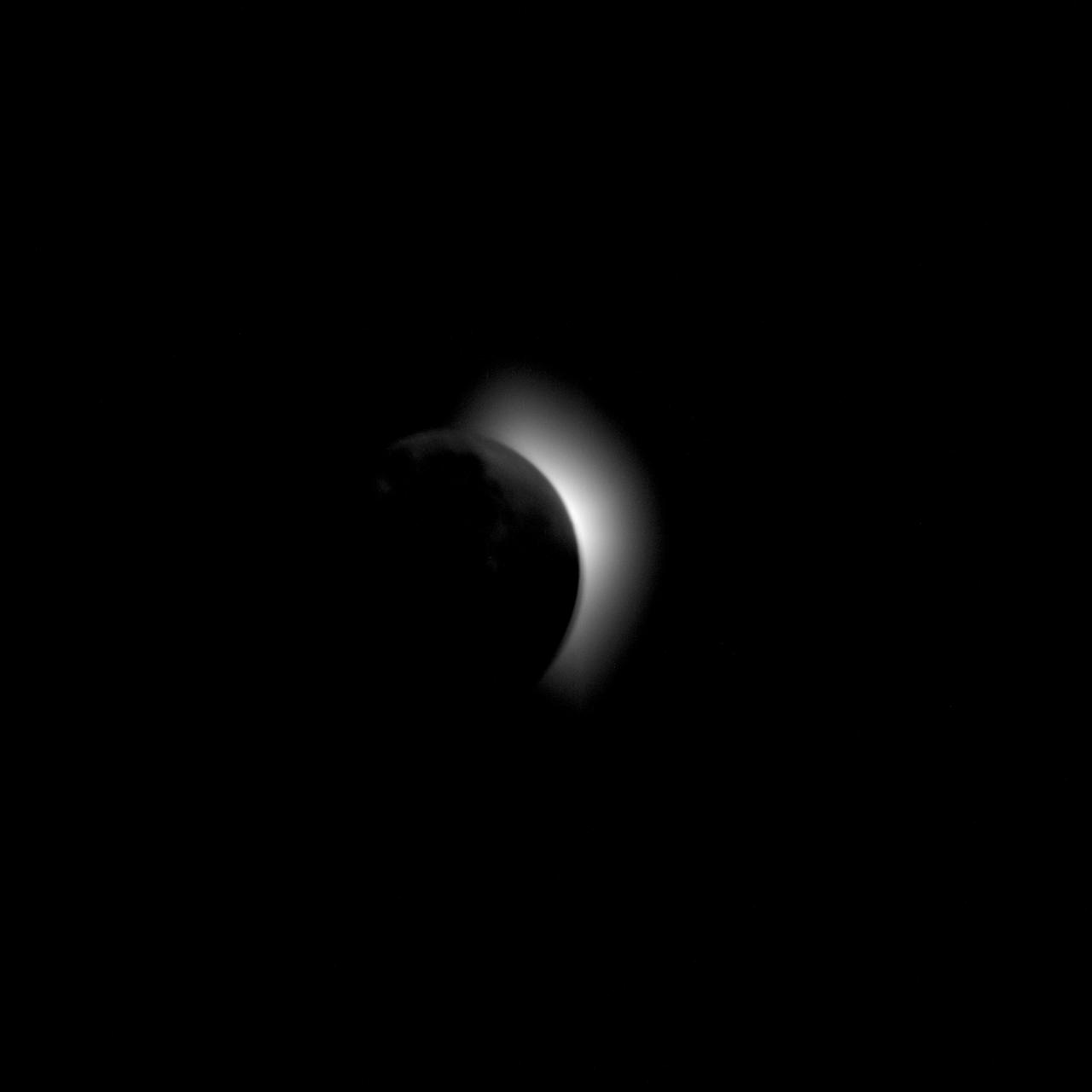

AS11-42-6179 (19 July 1969) --- This photograph of the solar corona was taken from the Apollo 11 spacecraft during trans-lunar coast and prior to lunar orbit insertion. The moon is the dark disc between the spacecraft and the sun.
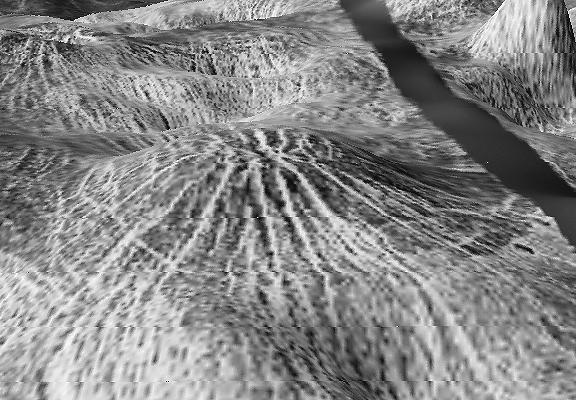

The view from NASA's Magellan spacecraft shows a 100-km-wide nova superposed on Yavine Corona. Coronae are roughly circular, volcanic features believed to form over hot upwellings of magma within the Venusian mantle. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00150
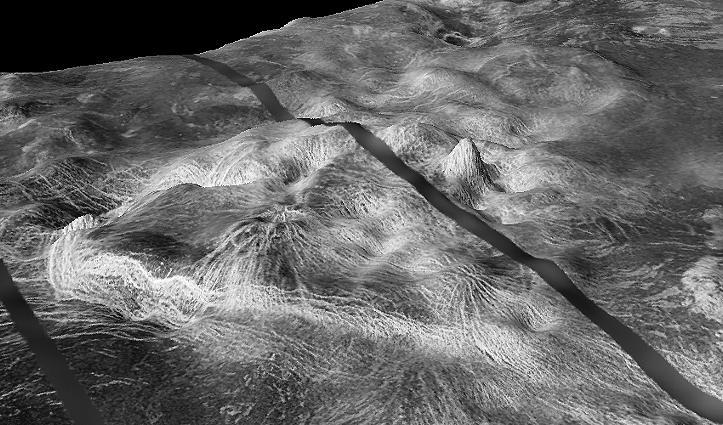

The view from NASA's Magellan spacecraft shows Yavine Corona, looking northeast. Coronae are roughly circular, volcanic features believed to form over hot upwellings of magma within the Venusian mantle. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00098
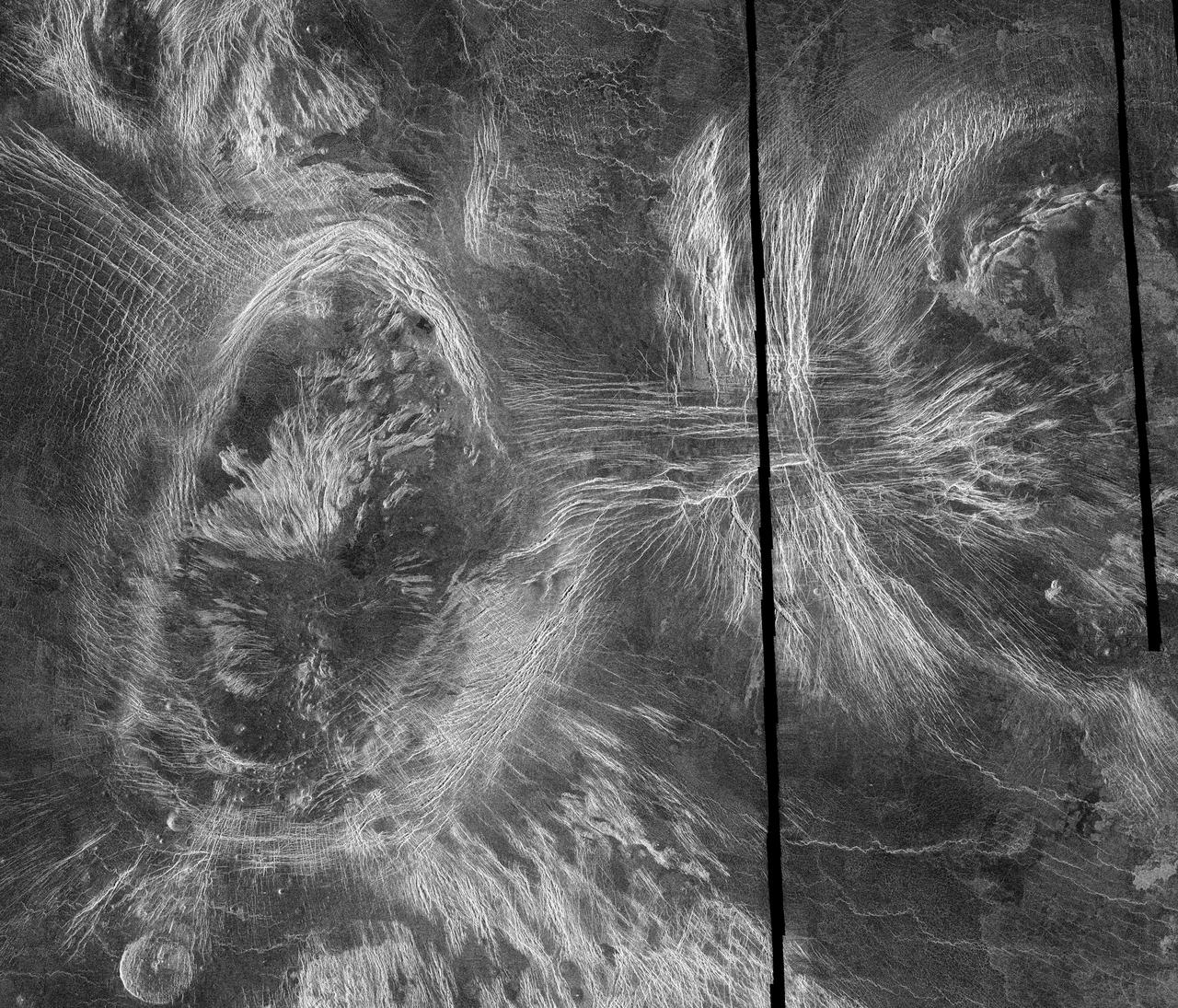
This mosaic of Magellan data in the Fortuna region of Venus, centered at 49 degrees north latitude, 2 degrees longitude, shows two coronae. Coronae are large circular or oval structures first identified in Soviet radar images of Venus. The structure on the left, Bahet Corona, is about 230 kilometers (138 miles) long and 150 kilometers (90 miles) across. A portion of Onatah Corona, over 350 kilometers (210 miles) in diameter, can be seen on the right of the mosaic. Both features are surrounded by a ring of ridges and troughs, which in places cut more radially-oriented fractures. The centers of the features also contain radial fractures as well as volcanic domes and flows. Coronae are thought to form due to the upwelling of hot material from deep in the interior of Venus. The two coronae may have formed at the same time over a single upwelling, or may indicate movement of the upwelling or the upper layers of the planet to the west over time. A 'pancake' dome, similar to low-relief domes see in the southern hemisphere, is located just to the southwest of Bahet. Resolution of the Magellan data is about 120 meters (400 feet). http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00461
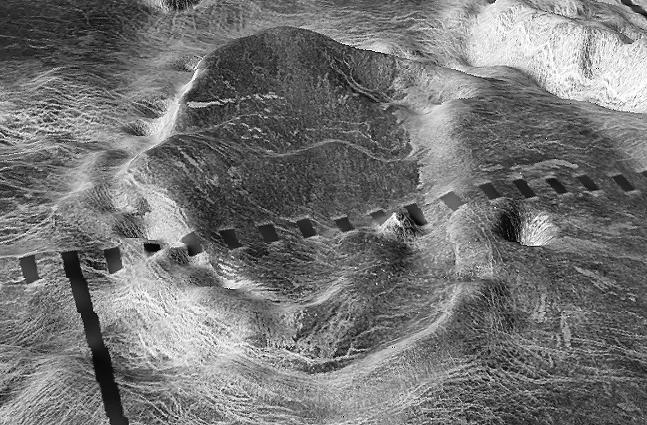

This view from NASA's Magellan spacecraft is a close-up of Atete Corona, a 600-km-long and 450-km-wide feature at latitude 16 degrees S., longitude 244 degrees; looking north. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00097
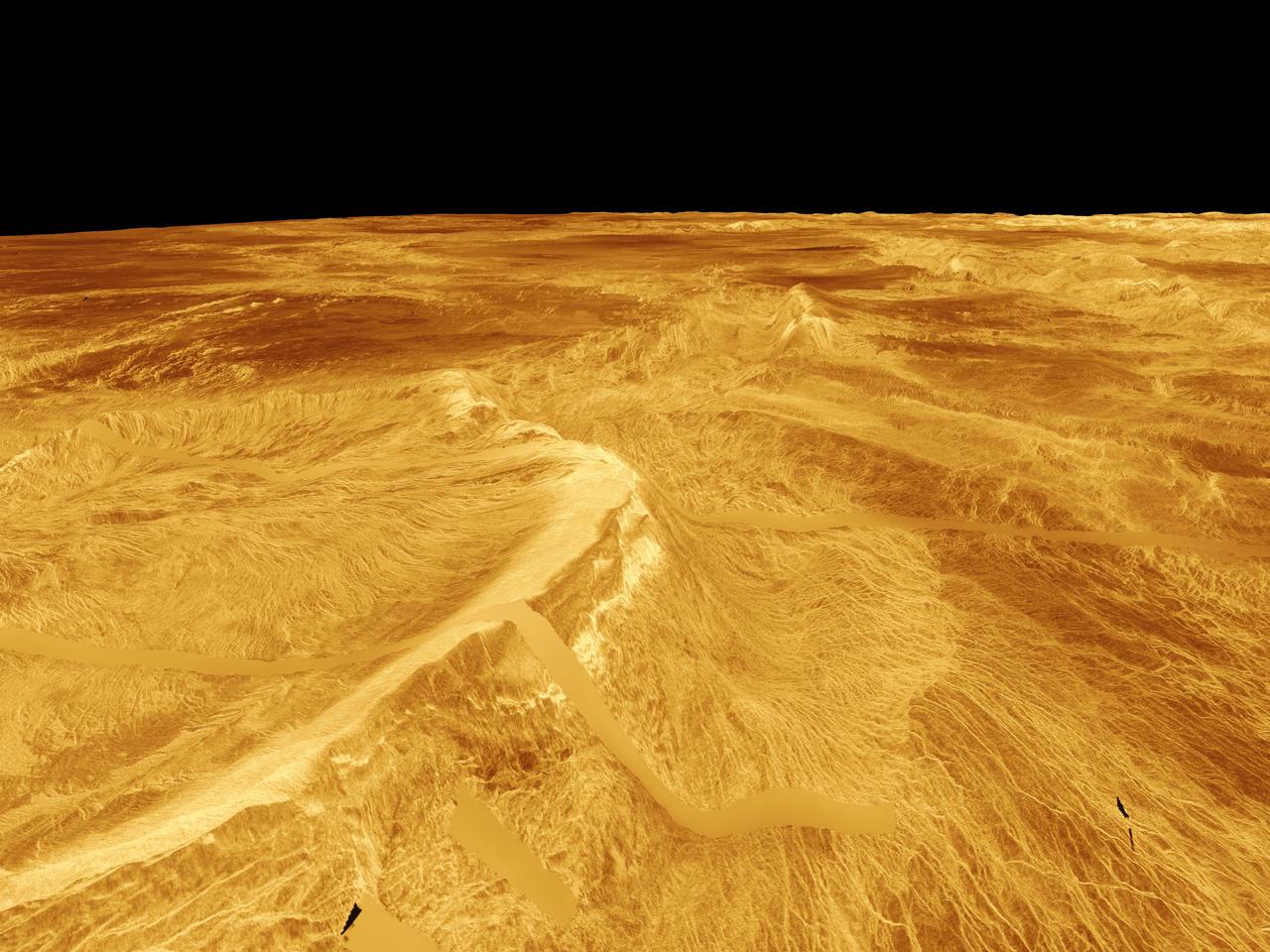
This computer-generated perspective view of Latona Corona and Dali Chasma on Venus shows NASA Magellan radar data superimposed on topography. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00268

This two-panel illustration shows a black hole surrounded by a disk of gas, before and after the disk is partially dispersed. In the left panel, the ball of white light above the black hole is the black hole corona, a collection of ultra-hot gas particles that forms as gas from the disk falls into the black hole. The streak of debris falling toward the disk is what remains of a star that was torn apart by the black hole's gravity. The right panel shows the black hole after the debris from the star has dispersed some of the gas in the disk, causing the corona to disappear. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23864
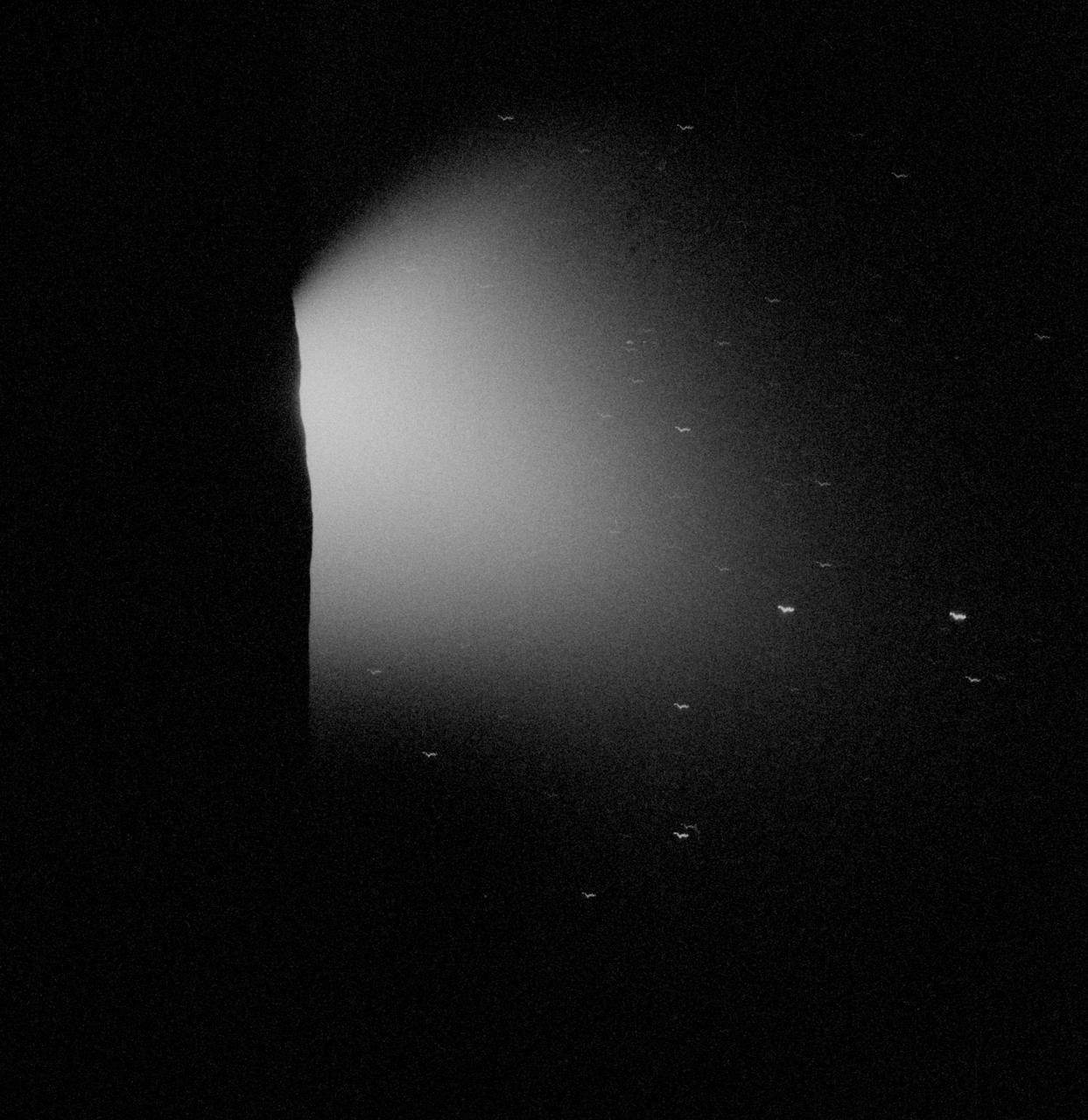

AS15-98-13311 (31 July 1971) --- The solar corona, as photographed from the Apollo 15 spacecraft about one minute prior to sunrise on July 31, 1971, is seen just beyond the lunar horizon. The bright object on the opposite of the frame is the planet Mercury. The bright star near the frame center is Regulus, and the lesser stars form the head of the constellation Leo. Mercury is approximately 28 degrees from the center of the sun. The solar coronal streamers, therefore, appear to extend about eight degrees from the sun's center. This solar corona photograph was the second in a series of seven. Three such series were obtained by astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, during the solo part of his lunar orbital flight. They represent man's first view of this part of the sun's light. While astronauts David R. Scott, commander, and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Falcon" to explore the Hadley-Apennine area of the moon, astronaut Worden remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.

A supermassive black hole is depicted in this artist's concept, surrounded by a swirling disk of material falling onto it. The purplish ball of light above the black hole, a feature called the corona, contains highly energetic particles that generate X-ray light. If you could view the corona with your eyes, it would appear nearly invisible since we can't see its X-ray light. The corona gathers inward (left), becoming brighter, before shooting away from the black hole (middle and right). Astronomers don't know why the coronas shift, but they have learned that this process leads to a brightening of X-ray light that can be observed by telescopes. Normally, before a black hole's corona shifts, there is already an effect at work called relativistic boosting. As X-ray light from the corona reflects off the black hole's surrounding disk of material -- which is traveling near half the speed of light -- the X-ray light becomes brightened, as seen on the left side of the illustration. This boosting occurs on the side of the disk where the material is traveling toward us. The opposite effect, a dimming of the X-ray light, occurs on the other side of the disk moving away from us. Another form of relativistic boosting happens when the corona shoots away from the black hole, and later collapses. Its X-ray light is also brightened as the corona travels toward us at very fast speeds, leading to X-ray flares. In 2014, NASA's Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array, or NuSTAR, and Swift space telescopes witnessed an X-flare from the supermassive black hole in a distant galaxy called Markarian 335. The observations allowed astronomers to link a shifting corona to an X-ray flare for the first time. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20051

NASA release July 27, 2011 These jets, known as spicules, were captured in an SDO image on April 25, 2010. Combined with the energy from ripples in the magnetic field, they may contain enough energy to power the solar wind that streams from the sun toward Earth at 1.5 million miles per hour. Credit: NASA/SDO/AIA Like giant strands of seaweed some 32,000 miles high, material shooting up from the sun sways back and forth with the atmosphere. In the ocean, it's moving water that pulls the seaweed along for a ride; in the sun's corona, magnetic field ripples called Alfvén waves cause the swaying. For years these waves were too difficult to detect directly, but NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) is now able to track the movements of this solar "seaweed" and measure how much energy is carried by the Alfvén waves. The research shows that the waves carry more energy than previously thought, and possibly enough to drive two solar phenomena whose causes remain points of debate: the intense heating of the corona to some 20 times hotter than the sun's surface and solar winds that blast up to 1.5 million miles per hour. "SDO has amazing resolution so you can actually see individual waves," says Scott McIntosh at the National Center for Atmospheric Research in Boulder, Colo. "Now we can see that instead of these waves having about 1000th the energy needed as we previously thought, it has the equivalent of about 1100W light bulb for every 11 square feet of the sun's surface, which is enough to heat the sun's atmosphere and drive the solar wind." To read more go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/sdo/news/alfven-waves.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/sdo/news/alfven-waves.html</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://web.stagram.com/n/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
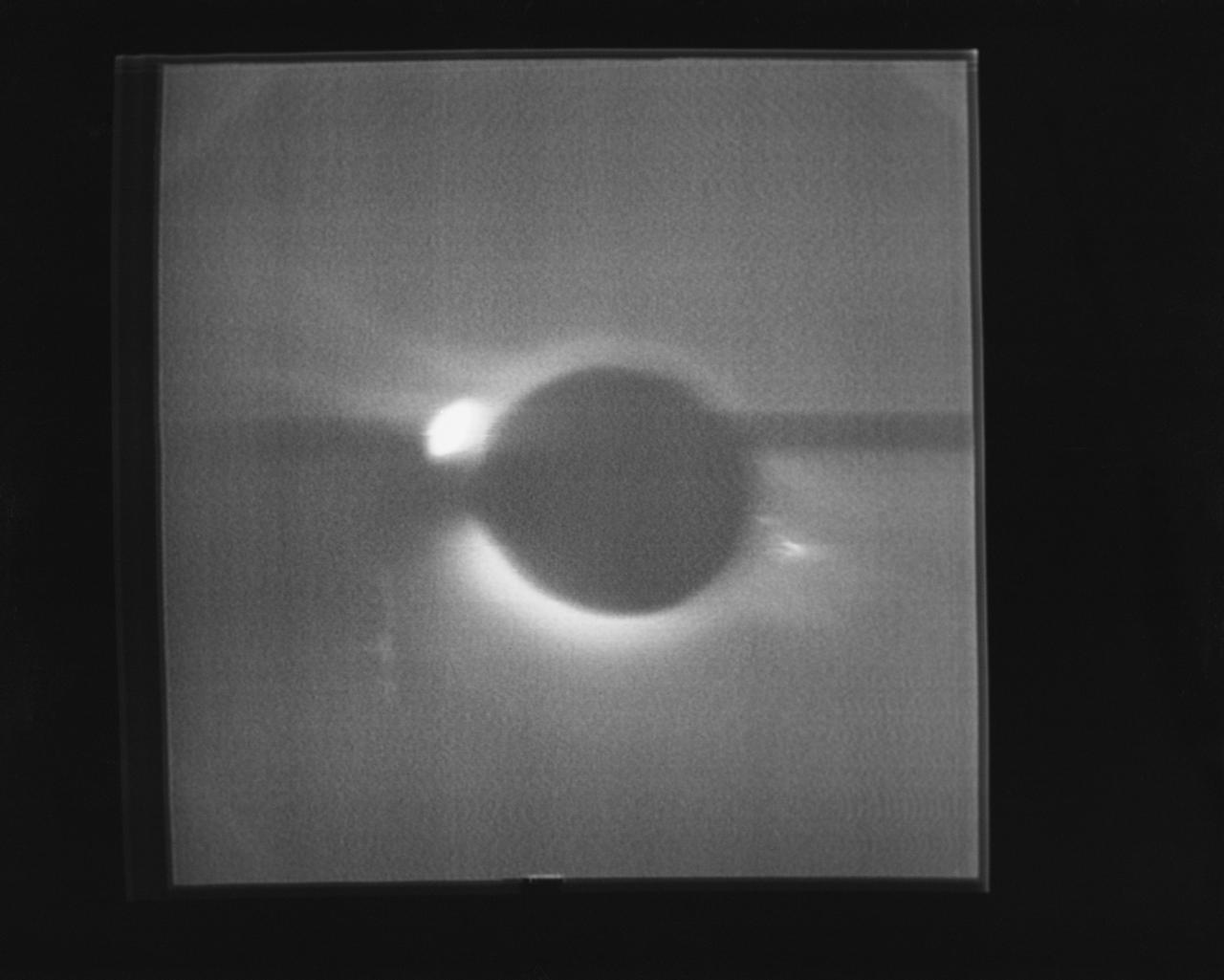

S74-15697 (17 Jan. 1974) --- The solar corona and a solar prominence as seen through the White Light Coronograph, Skylab Experiment S052, on Jan. 17, 1974. This view was reproduced from a television transmission made by a TV camera aboard the Skylab space station in Earth orbit. The bright spot is a burn in the vidicon. The solar corona is the halo around the sun which is normally visible only at the time of solar eclipse by the moon. The Skylab coronography uses an externally-mounted disk system which occults the brilliant solar surface while allowing the fainter radiation of the corona to enter an annulus and be photographed. A mirror system allows either TV viewing of the corona or photographic recording of the image. Photo credit: NASA
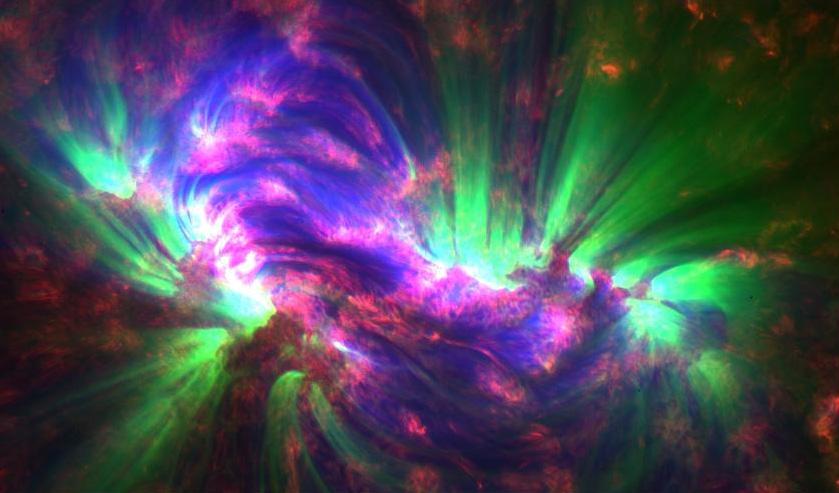

NASA release July 27, 2011 These jets, known as spicules, were captured in an SDO image on April 25, 2010. Combined with the energy from ripples in the magnetic field, they may contain enough energy to power the solar wind that streams from the sun toward Earth at 1.5 million miles per hour. Credit: NASA/SDO/AIA To see a full disk view go here: <a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/5982663752/in/photostream/">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/5982663752/in/photostream/</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://web.stagram.com/n/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
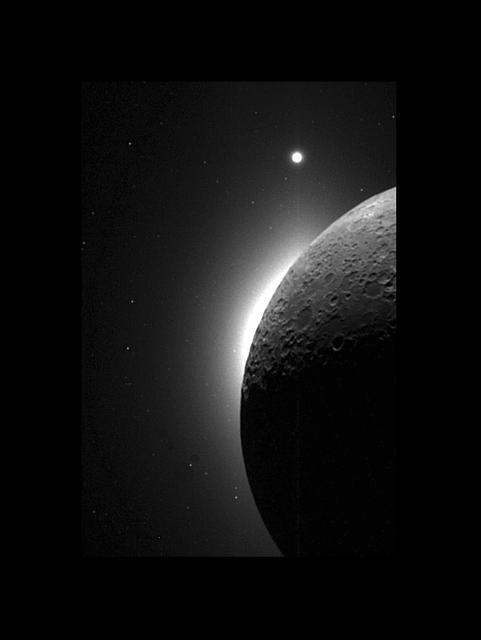

In 1994, during its flight, NASA's Clementine spacecraft returned images of the Moon. In addition to the geologic mapping cameras, the Clementine spacecraft also carried two Star Tracker cameras for navigation. These lightweight (0.3 kg) cameras kept the spacecraft on track by constantly observing the positions of stars, reminiscent of the age-old seafaring tradition of sextant/star navigation. These navigation cameras were also to take some spectacular wide angle images of the Moon. In this picture the Moon is seen illuminated solely by light reflected from the Earth--Earthshine! The bright glow on the lunar horizon is caused by light from the solar corona; the sun is just behind the lunar limb. Caught in this image is the planet Venus at the top of the frame. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00434
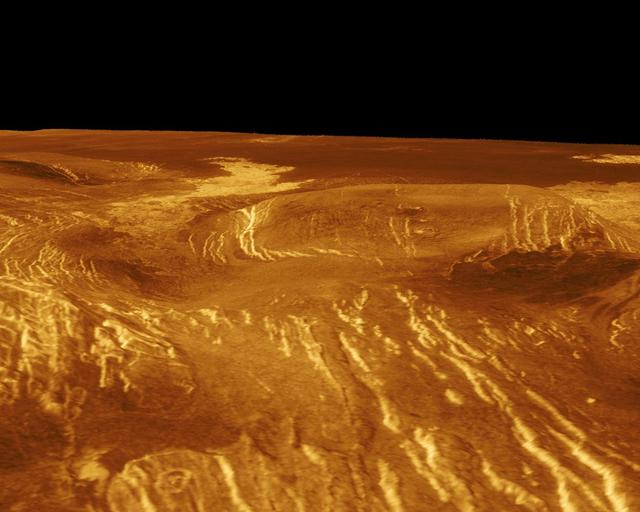
A corona is displayed in this computer-simulated view from NASA's Magellan spacecraft of the surface of Venus. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00109
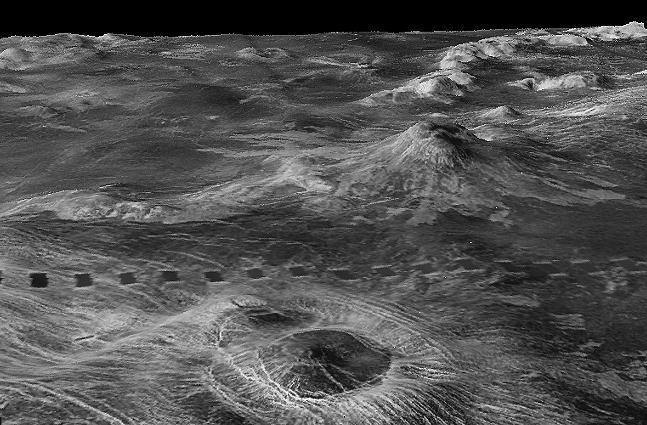
The view from NASA's Magellan spacecraft shows part of Galindo V40 quadrangle looking north; Nagavonyi Corona is in the foreground. Coronae are roughly circular, volcanic features believed to form over hot upwellings of magma within the Venusian mantle. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00095

A disk of hot gas swirls around a black hole in this illustration. Some of the gas came from a star that was pulled apart by the black hole, forming the long stream of hot gas on the right, feeding into the disk. These events are formally known as tidal disruption events, or TDEs. It can take just a matter or weeks or months from the destruction of the star to the formation of the disk. The gas gets hotter the closer it gets to the black hole, but the hottest material can be found above the black hole. This hottest material is cloud of plasma (gas atoms with their electrons stripped away) known as a corona. Most TDEs that result in the formation of a corona also produce jets of material that spew into space away from the black hole at its poles. A TDE called AT2021ehb is the first confirmed example of a corona forming without jets in a tidal disruption event. The observation of AT2021ehb makes it possible for scientists to study the formation of jets and coronae separately. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25440

NASA Solar TErrestrial RElations Observatory STEREO satellites have provided the first three-dimensional images of the Sun. The structure of the corona shows well in this image.

NASA Solar TErrestrial RElations Observatory STEREO satellites have provided the first three-dimensional images of the Sun. The structure of the corona shows well in this image.
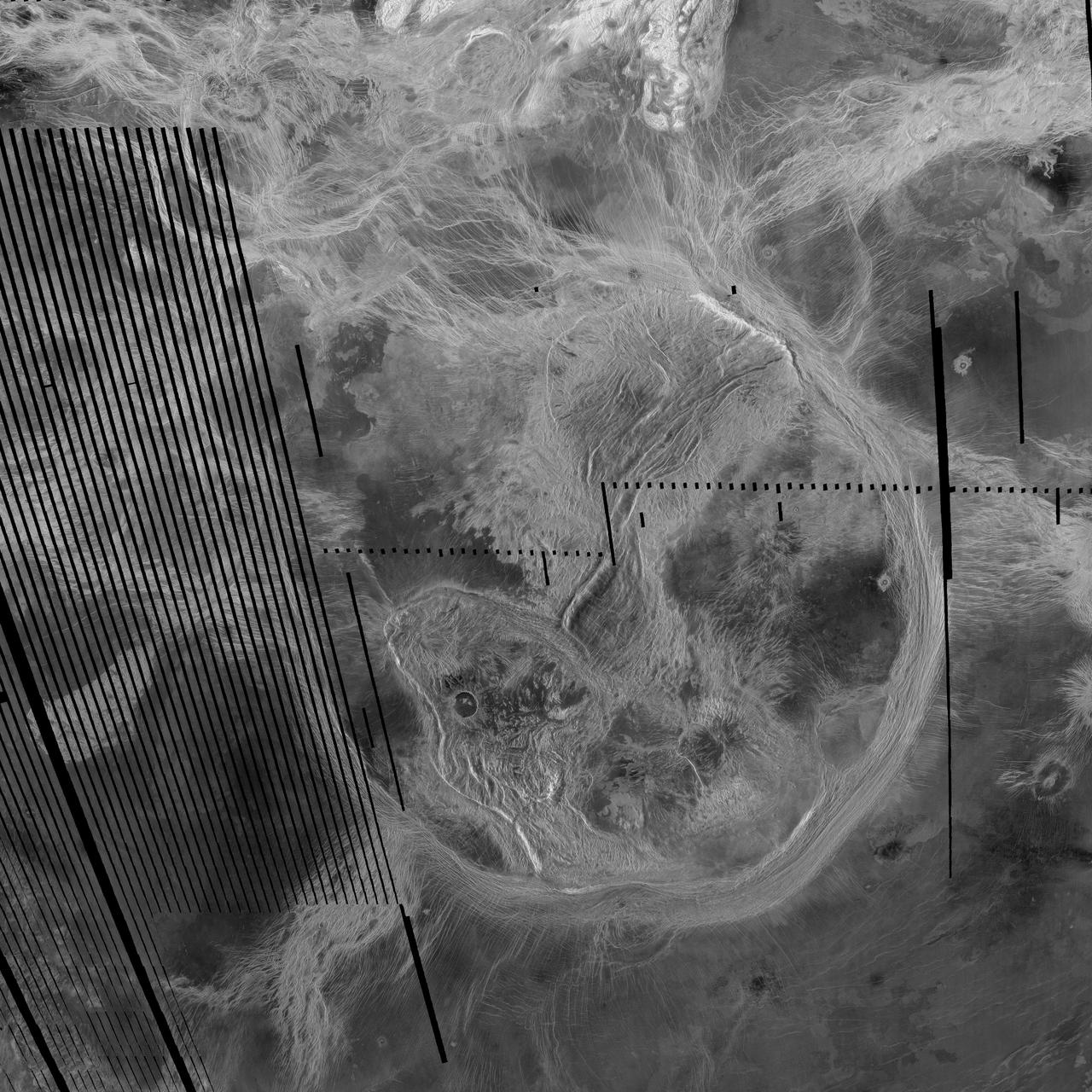
This spectacular image from NASA's Magellan spacecraft is centered on 30 degrees south latitude, 135 degrees east longitude, spans 3500 kilometers 2170 miles from east to west left to right, and shows the near-circular trough of Artemis Chasma. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00101
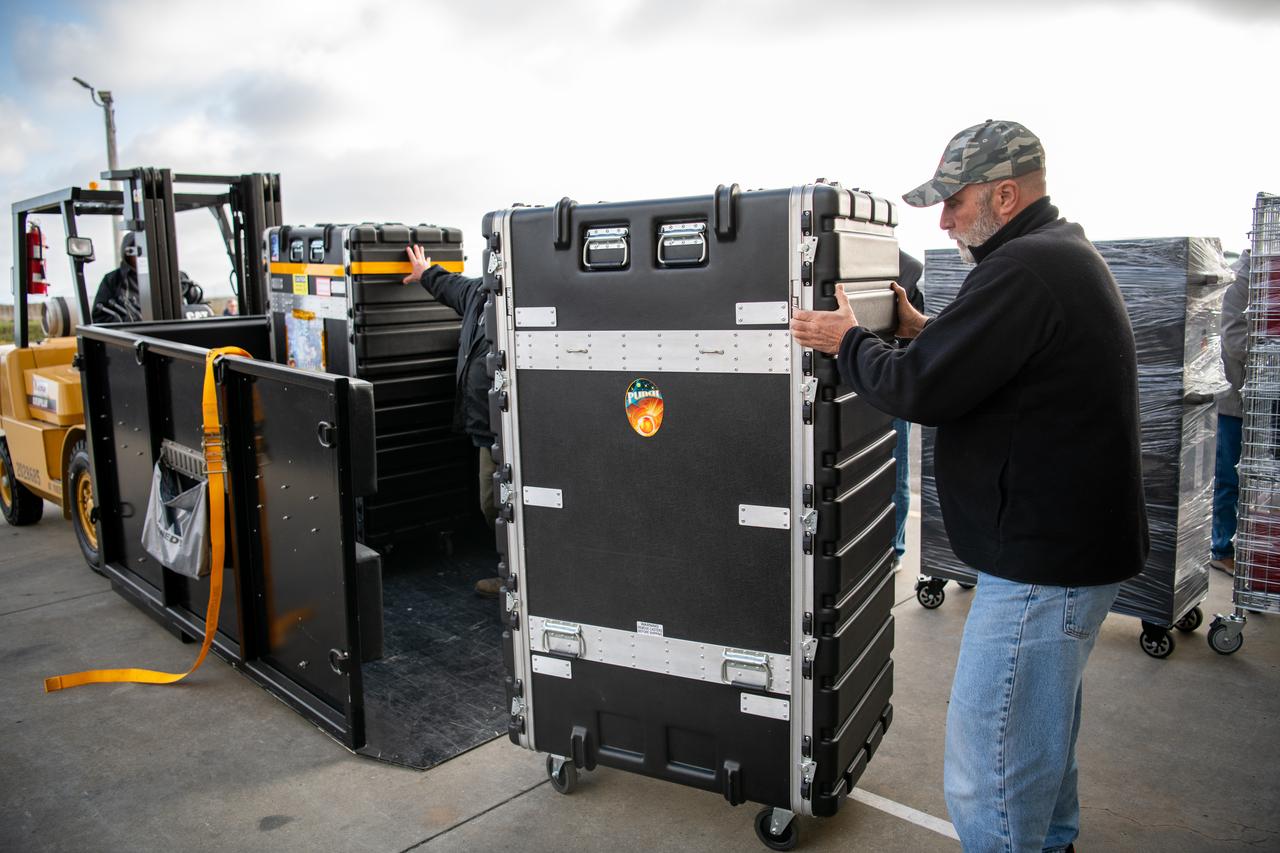

Teams at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California offload several shipping containers protecting NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites on Saturday, Jan. 18, 2025. PUNCH will make 3D observations of the Sun’s corona to learn how the mass and energy becomes solar wind. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.
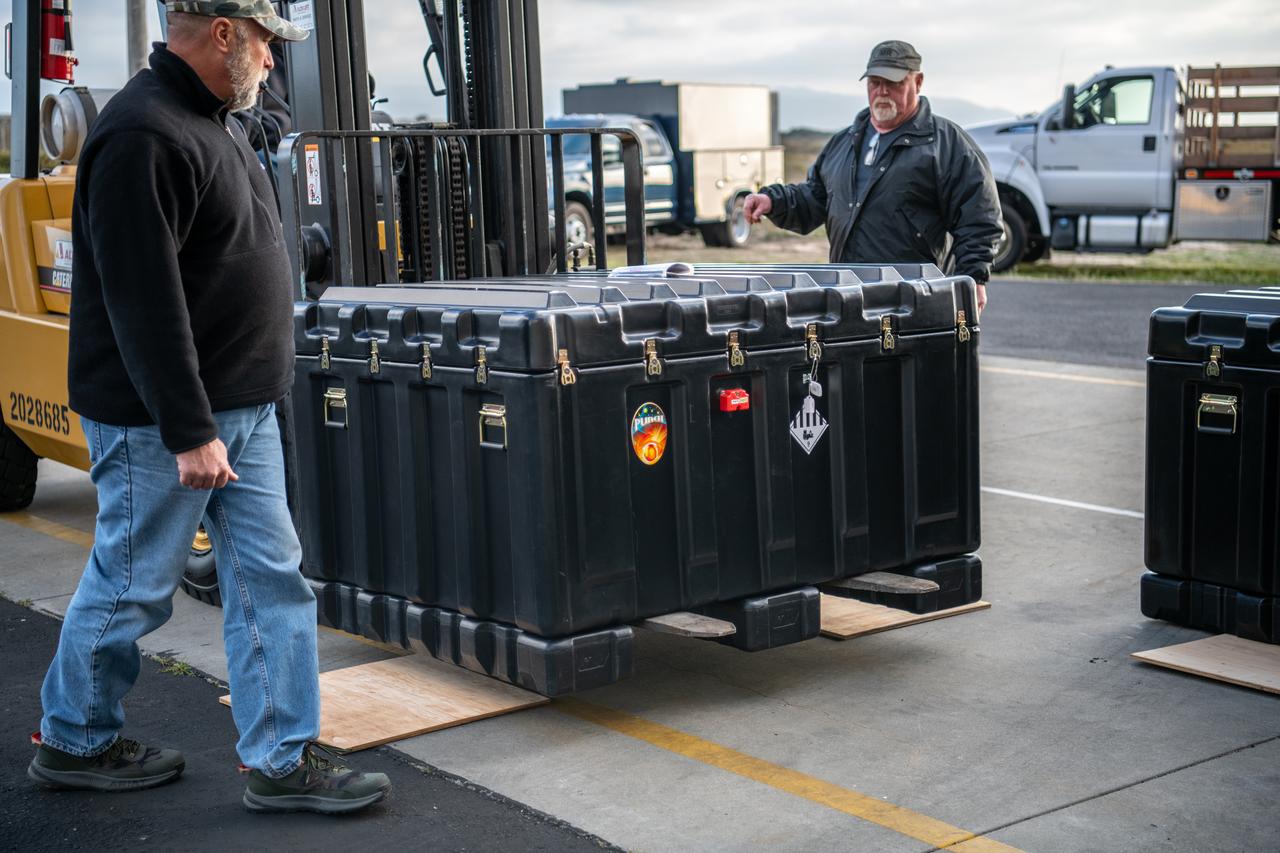

Teams at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California offload several shipping containers protecting NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites on Saturday, Jan. 18, 2025. PUNCH will make 3D observations of the Sun’s corona to learn how the mass and energy becomes solar wind. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.
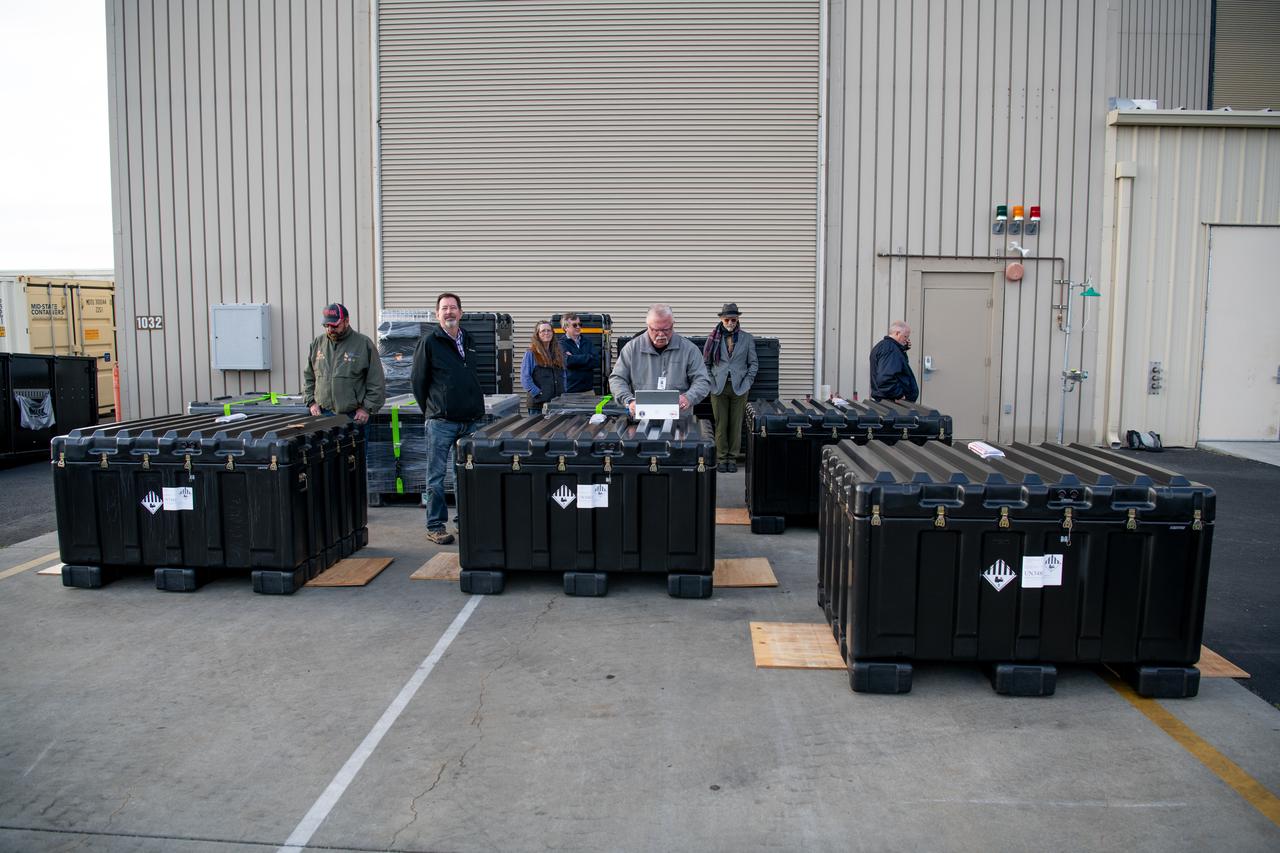

NASA’s four PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites arrive at Astrotech Space Operations located inside Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Saturday, Jan. 18, 2025. The four satellites of PUNCH will make 3D observations of the Sun’s corona to learn how the mass and energy becomes solar wind. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.
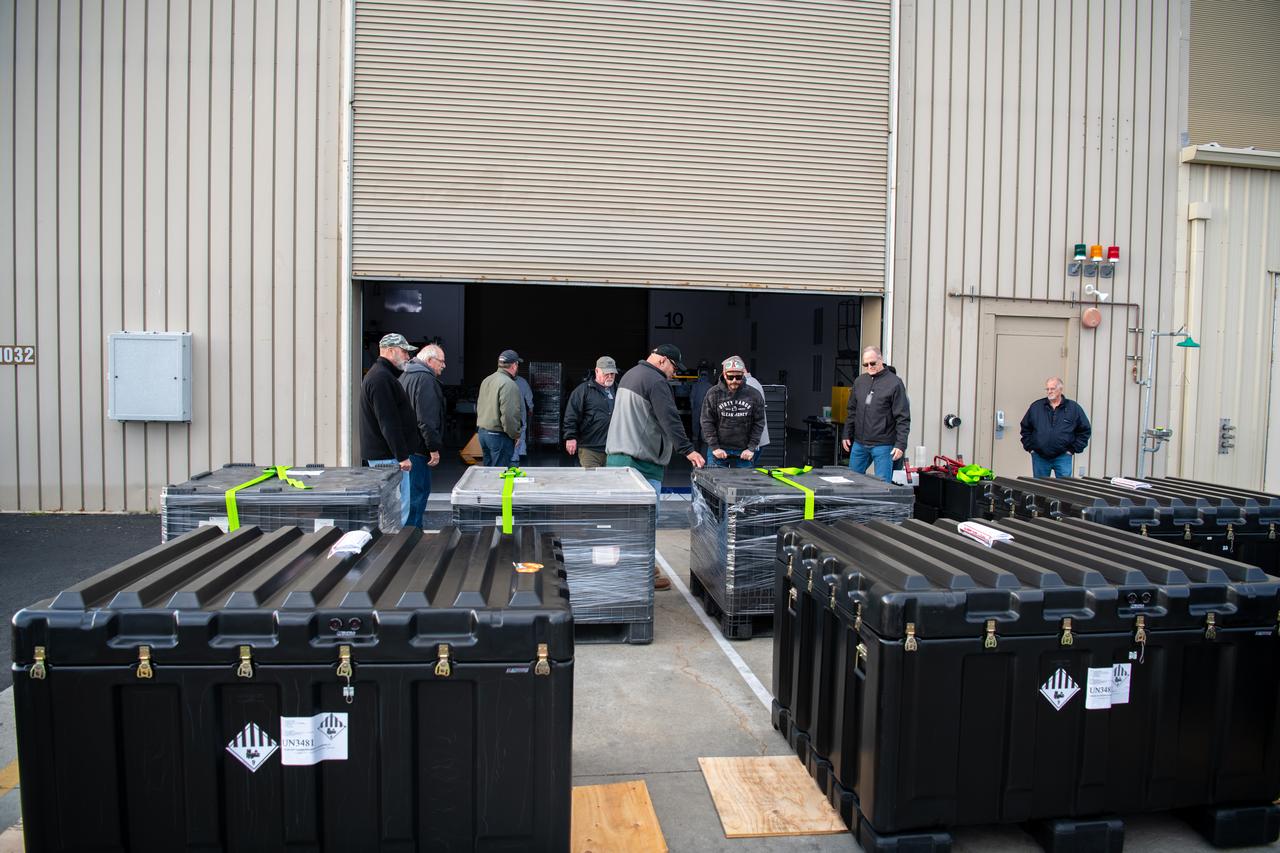

Teams at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California offload several shipping containers protecting NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites on Saturday, Jan. 18, 2025. PUNCH will make 3D observations of the Sun’s corona to learn how the mass and energy becomes solar wind. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.
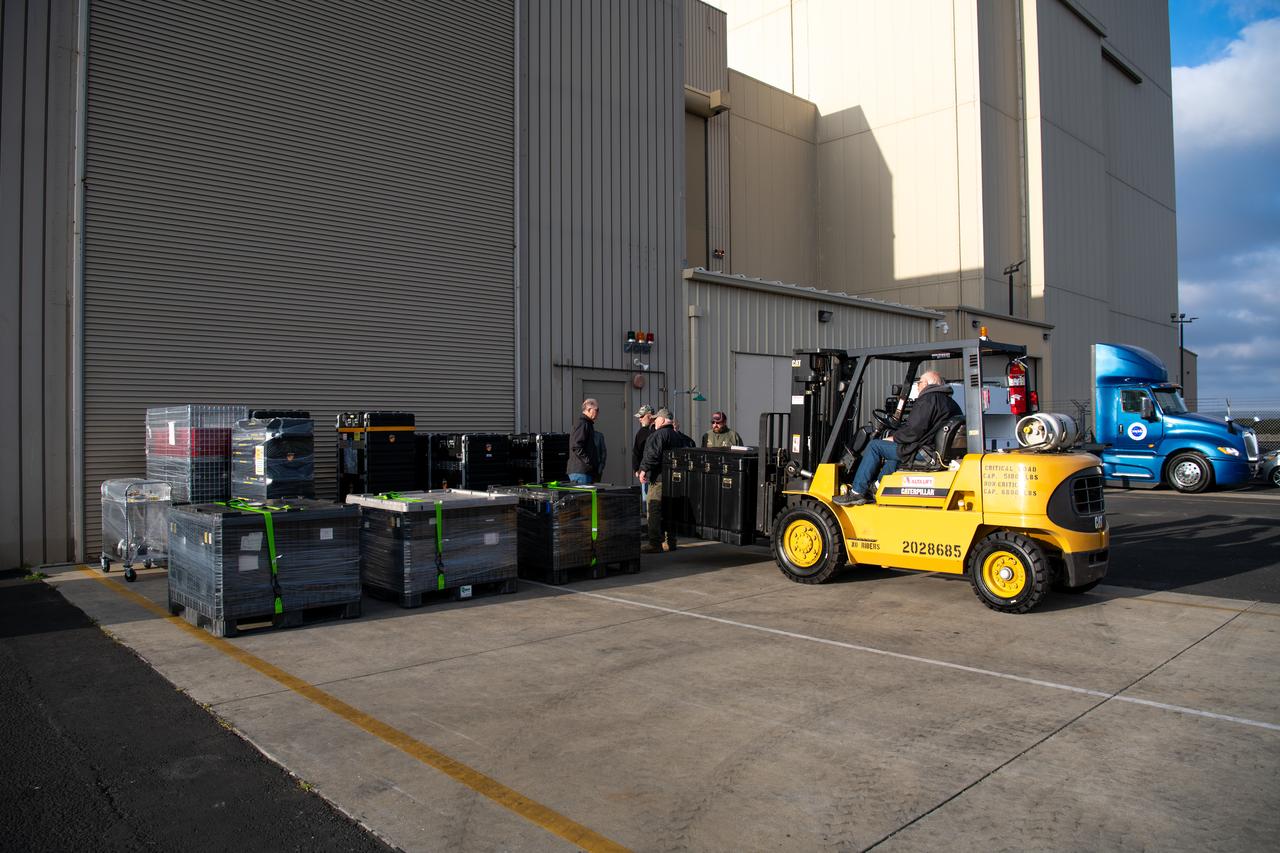

Teams at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California offload several shipping containers protecting NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites on Saturday, Jan. 18, 2025. PUNCH will make 3D observations of the Sun’s corona to learn how the mass and energy becomes solar wind. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.
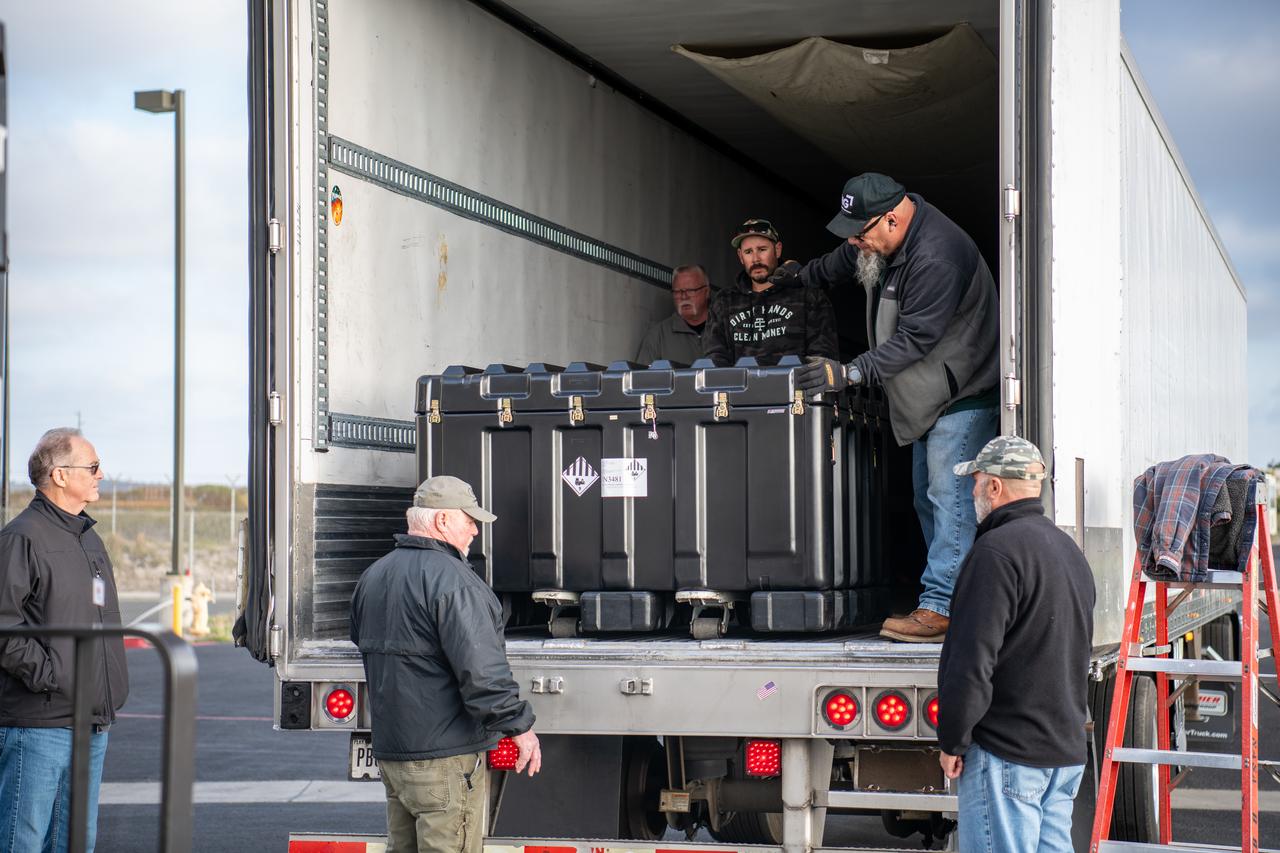

Teams at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California offload several shipping containers protecting NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites on Saturday, Jan. 18, 2025. PUNCH will make 3D observations of the Sun’s corona to learn how the mass and energy becomes solar wind. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.
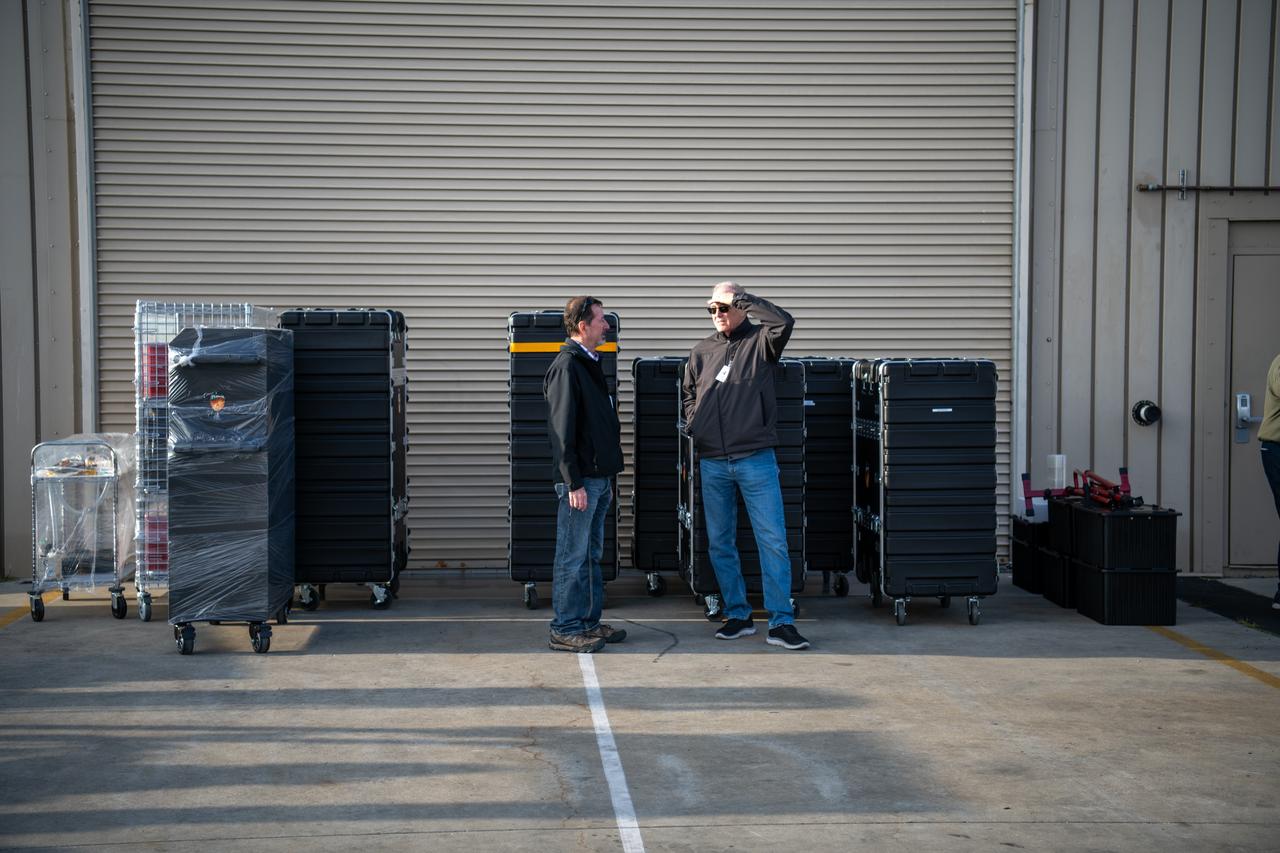

NASA’s four PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites arrive at Astrotech Space Operations located inside Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Saturday, Jan. 18, 2025. The four satellites of PUNCH will make 3D observations of the Sun’s corona to learn how the mass and energy becomes solar wind. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.
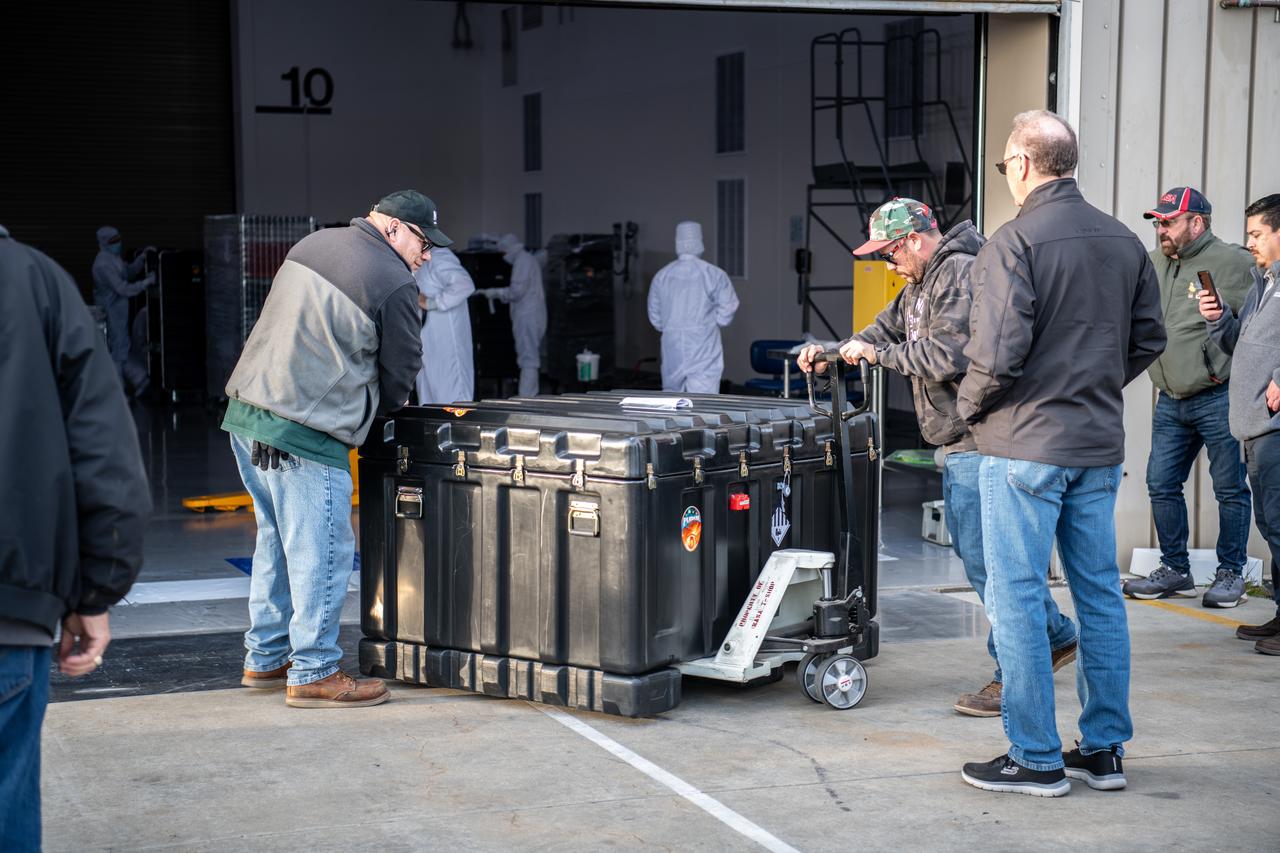

Teams at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California offload several shipping containers protecting NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites on Saturday, Jan. 18, 2025. PUNCH will make 3D observations of the Sun’s corona to learn how the mass and energy becomes solar wind. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.
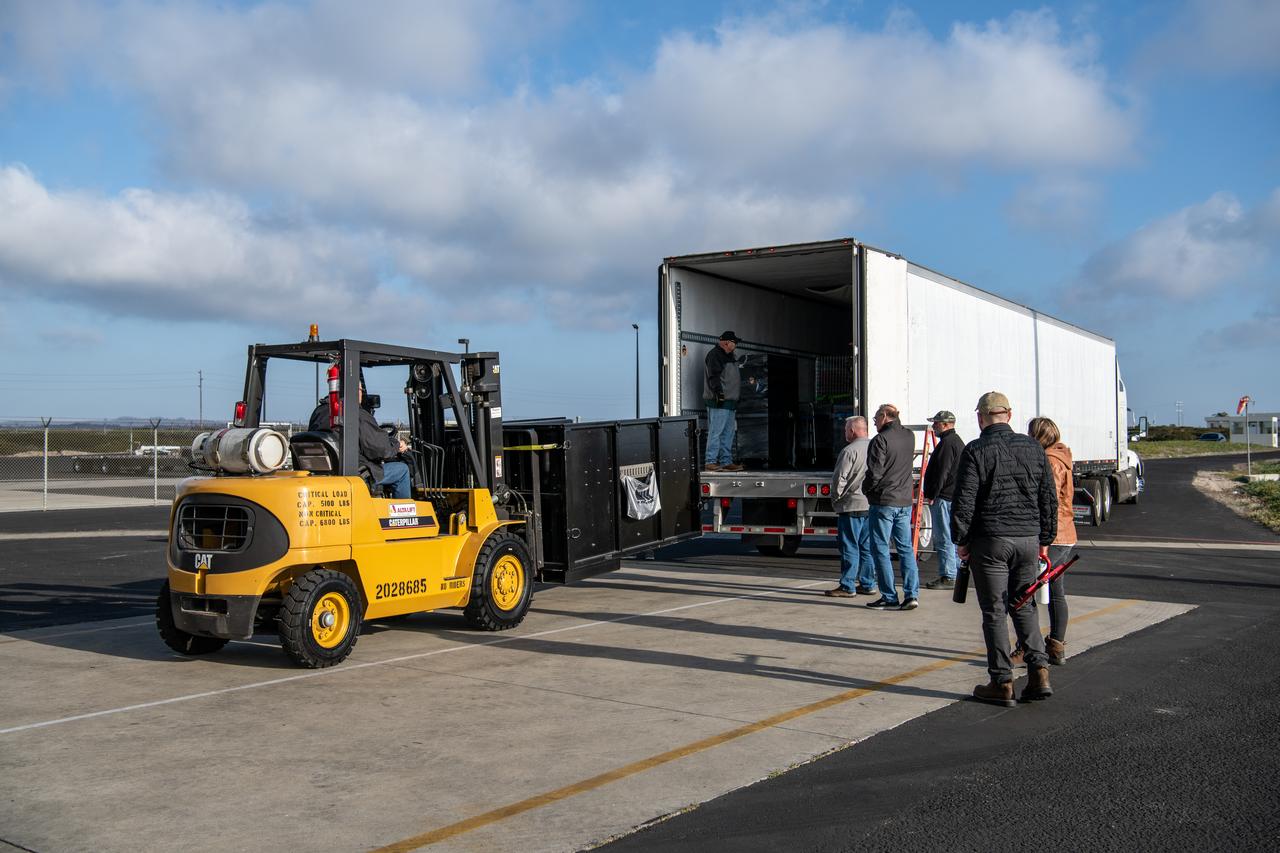

Teams at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California offload several shipping containers protecting NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites on Saturday, Jan. 18, 2025. PUNCH will make 3D observations of the Sun’s corona to learn how the mass and energy becomes solar wind. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.
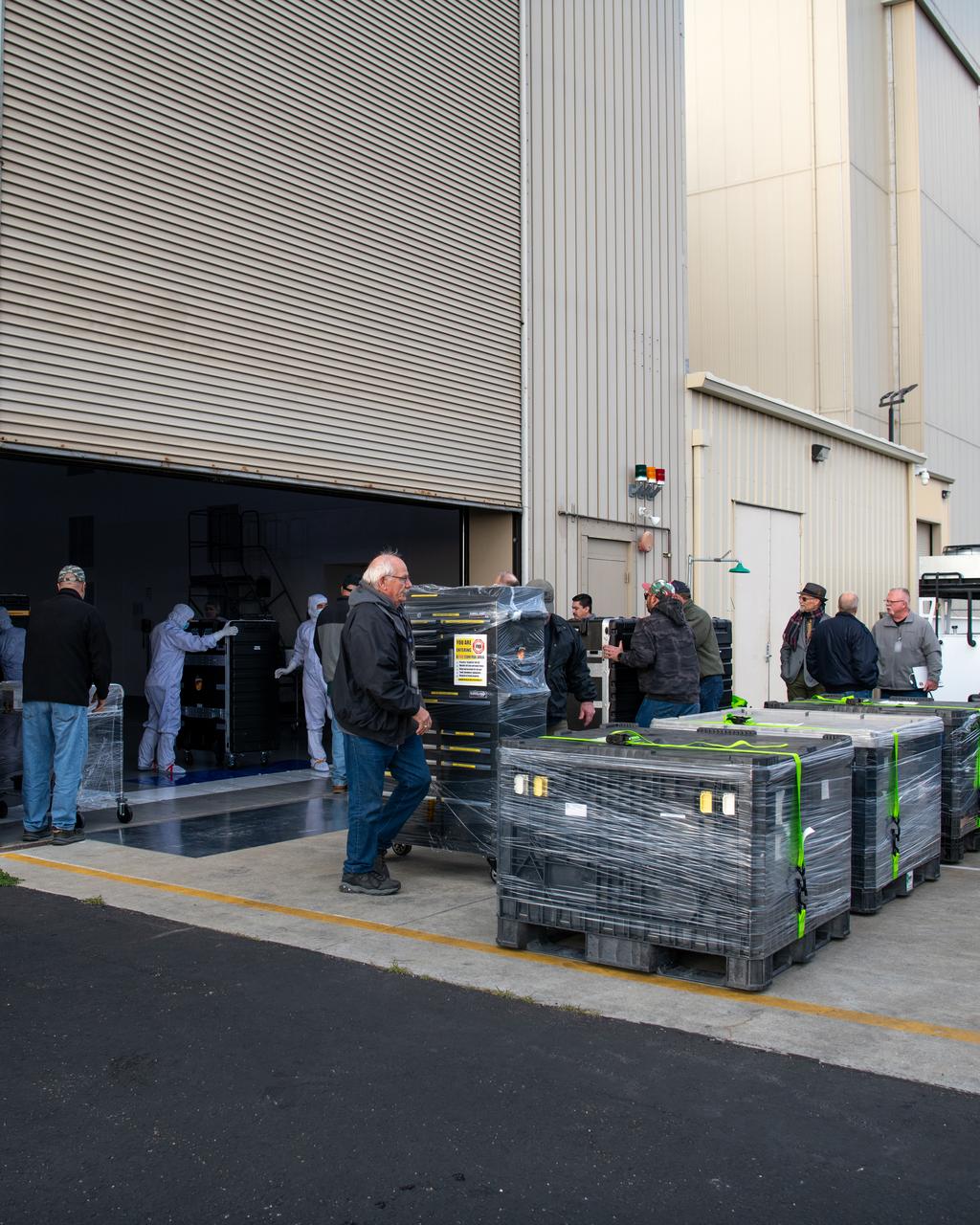

Teams at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California offload several shipping containers protecting NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites on Saturday, Jan. 18, 2025. PUNCH will make 3D observations of the Sun’s corona to learn how the mass and energy becomes solar wind. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.
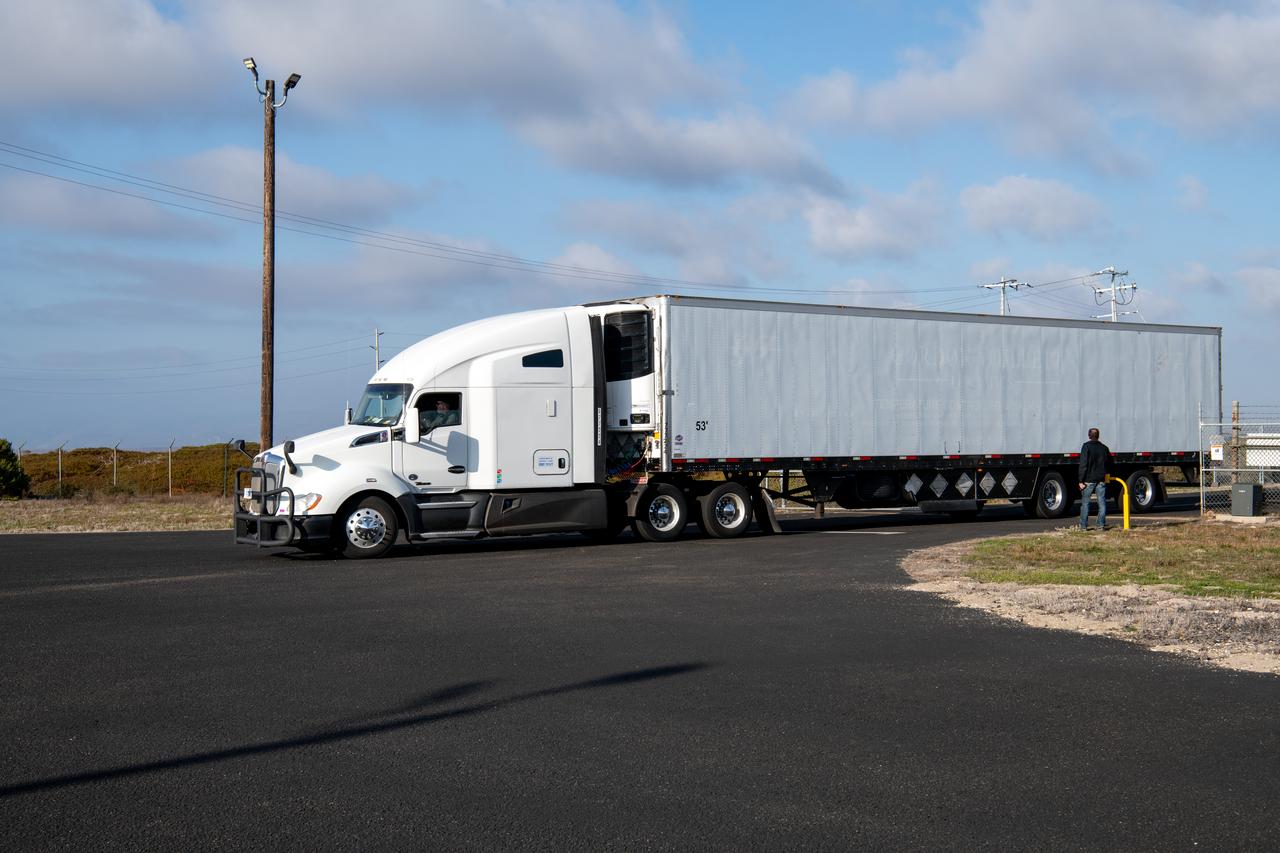

A transport truck carrying four small satellites of NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) arrives at Astrotech Space Operations located inside Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Saturday, Jan. 18, 2025. PUNCH will make 3D observations of the Sun’s corona to learn how the mass and energy becomes solar wind. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.

Teams at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California offload several shipping containers protecting NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites on Saturday, Jan. 18, 2025. PUNCH will make 3D observations of the Sun’s corona to learn how the mass and energy becomes solar wind. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.
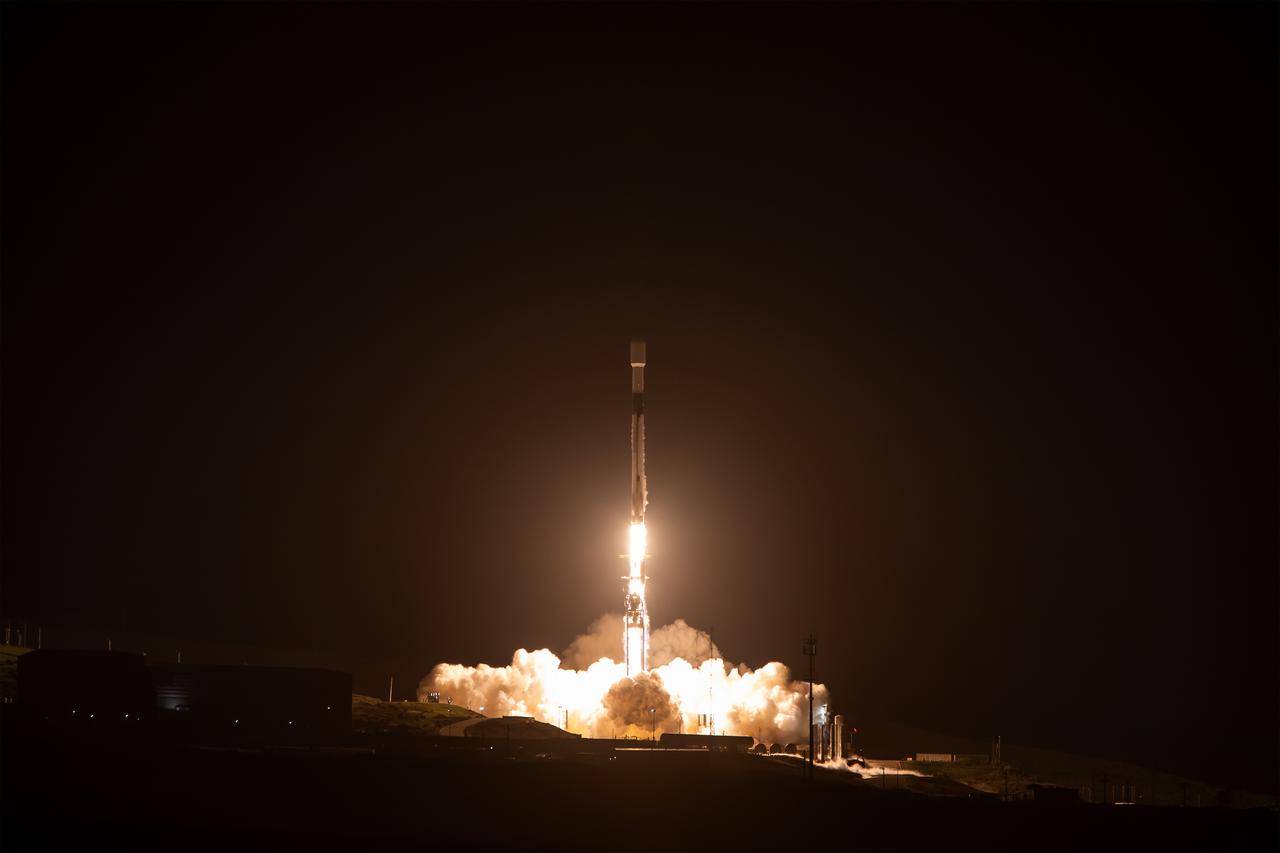

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, carrying NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory and PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites, launches from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Tuesday, March 11, 2025. SPHEREx will use its telescope to provide an all-sky spectral survey, creating a 3D map of the entire sky to help scientists investigate the origins of our universe. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system.
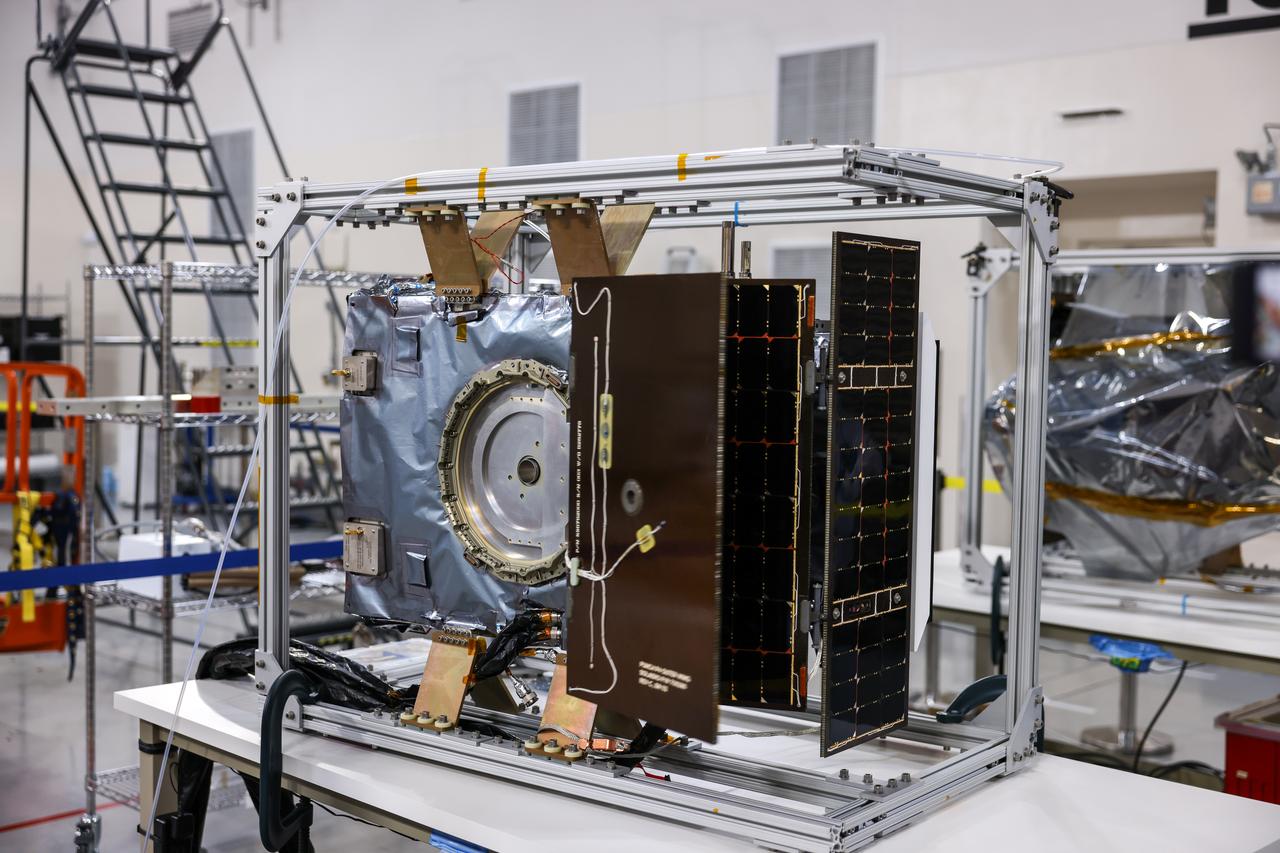

Crews conduct a solar array deployment test on the spacecraft of NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites at Astrotech Space Operations located on Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Tuesday, Jan. 21, 2025. The four satellites of PUNCH will make 3D observations of the Sun’s corona to learn how the mass and energy becomes solar wind. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.
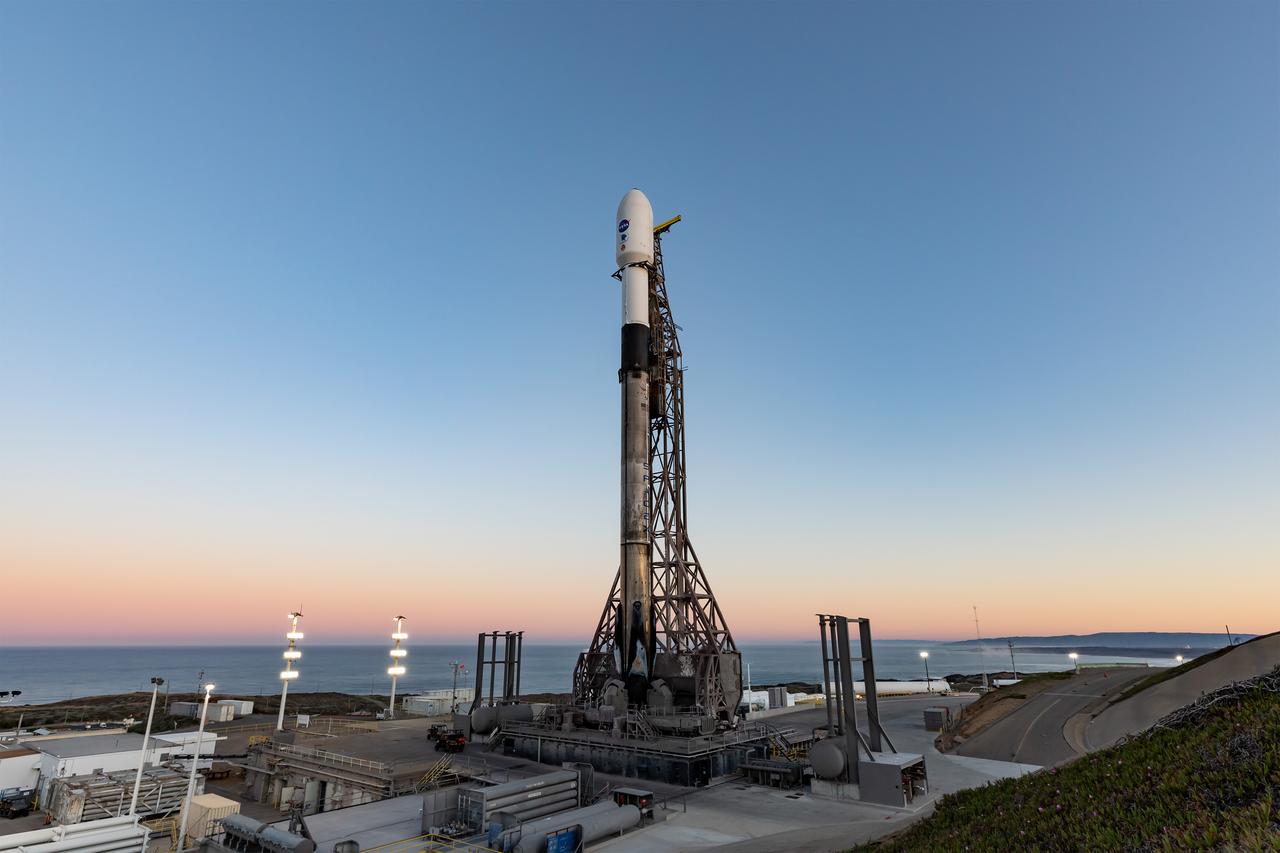

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, carrying NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory and PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites, is vertical at Space Launch Complex 4 East from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Saturday March 8, 2025. SPHEREx will use its telescope to provide an all-sky spectral survey, creating a 3D map of the entire sky to help scientists investigate the origins of our universe. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system.

Antenna's on NASA's Parker Solar Probe are deployed for testing at the Astrotech processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near NASA's Kennedy Space Center on Thursday, April 19, 2018. The Parker Solar Probe will launch on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida no earlier than Aug. 4, 2018. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
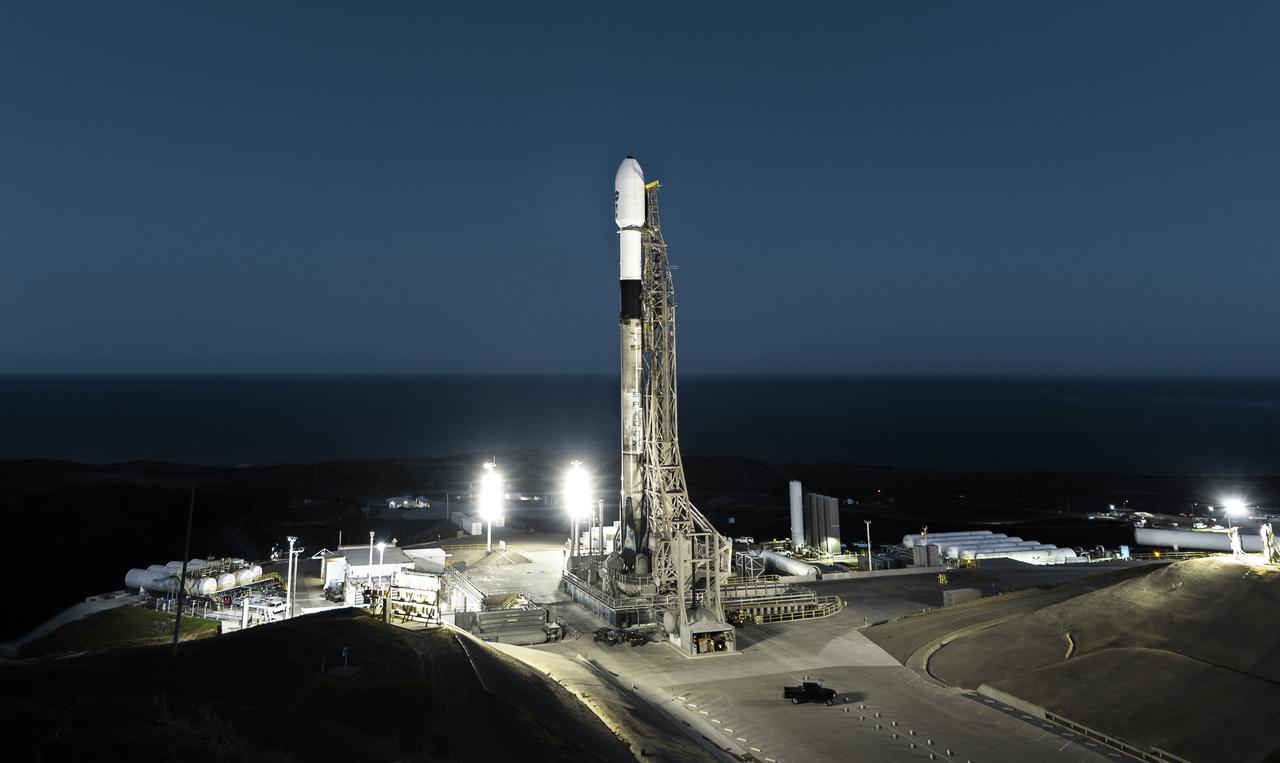

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, carrying NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory and PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites, is vertical at Space Launch Complex 4 East from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Saturday March 8, 2025. SPHEREx will use its telescope to provide an all-sky spectral survey, creating a 3D map of the entire sky to help scientists investigate the origins of our universe. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system.
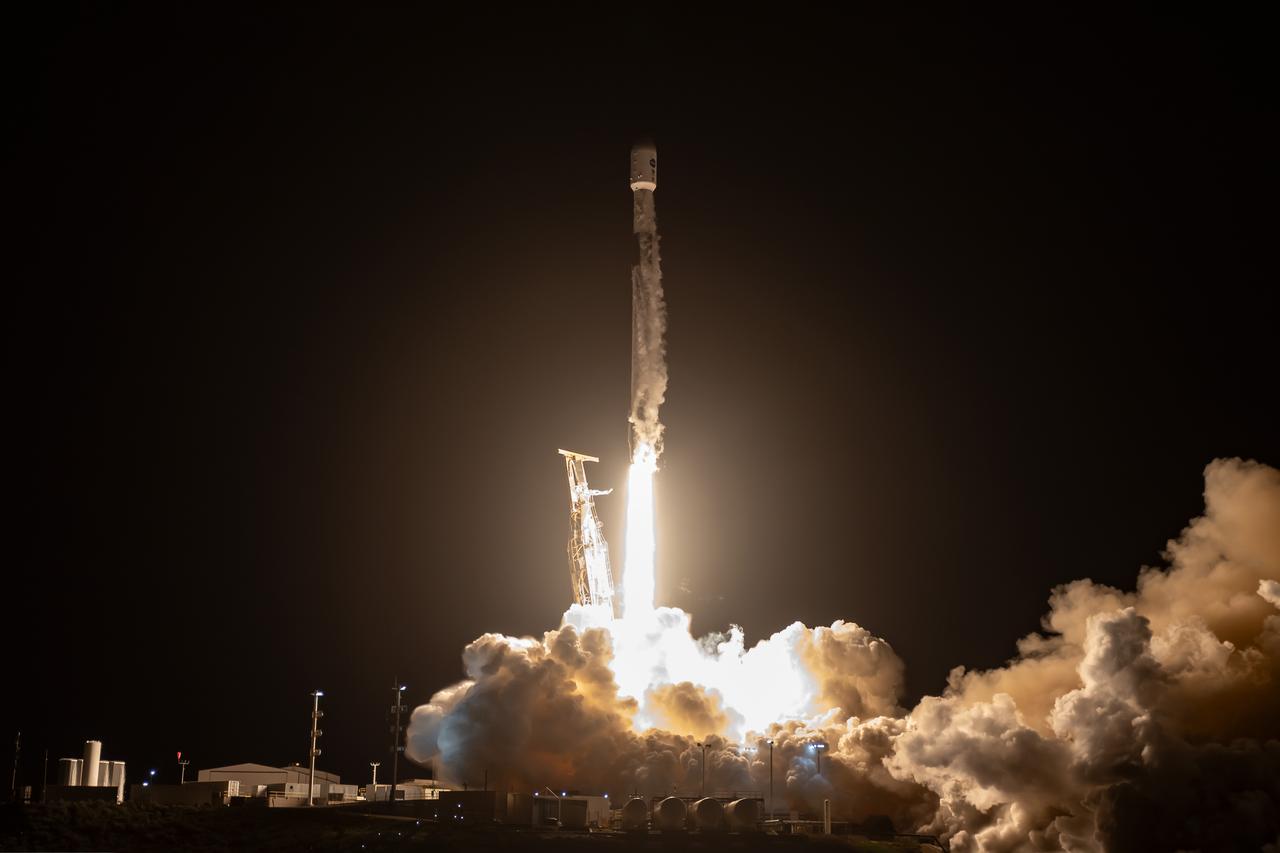

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, carrying NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory and PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites, launches from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Tuesday, March 11, 2025. SPHEREx will use its telescope to provide an all-sky spectral survey, creating a 3D map of the entire sky to help scientists investigate the origins of our universe. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system.
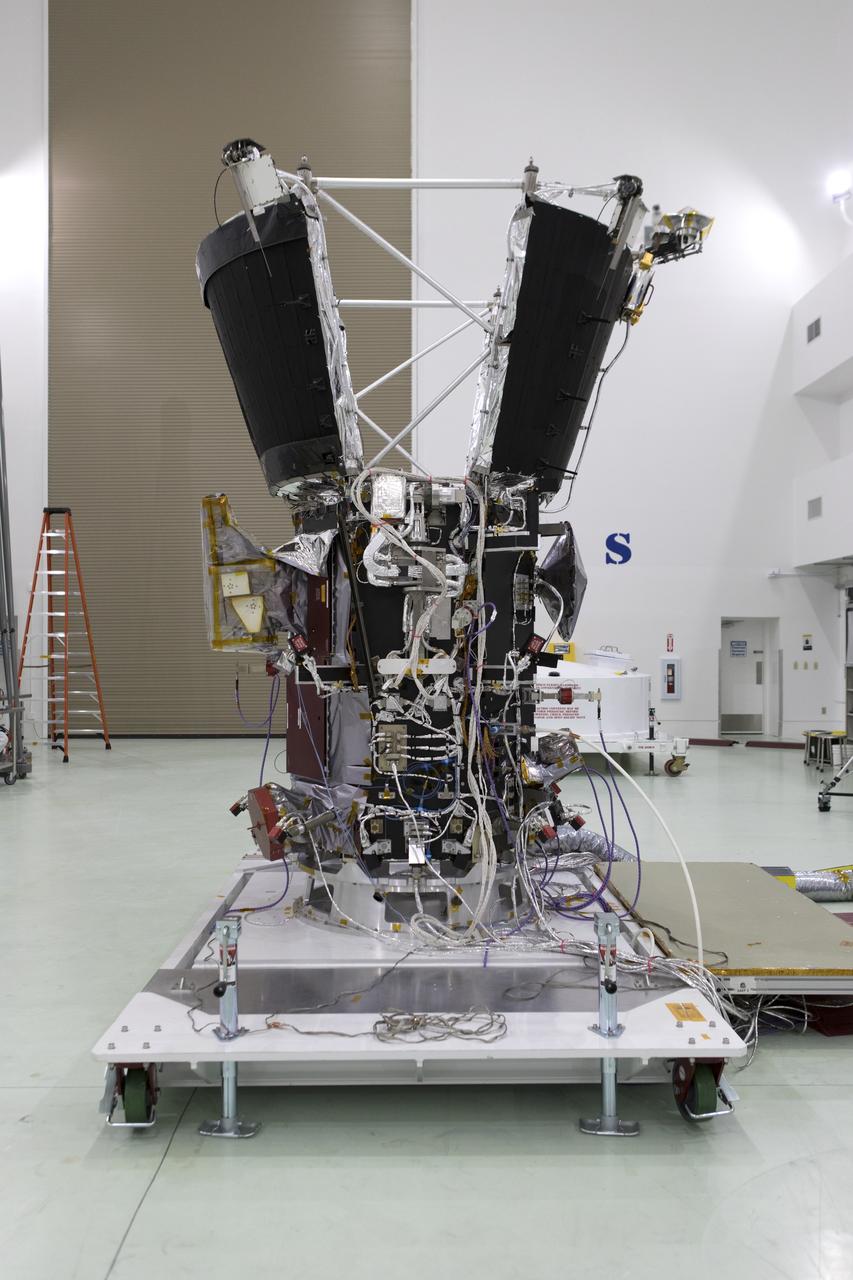

Antenna's on NASA's Parker Solar Probe are deployed for testing at the Astrotech processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near NASA's Kennedy Space Center on Thursday, April 19, 2018. The Parker Solar Probe will launch on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida no earlier than Aug. 4, 2018. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
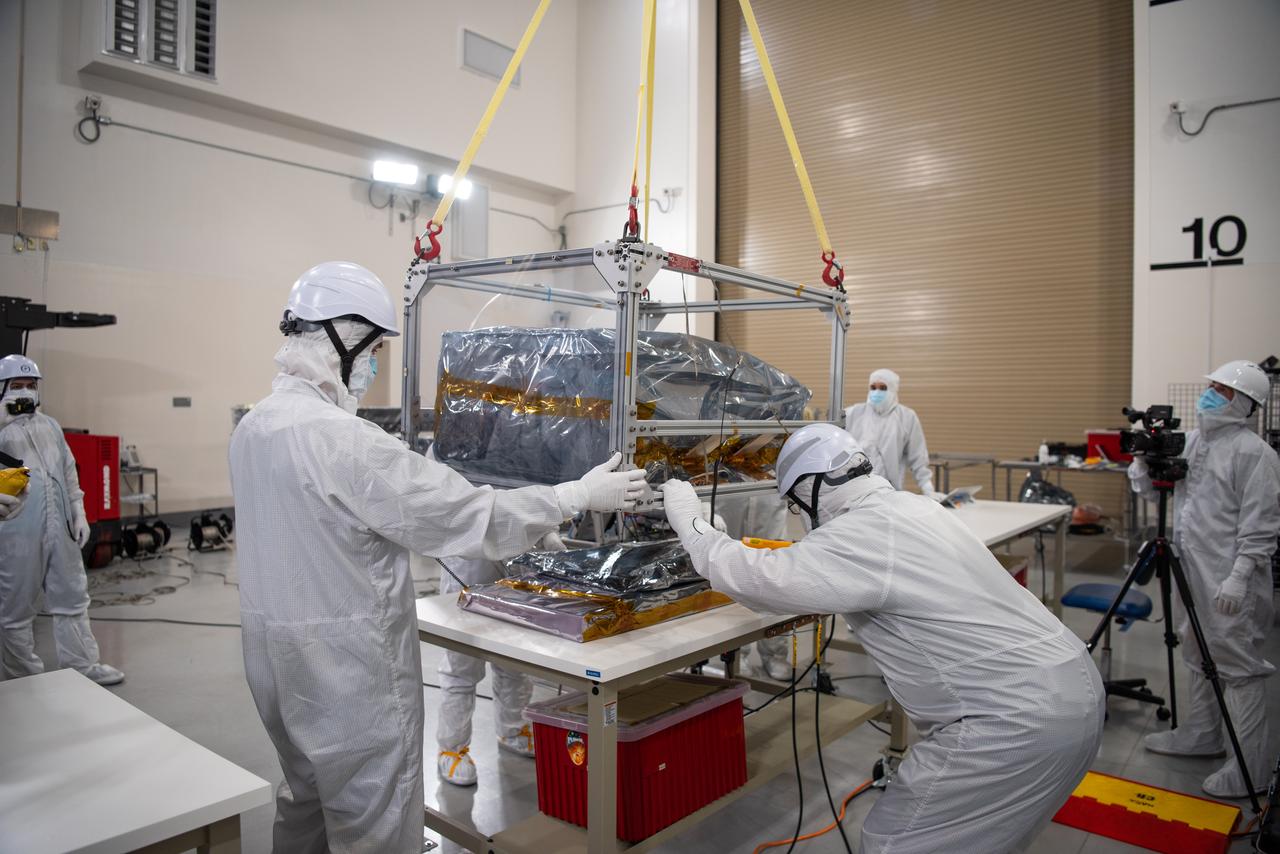

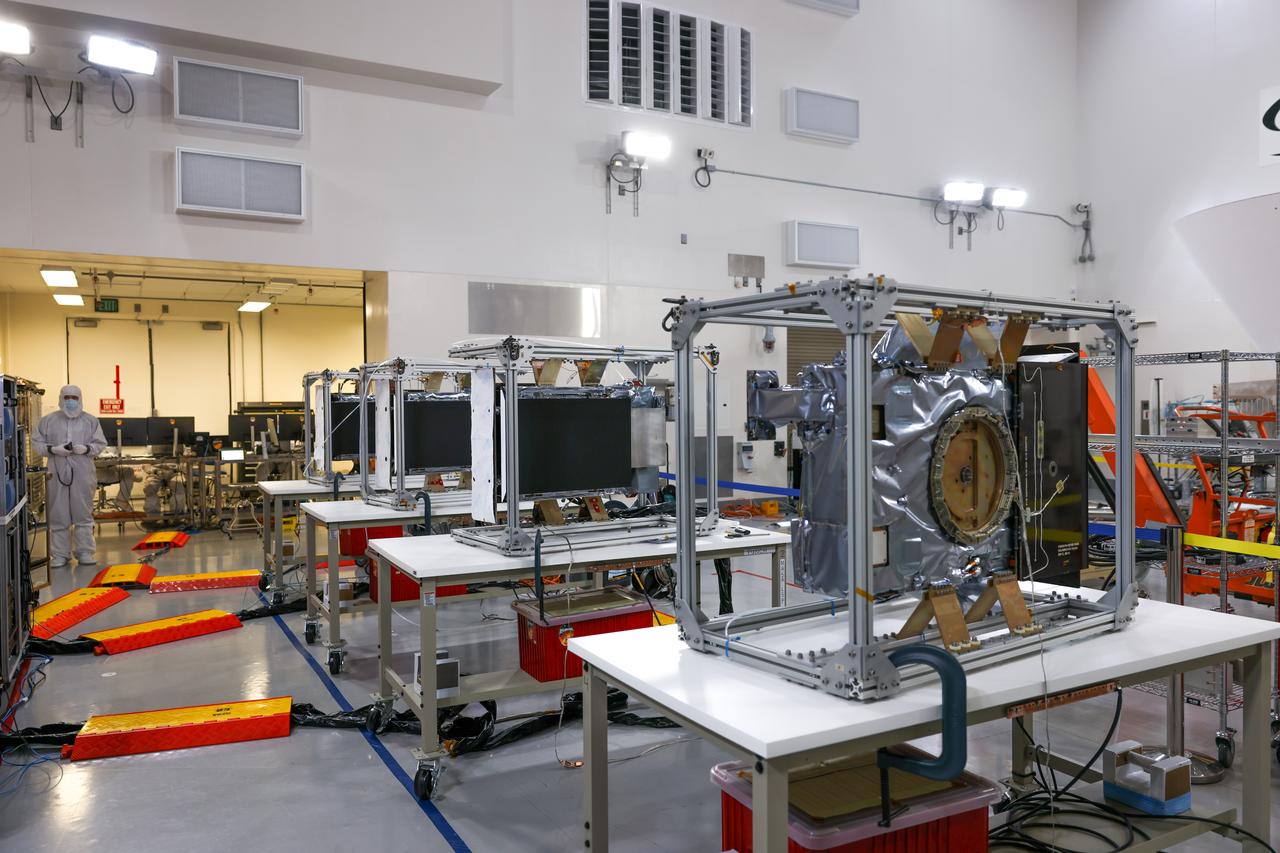
Technicians use an overheard crane to lift NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) spacecraft onto a work stand for testing operations at the Astrotech Processing Facility on Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Sunday, Jan. 19, 2025. PUNCH, consisting of four satellites, will produce continuous 3D images of the solar wind and solar storms as it travels from the Sun to Earth to better understand how material in the corona accelerates to become the solar wind that fills the solar system. PUNCH will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.
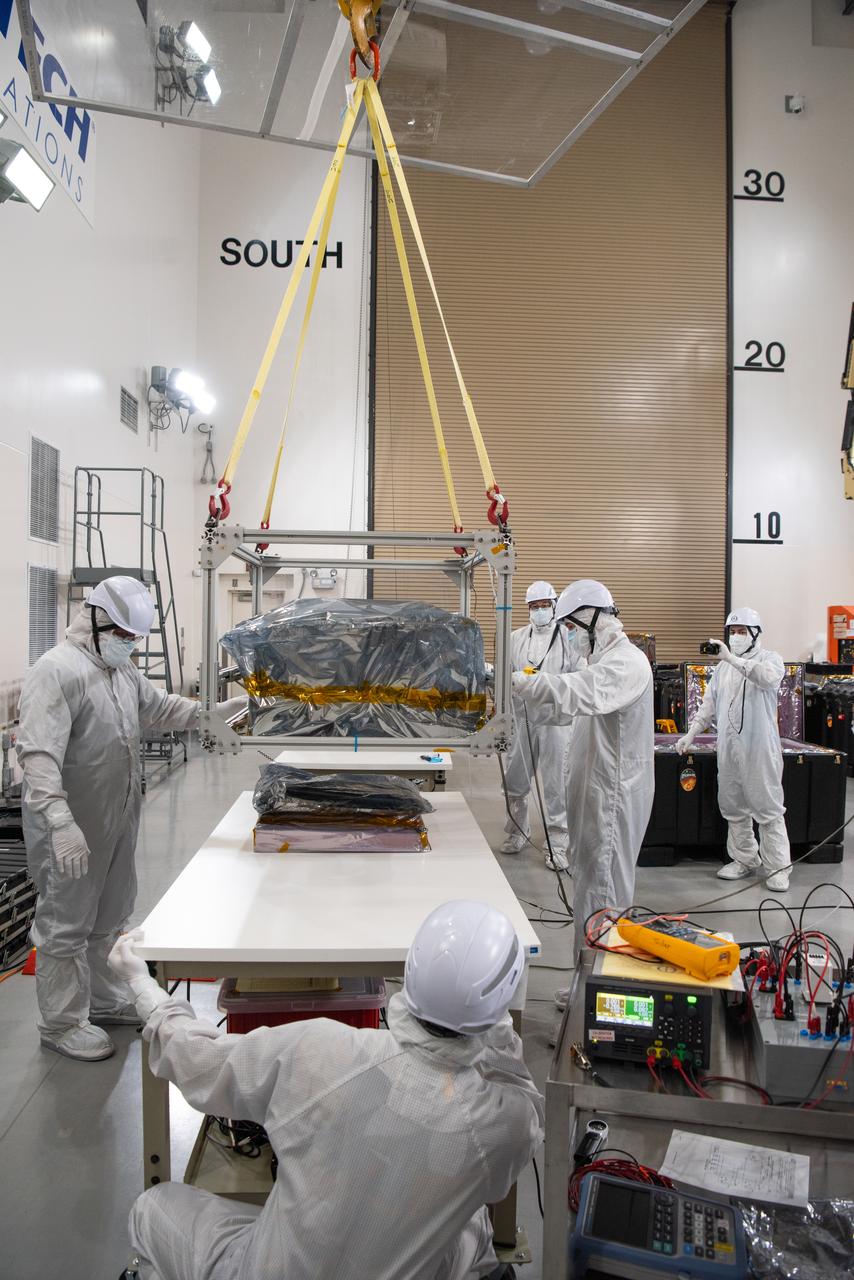

Technicians use an overheard crane to lift NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) spacecraft onto a work stand for testing operations at the Astrotech Processing Facility on Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Sunday, Jan. 19, 2025. PUNCH, consisting of four satellites, will produce continuous 3D images of the solar wind and solar storms as it travels from the Sun to Earth to better understand how material in the corona accelerates to become the solar wind that fills the solar system. PUNCH will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.

Nicholeen Viall, PUNCH Mission Scientist, NASA’s Goddard Flight Center, participates in a science briefing on Tuesday, Feb. 25, 2025, to discuss the upcoming launch of NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory and PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. SPHEREx will use its telescope to provide an all-sky spectral survey, creating a 3D map of the entire sky to help scientists investigate the origins of our universe. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system.
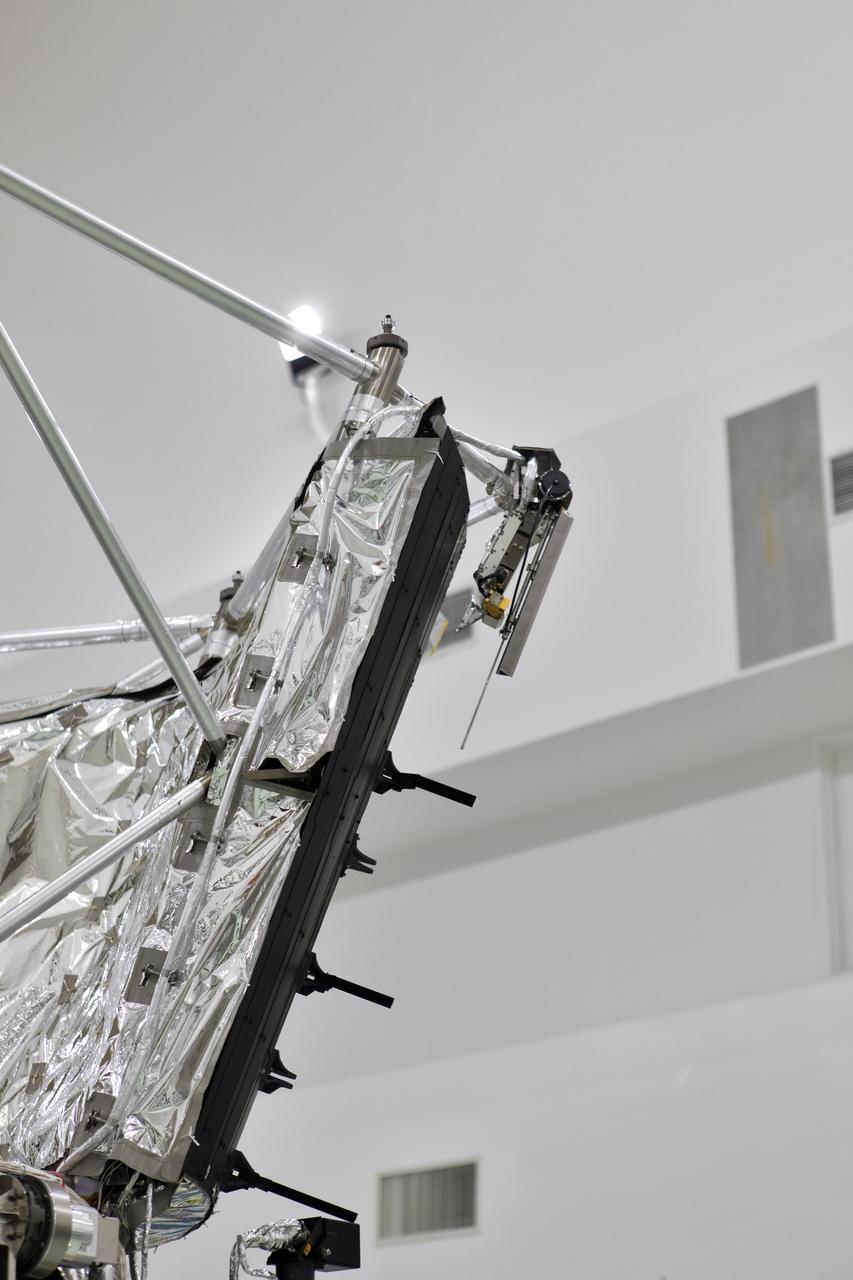

Antenna's on NASA's Parker Solar Probe are deployed for testing at the Astrotech processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near NASA's Kennedy Space Center on Thursday, April 19, 2018. The Parker Solar Probe will launch on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida no earlier than Aug. 4, 2018. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.

Shawn Domagal-Goldman, acting director, Astrophysics Division, NASA Headquarters, participates in a science briefing on Tuesday, Feb. 25, 2025, to discuss the upcoming launch of NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory and PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. SPHEREx will use its telescope to provide an all-sky spectral survey, creating a 3D map of the entire sky to help scientists investigate the origins of our universe. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system.

Crews conduct a solar array deployment test on the spacecraft of NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites at Astrotech Space Operations located on Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Tuesday, Jan. 21, 2025. The four satellites of PUNCH will make 3D observations of the Sun’s corona to learn how the mass and energy becomes solar wind. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.
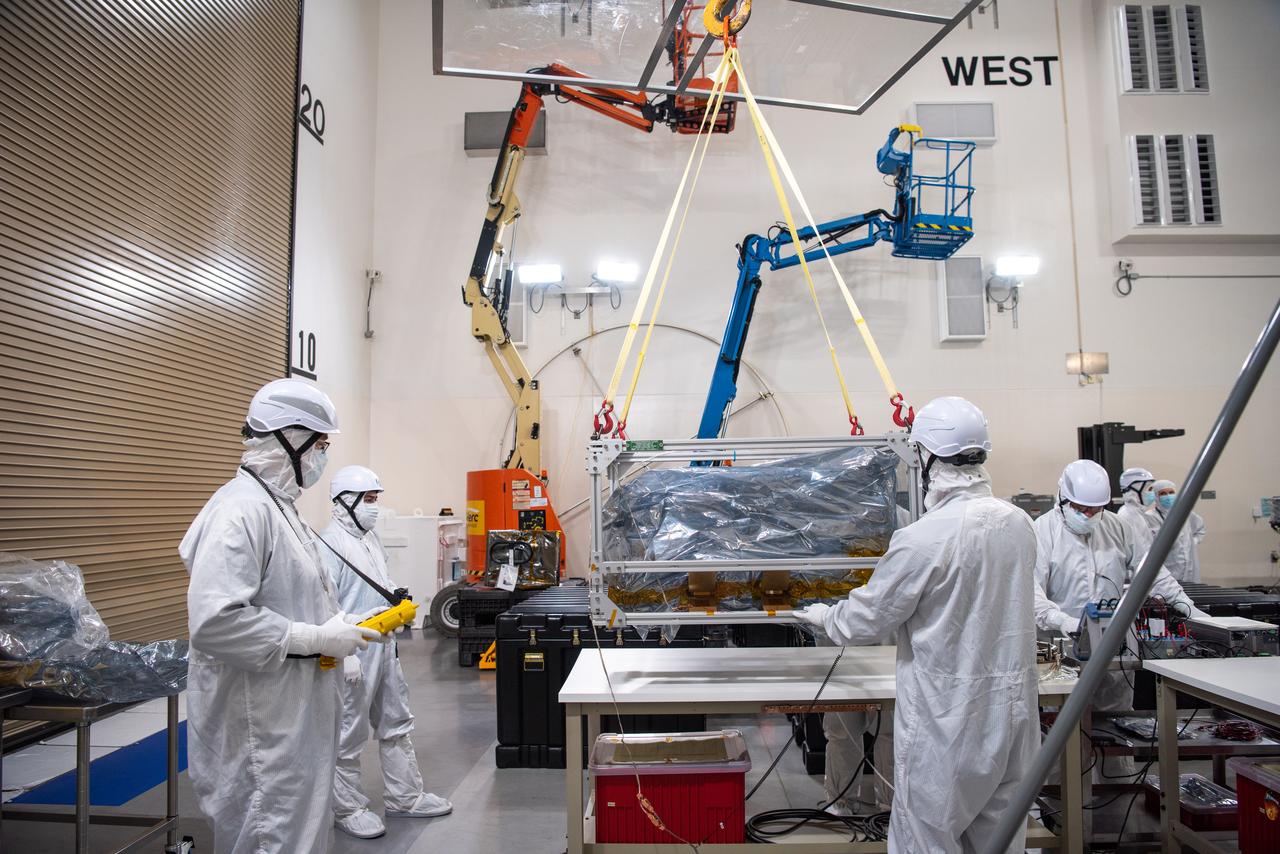

Technicians use an overheard crane to lift NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) spacecraft onto a work stand for testing operations at the Astrotech Processing Facility on Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Sunday, Jan. 19, 2025. PUNCH, consisting of four satellites, will produce continuous 3D images of the solar wind and solar storms as it travels from the Sun to Earth to better understand how material in the corona accelerates to become the solar wind that fills the solar system. PUNCH will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.
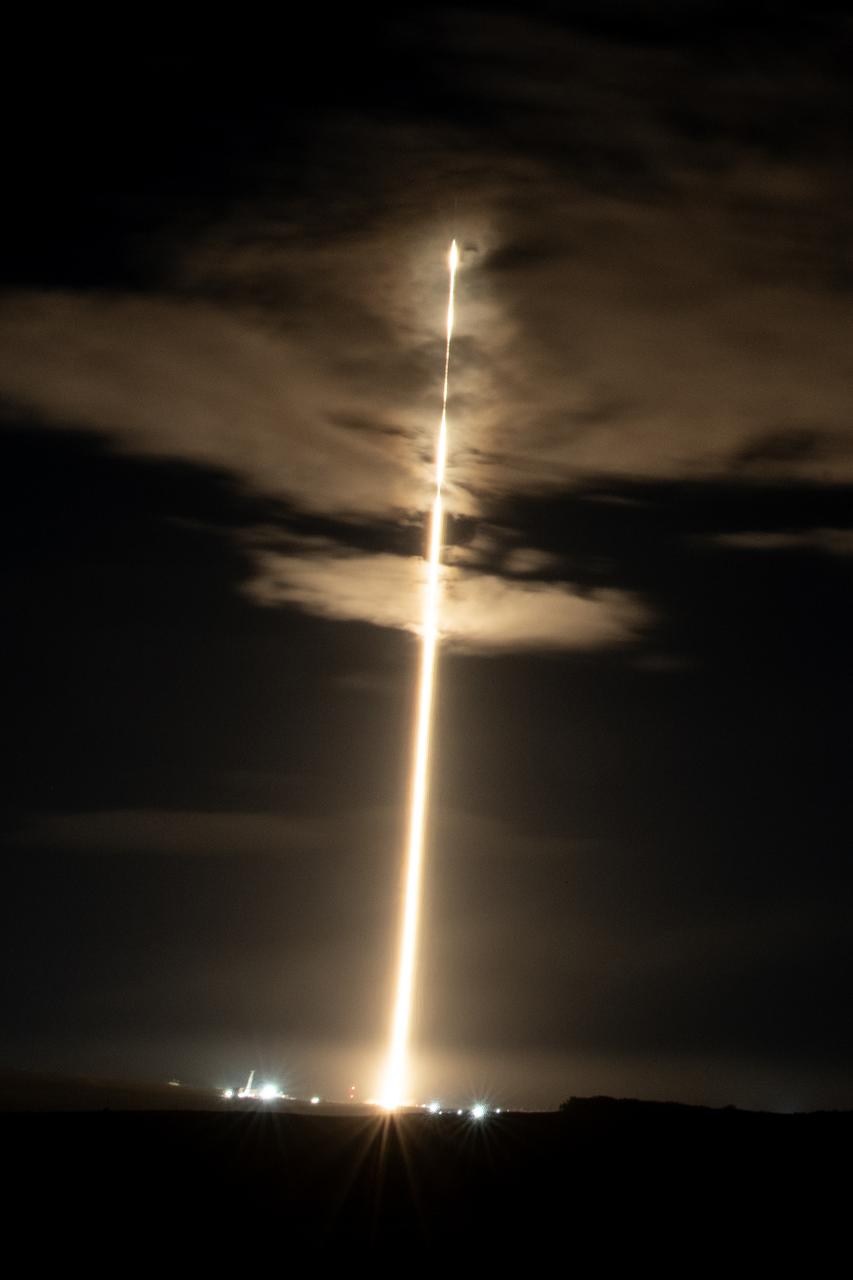

A streak lights up the sky as the first stage of a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket lands at Vandenberg Space Force Base’s Landing Zone 4 in California on Tuesday March 11, 2025, following the launch of NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory and PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites. SPHEREx will use its telescope to provide an all-sky spectral survey, creating a 3D map of the entire sky to help scientists investigate the origins of our universe. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system.
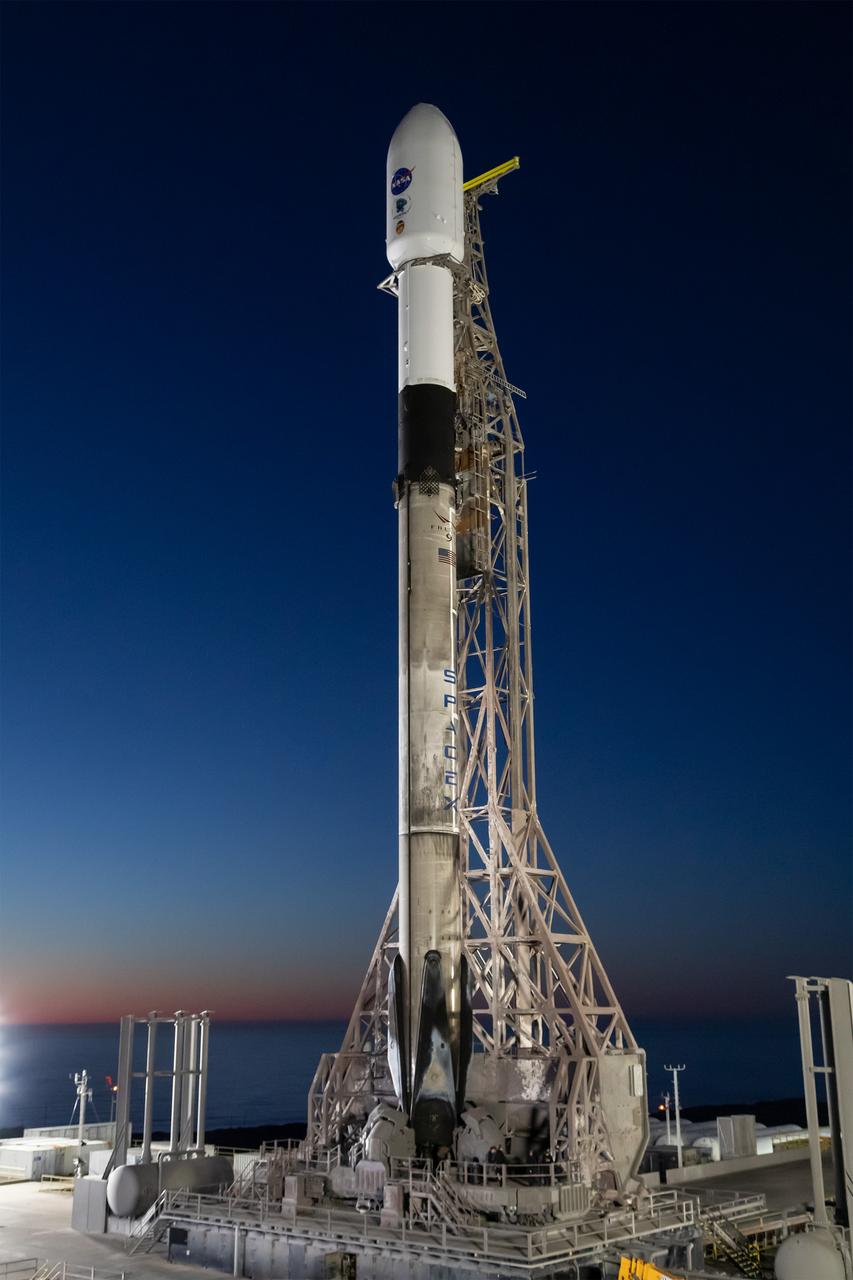

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, carrying NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory and PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites, is vertical at Space Launch Complex 4 East from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Saturday, March 8, 2025. SPHEREx will use its telescope to provide an all-sky spectral survey, creating a 3D map of the entire sky to help scientists investigate the origins of our universe. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system.
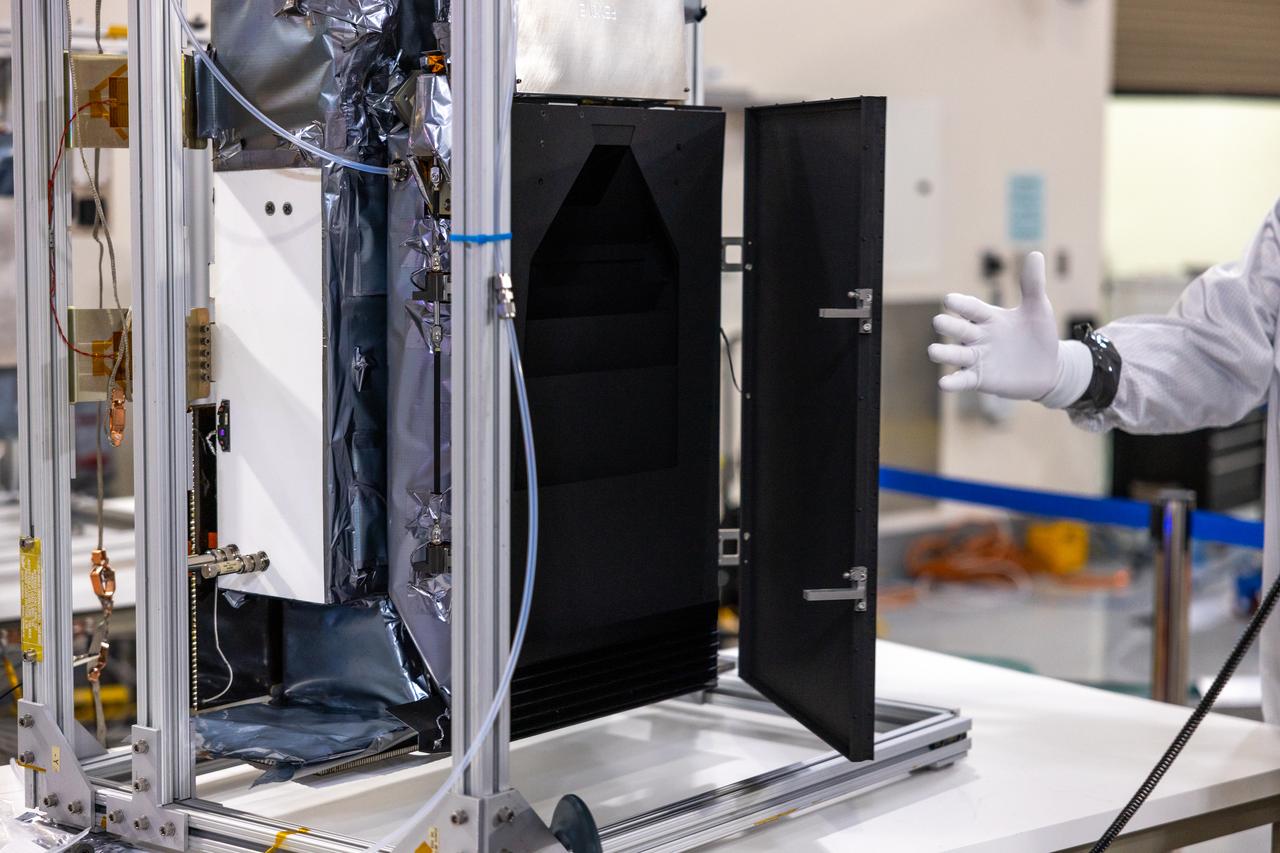

Crews conduct additional solar array deployment testing for NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites at Astrotech Space Operations located on Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Wednesday, Jan. 22, 2025. PUNCH, consisting of four satellites, will produce continuous 3D images of the solar wind and solar storms as it travels from the Sun to Earth to better understand how material in the corona accelerates. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in Central California on Thursday, Feb. 27, 2025.
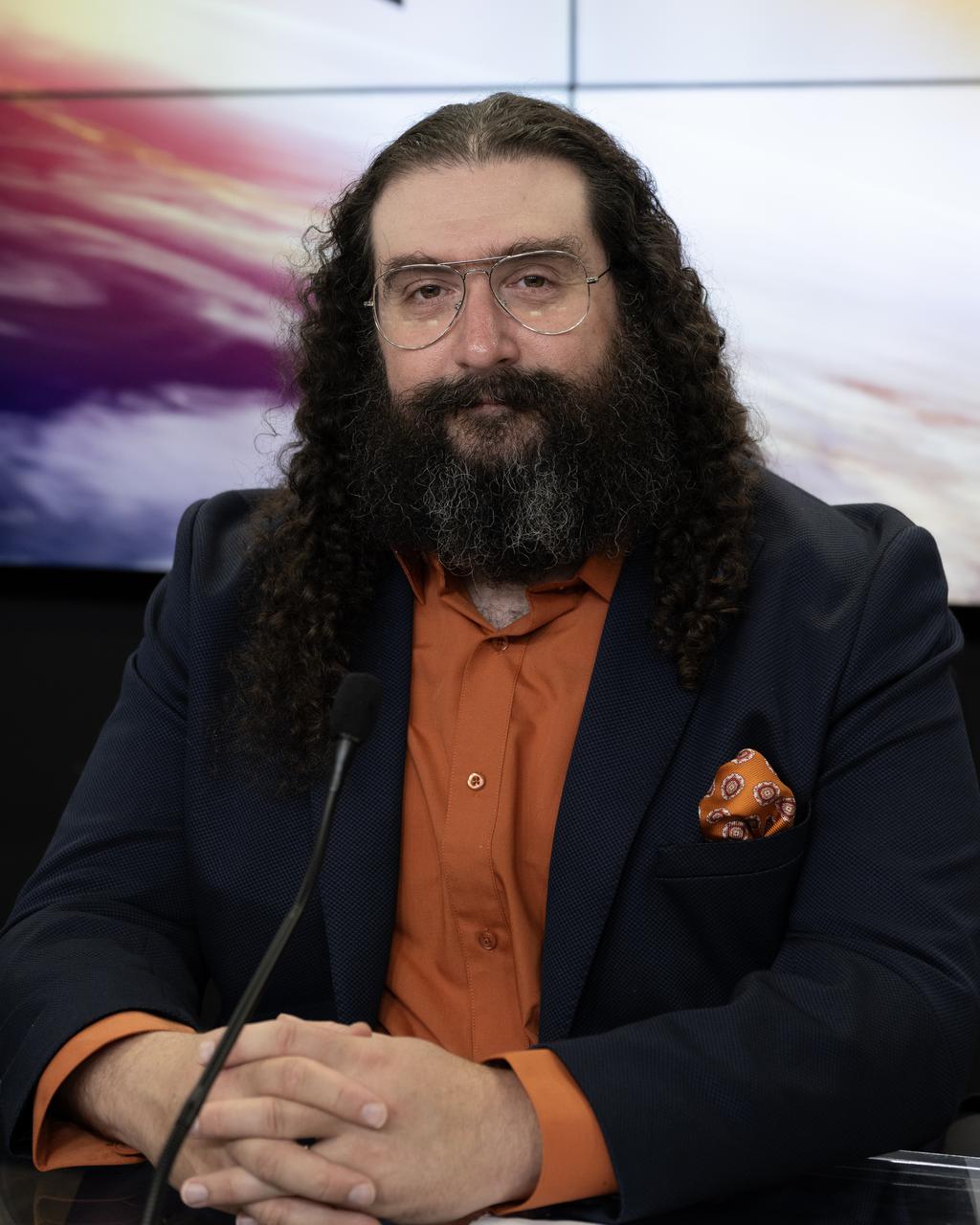

Phil Korngut, SPHEREx instrument scientist, Caltech, participates in a science briefing on Tuesday, Feb. 25, 2025, to discuss the upcoming launch of NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory and PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. SPHEREx will use its telescope to provide an all-sky spectral survey, creating a 3D map of the entire sky to help scientists investigate the origins of our universe. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system.

Antenna's on NASA's Parker Solar Probe are deployed for testing at the Astrotech processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near NASA's Kennedy Space Center on Thursday, April 19, 2018. The Parker Solar Probe will launch on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida no earlier than Aug. 4, 2018. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
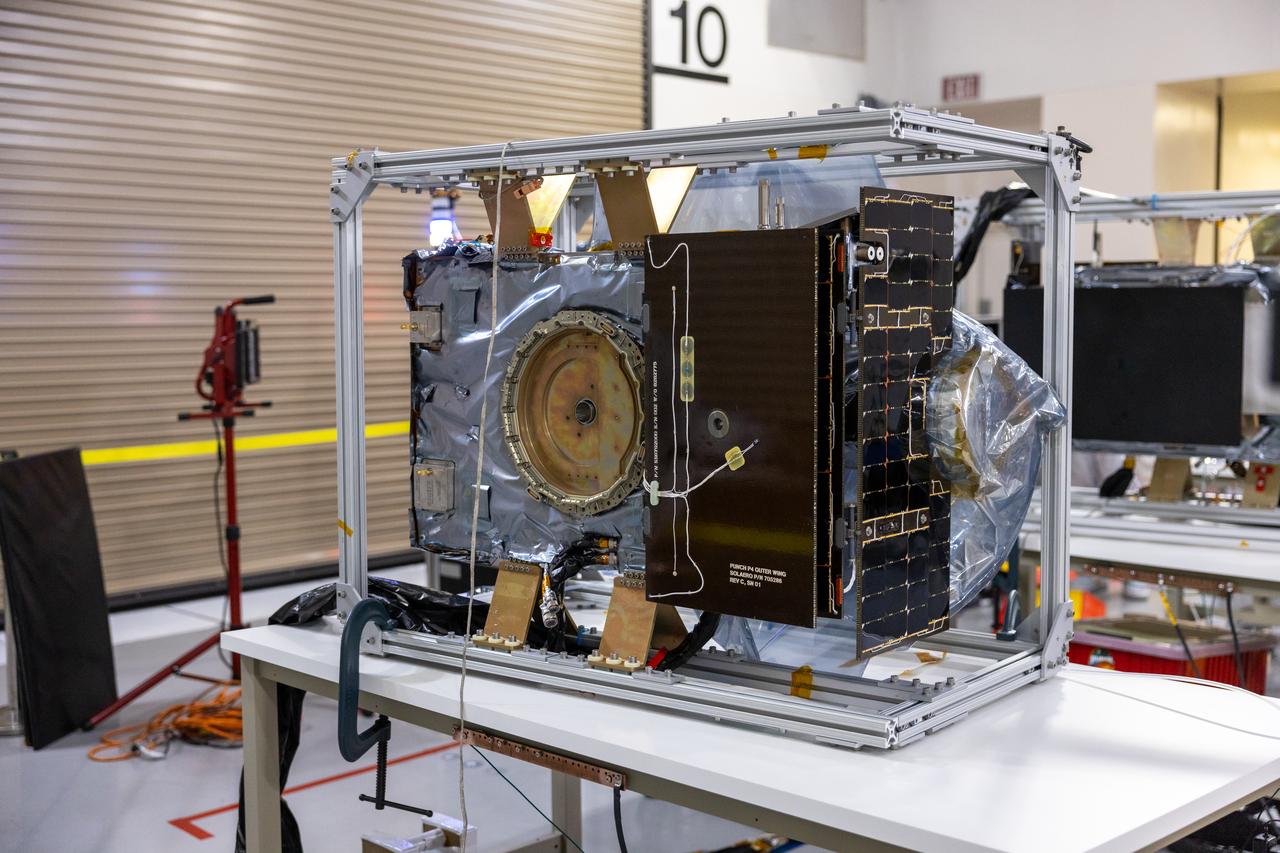
Crews conduct additional solar array deployment testing for NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites at Astrotech Space Operations located on Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Wednesday, Jan. 22, 2025. PUNCH, consisting of four satellites, will produce continuous 3D images of the solar wind and solar storms as it travels from the Sun to Earth to better understand how material in the corona accelerates. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in Central California on Thursday, Feb. 27, 2025.
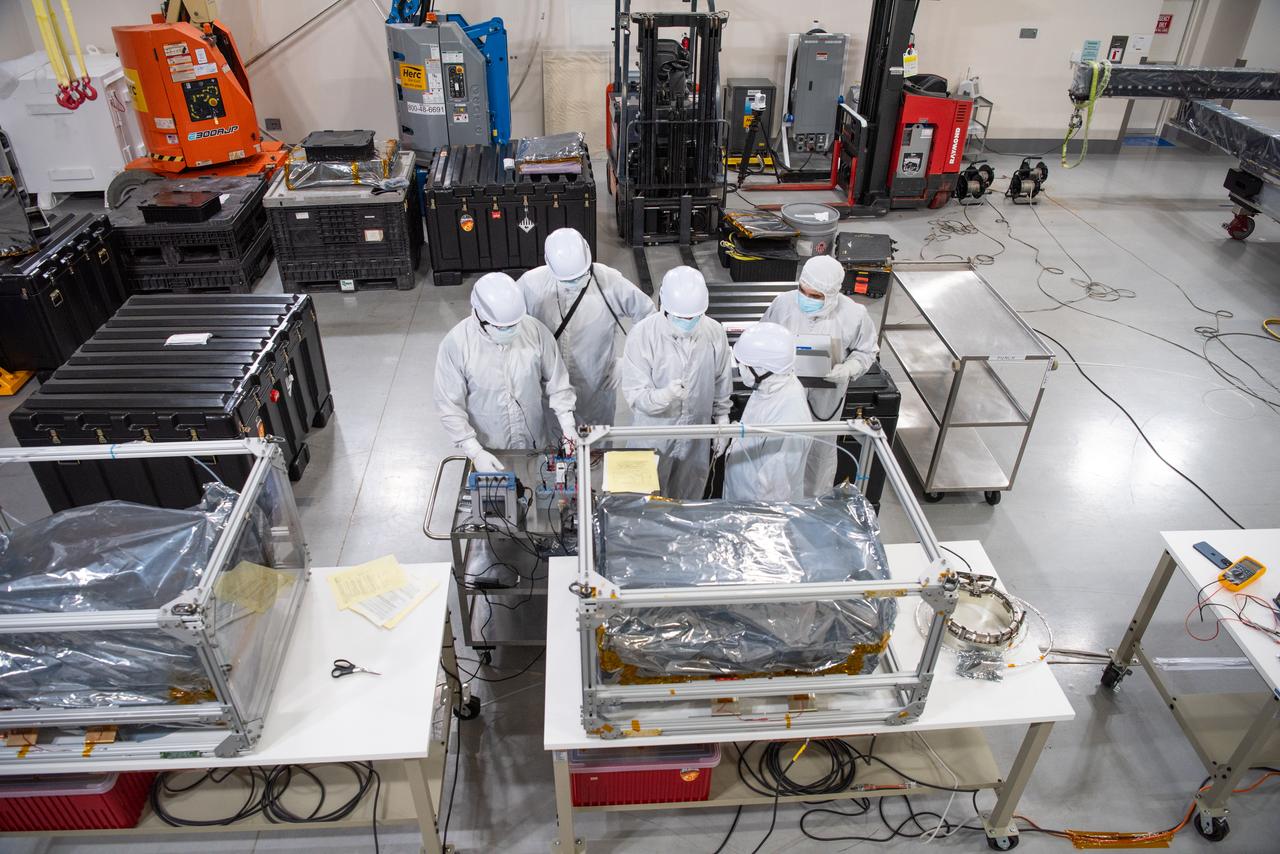

Technicians conduct testing operations on NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) spacecraft onto a work stand for testing operations at the Astrotech Processing Facility on Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Sunday, Jan. 19, 2025. PUNCH, consisting of four satellites, will produce continuous 3D images of the solar wind and solar storms as it travels from the Sun to Earth to better understand how material in the corona accelerates to become the solar wind that fills the solar system. PUNCH will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.
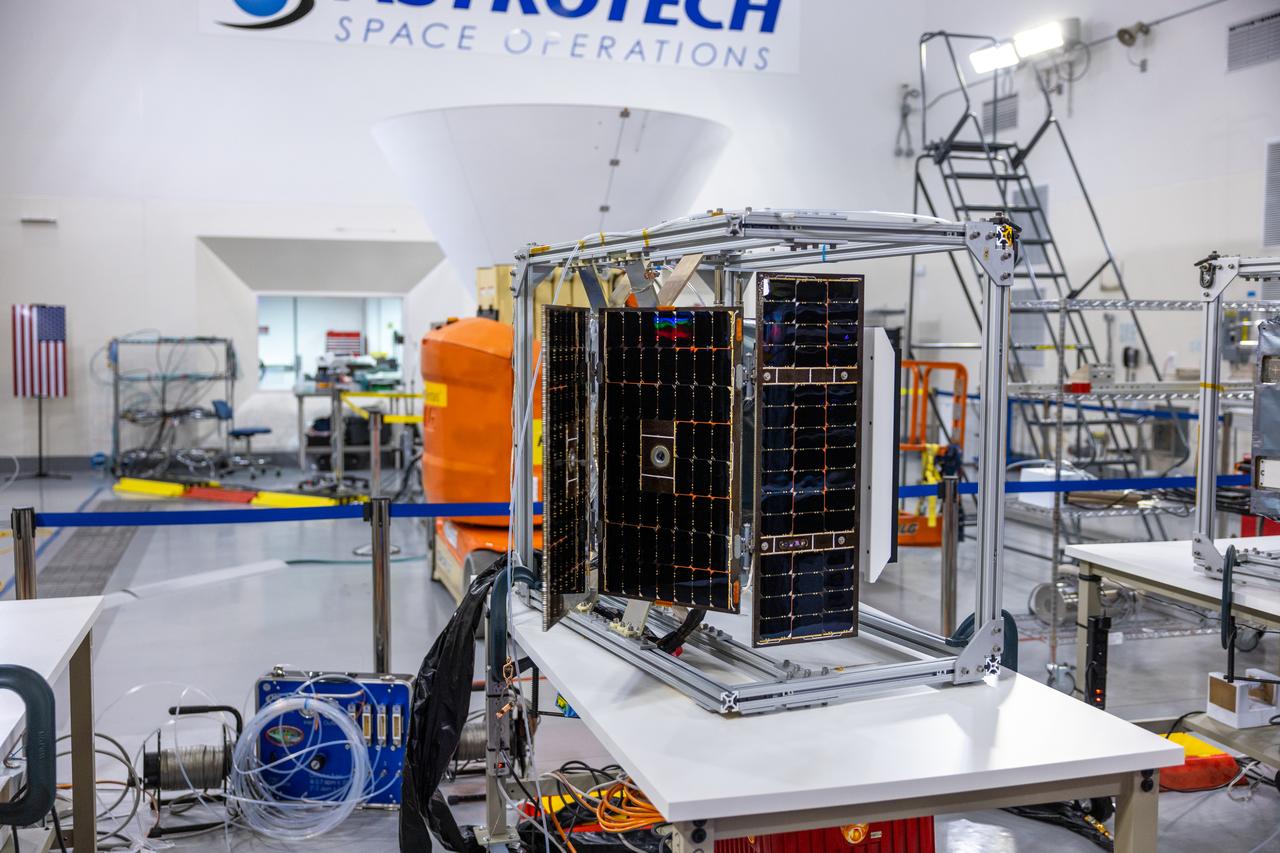

Crews conduct additional solar array deployment testing for NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites at Astrotech Space Operations located on Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Wednesday, Jan. 22, 2025. PUNCH, consisting of four satellites, will produce continuous 3D images of the solar wind and solar storms as it travels from the Sun to Earth to better understand how material in the corona accelerates. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in Central California on Thursday, Feb. 27, 2025.

Rachel Akeson, SPHEREx science data center lead, Caltech/IPAC, participates in a science briefing on Tuesday, Feb. 25, 2025, to discuss the upcoming launch of NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory and PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. SPHEREx will use its telescope to provide an all-sky spectral survey, creating a 3D map of the entire sky to help scientists investigate the origins of our universe. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system.
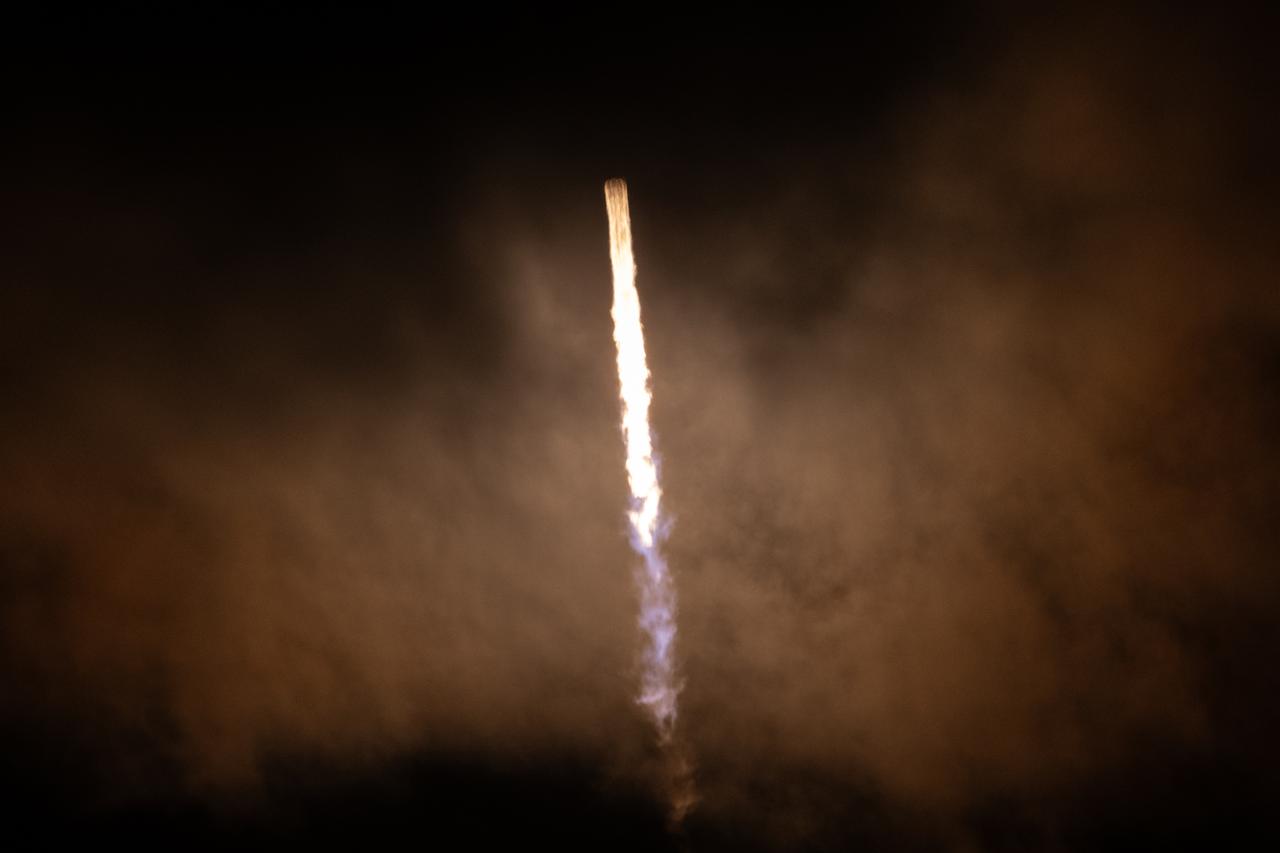

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, carrying NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory and PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites, launches from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Tuesday, March 11, 2025. SPHEREx will use its telescope to provide an all-sky spectral survey, creating a 3D map of the entire sky to help scientists investigate the origins of our universe. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system.
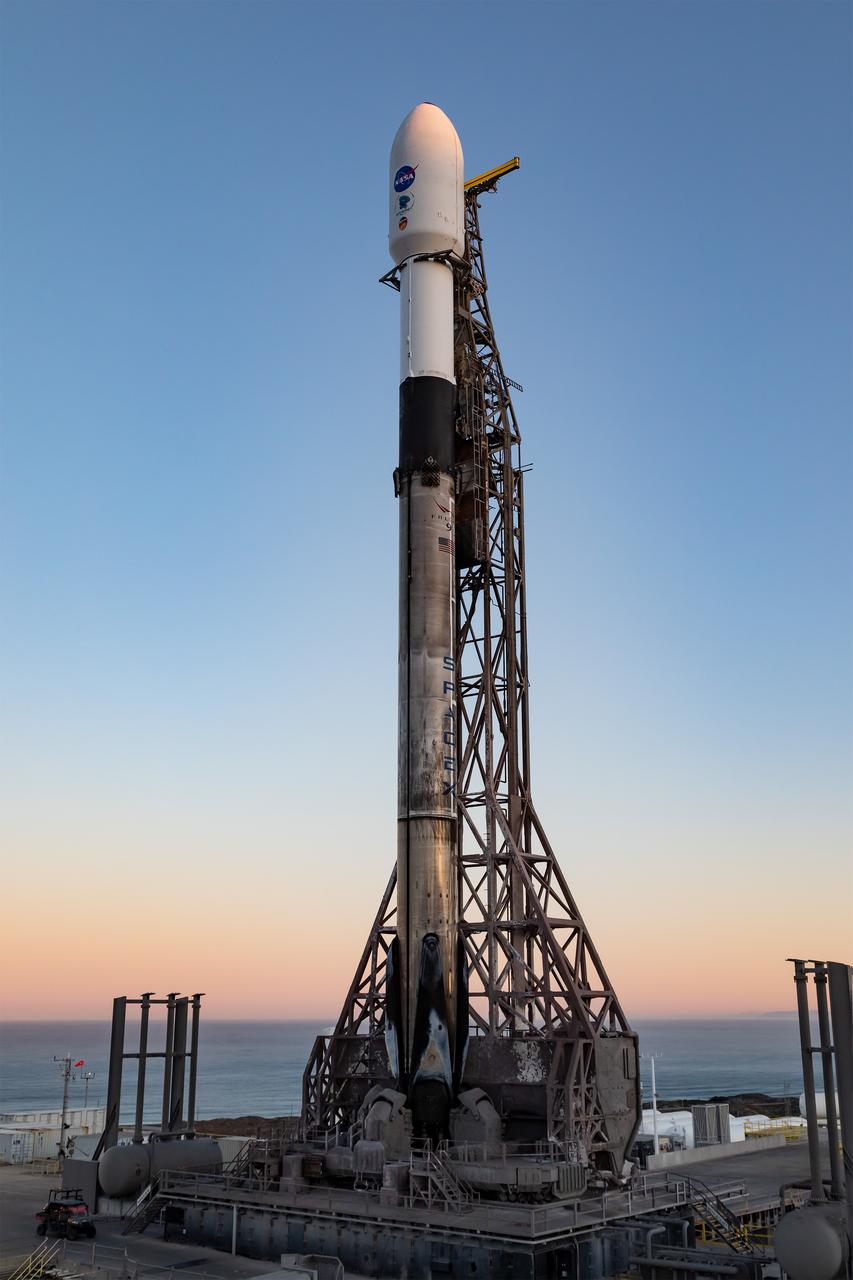

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, carrying NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory and PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites, is vertical at Space Launch Complex 4 East from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Saturday March 8, 2025. SPHEREx will use its telescope to provide an all-sky spectral survey, creating a 3D map of the entire sky to help scientists investigate the origins of our universe. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system.
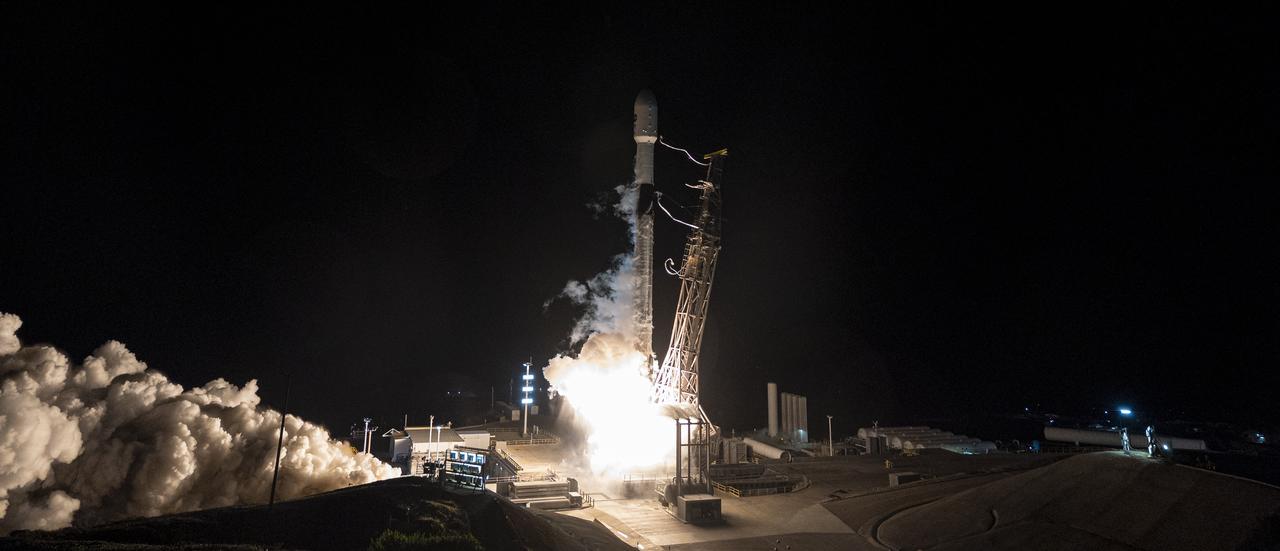

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, carrying NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory and PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites, launches from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Tuesday, March 11, 2025. SPHEREx will use its telescope to provide an all-sky spectral survey, creating a 3D map of the entire sky to help scientists investigate the origins of our universe. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system.
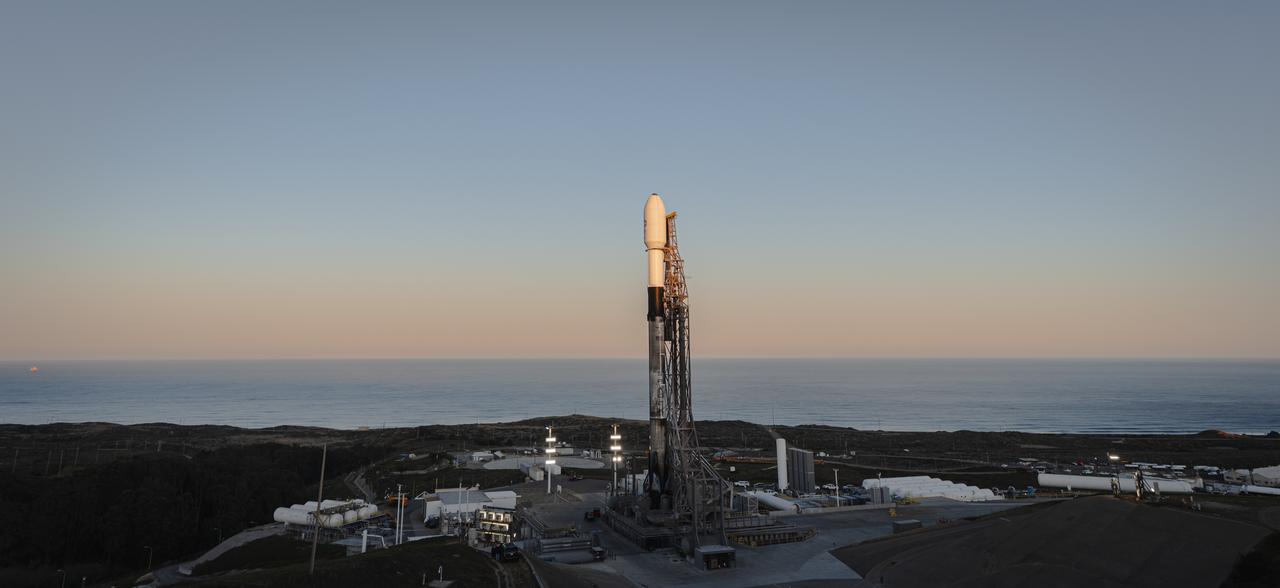

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, carrying NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory and PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites, is vertical at Space Launch Complex 4 East from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Saturday March 8, 2025. SPHEREx will use its telescope to provide an all-sky spectral survey, creating a 3D map of the entire sky to help scientists investigate the origins of our universe. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system.
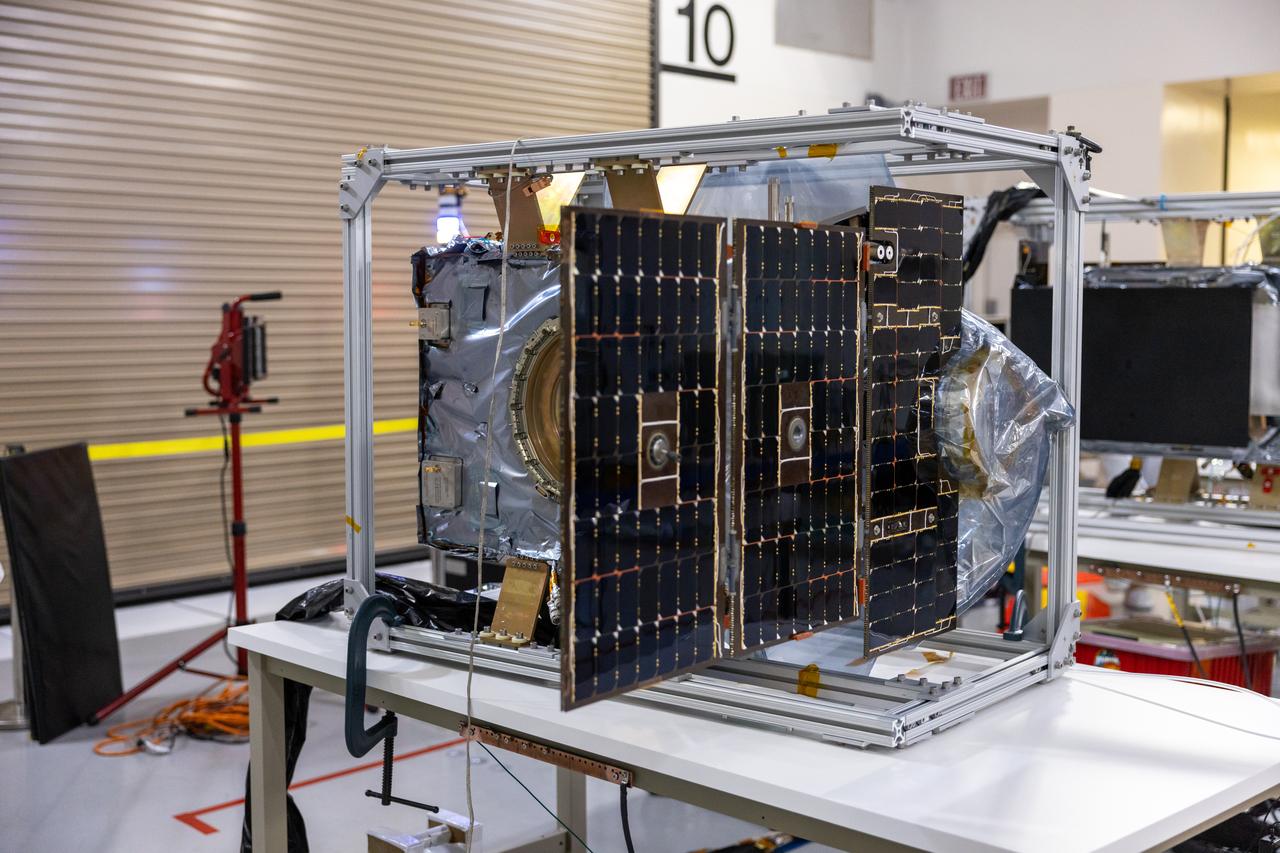

Crews conduct additional solar array deployment testing for NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites at Astrotech Space Operations located on Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Wednesday, Jan. 22, 2025. PUNCH, consisting of four satellites, will produce continuous 3D images of the solar wind and solar storms as it travels from the Sun to Earth to better understand how material in the corona accelerates. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in Central California on Thursday, Feb. 27, 2025.
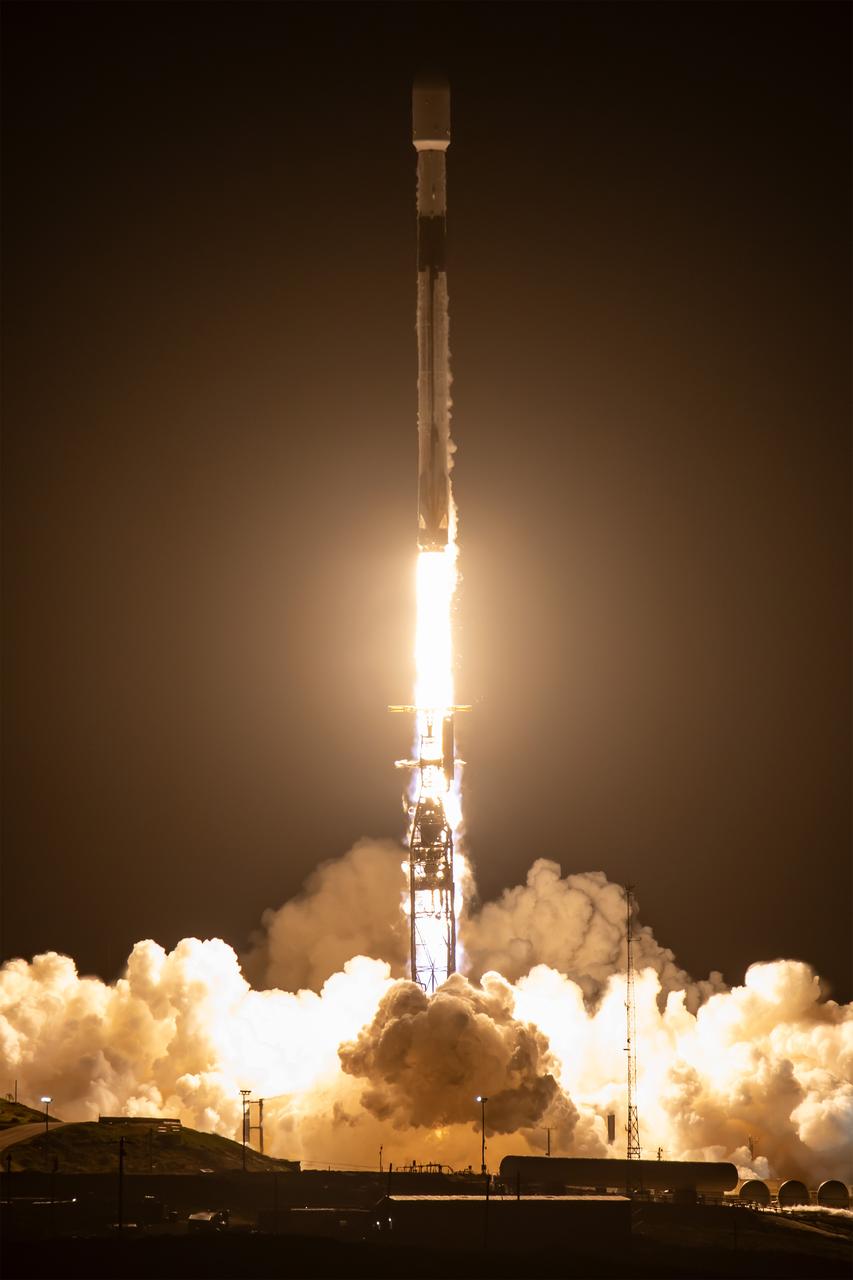

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, carrying NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory and PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites, launches from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Tuesday, March 11, 2025. SPHEREx will use its telescope to provide an all-sky spectral survey, creating a 3D map of the entire sky to help scientists investigate the origins of our universe. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system.
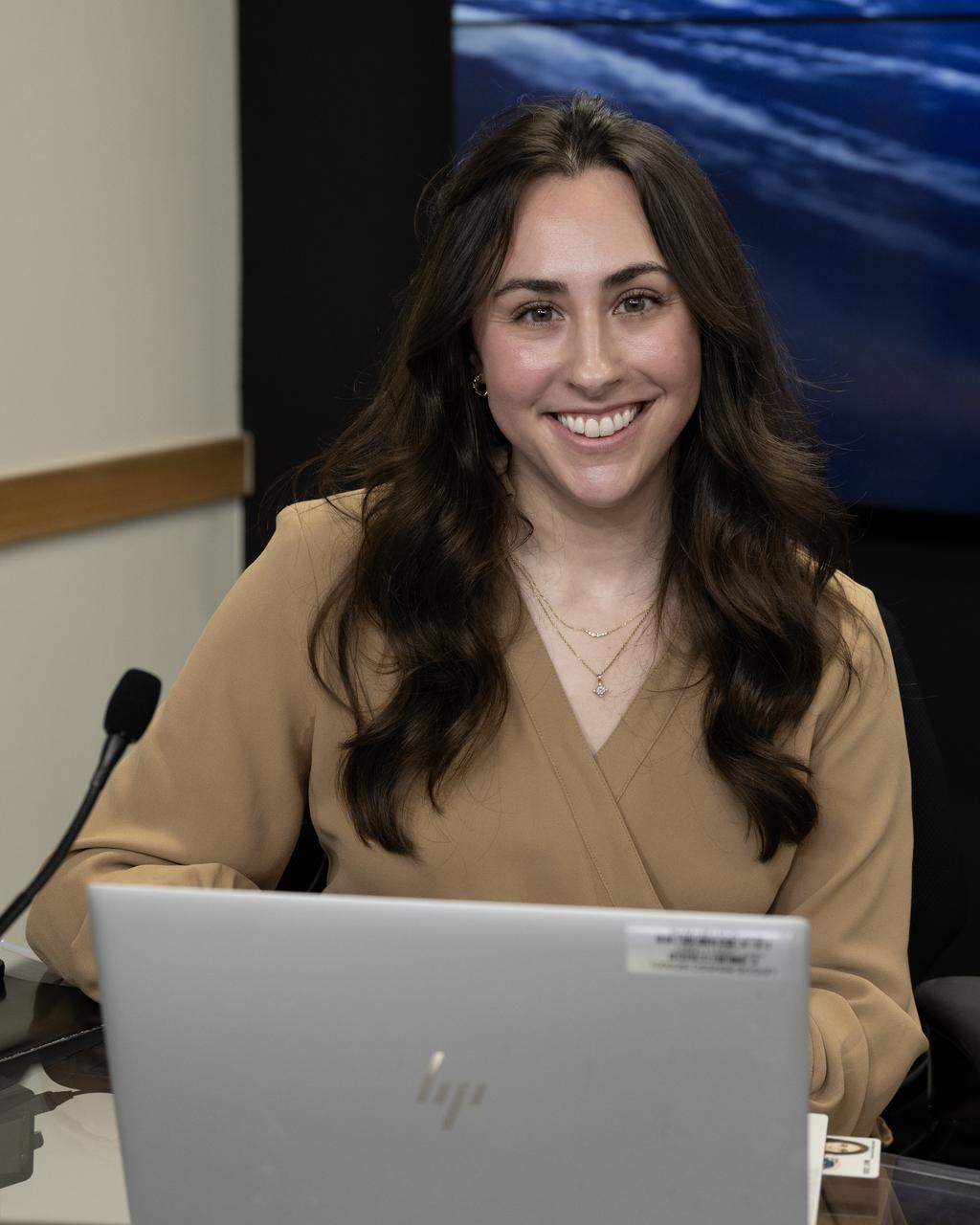

Alise Fischer, communications, NASA Headquarters participates in a science briefing on Tuesday, Feb. 25, 2025, to discuss the upcoming launch of NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory and PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. SPHEREx will use its telescope to provide an all-sky spectral survey, creating a 3D map of the entire sky to help scientists investigate the origins of our universe. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system.
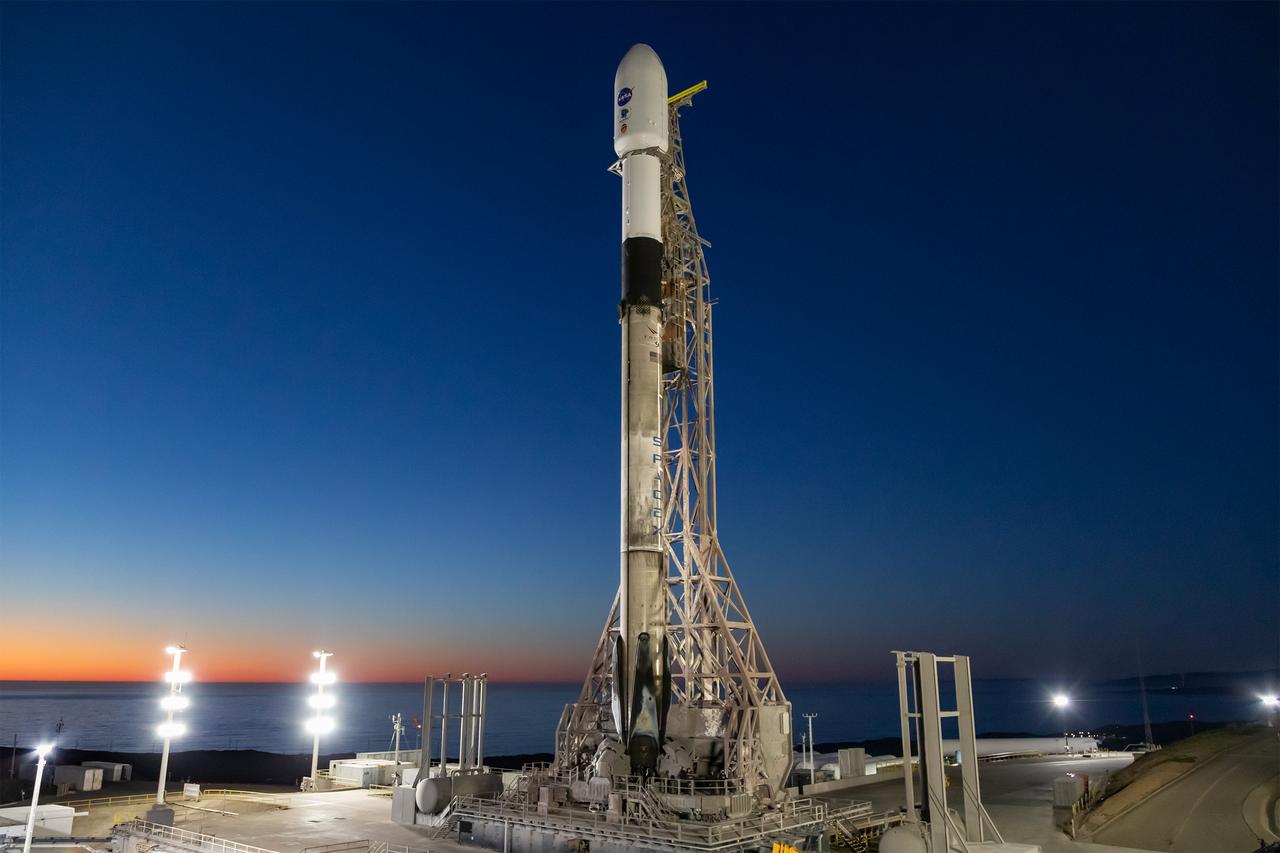

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, carrying NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory and PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites, is vertical at Space Launch Complex 4 East from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Saturday, March 8, 2025. SPHEREx will use its telescope to provide an all-sky spectral survey, creating a 3D map of the entire sky to help scientists investigate the origins of our universe. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system.
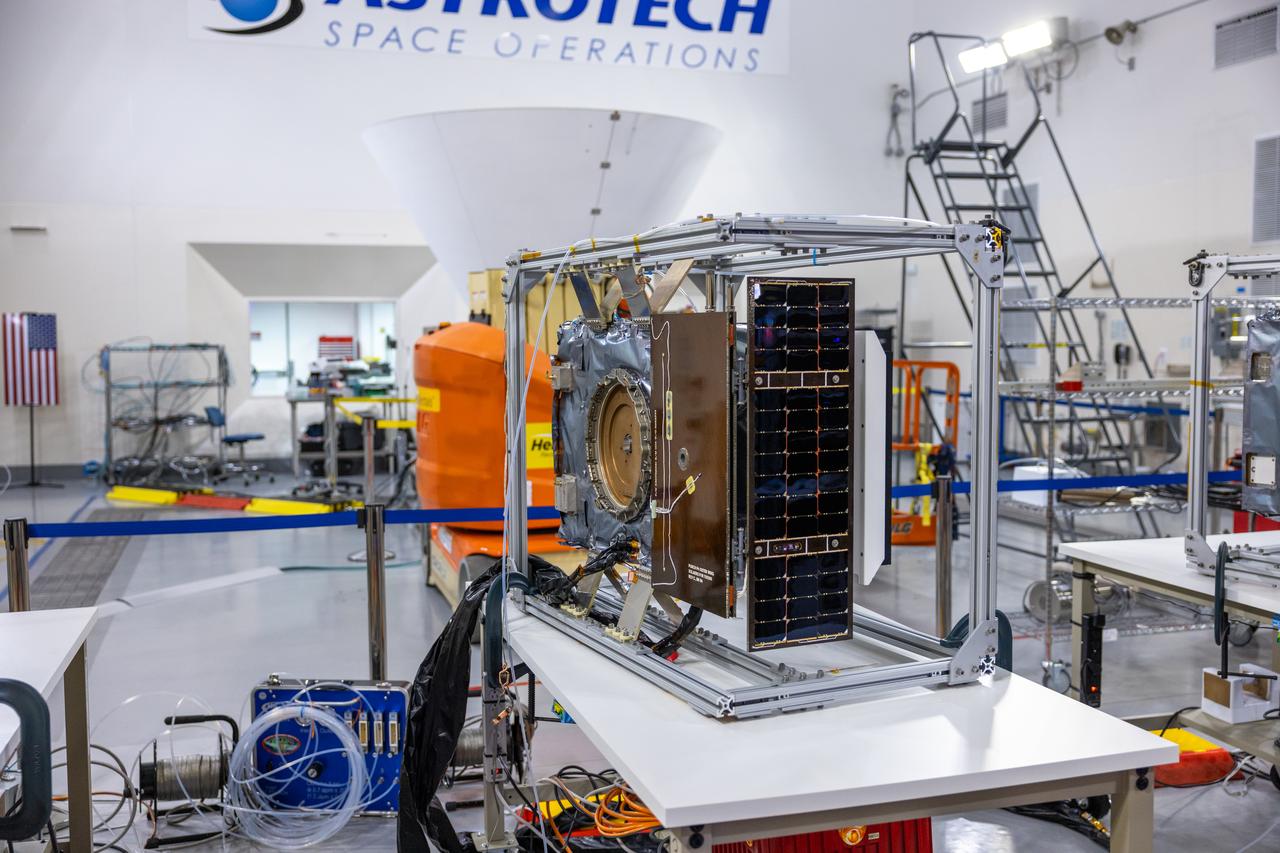

Crews conduct additional solar array deployment testing for NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites at Astrotech Space Operations located on Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Wednesday, Jan. 22, 2025. PUNCH, consisting of four satellites, will produce continuous 3D images of the solar wind and solar storms as it travels from the Sun to Earth to better understand how material in the corona accelerates. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in Central California on Thursday, Feb. 27, 2025.
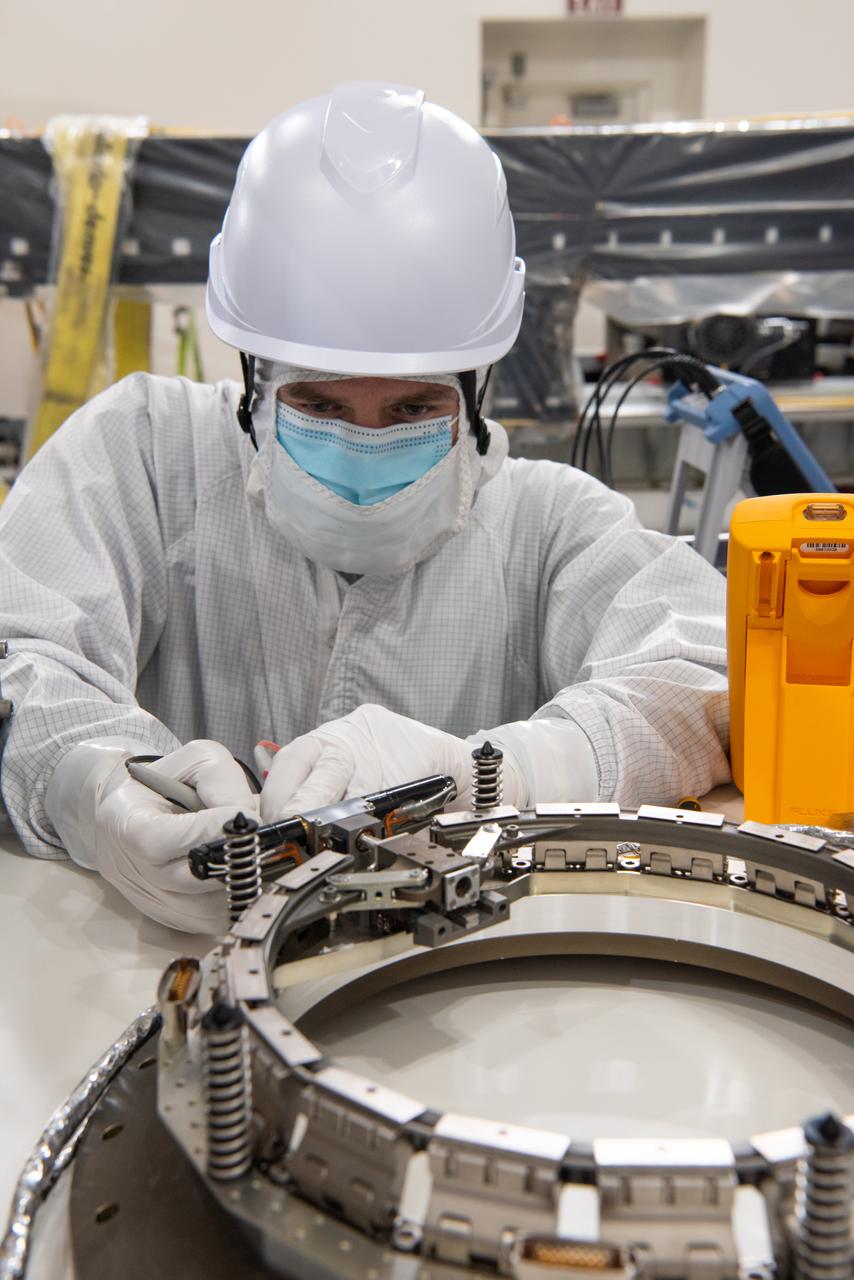

Technicians conduct testing operations on NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) spacecraft onto a work stand for testing operations at the Astrotech Processing Facility on Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Sunday, Jan. 19, 2025. PUNCH, consisting of four satellites, will produce continuous 3D images of the solar wind and solar storms as it travels from the Sun to Earth to better understand how material in the corona accelerates to become the solar wind that fills the solar system. PUNCH will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.
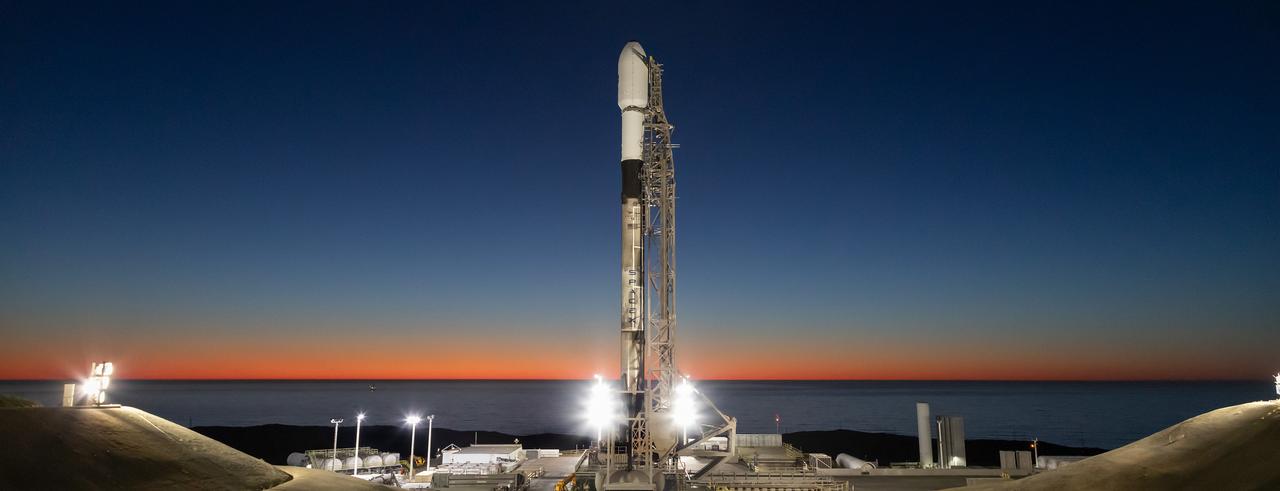

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, carrying NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory and PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites, is vertical at Space Launch Complex 4 East from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Saturday, March 8, 2025. SPHEREx will use its telescope to provide an all-sky spectral survey, creating a 3D map of the entire sky to help scientists investigate the origins of our universe. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system.
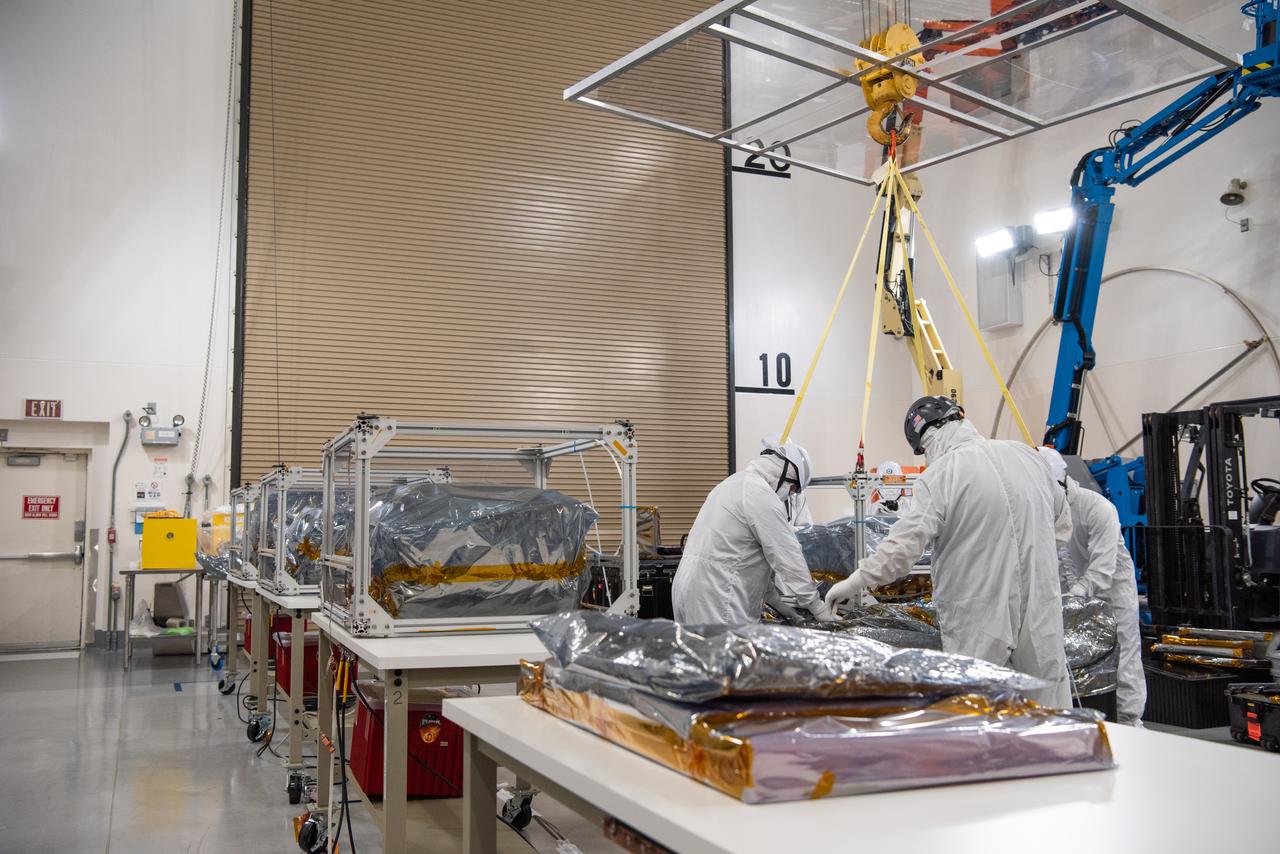

Technicians use an overheard crane to lift NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) spacecraft onto a work stand for testing operations at the Astrotech Processing Facility on Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Sunday, Jan. 19, 2025. PUNCH, consisting of four satellites, will produce continuous 3D images of the solar wind and solar storms as it travels from the Sun to Earth to better understand how material in the corona accelerates to become the solar wind that fills the solar system. PUNCH will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.
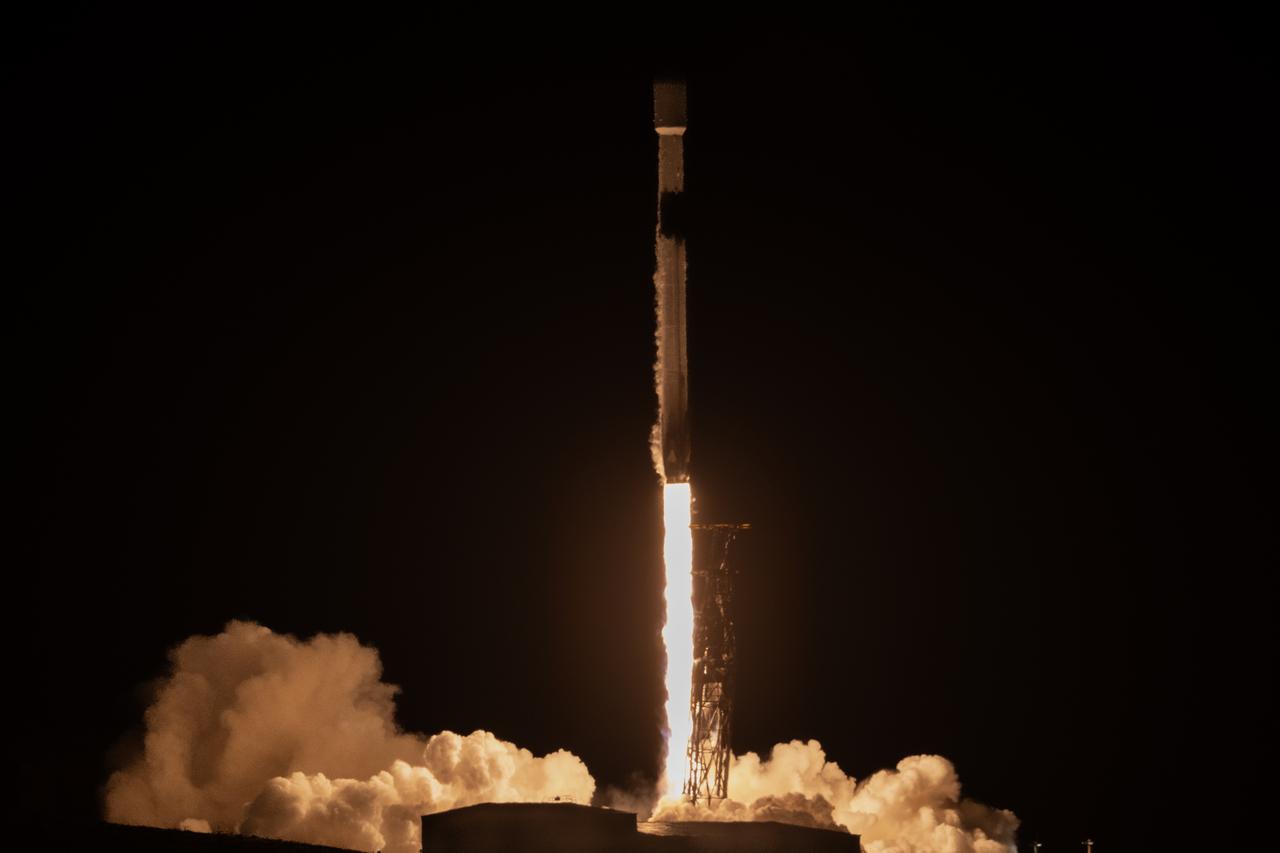

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, carrying NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory and PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites, launches from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Tuesday, March 11, 2025. SPHEREx will use its telescope to provide an all-sky spectral survey, creating a 3D map of the entire sky to help scientists investigate the origins of our universe. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system.
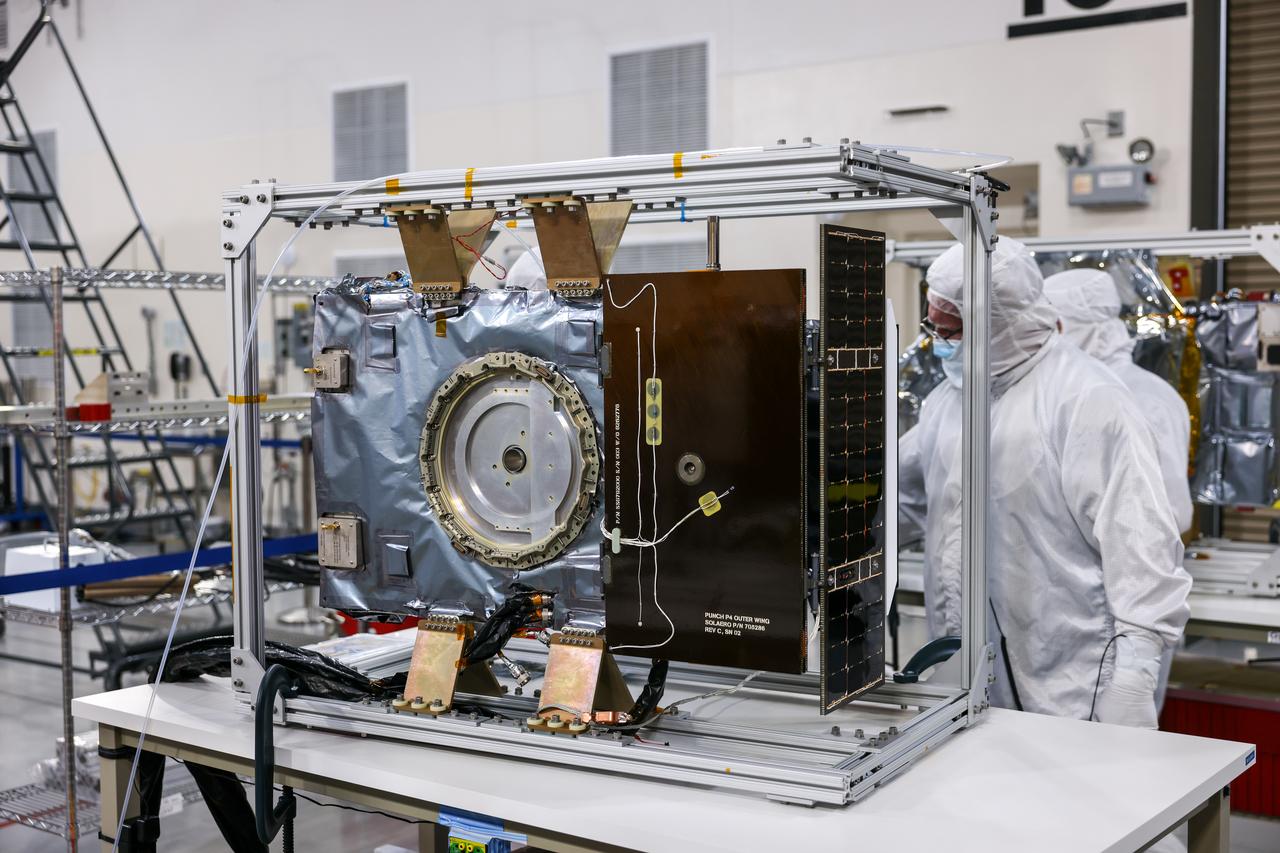
Crews conduct a solar array deployment test on the spacecraft of NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites at Astrotech Space Operations located on Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Tuesday, Jan. 21, 2025. The four satellites of PUNCH will make 3D observations of the Sun’s corona to learn how the mass and energy becomes solar wind. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.
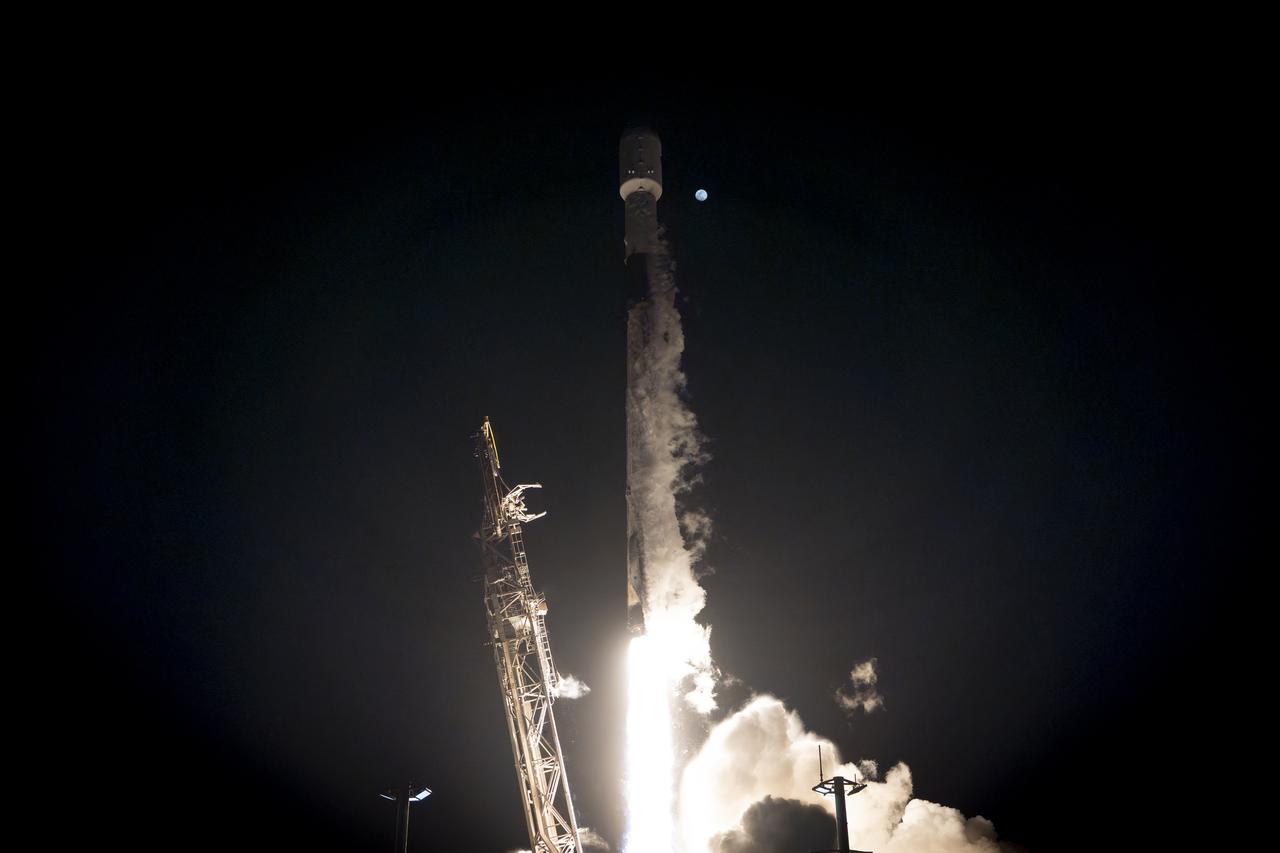

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, carrying NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory and PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites, launches from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Tuesday, March 11, 2025. SPHEREx will use its telescope to provide an all-sky spectral survey, creating a 3D map of the entire sky to help scientists investigate the origins of our universe. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system.
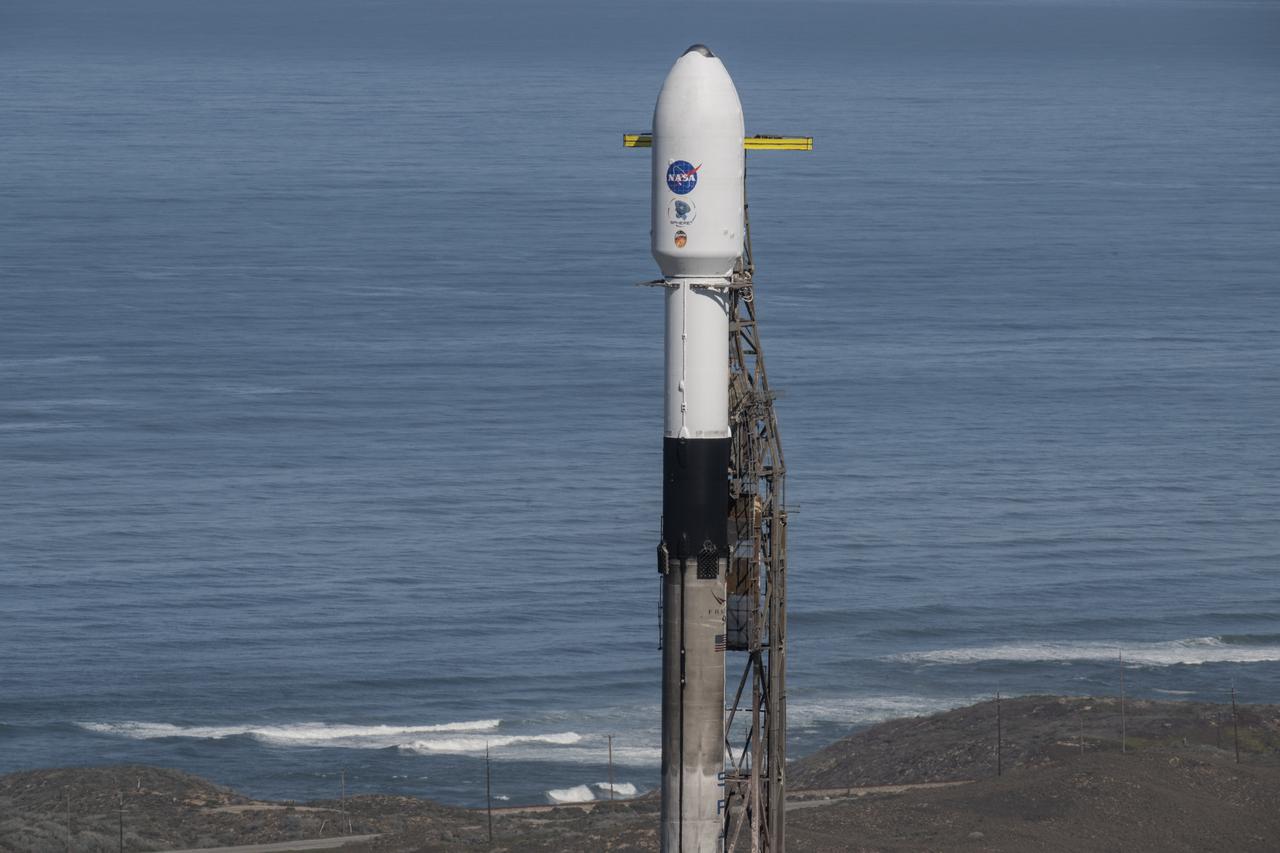

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, carrying NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory and PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites, is vertical at Space Launch Complex 4 East from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Saturday, March 8, 2025. SPHEREx will use its telescope to provide an all-sky spectral survey, creating a 3D map of the entire sky to help scientists investigate the origins of our universe. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system.

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, carrying NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory and PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites, is vertical at Space Launch Complex 4 East from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Saturday March 8, 2025. SPHEREx will use its telescope to provide an all-sky spectral survey, creating a 3D map of the entire sky to help scientists investigate the origins of our universe. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system.
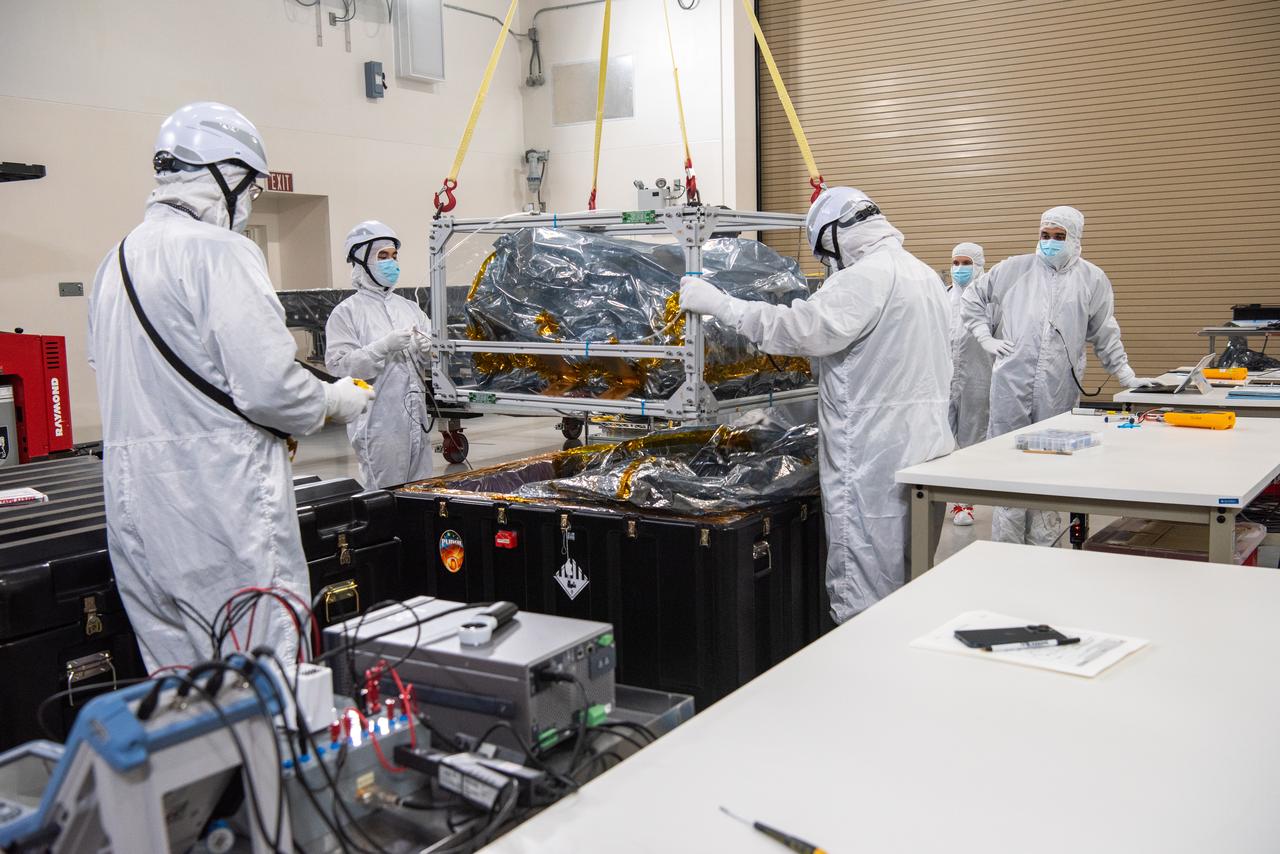

Technicians use an overheard crane to lift NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) spacecraft onto a work stand for testing operations at the Astrotech Processing Facility on Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Sunday, Jan. 19, 2025. PUNCH, consisting of four satellites, will produce continuous 3D images of the solar wind and solar storms as it travels from the Sun to Earth to better understand how material in the corona accelerates to become the solar wind that fills the solar system. PUNCH will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.
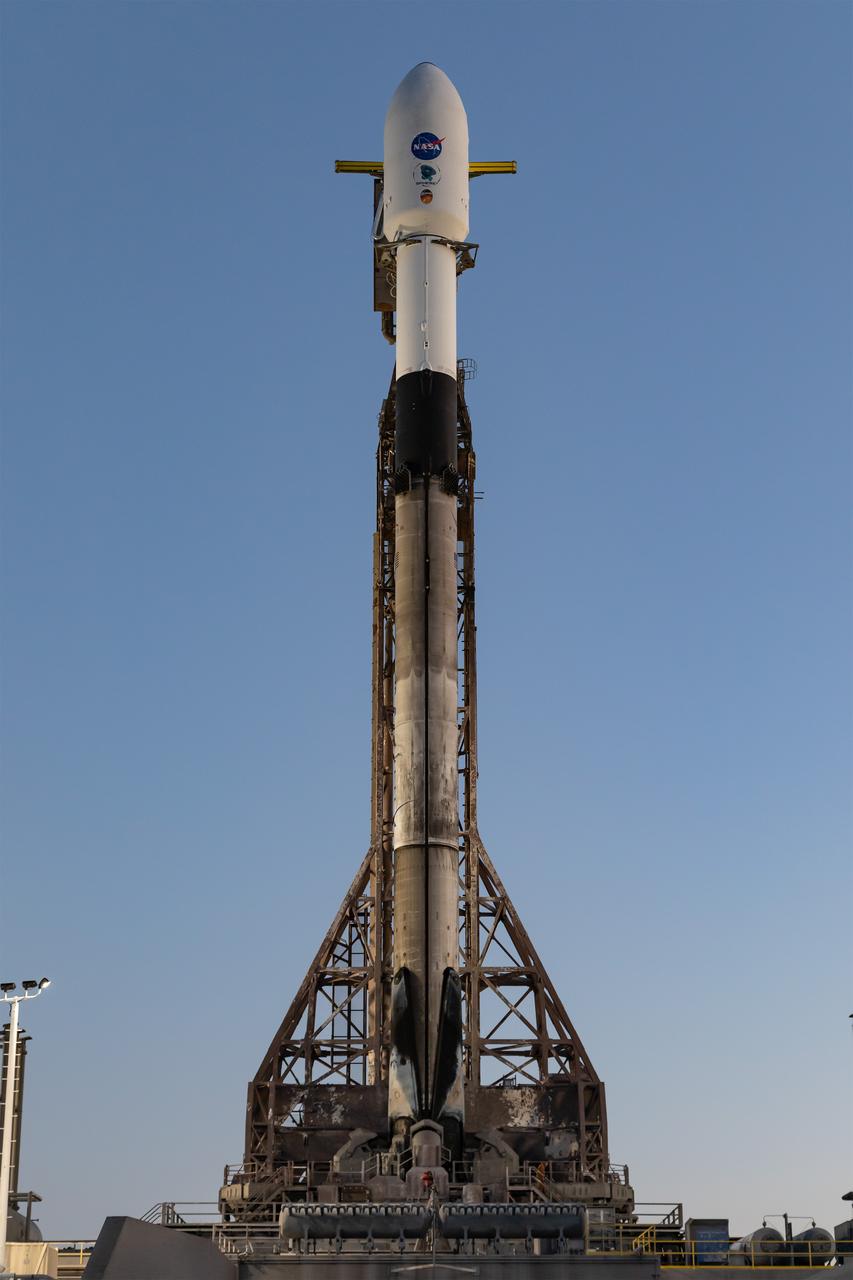

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, carrying NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory and PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites, is vertical at Space Launch Complex 4 East from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Saturday March 8, 2025. SPHEREx will use its telescope to provide an all-sky spectral survey, creating a 3D map of the entire sky to help scientists investigate the origins of our universe. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system.
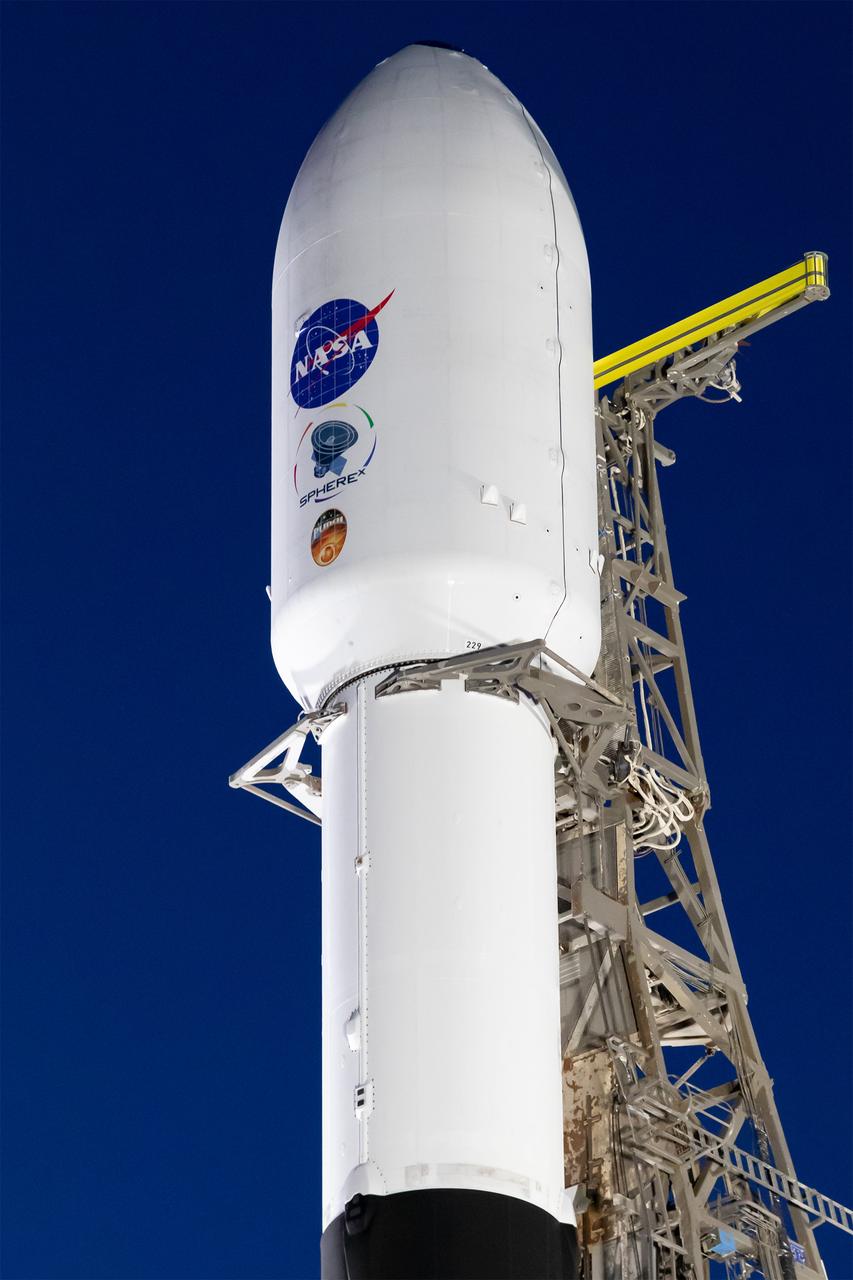

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, carrying NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory and PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites, is vertical at Space Launch Complex 4 East from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Saturday, March 8, 2025. SPHEREx will use its telescope to provide an all-sky spectral survey, creating a 3D map of the entire sky to help scientists investigate the origins of our universe. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system.
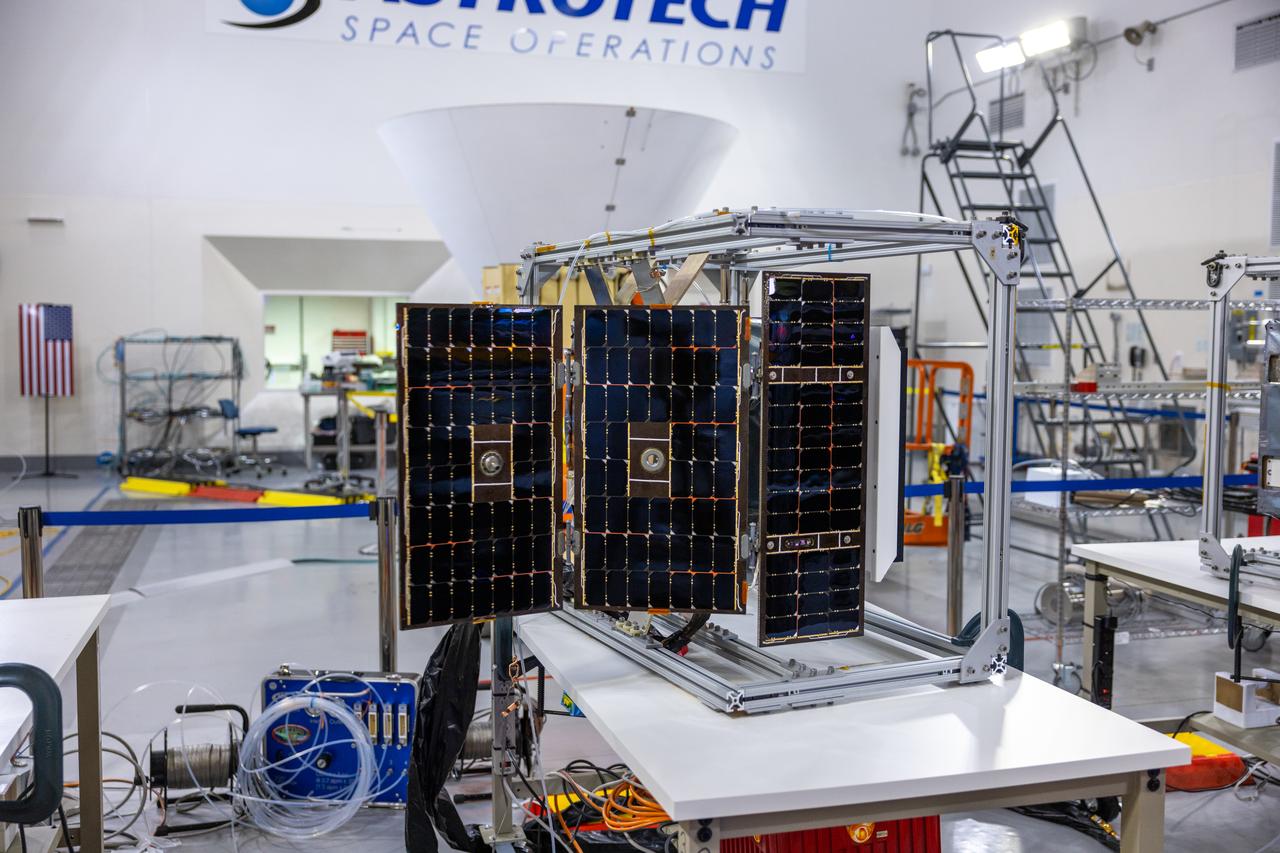

Crews conduct additional solar array deployment testing for NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites at Astrotech Space Operations located on Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Wednesday, Jan. 22, 2025. PUNCH, consisting of four satellites, will produce continuous 3D images of the solar wind and solar storms as it travels from the Sun to Earth to better understand how material in the corona accelerates. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in Central California on Thursday, Feb. 27, 2025.

Joe Westlake, director, Heliophysics Division, NASA Headquarters, participates in a science briefing on Tuesday, Feb. 25, 2025, to discuss the upcoming launch of NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory and PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. SPHEREx will use its telescope to provide an all-sky spectral survey, creating a 3D map of the entire sky to help scientists investigate the origins of our universe. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system.

NASA and Caltech participate in a science briefing on Tuesday, Feb. 25, 2025, to discuss the upcoming launch of NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory and PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. SPHEREx will use its telescope to provide an all-sky spectral survey, creating a 3D map of the entire sky to help scientists investigate the origins of our universe. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system.
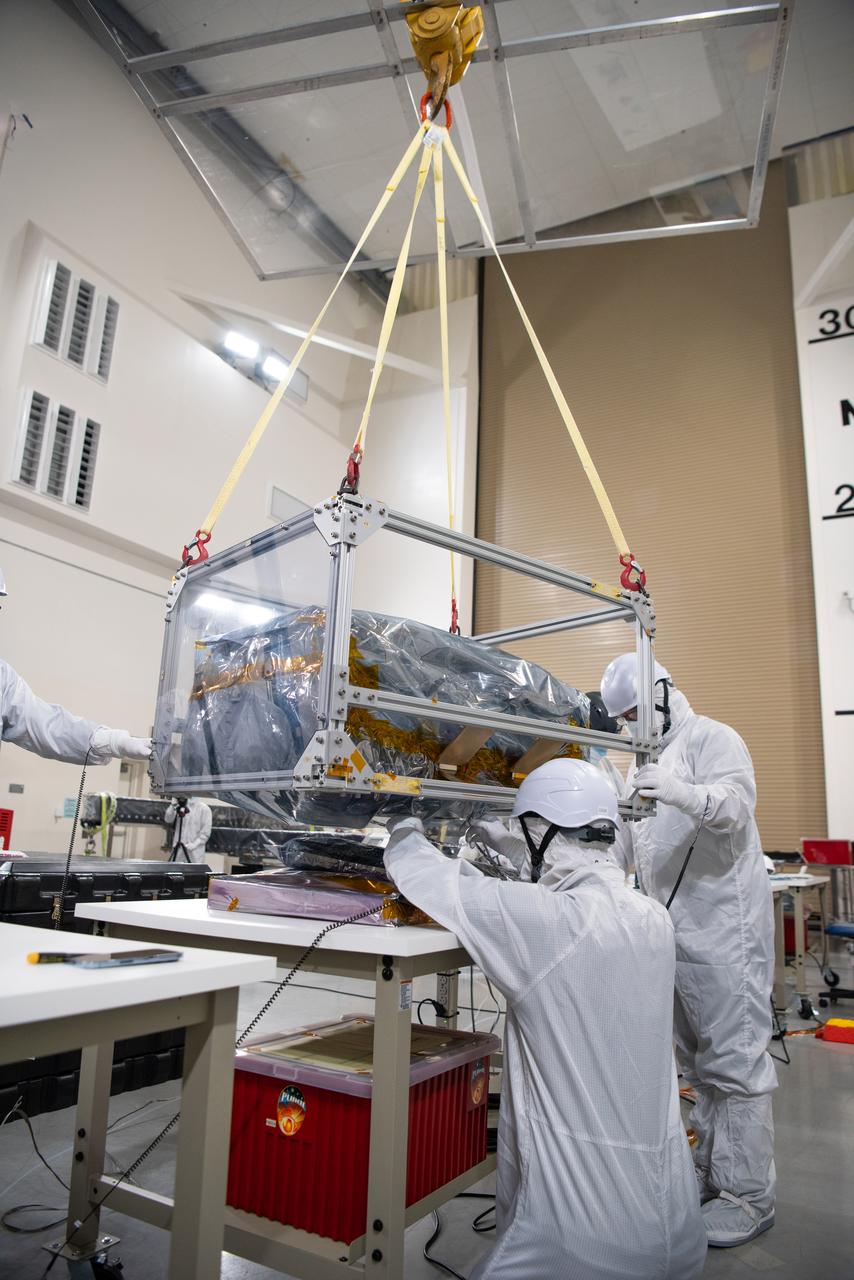

Technicians use an overheard crane to lift NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) spacecraft onto a work stand for testing operations at the Astrotech Processing Facility on Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Sunday, Jan. 19, 2025. PUNCH, consisting of four satellites, will produce continuous 3D images of the solar wind and solar storms as it travels from the Sun to Earth to better understand how material in the corona accelerates to become the solar wind that fills the solar system. PUNCH will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, carrying NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory and PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites, launches from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Tuesday, March 11, 2025. SPHEREx will use its telescope to provide an all-sky spectral survey, creating a 3D map of the entire sky to help scientists investigate the origins of our universe. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system.
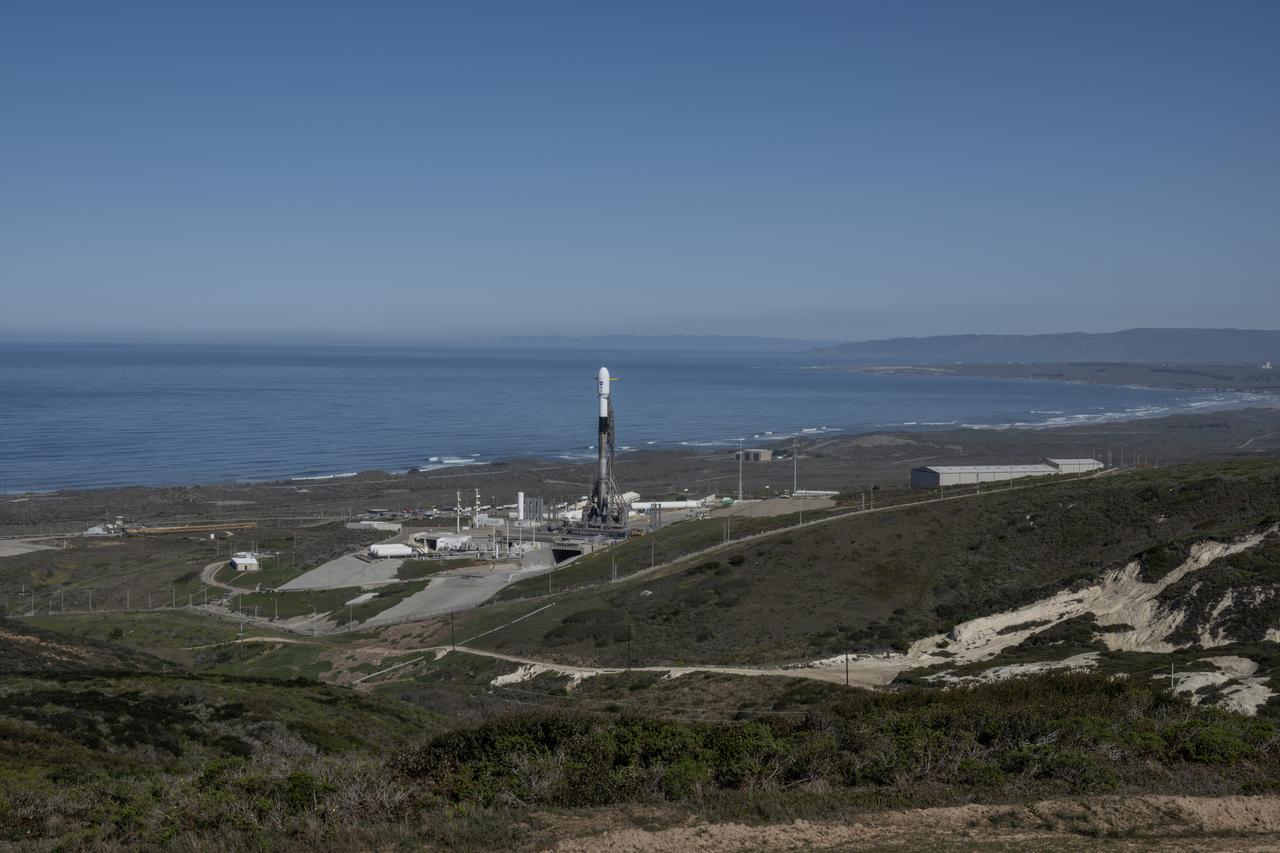

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, carrying NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory and PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites, is vertical at Space Launch Complex 4 East from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Saturday, March 8, 2025. SPHEREx will use its telescope to provide an all-sky spectral survey, creating a 3D map of the entire sky to help scientists investigate the origins of our universe. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system.
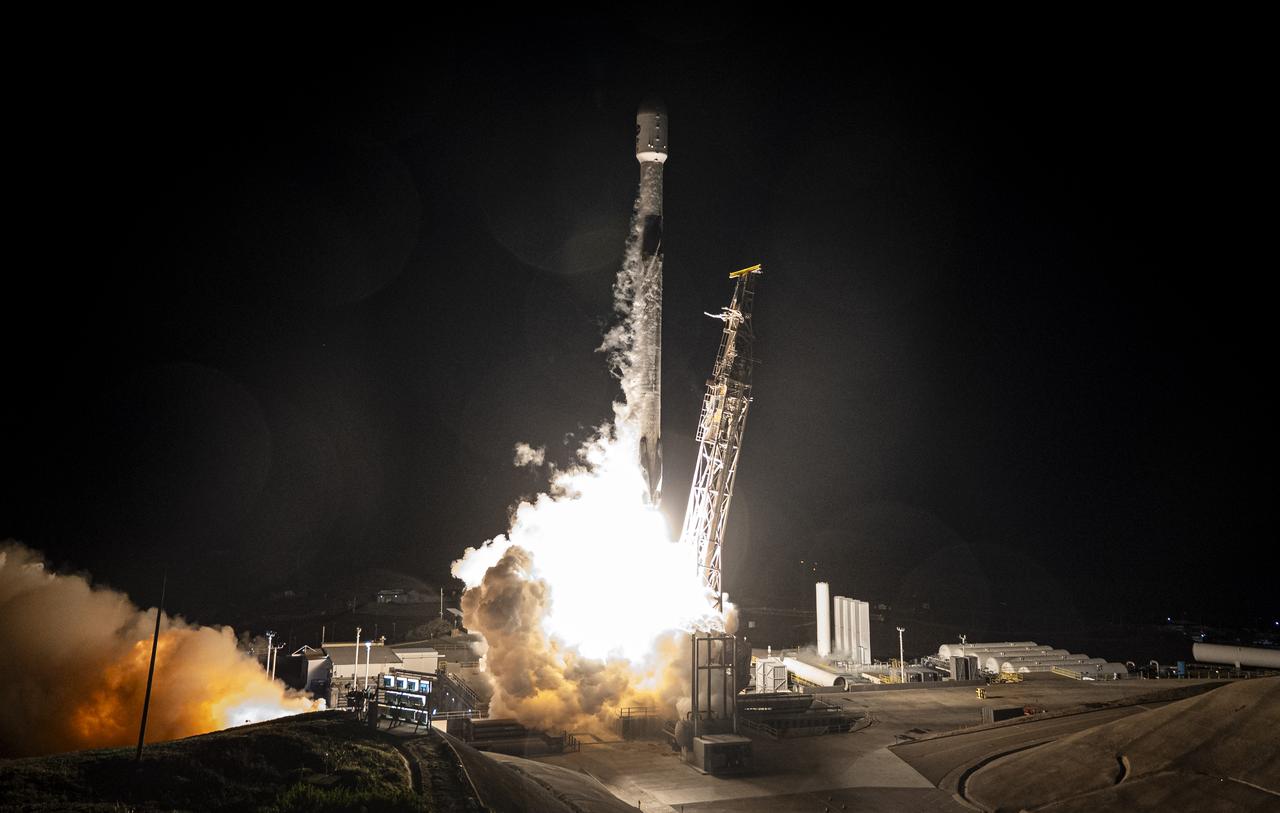

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, carrying NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory and PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites, launches from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Tuesday, March 11, 2025. SPHEREx will use its telescope to provide an all-sky spectral survey, creating a 3D map of the entire sky to help scientists investigate the origins of our universe. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system.
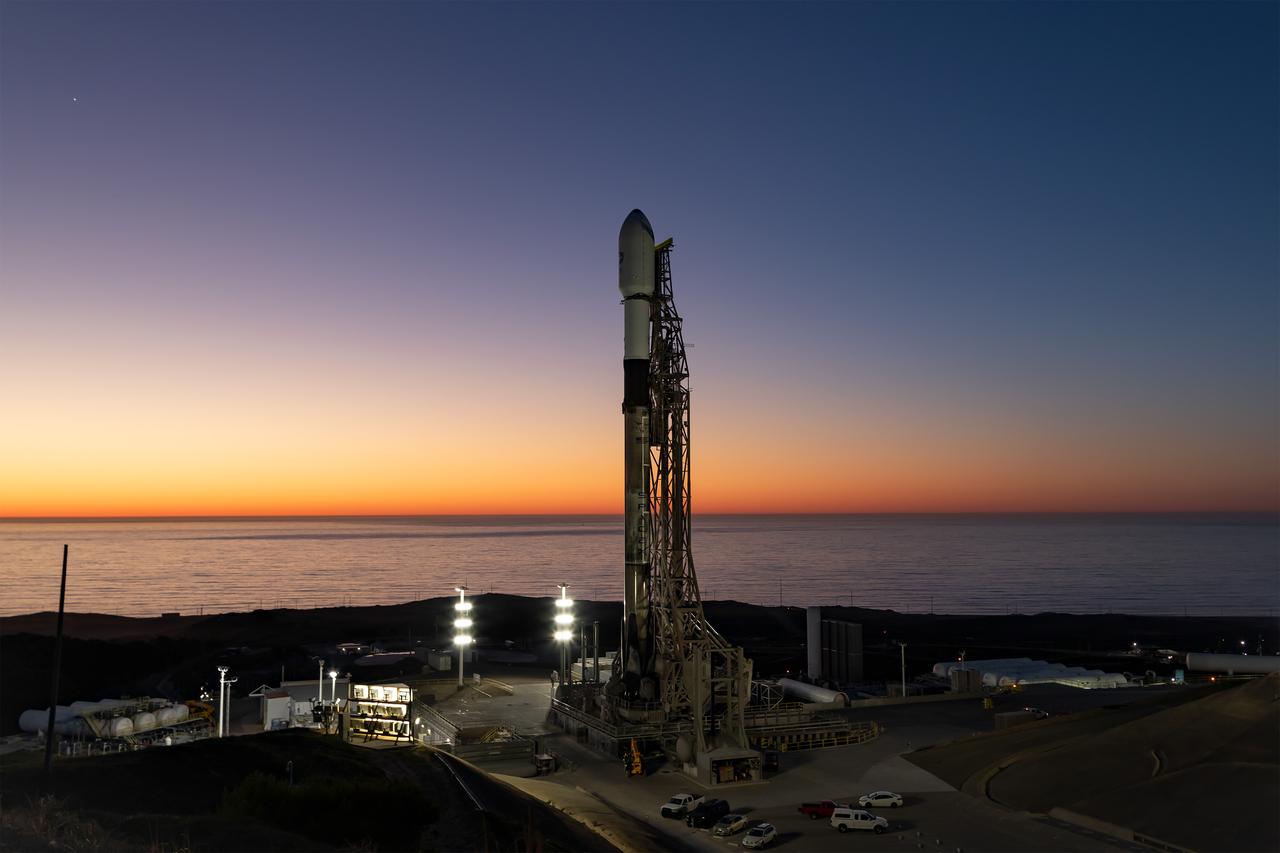

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, carrying NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory and PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites, is vertical at Space Launch Complex 4 East from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Saturday, March 8, 2025. SPHEREx will use its telescope to provide an all-sky spectral survey, creating a 3D map of the entire sky to help scientists investigate the origins of our universe. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system.
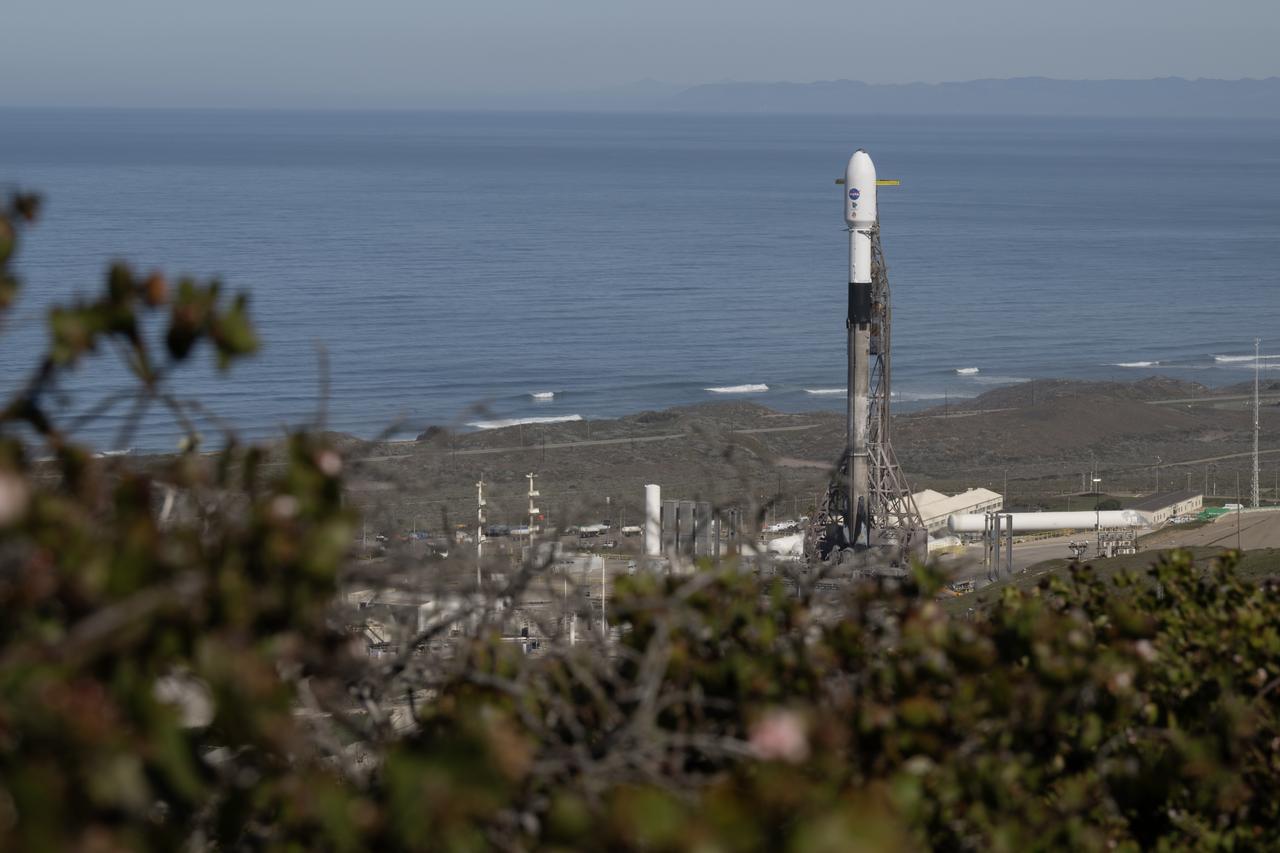

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, carrying NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory and PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites, is vertical at Space Launch Complex 4 East from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Saturday, March 8, 2025. SPHEREx will use its telescope to provide an all-sky spectral survey, creating a 3D map of the entire sky to help scientists investigate the origins of our universe. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system.
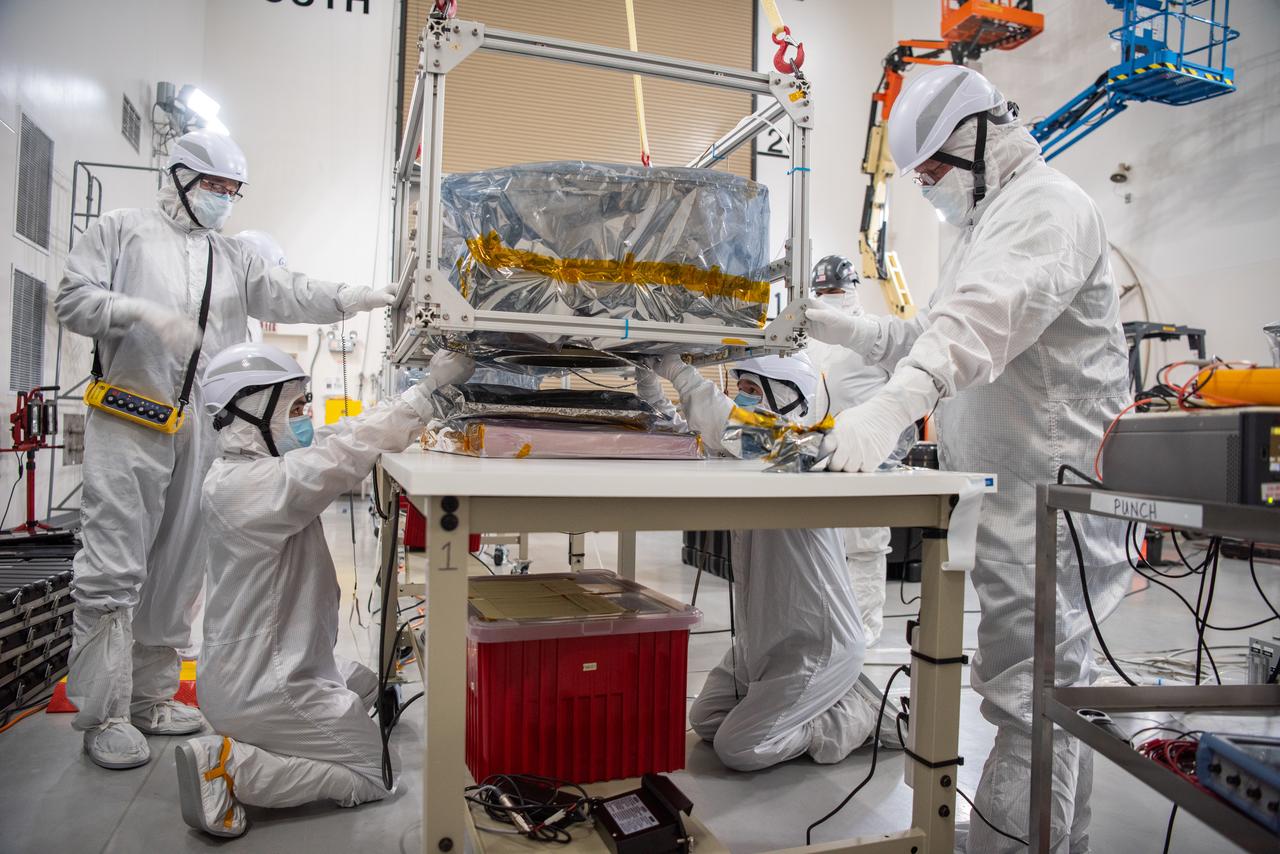

Technicians use an overheard crane to lift NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) spacecraft onto a work stand for testing operations at the Astrotech Processing Facility on Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Sunday, Jan. 19, 2025. PUNCH, consisting of four satellites, will produce continuous 3D images of the solar wind and solar storms as it travels from the Sun to Earth to better understand how material in the corona accelerates to become the solar wind that fills the solar system. PUNCH will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.
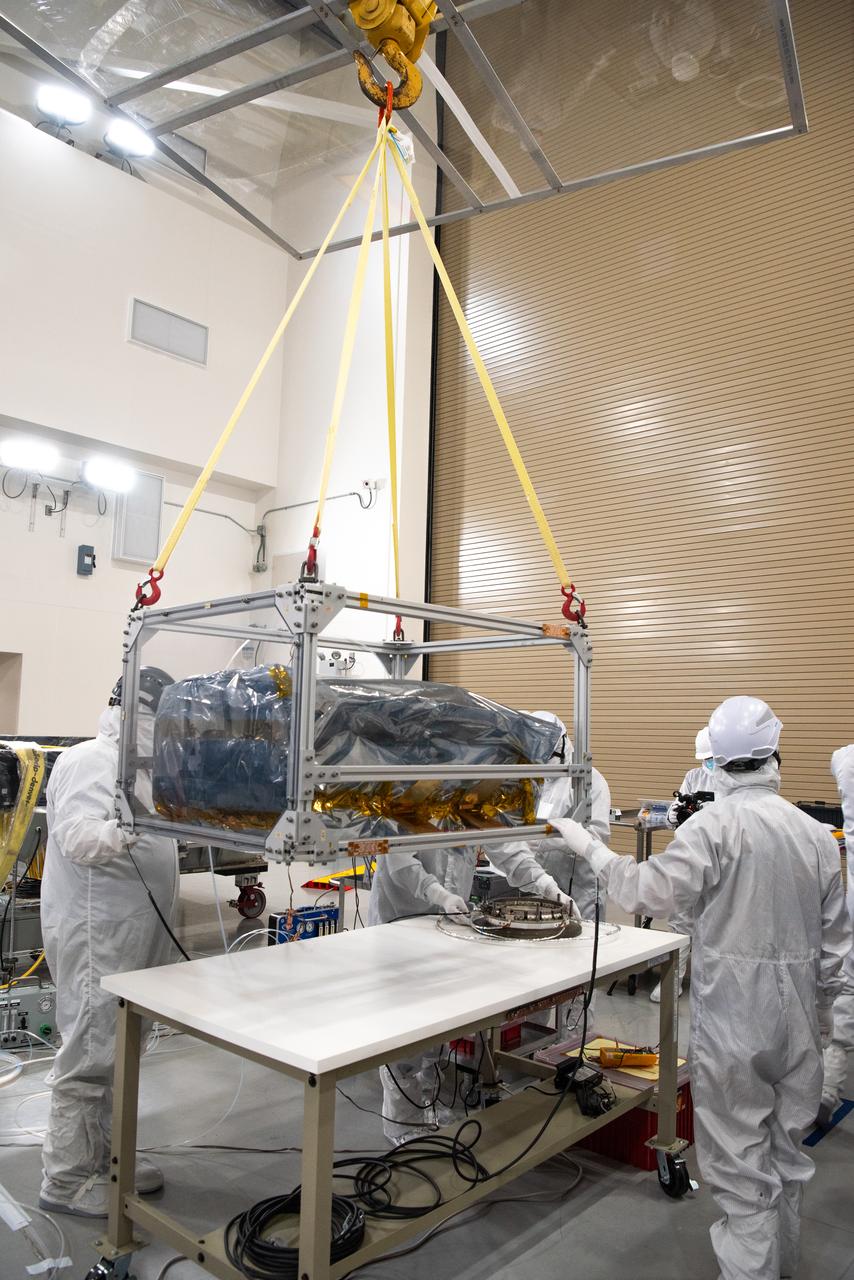

Technicians use an overheard crane to lift NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) spacecraft onto a work stand for testing operations at the Astrotech Processing Facility on Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Sunday, Jan. 19, 2025. PUNCH, consisting of four satellites, will produce continuous 3D images of the solar wind and solar storms as it travels from the Sun to Earth to better understand how material in the corona accelerates to become the solar wind that fills the solar system. PUNCH will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.
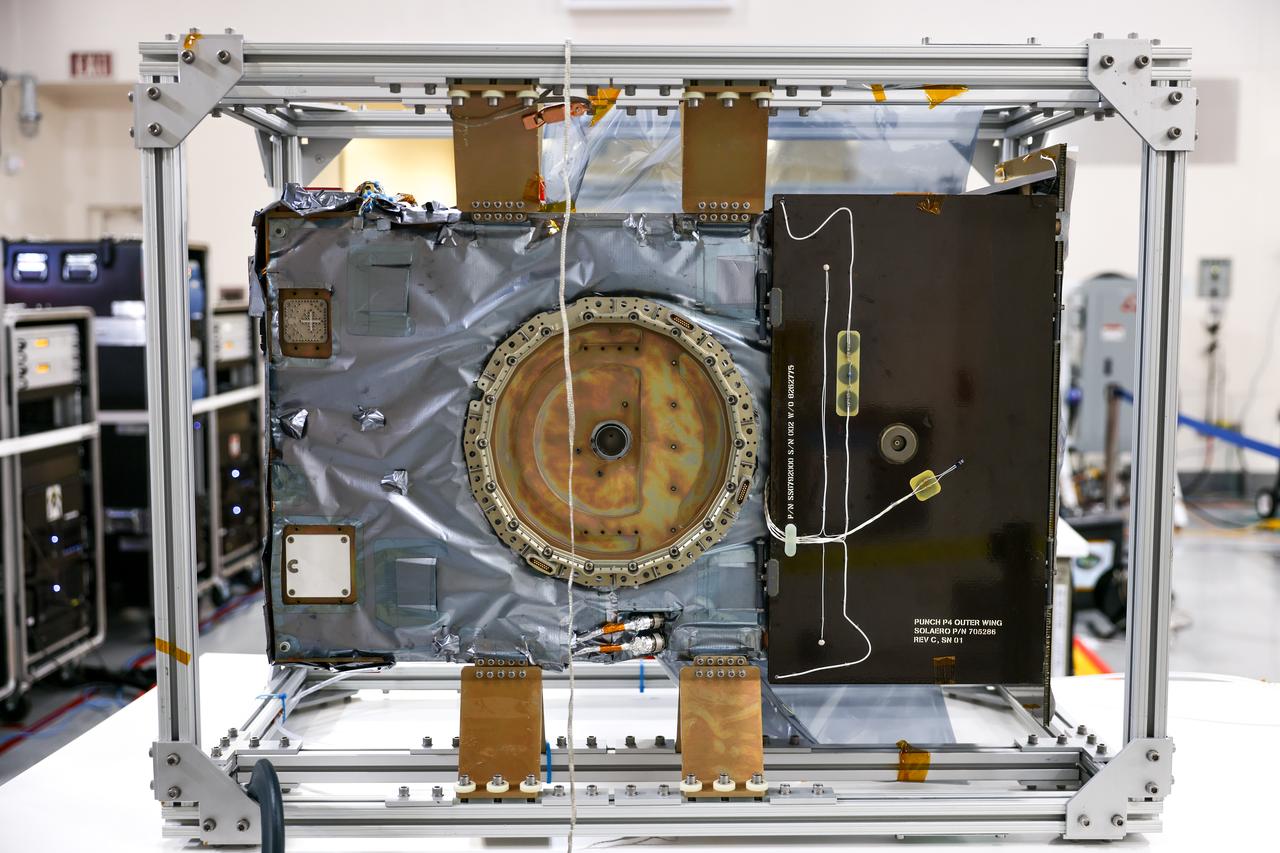
Crews conduct a solar array deployment test on the spacecraft of NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites at Astrotech Space Operations located on Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Tuesday, Jan. 21, 2025. The four satellites of PUNCH will make 3D observations of the Sun’s corona to learn how the mass and energy becomes solar wind. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.
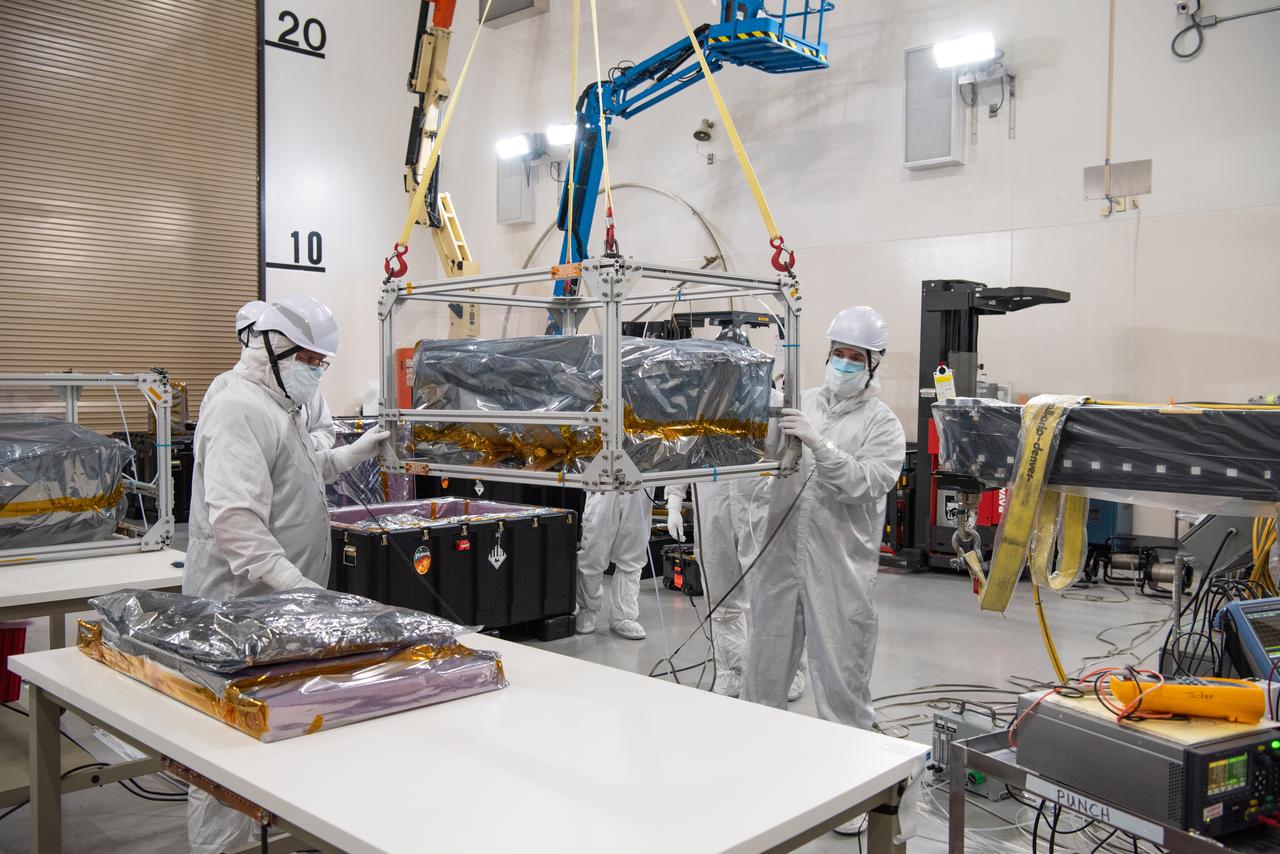

Technicians use an overheard crane to lift NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) spacecraft onto a work stand for testing operations at the Astrotech Processing Facility on Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Sunday, Jan. 19, 2025. PUNCH, consisting of four satellites, will produce continuous 3D images of the solar wind and solar storms as it travels from the Sun to Earth to better understand how material in the corona accelerates to become the solar wind that fills the solar system. PUNCH will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.
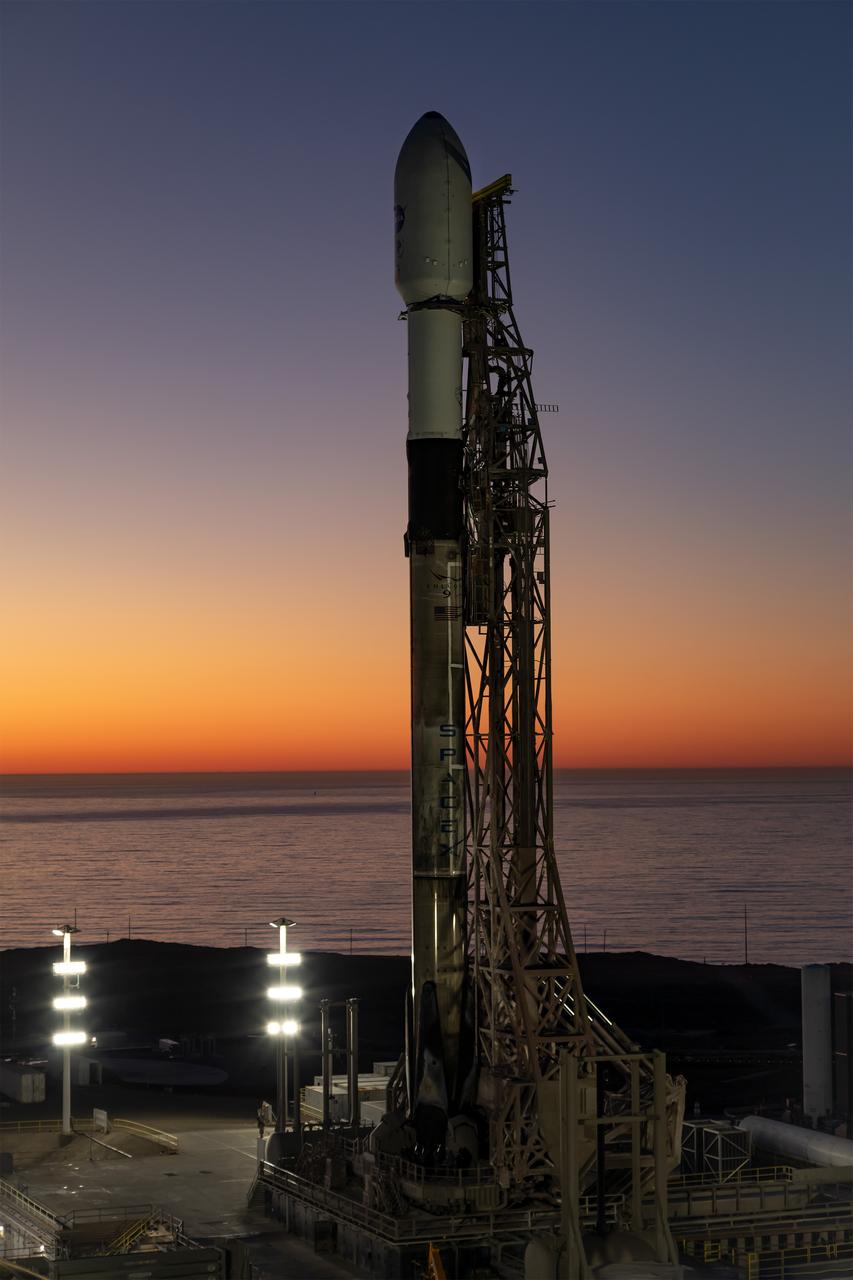

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, carrying NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory and PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites, is vertical at Space Launch Complex 4 East from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Saturday, March 8, 2025. SPHEREx will use its telescope to provide an all-sky spectral survey, creating a 3D map of the entire sky to help scientists investigate the origins of our universe. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system.
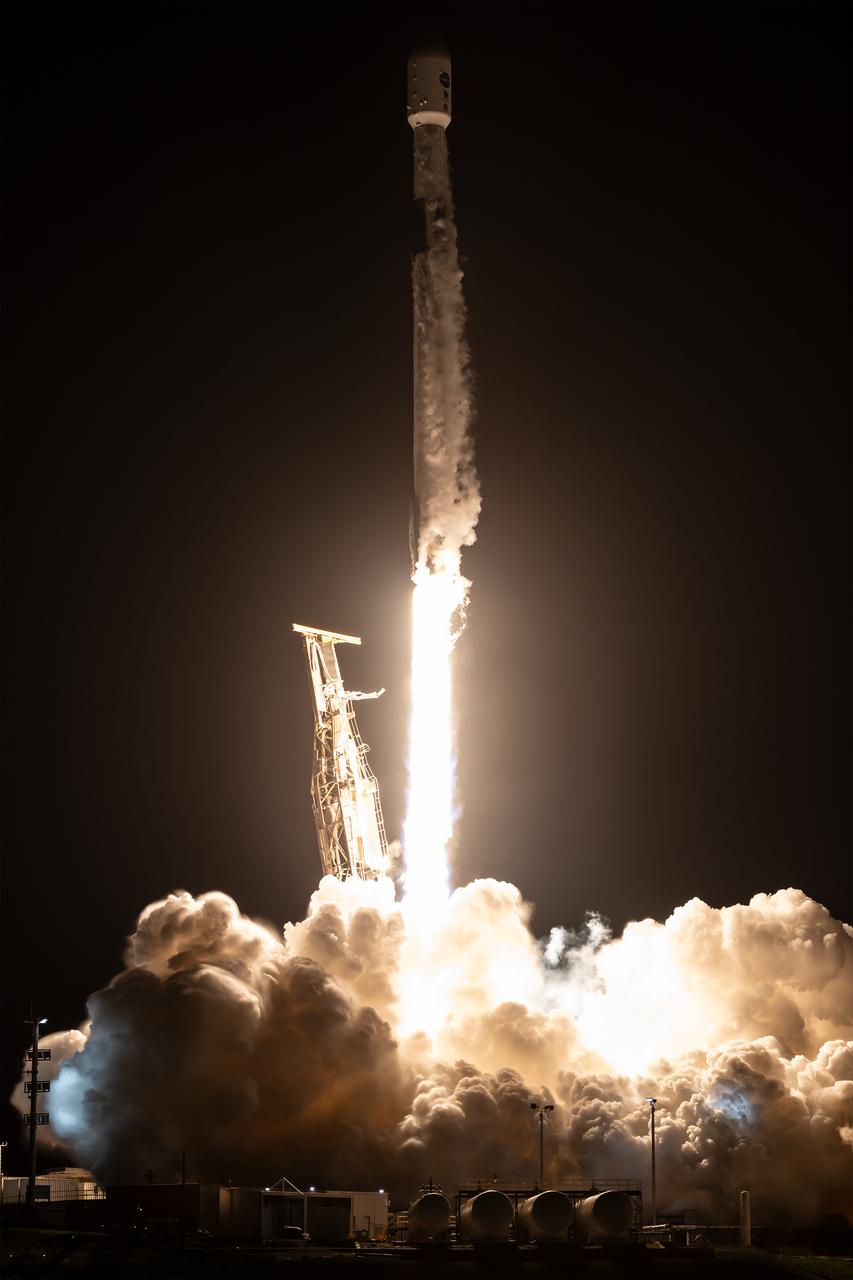

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, carrying NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory and PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites, launches from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Tuesday, March 11, 2025. SPHEREx will use its telescope to provide an all-sky spectral survey, creating a 3D map of the entire sky to help scientists investigate the origins of our universe. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system.
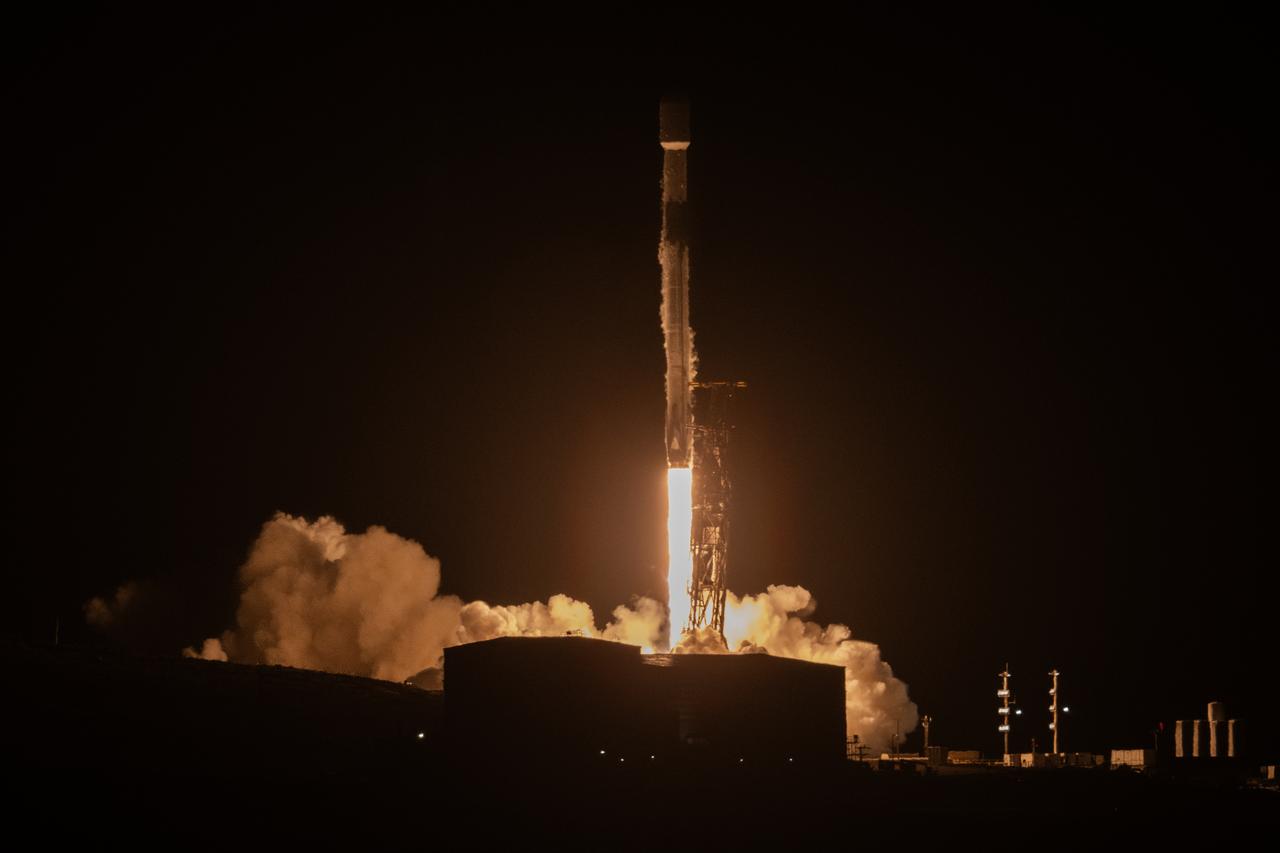

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, carrying NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory and PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites, launches from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Tuesday, March 11, 2025. SPHEREx will use its telescope to provide an all-sky spectral survey, creating a 3D map of the entire sky to help scientists investigate the origins of our universe. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system.
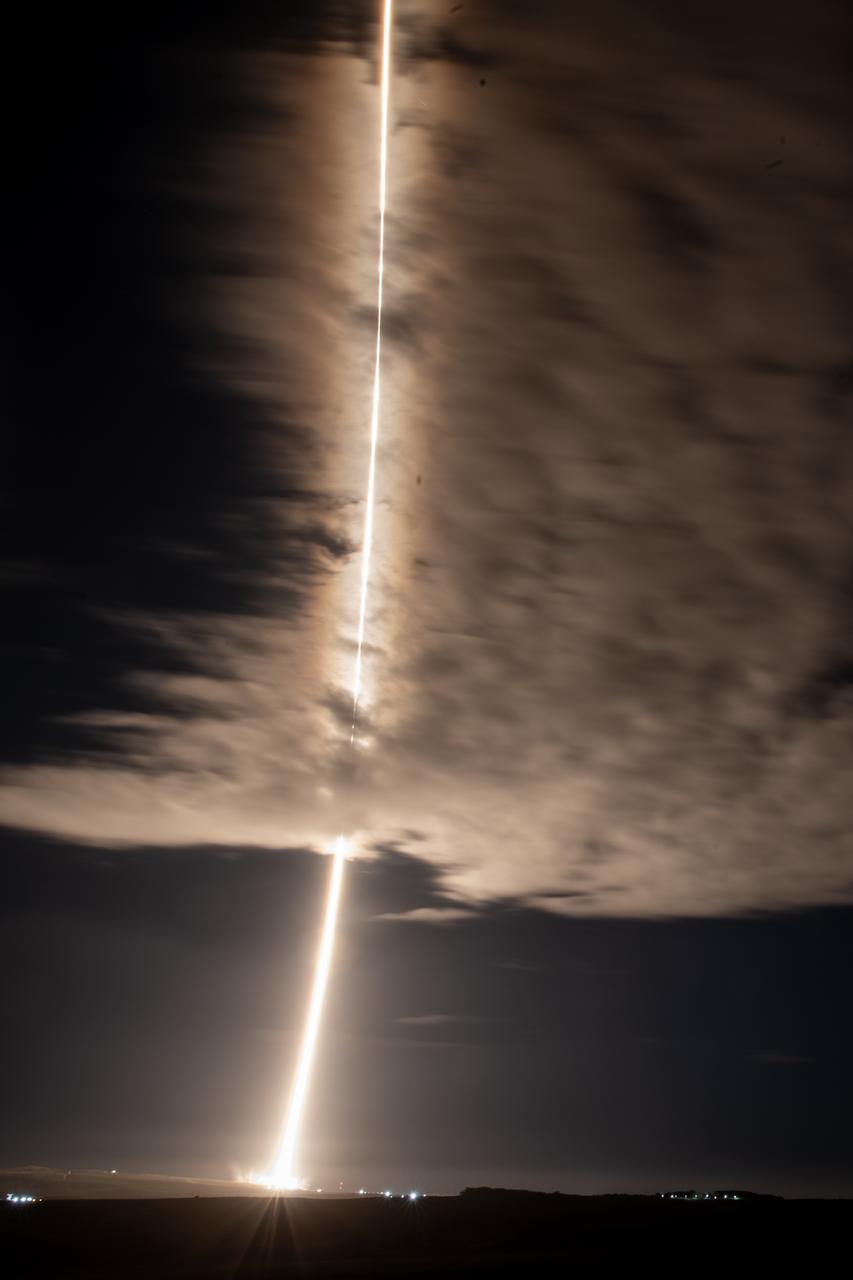

A streak lights up the sky following the launch of NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory and PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites at Space Launch Complex 4 East from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Tuesday, March 11, 2025. SPHEREx will use its telescope to provide an all-sky spectral survey, creating a 3D map of the entire sky to help scientists investigate the origins of our universe. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system.
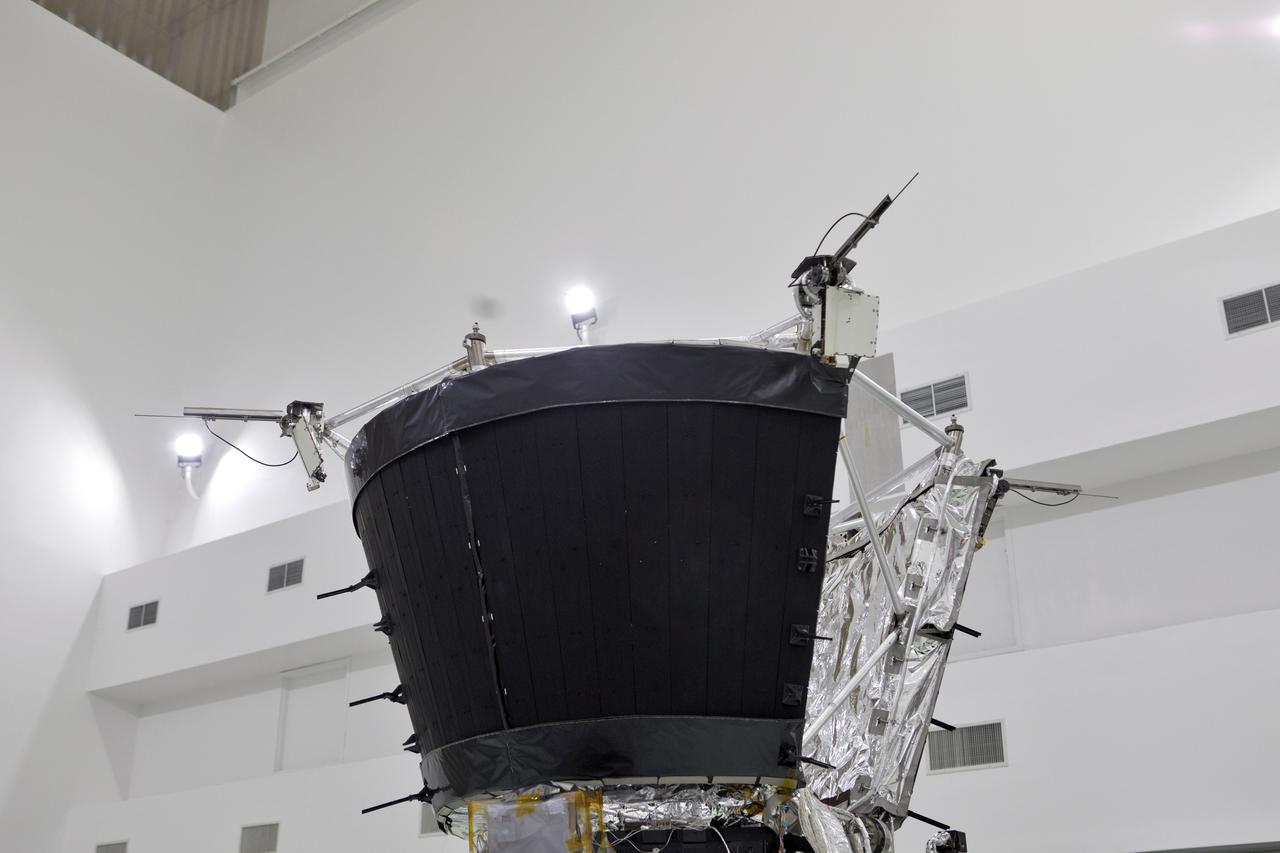

Antenna's on NASA's Parker Solar Probe are deployed for testing at the Astrotech processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near NASA's Kennedy Space Center on Thursday, April 19, 2018. The Parker Solar Probe will launch on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida no earlier than Aug. 4, 2018. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
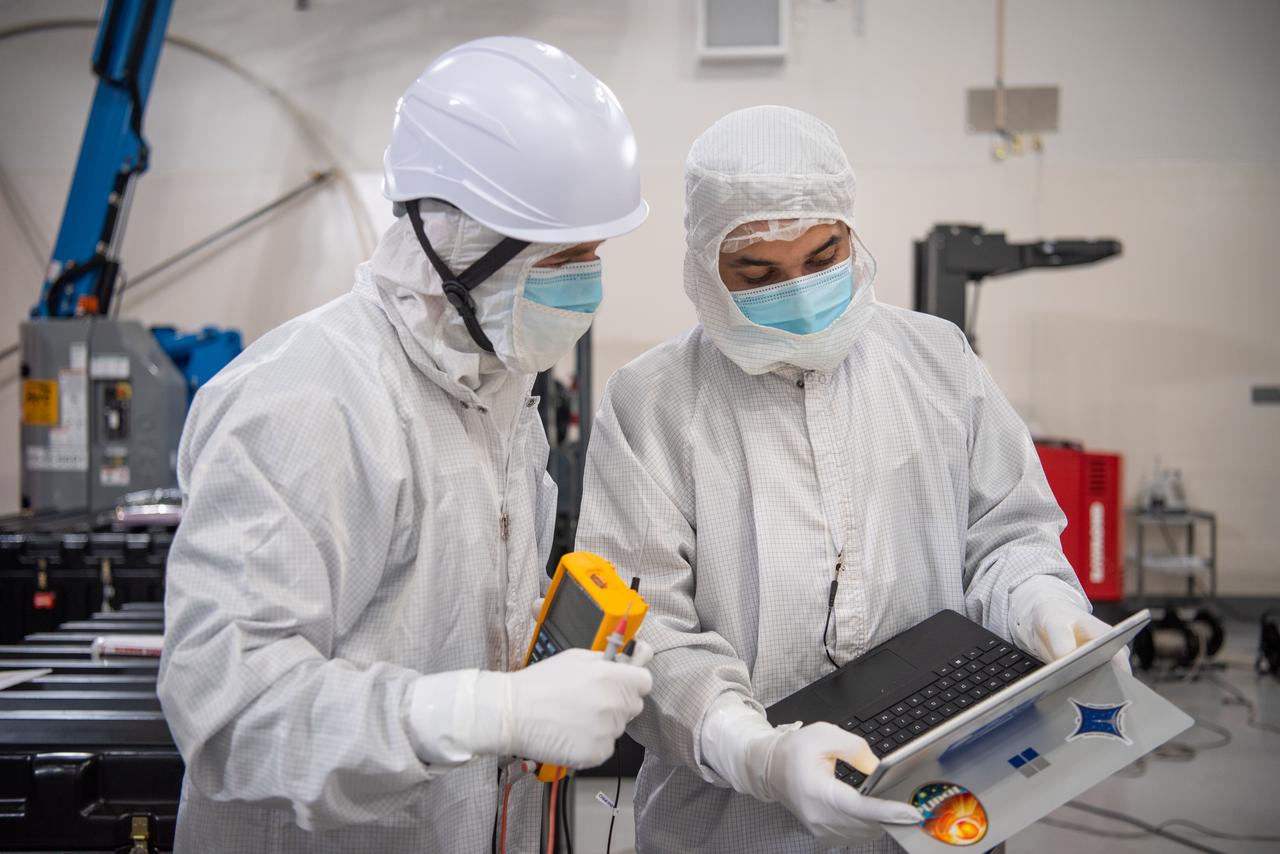

Technicians conduct testing operations on NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) spacecraft onto a work stand for testing operations at the Astrotech Processing Facility on Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Sunday, Jan. 19, 2025. PUNCH, consisting of four satellites, will produce continuous 3D images of the solar wind and solar storms as it travels from the Sun to Earth to better understand how material in the corona accelerates to become the solar wind that fills the solar system. PUNCH will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.
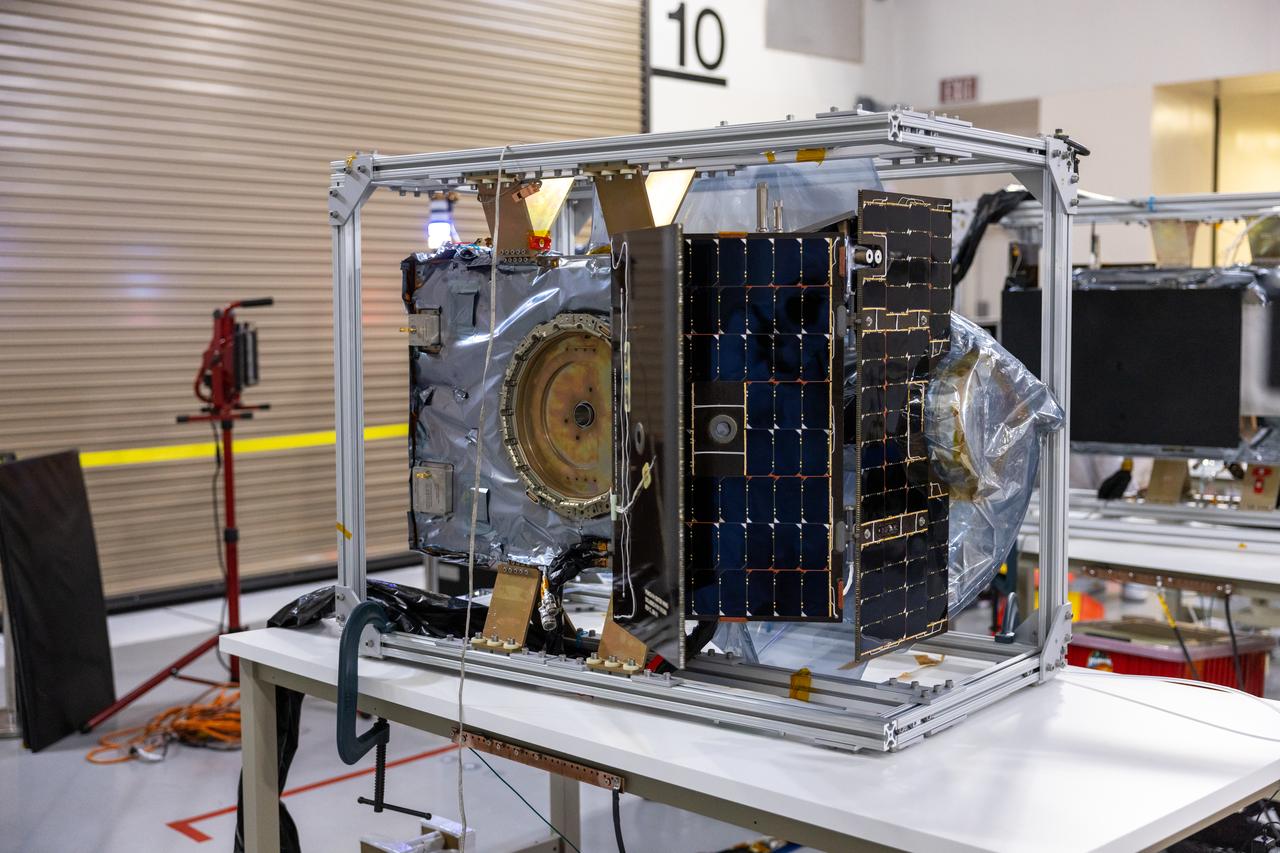

Crews conduct additional solar array deployment testing for NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites at Astrotech Space Operations located on Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Wednesday, Jan. 22, 2025. PUNCH, consisting of four satellites, will produce continuous 3D images of the solar wind and solar storms as it travels from the Sun to Earth to better understand how material in the corona accelerates. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in Central California on Thursday, Feb. 27, 2025.
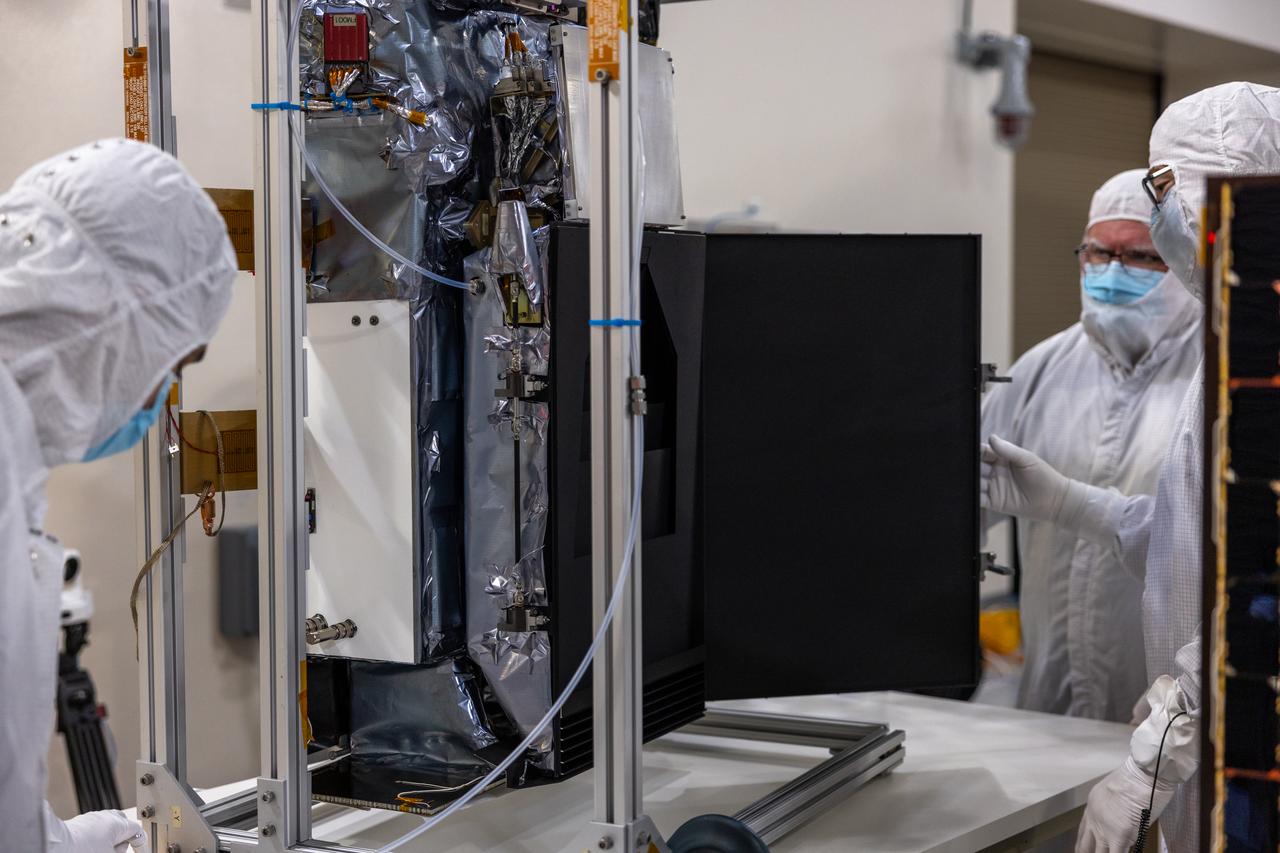

Crews conduct additional solar array deployment testing for NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites at Astrotech Space Operations located on Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Wednesday, Jan. 22, 2025. PUNCH, consisting of four satellites, will produce continuous 3D images of the solar wind and solar storms as it travels from the Sun to Earth to better understand how material in the corona accelerates. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in Central California on Thursday, Feb. 27, 2025.
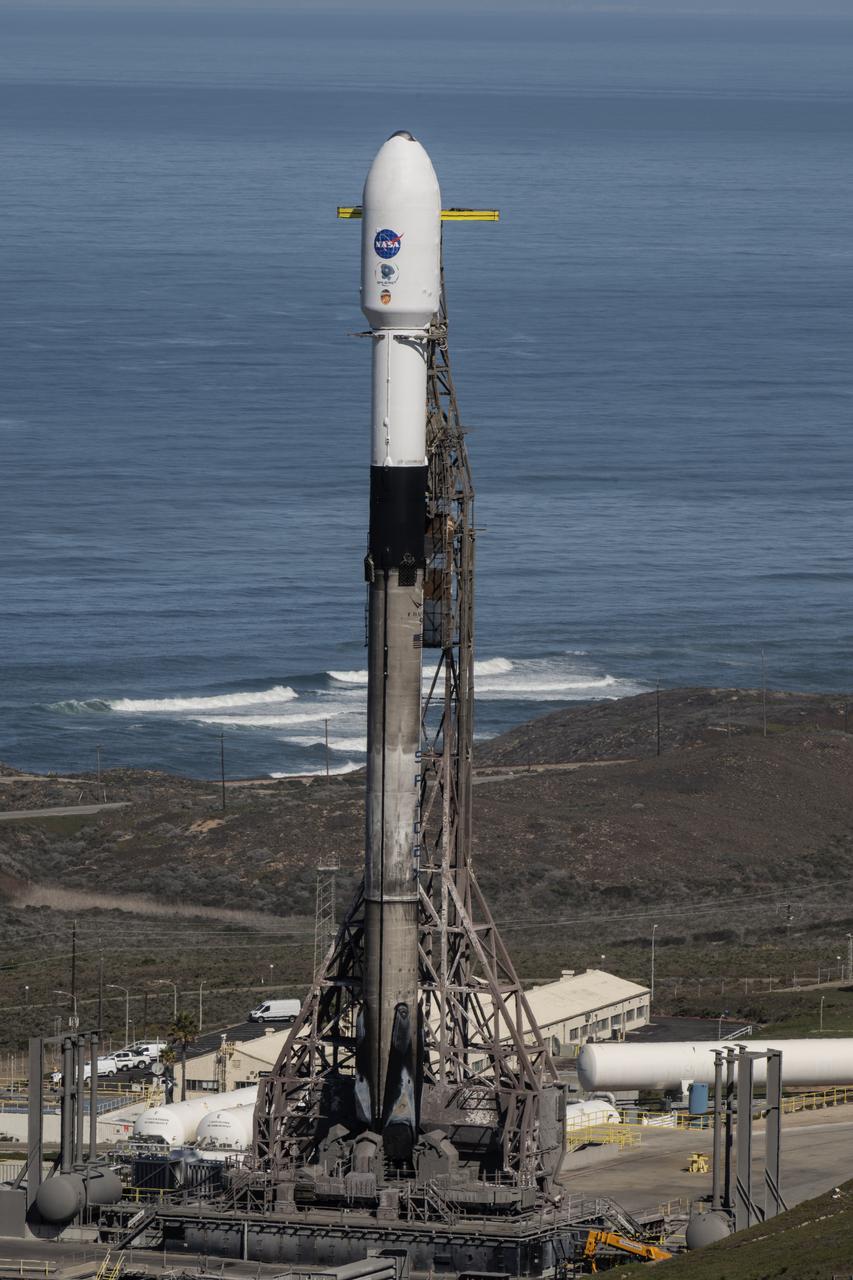

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, carrying NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory and PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites, is vertical at Space Launch Complex 4 East from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Saturday, March 8, 2025. SPHEREx will use its telescope to provide an all-sky spectral survey, creating a 3D map of the entire sky to help scientists investigate the origins of our universe. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system.

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, carrying NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory and PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites, launches from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Tuesday, March 11, 2025. SPHEREx will use its telescope to provide an all-sky spectral survey, creating a 3D map of the entire sky to help scientists investigate the origins of our universe. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system.
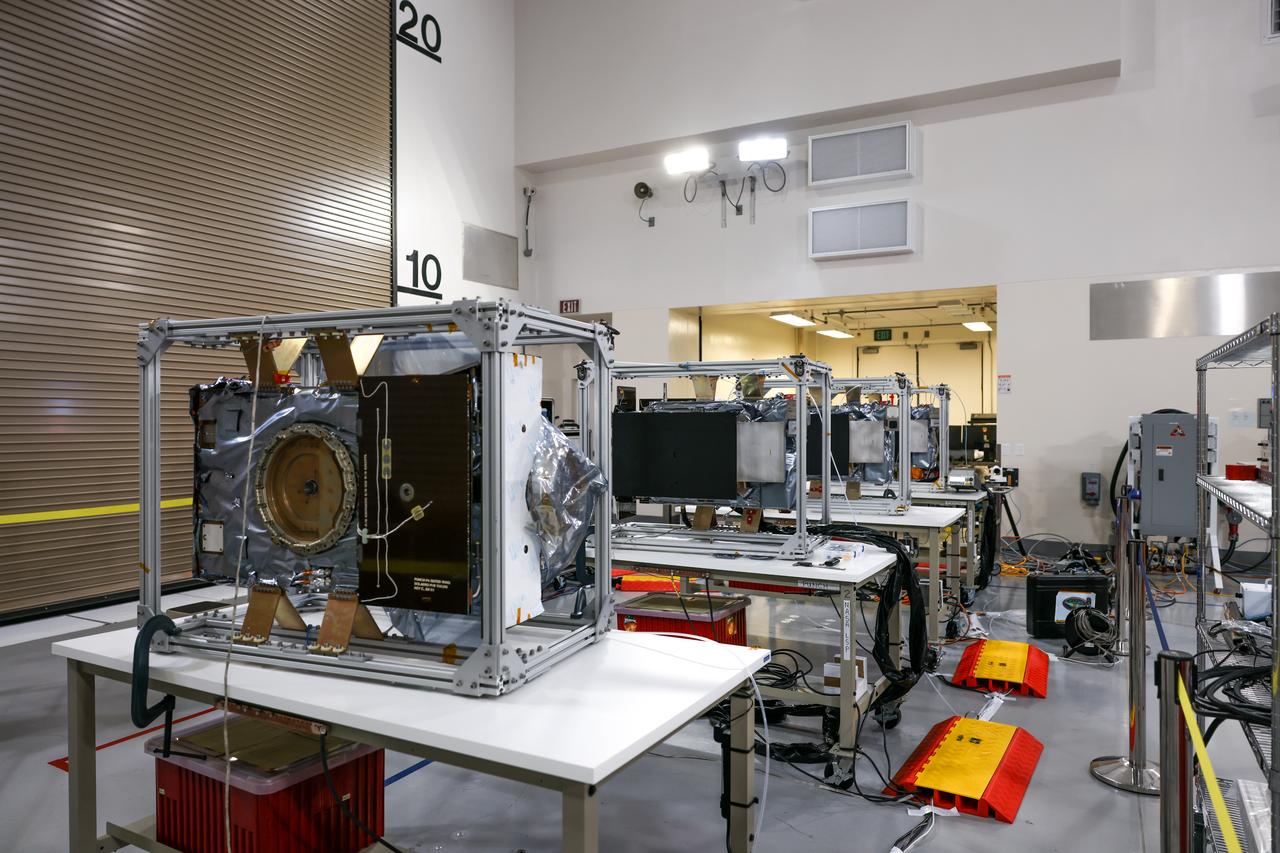

Crews conduct a solar array deployment test on the spacecraft of NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites at Astrotech Space Operations located on Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Tuesday, Jan. 21, 2025. The four satellites of PUNCH will make 3D observations of the Sun’s corona to learn how the mass and energy becomes solar wind. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.
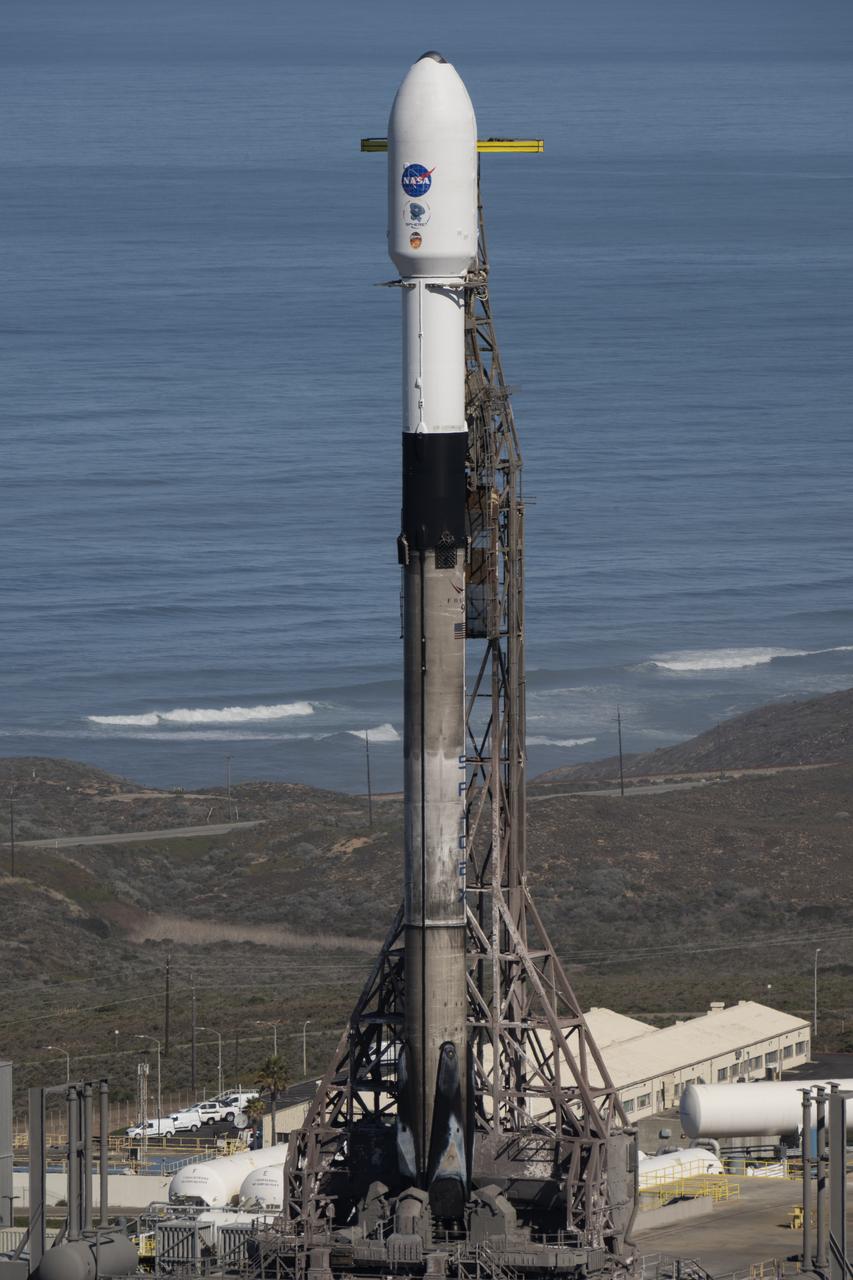

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, carrying NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) observatory and PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites, is vertical at Space Launch Complex 4 East from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Saturday, March 8, 2025. SPHEREx will use its telescope to provide an all-sky spectral survey, creating a 3D map of the entire sky to help scientists investigate the origins of our universe. PUNCH will study origins of the Sun’s outflow of material, or the solar wind, capturing continuous 3D images of the Sun’s corona and the solar wind’s journey into the solar system.
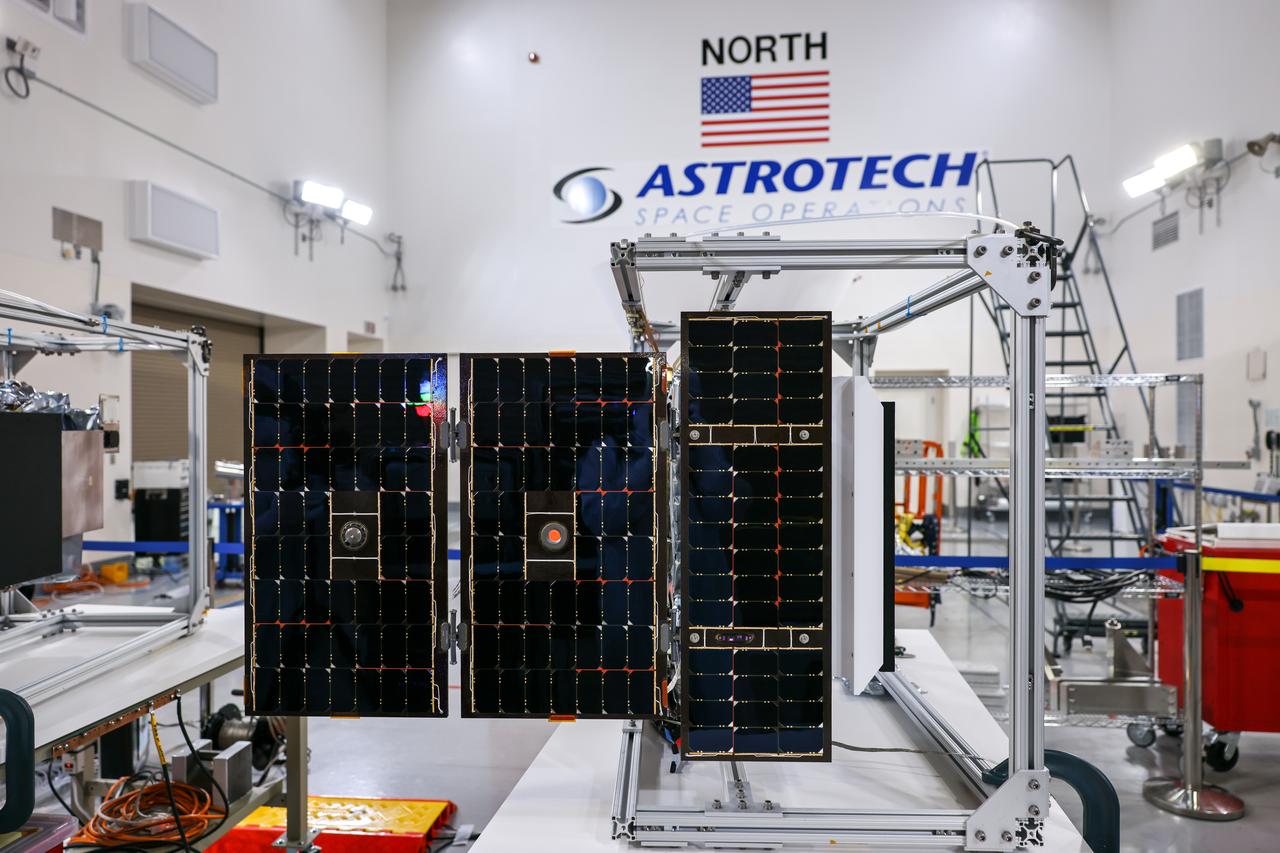

Crews conduct a solar array deployment test on the spacecraft of NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) satellites at Astrotech Space Operations located on Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Tuesday, Jan. 21, 2025. The four satellites of PUNCH will make 3D observations of the Sun’s corona to learn how the mass and energy becomes solar wind. PUNCH, along with NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer), a space telescope, will launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in late February 2025.