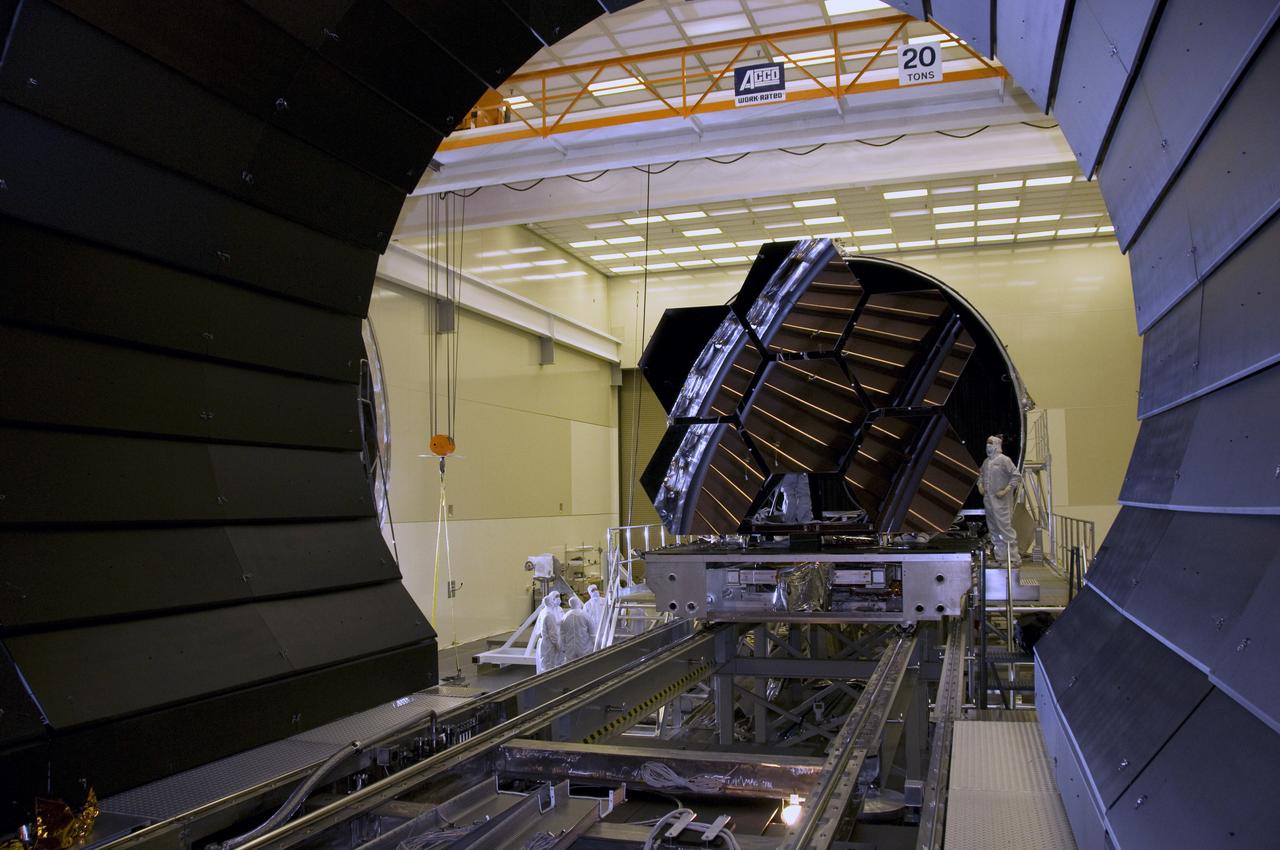

SIX MIRROR SEGMENTS OF THE JAMES WEBB SPACE TELESCOPE ARE REMOVED FROM THE CRYOGENIC TEST CHAMBER
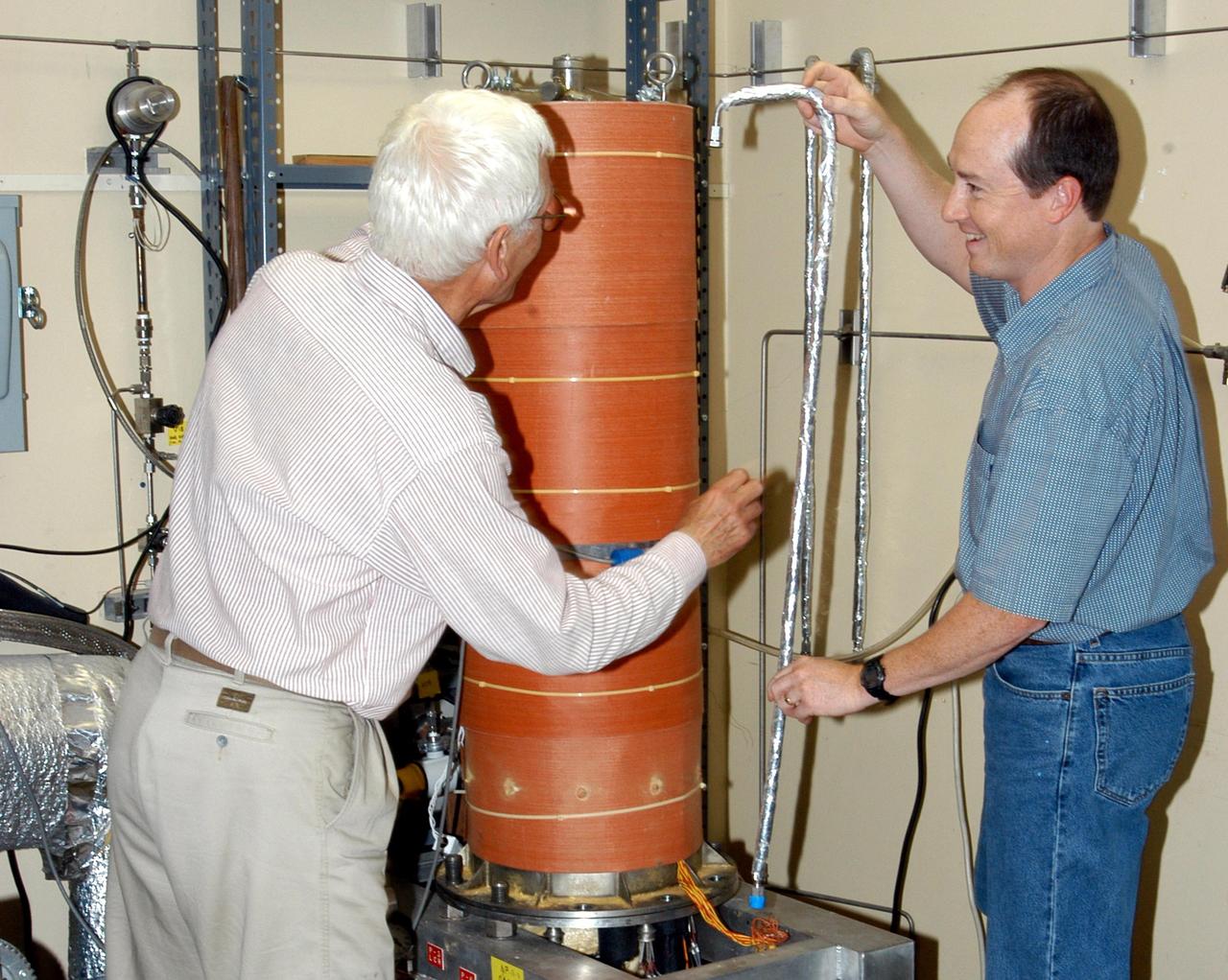

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - James E. Fesmire (right), NASA lead engineer for the KSC Cryogenics Testbed, works on Cryostat-1, the Methods of Testing Thermal Insulation and Association Test Apparatus, which he developed. At left is co-inventor Dr. Stan Augustynowicz, chief scientist with Sierra Lobo Inc. in Milan, Ohio. Cryostat-1 provides absolute thermal performance values of cryogenic insulation systems under real-world conditions. Cryogenic liquid is supplied to a test chamber and two guard chambers, and temperatures are sensed within the vacuum chamber to test aerogels, foams or other materials. The Cryostat-1 machine can detect the absolute heat leakage rates through materials under the full range of vacuum conditions. Fesmire recently acquired three patents for testing thermal insulation materials for cryogenic systems. The research team of the Cryogenics Testbed offers testing and support for a number of programs and initiatives for NASA and commercial customers.
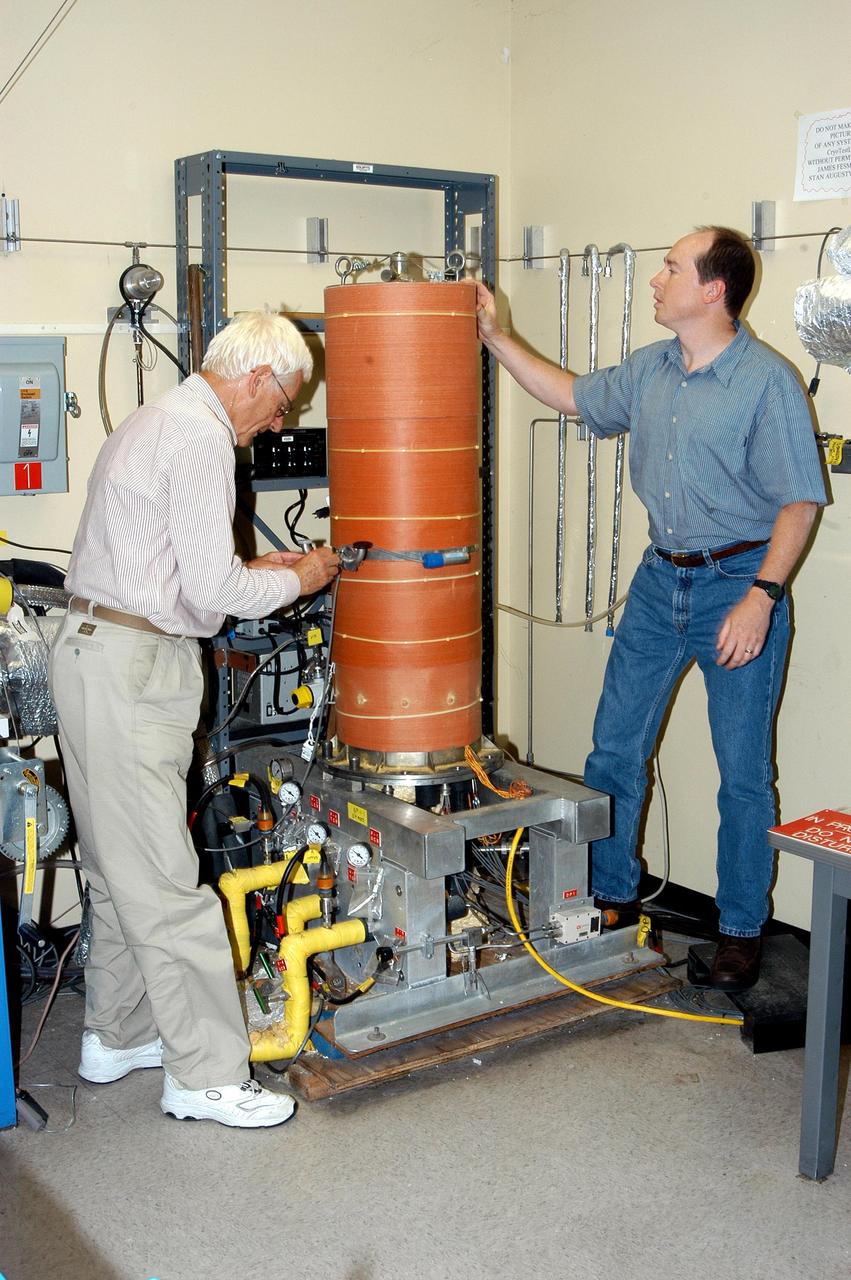

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - James E. Fesmire (right), NASA lead engineer for the KSC Cryogenics Testbed, works on Cryostat-1, the Methods of Testing Thermal Insulation and Association Test Apparatus, which he developed. At left is co-inventor Dr. Stan Augustynowicz, chief scientist with Sierra Lobo Inc. in Milan, Ohio. Cryostat-1 provides absolute thermal performance values of cryogenic insulation systems under real-world conditions. Cryogenic liquid is supplied to a test chamber and two guard chambers, and temperatures are sensed within the vacuum chamber to test aerogels, foams or other materials. The Cryostat-1 machine can detect the absolute heat leakage rates through materials under the full range of vacuum conditions. Fesmire recently acquired three patents for testing thermal insulation materials for cryogenic systems. The research team of the Cryogenics Testbed offers testing and support for a number of programs and initiatives for NASA and commercial customers.
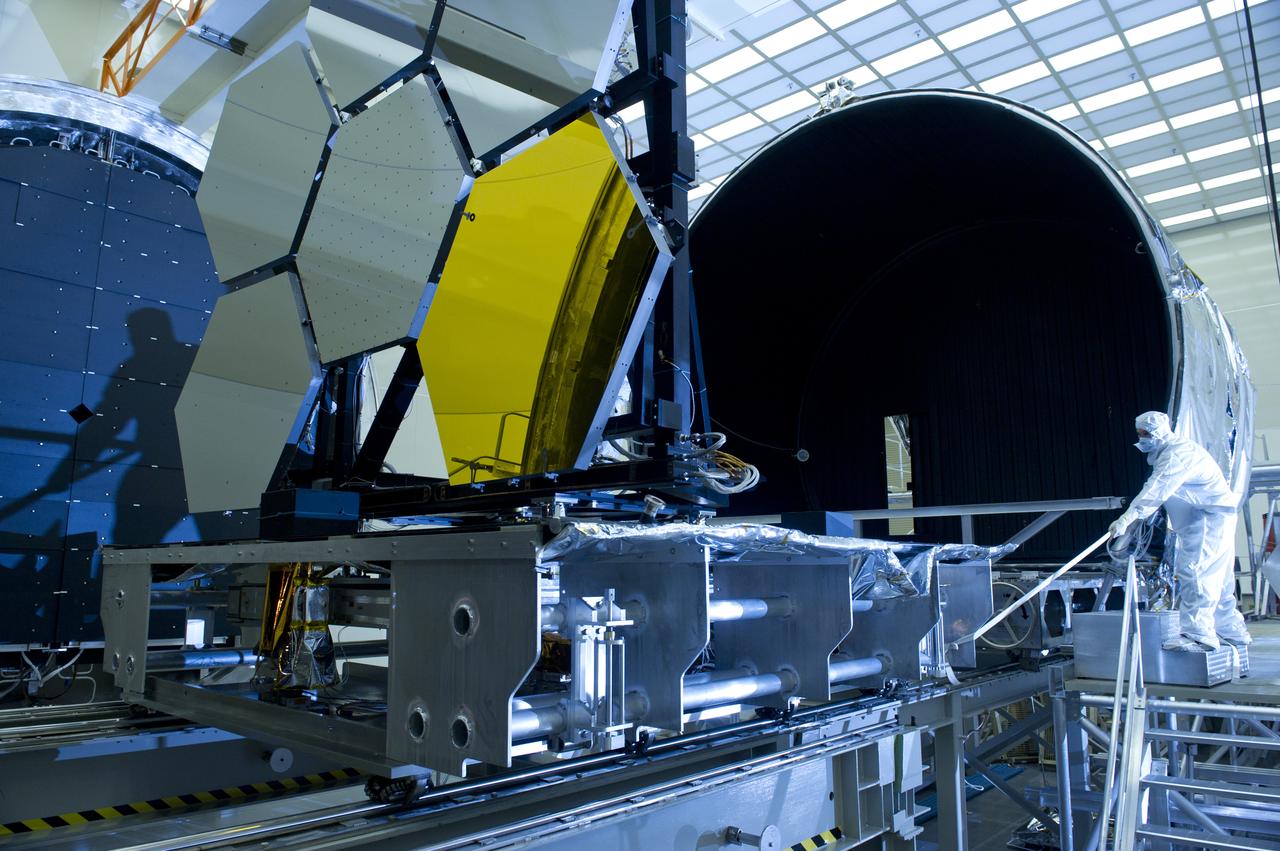

MARSHALL TEST ENGINEER HARLAN HAIGHT HELPS PULL JWST MIRROR ARRAY FROM CRYOGENICS CHAMBER.
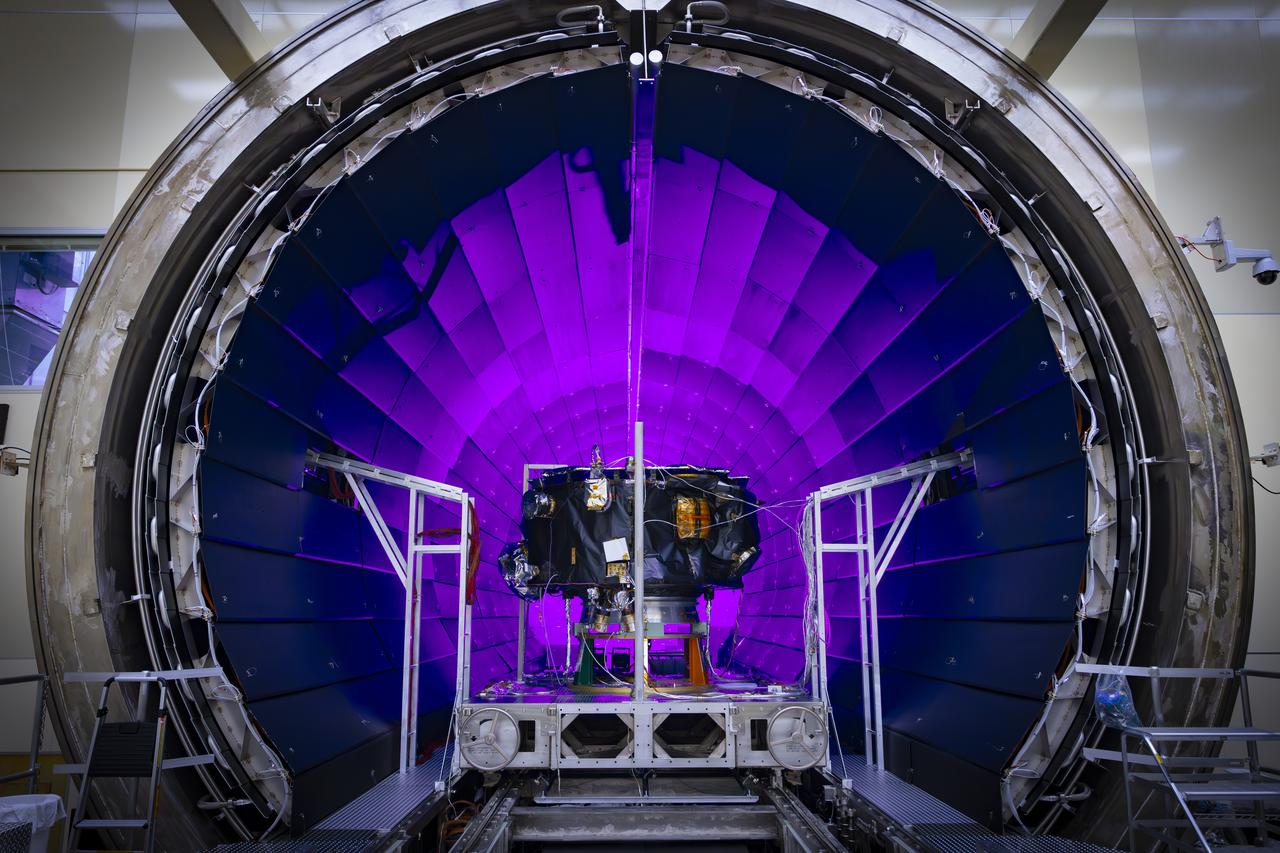

These photos and timelapse show NASA’s IMAP mission being loaded into the thermal vacuum chamber of NASA Marshall Space Flight Center’s X-Ray and Cryogenic Facility (XRCF) in Huntsville, Alabama. IMAP arrived at Marshall March 18 and was loaded into the chamber March 19. IMAP will undergo testing such as dramatic temperature changes to simulate the harsh environment of space. The XRCF’s vacuum chamber is is 20 feet in diameter and 60 feet long making it one of the largest across NASA. The IMAP mission is a modern-day celestial cartographer that will map the solar system by studying the heliosphere, a giant bubble created by the Sun’s solar wind that surrounds our solar system and protects it from harmful interstellar radiation. Photos and video courtesy of Ed Whitman from Johns Hopkins University’s Applied Physics Laboratory. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.
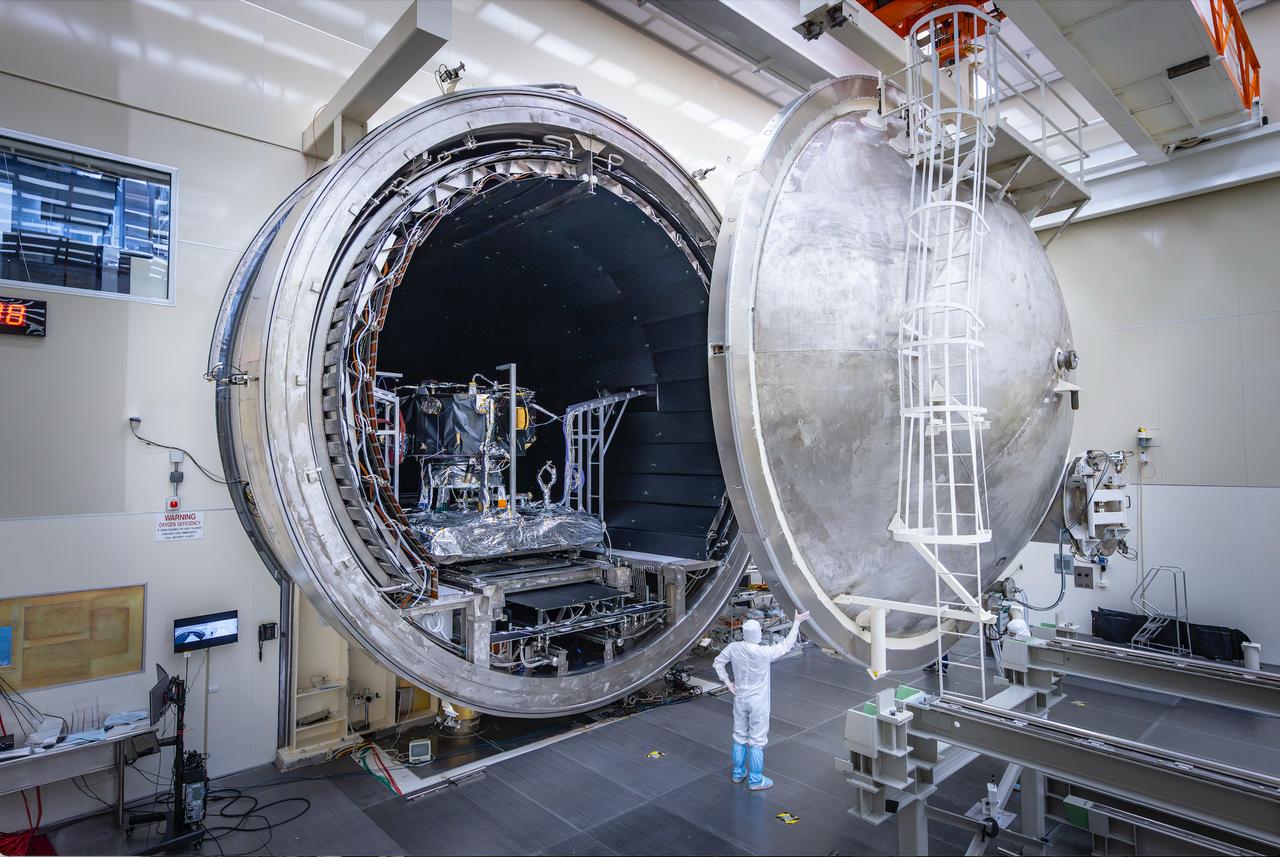
These photos and timelapse show NASA’s IMAP mission being loaded into the thermal vacuum chamber of NASA Marshall Space Flight Center’s X-Ray and Cryogenic Facility (XRCF) in Huntsville, Alabama. IMAP arrived at Marshall March 18 and was loaded into the chamber March 19. IMAP will undergo testing such as dramatic temperature changes to simulate the harsh environment of space. The XRCF’s vacuum chamber is is 20 feet in diameter and 60 feet long making it one of the largest across NASA. The IMAP mission is a modern-day celestial cartographer that will map the solar system by studying the heliosphere, a giant bubble created by the Sun’s solar wind that surrounds our solar system and protects it from harmful interstellar radiation. Photos and video courtesy of Ed Whitman from Johns Hopkins University’s Applied Physics Laboratory. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.
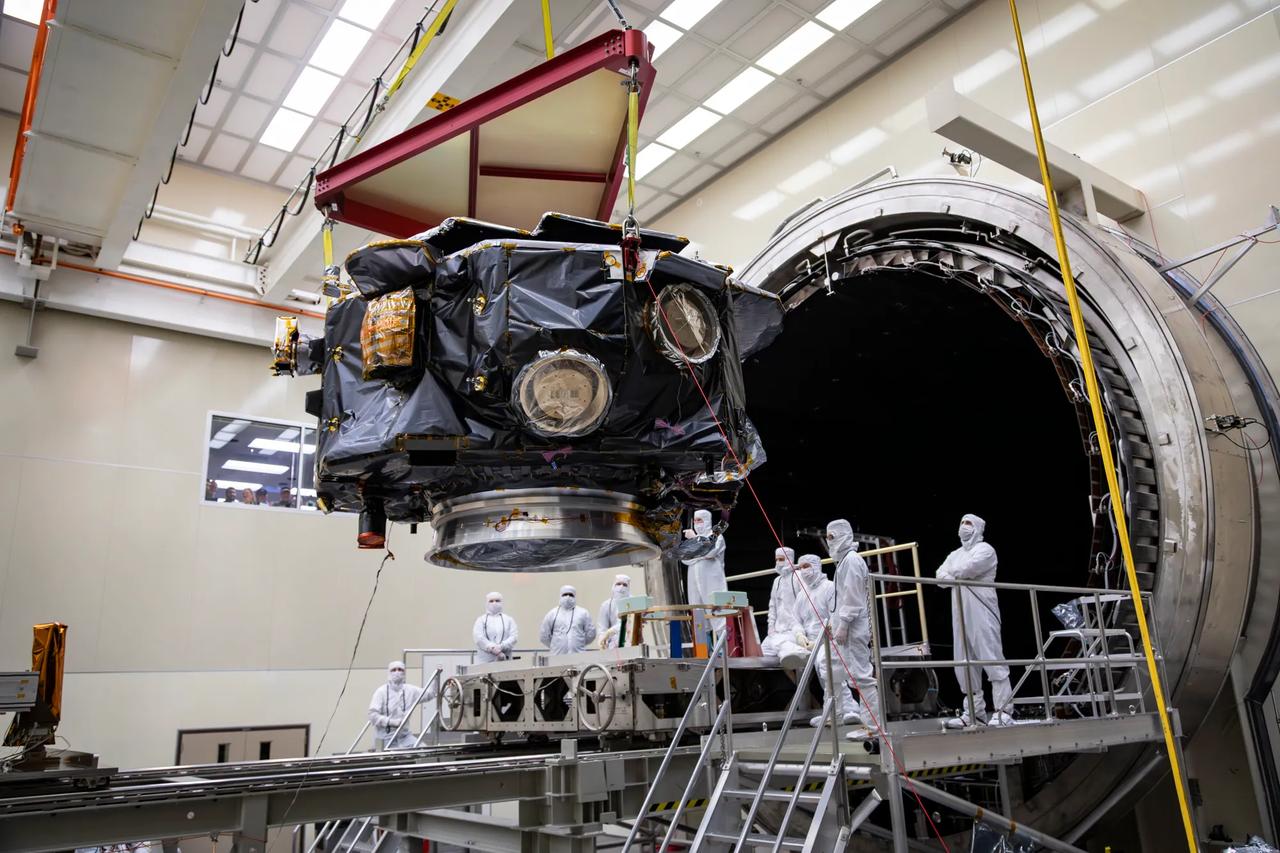

These photos and timelapse show NASA’s IMAP mission being loaded into the thermal vacuum chamber of NASA Marshall Space Flight Center’s X-Ray and Cryogenic Facility (XRCF) in Huntsville, Alabama. IMAP arrived at Marshall March 18 and was loaded into the chamber March 19. IMAP will undergo testing such as dramatic temperature changes to simulate the harsh environment of space. The XRCF’s vacuum chamber is is 20 feet in diameter and 60 feet long making it one of the largest across NASA. The IMAP mission is a modern-day celestial cartographer that will map the solar system by studying the heliosphere, a giant bubble created by the Sun’s solar wind that surrounds our solar system and protects it from harmful interstellar radiation. Photos and video courtesy of Ed Whitman from Johns Hopkins University’s Applied Physics Laboratory. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.
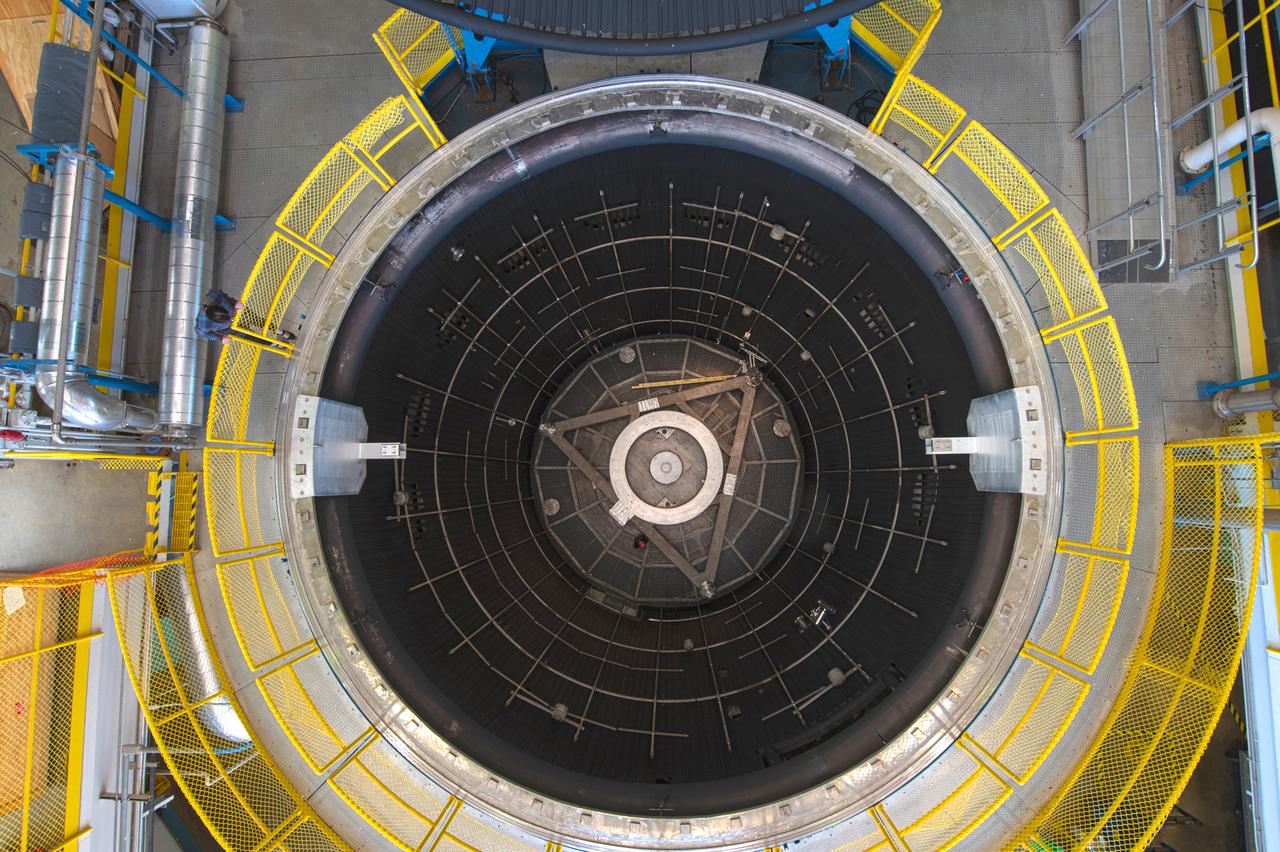

The test chamber is 38 ft in diameter by 62 ft deep amd made of stainless steel. It is vacuum rated at 10-7 torr long duration (Local atmospheric pressure to 100 statute miles altitude). The vacuum chamber surfaces are lined with a liquid nitrogen cold wall, capable of maintaining -320 °F. A quartz infrared heating system can be programmed to radiate a sinusoidal distribution, simulating rotational solar heating. Photo Credit: (NASA/Quentin Schwinn)
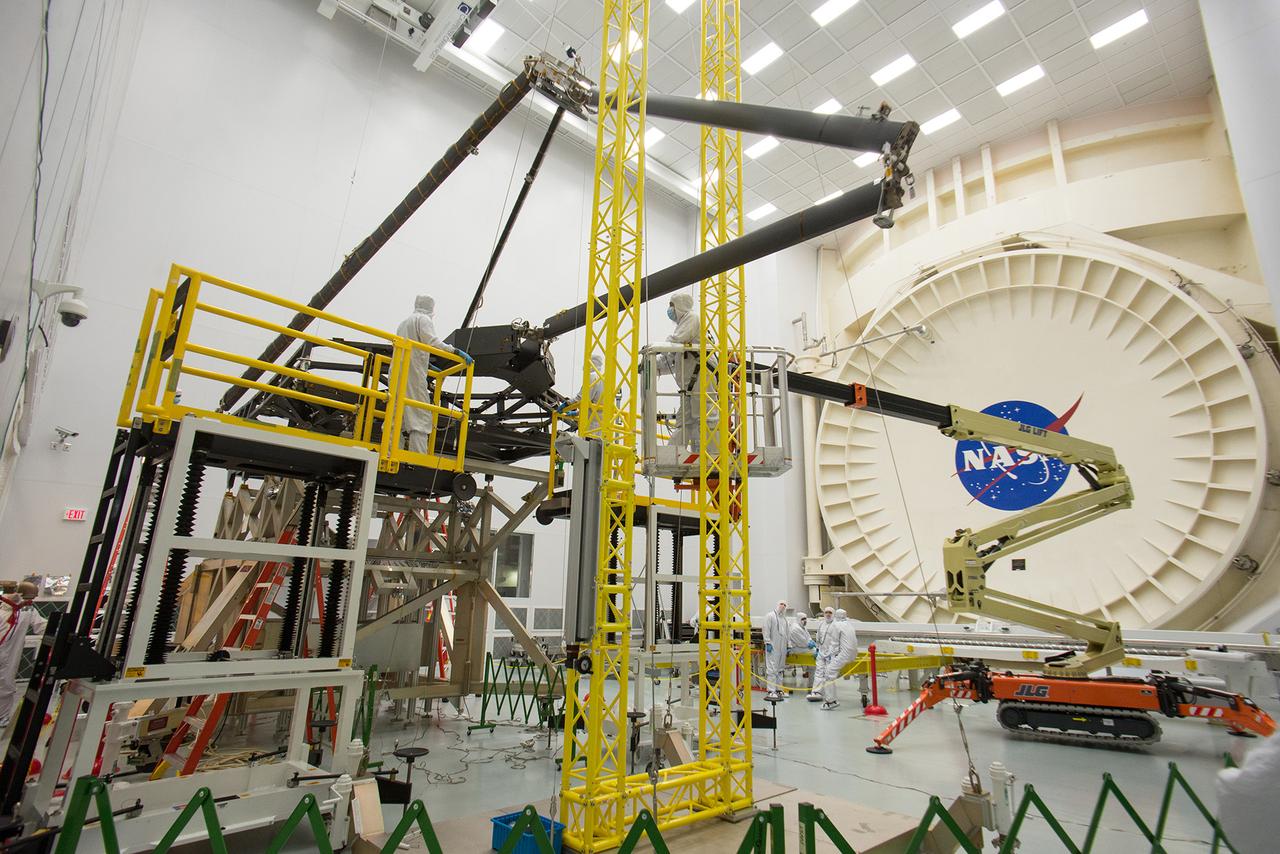

Engineers and technicians manually deployed the secondary mirror support structure (SMSS) of the James Webb Space Telescope's Pathfinder backplane test model, outside of a giant space simulation chamber called Chamber A, at NASA's Johnson Space Center in Houston. This historic test chamber was previously used in manned spaceflight missions and is being readied for a cryogenic test of a Webb telescope component. In the weightless environment of space, the SMSS is deployed by electric motors. On the ground, specially trained operators use a hand crank and a collection of mechanical ground support equipment to overcome the force of gravity. "This structure needs to be in the deployed configuration during the cryogenic test to see how the structure will operate in the frigid temperatures of space," said Will Rowland, senior mechanical test engineer for Northrop Grumman Aerospace Systems, Redondo Beach, California. "The test also demonstrates that the system works and can be successfully deployed." After the deployment was completed, Chamber A's circular door was opened and the rails (seen in the background of the photo) were installed so that the Pathfinder unit could be lifted, installed and rolled into the chamber on a cart. The team completed a fit check for the Pathfinder. Afterwards they readied the chamber for the cryogenic test, which will simulate the frigid temperatures the Webb telescope will encounter in space. “The team has been doing a great job keeping everything on schedule to getting our first optical test results, " said Lee Feinberg, NASA Optical Telescope Element Manager. The James Webb Space Telescope is the scientific successor to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. It will be the most powerful space telescope ever built. Webb is an international project led by NASA with its partners, the European Space Agency and the Canadian Space Agency. Image credit: NASA/Desiree Stover Text credit: Laura Betz, NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Maryland <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
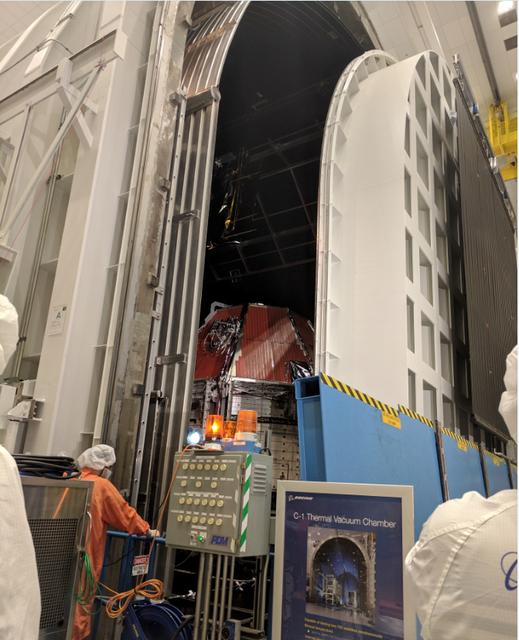

Boeing’s Crew Flight Test Starliner prepares for thermal vacuum testing at Boeing’s Space Environment Test Facility in El Segundo, Calif. During this test series, test teams outfitted Starliner with hot plates and radiators and placed in a vacuum chamber that could also be filled with a cryogenic nitrogen shroud. This allowed Boeing teams to simulate the vacuum environment in space as well as the drastic temperature swings Starliner will see as it moves to and from direct sunlight and the Earth’s shadow. This is the Starliner that will be used for Boeing’s Crew Flight Test as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, which is working with Boeing to return human spaceflight launches to the space station from U.S. soil.
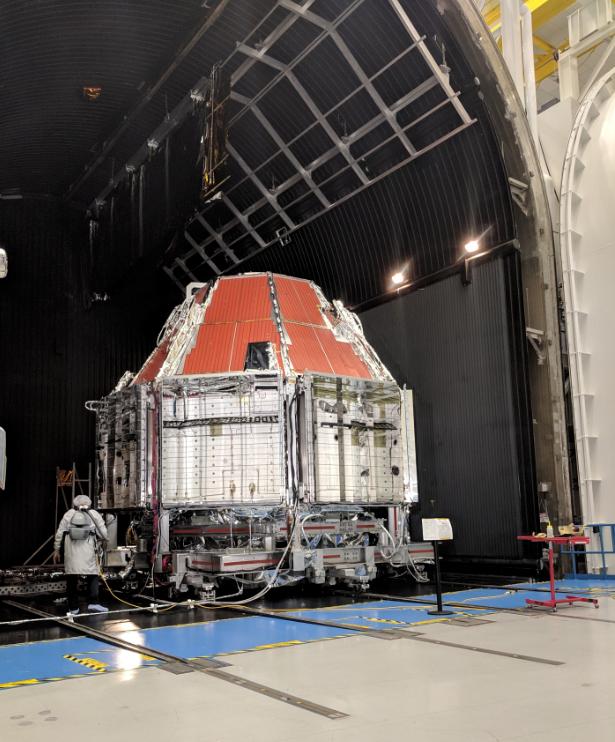

Boeing’s Crew Flight Test Starliner prepares for thermal vacuum testing at Boeing’s Space Environment Test Facility in El Segundo, Calif. During this test series, test teams outfitted Starliner with hot plates and radiators and placed in a vacuum chamber that could also be filled with a cryogenic nitrogen shroud. This allowed Boeing teams to simulate the vacuum environment in space as well as the drastic temperature swings Starliner will see as it moves to and from direct sunlight and the Earth’s shadow. This is the Starliner that will be used for Boeing’s Crew Flight Test as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, which is working with Boeing to return human spaceflight launches to the space station from U.S. soil.
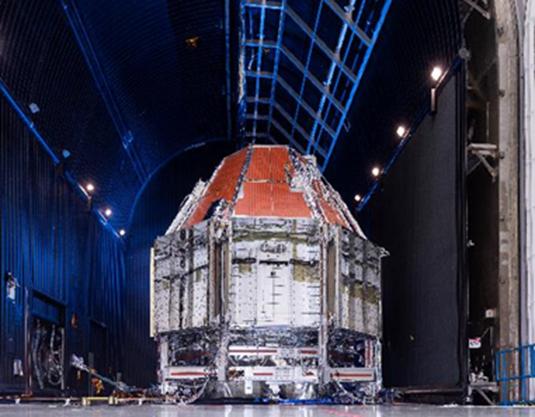

Boeing’s Crew Flight Test CST-100 Starliner prepares for thermal vacuum testing at Boeing’s Space Environment Test Facility in El Segundo, Calif. During this test series, test teams outfitted Starliner with hot plates and radiators and placed in a vacuum chamber that could also be filled with a cryogenic nitrogen shroud. This allowed Boeing teams to simulate the vacuum environment in space as well as the drastic temperature swings Starliner will see as it moves to and from direct sunlight and the Earth’s shadow. This is the Starliner that will be used for Boeing’s Crew Flight Test as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, which is working with Boeing to return human spaceflight launches to the space station from U.S. soil.
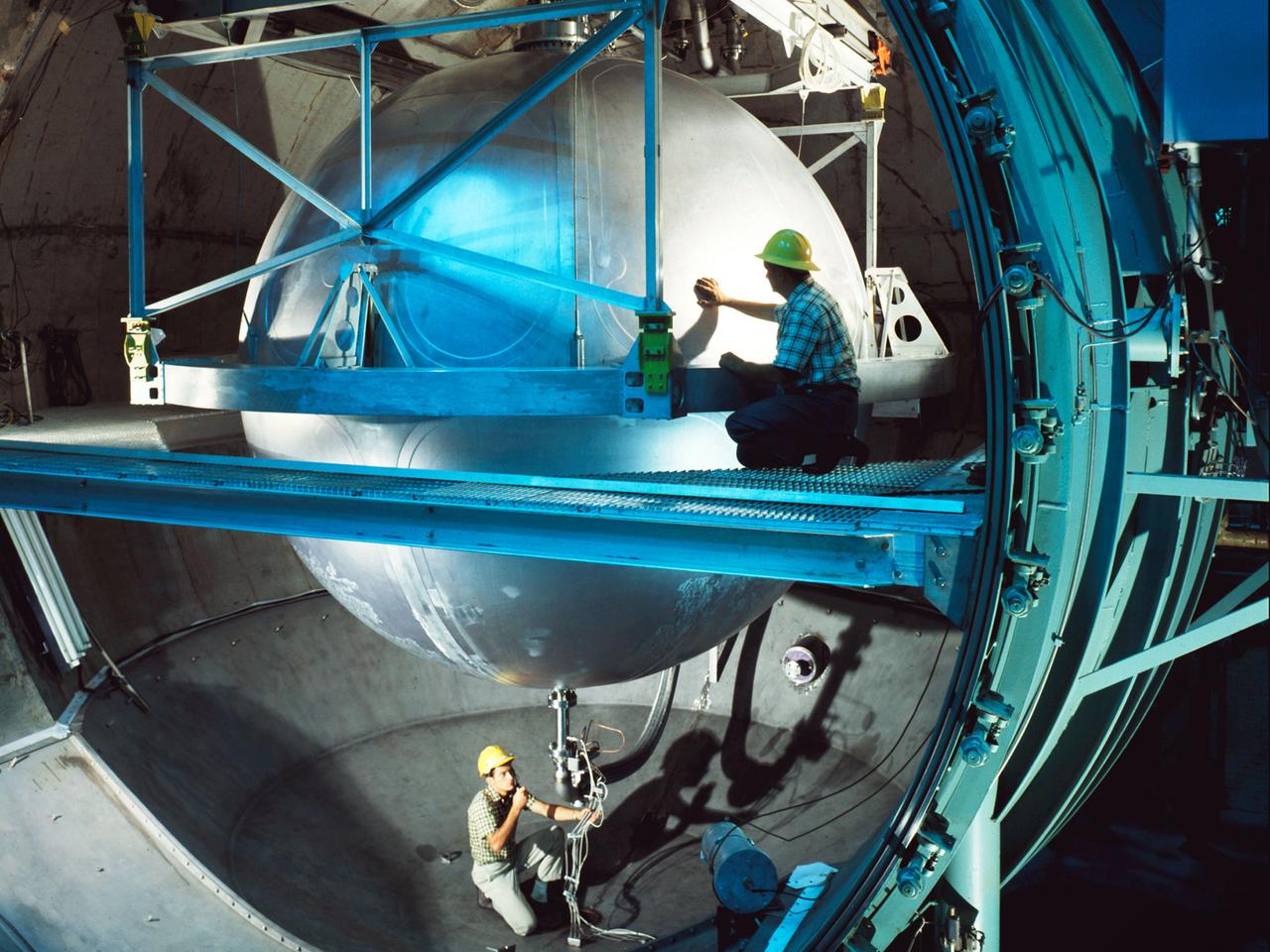

A 13-foot diameter mounted inside the large test chamber at the Cryogenic Propellant Tank, or K-Site, at National Aeronautics and Space Administration’s (NASA) Plum Brook Station. The 25-foot test chamber and 20-foot access door were designed to test liquid hydrogen fuel tanks up to 18 feet in diameter in conditions that simulated launches and spaceflight. Shakers were installed to test the effects of launch vibration on the tanks and their insulation. The K Site chamber was also equipped with cold walls that could be cooled with either liquid nitrogen or liquid hydrogen and vacuum pumps that could reduce pressure levels to 10-8 torr. This 13-foot tank passed its initial acceptance tests in K-Site on August 24, 1966. Delays in the modification of the tank postponed further tests of the tank until May 1967. Four pressure hold tests and expulsion runs were made in May using gaseous hydrogen or gaseous helium at 300R and 520R. In June a straight pipe injector test was run and two pressure effect tests at 35 and 75psi. Propellant slosh tests were successfully run in August. This photograph was taken the day after the program’s final runs on September 12, 1967.
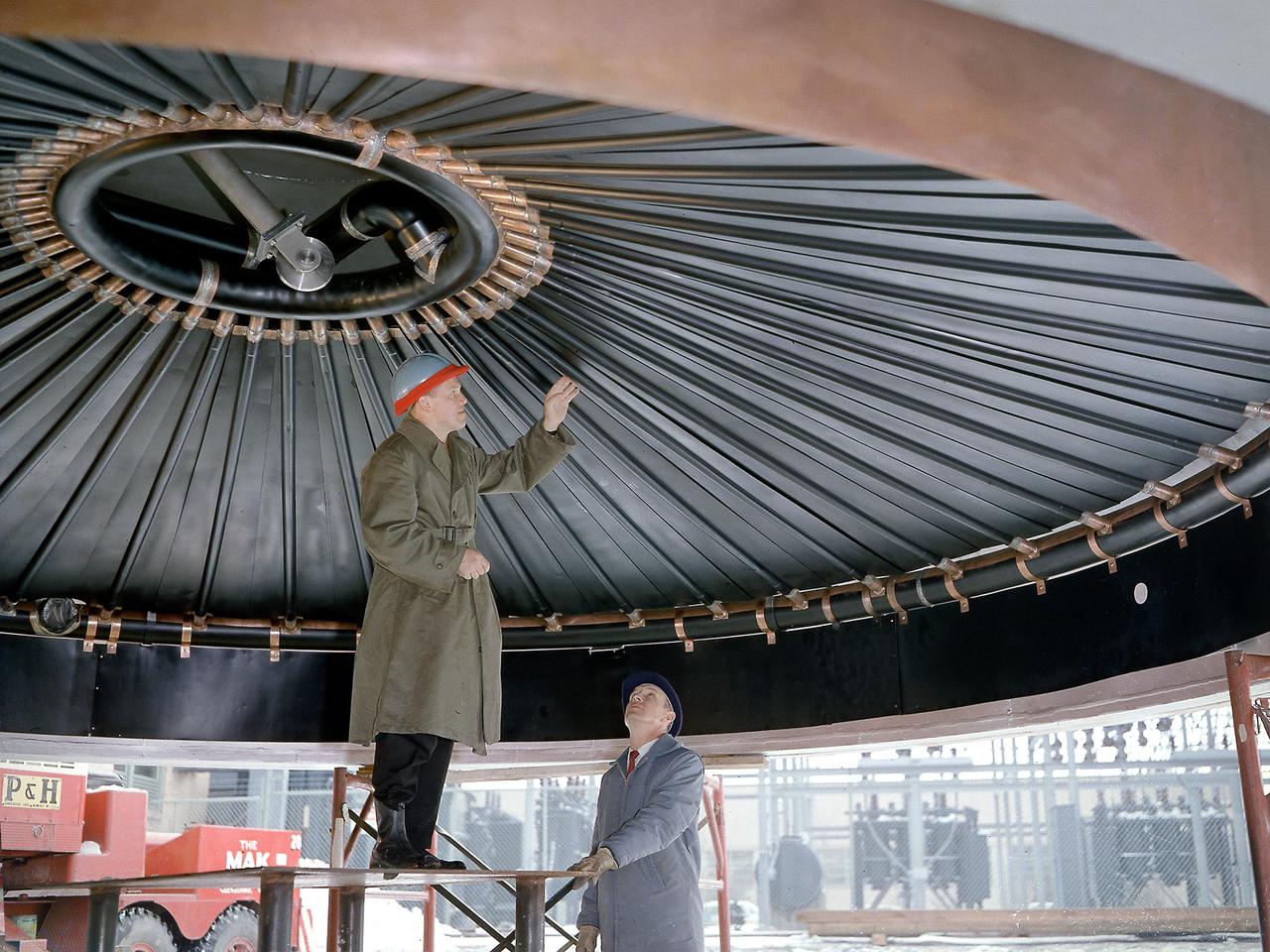

Engineers at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center inspect the nitrogen baffle in the interior of the 22.5-foot diameter dome at the Space Power Chambers. In 1961 NASA Lewis management decided to convert the Altitude Wind Tunnel into two large test chambers and renamed the facility the Space Power Chambers. The conversion, which took over two years, included removing the tunnel’s drive fan, exhaust scoop, and turning vanes from the east end and inserting bulkheads to seal off the new chambers within the tunnel. The eastern section of the tunnel became a vacuum chamber capable of simulating 100 miles altitude. In 1962 NASA management decided to use the new vacuum chamber exclusively to study the second-stage rocket. This required significant modifications to the new tank and extensive test equipment to create a space environment. The Lewis test engineers sought to subject the Centaur to long durations in conditions that would replicate those encountered during its missions in space. The chamber was already capable of creating the vacuum of space, but the test engineers also wanted to simulate the cryogenic temperatures and solar radiation found in space. Six panels of 500-watt tungsten-iodine lamps were arranged around the Centaur to simulate the effect of the Sun’s heat. A large copper cold wall with its interior coated with heat-absorbing black paint was created specifically for these tests and assembled around the Centaur. The 42-foot-high wall had vertical ribs filled with liquid nitrogen which produced the low temperatures.
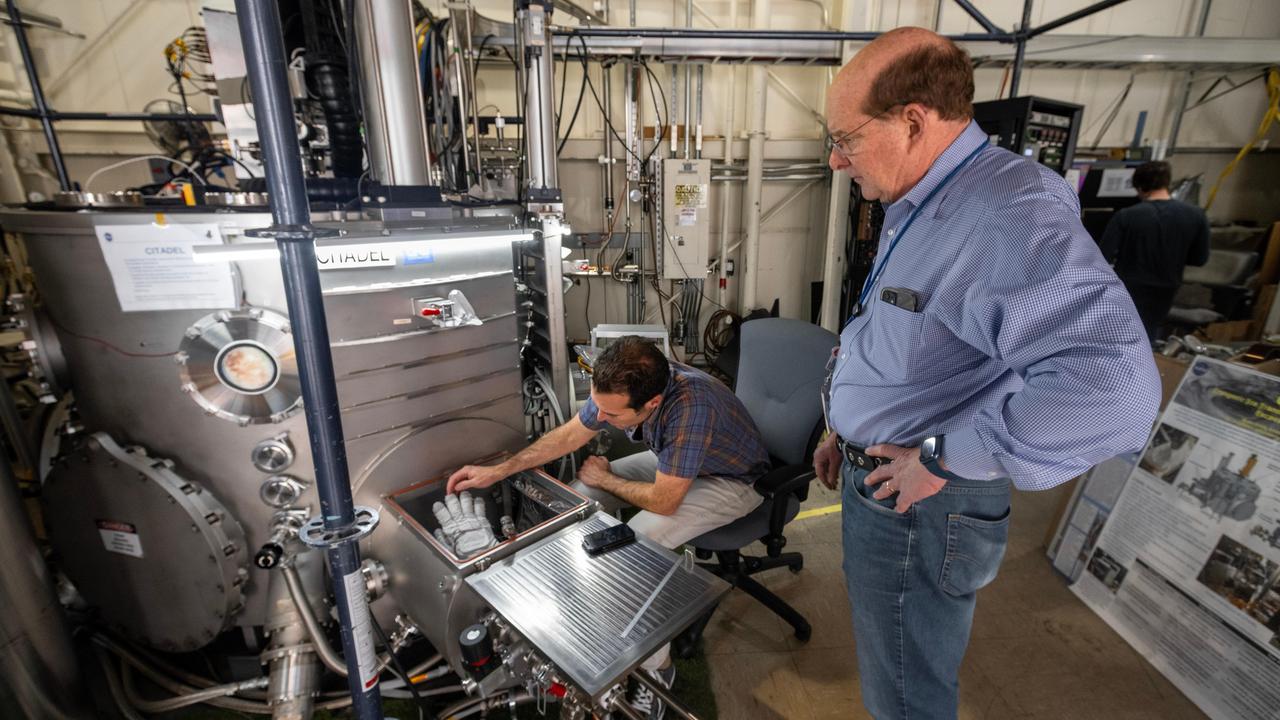

Spacesuit engineer Shane McFarland, left, of the Advanced Suit Team at NASA's Johnson Space Center prepares an astronaut glove for thermal vacuum testing inside a chamber at the agency's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California on Nov. 1, 2023. Tim Brady of the NASA Engineering and Safety Center (NESC), which spearheaded the glove testing campaign, looks on as McFarland positions the glove in a load lock – one of four small drawer-like chambers through which test materials are inserted into the larger main chamber of a facility called CITADEL (Cryogenic Ice Testing, Acquisition Development, and Excavation Laboratory). The glove was tested at vacuum and temperatures as low as minus 352 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 213 degrees Celsius) – temperatures as frigid as those Artemis III astronauts could experience on the Moon's South Pole. Built to prepare potential future robotic spacecraft for the frosty, low-pressure conditions on ocean worlds like Jupiter's frozen moon Europa, CITADEL has also proven key to evaluating how astronaut gloves and boots hold up in extraordinary cold. The NASA Engineering and Safety Center spearheaded a glove testing campaign in CITADEL from October 2023 to March 2024. Part of a spacesuit design called the Extravehicular Mobility Unit, the gloves tested in the chamber are the sixth version of a glove NASA began using in the 1980s. The testing in CITADEL showed that the legacy glove would not meet thermal requirements in the more challenging lunar South Pole environment. In addition to spotting vulnerabilities with existing suits, the CITADEL experiments will help NASA develop this unique test capability and prepare criteria for standardized, repeatable, and inexpensive test methods for the next-generation lunar suit being built by Axiom Space. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26591
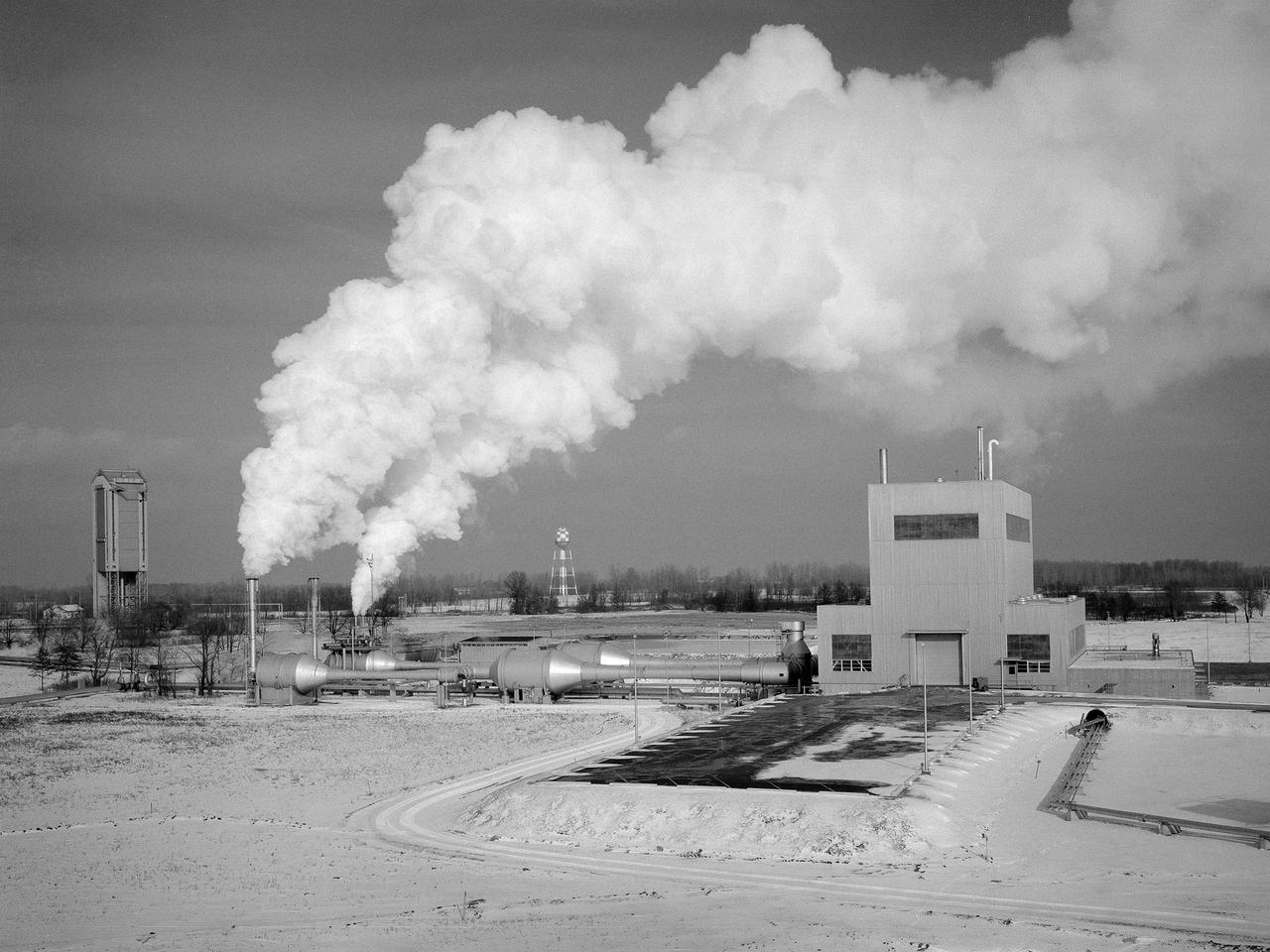

The Space Propulsion Research Facility, better known as B-2, operating at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration’s (NASA) Plum Brook Station in Sandusky, Ohio. B-2 is the world's only high altitude test facility capable of full-scale rocket engine and launch vehicle system level tests. It was created to test rocket propulsion systems with up to 100,000 pounds of thrust in a simulated space environment. The facility has the unique ability to maintain a vacuum at the rocket’s nozzle while the engine is firing. The rocket fires into a 120-foot deep spray chamber which cools the exhaust before it is ejected outside the facility. B-2 simulated space using giant diffusion pumps to reduce chamber pressure, nitrogen-filled cold walls create cryogenic temperatures, and quartz lamps replicate the radiation of the sun. This photograph shows the facility undergoing check-out runs prior to its first test in late 1969.The 38-foot diameter and 62-foot tall vacuum chamber is inside the high-bay on the right. Below that is a 67-foot diameter and 120-foot deep spray chamber. The hot rocket exhaust is cooled in the chamber by a spray of 250,000 gallons of water per minute. B-2’s first test was a hot firing of Centaur D-1A rocket on December 18, 1969. Since then the facility has fired more than 100 Pratt and Whitney RL-10 engines during the Centaur development, 80 current RL-10B-2 engines for Delta-3 development, and another 12 RL-10B-2s for the Delta 3 Upper Stage.
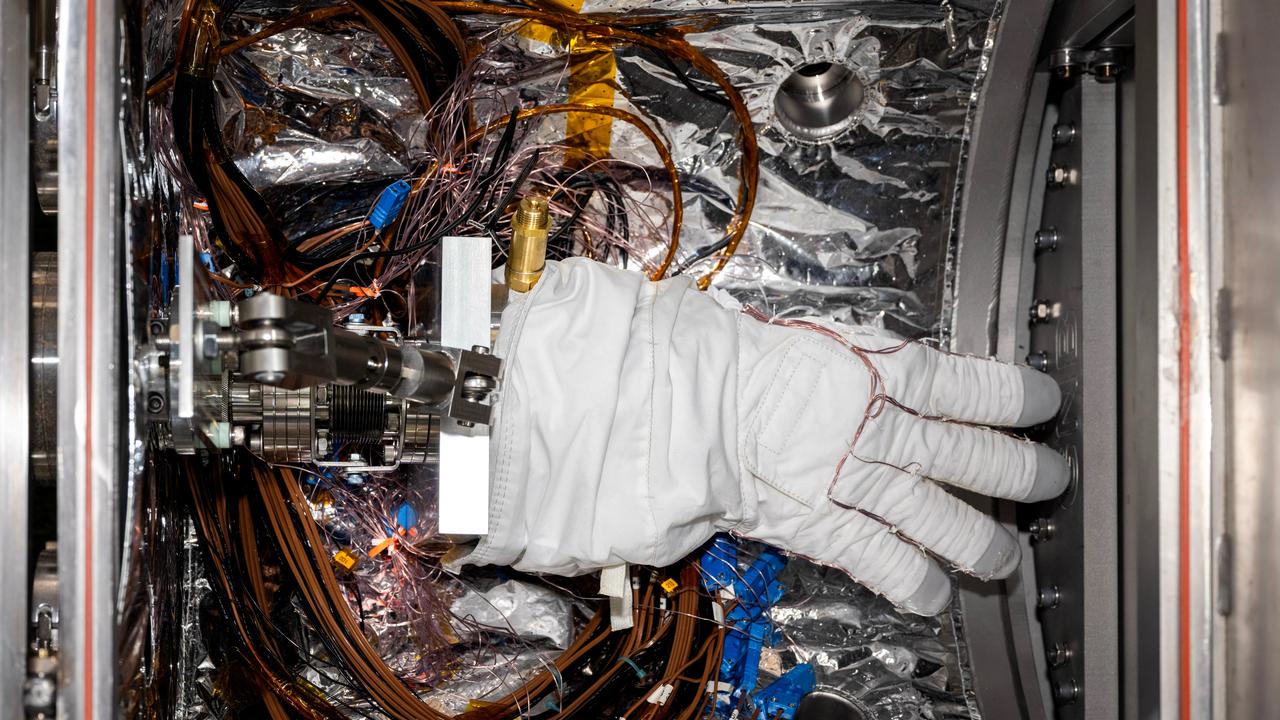

An astronaut glove designed for use during spacewalks on the International Space Station is prepared for thermal vacuum testing inside a chamber at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California on Nov. 1, 2023. The glove lies in a load lock, one of four small drawer-like chambers through which test materials are inserted into the larger main chamber of a facility called CITADEL (Cryogenic Ice Testing, Acquisition Development, and Excavation Laboratory). The glove was tested at vacuum and temperatures as low as minus 352 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 213 degrees Celsius) – temperatures as frigid as those Artemis III astronauts could experience on the Moon's South Pole. Built to prepare potential future robotic spacecraft for the frosty, low-pressure conditions on ocean worlds like Jupiter's frozen moon Europa, CITADEL has also proven key to evaluating how astronaut gloves and boots hold up in extraordinary cold. The NASA Engineering and Safety Center spearheaded a glove testing campaign in CITADEL from October 2023 to March 2024. Part of a spacesuit design called the Extravehicular Mobility Unit, the gloves tested in the chamber are the sixth version of a glove NASA began using in the 1980s. The testing in CITADEL showed that the legacy glove would not meet thermal requirements in the more challenging lunar South Pole environment. In addition to spotting vulnerabilities with existing suits, the CITADEL experiments will help NASA develop this unique test capability and prepare criteria for standardized, repeatable, and inexpensive test methods for the next-generation lunar suit being built by Axiom Space. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26430
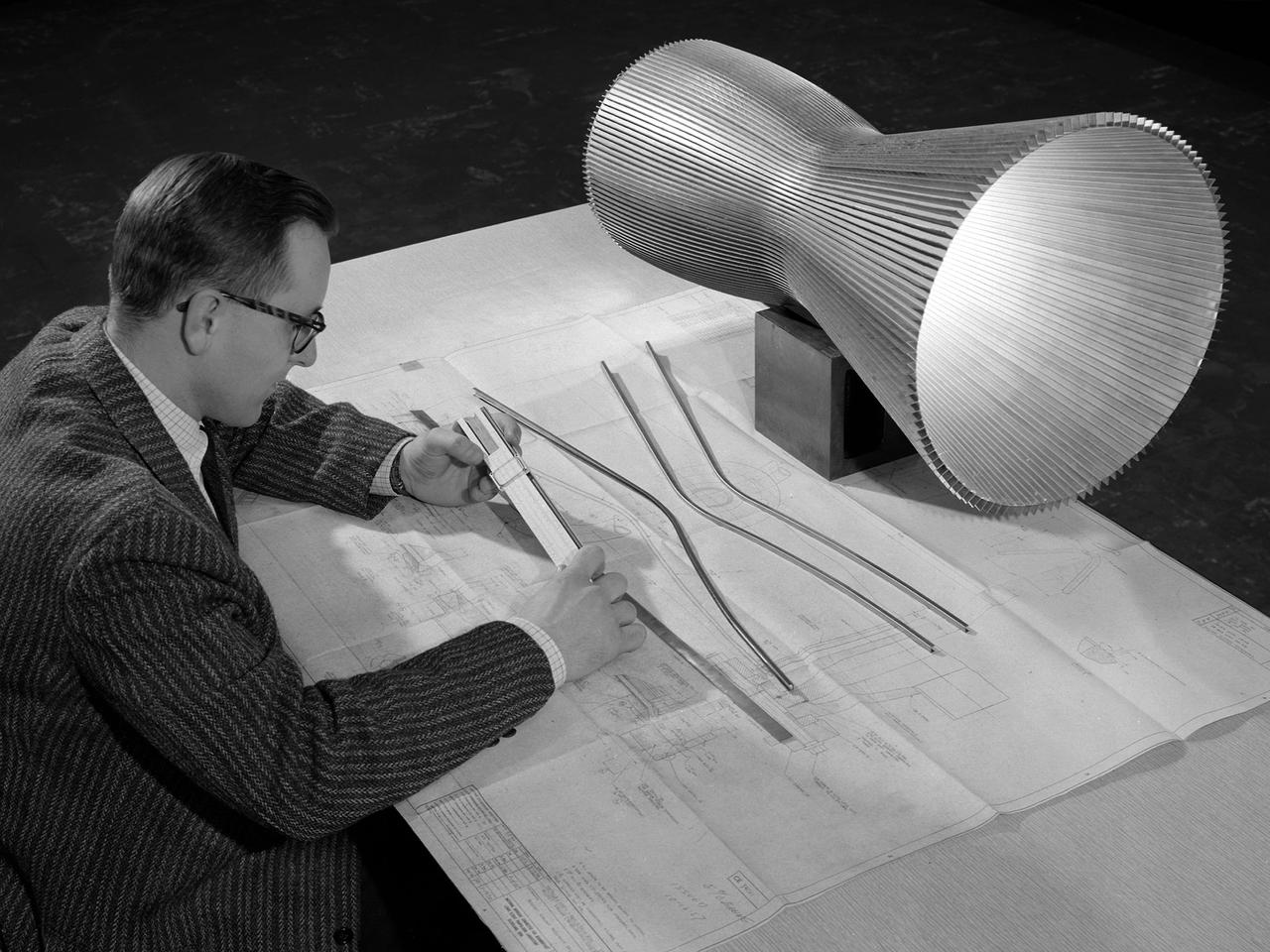
An engineer at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center examines a drawing showing the assembly and details of a 20,000-pound thrust regeneratively cooled rocket engine. The engine was being designed for testing in Lewis’ new Rocket Engine Test Facility, which began operating in the fall of 1957. The facility was the largest high-energy test facility in the country that was capable of handling liquid hydrogen and other liquid chemical fuels. The facility’s use of subscale engines up to 20,000 pounds of thrust permitted a cost-effective method of testing engines under various conditions. The Rocket Engine Test Facility was critical to the development of the technology that led to the use of hydrogen as a rocket fuel and the development of lightweight, regeneratively-cooled, hydrogen-fueled rocket engines. Regeneratively-cooled engines use the cryogenic liquid hydrogen as both the propellant and the coolant to prevent the engine from burning up. The fuel was fed through rows of narrow tubes that surrounded the combustion chamber and nozzle before being ignited inside the combustion chamber. The tubes are visible in the liner sitting on the desk. At the time, Pratt and Whitney was designing a 20,000-pound thrust liquid-hydrogen rocket engine, the RL-10. Two RL-10s would be used to power the Centaur second-stage rocket in the 1960s. The successful development of the Centaur rocket and the upper stages of the Saturn V were largely credited to the work carried out Lewis.
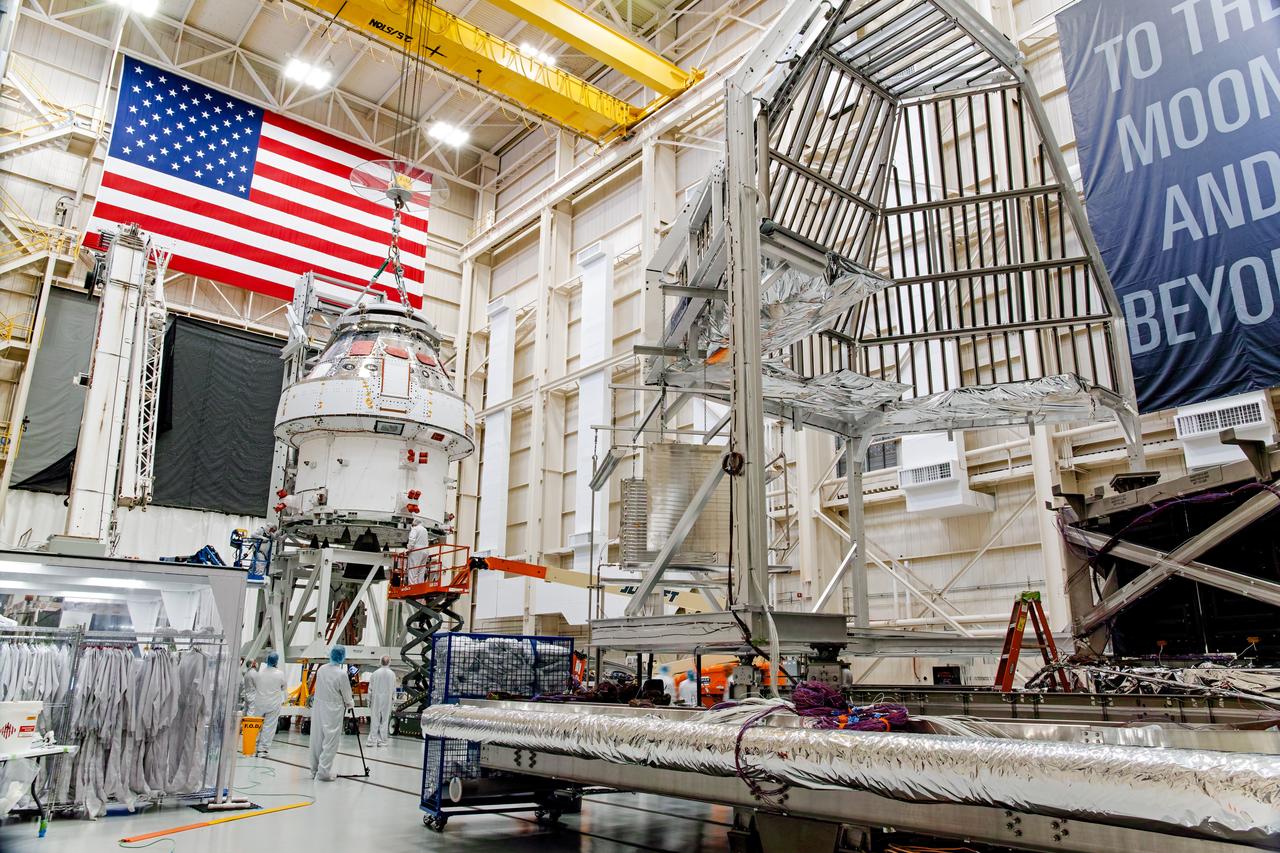

NASA’s Orion spacecraft–the crew module and European-built service module—is being lifted on Dec. 1, 2019 into a thermal cage and readied for its move into the vacuum chamber at NASA’s Neil A. Armstrong Test Facility in Ohio (formerly Plum Brook Station) for testing. Testing begins with a 60-day thermal test, where the spacecraft will be subjected to temperatures ranging from -250 to 300-degrees Fahrenheit to ensure it can withstand the harsh environment of space during Artemis missions. These extreme temperatures simulate flying in-and-out of sunlight and shadow in space using Heat Flux, a specially-designed system that heats specific parts of the spacecraft at any given time. Orion will also be surrounded on all sides by a set of large panels, called a cryogenic-shroud, that will provide the cold background temperatures of space.
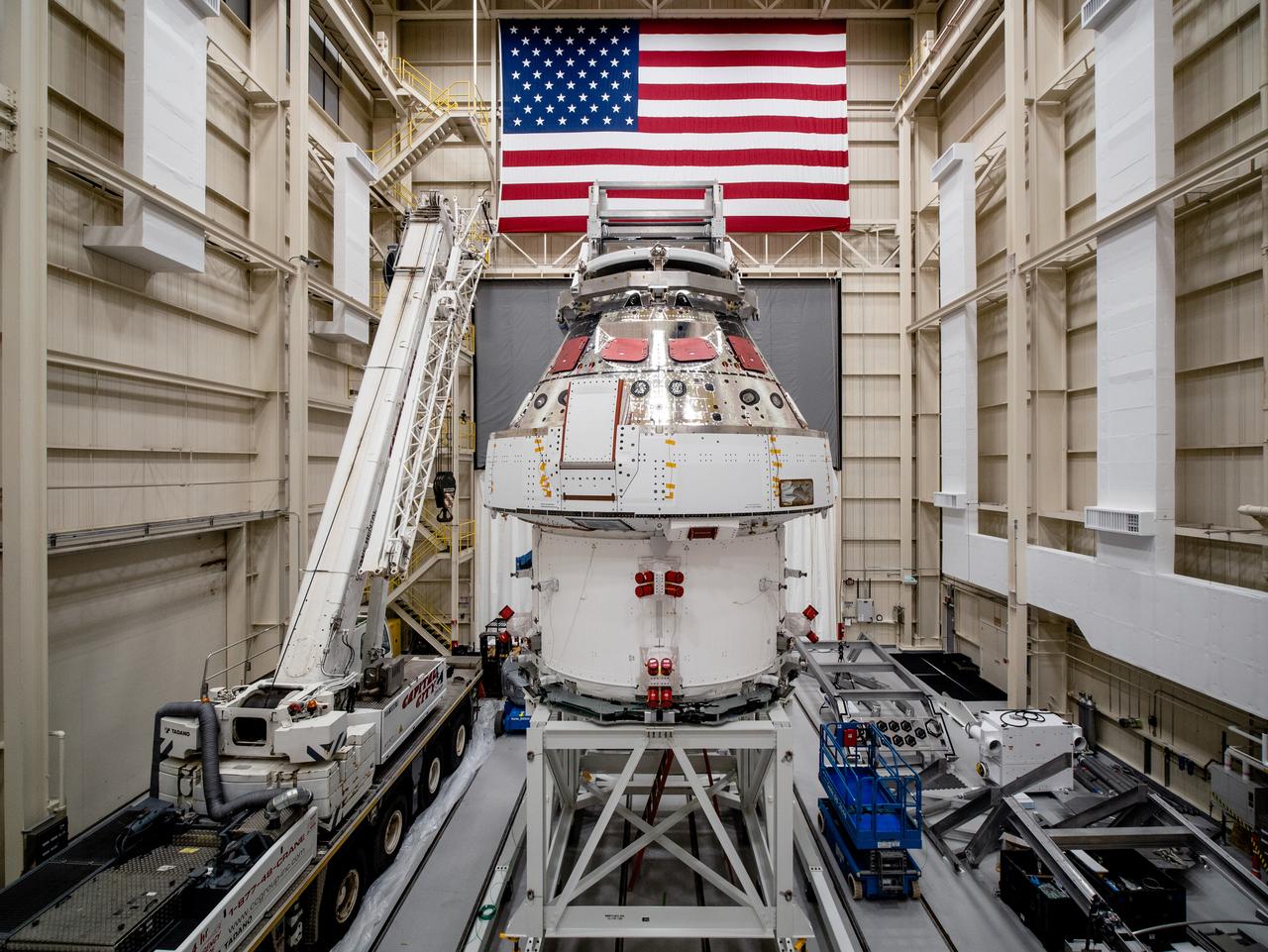
NASA’s Orion spacecraft–the crew module and European-built service module—is being lifted on Dec. 1, 2019 into a thermal cage and readied for its move into the vacuum chamber at NASA’s Neil A. Armstrong Test Facility in Ohio (formerly Plum Brook Station) for testing. Testing begins with a 60-day thermal test, where the spacecraft will be subjected to temperatures ranging from -250 to 300-degrees Fahrenheit to ensure it can withstand the harsh environment of space during Artemis missions. These extreme temperatures simulate flying in-and-out of sunlight and shadow in space using Heat Flux, a specially-designed system that heats specific parts of the spacecraft at any given time. Orion will also be surrounded on all sides by a set of large panels, called a cryogenic-shroud, that will provide the cold background temperatures of space.
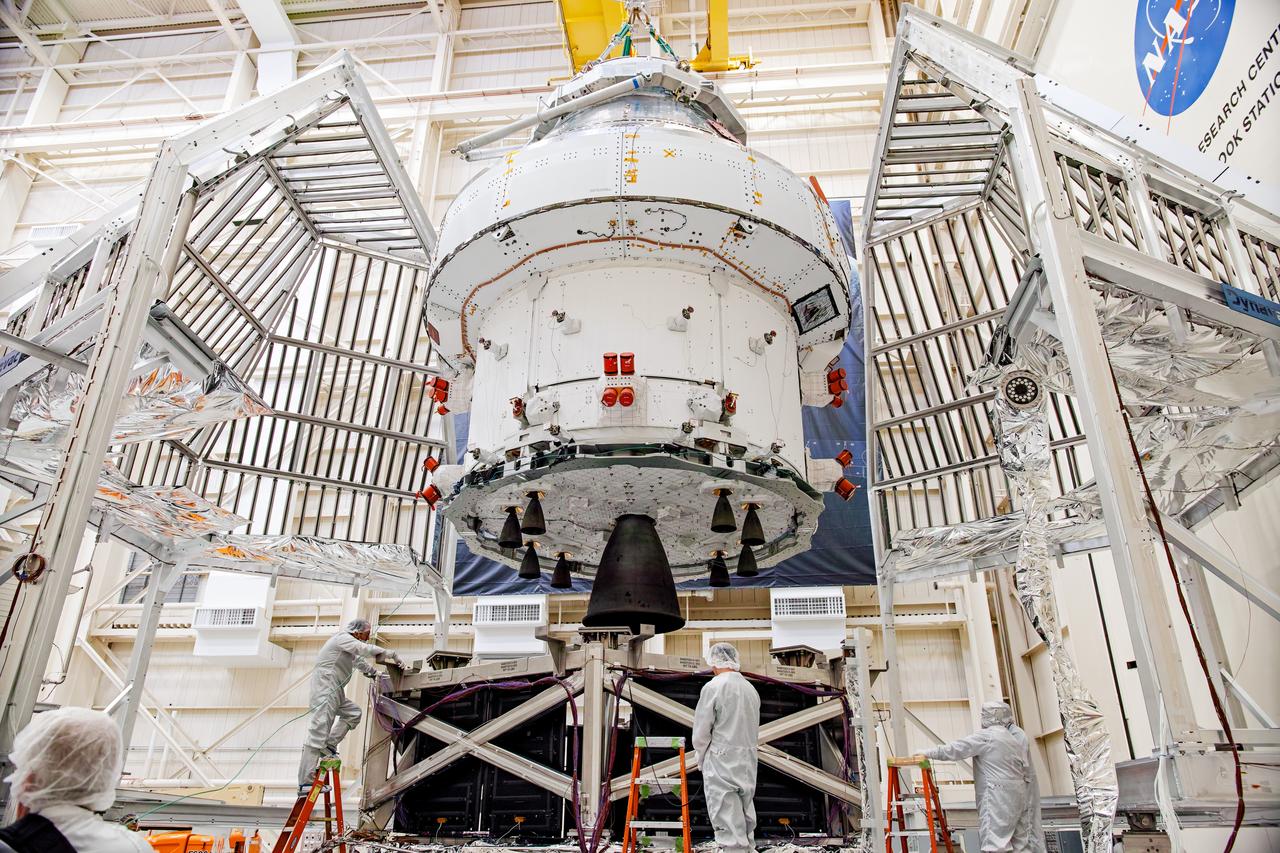
NASA’s Orion spacecraft–the crew module and European-built service module—is being lifted on Dec. 1, 2019 into a thermal cage and readied for its move into the vacuum chamber at NASA’s Neil A. Armstrong Test Facility in Ohio (formerly Plum Brook Station) for testing. Testing begins with a 60-day thermal test, where the spacecraft will be subjected to temperatures ranging from -250 to 300-degrees Fahrenheit to ensure it can withstand the harsh environment of space during Artemis missions. These extreme temperatures simulate flying in-and-out of sunlight and shadow in space using Heat Flux, a specially-designed system that heats specific parts of the spacecraft at any given time. Orion will also be surrounded on all sides by a set of large panels, called a cryogenic-shroud, that will provide the cold background temperatures of space.

NASA’s Orion spacecraft–the crew module and European-built service module—is being lifted on Dec. 1, 2019 into a thermal cage and readied for its move into the vacuum chamber at NASA’s Neil A. Armstrong Test Facility in Ohio (formerly Plum Brook Station) for testing. Testing begins with a 60-day thermal test, where the spacecraft will be subjected to temperatures ranging from -250 to 300-degrees Fahrenheit to ensure it can withstand the harsh environment of space during Artemis missions. These extreme temperatures simulate flying in-and-out of sunlight and shadow in space using Heat Flux, a specially-designed system that heats specific parts of the spacecraft at any given time. Orion will also be surrounded on all sides by a set of large panels, called a cryogenic-shroud, that will provide the cold background temperatures of space.
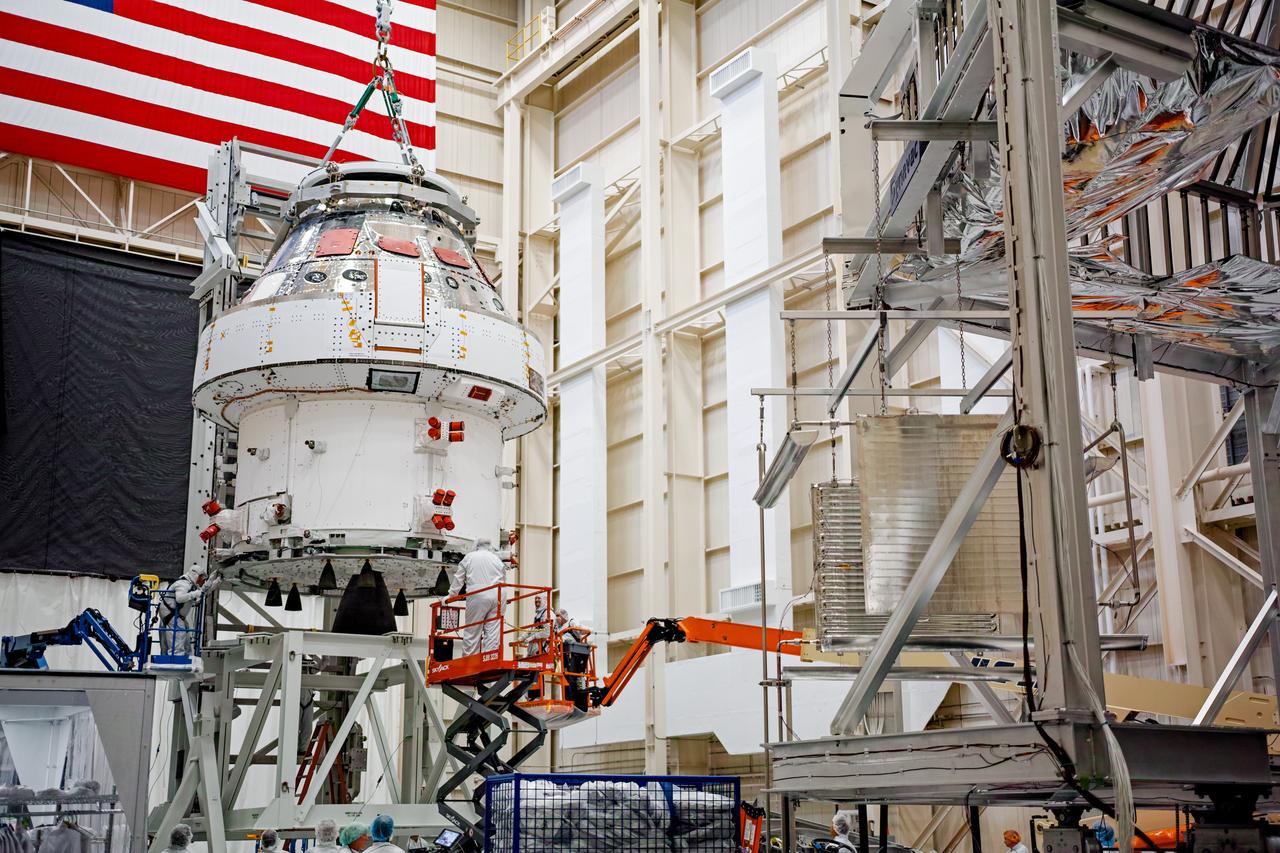

NASA’s Orion spacecraft–the crew module and European-built service module—is being lifted on Dec. 1, 2019 into a thermal cage and readied for its move into the vacuum chamber at NASA’s Neil A. Armstrong Test Facility in Ohio (formerly Plum Brook Station) for testing. Testing begins with a 60-day thermal test, where the spacecraft will be subjected to temperatures ranging from -250 to 300-degrees Fahrenheit to ensure it can withstand the harsh environment of space during Artemis missions. These extreme temperatures simulate flying in-and-out of sunlight and shadow in space using Heat Flux, a specially-designed system that heats specific parts of the spacecraft at any given time. Orion will also be surrounded on all sides by a set of large panels, called a cryogenic-shroud, that will provide the cold background temperatures of space.
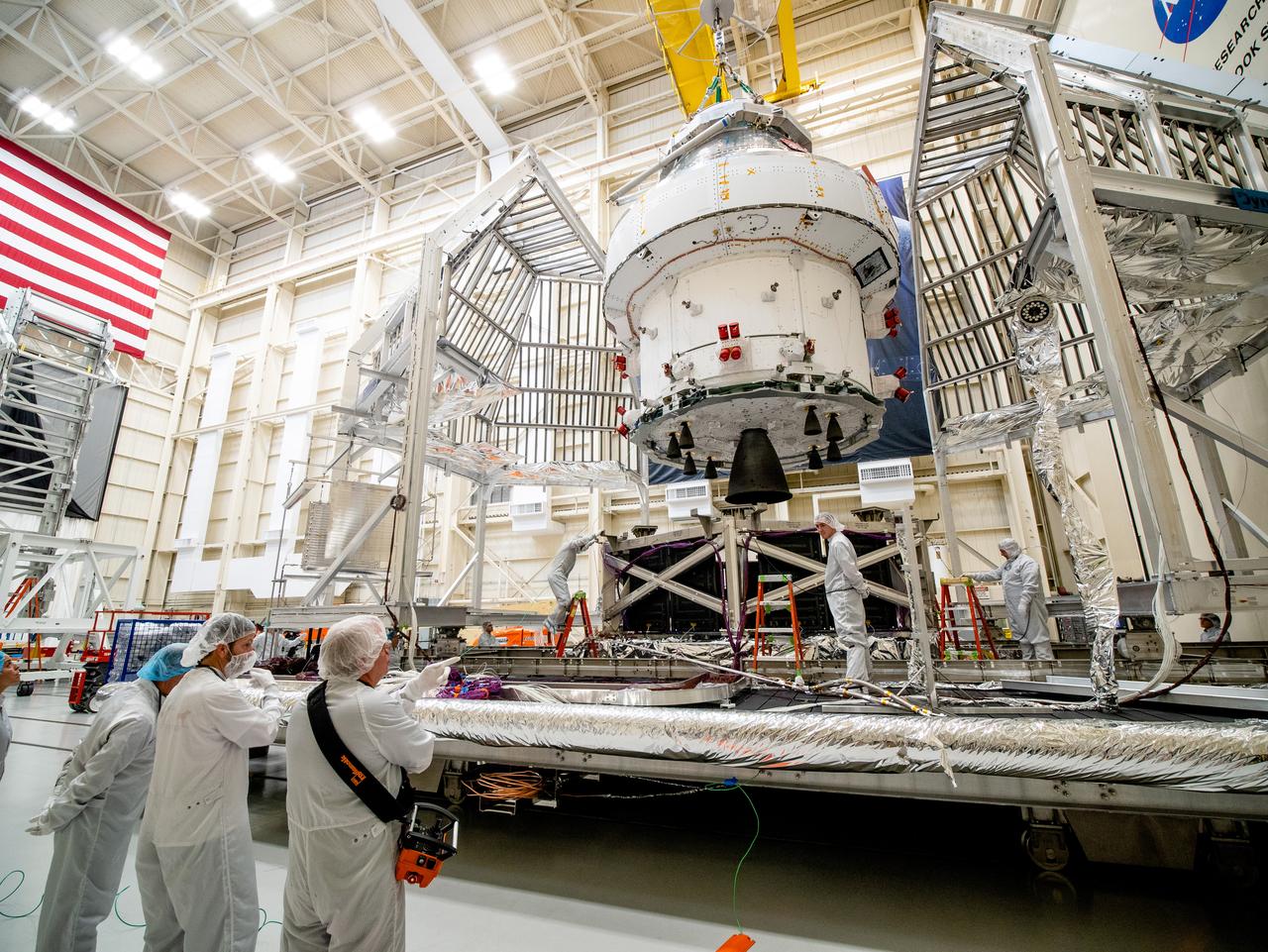

NASA’s Orion spacecraft–the crew module and European-built service module—is being lifted on Dec. 1, 2019 into a thermal cage and readied for its move into the vacuum chamber at NASA’s Neil A. Armstrong Test Facility in Ohio (formerly Plum Brook Station) for testing. Testing begins with a 60-day thermal test, where the spacecraft will be subjected to temperatures ranging from -250 to 300-degrees Fahrenheit to ensure it can withstand the harsh environment of space during Artemis missions. These extreme temperatures simulate flying in-and-out of sunlight and shadow in space using Heat Flux, a specially-designed system that heats specific parts of the spacecraft at any given time. Orion will also be surrounded on all sides by a set of large panels, called a cryogenic-shroud, that will provide the cold background temperatures of space.
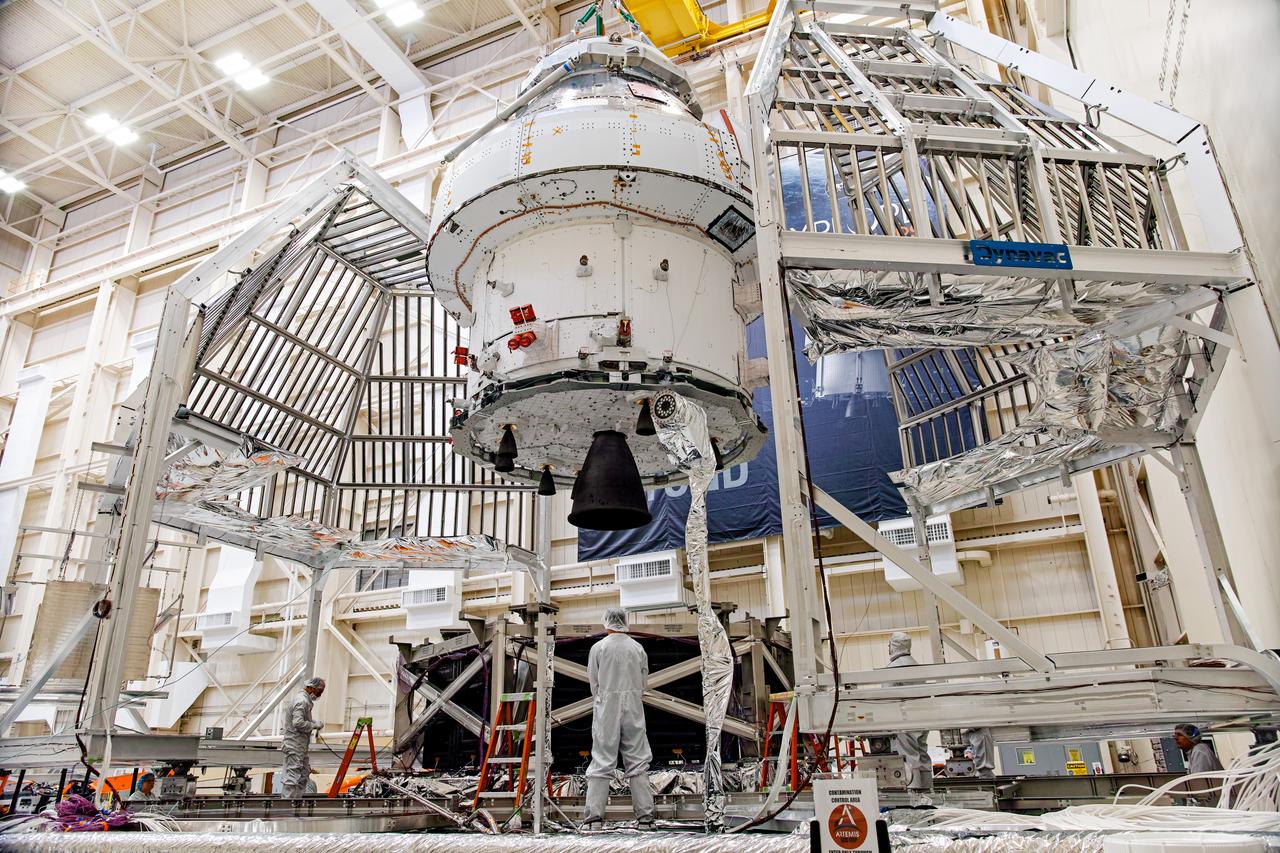

NASA’s Orion spacecraft–the crew module and European-built service module—is being lifted on Dec. 1, 2019 into a thermal cage and readied for its move into the vacuum chamber at NASA’s Neil A. Armstrong Test Facility in Ohio (formerly Plum Brook Station) for testing. Testing begins with a 60-day thermal test, where the spacecraft will be subjected to temperatures ranging from -250 to 300-degrees Fahrenheit to ensure it can withstand the harsh environment of space during Artemis missions. These extreme temperatures simulate flying in-and-out of sunlight and shadow in space using Heat Flux, a specially-designed system that heats specific parts of the spacecraft at any given time. Orion will also be surrounded on all sides by a set of large panels, called a cryogenic-shroud, that will provide the cold background temperatures of space.
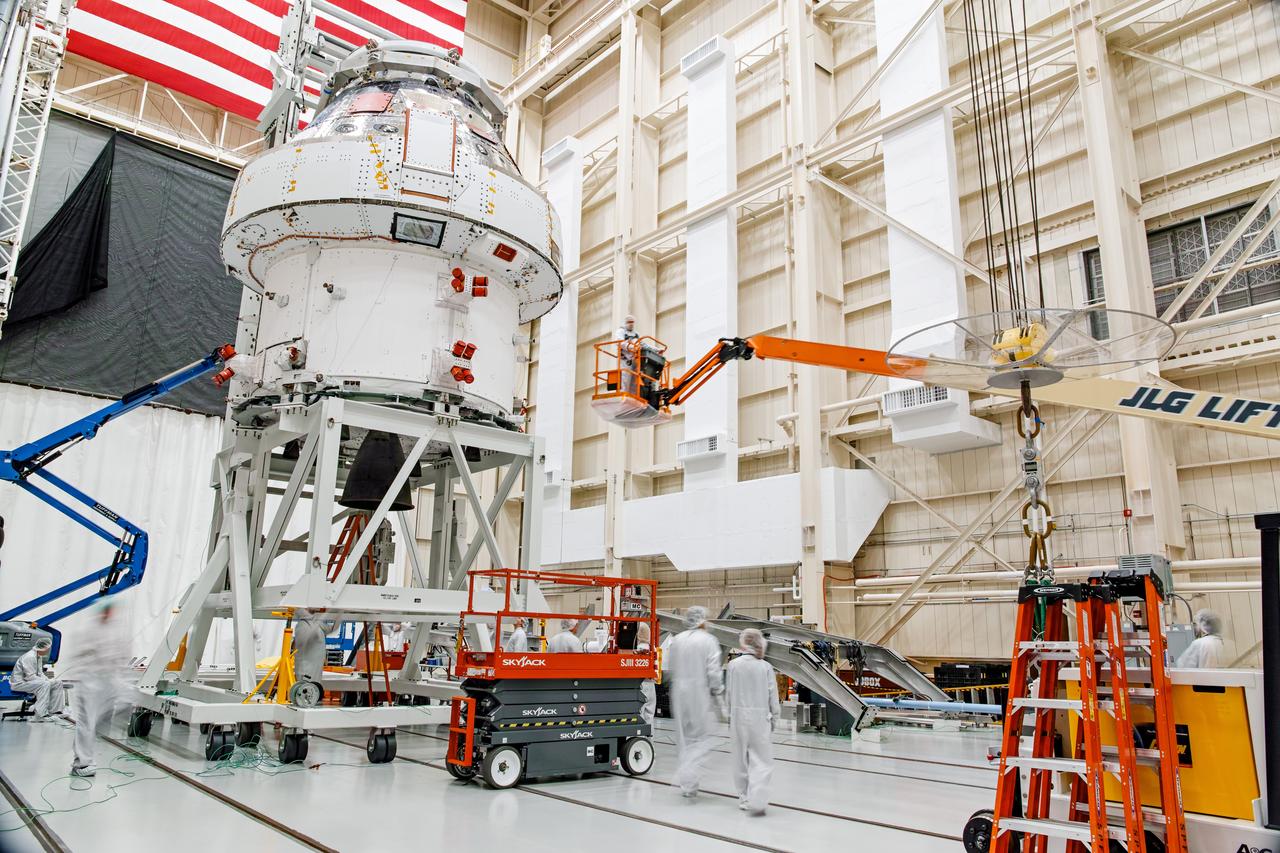

NASA’s Orion spacecraft–the crew module and European-built service module—is being lifted on Dec. 1, 2019 into a thermal cage and readied for its move into the vacuum chamber at NASA’s Neil A. Armstrong Test Facility in Ohio (formerly Plum Brook Station) for testing. Testing begins with a 60-day thermal test, where the spacecraft will be subjected to temperatures ranging from -250 to 300-degrees Fahrenheit to ensure it can withstand the harsh environment of space during Artemis missions. These extreme temperatures simulate flying in-and-out of sunlight and shadow in space using Heat Flux, a specially-designed system that heats specific parts of the spacecraft at any given time. Orion will also be surrounded on all sides by a set of large panels, called a cryogenic-shroud, that will provide the cold background temperatures of space.
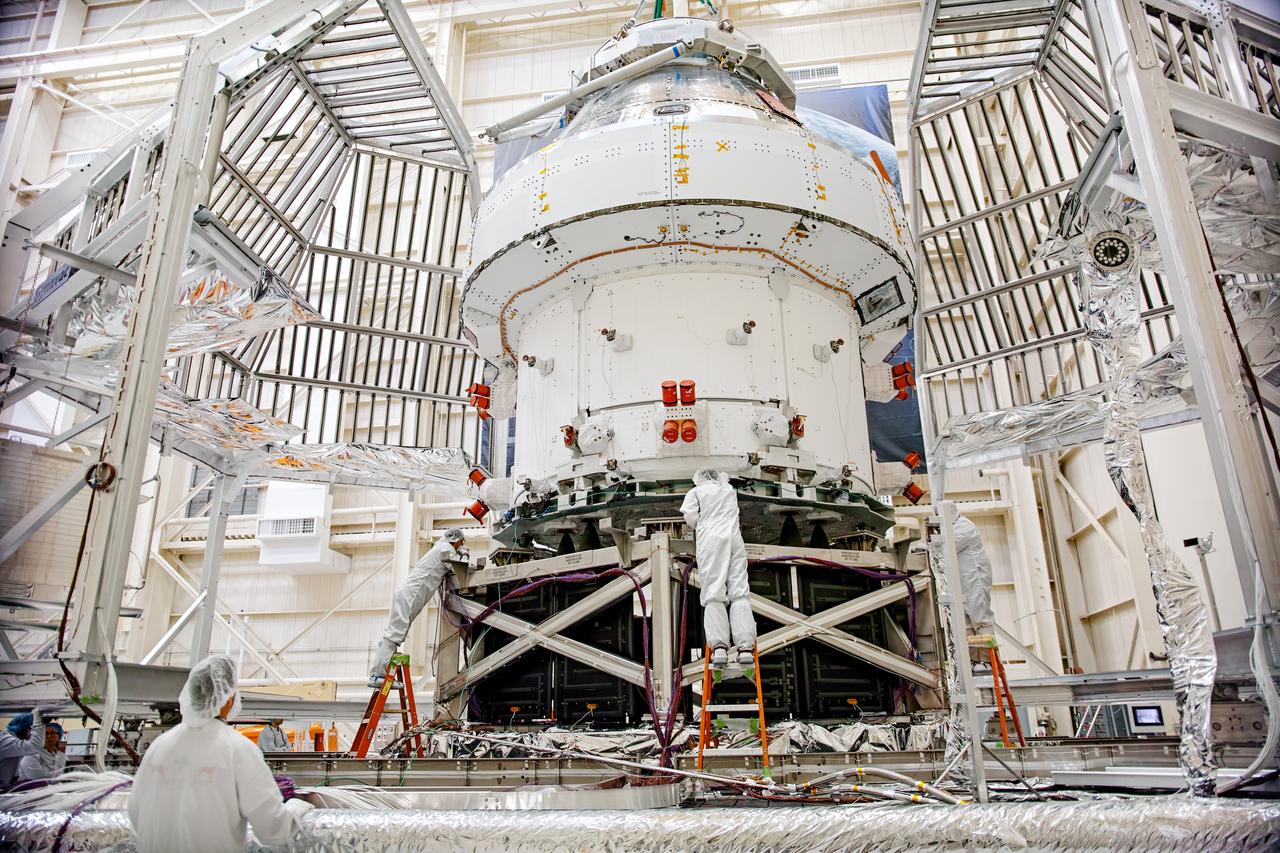
NASA’s Orion spacecraft–the crew module and European-built service module—is being lifted on Dec. 1, 2019 into a thermal cage and readied for its move into the vacuum chamber at NASA’s Neil A. Armstrong Test Facility in Ohio (formerly Plum Brook Station) for testing. Testing begins with a 60-day thermal test, where the spacecraft will be subjected to temperatures ranging from -250 to 300-degrees Fahrenheit to ensure it can withstand the harsh environment of space during Artemis missions. These extreme temperatures simulate flying in-and-out of sunlight and shadow in space using Heat Flux, a specially-designed system that heats specific parts of the spacecraft at any given time. Orion will also be surrounded on all sides by a set of large panels, called a cryogenic-shroud, that will provide the cold background temperatures of space.

NASA’s Orion spacecraft–the crew module and European-built service module—is being lifted on Dec. 1, 2019 into a thermal cage and readied for its move into the vacuum chamber at NASA’s Neil A. Armstrong Test Facility in Ohio (formerly Plum Brook Station) for testing. Testing begins with a 60-day thermal test, where the spacecraft will be subjected to temperatures ranging from -250 to 300-degrees Fahrenheit to ensure it can withstand the harsh environment of space during Artemis missions. These extreme temperatures simulate flying in-and-out of sunlight and shadow in space using Heat Flux, a specially-designed system that heats specific parts of the spacecraft at any given time. Orion will also be surrounded on all sides by a set of large panels, called a cryogenic-shroud, that will provide the cold background temperatures of space.
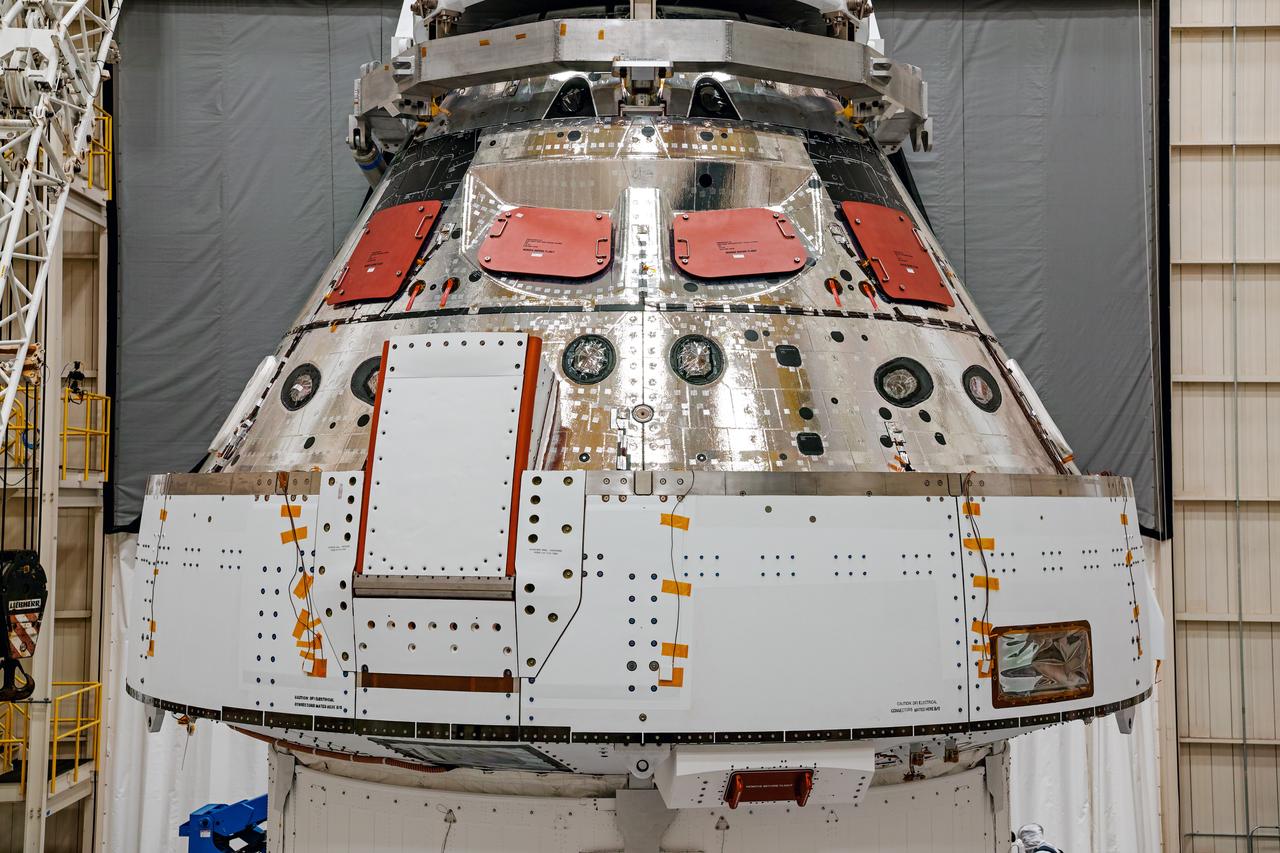

NASA’s Orion spacecraft–the crew module and European-built service module—is being lifted on Dec. 1, 2019 into a thermal cage and readied for its move into the vacuum chamber at NASA’s Neil A. Armstrong Test Facility in Ohio (formerly Plum Brook Station) for testing. Testing begins with a 60-day thermal test, where the spacecraft will be subjected to temperatures ranging from -250 to 300-degrees Fahrenheit to ensure it can withstand the harsh environment of space during Artemis missions. These extreme temperatures simulate flying in-and-out of sunlight and shadow in space using Heat Flux, a specially-designed system that heats specific parts of the spacecraft at any given time. Orion will also be surrounded on all sides by a set of large panels, called a cryogenic-shroud, that will provide the cold background temperatures of space.
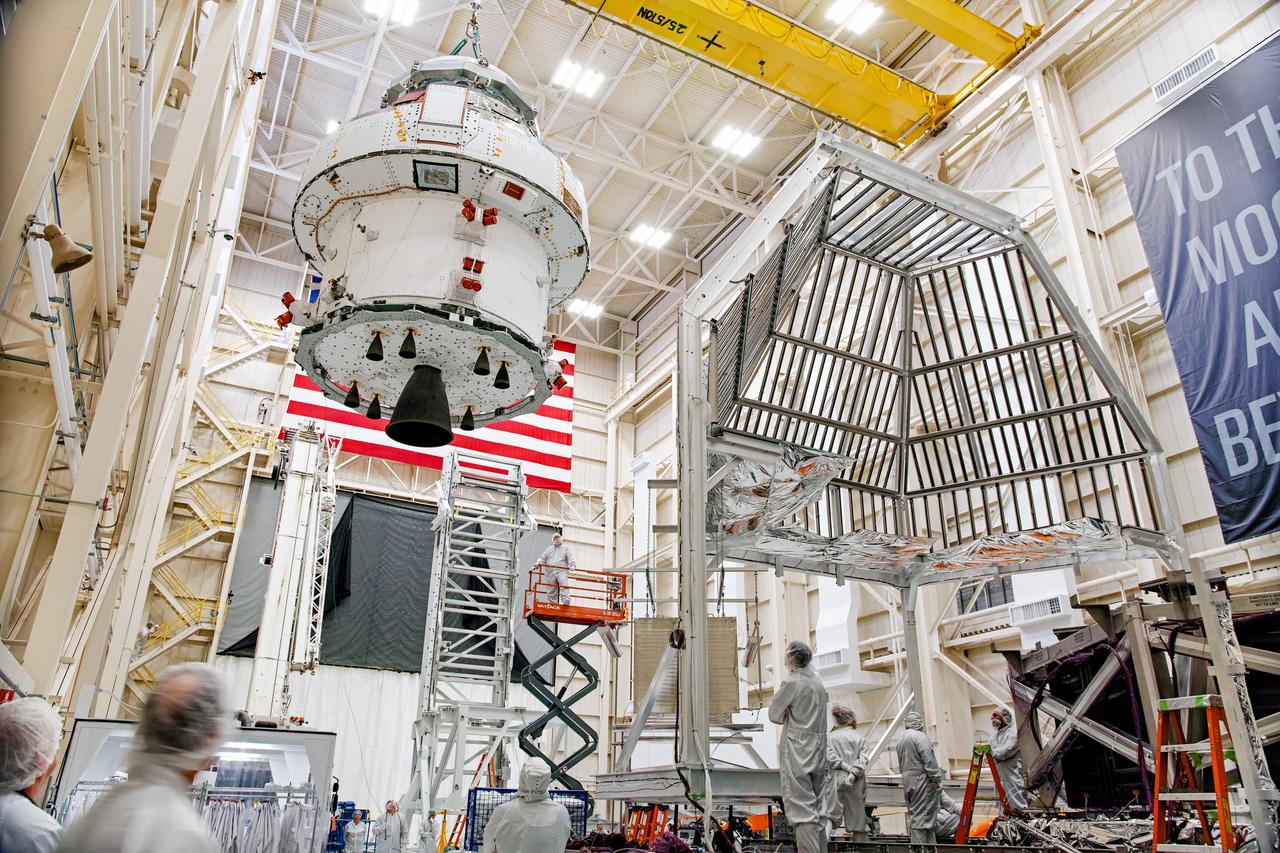
NASA’s Orion spacecraft–the crew module and European-built service module—is being lifted on Dec. 1, 2019 into a thermal cage and readied for its move into the vacuum chamber at NASA’s Neil A. Armstrong Test Facility in Ohio (formerly Plum Brook Station) for testing. Testing begins with a 60-day thermal test, where the spacecraft will be subjected to temperatures ranging from -250 to 300-degrees Fahrenheit to ensure it can withstand the harsh environment of space during Artemis missions. These extreme temperatures simulate flying in-and-out of sunlight and shadow in space using Heat Flux, a specially-designed system that heats specific parts of the spacecraft at any given time. Orion will also be surrounded on all sides by a set of large panels, called a cryogenic-shroud, that will provide the cold background temperatures of space.
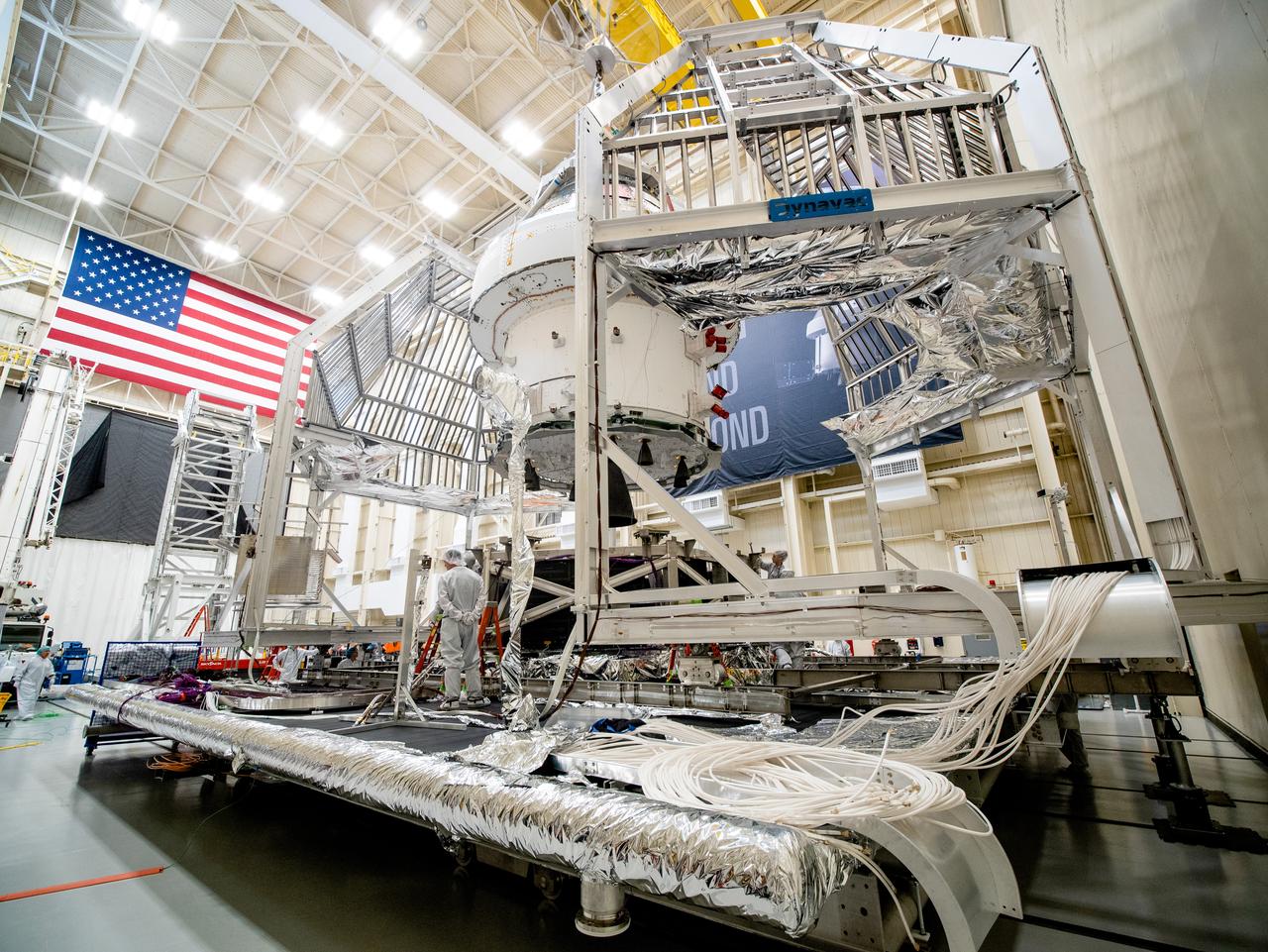

NASA’s Orion spacecraft–the crew module and European-built service module—is being lifted on Dec. 1, 2019 into a thermal cage and readied for its move into the vacuum chamber at NASA’s Neil A. Armstrong Test Facility in Ohio (formerly Plum Brook Station) for testing. Testing begins with a 60-day thermal test, where the spacecraft will be subjected to temperatures ranging from -250 to 300-degrees Fahrenheit to ensure it can withstand the harsh environment of space during Artemis missions. These extreme temperatures simulate flying in-and-out of sunlight and shadow in space using Heat Flux, a specially-designed system that heats specific parts of the spacecraft at any given time. Orion will also be surrounded on all sides by a set of large panels, called a cryogenic-shroud, that will provide the cold background temperatures of space.
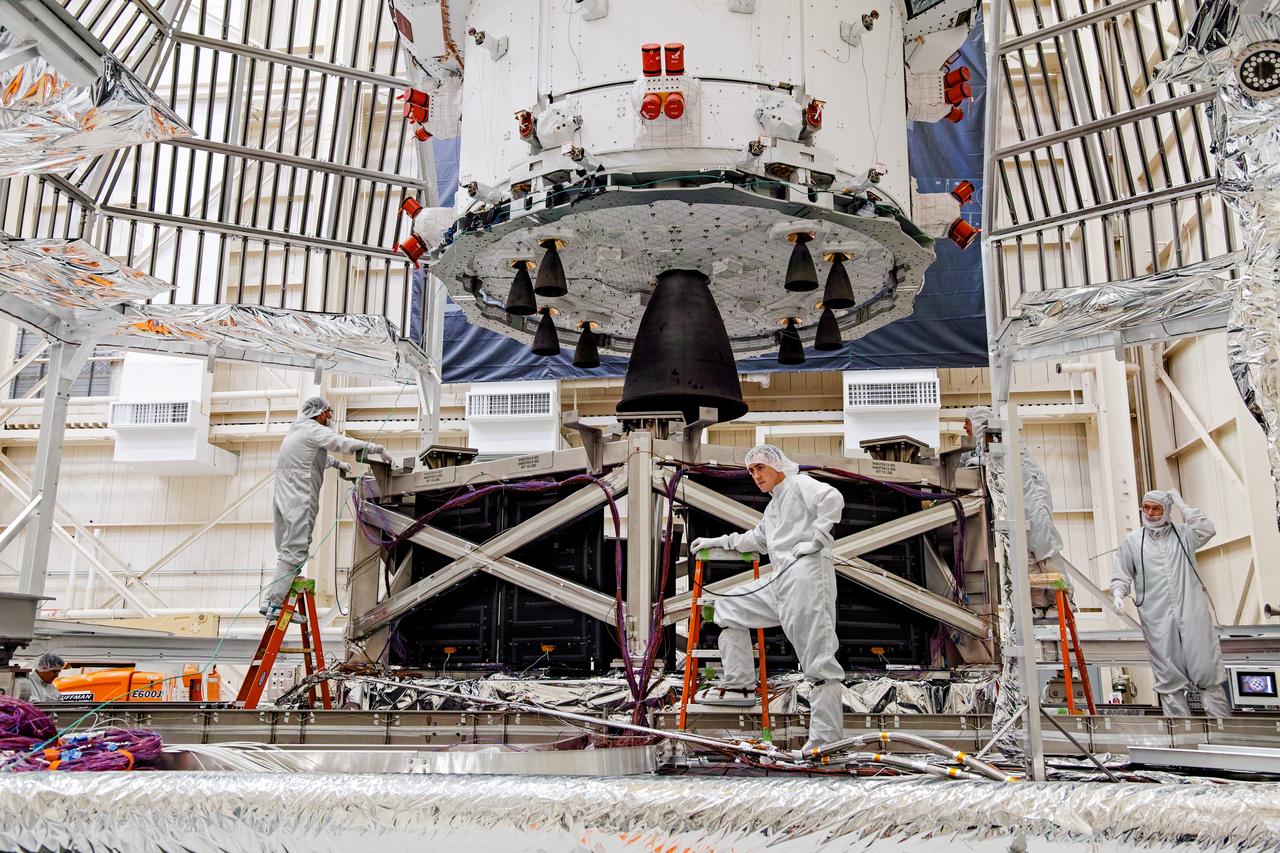

NASA’s Orion spacecraft–the crew module and European-built service module—is being lifted on Dec. 1, 2019 into a thermal cage and readied for its move into the vacuum chamber at NASA’s Neil A. Armstrong Test Facility in Ohio (formerly Plum Brook Station) for testing. Testing begins with a 60-day thermal test, where the spacecraft will be subjected to temperatures ranging from -250 to 300-degrees Fahrenheit to ensure it can withstand the harsh environment of space during Artemis missions. These extreme temperatures simulate flying in-and-out of sunlight and shadow in space using Heat Flux, a specially-designed system that heats specific parts of the spacecraft at any given time. Orion will also be surrounded on all sides by a set of large panels, called a cryogenic-shroud, that will provide the cold background temperatures of space.
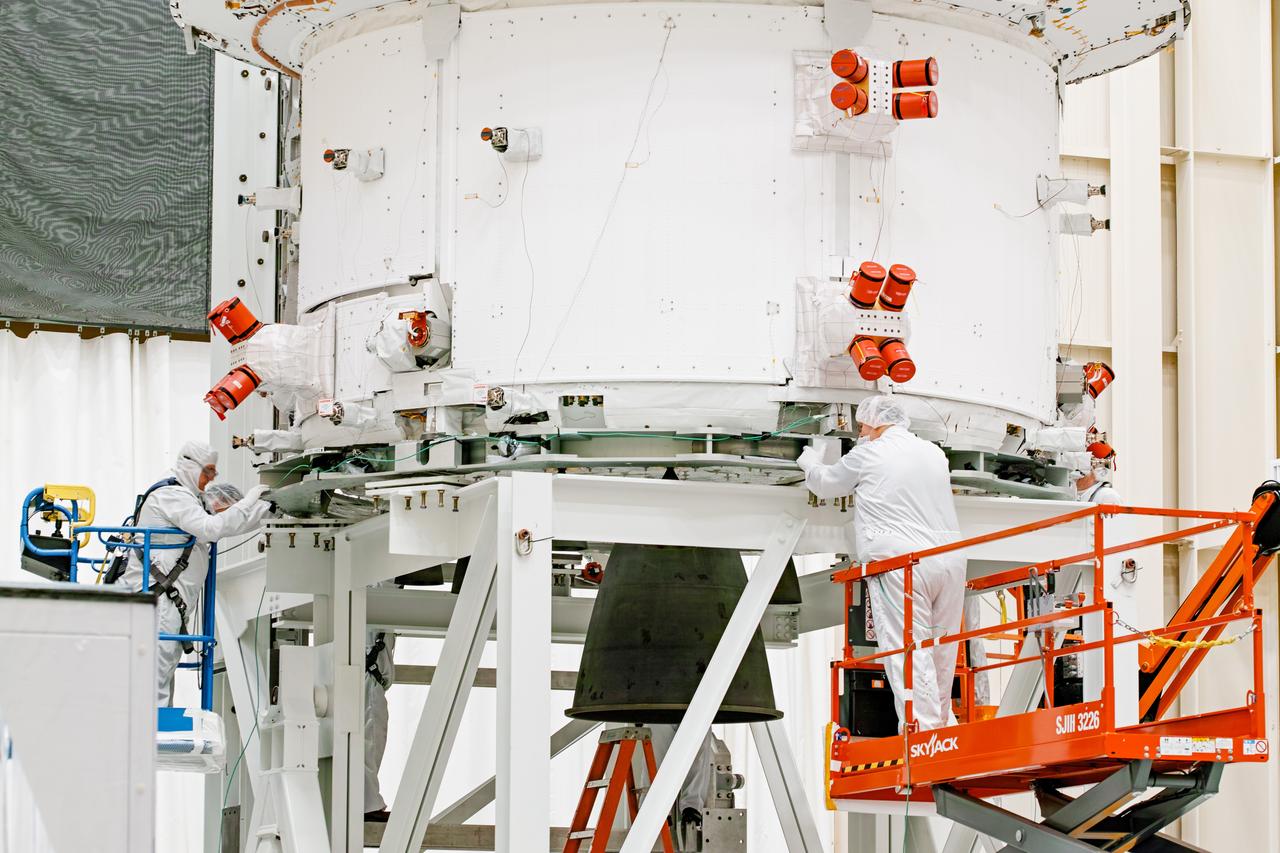

NASA’s Orion spacecraft–the crew module and European-built service module—is being lifted on Dec. 1, 2019 into a thermal cage and readied for its move into the vacuum chamber at NASA’s Neil A. Armstrong Test Facility in Ohio (formerly Plum Brook Station) for testing. Testing begins with a 60-day thermal test, where the spacecraft will be subjected to temperatures ranging from -250 to 300-degrees Fahrenheit to ensure it can withstand the harsh environment of space during Artemis missions. These extreme temperatures simulate flying in-and-out of sunlight and shadow in space using Heat Flux, a specially-designed system that heats specific parts of the spacecraft at any given time. Orion will also be surrounded on all sides by a set of large panels, called a cryogenic-shroud, that will provide the cold background temperatures of space.
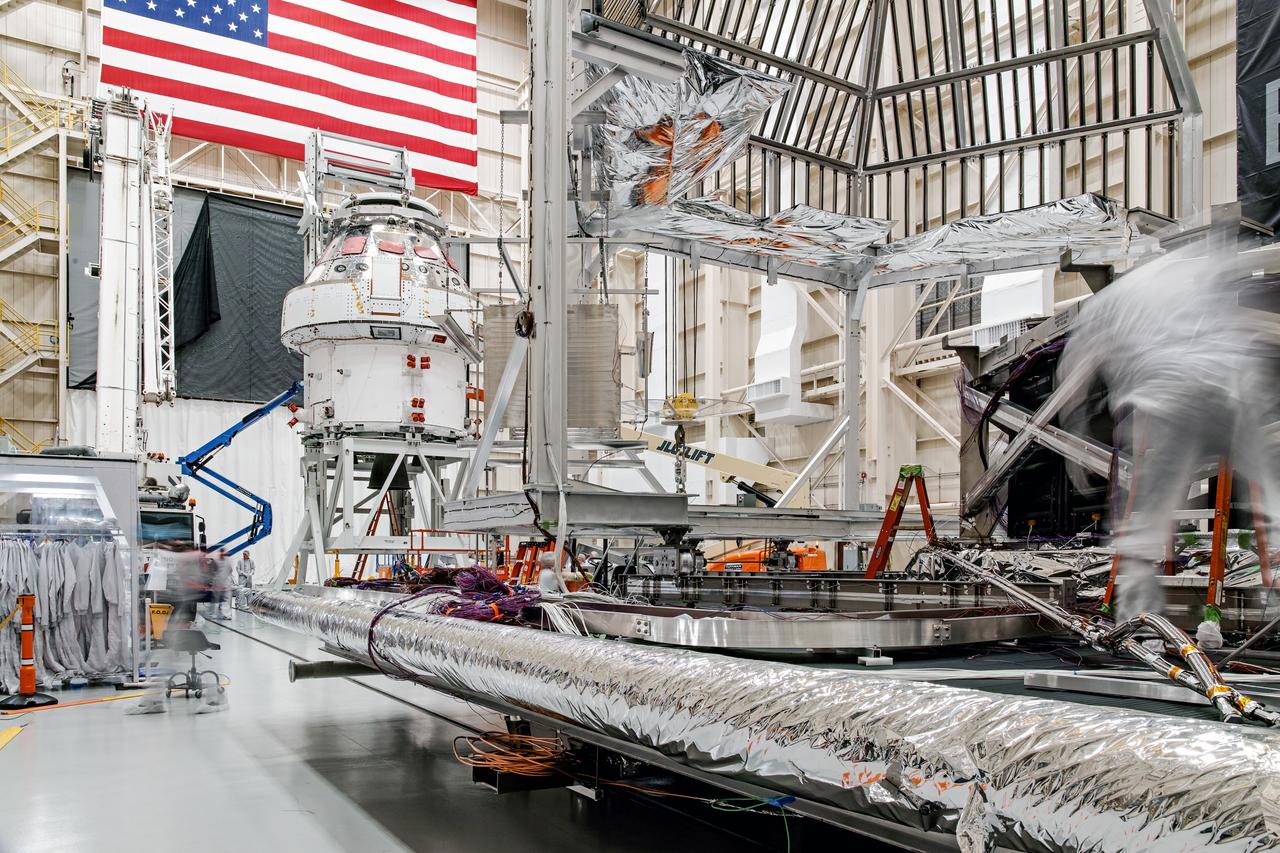

NASA’s Orion spacecraft–the crew module and European-built service module—is being lifted on Dec. 1, 2019 into a thermal cage and readied for its move into the vacuum chamber at NASA’s Neil A. Armstrong Test Facility in Ohio (formerly Plum Brook Station) for testing. Testing begins with a 60-day thermal test, where the spacecraft will be subjected to temperatures ranging from -250 to 300-degrees Fahrenheit to ensure it can withstand the harsh environment of space during Artemis missions. These extreme temperatures simulate flying in-and-out of sunlight and shadow in space using Heat Flux, a specially-designed system that heats specific parts of the spacecraft at any given time. Orion will also be surrounded on all sides by a set of large panels, called a cryogenic-shroud, that will provide the cold background temperatures of space.
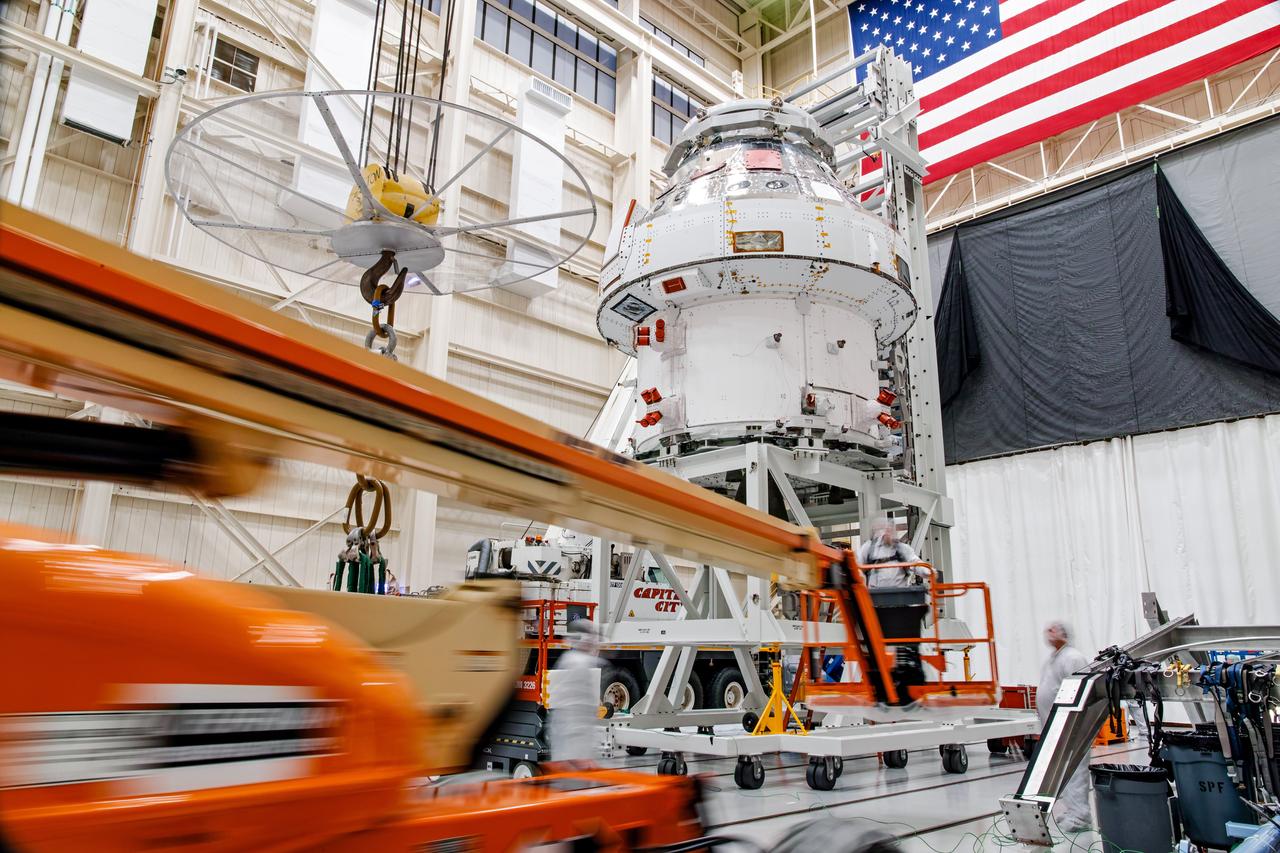
NASA’s Orion spacecraft–the crew module and European-built service module—is being lifted on Dec. 1, 2019 into a thermal cage and readied for its move into the vacuum chamber at NASA’s Neil A. Armstrong Test Facility in Ohio (formerly Plum Brook Station) for testing. Testing begins with a 60-day thermal test, where the spacecraft will be subjected to temperatures ranging from -250 to 300-degrees Fahrenheit to ensure it can withstand the harsh environment of space during Artemis missions. These extreme temperatures simulate flying in-and-out of sunlight and shadow in space using Heat Flux, a specially-designed system that heats specific parts of the spacecraft at any given time. Orion will also be surrounded on all sides by a set of large panels, called a cryogenic-shroud, that will provide the cold background temperatures of space.
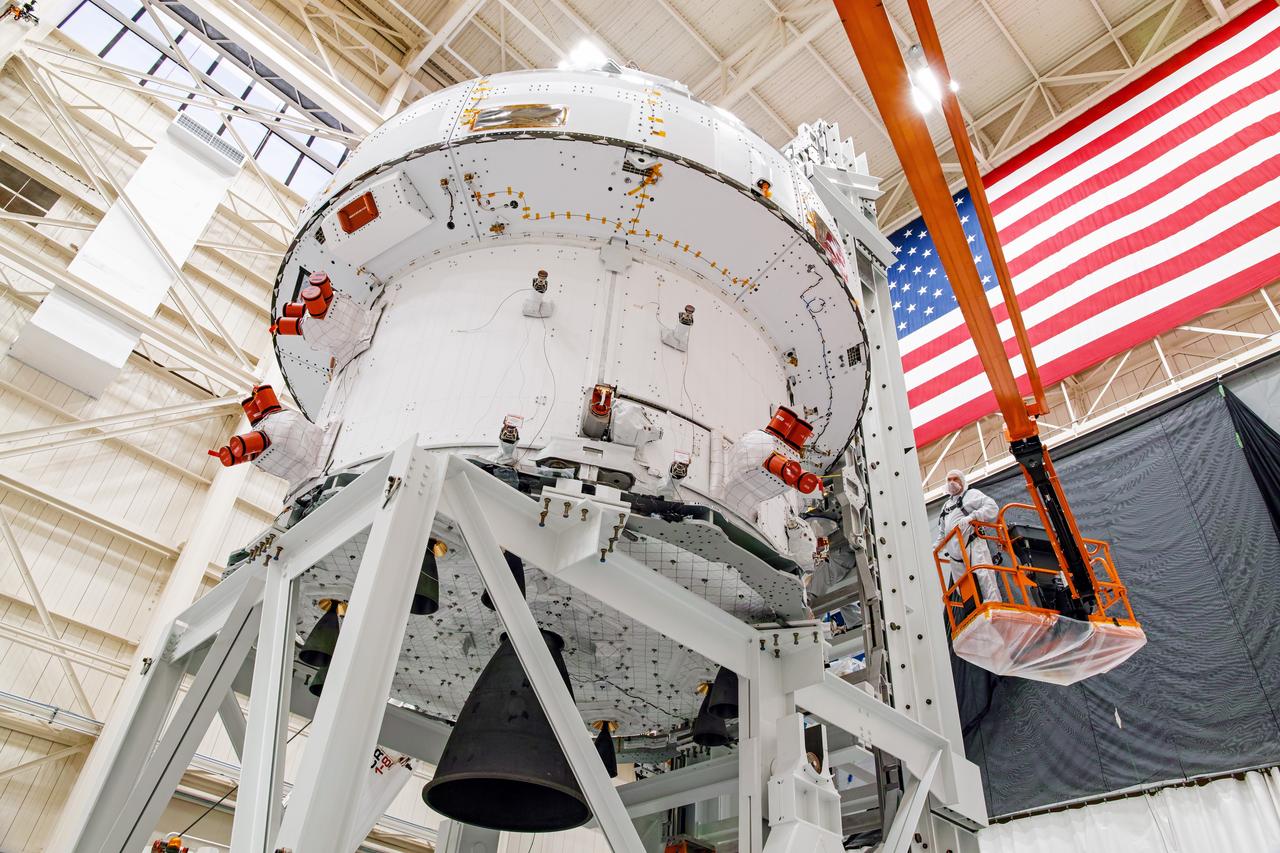

NASA’s Orion spacecraft–the crew module and European-built service module—is being lifted on Dec. 1, 2019 into a thermal cage and readied for its move into the vacuum chamber at NASA’s Neil A. Armstrong Test Facility in Ohio (formerly Plum Brook Station) for testing. Testing begins with a 60-day thermal test, where the spacecraft will be subjected to temperatures ranging from -250 to 300-degrees Fahrenheit to ensure it can withstand the harsh environment of space during Artemis missions. These extreme temperatures simulate flying in-and-out of sunlight and shadow in space using Heat Flux, a specially-designed system that heats specific parts of the spacecraft at any given time. Orion will also be surrounded on all sides by a set of large panels, called a cryogenic-shroud, that will provide the cold background temperatures of space.
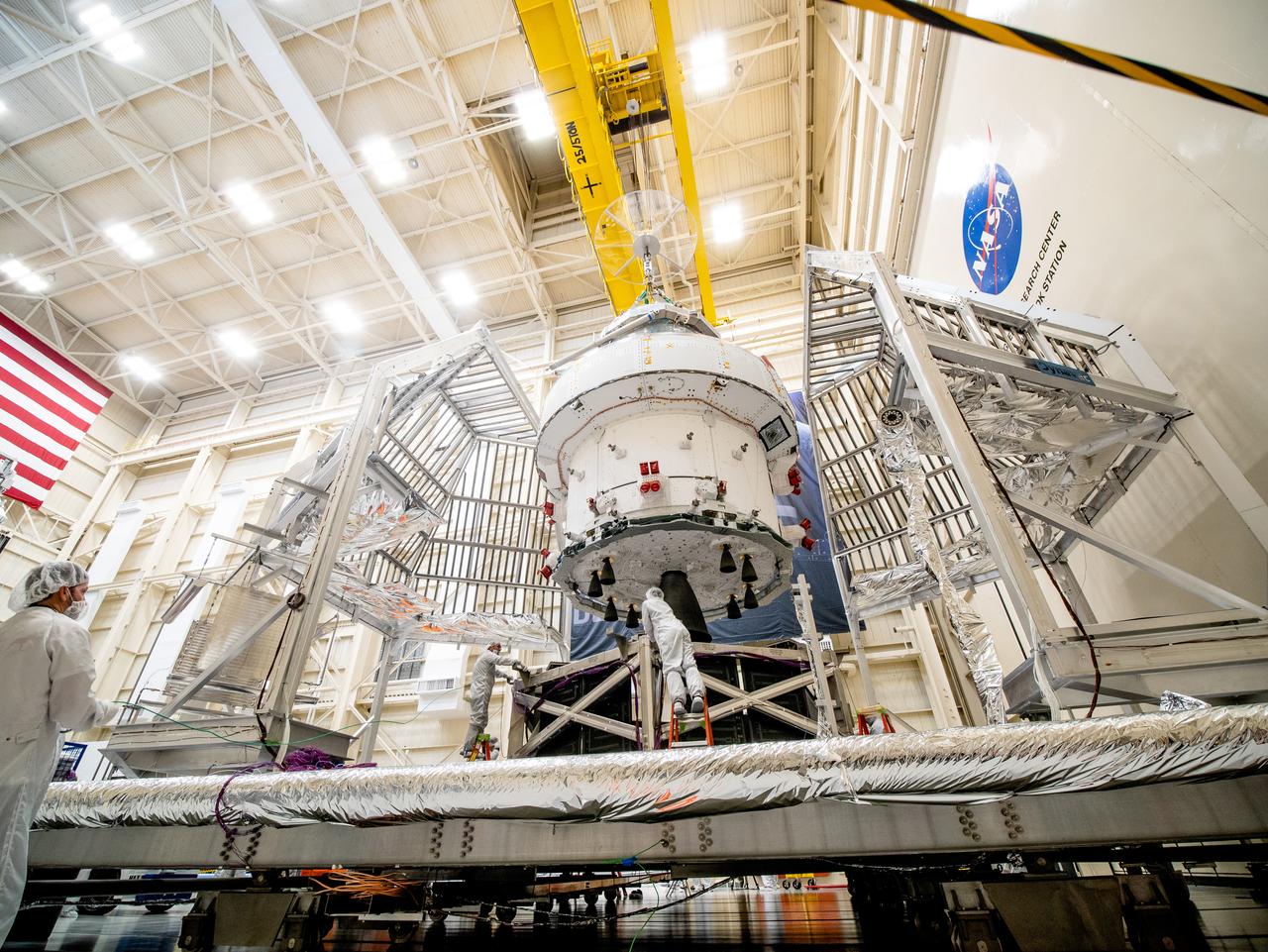

NASA’s Orion spacecraft–the crew module and European-built service module—is being lifted on Dec. 1, 2019 into a thermal cage and readied for its move into the vacuum chamber at NASA’s Neil A. Armstrong Test Facility in Ohio (formerly Plum Brook Station) for testing. Testing begins with a 60-day thermal test, where the spacecraft will be subjected to temperatures ranging from -250 to 300-degrees Fahrenheit to ensure it can withstand the harsh environment of space during Artemis missions. These extreme temperatures simulate flying in-and-out of sunlight and shadow in space using Heat Flux, a specially-designed system that heats specific parts of the spacecraft at any given time. Orion will also be surrounded on all sides by a set of large panels, called a cryogenic-shroud, that will provide the cold background temperatures of space.
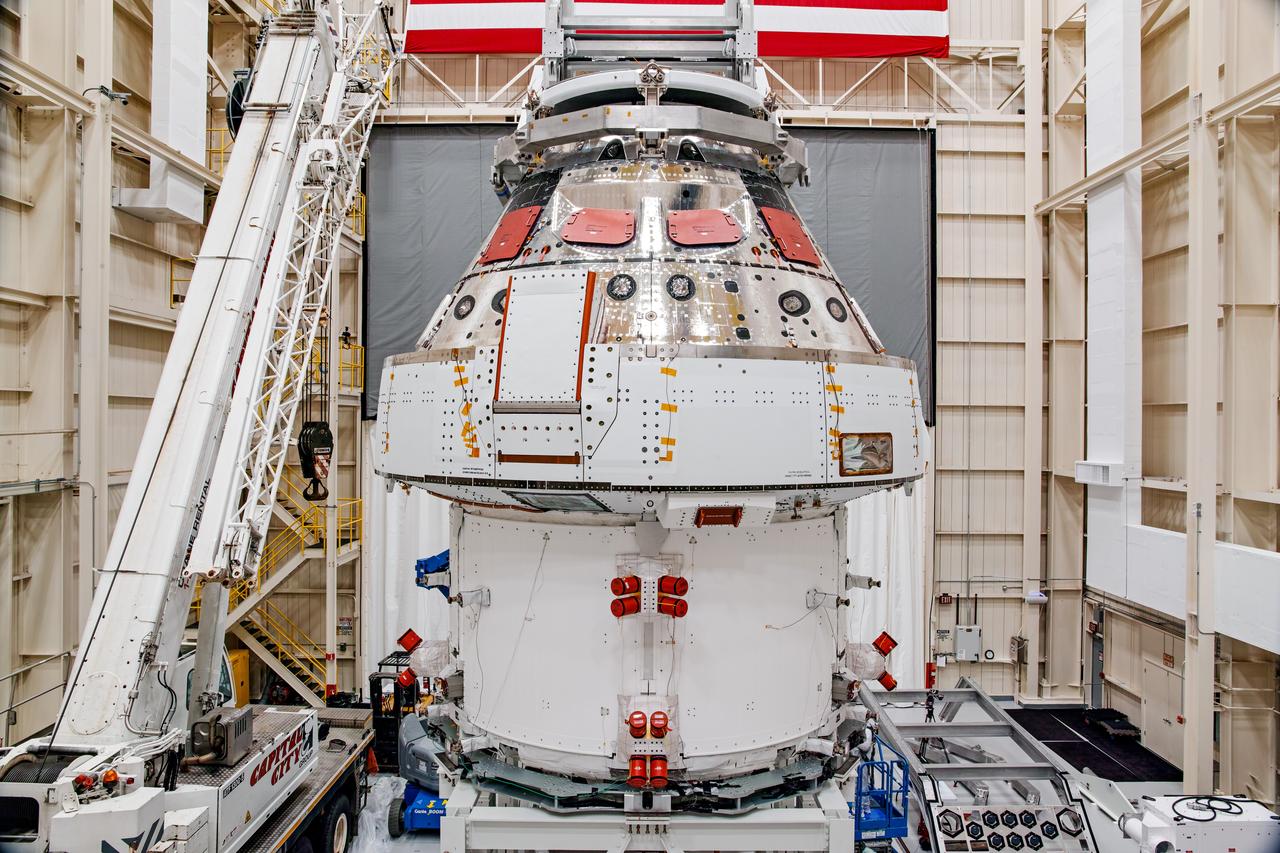
NASA’s Orion spacecraft–the crew module and European-built service module—is being lifted on Dec. 1, 2019 into a thermal cage and readied for its move into the vacuum chamber at NASA’s Neil A. Armstrong Test Facility in Ohio (formerly Plum Brook Station) for testing. Testing begins with a 60-day thermal test, where the spacecraft will be subjected to temperatures ranging from -250 to 300-degrees Fahrenheit to ensure it can withstand the harsh environment of space during Artemis missions. These extreme temperatures simulate flying in-and-out of sunlight and shadow in space using Heat Flux, a specially-designed system that heats specific parts of the spacecraft at any given time. Orion will also be surrounded on all sides by a set of large panels, called a cryogenic-shroud, that will provide the cold background temperatures of space.
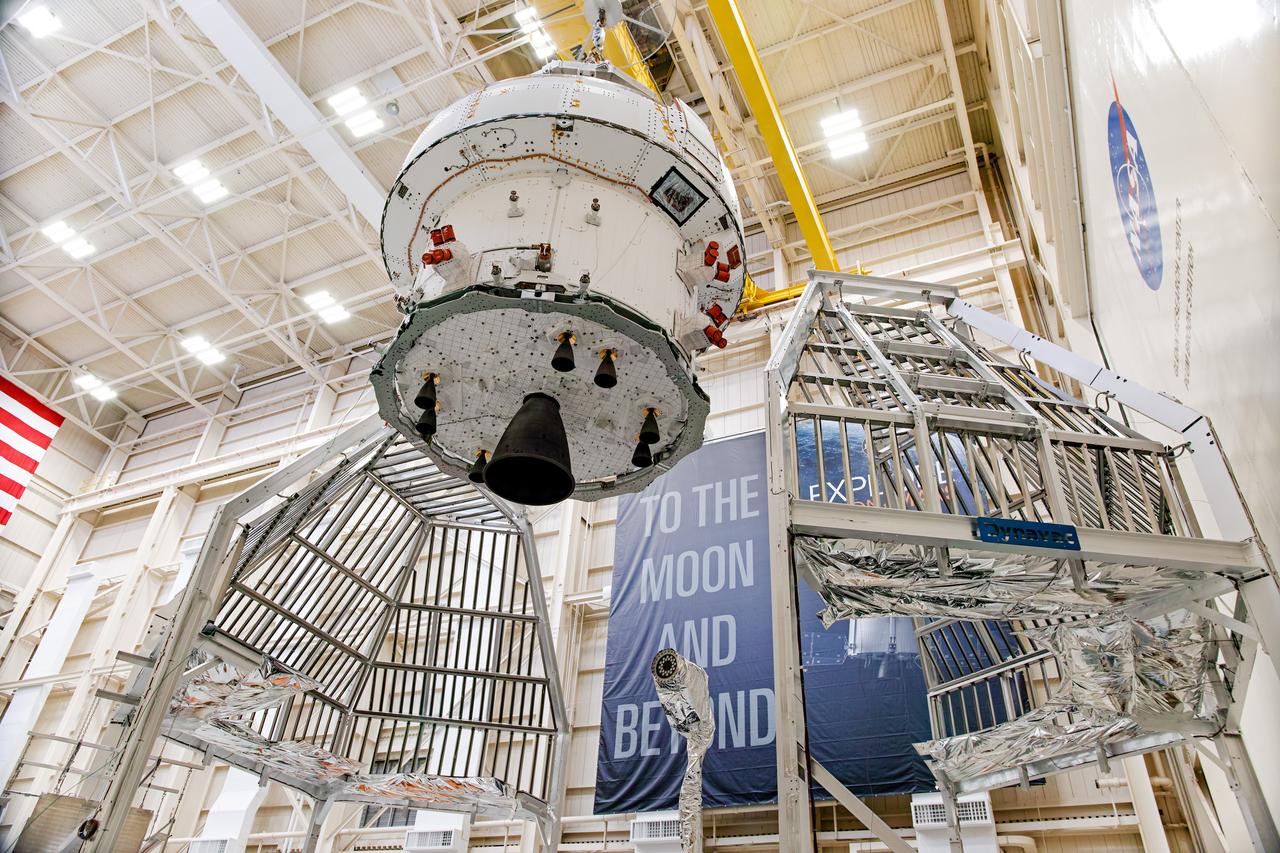

NASA’s Orion spacecraft–the crew module and European-built service module—is being lifted on Dec. 1, 2019 into a thermal cage and readied for its move into the vacuum chamber at NASA’s Neil A. Armstrong Test Facility in Ohio (formerly Plum Brook Station) for testing. Testing begins with a 60-day thermal test, where the spacecraft will be subjected to temperatures ranging from -250 to 300-degrees Fahrenheit to ensure it can withstand the harsh environment of space during Artemis missions. These extreme temperatures simulate flying in-and-out of sunlight and shadow in space using Heat Flux, a specially-designed system that heats specific parts of the spacecraft at any given time. Orion will also be surrounded on all sides by a set of large panels, called a cryogenic-shroud, that will provide the cold background temperatures of space.
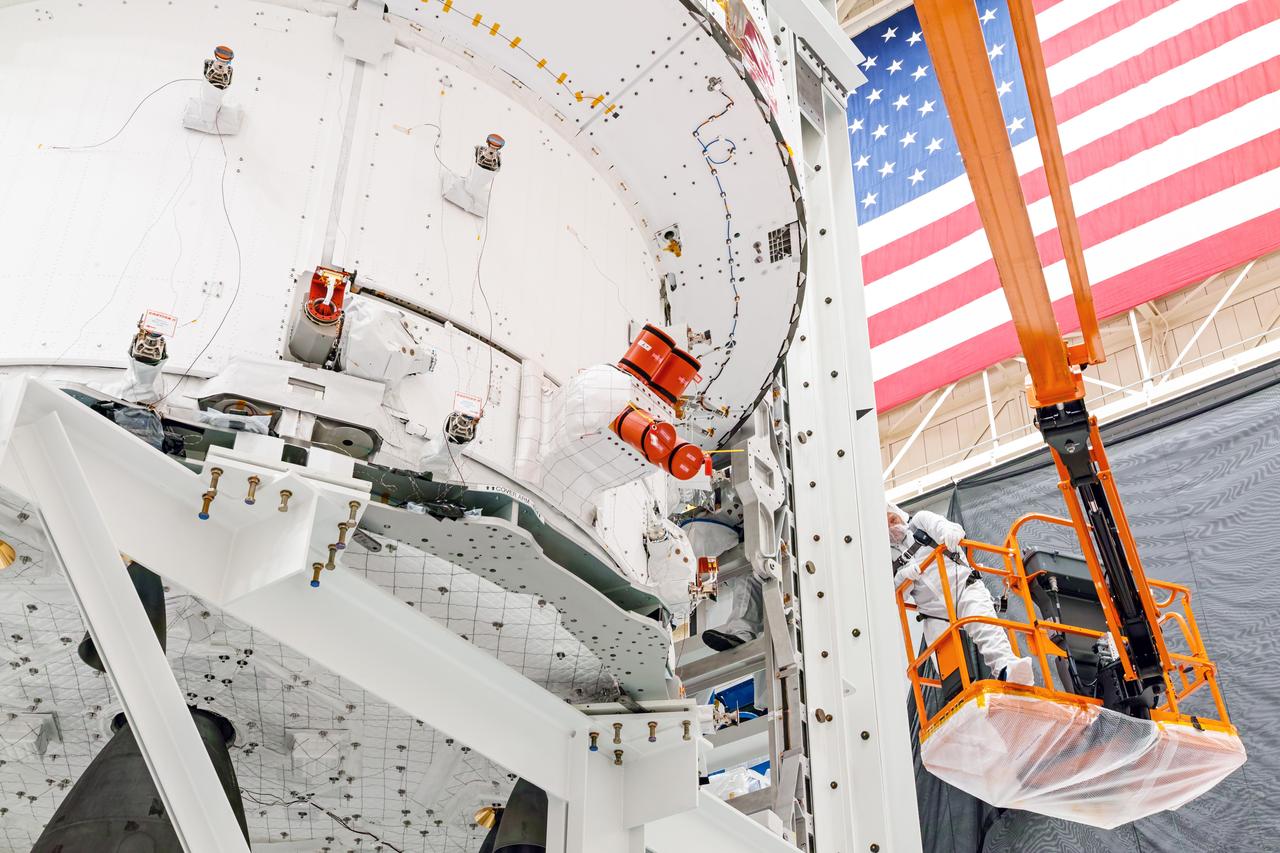

NASA’s Orion spacecraft–the crew module and European-built service module—is being lifted on Dec. 1, 2019 into a thermal cage and readied for its move into the vacuum chamber at NASA’s Neil A. Armstrong Test Facility in Ohio (formerly Plum Brook Station) for testing. Testing begins with a 60-day thermal test, where the spacecraft will be subjected to temperatures ranging from -250 to 300-degrees Fahrenheit to ensure it can withstand the harsh environment of space during Artemis missions. These extreme temperatures simulate flying in-and-out of sunlight and shadow in space using Heat Flux, a specially-designed system that heats specific parts of the spacecraft at any given time. Orion will also be surrounded on all sides by a set of large panels, called a cryogenic-shroud, that will provide the cold background temperatures of space.
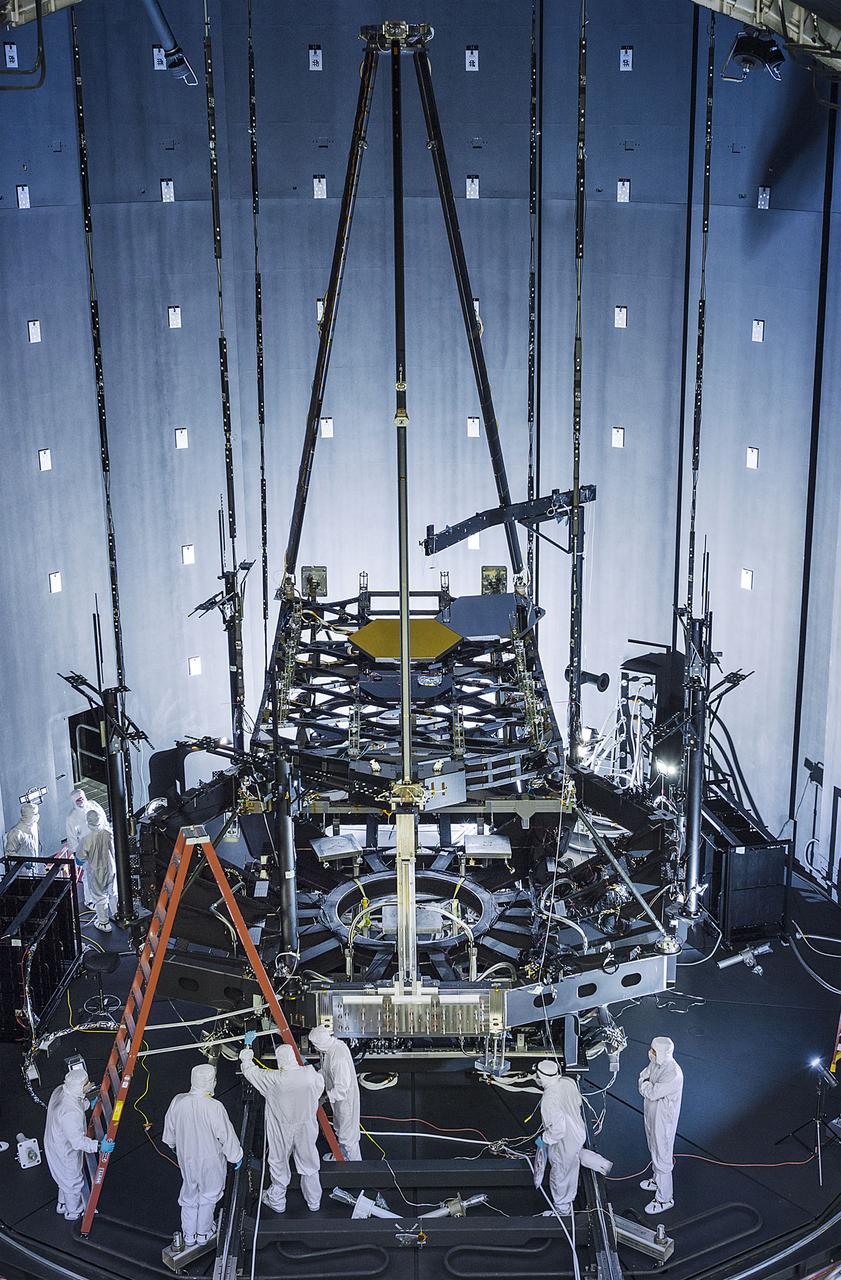
Inside NASA's giant thermal vacuum chamber, called Chamber A, at NASA's Johnson Space Center in Houston, the James Webb Space Telescope's Pathfinder backplane test model, is being prepared for its cryogenic test. Previously used for manned spaceflight missions, this historic chamber is now filled with engineers and technicians preparing for a crucial test. Exelis developed and installed the optical test equipment in the chamber. "The optical test equipment was developed and installed in the chamber by Exelis," said Thomas Scorse, Exelis JWST Program Manager. "The Pathfinder telescope gives us our first opportunity for an end-to-end checkout of our equipment." "This will be the first time on the program that we will be aligning two primary mirror segments together," said Lee Feinberg, NASA Optical Telescope Element Manager. "In the past, we have always tested one mirror at a time but this time we will use a single test system and align both mirrors to it as though they are a single monolithic mirror." The James Webb Space Telescope is the scientific successor to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. It will be the most powerful space telescope ever built. Webb is an international project led by NASA with its partners, the European Space Agency and the Canadian Space Agency. Image credit: NASA/Chris Gunn Text credit: Laura Betz, NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Maryland <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
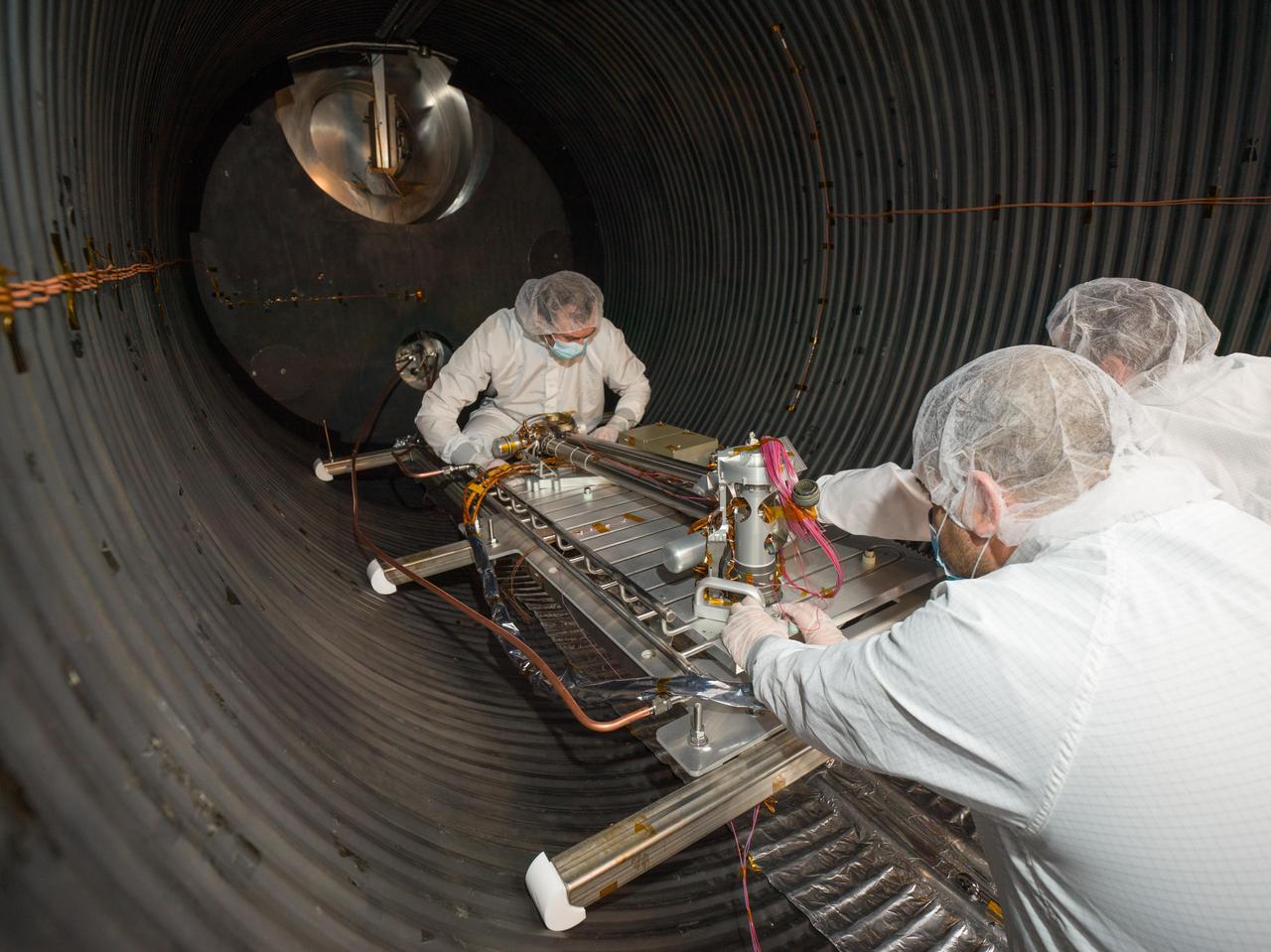

Engineers and technicians prepare NASA's Cold Operable Lunar Deployable Arm (COLDArm) robotic arm system for testing in a thermal vacuum chamber at the agency's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California in November 2023. Successful testing in this chamber, which was reduced to minus 292 F (minus 180 C), demonstrates the arm can withstand the conditions it would face on the surface of the Moon. To operate in the cold, COLDArm combines several key new technologies: gears made of bulk metallic glass, which require no wet lubrication or heating; cold motor controllers that don't need to be kept warm in an electronics box near the core of the spacecraft, and a cryogenic six-axis force torque sensor that lets the arm "feel" what it's doing and make adjustments. A variety of attachments and small instruments could go on the end of the arm, including a 3D-printed titanium scoop that could be used for collecting samples from a celestial body's surface. Like the arm on NASA's InSight Mars lander, COLDArm could deploy science instruments to the surface. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26162
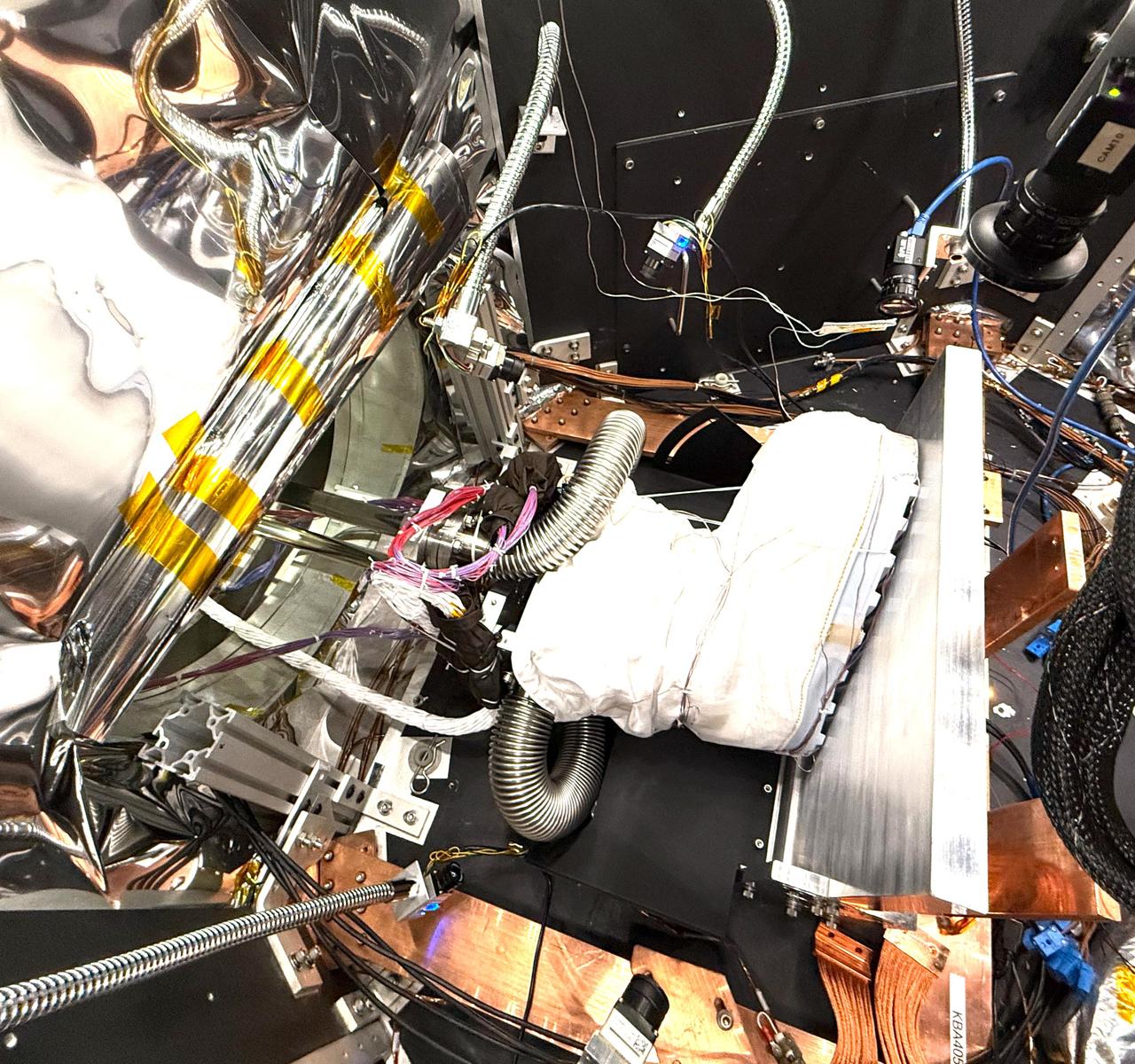
A boot that's part of a NASA lunar surface spacesuit prototype is readied for testing inside a thermal vacuum chamber called CITADEL at the agency's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California on Nov. 8, 2024. The thick aluminum plate at right stands in for the frigid surface of the lunar South Pole, where Artemis III astronauts will confront conditions more extreme than any previously experienced by humans. Built to prepare potential future robotic spacecraft for the frosty, low-pressure conditions on ocean worlds like Jupiter's frozen moon Europa, CITADEL (Cryogenic Ice Testing, Acquisition Development, and Excavation Laboratory) has also proven key to evaluating how astronaut gloves and boots hold up in extraordinary cold. It can reach temperatures as low as low as minus 370 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 223 degrees Celsius), approximating conditions in permanently shadowed regions that astronauts will explore. Figure A, showing the outer boot sole, was taken from inside CITADEL on Nov. 13, 2024. The boot is positioned in a load lock, one of four small drawer-like chambers through which test materials are inserted into the larger chamber. Initiated by the Extravehicular Activity and Human Surface Mobility Program at NASA's Johnson Space Center, the boot testing took place from October 2024 to January 2025. The boot is part of a NASA spacesuit called the Exploration Extravehicular Mobility Unit, or xEMU. Results haven't yet been fully analyzed. In addition to spotting vulnerabilities with existing suits, the experiments are intended to help NASA develop this unique test capability and prepare criteria for standardized, repeatable, and inexpensive test methods for the next-generation lunar suit being built by Axiom Space. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26592
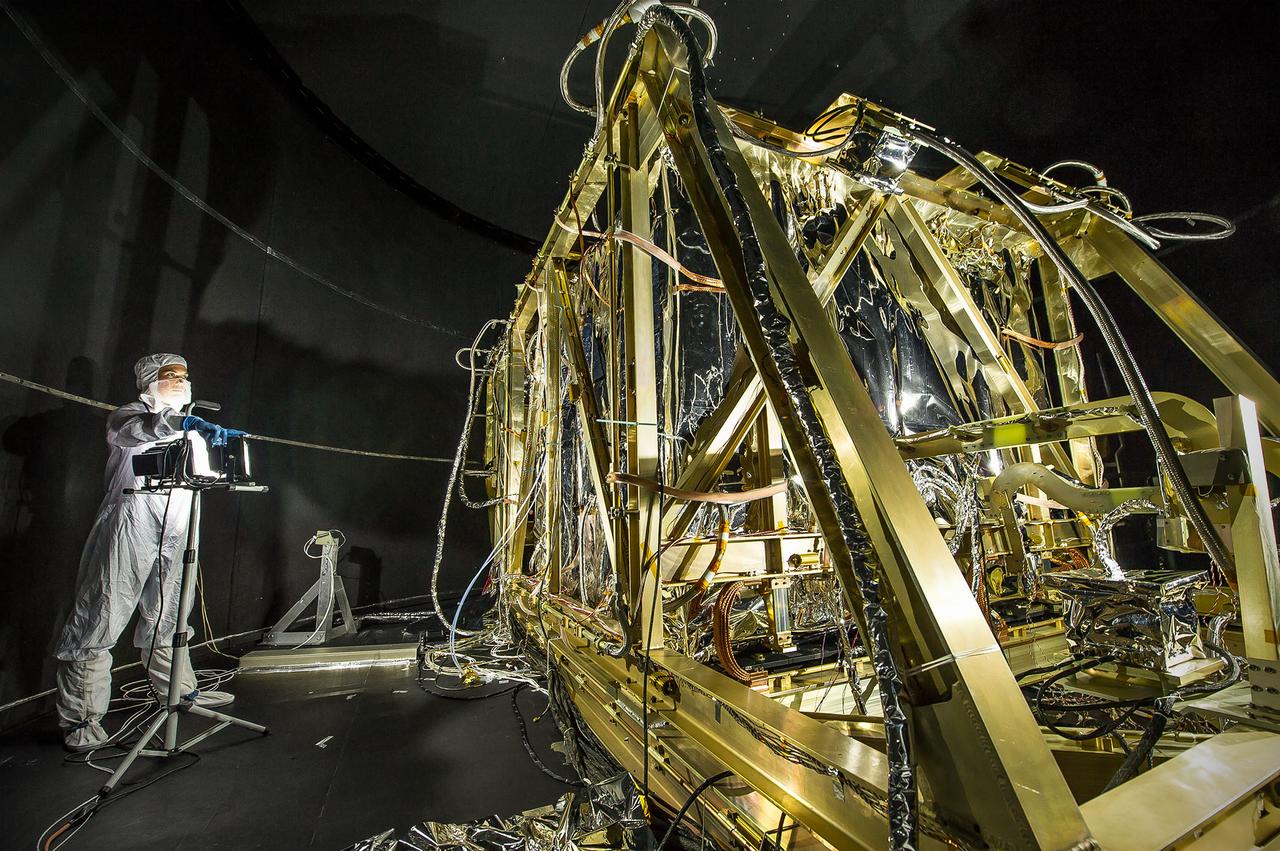

Dressed in a clean room suit, NASA photographer Desiree Stover shines a light on the Space Environment Simulator's Integration Frame inside the thermal vacuum chamber at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. Shortly after, the chamber was closed up and engineers used this frame to enclose and help cryogenic (cold) test the heart of the James Webb Space Telescope, the Integrated Science Instrument Module. Credit: NASA/Goddard/Chris Gunn <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
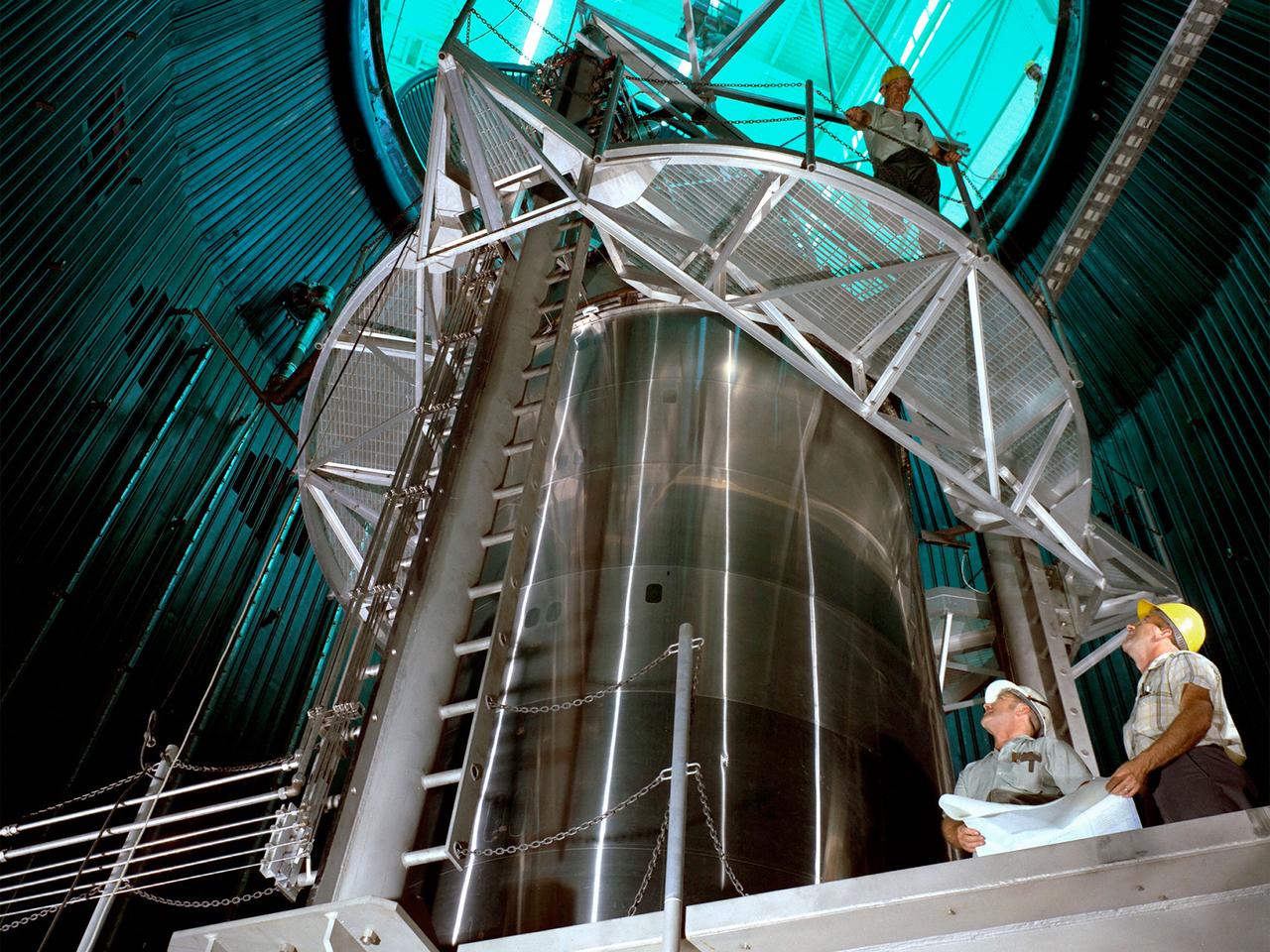

A Centaur second-stage rocket in the Space Propulsion Research Facility, better known as B‒2, operating at NASA’s Plum Brook Station in Sandusky, Ohio. Centaur was designed to be used with an Atlas booster to send the Surveyor spacecraft to the moon in the mid-1960s. After those missions, the rocket was modified to launch a series of astronomical observation satellites into orbit and send space probes to other planets. Researchers conducted a series of systems tests at the Plum Brook test stands to improve the Centaur fuel pumping system. Follow up full-scale tests in the B-2 facility led to the eventual removal of the boost pumps from the design. This reduced the system’s complexity and significantly reduced the cost of a Centaur rocket. The Centaur tests were the first use of the new B-2 facility. B‒2 was the world's only high altitude test facility capable of full-scale rocket engine and launch vehicle system level tests. It was created to test rocket propulsion systems with up to 100,000 pounds of thrust in a simulated space environment. The facility has the unique ability to maintain a vacuum at the rocket’s nozzle while the engine is firing. The rocket fires into a 120-foot deep spray chamber which cools the exhaust before it is ejected outside the facility. B‒2 simulated space using giant diffusion pumps to reduce chamber pressure 10-6 torr, nitrogen-filled cold walls create cryogenic temperatures, and quartz lamps replicate the radiation of the sun.
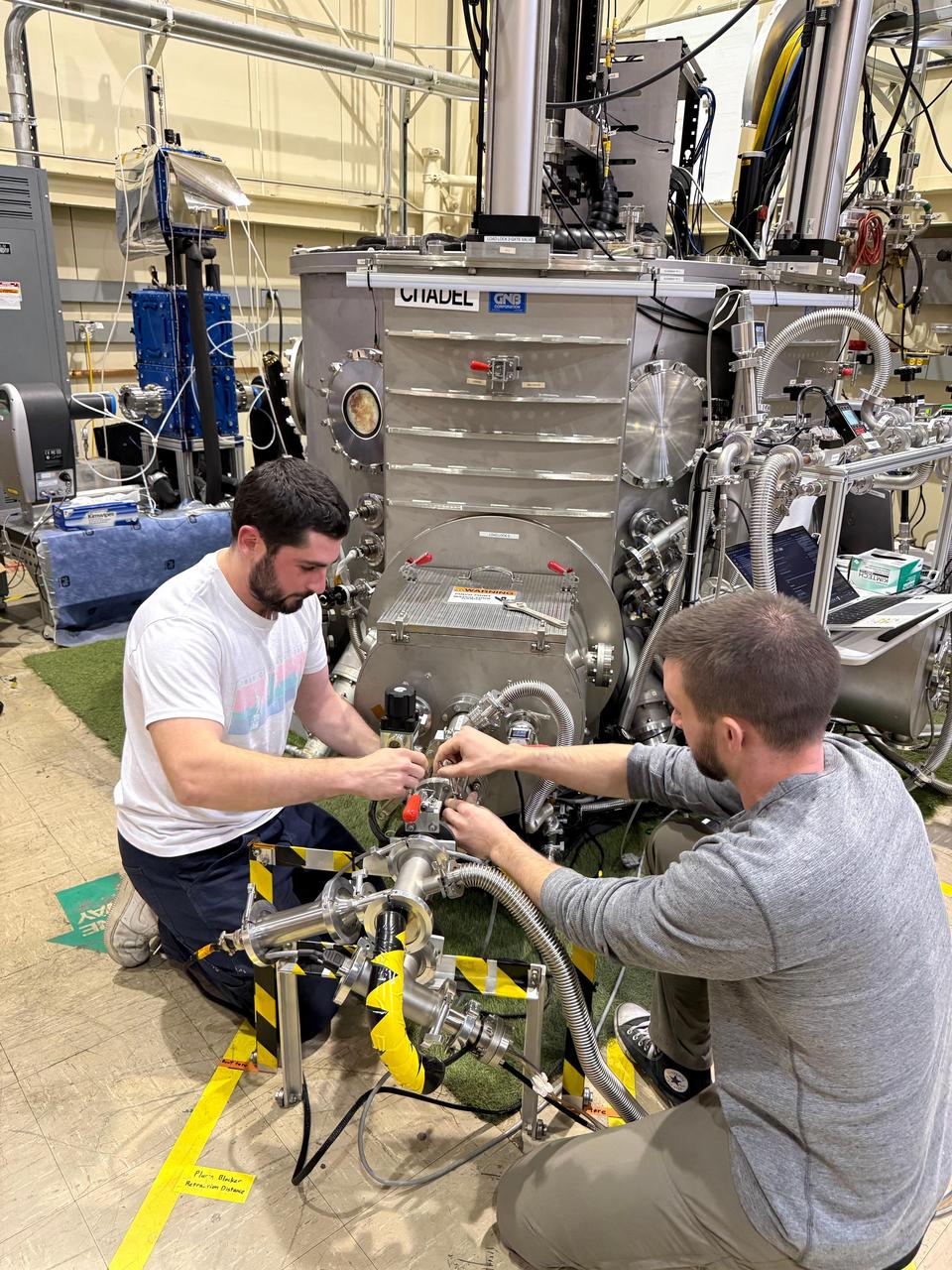

Robotics technologist Brendan Chamberlain-Simon, left, of NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory and spacesuit engineer Zach Fester of the agency's Johnson Space Center adjust a thermal vacuum chamber called CITADEL at JPL on Nov. 12, 2024, before testing an astronaut boot inside the chamber. Built to prepare potential robotic explorers for the frosty, low-pressure conditions on ocean worlds like Jupiter's frozen moon Europa, CITADEL (Cryogenic Ice Testing, Acquisition Development, and Excavation Laboratory) has also proven key to evaluating how astronaut gloves and boots hold up in extraordinary cold. It can reach temperatures as low as low as minus 370 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 223 degrees Celsius), approximating extreme conditions Artemis III astronauts will confront in permanently shadowed regions of the lunar South Pole. The boot testing was initiated by the Extravehicular Activity and Human Surface Mobility Program at NASA Johnson and took place from October 2024 to January 2025. The boot is part of a NASA spacesuit called the Exploration Extravehicular Mobility Unit, or xEMU. Test results haven't yet been fully analyzed. In addition to spotting vulnerabilities with existing suits, the experiments are intended to help NASA develop this unique test capability and prepare criteria for standardized, repeatable, and inexpensive test methods for the next-generation lunar suit being built by Axiom Space. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26593
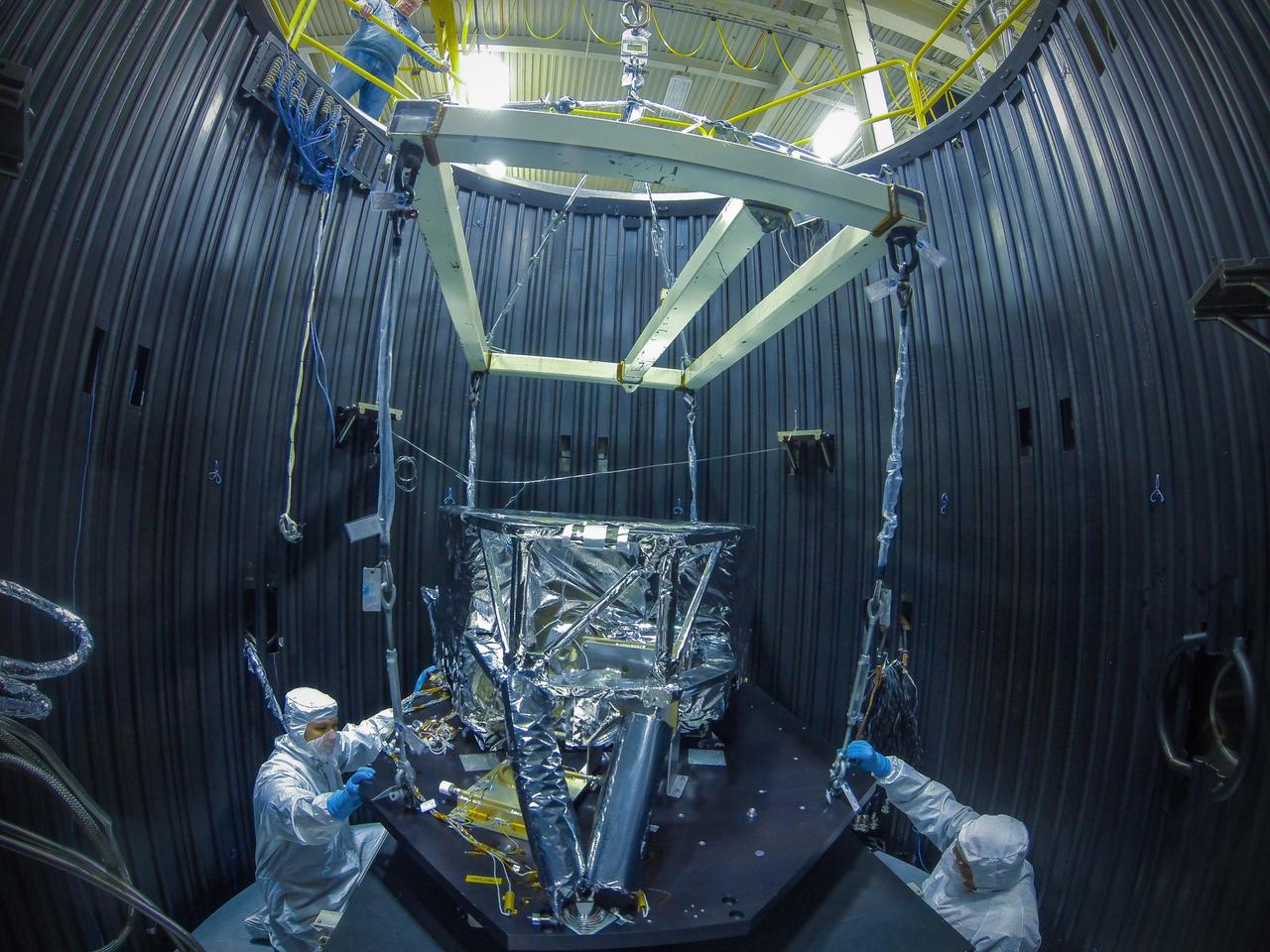

Goddard Technicians Tony Kiem (left) and George Mooney (right) guide the craned structure holding the Webb telescope's Mid-Infrared Instrument or MIRI Shield Environmental Test Unit into place in a cryogenic (cooling) test chamber. This shield will be used to simulate the MIRI instrument during prelaunch testing to verify that the MIRI cooling system will function properly in space. Goddard Safety Engineer Richard Bowlan watches from above. Image Credit: NASA/Chris Gunn <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
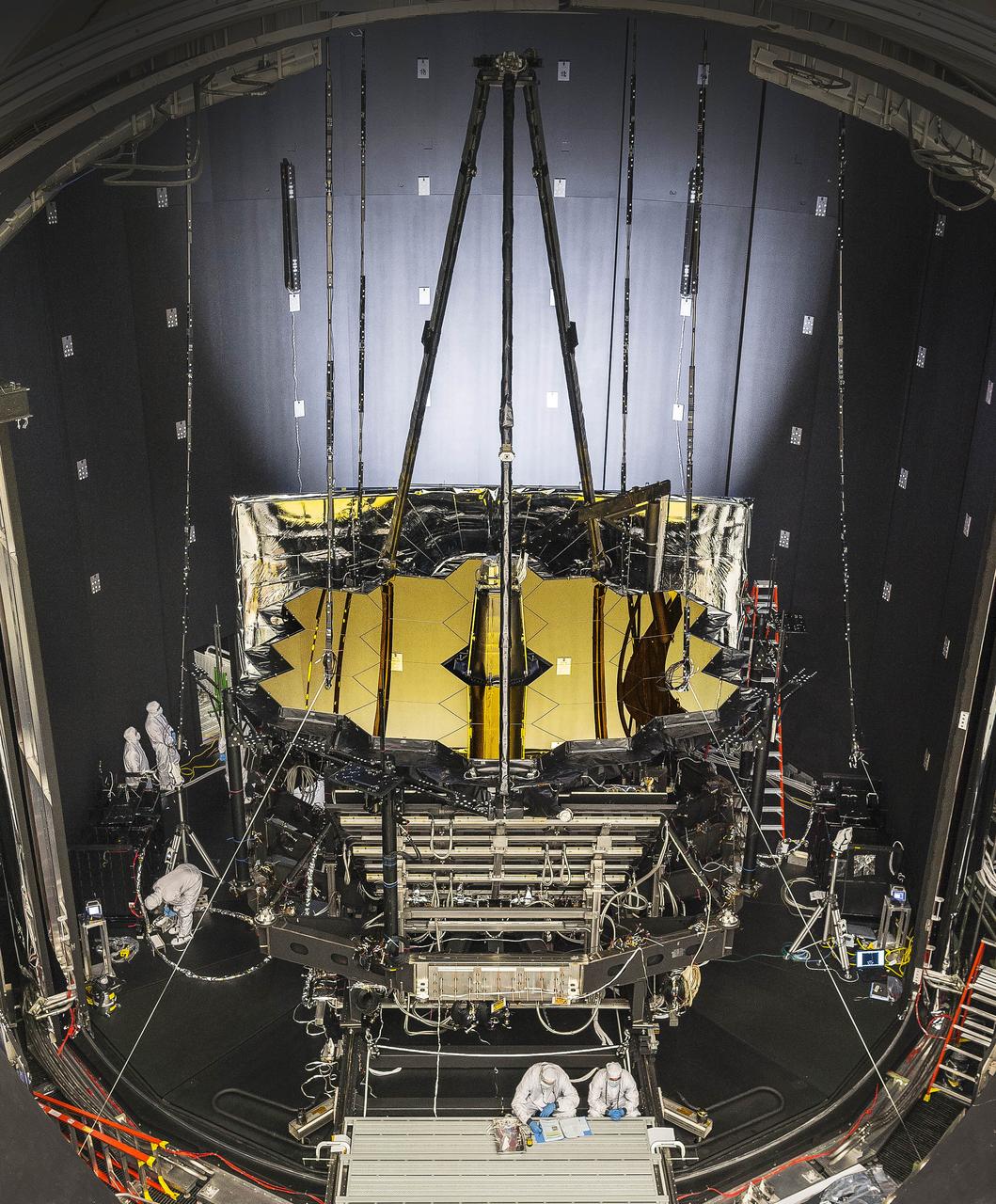

NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope was placed in Johnson Space Center’s historic Chamber A on June 20, 2017, to prepare for its final three months of testing in a cryogenic vacuum that mimics temperatures in space. Engineers will perform the test to prove that the telescope can operate in space at these temperatures. Chamber A will simulate an environment where the telescope will experience extreme cold -- around 37 Kelvin (minus 236 degrees Celsius or minus 393 degrees Fahrenheit). In space, the telescope must be kept extremely cold, in order to be able to detect the infrared light from very faint, distant objects. To protect the telescope from external sources of light and heat (like the sun, Earth, and moon), as well as from heat emitted by the observatory, a five-layer, tennis court-sized sunshield acts like a parasol that provides shade. The sunshield separates the observatory into a warm, sun-facing side (reaching temperatures close to 400 degrees Fahrenheit) and a cold side (185 degrees below zero). The sunshield blocks sunlight from interfering with the sensitive telescope instruments. Read more: <a href="https://go.nasa.gov/2sZAilS" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/2sZAilS</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Engineer Erin Wilson adds aluminum tape to electrical cables to protect them from the cold during environmental testing of special optical equipment. These tests will verify the alignment of the actual flight instruments that will fly aboard NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope. "Because the flight science instruments detect infrared light, they must be extremely cold to work, and so the environment we test them in must be extremely cold too," Wilson says. Wilson is working in the Space Environment Simulator thermal-vacuum chamber at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. The subject of the testing is the Optical Telescope Element (OTE) Simulator, or OSIM. The hardware seen in the background is the Beam Image Analyzer, which will be used to measure OSIM. It sits above the OSIM, which is under the platform that Wilson is working on. The OSIM is about two stories tall and almost as wide as the whole test chamber. The job of the OSIM is to generate a beam of light just like the one that the real telescope optics will feed into the actual flight science instruments. Because the real flight science instruments will be used to test the real flight telescope, their alignment and performance have to be verified first, using OSIM, and before that can happen, the OSIM has to tested and verified. In space, the telescope optics act as Webb’s eye, and on the ground, the OSIM substitutes for the telescope optics, says Robert Rashford, manager for the OSIM as well as the Integrated Science Instrument Module (ISIM) Electronics Compartment. This hardware is being tested in an environment that mimics the hard vacuum and cold temperatures that Webb will experience in space. After Erin and others were done setting things up in the test chamber, Goddard engineers sealed it up, evacuated all the air and lowered the temperature of the equipment being tested to 42 Kelvin (-384-point-1 Fahrenheit or -231-point-1 Celsius). "It has taken a little over a month to get temperatures cold enough to duplicate the temperatures that Webb will see in operation in space," Rashford says. In the next couple weeks Rashford and the team of Goddard engineers will measure the OSIM with the Beam Image Analyzer. This extremely cold or “cryogenic” optical testing and verification process will likely take 90 days to complete. Laura Betz NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>