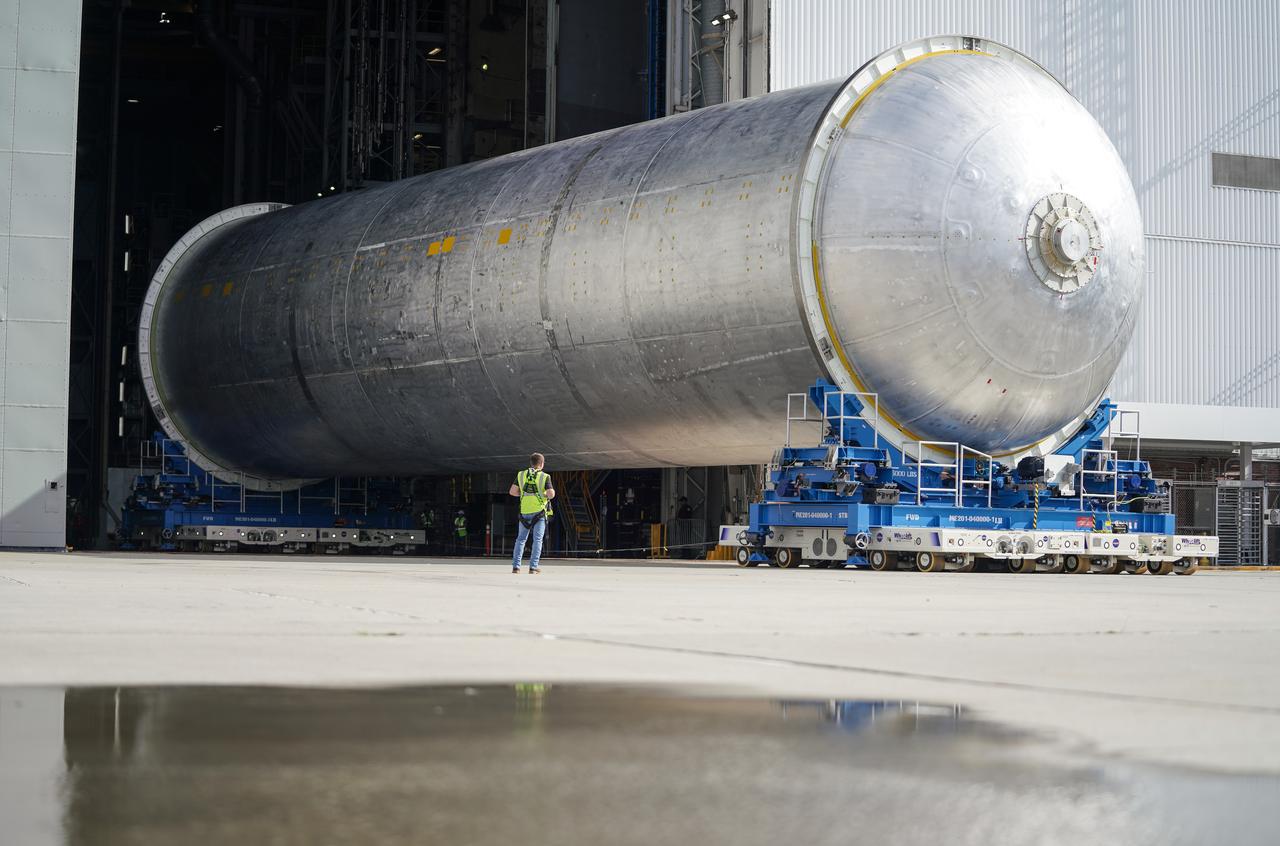

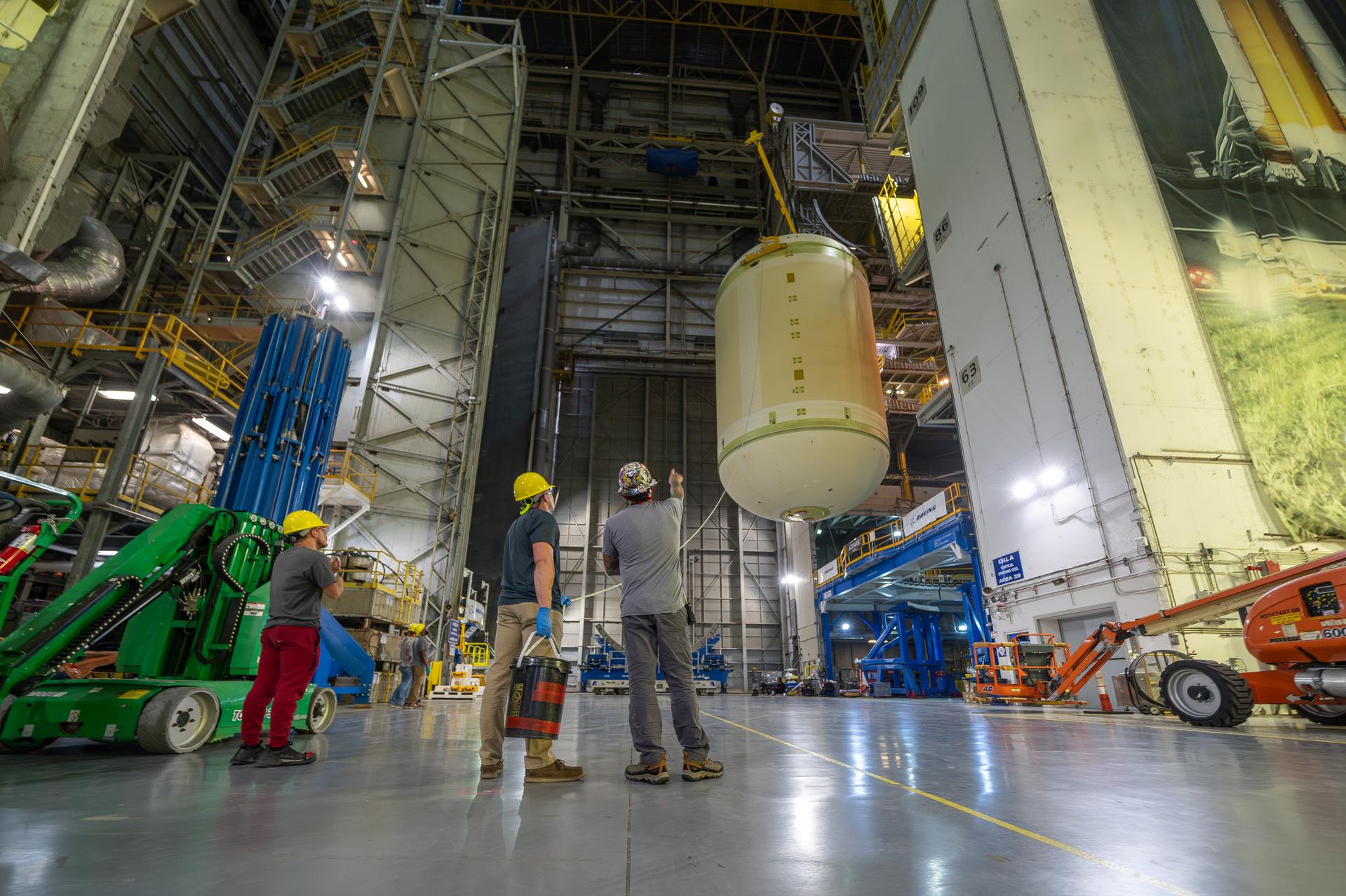
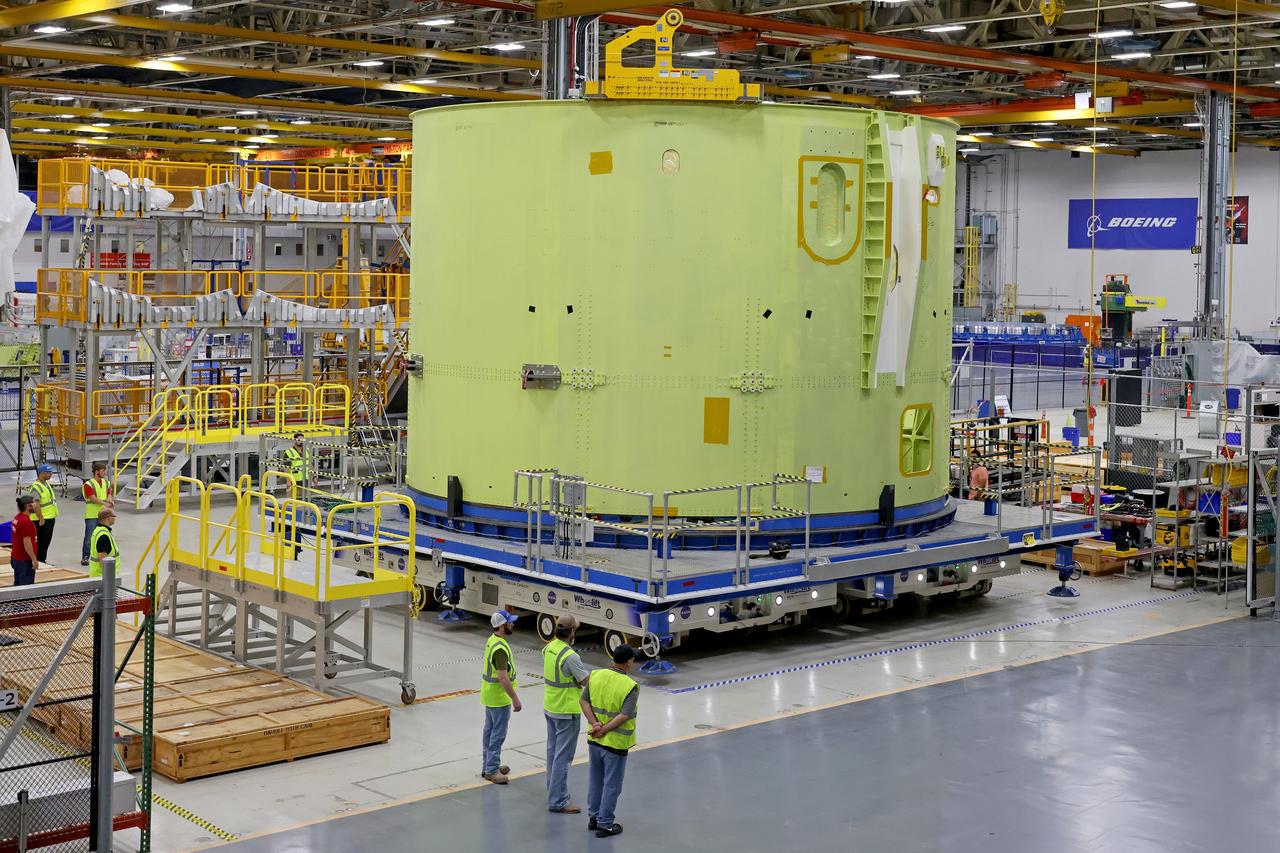
Teams move the core stage liquid hydrogen tank for the Artemis III mission to a priming cell near the Vertical Assembly Building at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans Nov. 21. Technichians will sand down and prepare the suface of the tank before coating it in a primer. Primer is applied to the barrel section of the tank by an automated robotic tool, whereas the forward and aft domes are primed manually. Once priming is complete, technicians with NASA and Boeing, the SLS core stage prime contractor, will apply a foam-based thermal protection system, which protects the propellant tank from the extreme temperatures it will face during launch and flight while also regulating the super-chilled propellant within it. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
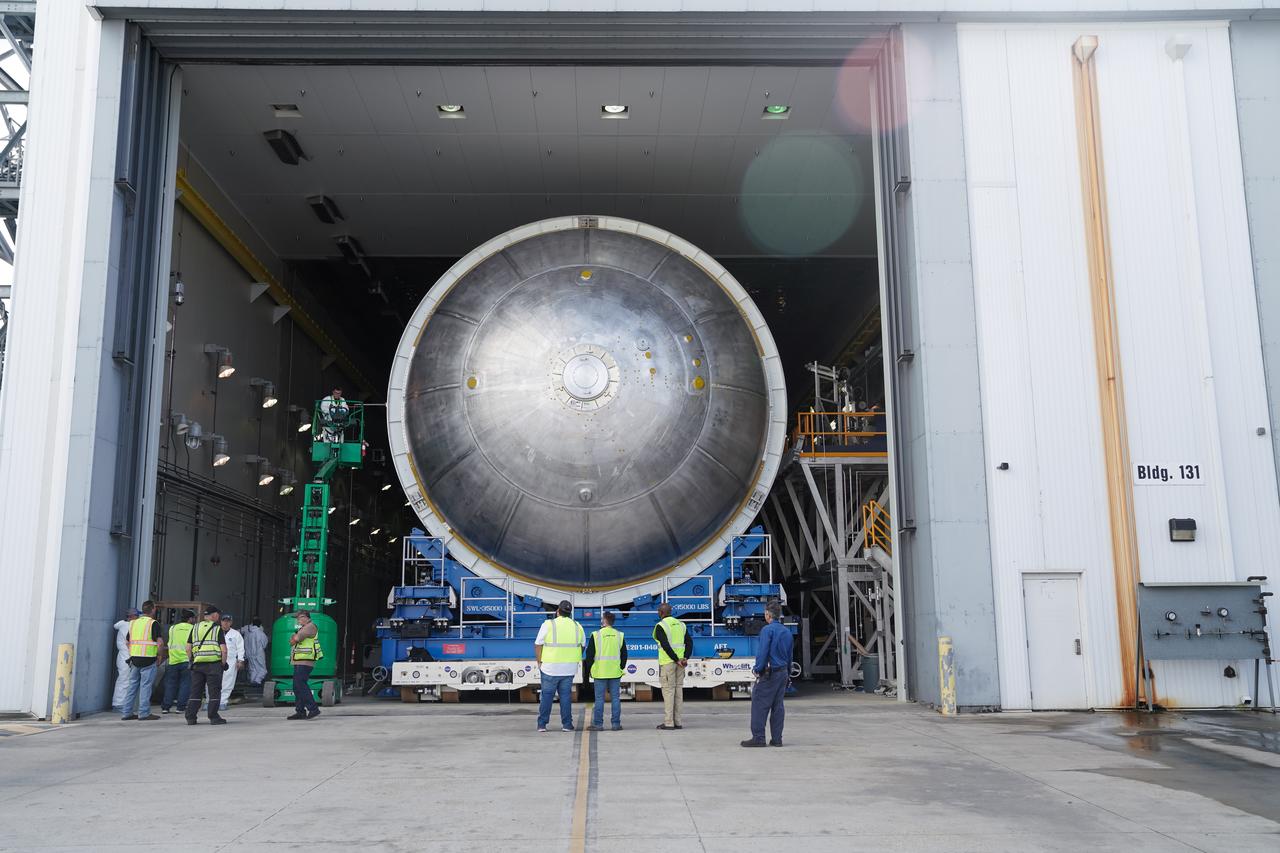

Teams move the core stage liquid hydrogen tank for the Artemis III mission to a priming cell near the Vertical Assembly Building at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans Nov. 21. Technichians will sand down and prepare the suface of the tank before coating it in a primer. Primer is applied to the barrel section of the tank by an automated robotic tool, whereas the forward and aft domes are primed manually. Once priming is complete, technicians with NASA and Boeing, the SLS core stage prime contractor, will apply a foam-based thermal protection system, which protects the propellant tank from the extreme temperatures it will face during launch and flight while also regulating the super-chilled propellant within it. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
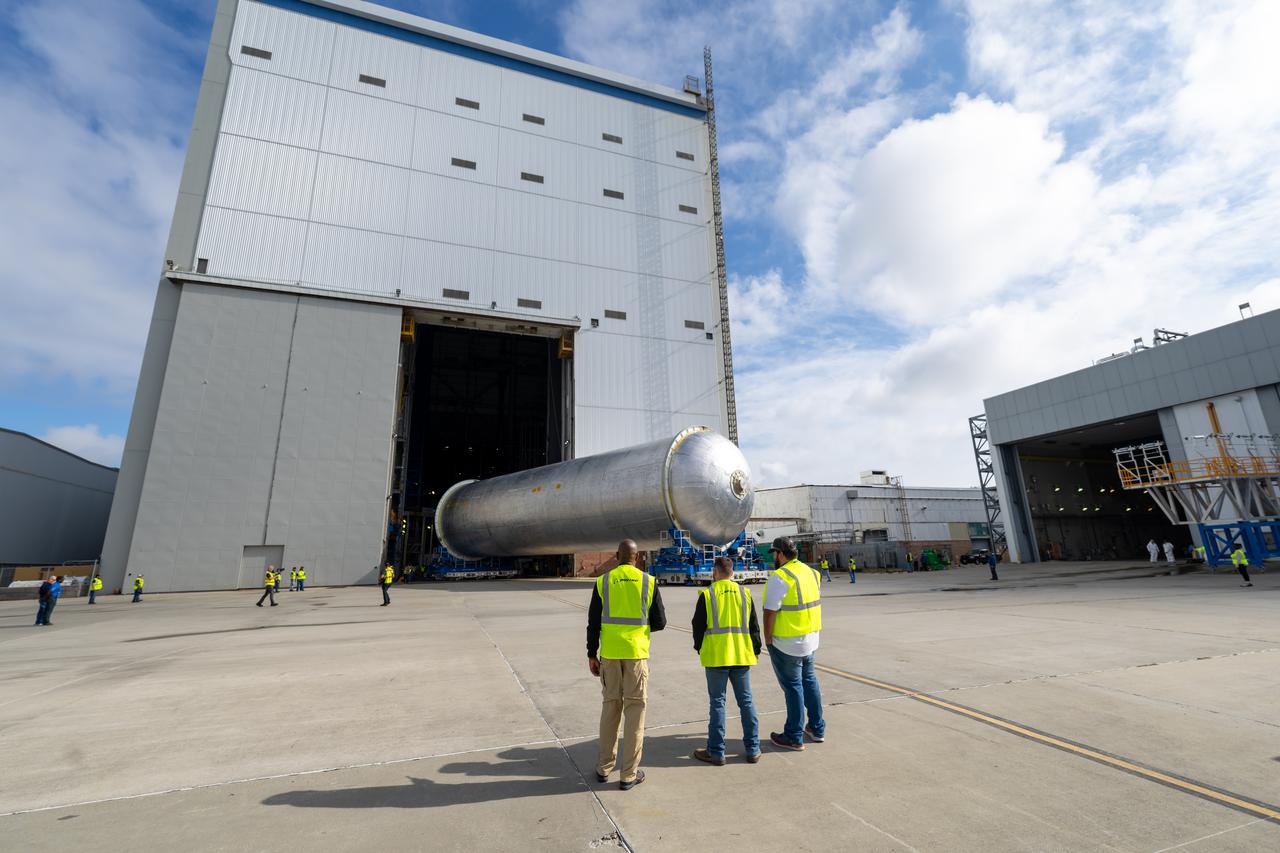

Teams move the core stage liquid hydrogen tank for the Artemis III mission to a priming cell near the Vertical Assembly Building at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans Nov. 21. Technichians will sand down and prepare the suface of the tank before coating it in a primer. Primer is applied to the barrel section of the tank by an automated robotic tool, whereas the forward and aft domes are primed manually. Once priming is complete, technicians with NASA and Boeing, the SLS core stage prime contractor, will apply a foam-based thermal protection system, which protects the propellant tank from the extreme temperatures it will face during launch and flight while also regulating the super-chilled propellant within it. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
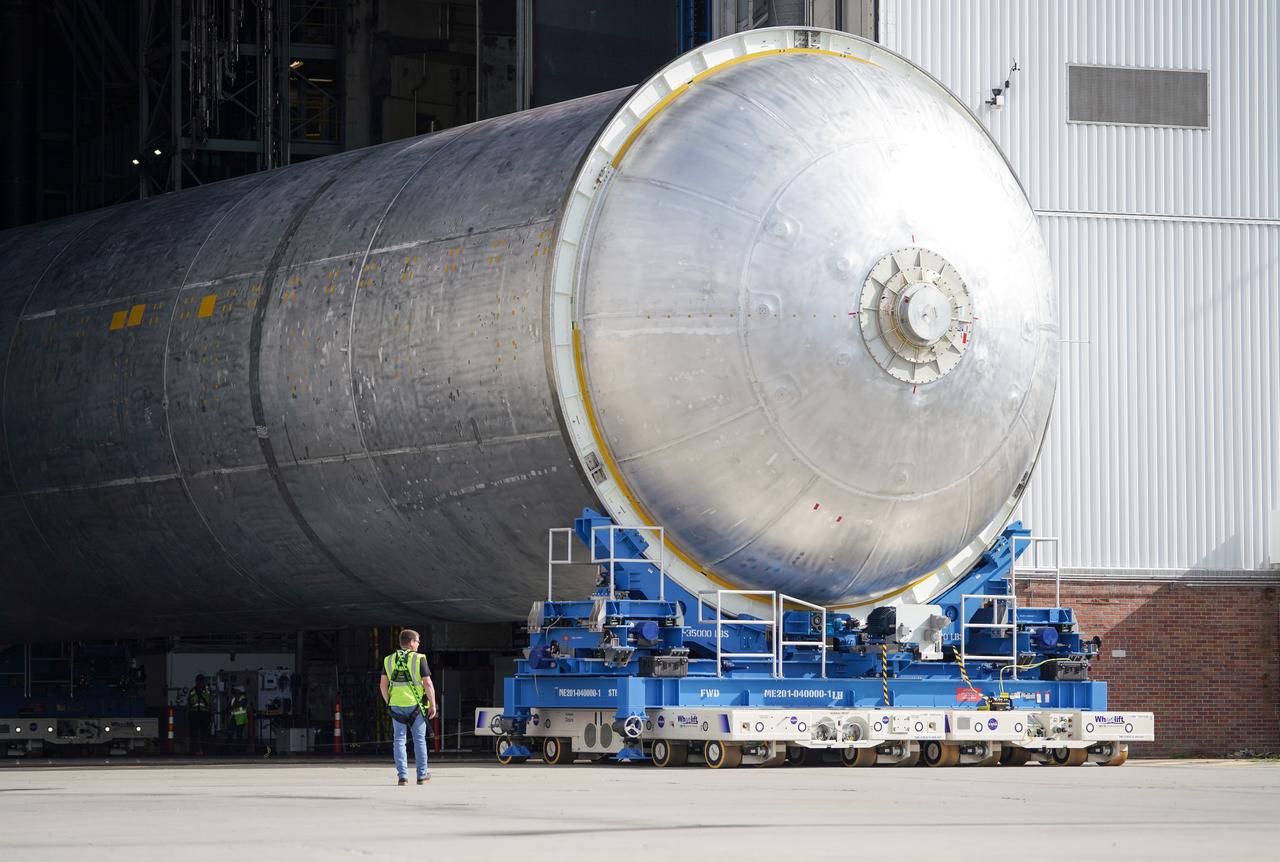

Teams move the core stage liquid hydrogen tank for the Artemis III mission to a priming cell near the Vertical Assembly Building at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans Nov. 21. Technichians will sand down and prepare the suface of the tank before coating it in a primer. Primer is applied to the barrel section of the tank by an automated robotic tool, whereas the forward and aft domes are primed manually. Once priming is complete, technicians with NASA and Boeing, the SLS core stage prime contractor, will apply a foam-based thermal protection system, which protects the propellant tank from the extreme temperatures it will face during launch and flight while also regulating the super-chilled propellant within it. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
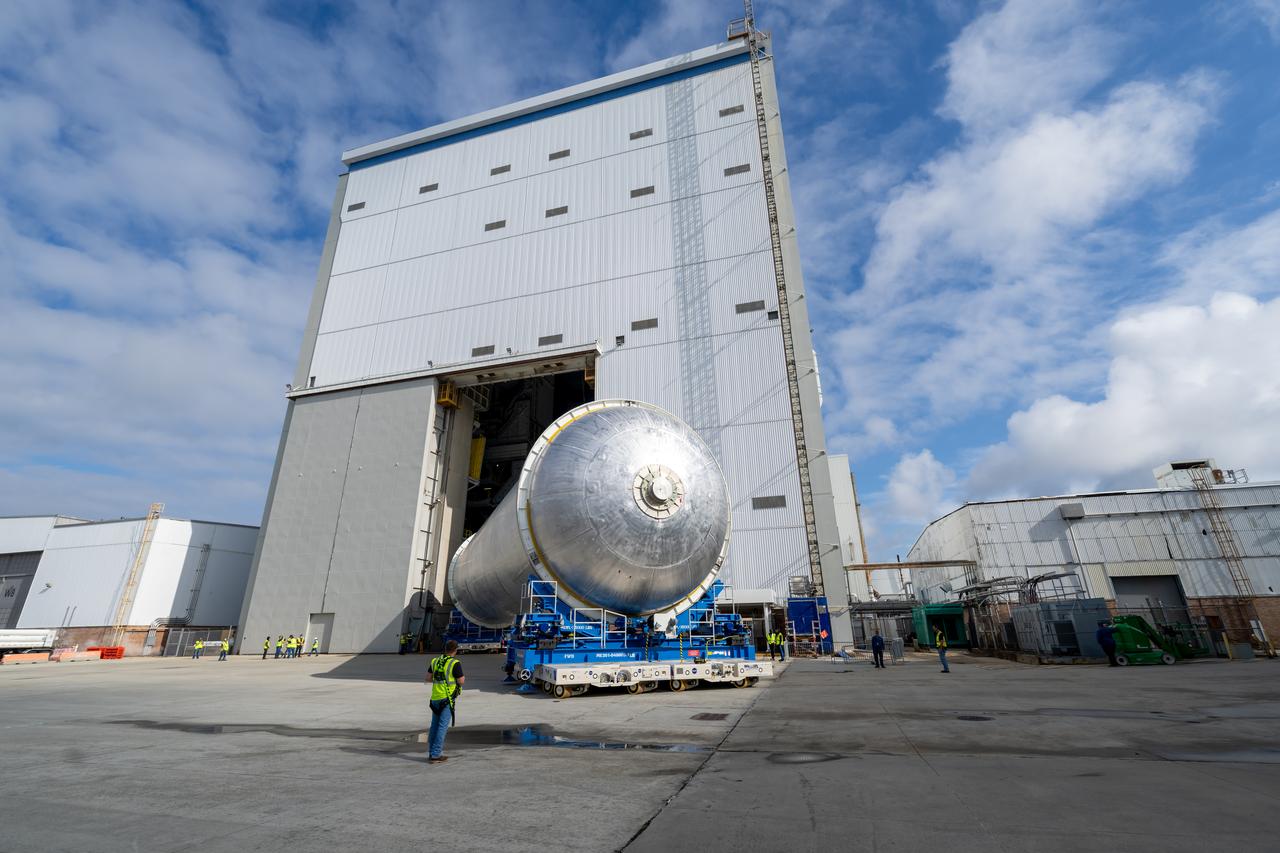

Teams move the core stage liquid hydrogen tank for the Artemis III mission to a priming cell near the Vertical Assembly Building at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans Nov. 21. Technichians will sand down and prepare the suface of the tank before coating it in a primer. Primer is applied to the barrel section of the tank by an automated robotic tool, whereas the forward and aft domes are primed manually. Once priming is complete, technicians with NASA and Boeing, the SLS core stage prime contractor, will apply a foam-based thermal protection system, which protects the propellant tank from the extreme temperatures it will face during launch and flight while also regulating the super-chilled propellant within it. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
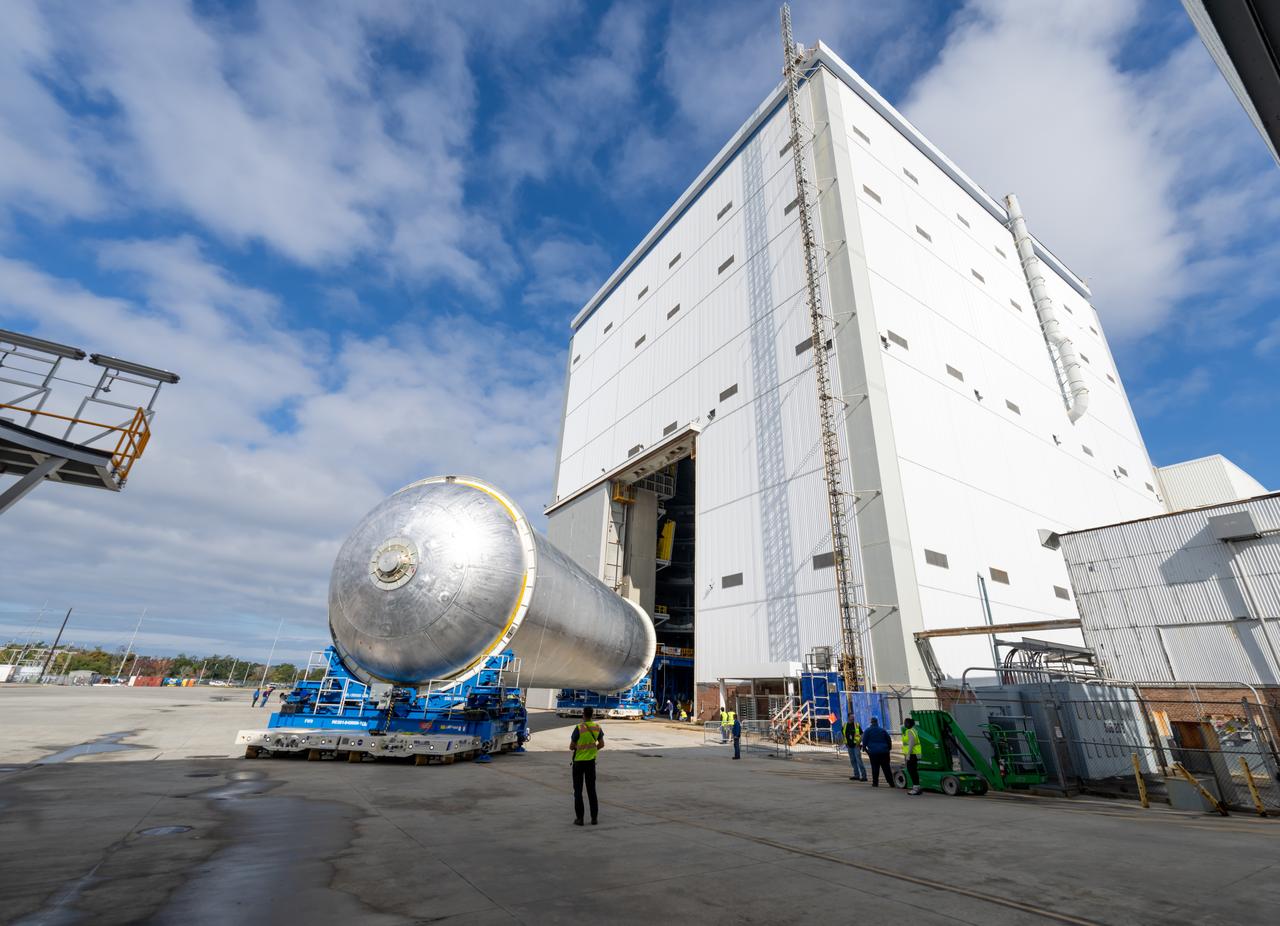

Teams move the core stage liquid hydrogen tank for the Artemis III mission to a priming cell near the Vertical Assembly Building at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans Nov. 21. Technichians will sand down and prepare the suface of the tank before coating it in a primer. Primer is applied to the barrel section of the tank by an automated robotic tool, whereas the forward and aft domes are primed manually. Once priming is complete, technicians with NASA and Boeing, the SLS core stage prime contractor, will apply a foam-based thermal protection system, which protects the propellant tank from the extreme temperatures it will face during launch and flight while also regulating the super-chilled propellant within it. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
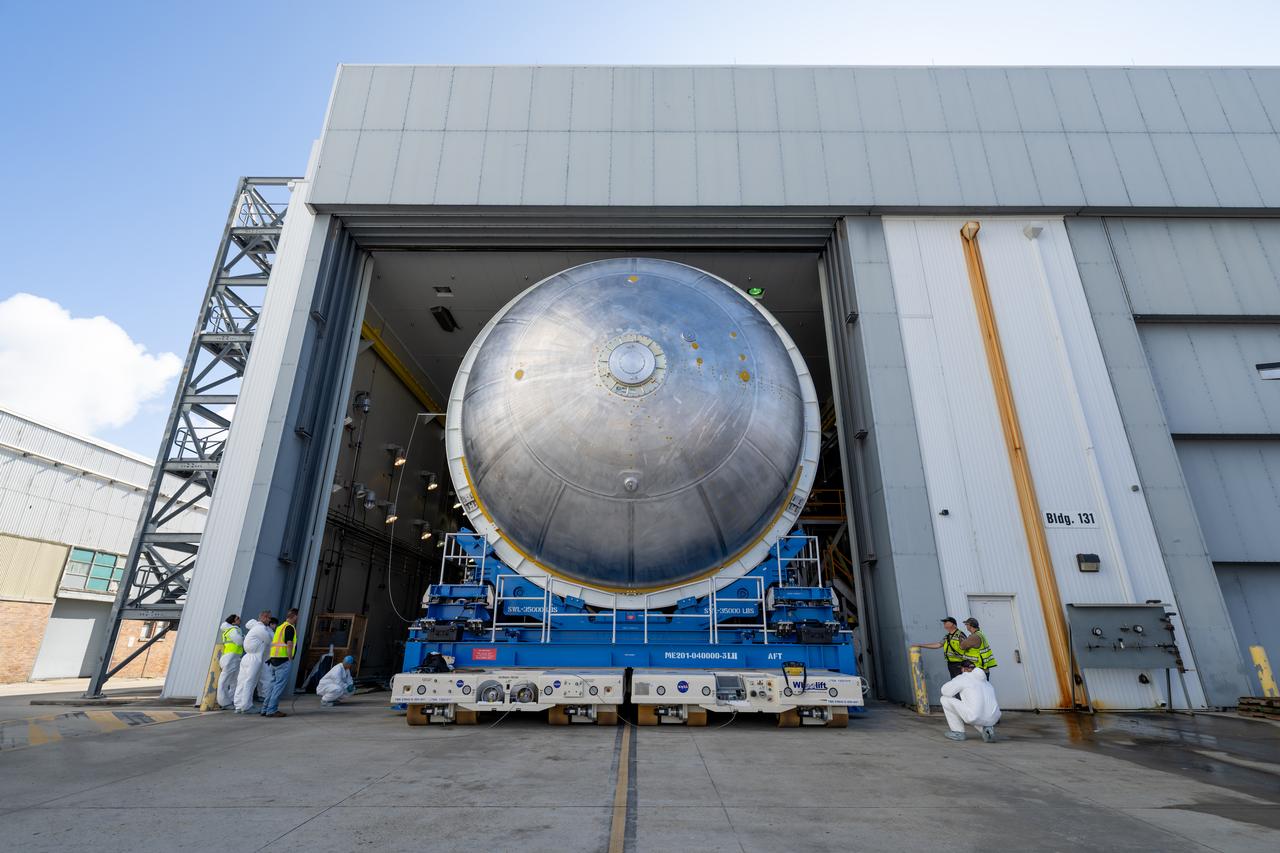

Teams move the core stage liquid hydrogen tank for the Artemis III mission to a priming cell near the Vertical Assembly Building at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans Nov. 21. Technichians will sand down and prepare the suface of the tank before coating it in a primer. Primer is applied to the barrel section of the tank by an automated robotic tool, whereas the forward and aft domes are primed manually. Once priming is complete, technicians with NASA and Boeing, the SLS core stage prime contractor, will apply a foam-based thermal protection system, which protects the propellant tank from the extreme temperatures it will face during launch and flight while also regulating the super-chilled propellant within it. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
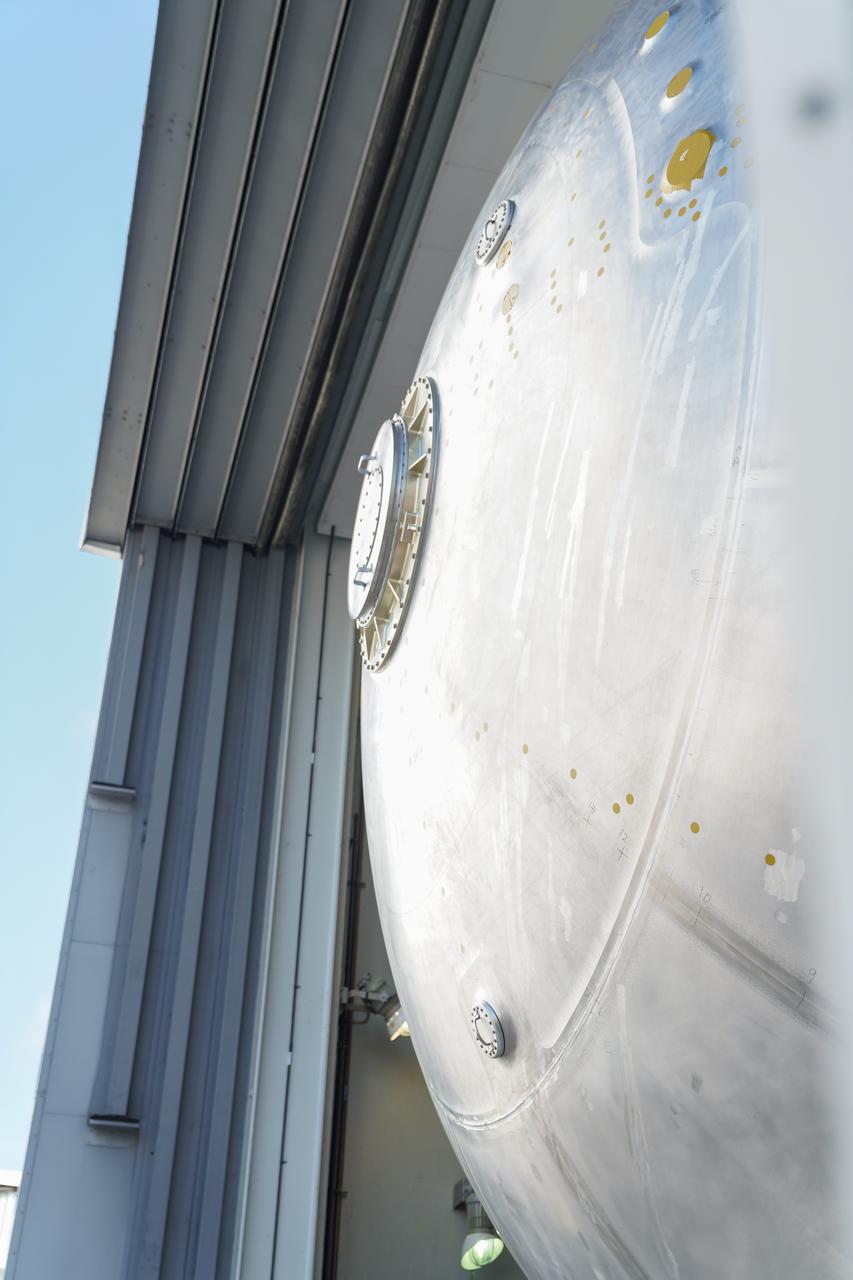

Teams move the core stage liquid hydrogen tank for the Artemis III mission to a priming cell near the Vertical Assembly Building at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans Nov. 21. Technichians will sand down and prepare the suface of the tank before coating it in a primer. Primer is applied to the barrel section of the tank by an automated robotic tool, whereas the forward and aft domes are primed manually. Once priming is complete, technicians with NASA and Boeing, the SLS core stage prime contractor, will apply a foam-based thermal protection system, which protects the propellant tank from the extreme temperatures it will face during launch and flight while also regulating the super-chilled propellant within it. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
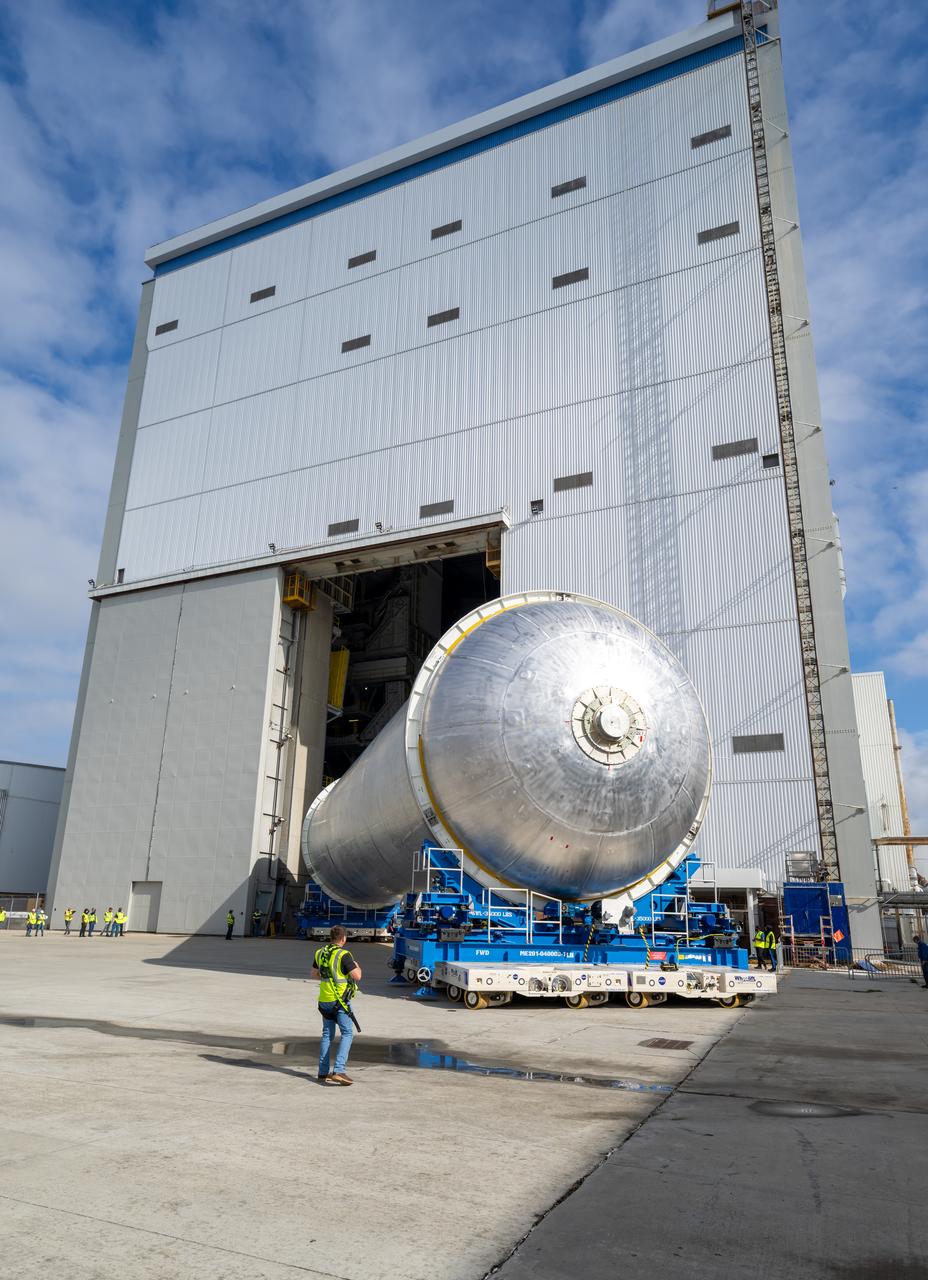

Teams move the core stage liquid hydrogen tank for the Artemis III mission to a priming cell near the Vertical Assembly Building at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans Nov. 21. Technichians will sand down and prepare the suface of the tank before coating it in a primer. Primer is applied to the barrel section of the tank by an automated robotic tool, whereas the forward and aft domes are primed manually. Once priming is complete, technicians with NASA and Boeing, the SLS core stage prime contractor, will apply a foam-based thermal protection system, which protects the propellant tank from the extreme temperatures it will face during launch and flight while also regulating the super-chilled propellant within it. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.

Teams move the core stage liquid hydrogen tank for the Artemis III mission to a priming cell near the Vertical Assembly Building at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans Nov. 21. Technichians will sand down and prepare the suface of the tank before coating it in a primer. Primer is applied to the barrel section of the tank by an automated robotic tool, whereas the forward and aft domes are primed manually. Once priming is complete, technicians with NASA and Boeing, the SLS core stage prime contractor, will apply a foam-based thermal protection system, which protects the propellant tank from the extreme temperatures it will face during launch and flight while also regulating the super-chilled propellant within it. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.

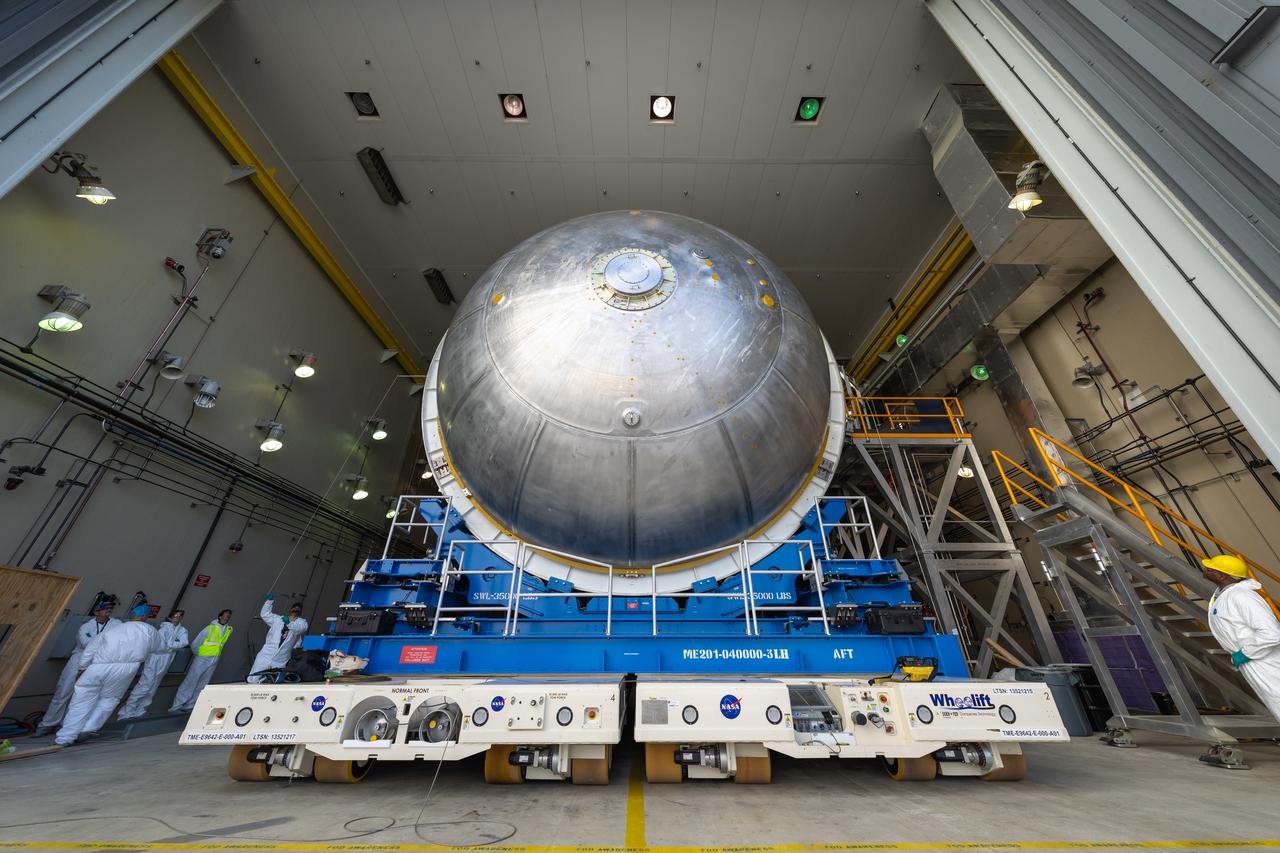
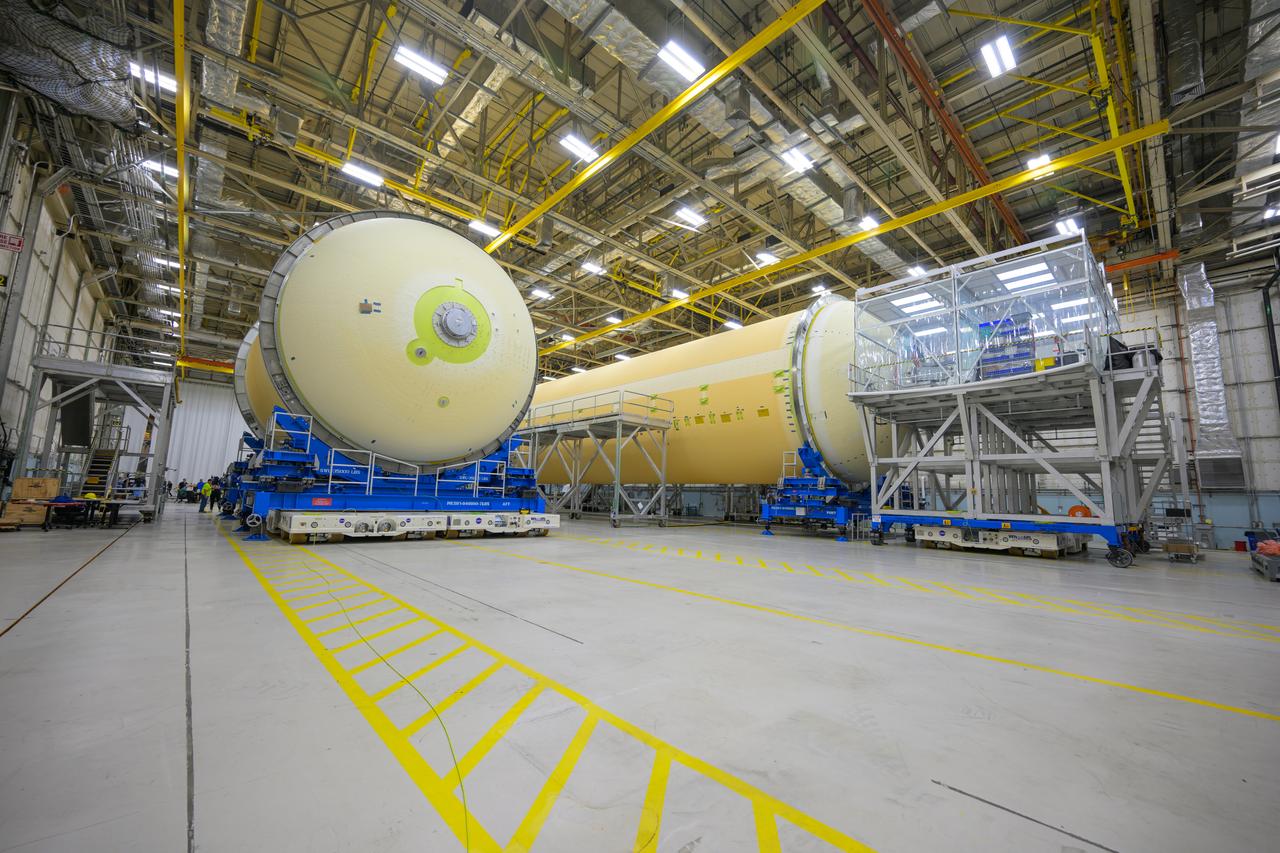
Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans perform “breakover” operations on a liquid oxygen tank in the facility’s vertical assembly building on Aug. 22, 2025. During the breakover, teams lifted the tank from its vertical configuration inside of a production cell and set it horizontally atop self-propelled mobile transporters for transfer to the final assembly production area. There, it will undergo integration of the forward dome by SLS (Space Launch System) prime contractor, Boeing. Eventually, the liquid oxygen tank will be moved back to the high bay where it will be mated with the intertank and forward skirt to complete the forward join of the Artemis III core stage. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans perform “breakover” operations on a liquid oxygen tank in the facility’s vertical assembly building on Aug. 22, 2025. During the breakover, teams lifted the tank from its vertical configuration inside of a production cell and set it horizontally atop self-propelled mobile transporters for transfer to the final assembly production area. There, it will undergo integration of the forward dome by SLS (Space Launch System) prime contractor, Boeing. Eventually, the liquid oxygen tank will be moved back to the high bay where it will be mated with the intertank and forward skirt to complete the forward join of the Artemis III core stage. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans perform “breakover” operations on a liquid oxygen tank in the facility’s vertical assembly building on Aug. 22, 2025. During the breakover, teams lifted the tank from its vertical configuration inside of a production cell and set it horizontally atop self-propelled mobile transporters for transfer to the final assembly production area. There, it will undergo integration of the forward dome by SLS (Space Launch System) prime contractor, Boeing. Eventually, the liquid oxygen tank will be moved back to the high bay where it will be mated with the intertank and forward skirt to complete the forward join of the Artemis III core stage. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the liquid oxygen tank into final assembly production area on Aug. 27, 2025. There, it will undergo integration of the forward dome by SLS (Space Launch System) prime contractor,Boeing. Eventually, the liquid oxygen tank will be moved back to the high bay where it will be mated with the intertank and forward skirt to complete the forward join of the Artemis III core stage. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
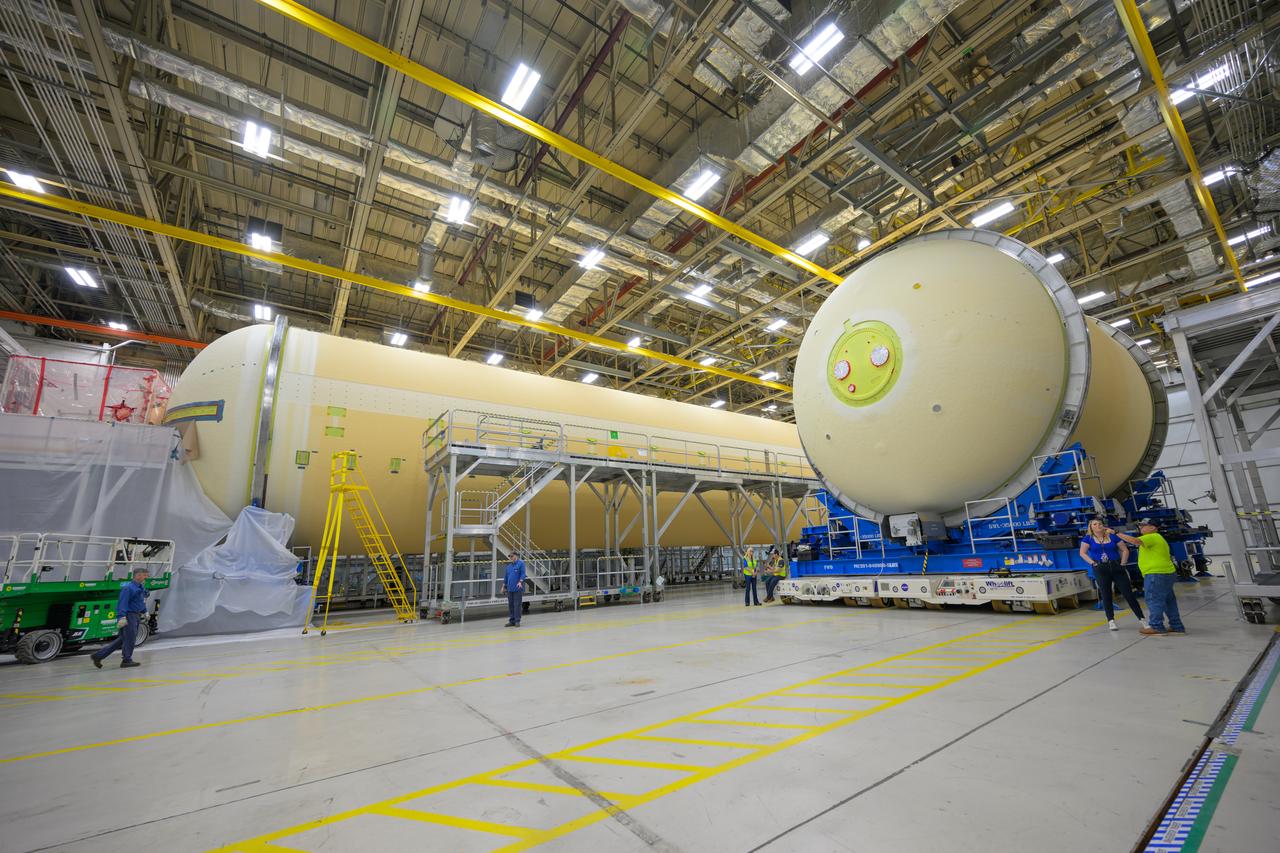

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the liquid oxygen tank into final assembly production area on Aug. 27, 2025. There, it will undergo integration of the forward dome by SLS (Space Launch System) prime contractor, Boeing. Eventually, the liquid oxygen tank will be moved back to the high bay where it will be mated with the intertank and forward skirt to complete the forward join of the Artemis III core stage. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
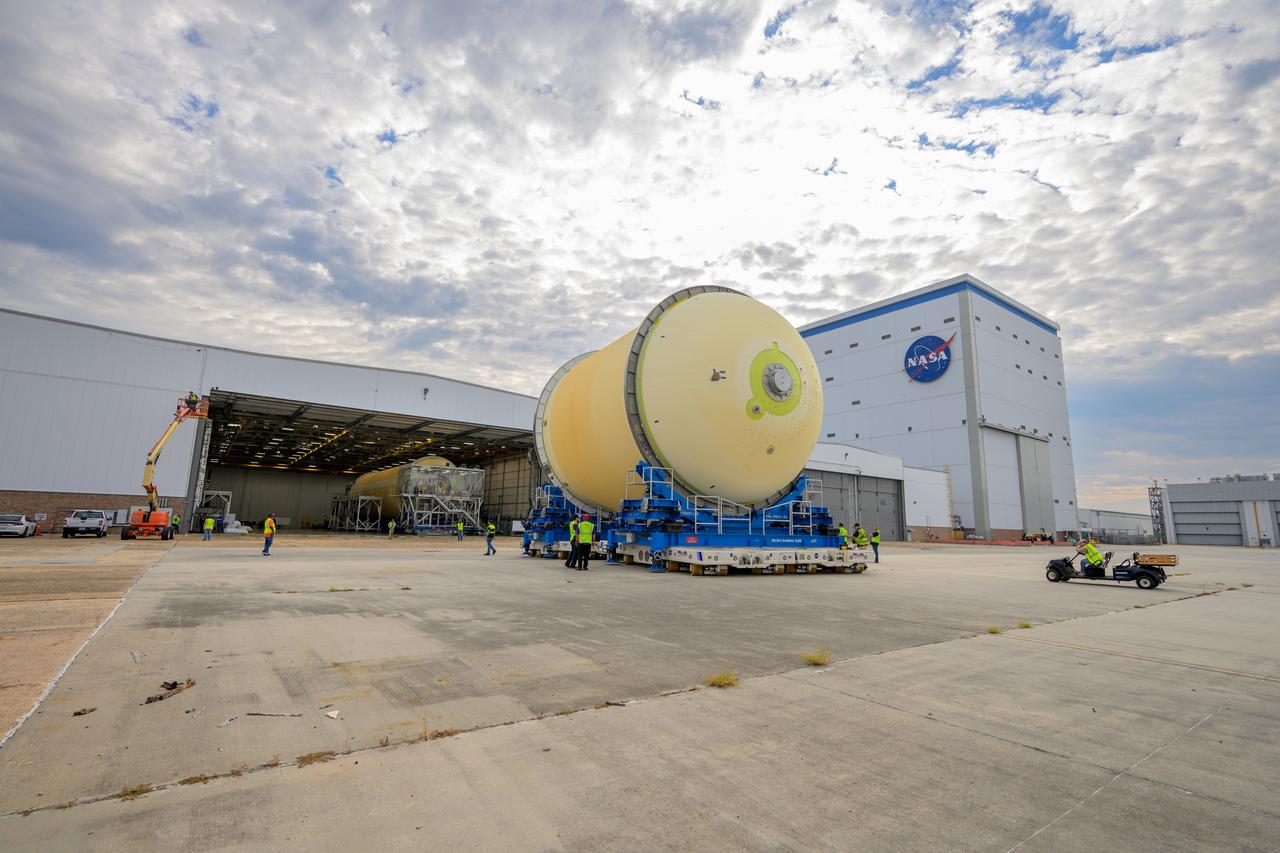

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the liquid oxygen tank into final assembly production area on Aug. 27, 2025. There, it will undergo integration of the forward dome by SLS (Space Launch System) prime contractor, Boeing. Eventually, the liquid oxygen tank will be moved back to the high bay where it will be mated with the intertank and forward skirt to complete the forward join of the Artemis III core stage. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
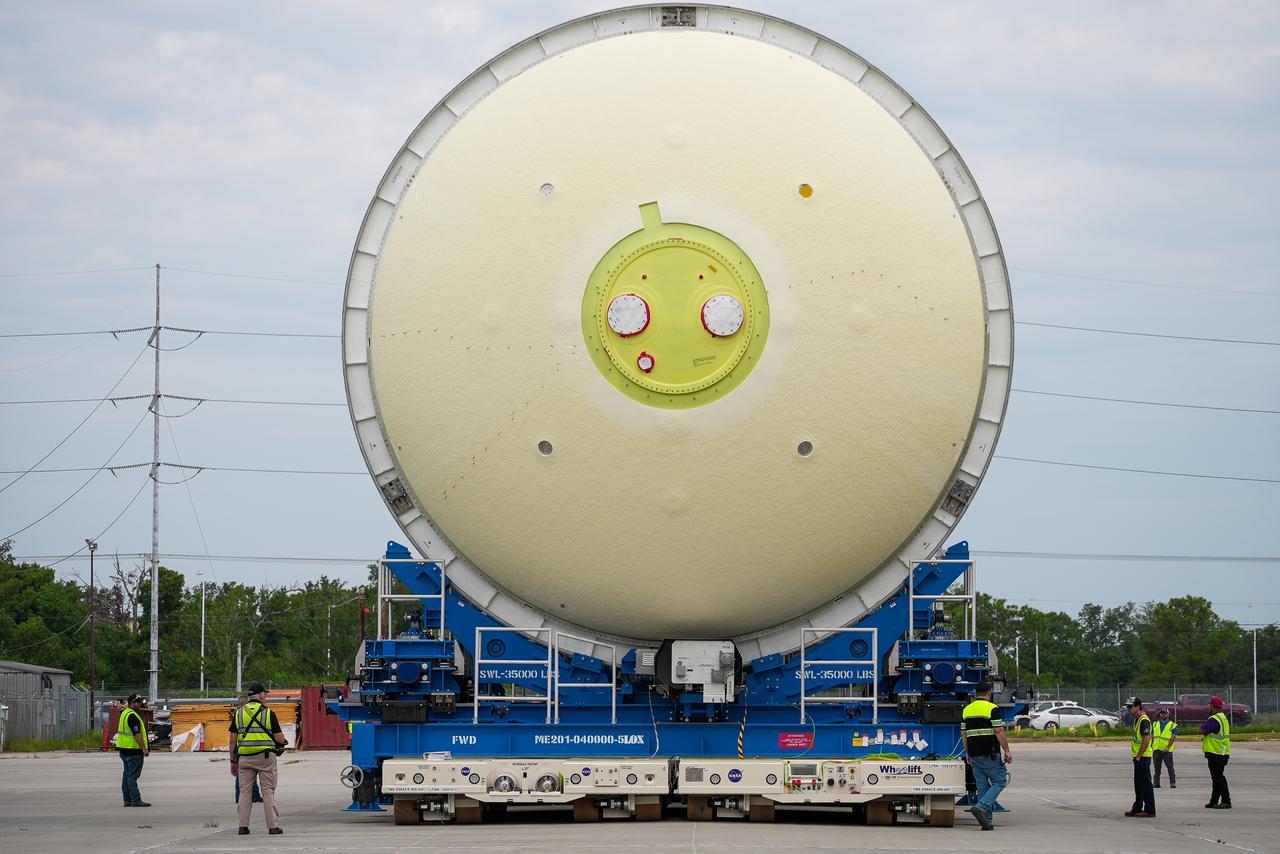

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the liquid oxygen tank into final assembly production area on Aug. 27, 2025. There, it will undergo integration of the forward dome by SLS (Space Launch System) prime contractor, Boeing. Eventually, the liquid oxygen tank will be moved back to the high bay where it will be mated with the intertank and forward skirt to complete the forward join of the Artemis III core stage. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
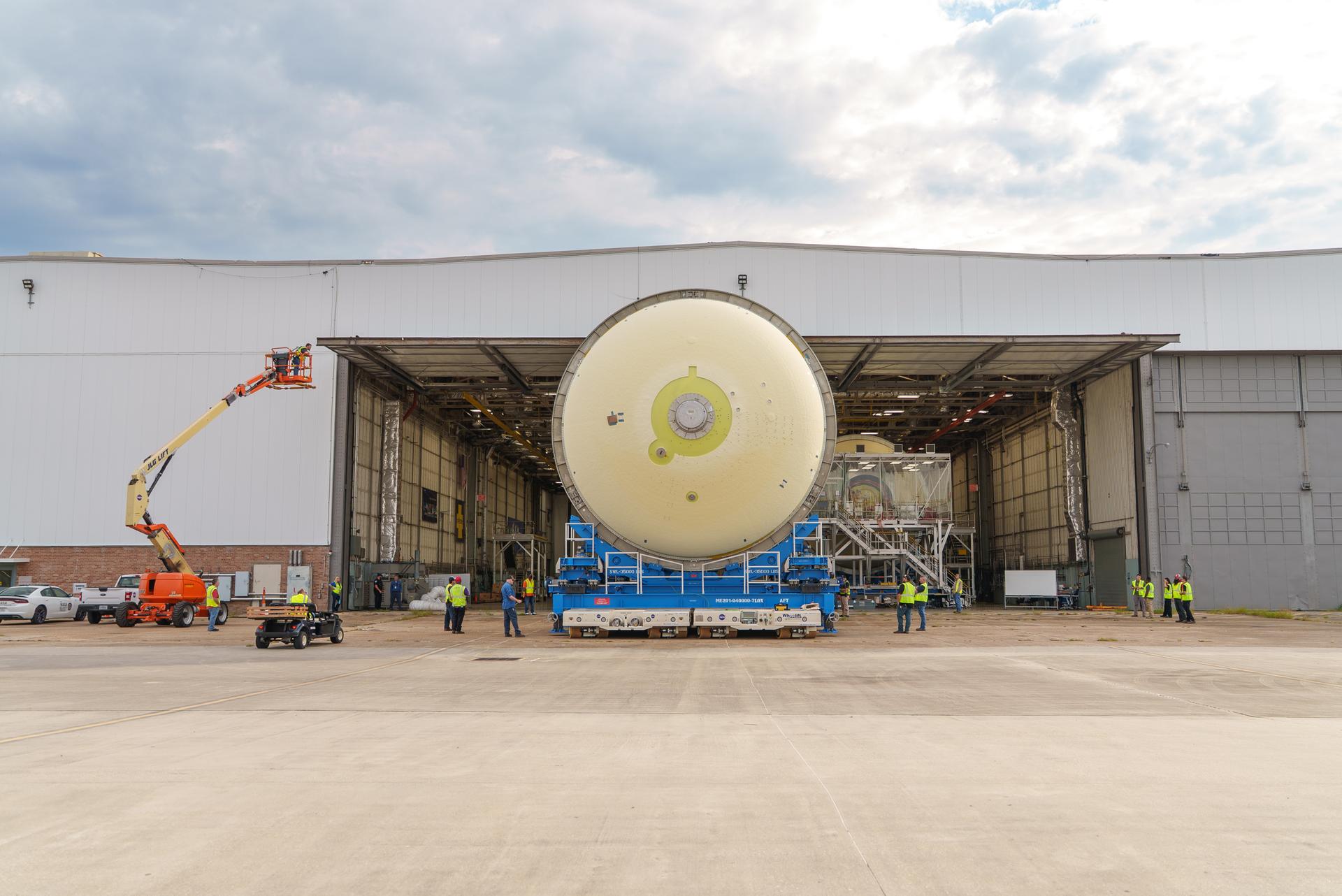

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the liquid oxygen tank into final assembly production area on Aug. 27, 2025. There, it will undergo integration of the forward dome by SLS (Space Launch System) prime contractor, Boeing. Eventually, the liquid oxygen tank will be moved back to the high bay where it will be mated with the intertank and forward skirt to complete the forward join of the Artemis III core stage. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
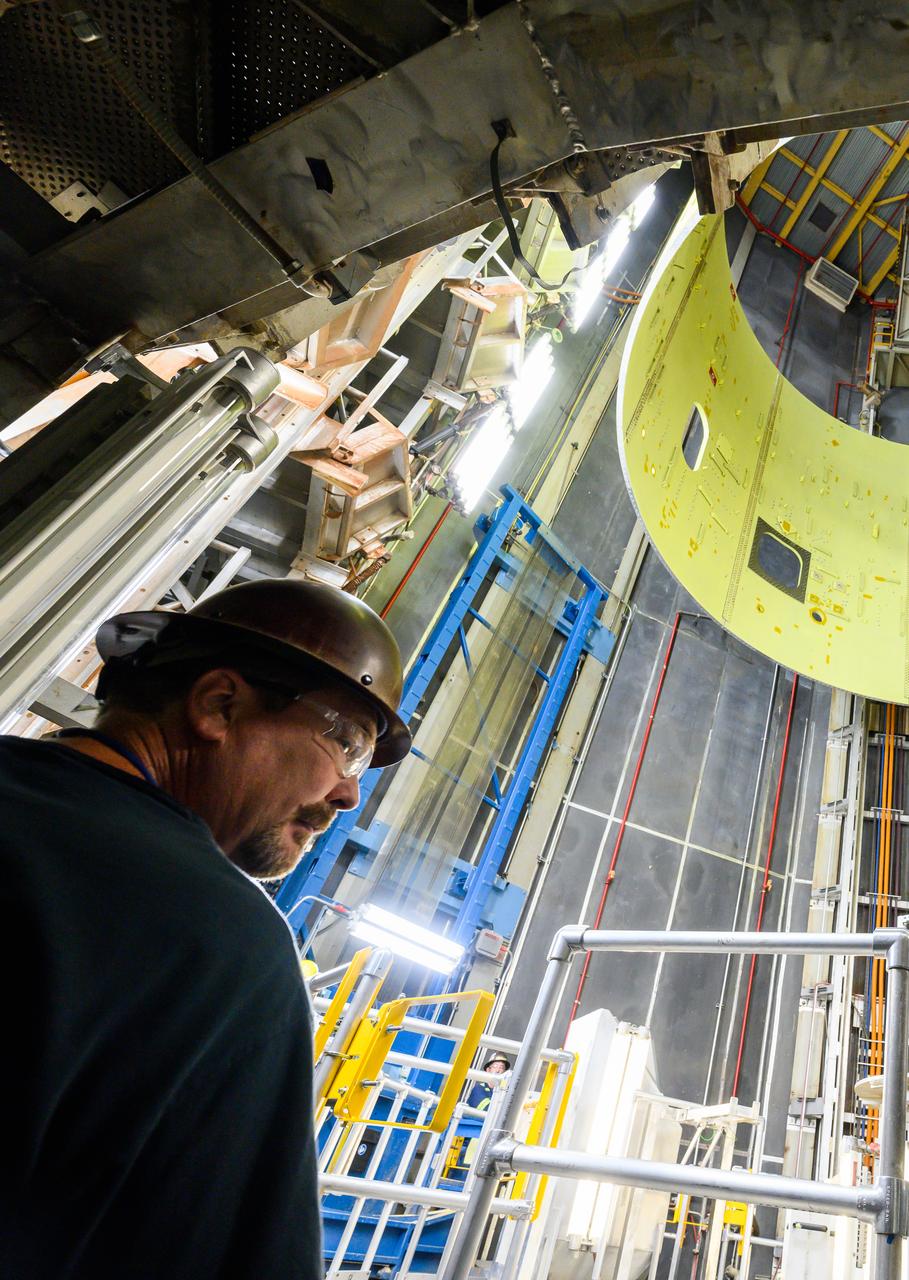

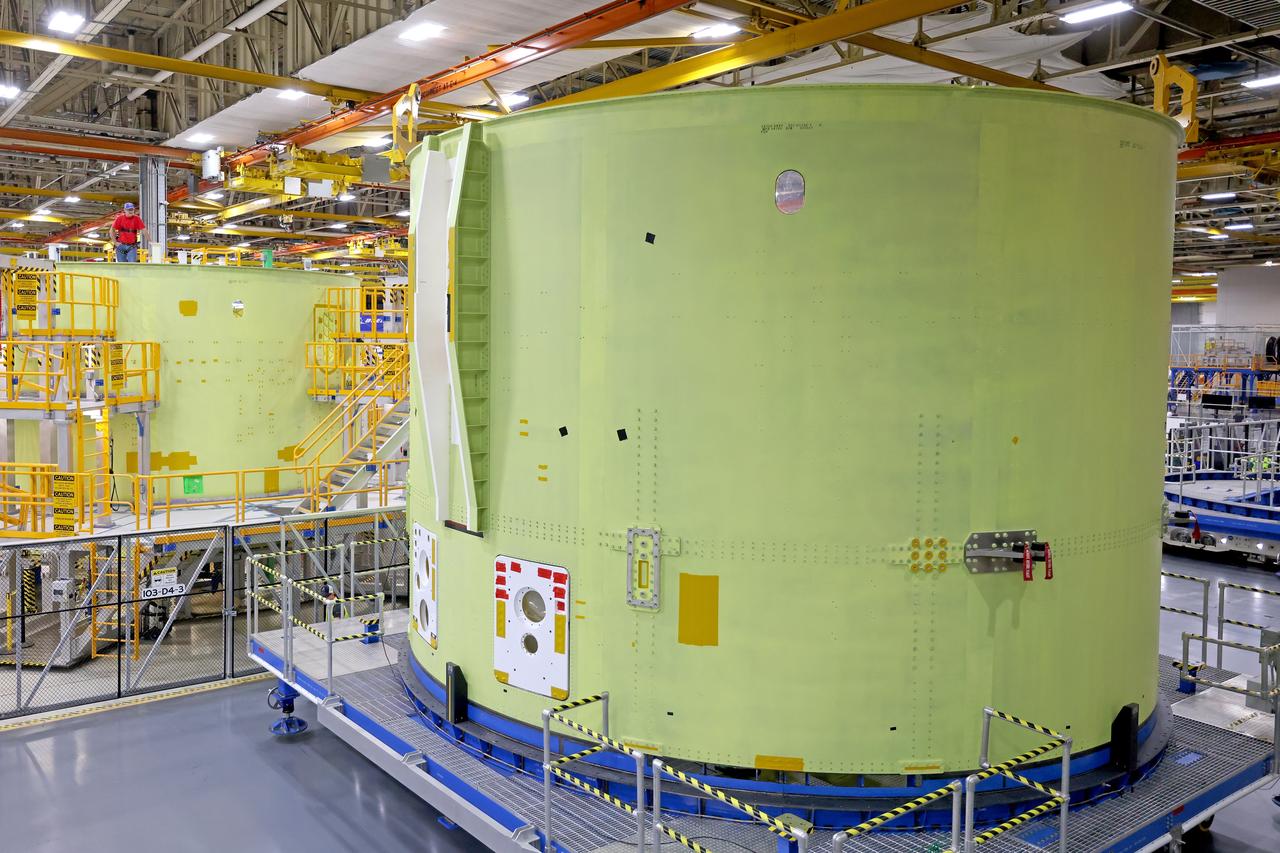
Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move the intertank of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis III to Cell G on October 26, 2022 to await application of the thermal protection system. Thermal protection systems protect space vehicles from aerodynamic heating during entry to planet atmosphere and re-entry to earth atmosphere. The intertank lays between the liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank. Together with the engine section and the forward skirt, they comprise the SLS core stage. The liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank hold 733,000 gallons of propellant to power the stage’s four RS-25 engines needed for liftoff and Artemis missions to the Moon and future missions to Mars.
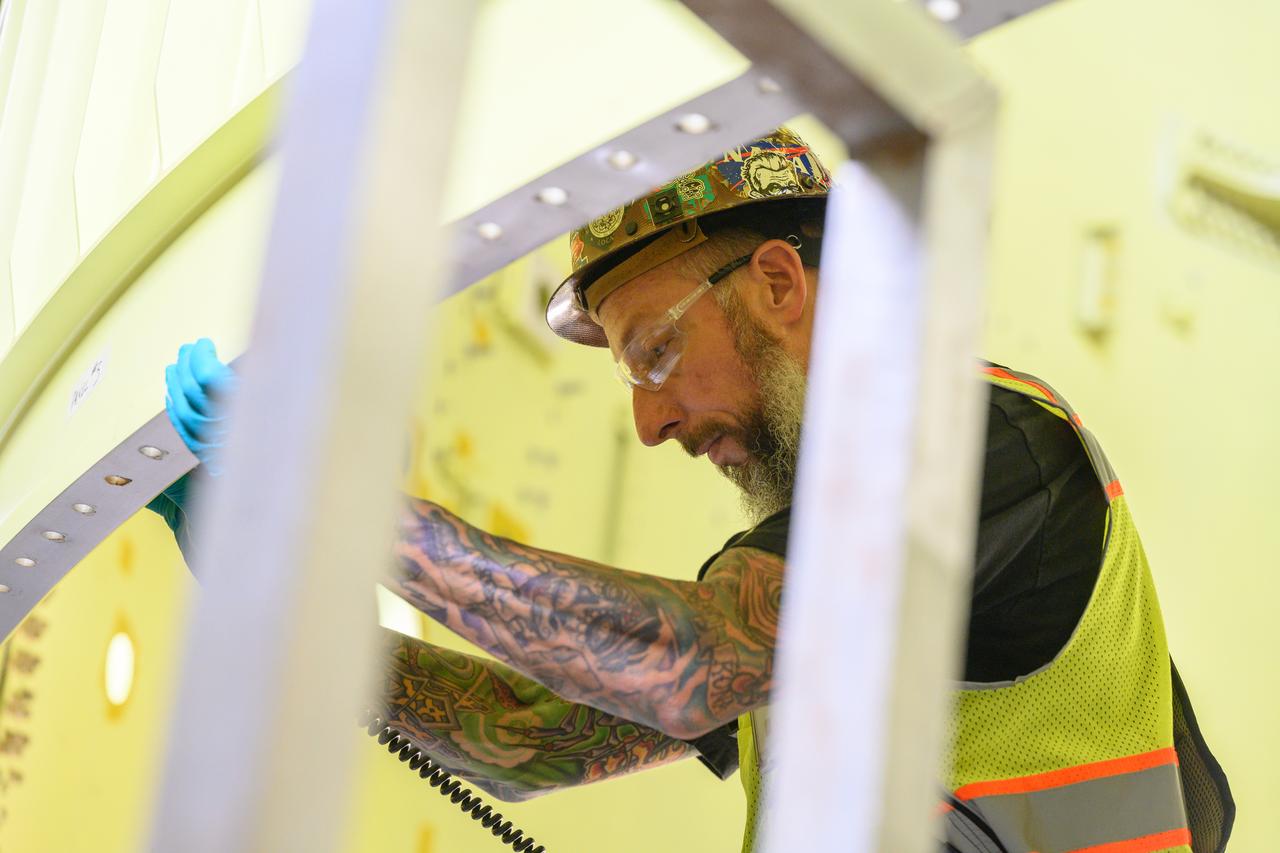

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move the intertank of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis III to Cell G on October 26, 2022 to await application of the thermal protection system. Thermal protection systems protect space vehicles from aerodynamic heating during entry to planet atmosphere and re-entry to earth atmosphere. The intertank lays between the liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank. Together with the engine section and the forward skirt, they comprise the SLS core stage. The liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank hold 733,000 gallons of propellant to power the stage’s four RS-25 engines needed for liftoff and Artemis missions to the Moon and future missions to Mars.
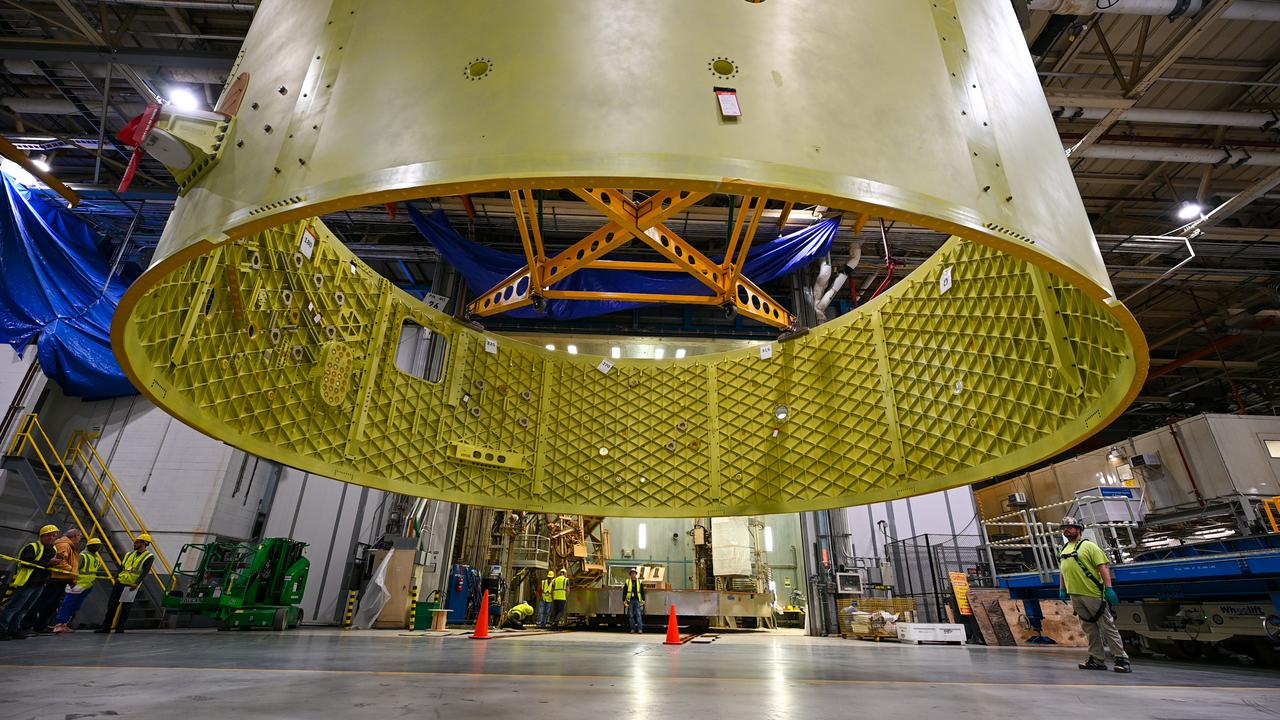

Crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the forward skirt of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility Dec. 15. Teams are preparing to apply the thermal protection system to the flight hardware, which will protect it from the extreme temperatures during launch and flight. The forward skirt is part of the core stage that will power the SLS rocket for the Artemis III mission. The forward skirt houses flight computers, cameras, and avionics.. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. When fully stacked, the forward skirt is located at the top of the core stage and connects the stage to the upper part of the rocket. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
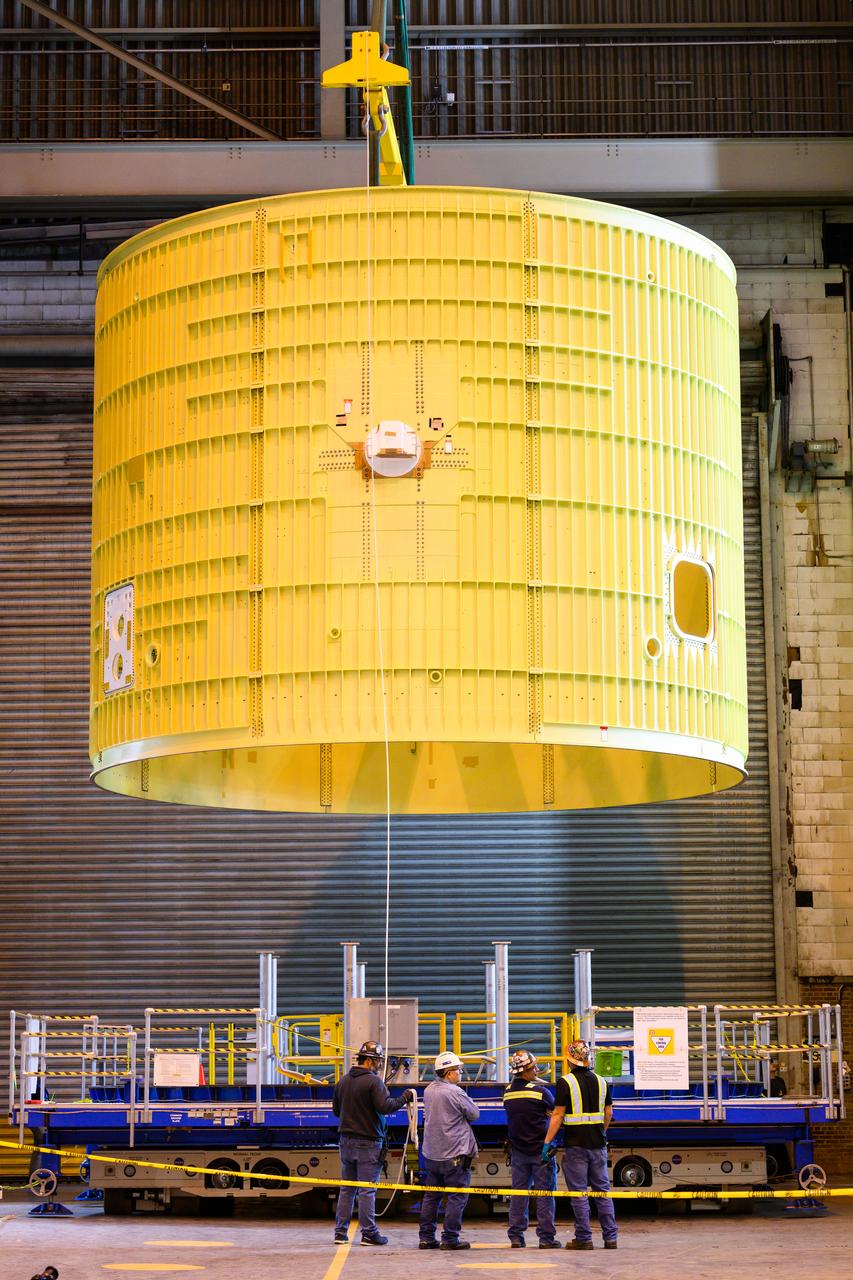

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move the intertank of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis III to Cell G on October 26, 2022 to await application of the thermal protection system. Thermal protection systems protect space vehicles from aerodynamic heating during entry to planet atmosphere and re-entry to earth atmosphere. The intertank lays between the liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank. Together with the engine section and the forward skirt, they comprise the SLS core stage. The liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank hold 733,000 gallons of propellant to power the stage’s four RS-25 engines needed for liftoff and Artemis missions to the Moon and future missions to Mars.

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move the intertank of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis III to Cell G on October 26, 2022 to await application of the thermal protection system. Thermal protection systems protect space vehicles from aerodynamic heating during entry to planet atmosphere and re-entry to earth atmosphere. The intertank lays between the liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank. Together with the engine section and the forward skirt, they comprise the SLS core stage. The liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank hold 733,000 gallons of propellant to power the stage’s four RS-25 engines needed for liftoff and Artemis missions to the Moon and future missions to Mars.

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move the intertank of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis III to Cell G on October 26, 2022 to await application of the thermal protection system. Thermal protection systems protect space vehicles from aerodynamic heating during entry to planet atmosphere and re-entry to earth atmosphere. The intertank lays between the liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank. Together with the engine section and the forward skirt, they comprise the SLS core stage. The liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank hold 733,000 gallons of propellant to power the stage’s four RS-25 engines needed for liftoff and Artemis missions to the Moon and future missions to Mars.
/MAF_20221027_CS3_IT_lifttoG-epb_004(1)~medium.jpg)
Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move the intertank of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis III to Cell G on October 26, 2022 to await application of the thermal protection system. Thermal protection systems protect space vehicles from aerodynamic heating during entry to planet atmosphere and re-entry to earth atmosphere. The intertank lays between the liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank. Together with the engine section and the forward skirt, they comprise the SLS core stage. The liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank hold 733,000 gallons of propellant to power the stage’s four RS-25 engines needed for liftoff and Artemis missions to the Moon and future missions to Mars.
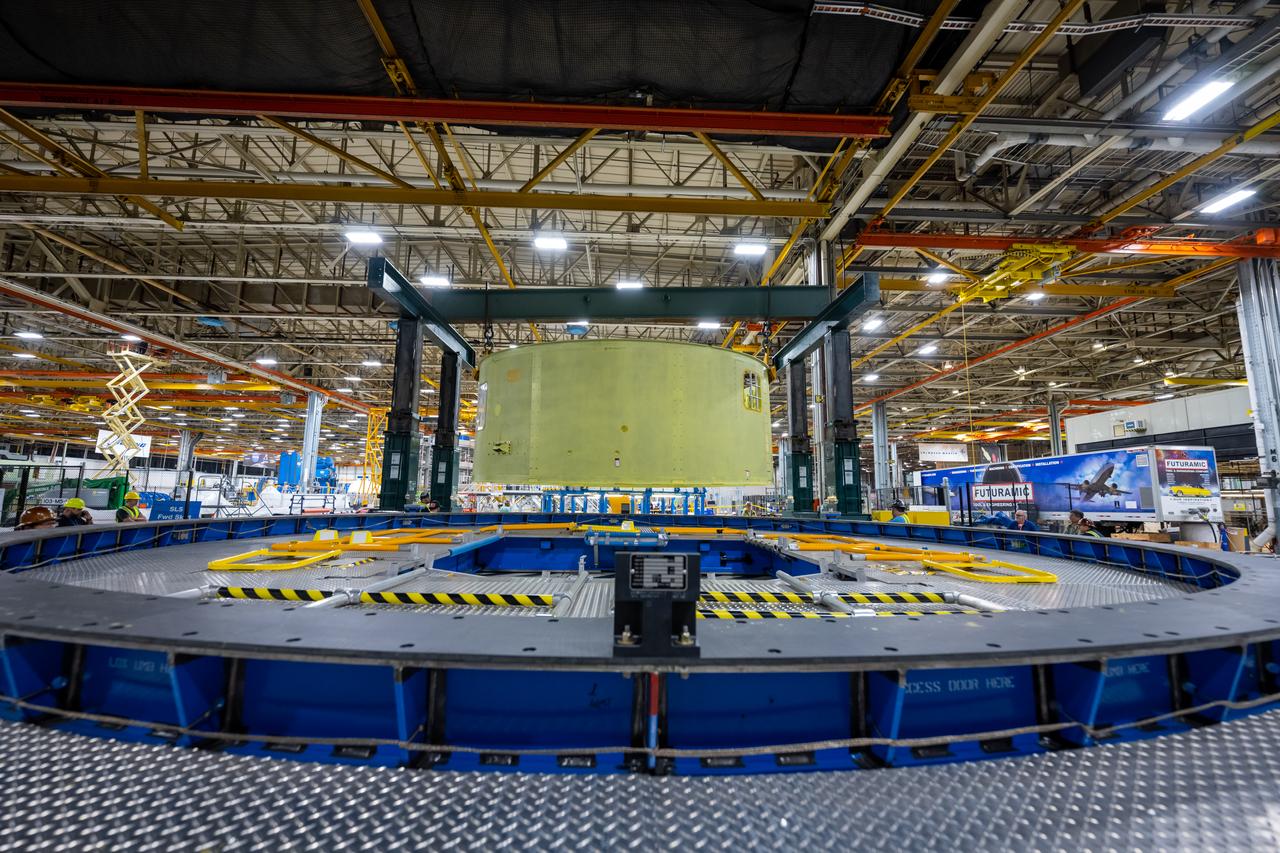

Crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the forward skirt of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility Dec. 15. Teams are preparing to apply the thermal protection system to the flight hardware, which will protect it from the extreme temperatures during launch and flight. The forward skirt is part of the core stage that will power the SLS rocket for the Artemis III mission. The forward skirt houses flight computers, cameras, and avionics.. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. When fully stacked, the forward skirt is located at the top of the core stage and connects the stage to the upper part of the rocket. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

Crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the forward skirt of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility Dec. 15. Teams are preparing to apply the thermal protection system to the flight hardware, which will protect it from the extreme temperatures during launch and flight. The forward skirt is part of the core stage that will power the SLS rocket for the Artemis III mission. The forward skirt houses flight computers, cameras, and avionics.. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. When fully stacked, the forward skirt is located at the top of the core stage and connects the stage to the upper part of the rocket. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

Crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the forward skirt of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility Dec. 15. Teams are preparing to apply the thermal protection system to the flight hardware, which will protect it from the extreme temperatures during launch and flight. The forward skirt is part of the core stage that will power the SLS rocket for the Artemis III mission. The forward skirt houses flight computers, cameras, and avionics.. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. When fully stacked, the forward skirt is located at the top of the core stage and connects the stage to the upper part of the rocket. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

Crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the forward skirt of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility Dec. 15. Teams are preparing to apply the thermal protection system to the flight hardware, which will protect it from the extreme temperatures during launch and flight. The forward skirt is part of the core stage that will power the SLS rocket for the Artemis III mission. The forward skirt houses flight computers, cameras, and avionics.. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. When fully stacked, the forward skirt is located at the top of the core stage and connects the stage to the upper part of the rocket. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
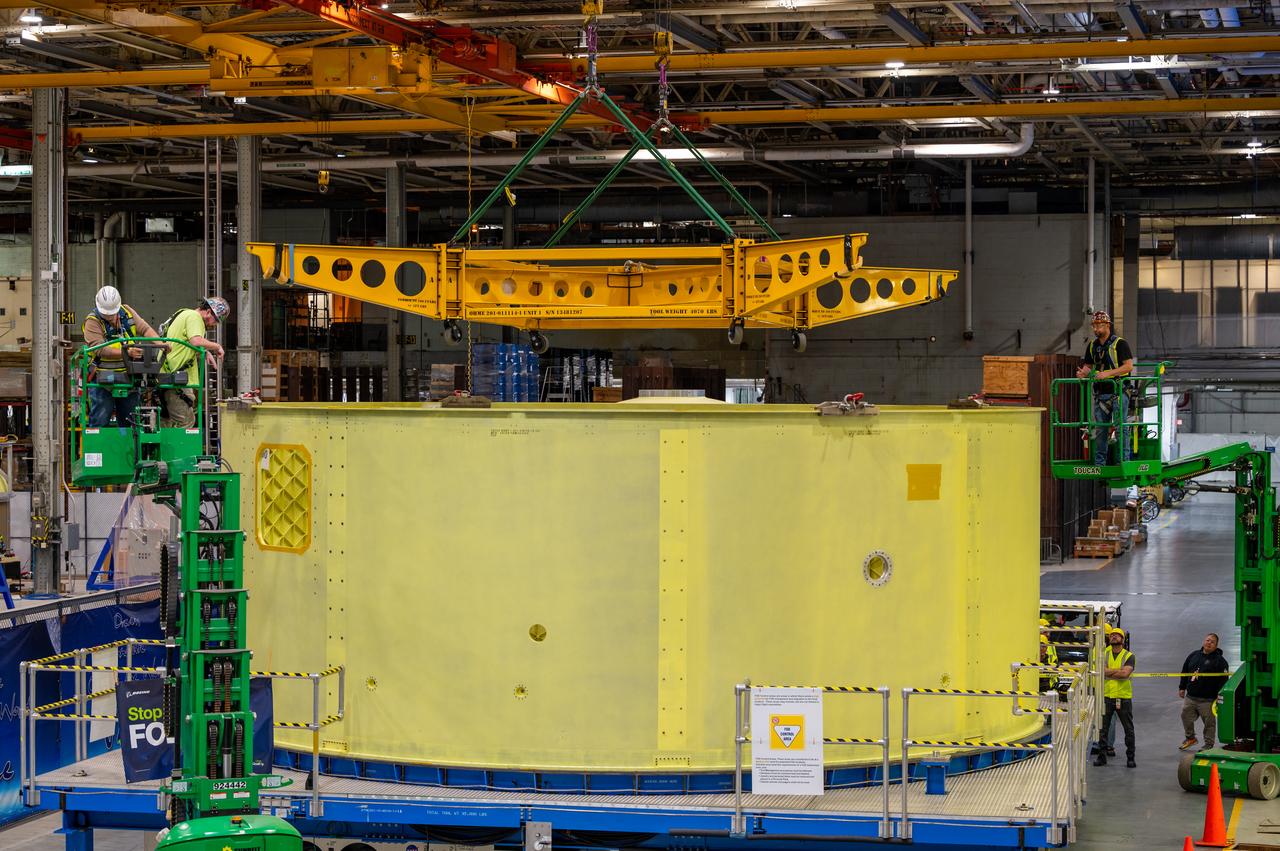
Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move the engine section of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis III to the VAB on November 7, 2022. This hardware makes up the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall core stage; and when complete, it will house the four RS-25 engines as well as vital systems for mounting, controlling, and delivering fuel from the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Together with its four RS-25 engines and its twin solid rocket boosters, it will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability, and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Humane Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
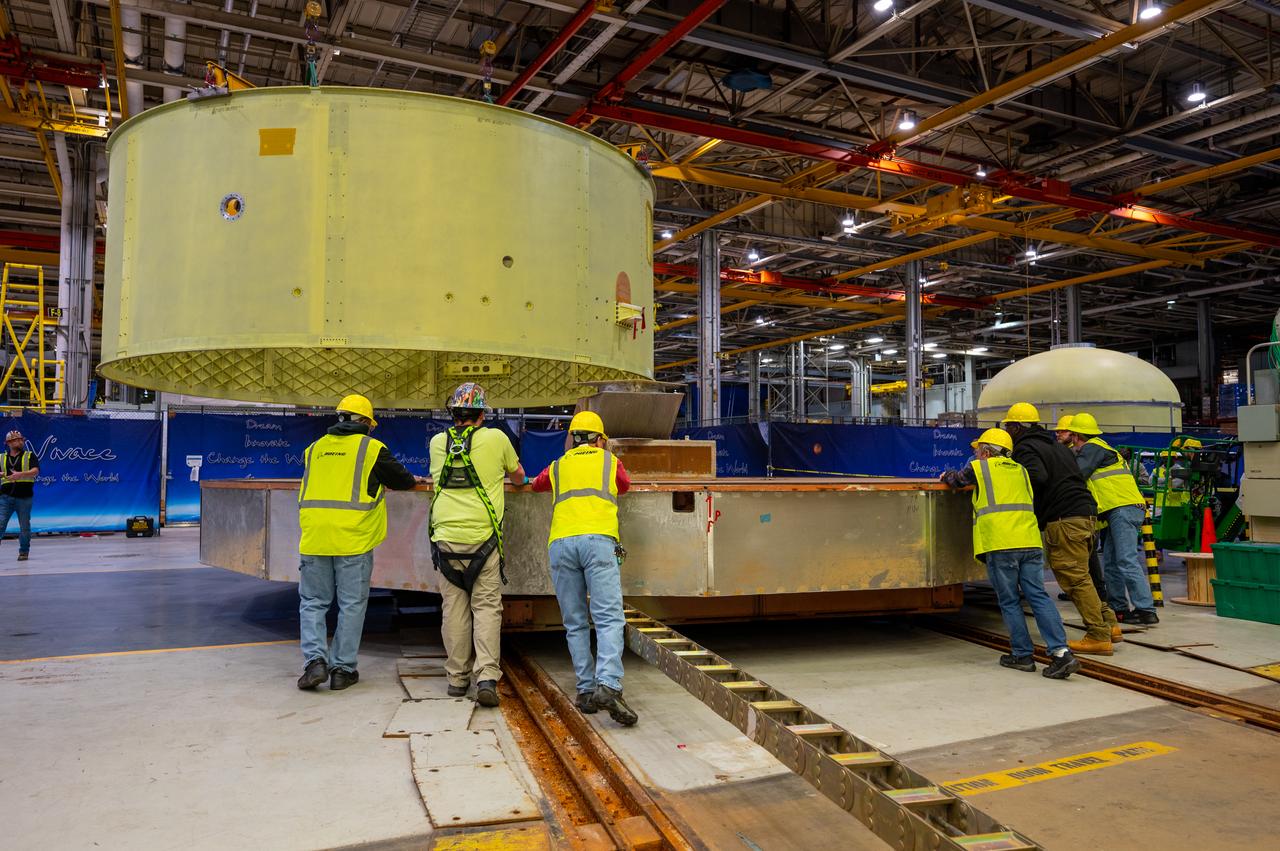

Crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the forward skirt of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility Dec. 15. Teams are preparing to apply the thermal protection system to the flight hardware, which will protect it from the extreme temperatures during launch and flight. The forward skirt is part of the core stage that will power the SLS rocket for the Artemis III mission. The forward skirt houses flight computers, cameras, and avionics.. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. When fully stacked, the forward skirt is located at the top of the core stage and connects the stage to the upper part of the rocket. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
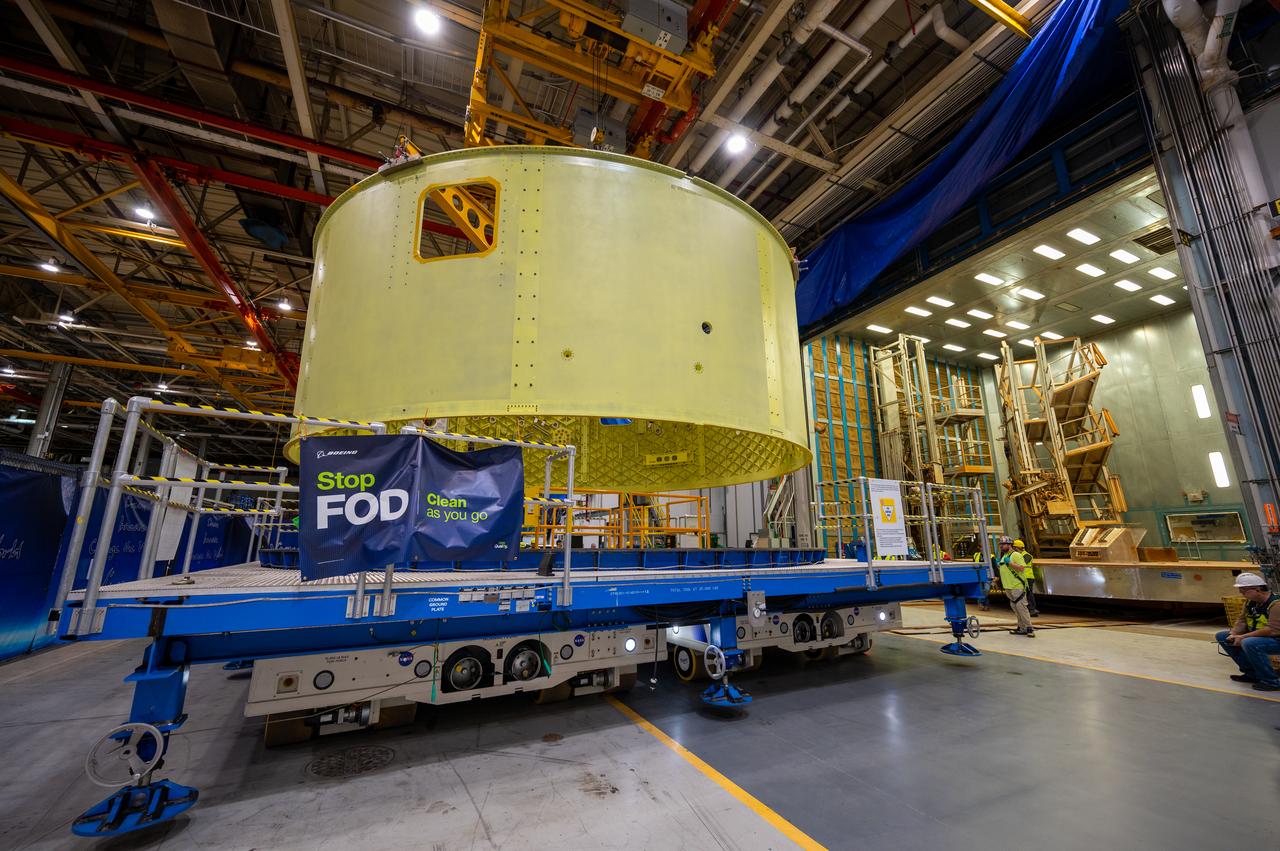

Crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the forward skirt of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility Dec. 15. Teams are preparing to apply the thermal protection system to the flight hardware, which will protect it from the extreme temperatures during launch and flight. The forward skirt is part of the core stage that will power the SLS rocket for the Artemis III mission. The forward skirt houses flight computers, cameras, and avionics.. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. When fully stacked, the forward skirt is located at the top of the core stage and connects the stage to the upper part of the rocket. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
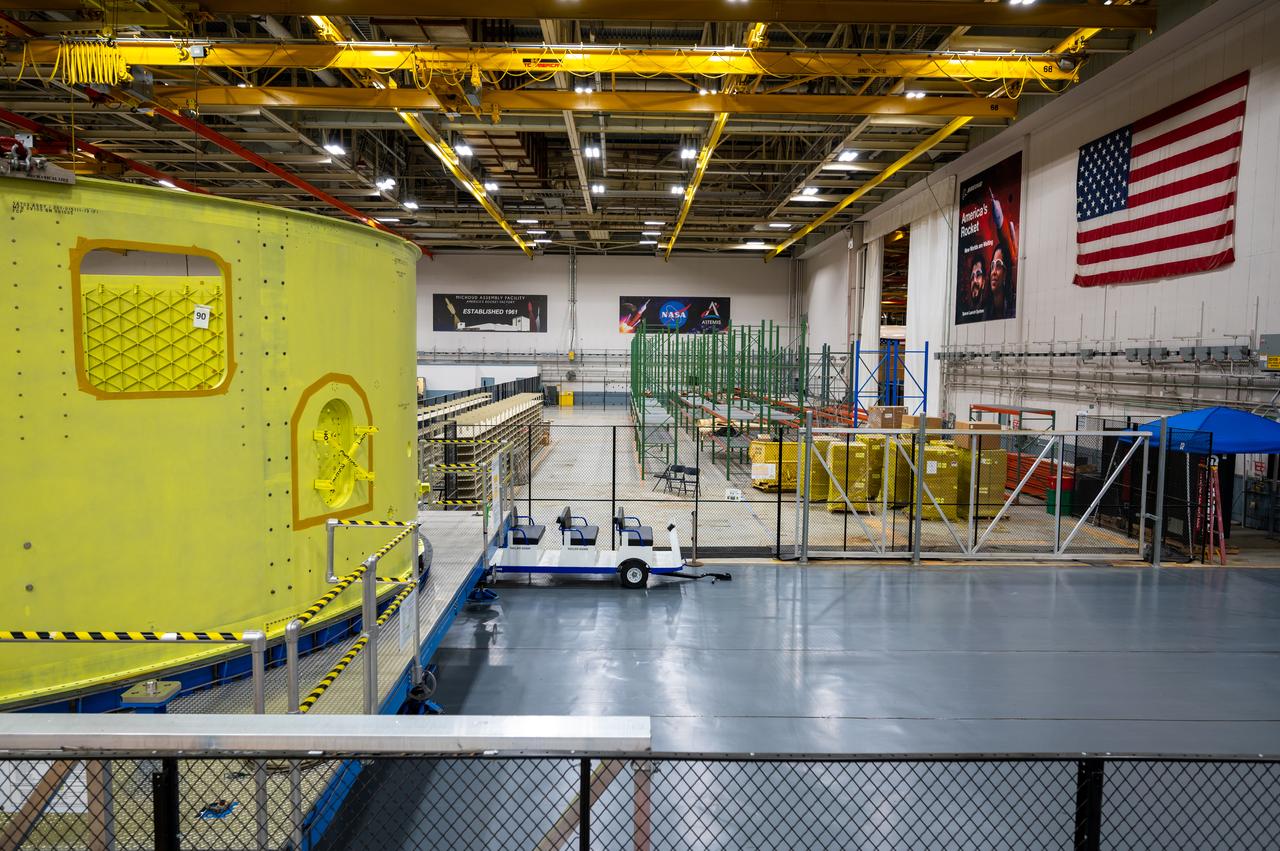

Crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the forward skirt of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility Dec. 15. Teams are preparing to apply the thermal protection system to the flight hardware, which will protect it from the extreme temperatures during launch and flight. The forward skirt is part of the core stage that will power the SLS rocket for the Artemis III mission. The forward skirt houses flight computers, cameras, and avionics.. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. When fully stacked, the forward skirt is located at the top of the core stage and connects the stage to the upper part of the rocket. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move the engine section of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis III to the VAB on November 7, 2022. This hardware makes up the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall core stage; and when complete, it will house the four RS-25 engines as well as vital systems for mounting, controlling, and delivering fuel from the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Together with its four RS-25 engines and its twin solid rocket boosters, it will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability, and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Humane Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

Crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the forward skirt of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility Dec. 15. Teams are preparing to apply the thermal protection system to the flight hardware, which will protect it from the extreme temperatures during launch and flight. The forward skirt is part of the core stage that will power the SLS rocket for the Artemis III mission. The forward skirt houses flight computers, cameras, and avionics.. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. When fully stacked, the forward skirt is located at the top of the core stage and connects the stage to the upper part of the rocket. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

Crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the forward skirt of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility Dec. 15. Teams are preparing to apply the thermal protection system to the flight hardware, which will protect it from the extreme temperatures during launch and flight. The forward skirt is part of the core stage that will power the SLS rocket for the Artemis III mission. The forward skirt houses flight computers, cameras, and avionics.. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. When fully stacked, the forward skirt is located at the top of the core stage and connects the stage to the upper part of the rocket. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

Crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the forward skirt of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility Dec. 15. Teams are preparing to apply the thermal protection system to the flight hardware, which will protect it from the extreme temperatures during launch and flight. The forward skirt is part of the core stage that will power the SLS rocket for the Artemis III mission. The forward skirt houses flight computers, cameras, and avionics.. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. When fully stacked, the forward skirt is located at the top of the core stage and connects the stage to the upper part of the rocket. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
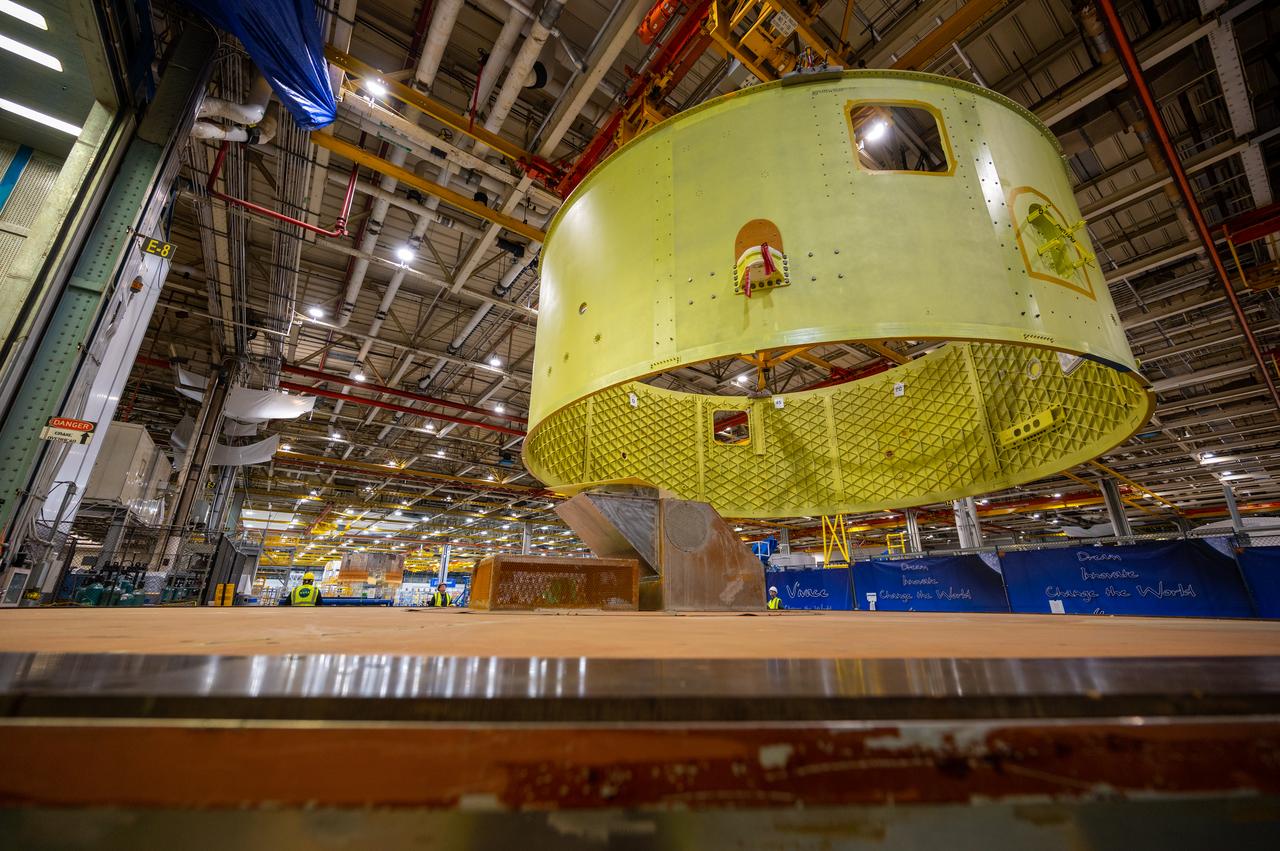

Crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the forward skirt of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility Dec. 15. Teams are preparing to apply the thermal protection system to the flight hardware, which will protect it from the extreme temperatures during launch and flight. The forward skirt is part of the core stage that will power the SLS rocket for the Artemis III mission. The forward skirt houses flight computers, cameras, and avionics.. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. When fully stacked, the forward skirt is located at the top of the core stage and connects the stage to the upper part of the rocket. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
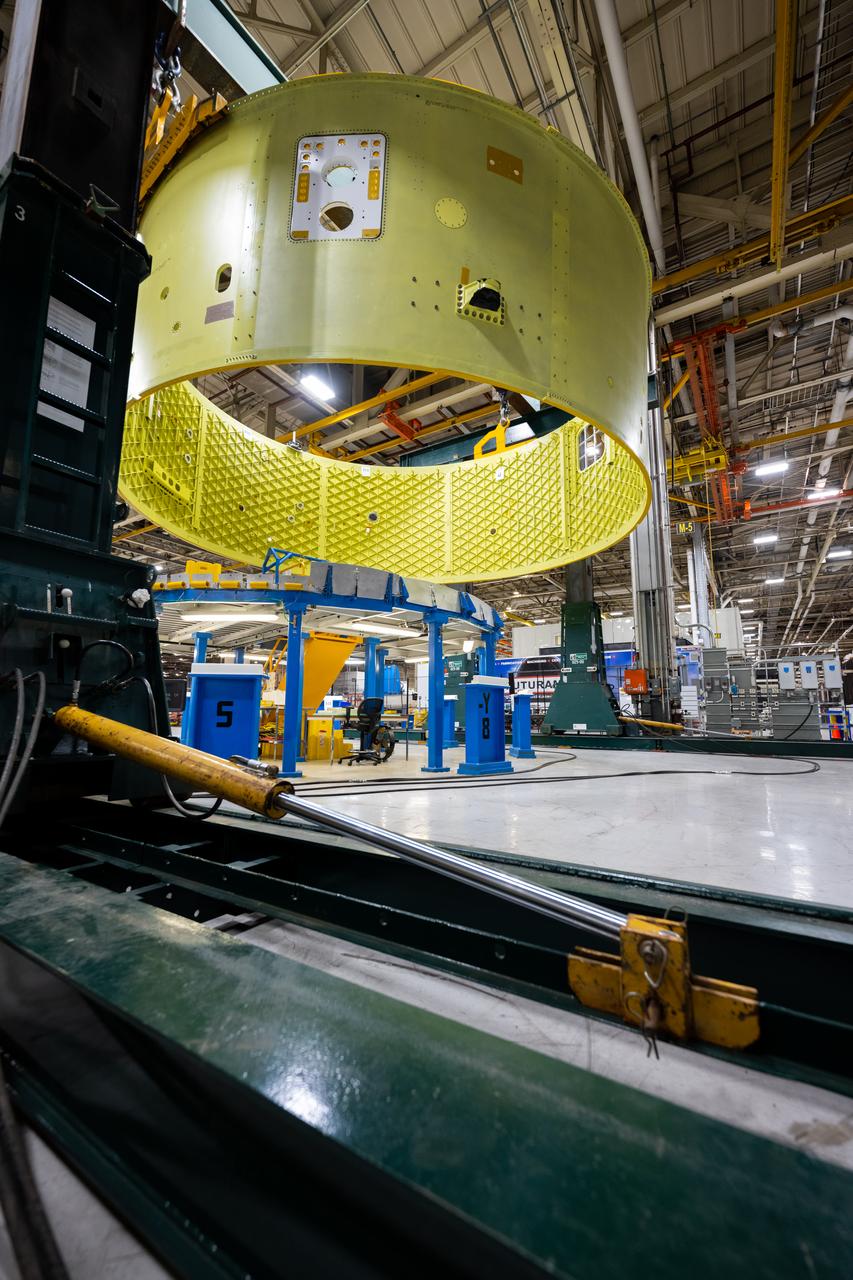

Crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the forward skirt of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility Dec. 15. Teams are preparing to apply the thermal protection system to the flight hardware, which will protect it from the extreme temperatures during launch and flight. The forward skirt is part of the core stage that will power the SLS rocket for the Artemis III mission. The forward skirt houses flight computers, cameras, and avionics.. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. When fully stacked, the forward skirt is located at the top of the core stage and connects the stage to the upper part of the rocket. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

Crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the forward skirt of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility Dec. 15. Teams are preparing to apply the thermal protection system to the flight hardware, which will protect it from the extreme temperatures during launch and flight. The forward skirt is part of the core stage that will power the SLS rocket for the Artemis III mission. The forward skirt houses flight computers, cameras, and avionics.. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. When fully stacked, the forward skirt is located at the top of the core stage and connects the stage to the upper part of the rocket. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
Crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the forward skirt of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility Dec. 15. Teams are preparing to apply the thermal protection system to the flight hardware, which will protect it from the extreme temperatures during launch and flight. The forward skirt is part of the core stage that will power the SLS rocket for the Artemis III mission. The forward skirt houses flight computers, cameras, and avionics.. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. When fully stacked, the forward skirt is located at the top of the core stage and connects the stage to the upper part of the rocket. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
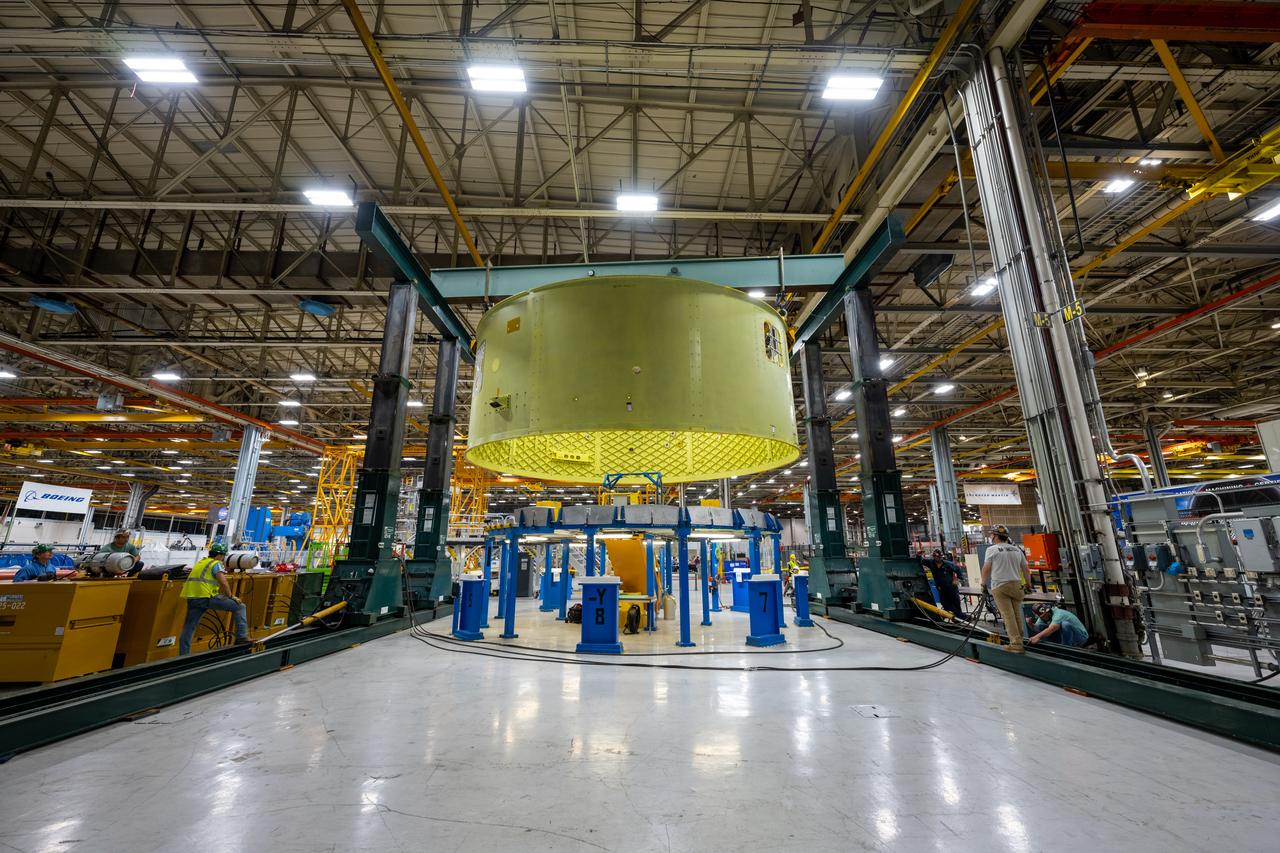

Crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the forward skirt of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility Dec. 15. Teams are preparing to apply the thermal protection system to the flight hardware, which will protect it from the extreme temperatures during launch and flight. The forward skirt is part of the core stage that will power the SLS rocket for the Artemis III mission. The forward skirt houses flight computers, cameras, and avionics.. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. When fully stacked, the forward skirt is located at the top of the core stage and connects the stage to the upper part of the rocket. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

Crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the forward skirt of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility Dec. 15. Teams are preparing to apply the thermal protection system to the flight hardware, which will protect it from the extreme temperatures during launch and flight. The forward skirt is part of the core stage that will power the SLS rocket for the Artemis III mission. The forward skirt houses flight computers, cameras, and avionics.. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. When fully stacked, the forward skirt is located at the top of the core stage and connects the stage to the upper part of the rocket. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

Crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the forward skirt of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility Dec. 15. Teams are preparing to apply the thermal protection system to the flight hardware, which will protect it from the extreme temperatures during launch and flight. The forward skirt is part of the core stage that will power the SLS rocket for the Artemis III mission. The forward skirt houses flight computers, cameras, and avionics.. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. When fully stacked, the forward skirt is located at the top of the core stage and connects the stage to the upper part of the rocket. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

Crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the forward skirt of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility Dec. 15. Teams are preparing to apply the thermal protection system to the flight hardware, which will protect it from the extreme temperatures during launch and flight. The forward skirt is part of the core stage that will power the SLS rocket for the Artemis III mission. The forward skirt houses flight computers, cameras, and avionics.. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. When fully stacked, the forward skirt is located at the top of the core stage and connects the stage to the upper part of the rocket. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

Crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the forward skirt of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility Dec. 15. Teams are preparing to apply the thermal protection system to the flight hardware, which will protect it from the extreme temperatures during launch and flight. The forward skirt is part of the core stage that will power the SLS rocket for the Artemis III mission. The forward skirt houses flight computers, cameras, and avionics.. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. When fully stacked, the forward skirt is located at the top of the core stage and connects the stage to the upper part of the rocket. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move the engine section of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis III to the VAB on November 7, 2022. This hardware makes up the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall core stage; and when complete, it will house the four RS-25 engines as well as vital systems for mounting, controlling, and delivering fuel from the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Together with its four RS-25 engines and its twin solid rocket boosters, it will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability, and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Humane Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

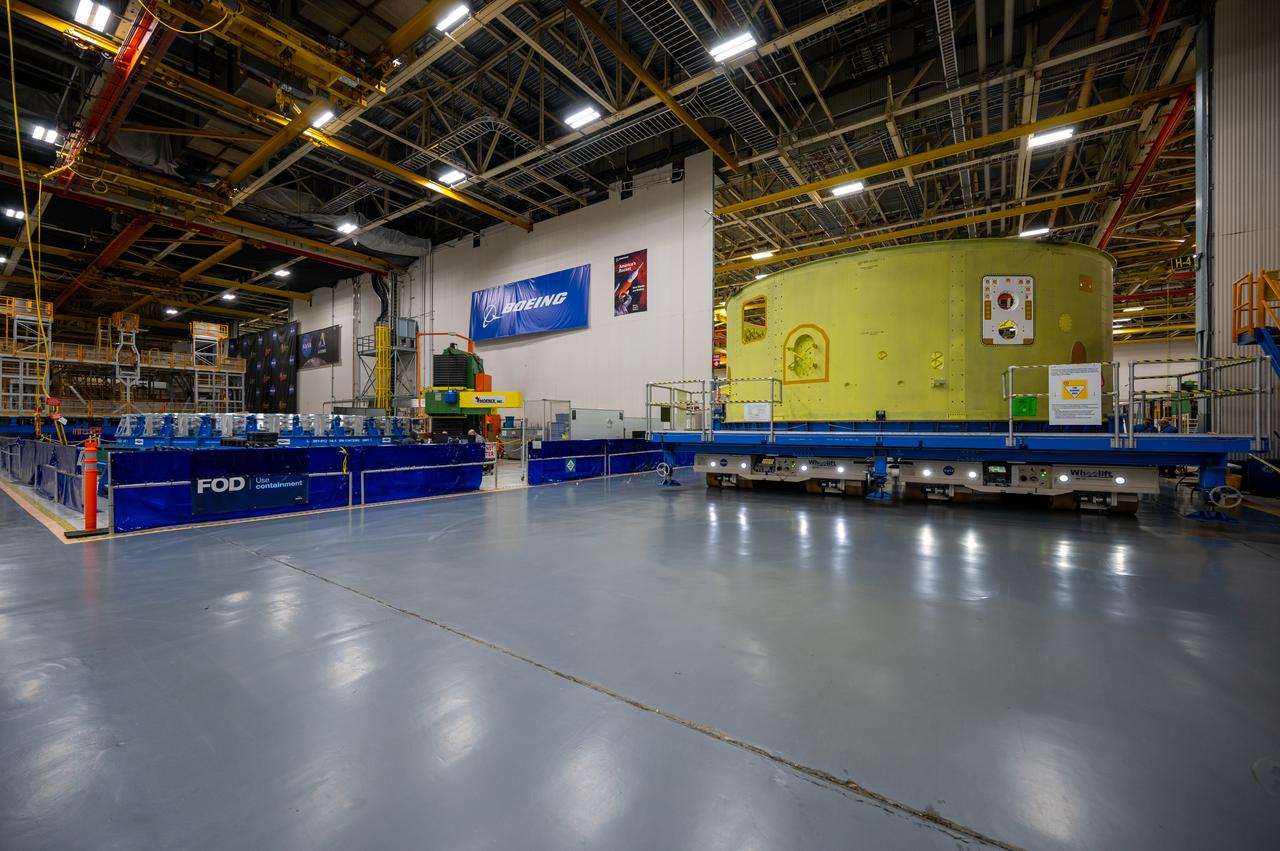
Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the liquid hydrogen tank of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Cell A for white light scans of the tank’s dimensions in preparation of multiple join activities throughout the manufacturing process. The flight hardware will be used for Artemis III, one of the first crewed Artemis missions. The liquid hydrogen tank holds 537,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen cooled to minus 432 degrees Fahrenheit and is the largest of the five elements that make up the rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage. The liquid hydrogen tank is situated between the core stage’s intertank and engine section. The liquid hydrogen hardware, along with the liquid oxygen tank, will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the core stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to launch NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the liquid hydrogen tank of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Cell A for white light scans of the tank’s dimensions in preparation of multiple join activities throughout the manufacturing process. The flight hardware will be used for Artemis III, one of the first crewed Artemis missions. The liquid hydrogen tank holds 537,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen cooled to minus 432 degrees Fahrenheit and is the largest of the five elements that make up the rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage. The liquid hydrogen tank is situated between the core stage’s intertank and engine section. The liquid hydrogen hardware, along with the liquid oxygen tank, will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the core stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to launch NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the liquid hydrogen tank of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Cell A for white light scans of the tank’s dimensions in preparation of multiple join activities throughout the manufacturing process. The flight hardware will be used for Artemis III, one of the first crewed Artemis missions. The liquid hydrogen tank holds 537,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen cooled to minus 432 degrees Fahrenheit and is the largest of the five elements that make up the rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage. The liquid hydrogen tank is situated between the core stage’s intertank and engine section. The liquid hydrogen hardware, along with the liquid oxygen tank, will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the core stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to launch NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the liquid hydrogen tank of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Cell A for white light scans of the tank’s dimensions in preparation of multiple join activities throughout the manufacturing process. The flight hardware will be used for Artemis III, one of the first crewed Artemis missions. The liquid hydrogen tank holds 537,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen cooled to minus 432 degrees Fahrenheit and is the largest of the five elements that make up the rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage. The liquid hydrogen tank is situated between the core stage’s intertank and engine section. The liquid hydrogen hardware, along with the liquid oxygen tank, will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the core stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to launch NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the liquid hydrogen tank of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Cell A for white light scans of the tank’s dimensions in preparation of multiple join activities throughout the manufacturing process. The flight hardware will be used for Artemis III, one of the first crewed Artemis missions. The liquid hydrogen tank holds 537,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen cooled to minus 432 degrees Fahrenheit and is the largest of the five elements that make up the rocket’s 212-foot-tall core stage. The liquid hydrogen tank is situated between the core stage’s intertank and engine section. The liquid hydrogen hardware, along with the liquid oxygen tank, will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the core stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to launch NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
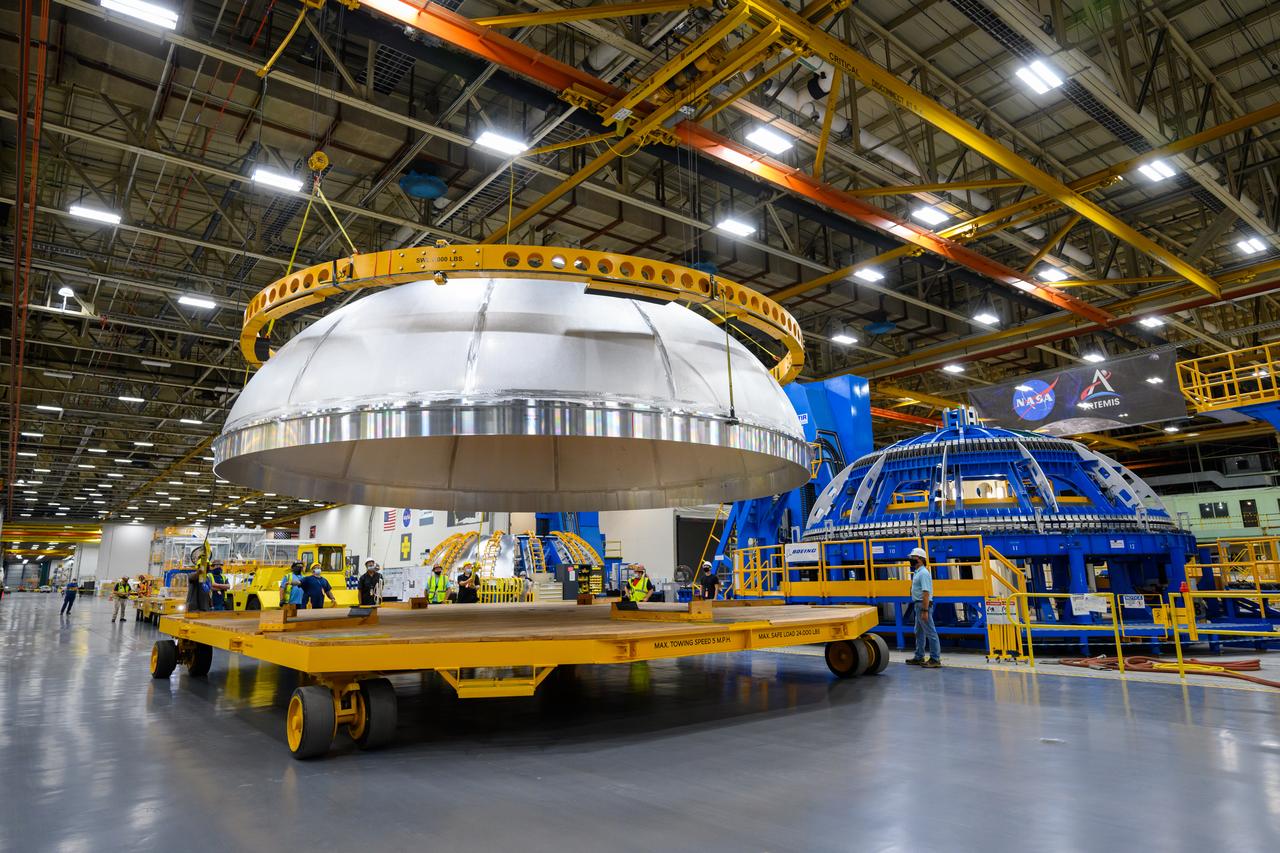

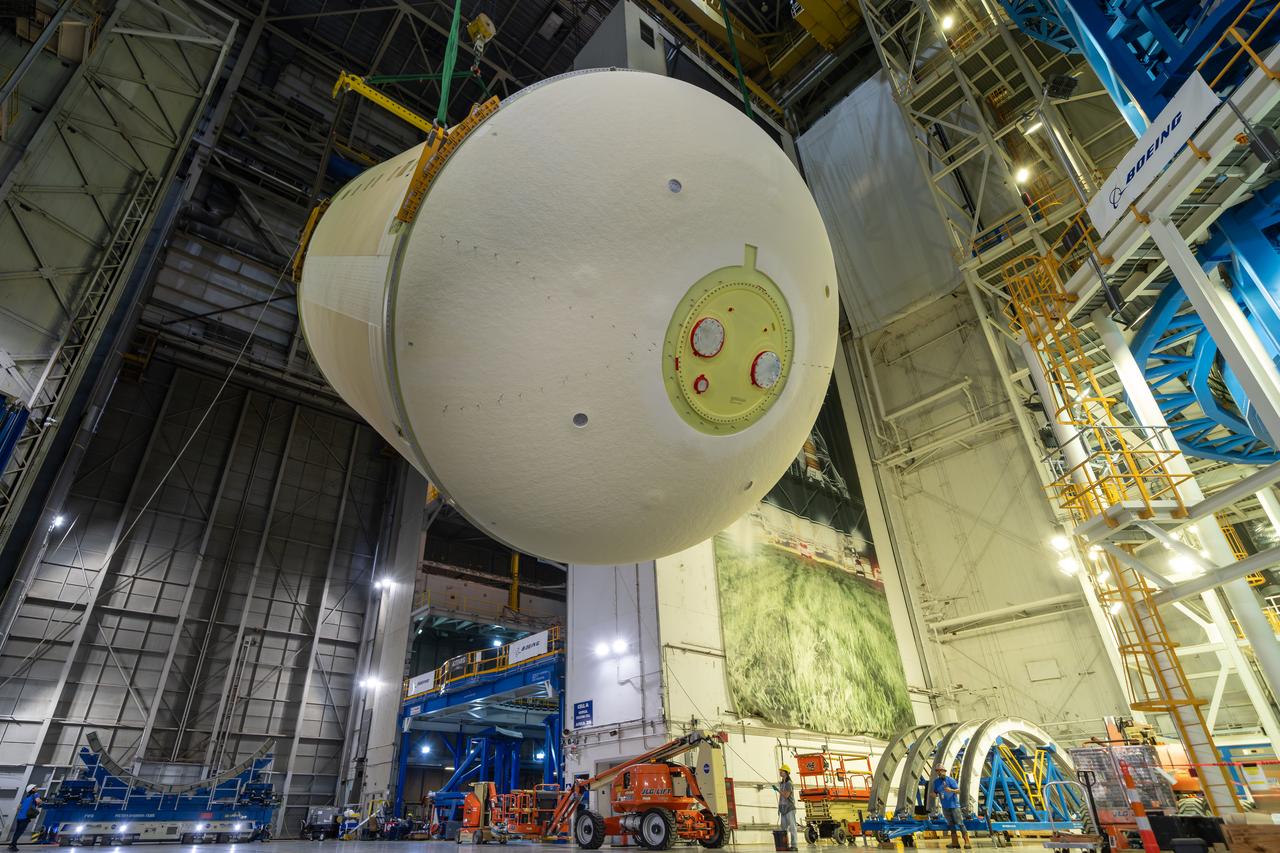
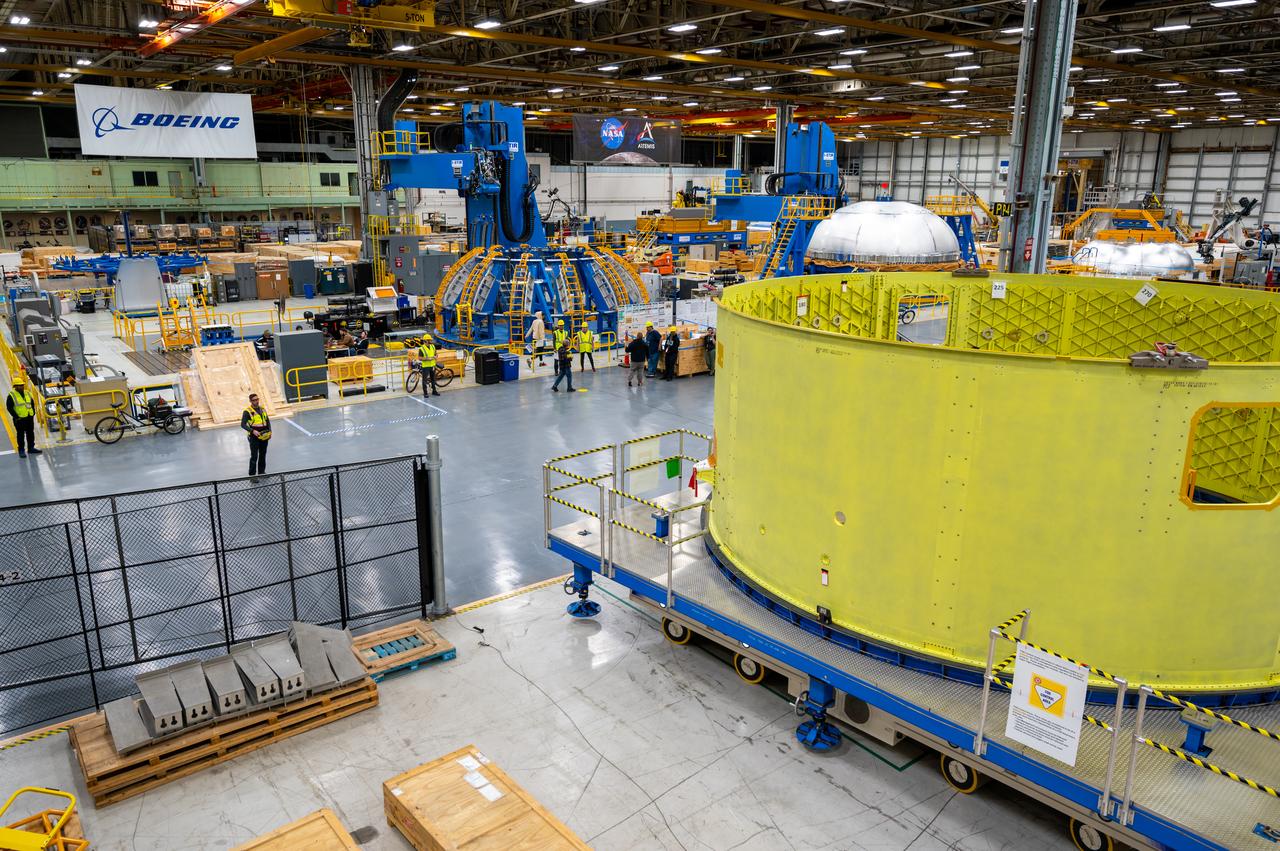
Teams completed the welding of the Artemis III core stage liquid oxygen tank dome at the NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the dome, which is the top of the tank. The dome was moved to an assembly area where it will be loaded into a robotic welder that will join it with the forward barrel to create half of the liquid oxygen tank. Later another barrel and dome will be added to complete the entire tank. The Space Launch System (SLS) core stage liquid oxygen tank holds 196,000 gallons of super-cooled liquid propellant that serves as one of the propellants for the four RS-25 engines. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The liquid oxygen and the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon.
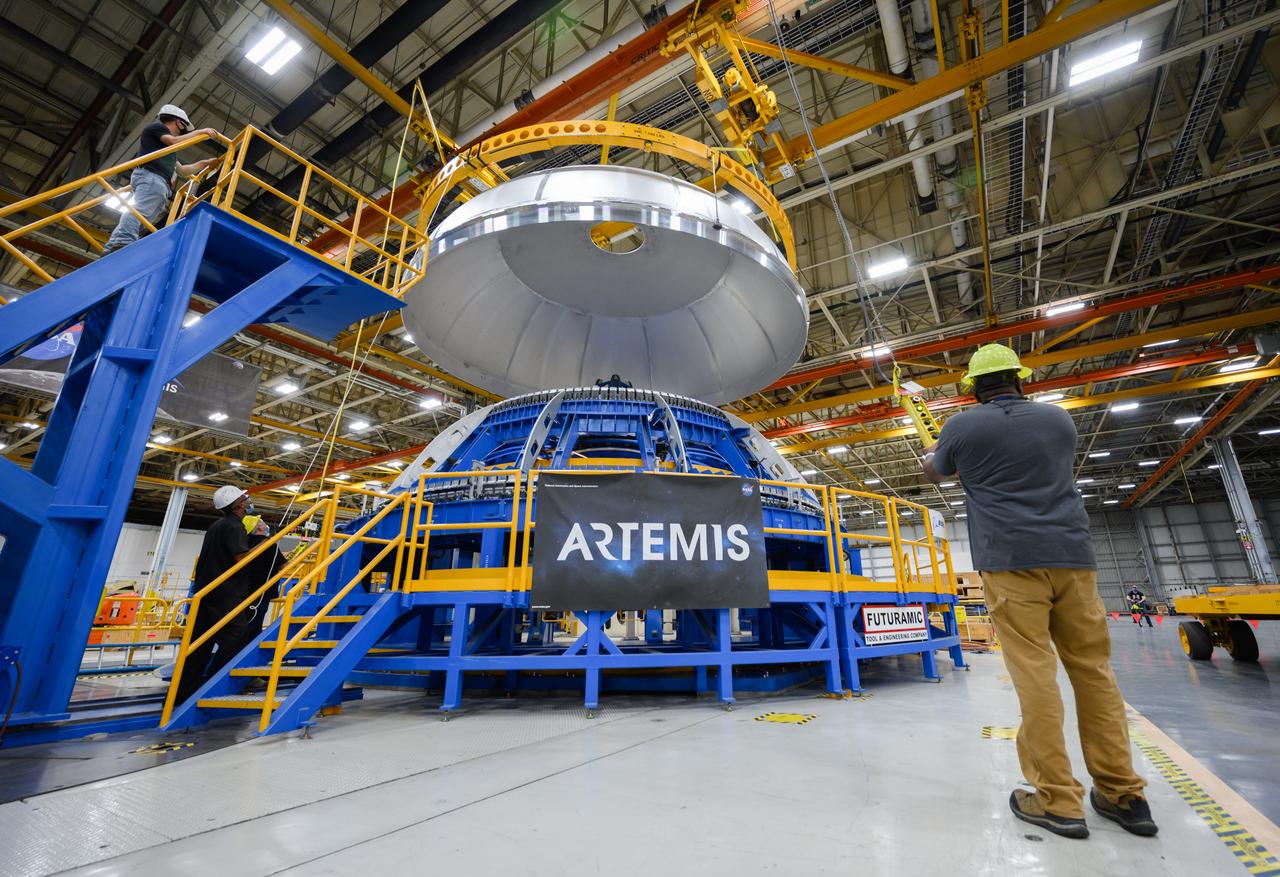

Teams completed the welding of the Artemis III core stage liquid oxygen tank dome at the NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the dome, which is the top of the tank. The dome was moved to an assembly area where it will be loaded into a robotic welder that will join it with the forward barrel to create half of the liquid oxygen tank. Later another barrel and dome will be added to complete the entire tank. The Space Launch System (SLS) core stage liquid oxygen tank holds 196,000 gallons of super-cooled liquid propellant that serves as one of the propellants for the four RS-25 engines. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The liquid oxygen and the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon.
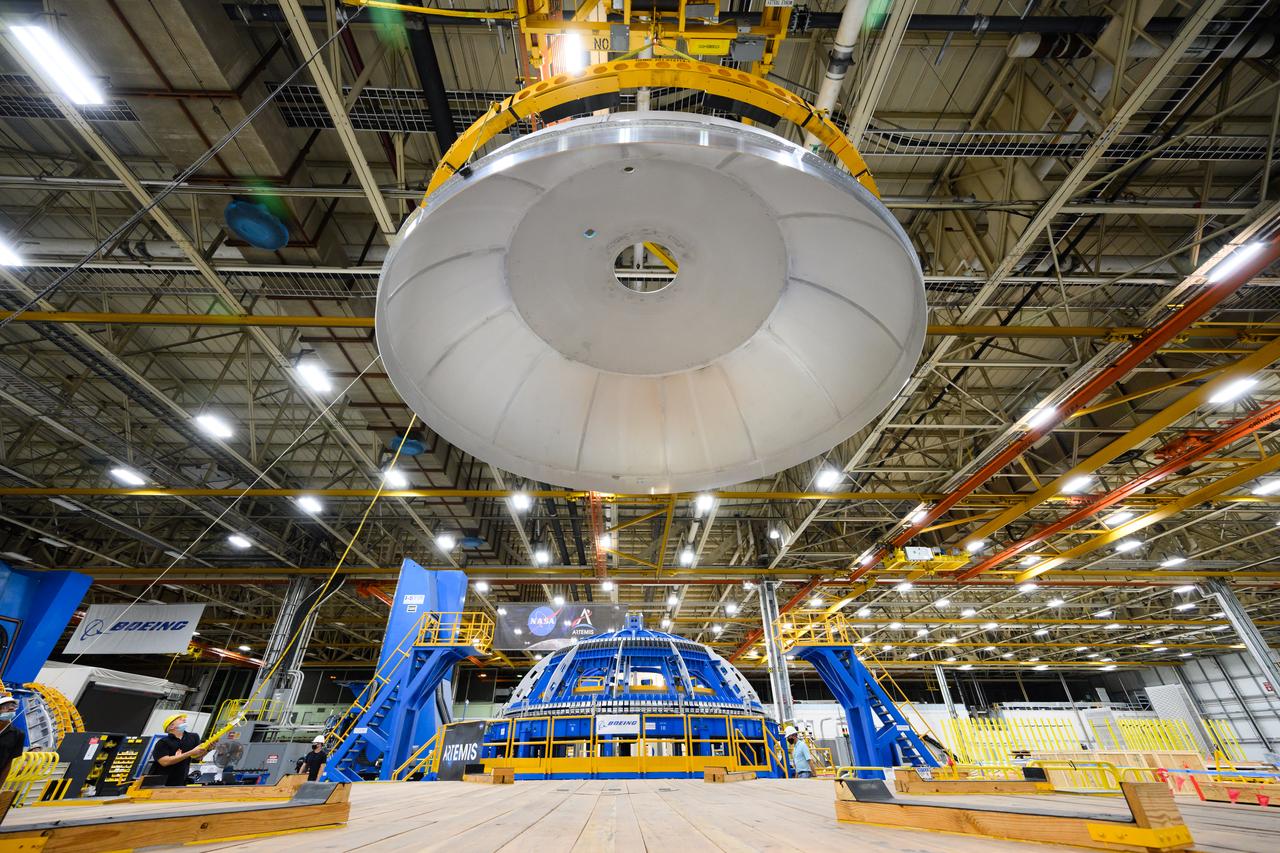

Teams completed the welding of the Artemis III core stage liquid oxygen tank dome at the NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the dome, which is the top of the tank. The dome was moved to an assembly area where it will be loaded into a robotic welder that will join it with the forward barrel to create half of the liquid oxygen tank. Later another barrel and dome will be added to complete the entire tank. The Space Launch System (SLS) core stage liquid oxygen tank holds 196,000 gallons of super-cooled liquid propellant that serves as one of the propellants for the four RS-25 engines. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The liquid oxygen and the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon.
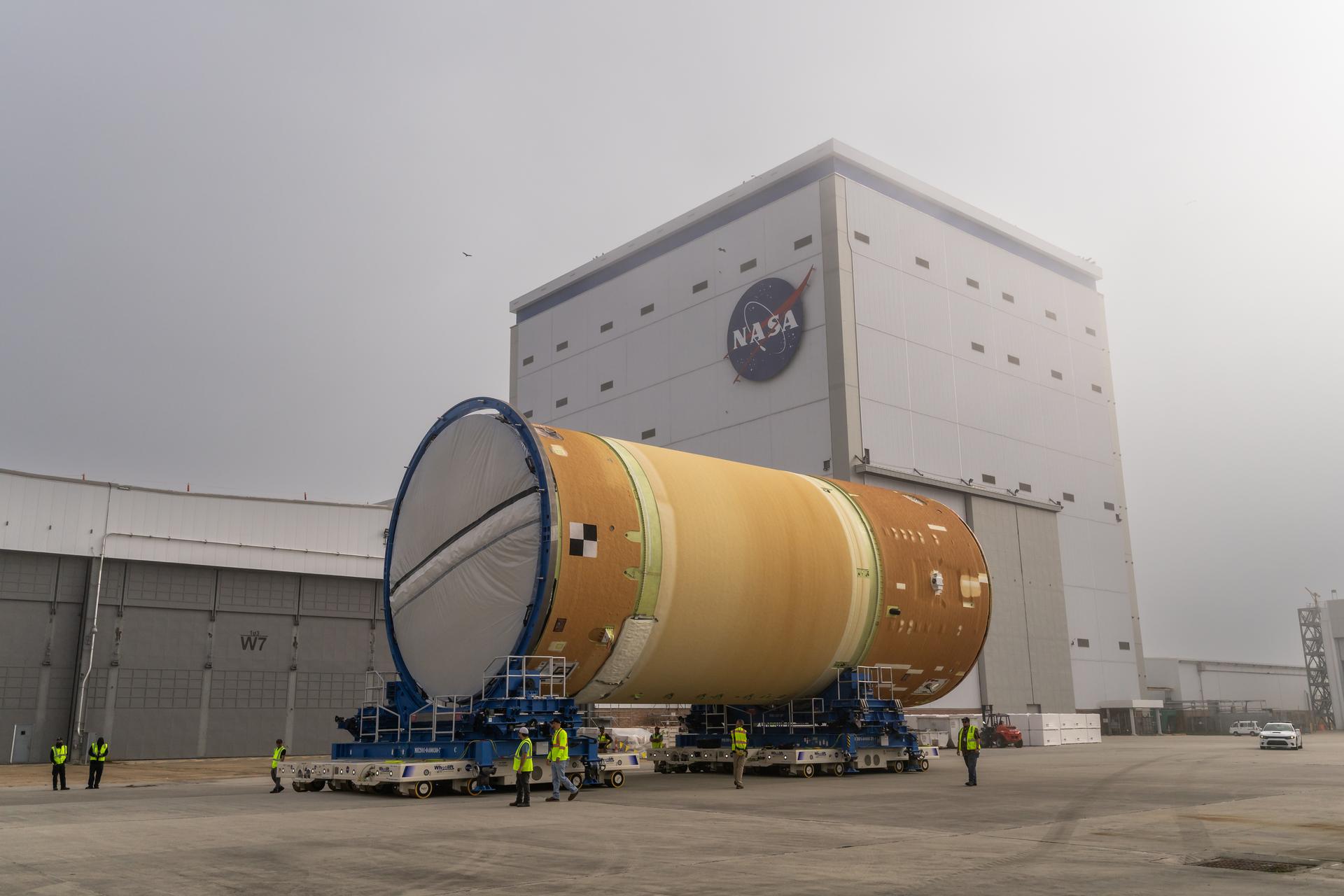

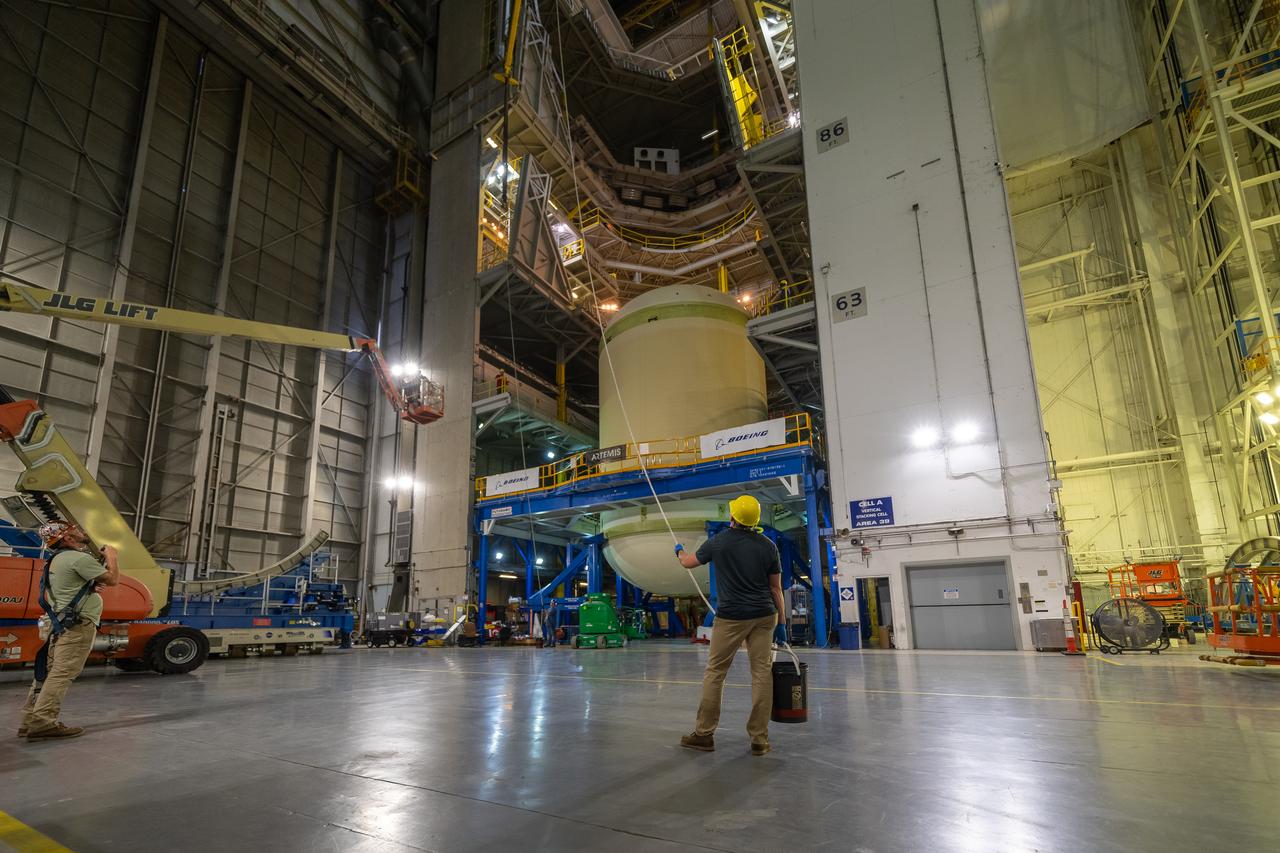
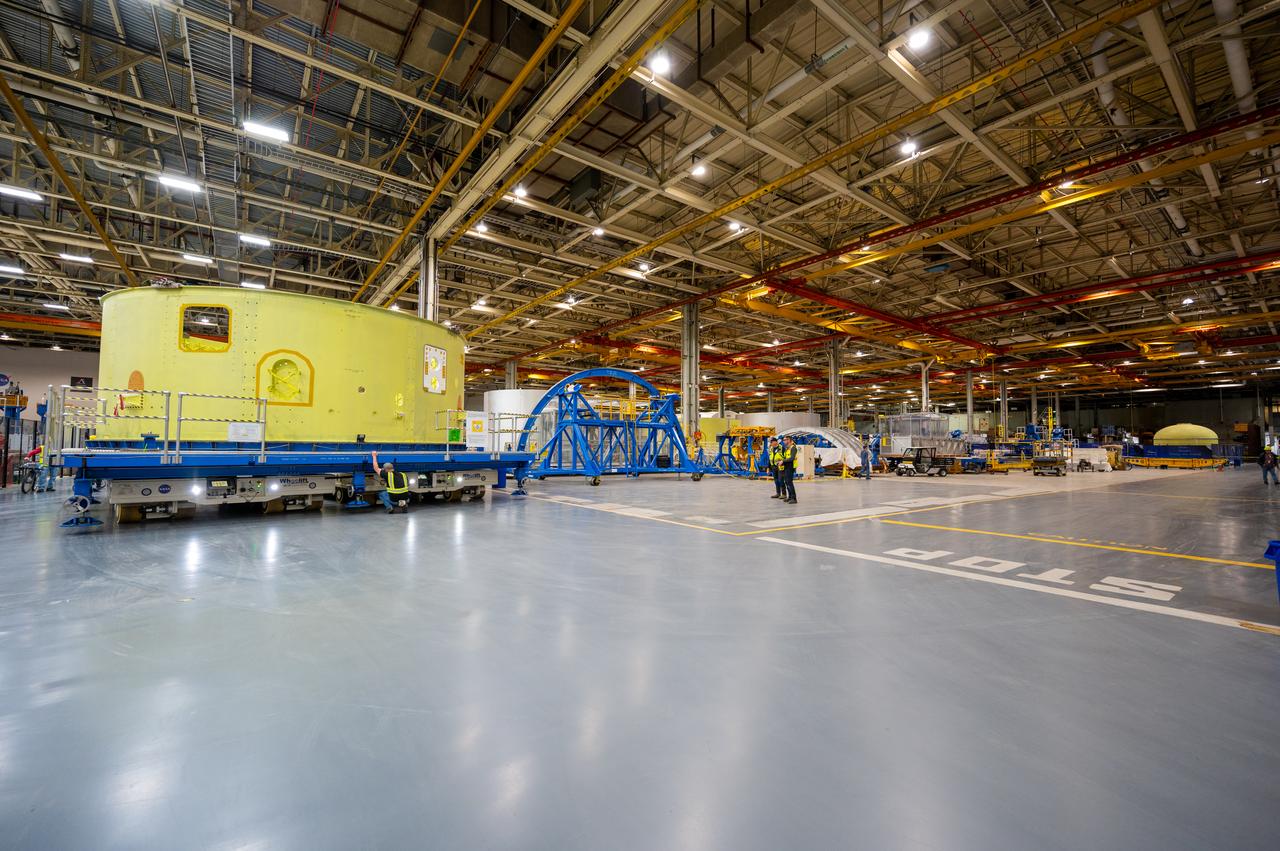
Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, lift the forward-joined flight hardware for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket out of a stacking cell in the vertical assembly building on Dec. 19, 2025. The forward join, which consists of the intertank, liquid oxygen tank, and forward skirt, will be used on the core stage slated for NASA’s Artemis III mission. Teams moved the flight hardware from the cell and set it atop self-propelled mobile transporters. The article was brought to the factory’s final assembly area on Dec. 27, 2025 where it will be mated to the core stage’s previously joined liquid hydrogen tank and undergo further integration. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
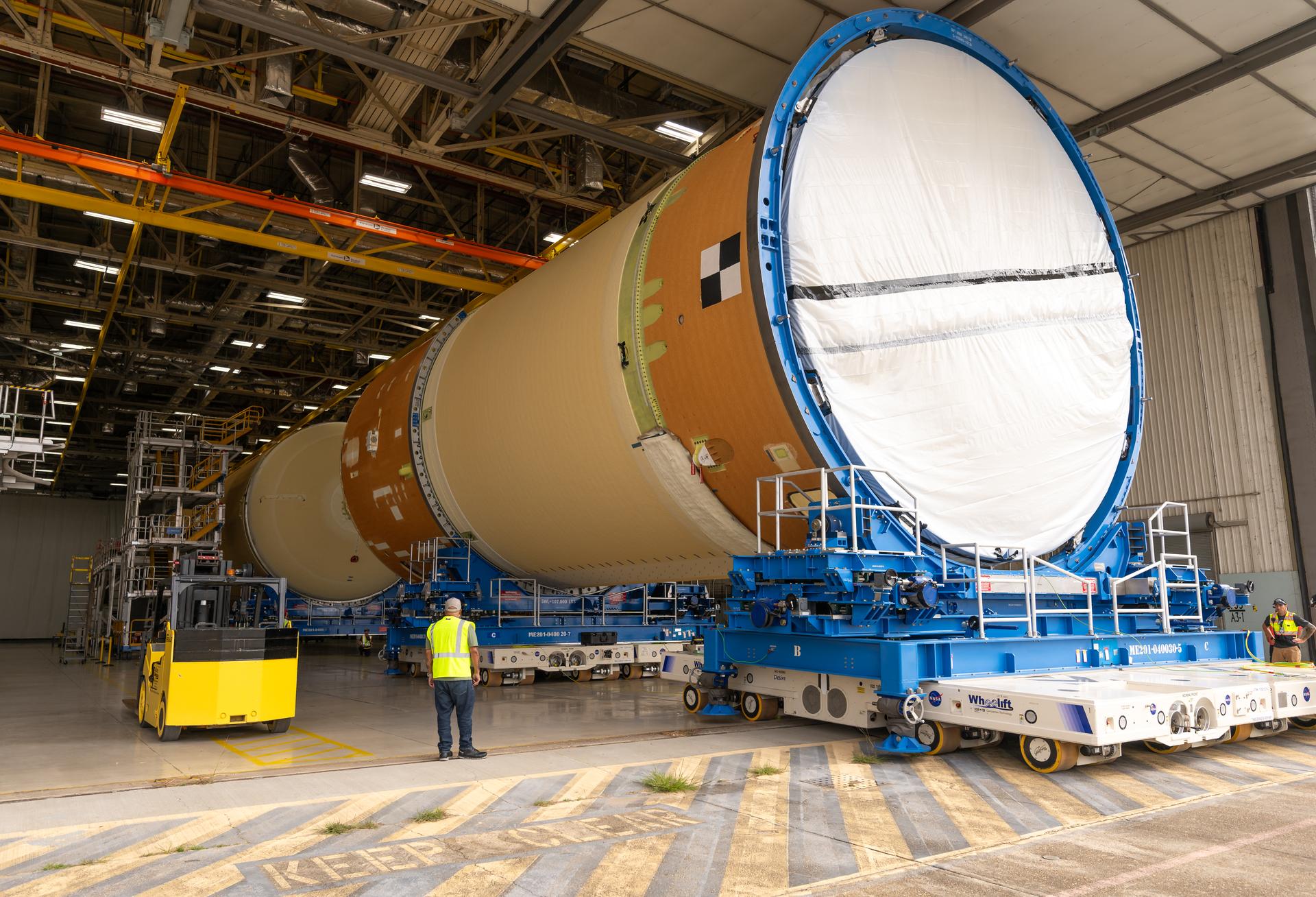

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, lift the forward-joined flight hardware for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket out of a stacking cell in the vertical assembly building on Dec. 19, 2025. The forward join, which consists of the intertank, liquid oxygen tank, and forward skirt, will be used on the core stage slated for NASA’s Artemis III mission. Teams moved the flight hardware from the cell and set it atop self-propelled mobile transporters. The article was brought to the factory’s final assembly area on Dec. 27, 2025 where it will be mated to the core stage’s previously joined liquid hydrogen tank and undergo further integration. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
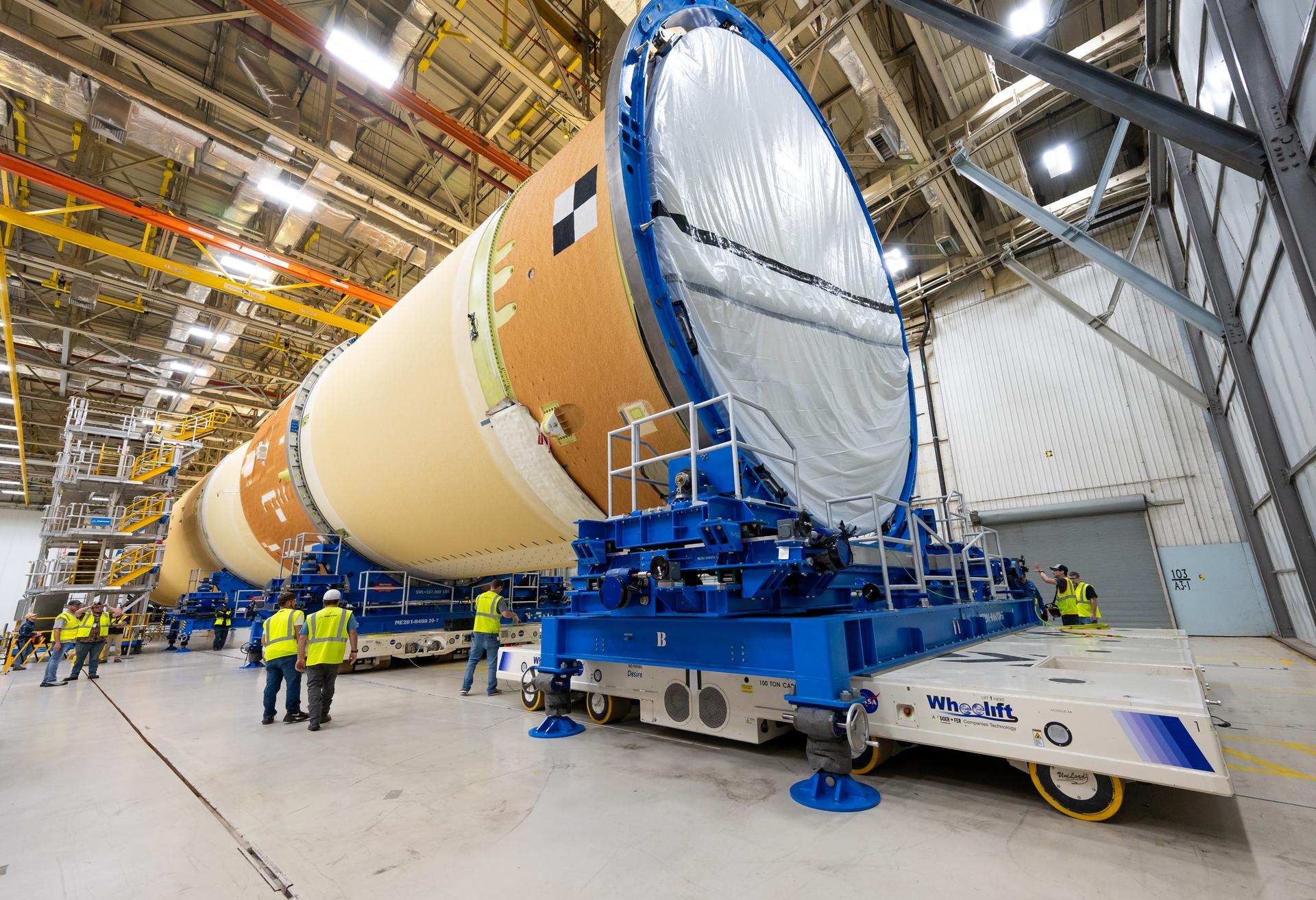

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, lift the forward-joined flight hardware for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket out of a stacking cell in the vertical assembly building on Dec. 19, 2025. The forward join, which consists of the intertank, liquid oxygen tank, and forward skirt, will be used on the core stage slated for NASA’s Artemis III mission. Teams moved the flight hardware from the cell and set it atop self-propelled mobile transporters. The article was brought to the factory’s final assembly area on Dec. 27, 2025 where it will be mated to the core stage’s previously joined liquid hydrogen tank and undergo further integration. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
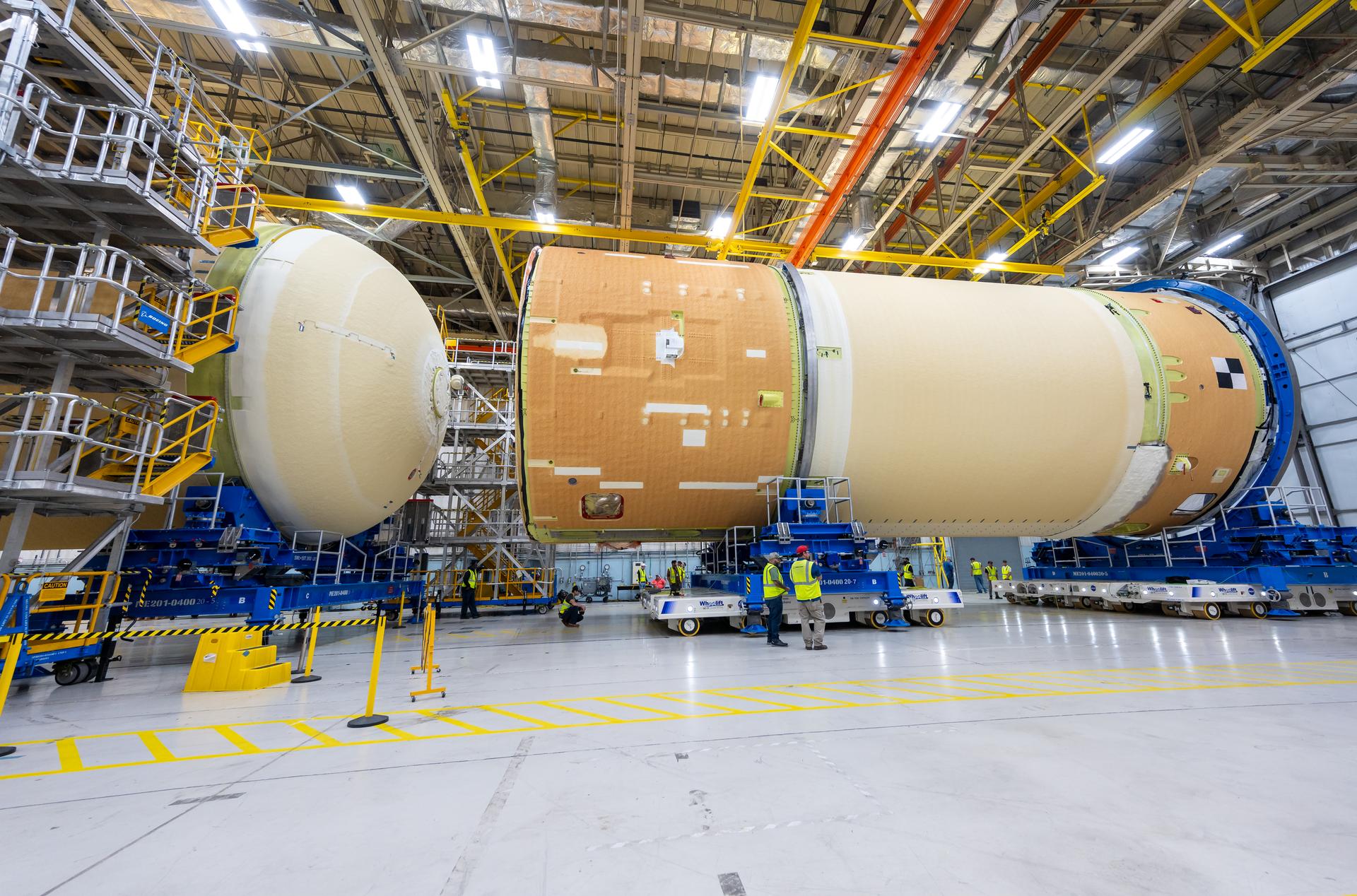

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, lift the forward-joined flight hardware for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket out of a stacking cell in the vertical assembly building on Dec. 19, 2025. The forward join, which consists of the intertank, liquid oxygen tank, and forward skirt, will be used on the core stage slated for NASA’s Artemis III mission. Teams moved the flight hardware from the cell and set it atop self-propelled mobile transporters. The article was brought to the factory’s final assembly area on Dec. 27, 2025 where it will be mated to the core stage’s previously joined liquid hydrogen tank and undergo further integration. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
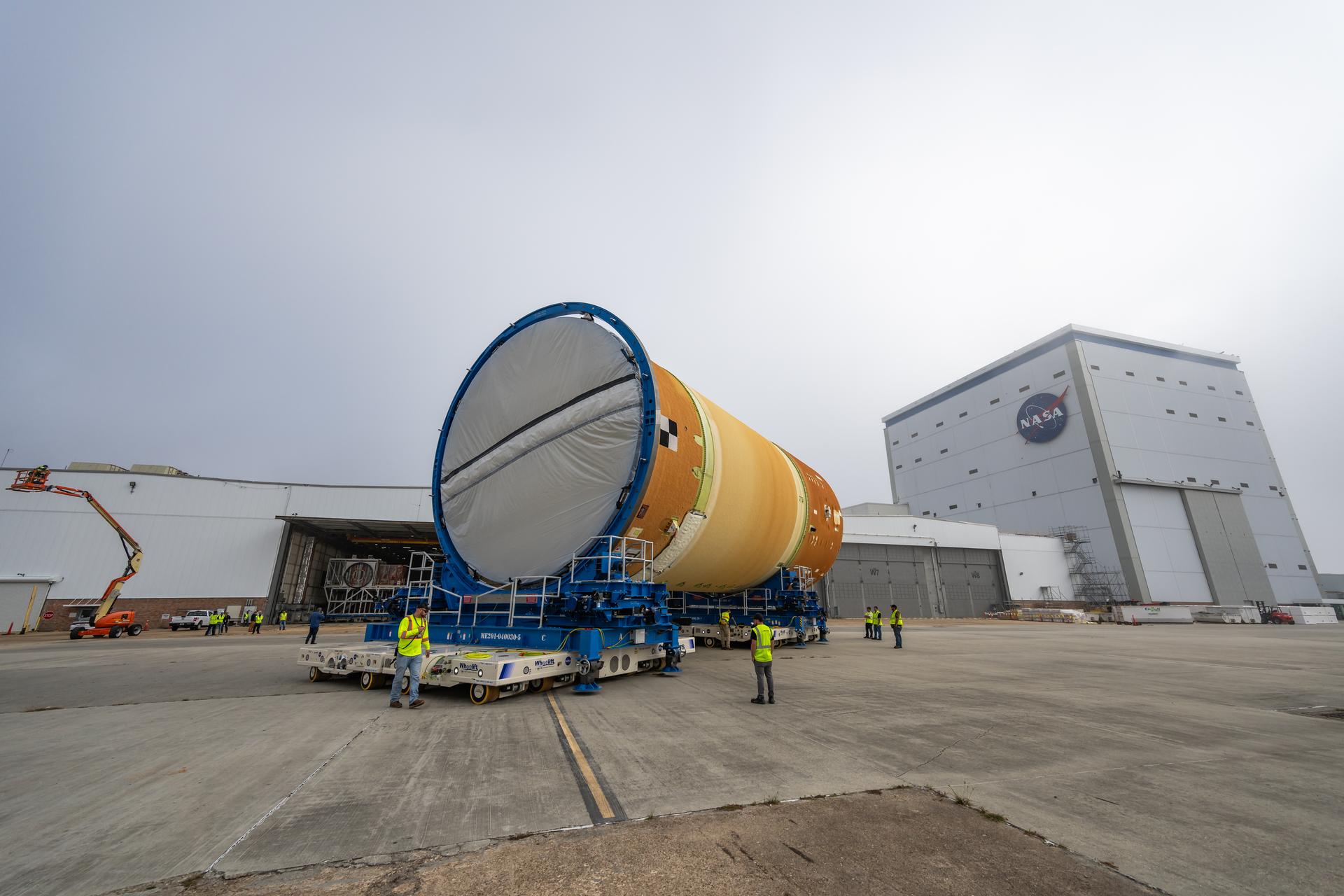

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, lift the forward-joined flight hardware for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket out of a stacking cell in the vertical assembly building on Dec. 19, 2025. The forward join, which consists of the intertank, liquid oxygen tank, and forward skirt, will be used on the core stage slated for NASA’s Artemis III mission. Teams moved the flight hardware from the cell and set it atop self-propelled mobile transporters. The article was brought to the factory’s final assembly area on Dec. 27, 2025 where it will be mated to the core stage’s previously joined liquid hydrogen tank and undergo further integration. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
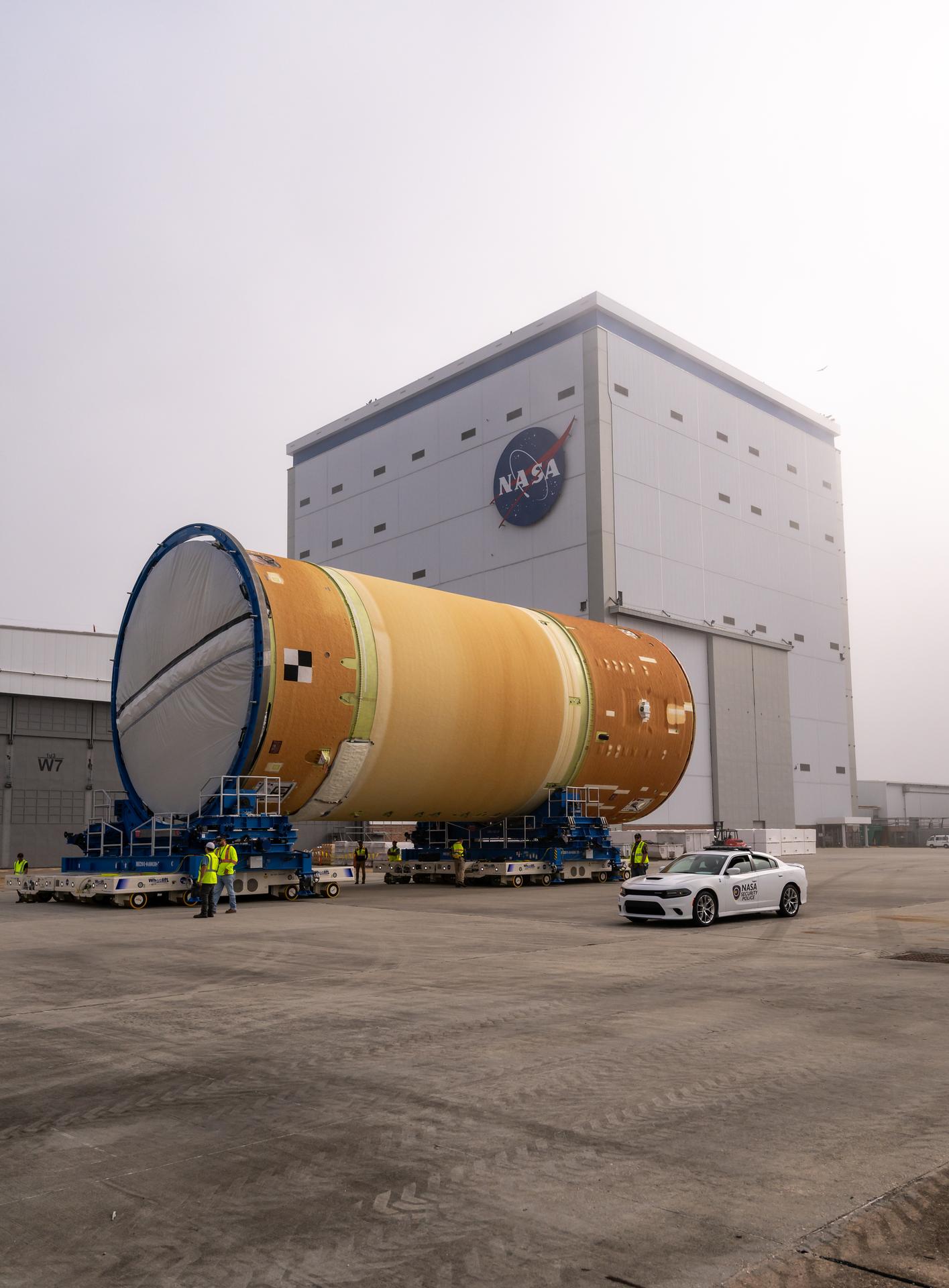

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, lift the forward-joined flight hardware for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket out of a stacking cell in the vertical assembly building on Dec. 19, 2025. The forward join, which consists of the intertank, liquid oxygen tank, and forward skirt, will be used on the core stage slated for NASA’s Artemis III mission. Teams moved the flight hardware from the cell and set it atop self-propelled mobile transporters. The article was brought to the factory’s final assembly area on Dec. 27, 2025 where it will be mated to the core stage’s previously joined liquid hydrogen tank and undergo further integration. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
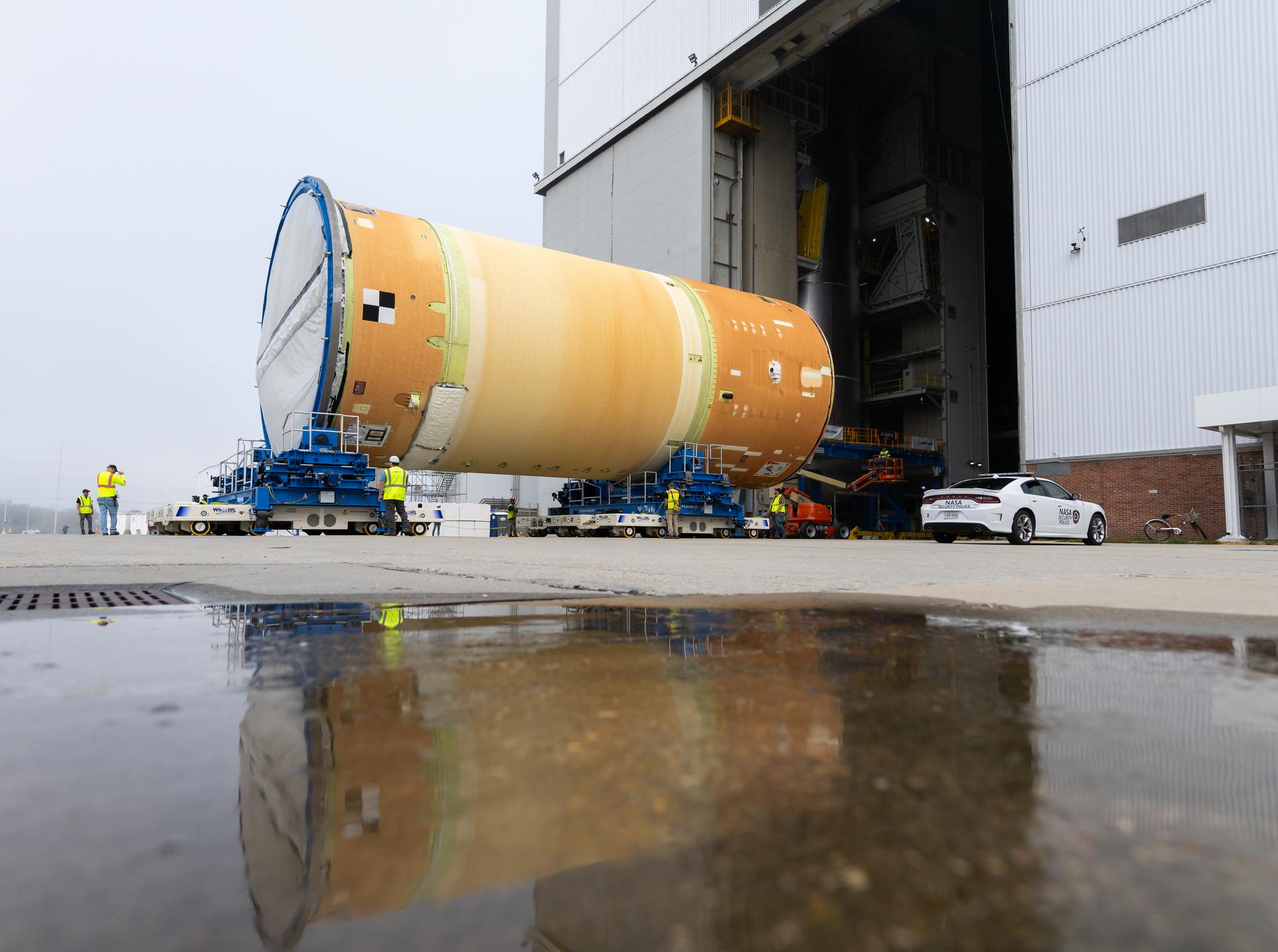

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, lift the forward-joined flight hardware for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket out of a stacking cell in the vertical assembly building on Dec. 19, 2025. The forward join, which consists of the intertank, liquid oxygen tank, and forward skirt, will be used on the core stage slated for NASA’s Artemis III mission. Teams moved the flight hardware from the cell and set it atop self-propelled mobile transporters. The article was brought to the factory’s final assembly area on Dec. 27, 2025 where it will be mated to the core stage’s previously joined liquid hydrogen tank and undergo further integration. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
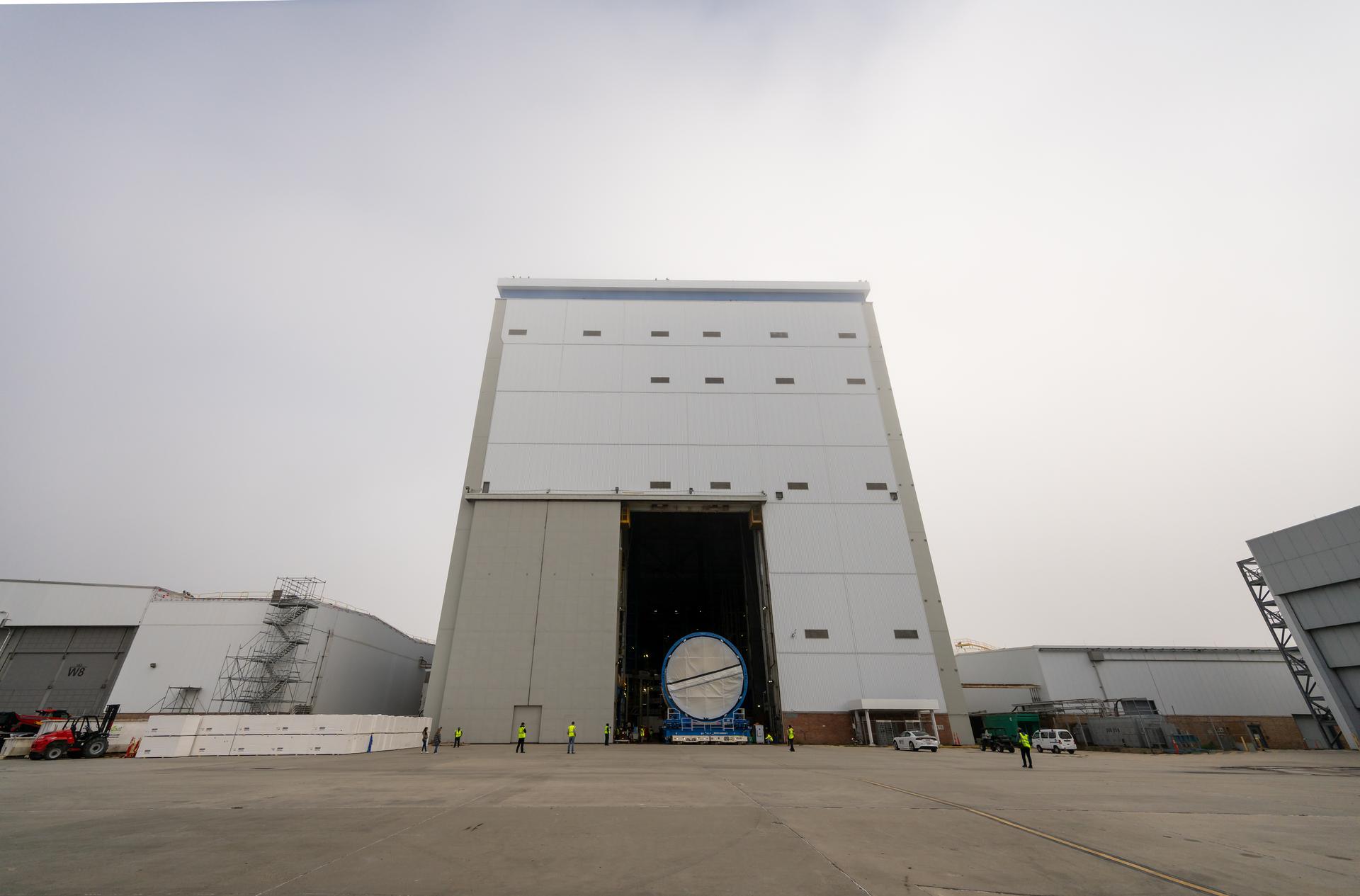

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, lift the forward-joined flight hardware for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket out of a stacking cell in the vertical assembly building on Dec. 19, 2025. The forward join, which consists of the intertank, liquid oxygen tank, and forward skirt, will be used on the core stage slated for NASA’s Artemis III mission. Teams moved the flight hardware from the cell and set it atop self-propelled mobile transporters. The article was brought to the factory’s final assembly area on Dec. 27, 2025 where it will be mated to the core stage’s previously joined liquid hydrogen tank and undergo further integration. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
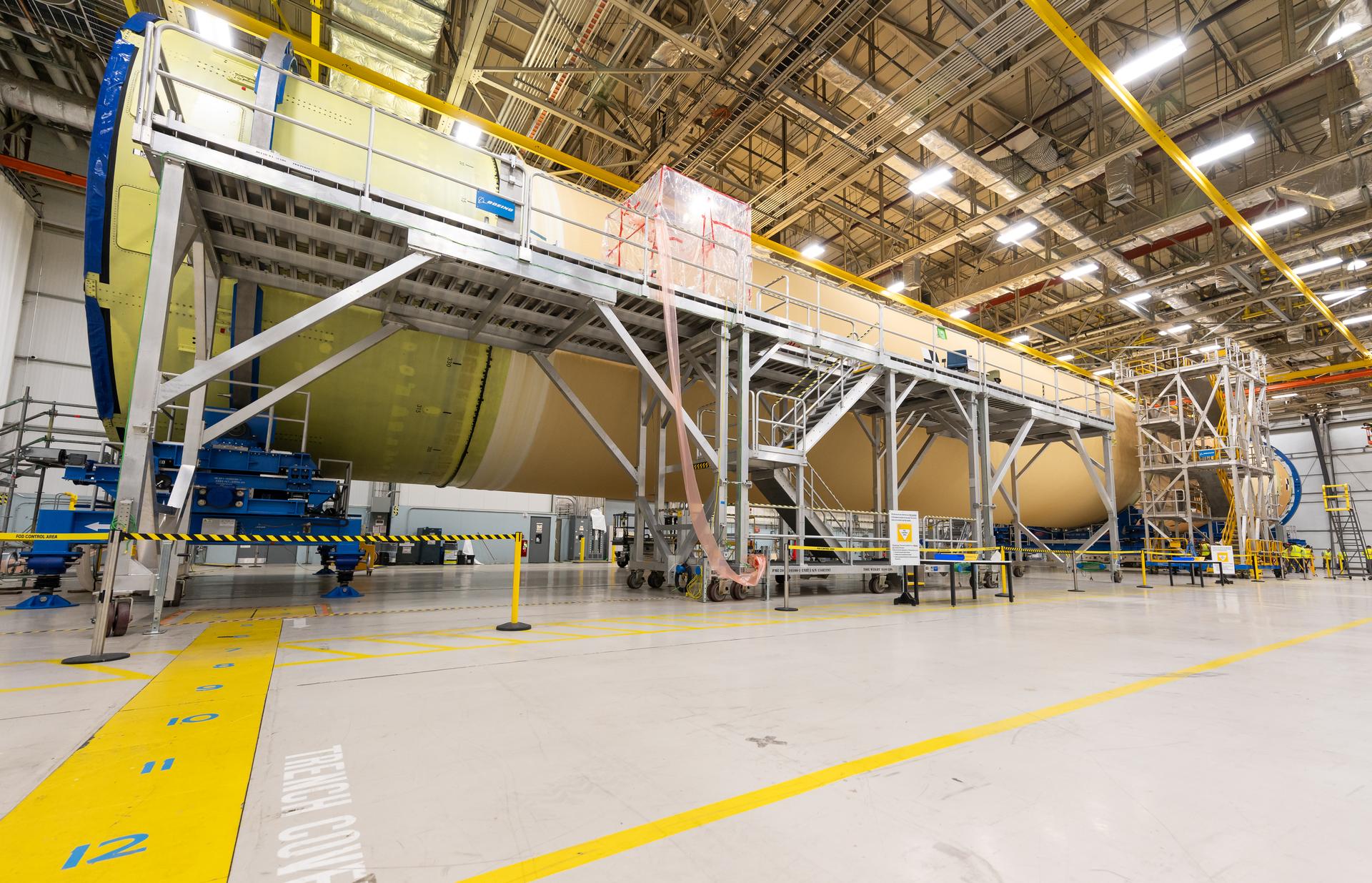

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, lift the forward-joined flight hardware for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket out of a stacking cell in the vertical assembly building on Dec. 19, 2025. The forward join, which consists of the intertank, liquid oxygen tank, and forward skirt, will be used on the core stage slated for NASA’s Artemis III mission. Teams moved the flight hardware from the cell and set it atop self-propelled mobile transporters. The article was brought to the factory’s final assembly area on Dec. 27, 2025 where it will be mated to the core stage’s previously joined liquid hydrogen tank and undergo further integration. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.

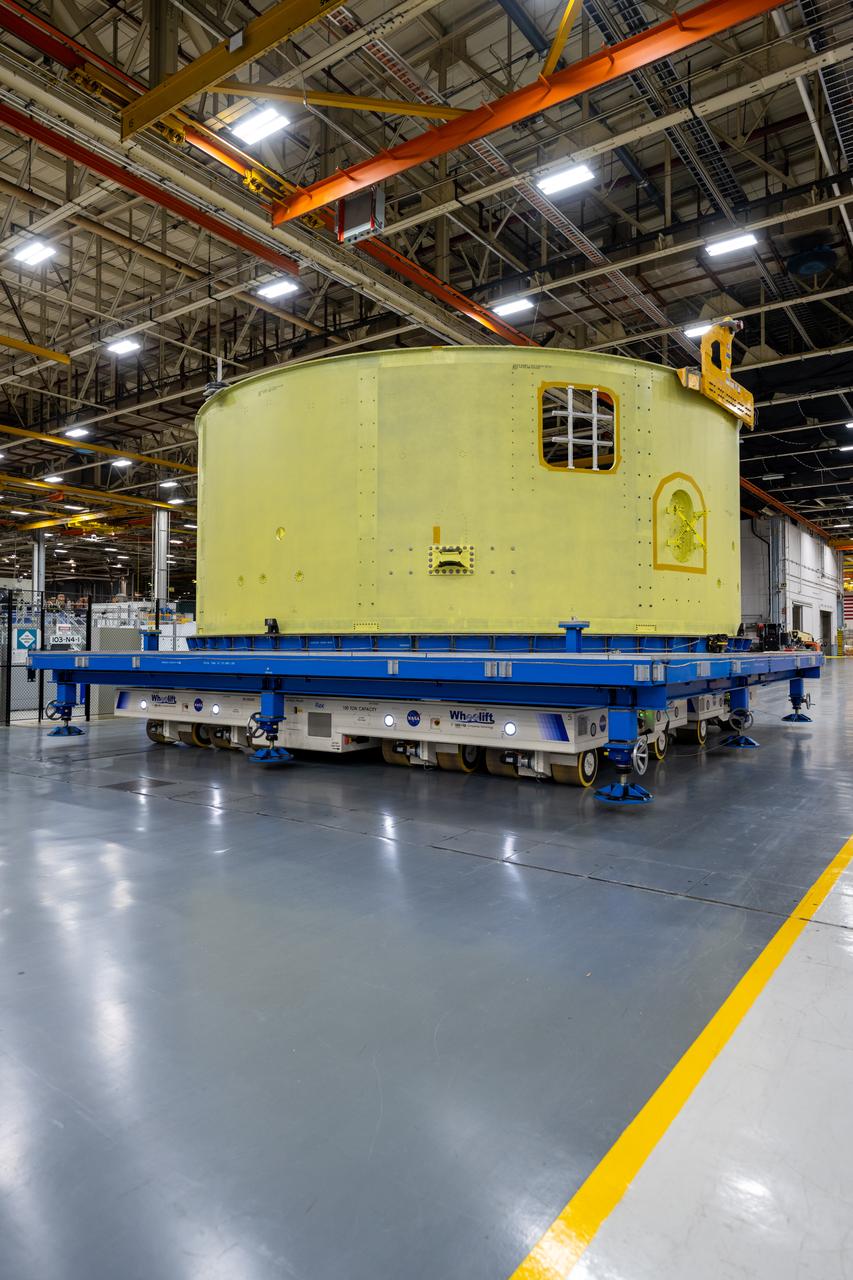
This imagery shows how technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility moved the aft dome of the liquid oxygen tank for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the next phase of production inside the Vertical Assembly center Dec. 18. The dome will form part of the core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis III mission. Engineers rotate the dome to attach it to the previously joined forward dome and aft barrel segments using friction-stir welding. The liquid oxygen tank is one of five major components that make up the SLS rocket’s core stage. Together with the forward skirt, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, engine section, along with the four RS-25 engines at its base, the 212-foot core stage will help power NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon.

This imagery shows how technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility moved the aft dome of the liquid oxygen tank for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the next phase of production inside the Vertical Assembly center Dec. 18. The dome will form part of the core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis III mission. Engineers rotate the dome to attach it to the previously joined forward dome and aft barrel segments using friction-stir welding. The liquid oxygen tank is one of five major components that make up the SLS rocket’s core stage. Together with the forward skirt, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, engine section, along with the four RS-25 engines at its base, the 212-foot core stage will help power NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon.

This imagery shows how technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility moved the aft dome of the liquid oxygen tank for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the next phase of production inside the Vertical Assembly center Dec. 18. The dome will form part of the core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis III mission. Engineers rotate the dome to attach it to the previously joined forward dome and aft barrel segments using friction-stir welding. The liquid oxygen tank is one of five major components that make up the SLS rocket’s core stage. Together with the forward skirt, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, engine section, along with the four RS-25 engines at its base, the 212-foot core stage will help power NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon.

This imagery shows how technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility moved the aft dome of the liquid oxygen tank for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the next phase of production inside the Vertical Assembly center Dec. 18. The dome will form part of the core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis III mission. Engineers rotate the dome to attach it to the previously joined forward dome and aft barrel segments using friction-stir welding. The liquid oxygen tank is one of five major components that make up the SLS rocket’s core stage. Together with the forward skirt, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, engine section, along with the four RS-25 engines at its base, the 212-foot core stage will help power NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon.

This imagery shows how technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility moved the aft dome of the liquid oxygen tank for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the next phase of production inside the Vertical Assembly center Dec. 18. The dome will form part of the core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis III mission. Engineers rotate the dome to attach it to the previously joined forward dome and aft barrel segments using friction-stir welding. The liquid oxygen tank is one of five major components that make up the SLS rocket’s core stage. Together with the forward skirt, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, engine section, along with the four RS-25 engines at its base, the 212-foot core stage will help power NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon.

This imagery shows how technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility moved the aft dome of the liquid oxygen tank for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the next phase of production inside the Vertical Assembly center Dec. 18. The dome will form part of the core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis III mission. Engineers rotate the dome to attach it to the previously joined forward dome and aft barrel segments using friction-stir welding. The liquid oxygen tank is one of five major components that make up the SLS rocket’s core stage. Together with the forward skirt, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, engine section, along with the four RS-25 engines at its base, the 212-foot core stage will help power NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon.

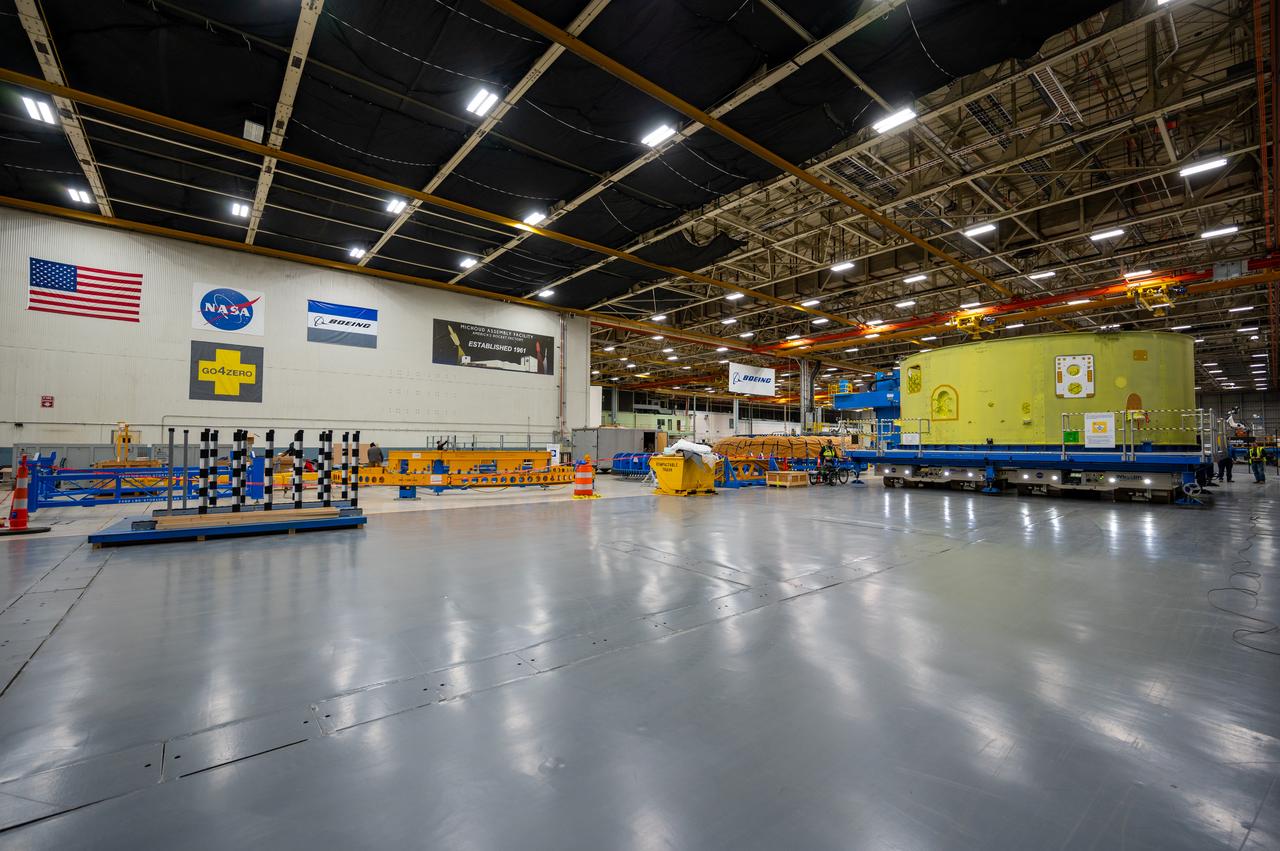
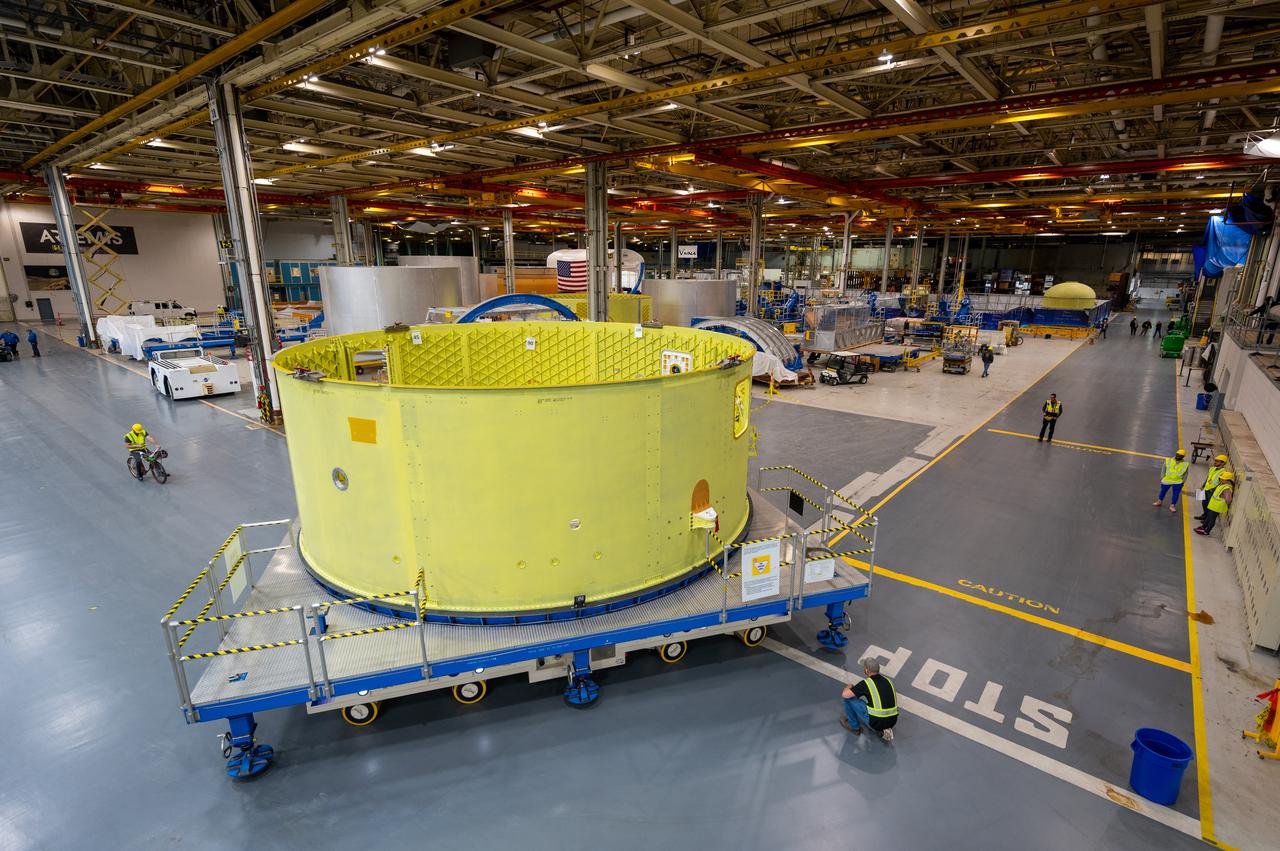
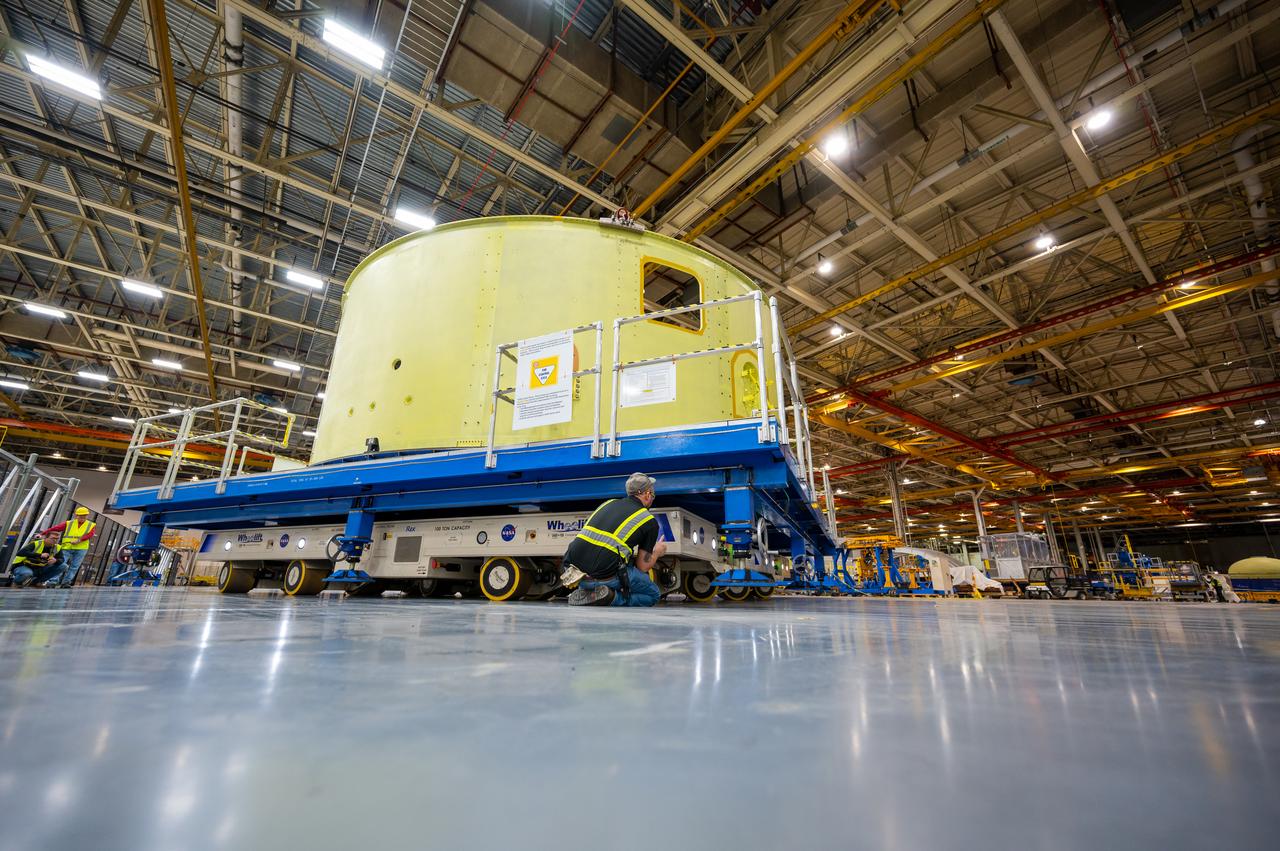
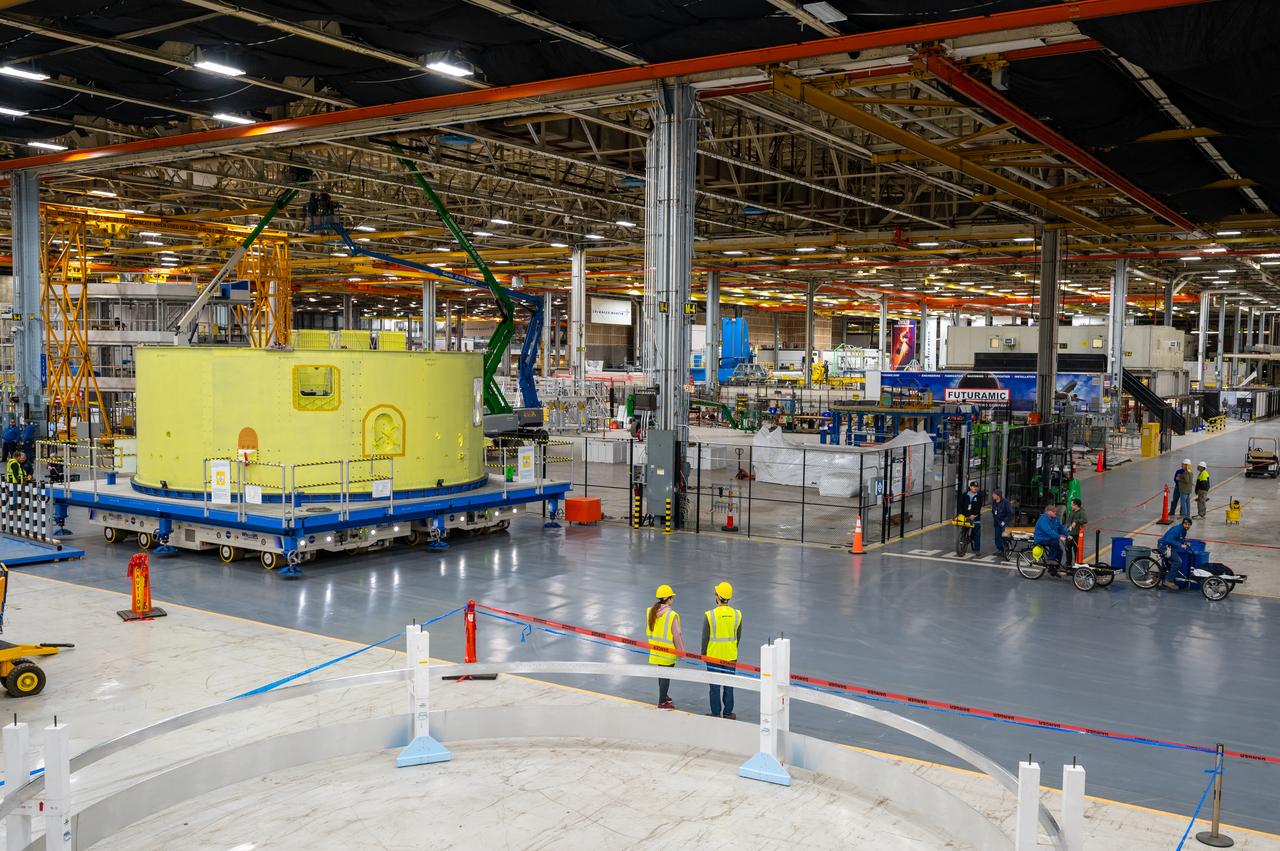
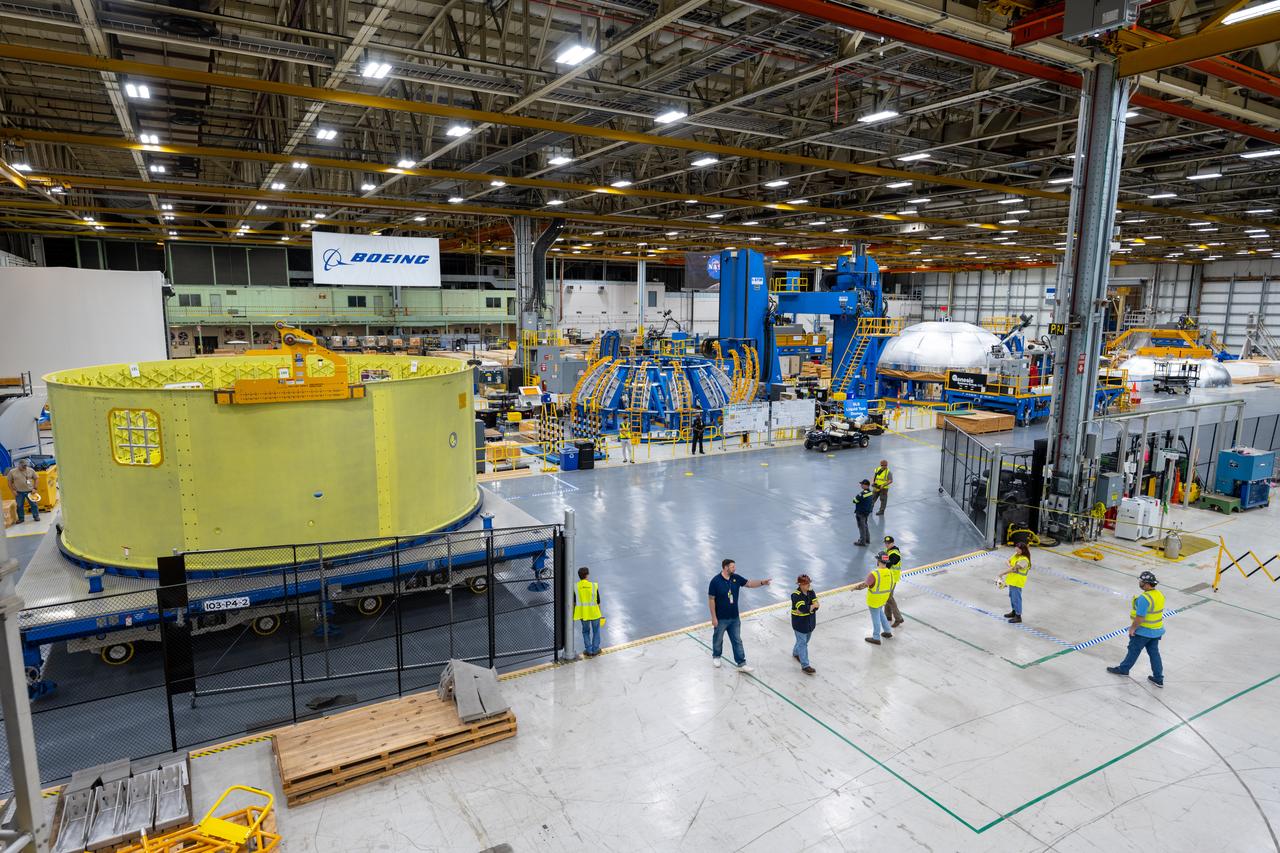
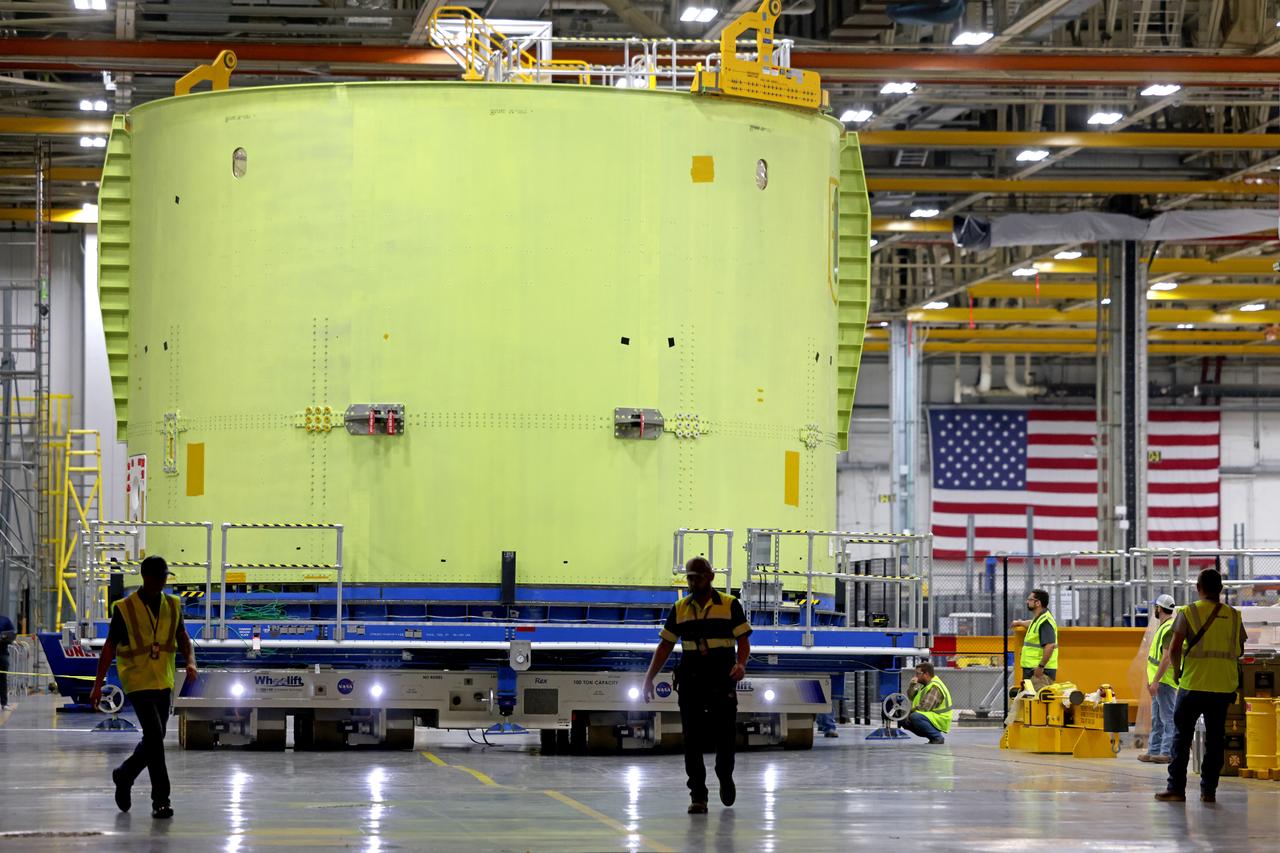
Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move a liquid hydrogen tank for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket into the factory’s final assembly area on April 22. Having recently completed application of the thermal protection system, teams will now continue outfitting the 130-foot-tall tank with critical systems to ready it for its designated Artemis III mission. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.

This imagery shows how technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility moved the aft dome of the liquid oxygen tank for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the next phase of production inside the Vertical Assembly center Dec. 18. The dome will form part of the core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis III mission. Engineers rotate the dome to attach it to the previously joined forward dome and aft barrel segments using friction-stir welding. The liquid oxygen tank is one of five major components that make up the SLS rocket’s core stage. Together with the forward skirt, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, engine section, along with the four RS-25 engines at its base, the 212-foot core stage will help power NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon.

This imagery shows how technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility moved the aft dome of the liquid oxygen tank for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the next phase of production inside the Vertical Assembly center Dec. 18. The dome will form part of the core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis III mission. Engineers rotate the dome to attach it to the previously joined forward dome and aft barrel segments using friction-stir welding. The liquid oxygen tank is one of five major components that make up the SLS rocket’s core stage. Together with the forward skirt, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, engine section, along with the four RS-25 engines at its base, the 212-foot core stage will help power NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon.

This imagery shows how technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility moved the aft dome of the liquid oxygen tank for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the next phase of production inside the Vertical Assembly center Dec. 18. The dome will form part of the core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis III mission. Engineers rotate the dome to attach it to the previously joined forward dome and aft barrel segments using friction-stir welding. The liquid oxygen tank is one of five major components that make up the SLS rocket’s core stage. Together with the forward skirt, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, engine section, along with the four RS-25 engines at its base, the 212-foot core stage will help power NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon.

This imagery shows how technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility moved the aft dome of the liquid oxygen tank for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the next phase of production inside the Vertical Assembly center Dec. 18. The dome will form part of the core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis III mission. Engineers rotate the dome to attach it to the previously joined forward dome and aft barrel segments using friction-stir welding. The liquid oxygen tank is one of five major components that make up the SLS rocket’s core stage. Together with the forward skirt, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, engine section, along with the four RS-25 engines at its base, the 212-foot core stage will help power NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon.

This imagery shows how technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility moved the aft dome of the liquid oxygen tank for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the next phase of production inside the Vertical Assembly center Dec. 18. The dome will form part of the core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis III mission. Engineers rotate the dome to attach it to the previously joined forward dome and aft barrel segments using friction-stir welding. The liquid oxygen tank is one of five major components that make up the SLS rocket’s core stage. Together with the forward skirt, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, engine section, along with the four RS-25 engines at its base, the 212-foot core stage will help power NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon.

This imagery shows how technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility moved the aft dome of the liquid oxygen tank for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the next phase of production inside the Vertical Assembly center Dec. 18. The dome will form part of the core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis III mission. Engineers rotate the dome to attach it to the previously joined forward dome and aft barrel segments using friction-stir welding. The liquid oxygen tank is one of five major components that make up the SLS rocket’s core stage. Together with the forward skirt, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, engine section, along with the four RS-25 engines at its base, the 212-foot core stage will help power NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon.