
The solar arrays for Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft are seen at Spectrolab in Sylmar, California. The solar arrays will power the Starliner as it flies through space and while it is docked to the International Space Station. Photo credit: Boeing

Engineers work with the solar array for Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft at Spectrolab in Sylmar, California. The solar arrays will power the Starliner as it flies through space and while it is docked to the International Space Station. Photo credit: Boeing

A boilerplate CST-100 Starliner is lifted skyward by a balloon for a drop test of the Starliner's parachute system. Boeing, which is building the Starliner, conducted the test in White Sands, New Mexico, as part of the testing campaign for certification by NASA's Commercial Crew Program. Photo credit: Boeing
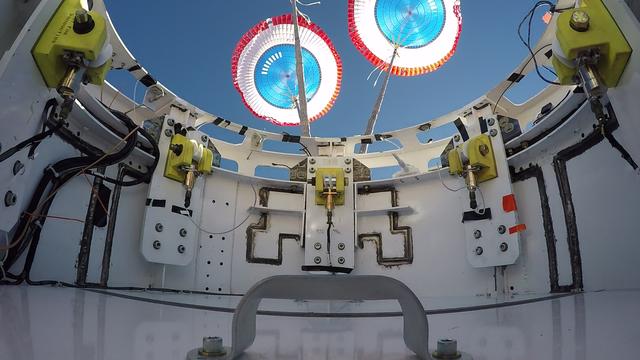
The parachute deployment is seen from the top hatch of a boilerplate CST-100 Starliner during a drop test of the Starliner's parachute system. Boeing, which is building the Starliner, conducted the test in White Sands, New Mexico, as part of the testing campaign for certification by NASA's Commercial Crew Program. Photo credit: Boeing

An engineer monitors a Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft inside Boeing's Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. This was the first time "Spacecraft 1," as the individual Starliner is known, was powered up. It is being assembled for use during a pad abort test that will demonstrate the Starliners' ability to lift astronauts out of danger in the unlikely event of an emergency. Later flight tests will demonstrate Starliners in orbital missions to the station without a crew, and then with astronauts aboard. The flight tests will preview the crew rotation missions future Starliners will perform as they take up to four astronauts at a time to the orbiting laboratory in order to enhance the research taking place there
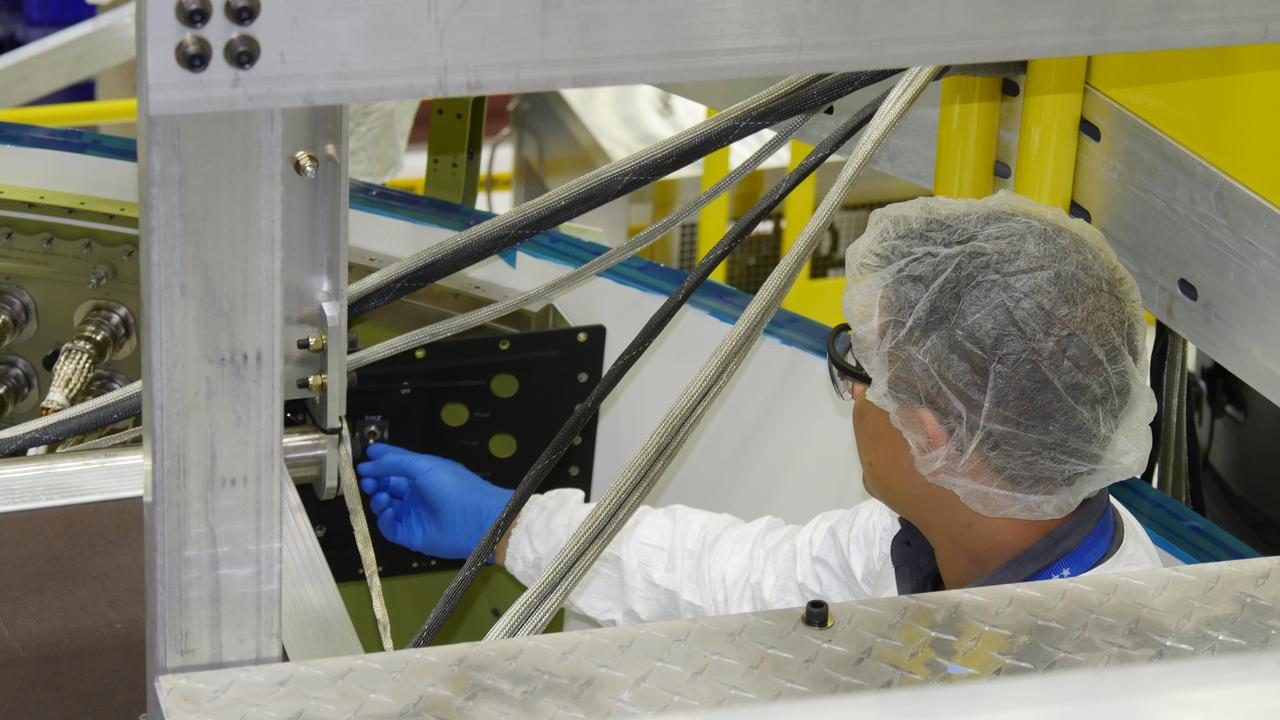

An engineer works the switch to power on a Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft inside Boeing's Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. This was the first time "Spacecraft 1," as the individual Starliner is known, was powered up. It is being assembled for use during a pad abort test that will demonstrate the Starliners' ability to lift astronauts out of danger in the unlikely event of an emergency. Later flight tests will demonstrate Starliners in orbital missions to the station without a crew, and then with astronauts aboard. The flight tests will preview the crew rotation missions future Starliners will perform as they take up to four astronauts at a time to the orbiting laboratory in order to enhance the research taking place there.
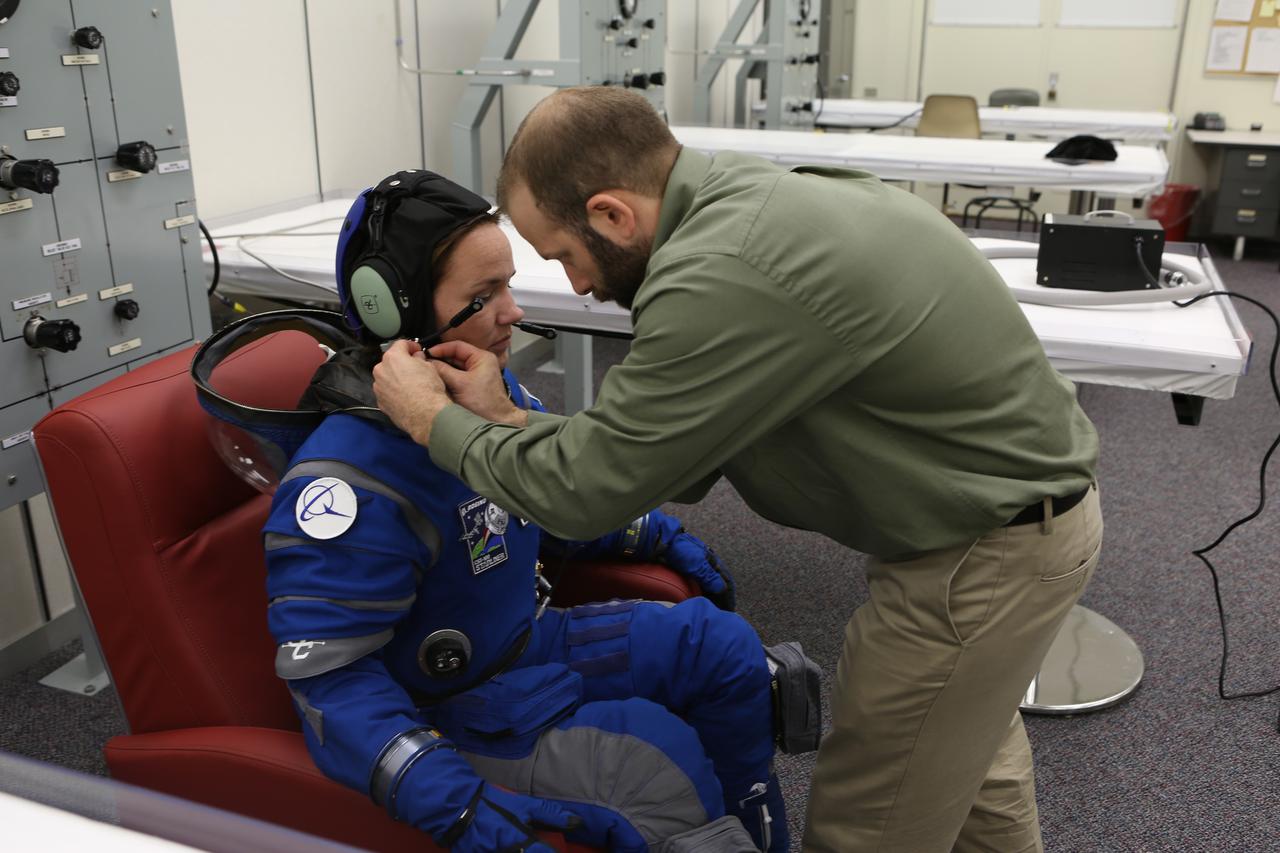

A suit technician prepares for a pressure test of Boeing's new spacesuit designed to be worn by astronauts flying on the CST-100 Starliner. Seen here being worn in the same manner as it will on launch day inside Crew Quarters at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the suit is lighter and more flexible than previous spacesuits but retains the ability to pressurize in an emergency. Astronauts will wear the suit throughout the launch and ascent into orbit as well as on the way back to Earth. Starliners will launch atop Atlas V rockets from United Launch Alliance on missions including flights to the International Space Station for NASA's Commercial Crew Program. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
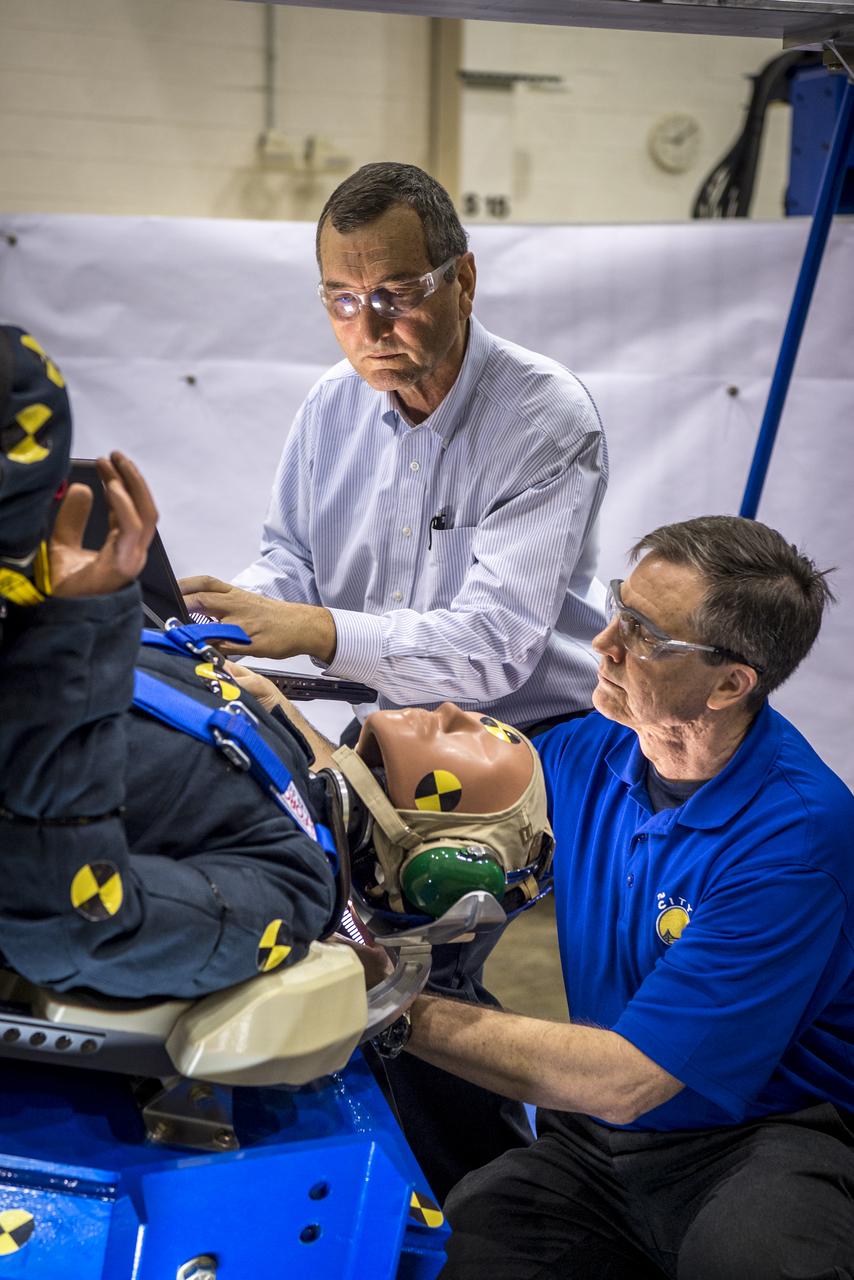
Engineers working with Boeing's CST-100 Starliner test the spacecraft's seat design in Mesa, Arizona, focusing on how the spacecraft seats would protect an astronaut's head, neck and spine during the 240-mile descent from the International Space Station. The company incorporated test dummies for a detailed analysis of impacts on a crew returning to earth. The human-sized dummies were equipped with sensitive instrumentation and secured in the seats for 30 drop tests at varying heights, angles, velocities and seat orientations in order to mimic actual landing conditions. High-speed cameras captured the footage for further analysis. The Starliner spacecraft is being developed in partnership with NASA's Commercial Crew Program.
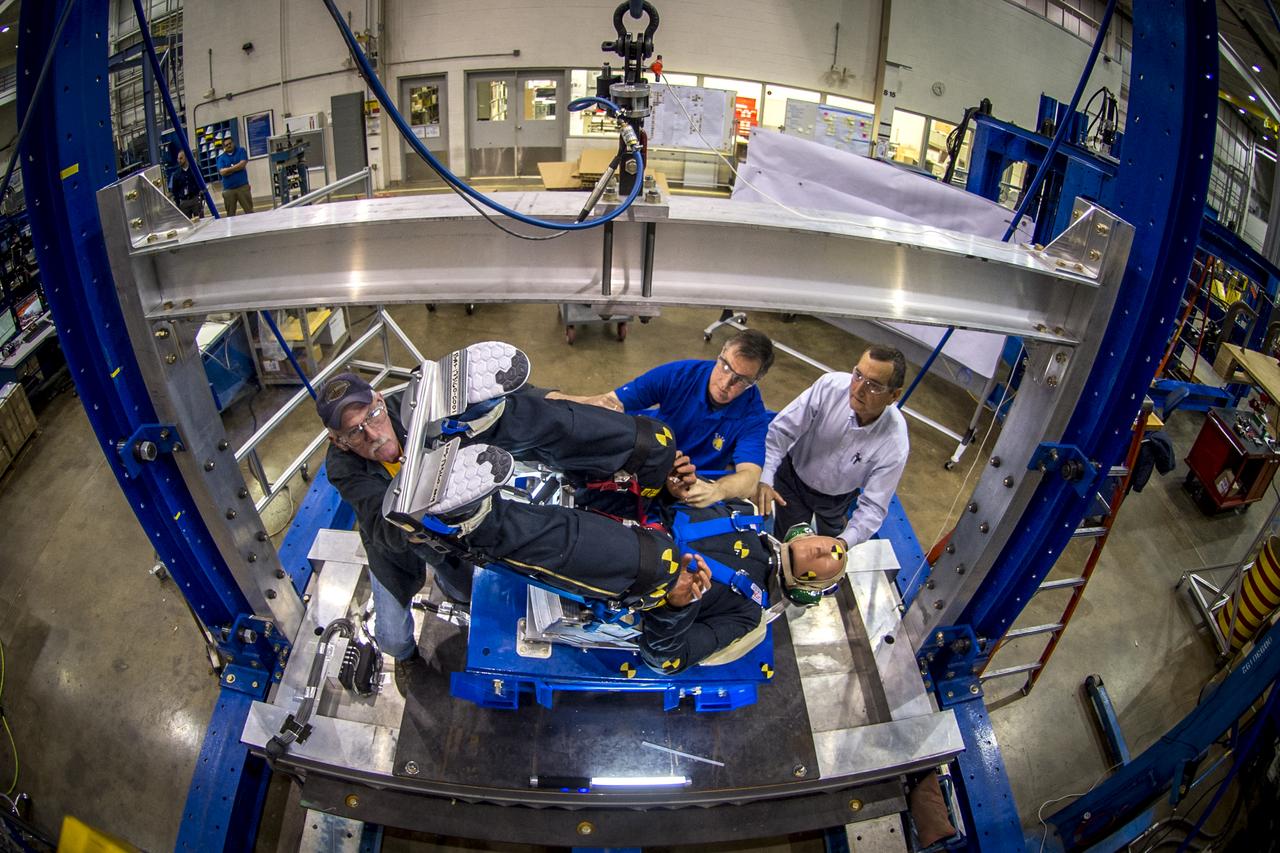

Engineers working with Boeing's CST-100 Starliner test the spacecraft's seat design in Mesa, Arizona, focusing on how the spacecraft seats would protect an astronaut's head, neck and spine during the 240-mile descent from the International Space Station. The company incorporated test dummies for a detailed analysis of impacts on a crew returning to earth. The human-sized dummies were equipped with sensitive instrumentation and secured in the seats for 30 drop tests at varying heights, angles, velocities and seat orientations in order to mimic actual landing conditions. High-speed cameras captured the footage for further analysis. The Starliner spacecraft is being developed in partnership with NASA's Commercial Crew Program.
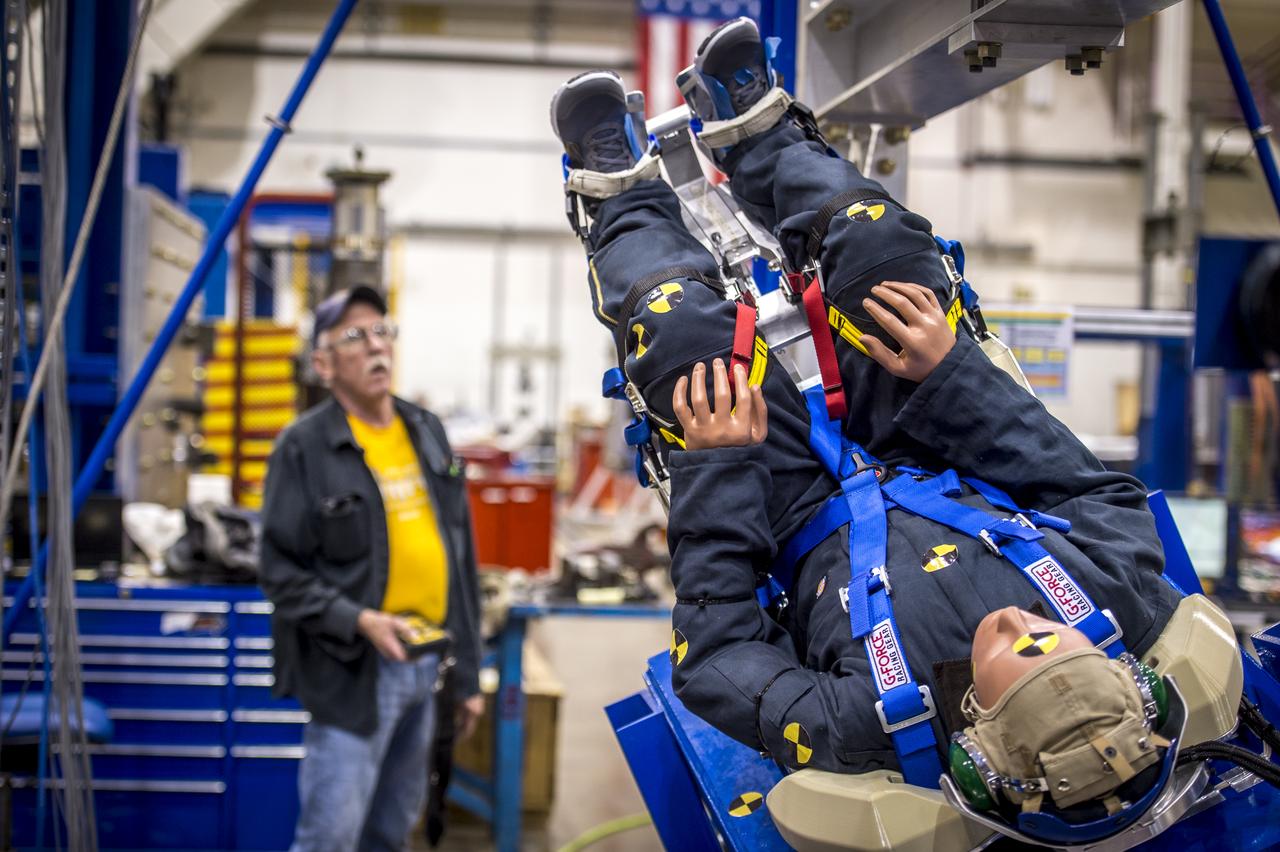

Engineers working with Boeing's CST-100 Starliner test the spacecraft's seat design in Mesa, Arizona, focusing on how the spacecraft seats would protect an astronaut's head, neck and spine during the 240-mile descent from the International Space Station. The company incorporated test dummies for a detailed analysis of impacts on a crew returning to earth. The human-sized dummies were equipped with sensitive instrumentation and secured in the seats for 30 drop tests at varying heights, angles, velocities and seat orientations in order to mimic actual landing conditions. High-speed cameras captured the footage for further analysis. The Starliner spacecraft is being developed in partnership with NASA's Commercial Crew Program.
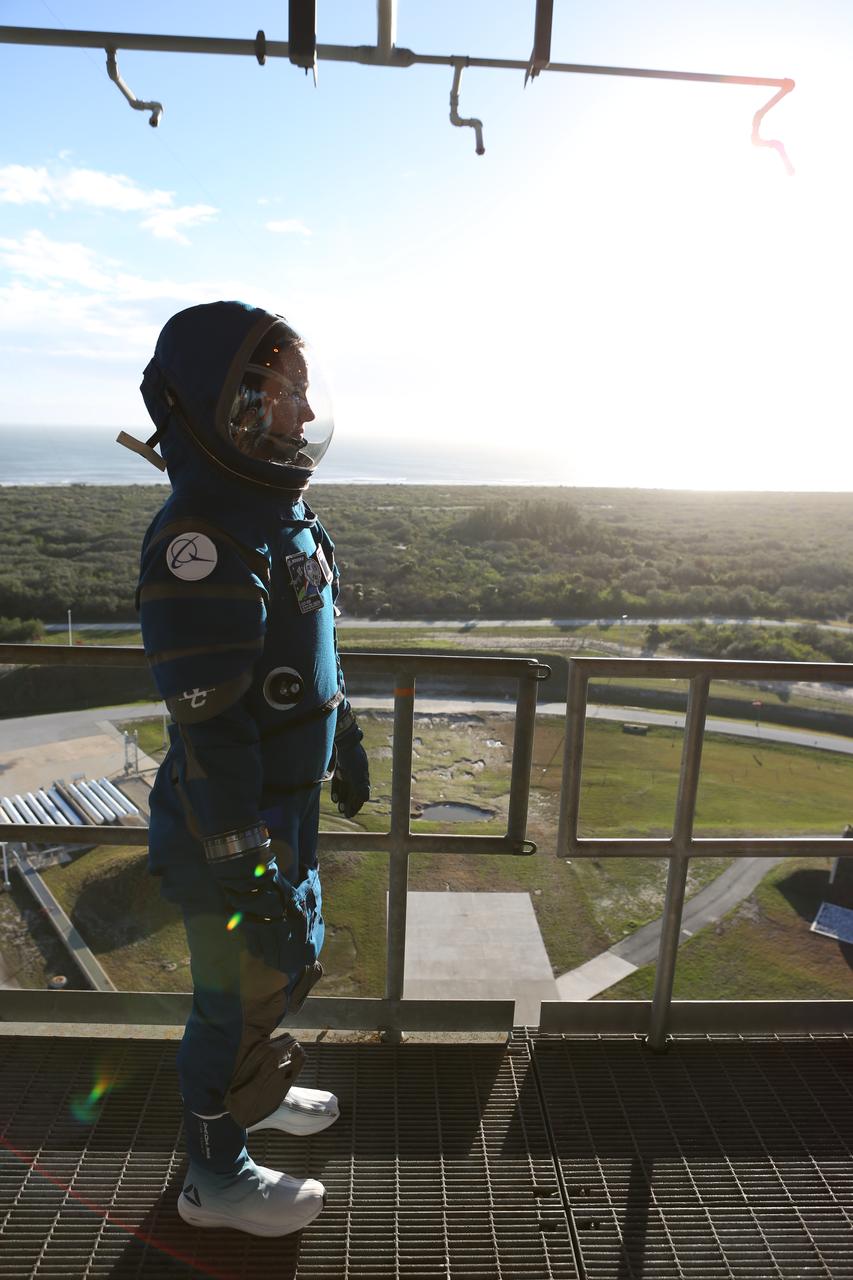

Boeing's new spacesuit designed to be worn by astronauts flying on the CST-100 Starliner. Seen here being worn in the same manner as it will on launch day for the walk to the spacecraft at Space Launch Complex 41, the suit is lighter and more flexible than previous spacesuits but retains the ability to pressurize in an emergency. Astronauts will wear the suit throughout the launch and ascent into orbit as well as on the way back to Earth. Starliners will launch atop Atlas V rockets from United Launch Alliance on missions including flights to the International Space Station for NASA's Commercial Crew Program. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
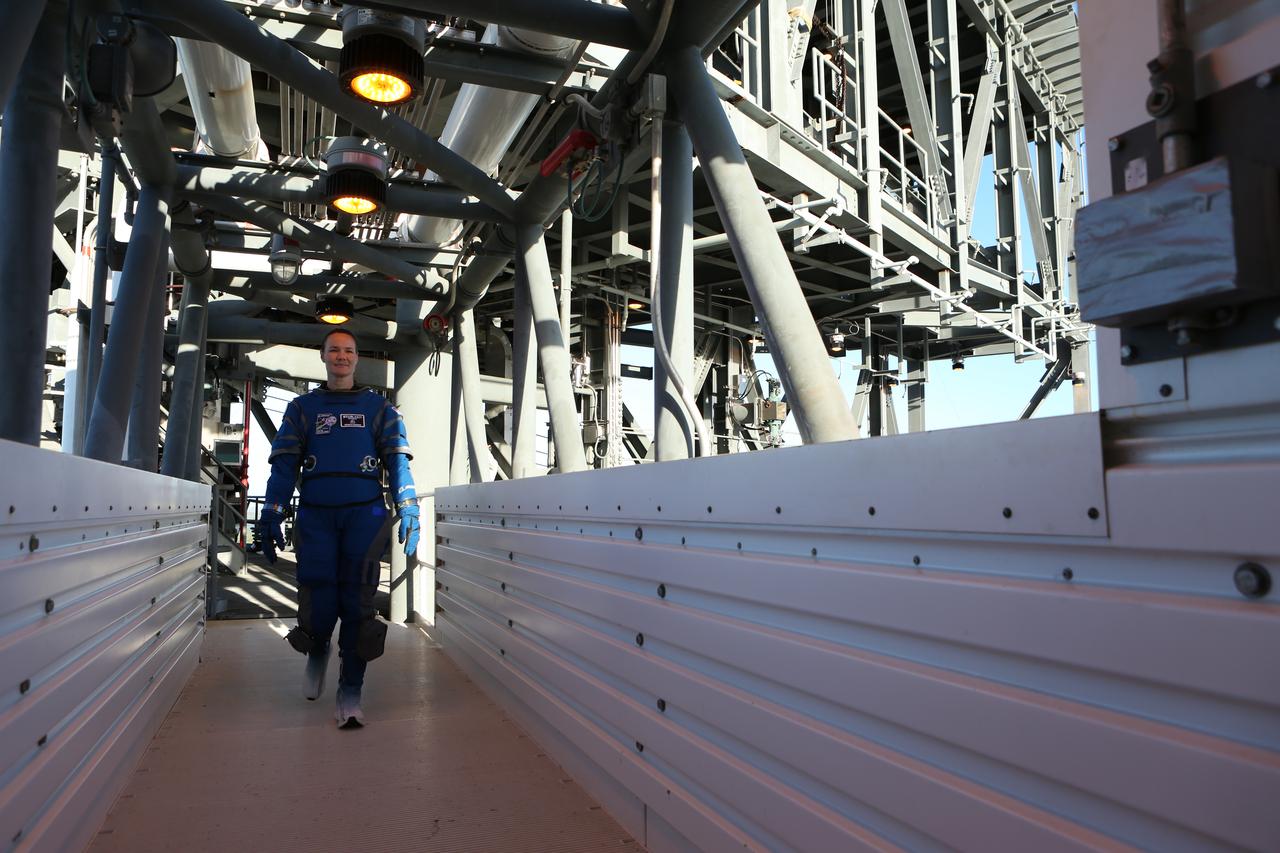

Boeing's new spacesuit designed to be worn by astronauts flying on the CST-100 Starliner. Seen here being worn in the same manner as it will on launch day for the walk to the spacecraft at Space Launch Complex 41, the suit is lighter and more flexible than previous spacesuits but retains the ability to pressurize in an emergency. Astronauts will wear the suit throughout the launch and ascent into orbit as well as on the way back to Earth. Starliners will launch atop Atlas V rockets from United Launch Alliance on missions including flights to the International Space Station for NASA's Commercial Crew Program. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
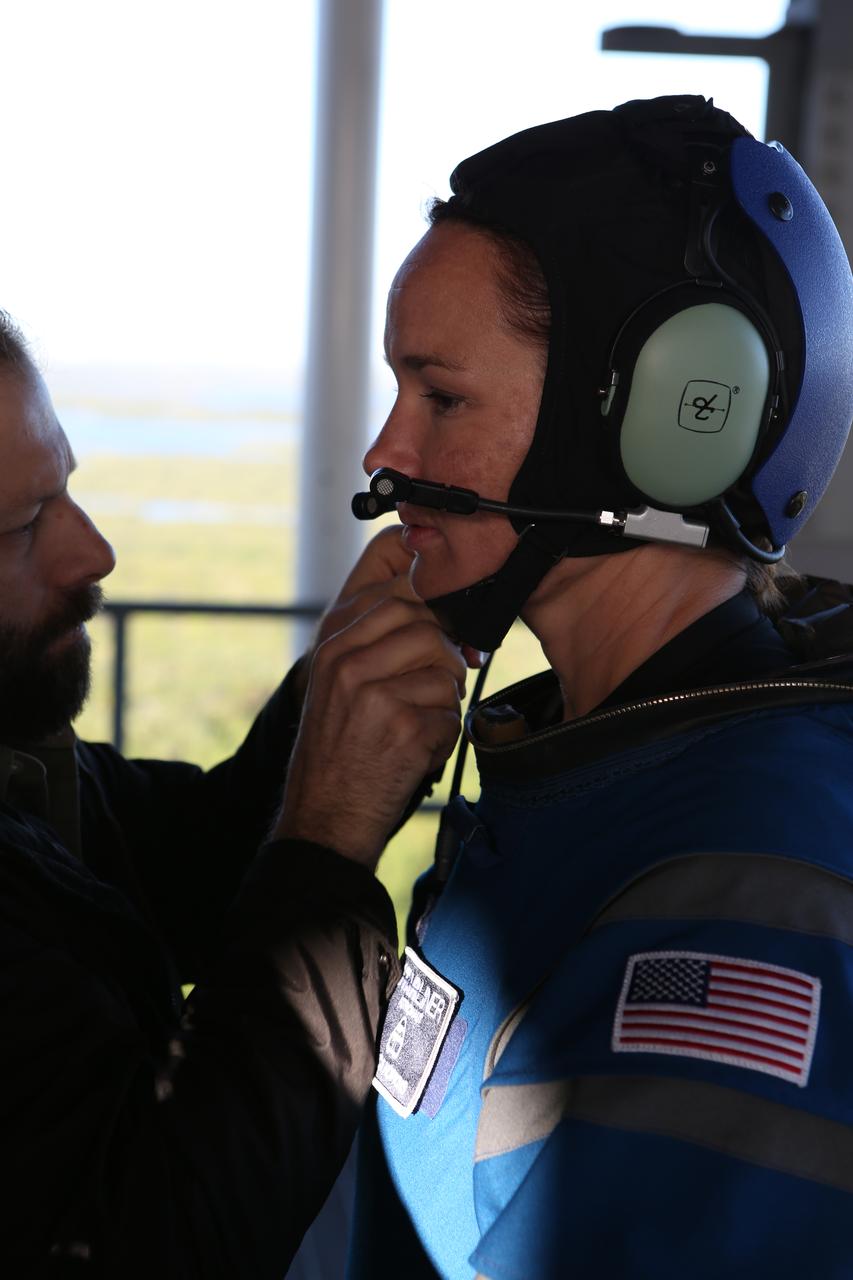

The communications carrier is placed as part of Boeing's new spacesuit designed to be worn by astronauts flying on the CST-100 Starliner. Seen here being worn in the same manner as it will on launch day for the walk to the spacecraft at Space Launch Complex 41, the suit is lighter and more flexible than previous spacesuits but retains the ability to pressurize in an emergency. Astronauts will wear the suit throughout the launch and ascent into orbit as well as on the way back to Earth. Starliners will launch atop Atlas V rockets from United Launch Alliance on missions including flights to the International Space Station for NASA's Commercial Crew Program. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston

Engineers working with Boeing's CST-100 Starliner test the spacecraft's seat design in Mesa, Arizona, focusing on how the spacecraft seats would protect an astronaut's head, neck and spine during the 240-mile descent from the International Space Station. The company incorporated test dummies for a detailed analysis of impacts on a crew returning to earth. The human-sized dummies were equipped with sensitive instrumentation and secured in the seats for 30 drop tests at varying heights, angles, velocities and seat orientations in order to mimic actual landing conditions. High-speed cameras captured the footage for further analysis. The Starliner spacecraft is being developed in partnership with NASA's Commercial Crew Program.
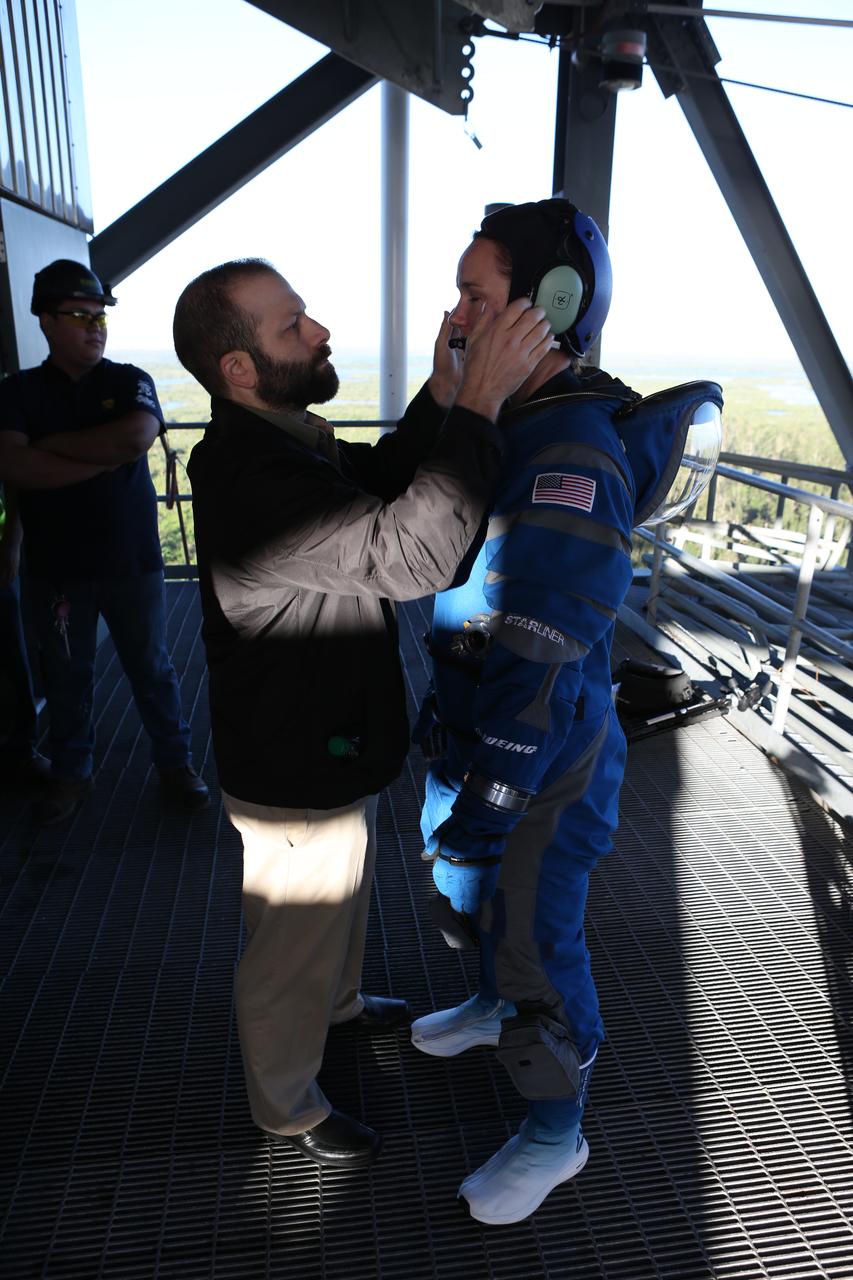

The communications carrier is placed as part of Boeing's new spacesuit designed to be worn by astronauts flying on the CST-100 Starliner. Seen here being worn in the same manner as it will on launch day for the walk to the spacecraft at Space Launch Complex 41, the suit is lighter and more flexible than previous spacesuits but retains the ability to pressurize in an emergency. Astronauts will wear the suit throughout the launch and ascent into orbit as well as on the way back to Earth. Starliners will launch atop Atlas V rockets from United Launch Alliance on missions including flights to the International Space Station for NASA's Commercial Crew Program. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
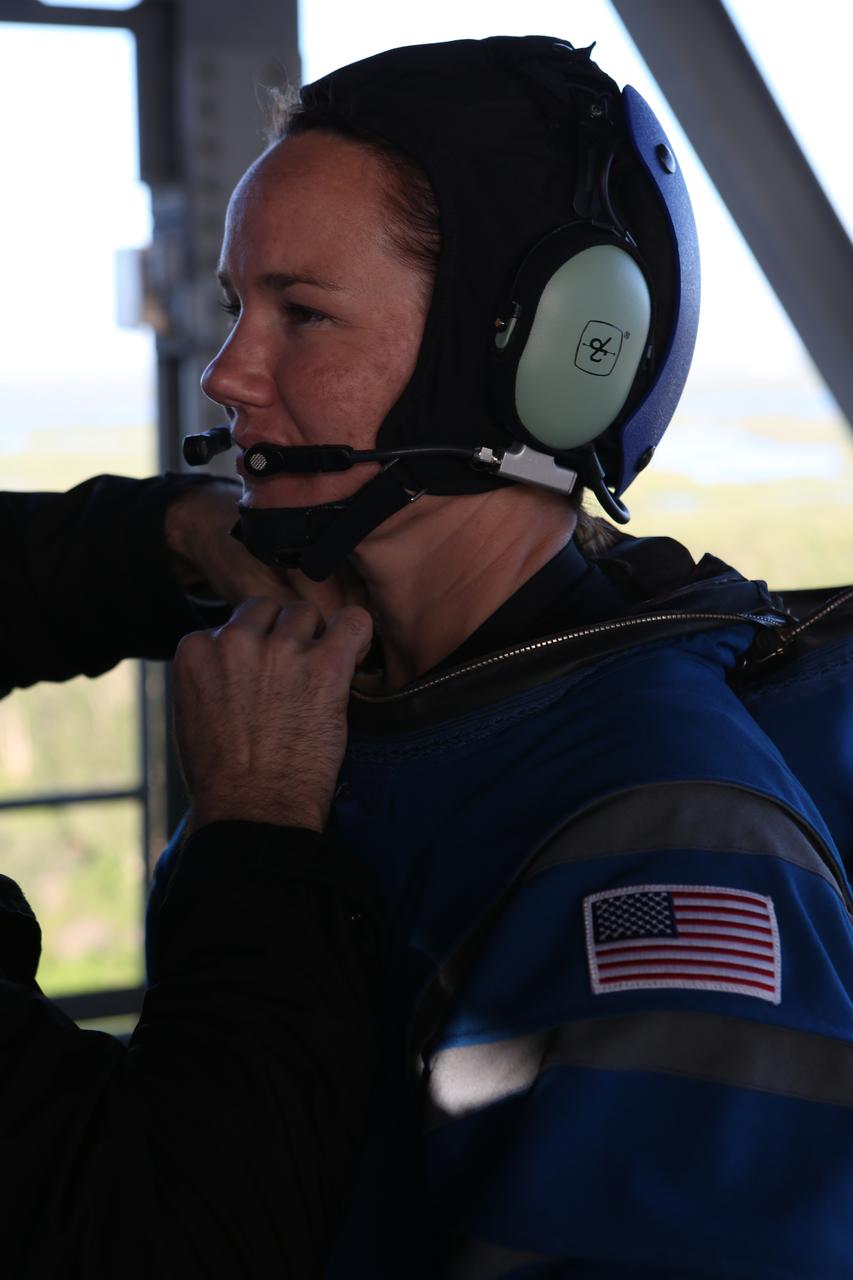

The communications carrier is placed as part of Boeing's new spacesuit designed to be worn by astronauts flying on the CST-100 Starliner. Seen here being worn in the same manner as it will on launch day for the walk to the spacecraft at Space Launch Complex 41, the suit is lighter and more flexible than previous spacesuits but retains the ability to pressurize in an emergency. Astronauts will wear the suit throughout the launch and ascent into orbit as well as on the way back to Earth. Starliners will launch atop Atlas V rockets from United Launch Alliance on missions including flights to the International Space Station for NASA's Commercial Crew Program. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
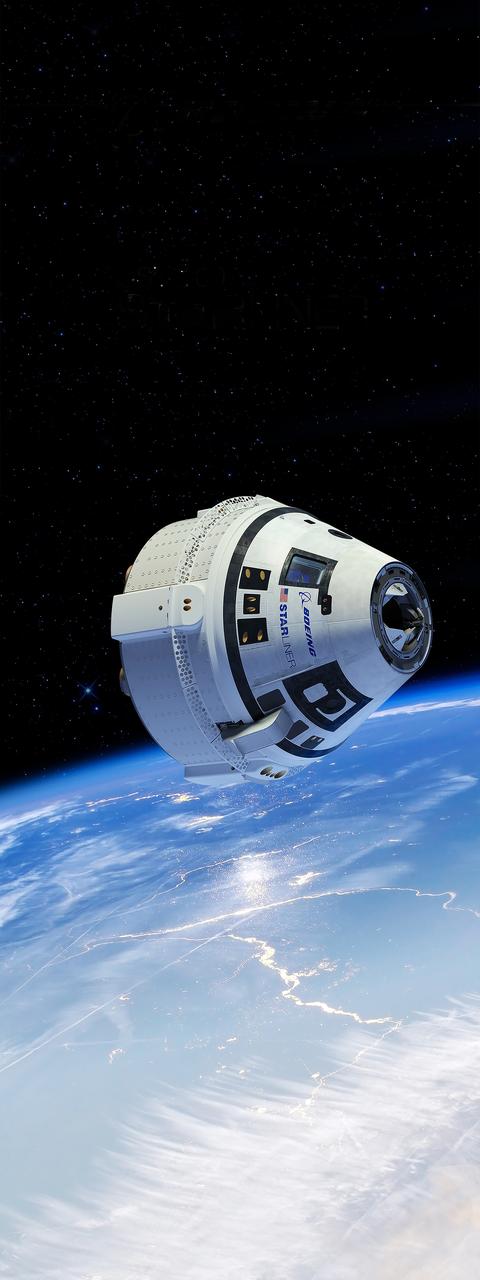

In this illustration, a Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft is shown in low-Earth orbit. NASA is partnering with Boeing and SpaceX to build a new generation of human-rated spacecraft capable of taking astronauts to the International Space Station and expanding research opportunities in orbit. Boeing's upcoming Orbital Flight Test is part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Transportation Capability contract with the goal of returning human spaceflight launch capabilities to the United States.

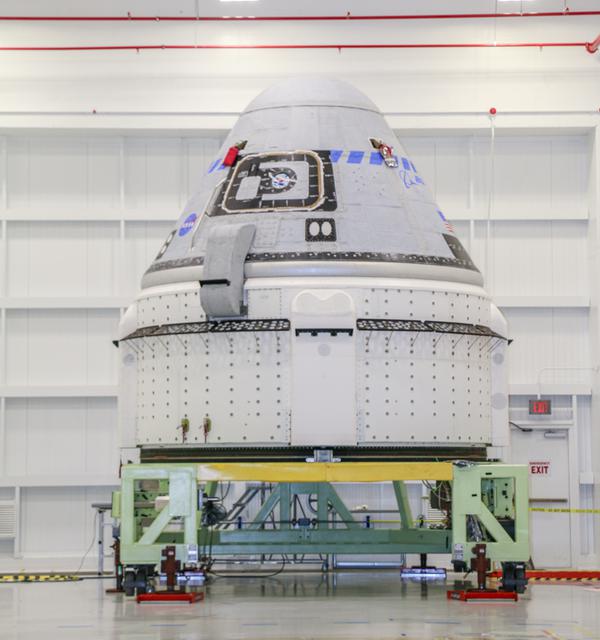
The CST-100 Starliner spacecraft to be flown on Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test (OFT) is viewed Nov. 2, 2019, while undergoing launch preparations inside the Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. During the OFT mission, the uncrewed Starliner spacecraft will fly to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.
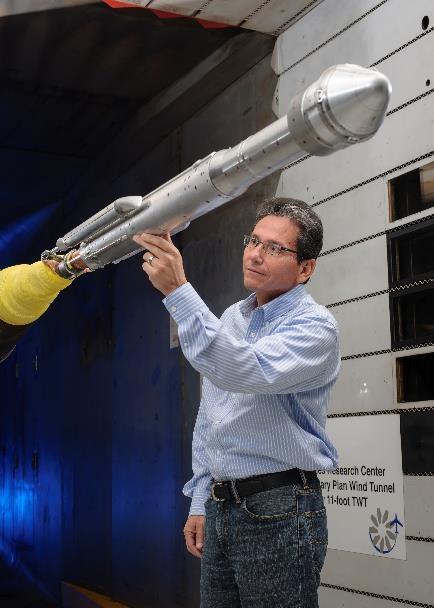

An engineer works with a model of a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with a Boeing CST-100 Starliner capsule inside a wind tunnel at NASA's Ames Research Center in California. The Starliner/Atlas V system is under development by Boeing and ULA in partnership with NASA's Commercial Crew Program to launch astronauts to the International Space Station.
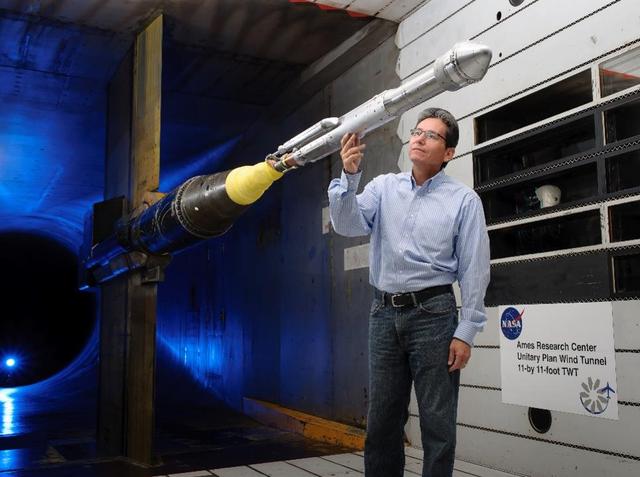

An engineer works with a model of a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with a Boeing CST-100 Starliner capsule inside a wind tunnel at NASA's Ames Research Center in California. The Starliner/Atlas V system is under development by Boeing and ULA in partnership with NASA's Commercial Crew Program to launch astronauts to the International Space Station.
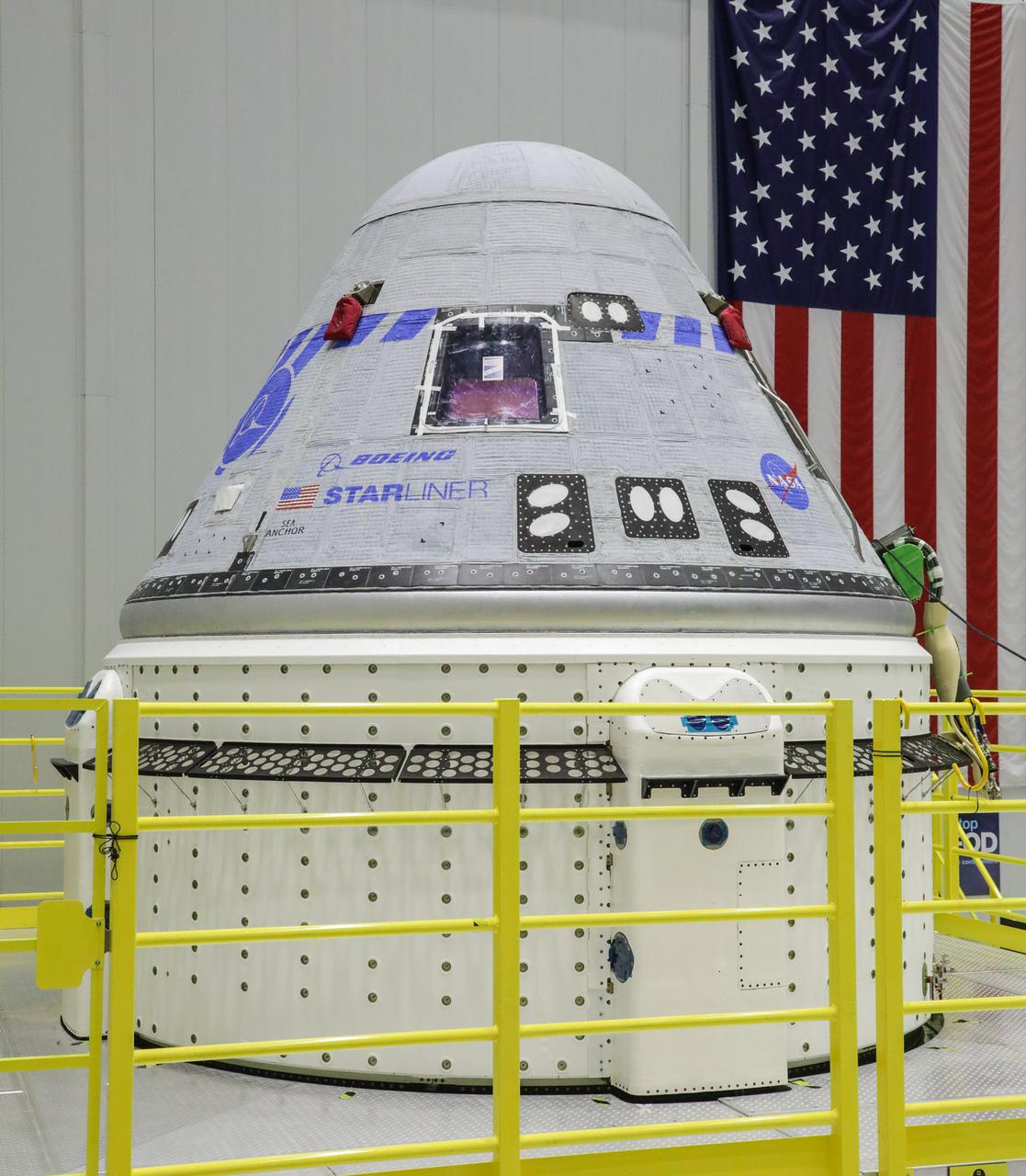

A new service module was mated to a Boeing CST-100 Starliner crew module to form a complete spacecraft on March 12, 2022, in Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Starliner will launch on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for Boeing’s second uncrewed Orbital Flight Test-2 (OFT-2) for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.
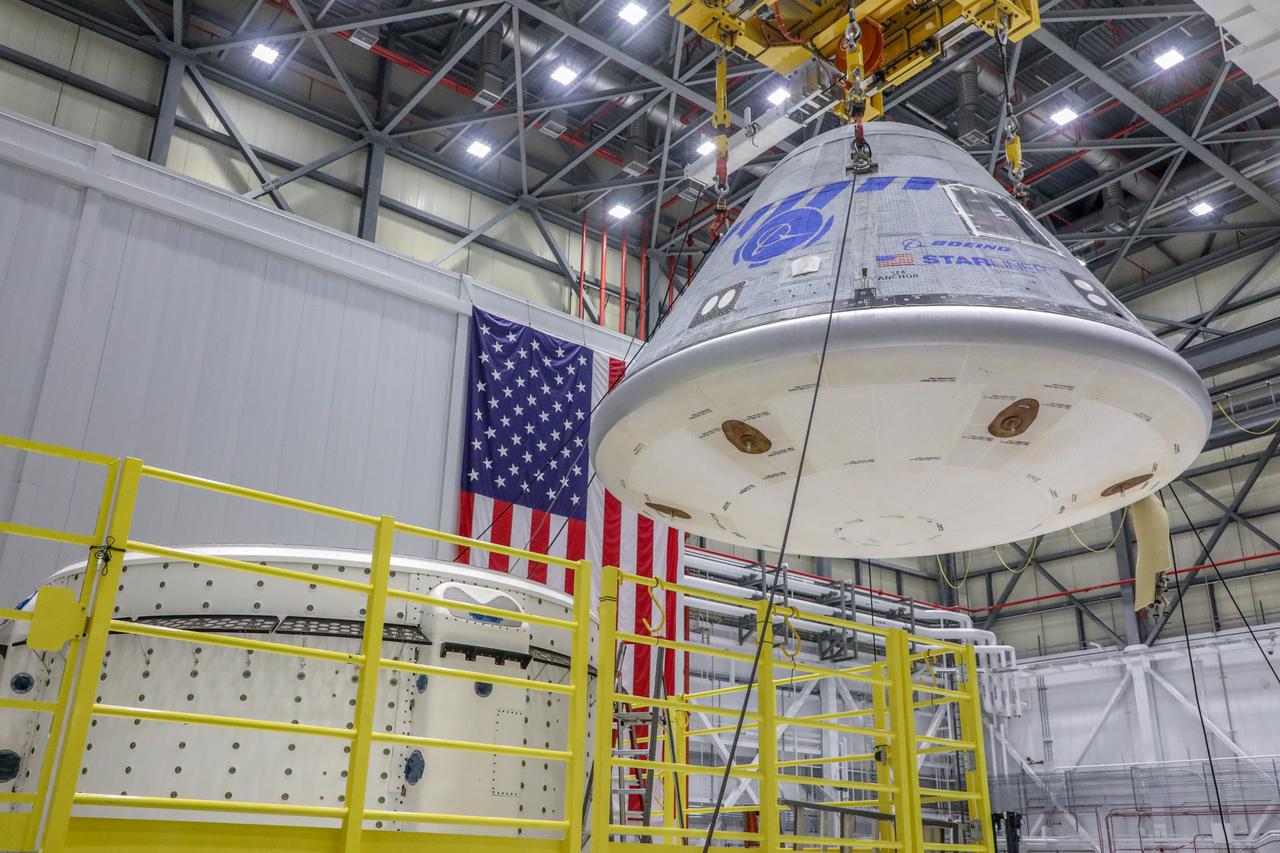

A new service module was mated to a Boeing CST-100 Starliner crew module to form a complete spacecraft on March 12, 2022, in Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Starliner will launch on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for Boeing’s second uncrewed Orbital Flight Test-2 (OFT-2) for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.
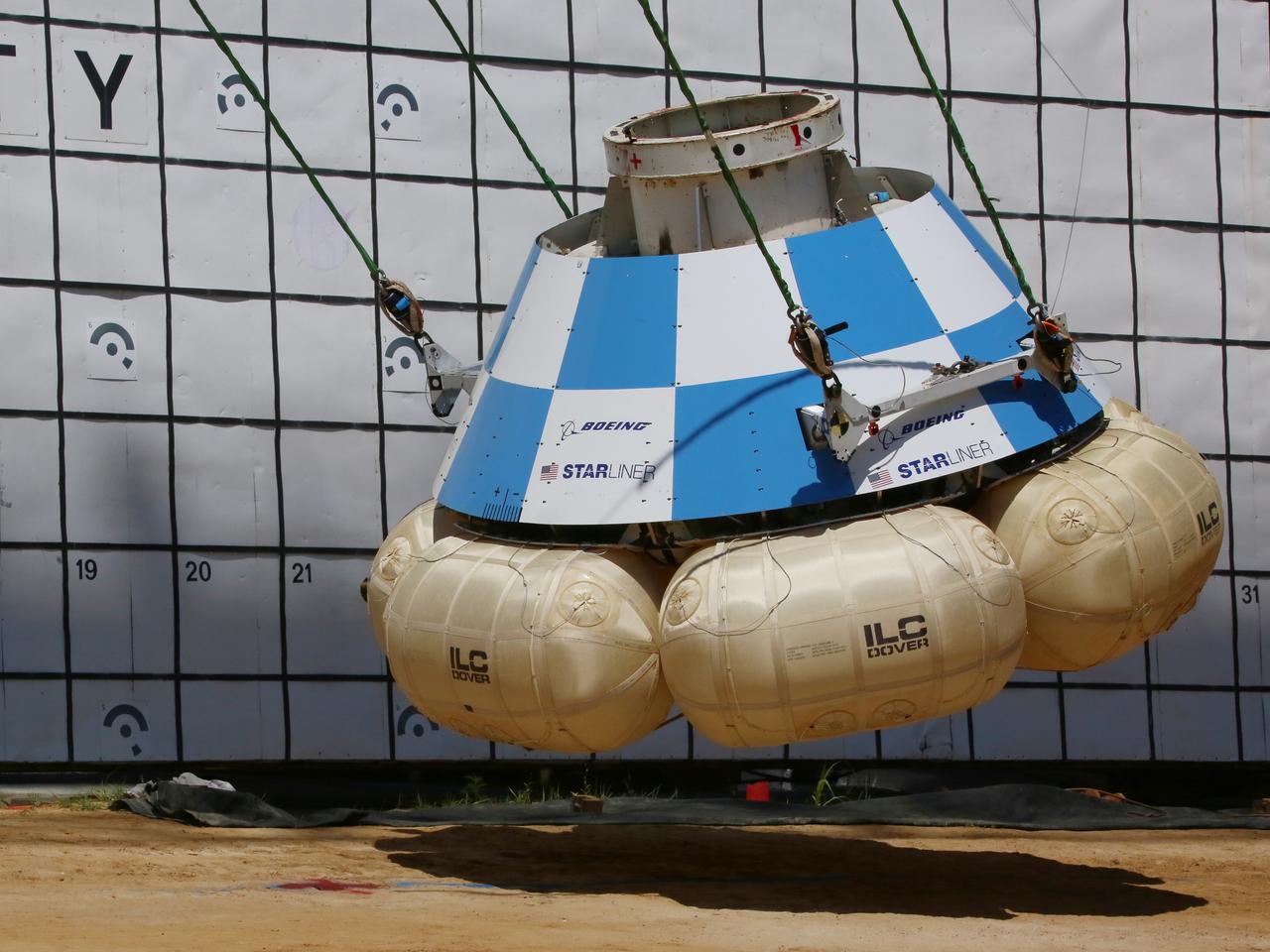

At NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia, a mock-up of the Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft goes through a series of land landing qualification tests to simulate what the actual spacecraft and crew members may experience while returning to Earth from space. The Starliner is being developed in collaboration with NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Along with SpaceX’s Crew Dragon, the spacecraft is part of the agency’s effort to return America’s capability to launch astronauts from the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to the International Space Station.
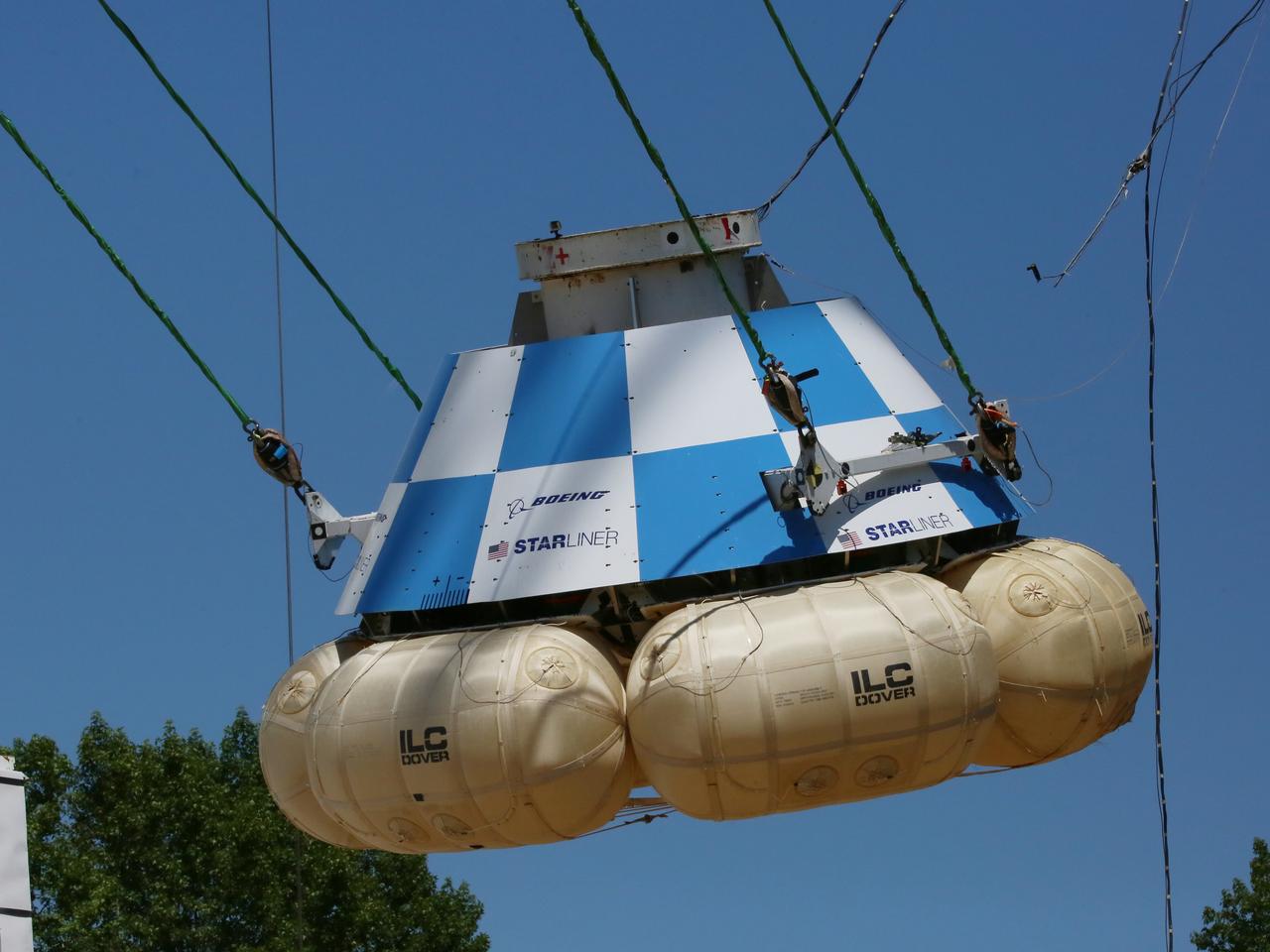

At NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia, a mock-up of the Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft goes through a series of land landing qualification tests to simulate what the actual spacecraft and crew members may experience while returning to Earth from space. The Starliner is being developed in collaboration with NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Along with SpaceX’s Crew Dragon, the spacecraft is part of the agency’s effort to return America’s capability to launch astronauts from the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to the International Space Station.
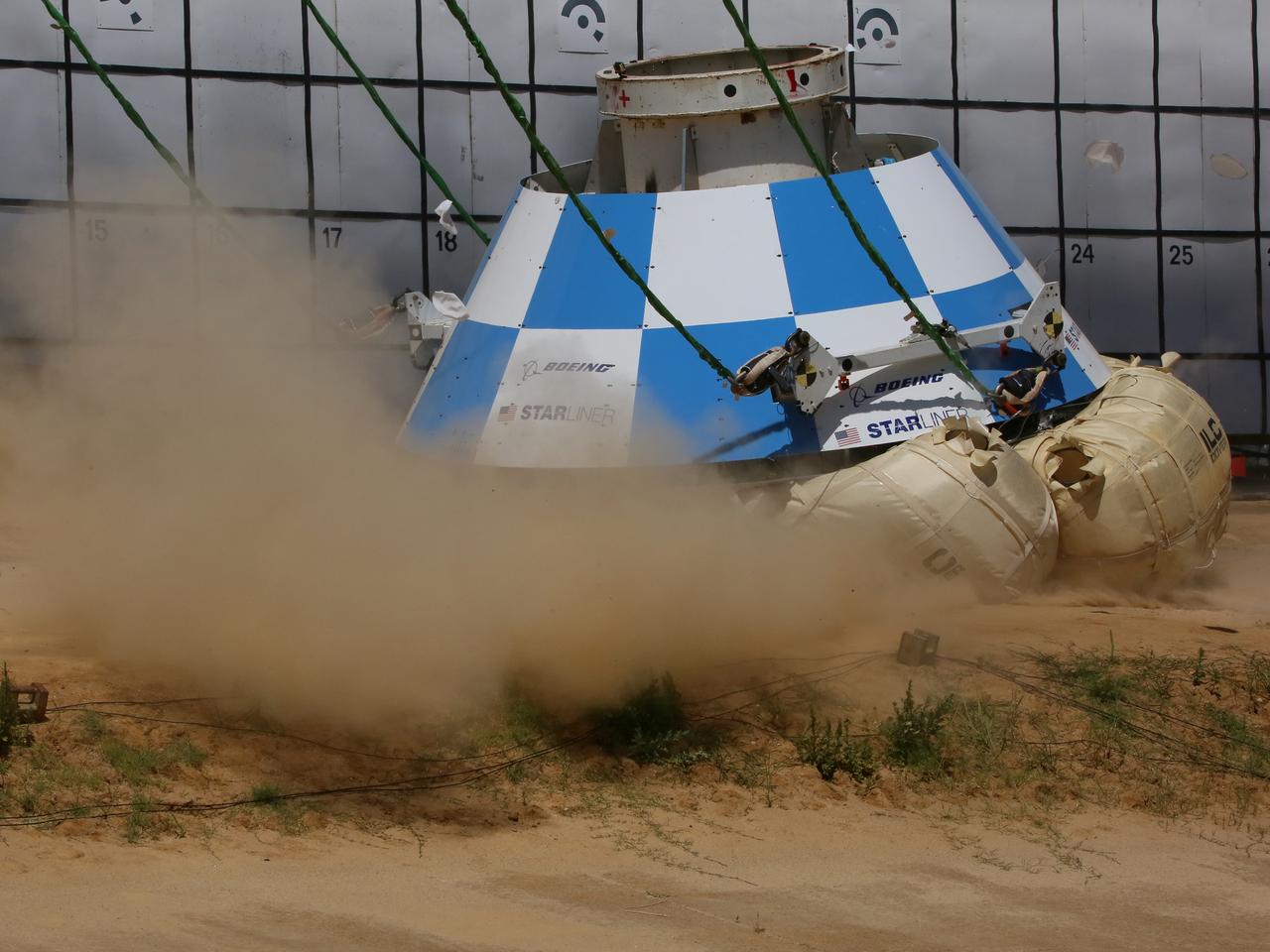

At NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia, a mock-up of the Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft goes through a series of land landing qualification tests to simulate what the actual spacecraft and crew members may experience while returning to Earth from space. The Starliner is being developed in collaboration with NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Along with SpaceX’s Crew Dragon, the spacecraft is part of the agency’s effort to return America’s capability to launch astronauts from the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to the International Space Station.
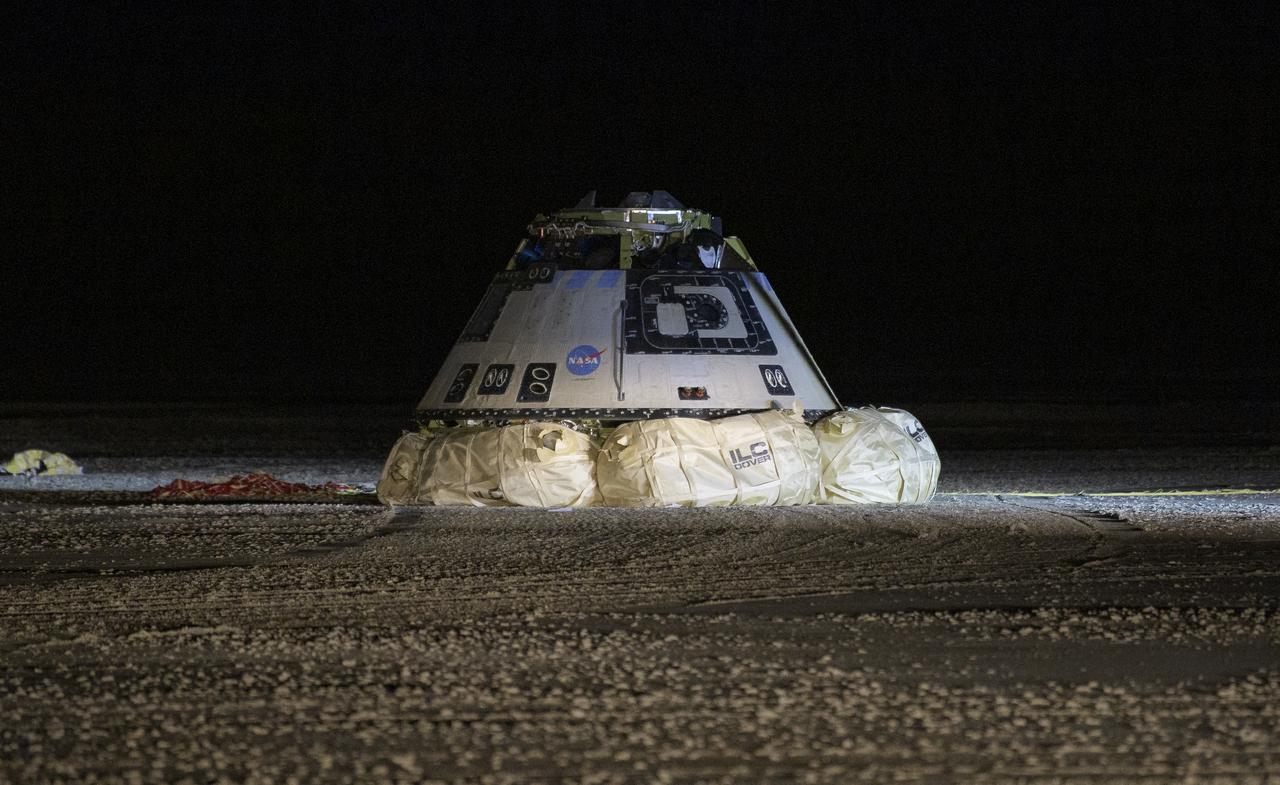

The Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft is seen after it landed in White Sands, New Mexico, Sunday, Dec. 22, 2019. The landing completes an abbreviated Orbital Flight Test for the company that still meets several mission objectives for NASA’s Commercial Crew program. The Starliner spacecraft launched on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket at 6:36 a.m. Friday, Dec. 20 from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner’s airbags inflate in preparation for landing in the New Mexico desert in the company’s Pad Abort Test for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The test, conducted Nov. 4 at the White Sands Missile Range, was designed to verify that each of Starliner’s systems will function not only separately, but in concert, to protect astronauts by carrying them safely away from the launch pad in the unlikely event of an emergency prior to liftoff. This is Boeing’s first test flight for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, which is working to launch astronauts on American rockets and spacecraft from American soil for the first time since 2011.

Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner’s airbags inflate in preparation for landing in the New Mexico desert in the company’s Pad Abort Test for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The test, conducted Nov. 4 at the White Sands Missile Range, was designed to verify that each of Starliner’s systems will function not only separately, but in concert, to protect astronauts by carrying them safely away from the launch pad in the unlikely event of an emergency prior to liftoff. This is Boeing’s first test flight for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, which is working to launch astronauts on American rockets and spacecraft from American soil for the first time since 2011.
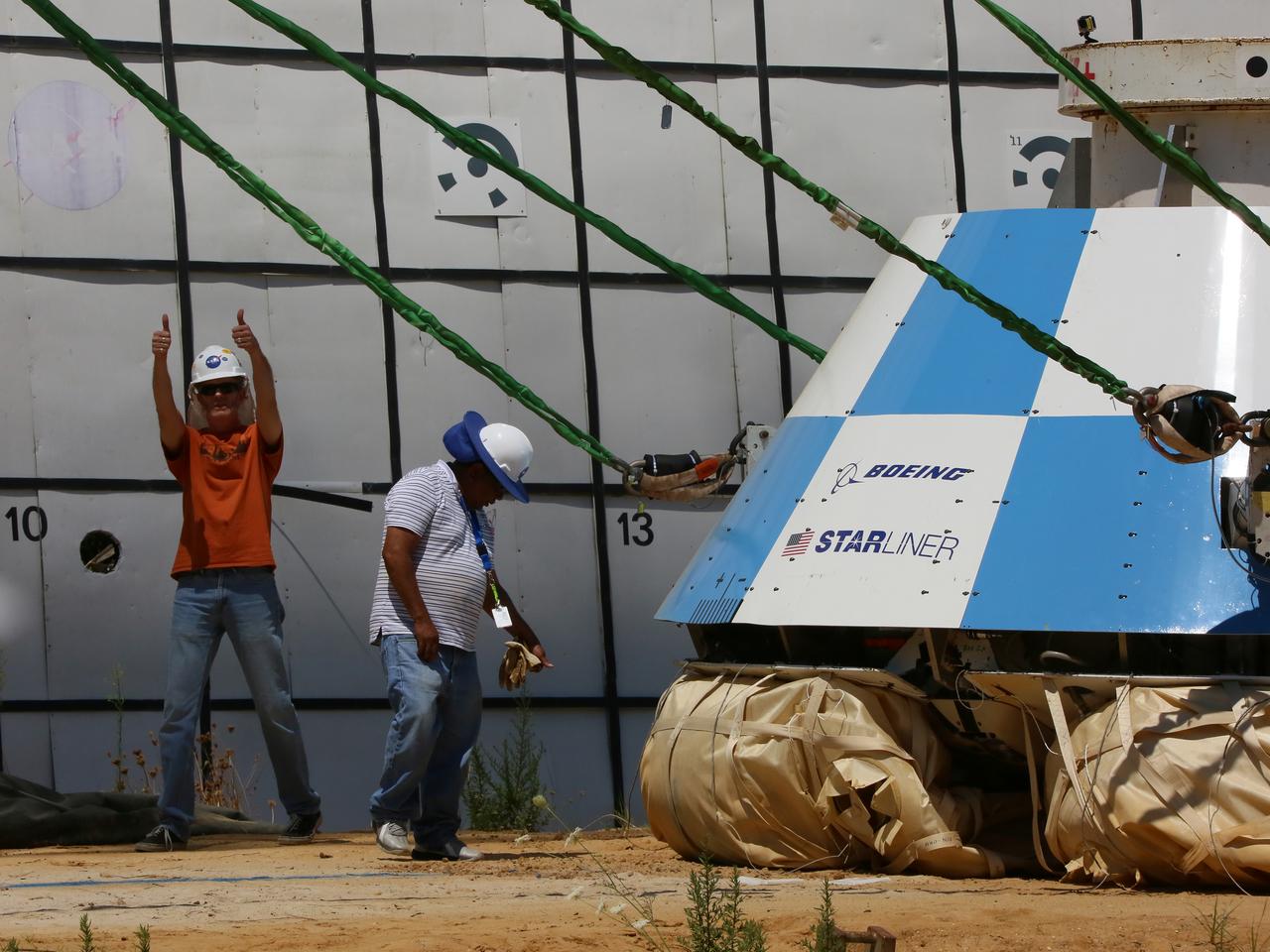

"Thumbs up" is signaled by ground personnel at NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia, after a mock-up of the Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft completed a land landing qualification test. The operation was to simulate what the actual spacecraft and crew members may experience while returning to Earth from space. The Starliner is being developed in collaboration with NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Along with SpaceX’s Crew Dragon, the spacecraft is part of the agency’s effort to return America’s capability to launch astronauts from the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to the International Space Station.

Parachutes deploy in in Boeing’s Pad Abort Test of its CST-100 Starliner spacecraft over the White Sands Missile Range in New Mexico, slowing the descent of the vehicle. The test, conducted Nov. 4, 2019, was designed to verify that each of Starliner’s systems will function not only separately, but in concert, to protect astronauts by carrying them safely away from the launch pad in the unlikely event of an emergency prior to liftoff. This is Boeing’s first test flight for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, which is working to launch astronauts on American rockets and spacecraft from American soil for the first time since 2011.
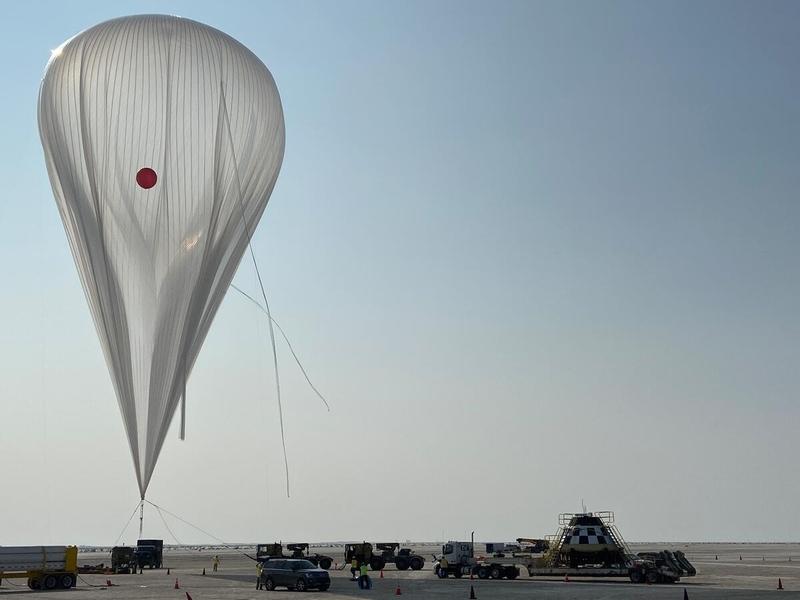

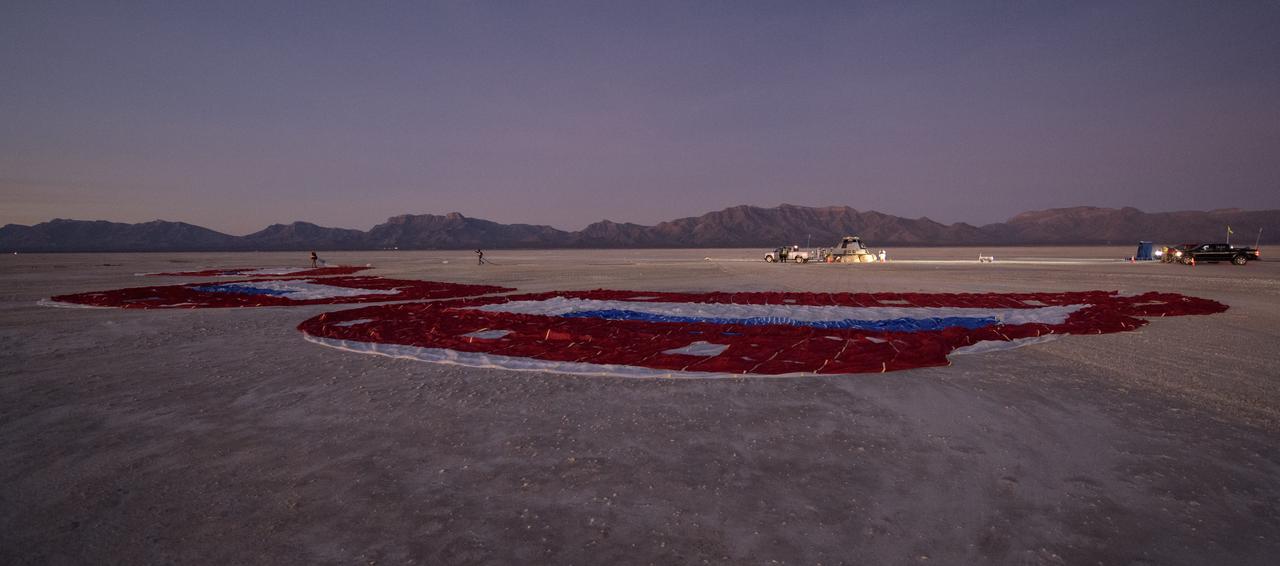
A Boeing CST-100 Starliner test article prepares to mate with a high altitude balloon ahead of its final parachute reliability drop test at White Sands, New Mexico, on Sept. 19, 2020. The test is part of a reliability campaign that will help strengthen the spacecraft’s landing system ahead of crewed flights to and from the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.
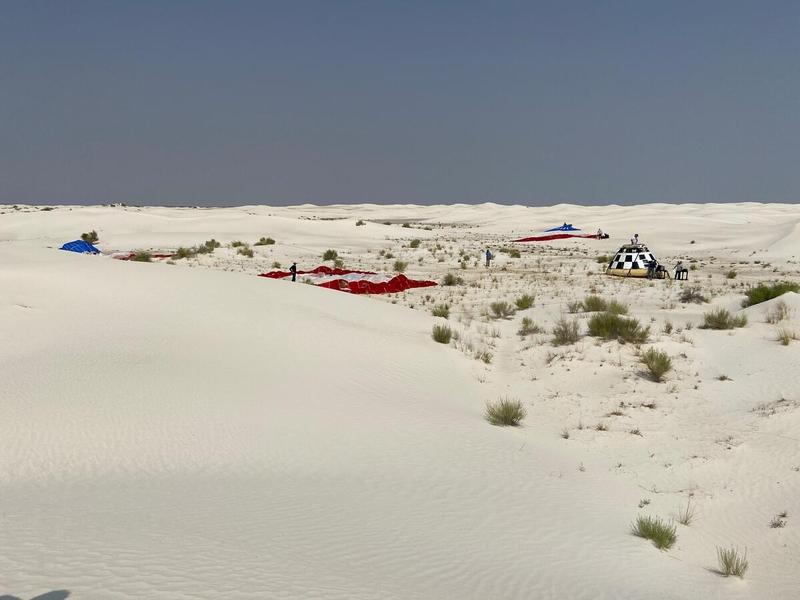

Recovery teams gather at the landing site of Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner test article used in the spacecraft's final parachute reliability test at White Sands Space Harbor, New Mexico, on Sept. 19, 2020. The test is part of a reliability campaign that will help strengthen the spacecraft’s landing system ahead of crewed flights to and from the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.

Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner's three main parachutes slow the test article to a safe and soft landing during the final balloon drop parachute test Sept. 19, 2020, at White Sands, New Mexico. The test is part of a reliability campaign that will help strengthen the spacecraft’s landing system ahead of crewed flights to and from the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.
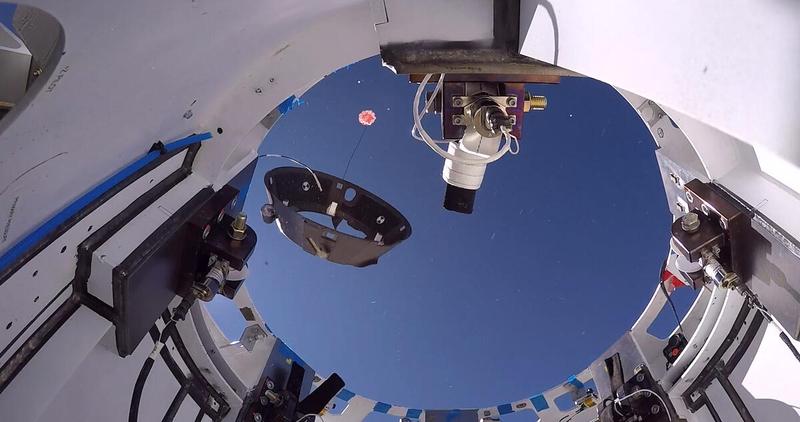

Boeing CST-100 Starliner’s forward heat shield jettisons from a test article during the vehicle’s final balloon drop parachute test at White Sands, New Mexico, on Sept 19, 2020. The test is part of a reliability campaign that will help strengthen the spacecraft’s landing system ahead of crewed flights to and from the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.
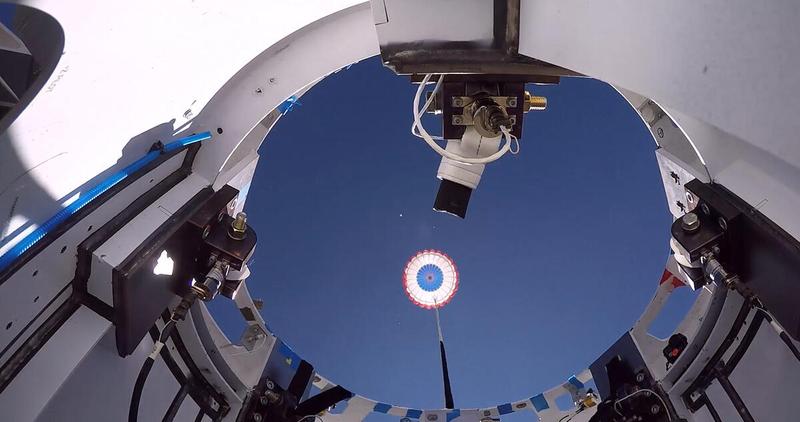
A reused drogue parachute deploys from Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner test article during the final balloon drop parachute test above White Sands, New Mexico, on Sept. 19, 2020. The test is part of a reliability campaign that will help strengthen the spacecraft’s landing system ahead of crewed flights to and from the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.
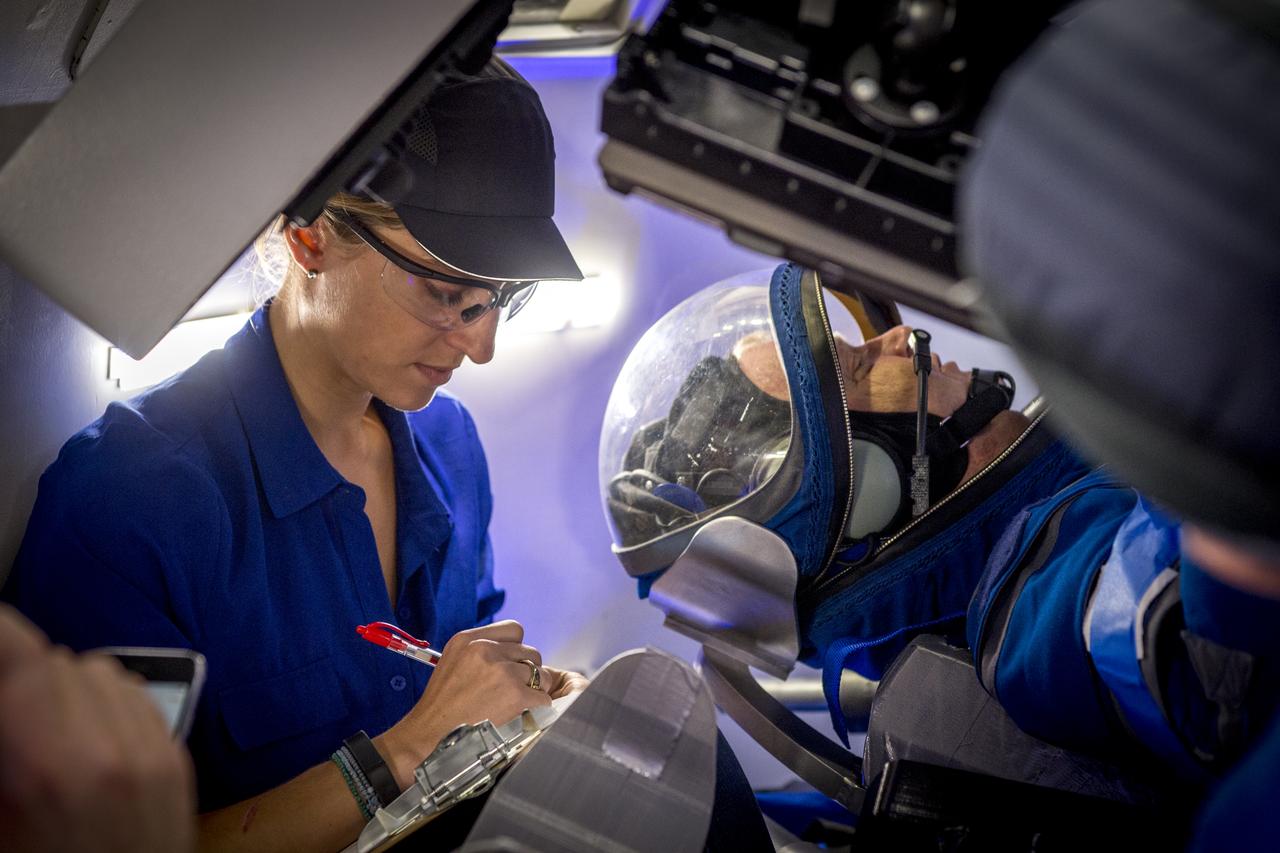

NASA astronaut Eric Boe wears Boeing's new spacesuit designed to be worn by astronauts flying on the CST-100 Starliner. The suit is lighter and more flexible than previous spacesuits but retains the ability to pressurize in an emergency. Astronauts will wear the suit throughout the launch and ascent into orbit as well as on the way back to Earth. Starliners will launch atop Atlas V rockets from United Launch Alliance on missions including flights to the International Space Station for NASA's Commercial Crew Program. NASA's commercial crew astronauts Boe and Suni Williams tried on the suits at Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. Boe, Williams, Bob Behnken, and Doug Hurley were selected by NASA in July 2015 to train for commercial crew test flights aboard the Starliner and SpaceX’s Crew Dragon spacecraft. The flight assignments have not been set, so all four of the astronauts are rehearsing heavily for flights aboard both vehicles. Photo credit: Boeing
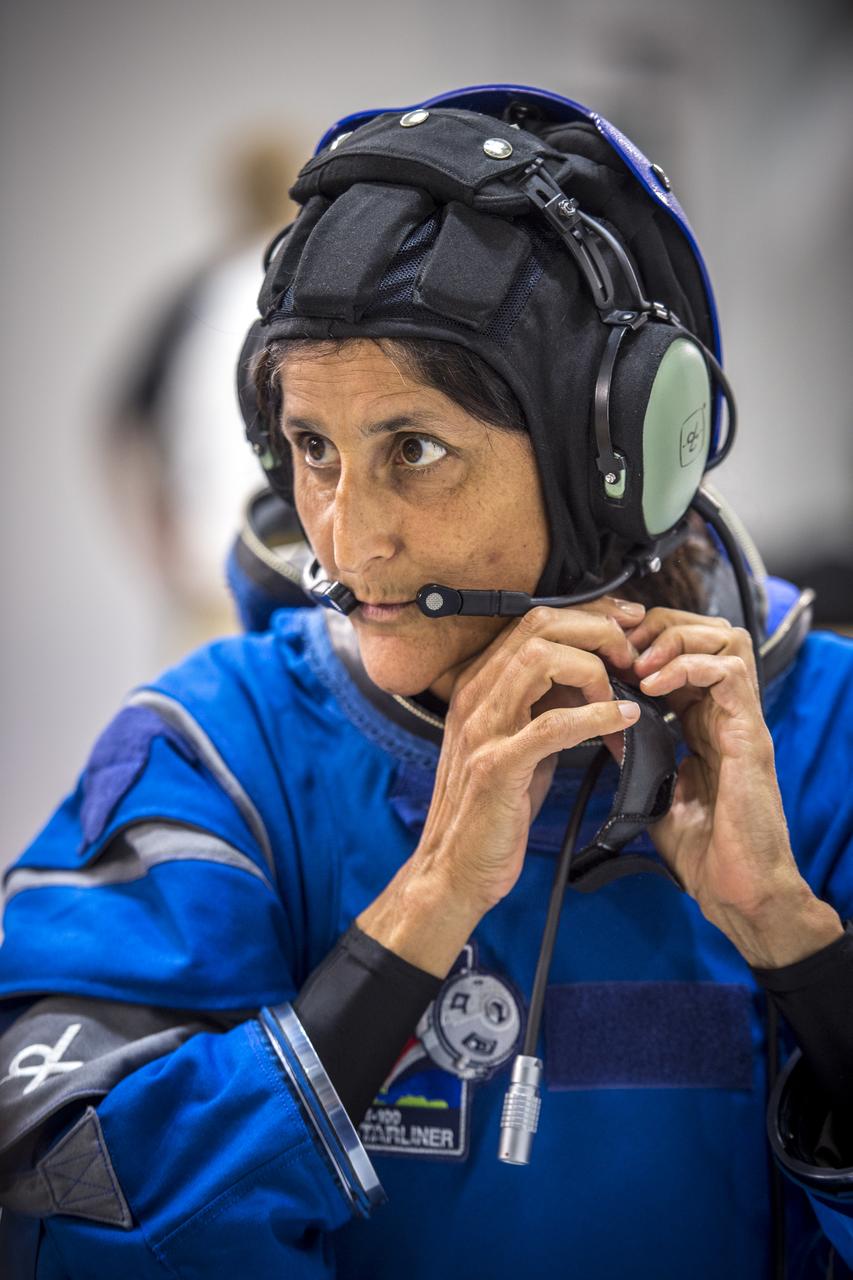

NASA astronaut Suni Williams wears Boeing's new spacesuit designed to be worn by astronauts flying on the CST-100 Starliner. The suit is lighter and more flexible than previous spacesuits but retains the ability to pressurize in an emergency. Astronauts will wear the suit throughout the launch and ascent into orbit as well as on the way back to Earth. Starliners will launch atop Atlas V rockets from United Launch Alliance on missions including flights to the International Space Station for NASA's Commercial Crew Program. NASA's commercial crew astronauts Eric Boe and Williams tried on the suits at Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. Boe, Williams, Bob Behnken, and Doug Hurley were selected by NASA in July 2015 to train for commercial crew test flights aboard the Starliner and SpaceX’s Crew Dragon spacecraft. The flight assignments have not been set, so all four of the astronauts are rehearsing heavily for flights aboard both vehicles. Photo credit: Boeing
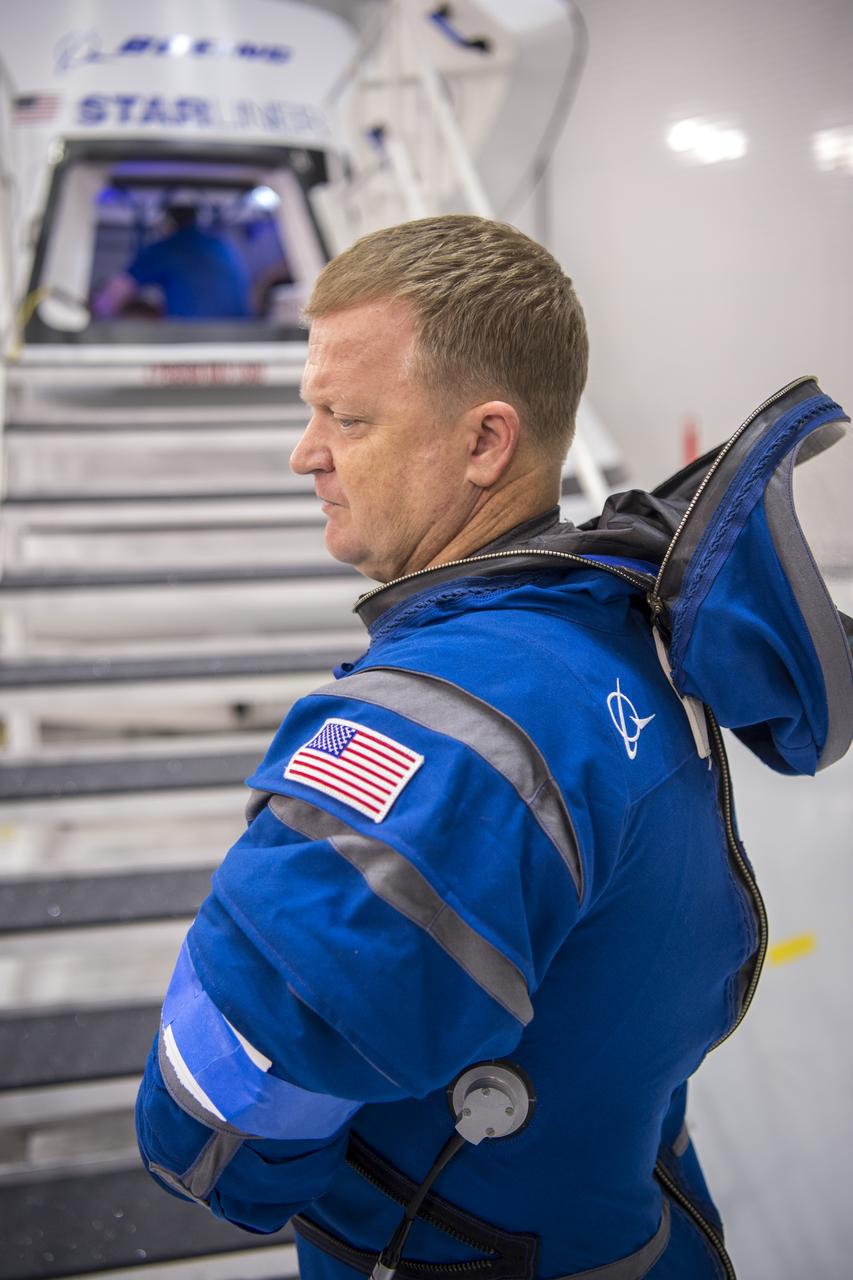

NASA astronaut Eric Boe wears Boeing's new spacesuit designed to be worn by astronauts flying on the CST-100 Starliner. The suit is lighter and more flexible than previous spacesuits but retains the ability to pressurize in an emergency. Astronauts will wear the suit throughout the launch and ascent into orbit as well as on the way back to Earth. Starliners will launch atop Atlas V rockets from United Launch Alliance on missions including flights to the International Space Station for NASA's Commercial Crew Program. NASA's commercial crew astronauts Boe and Suni Williams tried on the suits at Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. Boe, Williams, Bob Behnken, and Doug Hurley were selected by NASA in July 2015 to train for commercial crew test flights aboard the Starliner and SpaceX’s Crew Dragon spacecraft. The flight assignments have not been set, so all four of the astronauts are rehearsing heavily for flights aboard both vehicles. Photo credit: Boeing
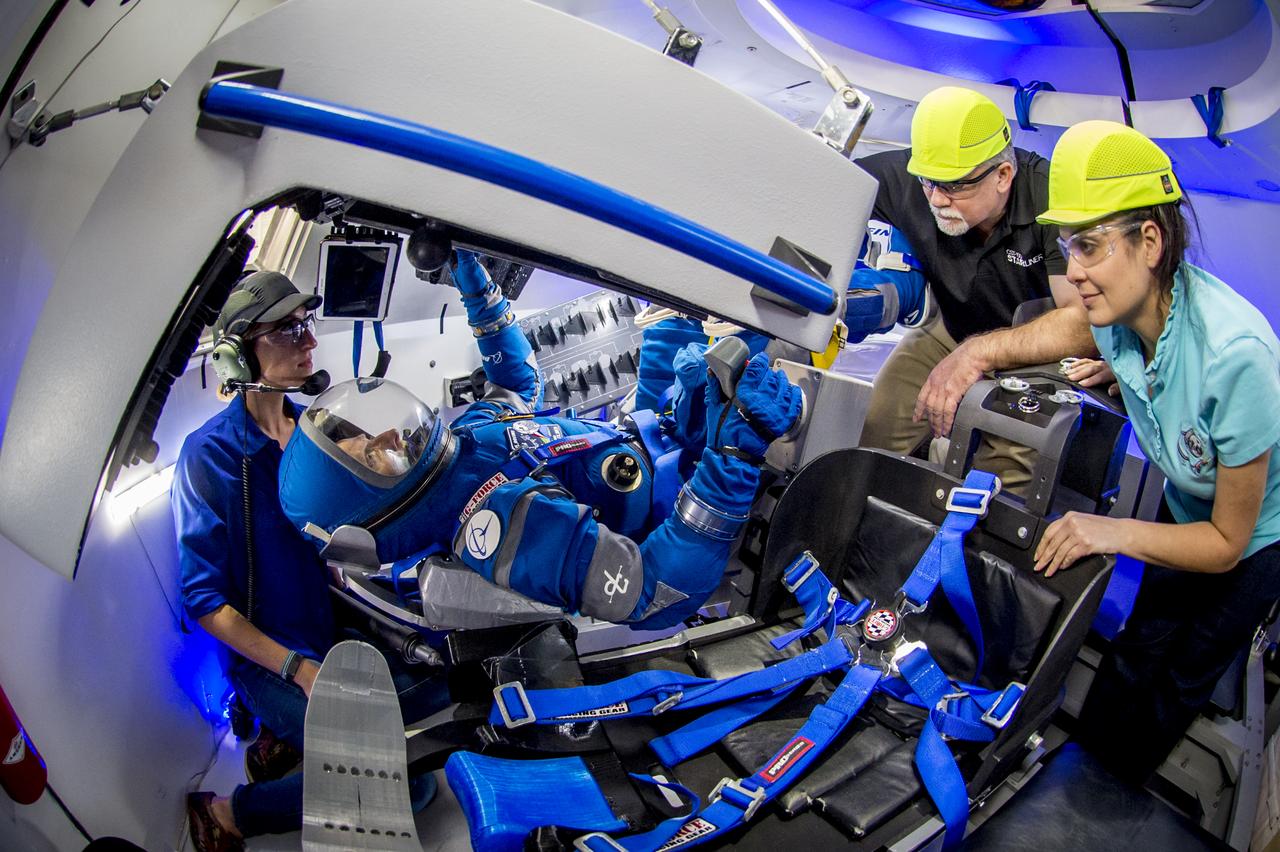

Boeing's Chris Ferguson wears Boeing's new spacesuit designed to be worn by astronauts flying on the CST-100 Starliner. The suit is lighter and more flexible than previous spacesuits but retains the ability to pressurize in an emergency. Astronauts will wear the suit throughout the launch and ascent into orbit as well as on the way back to Earth. Starliners will launch atop Atlas V rockets from United Launch Alliance on missions including flights to the International Space Station for NASA's Commercial Crew Program. NASA's commercial crew astronauts Eric Boe and Williams tried on the suits at Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. Boe, Williams, Bob Behnken, and Doug Hurley were selected by NASA in July 2015 to train for commercial crew test flights aboard the Starliner and SpaceX’s Crew Dragon spacecraft. The flight assignments have not been set, so all four of the astronauts are rehearsing heavily for flights aboard both vehicles. Photo credit: Boeing
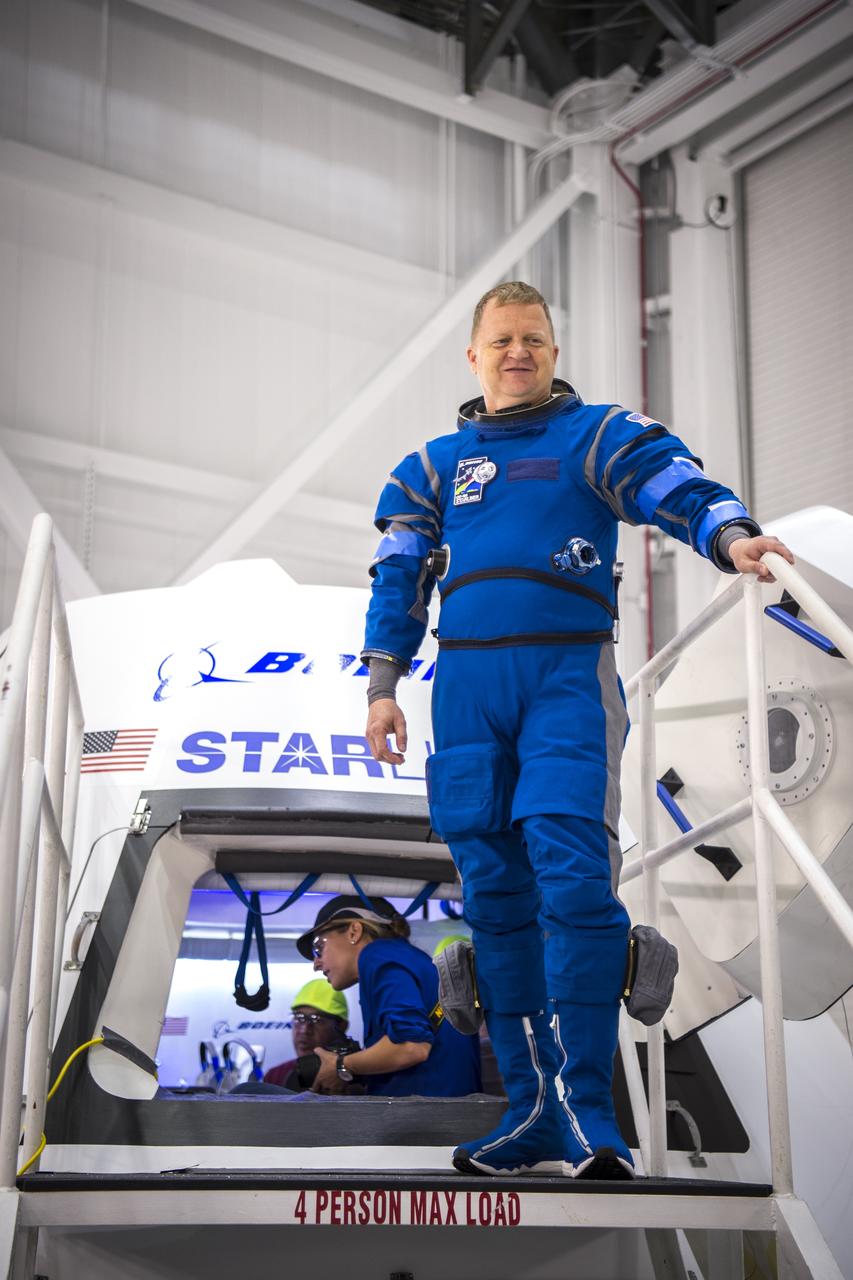

NASA astronaut Eric Boe wears Boeing's new spacesuit designed to be worn by astronauts flying on the CST-100 Starliner. The suit is lighter and more flexible than previous spacesuits but retains the ability to pressurize in an emergency. Astronauts will wear the suit throughout the launch and ascent into orbit as well as on the way back to Earth. Starliners will launch atop Atlas V rockets from United Launch Alliance on missions including flights to the International Space Station for NASA's Commercial Crew Program. NASA's commercial crew astronauts Boe and Suni Williams tried on the suits at Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. Boe, Williams, Bob Behnken, and Doug Hurley were selected by NASA in July 2015 to train for commercial crew test flights aboard the Starliner and SpaceX’s Crew Dragon spacecraft. The flight assignments have not been set, so all four of the astronauts are rehearsing heavily for flights aboard both vehicles. Photo credit: Boeing

NASA astronaut Eric Boe wears Boeing's new spacesuit designed to be worn by astronauts flying on the CST-100 Starliner. The suit is lighter and more flexible than previous spacesuits but retains the ability to pressurize in an emergency. Astronauts will wear the suit throughout the launch and ascent into orbit as well as on the way back to Earth. Starliners will launch atop Atlas V rockets from United Launch Alliance on missions including flights to the International Space Station for NASA's Commercial Crew Program. NASA's commercial crew astronauts Boe and Suni Williams tried on the suits at Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. Boe, Williams, Bob Behnken, and Doug Hurley were selected by NASA in July 2015 to train for commercial crew test flights aboard the Starliner and SpaceX’s Crew Dragon spacecraft. The flight assignments have not been set, so all four of the astronauts are rehearsing heavily for flights aboard both vehicles. Photo credit: Boeing

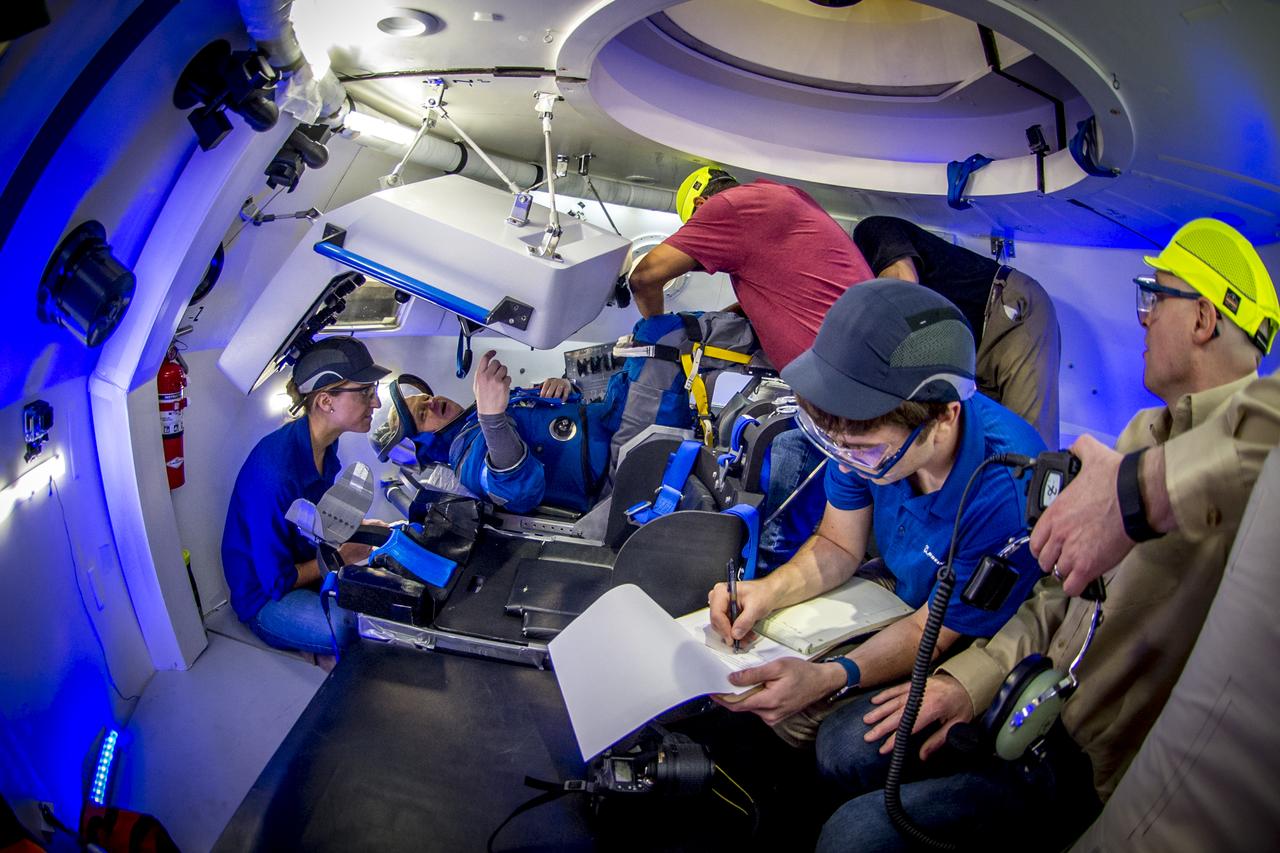
Boeing, NASA and U.S. Army teams rehearse safely bringing the CST-100 Starliner spacecraft home to Earth on Wed., June 6, 2018, at the U.S. Army's White Sands Missile Range in New Mexico. During the detailed landing simulation, engineers, technicians and spaceflight specialists worked through tight timelines and intense heat running through simulations of the spacecraft's landing and recovery, an operation that will cap each Starliner mission. For flight controllers at Mission Control in Houston, the simulation offered the chance to evaluate their own processes and rehearse everything from undocking the Starliner from the space station to communicating with the recovery teams in the field.

Boeing, NASA and U.S. Army teams rehearse safely bringing the CST-100 Starliner spacecraft home to Earth on Wed., June 6, 2018, at the U.S. Army's White Sands Missile Range in New Mexico. During the detailed landing simulation, engineers, technicians and spaceflight specialists worked through tight timelines and intense heat running through simulations of the spacecraft's landing and recovery, an operation that will cap each Starliner mission. For flight controllers at Mission Control in Houston, the simulation offered the chance to evaluate their own processes and rehearse everything from undocking the Starliner from the space station to communicating with the recovery teams in the field.

Boeing, NASA and U.S. Army teams rehearse safely bringing the CST-100 Starliner spacecraft home to Earth on Wed., June 6, 2018, at the U.S. Army's White Sands Missile Range in New Mexico. During the detailed landing simulation, engineers, technicians and spaceflight specialists worked through tight timelines and intense heat running through simulations of the spacecraft's landing and recovery, an operation that will cap each Starliner mission. For flight controllers at Mission Control in Houston, the simulation offered the chance to evaluate their own processes and rehearse everything from undocking the Starliner from the space station to communicating with the recovery teams in the field.

Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner lands in the New Mexico desert in the company’s Pad Abort Test for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The test, conducted Nov. 4 at the White Sands Missile Range, was designed to verify that each of Starliner’s systems will function not only separately, but in concert, to protect astronauts by carrying them safely away from the launch pad in the unlikely event of an emergency prior to liftoff. Starliner touched down on land approximately 90 seconds after the test began, about one mile from the test stand at Launch Complex 32. This is Boeing’s first test flight for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, which is working to launch astronauts on American rockets and spacecraft from American soil for the first time since 2011.

Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner lands in the New Mexico desert in the company’s Pad Abort Test for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The test, conducted Nov. 4 at the White Sands Missile Range, was designed to verify that each of Starliner’s systems will function not only separately, but in concert, to protect astronauts by carrying them safely away from the launch pad in the unlikely event of an emergency prior to liftoff. Starliner touched down on land approximately 90 seconds after the test began, about one mile from the test stand at Launch Complex 32. This is Boeing’s first test flight for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, which is working to launch astronauts on American rockets and spacecraft from American soil for the first time since 2011.

Boeing, NASA, and U.S. Army personnel work around the Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft shortly after it landed in White Sands, New Mexico, Sunday, Dec. 22, 2019. The landing completes an abbreviated Orbital Flight Test for the company that still meets several mission objectives for NASA’s Commercial Crew program. The Starliner spacecraft launched on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket at 6:36 a.m. Friday, Dec. 20 from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Boeing, NASA, and U.S. Army personnel prepare for the Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft landing in White Sands, New Mexico, Sunday, Dec. 22, 2019. The landing will complete an abbreviated Orbital Flight Test for the company that still meets several mission objectives for NASA’s Commercial Crew program. The Starliner spacecraft launched on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket at 6:36 a.m. Friday, Dec. 20 from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
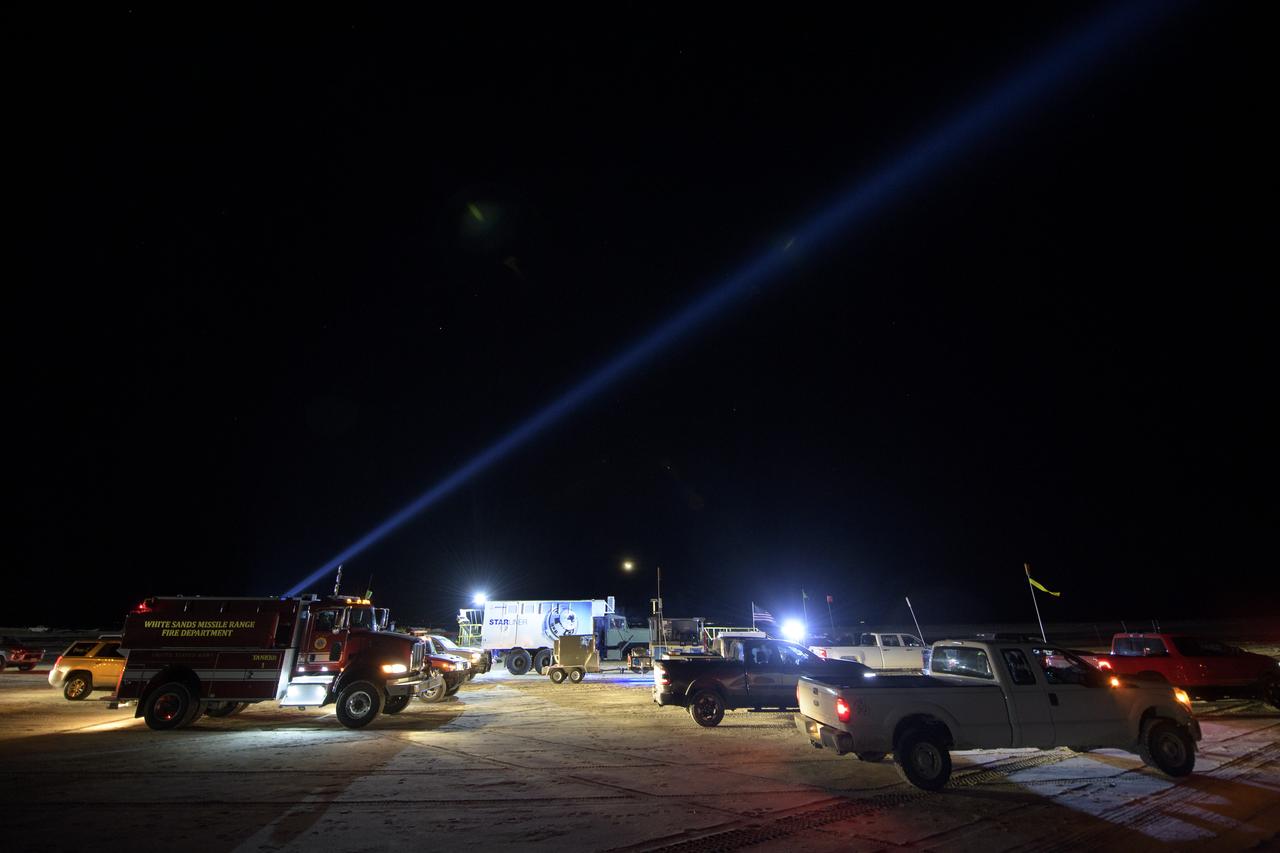

Boeing, NASA, and U.S. Army personnel prepare for the Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft landing in White Sands, New Mexico, Sunday, Dec. 22, 2019. The landing will complete an abbreviated Orbital Flight Test for the company that still meets several mission objectives for NASA’s Commercial Crew program. The Starliner spacecraft launched on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket at 6:36 a.m. Friday, Dec. 20 from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
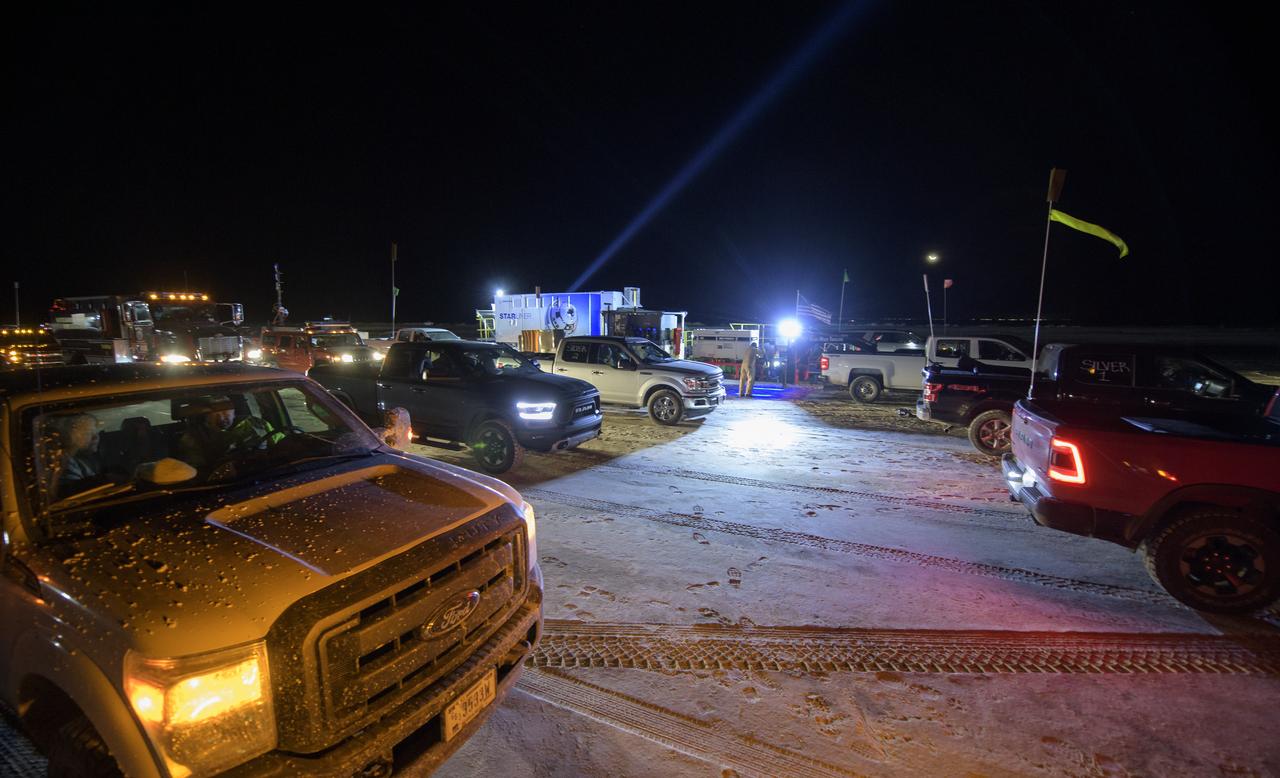

Boeing, NASA, and U.S. Army personnel prepare for the Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft landing in White Sands, New Mexico, Sunday, Dec. 22, 2019. The landing will complete an abbreviated Orbital Flight Test for the company that still meets several mission objectives for NASA’s Commercial Crew program. The Starliner spacecraft launched on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket at 6:36 a.m. Friday, Dec. 20 from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
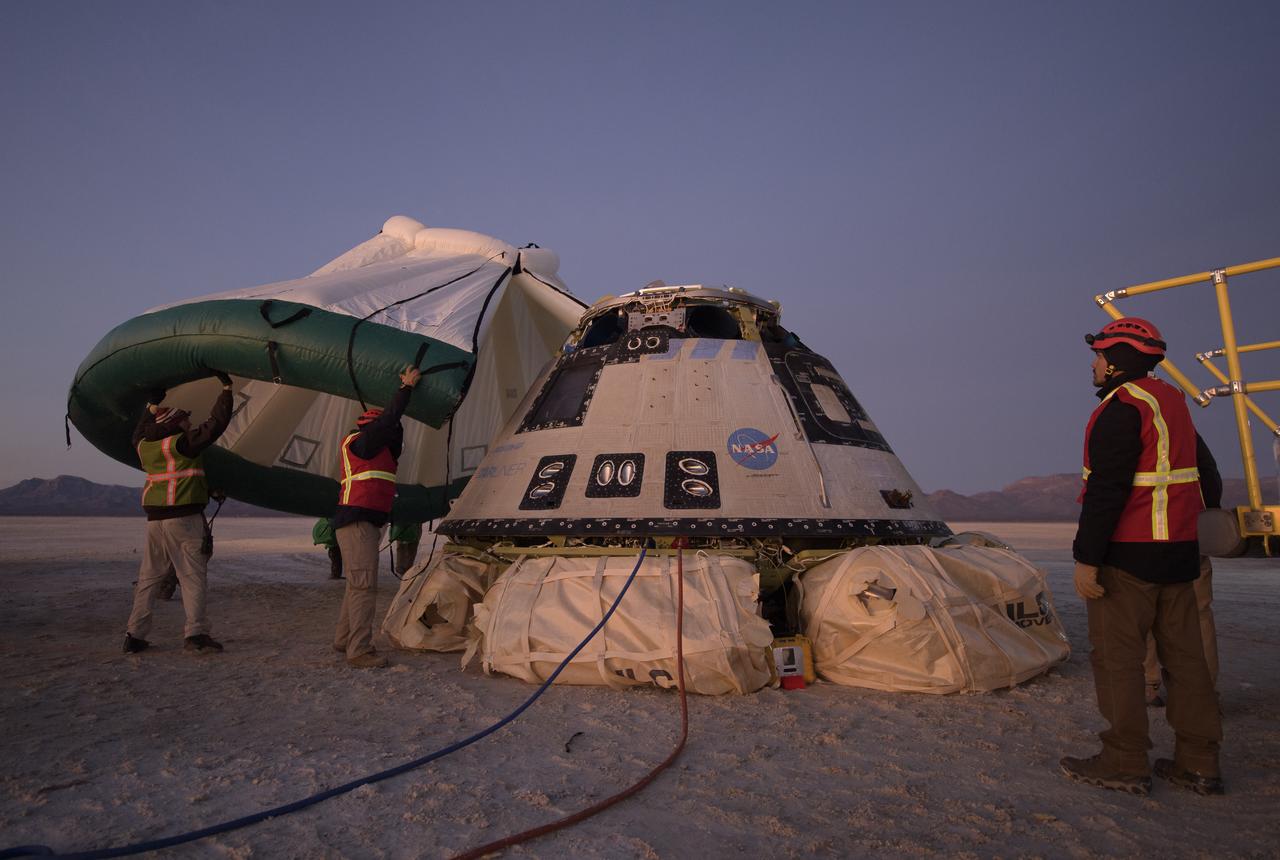

Boeing, NASA, and U.S. Army personnel work around the Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft shortly after it landed in White Sands, New Mexico, Sunday, Dec. 22, 2019. The landing completes an abbreviated Orbital Flight Test for the company that still meets several mission objectives for NASA’s Commercial Crew program. The Starliner spacecraft launched on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket at 6:36 a.m. Friday, Dec. 20 from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
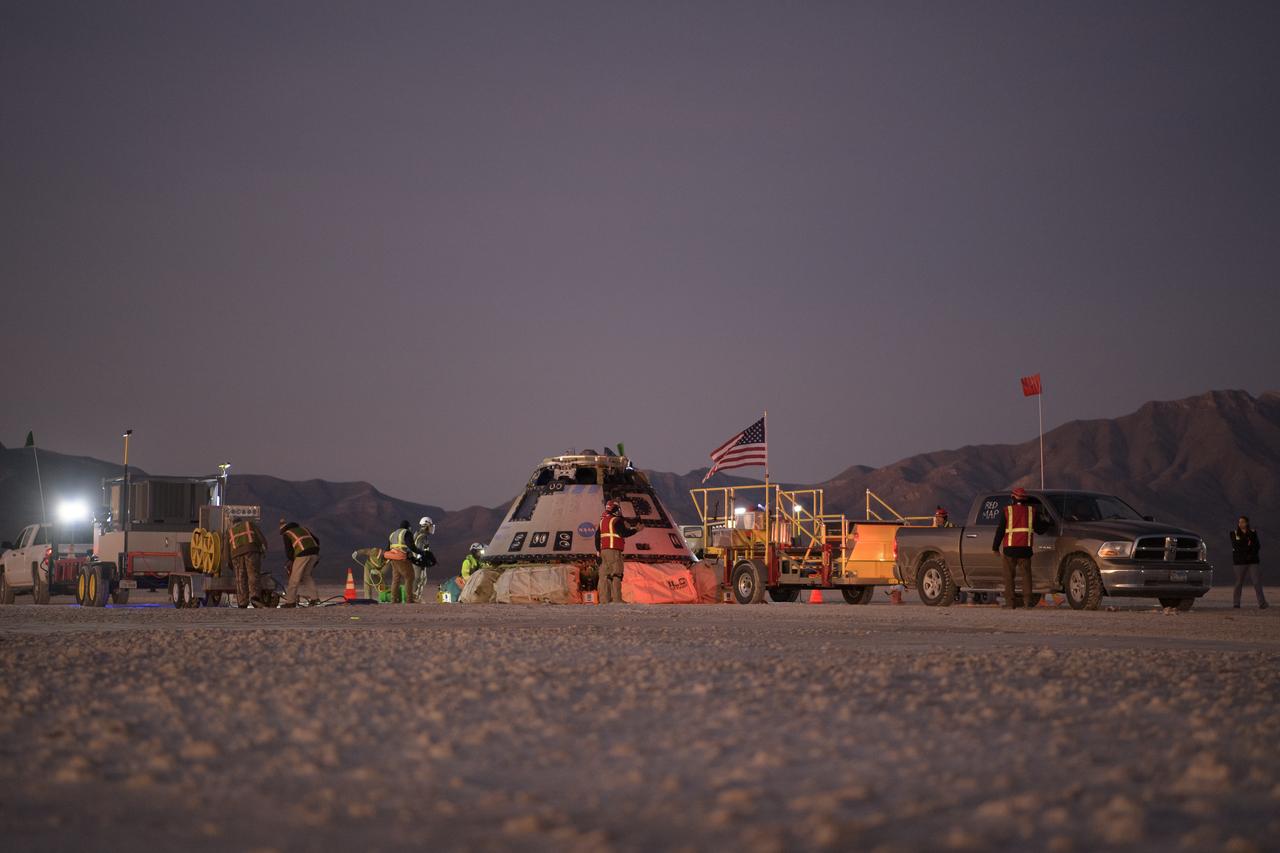

Boeing, NASA, and U.S. Army personnel work around the Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft shortly after it landed in White Sands, New Mexico, Sunday, Dec. 22, 2019. The landing completes an abbreviated Orbital Flight Test for the company that still meets several mission objectives for NASA’s Commercial Crew program. The Starliner spacecraft launched on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket at 6:36 a.m. Friday, Dec. 20 from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
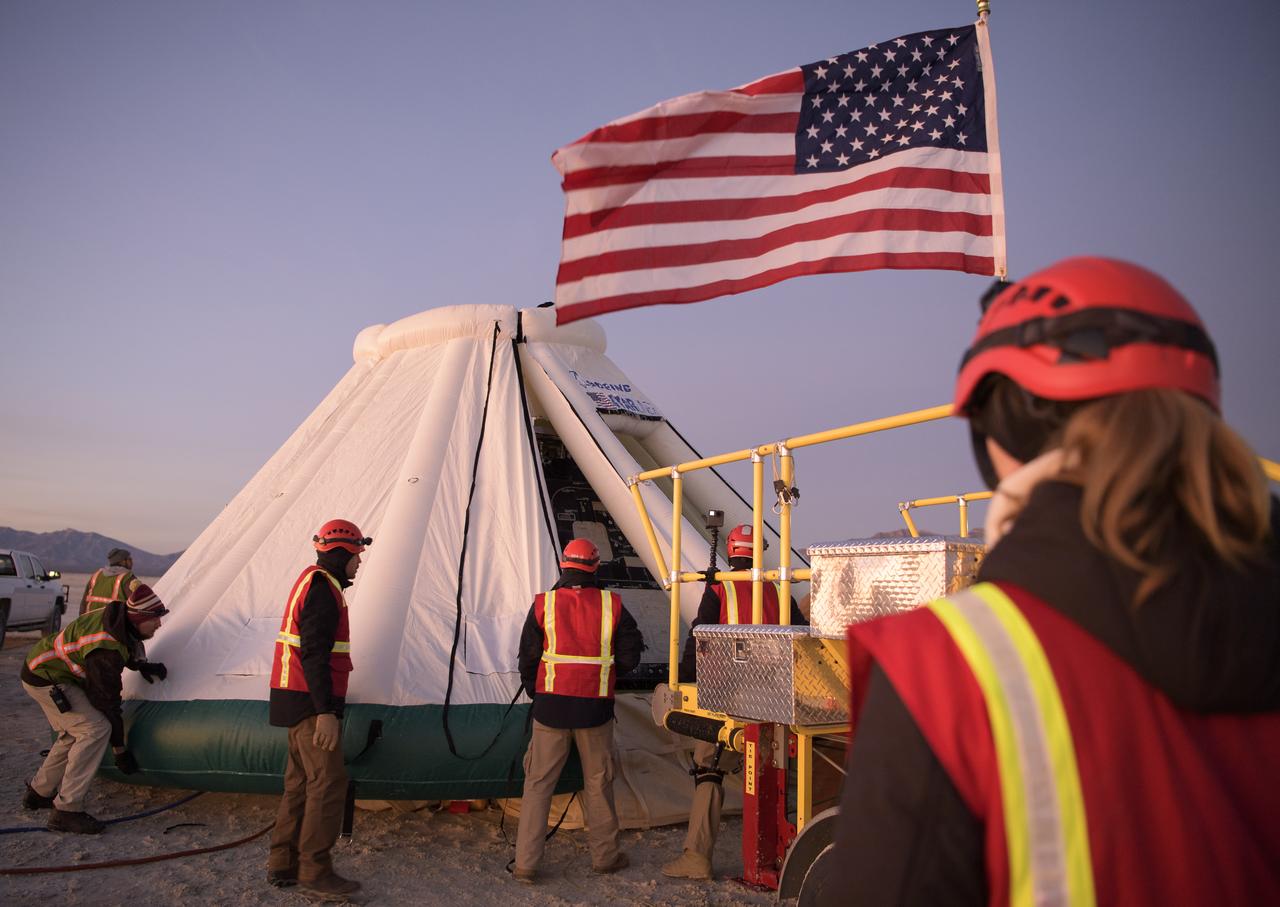

Boeing, NASA, and U.S. Army personnel work around the Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft shortly after it landed in White Sands, New Mexico, Sunday, Dec. 22, 2019. The landing completes an abbreviated Orbital Flight Test for the company that still meets several mission objectives for NASA’s Commercial Crew program. The Starliner spacecraft launched on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket at 6:36 a.m. Friday, Dec. 20 from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
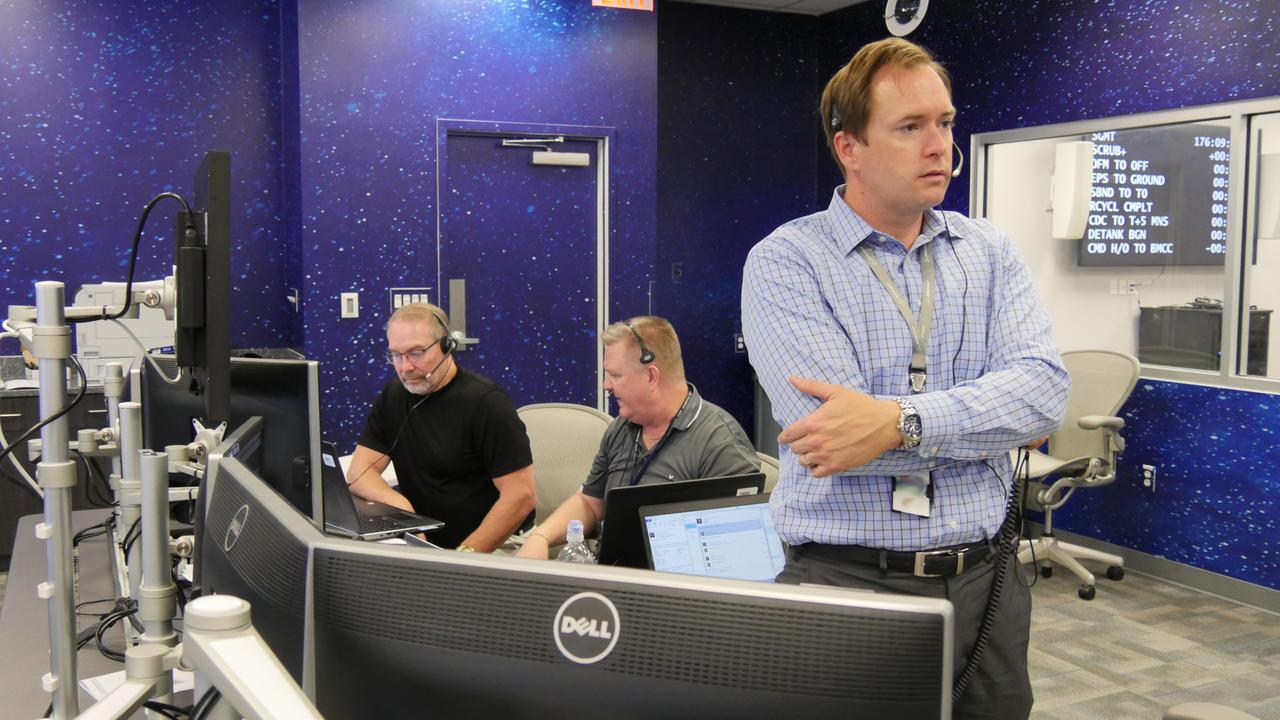

Inside the Boeing Mission Control Center at Kennedy Space Center, Fla., launch control teams for the CST-100 Starliner rehearse a fully integrated prelaunch simulation of the spacecraft’s upcoming Orbital Flight Test. Boeing Spacecraft Launch Conductor Louis Atchison speaks on console to the Mission Management Team as the countdown in the launch simulation progresses.
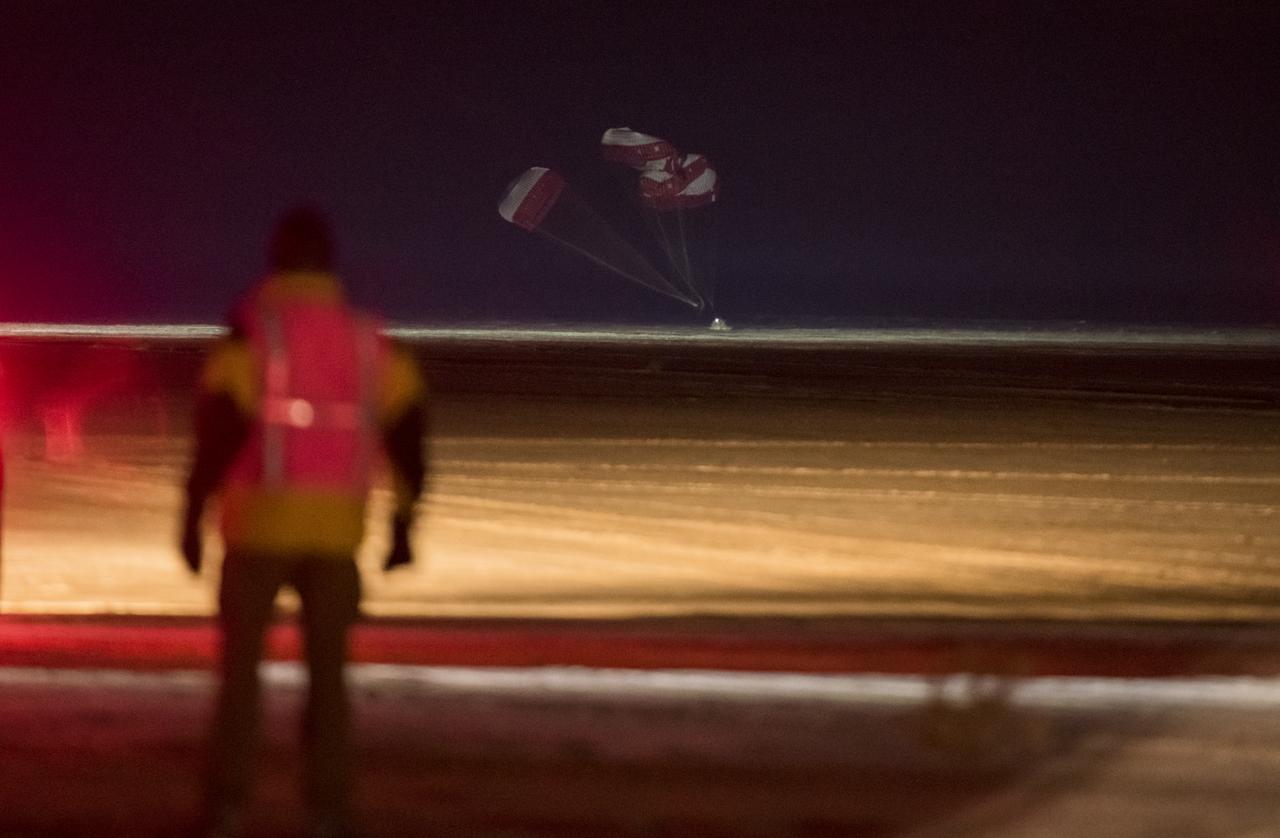

The Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft lands in White Sands, New Mexico, Sunday, Dec. 22, 2019. The landing completes an abbreviated Orbital Flight Test for the company that still meets several mission objectives for NASA’s Commercial Crew program. The Starliner spacecraft launched on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket at 6:36 a.m. Friday, Dec. 20 from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
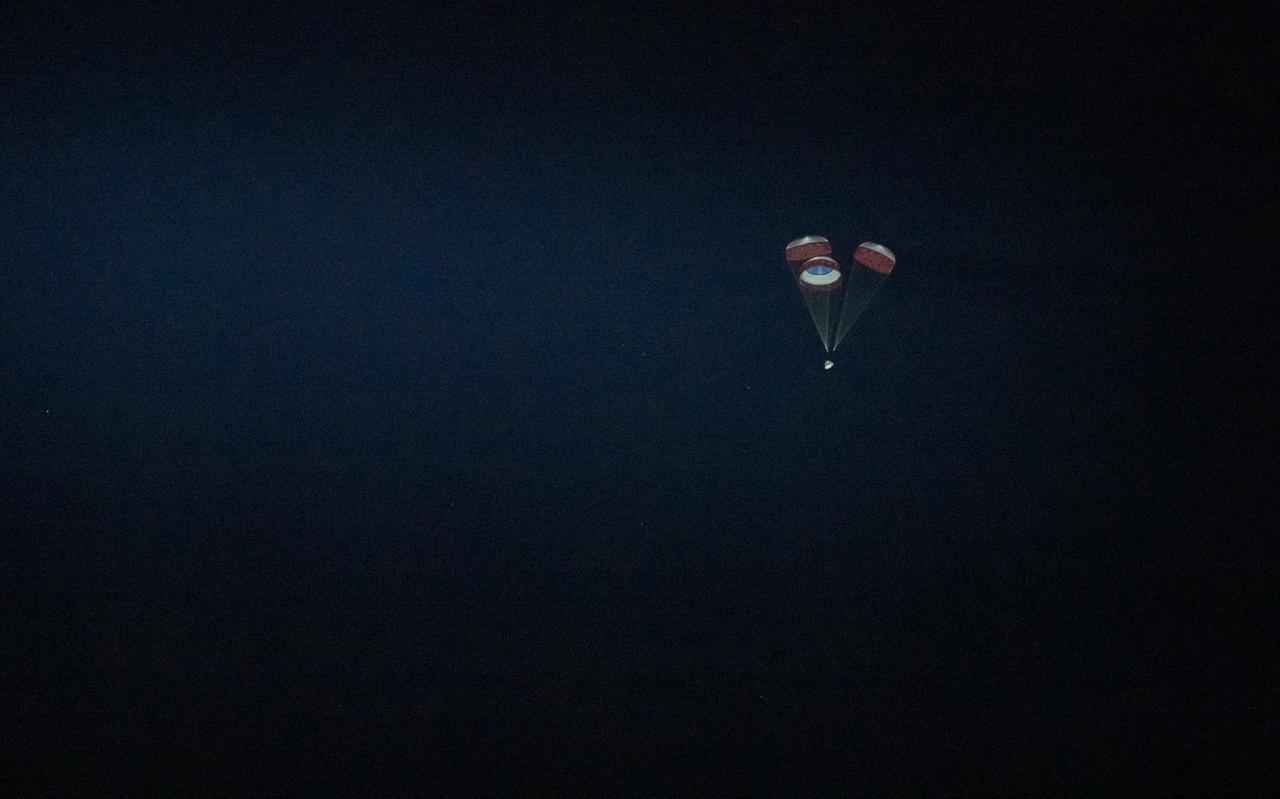

The Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft lands in White Sands, New Mexico, Sunday, Dec. 22, 2019. The landing completes an abbreviated Orbital Flight Test for the company that still meets several mission objectives for NASA’s Commercial Crew program. The Starliner spacecraft launched on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket at 6:36 a.m. Friday, Dec. 20 from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
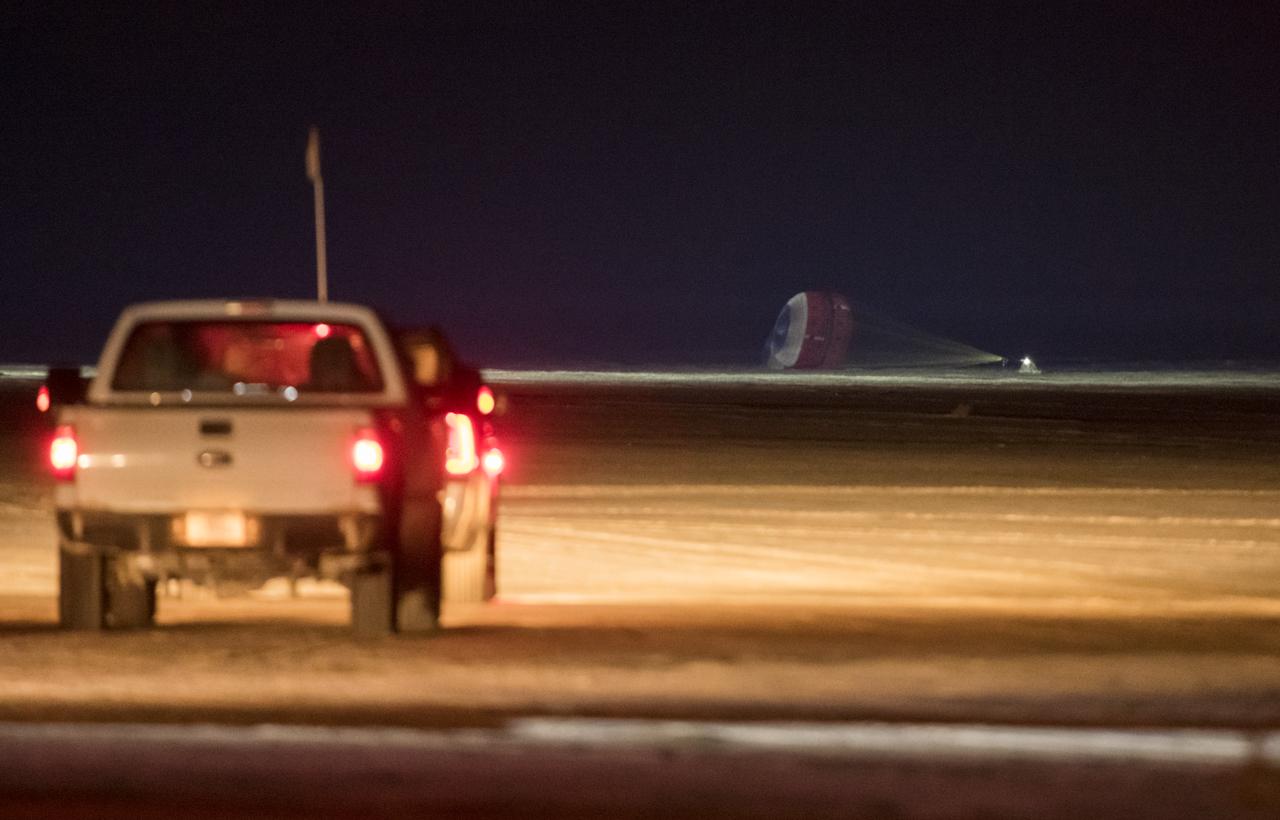

The Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft lands in White Sands, New Mexico, Sunday, Dec. 22, 2019. The landing completes an abbreviated Orbital Flight Test for the company that still meets several mission objectives for NASA’s Commercial Crew program. The Starliner spacecraft launched on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket at 6:36 a.m. Friday, Dec. 20 from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
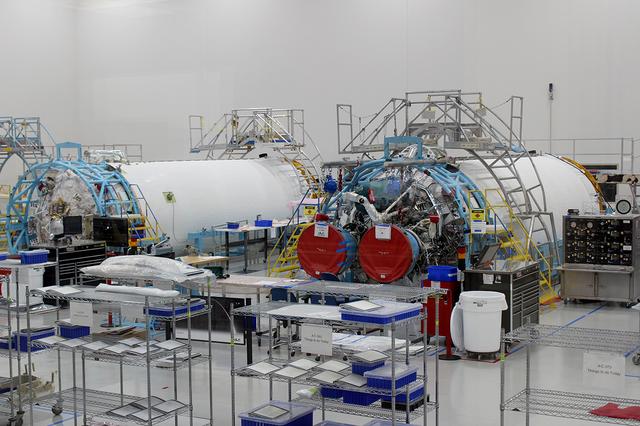

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Crew Flight Test dual engine, at left, and the Orbital Flight test dual engine, at right, for the Centaur stage of the Atlas V rocket are in production on June 11, 2018, at ULA's factory in Decatur, Alabama. Boeing's CST-100 Starliner will launch on its first uncrewed flight test on the ULA Atlas V rocket. The Starliner is being developed and manufactured in partnership with NASA's Commercial Crew Program to return human spaceflight capabilities to the U.S.
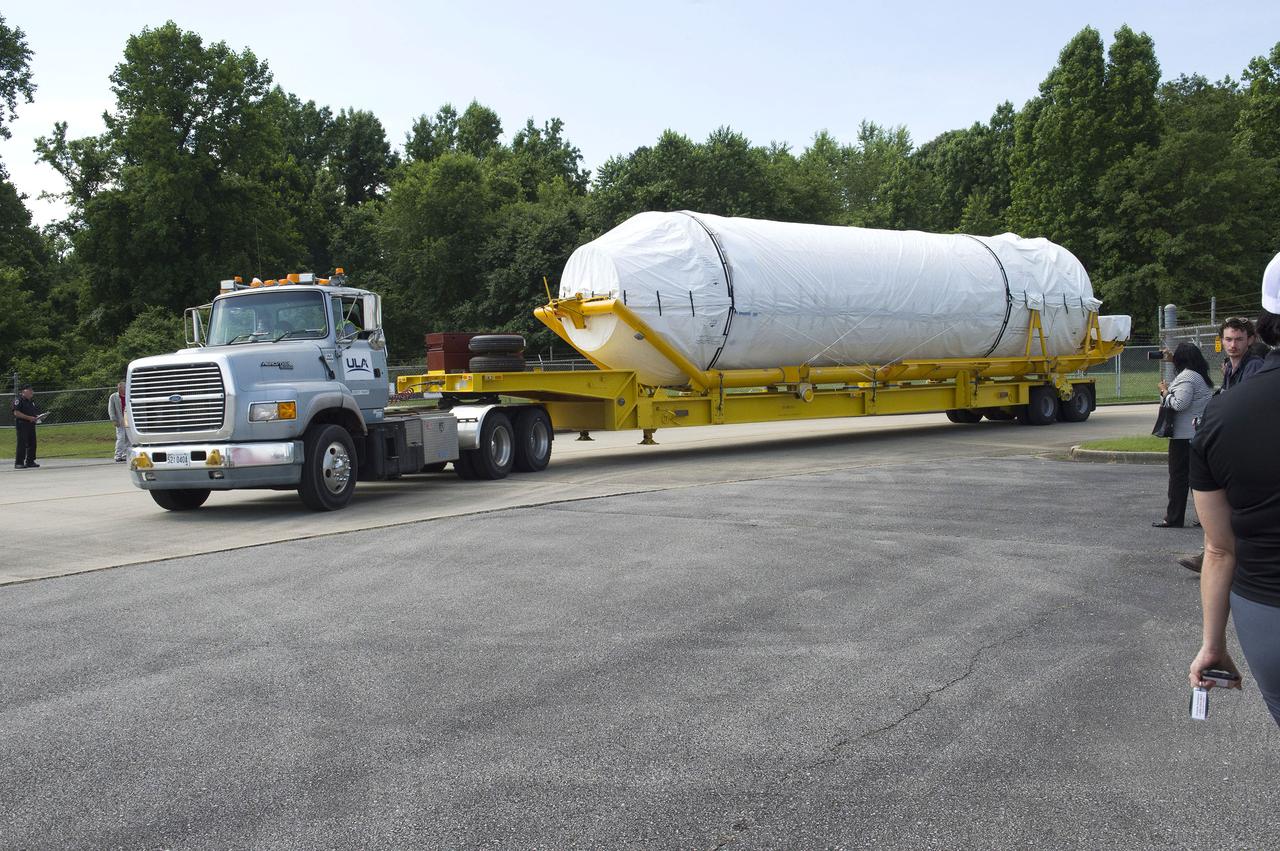

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket that will launch Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner on the Crew Flight Test (CFT) mission to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program emerged from the factory on May 24, 2019, rolling into a giant cargo ship for transport to Cape Canaveral.
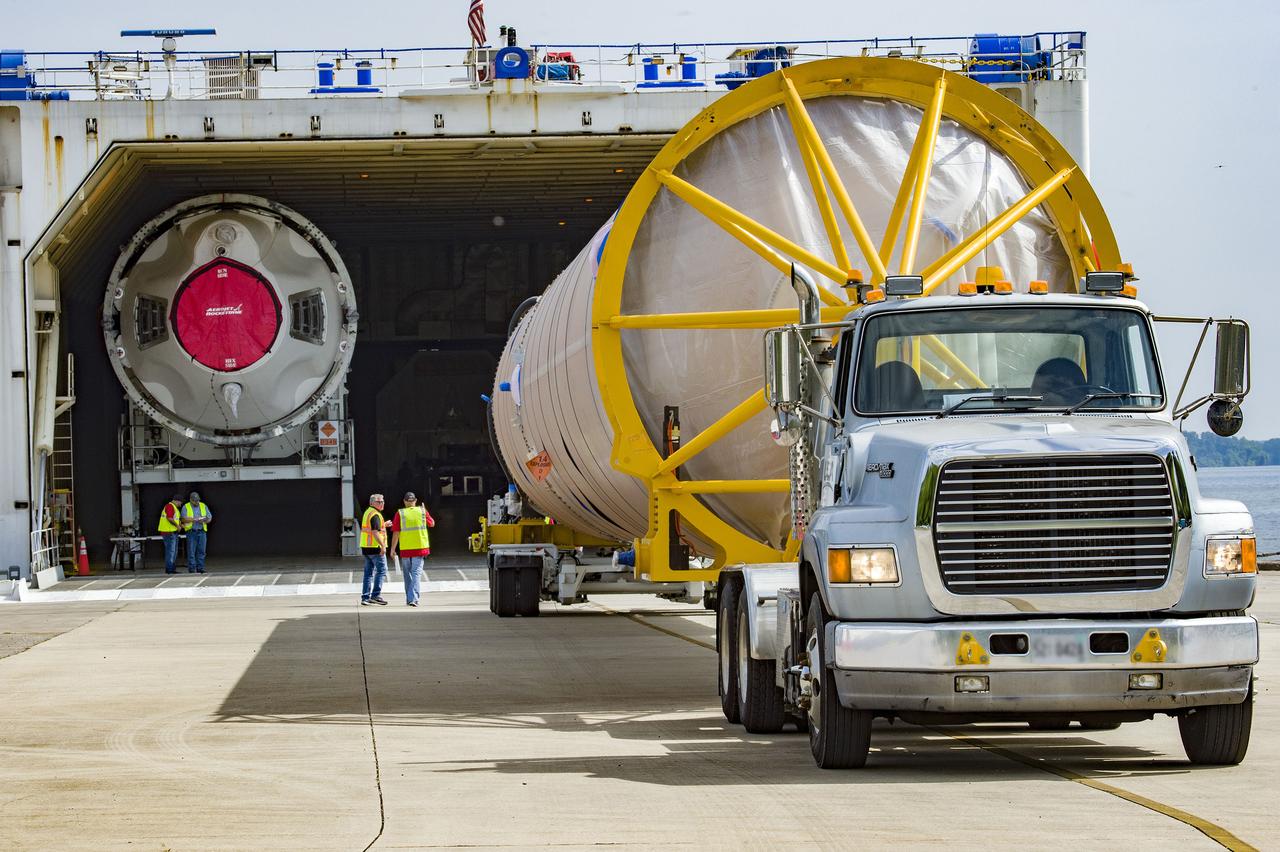

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket that will launch Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner on the Crew Flight Test (CFT) mission to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program emerged from the factory on May 24, 2019, rolling into a giant cargo ship for transport to Cape Canaveral.
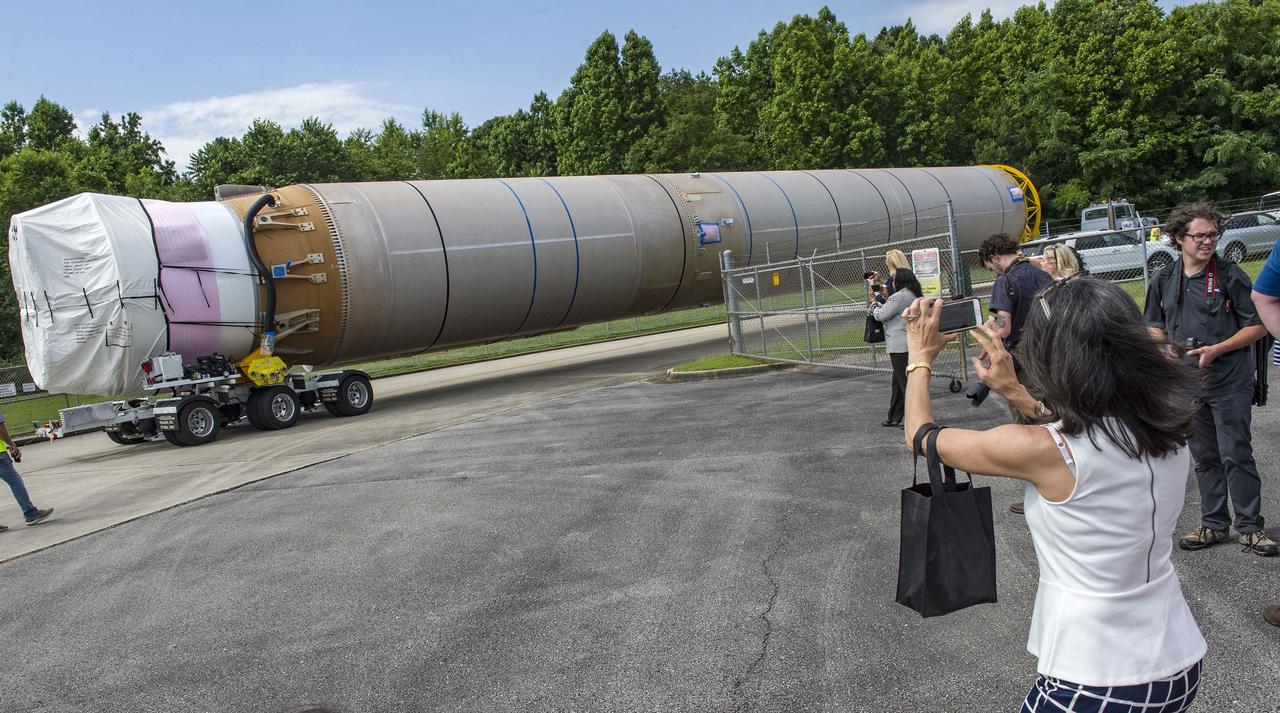

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket that will launch Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner on the Crew Flight Test (CFT) mission to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program emerged from the factory on May 24, 2019, rolling into a giant cargo ship for transport to Cape Canaveral.
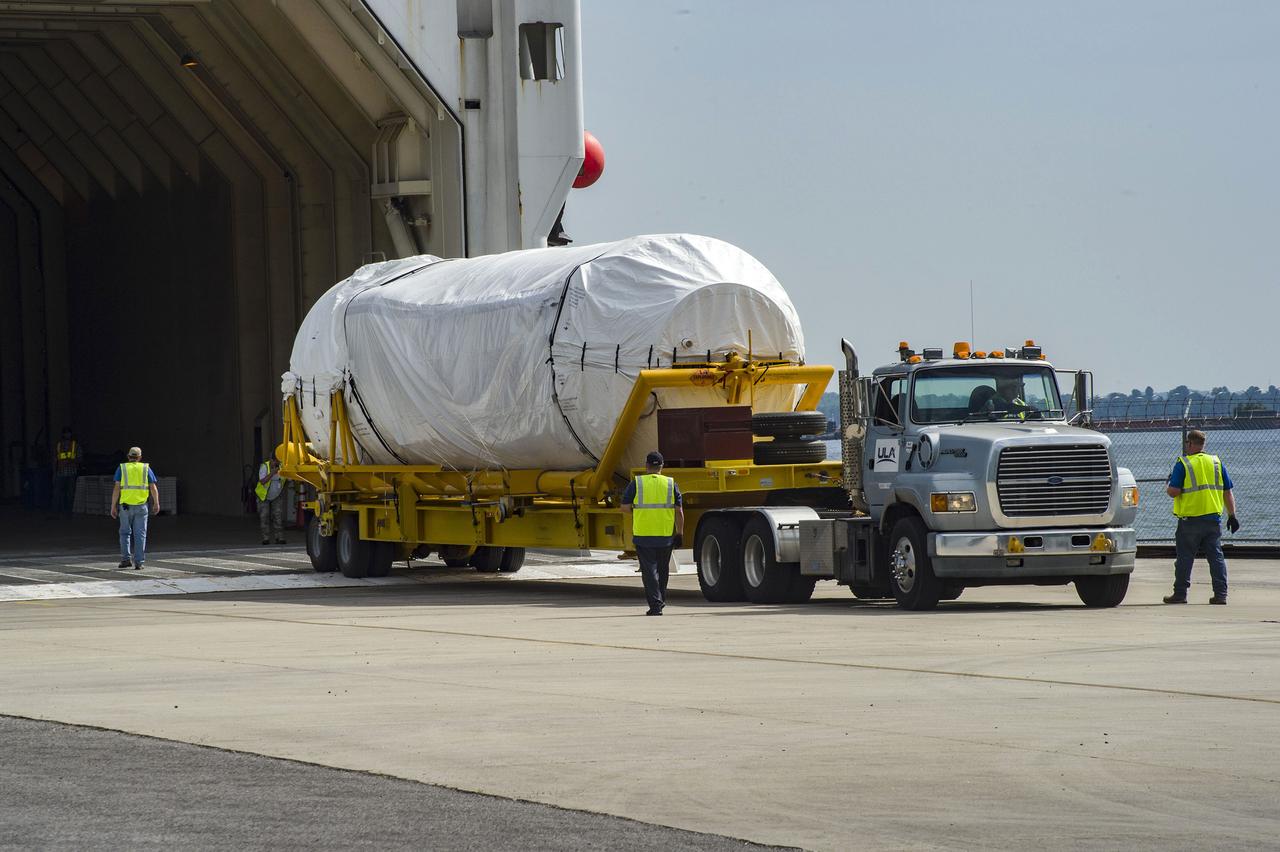

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket that will launch Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner on the Crew Flight Test (CFT) mission to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program emerged from the factory on May 24, 2019, rolling into a giant cargo ship for transport to Cape Canaveral.

Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner’s four launch abort engines and several orbital maneuvering and attitude control thrusters ignite in the company’s Pad Abort Test, pushing the spacecraft away from the test stand with a combined 160,000 pounds of thrust, from Launch Complex 32 on White Sands Missile Range in New Mexico. The test, conducted Nov. 4, 2019, was designed to verify that each of Starliner’s systems will function not only separately, but in concert, to protect astronauts by carrying them safely away from the launch pad in the unlikely event of an emergency prior to liftoff. The Pad Abort Test is Boeing’s first test flight for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, which is working to launch astronauts on American rockets and spacecraft from American soil for the first time since 2011.

Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner’s four launch abort engines and several orbital maneuvering and attitude control thrusters ignite in the company’s Pad Abort Test, pushing the spacecraft away from the test stand with a combined 160,000 pounds of thrust, from Launch Complex 32 on White Sands Missile Range in New Mexico. The test, conducted Nov. 4, 2019, was designed to verify that each of Starliner’s systems will function not only separately, but in concert, to protect astronauts by carrying them safely away from the launch pad in the unlikely event of an emergency prior to liftoff. The Pad Abort Test is Boeing’s first test flight for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, which is working to launch astronauts on American rockets and spacecraft from American soil for the first time since 2011.

The Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft to be flown on Orbital Flight Test-2 (OFT-2) is seen in the Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 12, 2021. Part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program, OFT-2 is a critical developmental milestone on the company’s path to fly crew missions for NASA.
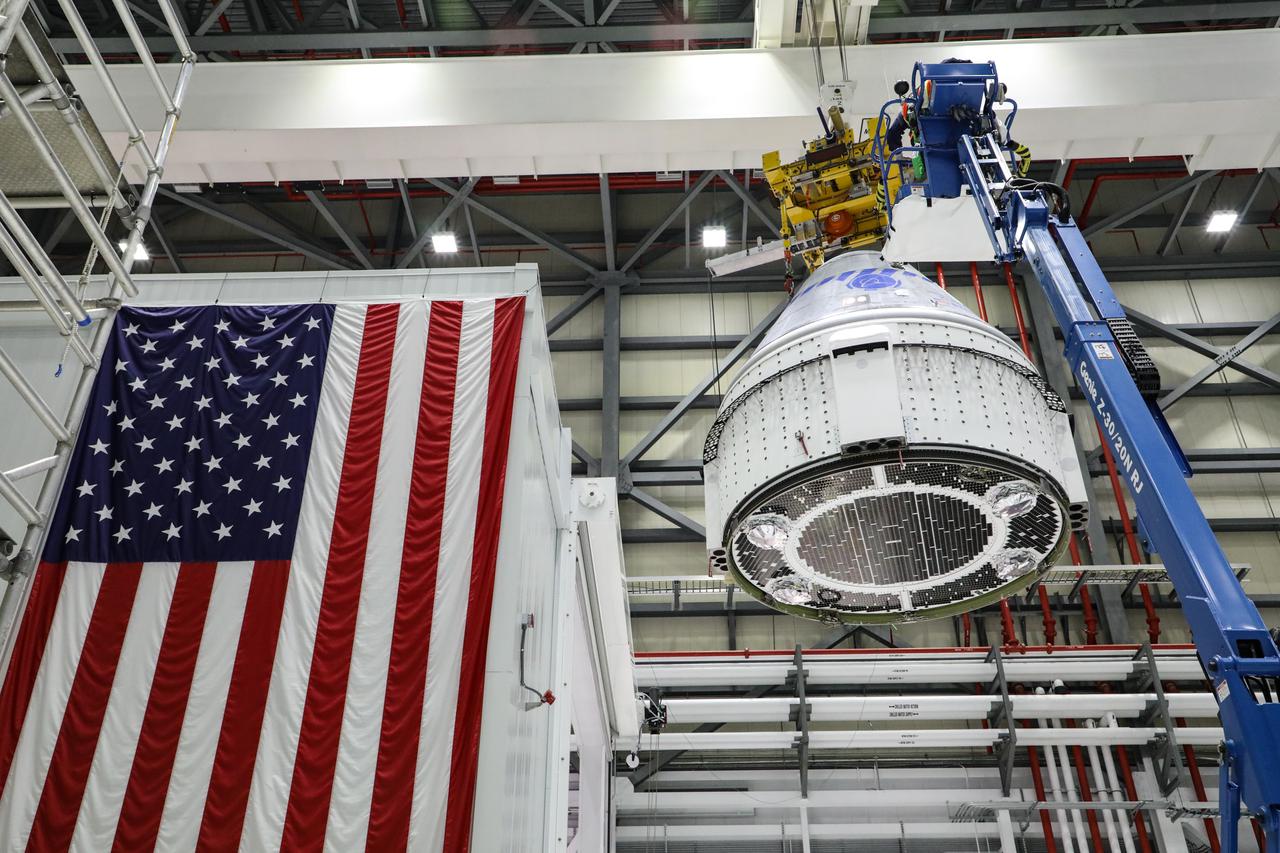

On July 13, 2021, inside the Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft moved from Hazardous Processing Area to the Weight and Center of Gravity machine and then transferred to the KMAG. The operations are in preparation for the company’s second Orbital Flight Test (OFT-2), as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.
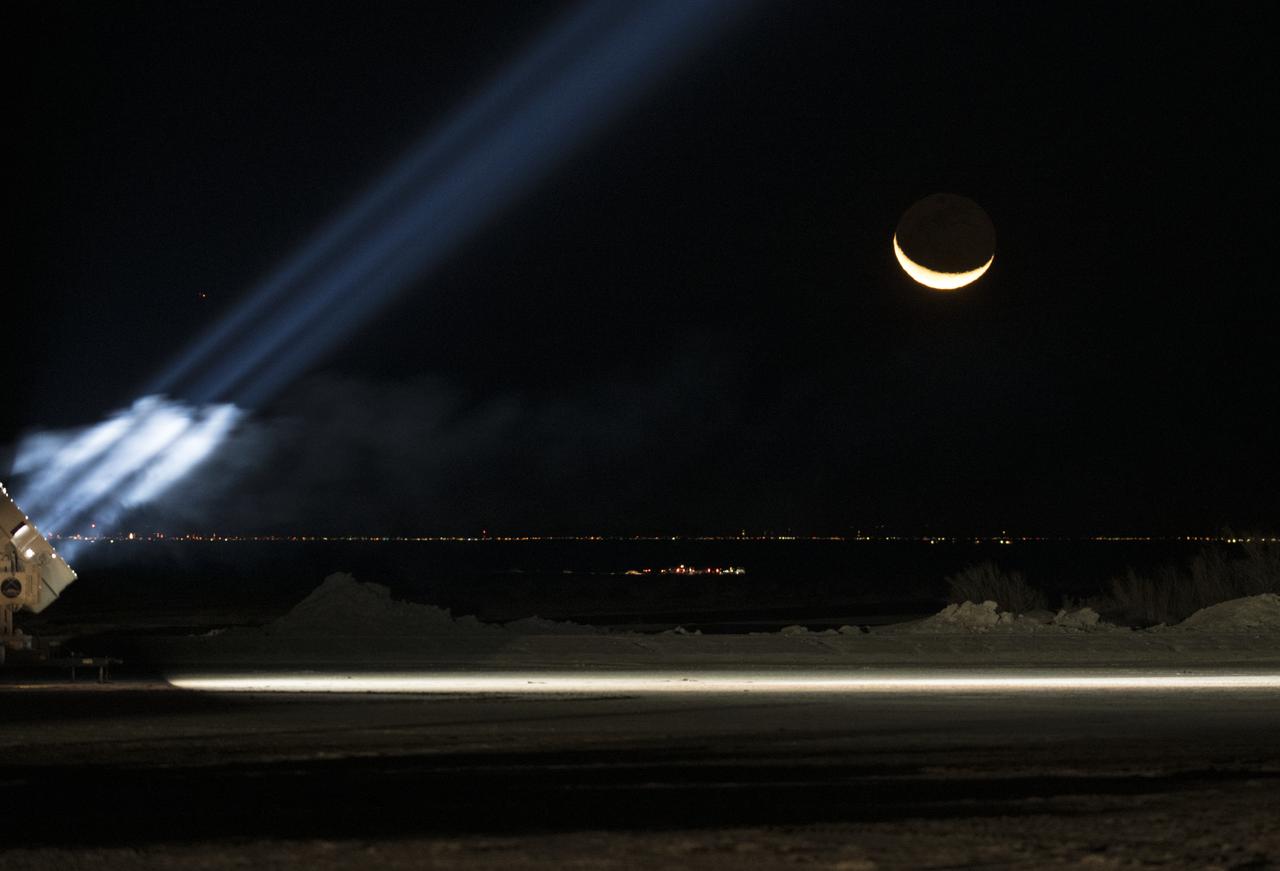

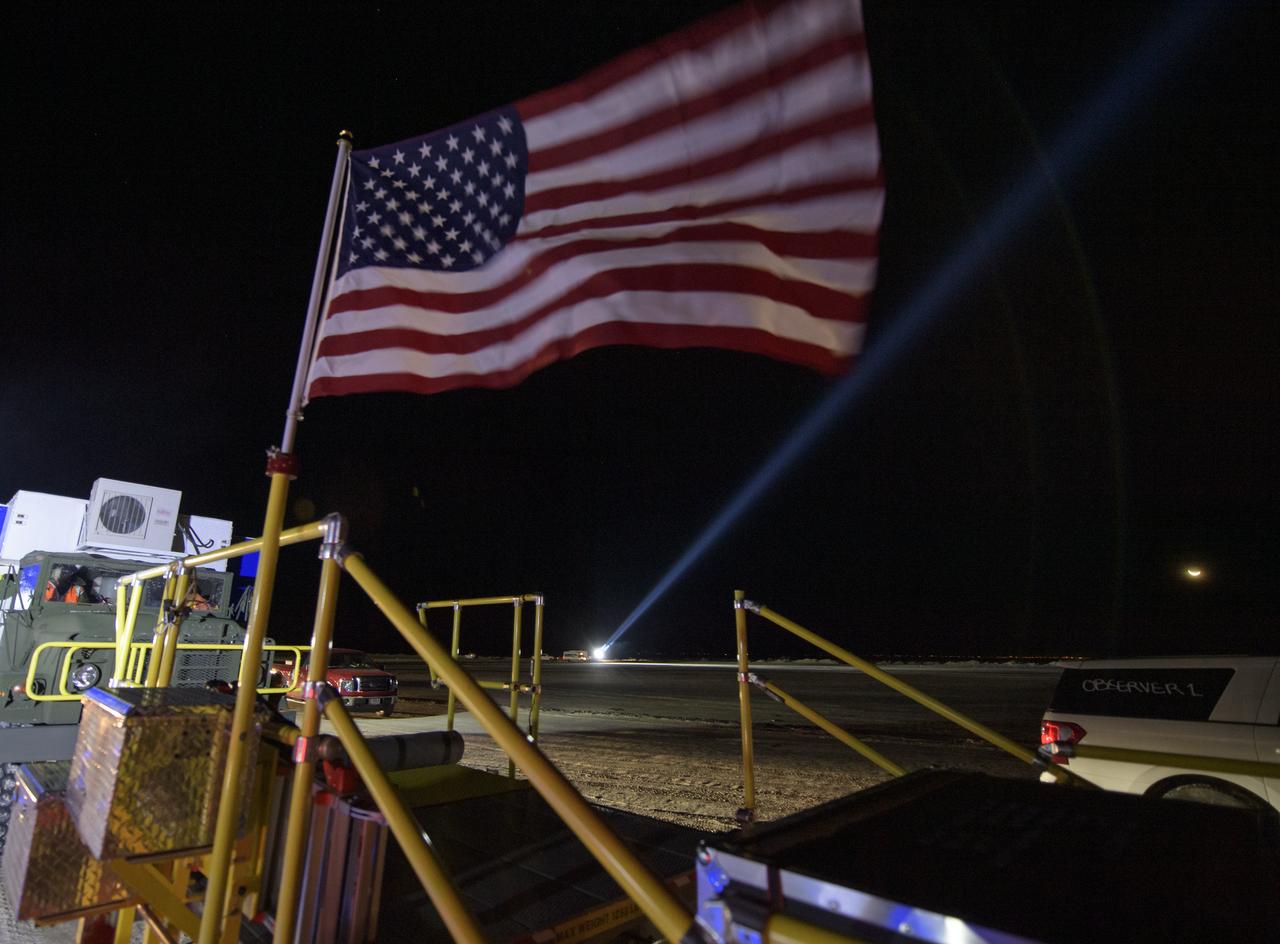
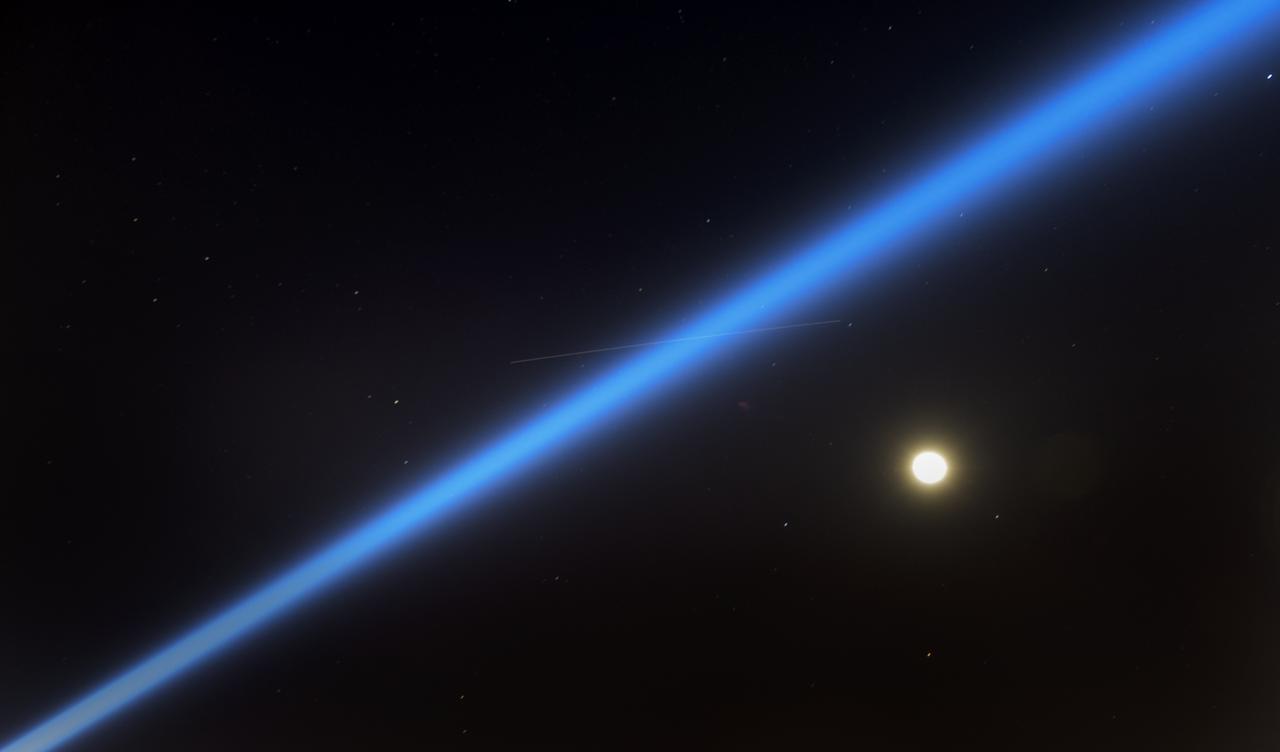
The moon is seen behind the spotlight that will follow the Boeing CST-100 Starliner as it lands in White Sands, New Mexico, Sunday, Dec. 22, 2019. The spacecraft is scheduled to land around 5:57am after an abbreviated Orbital Flight Test for the company that still meets several mission objectives for NASA’s Commercial Crew program. The Starliner spacecraft launched on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket at 6:36 a.m. Friday, Dec. 20 from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
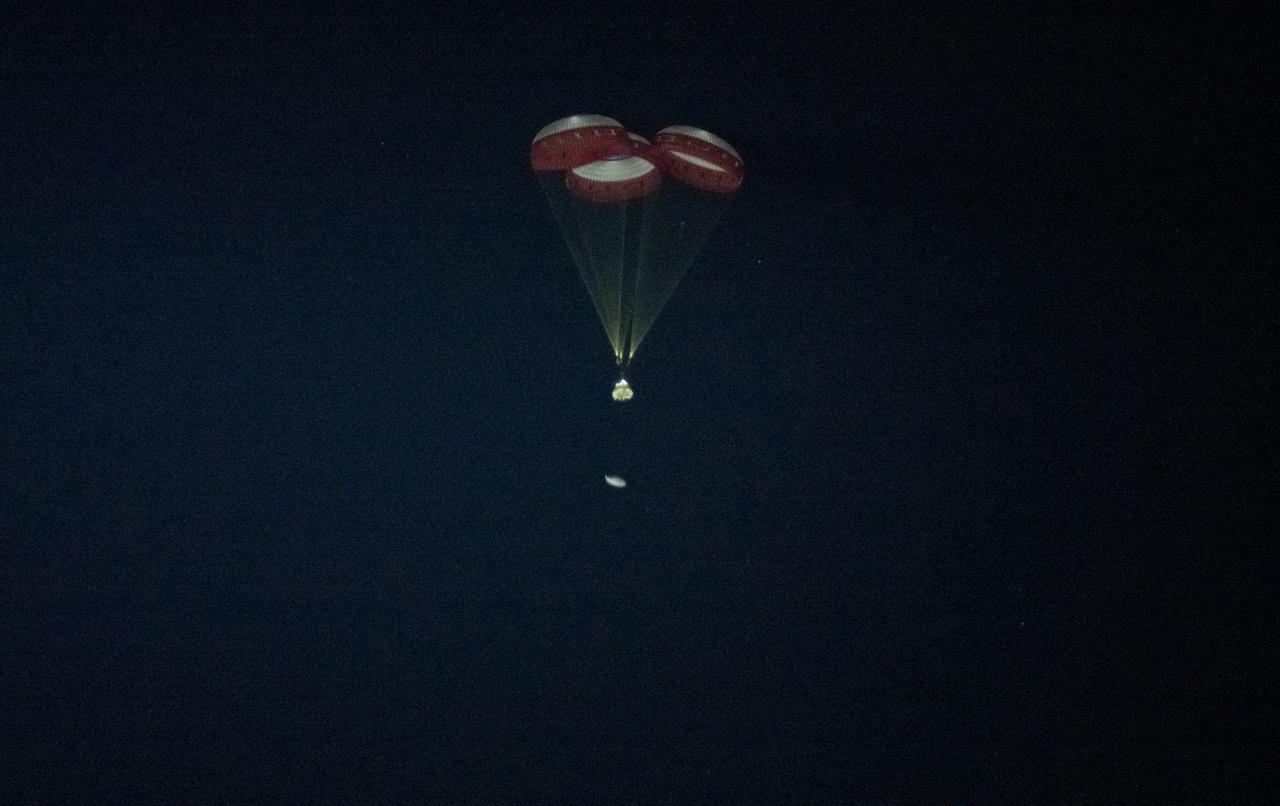

The Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft jettisons the heat shield before it lands in White Sands, New Mexico, Sunday, Dec. 22, 2019. The landing completes an abbreviated Orbital Flight Test for the company that still meets several mission objectives for NASA’s Commercial Crew program. The Starliner spacecraft launched on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket at 6:36 a.m. Friday, Dec. 20 from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
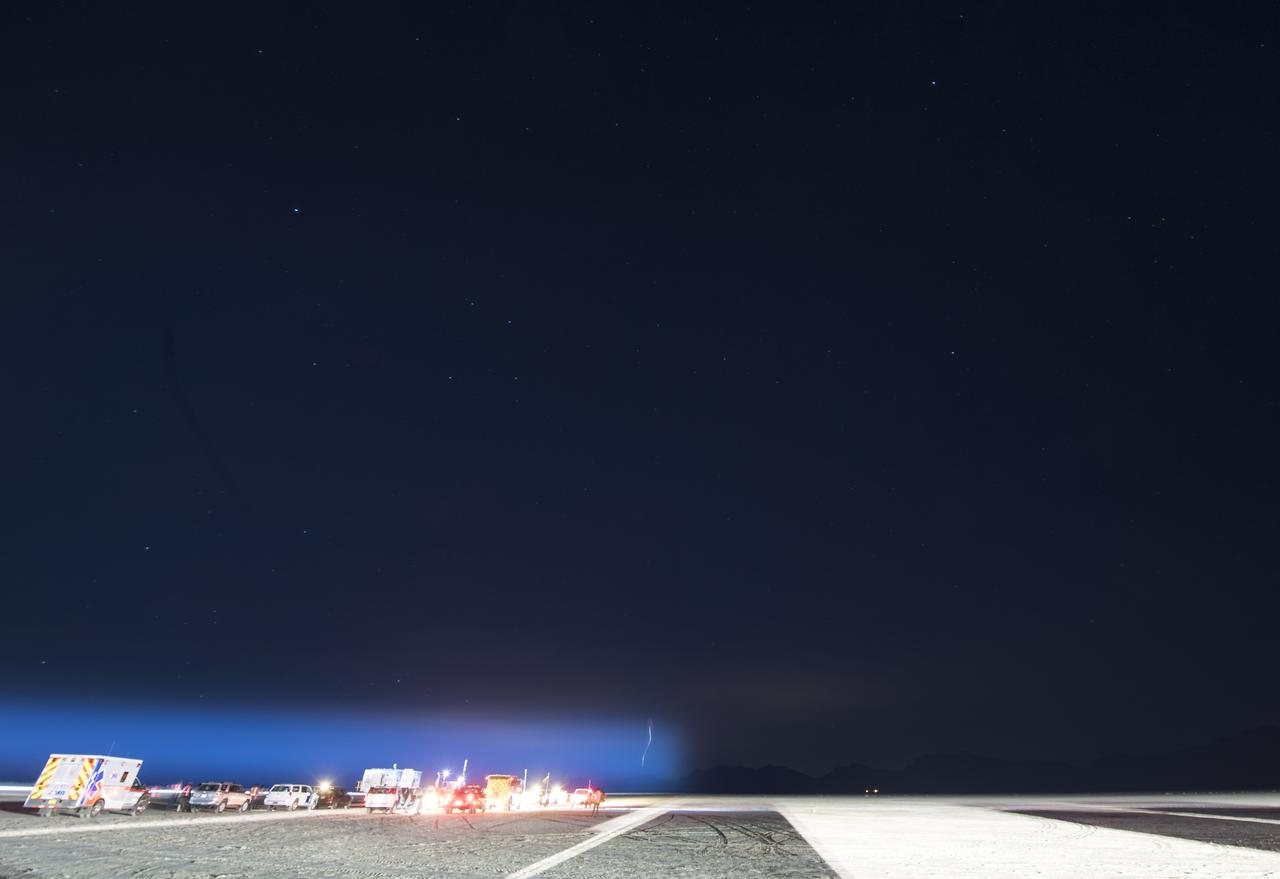

The Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft is seen landing in this 30 sec. exposure in White Sands, New Mexico, Sunday, Dec. 22, 2019. The landing completes an abbreviated Orbital Flight Test for the company that still meets several mission objectives for NASA’s Commercial Crew program. The Starliner spacecraft launched on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket at 6:36 a.m. Friday, Dec. 20 from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
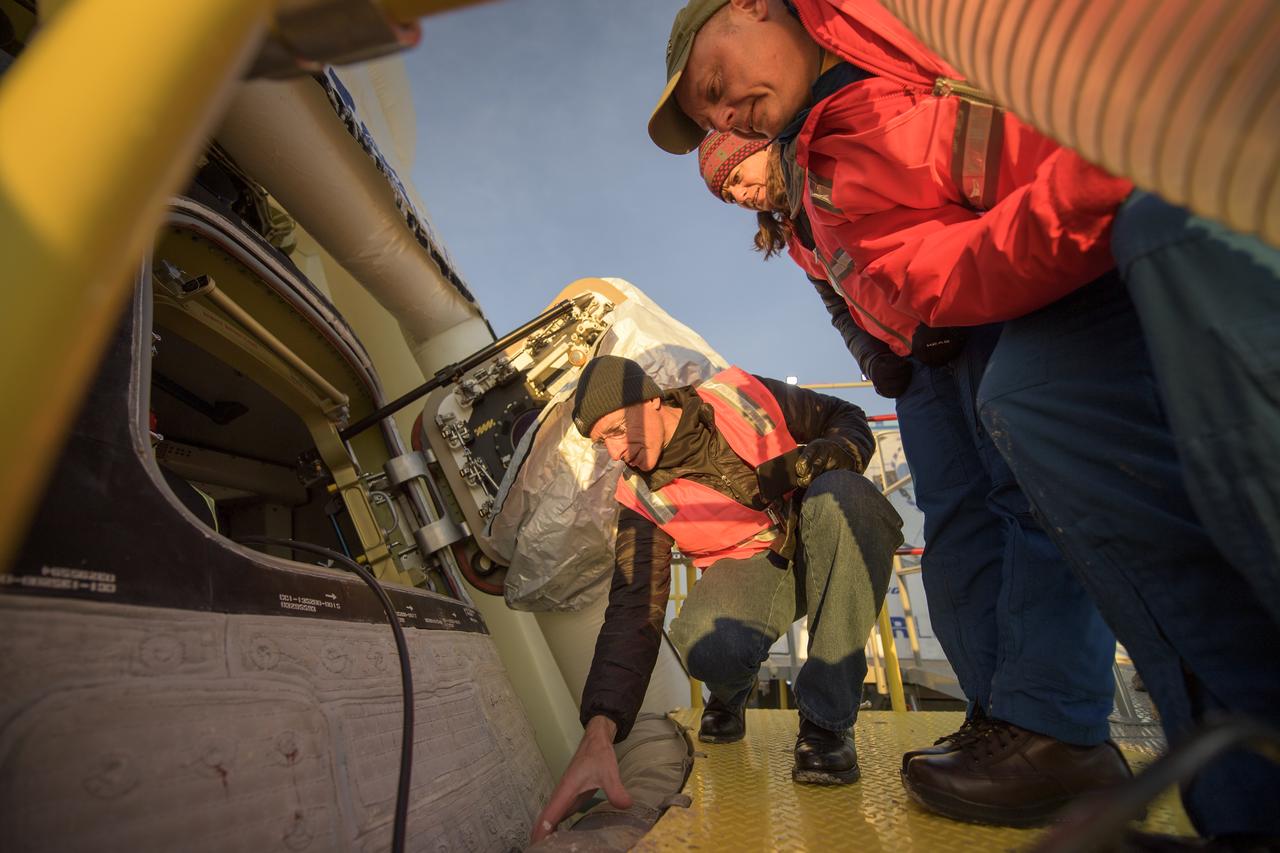

Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson, left, and NASA astronauts Nicole Mann, and Mike Fincke inspect the Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft shortly after it landed in White Sands, New Mexico, Sunday, Dec. 22, 2019. The landing completes an abbreviated Orbital Flight Test for the company that still meets several mission objectives for NASA’s Commercial Crew program. The Starliner spacecraft launched on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket at 6:36 a.m. Friday, Dec. 20 from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
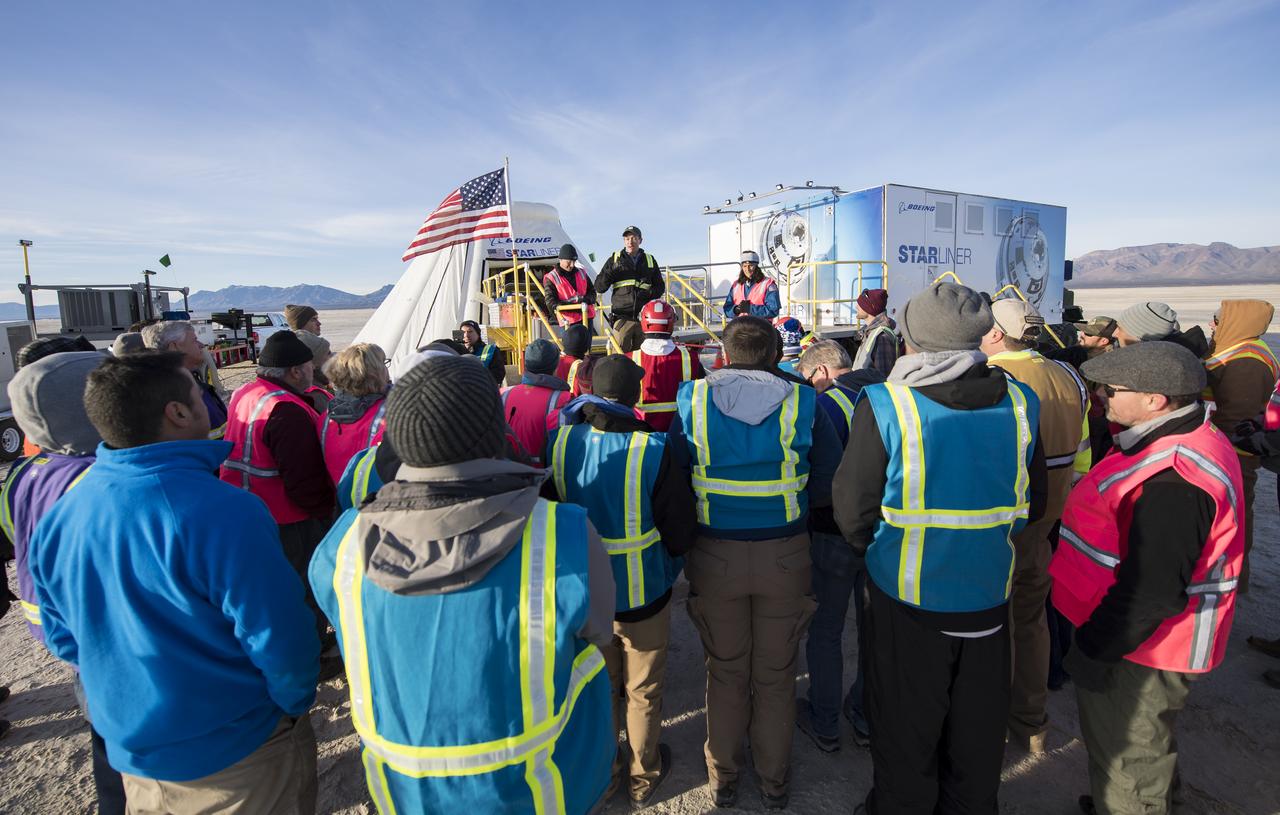

Louis Atchison, chief of launch and recovery operations, Boeing Commercial Crew Program, speaks to the teams from NASA, Boeing, and the White Sands Missile Range, after the Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft landed in White Sands, New Mexico, Sunday, Dec. 22, 2019. The landing completes an abbreviated Orbital Flight Test for the company that still meets several mission objectives for NASA’s Commercial Crew program. The Starliner spacecraft launched on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket at 6:36 a.m. Friday, Dec. 20 from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

The Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft is seen landing in this 30 sec. exposure in White Sands, New Mexico, Sunday, Dec. 22, 2019. The landing completes an abbreviated Orbital Flight Test for the company that still meets several mission objectives for NASA’s Commercial Crew program. The Starliner spacecraft launched on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket at 6:36 a.m. Friday, Dec. 20 from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
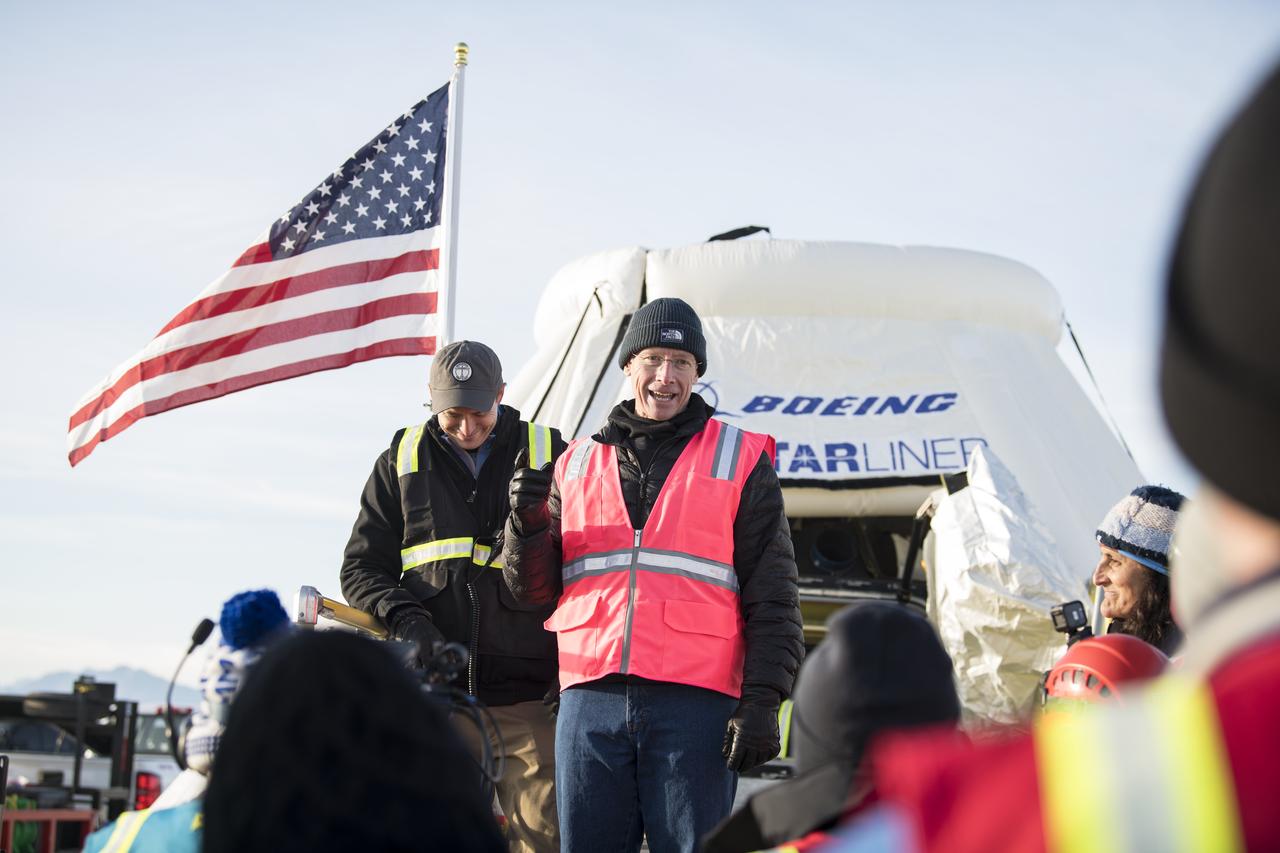

Former NASA astronaut and test flight pilot for the first manned flight of the Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft, Chris Ferguson, speaks after the capsule landed in White Sands, New Mexico, Sunday, Dec. 22, 2019. The landing completes an abbreviated Orbital Flight Test for the company that still meets several mission objectives for NASA’s Commercial Crew program. The Starliner spacecraft launched on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket at 6:36 a.m. Friday, Dec. 20 from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

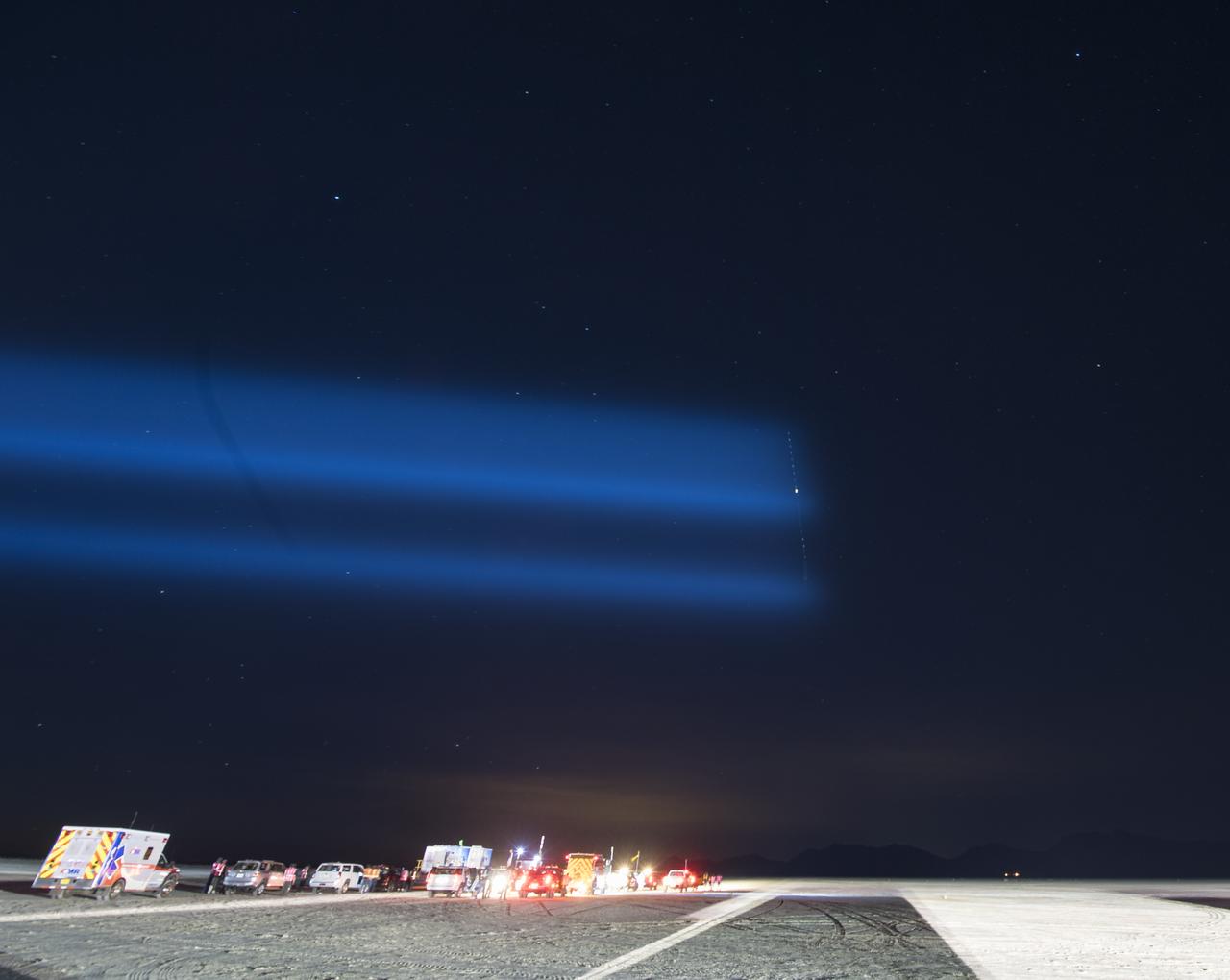
The International Space Station, a search light, and the Moon are seen in this long exposure photograph as teams from Boeing, NASA, and U.S. Army personnel prepare for the Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft landing in White Sands, New Mexico, Sunday, Dec. 22, 2019. The landing will complete an abbreviated Orbital Flight Test for the company that still meets several mission objectives for NASA’s Commercial Crew program. The Starliner spacecraft launched on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket at 6:36 a.m. Friday, Dec. 20 from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
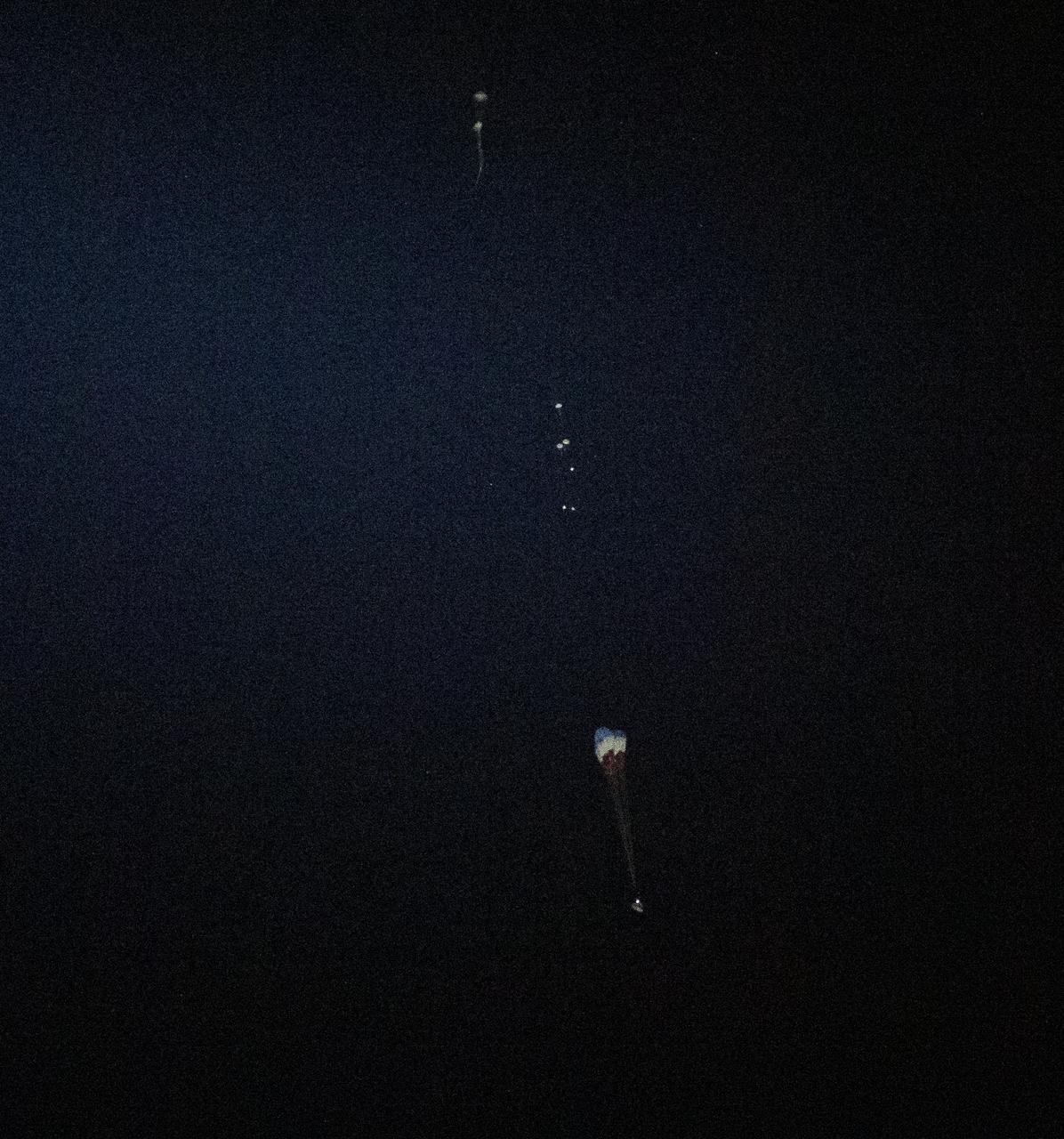

The main parachutes begin to deploy as the Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft lands in White Sands, New Mexico, Sunday, Dec. 22, 2019. The landing completes an abbreviated Orbital Flight Test for the company that still meets several mission objectives for NASA’s Commercial Crew program. The Starliner spacecraft launched on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket at 6:36 a.m. Friday, Dec. 20 from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
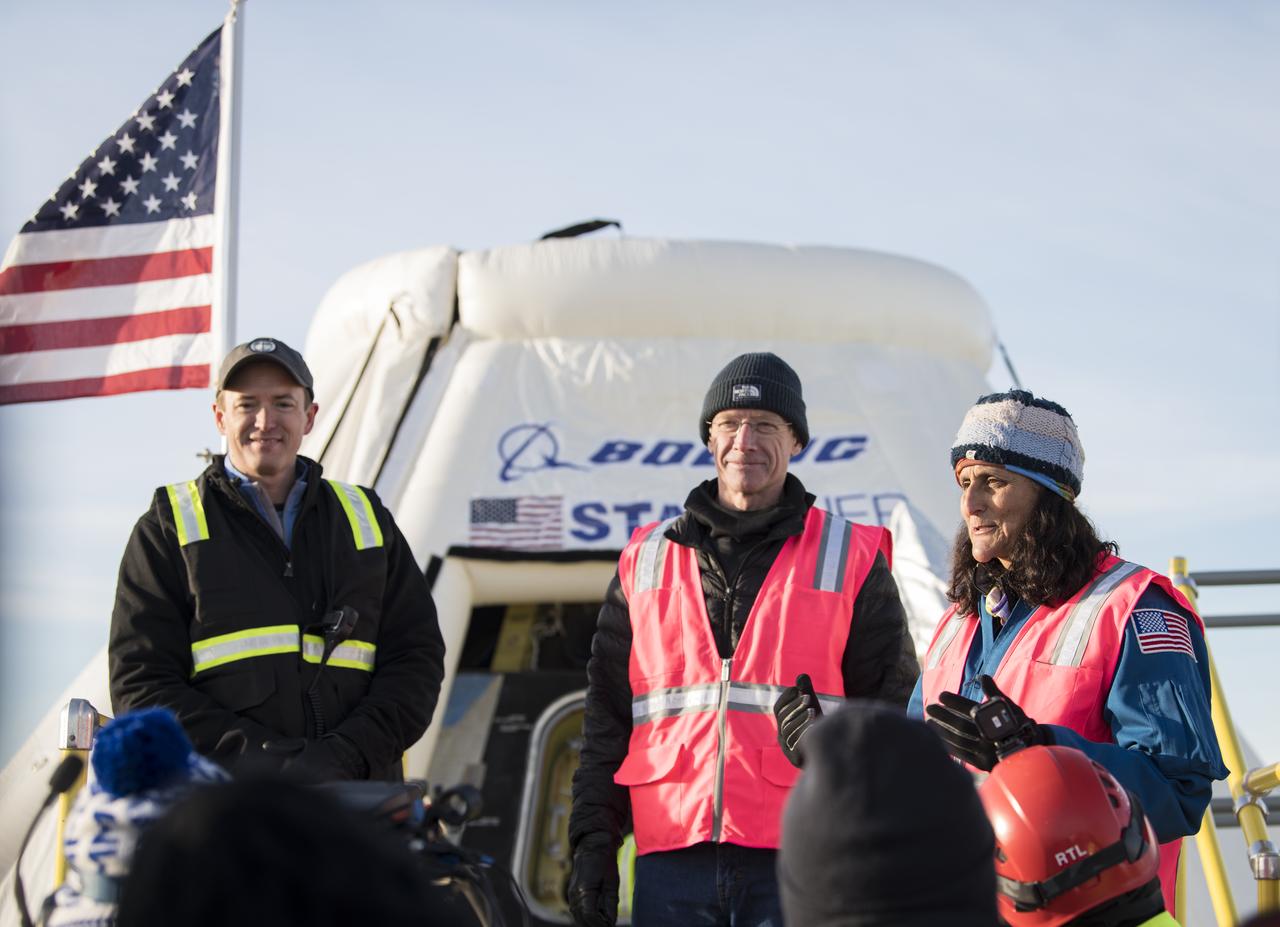

NASA astronaut, Suni Williams, who will command the first manned launch of the capsule, names the Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft, Calypso, after it landed in White Sands, New Mexico, Sunday, Dec. 22, 2019. The landing completes an abbreviated Orbital Flight Test for the company that still meets several mission objectives for NASA’s Commercial Crew program. The Starliner spacecraft launched on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket at 6:36 a.m. Friday, Dec. 20 from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
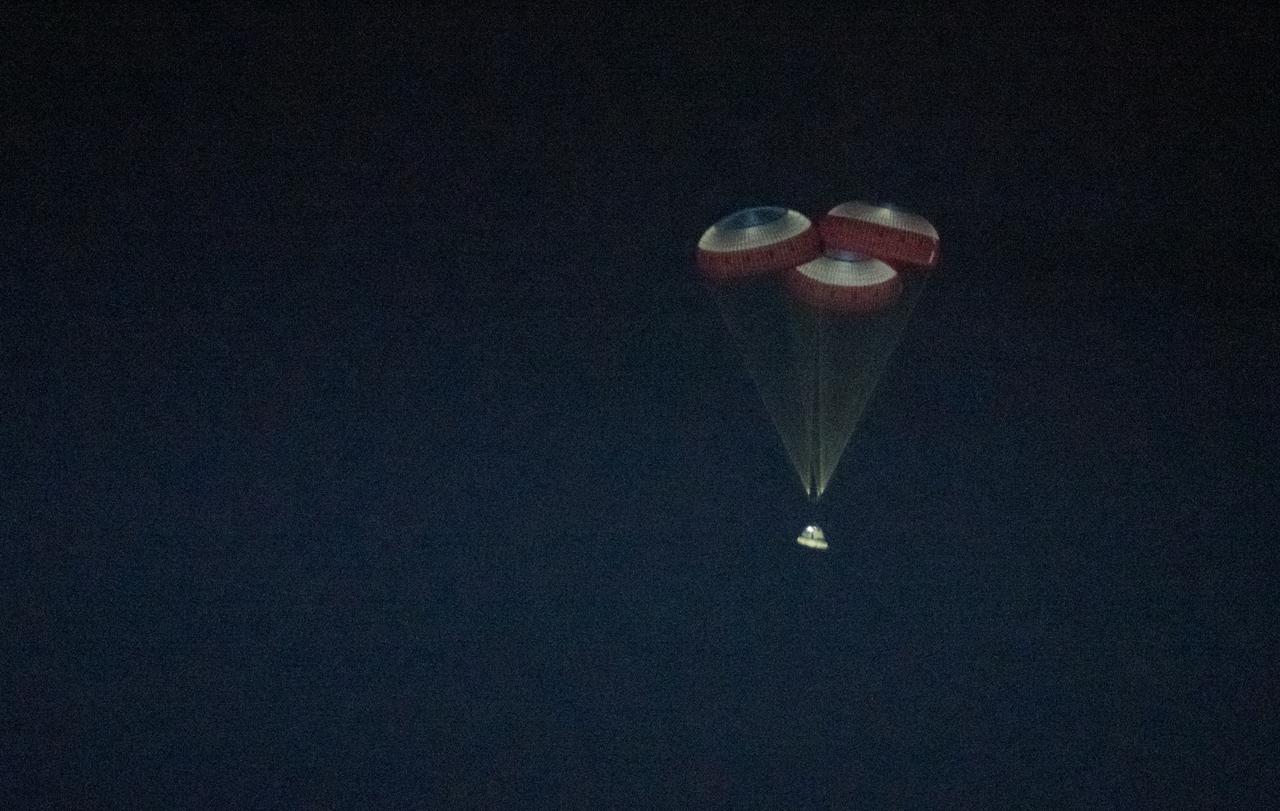

The Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft is seen with landing support inflated as it lands in White Sands, New Mexico, Sunday, Dec. 22, 2019. The landing completes an abbreviated Orbital Flight Test for the company that still meets several mission objectives for NASA’s Commercial Crew program. The Starliner spacecraft launched on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket at 6:36 a.m. Friday, Dec. 20 from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
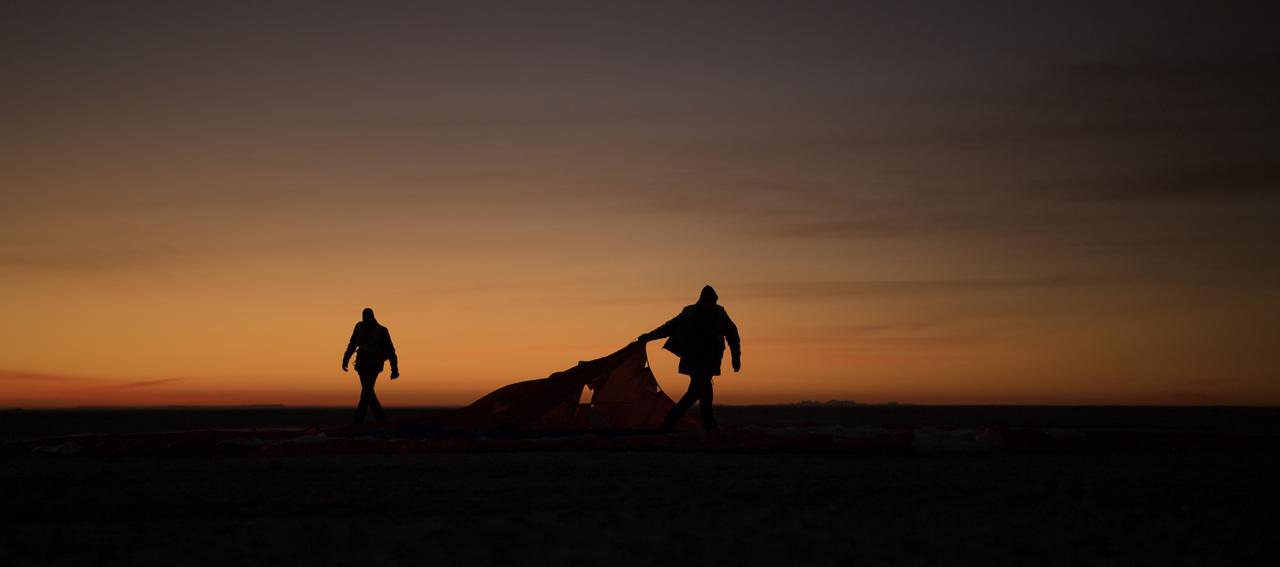

Boeing, NASA, and U.S. Army personnel collect parachutes around the Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft shortly after it landed in White Sands, New Mexico, Sunday, Dec. 22, 2019. The landing completes an abbreviated Orbital Flight Test for the company that still meets several mission objectives for NASA’s Commercial Crew program. The Starliner spacecraft launched on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket at 6:36 a.m. Friday, Dec. 20 from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
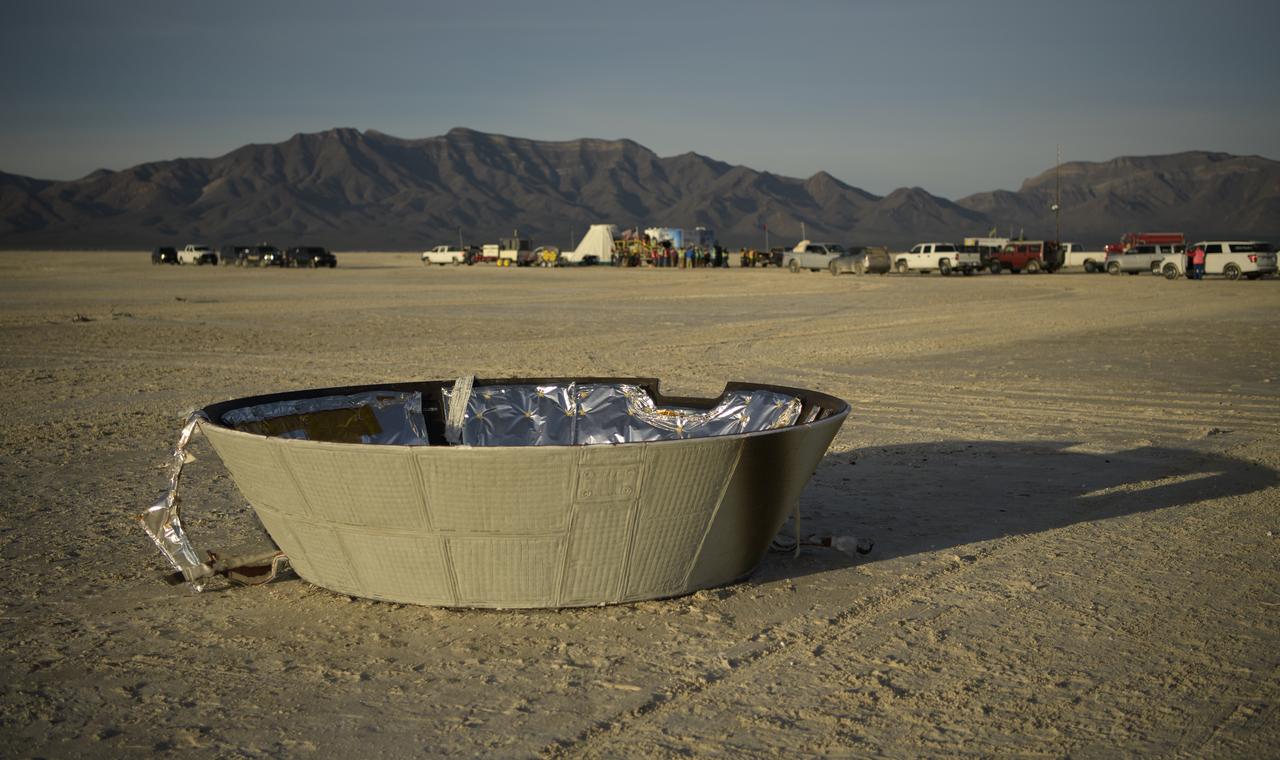

The forward heat shield is seen in the foreground of the Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft landing zone shortly after the landing in White Sands, New Mexico, Sunday, Dec. 22, 2019. The landing completes an abbreviated Orbital Flight Test for the company that still meets several mission objectives for NASA’s Commercial Crew program. The Starliner spacecraft launched on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket at 6:36 a.m. Friday, Dec. 20 from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
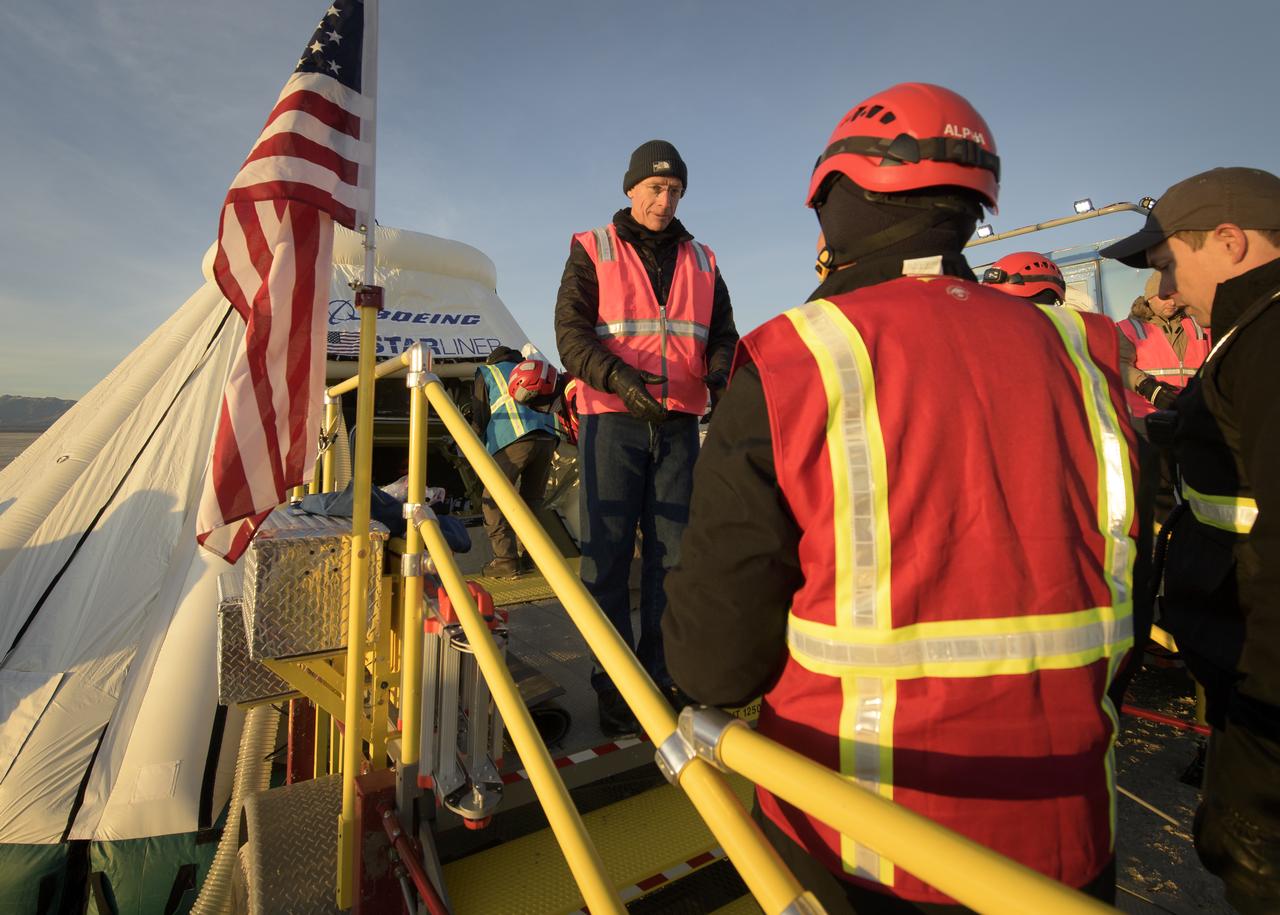

Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson, talks with support personnel outside of the Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft shortly after it landed in White Sands, New Mexico, Sunday, Dec. 22, 2019. The landing completes an abbreviated Orbital Flight Test for the company that still meets several mission objectives for NASA’s Commercial Crew program. The Starliner spacecraft launched on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket at 6:36 a.m. Friday, Dec. 20 from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
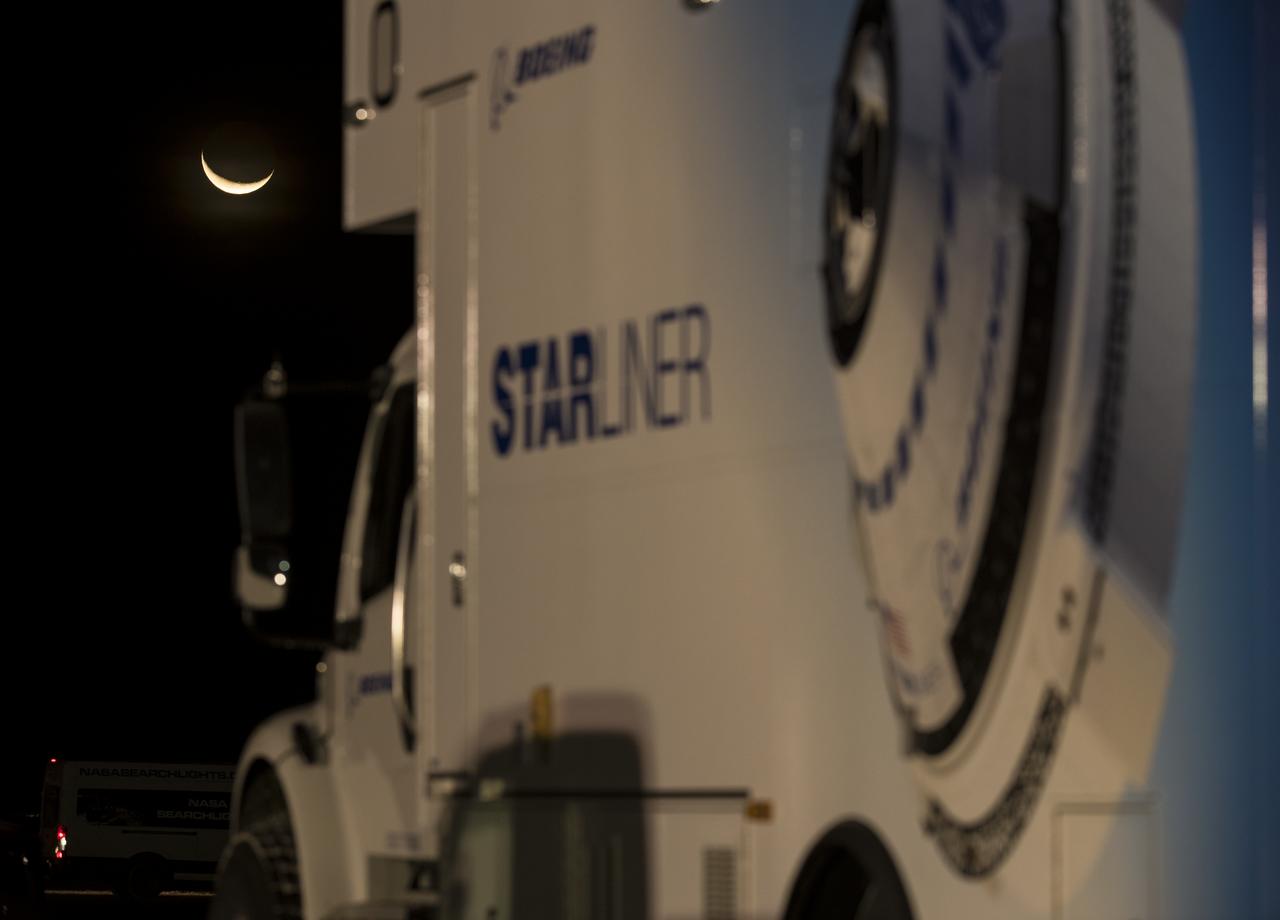

The moon is seen behind one of the Boeing vehicles staged for the Boeing CST-100 Starliner landing in White Sands, New Mexico, Sunday, Dec. 22, 2019. The spacecraft is scheduled to land around 5:57am after an abbreviated Orbital Flight Test for the company that still meets several mission objectives for NASA’s Commercial Crew program. The Starliner spacecraft launched on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket at 6:36 a.m. Friday, Dec. 20 from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
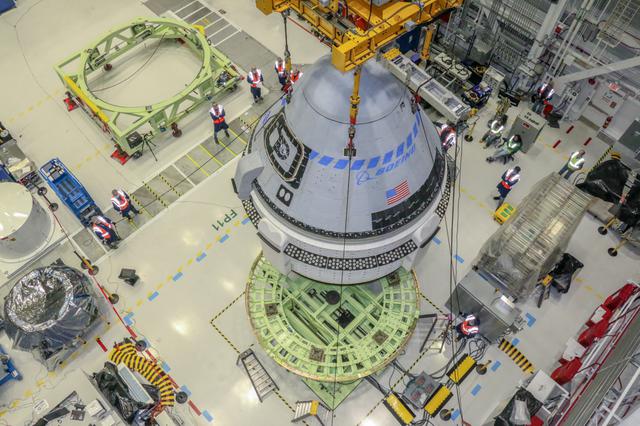

Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner undergoes weight and center of gravity checks in the Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 13, 2021. The operations are in preparation for the company’s second Orbital Flight Test (OFT-2), as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.
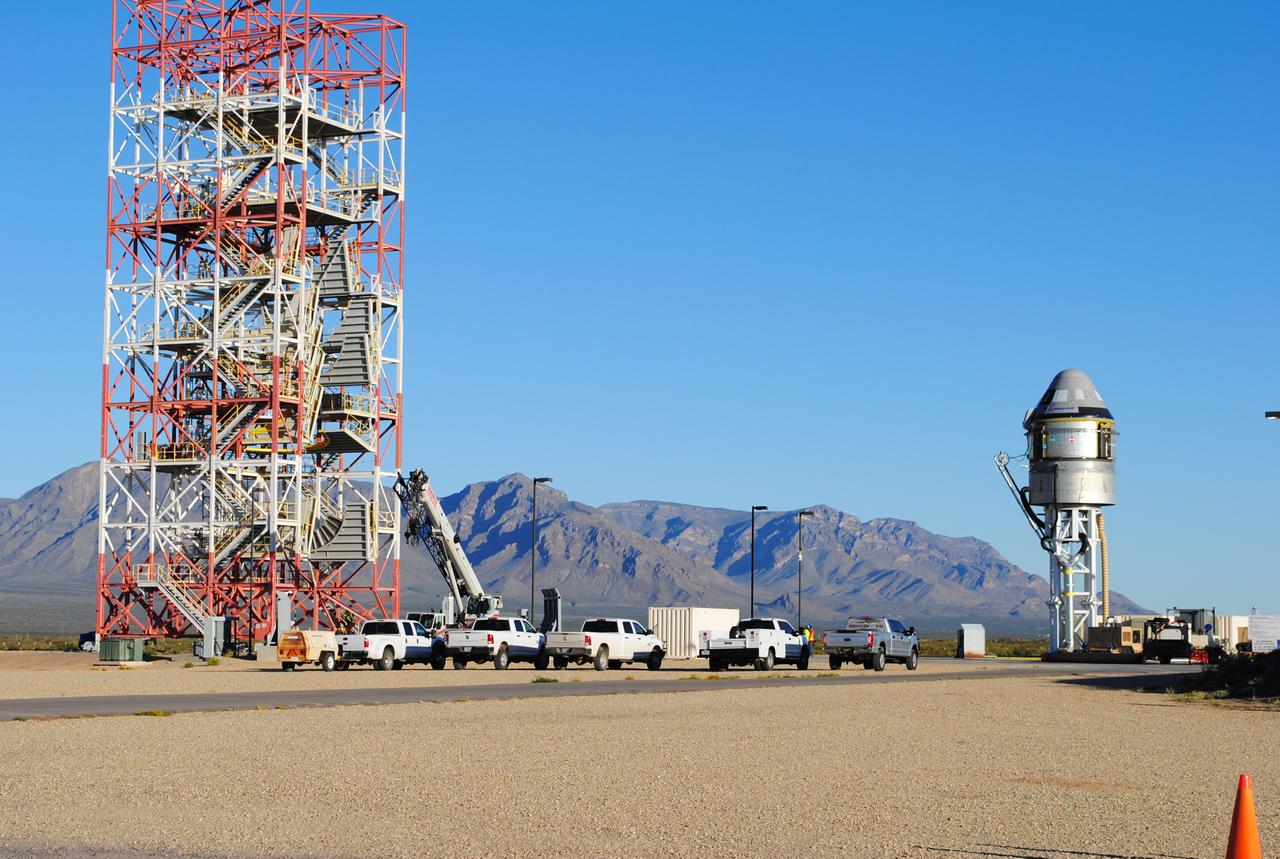

Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft and its service module stand atop the test stand at Launch Complex 32, White Sands Missile Range, New Mexico, in preparation for the Pad Abort Test. Boeing’s Pad Abort Test is designed to verify that each of Starliner’s systems will function not only separately, but in concert, to protect astronauts by carrying them safely away from the launch pad in the unlikely event of an emergency prior to liftoff. This will be Boeing’s first flight test as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The Pad Abort Test is scheduled for Nov. 4, 2019.
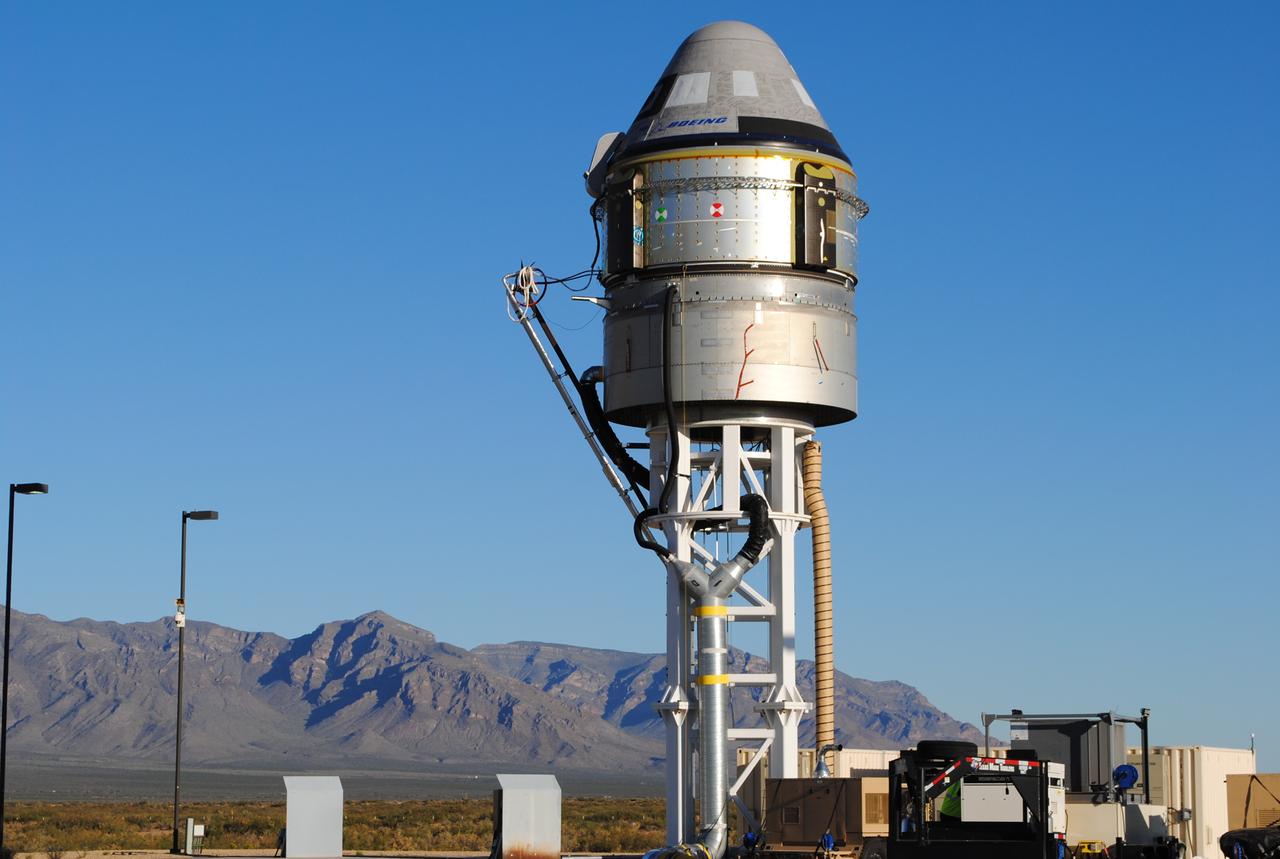

Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft and its service module stand atop the test stand at Launch Complex 32, White Sands Missile Range, New Mexico, in preparation for the Pad Abort Test. Boeing’s Pad Abort Test is designed to verify that each of Starliner’s systems will function not only separately, but in concert, to protect astronauts by carrying them safely away from the launch pad in the unlikely event of an emergency prior to liftoff. This will be Boeing’s first flight test as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The Pad Abort Test is scheduled for Nov. 4, 2019.

On March 15, the base heat shield for Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner was freshly installed on the bottom of Spacecraft 1 in the High Bay of the Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center. This is the spacecraft that will fly during the Pad Abort Test. The next step involves installation of the back shells and forward heat shield, and then the crew module will be mated to the service module for a fit check. Finally, the vehicle will head out to White Sands Missile Range in New Mexico for testing.
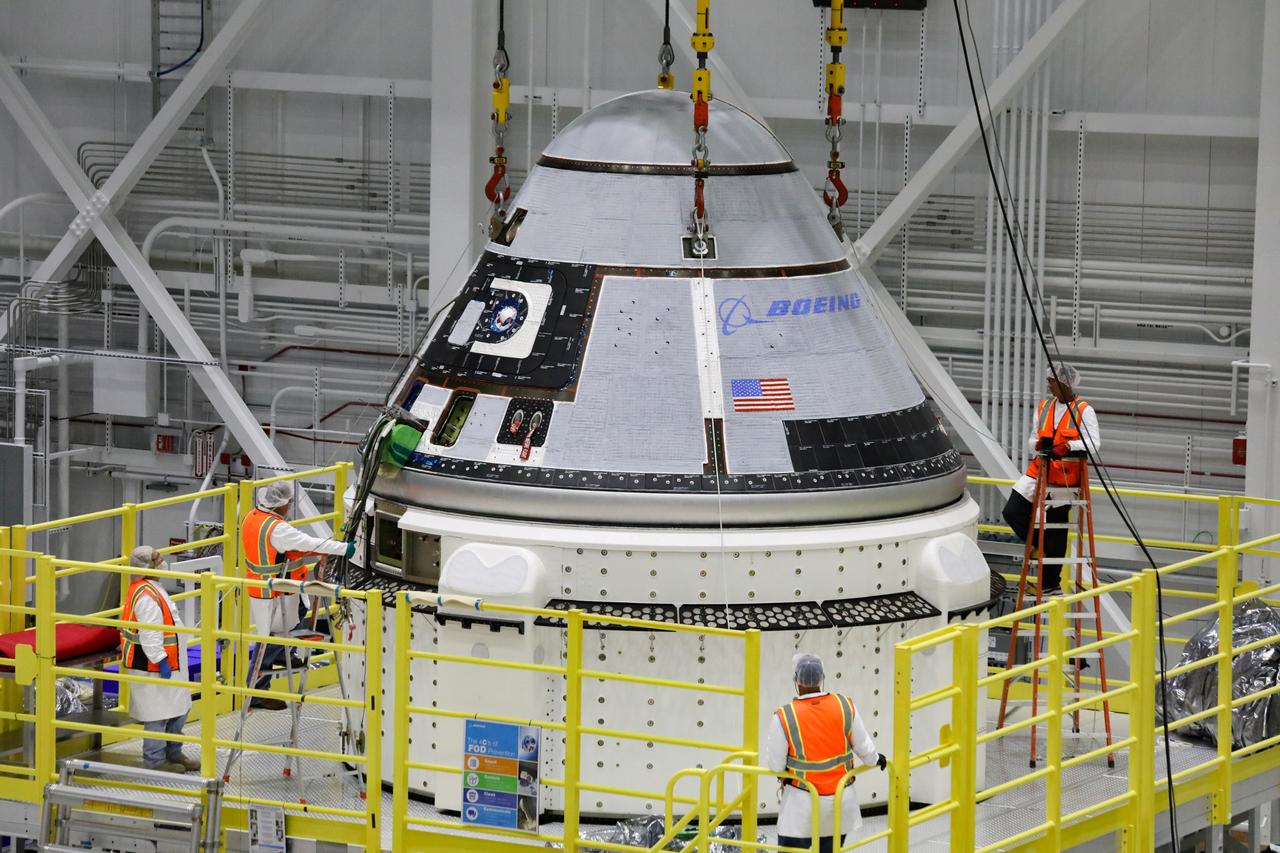

The crew module of Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft is lifted onto its service module on Oct. 16, 2019, inside the Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility (C3PF) at Kennedy Space Center in Florida ahead of the company's Orbital Flight Test to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program.
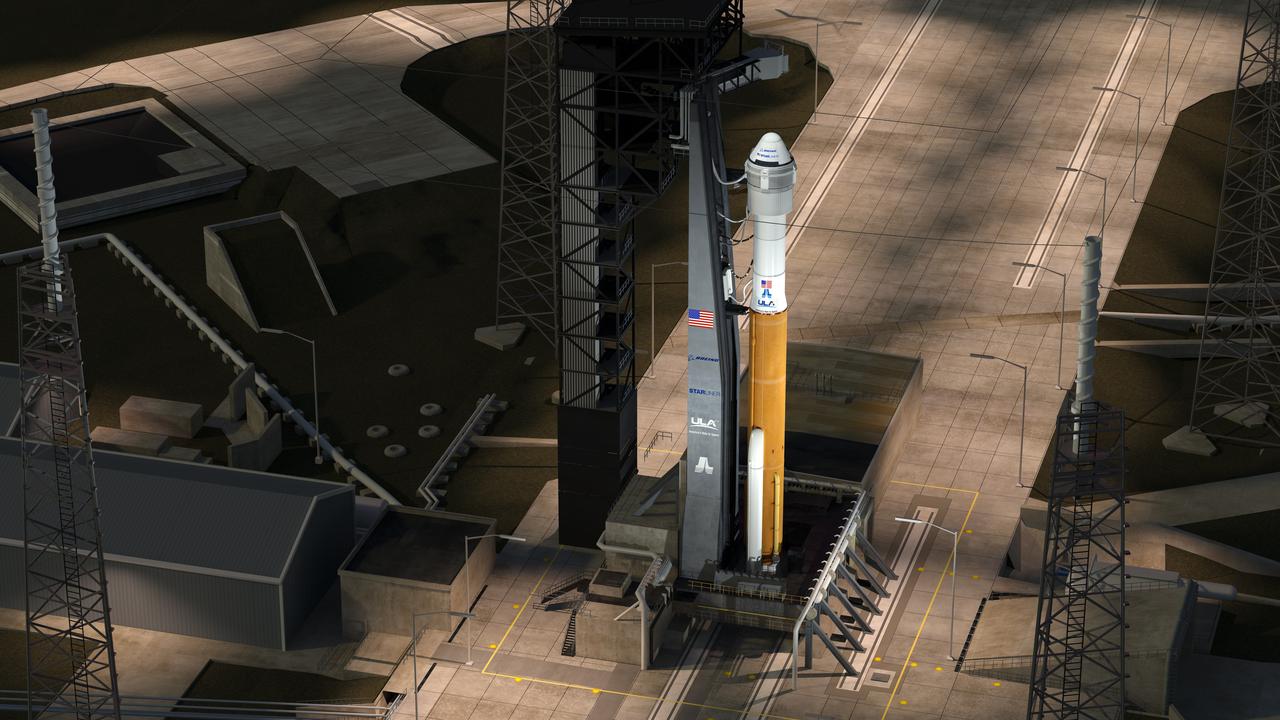

This artist concept shows a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with a Boeing CST-100 Starliner capsule at Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Starliner/Atlas V system is under development by Boeing and ULA in partnership with NASA's Commercial Crew Program to launch astronauts to the International Space Station.
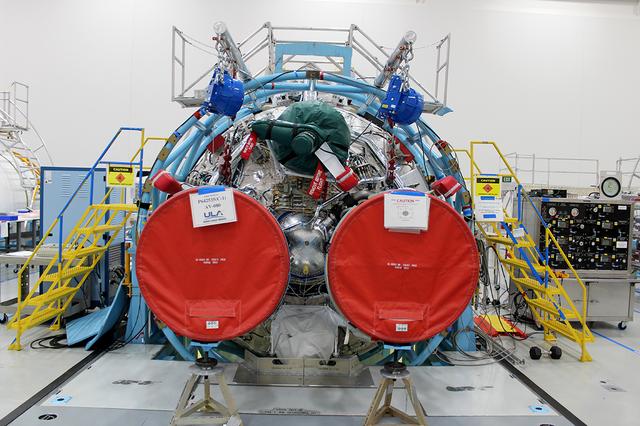

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Orbital Flight Test dual engine Centaur stage of the Atlas V rocket is in the final stage of production and checkout on May 22, 2018, at ULA's factory in Decatur, Alabama. Boeing's CST-100 Starliner will launch on its first uncrewed flight test on the ULA Atlas V rocket. The Starliner is being developed and manufactured in partnership with NASA's Commercial Crew Program to return human spaceflight capabilities to the U.S.
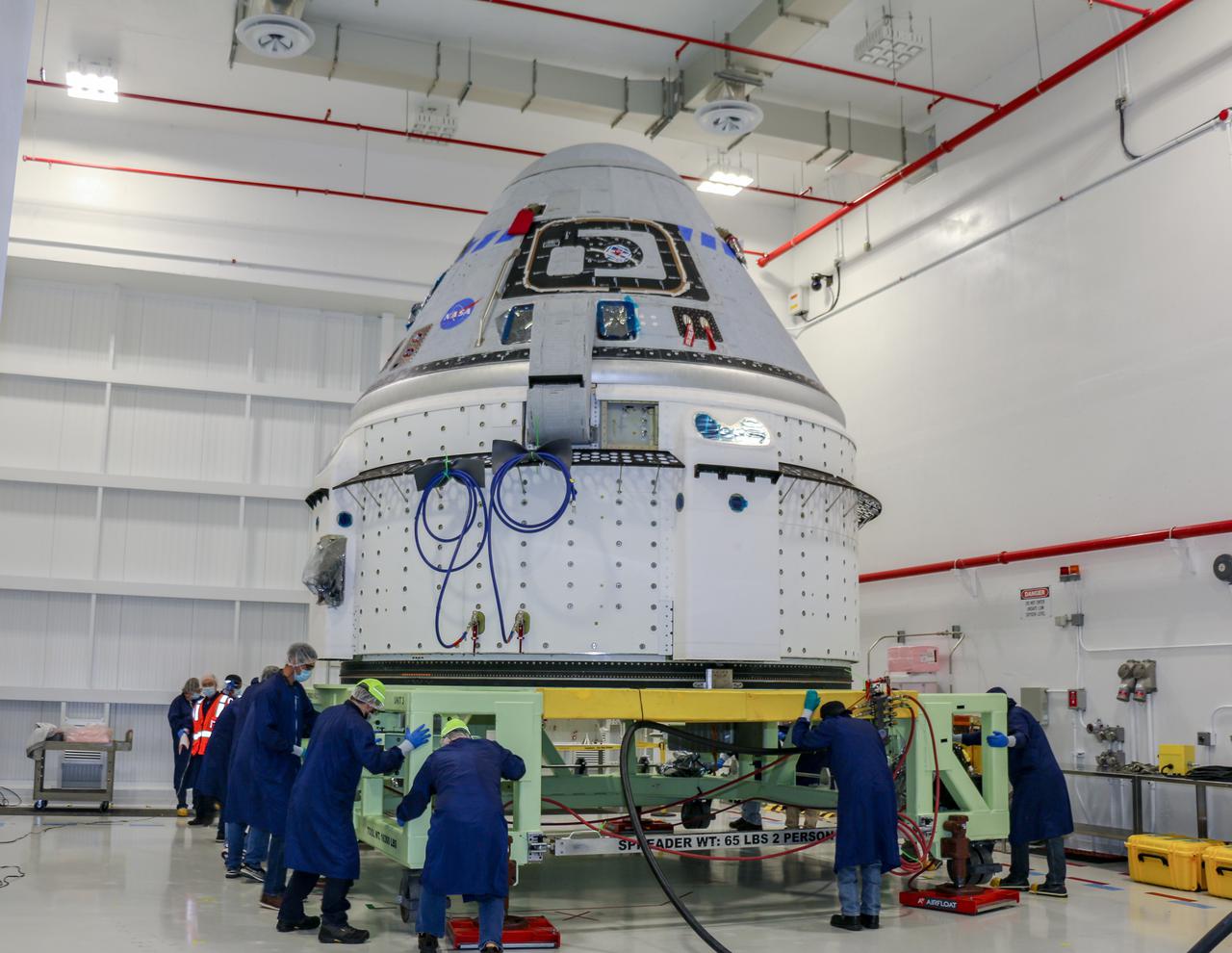

Technicians prepare Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner for the company’s Orbital Flight Test-2 (OFT-2) in the Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 2. Part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program, OFT-2 is a critical developmental milestone on the company’s path to fly crew missions for NASA.
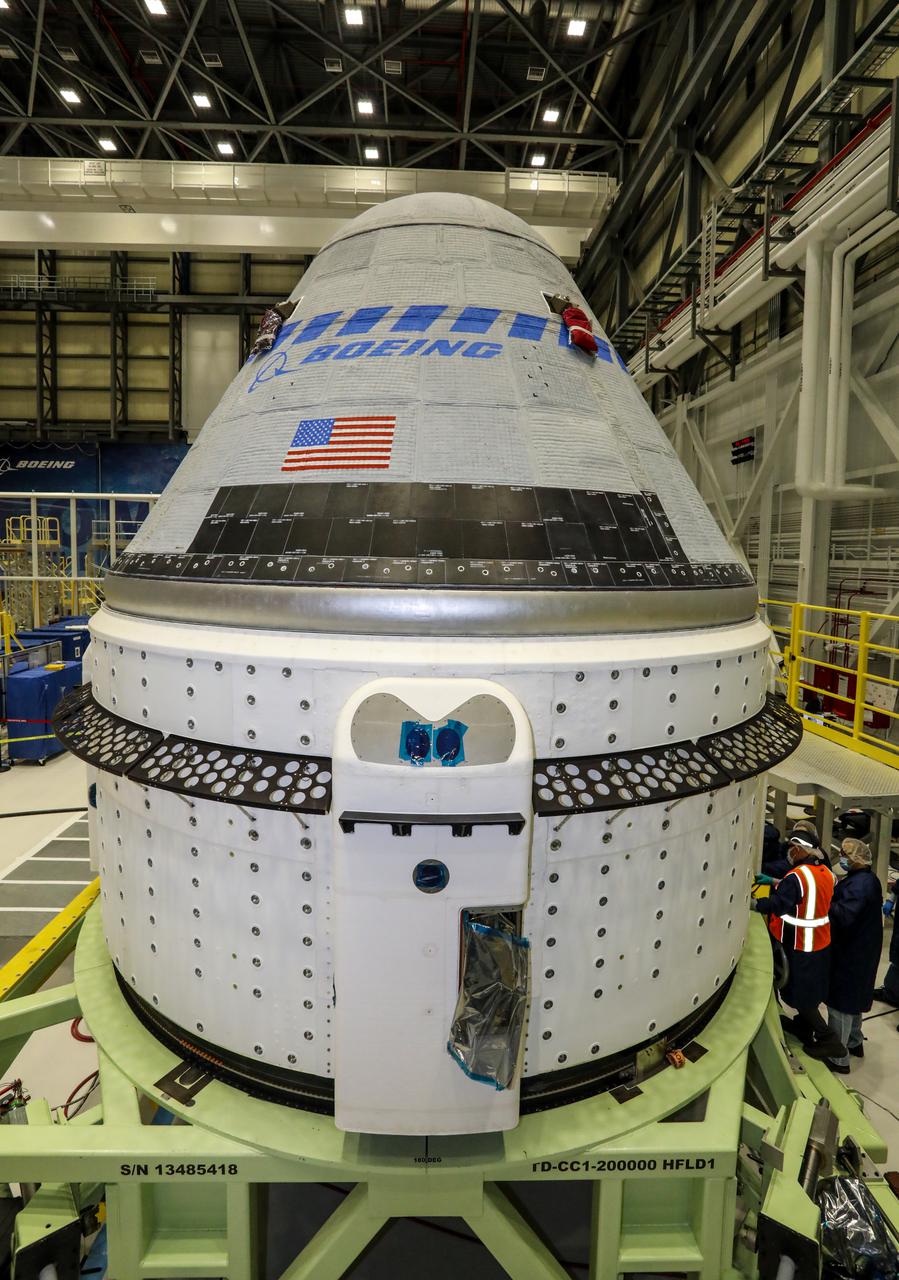

The Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft to be flown on Orbital Flight Test-2 (OFT-2) is seen in the Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 2. Part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program, OFT-2 is a critical developmental milestone on the company’s path to fly crew missions for NASA.
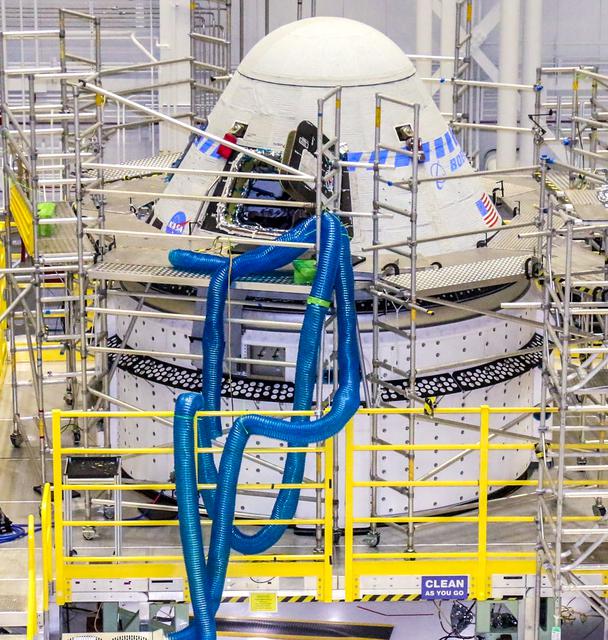

Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft undergoes preparations for the company’s Orbital Flight Test-2 (OFT-2) in the Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Wednesday, April 28, 2021. As part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, OFT-2 is a critical developmental milestone on Boeing’s path to fly crew missions for NASA.
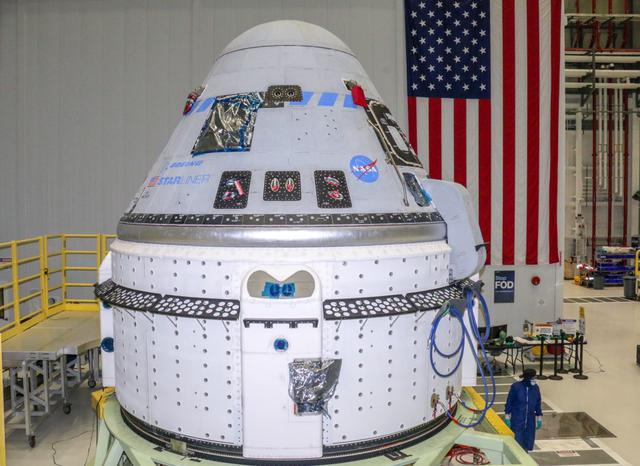
The Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft to be flown on Orbital Flight Test-2 (OFT-2) is seen in the Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 2. Part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program, OFT-2 is a critical developmental milestone on the company’s path to fly crew missions for NASA.
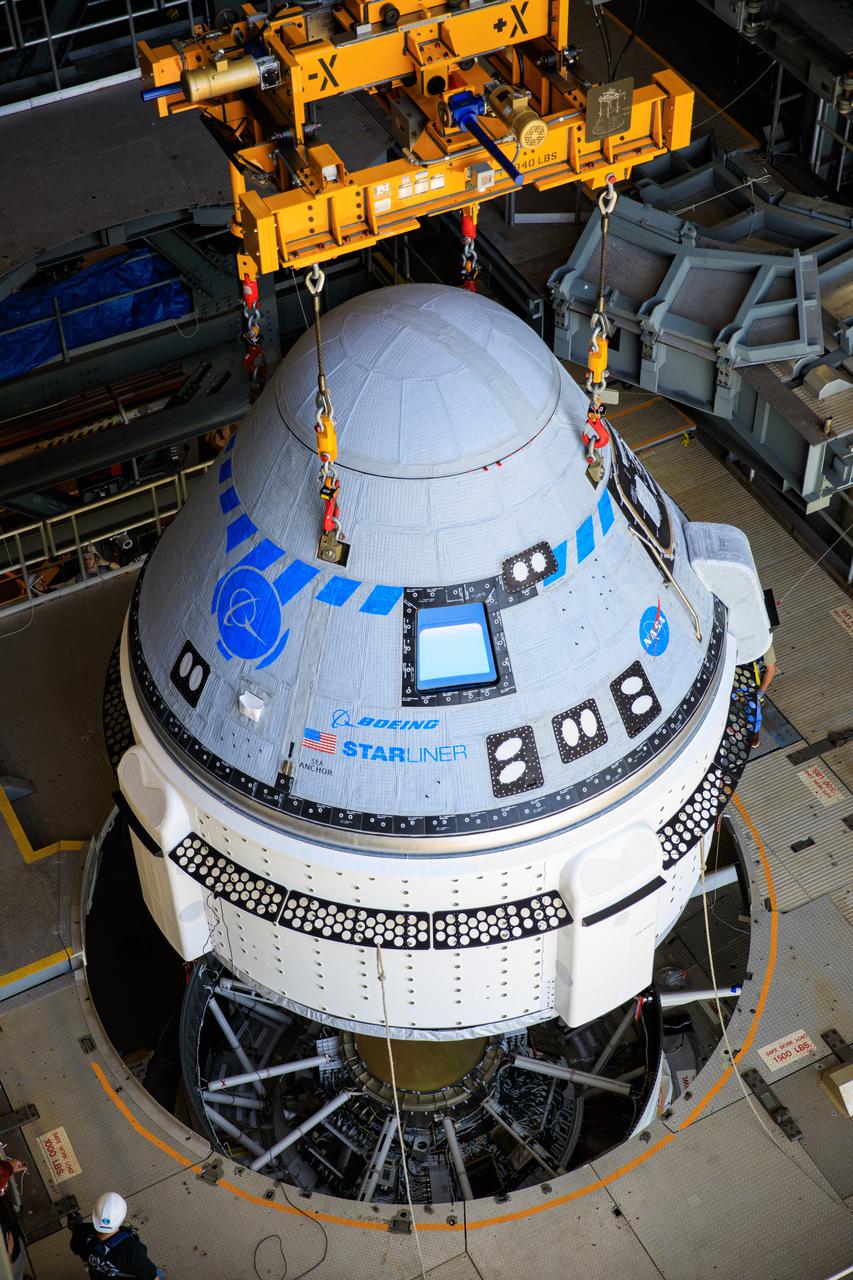

The Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft is lifted at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex-41 at Florida's Cape Canaveral Space Force Station on May 4th, 2022. Starliner will be secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for Boeing's second Orbital Flight Test (OFT-2) to the International Space Station for NASA's Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing's Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.
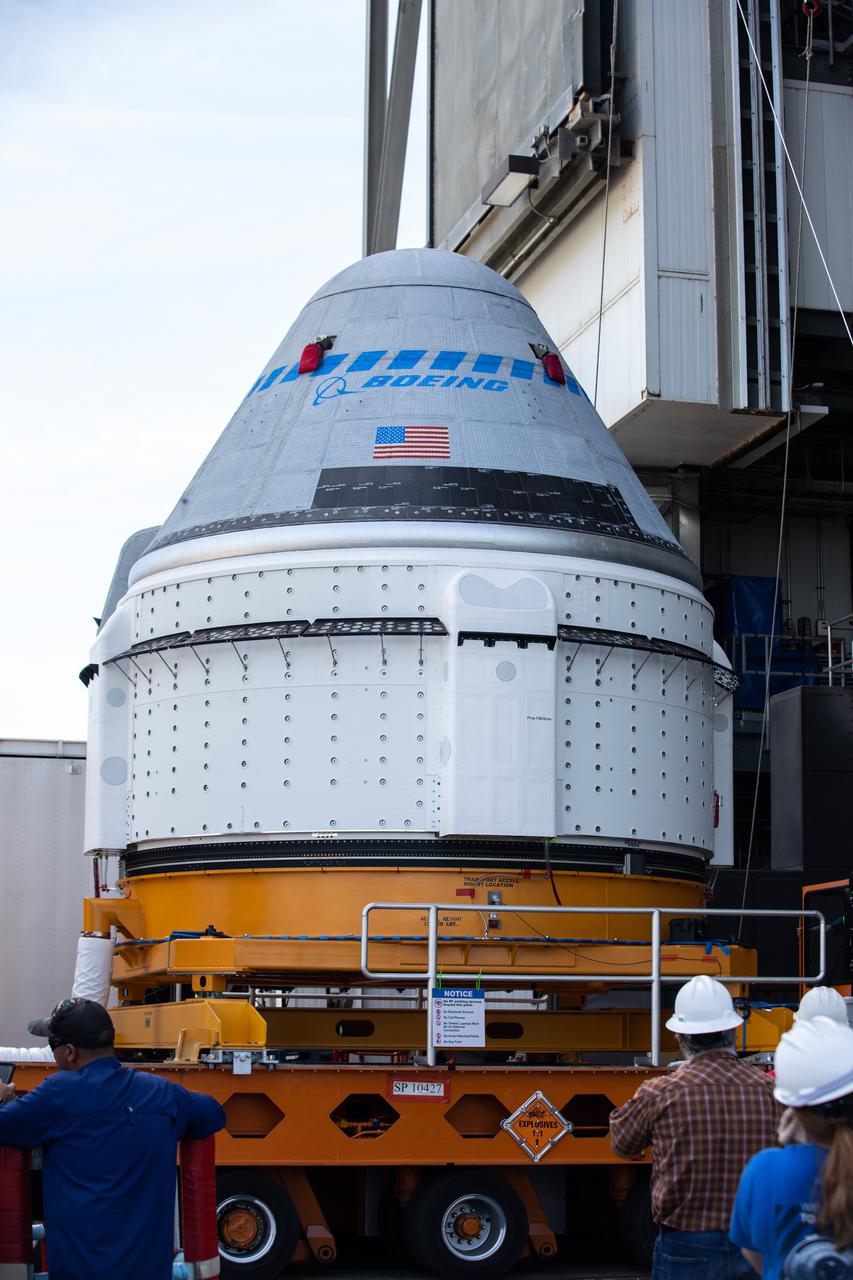

Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft arrives at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on May 4, 2022. Starliner will be secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for Boeing’s second Orbital Flight Test (OFT-2) to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.
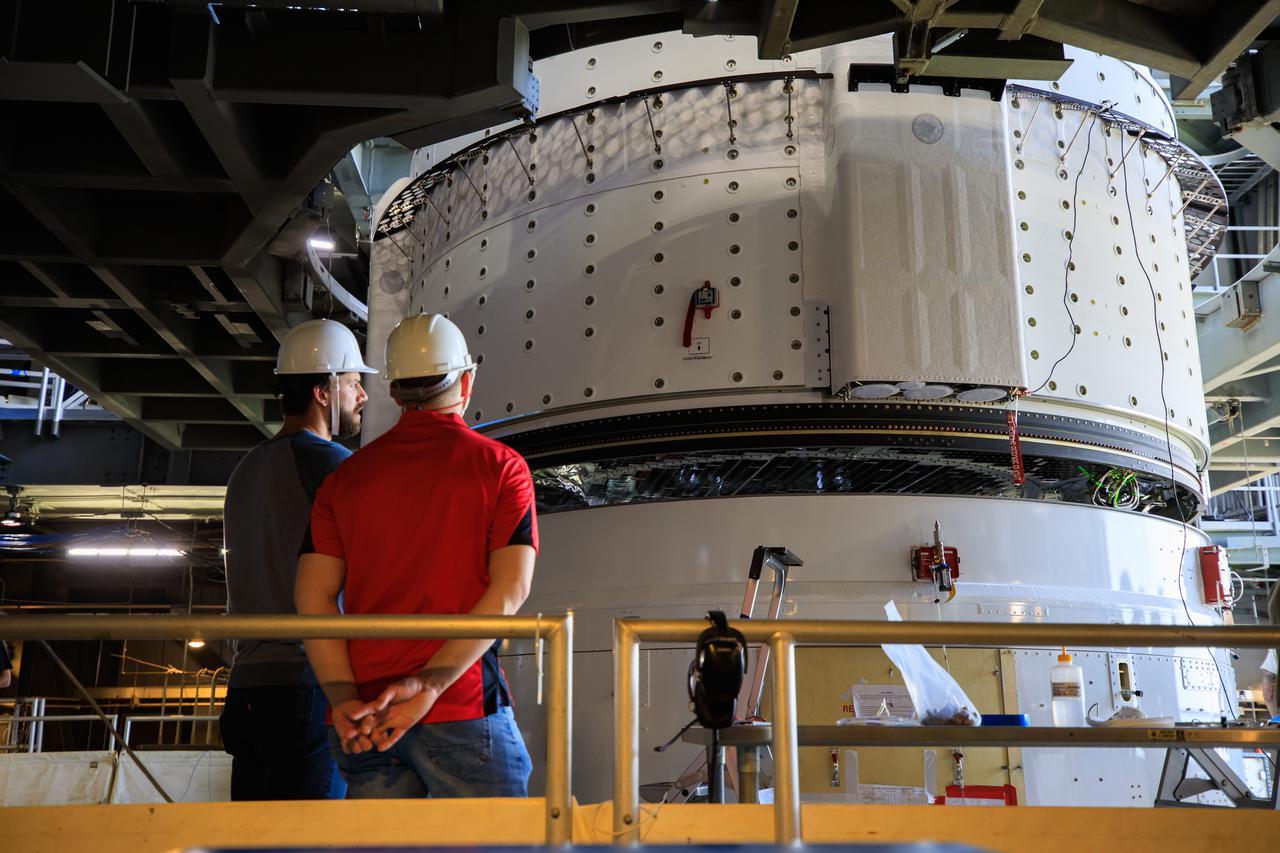
The Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft is lifted at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex-41 at Florida's Cape Canaveral Space Force Station on May 4th, 2022. Starliner will be secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for Boeing's second Orbital Flight Test (OFT-2) to the International Space Station for NASA's Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing's Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.
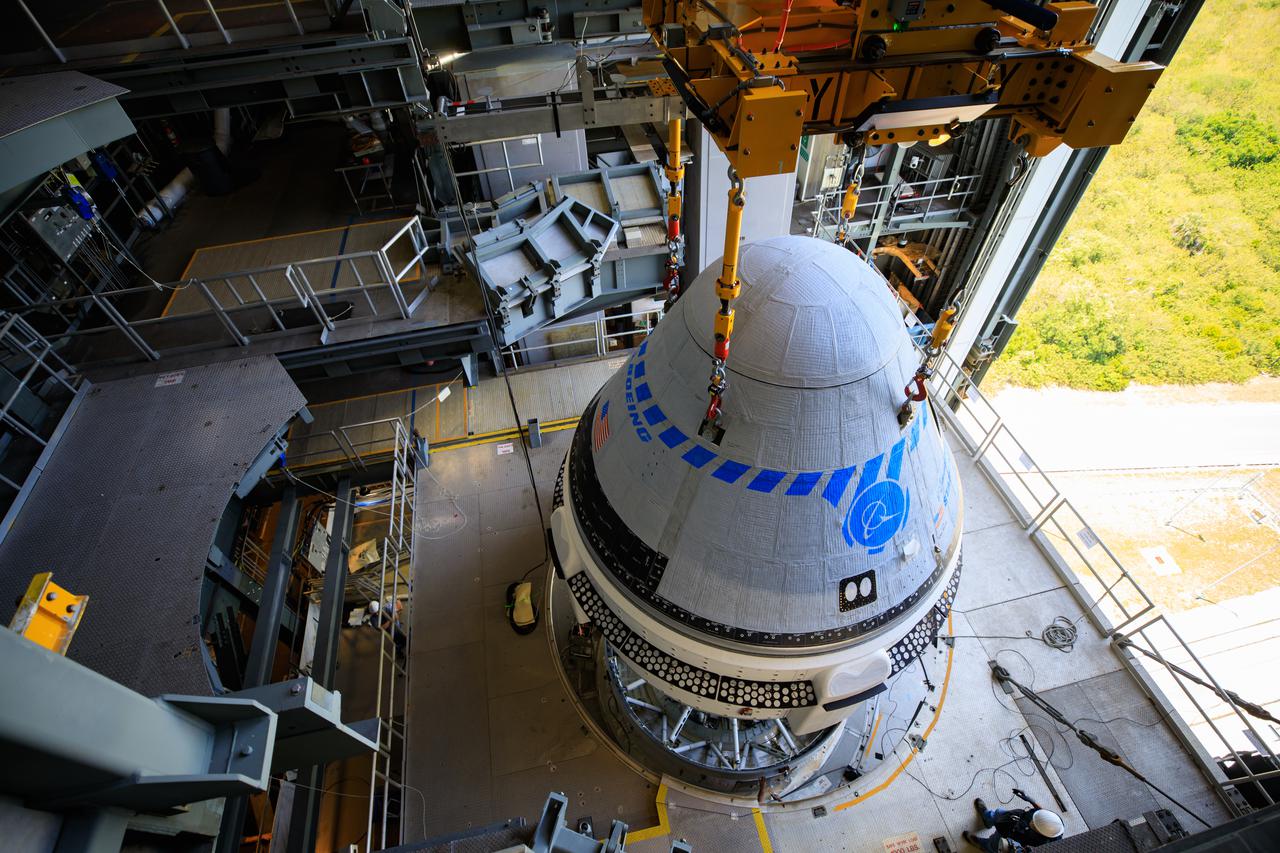
The Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft is lifted at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex-41 at Florida's Cape Canaveral Space Force Station on May 4th, 2022. Starliner will be secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for Boeing's second Orbital Flight Test (OFT-2) to the International Space Station for NASA's Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing's Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.
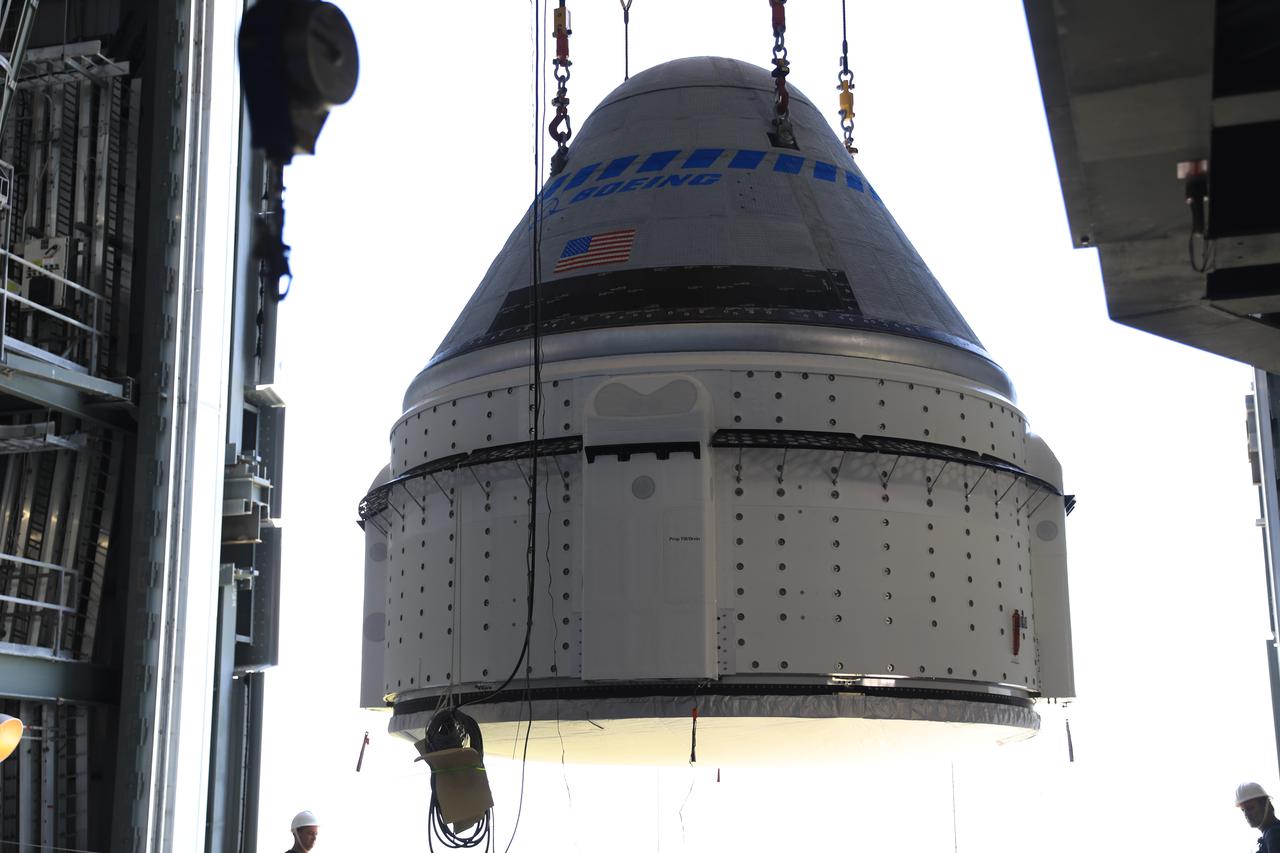

The Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft is lifted at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex-41 at Florida’s Cape Canaveral Space Force Station on May 4, 2022. Starliner will be secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for Boeing’s second Orbital Flight Test (OFT-2) to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.
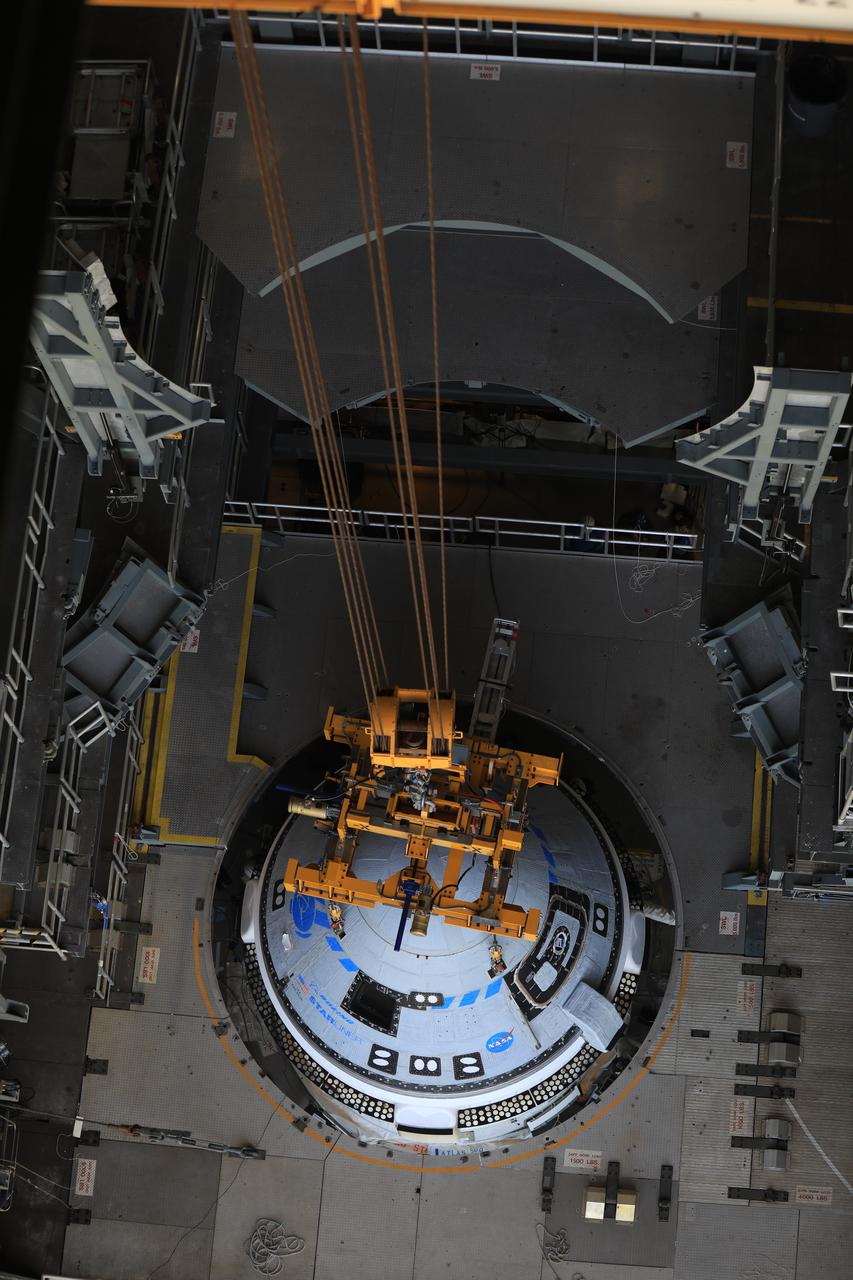
The Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft is lifted at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex-41 at Florida’s Cape Canaveral Space Force Station on May 4, 2022. Starliner will be secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for Boeing’s second Orbital Flight Test (OFT-2) to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.
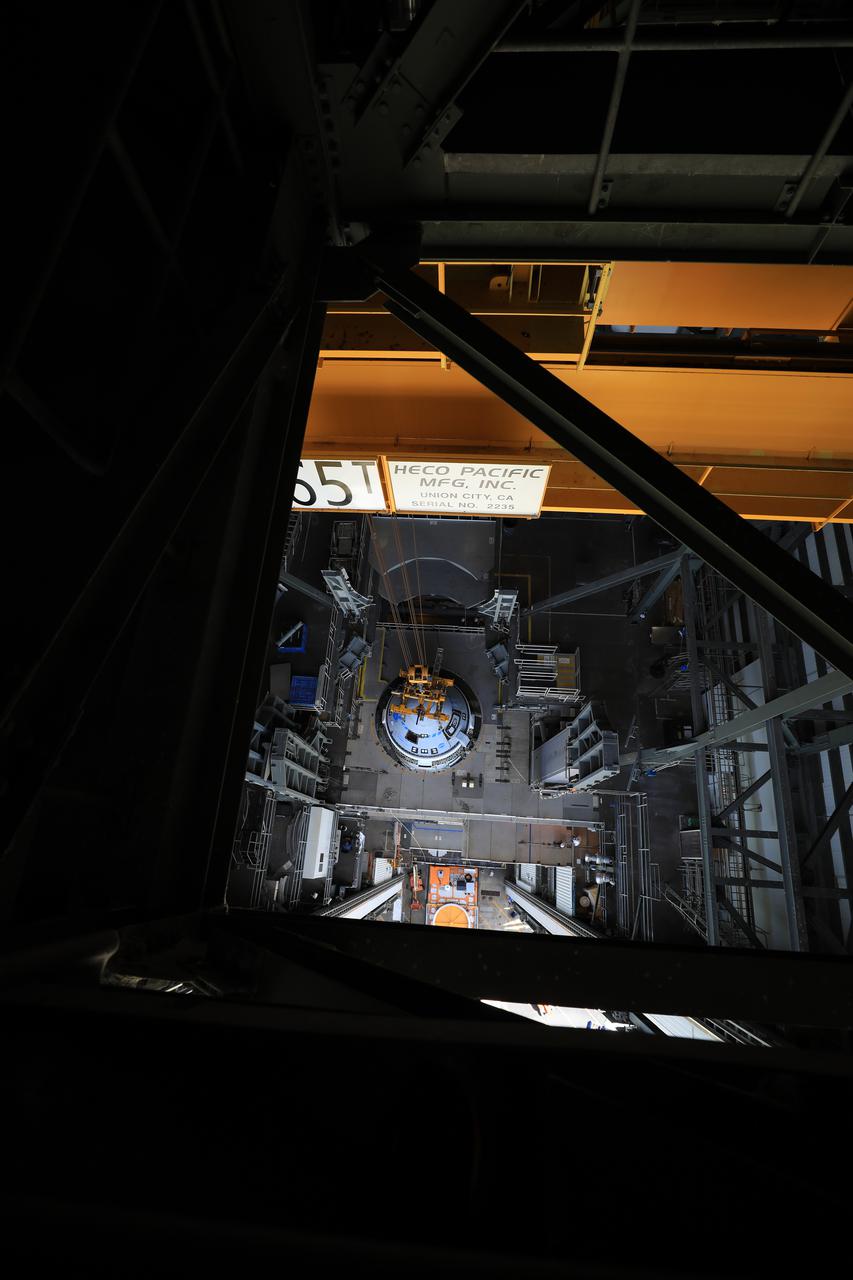

The Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft is lifted at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex-41 at Florida’s Cape Canaveral Space Force Station on May 4, 2022. Starliner will be secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for Boeing’s second Orbital Flight Test (OFT-2) to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.
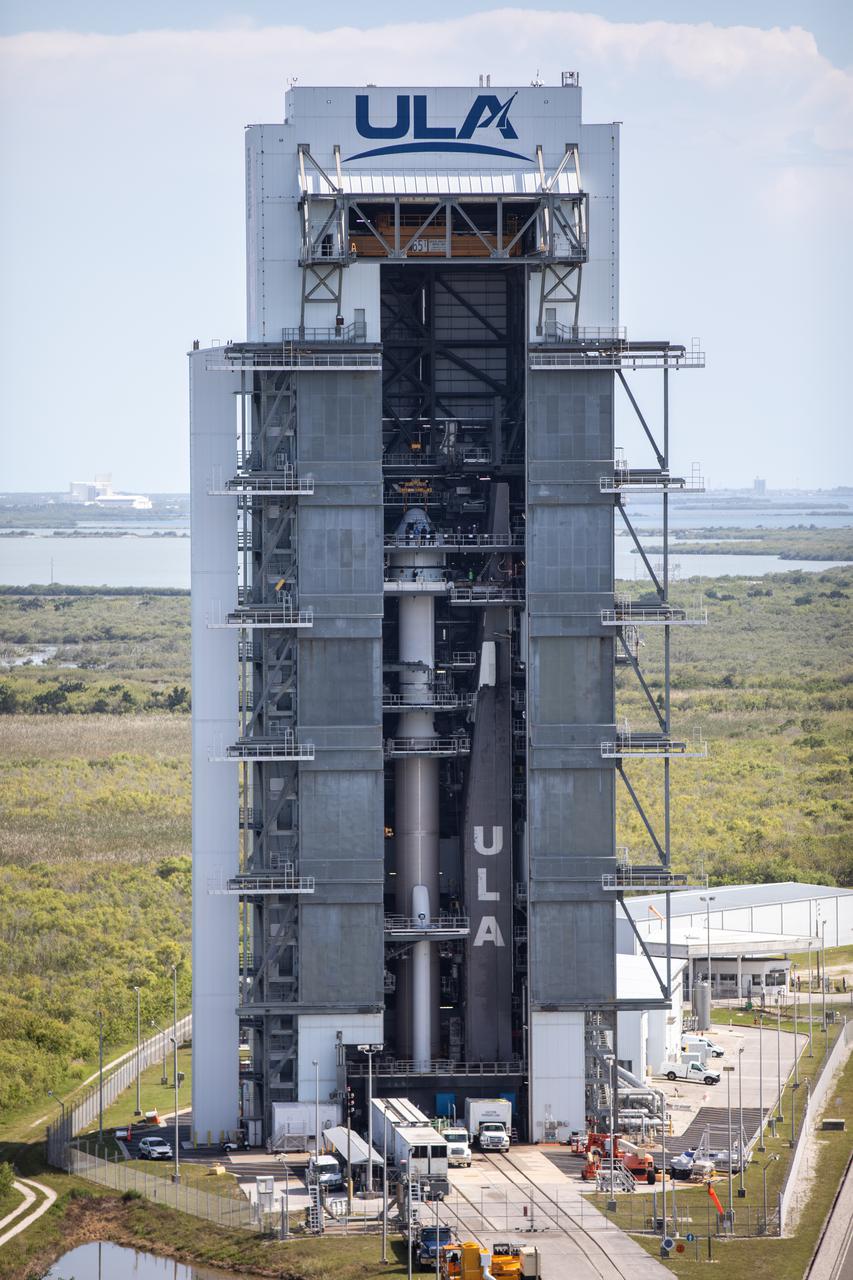

The Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft is lifted at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex-41 at Florida’s Cape Canaveral Space Force Station on May 4, 2022. Starliner will be secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for Boeing’s second Orbital Flight Test (OFT-2) to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.