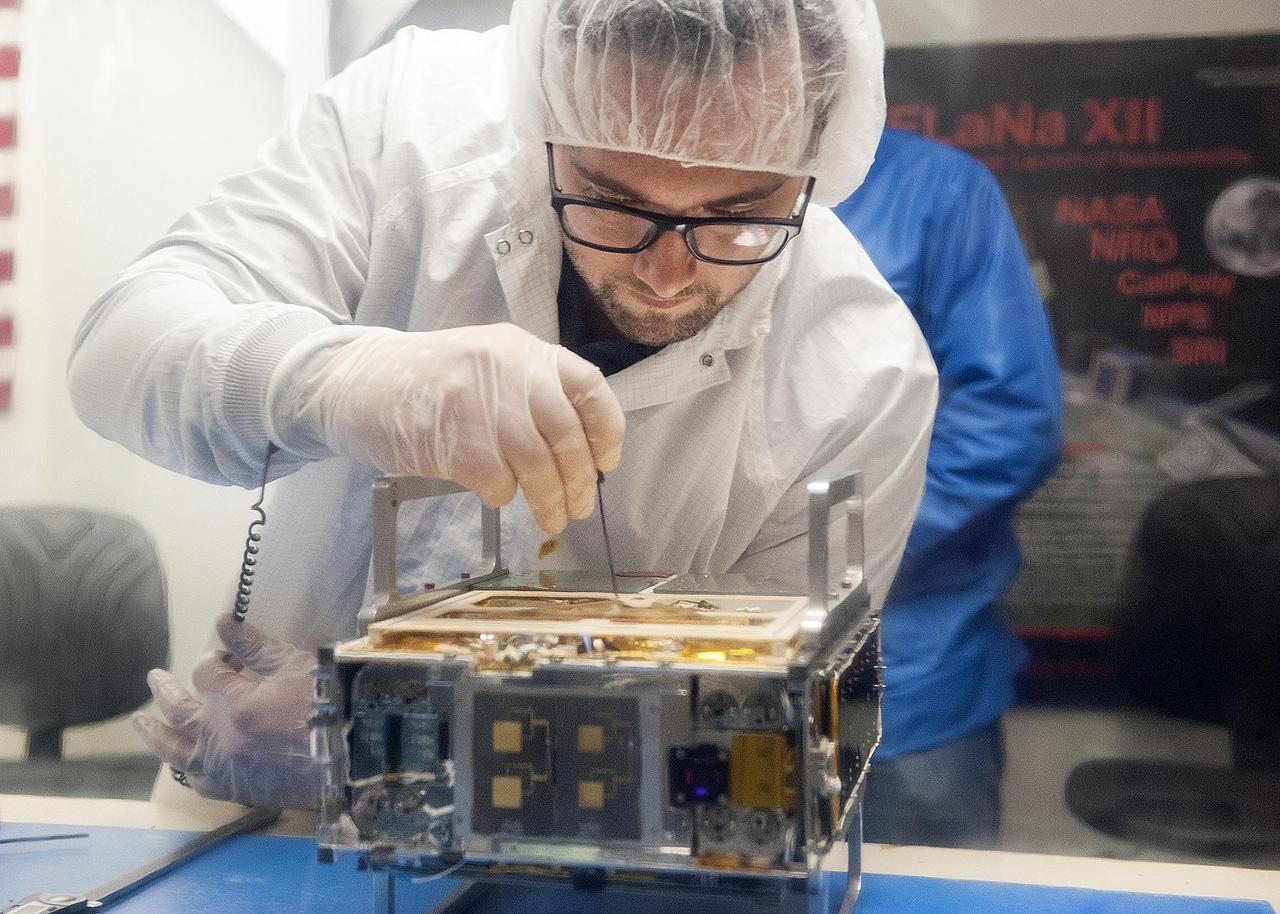

Joel Steinkraus, MarCO lead mechanical engineer from JPL, makes an adjustment on the CubeSat prior to integration in a deployment box as seen inside the cleanroom lab at Cal Poly San Luis Obispo on Monday, March 12, 2018. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22321
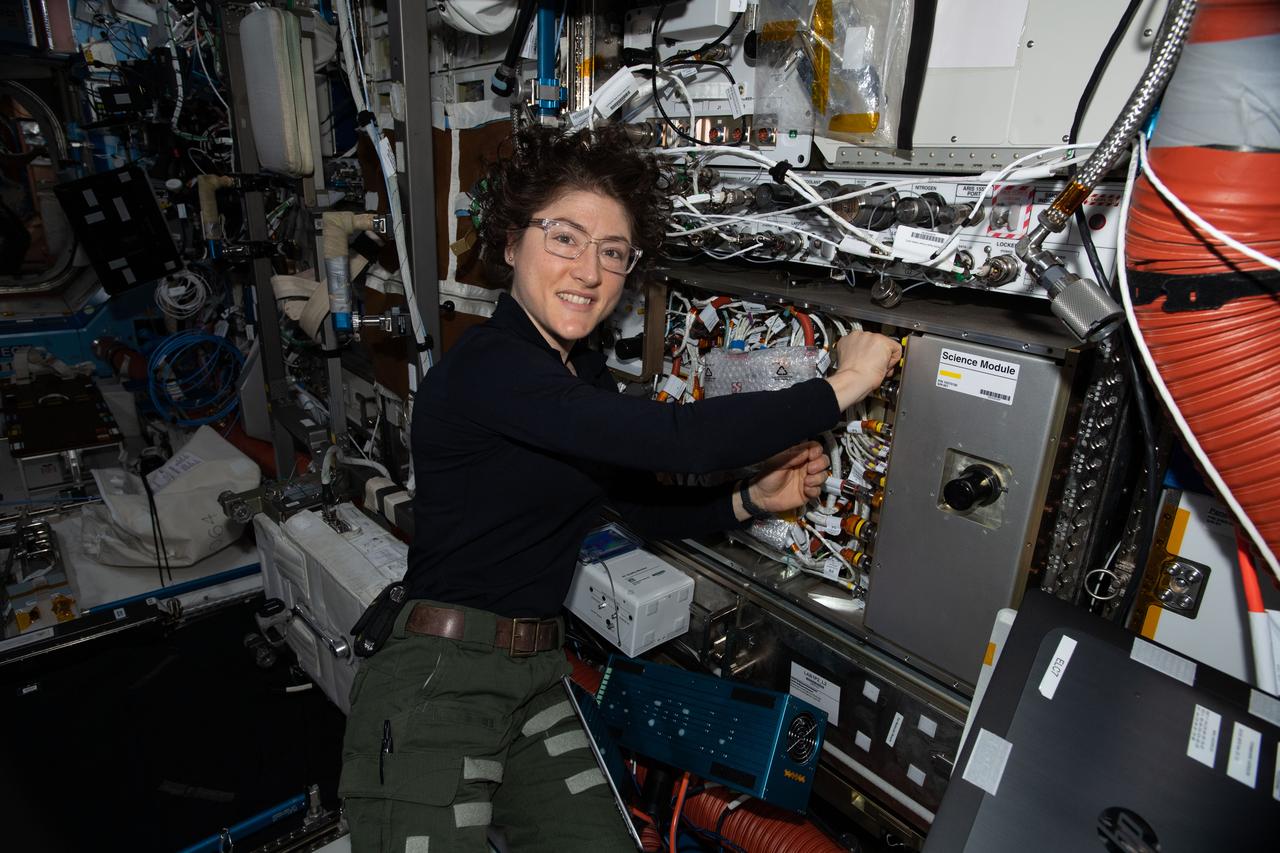

iss061e145487 (Jan. 28, 2020) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 61 Flight Engineer Jessica Koch works on the Cold Atom Lab (CAL) swapping and cleaning hardware inside the quantum research device. The CAL enables research into the quantum effects of gases chilled to nearly absolute zero, which is colder than the average temperature of the universe.
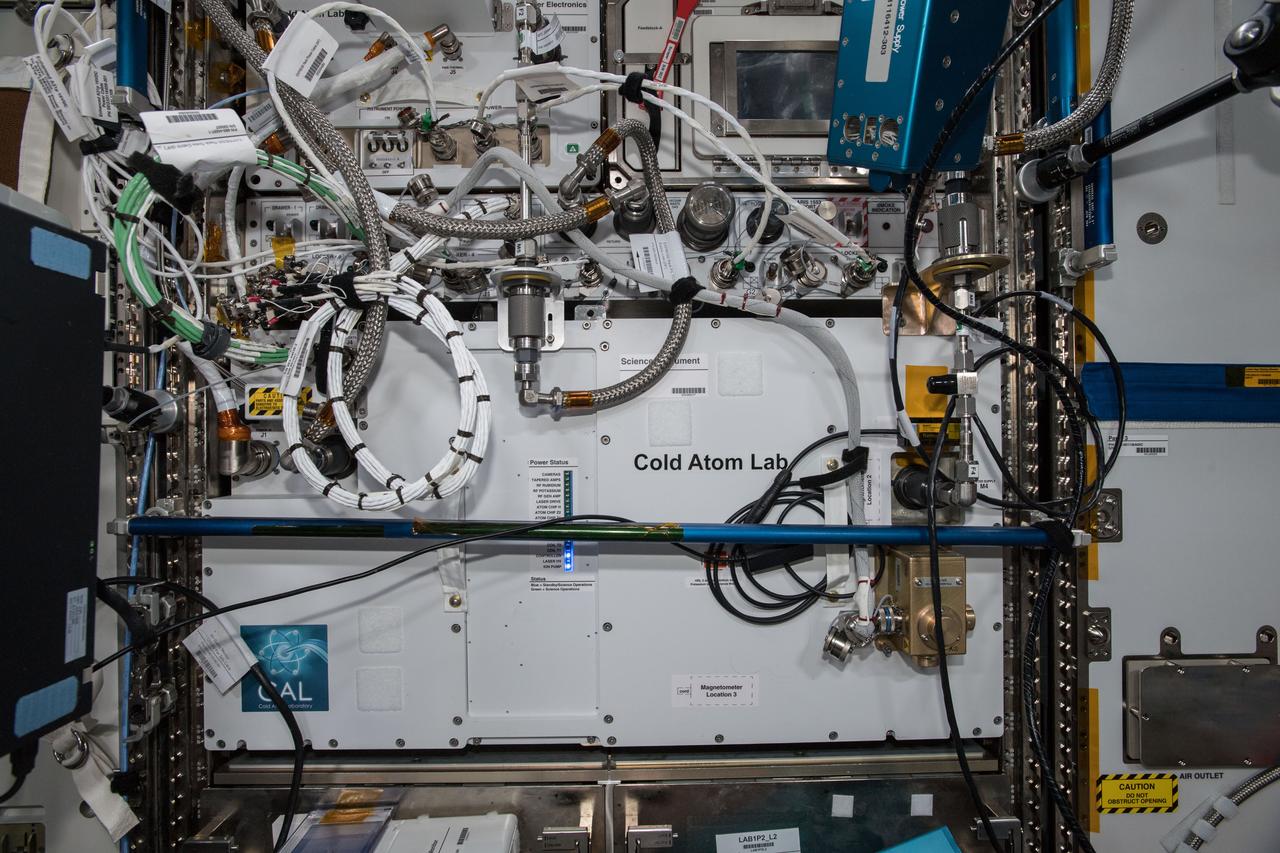

iss057e106407 (11/20/2018) -- A view of the Cold Atom Lab (CAL) in the Destiny module aboard the International Space Station (ISS). The Cold Atom Laboratory (CAL) produces clouds of atoms that are chilled to about one ten billionth of a degree above absolute zero -- much colder than the average temperature of deep space. At these low temperatures, atoms have almost no motion, allowing scientists to study fundamental behaviors and quantum characteristics that are difficult or impossible to probe at higher temperatures
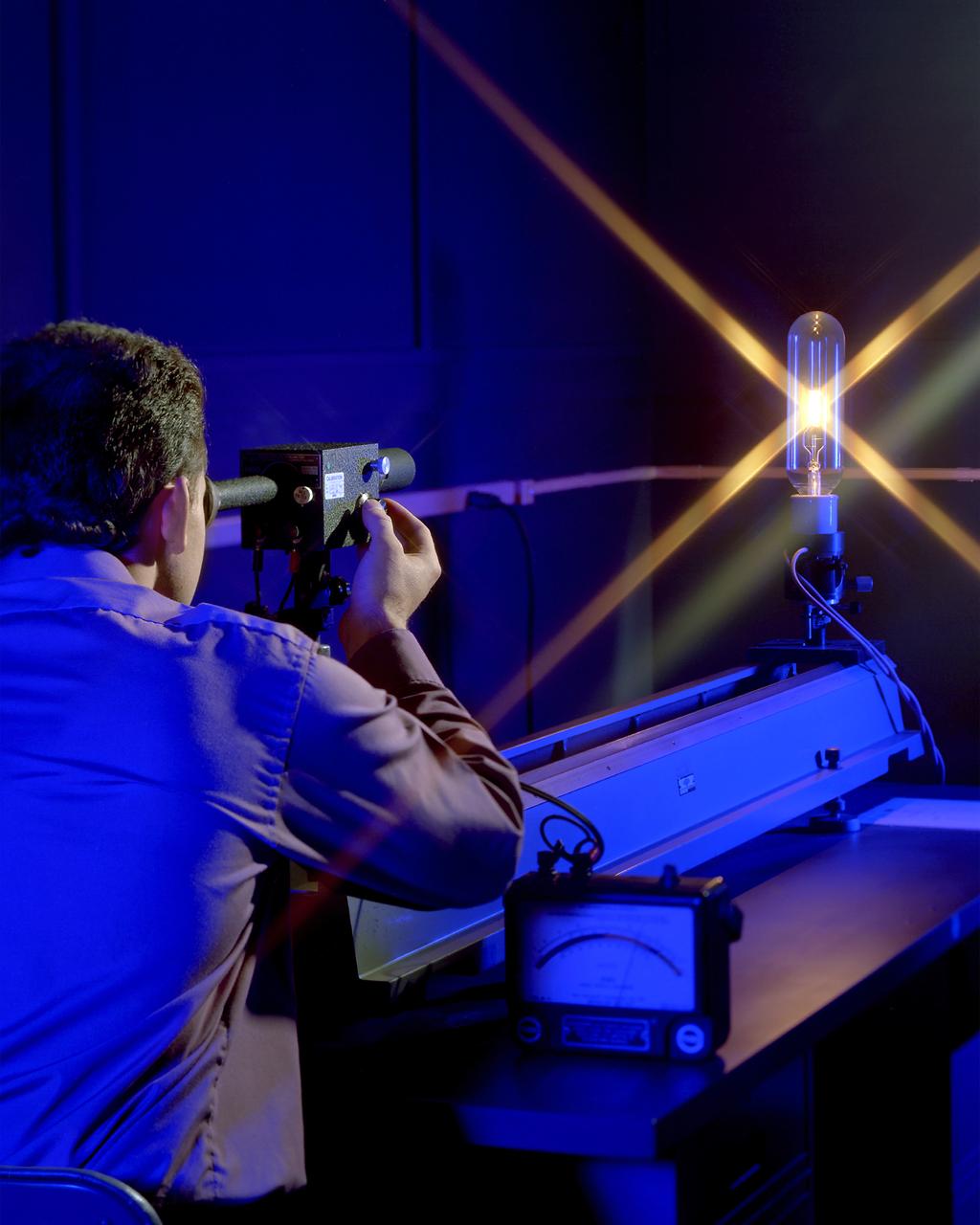

Pictured is a method for testing high temperature measurements by comparing the color spectrum of light at various power settings with an Optical Pyrometer. The devices are calibrated at NIST. The power through the bulb is varied and monitored by the meter on the table. The scanning device that the technician is looking though is adjusted till the color scheme viewed within in the device matches the color of the emanating from the bulb at the particular power setting. Using a relationship table provided, the technicians can then identify the temperature. The light source pictured is used to calibrate the device that the technician looks through. The technician would then go to a source of heat such as an oven and by aligning the color given off by the unit under test (UUT), he would use the reference table to determine the source’s heat output.
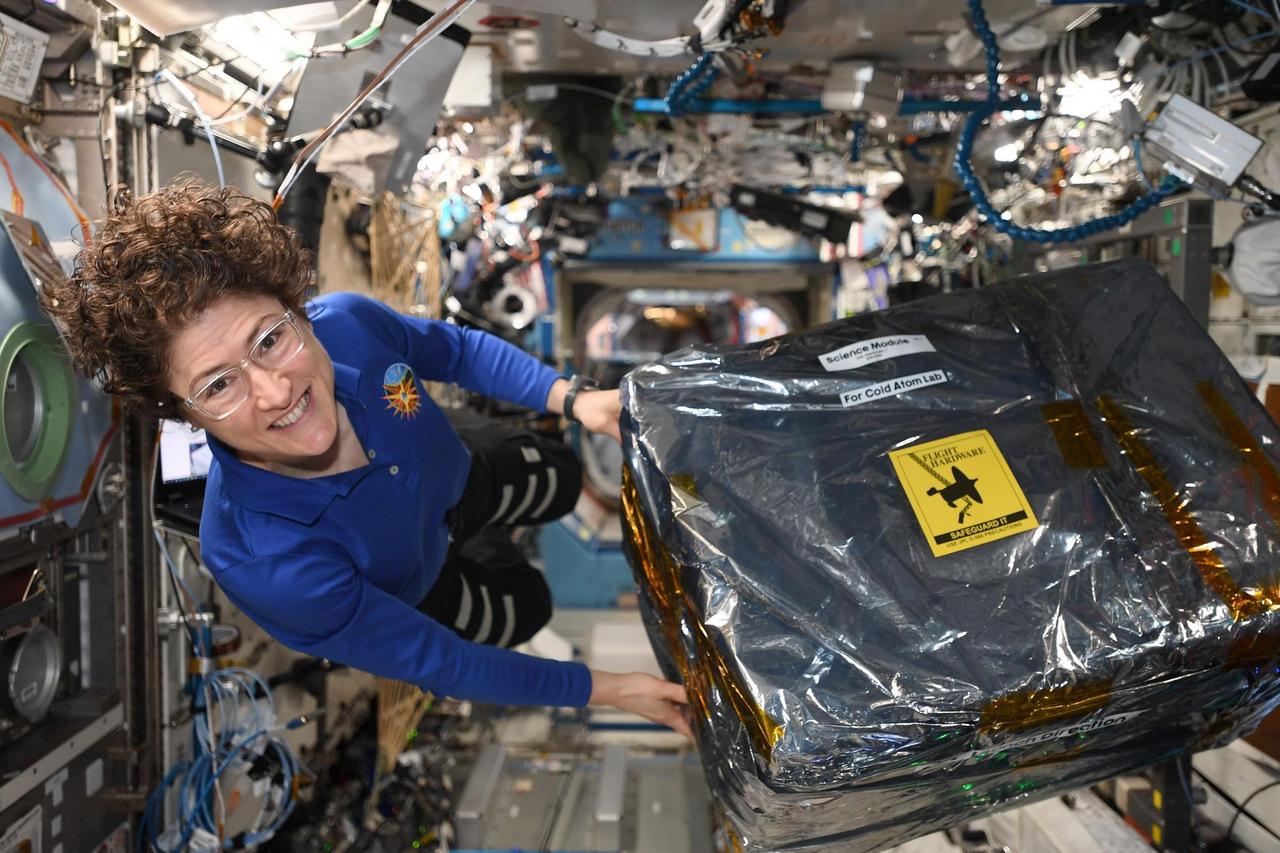

Astronaut Christina Koch unloads new hardware for the Cold Atom Lab aboard the International Space Station the week of Dec. 9, 2020. The Cold Atom Laboratory launched to the space station on May 21, 2018, aboard a Northrop Grumman (formerly Orbital ATK) Cygnus spacecraft from NASA's Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia. Designed and built at JPL, CAL is sponsored by the International Space Station Program at NASA's Johnson Space Center in Houston, and the Space Life and Physical Sciences Research and Applications (SLPSRA) Division of NASA's Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters in Washington. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23404
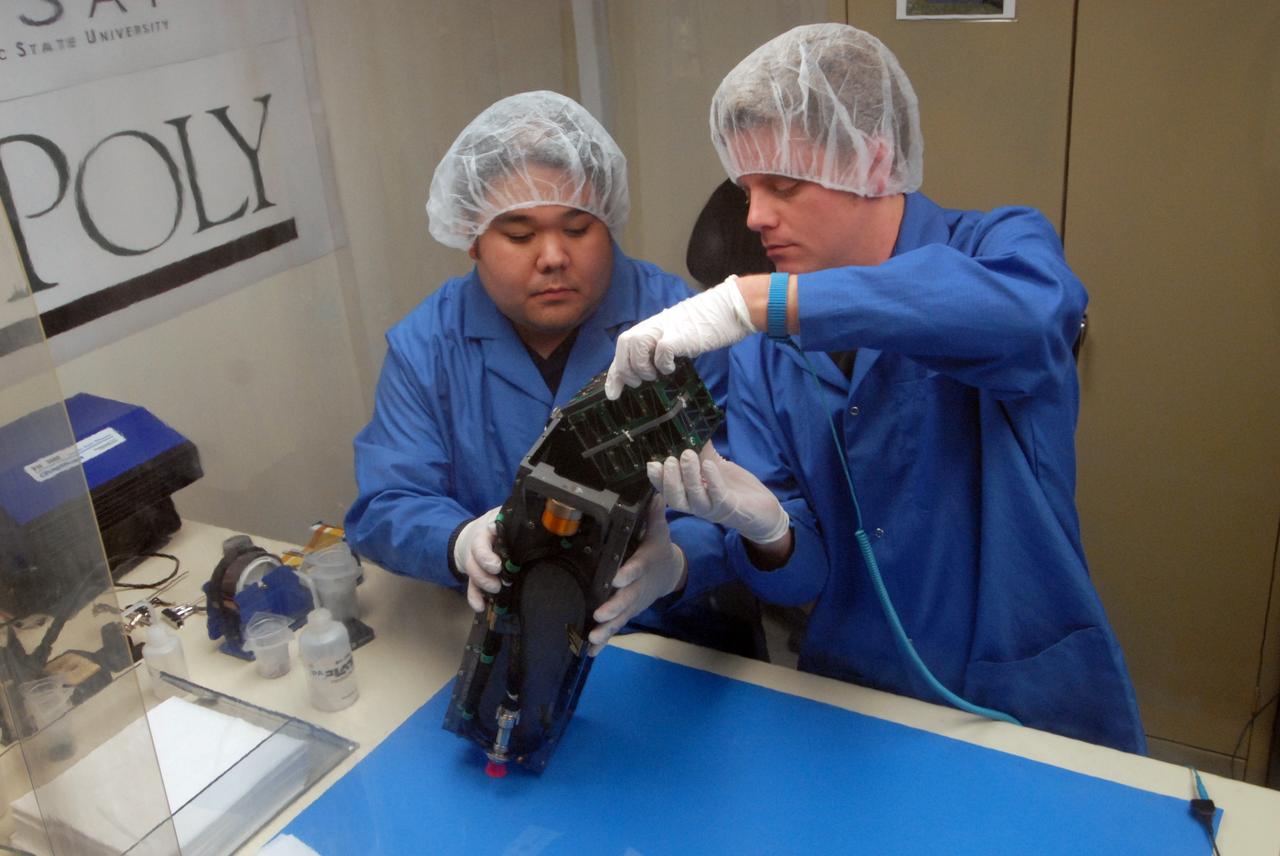

San Luis Obispo, Calif. -- 101116-F-8290C-054 -- Roland Coelho and Ryan Nugent, students at California Polytechnic State University Cal Poly, integrate miniature research satellites called CubeSats into a Poly Picosatellite Orbital Deployer PPOD container. The PPOD and CubeSat Project were developed by Cal Poly and Stanford University’s Space Systems Development Lab for use on NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellite ELaNa missions. Each CubeSat measures about 4-inches cubed and is about the same volume as a quart. The CubeSats weigh about 2.2 pounds, must conform to standard aerospace materials and must operate without propulsion. The satellites are being prepared to launch with NASA's Glory spacecraft aboard an Orbital Sciences Corp. Taurus XL rocket, targeted to lift off Feb. 23, 2011, from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 576-E. Glory is scheduled to collect data on the properties of aerosols and black carbon from its place in low Earth orbit. It also will help scientists understand how the sun's irradiance affects Earth's climate. Photo credit: U.S. Air Force/Jerry E. Clemens Jr.
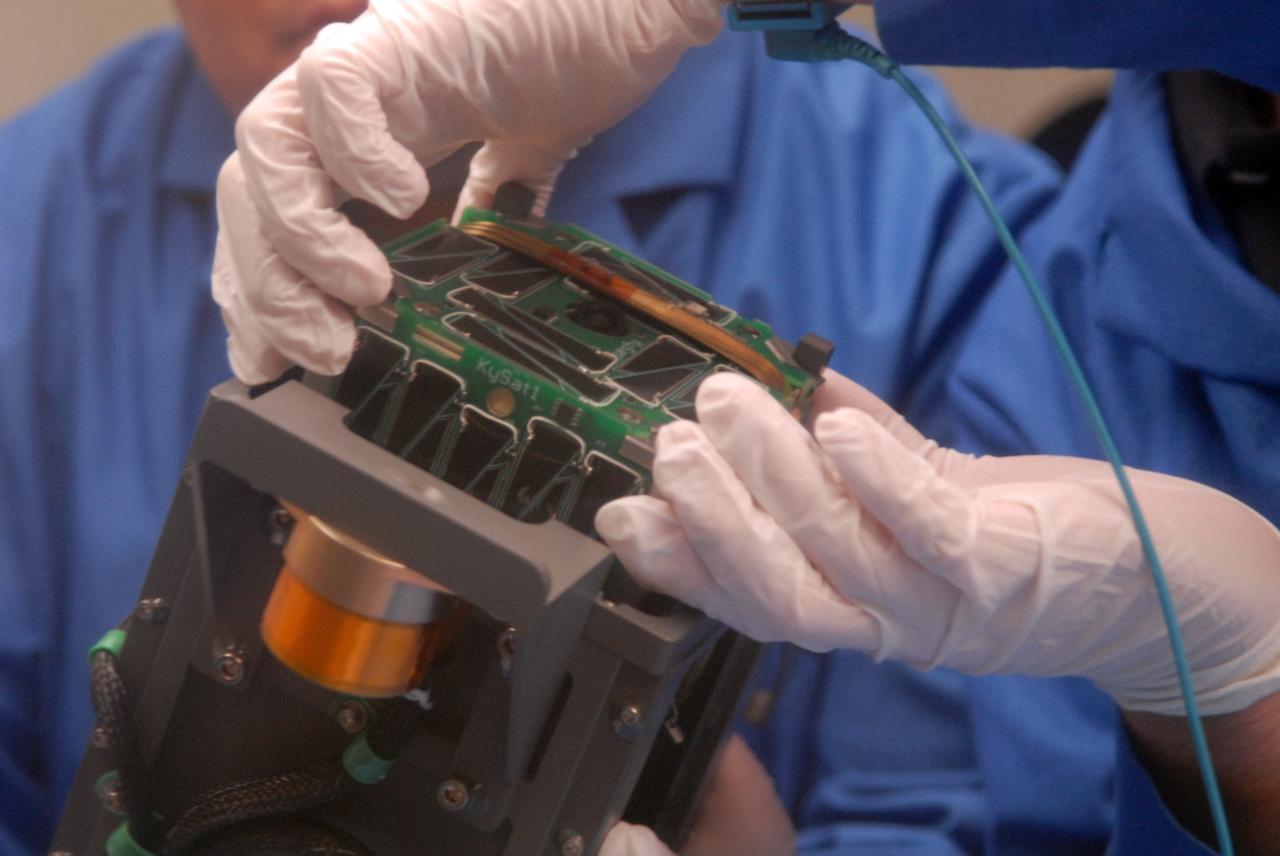
San Luis Obispo, Calif. -- 101116-F-8290C-059 -- Roland Coelho and Ryan Nugent, students at California Polytechnic State University Cal Poly, integrate miniature research satellites called CubeSats into a Poly Picosatellite Orbital Deployer PPOD container. The PPOD and CubeSat Project were developed by Cal Poly and Stanford University’s Space Systems Development Lab for use on NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellite ELaNa missions. Each CubeSat measures about 4-inches cubed and is about the same volume as a quart. The CubeSats weigh about 2.2 pounds, must conform to standard aerospace materials and must operate without propulsion. The satellites are being prepared to launch with NASA's Glory spacecraft aboard an Orbital Sciences Corp. Taurus XL rocket, targeted to lift off Feb. 23, 2011, from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 576-E. Glory is scheduled to collect data on the properties of aerosols and black carbon from its place in low Earth orbit. It also will help scientists understand how the sun's irradiance affects Earth's climate. Photo credit: U.S. Air Force/Jerry E. Clemens Jr.
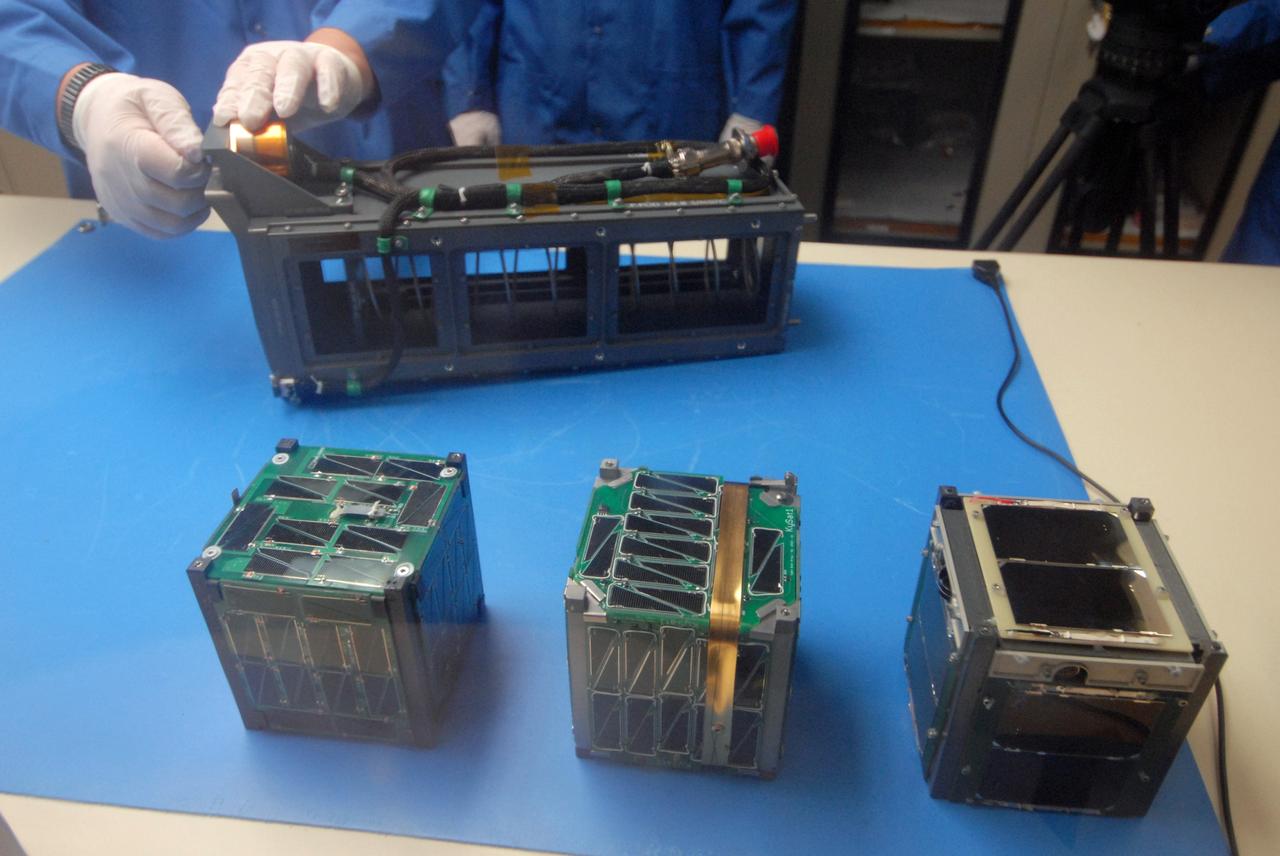
San Luis Obispo, Calif. -- 101116-F-8290C-045 -- Students at California Polytechnic State University Cal Poly prepare to integrate miniature research satellites called CubeSats into a Poly Picosatellite Orbital Deployer PPOD container. The PPOD and CubeSat Project were developed by Cal Poly and Stanford University’s Space Systems Development Lab for use on NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellite ELaNa missions. Each CubeSat measures about 4-inches cubed and is about the same volume as a quart. The CubeSats weigh about 2.2 pounds, must conform to standard aerospace materials and must operate without propulsion. The satellites are being prepared to launch with NASA's Glory spacecraft aboard an Orbital Sciences Corp. Taurus XL rocket, targeted to lift off Feb. 23, 2011, from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 576-E. Glory is scheduled to collect data on the properties of aerosols and black carbon from its place in low Earth orbit. It also will help scientists understand how the sun's irradiance affects Earth's climate. Photo credit: U.S. Air Force/Jerry E. Clemens Jr.

San Luis Obispo, Calif. -- 101116-F-8290C-060 -- Roland Coelho, a student at California Polytechnic State University Cal Poly, inspects the integration alignment of miniature research satellites called a CubeSats into a Poly Picosatellite Orbital Deployer PPOD container. The PPOD and CubeSat Project were developed by Cal Poly and Stanford University’s Space Systems Development Lab for use on NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellite ELaNa missions. Each CubeSat measures about 4-inches cubed and is about the same volume as a quart. The CubeSats weigh about 2.2 pounds, must conform to standard aerospace materials and must operate without propulsion. The satellites are being prepared to launch with NASA's Glory spacecraft aboard an Orbital Sciences Corp. Taurus XL rocket, targeted to lift off Feb. 23, 2011, from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 576-E. Glory is scheduled to collect data on the properties of aerosols and black carbon from its place in low Earth orbit. It also will help scientists understand how the sun's irradiance affects Earth's climate. Photo credit: U.S. Air Force/Jerry E. Clemens Jr.