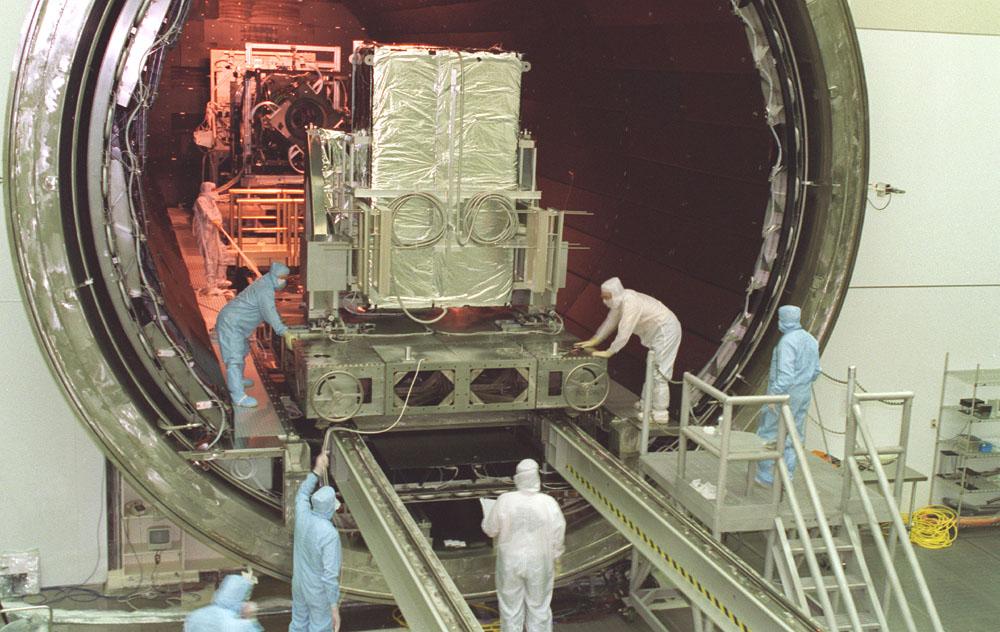
This photograph captures the installation of the Chandra X-Ray Observatory, formerly Advanced X-Ray Astrophysics Facility (AXAF), Advanced Charged-Coupled Device (CCD) Imaging Spectrometer (ACIS) into the Vacuum Chamber at the X-Ray Calibration Facility (XRCF) at Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The AXAF was renamed Chandra X-Ray Observatory (CXO) in 1999. The CXO is the most sophisticated and the world's most powerful x-ray telescope ever built. It observes x-rays from high-energy regions of the universe, such as hot gas in the remnants of exploded stars. The ACIS is one of two focal plane instruments. As the name suggests, this instrument is an array of CCDs similar to those used in a camcorder. This instrument will be especially useful because it can make x-ray images and measure the energies of incoming x-rays. It is the instrument of choice for studying the temperature variation across x-ray sources, such as vast clouds of hot-gas intergalactic space. MSFC's XRCF is the world's largest, most advanced laboratory for simulating x-ray emissions from distant celestial objects. It produces a space-like environment in which components related to x-ray telescope imaging are tested and the quality of their performances in space is predicted. TRW, Inc. was the prime contractor for the development of the CXO and NASA's MSFC was responsible for its project management. The Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory controls science and flight operations of the CXO for NASA from Cambridge, Massachusetts. The CXO was launched July 22, 1999 aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-93).
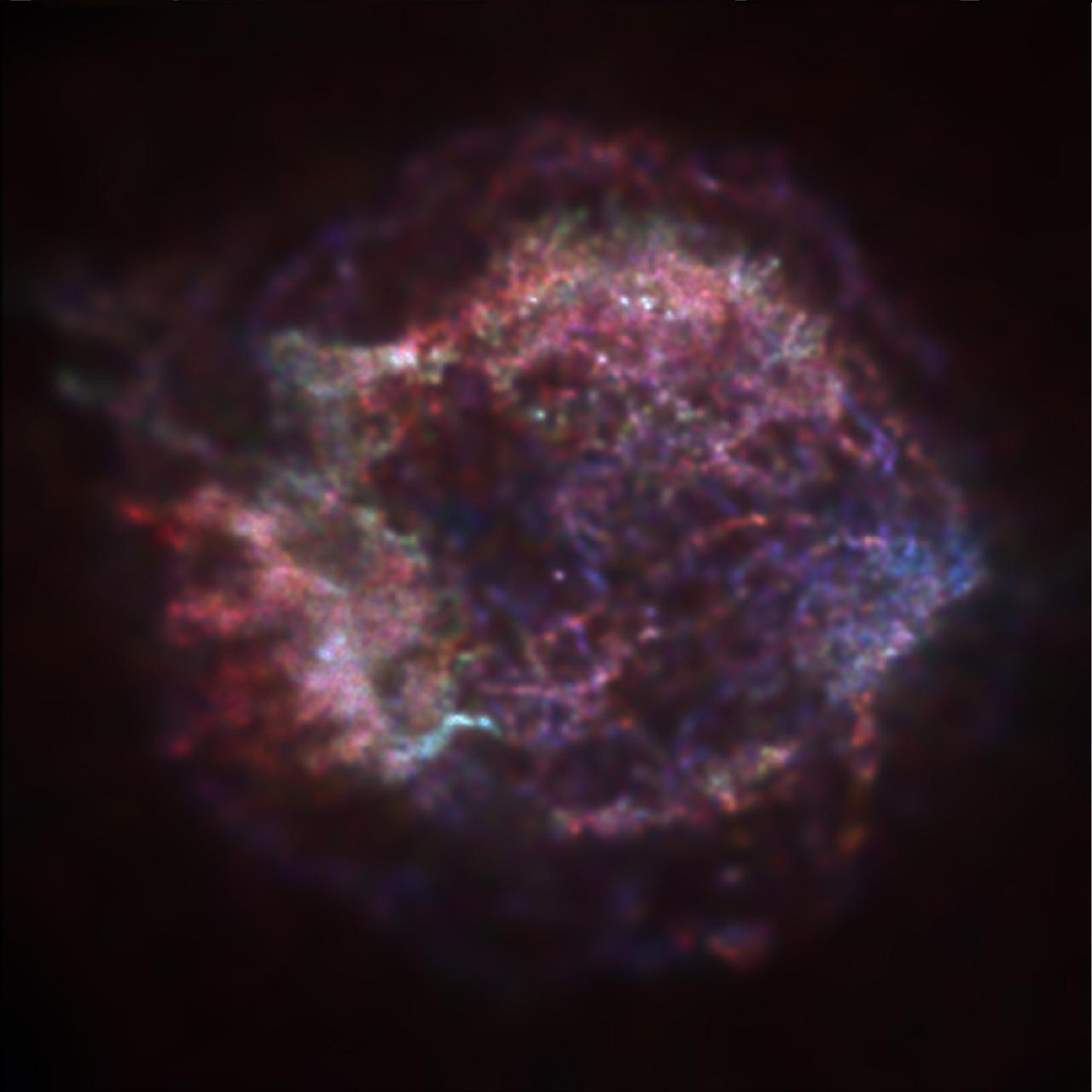

This is an extraordinary first image from the Chandra X-Ray Observatory (CXO), the supernova remnant Cassiopeia A, tracing the aftermath of a gigantic stellar explosion in such sturning detail that scientists can see evidence of what may be a neutron star or black hole near the center. The red, green, and blue regions in this image of the supernova remnant Cassiopeia A show where the intensity of low, medium, and high energy X-rays, respectively, is greatest. The red material on the left outer edge is enriched in iron, whereas the bright greenish white region on the low left is enriched in silicon and sulfur. In the blue region on the right edge, low and medium energy X-rays have been filtered out by a cloud of dust and gas in the remnant . The image was made with the CXO's Advanced Charged-Coupled Device (CCD) Imaging Spectrometer (ACIS). Photo credit: NASA/CXC/SAO/Rutgers/J.Hughes

After barely 2 months in space, the Chandra X-Ray Observatory (CXO) took this sturning image of the Crab Nebula, the spectacular remains of a stellar explosion, revealing something never seen before, a brilliant ring around the nebula's heart. The image shows the central pulsar surrounded by tilted rings of high-energy particles that appear to have been flung outward over a distance of more than a light-year from the pulsar. Perpendicular to the rings, jet-like structures produced by high-energy particles blast away from the pulsar. Hubble Space Telescope images have shown moving knots and wisps around the neutron star, and previous x-ray images have shown the outer parts of the jet and hinted at the ring structure. With CXO's exceptional resolution, the jet can be traced all the way in to the neutron star, and the ring pattern clearly appears. The image was made with CXO's Advanced Charge-Coupled Device (CCD) Imaging Spectrometer (ACIS) and High Energy Transmission Grating. The Crab Nebula, easily the most intensively studied object beyond our solar system, has been observed using virtually every astronomical instrument that could see that part of the sky
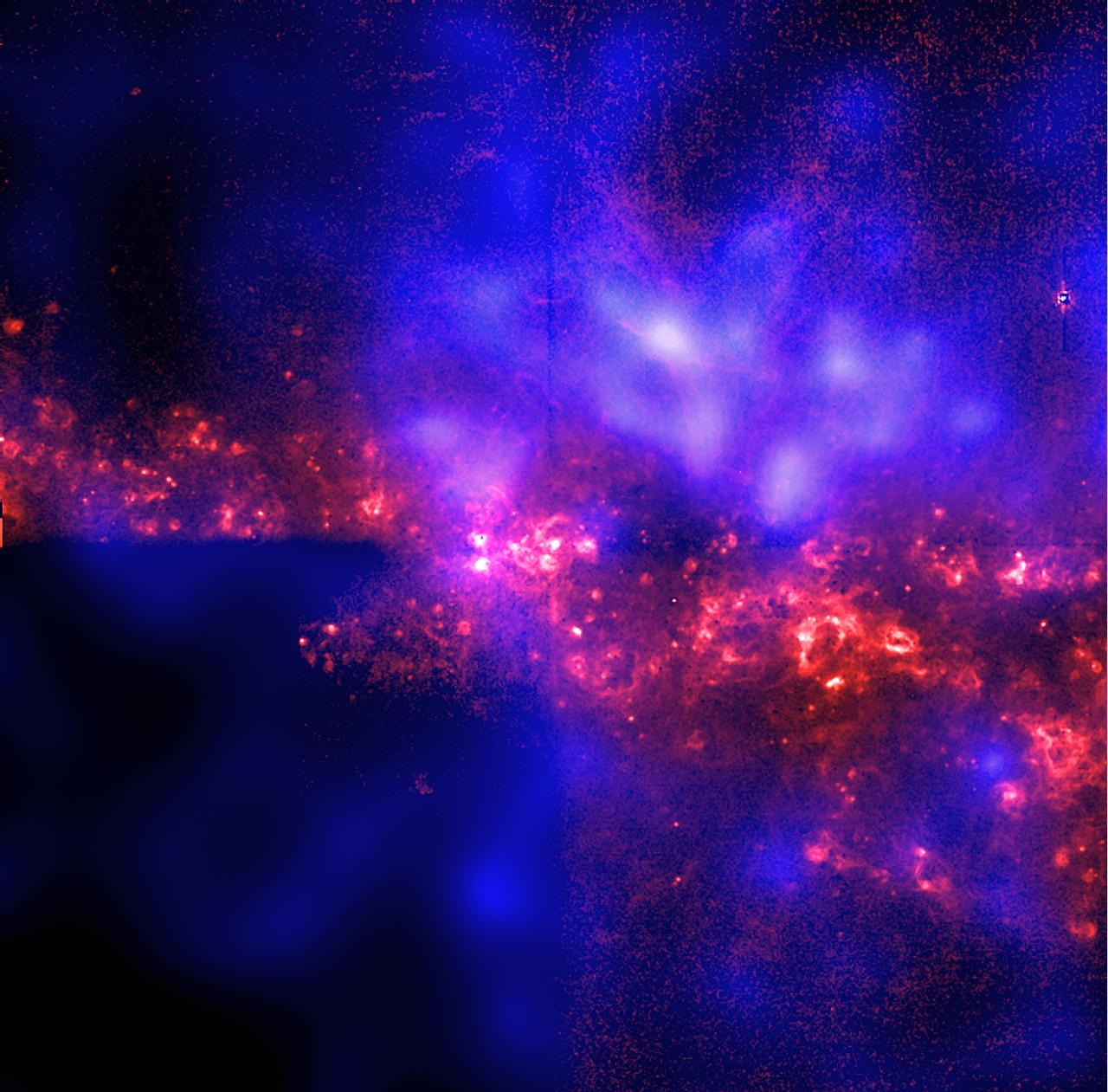

This image shows the central region of the spiral galaxy NGC 4631 as seen edge-on from the Chandra X-Ray Observatory (CXO) and the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The Chandra data, shown in blue and purple, provide the first unambiguous evidence for a halo of hot gas surrounding a galaxy that is very similar to our Milky Way. The structure across the middle of the image and the extended faint filaments, shown in orange, represent the observation from the HST that reveals giant bursting bubbles created by clusters of massive stars. Scientists have debated for more than 40 years whether the Milky Way has an extended corona, or halo, of hot gas. Observations of NGC 4631 and similar galaxies provide astronomers with an important tool in the understanding our own galactic environment. A team of astronomers, led by Daniel Wang of the University of Massachusetts at Amherst, observed NGC 4631 with CXO's Advanced Charge-Coupled Device (CCD) Imaging Spectrometer (ACIS). The observation took place on April 15, 2000, and its duration was approximately 60,000 seconds.
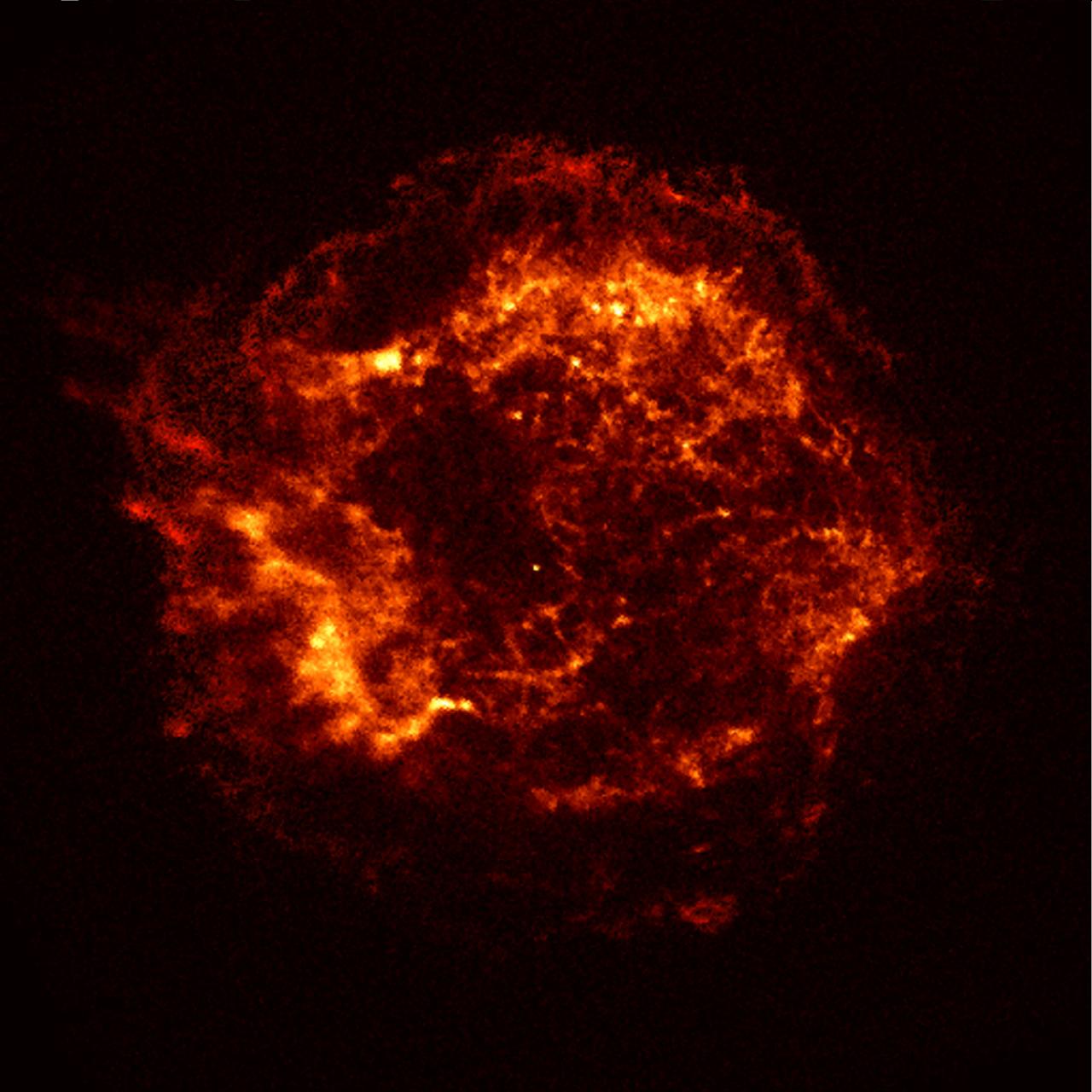
This x-ray image of the Cassiopeia A (CAS A) supernova remnant is the official first light image of the Chandra X-Ray Observatory (CXO). The 5,000-second image was made with the Advanced Charged Coupled Device (CCD) Image Spectrometer (ACIS). Two shock waves are visible: A fast outer shock and a slower irner shock. The inner shock wave is believed to be due to the collision of ejecta from the supernova explosion with a circumstellar shell of material, heating it to a temperature of 10 million-degrees Celsius. The outer shock wave is analogous to an awesome sonic boom resulting from this collision The x-rays reveal a bright object near the center, which may be the long-sought neutron star or black hole remnant of the explosion that produced Cassiopeia A. Cassiopeia A is the 320-year-old remnant of a massive star that exploded. Located in the constellation Cassiopeia, it is 10 light-years across and 10,000 light-years from Earth. A supernova occurs when a massive star has used up its nuclear fuel and the pressure drops in the central core of the star. The matter in the core is crushed by gravity to higher and higher densities, and temperatures reach billions of degrees. Under these extreme conditions, nuclear reactions occur violently and catastrophically, reversing the collapse. A thermonuclear shock wave races through the now expanding stellar debris, fusing lighter elements into heavier ones and producing a brilliant visual outburst.