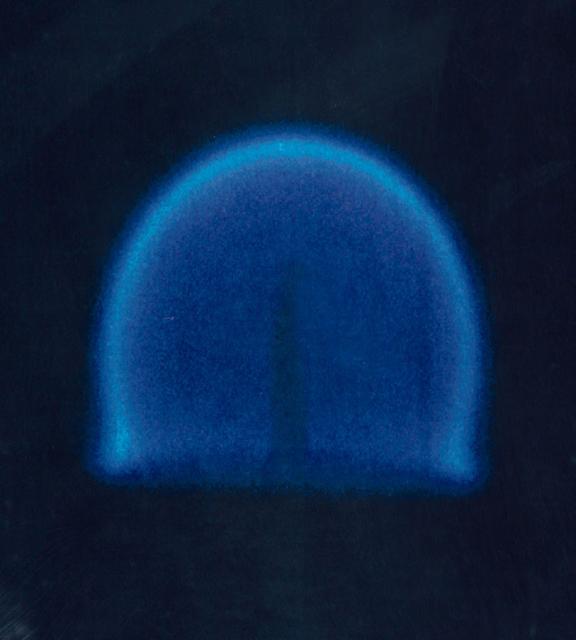
This photograph from CFM is a candle flame burning over time in microgravity, it shows that the candle flame continues to grow and exhibits less soot.
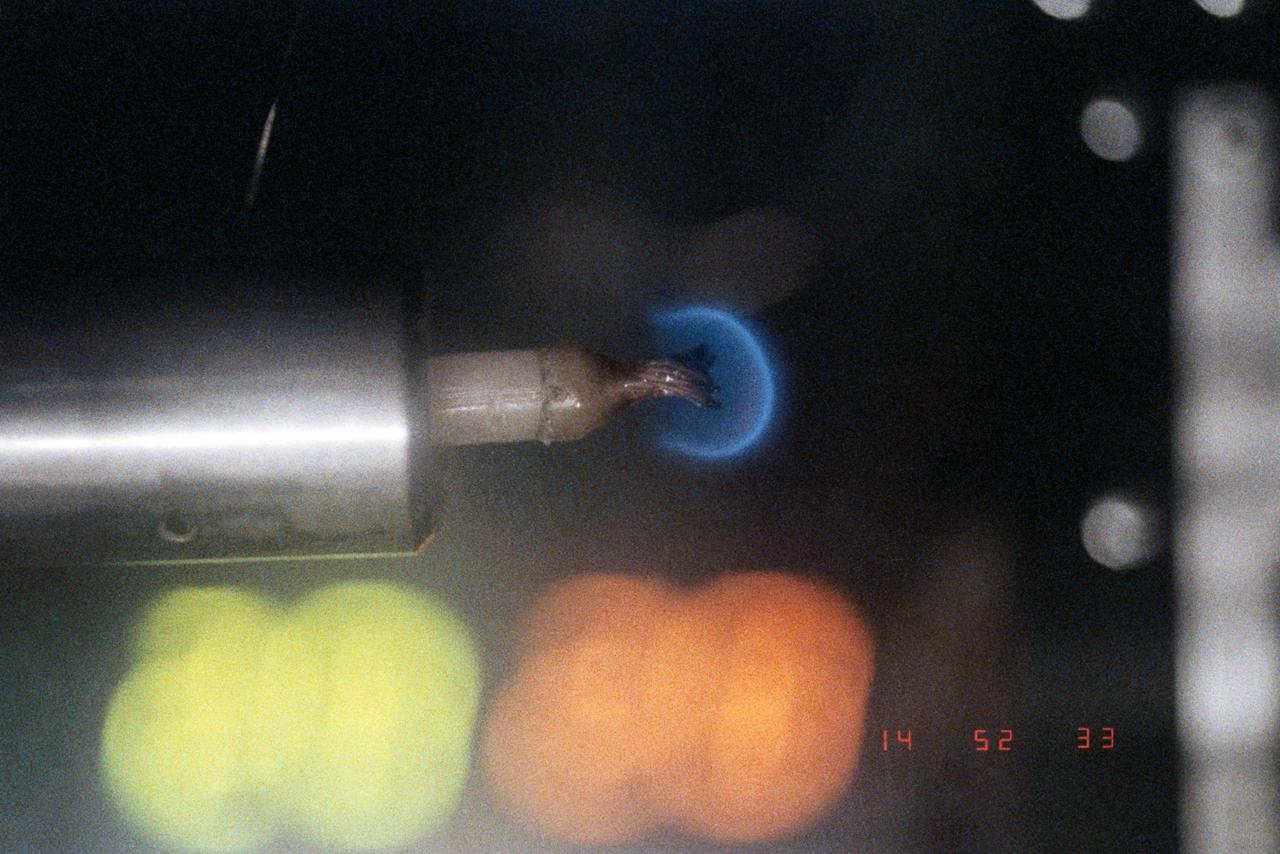
Closeup view inside glovebox showing a candle flame. The Candle Flames in Microgravity experiment is carried onboard Columbia to examine whether candle flames can be sustained in space; to study the interaction and physical properties of diffusion flames. In space, where buoyancy-driven convection is reduced, the role diffusion plays in sustaining candle flames can be isolated. Results have implications for other diffusion flame studies. Diffusion flames are the most common type of flame on Earth.
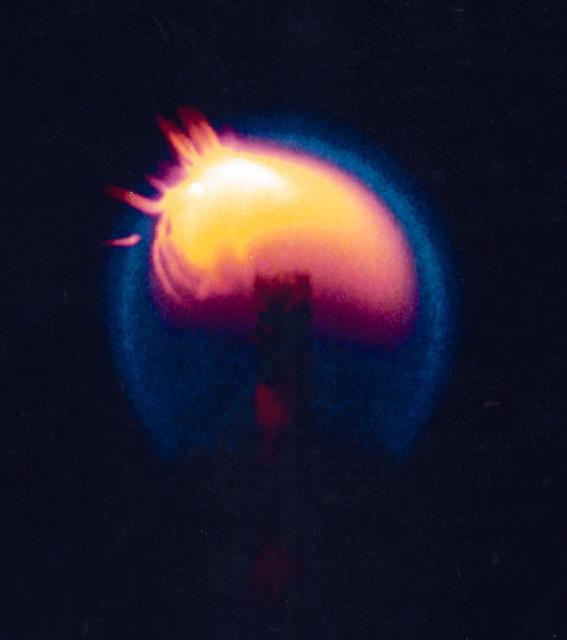

This photograph from CFM shows a candle flame burning over time in microgravity, it shows pieces of wax or soot moving through the flame about 25 seconds after ignition.
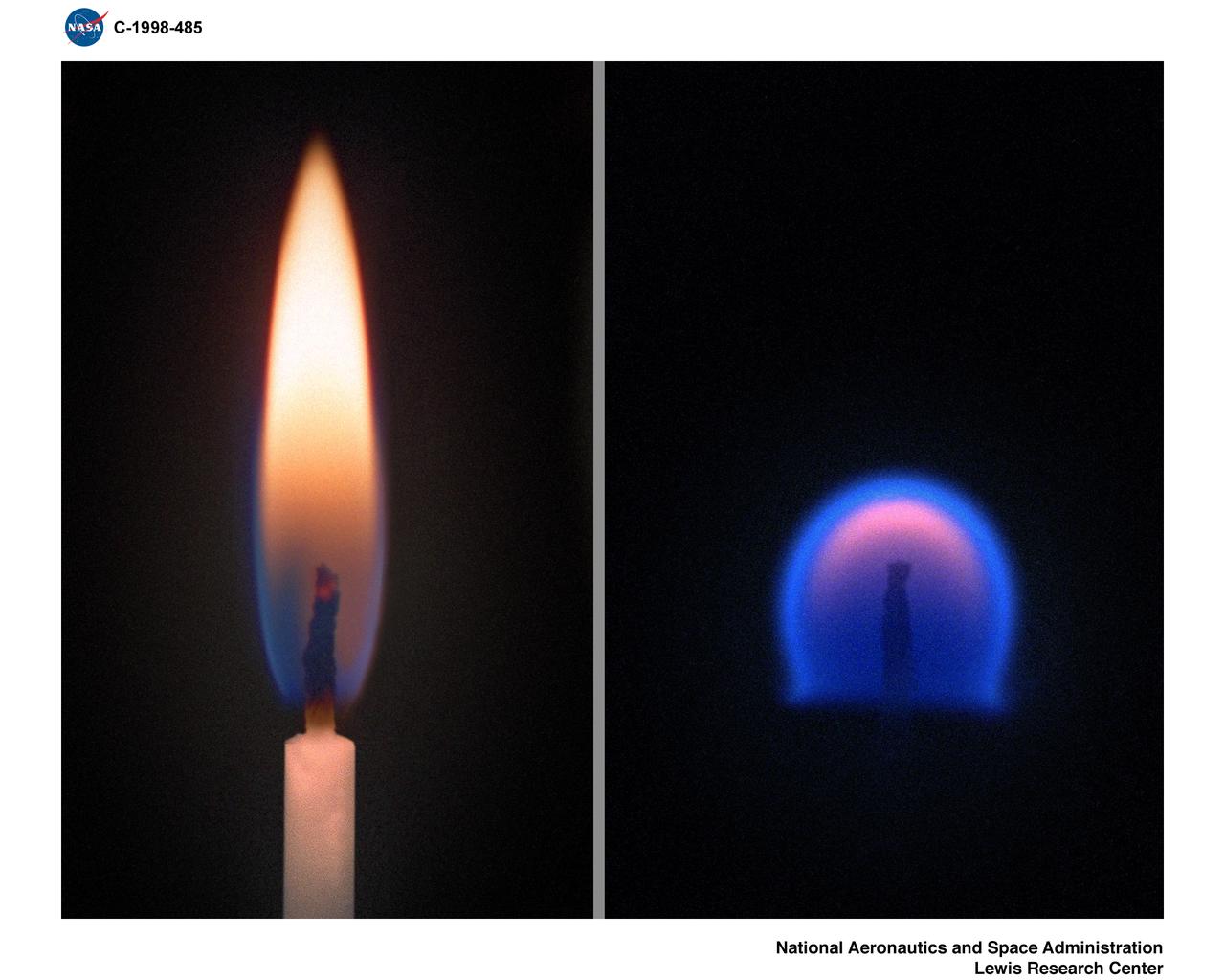

Comparison of a Candle Flame burning in normal gravity or 1-G (left) and a flame burning in Microgravity.
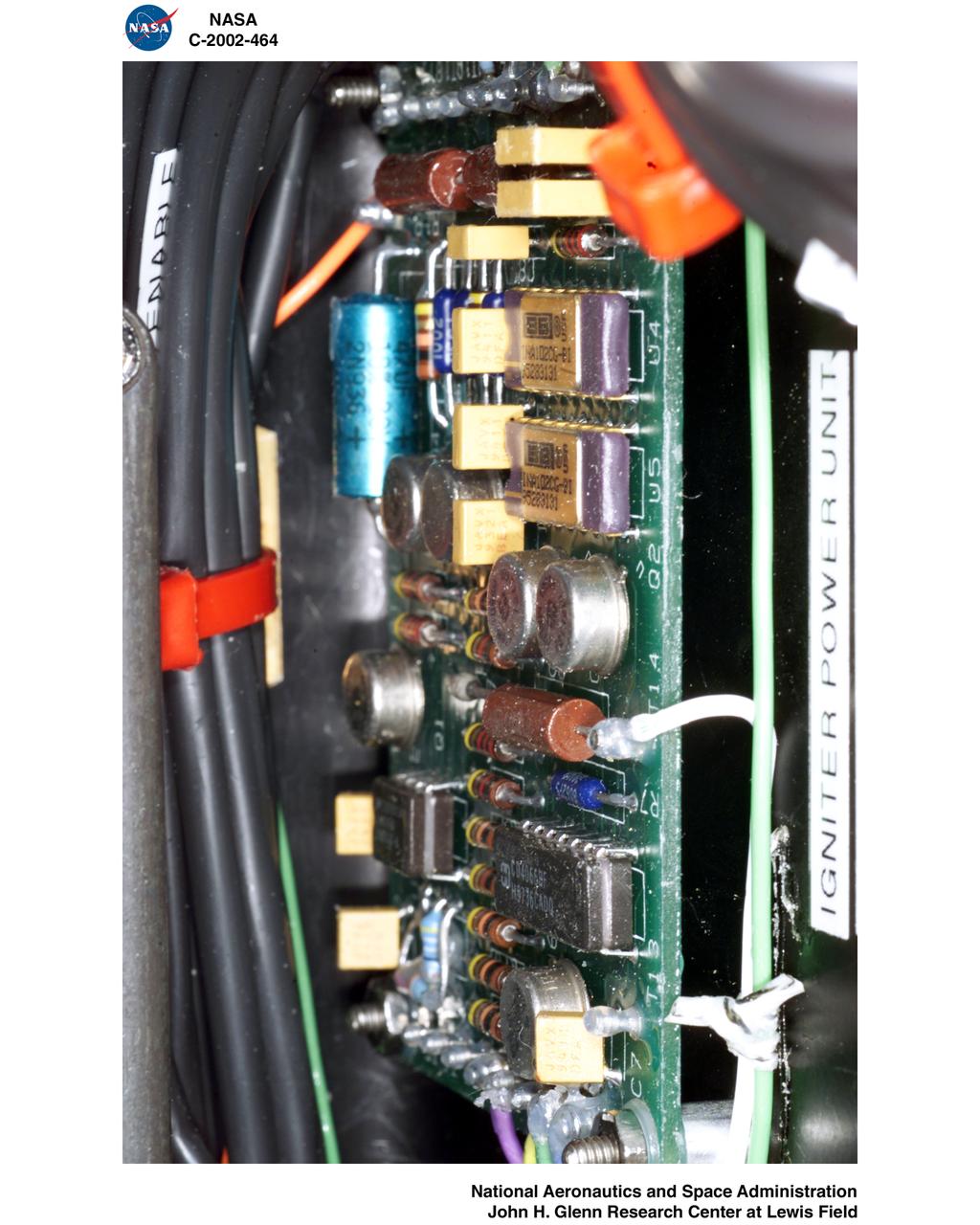

CANDLE FLAME IN MICROGRAVITY 2
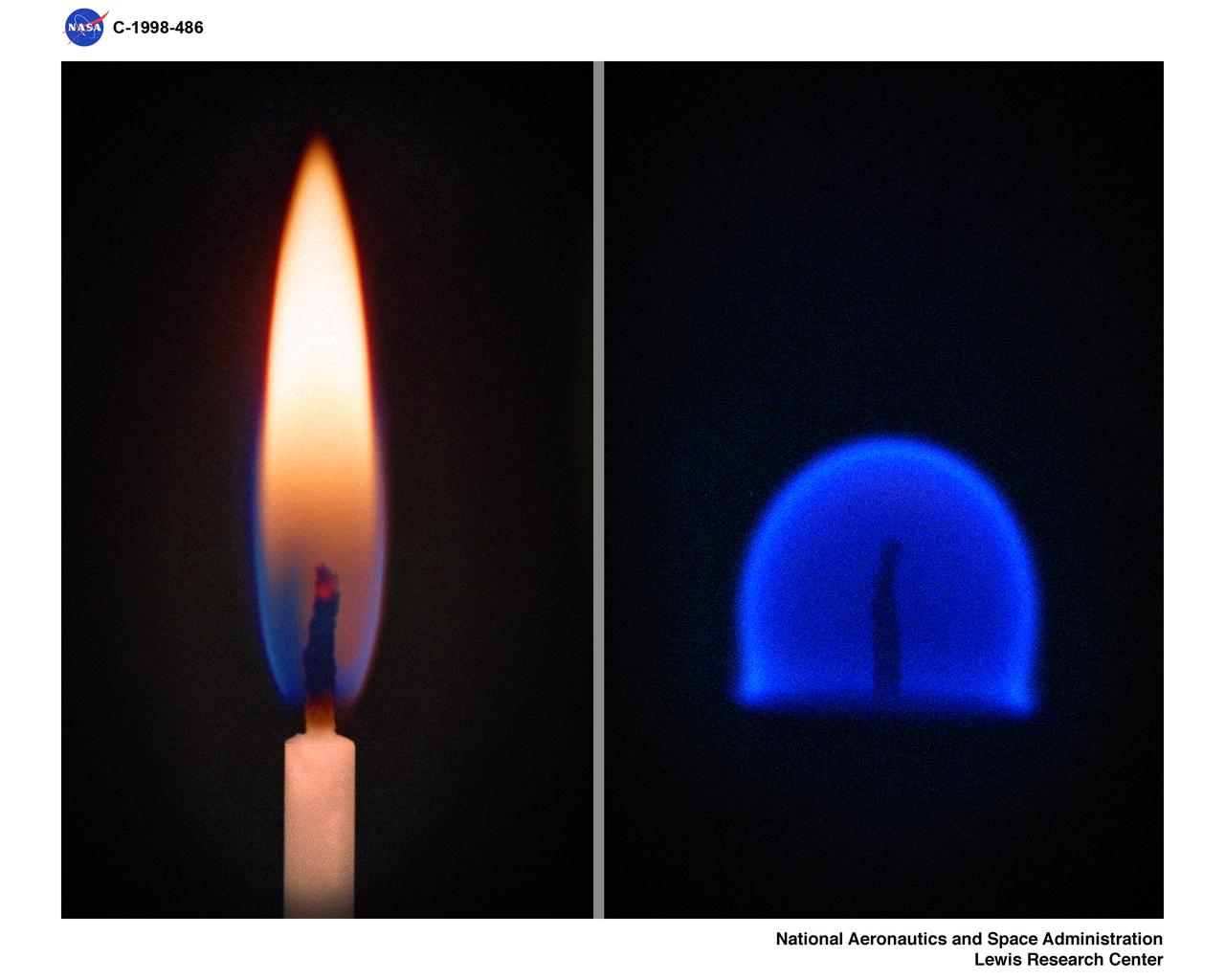

CANDLE FLAME NORMAL 1-G ONE GRAVITY AND MICROGRAVITY 0-G ZERO GRAVITY COMPARISON
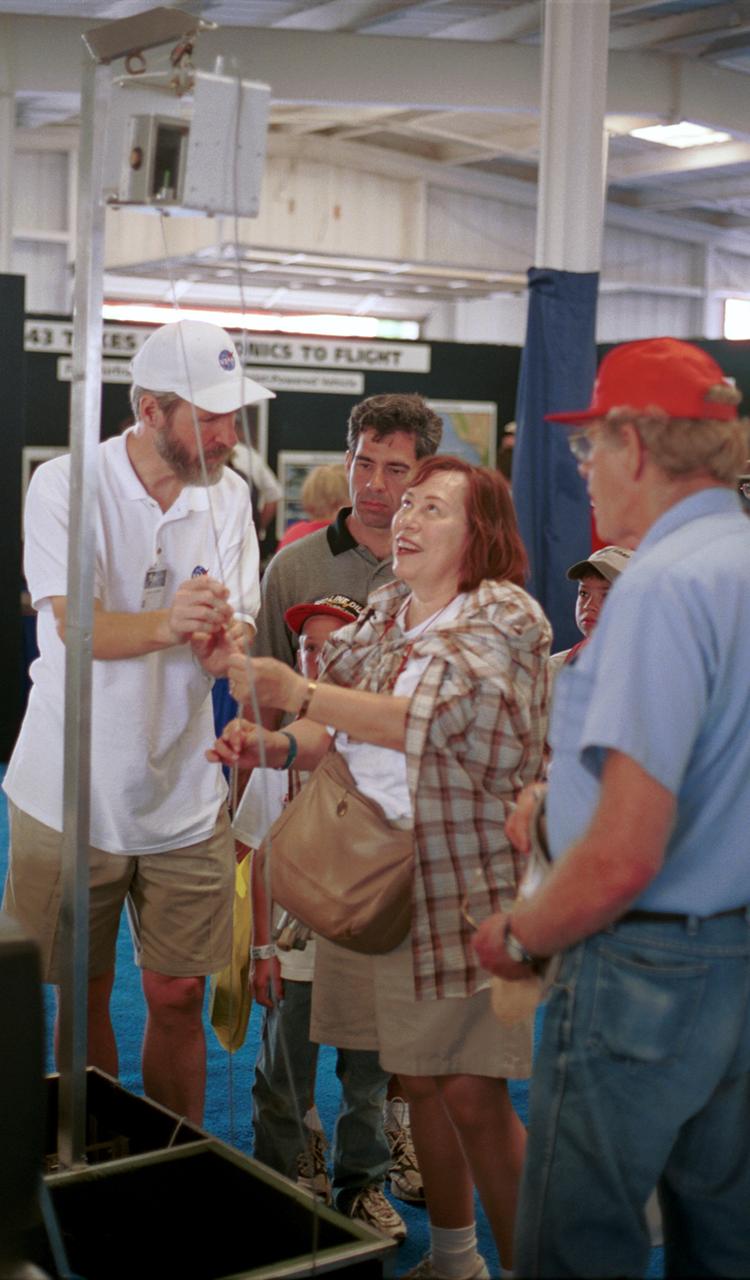

Dr. Richard DeLombard of NASA's Glenn Research Center, hands the relase line for the Microgravity Demonstrator to a visitor for her to start a short experiment showing the effects of microgravity on candle flames. Combustion physics will be a major line of investigation for NASA aboard the International Space Station (ISS). The Microgravity Demonstrator is frequently used at shows and schools to illustrate how phenomena change in microgravity. The exhibit was part of the NASA outreach activity at AirVenture 2000 sponsored by the Experimental Aircraft Association in Oshkosh, WI
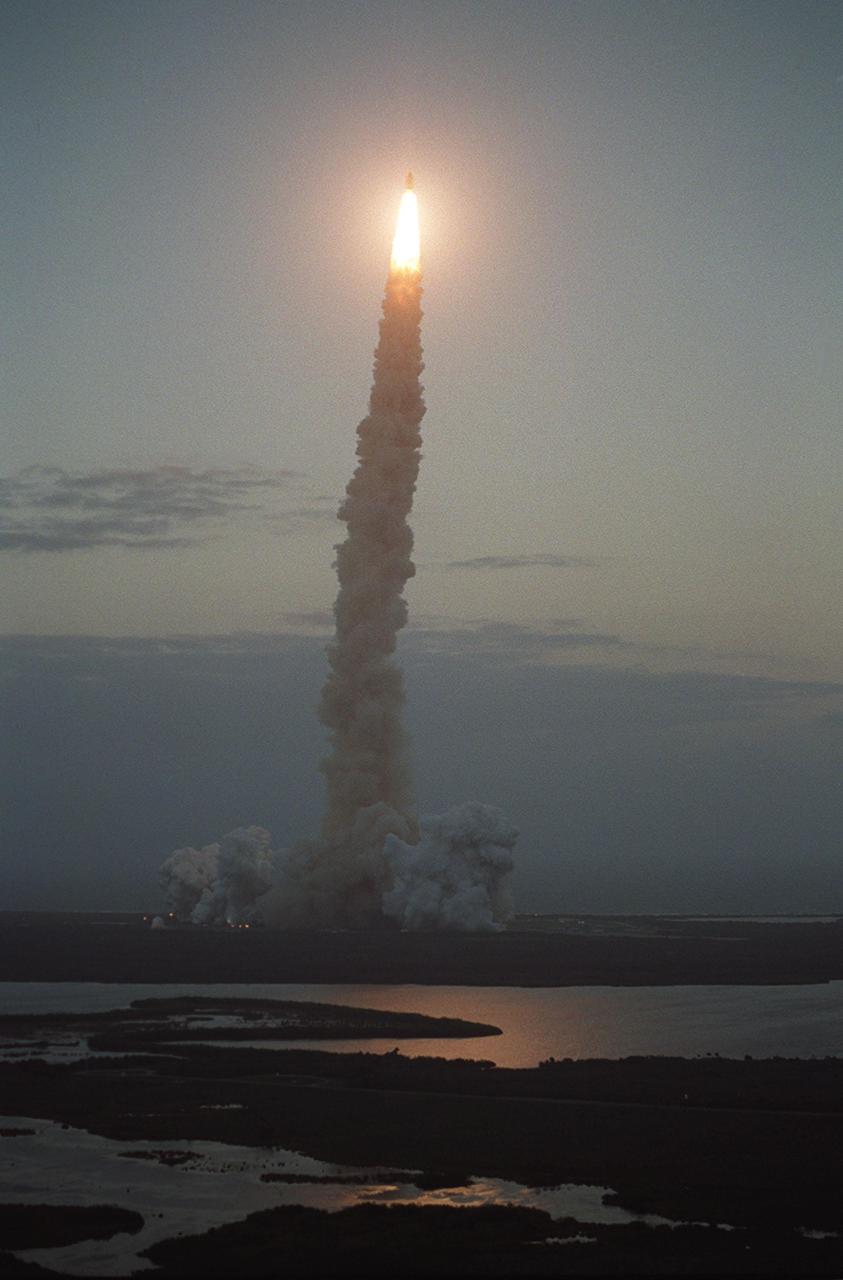

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Like a lighted candle, Space Shuttle Endeavour appears like a flame atop its twisted column of smoke as it soars into space on mission STS-108. Liftoff occurred at 5:19:28 p.m. EST (22:19.28 GMT). Endeavour will dock with the International Space Station on Dec. 7. STS-108 is the final Shuttle mission of 2001and the 107th Shuttle flight overall. It is the 12th flight to the Space Station. Landing of the orbiter at KSC's Shuttle Landing Facility is targeted for 1:05 p.m. EST (18:05 p.m. GMT) Dec. 16