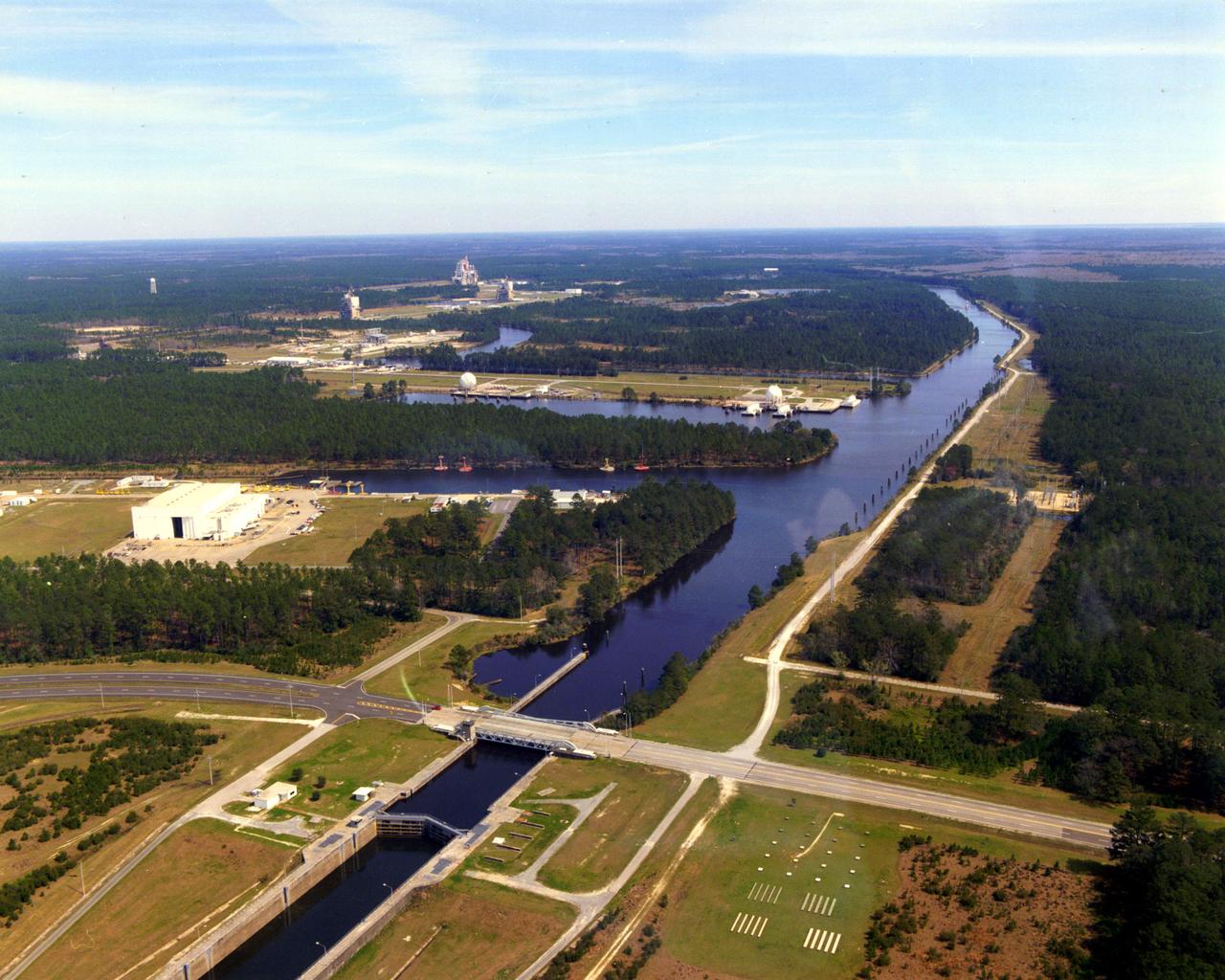

This aerial view of Stennis Space Center's unique lock and canal system
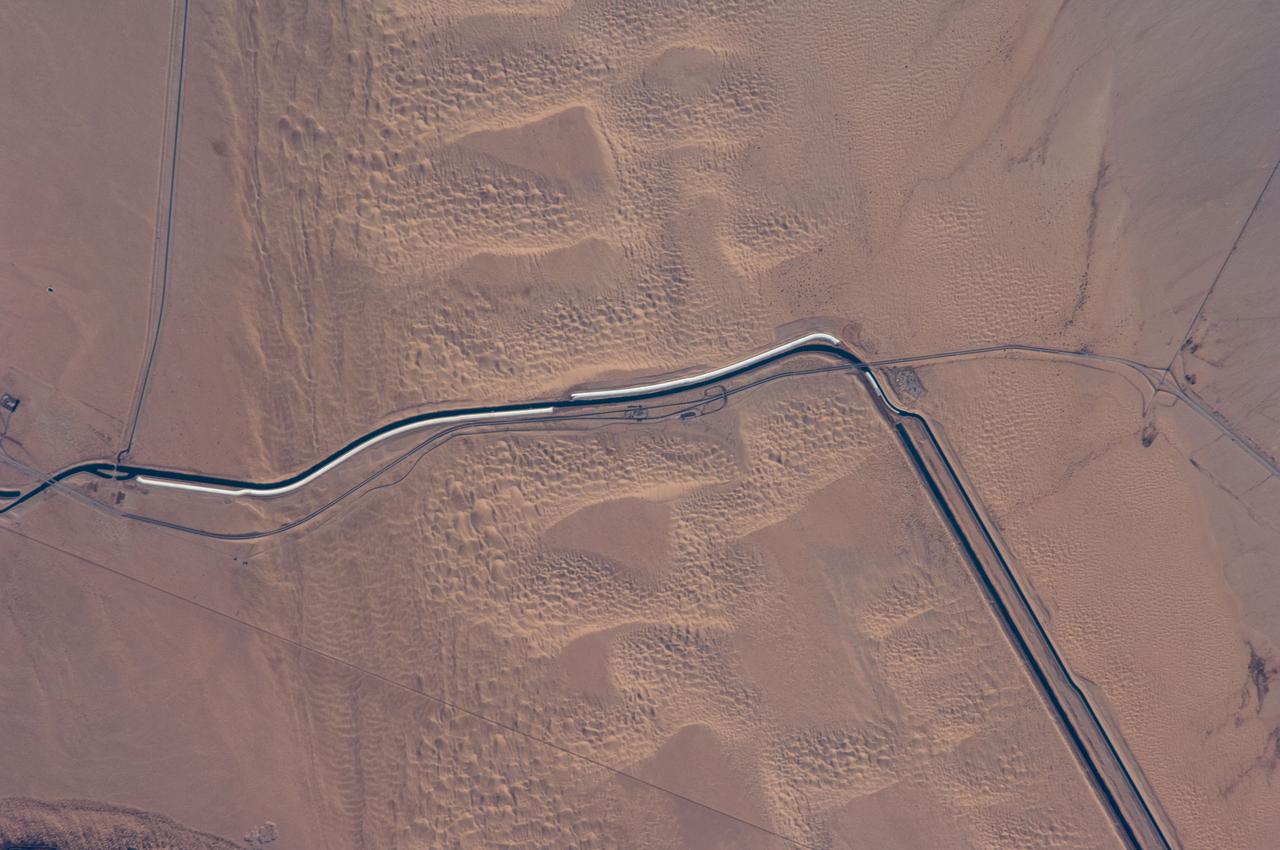

ISS018-E-024949 (31 Jan. 2009) --- The All-American Canal, the largest irrigation canal in the world and a key landmark along the California-Mexico border, is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 18 crewmember on the International Space Station. This image captures about 15 kilometers of the important infrastructure corridor just west of Yuma, AZ. The prominent dark line crossing the image is the Canal which is crossed, in this view, by Interstate Highway 8. The canal carries 740.6 cubic meters (26,155 cubic feet) of water per second from the Colorado River westward to support the intensive agriculture of California?s Imperial Valley to the northwest, and to nine cities including San Diego, CA. The canal system is the Imperial Valley?s only source of water, and allows irrigation of more than 2,000 square kilometers (500,000 acres) of agricultural fields. The Coachella Canal, one of four main branch canals, leads water north to Imperial Valley. This section of the canal requires constant maintenance. Approximately 68,000 acre-feet of water per year are lost by seepage from the All-American Canal - especially where the canal crosses the great Algodones Dune Field, a portion of which is visible extending from top to bottom in the center of the image. Additionally, dune sand is constantly blown to the southeast, and into the canal. As part of California?s Colorado River Water Use Plan, 37 kilometers (23 miles) of the canal is being lined to prevent water loss by seepage. A recently opened sector parallels the old canal (right) and new lined sectors are under construction (bright lines, center). Engineers have sited new sections of the canal to avoid the worst areas of dune-sand invasion, so that the new configuration will be significantly cheaper to maintain and operate. A new road crosses the dunes and marks the US?Mexico border as part of border fence construction efforts. The margin of the Colorado River floodplain in Mexico is just visible two kilometers south of the border (lower left corner). This floodplain is Mexico?s equivalent of the Imperial Valley in terms of its enormous irrigated agricultural production.

Site of the original Plymouth Colony in Massachusetts (42.0N, 70.5), This detailed photo is rich in early American history. Plymouth Rock, the Pilgrims first stepping stone on North America and site of Plymouth Colony is located just behind the natural breakwater on the south shore of Plymouth Bay seen in the middle of the photo. The through canal to the south is part of the Intercoastal Canal system. Cape Cod is just south of the canal.
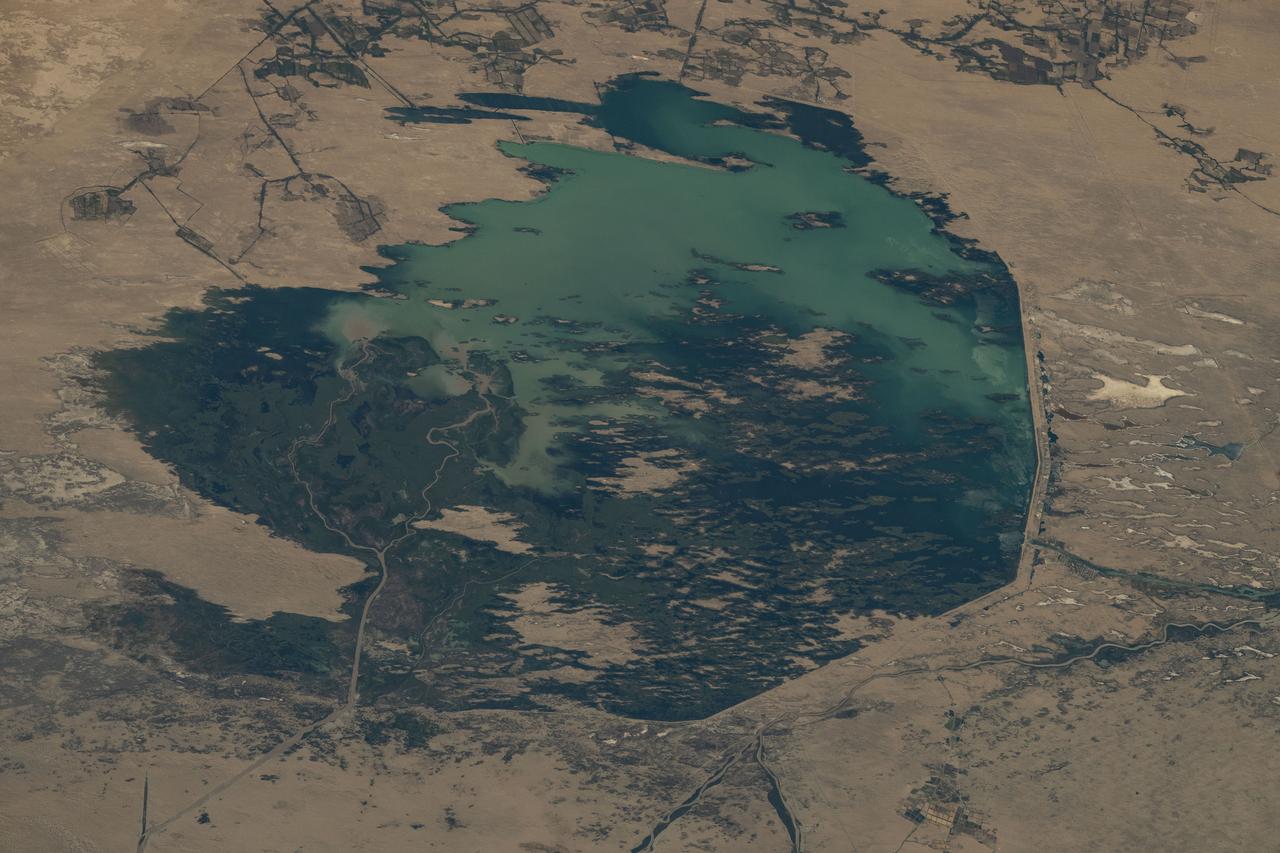

iss073e0423962 (Aug. 7, 2025) --- The Zeid Reservoir in Turkmenistan is pictured from the International Space Station as it orbited 260 miles above Central Asia. The reservoir was designed to capture some of the sand and sediment flowing in from the nearby Amu Darya River and the Karakum Canal. This helps keep the water cleaner and protects the canal system from getting clogged.
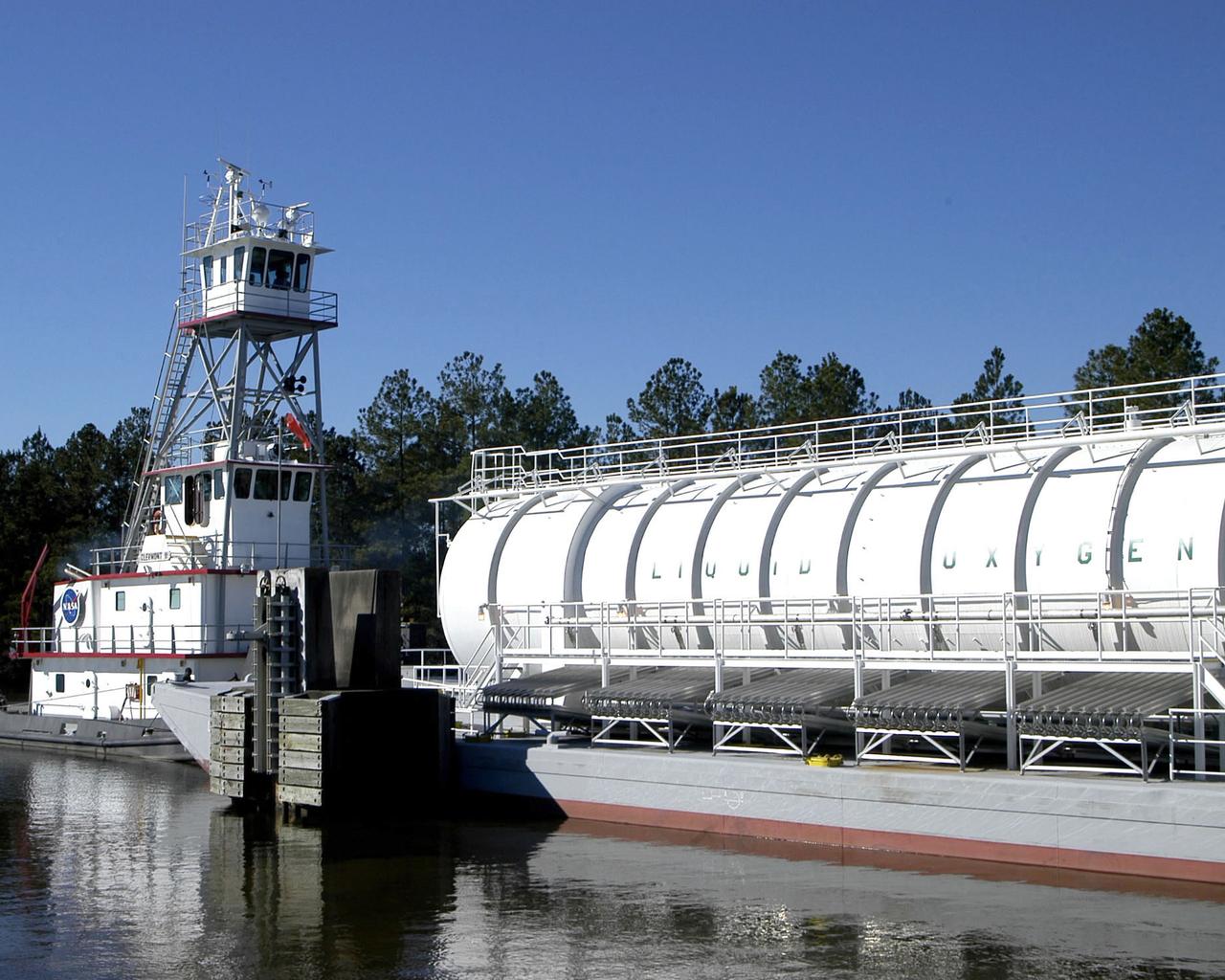

The crew of the NASA tugboat Clermont II navigates a barge of super-cool liquid oxygen through the 7 -mile canal system at SSC prior to a Space Shuttle Main Engine test.
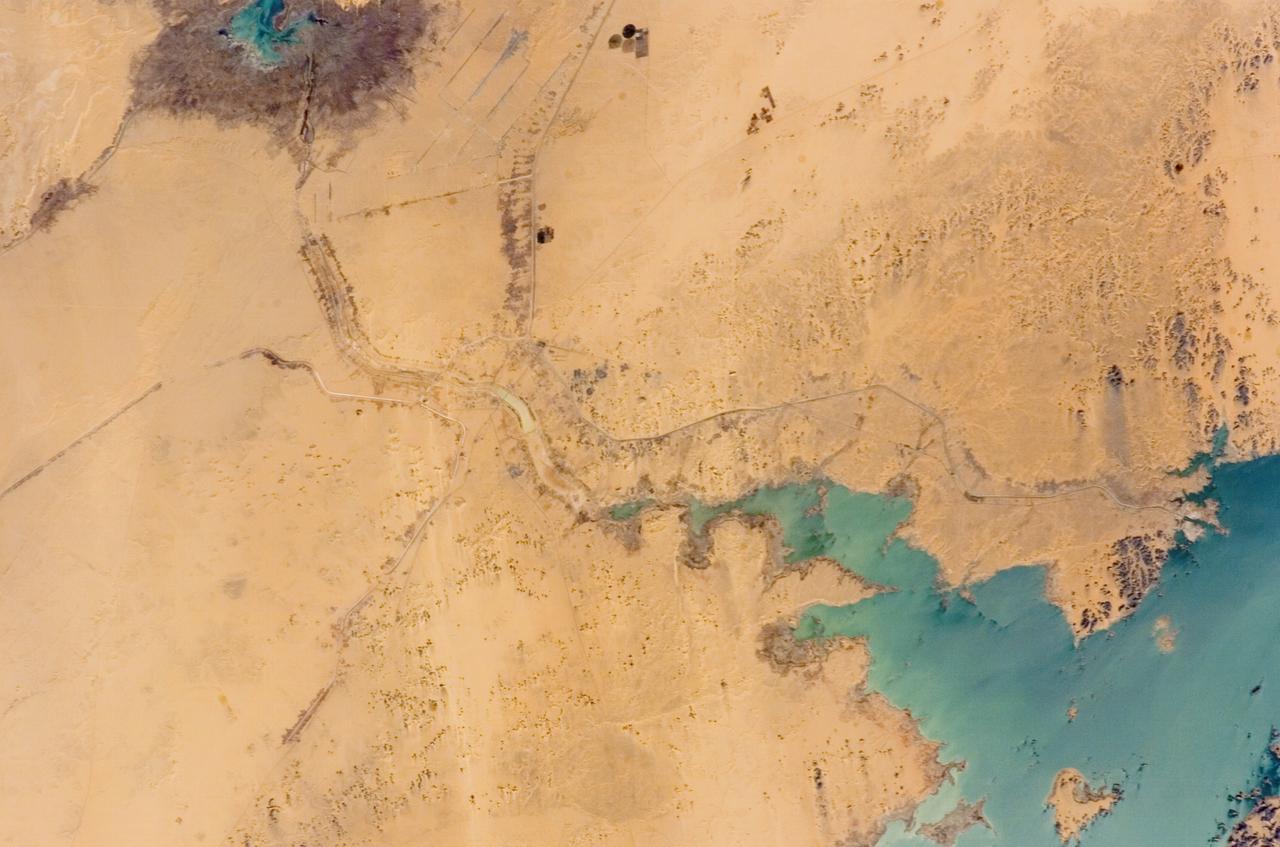

ISS012-E-11654 (11 Dec. 2005) --- Lake Nasser and New Valley, Egypt are featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 12 crew member on the International Space Station. Cycles of flood and drought in the African Sahel are legendary, and they have provided the impetus for major waterworks on Africa’s great rivers. The construction of the Aswan High Dam on the Nile River, creating Lake Nasser in the 1960s, is the biggest and most visible project. Heavy rains in the source regions of the Nile in the 1990s resulted in record water levels in Lake Nasser. The abundance of water facilitated the Egyptian government’s promotion of another massive water distribution system called New Valley. In 1997, Lake Nasser flooded westward down a spillway into the Toshka depression in southern Egypt, creating four new lakes over the next few years. Following the initial flooding, a pumping station and canal were constructed in 2000 to maintain water flow into the region, allowing for industrial and agricultural development in the desert. This view shows the completed Mubarek Pumping Station on Lake Nasser; the spillway that originally flooded the Toshka depression and the southern end of the first of the Toshka Lakes; part of the 50-kilometer-long main canal (the Sheikh Zayed Canal); side canals; and several new fields in the Egyptian desert northwest of Lake Nasser. Astronauts, cosmonauts and space-based sensors have been monitoring these developments in Egypt since their inception in the late 1990s. New Valley’s Toshka Lakes, and the new developments surrounding them, represent one of the most visible and rapid man-made changes on Earth’s surface.
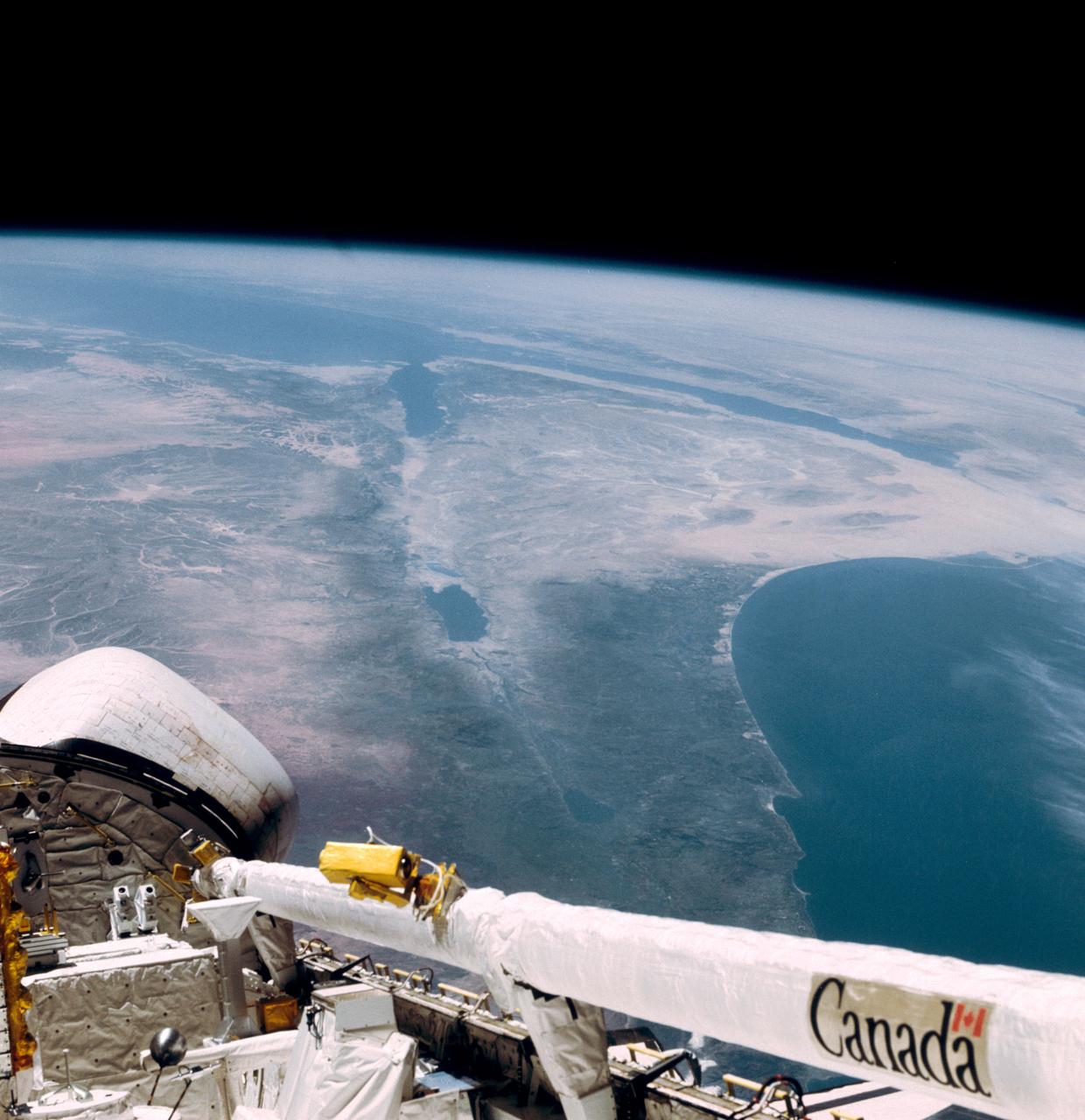

This southerly looking view photographed from the orbiting Space Shuttle Columbia shows a small portion of the vehichle's aft section. The 50-ft Canadian built remote manipulator system (RMS) is in a resting posture (lower right corner) stretched out along the 60-ft. long cargo bay. Many of the components of the OSS-1 payload package are in the bottom center. The Mediterranean Sea is at right foreground. Parts of the Sinai peninsula, Israel, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Jordan, Palestine, Syria, and Lebanon can be located in the photo. The Red Sea, Gulf of Aqaba, Suez Canal are near the photo's horizon.
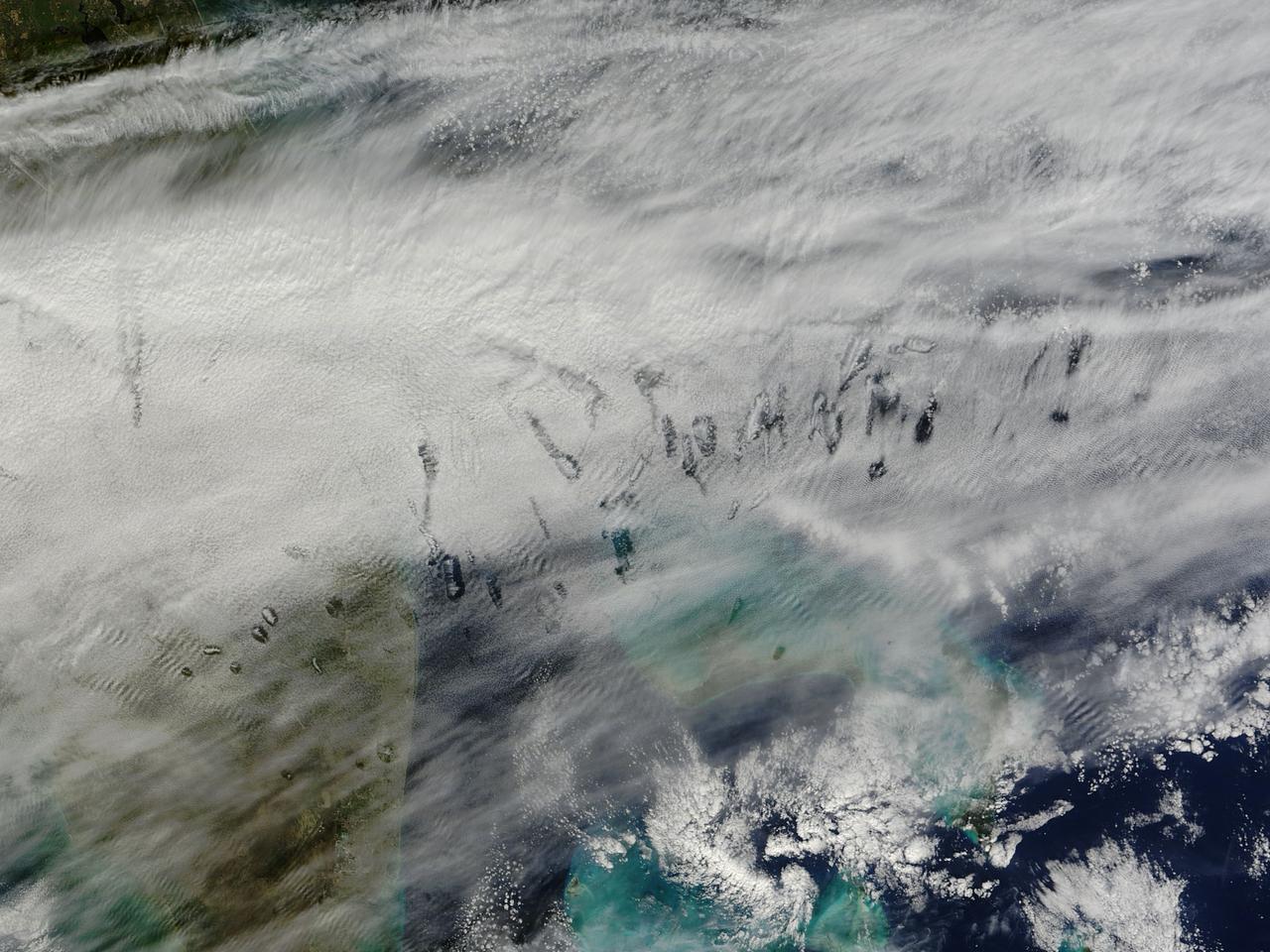
In elementary school, students learn that water freezes at 0 degrees Celsius (32 degrees Fahrenheit). That is true most of the time, but there are exceptions to the rule. For instance, water with very few impurities (such as dust or pollution particles, fungal spores, bacteria) can be chilled to much cooler temperatures and still remain liquid—a process known as supercooling. Supercooling may sound exotic, but it occurs pretty routinely in Earth’s atmosphere. Altocumulus clouds, a common type of mid-altitude cloud, are mostly composed of water droplets supercooled to a temperature of about -15 degrees C. Altocumulus clouds with supercooled tops cover about 8 percent of Earth’s surface at any given time. Supercooled water droplets play a key role in the formation of hole-punch and canal clouds, the distinctive clouds shown in these satellite images. Hole-punch clouds usually appear as circular gaps in decks of altocumulus clouds; canal clouds look similar but the gaps are longer and thinner. This true-color image shows hole-punch and canal clouds off the coast of Florida, as observed on December 12, 2014, by the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on NASA’s Terra satellite. Both types of cloud form when aircraft fly through cloud decks rich with supercooled water droplets and produce aerodynamic contrails. Air expands and cools as it moves around the wings and past the propeller, a process known as adiabatic cooling. Air temperatures over jet wings often cool by as much as 20 degrees Celsius, pushing supercooled water droplets to the point of freezing. As ice crystals form, they absorb nearby water droplets. Since ice crystals are relatively heavy, they tend to sink. This triggers tiny bursts of snow or rain that leave gaps in the cloud cover. Whether a cloud formation becomes a hole-punch or canal depends on the thickness of the cloud layer, the air temperature, and the degree of horizontal wind shear. Both descending and ascending aircraft—including jets and propeller planes—can trigger hole-punch and canal clouds. The nearest major airports in the images above include Miami International, Fort Lauderdale International, Grand Bahama International, and Palm Beach International. Credit: NASA/GSFC/Jeff Schmaltz/MODIS Land Rapid Response Team <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
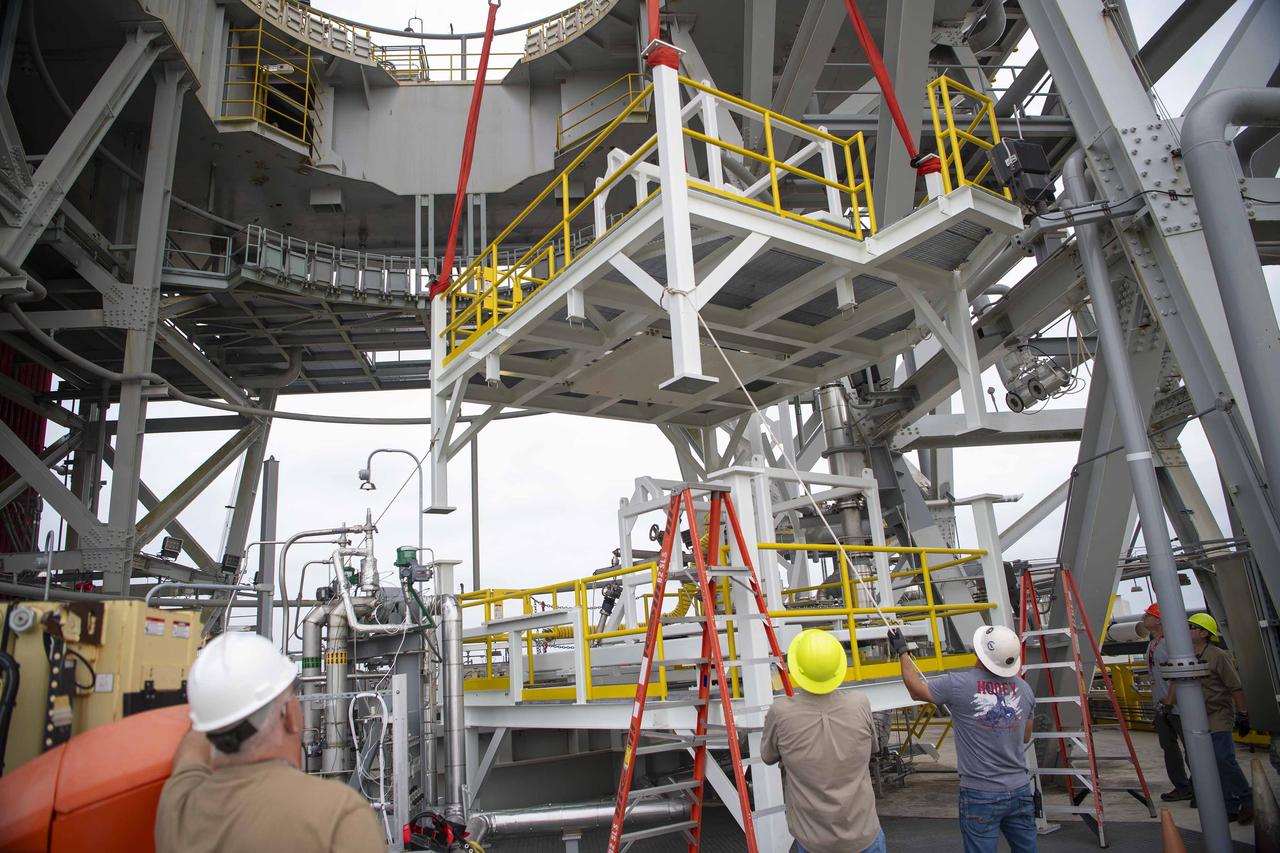

A pair of umbilical support structures needed for future testing of NASA’s exploration upper stage (EUS) were installed in the B-2 position of the Thad Cochran Test Stand on Oct. 30-31 at NASA’s Stennis Space Center. The support structures arrived from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans via the unique NASA Stennis seven-and-a-half-mile canal system in 2023. Since then, crews have prepared the structures that will align with the EUS unit for installation. In addition to helping secure the unit in place during hot fire testing, the umbilical support structures are where the command, control, and data electrical connections are mated to connect the ground systems to the vehicle systems, as well as most the commodity connections such as liquid hydrogen, liquid oxygen, hydrogen vent, helium bottle fill pressure, and purges. Prior to its initial flight, the EUS unit will undergo a series of so-called Green Run tests at NASA Stennis to ensure all systems are ready to go. The test series will culminate with a hot fire of the stage’s four RL10 engines, made by Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company and lead SLS engines contractor. The new upper stage will enable NASA to carry larger payloads on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond.
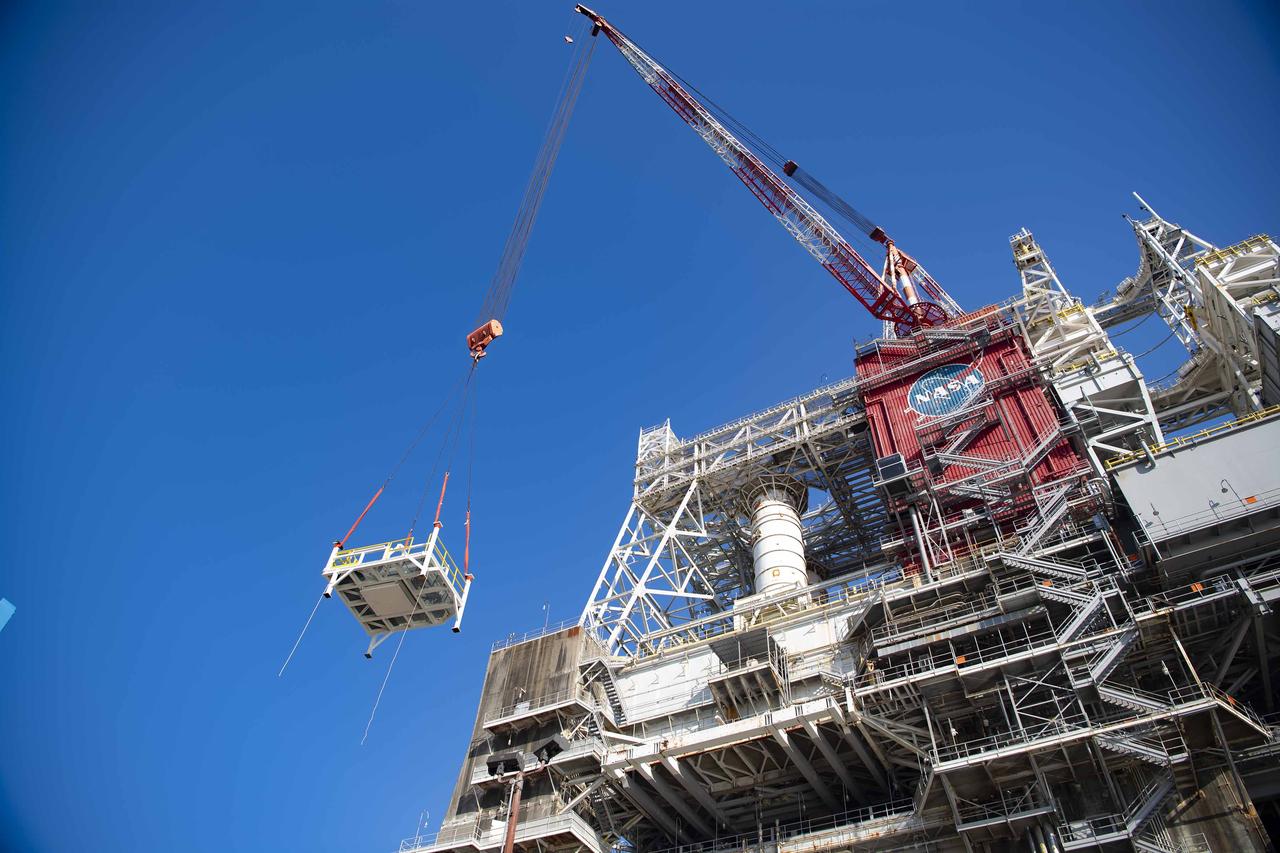

A pair of umbilical support structures needed for future testing of NASA’s exploration upper stage (EUS) were installed in the B-2 position of the Thad Cochran Test Stand on Oct. 30-31 at NASA’s Stennis Space Center. The support structures arrived from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans via the unique NASA Stennis seven-and-a-half-mile canal system in 2023. Since then, crews have prepared the structures that will align with the EUS unit for installation. In addition to helping secure the unit in place during hot fire testing, the umbilical support structures are where the command, control, and data electrical connections are mated to connect the ground systems to the vehicle systems, as well as most the commodity connections such as liquid hydrogen, liquid oxygen, hydrogen vent, helium bottle fill pressure, and purges. Prior to its initial flight, the EUS unit will undergo a series of so-called Green Run tests at NASA Stennis to ensure all systems are ready to go. The test series will culminate with a hot fire of the stage’s four RL10 engines, made by Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company and lead SLS engines contractor. The new upper stage will enable NASA to carry larger payloads on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond.
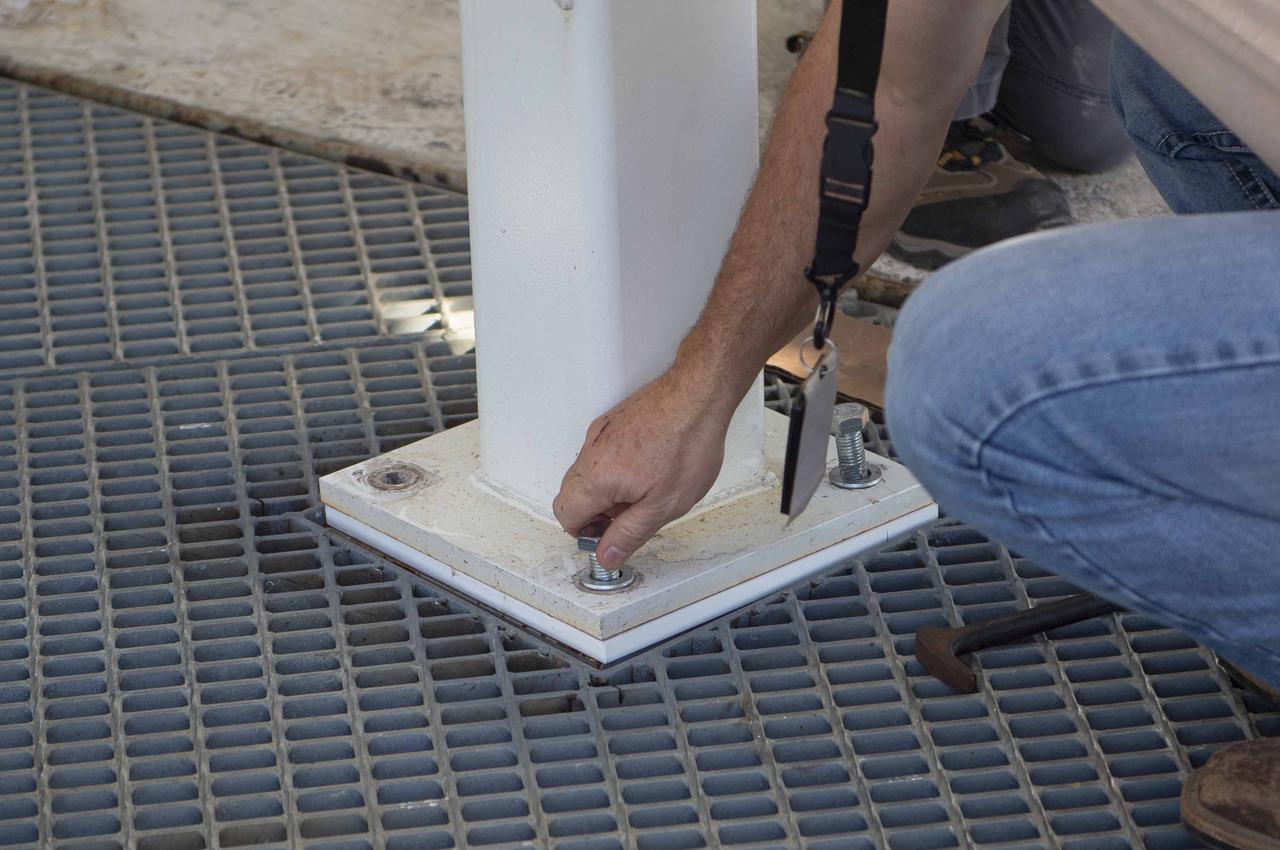

A pair of umbilical support structures needed for future testing of NASA’s exploration upper stage (EUS) were installed in the B-2 position of the Thad Cochran Test Stand on Oct. 30-31 at NASA’s Stennis Space Center. The support structures arrived from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans via the unique NASA Stennis seven-and-a-half-mile canal system in 2023. Since then, crews have prepared the structures that will align with the EUS unit for installation. In addition to helping secure the unit in place during hot fire testing, the umbilical support structures are where the command, control, and data electrical connections are mated to connect the ground systems to the vehicle systems, as well as most the commodity connections such as liquid hydrogen, liquid oxygen, hydrogen vent, helium bottle fill pressure, and purges. Prior to its initial flight, the EUS unit will undergo a series of so-called Green Run tests at NASA Stennis to ensure all systems are ready to go. The test series will culminate with a hot fire of the stage’s four RL10 engines, made by Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company and lead SLS engines contractor. The new upper stage will enable NASA to carry larger payloads on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond.
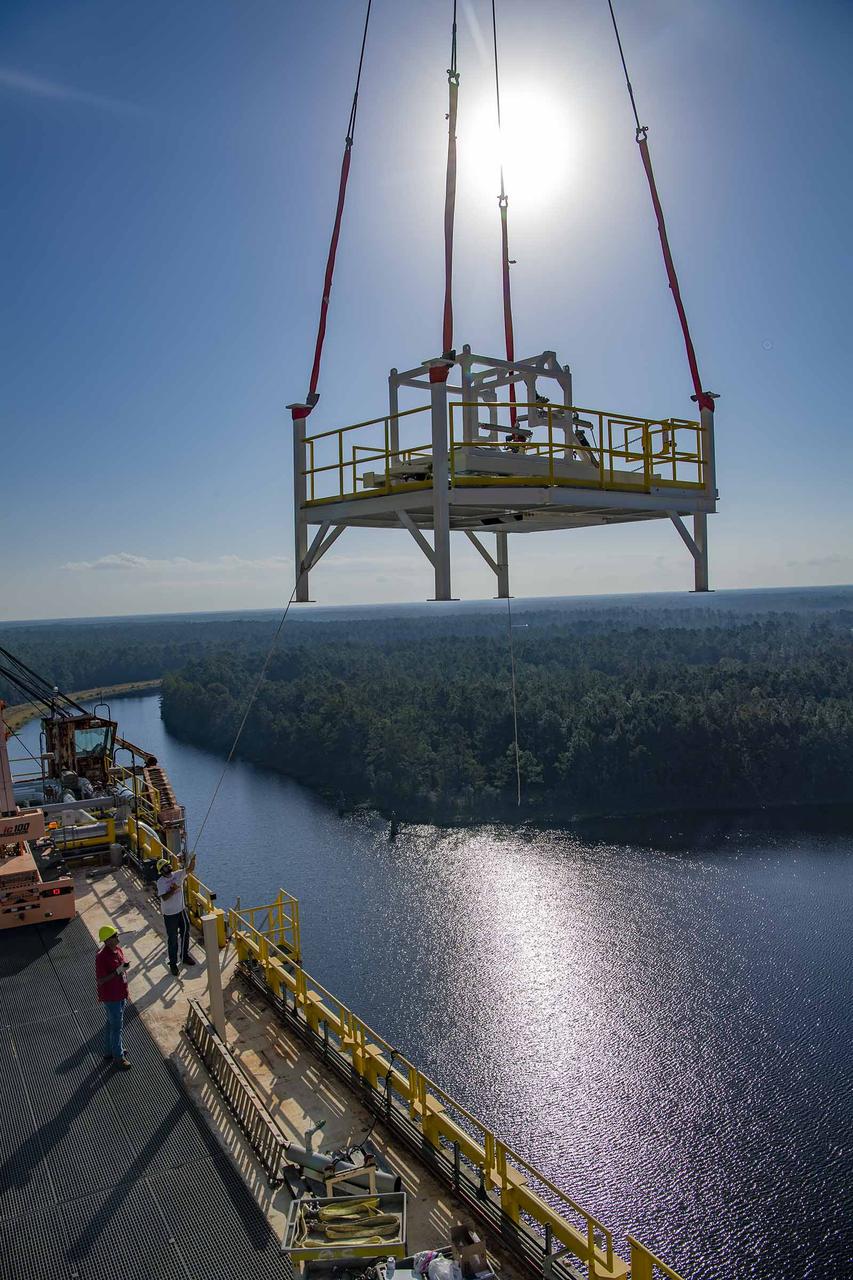

A pair of umbilical support structures needed for future testing of NASA’s exploration upper stage (EUS) were installed in the B-2 position of the Thad Cochran Test Stand on Oct. 30-31 at NASA’s Stennis Space Center. The support structures arrived from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans via the unique NASA Stennis seven-and-a-half-mile canal system in 2023. Since then, crews have prepared the structures that will align with the EUS unit for installation. In addition to helping secure the unit in place during hot fire testing, the umbilical support structures are where the command, control, and data electrical connections are mated to connect the ground systems to the vehicle systems, as well as most the commodity connections such as liquid hydrogen, liquid oxygen, hydrogen vent, helium bottle fill pressure, and purges. Prior to its initial flight, the EUS unit will undergo a series of so-called Green Run tests at NASA Stennis to ensure all systems are ready to go. The test series will culminate with a hot fire of the stage’s four RL10 engines, made by Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company and lead SLS engines contractor. The new upper stage will enable NASA to carry larger payloads on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond.
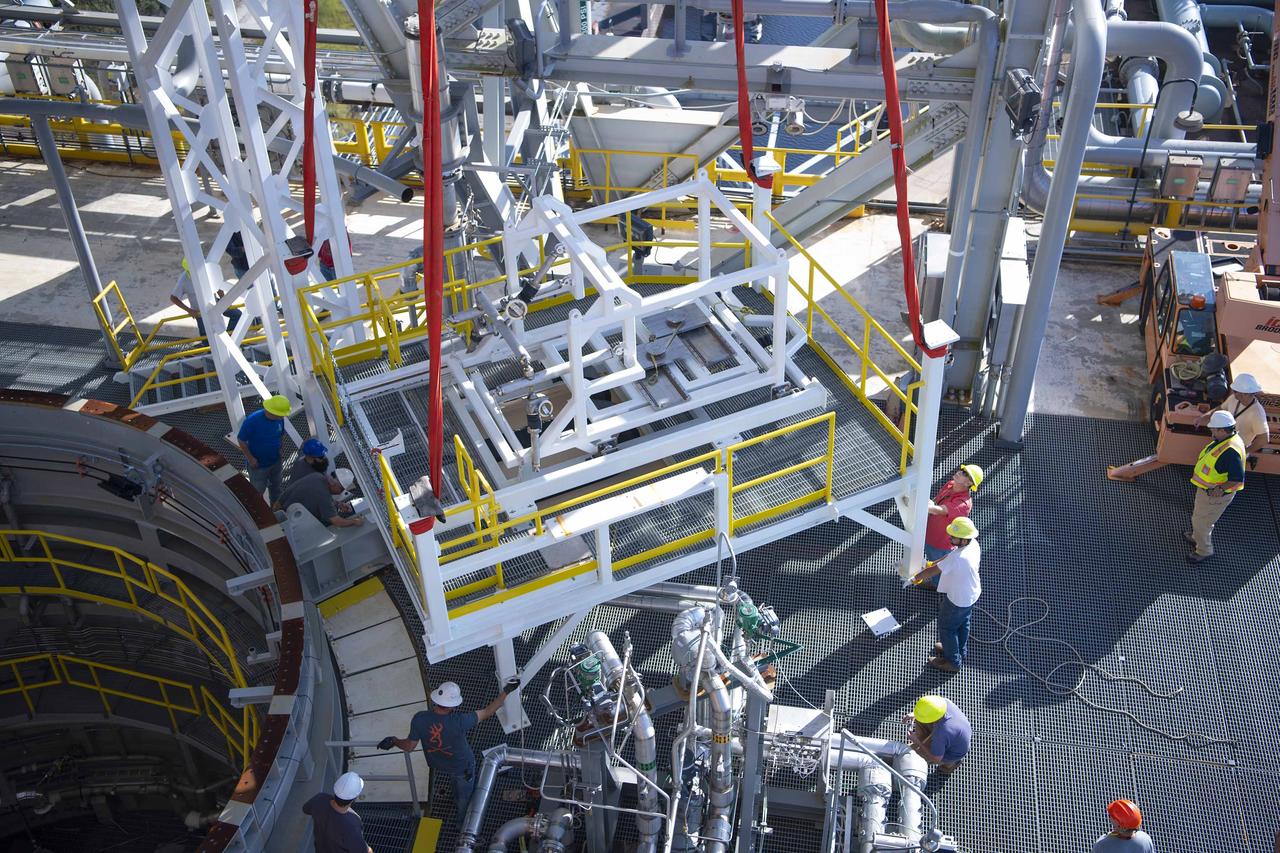

A pair of umbilical support structures needed for future testing of NASA’s exploration upper stage (EUS) were installed in the B-2 position of the Thad Cochran Test Stand on Oct. 30-31 at NASA’s Stennis Space Center. The support structures arrived from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans via the unique NASA Stennis seven-and-a-half-mile canal system in 2023. Since then, crews have prepared the structures that will align with the EUS unit for installation. In addition to helping secure the unit in place during hot fire testing, the umbilical support structures are where the command, control, and data electrical connections are mated to connect the ground systems to the vehicle systems, as well as most the commodity connections such as liquid hydrogen, liquid oxygen, hydrogen vent, helium bottle fill pressure, and purges. Prior to its initial flight, the EUS unit will undergo a series of so-called Green Run tests at NASA Stennis to ensure all systems are ready to go. The test series will culminate with a hot fire of the stage’s four RL10 engines, made by Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company and lead SLS engines contractor. The new upper stage will enable NASA to carry larger payloads on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond.
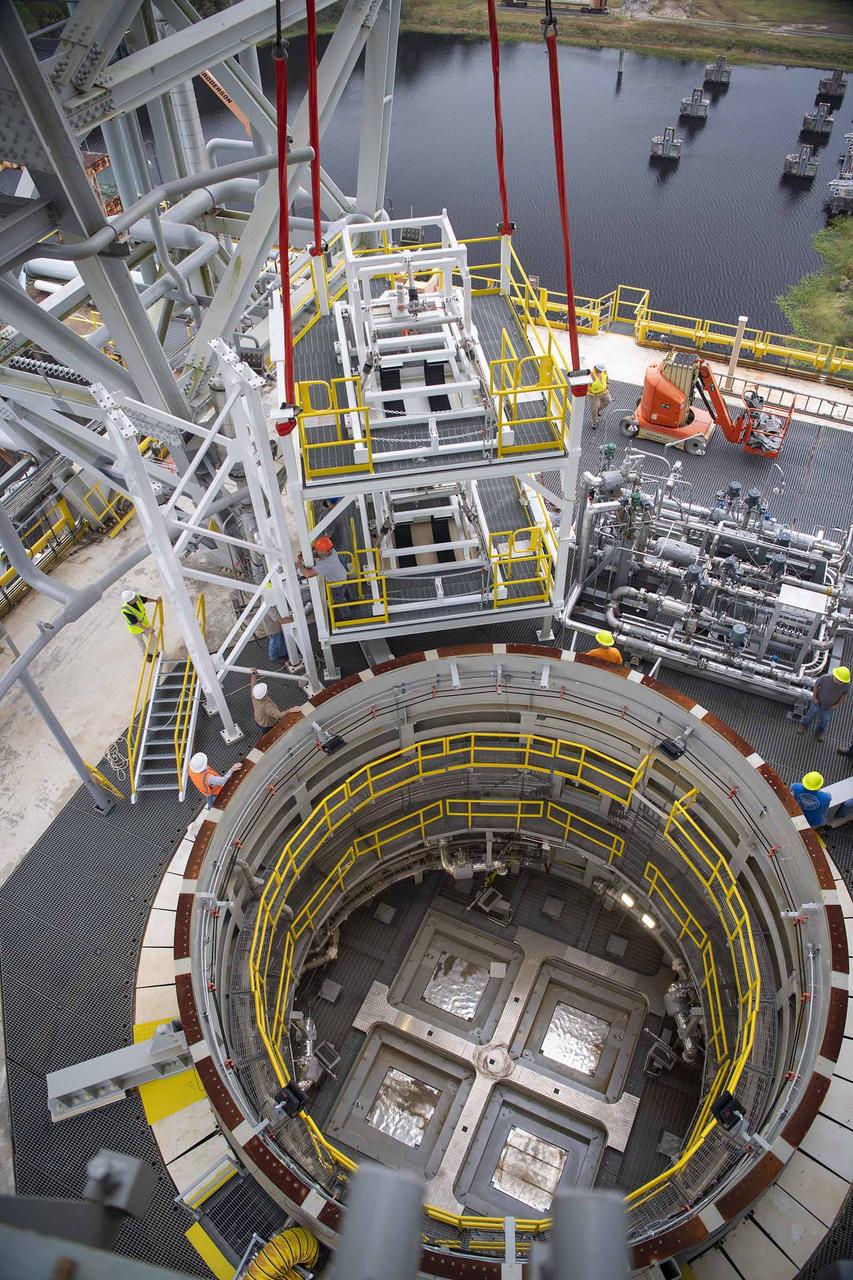
A pair of umbilical support structures needed for future testing of NASA’s exploration upper stage (EUS) were installed in the B-2 position of the Thad Cochran Test Stand on Oct. 30-31 at NASA’s Stennis Space Center. The support structures arrived from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans via the unique NASA Stennis seven-and-a-half-mile canal system in 2023. Since then, crews have prepared the structures that will align with the EUS unit for installation. In addition to helping secure the unit in place during hot fire testing, the umbilical support structures are where the command, control, and data electrical connections are mated to connect the ground systems to the vehicle systems, as well as most the commodity connections such as liquid hydrogen, liquid oxygen, hydrogen vent, helium bottle fill pressure, and purges. Prior to its initial flight, the EUS unit will undergo a series of so-called Green Run tests at NASA Stennis to ensure all systems are ready to go. The test series will culminate with a hot fire of the stage’s four RL10 engines, made by Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company and lead SLS engines contractor. The new upper stage will enable NASA to carry larger payloads on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond.
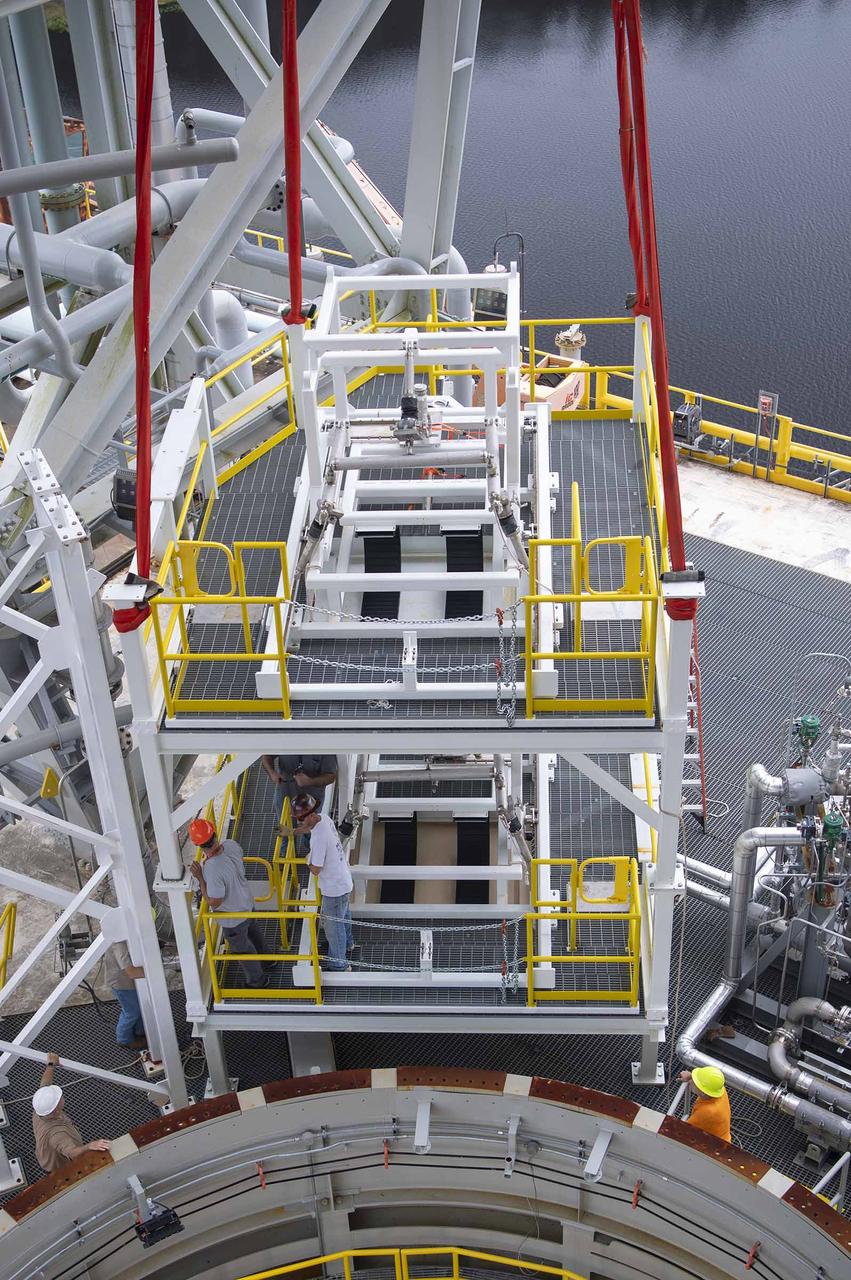

A pair of umbilical support structures needed for future testing of NASA’s exploration upper stage (EUS) were installed in the B-2 position of the Thad Cochran Test Stand on Oct. 30-31 at NASA’s Stennis Space Center. The support structures arrived from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans via the unique NASA Stennis seven-and-a-half-mile canal system in 2023. Since then, crews have prepared the structures that will align with the EUS unit for installation. In addition to helping secure the unit in place during hot fire testing, the umbilical support structures are where the command, control, and data electrical connections are mated to connect the ground systems to the vehicle systems, as well as most the commodity connections such as liquid hydrogen, liquid oxygen, hydrogen vent, helium bottle fill pressure, and purges. Prior to its initial flight, the EUS unit will undergo a series of so-called Green Run tests at NASA Stennis to ensure all systems are ready to go. The test series will culminate with a hot fire of the stage’s four RL10 engines, made by Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company and lead SLS engines contractor. The new upper stage will enable NASA to carry larger payloads on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond.
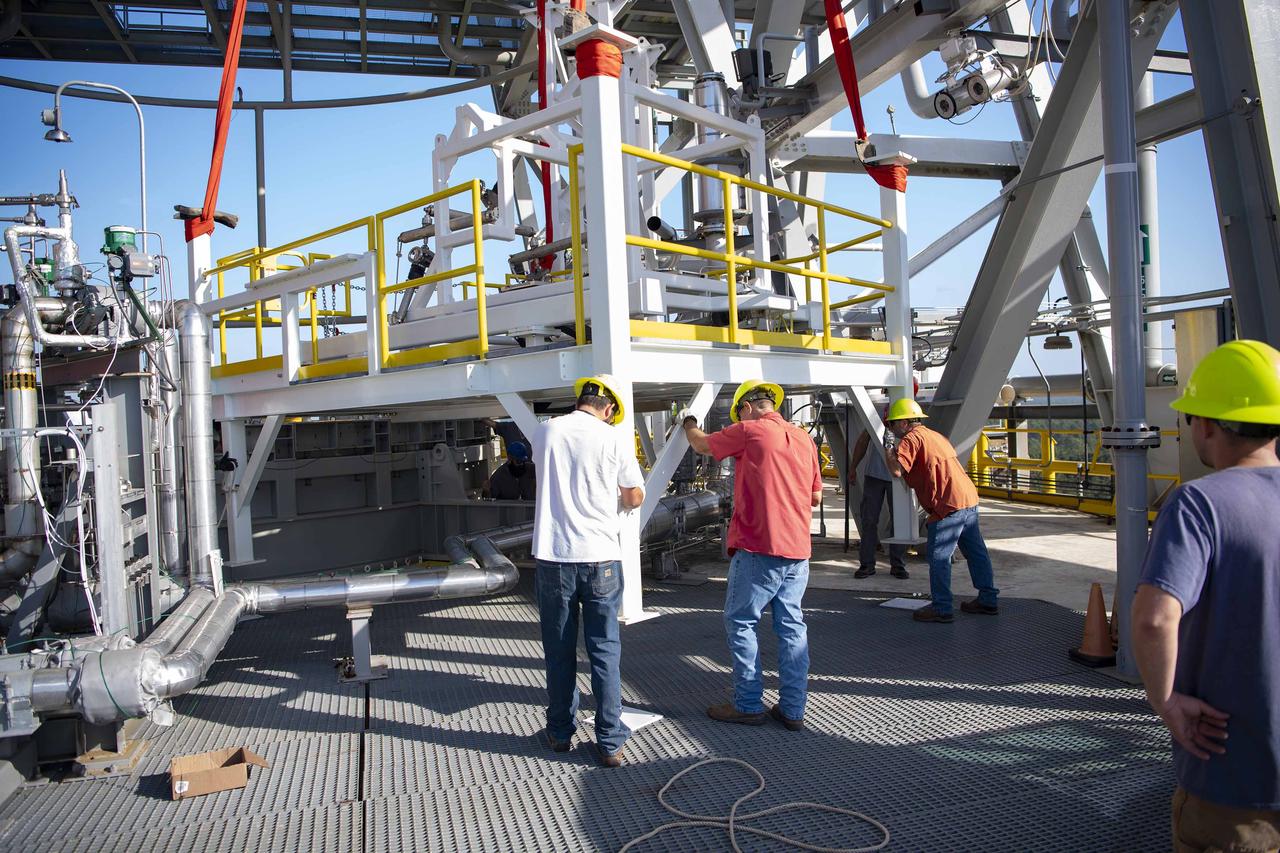

A pair of umbilical support structures needed for future testing of NASA’s exploration upper stage (EUS) were installed in the B-2 position of the Thad Cochran Test Stand on Oct. 30-31 at NASA’s Stennis Space Center. The support structures arrived from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans via the unique NASA Stennis seven-and-a-half-mile canal system in 2023. Since then, crews have prepared the structures that will align with the EUS unit for installation. In addition to helping secure the unit in place during hot fire testing, the umbilical support structures are where the command, control, and data electrical connections are mated to connect the ground systems to the vehicle systems, as well as most the commodity connections such as liquid hydrogen, liquid oxygen, hydrogen vent, helium bottle fill pressure, and purges. Prior to its initial flight, the EUS unit will undergo a series of so-called Green Run tests at NASA Stennis to ensure all systems are ready to go. The test series will culminate with a hot fire of the stage’s four RL10 engines, made by Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company and lead SLS engines contractor. The new upper stage will enable NASA to carry larger payloads on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond.
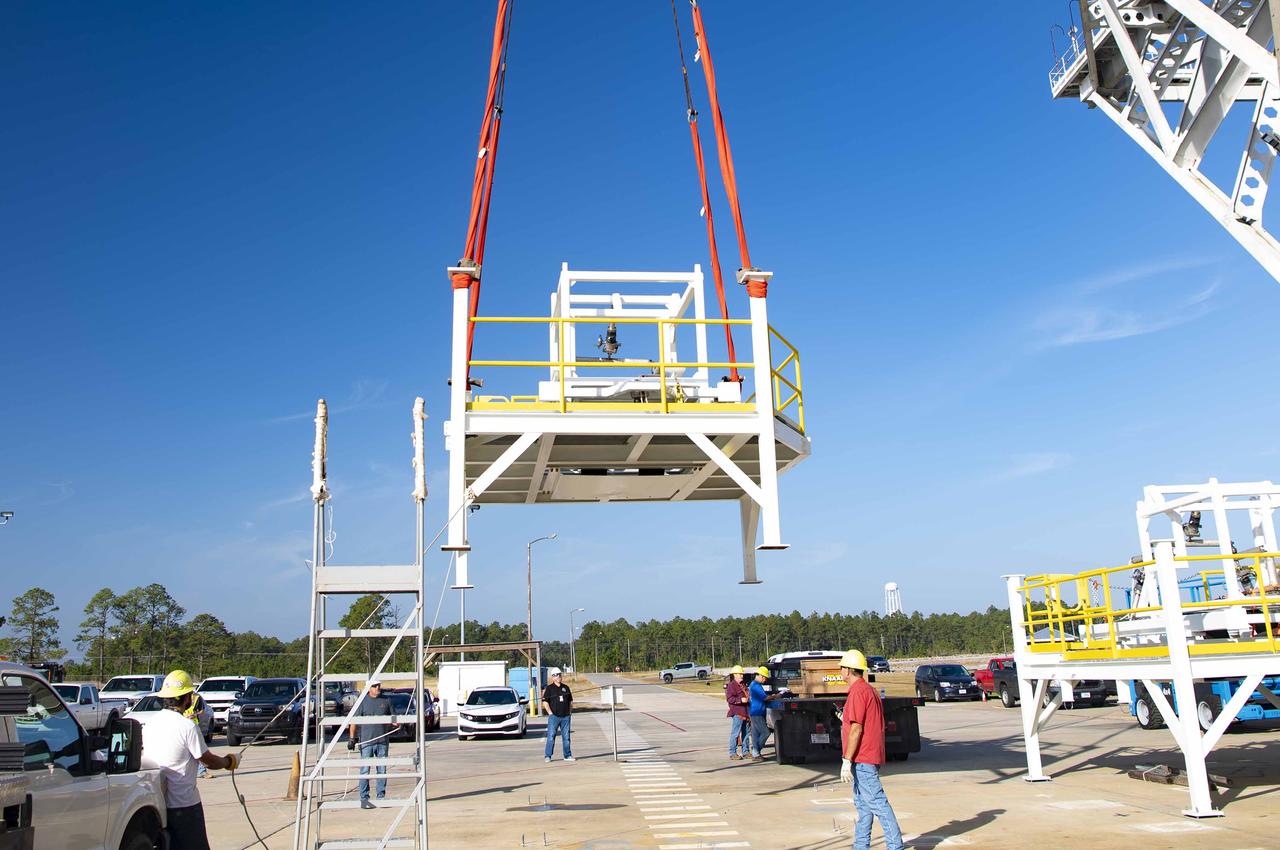

A pair of umbilical support structures needed for future testing of NASA’s exploration upper stage (EUS) were installed in the B-2 position of the Thad Cochran Test Stand on Oct. 30-31 at NASA’s Stennis Space Center. The support structures arrived from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans via the unique NASA Stennis seven-and-a-half-mile canal system in 2023. Since then, crews have prepared the structures that will align with the EUS unit for installation. In addition to helping secure the unit in place during hot fire testing, the umbilical support structures are where the command, control, and data electrical connections are mated to connect the ground systems to the vehicle systems, as well as most the commodity connections such as liquid hydrogen, liquid oxygen, hydrogen vent, helium bottle fill pressure, and purges. Prior to its initial flight, the EUS unit will undergo a series of so-called Green Run tests at NASA Stennis to ensure all systems are ready to go. The test series will culminate with a hot fire of the stage’s four RL10 engines, made by Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company and lead SLS engines contractor. The new upper stage will enable NASA to carry larger payloads on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond.
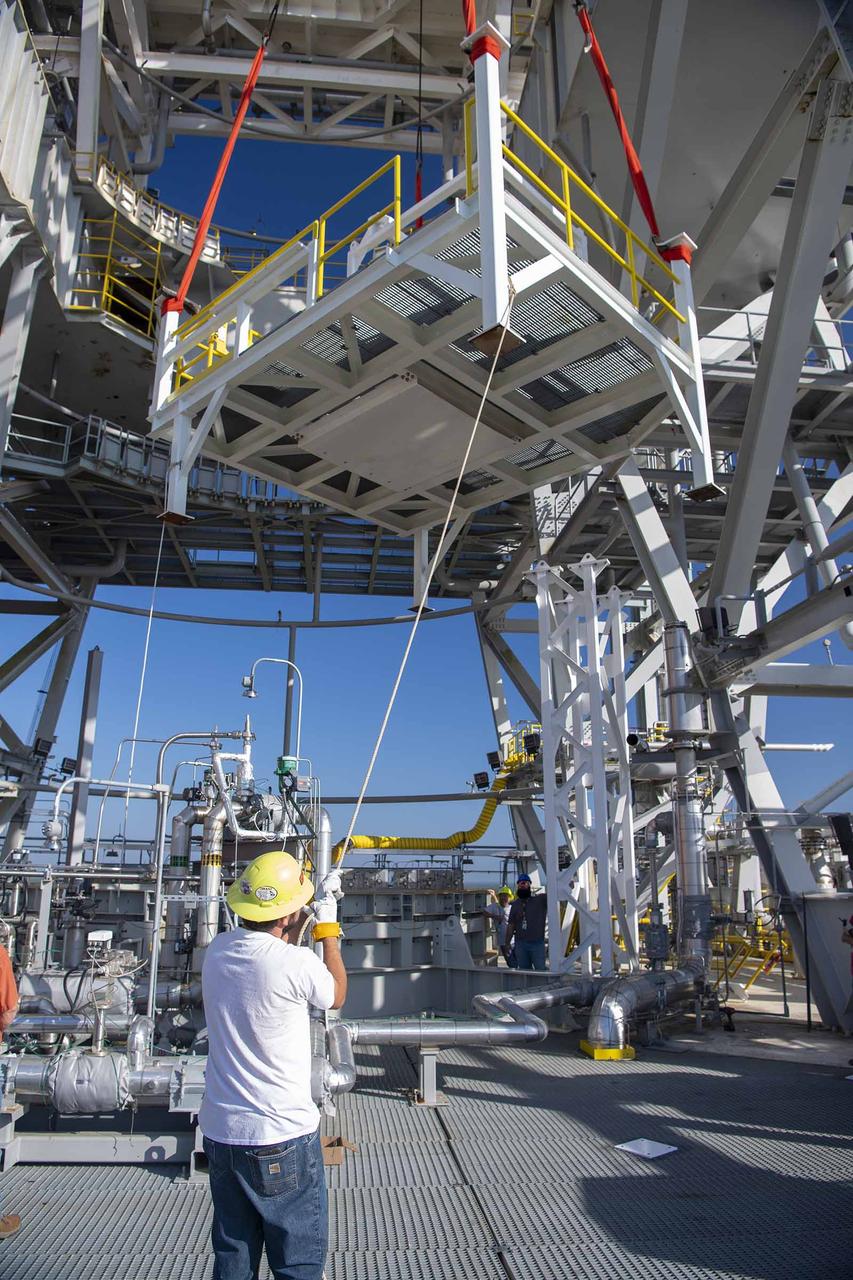

A pair of umbilical support structures needed for future testing of NASA’s exploration upper stage (EUS) were installed in the B-2 position of the Thad Cochran Test Stand on Oct. 30-31 at NASA’s Stennis Space Center. The support structures arrived from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans via the unique NASA Stennis seven-and-a-half-mile canal system in 2023. Since then, crews have prepared the structures that will align with the EUS unit for installation. In addition to helping secure the unit in place during hot fire testing, the umbilical support structures are where the command, control, and data electrical connections are mated to connect the ground systems to the vehicle systems, as well as most the commodity connections such as liquid hydrogen, liquid oxygen, hydrogen vent, helium bottle fill pressure, and purges. Prior to its initial flight, the EUS unit will undergo a series of so-called Green Run tests at NASA Stennis to ensure all systems are ready to go. The test series will culminate with a hot fire of the stage’s four RL10 engines, made by Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company and lead SLS engines contractor. The new upper stage will enable NASA to carry larger payloads on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond.
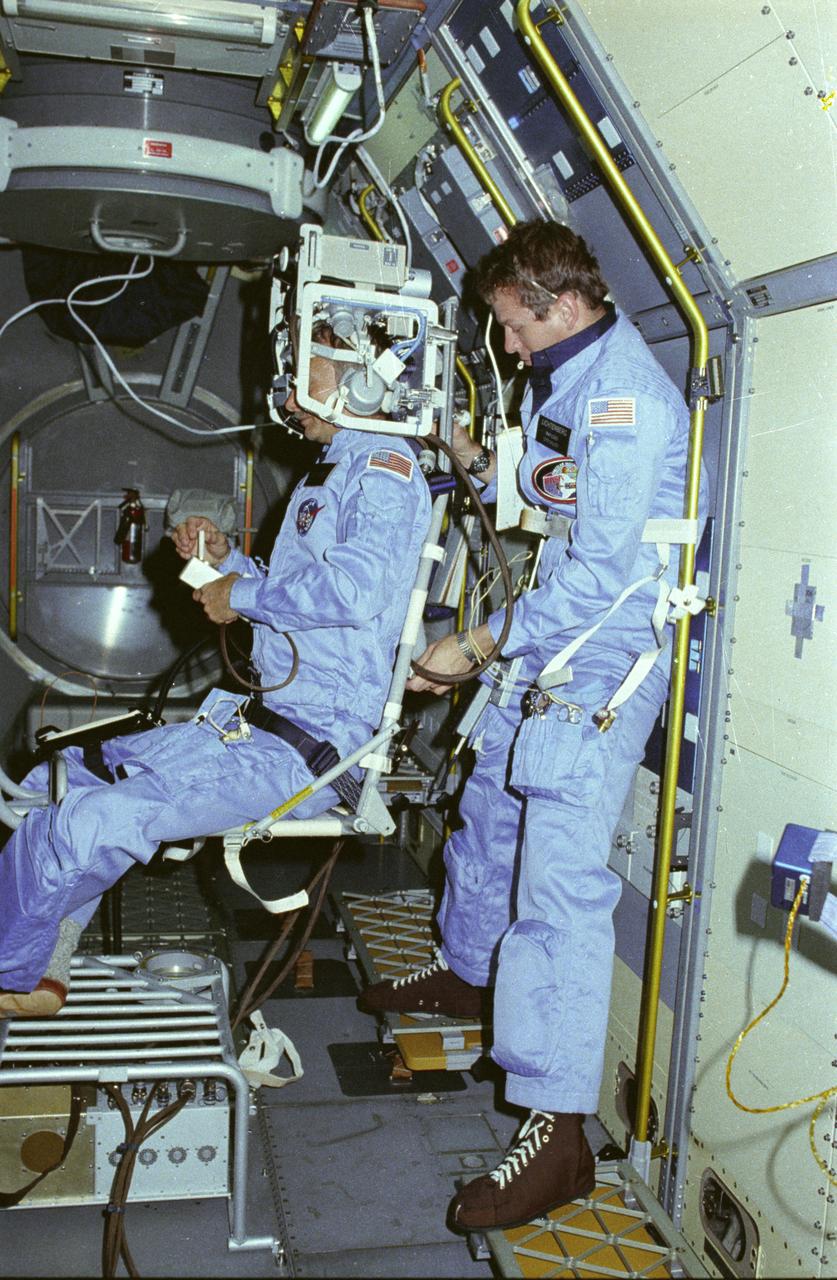

In this photograph, astronauts Owen Garriott on the body restriant system and Byron Lichtenberg prepare for a Vestibular Experiment during the Spacelab-1 mission. The Vestibular Experiments in Space were the study of the interaction among the otoliths, semicircular canals, vision, and spinal reflexes in humans. The main objective was to determine how the body, which receives redundant information for several sensory sources, interprets this information in microgravity. Another objective was to record and characterize the symptoms of space sickness experienced by crewmembers. The body restraint system was a rotating chair with a harness to hold the test subject in place. The crewmember wore an accelerometer and electrodes to record head motion and horizontal and vertical eye movement as the body rotated. The first Spacelab mission, Spacelab-1, sponsored jointly and shared equally by NASA and the European Space Agency, was a multidisciplinary mission; that is, investigations were performed in several different fields of scientific research. The overall goal of the mission was to verify Spacelab performance through a variety of scientific experiments. The Spacelab-1 was launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia for the STS-9 mission on November 28, 1983. The Marshall Space Flight Center had management responsibilities for the mission.
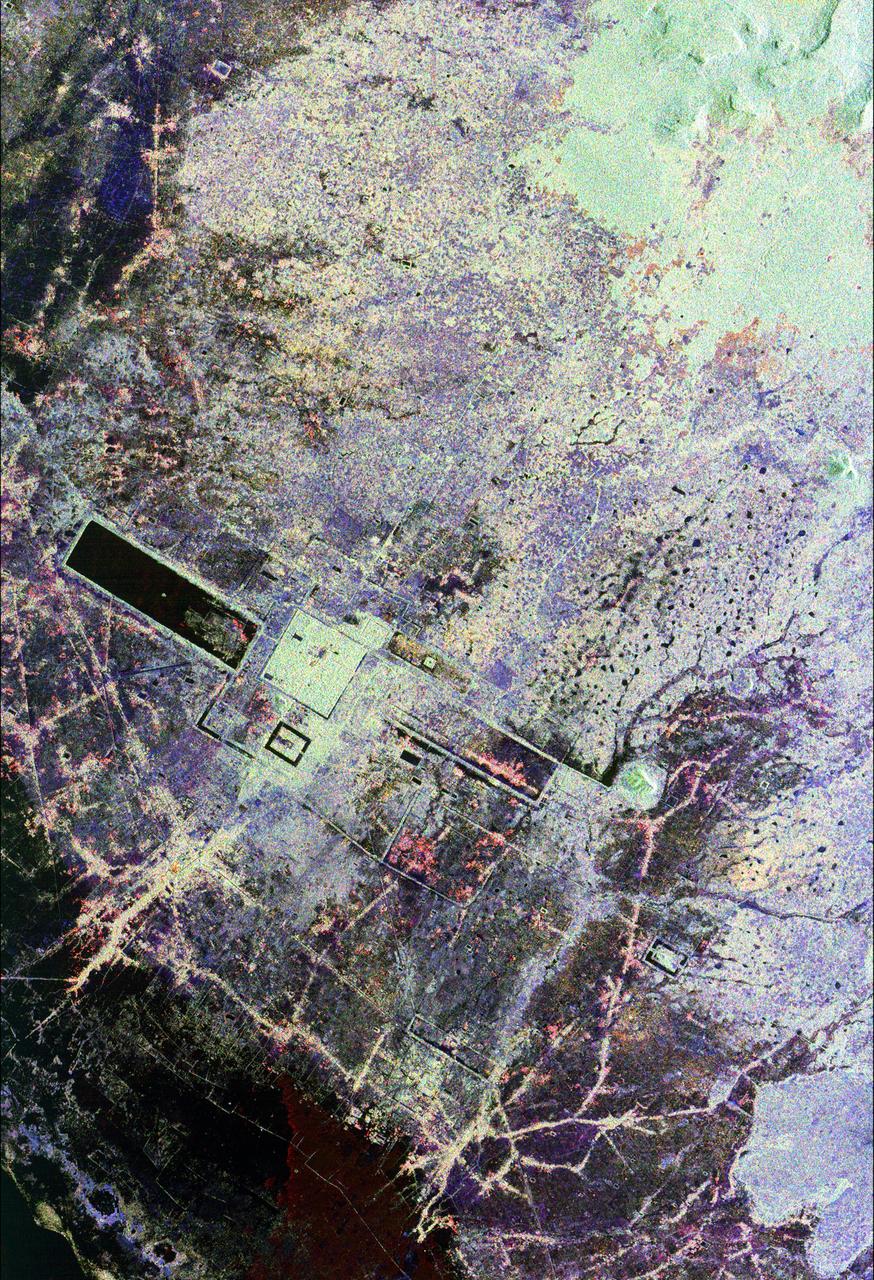

This is an image of the area around the city of Angkor, Cambodia. The city houses an ancient complex of more than 60 temples dating back to the 9th century. The principal complex, Angkor Wat, is the bright square just left of the center of the image. It is surrounded by a reservoir that appears in this image as a thick black line. The larger bright square above Angkor Wat is another temple complex called Angkor Thom. Archeologists studying this image believe the blue-purple area slightly north of Angkor Thom may be previously undiscovered structures. In the lower right is a bright rectangle surrounded by a dark reservoir, which houses the temple complex Chau Srei Vibol. In its heyday, Angkor had a population of 1 million residents and was the spiritual center for the Khmer people until it was abandoned in the 15th century. The image was acquired by the Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C/X-band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR) on the 15th orbit of the space shuttle Endeavour on September 30, 1994. The image shows an area approximately 55 kilometers by 85 kilometers (34 miles by 53 miles) that is centered at 13.43 degrees north latitude and 103.9 degrees east longitude. The colors in this image were obtained using the following radar channels: red represents the L-band (horizontally transmitted and received); green represents the L-band (horizontally transmitted and vertically received); blue represents the C-band (horizontally transmitted and vertically received). The body of water in the south-southwest corner is Tonle Sap, Cambodia's great central lake. The urban area at the lower left of the image is the present-day town of Siem Reap. The adjoining lines are both modern and ancient roads and the remains of Angkor's vast canal system that was used for both irrigation and transportation. The large black rectangles are ancient reservoirs. Today the Angkor complex is hidden beneath a dense rainforest canopy, making it difficult for researchers on the ground to study the ancient city. The SIR-C/X-SAR data are being used by archaeologists at the World Monuments Fund and the Royal Angkor Foundation to understand how the city grew, flourished and later fell into disuse over an 800-year period. The data are also being used to help reconstruct the vast system of hydrological works, canals and reservoirs, which have gone out of use over time. Research teams from more than 11 countries will be using this data to study the Angkor complex. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00505
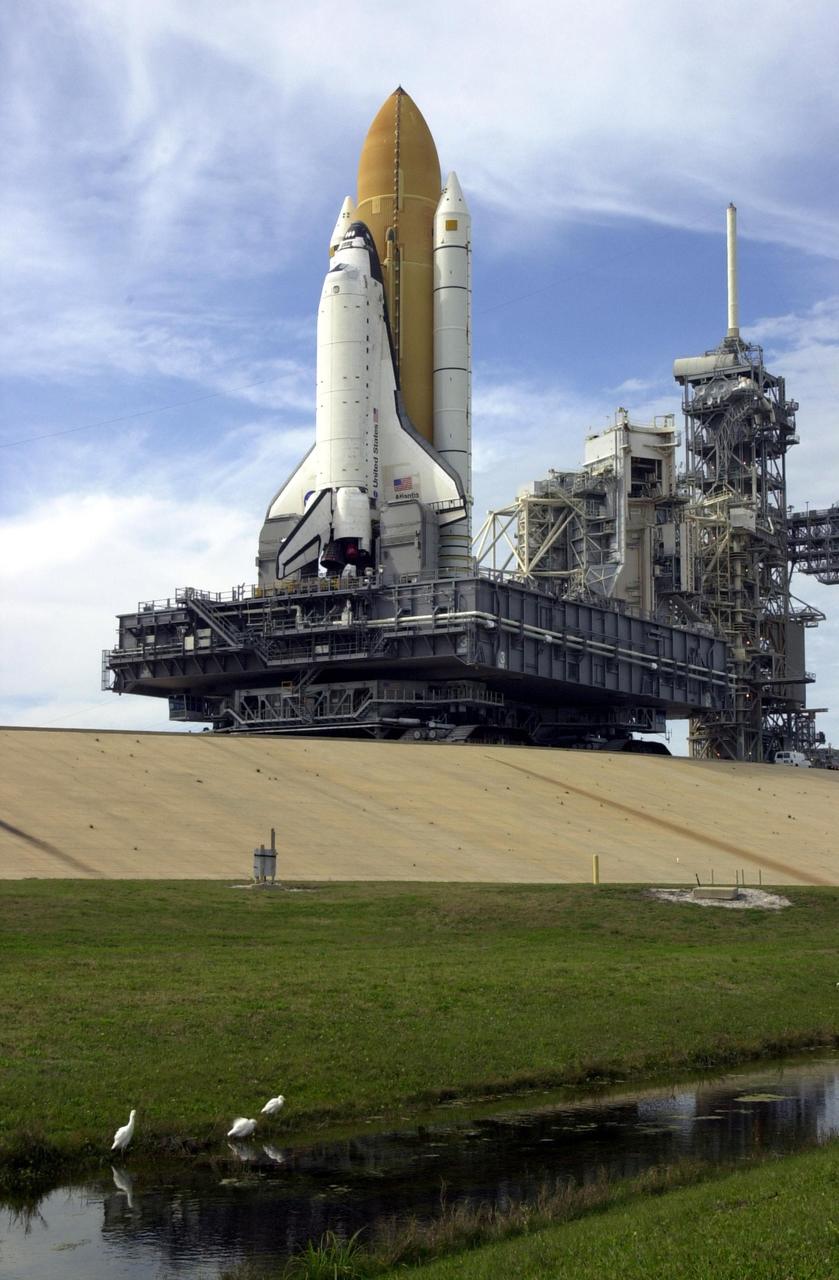

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the foreground, white herons at the canal's edge pay scant attention the immense Space Shuttle towering above them. The Shuttle is inching its way to the top of the launch pad. In the background are seen the Rotating Service Structure (open) and the Fixed Service Structure, which holds the 80-foot lightning mast on top. The Shuttle sits on top of the Mobile Launcher Platform, which rests on the crawler-transporter. Atlantis is scheduled for launch April 4 on mission STS-110, which will install the S0 truss, the framework that eventually will hold the power and cooling systems needed for future international research laboratories on the International Space Station. The Canadarm2 robotic arm will be used exclusively to hoist the 13-ton truss from the payload bay to the Station. The S0 truss will be the first major U.S. component launched to the Station since the addition of the Quest airlock in July 2001. The four spacewalks planned for the construction will all originate from the airlock. The mission will be Atlantis' 25th trip to space

A truck arrives at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California on June 3, 2024, to deliver the Medium Articulating Transportation System (MATS), which will be used during the construction and transportation of components for NASA's Near-Earth Object Surveyor mission. Originating at the aerospace company Beyond Gravity in Vienna, Austria, the MATS traveled via ship through the Panama Canal to Port Hueneme, California, before arriving by road at JPL. Construction has begun on NEO Surveyor's instrument enclosure in the High Bay 1 clean room at JPL's Spacecraft Assembly Facility. When the enclosure is complete later this year, it will be moved inside the MATS to NASA's Johnson Space Center in Houston for environmental testing. The MATS is a transportable clean room with its own filtration and climate control systems that keep the spacecraft and components clean, stable, and safe while being moved between facilities. NEO Surveyor's instrument enclosure contains the spacecraft's telescope, mirrors, and infrared sensors that will be used to detect, track, and characterize the most hazardous near-Earth objects. BAE Systems, Space Dynamics Laboratory, and Teledyne are among the aerospace and engineering companies contracted to build the spacecraft and its instrumentation. The Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics at the University of Colorado, Boulder will support operations, and IPAC at Caltech in Pasadena, California, is responsible for processing survey data and producing the mission's data products. JPL manages the project; Caltech manages JPL for NASA. Launching no earlier than 2027, NEO Surveyor supports the objectives of NASA's Planetary Defense Coordination Office (PDCO) at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The NASA Authorization Act of 2005 directed NASA to discover and characterize at least 90% of the near-Earth objects more than 140 meters (460 feet) across that come within 30 million miles (48 million kilometers) of our planet's orbit. Objects of this size can cause significant regional damage, or worse, should they impact the Earth. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26381
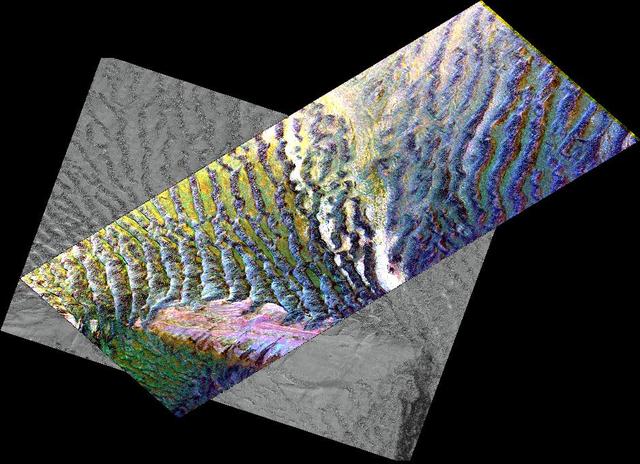
This composite image is of an area thought to contain the ruins of the ancient settlement of Niya. It is located in the southwest corner of the Taklamakan Desert in China Sinjiang Province. This region was part of some of China's earliest dynasties and from the third century BC on was traversed by the famous Silk Road. The Silk Road, passing east-west through this image, was an ancient trade route that led across Central Asia's desert to Persia, Byzantium and Rome. The multi-frequency, multi-polarized radar imagery was acquired on orbit 106 of the space shuttle Endeavour on April 16, 1994 by the Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C/X-band Synthetic Aperture Radar. The image is centered at 37.78 degrees north latitude and 82.41 degrees east longitude. The area shown is approximately 35 kilometers by 83 kilometers (22 miles by 51 miles). The image is a composite of an image from an Earth-orbiting satellite called Systeme Probatoire d'Observation de la Terre (SPOT) and a SIR-C multi-frequency, multi-polarized radar image. The false-color radar image was created by displaying the C-band (horizontally transmitted and received) return in red, the L-band (horizontally transmitted and received) return in green, and the L-band (horizontally transmitted and vertically received) return in blue. The prominent east/west pink formation at the bottom of the image is most likely a ridge of loosely consolidated sedimentary rock. The Niya River -- the black feature in the lower right of the French satellite image -- meanders north-northeast until it clears the sedimentary ridge, at which point it abruptly turns northwest. Sediment and evaporite deposits left by the river over millennia dominate the center and upper right of the radar image (in light pink). High ground, ridges and dunes are seen among the riverbed meanderings as mottled blue. Through image enhancement and analysis, a new feature probably representing a man-made canal has been discovered and mapped. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA01726
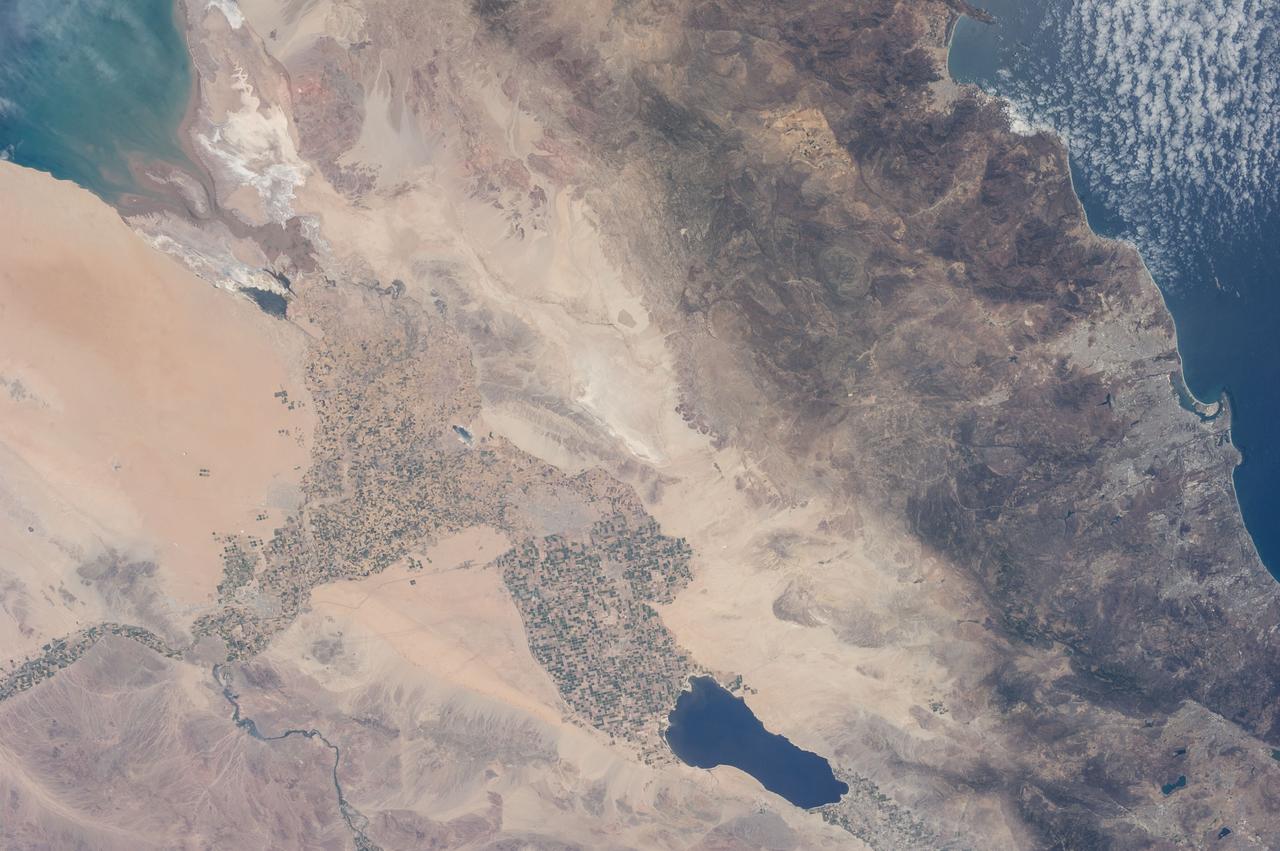

ISS036-E-011034 (21 June 2013) --- The Salton Trough is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 36 crew member on the International Space Station. The Imperial and Coachella Valleys of southern California – and the corresponding Mexicali Valley and Colorado River Delta in Mexico – are part of the Salton Trough, a large geologic structure known to geologists as a graben or rift valley that extends into the Gulf of California. The trough is a geologically complex zone formed by interaction of the San Andreas transform fault system that is, broadly speaking, moving southern California towards Alaska; and the northward motion of the Gulf of California segment of the East Pacific Rise that continues to widen the Gulf of California by sea-floor spreading. According to scientists, sediments deposited by the Colorado River have been filling the northern rift valley (the Salton Trough) for the past several million years, excluding the waters of the Gulf of California and providing a fertile environment – together with irrigation—for the development of extensive agriculture in the region (visible as green and yellow-brown fields at center). The Salton Sea, a favorite landmark of astronauts in low Earth orbit, was formed by an irrigation canal rupture in 1905, and today is sustained by agricultural runoff water. A wide array of varying landforms and land uses in the Salton Trough are visible from space. In addition to the agricultural fields and Salton Sea, easily visible metropolitan areas include Yuma, AZ (lower left); Mexicali, Baja California, Mexico (center); and the San Diego-Tijuana conurbation on the Pacific Coast (right). The approximately 72-kilometer-long Algodones Dunefield is visible at lower left.
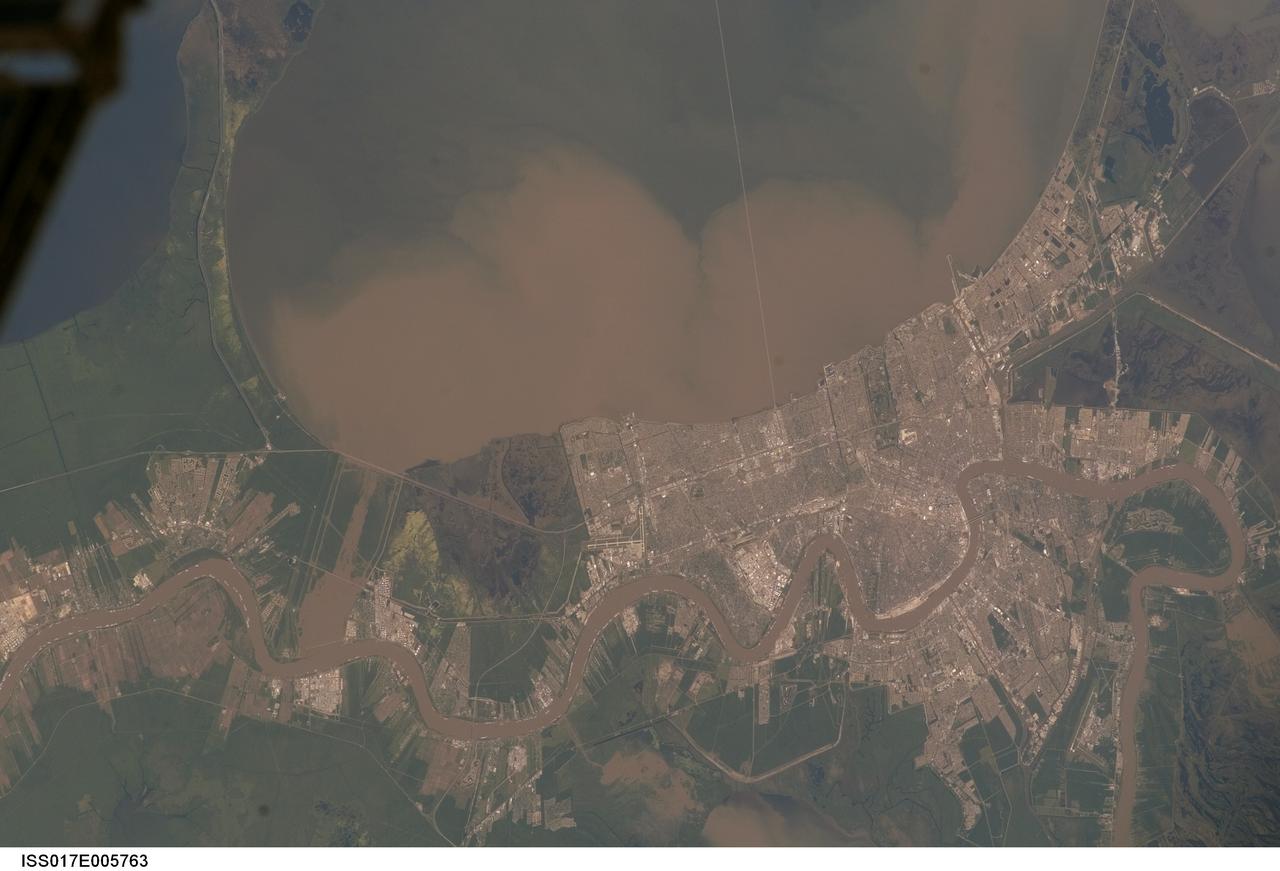

ISS017-E-005763 (29 April 2008) --- Lake Pontchartrain and the Bonnet Carre Spillway, Louisiana, are featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 17 crewmember on the International Space Station. Lake Pontchartrain, a big body of water immediately north of New Orleans, occupies the upper part of this view, with the winding course of the muddy Mississippi River snaking across the bottom of the image (flow is east, from left to right). The city of New Orleans is sandwiched between the lake and river. Heavy rain in March and April 2008 in the Mississippi's catchment area raised water levels in the river sufficiently to make the Army Corps of Engineers take action. To reduce the volume of the river where it passes through New Orleans, the Corps opened the Bonnet Carre Spillway (lower left), a major engineering structure 18 kilometers upriver from New Orleans. The spillway, a 1.6 kilometer-wide gap in the developments along the Mississippi levees, is an integral part of the river and canal system that allows Mississippi river water to flow into Lake Pontchartrain. The spillway control structure itself is visible as a thin, discontinuous, white line along the river's edge in this image. The spillway has only been opened eight times since 1937. News of the opening in April 2008 was transmitted to crewmembers aboard the International Space Station who managed to capture the immediate effect of muddy water flowing down the spillway and into Lake Pontchartrain, where it forms great brown lobes in the otherwise green water. These lobes moved slowly east along the New Orleans shoreline, where the line of the Lake Pontchartrain Causeway, the longest bridge in the U.S., can be seen, top right. Opening the spillway protects New Orleans in various ways. First, it reduces pressure on the levees, which famously collapsed at some points during the onslaught of Hurricane Katrina in 2005. Keeping water levels below critical high levels also helps the river channel to accommodate the discharge of water, and reduces both the speed of flow and cross currents in the river which can interfere with vessels navigating the river -- or even cause collisions with levees.
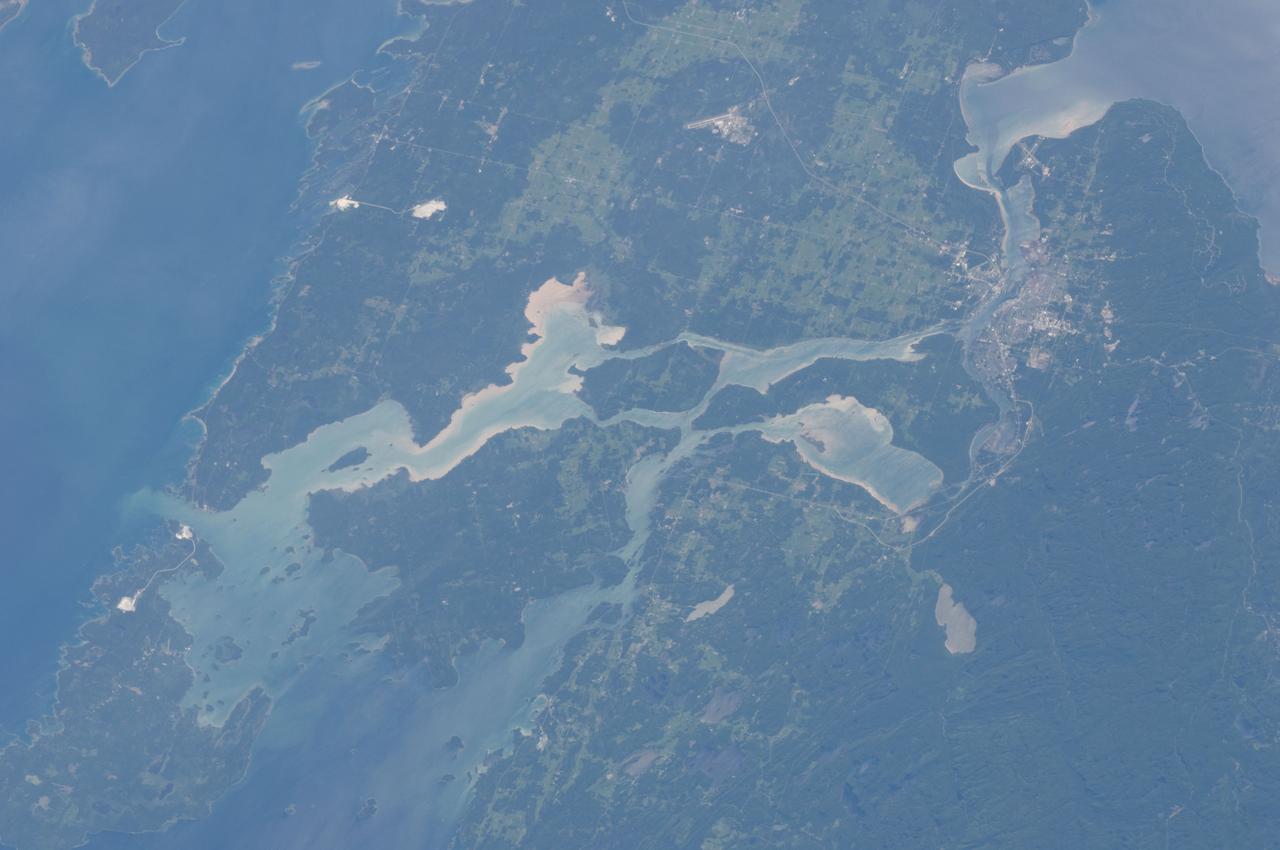

ISS028-E-010162 (29 June 2011) --- Sault Ste Marie, Ontario and Michigan are featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 28 crew member on the International Space Station. The twin cities of Sault Ste Marie are located across the St. Mary?s River that forms part of the international boundary between Canada (Province of Ontario) and the United States (State of Michigan). This photograph highlights the two cities, together with the region of lakes and islands that separates Lakes Huron and Superior, two of the Great Lakes of North America. Smaller lakes include Lake George to the west; the large forested islands of St. Joseph and Drummond are visible at lower left. The Sault Ste Marie urban areas (upper right) have a distinctive gray to white coloration in the image, contrasting with the deep green of forested areas in Ontario and the lighter green of agricultural fields in Michigan. The coloration of water surfaces in the lakes and rivers varies from blue to blue-green to silver, and is likely caused by varying degrees of sediment and sunglint ? light reflecting back to the observer on the space station from the water surface, much as light reflects from a mirror. Prior to formalization of the US/Canada border in 1817, Sault Ste Marie was a single community. Archeological evidence suggests that the region had been occupied by Native Americans at least five hundred years ago. A mission ? the first European settlement in Michigan ? was established there in 1668 by the French Jesuit Father Jacques Marquette. Today, shipping locks and canals in both urban areas are an important part of the Great Lakes shipping traffic system.
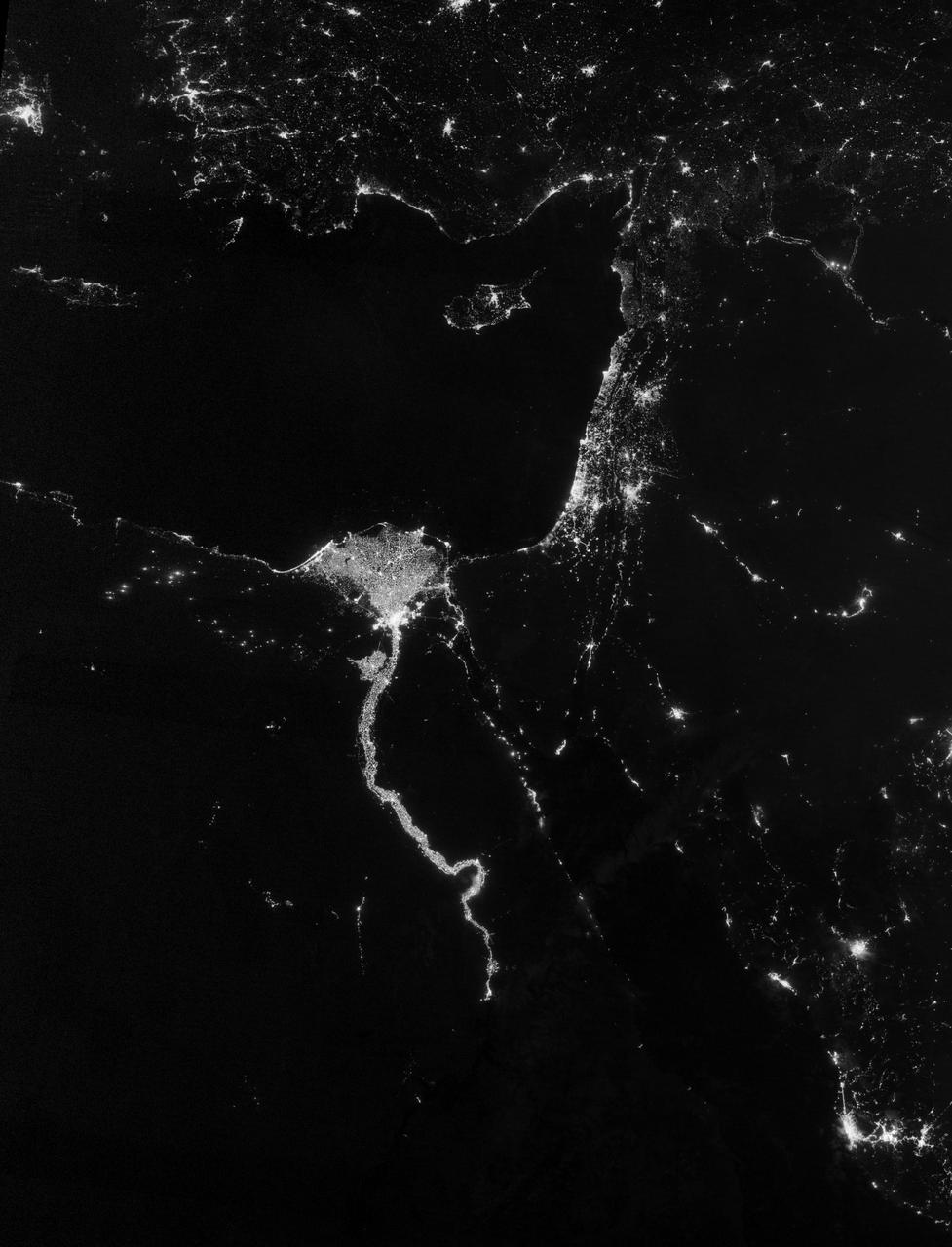

NASA image acquired October 13, 2012 The Nile River Valley and Delta comprise less than 5 percent of Egypt’s land area, but provide a home to roughly 97 percent of the country’s population. Nothing makes the location of human population clearer than the lights illuminating the valley and delta at night. On October 13, 2012, the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) on the Suomi NPP satellite captured this nighttime view of the Nile River Valley and Delta. This image is from the VIIRS “day-night band,” which detects light in a range of wavelengths from green to near-infrared and uses filtering techniques to observe signals such as gas flares, auroras, wildfires, city lights, and reflected moonlight. The city lights resemble a giant calla lily, just one with a kink in its stem near the city of Luxor. Some of the brightest lights occur around Cairo, but lights are abundant along the length of the river. Bright city lights also occur along the Suez Canal and around Tel Aviv. Away from the lights, however, land and water appear uniformly black. This image was acquired near the time of the new Moon, and little moonlight was available to brighten land and water surfaces. NASA Earth Observatory image by Jesse Allen and Robert Simmon, using VIIRS Day-Night Band data from the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership. Suomi NPP is the result of a partnership between NASA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, and the Department of Defense. Caption by Michon Scott. Instrument: Suomi NPP - VIIRS Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> <b>Click here to view all of the <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/Features/NightLights/" rel="nofollow"> Earth at Night 2012 images </a></b> <b>Click here to <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/NaturalHazards/view.php?id=79807" rel="nofollow"> read more </a> about this image </b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
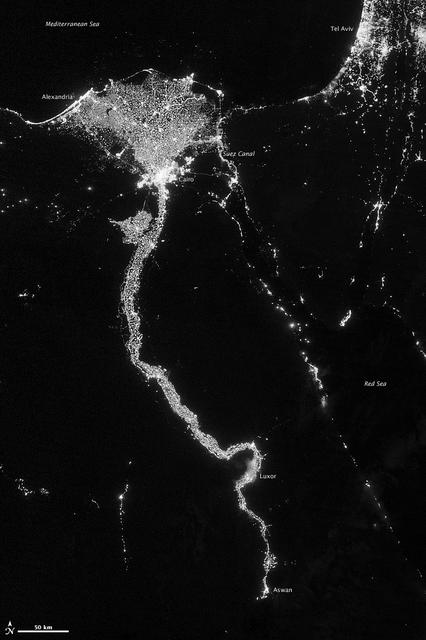
NASA image acquired October 13, 2012 The Nile River Valley and Delta comprise less than 5 percent of Egypt’s land area, but provide a home to roughly 97 percent of the country’s population. Nothing makes the location of human population clearer than the lights illuminating the valley and delta at night. On October 13, 2012, the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) on the Suomi NPP satellite captured this nighttime view of the Nile River Valley and Delta. This image is from the VIIRS “day-night band,” which detects light in a range of wavelengths from green to near-infrared and uses filtering techniques to observe signals such as gas flares, auroras, wildfires, city lights, and reflected moonlight. The city lights resemble a giant calla lily, just one with a kink in its stem near the city of Luxor. Some of the brightest lights occur around Cairo, but lights are abundant along the length of the river. Bright city lights also occur along the Suez Canal and around Tel Aviv. Away from the lights, however, land and water appear uniformly black. This image was acquired near the time of the new Moon, and little moonlight was available to brighten land and water surfaces. NASA Earth Observatory image by Jesse Allen and Robert Simmon, using VIIRS Day-Night Band data from the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership. Suomi NPP is the result of a partnership between NASA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, and the Department of Defense. Caption by Michon Scott. Instrument: Suomi NPP - VIIRS Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> <b>Click here to view all of the <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/Features/NightLights/" rel="nofollow"> Earth at Night 2012 images </a></b> <b>Click here to <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/NaturalHazards/view.php?id=79807" rel="nofollow"> read more </a> about this image </b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
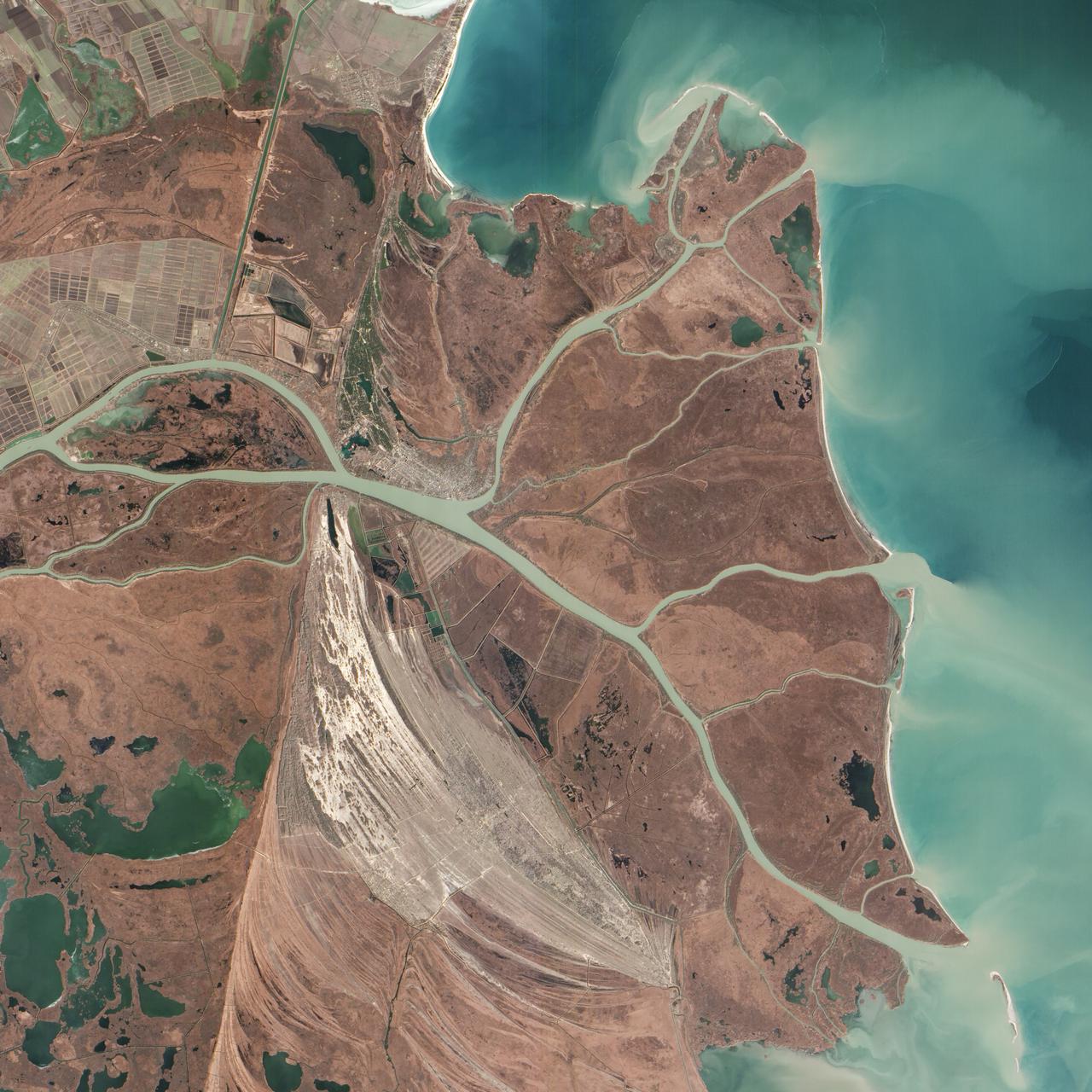

Acquired February 5, 2013 The Danube River is the largest in the European Union, its watershed draining 801,463 square kilometers (309,447 square miles) of land across 19 countries. Where that great river reaches the Black Sea, a remarkable delta has formed—the “Everglades” of Europe. The Danube Delta is home to more than 300 species of bird and 45 species of freshwater fish. The Danube Delta has been home to human settlements since the end of the Stone Age (the Neolithic Period), and the ancient Greeks, Romans, and Byzantines all built trading ports and military outposts along this coast. Today, the border between Romania and Ukraine cuts through the northern part of the delta. The area is a United Nations World Heritage Site, both for its natural and human history, and for the traditional maritime culture that persists in its marshes. All the while, the landscape has been shaped and re-shaped by nature and man. The image above was acquired on February 5, 2013, by the Advanced Land Imager (ALI) on NASA’s Earth Observing-1 (EO-1) satellite. The Danube Delta has a number of lobes formed over the past several thousand years, and this image is focused largely on the northernmost Chilia (or Kilia) lobe. It is the youngest section of the delta—somewhere between 300 to 400 years old—and lies mostly within Ukraine. Much of the land in the image above is officially considered part of the Danube Biosphere Reserve. Near the center of the image, the small city of Vylkove is known as the “Ukranian Venice,” due to its canals. To the lower left, the older Sulina lobe of the delta stretches to the south and further inland into Romania. White and brown curved lines reveal beach ridges and former shorelines, with the whiter ridges composed almost entirely of pure quartz sand in high dunes. To the east of the ridges, most of the landscape is flat marshland that is mostly brown in the barren days of winter. The Bystroye Canal through the center of the Chilia lobe has been the subject of heated debate over the past two decades. Over the centuries, damming and channeling of the Danube throughout Europe has reduced its water flow and sediment load to roughly 30 percent of what it once was, according to coastal geologist Liviu Giosan of the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution. In recent years, the Ukrainian government has dredged some delta channels (including Bystroye) and proposed extensive dredging of others in order to provide navigational channels for large ships. Proponents argue for the economic needs of water transportation routes. Opponents note that deeper, faster channels mean less mud and sand is deposited in the delta; in some places, more is carried away by swifter currents. Both affect the sensitive ecosystems and the ability of the delta to restore itself and grow. In a 2012 report led by Giosan, scientists noted that the shape, water chemistry, and biology of Danube Delta was being altered long before the modern Industrial Era. Land use practices—particularly farming and forest clearing—added significant amounts of nutrients into the water and reduced salinity in the Black Sea, changing the dominant species of phytoplankton and sending a ripple of effects through the entire food web. NASA Earth Observatory image by Jesse Allen and Robert Simmon, using EO-1 ALI data provided courtesy of the NASA EO-1 team and the U.S. Geological Survey. Caption by Mike Carlowicz. Instrument: EO-1 - ALI More info: <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=80459" rel="nofollow">earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=80459</a> Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>