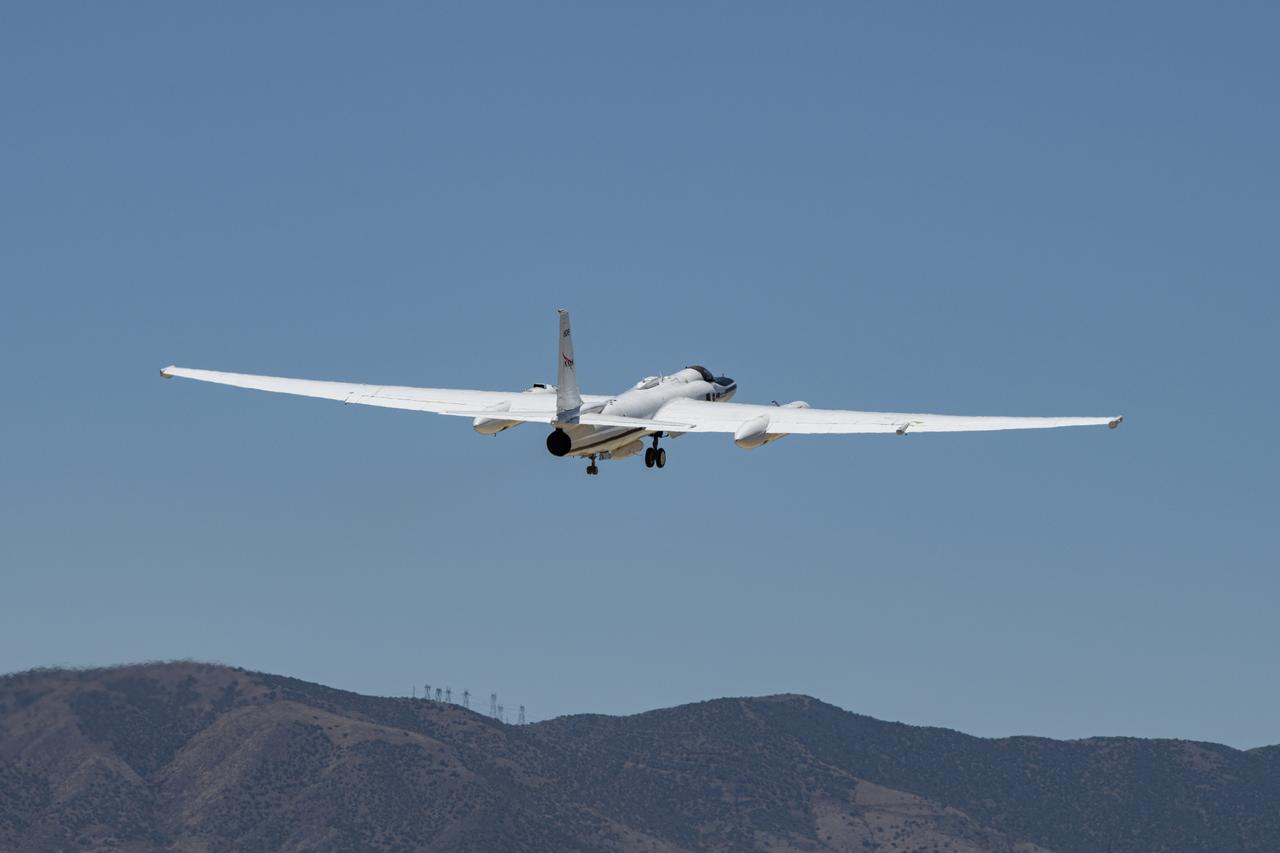

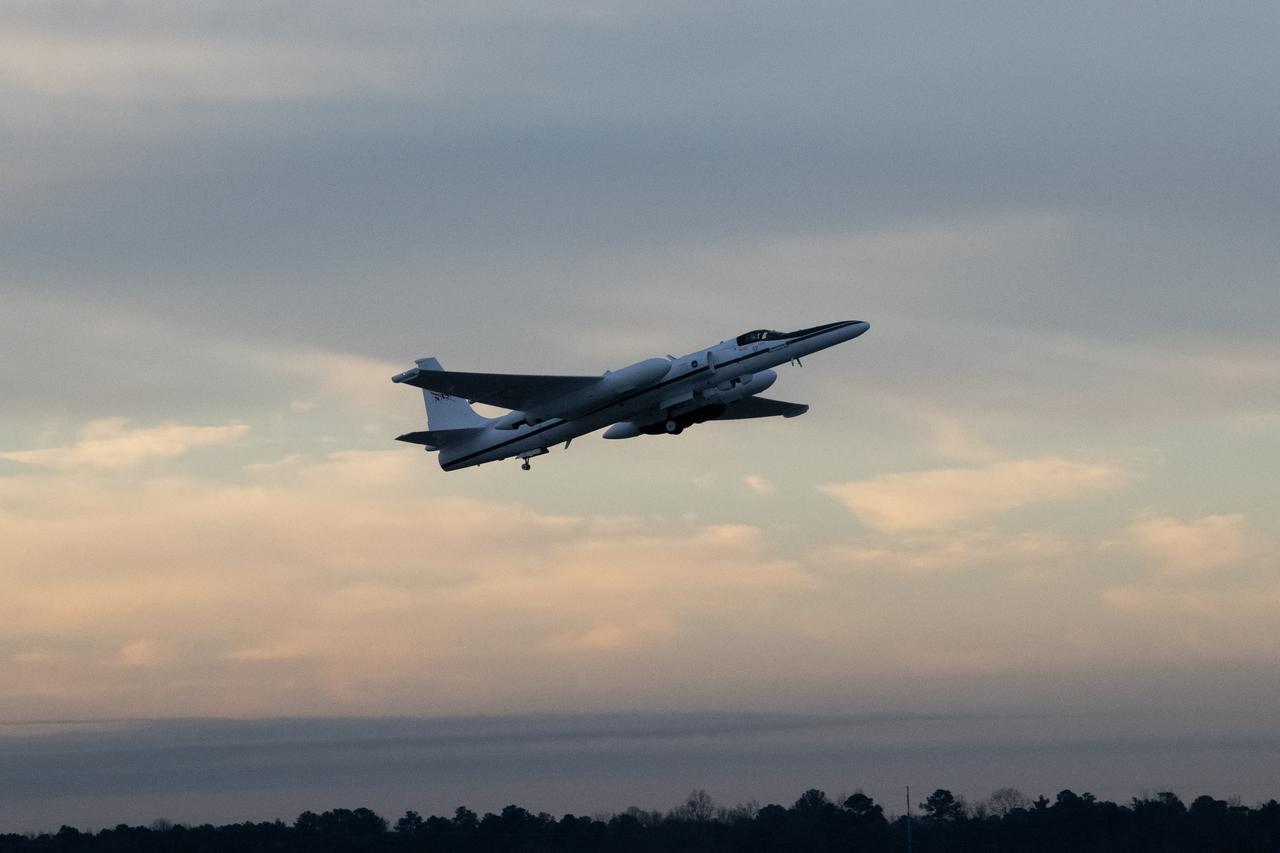
NASA’s ER-2 aircraft performs a check flight for the Dynamics and Chemistry of the Summer Stratosphere, or DCOTSS, 2022 campaign on May 13, 2022.
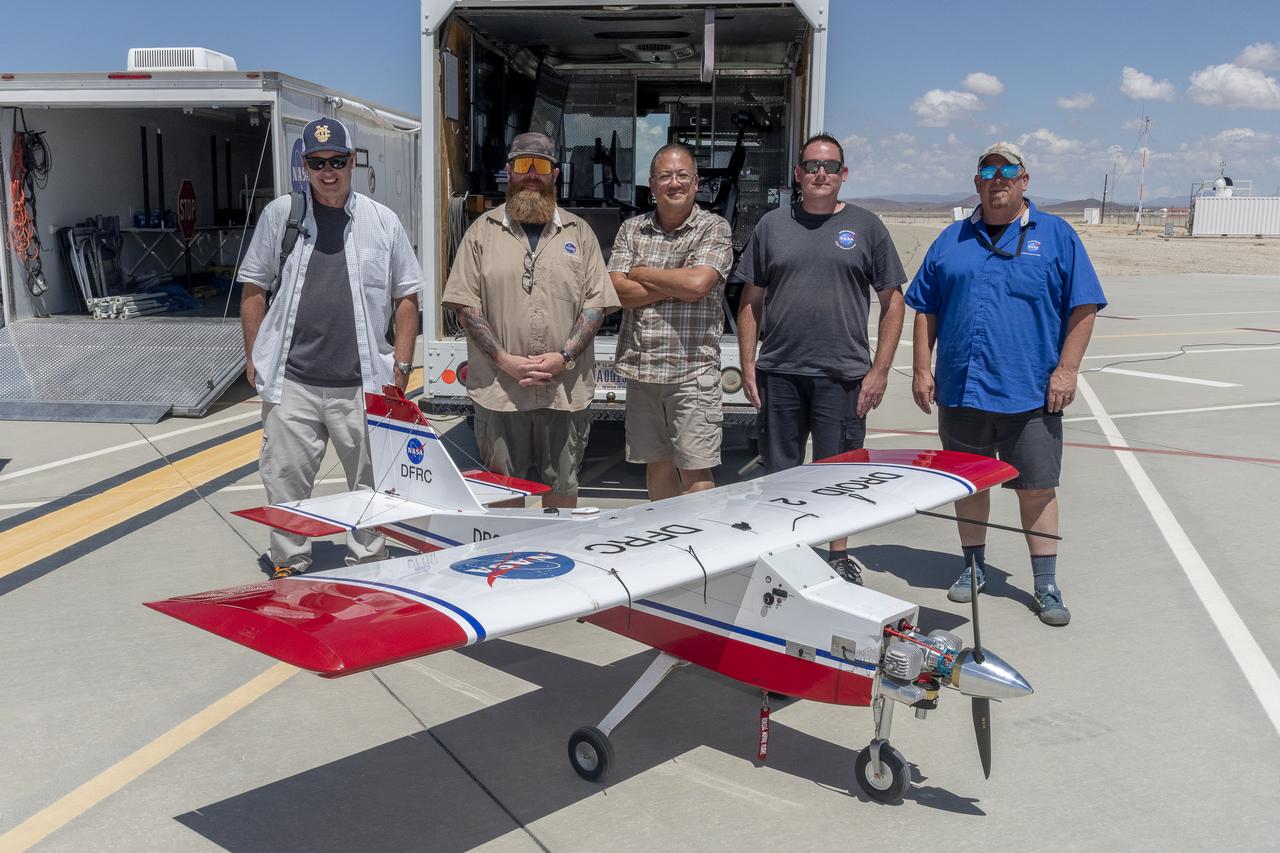

John Melton, Justin Hall, Derek Abramson, Justin Link, and Robert "Red" Jensen were key on mission day for the Advanced Exploration of Reliable Operation at Low Altitudes: Meteorology, Simulation, and Technology campaign. The DROID 2 (Dryden Remotely Operated Integrated Drone 2) aircraft supported the campaign at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. The focus was to study wind to provide data for safe takeoff and landing of future air taxis.
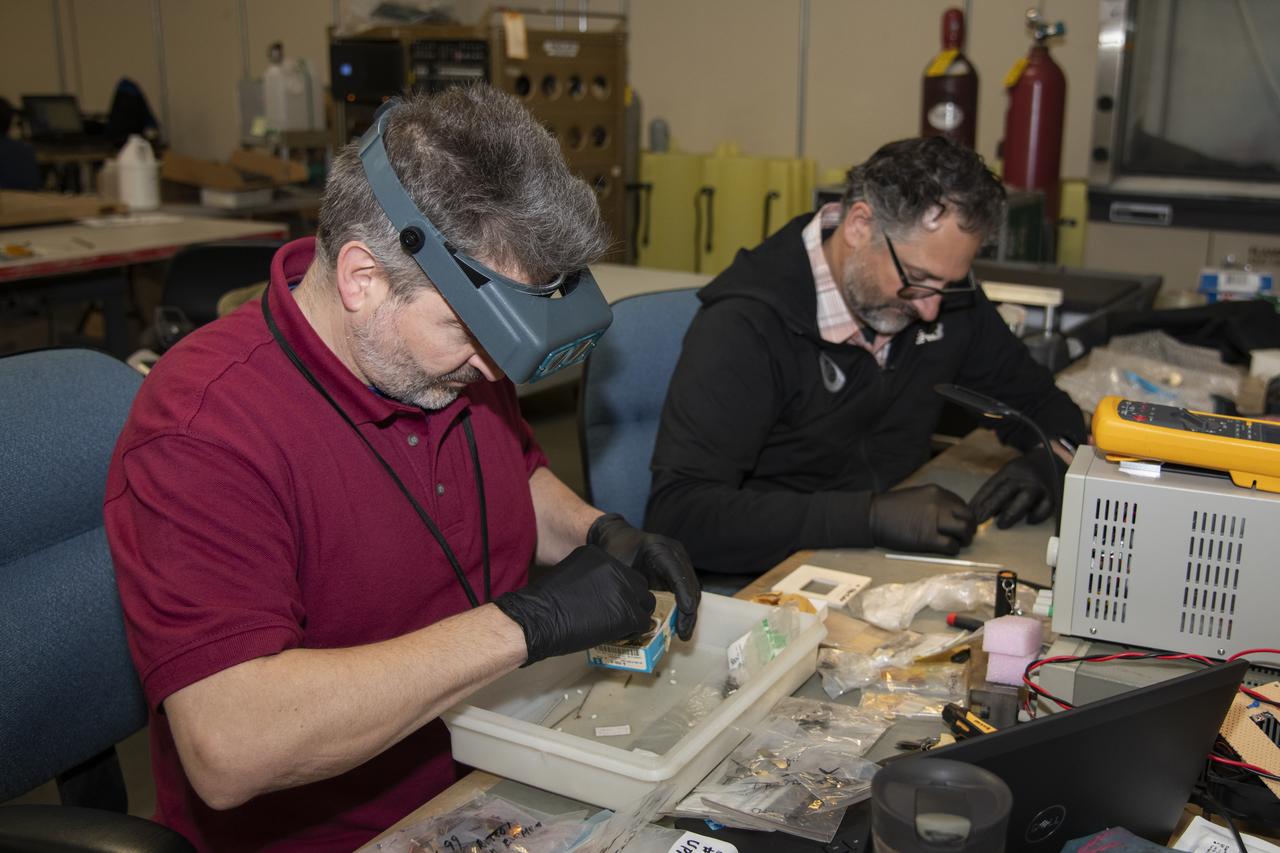

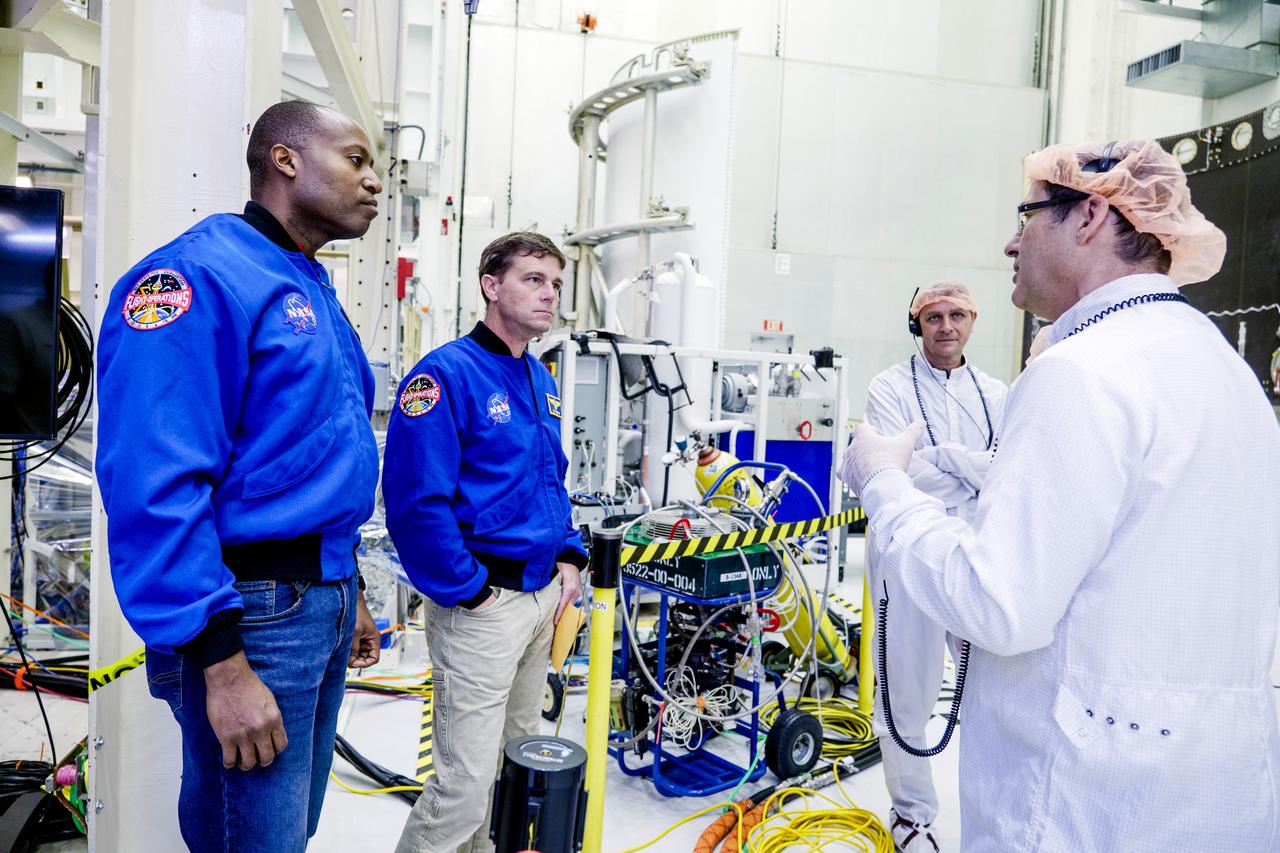
The Harvard Halogen Instrument (HAL) is prepared for integration on NASA's ER-2 by electrical engineer Marco Rivero and mechanical engineer Michael Greenberg for the Dynamics and Chemistry of the Summer Stratosphere, or DCOTSS, 2022 campaign.
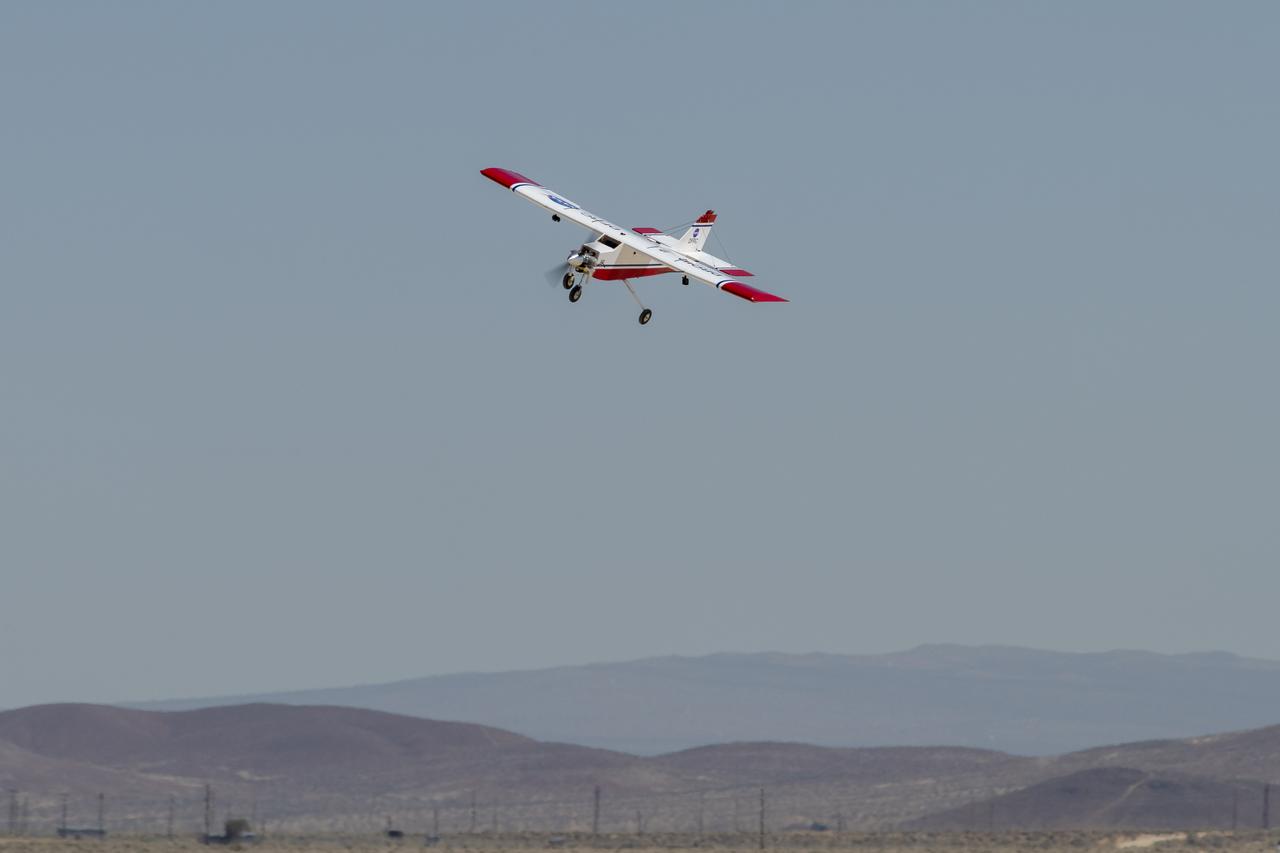

The DROID 2 (Dryden Remotely Operated Integrated Drone 2) flies at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, as part of the Advanced Exploration of Reliable Operation at Low Altitudes: Meteorology, Simulation, and Technology campaign. The focus was to study wind to provide data for safe takeoff and landing of future air taxis.
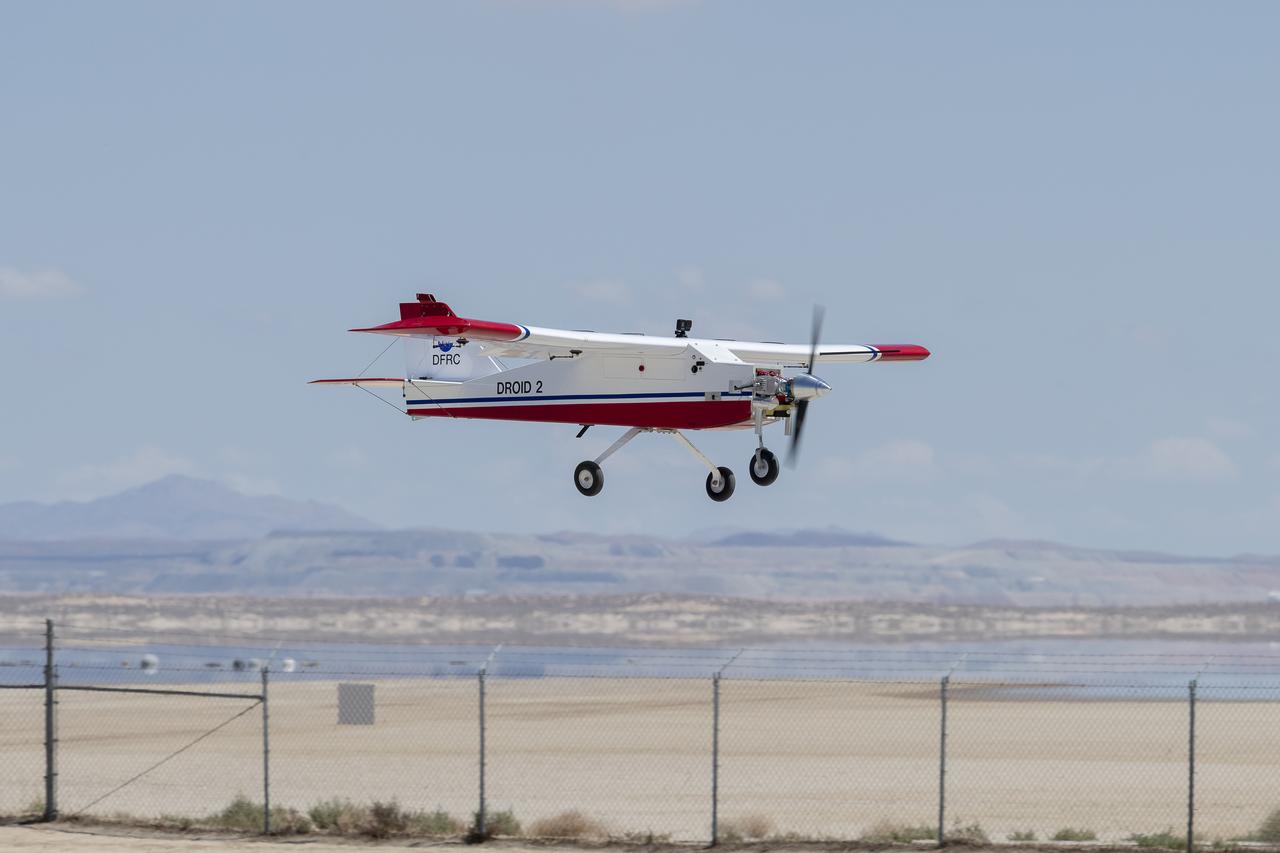

The DROID 2 (Dryden Remotely Operated Integrated Drone 2) prepares to land at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, as part of the Advanced Exploration of Reliable Operation at Low Altitudes: Meteorology, Simulation, and Technology campaign. The focus was to study wind to provide data for safe takeoff and landing of future air taxis.
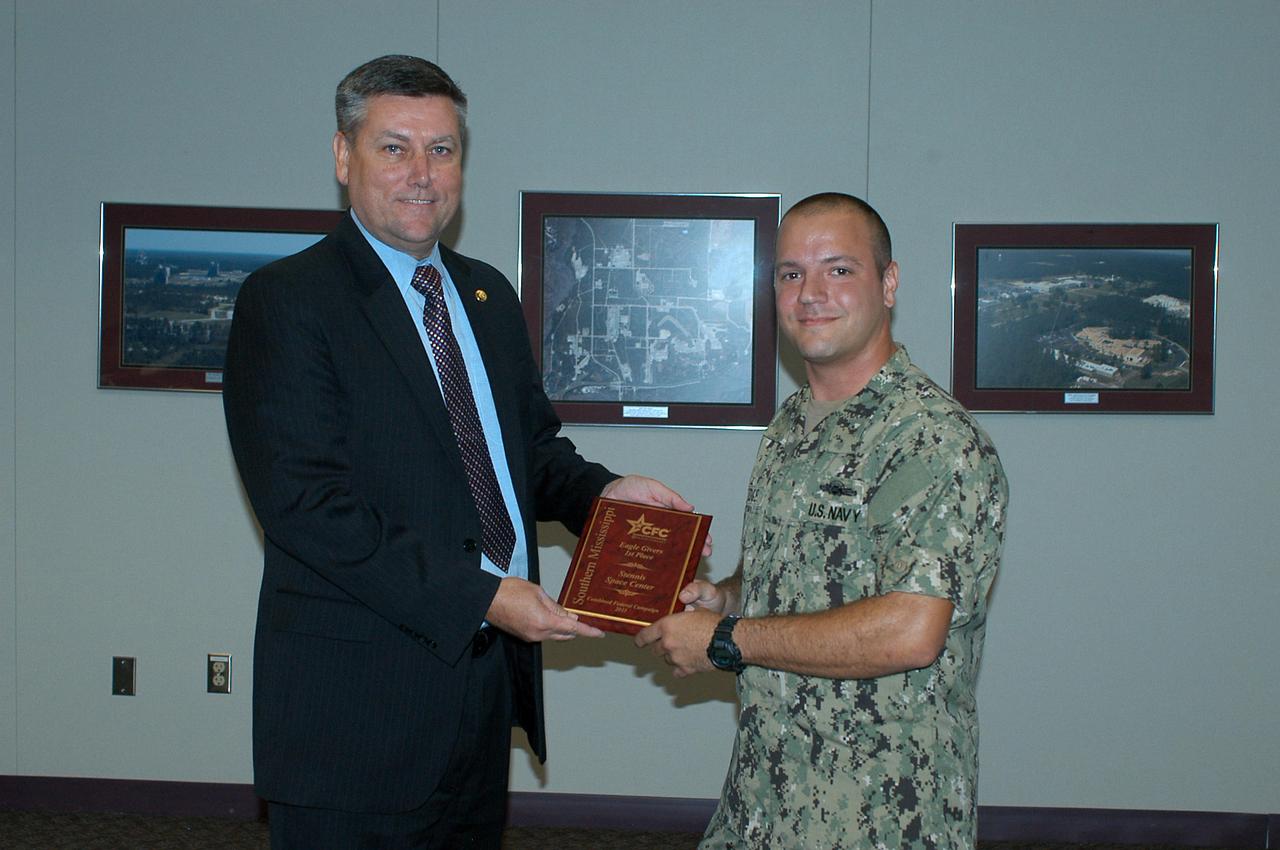

U.S. Navy HT 2 Ryan Vinnedge (right) presents a Combined Federal Campaign award to Stennis Space Center Director Patrick Scheuermann during a May 16, 2012, ceremony. Stennis employees led the way in two categories in the 2011 Southern Mississippi CFC effort, ranking first in the number of Eagle Givers (more than $480 each) and in dollar increase of contributions. Stennis Space Center employees contributed $221,000 through the campaign.
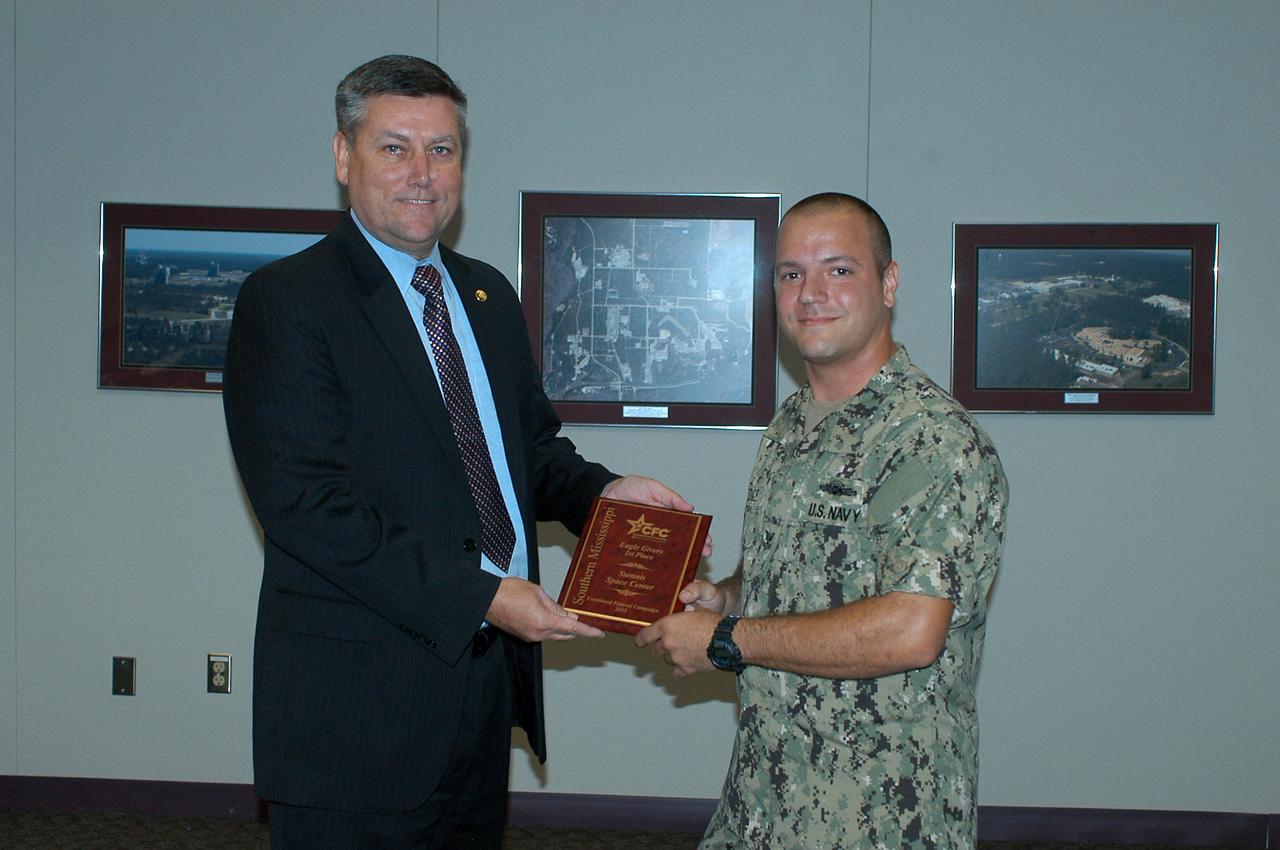

U.S. Navy HT 2 Ryan Vinnedge (right) presents a Combined Federal Campaign award to Stennis Space Center Director Patrick Scheuermann during a May 16, 2012, ceremony. Stennis employees led the way in two categories in the 2011 Southern Mississippi CFC effort, ranking first in the number of Eagle Givers (more than $480 each) and in dollar increase of contributions. Stennis Space Center employees contributed $221,000 through the campaign.
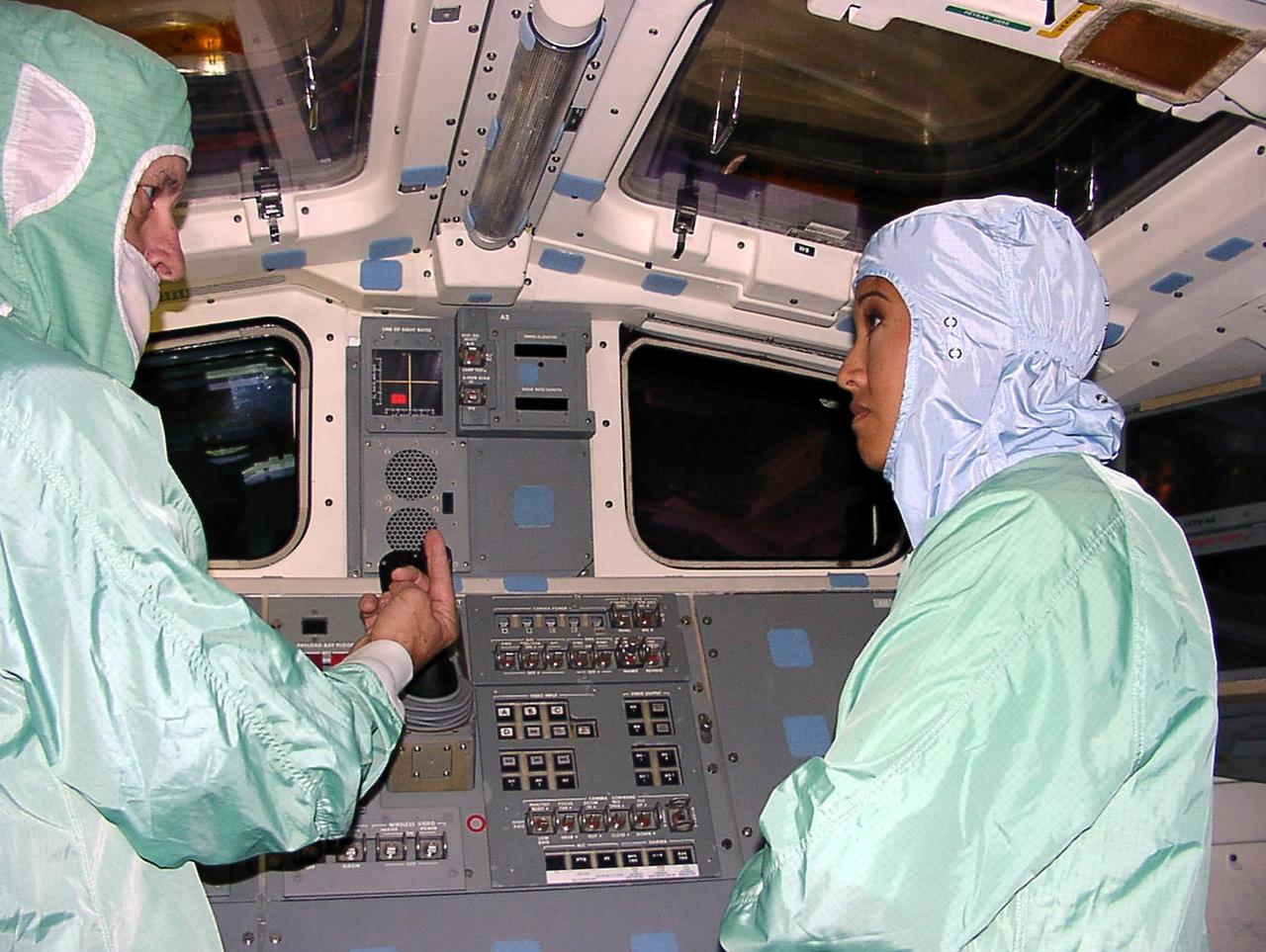

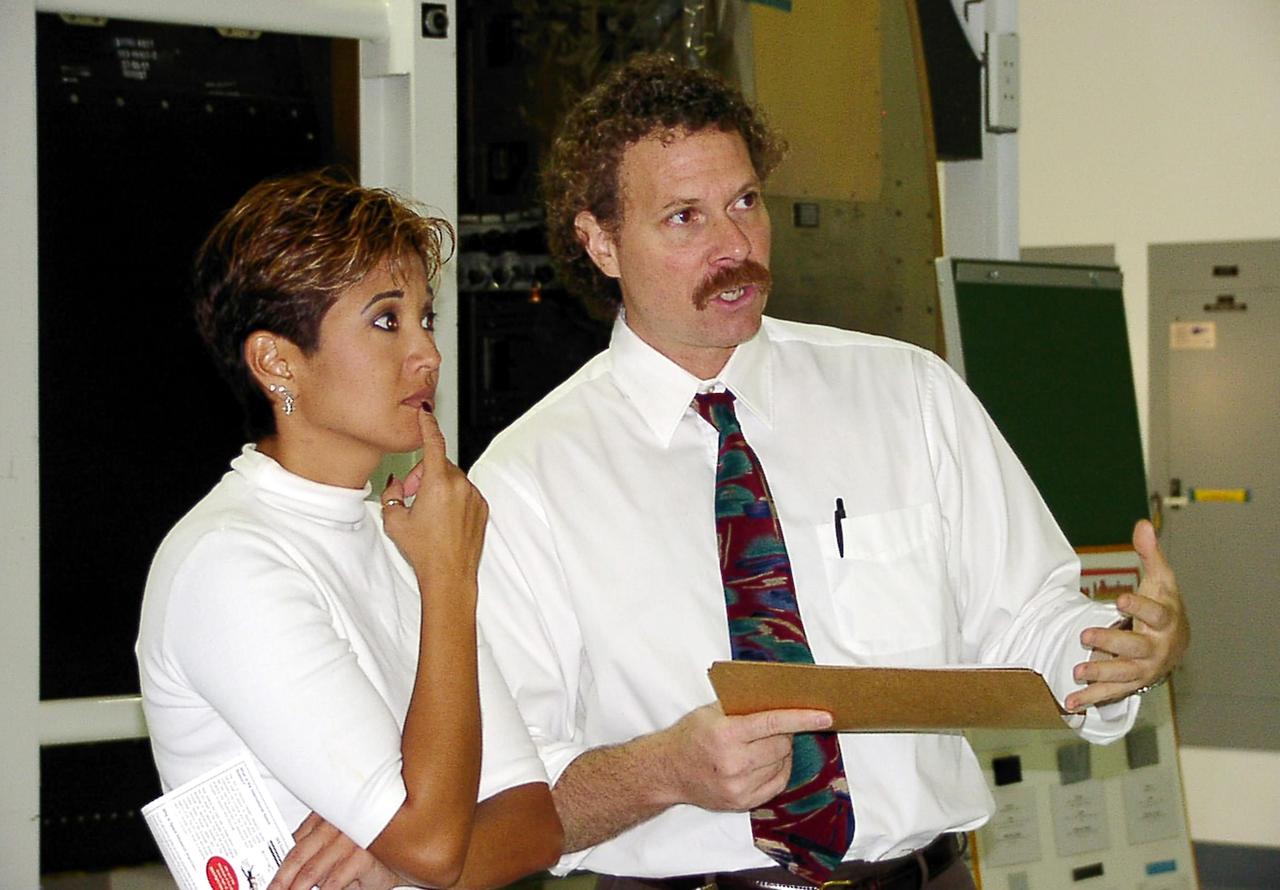
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- WESH-TV 2 News Anchor Wendy Chioji (right) is given a briefing on how to pilot a Space Shuttle orbiter during a tour inside the cockpit of an orbiter. Chioji was at KSC to speak at the 2002 Combined Federal Campaign (CFC) kickoff rally.
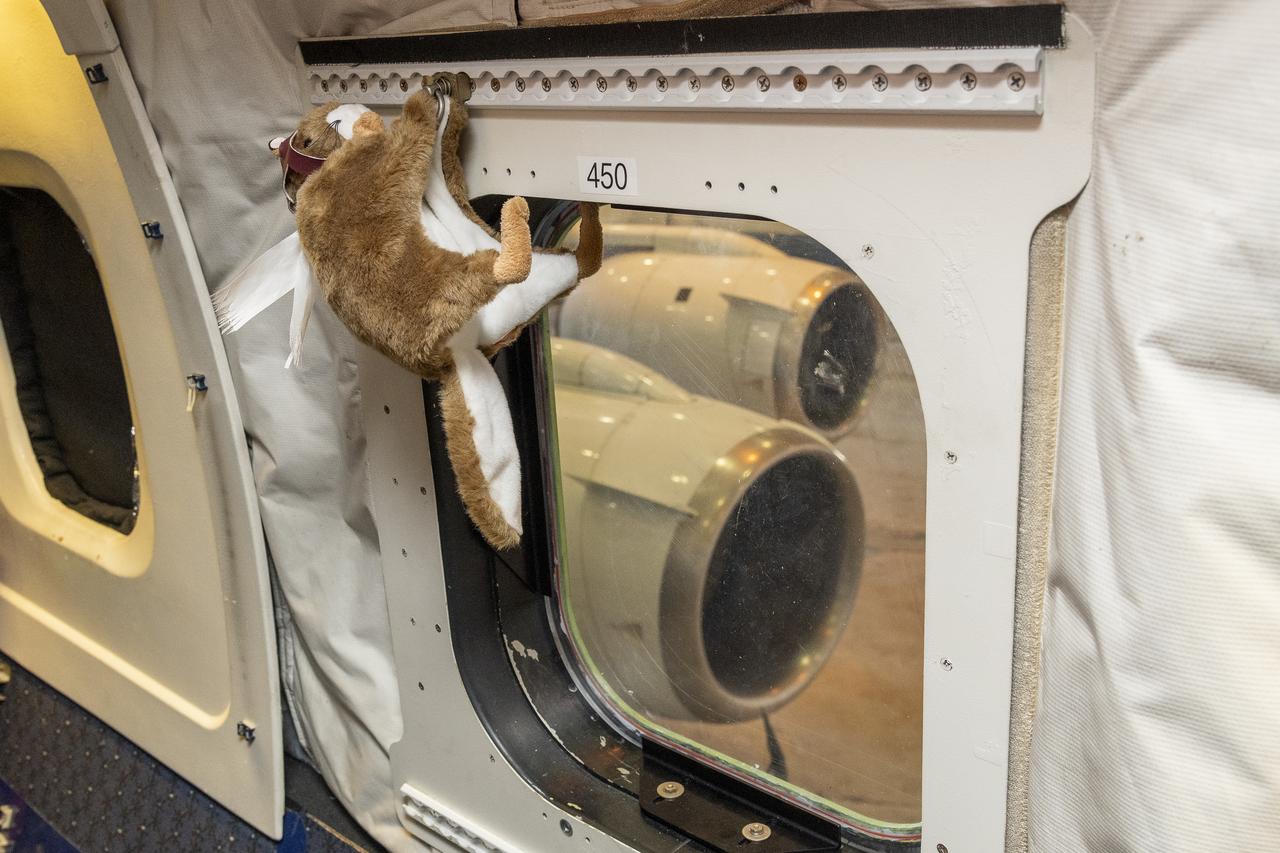

Orville, NASA’s high-flying squirrel, hangs onto the DC-8 aircraft at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center Building 703 in Palmdale, California. On May 2, 2024, NASA personnel, friends, and family celebrated the DC-8 staff, aircraft, and science campaigns.
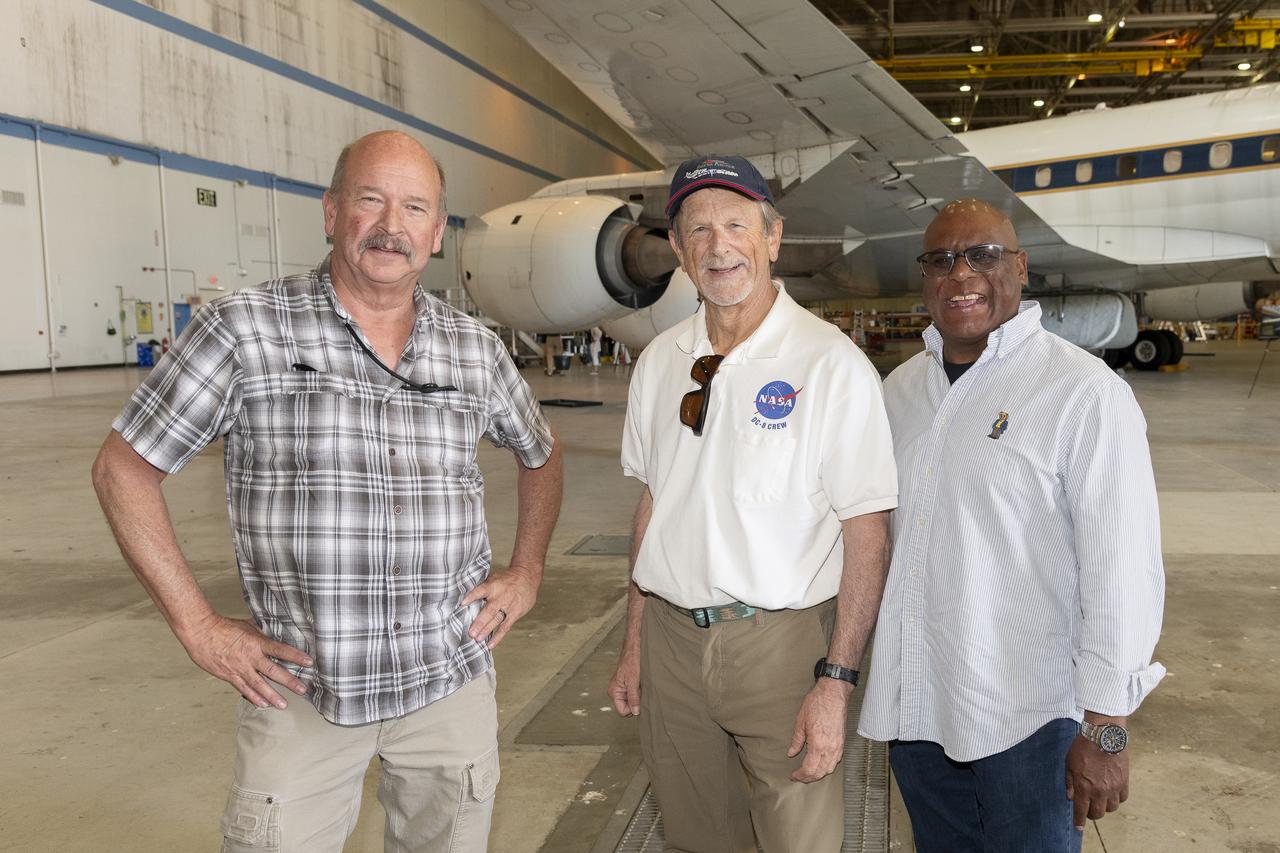

Rocky Radcliff, Kevin Hall, and Herman “Chico” Rijfkogel stand in front of NASA’s DC-8 aircraft at the agency’s Armstrong Flight Research Center Building 703 in Palmdale, California. On May 2, 2024, NASA personnel, friends, and family celebrated the DC-8 staff, aircraft, and science campaigns.
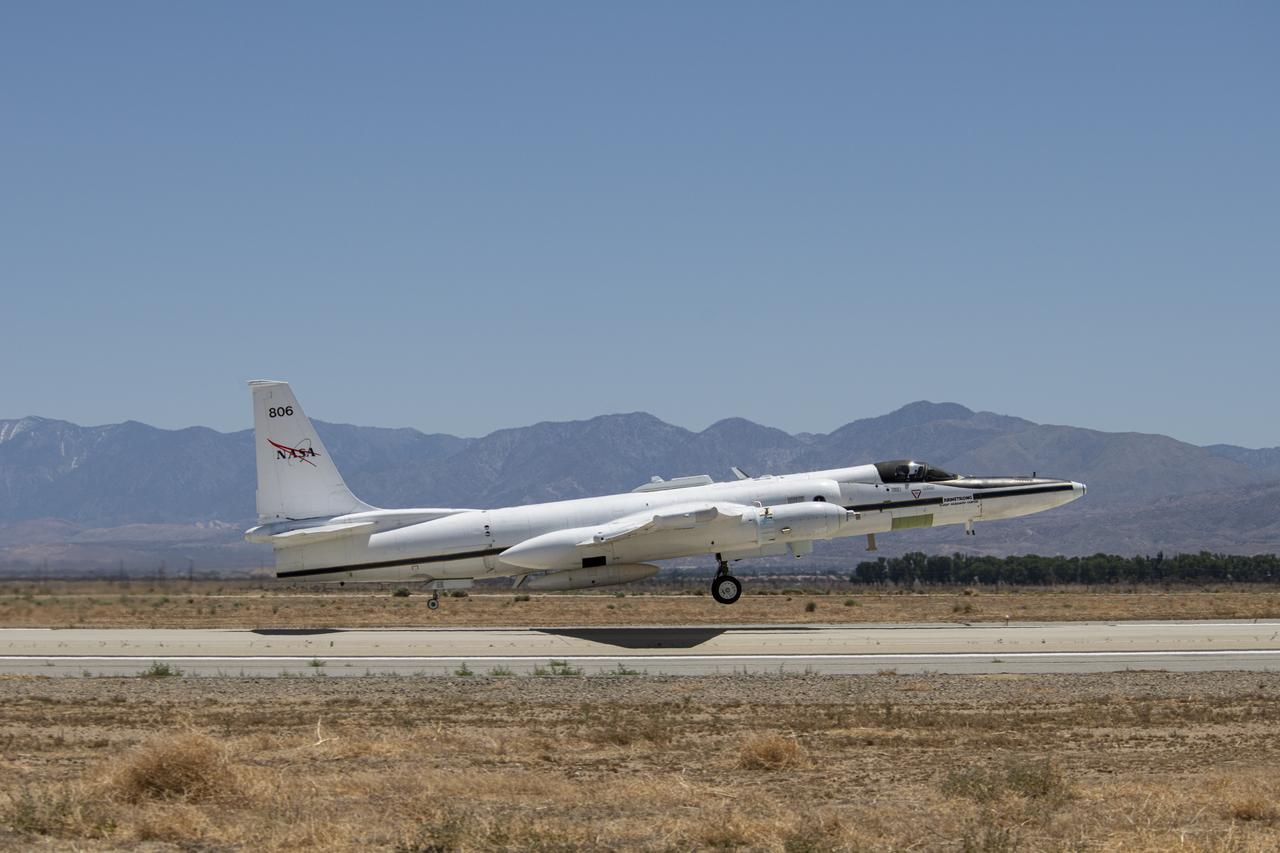

NASA's ER-2 high altitude aircraft takes off from Armstrong Flight Research Center Building 703 in Palmdale, California to perform a check flight for the the Dynamics and Chemistry of the Summer Stratosphere, or DCOTSS, 2022 campaign on May 13, 2022.
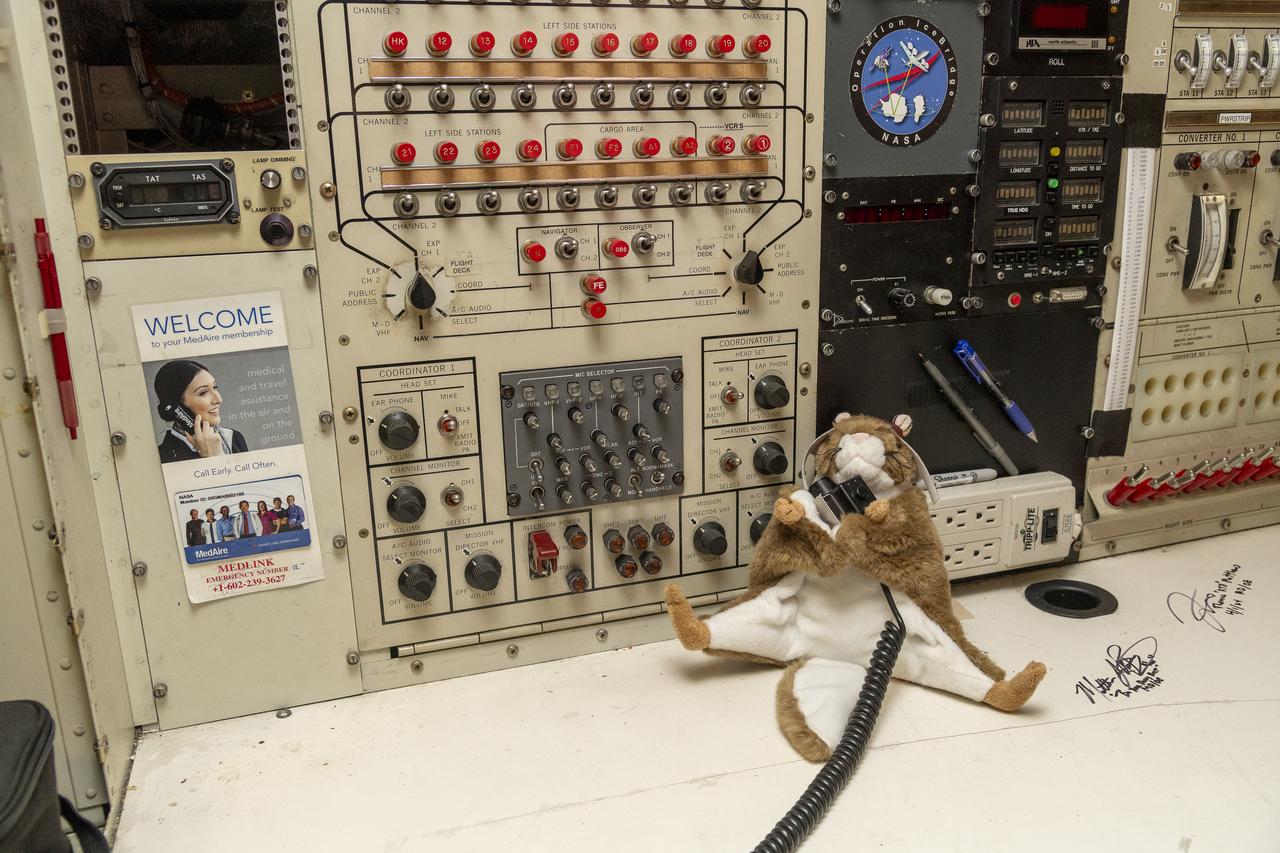

Orville, NASA’s high-flying squirrel, uses the microphone at the mission director station onboard the DC-8 aircraft at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center Building 703 in Palmdale, California. On May 2, 2024, NASA personnel, friends, and family celebrated the DC-8 staff, aircraft, and science campaigns.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- WESH-TV 2 News Anchor Wendy Chioji (right) is given a tour of Launch Complex 39B by NASA's Stephen Bulloch. Chioji was at KSC to speak at the 2002 Combined Federal Campaign (CFC) kickoff rally.

People tour the inside of the DC-8 aircraft at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center Building 703 in Palmdale, California. On May 2, 2024, NASA personnel, friends, and family celebrated the DC-8 staff, aircraft, and science campaigns.
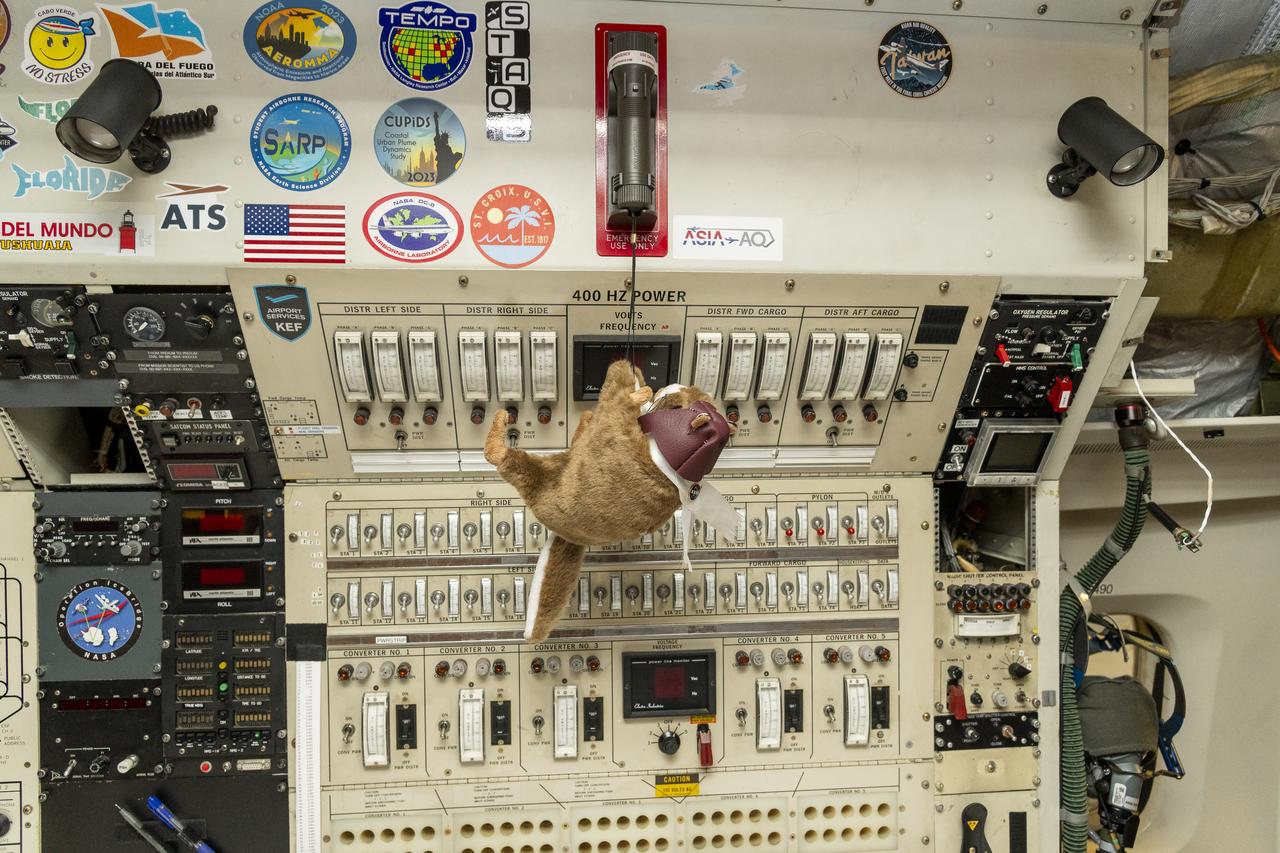

Orville, NASA’s high-flying squirrel, finds mischief onboard the DC-8 aircraft at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center Building 703 in Palmdale, California. On May 2, 2024, NASA personnel, friends, and family celebrated the DC-8 staff, aircraft, and science campaigns.

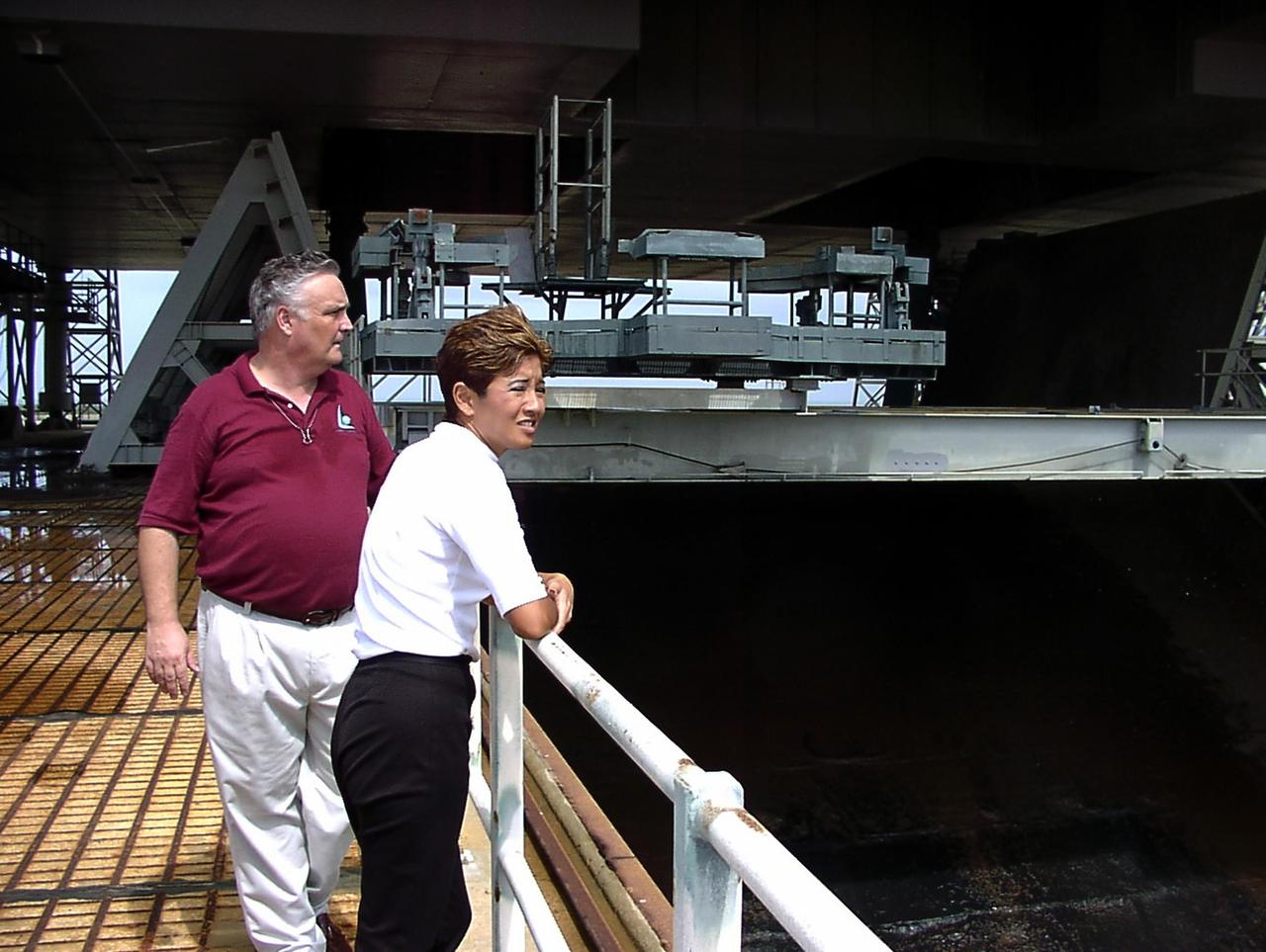
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- WESH-TV 2 News Anchor Wendy Chioji (left) is given a tour of the Space Station Processing Facility by Russell Romanella, Deputy Director for Program Management in the International Space Staton / Payloads Processing Directorate. Chioji was at KSC to speak at the 2002 Combined Federal Campaign (CFC) kickoff rally.
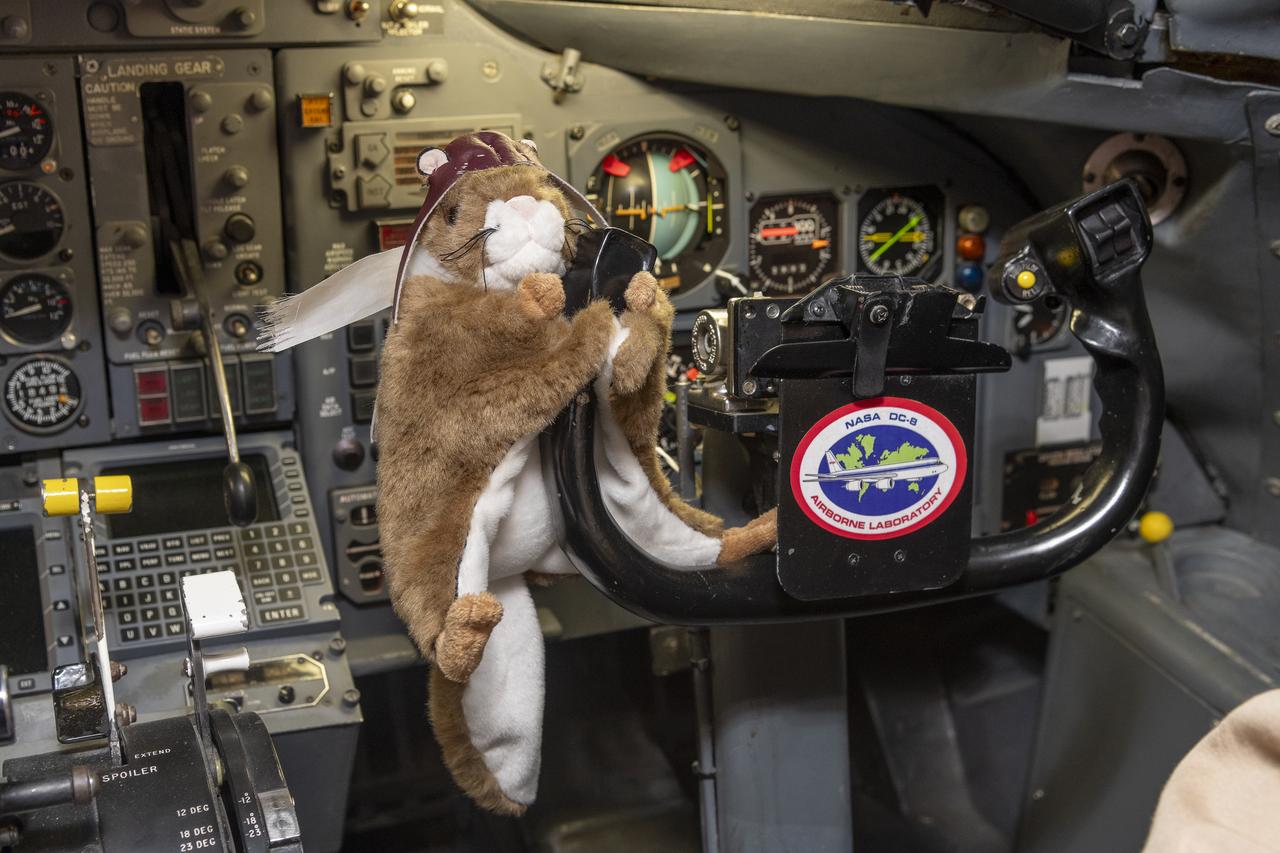

Orville, NASA’s high-flying squirrel, tries his paw at piloting the DC-8 aircraft at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center Building 703 in Palmdale, California. On May 2, 2024, NASA personnel, friends, and family celebrated the DC-8 staff, aircraft, and science campaigns.
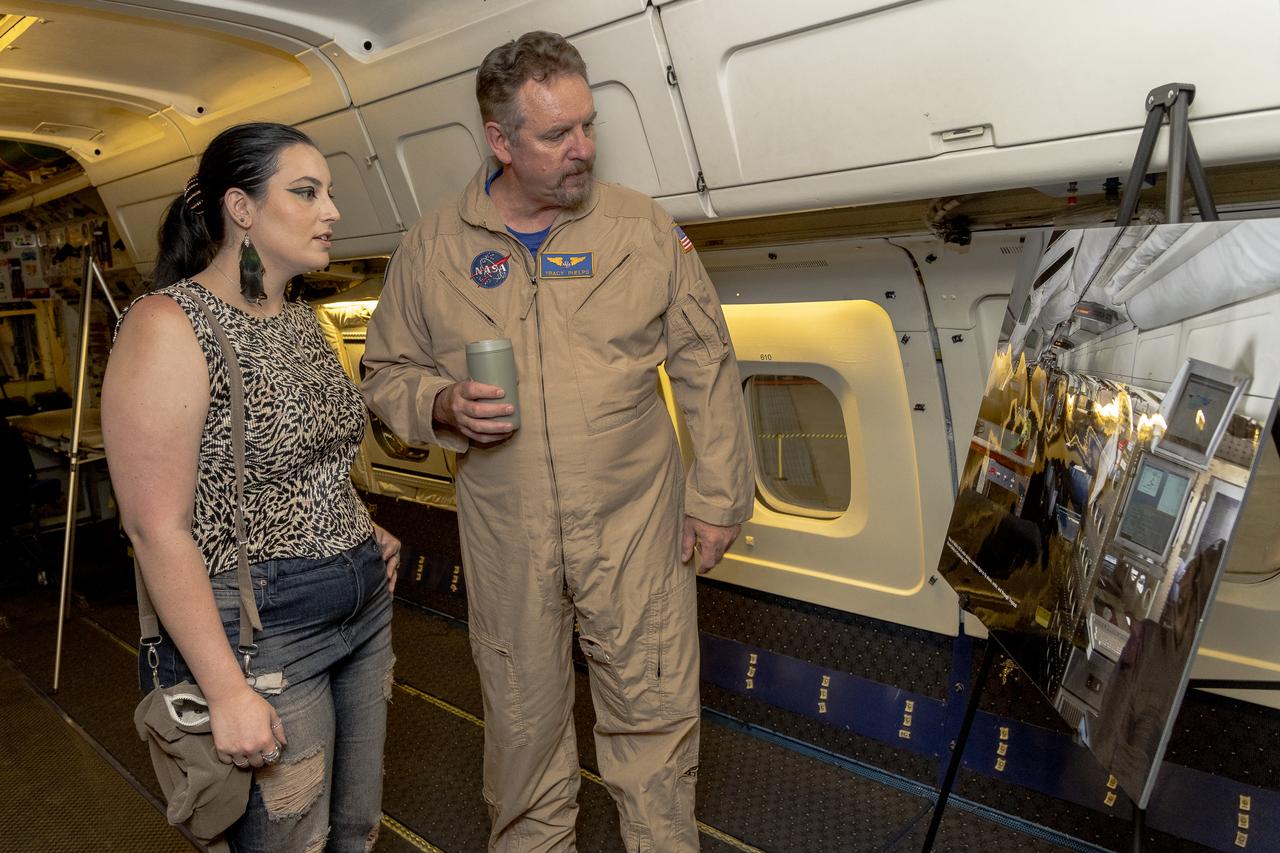

NASA pilot Tracy Phelps and his daughter Rachael Phelps look at a poster onboard the DC-8 at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center Building 703 in Palmdale, California. On May 2, 2024, NASA personnel, friends, and family celebrated the DC-8 staff, aircraft, and science campaigns.
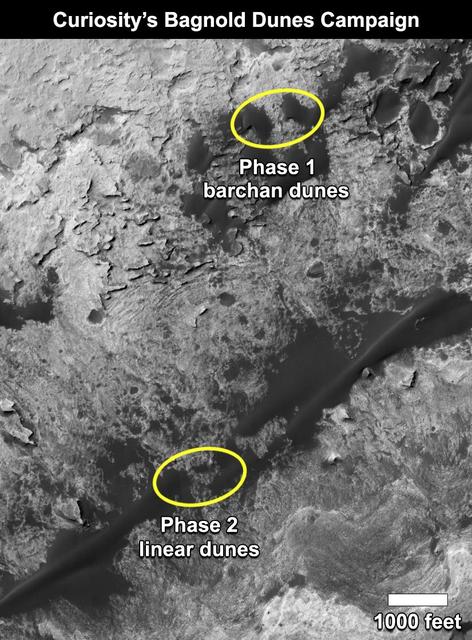

This map shows the two locations of a research campaign by NASA's Curiosity Mars rover mission to investigate active sand dunes inside Gale Crater on Mars. The Bagnold Dunes form a dark band on the northwestern flank of Mount Sharp, inside the crater. In late 2015 and early 2016, Curiosity examined crescent-shaped dunes, called barchans, which are convex on the downwind (leeward) side. This was the first close-up study of active sand dunes anywhere other than Earth. In February 2017, the rover reached a location where the dunes are linear in shape, and the mission began Phase 2 of its dunes campaign. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21269
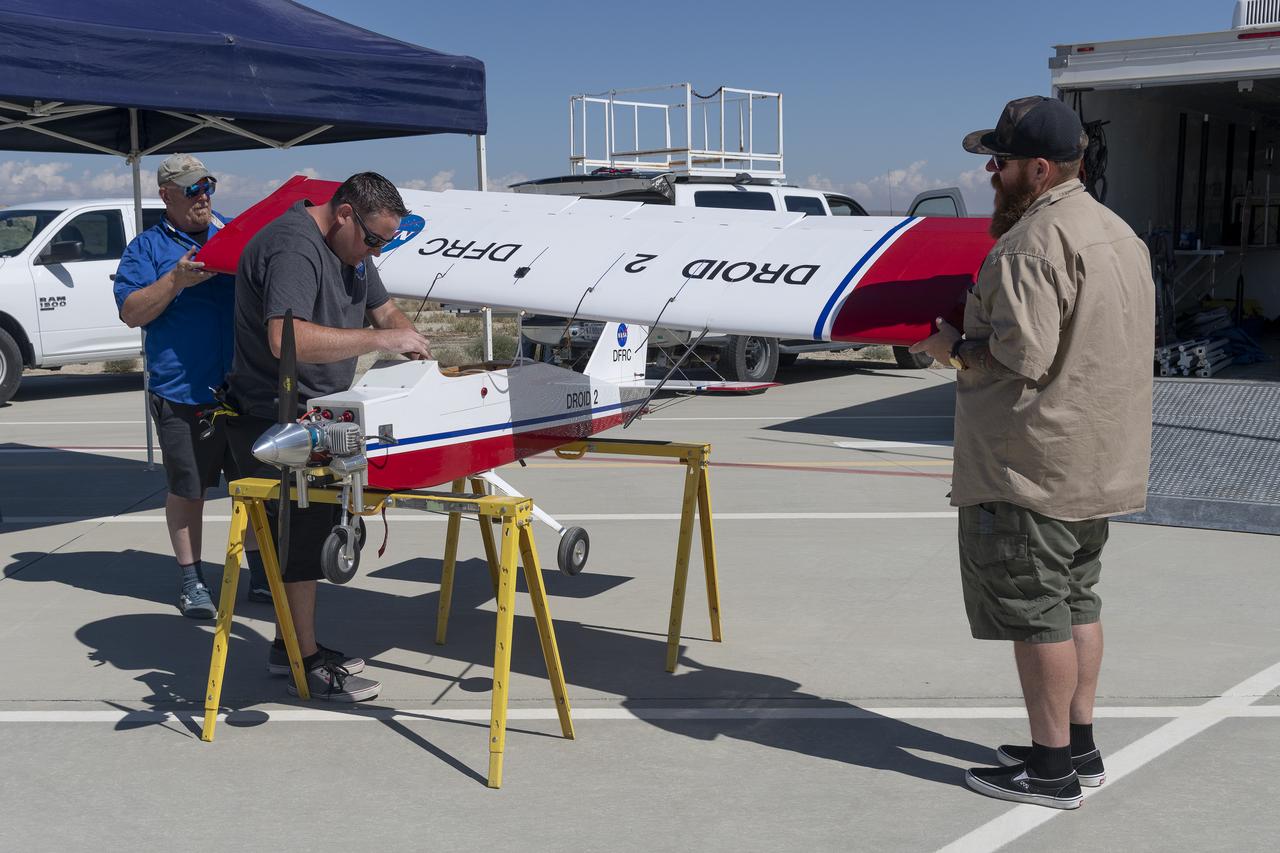

Robert "Red" Jensen, Justin Link, and Justin Hall prepare the DROID 2 (Dryden Remotely Operated Integrated Drone 2) for the Advanced Exploration of Reliable Operation at Low Altitudes: Meteorology, Simulation, and Technology campaign flights. The weather study was at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. The focus was to study wind to provide data for safe takeoff and landing of future air taxis.
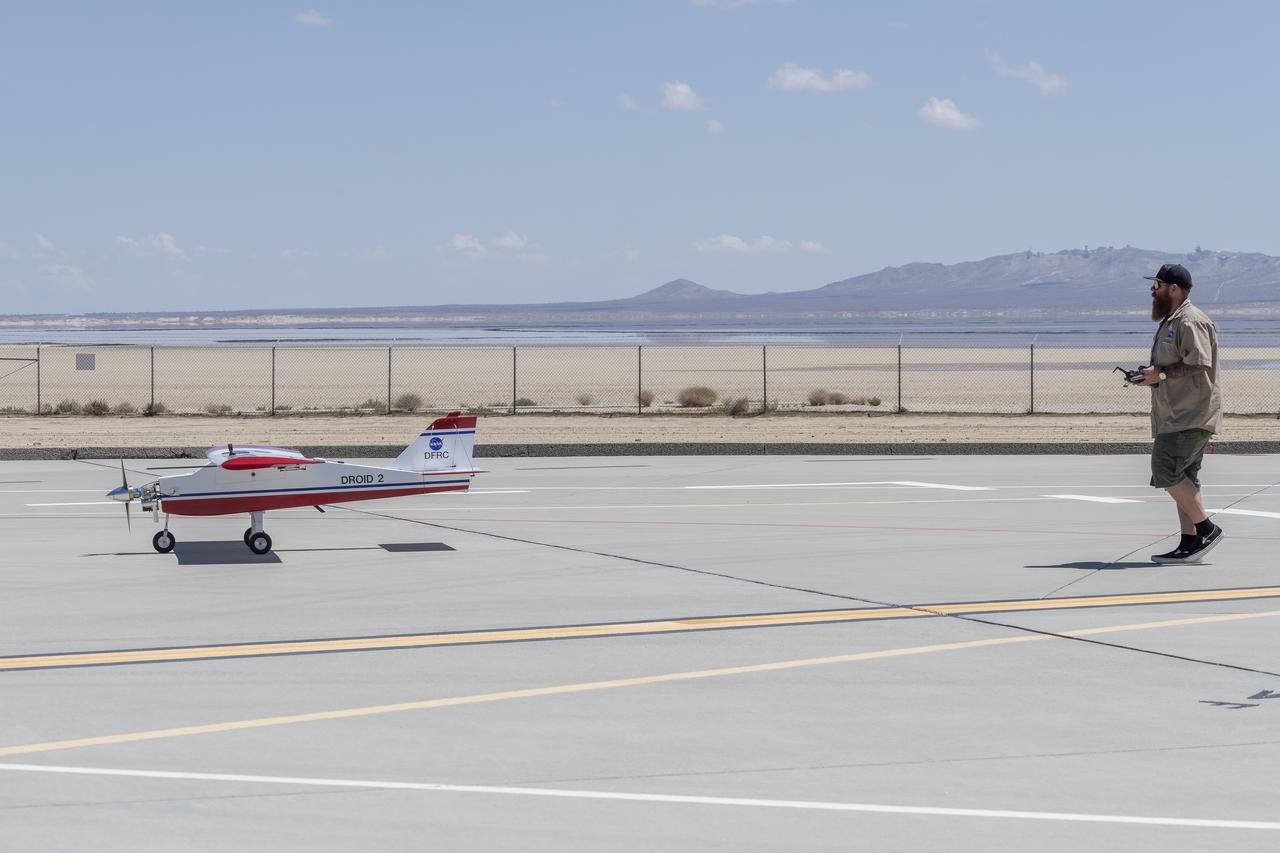

Justin Hall lands the DROID 2 (Dryden Remotely Operated Integrated Drone 2) aircraft at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, as part of the Advanced Exploration of Reliable Operation at Low Altitudes: Meteorology, Simulation, and Technology campaign. The focus was to study wind to provide data for safe takeoff and landing of future air taxis.
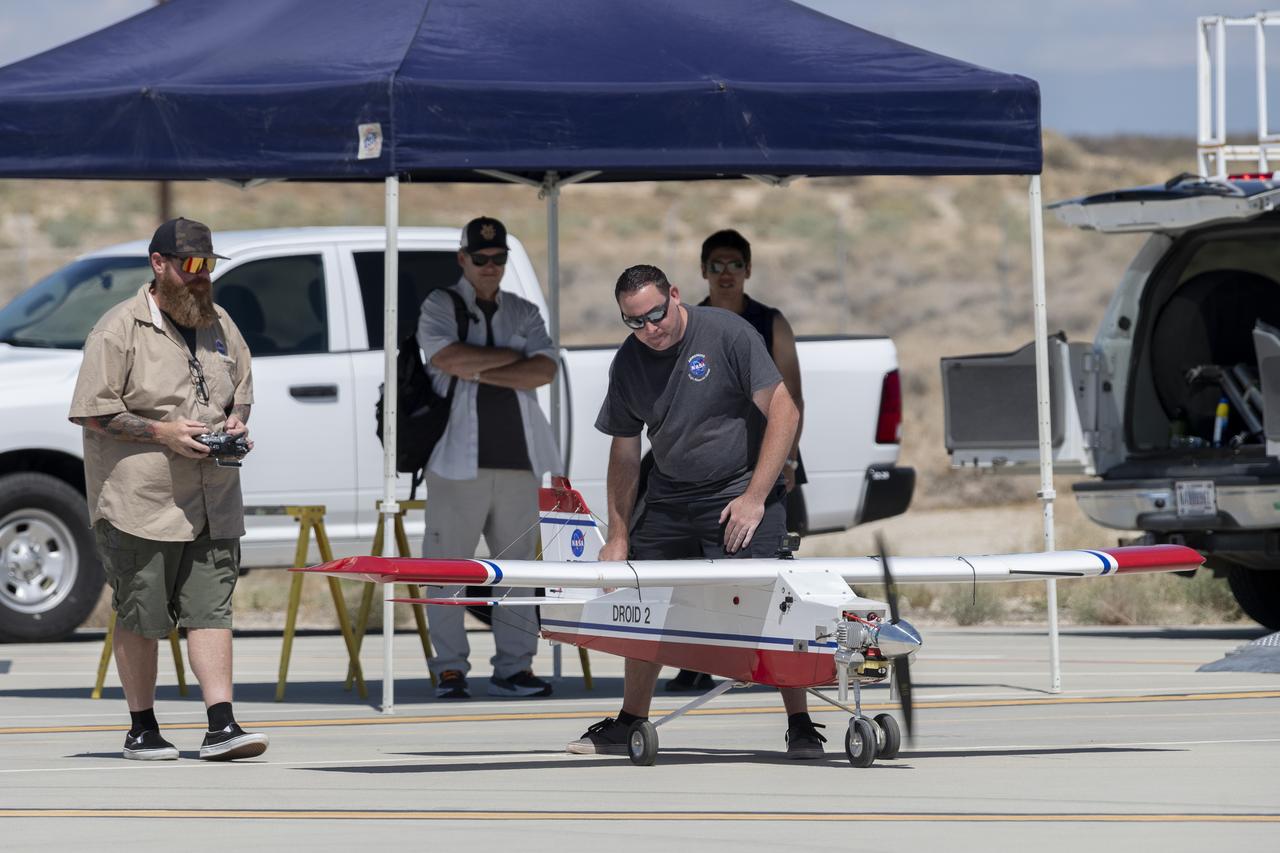

Justin Hall, left, prepares to pilot the DROID 2 (Dryden Remotely Operated Integrated Drone 2) aircraft, as John Melton watches and Justin Link makes a final adjustment. The flight was part of the Advanced Exploration of Reliable Operation at Low Altitudes: Meteorology, Simulation, and Technology campaign. The weather study was at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. The focus was to study wind to provide data for safe takeoff and landing of future air taxis.
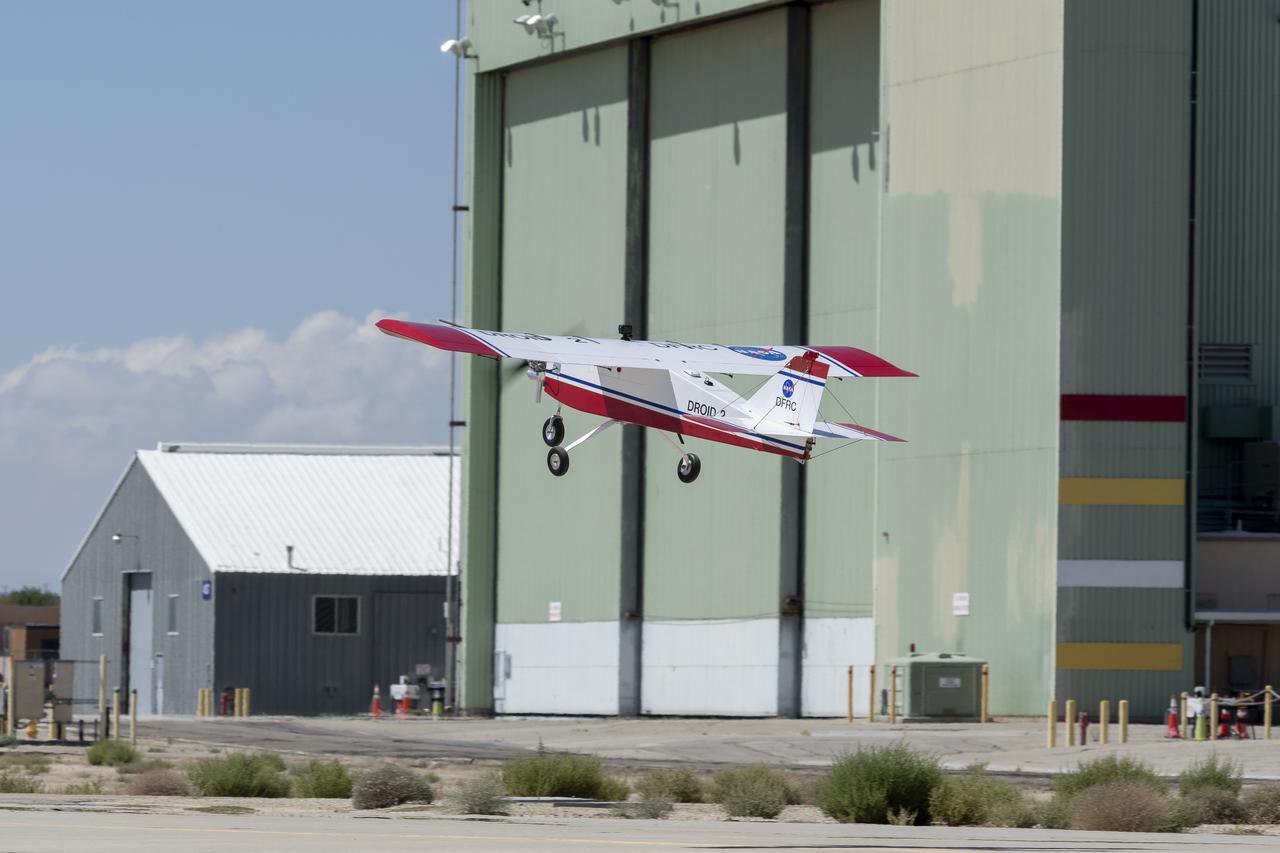

The DROID 2 (Dryden Remotely Operated Integrated Drone 2) aircraft flies by the former space shuttle hangar at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, as part of the Advanced Exploration of Reliable Operation at Low Altitudes: Meteorology, Simulation, and Technology campaign. The focus was to study wind to provide data for safe takeoff and landing of future air taxis.
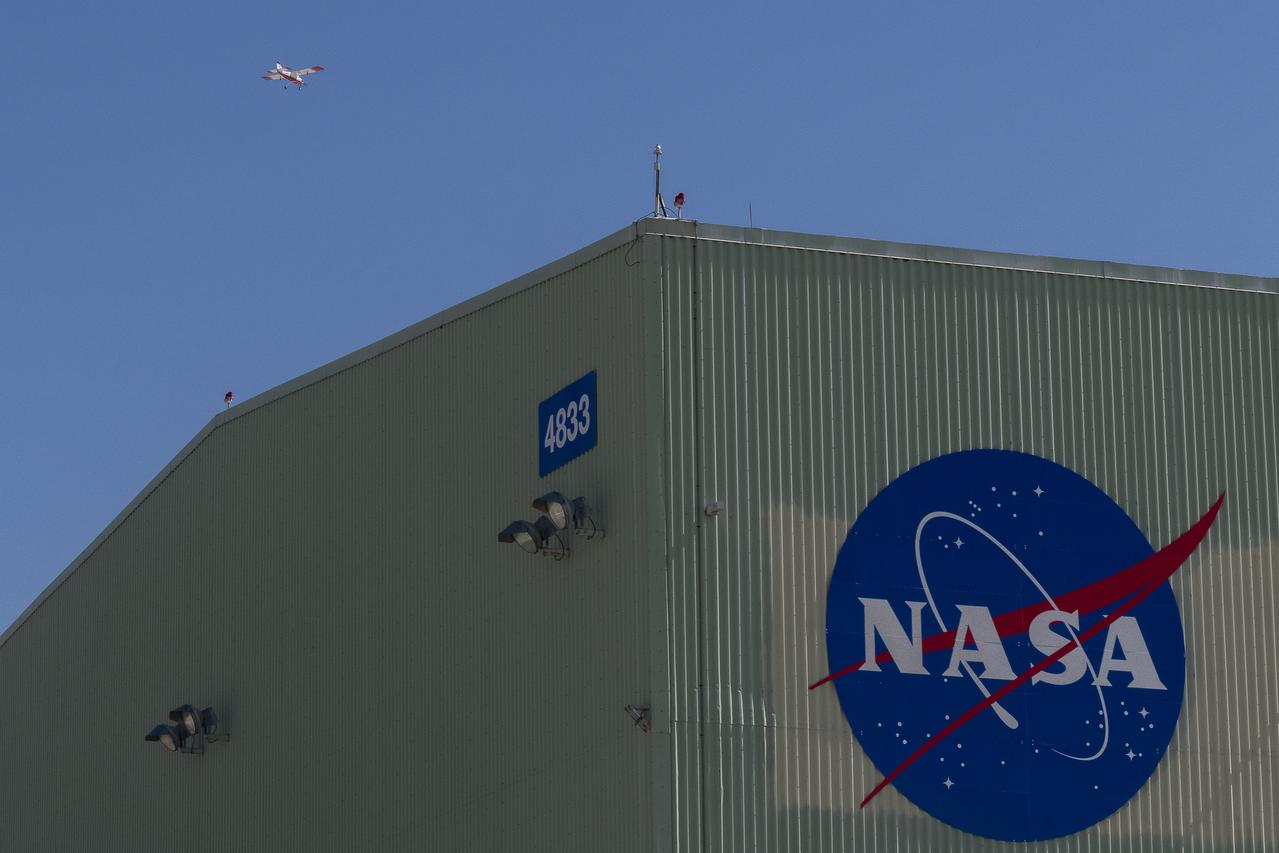

The DROID 2 (Dryden Remotely Operated Integrated Drone 2) aircraft flies by the former space shuttle hangar at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, as part of the Advanced Exploration of Reliable Operation at Low Altitudes: Meteorology, Simulation, and Technology campaign. The focus was to study wind to provide data for safe takeoff and landing of future air taxis.
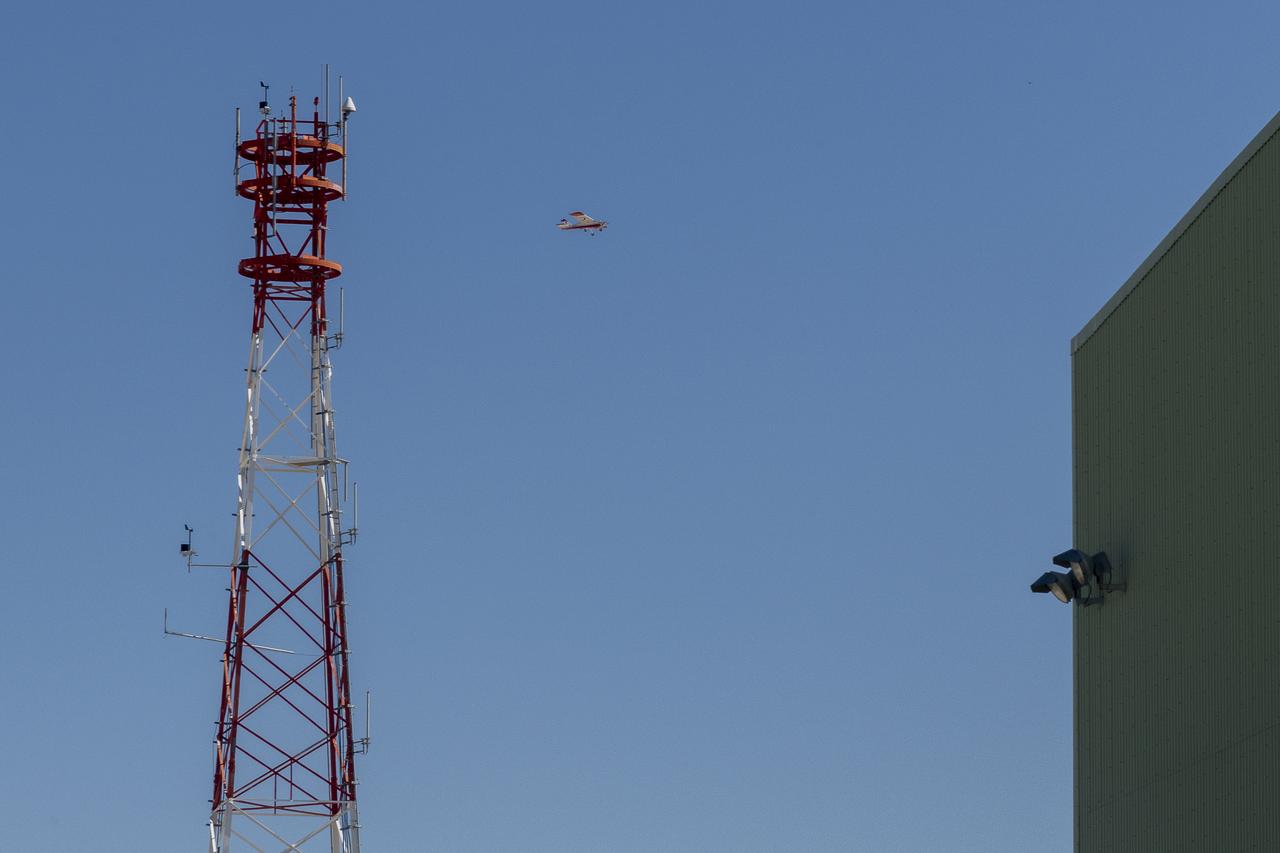

The DROID 2 (Dryden Remotely Operated Integrated Drone 2) flies by a 140-foot instrumented tower and the former space shuttle hangar at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, as part of the Advanced Exploration of Reliable Operation at Low Altitudes: Meteorology, Simulation, and Technology campaign. The focus was to study wind to provide data for safe takeoff and landing of future air taxis.
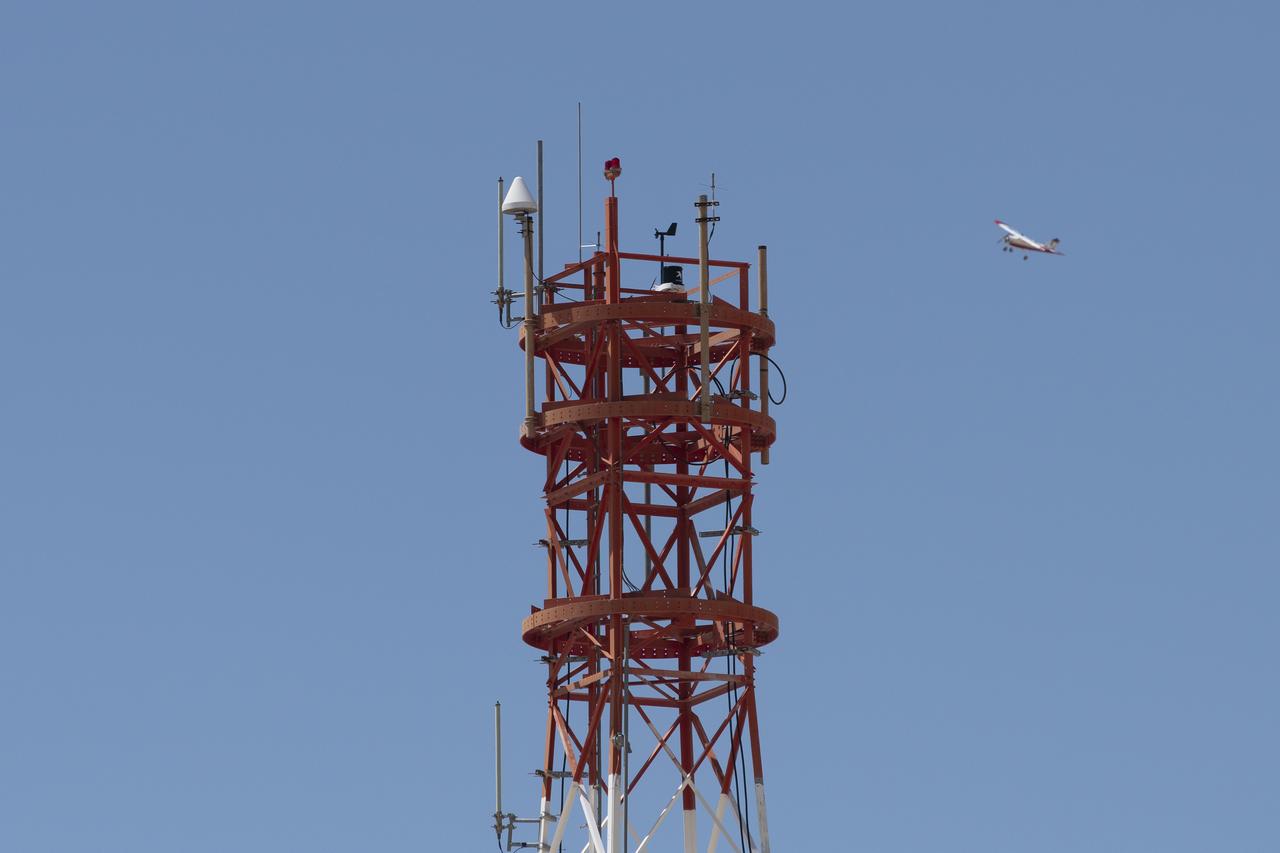

The DROID 2 (Dryden Remotely Operated Integrated Drone 2) flies by a 140-foot instrumented tower at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, as part of the Advanced Exploration of Reliable Operation at Low Altitudes: Meteorology, Simulation, and Technology campaign. The focus was to study wind to provide data for safe takeoff and landing of future air taxis.

Robert "Red" Jensen lands the DROID 2 (Dryden Remotely Operated Integrated Drone 2) aircraft at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, as part of the Advanced Exploration of Reliable Operation at Low Altitudes: Meteorology, Simulation, and Technology campaign. The focus was to study wind to provide data for safe takeoff and landing of future air taxis.
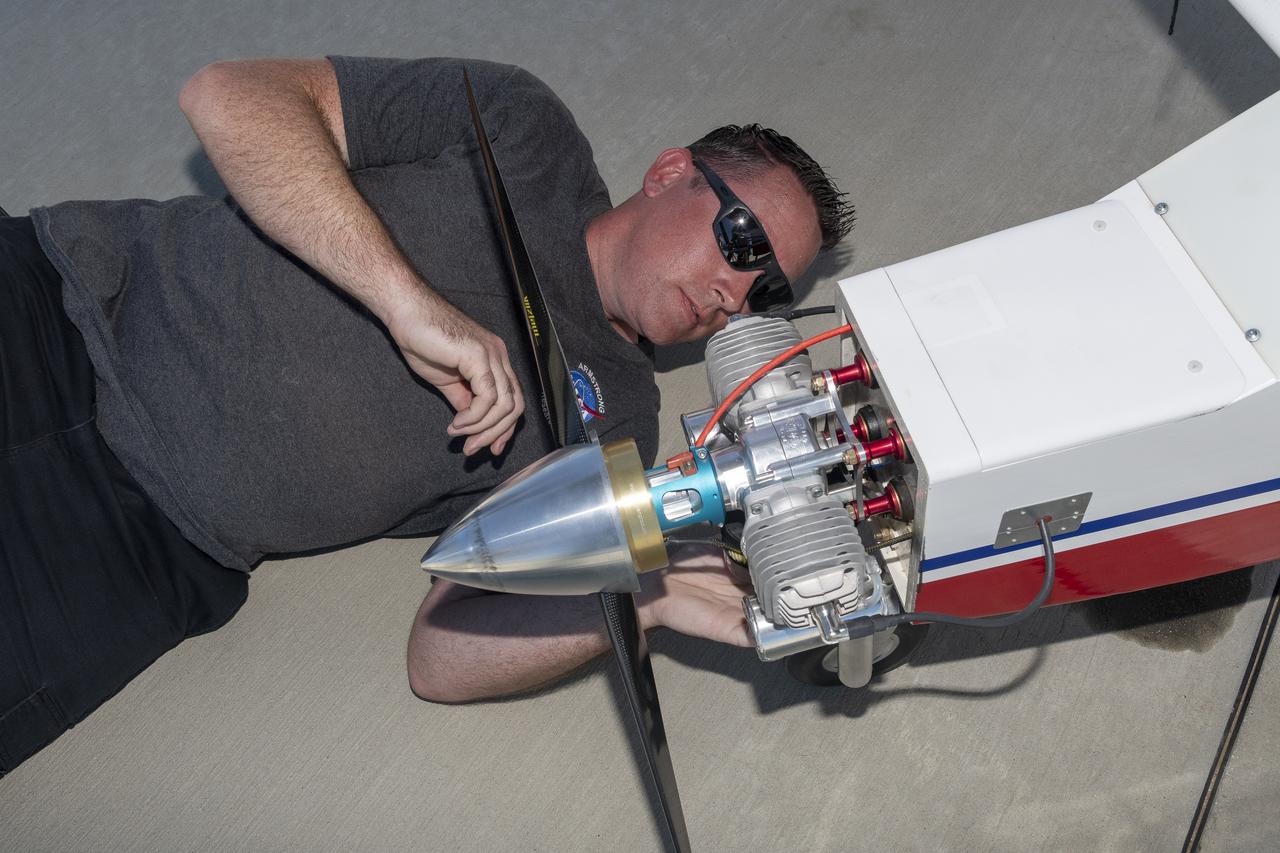

Justin Link prepares the DROID 2 (Dryden Remotely Operated Integrated Drone 2) aircraft before a flight for the Advanced Exploration of Reliable Operation at Low Altitudes: Meteorology, Simulation, and Technology campaign. The weather study was at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. The focus was to study wind to provide data for safe takeoff and landing of future air taxis.
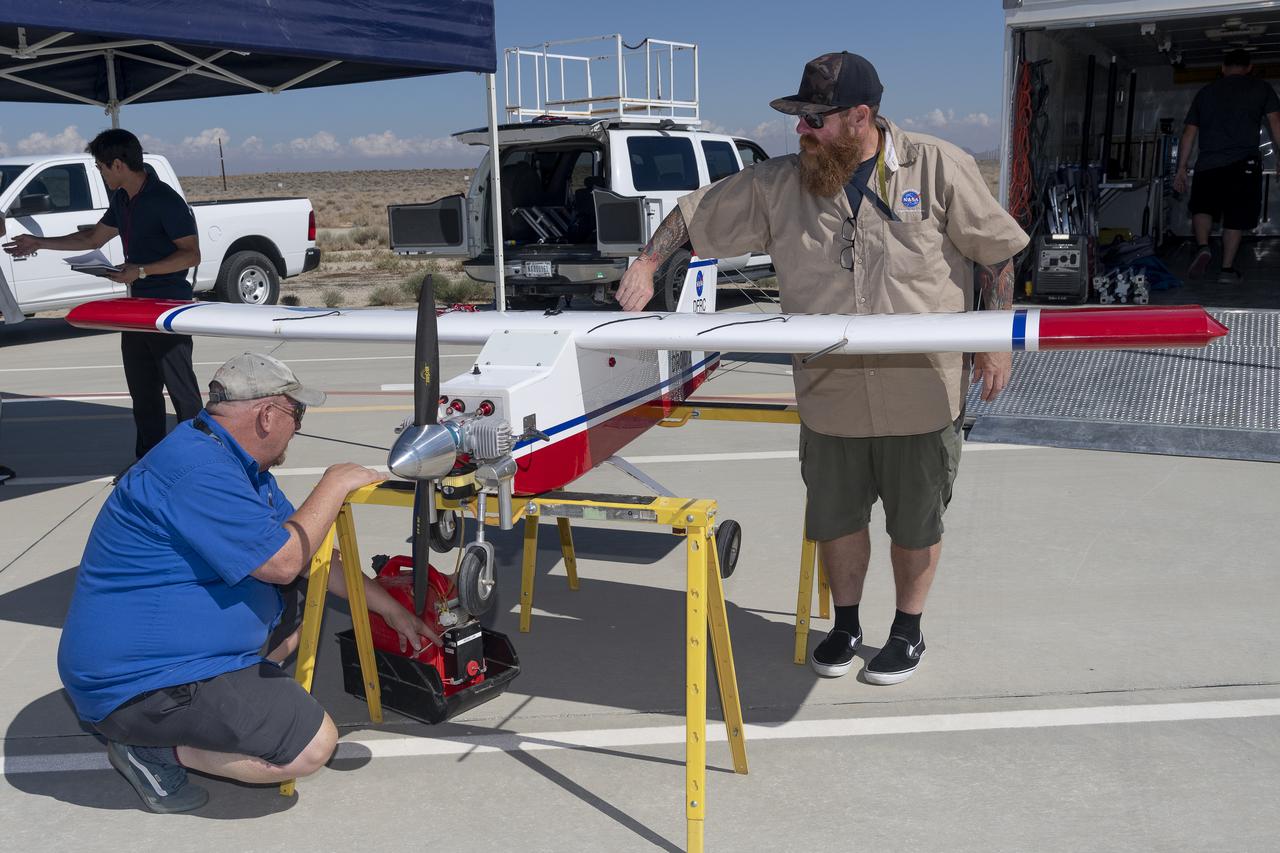

Robert "Red" Jensen and Justin Hall prepare the DROID 2 (Dryden Remotely Operated Integrated Drone 2) aircraft for the Advanced Exploration of Reliable Operation at Low Altitudes: Meteorology, Simulation, and Technology campaign flights. The weather study was at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. The focus was to study wind to provide data for safe takeoff and landing of future air taxis.
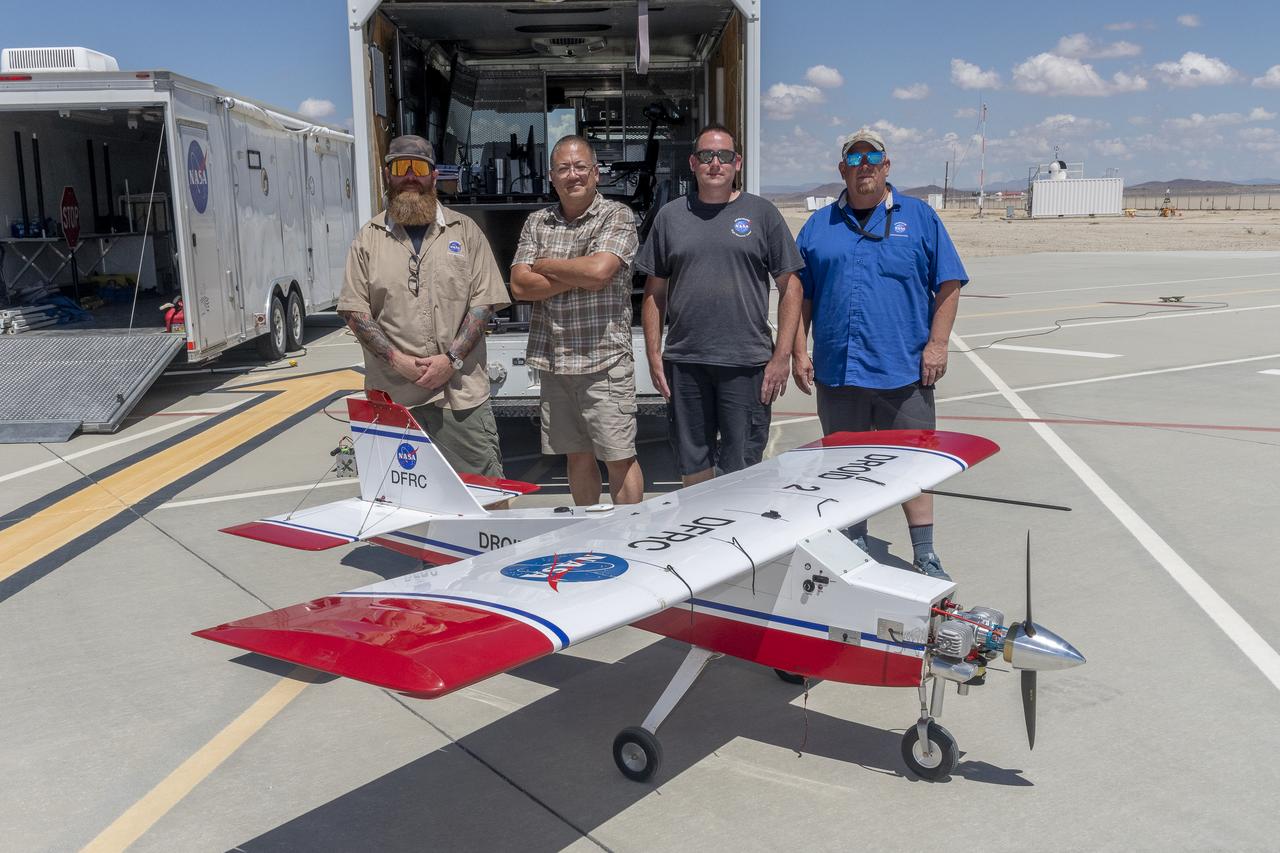

Justin Hall, Derek Abramson, Justin Link, and Robert "Red" Jensen were key to a successful mission for the DROID 2 (Dryden Remotely Operated Integrated Drone 2) aircraft at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. The aircraft flew as part of the Advanced Exploration of Reliable Operation at Low Altitudes: Meteorology, Simulation, and Technology campaign. The focus was to study wind to provide data for safe takeoff and landing of future air taxis.
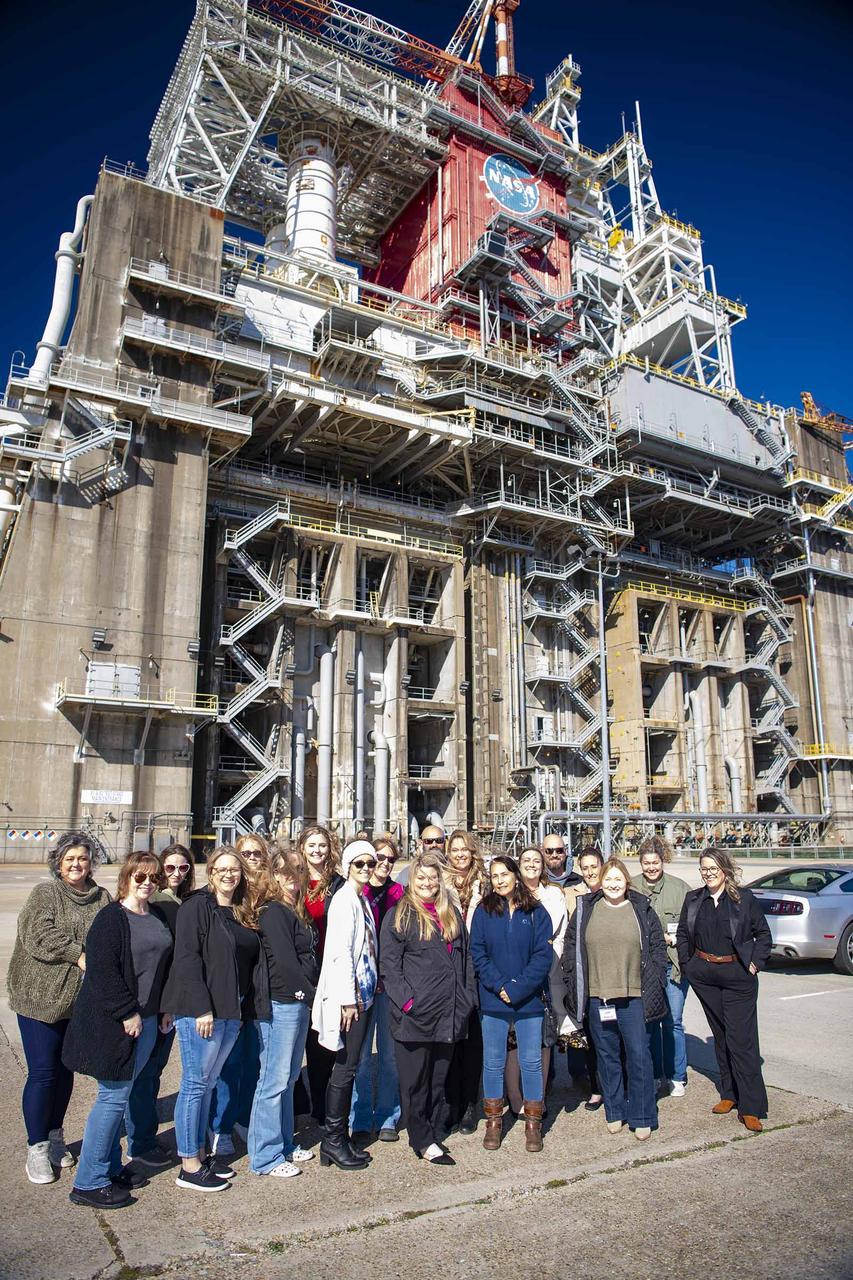

The Pearl River County Leadership Class visits the Thad Cochran Test Stand (B-1/B-2) during a NASA Stennis tour on Feb. 20. NASA Stennis is at the front end of the critical path for the future of human deep space exploration through NASA’s Artemis campaign. The B-2 side of the Thad Cochran Test Stand is undergoing preparations for exploration upper stage testing. The upper stage is scheduled to undergo Green Run tests of its integrated systems before its first flight on the Artemis IV mission. The test series will culminate with a hot fire of the stage’s four RL10 engines, just as during an actual mission.
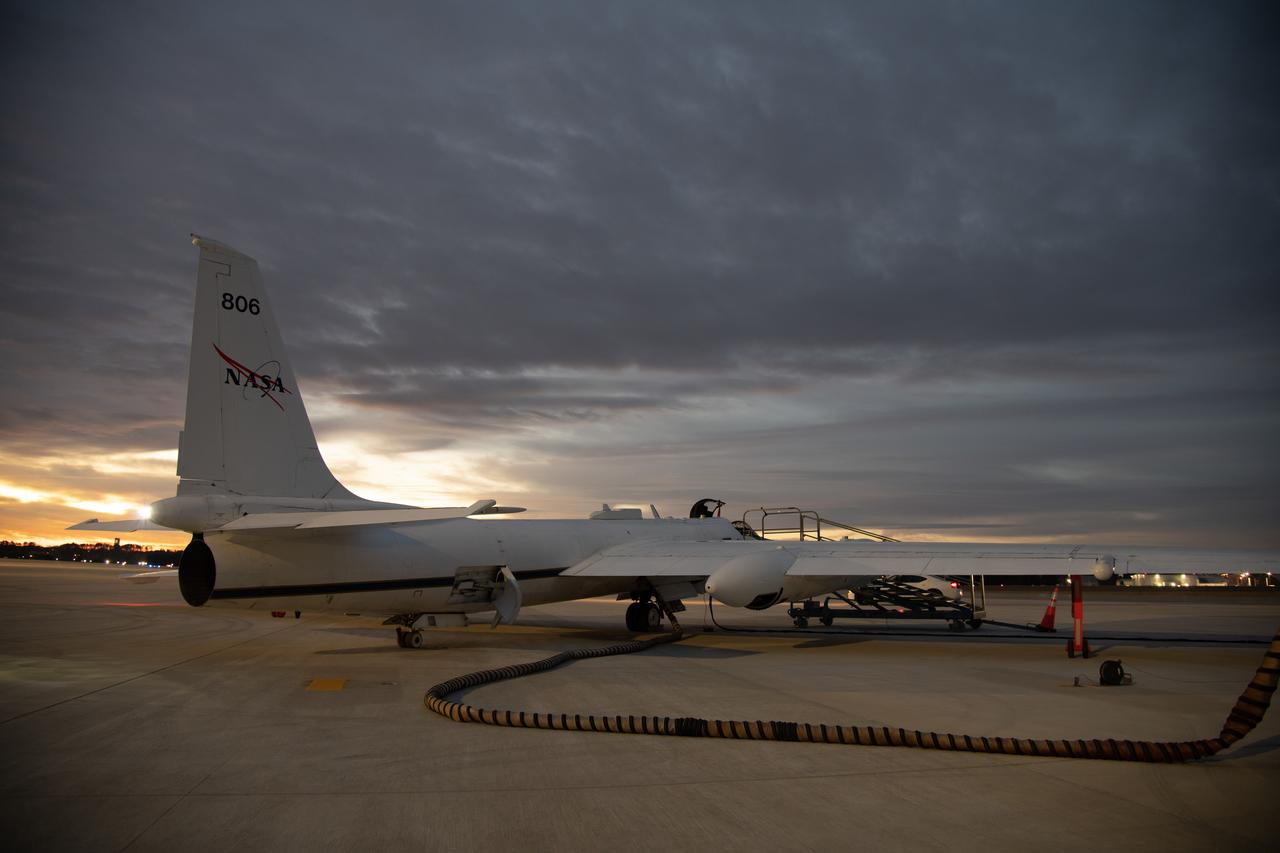

The NASA ER-2 high-altitude aircraft was prepared to support the Investigation of Microphysics and Precipitation for Atlantic Coast-Threatening Storms (IMPACTS) mission. For this mission, the IMPACTS team tracked storms across the Eastern United States to help understand how winter storms form and develop. The aircraft, which is based at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center Building 703 in Palmdale, California, was temporarily based at Dobbins Air Reserve Base in Marietta, Georgia. The three-year IMPACTS campaign concluded on Feb. 28, 2023.
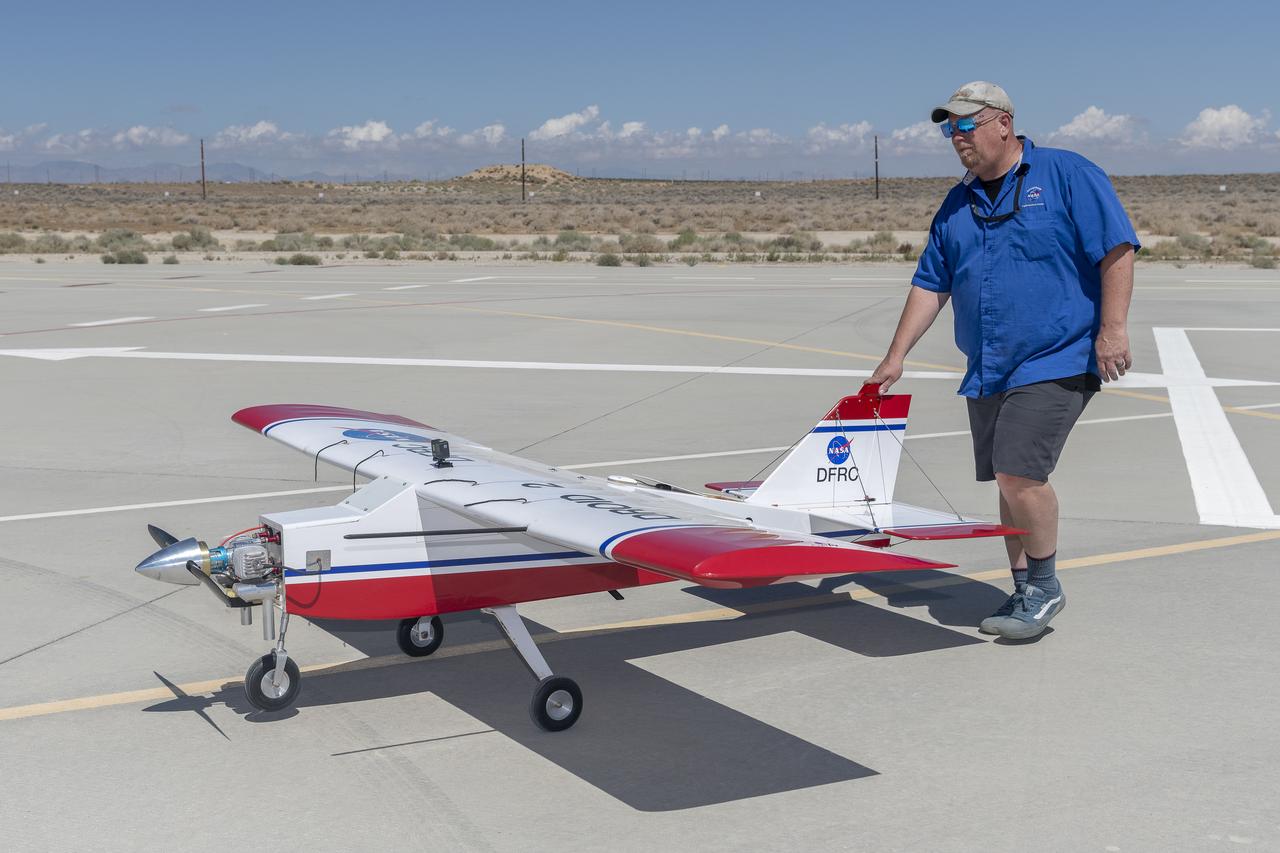

Robert "Red" Jensen positions the DROID 2 (Dryden Remotely Operated Integrated Drone) aircraft before a flight for the Advanced Exploration of Reliable Operation at Low Altitudes: Meteorology, Simulation, and Technology campaign. The weather study was at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. The focus was to study wind to provide data for safe takeoff and landing of future air taxis.

The NASA ER-2 high-altitude aircraft supported the Investigation of Microphysics and Precipitation for Atlantic Coast-Threatening Storms (IMPACTS) mission. For this mission, the IMPACTS team tracked storms across the Eastern United States to help understand how winter storms form and develop. The aircraft, which is based at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center Building 703 in Palmdale, California, was temporarily based at Dobbins Air Reserve Base in Marietta, Georgia. The three-year IMPACTS campaign concluded on Feb. 28, 2023.
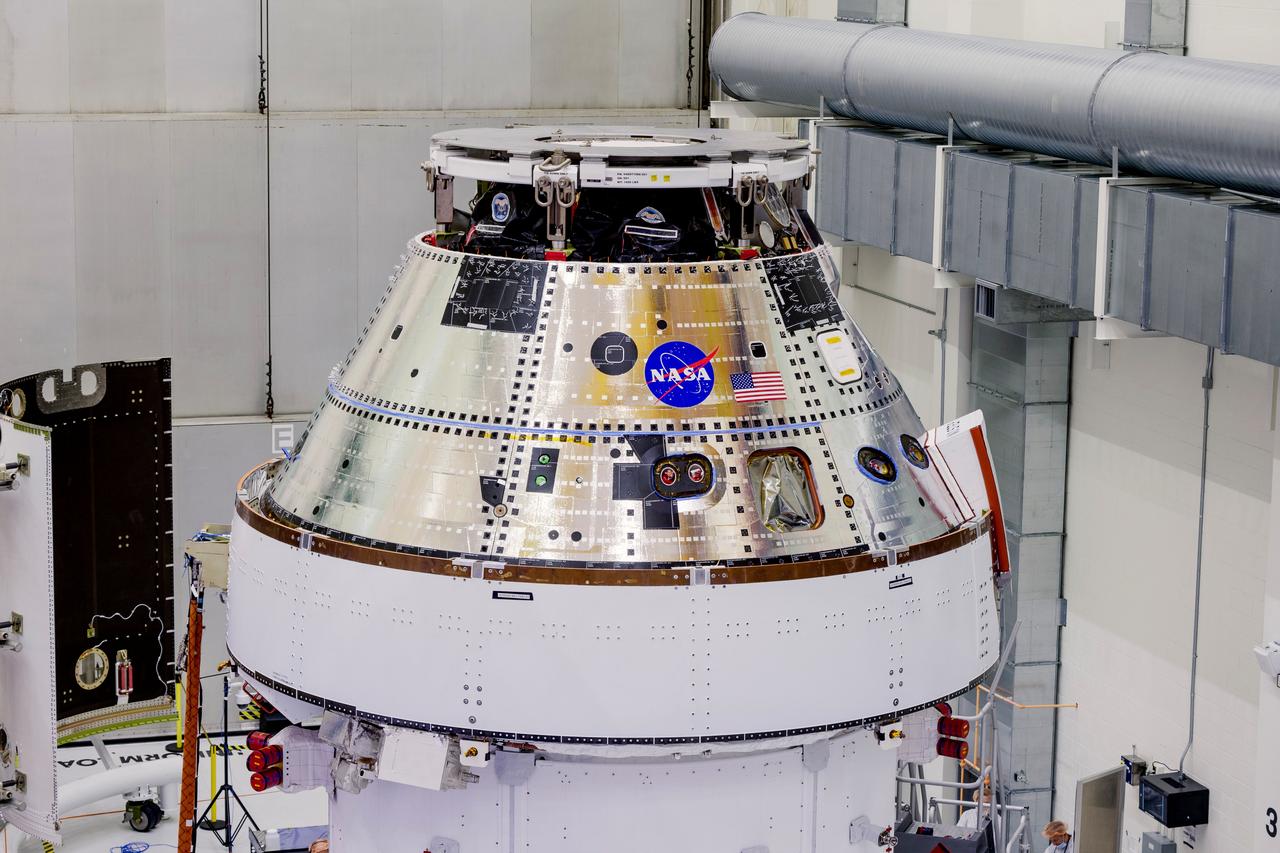

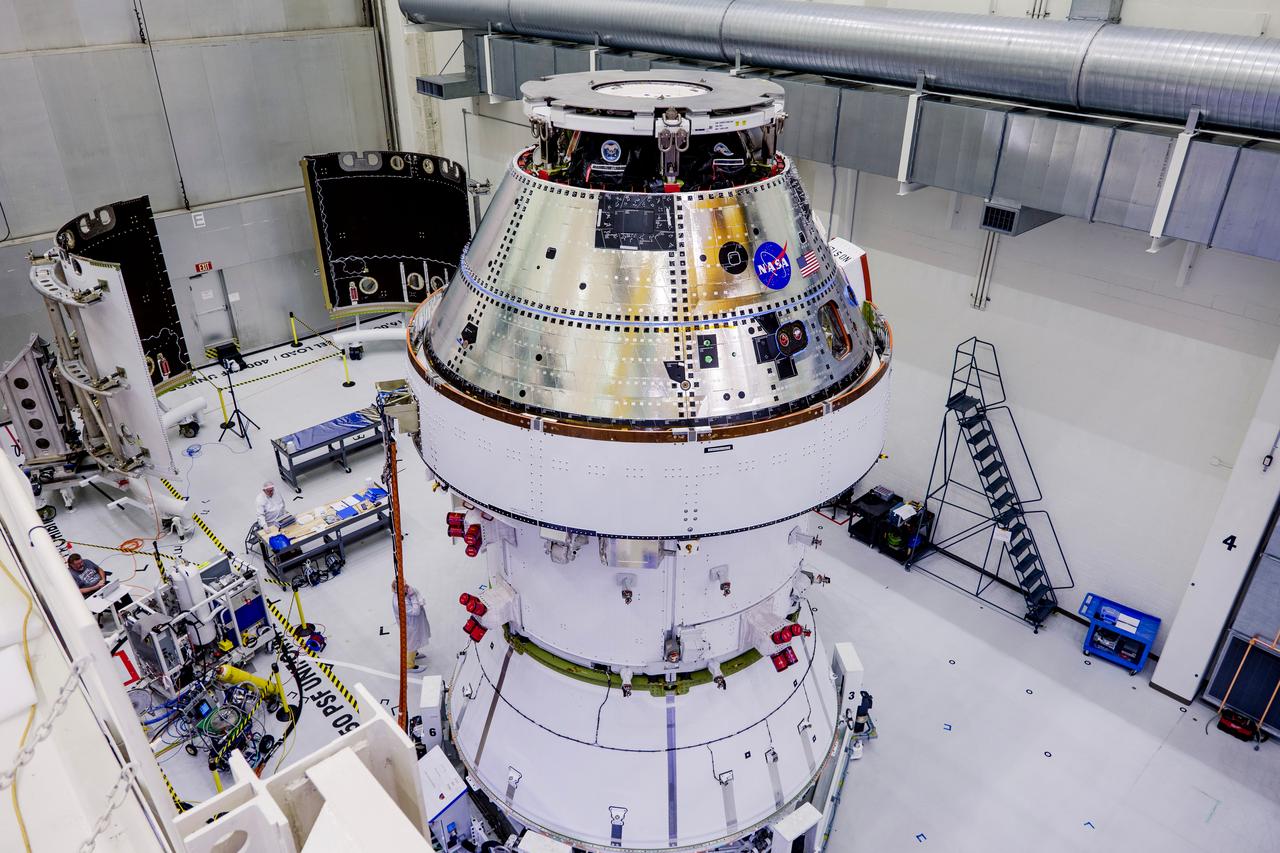
Date: 2/27/2025 Photographer: NASA/Rad Sinyak Caption: Technicians begin working on the installation of the four solar array wings for NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft inside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Feb. 27, 2025. Artemis II is Orion’s first crewed flight test around the Moon under the agency’s Artemis campaign.
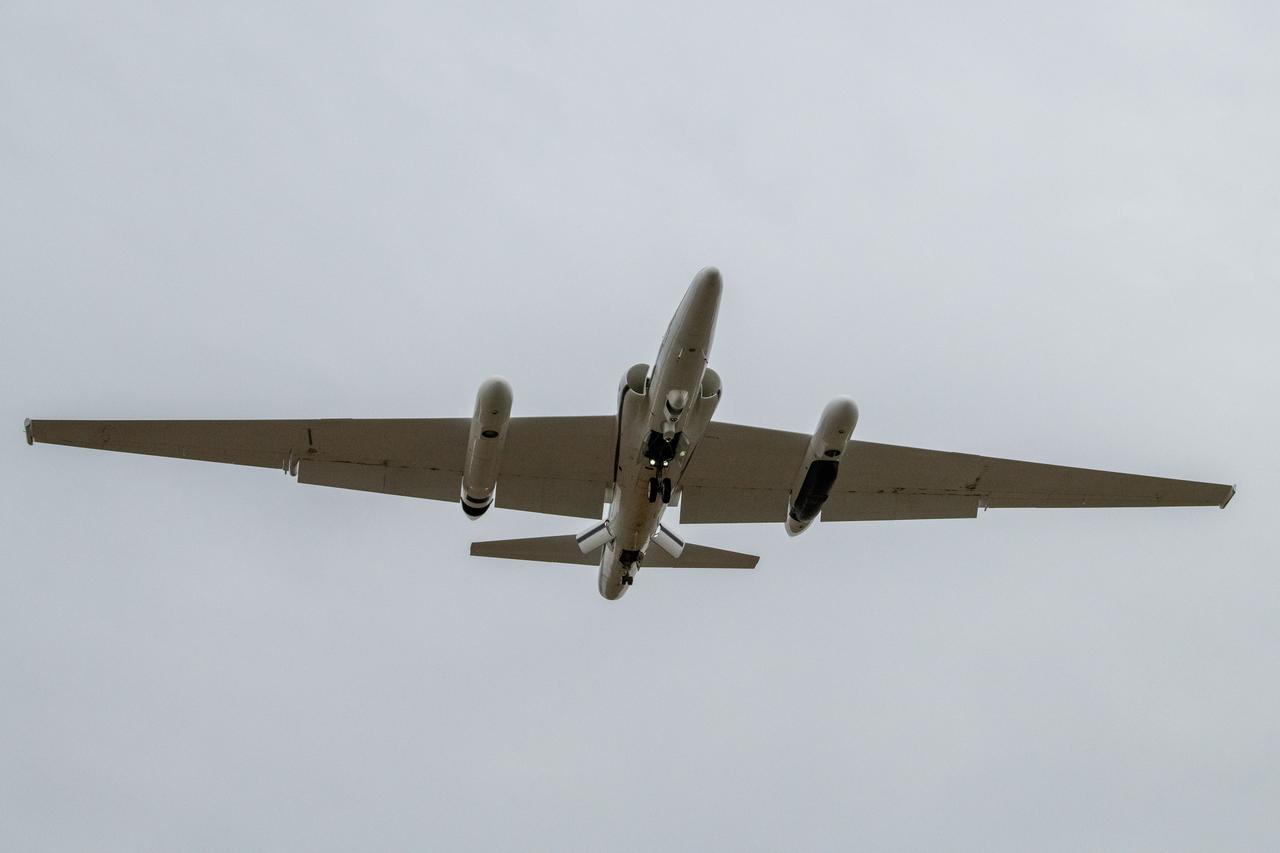

The NASA ER-2 high-altitude aircraft supported the Investigation of Microphysics and Precipitation for Atlantic Coast-Threatening Storms (IMPACTS) mission. For this mission, the IMPACTS team tracked storms across the Eastern United States to help understand how winter storms form and develop. The aircraft, which is based at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center Building 703 in Palmdale, California, was temporarily based at Dobbins Air Reserve Base in Marietta, Georgia. The three-year IMPACTS campaign concluded on Feb. 28, 2023.
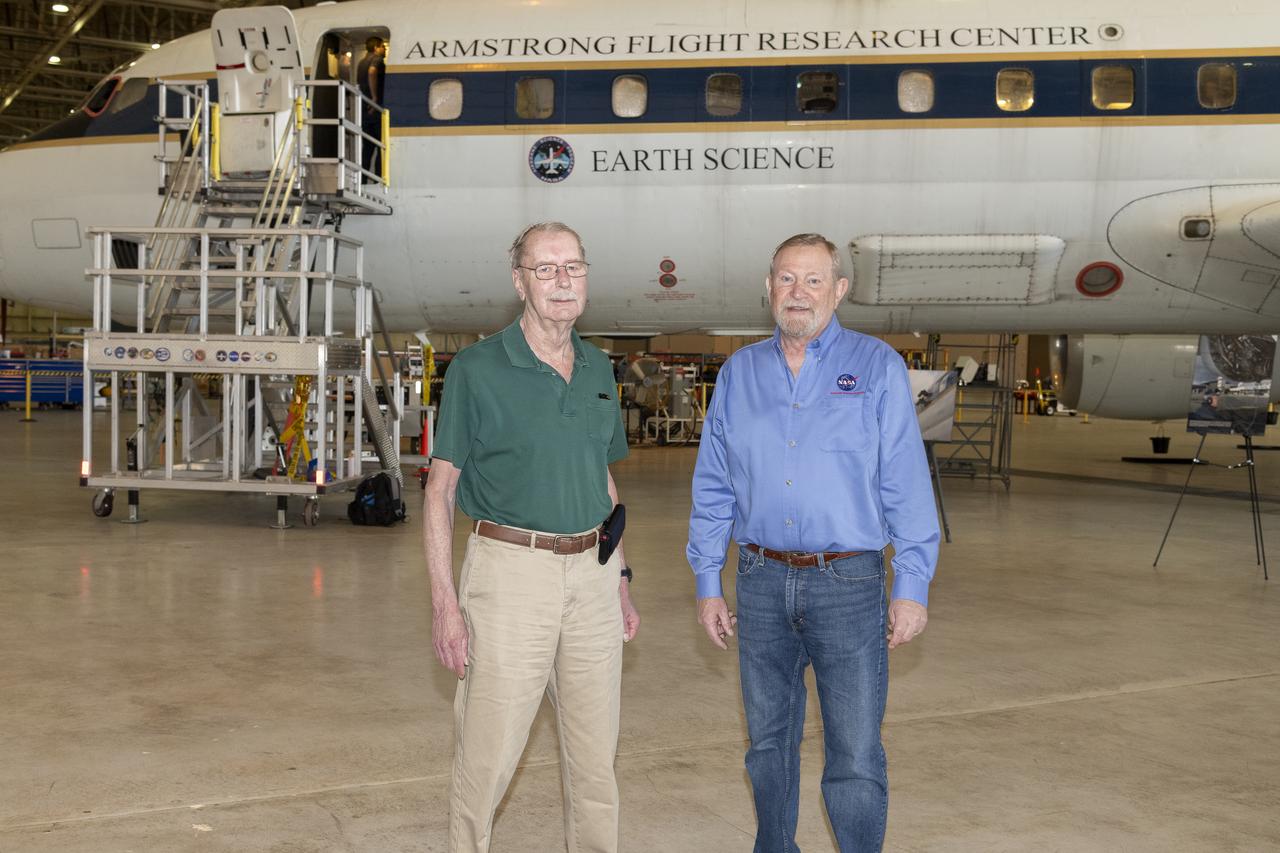

Retired NASA mission manager Chris Jennison and Randy Albertson, right, who retired in 2019 as NASA’s Airborne Science Program deputy director, stand in front of the DC-8 aircraft at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center Building 703 in Palmdale, California. On May 2, 2024, NASA personnel, friends, and family celebrated the DC-8 staff, aircraft, and science campaigns.

Date: 2/27/2025 Photographer: NASA/Rad Sinyak Caption: Technicians begin working on the installation of the four solar array wings for NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft inside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Feb. 27, 2025. Artemis II is Orion’s first crewed flight test around the Moon under the agency’s Artemis campaign.

Date: 2/27/2025 Photographer: NASA/Rad Sinyak Caption: Technicians begin working on the installation of the four solar array wings for NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft inside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Feb. 27, 2025. Artemis II is Orion’s first crewed flight test around the Moon under the agency’s Artemis campaign.

Date: 2/27/2025 Photographer: NASA/Rad Sinyak Caption: Technicians begin working on the installation of the four solar array wings for NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft inside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Feb. 27, 2025. Artemis II is Orion’s first crewed flight test around the Moon under the agency’s Artemis campaign.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- WESH-TV 2 News Anchor Wendy Chioji (right) is given a tour of Launch Complex 39B by NASA's Stephen Bulloch. Space Shuttle Atlantis awaits launch on mission STS-112 to the International Space Station in the background. Chioji was at KSC to speak at the 2002 Combined Federal Campaign (CFC) kickoff rally.

Date: 2/27/2025 Photographer: NASA/Rad Sinyak Caption: Technicians begin working on the installation of the four solar array wings for NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft inside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Feb. 27, 2025. Artemis II is Orion’s first crewed flight test around the Moon under the agency’s Artemis campaign.

Date: 2/27/2025 Photographer: NASA/Rad Sinyak Caption: Technicians begin working on the installation of the four solar array wings for NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft inside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Feb. 27, 2025. Artemis II is Orion’s first crewed flight test around the Moon under the agency’s Artemis campaign.
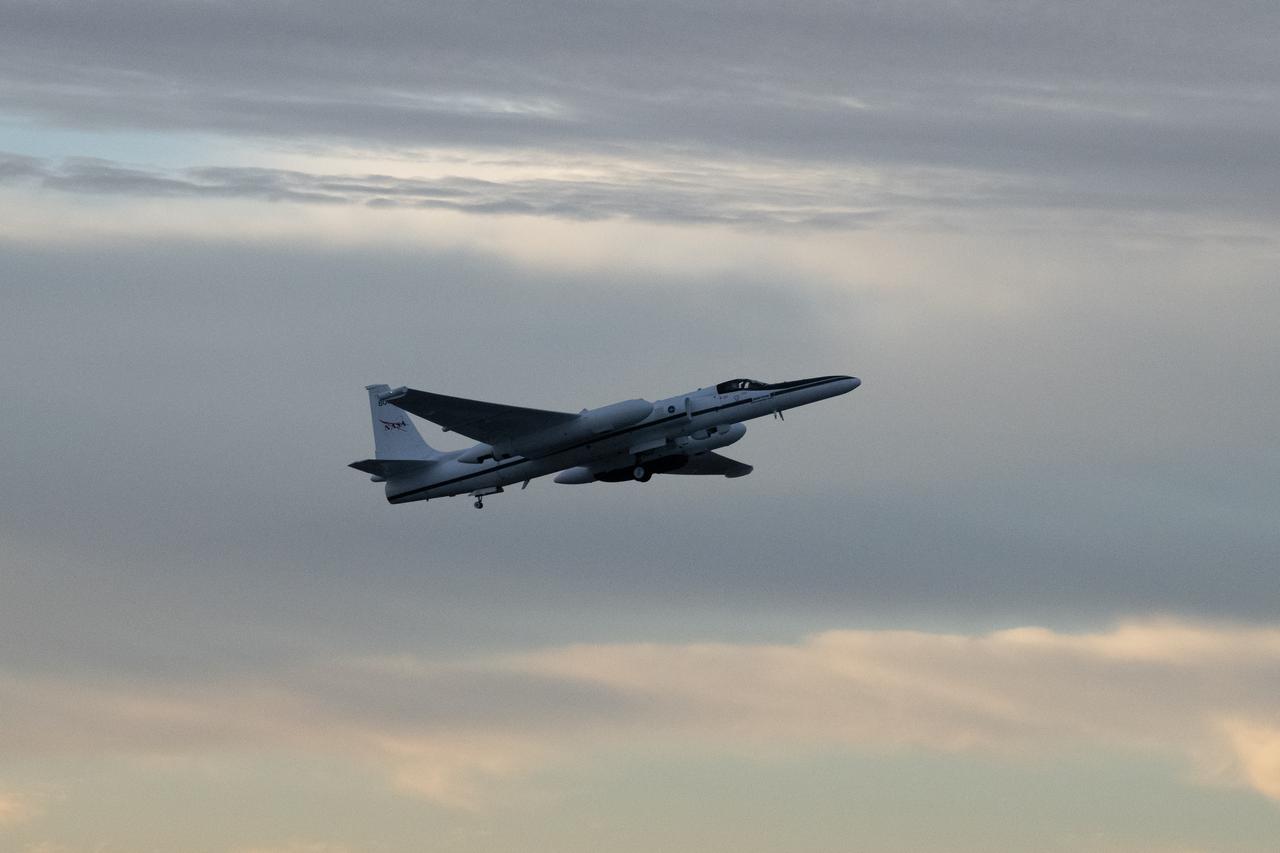

The NASA ER-2 high-altitude aircraft supported the Investigation of Microphysics and Precipitation for Atlantic Coast-Threatening Storms (IMPACTS) mission. For this mission, the IMPACTS team tracked storms across the Eastern United States to help understand how winter storms form and develop. The aircraft, which is based at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center Building 703 in Palmdale, California, was temporarily based at Dobbins Air Reserve Base in Marietta, Georgia. The three-year IMPACTS campaign concluded on Feb. 28, 2023.
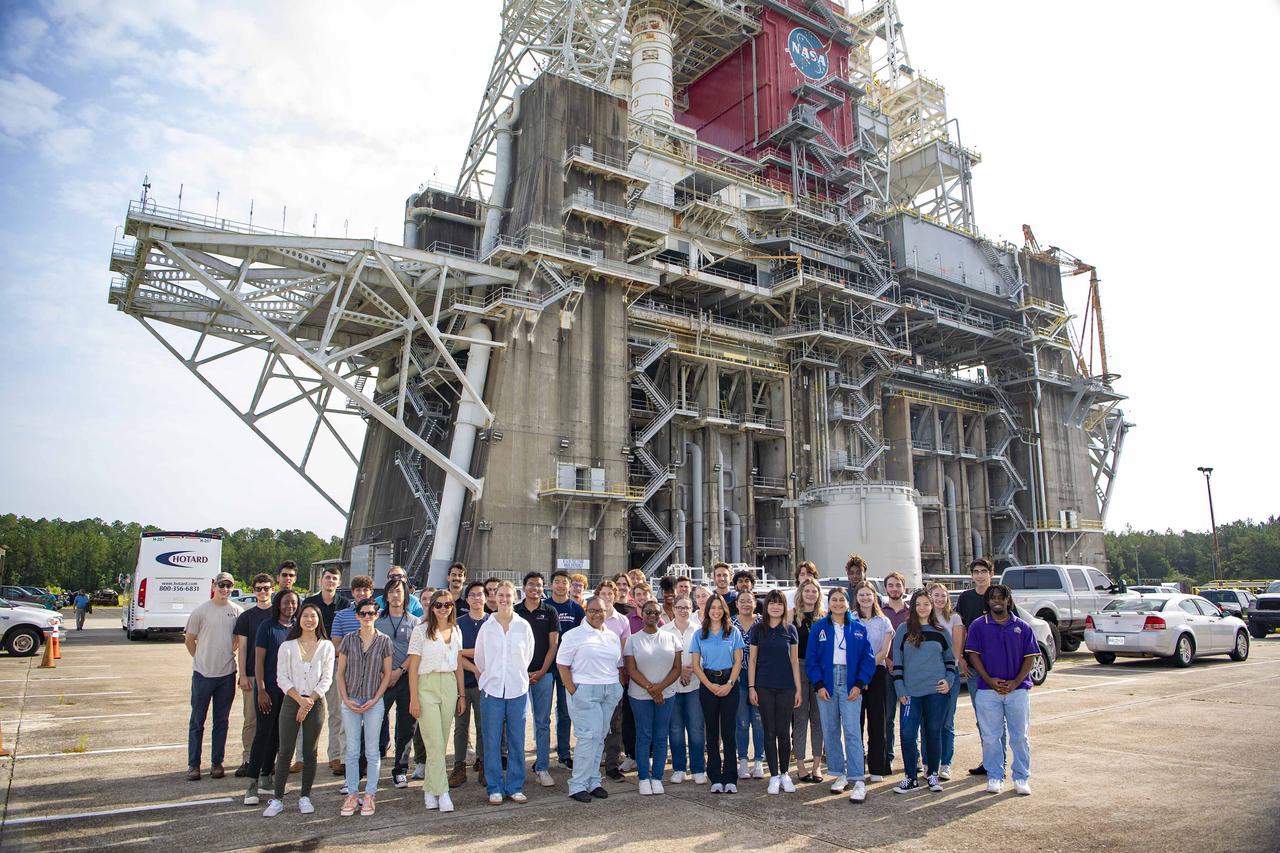

Interns at NASA Stennis visit the Thad Cochran Test Stand (B-1/B-2) on July 25 during a test complex tour on National Intern Day. As NASA continues to progress with the Artemis campaign, students across the nation are invited to join the journey. NASA’s internships aim to inspire the Artemis Generation to pursue STEM careers across the nation.
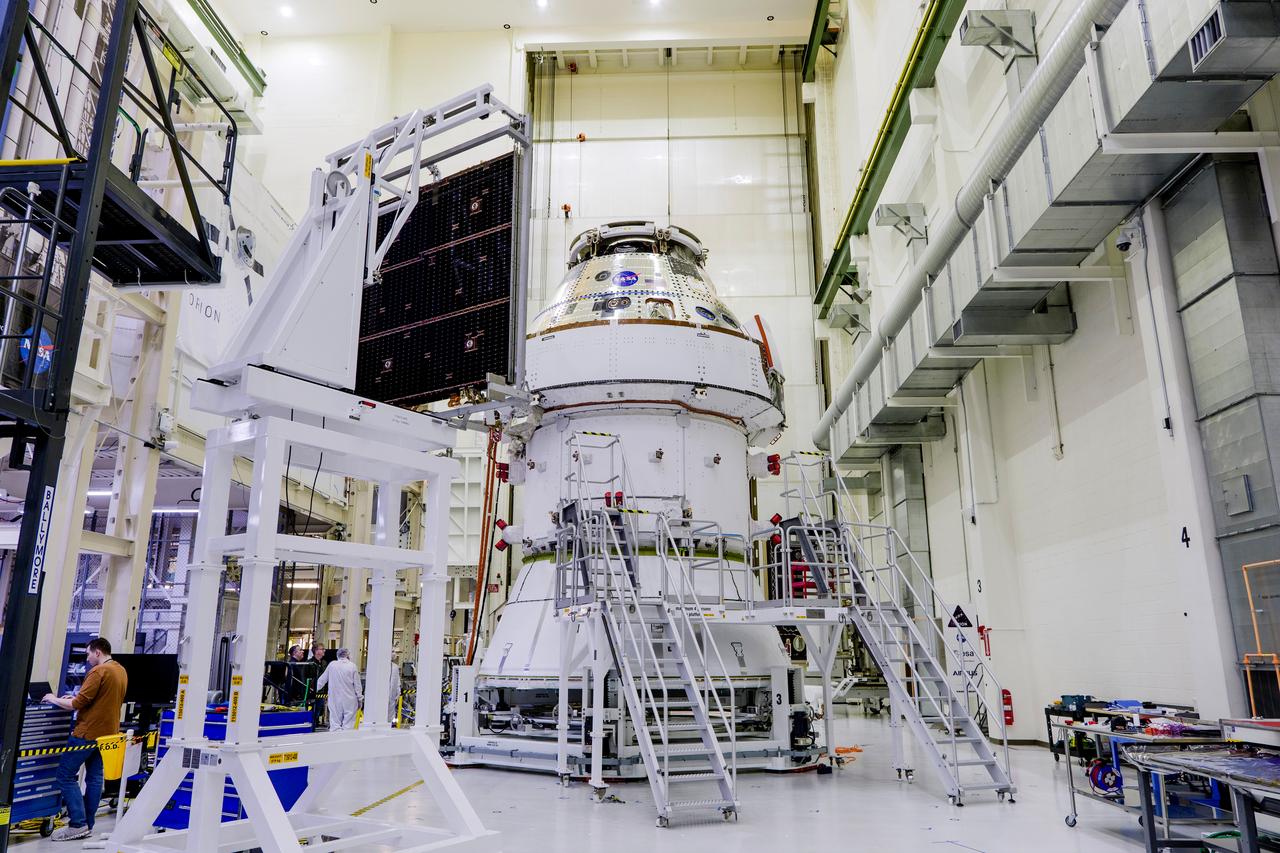

Date: 2/27/2025 Photographer: NASA/Rad Sinyak Caption: Technicians begin working on the installation of the four solar array wings for NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft inside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Feb. 27, 2025. Artemis II is Orion’s first crewed flight test around the Moon under the agency’s Artemis campaign.
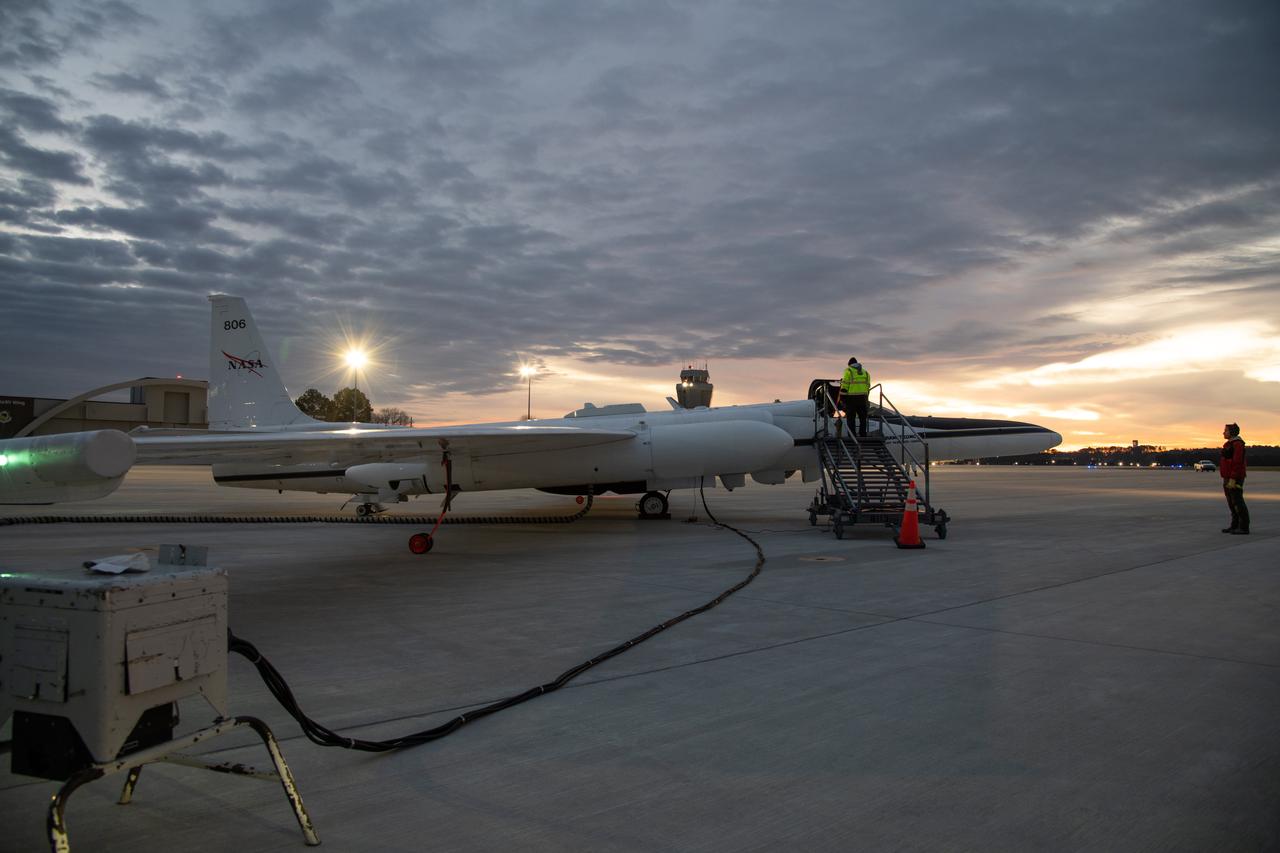

The NASA ER-2 high-altitude aircraft was prepared to support the Investigation of Microphysics and Precipitation for Atlantic Coast-Threatening Storms (IMPACTS) mission. For this mission, the IMPACTS team tracked storms across the Eastern United States to help understand how winter storms form and develop. The aircraft, which is based at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center Building 703 in Palmdale, California, was temporarily based at Dobbins Air Reserve Base in Marietta, Georgia. The three-year IMPACTS campaign concluded on Feb. 28, 2023.
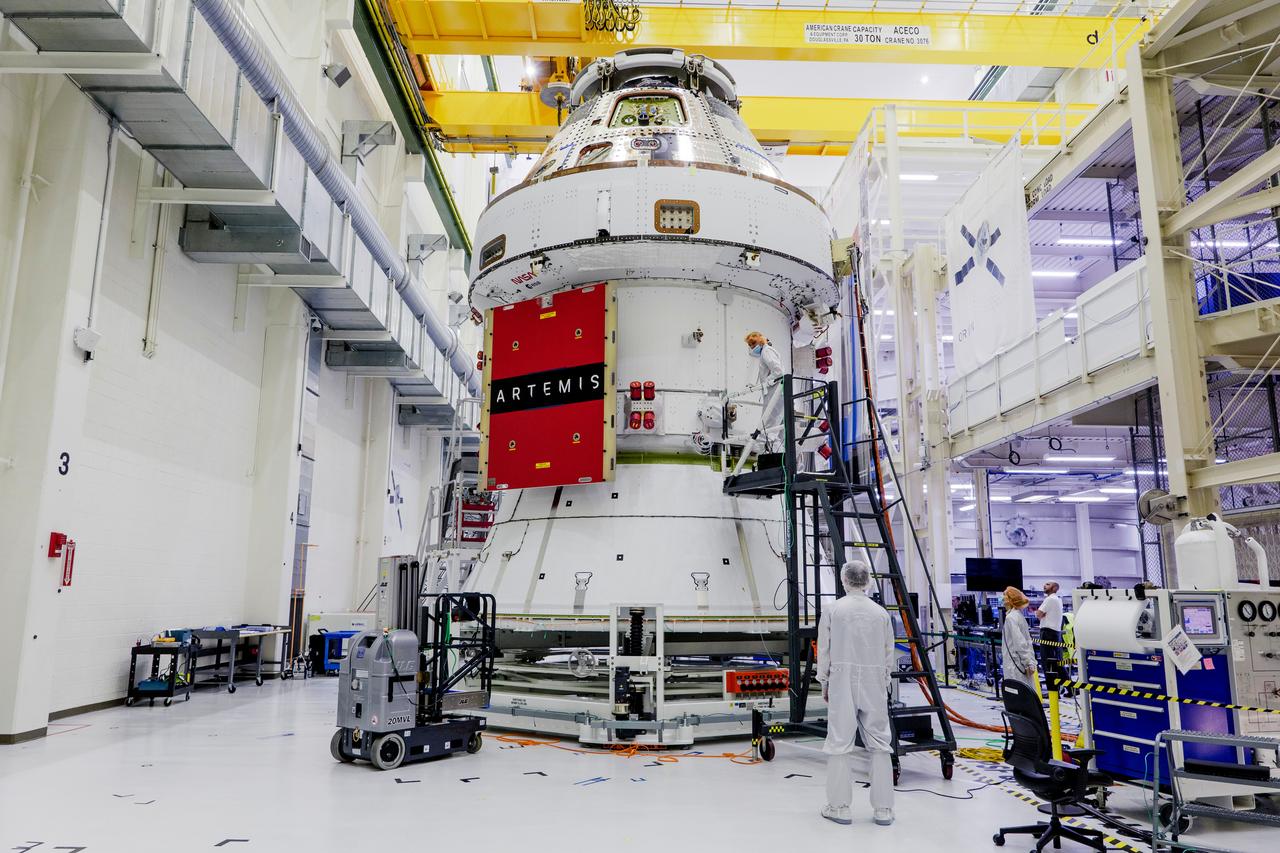

Date: 2/27/2025 Photographer: NASA/Rad Sinyak Caption: Technicians begin working on the installation of the four solar array wings for NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft inside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Feb. 27, 2025. Artemis II is Orion’s first crewed flight test around the Moon under the agency’s Artemis campaign.
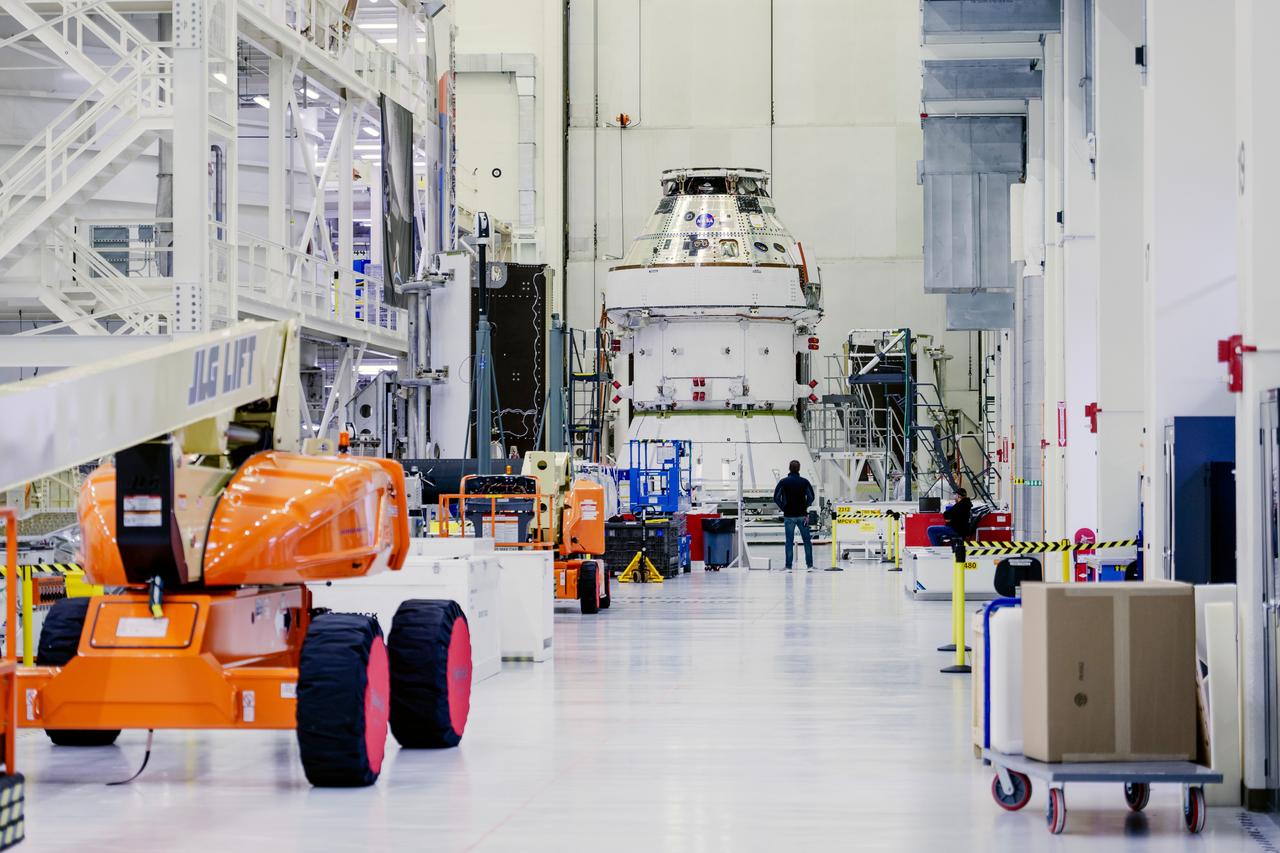

Date: 2/27/2025 Photographer: NASA/Rad Sinyak Caption: Technicians begin working on the installation of the four solar array wings for NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft inside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Feb. 27, 2025. Artemis II is Orion’s first crewed flight test around the Moon under the agency’s Artemis campaign.
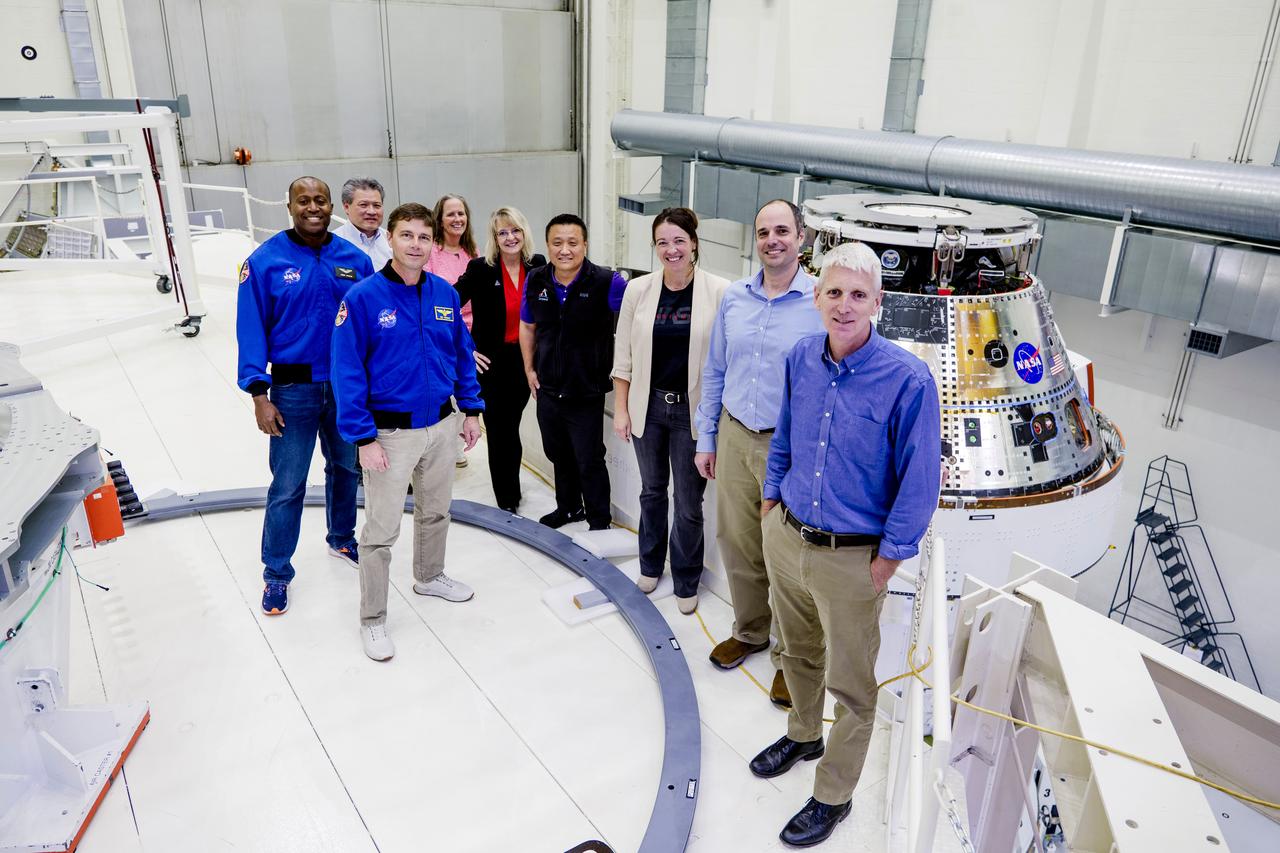

Date: 2/27/2025 Photographer: NASA/Rad Sinyak Caption: Technicians begin working on the installation of the four solar array wings for NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft inside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Feb. 27, 2025. Artemis II is Orion’s first crewed flight test around the Moon under the agency’s Artemis campaign.
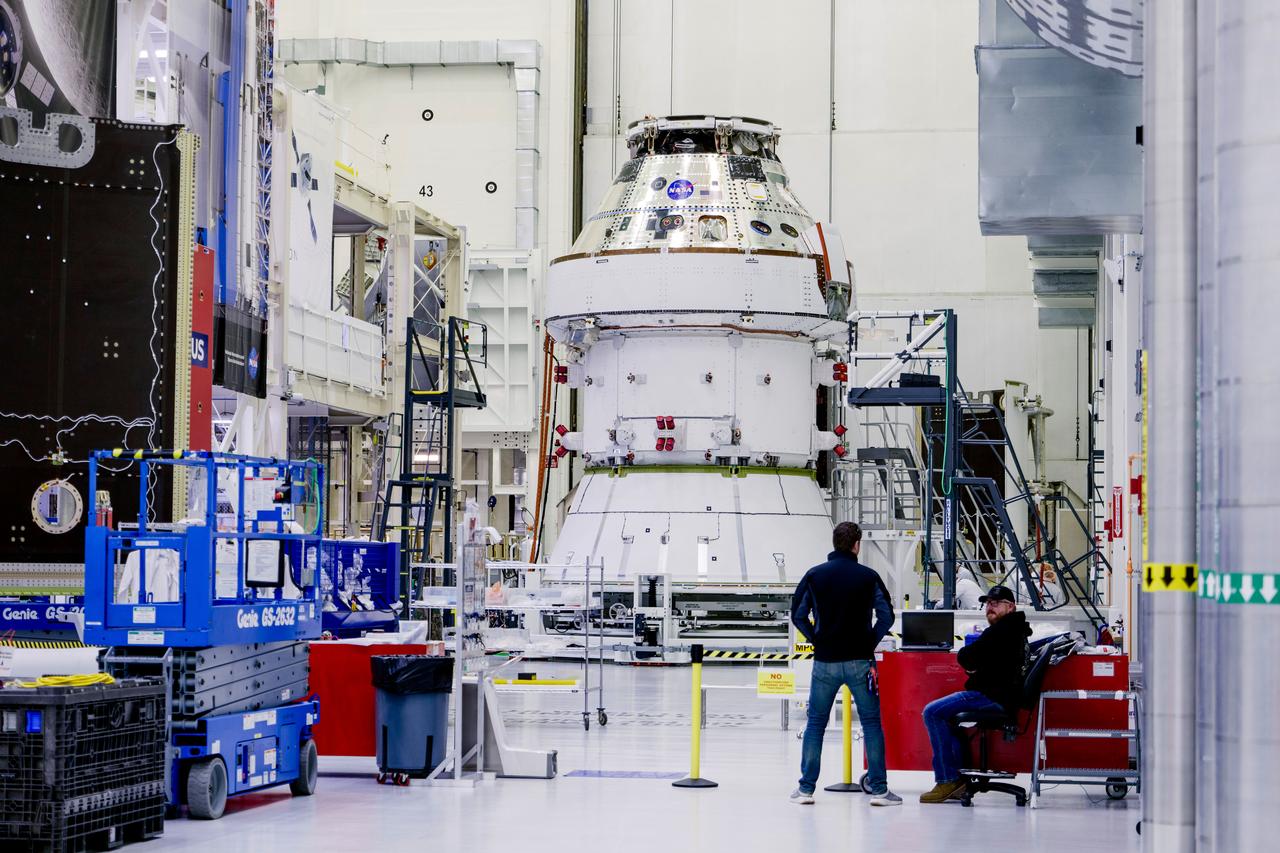

Date: 2/27/2025 Photographer: NASA/Rad Sinyak Caption: Technicians begin working on the installation of the four solar array wings for NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft inside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Feb. 27, 2025. Artemis II is Orion’s first crewed flight test around the Moon under the agency’s Artemis campaign.
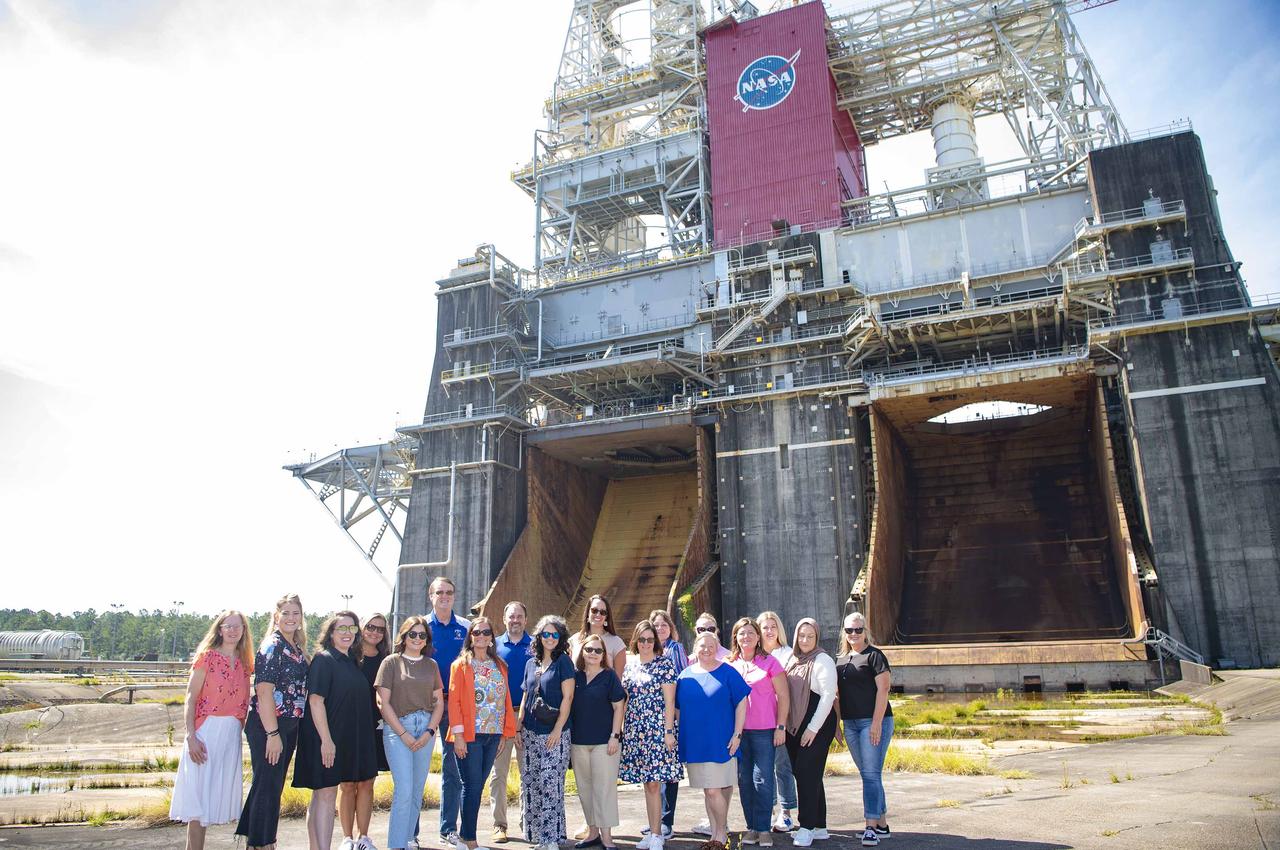

Pearl River County Elementary School leaders visit the Thad Cochran Test Stand (B-1/B-2) during a NASA Stennis tour on July 15. The school leaders received an overview of work conducted at NASA Stennis, including how the south Mississippi site is contributing to NASA’s return to the Moon through the Artemis campaign by testing engines and stages to help power the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket.

Date: 2/27/2025 Photographer: NASA/Rad Sinyak Caption: Technicians begin working on the installation of the four solar array wings for NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft inside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Feb. 27, 2025. Artemis II is Orion’s first crewed flight test around the Moon under the agency’s Artemis campaign.
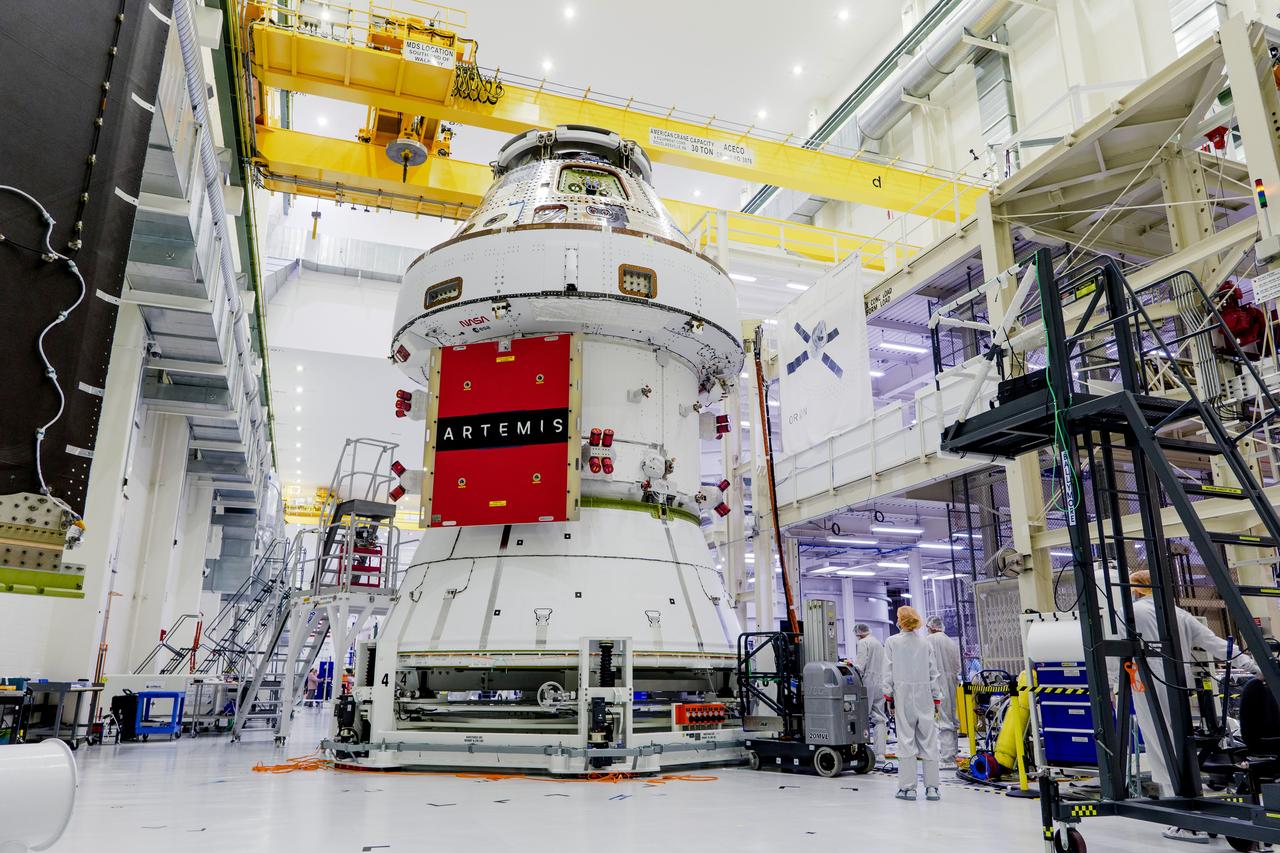

Date: 2/27/2025 Photographer: NASA/Rad Sinyak Caption: Technicians begin working on the installation of the four solar array wings for NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft inside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Feb. 27, 2025. Artemis II is Orion’s first crewed flight test around the Moon under the agency’s Artemis campaign.
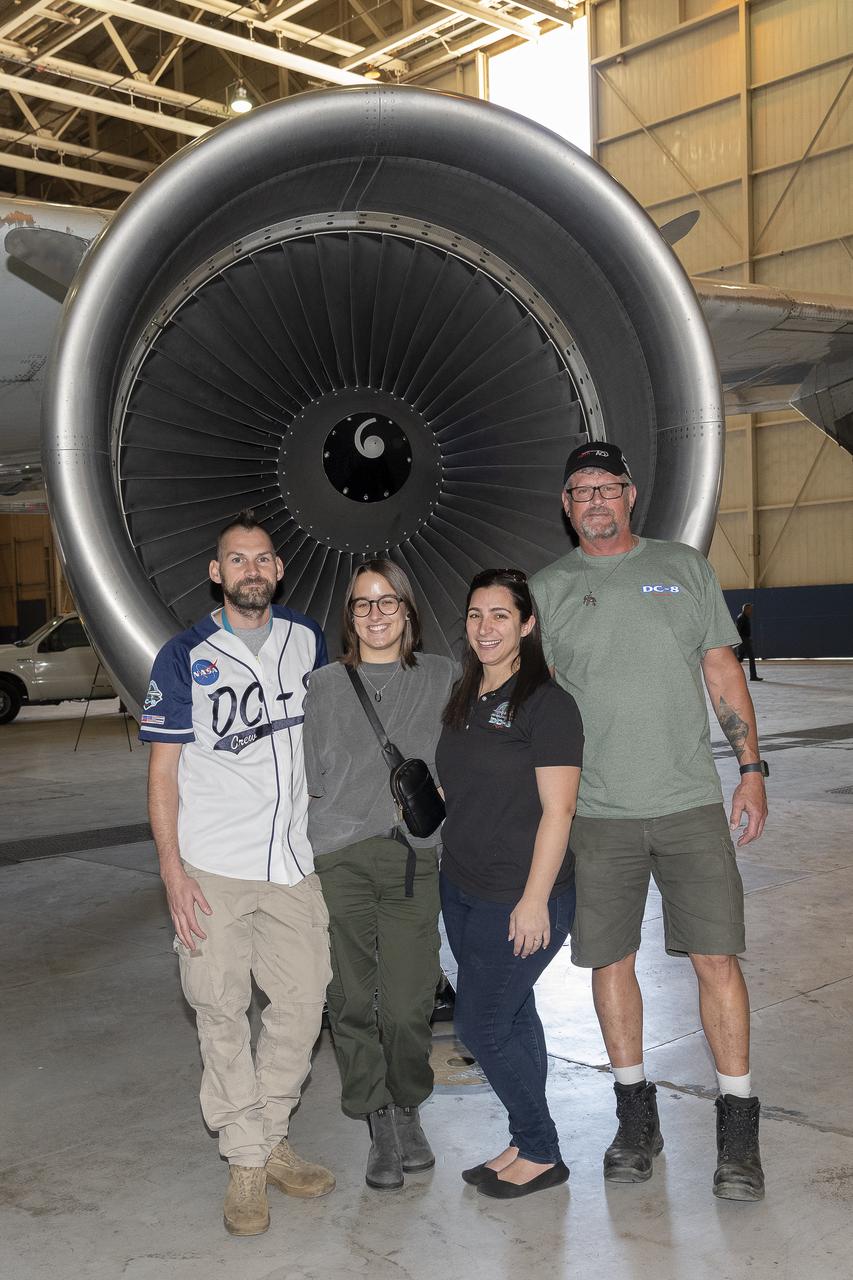

Members of past science missions pose together in front of the DC-8 aircraft’s left engine turbine at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center Building 703 in Palmdale, California. From left are avionics lead Kelly Jellison, chemical scientist Katherine Ball, DC-8 Deputy Program Manager Kirsten Boogaard, and DC-8 safety engineer Garry Moors. On May 2, 2024, NASA personnel, friends, and family celebrated the DC-8 staff, aircraft, and science campaigns.
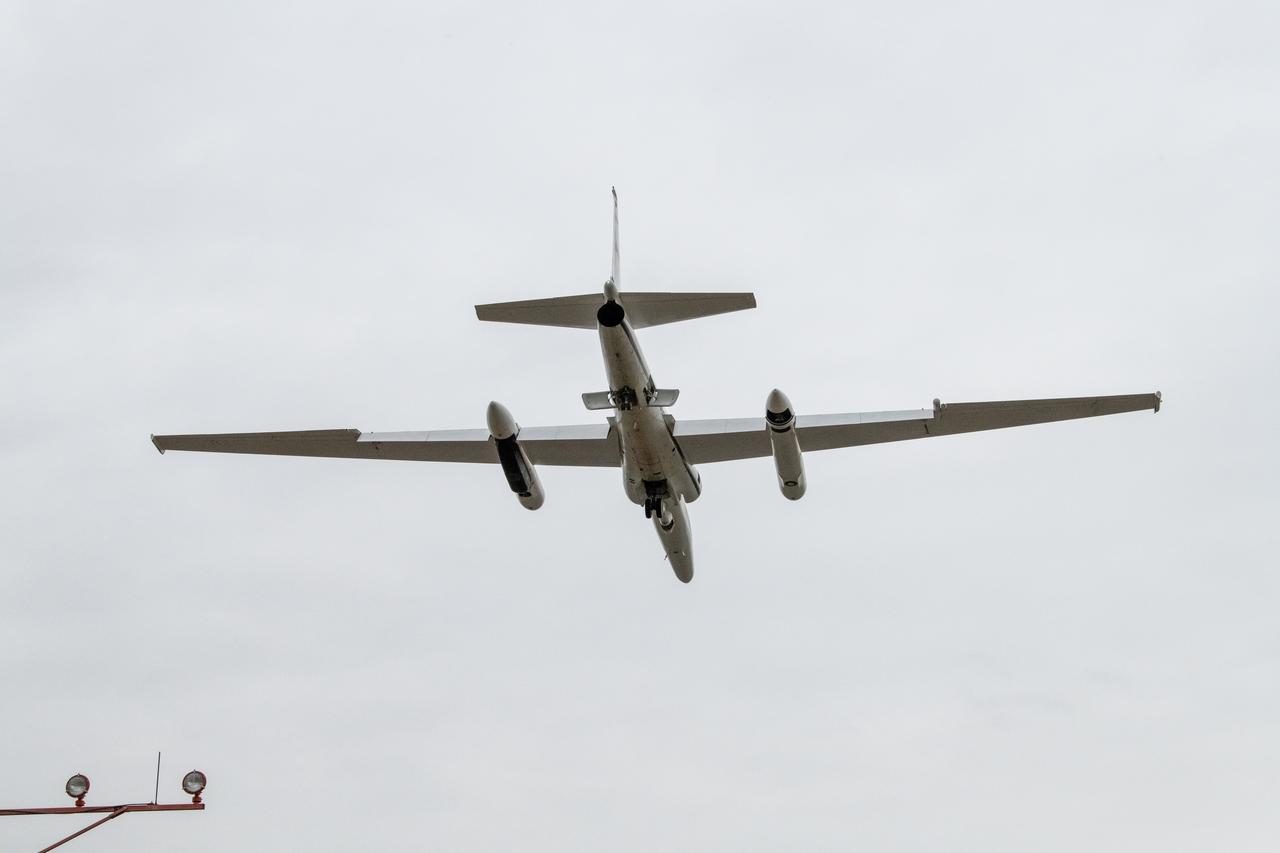

The NASA ER-2 high-altitude aircraft supported the Investigation of Microphysics and Precipitation for Atlantic Coast-Threatening Storms (IMPACTS) mission. For this mission, the IMPACTS team tracked storms across the Eastern United States to help understand how winter storms form and develop. The aircraft, which is based at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center Building 703 in Palmdale, California, was temporarily based at Dobbins Air Reserve Base in Marietta, Georgia. The three-year IMPACTS campaign concluded on Feb. 28, 2023.
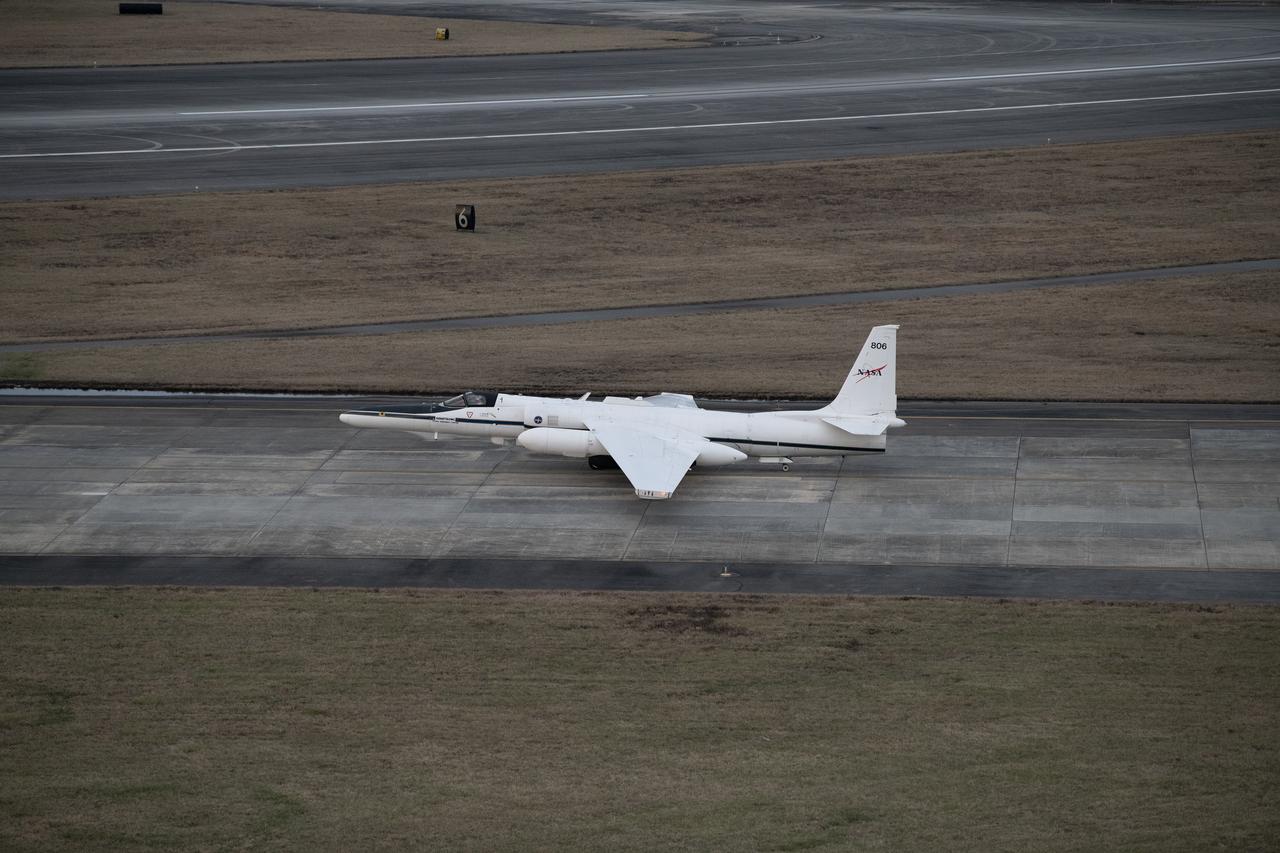

The NASA ER-2 high-altitude aircraft was prepared to support the Investigation of Microphysics and Precipitation for Atlantic Coast-Threatening Storms (IMPACTS) mission. For this mission, the IMPACTS team tracked storms across the Eastern United States to help understand how winter storms form and develop. The aircraft, which is based at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center Building 703 in Palmdale, California, was temporarily based at Dobbins Air Reserve Base in Marietta, Georgia. The three-year IMPACTS campaign concluded on Feb. 28, 2023.
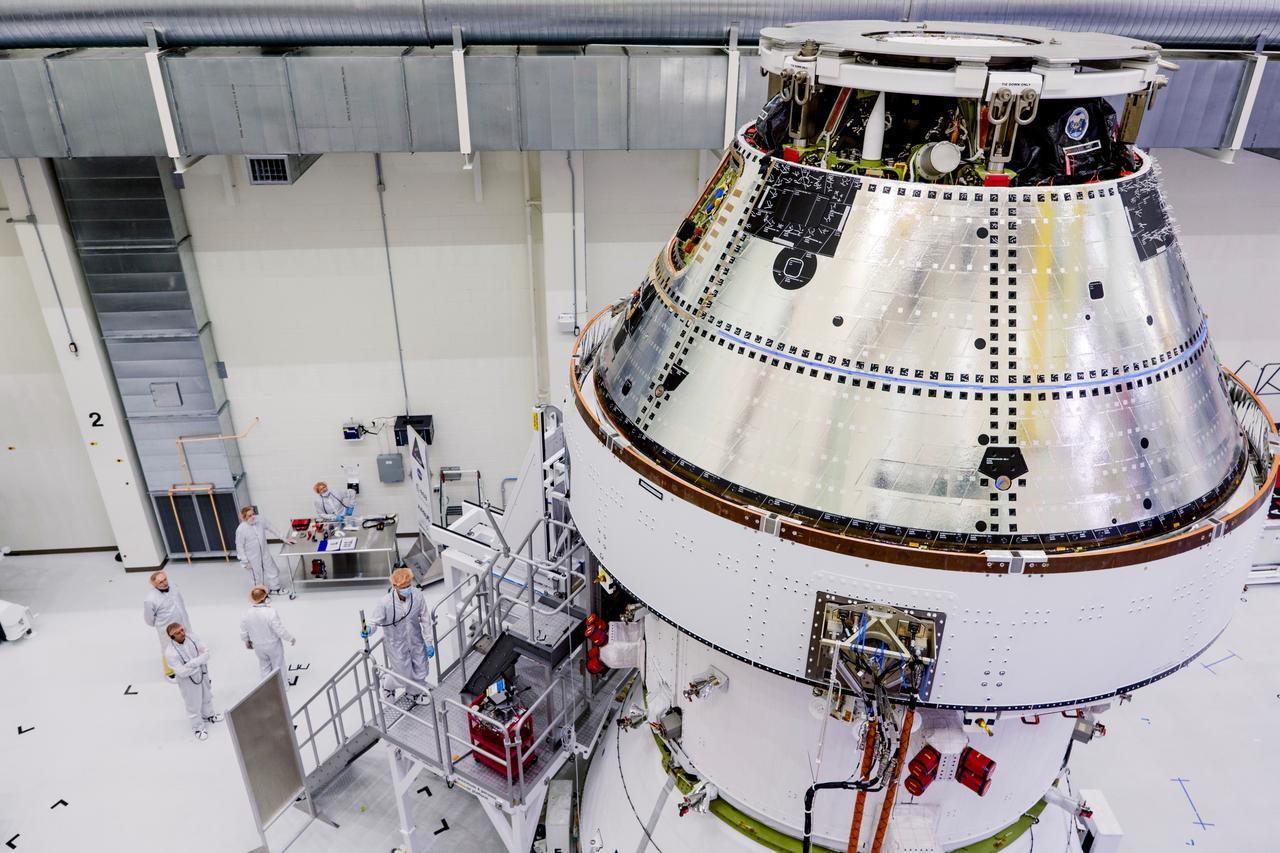
Date: 2/27/2025 Photographer: NASA/Rad Sinyak Caption: Technicians begin working on the installation of the four solar array wings for NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft inside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Feb. 27, 2025. Artemis II is Orion’s first crewed flight test around the Moon under the agency’s Artemis campaign.
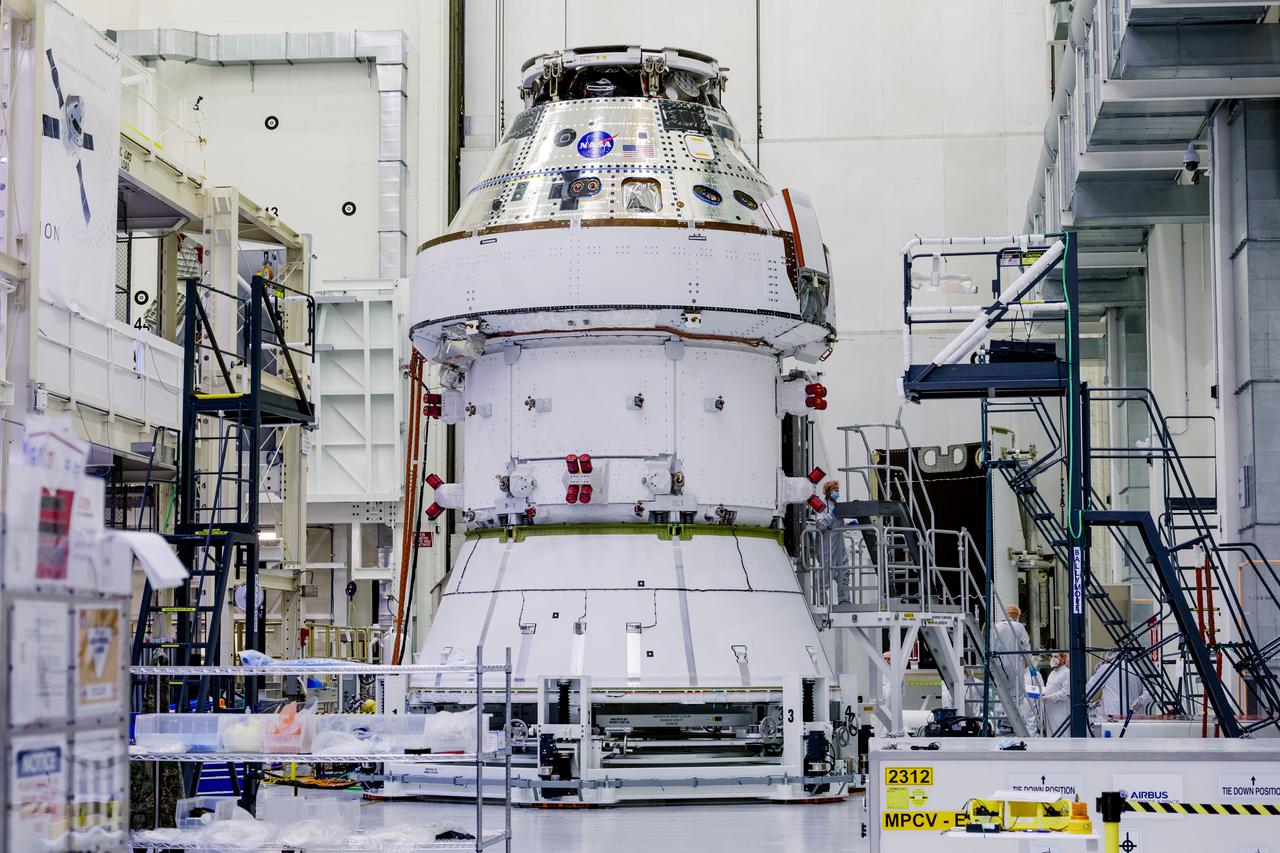
Date: 2/27/2025 Photographer: NASA/Rad Sinyak Caption: Technicians begin working on the installation of the four solar array wings for NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft inside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Feb. 27, 2025. Artemis II is Orion’s first crewed flight test around the Moon under the agency’s Artemis campaign.
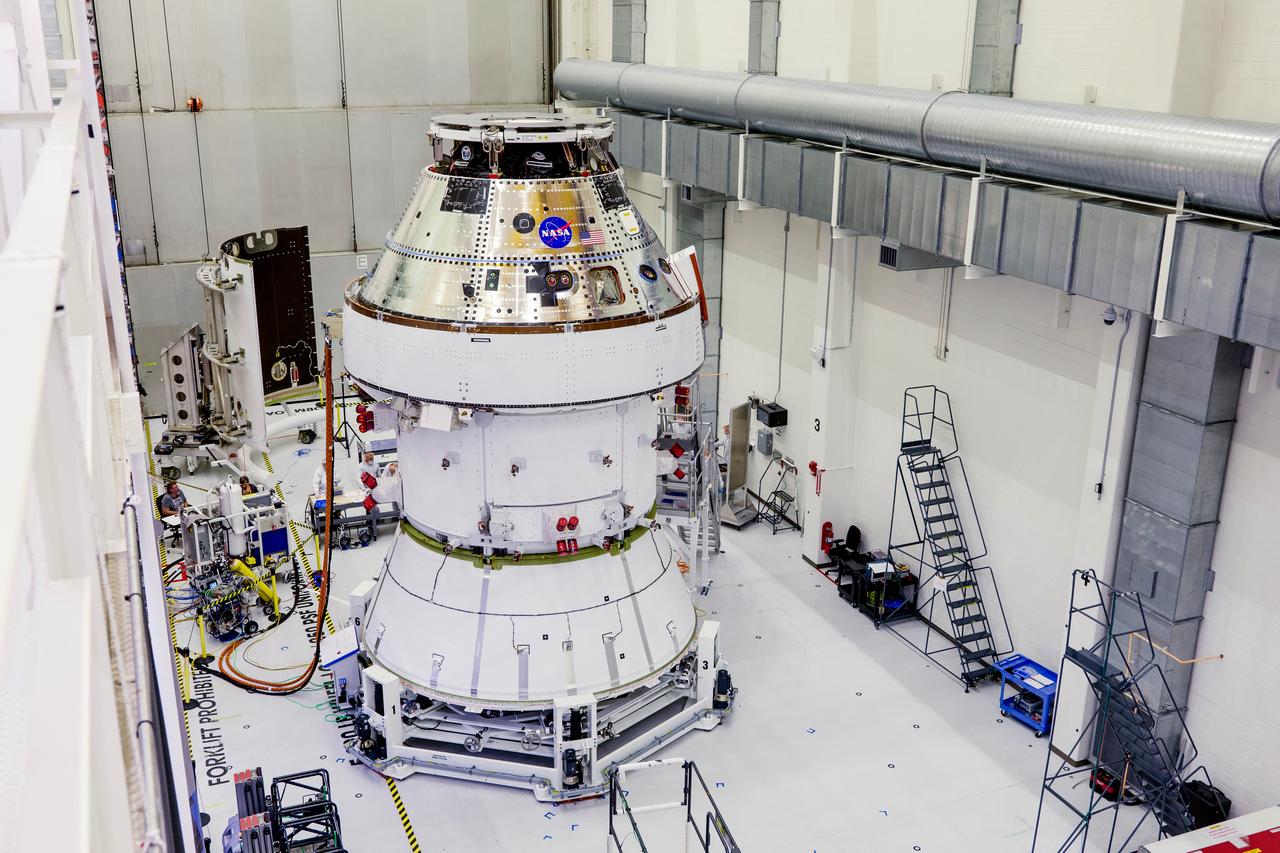

Date: 2/27/2025 Photographer: NASA/Rad Sinyak Caption: Technicians begin working on the installation of the four solar array wings for NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft inside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Feb. 27, 2025. Artemis II is Orion’s first crewed flight test around the Moon under the agency’s Artemis campaign.
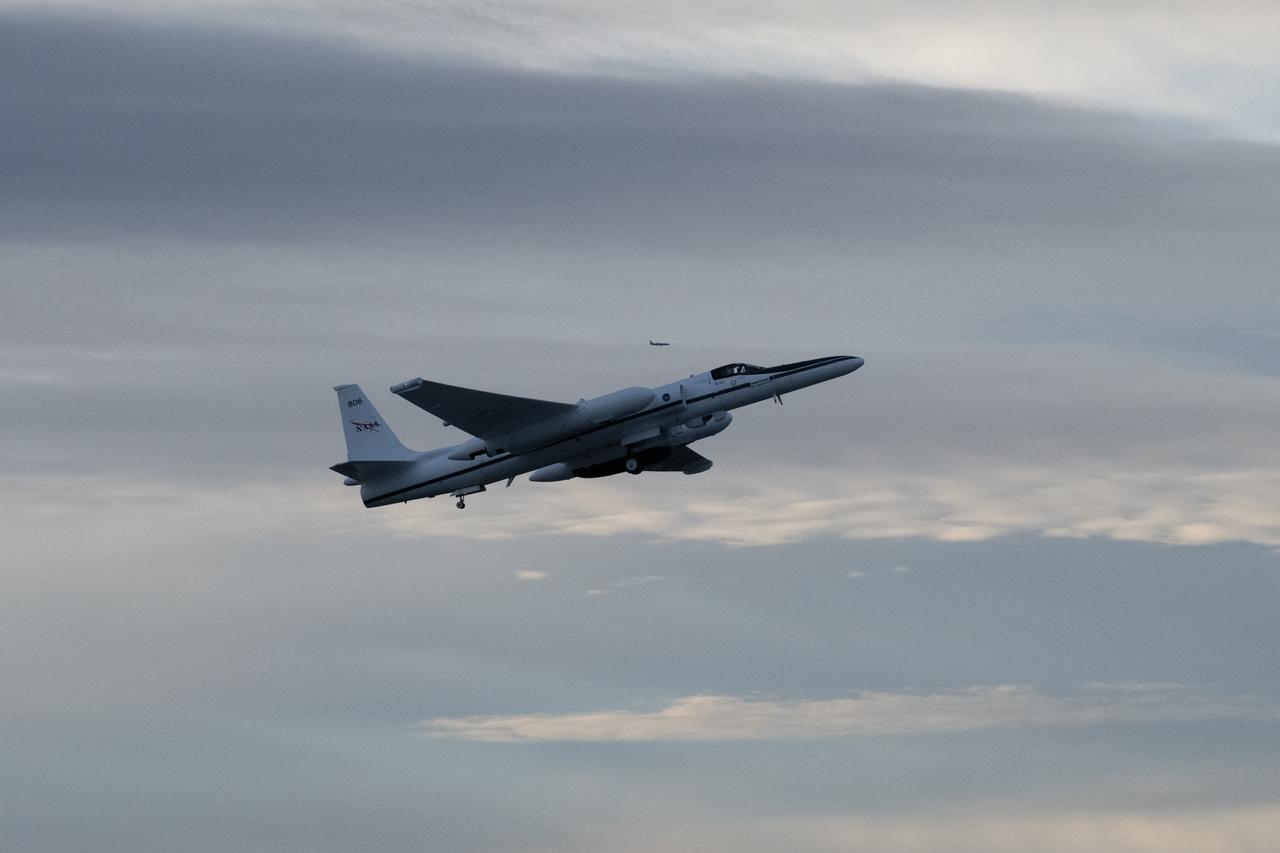

The NASA ER-2 high-altitude aircraft supported the Investigation of Microphysics and Precipitation for Atlantic Coast-Threatening Storms (IMPACTS) mission. For this mission, the IMPACTS team tracked storms across the Eastern United States to help understand how winter storms form and develop. The aircraft, which is based at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center Building 703 in Palmdale, California, was temporarily based at Dobbins Air Reserve Base in Marietta, Georgia. The three-year IMPACTS campaign concluded on Feb. 28, 2023.
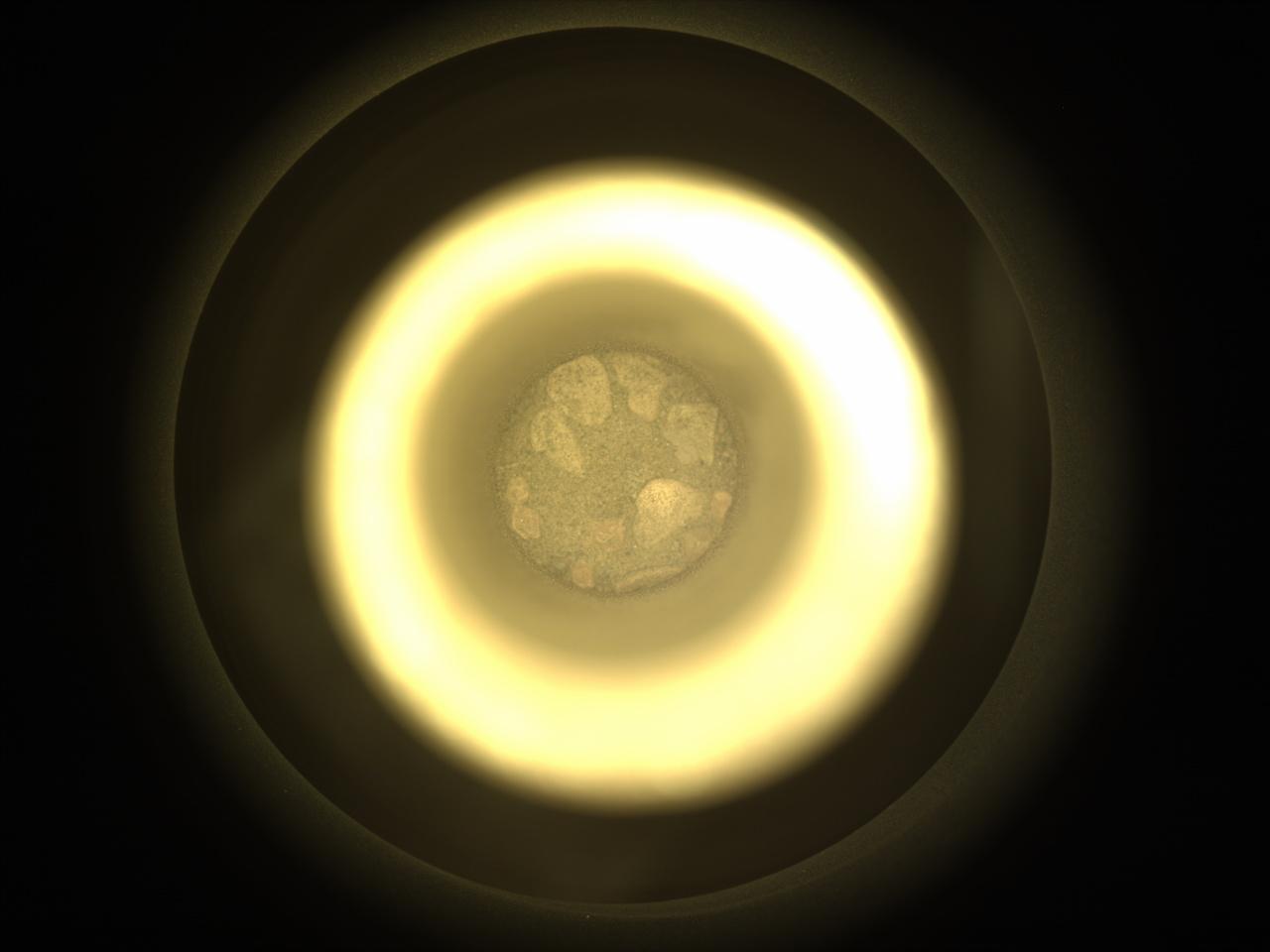
This image of Martian regolith – broken rock and dust – was captured Dec. 2, 2022, by the Sampling and Caching System Camera (known as CacheCam) on NASA's Perseverance Mars rover. The regolith, contained inside a metal tube, is one of two samples that will be considered for deposit on the Martian surface this month as part of the Mars Sample Return campaign. The sample was collected in Mars' Jezero Crater from a pile of wind-blown sand and dust called a "mega-ripple" – a feature similar to but smaller than a dune. Studying regolith with powerful lab equipment back on Earth will allow scientists to better understand the processes that have shaped the surface of Mars and help engineers design future missions as well as equipment used by future Martian astronauts. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25588
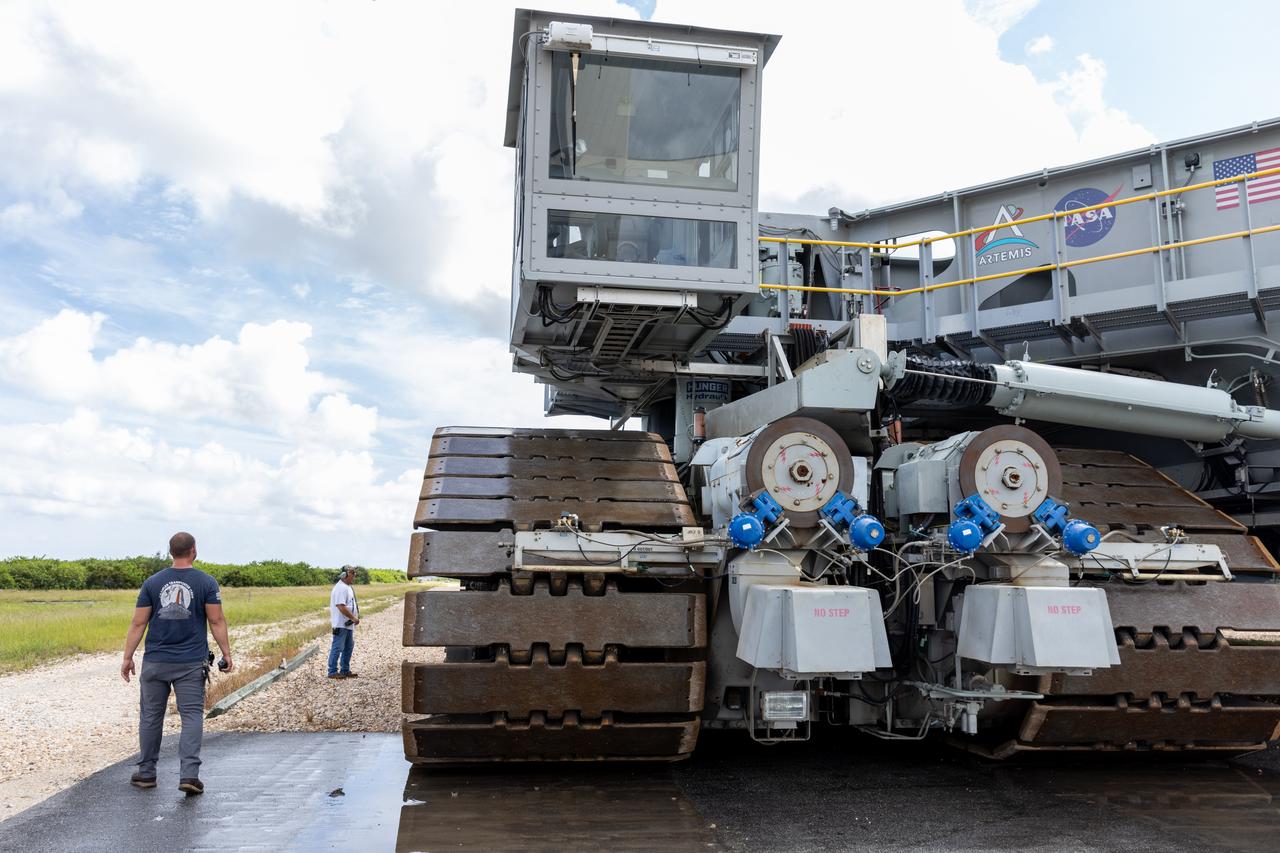

NASA’s crawler-transporter 2 moves slowly along the crawlerway towards Launch Pad 39B at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Sept. 25, 2024, after reaching the milestone of 2,500 miles traveled since its construction in 1965. Crawler-transporter 2 reached the milestone while teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems took it on a trip in preparation for supporting the roll of the mobile launcher back into the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building ahead of the Artemis II launch. Built originally to transport massive Saturn V rockets during the Apollo Program, crawler-transporter 2 continued its service during the Space Shuttle Program, and currently transports the massive SLS (Space Launch System) rocket and Orion spacecraft atop the mobile launcher as part of the agency’s Artemis campaign.
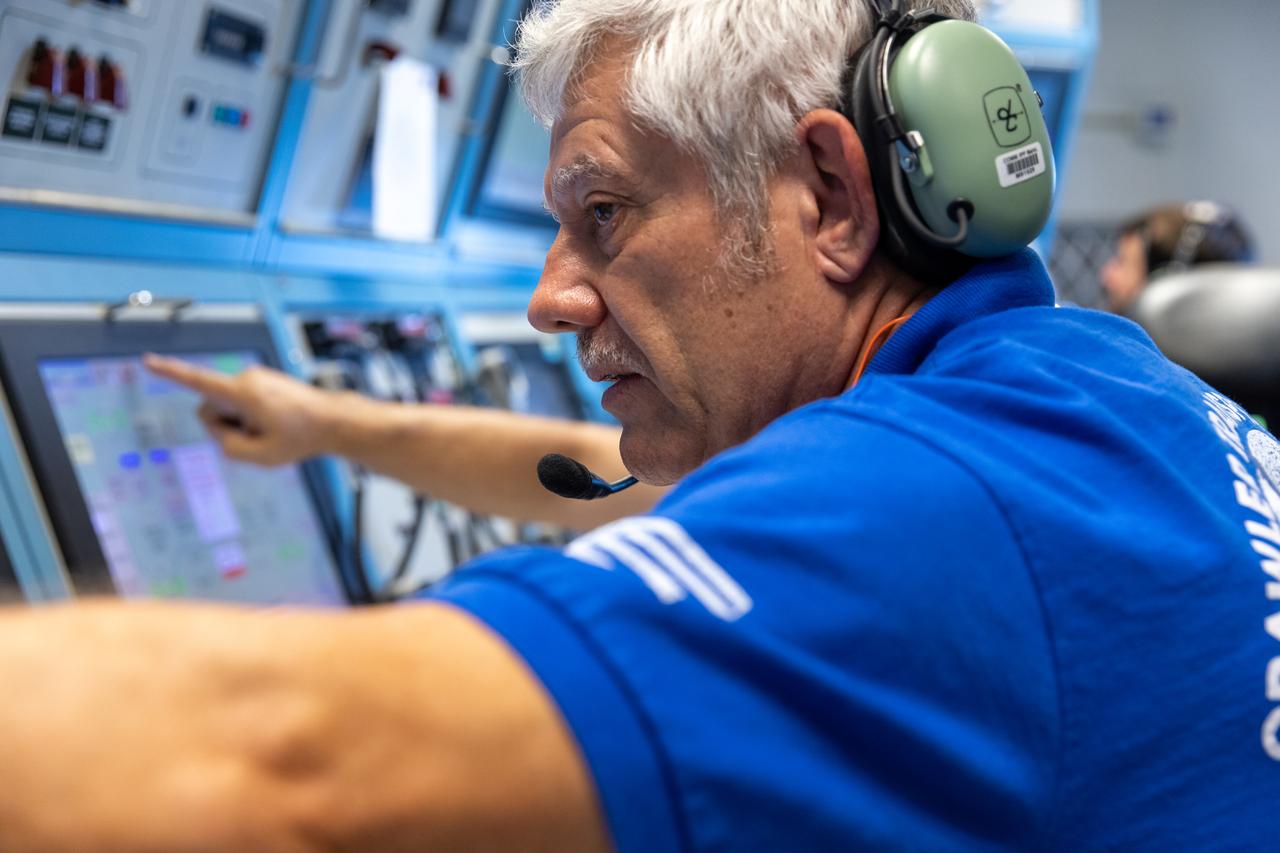

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida celebrate on Wednesday, Sept. 25, 2024, the agency’s crawler-transporter 2 reaching the milestone of 2,500 miles traveled since its construction in 1965. Crawler-transporter 2 reached the milestone while teams took it on a trip in preparation for supporting the roll of the mobile launcher from Launch Pad 39B back into the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building ahead of the Artemis II launch. Built originally to transport massive Saturn V rockets during the Apollo Program, crawler-transporter 2 continued its service during the Space Shuttle Program, and currently transports the massive SLS (Space Launch System) rocket and Orion spacecraft atop the mobile launcher as part of the agency’s Artemis campaign.
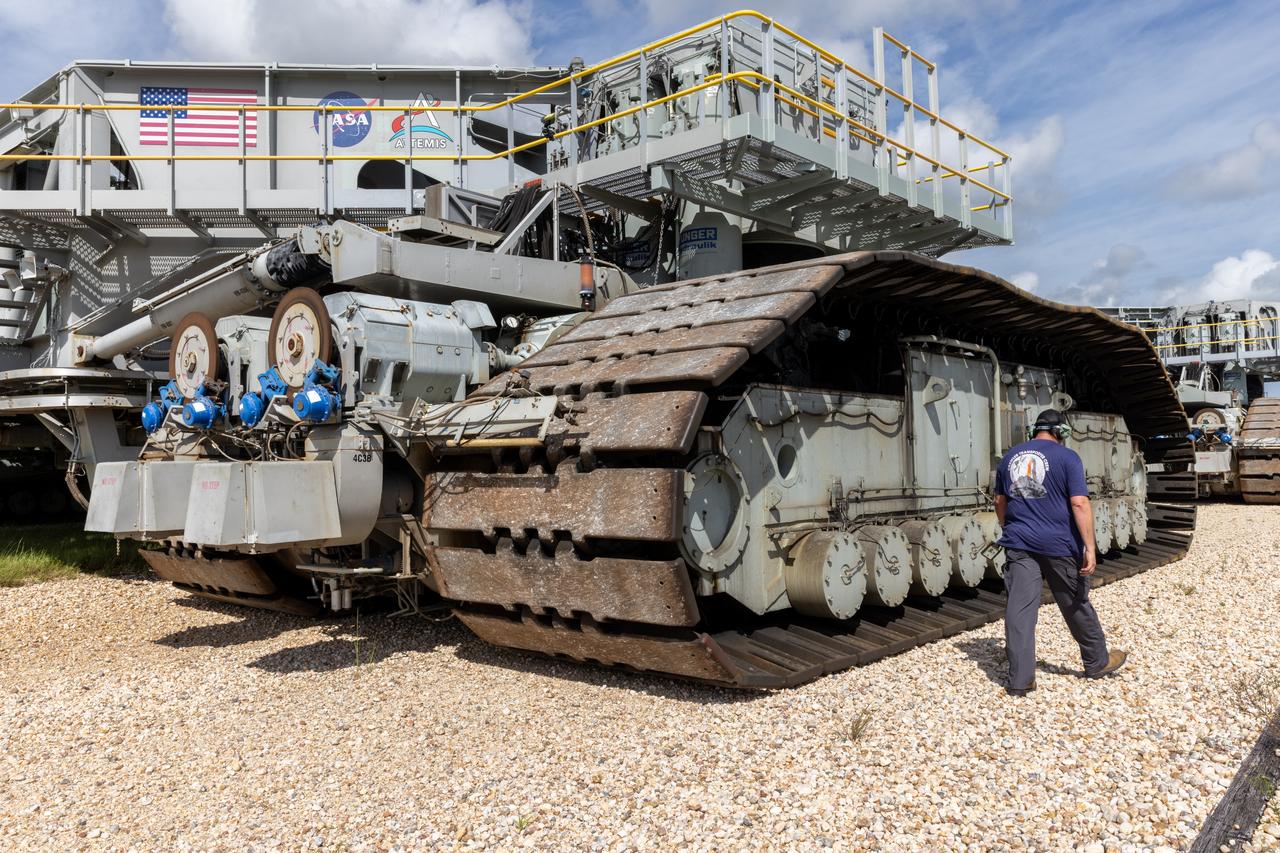

NASA’s crawler-transporter 2 moves slowly along the crawlerway towards Launch Pad 39B at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Sept. 25, 2024, after reaching the milestone of 2,500 miles traveled since its construction in 1965. Crawler-transporter 2 reached the milestone while teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems took it on a trip in preparation for supporting the roll of the mobile launcher back into the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building ahead of the Artemis II launch. Built originally to transport massive Saturn V rockets during the Apollo Program, crawler-transporter 2 continued its service during the Space Shuttle Program, and currently transports the massive SLS (Space Launch System) rocket and Orion spacecraft atop the mobile launcher as part of the agency’s Artemis campaign.

John Giles, crawler element operations manager for NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems, holds a plaque near the odometer of the agency’s crawler-transporter 2, on Wednesday, Sept. 25, 2024, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, commemorating the milestone of 2,500 miles traveled since its construction in 1965. Crawler-transporter 2 reached the milestone while teams took it on a trip in preparation for supporting the roll of the mobile launcher from Launch Pad 39B back into the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building ahead of the Artemis II launch. Built originally to transport massive Saturn V rockets during the Apollo Program, crawler-transporter 2 continued its service during the Space Shuttle Program, and currently transports the massive SLS (Space Launch System) rocket and Orion spacecraft atop the mobile launcher as part of the agency’s Artemis campaign.
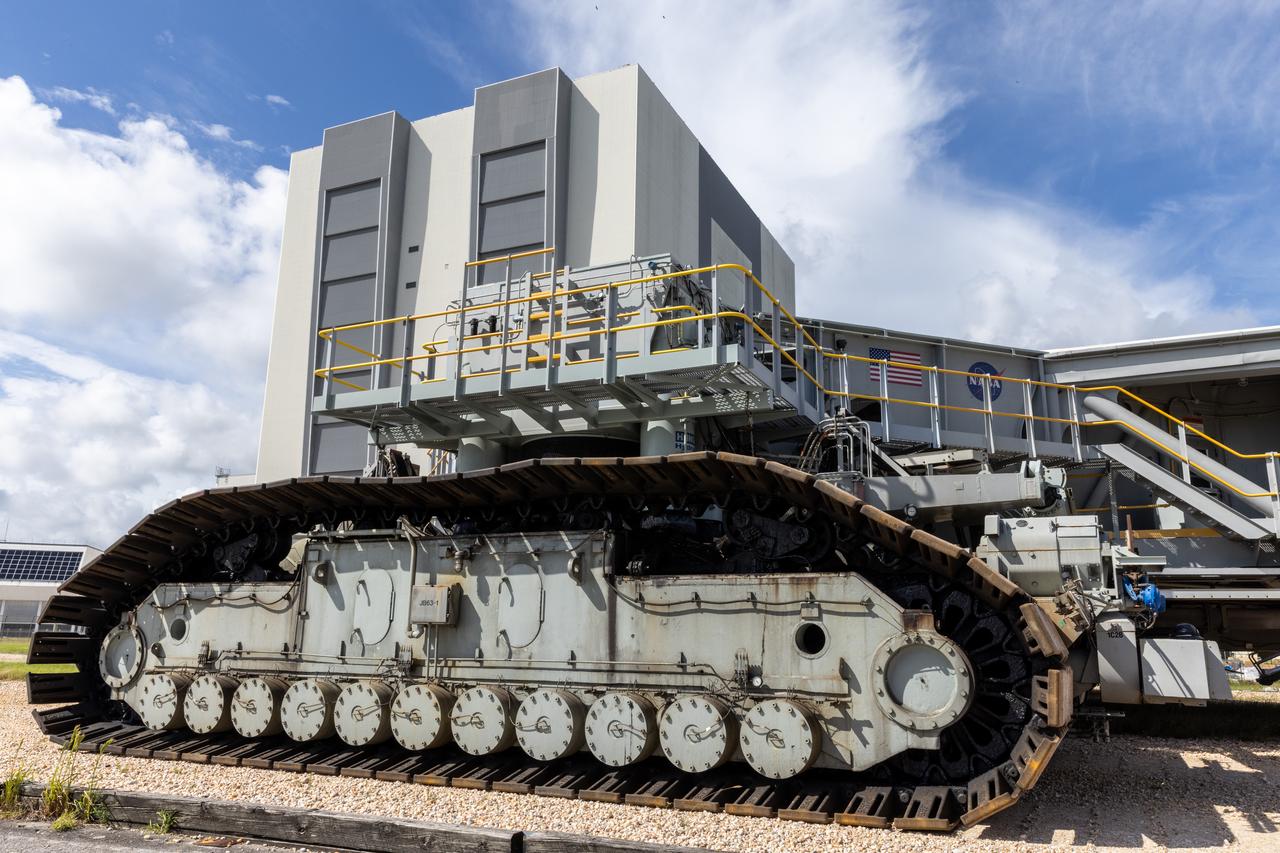

NASA’s crawler-transporter 2 moves slowly along the crawlerway towards Launch Pad 39B at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Sept. 25, 2024, after reaching the milestone of 2,500 miles traveled since its construction in 1965. Crawler-transporter 2 reached the milestone while teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems took it on a trip in preparation for supporting the roll of the mobile launcher back into the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building ahead of the Artemis II launch. Built originally to transport massive Saturn V rockets during the Apollo Program, crawler-transporter 2 continued its service during the Space Shuttle Program, and currently transports the massive SLS (Space Launch System) rocket and Orion spacecraft atop the mobile launcher as part of the agency’s Artemis campaign.

A photo of NASA’s crawler-transporter 2 odometer on Wednesday, Sept. 25, 2024, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, commemorates the milestone of reaching 2,500 miles traveled since its construction in 1965. Crawler-transporter 2’s original odometer ceased working in 1977 at 644 miles, so teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems added the original figure to the new odometer to calculate the milestone. Built originally to transport massive Saturn V rockets during the Apollo Program, crawler-transporter 2 continued its service during the Space Shuttle Program, and currently transports the massive SLS (Space Launch System) rocket and Orion spacecraft atop the mobile launcher as part of the agency’s Artemis campaign.
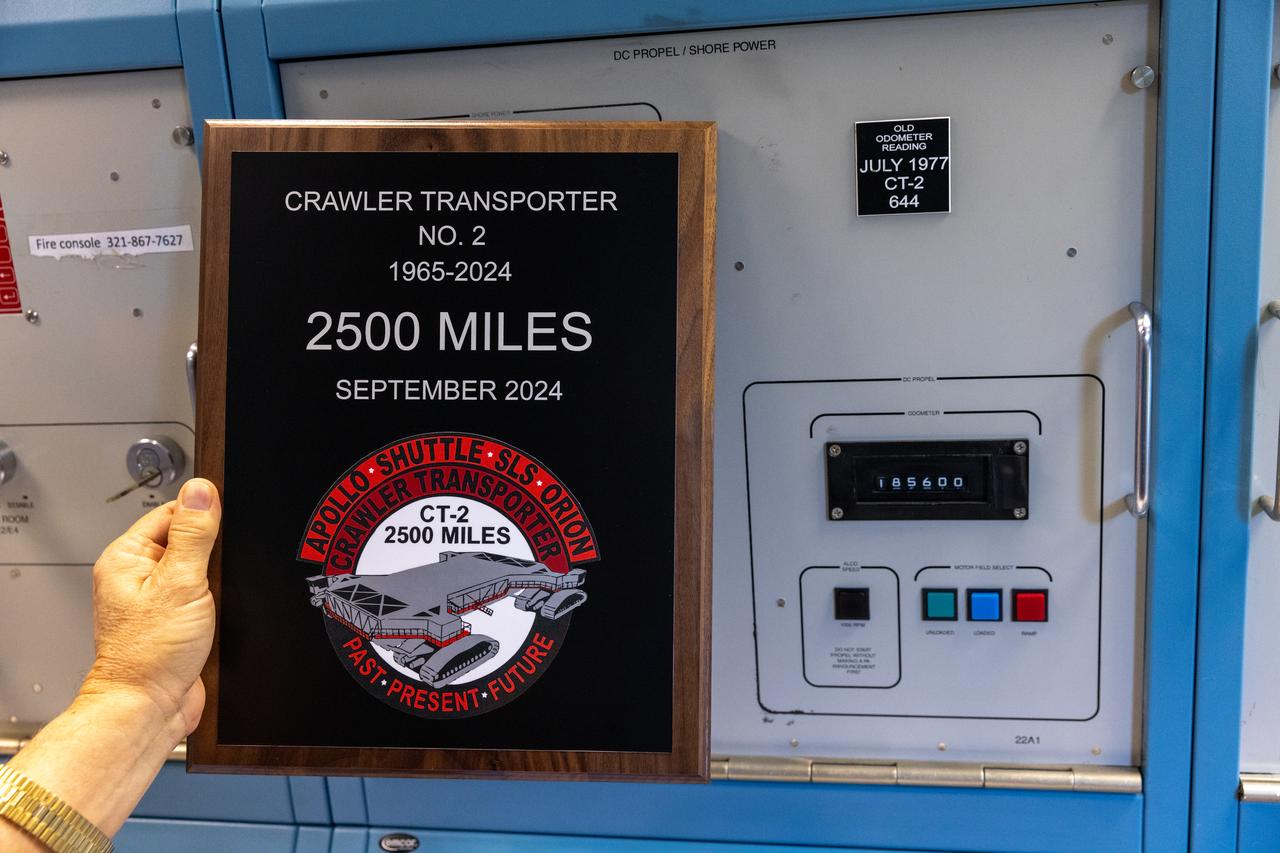
A plaque is held near the odometer of the agency’s crawler-transporter 2, on Wednesday, Sept. 25, 2024, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, commemorating the milestone of 2,500 miles traveled since its construction in 1965. Crawler-transporter 2 reached the milestone while teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems took it on a trip in preparation for supporting the roll of the mobile launcher from Launch Pad 39B back into the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building ahead of the Artemis II launch. Built originally to transport massive Saturn V rockets during the Apollo Program, crawler-transporter 2 continued its service during the Space Shuttle Program, and currently transports the massive SLS (Space Launch System) rocket and Orion spacecraft atop the mobile launcher as part of the agency’s Artemis campaign.
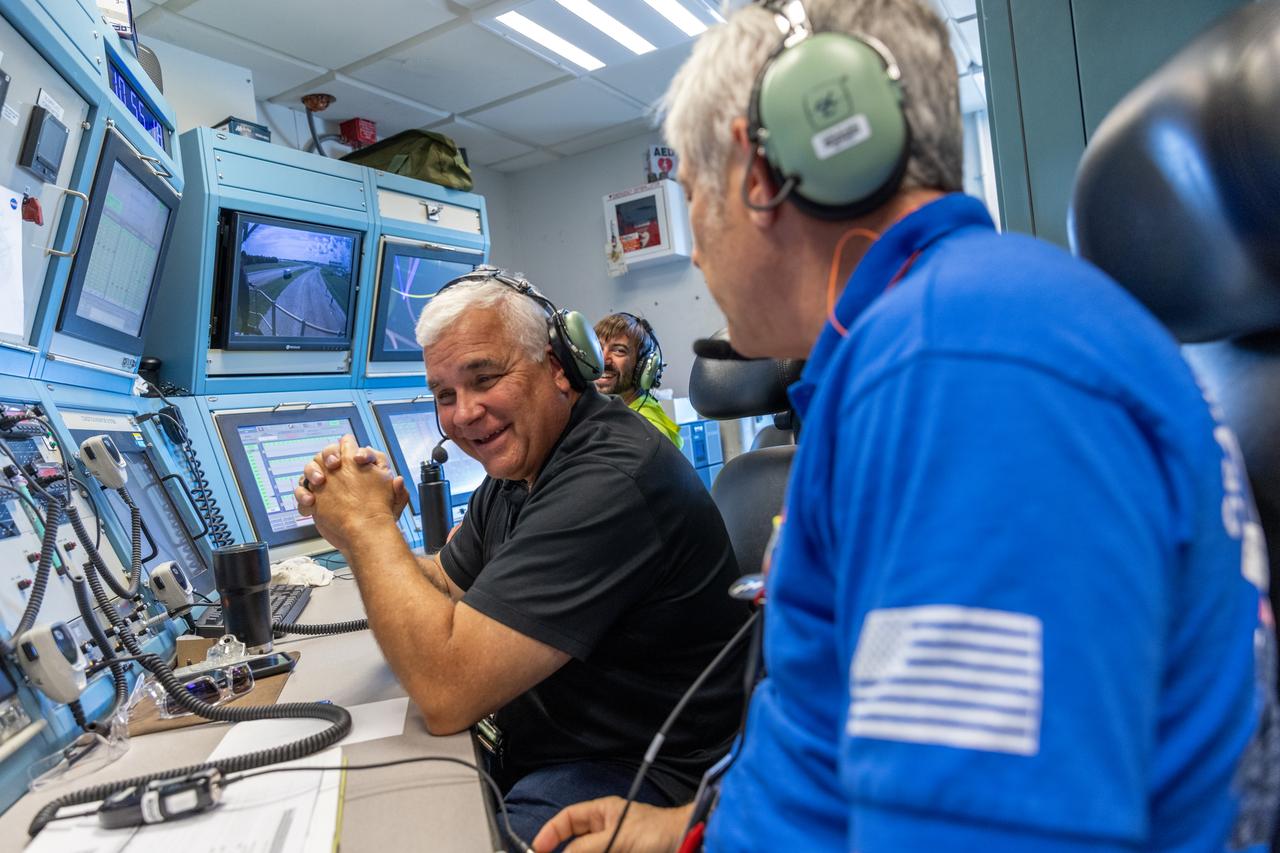

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida celebrate on Wednesday, Sept. 25, 2024, the agency’s crawler-transporter 2 reaching the milestone of 2,500 miles traveled since its construction in 1965. Crawler-transporter 2 reached the milestone while teams took it on a trip in preparation for supporting the roll of the mobile launcher from Launch Pad 39B back into the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building ahead of the Artemis II launch. Built originally to transport massive Saturn V rockets during the Apollo Program, crawler-transporter 2 continued its service during the Space Shuttle Program, and currently transports the massive SLS (Space Launch System) rocket and Orion spacecraft atop the mobile launcher as part of the agency’s Artemis campaign.
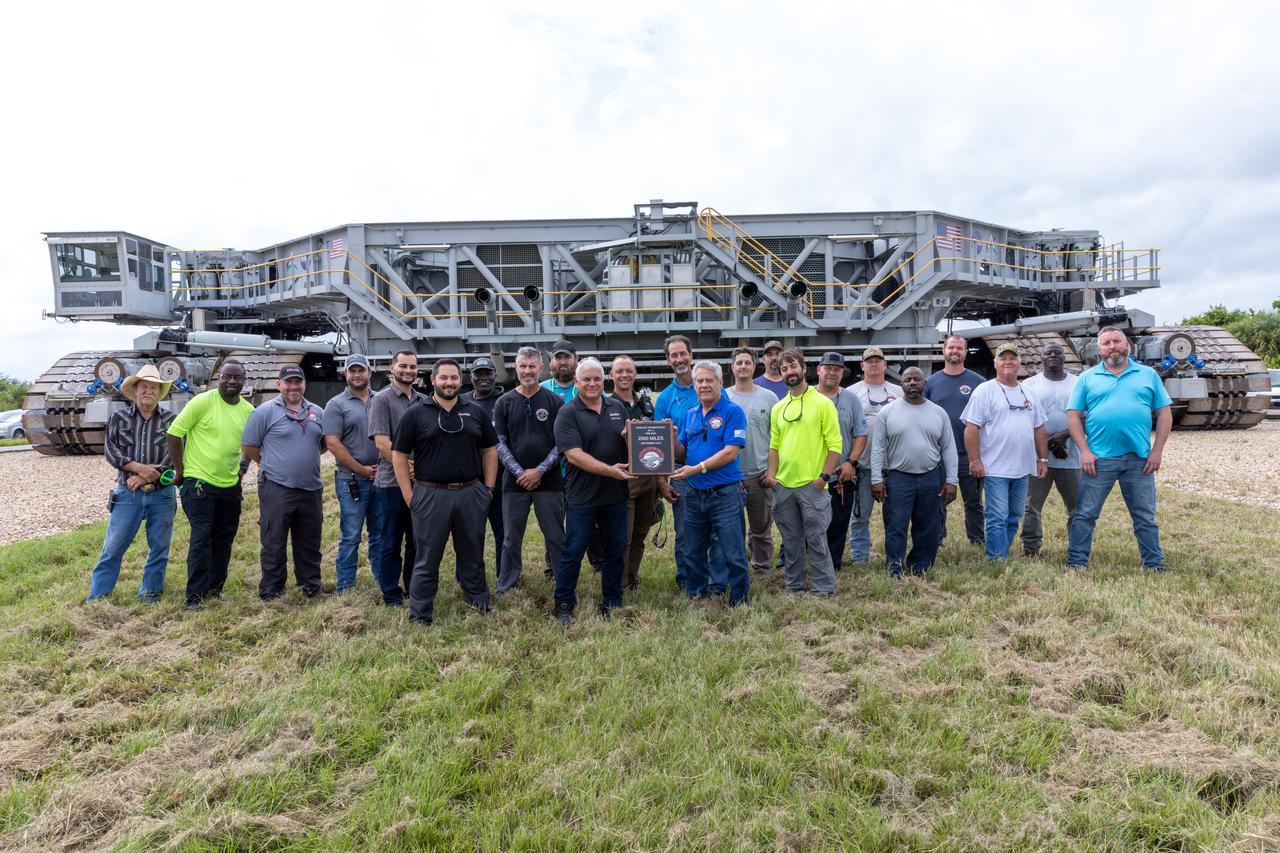

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida celebrate on Wednesday, Sept. 25, 2024, the agency’s crawler-transporter 2 reaching the milestone of 2,500 miles traveled since its construction in 1965. Crawler-transporter 2 reached the milestone while teams took it on a trip in preparation for supporting the roll of the mobile launcher from Launch Pad 39B back into the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building ahead of the Artemis II launch. Built originally to transport massive Saturn V rockets during the Apollo Program, crawler-transporter 2 continued its service during the Space Shuttle Program, and currently transports the massive SLS (Space Launch System) rocket and Orion spacecraft atop the mobile launcher as part of the agency’s Artemis campaign.

The Kepler space telescope examined twenty-one patches of the sky during it’s nine and a half years of operation. Within these regions, Kepler gathered high precision brightness measurements of over half a million stars facilitating the discovery of thousands of exoplanets and yielding insight into a multitude of other astrophysical phenomena. Illustration by Wendy Stenzel. Science content: Jeff Coughlin, Kenneth Mighell, Doug Caldwell, all of NASA Ames. Key words: Kepler, K2, Missions, nasa, Ames research center, spacecraft, FFI, Full Frame Image, fields of view, science.

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Logos affixed to the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California represent the principal players in the launch campaign underway at the pad. From the top are the logos for the National Aeronautics and Space Administration, or NASA the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, or OCO-2 and the United Launch Alliance, or ULA. Launch of NASA's OCO-2 satellite aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is scheduled for 5:56 a.m. EDT on July 1. OCO-2 is NASA’s first mission dedicated to studying atmospheric carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 will provide a new tool for understanding the human and natural sources of carbon dioxide emissions and the natural "sinks" that absorb carbon dioxide and help control its buildup. The observatory will measure the global geographic distribution of these sources and sinks and study their changes over time. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://www.nasa.gov/oco2. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
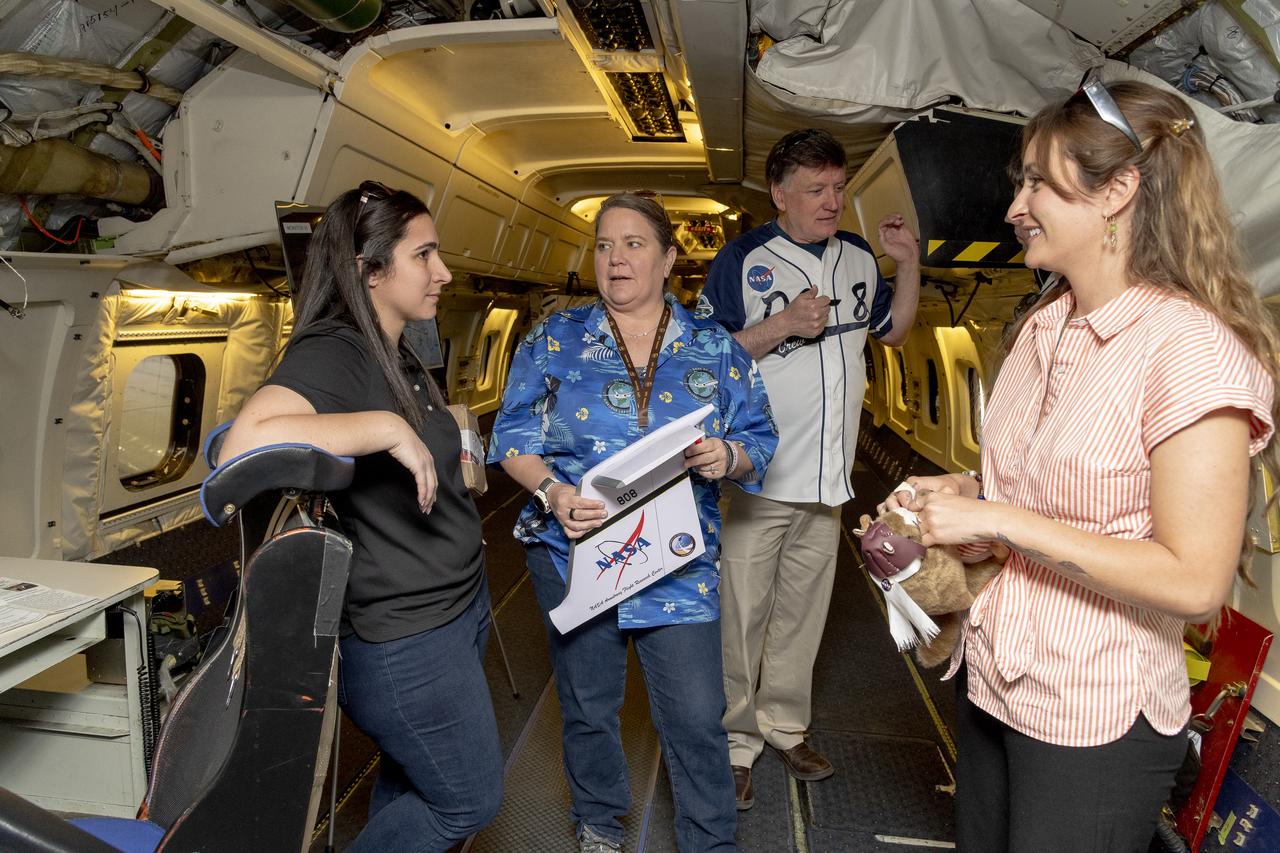

Members of the DC-8 program team tour an empty aircraft and recall past missions. Usually the DC-8 has between 15 and 30 instrument racks installed for a given science mission. The aircraft was spacious by comparison on May 2, 2024, when NASA personnel, friends, and family gathered at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center Building 703 in Palmdale, California to celebrate the DC-8 staff, aircraft, and science campaigns. Conversing here are DC-8 aircraft deputy manager Kirsten Boogaard, left, with NASA Armstrong pilot Carrie Worth, Mike Zimmerman, and NASA Armstrong public affairs specialist for airborne science, Erica Heim.
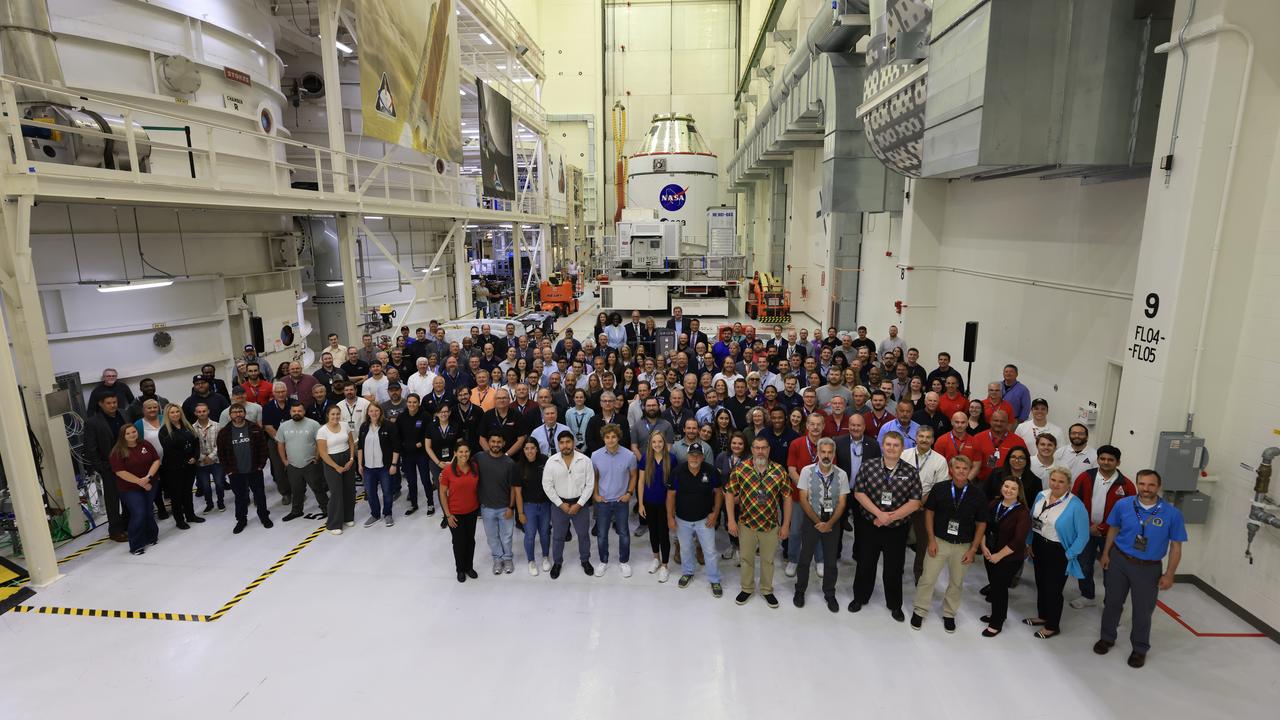

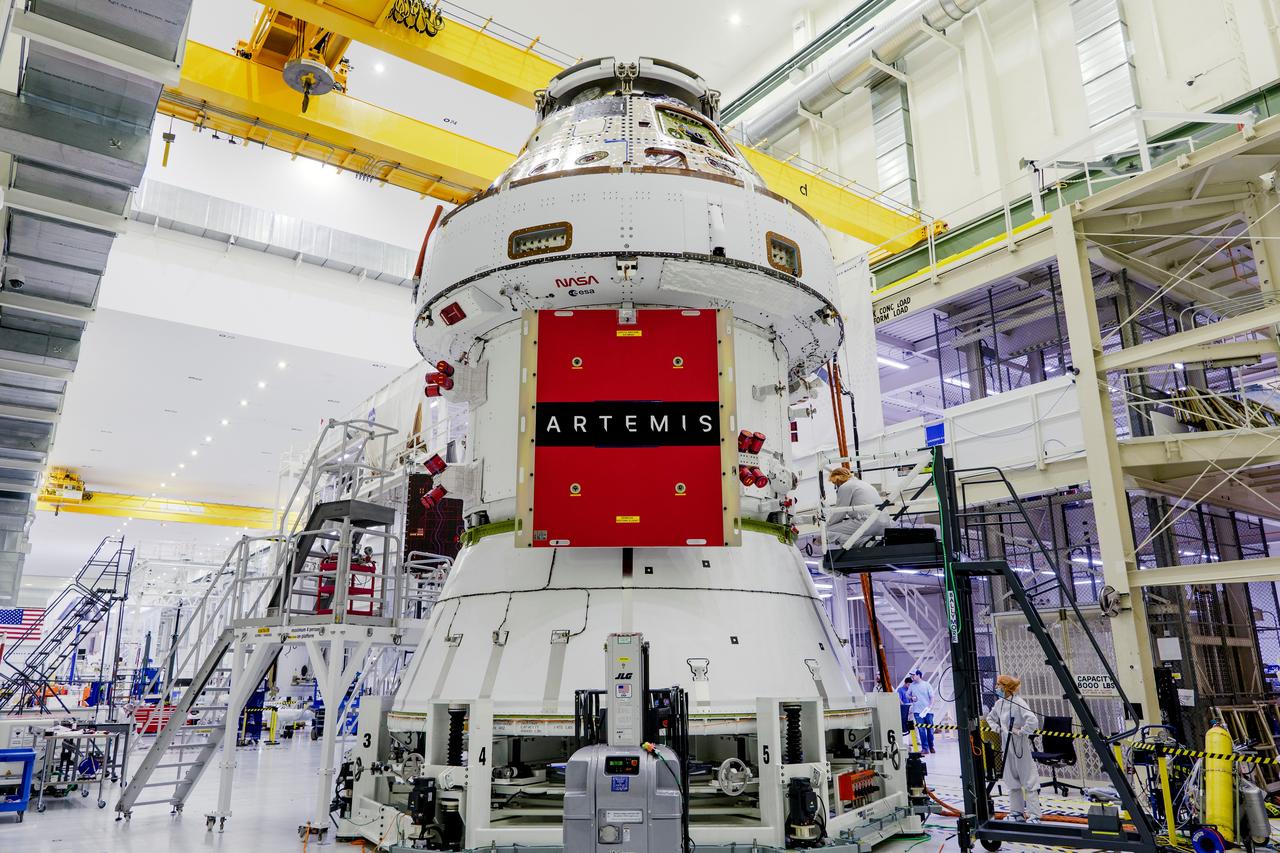
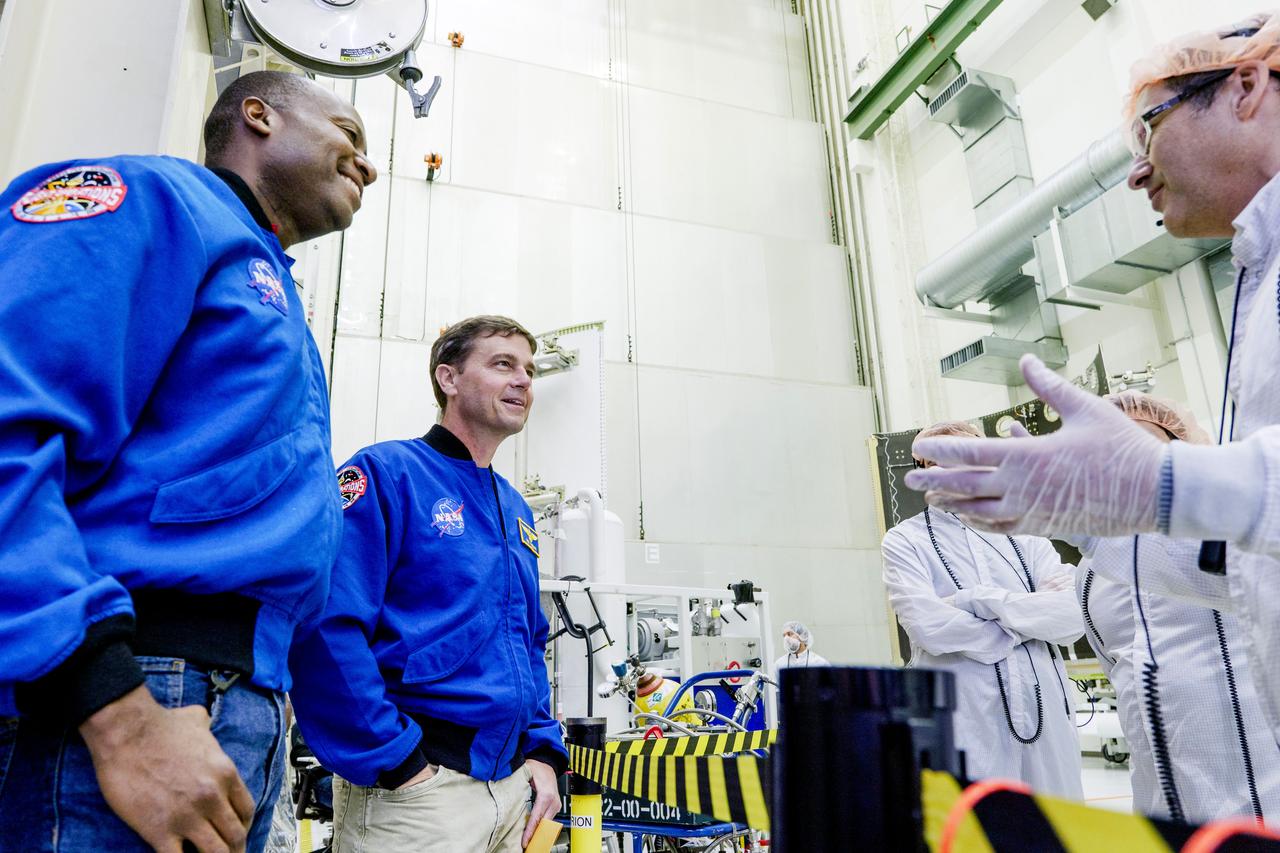
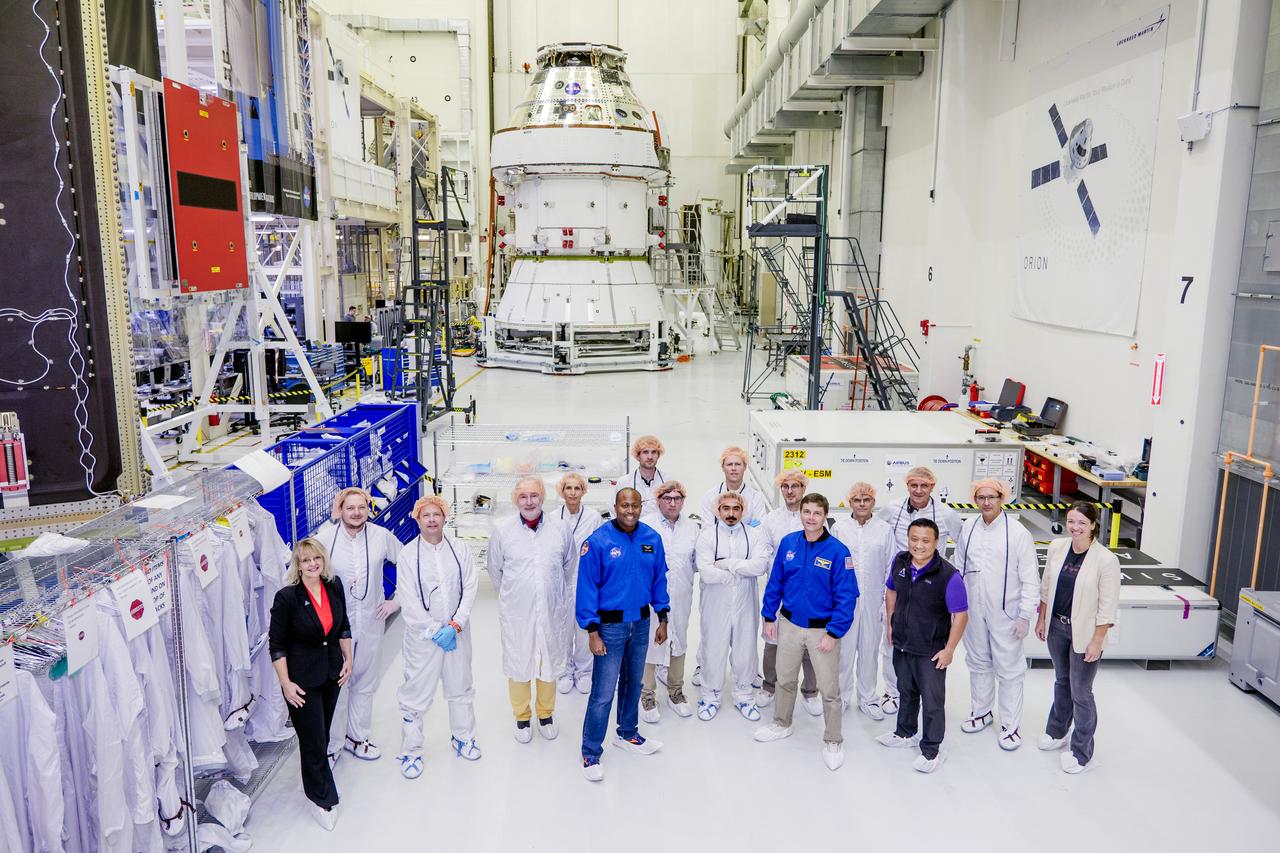
Teams from NASA and Lockheed Martin pose for a photo in front of NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft, connected to a massive crane ahead atop the agency’s KAMAG transporter inside the Neil A. Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Friday, May 2, 2025. The spacecraft will be transported to the spaceport’s Multi-Payload Processing Facility to undergo fueling and processing for prelaunch operations. The Artemis II test flight is the first crewed flight under NASA’s Artemis campaign and is another step toward missions on the lunar surface and helping the agency prepare for future human missions to Mars.
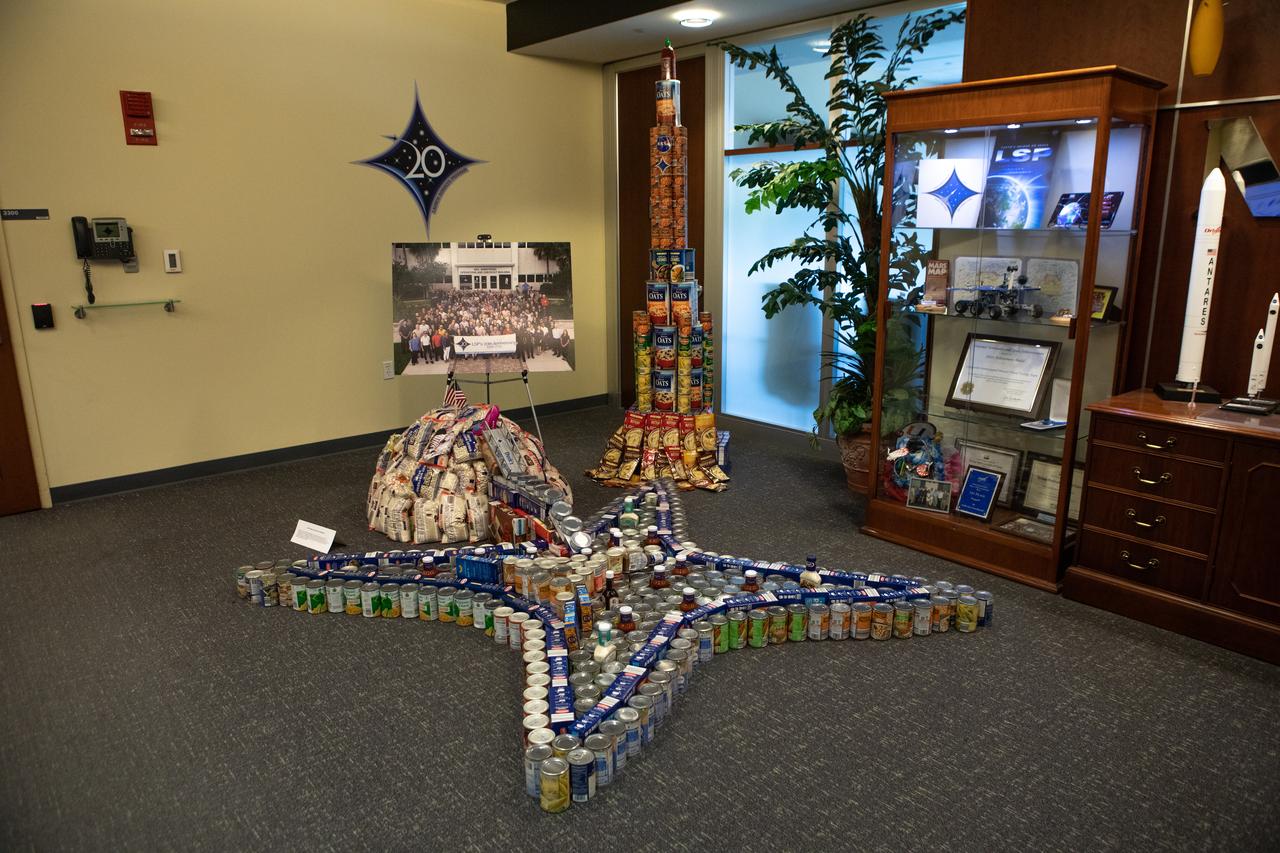

A sculpture created out of non-perishable canned and boxed foods by NASA’s Launch Services Program is on display at Kennedy Space Center in Florida as part of the 2019 Feds Feeds Families campaign. Kennedy employees had the opportunity to work in teams to construct sculptures reflecting this year’s theme – The Moon Lights the Way – to pay tribute to the 50th anniversary of the first Apollo Moon landing. As part of the theme, the can sculptures highlighted the accomplishments of the Apollo Program while incorporating aspects of NASA’s aim to return to the Moon and beyond to Mars. On Aug. 2, 2019, all sculptures will be deconstructed and boxed for donation.
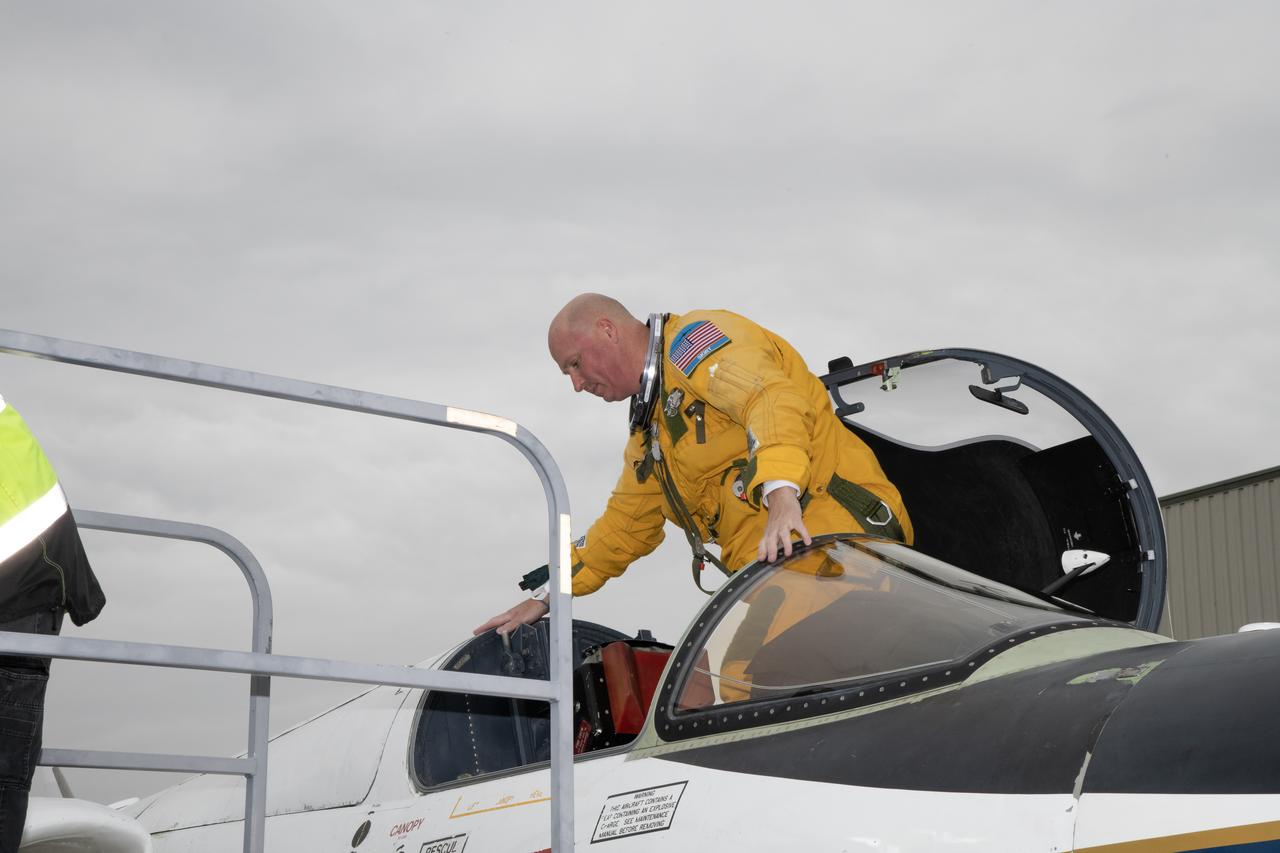

Kirt Stallings, an ER-2 pilot from NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards California, completed a flight in support of the Investigation of Microphysics and Precipitation for Atlantic Coast-Threatening Storms (IMPACTS) mission. The IMPACTS team tracked storms across the Eastern United States to help understand how winter storms form and develop. The aircraft, which is based at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center Building 703 in Palmdale, California, was temporarily based at Dobbins Air Reserve Base in Marietta, Georgia. The three-year IMPACTS campaign concluded on Feb. 28, 2023.

A sign explaining the construction of a sculpture created out of non-perishable canned and boxed foods is on display at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida as part of the 2019 Feds Feeds Families campaign. Kennedy employees had the opportunity to work in teams to construct sculptures reflecting this year’s theme – The Moon Lights the Way – to pay tribute to the 50th anniversary of the first Apollo Moon landing. As part of the theme, the can sculptures highlighted the accomplishments of the Apollo Program while incorporating aspects of NASA’s aim to return to the Moon and beyond to Mars. On Aug. 2, 2019, all sculptures will be deconstructed and boxed for donation.
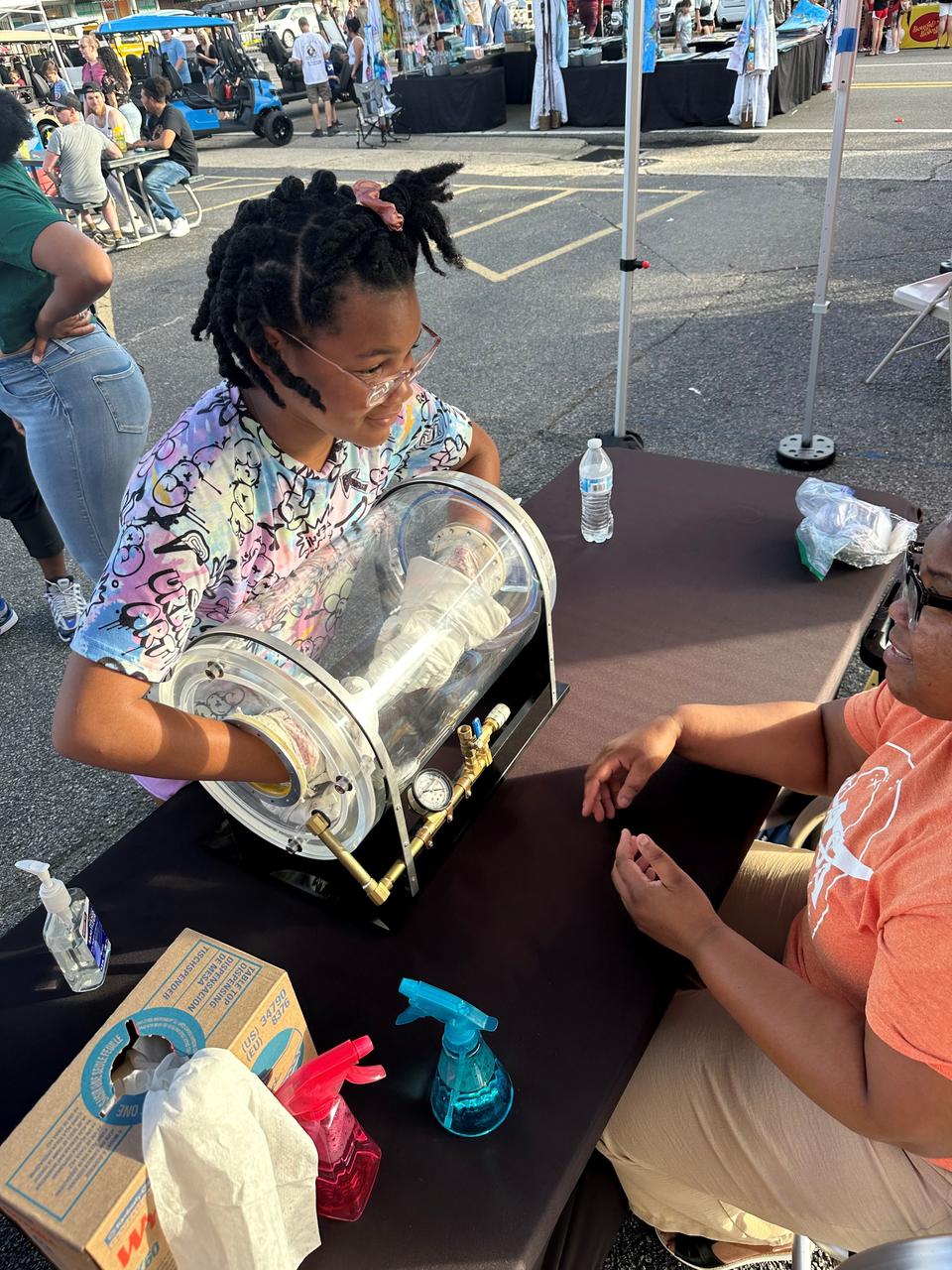
NASA Stennis representatives engage with the Artemis Generation at the Picayune Street Fair in Picayune, Mississippi on Nov. 2-3. The south Mississippi NASA center is located less than 15 miles from Picayune with many employees living in the community. NASA Stennis tests all RS-25 engines to help power NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket on Artemis missions. The NASA center is also preparing to conduct a full series of tests on the agency’s exploration upper stage to demonstrate it is ready to fly on future Artemis missions. With the Artemis campaign, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever.
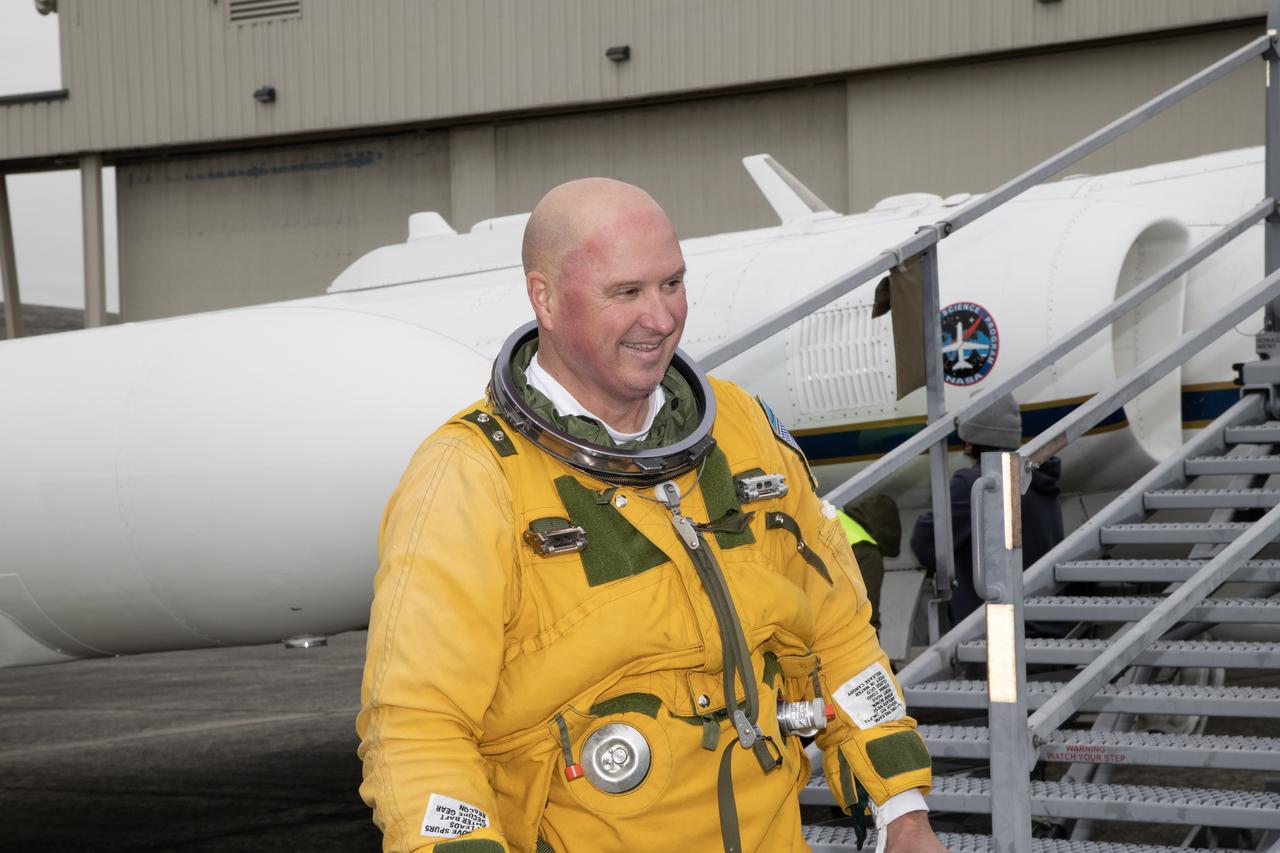

Kirt Stallings, an ER-2 pilot from NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards California, completed a flight in support of the Investigation of Microphysics and Precipitation for Atlantic Coast-Threatening Storms (IMPACTS) mission. The IMPACTS team tracked storms across the Eastern United States to help understand how winter storms form and develop. The aircraft, which is based at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center Building 703 in Palmdale, California, was temporarily based at Dobbins Air Reserve Base in Marietta, Georgia. The three-year IMPACTS campaign concluded on Feb. 28, 2023.
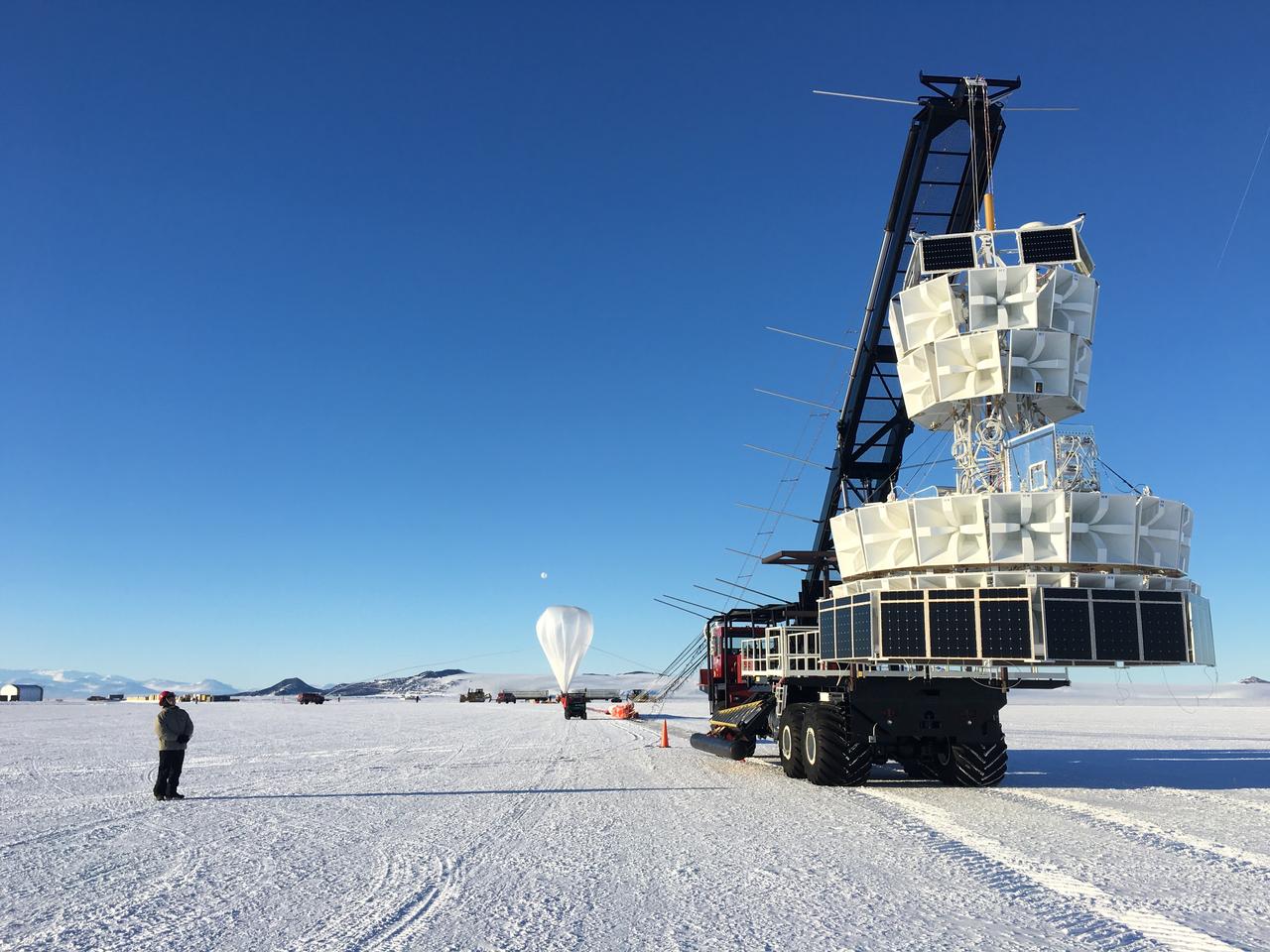

The second of three missions as part of NASA’s Antarctica Long Duration Balloon Flight Campaign was successfully launched at 8:10 a.m. EDT, Dec. 2. The Antarctic Impulsive Transient Antenna (ANITA) from the University of Hawaii at Manoa was launched from Antarctica’s Ross Ice Shelf near McMurdo Station with support from the National Science Foundation’s United States Antarctic Program. Scientists will use ANITA’s instruments to study the reactions in the core of stars and as they explode via the release of neutrinos that travel to Earth and interact with the Antarctica ice. More: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/2ghR6Le" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/2ghR6Le</a>

A sculpture created out of non-perishable canned and boxed foods is on display at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida as part of the 2019 Feds Feeds Families campaign. Kennedy employees had the opportunity to work in teams to construct sculptures reflecting this year’s theme – The Moon Lights the Way – to pay tribute to the 50th anniversary of the first Apollo Moon landing. As part of the theme, the can sculptures highlighted the accomplishments of the Apollo Program while incorporating aspects of NASA’s aim to return to the Moon and beyond to Mars. On Aug. 2, 2019, all sculptures will be deconstructed and boxed for donation.
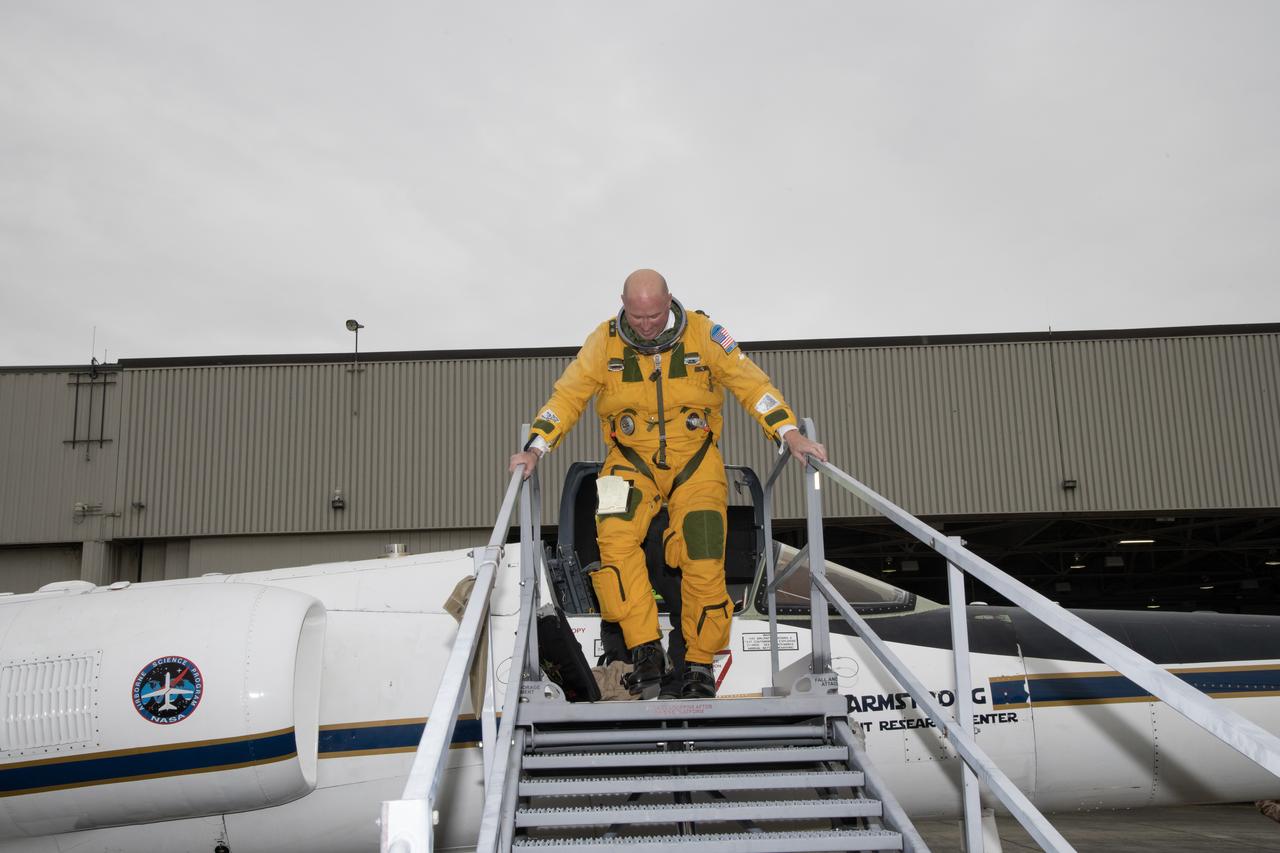

Kirt Stallings, an ER-2 pilot from NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards California, completed a flight in support of the Investigation of Microphysics and Precipitation for Atlantic Coast-Threatening Storms (IMPACTS) mission. The IMPACTS team tracked storms across the Eastern United States to help understand how winter storms form and develop. The aircraft, which is based at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center Building 703 in Palmdale, California, was temporarily based at Dobbins Air Reserve Base in Marietta, Georgia. The three-year IMPACTS campaign concluded on Feb. 28, 2023.
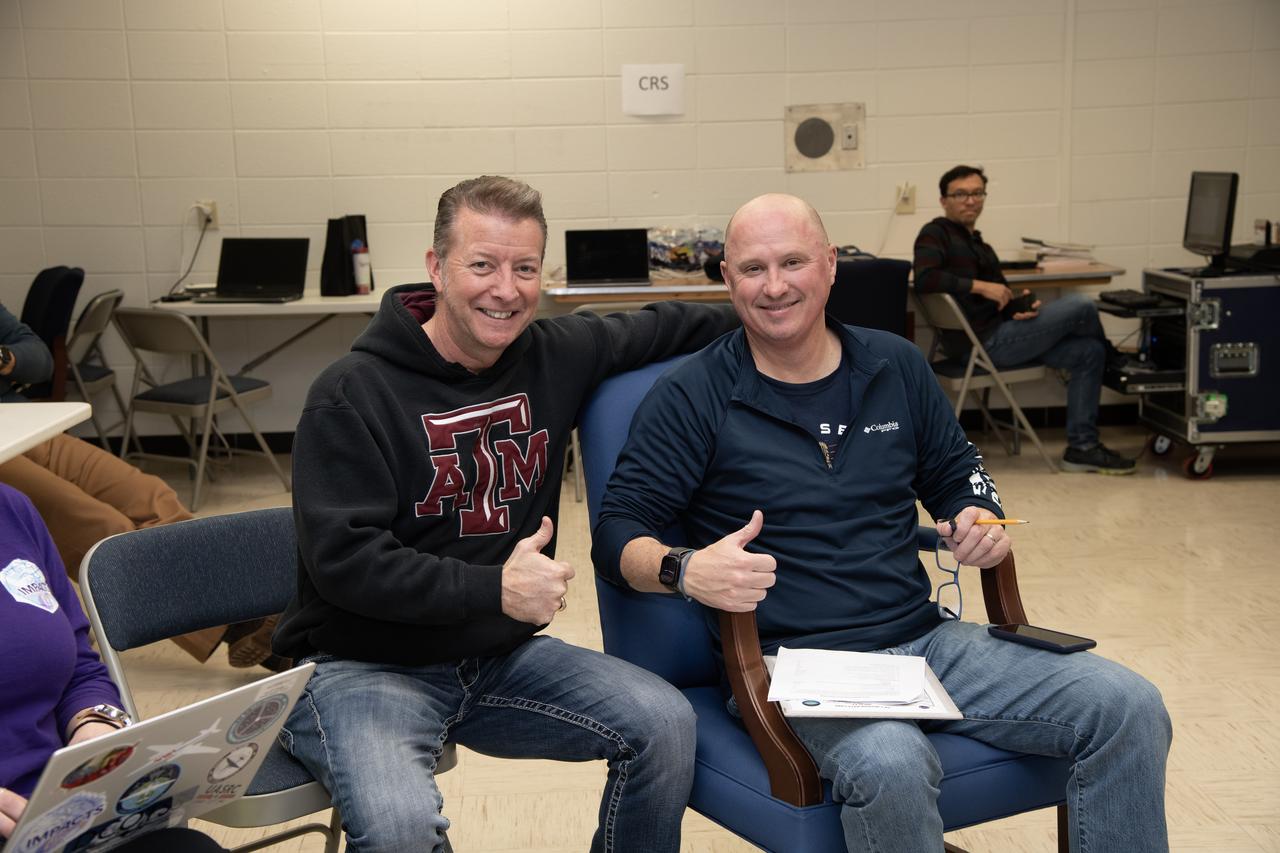

Dean Neeley and Kirt Stallings, ER-2 pilots from NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards California, completed flights in support of the Investigation of Microphysics and Precipitation for Atlantic Coast-Threatening Storms (IMPACTS) mission. The IMPACTS team tracked storms across the Eastern United States to help understand how winter storms form and develop. Here Neeley and Stallings are seen in a lighter moment at debrief. The aircraft, which is based at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center Building 703 in Palmdale, California, was temporarily based at Dobbins Air Reserve Base in Marietta, Georgia. The three-year IMPACTS campaign concluded on Feb. 28, 2023.
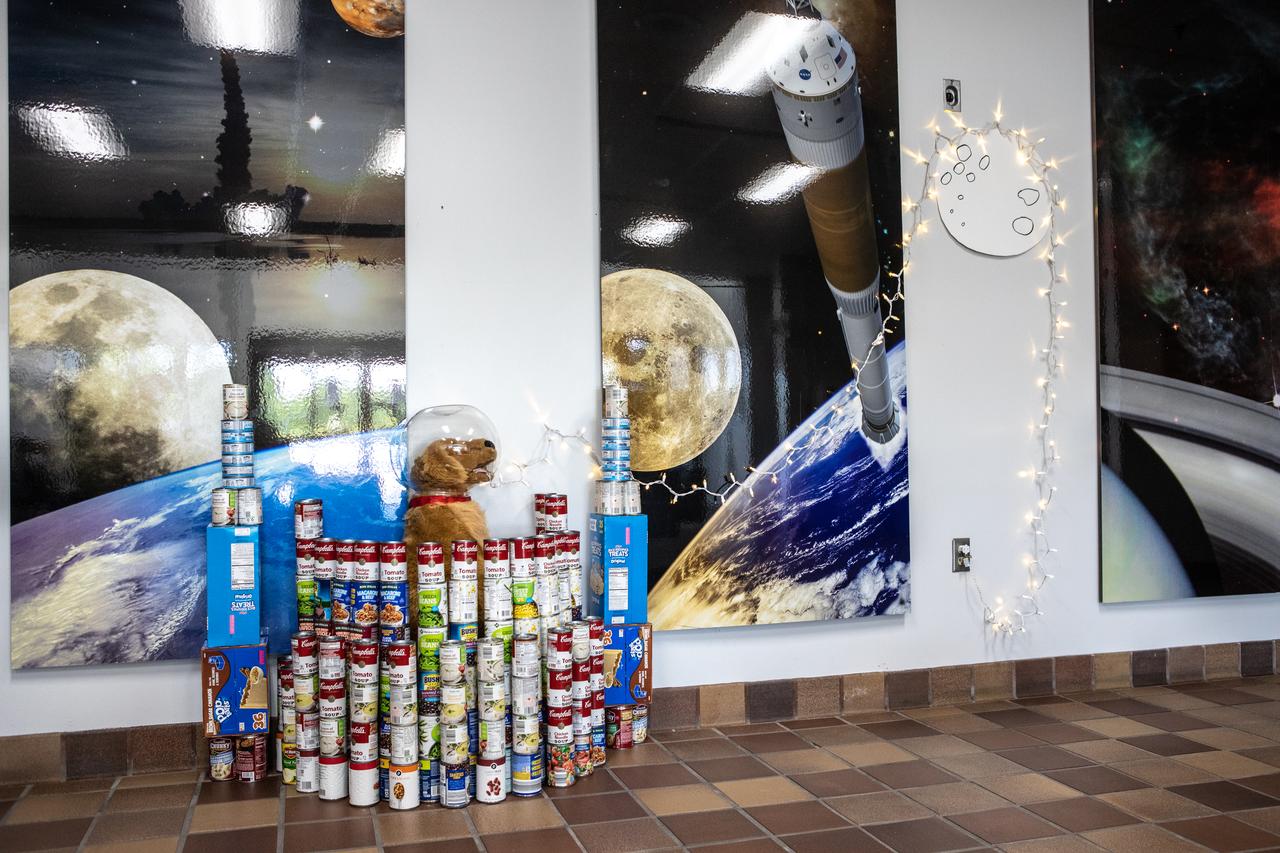

A sculpture created out of non-perishable canned and boxed foods is on display at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida as part of the 2019 Feds Feeds Families campaign. Kennedy employees had the opportunity to work in teams to construct sculptures reflecting this year’s theme – The Moon Lights the Way – to pay tribute to the 50th anniversary of the first Apollo Moon landing. As part of the theme, the can sculptures highlighted the accomplishments of the Apollo Program while incorporating aspects of NASA’s aim to return to the Moon and beyond to Mars. On Aug. 2, 2019, all sculptures will be deconstructed and boxed for donation.
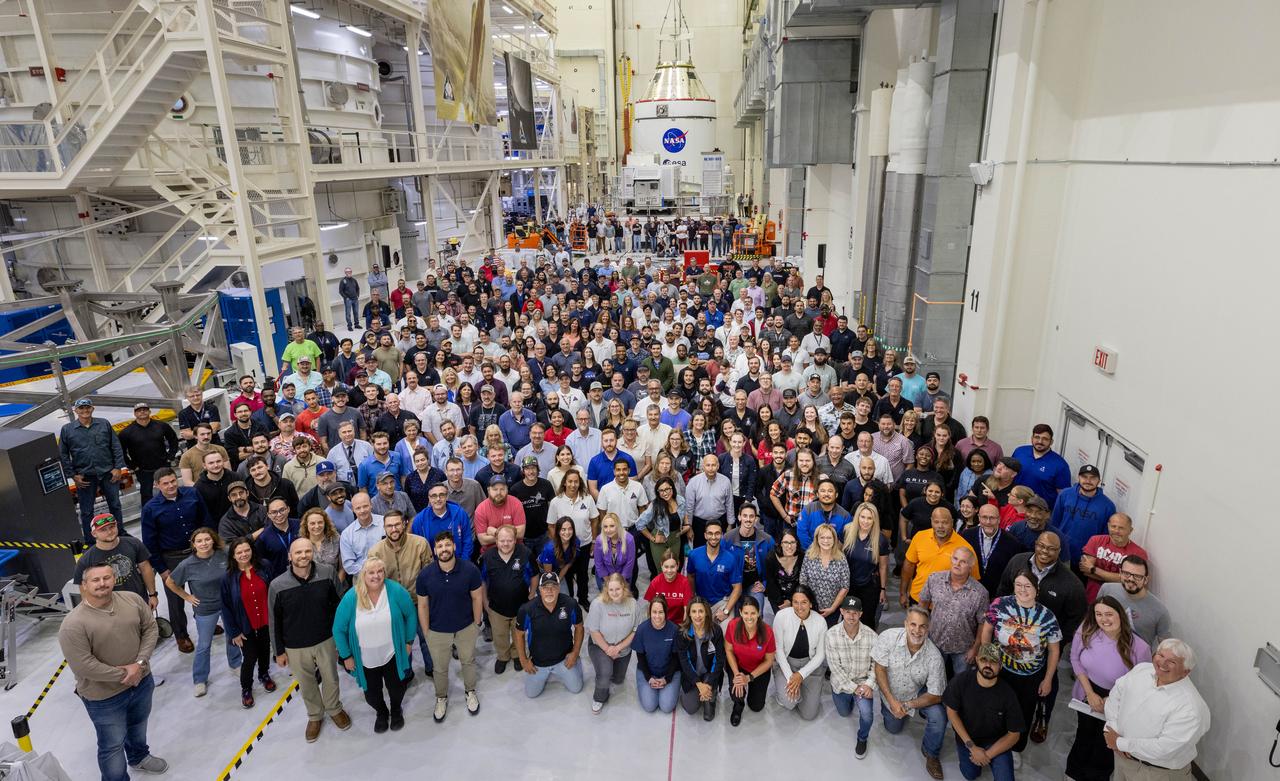

Teams from NASA and Lockheed Martin pose for a photo in front of NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft, connected to a massive crane ahead atop the agency’s KAMAG transporter inside the Neil A. Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Friday, May 2, 2025. The spacecraft will be transported to the spaceport’s Multi-Payload Processing Facility to undergo fueling and processing for prelaunch operations. The Artemis II test flight is the first crewed flight under NASA’s Artemis campaign and is another step toward missions on the lunar surface and helping the agency prepare for future human missions to Mars.
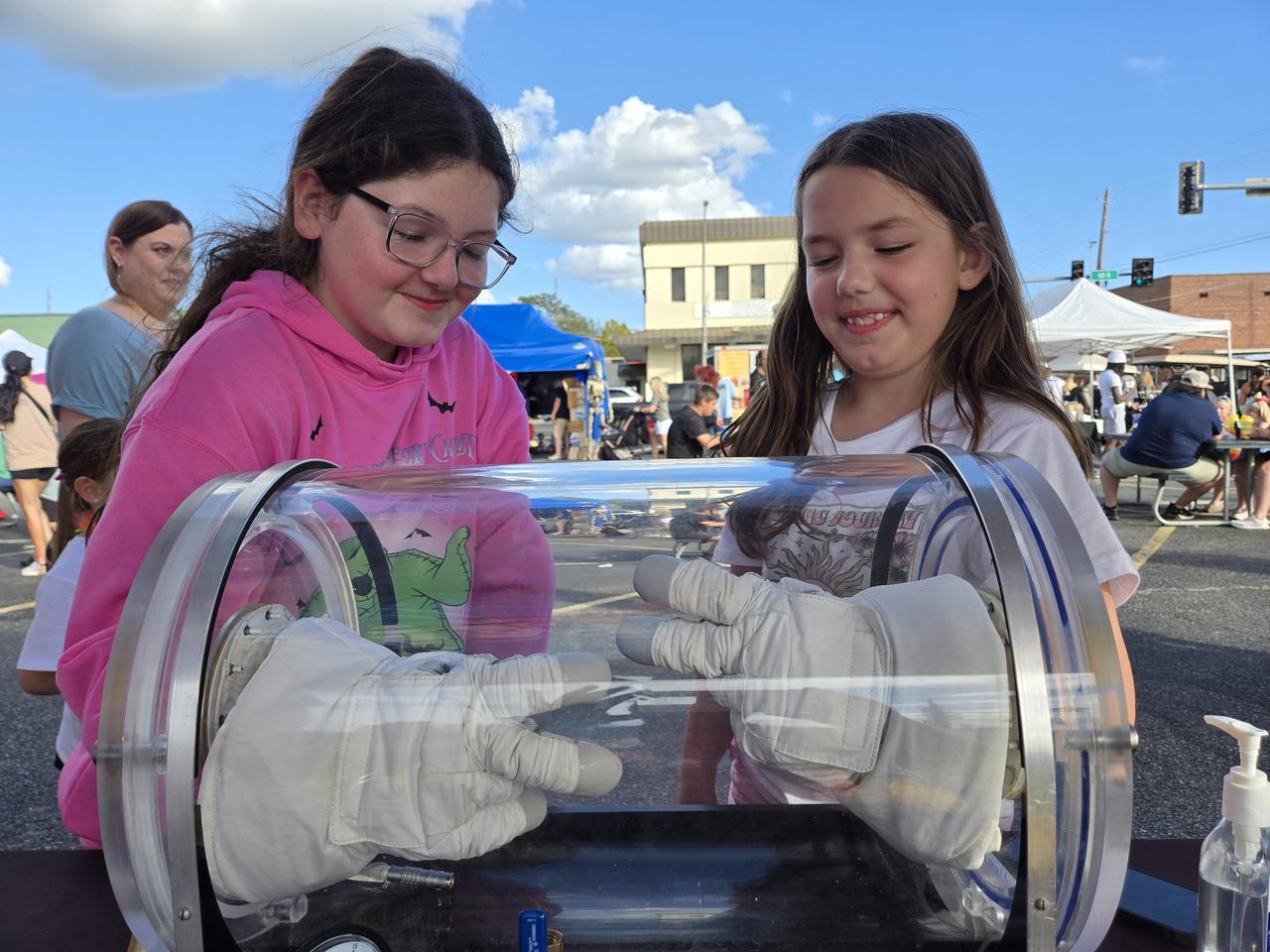

NASA Stennis representatives engage with the Artemis Generation at the Picayune Street Fair in Picayune, Mississippi on Nov. 2-3. The south Mississippi NASA center is located less than 15 miles from Picayune with many employees living in the community. NASA Stennis tests all RS-25 engines to help power NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket on Artemis missions. The NASA center is also preparing to conduct a full series of tests on the agency’s exploration upper stage to demonstrate it is ready to fly on future Artemis missions. With the Artemis campaign, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever.

A sculpture created out of non-perishable canned and boxed foods is on display at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida as part of the 2019 Feds Feeds Families campaign. Kennedy employees had the opportunity to work in teams to construct sculptures reflecting this year’s theme – The Moon Lights the Way – to pay tribute to the 50th anniversary of the first Apollo Moon landing. As part of the theme, the can sculptures highlighted the accomplishments of the Apollo Program while incorporating aspects of NASA’s aim to return to the Moon and beyond to Mars. On Aug. 2, 2019, all sculptures will be deconstructed and boxed for donation.
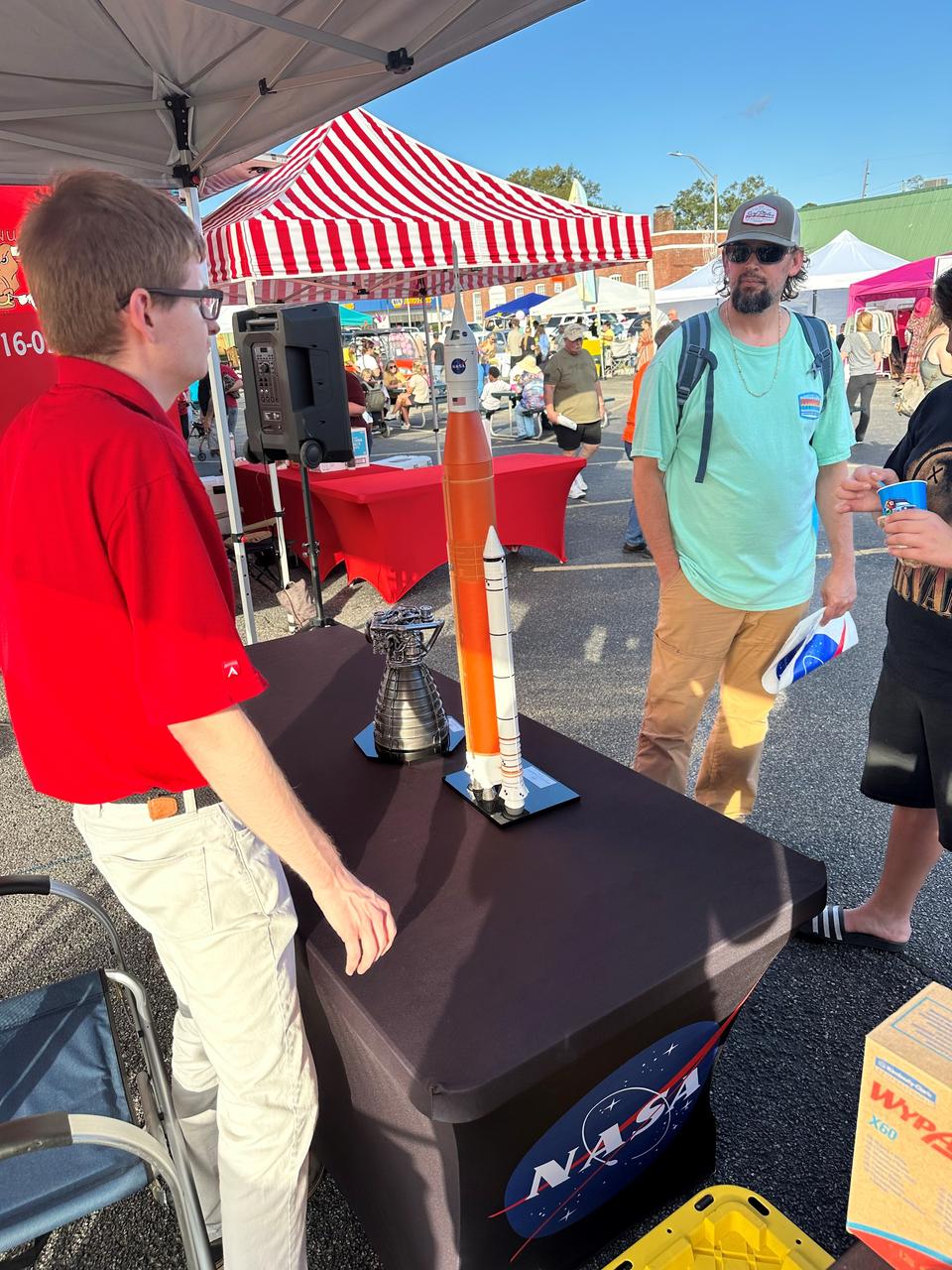

NASA Stennis representatives engage with the Artemis Generation at the Picayune Street Fair in Picayune, Mississippi on Nov. 2-3. The south Mississippi NASA center is located less than 15 miles from Picayune with many employees living in the community. NASA Stennis tests all RS-25 engines to help power NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket on Artemis missions. The NASA center is also preparing to conduct a full series of tests on the agency’s exploration upper stage to demonstrate it is ready to fly on future Artemis missions. With the Artemis campaign, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever.

A sculpture created out of non-perishable canned and boxed foods is on display at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida as part of the 2019 Feds Feeds Families campaign. Kennedy employees had the opportunity to work in teams to construct sculptures reflecting this year’s theme – The Moon Lights the Way – to pay tribute to the 50th anniversary of the first Apollo Moon landing. As part of the theme, the can sculptures highlighted the accomplishments of the Apollo Program while incorporating aspects of NASA’s aim to return to the Moon and beyond to Mars. On Aug. 2, 2019, all sculptures will be deconstructed and boxed for donation.
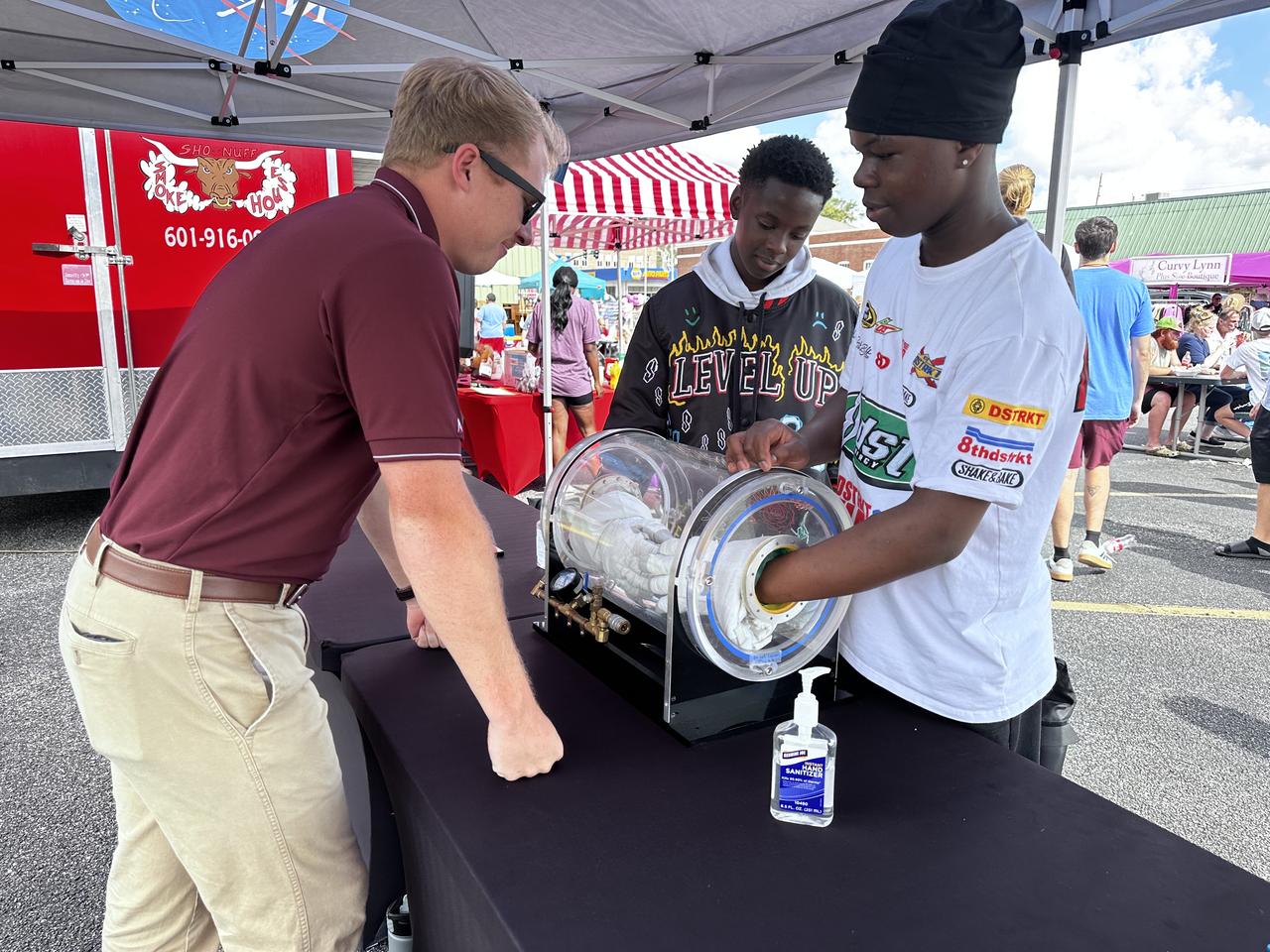

NASA Stennis representatives engage with the Artemis Generation at the Picayune Street Fair in Picayune, Mississippi on Nov. 2-3. The south Mississippi NASA center is located less than 15 miles from Picayune with many employees living in the community. NASA Stennis tests all RS-25 engines to help power NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket on Artemis missions. The NASA center is also preparing to conduct a full series of tests on the agency’s exploration upper stage to demonstrate it is ready to fly on future Artemis missions. With the Artemis campaign, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever.
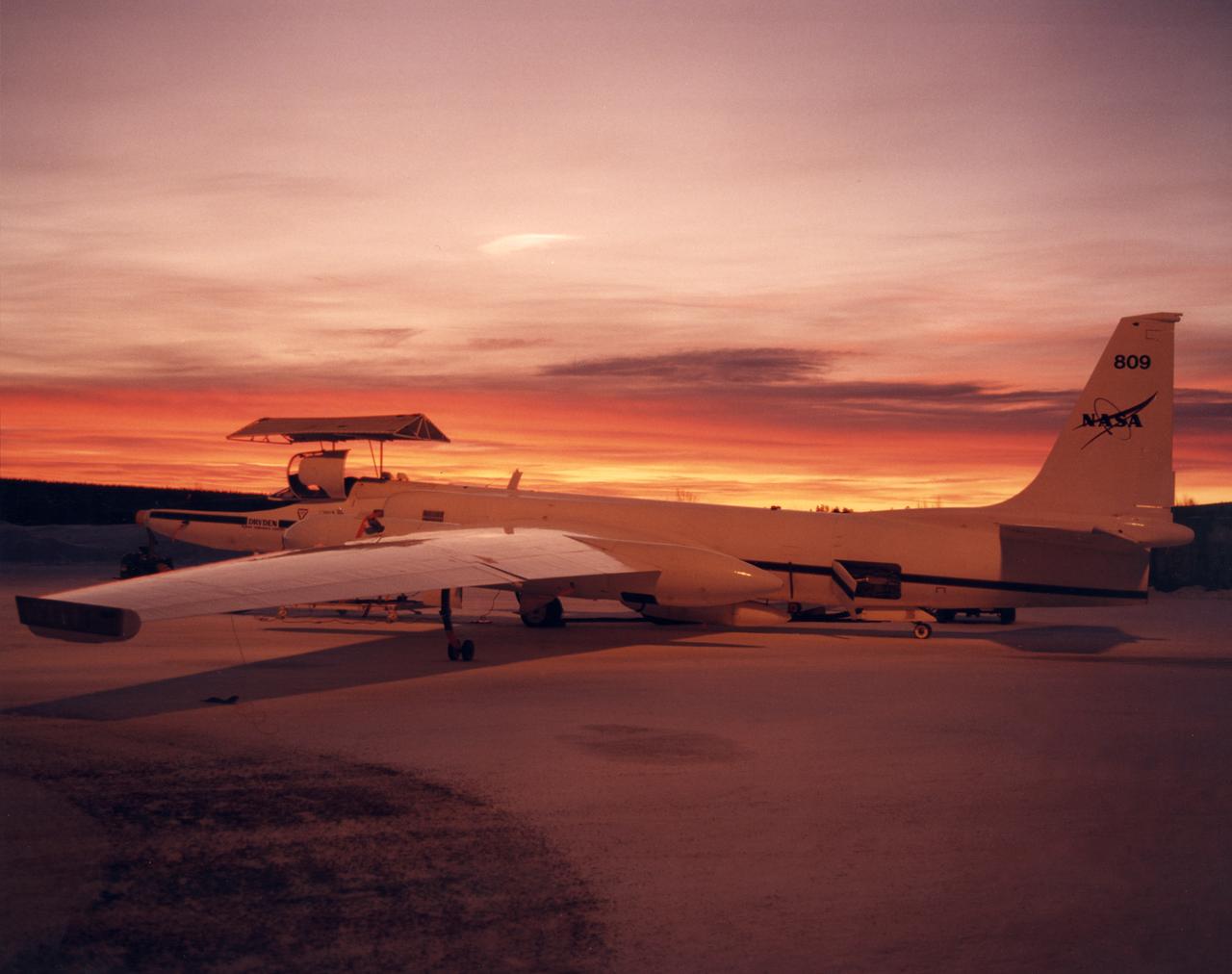

ER-2 #809 awaiting pilot entry for the third flight of the SAGE III Ozone Loss and Validation Experiment (SOLVE). The ER-2, a civilian variant of Lockheed's U-2, and another NASA flying laboratory, Dryden's DC-8, were based north of the Arctic Circle in Kiruna, Sweden during the winter of 2000 to study ozone depletion as part of SOLVE. A large hangar built especially for research, "Arena Arctica" housed the instrumented aircraft and the scientists. Scientists have observed unusually low levels of ozone over the Arctic during recent winters, raising concerns that ozone depletion there could become more widespread as in the Antarctic ozone hole. The NASA-sponsored international mission took place between November 1999 and March 2000 and was divided into three phases. The DC-8 was involved in all three phases returning to Dryden between each phase. The ER-2 flew sample collection flights between January and March, remaining in Sweden from Jan. 9 through March 16. "The collaborative campaign will provide an immense new body of information about the Arctic stratosphere," said program scientist Dr. Michael Kurylo, NASA Headquarters. "Our understanding of the Earth's ozone will be greatly enhanced by this research."
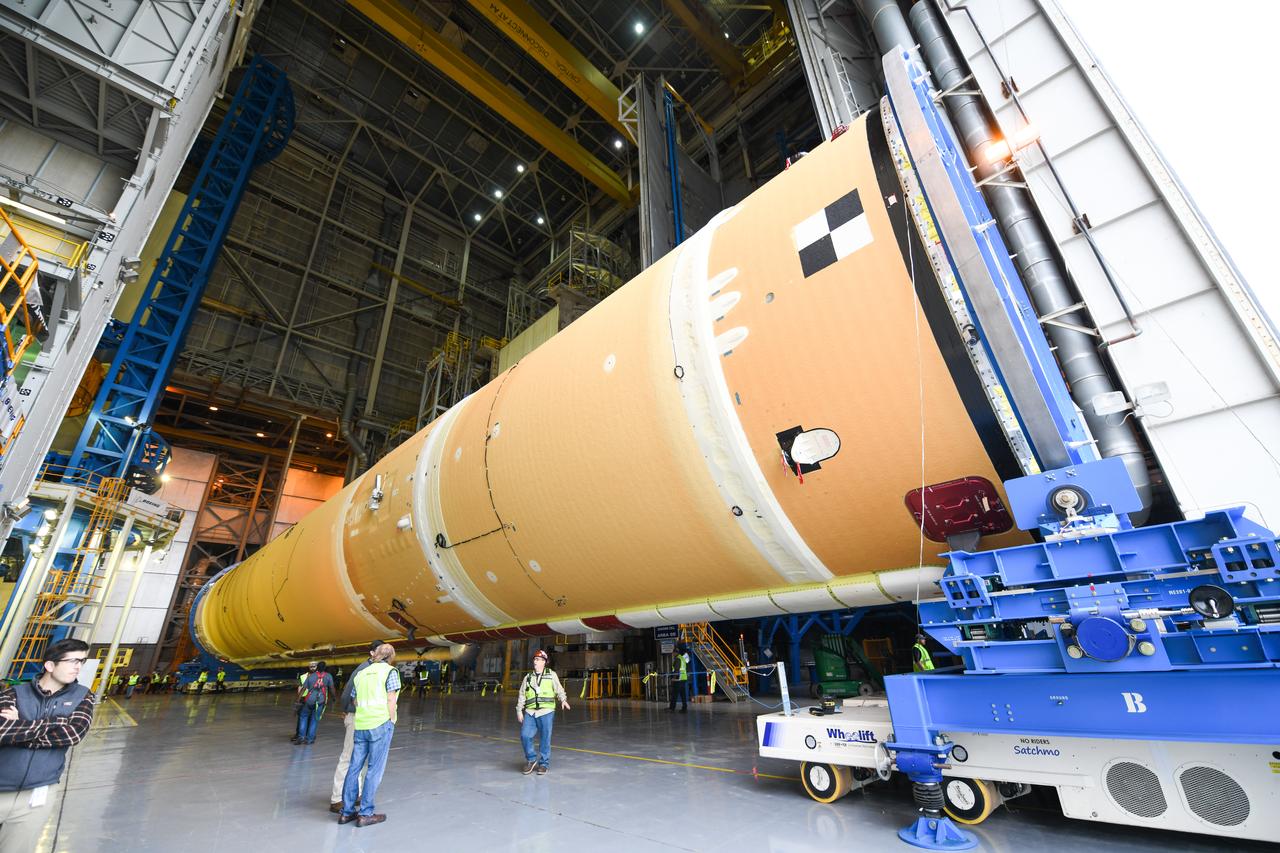

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
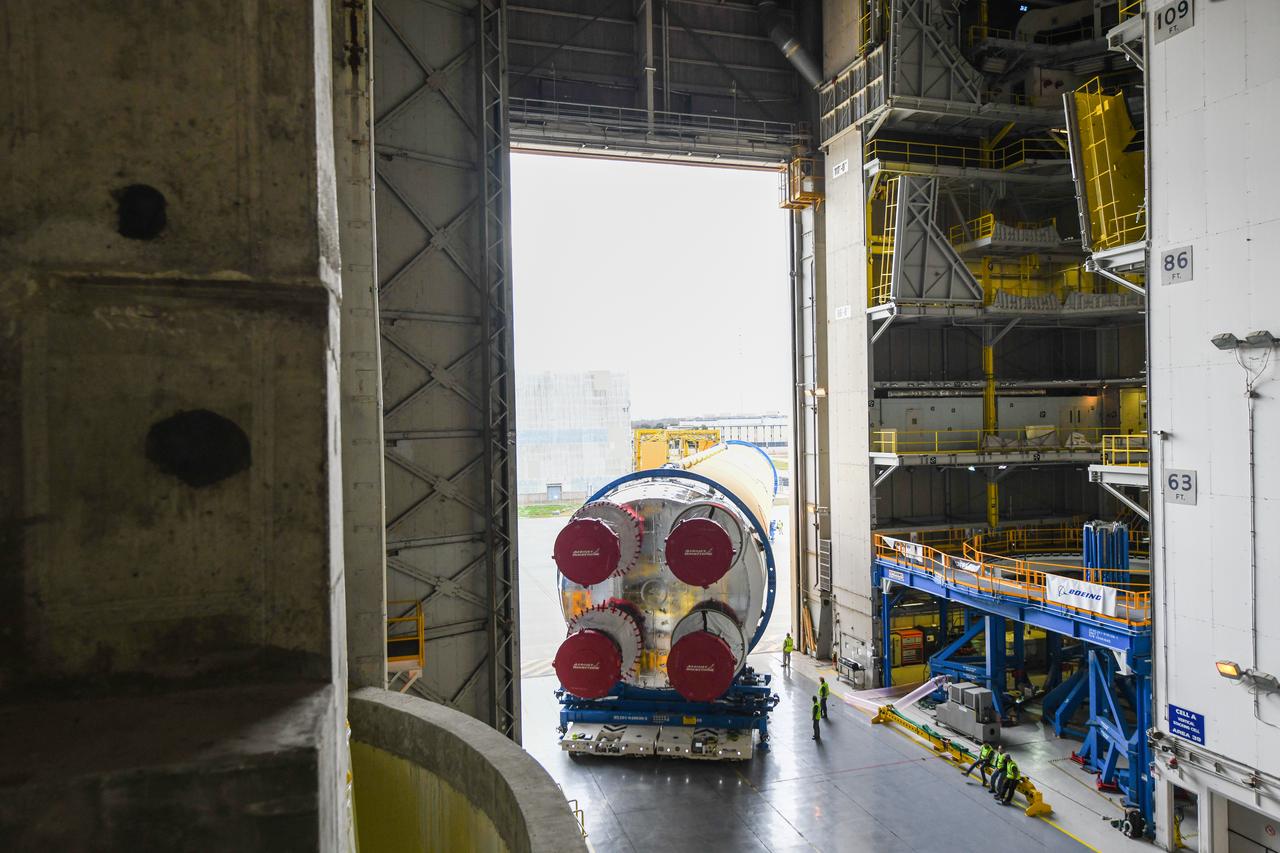

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
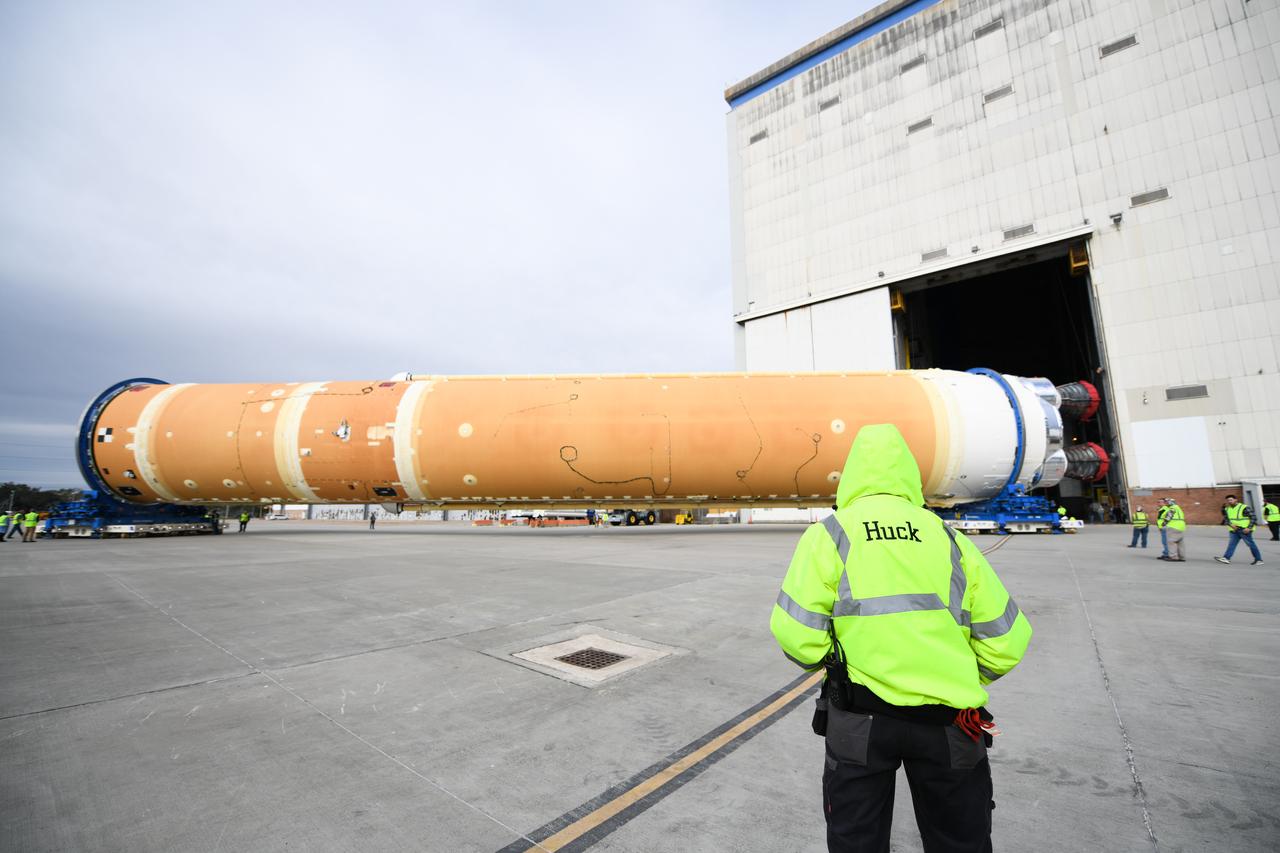

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
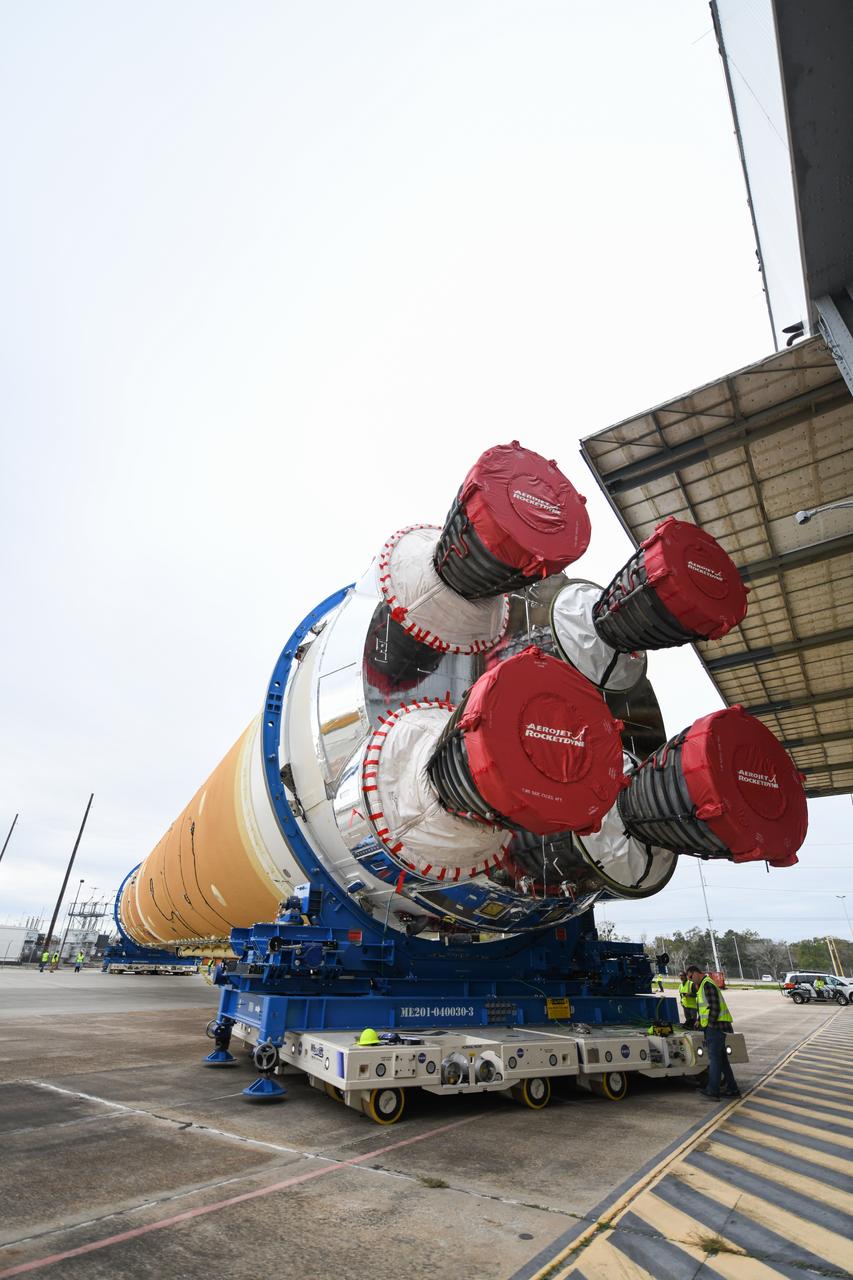

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
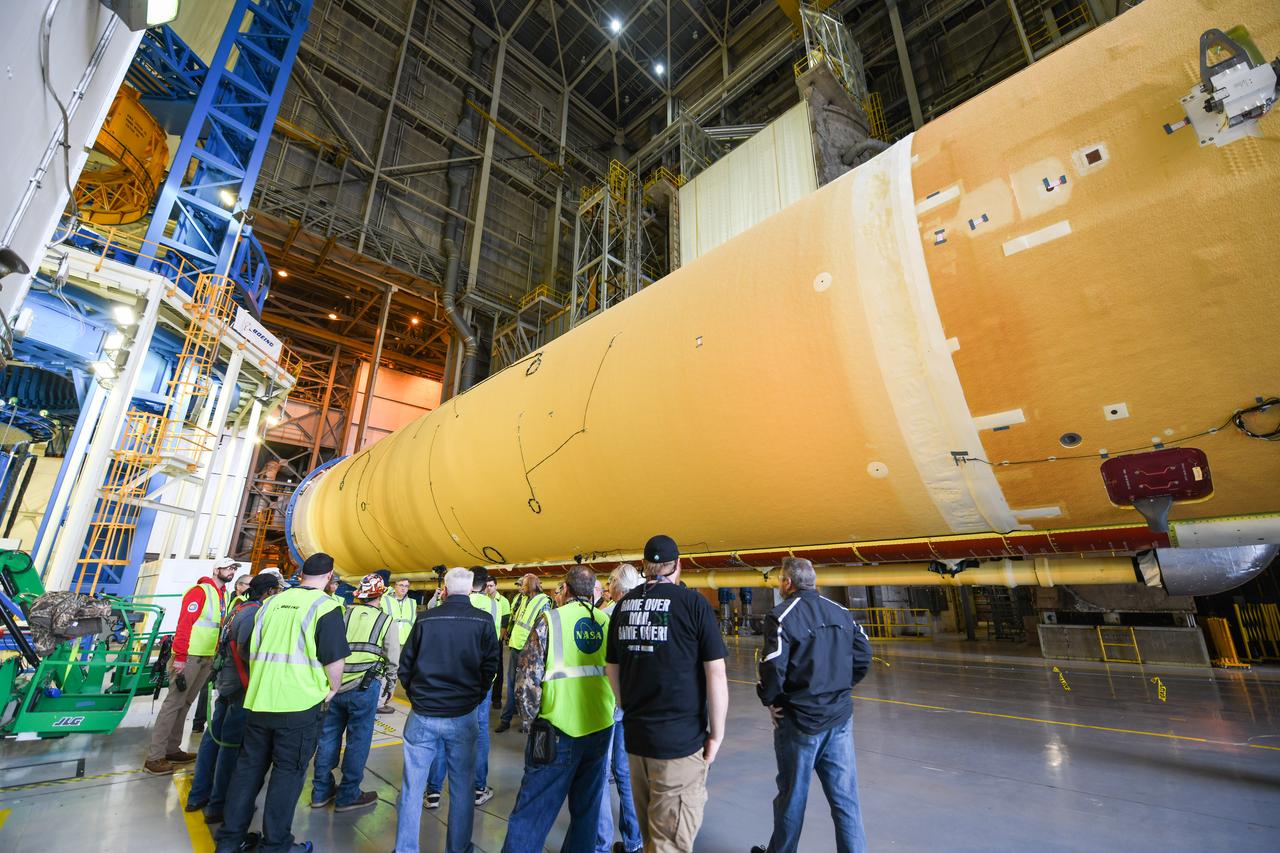

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
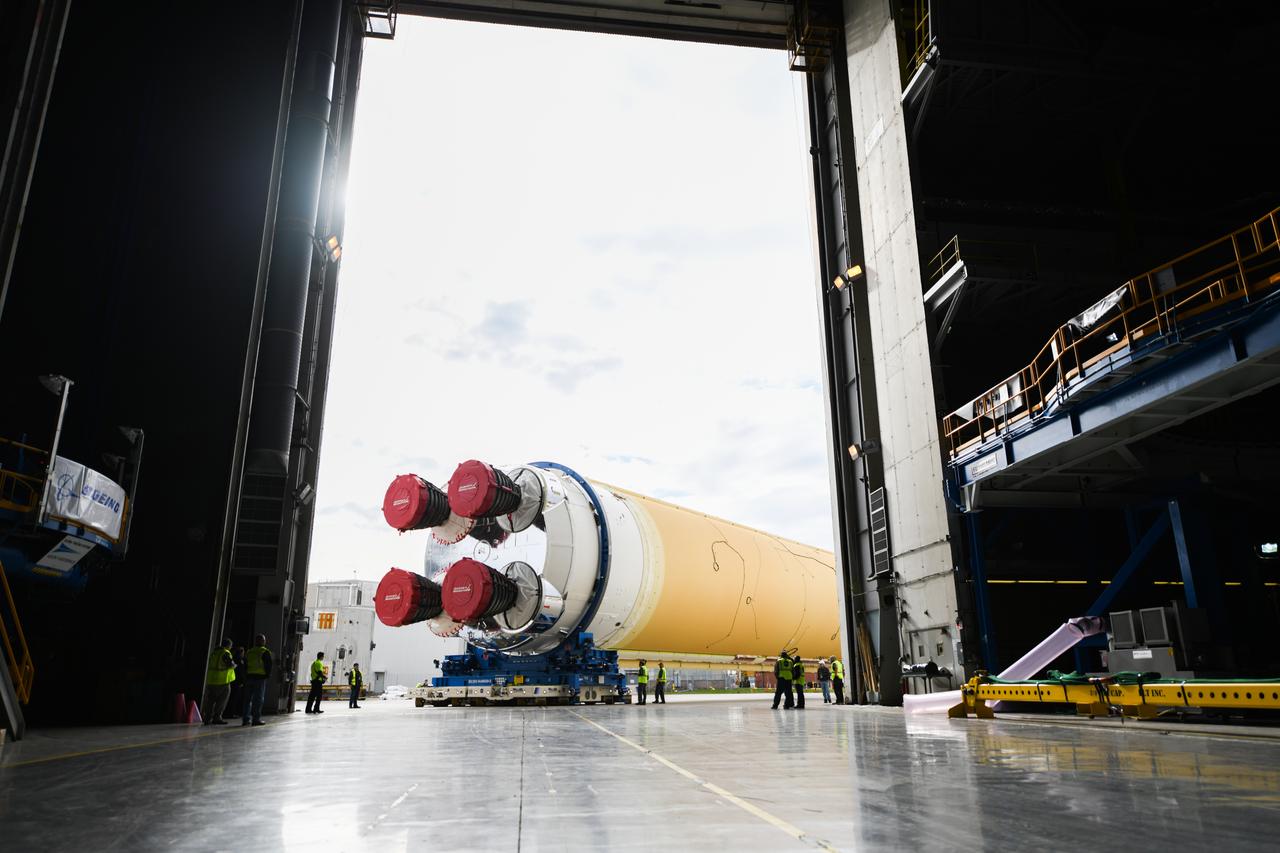

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
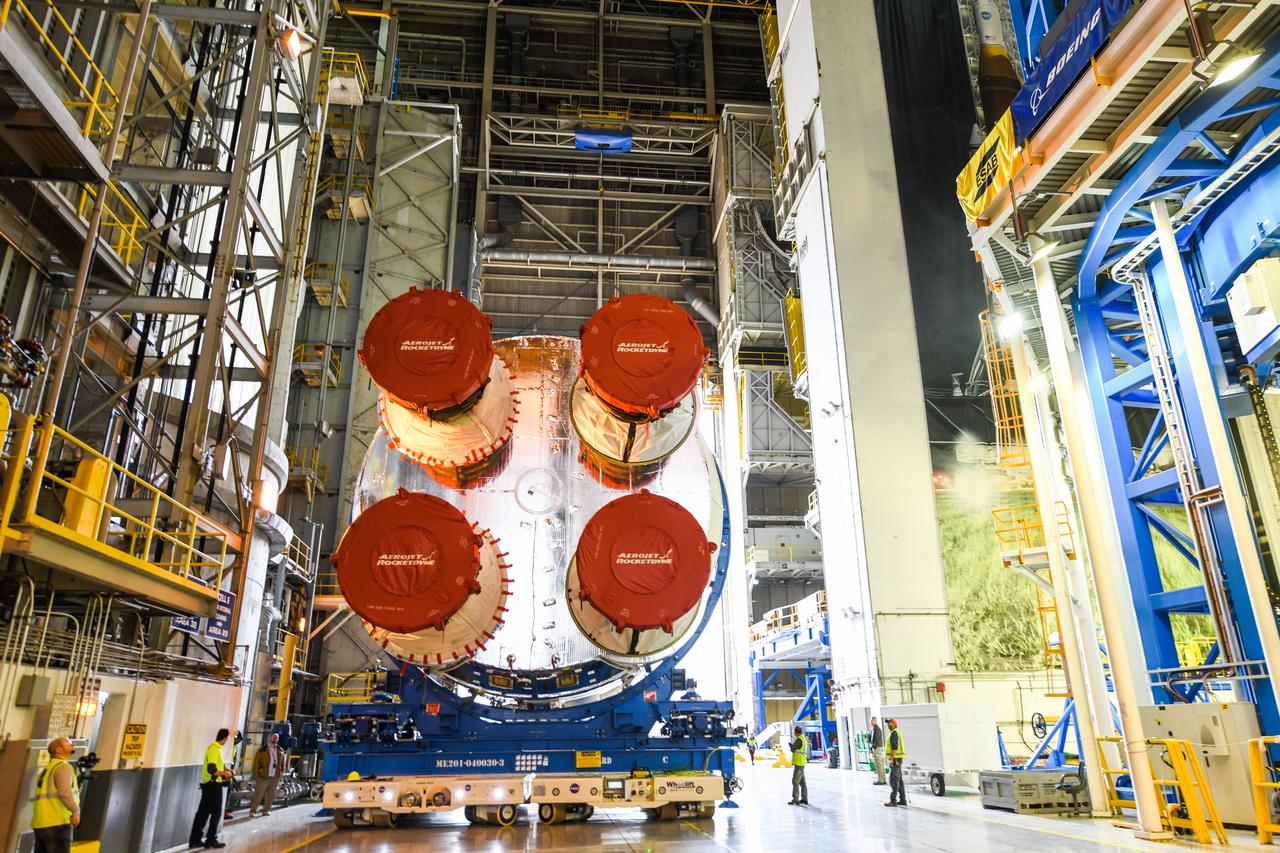
These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
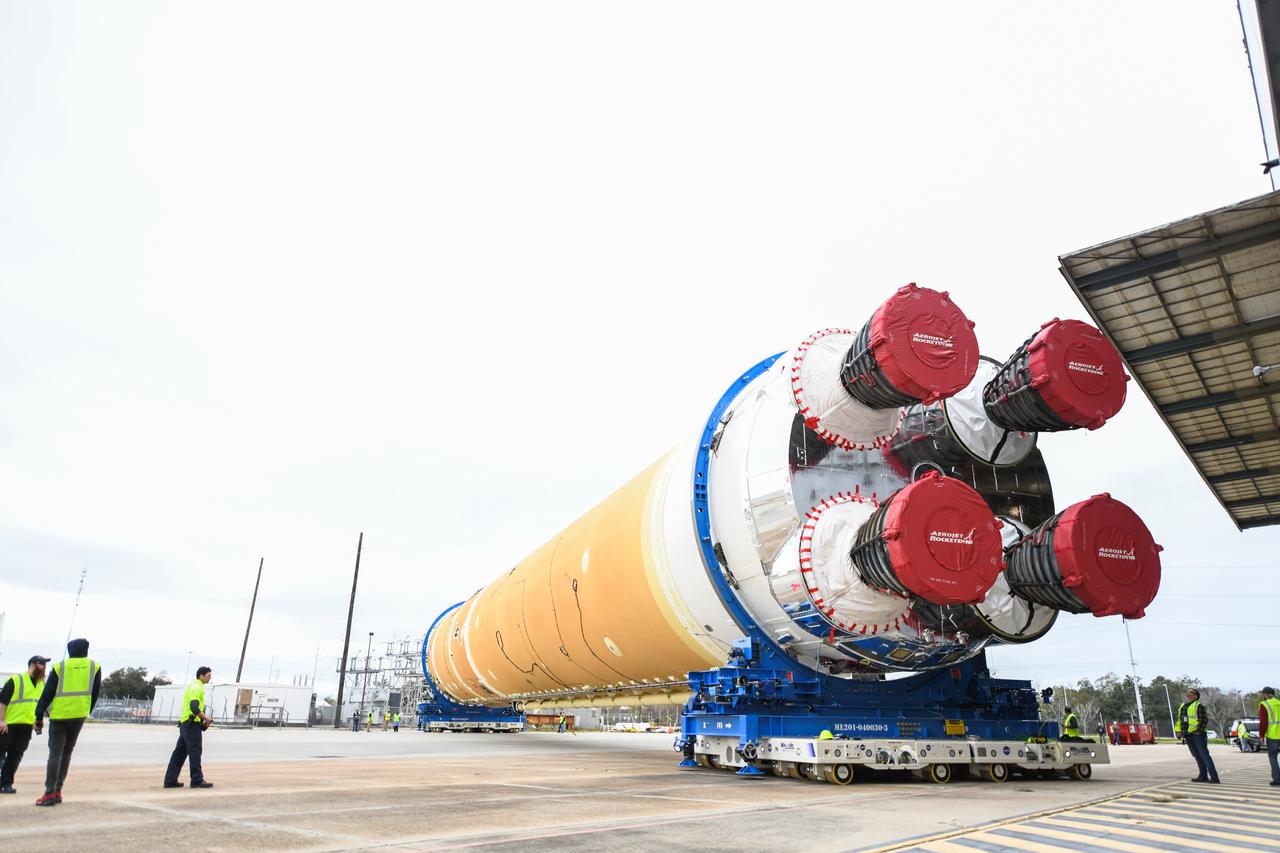

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.