Compositional Medley
Mozart Composition
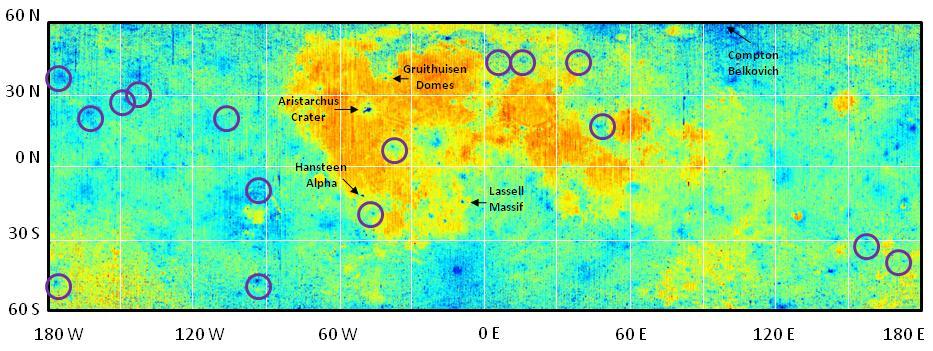
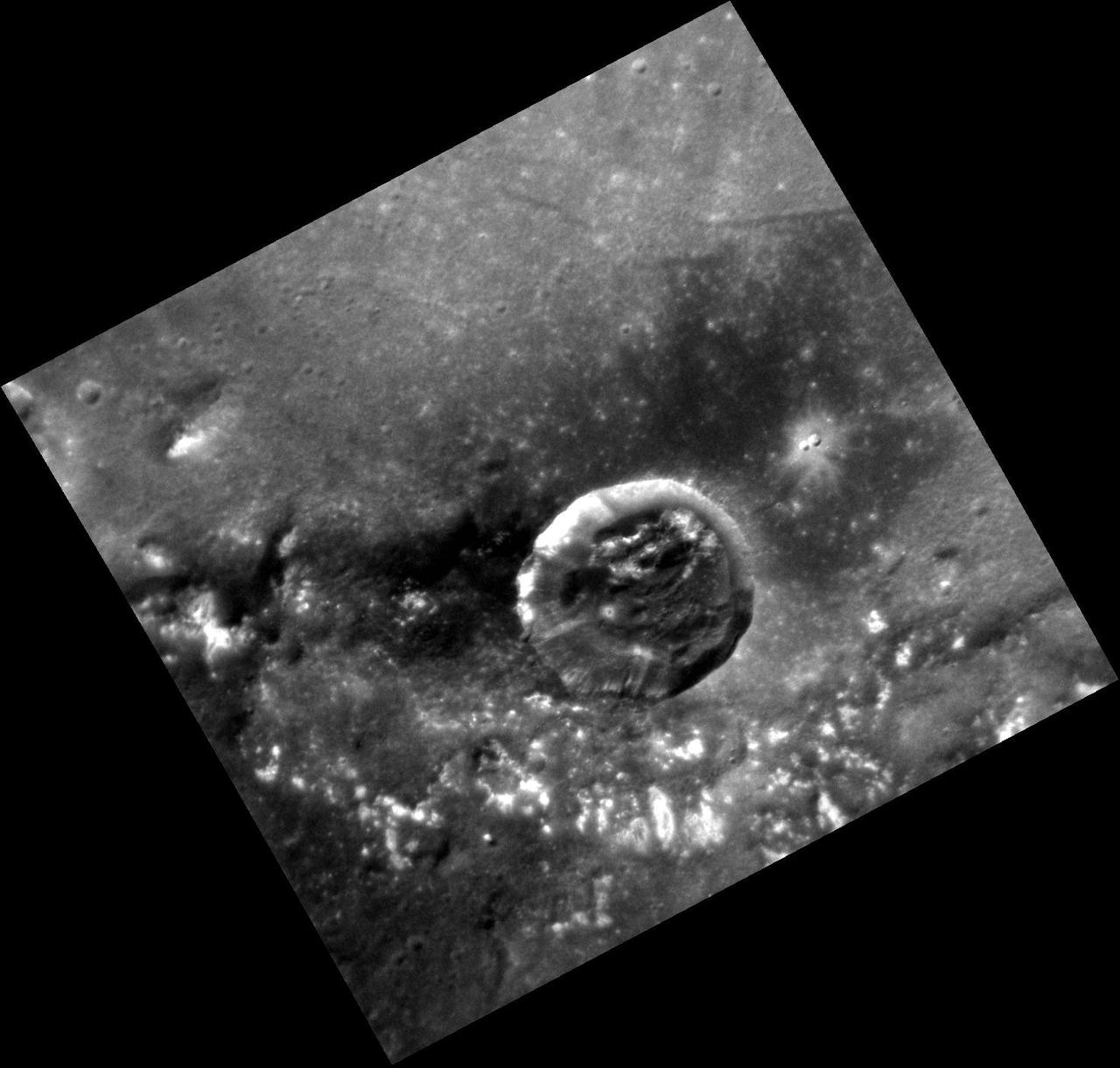
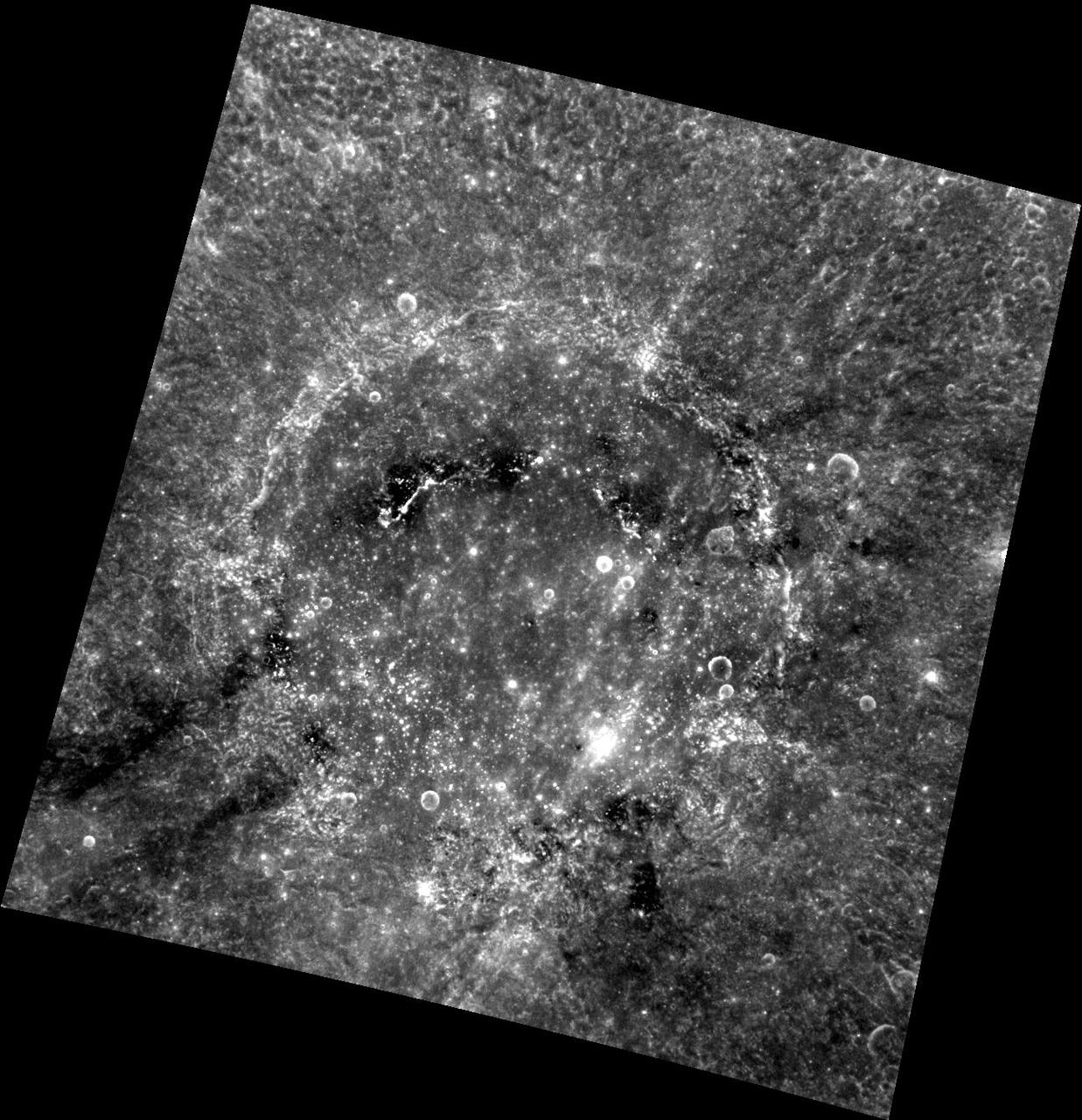
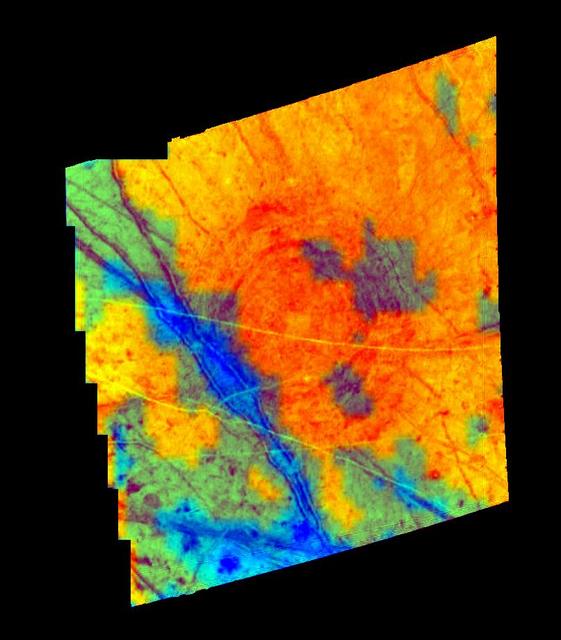
Diviner Global Composition

Iapetus Surface Composition
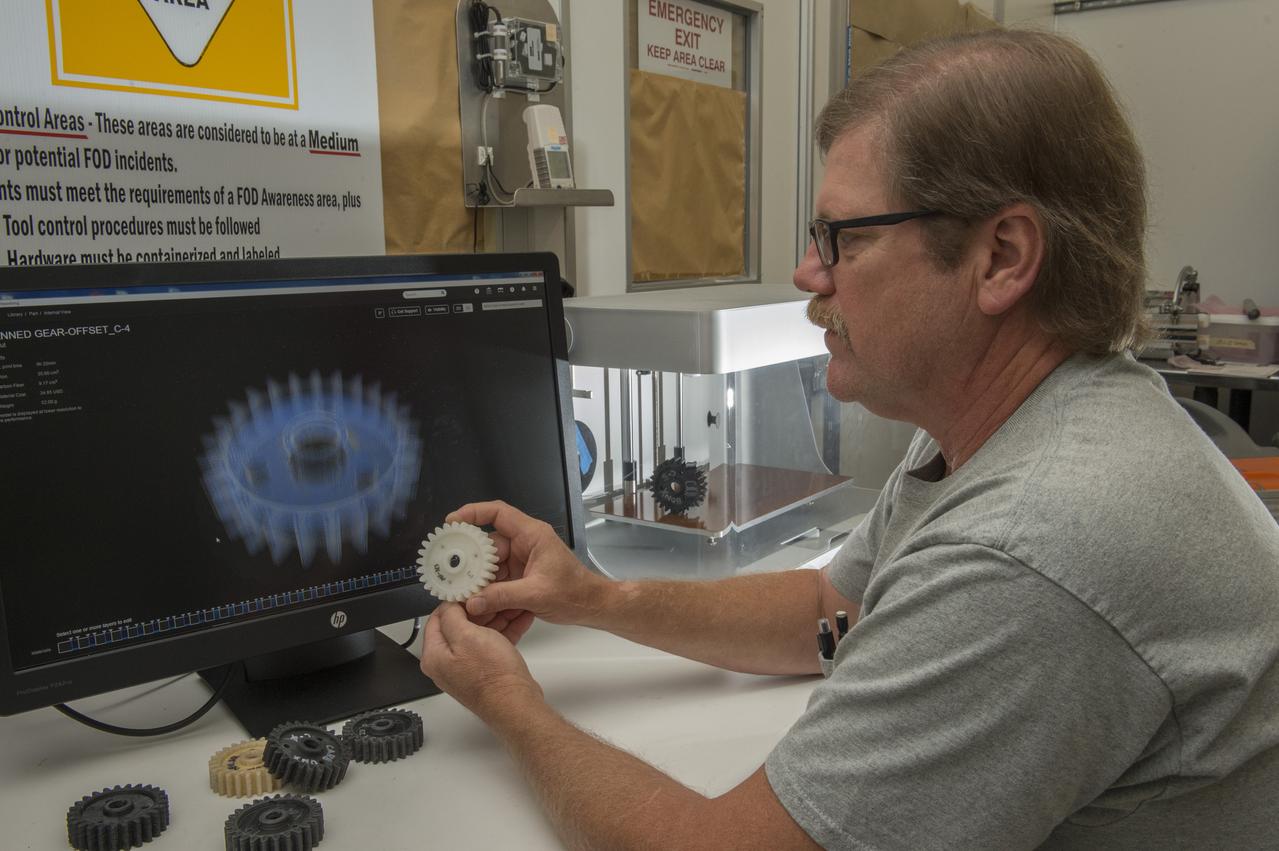

Phillip Steele (EM42/ESSSA) examines composite material gears printed with Marshall’s MarkForged® 3D Printer (background).
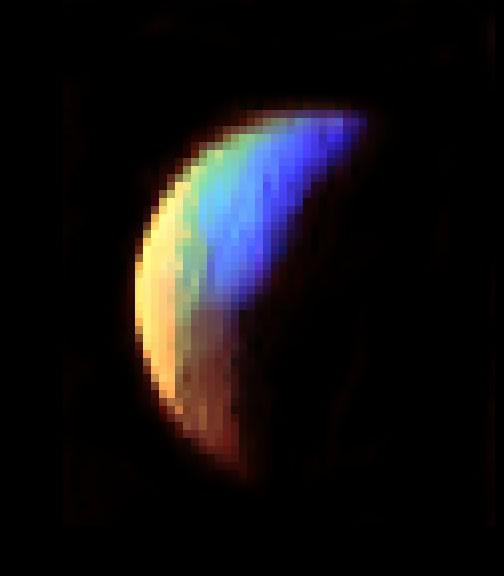

VIMS Shows Iapetus Surface Composition
A Compositional Map of the Tyre Region of Europa
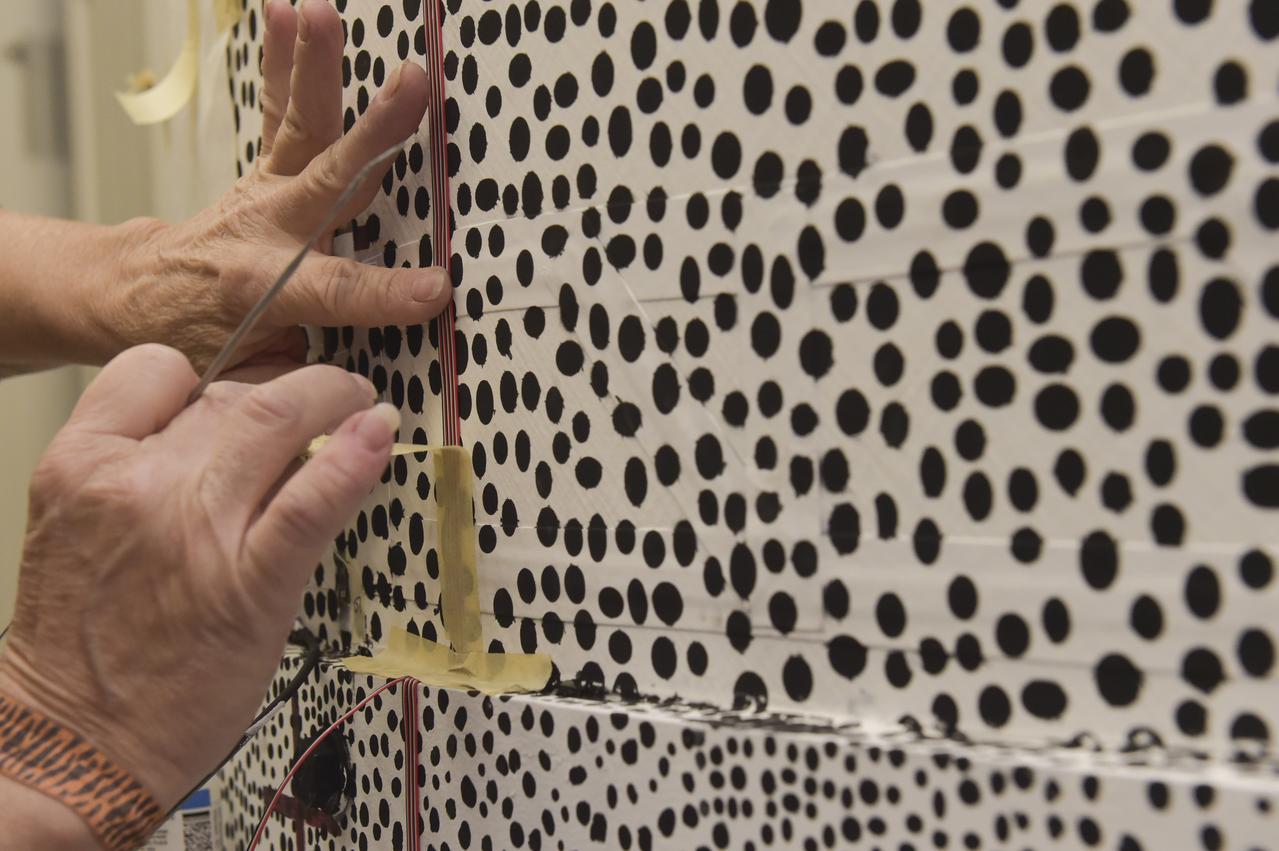

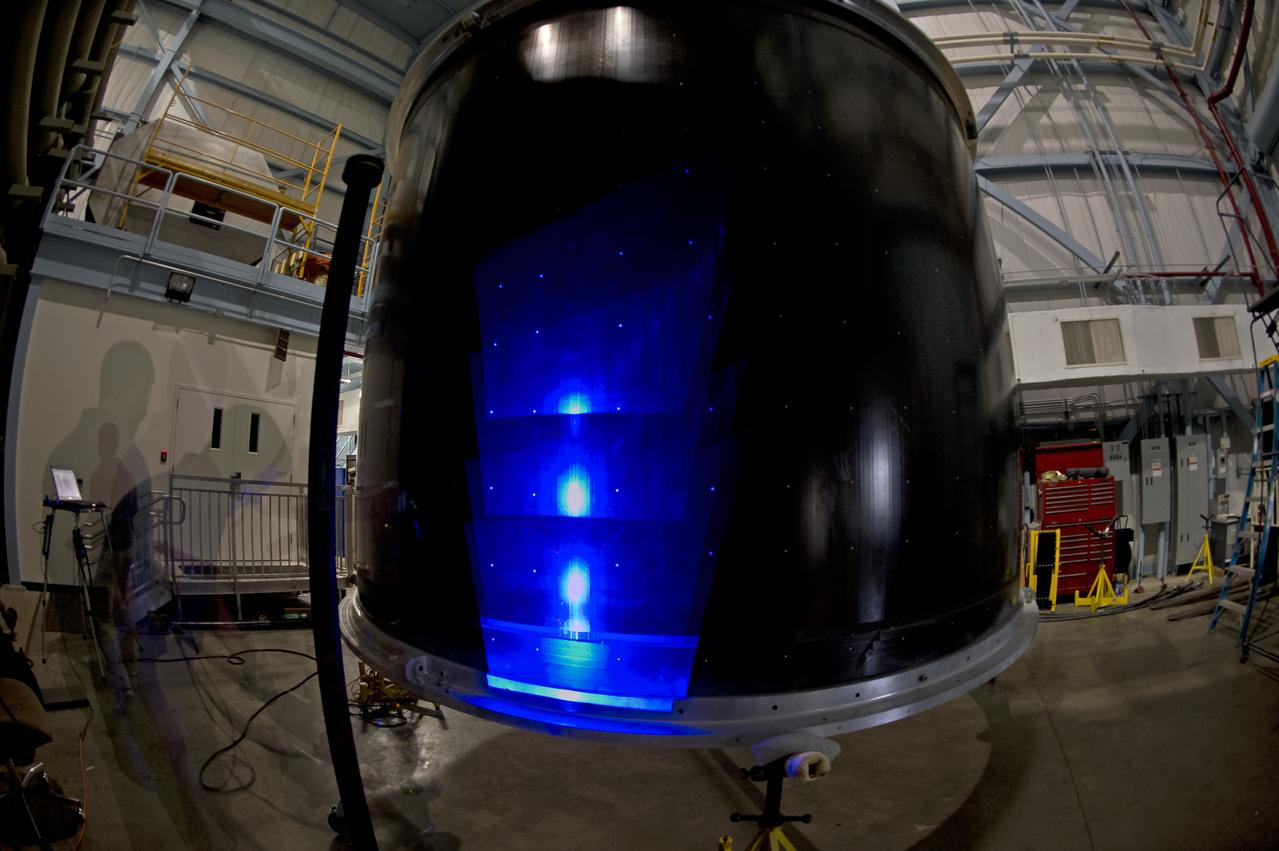
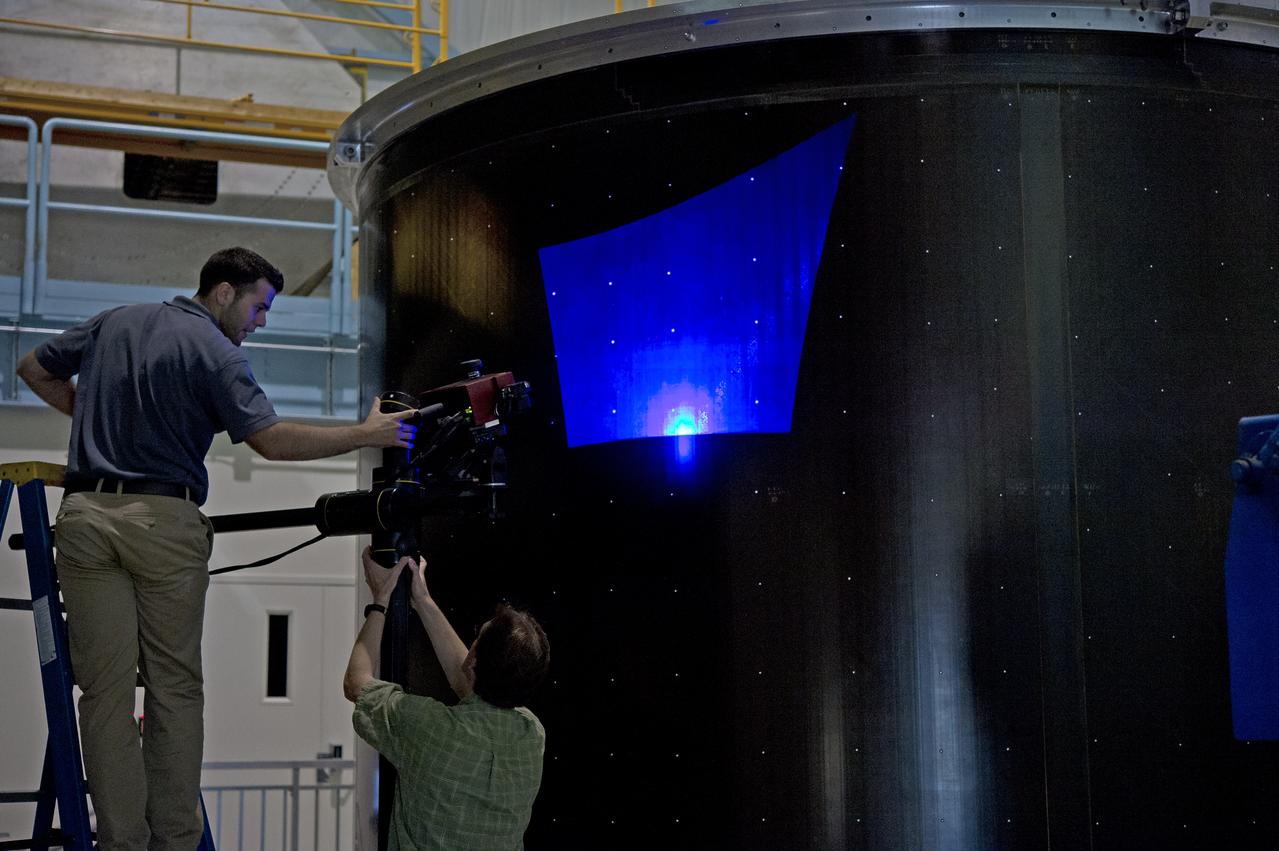
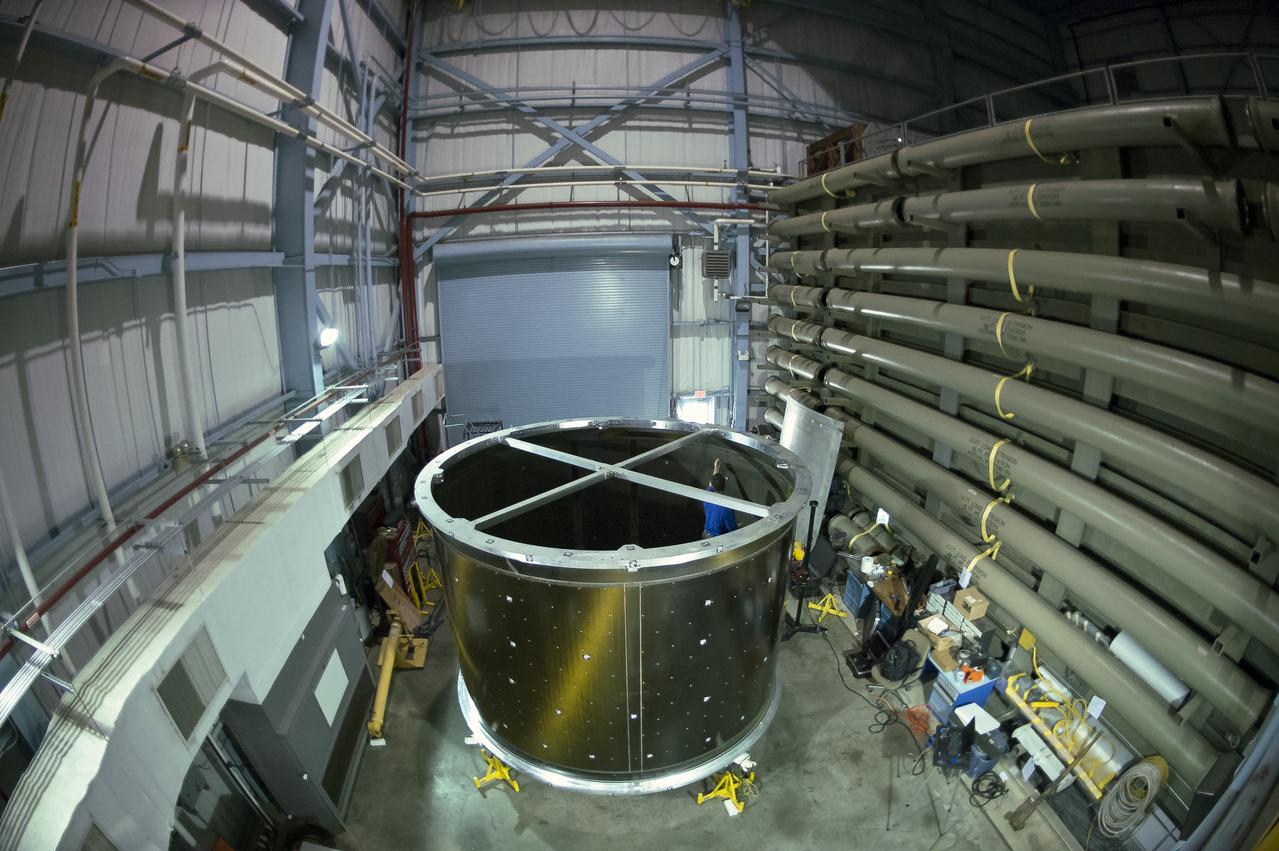
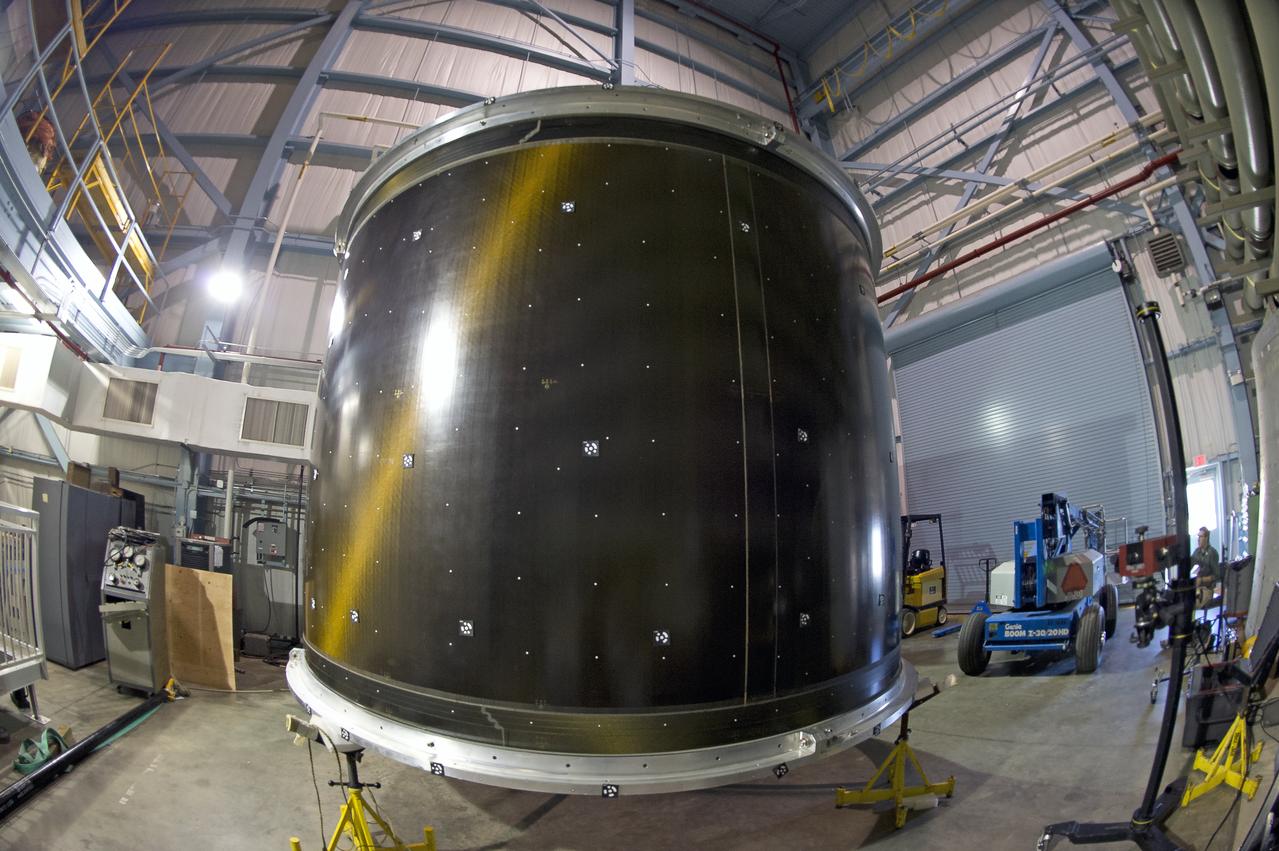
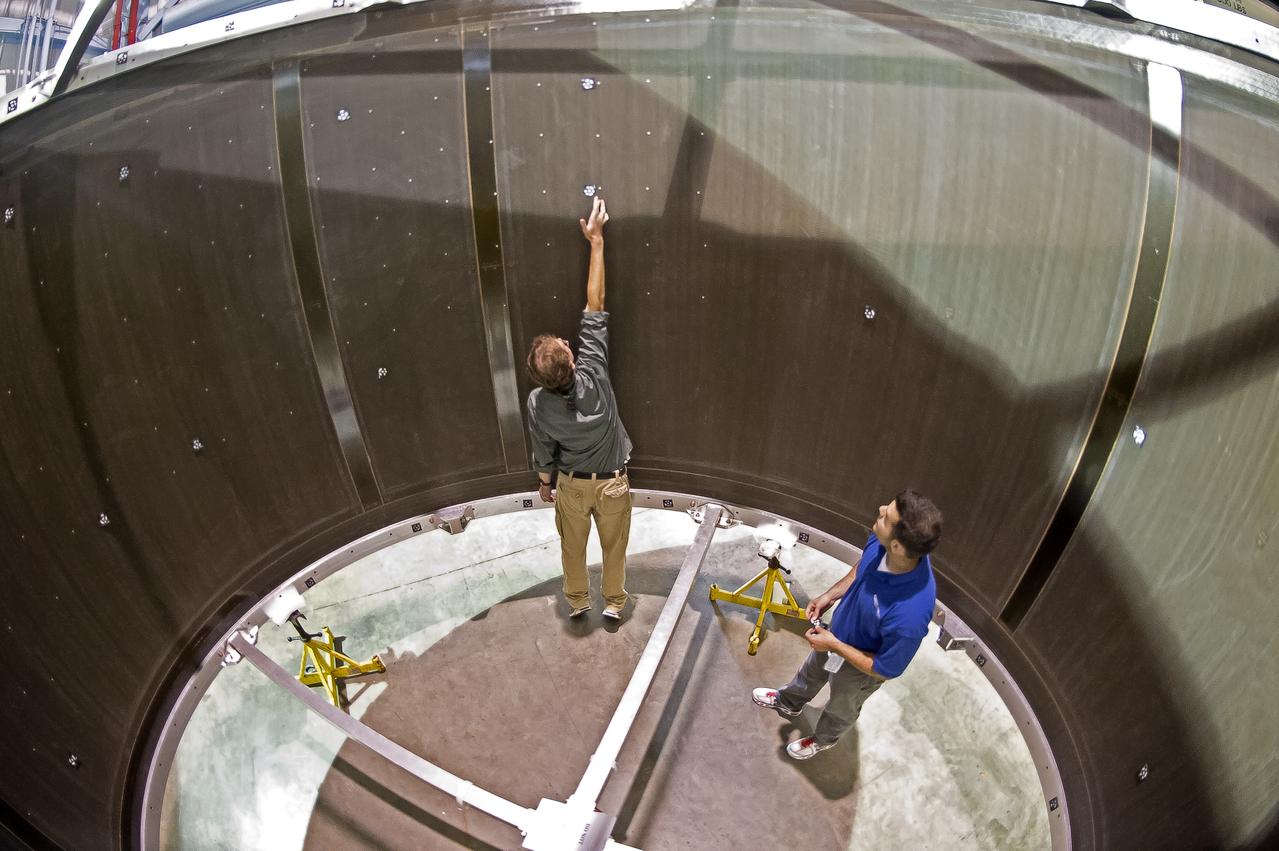
INSTALLATION OF STRESS SENSORS TO SHELL BUCKLE KNOCKDOWN FACTOR COMPOSITE TANK.
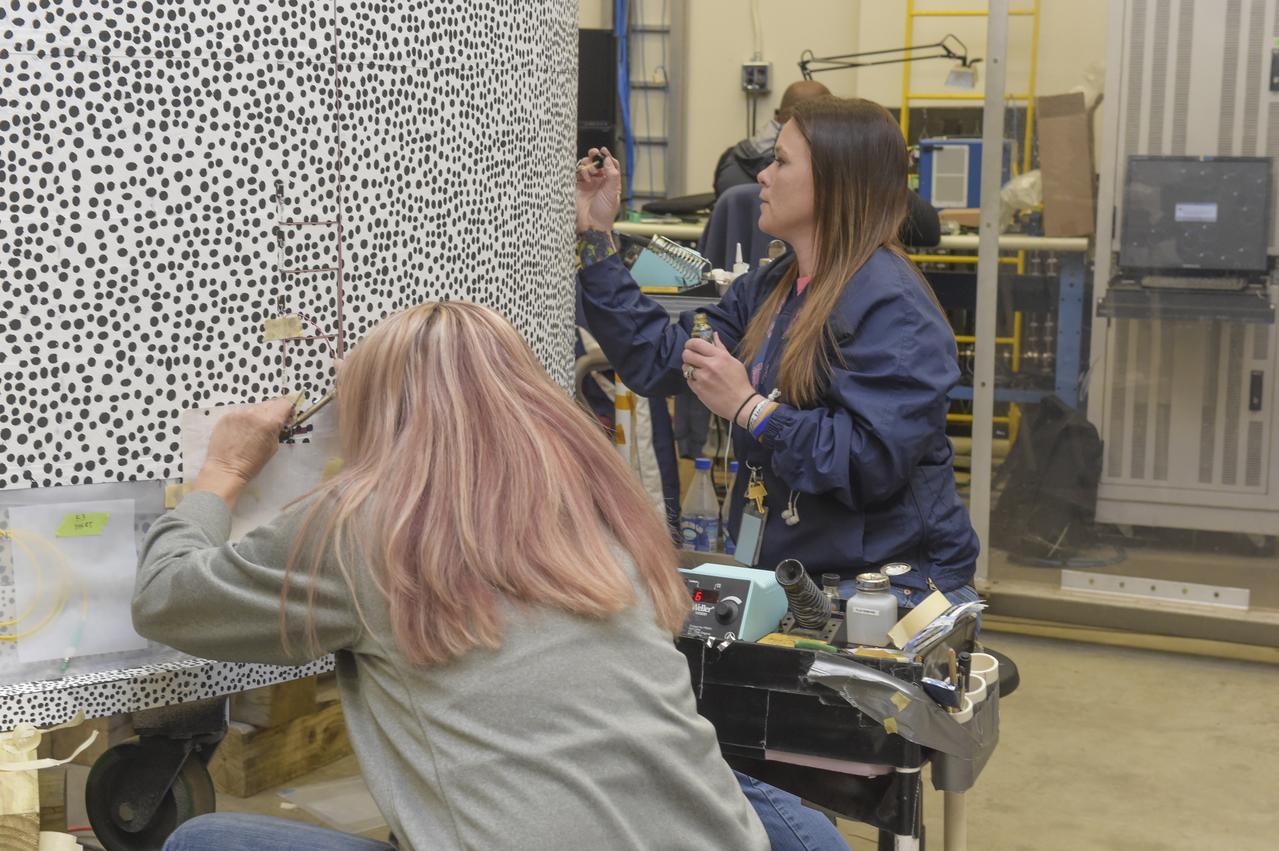

INSTALLATION OF STRESS SENSORS TO SHELL BUCKLE KNOCKDOWN FACTOR COMPOSITE TANK.
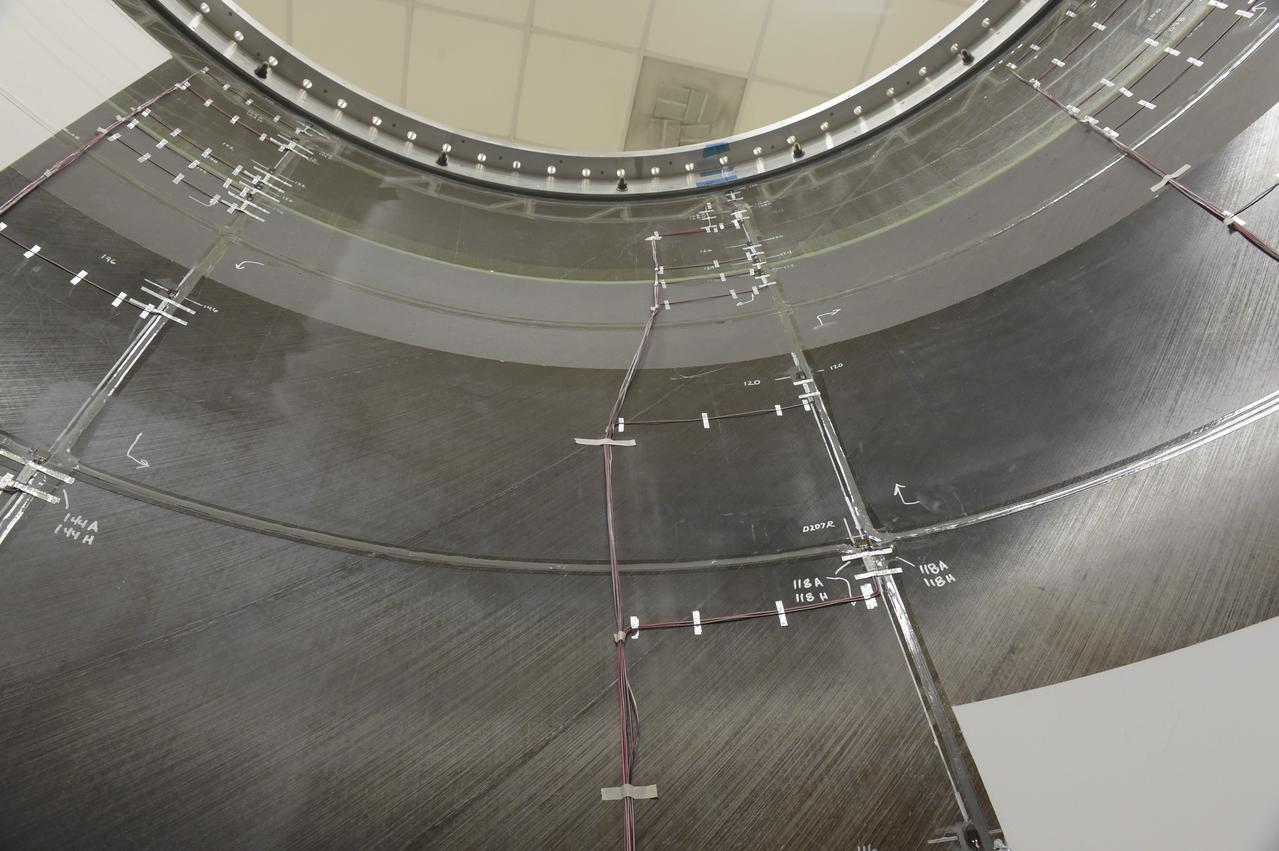

INSTALLATION OF STRESS SENSORS TO SHELL BUCKLE KNOCKDOWN FACTOR COMPOSITE TANK.
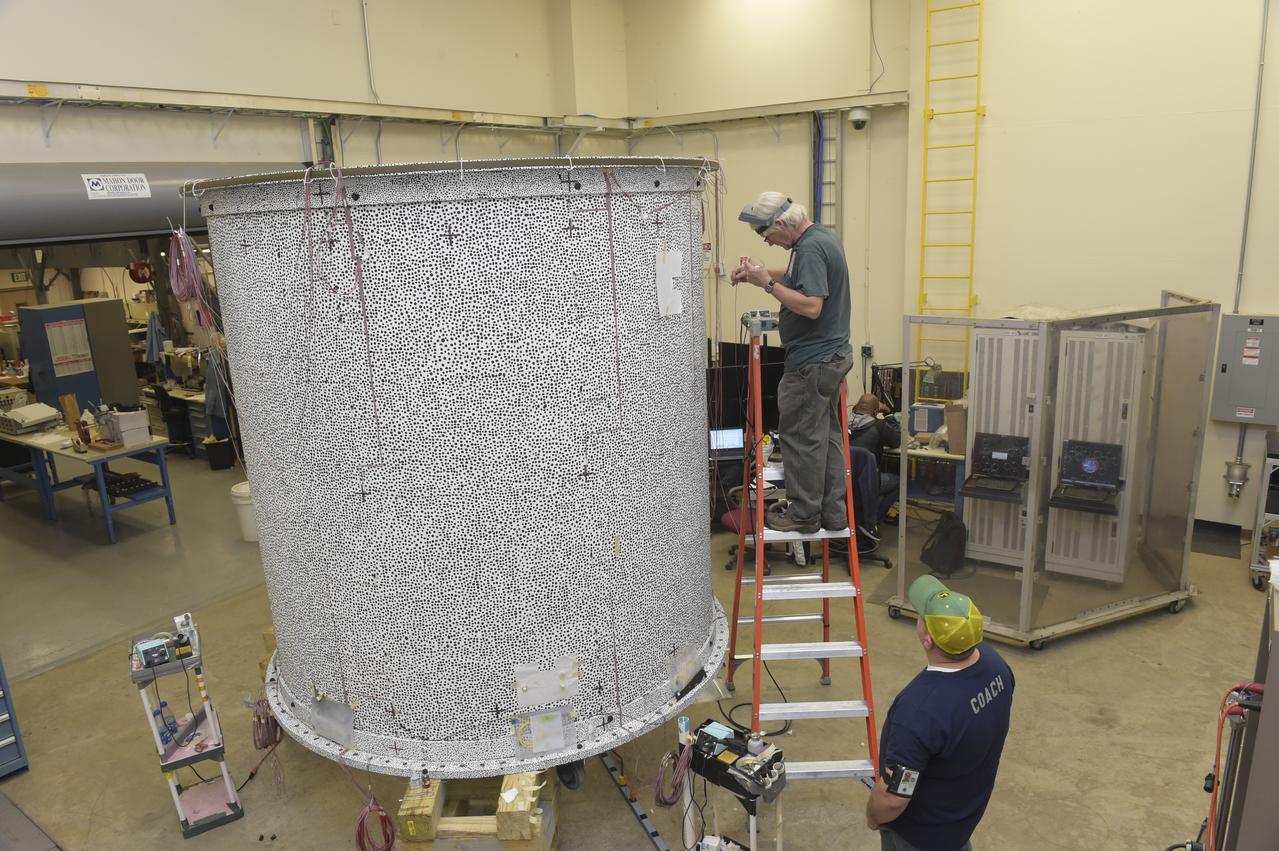

INSTALLATION OF STRESS SENSORS TO SHELL BUCKLE KNOCKDOWN FACTOR COMPOSITE TANK.
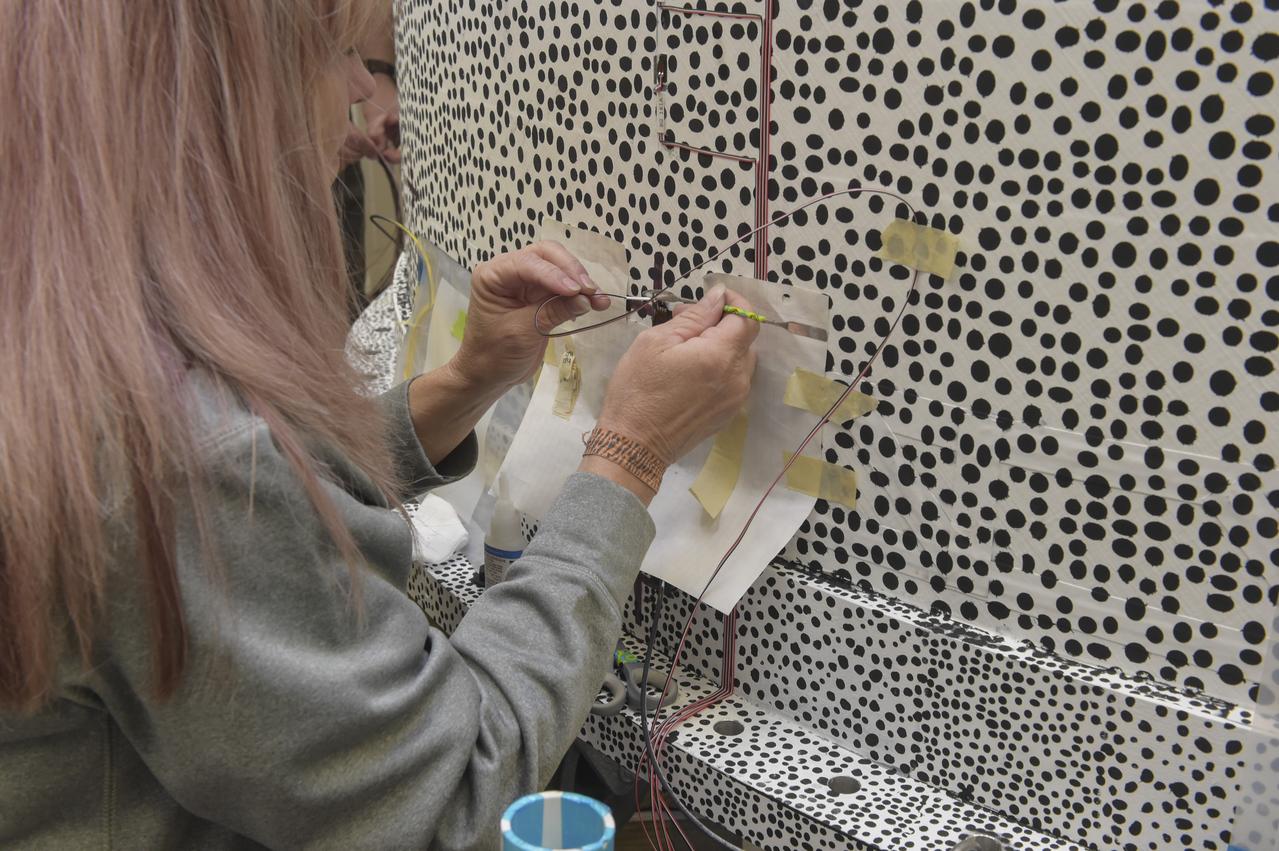

INSTALLATION OF STRESS SENSORS TO SHELL BUCKLE KNOCKDOWN FACTOR COMPOSITE TANK.
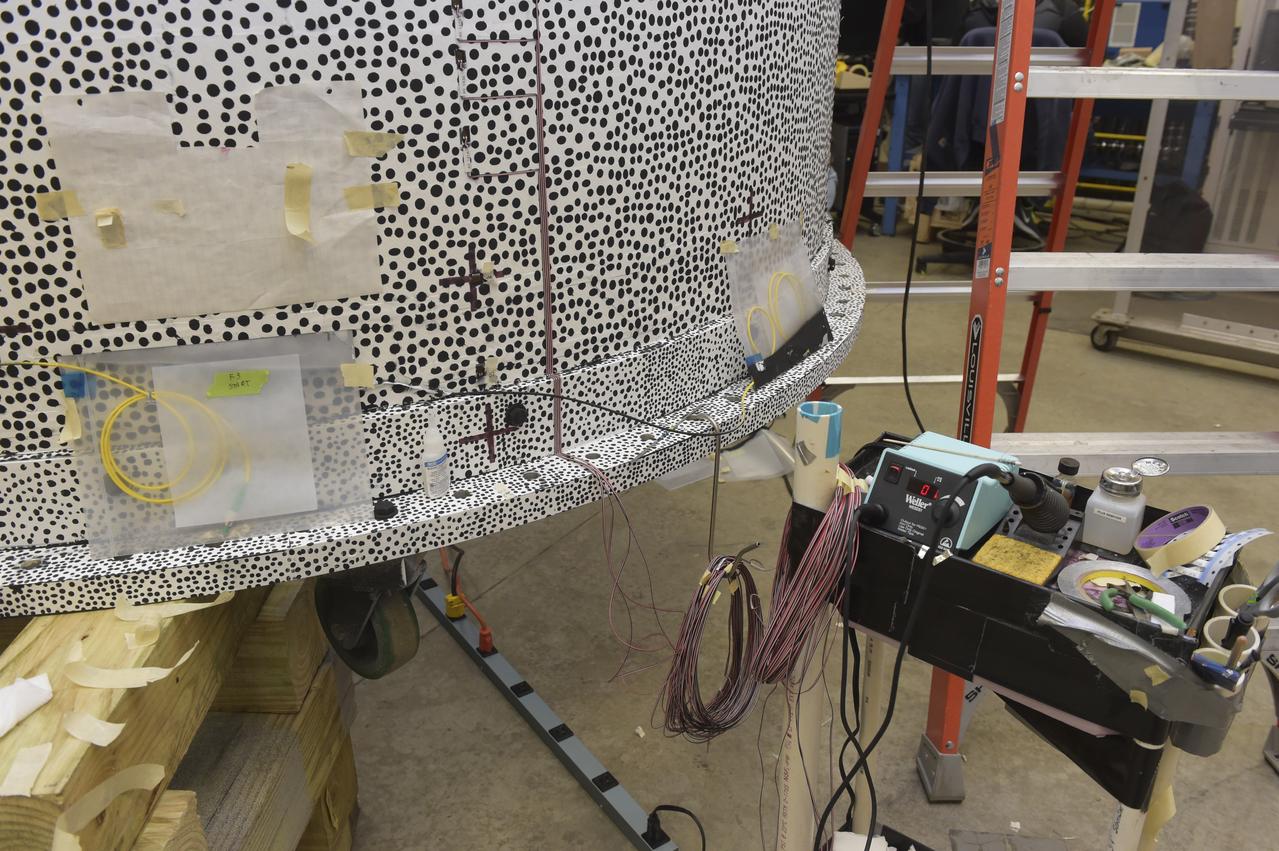

INSTALLATION OF STRESS SENSORS TO SHELL BUCKLE KNOCKDOWN FACTOR COMPOSITE TANK.
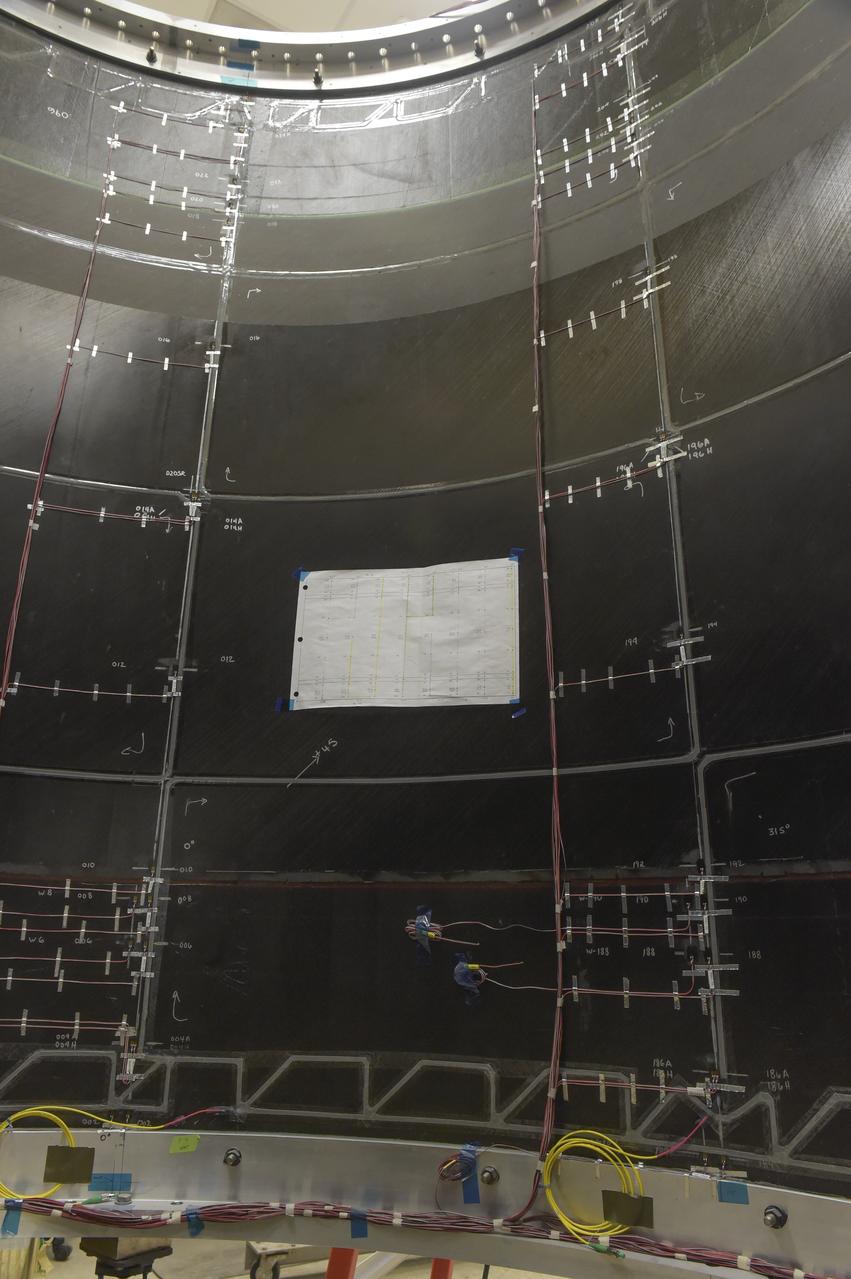

INSTALLATION OF STRESS SENSORS TO SHELL BUCKLE KNOCKDOWN FACTOR COMPOSITE TANK.
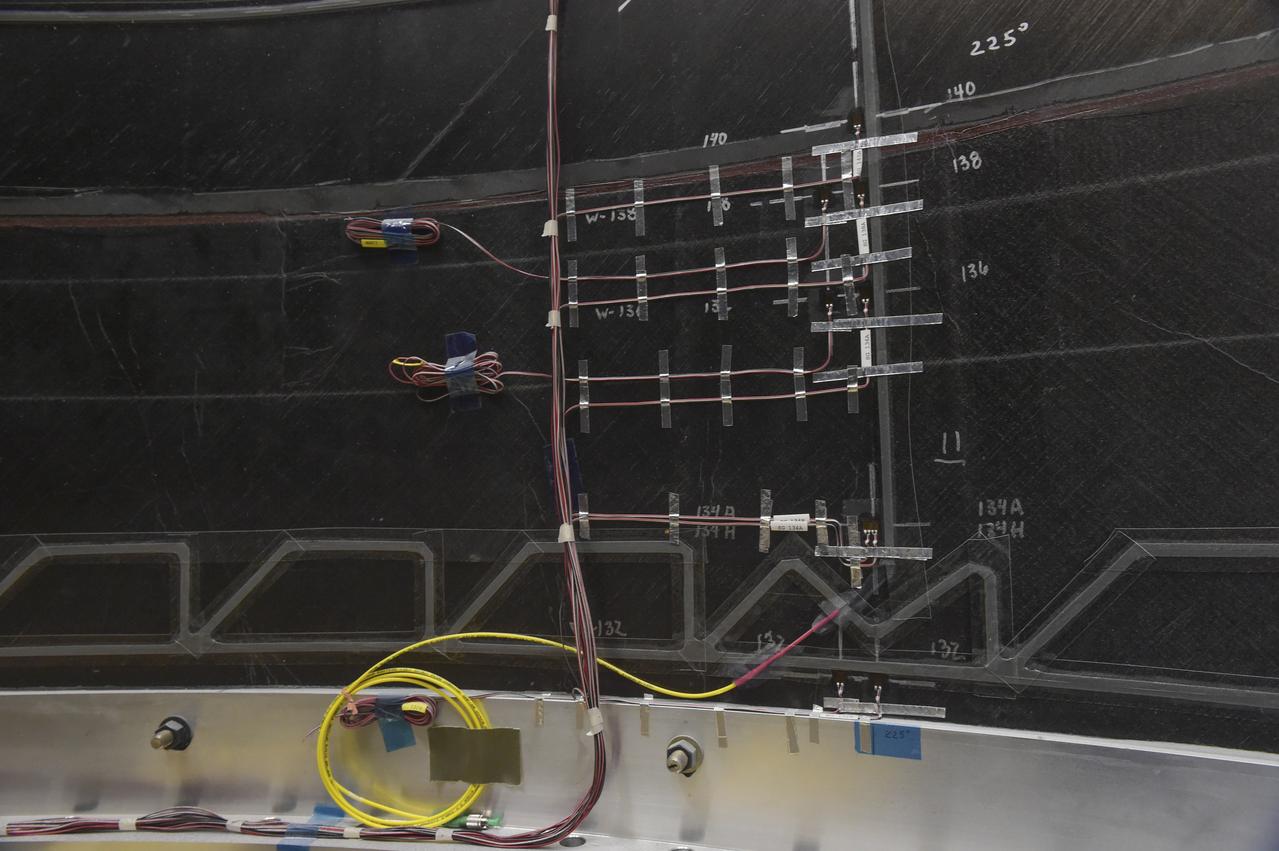

INSTALLATION OF STRESS SENSORS TO SHELL BUCKLE KNOCKDOWN FACTOR COMPOSITE TANK.
INSTALLATION OF STRESS SENSORS TO SHELL BUCKLE KNOCKDOWN FACTOR COMPOSITE TANK.
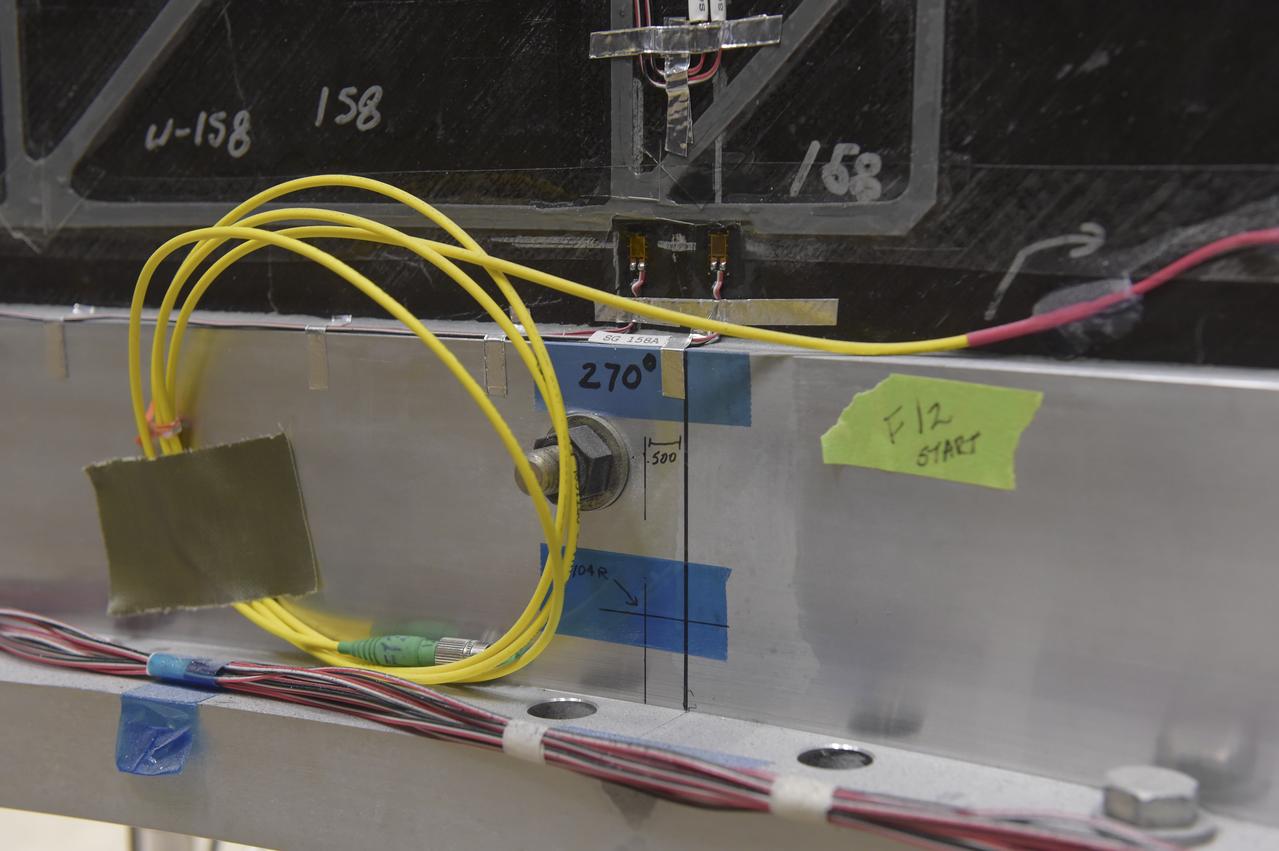

INSTALLATION OF STRESS SENSORS TO SHELL BUCKLE KNOCKDOWN FACTOR COMPOSITE TANK.
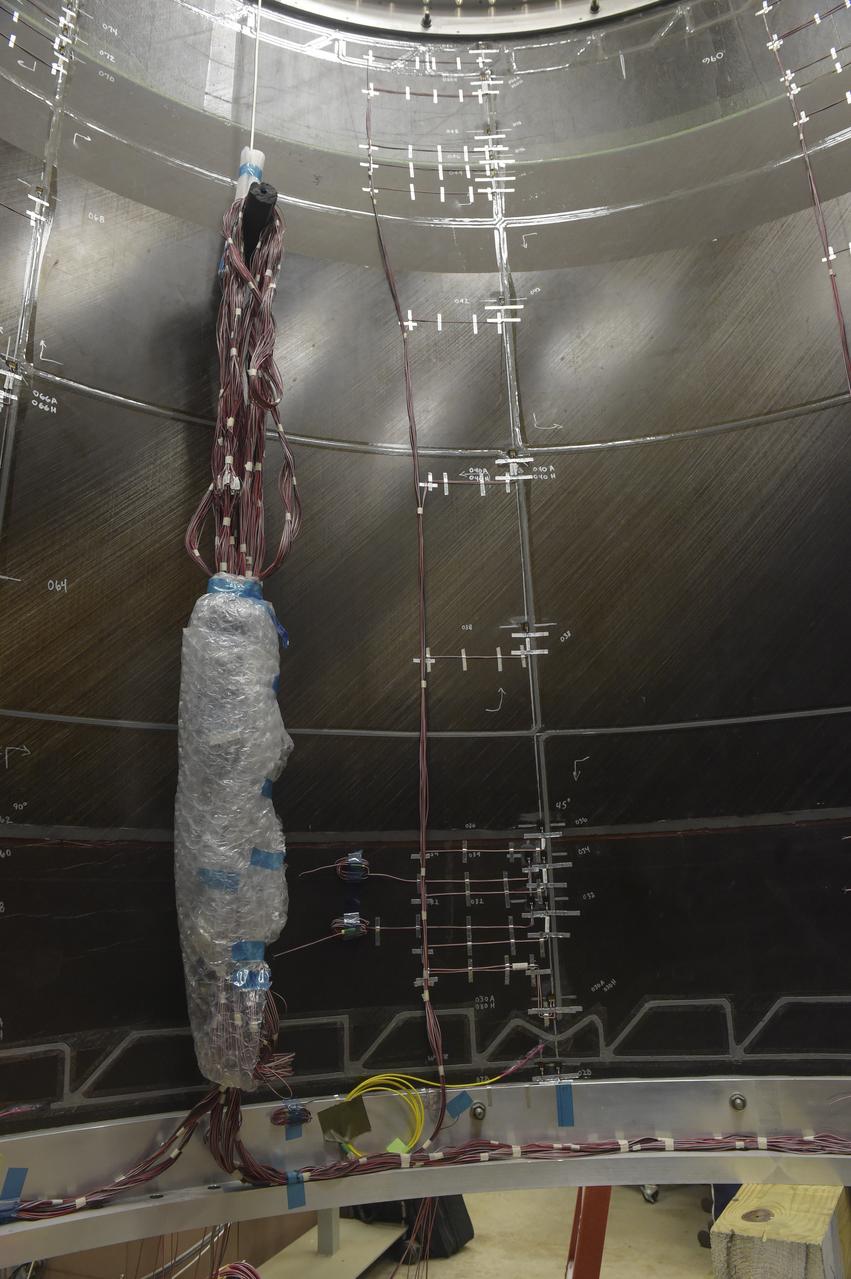

INSTALLATION OF STRESS SENSORS TO SHELL BUCKLE KNOCKDOWN FACTOR COMPOSITE TANK.
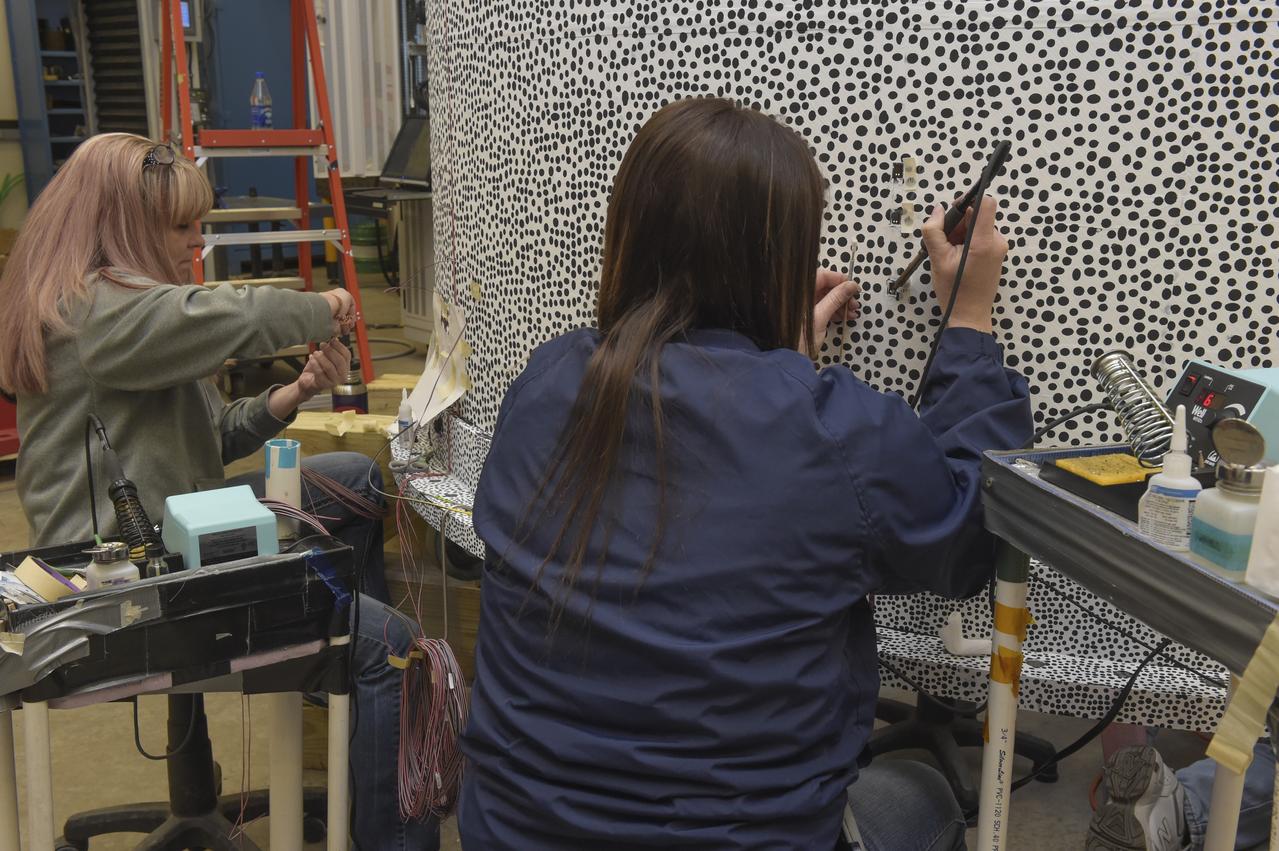

INSTALLATION OF STRESS SENSORS TO SHELL BUCKLE KNOCKDOWN FACTOR COMPOSITE TANK.
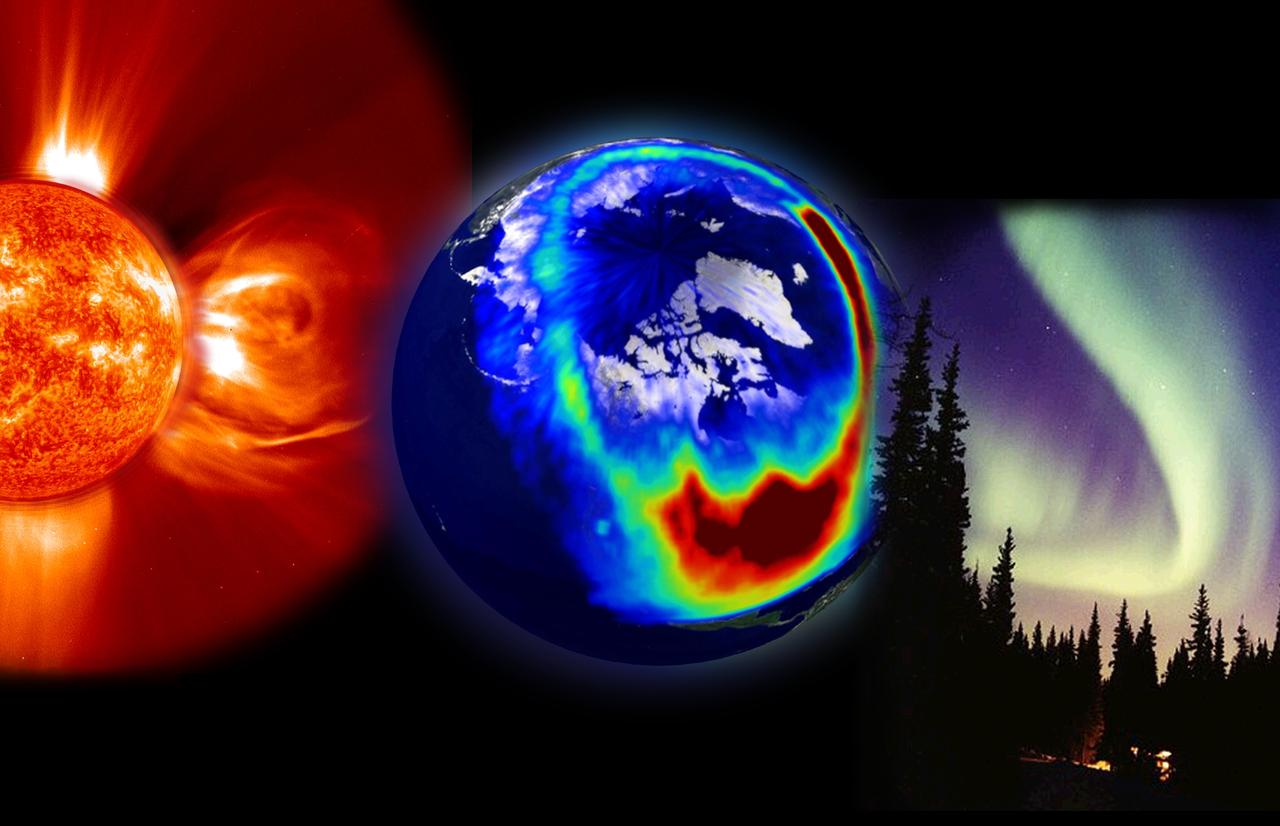
This composite image presents the three most visible elements of space weather: a storm from the Sun, aurora as seen from space, and aurora as seen from the Earth. The solar storm is a corona mass ejection (CME) composite from EIT 304Å superimposed on a LASCO C2 image, both from SOHO. The middle image from Polar’s VIS imager shows charged particles as they spread down across the U.S. during a large solar storm event on July 14, 2000. Lastly, Jan Curtis took this image of an aurora display in Alaska, the visible evidence of space weather that we see here on Earth. Credit: NASA/GSFC/SOHO/ESA To learn more go to the SOHO website: <a href="http://sohowww.nascom.nasa.gov/home.html" rel="nofollow">sohowww.nascom.nasa.gov/home.html</a> To learn more about NASA's Sun Earth Day go here: <a href="http://sunearthday.nasa.gov/2010/index.php" rel="nofollow">sunearthday.nasa.gov/2010/index.php</a>

White light shape and measurement of a 13.1 Foot diameter fluted-core sandwich composite test article designed by LaRC and fabricated by Boeing Under Space Act Agreement SAA1-737, Annex 14. to be tested in LaRC's combined Loads Testing System (COLTS).
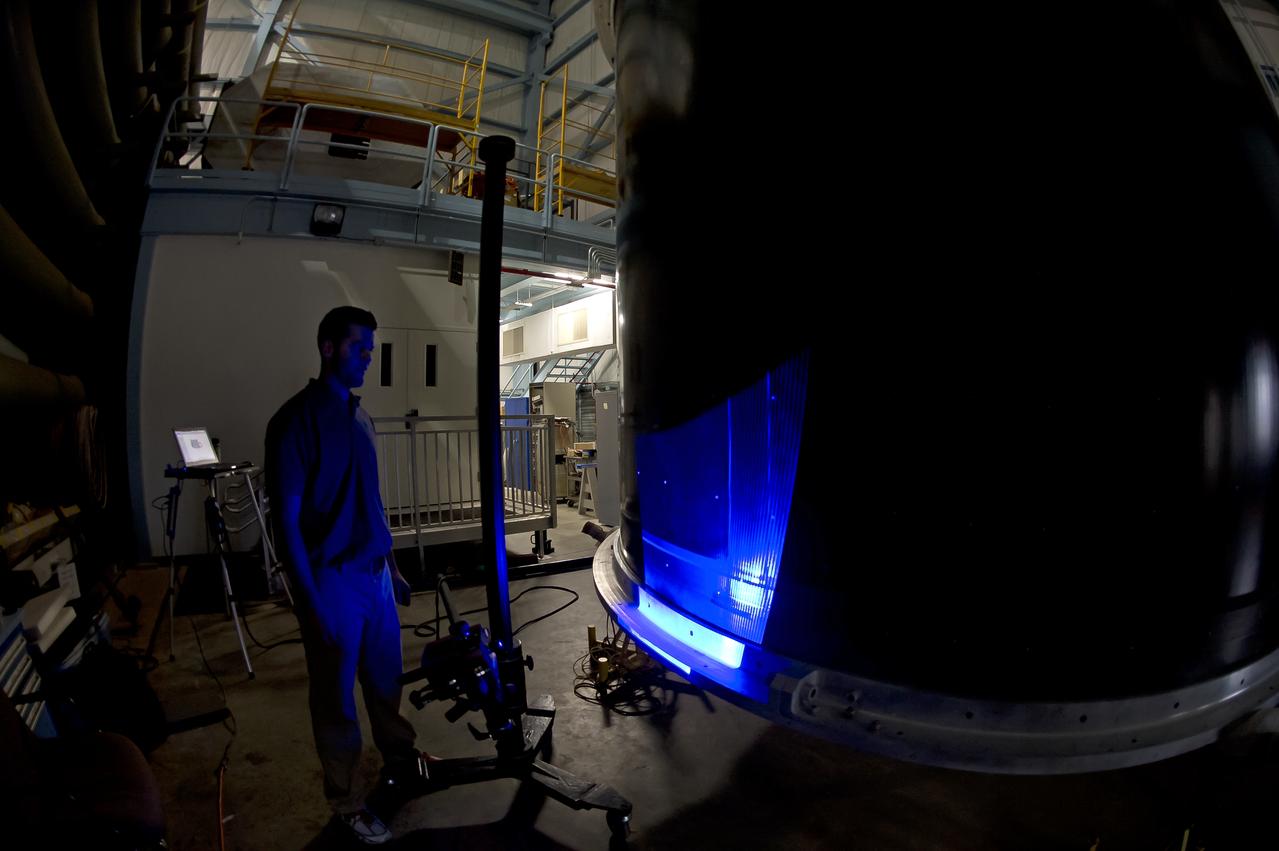

White light shape and measurement of a 13.1 Foot diameter fluted-core sandwich composite test article designed by LaRC and fabricated by Boeing Under Space Act Agreement SAA1-737, Annex 14. to be tested in LaRC's combined Loads Testing System (COLTS).
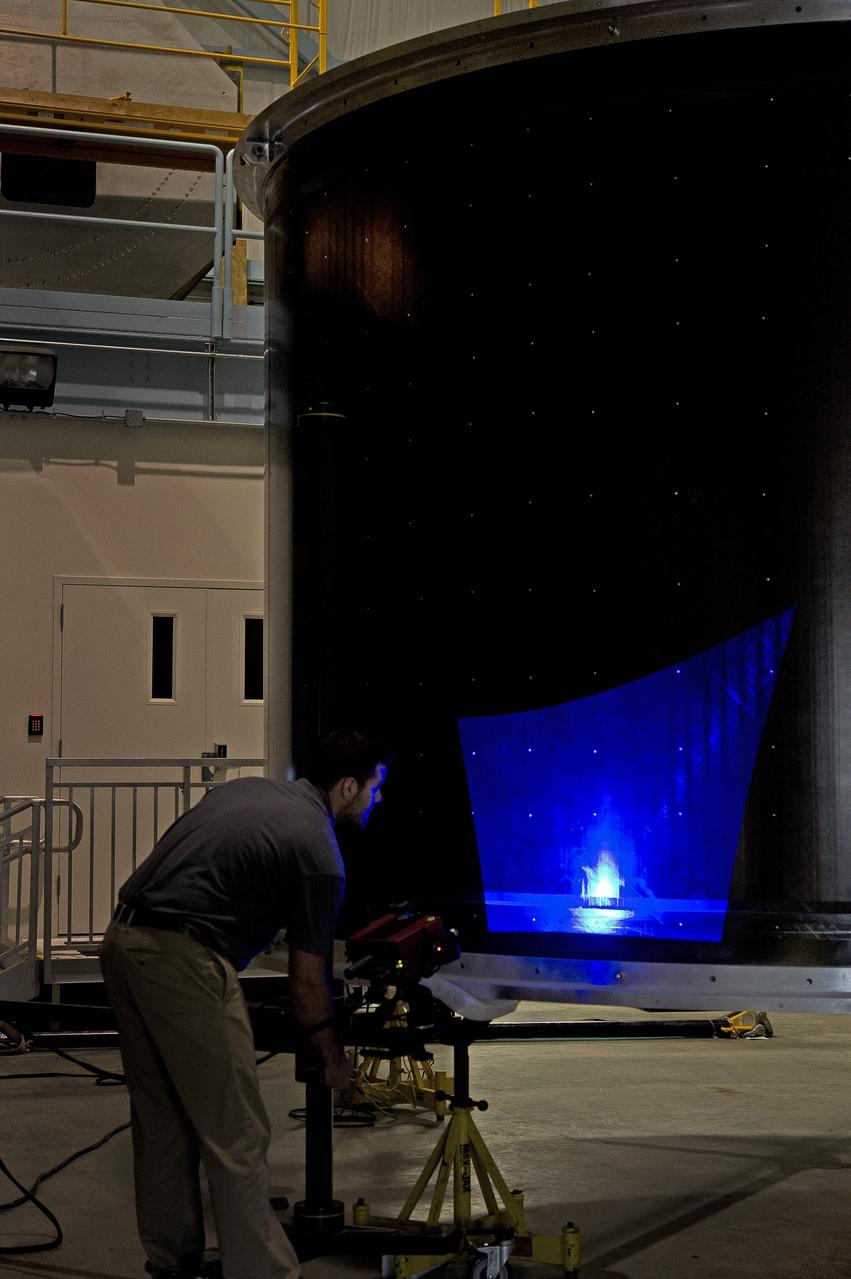

White light shape and measurement of a 13.1 Foot diameter fluted-core sandwich composite test article designed by LaRC and fabricated by Boeing Under Space Act Agreement SAA1-737, Annex 14. to be tested in LaRC's combined Loads Testing System (COLTS).

White light shape and measurement of a 13.1 Foot diameter fluted-core sandwich composite test article designed by LaRC and fabricated by Boeing Under Space Act Agreement SAA1-737, Annex 14. to be tested in LaRC's combined Loads Testing System (COLTS).

White light shape and measurement of a 13.1 Foot diameter fluted-core sandwich composite test article designed by LaRC and fabricated by Boeing Under Space Act Agreement SAA1-737, Annex 14. to be tested in LaRC's combined Loads Testing System (COLTS).

White light shape and measurement of a 13.1 Foot diameter fluted-core sandwich composite test article designed by LaRC and fabricated by Boeing Under Space Act Agreement SAA1-737, Annex 14. to be tested in LaRC's combined Loads Testing System (COLTS).

White light shape and measurement of a 13.1 Foot diameter fluted-core sandwich composite test article designed by LaRC and fabricated by Boeing Under Space Act Agreement SAA1-737, Annex 14. to be tested in LaRC's combined Loads Testing System (COLTS).

White light shape and measurement of a 13.1 Foot diameter fluted-core sandwich composite test article designed by LaRC and fabricated by Boeing Under Space Act Agreement SAA1-737, Annex 14. to be tested in LaRC's combined Loads Testing System (COLTS).

White light shape and measurement of a 13.1 Foot diameter fluted-core sandwich composite test article designed by LaRC and fabricated by Boeing Under Space Act Agreement SAA1-737, Annex 14. to be tested in LaRC's combined Loads Testing System (COLTS).

White light shape and measurement of a 13.1 Foot diameter fluted-core sandwich composite test article designed by LaRC and fabricated by Boeing Under Space Act Agreement SAA1-737, Annex 14. to be tested in LaRC's combined Loads Testing System (COLTS).

White light shape and measurement of a 13.1 Foot diameter fluted-core sandwich composite test article designed by LaRC and fabricated by Boeing Under Space Act Agreement SAA1-737, Annex 14. to be tested in LaRC's combined Loads Testing System (COLTS).

White light shape and measurement of a 13.1 Foot diameter fluted-core sandwich composite test article designed by LaRC and fabricated by Boeing Under Space Act Agreement SAA1-737, Annex 14. to be tested in LaRC's combined Loads Testing System (COLTS).

NASA’s Advanced Composite Solar Sail System is seen orbiting Earth in this 13-second exposure photograph, Monday, Sept. 2, 2024, from Arlington, Virginia. The mission team confirmed the spacecraft’s unique composite boom system unfurled its reflective sail on Thursday, accomplishing a critical milestone in the agency’s demonstration of next-generation solar sail technology that will allow small spacecraft to “sail on sunlight.” Just as a sailboat is powered by wind in a sail, a spacecraft can use the pressure of sunlight on a solar sail for propulsion. This technology demonstration serves as a pathfinder for future missions powered by solar sail technology. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
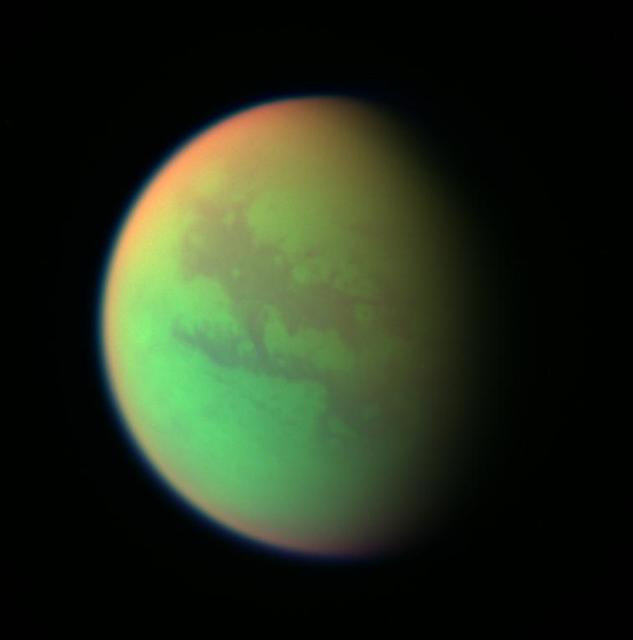

Cassini Views of Titan: False Color Composite
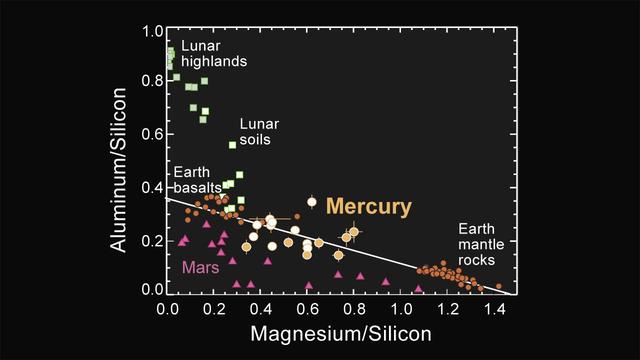
Major-element Composition of Mercury Surface Materials
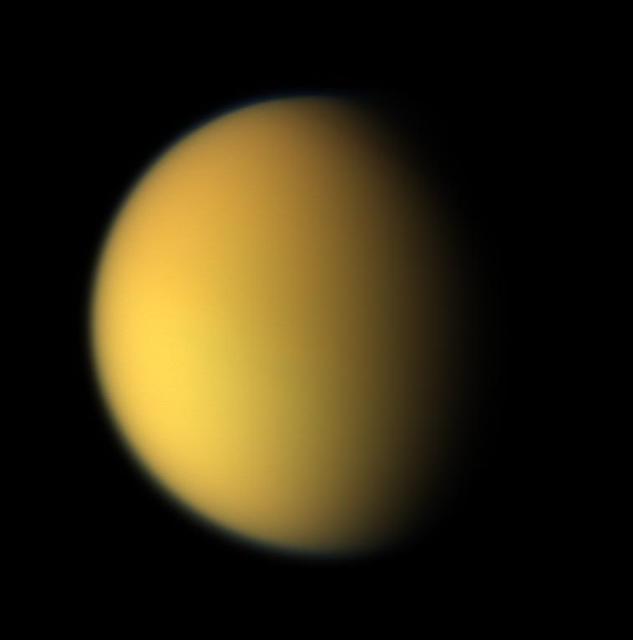

Cassini View of Titan: Natural Color Composite
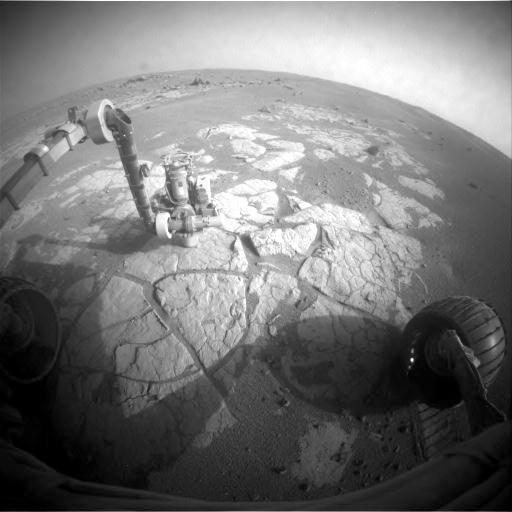

Opportunity Examining Composition of Cook Islands Outcrop
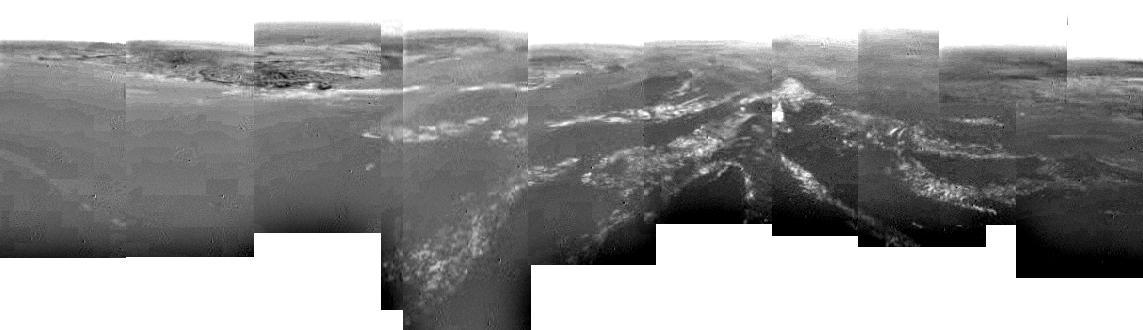
Composite of Titan Surface Seen During Descent

These composite images from NASA Dawn spacecraft images show the spectacular spectral diversity of asteroid Vesta surface.
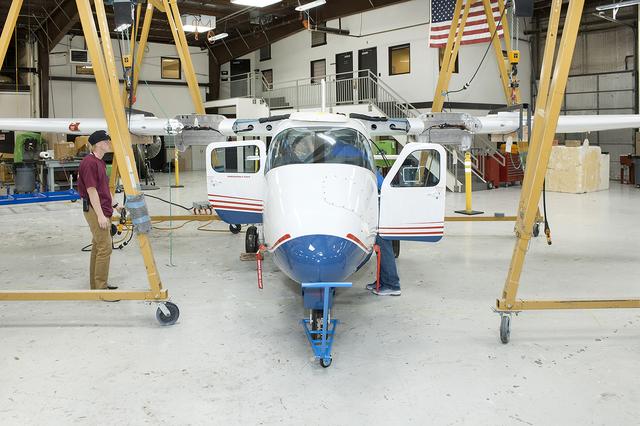

The Tecnam P2006T undergoes wing integration at Scaled Composites in Mojave, California, where the aircraft’s system will be converted to feature electric propulsion.

On May 9, 2016, Mercury passed directly between the sun and Earth. This event – which happens about 13 times each century – is called a transit. NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO, studies the sun 24/7 and captured the entire seven-and-a-half-hour event. This composite image of Mercury’s journey across the sun was created with visible-light images from the Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager on SDO. Image Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/SDO/Genna Duberstein <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Variations in the appearance of the giant plume from the Tvashtar volcano on Jupiter moon Io are seen in this composite of the best photos taken by the New Horizons Long Range Reconnaissance Imager LORRI during its Jupiter flyby in late February.
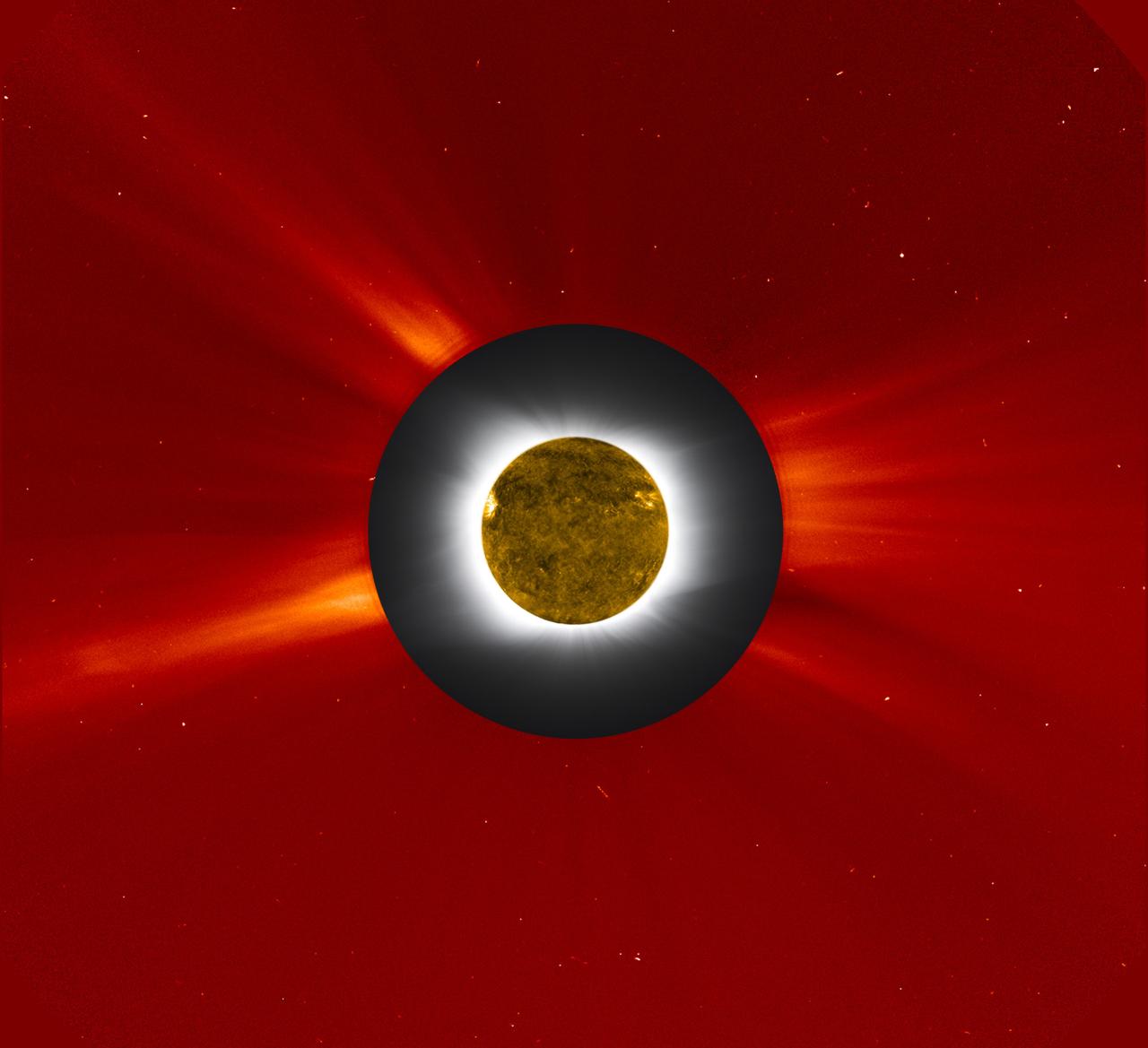

Eclipse 2010 Composite A solar eclipse photo (gray and white) from the Williams College Expedition to Easter Island in the South Pacific (July 11, 2010) was embedded with an image of the Sun’s outer corona taken by the Large Angle Spectrometric Coronagraph (LASCO) on the SOHO spacecraft and shown in red false color. LASCO uses a disk to blot out the bright sun and the inner corona so that the faint outer corona can be monitored and studied. Further, the dark silhouette of the moon was covered with an image of the Sun taken in extreme ultraviolet light at about the same time by the Atmospheric Imaging Assembly on Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). The composite brings out the correlation of structures in the inner and outer corona. Credits: Williams College Eclipse Expedition -- Jay M. Pasachoff, Muzhou Lu, and Craig Malamut; SOHO’s LASCO image courtesy of NASA/ESA; solar disk image from NASA’s SDO; compositing by Steele Hill, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. NASA Goddard Space Flight Center is home to the nation's largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe.
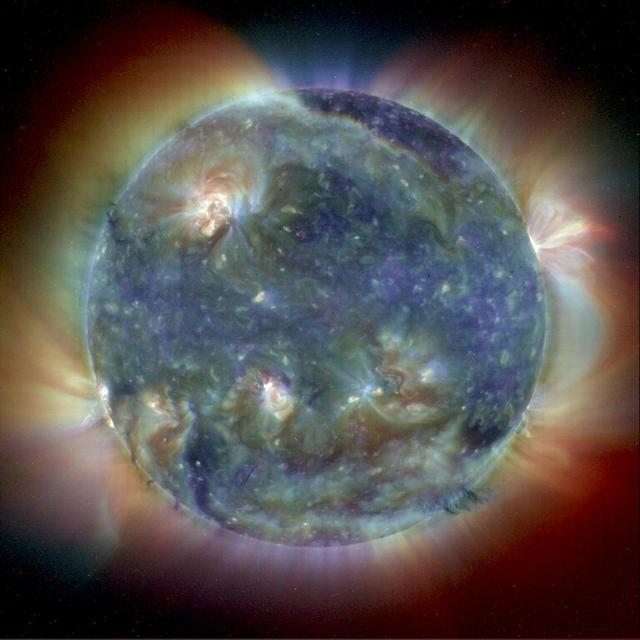
This composite image combines NASA Extreme Ultravoilet Imaging Telescope images from three wavelengths into one that reveals solar features unique to each wavelength.
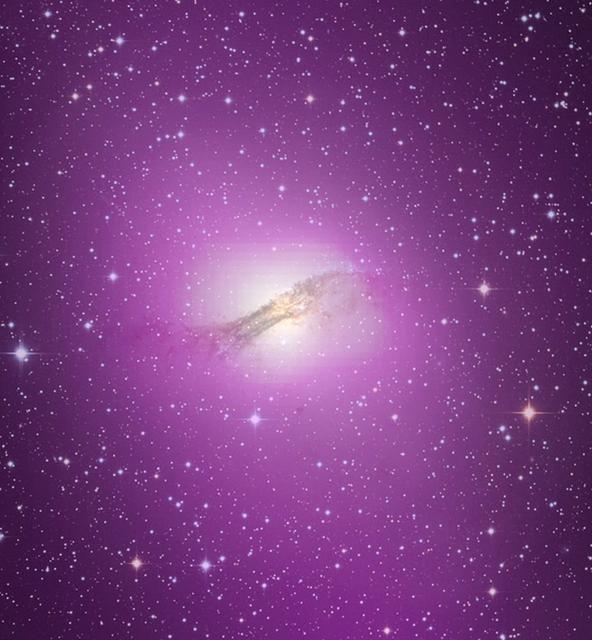

NASA release April 1, 2010 The gamma-ray output from Cen A's lobes exceeds their radio output by more than ten times. High-energy gamma rays detected by Fermi's Large Area Telescope are depicted as purple in this gamma ray/optical composite of the galaxy. Credit: NASA/DOE/Fermi LAT Collaboration, Capella Observatory To learn more about these images go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/GLAST/news/smokestack-plumes.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/GLAST/news/smokestack-plumes.html</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> is home to the nation's largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe.

NASA release April 1, 2010 The gamma-ray output from Cen A's lobes exceeds their radio output by more than ten times. High-energy gamma rays detected by Fermi's Large Area Telescope are depicted as purple in this gamma ray/optical composite of the galaxy. Credit: NASA/DOE/Fermi LAT Collaboration, Capella Observatory To learn more about these images go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/GLAST/news/smokestack-plumes.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/GLAST/news/smokestack-plumes.html</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> is home to the nation's largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe.
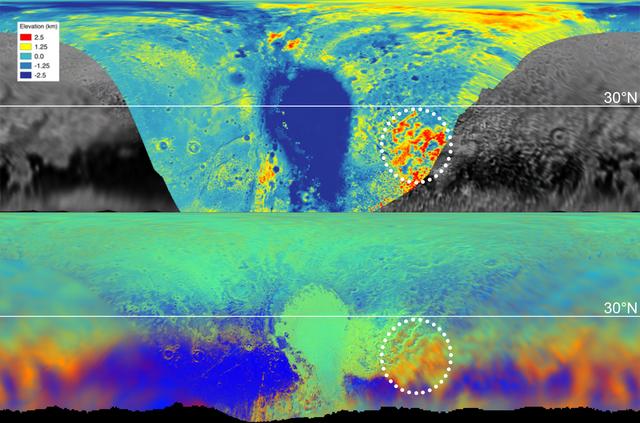
These maps are from New Horizons' data on the topography (top) and composition (bottom) of Pluto's surface. In the high-resolution topographical map, the highlighted red region is high in elevation. The map below, showing the composition, indicates the same section also contains methane, color-coded in orange. One can see the orange features spread into the fuzzier, lower-resolution data that covers the rest of the globe, meaning those areas, too, are high in methane, and therefore likely to be high in elevation. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22036
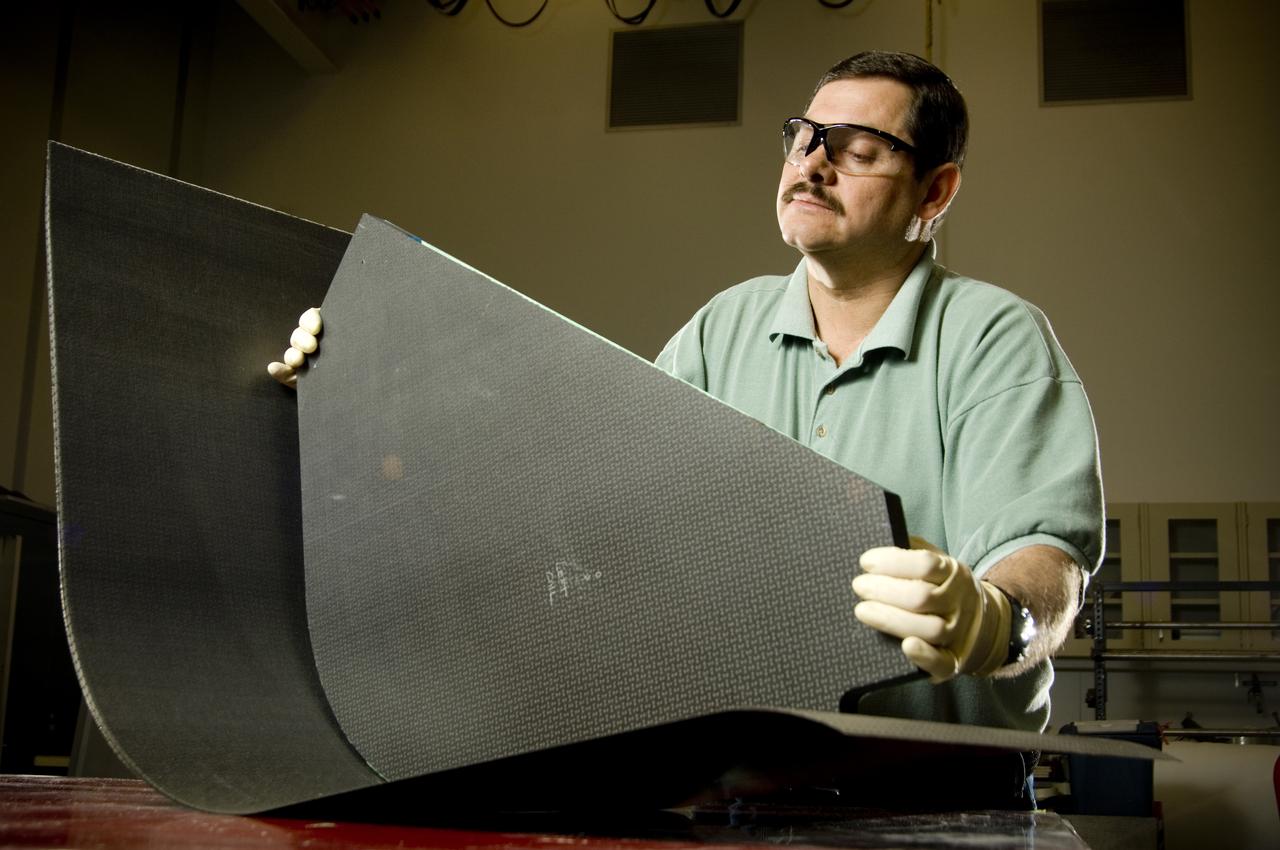

PHILLIP THOMPSON (ENGINEERING TECHNICIAN, ATK LS) ASSEMBLES A COMPOSITE

PHILLIP THOMPSON (ENGINEERING TECHNICIAN, ATK LS) ASSEMBLES A COMPOSITE
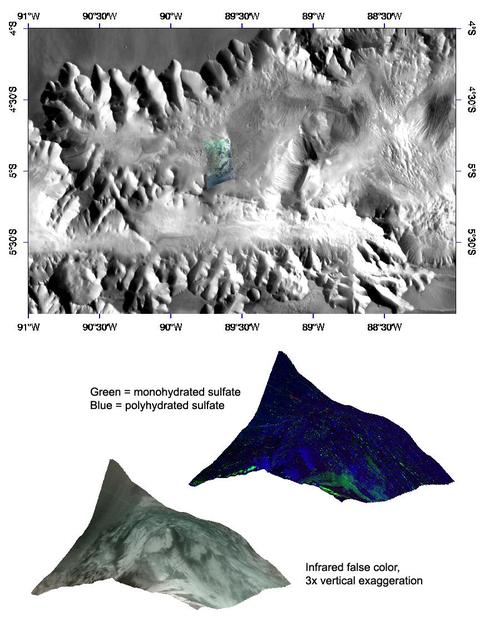
Interior Layered Deposits in Tithonium Chasma Reveal Diverse Compositions
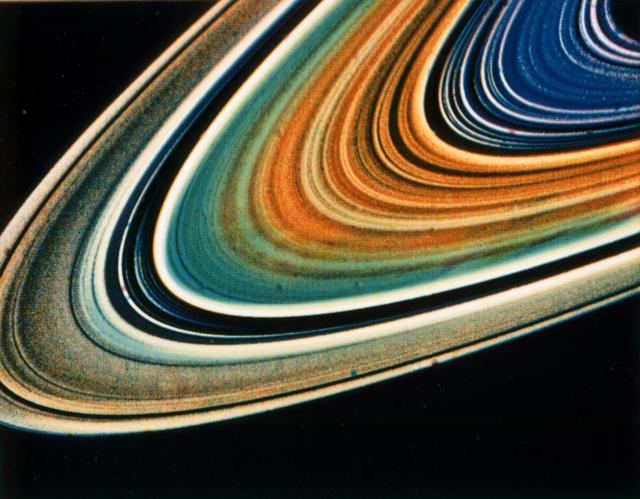

Possible variations in chemical composition from one part of Saturn ring system to another are visible in this archival image from NASA Voyager 2.

Color differences in this daytime infrared image taken by NASA Mars Odyssey spacecraft represent differences in the mineral composition of the rocks, sediments and dust on the surface.
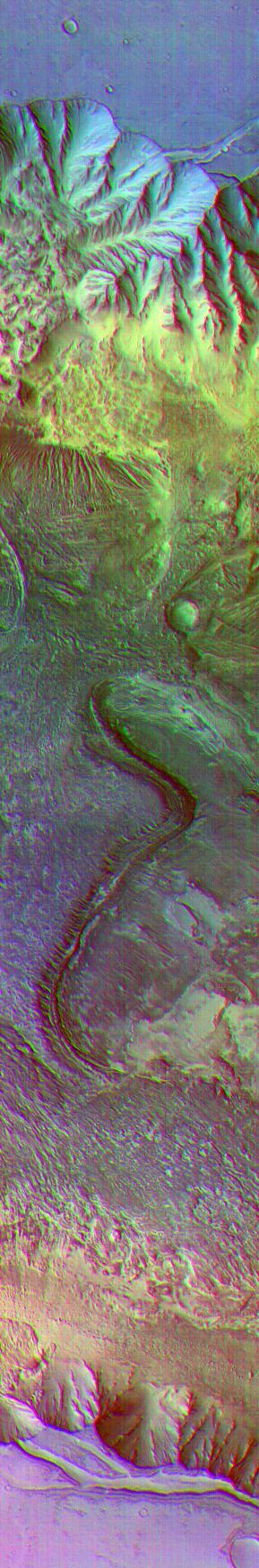
Color differences in this daytime infrared image taken by the camera on NASA Mars Odyssey spacecraft represent differences in the mineral composition of the rocks, sediments and dust on the surface.
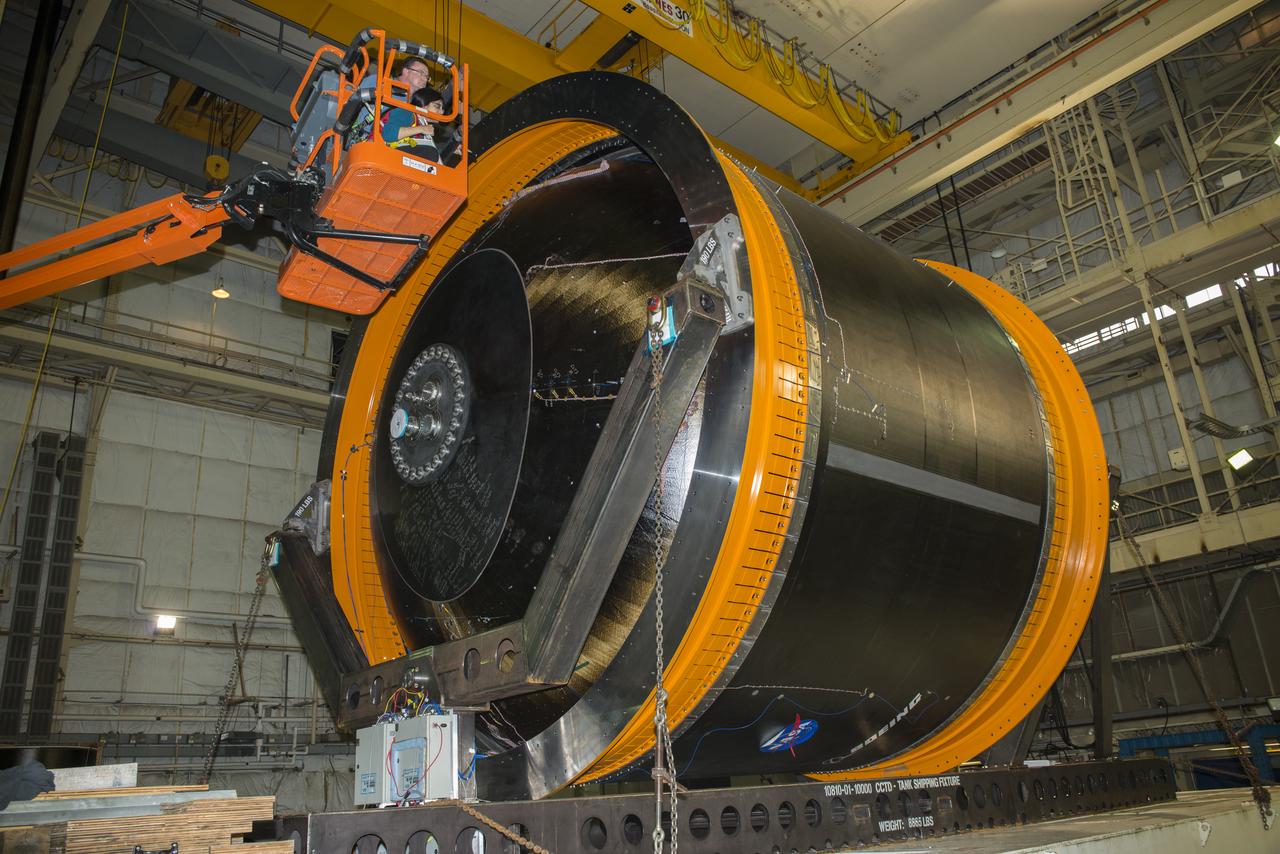

NASA AND BOEING ENGINEERS INSPECT AND PREPARE ONE OF THE LARGEST COMPSITE ROCKET PROPELLANT TANKS EVER MANUFACTURED. THE COMPOSITE CRYOTANK PROMISES A 30% WEIGHT REDUCTION AND A 25 % COST REDUCTION OVER THE PREVIOUSLY USED METAL TANKS.
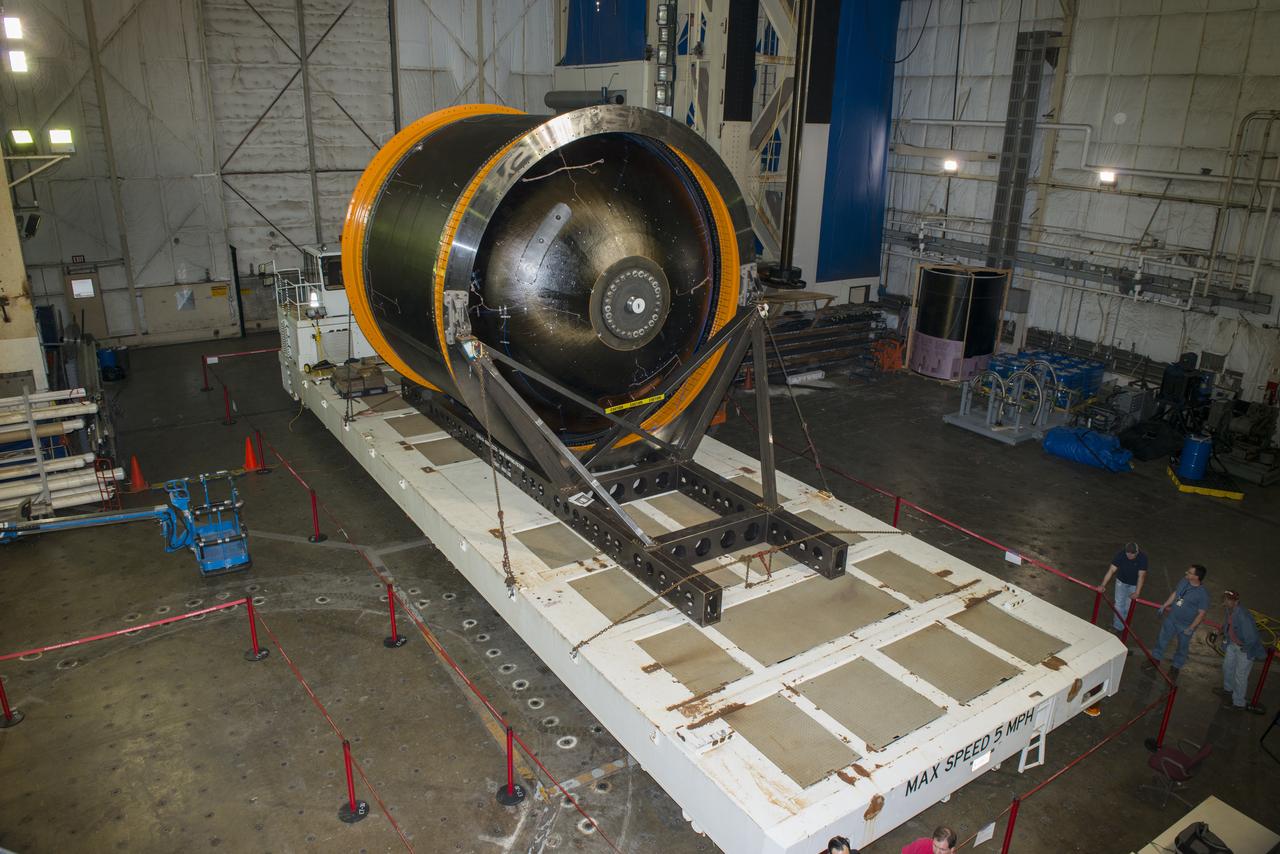

NASA AND BOEING ENGINEERS INSPECT AND PREPARE ONE OF THE LARGEST COMPSITE ROCKET PROPELLANT TANKS EVER MANUFACTURED. THE COMPOSITE CRYOTANK PROMISES A 30% WEIGHT REDUCTION AND A 25 % COST REDUCTION OVER THE PREVIOUSLY USED METAL TANKS.
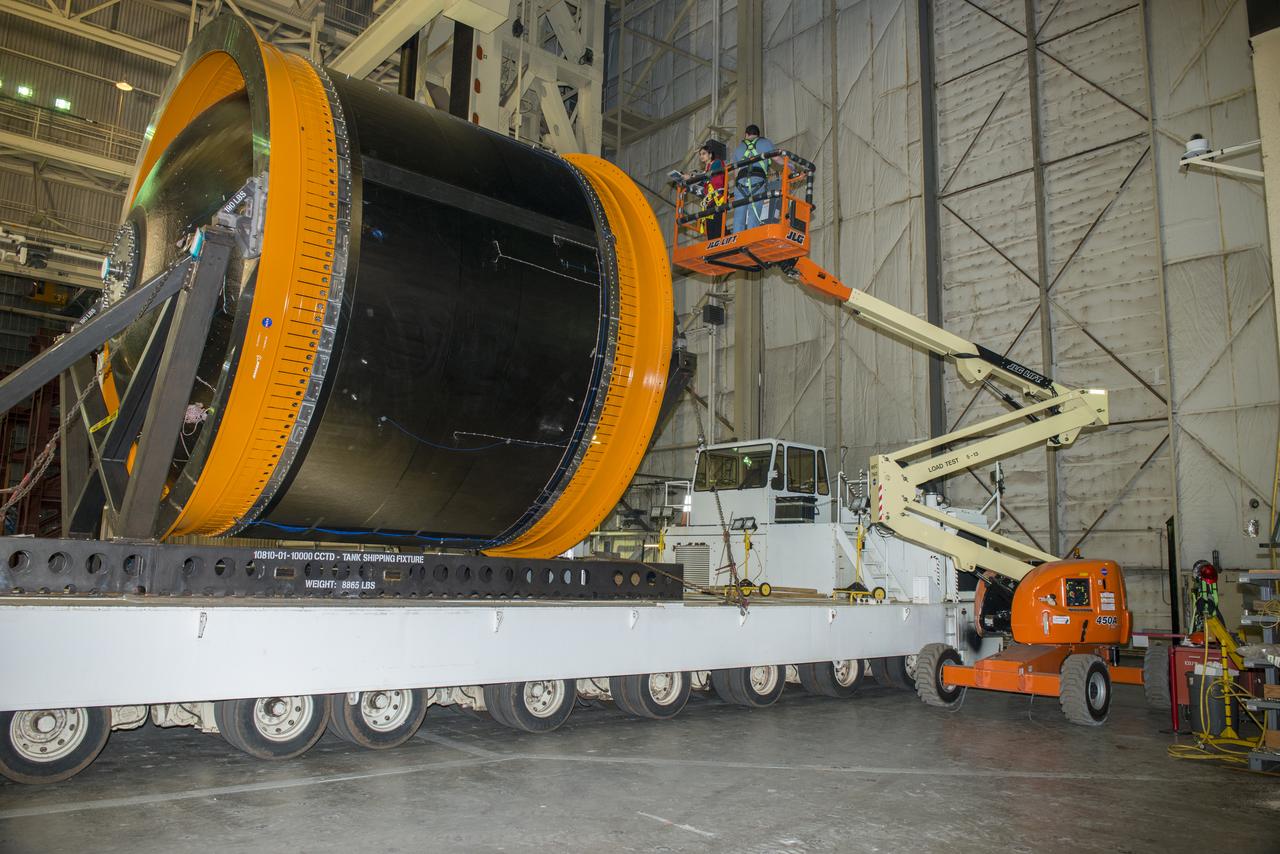

NASA AND BOEING ENGINEERS INSPECT AND PREPARE ONE OF THE LARGEST COMPSITE ROCKET PROPELLANT TANKS EVER MANUFACTURED. THE COMPOSITE CRYOTANK PROMISES A 30% WEIGHT REDUCTION AND A 25 % COST REDUCTION OVER THE PREVIOUSLY USED METAL TANKS.
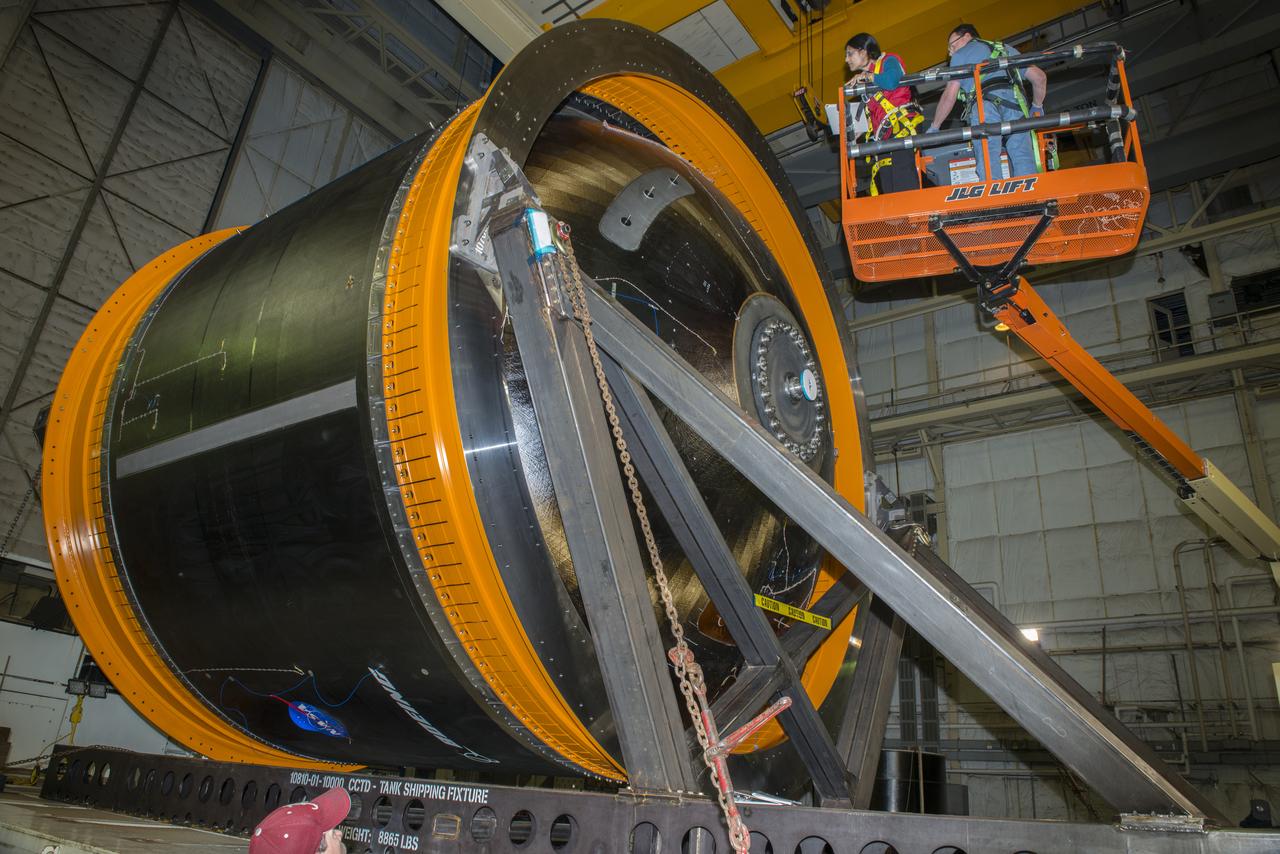

NASA AND BOEING ENGINEERS INSPECT AND PREPARE ONE OF THE LARGEST COMPSITE ROCKET PROPELLANT TANKS EVER MANUFACTURED. THE COMPOSITE CRYOTANK PROMISES A 30% WEIGHT REDUCTION AND A 25 % COST REDUCTION OVER THE PREVIOUSLY USED METAL TANKS.

NASA AND BOEING ENGINEERS INSPECT AND PREPARE ONE OF THE LARGEST COMPSITE ROCKET PROPELLANT TANKS EVER MANUFACTURED. THE COMPOSITE CRYOTANK PROMISES A 30% WEIGHT REDUCTION AND A 25 % COST REDUCTION OVER THE PREVIOUSLY USED METAL TANKS.

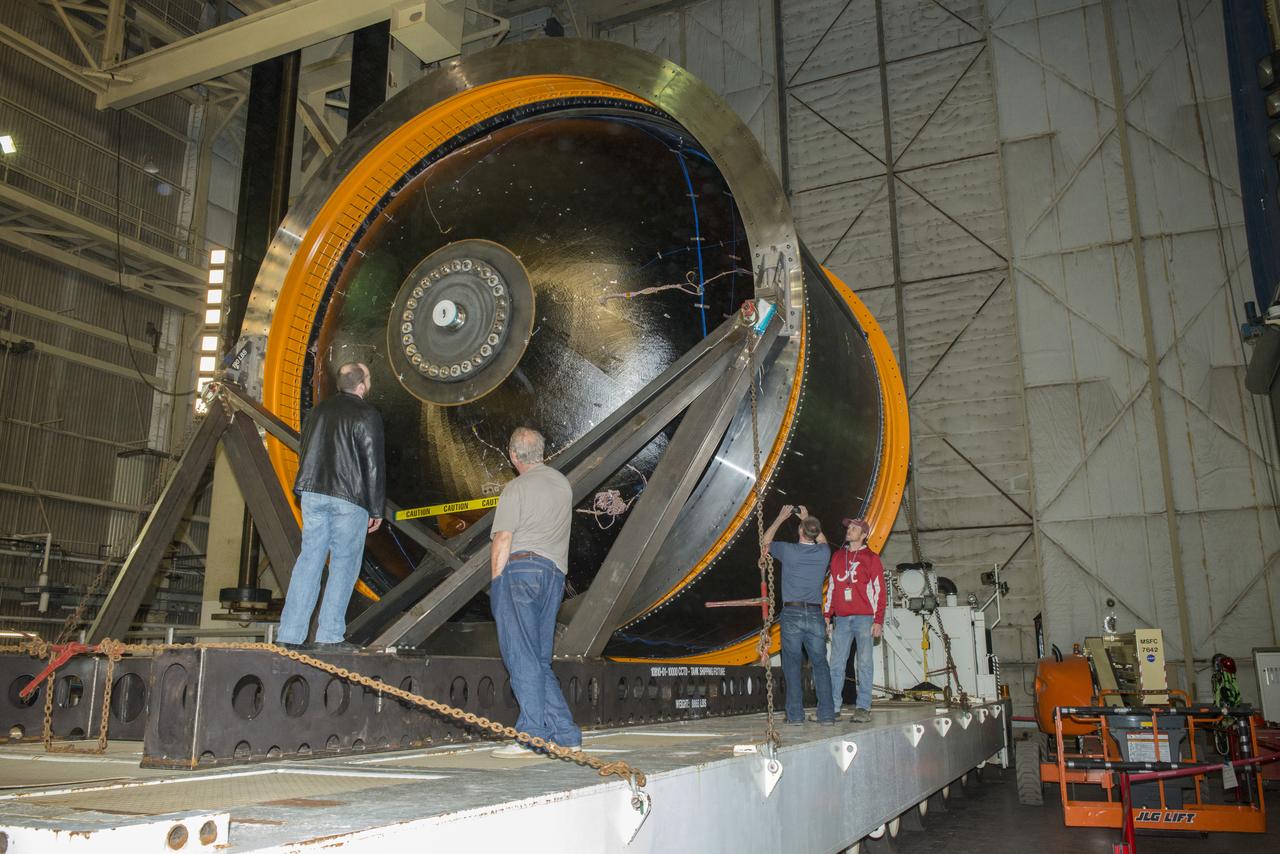
NASA AND BOEING ENGINEERS INSPECT AND PREPARE ONE OF THE LARGEST COMPSITE ROCKET PROPELLANT TANKS EVER MANUFACTURED. THE COMPOSITE CRYOTANK PROMISES A 30% WEIGHT REDUCTION AND A 25 % COST REDUCTION OVER THE PREVIOUSLY USED METAL TANKS.
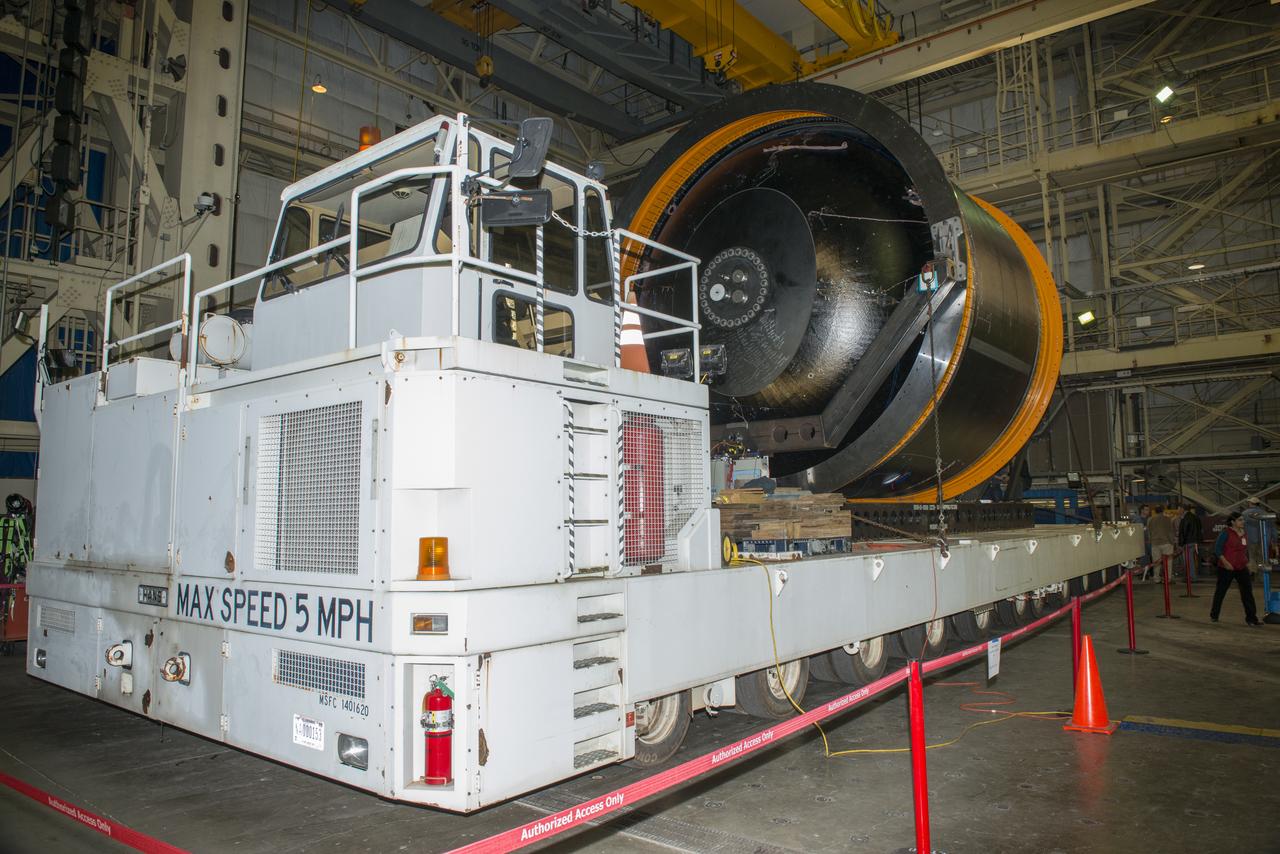

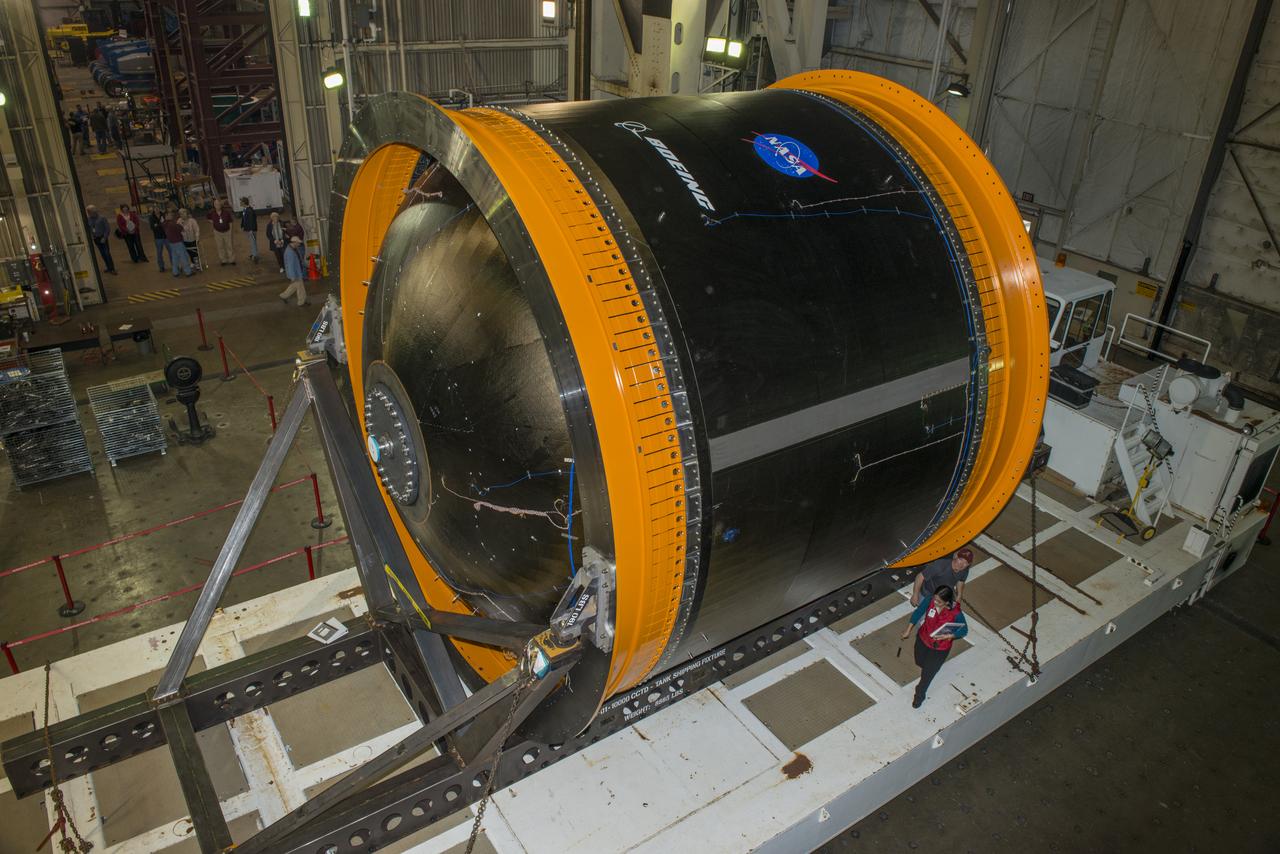
NASA AND BOEING ENGINEERS INSPECT AND PREPARE ONE OF THE LARGEST COMPSITE ROCKET PROPELLANT TANKS EVER MANUFACTURED. THE COMPOSITE CRYOTANK PROMISES A 30% WEIGHT REDUCTION AND A 25 % COST REDUCTION OVER THE PREVIOUSLY USED METAL TANKS.
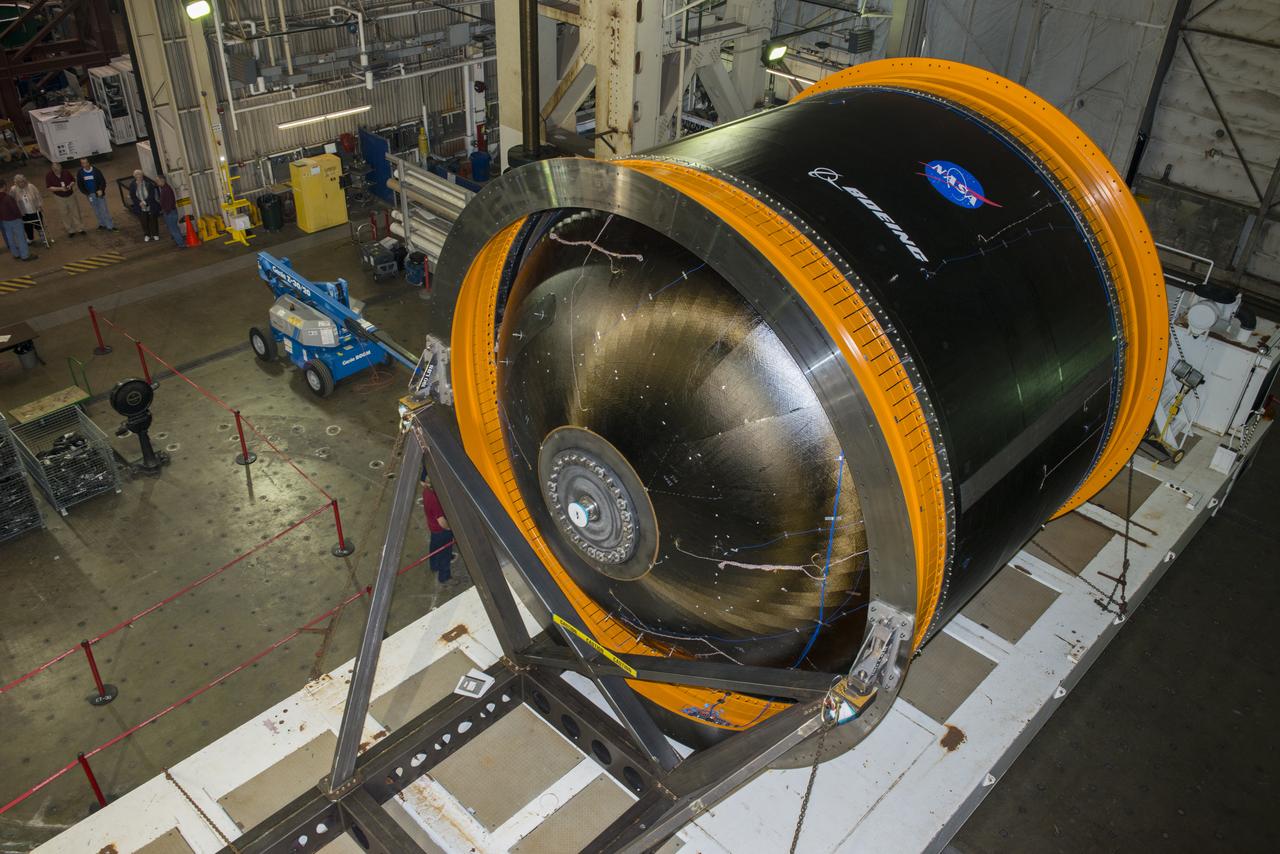

NASA AND BOEING ENGINEERS INSPECT AND PREPARE ONE OF THE LARGEST COMPSITE ROCKET PROPELLANT TANKS EVER MANUFACTURED. THE COMPOSITE CRYOTANK PROMISES A 30% WEIGHT REDUCTION AND A 25 % COST REDUCTION OVER THE PREVIOUSLY USED METAL TANKS.
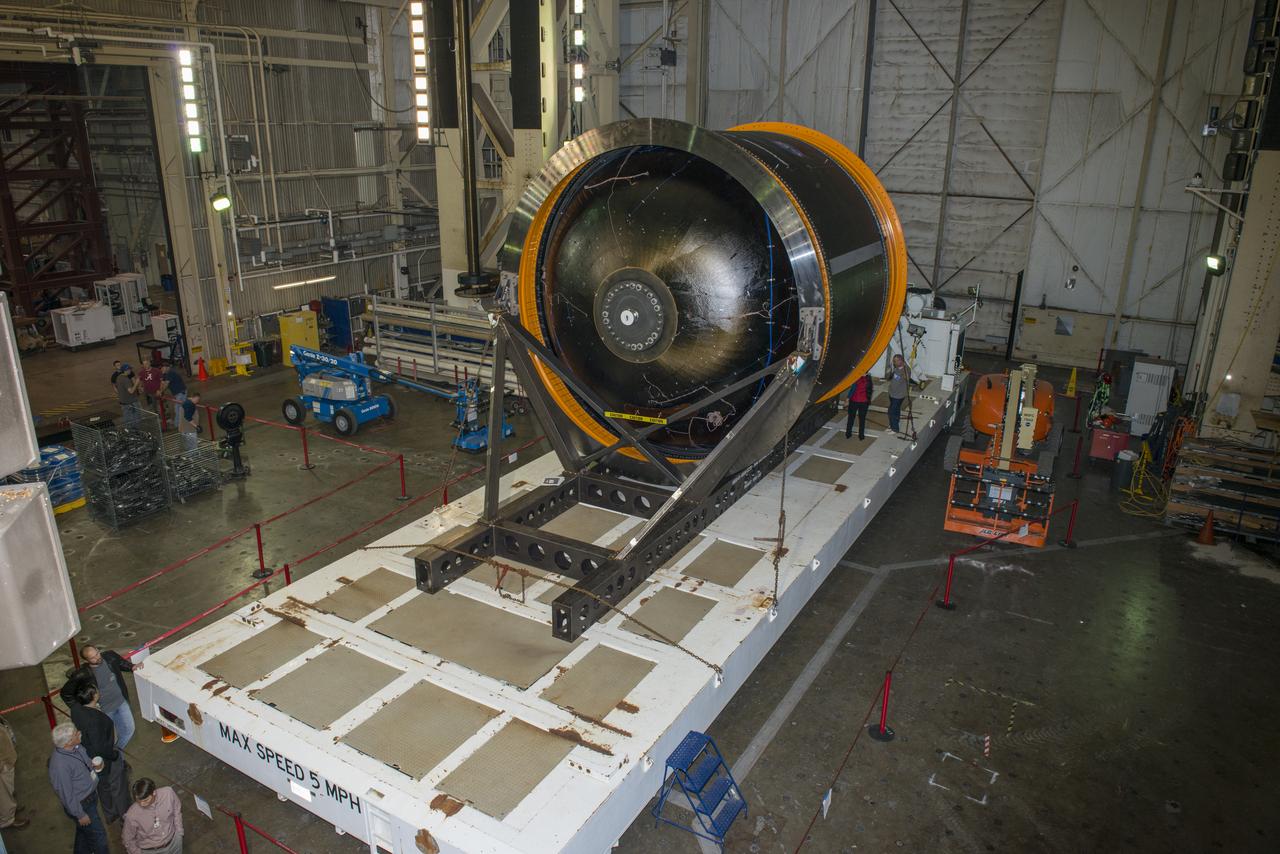

NASA AND BOEING ENGINEERS INSPECT AND PREPARE ONE OF THE LARGEST COMPSITE ROCKET PROPELLANT TANKS EVER MANUFACTURED. THE COMPOSITE CRYOTANK PROMISES A 30% WEIGHT REDUCTION AND A 25 % COST REDUCTION OVER THE PREVIOUSLY USED METAL TANKS.
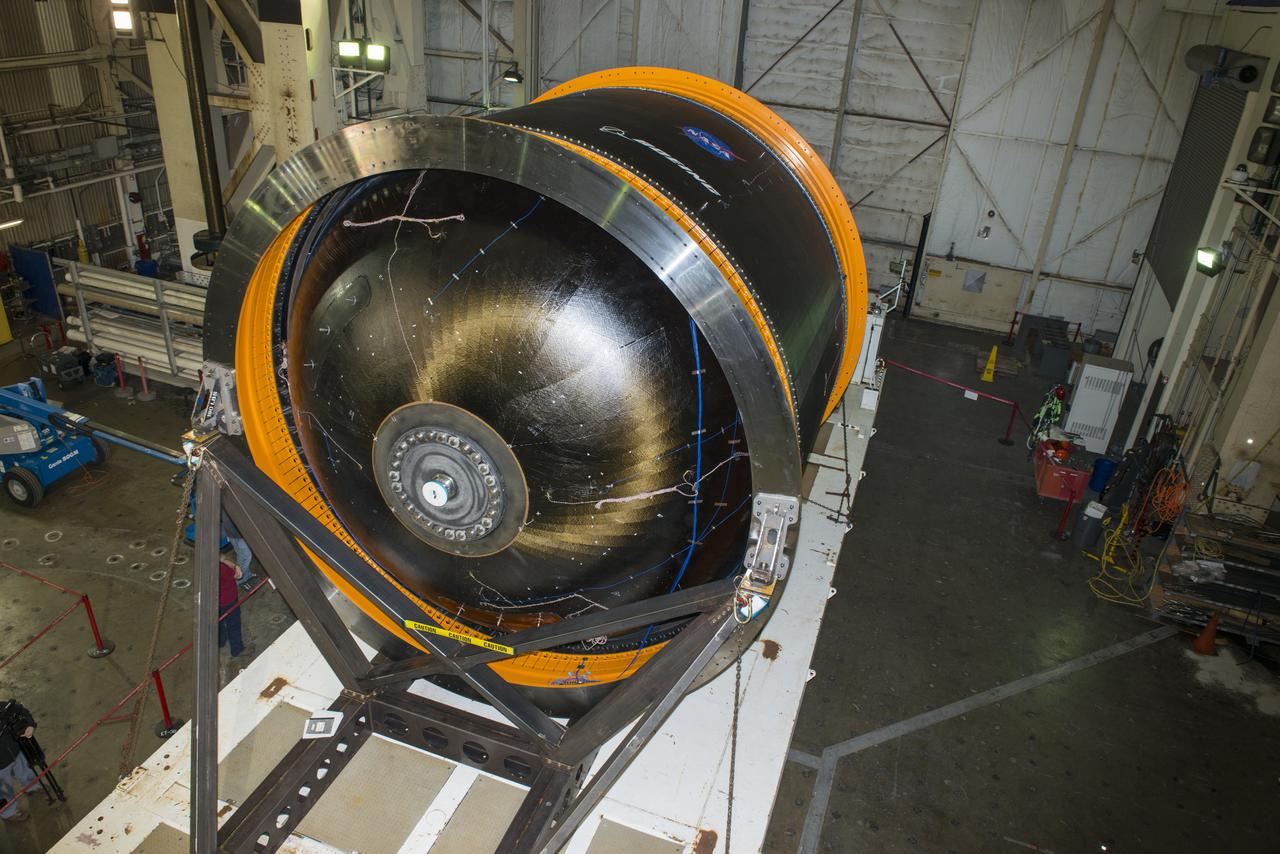

NASA AND BOEING ENGINEERS INSPECT AND PREPARE ONE OF THE LARGEST COMPSITE ROCKET PROPELLANT TANKS EVER MANUFACTURED. THE COMPOSITE CRYOTANK PROMISES A 30% WEIGHT REDUCTION AND A 25 % COST REDUCTION OVER THE PREVIOUSLY USED METAL TANKS.
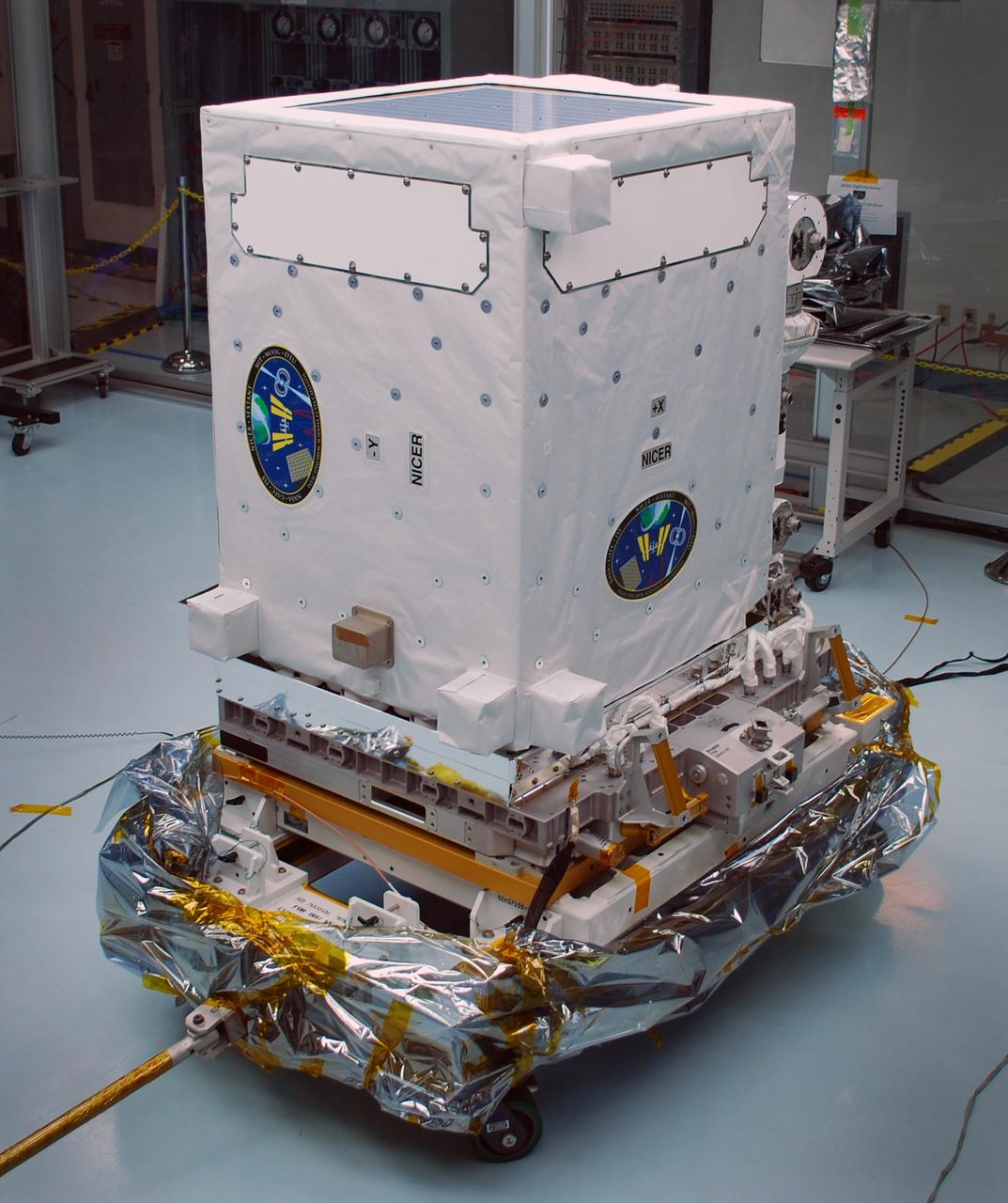

The NICER payload, blanketed and waiting for launch in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral, Florida. The instrument is in its stowed configuration for launch. The Neutron star Interior Composition Explorer (NICER) is a NASA Explorer Mission of Opportunity dedicated to studying the extraordinary environments — strong gravity, ultra-dense matter, and the most powerful magnetic fields in the universe — embodied by neutron stars. An attached payload aboard the International Space Station, NICER will deploy an instrument with unique capabilities for timing and spectroscopy of fast X-ray brightness fluctuations. The embedded Station Explorer for X-ray Timing and Navigation Technology demonstration (SEXTANT) will use NICER data to validate, for the first time in space, technology that exploits pulsars as natural navigation beacons. Credit: NASA/Goddard/ Keith Gendreau <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

NICER team members Takashi Okajima, Yang Soong, and Steven Kenyon apply epoxy to the X-ray concentrator mounts after alignment. The epoxy holds the optics assemblies fixed in position through the vibrations experienced during launch to the International Space Station. The payload’s 56 mirror assemblies concentrate X-rays onto silicon detectors to gather data that will probe the interior makeup of neutron stars, including those that appear to flash regularly, called pulsars. The Neutron star Interior Composition Explorer (NICER) is a NASA Explorer Mission of Opportunity dedicated to studying the extraordinary environments — strong gravity, ultra-dense matter, and the most powerful magnetic fields in the universe — embodied by neutron stars. An attached payload aboard the International Space Station, NICER will deploy an instrument with unique capabilities for timing and spectroscopy of fast X-ray brightness fluctuations. The embedded Station Explorer for X-ray Timing and Navigation Technology demonstration (SEXTANT) will use NICER data to validate, for the first time in space, technology that exploits pulsars as natural navigation beacons. Credit: NASA/Goddard/ Keith Gendreau <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Many of NICER’s 56 X-ray “concentrators” seen from within the instrument optical bench. Light reflected from the gold surfaces of the 24 concentric foils in each concentrator is focused onto detectors slightly more than 1 meter (3.5 feet) away. The payload’s 56 mirror assemblies concentrate X-rays onto silicon detectors to gather data that will probe the interior makeup of neutron stars, including those that appear to flash regularly, called pulsars. The Neutron star Interior Composition Explorer (NICER) is a NASA Explorer Mission of Opportunity dedicated to studying the extraordinary environments — strong gravity, ultra-dense matter, and the most powerful magnetic fields in the universe — embodied by neutron stars. An attached payload aboard the International Space Station, NICER will deploy an instrument with unique capabilities for timing and spectroscopy of fast X-ray brightness fluctuations. The embedded Station Explorer for X-ray Timing and Navigation Technology demonstration (SEXTANT) will use NICER data to validate, for the first time in space, technology that exploits pulsars as natural navigation beacons. Credit: NASA/Goddard/ Keith Gendreau <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
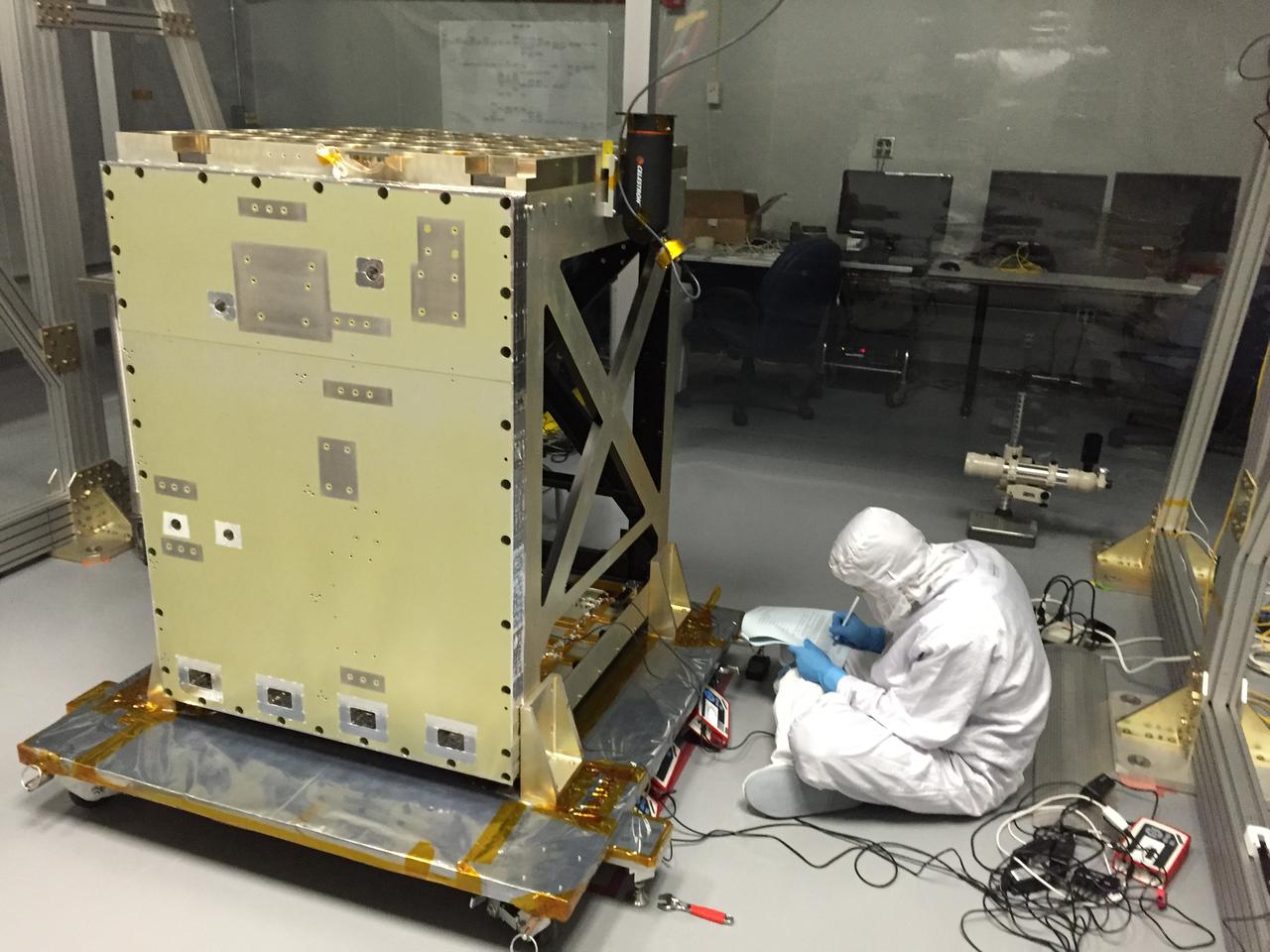

A NICER team member measures the focused optical power of each X-ray concentrator in a clean tent at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center. The Neutron star Interior Composition Explorer (NICER) is a NASA Explorer Mission of Opportunity dedicated to studying the extraordinary environments — strong gravity, ultra-dense matter, and the most powerful magnetic fields in the universe — embodied by neutron stars. An attached payload aboard the International Space Station, NICER will deploy an instrument with unique capabilities for timing and spectroscopy of fast X-ray brightness fluctuations. The embedded Station Explorer for X-ray Timing and Navigation Technology demonstration (SEXTANT) will use NICER data to validate, for the first time in space, technology that exploits pulsars as natural navigation beacons. Credit: NASA/Goddard/ Keith Gendreau <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

NICER’s X-ray concentrator optics are inspected under a black light for dust and foreign object debris that could impair functionality once in space. The payload’s 56 mirror assemblies concentrate X-rays onto silicon detectors to gather data that will probe the interior makeup of neutron stars, including those that appear to flash regularly, called pulsars. The Neutron star Interior Composition Explorer (NICER) is a NASA Explorer Mission of Opportunity dedicated to studying the extraordinary environments — strong gravity, ultra-dense matter, and the most powerful magnetic fields in the universe — embodied by neutron stars. An attached payload aboard the International Space Station, NICER will deploy an instrument with unique capabilities for timing and spectroscopy of fast X-ray brightness fluctuations. The embedded Station Explorer for X-ray Timing and Navigation Technology demonstration (SEXTANT) will use NICER data to validate, for the first time in space, technology that exploits pulsars as natural navigation beacons. Credit: NASA/Goddard/ Keith Gendreau <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

NICER Optics Lead Takashi Okajima installs one of NICER’s 56 X-ray “concentrators,” each consisting of 24 concentric foils. To minimize the effects of Earth’s gravity on their alignment, the concentrator assemblies were installed from the outside edges toward the center of the plate that houses them. The payload’s 56 mirror assemblies concentrate X-rays onto silicon detectors to gather data that will probe the interior makeup of neutron stars, including those that appear to flash regularly, called pulsars. The Neutron star Interior Composition Explorer (NICER) is a NASA Explorer Mission of Opportunity dedicated to studying the extraordinary environments — strong gravity, ultra-dense matter, and the most powerful magnetic fields in the universe — embodied by neutron stars. An attached payload aboard the International Space Station, NICER will deploy an instrument with unique capabilities for timing and spectroscopy of fast X-ray brightness fluctuations. The embedded Station Explorer for X-ray Timing and Navigation Technology demonstration (SEXTANT) will use NICER data to validate, for the first time in space, technology that exploits pulsars as natural navigation beacons. Credit: NASA/Goddard/ Keith Gendreau <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

NICER engineer Steven Kenyon prepares seven of the 56 X-ray concentrators for installation in the NICER instrument. The payload’s 56 mirror assemblies concentrate X-rays onto silicon detectors to gather data that will probe the interior makeup of neutron stars, including those that appear to flash regularly, called pulsars. The Neutron star Interior Composition Explorer (NICER) is a NASA Explorer Mission of Opportunity dedicated to studying the extraordinary environments — strong gravity, ultra-dense matter, and the most powerful magnetic fields in the universe — embodied by neutron stars. An attached payload aboard the International Space Station, NICER will deploy an instrument with unique capabilities for timing and spectroscopy of fast X-ray brightness fluctuations. The embedded Station Explorer for X-ray Timing and Navigation Technology demonstration (SEXTANT) will use NICER data to validate, for the first time in space, technology that exploits pulsars as natural navigation beacons. Credit: NASA/Goddard/ Keith Gendreau <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

NICER Optics Lead Takashi Okajima makes a fine adjustment to the orientation of one X-ray “concentrator” optic. The 56 optics must point in the same direction in order for NICER to achieve its science goals. The payload’s 56 mirror assemblies concentrate X-rays onto silicon detectors to gather data that will probe the interior makeup of neutron stars, including those that appear to flash regularly, called pulsars. The Neutron star Interior Composition Explorer (NICER) is a NASA Explorer Mission of Opportunity dedicated to studying the extraordinary environments — strong gravity, ultra-dense matter, and the most powerful magnetic fields in the universe — embodied by neutron stars. An attached payload aboard the International Space Station, NICER will deploy an instrument with unique capabilities for timing and spectroscopy of fast X-ray brightness fluctuations. The embedded Station Explorer for X-ray Timing and Navigation Technology demonstration (SEXTANT) will use NICER data to validate, for the first time in space, technology that exploits pulsars as natural navigation beacons. Credit: NASA/Goddard/ Keith Gendreau <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
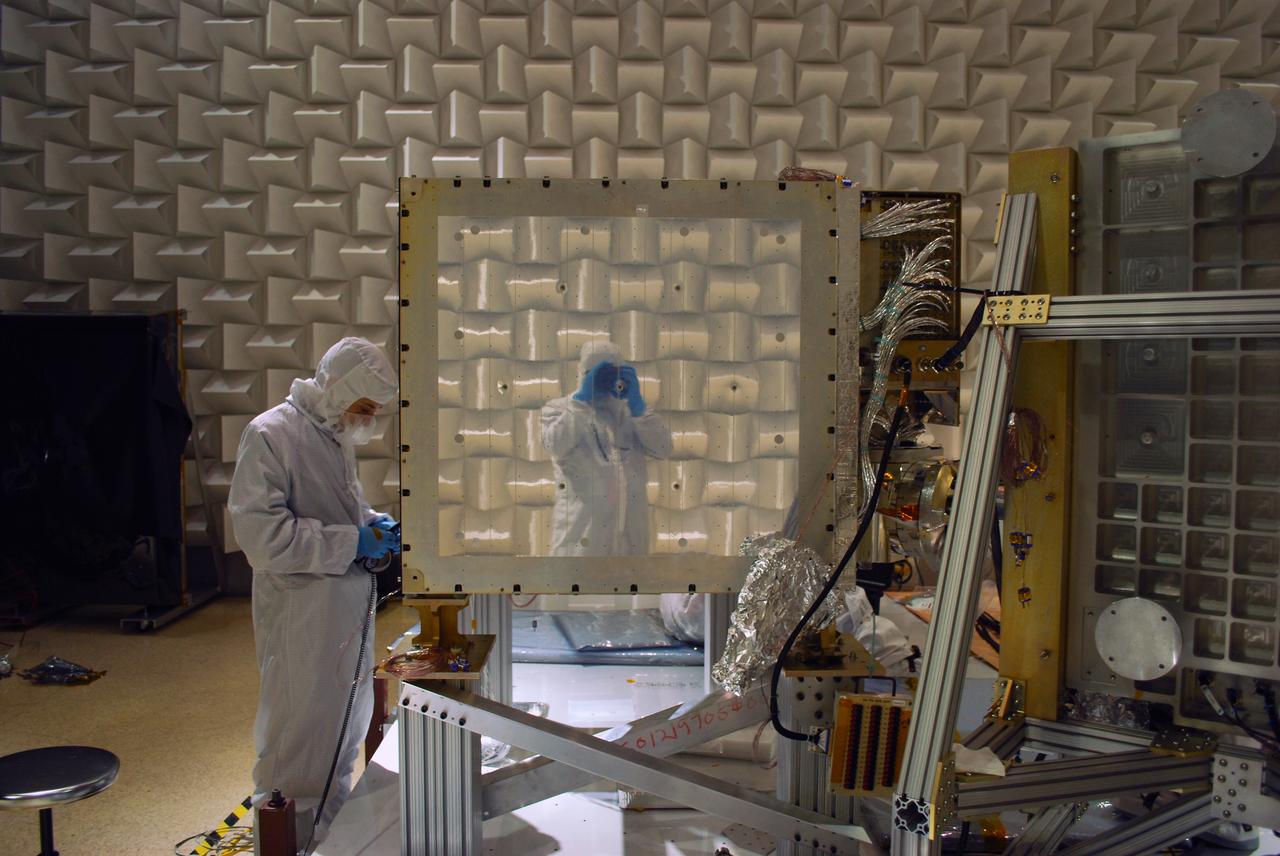

A photo taken during the NICER range-of-motion test at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center shows the photographer’s reflection in the mirror-like radiator surface of the detector plate. Teflon-coated silver tape is used to keep NICER’s detectors cool. The Neutron star Interior Composition Explorer (NICER) is a NASA Explorer Mission of Opportunity dedicated to studying the extraordinary environments — strong gravity, ultra-dense matter, and the most powerful magnetic fields in the universe — embodied by neutron stars. An attached payload aboard the International Space Station, NICER will deploy an instrument with unique capabilities for timing and spectroscopy of fast X-ray brightness fluctuations. The embedded Station Explorer for X-ray Timing and Navigation Technology demonstration (SEXTANT) will use NICER data to validate, for the first time in space, technology that exploits pulsars as natural navigation beacons. Credit: NASA/Goddard/ Keith Gendreau <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
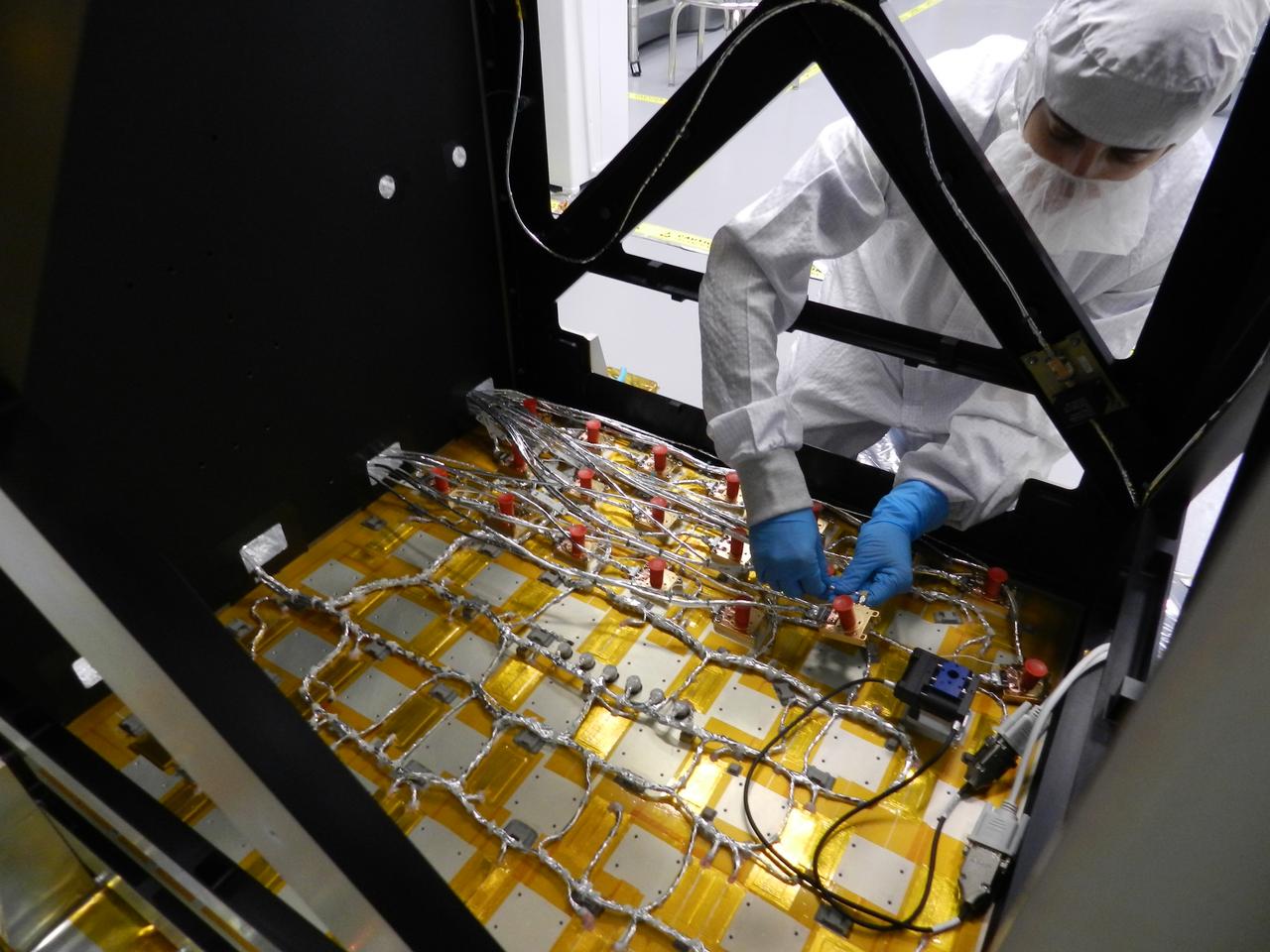
NICER engineer Steven Kenyon installs an X-ray detector onto the payload’s detector plate. The detectors are protected by red caps during installation because they are very sensitive to dust and other foreign object debris. The Neutron star Interior Composition Explorer (NICER) is a NASA Explorer Mission of Opportunity dedicated to studying the extraordinary environments — strong gravity, ultra-dense matter, and the most powerful magnetic fields in the universe — embodied by neutron stars. An attached payload aboard the International Space Station, NICER will deploy an instrument with unique capabilities for timing and spectroscopy of fast X-ray brightness fluctuations. The embedded Station Explorer for X-ray Timing and Navigation Technology demonstration (SEXTANT) will use NICER data to validate, for the first time in space, technology that exploits pulsars as natural navigation beacons. Credit: NASA/Goddard/ Keith Gendreau <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

This observation of a small section of the Asgard terrain reveals compositional variations over the surface of Callisto was captured by NASA Galileo spacecraft in 1996.
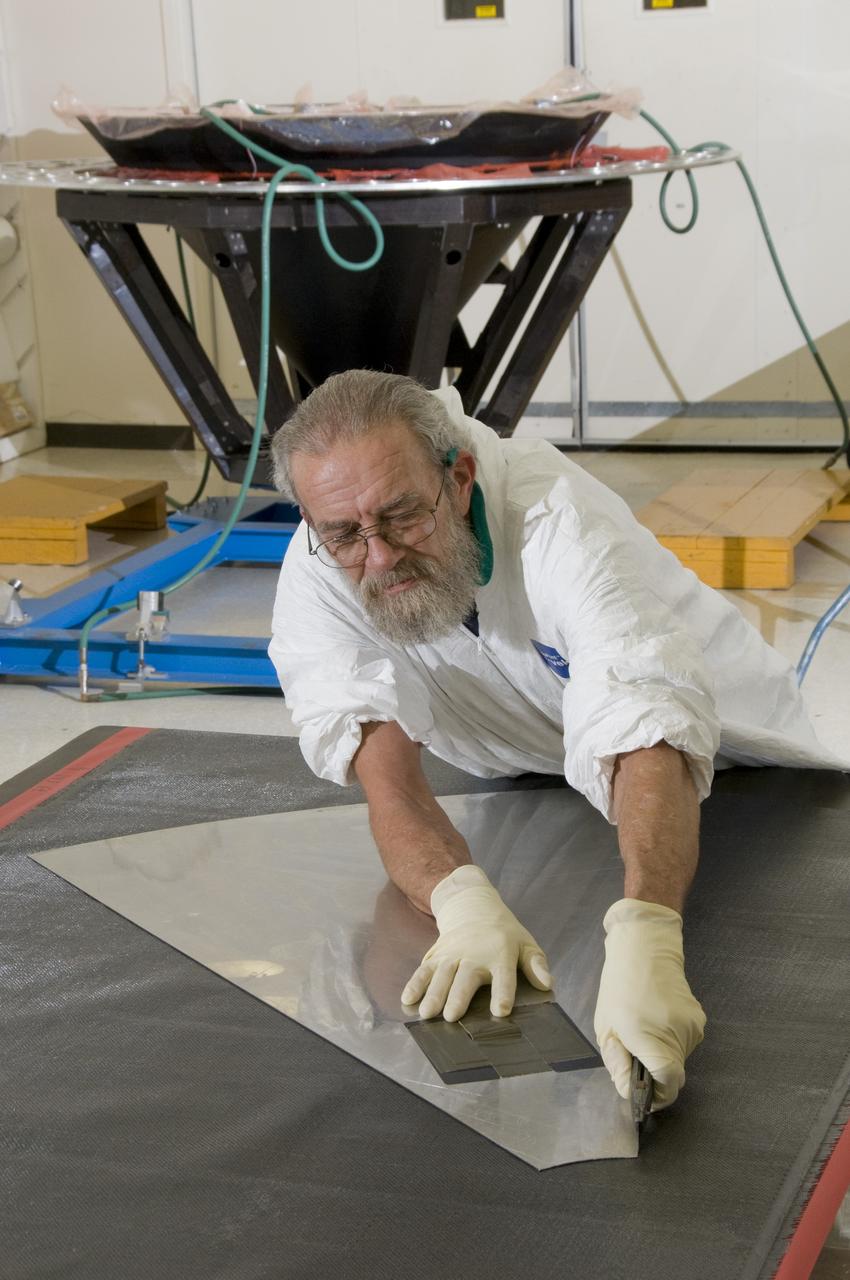

ED KIRCH, A LOCKHEED MARTIN TECHNICIAN, CUTS A PATTERN FROM COMPOSITE MATERIAL THAT WILL BE PLACED IN A MOLD TO BUILD A SPACE SHUTTLE EXTERNAL TANK COMPOSITE NOSE CONE.
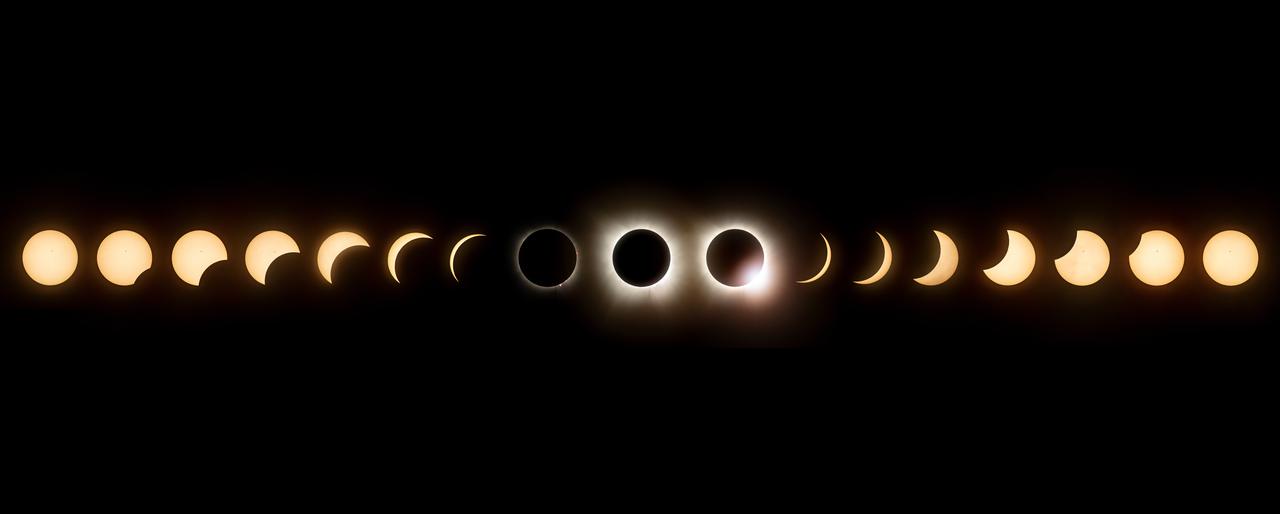

This composite image of seventeen images shows the progression of a total solar eclipse at the NASA's Glenn Research Center in Cleveland, Ohio on Monday, April 8, 2024. A total solar eclipse swept across a narrow portion of the North American continent from Mexico’s Pacific coast to the Atlantic coast of Newfoundland, Canada. A partial solar eclipse was visible across the entire North American continent along with parts of Central America and Europe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)
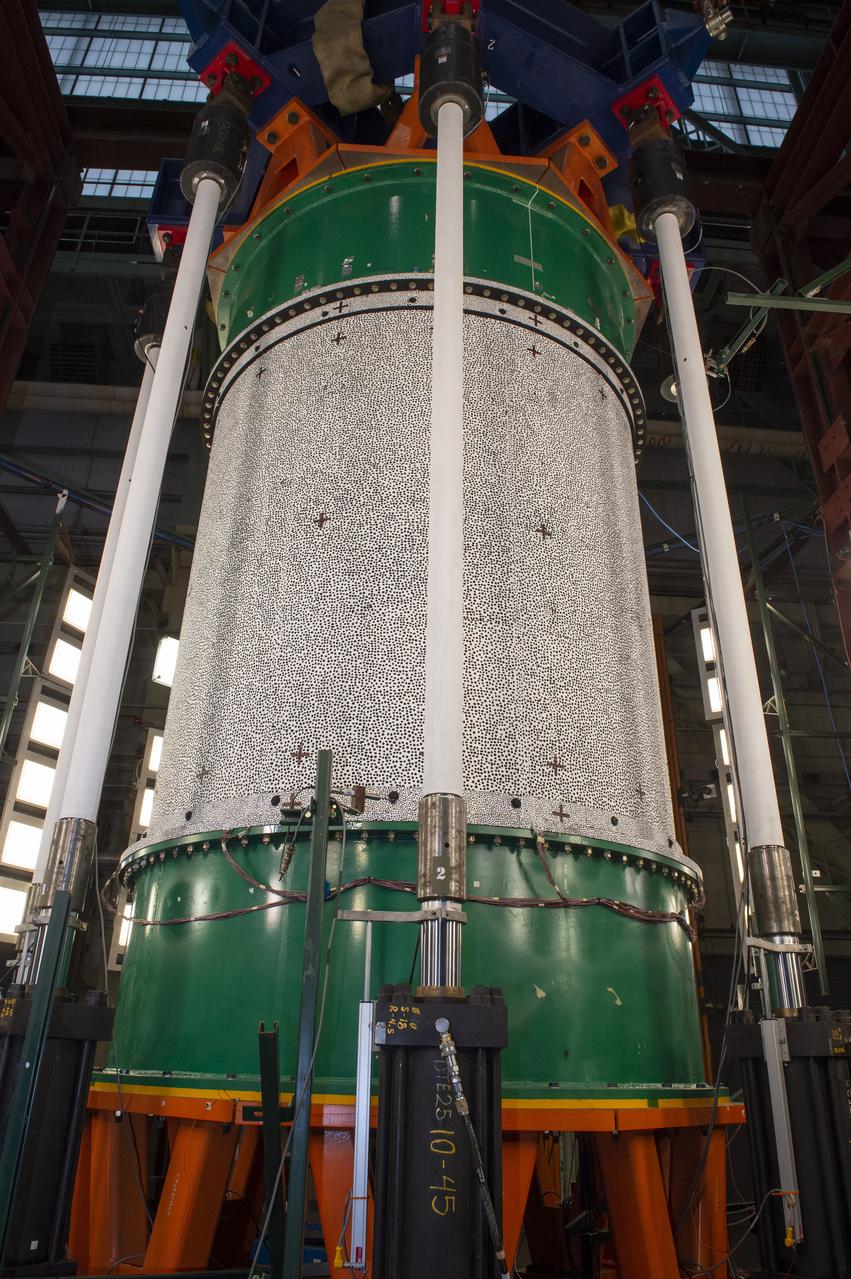

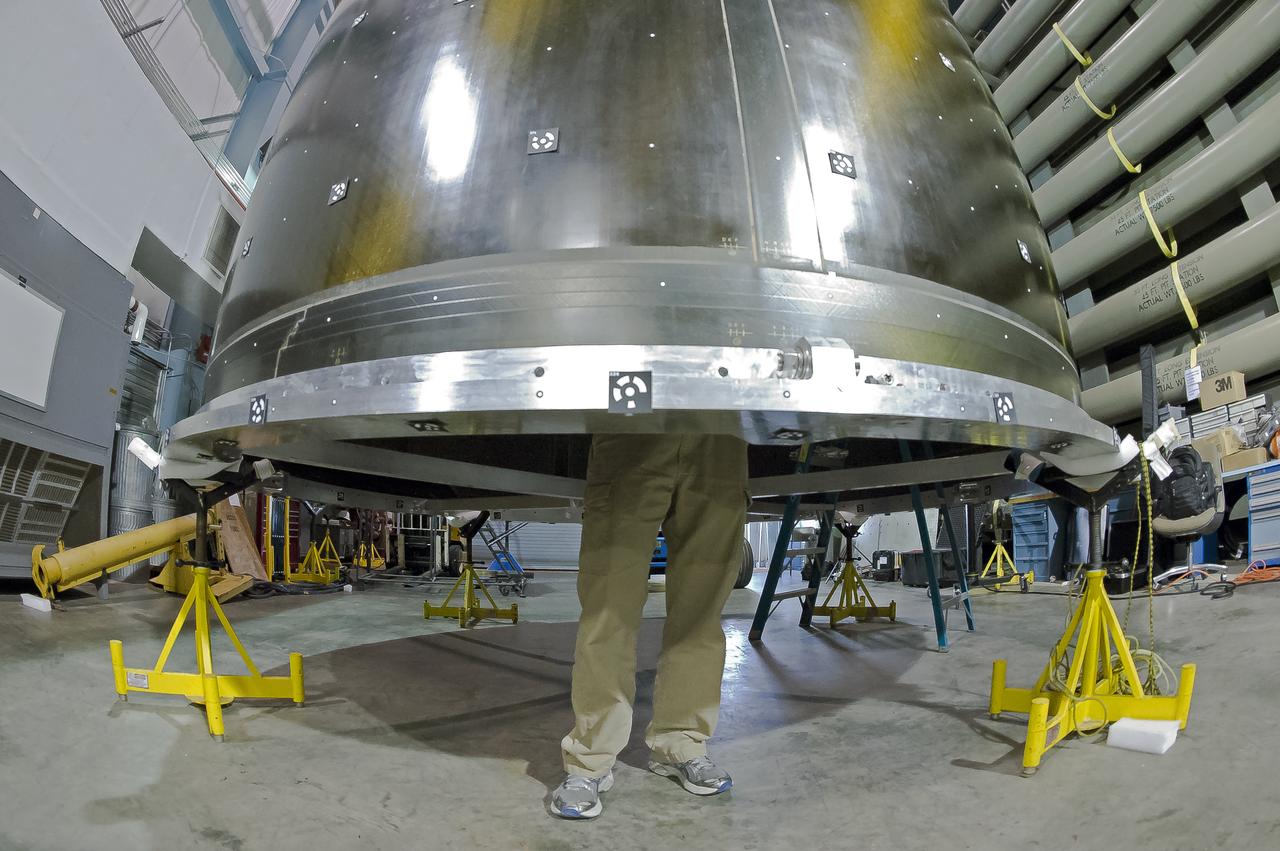
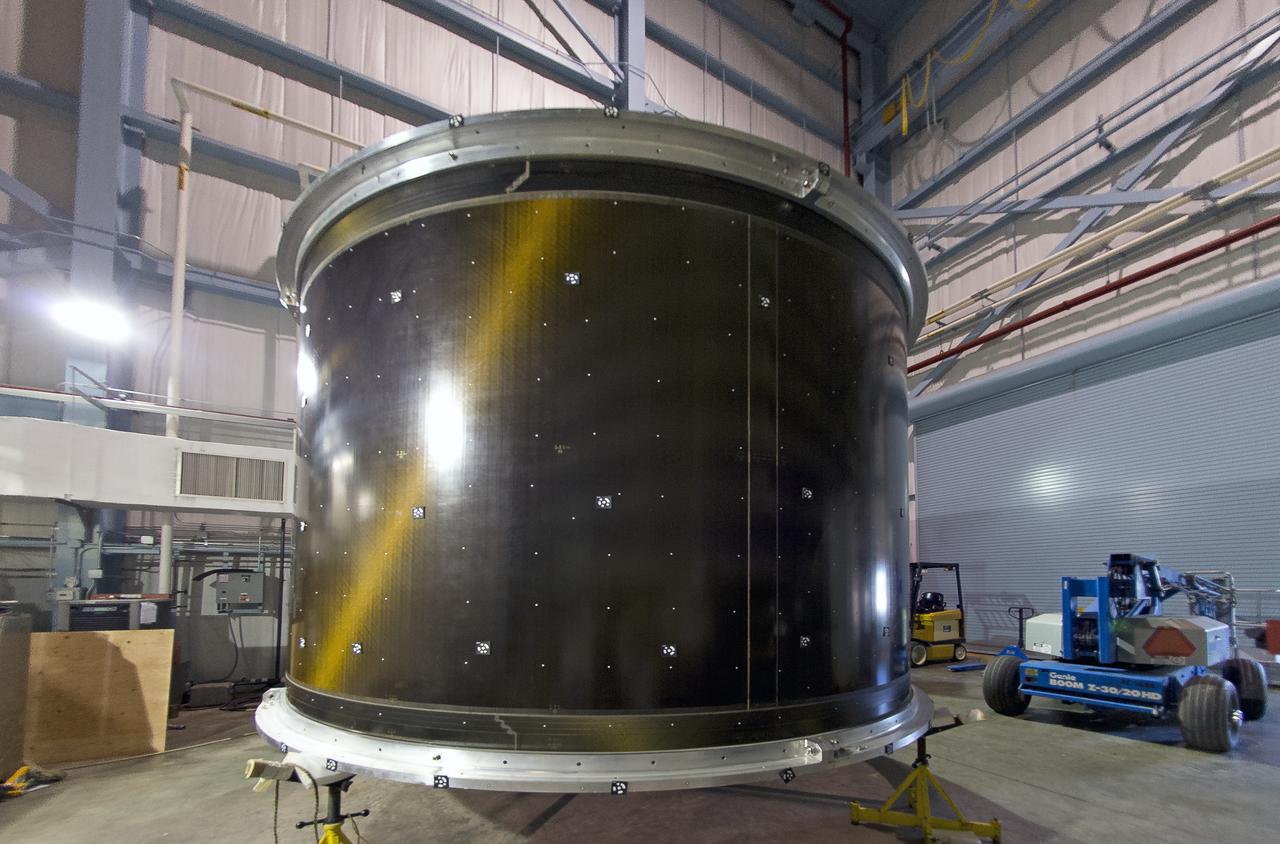
SHELL BUCKLING KNOCKDOWN FACTOR (SBKF) PROJECT - COMPOSITE TEST ARTICLE, (CTA) 8.3 – 12/17/19 – VIEW 1 OF 12
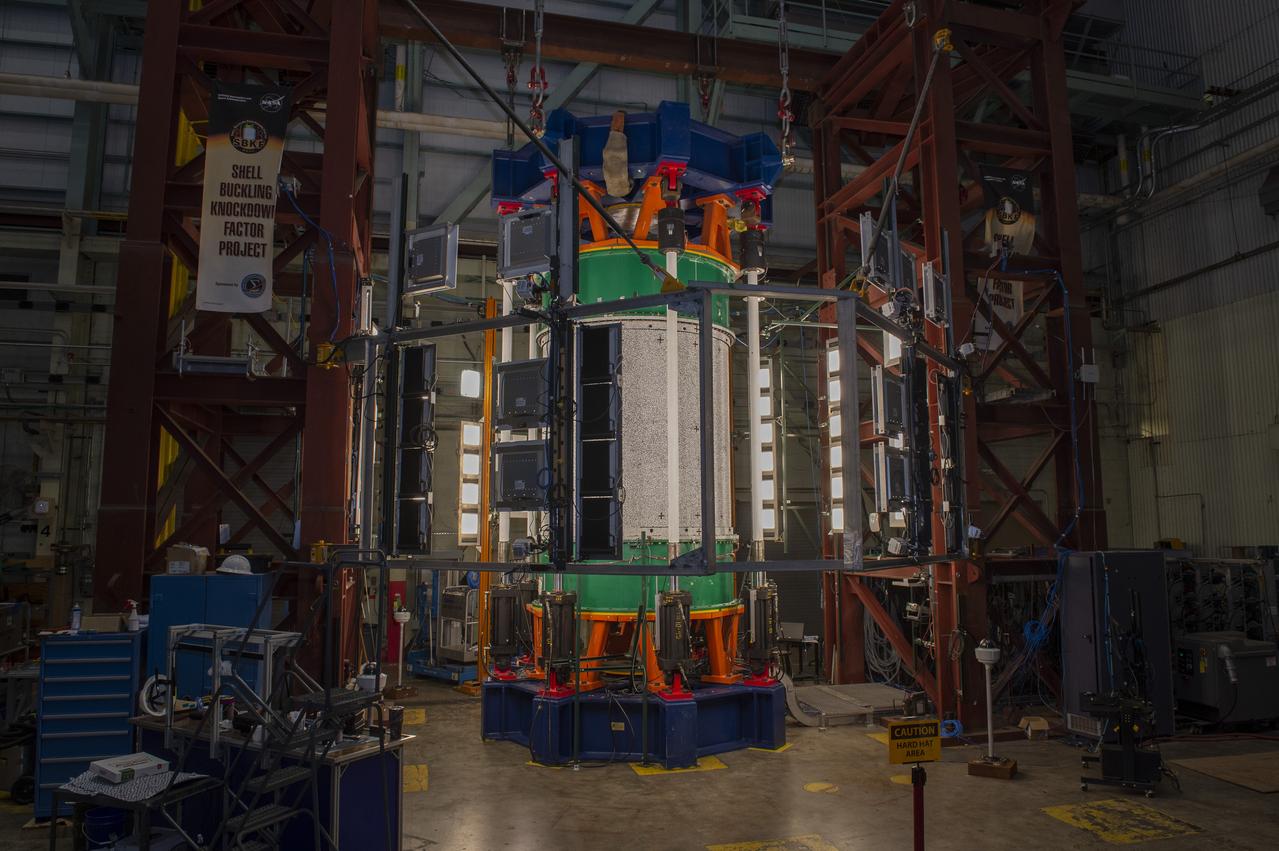

SHELL BUCKLING KNOCKDOWN FACTOR (SBKF) PROJECT - COMPOSITE TEST ARTICLE, (CTA) 8.3 – 12/17/19 – VIEW 1 OF 12
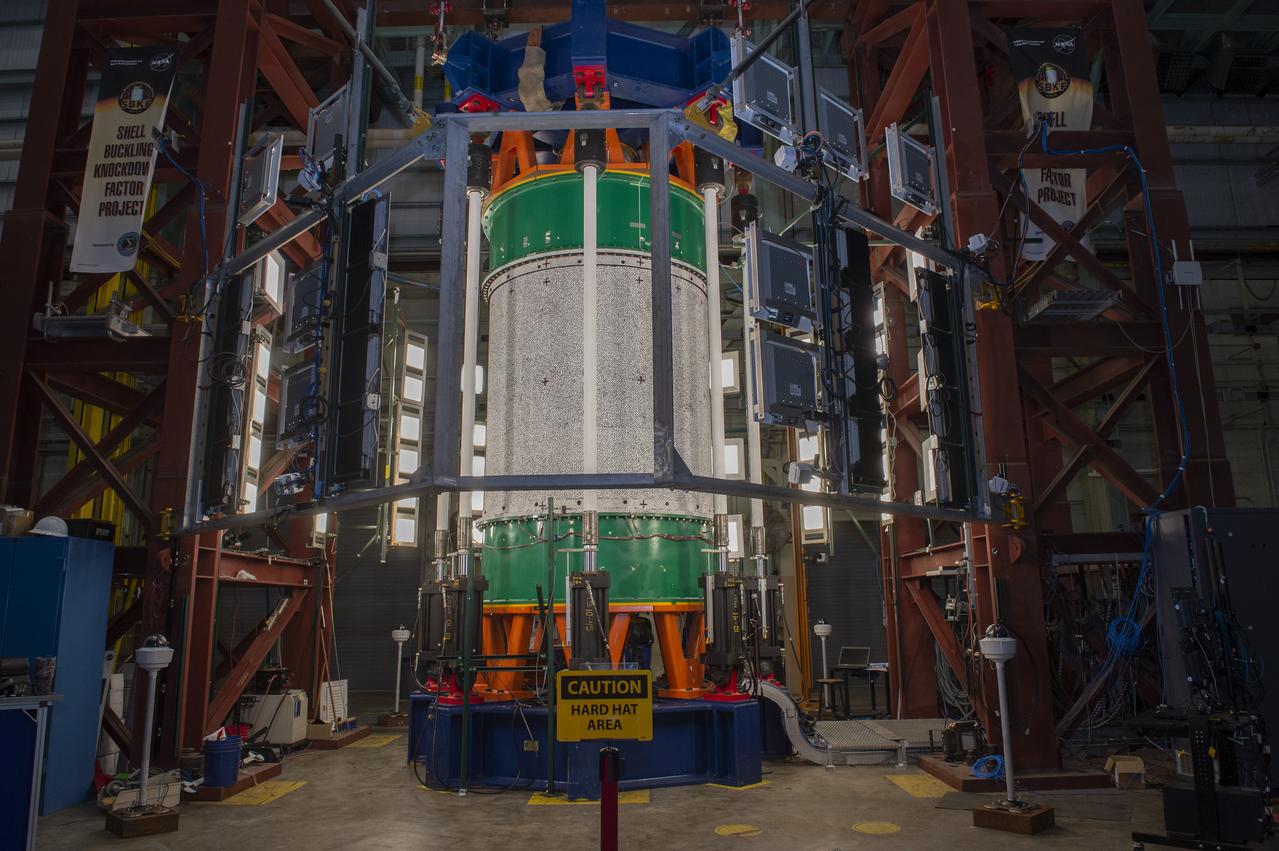

SHELL BUCKLING KNOCKDOWN FACTOR (SBKF) PROJECT - COMPOSITE TEST ARTICLE, (CTA) 8.3 – 12/17/19 – VIEW 1 OF 12
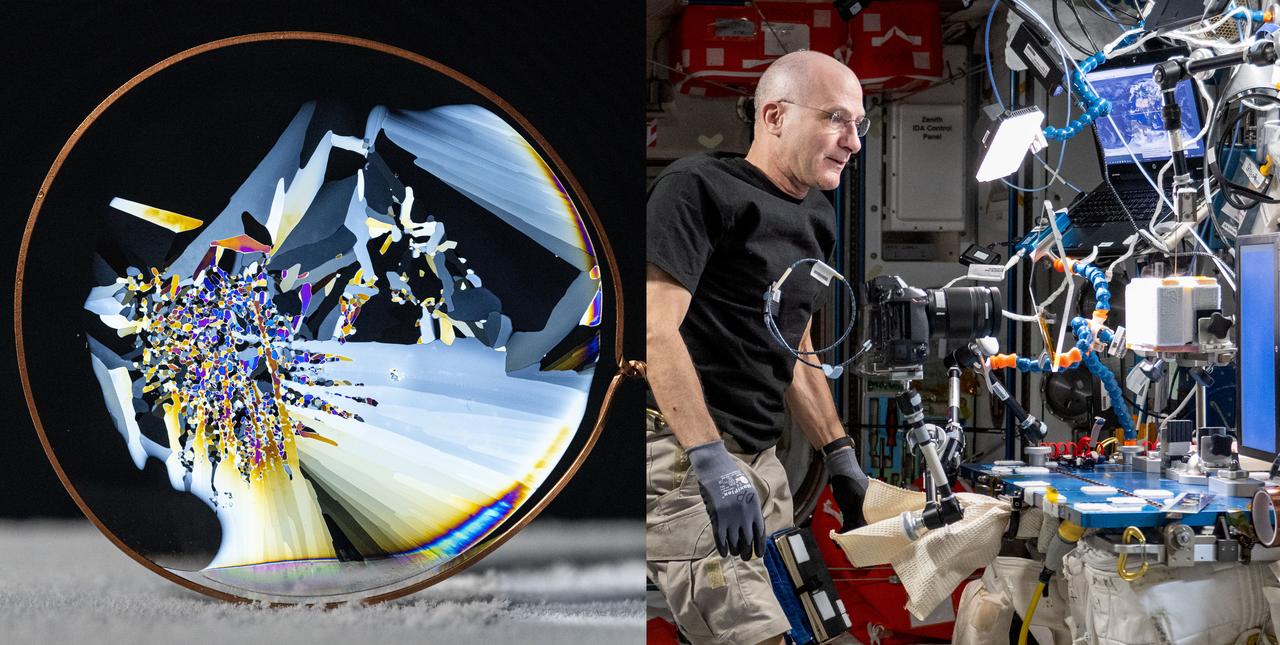

iss072e096196 and iss072e098100 (Oct. 23, 2024) -- NASA Astronaut Don Pettit views thin wafers of ice under polarized filters on the International Space Station. Pettit conducts “science of opportunity” using station’s MELFI freezer to understand the behaviors of freezing water under microgravity conditions without gravitational buoyancy. This ice wafer was photographed between a polarized filter and a laptop display used to illuminate and cross-polarize the thin ice, giving a colorful image highlighting the fragmented crystals. This is a composite image of iss072e098100 and iss072e096196.
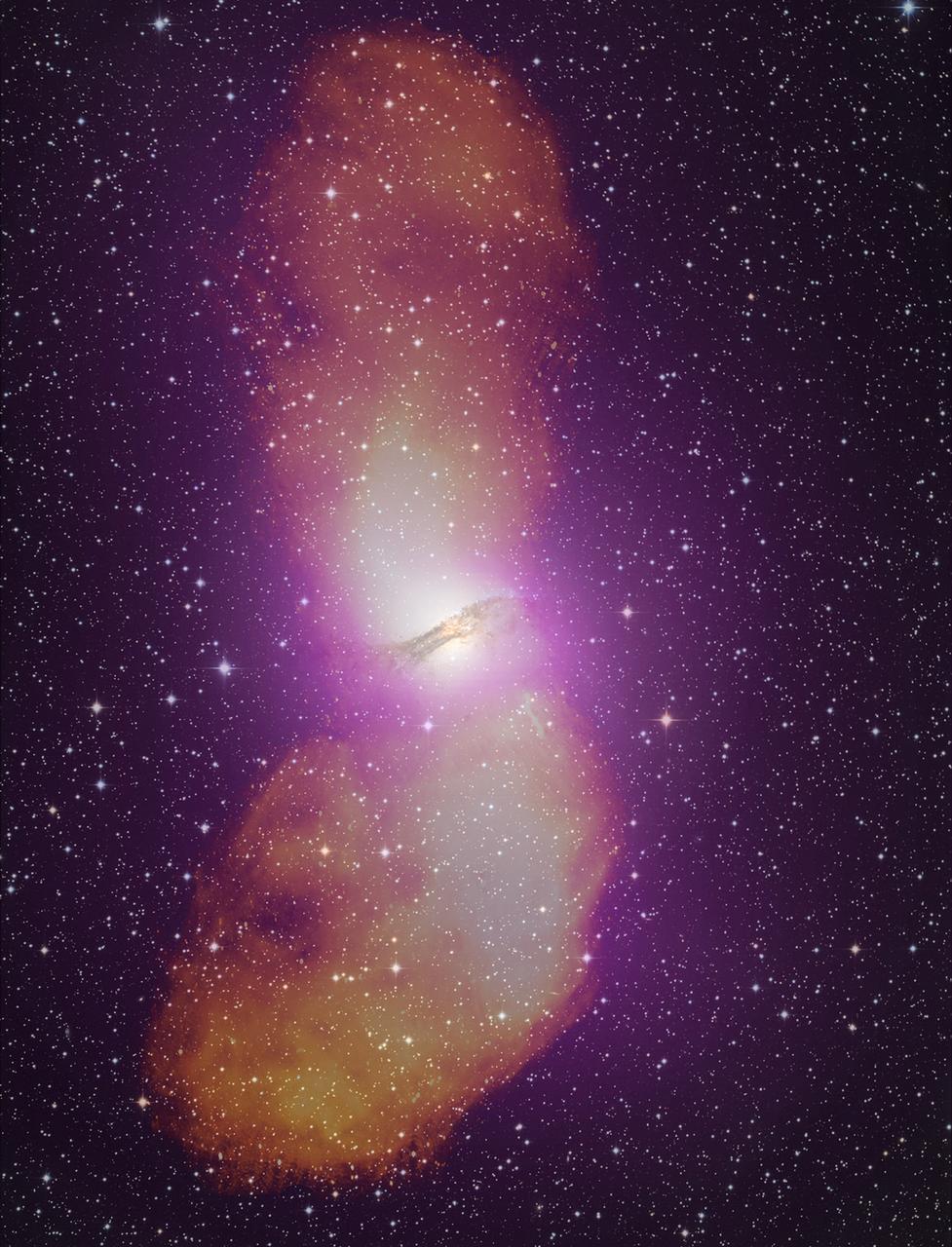

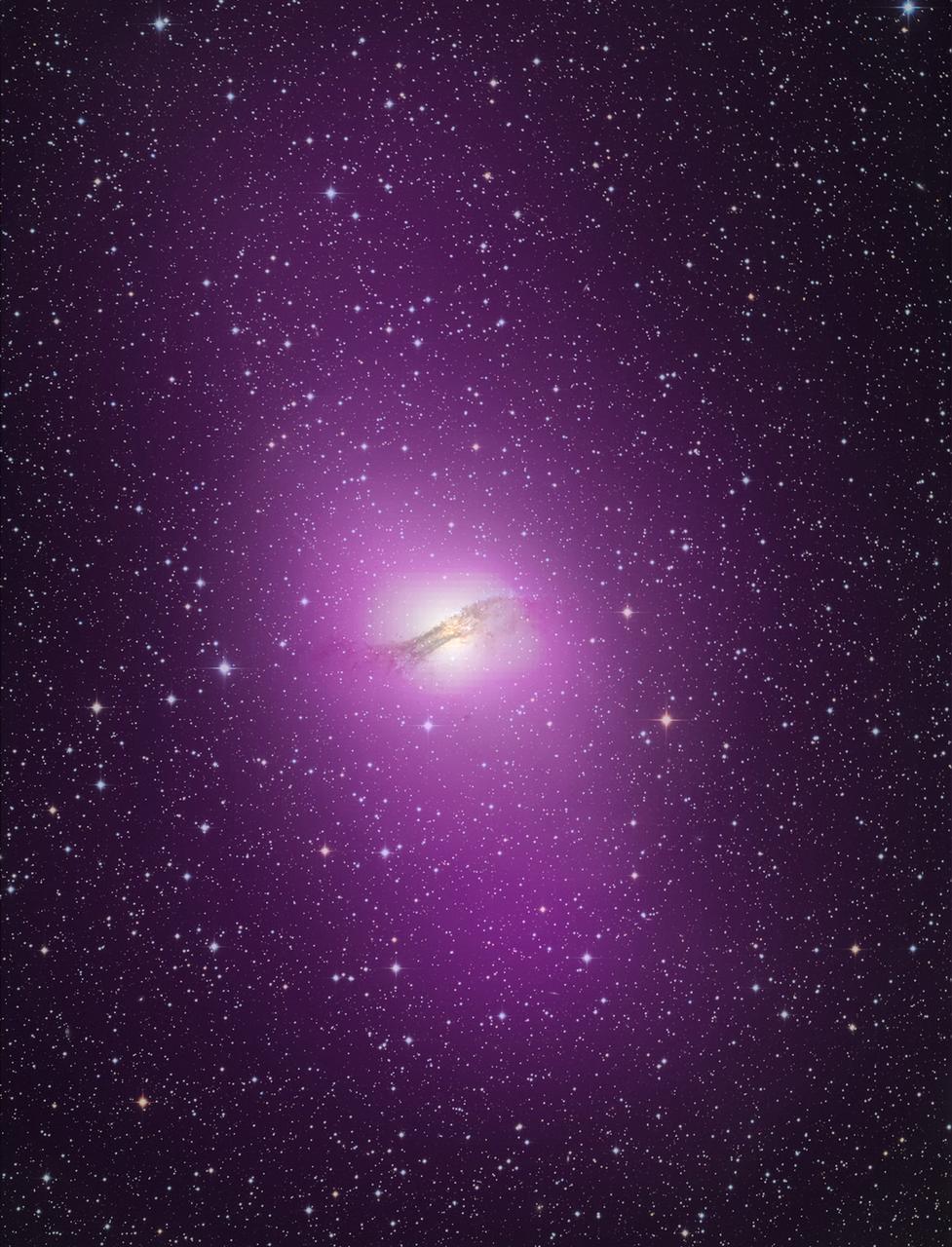
NASA release April 1, 2010 It takes the addition of radio data (orange) to fully appreciate the scale of Cen A's giant radio-emitting lobes, which stretch more than 1.4 million light-years. Gamma-rays from Fermi's Large Area Telescope (purple) and an image of the galaxy in visible light are also included in this composite. Credit: NASA/DOE/Fermi LAT Collaboration, Capella Observatory, and Ilana Feain, Tim Cornwell, and Ron Ekers (CSIRO/ATNF), R. Morganti (ASTRON), and N. Junkes (MPIfR) To learn more about these images go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/GLAST/news/smokestack-plumes.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/GLAST/news/smokestack-plumes.html</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> is home to the nation's largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe.
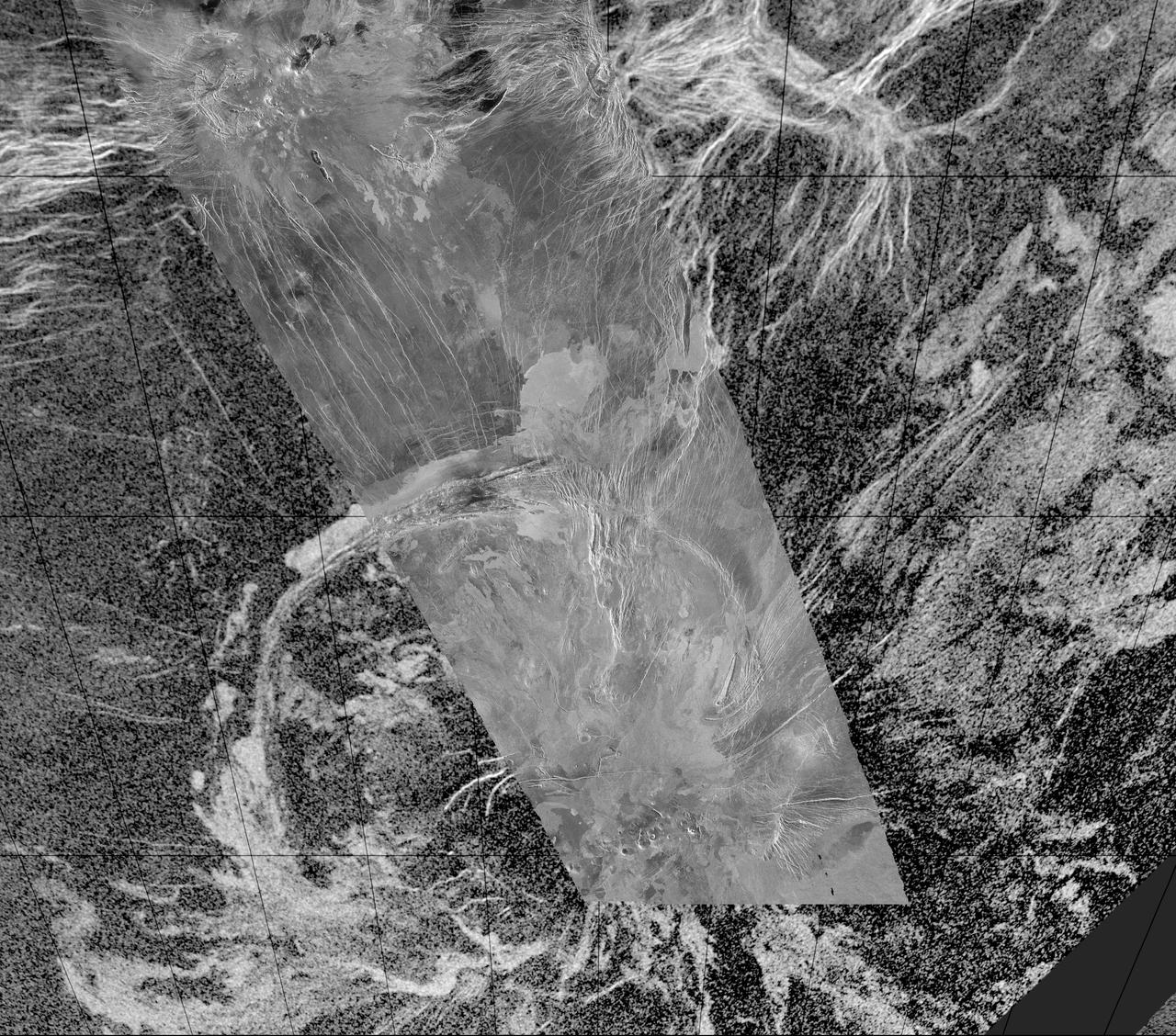

This composite image was created by inserting approximately 70 orbits of NASA Magellan data into an image obtained at the Arecibo, Puerto Rico radiotelescope and shows a geologically complex region in the southern hemisphere of Venus. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00217
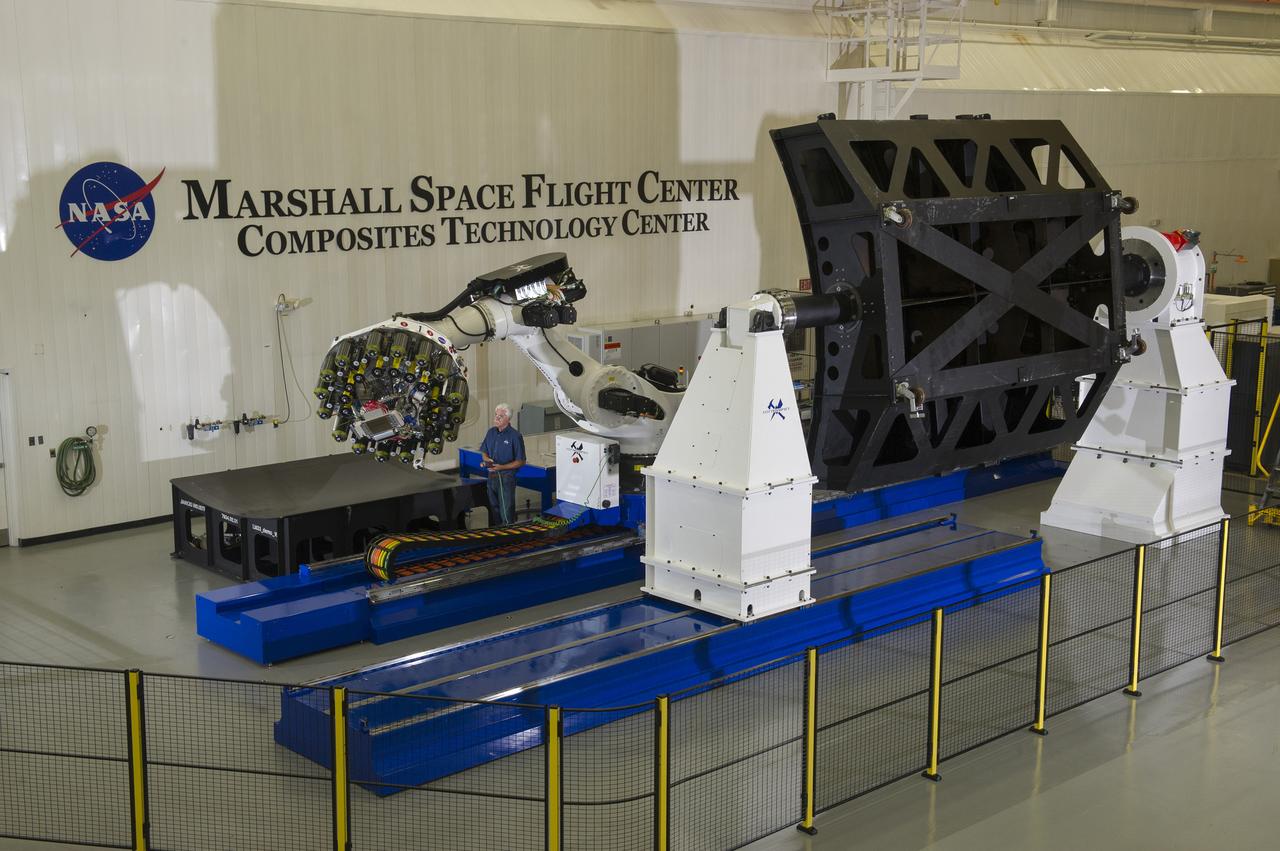
OVERVIEW OF MSFC COMPOSITES TECHNOLOGY CENTER AND THE AUTOMATED FIBER PLACEMENT TOOL WITH MATERIALS ENGINEER LARRY PELHAM
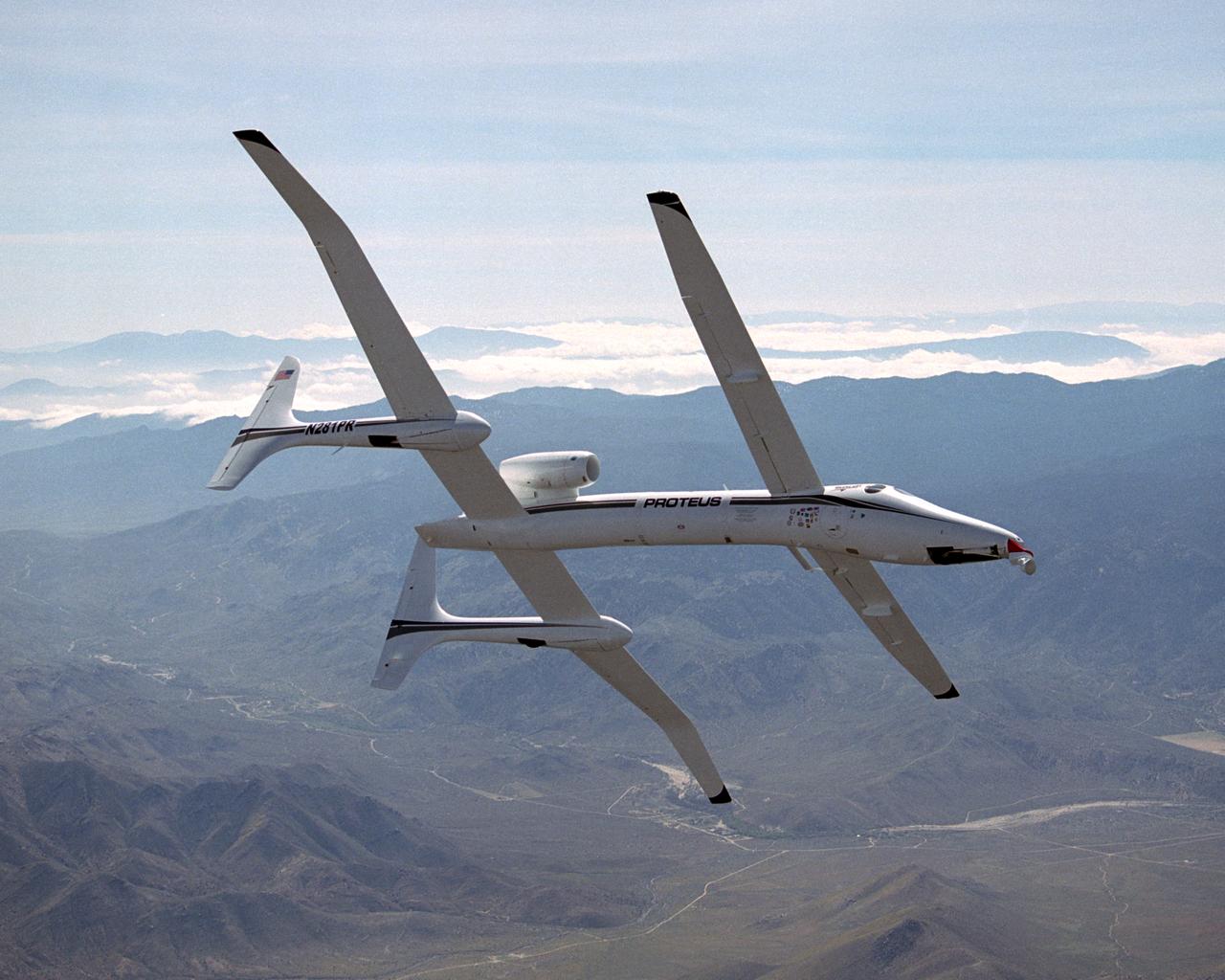

Scaled Composites' unique tandem-wing Proteus was the testbed for a series of UAV collision-avoidance flight demonstrations. An Amphitech 35GHz radar unit installed below Proteus' nose was the primary sensor for the Detect, See and Avoid tests.
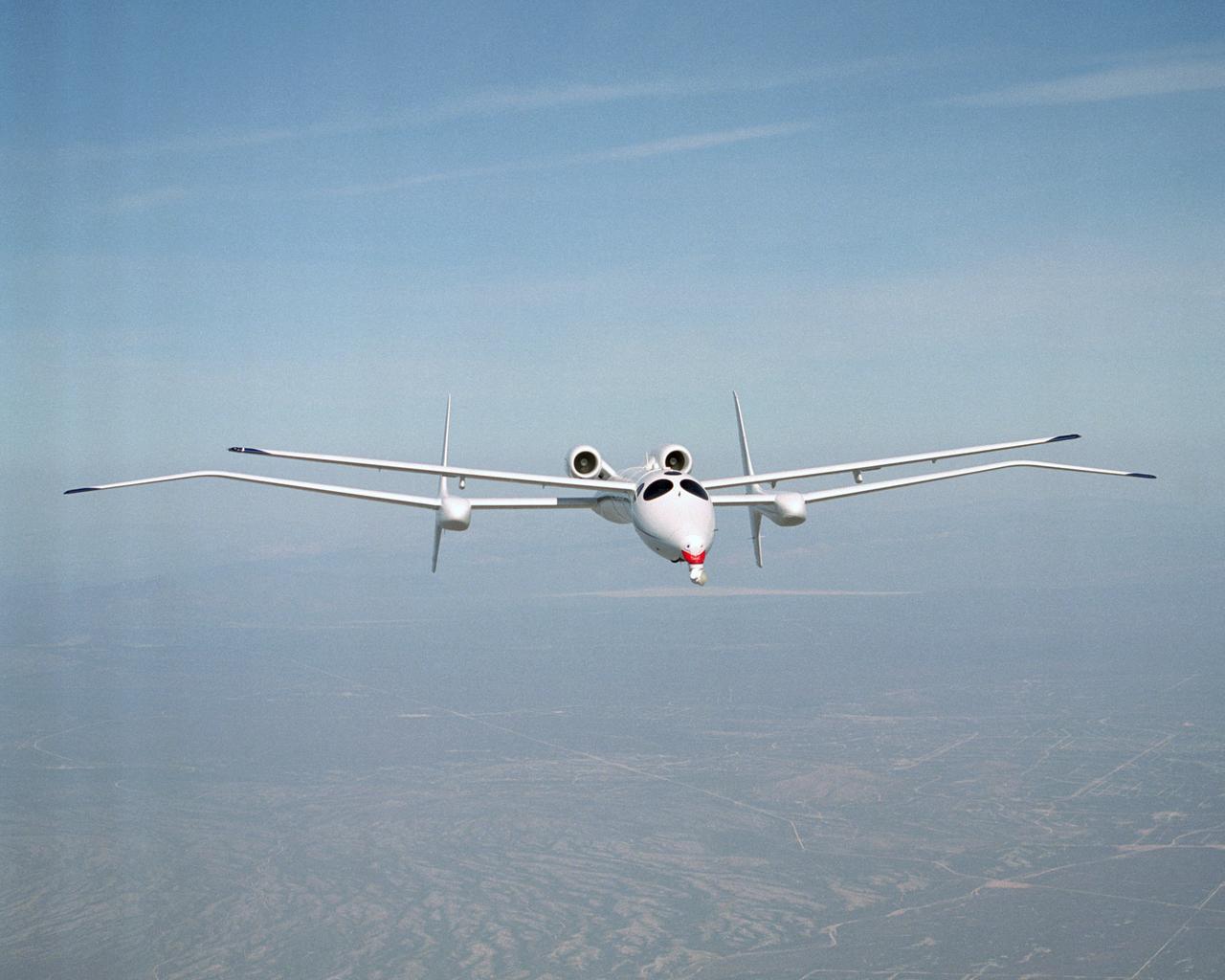

Scaled Composites' unique tandem-wing Proteus was the testbed for a series of UAV collision-avoidance flight demonstrations. An Amphitech 35GHz radar unit installed below Proteus' nose was the primary sensor for the Detect, See and Avoid tests.
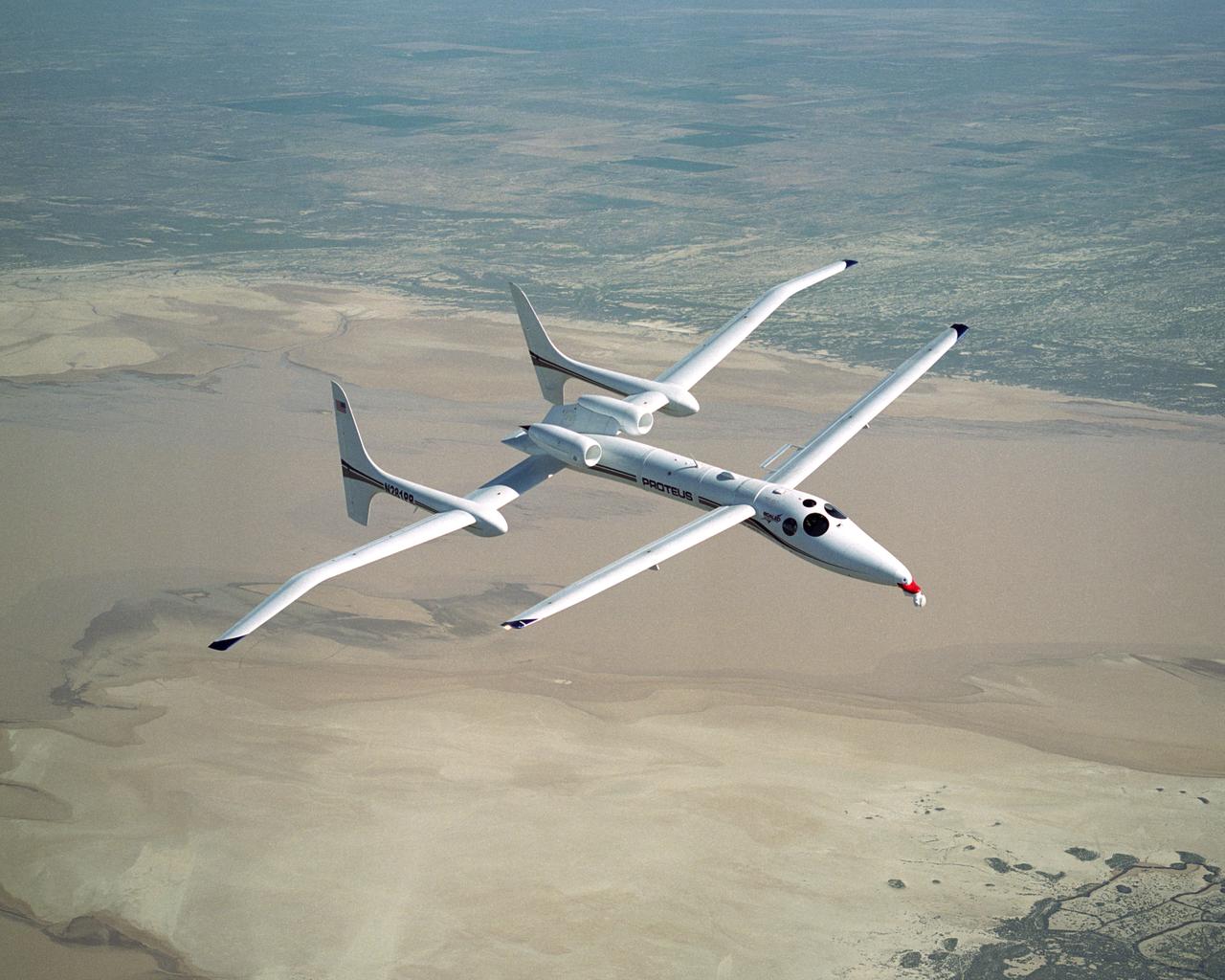

Scaled Composites' unique tandem-wing Proteus was the testbed for a series of UAV collision-avoidance flight demonstrations. An Amphitech 35GHz radar unit installed below Proteus' nose was the primary sensor for the Detect, See and Avoid tests.
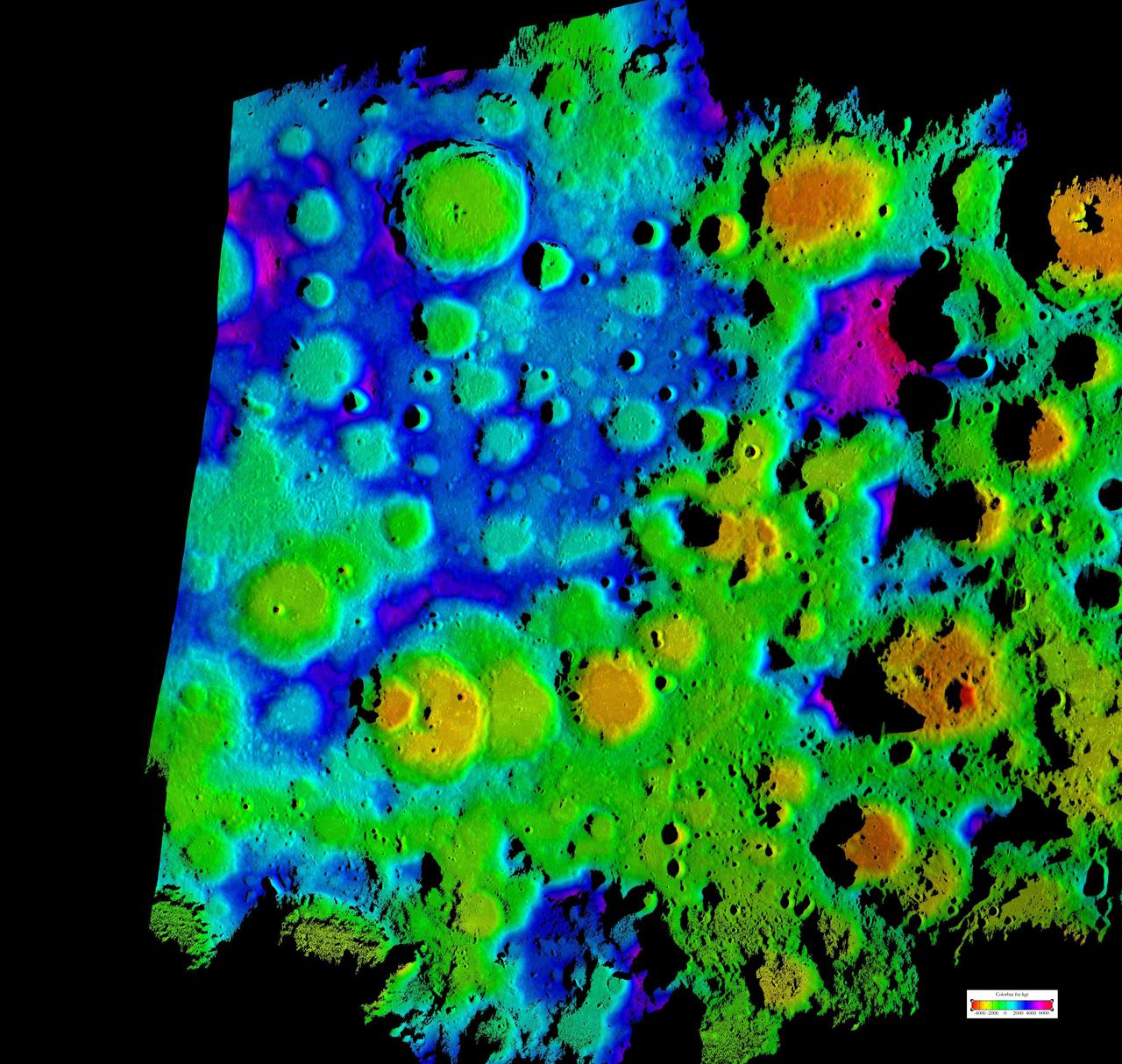
This composite image depicts the moon rugged south polar region in two lights. The color image is the highest resolution topography map to date of the moon south pole.
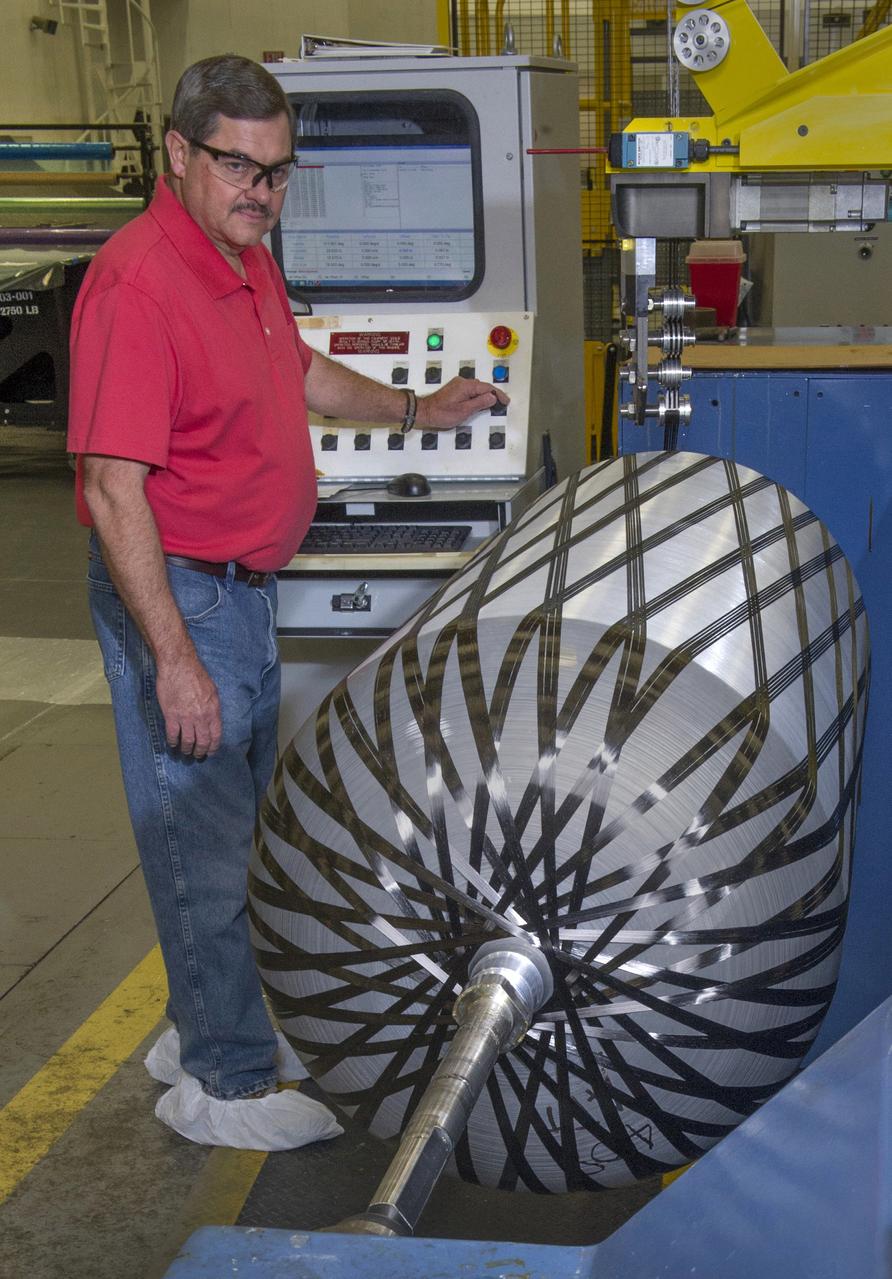

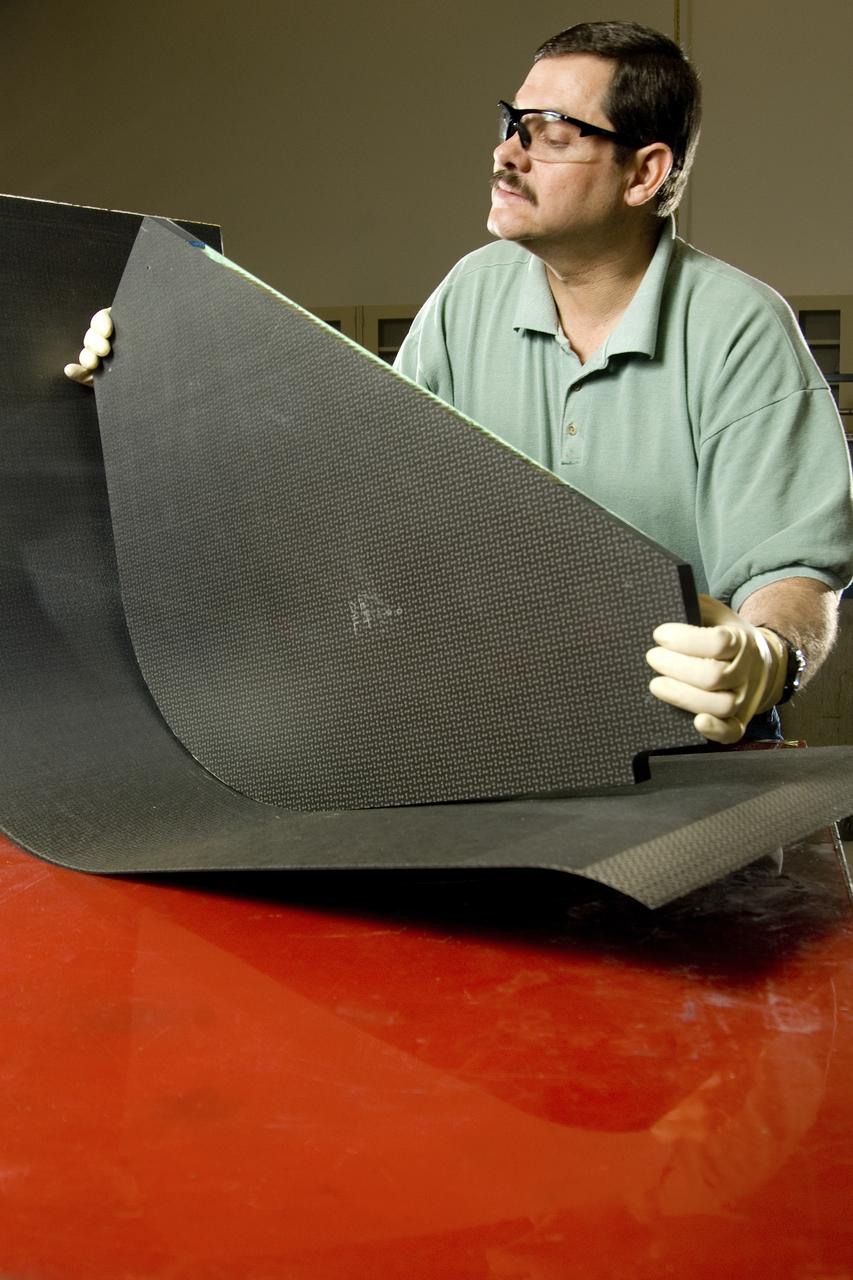
PHILLIP THOMPSON WRAPS PRESSURE VESSEL WITH COMPOSITE MATERIAL

Optics Lead Takashi Okajima prepares to align NICER’s X-ray optics. The payload’s 56 mirror assemblies concentrate X-rays onto silicon detectors to gather data that will probe the interior makeup of neutron stars, including those that appear to flash regularly, called pulsars. The Neutron star Interior Composition Explorer (NICER) is a NASA Explorer Mission of Opportunity dedicated to studying the extraordinary environments — strong gravity, ultra-dense matter, and the most powerful magnetic fields in the universe — embodied by neutron stars. An attached payload aboard the International Space Station, NICER will deploy an instrument with unique capabilities for timing and spectroscopy of fast X-ray brightness fluctuations. The embedded Station Explorer for X-ray Timing and Navigation Technology demonstration (SEXTANT) will use NICER data to validate, for the first time in space, technology that exploits pulsars as natural navigation beacons. Credit: NASA/Goddard/ Keith Gendreau <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
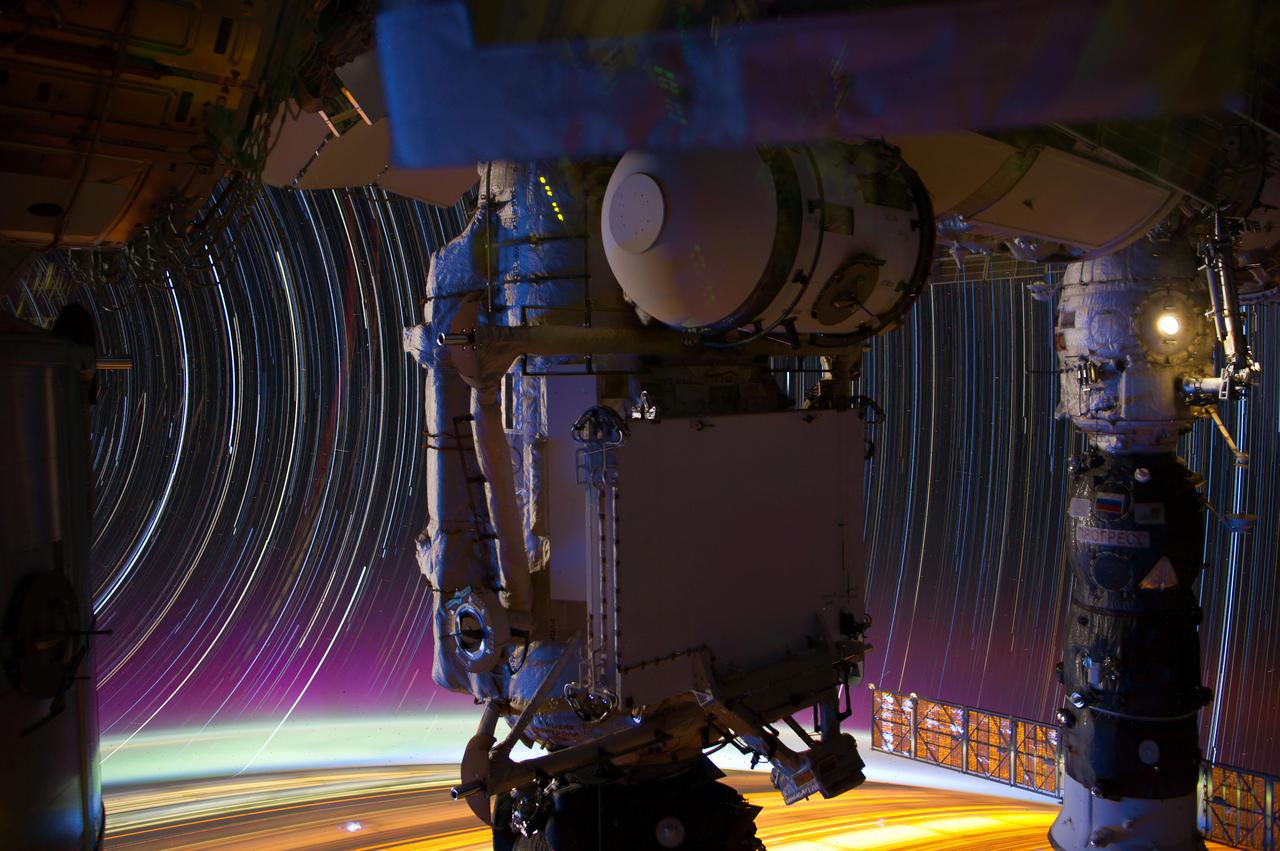

ISS030 star trail composite using iss030e159064 thru iss030e159110
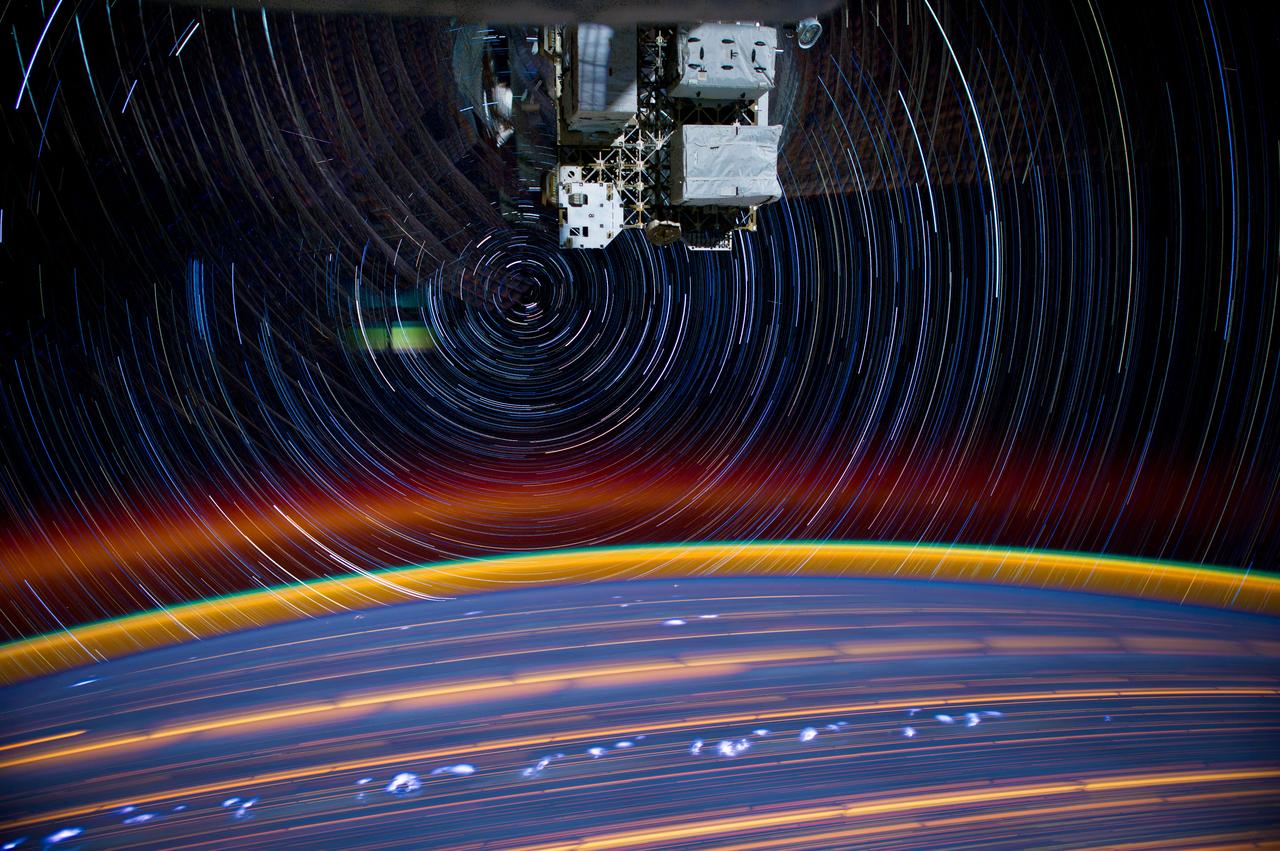

ISS030 star trail composite using iss030e158927 thru iss030e158944
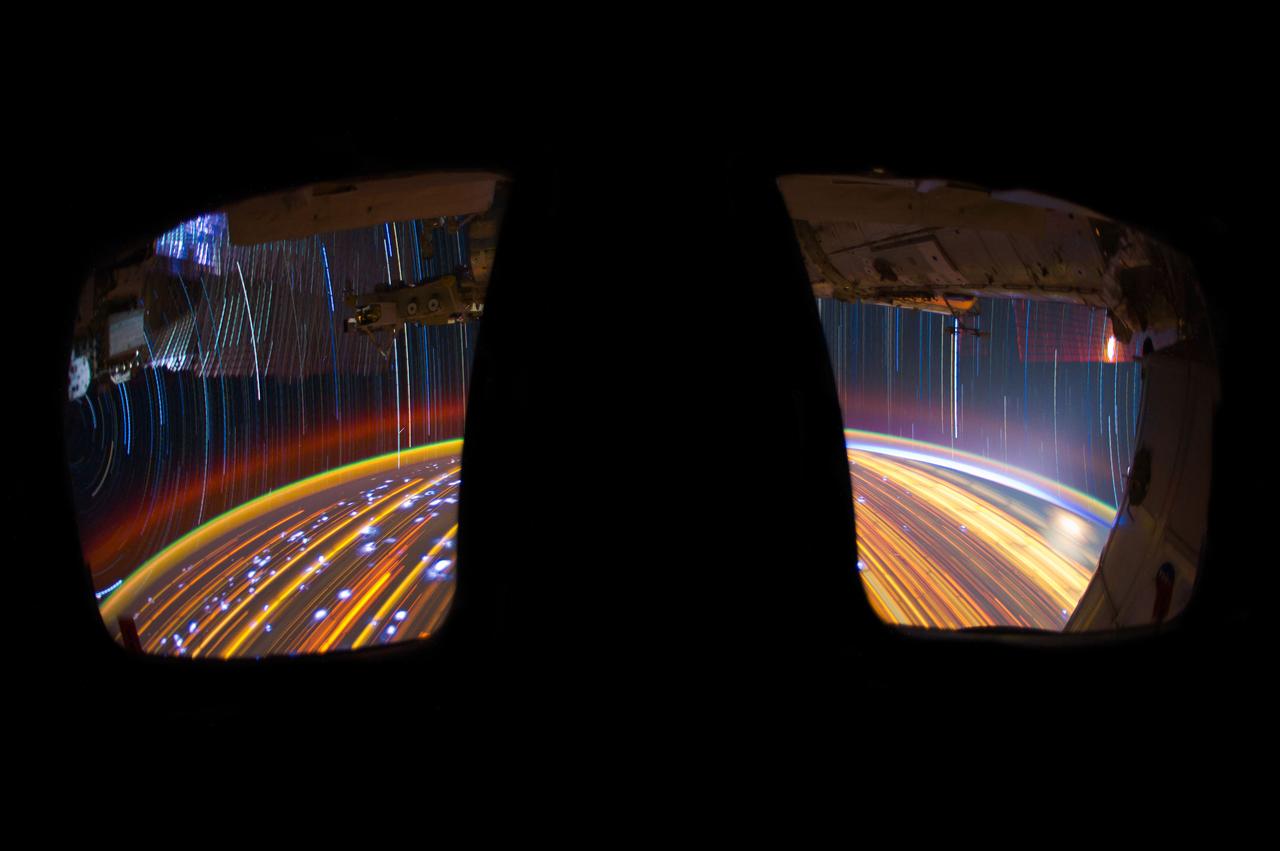

ISS030 star trail composite using iss030e158947 thru iss030e158992
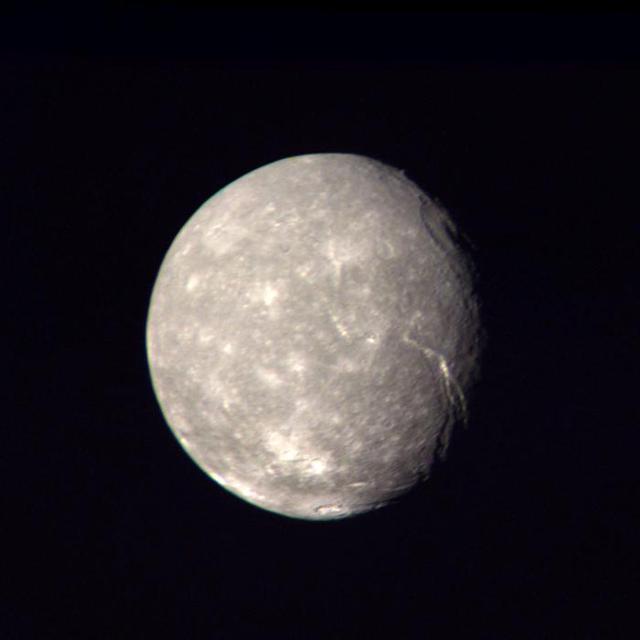

This high-resolution color composite of Titania was made from NASA Voyager 2 images taken Jan. 24, 1986, as the spacecraft neared its closest approach to Uranus. A large, trenchlike feature is seen near the terminator. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00036
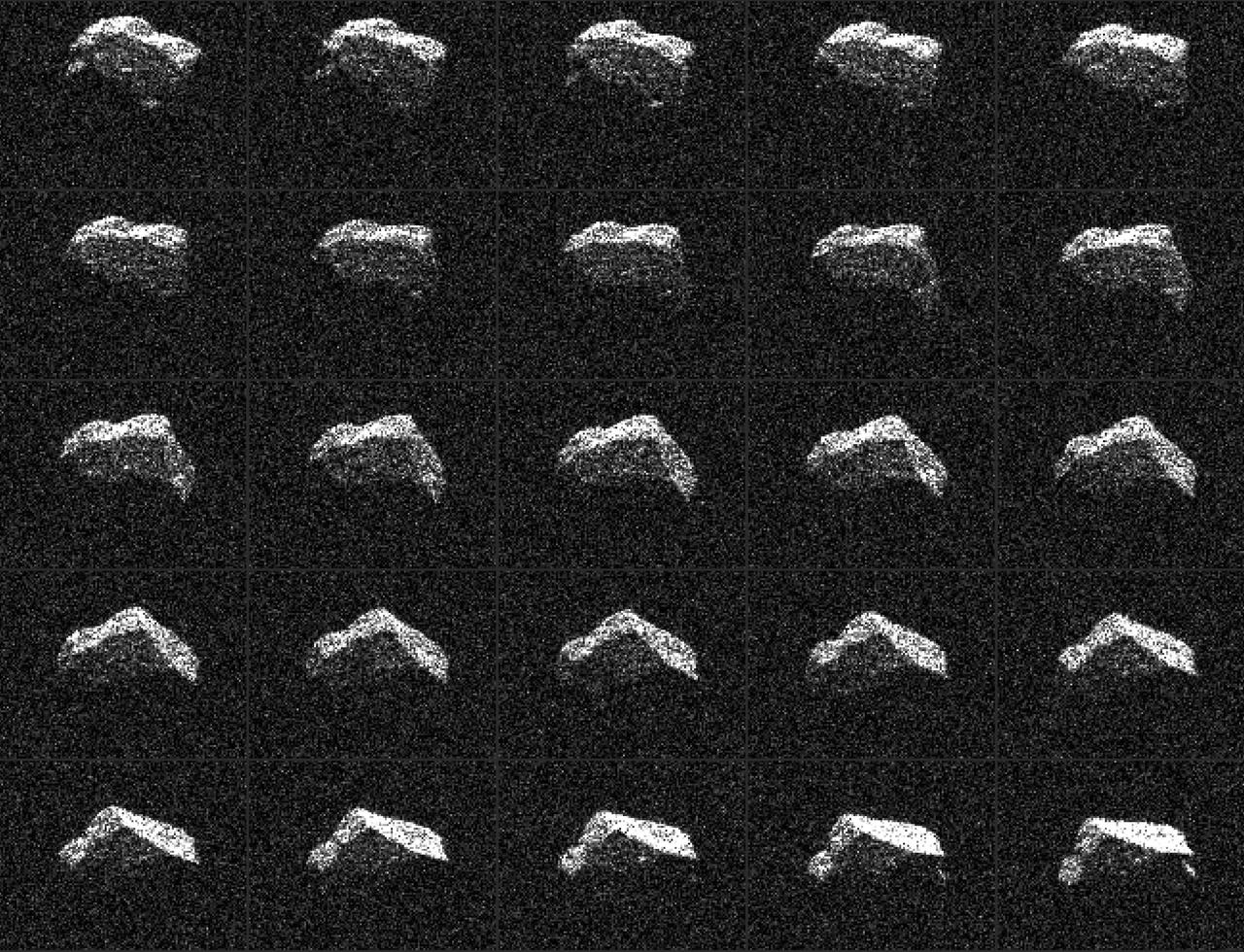
This composite of 25 images of asteroid 2017 BQ6 was generated with radar data collected using NASA's Goldstone Solar System Radar in California's Mojave Desert. The images were gathered on Feb. 7, 2017, between 8:39 and 9:50 p.m. PST (11:39 p.m. EST and 12:50 a.m., Feb. 7), revealing an irregular, angular-appearing asteroid about 660 feet (200 meters) in size that rotates about once every three hours. The images have resolutions as fine as 12 feet (3.75 meters) per pixel. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21452
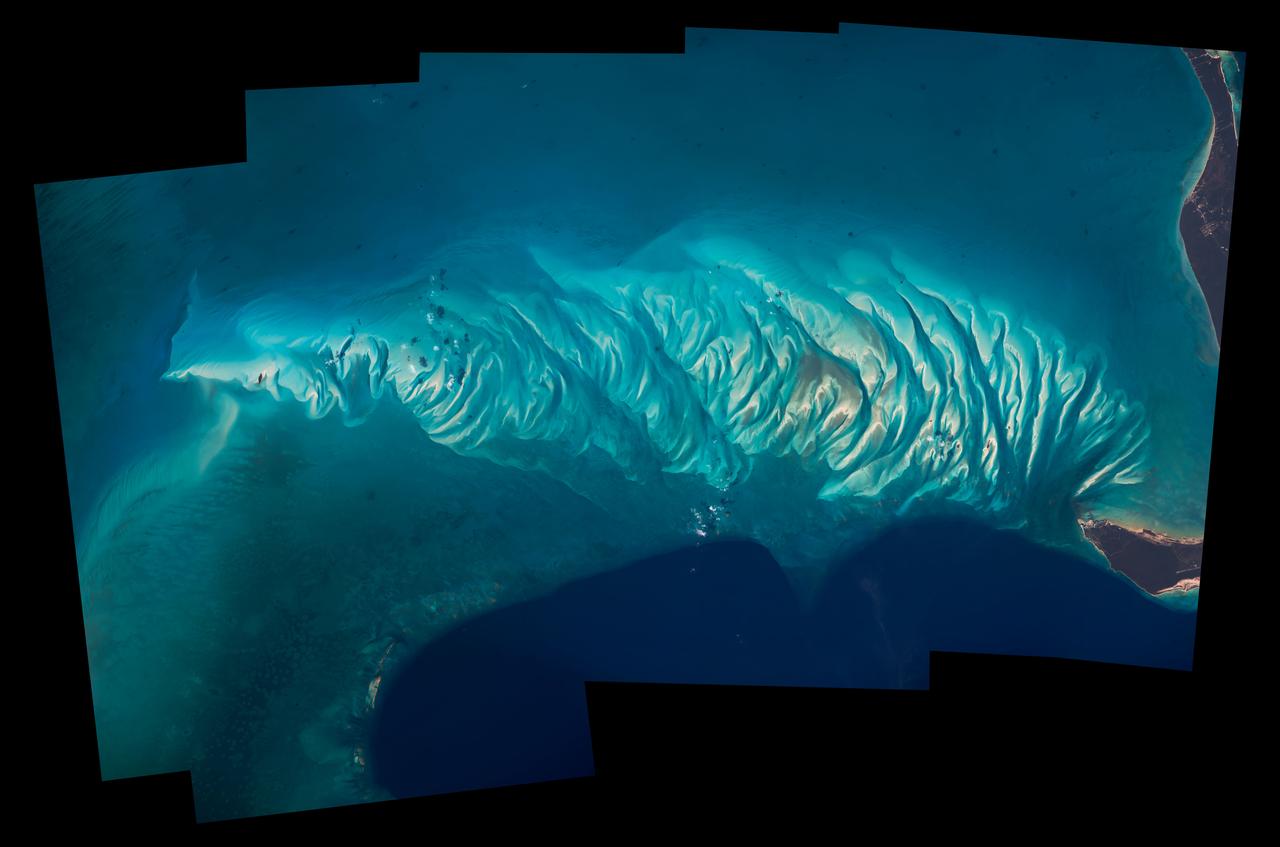

Expedition 47 Earth observation composite created with iss047e051337 - iss047e051343 135A8768 – 135A8774 Bahamas
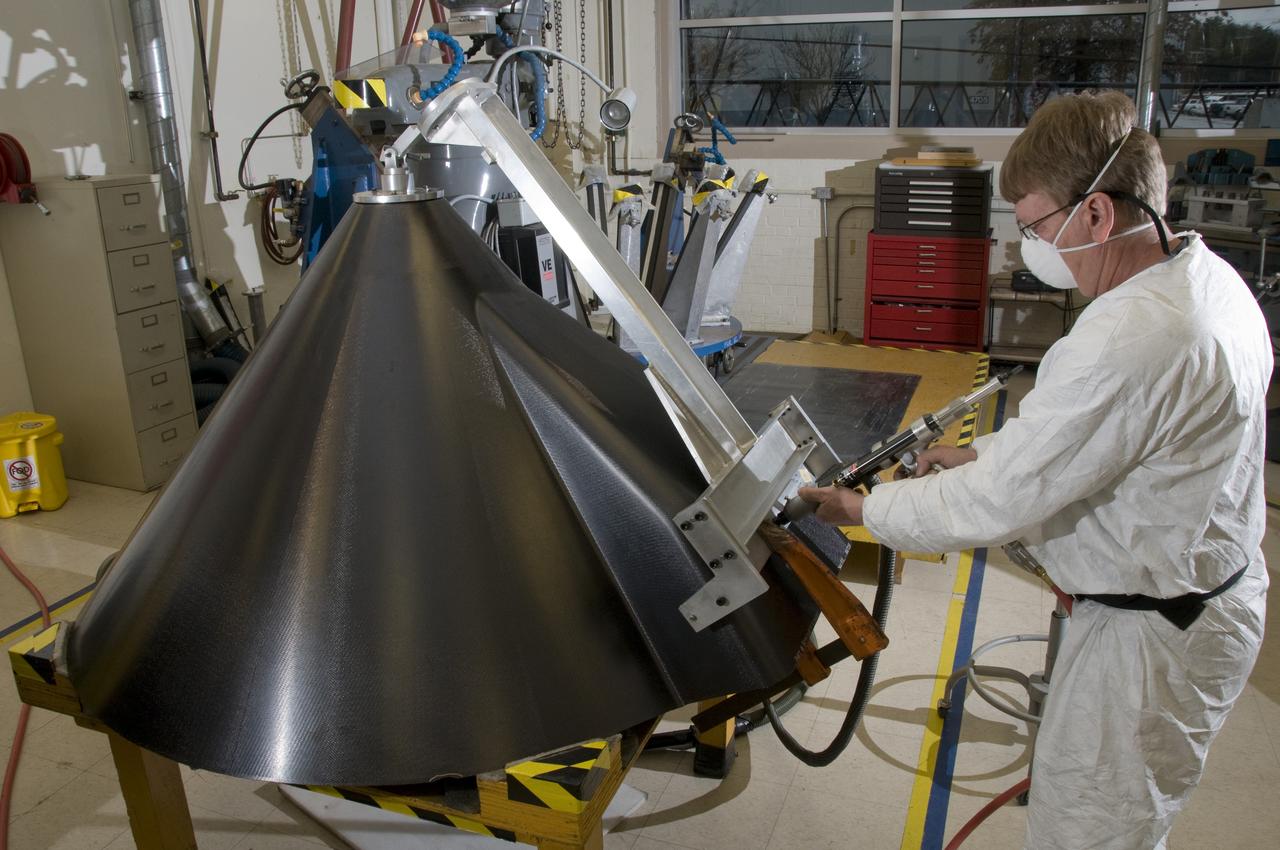

ROBERT CARROLL, A MACHINIST WITH LOCKHEED MARTIN, DRILLS ALIGNMENT HOLES ON THE EXTERNAL TANK COMPOSITE NOSE CONE
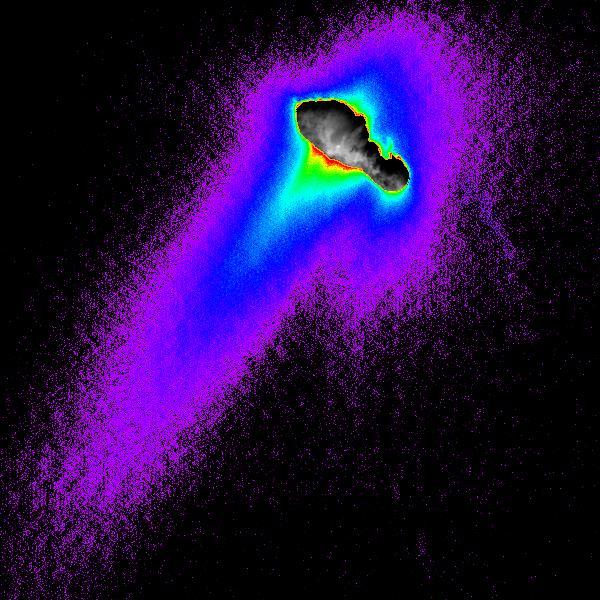
A composite of images from NASA Deep Space 1 spacecraft shows features of comet Borrelly nucleus, dust jets escaping the nucleus and the cloud-like coma of dust and gases surrounding the nucleus.
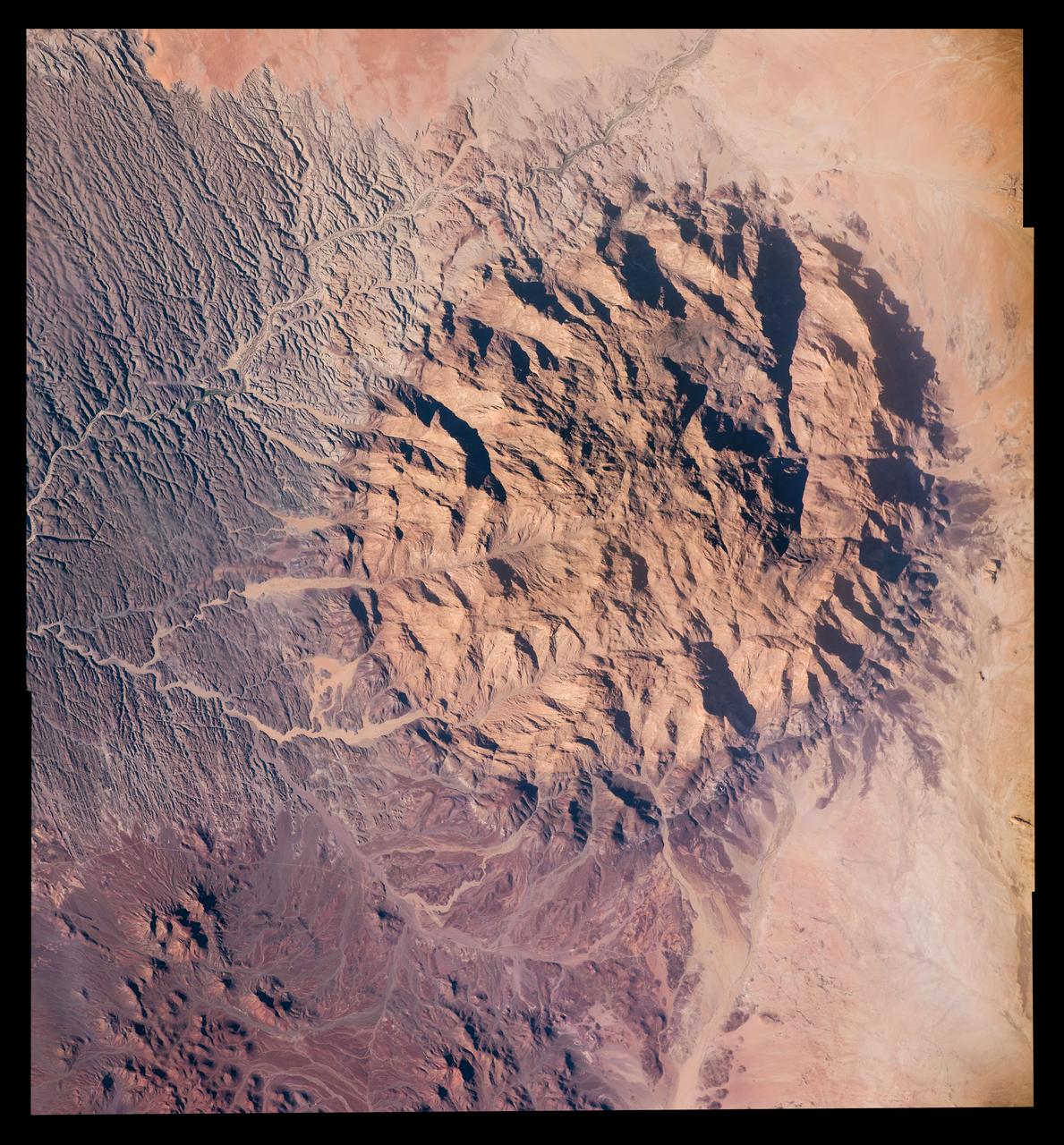

Expedition 47 Earth observation composite created with iss047e028742 - iss047e028744 135A2099 – 135A2101 Unique structure in Namibia Mt Brandberg Nature Reserve
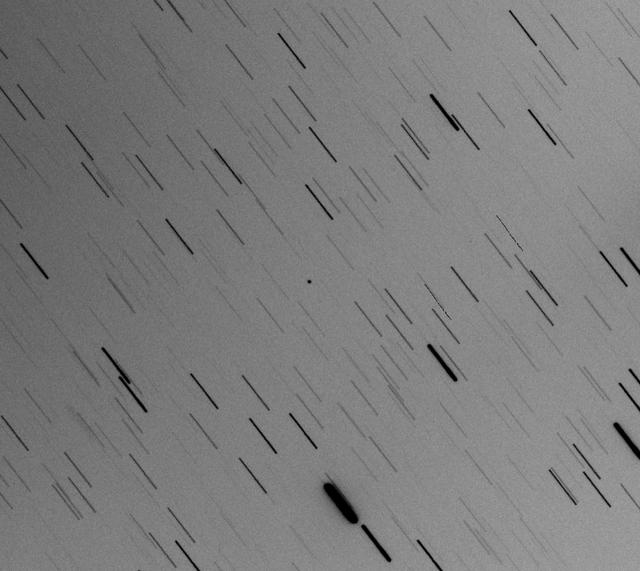

This optical composite image shows asteroid 2017 YE5, taken on June 30, 2018, by the Cadi Ayyad University Morocco Oukaimeden Sky Survey, one of the first surveys to identify 2017 YE5 in December 2017. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22558
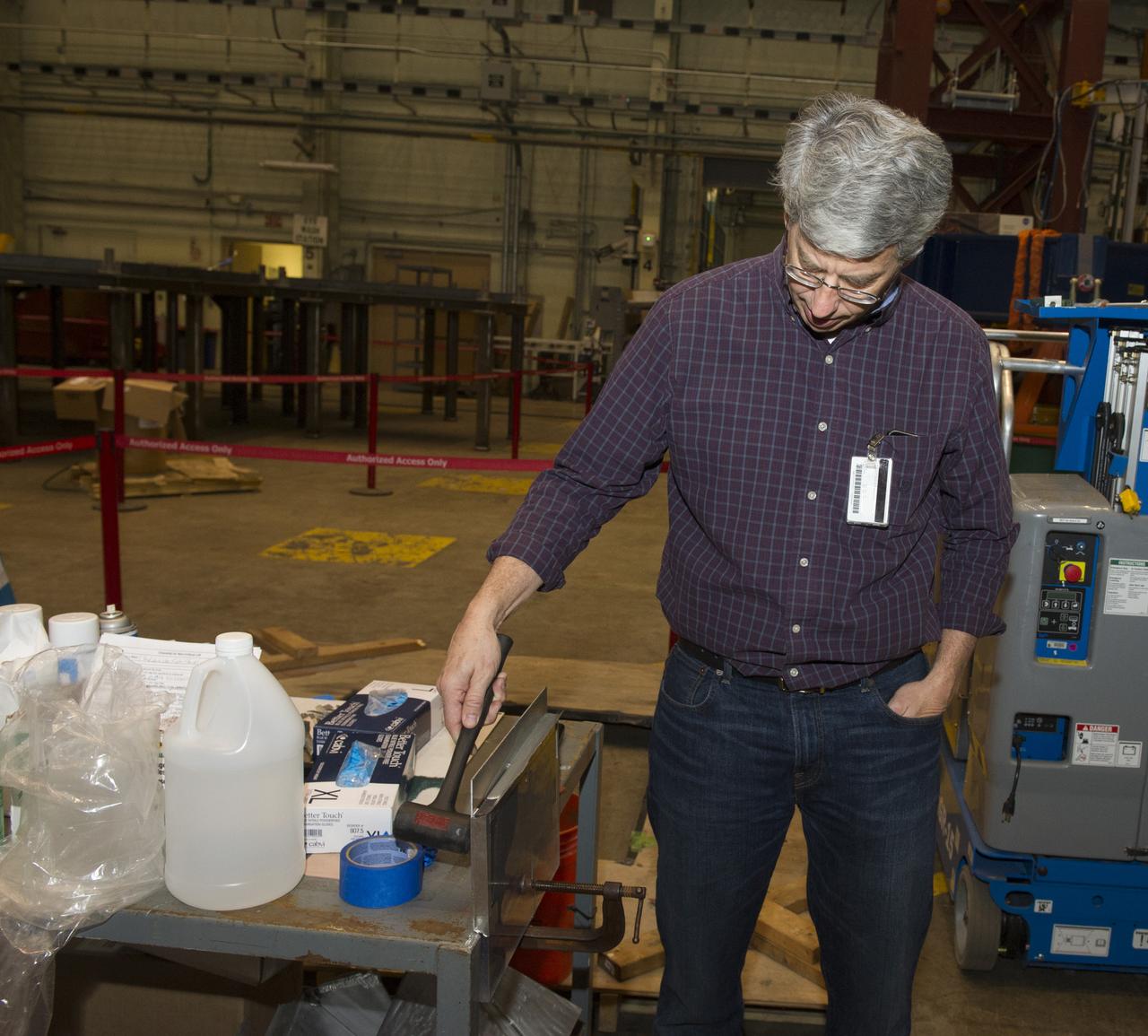

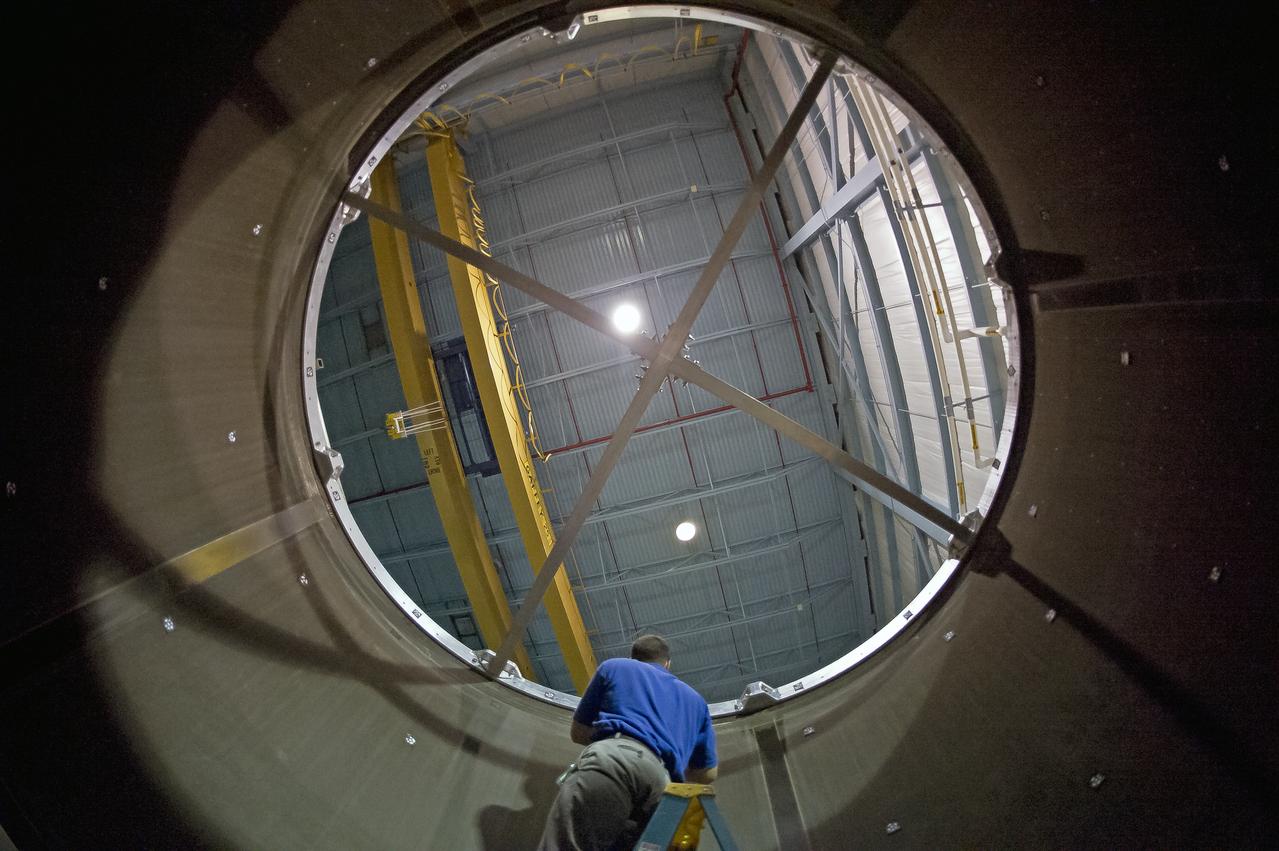
SHELL BUCKLE KNOCKDOWN FACTOR (SBKF) COMPOSITE BARREL EPOXY POUR