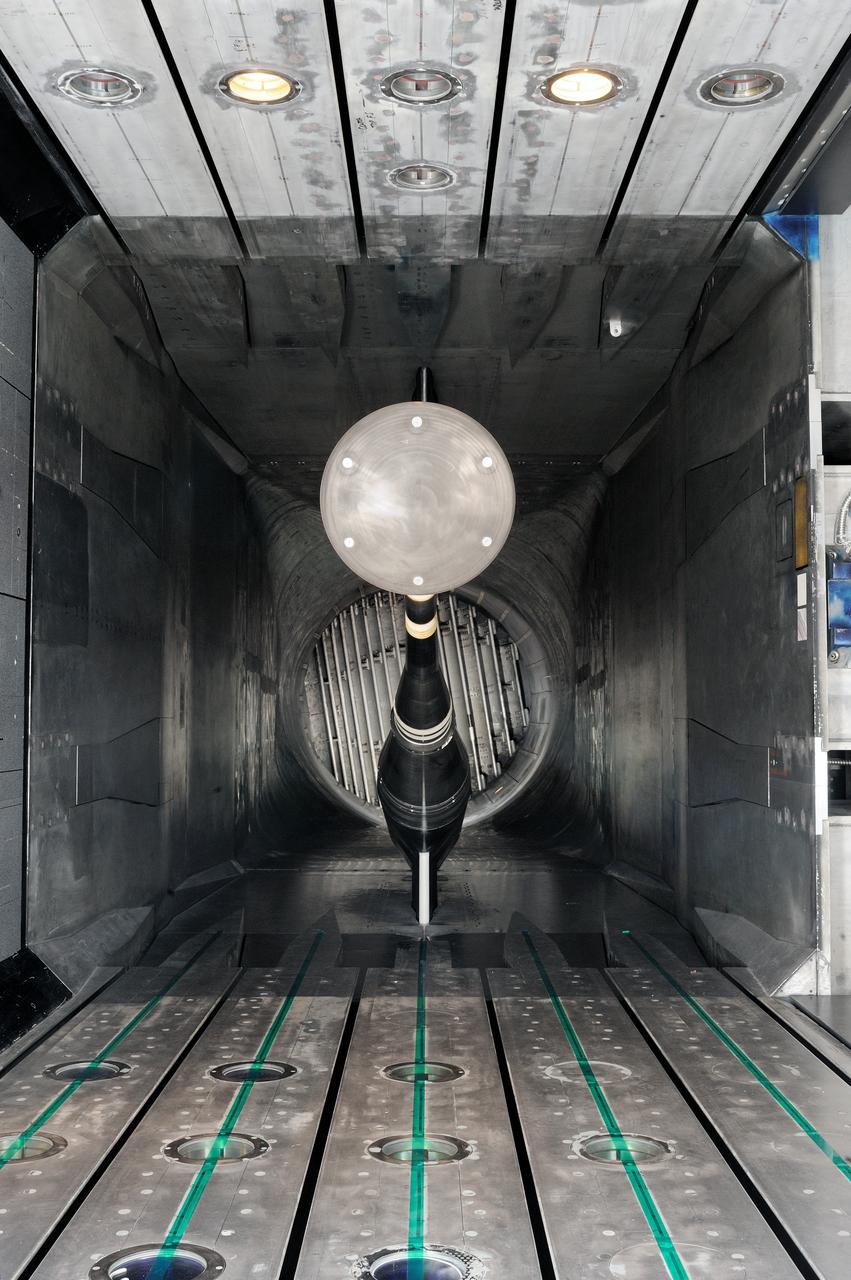
MPCV Orion 7% Crew Module in (NTF) National Transonic Facility, Test team for T211, 7% Orion CM in NTF

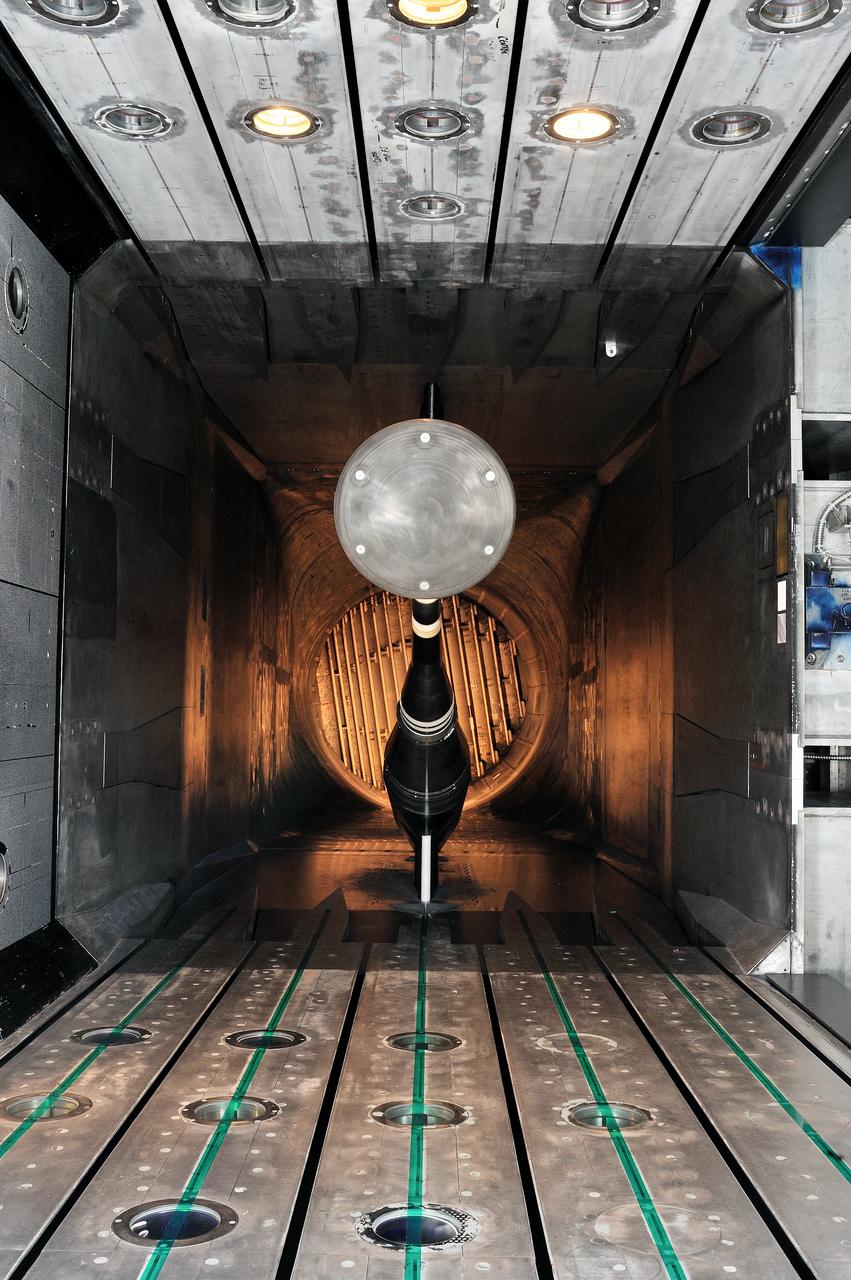
MPCV Orion 7% Crew Module in (NTF) National Transonic Facility, Test team for T211, 7% Orion CM in NTF

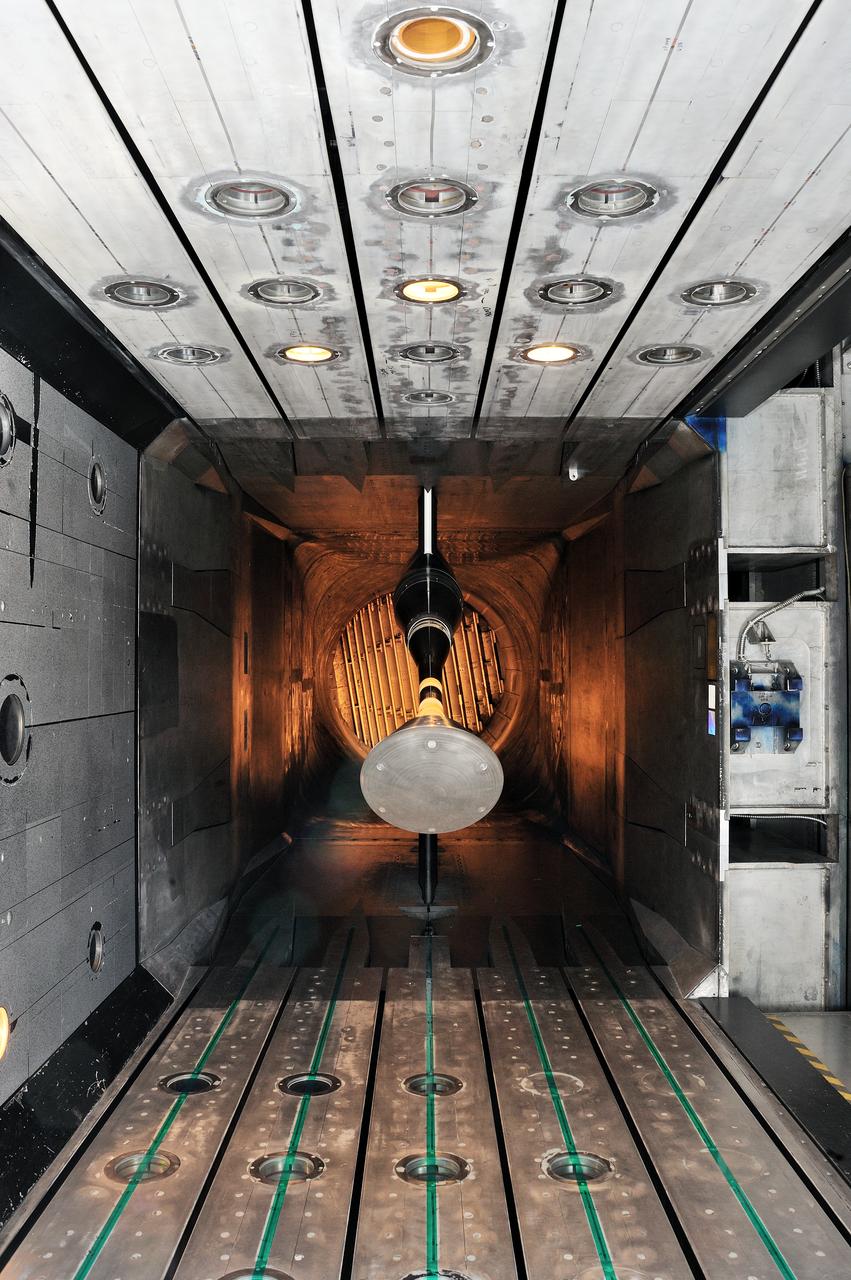
MPCV Orion 7% Crew Module in (NTF) National Transonic Facility, Test team for T211, 7% Orion CM in NTF

MPCV Orion 7% Crew Module in (NTF) National Transonic Facility, Test team for T211, 7% Orion CM in NTF

MPCV Orion 7% Crew Module in (NTF) National Transonic Facility, Test team for T211, 7% Orion CM in NTF

MPCV Orion 7% Crew Module in (NTF) National Transonic Facility, Test team for T211, 7% Orion CM in NTF

Perseid Meteor flight on Google's Gulfstream Aircraft. P.I. Peter Jenniskens, SETI Group with D.K. Holman, CMS/IMO
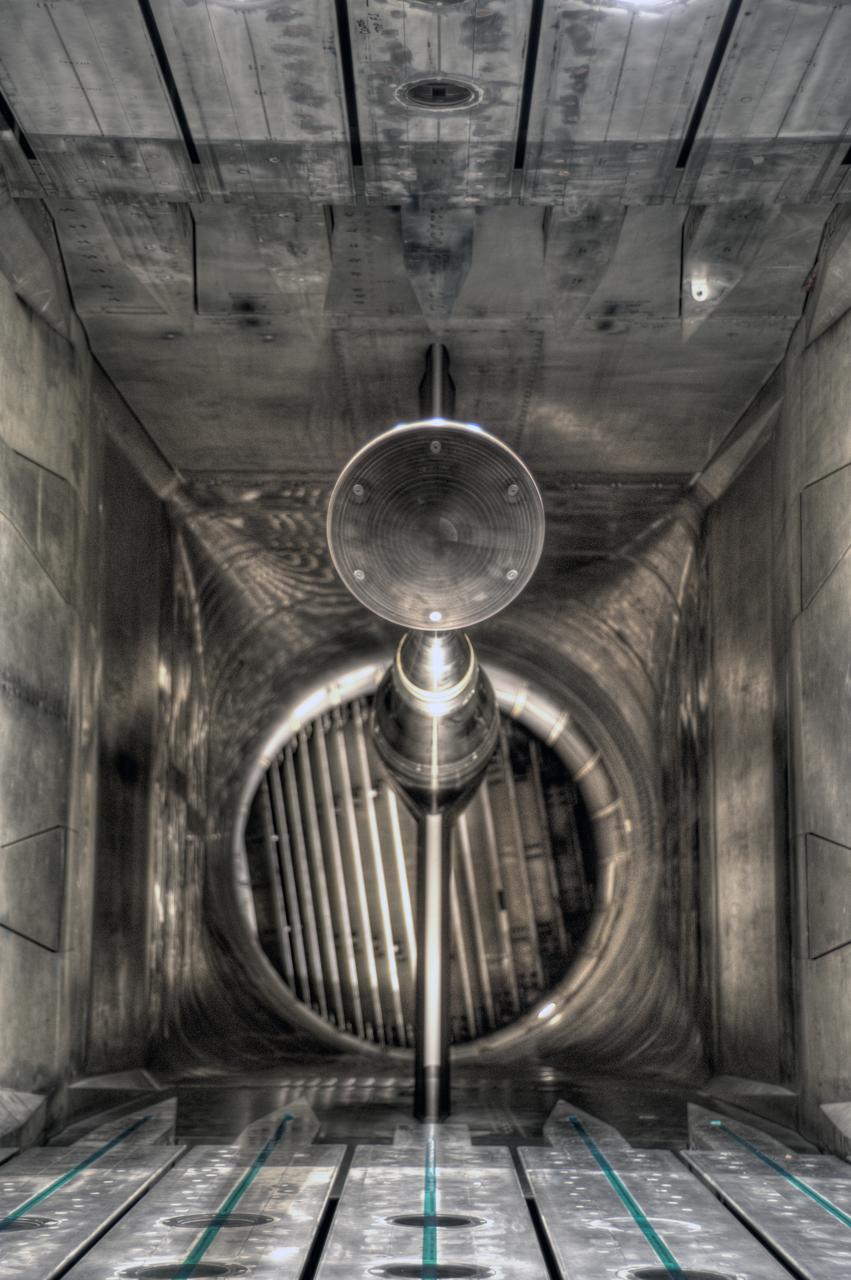

MPCV Orion 7% Crew Module in (NTF) National Transonic Facility, Test team for T211, 7% Orion CM in NTF
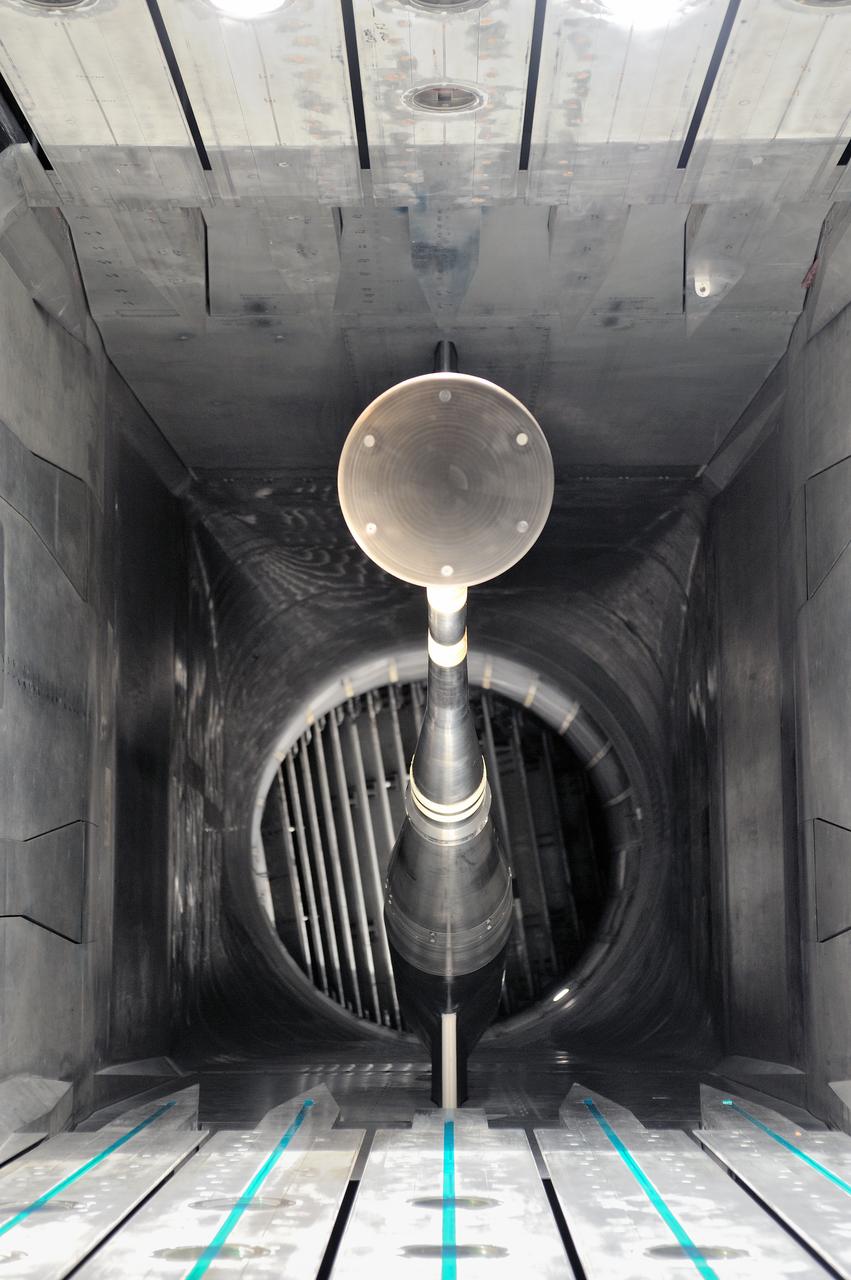

MPCV Orion 7% Crew Module in (NTF) National Transonic Facility, Test team for T211, 7% Orion CM in NTF
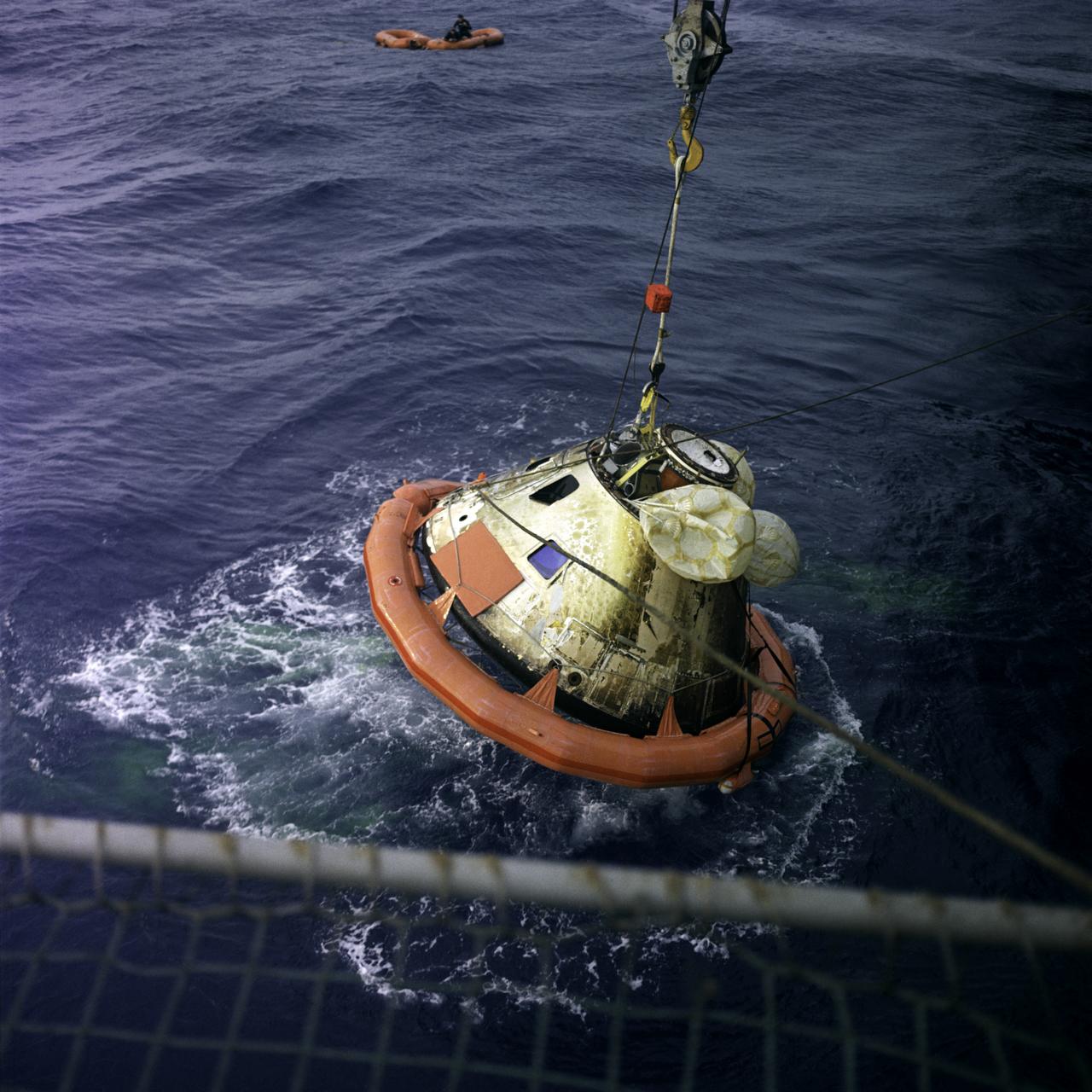

RECOVERY - APOLLO 8 Recovery and inspection of the Apollo 8 Command Module (CM)-103 spacecraft.

MPCV Orion 7% Crew Module in (NTF) National Transonic Facility, Test team for T211, 7% Orion CM in NTF
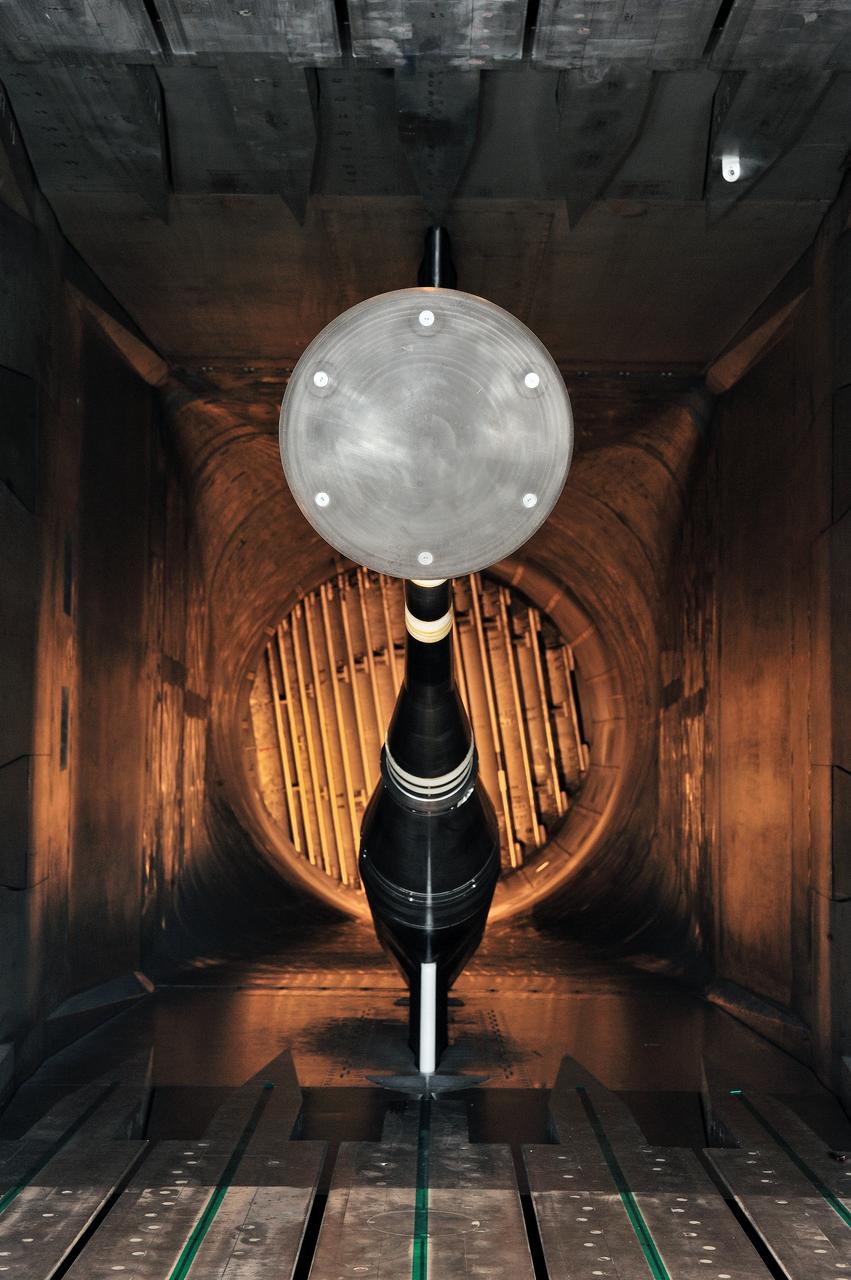

MPCV Orion 7% Crew Module in (NTF) National Transonic Facility, Test team for T211, 7% Orion CM in NTF
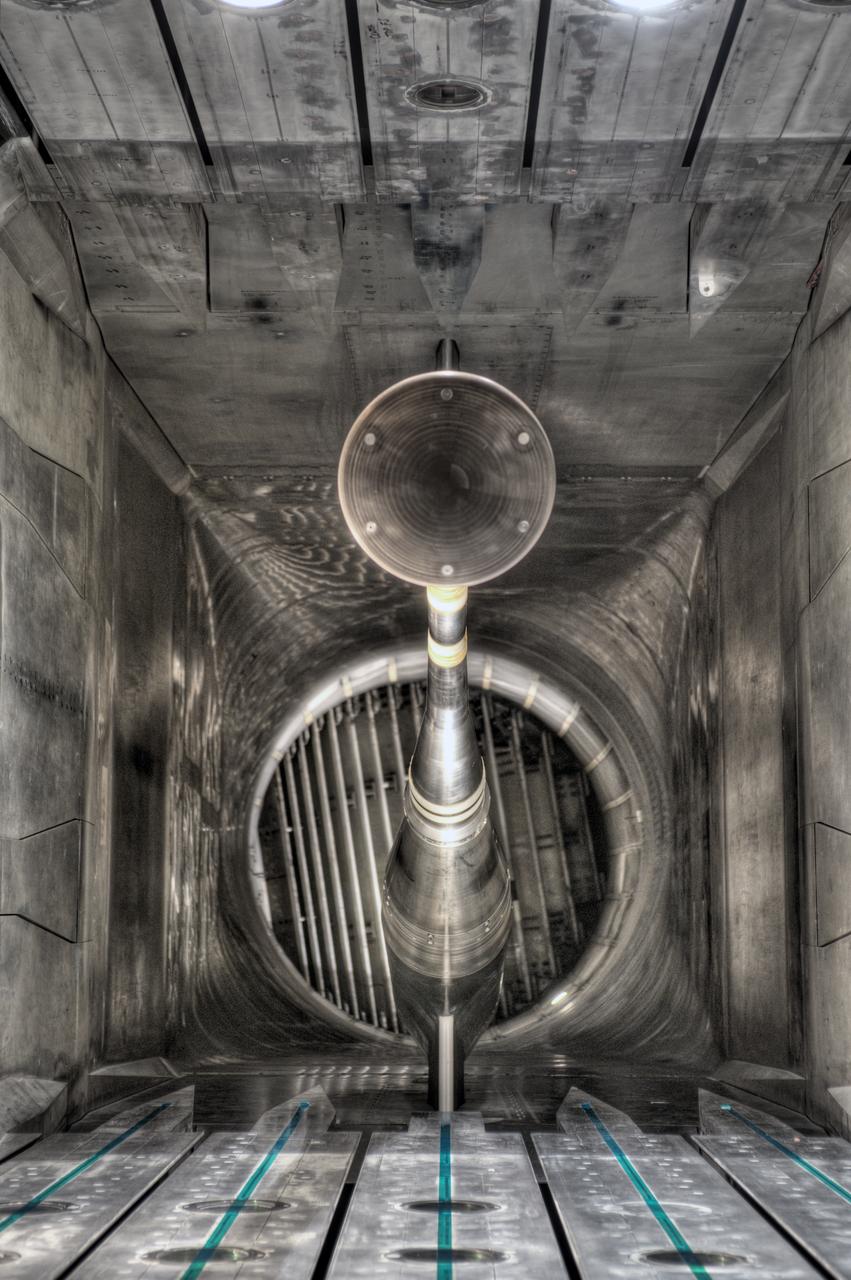

MPCV Orion 7% Crew Module in (NTF) National Transonic Facility, Test team for T211, 7% Orion CM in NTF

Perseid Meteor flight on Google's Gulfstream Aircraft. P.I. Peter Jenniskens, SETI Group with D.K. Holman, CMS/IMO
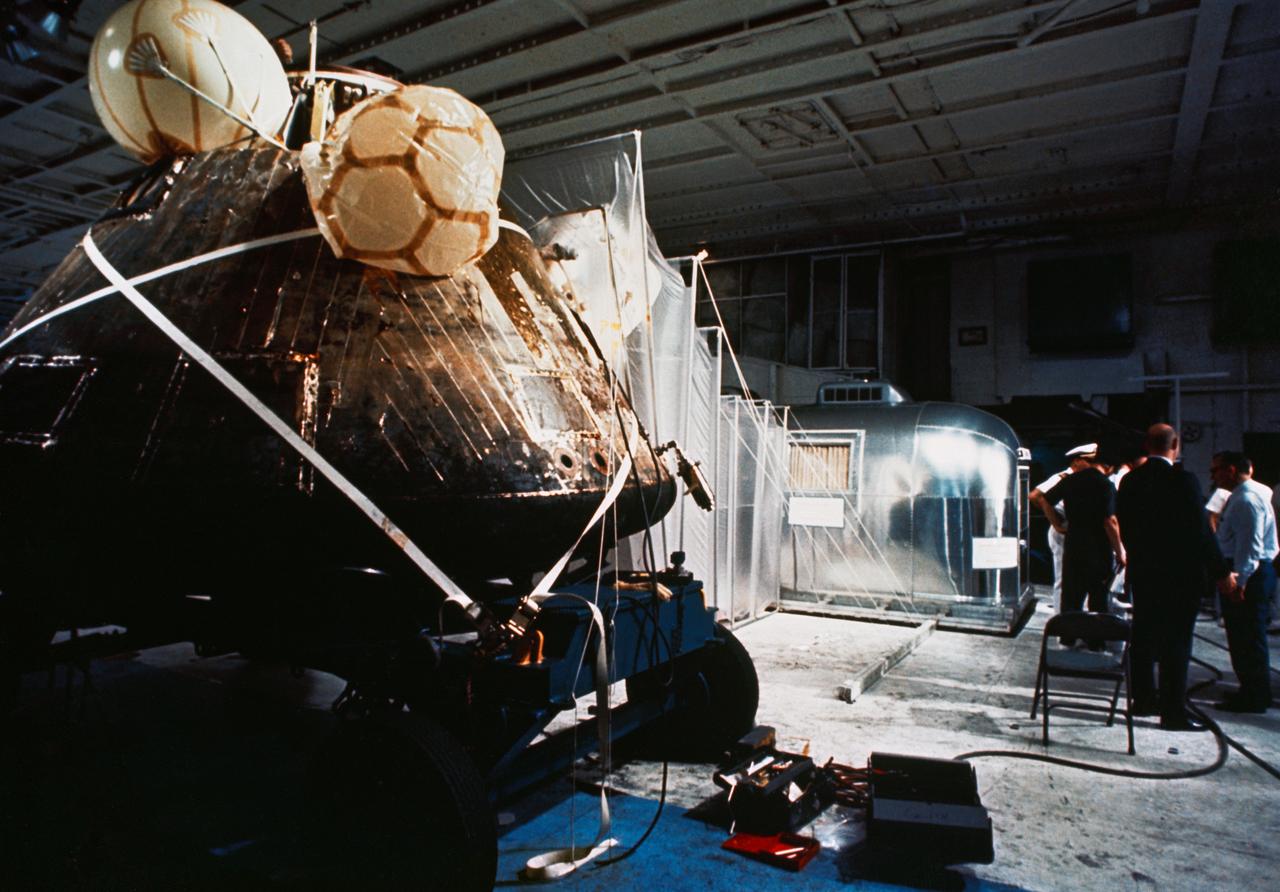

S69-40758 (24 July 1969) --- The Apollo 11 spacecraft Command Module (CM) and the Mobile Quarantine Facility (MQF) are photographed aboard the USS Hornet, prime recovery ship for the historic first lunar landing mission. The three crewmen are already in the MQF. Apollo 11 with astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, Michael Collins and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. aboard splashed down at 11:49 a.m. (CDT), July 24, 1969, about 812 nautical miles southwest of Hawaii and only 12 nautical miles from the USS Hornet. While astronauts Armstrong, commander, and Aldrin, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Eagle" to explore the Sea of Tranquility region of the moon, astronaut Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Columbia" in lunar orbit.
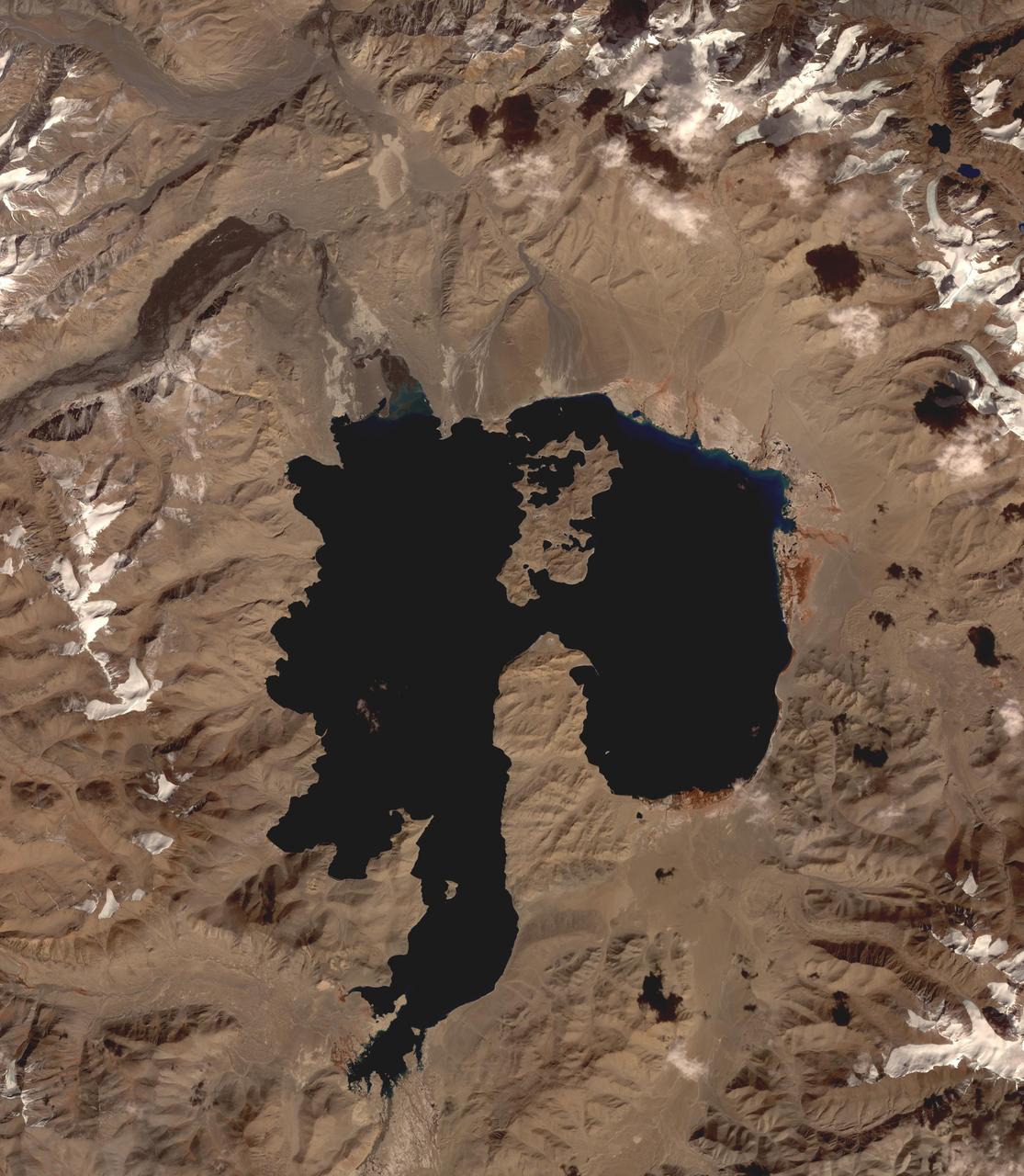

Lake Karakul in northeast Tajikistan is a hypersaline lake with no external drainage, receiving less than 3 cm precipitation per year. It is on the highest part of the fabled Pamir highway at 3900 m. In the local Kyrgyz language, the lake is called "The Black Lake". Recently, Russian scientists have suggested that the lake occupies a 200 million year old meteor impact crater. The image was acquired October 16, 2016, covers an area of 48 by 55 km, and is located at 39 degrees north, 73.4 degrees east. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23102

N-258 NAS COMPUTER ROOM SHOWING PARRALLEL PROCESSORS, INTEL PARGON, THINKING MACHINE (CM-5), & CRAY C-90
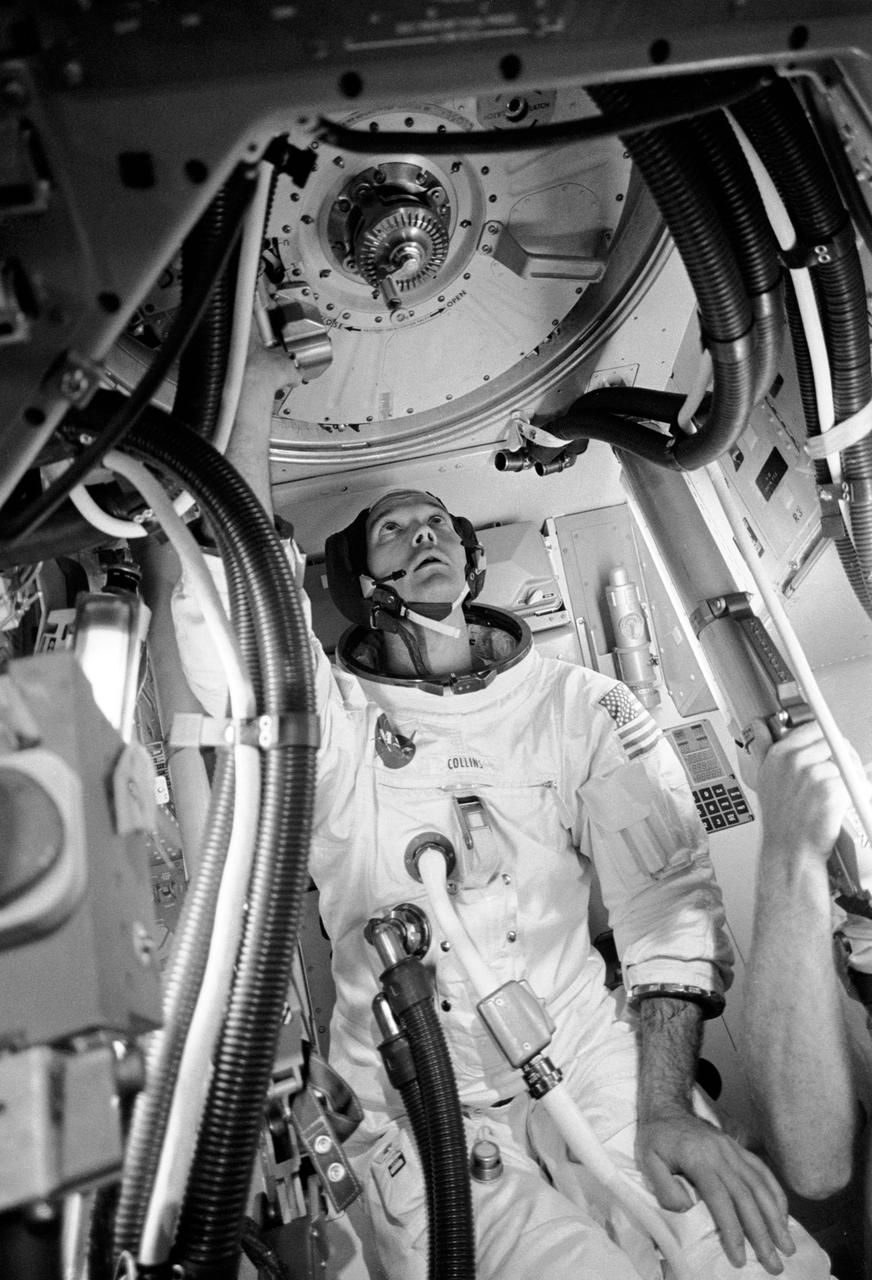

S69-38323 (28 June 1969) --- Astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot of the Apollo 11 flight, is seen inside an Apollo Command Module (CM) mockup in Building 5 practicing procedures with the Apollo docking mechanism in preparation for the scheduled Apollo 11 lunar landing mission. Collins is at the CM's docking tunnel which provides passageway to and from the Lunar Module (LM) following docking, and after removal of the tunnel hatches, docking probe and drogue.

AS13-59-8562 (17 April 1970) --- This view of the Apollo 13 Lunar Module (LM) was photographed from the Command Module (CM) just after the LM had been jettisoned. The jettisoning occurred a few minutes before 11 a.m. (CST), April 17, 1970, just over an hour prior to splashdown of the CM in the south Pacific Ocean. The apparent explosion of oxygen tank number two in the Apollo 13 Service Module (SM) caused the Apollo 13 crew members to rely on the LM as a "lifeboat".

AST-06-318 (15-24 July 1975) --- Astronaut Vance D. Brand, command module pilot of the American ASTP crew, is seen in the hatchway leading from the Apollo Command Module (CM) into the Apollo Docking Module (DM) during the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project docking mission in Earth orbit. The 35mm camera is looking from the DM into the CM.
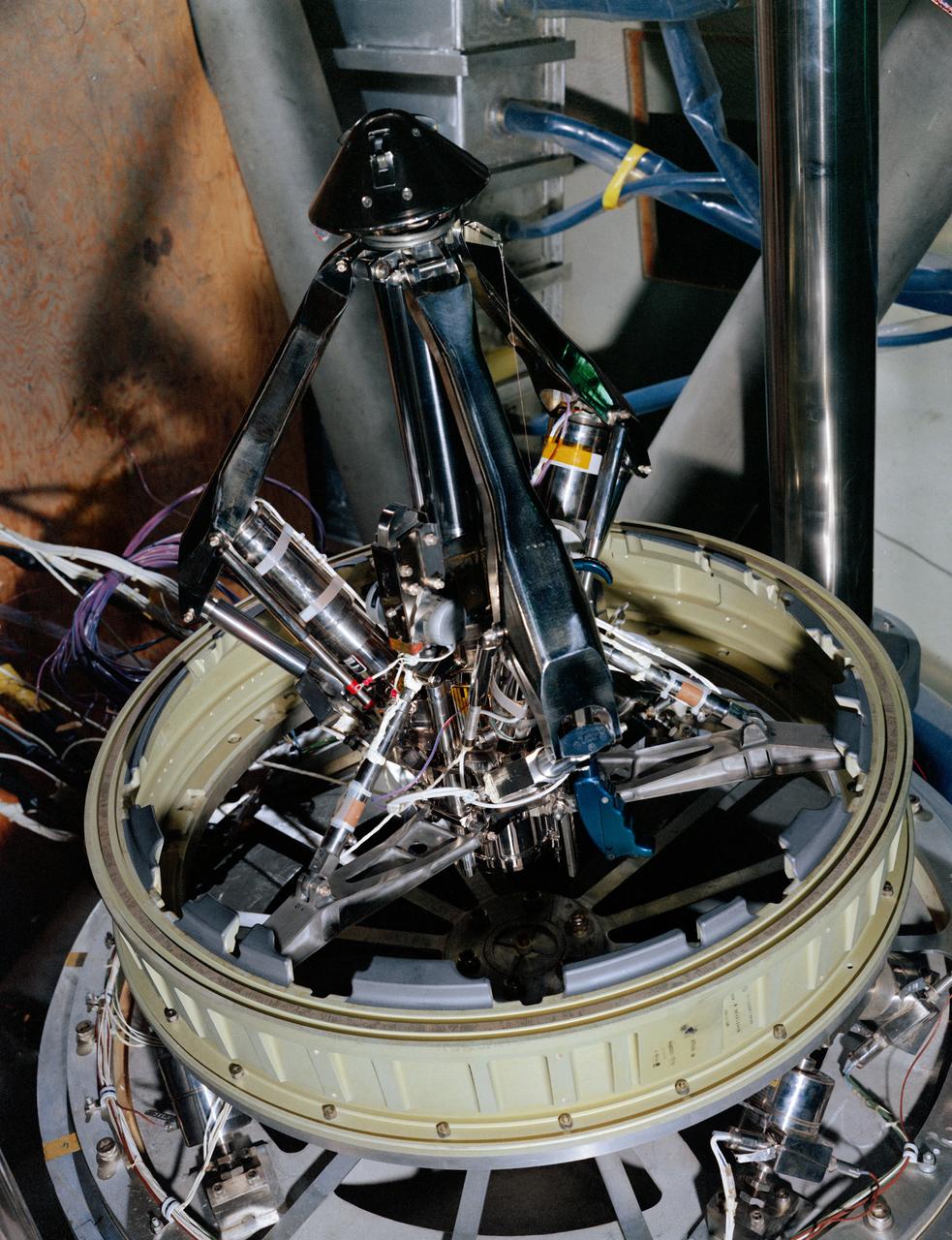

S68-50870 (1968) --- An engineering set up illustrating the probe portion of the docking system of the Apollo spacecraft. During docking maneuvers the docking probe on the Command Module (CM) engages the cone shaped drogue of the Lunar Module (LM). The primary docking structure is the tunnel through which the astronauts transfer from one module to the other. This tunnel is partly in the nose of the CM and partly in the top of the LM. Following CSM/LM docking the drogue and probe are removed to open the passageway between the modules.
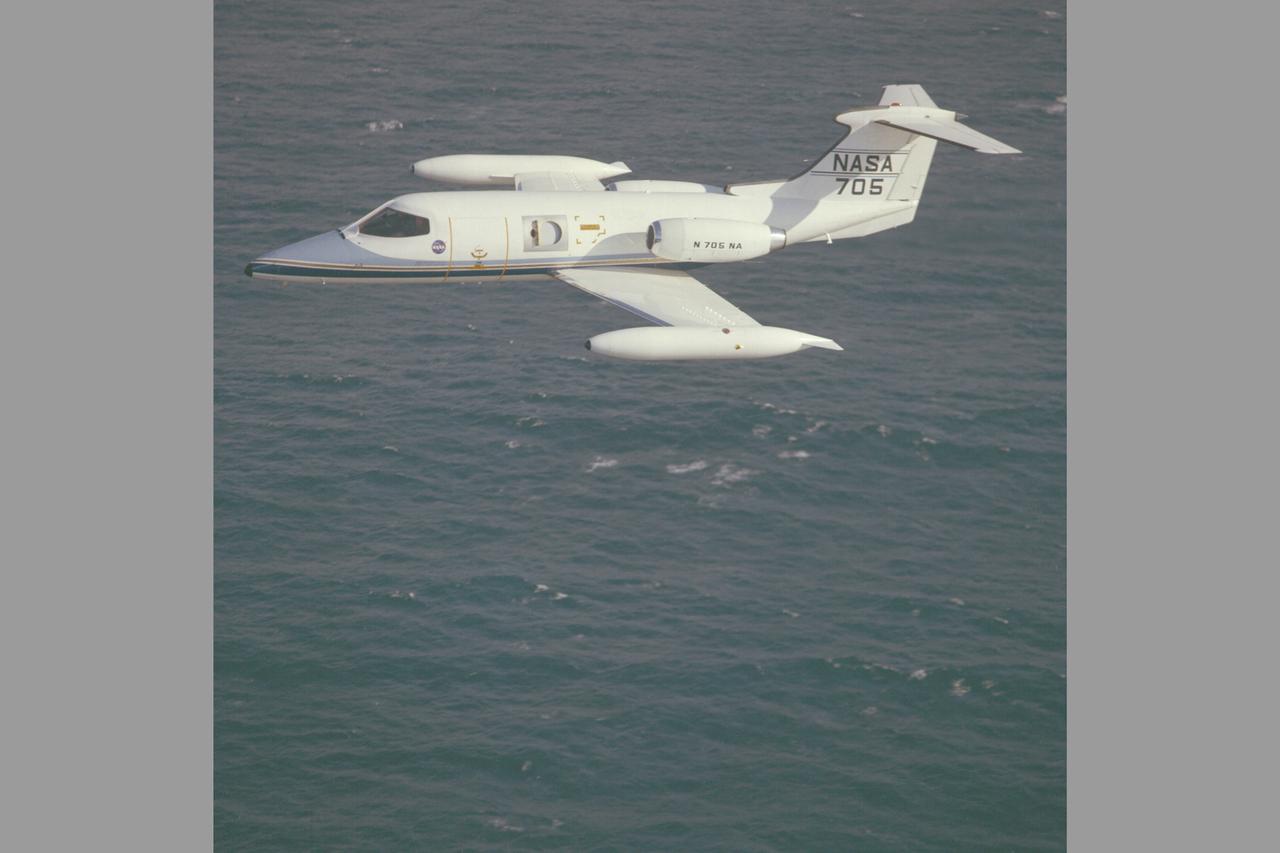

Lear Jet 24B (NASA-705) in flight along California coast is used primarily as a high altitude observation platform carrying a 12' telescope with a special hatch on the starboard side for upward viewing. The hatch has a maximum circular clear aperture of 37.6 cm and can contain a 30 cm aperture open-port gyro-stabilized telescope designed especially for infrared astronomical research.
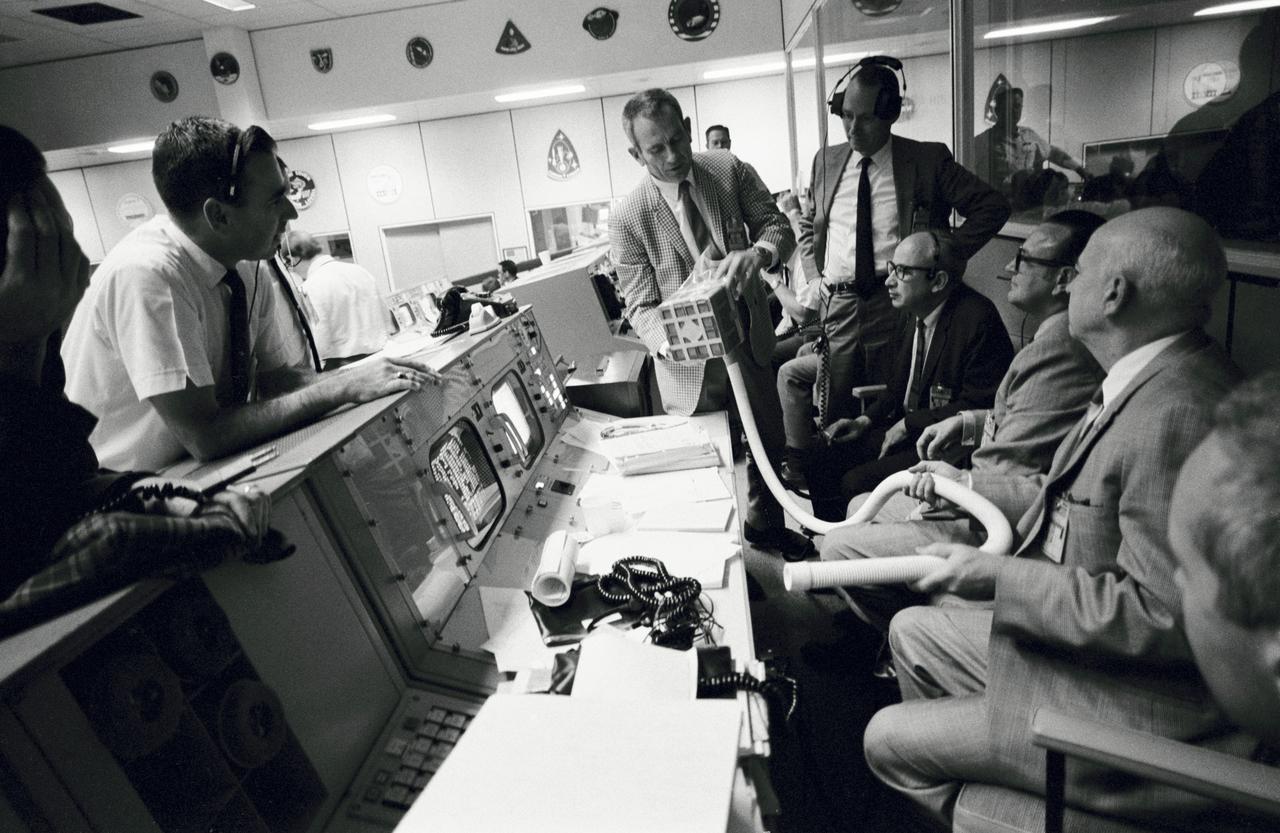

S70-35013 (15 April 1970) --- Prototype of the "mail box" constructed at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC) to remove carbon dioxide from the Apollo 13 Command Module (CM) is displayed in the Mission Control Center (MCC). The "mail box" was constructed when it became apparent CO2 was prevalent in the CM and the spacecraft's lithium hydroxide system was not removing it sufficiently. A space suit exhaust hose is connected to a lithium hydroxide canister to purge the cabin air. There are 16 such canisters in the CM and each will last approximately 12 hours. Looking at the "mail box" are (from the left): Milton L. Windler, shift 1 flight director; Dr. Donald K. (Deke) Slayton, director of flight crew operations, MSC; Howard W. Tindall, deputy director, flight operations, MSC; Sigurd A. Sjoberg, director, flight operations, MSC; Dr. Christopher C. Kraft, deputy director, MSC; and Dr. Robert R. Gilruth, director, MSC.
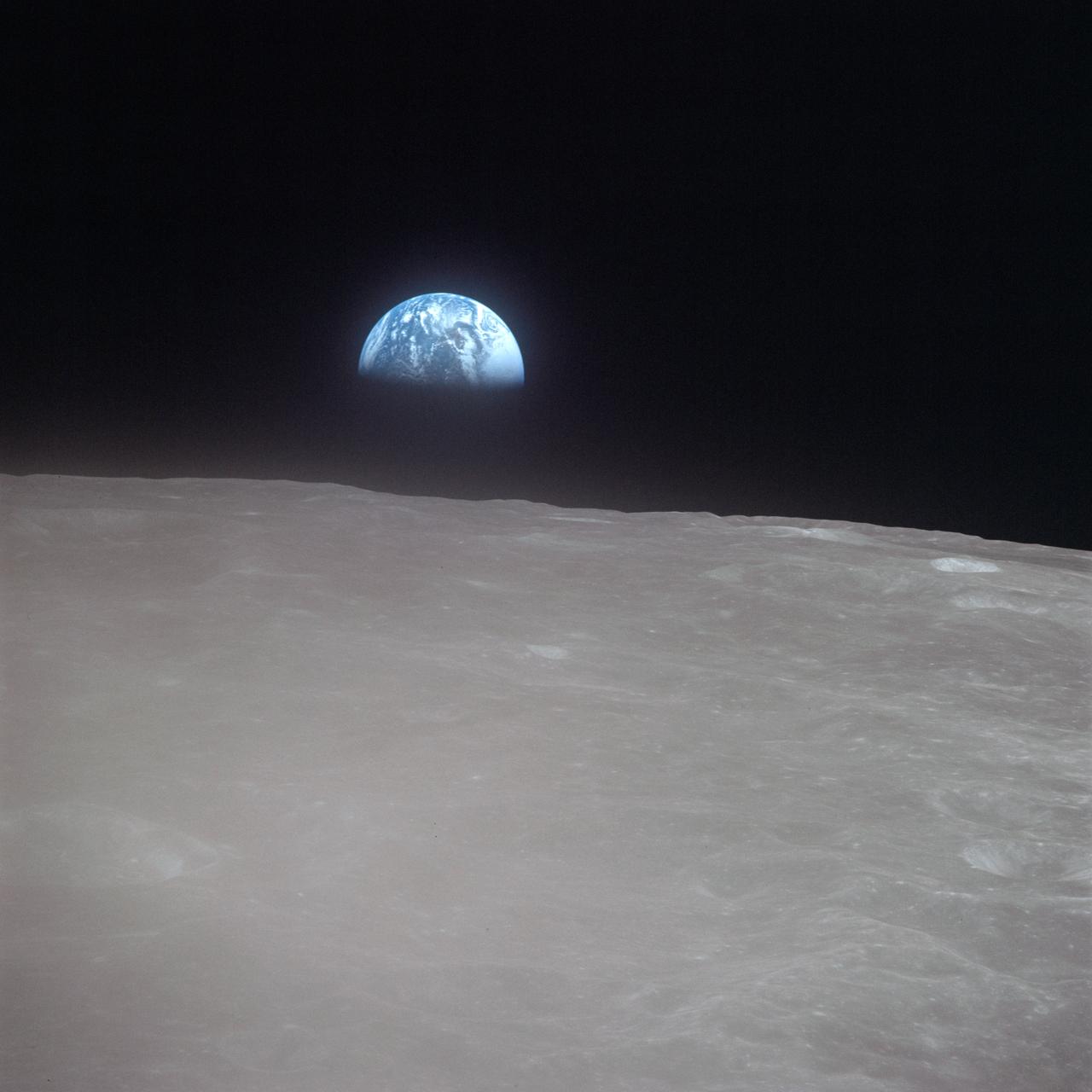

AS16-120-19187 (19 April 1972) --- Apollo 16 astronauts captured this Earth rise scene with a handheld Hasselblad camera during the second revolution of the moon. Identifiable craters seen on the moon include Saha, Wyld, and Saenger. Much of the terrain seen here is never visible from Earth, as the Command Module (CM) was just passing onto what is known as the dark side or far side of the moon. Crewmen aboard the CM at the time the photo was made were astronauts John W. Young, Thomas K. Mattingly II and Charles M. Duke Jr. Mattingly remained later with the CM in lunar orbit while Young and Duke descended in the lunar module (LM) to explore the surface of the moon.
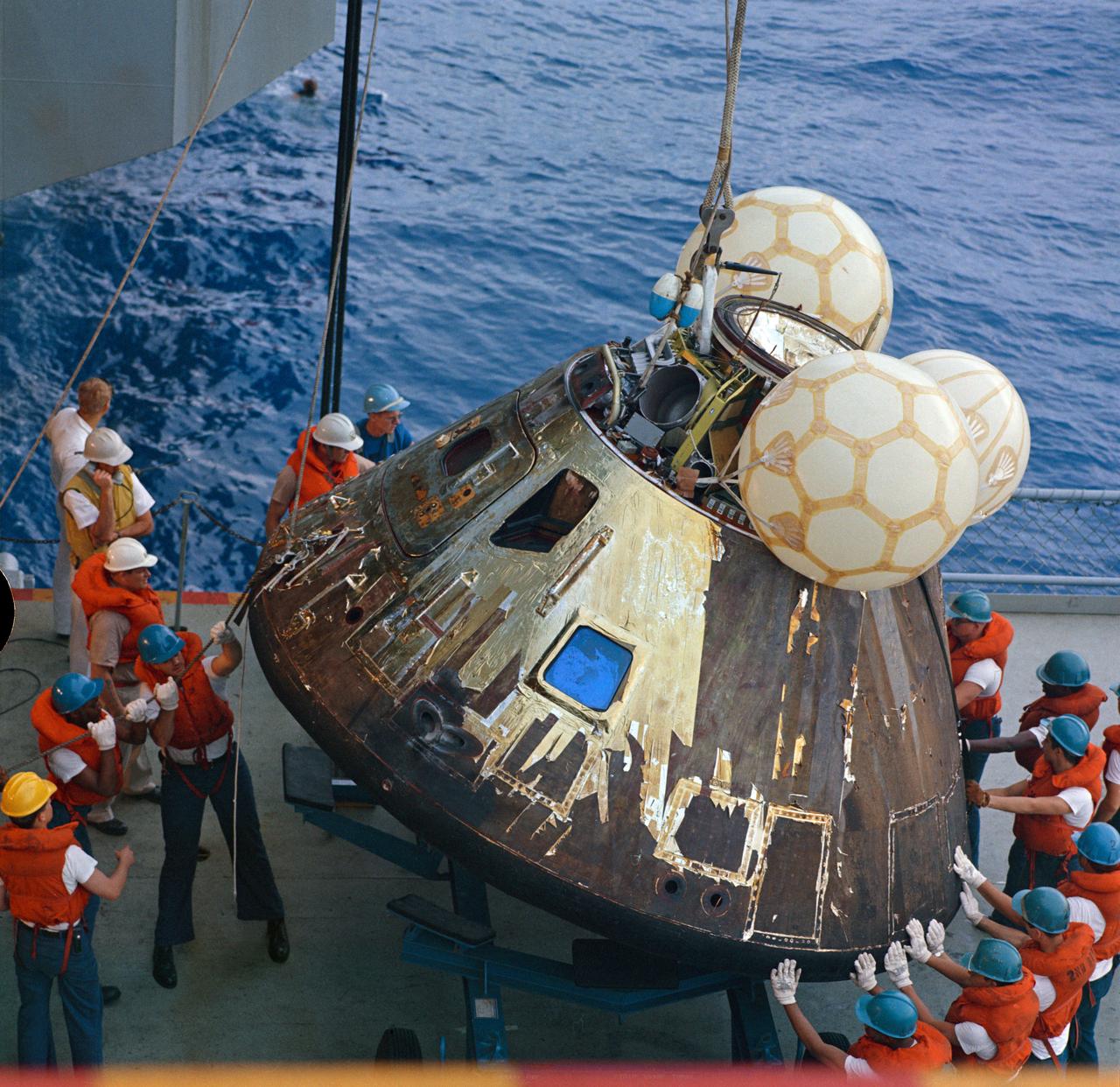

S70-35632 (17 April 1970) --- Crewmen aboard the USS Iwo Jima, prime recovery ship for the Apollo 13 mission, guide the Command Module (CM) atop a dolly onboard the ship. The CM is connected by strong cable to a hoist on the vessel. The Apollo 13 crewmembers, astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., commander; John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot, were already aboard the USS Iwo Jima when this photograph was made. The CM, with the three tired crewmen aboard, splashed down at 12:07:44 p.m. (CST), April 17, 1970, only about four miles from the recovery vessel in the South Pacific Ocean.
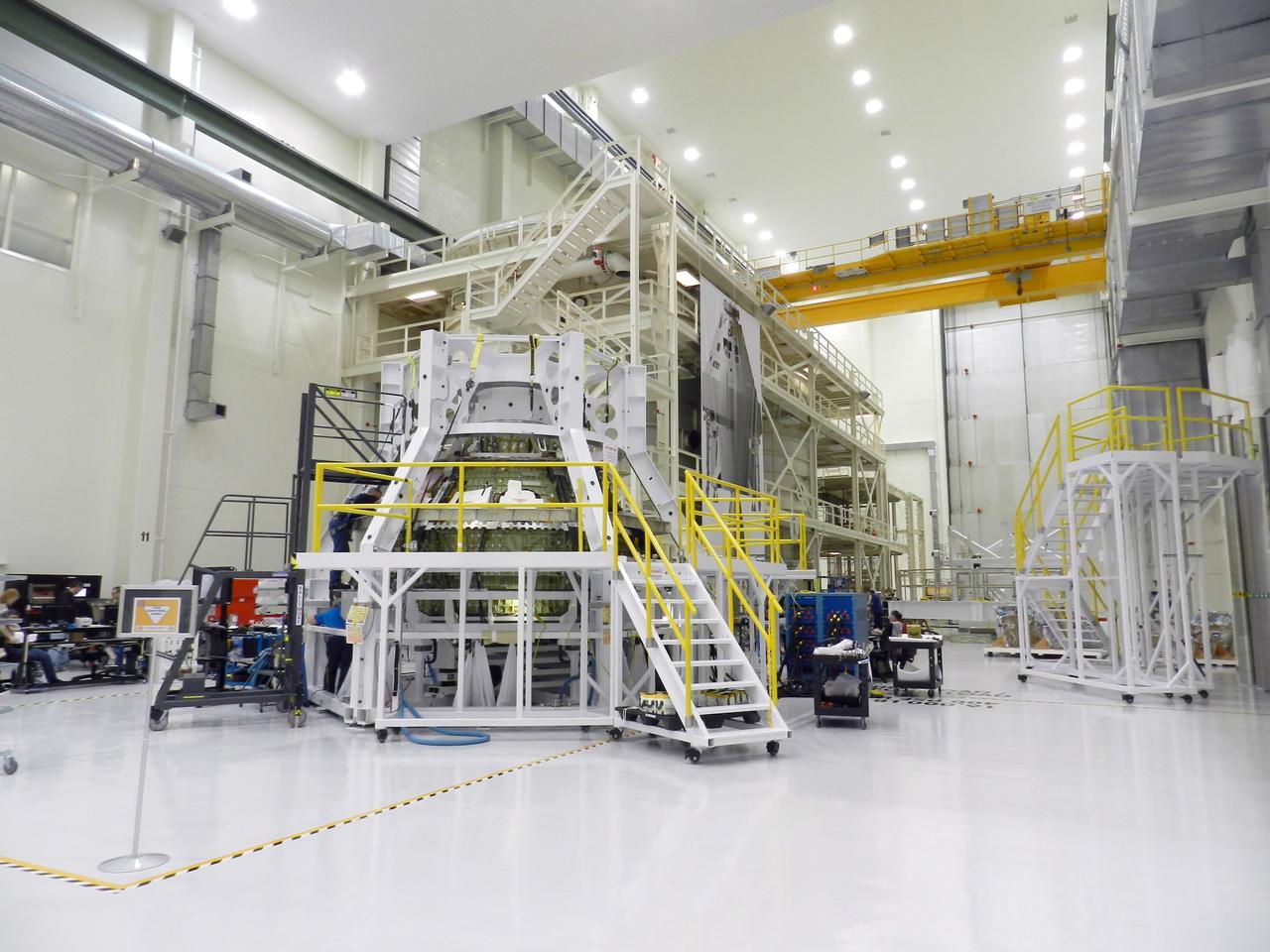

The Orion Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) crew module inside the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Feb. 26, 2013. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
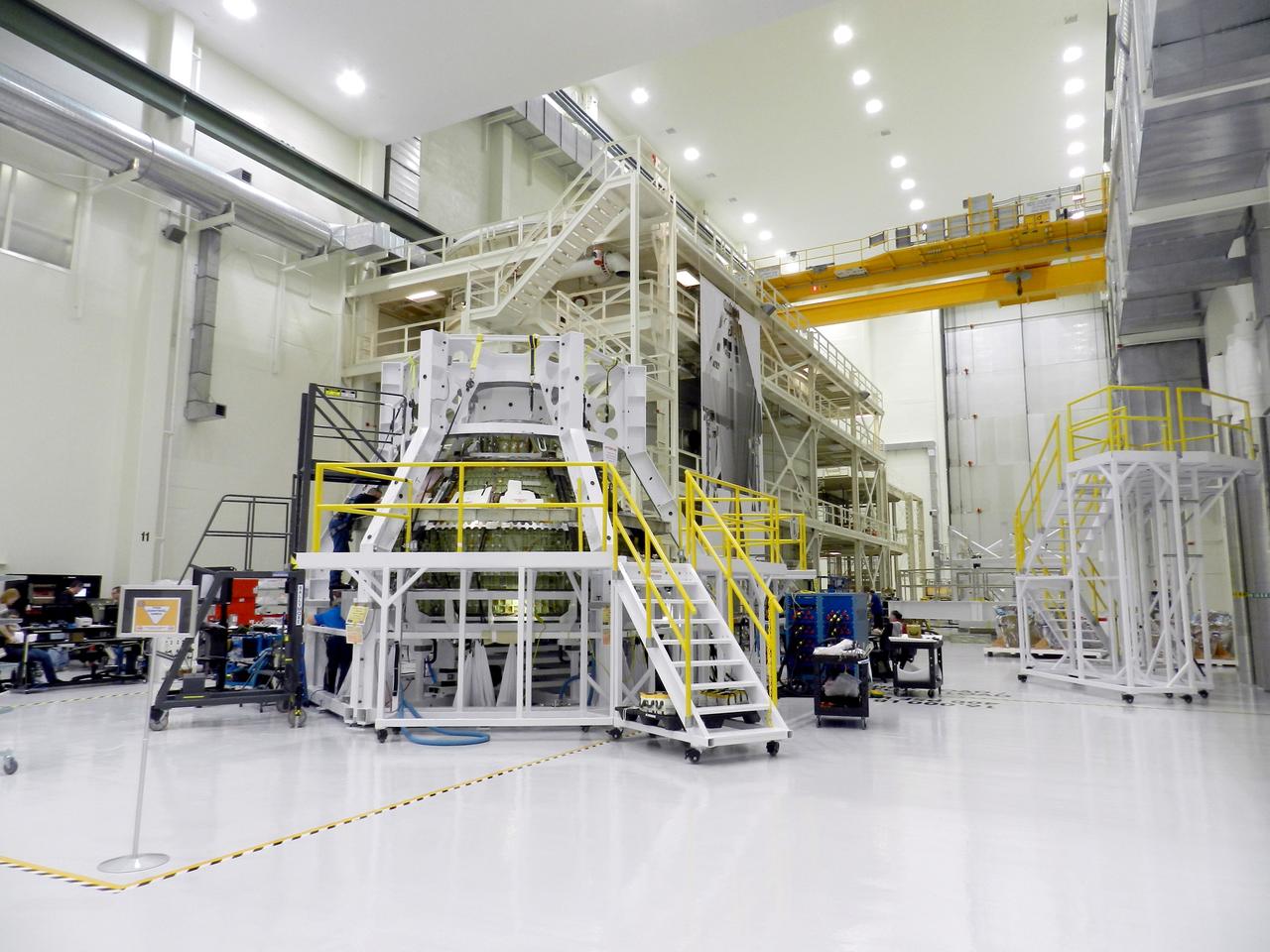

The Orion Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) crew module inside the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Feb. 26, 2013. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
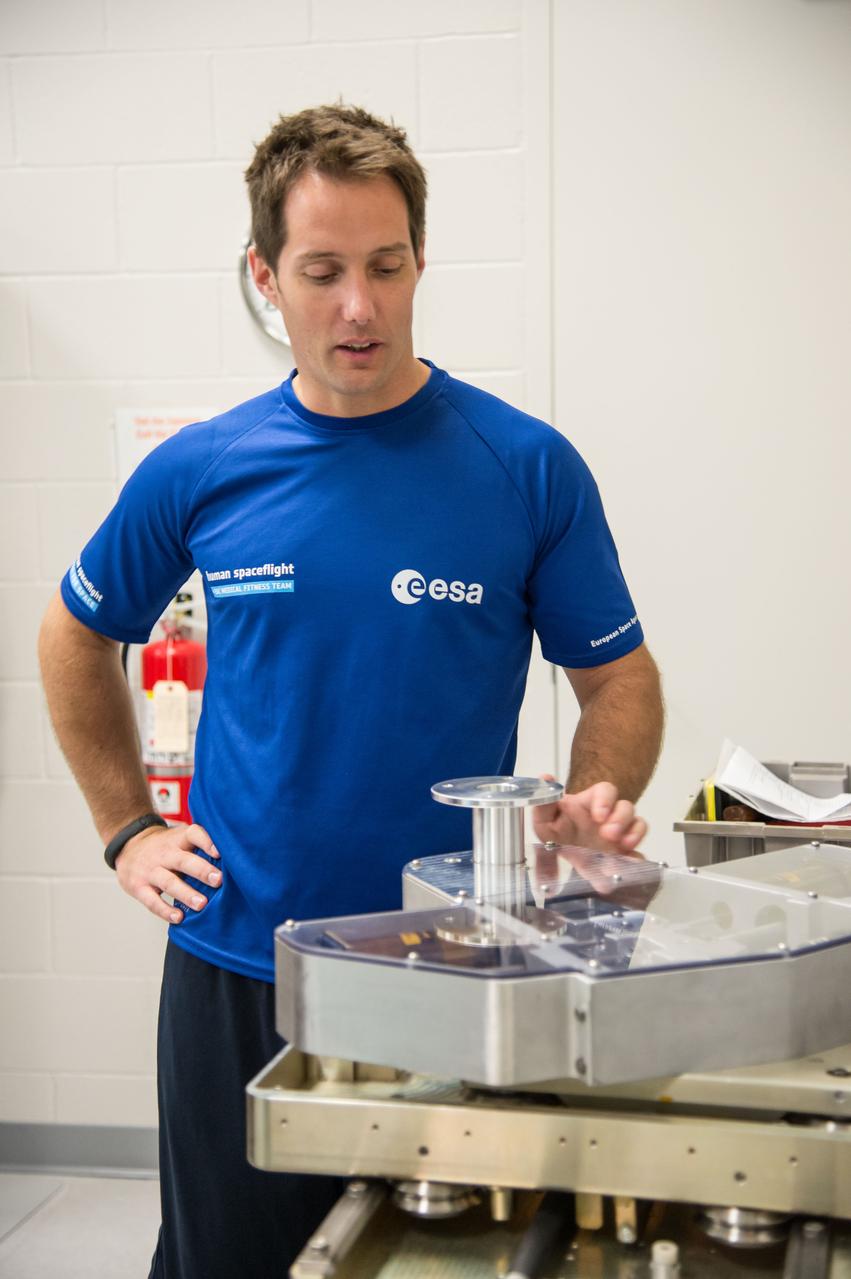

ESA Astronaut Thomas Pesquet during CMS ARED OPS training with instructor Kimberlee Jadwick . Photo Date: September 16, 2014. Location: Building 26. Photographer: Robert Markowitz
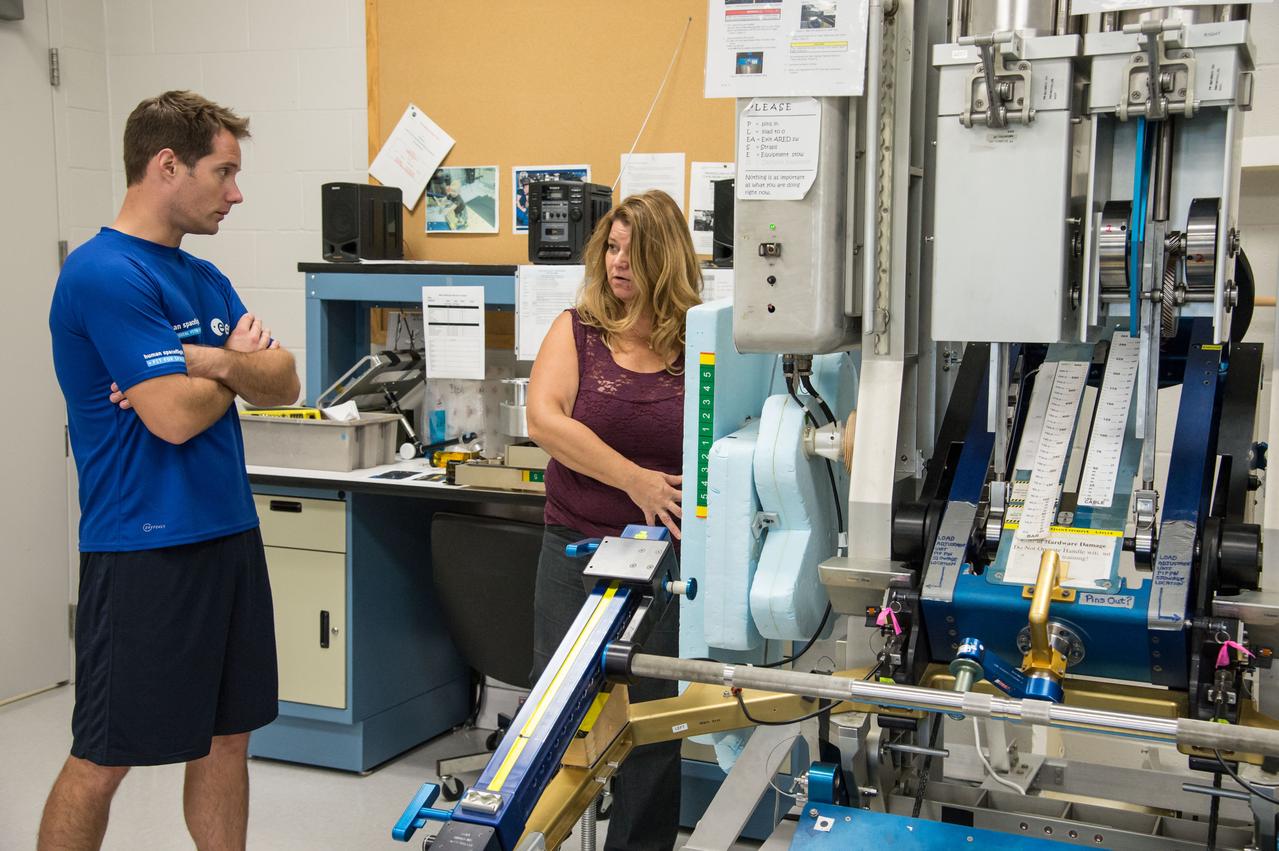

ESA Astronaut Thomas Pesquet during CMS ARED OPS training with instructor Kimberlee Jadwick . Photo Date: September 16, 2014. Location: Building 26. Photographer: Robert Markowitz
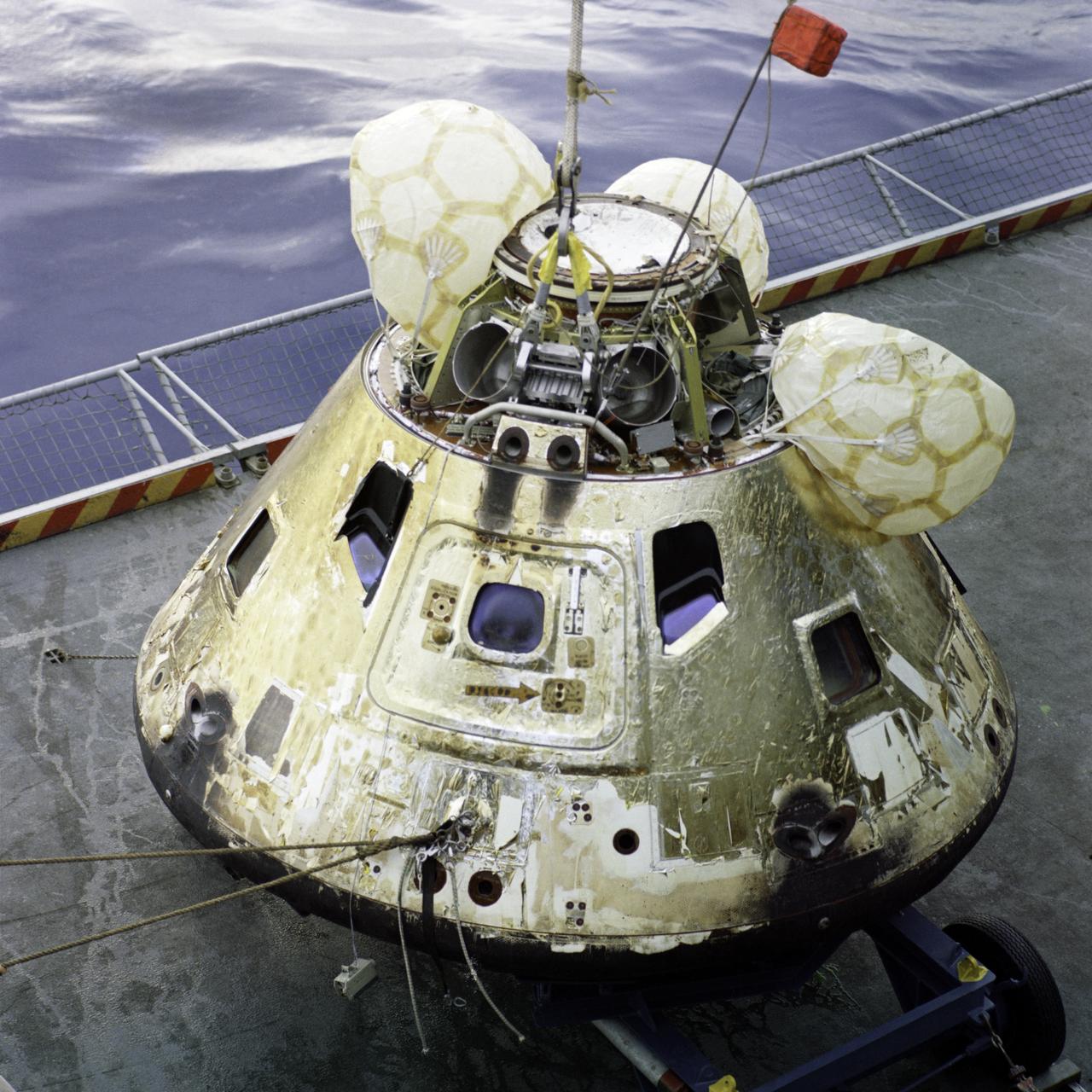

RECOVERY - APOLLO 8 - USS YORKTOWN Recovery activities of the Apollo 8 Crew and Command Module (CM)-103 Spacecraft inspection onboard the USS Yorktown. USS YORKTOWN
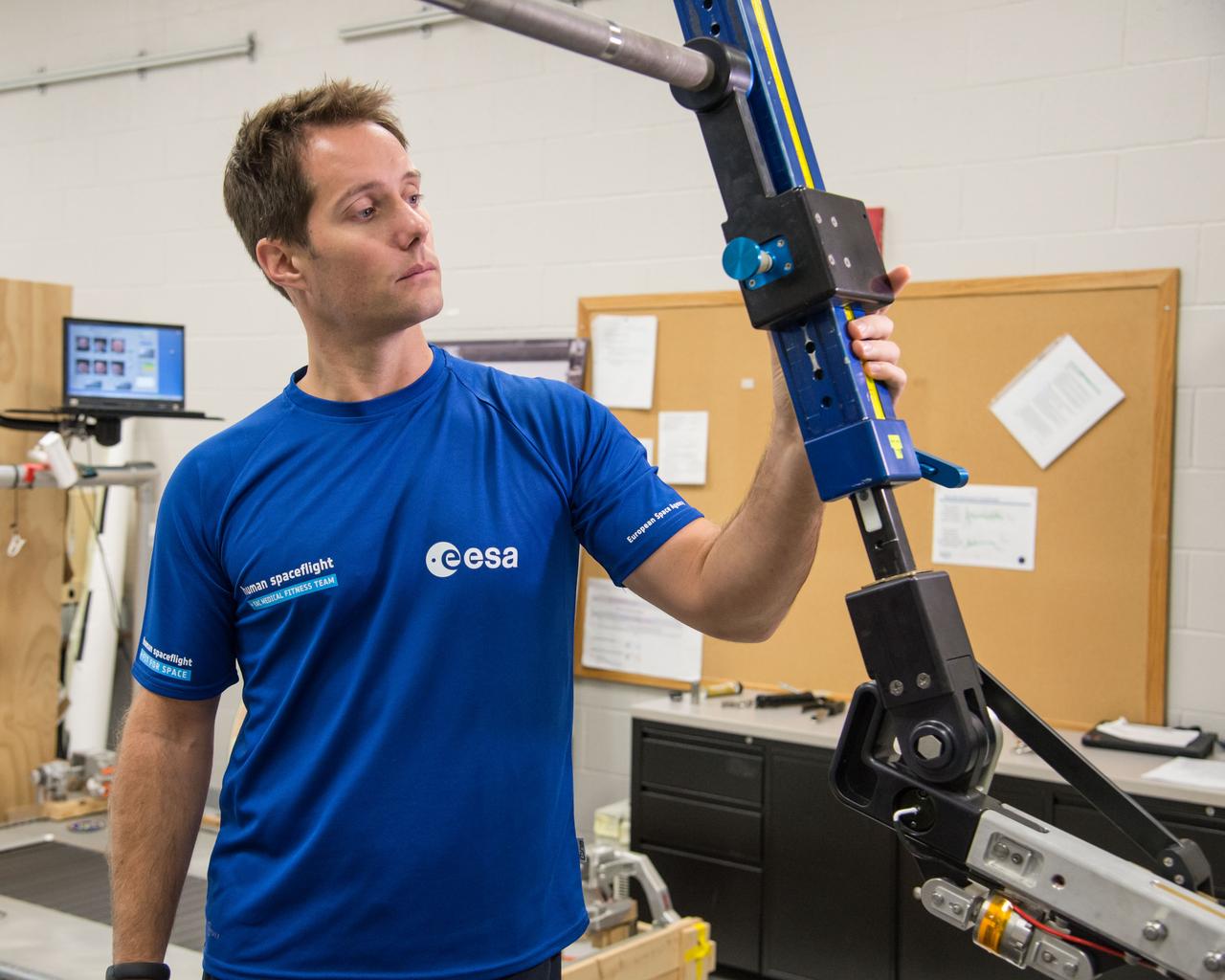

ESA Astronaut Thomas Pesquet during CMS ARED OPS training with instructor Kimberlee Jadwick . Photo Date: September 16, 2014. Location: Building 26. Photographer: Robert Markowitz
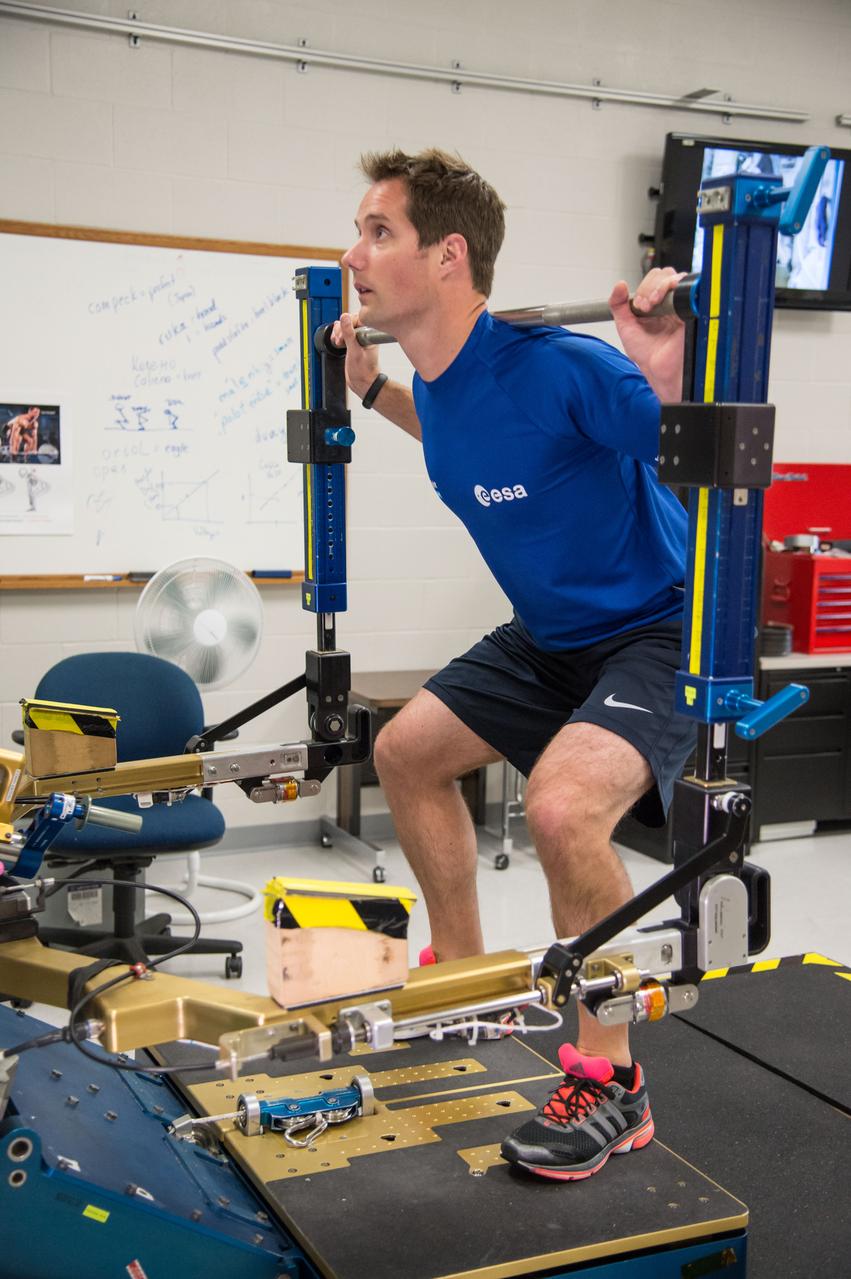

ESA Astronaut Thomas Pesquet during CMS ARED OPS training with instructor Kimberlee Jadwick . Photo Date: September 16, 2014. Location: Building 26. Photographer: Robert Markowitz

ESA Astronaut Thomas Pesquet during CMS ARED OPS training with instructor Kimberlee Jadwick . Photo Date: September 16, 2014. Location: Building 26. Photographer: Robert Markowitz
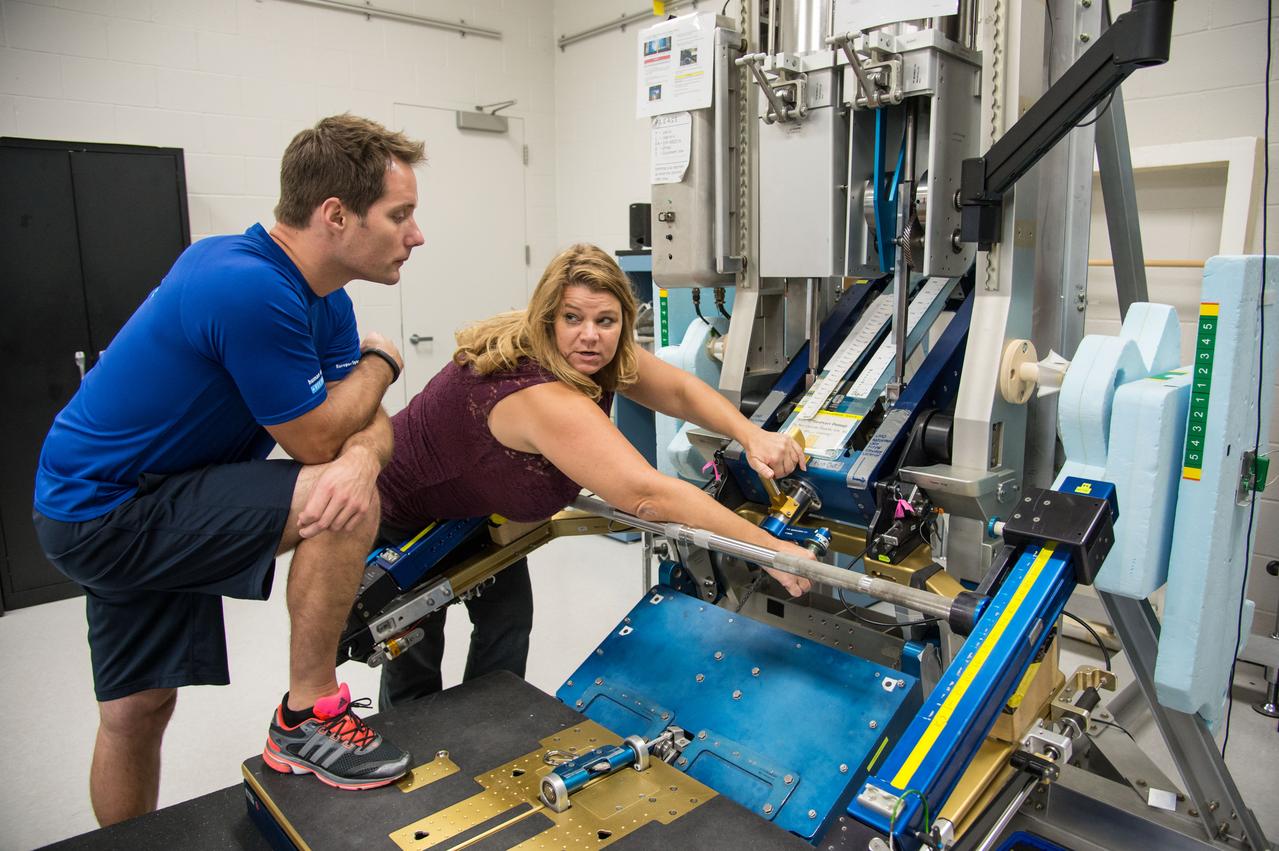

ESA Astronaut Thomas Pesquet during CMS ARED OPS training with instructor Kimberlee Jadwick . Photo Date: September 16, 2014. Location: Building 26. Photographer: Robert Markowitz
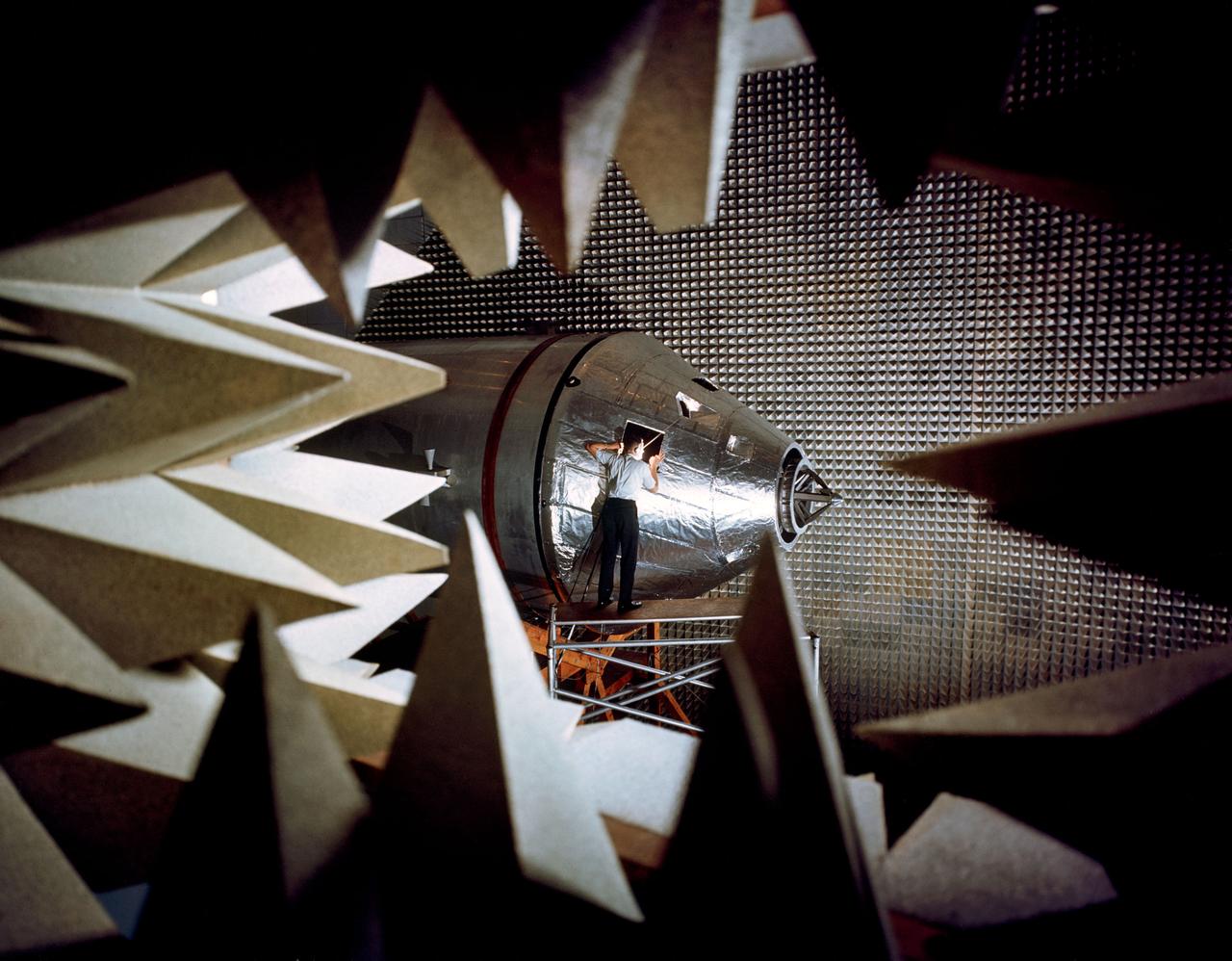
ASTRONAUT TRAINING APOLLO - LEM APOLLO MISSION SIMULATOR; NEUTRAL BOUYANCY FACILITY TANK; DYNAMIC CREW SIMULATOR; LUNAR MODULE SIMULATOR; CM PROCEDURES SIMULATOR; ANECHOIC CHAMBER;

RECOVERY - APOLLO 8 - USS YORKTOWN Recovery activities of the Apollo 8 Crew and Command Module (CM)-103 Spacecraft inspection onboard the USS Yorktown. USS YORKTOWN
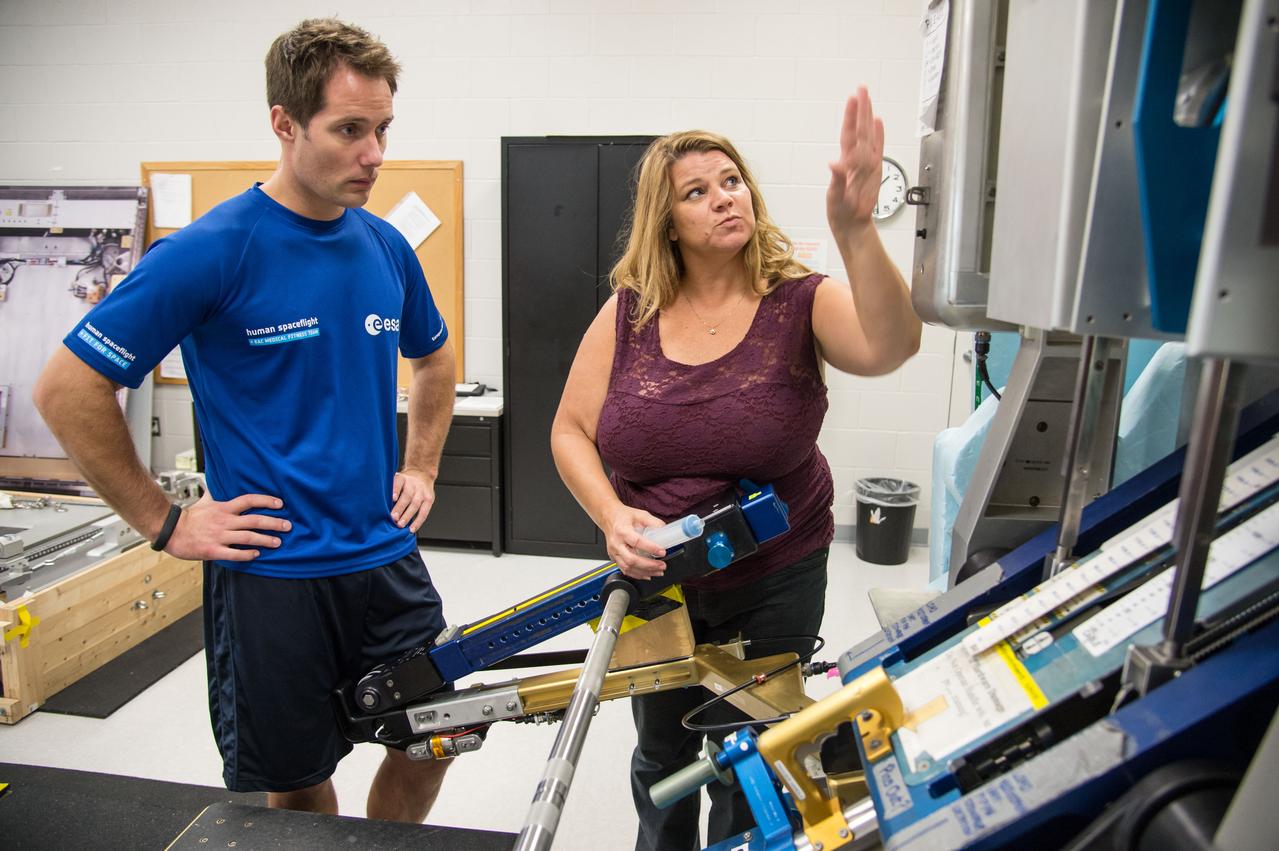

ESA Astronaut Thomas Pesquet during CMS ARED OPS training with instructor Kimberlee Jadwick . Photo Date: September 16, 2014. Location: Building 26. Photographer: Robert Markowitz
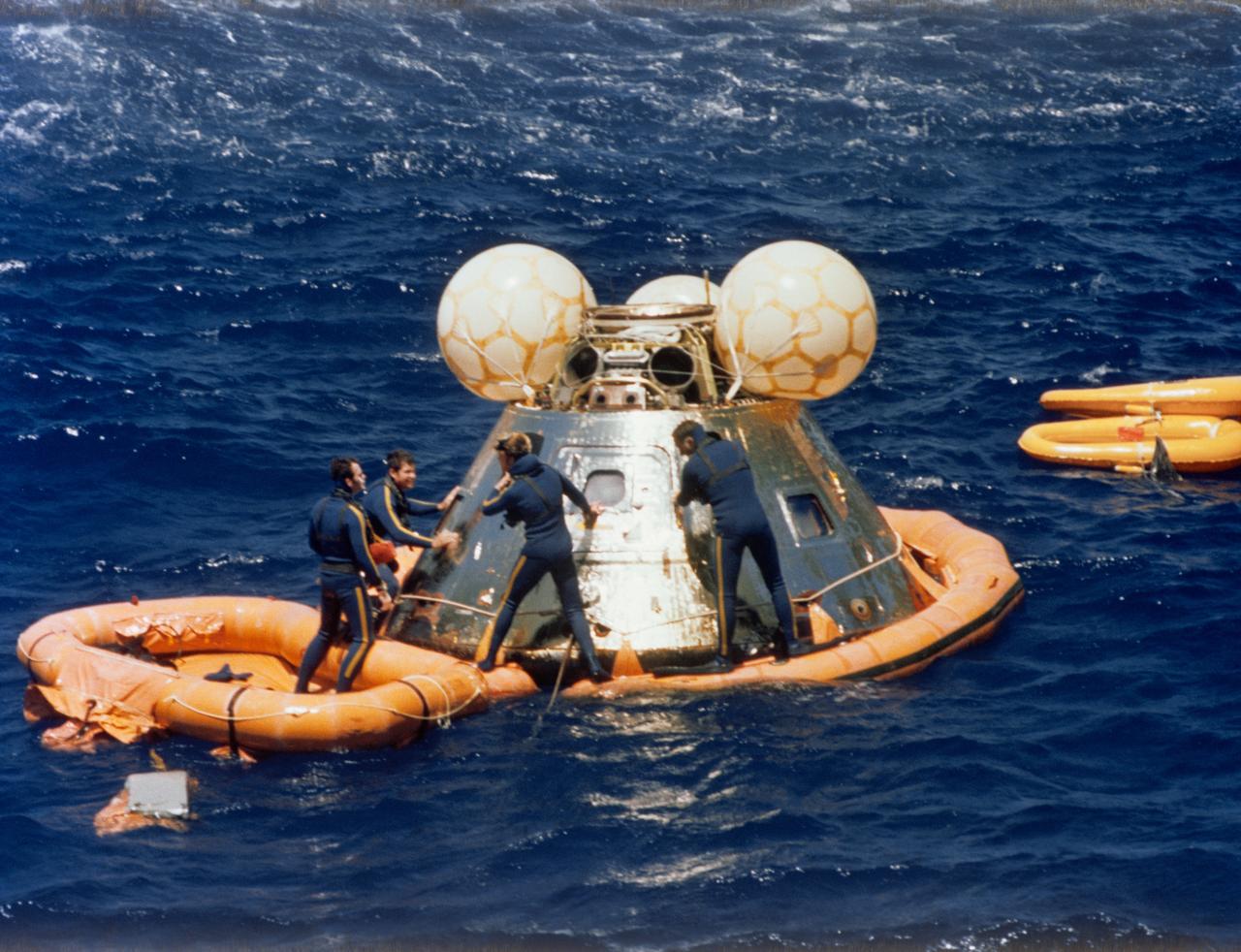

S75-29715 (24 July 1975) --- A team of U.S. Navy swimmers assists with the recovery of the ASTP Apollo Command Module following its splashdown in the Central Pacific Ocean to conclude the historic joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project docking mission in Earth orbit. The swimmers have already attached a flotation collar to the spacecraft. The CM touched down in the Hawaiian Islands area at 4:18 p.m. (CDT), July 24, 1975. The crewmen, astronauts Thomas P. Stafford, Vance D. Brand and Donald K. Slayton, remained in the CM until it was hoisted aboard the prime recovery ship, the USS New Orleans.
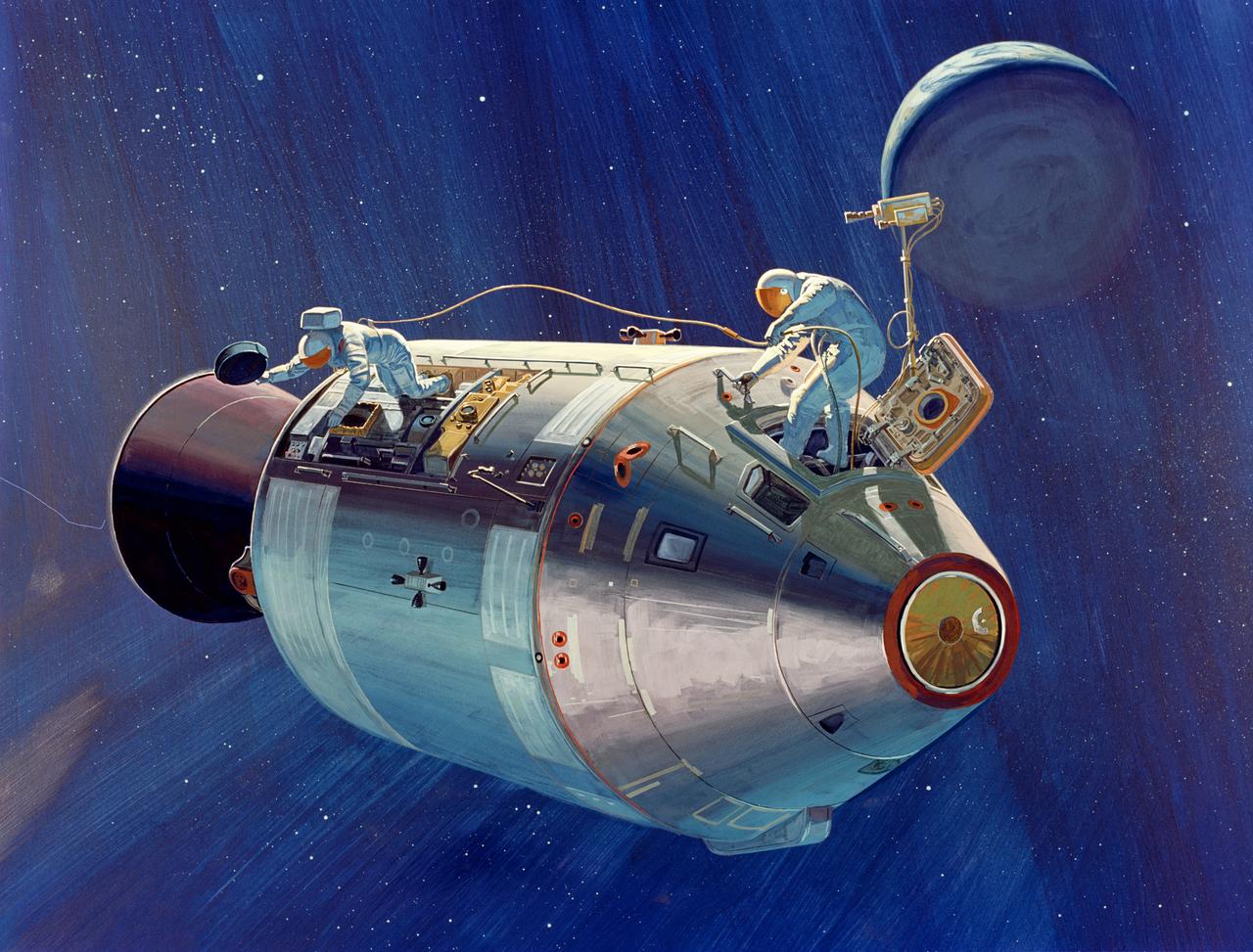
S71-39614 (July 1971) --- An artist's concept of the Apollo 15 Command and Service Modules (CSM), showing two crewmembers performing a new-to-Apollo extravehicular activity (EVA). The figure at left represents astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, connected by an umbilical tether to the CM, at right, where a figure representing astronaut James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, stands at the open CM hatch. Worden is working with the panoramic camera in the Scientific Instrument Module (SIM). Behind Irwin is the 16mm data acquisition camera. Artwork by North American Rockwell.
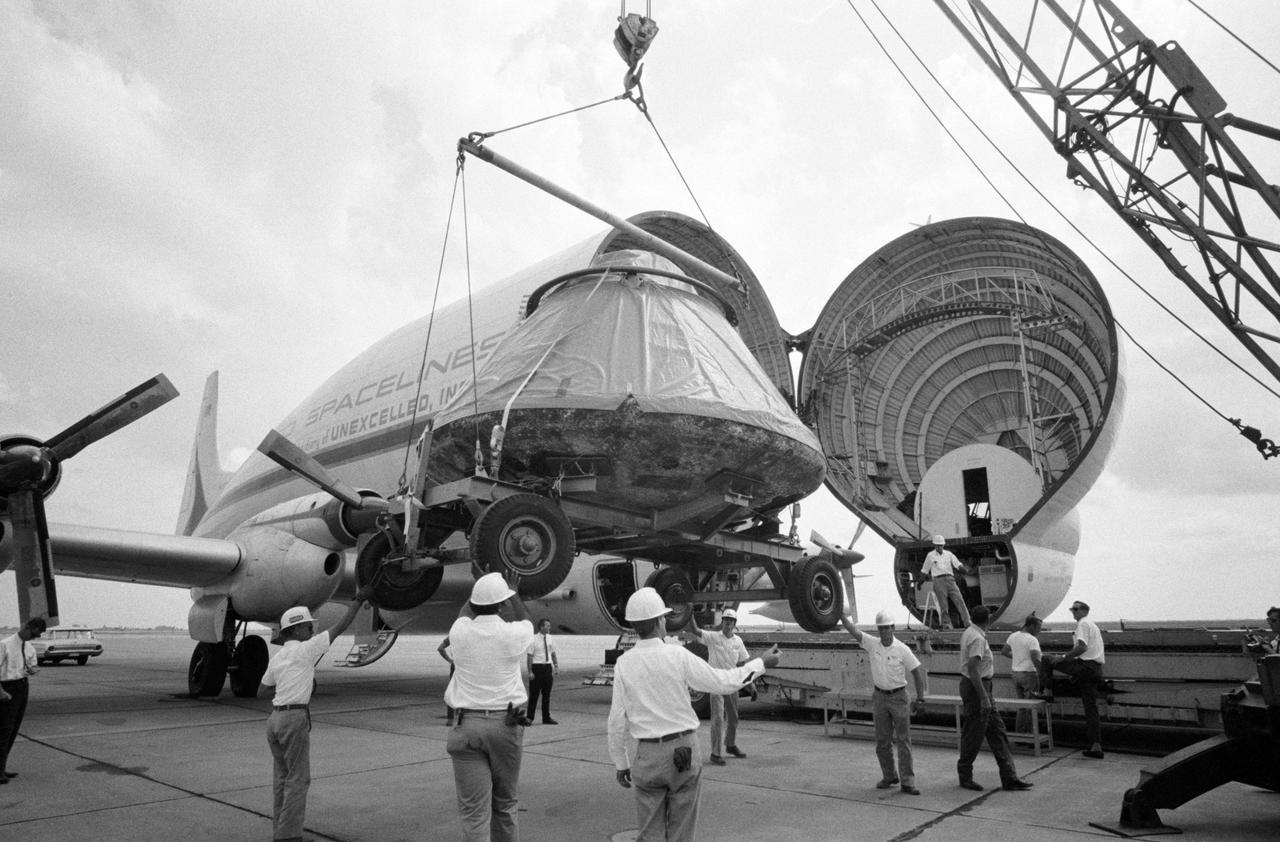

S69-41985 (14 Aug. 1969) --- The Apollo 11 spacecraft Command Module (CM) is loaded aboard a Super Guppy Aircraft at Ellington Air Force Base for shipment to the North American Rockwell Corporation at Downey, California. The CM was just released from its postflight quarantine at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). The Apollo 11 spacecraft was flown by astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, command module pilot; and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, during their lunar landing mission. Note damage to aft heat shield caused by extreme heat of Earth reentry. North American Rockwell is the prime contractor for the Apollo Command and Service Modules (CSM).
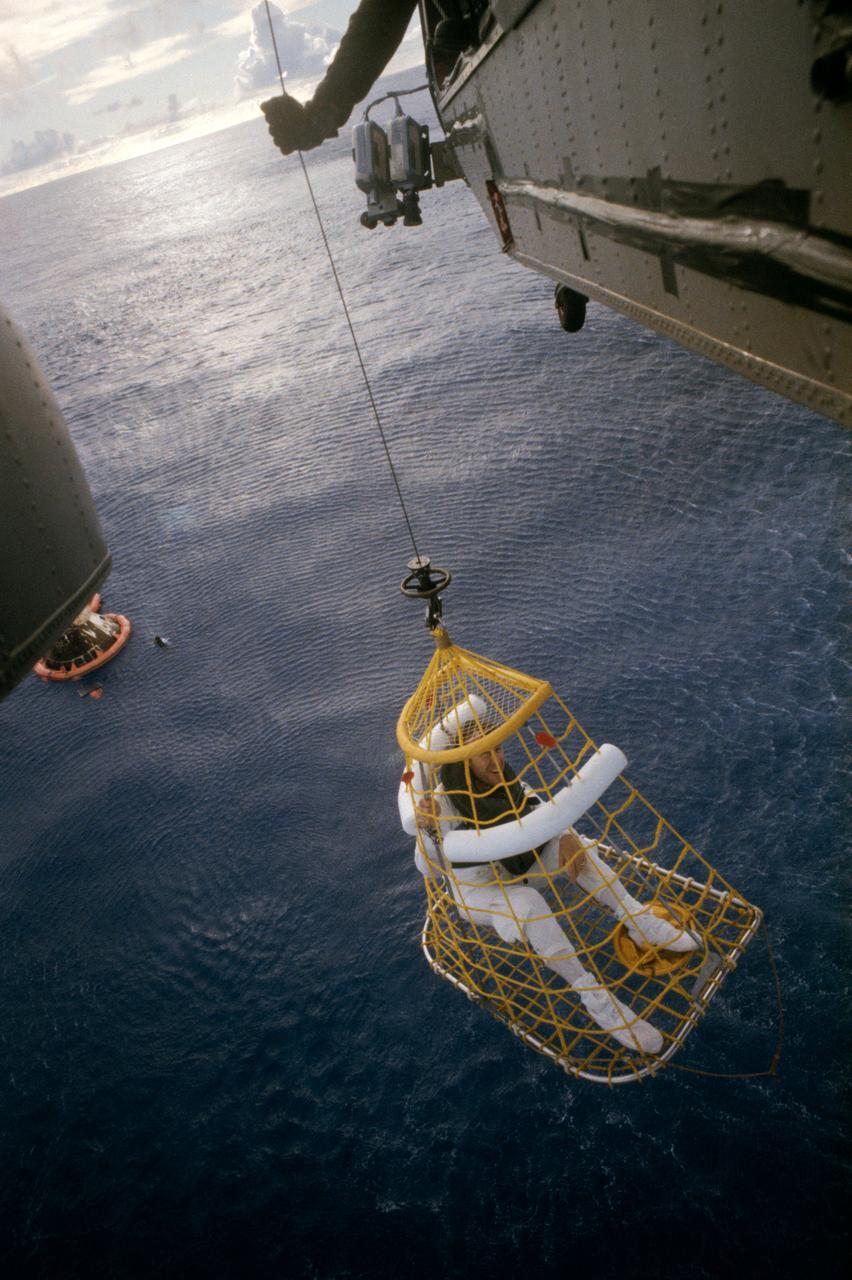

S70-35645 (17 April 1970) --- Astronaut James A. Lovell Jr., commander, is hoisted aboard a helicopter from the USS Iwo Jima, prime recovery vessel for the mission. Lovell was the last of the three Apollo 13 crewmembers to egress the Command Module (CM) and the last to be lifted aboard the helicopter. He was preceded by astronauts John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot. The CM and a U.S. Navy underwater demolition team swimmer can be seen in the ocean background. Apollo 13 splashed down at 12:07:44 p.m. (CST), April 17, 1970.