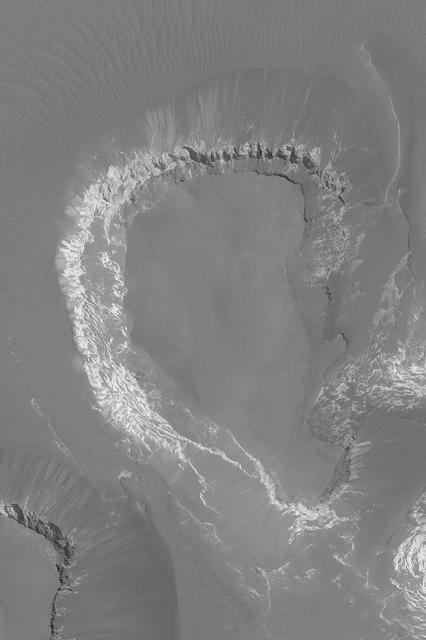

Mesa in Capri Chasma

Capri Chasma is located in the eastern portion of the Valles Marineris canyon system, the largest known canyon system in the Solar System. Deeply incised canyons such as this are excellent targets for studying the Martian crust, as the walls may reveal many distinct types of bedrock. This section of the canyon was targeted by HiRISE based on a previous spectral detection of hematite-rich deposits in the area. Hematite, a common iron-oxide mineral, was first identified here by the Mars Global Surveyor Thermal Emission Spectrometer (TES). In this TES image, red pixels indicate higher abundances of hematite, while the blue and green pixels represent different types of volcanic rocks (e.g., basalt). Hematite in the Meridiani Planum region was also detected with the TES instrument (which we can see with the bright red spot on the Global TES mineral map). As a consequence, Meridiani Planum was the first landing site selected on Mars due to the spectral detection of a mineral that may have formed in the presence of liquid water. Shortly after landing, the Opportunity rover detected the presence of hematite in the form of concretions called "blueberries." The blueberries are found in association with layers of sulfate salt-rich rocks. The salts are hypothesized to have formed through the raising and lowering of the groundwater table. During one such an event, the rock altered to form the hematite-rich blueberries. As the rock was eroded away, the more resistant hematite-rich blueberries were plucked out and concentrated on the plains as a "lag" deposit. Martian blueberries are observed to be scattered across the plains of Meridiani along Opportunity's traverse from Eagle Crater to Endeavor Crater, where Opportunity continues to explore after its mission began over 10 years ago. This infrared-color image close-up highlights what is possibly the hematite-rich deposits nestled between different types of bedrock terraces in Capri Chasma. The bluish terrace is likely volcanic in origin, possibly basaltic, whereas the greenish rocks remain unidentified. The central reddish terrace is possibly where some of the hematite may be concentrated. The higher elevation terrace with the lighter-colored materials is likely a sulfate-rich rock (based on CRISM data in the area). Given the presence of both sulfate salts and hematite in this area, akin to the deposits and associations explored by the Opportunity rover in Meridiani Planum, it might be that these materials in Capri Chasma may share a similar origin. The yellow rectangular box shown on the TES spectral map outlines the corresponding location of the HiRISE image. Although the outline does not appear to contain a high hematite abundance, we note that the lower resolution of TES (about 3 to 6 kilometers per pixel) may exclude smaller exposures and finer sub-pixel details not-yet captured, but could be with HiRISE. A follow-up observation by the CRISM spectrometer may reveal additional details and a spectral signature for hematite in the vicinity at a finer resolution than TES. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21274

This 2001 Mars Odyssey image of Capri Chasma shows multiple landslide deposits.

This image from NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey shows a portion of Capri Chasma. Dunes are found on the floor of this chasma.

Today's VIS image shows a small section of Capri Chasma. Landslide deposits dominate this part of Capri Chasma. The downslope movement of materials flowed all the way to the center of the chasm, with the one from the northern cliff overlapping one from the southern cliff. Radial grooves and lobate margins are common on martian landslides. Orbit Number: 88212 Latitude: -8.70795 Longitude: 318.685 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2021-11-02 16:16 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25194

This 2001 Mars Odyssey image shows multiple landslides are visible in this daytime infrared image of Capri Chasma.

Taken by NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft, this image shows a small portion of the floor of Capri Chasma. Bright layered deposits and dunes are visible.
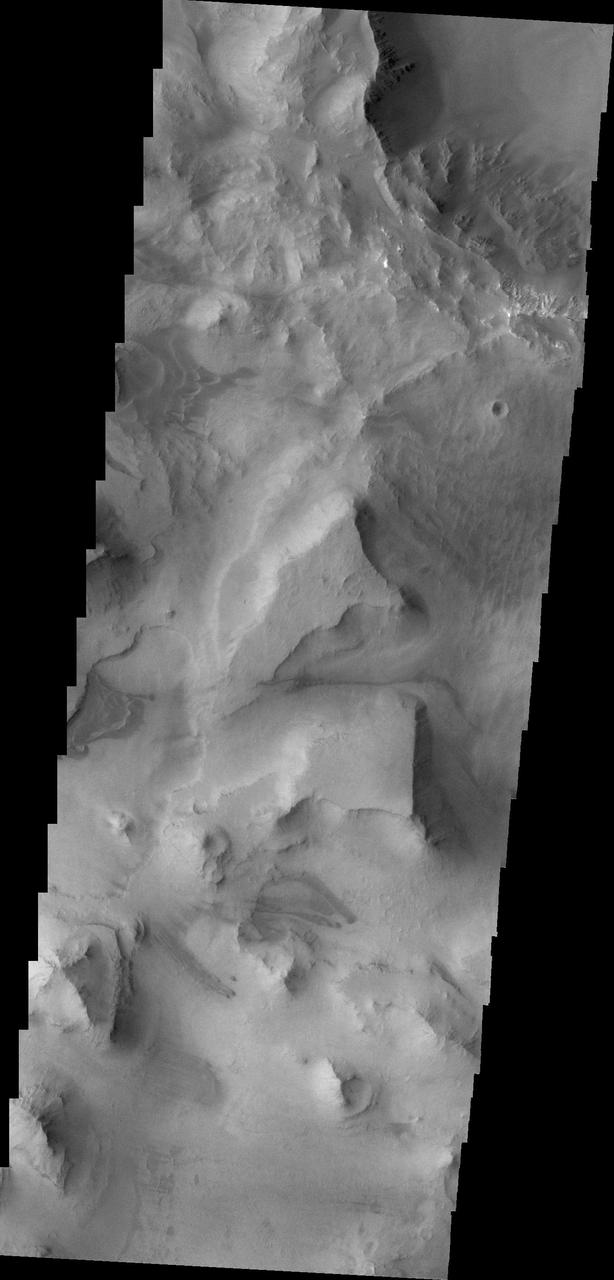

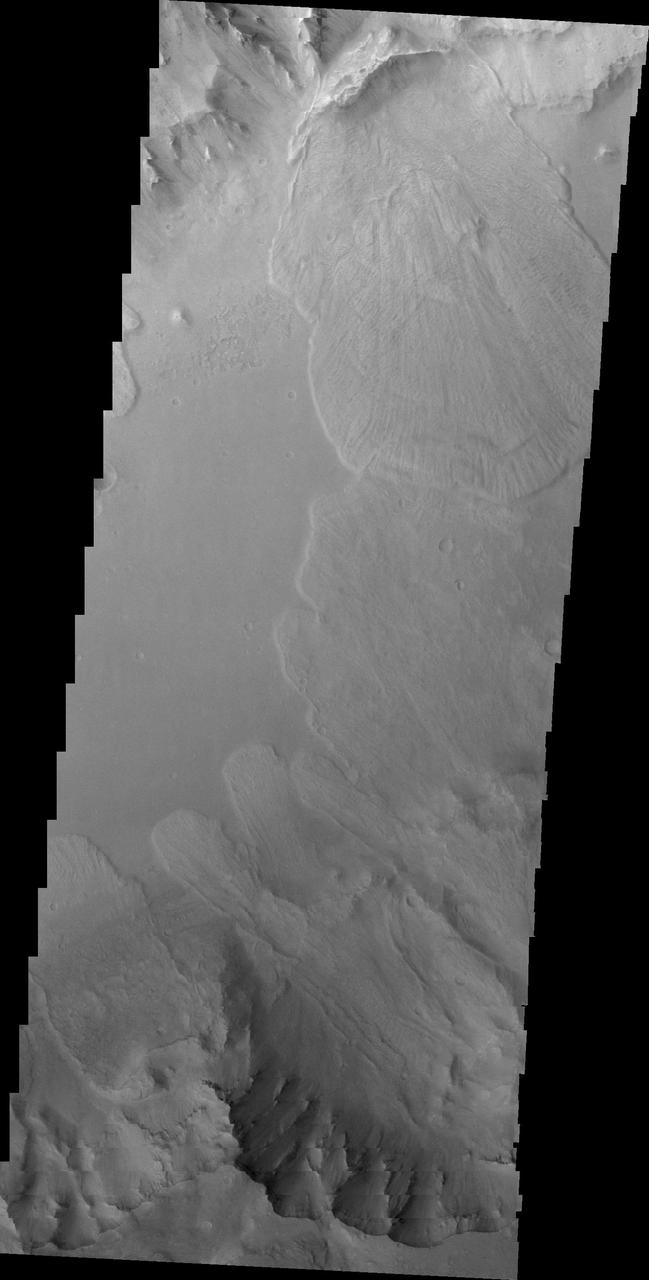
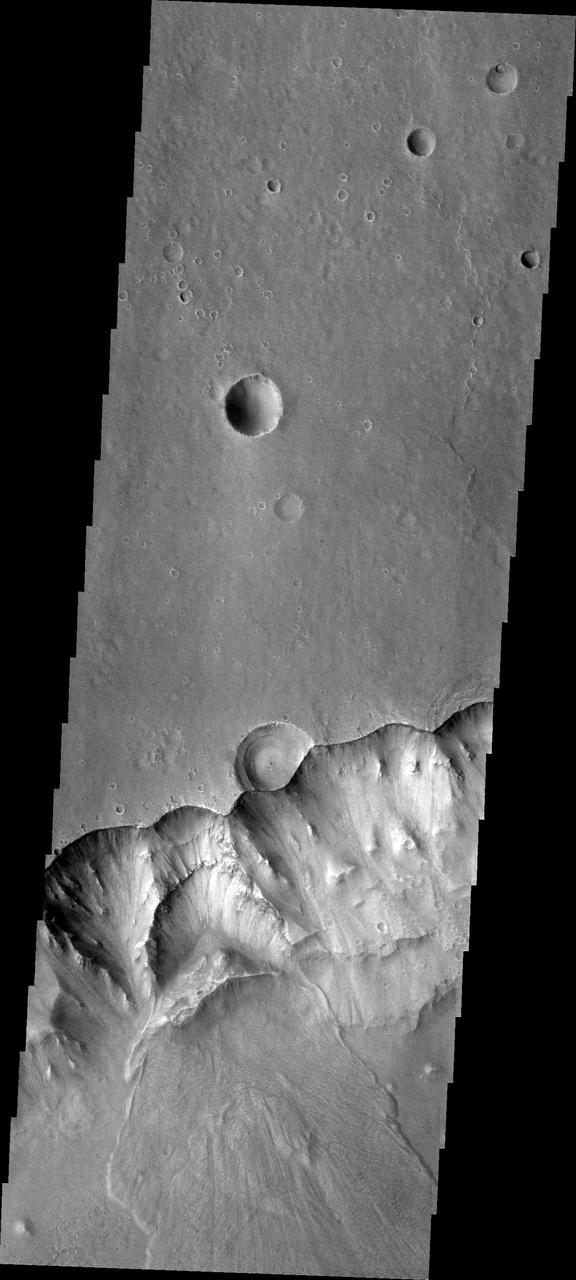
This image from NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey shows the mesas and mountain tops of Capri Chasma.
This 2001 Mars Odyssey THEMIS VIS image shows a landslide in Capri Chasma.
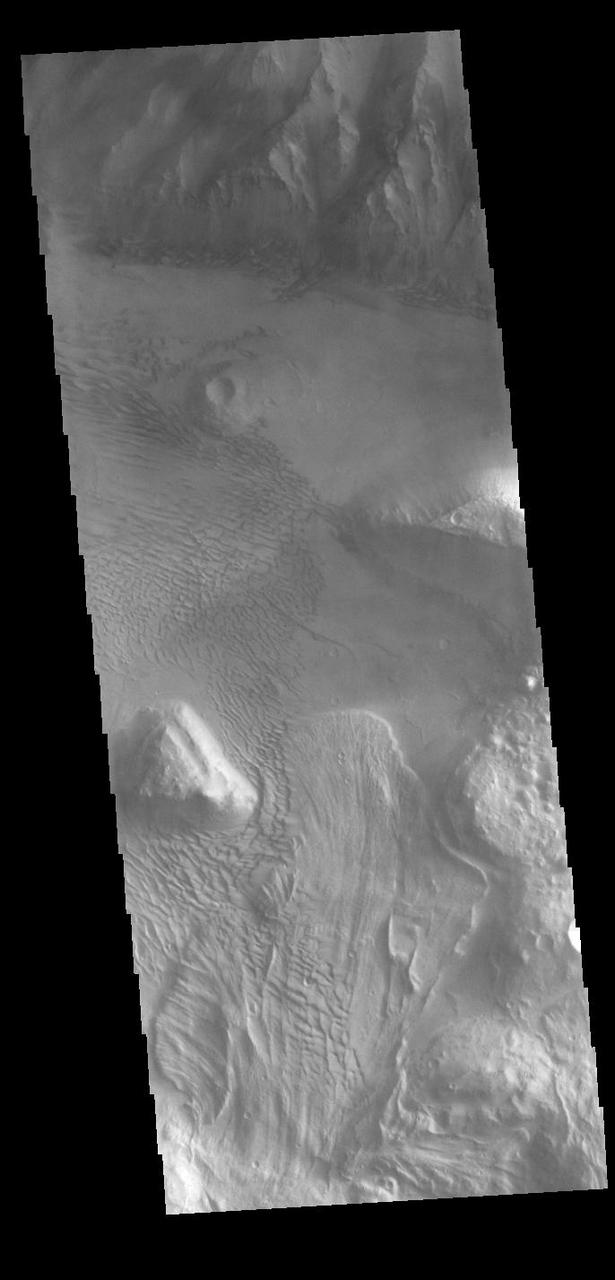

This VIS image is located on the eastern side of Coprates Chasma, near Capri Chasma. The image shows a large lobe shaped landslide deposit at the bottom of the canyon cliff face. Sand dunes are visible both on the landslide deposit and other parts of the canyon floor. Coprates Chasma is one of the numerous canyons that make up Valles Marineris. The chasma stretches for 960 km (600 miles) from Melas Chasma to the west and Capri Chasma to the east. Landslide deposits, layered materials and sand dunes cover a large portion of the chasma floor. Orbit Number: 88225 Latitude: -15.0285 Longitude: 304.496 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2021-11-03 17:56 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25196
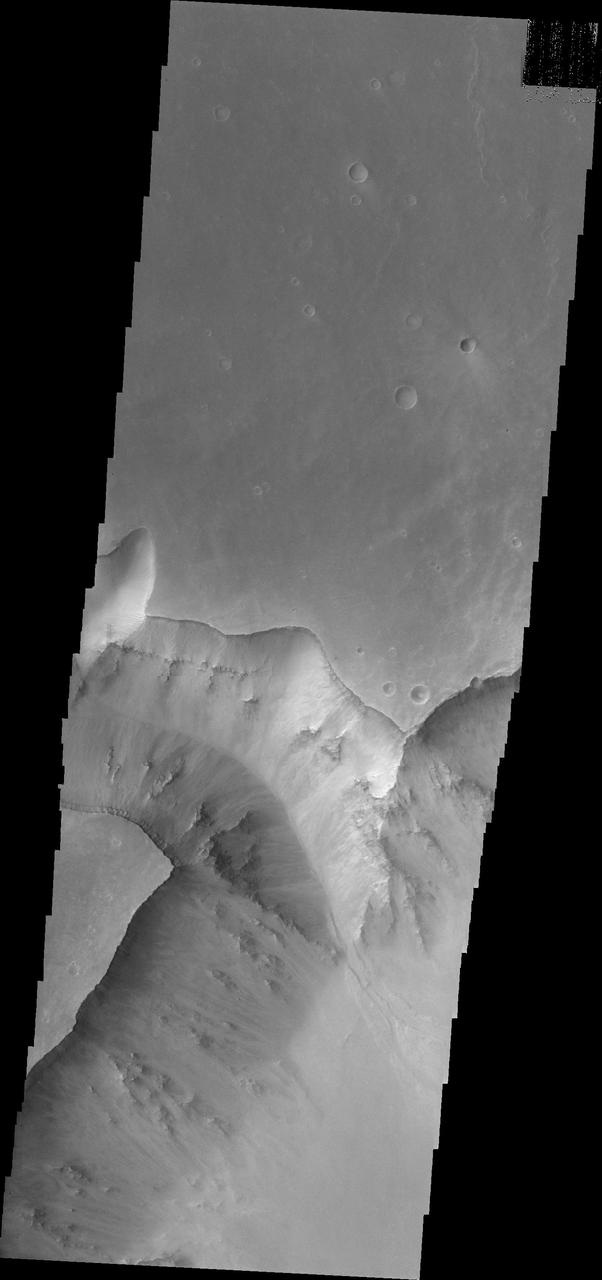

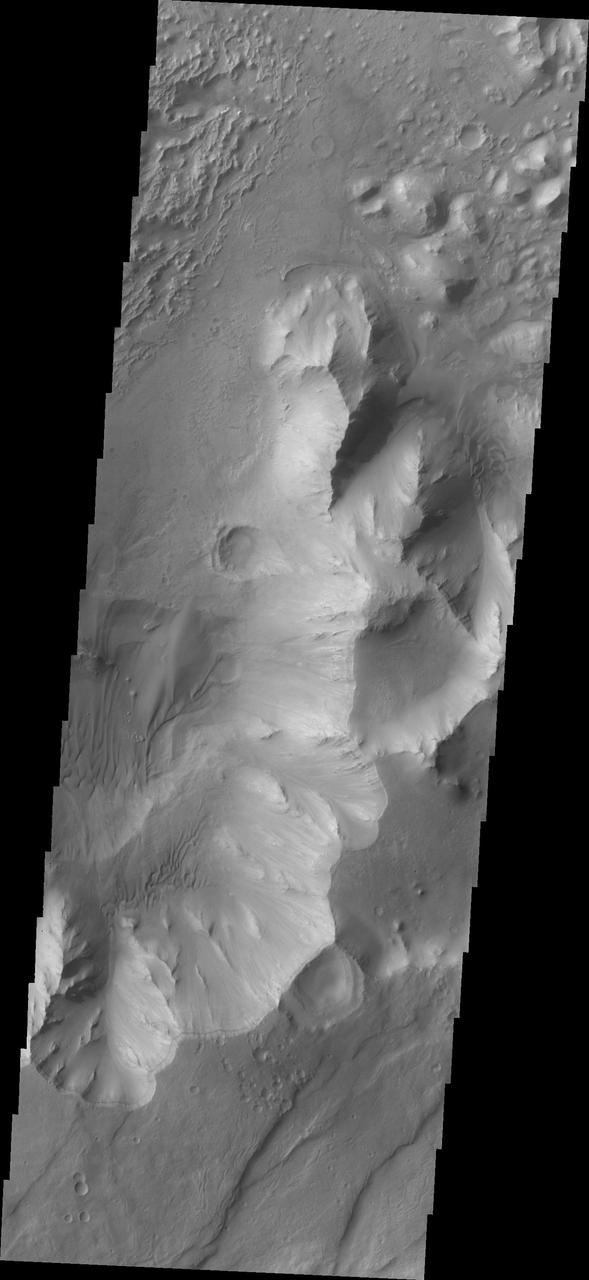
This image from NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft shows part of the Valles Marineris canyon system -- a mega gully enters Capri Chasma.

The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. This image from NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft shows part of Capri Mensa and Capri Chasma.
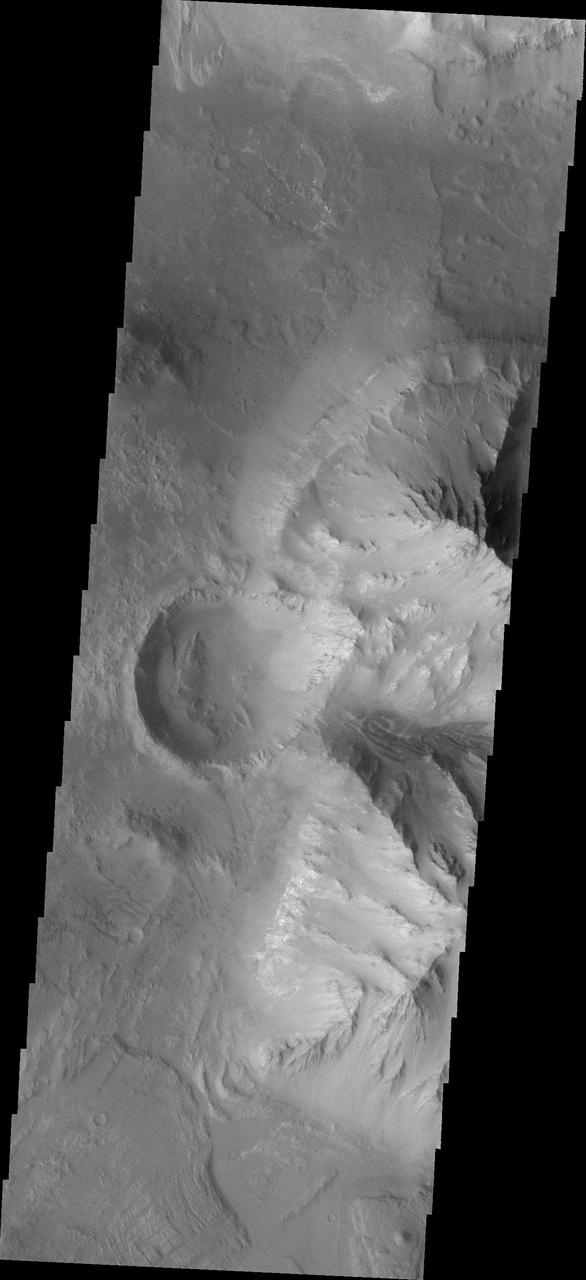

Coprates Chasma is one of the numerous canyons that make up Valles Marineris. The chasma stretches for 960 km (600 miles) from Melas Chasma to the west and Capri Chasma to the east. Landslide deposits, layered materials and sand dunes cover a large portion of the chasma floor. This image is located on the eastern side of Coprates Chasma, near Capri Chasma. The image shows multiple landslide features, which form lobed shaped deposits at the bottom of the canyon cliff face. Sand dunes are visible both on the landslide deposit and other parts of the canyon floor. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 16653 Latitude: -14.2759 Longitude: 303.707 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2005-09-15 12:01 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21991
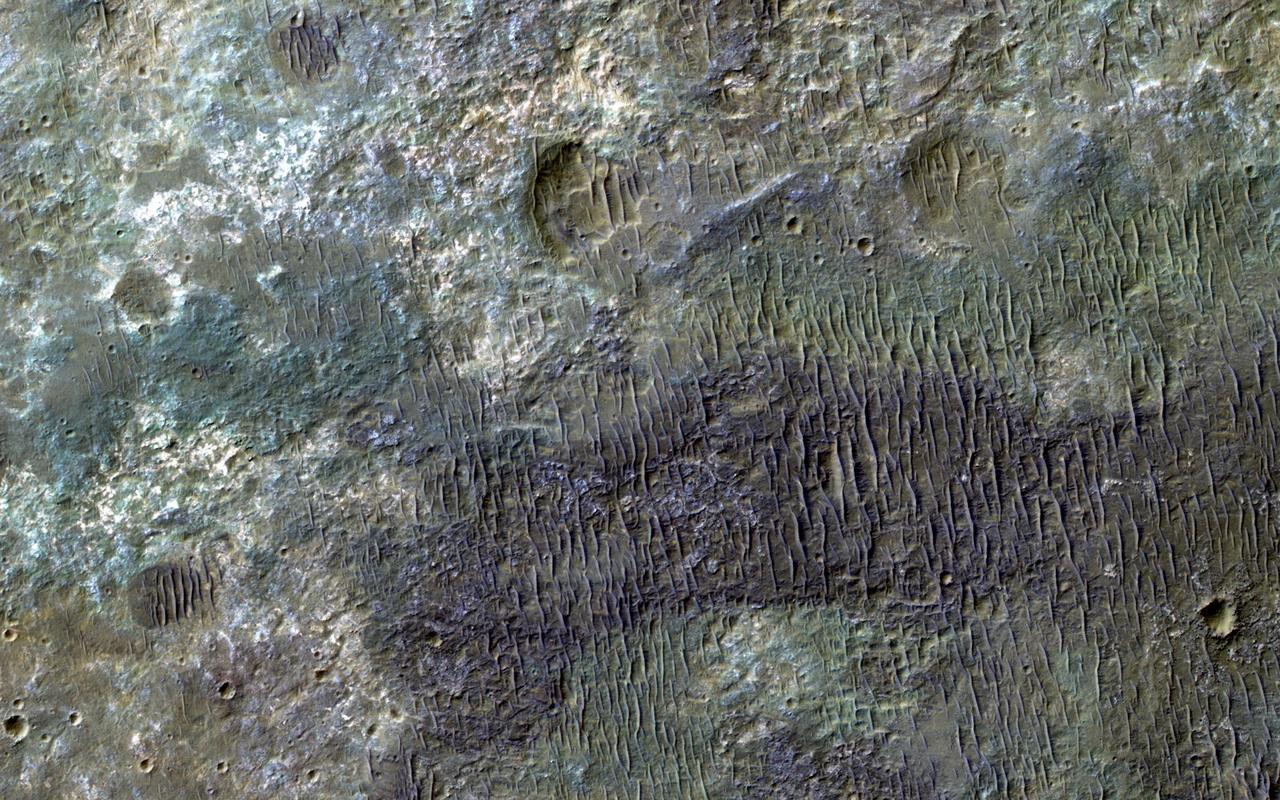

This image from NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter spacecraft covers some of the plains south of Capri Chasma in eastern Valles Marineris. Where the aeolian (wind-blown) sedimentary cover has been stripped away, we see diverse colors indicative of of a variety of altered minerals formed in Mars' wetter past. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20730
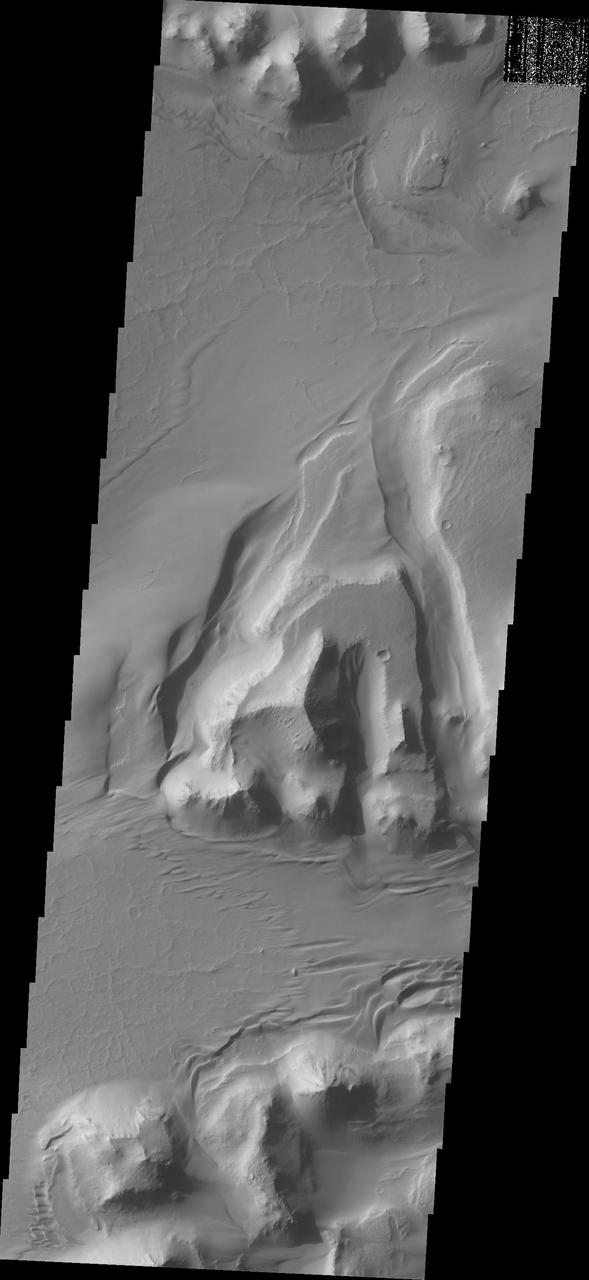

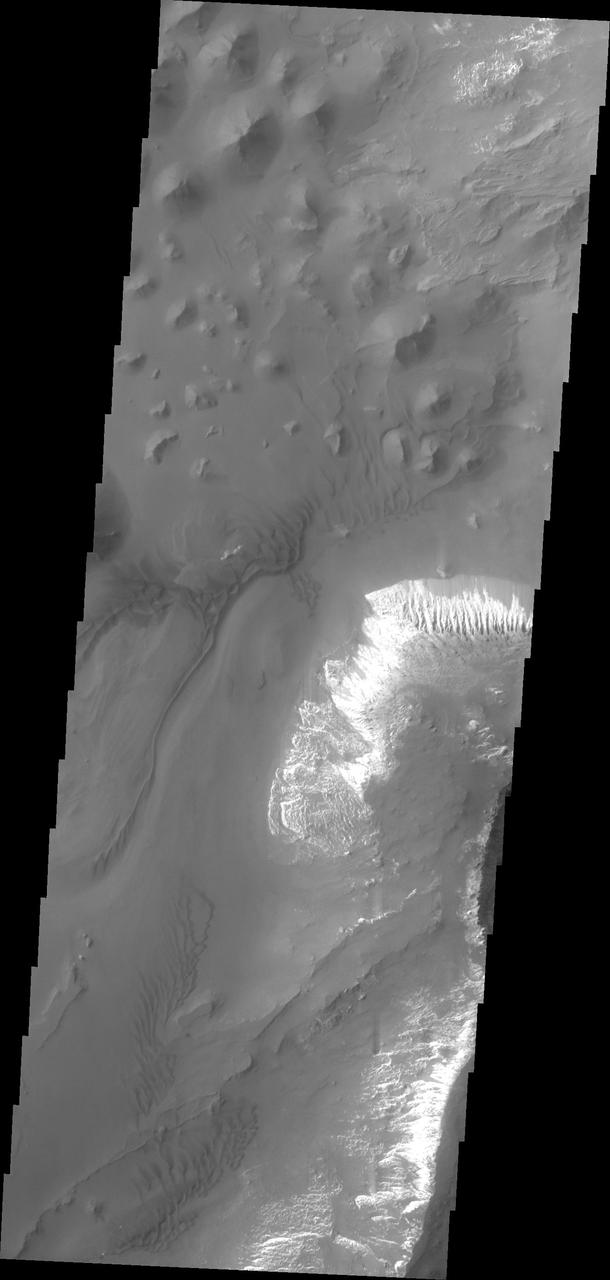
A sand sheet and dune forms are present on the floor of Capri Chasmain this image from NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft.
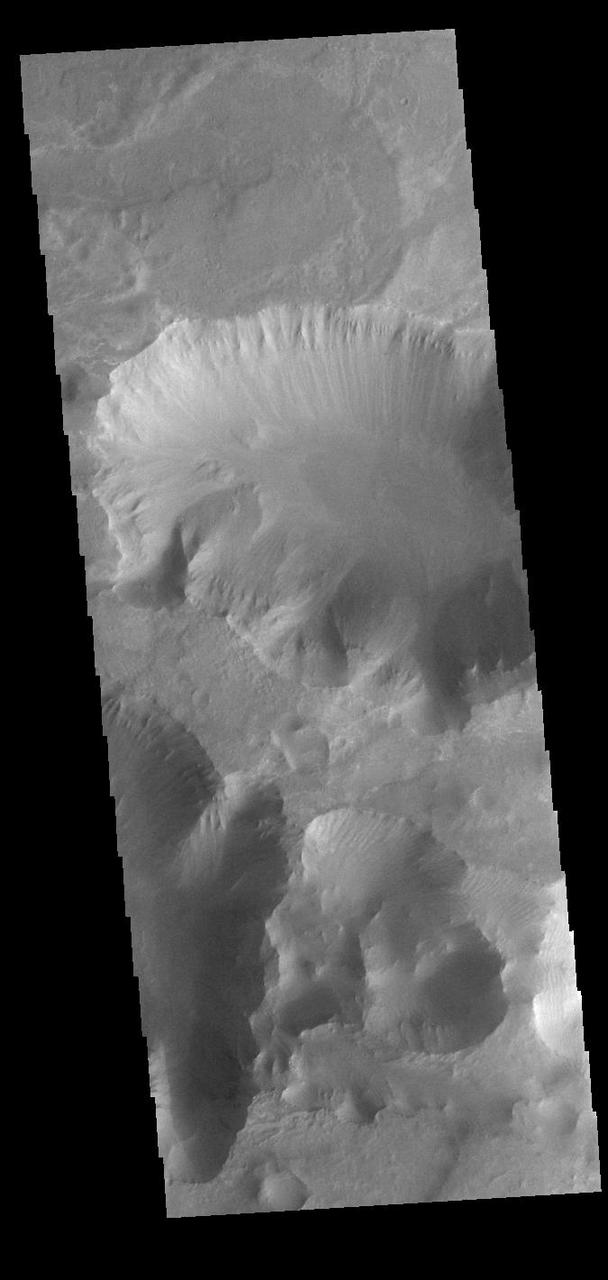

Today's VIS image is located between the main part of Coprates Chasma (north) and Coprates Catena (south). The canyon in this area is much shallower than the main canyon. Coprates Chasma is one of the numerous canyons that make up Valles Marineris. The chasma stretches for 960 km (600 miles) from Melas Chasma to the west and Capri Chasma to the east. Orbit Number: 90883 Latitude: -15.0445 Longitude: 301.518 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2022-06-10 14:37 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25516

Today's VIS image shows a cross section of Coprates Chasma. The floor of the canyon is covered by large landslide deposits. Coprates Chasma is one of the numerous canyons that make up Valles Marineris. The chasma stretches for 960 km (600 miles) from Melas Chasma to the west and Capri Chasma to the east. Paralleling the chasma to the south runs a narrower and shallower chain of linked pits and depressions called Coprates Catena. Orbit Number: 93011 Latitude: -14.3186 Longitude: 299.989 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2022-12-02 19:04 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25811

Today's VIS image shows a cross section of Coprates Chasma. In this region the chasma has two sections – a deep, flat floored canyon at the top of the image, and a shallower section in the lower part of the image. The sections are divided by a large ridge. The floor of the bottom canyon is covered by large landslide deposits. Coprates Chasma is one of the numerous canyons that make up Valles Marineris. The chasma stretches for 960 km (600 miles) from Melas Chasma to the west and Capri Chasma to the east. Orbit Number: 91988 Latitude: -12.6995 Longitude: 293.287 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2022-09-09 13:27 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25717
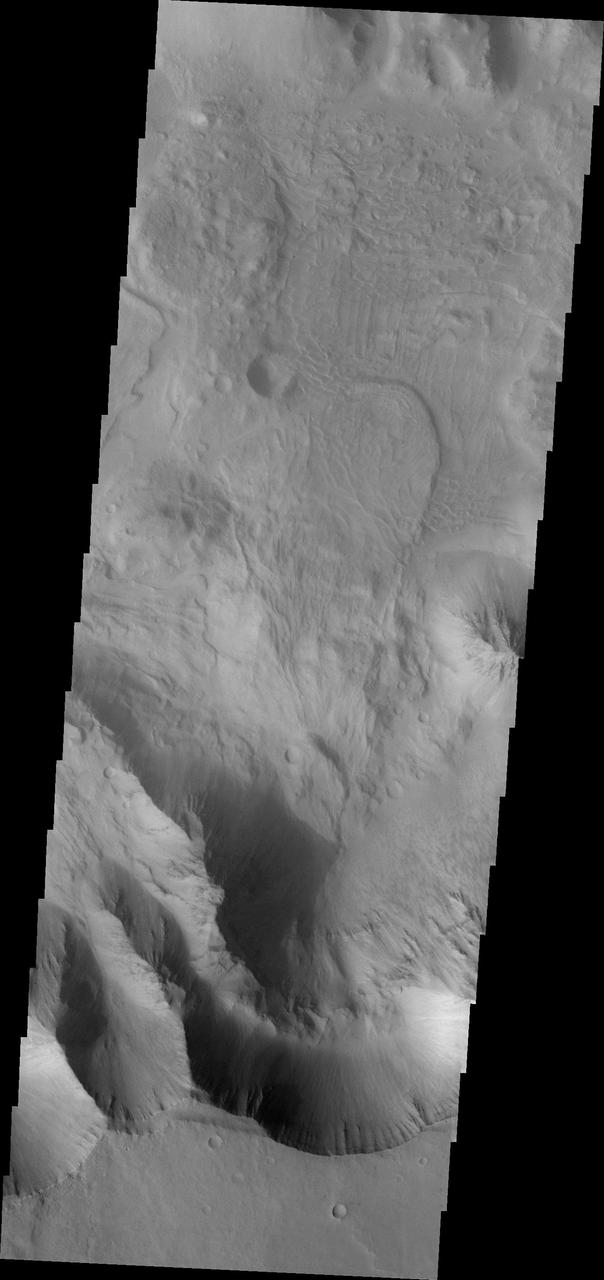

Coprates Chasma is one of the numerous canyons that make up Valles Marineris. The chasma stretches for 960 km (600 miles) from Melas Chasma to the west and Capri Chasma to the east. Landslide deposits, layered materials and sand dunes cover a large portion of the chasma floor. This image is located on the eastern side of Coprates Chasma, near Capri Chasma. The image shows multiple landslide features, which form lobed shaped deposits at the bottom of the canyon cliff face. Sand dunes are visible both on the landslide deposit and other parts of the canyon floor. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 16628 Latitude: -15.4094 Longitude: 304.726 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2005-09-13 10:38 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21990

Today's VIS image shows a cross section of Coprates Chasma. In this region the chasma has two sections – a deep, flat floored canyon at the top of the image (the northern cliff face is not visible in this image), and the second section below that separated by a large ridge. Paralleling it to the south runs a narrower and shallower chain of linked pits and depressions called Coprates Catena. Landslide deposits, layered materials and sand dunes cover a large portion of the chasma floor. The brighter materials at the top of the image are layered deposits. It is unknown how deep these canyon deposits were when they formed. The layering is only visible due to erosion, making it difficult to estimate the original thickness. While layered deposits can be found on the floor of Coprates Chasma, they are most commonly found along the lower elevations and at the bottom of the cliff faces in the canyon. Coprates Chasma is one of the numerous canyons that make up Valles Marineris. The chasma stretches for 960 km (600 miles) from Melas Chasma to the west and Capri Chasma to the east. Orbit Number: 93111 Latitude: -14.0758 Longitude: 295.079 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2022-12-11 00:40 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25816

Coprates Chasma is one of the numerous canyons that make up Valles Marineris. The chasma stretches for 960 km (600 miles) from Melas Chasma to the west and Capri Chasma to the east. Landslide deposits, layered materials and sand dunes cover a large portion of the chasma floor. This image is located in eastern Coprates Chasma. The plateau above the chasma is visible in this image. The cliff face is very steep, with the elevation dropping over 3 miles from the plateau to the canyon floor. Craters are relatively rare on the chasma floor, the one in this image is fairly large. The crater rim has affected winds in this region, causing the interior dunes within the crater as well as the dunes outside the crater rim. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 37804 Latitude: -14.4843 Longitude: 302.193 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2010-06-23 01:14 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21999
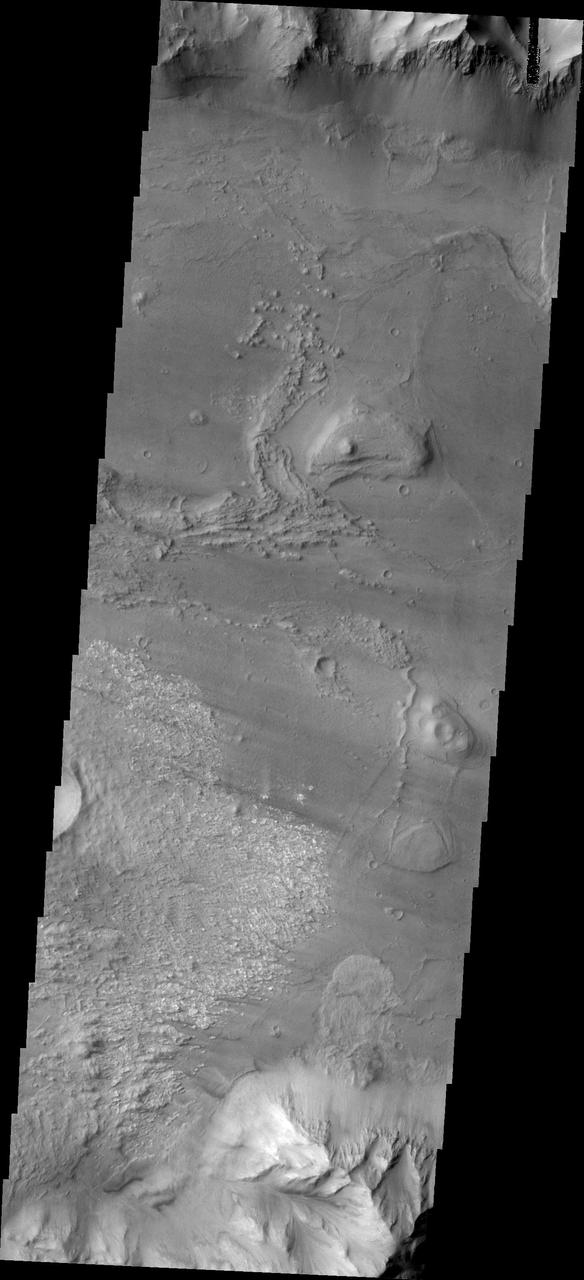

Coprates Chasma is one of the numerous canyons that make up Valles Marineris. The chasma stretches for 960 km (600 miles) from Melas Chasma to the west and Capri Chasma to the east. Landslide deposits, layered materials and sand dunes cover a large portion of the chasma floor. This image is located in central Coprates Chasma. In this image, there is a landslide deposit at the bottom of the image. The brighter material to the left of the landslide appears to be a rough surface likely etched by wind action. The chasma contains numerous regions of sand dunes, indicating that the wind plays a part in the erosion and deposition of fine materials in the canyon. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 35820 Latitude: -12.793 Longitude: 297.407 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2010-01-10 16:39 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21996

Coprates Chasma is one of the numerous canyons that make up Valles Marineris. The chasma stretches for 960 km (600 miles) from Melas Chasma to the west and Capri Chasma to the east. Landslide deposits, layered materials and sand dunes cover a large portion of the chasma floor. This image is located in central Coprates Chasma. The image shows multiple landslide features, which form the bright lobed shaped deposits at the bottom of the canyon cliff face (top of image). The linear grooves on the top of the large landslide deposit were formed as the material came to rest on the canyon floor. The other features on the chasma floor are layered materials that have been weathered. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 16803 Latitude: -12.5614 Longitude: 296.887 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2005-09-27 20:25 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21992
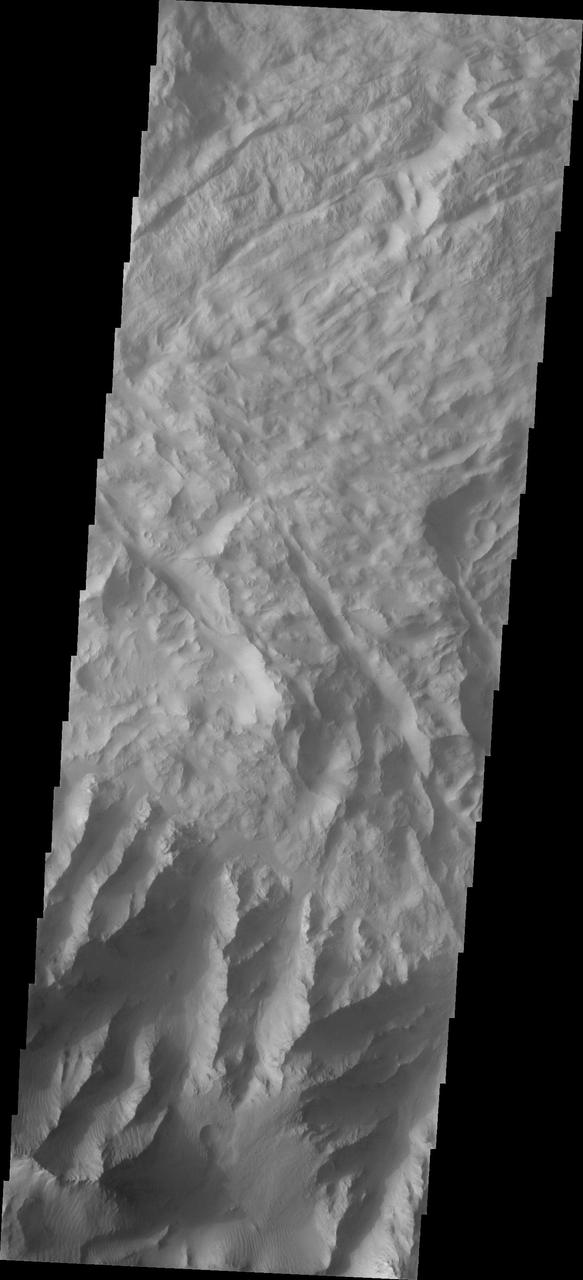

Coprates Chasma is one of the numerous canyons that make up Valles Marineris. The chasma stretches for 960 km (600 miles) from Melas Chasma to the west and Capri Chasma to the east. Landslide deposits, layered materials and sand dunes cover a large portion of the chasma floor. This image is located in central Coprates Chasma. The floor of the chasma is covered by a complex deposit of material. This chaotic surface differs from most of the floor of the canyon and indicate a local process, perhaps a very large landslide or failure of the cliff face. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 27086 Latitude: -13.564 Longitude: 300.618 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2008-01-22 12:04 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21994
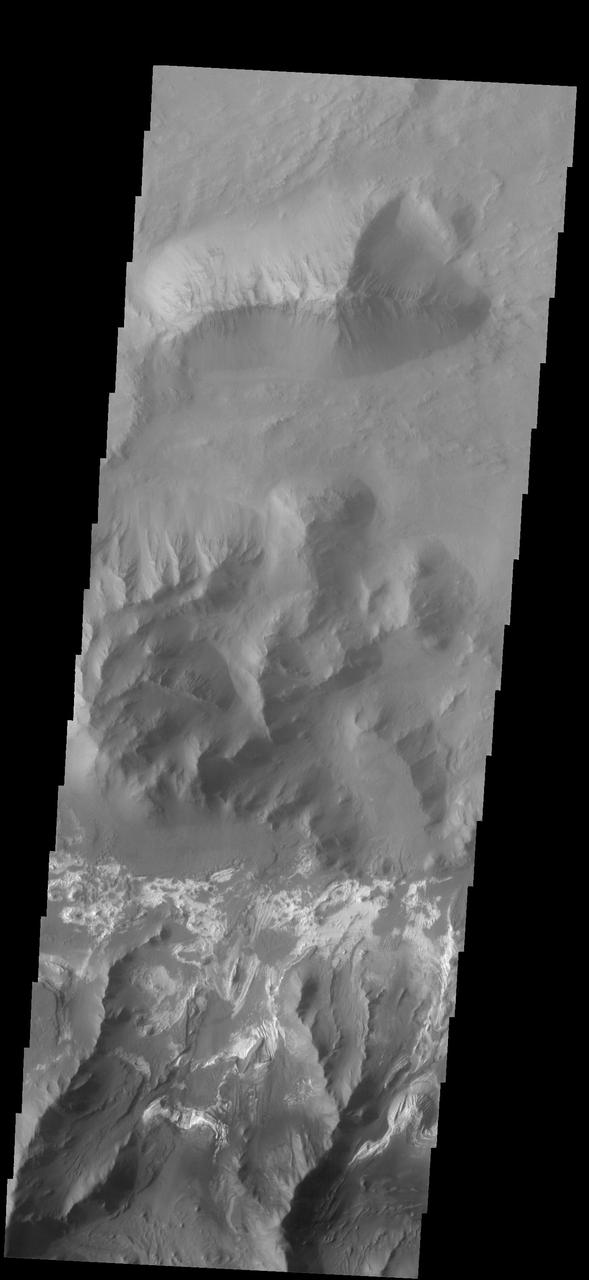

Coprates Chasma is one of the numerous canyons that make up Valles Marineris. The chasma stretches for 960 km (600 miles) from Melas Chasma to the west and Capri Chasma to the east. Landslide deposits, layered materials and sand dunes cover a large portion of the chasma floor. This image is located in central Coprates Chasma. The brighter materials at the bottom of the image are layered deposits. It is unknown how deep these canyon deposits were when they formed. The layering is only visible due to erosion, making it difficult to estimate the original thickness. While layered deposits can be found on the floor of Coprates Chasma, they are most commonly found along the lower elevations and at the bottom of the cliff faces in the canyon. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 51810 Latitude: -12.6848 Longitude: 295.197 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2013-08-18 22:56 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22000
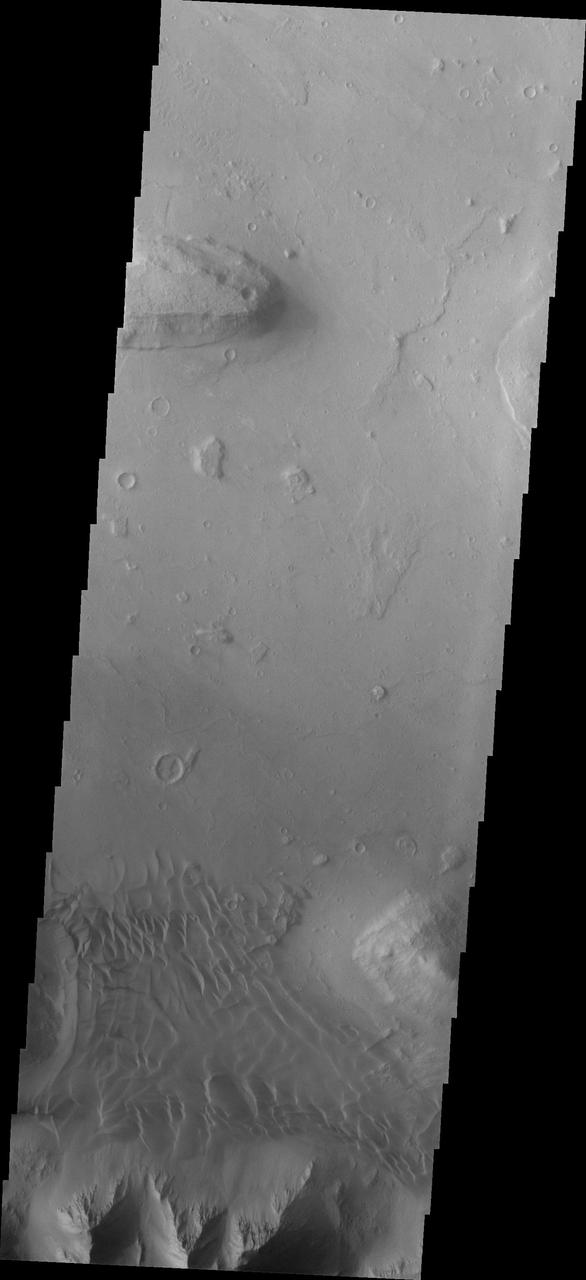

Coprates Chasma is one of the numerous canyons that make up Valles Marineris. The chasma stretches for 960 km (600 miles) from Melas Chasma to the west and Capri Chasma to the east. Landslide deposits, layered materials and sand dunes cover a large portion of the chasma floor. This image is located in eastern Coprates Chasma. The image shows a relatively smooth floor, with a group of sand dune forms located against the wall of the chasma (bottom of image). The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 27061 Latitude: -13.9602 Longitude: 301.82 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2008-01-20 10:39 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21993
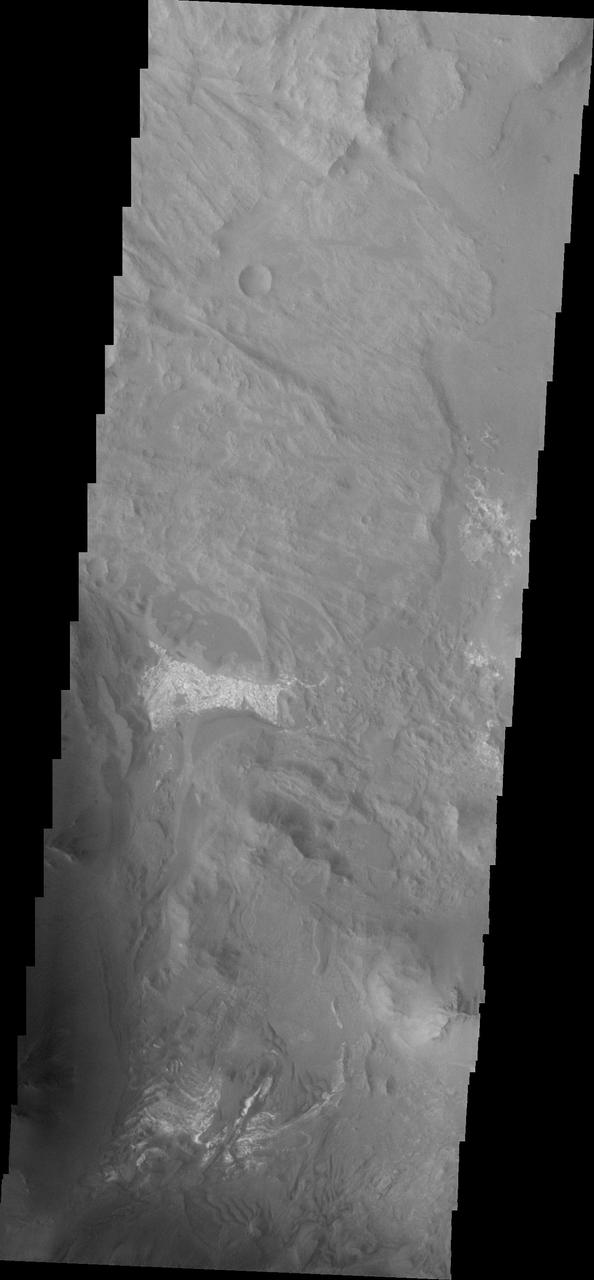

Coprates Chasma is one of the numerous canyons that make up Valles Marineris. The chasma stretches for 960 km (600 miles) from Melas Chasma to the west and Capri Chasma to the east. Landslide deposits, layered materials and sand dunes cover a large portion of the chasma floor. This image is located in eastern Coprates Chasma, just east of the previous image. In this image, the lobate margins of several landslide deposits are easy to identify. This indicates the chaotic surface in yesterday's image are materials emplaced by landslides. The brighter features at the bottom of the image are layered materials. There are also dunes in the region with the layered deposits. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 33037 Latitude: -13.8409 Longitude: 301.104 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2009-05-26 13:16 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21995
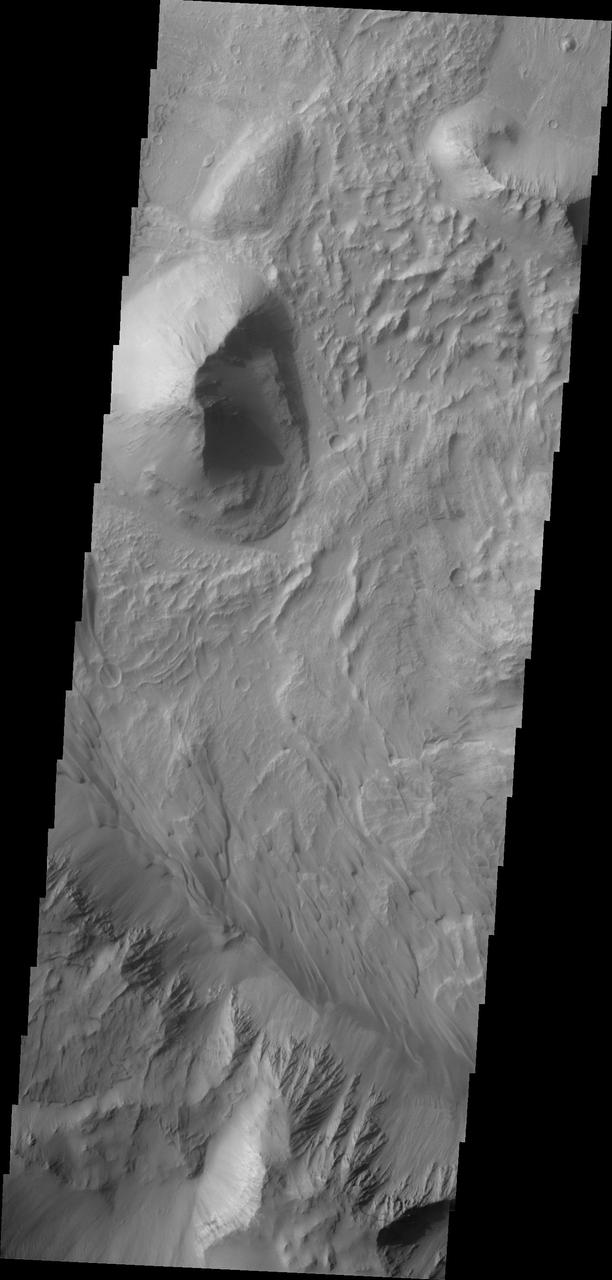

Coprates Chasma is one of the numerous canyons that make up Valles Marineris. The chasma stretches for 960 km (600 miles) from Melas Chasma to the west and Capri Chasma to the east. Landslide deposits, layered materials and sand dunes cover a large portion of the chasma floor. This image is located in eastern Coprates Chasma. The branching features near the bottom of the image are spurs of rock in the cliff face. The rock is more resistant to erosion that fine materials like sand and dust. Those materials are visible below the spurs, and then onto the canyon floor. Unlike the large landslide deposits, these small fans of material build up over time as the material above erodes. There are sand dunes along the edge of the fans in this image. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 36294 Latitude: -14.7055 Longitude: 303.066 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2010-02-18 17:20 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21998
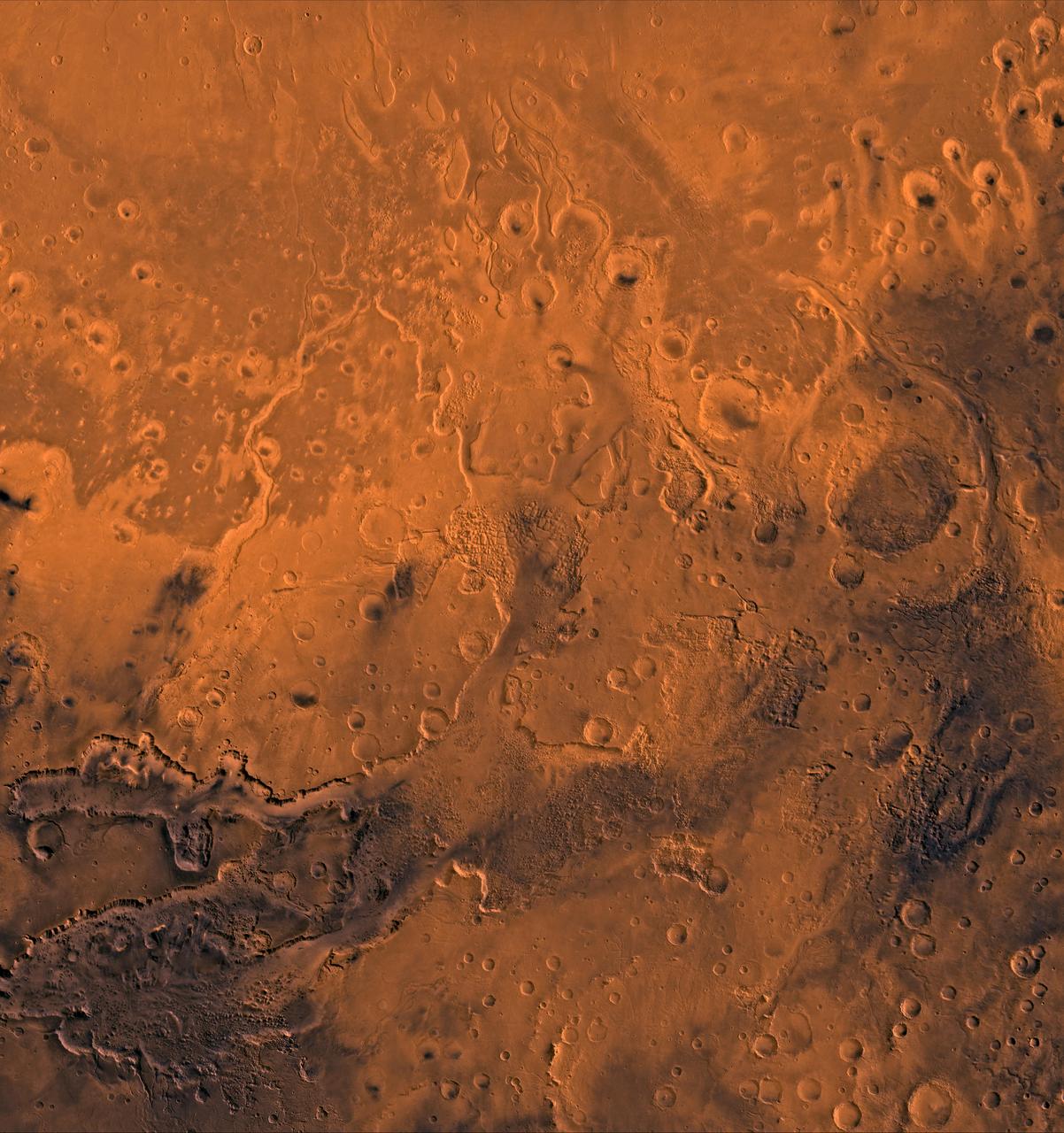

A color image of the south Chryse basin Valles Marineris outflow channels on Mars; north toward top. The scene shows on the southwest corner the chaotic terrain of the east part of Valles Marineris and two of its related canyons: Eos and Capri Chasmata (south to north). Ganges Chasma lies directly north. The chaos in the southern part of the image gives rise to several outflow channels, Shalbatana, Simud, Tiu, and Ares Valles (left to right), that drained north into the Chryse basin. The mouth of Ares Valles is the site of the Mars Pathfinder lander. This image is a composite of NASA's Viking medium-resolution images in black and white and low-resolution images in color. The image extends from latitude 20 degrees S. to 20 degrees N. and from longitude 15 degrees to 53 degrees; Mercator projection. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00418

This observation from NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbite shows a candidate 2018 European Space Agency ExoMars landing site in Hypanis Vallis. Instead of imaging ancient fluvial deposits (thought to be the remnants of a delta feed lake), the image shows patchy concentrations of dust clouds. These clouds are part of the annually occurring Acidalia storm track, a regional dust storm system that originates in the Acidalia-Chryse-Kasei region and propagates southward into equatorial Valles Marineris and beyond. While this image is only partially obscured by dust, many others captured around this time frame were completely dominated by think clouds of dust. For example, this image in Capri Chasma was rendered useless for geology and will have to be reacquired. Landing by the ExoMars rover in these kinds of atmospheric conditions would be complicated. That mission is set to touchdown on Mars in January 2019, hopefully with clear skies. HiRISE will continue to image Hypanis Vallis and other interesting sites on Mars despite the changing weather. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19846
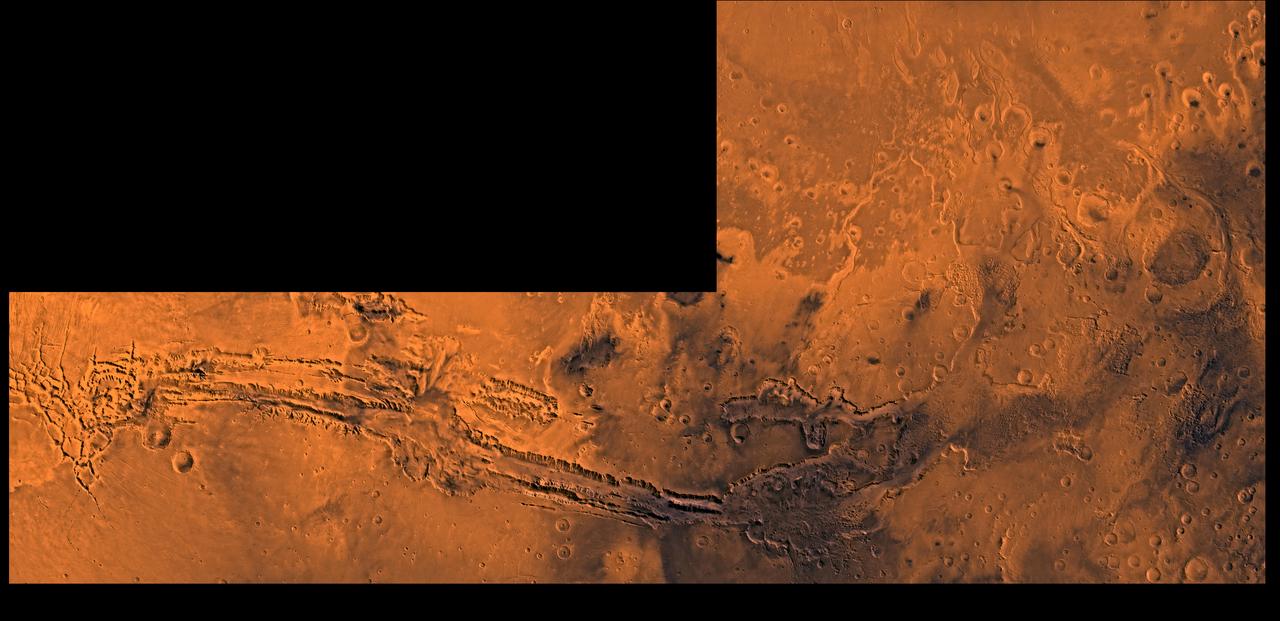

A color image of Valles Marineris, the great canyon and the south Chryse basin-Valles Marineris outflow channels of Mars; north toward top. The scene shows the entire Valles Marineris canyon system, over 3,000 km long and averaging 8 km deep, extending from Noctis Labyrinthus, the arcuate system of graben to the west, to the chaotic terrain to the east and related outflow canyons that drain toward the Chryse basin. Eos and Capri Chasmata (south to north) are two canyons connected to Valles Marineris. Ganges Chasma lies directly north. The chaos in the southeast part of the image gives rise to several outflow channels, Shalbatana, Simud, Tiu, and Ares Valles (left to right), that drained north into the Chryse basin. The mouth of Ares Valles is the site of the Mars Pathfinder lander. This image is a composite of Viking medium-resolution images in black and white and low-resolution images in color; Mercator projection. The image roughly extends from latitude 20 degrees S. to 20 degrees N. and from longitude 15 degrees to 102.5 degrees. The connected chasma or valleys of Valles Marineris may have formed from a combination of erosional collapse and structural activity. Layers of material in the eastern canyons might consist of carbonates deposited in ancient lakes, eolian deposits, or volcanic materials. Huge ancient river channels began from Valles Marineris and from adjacent canyons and ran north. Many of the channels flowed north into Chryse Basin. The south Chryse outflow channels are cut an average of 1 km into the cratered highland terrain. This terrain is about 9 km above datum near Valles Marineris and steadily decreases in elevation to 1 km below datum in the Chryse basin. Shalbatana is relatively narrow (10 km wide) but can reach 3 km in depth. The channel begins at a 2- to 3-km-deep circular depression within a large impact crater, whose floor is partly covered by chaotic material, and ends in Simud Valles. Tiu and Simud Valles consist of a complex of connected channel floors and chaotic terrain and extend as far south as and connect to eastern Valles Marineris. Ares Vallis originates from discontinuous patches of chaotic terrain within large craters. In the Chryse basin the Ares channel forks; one branch continues northwest into central Chryse Planitia and the other extends north into eastern Chryse Planitia. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00426