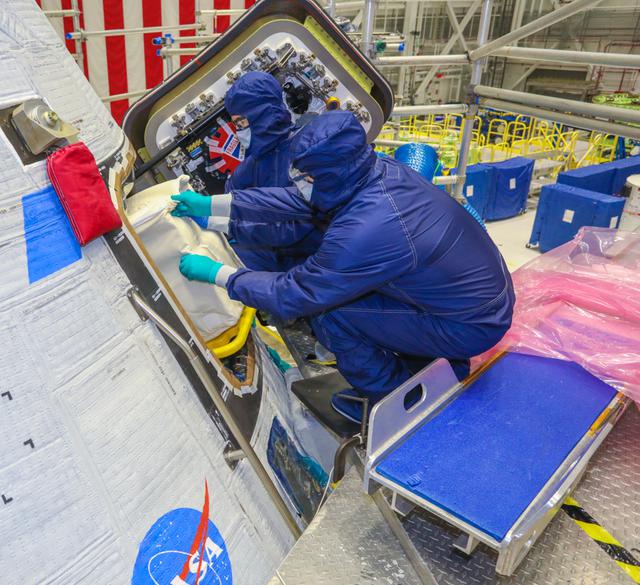

Technicians place cargo inside Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner ahead of Orbital Flight Test-2 (OFT-2) in the Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 28, 2021. Part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program, OFT-2 is a critical developmental milestone on the company’s path to fly crew missions for NASA.
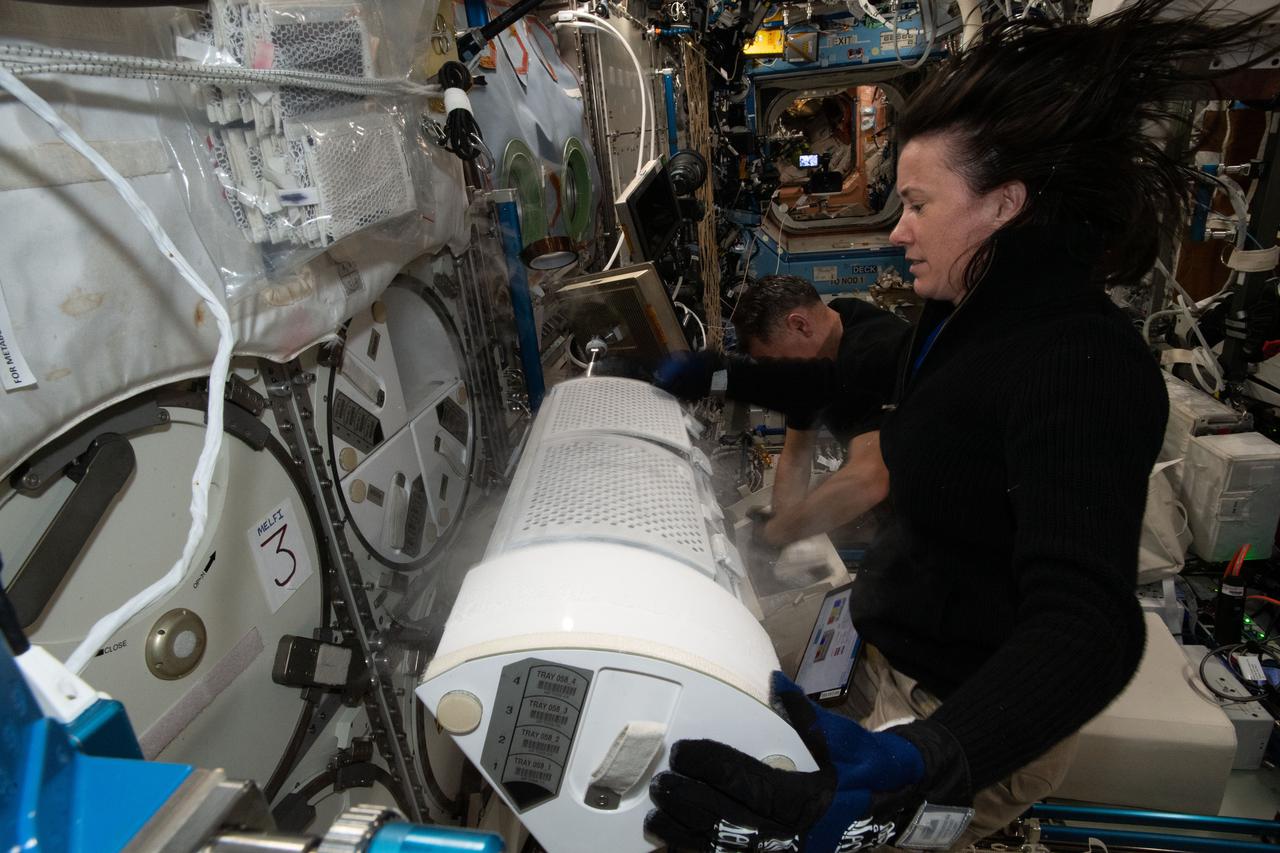

iss065e158844 (July 8, 2021) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 65 Flight Engineer Megan McArthur prepares frozen research samples for transfer and stowage inside the SpaceX Cargo Dragon resupply ship ahead of the U.S. cargo craft's undocking and splashdown in the Gulf of Mexico.
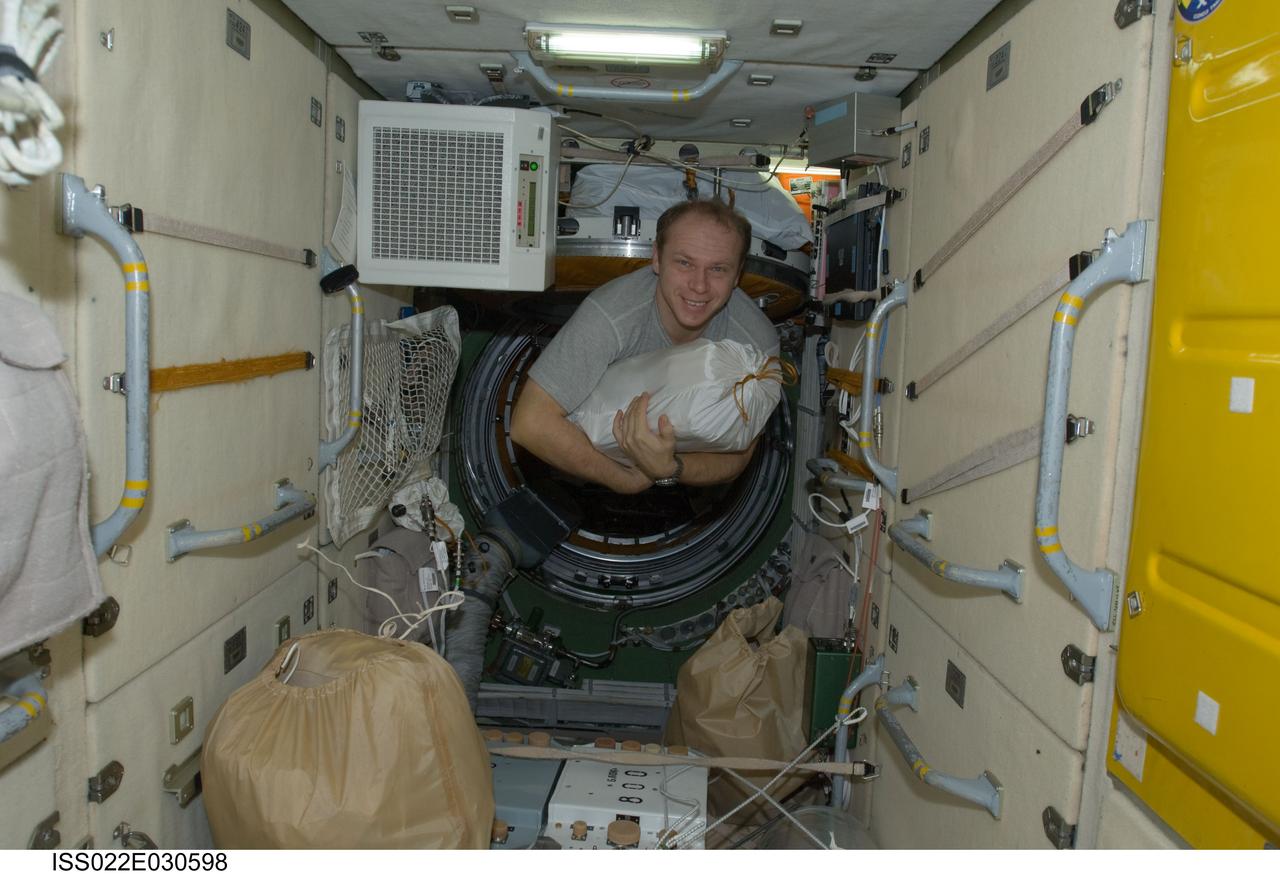

ISS022-E-030598 (19 Jan. 2010) --- Russian cosmonaut Oleg Kotov, Expedition 22 flight engineer, moves a stowage bag in the Zarya Functional Cargo Block (FGB) of the International Space Station.
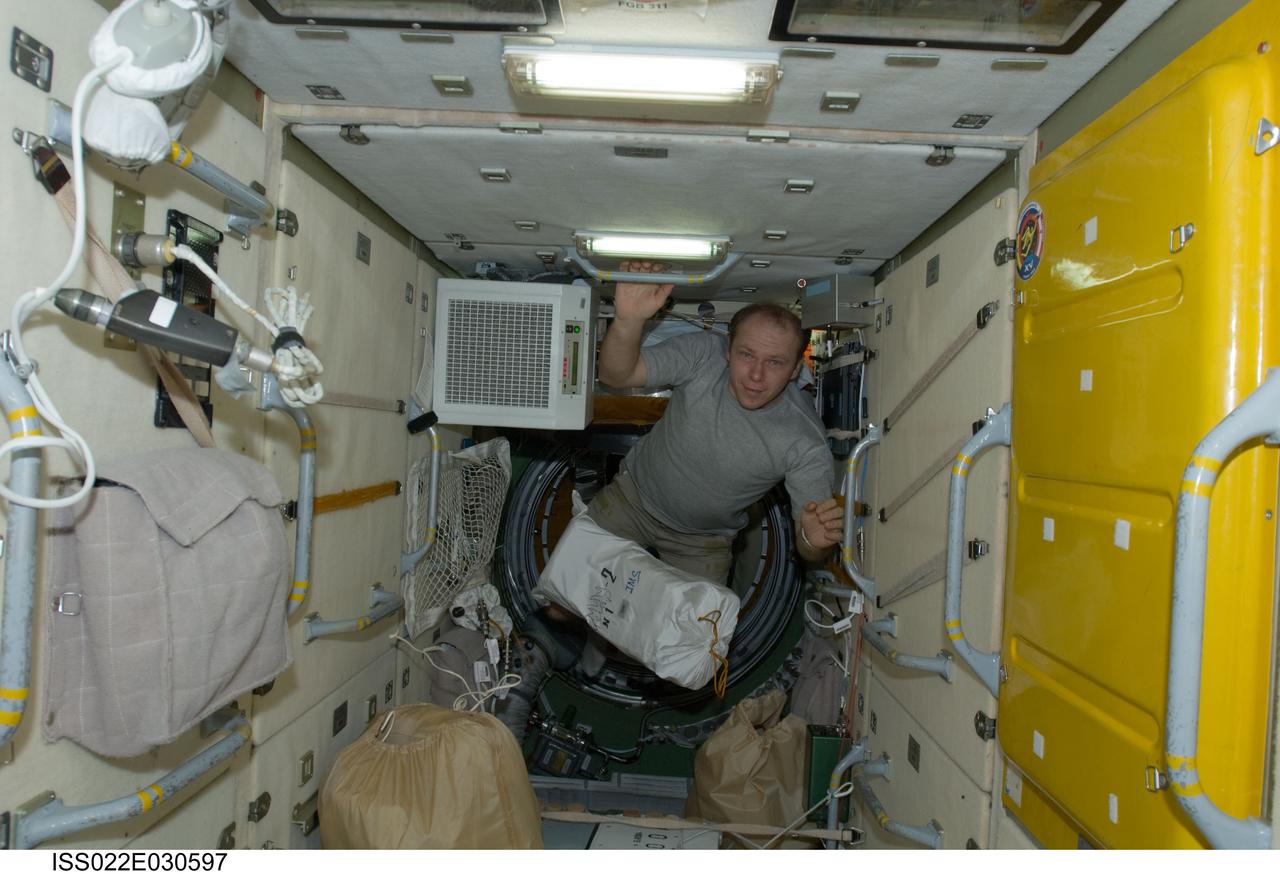

ISS022-E-030597 (19 Jan. 2010) --- Russian cosmonaut Oleg Kotov, Expedition 22 flight engineer, is pictured near a stowage bag floating freely in the Zarya Functional Cargo Block (FGB) of the International Space Station.
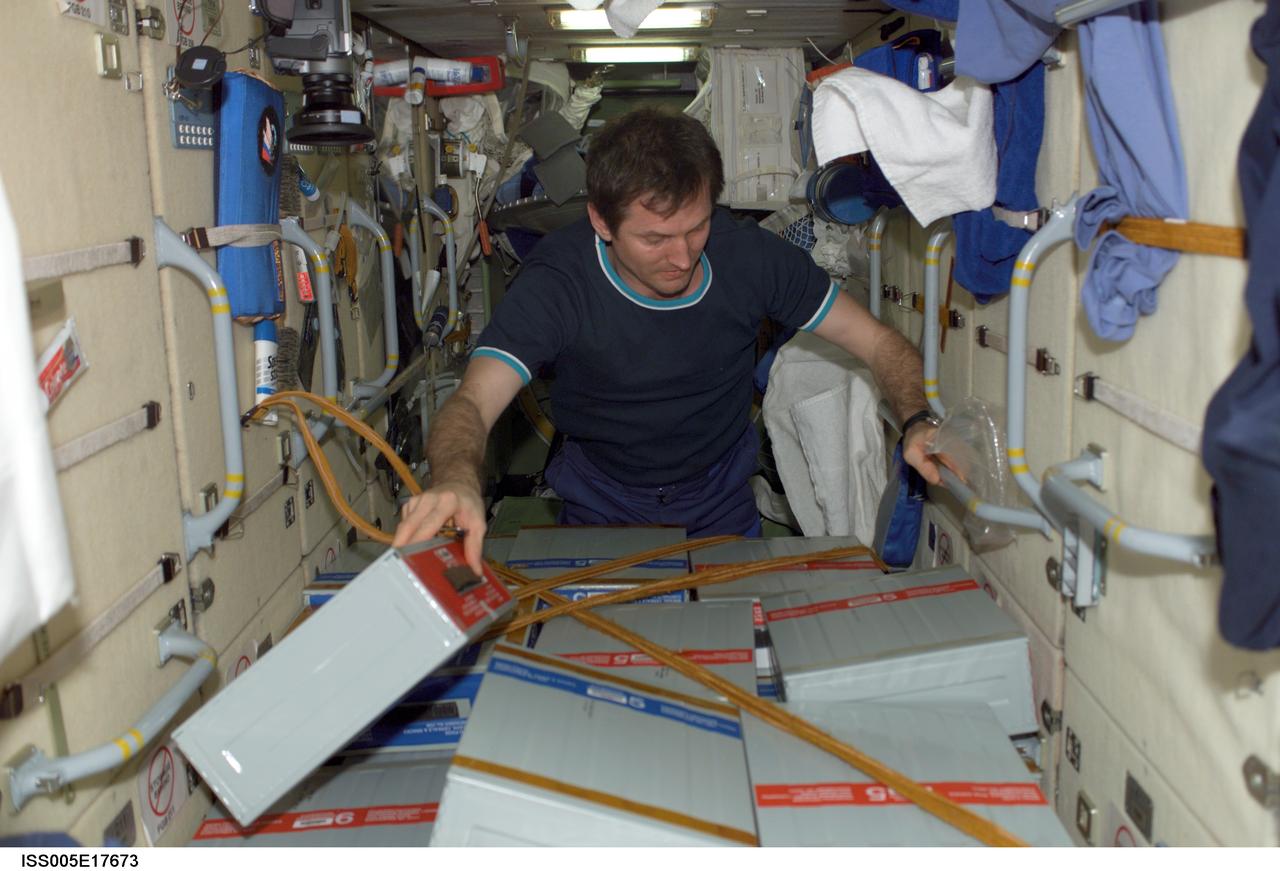

ISS005-E-17673 (17 October 2002) --- Cosmonaut Sergei Y. Treschev, Expedition Five flight engineer representing Rosaviakosmos, checks stowage boxes in the functional cargo block (FGB), or Zarya, on the International Space Station (ISS).
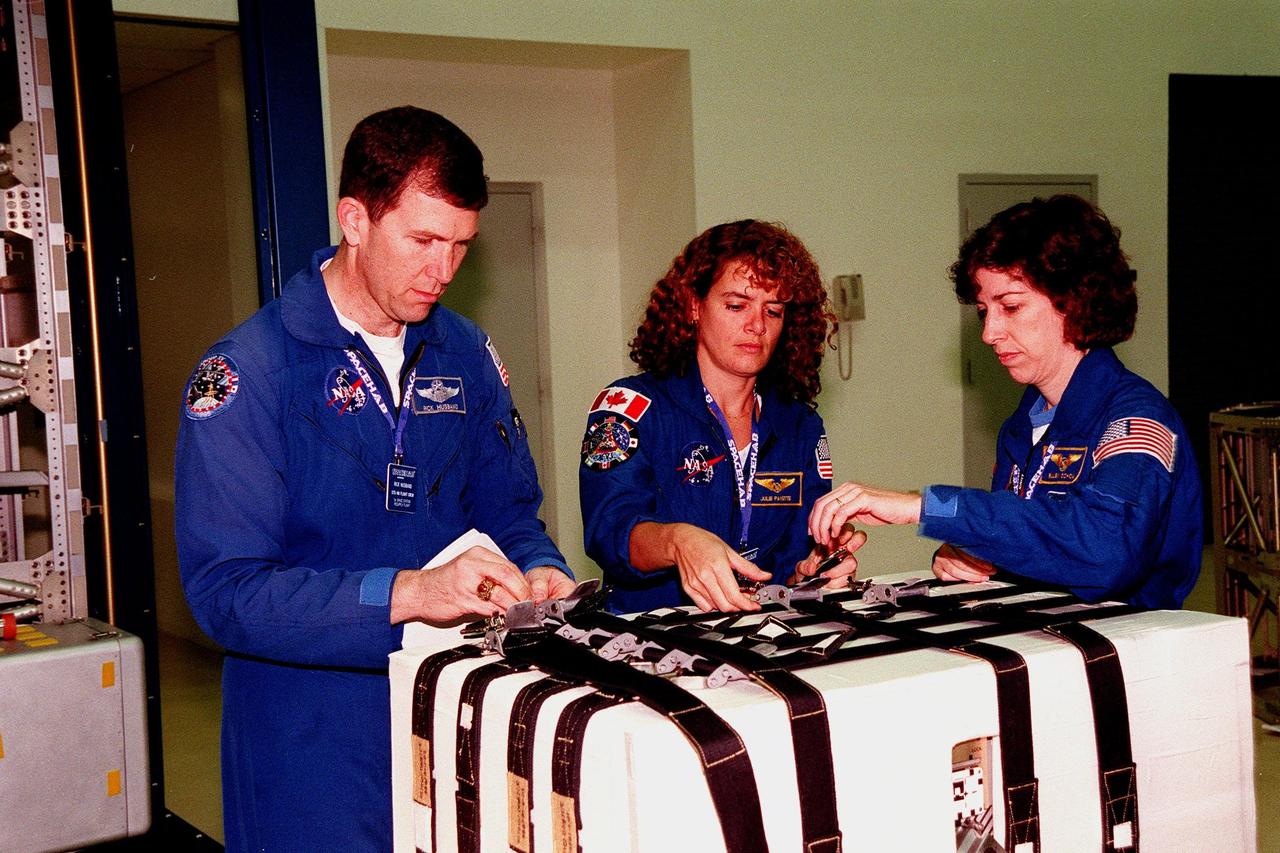

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the SPACEHAB Facility, (left to right) STS-96 Pilot Rick Husband and Mission Specialists Julie Payette and Ellen Ochoa work the straps on the Sequential Shunt Unit (SSU) in front of them. The STS-96 crew is at KSC for a payload Interface Verification Test (IVT) for its upcoming mission to the International Space Station . Other crew members at KSC for the IVT are Commander Kent Rominger and Mission Specialists Tamara Jernigan, Dan Barry and Valery Tokarev of Russia. The SSU is part of the cargo on Mission STS-96, which carries the SPACEHAB Logistics Double Module, with equipment to further outfit the International Space Station service module and equipment that can be off-loaded from the early U.S. assembly flights. The SPACEHAB carries internal logistics and resupply cargo for station outfitting, plus an external Russian cargo crane to be mounted to the exterior of the Russian station segment and used to perform space walking maintenance activities. The double module stowage provides capacity of up to 10,000 lbs. with the ability to accommodate powered payloads, four external rooftop stowage locations, four double-rack locations (two powered), up to 61 bulkhead-mounted middeck locker locations, and floor storage for large unique items and Soft Stowage. STS-96 is targeted to launch May 20 about 9:32 a.m
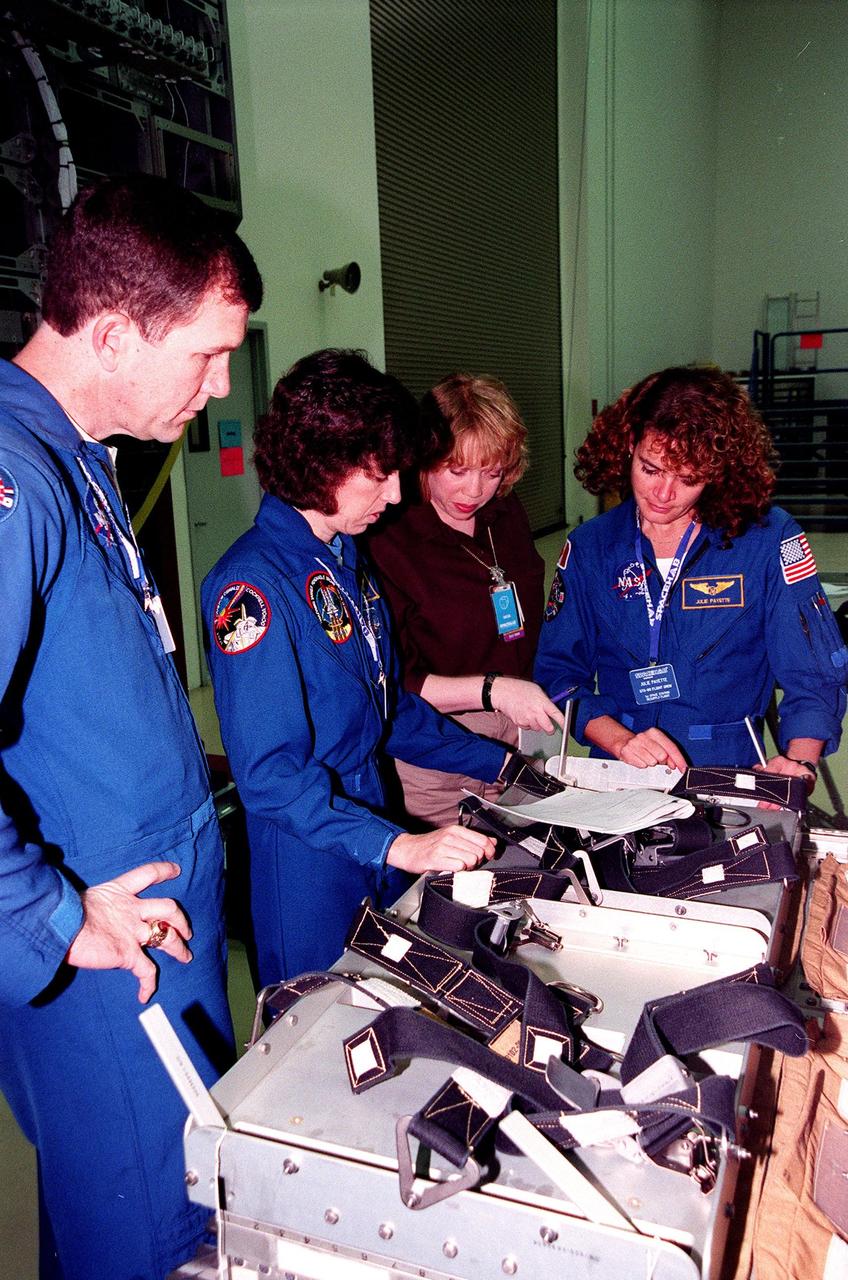

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- During a payload Interface Verification Test (IVT) in the SPACEHAB Facility, STS-96 Pilot Rick Husband and Mission Specialist Ellen Ochoa (on the left) and Mission Specialist Julie Payette (on the far right) listen to Khristal Parker (second from right), with Boeing, explain about the equipment in front of them. Other crew members at KSC for the IVT are Commander Kent Rominger and Mission Specialists Tamara Jernigan, Dan Barry and Valery Tokarev of Russia. The SSU is part of the cargo on Mission STS-96, which carries the SPACEHAB Logistics Double Module, with equipment to further outfit the International Space Station service module and equipment that can be off-loaded from the early U.S. assembly flights. The SPACEHAB carries internal logistics and resupply cargo for station outfitting, plus an external Russian cargo crane to be mounted to the exterior of the Russian station segment and used to perform space walking maintenance activities. The double module stowage provides capacity of up to 10,000 lbs. with the ability to accommodate powered payloads, four external rooftop stowage locations, four double-rack locations (two powered), up to 61 bulkhead-mounted middeck locker locations, and floor storage for large unique items and Soft Stowage. STS-96 is targeted to launch May 20 about 9:32 a.m

iss064e021970 (Jan. 9, 2021) --- The SpaceX Cargo Dragon resupply ship is pictured docked to the Harmony module's space-facing international docking adapter. At right, a portion of the JAXA Kibo laboratory module, the Experiment Logistics Module (Kibo's stowage facility), is pictured.
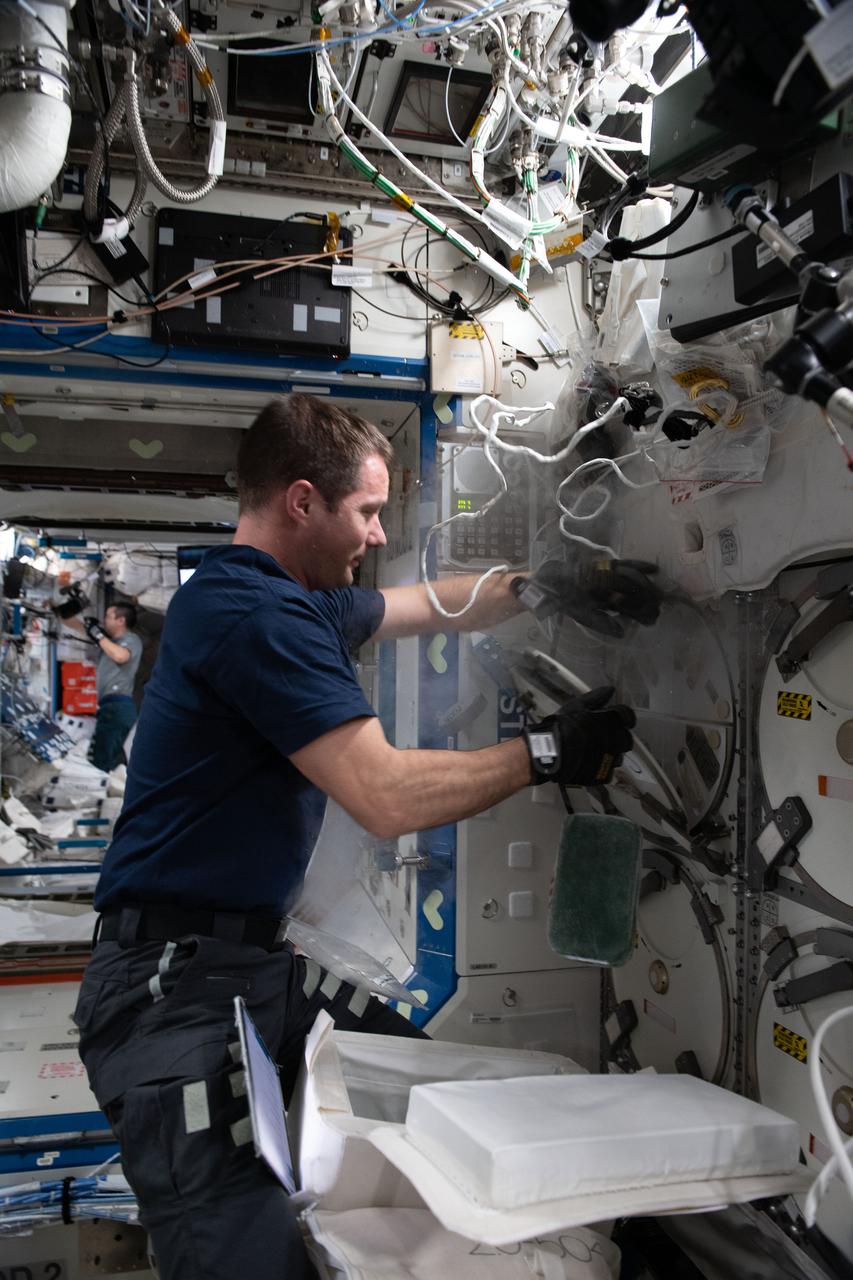

iss065e431756 (Oct. 2, 2021) --- Expedition 65 Commander Thomas Pesquet of ESA (European Space Agency) collects research samples preserved in science freezers aboard the International Space Station in preparation for stowage inside the SpaceX Cargo Dragon resupply ship for return and analysis on Earth.
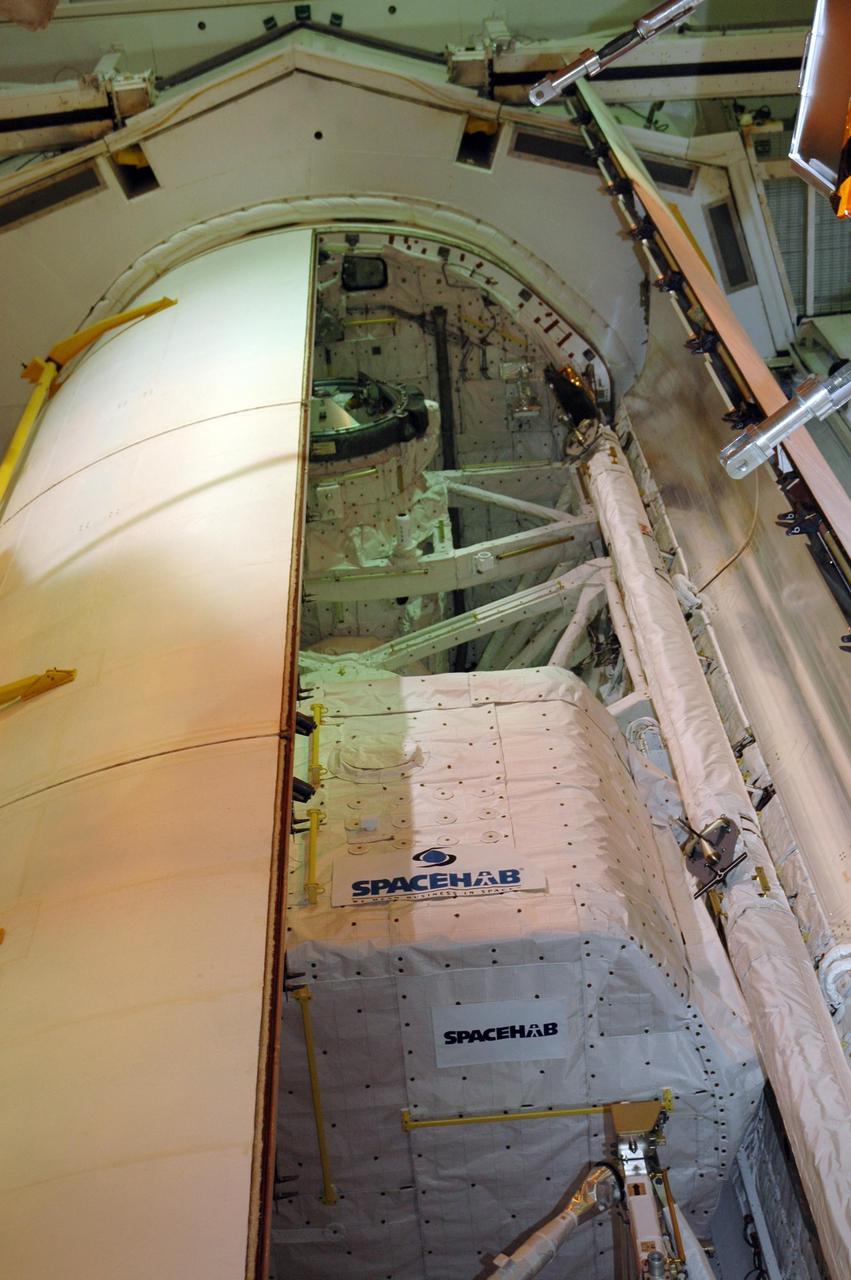

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. — At Launch Pad 39A, the second payload bay door of Endeavour closes over the cargo inside. The payload includes the S5 truss, the SPACEHAB module and external stowage platform 3. The mission is the 22nd flight to the International Space Station and is targeted for launch on Aug. 7. NASA/Charisse Nahser
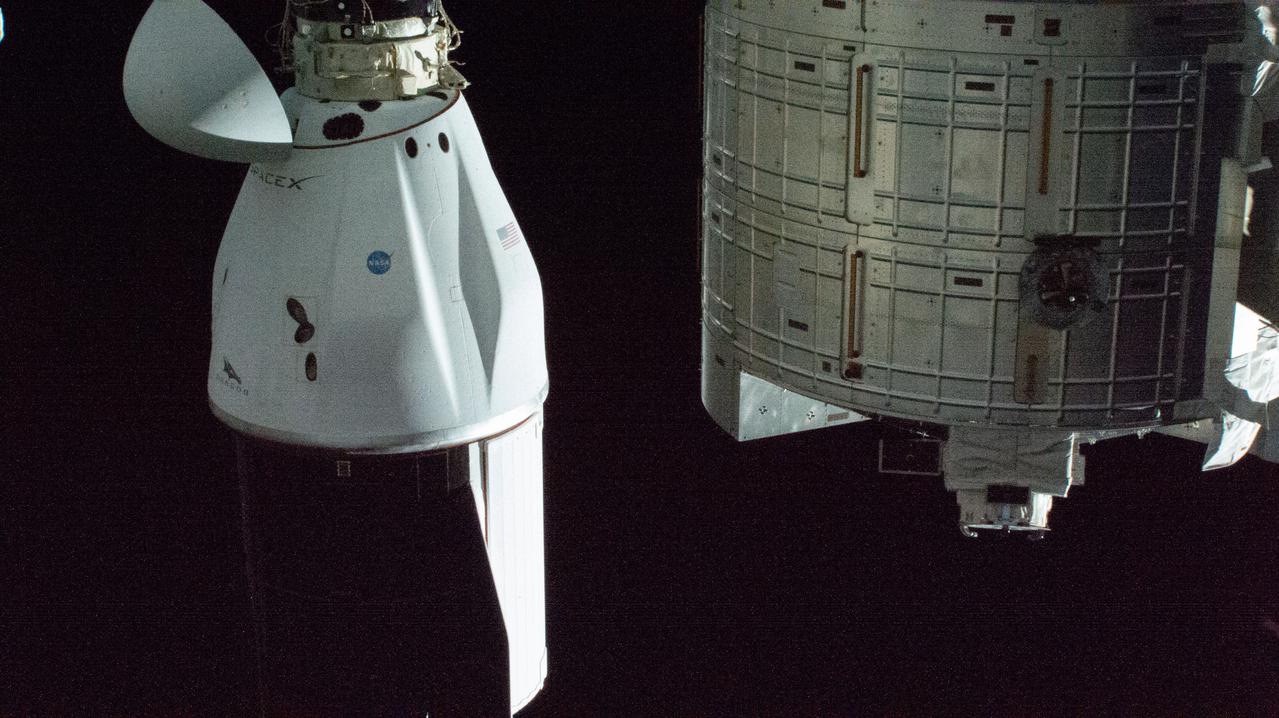

iss064e021974 (Jan. 9, 2021) --- The SpaceX Cargo Dragon resupply ship is pictured docked to the Harmony module's space-facing international docking adapter. At right, a portion of the JAXA Kibo laboratory module, the Experiment Logistics Module (Kibo's stowage facility), is pictured.
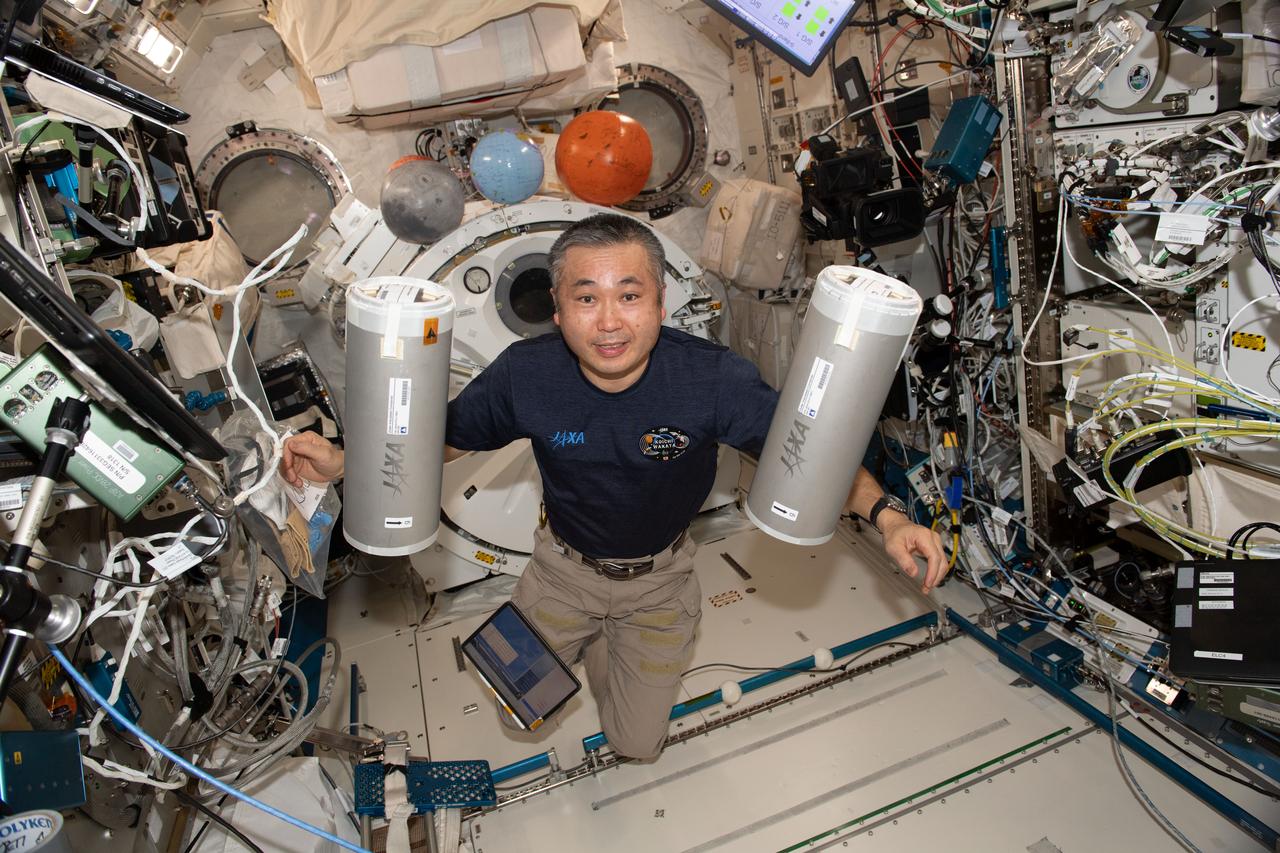

iss068e039389 (Jan. 9, 2023) --- Expedition 68 Flight Engineer Koichi Wakata of the Japan Aerospace Exploration (JAXA) retrieves research samples from science freezers inside the Kibo laboratory module in preparation for stowage inside the SpaceX Dragon cargo craft before its undocking from the International Space Station and return to Earth.
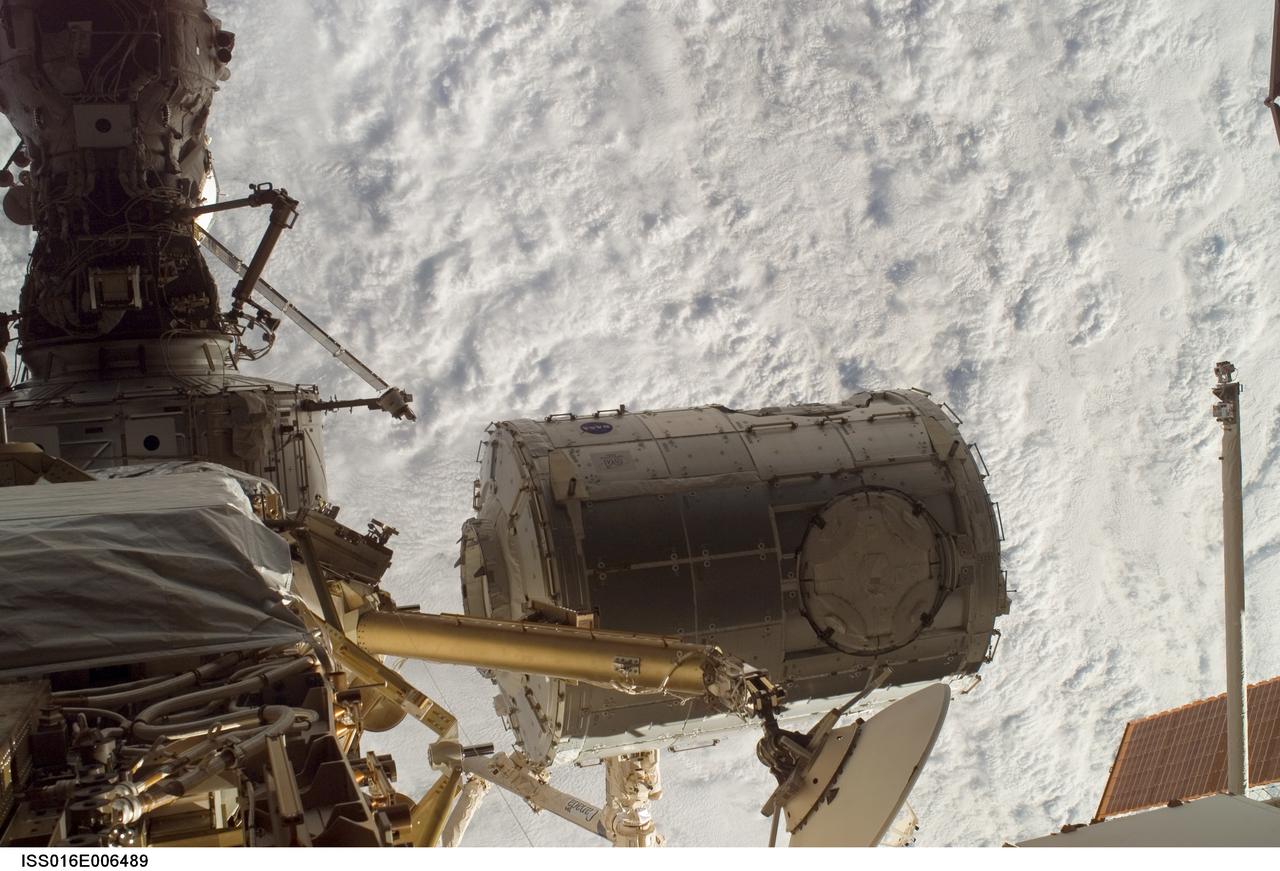

ISS016-E-006489 (26 Oct. 2007) --- In the grasp of the station's Canadarm2, the Harmony module (center) is moved from its stowage position in the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-120) to its temporary location on the International Space Station.
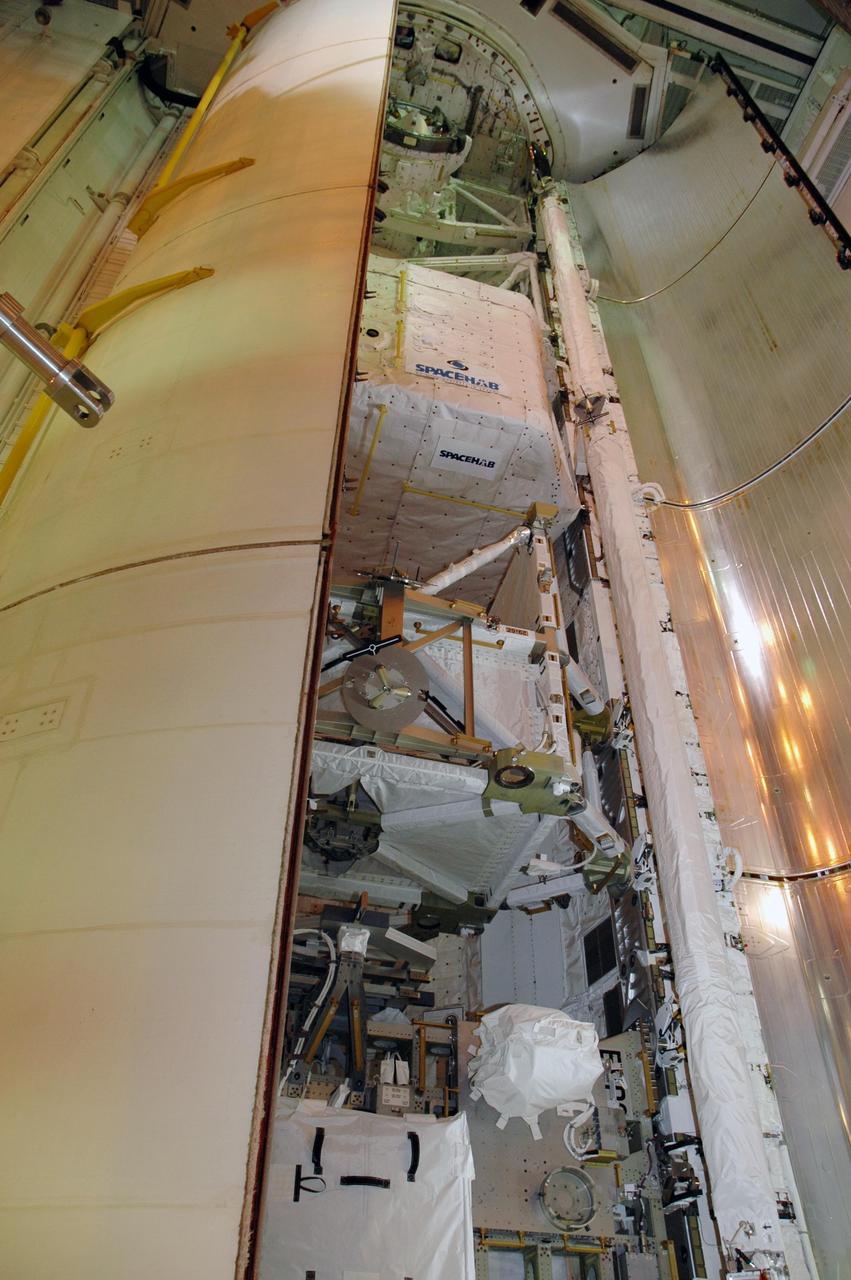

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. — At Launch Pad 39A, the first payload bay door on Endeavour closes over its cargo. The payload includes the S5 truss, the SPACEHAB module and external stowage platform 3. The mission is the 22nd flight to the International Space Station and is targeted for launch on Aug. 7. NASA/Charisse Nahser
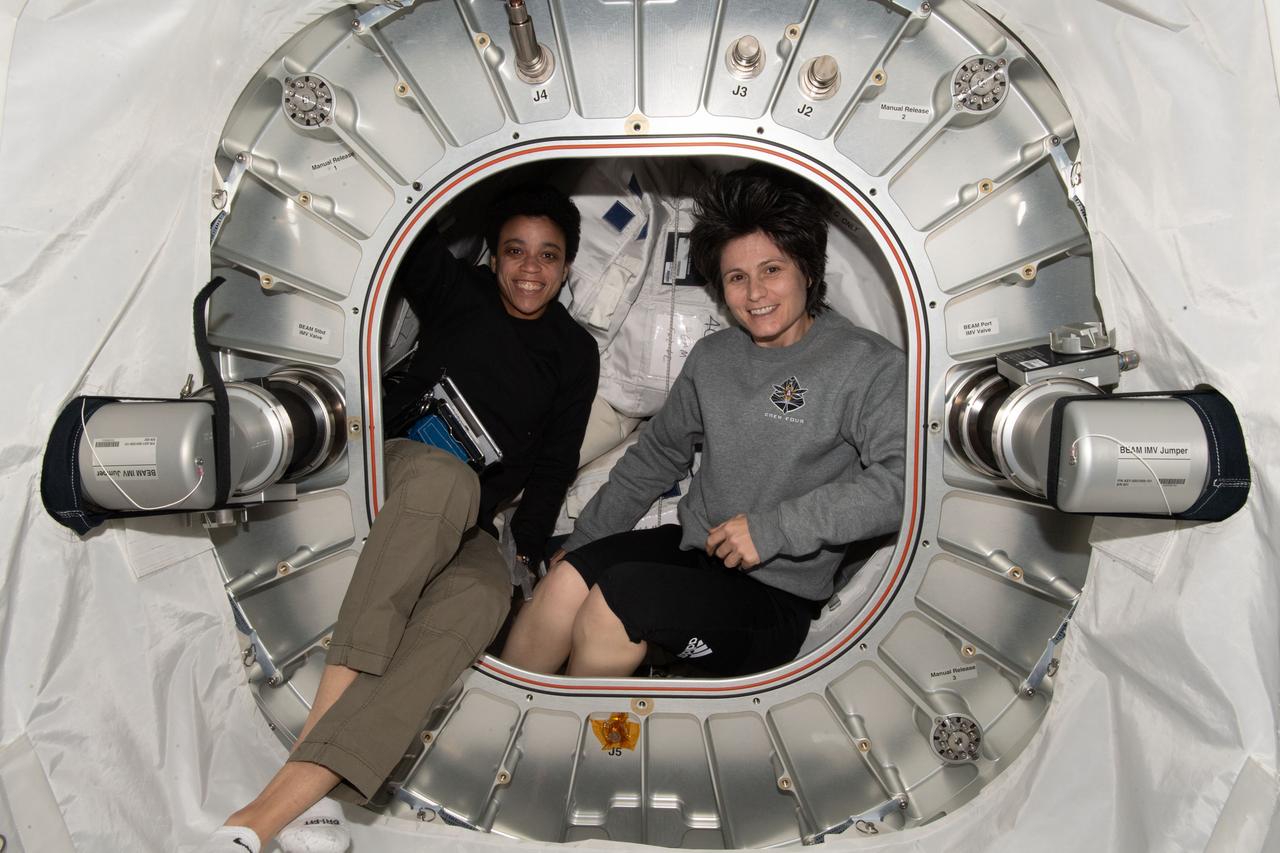

iss067e124526 (June 10, 2022) --- Expedition 67 Flight Engineers (from left) Jessica Watkins of NASA and Samantha Cristoforetti of ESA (European Space Agency) are pictured inside the Bigelow Expandable Activity Module (BEAM) during cargo stowage activities.
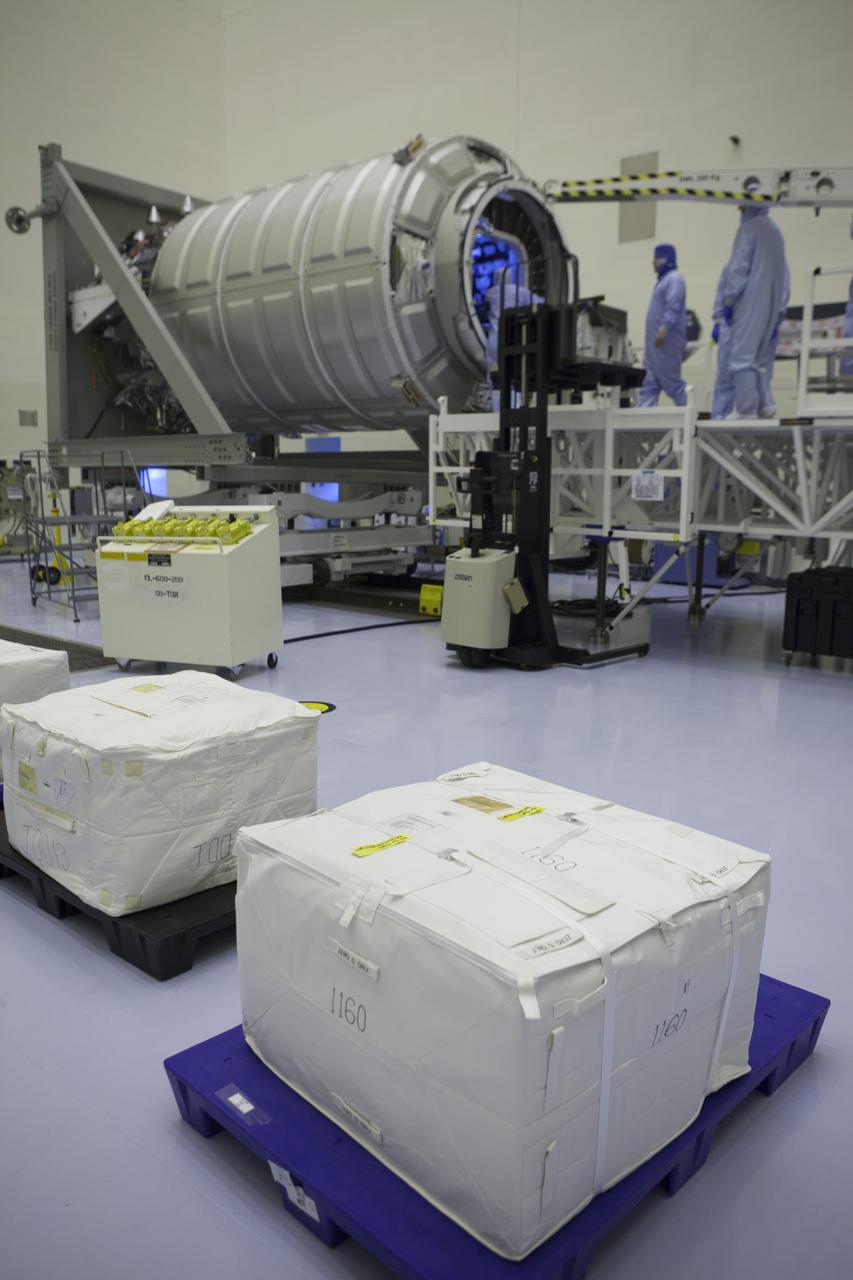

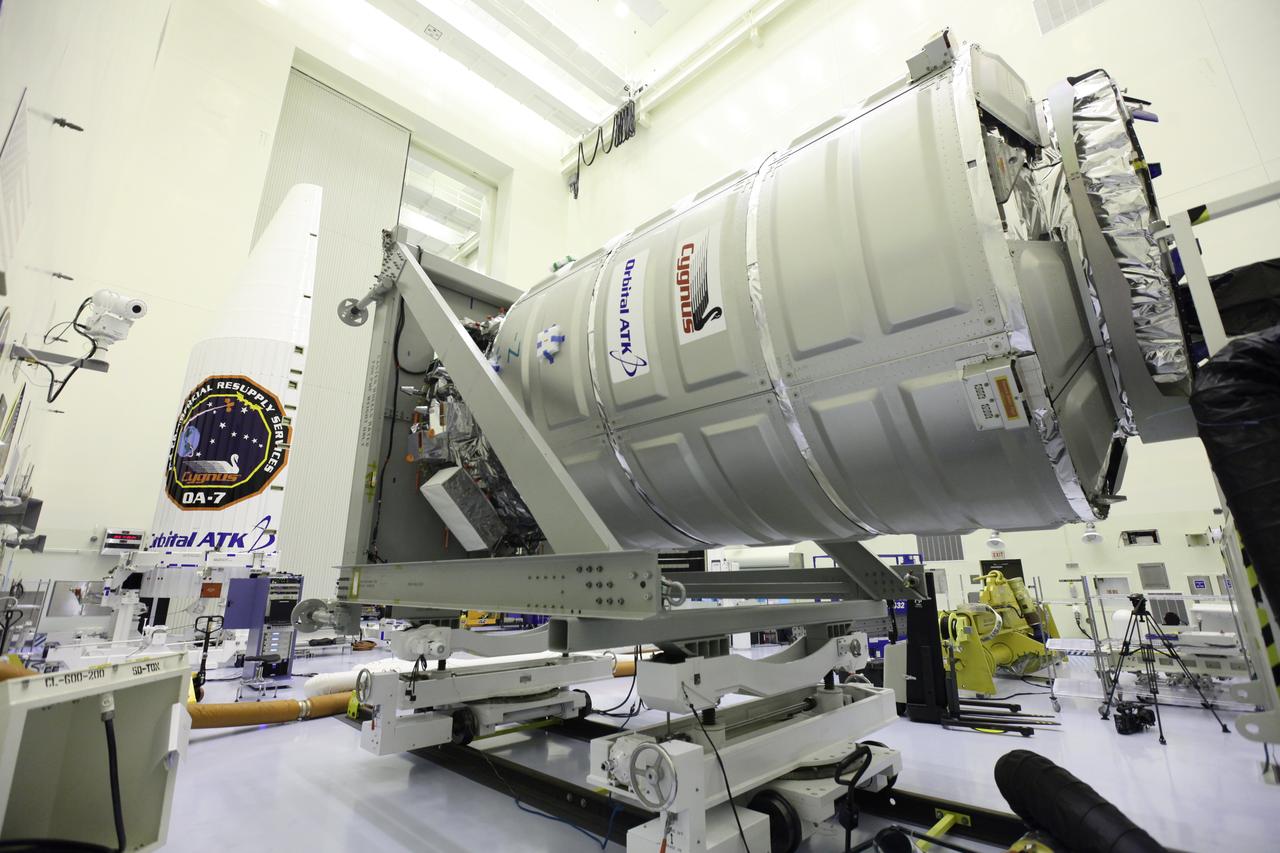
Carefully packaged cargo waits on pallets inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In the background, technicians prepare to begin loading the cargo into the Orbital ATK Cygnus pressurized module during late stowage operations. The spacecraft is scheduled for the upcoming Orbital ATK Commercial Resupply Services-6 mission to deliver hardware and supplies to the International Space Station. The Cygnus is scheduled to lift off atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on March 22.
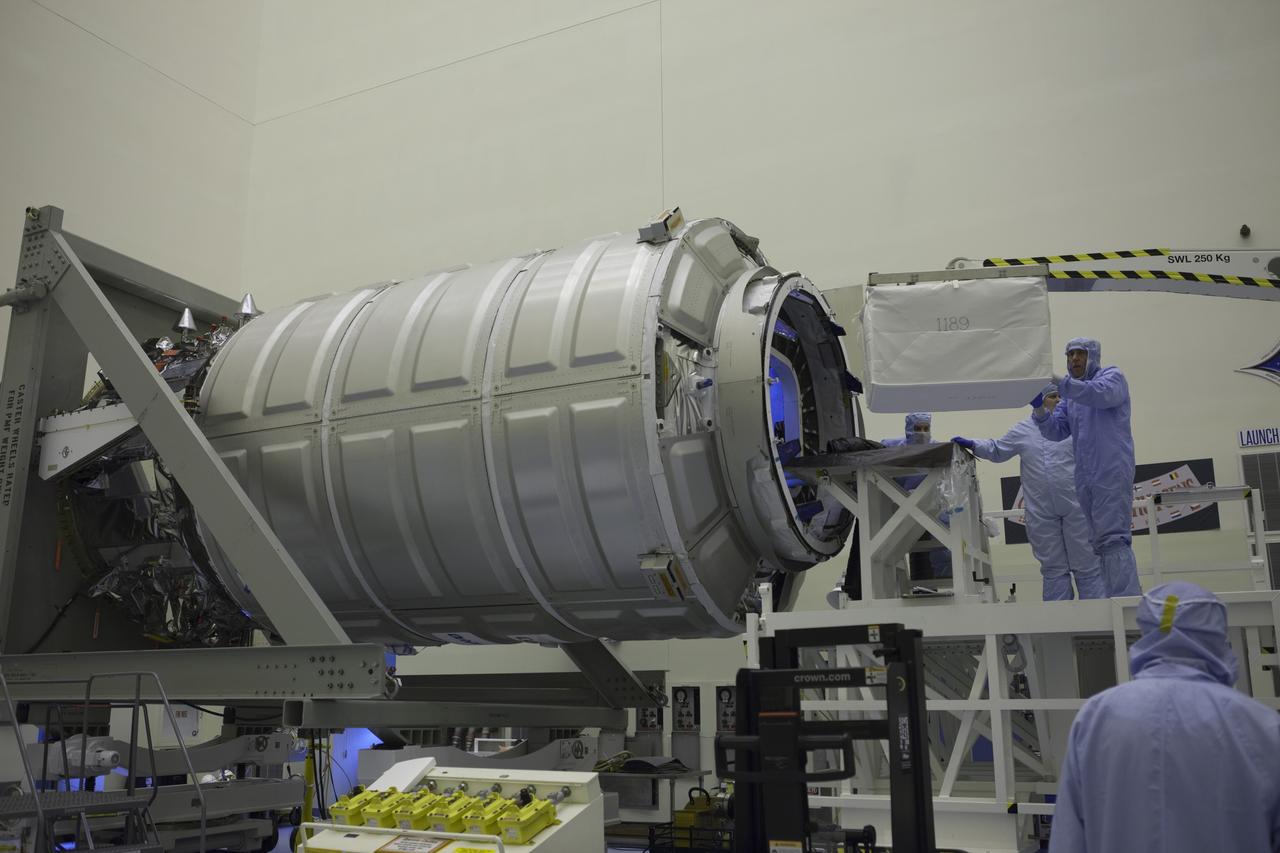

Technicians move cargo into the Orbital ATK CRS-6 pressurized cargo module during late stowage inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft is scheduled for the upcoming Orbital ATK Commercial Resupply Services-6 mission to deliver hardware and supplies to the International Space Station. The Cygnus is scheduled to lift off atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on March 22.
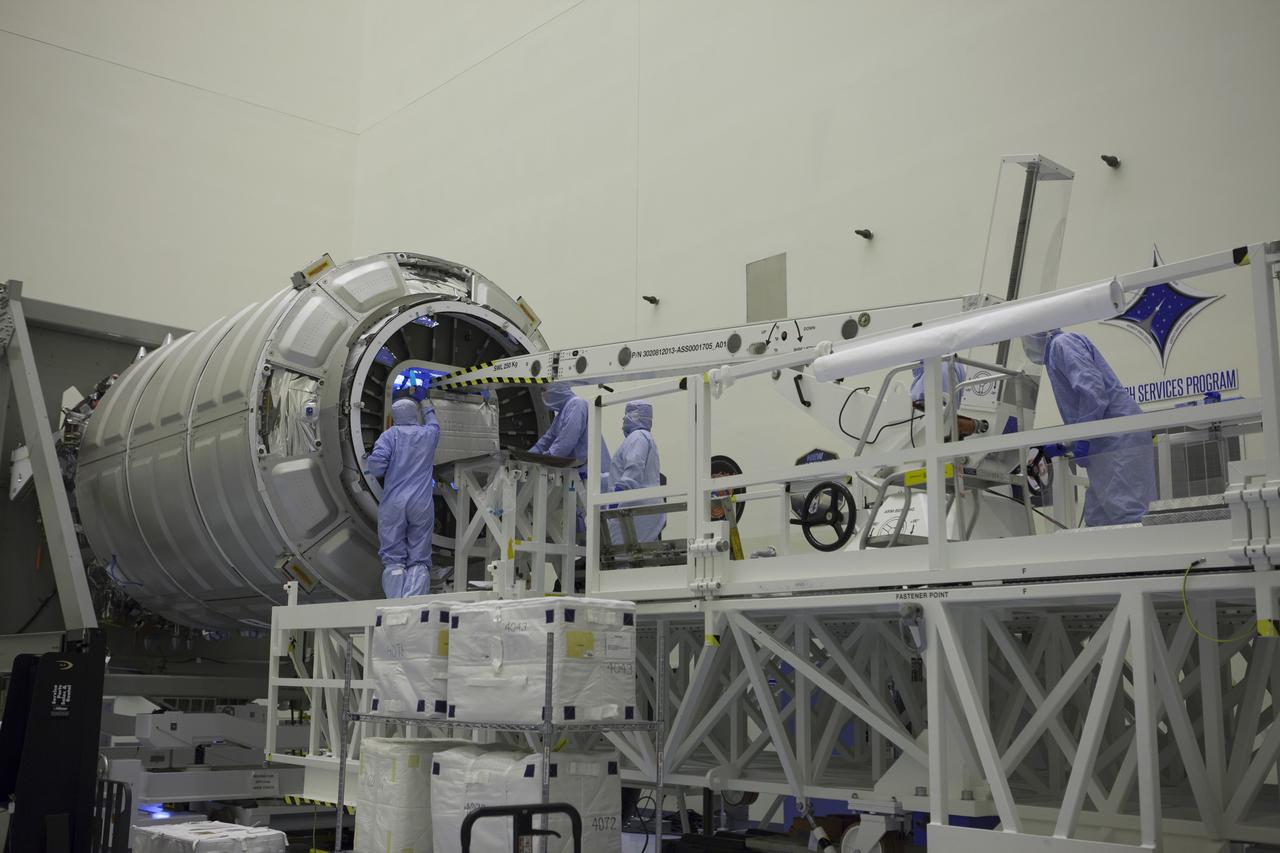

Technicians move cargo into the Orbital ATK CRS-6 pressurized cargo module during late stowage inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft is scheduled for the upcoming Orbital ATK Commercial Resupply Services-6 mission to deliver hardware and supplies to the International Space Station. The Cygnus is scheduled to lift off atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on March 22.
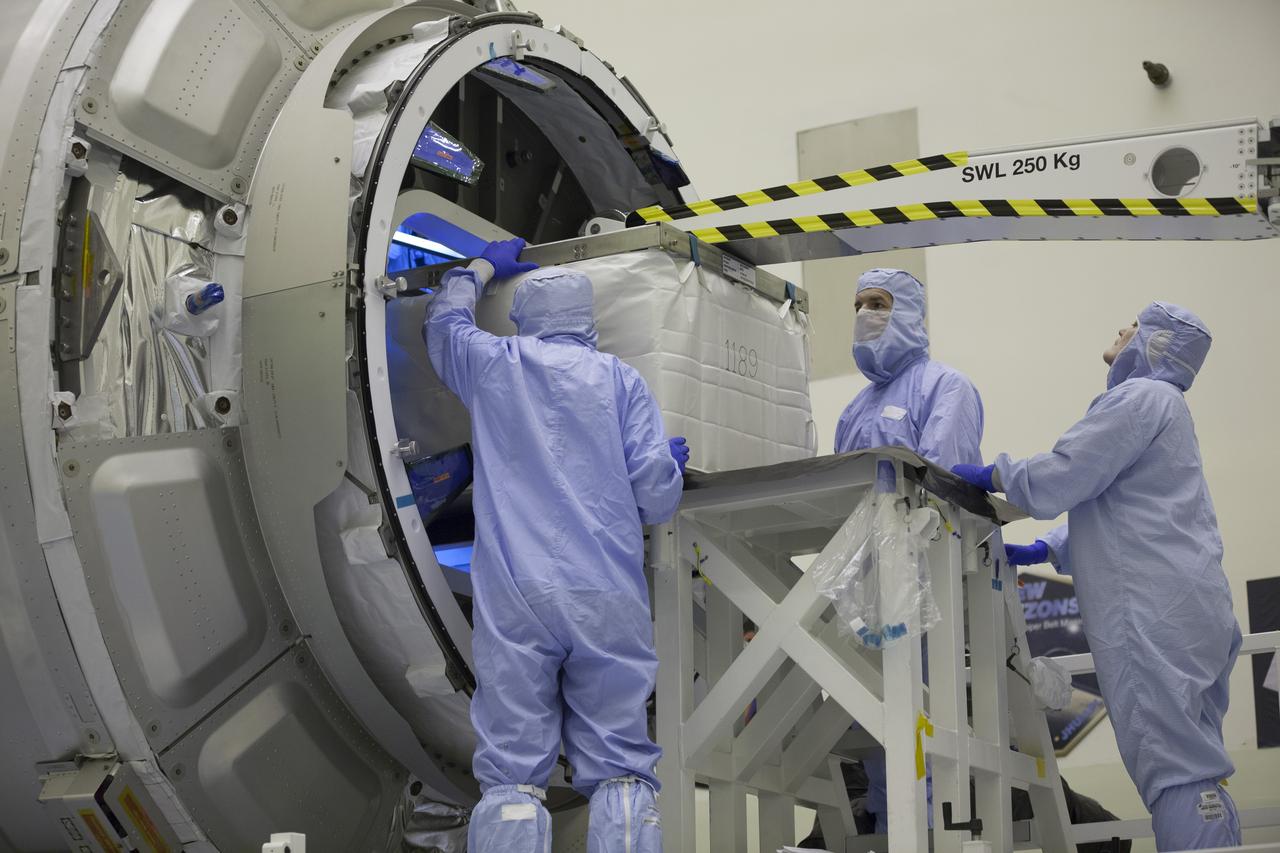

Technicians move cargo into the Orbital ATK CRS-6 pressurized cargo module during late stowage inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft is scheduled for the upcoming Orbital ATK Commercial Resupply Services-6 mission to deliver hardware and supplies to the International Space Station. The Cygnus is scheduled to lift off atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on March 22.
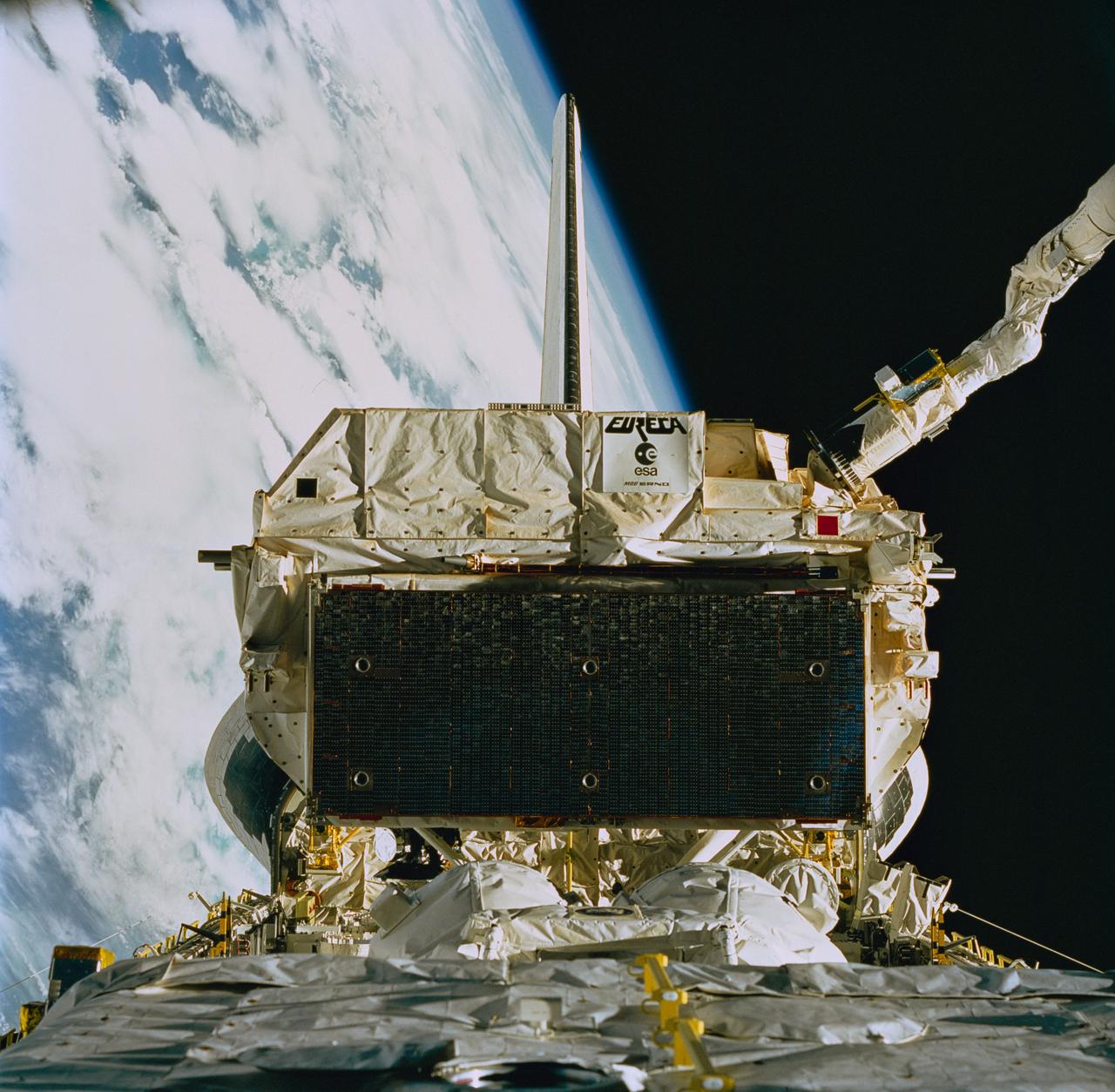

STS057-84-000AD (24 June 1993) --- The recently "captured" European Retrievable Carrier (EURECA) was recorded on 70mm film as it was berthed in the Space Shuttle Endeavour's aft cargo bay, assisted by the Canadian-built Remote Manipulator System (RMS), partially visible in upper right. Moments later the RMS eased EURECA into its stowage area between Endeavour's aft cargo bay firewall and the SpaceHab module (partially visible in foreground).
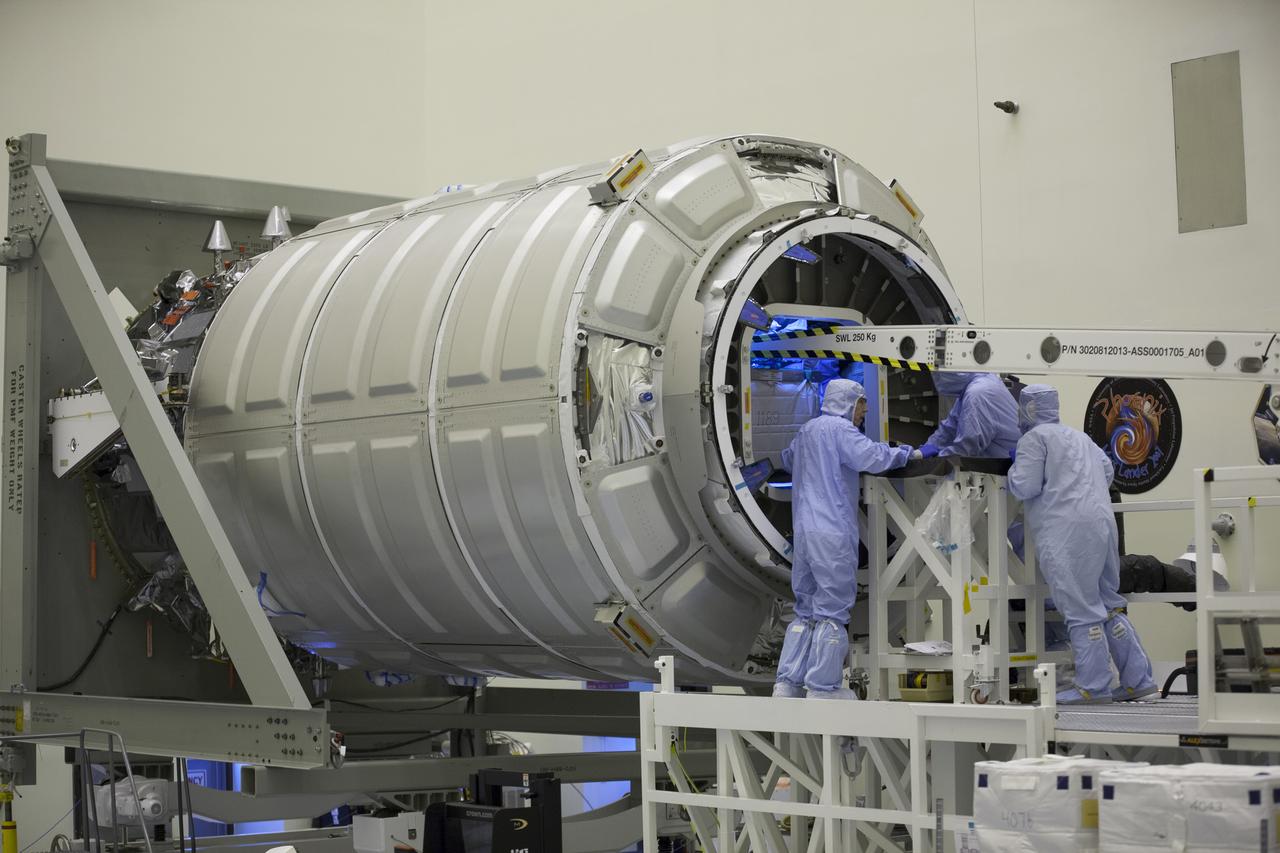

Technicians move cargo into the Orbital ATK CRS-6 pressurized cargo module during late stowage inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft is scheduled for the upcoming Orbital ATK Commercial Resupply Services-6 mission to deliver hardware and supplies to the International Space Station. The Cygnus is scheduled to lift off atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on March 22.
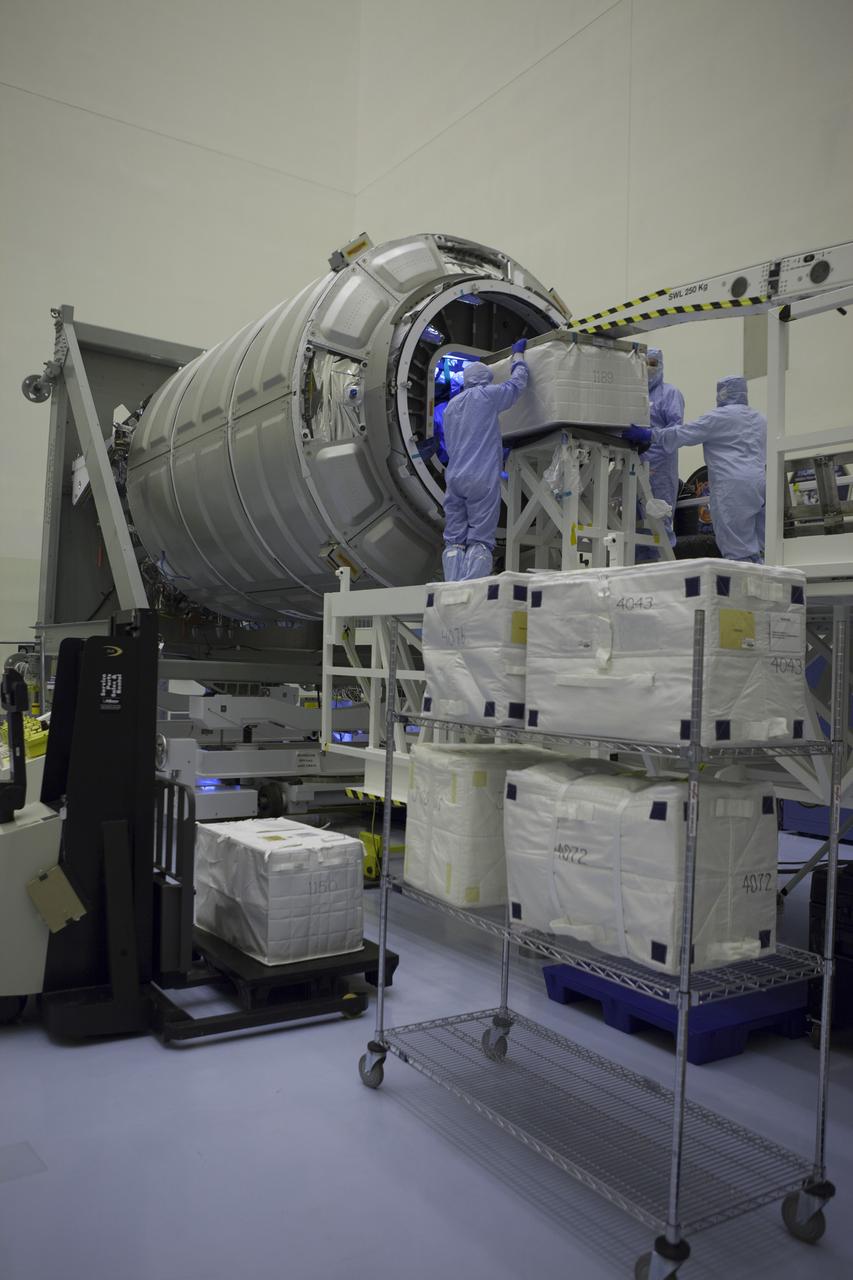

Technicians move cargo into the Orbital ATK CRS-6 pressurized cargo module during late stowage inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft is scheduled for the upcoming Orbital ATK Commercial Resupply Services-6 mission to deliver hardware and supplies to the International Space Station. The Cygnus is scheduled to lift off atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on March 22.
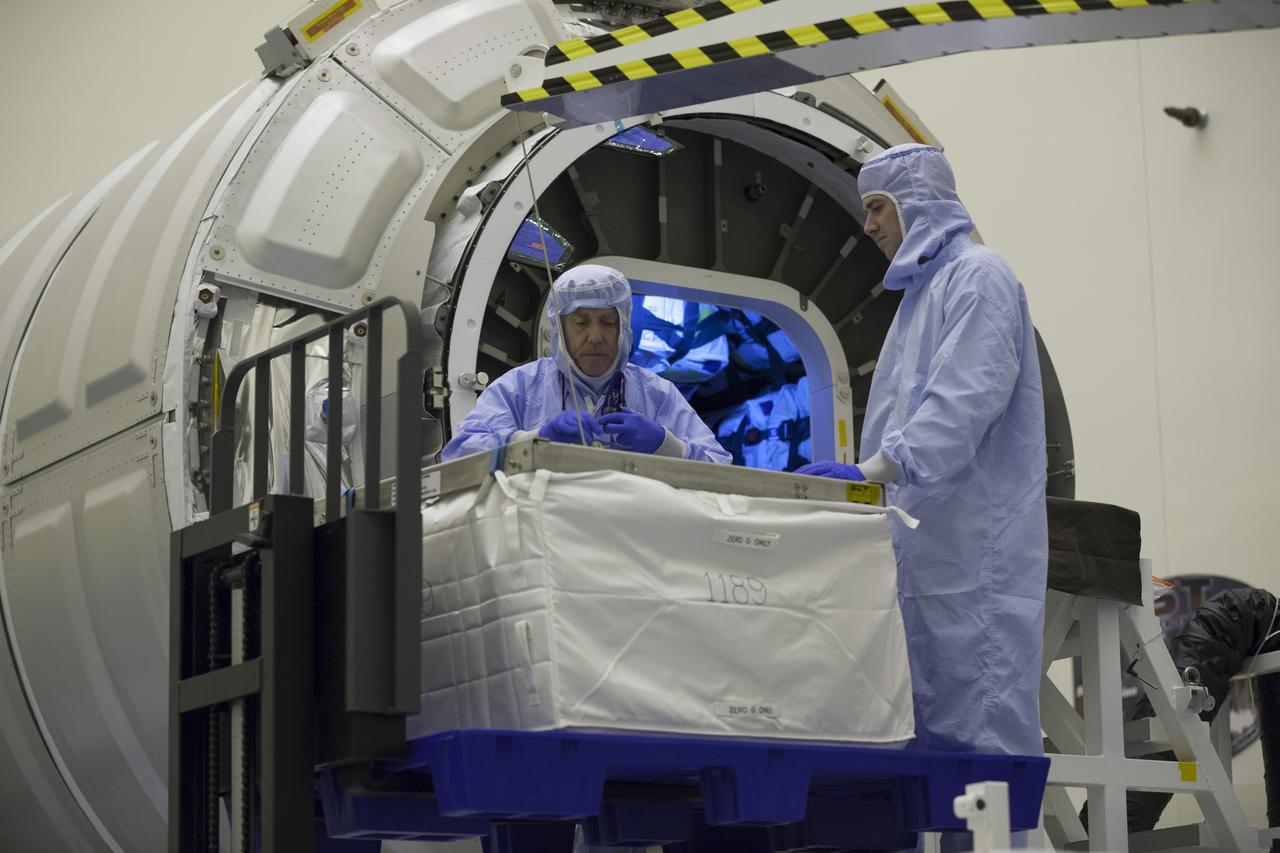

Technicians prepare to move cargo into the Orbital ATK CRS-6 pressurized cargo module during late stowage inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft is scheduled for the upcoming Orbital ATK Commercial Resupply Services-6 mission to deliver hardware and supplies to the International Space Station. The Cygnus is scheduled to lift off atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on March 22.
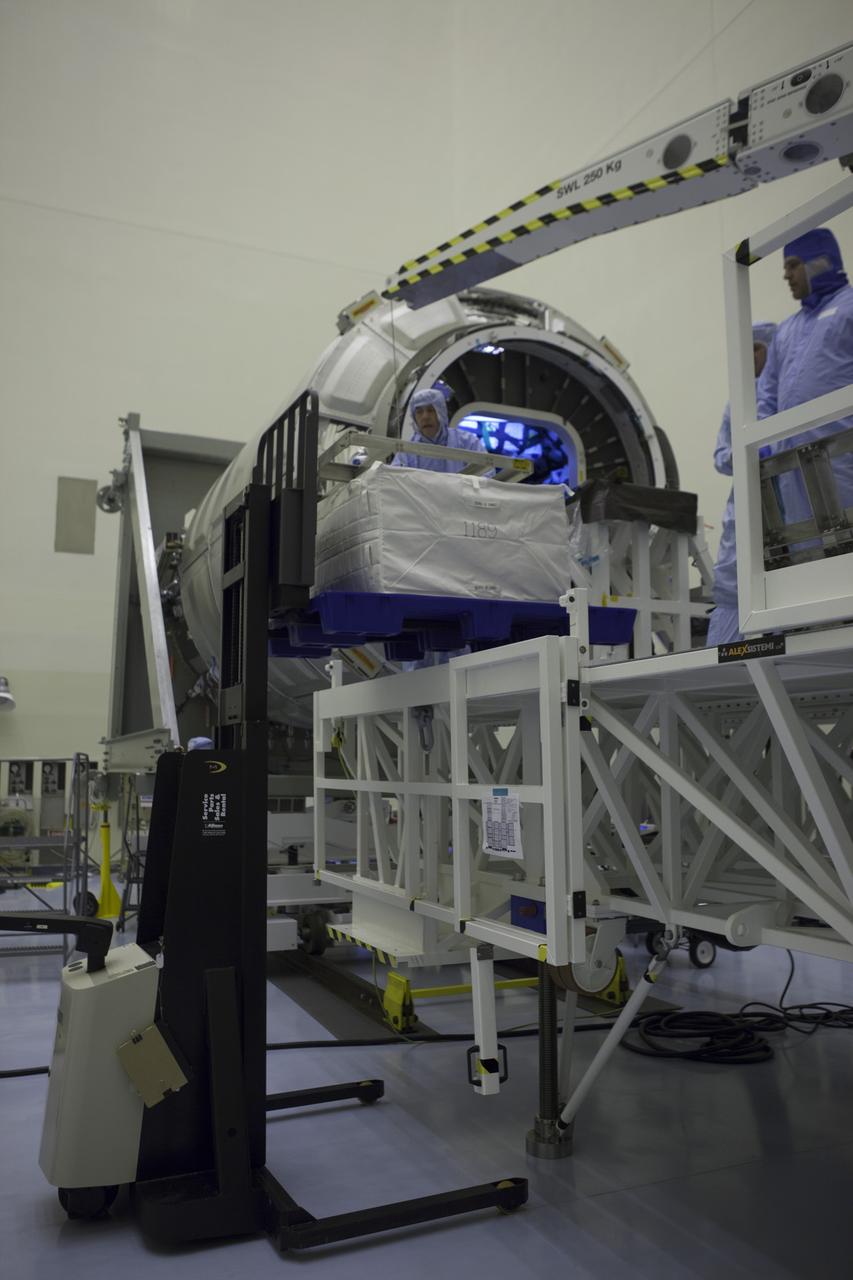

Technicians prepare to move a cargo package from a forklift into the Orbital ATK CRS-6 pressurized cargo module during late stowage inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft is scheduled for the upcoming Orbital ATK Commercial Resupply Services-6 mission to deliver hardware and supplies to the International Space Station. The Cygnus is scheduled to lift off atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on March 22.

iss065e004417 (April 25, 2021) --- The International Space Station's newest component is the NanoRacks Bishop Airlock (center left) attached to the end of the Tranquility module. Bishop will enable more commercial research, satellite deployments, and cargo operations outside in the vacuum of space. Located on the other side of Bishop on Tranquility is BEAM, or the Bigelow Expandable Activity Module, which is a cargo stowage module outfitted with sensors continuously monitoring its environment.
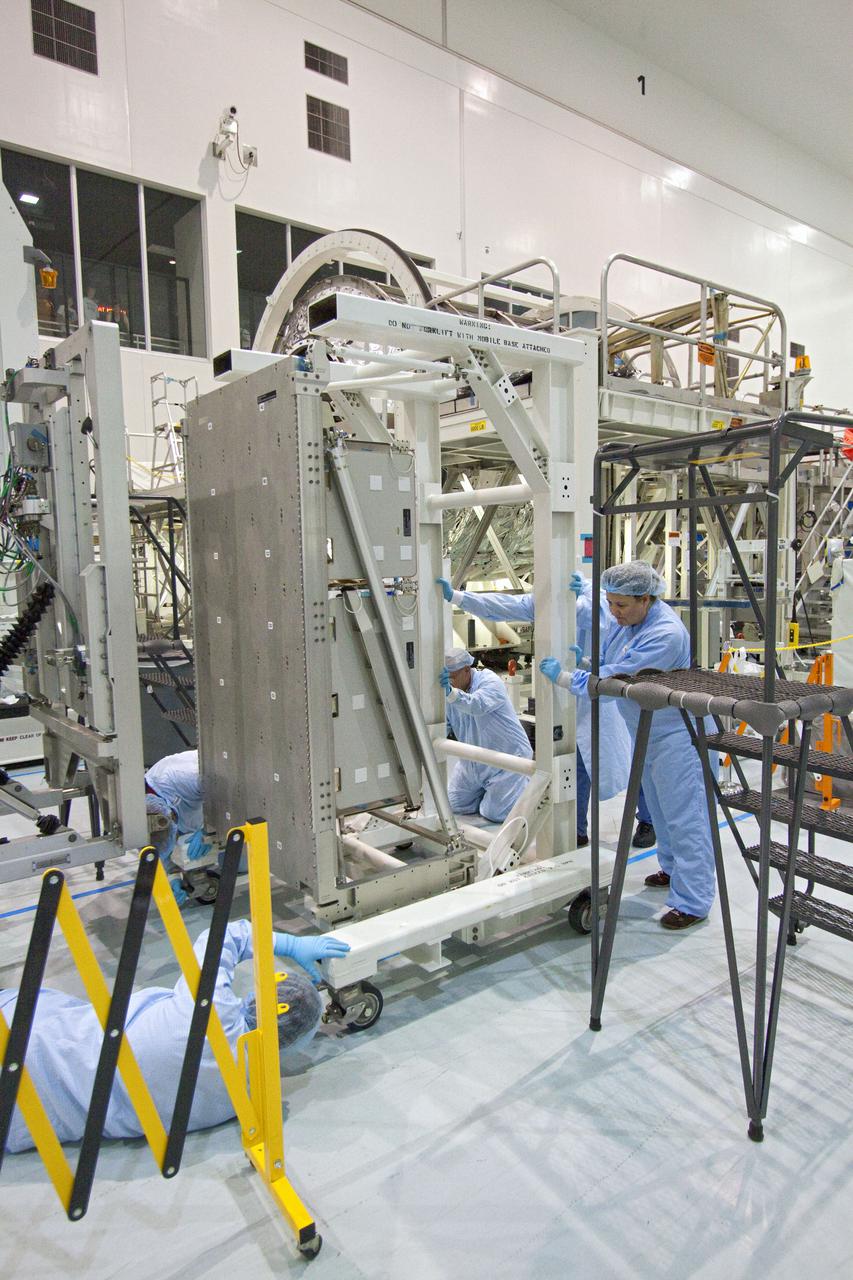

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers prepare a resupply stowage platform prior to installation of cargo headed to the International Space Station. The stowage platforms will then be moved into the Permanent Multipurpose Module, or PMM. The PMM will be used to carry supplies and critical spare parts to the station. The module will be left behind so it can be used for microgravity experiments in fluid physics, materials science, biology and biotechnology. Space shuttle Discovery will deliver its payload to the station on the STS-133 mission. Launch is targeted for Nov. 1 at 4:33 p.m. EDT. Photo credit: NASA_Jack Pfaller
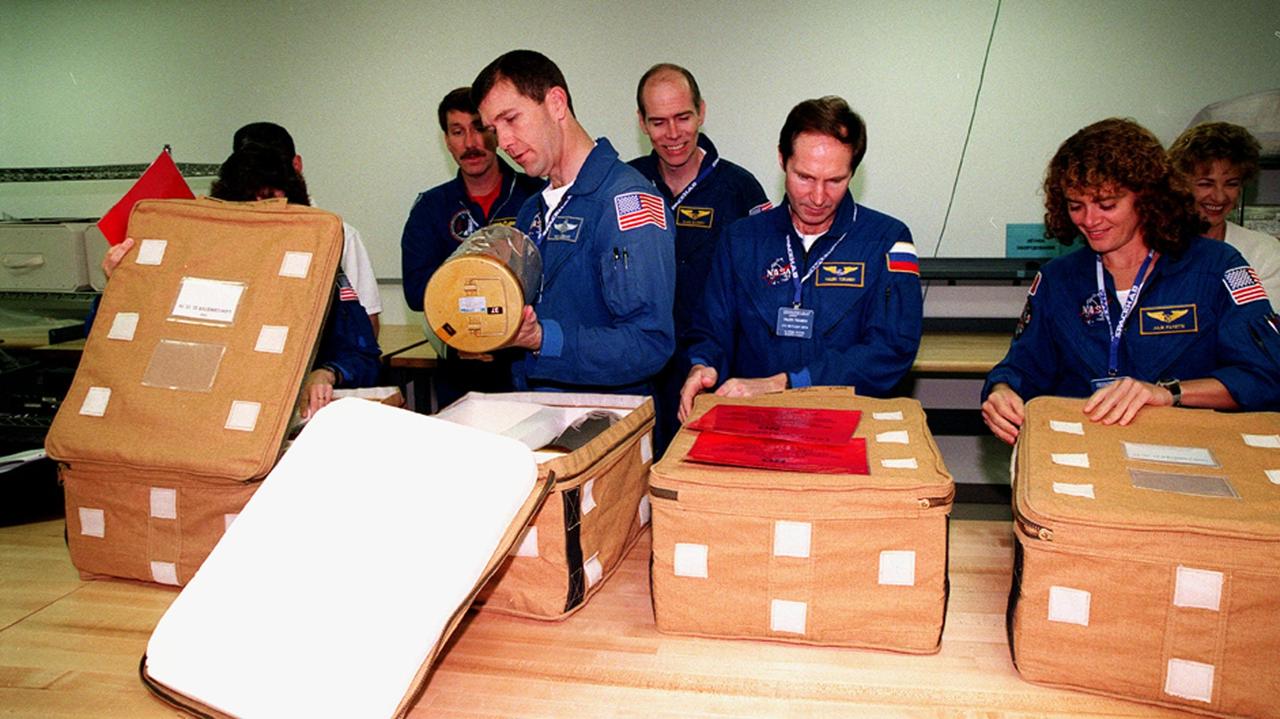

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the SPACEHAB Facility, the STS-96 crew looks at equipment as part of a payload Interface Verification Test (IVT) for their upcoming mission to the International Space Station . From left are Mission Specialist Ellen Ochoa (behind the opened storage cover ), Commander Kent Rominger, Pilot Rick Husband (holding a lithium hydroxide canister) and Mission Specialists Dan Barry, Valery Tokarev of Russia and Julie Payette. In the background is TTI interpreter Valentina Maydell. The other crew member at KSC for the IVT is Mission Specialist Tamara Jernigan. Mission STS-96 carries the SPACEHAB Logistics Double Module, which has equipment to further outfit the International Space Station service module and equipment that can be off-loaded from the early U.S. assembly flights. The SPACEHAB carries internal logistics and resupply cargo for station outfitting, plus an external Russian cargo crane to be mounted to the exterior of the Russian station segment and used to perform space walking maintenance activities. The double module stowage provides capacity of up to 10,000 lbs. with the ability to accommodate powered payloads, four external rooftop stowage locations, four double-rack locations (two powered), up to 61 bulkhead-mounted middeck locker locations, and floor storage for large unique items and Soft Stowage. STS-96 is targeted to launch May 20 about 9:32 a.m
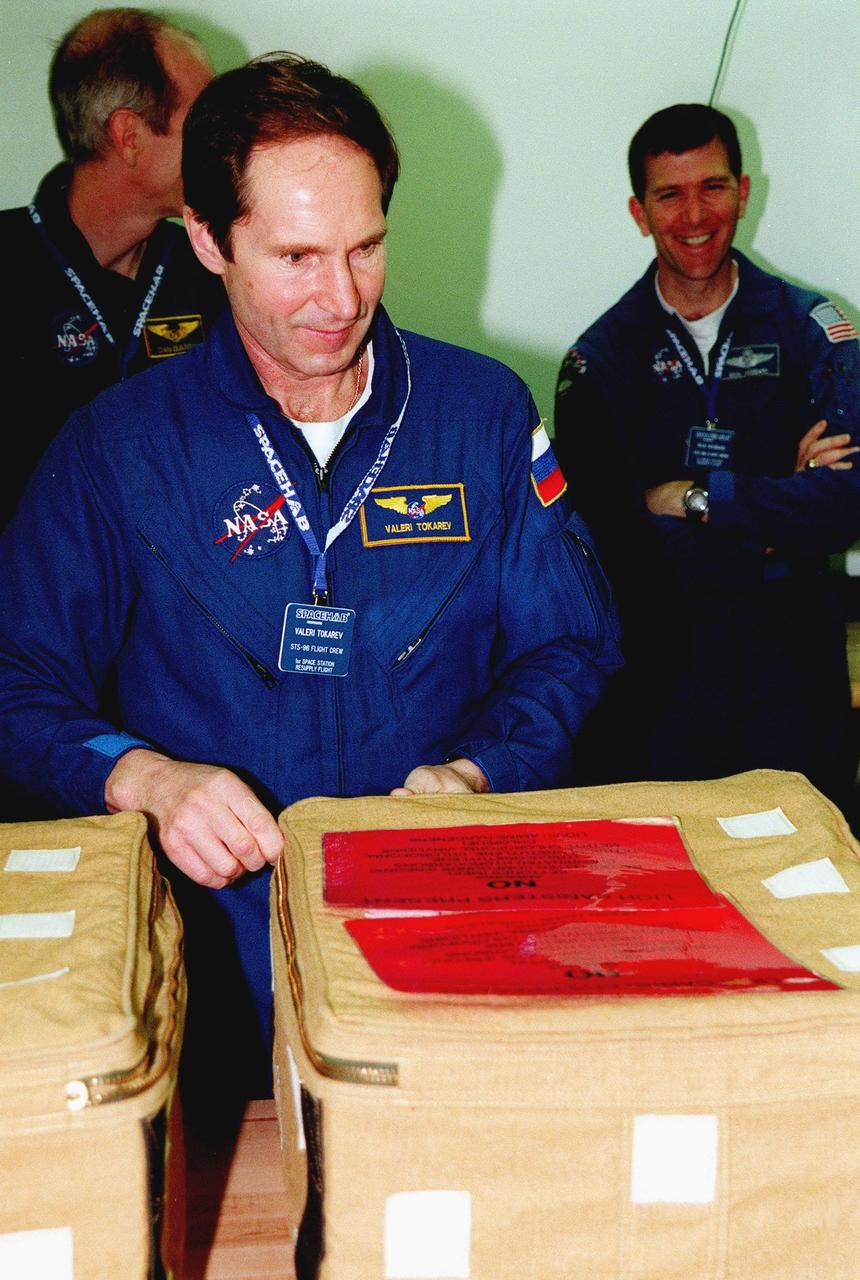

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the SPACEHAB Facility, STS-96 Mission Specialist Valery Tokarev (in foreground) of the Russian Space Agency closes a container, part of the equipment that will be in the SPACEHAB module on mission STS-96. Behind Tokarev are Mission Specialist Dan Barry (left) and Pilot Rick Husband right). Other crew members at KSC for a payload Interface Verification Test for the upcoming mission to the International Space Station are Commander Kent Rominger and Mission Specialists Ellen Ochoa, Tamara Jernigan and Julie Payette. Mission STS-96 carries the SPACEHAB Logistics Double Module, which has equipment to further outfit the International Space Station service module and equipment that can be off-loaded from the early U.S. assembly flights. The SPACEHAB carries internal logistics and resupply cargo for station outfitting, plus an external Russian cargo crane to be mounted to the exterior of the Russian station segment and used to perform space walking maintenance activities. The double module stowage provides capacity of up to 10,000 lbs. with the ability to accommodate powered payloads, four external rooftop stowage locations, four double-rack locations (two powered), up to 61 bulkhead-mounted middeck locker locations, and floor storage for large unique items and Soft Stowage. STS-96 is targeted to launch May 20 about 9:32 a.m

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the SPACEHAB Facility for a payload Interface Verification Test (IVT) for their upcoming mission to the International Space Station are (kneeling) STS-96 Mission Specialists Julie Payette and Ellen Ochoa, Pilot Rick Husband, and (standing at right) Mission Specialist Dan Barry. At the left is James Behling, with Boeing, explaining some of the equipment that will be on board STS-96. Other STS-96 crew members at KSC for the IVT are Commander Kent Rominger and Mission Specialists Tamara Jernigan and Valery Tokarev of Russia. Mission STS-96 carries the SPACEHAB Logistics Double Module, which will have equipment to further outfit the International Space Station service module and equipment that can be off-loaded from the early U.S. assembly flights. It carries internal logistics and resupply cargo for station outfitting, plus an external Russian cargo crane to be mounted to the exterior of the Russian station segment and used to perform space walking maintenance activities. The double module stowage provides capacity of up to 10,000 lbs. with the ability to accommodate powered payloads, four external rooftop stowage locations, four double-rack locations (two powered), up to 61 bulkhead-mounted middeck locker locations, and floor storage for large unique items and Soft Stowage. STS-96 is targeted to launch May 20 about 9:32 a.m
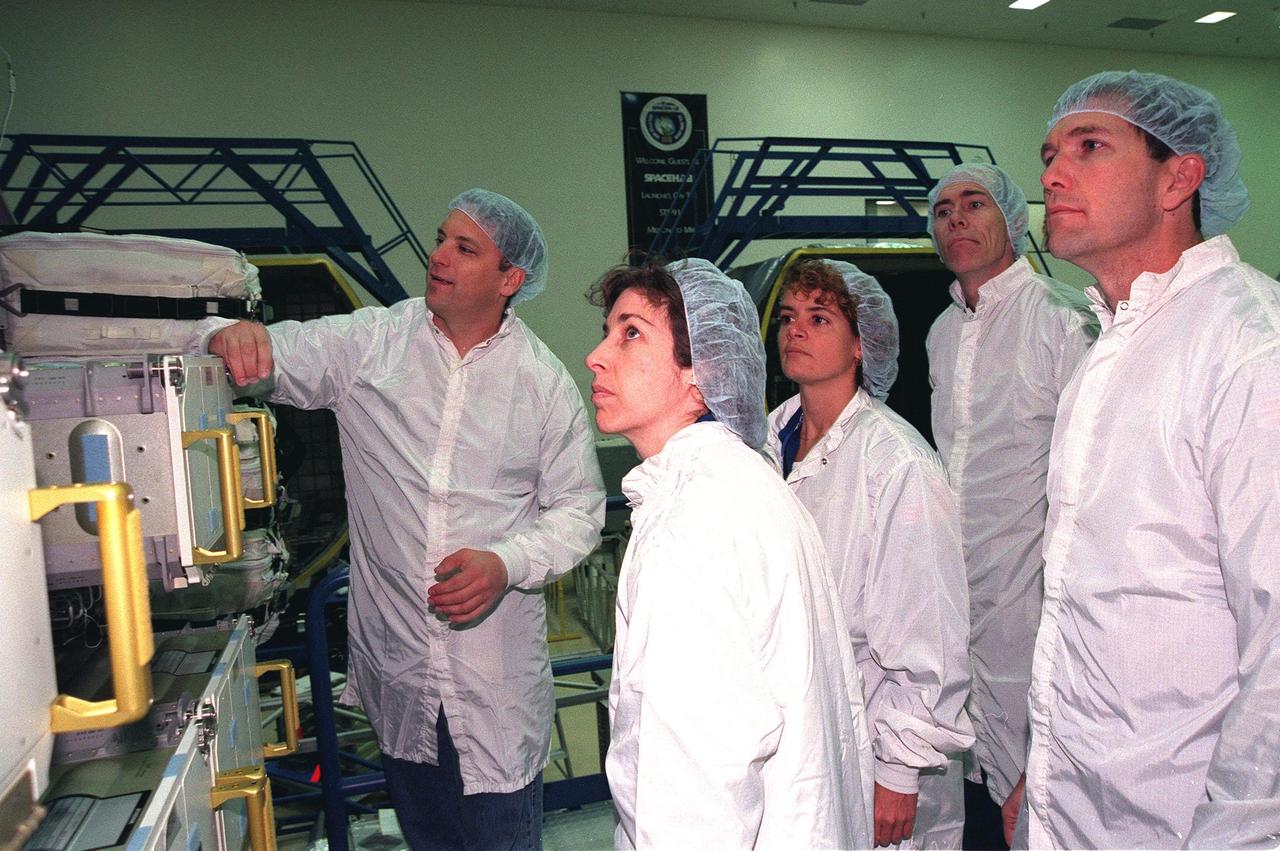

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the SPACEHAB Facility, James Behling, with Boeing, talks about equipment for mission STS-96 during a payload Interface Verification Test (IVT). Watching are (from left) Mission Specialists Ellen Ochoa, Julie Payette and Dan Berry, and Pilot Rick Husband. Other STS-96 crew members at KSC for the IVT are Commander Kent Rominger and Mission Specialists Tamara Jernigan and Valery Tokarev of Russia. Mission STS-96 carries the SPACEHAB Logistics Double Module, which will have equipment to further outfit the International Space Station service module and equipment that can be off-loaded from the early U.S. assembly flights. It carries internal logistics and resupply cargo for station outfitting, plus an external Russian cargo crane to be mounted to the exterior of the Russian station segment and used to perform space walking maintenance activities. The double module stowage provides capacity of up to 10,000 lbs. with the ability to accommodate powered payloads, four external rooftop stowage locations, four double-rack locations (two powered), up to 61 bulkhead-mounted middeck locker locations, and floor storage for large unique items and Soft Stowage. STS-96 is targeted to launch May 20 about 9:32 a.m
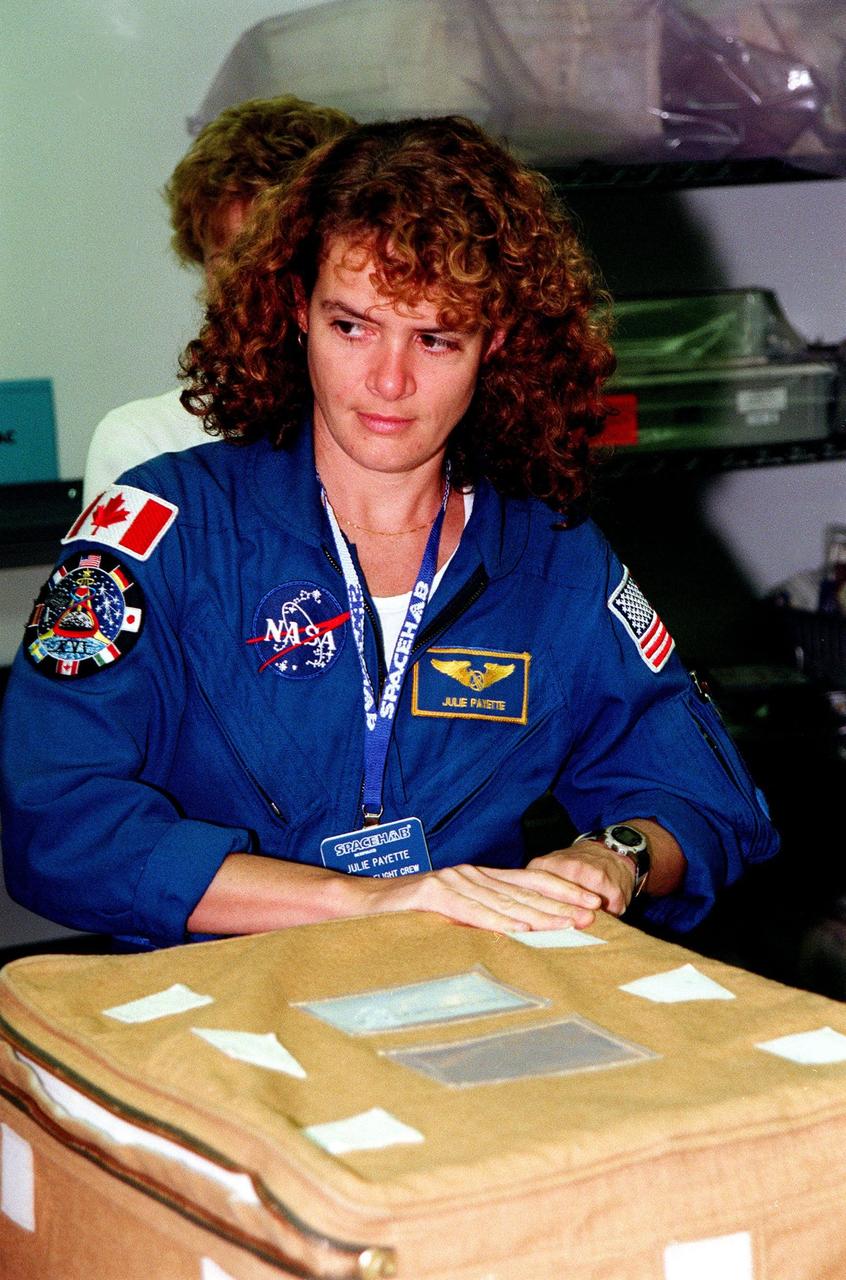

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the SPACEHAB Facility, STS-96 Mission Specialist Julie Payette closes a container, part of the equipment to be carried on the SPACEHAB and mission STS-96. She and other crew members Commander Kent Rominger, Pilot Rick Husband, and Mission Speciaists Ellen Ochoa, Tamara Jernigan, Dan Barry and Valery Tokarev of Russia are at KSC for a payload Interface Verification Test for the upcoming mission to the International Space Station . Mission STS-96 carries the SPACEHAB Logistics Double Module, which has equipment to further outfit the International Space Station service module and equipment that can be off-loaded from the early U.S. assembly flights. The SPACEHAB carries internal logistics and resupply cargo for station outfitting, plus an external Russian cargo crane to be mounted to the exterior of the Russian station segment and used to perform space walking maintenance activities. The double module stowage provides capacity of up to 10,000 lbs. with the ability to accommodate powered payloads, four external rooftop stowage locations, four double-rack locations (two powered), up to 61 bulkhead-mounted middeck locker locations, and floor storage for large unique items and Soft Stowage. STS-96 is targeted to launch May 20 about 9:32 a.m

In the SPACEHAB Facility, STS-96 Mission Specialists Dan Barry and Tamara Jernigan discuss procedures during a payload Interface Verification Test (IVT) for their upcoming mission to the International Space Station. Other STS-96 crew members at KSC for the IVT are Commander Kent Rominger, Pilot Rick Husband and Mission Specialists Ellen Ochoa, Julie Payette and Valery Tokarev of Russia. Mission STS-96 carries the SPACEHAB Logistics Double Module, which will have equipment to further outfit the International Space Station service module and equipment that can be off-loaded from the early U.S. assembly flights. It carries internal logistics and resupply cargo for station outfitting, plus an external Russian cargo crane to be mounted to the exterior of the Russian station segment and used to perform space walking maintenance activities. The double module stowage provides capacity of up to 10,000 lbs. with the ability to accommodate powered payloads, four external rooftop stowage locations, four double-rack locations (two powered), up to 61 bulkhead-mounted middeck locker locations, and floor storage for large unique items and Soft Stowage. STS-96 is targeted to launch May 20 about 9:32 a.m
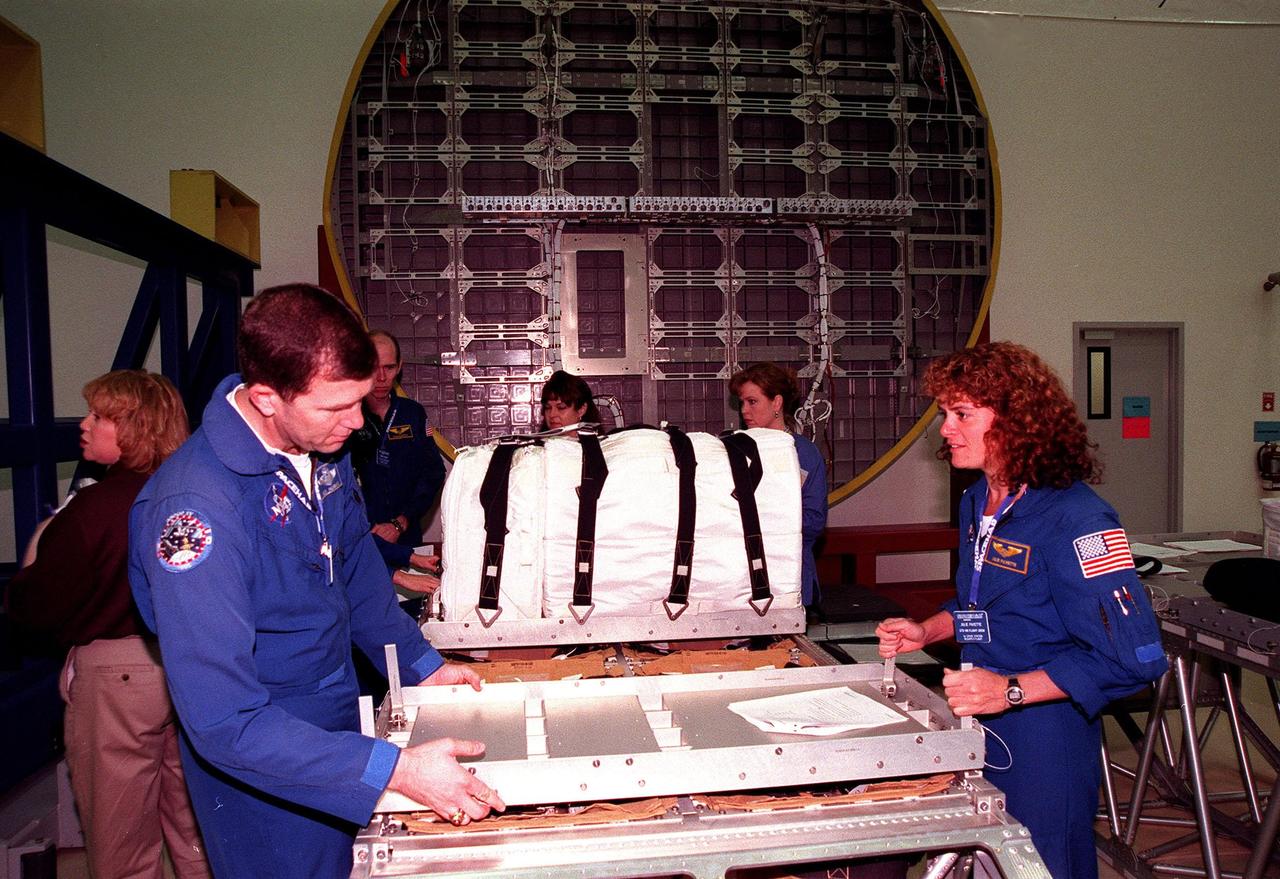

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the SPACEHAB Facility, STS-96 crew members look over equipment during a payload Interface Verification Test (IVT) for their upcoming mission to the International Space Station. From left are Khristal Parker, with Boeing; Mission Specialist Dan Barry, Pilot Rick Husband, Mission Specialist Tamara Jernigan, and at the far right, Mission Specialist Julie Payette. An unidentified worker is in the background. Also at KSC for the IVT are Commander Kent Rominger and Mission Specialists Ellen Ochoa and Valery Tokarev of Russia. Mission STS-96 carries the SPACEHAB Logistics Double Module, which will have equipment to further outfit the International Space Station service module and equipment that can be off-loaded from the early U.S. assembly flights. It carries internal logistics and resupply cargo for station outfitting, plus an external Russian cargo crane to be mounted to the exterior of the Russian station segment and used to perform space walking maintenance activities. The double module stowage provides capacity of up to 10,000 lbs. with the ability to accommodate powered payloads, four external rooftop stowage locations, four double-rack locations (two powered), up to 61 bulkhead-mounted middeck locker locations, and floor storage for large unique items and Soft Stowage. STS-96 is targeted to launch May 20 about 9:32 a.m

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- During a payload Interface Verification Test (IVT) for their upcoming mission to the International Space Station, STS-96 Mission Specialists Julie Payette, Dan Barry, and Valery Tokarev of Russia, look at a Sequential Shunt Unit in the SPACEHAB Facility. Other crew members at KSC for the IVT are Commander Kent Rominger, Pilot Rick Husband, and Mission Specialists Ellen Ochoa and Tamara Jernigan. Mission STS-96 carries the SPACEHAB Logistics Double Module, which will have equipment to further outfit the International Space Station service module and equipment that can be off-loaded from the early U.S. assembly flights. It carries internal logistics and resupply cargo for station outfitting, plus an external Russian cargo crane to be mounted to the exterior of the Russian station segment and used to perform space walking maintenance activities. The double module stowage provides capacity of up to 10,000 lbs. with the ability to accommodate powered payloads, four external rooftop stowage locations, four double-rack locations (two powered), up to 61 bulkhead-mounted middeck locker locations, and floor storage for large unique items and Soft Stowage. STS-96 is targeted to launch May 20 about 9:32 a.m. EDT
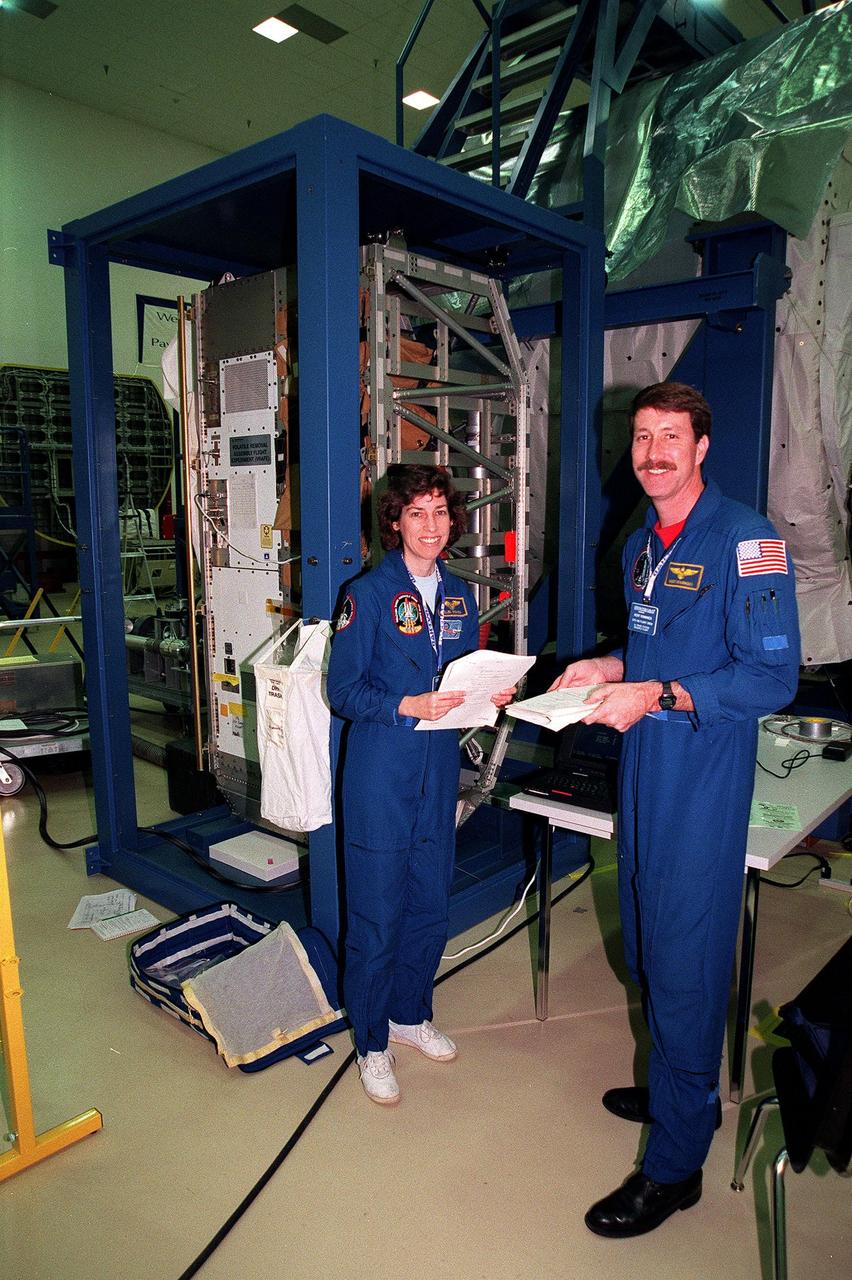

At the SPACEHAB Facility, STS-96 Mission Specialist Ellen Ochoa and Commander Kent Rominger pause during a payload Interface Verification Test (IVT) for their upcoming mission to the International Space Station. Other crew members at KSC for the IVT are Pilot Rick Husband and Mission Specialists Tamara Jernigan, Dan Barry, Julie Payette and Valery Tokarev of Russia. Mission STS-96 carries the SPACEHAB Logistics Double Module, which will have equipment to further outfit the International Space Station service module and equipment that can be off-loaded from the early U.S. assembly flights. It carries internal logistics and resupply cargo for station outfitting, plus an external Russian cargo crane to be mounted to the exterior of the Russian station segment and used to perform space walking maintenance activities. The double module stowage provides capacity of up to 10,000 lbs. with the ability to accommodate powered payloads, four external rooftop stowage locations, four double-rack locations (two powered), up to 61 bulkhead-mounted middeck locker locations, and floor storage for large unique items and Soft Stowage. STS-96 is targeted to launch May 20 about 9:32 a.m. EDT

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the SPACEHAB Facility, the STS-96 crew looks over equipment during a payload Interface Verification Test for the upcoming mission to the International Space Station. From left are Commander Kent Rominger, Mission Specialists Tamara Jernigan and Valery Tokarev of Russia, Pilot Rick Husband, and Mission Specialists Ellen Ochoa and Julie Payette (backs to the camera). They are listening to Chris Jaskolka of Boeing talk about the equipment. Mission STS-96 carries the SPACEHAB Logistics Double Module, which will have equipment to further outfit the International Space Station service module and equipment that can be off-loaded from the early U.S. assembly flights. It carries internal logistics and resupply cargo for station outfitting, plus an external Russian cargo crane to be mounted to the exterior of the Russian station segment and used to perform space walking maintenance activities. The double module stowage provides capacity of up to 10,000 lbs. with the ability to accommodate powered payloads, four external rooftop stowage locations, four double-rack locations (two powered), up to 61 bulkhead-mounted middeck locker locations, and floor storage for large unique items and Soft Stowage. STS-96 is targeted to launch May 20 about 9:32 a.m. EDT
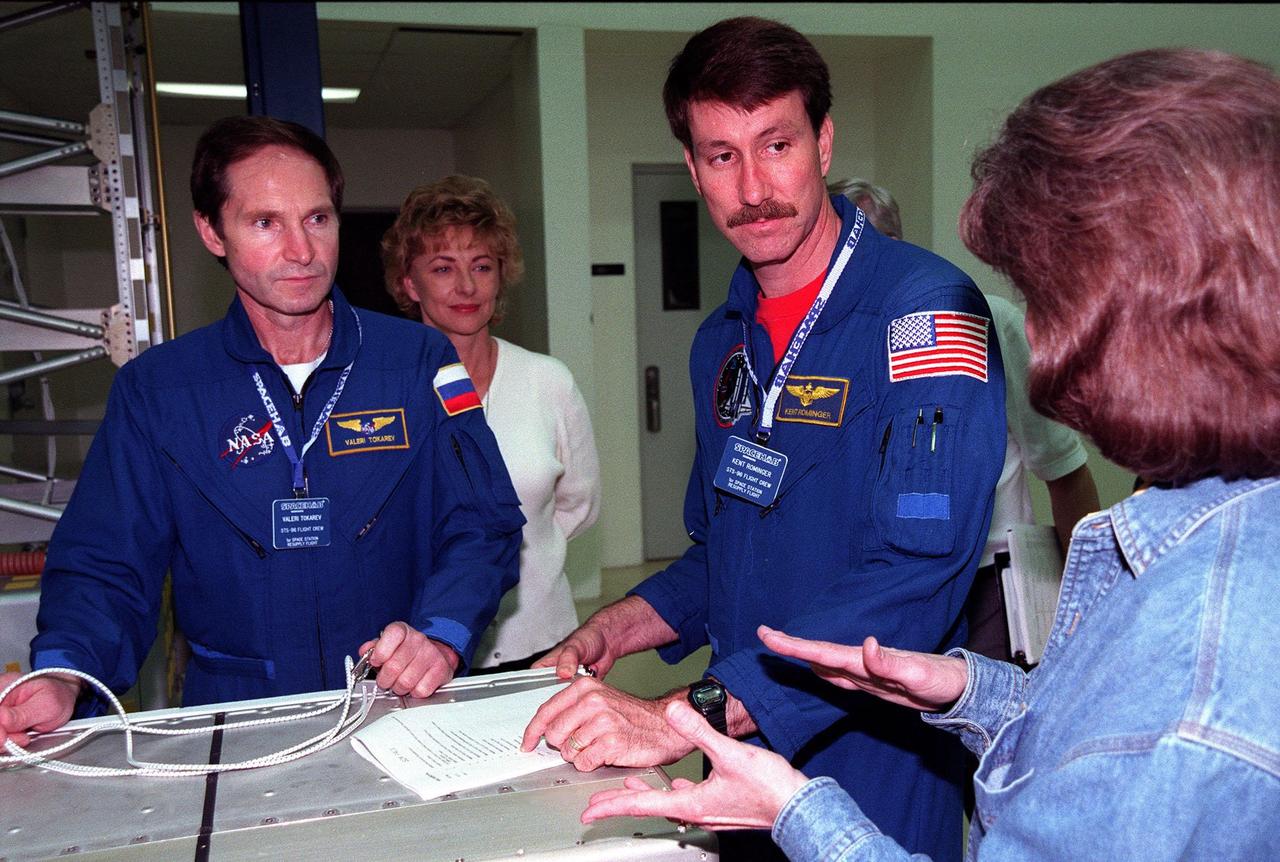

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the SPACEHAB Facility, STS-96 Mission Specialist Valery Tokarev of Russia (left) and Commander Kent Rominger (second from right) listen to Lynn Ashby (far right), with JSC, talking about the SPACEHAB equipment in front of them during a payload Interface Verification Test (IVT). In the background behind Tokarev is TTI interpreter Valentina Maydell. Other STS-96 crew members at KSC for the IVT are Pilot Rick Husband and Mission Specialists Dan Barry, Ellen Ochoa, Tamara Jernigan and Julie Payette. Mission STS-96 carries the SPACEHAB Logistics Double Module, which will have equipment to further outfit the International Space Station service module and equipment that can be off-loaded from the early U.S. assembly flights. It carries internal logistics and resupply cargo for station outfitting, plus an external Russian cargo crane to be mounted to the exterior of the Russian station segment and used to perform space walking maintenance activities. The double module stowage provides capacity of up to 10,000 lbs. with the ability to accommodate powered payloads, four external rooftop stowage locations, four double-rack locations (two powered), up to 61 bulkhead-mounted middeck locker locations, and floor storage for large unique items and Soft Stowage. STS-96 is targeted to launch May 20 about 9:32 a.m
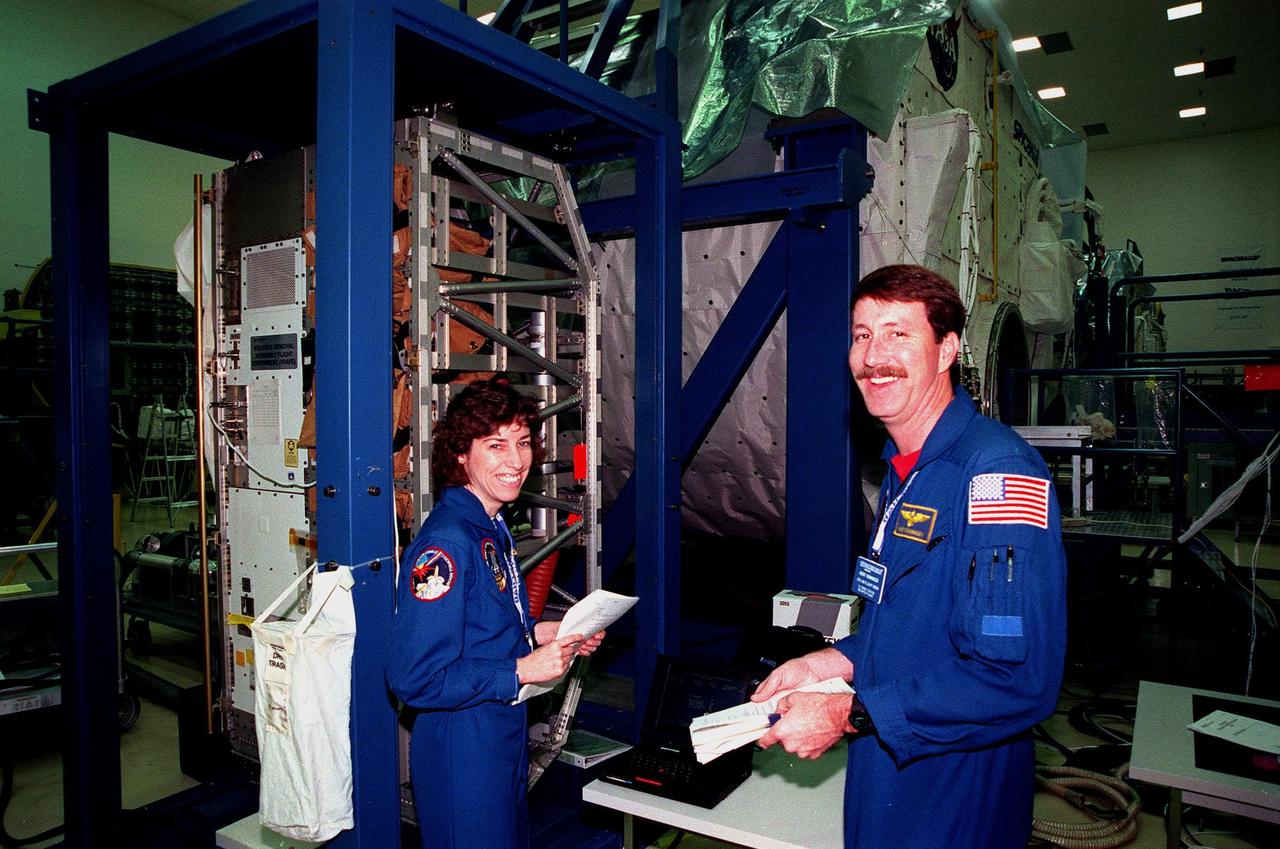

At the SPACEHAB Facility, STS-96 Mission Specialist Ellen Ochoa and Commander Kent Rominger smile for the camera during a payload Interface Verification Test (IVT) for their upcoming mission to the International Space Station. Other crew members at KSC for the IVT are Pilot Rick Husband and Mission Specialists Tamara Jernigan, Dan Barry, Julie Payette and Valery Tokarev of Russia. Mission STS-96 carries the SPACEHAB Logistics Double Module, which will have equipment to further outfit the International Space Station service module and equipment that can be off-loaded from the early U.S. assembly flights. It carries internal logistics and resupply cargo for station outfitting, plus an external Russian cargo crane to be mounted to the exterior of the Russian station segment and used to perform space walking maintenance activities. The double module stowage provides capacity of up to 10,000 lbs. with the ability to accommodate powered payloads, four external rooftop stowage locations, four double-rack locations (two powered), up to 61 bulkhead-mounted middeck locker locations, and floor storage for large unique items and Soft Stowage. STS-96 is targeted to launch May 20 about 9:32 a.m. EDT
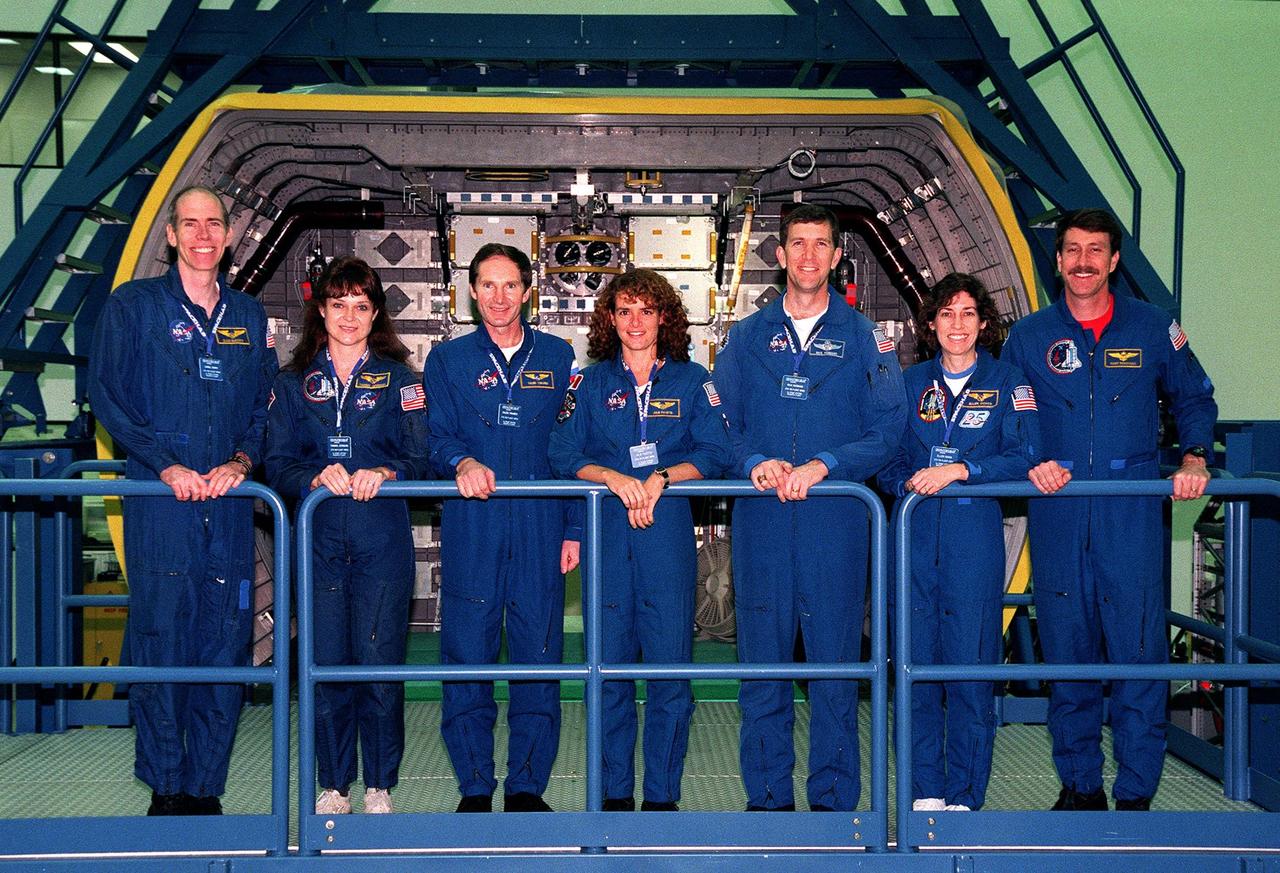

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Posing on the platform next to the SPACEHAB Logistics Double Module in the SPACEHAB Facility are the STS-96 crew (from left) Mission Specialists Dan Barry, Tamara Jernigan, Valery Tokarev of Russia, and Julie Payette; Pilot Rick Husband; Mission Specialist Ellen Ochoa; and Commander Kent Rominger. The crew is at KSC for a payload Interface Verification Test for their upcoming mission to the International Space Station. Mission STS-96 carries the SPACEHAB Logistics Double Module, which will have equipment to further outfit the International Space Station service module and equipment that can be off-loaded from the early U.S. assembly flights. It carries internal logistics and resupply cargo for station outfitting, plus an external Russian cargo crane to be mounted to the exterior of the Russian station segment and used to perform space walking maintenance activities. The double module stowage provides capacity of up to 10,000 lbs. with the ability to accommodate powered payloads, four external rooftop stowage locations, four double-rack locations (two powered), up to 61 bulkhead-mounted middeck locker locations, and floor storage for large unique items and Soft Stowage. STS-96 is targeted to launch May 20 about 9:32 a.m
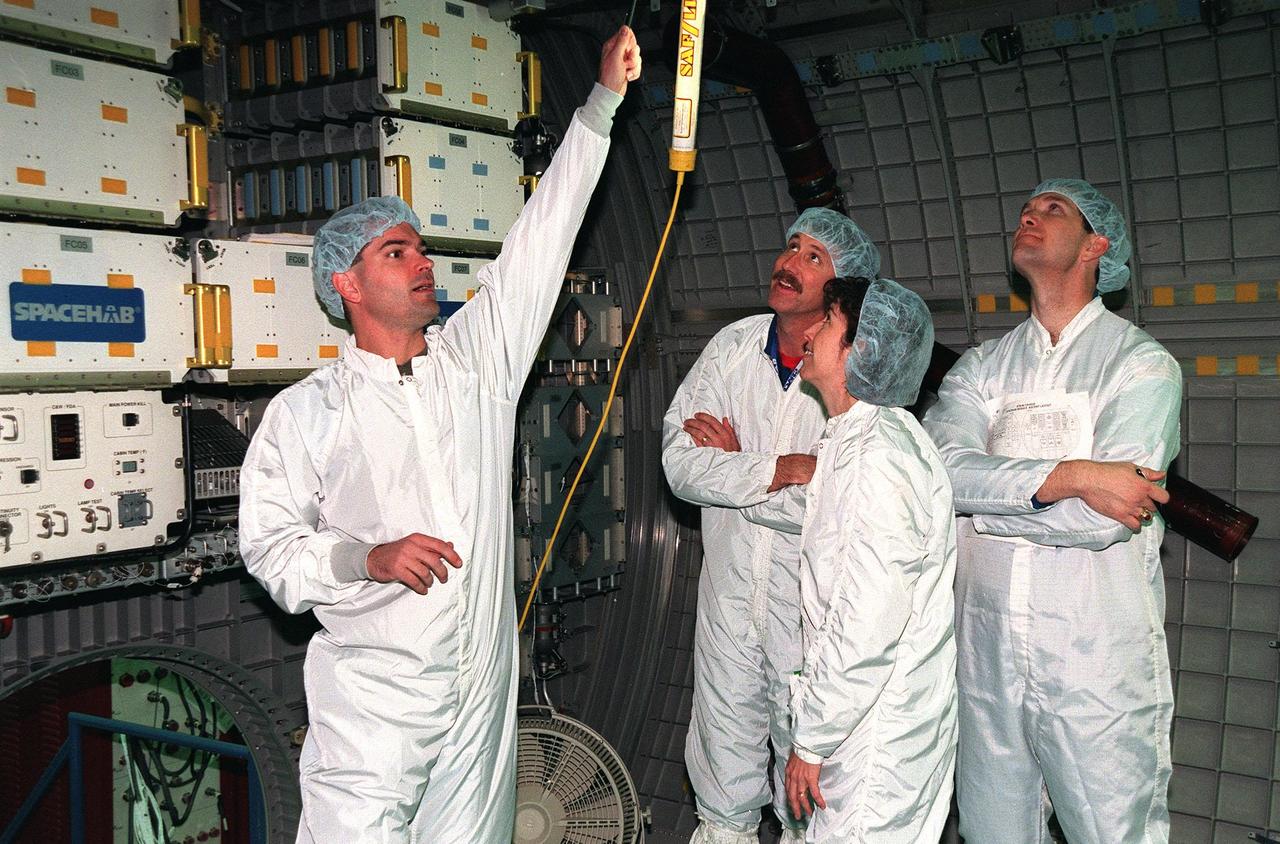

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- During a payload Interface Verification Test (IVT) for the upcoming mission to the International Space Station , Chris Jaskolka of Boeing points out a piece of equipment in the SPACEHAB module to STS-96 Commander Kent Rominger, Mission Specialist Ellen Ochoa and Pilot Rick Husband. Other crew members visiting KSC for the IVT are Mission Specialists Tamara Jernigan, Dan Barry, Julie Payette and Valery Tokarev of Russia. Mission STS-96 carries the SPACEHAB Logistics Double Module, which will have equipment to further outfit the International Space Station service module and equipment that can be off-loaded from the early U.S. assembly flights. It carries internal logistics and resupply cargo for station outfitting, plus an external Russian cargo crane to be mounted to the exterior of the Russian station segment and used to perform space walking maintenance activities. The double module stowage provides capacity of up to 10,000 lbs. with the ability to accommodate powered payloads, four external rooftop stowage locations, four double-rack locations (two powered), up to 61 bulkhead-mounted middeck locker locations, and floor storage for large unique items and Soft Stowage. STS-96 is targeted to launch May 20 about 9:32 a.m. EDT
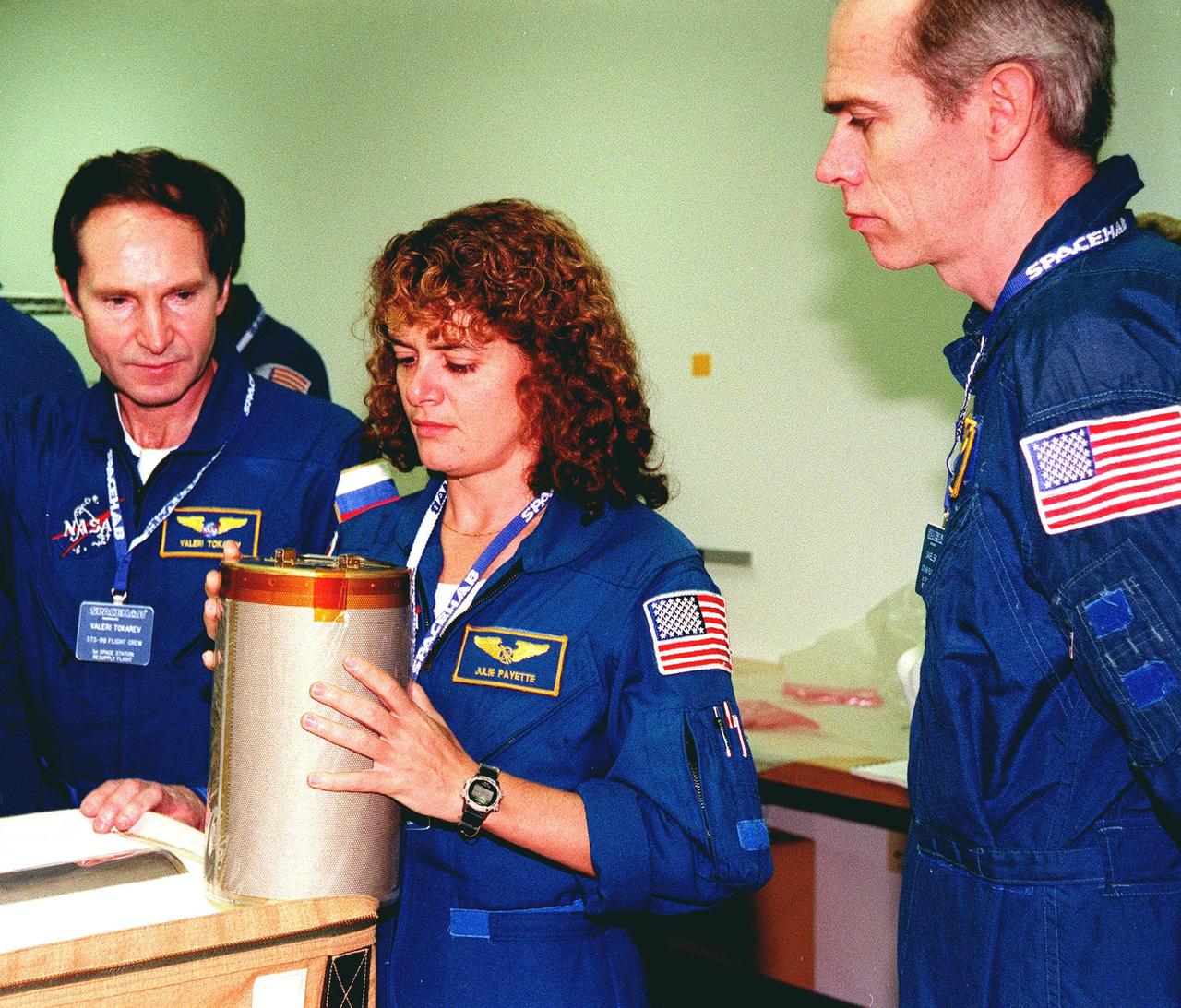

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the SPACEHAB Facility for a payload Interface Verification Test (IVT) for their upcoming mission to the International Space Station are (left to right) Mission Specialists Valery Tokarev, Julie Payette (holding a lithium hydroxide canister) and Dan Barry. Other crew members at KSC for the IVT are Commander Kent Rominger, Pilot Rick Husband and Mission Specialists Ellen Ochoa and Tamara Jernigan. Mission STS-96 carries the SPACEHAB Logistics Double Module, which has equipment to further outfit the International Space Station service module and equipment that can be off-loaded from the early U.S. assembly flights. The SPACEHAB carries internal logistics and resupply cargo for station outfitting, plus an external Russian cargo crane to be mounted to the exterior of the Russian station segment and used to perform space walking maintenance activities. The double module stowage provides capacity of up to 10,000 lbs. with the ability to accommodate powered payloads, four external rooftop stowage locations, four double-rack locations (two powered), up to 61 bulkhead-mounted middeck locker locations, and floor storage for large unique items and Soft Stowage. STS-96 is targeted to launch May 20 about 9:32 a.m
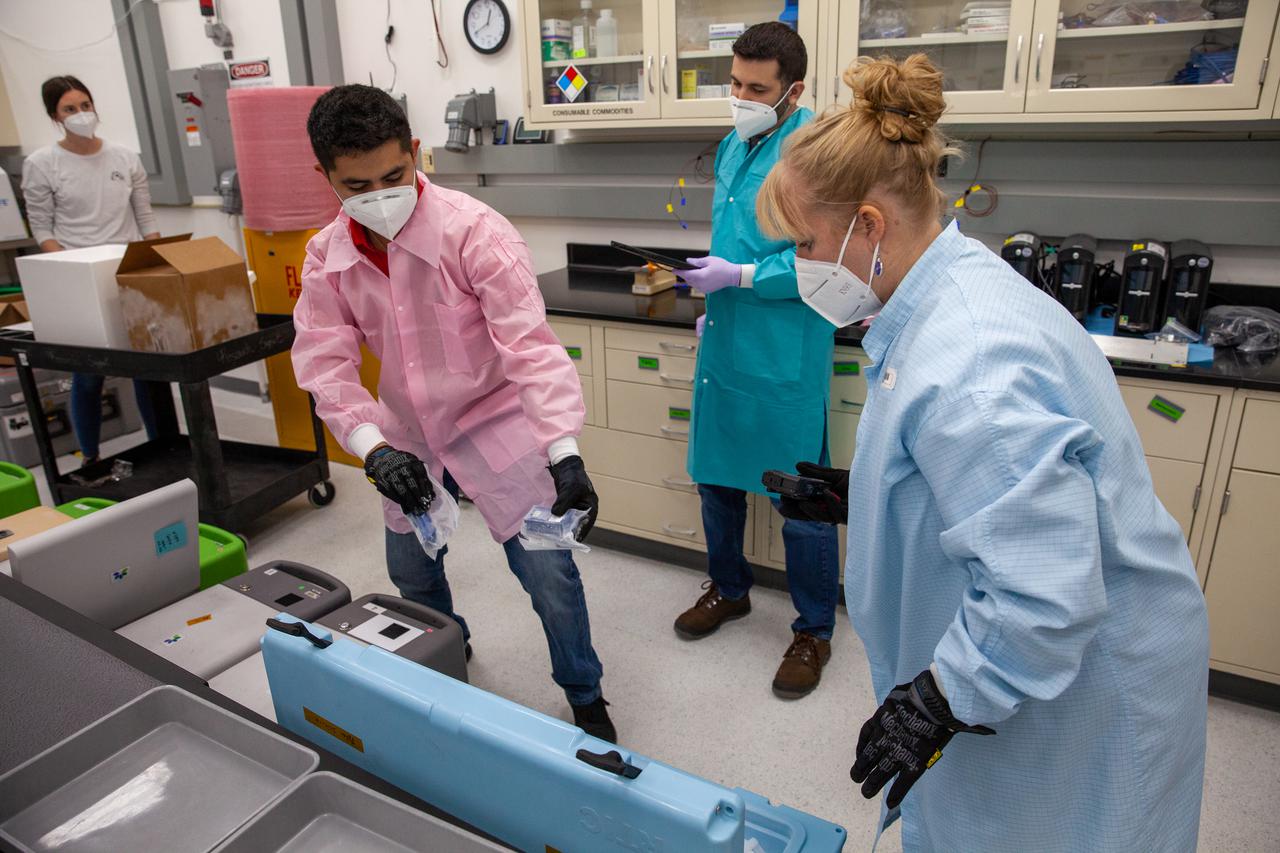

Members of the cold stowage team unpack science experiments inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 14, 2021. The experiments returned to Earth on SpaceX’s 21st commercial resupply services mission (CRS-21). Making its successful parachute-assisted splashdown west of Tampa off the Florida coast, at 8:26 p.m. EST on Jan. 13, the SpaceX cargo Dragon returned more than 4,400 pounds of scientific experiments and other cargo from the International Space Station. After splashdown, SpaceX loaded Dragon aboard their Go Navigator recovery ship and packed an Airbus H225 helicopter with the time-sensitive research cargo for delivery to Kennedy. The upgraded cargo Dragon capsule also boasts double the powered locker capacity to preserve science samples, allowing for a significant increase in the research that can be carried back to Earth.
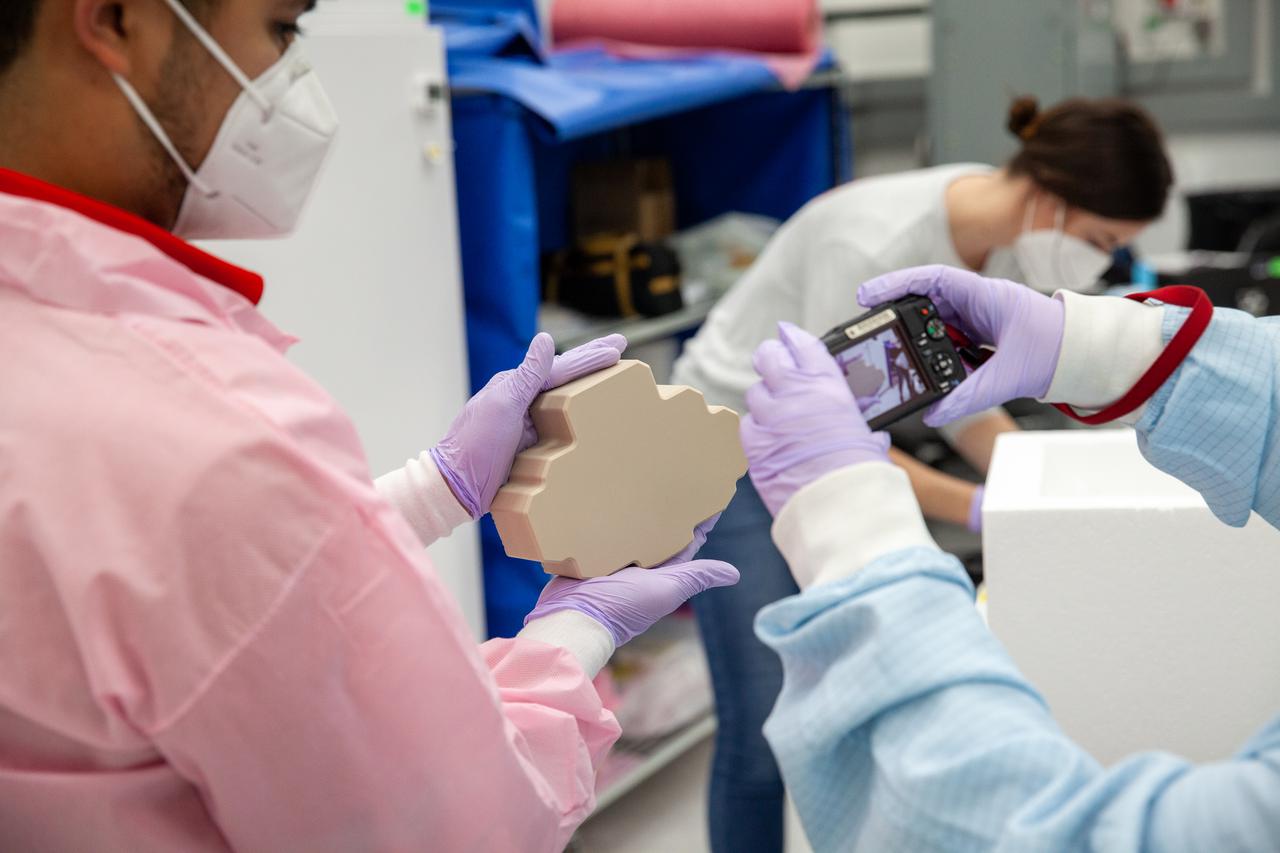

Members of the cold stowage team unpack science experiments inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 14, 2021. The experiments returned to Earth on SpaceX’s 21st commercial resupply services mission (CRS-21). Making its successful parachute-assisted splashdown west of Tampa off the Florida coast, at 8:26 p.m. EST on Jan. 13, the SpaceX cargo Dragon returned more than 4,400 pounds of scientific experiments and other cargo from the International Space Station. After splashdown, SpaceX loaded Dragon aboard their Go Navigator recovery ship and packed an Airbus H225 helicopter with the time-sensitive research cargo for delivery to Kennedy. The upgraded cargo Dragon capsule also boasts double the powered locker capacity to preserve science samples, allowing for a significant increase in the research that can be carried back to Earth.
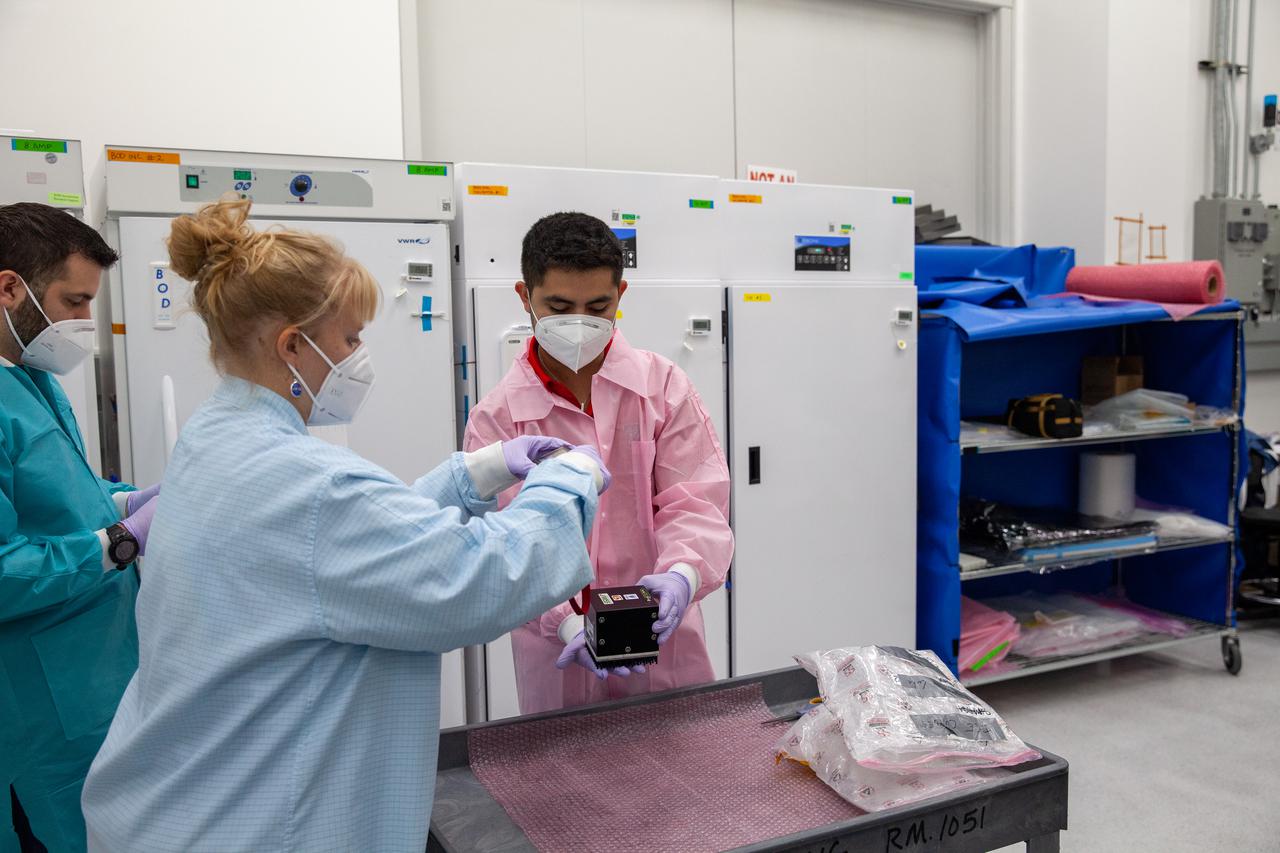

Members of the cold stowage team unpack science experiments inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 14, 2021. The experiments returned to Earth on SpaceX’s 21st commercial resupply services mission (CRS-21). Making its successful parachute-assisted splashdown west of Tampa off the Florida coast, at 8:26 p.m. EST on Jan. 13, the SpaceX cargo Dragon returned more than 4,400 pounds of scientific experiments and other cargo from the International Space Station. After splashdown, SpaceX loaded Dragon aboard their Go Navigator recovery ship and packed an Airbus H225 helicopter with the time-sensitive research cargo for delivery to Kennedy. The upgraded cargo Dragon capsule also boasts double the powered locker capacity to preserve science samples, allowing for a significant increase in the research that can be carried back to Earth.
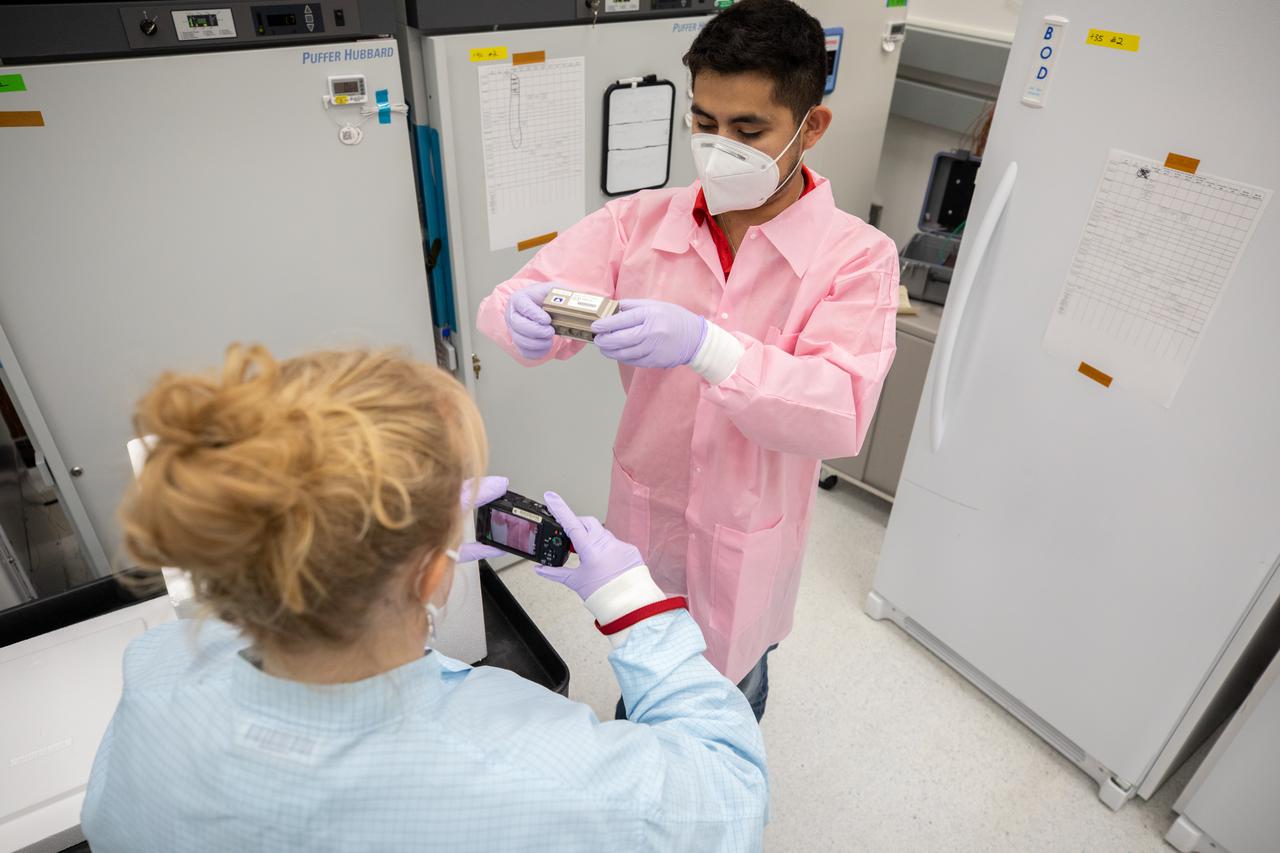
Members of the cold stowage team unpack science experiments inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 14, 2021. The experiments returned to Earth on SpaceX’s 21st commercial resupply services mission (CRS-21). Making its successful parachute-assisted splashdown west of Tampa off the Florida coast, at 8:26 p.m. EST on Jan. 13, the SpaceX cargo Dragon returned more than 4,400 pounds of scientific experiments and other cargo from the International Space Station. After splashdown, SpaceX loaded Dragon aboard their Go Navigator recovery ship and packed an Airbus H225 helicopter with the time-sensitive research cargo for delivery to Kennedy. The upgraded cargo Dragon capsule also boasts double the powered locker capacity to preserve science samples, allowing for a significant increase in the research that can be carried back to Earth.
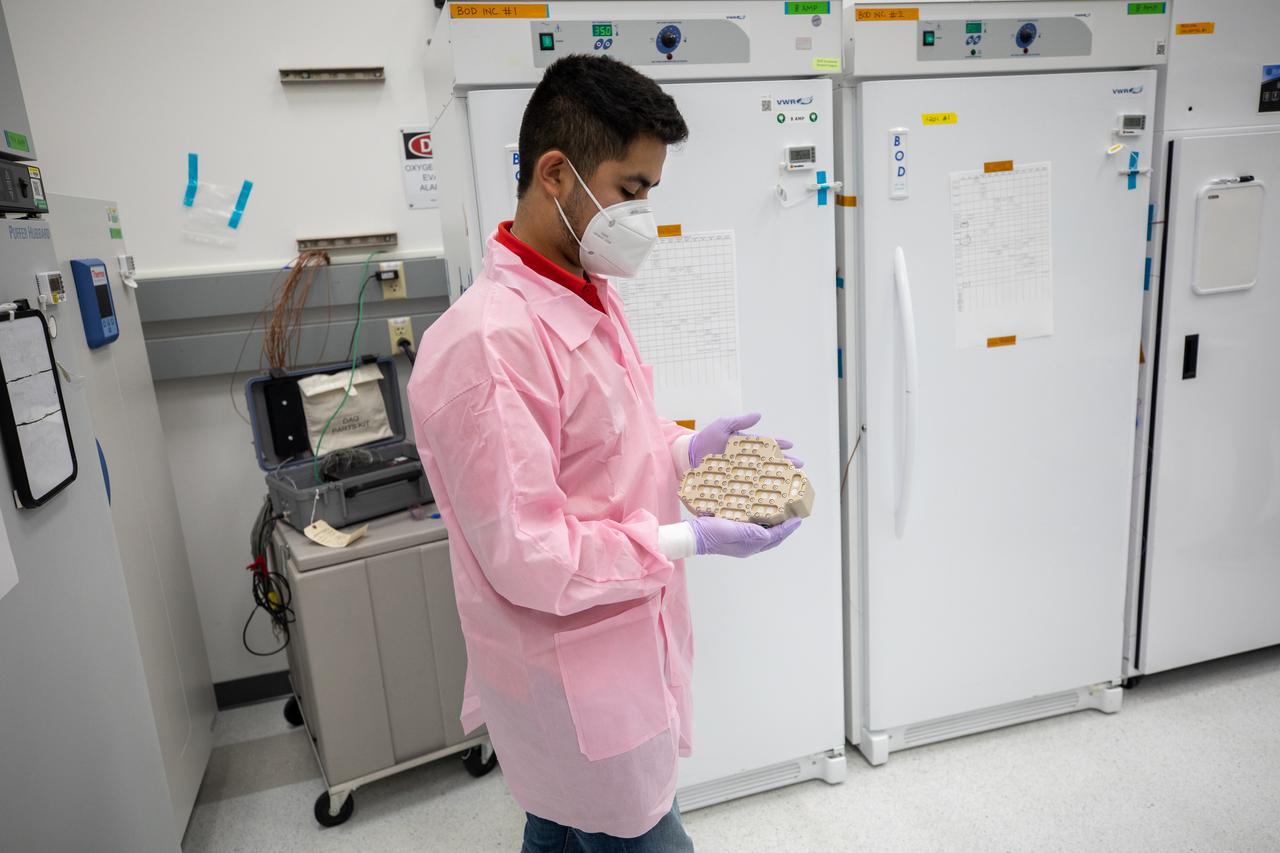

A member of the cold stowage team unpacks science experiments inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 14, 2021. The experiments returned to Earth on SpaceX’s 21st commercial resupply services mission (CRS-21). Making its successful parachute-assisted splashdown west of Tampa off the Florida coast, at 8:26 p.m. EST on Jan. 13, the SpaceX cargo Dragon returned more than 4,400 pounds of scientific experiments and other cargo from the International Space Station. After splashdown, SpaceX loaded Dragon aboard their Go Navigator recovery ship and packed an Airbus H225 helicopter with the time-sensitive research cargo for delivery to Kennedy. The upgraded cargo Dragon capsule also boasts double the powered locker capacity to preserve science samples, allowing for a significant increase in the research that can be carried back to Earth.
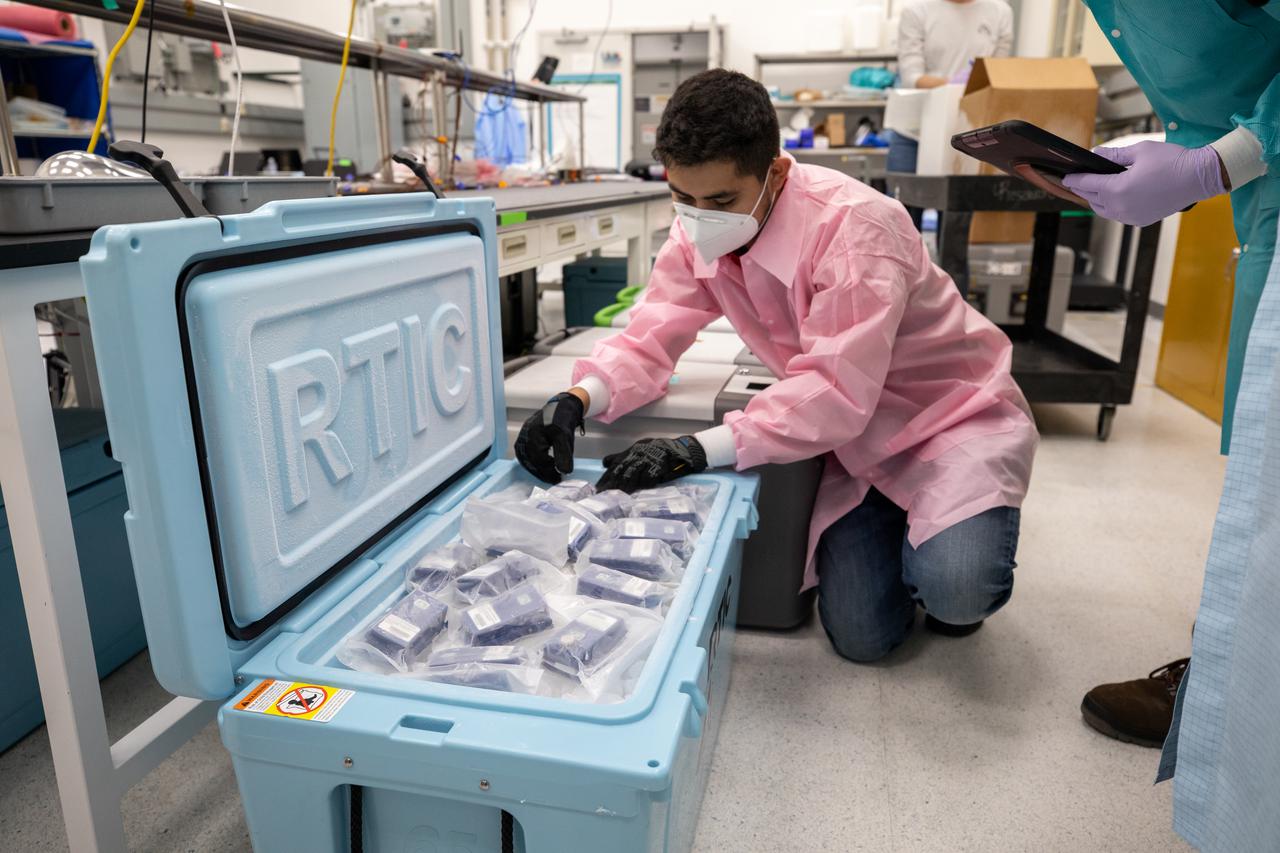

Members of the cold stowage team unpack science experiments inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 14, 2021. The experiments returned to Earth on SpaceX’s 21st commercial resupply services mission (CRS-21). Making its successful parachute-assisted splashdown west of Tampa off the Florida coast, at 8:26 p.m. EST on Jan. 13, the SpaceX cargo Dragon returned more than 4,400 pounds of scientific experiments and other cargo from the International Space Station. After splashdown, SpaceX loaded Dragon aboard their Go Navigator recovery ship and packed an Airbus H225 helicopter with the time-sensitive research cargo for delivery to Kennedy. The upgraded cargo Dragon capsule also boasts double the powered locker capacity to preserve science samples, allowing for a significant increase in the research that can be carried back to Earth.
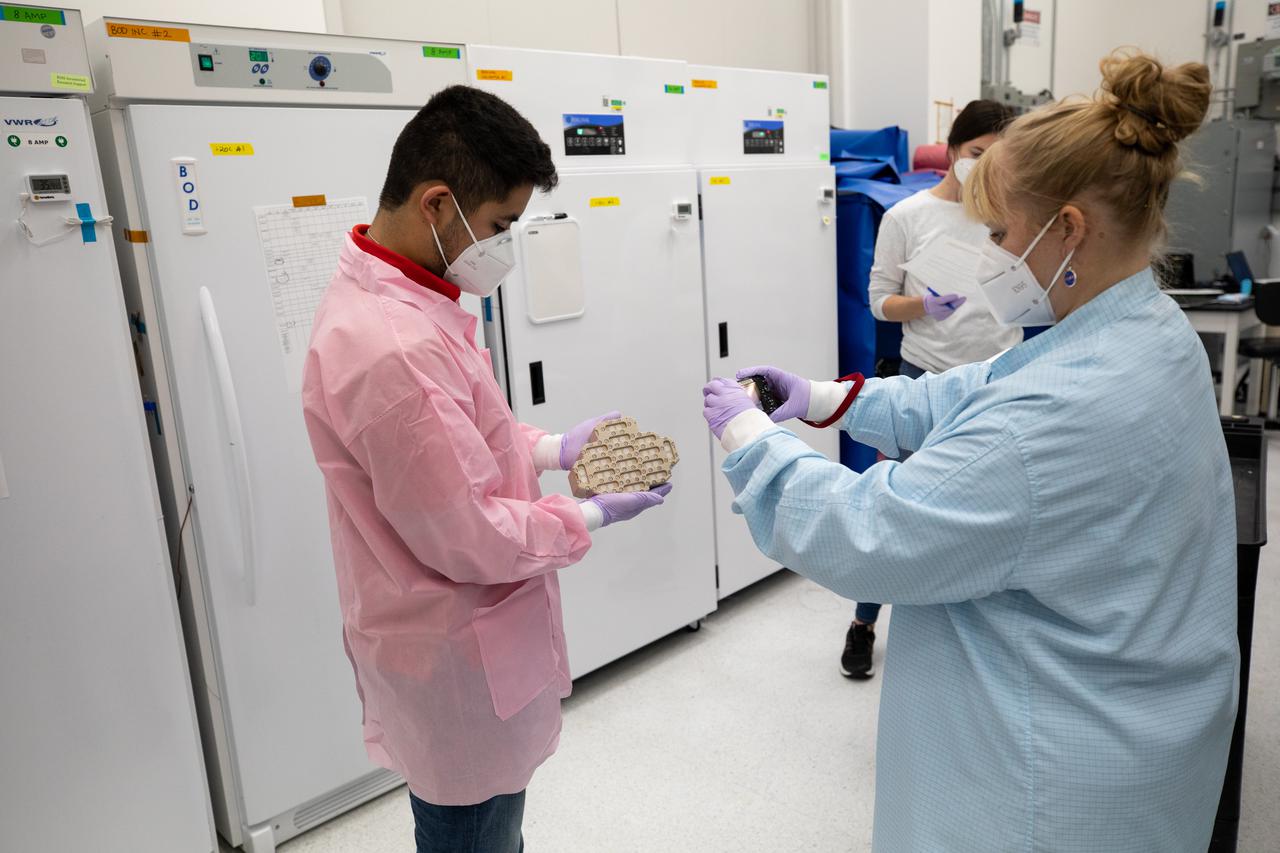

Members of the cold stowage team unpack science experiments inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 14, 2021. The experiments returned to Earth on SpaceX’s 21st commercial resupply services mission (CRS-21). Making its successful parachute-assisted splashdown west of Tampa off the Florida coast, at 8:26 p.m. EST on Jan. 13, the SpaceX cargo Dragon returned more than 4,400 pounds of scientific experiments and other cargo from the International Space Station. After splashdown, SpaceX loaded Dragon aboard their Go Navigator recovery ship and packed an Airbus H225 helicopter with the time-sensitive research cargo for delivery to Kennedy. The upgraded cargo Dragon capsule also boasts double the powered locker capacity to preserve science samples, allowing for a significant increase in the research that can be carried back to Earth.
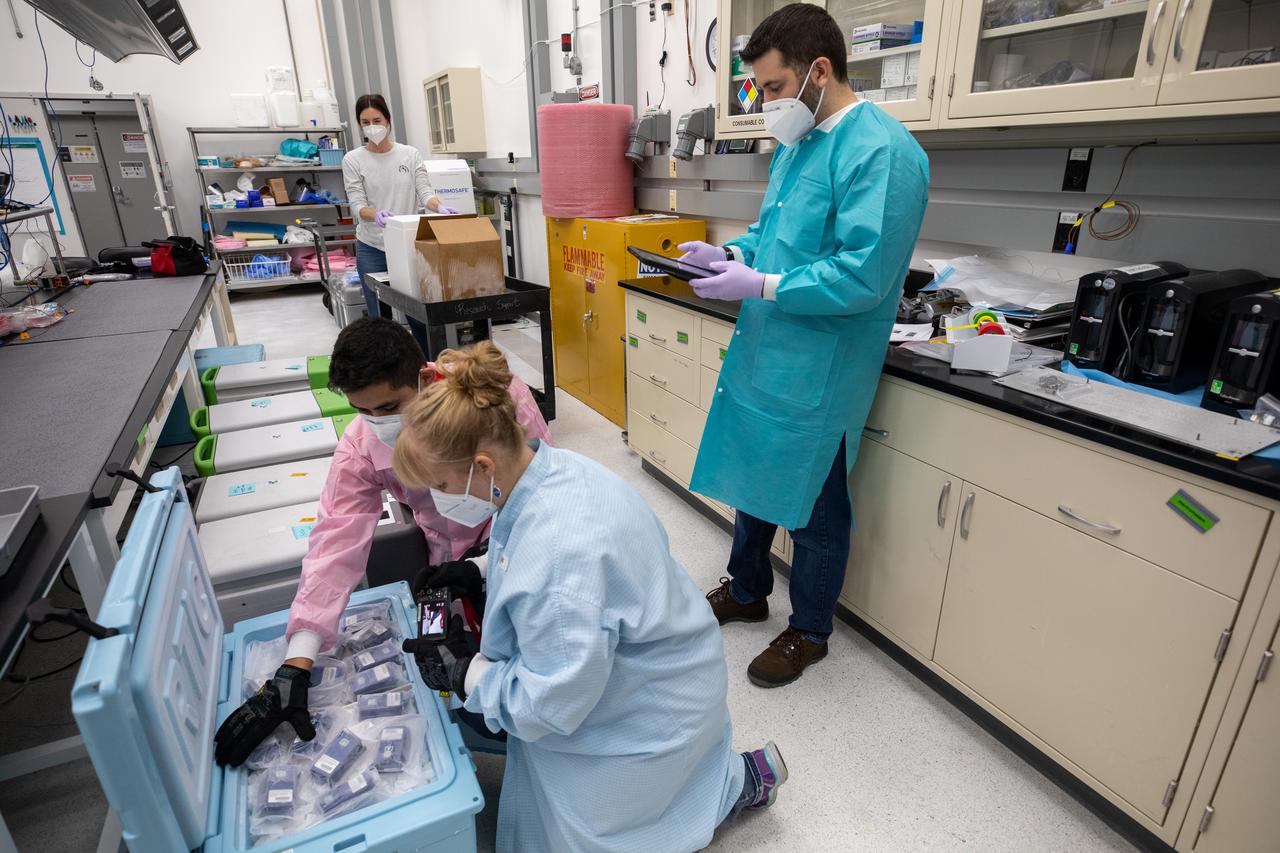

Members of the cold stowage team unpack science experiments inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 14, 2021. The experiments returned to Earth on SpaceX’s 21st commercial resupply services mission (CRS-21). Making its successful parachute-assisted splashdown west of Tampa off the Florida coast, at 8:26 p.m. EST on Jan. 13, the SpaceX cargo Dragon returned more than 4,400 pounds of scientific experiments and other cargo from the International Space Station. After splashdown, SpaceX loaded Dragon aboard their Go Navigator recovery ship and packed an Airbus H225 helicopter with the time-sensitive research cargo for delivery to Kennedy. The upgraded cargo Dragon capsule also boasts double the powered locker capacity to preserve science samples, allowing for a significant increase in the research that can be carried back to Earth.
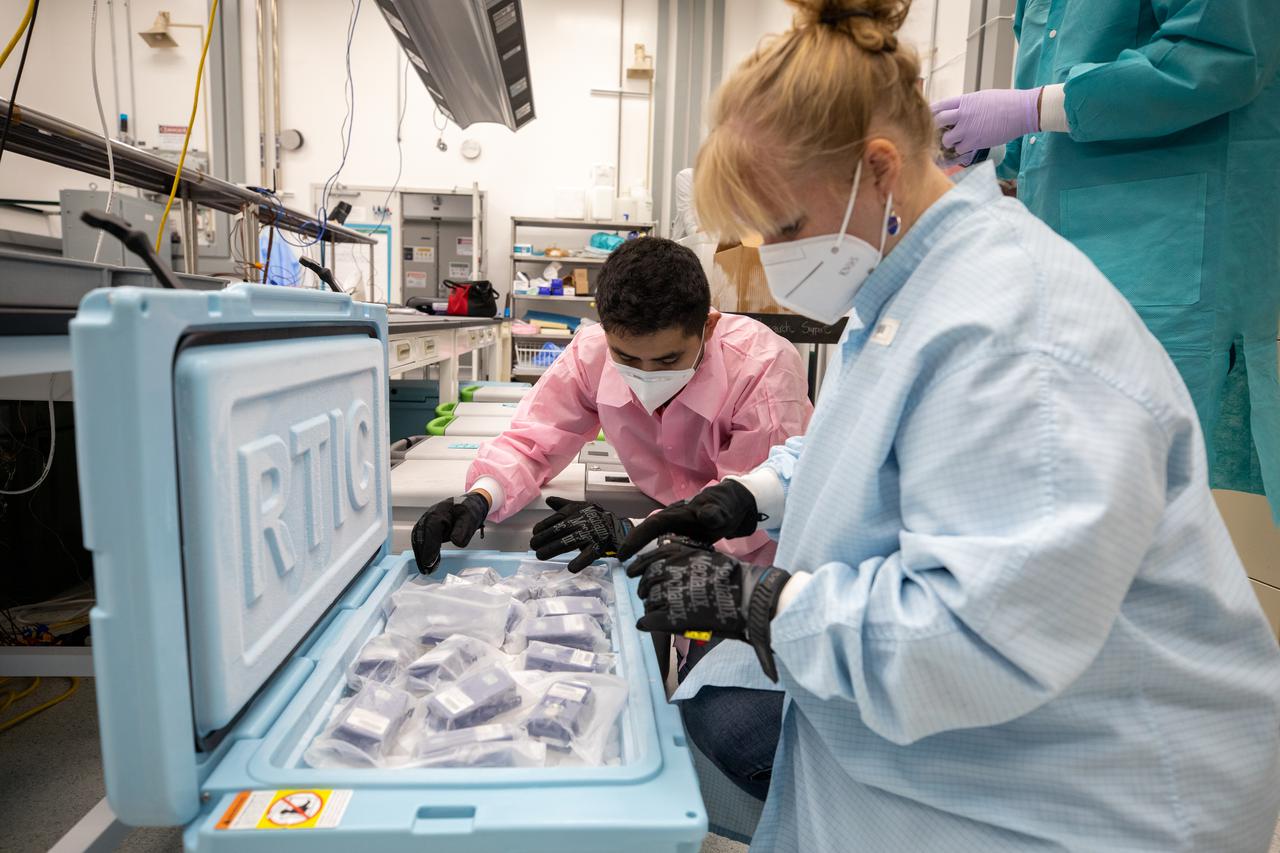

Members of the cold stowage team unpack science experiments inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 14, 2021. The experiments returned to Earth on SpaceX’s 21st commercial resupply services mission (CRS-21). Making its successful parachute-assisted splashdown west of Tampa off the Florida coast, at 8:26 p.m. EST on Jan. 13, the SpaceX cargo Dragon returned more than 4,400 pounds of scientific experiments and other cargo from the International Space Station. After splashdown, SpaceX loaded Dragon aboard their Go Navigator recovery ship and packed an Airbus H225 helicopter with the time-sensitive research cargo for delivery to Kennedy. The upgraded cargo Dragon capsule also boasts double the powered locker capacity to preserve science samples, allowing for a significant increase in the research that can be carried back to Earth.

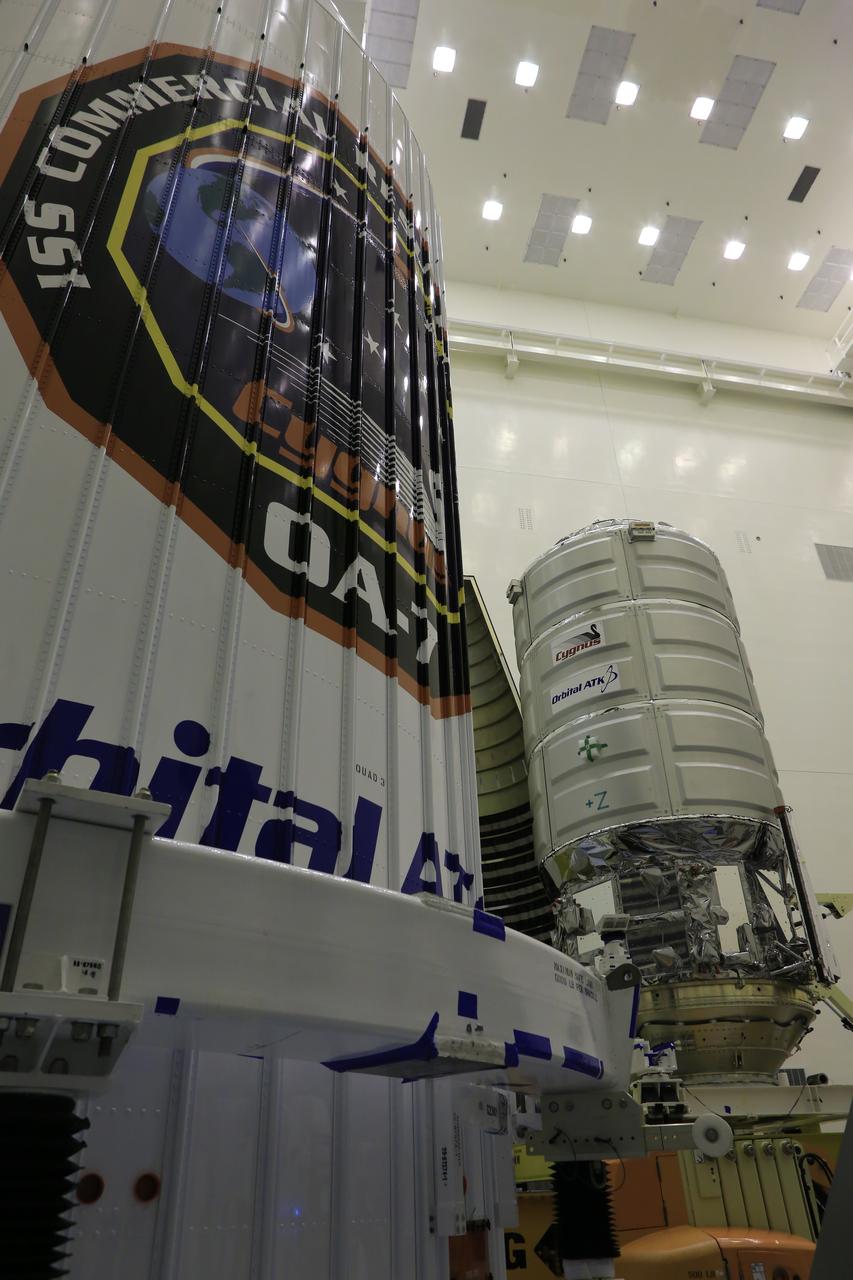
A KAMAG transporter with Orbital ATK's CYGNUS pressurized cargo module secured on top moves from the airlock into the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Cygnus will be moved to a work stand for final propellant loading and late cargo stowage. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on March 19, 2017. CYGNUS will deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
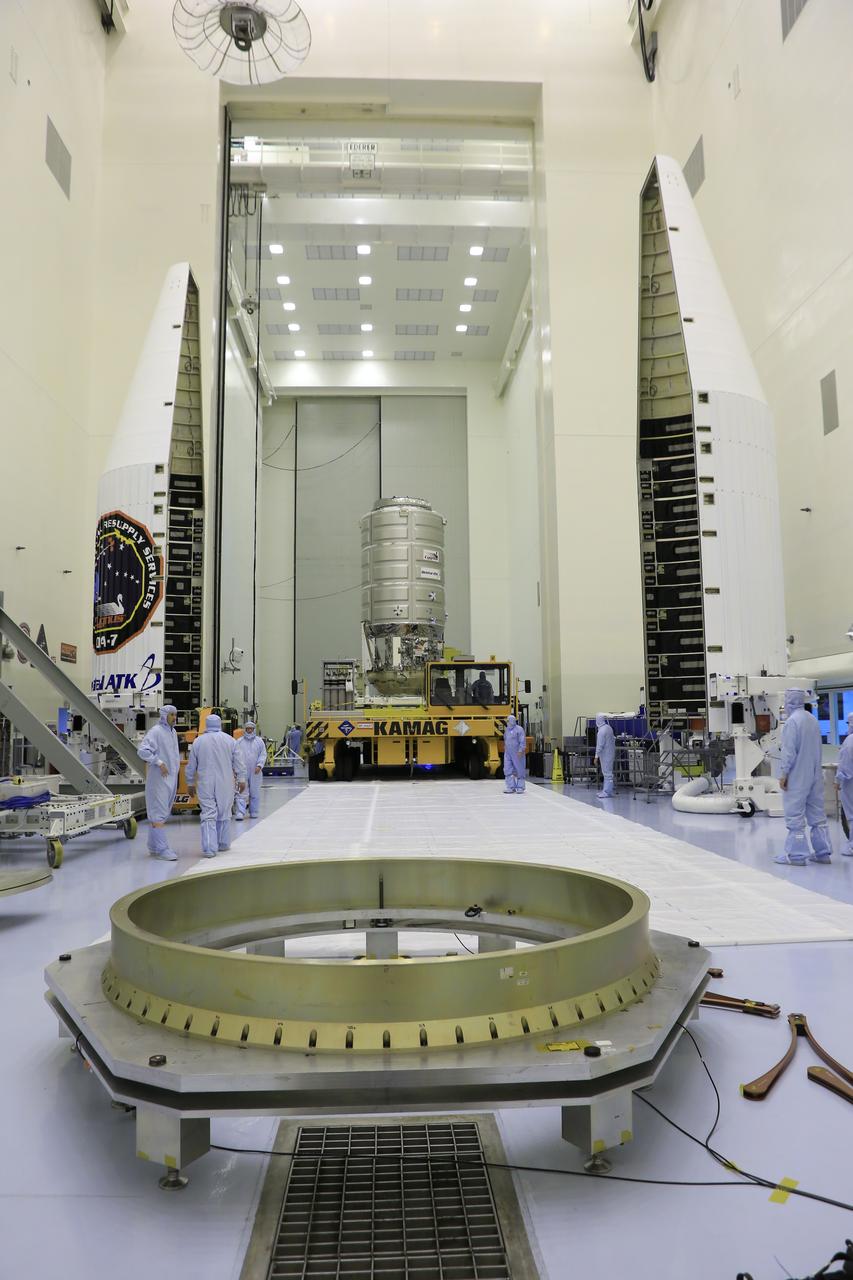

A KAMAG transporter with Orbital ATK's CYGNUS pressurized cargo module secured on top slowly moves from the airlock into the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Cygnus will be moved to a work stand for final propellant loading and late cargo stowage. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on March 19, 2017. CYGNUS will deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.

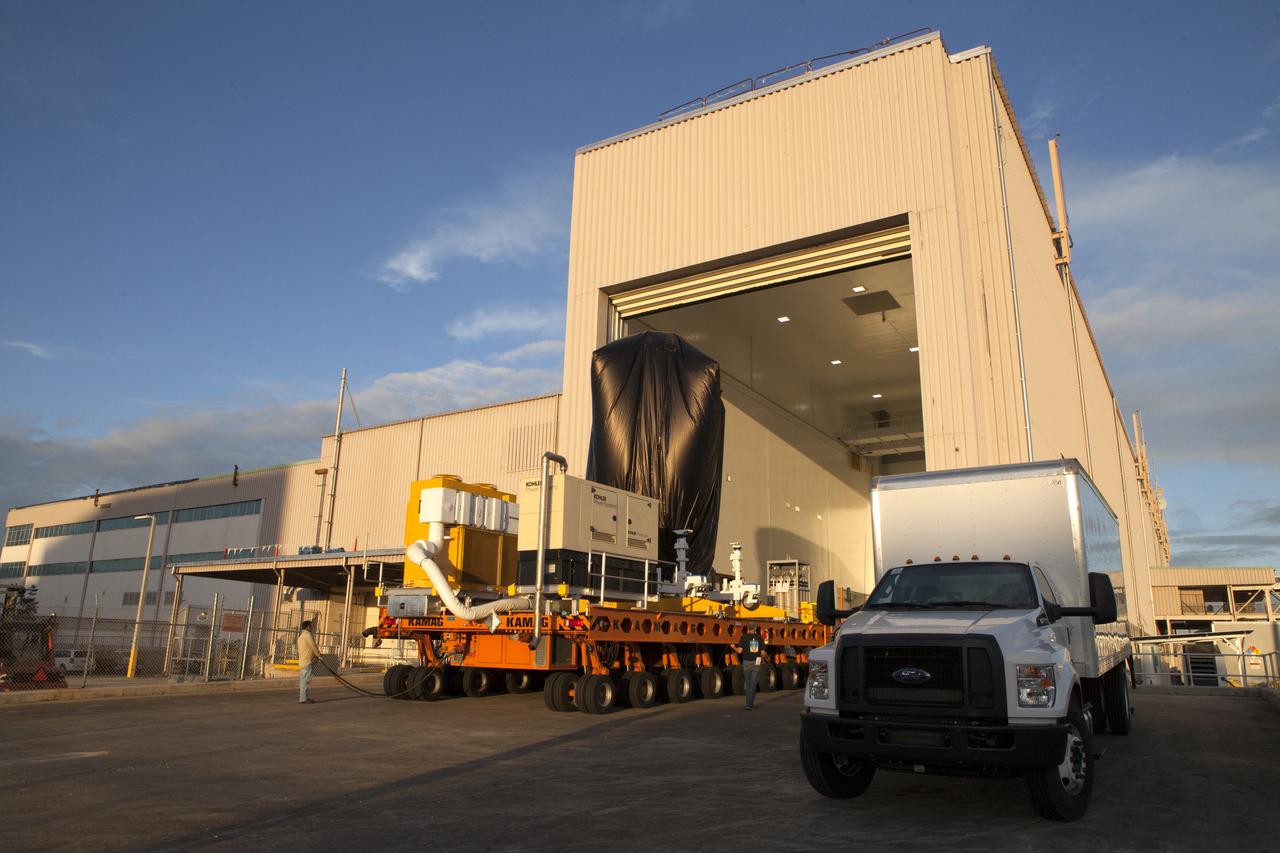
A KAMAG transporter with Orbital ATK's CYGNUS pressurized cargo module secured on top is moved inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. CYGNUS will be lifted off of the transporter and lowered onto a processing stand for final propellant loading and late cargo stowage. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on March 19, 2017. CYGNUS will deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
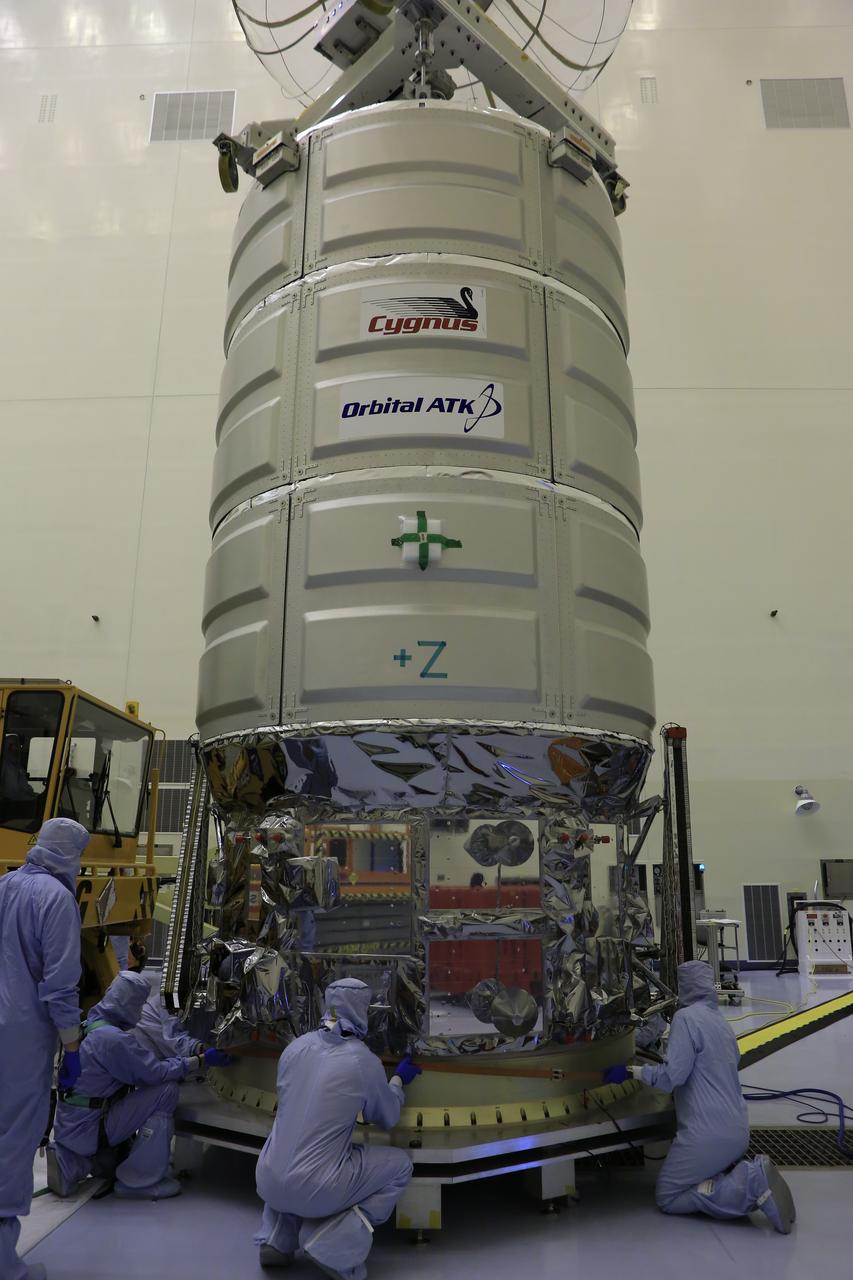

Technicians assist as a crane lowers Orbital ATK's CYGNUS pressurized cargo module onto a work stand inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. CYGNUS will be secured on the work stand for final propellant loading and late cargo stowage. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on March 19, 2017. CYGNUS will deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.

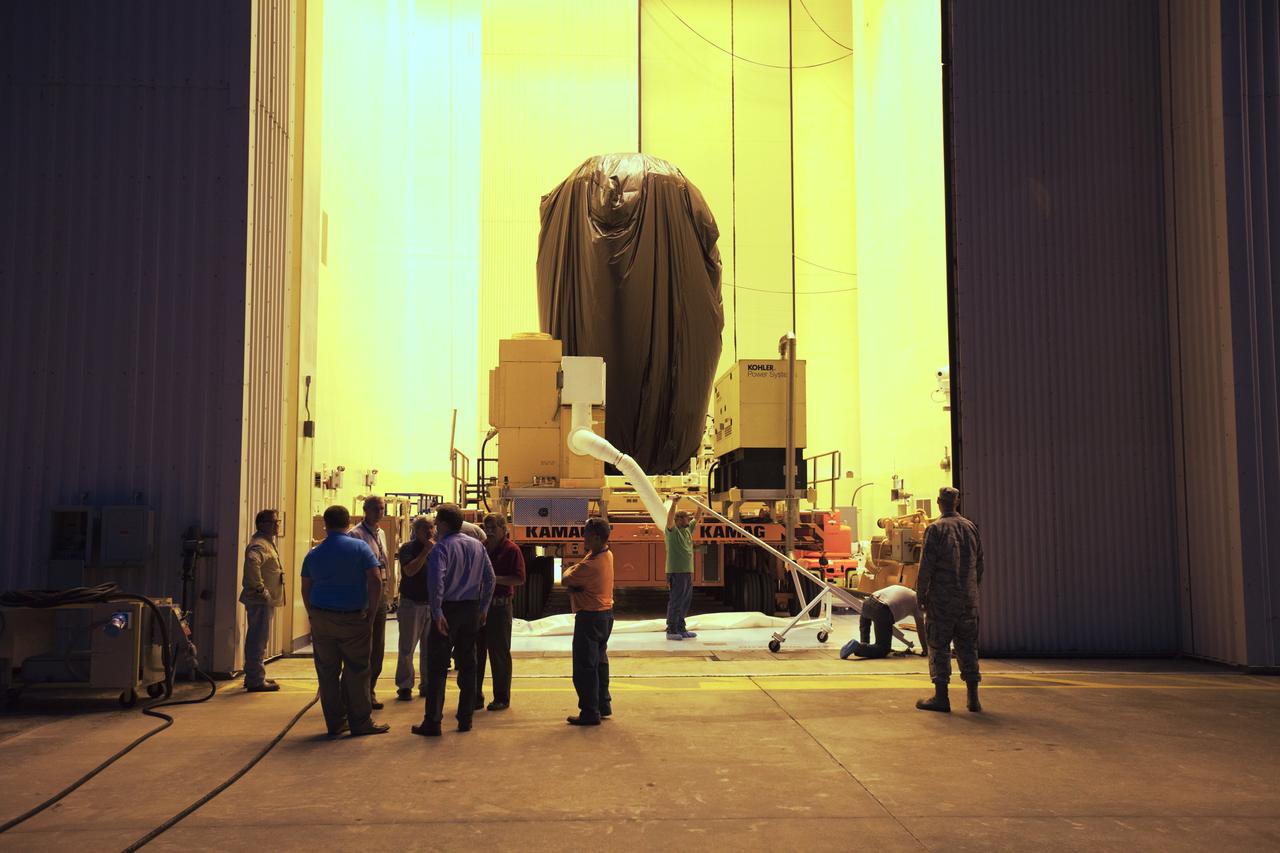
A KAMAG transporter with Orbital ATK's CYGNUS pressurized cargo module secured on top exits the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. CYGNUS will be transported to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility for final propellant loading and late cargo stowage. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on March 19, 2017. CYGNUS will deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
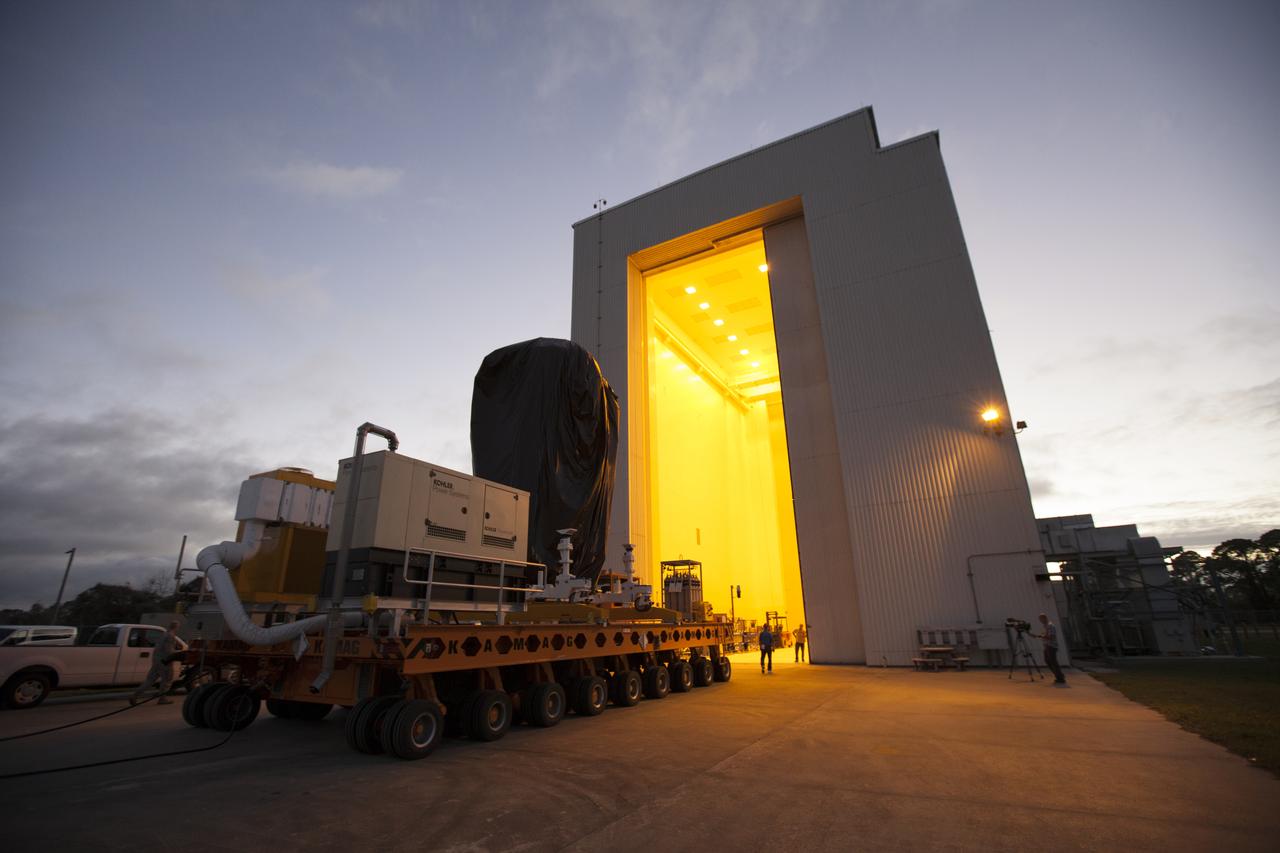

A KAMAG transporter with Orbital ATK's CYGNUS pressurized cargo module secured on top arrives at the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. CYGNUS will be moved inside the facility for final propellant loading and late cargo stowage. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on March 19, 2017. CYGNUS will deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.

A crane is attached to Orbital ATK's CYGNUS pressurized cargo module to lift it up from the KAMAG transporter inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. CYGNUS will be lowered onto a work stand for final propellant loading and late cargo stowage. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on March 19, 2017. CYGNUS will deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.

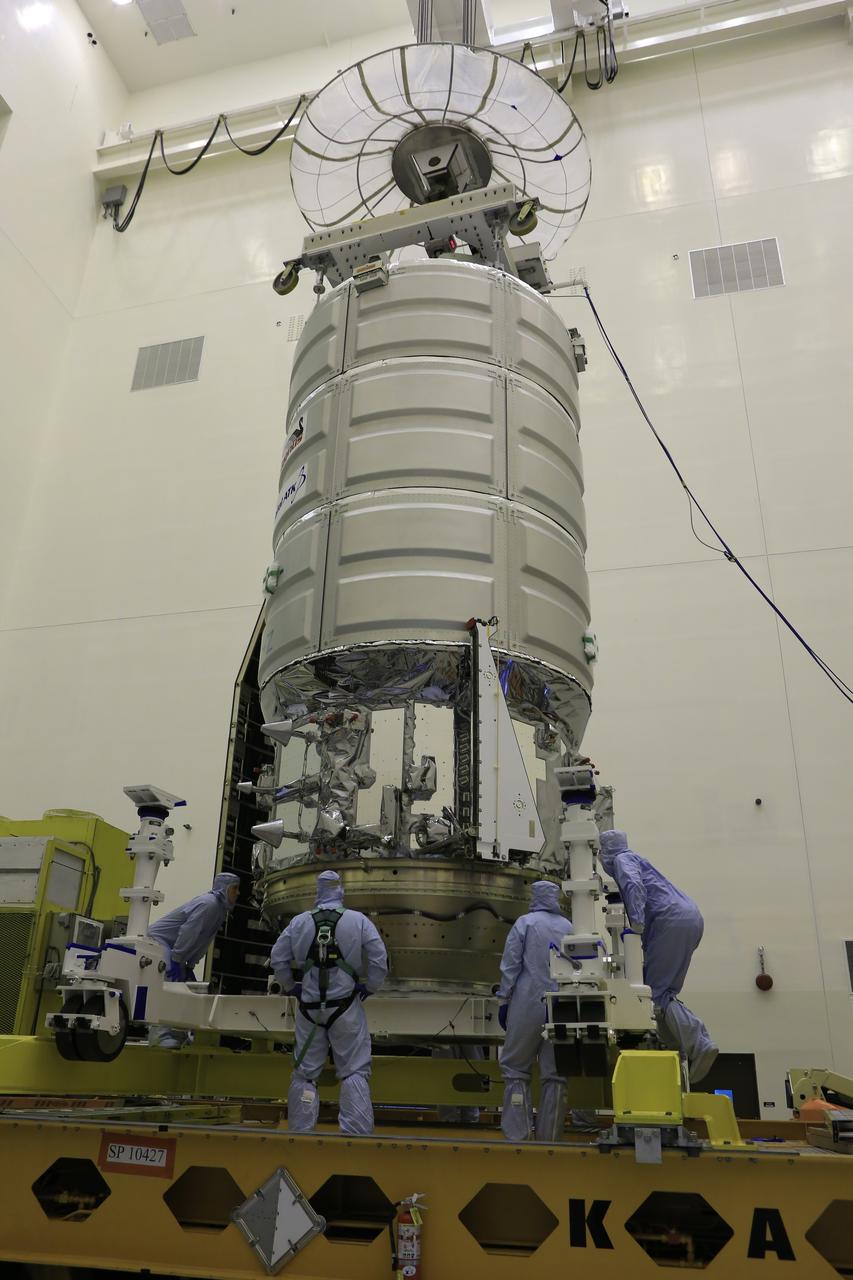
Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, preparations are underway for final stowage of powered cargo in the Orbital ATK Cygnus pressurized cargo module. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station targeted for March 24, 2017. Cygnus will deliver 7,600 pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
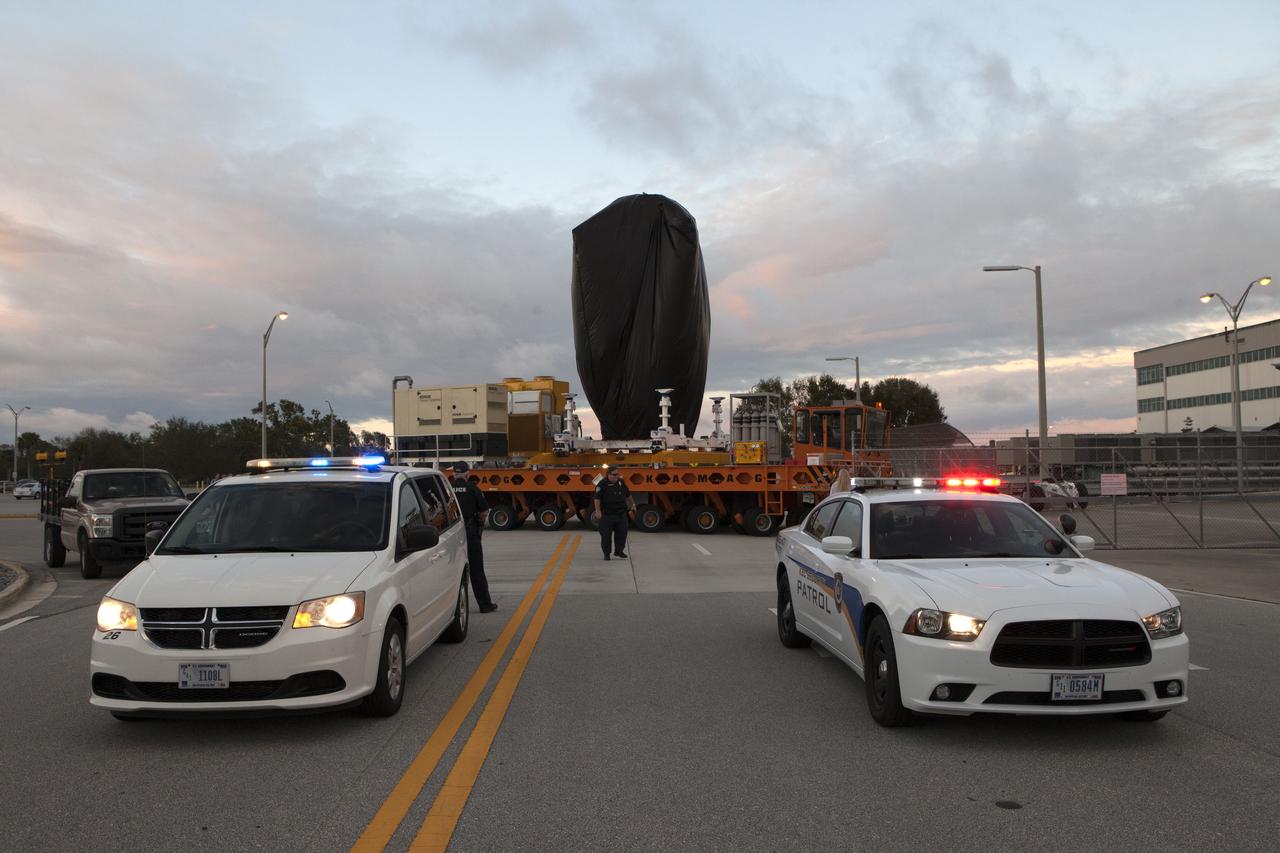

A KAMAG transporter with Orbital ATK's CYGNUS pressurized cargo module secured on top departs the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. CYGNUS will be transported to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility for final propellant loading and late cargo stowage. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on March 19, 2017. CYGNUS will deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
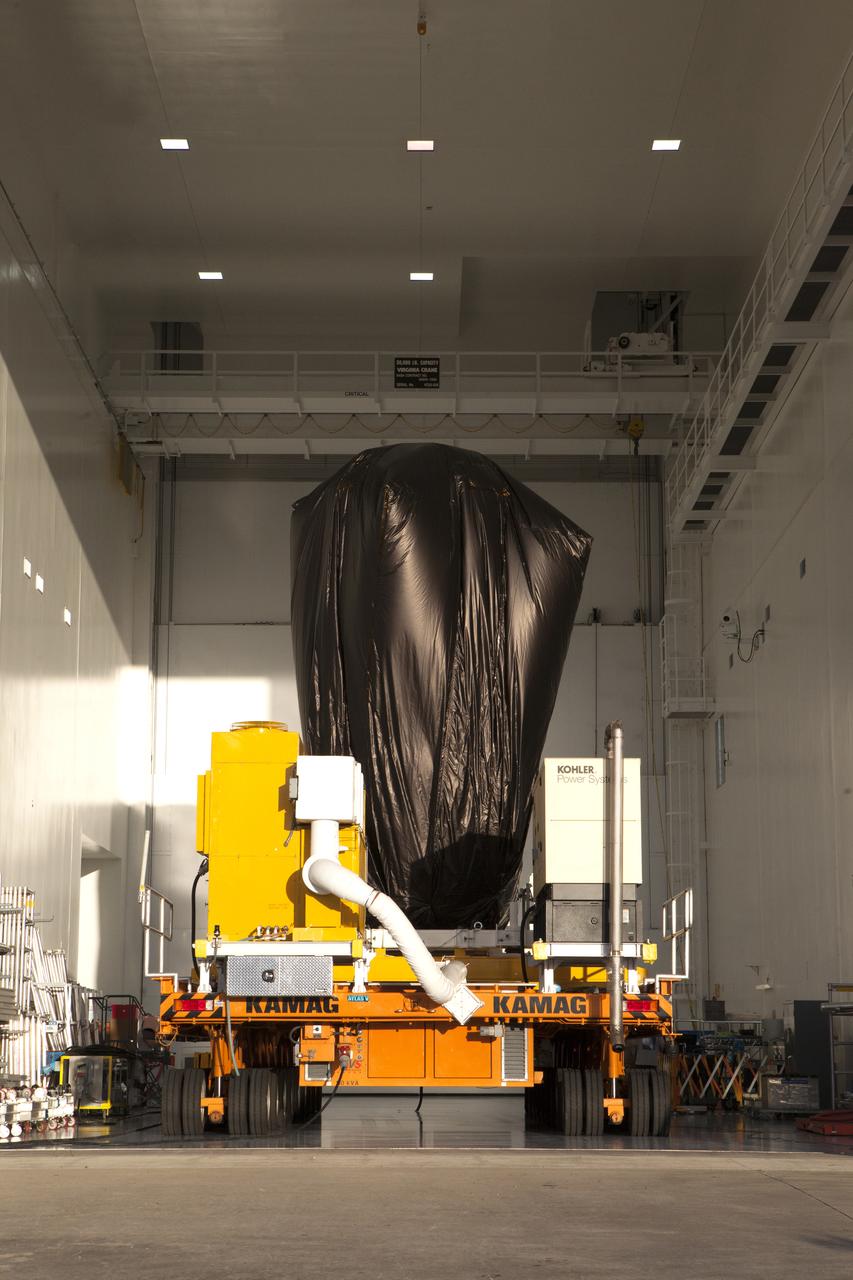

A KAMAG transporter with Orbital ATK's CYGNUS pressurized cargo module secured on top begins to move out of the high bay in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. CYGNUS will be transported to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility for final propellant loading and late cargo stowage. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on March 19, 2017. CYGNUS will deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
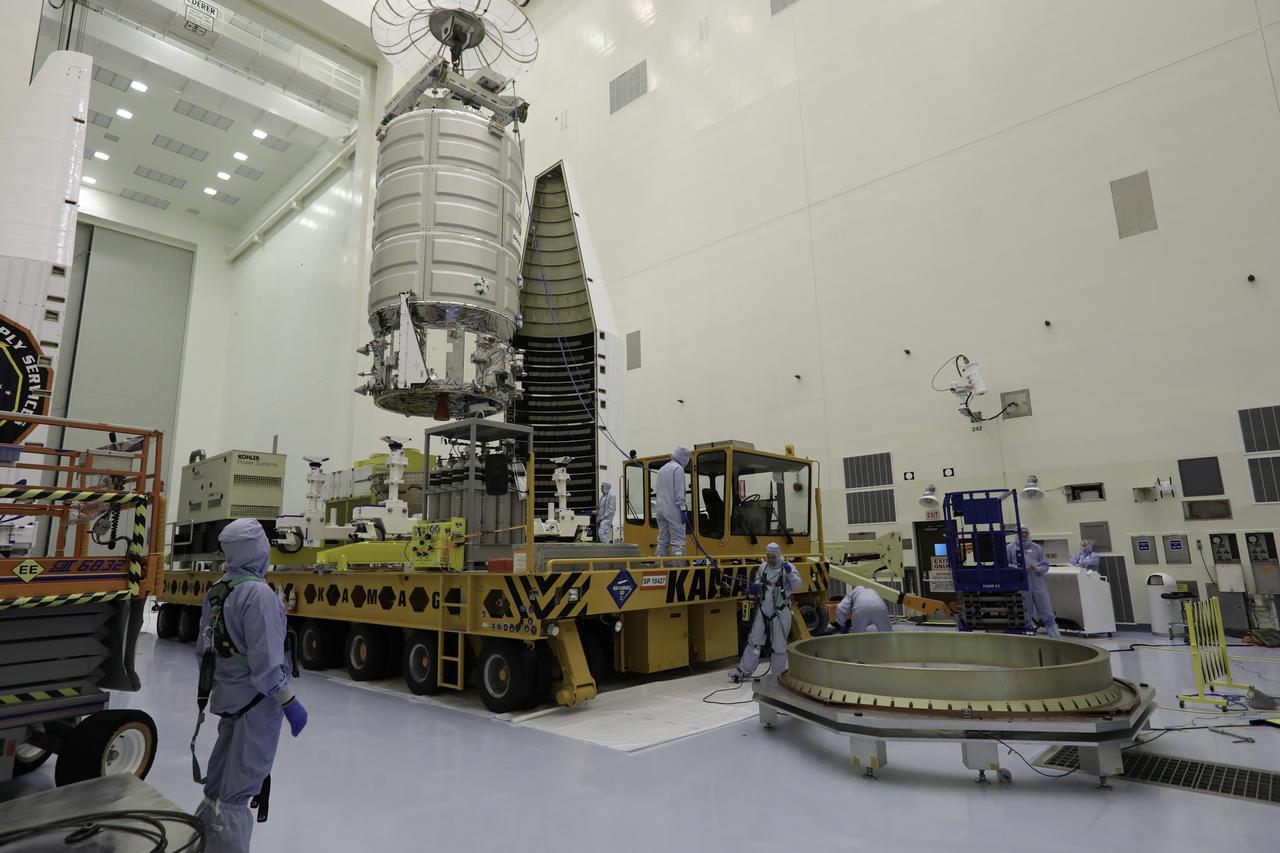

A crane lifts Orbital ATK's CYGNUS pressurized cargo module up from the KAMAG transporter inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. CYGNUS will be lowered onto a work stand for final propellant loading and late cargo stowage. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on March 19, 2017. CYGNUS will deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
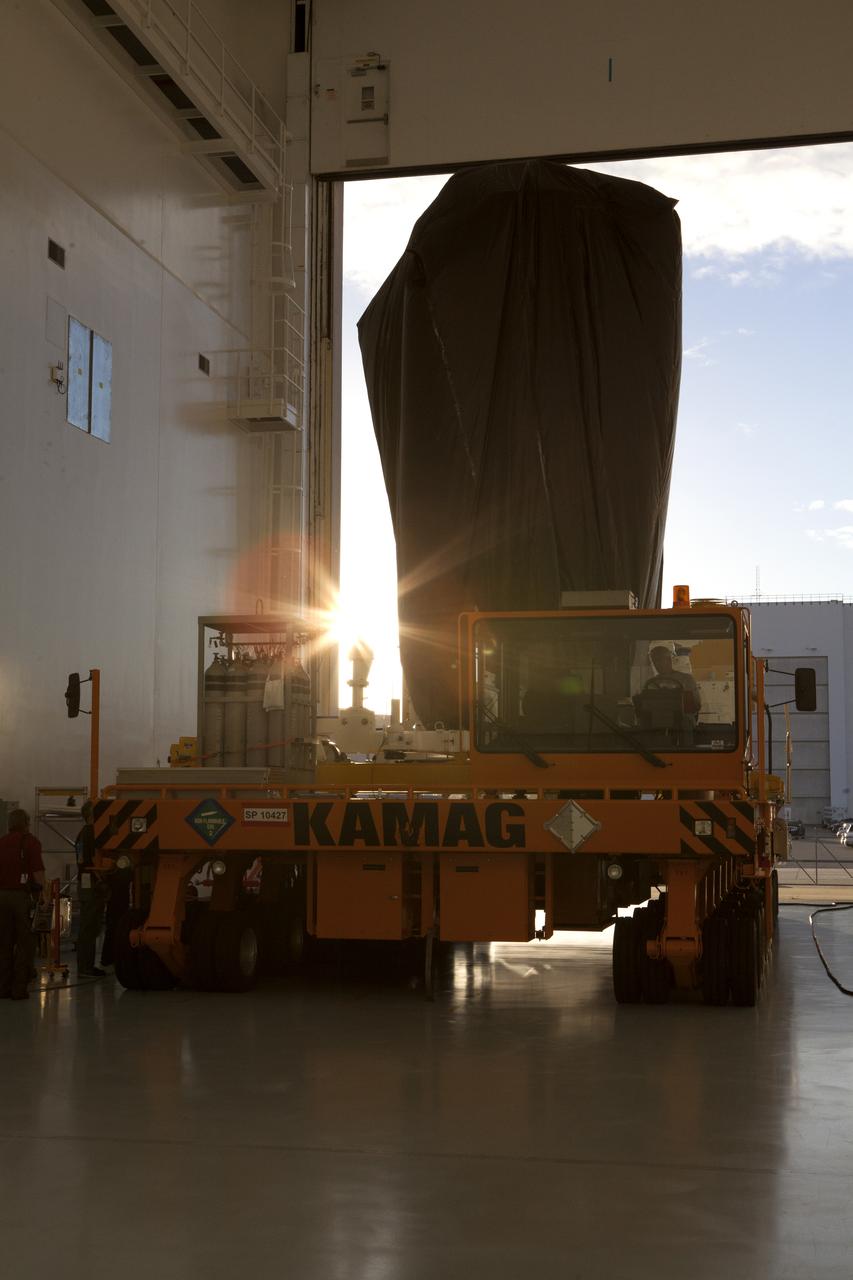

A KAMAG transporter with Orbital ATK's CYGNUS pressurized cargo module secured on top exits the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. CYGNUS will be transported to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility for final propellant loading and late cargo stowage. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on March 19, 2017. CYGNUS will deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
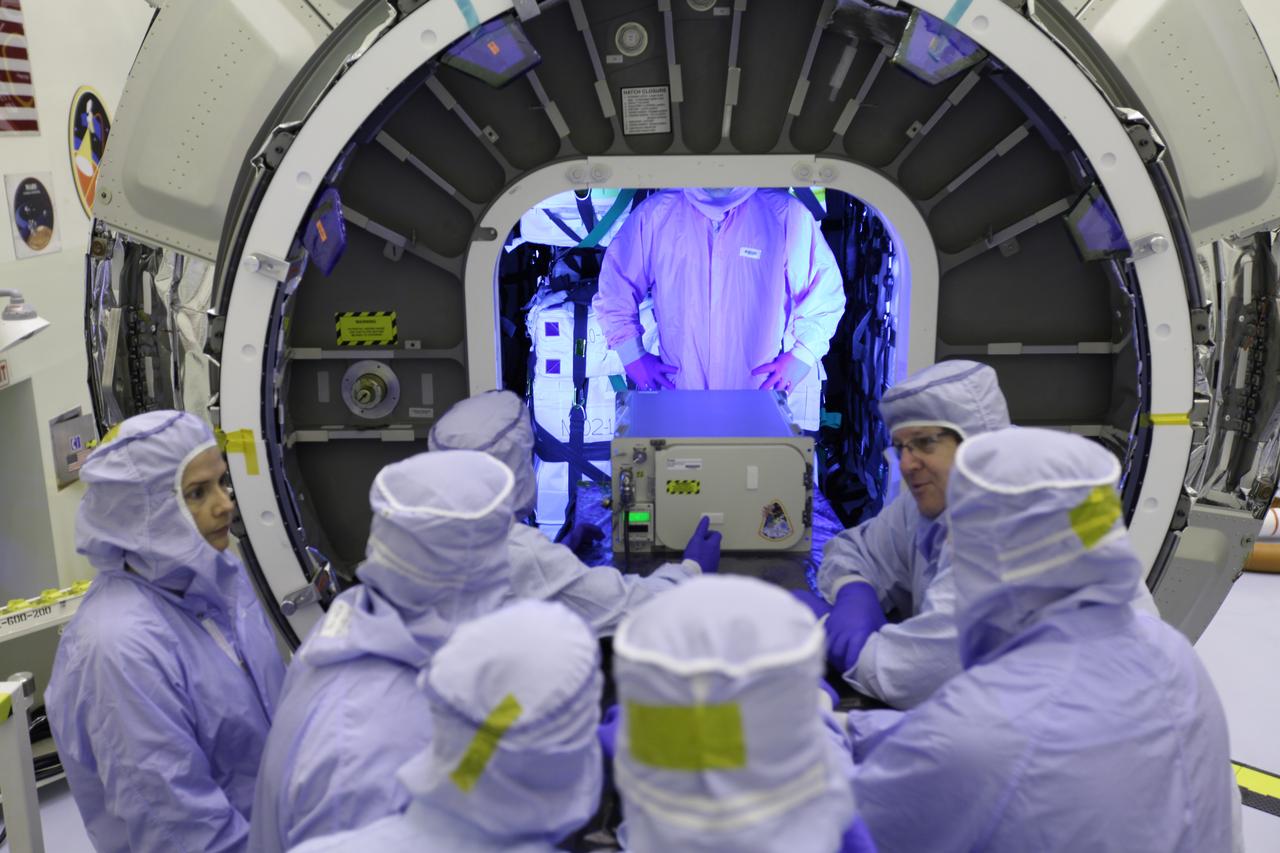

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians load a powered cargo unit into the Orbital ATK Cygnus pressurized cargo module during final stowage. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station targeted for March 24, 2017. Cygnus will deliver 7,600 pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
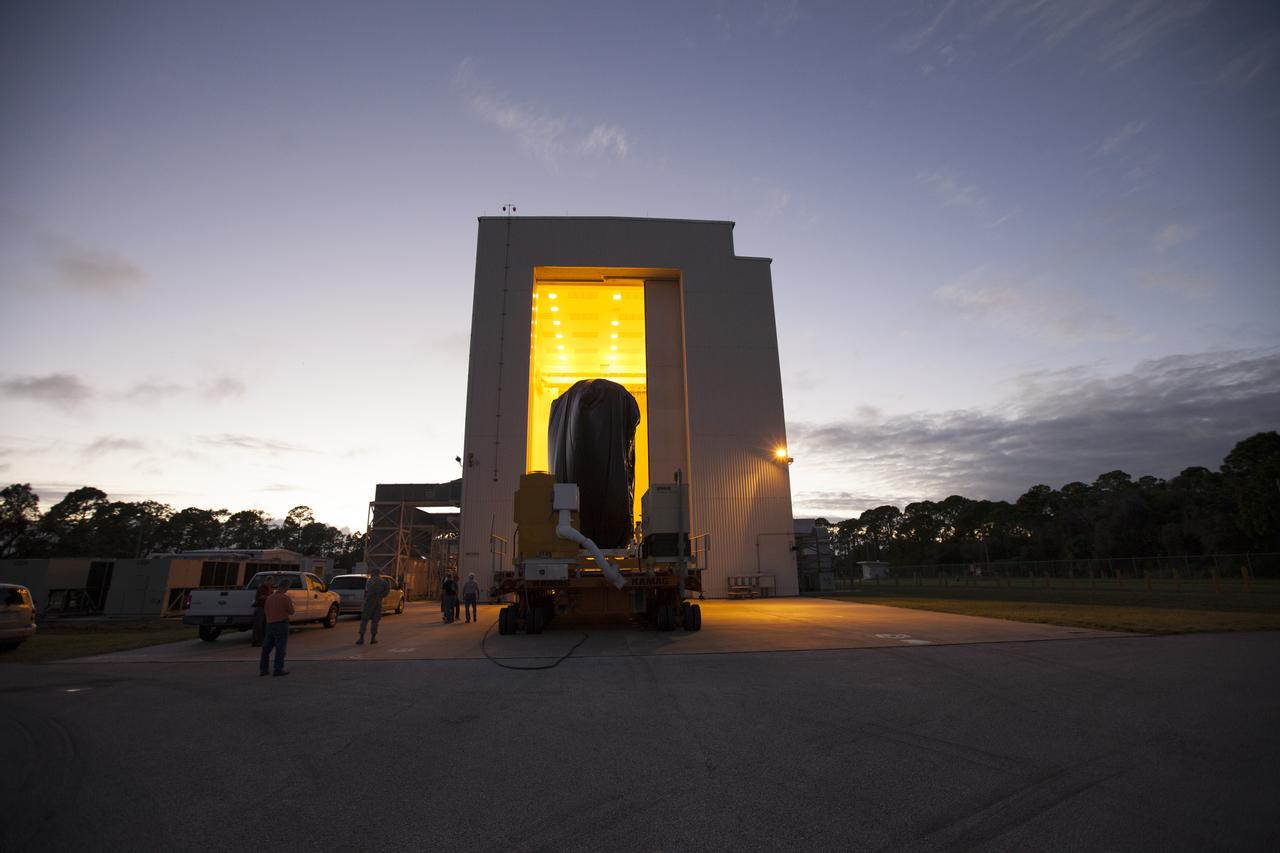

A KAMAG transporter with Orbital ATK's CYGNUS pressurized cargo module secured on top arrives at the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. CYGNUS will be moved inside the facility for final propellant loading and late cargo stowage. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on March 19, 2017. CYGNUS will deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
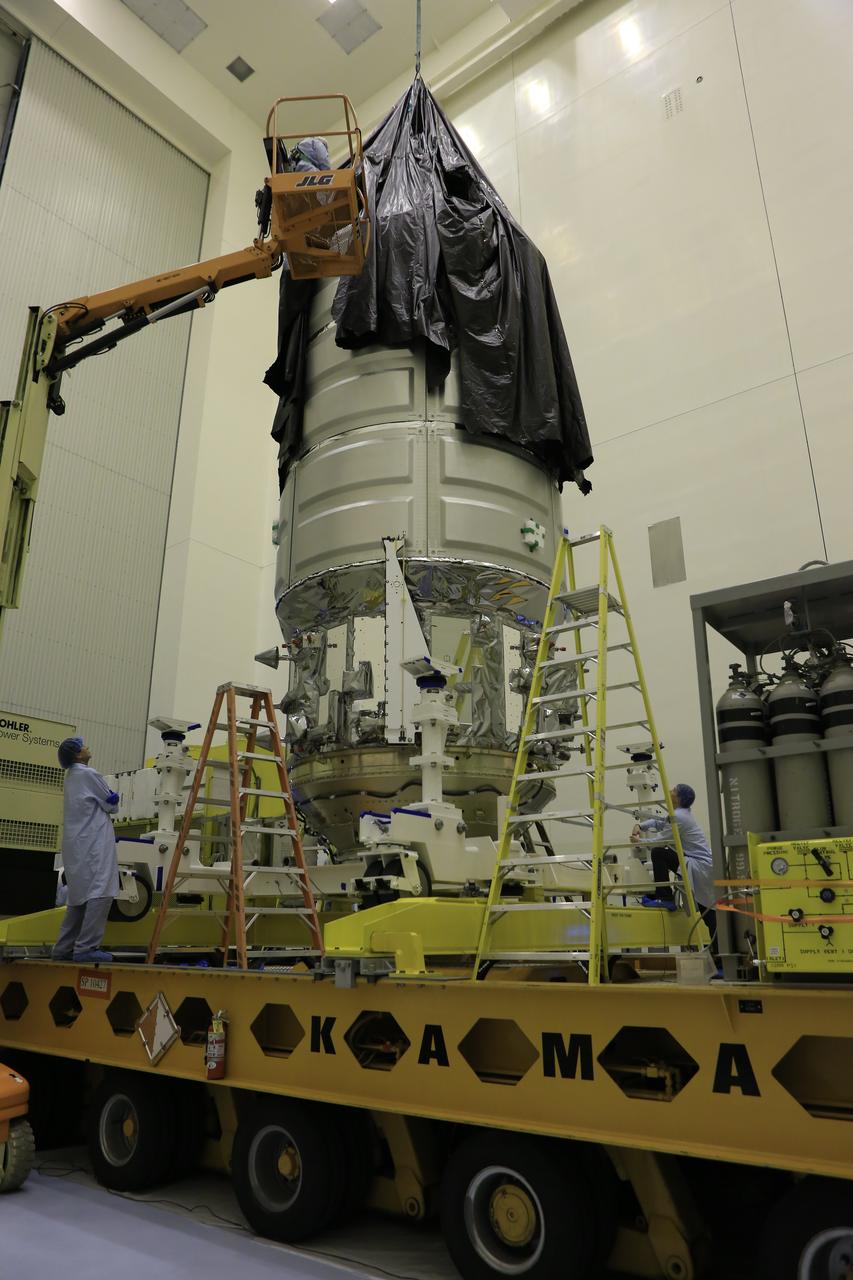

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians assist as a crane is used to remove the protective covering from Orbital ATK's CYGNUS pressurized cargo module on a KAMAG transporter. In the PHSF, Cygnus will be moved to a work stand for final propellant loading and late cargo stowage. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on March 19, 2017. CYGNUS will deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Orbital ATK Cygnus pressurized cargo module is tilted to the horizontal position to prepare for final stowage of powered cargo. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station targeted for March 24, 2017. Cygnus will deliver 7,600 pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
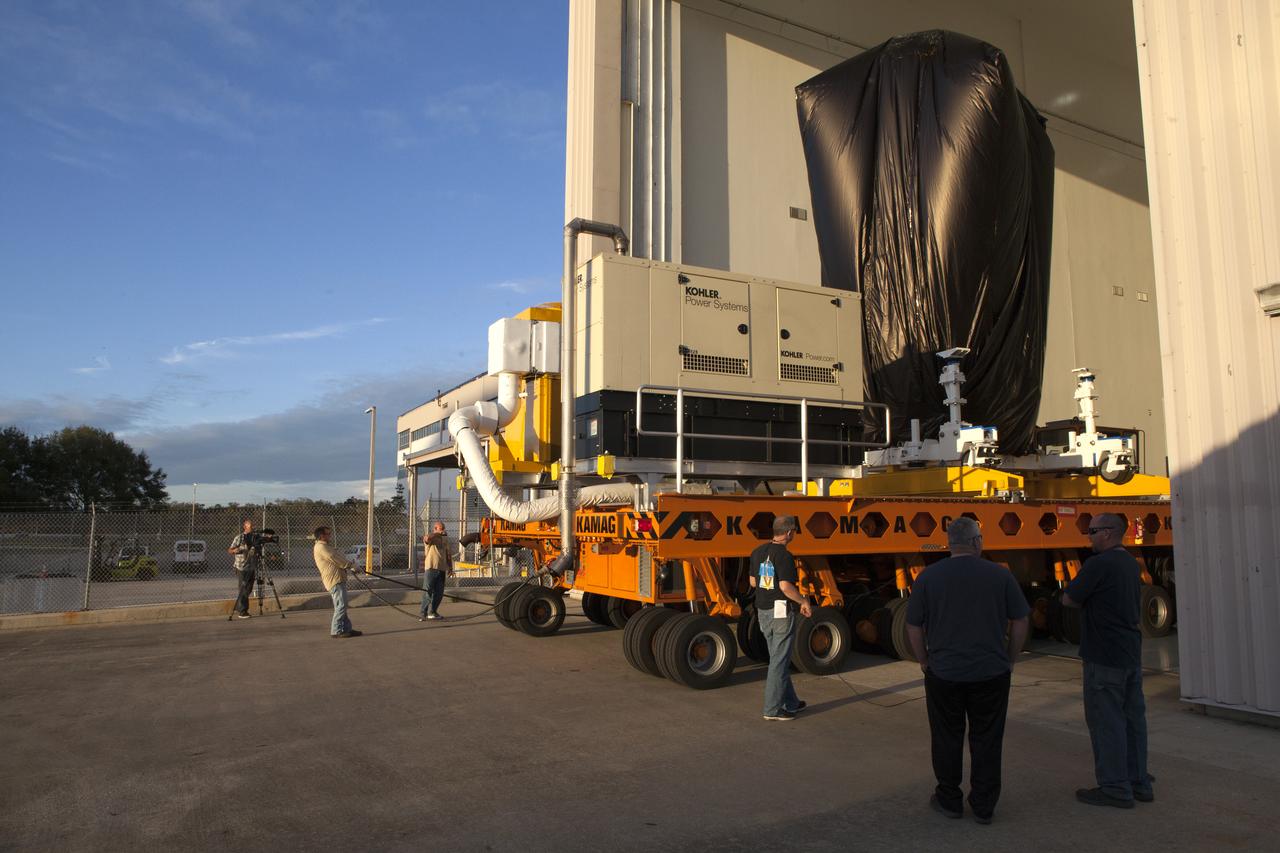

A KAMAG transporter with Orbital ATK's CYGNUS pressurized cargo module secured on top exits the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. CYGNUS will be transported to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility for final propellant loading and late cargo stowage. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on March 19, 2017. CYGNUS will deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
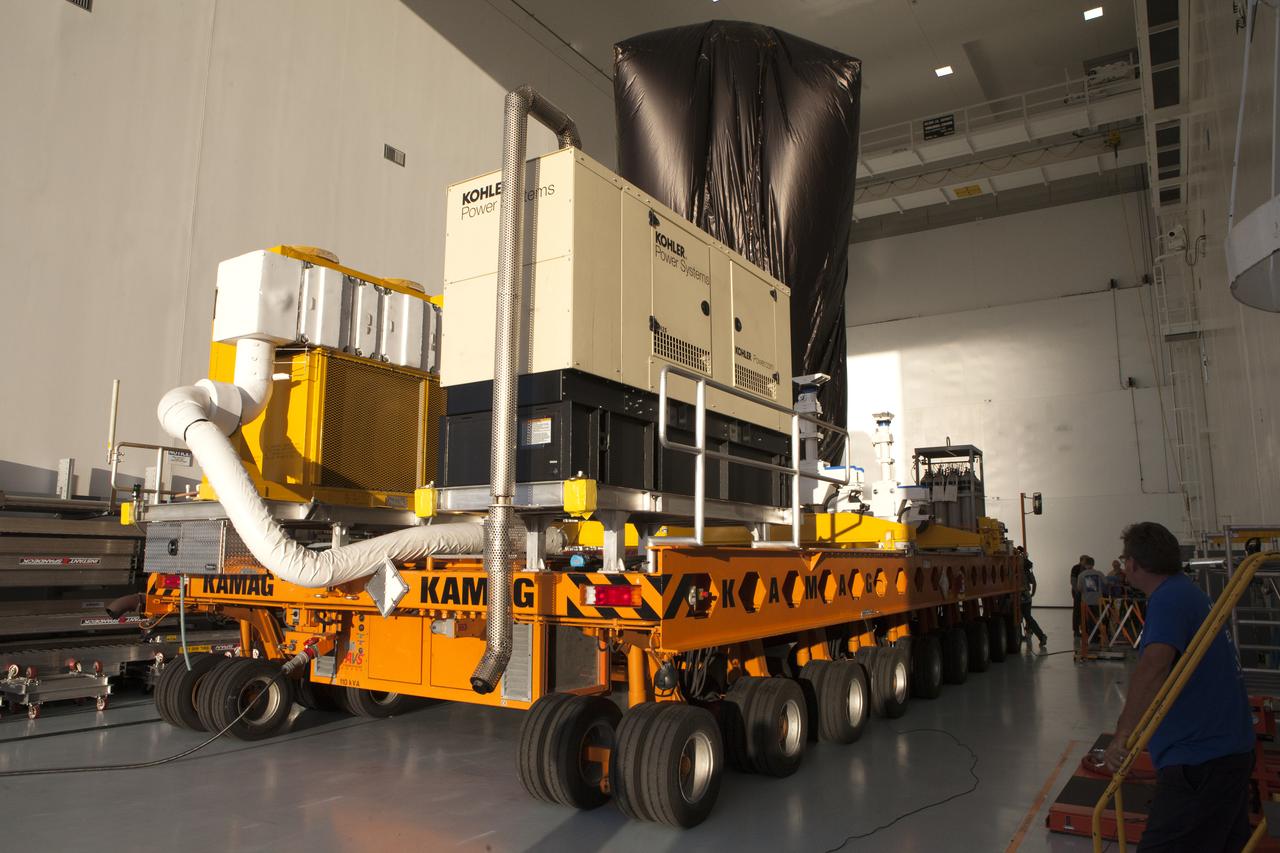

A KAMAG transporter with Orbital ATK's CYGNUS pressurized cargo module secured on top begins to move out of the high bay in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. CYGNUS will be transported to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility for final propellant loading and late cargo stowage. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on March 19, 2017. CYGNUS will deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
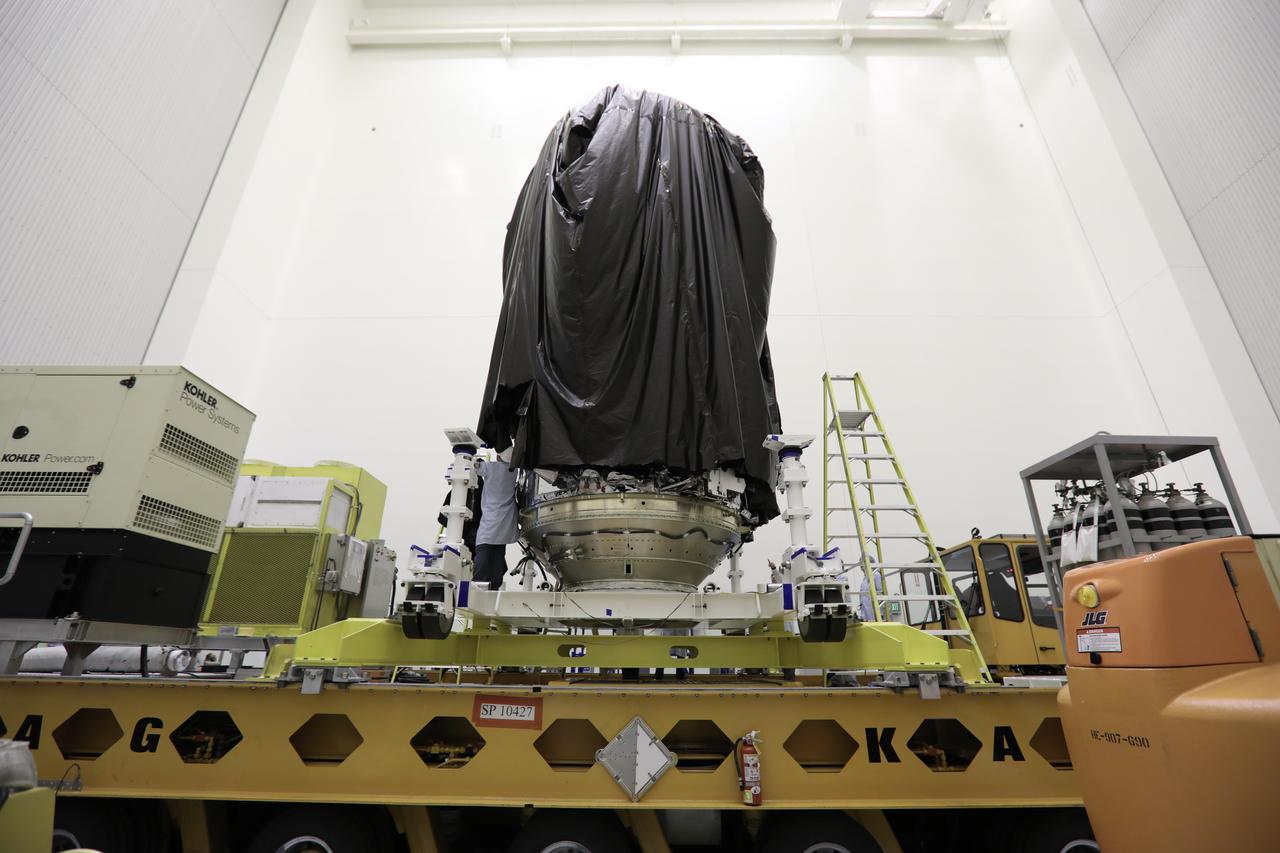

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians begin to remove the protective covering from Orbital ATK's CYGNUS pressurized cargo module on a KAMAG transporter. In the PHSF, Cygnus will be move to a work stand for final propellant loading and late cargo stowage. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on March 19, 2017. CYGNUS will deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
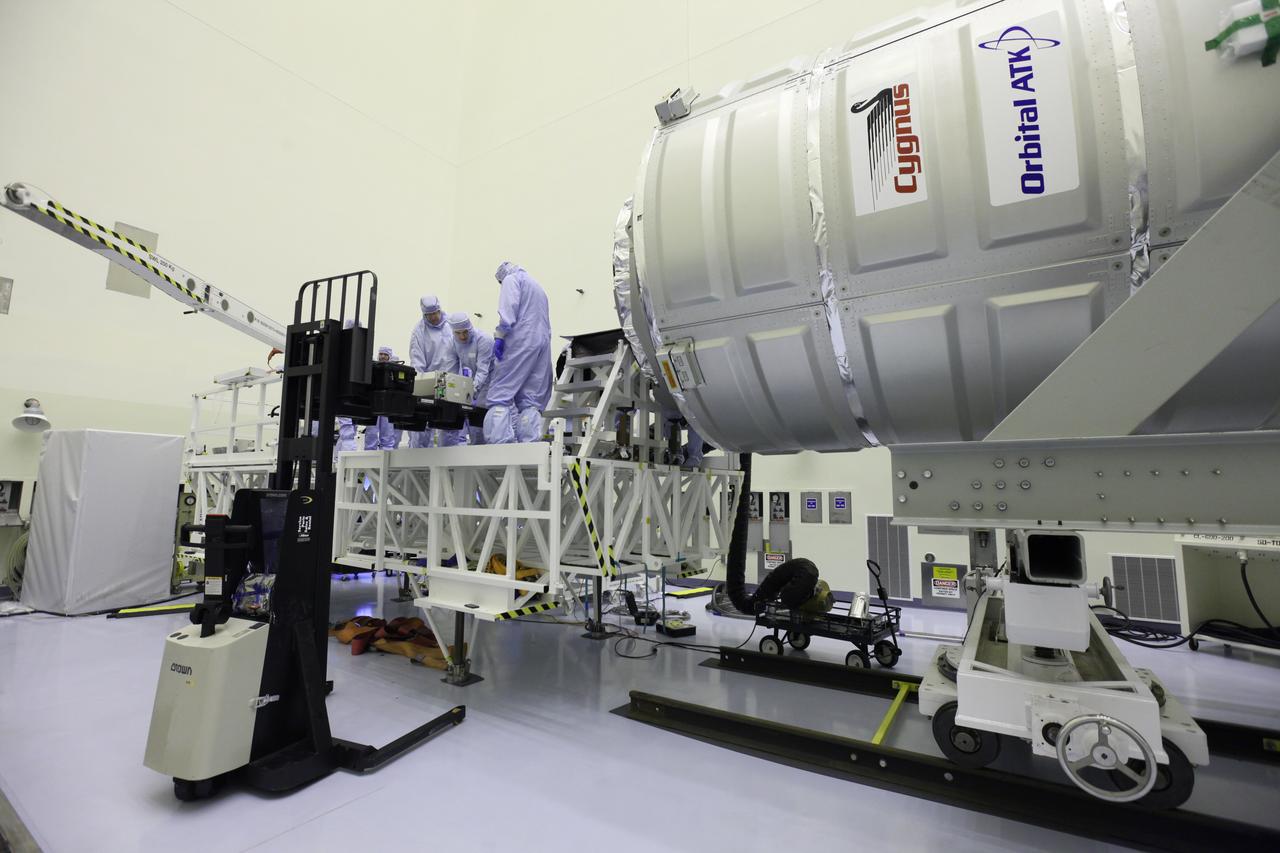

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians prepare a powered cargo unit for late stowage in the Orbital ATK Cygnus pressurized cargo module. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station targeted for March 24, 2017. Cygnus will deliver 7,600 pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
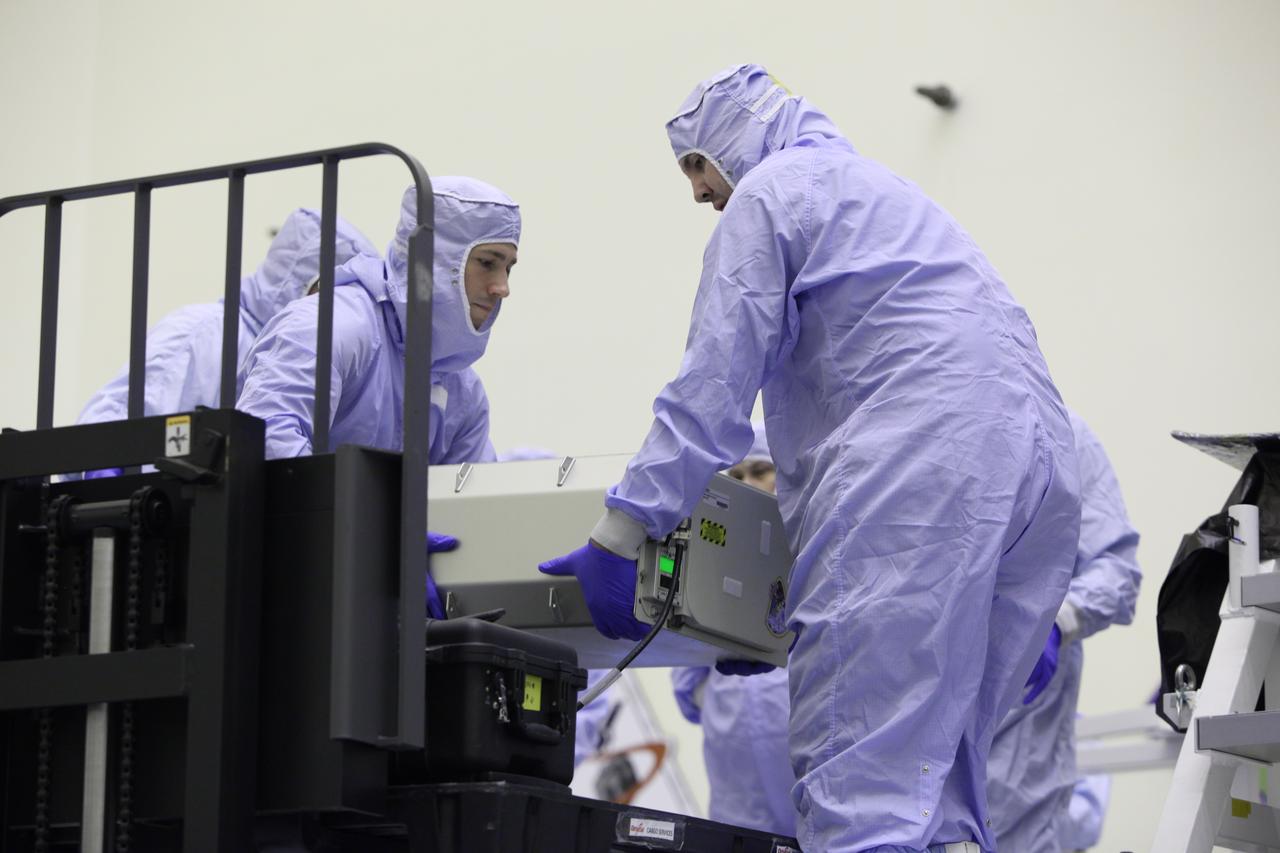

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians prepare a powered cargo unit for late stowage in the Orbital ATK Cygnus pressurized cargo module. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station targeted for March 24, 2017. Cygnus will deliver 7,600 pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.

A KAMAG transporter with Orbital ATK's CYGNUS pressurized cargo module secured on top moves into the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Cygnus will be moved to a work stand for final propellant loading and late cargo stowage. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on March 19, 2017. CYGNUS will deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
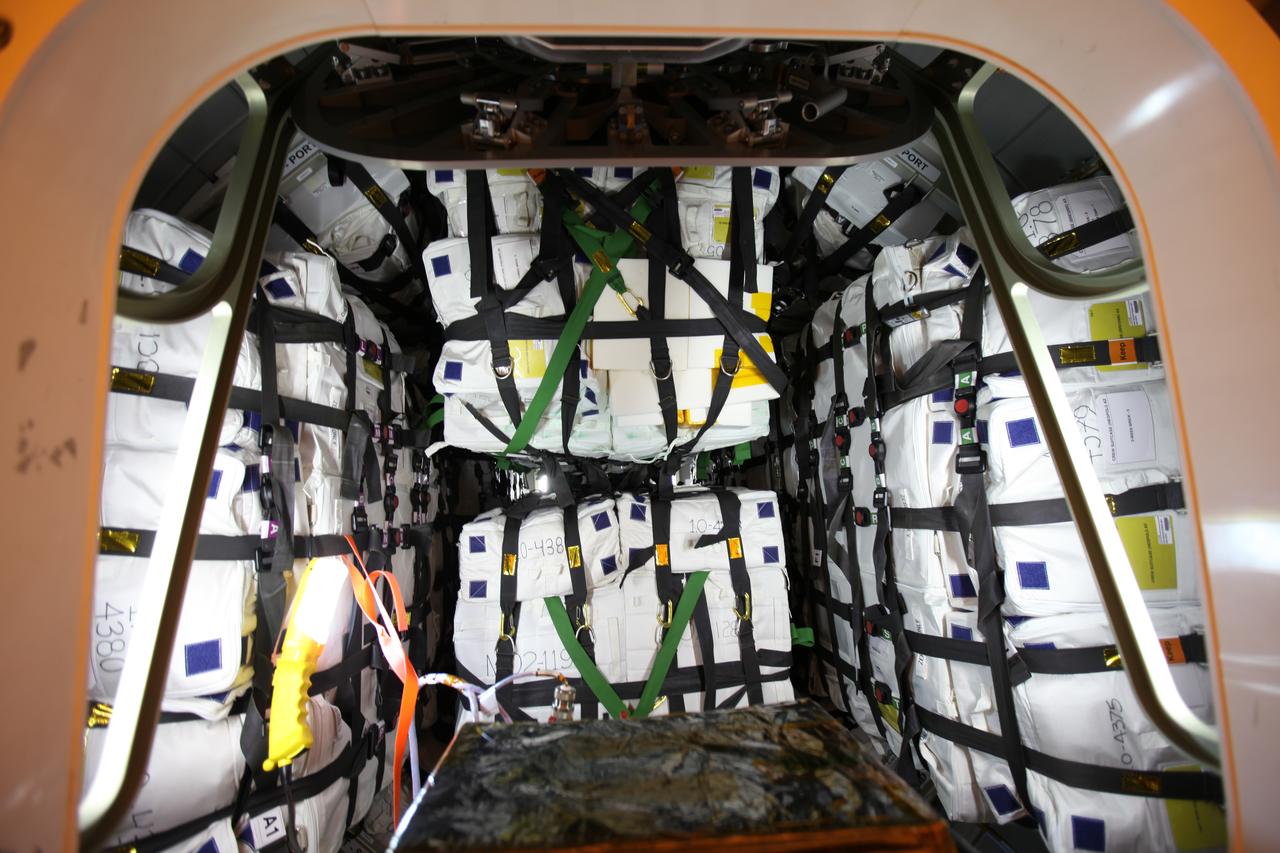

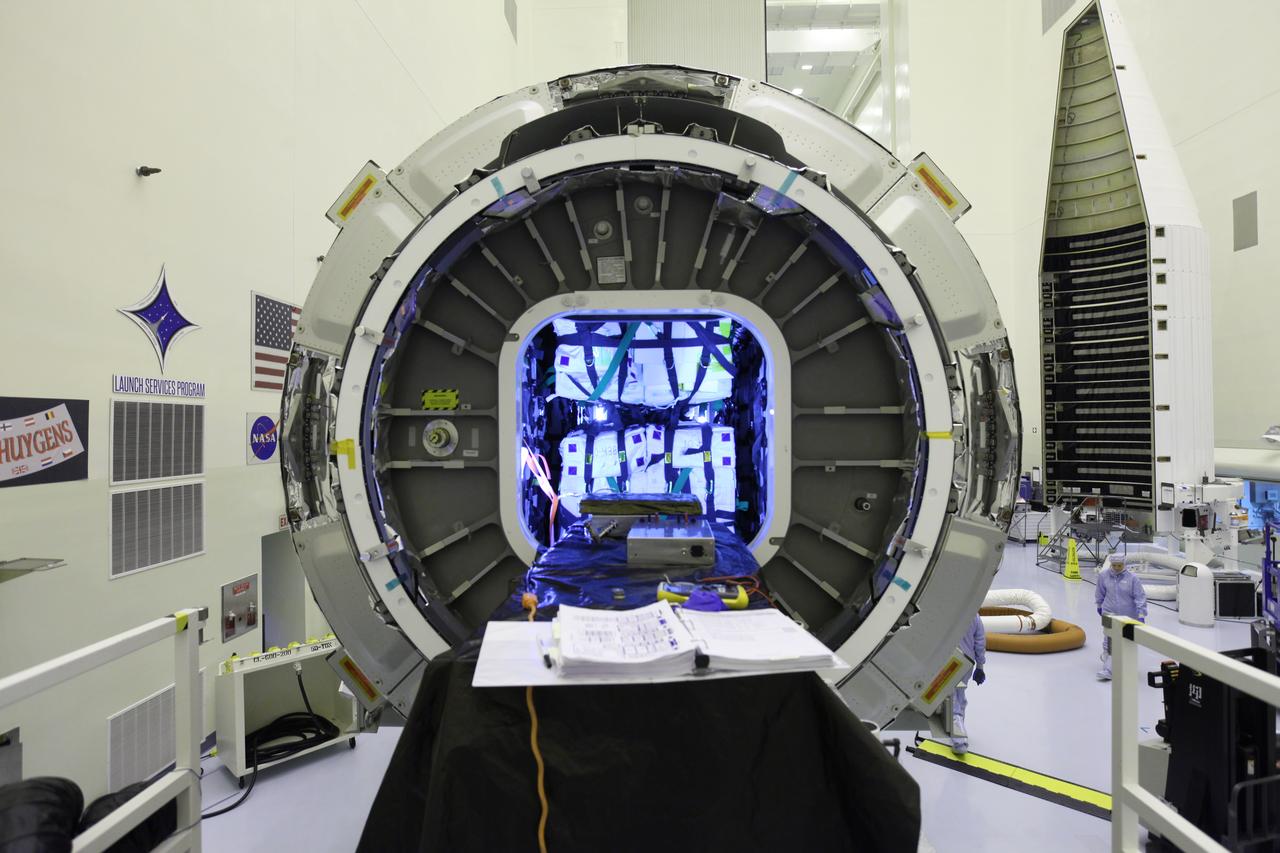
Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the hatch on the Orbital ATK Cygnus pressurized cargo module is open for final stowage of powered cargo. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station targeted for March 24, 2017. Cygnus will deliver 7,600 pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
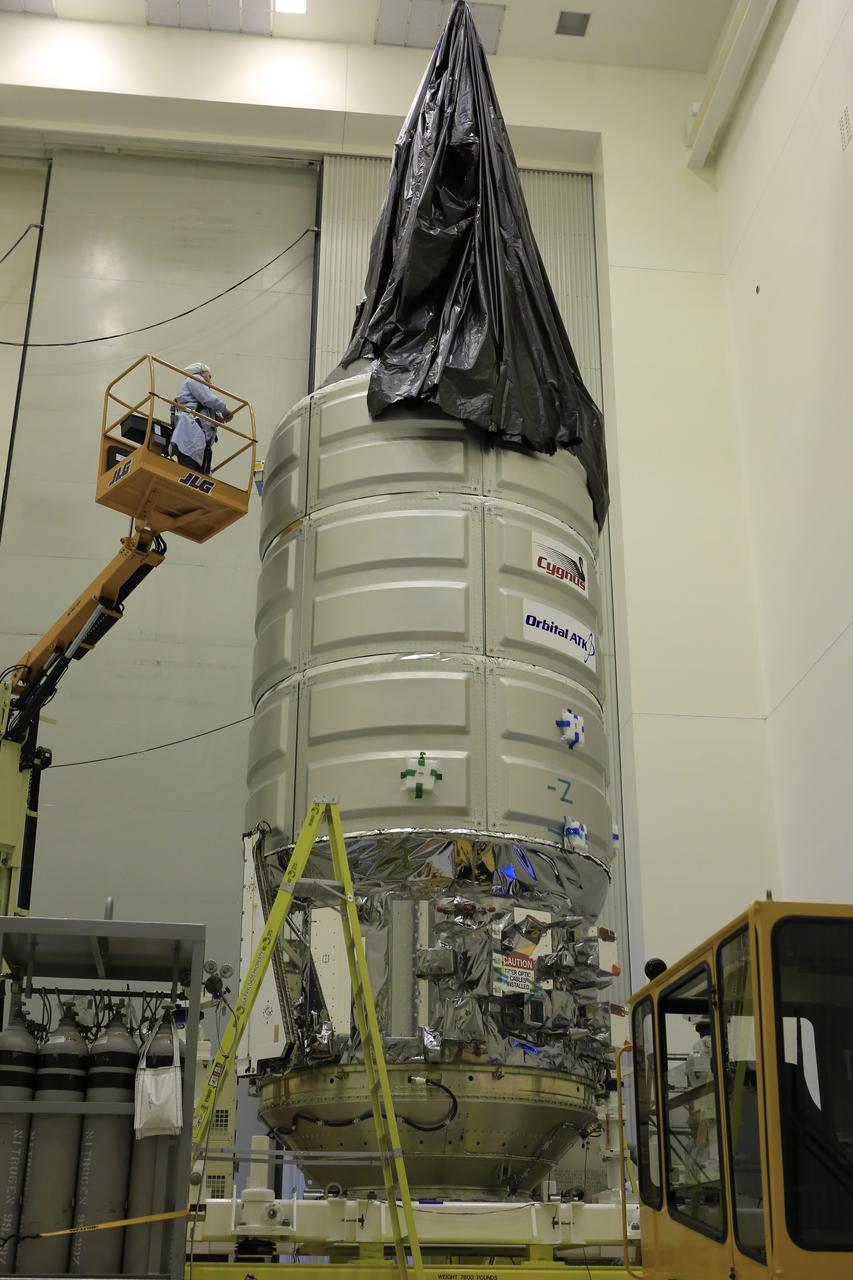

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians assist as a crane is used to remove the protective covering from Orbital ATK's CYGNUS pressurized cargo module on a KAMAG transporter. In the PHSF, Cygnus will be moved to a work stand for final propellant loading and late cargo stowage. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on March 19, 2017. CYGNUS will deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
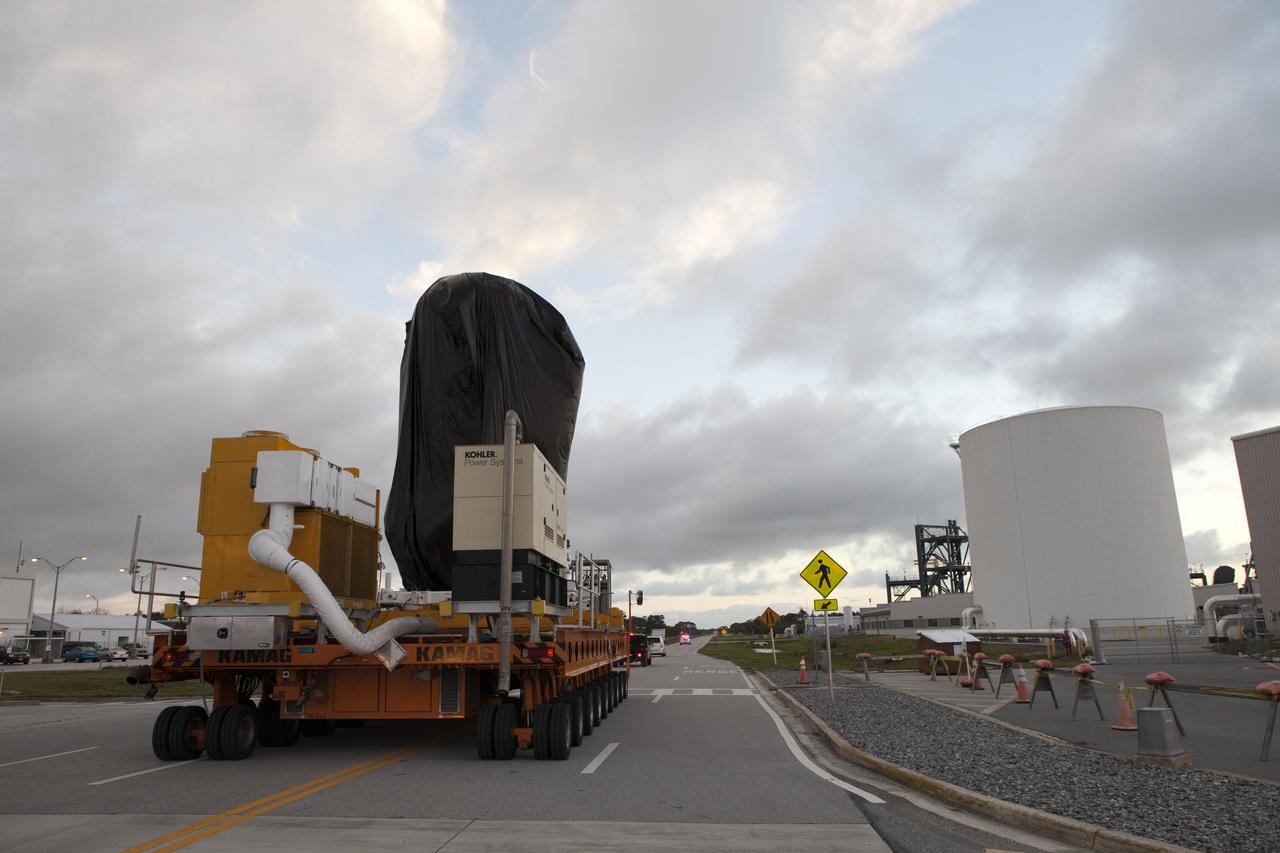

A KAMAG transporter with Orbital ATK's CYGNUS pressurized cargo module secured on top moves slowly along the road after exiting the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. CYGNUS will be transported to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility for final propellant loading and late cargo stowage. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on March 19, 2017. CYGNUS will deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
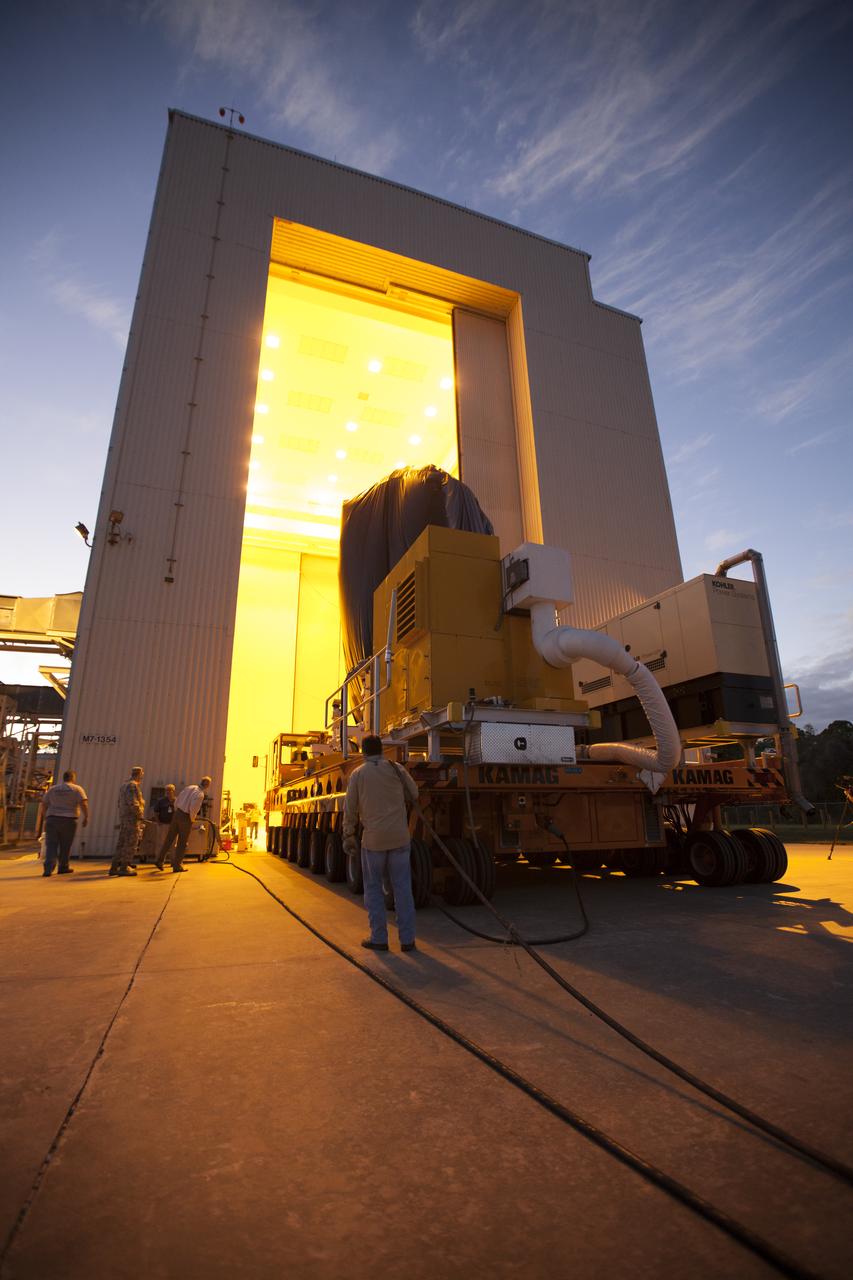

A KAMAG transporter with Orbital ATK's CYGNUS pressurized cargo module secured on top arrives at the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. CYGNUS will be moved inside the facility for final propellant loading and late cargo stowage. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on March 19, 2017. CYGNUS will deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
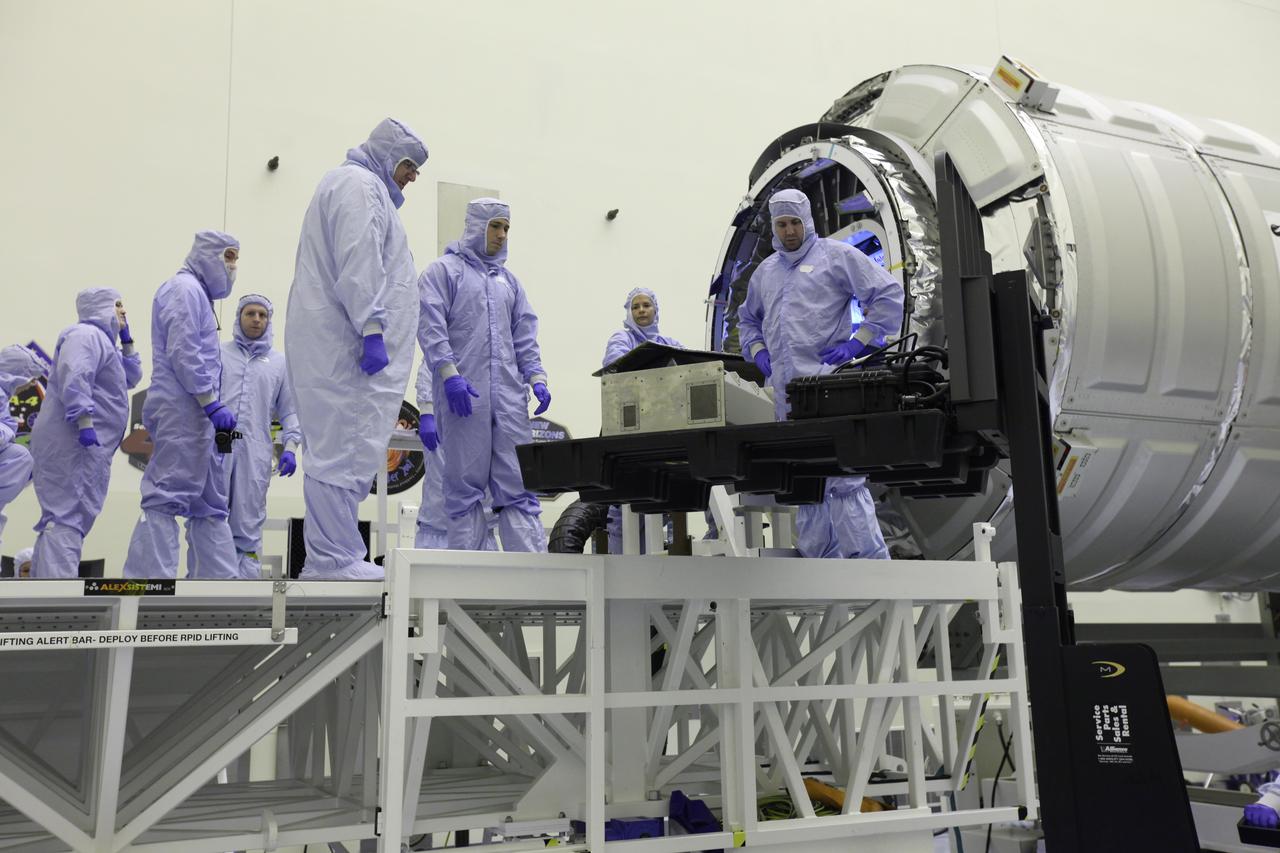

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians prepare a powered cargo unit for late stowage in the Orbital ATK Cygnus pressurized cargo module. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station targeted for March 24, 2017. Cygnus will deliver 7,600 pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
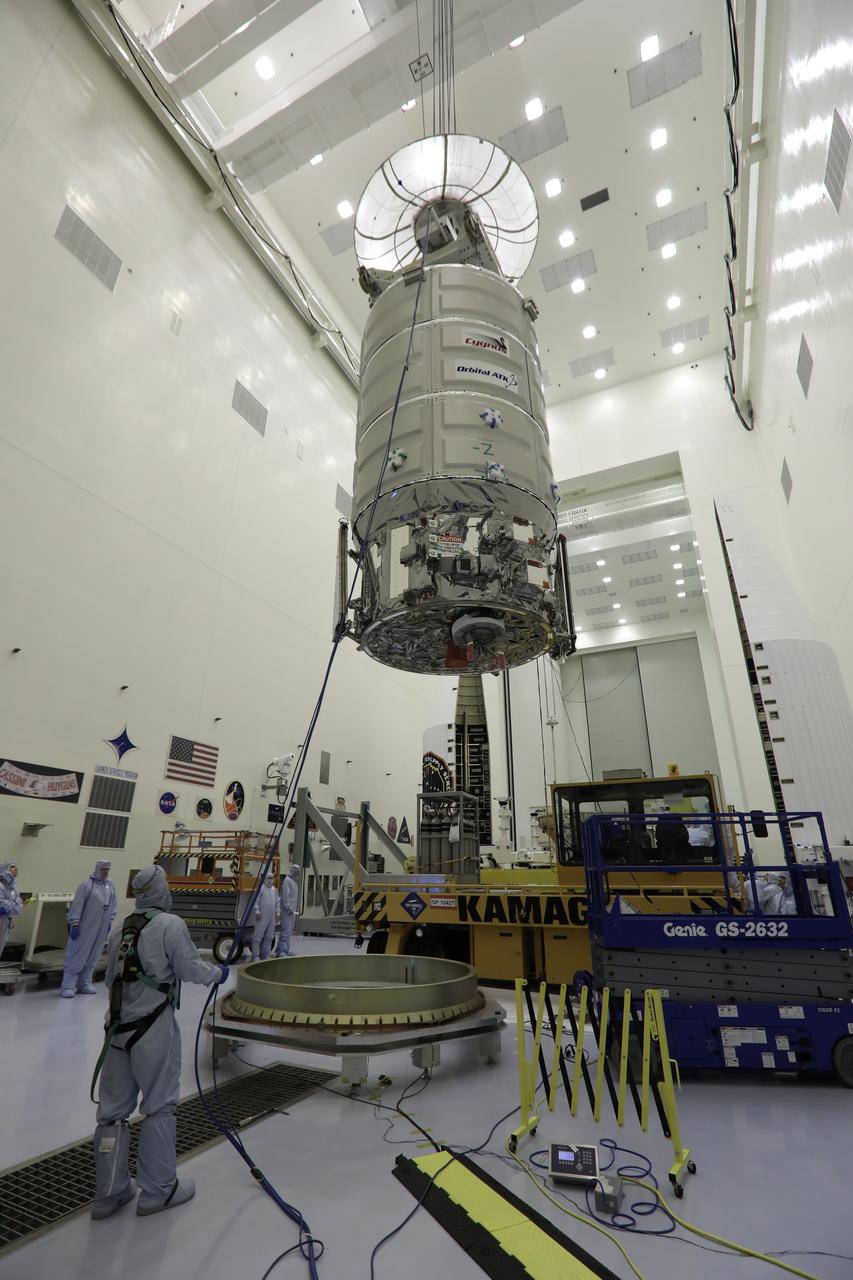

A crane lifts Orbital ATK's CYGNUS pressurized cargo module up and away from the KAMAG transporter inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. CYGNUS will be lowered onto a work stand for final propellant loading and late cargo stowage. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on March 19, 2017. CYGNUS will deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
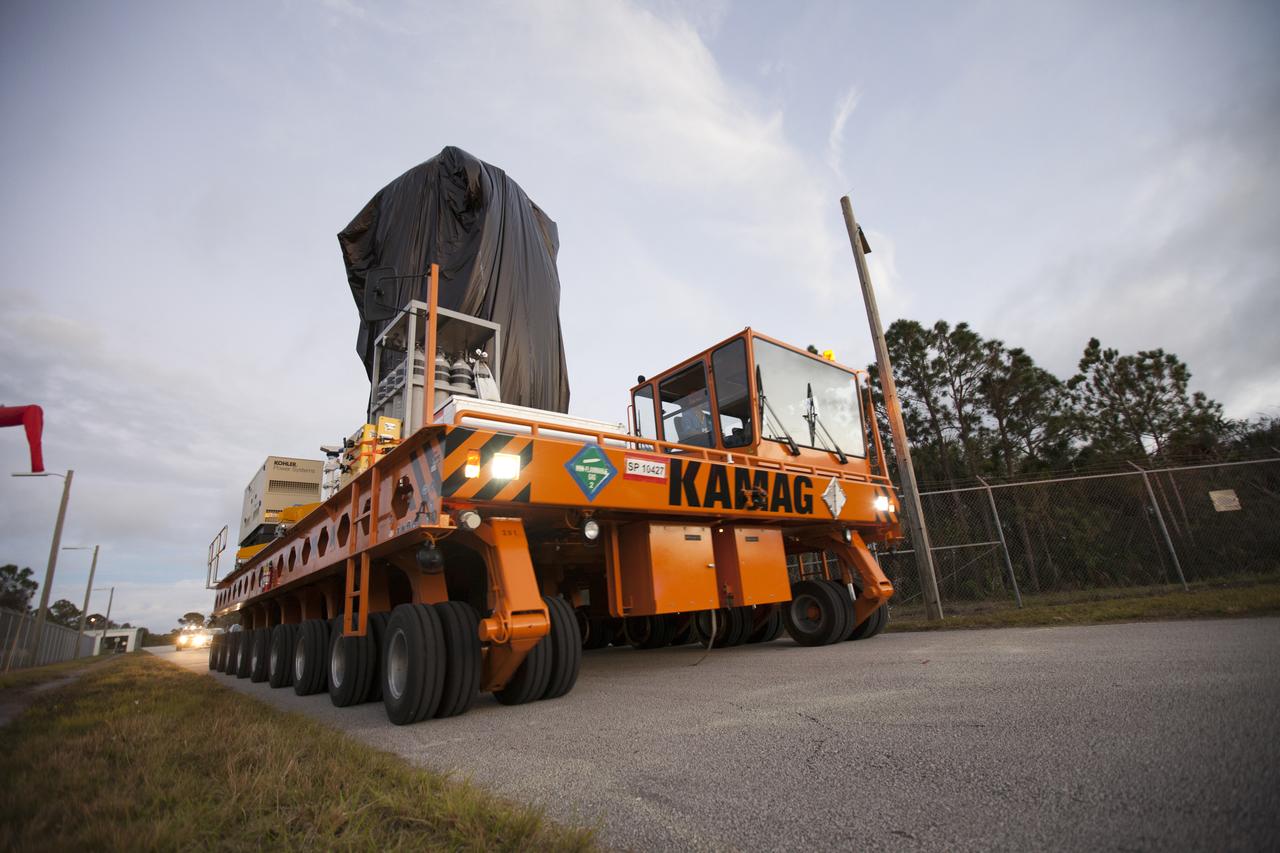

A KAMAG transporter with Orbital ATK's CYGNUS pressurized cargo module secured on top moves slowly along the road after exiting the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. CYGNUS will be transported to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility for final propellant loading and late cargo stowage. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on March 19, 2017. CYGNUS will deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
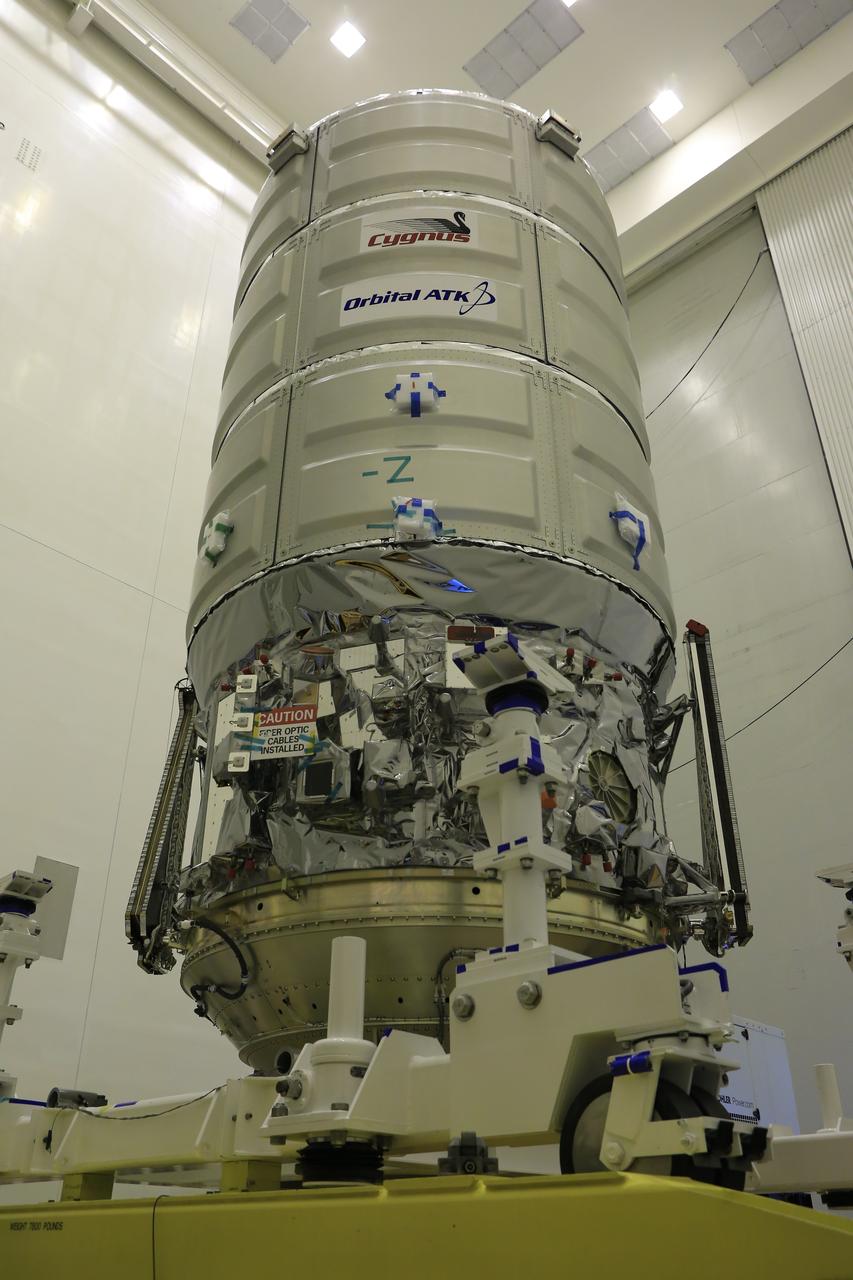

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the protective covering was removed from Orbital ATK's CYGNUS pressurized cargo module on a KAMAG transporter. In the PHSF, Cygnus will be moved to a work stand for final propellant loading and late cargo stowage. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on March 19, 2017. CYGNUS will deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
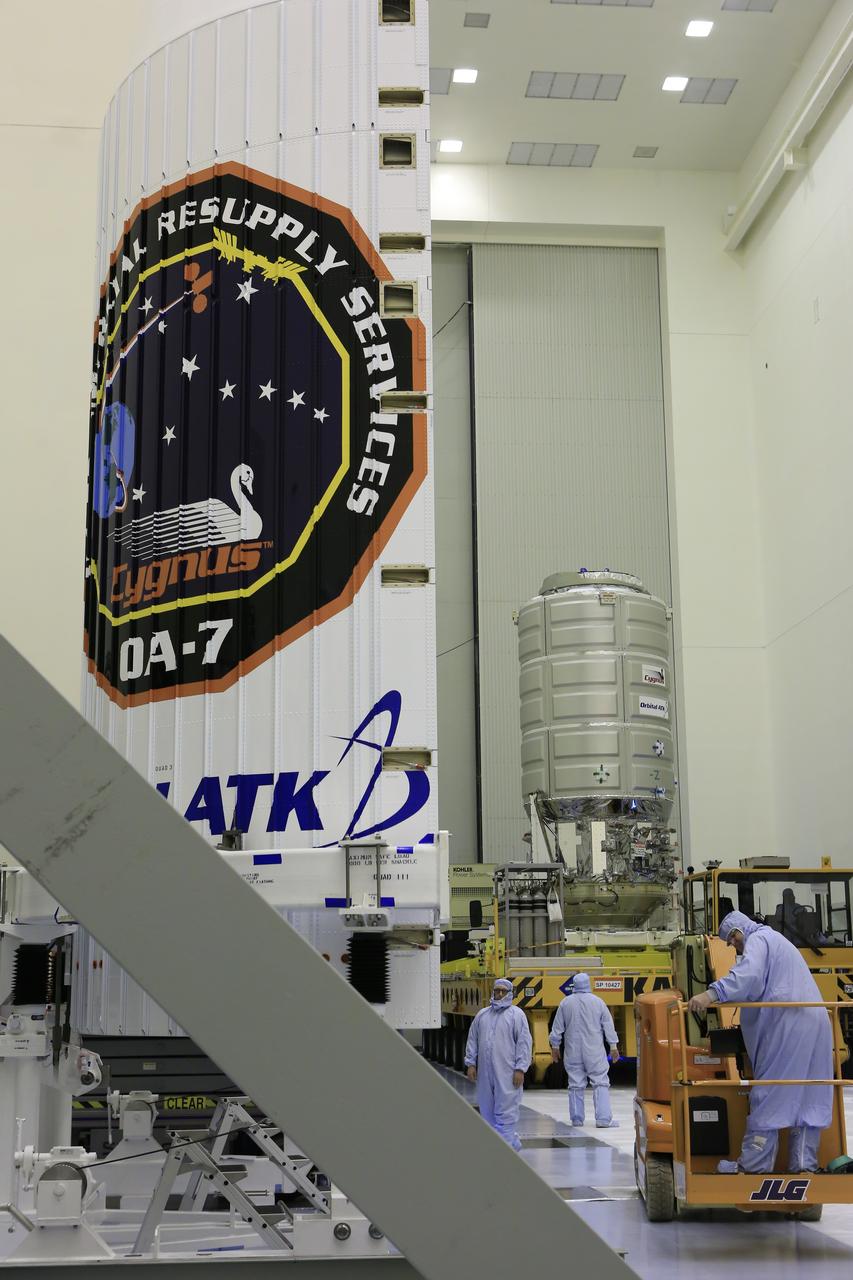

A KAMAG transporter with Orbital ATK's CYGNUS pressurized cargo module secured on top slowly moves from the airlock into the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Cygnus will be moved to a work stand for final propellant loading and late cargo stowage. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on March 19, 2017. CYGNUS will deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
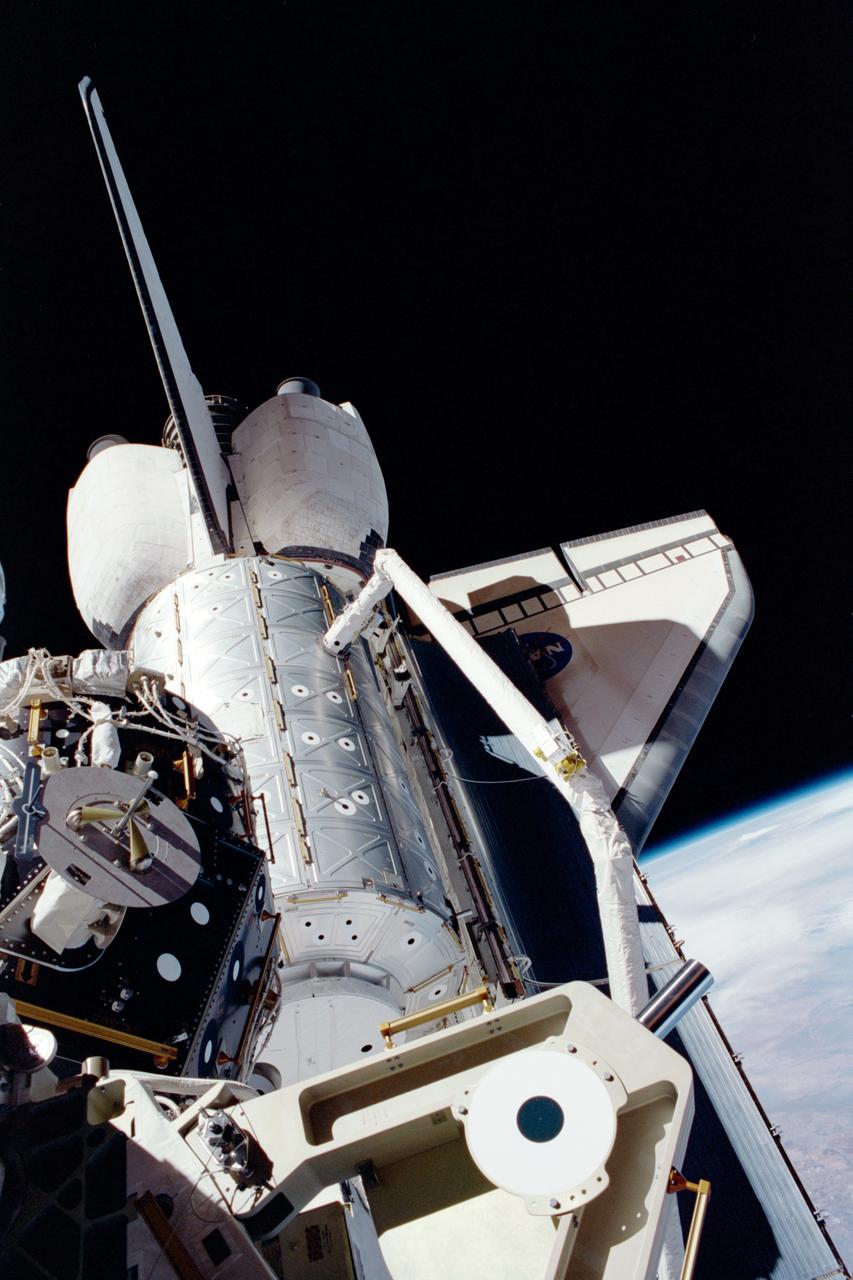

STS098-331-005 (7-20 February 2001) --- In the grasp of the shuttle’s remote manipulator system (RMS) robot arm, the Destiny laboratory is moved from its stowage position in the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Atlantis. The photo was taken by astronaut Thomas D. Jones, who was participating in one of three STS-98/5a spacewalks at the time. Astronaut Robert L. Curbeam (out of frame) also made the three spacewalks.
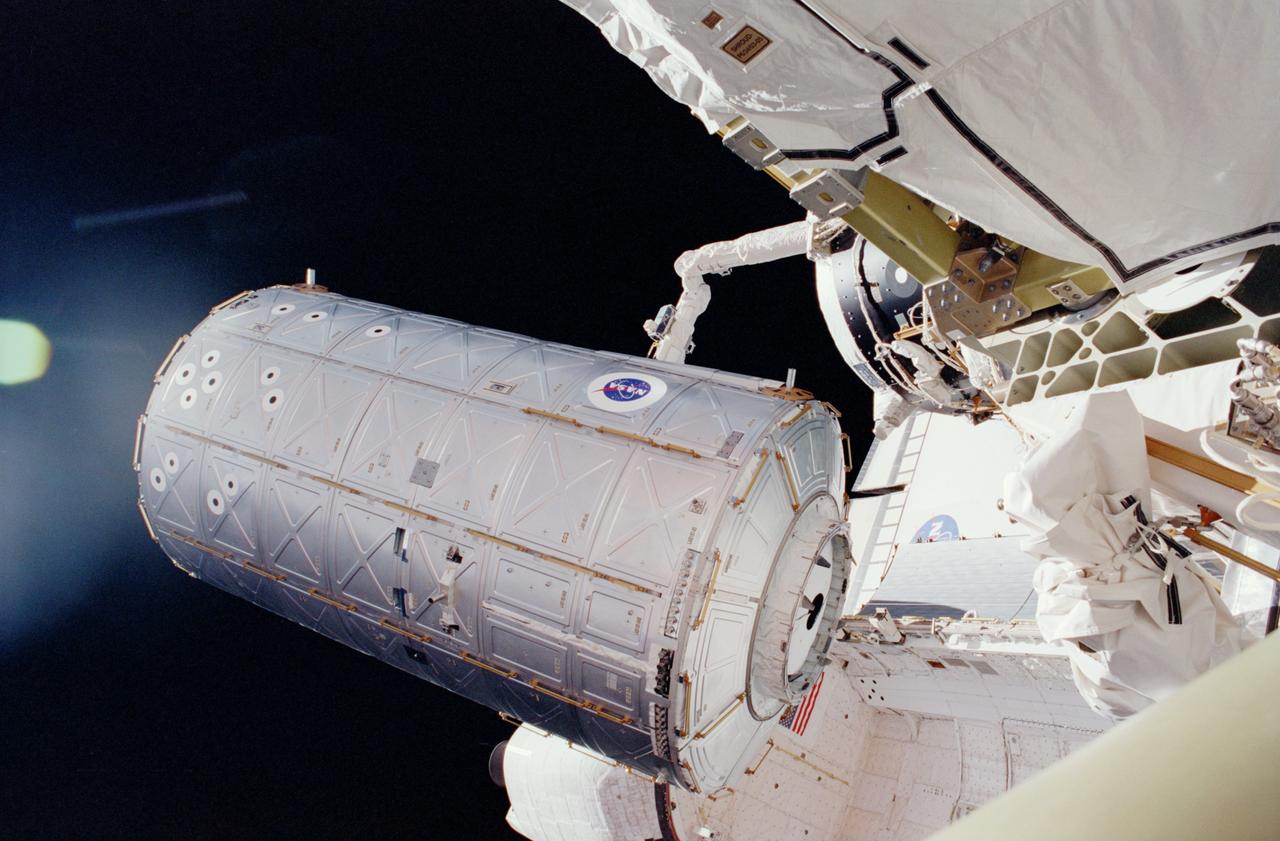

STS098-331-0017 (7-20 February 2001) --- In the grasp of the shuttle's remote manipulator system (RMS) robot arm, the Destiny laboratory is moved from its stowage position in the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Atlantis. The photo was taken by astronaut Thomas D. Jones, who was participating in one of three STS-98/5a space walks at the time. Astronaut Robert L. Curbeam (out of frame) also made the three space walks.
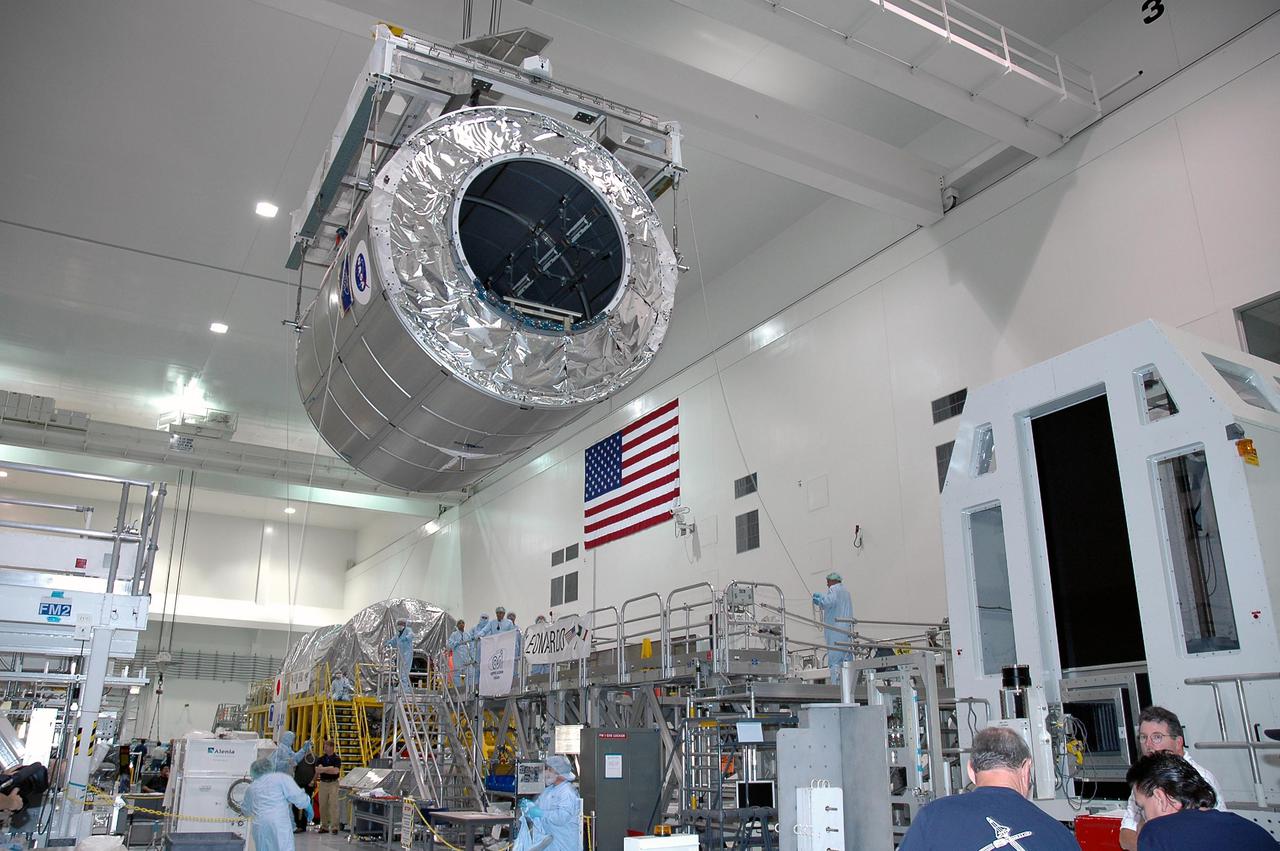

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Raffaello, the MPLM scheduled to fly on the STS-114 Return to Flight mission, is being moved from a cargo element work stand to an element rotation stand. The latter allows the module to be rotated around its x-axis to facilitate better access to the MPLM during final pre-flight processing operations. STS-114 is a logistics flight (LF1) that will carry the External Stowage Platform plus supplies and equipment to the International Space Station. The planning window for launch is May 12 to June 3, 2005.
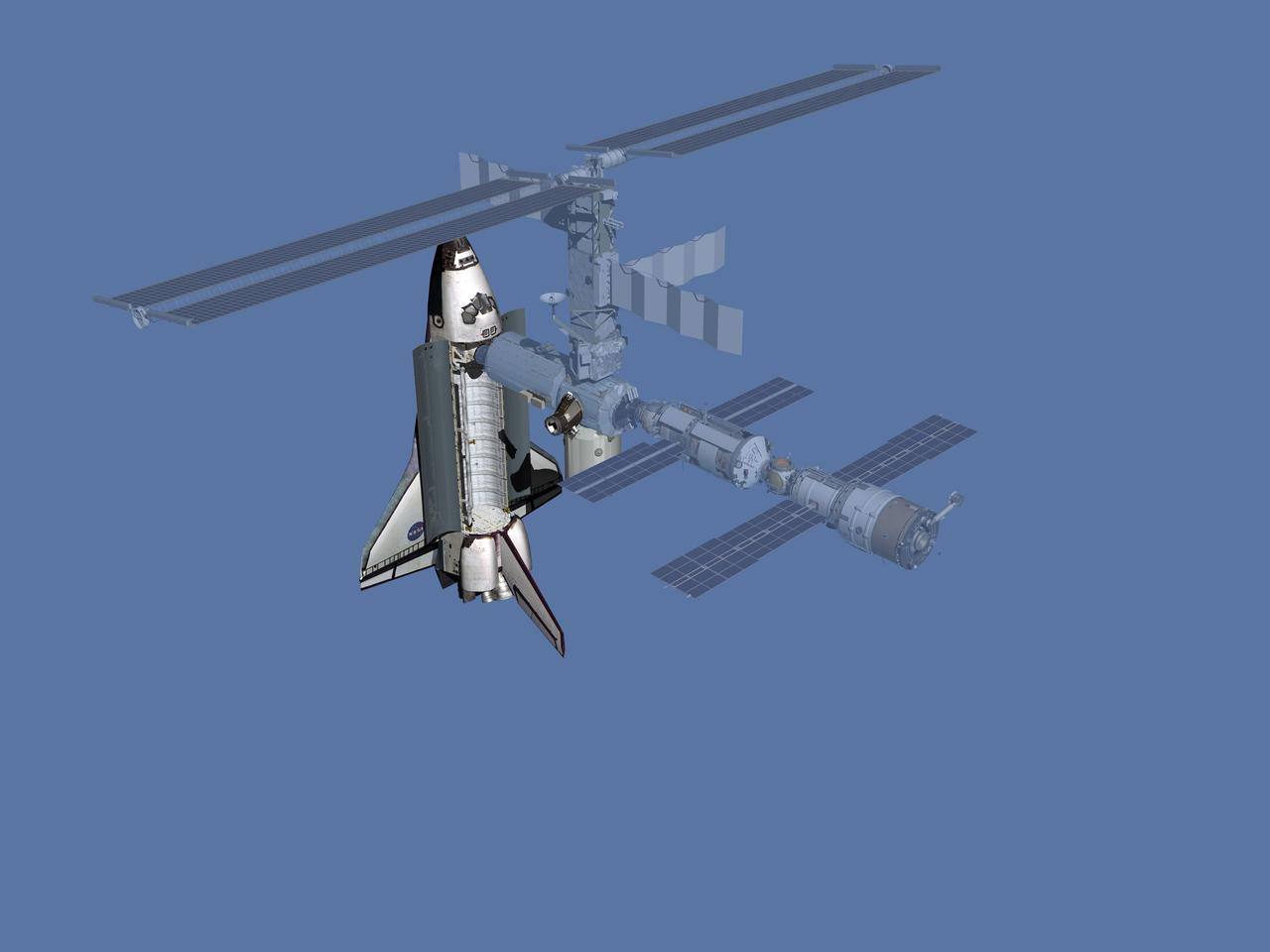
JSC2006-E-43486 (March 2001) --- Computer-generated artist's rendering of the International Space Station after flight STS-102/5A.1. Space Shuttle Discovery re-supplied the station with cargo from the Italian-built Leonardo Multi-Purpose Logistics Module (MPLM). The shuttle also arrived with the Expedition Two crew and returned with the Expedition One crew. The Pressurized Mating Adapter-3 (PMA-3) was relocated to the port side of the Unity node and the External Stowage Platform-1 was installed on the Destiny laboratory.
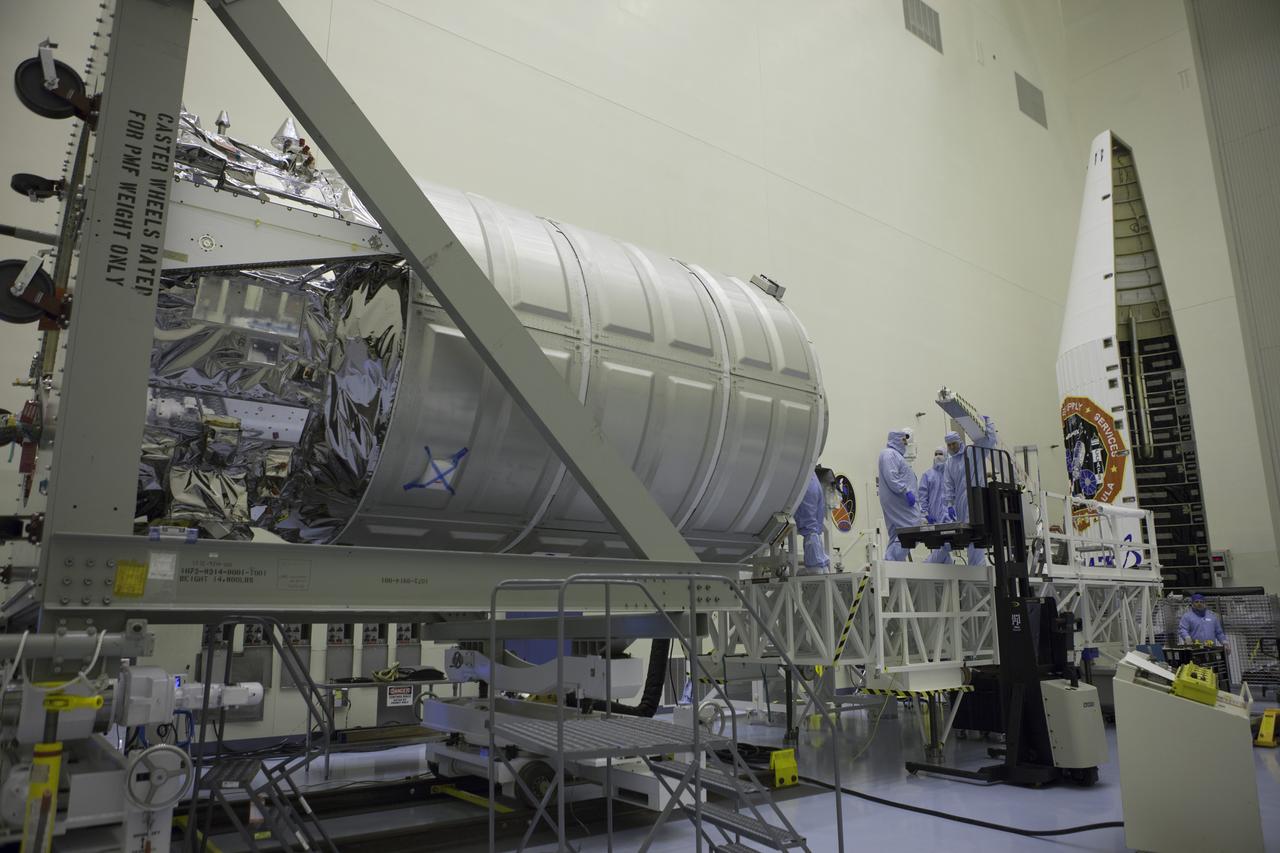

Technicians prepare load cargo into the Orbital ATK Cygnus pressurized module during late stowage operations inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft is scheduled for the upcoming Orbital ATK Commercial Resupply Services-6 mission to deliver hardware and supplies to the International Space Station. The Cygnus is scheduled to lift off atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on March 22.

STS109-E-5389 (5 March 2002) --- Astronaut James H. Newman, mission specialist, returns to a stowage area in the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Columbia during the STS-109 mission's second day of extravehicular activity (EVA). Astronauts Newman and Michael J. Massimino worked to replace the second set of solar arrays on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The image was recorded with a digital still camera.
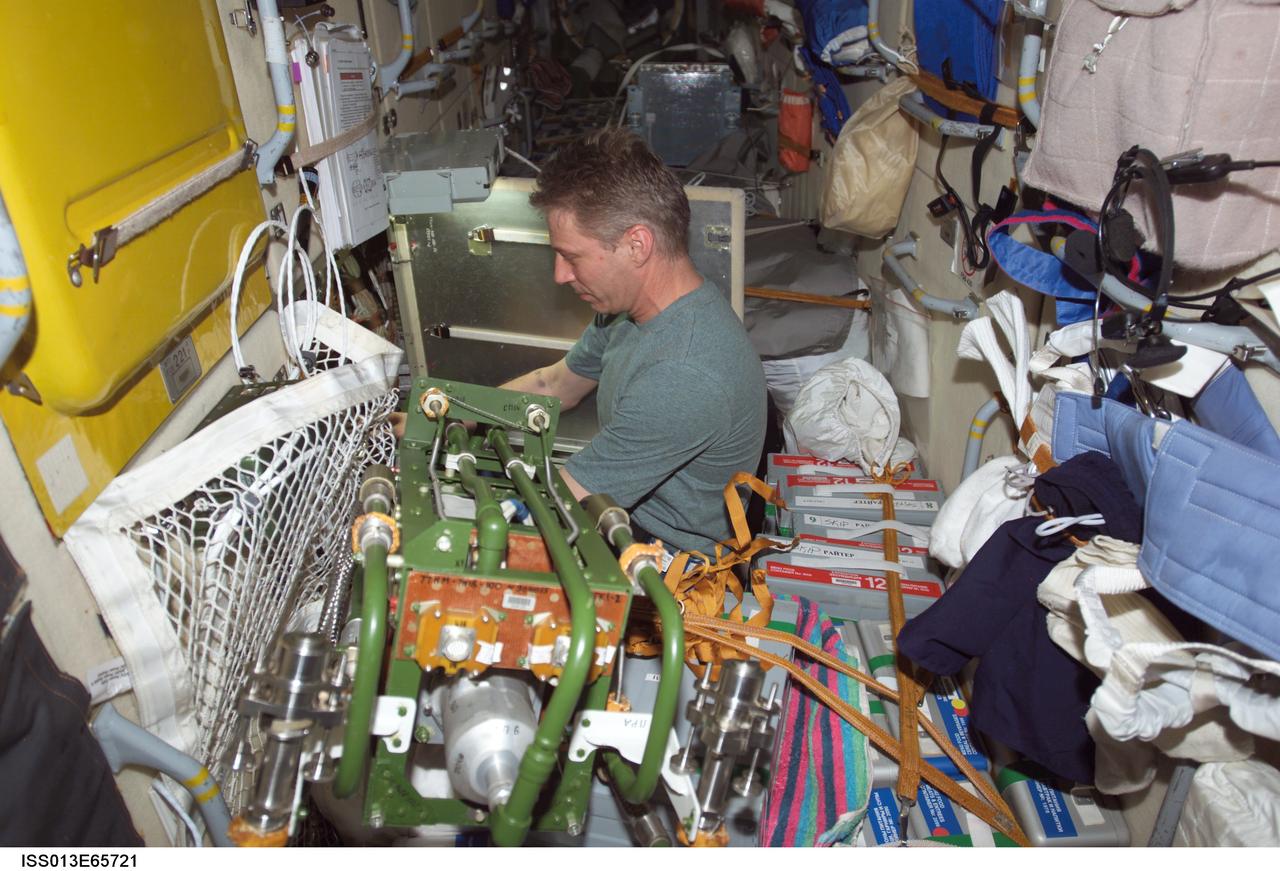

ISS013-E-65721 (10 Aug. 2006) --- European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Thomas Reiter, Expedition 13 flight engineer, replaces the number two replaceable pump panel (SPN) in the number one loop (VGK1) of the International Space Station's Zarya functional cargo block (FGB) thermal control system with a new spare from stowage.
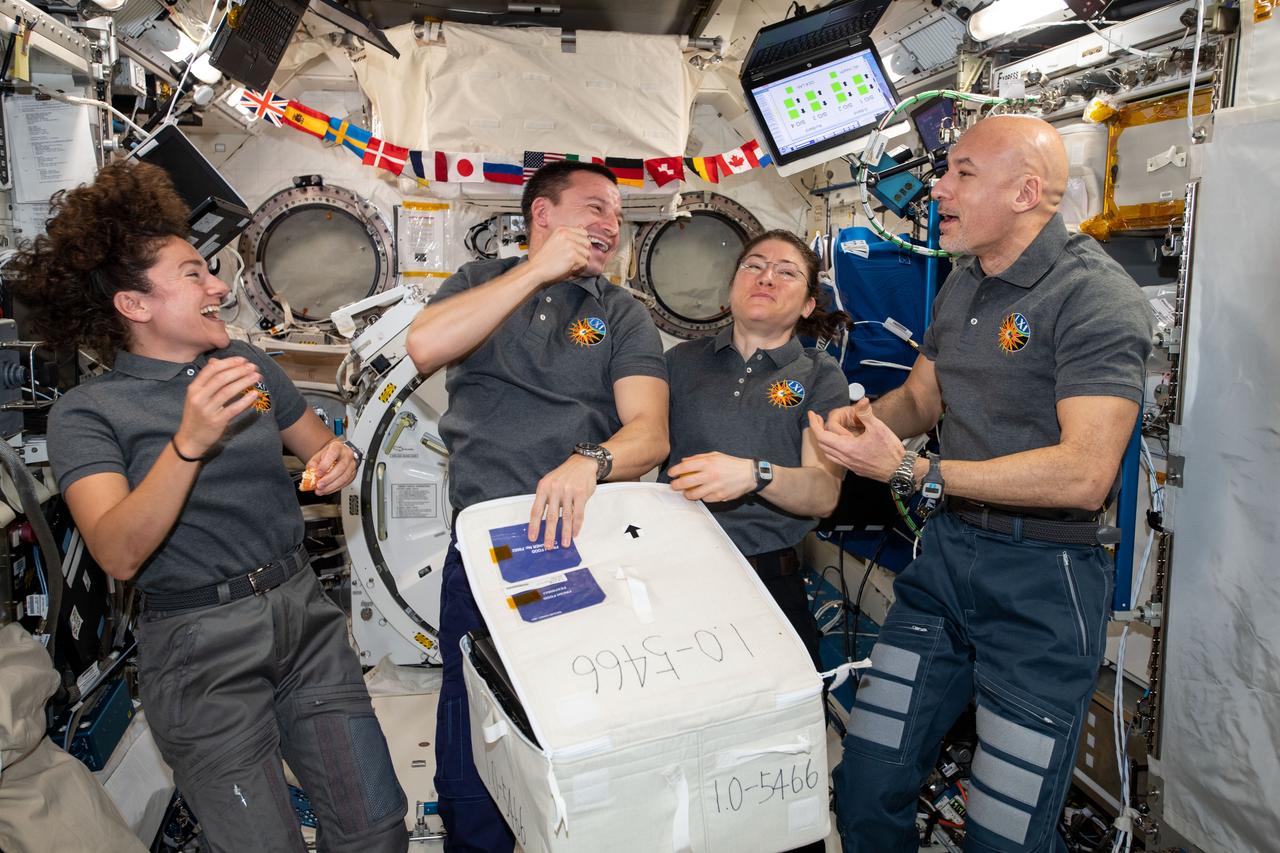

iss061e003995 (Oct. 7, 2019) --- Four Expedition 61 crewmembers open a stowage case packed with fresh fruit and other goodies delivered aboard Japan's HTV-8 cargo craft. From left are, NASA Flight Engineers Jessica Meir, Andrew Morgan and Christina Koch with Commander Luca Parmitano of ESA (European Space Agency).
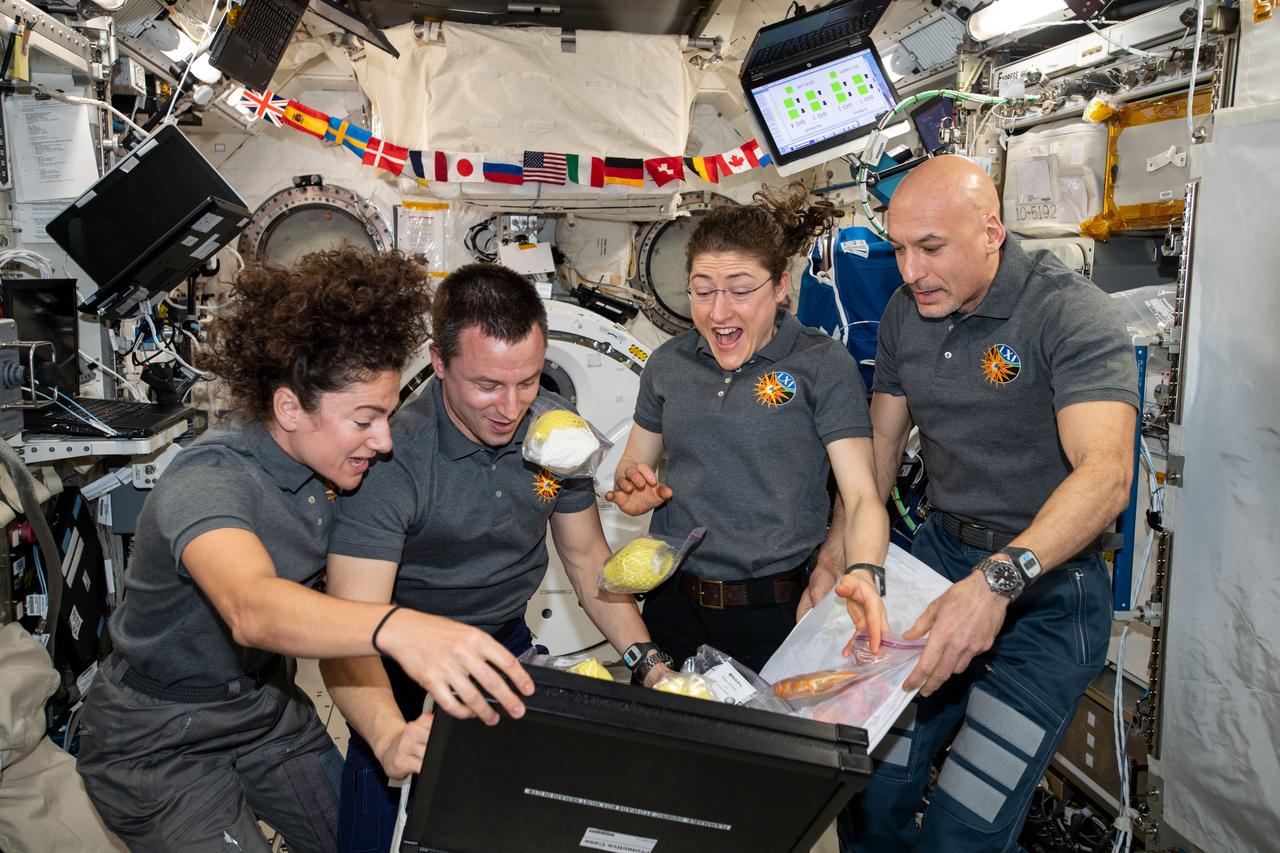

iss061e004031 (Oct. 7, 2019) --- Four Expedition 61 crewmembers unpack fresh fruit and other goodies from a stowage bag delivered aboard Japan's HTV-8 cargo craft. From left are, NASA Flight Engineers Jessica Meir, Andrew Morgan and Christina Koch with Commander Luca Parmitano of ESA (European Space Agency).
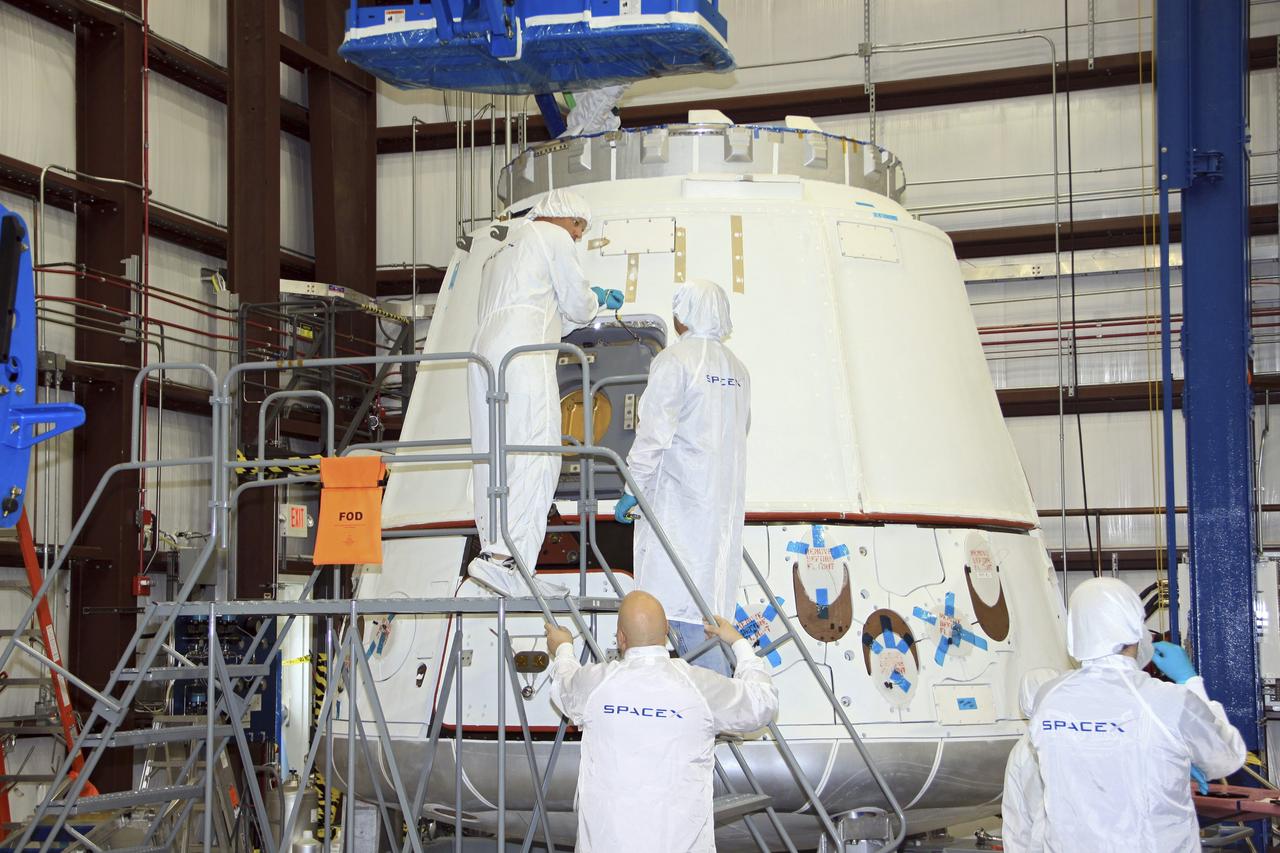

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In a processing hangar at Space Launch Complex-40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the hatch of the Space Exploration Technologies Dragon capsule has been closed following stowage of cargo in preparation for its scheduled April 30 liftoff aboard a Falcon 9 rocket. Known as SpaceX, the launch will be the company's second demonstration test flight for NASA's Commercial Orbital Transportation Services program, or COTS. During the flight, the capsule will conduct a series of checkout procedures to test and prove its systems, including rendezvous and berthing with the International Space Station. The cargo includes food and provisions for the station’s Expedition crews, such as clothing, batteries, and computer equipment. Under COTS, NASA has partnered with two private companies to launch cargo safely to the station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/spacex. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
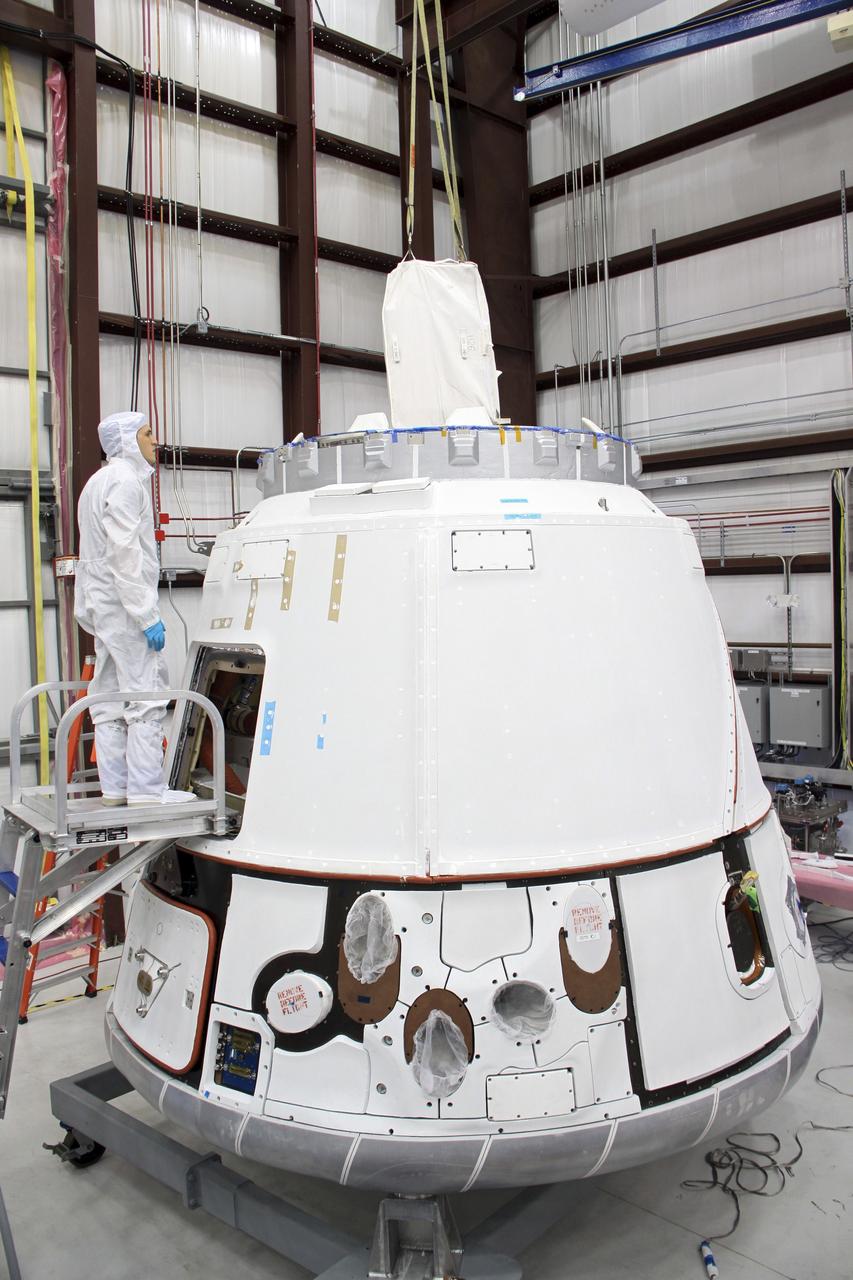

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In a processing hangar at Space Launch Complex-40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, a cargo bag slides through the docking ring into the Space Exploration Technologies Dragon capsule for stowage for its scheduled April 30 liftoff aboard a Falcon 9 rocket. Known as SpaceX, the launch will be the company's second demonstration test flight for NASA's Commercial Orbital Transportation Services program, or COTS. During the flight, the capsule will conduct a series of checkout procedures to test and prove its systems, including rendezvous and berthing with the International Space Station. The cargo includes food and provisions for the station’s Expedition crews, such as clothing, batteries, and computer equipment. Under COTS, NASA has partnered with two private companies to launch cargo safely to the station. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/spacex. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
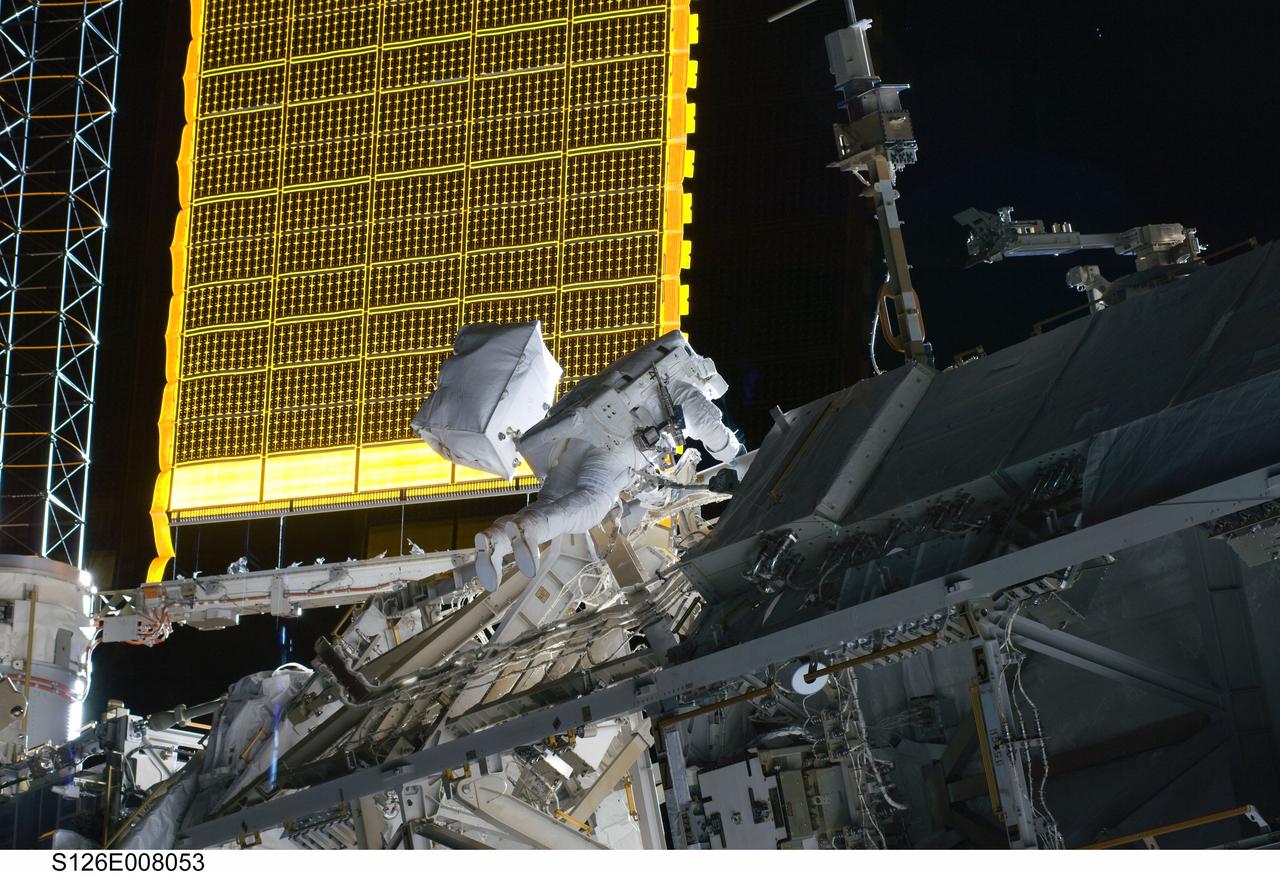

S126-E-008053 (18 Nov. 2008) --- Astronaut Steve Bowen, STS-126 mission specialist, participates in the mission's first session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 52-minute spacewalk, Bowen and astronaut Heidemarie Stefanyshyn-Piper (out of frame), mission specialist, worked to clean and lubricate part of the station's starboard Solar Alpha Rotary Joints (SARJ) and to remove two of SARJ's 12 trundle bearing assemblies. The spacewalkers also removed a depleted nitrogen tank from a stowage platform on the outside of the complex and moved it into Endeavour's cargo bay. They also moved a flex hose rotary coupler from the shuttle to the station stowage platform, as well as removing some insulation blankets from the common berthing mechanism on the Kibo laboratory.
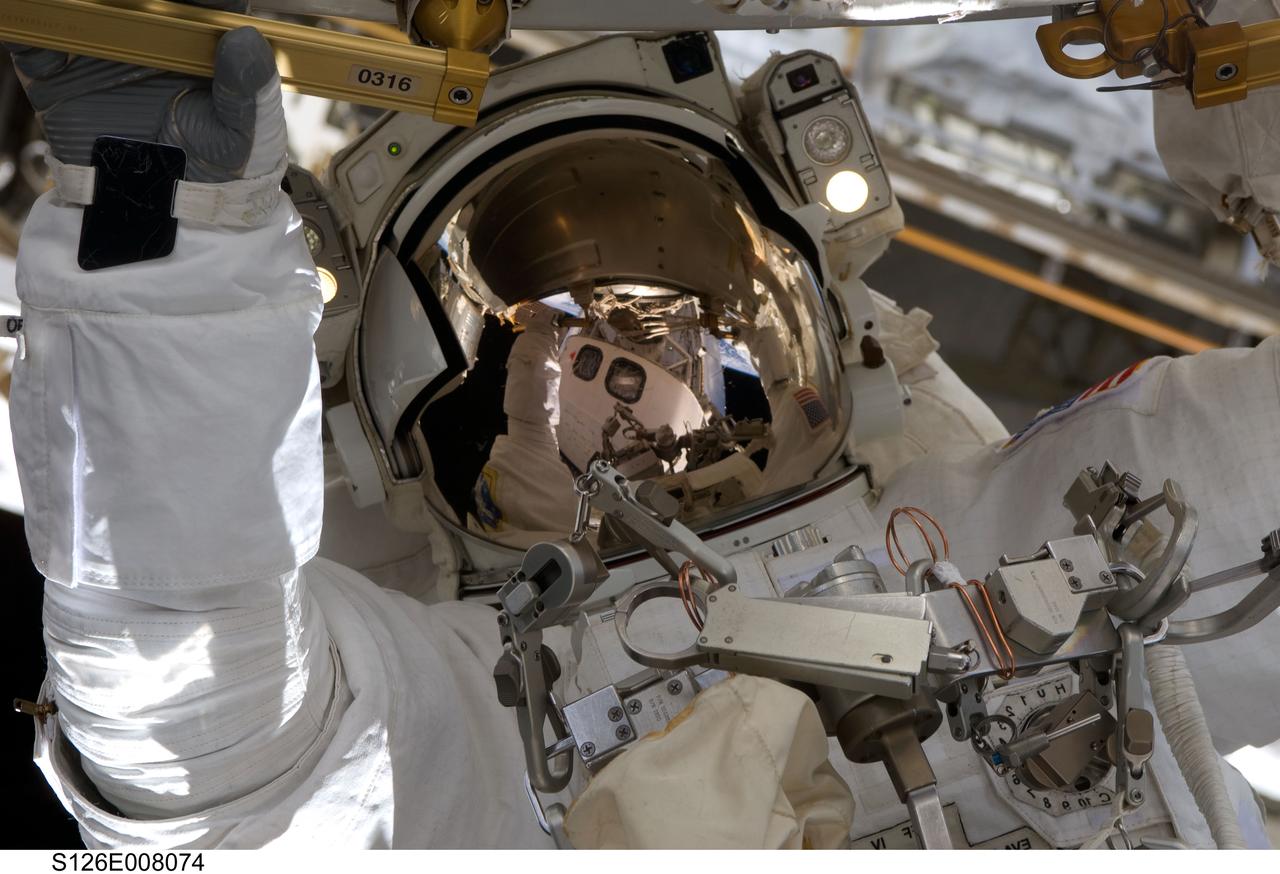

S126-E-008074 (18 Nov. 2008) --- Astronaut Steve Bowen, STS-126 mission specialist, participates in the mission's first session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 52-minute spacewalk, Bowen and astronaut Heidemarie Stefanyshyn-Piper (out of frame), mission specialist, worked to clean and lubricate part of the station's starboard Solar Alpha Rotary Joints (SARJ) and to remove two of SARJ's 12 trundle bearing assemblies. The spacewalkers also removed a depleted nitrogen tank from a stowage platform on the outside of the complex and moved it into Endeavour's cargo bay. They also moved a flex hose rotary coupler from the shuttle to the station stowage platform, as well as removing some insulation blankets from the common berthing mechanism on the Kibo laboratory.
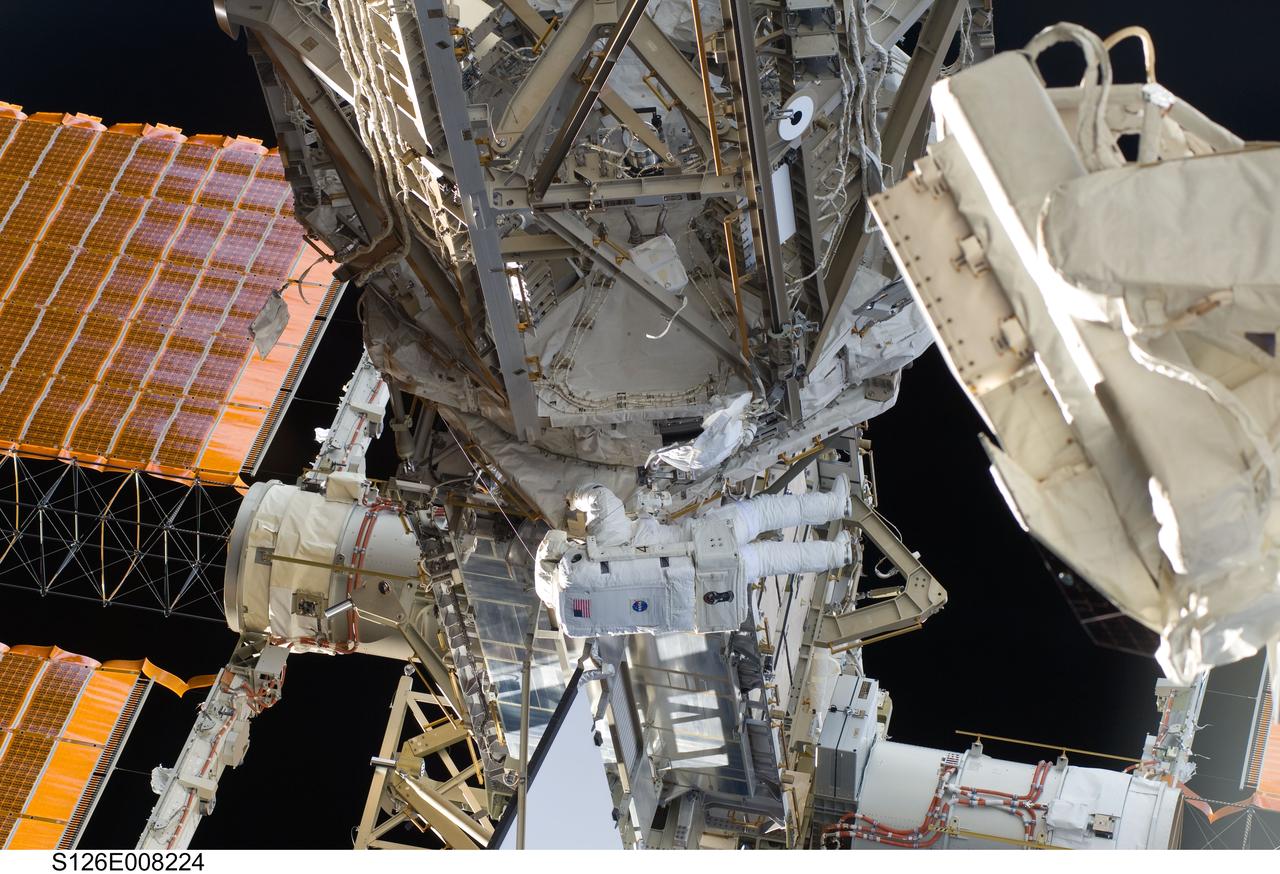

S126-E-008224 (18 Nov. 2008) --- Astronaut Steve Bowen, STS-126 mission specialist, participates in the mission's first session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 52-minute spacewalk, Bowen and astronaut Heidemarie Stefanyshyn-Piper (out of frame), mission specialist, worked to clean and lubricate part of the station's starboard Solar Alpha Rotary Joints (SARJ) and to remove two of SARJ's 12 trundle bearing assemblies. The spacewalkers also removed a depleted nitrogen tank from a stowage platform on the outside of the complex and moved it into Endeavour's cargo bay. They also moved a flex hose rotary coupler from the shuttle to the station stowage platform, as well as removing some insulation blankets from the common berthing mechanism on the Kibo laboratory.
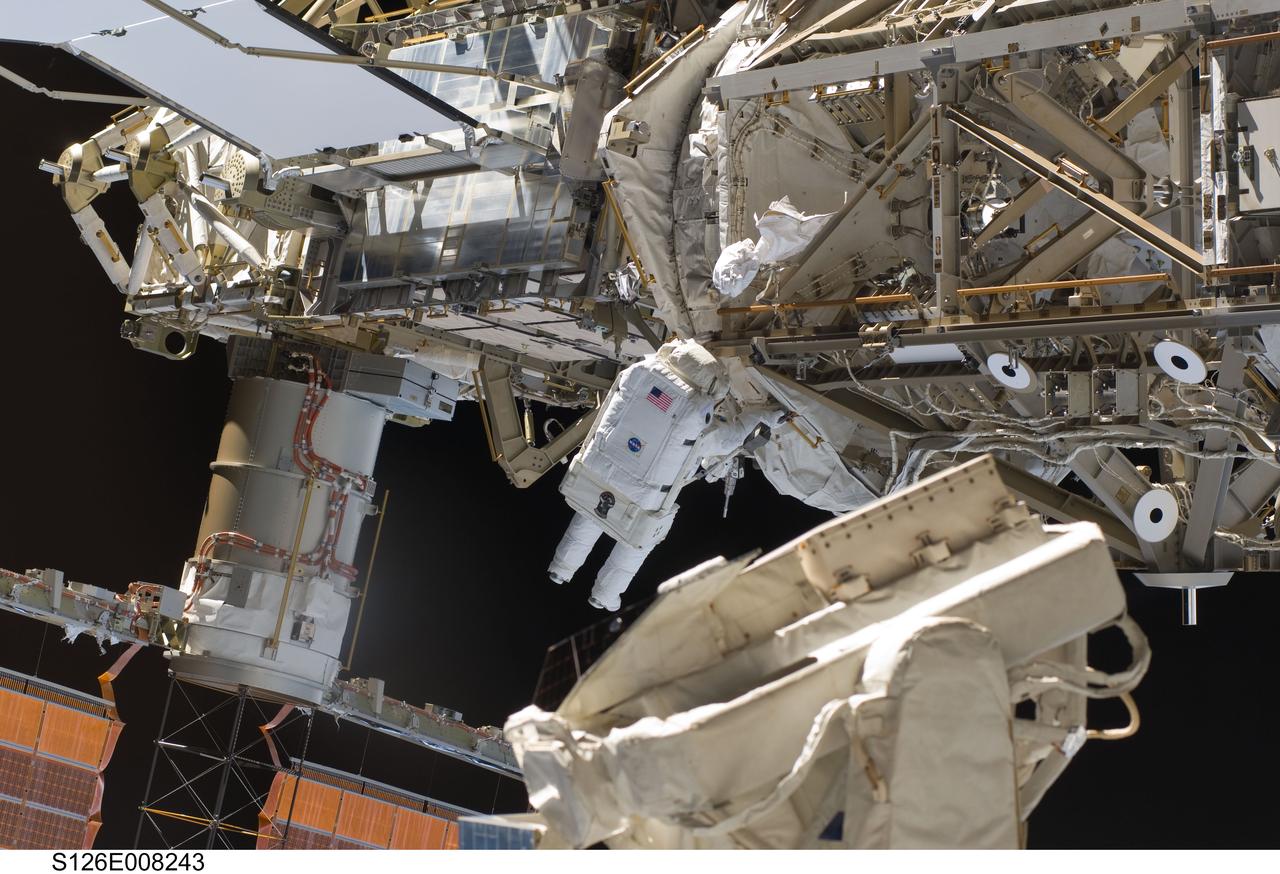

S126-E-008243 (18 Nov. 2008) --- Astronaut Steve Bowen, STS-126 mission specialist, participates in the mission's first session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 52-minute spacewalk, Bowen and astronaut Heidemarie Stefanyshyn-Piper (out of frame), mission specialist, worked to clean and lubricate part of the station's starboard Solar Alpha Rotary Joints (SARJ) and to remove two of SARJ's 12 trundle bearing assemblies. The spacewalkers also removed a depleted nitrogen tank from a stowage platform on the outside of the complex and moved it into Endeavour's cargo bay. They also moved a flex hose rotary coupler from the shuttle to the station stowage platform, as well as removing some insulation blankets from the common berthing mechanism on the Kibo laboratory.
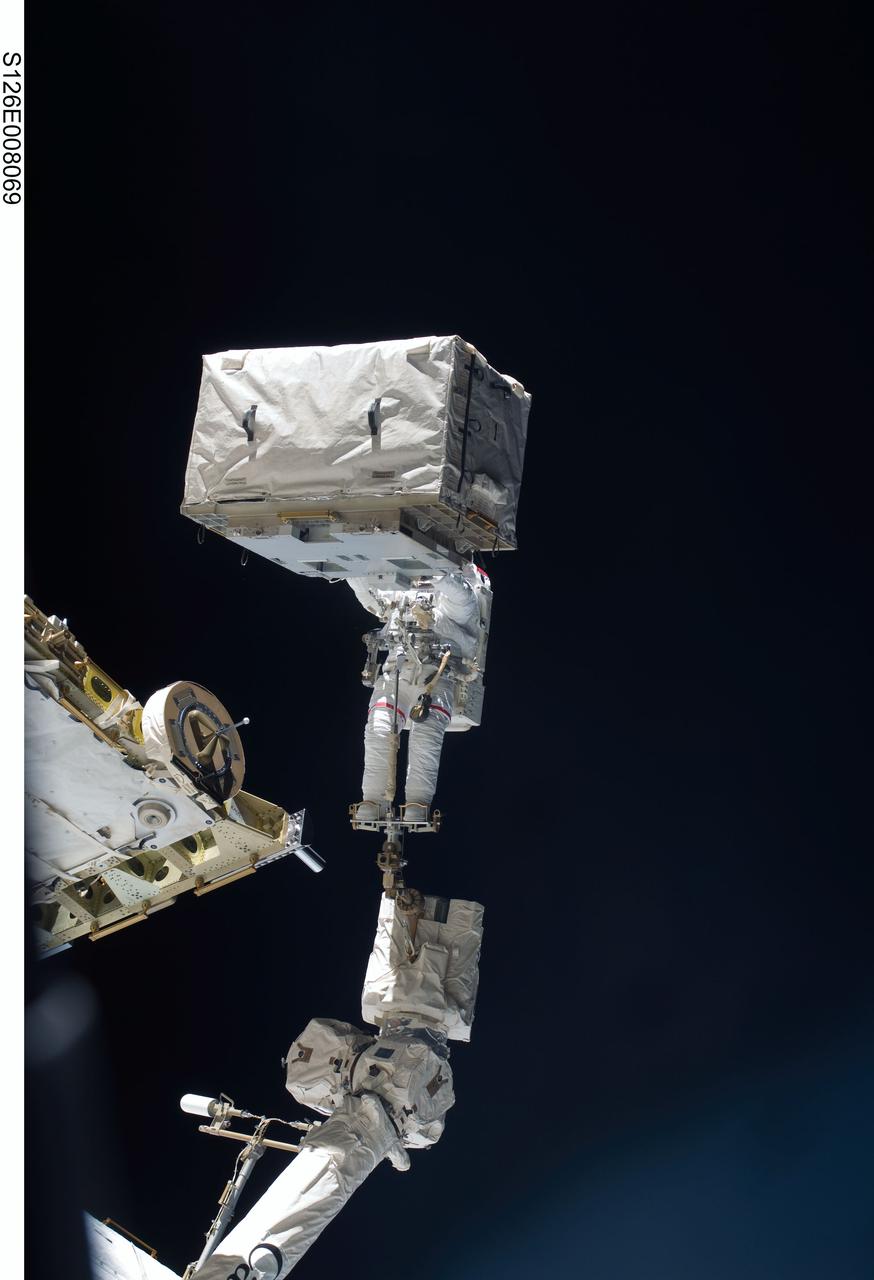

S126-E-008069 (18 Nov. 2008) --- Anchored to a Canadarm2 mobile foot restraint, astronaut Heidemarie Stefanyshyn-Piper, STS-126 mission specialist, participates in the mission's first session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 52-minute spacewalk, Piper and astronaut Steve Bowen (out of frame), mission specialist, worked to clean and lubricate part of the station's starboard Solar Alpha Rotary Joints (SARJ) and to remove two of SARJ's 12 trundle bearing assemblies. The spacewalkers also removed a depleted nitrogen tank from a stowage platform on the outside of the complex and moved it into Endeavour's cargo bay. They also moved a flex hose rotary coupler from the shuttle to the station stowage platform, as well as removing some insulation blankets from the common berthing mechanism on the Kibo laboratory.
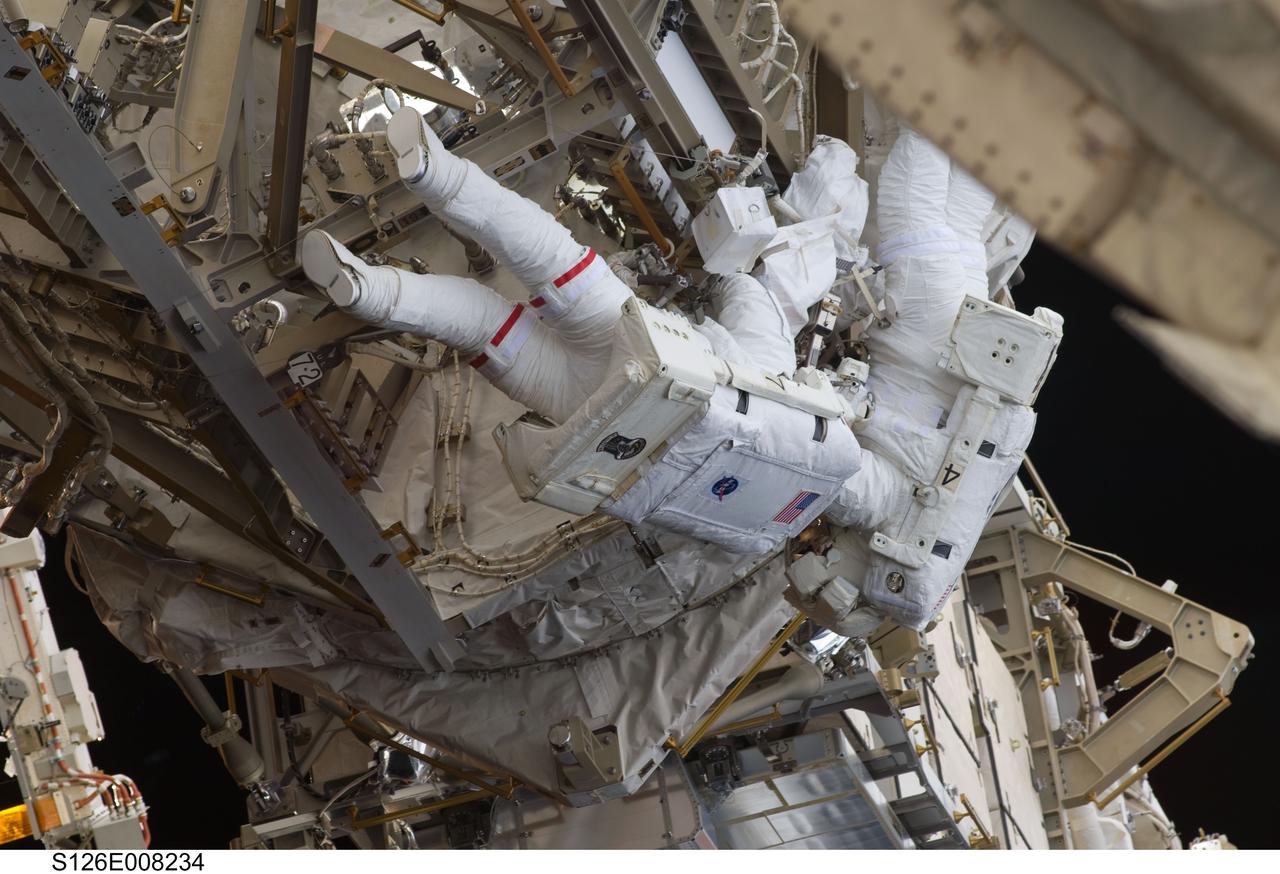

S126-E-008234 (18 Nov. 2008) --- Astronauts Heidemarie Stefanyshyn-Piper (left) and Steve Bowen, both STS-126 mission specialists, participate in the mission's first session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 52-minute spacewalk, Piper and Bowen worked to clean and lubricate part of the station's starboard Solar Alpha Rotary Joints (SARJ) and to remove two of SARJ's 12 trundle bearing assemblies. The spacewalkers also removed a depleted nitrogen tank from a stowage platform on the outside of the complex and moved it into Endeavour's cargo bay. They also moved a flex hose rotary coupler from the shuttle to the station stowage platform, as well as removing some insulation blankets from the common berthing mechanism on the Kibo laboratory.
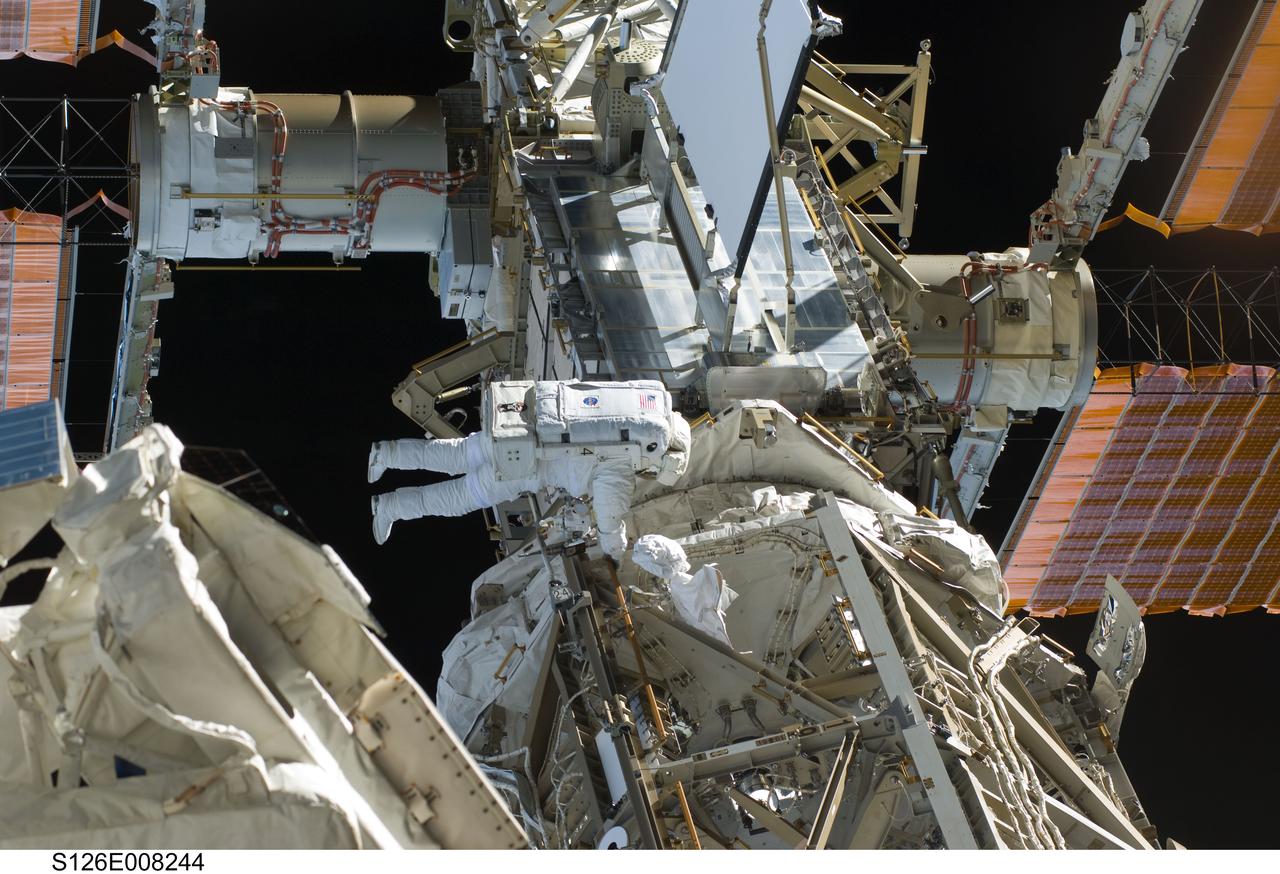

S126-E-008244 (18 Nov. 2008) --- Astronaut Steve Bowen, STS-126 mission specialist, participates in the mission's first session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 52-minute spacewalk, Bowen and astronaut Heidemarie Stefanyshyn-Piper (out of frame), mission specialist, worked to clean and lubricate part of the station's starboard Solar Alpha Rotary Joints (SARJ) and to remove two of SARJ's 12 trundle bearing assemblies. The spacewalkers also removed a depleted nitrogen tank from a stowage platform on the outside of the complex and moved it into Endeavour's cargo bay. They also moved a flex hose rotary coupler from the shuttle to the station stowage platform, as well as removing some insulation blankets from the common berthing mechanism on the Kibo laboratory.
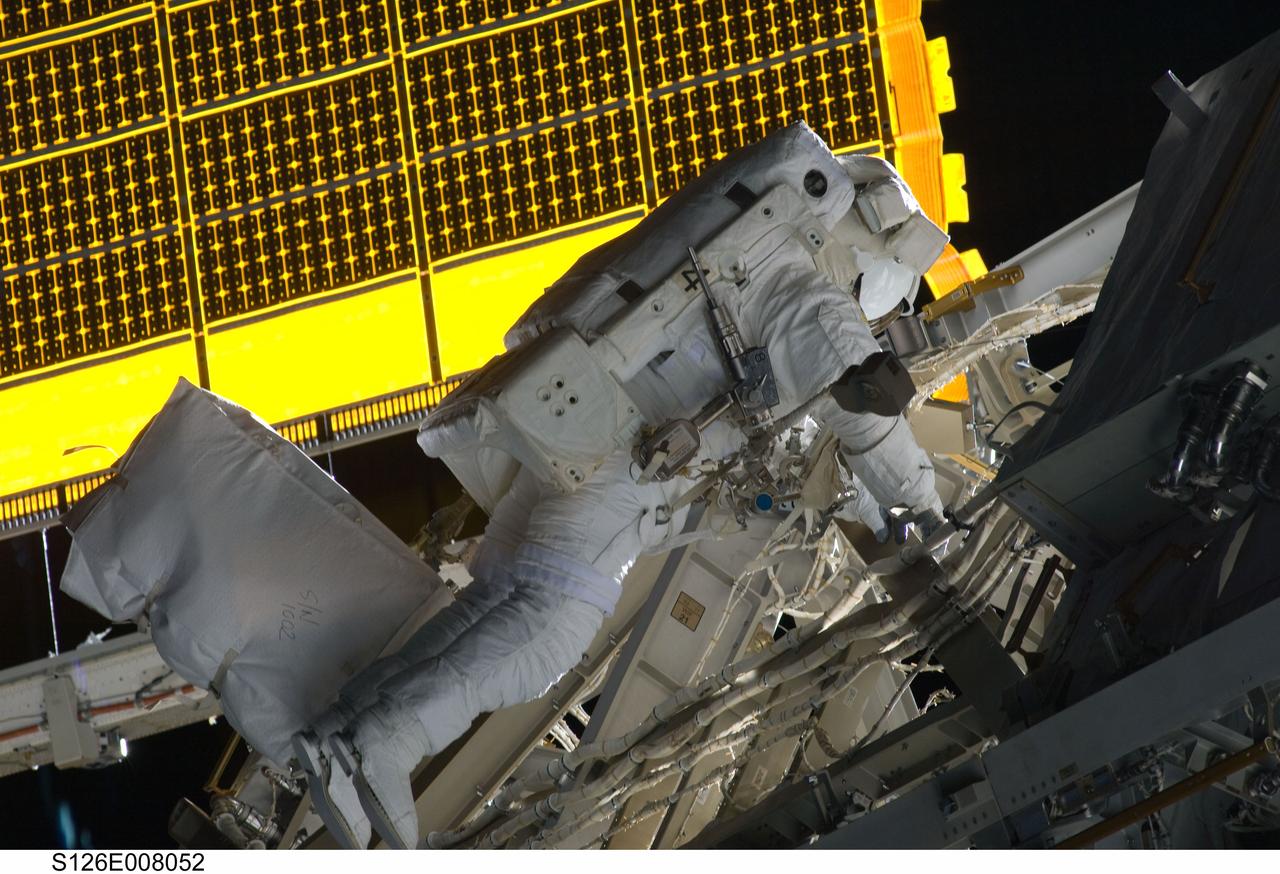

S126-E-008052 (18 Nov. 2008) --- Astronaut Steve Bowen, STS-126 mission specialist, participates in the mission's first session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 52-minute spacewalk, Bowen and astronaut Heidemarie Stefanyshyn-Piper (out of frame), mission specialist, worked to clean and lubricate part of the station's starboard Solar Alpha Rotary Joints (SARJ) and to remove two of SARJ's 12 trundle bearing assemblies. The spacewalkers also removed a depleted nitrogen tank from a stowage platform on the outside of the complex and moved it into Endeavour's cargo bay. They also moved a flex hose rotary coupler from the shuttle to the station stowage platform, as well as removing some insulation blankets from the common berthing mechanism on the Kibo laboratory.