
CRS-17 Payload STP-H6 move to SpaceX

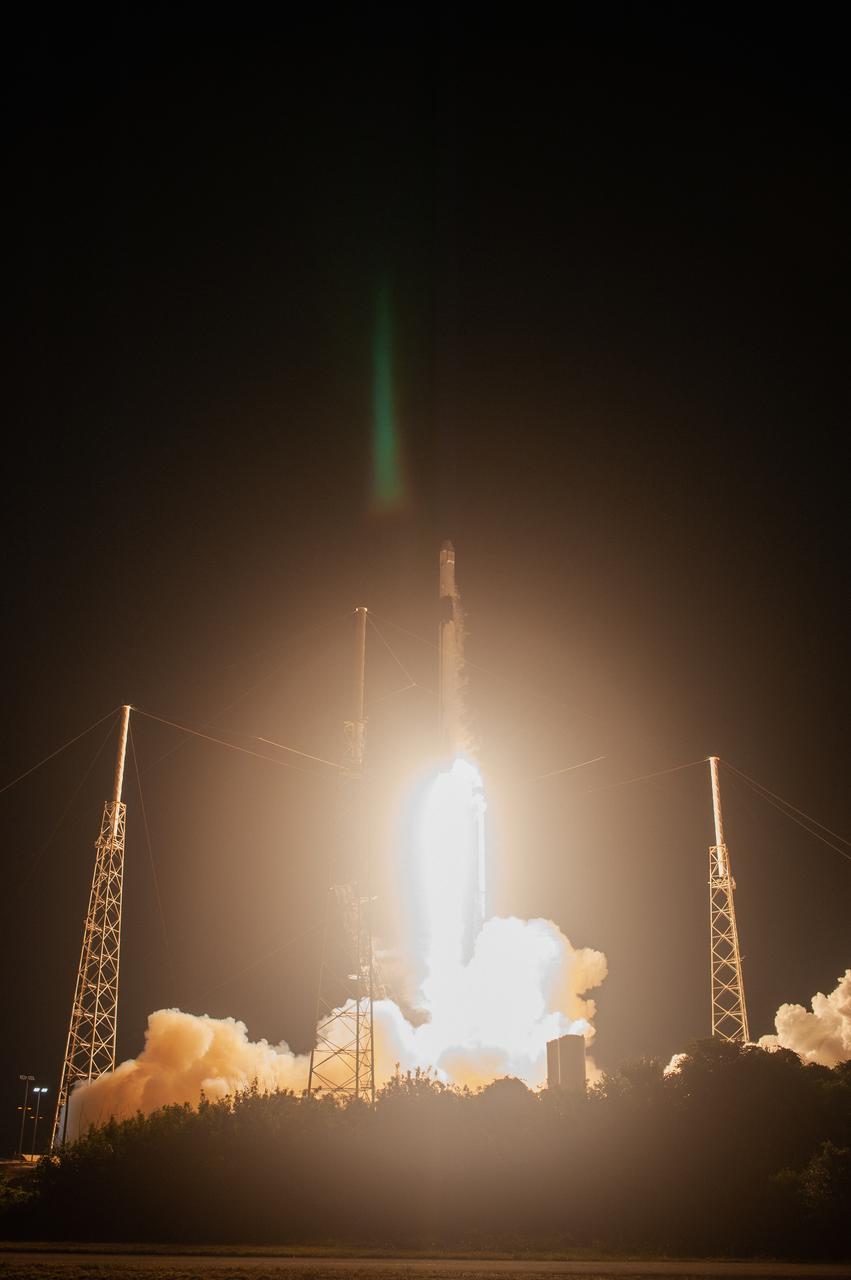
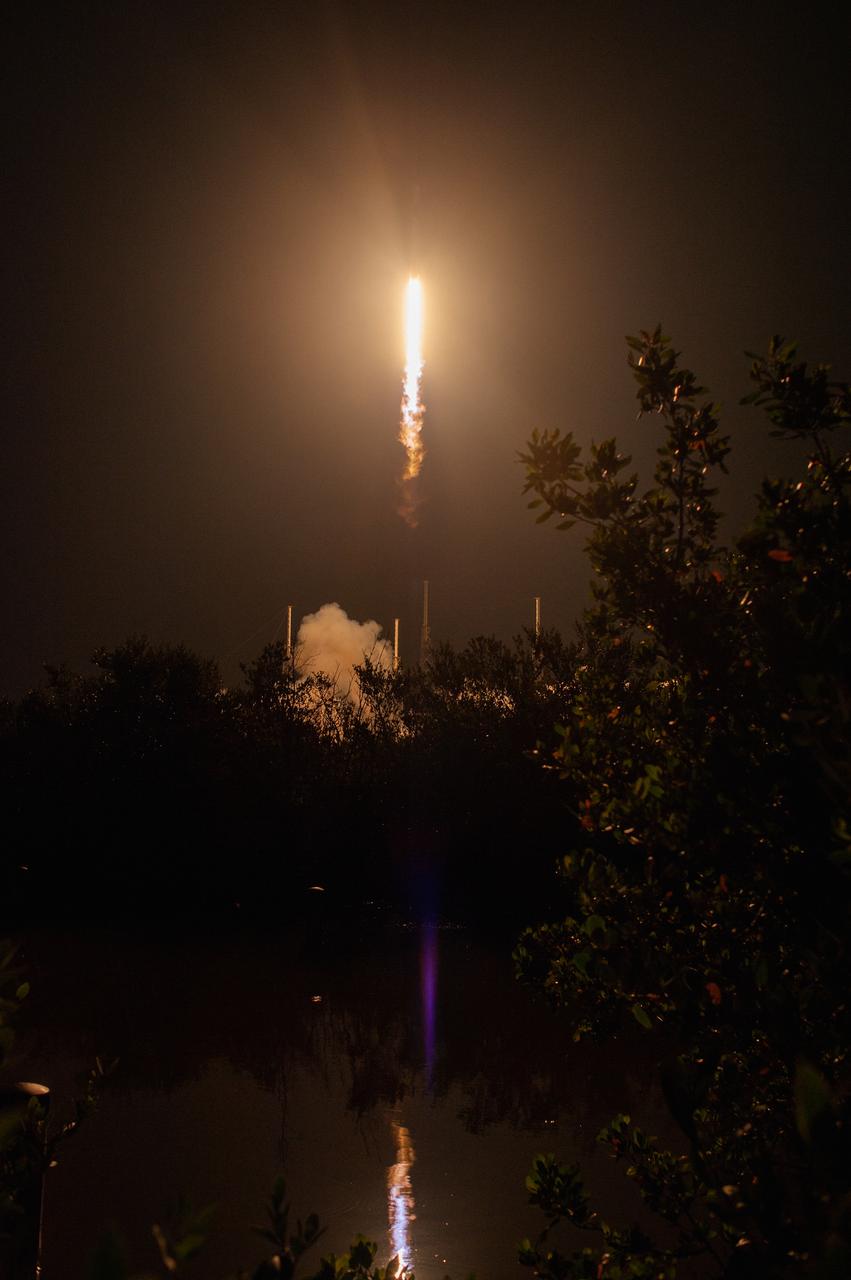
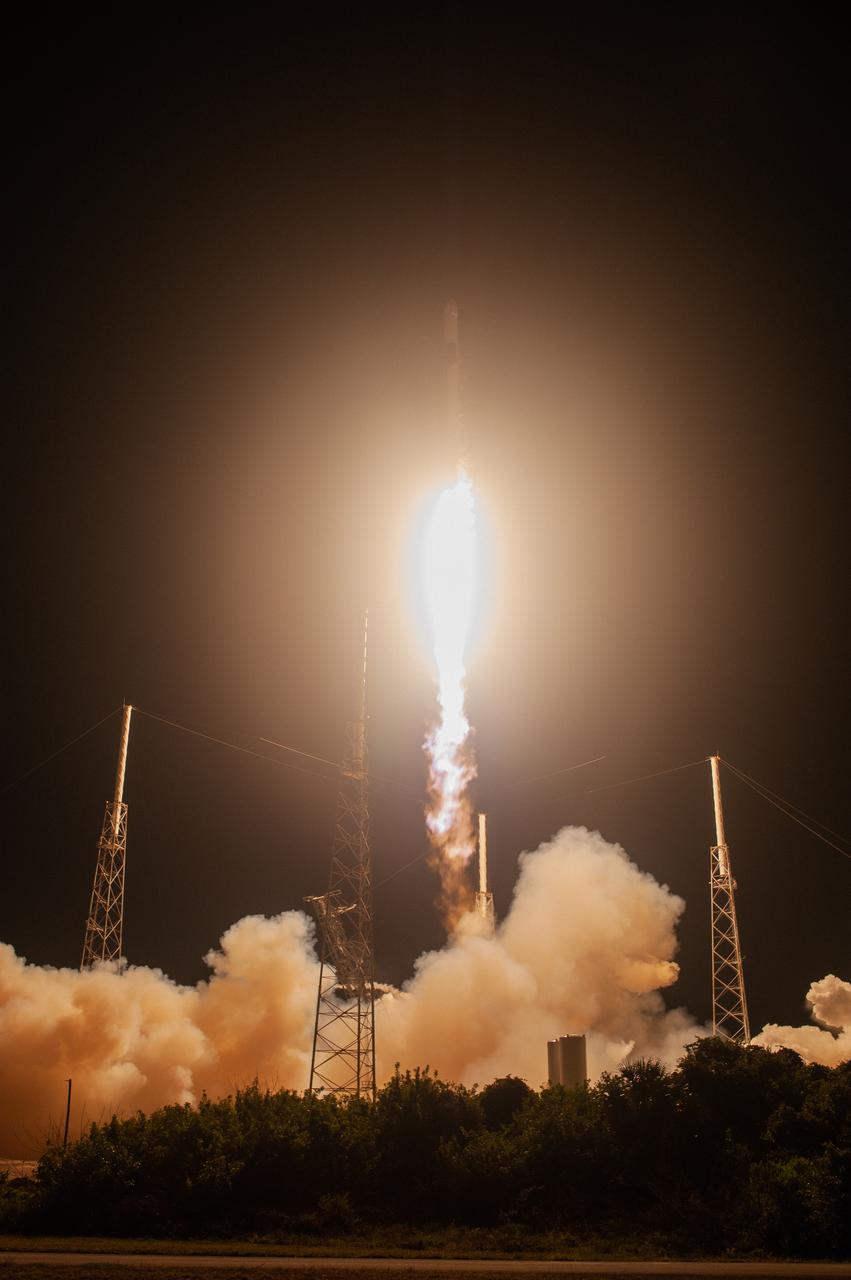
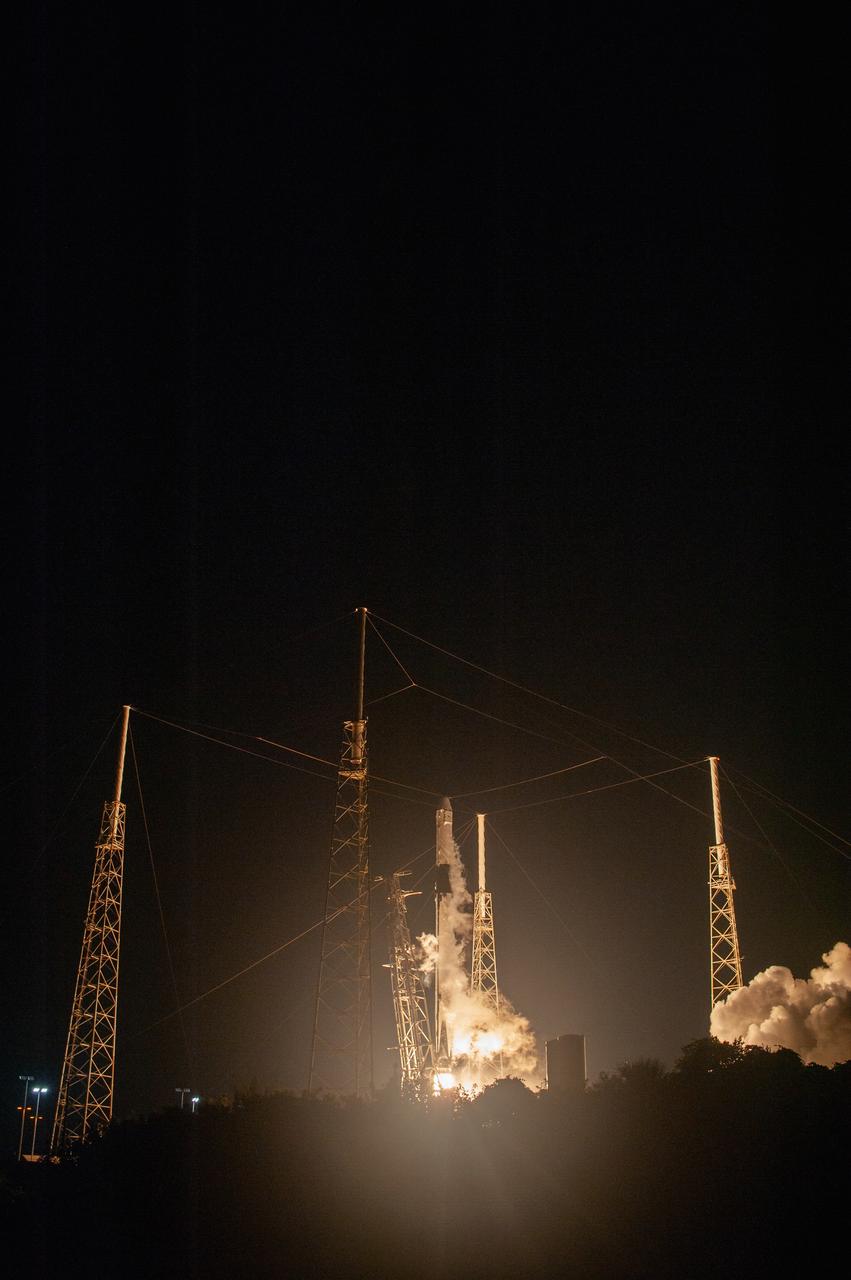
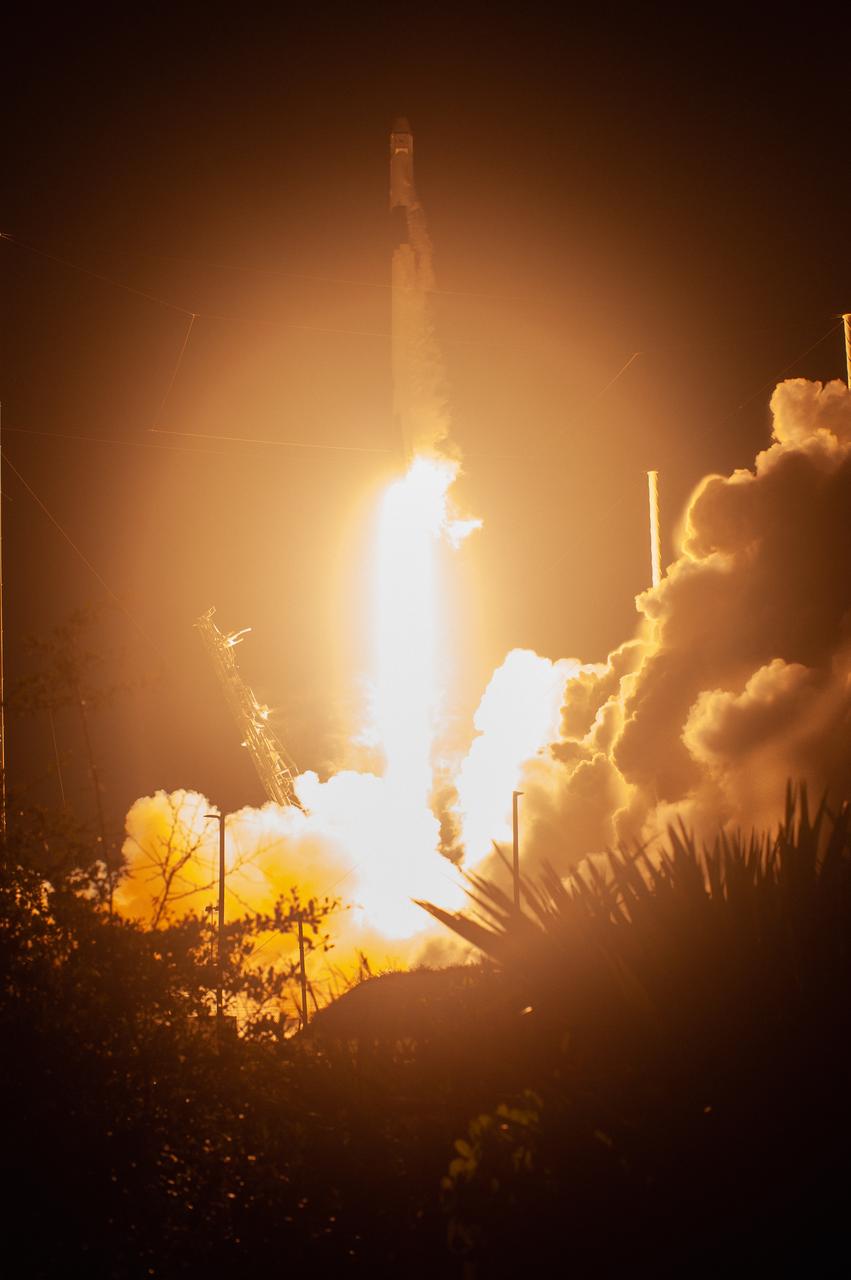
The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module climbs upward after liftoff from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in the early morning May 4, 2019. Liftoff was at 2:48 a.m. EDT. This is SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.
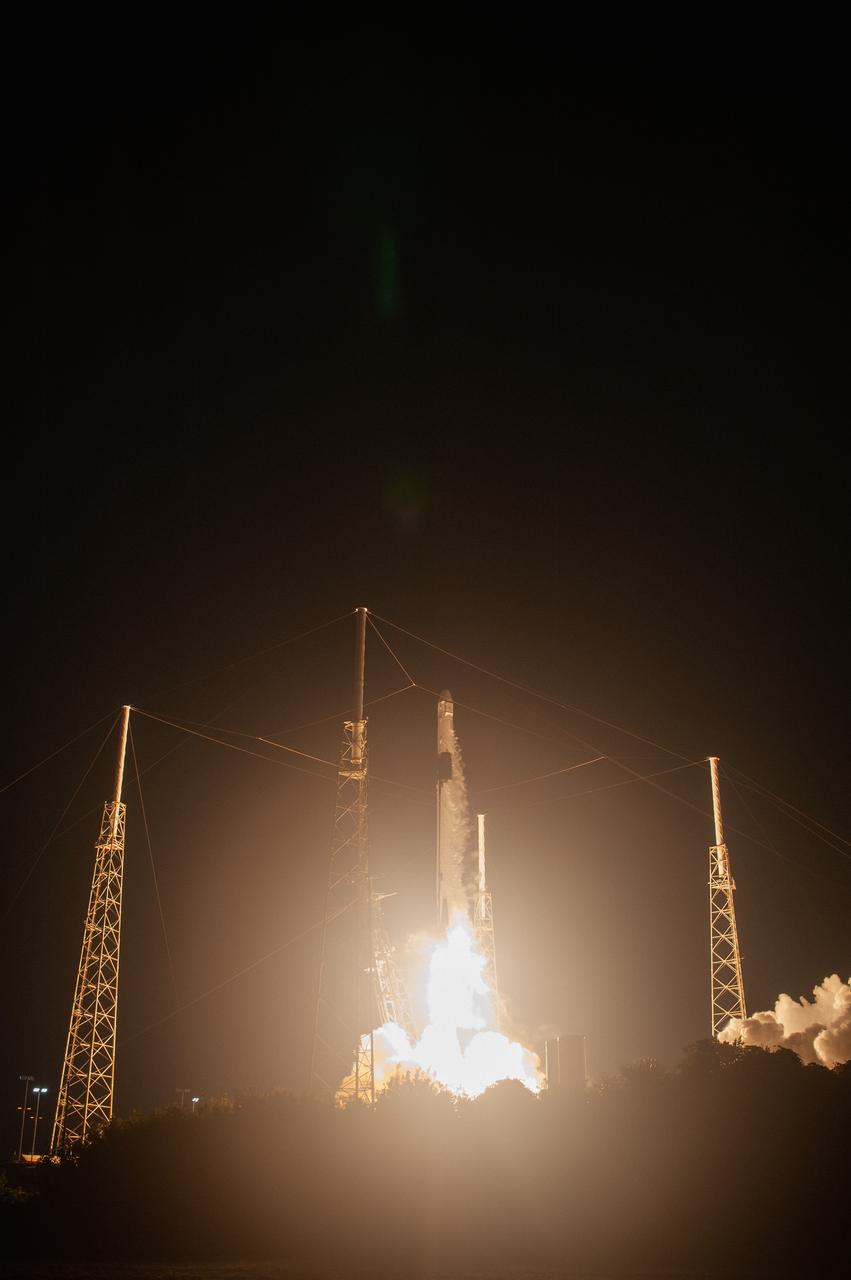

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module lifts off Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in the early morning May 4, 2019. Liftoff was at 2:48 a.m. EDT. This is SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module climbs upward after liftoff from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in the early morning May 4, 2019. Liftoff was at 2:48 a.m. EDT. This is SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.

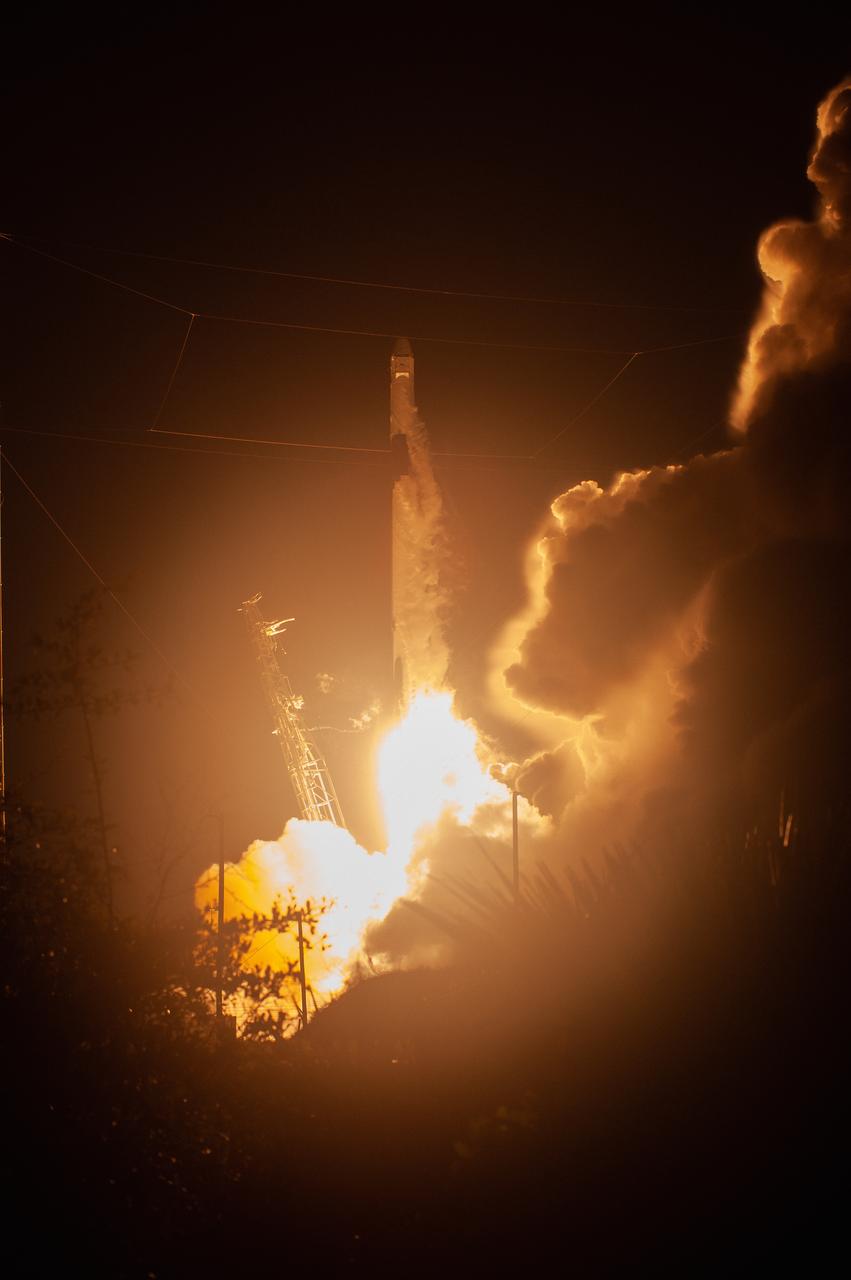
The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module lifts off Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in the early morning May 4, 2019. Liftoff was at 2:48 a.m. EDT. This is SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module lifts off Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in the early morning May 4, 2019. Liftoff was at 2:48 a.m. EDT. This is SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.

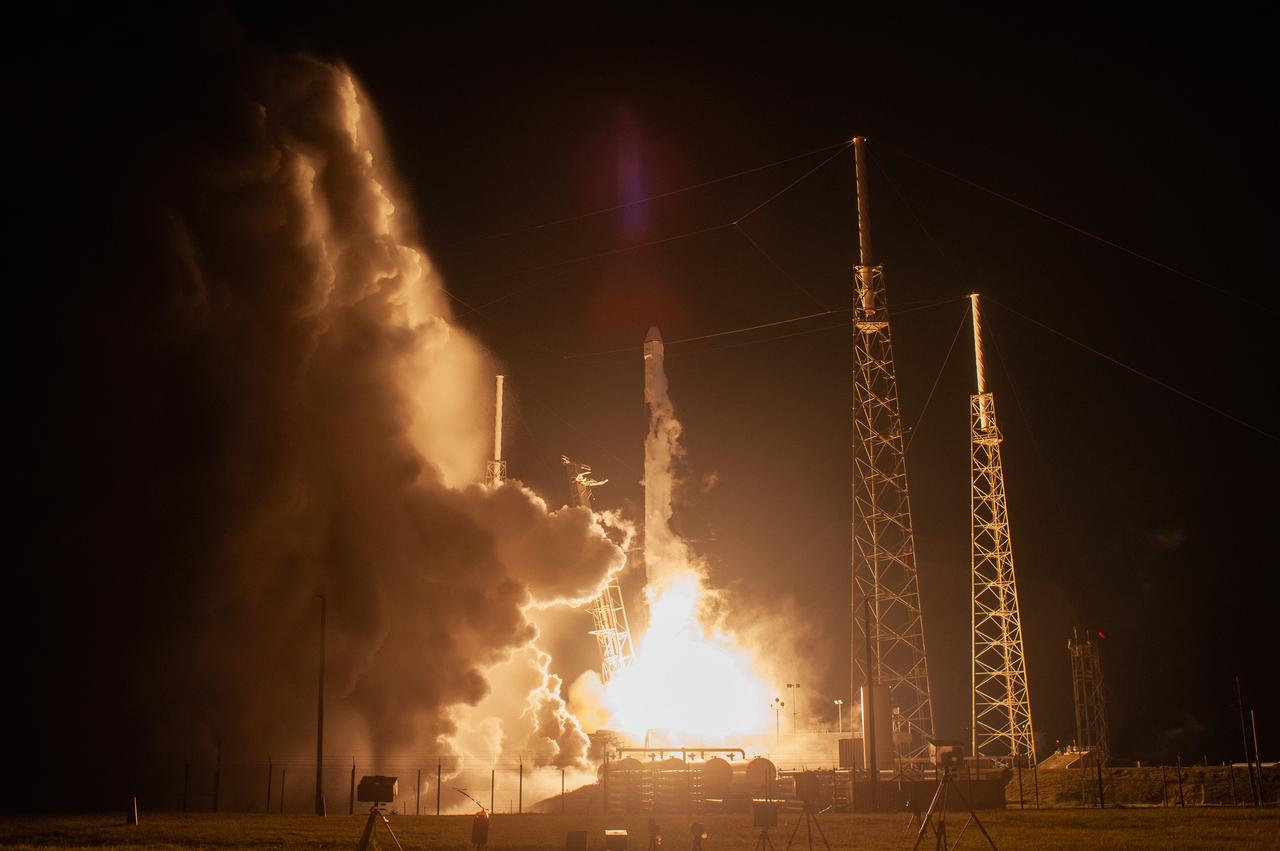
The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module climbs upward after liftoff from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in the early morning May 4, 2019. Liftoff was at 2:48 a.m. EDT. This is SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module climbs upward after liftoff from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in the early morning May 4, 2019. Liftoff was at 2:48 a.m. EDT. This is SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module climbs upward after liftoff from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in the early morning May 4, 2019. Liftoff was at 2:48 a.m. EDT. This is SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module lifts off Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in the early morning May 4, 2019. Liftoff was at 2:48 a.m. EDT. This is SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module climbs upward after liftoff from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in the early morning May 4, 2019. Liftoff was at 2:48 a.m. EDT. This is SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module lifts off Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in the early morning May 4, 2019. Liftoff was at 2:48 a.m. EDT. This is SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.
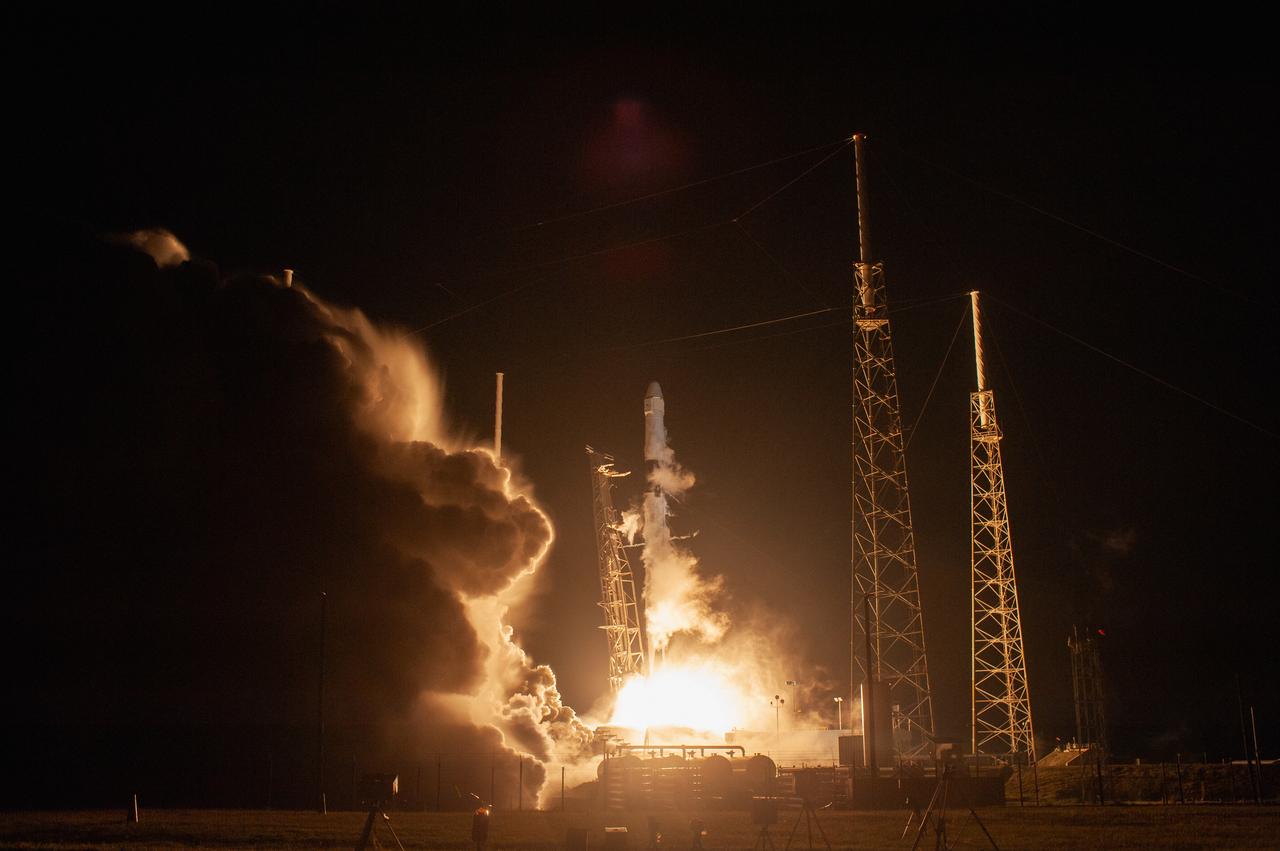

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module lifts off Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in the early morning May 4, 2019. Liftoff was at 2:48 a.m. EDT. This is SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.
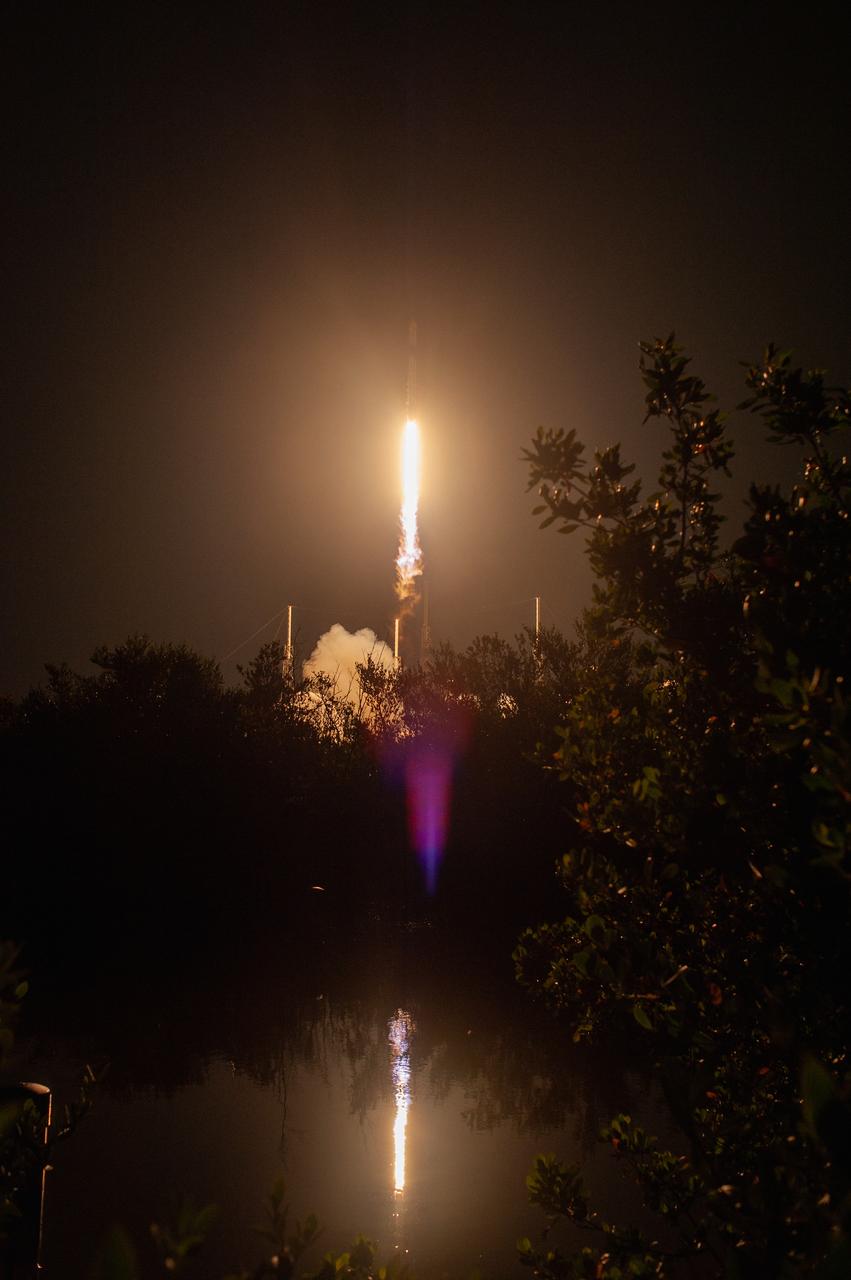

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module climbs upward after liftoff from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in the early morning May 4, 2019. Liftoff was at 2:48 a.m. EDT. This is SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.
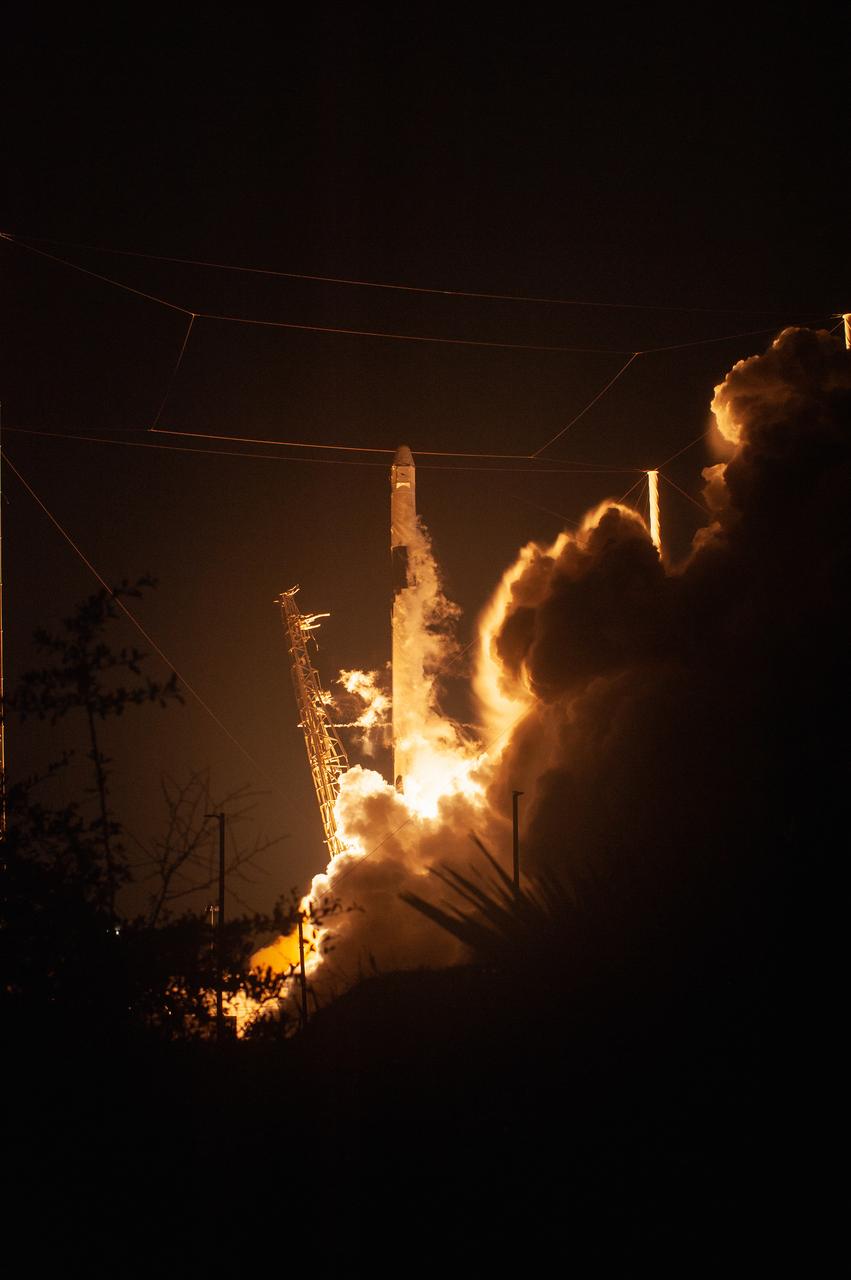

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module climbs upward after liftoff from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in the early morning May 4, 2019. Liftoff was at 2:48 a.m. EDT. This is SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.
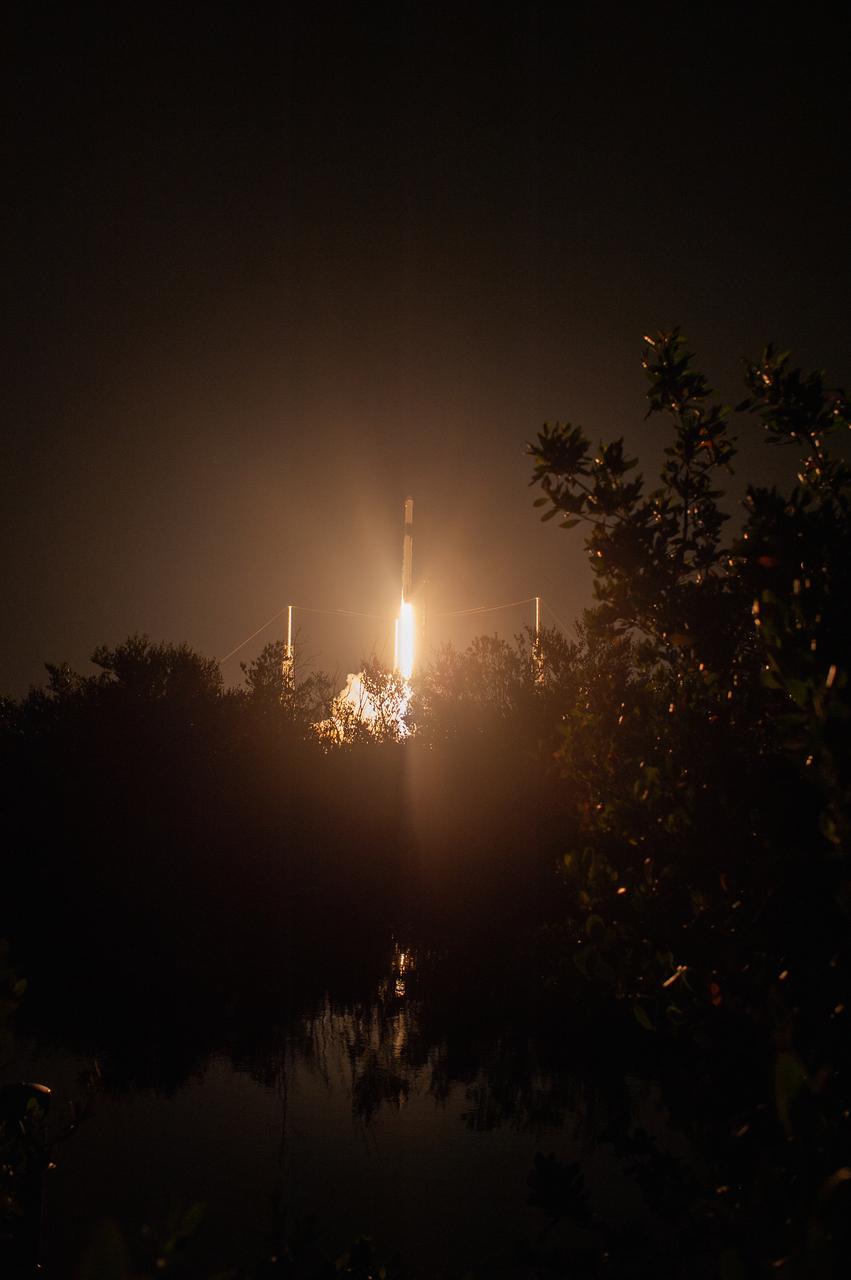

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module lifts off Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in the early morning May 4, 2019. Liftoff was at 2:48 a.m. EDT. This is SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.
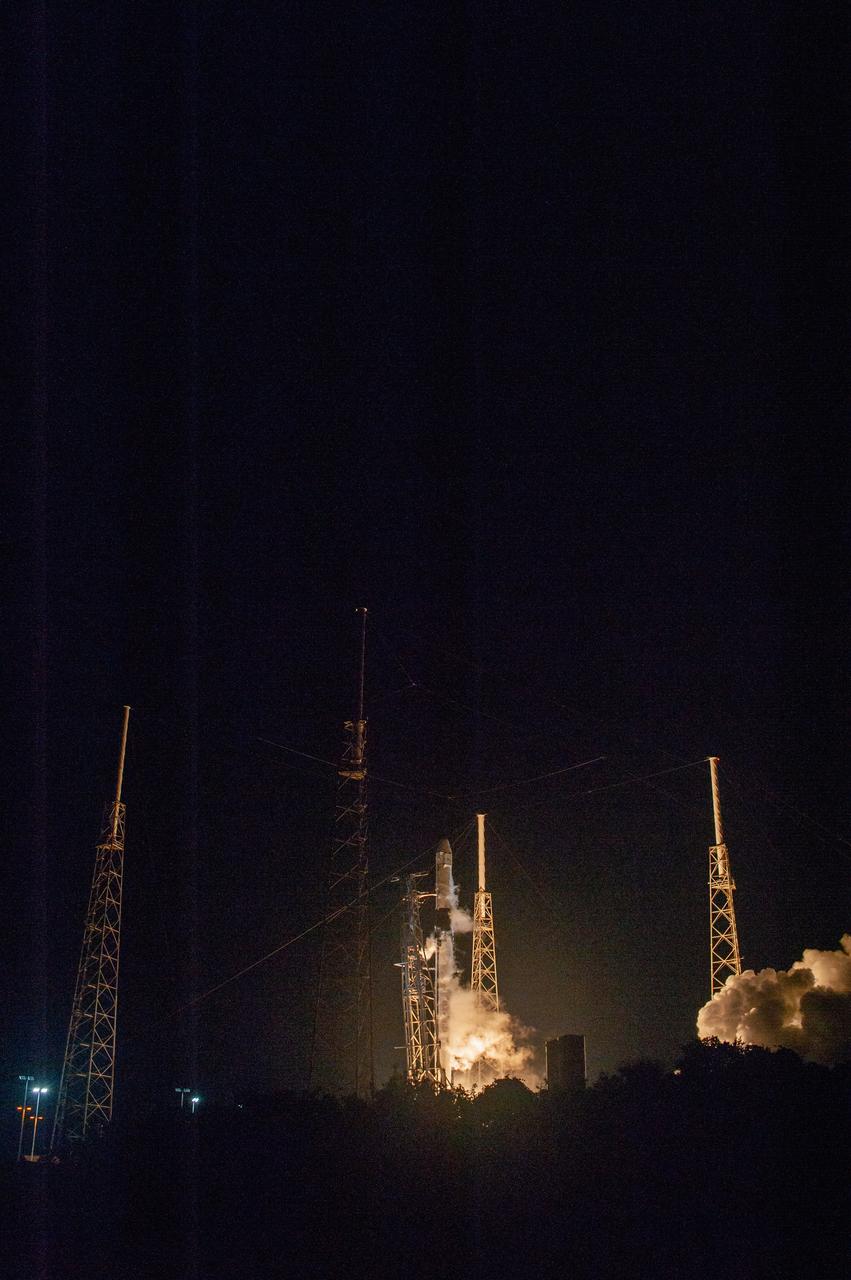

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module lifts off Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in the early morning May 4, 2019. Liftoff was at 2:48 a.m. EDT. This is SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.
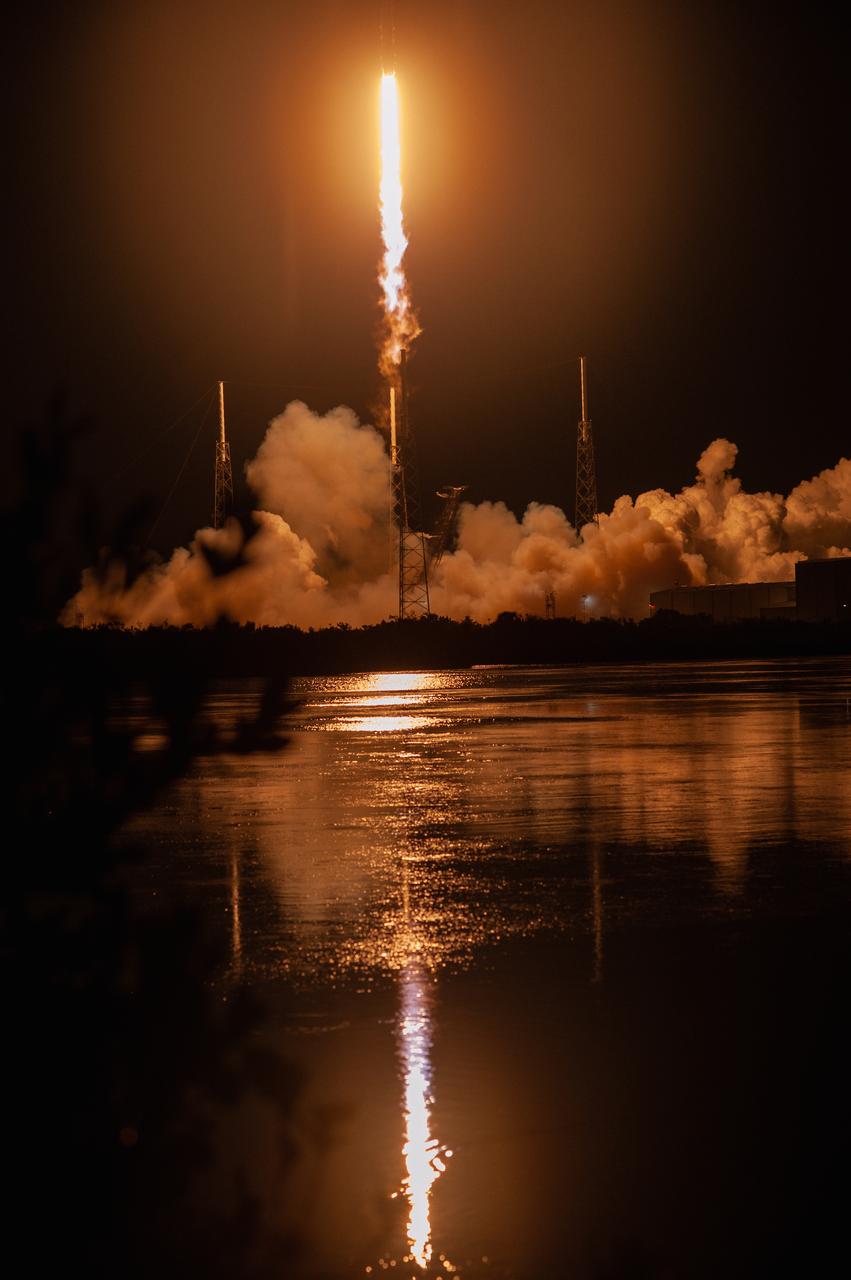

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module lifts off Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in the early morning May 4, 2019. Liftoff was at 2:48 a.m. EDT. This is SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.
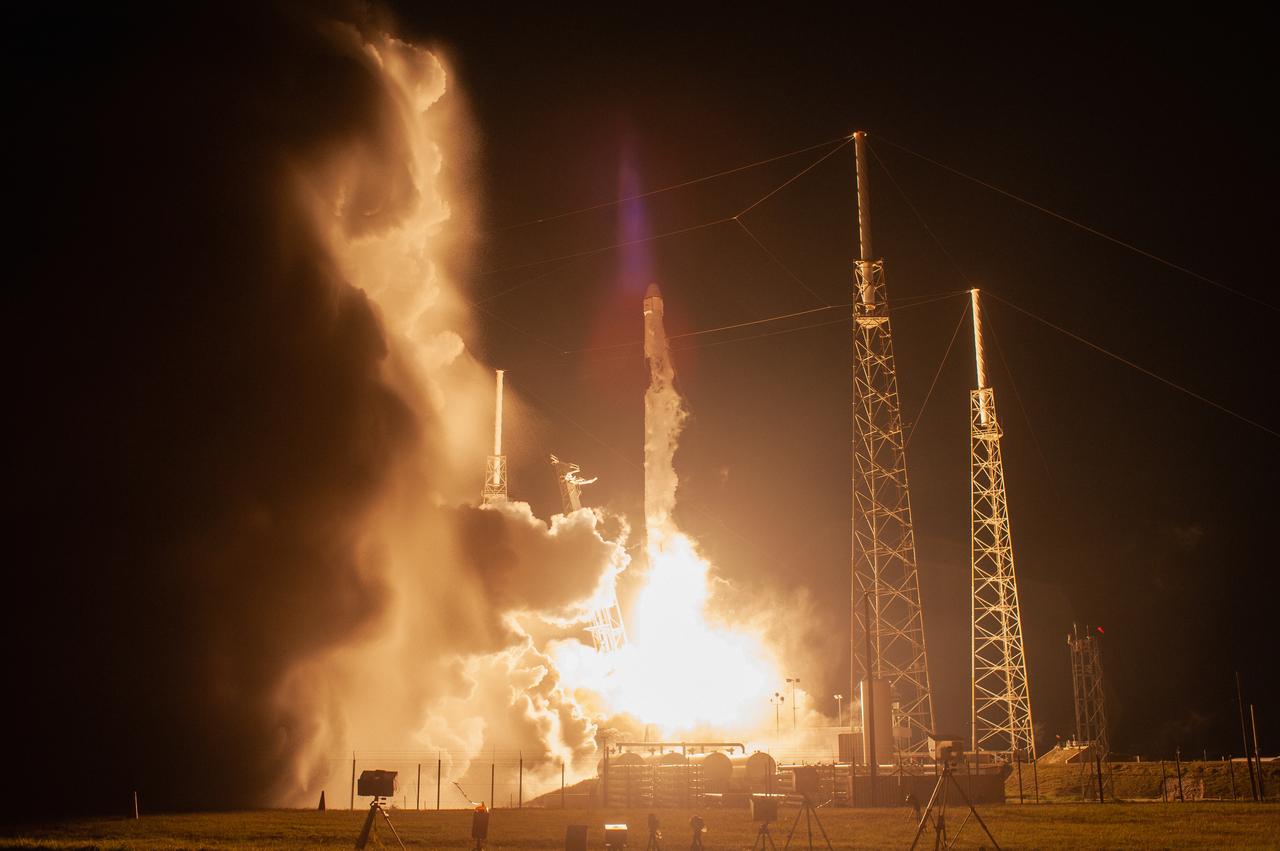

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module lifts off Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in the early morning May 4, 2019. Liftoff was at 2:48 a.m. EDT. This is SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module lifts off Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in the early morning May 4, 2019. Liftoff was at 2:48 a.m. EDT. This is SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.
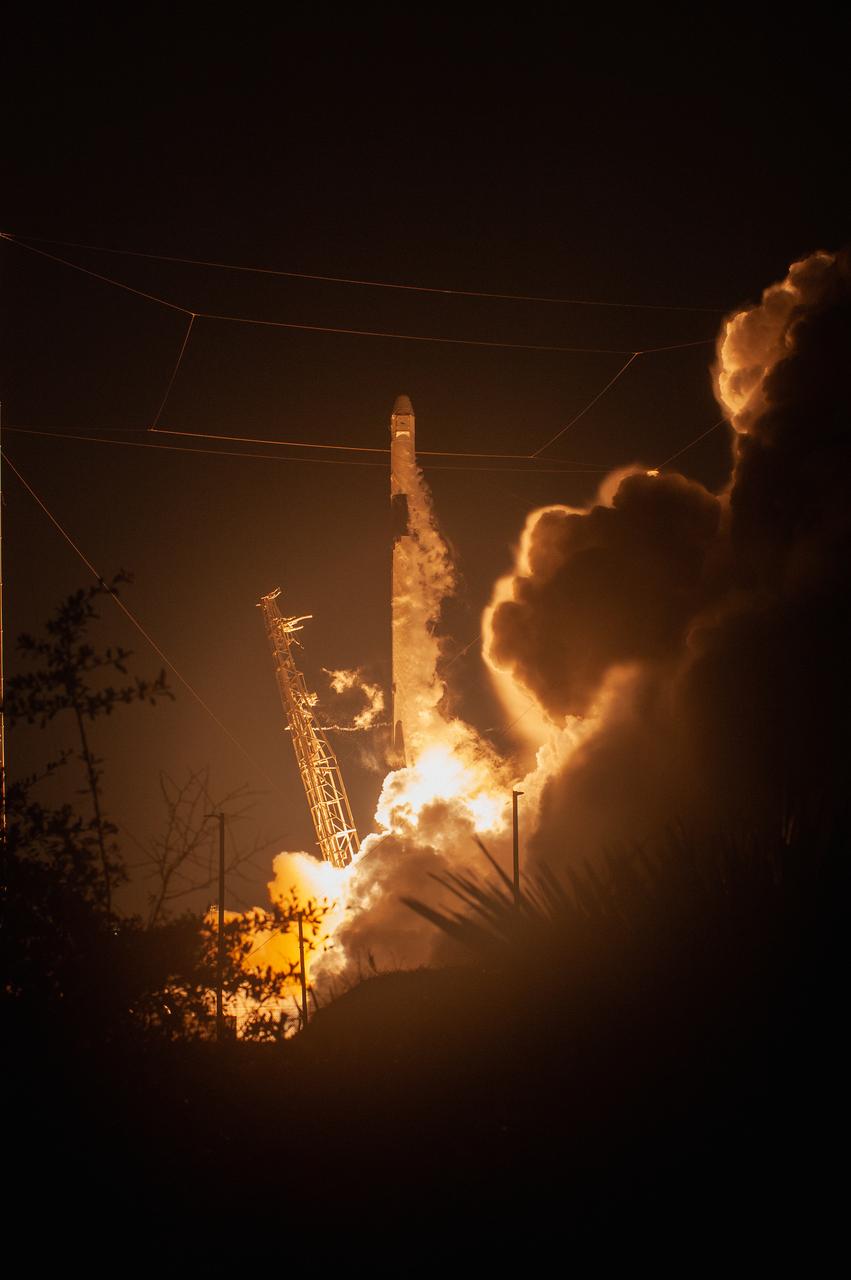

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module climbs upward after liftoff from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in the early morning May 4, 2019. Liftoff was at 2:48 a.m. EDT. This is SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.
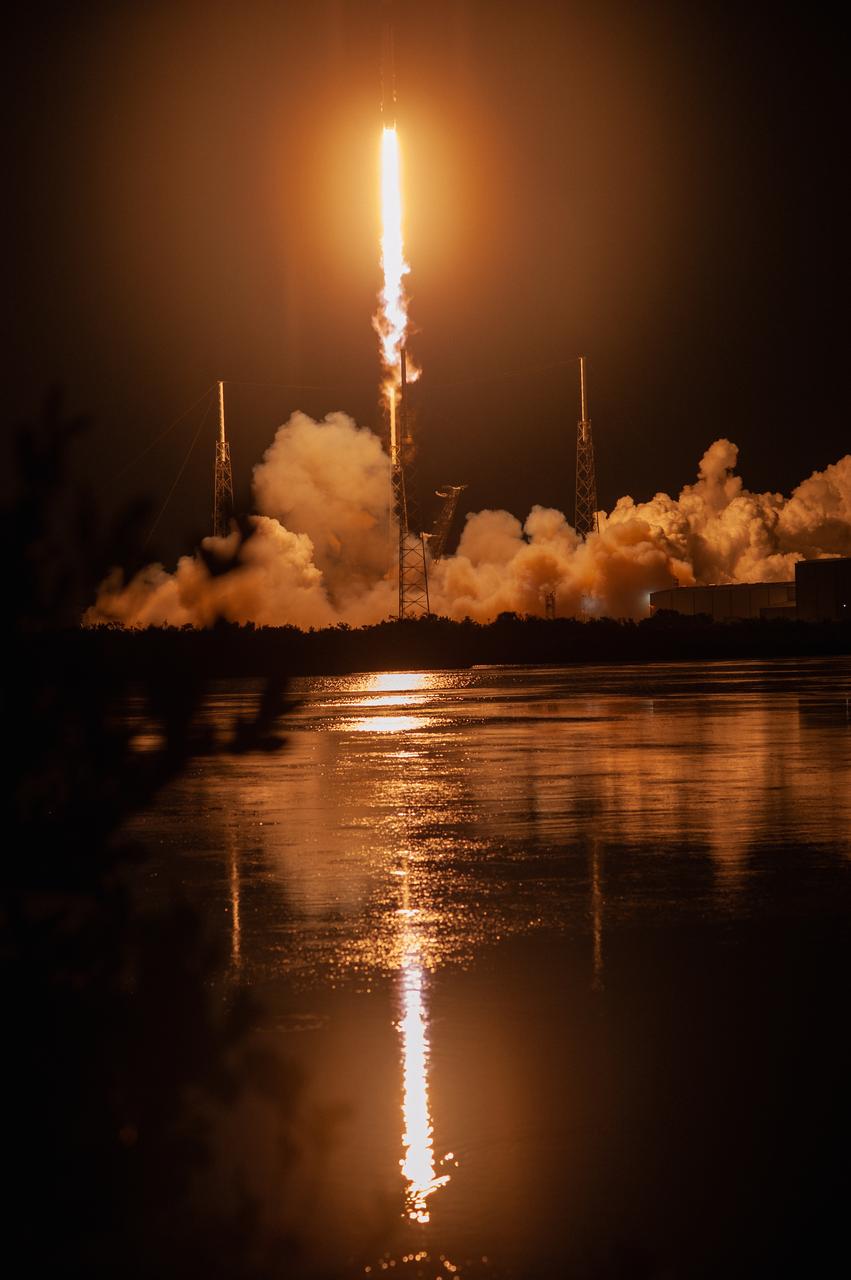

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module lifts off Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in the early morning May 4, 2019. Liftoff was at 2:48 a.m. EDT. This is SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module lifts off Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in the early morning May 4, 2019. Liftoff was at 2:48 a.m. EDT. This is SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.
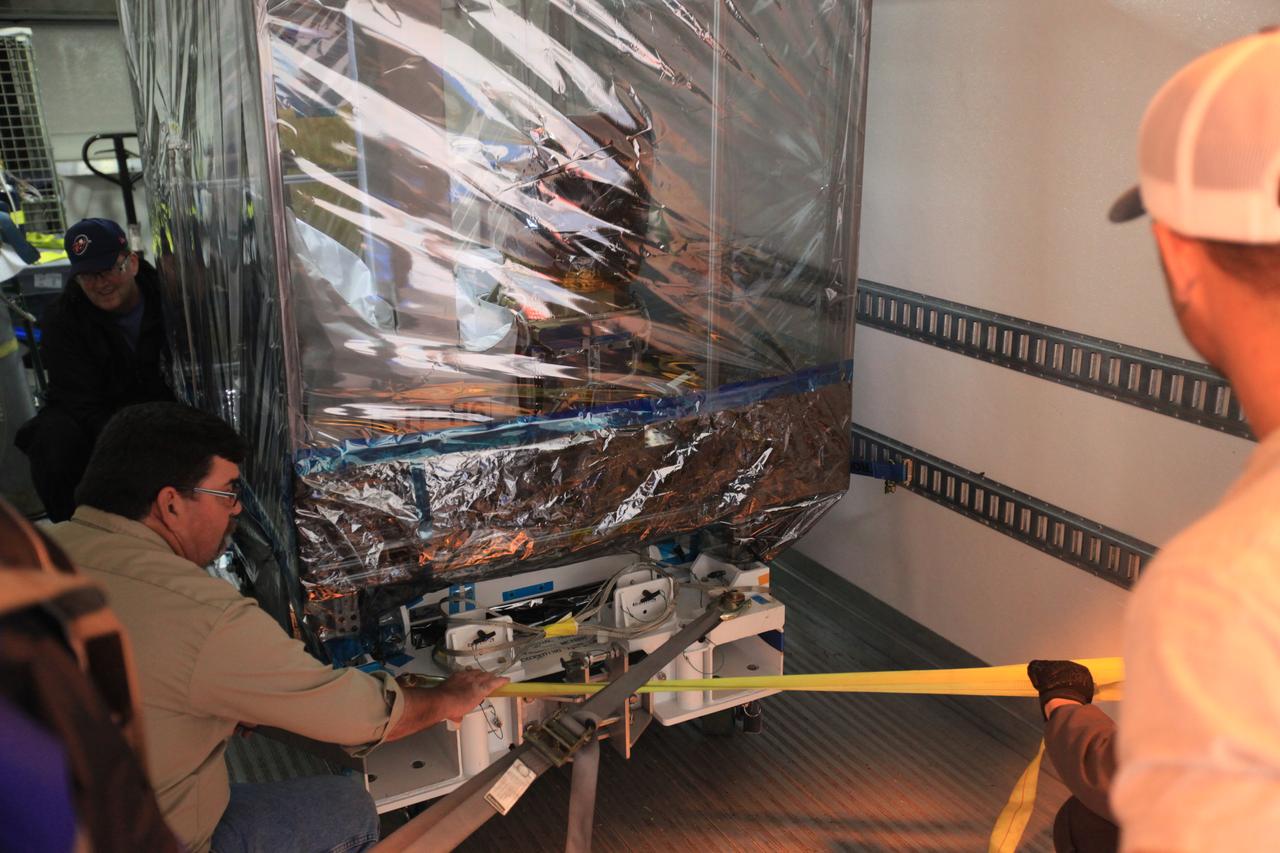

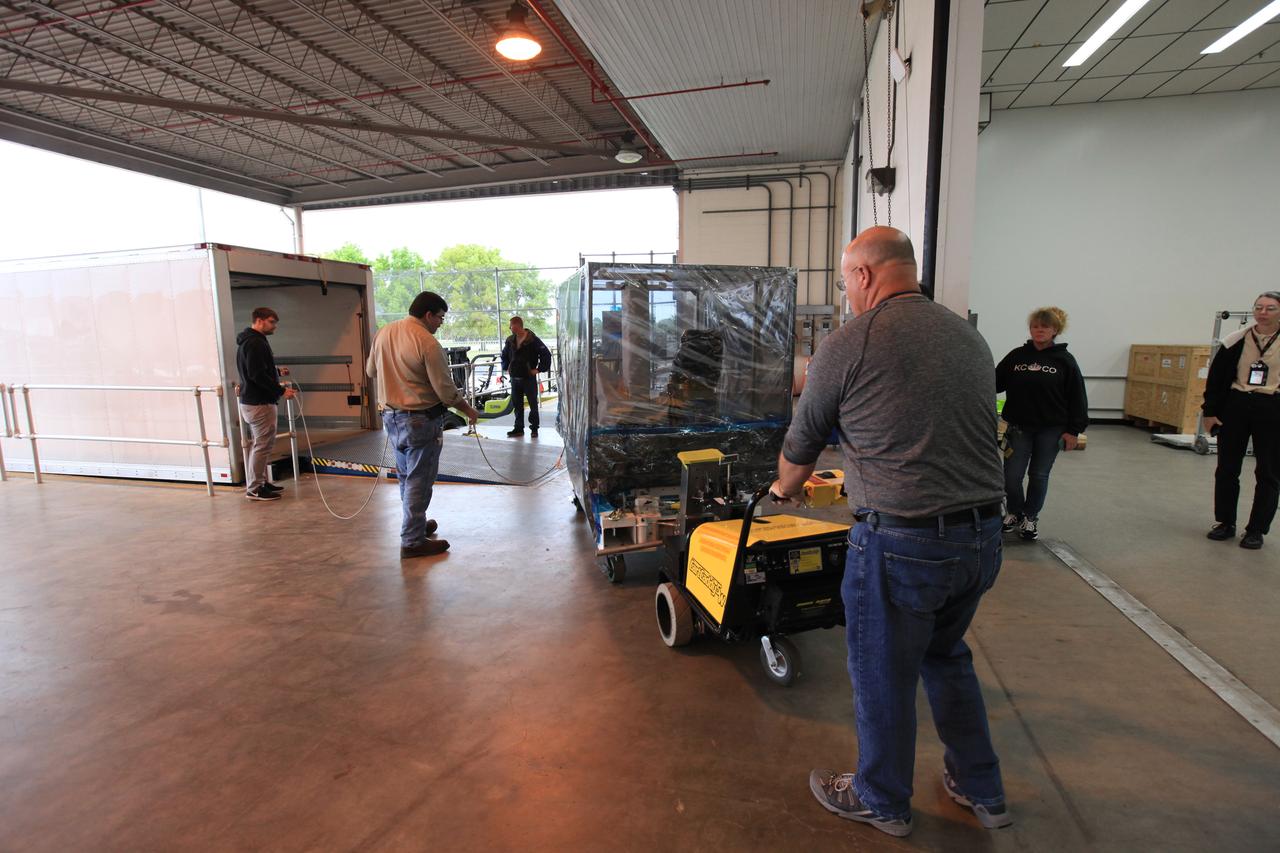
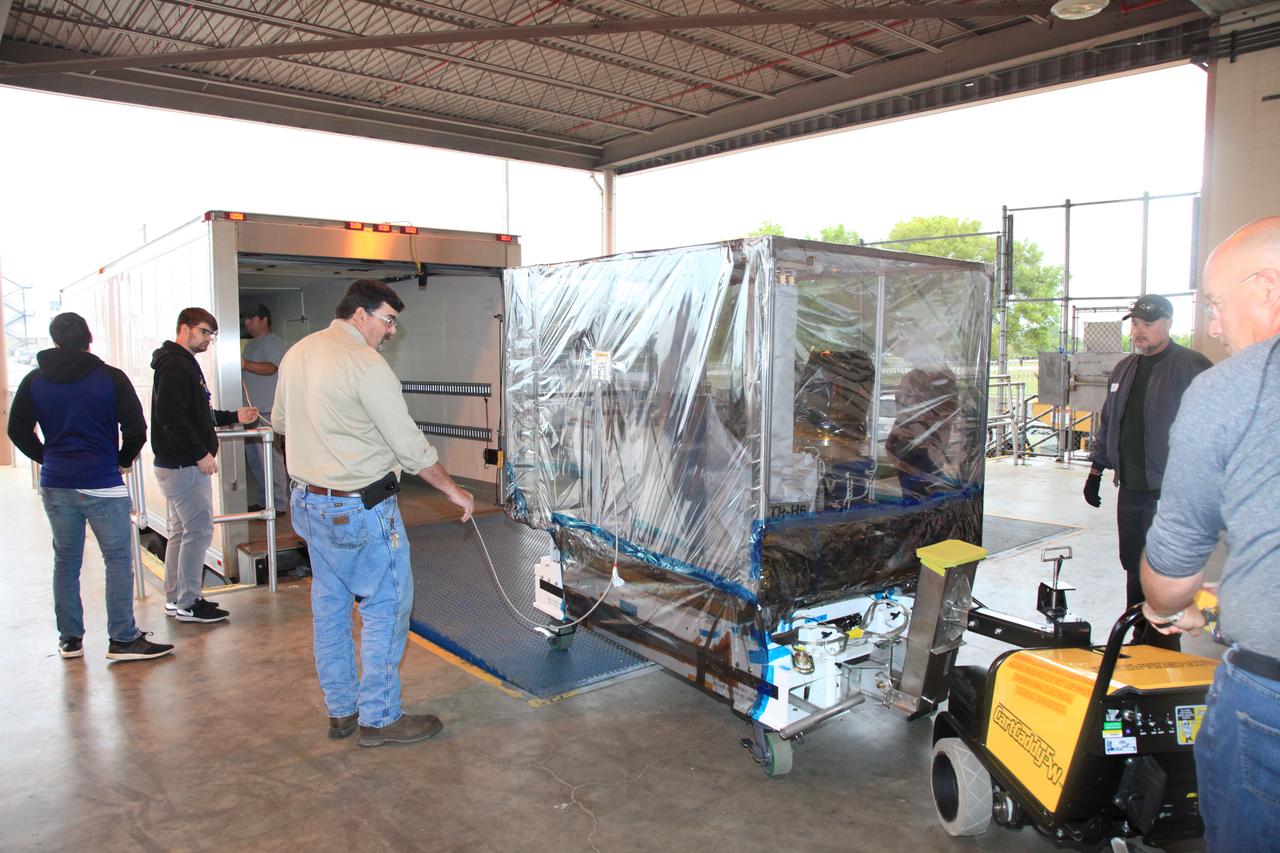
Technicians secure the Space Test Program-Houston 6 (STP-H6) inside a transport truck at the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 19, 2019. The payload will be moved to the SpaceX facility where it will be stowed in the trunk of the Dragon spacecraft for delivery to the International Space Station on SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services mission (CRS-17) for NASA. STP-H6 is an x-ray communication investigation that will be used to perform a space-based demonstration of a new technology for generating beams of modulated x-rays. This technology may be useful for providing efficient communication to deep space probes, or communicating with hypersonic vehicles where plasma sheaths prevent traditional radio communications. CRS-17 is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in late April.
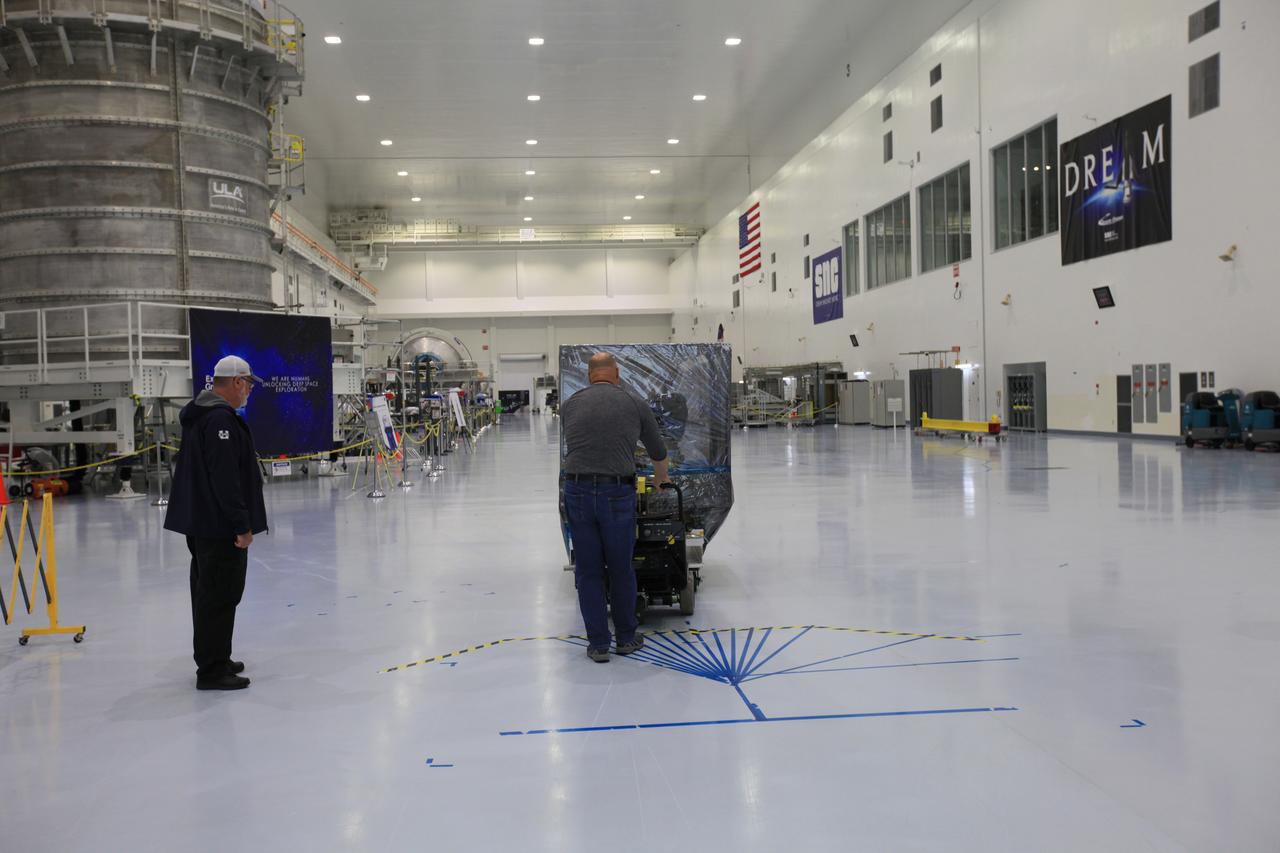

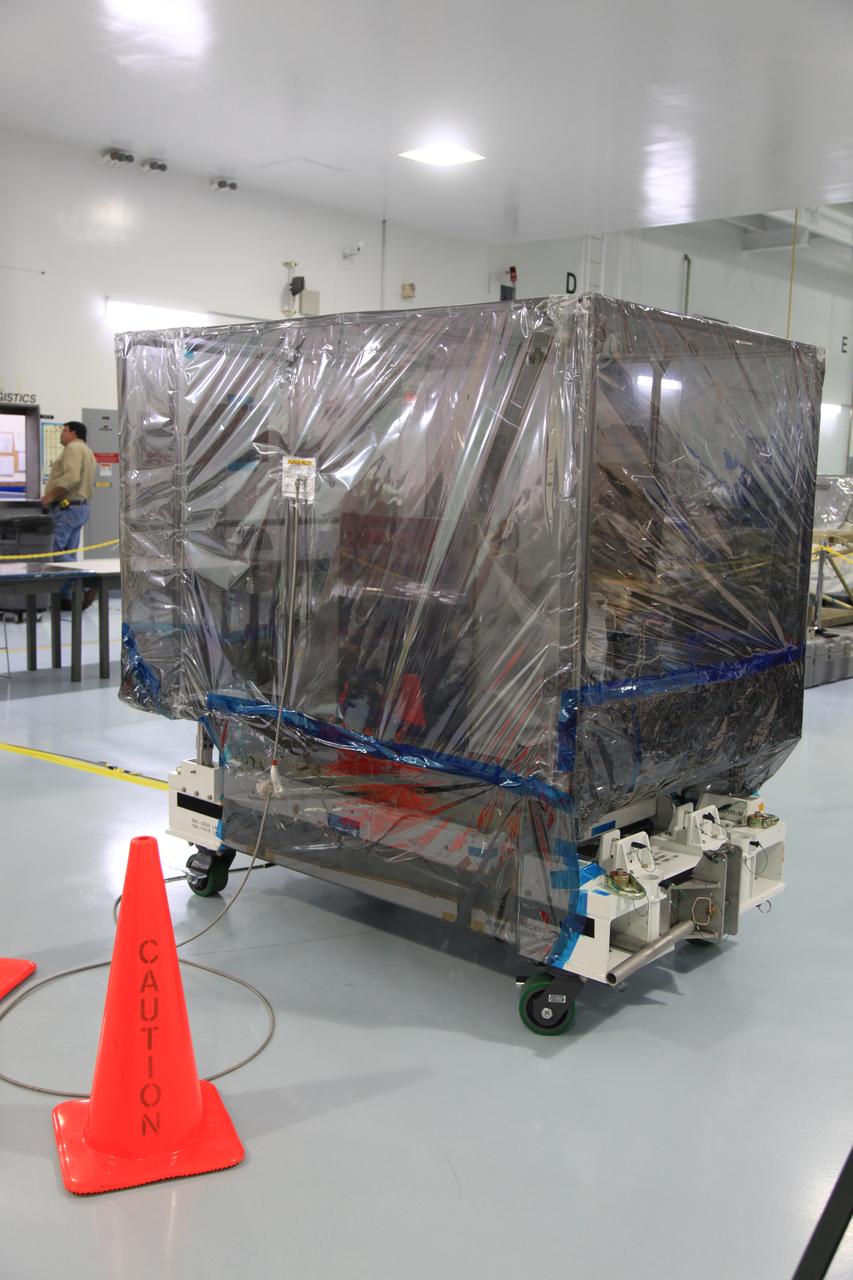
The Space Test Program-Houston 6 (STP-H6) payload is being moved out of the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 19, 2019. The payload will be moved to the SpaceX facility where it will be stowed in the trunk of the Dragon spacecraft for delivery to the International Space Station on SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services mission (CRS-17) for NASA. STP-H6 is an x-ray communication investigation that will be used to perform a space-based demonstration of a new technology for generating beams of modulated x-rays. This technology may be useful for providing efficient communication to deep space probes, or communicating with hypersonic vehicles where plasma sheaths prevent traditional radio communications. CRS-17 is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in late April.
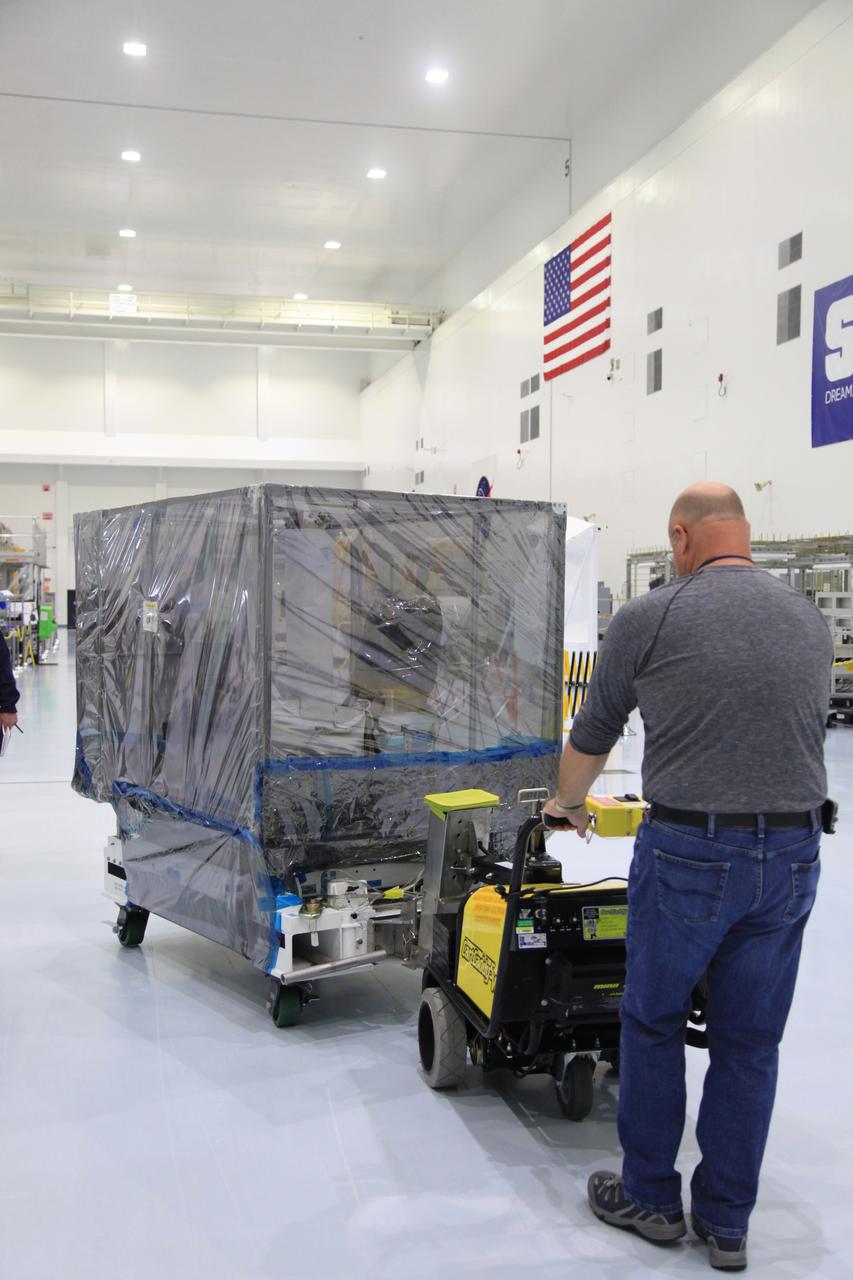

The Space Test Program-Houston 6 (STP-H6) payload is being moved out of the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 19, 2019. The payload will be moved to the SpaceX facility where it will be stowed in the trunk of the Dragon spacecraft for delivery to the International Space Station on SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services mission (CRS-17) for NASA. STP-H6 is an x-ray communication investigation that will be used to perform a space-based demonstration of a new technology for generating beams of modulated x-rays. This technology may be useful for providing efficient communication to deep space probes, or communicating with hypersonic vehicles where plasma sheaths prevent traditional radio communications. CRS-17 is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in late April.
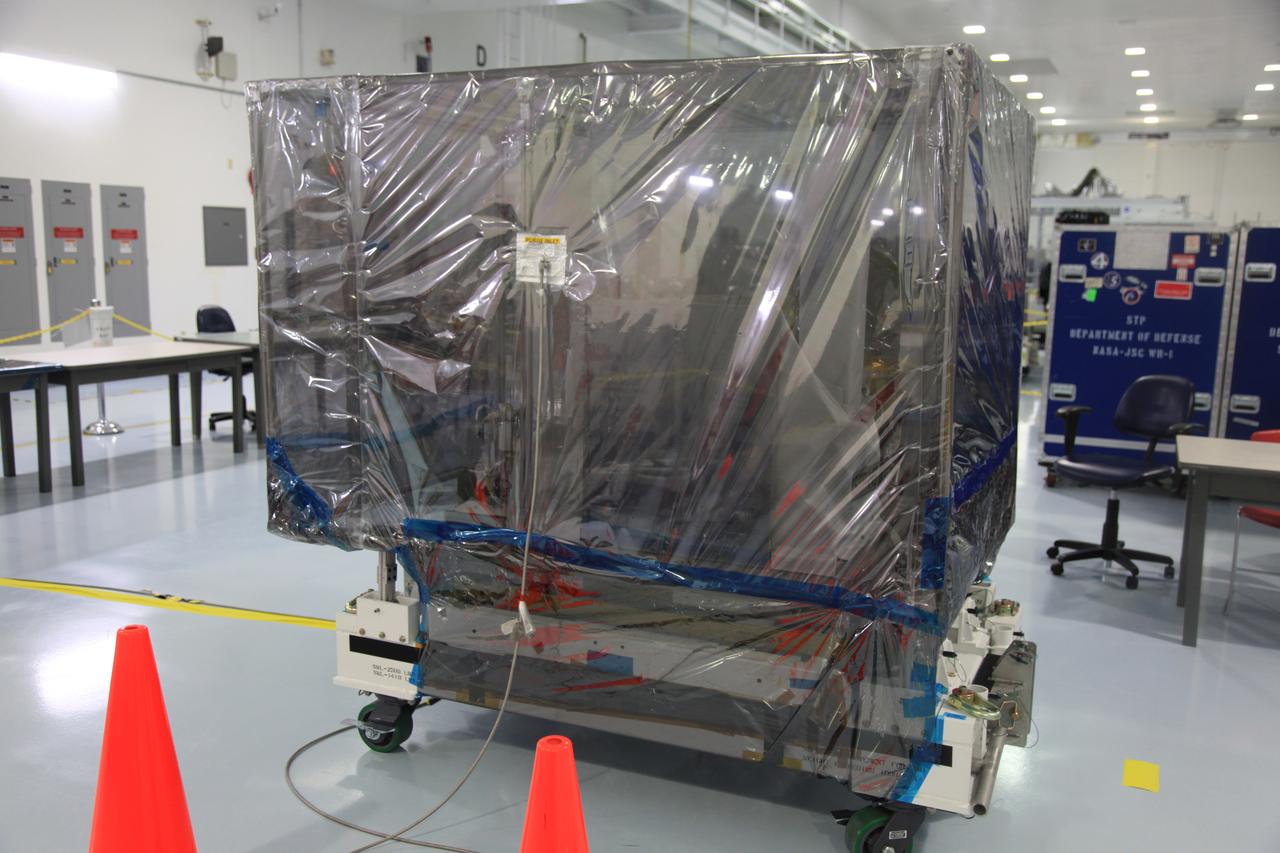

The Space Test Program-Houston 6 (STP-H6) payload is inside the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 19, 2019. It is being prepared for its move to the SpaceX facility where it will be will be stowed in the trunk of the Dragon spacecraft for delivery to the International Space Station on SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services mission (CRS-17) for NASA. STP-H6 is an x-ray communication investigation that will be used to perform a space-based demonstration of a new technology for generating beams of modulated x-rays. This technology may be useful for providing efficient communication to deep space probes, or communicating with hypersonic vehicles where plasma sheaths prevent traditional radio communications. CRS-17 is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in late April.

The Space Test Program-Houston 6 (STP-H6) payload is inside the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 19, 2019. It is being prepared for its move to the SpaceX facility where it will be will be stowed in the trunk of the Dragon spacecraft for delivery to the International Space Station on SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services mission (CRS-17) for NASA. STP-H6 is an x-ray communication investigation that will be used to perform a space-based demonstration of a new technology for generating beams of modulated x-rays. This technology may be useful for providing efficient communication to deep space probes, or communicating with hypersonic vehicles where plasma sheaths prevent traditional radio communications. CRS-17 is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in late April.

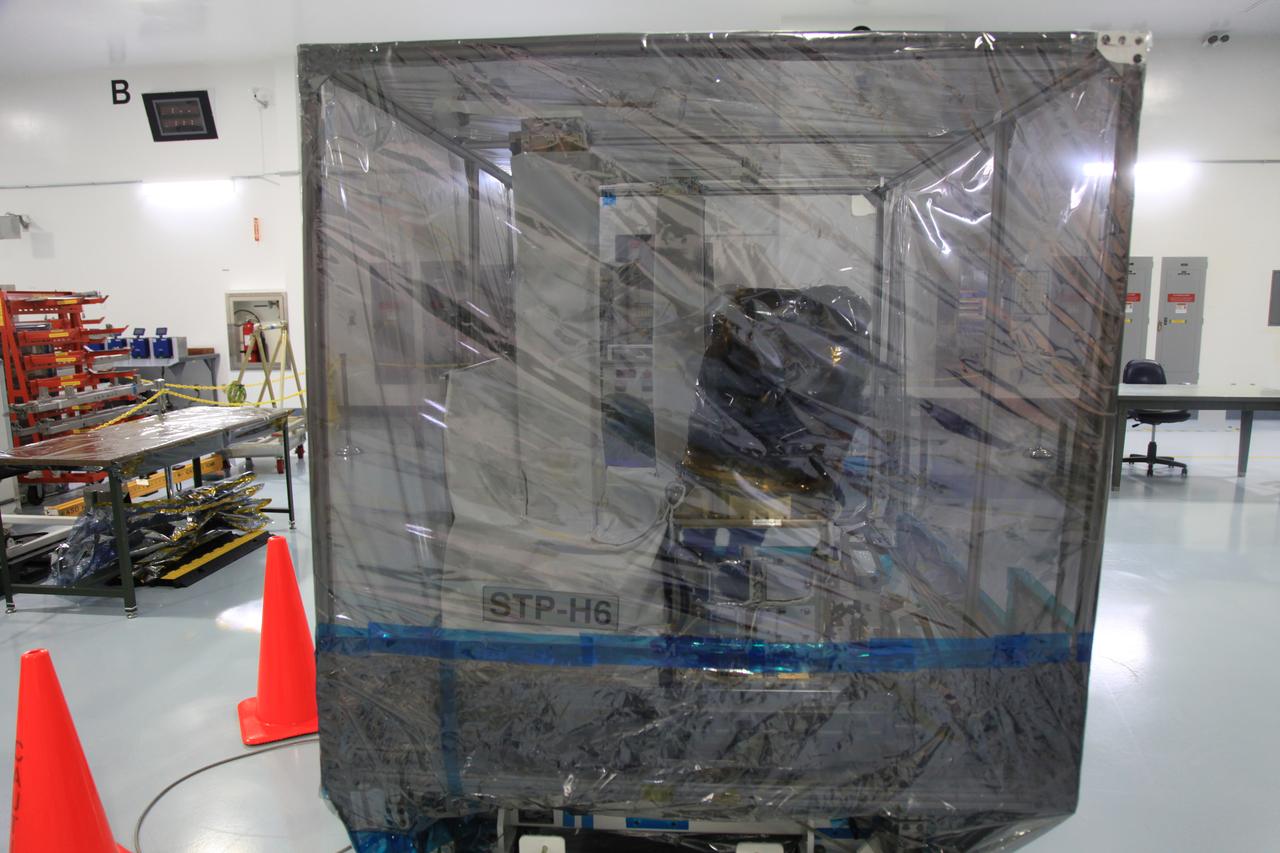
The Space Test Program-Houston 6 (STP-H6) payload is moved to a transport truck at the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 19, 2019. The payload will be moved to the SpaceX facility where it will be stowed in the trunk of the Dragon spacecraft for delivery to the International Space Station on SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services mission (CRS-17) for NASA. STP-H6 is an x-ray communication investigation that will be used to perform a space-based demonstration of a new technology for generating beams of modulated x-rays. This technology may be useful for providing efficient communication to deep space probes, or communicating with hypersonic vehicles where plasma sheaths prevent traditional radio communications. CRS-17 is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in late April.
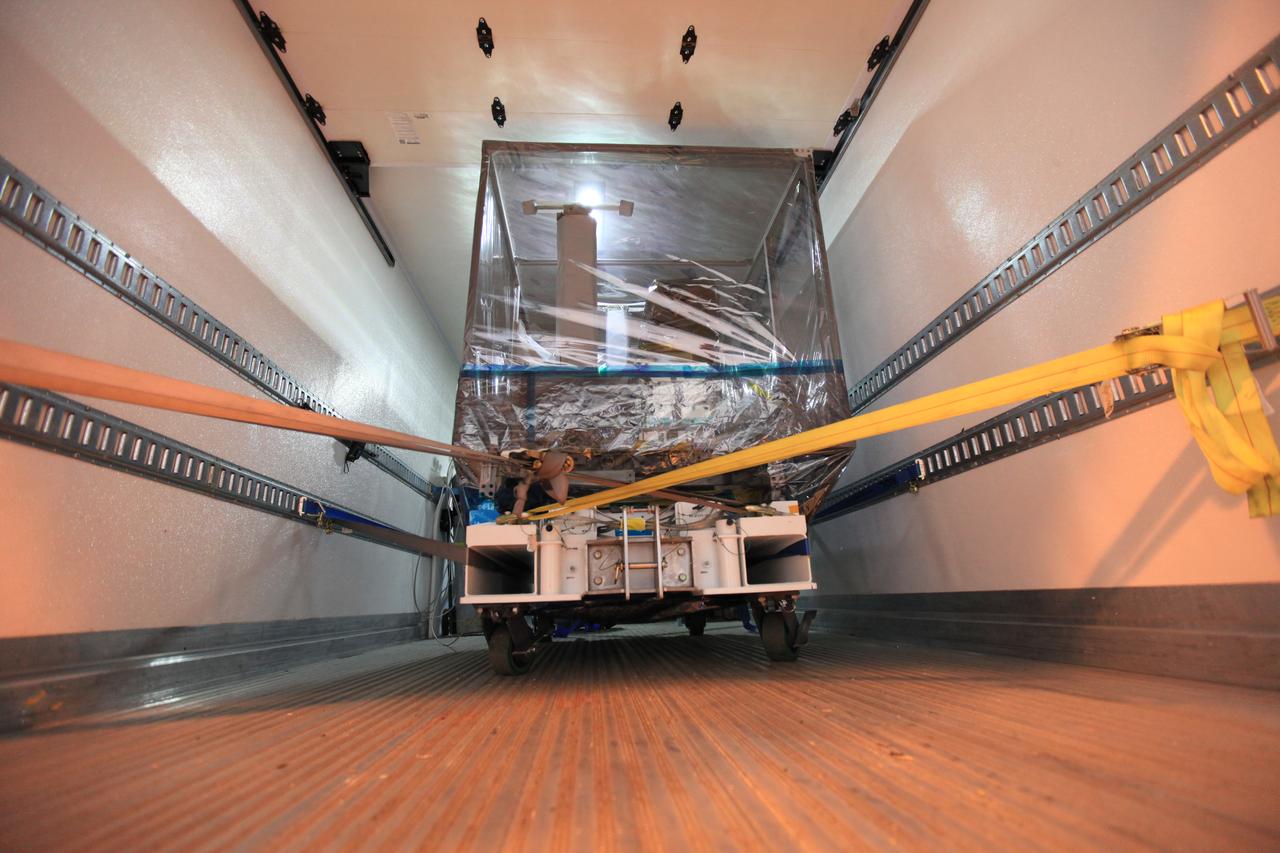

The Space Test Program-Houston 6 (STP-H6) payload is secured inside a truck at the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 19, 2019. The payload will be moved to the SpaceX facility where it will be stowed in the trunk of the Dragon spacecraft for delivery to the International Space Station on SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services mission (CRS-17) for NASA. STP-H6 is an x-ray communication investigation that will be used to perform a space-based demonstration of a new technology for generating beams of modulated x-rays. This technology may be useful for providing efficient communication to deep space probes, or communicating with hypersonic vehicles where plasma sheaths prevent traditional radio communications. CRS-17 is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in late April.
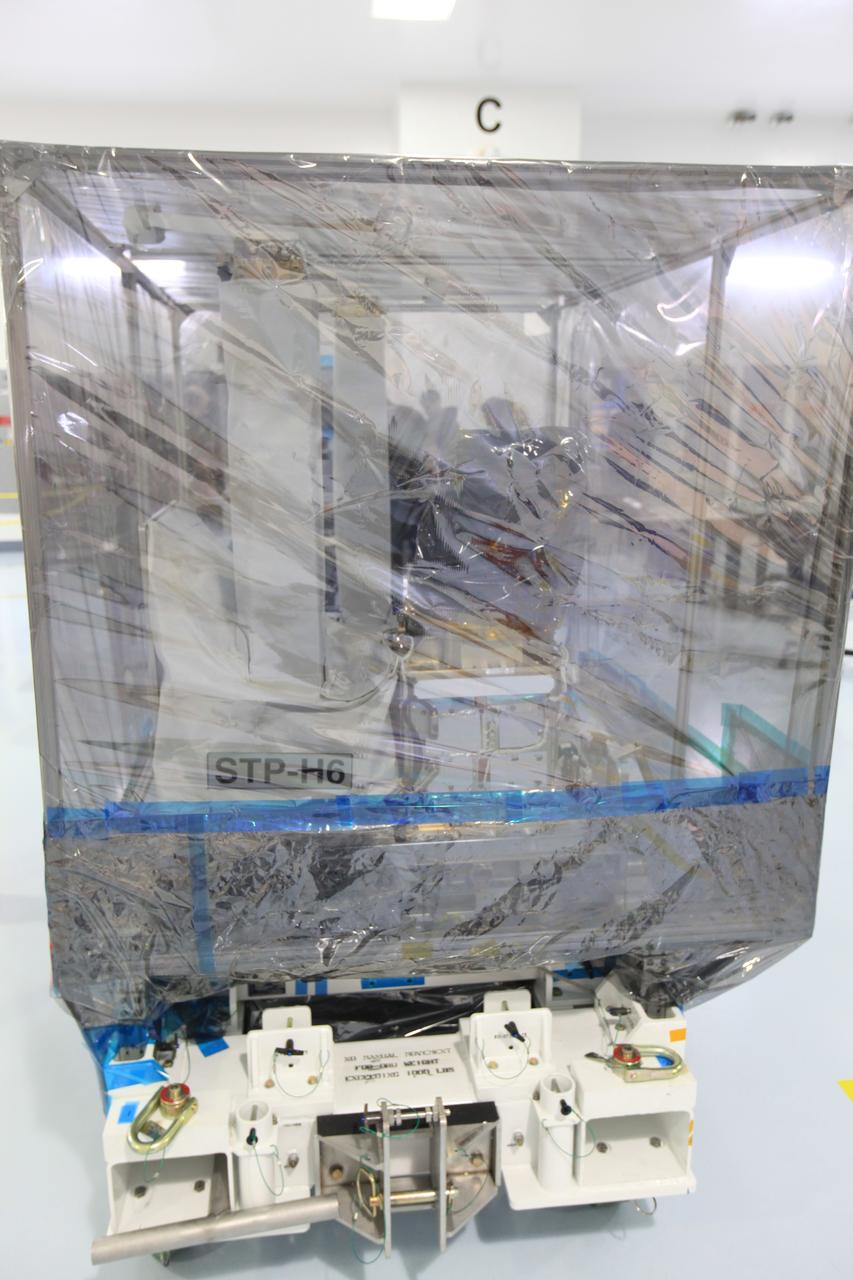

The Space Test Program-Houston 6 (STP-H6) payload is inside the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 19, 2019. It is being prepared for its move to the SpaceX facility where it will be will be stowed in the trunk of the Dragon spacecraft for delivery to the International Space Station on SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services mission (CRS-17) for NASA. STP-H6 is an x-ray communication investigation that will be used to perform a space-based demonstration of a new technology for generating beams of modulated x-rays. This technology may be useful for providing efficient communication to deep space probes, or communicating with hypersonic vehicles where plasma sheaths prevent traditional radio communications. CRS-17 is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in late April.

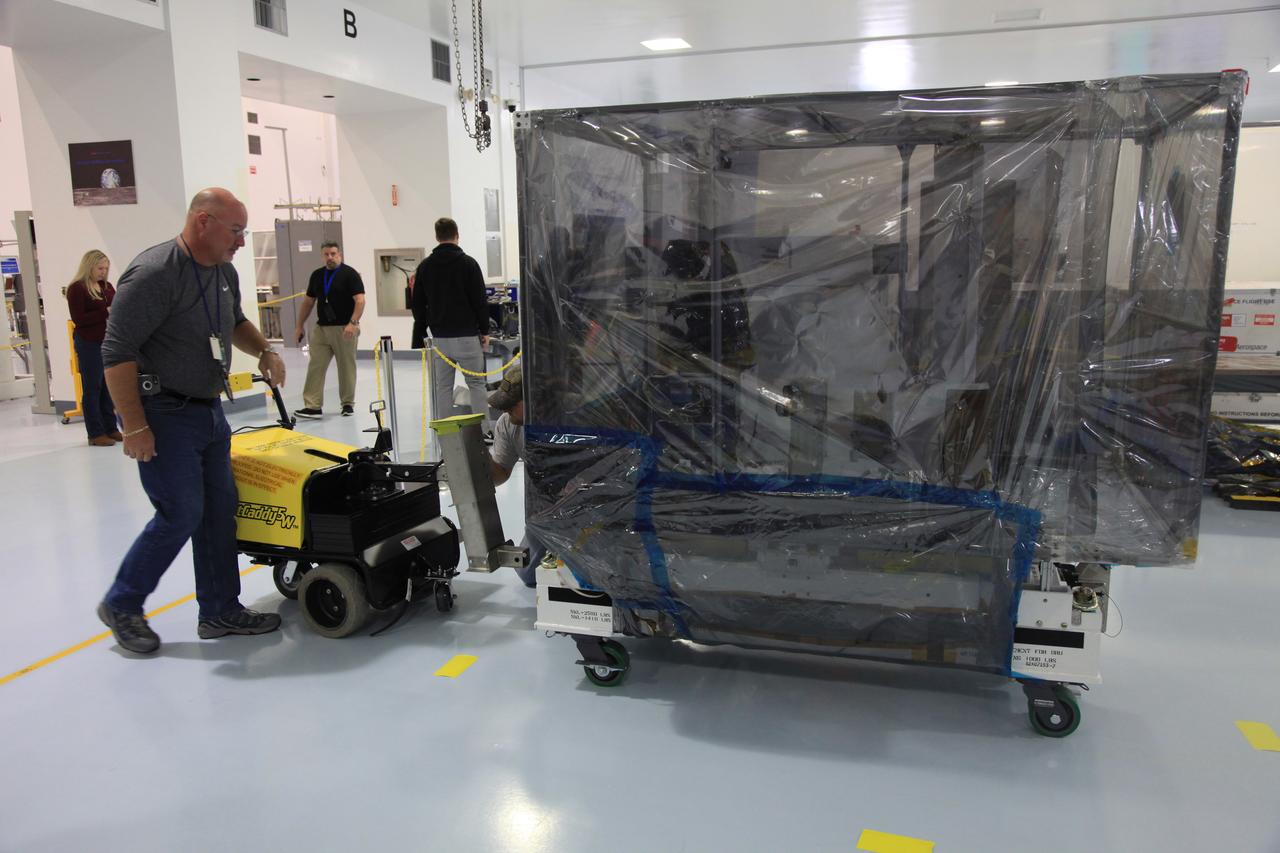
The Space Test Program-Houston 6 (STP-H6) payload is being loaded into a transport truck at the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 19, 2019. The payload will be moved to the SpaceX facility where it will be stowed in the trunk of the Dragon spacecraft for delivery to the International Space Station on SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services mission (CRS-17) for NASA. STP-H6 is an x-ray communication investigation that will be used to perform a space-based demonstration of a new technology for generating beams of modulated x-rays. This technology may be useful for providing efficient communication to deep space probes, or communicating with hypersonic vehicles where plasma sheaths prevent traditional radio communications. CRS-17 is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in late April.

The Space Test Program-Houston 6 (STP-H6) payload is inside the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 19, 2019. It is being prepared for its move to the SpaceX facility where it will be will be stowed in the trunk of the Dragon spacecraft for delivery to the International Space Station on SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services mission (CRS-17) for NASA. STP-H6 is an x-ray communication investigation that will be used to perform a space-based demonstration of a new technology for generating beams of modulated x-rays. This technology may be useful for providing efficient communication to deep space probes, or communicating with hypersonic vehicles where plasma sheaths prevent traditional radio communications. CRS-17 is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in late April.

The Space Test Program-Houston 6 (STP-H6) payload is being prepared for its move from the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 19, 2019. The payload will be moved to the SpaceX facility where it will be stowed in the trunk of the Dragon spacecraft for delivery to the International Space Station on SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services mission (CRS-17) for NASA. STP-H6 is an x-ray communication investigation that will be used to perform a space-based demonstration of a new technology for generating beams of modulated x-rays. This technology may be useful for providing efficient communication to deep space probes, or communicating with hypersonic vehicles where plasma sheaths prevent traditional radio communications. CRS-17 is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in late April.
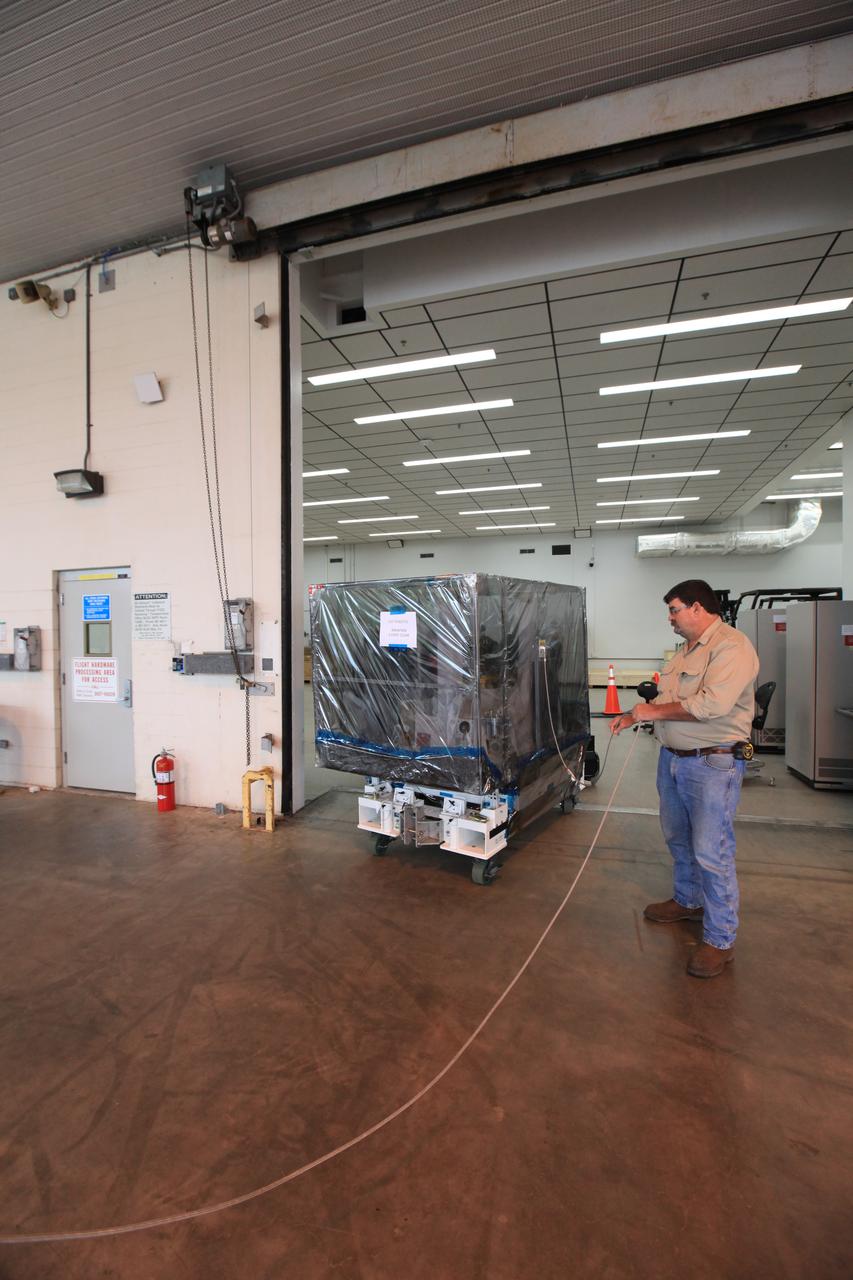

The Space Test Program-Houston 6 (STP-H6) payload is moved out of the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 19, 2019. The payload will be moved to the SpaceX facility where it will be stowed in the trunk of the Dragon spacecraft for delivery to the International Space Station on SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services mission (CRS-17) for NASA. STP-H6 is an x-ray communication investigation that will be used to perform a space-based demonstration of a new technology for generating beams of modulated x-rays. This technology may be useful for providing efficient communication to deep space probes, or communicating with hypersonic vehicles where plasma sheaths prevent traditional radio communications. CRS-17 is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in late April.
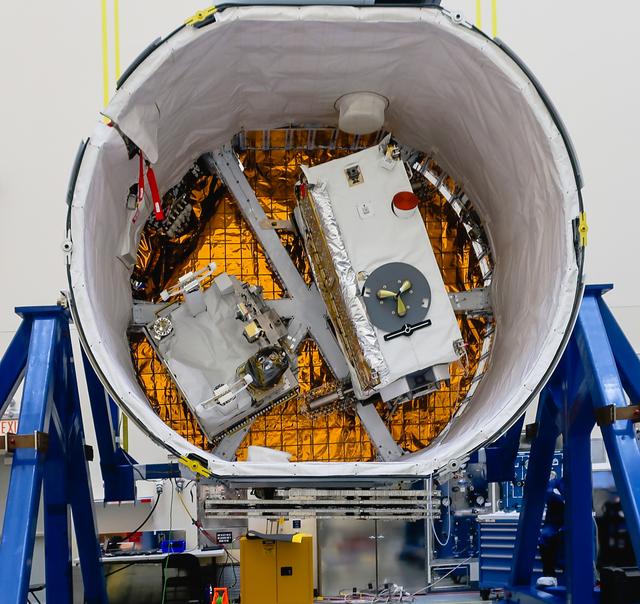

NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory-3 (OCO-3) and Space Test Program-Houston 6 (STP-H6) are in view installed in the truck of SpaceX’s Dragon spacecraft inside the SpaceX facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 23, 2019. OCO-3 and STP-H6 will be delivered to the International Space Station on SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services mission (CRS-17) for NASA. STP-H6 is an x-ray communication investigation that will be used to perform a space-based demonstration of a new technology for generating beams of modulated x-rays. This technology may be useful for providing efficient communication to deep space probes, or communicating with hypersonic vehicles where plasma sheaths prevent traditional radio communications. OCO-3 will be robotically installed on the exterior of the space station’s Japanese Experiment Module Exposed Facility Unit, where it will measure and map carbon dioxide from space to provide further understanding of the relationship between carbon and climate. CRS-17 is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in late April.
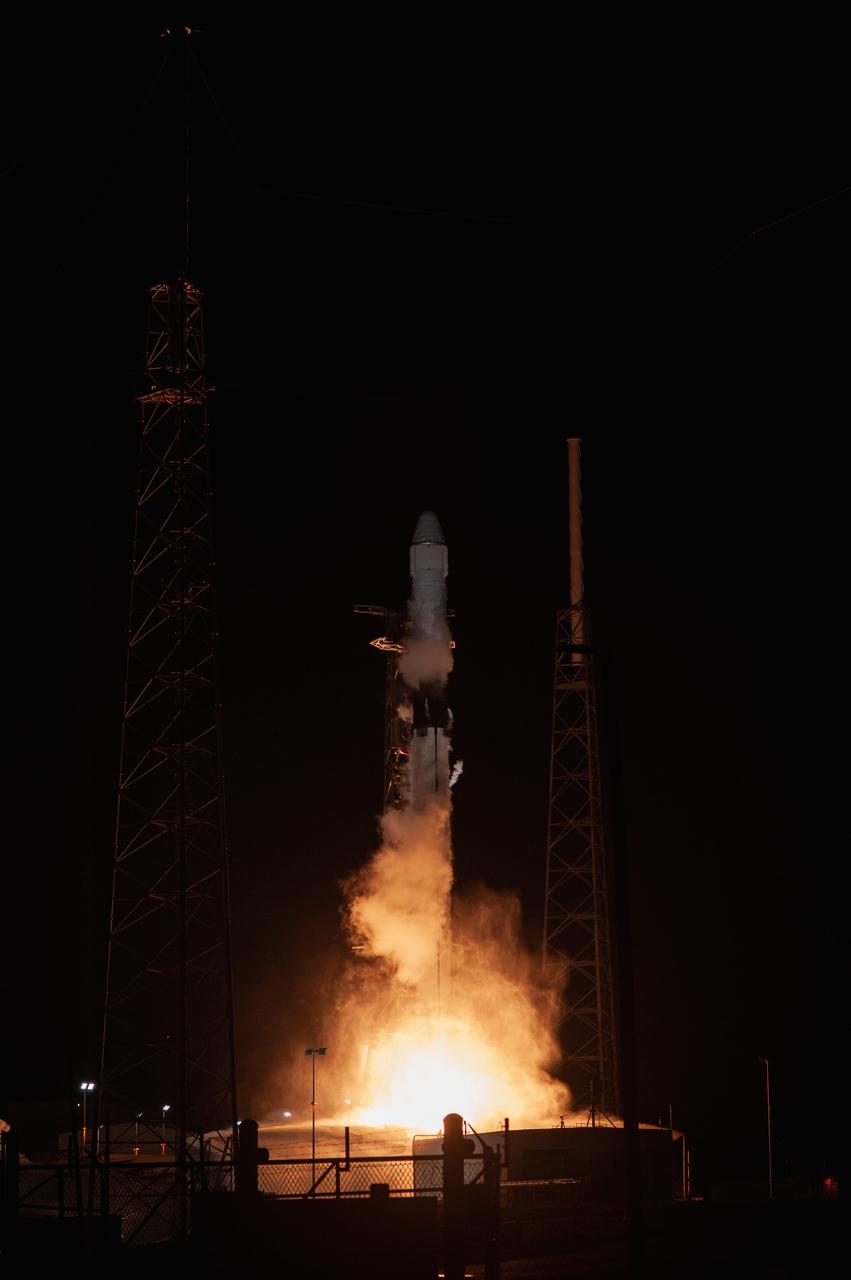

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module lifts off Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in the early morning May 4, 2019. Liftoff was at 2:48 a.m. EDT. This is SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.
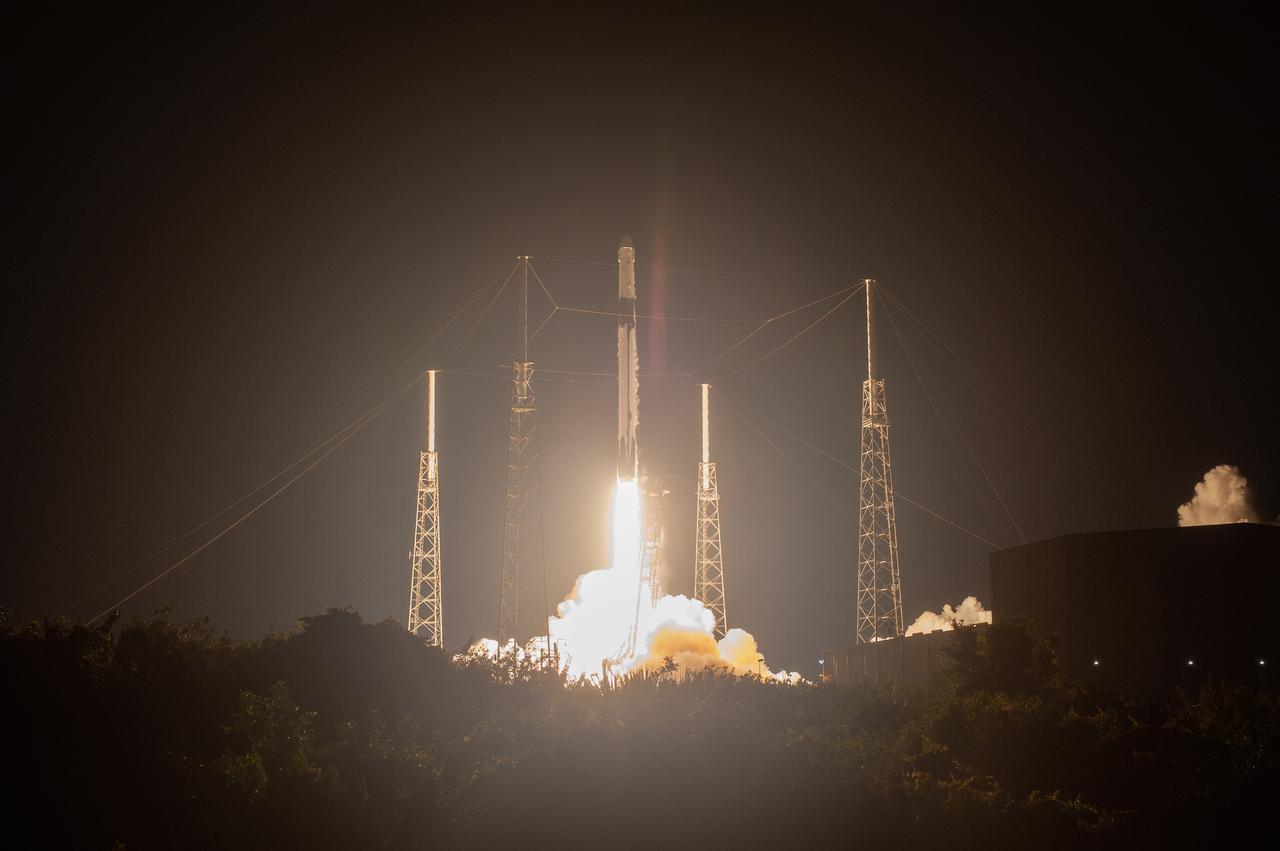

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module lifts off Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in the early morning May 4, 2019. Liftoff was at 2:48 a.m. EDT. This is SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module lifts off Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in the early morning May 4, 2019. Liftoff was at 2:48 a.m. EDT. This is SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.
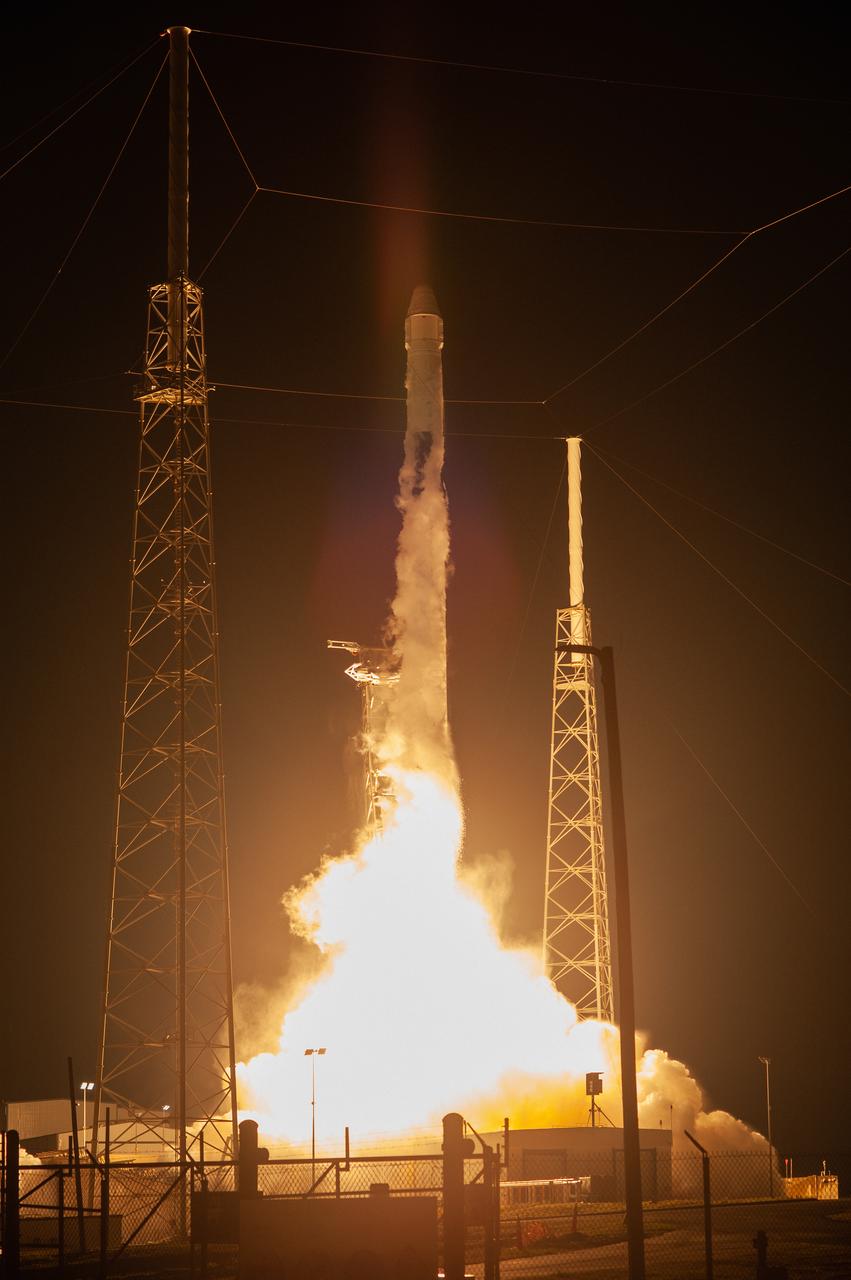

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module lifts off Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in the early morning May 4, 2019. Liftoff was at 2:48 a.m. EDT. This is SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.
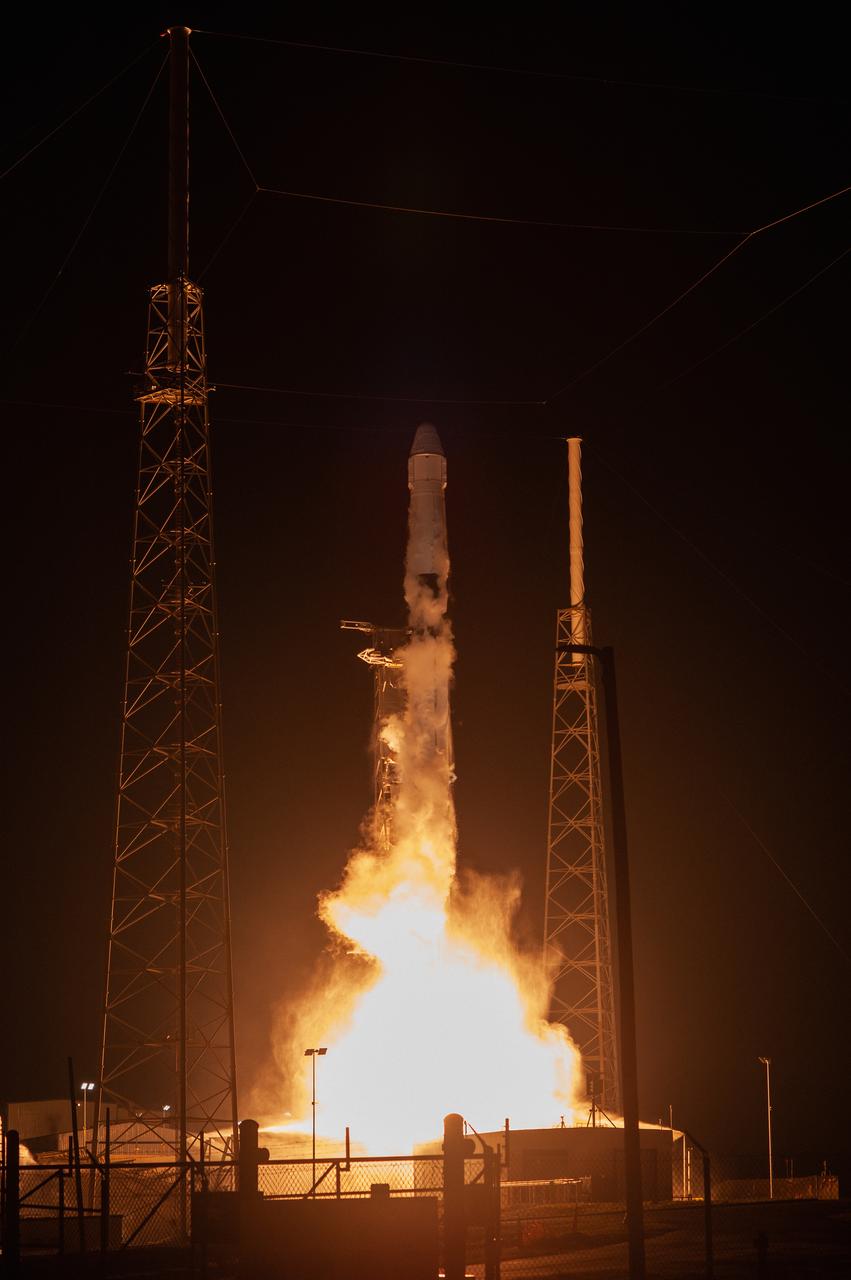

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module lifts off Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in the early morning May 4, 2019. Liftoff was at 2:48 a.m. EDT. This is SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.
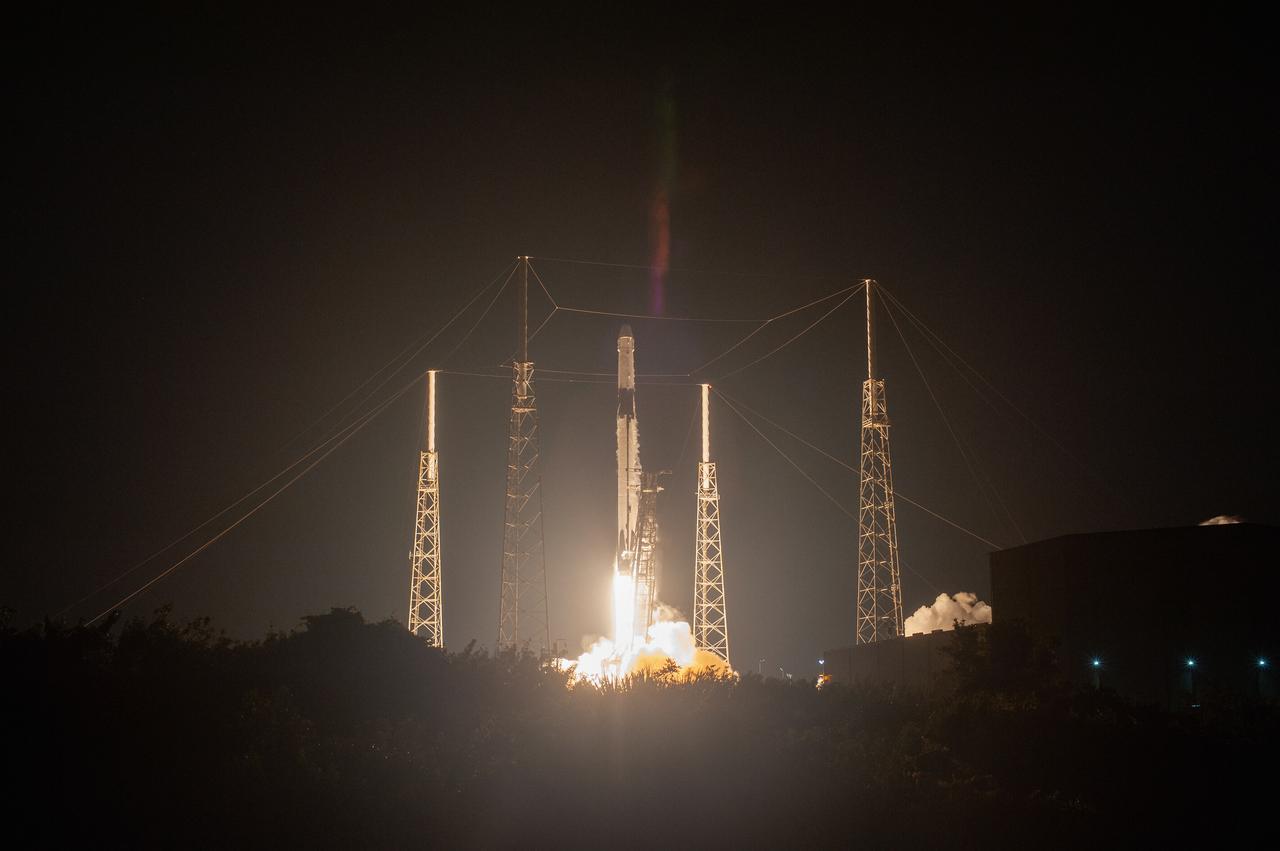

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module lifts off Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in the early morning May 4, 2019. Liftoff was at 2:48 a.m. EDT. This is SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.
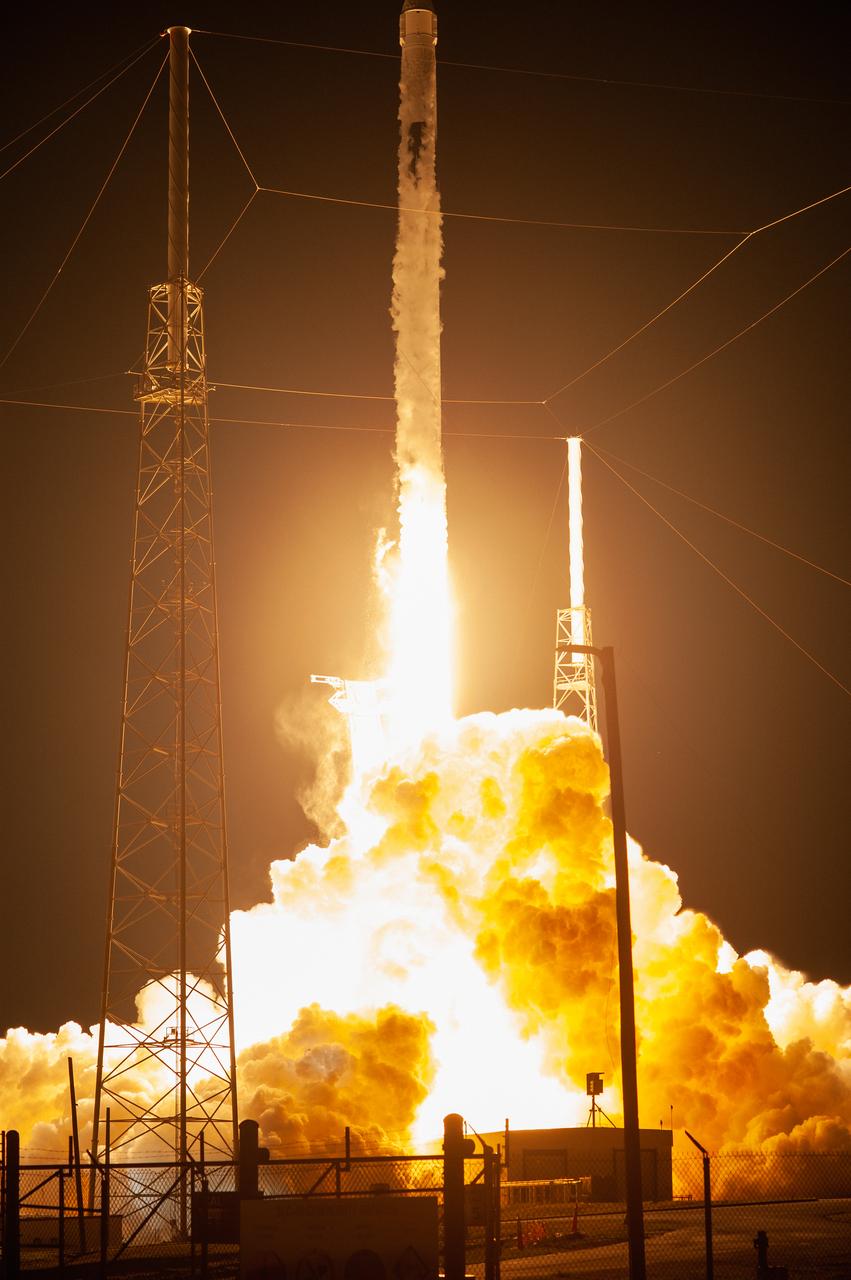

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module lifts off Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in the early morning May 4, 2019. Liftoff was at 2:48 a.m. EDT. This is SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.
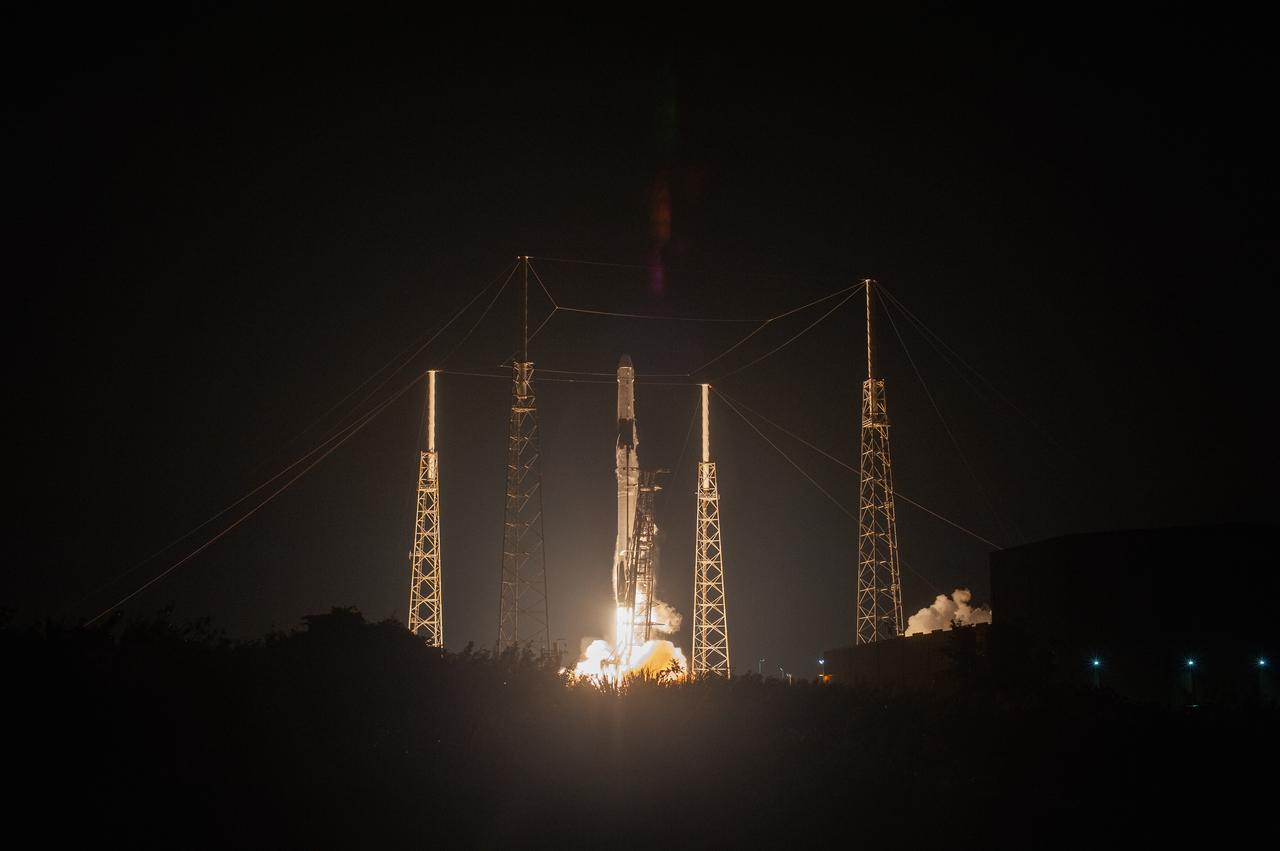

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module lifts off Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in the early morning May 4, 2019. Liftoff was at 2:48 a.m. EDT. This is SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.
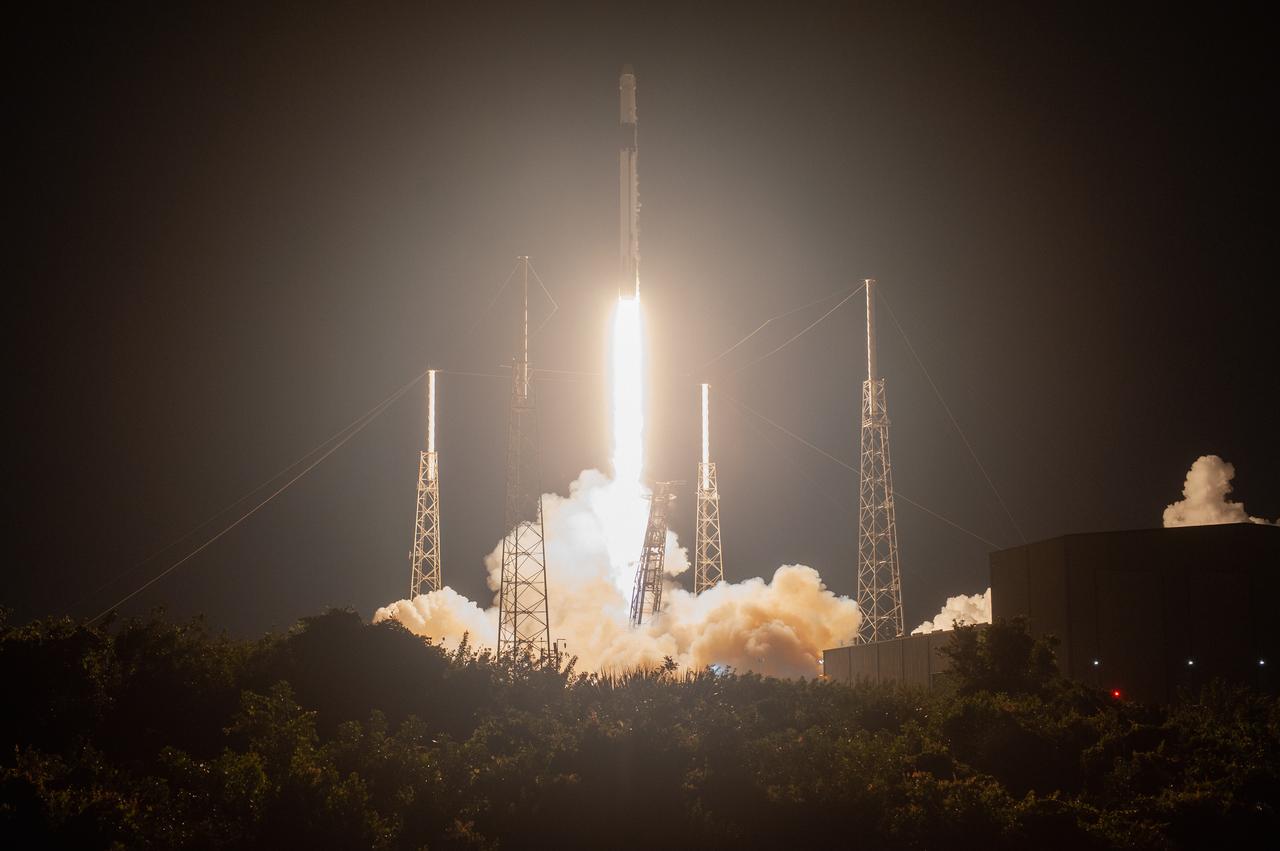

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module lifts off Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in the early morning May 4, 2019. Liftoff was at 2:48 a.m. EDT. This is SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module climbs upward after liftoff from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in the early morning May 4, 2019. Liftoff was at 2:48 a.m. EDT. This is SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.
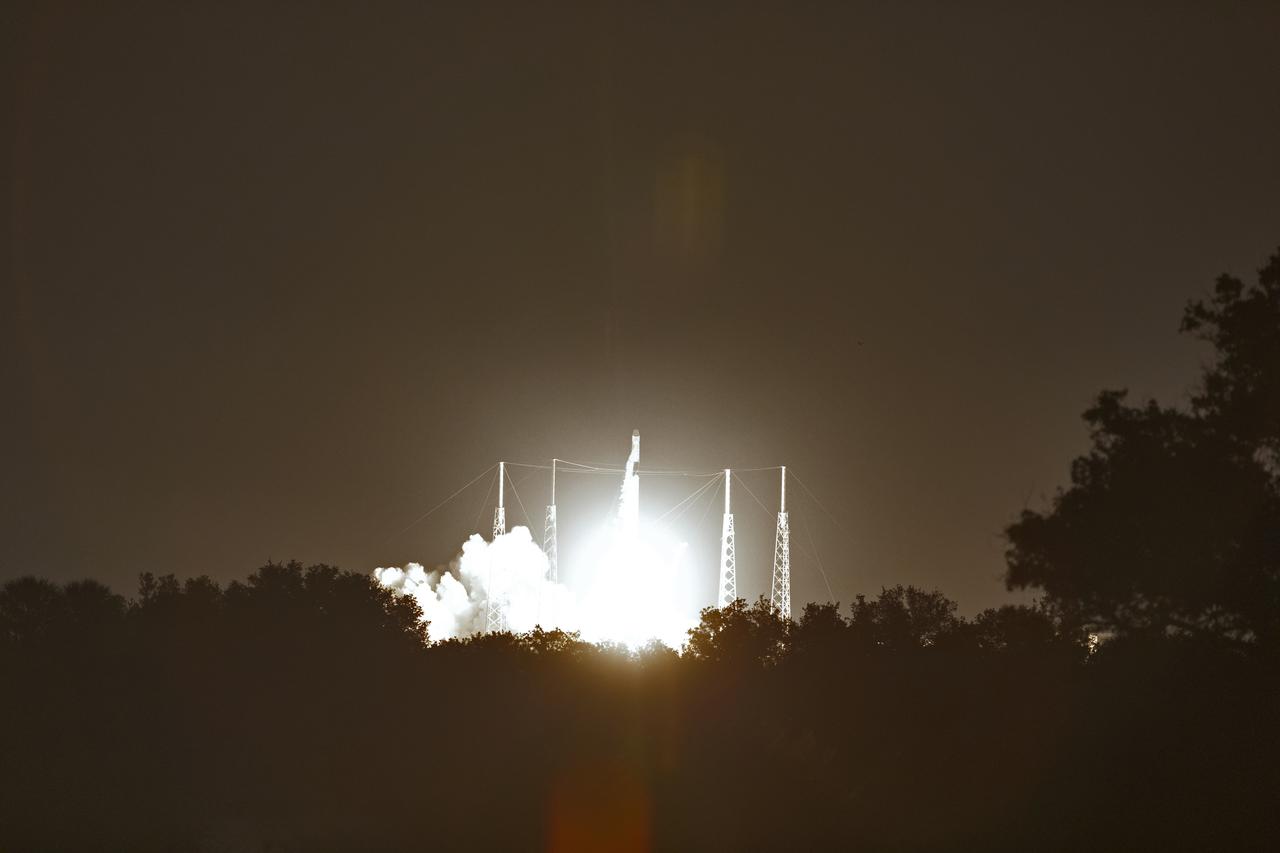

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module lifts off Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in the early morning May 4, 2019. Liftoff was at 2:48 a.m. EDT. This is SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module lifts off Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in the early morning May 4, 2019. Liftoff was at 2:48 a.m. EDT. This is SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.

Derrol Nail, NASA Communications moderates a prelaunch news conference for SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station on May 2, 2019, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon cargo module are scheduled to launch no earlier than May 3, 2019, from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
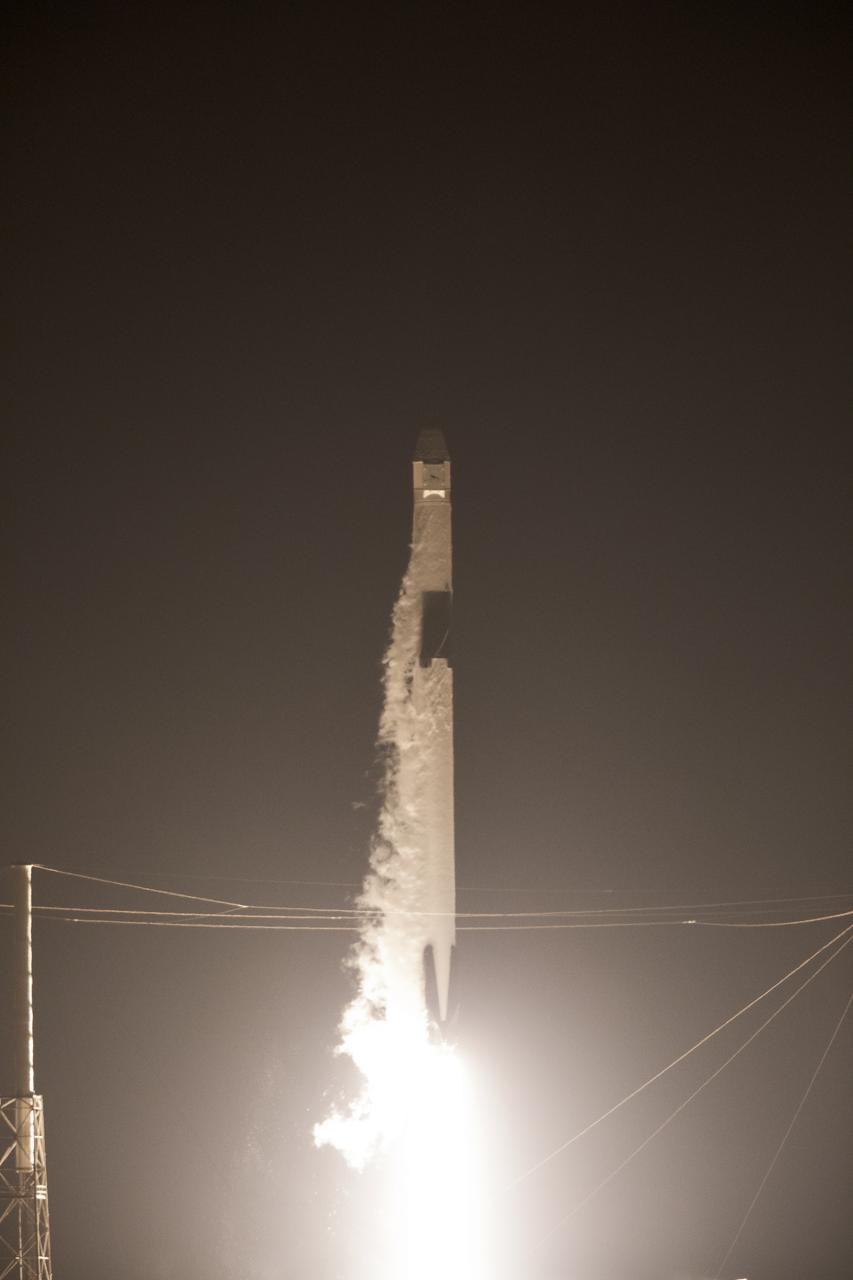

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module lifts off Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in the early morning May 4, 2019. Liftoff was at 2:48 a.m. EDT. This is SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module lifts off Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in the early morning May 4, 2019. Liftoff was at 2:48 a.m. EDT. This is SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.
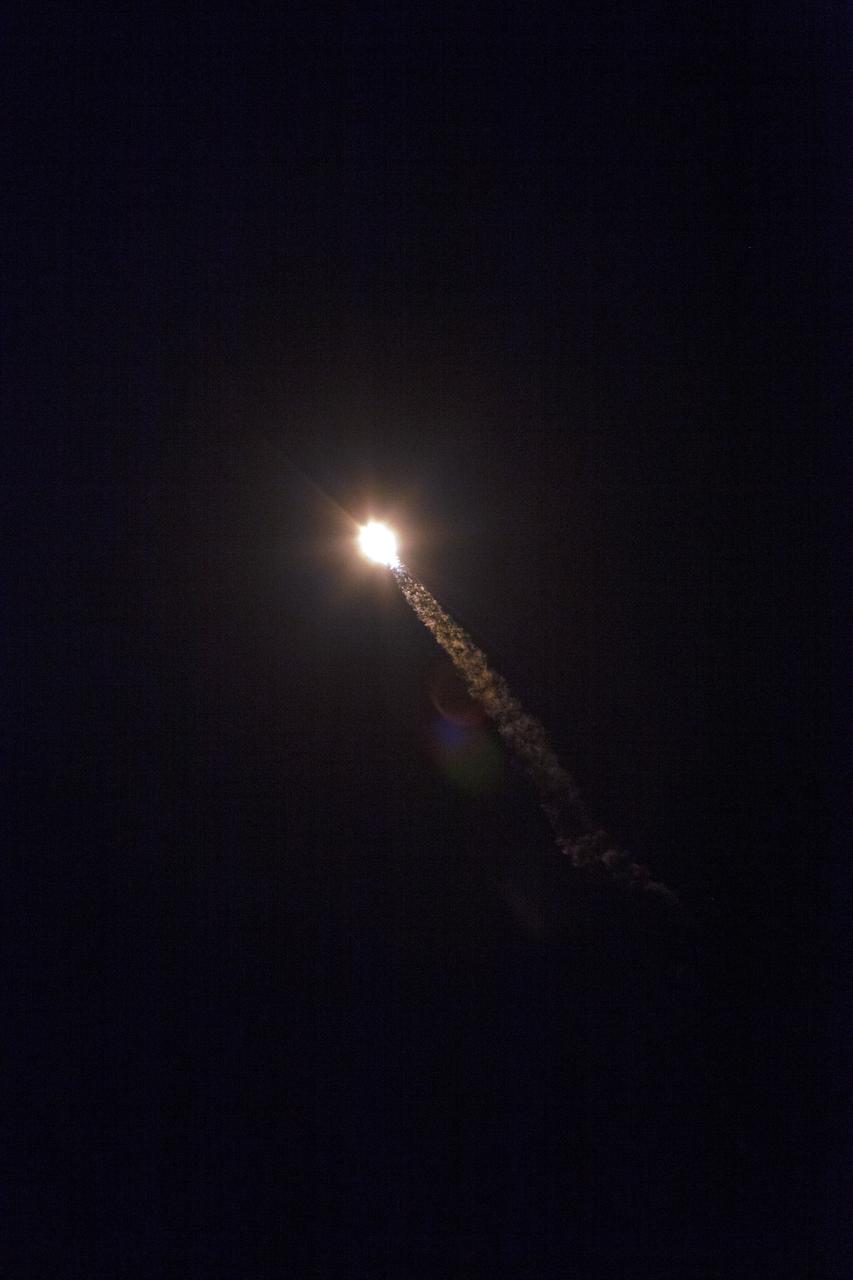

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module climbs upward after liftoff from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in the early morning May 4, 2019. Liftoff was at 2:48 a.m. EDT. This is SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.
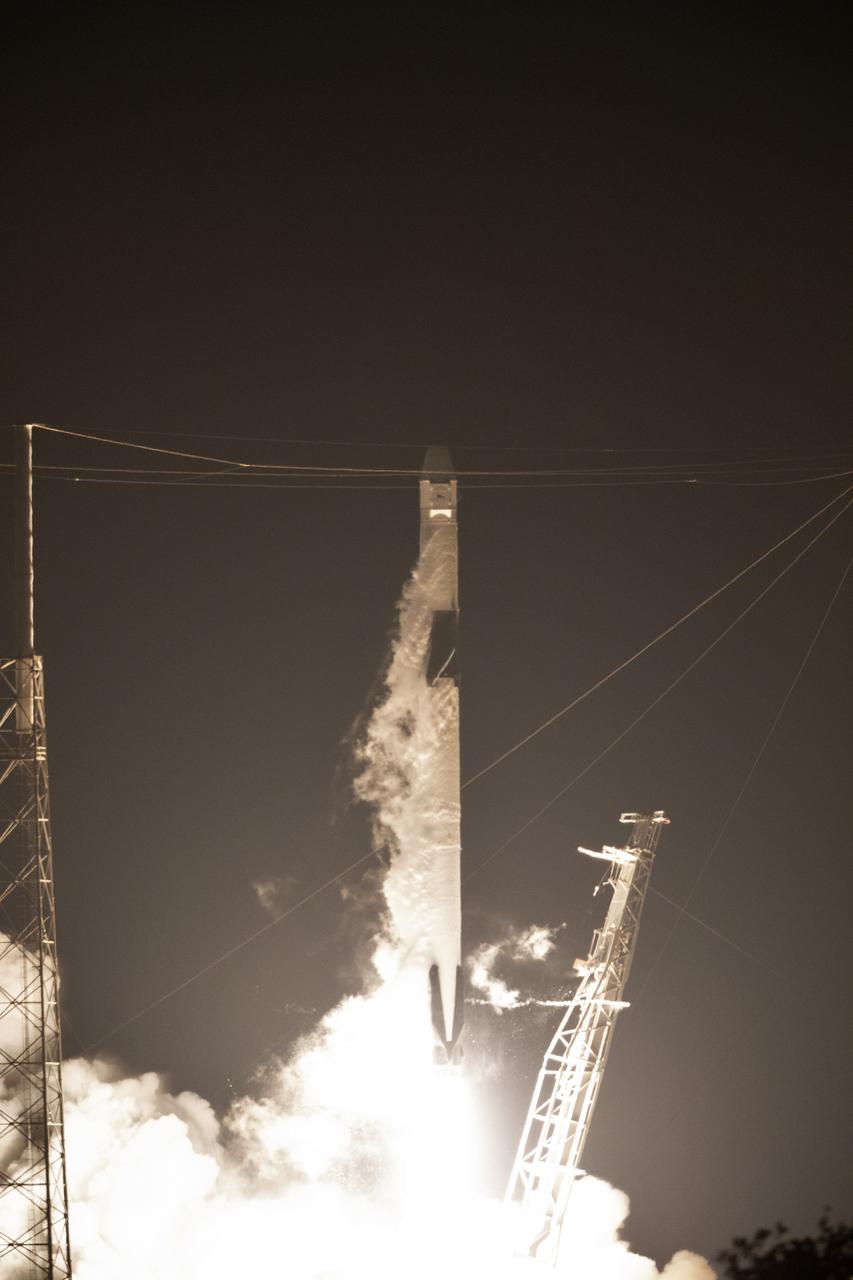

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module lifts off Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in the early morning May 4, 2019. Liftoff was at 2:48 a.m. EDT. This is SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.
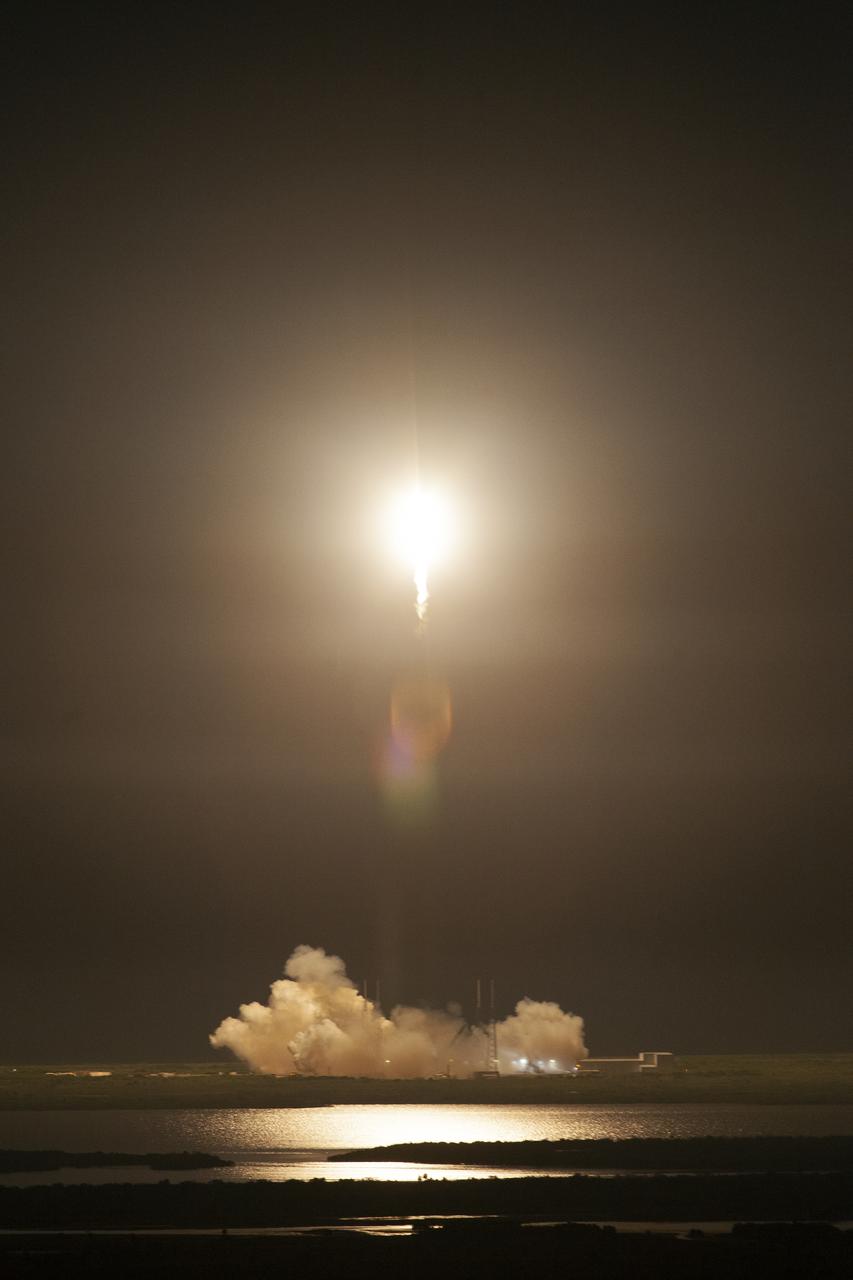

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module climbs upward after liftoff from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in the early morning May 4, 2019. Liftoff was at 2:48 a.m. EDT. This is SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.
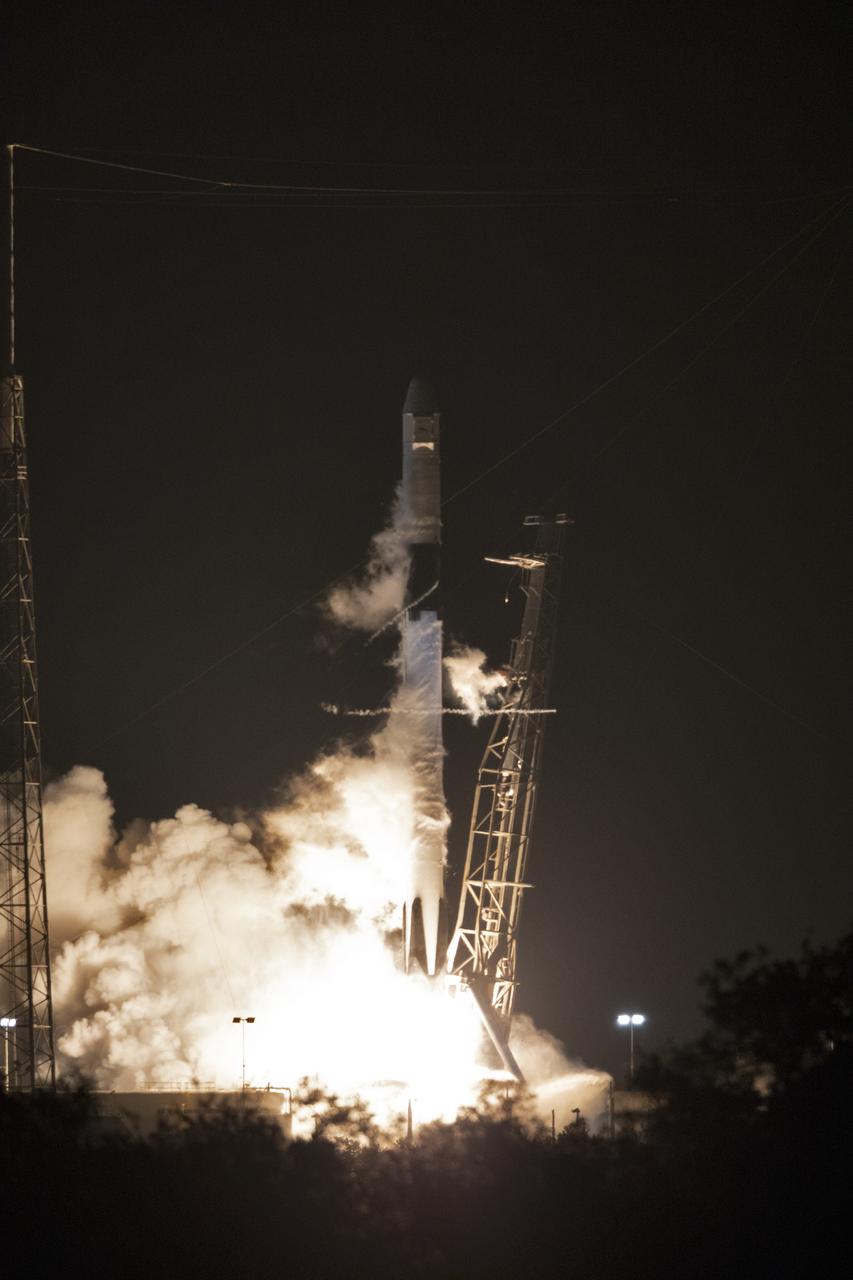

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module lifts off Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in the early morning May 4, 2019. Liftoff was at 2:48 a.m. EDT. This is SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.
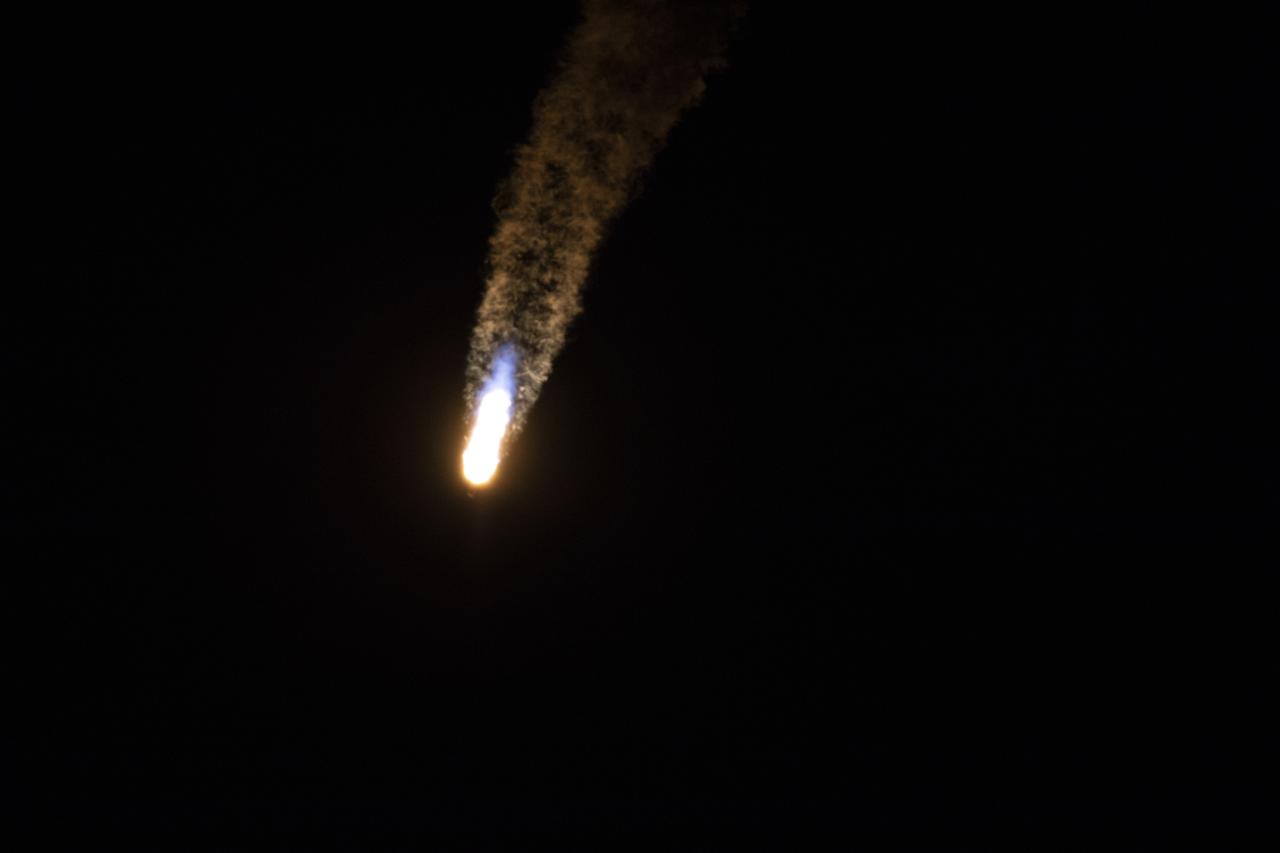

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module climbs upward after liftoff from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in the early morning May 4, 2019. Liftoff was at 2:48 a.m. EDT. This is SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.
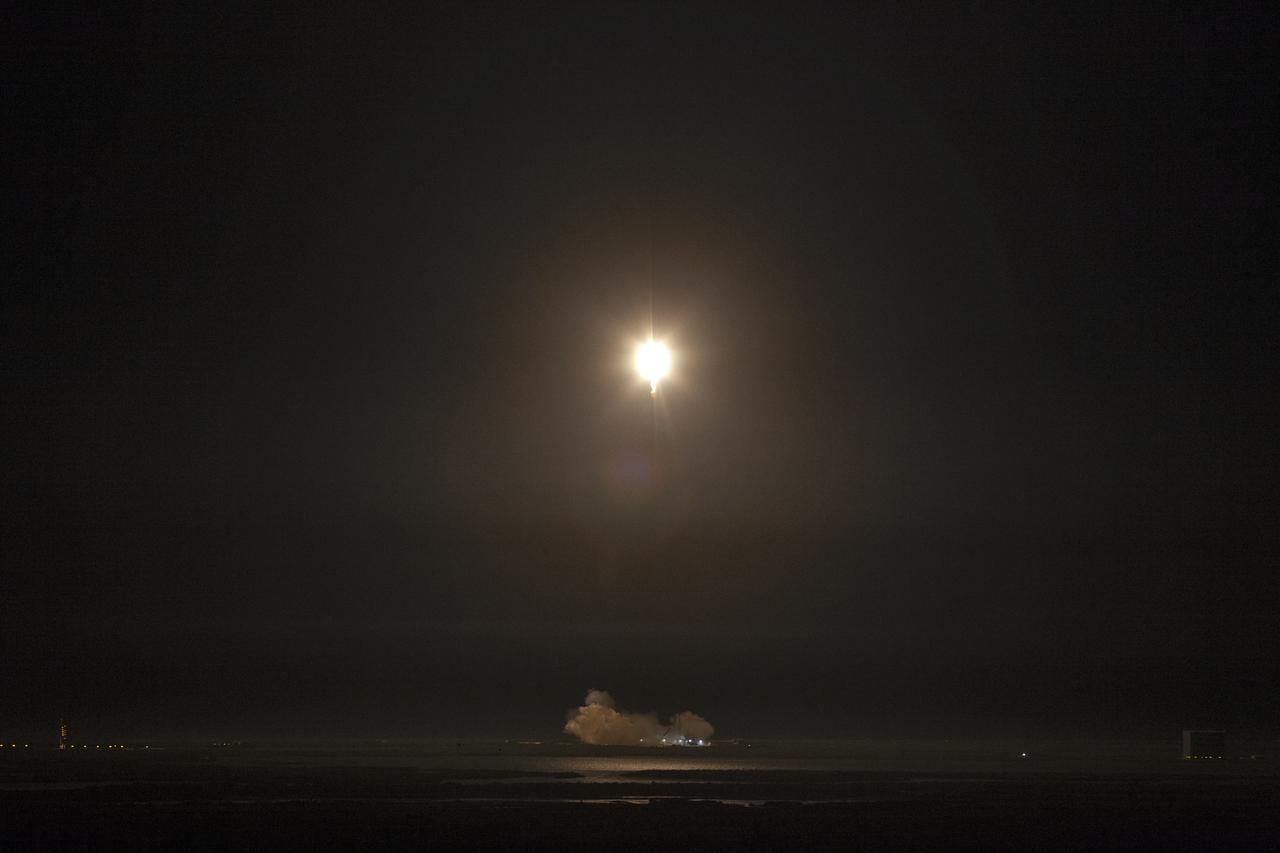

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module climbs upward after liftoff from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in the early morning May 4, 2019. Liftoff was at 2:48 a.m. EDT. This is SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.
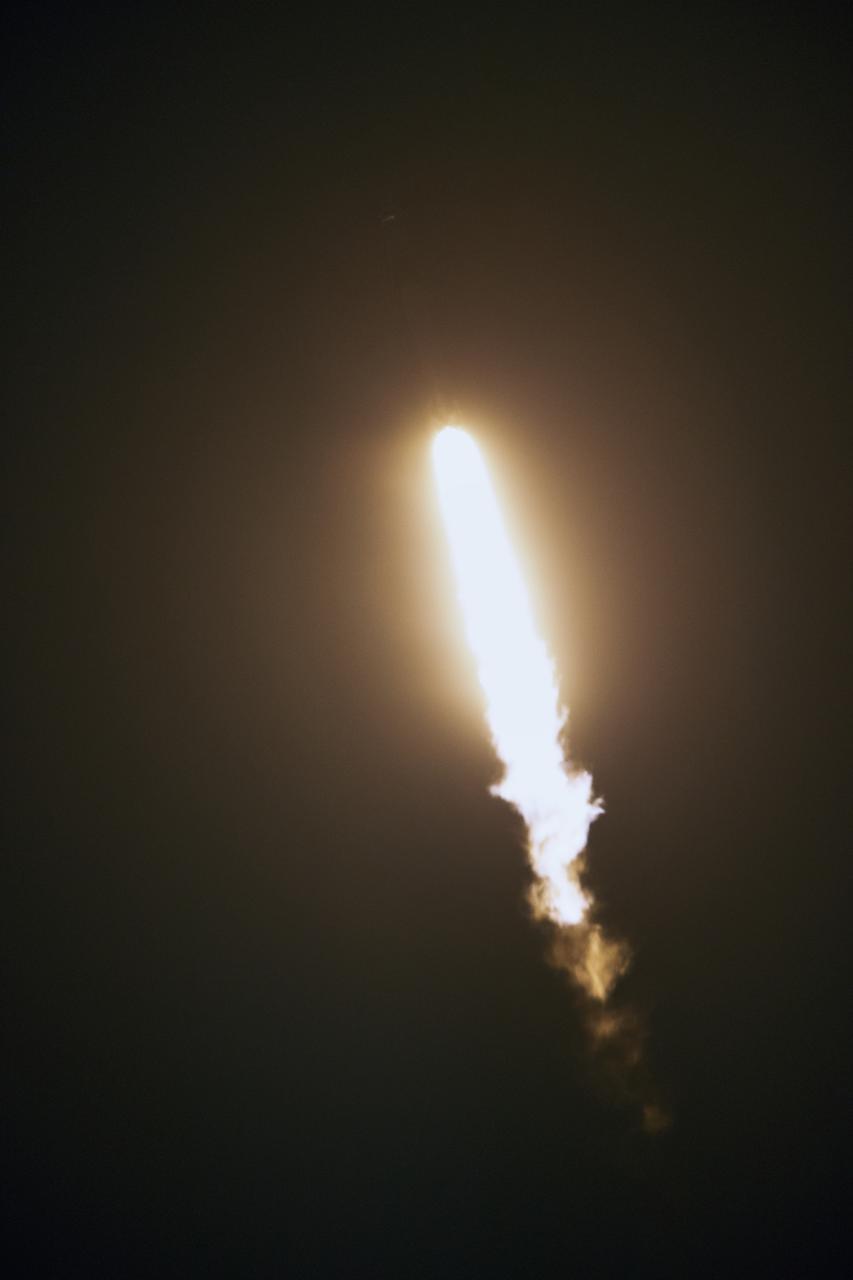

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module climbs upward after liftoff from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in the early morning May 4, 2019. Liftoff was at 2:48 a.m. EDT. This is SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.
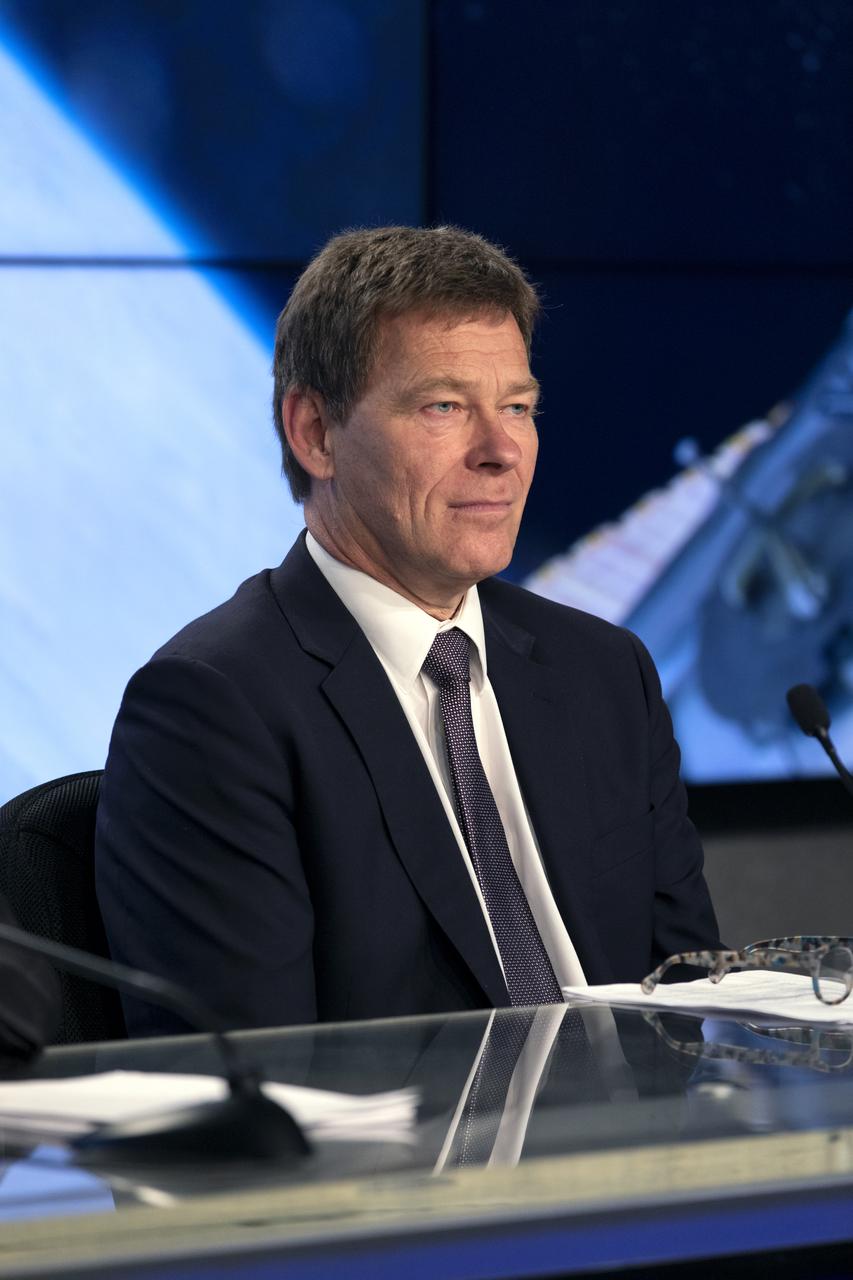

Hans Koenigsmann, VP, Build and Flight Reliability with SpaceX, speaks to members of the news media during a prelaunch news conference for SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station on May 2, 2019, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon cargo module are scheduled to launch no earlier than May 3, 2019, from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
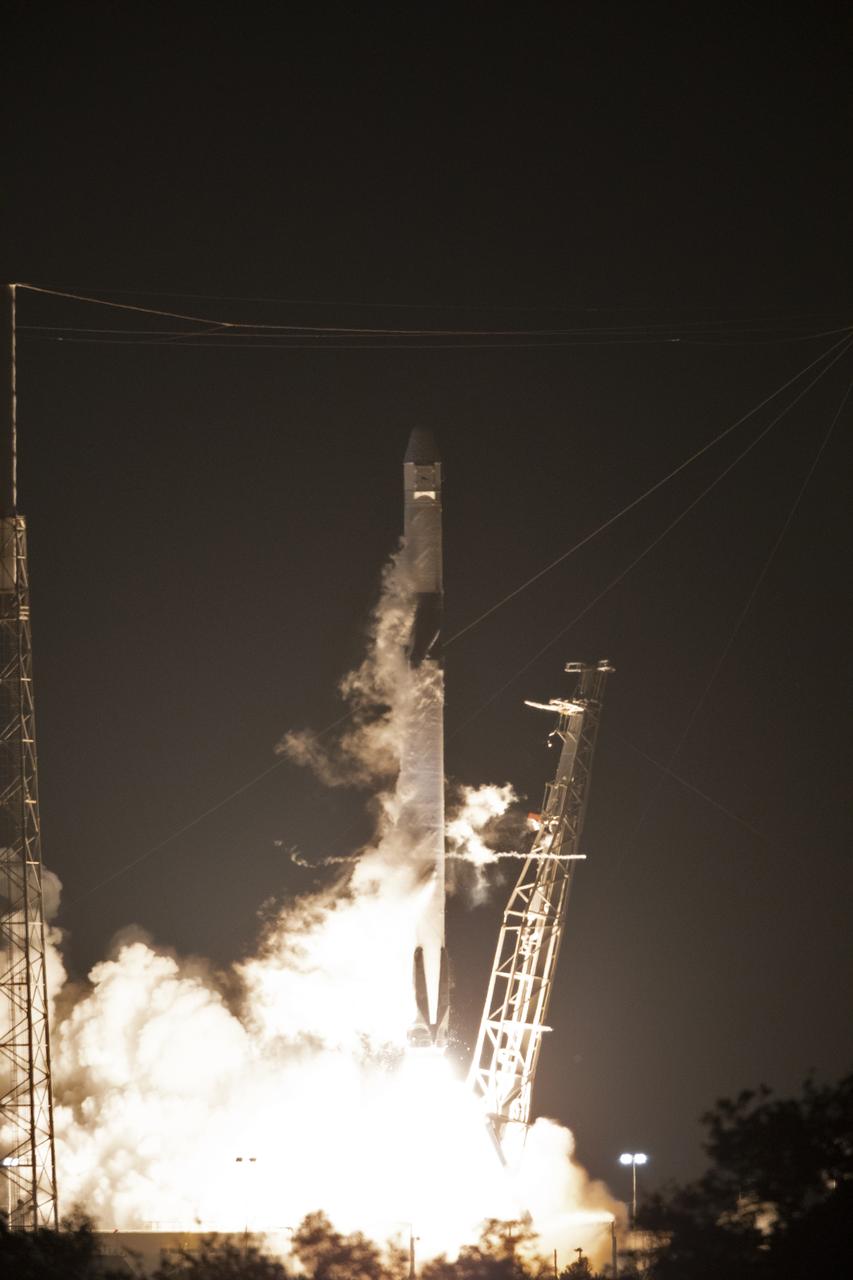

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module lifts off Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in the early morning May 4, 2019. Liftoff was at 2:48 a.m. EDT. This is SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.
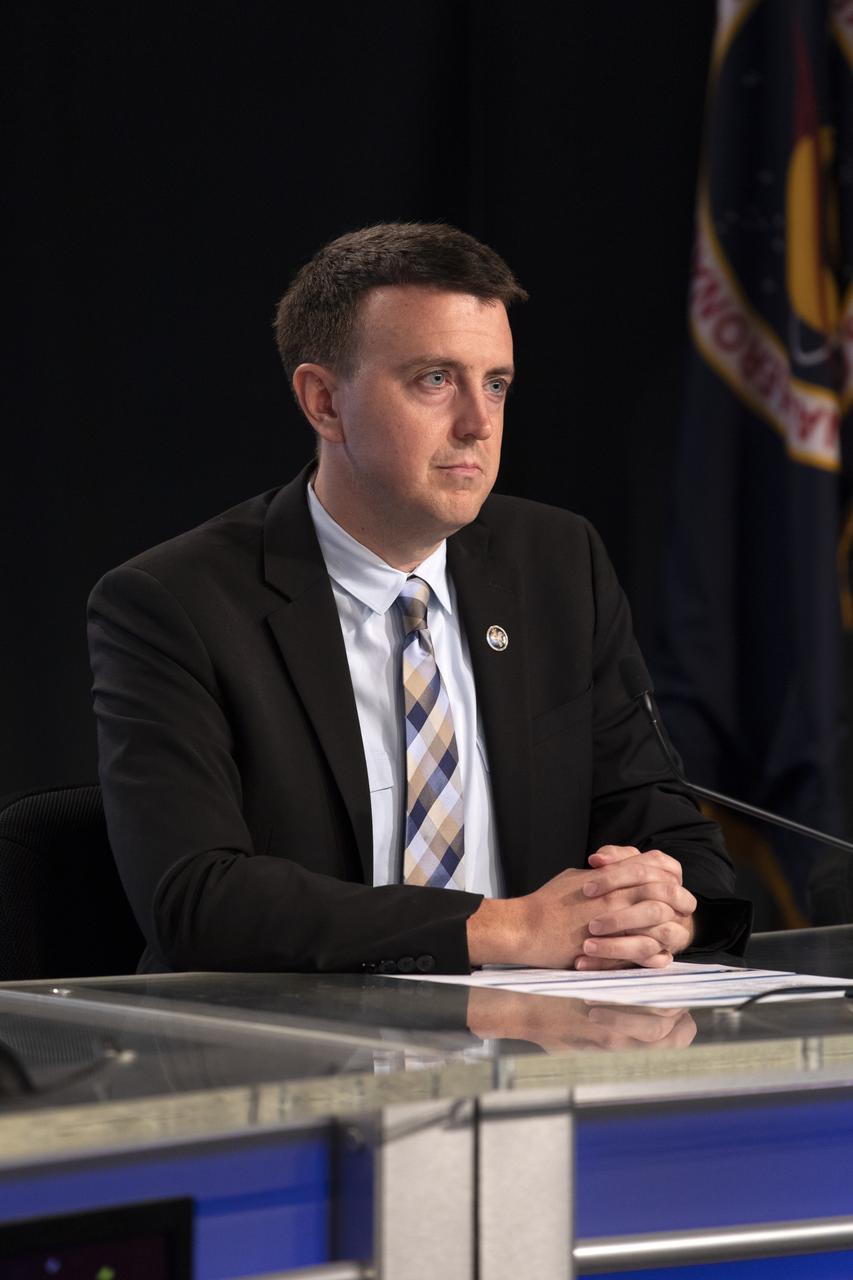

Will Ulrich, 45th Space Wing weather officer with the U.S. Air Force, speaks to members of the news media during a prelaunch news conference for SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station on May 2, 2019, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon cargo module are scheduled to launch no earlier than May 3, 2019, from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module lifts off Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in the early morning May 4, 2019. Liftoff was at 2:48 a.m. EDT. This is SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.
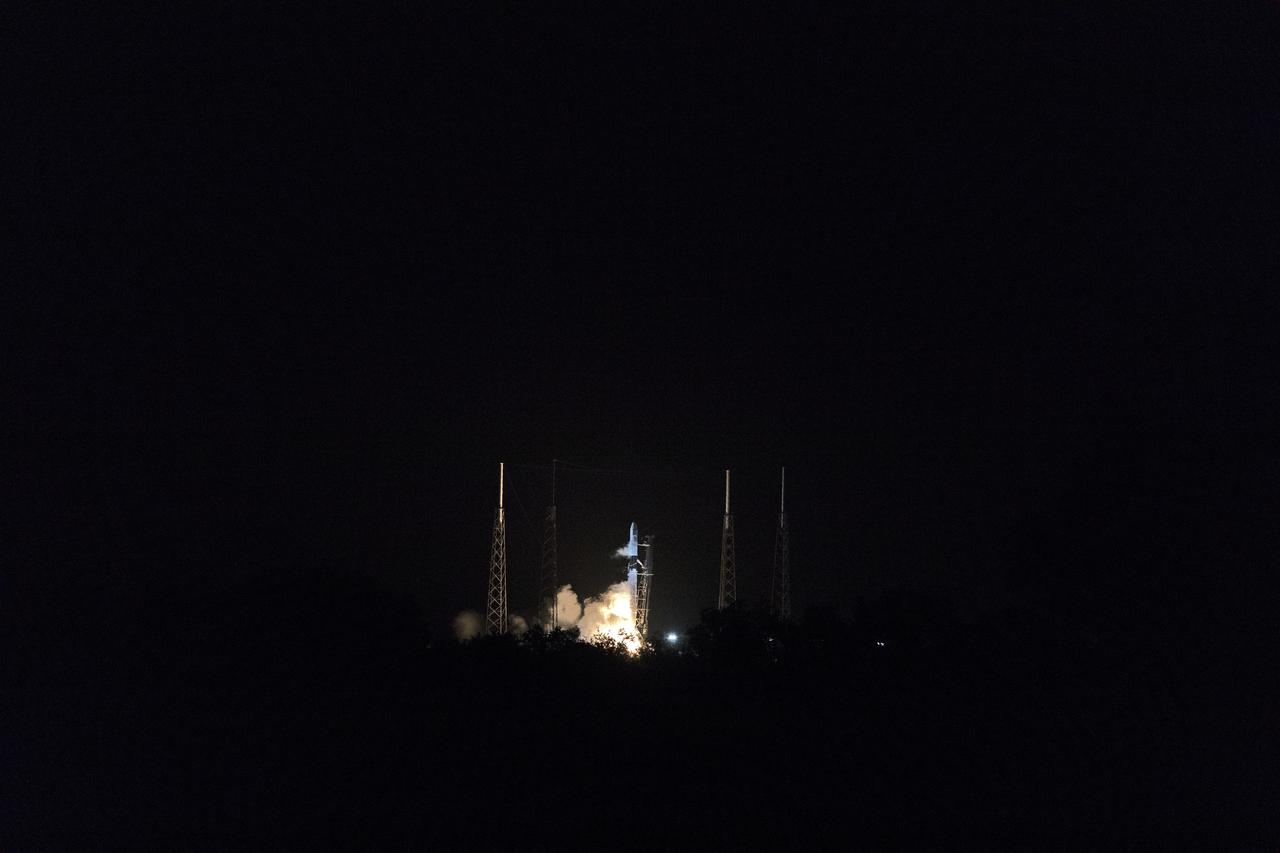

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module lifts off Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in the early morning May 4, 2019. Liftoff was at 2:48 a.m. EDT. This is SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module lifts off Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in the early morning May 4, 2019. Liftoff was at 2:48 a.m. EDT. This is SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module lifts off Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in the early morning May 4, 2019. Liftoff was at 2:48 a.m. EDT. This is SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.
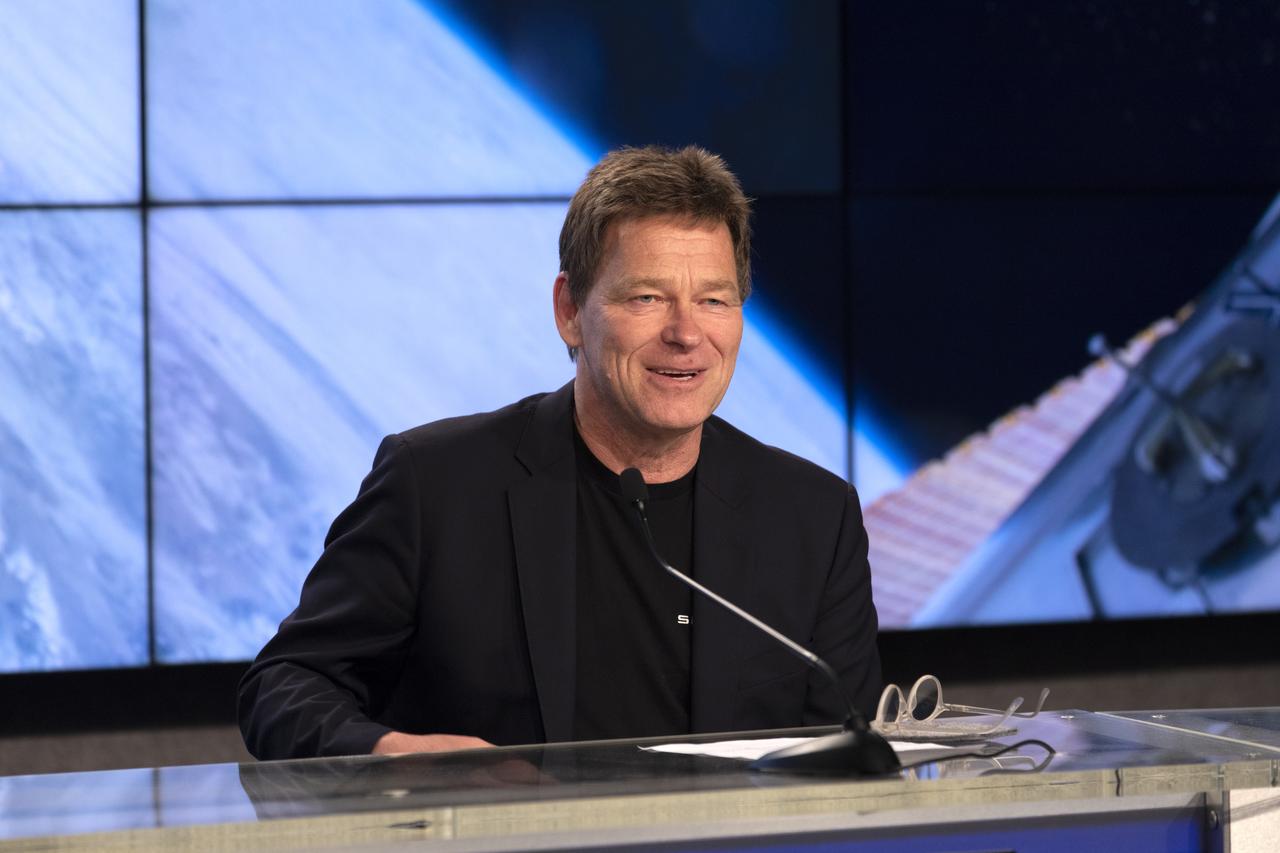

Hans Koenigsmann, vice president, Build and Flight Reliability with SpaceX, speaks to members of the news media during a postlaunch news conference at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 4, 2019, for SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission to the International Space Station for the agency. The company’s Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module lifted off from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida at 2:48 a.m. EDT. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.
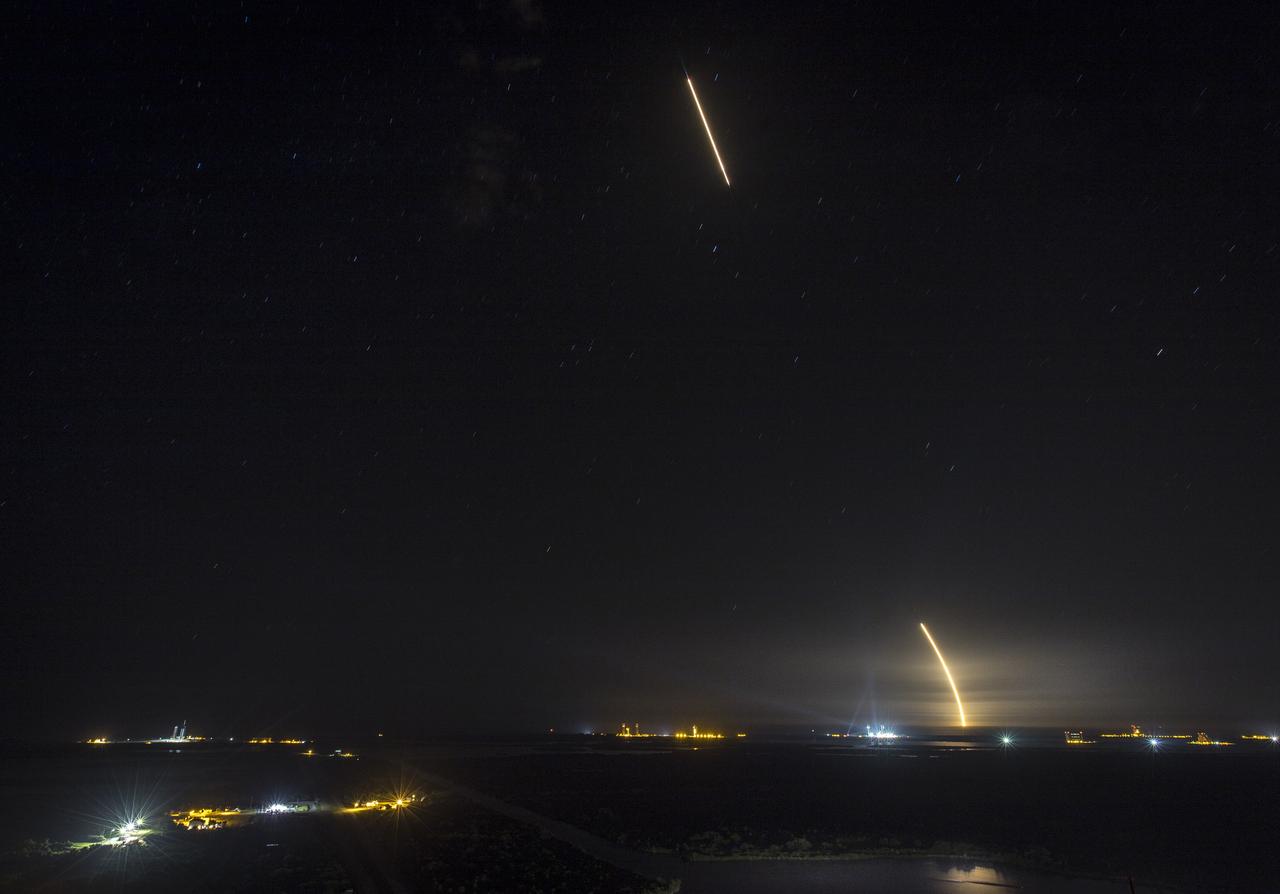

In this long exposure photograph, the first stage of the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket lands on the company's drone ship in the Atlantic Ocean on May 4, 2019. The Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module lifted off Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida at 2:48 a.m. EDT. This is SpaceX's 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module creates a streak across the sky as it climbs upward after liftoff from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in the early morning May 4, 2019. Liftoff was at 2:48 a.m. EDT. This is SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.
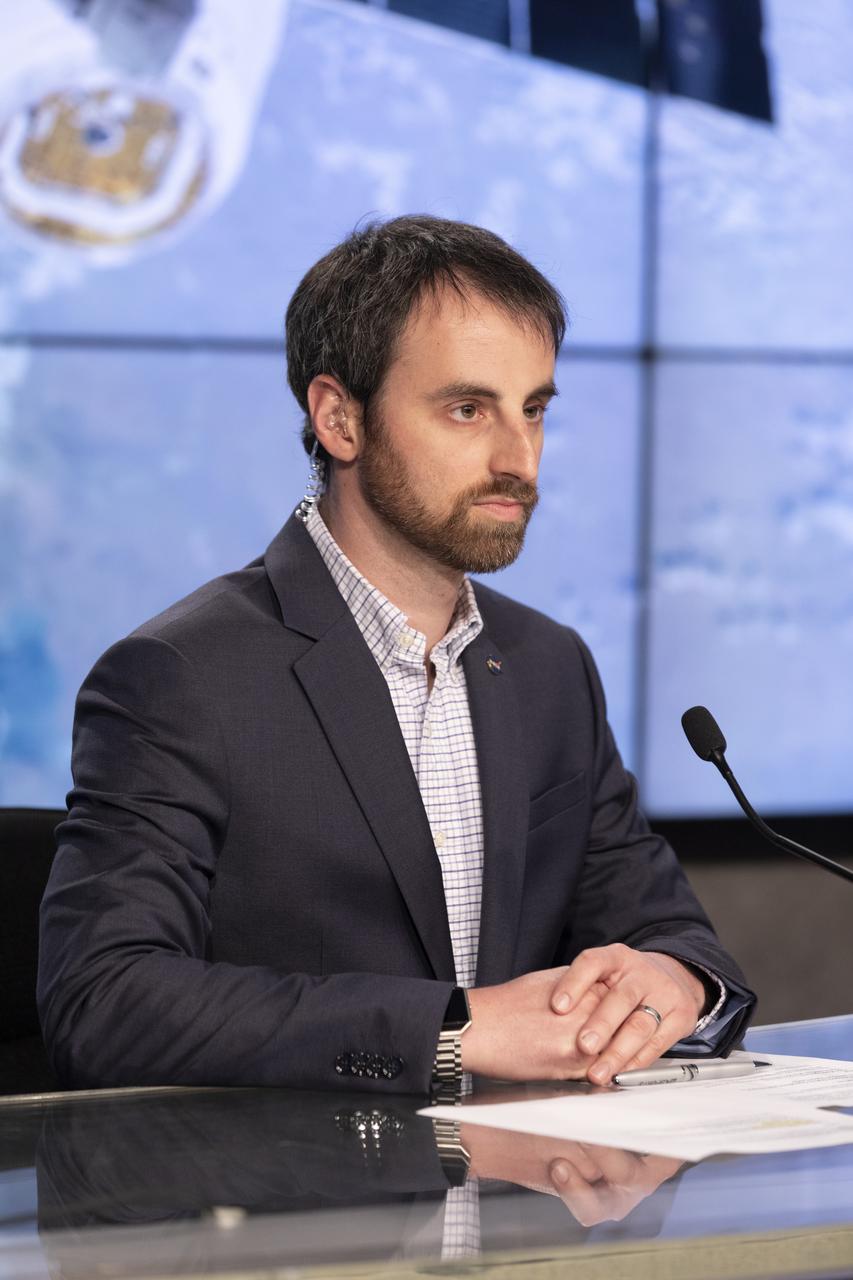

Josh Santora, with NASA Communications, moderates a postlaunch news conference at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 4, 2019, for SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission to the International Space Station for the agency. The company’s Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module lifted off from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida at 2:48 a.m. EDT. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.
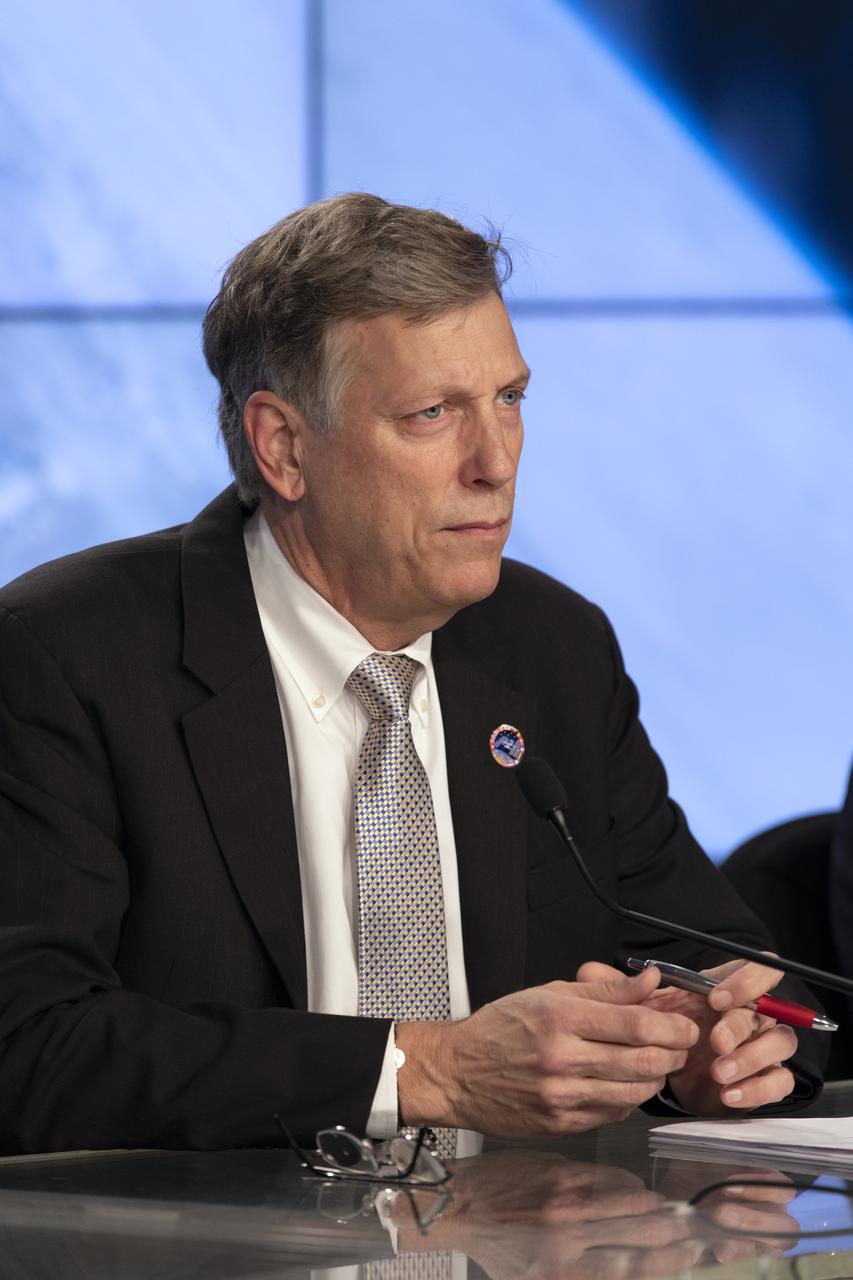

Kenny Todd, manager, International Space Station Operations and Integration, NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, speaks to members of the news media during a prelaunch news conference for SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission for NASA to the International Space Station on May 2, 2019, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon cargo module are scheduled to launch no earlier than May 3, 2019, from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
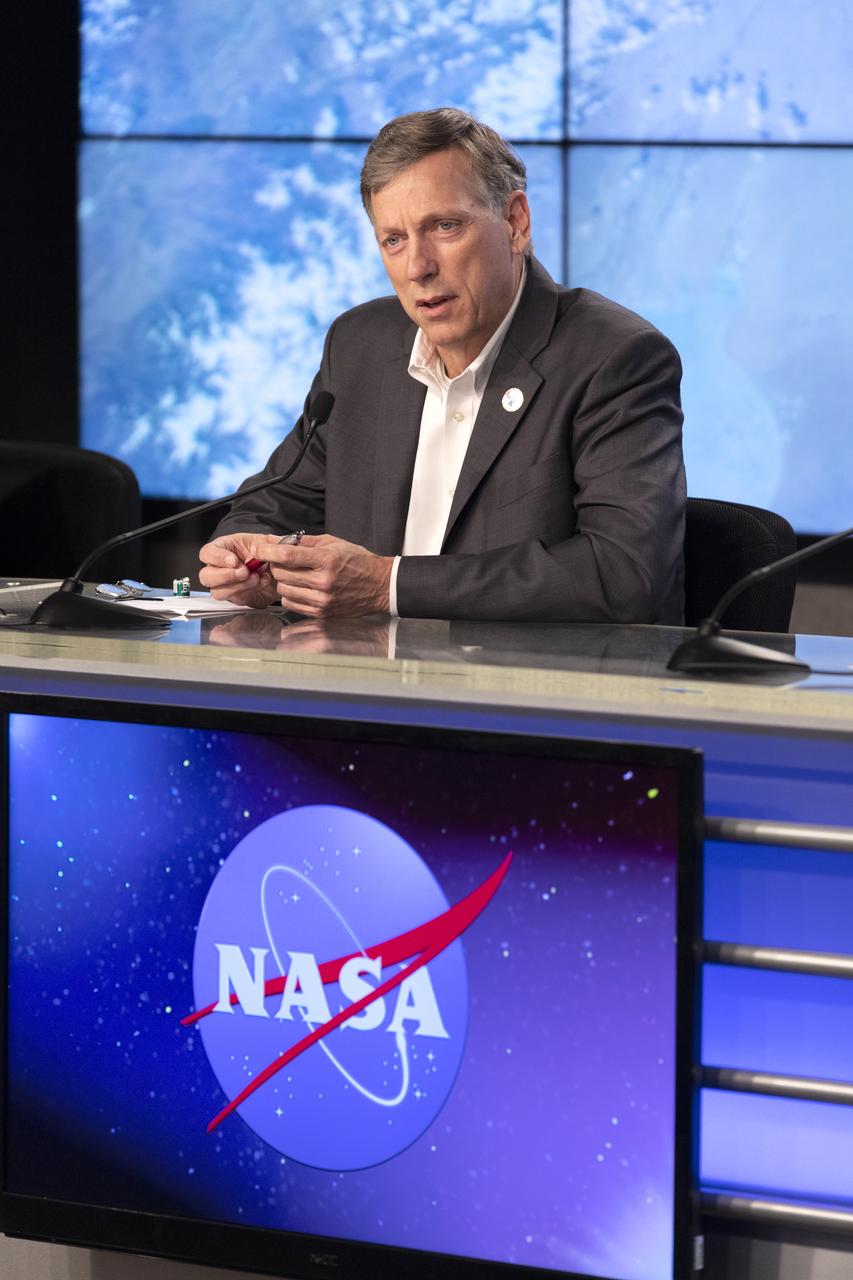

Kenny Todd, manager, International Space Station Operations and Integration at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston speaks to members of the news media during a postlaunch news conference at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 4, 2019, for SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission to the International Space Station for the agency. The company’s Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module lifted off from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida at 2:48 a.m. EDT. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.
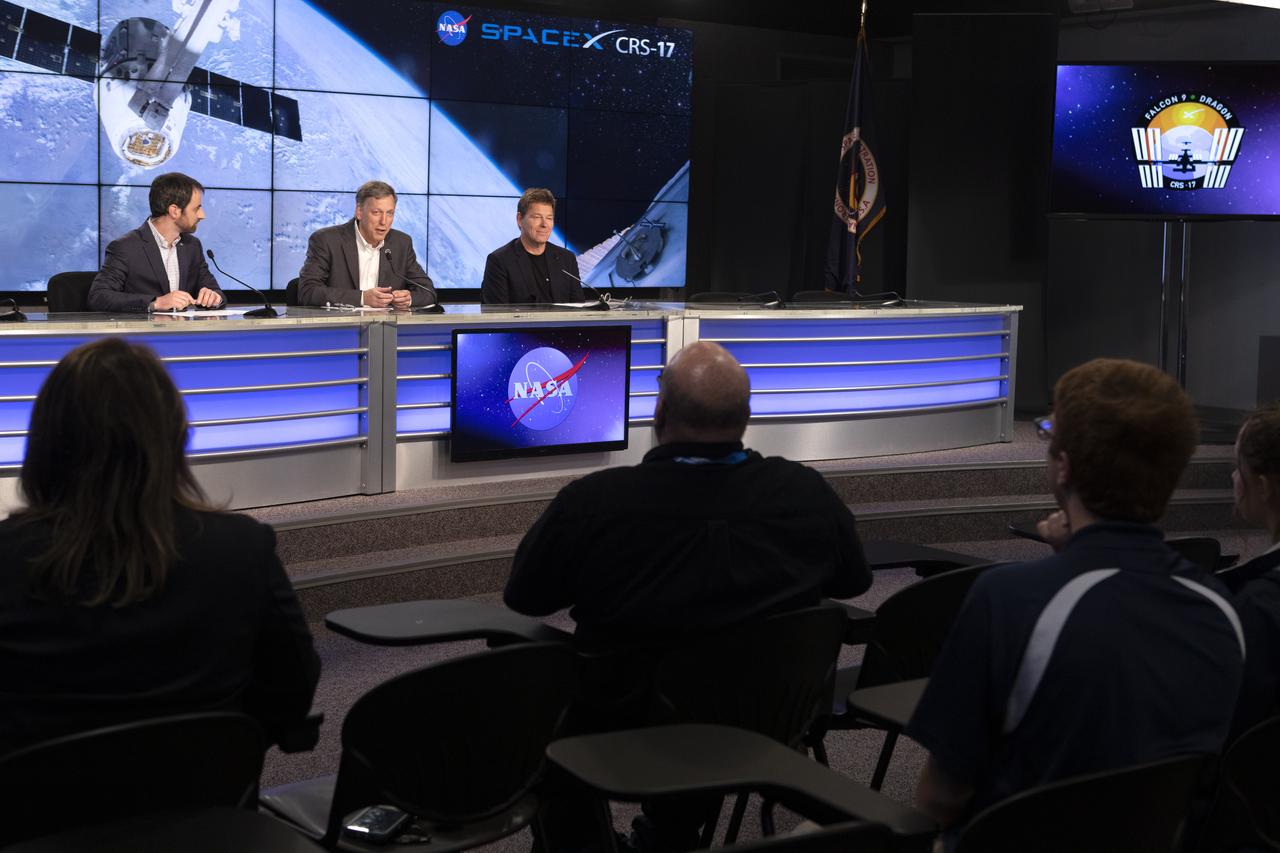

From left, Josh Santora, moderator with NASA Communications; Kenny Todd, manager, International Space Station Operations and Integration at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston; and Hans Koenigsmann, vice president, Build and Flight Reliability with SpaceX, speak to members of the news media during a postlaunch news conference at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 4, 2019, for SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission to the International Space Station for the agency. The company’s Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module lifted off from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida at 2:48 a.m. EDT. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.

From left, Josh Santora, moderator with NASA Communications; Kenny Todd, manager, International Space Station Operations and Integration at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston; and Hans Koenigsmann, vice president, Build and Flight Reliability with SpaceX, speak to members of the news media during a postlaunch news conference at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 4, 2019, for SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission to the International Space Station for the agency. The company’s Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module lifted off from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida at 2:48 a.m. EDT. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.
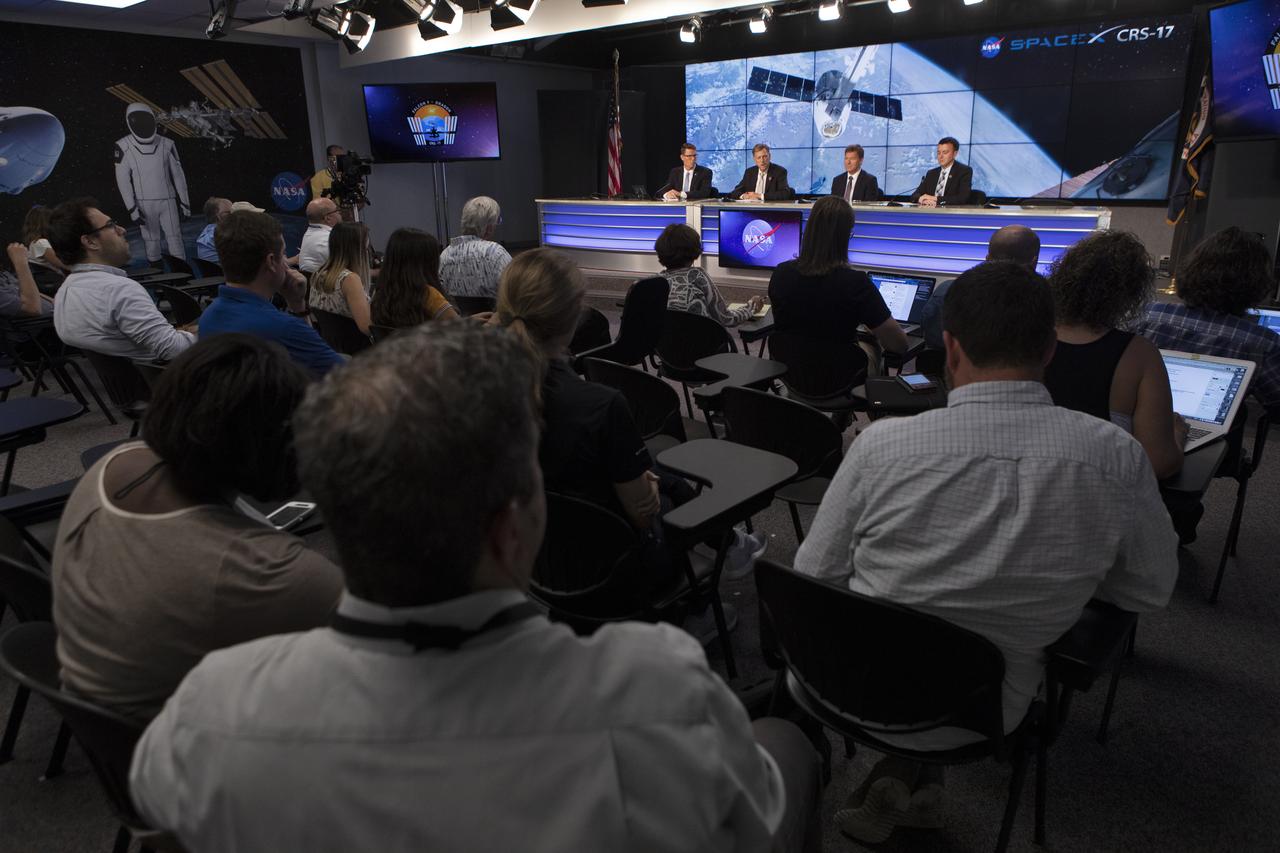

Members of the news media attend a prelaunch news conference for SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission to the International Space Station for NASA on May 2, 2019, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. From left, are Derrol Nail, NASA Communications moderator; Kenny Todd, Manager, International Space Station Operations and Integration at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston; Hans Koenigsmann, VP, Build and Flight Reliability with SpaceX; and Will Ulrich, 45th launch weather officer with the U.S. Air Force. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon cargo module are scheduled to launch no earlier than May 3, 2019, from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.

From left, Kenny Todd, manager, International Space Station Operations and Integration at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston; and Hans Koenigsmann, vice president, Build and Flight Reliability with SpaceX, speak to members of the news media during a postlaunch news conference at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 4, 2019, for SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission to the International Space Station for the agency. The company’s Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module lifted off from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida at 2:48 a.m. EDT. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.

From left, Josh Santora, moderator with NASA Communications; Kenny Todd, manager, International Space Station Operations and Integration at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston; and Hans Koenigsmann, vice president, Build and Flight Reliability with SpaceX, speak to members of the news media during a postlaunch news conference at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 4, 2019, for SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission to the International Space Station for the agency. The company’s Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon cargo module lifted off from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida at 2:48 a.m. EDT. The Dragon cargo module will deliver about 5,500 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew.

A prelaunch news conference for SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission to the International Space Station for NASA is held at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 2, 2019. From left, are Derrol Nail, NASA Communications moderator; Kenny Todd, Manager, International Space Station Operations and Integration at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston; Hans Koenigsmann, VP, Build and Flight Reliability with SpaceX; and Will Ulrich, 45th launch weather officer with the U.S. Air Force. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon cargo module are scheduled to launch no earlier than May 3, 2019, from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.

A prelaunch news conference for SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission to the International Space Station for NASA is held at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 2, 2019. From left, are Derrol Nail, NASA Communications moderator; Kenny Todd, Manager, International Space Station Operations and Integration at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston; Hans Koenigsmann, VP, Build and Flight Reliability with SpaceX; and Will Ulrich, 45th launch weather officer with the U.S. Air Force. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon cargo module are scheduled to launch no earlier than May 3, 2019, from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
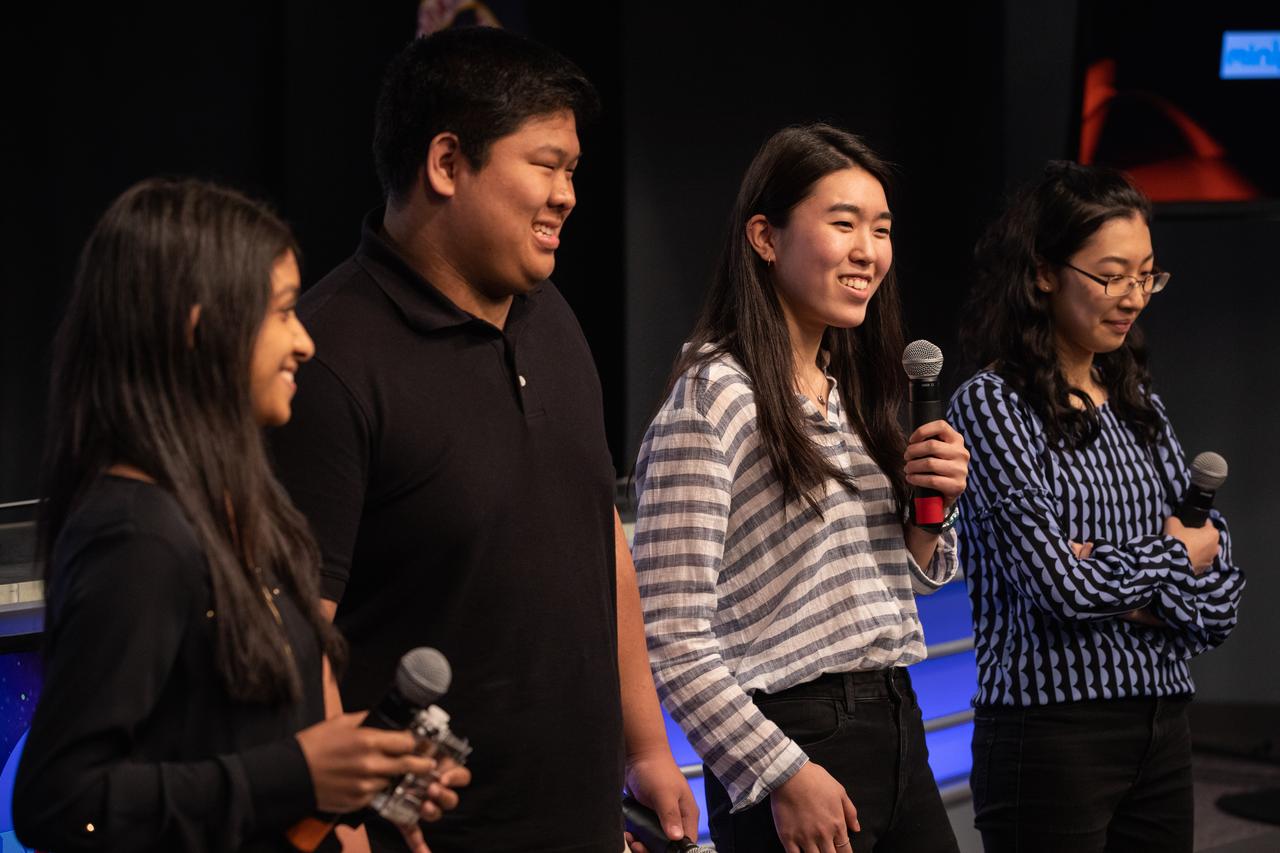

From left, high school student Aarthi Vijayakumar, MIT student David Li, and high school students Michelle Sung and Rebecca Li talk about their winning Genes in Space experiment for NASA during a What’s On Board science briefing to NASA Social participants at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 29, 2019. The briefing was held for SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission to the International Space Station. NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory-3 (OCO-3) and Space Test Program-Houston 6 (STP-H6) are two of the experiments that also will be delivered to the space station on CRS-17. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon cargo module are scheduled to launch no earlier than May 3, 2019, from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
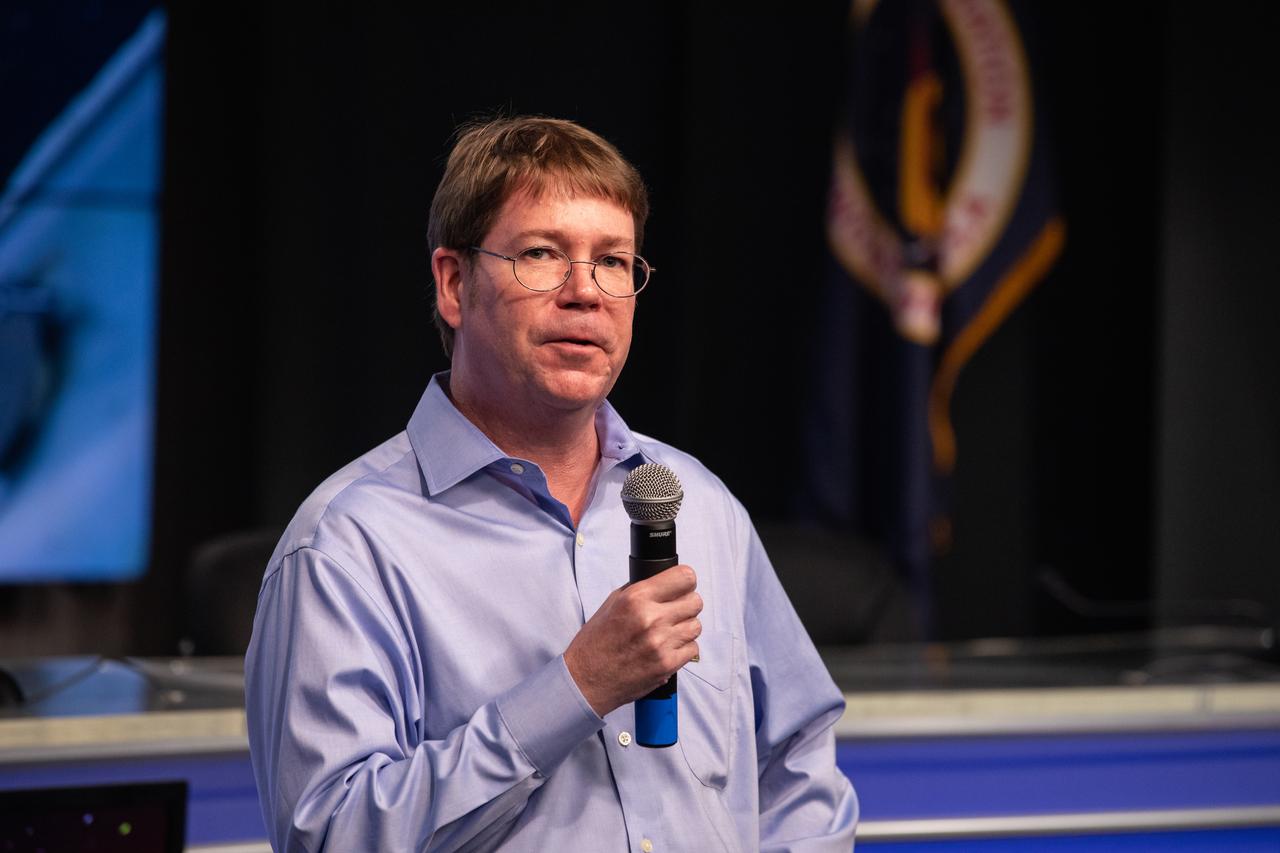

Dr. Edward Kelly, with the University of Washington School of Pharmacy, discusses The Tissue Chips in Space project during a What’s On Board science briefing to NASA Social participants at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 29, 2019. The briefing was held for SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission to the International Space Station. Kelly and other researchers will send kidney tissue chip models to the space station to understand how microgravity affects kidney function, such as changes in vitamin D metabolism and formation of kidney stones. NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory-3 (OCO-3) and Space Test Program-Houston 6 (STP-H6) are two of the experiments that also will be delivered to the space station on CRS-17. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon cargo module are scheduled to launch no earlier than May 3, 2019, from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
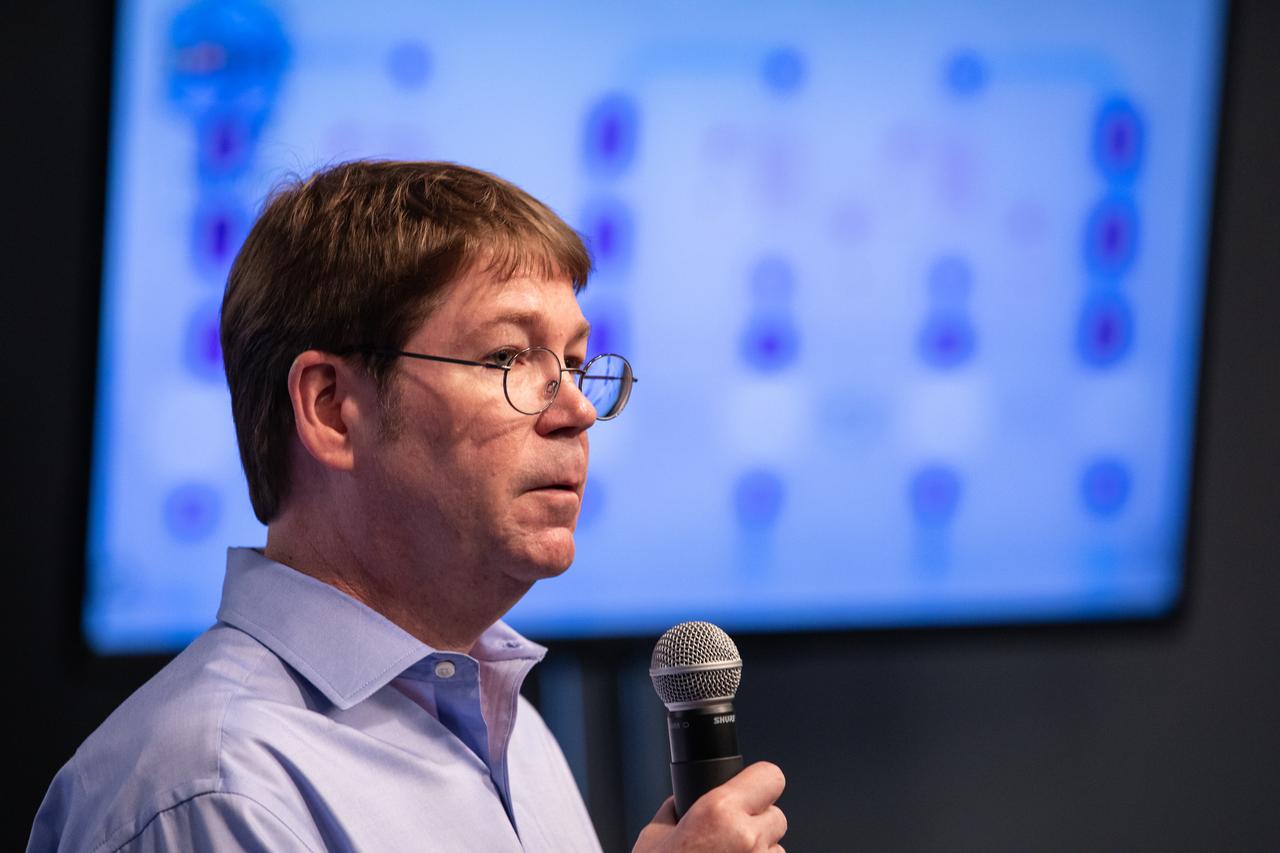

Dr. Edward Kelly, with the University of Washington School of Pharmacy, discusses The Tissue Chips in Space project during a What’s On Board science briefing to NASA Social participants at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 29, 2019. The briefing was held for SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission to the International Space Station. Kelly and other researchers will send kidney tissue chip models to the space station to understand how microgravity affects kidney function, such as changes in vitamin D metabolism and formation of kidney stones. NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory-3 (OCO-3) and Space Test Program-Houston 6 (STP-H6) are two of the experiments that also will be delivered to the space station on CRS-17. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon cargo module are scheduled to launch no earlier than May 3, 2019, from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
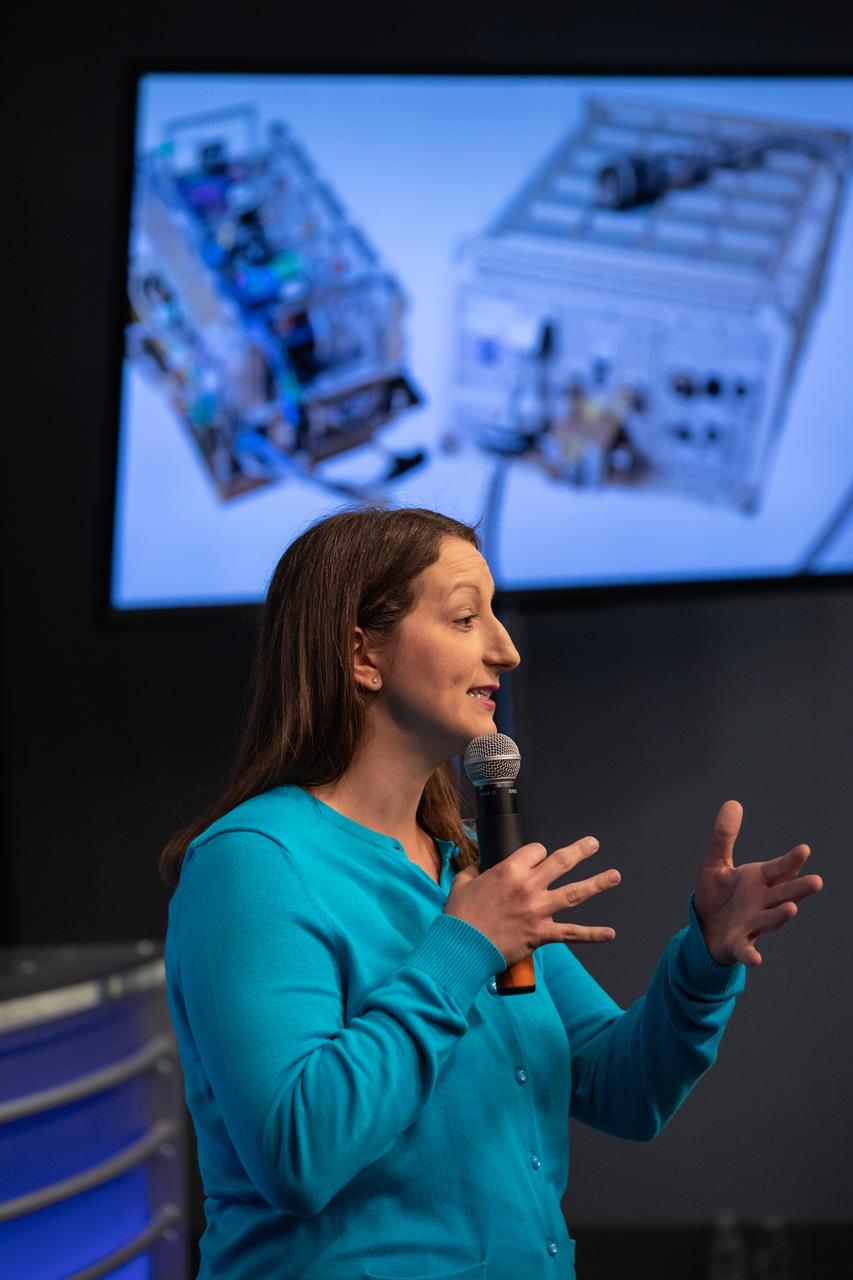
Dr. Kristen John, principal investigator for Hermes at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, talks to NASA Social participants during a What’s On Board science briefing at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 29, 2019. The briefing was held for SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission to the International Space Station. John presented on the Hermes Facility, an experimental microgravity facility that enables science experiments, microgravity exposure testing, testing of engineering components and CubeSats and any payloads that can fit in the Hermes design and operations constraints. NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory-3 (OCO-3) and Space Test Program-Houston 6 (STP-H6) are two of the experiments that also will be delivered to the space station on CRS-17. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon cargo module are scheduled to launch no earlier than May 3, 2019, from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
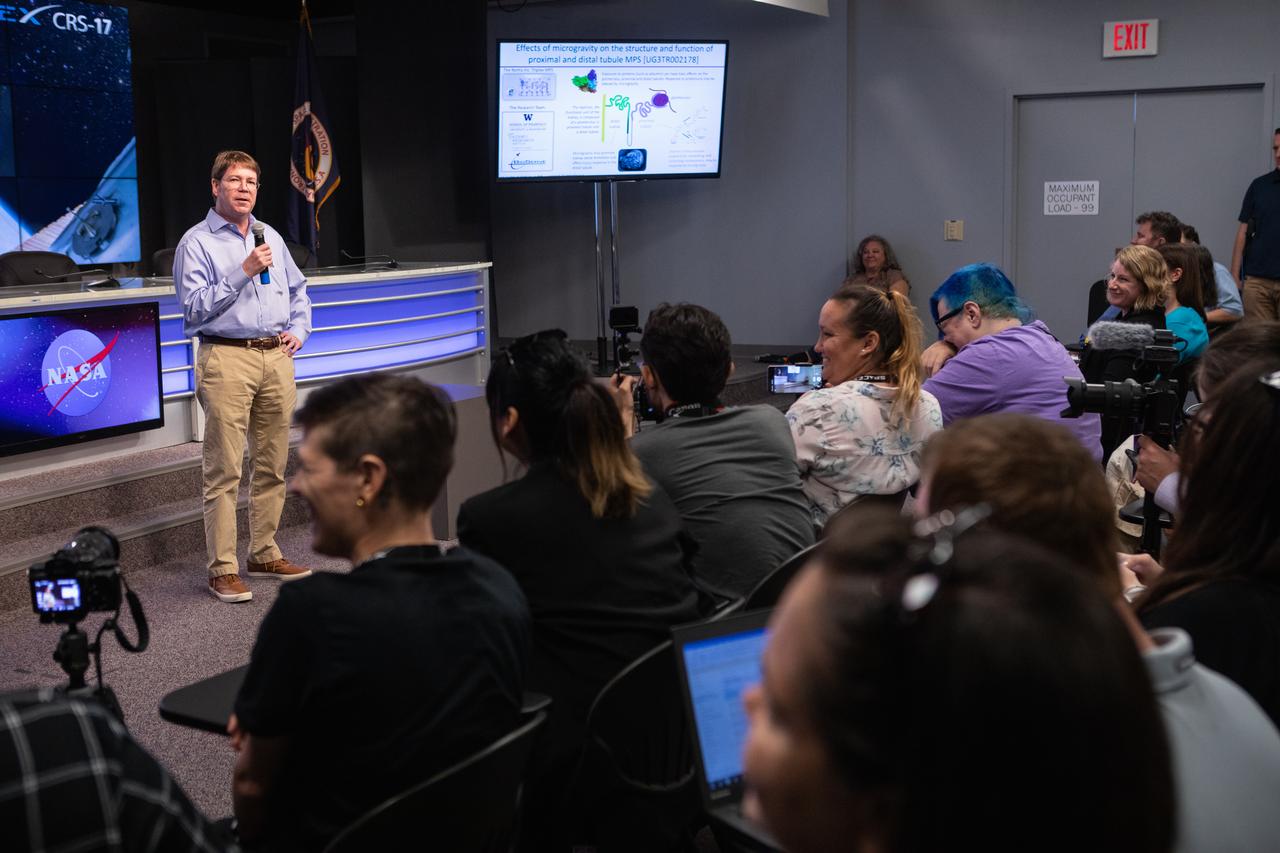

Dr. Edward Kelly, with the University of Washington School of Pharmacy, discusses The Tissue Chips in Space project during a What’s On Board science briefing to NASA Social participants at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 29, 2019. The briefing was held for SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission to the International Space Station. Kelly and other researchers will send kidney tissue chip models to the space station to understand how microgravity affects kidney function, such as changes in vitamin D metabolism and formation of kidney stones. NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory-3 (OCO-3) and Space Test Program-Houston 6 (STP-H6) are two of the experiments that also will be delivered to the space station on CRS-17. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon cargo module are scheduled to launch no earlier than May 3, 2019, from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
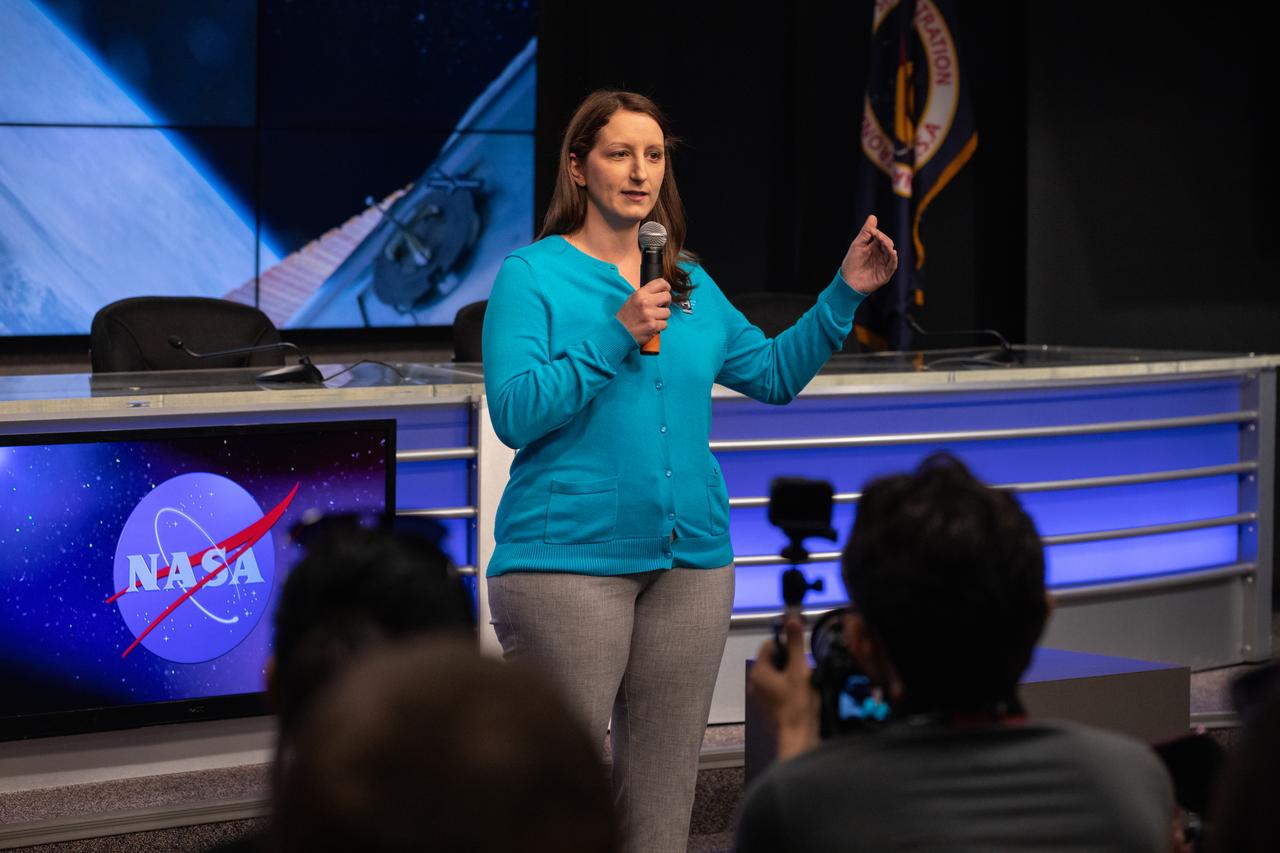

Dr. Kristen John, principal investigator for Hermes at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, talks to NASA Social participants during a What’s On Board science briefing at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 29, 2019. The briefing was held for SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission to the International Space Station. John presented on the Hermes Facility, an experimental microgravity facility that enables science experiments, microgravity exposure testing, testing of engineering components and CubeSats and any payloads that can fit in the Hermes design and operations constraints. NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory-3 (OCO-3) and Space Test Program-Houston 6 (STP-H6) are two of the experiments that also will be delivered to the space station on CRS-17. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon cargo module are scheduled to launch no earlier than May 3, 2019, from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
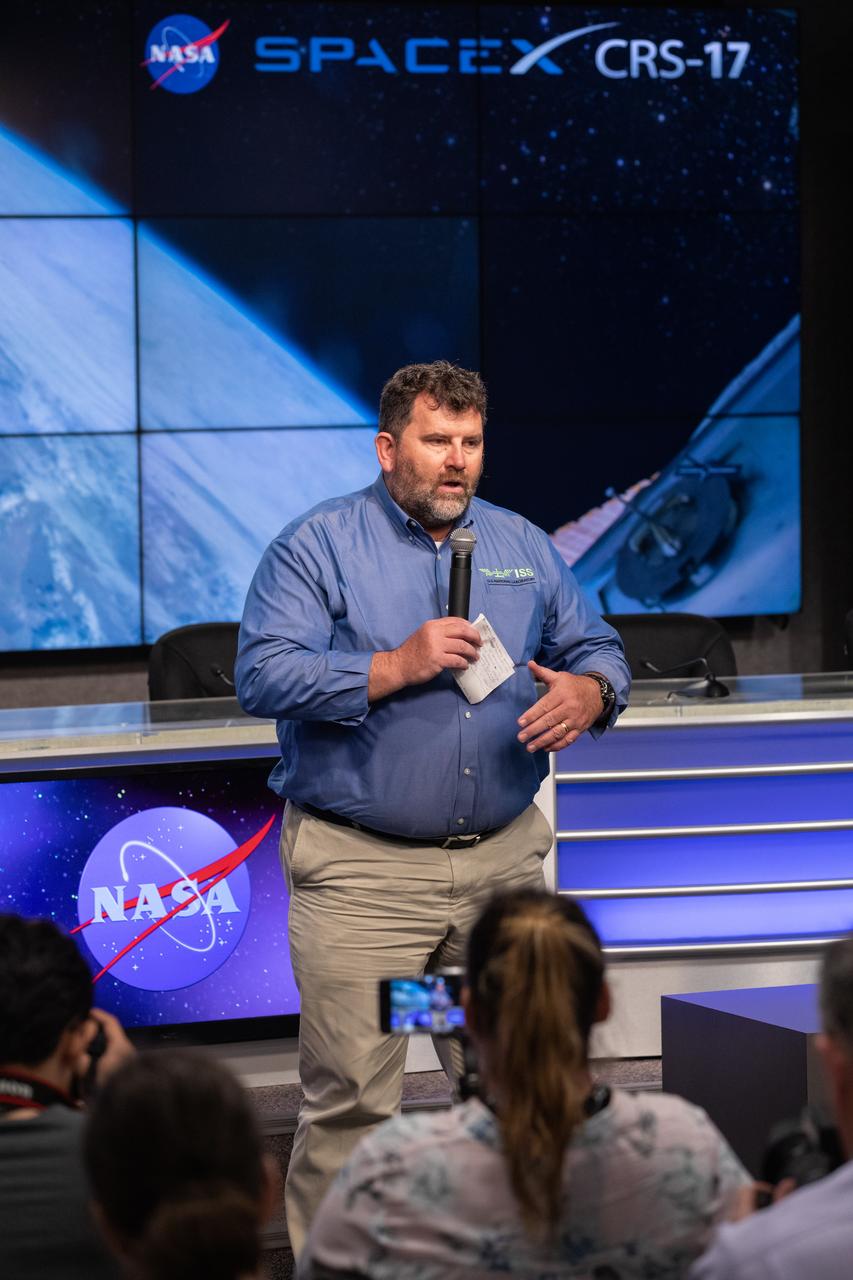

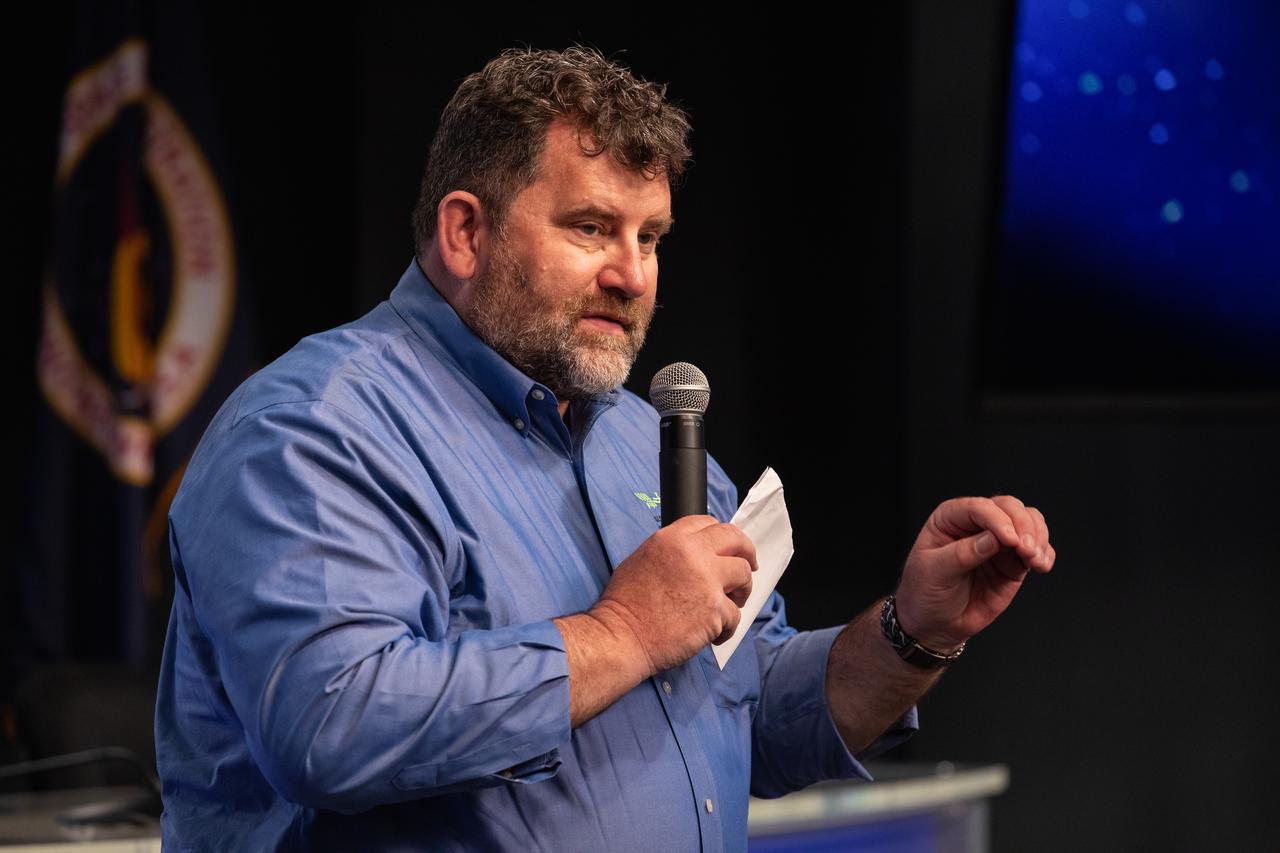
Mike Roberts, deputy chief scientist for the ISS Program at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, talks to NASA Social participants during a What’s On Board science briefing at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 29, 2019. The briefing was held for SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission to the International Space Station. NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory-3 (OCO-3) and Space Test Program-Houston 6 (STP-H6) are two of the experiments that will be delivered to the space station on CRS-17. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon cargo module are scheduled to launch no earlier than May 3, 2019, from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
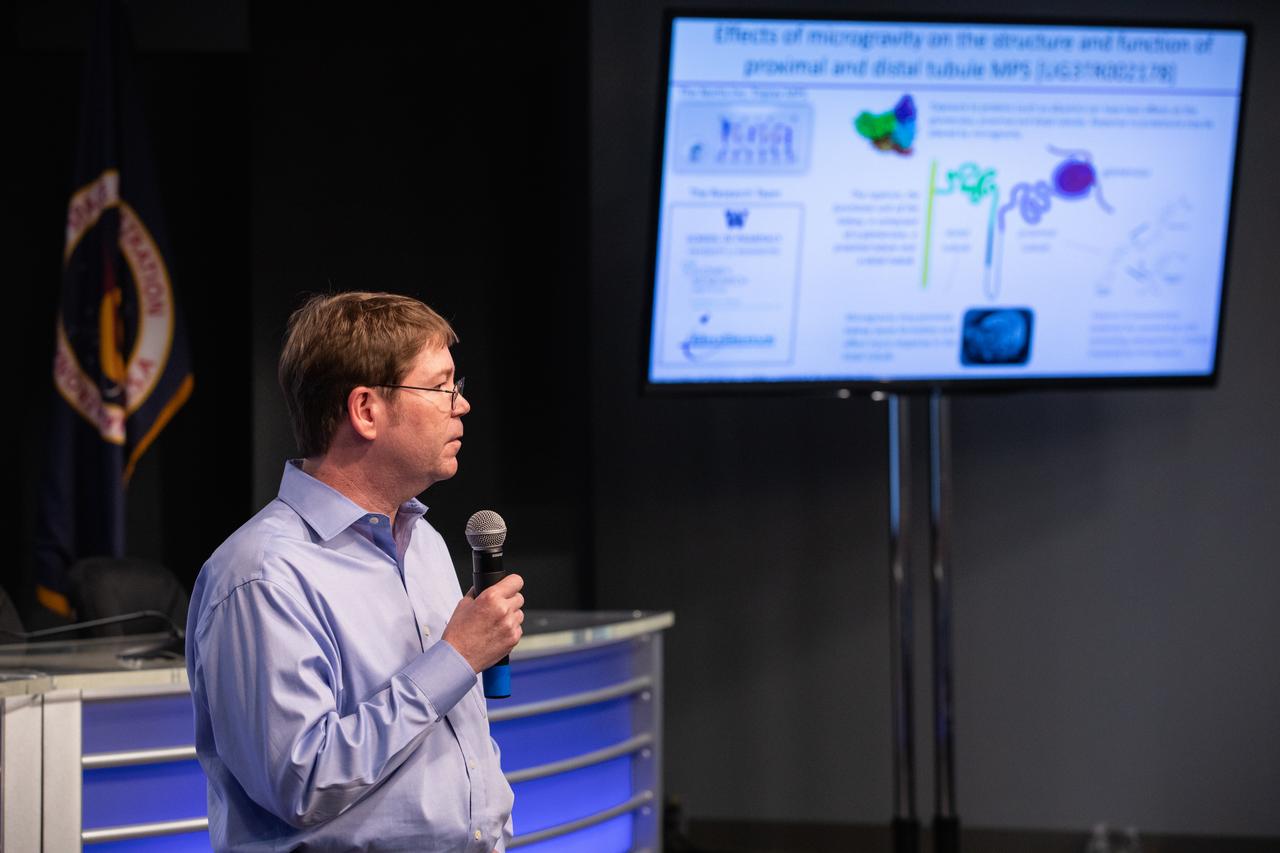

Dr. Edward Kelly, with the University of Washington School of Pharmacy, discusses The Tissue Chips in Space project during a What’s On Board science briefing to NASA Social participants at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 29, 2019. The briefing was held for SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission to the International Space Station. Kelly and other researchers will send kidney tissue chip models to the space station to understand how microgravity affects kidney function, such as changes in vitamin D metabolism and formation of kidney stones. NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory-3 (OCO-3) and Space Test Program-Houston 6 (STP-H6) are two of the experiments that also will be delivered to the space station on CRS-17. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon cargo module are scheduled to launch no earlier than May 3, 2019, from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
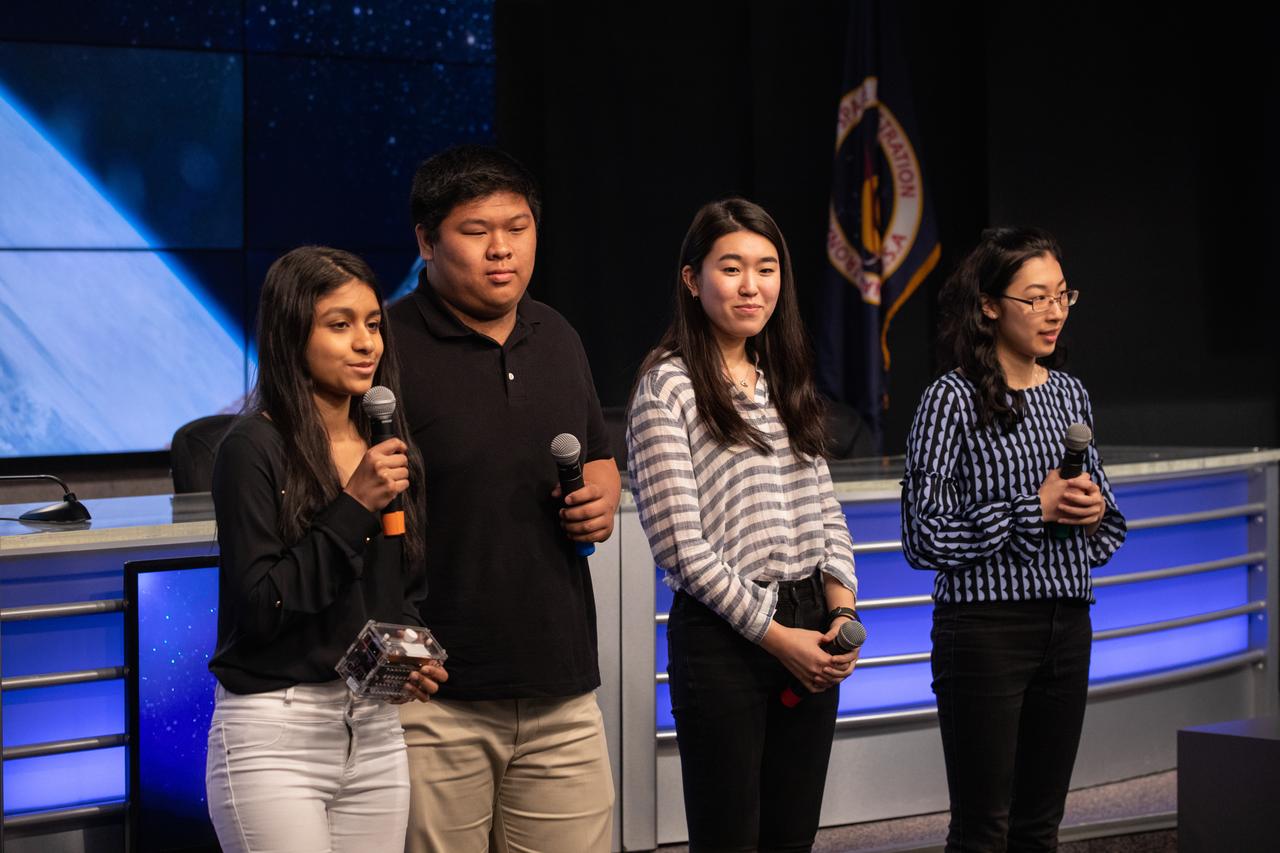

From left, high school student Aarthi Vijayakumar, MIT student David Li, and high school students Michelle Sung and Rebecca Li talk about their winning Genes in Space experiment for NASA during a What’s On Board science briefing to NASA Social participants at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 29, 2019. The briefing was held for SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission to the International Space Station. NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory-3 (OCO-3) and Space Test Program-Houston 6 (STP-H6) are two of the experiments that also will be delivered to the space station on CRS-17. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon cargo module are scheduled to launch no earlier than May 3, 2019, from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.

Dr. Kristen John, principal investigator for Hermes at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, talks to NASA Social participants during a What’s On Board science briefing at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 29, 2019. The briefing was held for SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission to the International Space Station. John presented on the Hermes Facility, an experimental microgravity facility that enables science experiments, microgravity exposure testing, testing of engineering components and CubeSats and any payloads that can fit in the Hermes design and operations constraints. NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory-3 (OCO-3) and Space Test Program-Houston 6 (STP-H6) are two of the experiments that also will be delivered to the space station on CRS-17. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon cargo module are scheduled to launch no earlier than May 3, 2019, from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.

Mike Roberts, deputy chief scientist for the ISS Program at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, talks to NASA Social participants during a What’s On Board science briefing at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 29, 2019. The briefing was held for SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission to the International Space Station. NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory-3 (OCO-3) and Space Test Program-Houston 6 (STP-H6) are two of the experiments that will be delivered to the space station on CRS-17. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon cargo module are scheduled to launch no earlier than May 3, 2019, from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
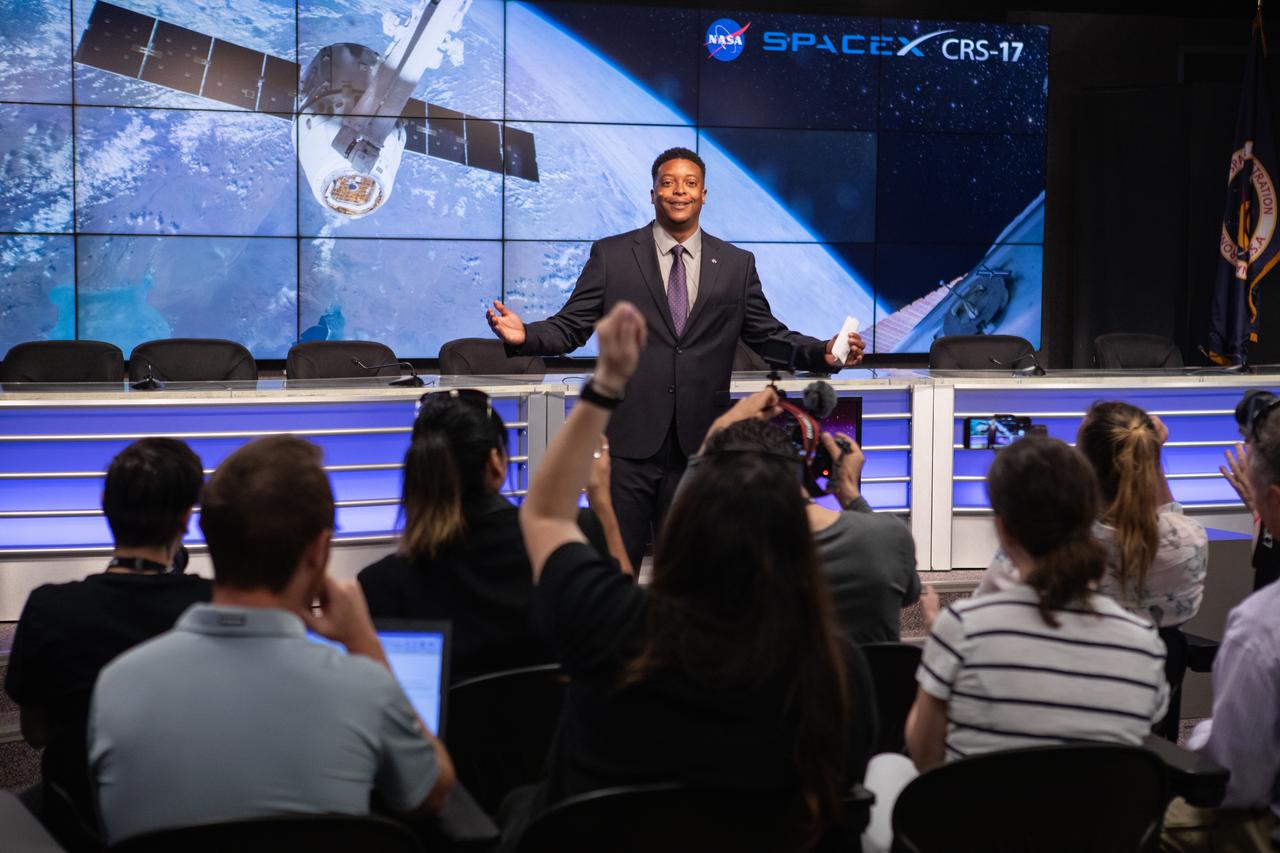

Derrick Matthews, moderator with NASA Communications, fields questions from NASA Social participants during a What’s On Board science briefing at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 29, 2019. The briefing was held for SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission to the International Space Station. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon cargo module are scheduled to launch no earlier than May 3, 2019, from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
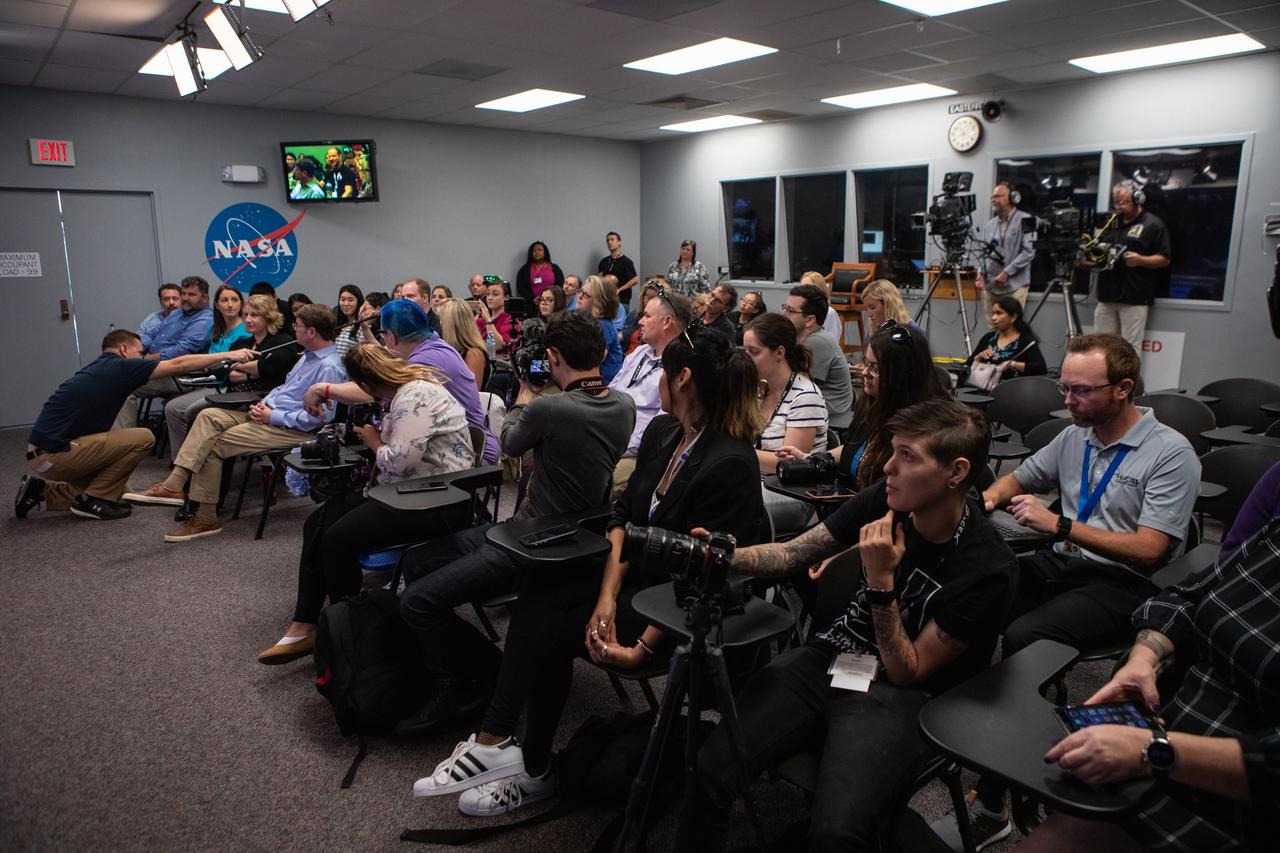

NASA Social participants attend a What’s On Board science briefing at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 29, 2019. The briefing was held for SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission to the International Space Station. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon cargo module are scheduled to launch no earlier than May 3, 2019, from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
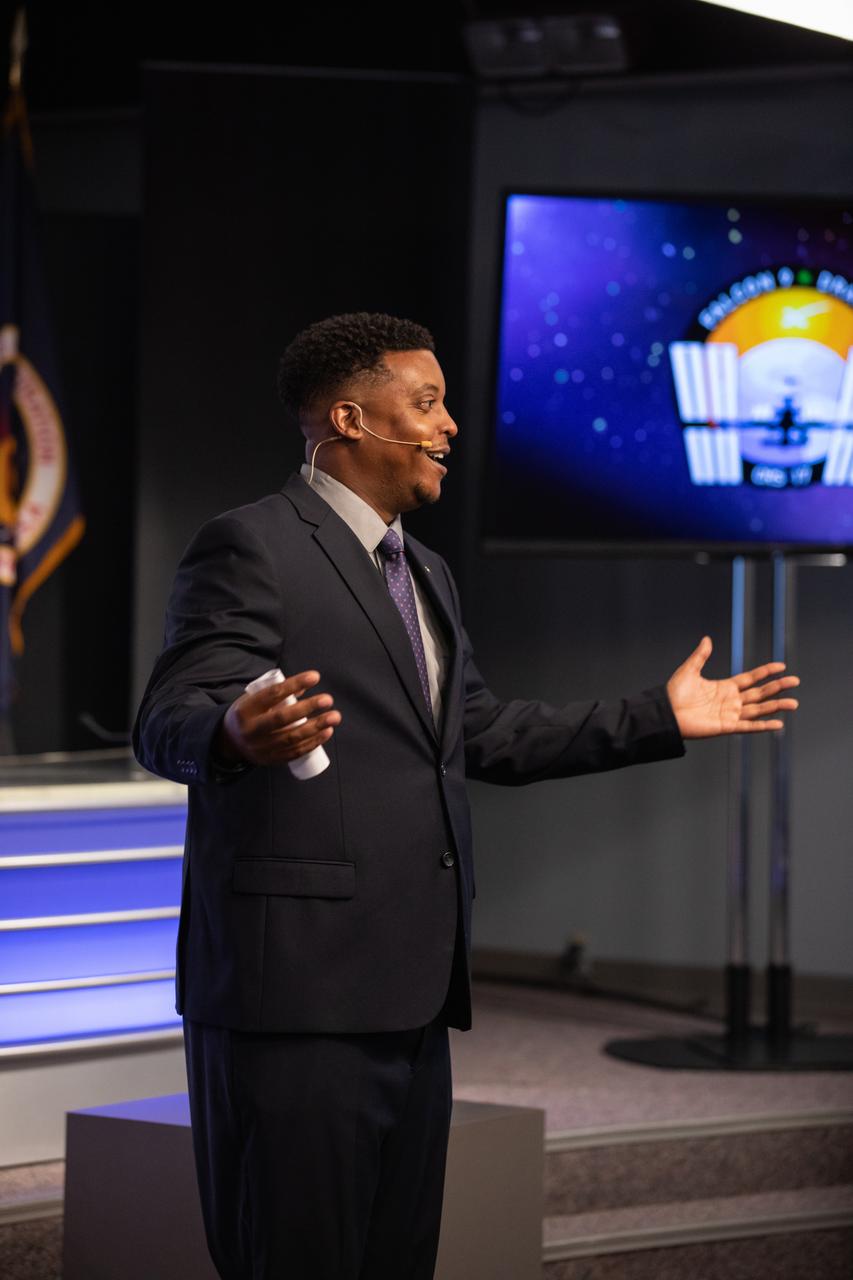

Derrick Matthews, moderator with NASA Communications, concludes a What’s On Board science briefing to NASA Social participants at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 29, 2019. The briefing was held for SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission to the International Space Station. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon cargo module are scheduled to launch no earlier than May 3, 2019, from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
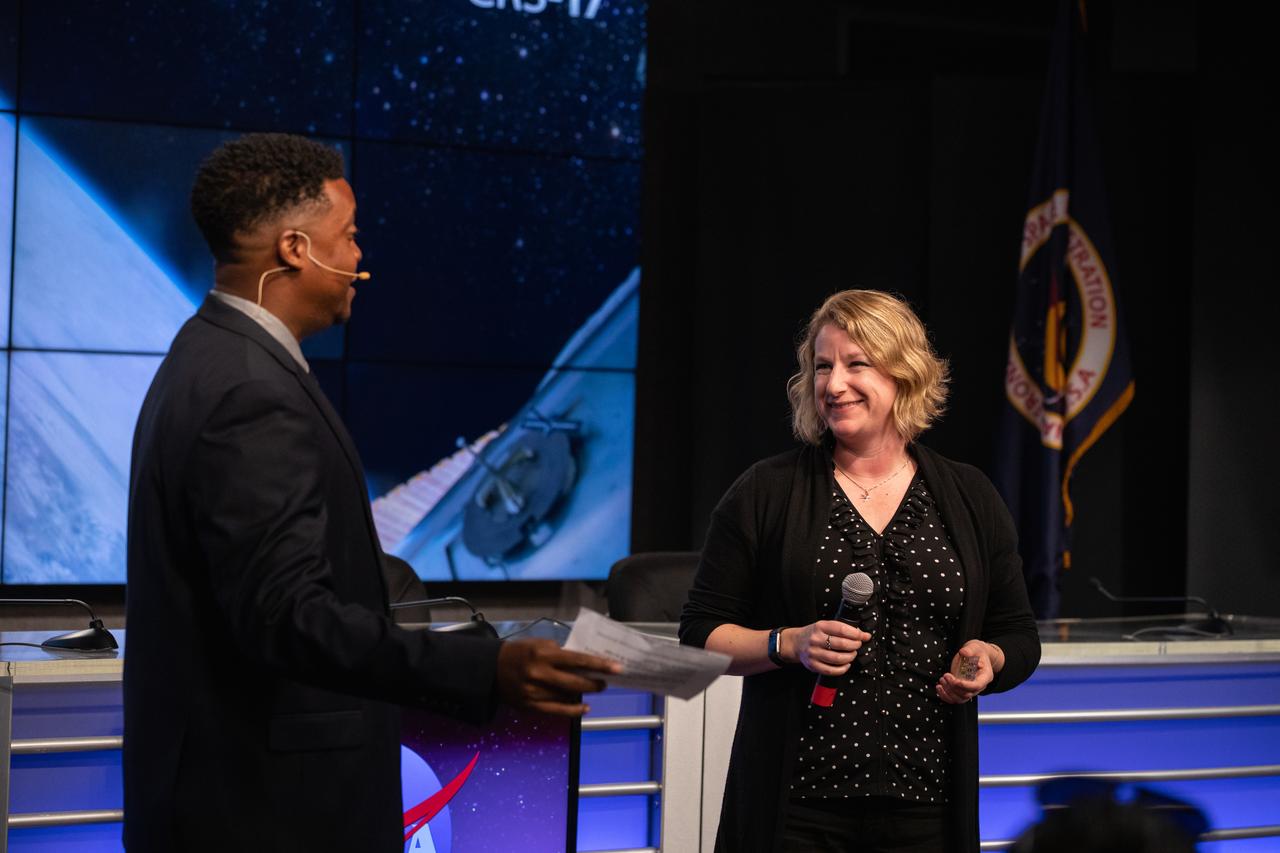

Derrick Matthews, at left, moderator with NASA Communications, introduces Dr. Lucy Low, with the National Institutes of Health, during a What’s On Board science briefing to NASA Social participants at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 29, 2019. The briefing was held for SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission to the International Space Station. Low presented on the Tissue Chips in Space project that will test the ability of tissue chip technology to mimic how human organs work and reveal what effects microgravity has on tissue function. Headed to the space station will be lung and bone marrow chips, kidney chips, chips modeling the blood-brain barrier, and bone and cartilage chips. NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory-3 (OCO-3) and Space Test Program-Houston 6 (STP-H6) are two of the experiments that also will be delivered to the space station on CRS-17. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon cargo module are scheduled to launch no earlier than May 3, 2019, from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
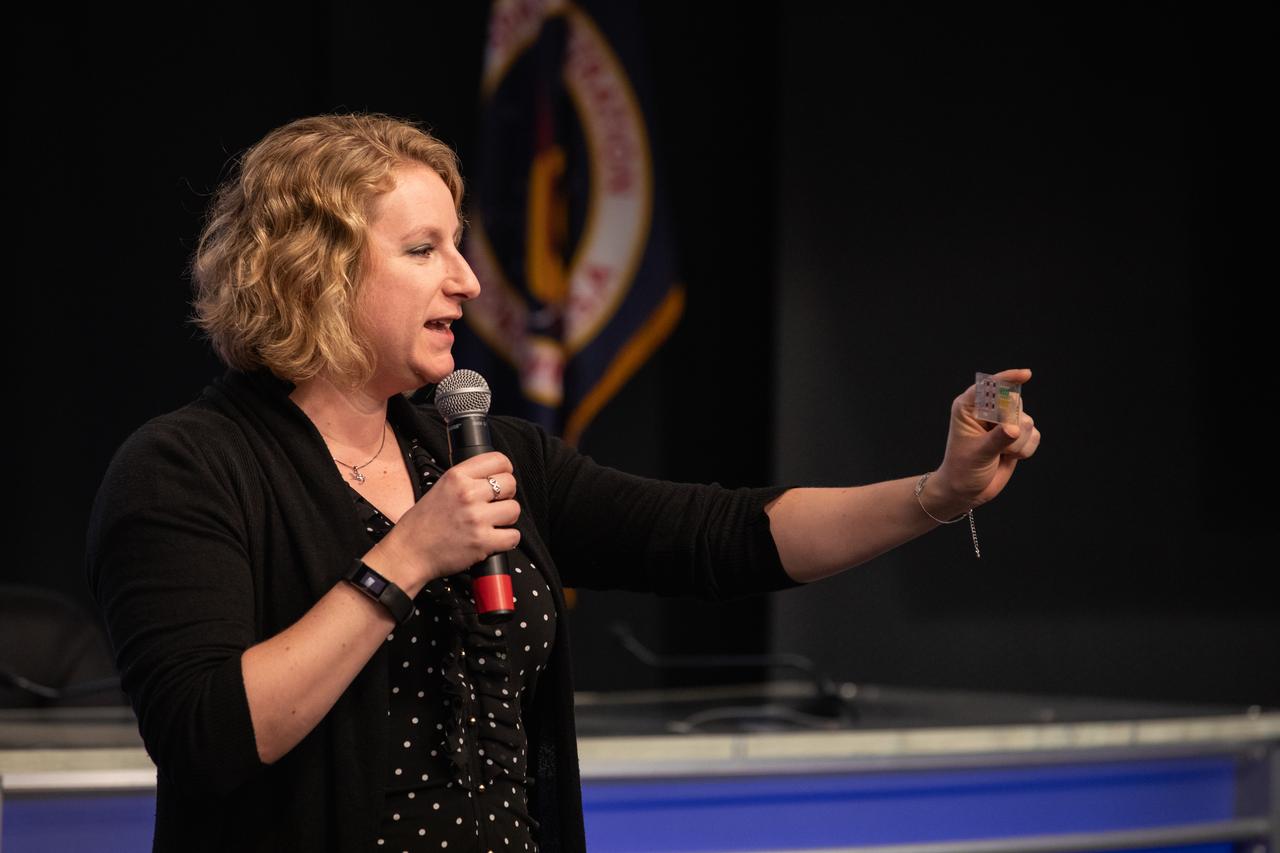

Dr. Lucy Low, with the National Institutes of Health, talks to NASA Social participants during a What’s On Board science briefing at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 29, 2019. The briefing was held for SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission to the International Space Station. Low presented on the Tissue Chips in Space project that will test the ability of tissue chip technology to mimic how human organs work and reveal what effects microgravity has on tissue function. Headed to the space station will be lung and bone marrow chips, kidney chips, chips modeling the blood-brain barrier, and bone and cartilage chips. NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory-3 (OCO-3) and Space Test Program-Houston 6 (STP-H6) are two of the experiments that also will be delivered to the space station on CRS-17. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon cargo module are scheduled to launch no earlier than May 3, 2019, from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
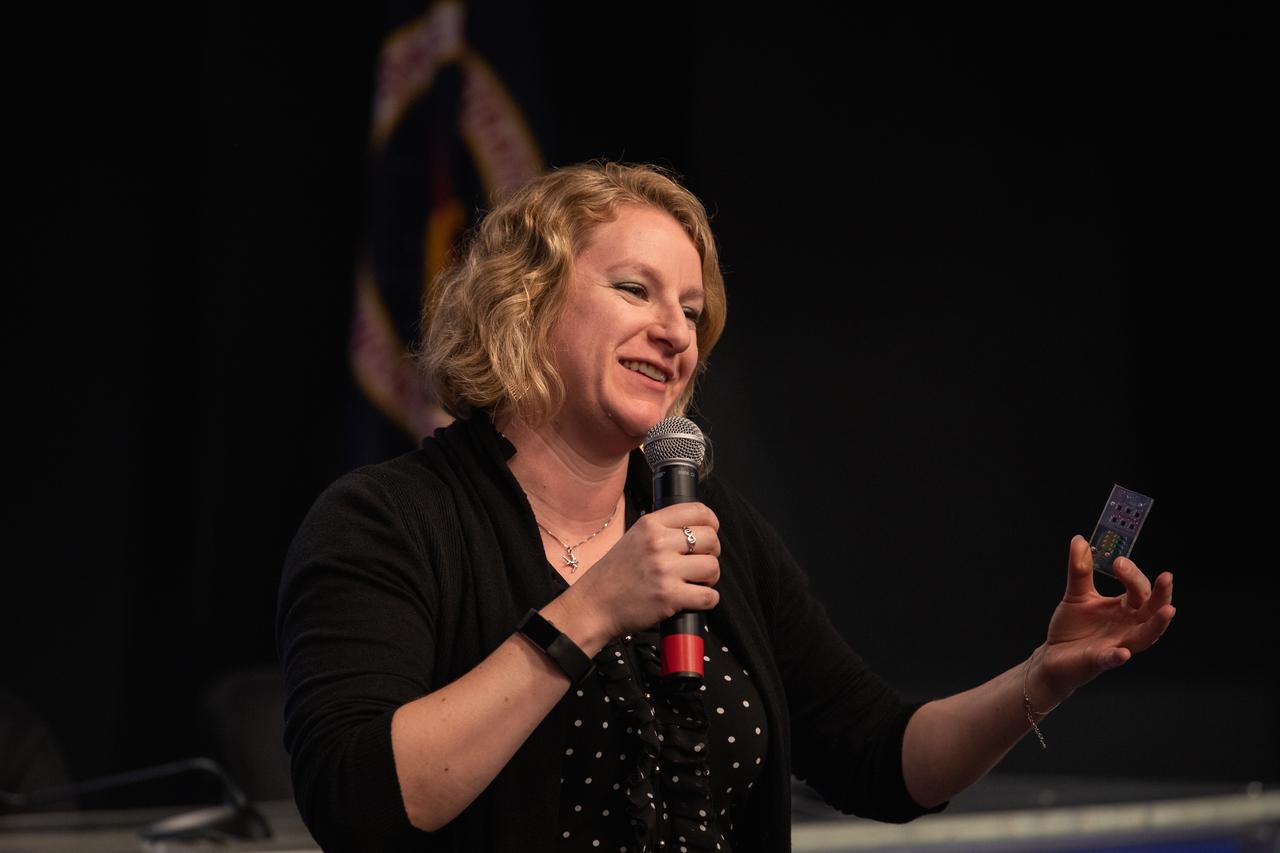

Dr. Lucy Low, with the National Institutes of Health, talks to NASA Social participants during a What’s On Board science briefing at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 29, 2019. The briefing was held for SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission to the International Space Station. Low presented on the Tissue Chips in Space project that will test the ability of tissue chip technology to mimic how human organs work and reveal what effects microgravity has on tissue function. Headed to the space station will be lung and bone marrow chips, kidney chips, chips modeling the blood-brain barrier, and bone and cartilage chips. NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory-3 (OCO-3) and Space Test Program-Houston 6 (STP-H6) are two of the experiments that also will be delivered to the space station on CRS-17. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon cargo module are scheduled to launch no earlier than May 3, 2019, from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
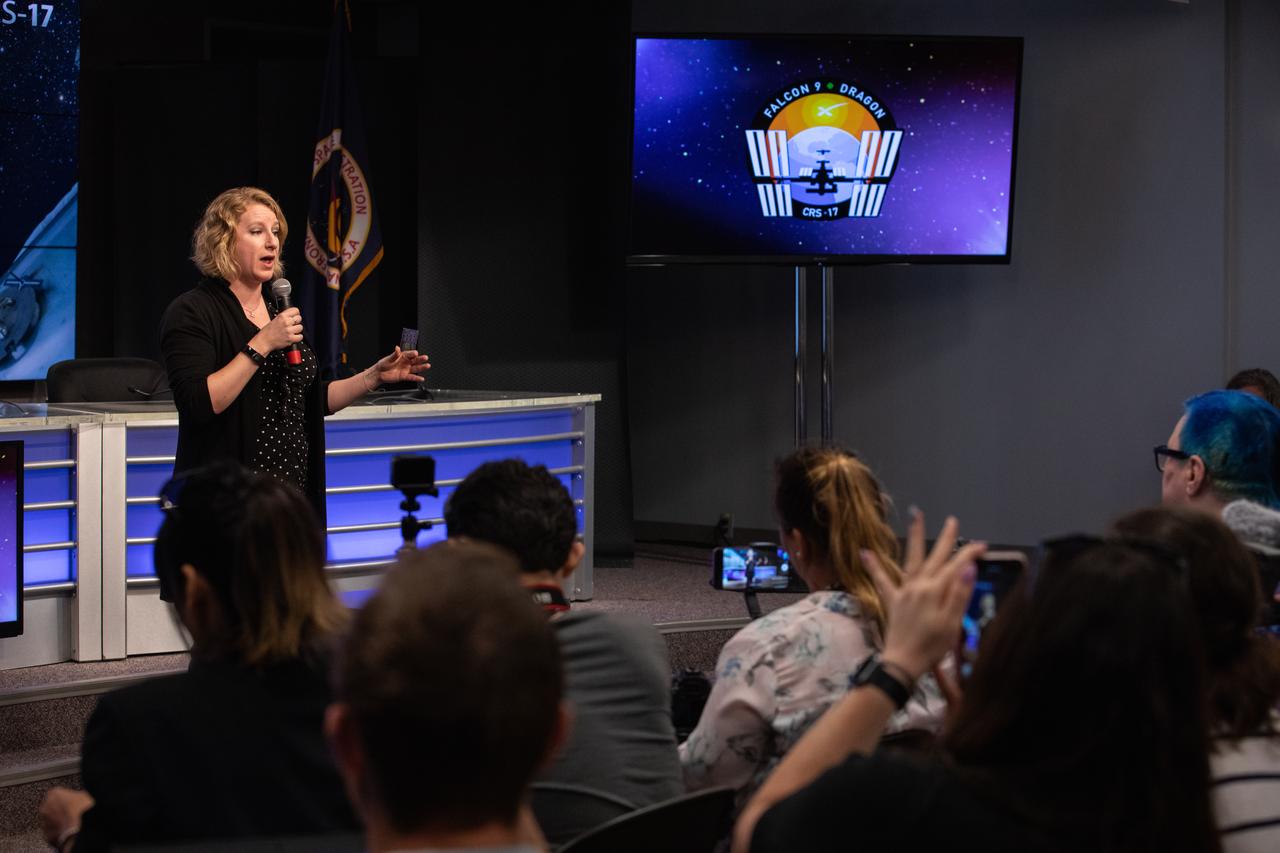

Dr. Lucy Low, with the National Institutes of Health, talks to NASA Social participants during a What’s On Board science briefing at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 29, 2019. The briefing was held for SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission to the International Space Station. Low presented on the Tissue Chips in Space project that will test the ability of tissue chip technology to mimic how human organs work and reveal what effects microgravity has on tissue function. Headed to the space station will be lung and bone marrow chips, kidney chips, chips modeling the blood-brain barrier, and bone and cartilage chips. NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory-3 (OCO-3) and Space Test Program-Houston 6 (STP-H6) are two of the experiments that also will be delivered to the space station on CRS-17. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon cargo module are scheduled to launch no earlier than May 3, 2019, from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
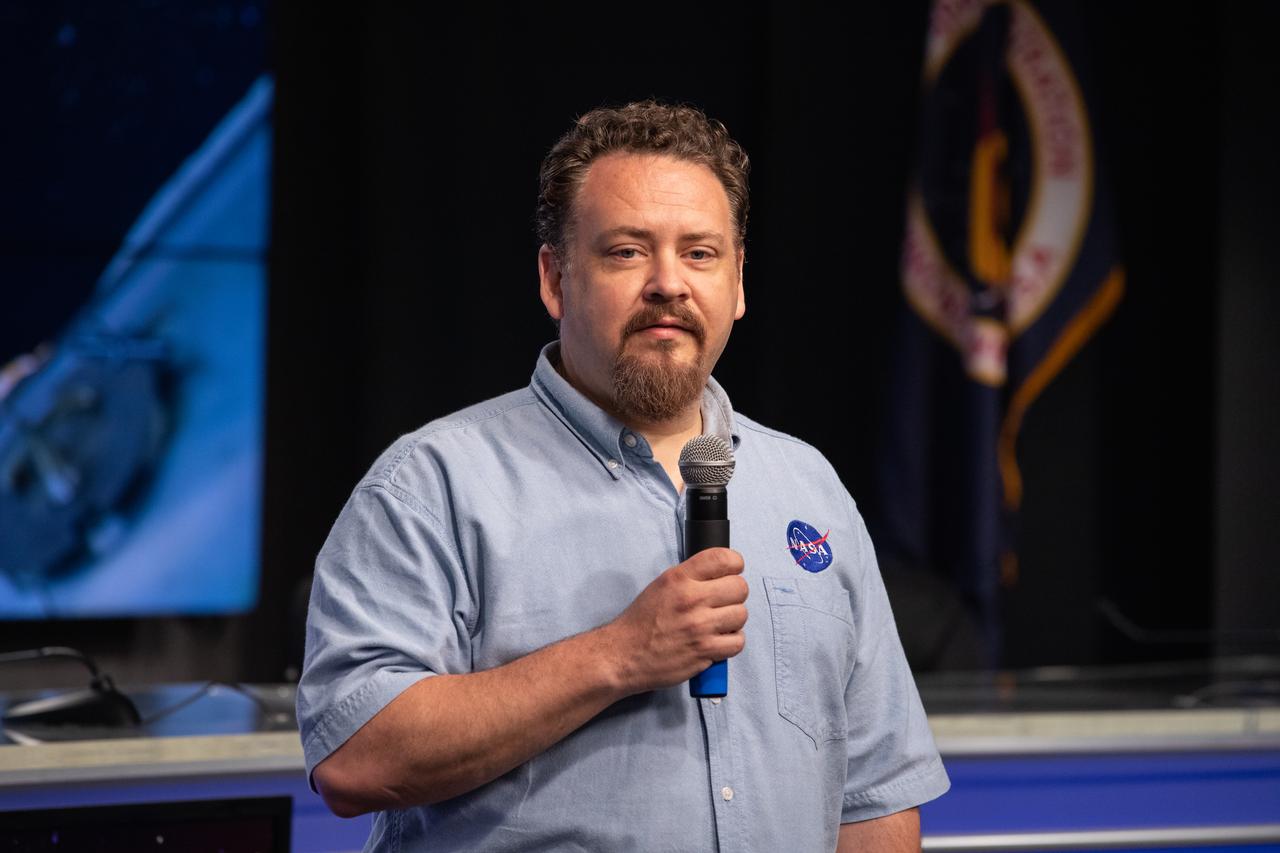

Dr. Kirt Costello, chief scientist for the ISS Program at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, talks to NASA Social participants during a What’s On Board science briefing at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 29, 2019. The briefing was held for SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission to the International Space Station. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon cargo module are scheduled to launch no earlier than May 3, 2019, from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
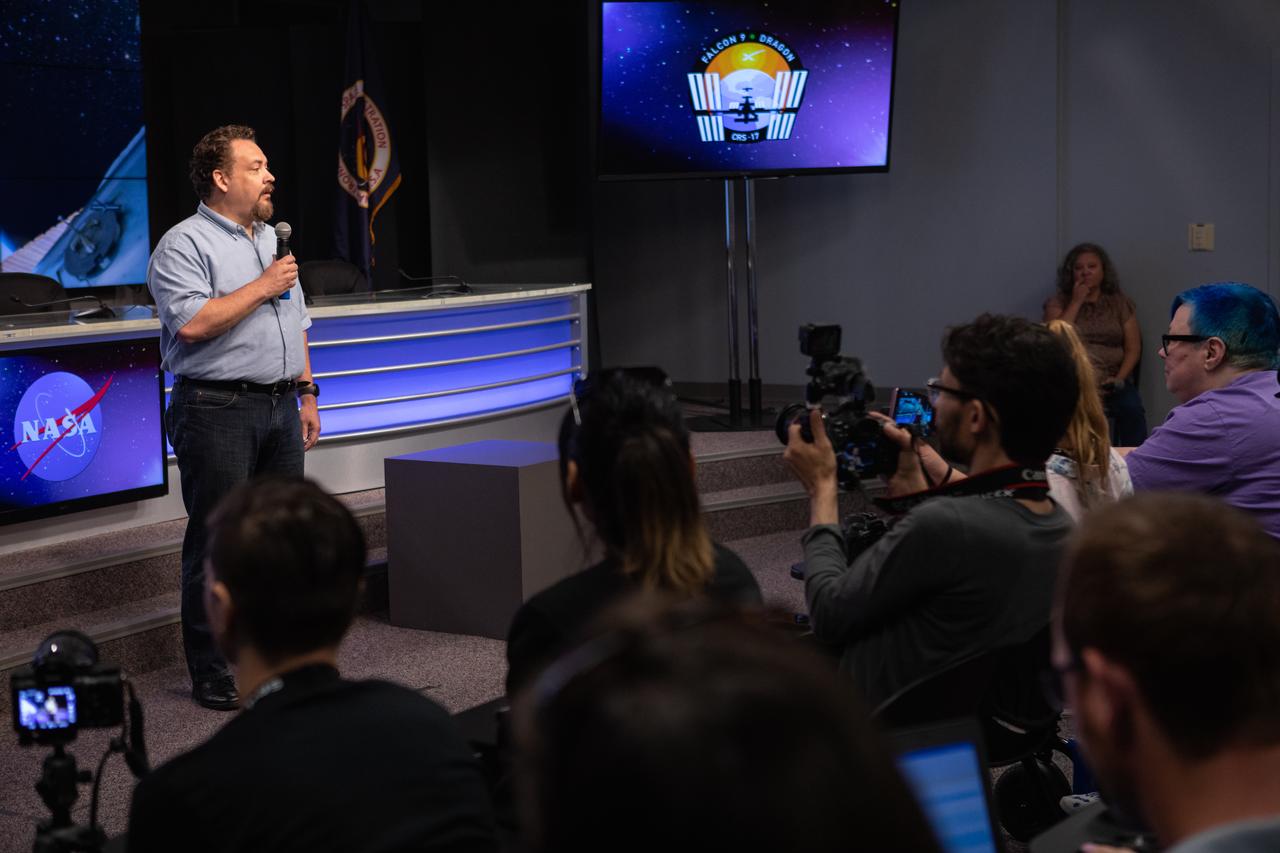

Dr. Kirt Costello, chief scientist for the ISS Program at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, talks to NASA Social participants during a What’s On Board science briefing at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 29, 2019. The briefing was held for SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission to the International Space Station. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon cargo module are scheduled to launch no earlier than May 3, 2019, from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
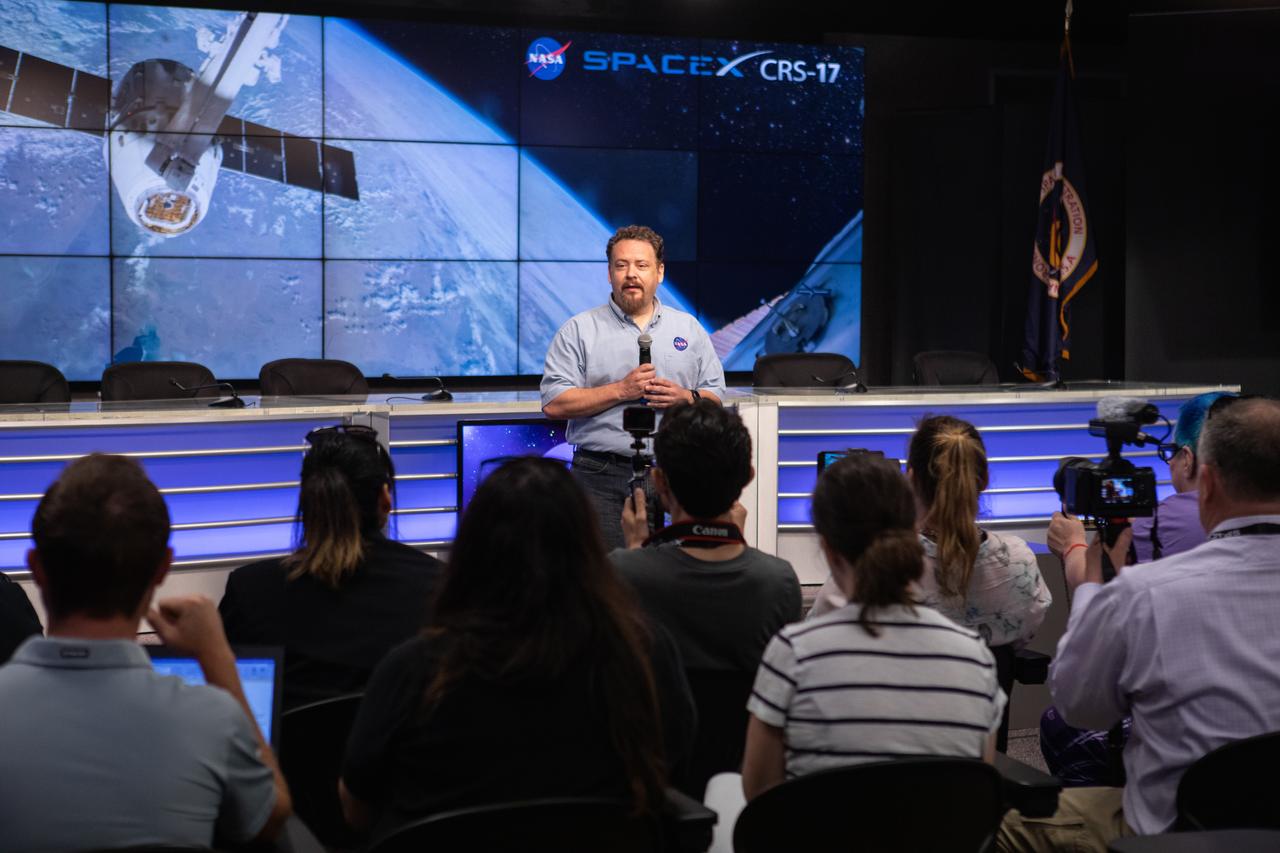

Dr. Kirt Costello, chief scientist for the ISS Program at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, talks to NASA Social participants during a What’s On Board science briefing at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 29, 2019. The briefing was held for SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-17) mission to the International Space Station. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon cargo module are scheduled to launch no earlier than May 3, 2019, from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
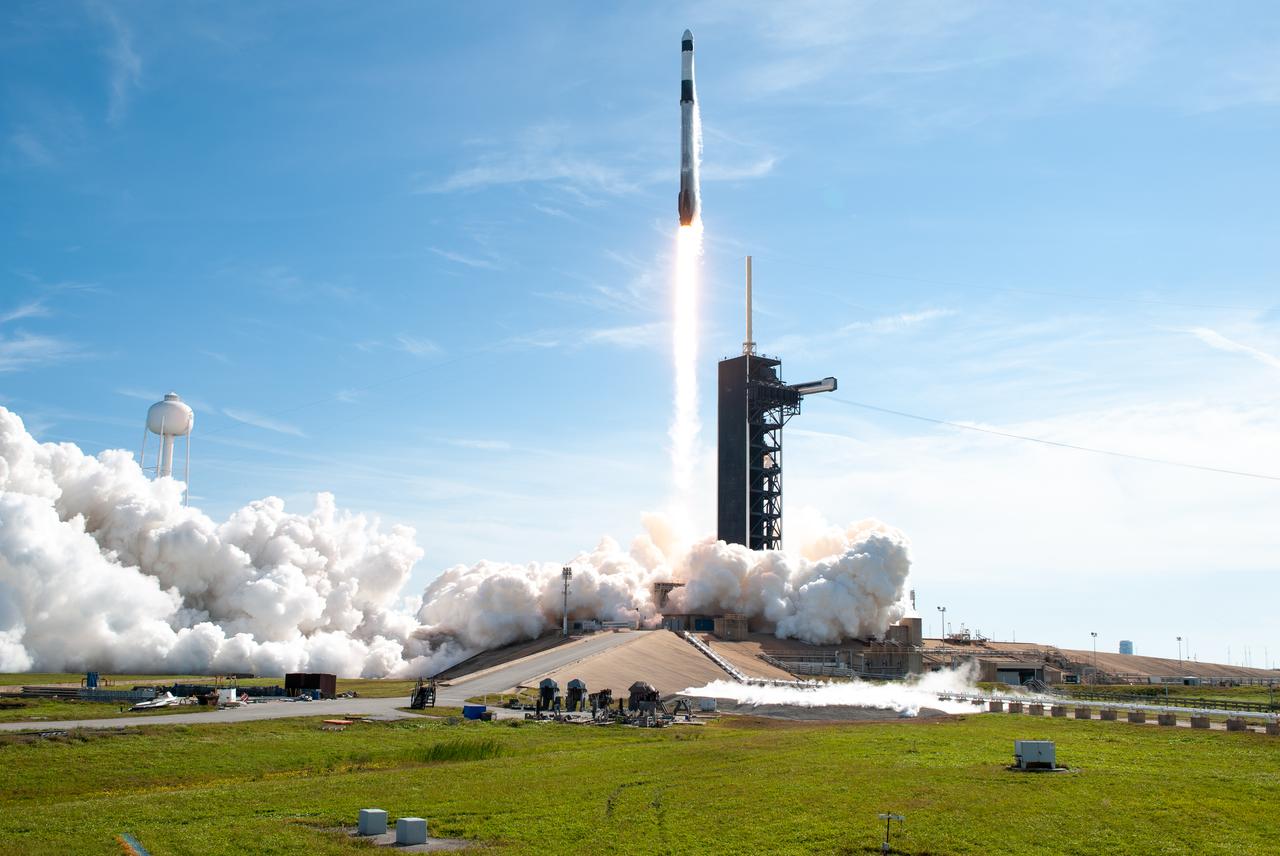

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 11:17 a.m. EST on Dec. 6, 2020, carrying the uncrewed cargo Dragon spacecraft on its journey to the International Space Station for NASA and SpaceX’s 21st Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-21) mission. Dragon will deliver more than 6,400 pounds of science investigations and cargo to the orbiting laboratory. The mission marks the first launch for SpaceX under NASA’s CRS-2 contract.