
This is image is of the 200-inch Hale Telescope at the Palomar Observatory, located in north San Diego County, California which is owned and operated by the California Institute of Technology.

This image of the Crab Pulsar was taken with CHIMERA, an instrument at the Palomar Observatory, which is operated by the California Institute of Technology.
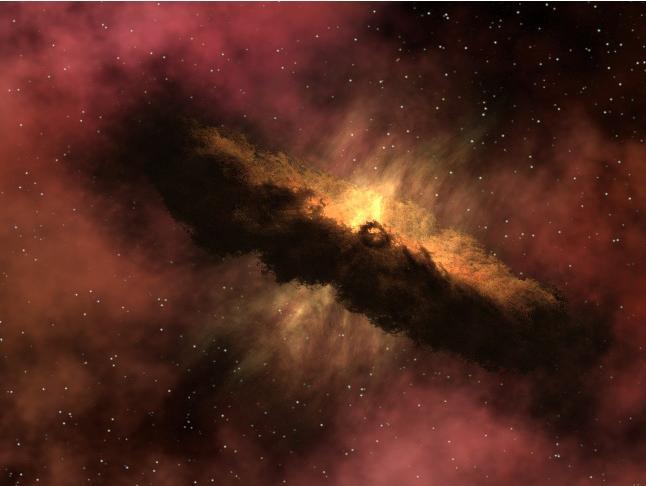

This artist animation depicts one of the most widely accepted theories pertaining to the origin of comets. This image is courtesy of NASA Spitzer Science Center at the California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, Calif.
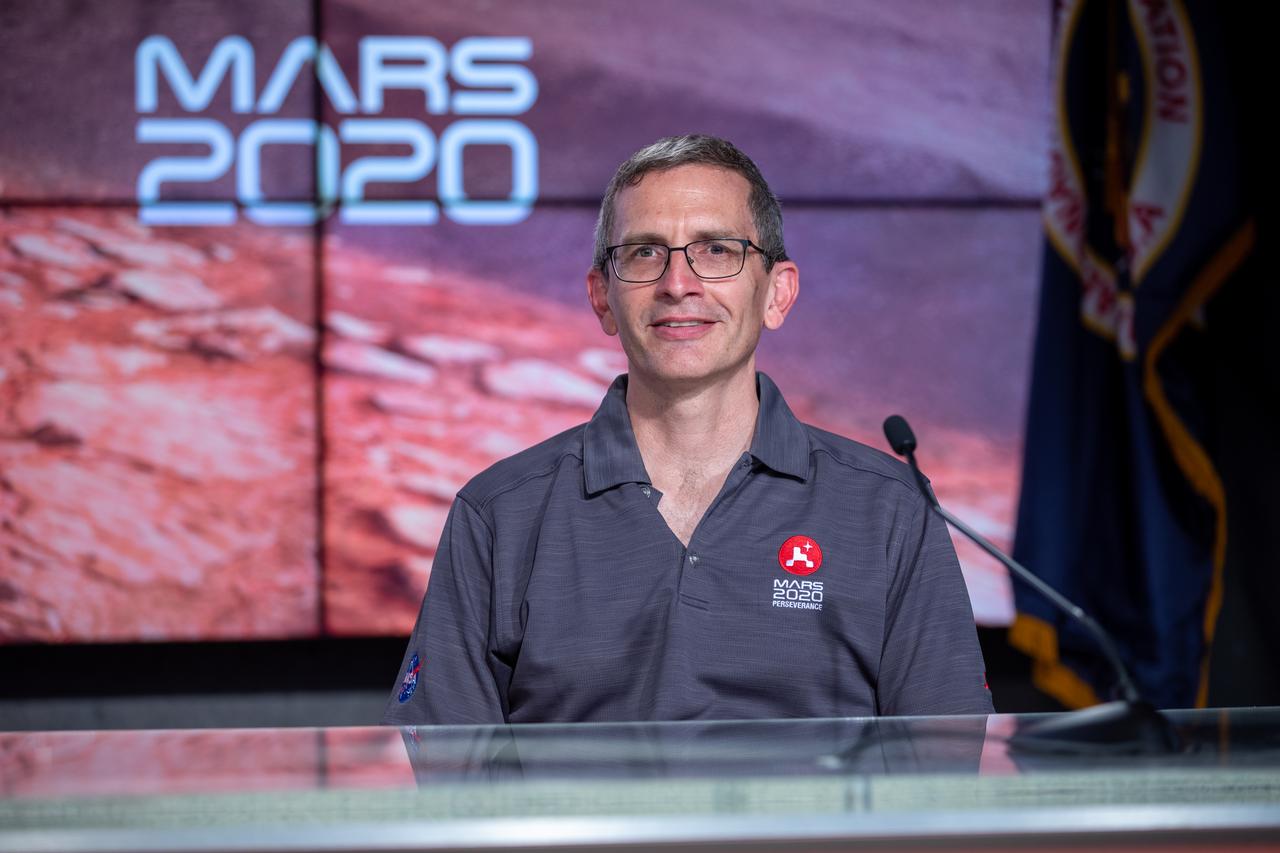

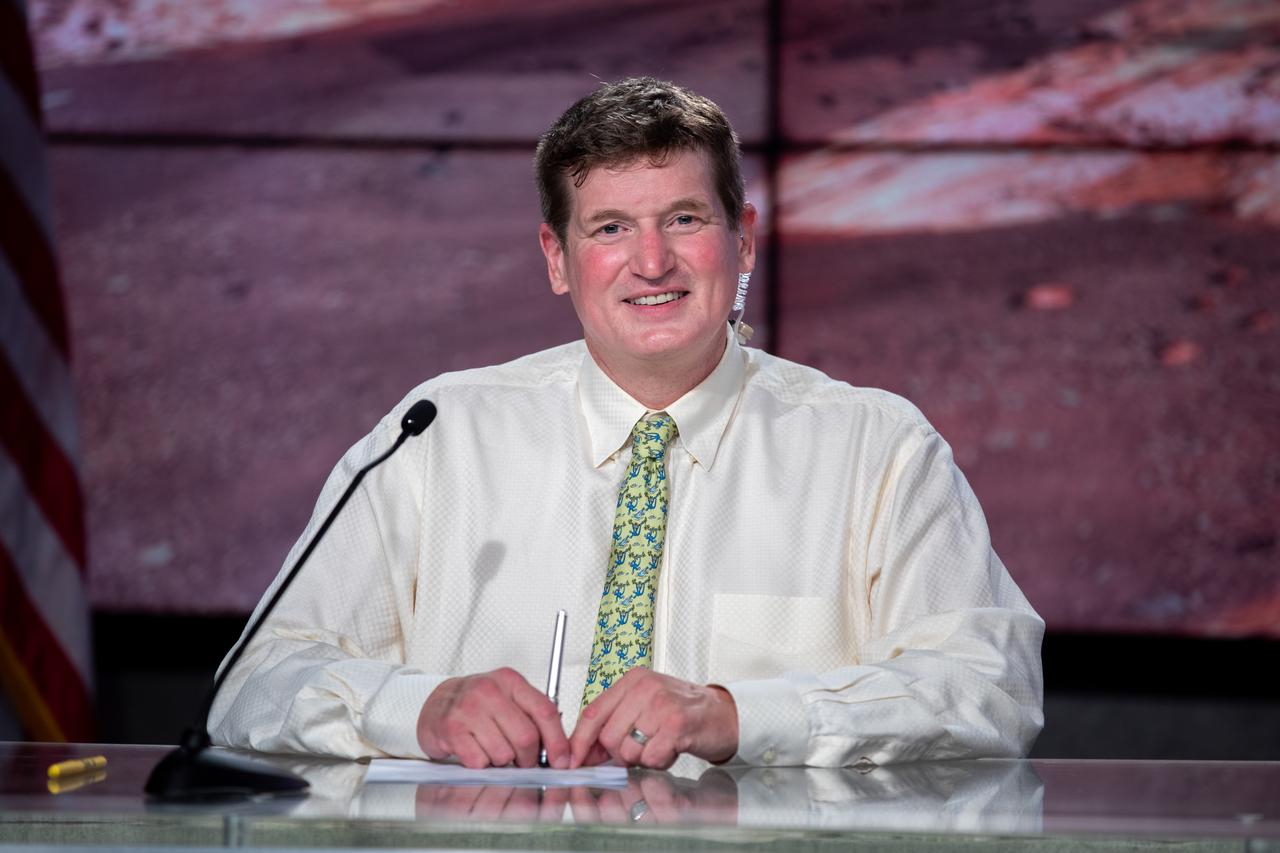
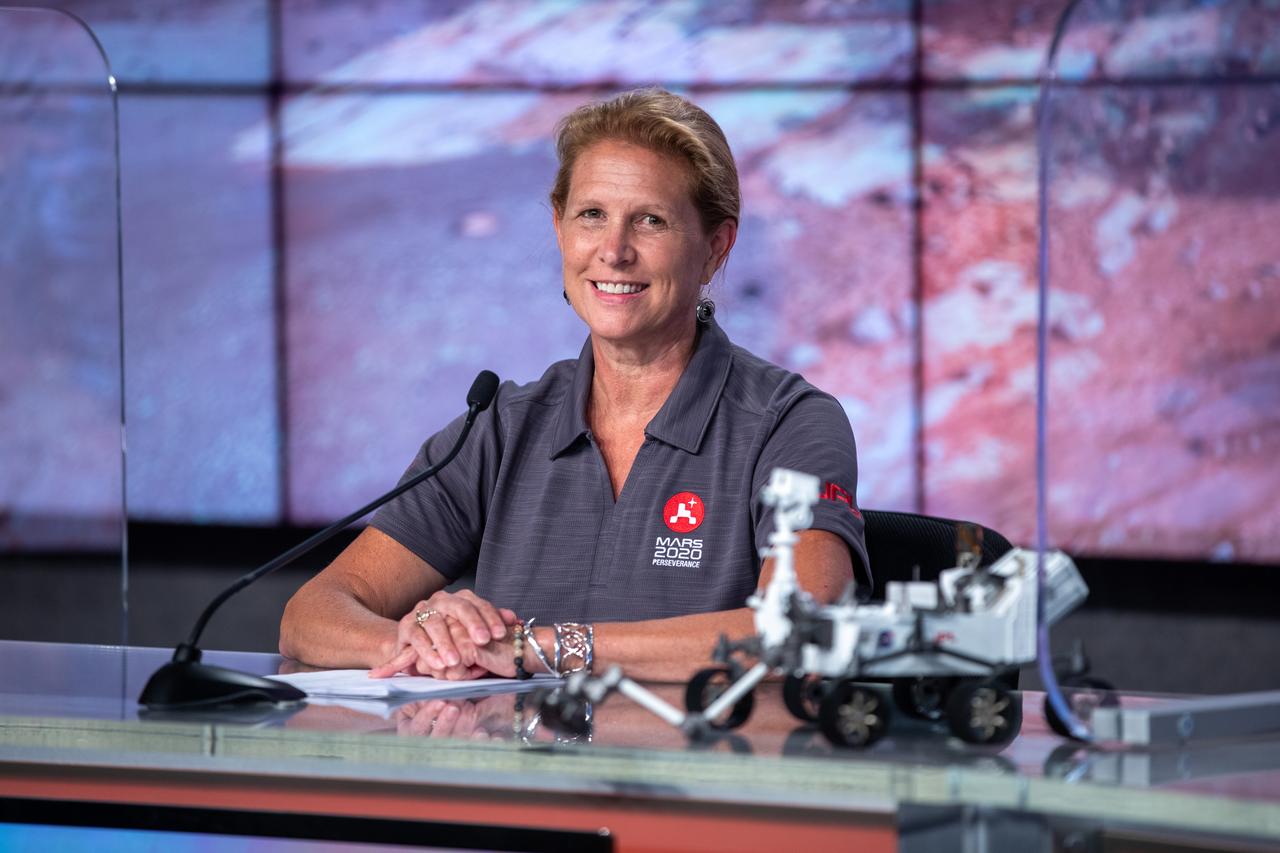
Ken Farley, project scientist, California Institute of Technology, participates in a Mars 2020 Mission Engineering and Science Briefing at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 27, 2020. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch July 30, on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at nearby Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
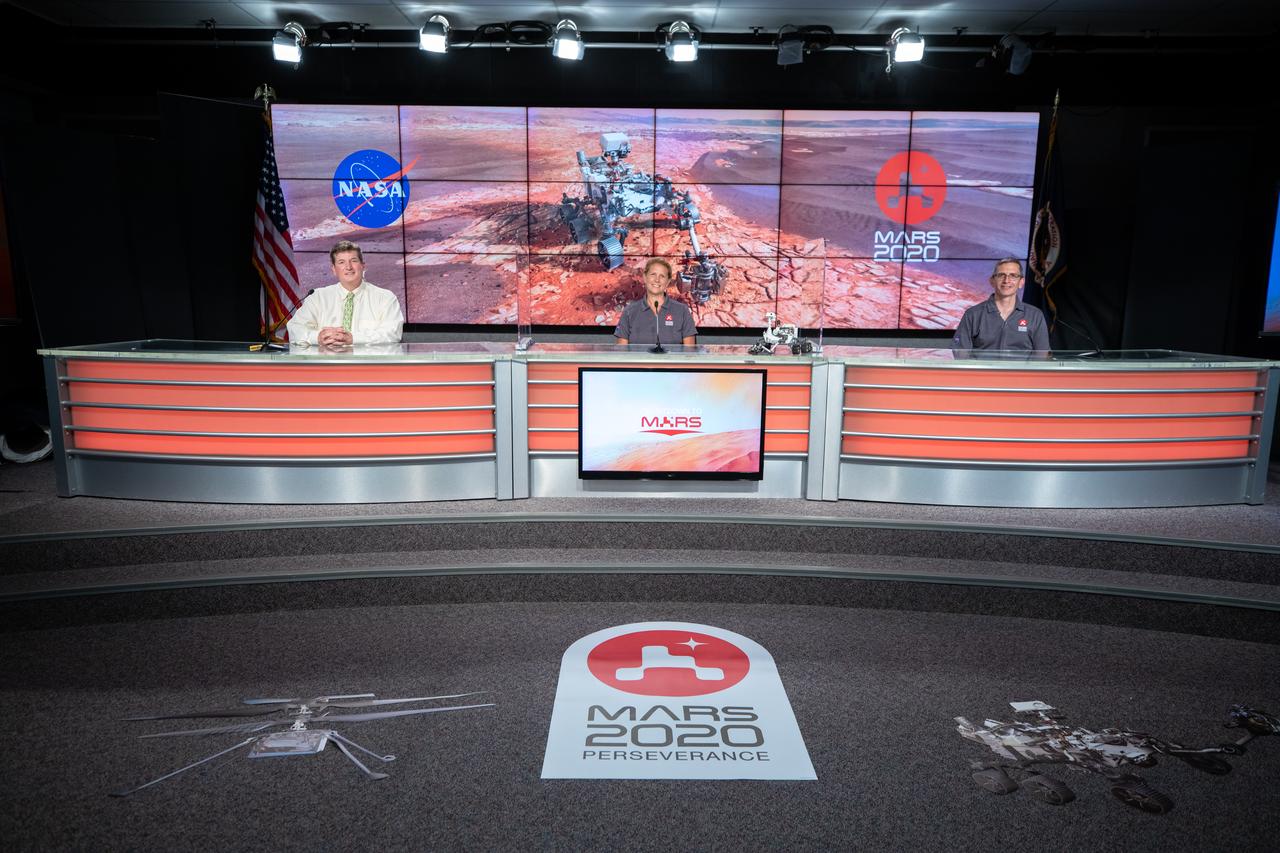

A Mars 2020 Mission Engineering and Science Briefing is held at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 27, 2020. Participating in the briefing from left, are Moderator DC Agle, NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory; Lori Glaze, Planetary Science Division director, NASA Headquarters; and Ken Farley, project scientist, California Institute of Technology. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch July 30, on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at nearby Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.

A Mars 2020 Mission Engineering and Science Briefing is held at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 27, 2020. Participating in the briefing from left, are Moderator DC Agle, NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory; Lori Glaze, Planetary Science Division director, NASA Headquarters; and Ken Farley, project scientist, California Institute of Technology. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch July 30, on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at nearby Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Logo for the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) mission, managed for NASA by JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology, Pasadena.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Press Site auditorium at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, media were briefed about NASA's future science missions. Seen here are NASA Public Affairs Officer George Diller (left); Waleed Abdalati, NASA chief scientist; Amanda Mitskevich, NASA Launch Services Program manager; Scott Bolton, Juno principal investigator with the Southwest Research Institute, San Antonio; Maria Zuber, GRAIL principal investigator with the Massachusetts Institute of Technology; John Grotzinger, Mars Science Lab project scientist with the California Institute of Technology and Daniel Stern, NuStar project scientist with NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Calif. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
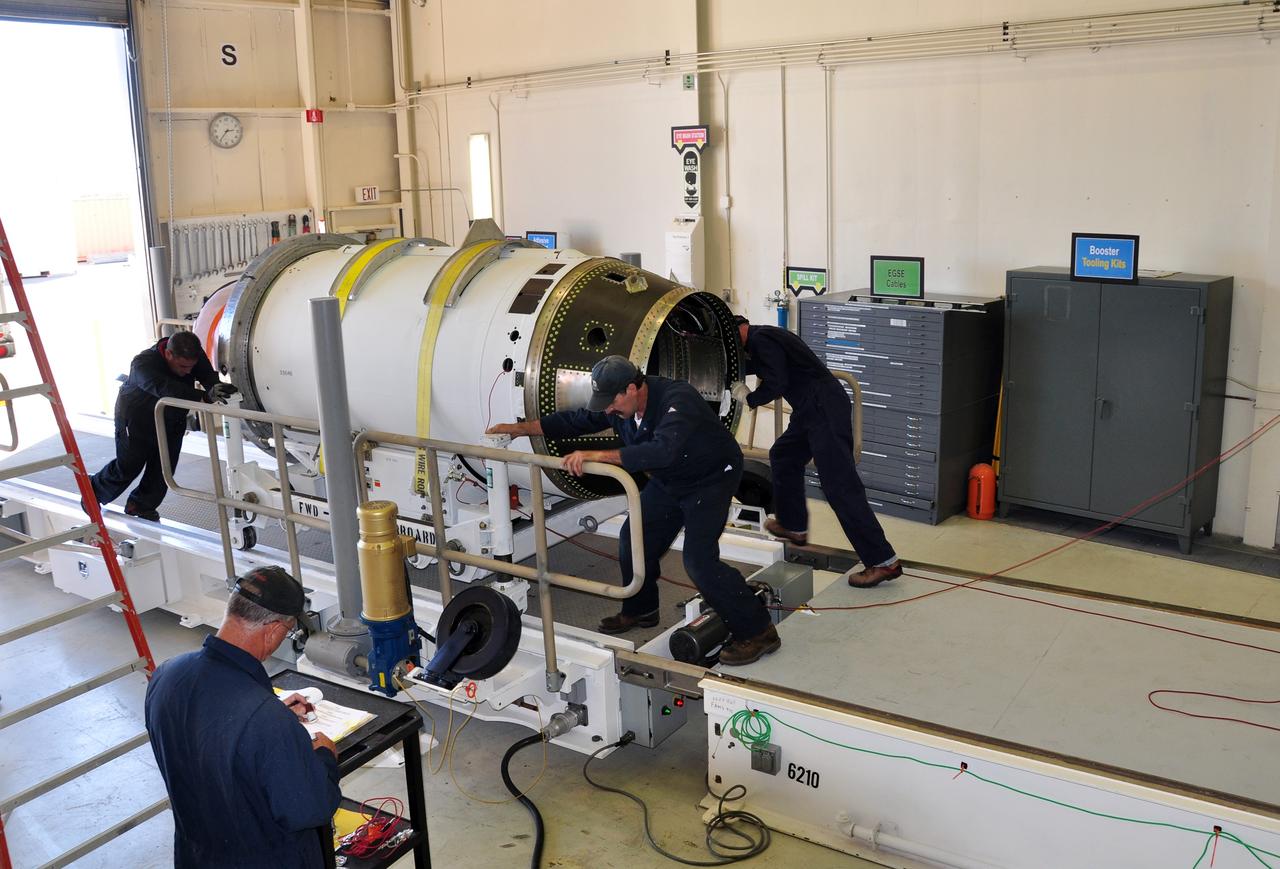

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the second stage of the Pegasus XL rocket that will launch the Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) to orbit is moved to a stationary rail in Building 1555 for processing. After the rocket and spacecraft are processed at Vandenberg, they will be shipped to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site located at the Pacific Ocean’s Kwajalein Atoll for launch. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
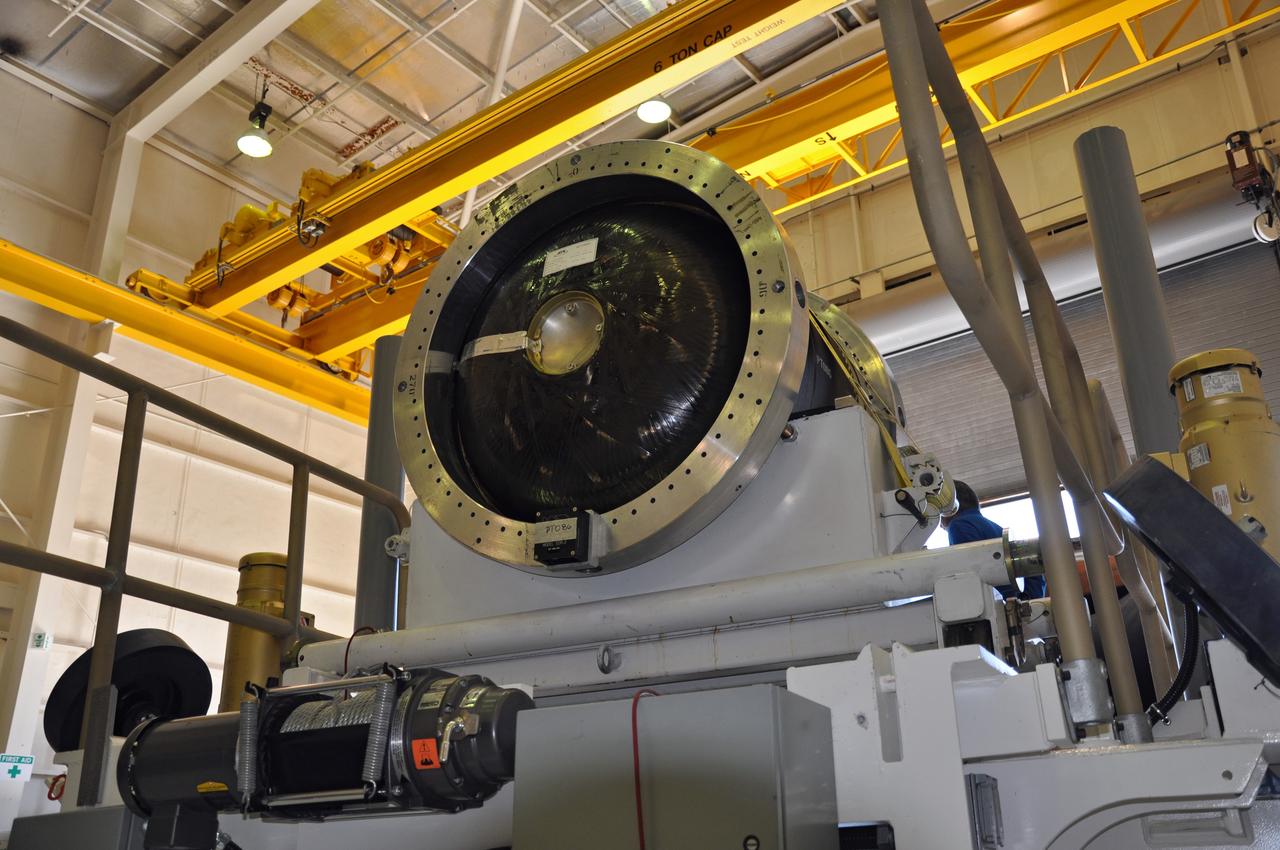

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the third stage of the Pegasus XL rocket that will launch the Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) to orbit is offloaded for processing in Building 1555. After the rocket and spacecraft are processed at Vandenberg, they will be shipped to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site located at the Pacific Ocean’s Kwajalein Atoll for launch. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
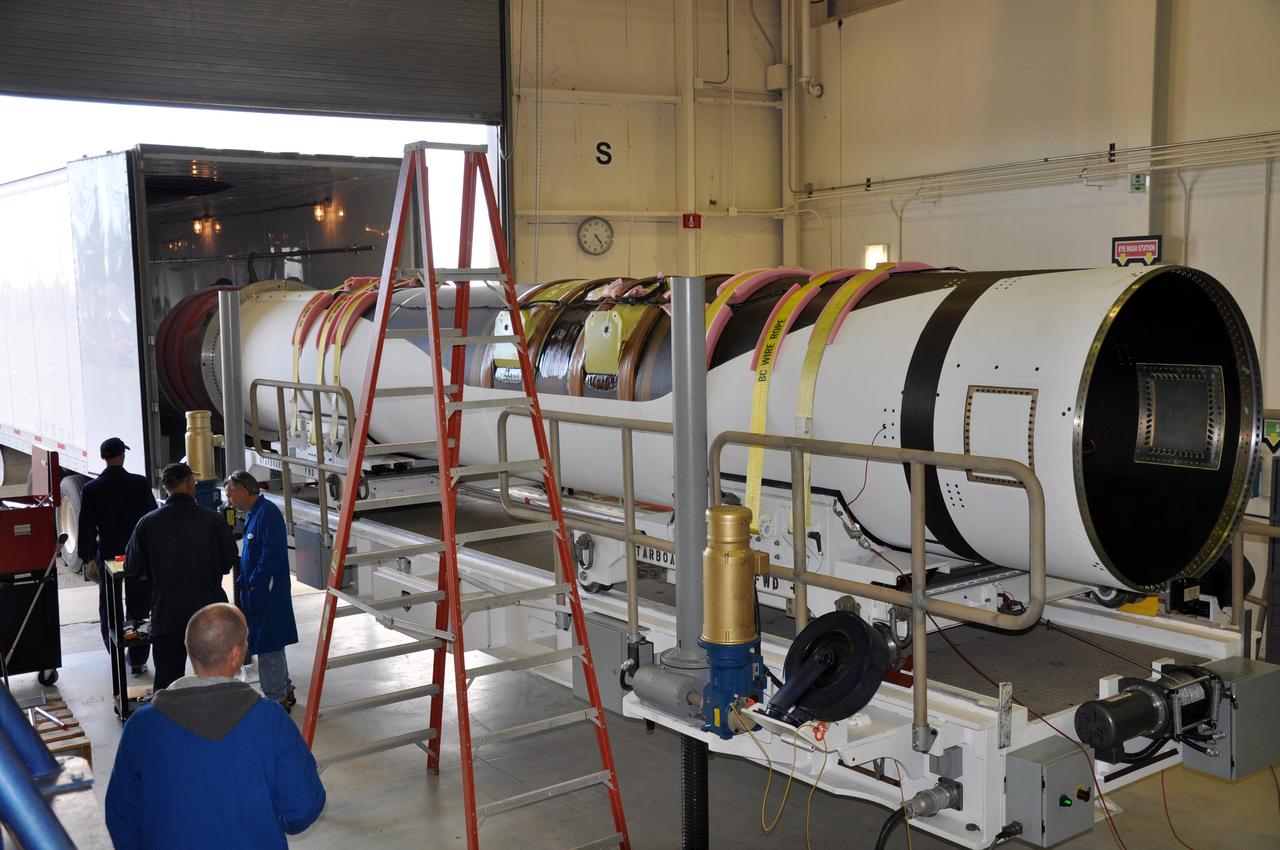

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the first stage of the Pegasus XL rocket that will launch the Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) to orbit is offloaded for processing in Building 1555. After the rocket and spacecraft are processed at Vandenberg, they will be shipped to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site located at the Pacific Ocean’s Kwajalein Atoll for launch. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
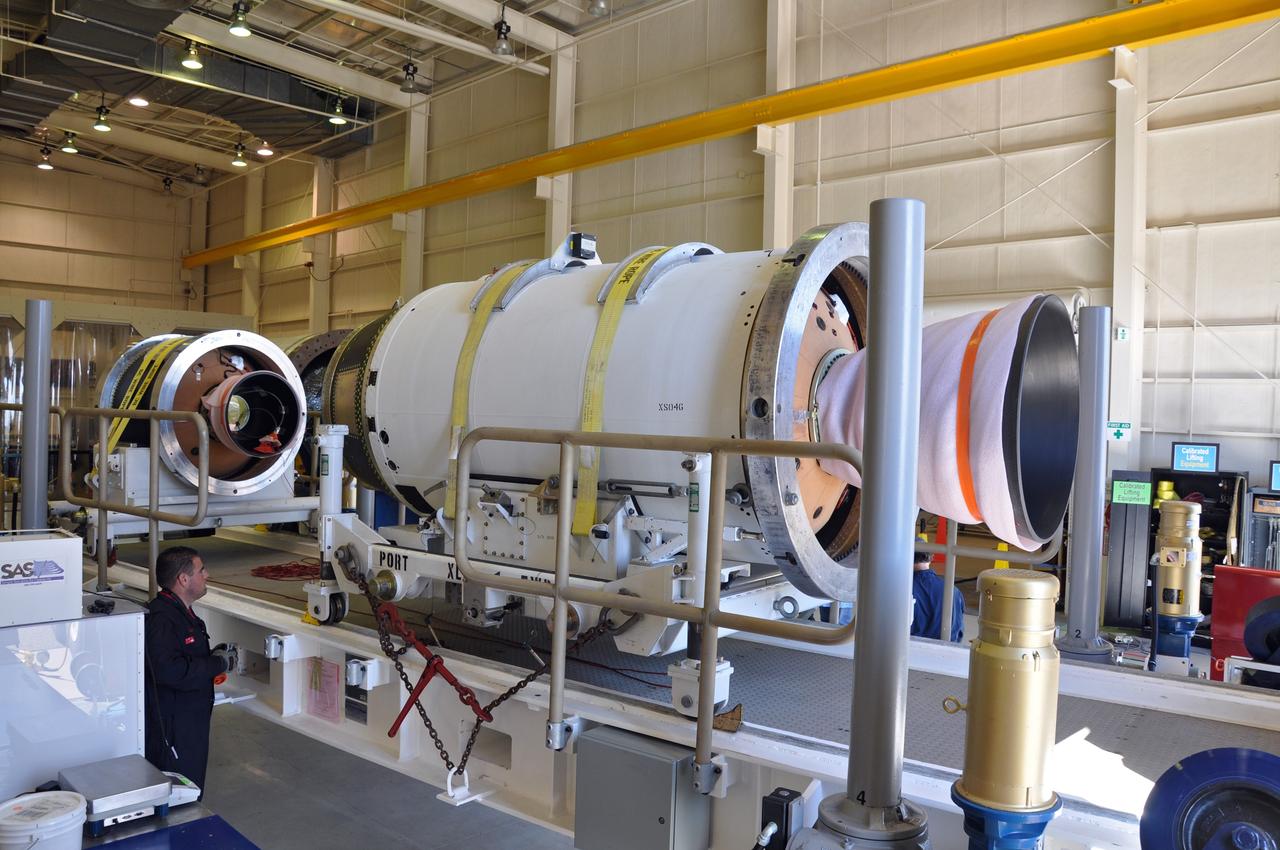

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the second stage of the Pegasus XL rocket that will launch the Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) to orbit is ready to move from a jackable rail to a stationary one for processing in Building 1555. After the rocket and spacecraft are processed at Vandenberg, they will be shipped to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site located at the Pacific Ocean’s Kwajalein Atoll for launch. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
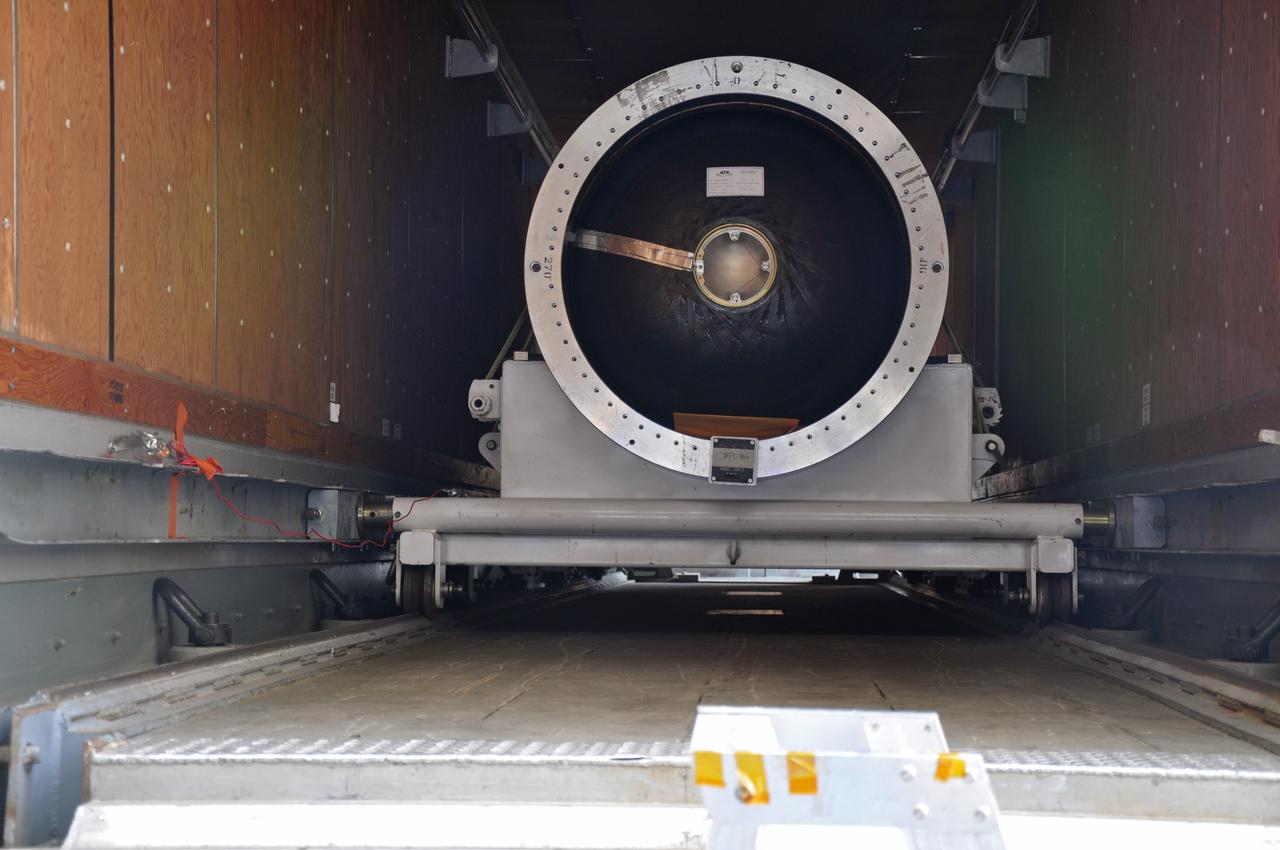

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the third stage of the Pegasus XL rocket that will launch the Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) to orbit is offloaded for processing in Building 1555. After the rocket and spacecraft are processed at Vandenberg, they will be shipped to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site located at the Pacific Ocean’s Kwajalein Atoll for launch. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
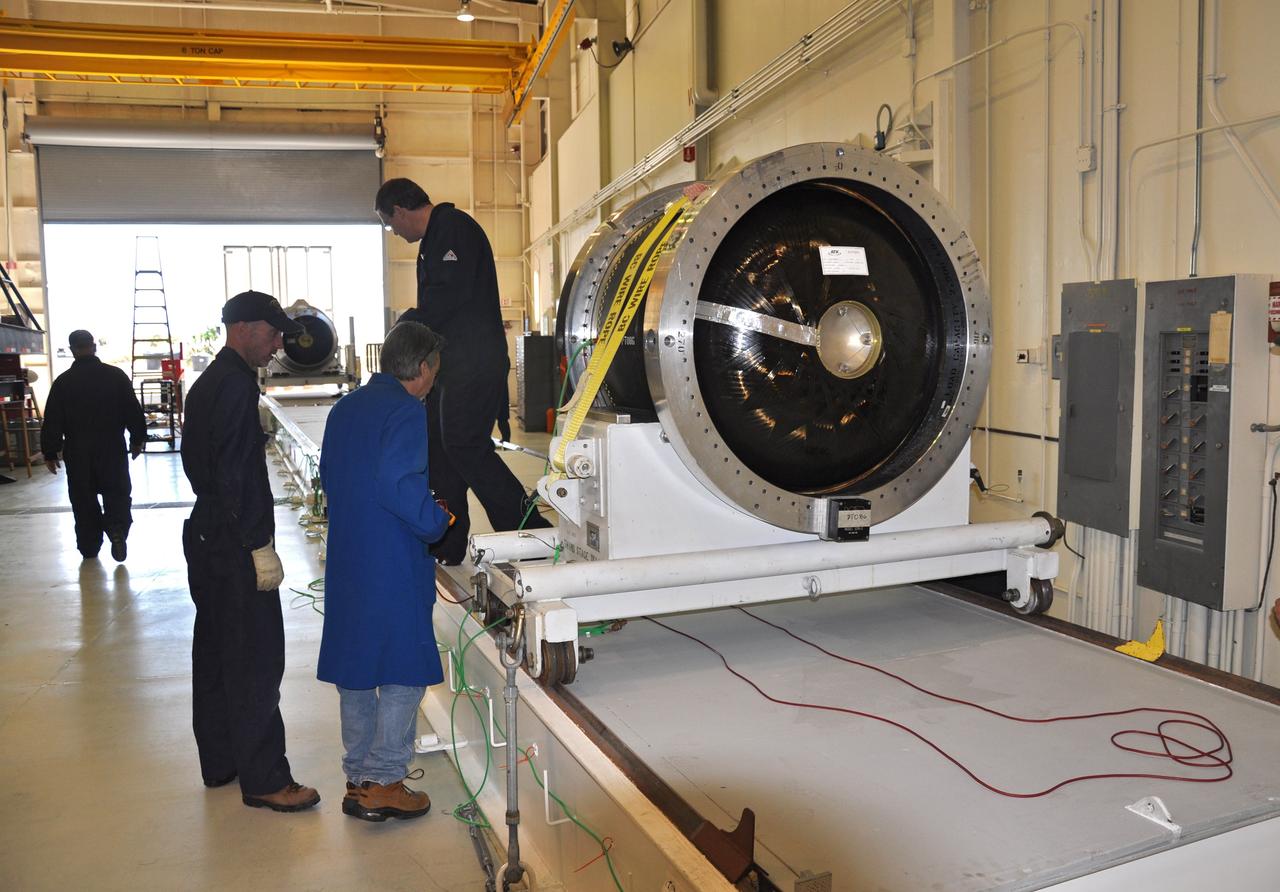

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the second stage of the Pegasus XL rocket that will launch the Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) to orbit is moved to a stationary rail in Building 1555 for processing. After the rocket and spacecraft are processed at Vandenberg, they will be shipped to the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site located at the Pacific Ocean’s Kwajalein Atoll for launch. The high-energy X-ray telescope will conduct a census for black holes, map radioactive material in young supernovae remnants, and study the origins of cosmic rays and the extreme physics around collapsed stars. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
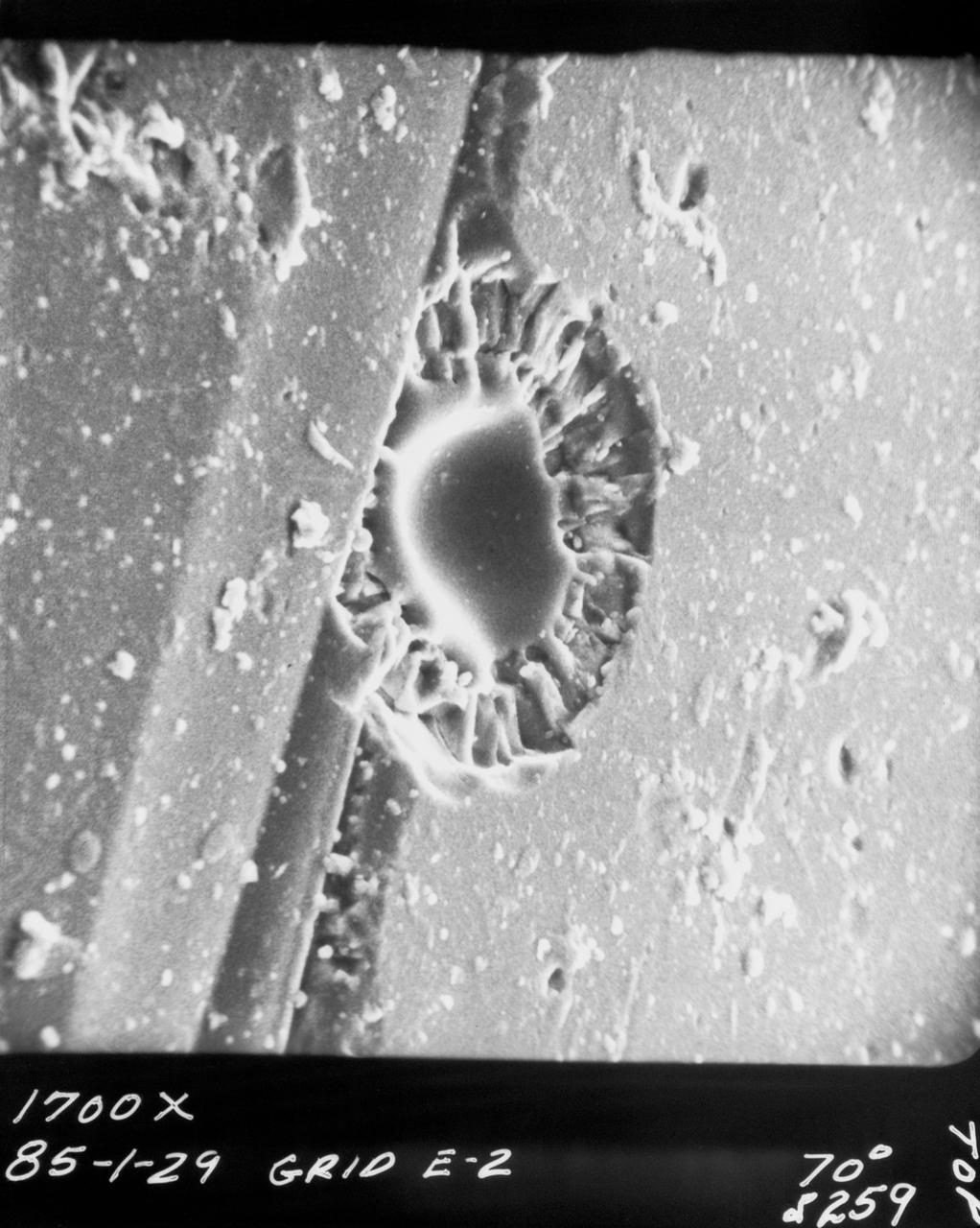
S70-20418 (December 1969) --- Enlarged view shows cosmic dust on broken glass particles, photographed by Dr. G. J. Wasserberg, J. DeVaney and K. Evans at California Institute of Technology during examination of the Apollo 11 lunar material. The photograph was enlarged to 1,700 time its actual size.
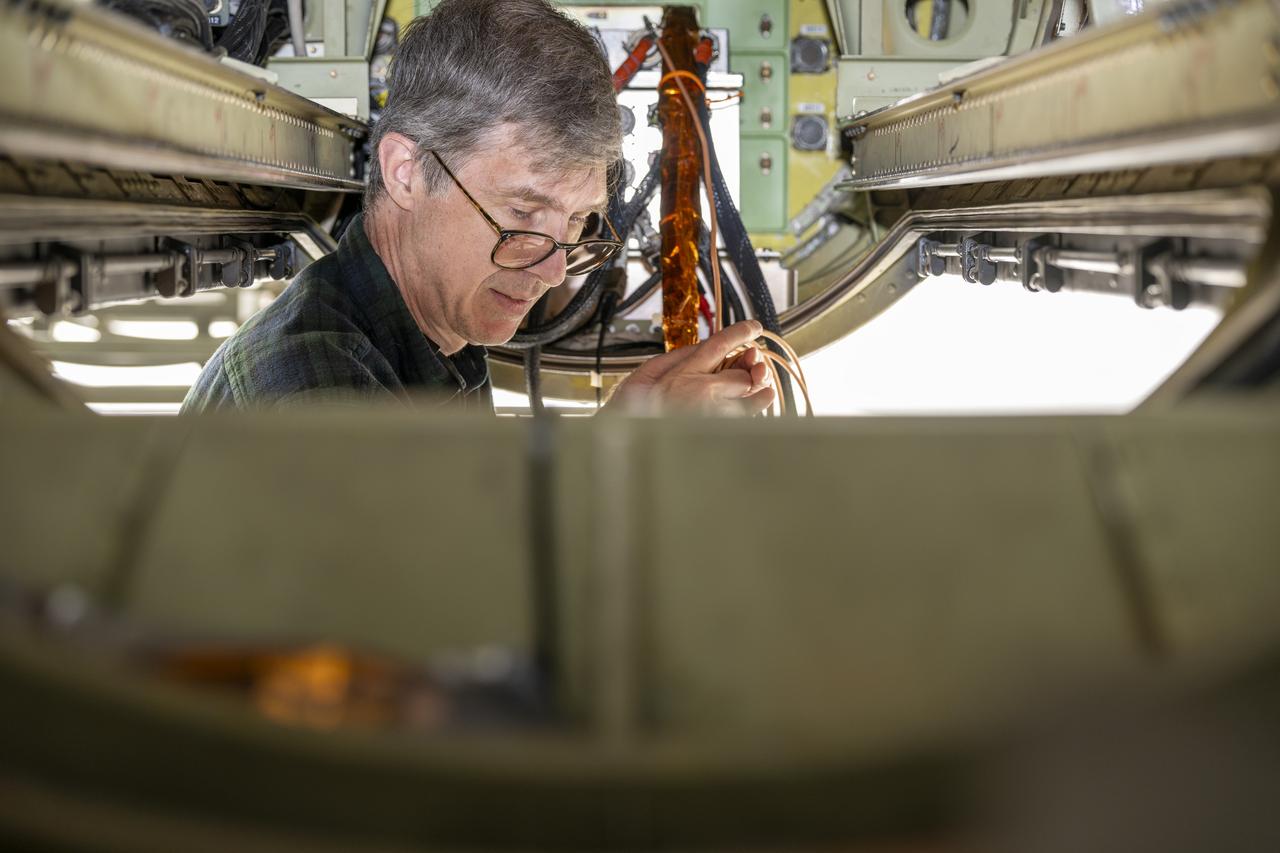

Dr. John Woodward, of the National Institute of Standards and Technology and co-investigator on the airborne Lunar Spectral Irradiance (air-LUSI) mission, prepares the instrument for upload onto the ER-2 aircraft in March 2025 at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California.
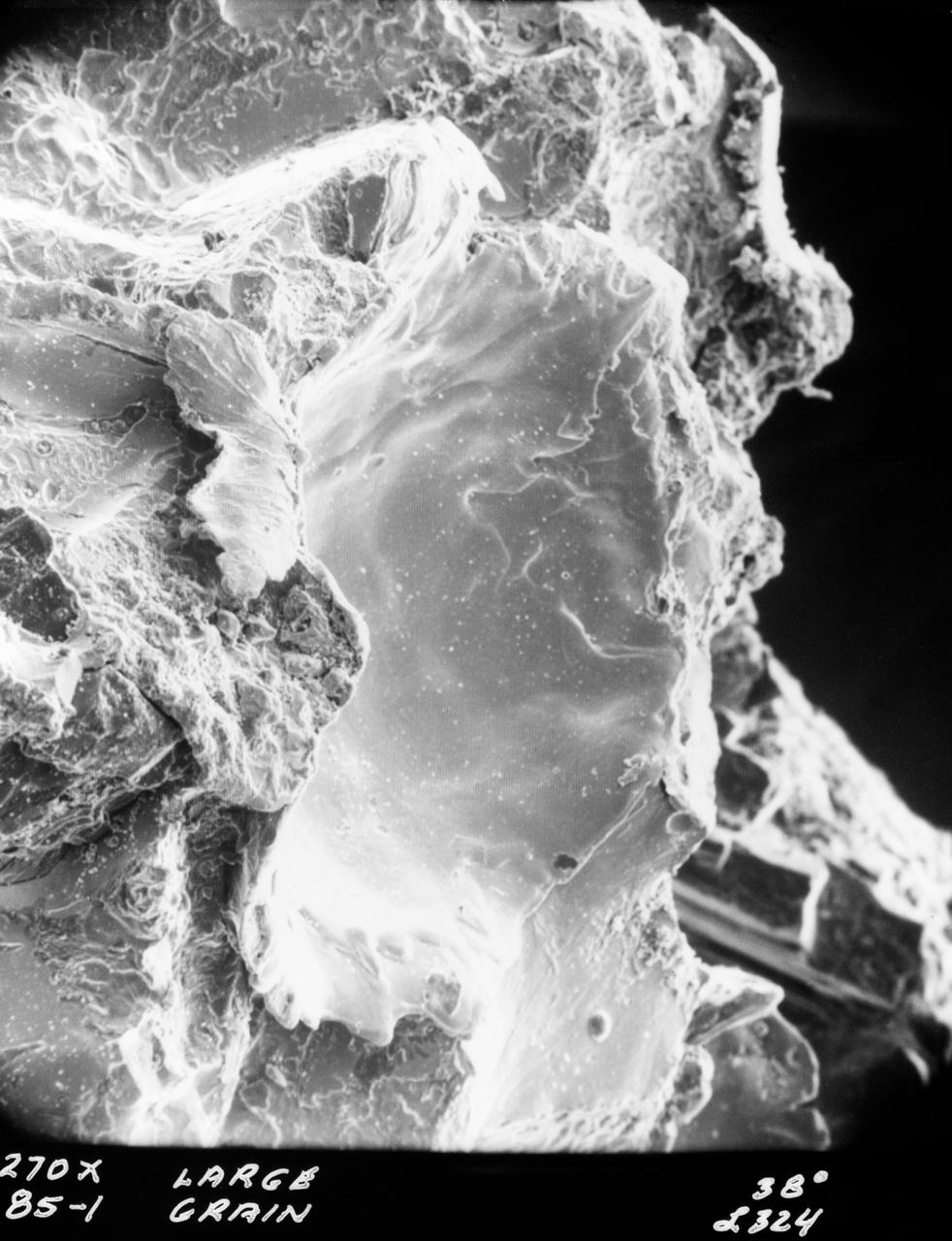
S70-20416 (December 1969) --- Enlarged view show hypervelocity impact on iron particles of lunar surface material returned to Earth by the crew of the Apollo 11 lunar landing mission. This photograph, enlarged to 270 times the actual size, was taken by Dr. G. J. Wasserberg, J. DeVaney and K. Evans at the California Institute of Technology.
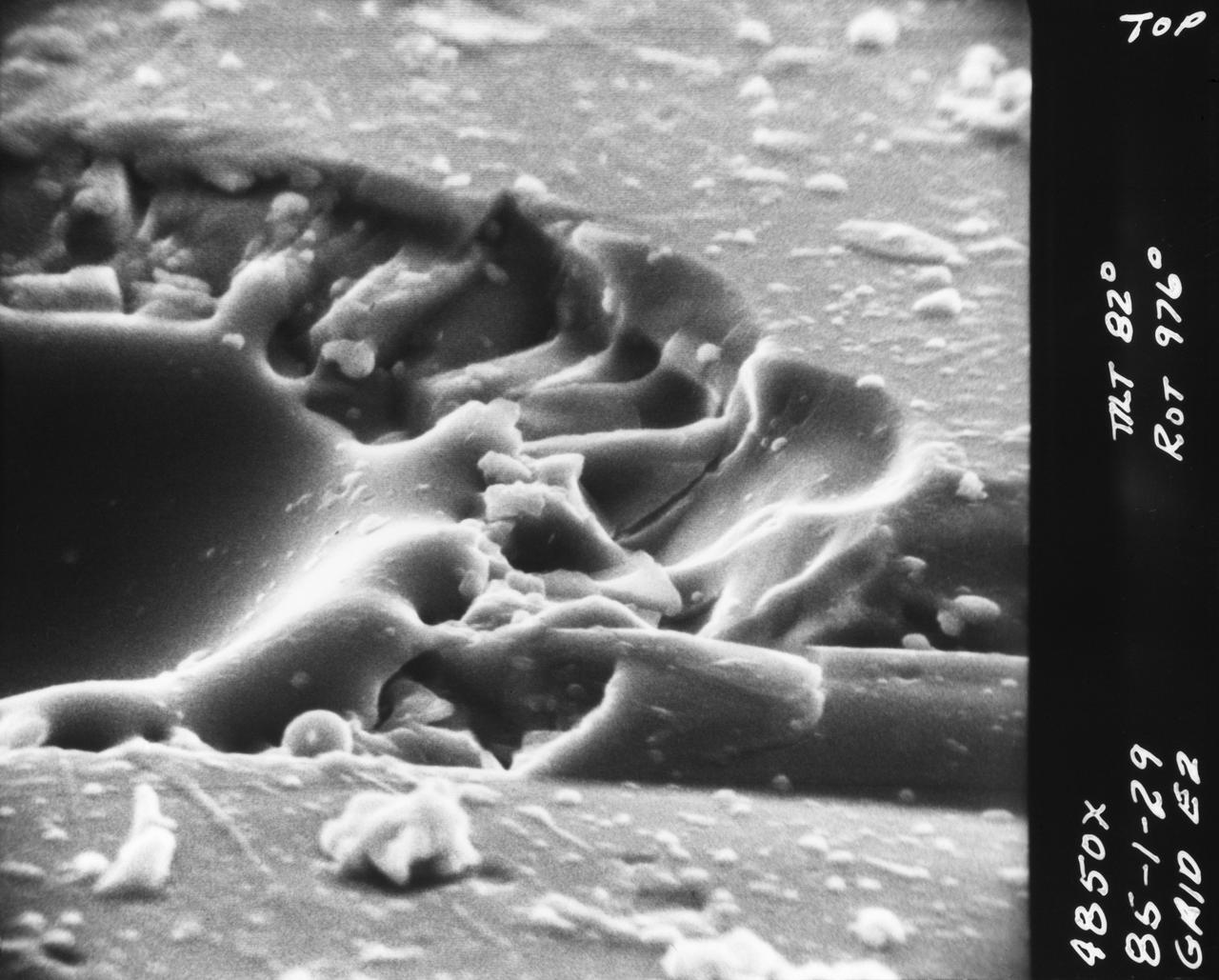
S70-20417 (December 1969) --- Enlarged view shows hypervelocity impact of cosmic dust on broken glass particles, taken during the examination of Apollo 11 lunar material by Dr. G. J. Wasserberg, J. DeVaney and K. Evans at California Institute of Technology. The photograph is enlarged 4,850 times actual size.
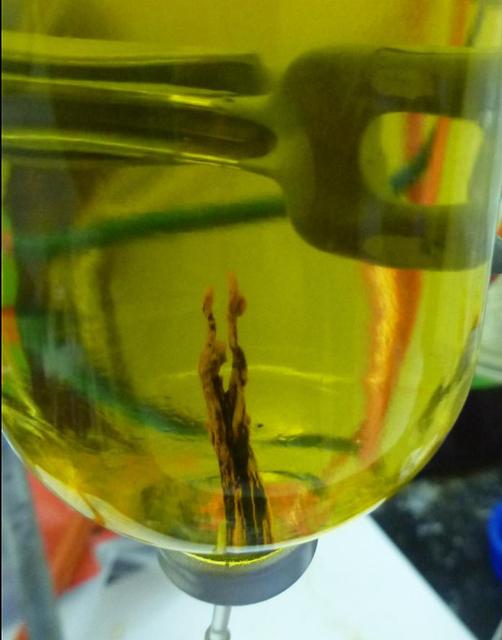

A laboratory-created "chemical garden" made of a combination of black iron sulfide and orange iron hydroxide/oxide is shown in this photo. Chemical gardens are a nickname for chimney-like structures that form at bubbling vents on the seafloor. Some researchers think that life may have originated at structures like these billions of years ago. JPL's research team is part of the Icy Worlds team of the NASA Astrobiology Institute, based at NASA's Ames Research Center in Moffett Field, California. JPL is managed by the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena for NASA. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19835
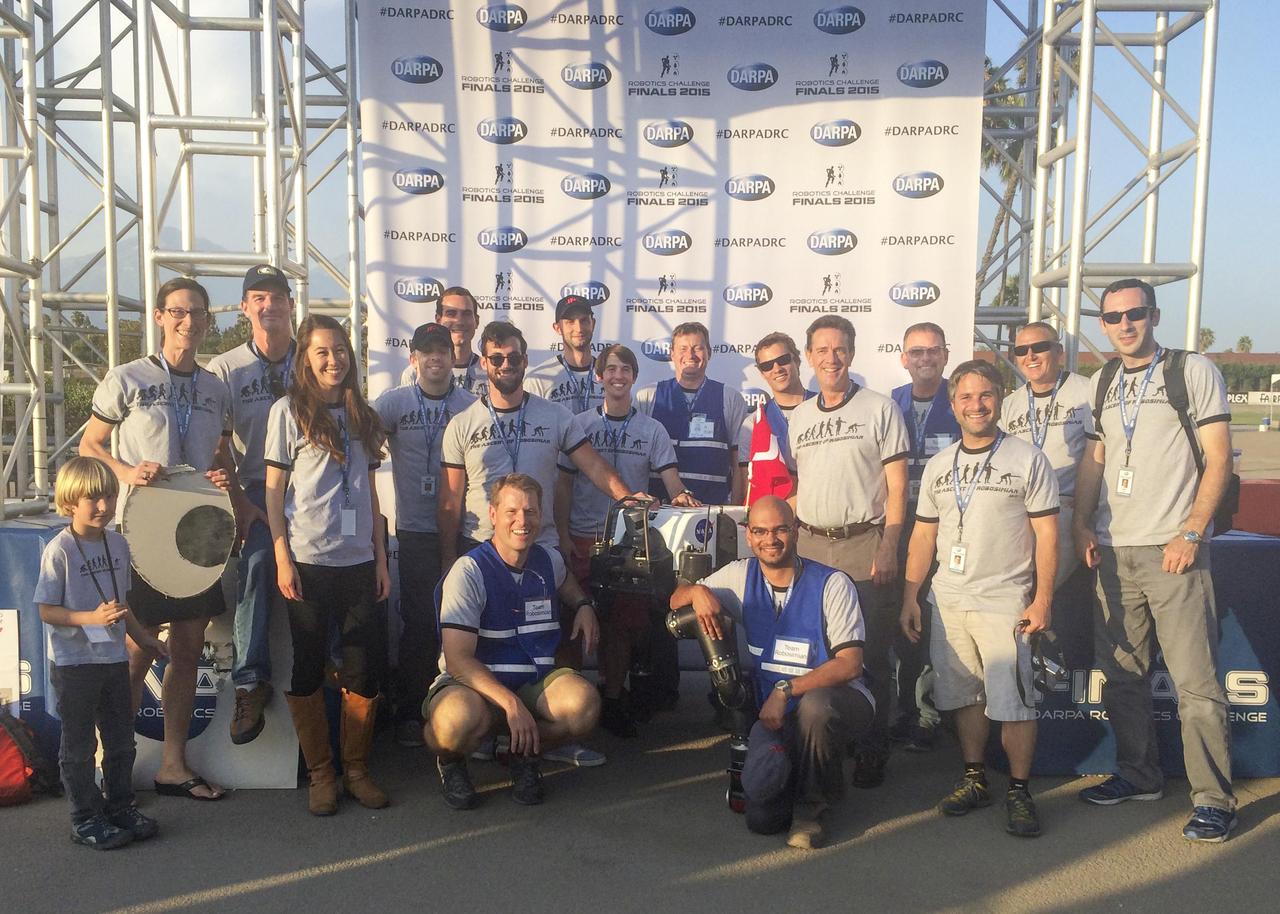

Many members of Team RoboSimian and a few guests gather with competition hardware at a "Meet the Robots" event during the DARPA Robotics Challenge Finals in Pomona, California, on June 6, 2015. The RoboSimian team at JPL is collaborating with partners at the University of California, Santa Barbara, and the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena. Caltech manages JPL for NASA. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19329

This artist's concept shows RoboSimian, a robot intended to assist with disaster relief and mitigation. RoboSimian is an ape-like robot that moves around on four limbs. It was designed and built at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. It will compete in the 2015 DARPA Robotics Challenge Finals. To get the robot in shape for the contest, researchers at JPL are collaborating with partners at University of California, Santa Barbara, and the California Institute of Technology. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19313
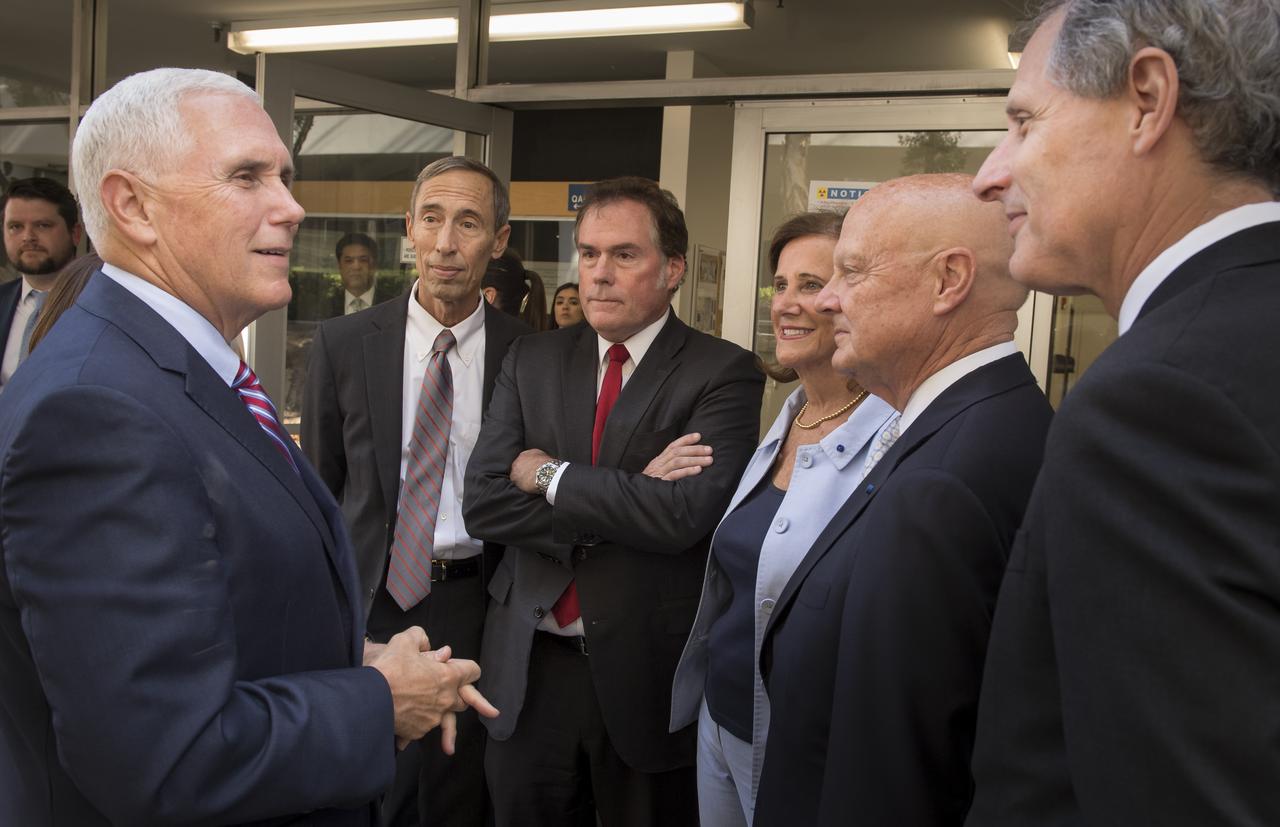

U.S. Vice President Mike Pence, left, thanks JPL Deputy Director Lt. Gen. (Ret) Larry James, JPL Director Michael Watkins, JPL Distinguished Visiting Scientist and Spouse of UAG Chairman James Ellis, Elisabeth Pate-Cornell , UAG Chairman, Admiral (Ret) James Ellis , and California Institute of Technology President Thomas Rosenbaum, right, for giving him a tour of NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Saturday, April 28, 2018 in Pasadena, California. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
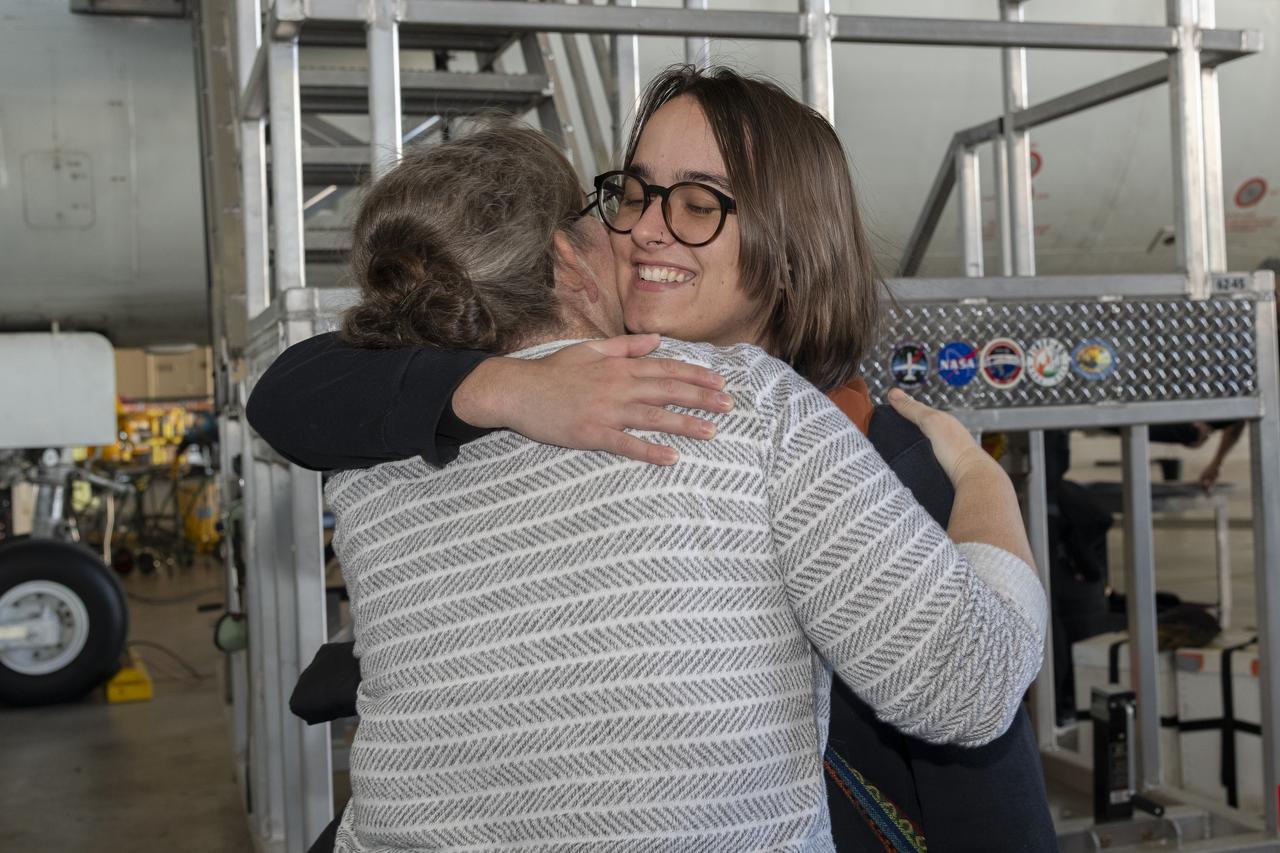

NASA’s DC-8 operations engineer, Nickelle “Nicki” Reid, left, embraces Katherine Ball, chemical engineering Ph.D. candidate at California Institute of Technology, after the DC-8 aircraft and crew return to NASA Armstrong’s Building 703 in Palmdale, California, on April 1, 2024, following the aircraft’s final mission in support of the Airborne and Satellite Investigation of Asian Air Quality (ASIA-AQ).
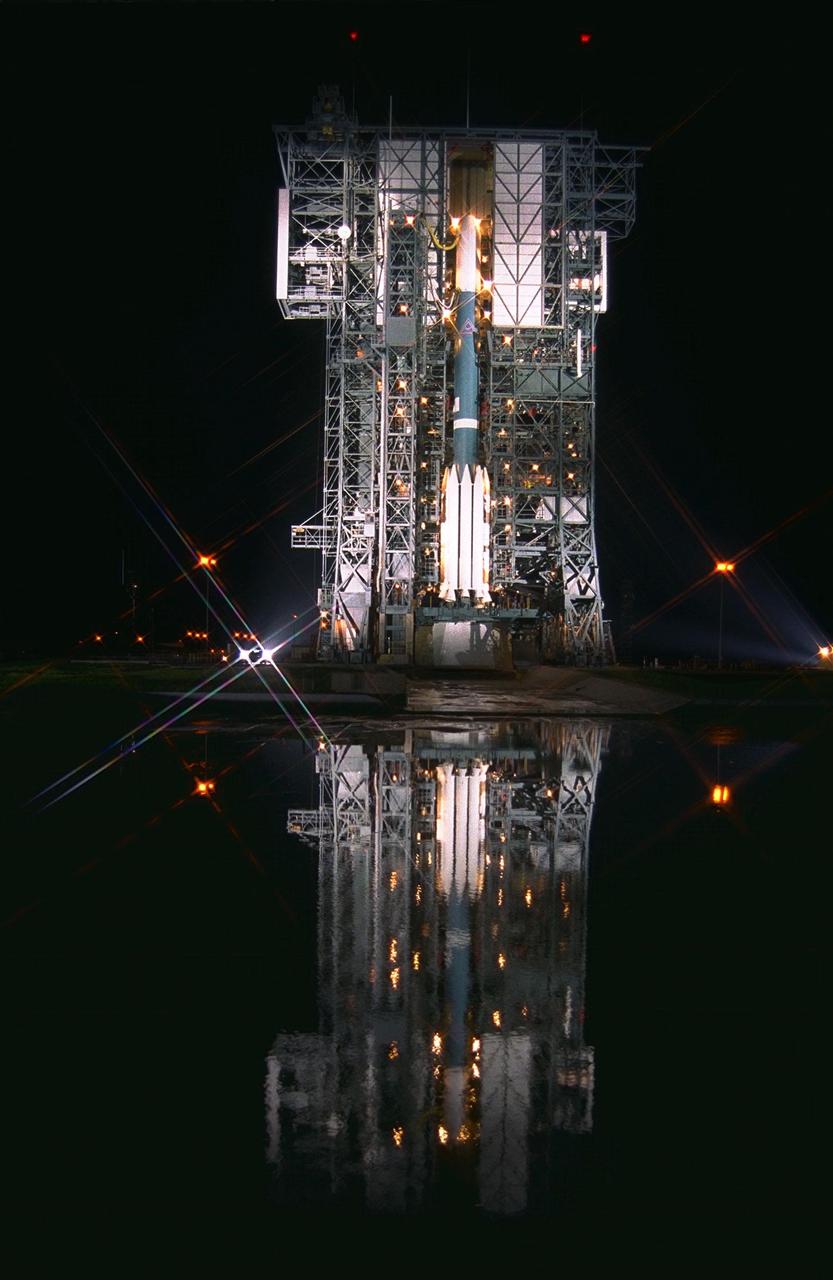

After launch tower retraction, the Boeing Delta II expendable launch vehicle carrying the Advanced Composition Explorer (ACE) undergoes final preparations for liftoff in the predawn hours of Aug. 24, 1997, at Launch Complex 17A, Cape Canaveral Air Station. This is the second Delta launch under the Boeing name and the first from Cape Canaveral. ACE with its combination of nine sensors and instruments will investigate the origin and evolution of solar phenomenon, the formation of solar corona, solar flares and acceleration of the solar wind. ACE was built for NASA by the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory and is managed by the Explorer Project Office at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center. The lead scientific institution is the California Institute of Technology
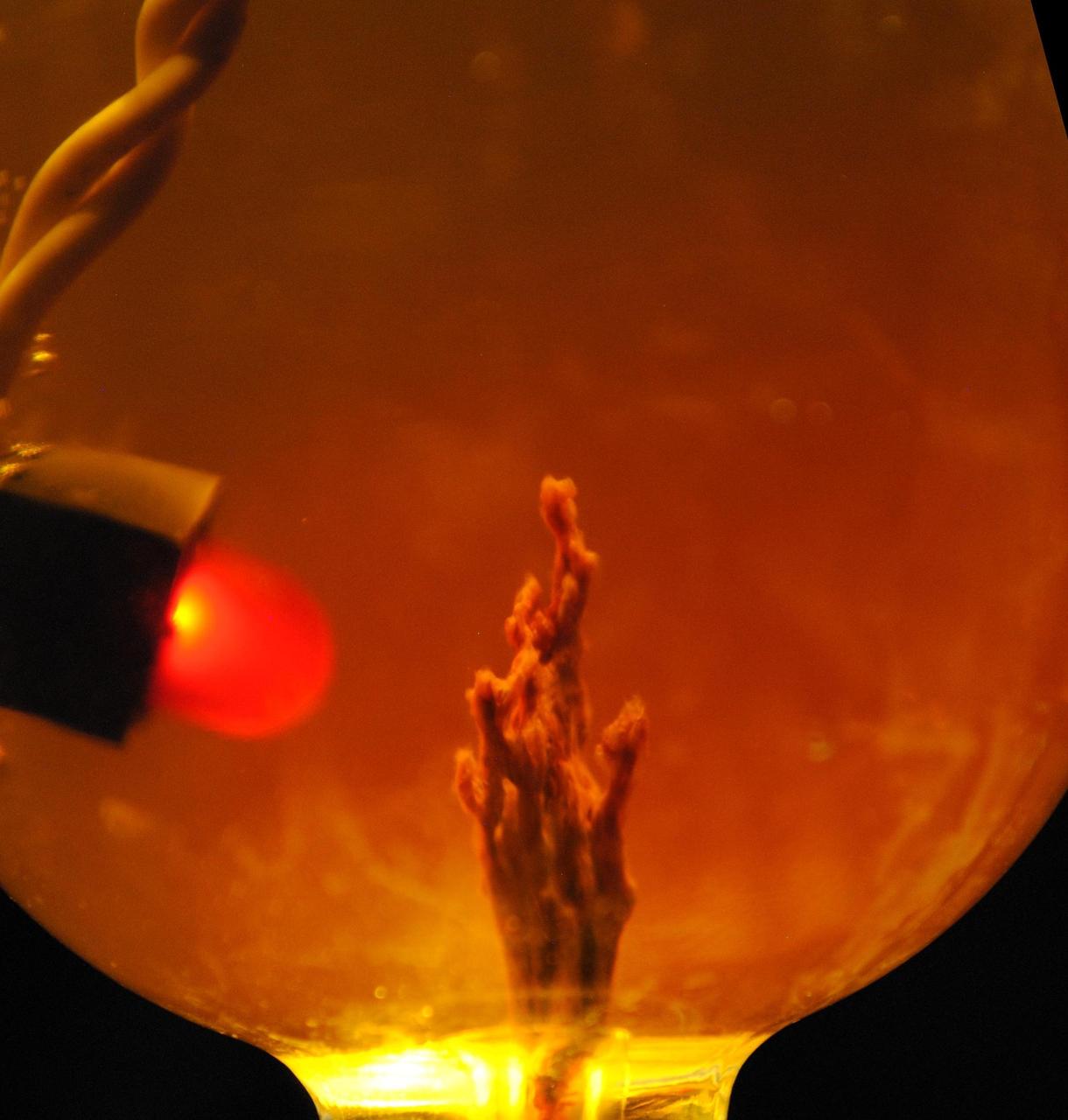

This photo simulation shows a laboratory-created "chemical garden," which is a chimney-like structure found at bubbling vents on the seafloor. Some researchers think life on Earth might have got its start at structures like these billions of years ago, partly due to their ability to transfer electrical currents -- an essential trait of life as we know it. The battery-like property of these chemical gardens was demonstrated by linking several together in series to light an LED (light-emitting diode) bulb. In this photo simulation, the bulb is not really attached to the chimney. The chimney membranes are made of iron sulfides and iron hydroxides, geologic materials that conduct electrons. JPL's research team is part of the Icy Worlds team of the NASA Astrobiology Institute, based at NASA's Ames Research Center in Moffett Field, California. JPL is managed by the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena for NASA. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19834
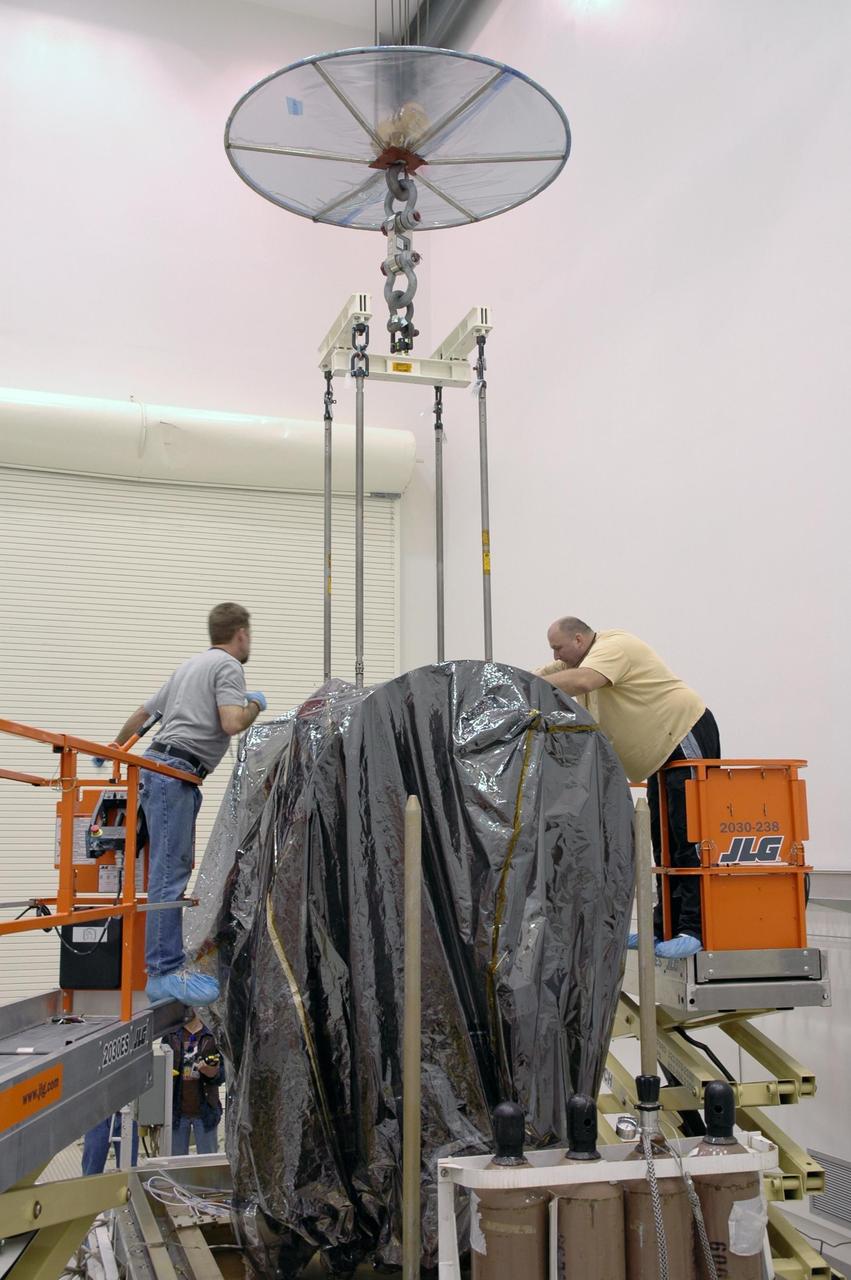

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Astrotech's Payload Processing Facility, a crane is being attached to the Dawn spacecraft to lift it from the transporter. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. The Dawn mission is managed by JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington, D.C. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
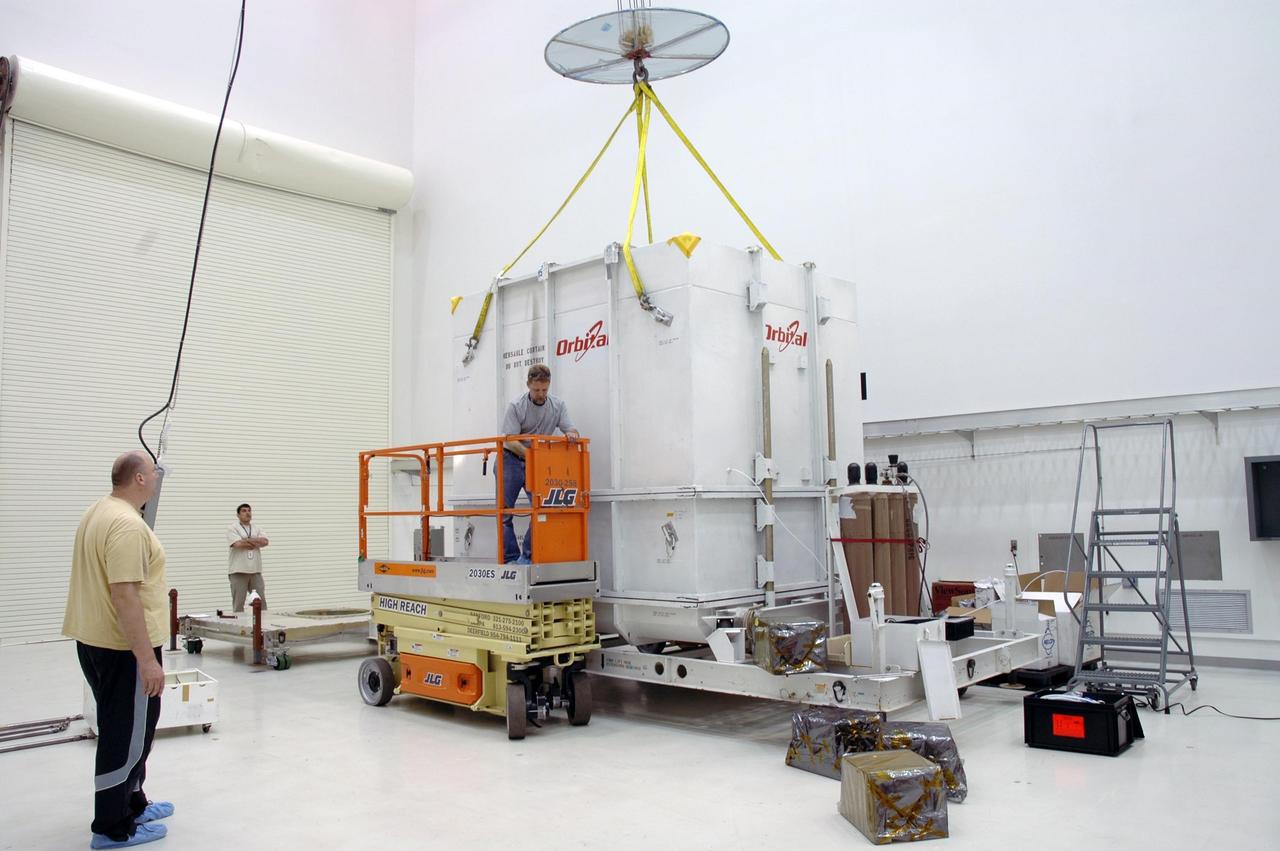

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Astrotech's Payload Processing Facility, a crane is attached to the shipping container to remove it from around the Dawn spacecraft. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. The Dawn mission is managed by JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington, D.C. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
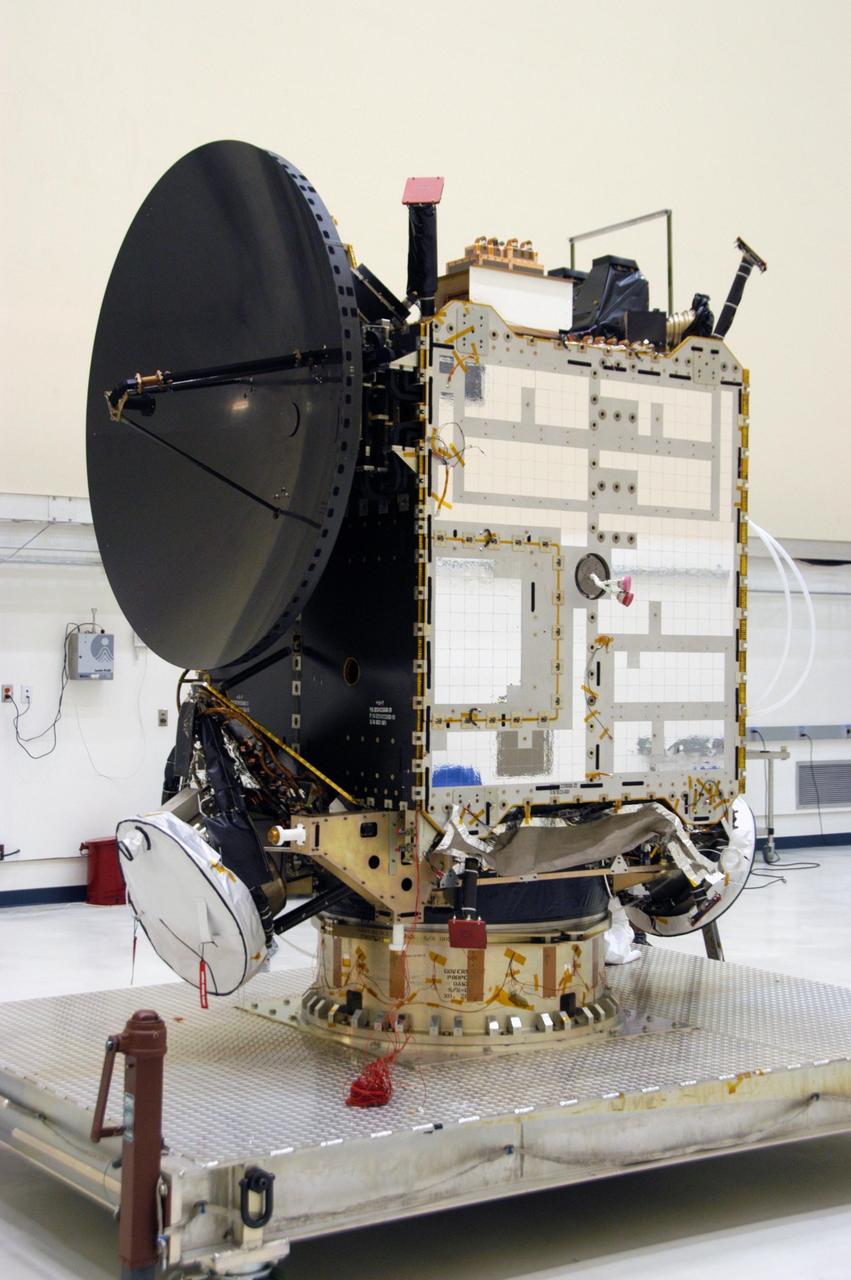
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Dawn spacecraft is seen here in clean room C of Astrotech's Payload Processing Facility. In the clean room, the spacecraft will undergo further processing. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. The Dawn mission is managed by JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington, D.C. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Astrotech, an external cover is removed from around the shipping container holding the Dawn spacecraft. The container will then be moved into the high bay of the Payload Processing Facility and the spacecraft removed. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. The Dawn mission is managed by JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington, D.C. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

In clean room C of Astrotech's Payload Processing Facility, technicians dressed in "bunny suits," or clean-room attire, begin working on the Dawn spacecraft. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. The Dawn mission is managed by JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington, D.C.
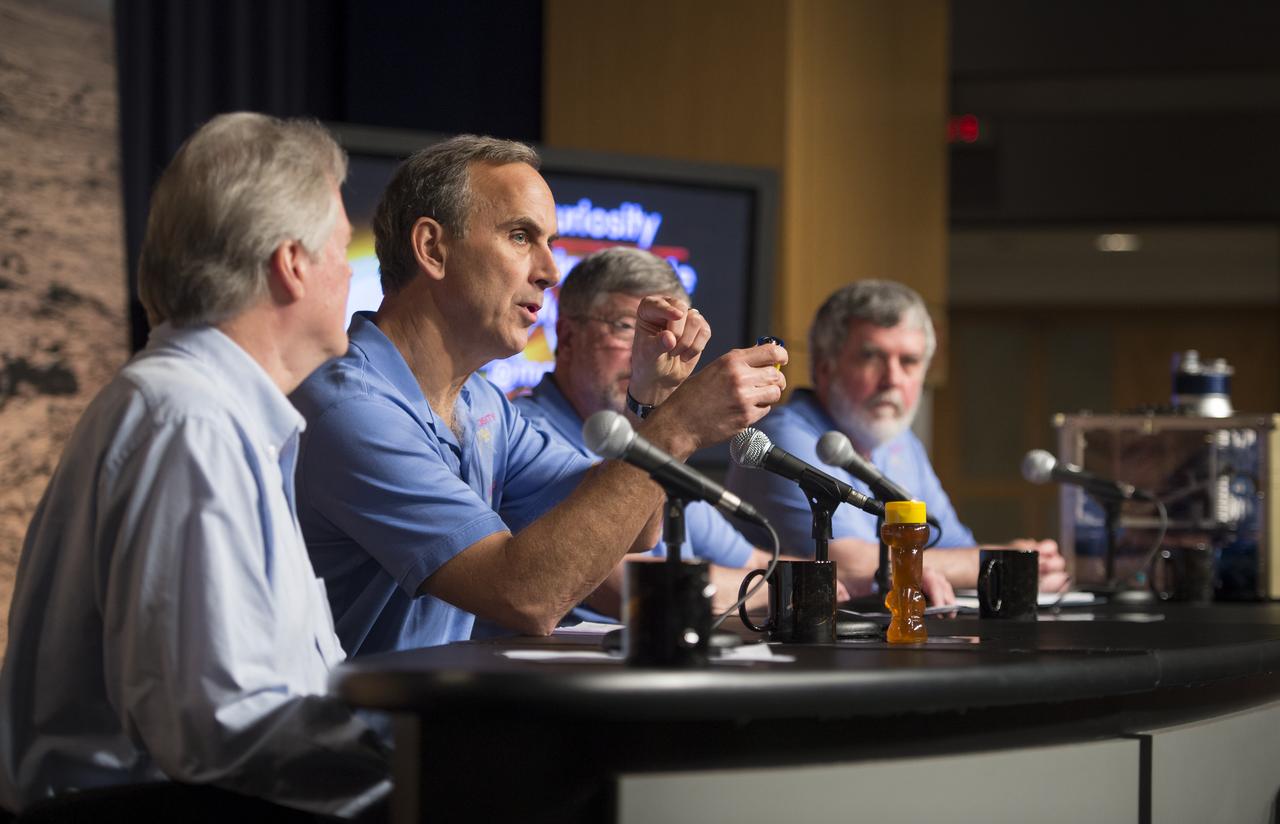

John Grotzinger (second from left), Curiosity project scientist, California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, speaks at a news conference presenting findings of the Curiosity rover's analysis of the first sample of rock powder collected on Mars, Tuesday, March 12, 2013 in Washington. The rock sample collected shows ancient Mars could have supported living microbes. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
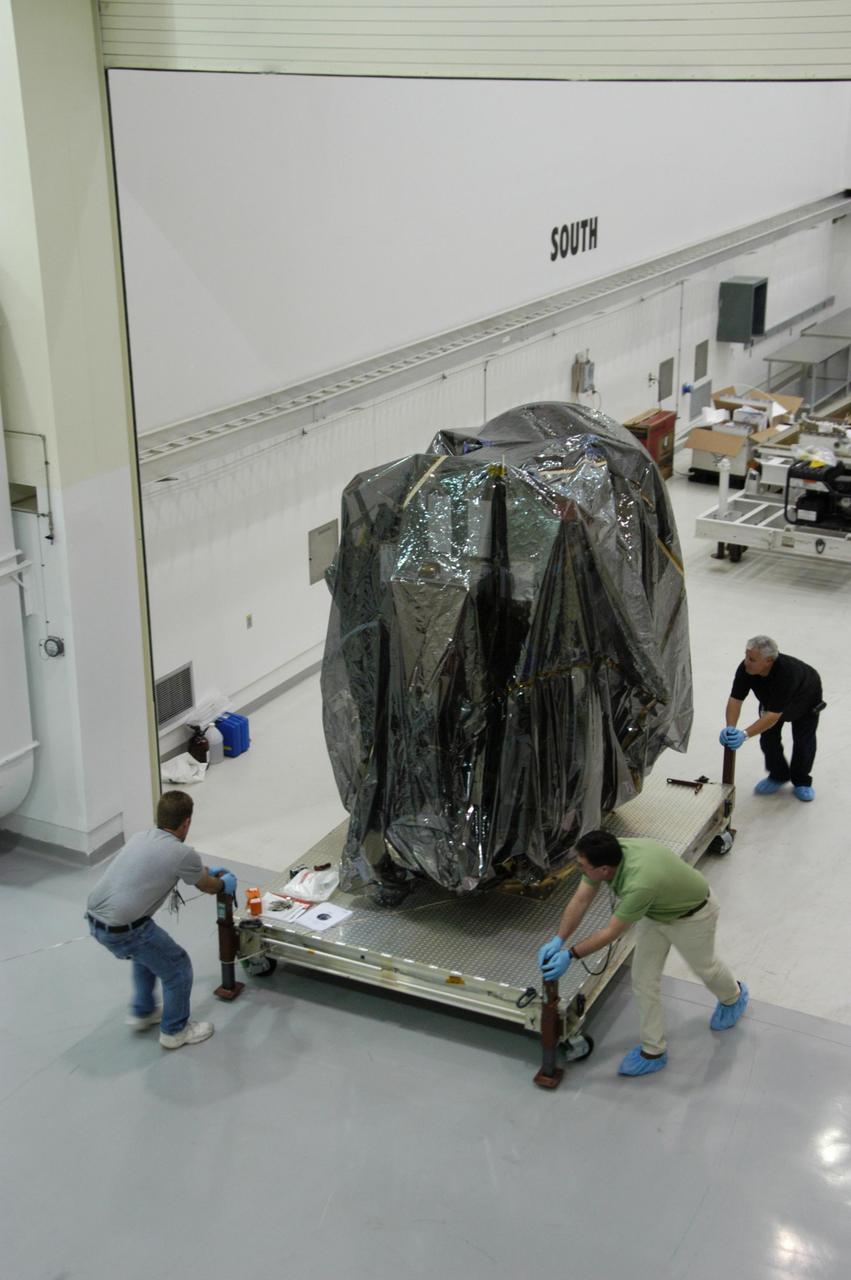

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Astrotech's Payload Processing Facility, technicians roll the Dawn spacecraft into clean room C for unbagging and further processing. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. The Dawn mission is managed by JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington, D.C. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton

Dr. Lee Silver (pointing foregroung), California Institute of Technology, calls a geological feature near Taos, New Mexico, to the attention of Apollo 16 prime and backup crewmen during a geological field trip. The crewmen, from left to right, are Astronauts Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot; Fred W. Haise Jr., backup commander; Edgar D. Mitchell, backup Lunar Module pilot; and John W. Young, commander.

Michael Meyer (left), lead scientist, Mars Exploration Program at NASA Headquarters, speaks at a news conference presenting findings of the Curiosity rover's analysis of the first sample of rock powder collected on Mars, Tuesday, March 12, 2013 in Washington. The rock sample collected shows ancient Mars could have supported living microbes. John Grotzinger, Curiosity project scientist, California Institute of Technology is seen on the right. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)

In clean room C of Astrotech's Payload Processing Facility, a worker wears a "bunny suit," or clean-room attire, next to the Dawn spacecraft, which will be unbagged and undergo further processing. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. The Dawn mission is managed by JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington, D.C.
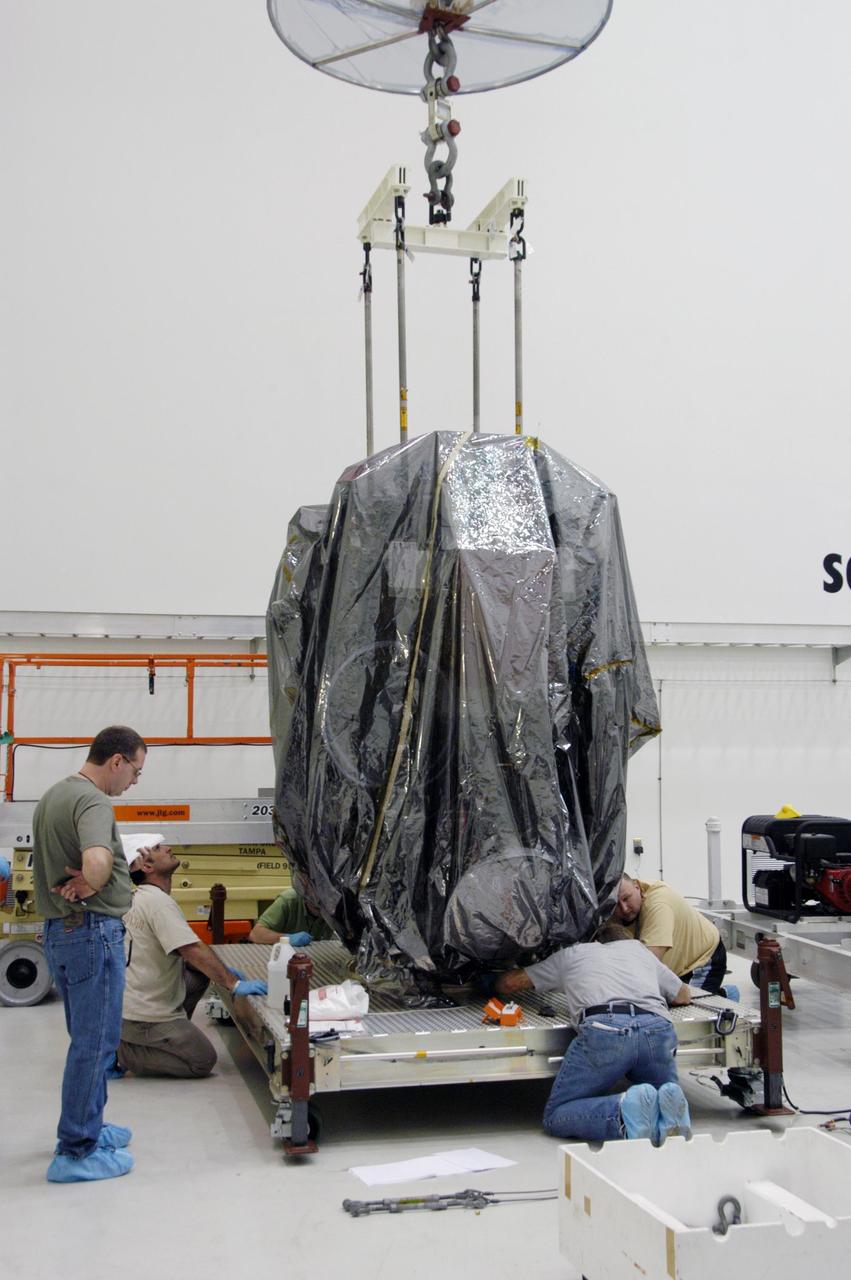

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Astrotech's Payload Processing Facility, technicians help secure the Dawn spacecraft onto a moveable stand. Dawn will be moved into clean room C for unbagging and further processing. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. The Dawn mission is managed by JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington, D.C. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
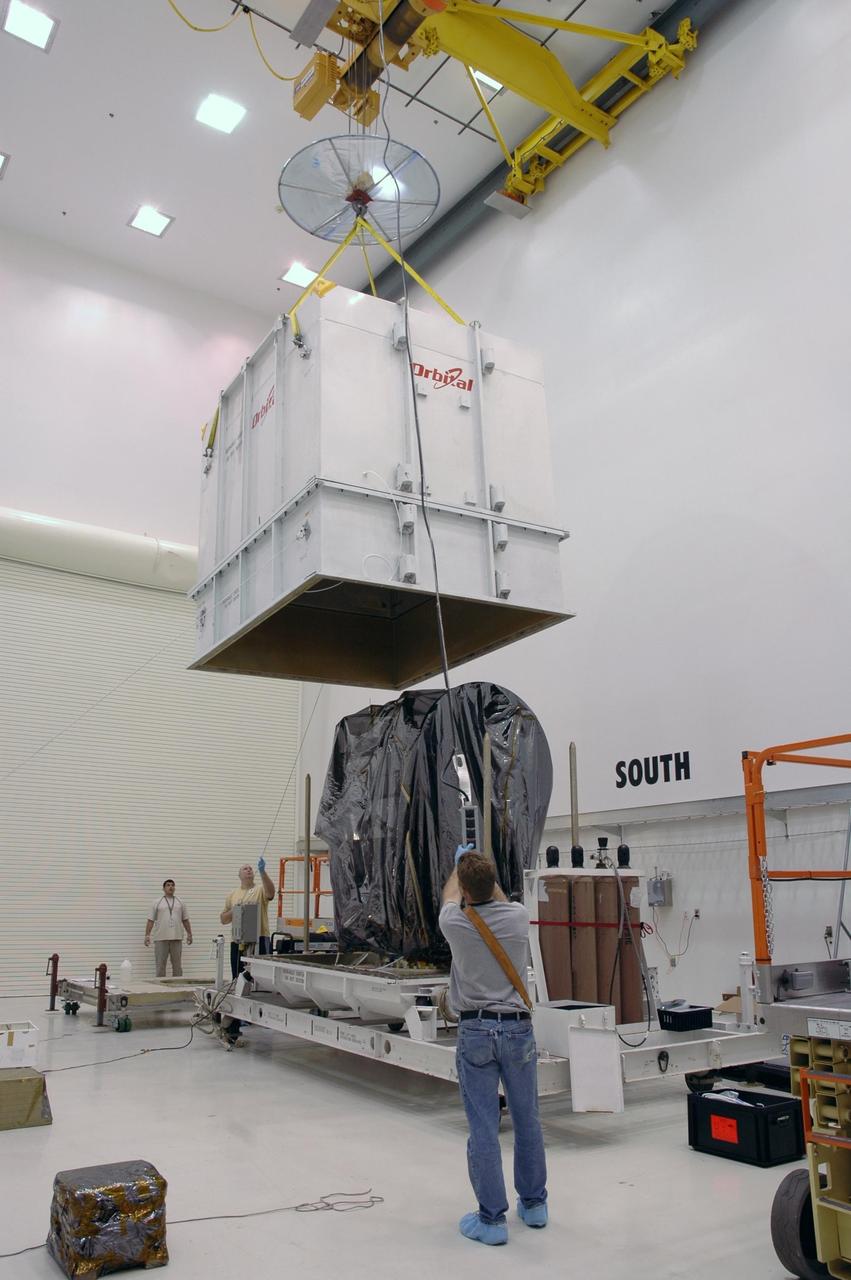

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Astrotech's Payload Processing Facility, a crane lifts the shipping container from the Dawn spacecraft. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. The Dawn mission is managed by JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington, D.C. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In clean room C of Astrotech's Payload Processing Facility, technicians dressed in "bunny suits," or clean-room attire, begin working on the Dawn spacecraft. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. The Dawn mission is managed by JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington, D.C. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
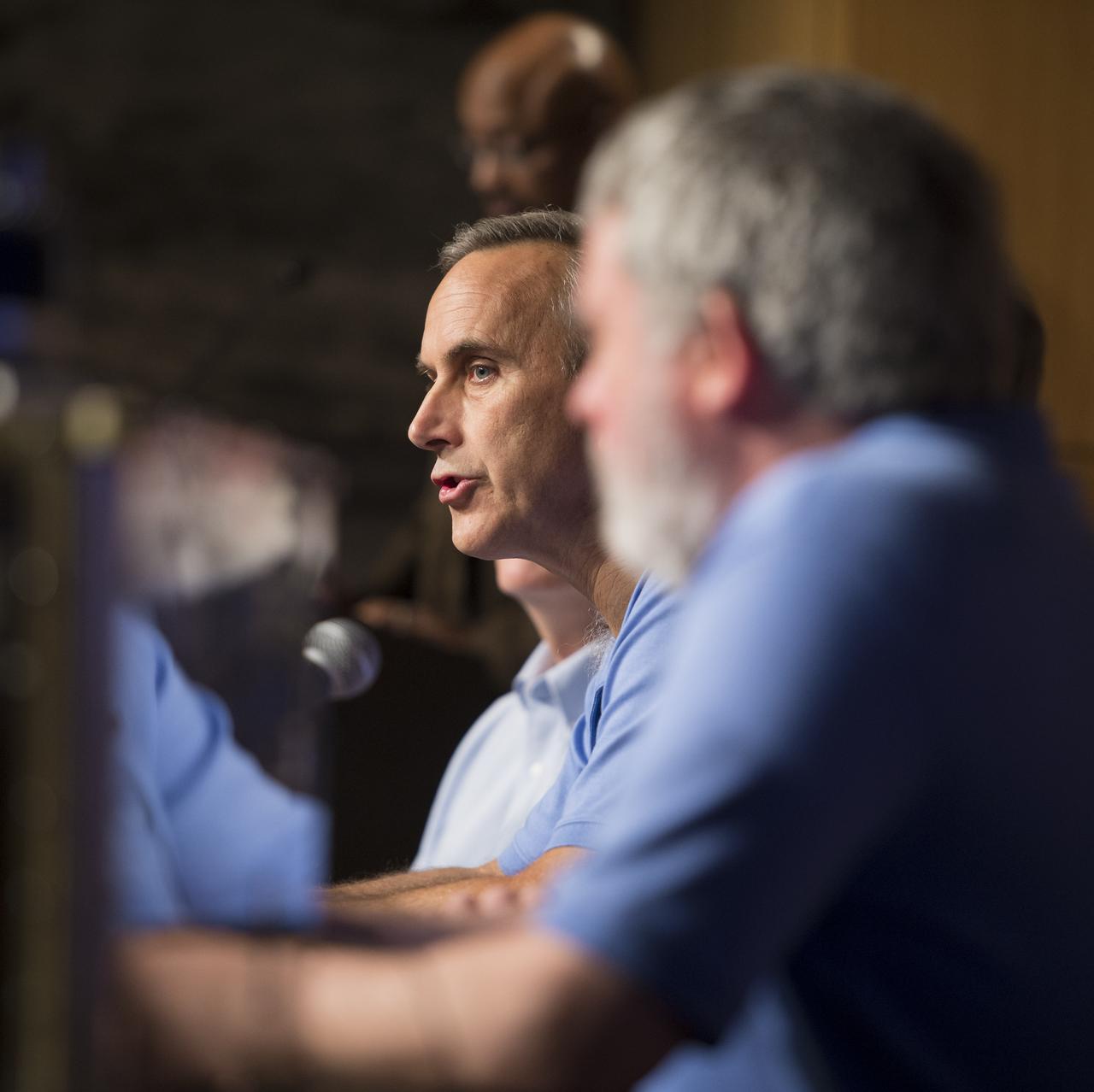

John Grotzinger (center), Curiosity project scientist, California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, speaks at a news conference presenting findings of the Curiosity rover's analysis of the first sample of rock powder collected on Mars, Tuesday, March 12, 2013 in Washington. The rock sample collected shows ancient Mars could have supported living microbes. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)

In Astrotech's Payload Processing Facility, an overhead crane lifts the Dawn spacecraft from its transporter. Dawn will be moved into clean room C for unbagging and further processing. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. The Dawn mission is managed by JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington, D.C

John Grotzinger, Curiosity project scientist, California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, answers a reporter's question at a news conference where findings of the Curiosity rover's analysis of the first sample of rock powder collected on Mars were presented, Tuesday, March 12, 2013 in Washington. The rock sample collected shows ancient Mars could have supported living microbes. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
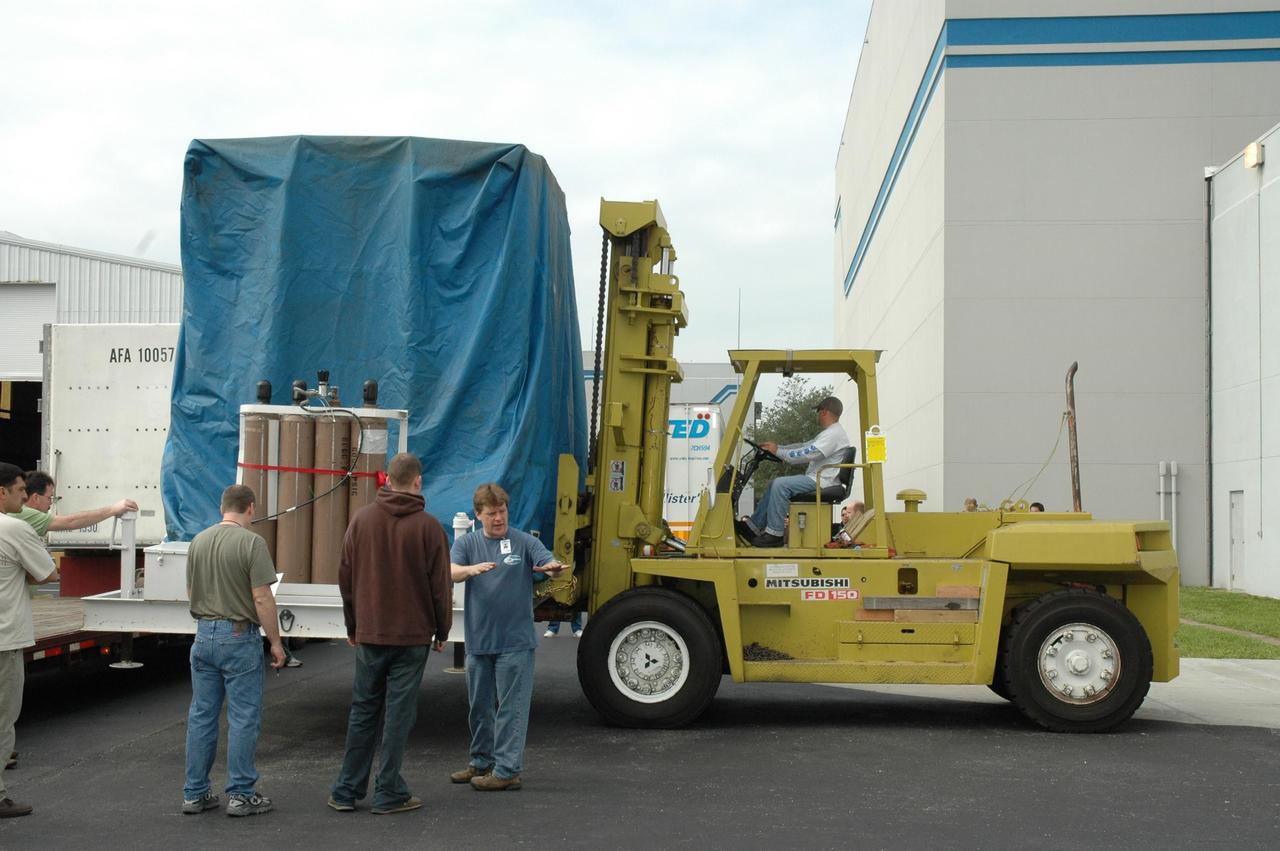

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Astrotech, the shipping container holding the Dawn spacecraft is removed from the truck. The container will then be moved into the high bay of the Payload Processing Facility and the spacecraft removed. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. The Dawn mission is managed by JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington, D.C. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
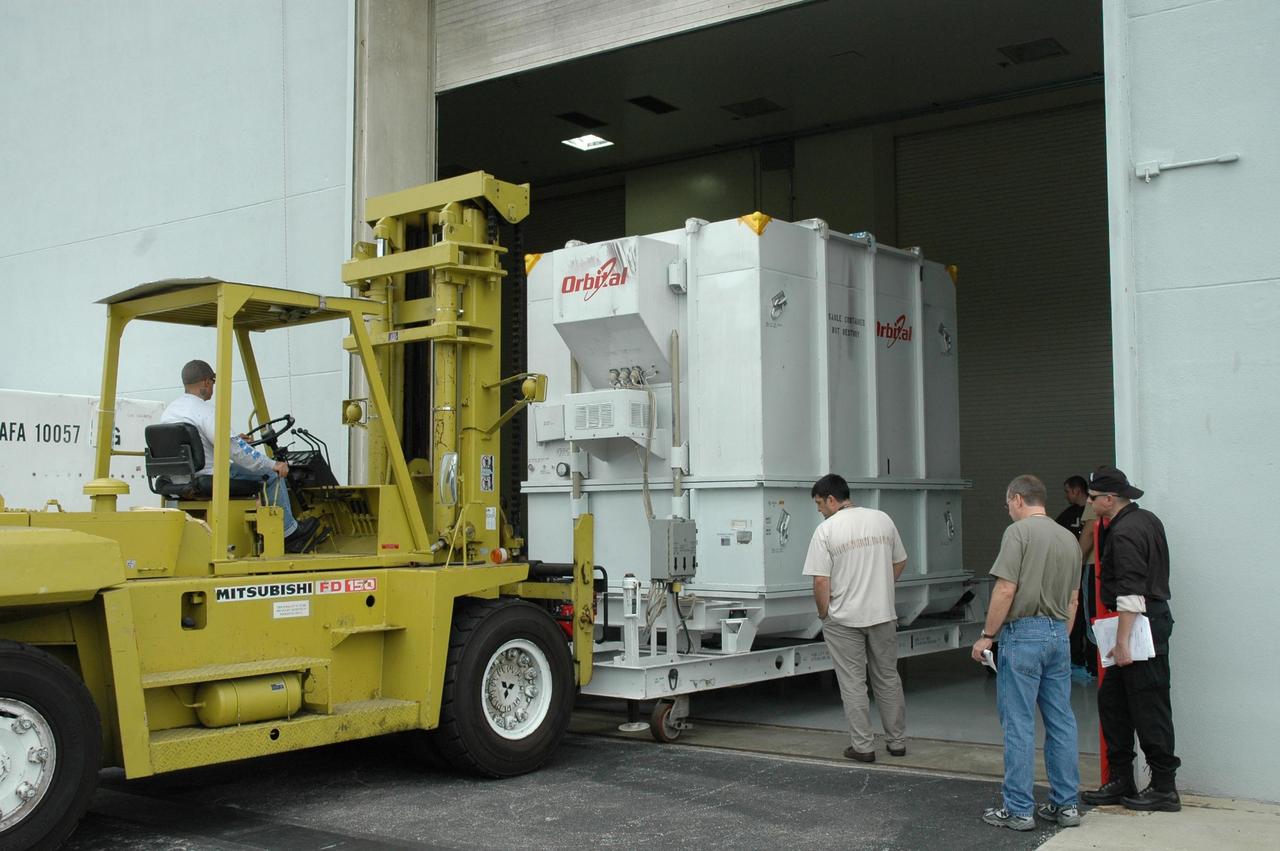

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Astrotech, the shipping container holding the Dawn spacecraft is moved into the high bay of the Payload Processing Facility. The spacecraft will next be removed from the container. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. The Dawn mission is managed by JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington, D.C. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

In clean room C of Astrotech's Payload Processing Facility, a worker wearing a "bunny suit," or clean-room attire, looks over the Dawn spacecraft after removing the protective cover, at bottom right. In the clean room, the spacecraft will undergo further processing. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. The Dawn mission is managed by JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington, D.C.

In Astrotech's Payload Processing Facility, technicians help secure the Dawn spacecraft onto a moveable stand. Dawn will be moved into clean room C for unbagging and further processing. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. The Dawn mission is managed by JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington, D.C.
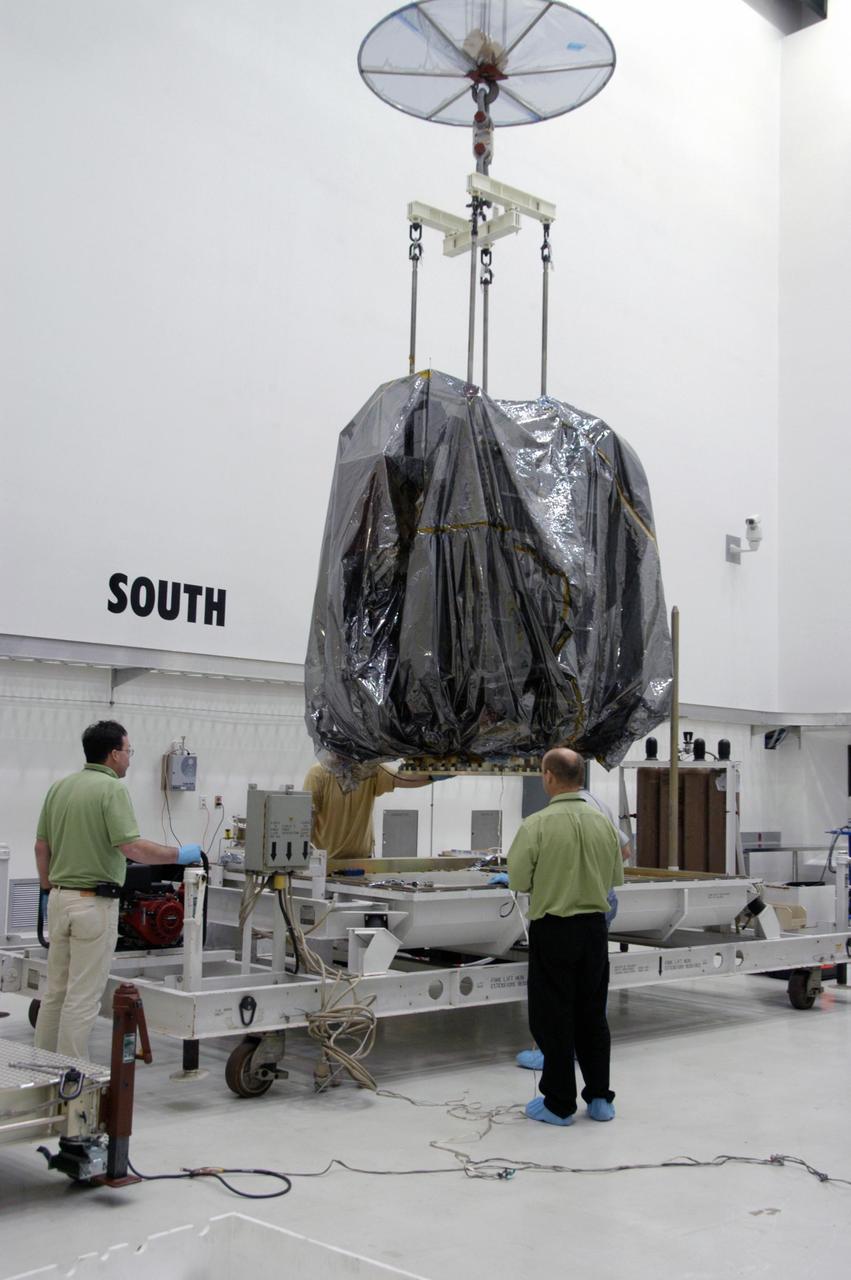

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Astrotech's Payload Processing Facility, an overhead crane lifts the Dawn spacecraft from its transporter. Dawn will be moved into clean room C for unbagging and further processing. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. The Dawn mission is managed by JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington, D.C. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton

The Dawn spacecraft is seen here in clean room C of Astrotech's Payload Processing Facility. In the clean room, the spacecraft will undergo further processing. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. The Dawn mission is managed by JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington, D.C.

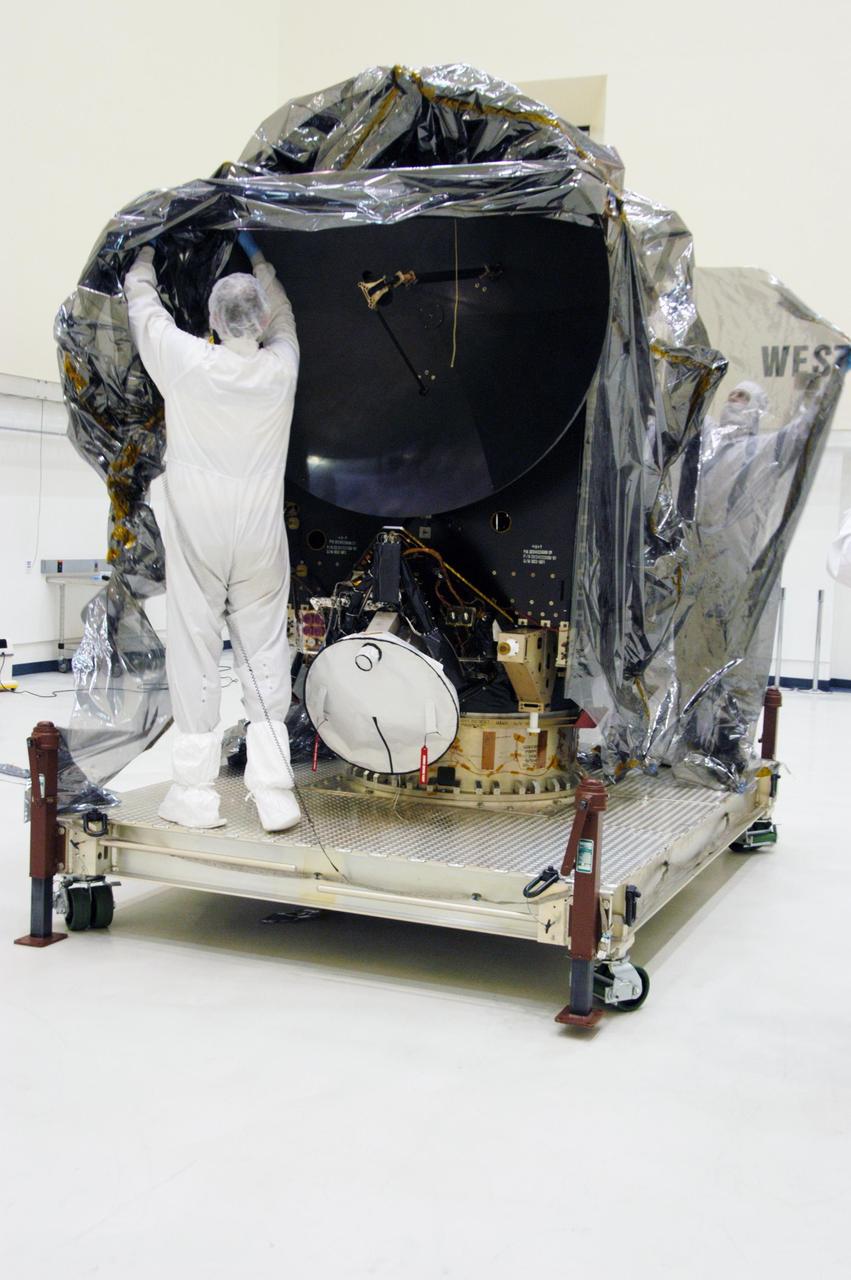
In clean room C of Astrotech's Payload Processing Facility, a worker wearing a "bunny suit," or clean-room attire, begins removing the protective cover surrounding the Dawn spacecraft. In the clean room, the spacecraft will undergo further processing. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. The Dawn mission is managed by JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington, D.C.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- This logo represents the mission of the Dawn spacecraft. During its nearly decade-long mission, Dawn will study the asteroid Vesta and dwarf planet Ceres, celestial bodies believed to have accreted early in the history of the solar system. The mission hopes to unlock some of the mysteries of planetary formation, including the building blocks and the processes leading to their state today. The Dawn mission is managed by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, Calif., for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington, D.C.
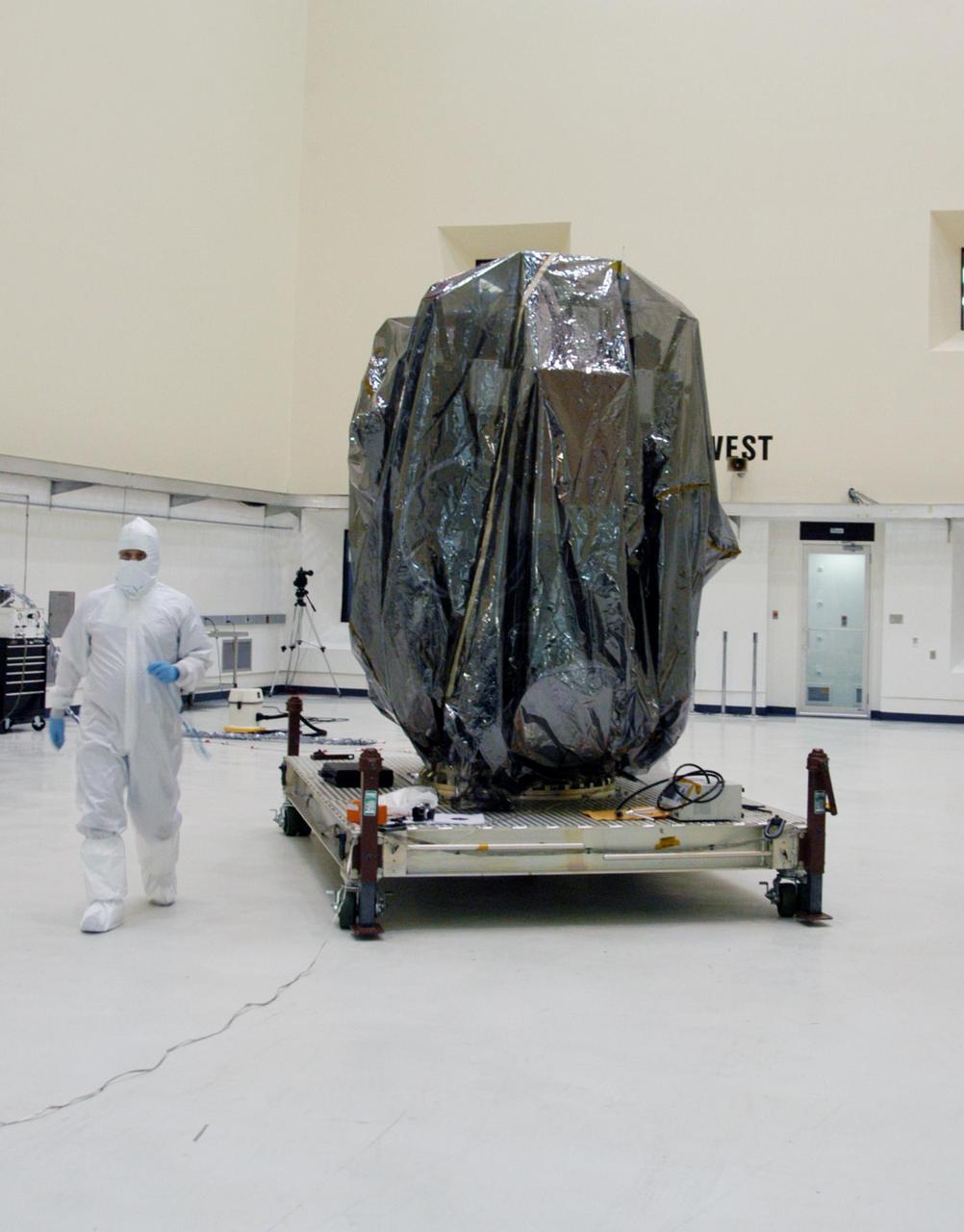

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In clean room C of Astrotech's Payload Processing Facility, a worker wears a "bunny suit," or clean-room attire, next to the Dawn spacecraft, which will be unbagged and undergo further processing. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. The Dawn mission is managed by JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington, D.C. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
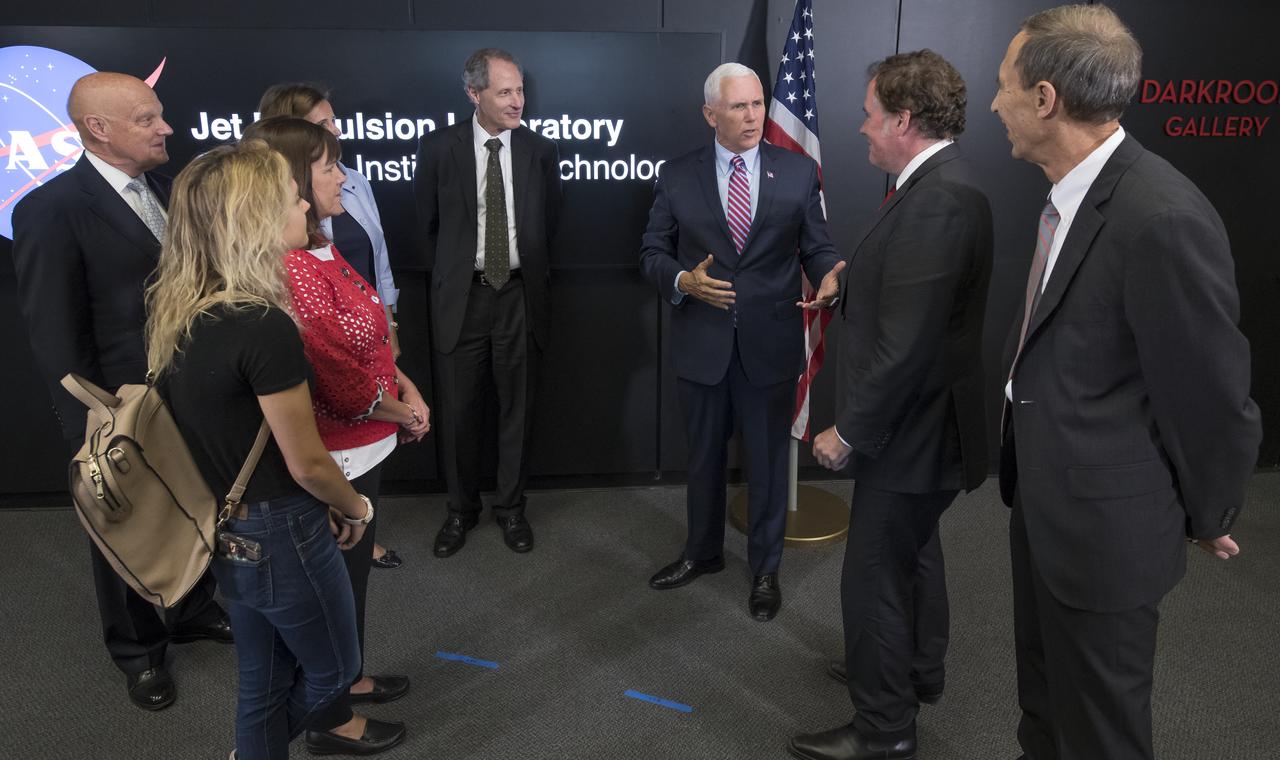

U.S. Vice President Mike Pence, 3rd from right, tours NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory along with his wife Karen, and daughter Charlotte, Saturday, April 28, 2018 in Pasadena, California. Joining the Vice President t and his family on the tour are: UAG Chairman, Admiral (Ret) James Ellis , left, JPL Distinguished Visiting Scientist and Spouse of UAG Chairman James Ellis, Elisabeth Pate-Cornell, behind Mrs. Pence, California Institute of Technology President Thomas Rosenbaum, JPL Director Michael Watkins, and JPL Deputy Director Lt. Gen. (Ret) Larry James, right. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
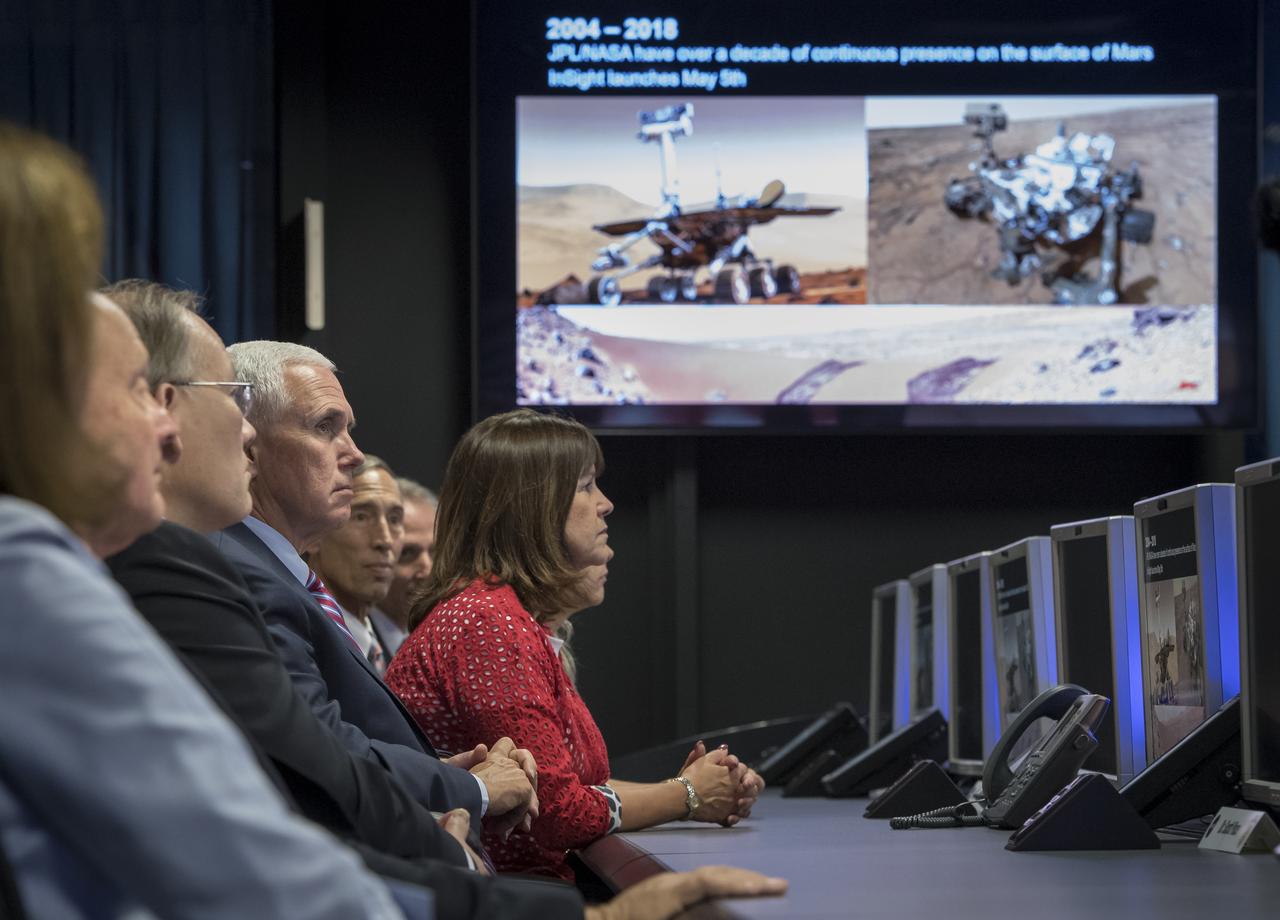

U.S. Vice President Mike Pence can be seen with his wife Karen Pence as they toured NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Saturday, April 28, 2018 in Pasadena, California. The vice President was also joined by his daughter Charlotte Pence, JPL Distinguished Visiting Scientist and Spouse of UAG Chairman James Ellis, Elisabeth Pate-Cornell , UAG Chairman, Admiral (Ret) James Ellis , Executive Director of the National Space Council Scott Pace, JPL Deputy Director Lt. Gen. (Ret) Larry James, and California Institute of Technology President Thomas Rosenbaum. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
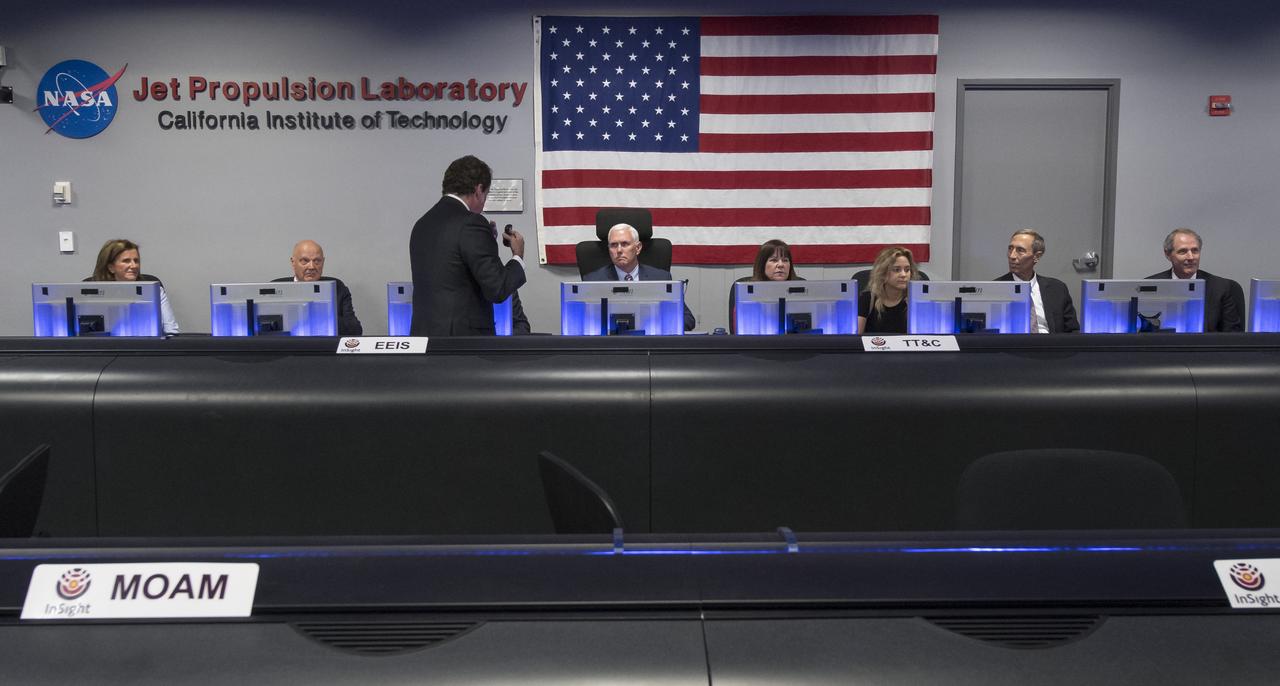

JPL Director Michael Watkins, standing, explains the history of NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory and the use of the Mission Support Area to Vice President Mike Pence, seated next to his wife Karen and daughter Charlotte Pence, during a tour of JPL, Saturday, April 28, 2018 in Pasadena, California. Joining the Vice President was, JPL Distinguished Visiting Scientist and Spouse of UAG Chairman James Ellis, Elisabeth Pate-Cornell, left, UAG Chairman, Admiral (Ret) James Ellis, JPL Deputy Director Lt. Gen. (Ret) Larry James, and California Institute of Technology President Thomas Rosenbaum. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
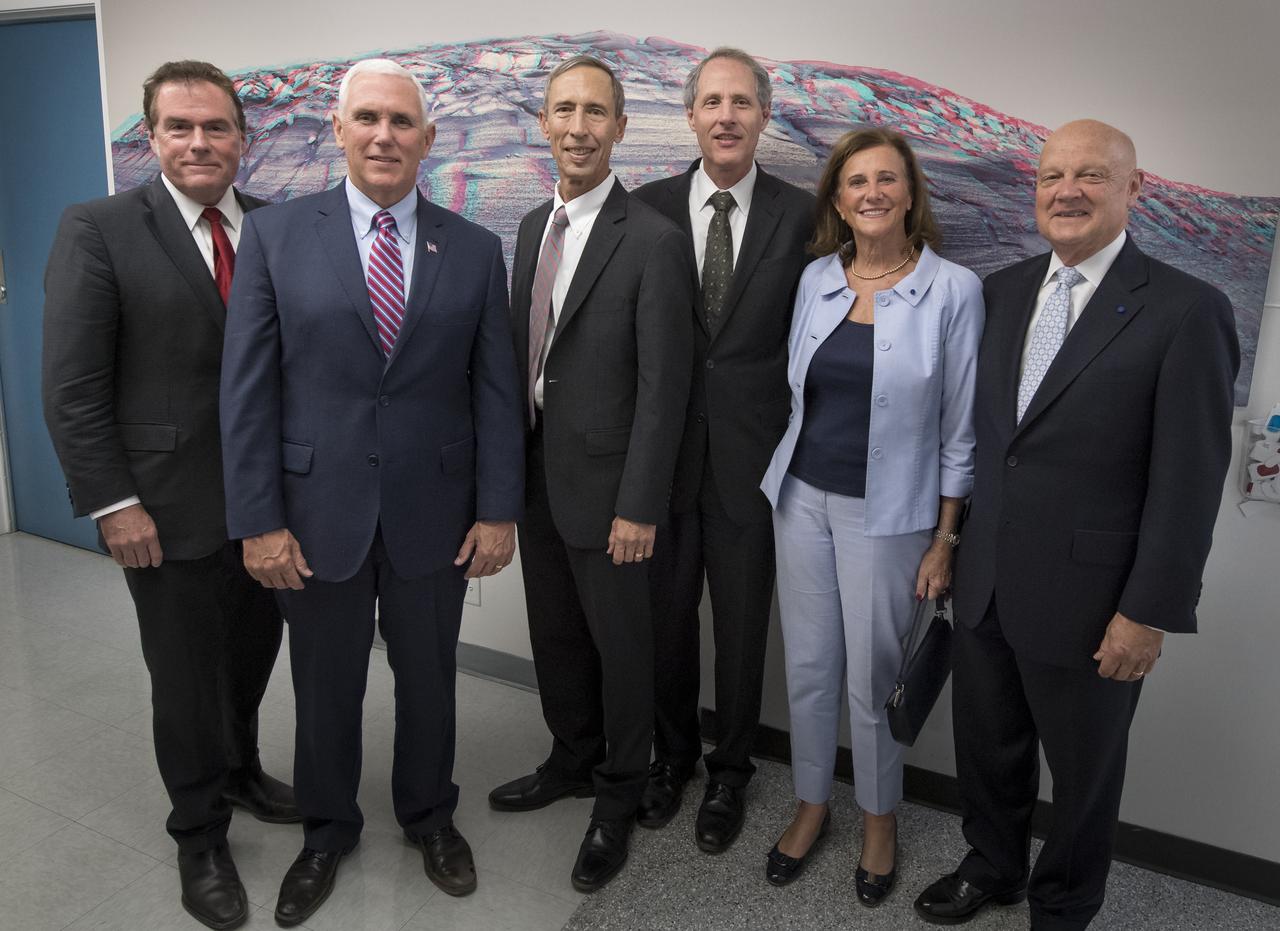

U.S. Vice President Mike Pence, 2nd from left, poses for a group photograph with JPL Director Michael Watkins, left, JPL Deputy Director Lt. Gen. (Ret) Larry James, California Institute of Technology President Thomas Rosenbaum, JPL Distinguished Visiting Scientist and Spouse of UAG Chairman James Ellis, Elisabeth Pate-Cornell, and UAG Chairman, Admiral (Ret) James Ellis, right, after having toured NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Saturday, April 28, 2018 in Pasadena, California. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
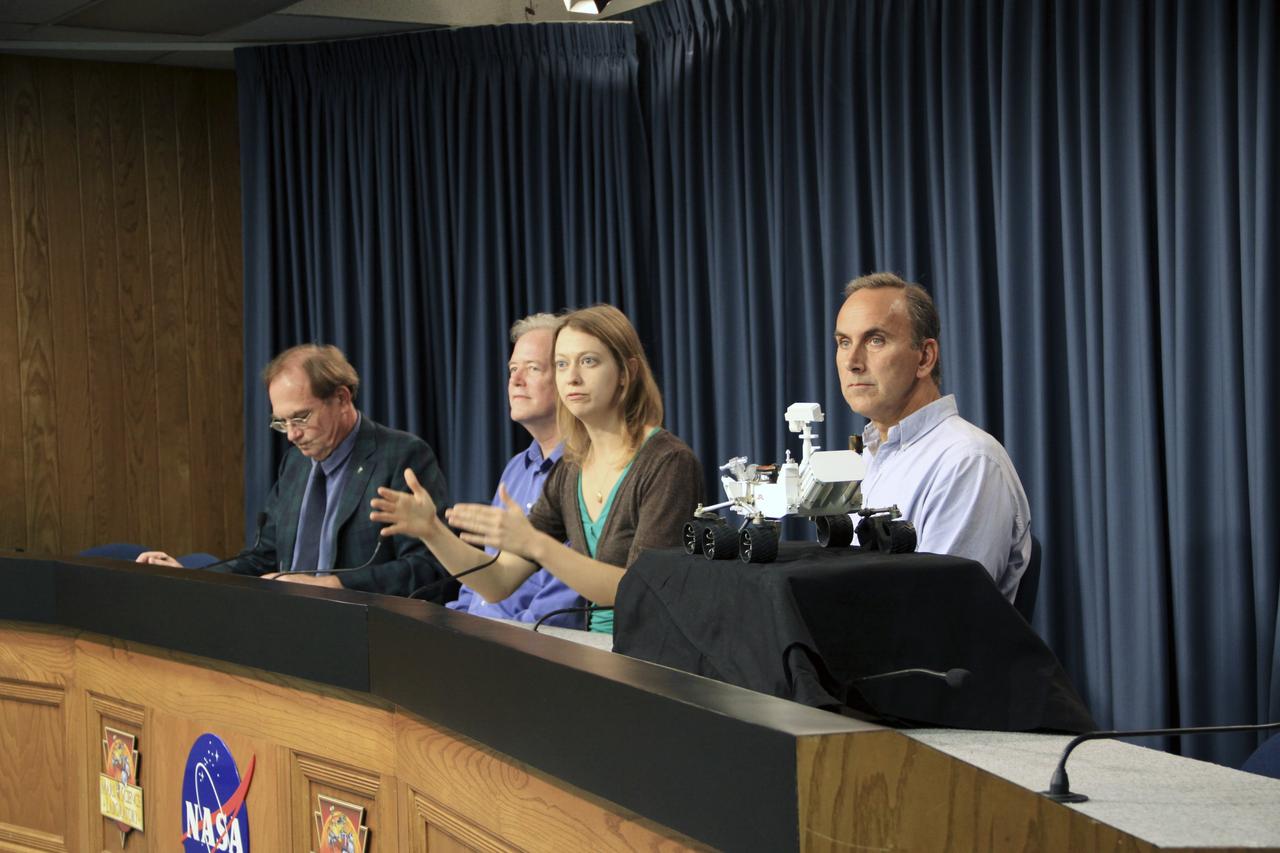

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Scientist and Assistant Professor Bethany Ehlmann with the California Institute of Technology and Jet Propulsion Laboratory, answers a question from the media during a “What Do We Know About Mars” news conference, Nov. 21. The press conference was part of preflight activities for the Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. NASA Public Affairs Officer George Diller, at left, moderates the conference that also features Lead Scientist Michael Meyer, Mars Exploration Program and Mars Science Laboratory Project Scientist John Grotzinger from the California Institute of Technology. MSL’s components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 26 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
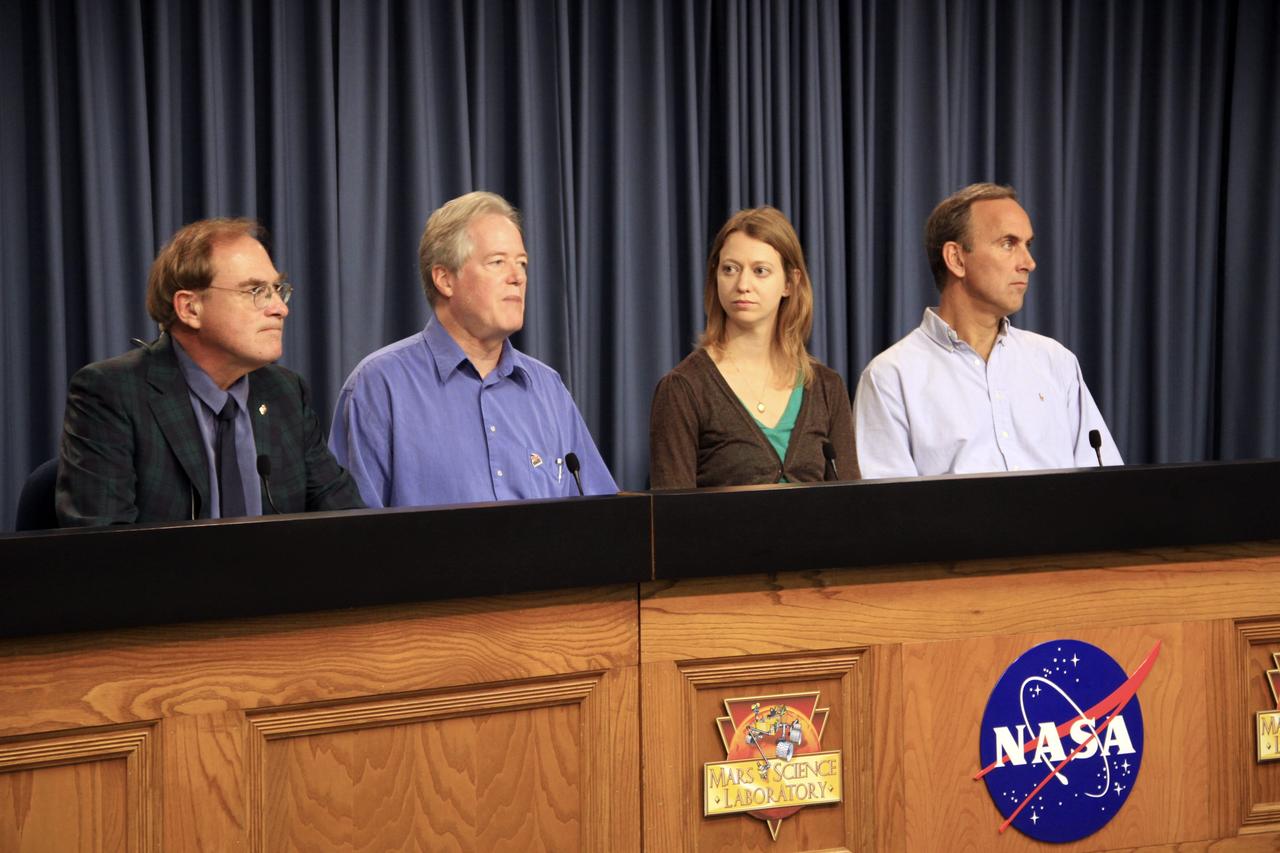

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida is host to a “What Do We Know About Mars” news conference, Nov. 21, as part of preflight activities for the Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. NASA Public Affairs Officer George Diller, at left, moderates the conference featuring Lead Scientist Michael Meyer, Mars Exploration Program; Scientist and Assistant Professor Bethany Ehlmann with the California Institute of Technology and Jet Propulsion Laboratory; and Mars Science Laboratory Project Scientist John Grotzinger from the California Institute of Technology. MSL’s components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 26 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
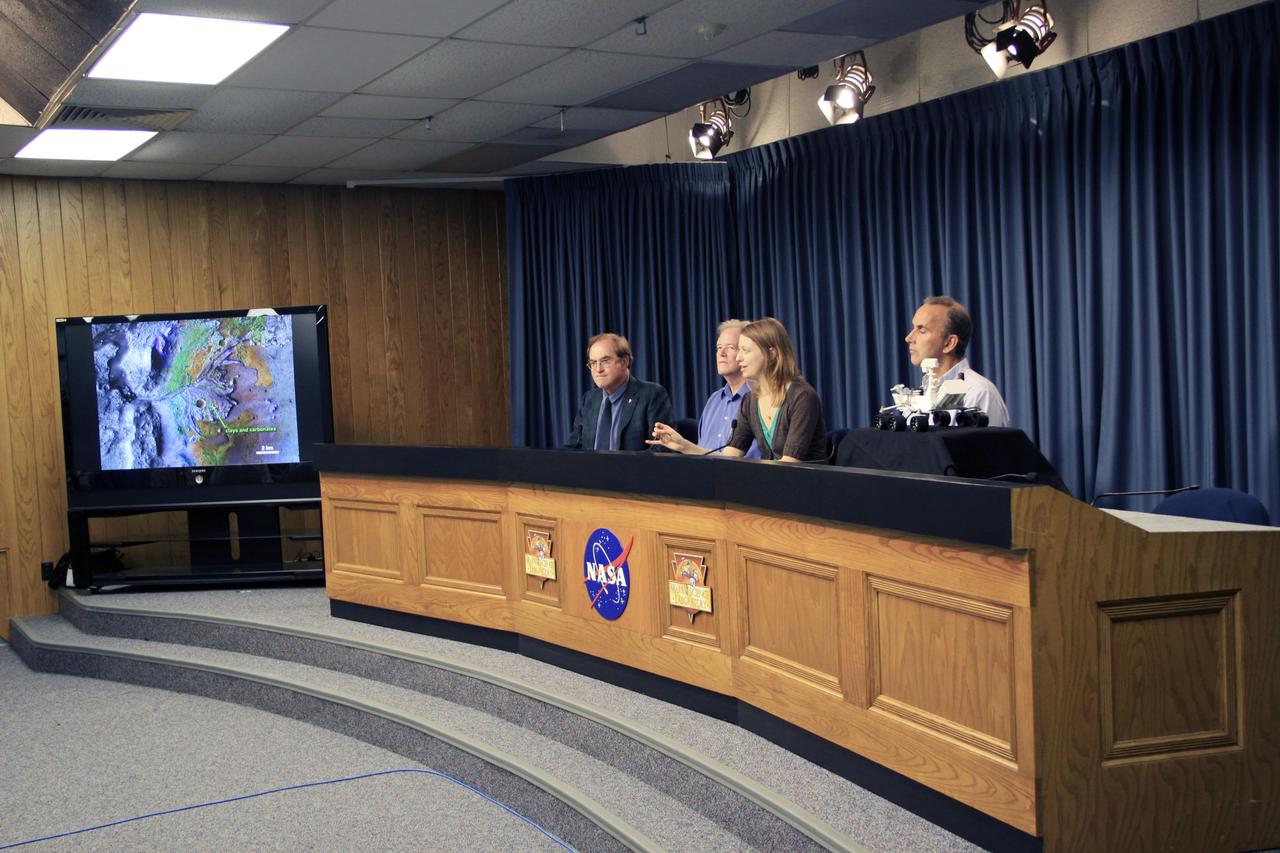

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Scientist and Assistant Professor Bethany Ehlmann with the California Institute of Technology and Jet Propulsion Laboratory, answers a question from the media during a “What Do We Know About Mars” news conference, Nov. 21. The press conference was part of preflight activities for the Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission. NASA Public Affairs Officer George Diller, at left, moderates the conference that also features Lead Scientist Michael Meyer, Mars Exploration Program and Mars Science Laboratory Project Scientist John Grotzinger from the California Institute of Technology. MSL’s components include a car-sized rover, Curiosity, which has 10 science instruments designed to search for signs of life, including methane, and help determine if the gas is from a biological or geological source. Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is targeted for Nov. 26 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

NASA and industry leaders speak to NASA Social participants about the agency's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) in the Press Site auditorium at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Speaking to the group from center, are Martin Still, TESS Program Scientist, NASA Headquarters, and Jessie Christiansen, Staff scientist, NASA Exoplanet Science Institute, California Institute of Technology. At far left is Jason Townsend, NASA Communications. TESS is the next step in the search for planets outside of our solar system. The mission will find exoplanets that periodically block part of the light from their host stars, events called transits. The satellite will survey the nearest and brightest stars for two years to search for transiting exoplanets. TESS will launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station no earlier than 6:32 p.m. EDT on Monday, April 16.

NASA and industry leaders speak to NASA Social participants about the agency's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) in the Press Site auditorium at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Speaking to the group is Jessie Christiansen, staff scientiest, NASA Exoplaneet Science Institute, California Institute of Technology. TESS is the next step in the search for planets outside of our solar system. The mission will find exoplanets that periodically block part of the light from their host stars, events called transits. The satellite will survey the nearest and brightest stars for two years to search for transiting exoplanets. TESS will launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station no earlier than 6:32 p.m. EDT on Monday, April 16.
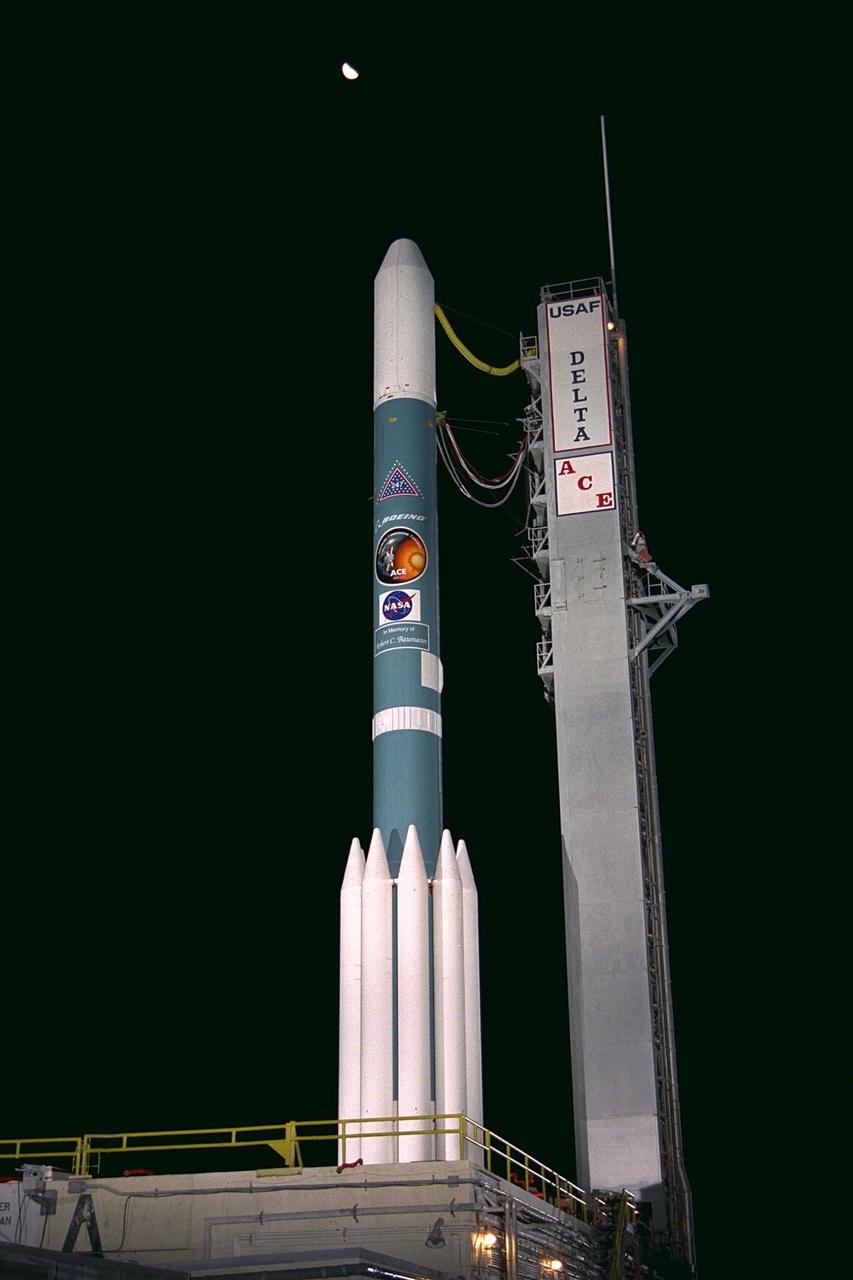

The Boeing Delta II expendable launch vehicle carrying the Advanced Composition Explorer (ACE) undergoes final preparations for liftoff in the predawn hours of Aug. 25, 1997, at Launch Complex 17A, Cape Canaveral Air Station. This is the second Delta launch under the Boeing name and the first from Cape Canaveral. The first launch attempt on Aug. 24 was scrubbed by Air Force range safety personnel because two commercial fishing vessels were within the Delta’s launch danger area. ACE with its combination of nine sensors and instruments will investigate the origin and evolution of solar phenomenon, the formation of solar corona, solar flares and acceleration of the solar wind. ACE was built for NASA by the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory and is managed by the Explorer Project Office at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center. The lead scientific institution is the California Institute of Technology
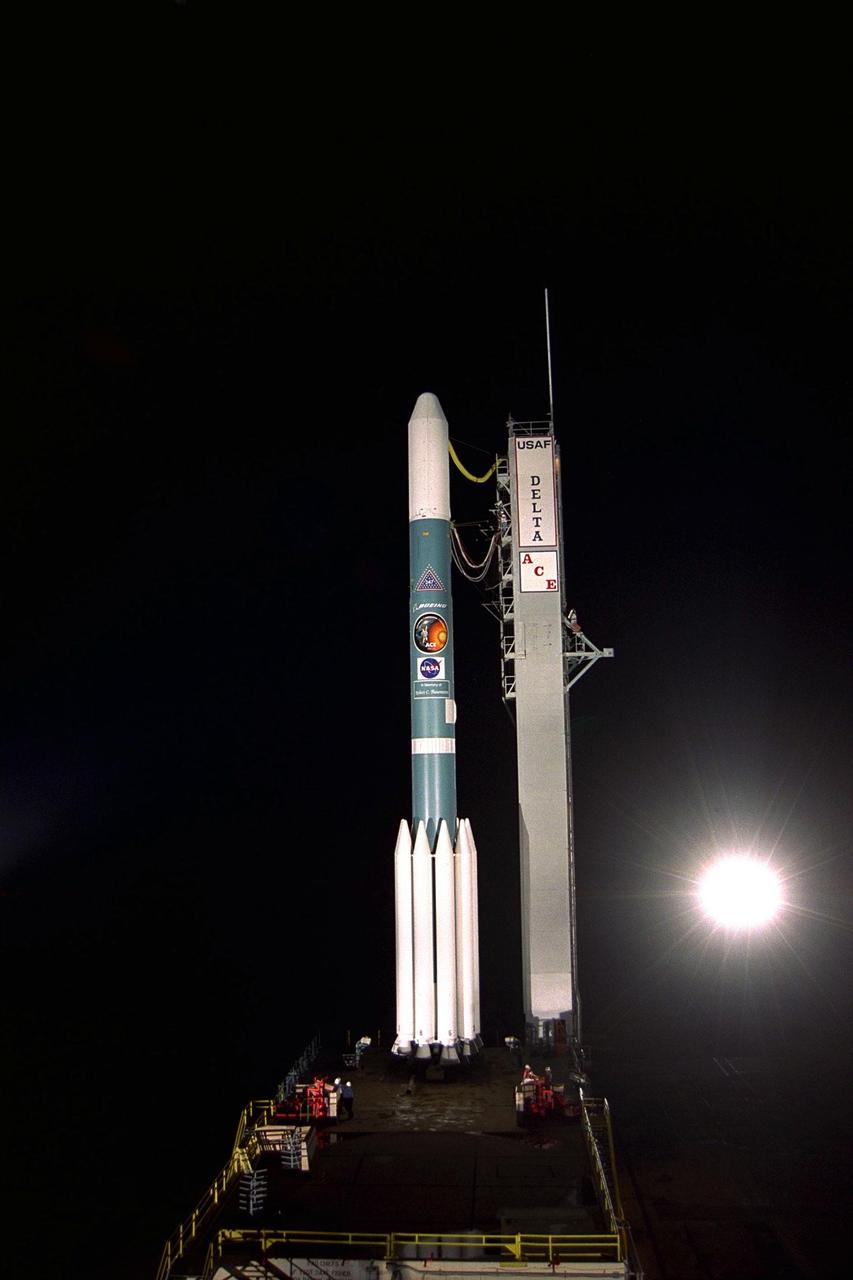

The Boeing Delta II expendable launch vehicle carrying the Advanced Composition Explorer (ACE) undergoes final preparations for liftoff in the predawn hours of Aug. 25, 1997, at Launch Complex 17A, Cape Canaveral Air Station. This is the second Delta launch under the Boeing name and the first from Cape Canaveral. The first launch attempt on Aug. 24 was scrubbed by Air Force range safety personnel because two commercial fishing vessels were within the Delta’s launch danger area. ACE with its combination of nine sensors and instruments will investigate the origin and evolution of solar phenomenon, the formation of solar corona, solar flares and acceleration of the solar wind. ACE was built for NASA by the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory and is managed by the Explorer Project Office at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center. The lead scientific institution is the California Institute of Technology
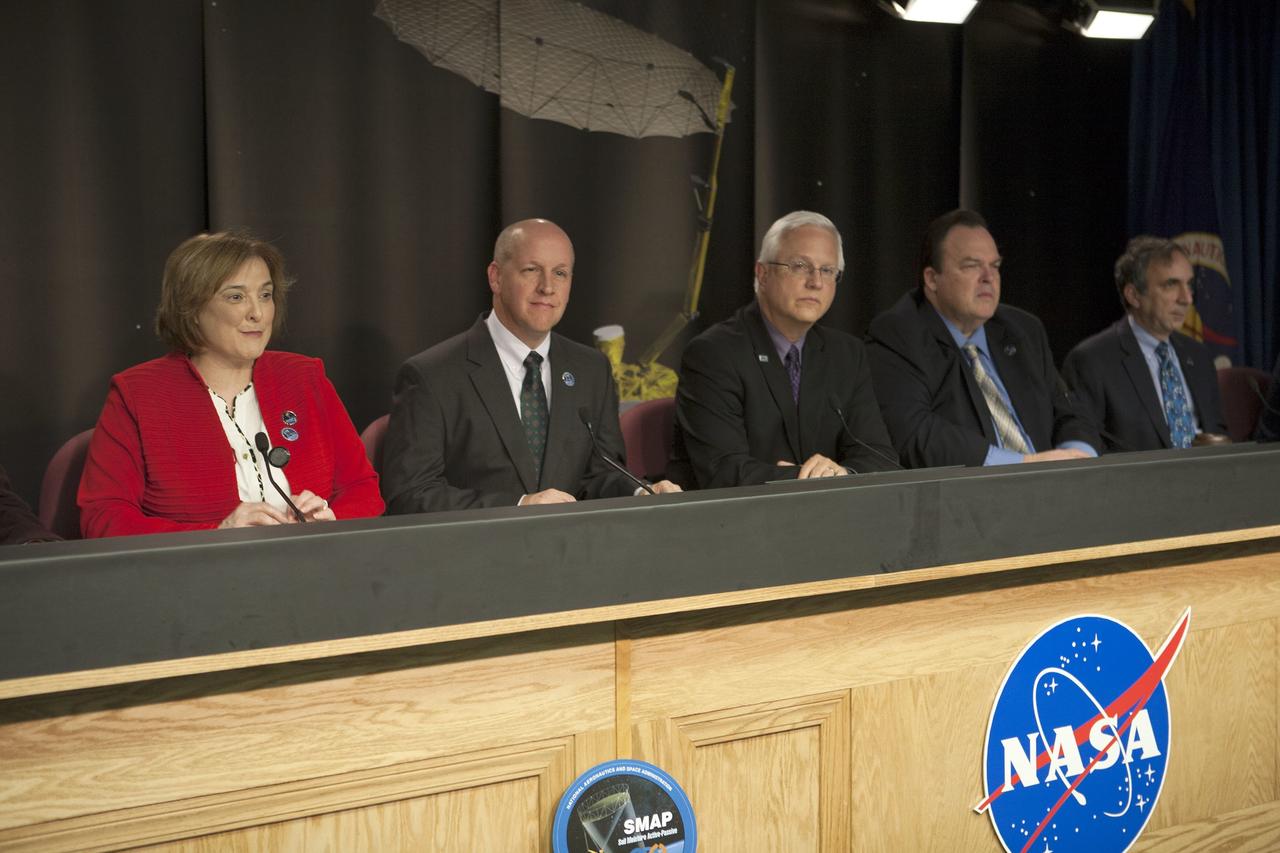

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, California – At Vandenberg Air Force Base, California, agency and industry leaders spoke to members of the news media as the Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, satellite and its Delta II rocket were being prepared for launch. From left are: Christine Bonniksen, SMAP program executive at NASA Headquarters, Tim Dunn, NASA launch manager at Kennedy Space Center, Florida, Vern Thorp, program manager for NASA Missions for United Launch Alliance in Centennial, Colorado, Kent Kellogg, SMAP Project manager at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, Dara Entekhabi, SMAP science team leader at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and 1st Lt. John Martin, launch weather officer, 30th Operations Support Squadron at Vandenberg. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, California – At Vandenberg Air Force Base, California, agency and industry leaders spoke to members of the news media as the Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, satellite and its Delta II rocket were being prepared for launch. From left are: George Diller of NASA Public Affairs, Christine Bonniksen, SMAP program executive at NASA Headquarters, Tim Dunn, NASA launch manager at Kennedy Space Center, Florida Vern Thorp, program manager for NASA Missions for United Launch Alliance in Centennial, Colorado, Kent Kellogg, SMAP Project manager at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, Dara Entekhabi, SMAP science team leader at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and 1st Lt. John Martin, launch weather officer, 30th Operations Support Squadron at Vandenberg. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

Participants at a news conference discussing findings of the analysis of a rock sample from Mars are seen, Tuesday, March 12, 2013 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. From left to right are seen: Michael Meyer, lead scientist, Mars Exploration Program at NASA Headquarters; John Grotzinger, Curiosity project scientist, California Institute of Technology in Pasadena; David Blake, principal investigator for Curiosity's Chemistry and Mineralogy investigation at NASA's Ames Research Center in Calif.; and Paul Mahaffy, principal investigator for Curiosity's Sample Analysis at Mars (SAM) investigation at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
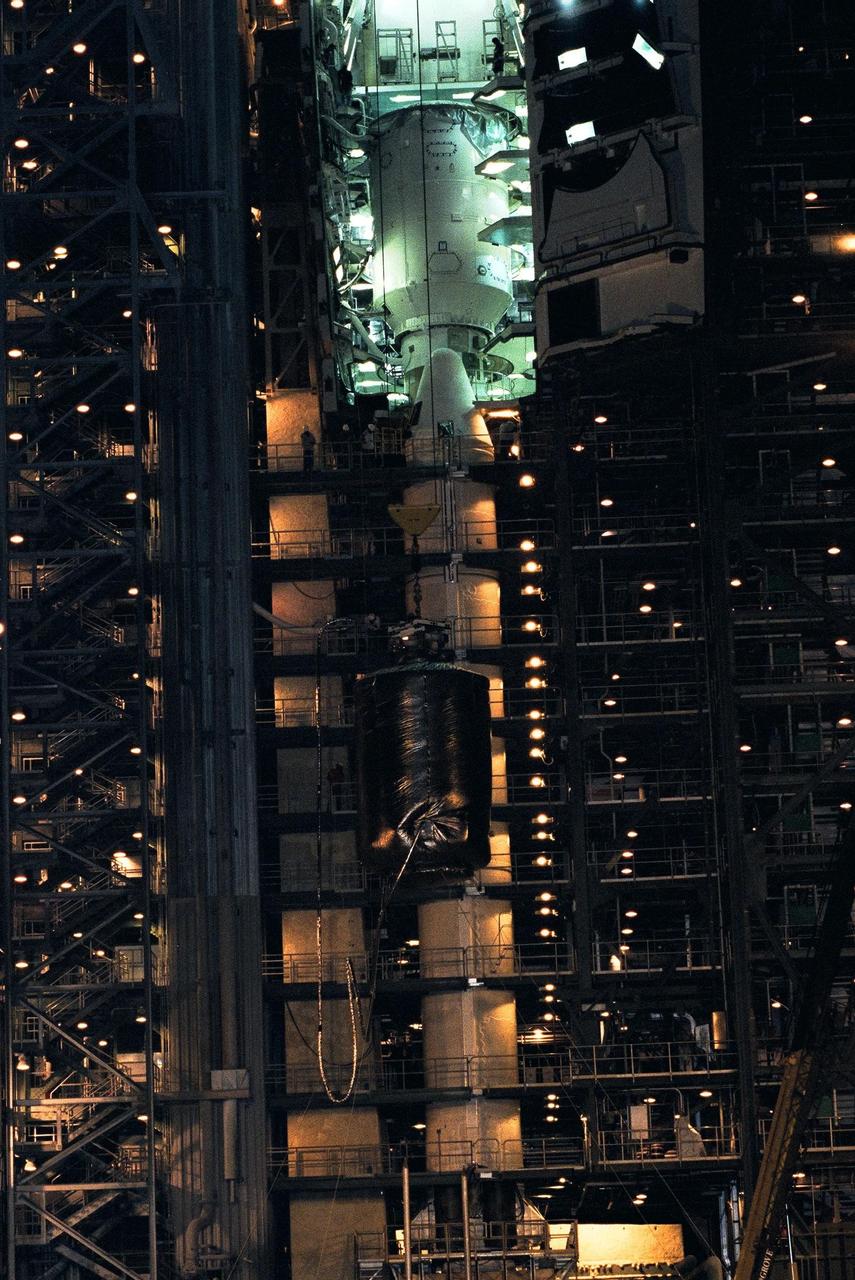

Technicians at Launch Complex 40, Cape Canaveral Air Station (CCAS), connect the crane to the top of the Cassini spacecraft in preparation for the lift to the top of its Titan IV/Centaur launch vehicle. Cassini is an international mission conducted by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), the European Space Agency (ESA), and the Italian Space Agency (ASI). The two-story-tall spacecraft, scheduled for launch on Oct. 6, is destined to arrive at Saturn in July 2004, where it will orbit and study Saturn, its rings, moons and magnetic environment in detail over a four-year period. The Cassini mission is managed for NASA's Office of Space Science by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology

The Cassini spacecraft, covered by an environmentally controlled protective enclosure, is lifted at Launch Complex 40, Cape Canaveral Air Station (CCAS), in preparation to mate it to the top of its Titan IV/Centaur launch vehicle. Cassini is an international mission conducted by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), the European Space Agency (ESA), and the Italian Space Agency (ASI). The two-story-tall spacecraft, scheduled for launch on Oct. 13, is destined to arrive at Saturn in July 2004, where it will orbit and study Saturn, its rings, moons and magnetic environment in detail over a four-year period. The Cassini mission is managed for NASA's Office of Space Science by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology

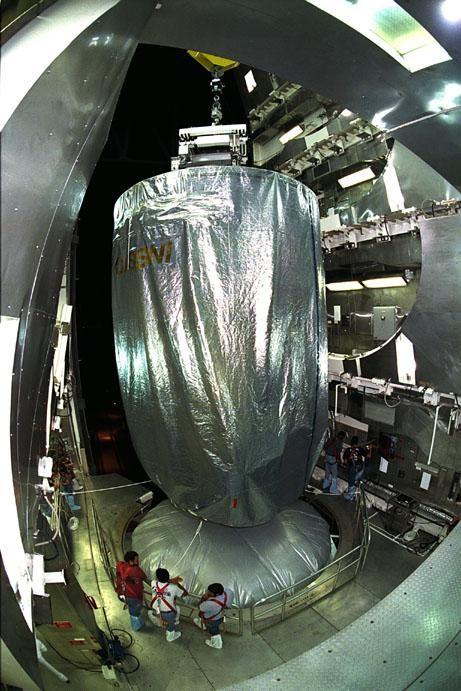
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In clean room C of Astrotech's Payload Processing Facility, a worker wearing a "bunny suit," or clean-room attire, begins removing the protective cover surrounding the Dawn spacecraft. In the clean room, the spacecraft will undergo further processing. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. The Dawn mission is managed by JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington, D.C. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
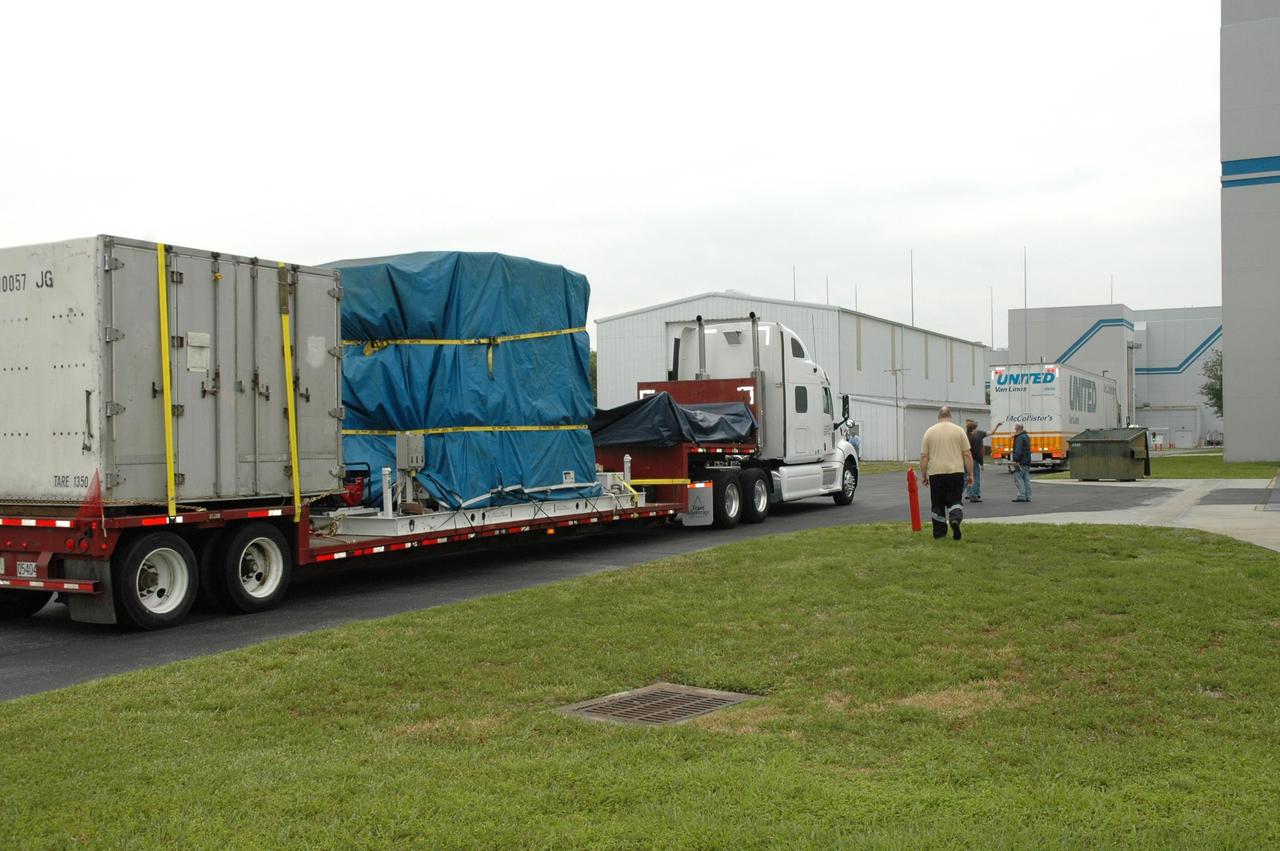

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Two trucks (one air-ride, one flat-bed) deliver the Dawn spacecraft, as well as additional electrical and ground support equipment and xenon ground support equipment, to Astrotech. Dawn will be moved from the truck and the shipping container removed. The spacecraft will then be moved into the high bay of the Payload Processing Facility. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. The Dawn mission is managed by JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington, D.C. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
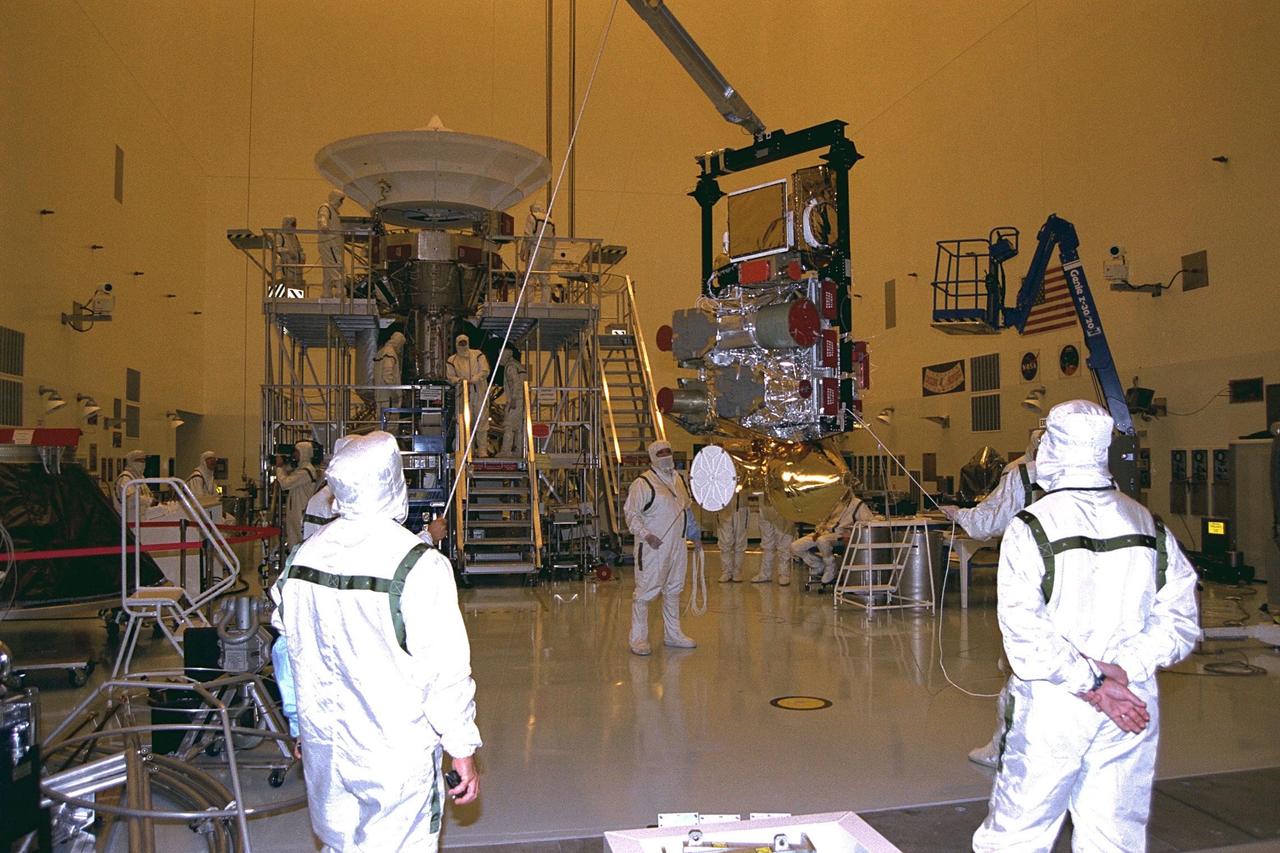

Technicians from the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) of the California Institute of Technology lift the remote sensing pallet in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at KSC in July prior to installation on the Cassini spacecraft. A four- year, close-up study of the Saturnian system, the Cassini mission is scheduled for launch from Cape Canaveral Air Station in October 1997. It will take seven years for the spacecraft to reach Saturn. Scientific instruments carried aboard the spacecraft will study Saturn’s atmosphere, magnetic field, rings, and several moons. JPL is managing the Cassini project for NASA
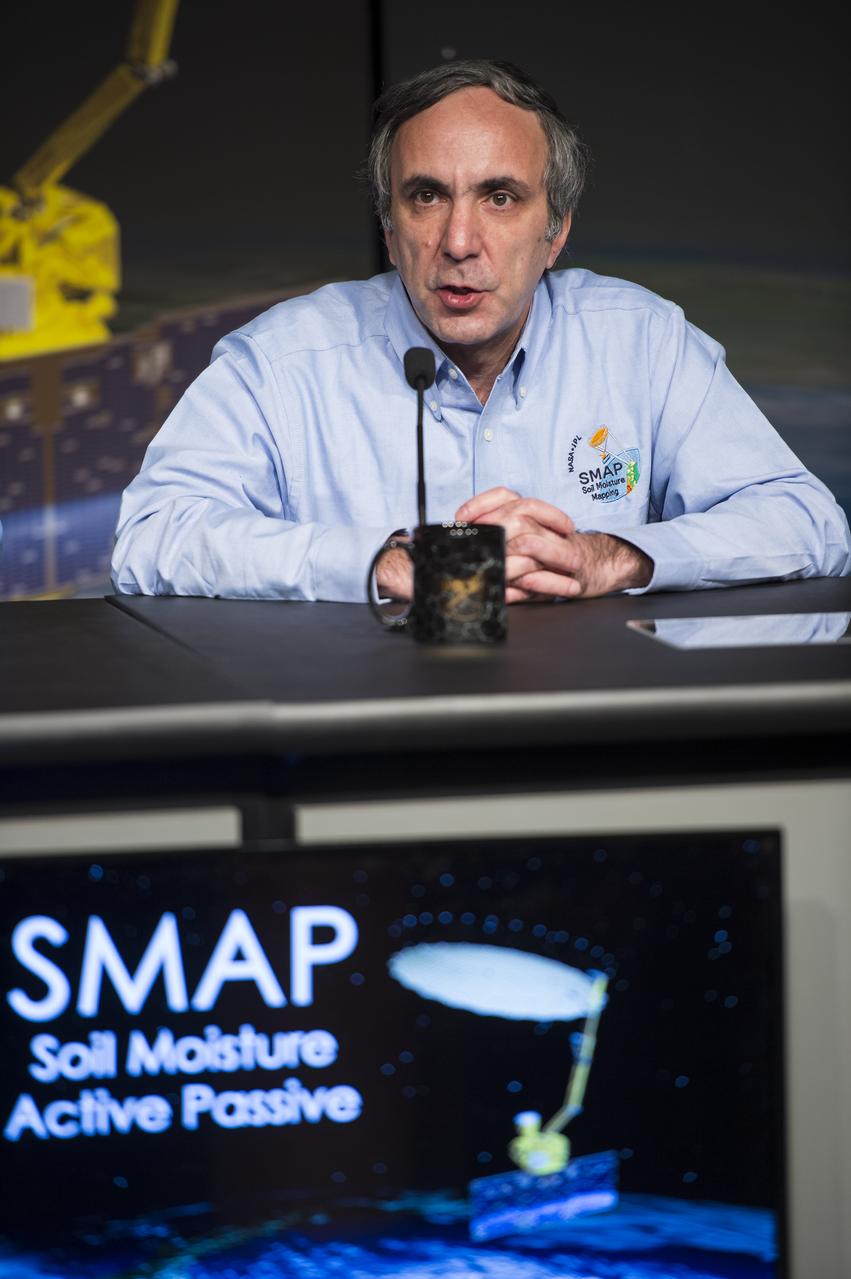

Dara Entekhabi, SMAP science team lead, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, speaks during a briefing about the upcoming launch of the Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) mission, Thursday, Jan. 08, 2015, at NASA Headquarters in Washington DC. The mission is scheduled for a Jan. 29 launch from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, and will provide the most accurate, highest-resolution global measurements of soil moisture ever obtained from space. The data will be used to enhance scientists' understanding of the processes that link Earth's water, energy and carbon cycles. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

The Cassini spacecraft arrives at Complex 40, Cape Canaveral Air Station (CCAS), where it will be lifted to the top of its Titan IV/Centaur launch vehicle. Cassini is an international mission conducted by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), the European Space Agency (ESA), and the Italian Space Agency (ASI). The two-story-tall spacecraft, scheduled for launch on Oct. 6, is destined to arrive at Saturn in July 2004, where it will orbit and study Saturn, its rings, moons and magnetic environment in detail over a four-year period. The Cassini mission is managed for NASA's Office of Space Science by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology

Technicians at Cape Canaveral Air Station (CCAS) begin to remove the transportation cover from the Cassini spacecraft after it was lifted to the top of the Titan IV/Centaur launch vehicle at Complex 40. Cassini is an international mission conducted by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), the European Space Agency (ESA), and the Italian Space Agency (ASI). The two-story-tall spacecraft, scheduled for launch on Oct. 6, is destined to arrive at Saturn in July 2004, where it will orbit and study Saturn, its rings, moons and magnetic environment in detail over a four-year period. The Cassini mission is managed for NASA's Office of Space Science by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology

One investigation on NASA's Mars 2020 rover will extract oxygen from the Martian atmosphere. It is called MOXIE, for Mars Oxygen In-Situ Resource Utilization Experiment. In this image, MOXIE Principal Investigator Michael Hecht, of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, is in the MOXIE development laboratory at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California. Mars' atmosphere is mostly carbon dioxide. Demonstration of the capability for extracting oxygen from it, under Martian environmental conditions, will be a pioneering step toward how humans on Mars will use the Red Planet's natural resources. Oxygen can be used in the rocket http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20761
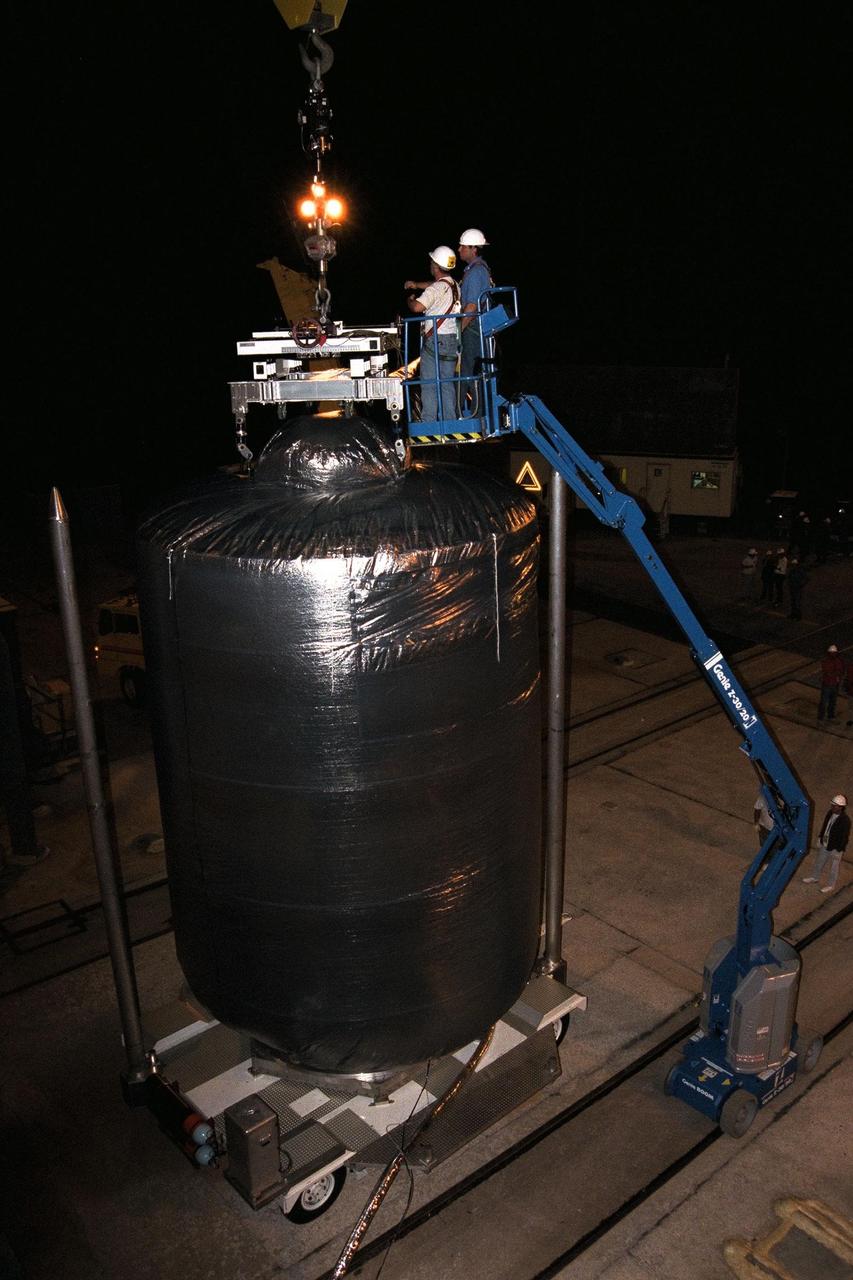

Technicians at Launch Complex 40, Cape Canaveral Air Station (CCAS), connect the crane to the top of the Cassini spacecraft in preparation for the lift to the top of its Titan IV/Centaur launch vehicle. Cassini is an international mission conducted by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), the European Space Agency (ESA), and the Italian Space Agency (ASI). The two-story-tall spacecraft, scheduled for launch on Oct. 6, is destined to arrive at Saturn in July 2004, where it will orbit and study Saturn, its rings, moons and magnetic environment in detail over a four-year period. The Cassini mission is managed for NASA's Office of Space Science by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology
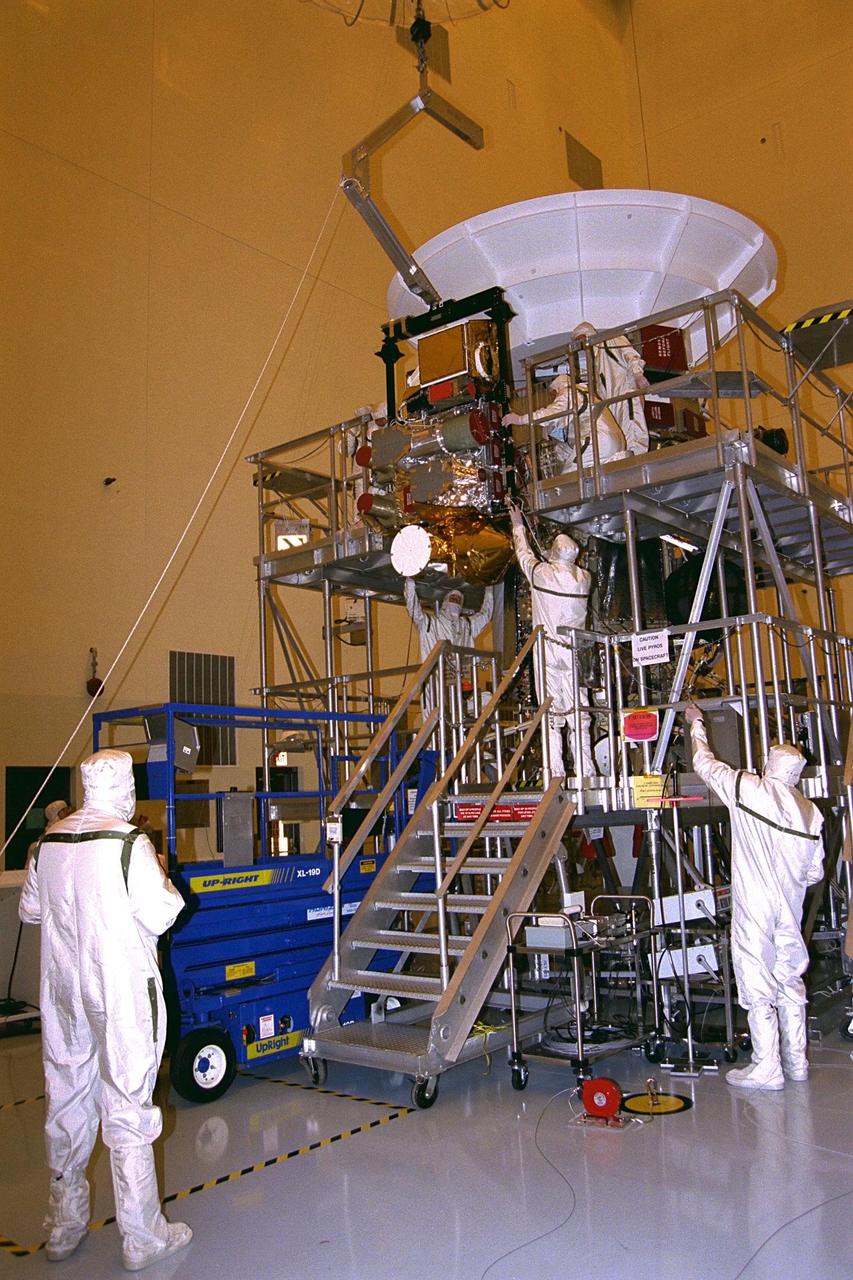

The complete remote sensing pallet is lowered by technicians from the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) of the California Institute of Technology and mated at the interface with the Cassini spacecraft in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at KSC in July. A four-year, close-up study of the Saturnian system, the Cassini mission is scheduled for launch from Cape Canaveral Air Station in October 1997. It will take seven years for the spacecraft to reach Saturn. Scientific instruments carried aboard the spacecraft will study Saturn’s atmosphere, magnetic field, rings, and several moons. JPL is managing the Cassini project for NASA
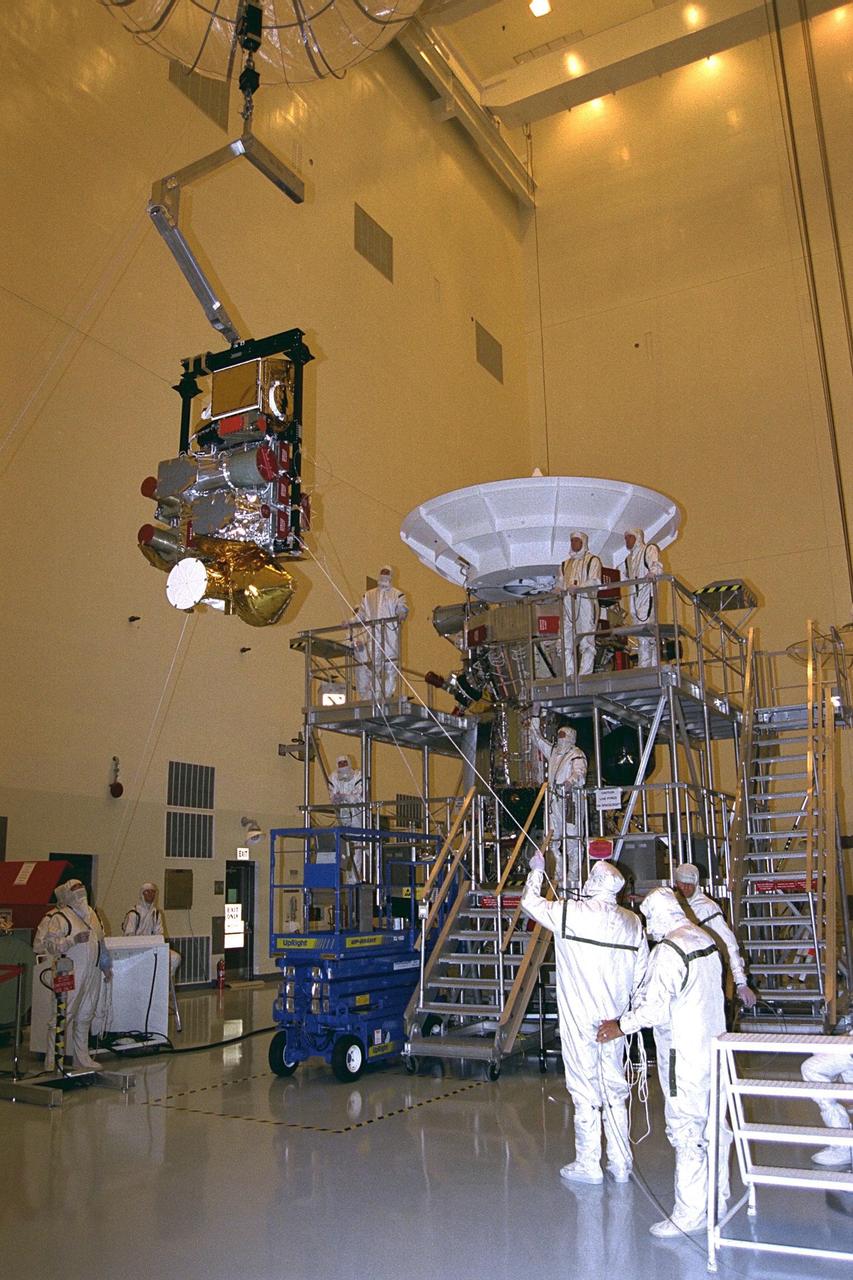

The complete remote sensing pallet is lowered by technicians from the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) of the California Institute of Technology to mate with the Cassini spacecraft in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at KSC in July. A four-year, close-up study of the Saturnian system, the Cassini mission is scheduled for launch from Cape Canaveral Air Station in October 1997. It will take seven years for the spacecraft to reach Saturn. Scientific instruments carried aboard the spacecraft will study Saturn’s atmosphere, magnetic field, rings, and several moons. JPL is managing the Cassini project for NASA
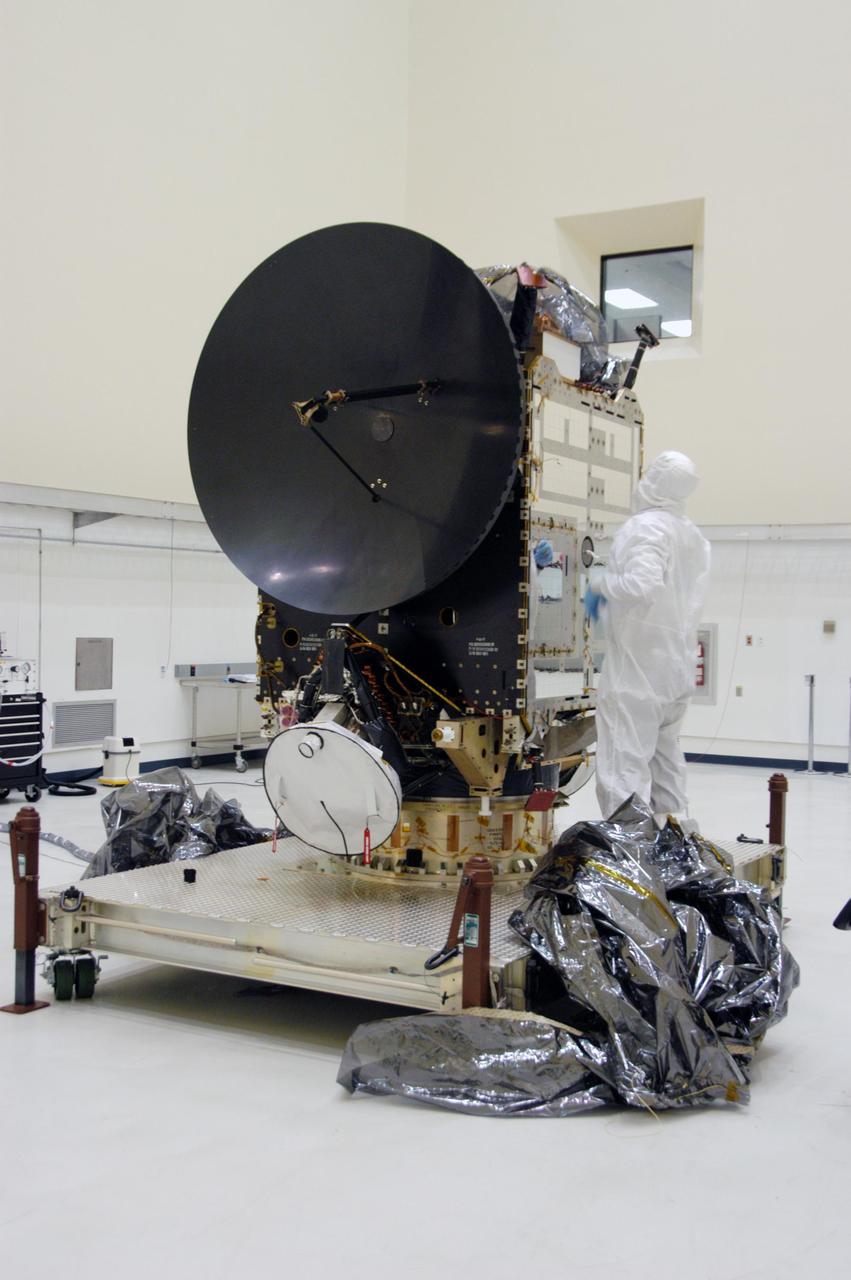

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In clean room C of Astrotech's Payload Processing Facility, a worker wearing a "bunny suit," or clean-room attire, looks over the Dawn spacecraft after removing the protective cover, at bottom right. In the clean room, the spacecraft will undergo further processing. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. The Dawn mission is managed by JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington, D.C. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton

Dara Entekhabi, SMAP science team lead, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, center, speaks during a briefing about the upcoming launch of the Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) mission, Thursday, Jan. 08, 2015, at NASA Headquarters in Washington DC. The mission is scheduled for a Jan. 29 launch from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, and will provide the most accurate, highest-resolution global measurements of soil moisture ever obtained from space. The data will be used to enhance scientists' understanding of the processes that link Earth's water, energy and carbon cycles. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
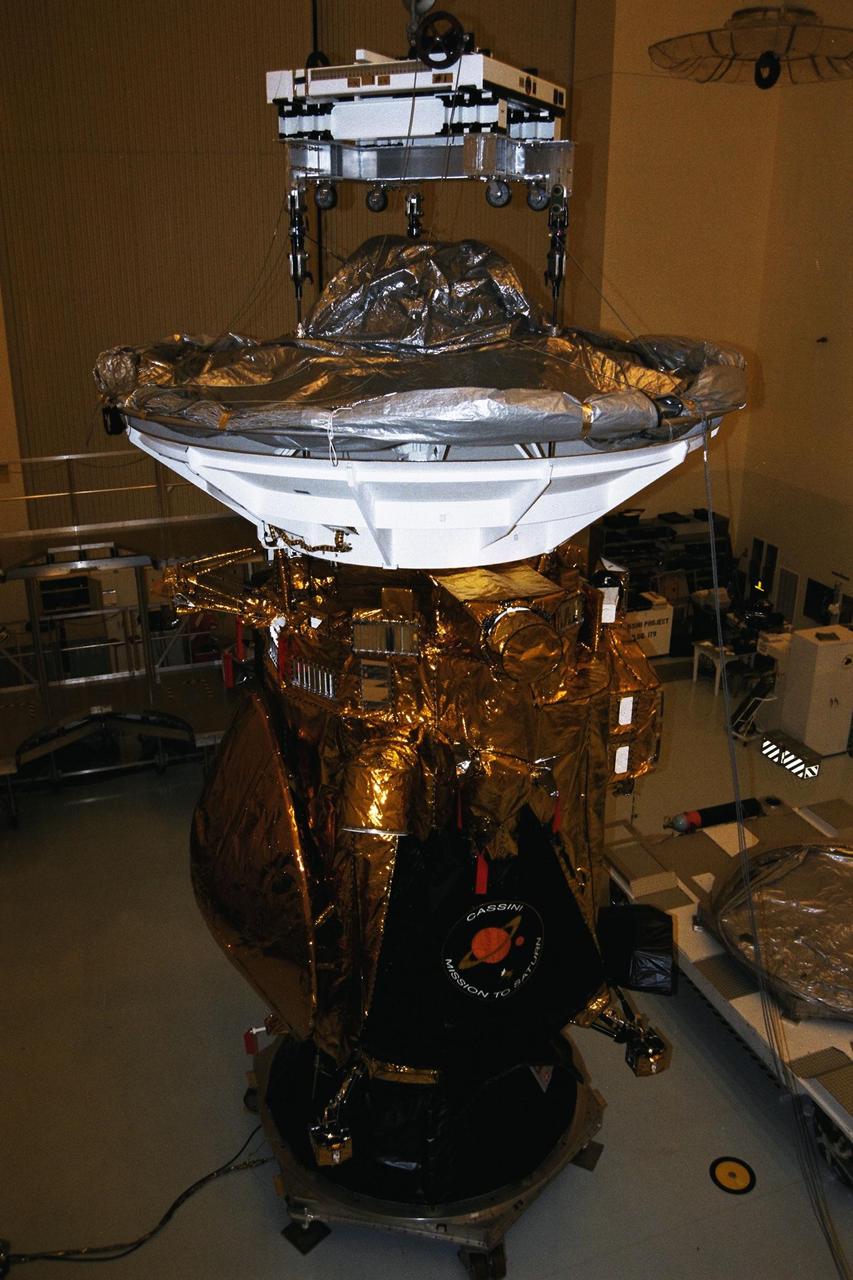

In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF), the Cassini spacecraft is prepared for its lift onto a transporter which will move it to Launch Complex 40, Cape Canaveral Air Station (CCAS). Cassini is an international mission conducted by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), the European Space Agency (ESA), and the Italian Space Agency (ASI). The two-story-tall spacecraft, scheduled for launch on Oct. 6, is destined to arrive at Saturn in July 2004, where it will study the planet, its rings, moons and magnetic environment in detail over a four-year period. The Cassini mission is managed for NASA's Office of Space Science by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology
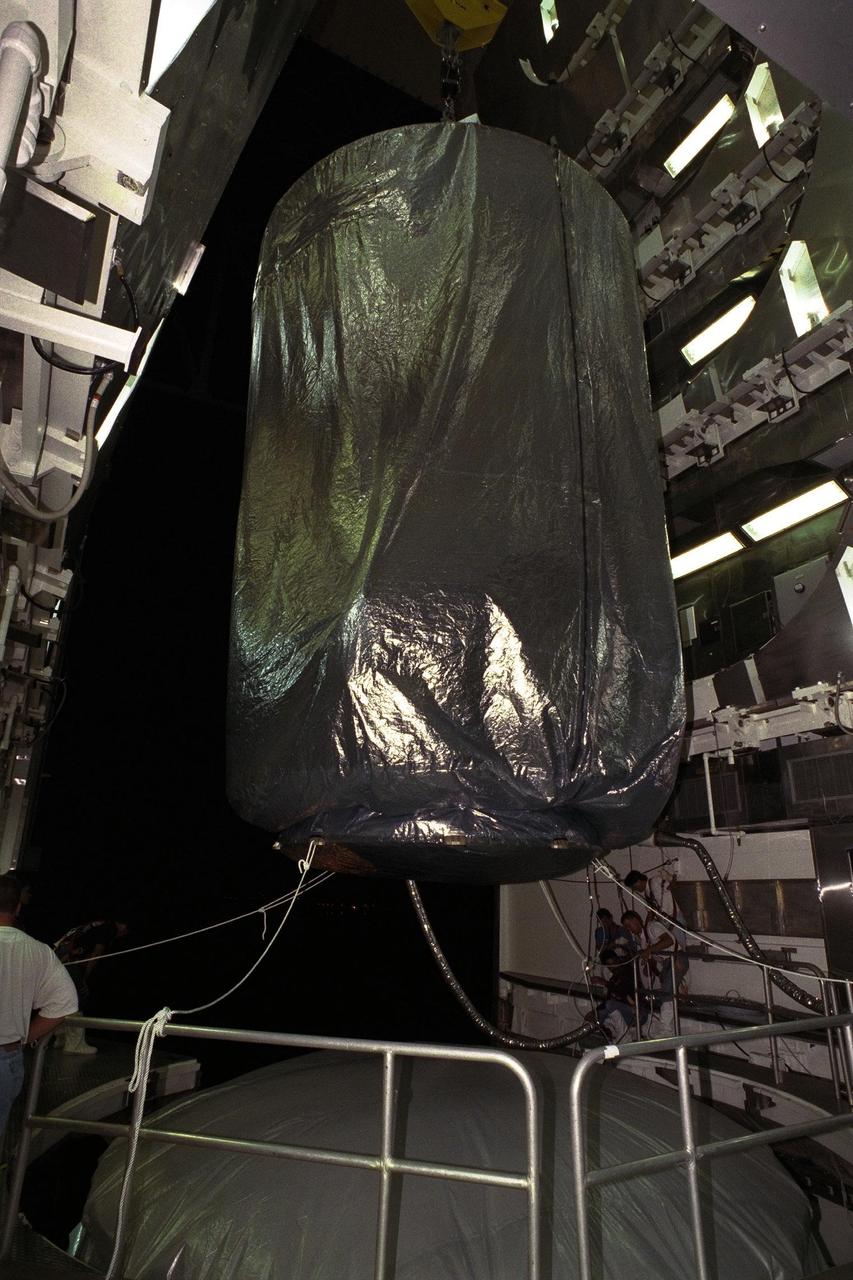

The Cassini spacecraft is lowered to the top of its Titan IV/Centaur launch vehicle at Launch Complex 40, Cape Canaveral Air Station (CCAS). Cassini is an international mission conducted by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), the European Space Agency (ESA), and the Italian Space Agency (ASI). The two-story-tall spacecraft, scheduled for launch on Oct. 6, is destined to arrive at Saturn in July 2004, where it will orbit and study Saturn, its rings, moons and magnetic environment in detail over a four-year period. The Cassini mission is managed for NASA's Office of Space Science by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology

The University of California Santa Cruz Rover Team's robot is seen prior to starting it's second attempt at the level one challenge during the 2014 NASA Centennial Challenges Sample Return Robot Challenge, Saturday, June 14, 2014, at the Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) in Worcester, Mass. Eighteen teams are competing for a $1.5 million NASA prize purse. Teams will be required to demonstrate autonomous robots that can locate and collect samples from a wide and varied terrain, operating without human control. The objective of this NASA-WPI Centennial Challenge is to encourage innovations in autonomous navigation and robotics technologies. Innovations stemming from the challenge may improve NASA's capability to explore a variety of destinations in space, as well as enhance the nation's robotic technology for use in industries and applications on Earth. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
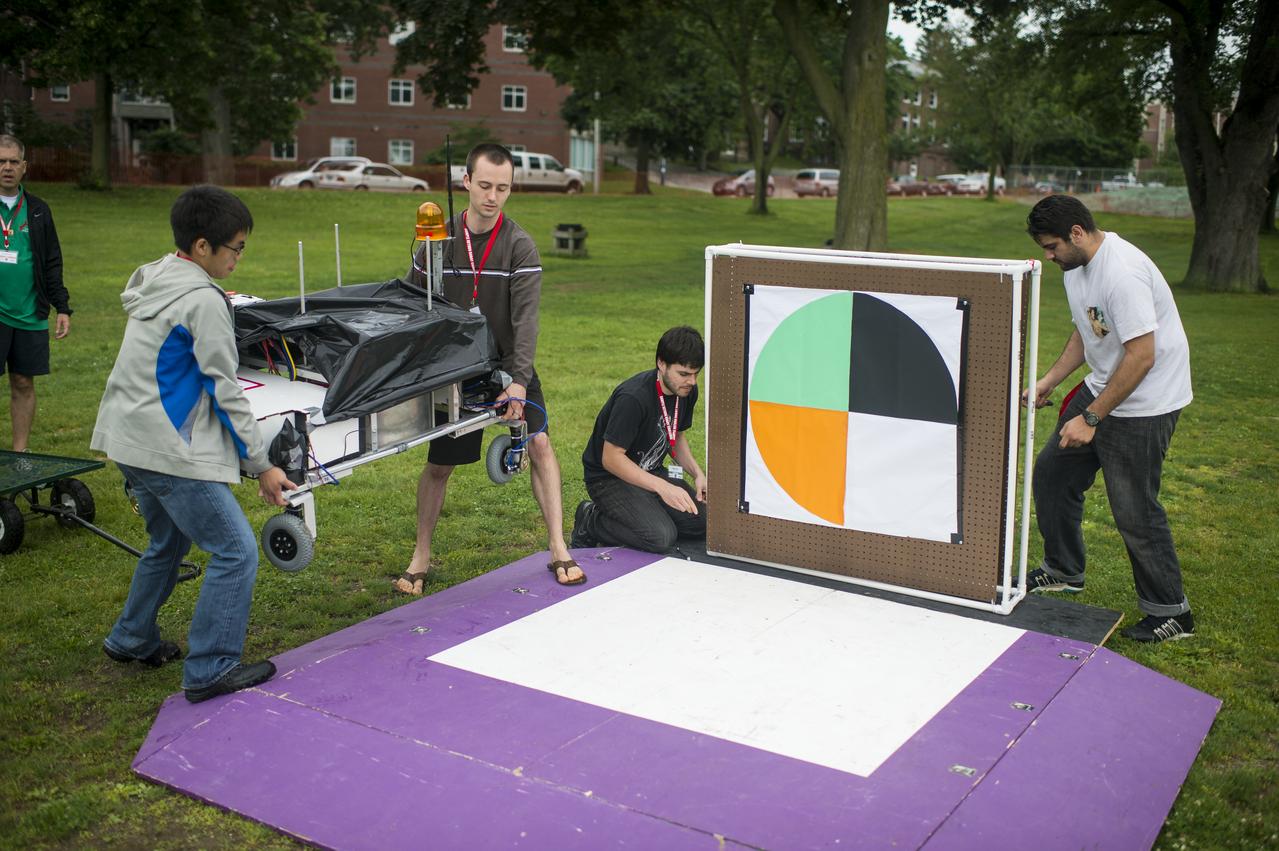

The University of California Santa Cruz Rover Team prepares their rover for the rerun of the level one challenge during the 2014 NASA Centennial Challenges Sample Return Robot Challenge, Saturday, June 14, 2014, at the Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) in Worcester, Mass. Eighteen teams are competing for a $1.5 million NASA prize purse. Teams will be required to demonstrate autonomous robots that can locate and collect samples from a wide and varied terrain, operating without human control. The objective of this NASA-WPI Centennial Challenge is to encourage innovations in autonomous navigation and robotics technologies. Innovations stemming from the challenge may improve NASA's capability to explore a variety of destinations in space, as well as enhance the nation's robotic technology for use in industries and applications on Earth. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

The University of California Santa Cruz Rover Team poses for a picture with their robot after attempting the level one challenge during the 2014 NASA Centennial Challenges Sample Return Robot Challenge, Wednesday, June 11, 2014, at the Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) in Worcester, Mass. is one of eighteen teams competing for a $1.5 million NASA prize purse. Teams will be required to demonstrate autonomous robots that can locate and collect samples from a wide and varied terrain, operating without human control. The objective of this NASA-WPI Centennial Challenge is to encourage innovations in autonomous navigation and robotics technologies. Innovations stemming from the challenge may improve NASA's capability to explore a variety of destinations in space, as well as enhance the nation's robotic technology for use in industries and applications on Earth. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
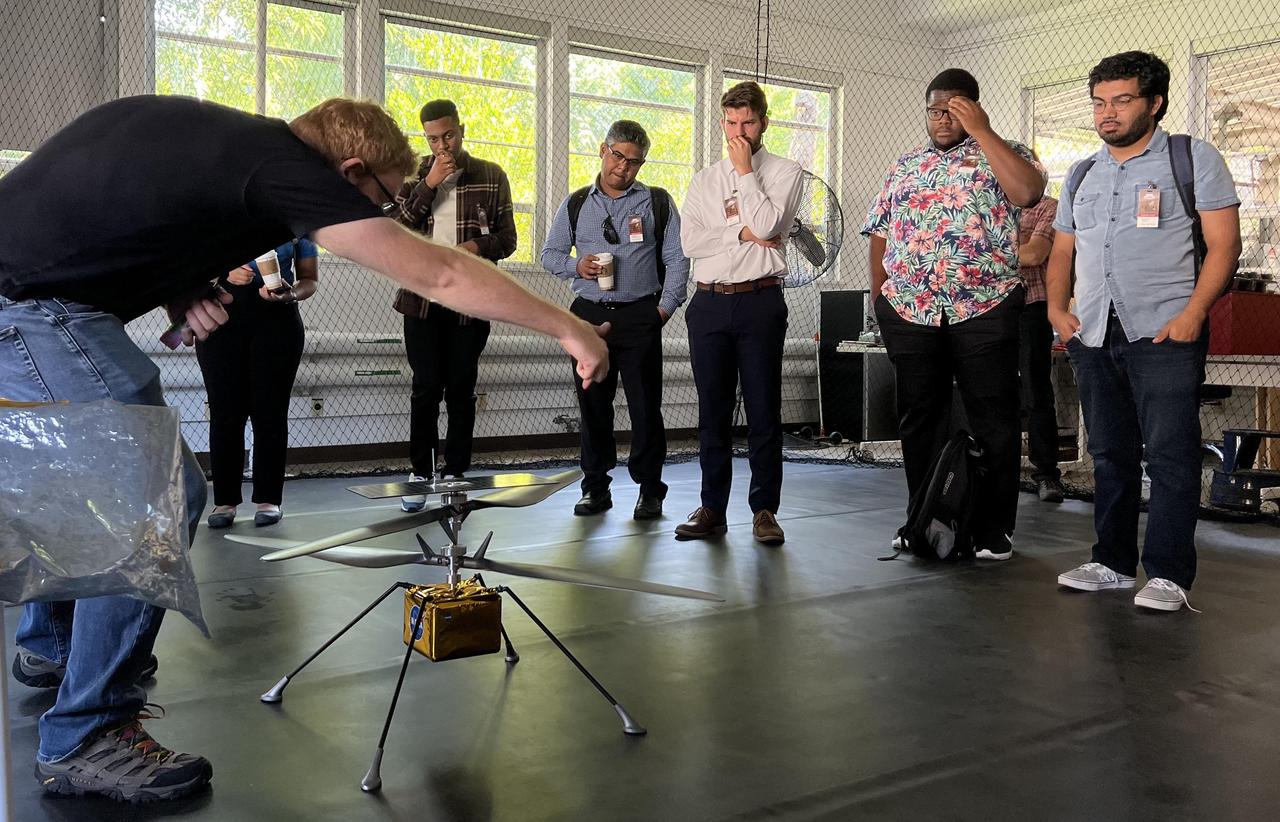

Participants in NASA's Minority Serving Institutions Space Accelerator program surround a full-scale model of NASA's Mars Ingenuity Helicopter as engineer Michael Starch discusses the mission. The group was visiting NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory on Aug. 18, 2022. These participants were members of three teams named as awardees in the first-of-its-kind accelerator program, a competition to advance the NASA's goals and meet its needs in the areas of machine learning, artificial intelligence, and development of autonomous systems while also engaging underrepresented academic institutions and reducing barriers for them to submit ideas to the agency. The program provides funding, business training through a 10-week accelerator course, and mentorship to help the teams develop ideas for systems that can operate without human oversight for future science missions in space and on Earth. The teams were made up of professors and students from Fayetteville State University in North Carolina, University of Massachusetts Boston, and California State University, Northridge. At the conclusion of the accelerator, participants arrived in Southern California for a variety of events, including two days at JPL. The program is a partnership between NASA's Science Mission Directorate, its Earth Science Technology Office, the Minority University Research Education Project within the agency's Office of STEM Engagement, JPL, and Starburst, a global aerospace accelerator company based in Los Angeles. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25315
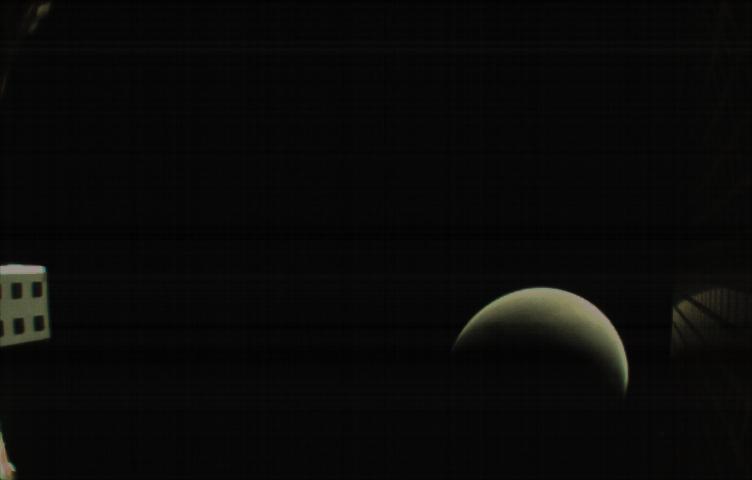

MarCO-B, one of the experimental Mars Cube One (MarCO) CubeSats, took this image of Mars from about 10,900 miles (17,500 kilometers) away just after NASA’s InSight spacecraft landed on Mars on Nov. 26, 2018. MarCO-B flew by Mars with its twin, MarCO-A, to serve as communications relays for InSight as it touched down on the Red Planet around noon PST (3 p.m. EST). This image was taken at 1 p.m. PST (4 p.m. EST). A crescent Mars with its south pole in the 4 o’clock position is visible in this picture. MarCO-B’s antenna reflector mirrors a portion of the illuminated part of Mars on the bottom right. The antenna feed (white rectangle with gold squares) is visible on the left. This image was taken about 50 minutes after PIA22833 and 10 seconds after PIA22832. The MarCO and InSight projects are managed for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington, by JPL, a division of Caltech, Pasadena. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
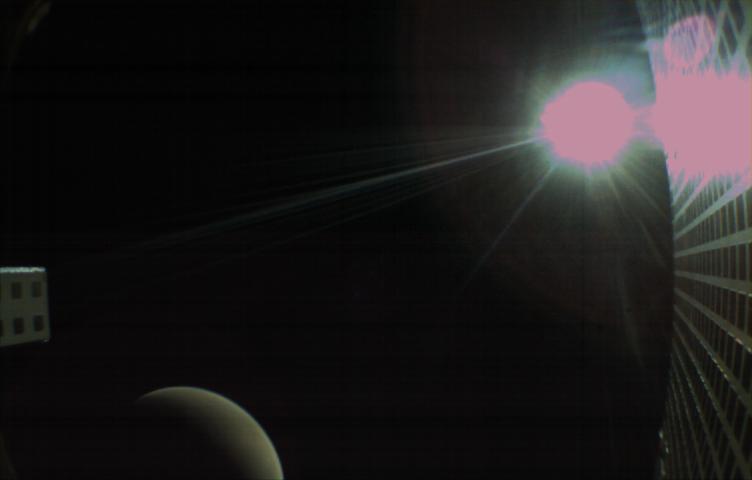

MarCO-B, one of the experimental Mars Cube One (MarCO) CubeSats, took this image of Mars from about 10,900 miles (17,500 kilometers) away just after NASA’s InSight spacecraft landed on Mars on Nov. 26, 2018. MarCO-B flew by Mars with its twin, MarCO-A, to serve as communications relays for InSight as it touched down on the Red Planet around noon PST (3 p.m. EST). This image was taken at 1 p.m. PST (4 p.m. EST). Mars’ south pole is facing the viewer in this image. MarCO-B’s antenna reflector is on the right and antenna feed (white rectangle with gold square) is on the left. The Sun at upper right overexposed part of the image. This image was taken after PIA22833 and shortly before PIA22834. The MarCO and InSight projects are managed for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington, by JPL, a division of Caltech, Pasadena. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech

DC Agle, with NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, moderates a Mars 2020 Mission Engineering and Science Briefing at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 27, 2020. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch July 30, on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at nearby Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.

Lori Glaze, Planetary Science Division director, NASA Headquarters, participates in a Mars 2020 Mission Engineering and Science Briefing at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 27, 2020. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch July 30, on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at nearby Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.

This view of a test rover at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, results from advance testing of arm positions and camera pointings for taking a low-angle self-portrait of NASA's Curiosity Mars rover. This rehearsal in California led to a dramatic Aug. 5, 2015, selfie of Curiosity, online at PIA19807. Curiosity's arm-mounted Mars Hand Lens Imager (MAHLI) camera took 92 of component images that were assembled into that mosaic. The rover team positioned the camera lower in relation to the rover body than for any previous full self-portrait of Curiosity. This practice version was taken at JPL's Mars Yard in July 2013, using the Vehicle System Test Bed (VSTB) rover, which has a test copy of MAHLI on its robotic arm. MAHLI was built by Malin Space Science Systems, San Diego. JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, manages the Mars Science Laboratory Project for the NASA Science Mission Directorate, Washington. JPL designed and built the project's Curiosity rover. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19810
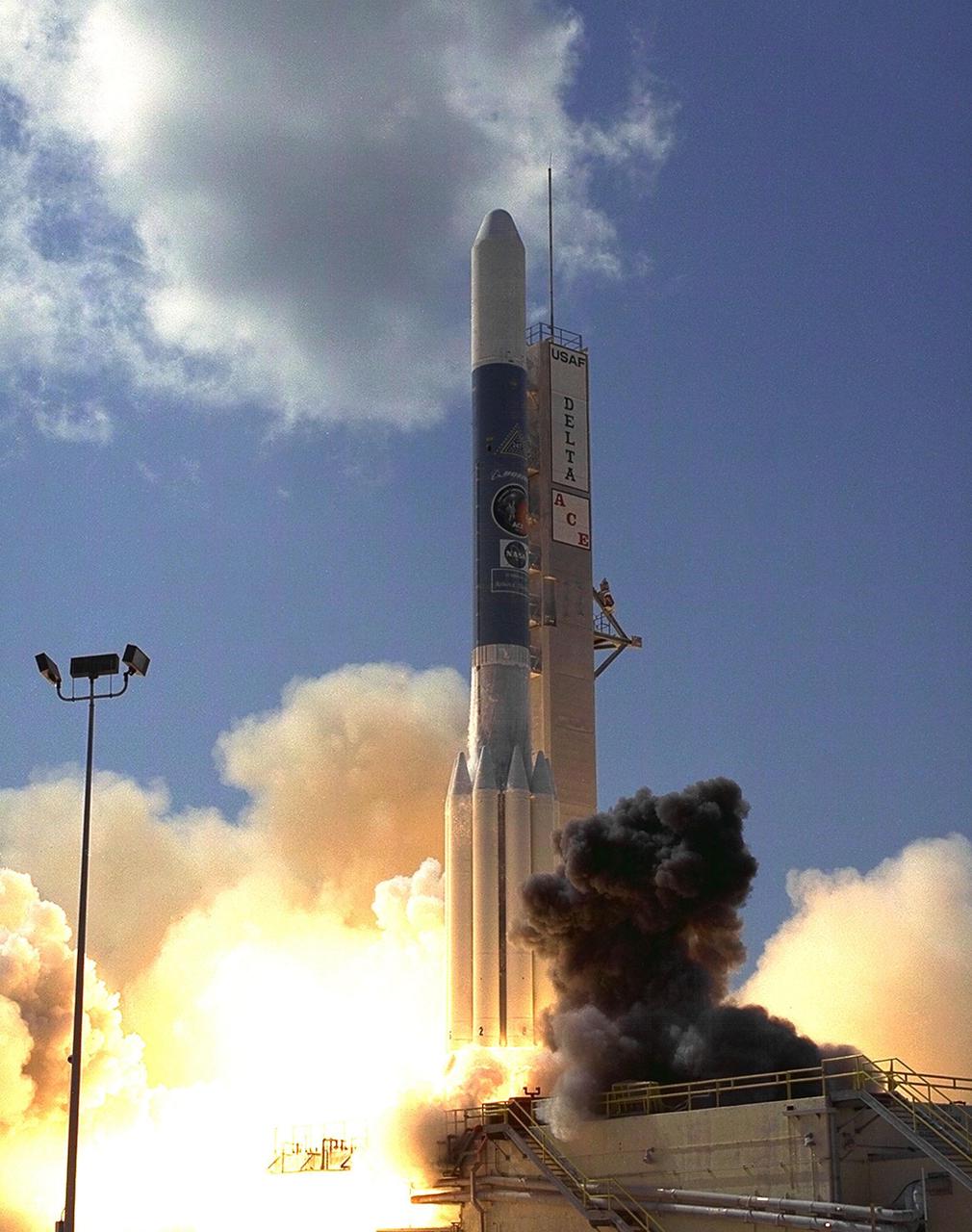

A Boeing Delta II expendable launch vehicle lifts off with NASA’s Advanced Composition Explorer (ACE) observatory at 10:39 a.m. EDT, on Aug. 25, 1997, from Launch Complex 17A, Cape Canaveral Air Station. This is the second Delta launch under the Boeing name and the first from Cape Canaveral. Launch was scrubbed one day by Air Force range safety personnel because two commercial fishing vessels were within the Delta’s launch danger area. The ACE spacecraft will study low-energy particles of solar origin and high-energy galactic particles on its one-million-mile journey. The collecting power of instruments aboard ACE is 10 to 1,000 times greater than anything previously flown to collect similar data by NASA. Study of these energetic particles may contribute to our understanding of the formation and evolution of the solar system. ACE has a two-year minimum mission lifetime and a goal of five years of service. ACE was built for NASA by the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory and is managed by the Explorer Project Office at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center. The lead scientific institution is the California Institute of Technology (Caltech) in Pasadena, Calif

Photographers and other onlookers watch as a Boeing Delta II expendable launch vehicle lifts off with NASA’s Advanced Composition Explorer (ACE) observatory at 10:39 a.m. EDT, on Aug. 25, 1997, from Launch Complex 17A, Cape Canaveral Air Station. This is the second Delta launch under the Boeing name and the first from Cape Canaveral. Liftoff had been scheduled for Aug. 24, but was scrubbed one day by Air Force range safety personnel because two commercial fishing vessels were within the Delta’s launch danger area. The ACE spacecraft will study low-energy particles of solar origin and high-energy galactic particles on its one-million-mile journey. The collecting power of instruments aboard ACE is 10 to 1,000 times greater than anything previously flown to collect similar data by NASA. Study of these energetic particles may contribute to our understanding of the formation and evolution of the solar system. ACE has a two-year minimum mission lifetime and a goal of five years of service. ACE was built for NASA by the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory and is managed by the Explorer Project Office at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center. The lead scientific institution is the California Institute of Technology (Caltech) in Pasadena, Calif
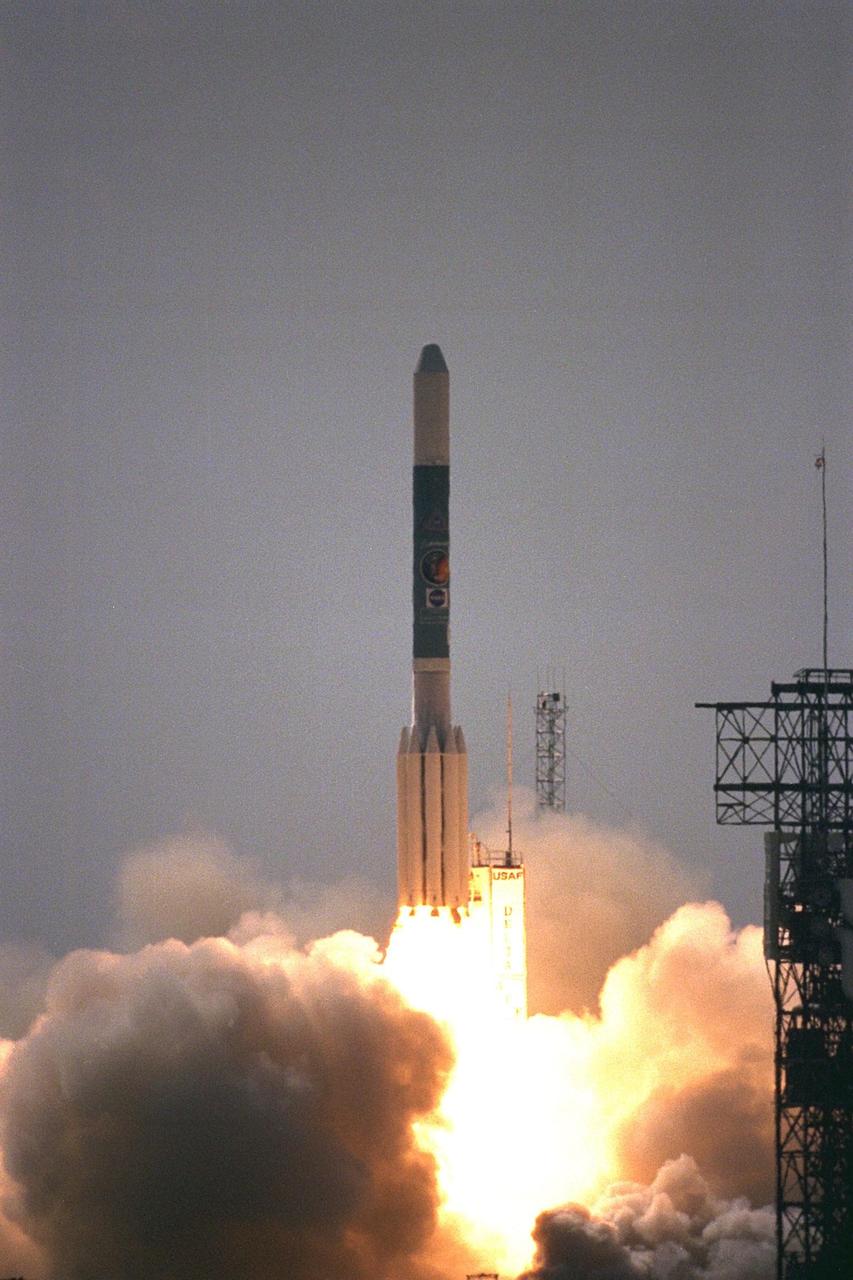

A Boeing Delta II expendable launch vehicle lifts off with NASA’s Advanced Composition Explorer (ACE) observatory at 10:39 a.m. EDT, on Aug. 25, 1997, from Launch Complex 17A, Cape Canaveral Air Station. This is the second Delta launch under the Boeing name and the first from Cape Canaveral. Launch was scrubbed one day by Air Force range safety personnel because two commercial fishing vessels were within the Delta’s launch danger area. The ACE spacecraft will study low-energy particles of solar origin and high-energy galactic particles on its one-million-mile journey. The collecting power of instruments aboard ACE is 10 to 1,000 times greater than anything previously flown to collect similar data by NASA. Study of these energetic particles may contribute to our understanding of the formation and evolution of the solar system. ACE has a two-year minimum mission lifetime and a goal of five years of service. ACE was built for NASA by the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory and is managed by the Explorer Project Office at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center. The lead scientific institution is the California Institute of Technology (Caltech) in Pasadena, Calif
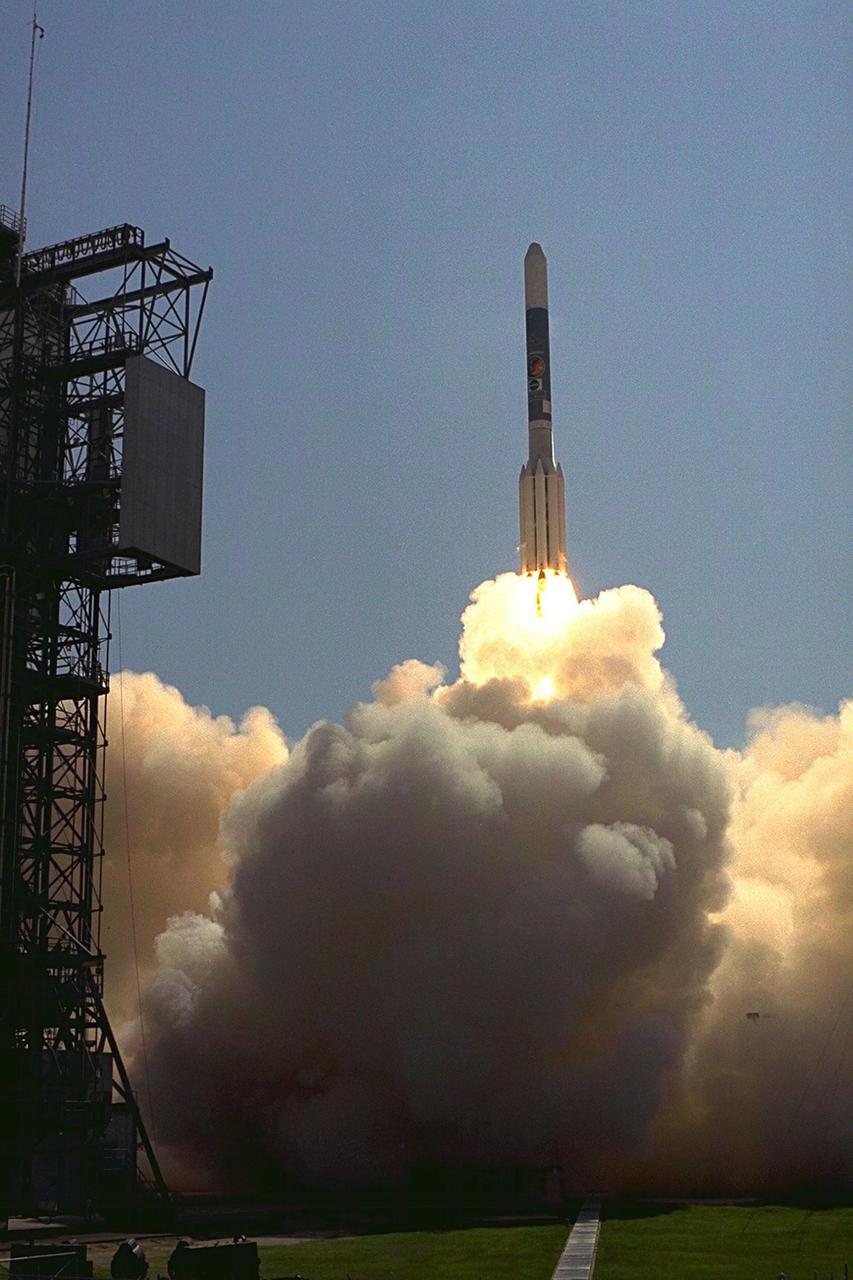

A Boeing Delta II expendable launch vehicle lifts off with NASA’s Advanced Composition Explorer (ACE) observatory at 10:39 a.m. EDT, on Aug. 25, 1997, from Launch Complex 17A, Cape Canaveral Air Station. This is the second Delta launch under the Boeing name and the first from Cape Canaveral. Launch was scrubbed one day by Air Force range safety personnel because two commercial fishing vessels were within the Delta’s launch danger area. The ACE spacecraft will study low-energy particles of solar origin and high-energy galactic particles on its one-million-mile journey. The collecting power of instruments aboard ACE is 10 to 1,000 times greater than anything previously flown to collect similar data by NASA. Study of these energetic particles may contribute to our understanding of the formation and evolution of the solar system. ACE has a two-year minimum mission lifetime and a goal of five years of service. ACE was built for NASA by the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory and is managed by the Explorer Project Office at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center. The lead scientific institution is the California Institute of Technology (Caltech) in Pasadena, Calif
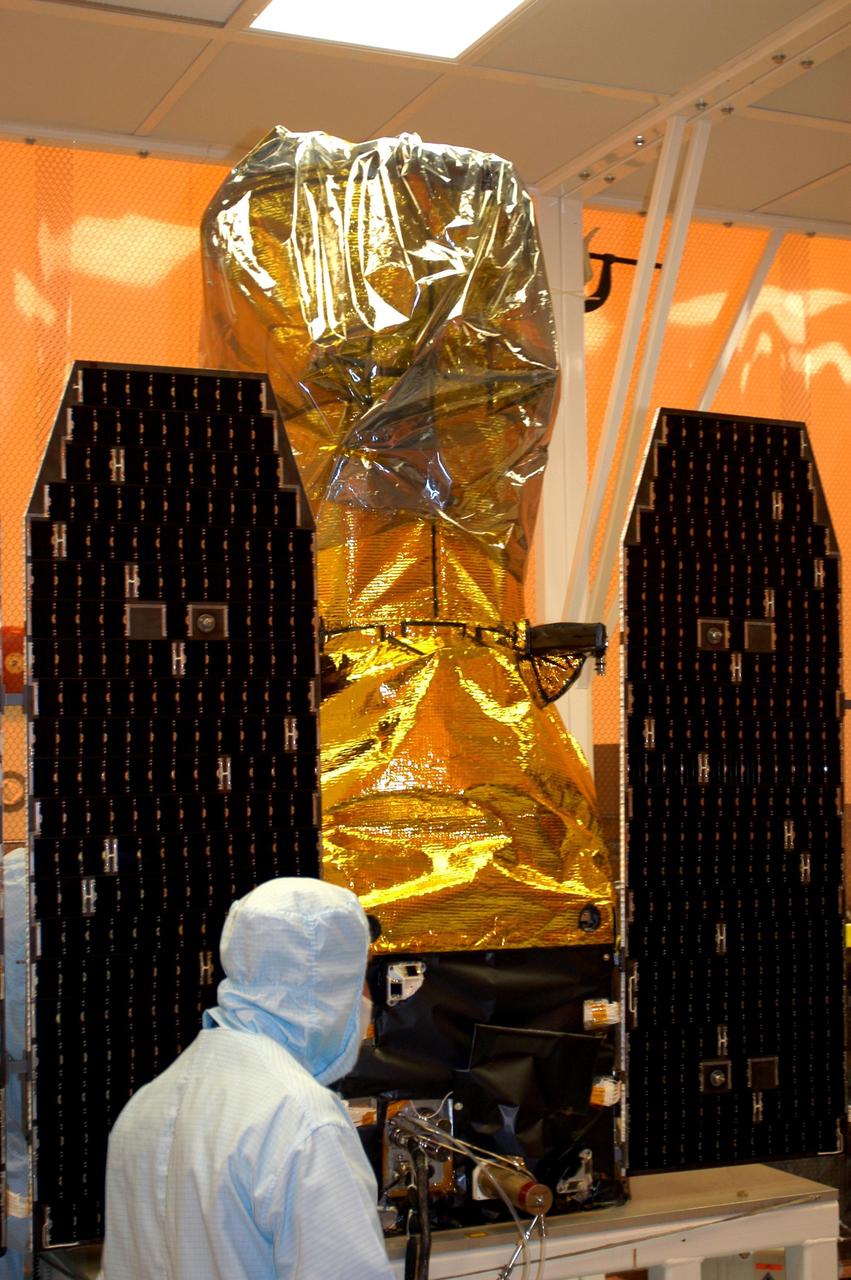

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The solar array panels on the Galaxy Evolution Explorer (GALEX) satellite are deployed during processing in the Multi-Payload Processing Facility. The GALEX is an orbiting space telescope that will observe galaxies in ultraviolet light across 10 billion years of cosmic history. Led by the California Institute of Technology, GALEX will conduct several first-of-a-kind sky surveys, including an extra-galactic (beyond our galaxy) ultraviolet all-sky survey. During its 29-month mission GALEX will produce the first comprehensive map of a Universe of galaxies under construction, bringing more understanding of how galaxies like the Milky Way were formed. GALEX is due to be launched from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station March 25 via a Pegasus rocket.
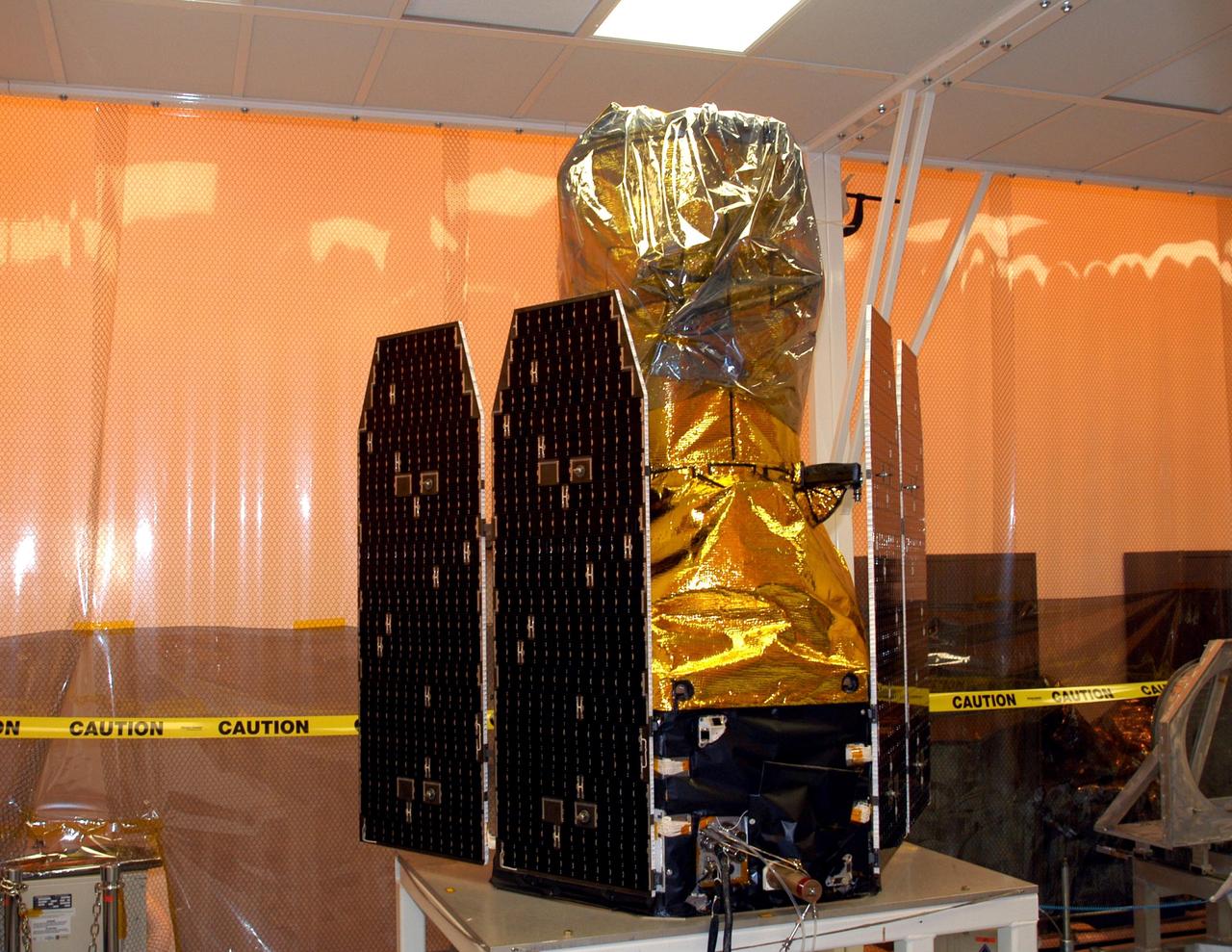

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Galaxy Evolution Explorer (GALEX) satellite is ready for deployment of its solar array panels during processing in the Multi-Payload Processing Facility. The GALEX is an orbiting space telescope that will observe galaxies in ultraviolet light across 10 billion years of cosmic history. Led by the California Institute of Technology, GALEX will conduct several first-of-a-kind sky surveys, including an extra-galactic (beyond our galaxy) ultraviolet all-sky survey. During its 29-month mission GALEX will produce the first comprehensive map of a Universe of galaxies under construction, bringing more understanding of how galaxies like the Milky Way were formed. GALEX is due to be launched from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station March 25 via a Pegasus rocket.
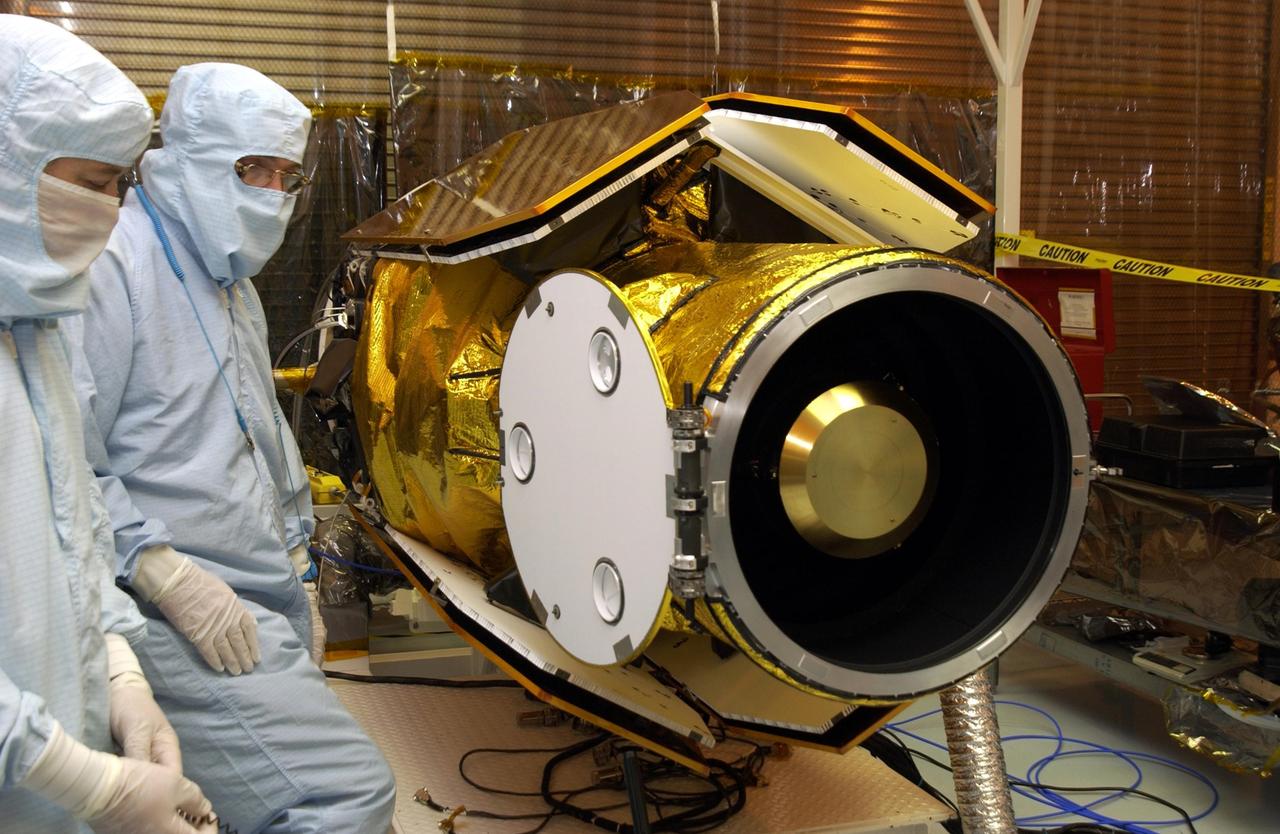

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Multi-Payload Processing Facility, workers check the deployment of the cover of the telescope on the GALEX satellite. The Galaxy Evolution Explorer (GALEX) is an orbiting space telescope that will observe galaxies in ultraviolet light across 10 billion years of cosmic history. Led by the California Institute of Technology, GALEX will conduct several first-of-a-kind sky surveys, including an extra-galactic (beyond our galaxy) ultraviolet all-sky survey. During its 29-month mission GALEX will produce the first comprehensive map of a Universe of galaxies under construction, bringing more understanding of how galaxies like the Milky Way were formed. GALEX is due to be launched from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station March 25 via a Pegasus rocket.
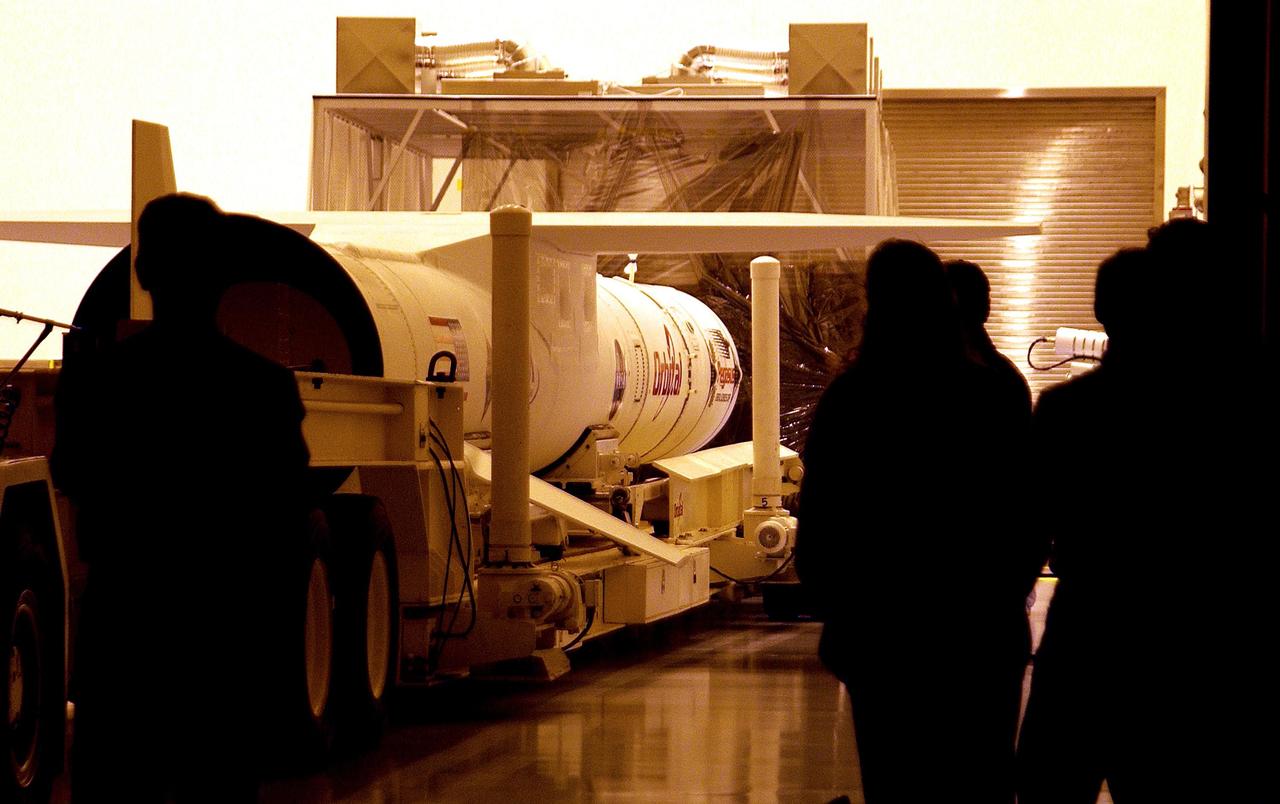

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Pegasus launch vehicle is inside the Multi-Payload Processing Facility (MPPF) at KSC. There it will be mated to the Galaxy Evolution Explorer (GALEX). The Pegasus will carry into orbit the GALEX, a space telescope that will observe galaxies in ultraviolet light across 10 billion years of cosmic history. Led by the California Institute of Technology, GALEX will conduct several first-of-a-kind sky surveys, including an extra-galactic (beyond our galaxy) ultraviolet all-sky survey. During its 29-month mission GALEX will produce the first comprehensive map of a Universe of galaxies under construction, bringing more understanding of how galaxies like the Milky Way were formed. GALEX is due to be launched from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station March 25.
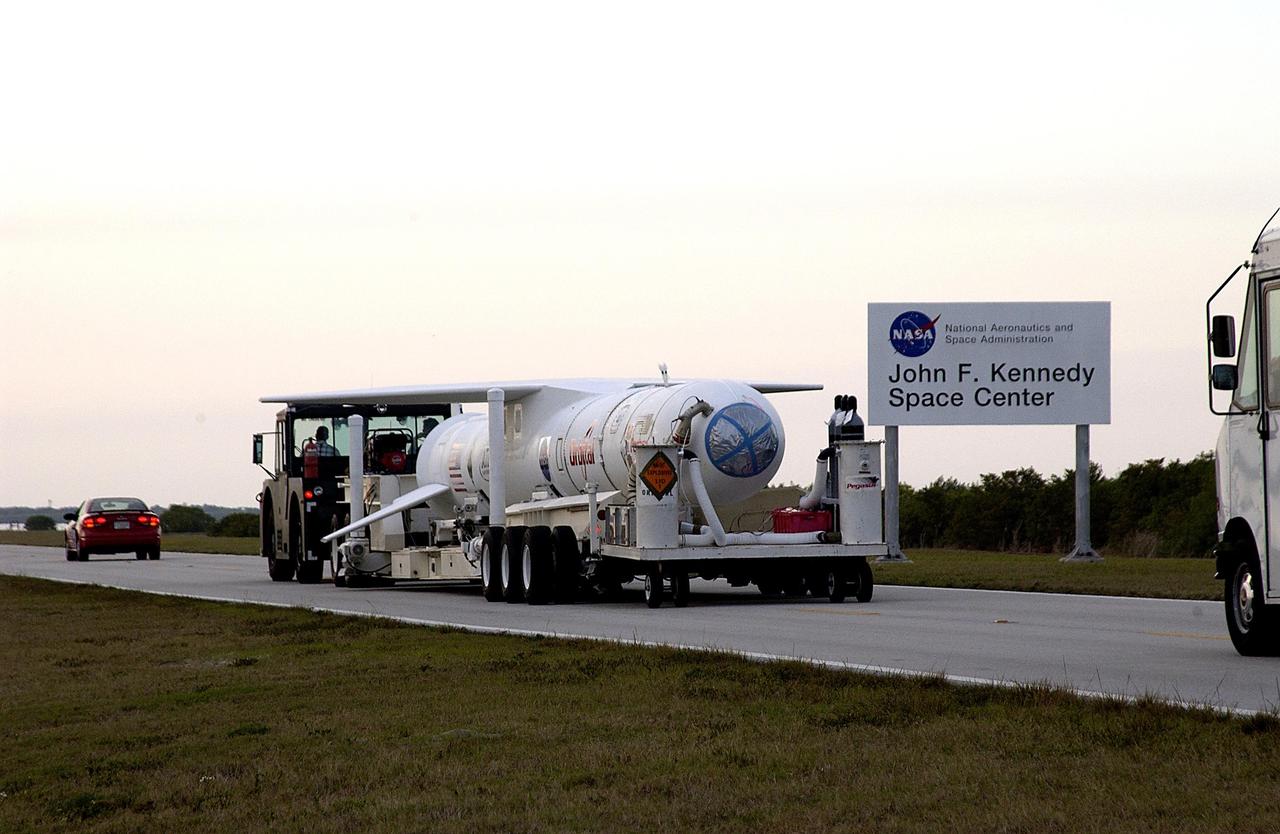

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Pegasus launch vehicle is moved from the Skid Strip, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, to the Multi-Payload Processing Facility (MPPF) at KSC. There it will be mated to the Galaxy Evolution Explorer (GALEX). The Pegasus will carry into orbit the GALEX, a space telescope that will observe galaxies in ultraviolet light across 10 billion years of cosmic history. Led by the California Institute of Technology, GALEX will conduct several first-of-a-kind sky surveys, including an extra-galactic (beyond our galaxy) ultraviolet all-sky survey. During its 29-month mission GALEX will produce the first comprehensive map of a Universe of galaxies under construction, bringing more understanding of how galaxies like the Milky Way were formed. GALEX is due to be launched from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station March 25.
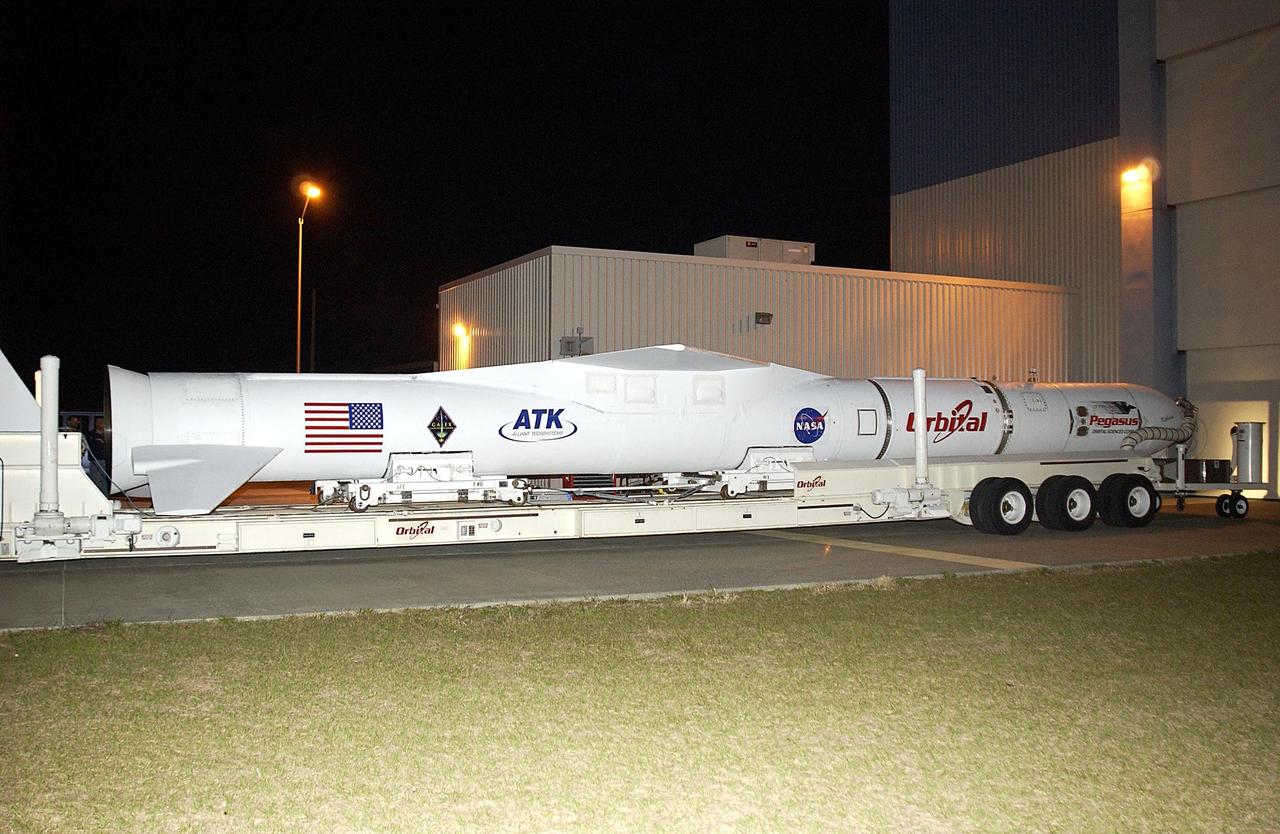

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - As darkness falls, the Pegasus launch vehicle arrives at the Multi-Payload Processing Facility (MPPF) at KSC. There it will be mated to the Galaxy Evolution Explorer (GALEX). The Pegasus will carry into orbit the GALEX, a space telescope that will observe galaxies in ultraviolet light across 10 billion years of cosmic history. Led by the California Institute of Technology, GALEX will conduct several first-of-a-kind sky surveys, including an extra-galactic (beyond our galaxy) ultraviolet all-sky survey. During its 29-month mission GALEX will produce the first comprehensive map of a Universe of galaxies under construction, bringing more understanding of how galaxies like the Milky Way were formed. GALEX is due to be launched from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station March 25.
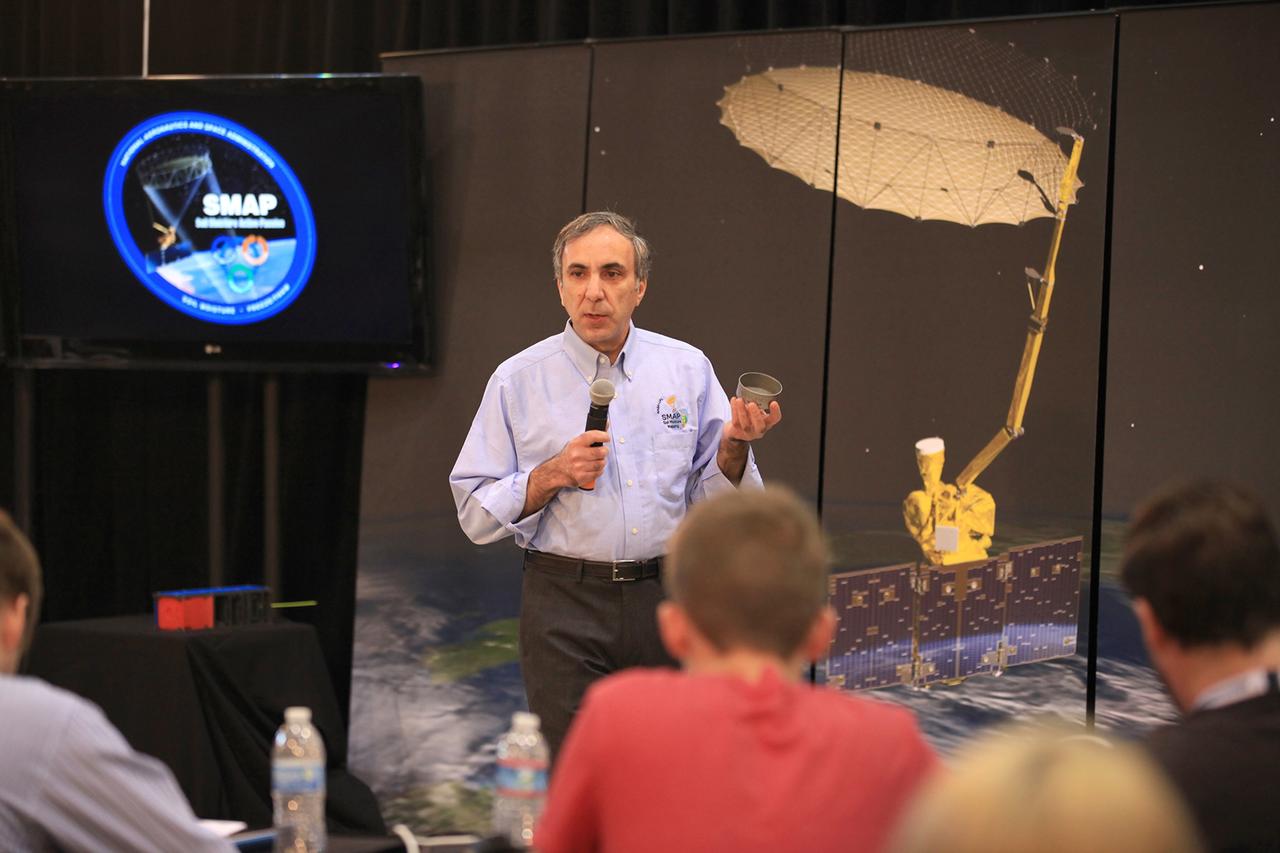

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Dara Entekhabi, science team leader at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in Cambridge, Massachusetts, discusses the science and engineering of NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive mission, or SMAP, with the audience of a NASA Social held at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. This NASA Social brought together mission scientists and engineers with an audience of 70 students, educators, social media managers, bloggers, photographers and videographers who were selected from a pool of 325 applicants from 45 countries to participate in launch activities and communicate their experience with social media followers. The SMAP mission is scheduled to launch from Vandenberg on Jan. 29. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://www.nasa.gov/smap. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett