
Huygens Probe Shines for Cassini Cameras #1

Cassini Snaps Image of ESA Huygens Probe
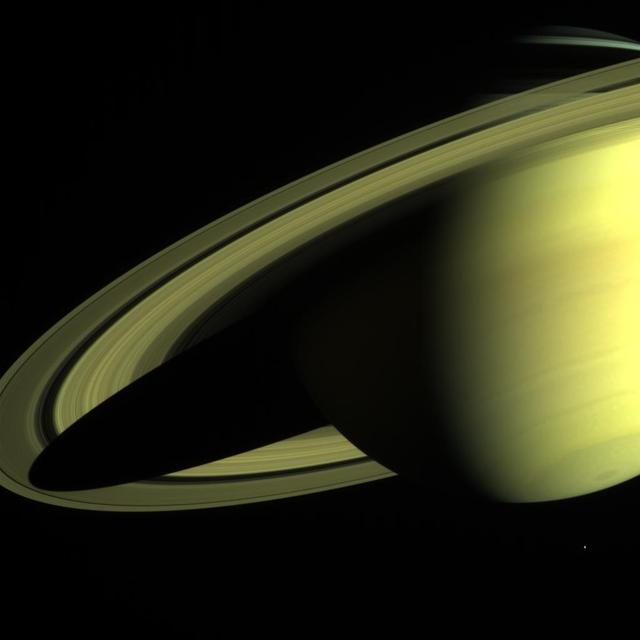

Saturn from Far and Near Cassini-Huygens
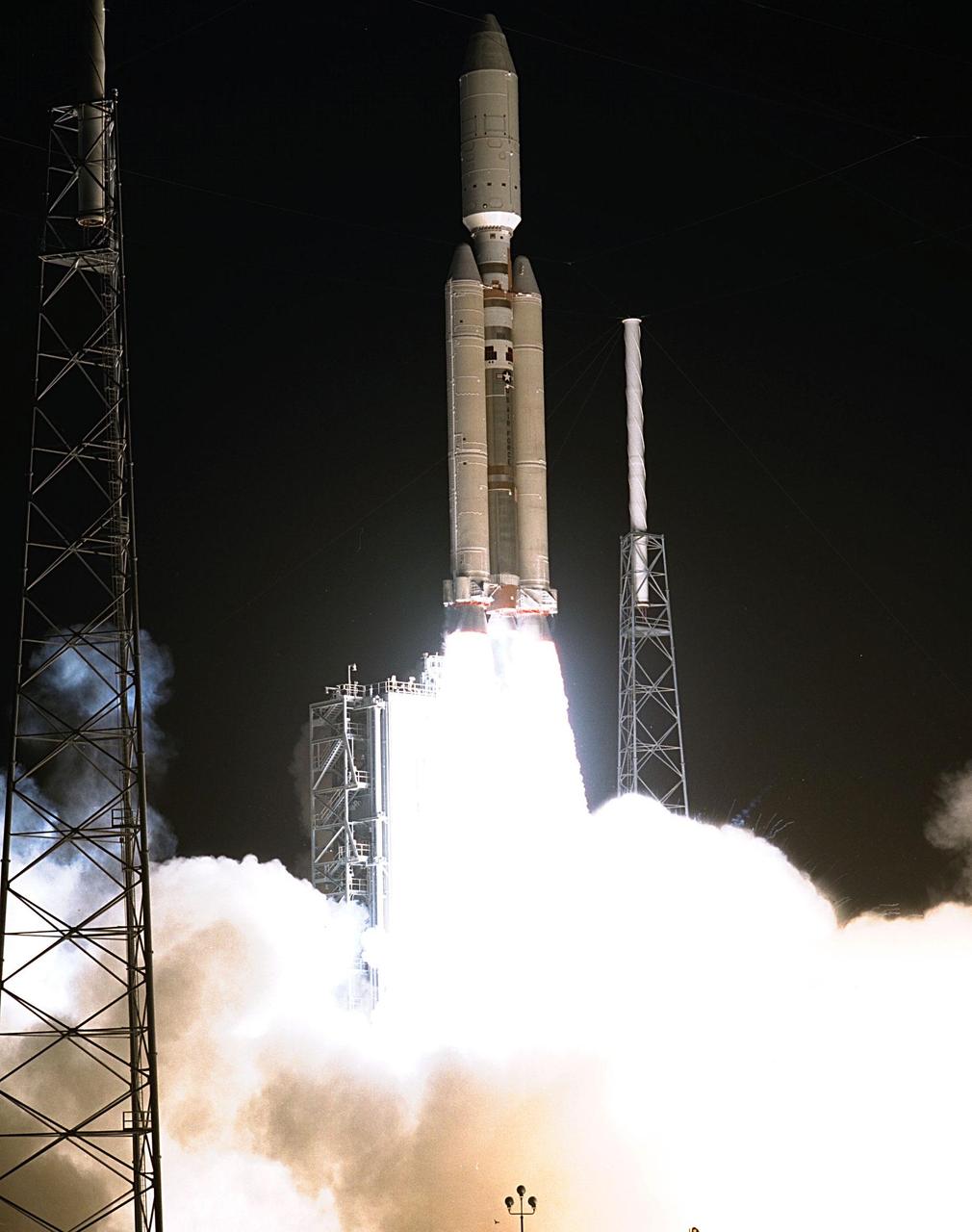

A seven-year journey to the ringed planet Saturn begins with the liftoff of a Titan IVB/Centaur carrying NASA Cassini orbiter and its attached Huygens probe.
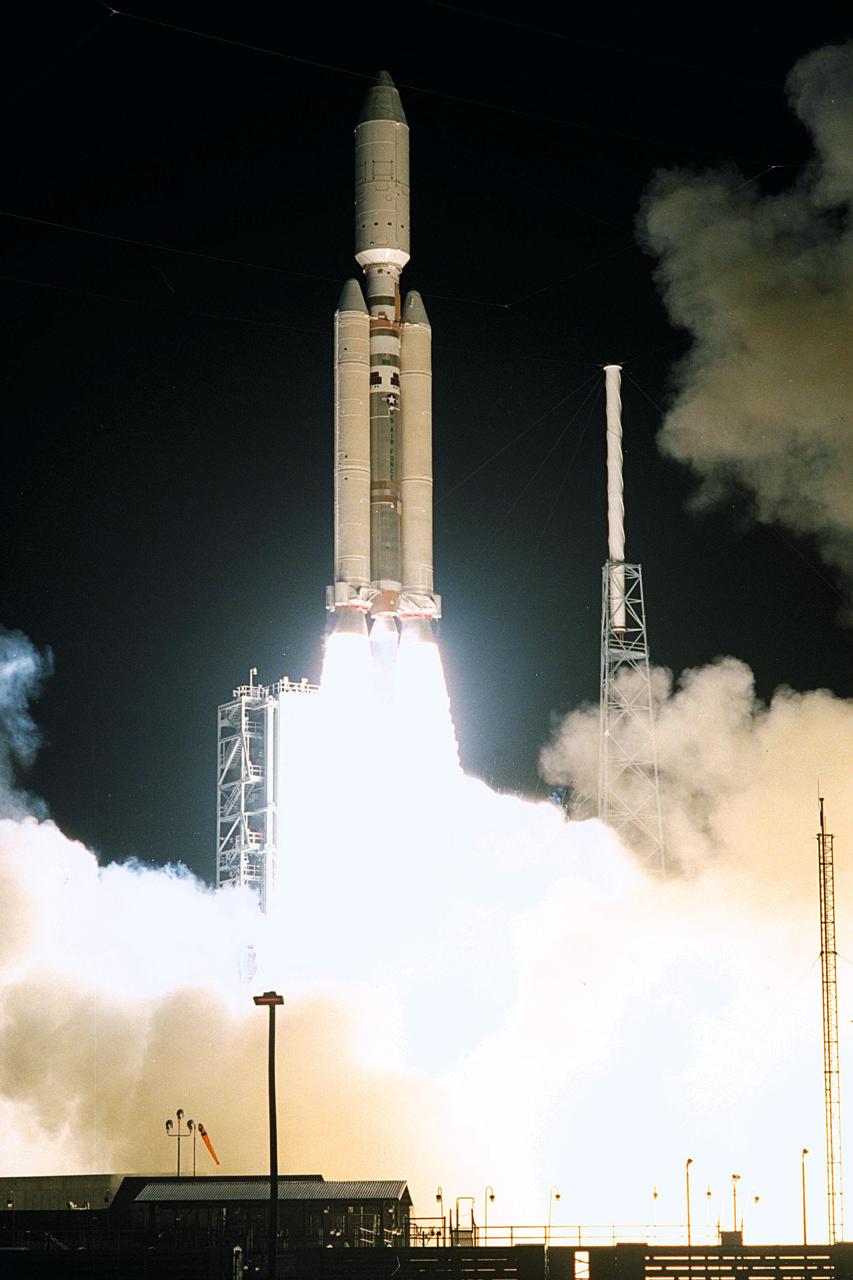

A seven-year journey to the ringed planet Saturn begins with the liftoff of a Titan IVB/Centaur carrying the Cassini orbiter and its attached Huygens probe.
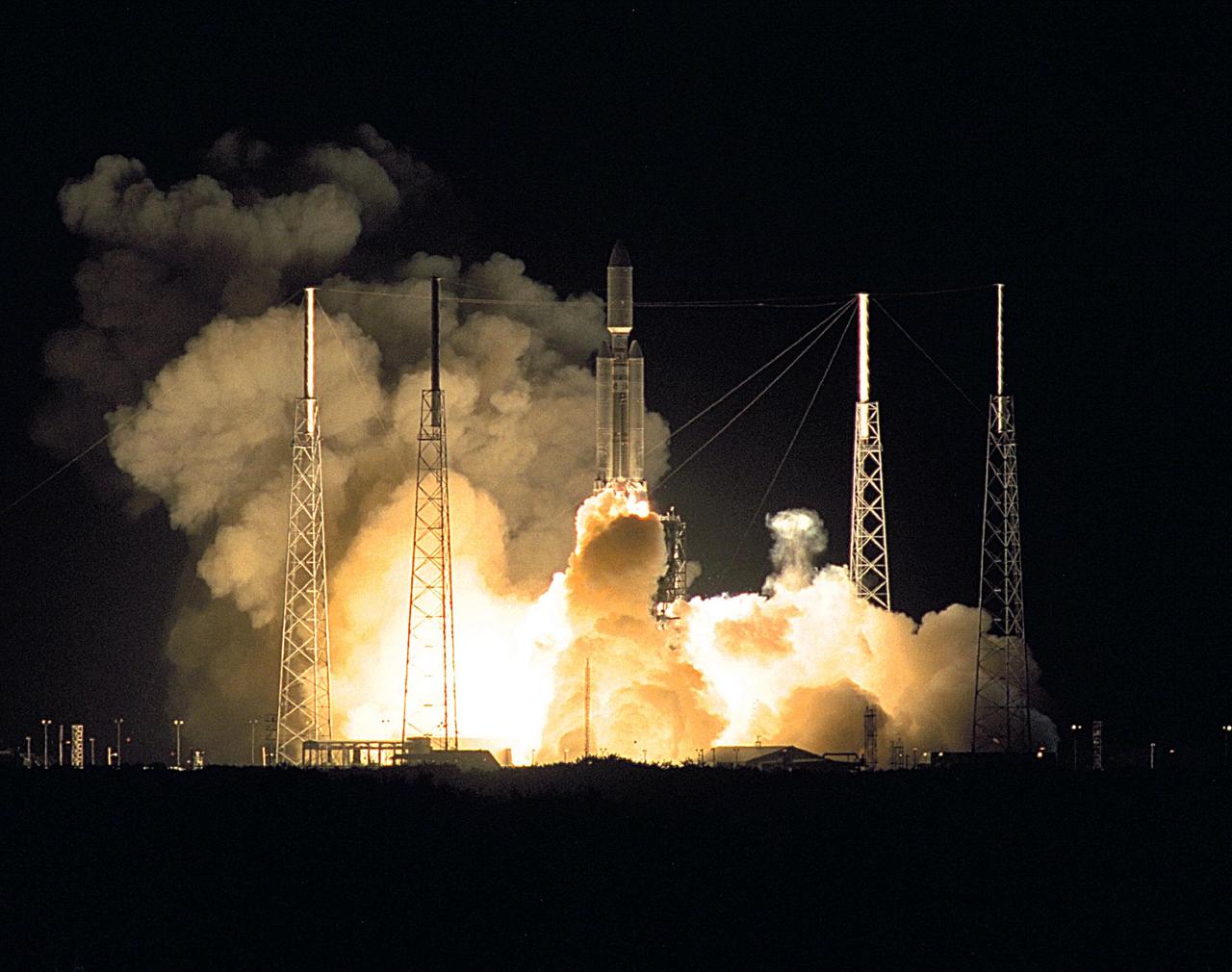

A seven-year journey to the ringed planet Saturn began on Oct. 15, 1997 with the liftoff of a Titan IVB/Centaur carrying NASA Cassini orbiter and its attached Huygens probe
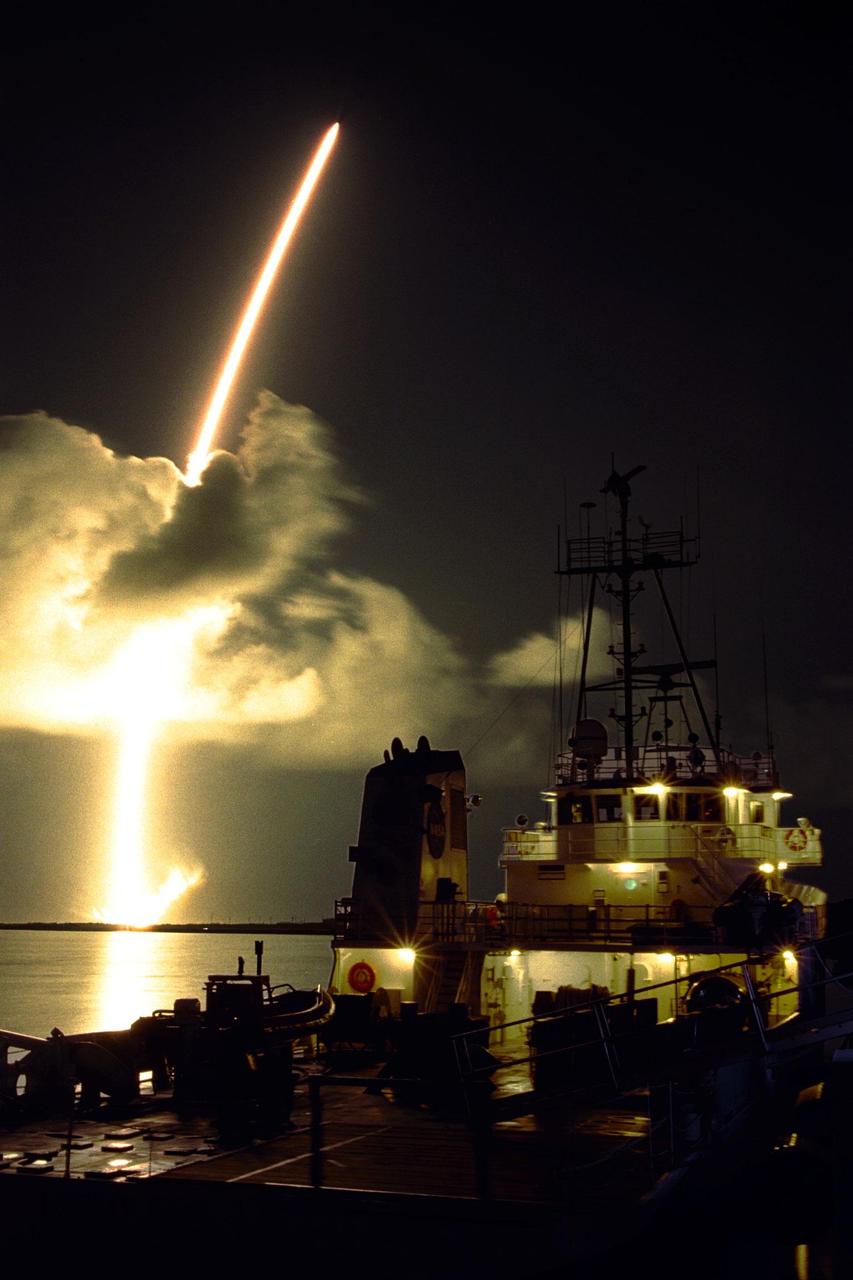

A seven-year journey to the ringed planet Saturn began on Oct. 15, 1997 with the liftoff of a Titan IVB/Centaur carrying NASA Cassini orbiter and its attached Huygens probe.
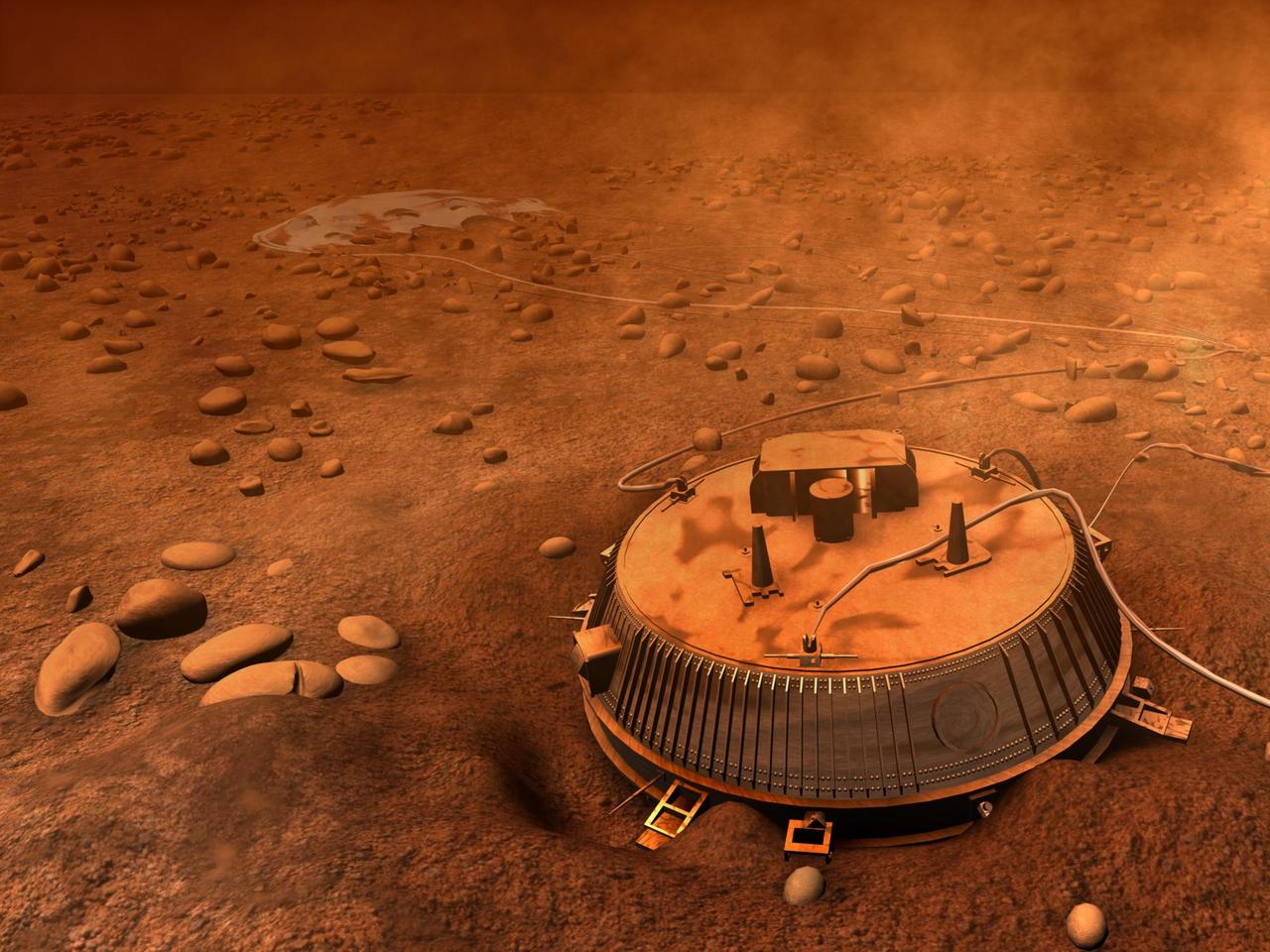
This is an artist interpretation of the area surrounding Huygens landing site, based on images and data returned Jan. 14, 2005. The Cassini-Huygens mission is a cooperative project of NASA, the European Space Agency and the Italian Space Agency.
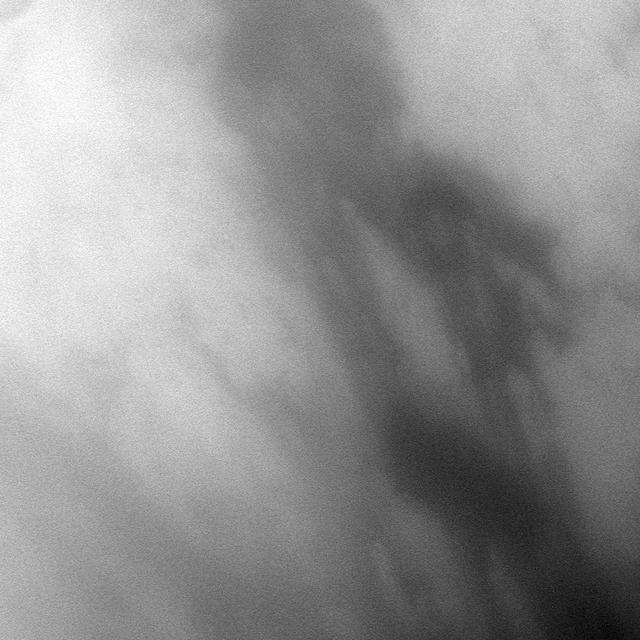

NASA Cassini spacecraft peers through Titan atmosphere at the region called Adiri, west of the landing site of the Huygens probe on the anti-Saturn side of the moon.
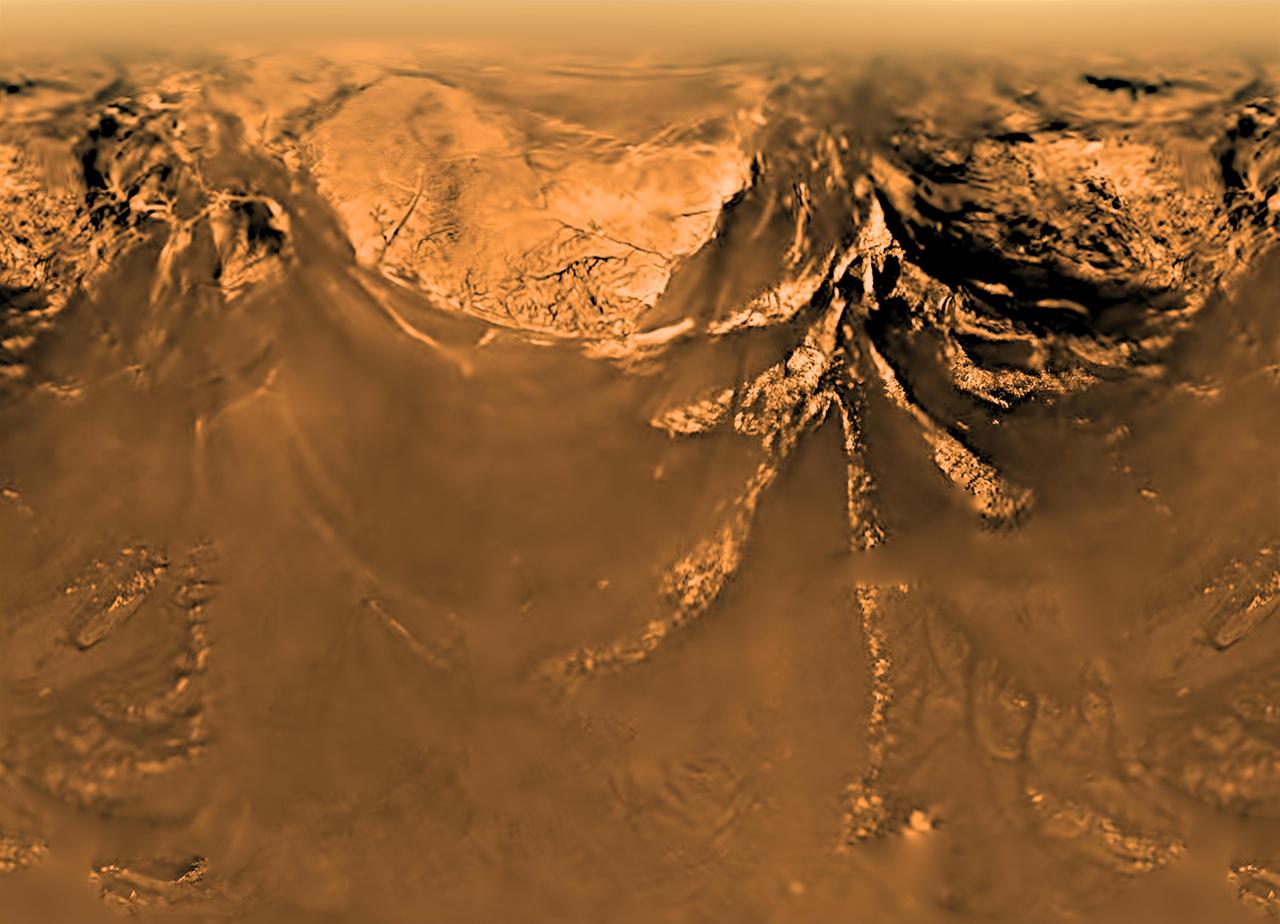
This poster shows a flattened (Mercator) projection of the Huygens probe's view from 10 kilometers altitude (6 miles). The images that make up this view were taken on Jan. 14, 2005, with the descent imager/spectral radiometer onboard the European Space Agency's Huygens probe. The Huygens probe was delivered to Saturn's moon Titan by the Cassini spacecraft, which is managed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif. NASA supplied two instruments on the probe, the descent imager/spectral radiometer and the gas chromatograph mass spectrometer. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA08113
Saturn rings lie in the distance as NASA Cassini spacecraft looks toward Titan and its dark region called Shangri-La, east of the landing site of the Huygens Probe.

This image was obtained by NASA Cassini radar instrument during a flyby on Oct. 28, 2005. Equatorial Pass Trailing hemisphere, Central Adiri, Central Belet, Huygens Landing Site, Antillia Faculae.
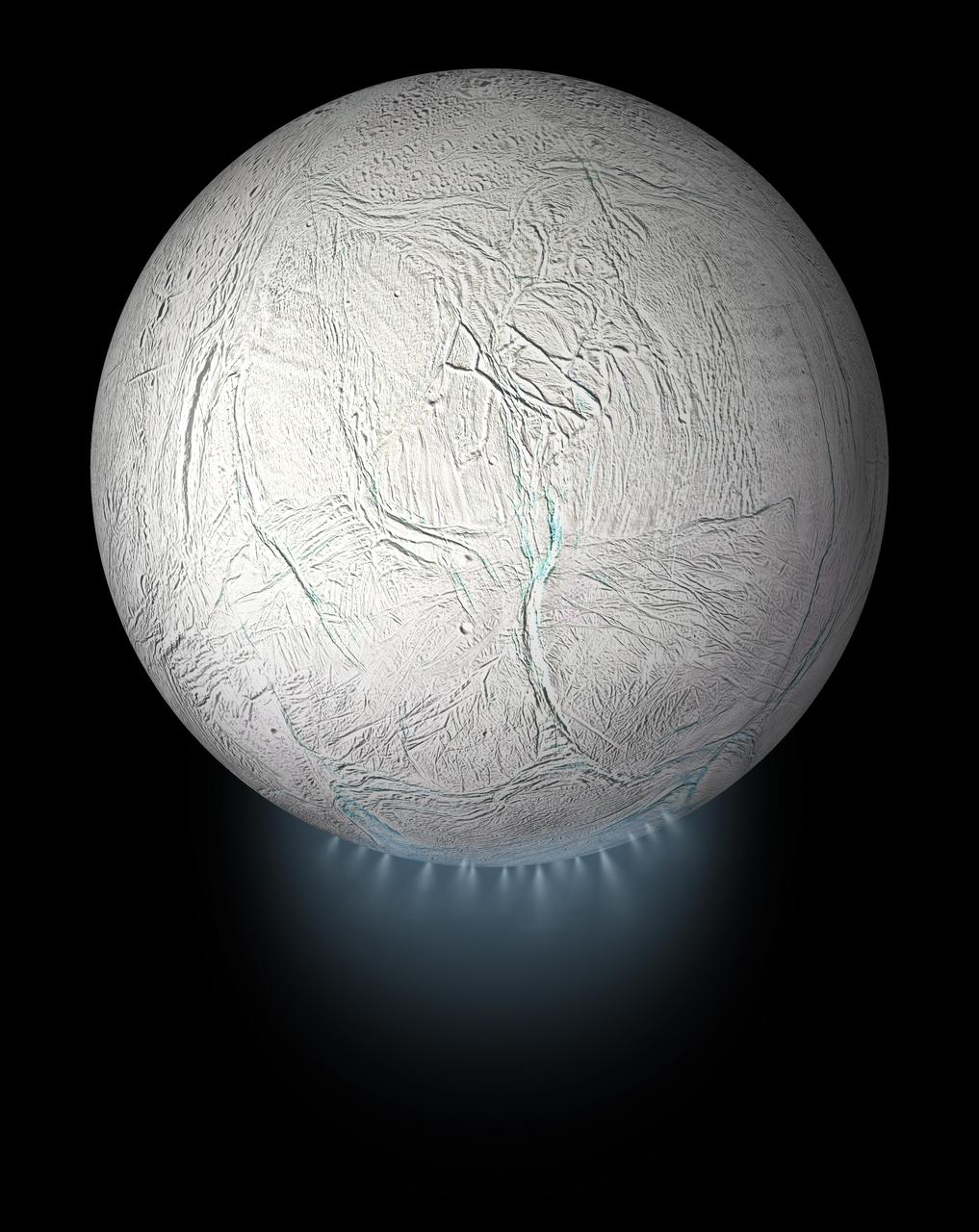

This illustration shows Saturn's icy moon Enceladus with the plume of ice particles, water vapor and organic molecules that sprays from fractures in the moon's south polar region. A cutaway version of this graphic is also available, showing the moon's interior ocean and hydrothermal activity — both of which were discovered by NASA's Cassini mission (see PIA20013). This global view was created using a Cassini-derived map of Enceladus (see PIA18435). More information about Enceladus is available at https://solarsystem.nasa.gov/moons/saturn-moons/enceladus/in-depth/. For more information about the Cassini-Huygens mission visit https://solarsystem.nasa.gov/missions/cassini/overview/. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23175
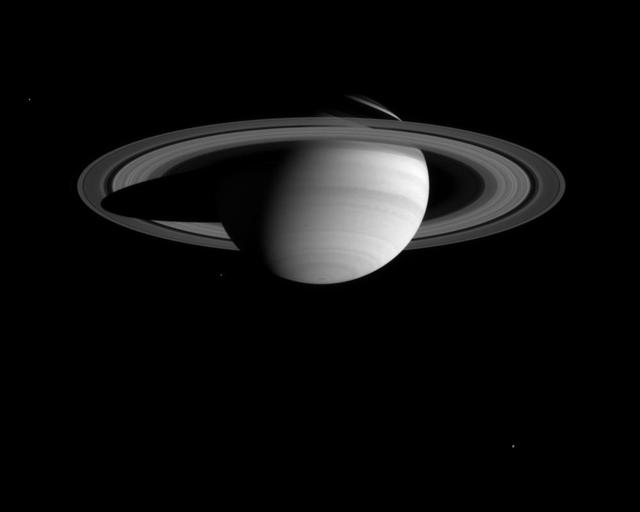

Bands and spots in Saturn's atmosphere, including a dark band south of the equator with a scalloped border, are visible in this image from the Cassini-Huygens spacecraft. The narrow angle camera took the image in blue light on Feb. 29, 2004. The distance to Saturn was 59.9 million kilometers (37.2 million miles). The image scale is 359 kilometers (223 miles) per pixel. Three of Saturn's moons are seen in the image: Enceladus (499 kilometers, or 310 miles across) at left; Mimas (398 kilometers, or 247 miles across) left of Saturn's south pole; and Rhea (1,528 kilometers, or 949 miles across) at lower right. The imaging team enhanced the brightness of the moons to aid visibility. The BL1 broadband spectral filter (centered at 451 nanometers) allows Cassini to "see" light in a part of the spectrum visible as the color blue to human eyes. Scientist can combine images made with this filter with those taken with red and green filters to create full-color composites. Scientists can also assess cloud heights by combining images from the blue filter with images taken in other spectral regions. For example, the bright clouds that form the equatorial zone are the highest in altitude and have pressures at their tops of about one quarter of Earth's atmospheric pressure at sea level. The cloud tops at middle latitudes are lower in altitude and have higher pressures of about half that found at sea level. Analysis of Saturn images like this one will be extremely useful to researchers assessing cloud altitudes during the Cassini-Huygens mission. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA05383
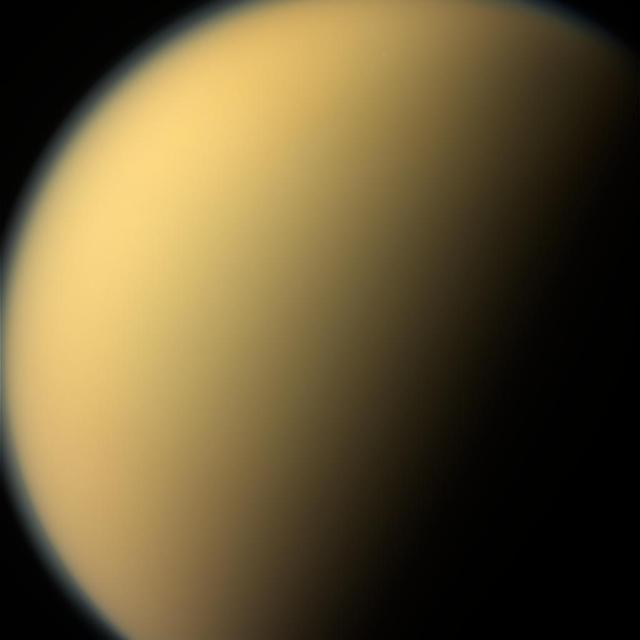

As it glanced around the Saturn system one final time, NASA's Cassini spacecraft captured this view of the planet's giant moon Titan. Interest in mysterious Titan was a major motivating factor to return to Saturn with Cassini-Huygens following the Voyager mission flybys of the early 1980s. Cassini and its Huygens probe, supplied by European Space Agency, revealed the moon to be every bit as fascinating as scientists had hoped. These views were obtained by Cassini's narrow-angle camera on Sept. 13, 2017. They are among the last images Cassini sent back to Earth. This natural color view, made from images taken using red, green and blue spectral filters, shows Titan much as Voyager saw it -- a mostly featureless golden orb, swathed in a dense atmospheric haze. An enhanced-color view (Figure 1) adds to this color a separate view taken using a spectral filter (centered at 938 nanometers) that can partially see through the haze. The views were acquired at a distance of 481,000 miles (774,000 kilometers) from Titan. The image scale is about 3 miles (5 kilometers) per pixel. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21890
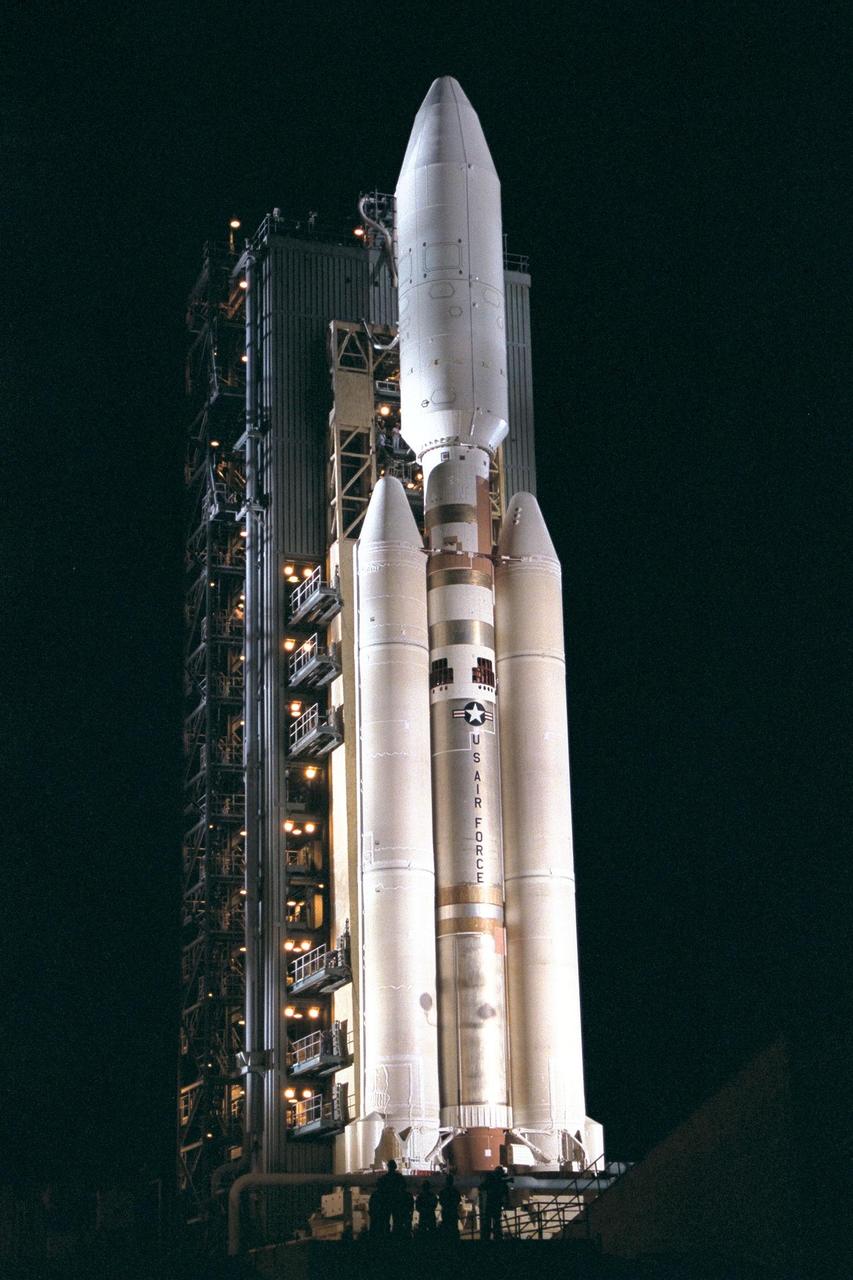

This image from 1997 is of the Titan IVB/Centaur carrying NASA Cassini spacecraft at Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Station, the Mobile Service Tower has been retracted away.
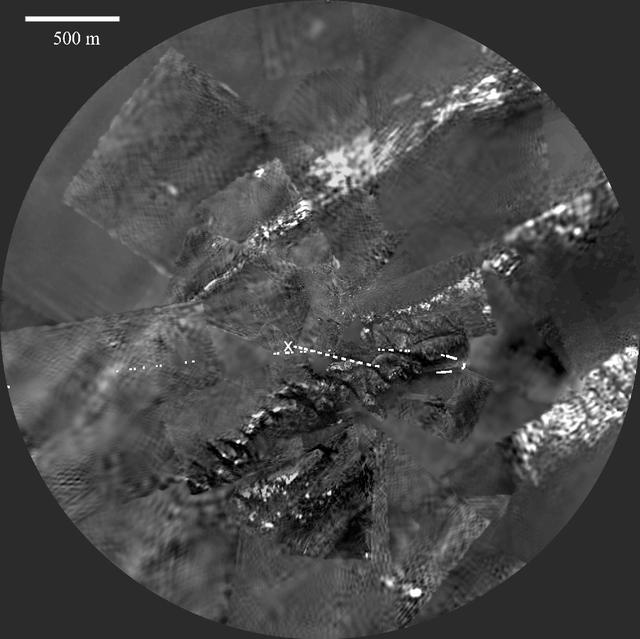

Images recorded by the European Space Agency's Huygens probe descent imager/spectral radiometer between 4 and 0.3 miles (7 and 0.5 kilometers) were assembled to produce this panoramic mosaic. The probe ground track is indicated as points in white. North is up. The ridge near the centre is cut by a dozen darker lanes or channels. The landing site is marked with an "X" near the continuation of one of the channels. The Huygens probe was delivered to Saturn's moon Titan by the Cassini spacecraft, which is managed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif. NASA supplied two instruments on the probe, the descent imager/spectral radiometer and the gas chromatograph mass spectrometer. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA06439
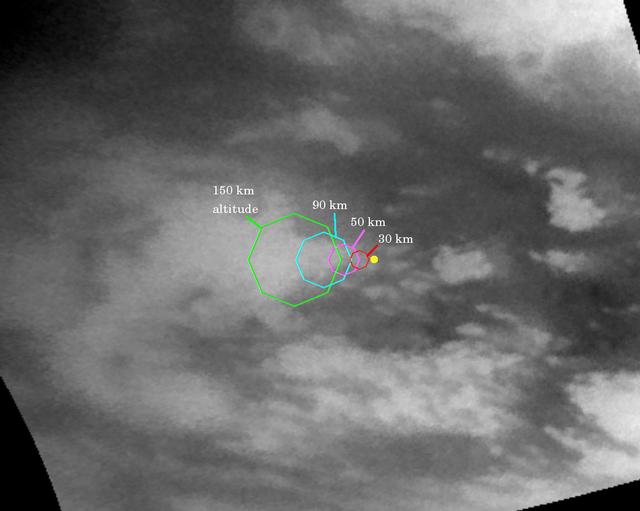

This map illustrates the planned imaging coverage for the Descent Imager/Spectral Radiometer, onboard the European Space Agency's Huygens probe during the probe's descent toward Titan's surface on Jan. 14, 2005. The Descent Imager/Spectral Radiometer is one of two NASA instruments on the probe. The colored lines delineate regions that will be imaged at different resolutions as the probe descends. On each map, the site where Huygens is predicted to land is marked with a yellow dot. This area is in a boundary between dark and bright regions. This map was made from the images taken by the Cassini spacecraft cameras on Oct. 26, 2004, at image scales of 4 to 6 kilometers (2.5 to 3.7 miles) per pixel. The images were obtained using a narrow band filter centered at 938 nanometers -- a near-infrared wavelength (invisible to the human eye) at which light can penetrate Titan's atmosphere to reach the surface and return through the atmosphere to be detected by the camera. The images have been processed to enhance surface details. Only brightness variations on Titan's surface are seen; the illumination is such that there is no shading due to topographic variations. For about two hours, the probe will fall by parachute from an altitude of 160 kilometers (99 miles) to Titan's surface. During the descent the camera on the probe and five other science instruments will send data about the moon's atmosphere and surface back to the Cassini spacecraft for relay to Earth. The Descent Imager/Spectral Radiometer will take pictures as the probe slowly spins, and some these will be made into panoramic views of Titan's surface. This map shows the planned coverage by the medium- and high-resolution. PIA06173 shows expected coverage by the Descent Imager/Spectral Radiometer side-looking imager and two downward-looking imagers - one providing medium-resolution and the other high-resolution coverage. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA06173

Saturn appears serene and majestic in the first color composite made of images taken by NASA's Cassini spacecraft on its approach to the ringed planet, with arrival still 20 months away. The planet was 285 million kilometers (177 million miles) away from the spacecraft, nearly twice the distance between the Sun and Earth, when Cassini took images of it in various filters as an engineering test on Oct. 21, 2002. It is summer in Saturn's southern hemisphere. The Sun is a lofty 27 degrees below the equator and casts a semi-circular shadow of the planet on the rings. The shadow extends partway across the rings, leaving the outer A ring in sunlight. The last Saturn-bound spacecraft, Voyager 2, arrived in early northern spring. Many features seen in Voyager images -- spoke-like markings on the rings, clouds and eddies in the hazy atmosphere, ring-shepherding moons -- are not yet visible to Cassini. Titan, Saturn's largest moon, appears in the upper left. It is the only moon resolved from this distance. This composite uses a threefold enhancement in the brightness of Titan relative to the brightness of Saturn. Titan is a major attraction for scientists of the Cassini-Huygens mission. They will study its haze-enshrouded atmosphere and peer down, with special instrumentation, to its surface to look for evidence of organic processes similar to those that might have occurred on the early Earth, prior to the emergence of life. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA02884
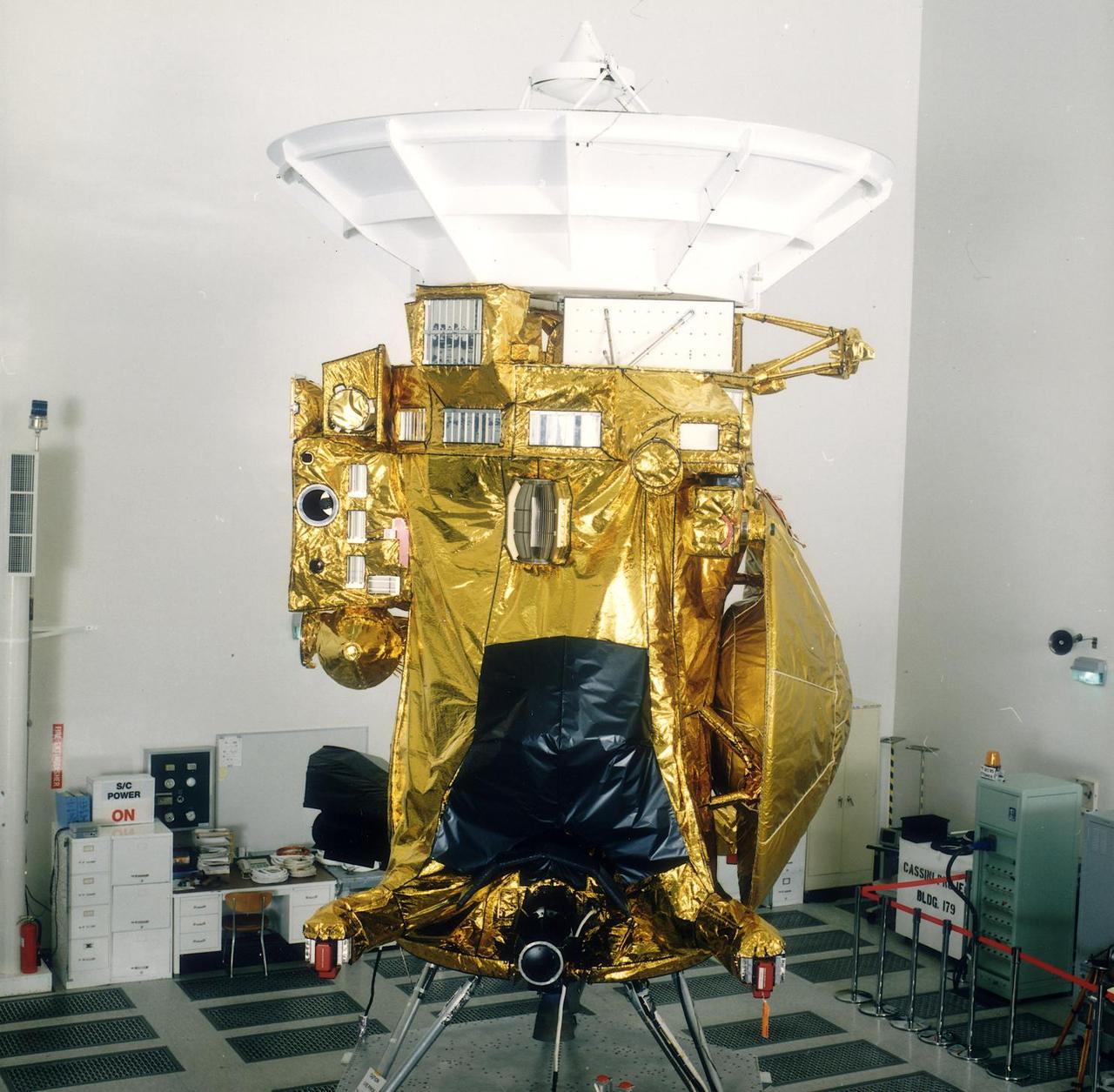

On October of 1997, a two-story-tall robotic spacecraft will begin a journey of many years to reach and explore the exciting realm of Saturn, the most distant planet that can easily be seen by the unaided human eye. In addition to Saturn's interesting atmosphere and interior, its vast system contains the most spectacular of the four planetary ring systems, numerous icy satellites with a variety of unique surface features. A huge magnetosphere teeming with particles that interact with the rings and moons, and the intriguing moon Titan, which is slightly larger than the planet Mercury, and whose hazy atmosphere is denser than that of Earth, make Saturn a fascinating planet to study. The Cassini mission is an international venture involving NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA), the Italian Space Agency (ASI), and several separate European academic and industrial partners. The mission is managed for NASA by JPL. The spacecraft will carry a sophisticated complement of scientific sensors to support 27 different investigations to probe the mysteries of the Saturn system. The large spacecraft will consist of an orbiter and ESA's Huygens Titan probe. The orbiter mass at launch will be nearly 5300 kg, over half of which is propellant for trajectory control. The mass of the Titan probe (2.7 m diameter) is roughly 350 kg. The mission is named in honor of the seventeenth-century, French-Italian astronomer Jean Dominique Cassini, who discovered the prominent gap in Saturn's main rings, as well as the icy moons Iapetus, Rhea, Dione, and Tethys. The ESA Titan probe is named in honor of the exceptional Dutch scientist Christiaan Huygens, who discovered Titan in 1655, followed in 1659 by his announcement that the strange Saturn "moons" seen by Galileo in 1610 were actually a ring system surrounding the planet. Huygens was also famous for his invention of the pendulum clock, the first accurate timekeeping device. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA04603
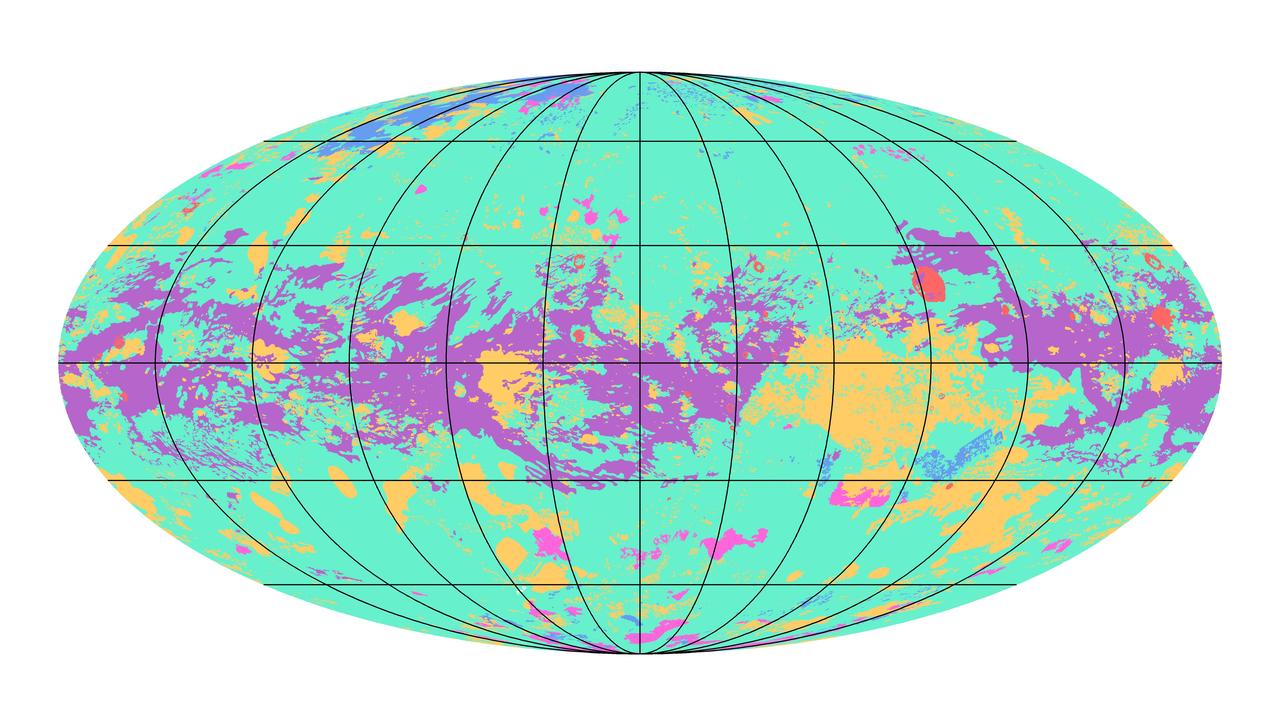
The first global geologic map of Saturn's largest moon, Titan, is based on radar and visible and infrared images from NASA's Cassini mission, which orbited Saturn from 2004 to 2017. Black lines mark 30 degrees of latitude and longitude. Map is in Mollweide projection, a global view that attempts to minimize the size or area distortion, especially at the poles (although shapes are increasingly distorted away from the center of the map). It is centered on 0 degrees latitude, 180 degrees longitude. Map scale is 1:20,000,000. In the annotated figure, the map is labeled with several of the named surface features. Also located is the landing site of the European Space Agency's (ESA) Huygens Probe, part of NASA's Cassini mission. The map legend colors represent the broad types of geologic units found on Titan: plains (broad, relatively flat regions), labyrinth (tectonically disrupted regions often containing fluvial channels), hummocky (hilly, with some mountains), dunes (mostly linear dunes, produced by winds in Titan's atmosphere), craters (formed by impacts) and lakes (regions now or previously filled with liquid methane or ethane). Titan is the only planetary body in our solar system other than Earth known to have stable liquid on its surface — methane and ethane. The map was developed using Cassini radar data and Imaging Science Subsystem (ISS) images. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23174

Images from the European Space Agency's Huygens probe descent imager/spectral radiometer side-looking imager and from the medium resolution imager, acquired after landing, were merged to produce this image. The horizon's position implies a pitch of the imager/spectral radiometer, nose-upward, by 1 to 2 degrees with no measurable roll. "Stones" in the foreground are 4 to 6 inches (10 to 15 centimeters) in size, presumably made of water ice, and these lie on a darker, finer-grained substrate. A region with a relatively low number of rocks lies between clusters of rocks in the foreground and the background and matches the general orientation of channel-like features in the panorama of PIA06439). The scene evokes the possibility of a dry lakebed. The Huygens probe was delivered to Saturn's moon Titan by the Cassini spacecraft, which is managed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif. NASA supplied two instruments on the probe, the descent imager/spectral radiometer and the gas chromatograph mass spectrometer. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA06440
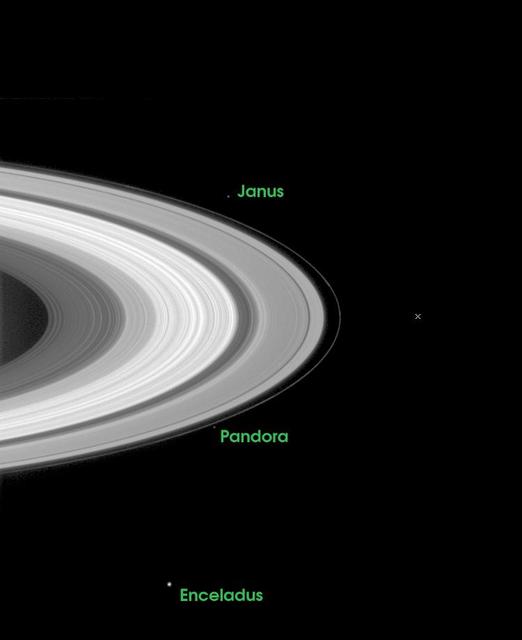

The path that lies ahead for the Cassini-Huygens mission is indicated in this image which illustrates where the spacecraft will be just 27 days from now, when it arrives at Saturn and crosses the ring plane 33 minutes before performing its critical orbital insertion maneuver. The X indicates the point where Cassini will pierce the ring plane on June 30, 2004, going from south to north of the ring plane, 33 minutes before the main engine fires to begin orbital insertion. The indicated point is between the narrow F-ring on the left and Saturn's tenuous G-ring which is too faint to be seen in this exposure. The image was taken on May 11, 2004 when the spacecraft was 26.3 million kilometers (16.3 million miles) from Saturn. Image scale is 158 kilometers (98 miles) per pixel. Moons visible in this image: Janus (181 kilometers or 113 miles across), one of the co-orbital moons; Pandora (84 kilometers or 52 miles across), one of the F ring shepherding moons; and Enceladus (499 kilometers or 310 miles across), a moon which may be heated from within and thus have a liquid sub-surface ocean. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA06061
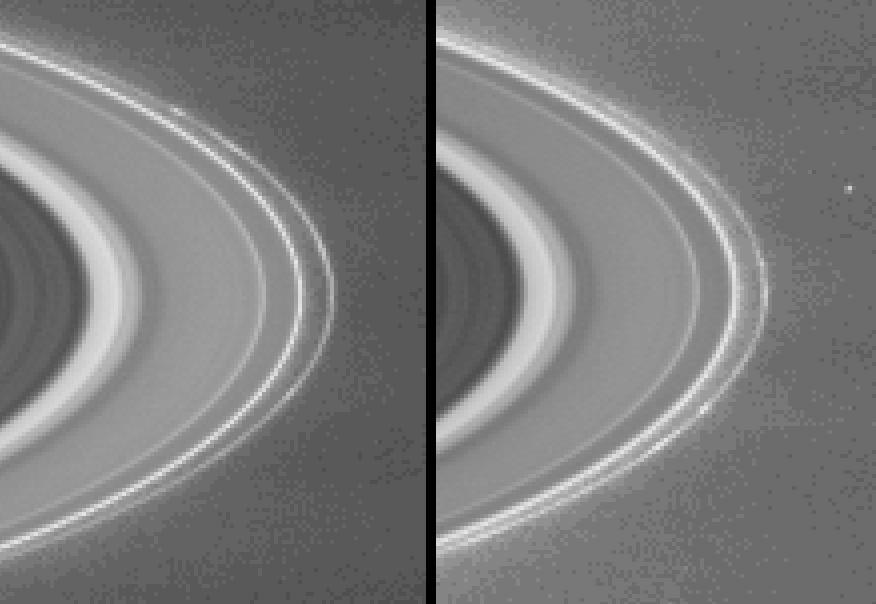

Scientists have only a rough idea of the lifetime of clumps in Saturn's rings - a mystery that Cassini may help answer. The latest images taken by the Cassini-Huygens spacecraft show clumps seemingly embedded within Saturn's narrow, outermost F ring. The narrow angle camera took the images on Feb. 23, 2004, from a distance of 62.9 million kilometers (39 million miles). The two images taken nearly two hours apart show these clumps as they revolve about the planet. The small dot at center right in the second image is one of Saturn's small moons, Janus, which is 181 kilometers, (112 miles) across. Like all particles in Saturn's ring system, these clump features orbit the planet in the same direction in which the planet rotates. This direction is clockwise as seen from Cassini's southern vantage point below the ring plane. Two clumps in particular, one of them extended, is visible in the upper part of the F ring in the image on the left, and in the lower part of the ring in the image on the right. Other knot-like irregularities in the ring's brightness are visible in the image on the right. The core of the F ring is about 50 kilometers (31miles) wide, and from Cassini's current distance, is not fully visible. The imaging team enhanced the contrast of the images and magnified them to aid visibility of the F ring and the clump features. The camera took the images with the green filter, which is centered at 568 nanometers. The image scale is 377 kilometers (234 miles) per pixel. NASA's two Voyager spacecraft that flew past Saturn in 1980 and 1981 were the first to see these clumps. The Voyager data suggest that the clumps change very little and can be tracked as they orbit for 30 days or more. No clump survived from the time of the first Voyager flyby to the Voyager 2 flyby nine months later. Scientists are not certain of the cause of these features. Among the theories proposed are meteoroid bombardments and inter-particle collisions in the F ring. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA05382
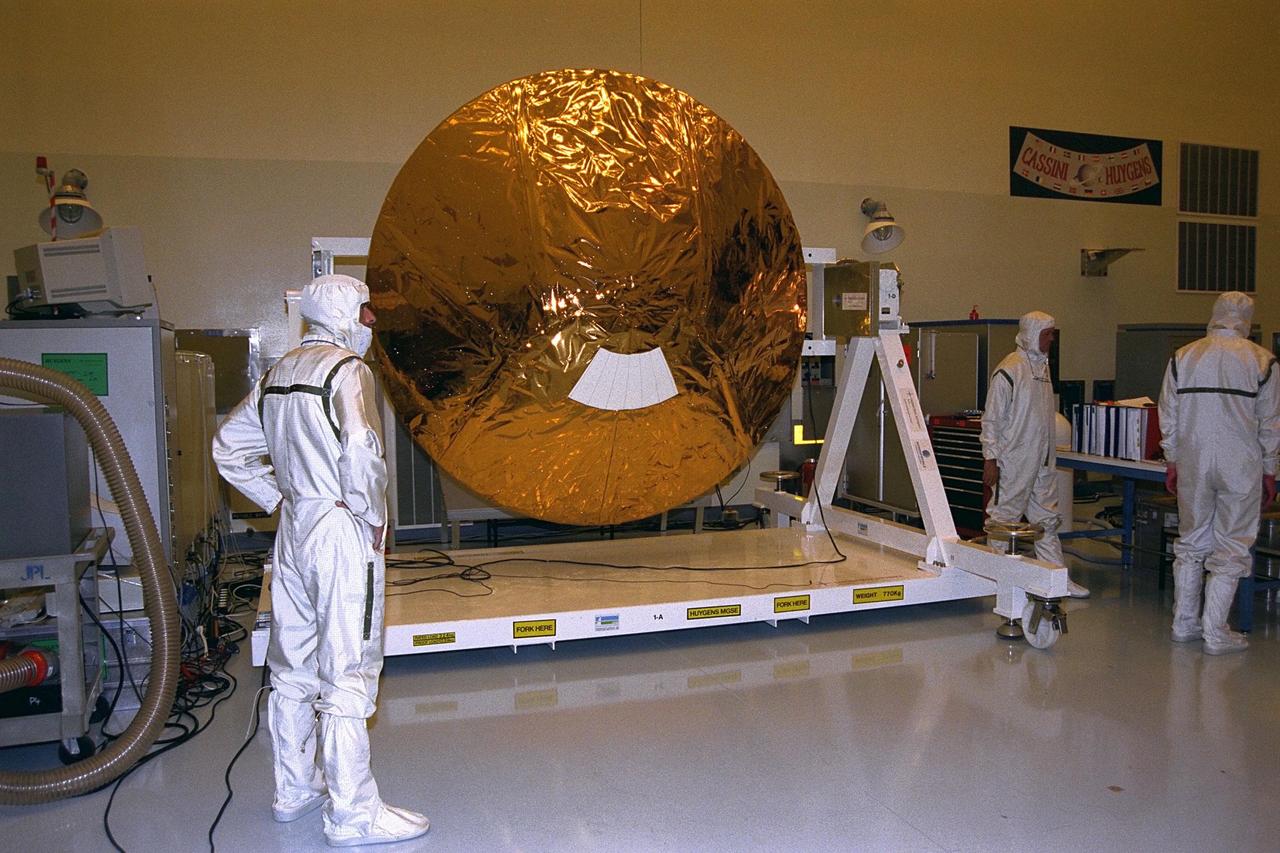

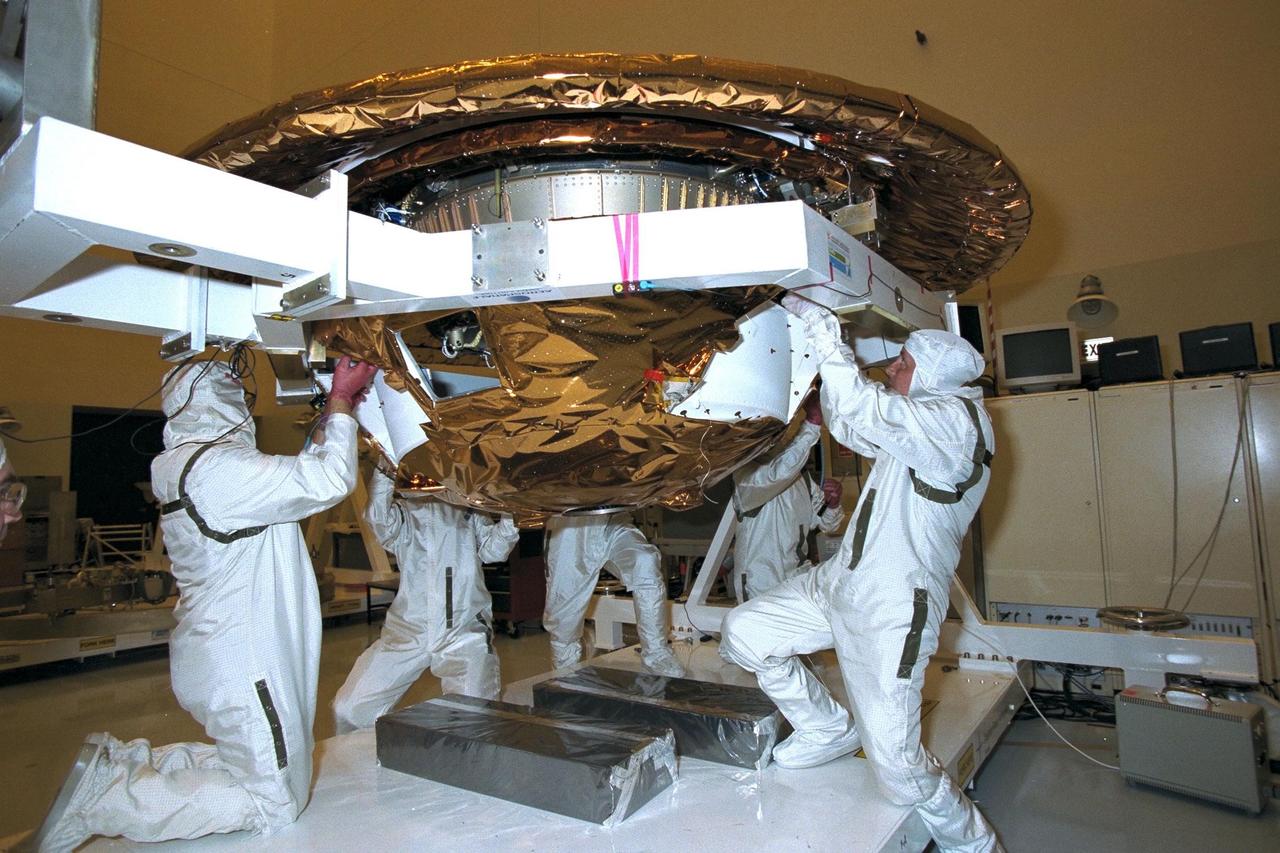
The Huygens probe is installed into the Cassini orbiter in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF)
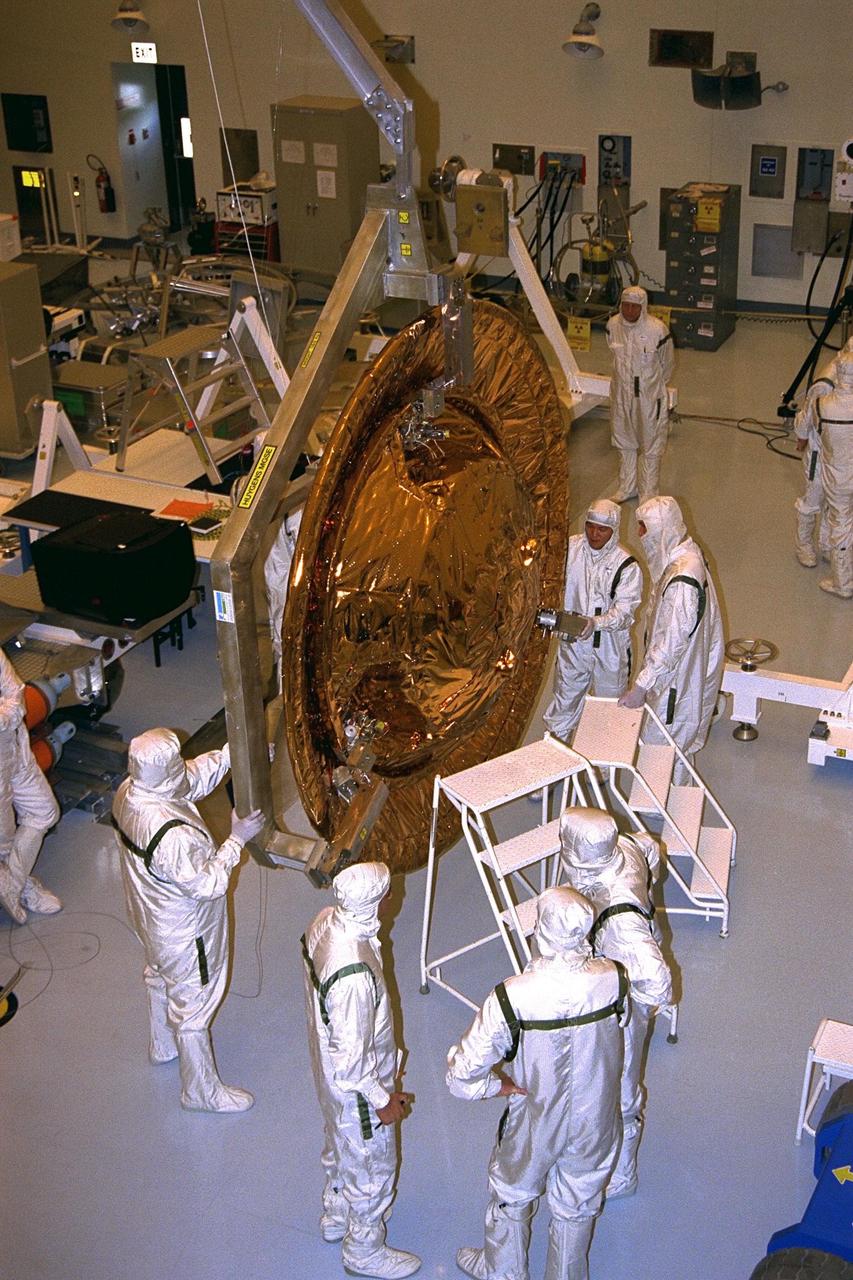

The Huygens probe is installed into the Cassini orbiter in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF)
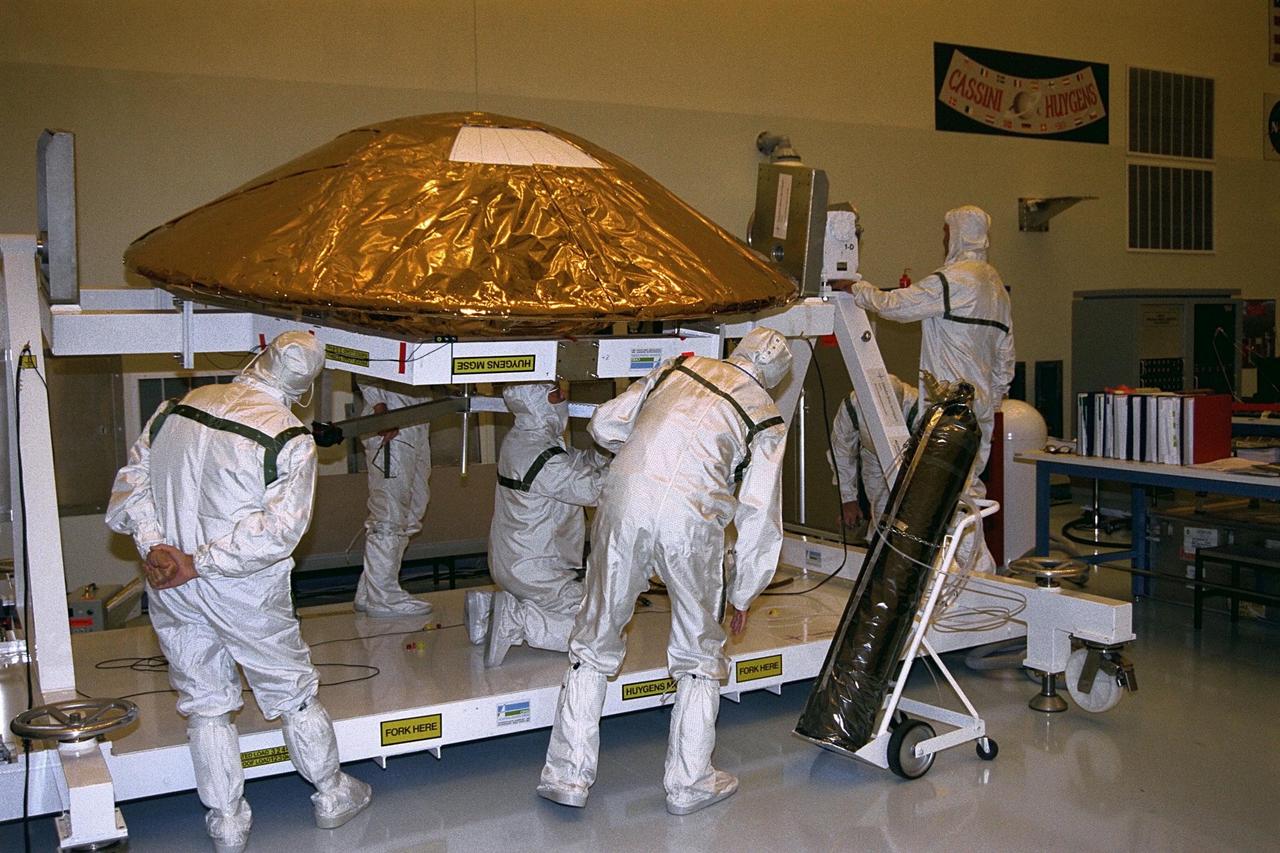

The Huygens probe is installed into the Cassini orbiter in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF)
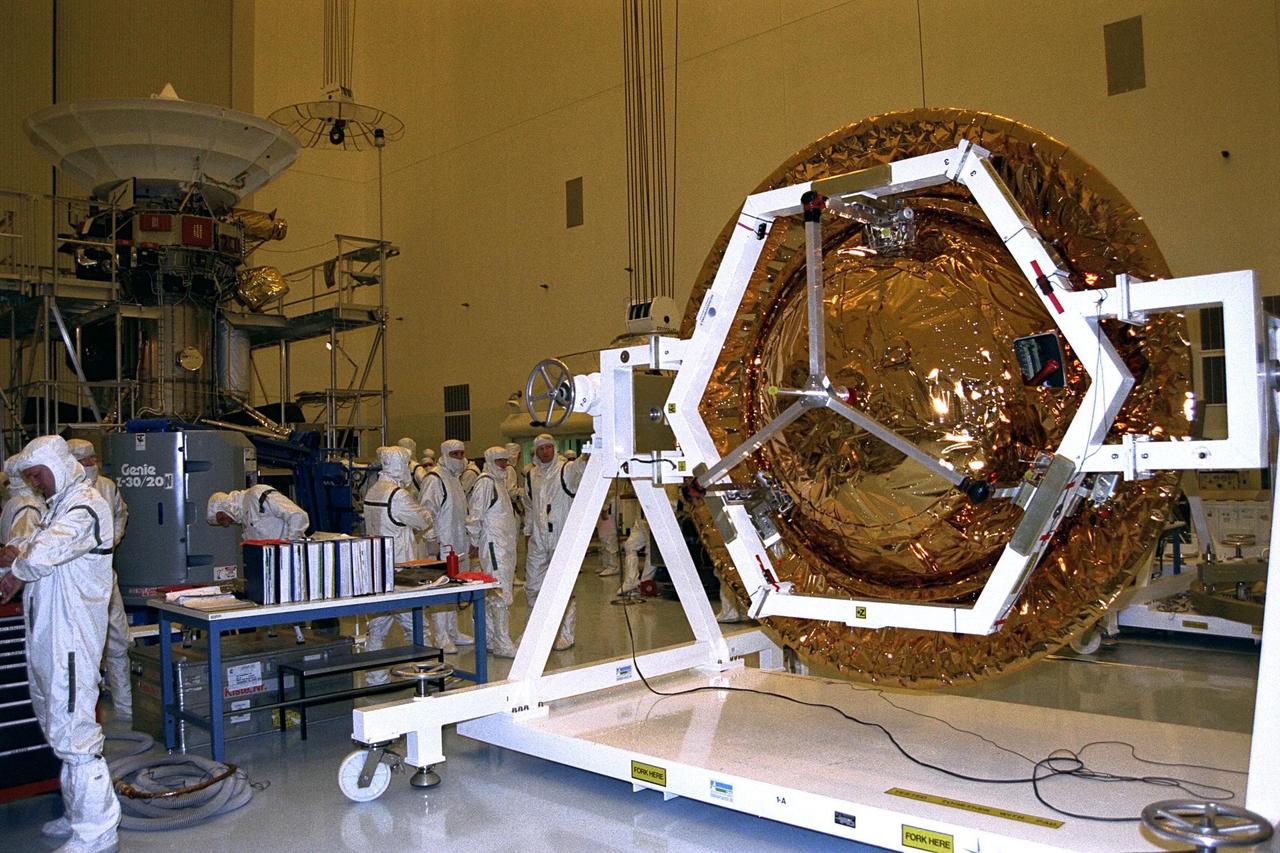

The Huygens probe is installed into the Cassini orbiter in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF)
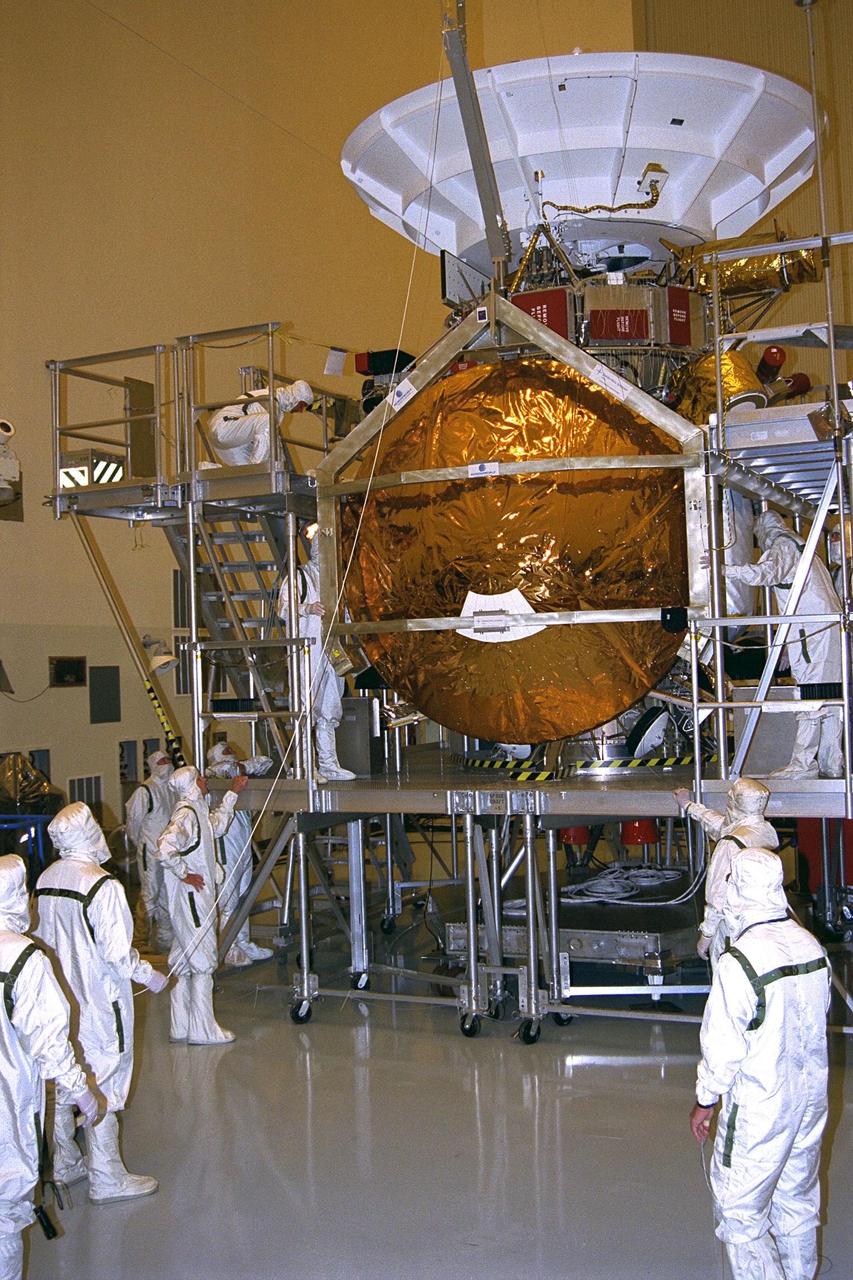

The Huygens probe is installed into the Cassini orbiter in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF)
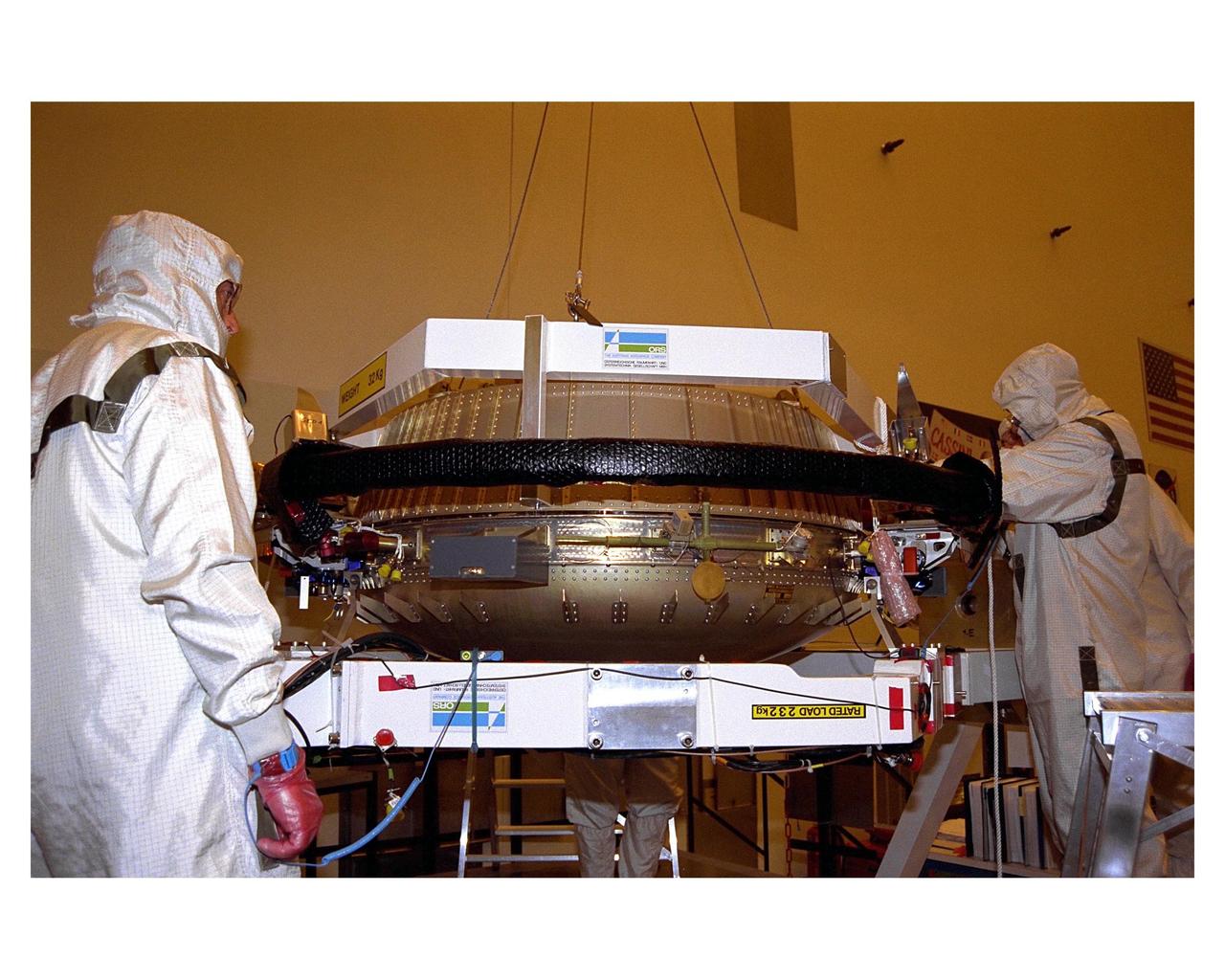

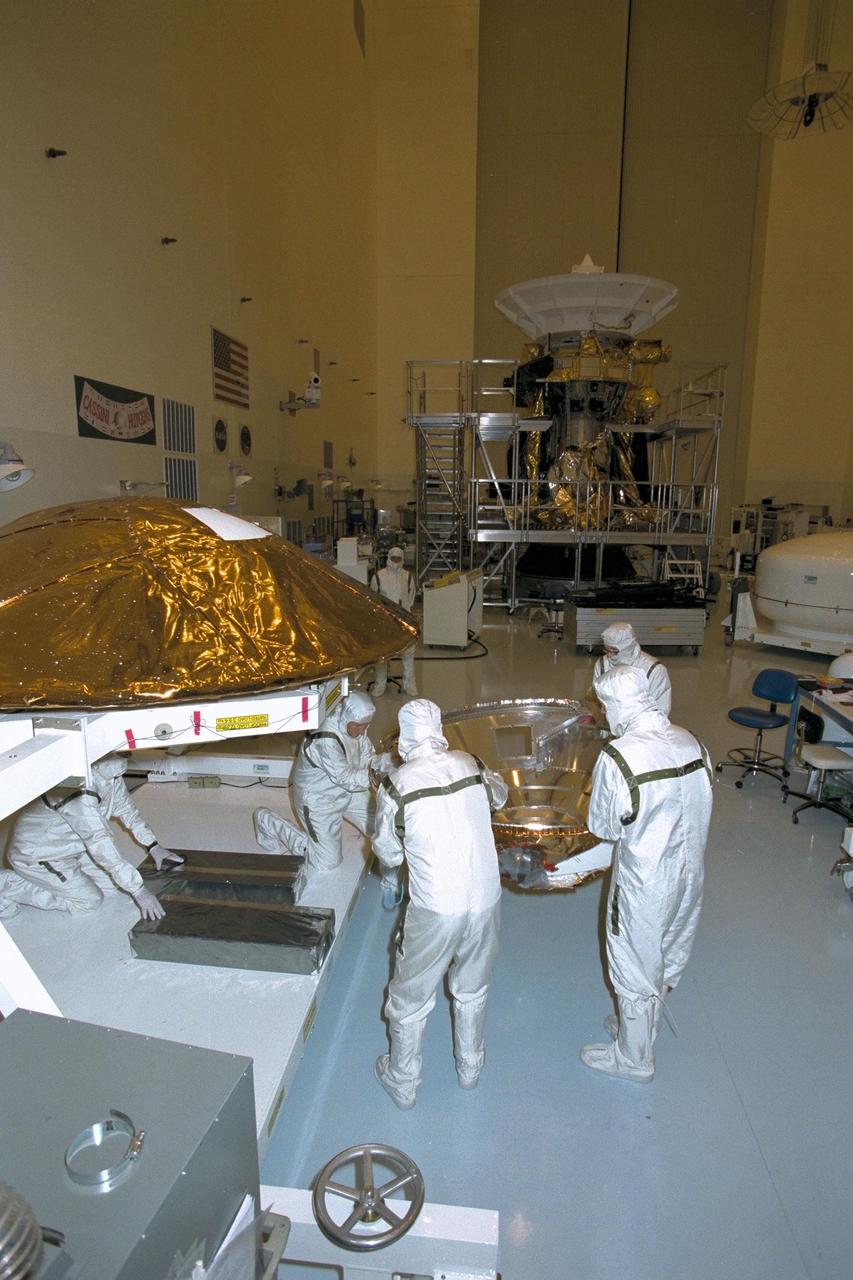
The aft shield is installed on the Huygens probe in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF). The European Space Agency's Huygens probe will be attached to the Cassini spacecraft which will explore the Titan moon of the Saturnian system
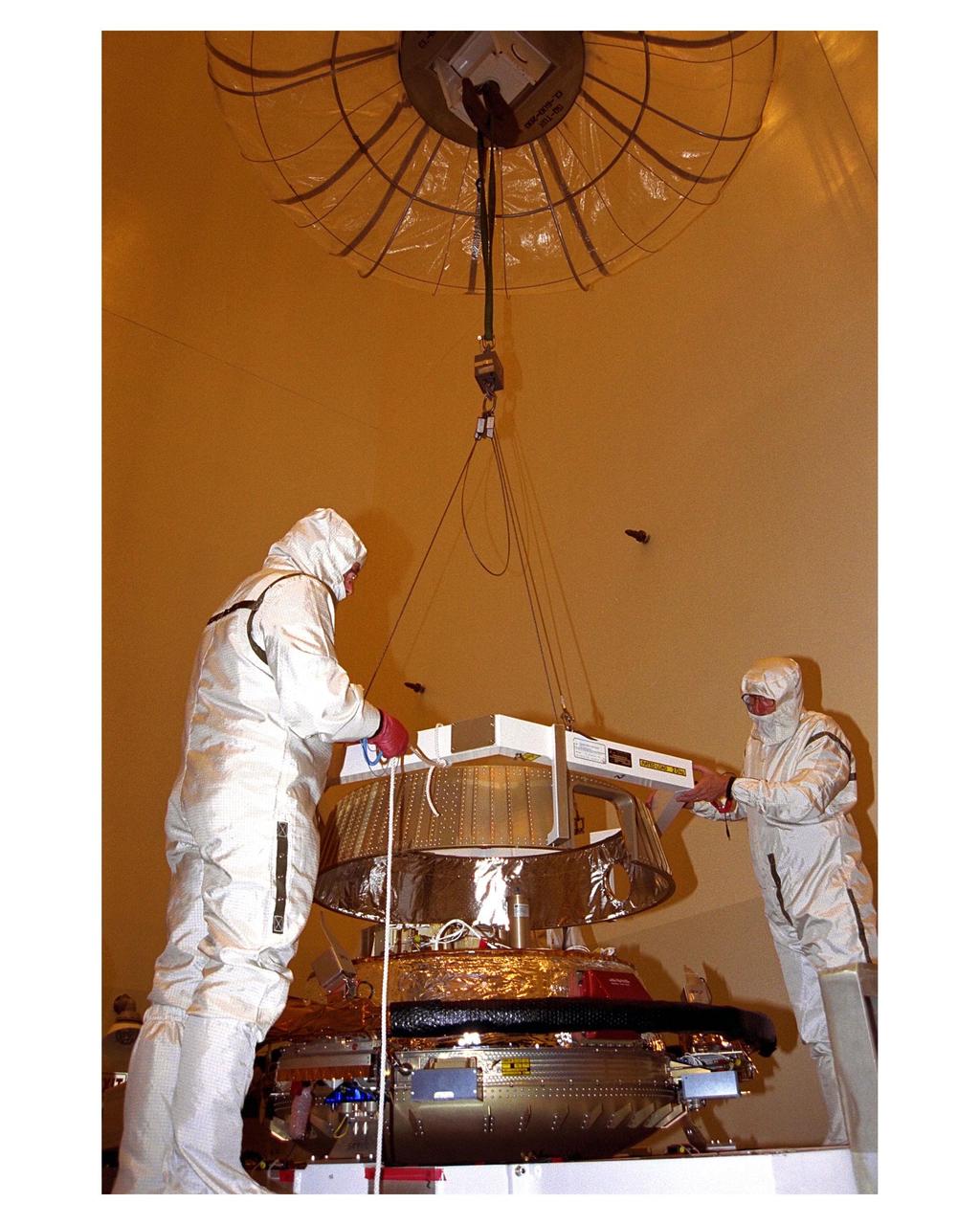

The aft shield is installed on the Huygens probe in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF). The European Space Agency's Huygens probe will be attached to the Cassini spacecraft which will explore the Titan moon of the Saturnian system
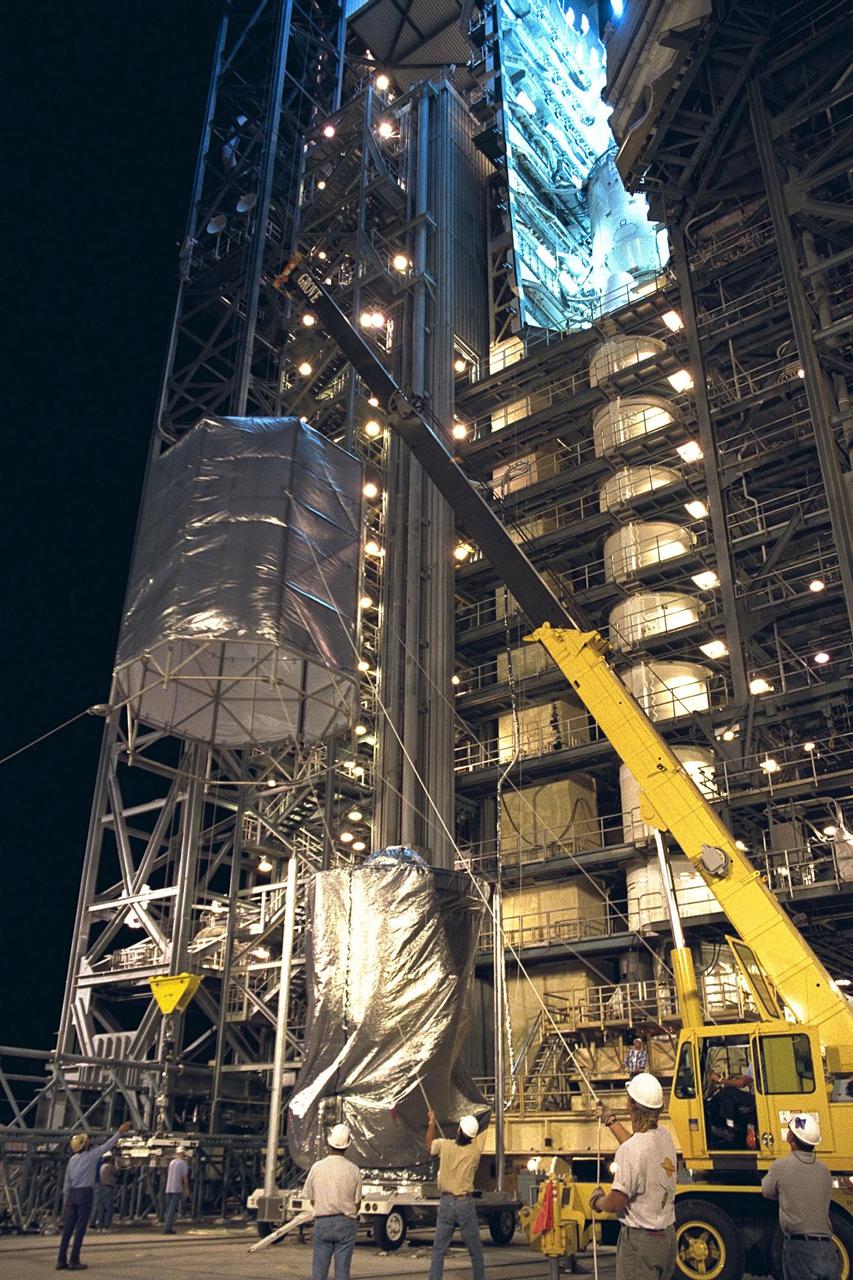

A crane lowers a protective transportation cover over the Cassini spacecraft, with its attached Huygens probe, at Launch Pad 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Station for the spacecraft’s return trip to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF). Damage to thermal insulation was discovered inside Huygens from an abnormally high flow of conditioned air. Further internal inspection, insulation repair and a cleaning of the probe are now required. Mission managers are targeting a mid-October launch date after Cassini returns to the pad and is once again placed atop its Titan IVB expendable launch vehicle. Cassini will explore the Saturnian system, including the planet’s rings, while the Huygens probe will explore the moon Titan
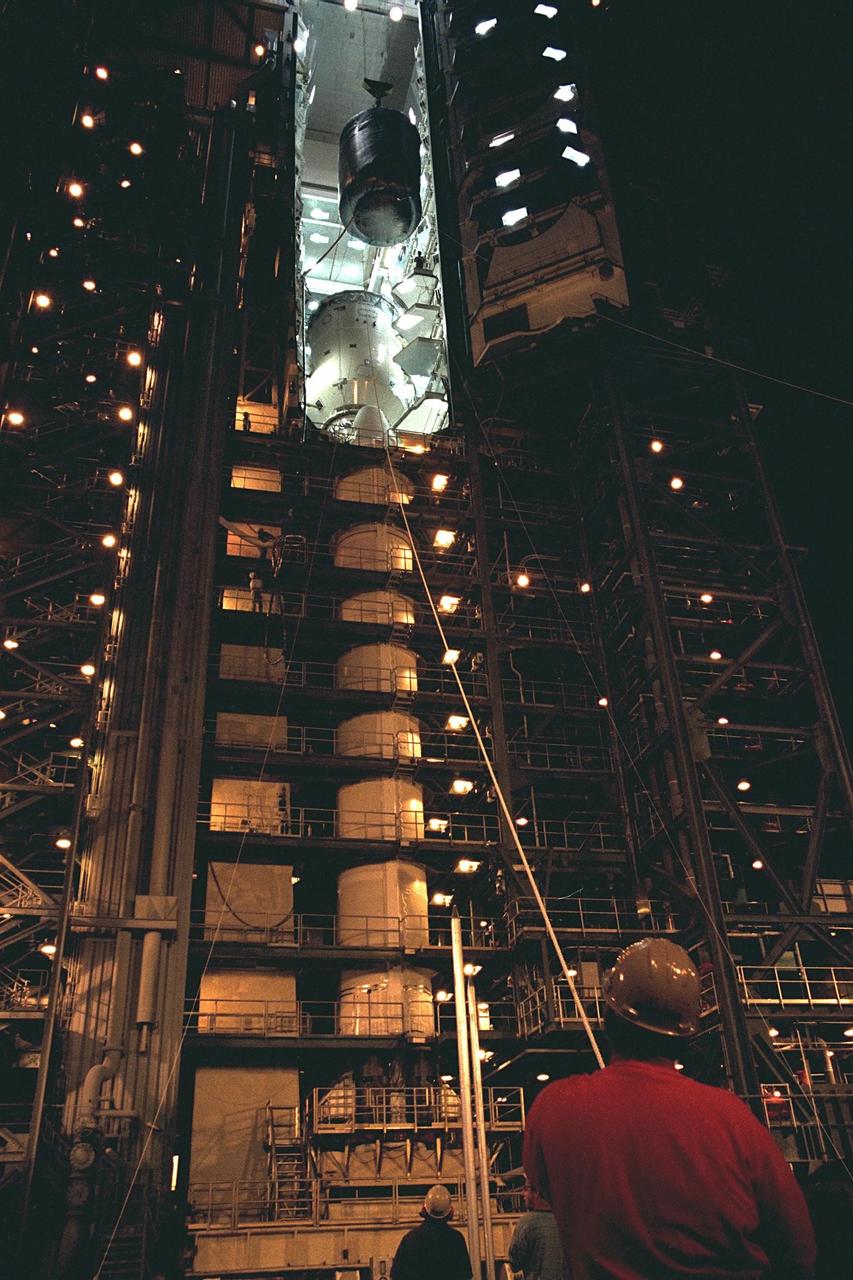

The Cassini spacecraft, with its attached Huygens probe, is lowered from Launch Pad 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Station for its return trip to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF). Damage to thermal insulation was discovered inside Huygens from an abnormally high flow of conditioned air. Further internal inspection, insulation repair and a cleaning of the probe are now required. Mission managers are targeting a mid-October launch date after Cassini returns to the pad and is once again placed atop its Titan IVB expendable launch vehicle. Cassini will explore the Saturnian system, including the planet’s rings, while the Huygens probe will explore the moon Titan
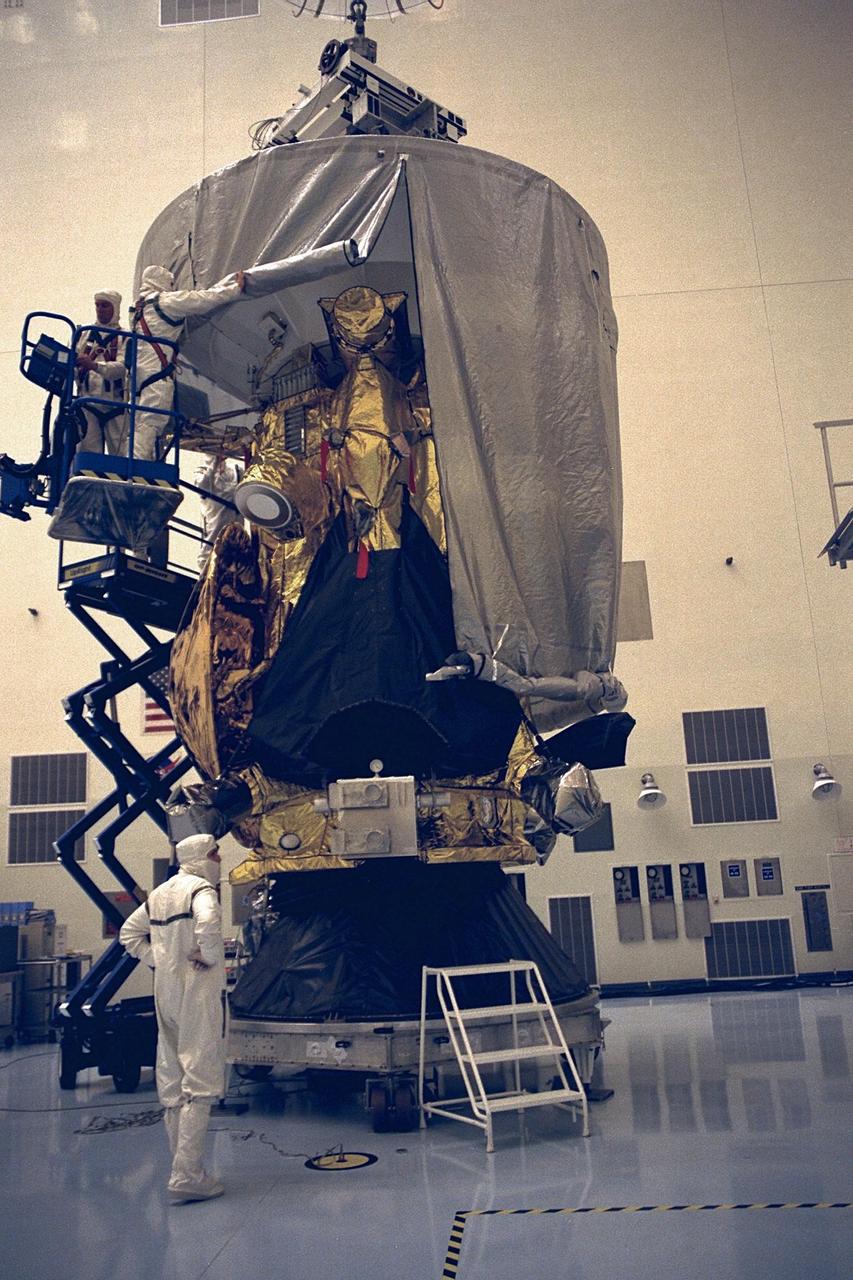

Workers in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) begin to remove a protective cover from the Cassini spacecraft with its attached Huygens probe. Damage to thermal insulation was discovered inside Huygens from an abnormally high flow of conditioned air. Further internal inspection, insulation repair and a cleaning of the probe are now required. Mission managers are targeting a mid-October launch date after Cassini returns to the pad and is once again placed atop its Titan IVB expendable launch vehicle at Launch Pad 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Station. Cassini will explore the Saturnian system, including the planet’s rings, while the Huygens probe will explore the moon Titan

Workers in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) finish the removal of a protective cover from the Cassini spacecraft with its attached Huygens probe. Damage to thermal insulation was discovered inside Huygens from an abnormally high flow of conditioned air. Further internal inspection, insulation repair and a cleaning of the probe are now required. Mission managers are targeting a mid-October launch date after Cassini returns to the pad and is once again placed atop its Titan IVB expendable launch vehicle at Launch Pad 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Station. Cassini will explore the Saturnian system, including the planet’s rings, while the Huygens probe will explore the moon Titan
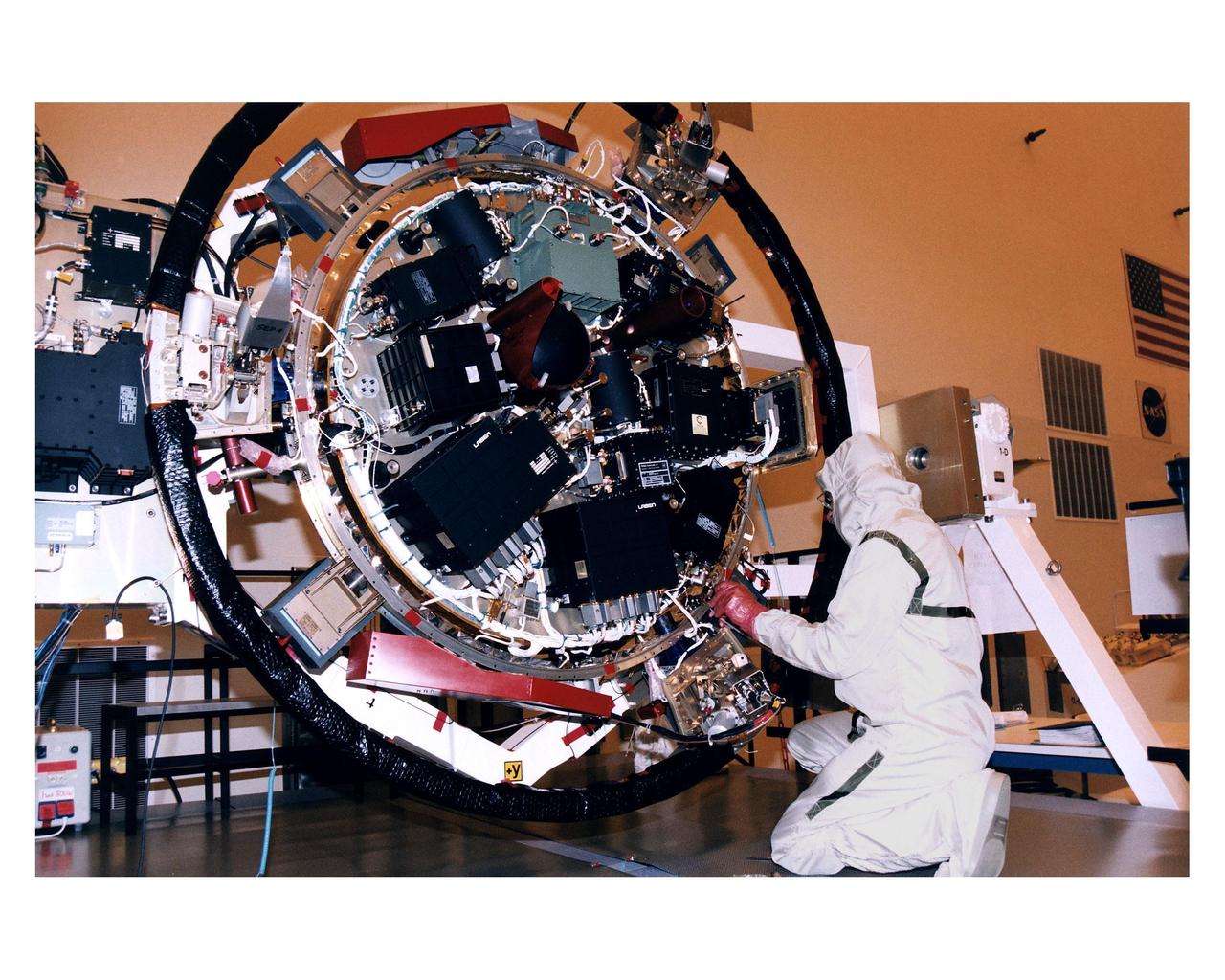
An employee in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) works on the top side of the experiment platform for the Huygens probe that will accompany the Cassini orbiter to Saturn during prelaunch processing, testing and integration in that facility. The Huygens probe and the Cassini orbiter being processed at KSC are the two primary components of the Cassini spacecraft, which will be launched on a Titan IVB/Centaur expendable launch vehicle from Cape Canaveral Air Station. Cassini will explore Saturn, its rings and moons for four years. The Huygens probe, designed and developed for the European Space Agency (ESA), will be deployed from the orbiter to study the clouds, atmosphere and surface of Saturn’s largest moon, Titan. The orbiter was designed and assembled at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California. Following postflight inspections, integration of the 12 science instruments not already installed on the orbiter will be completed. Then, the parabolic high-gain antenna and the propulsion module will be mated to the orbiter, followed by the Huygens probe, which will complete spacecraft integration. The Cassini mission is targeted for an Oct. 6 launch to begin its 6.7-year journey to the Saturnian system. Arrival at the planet is expected to occur around July 1, 2004
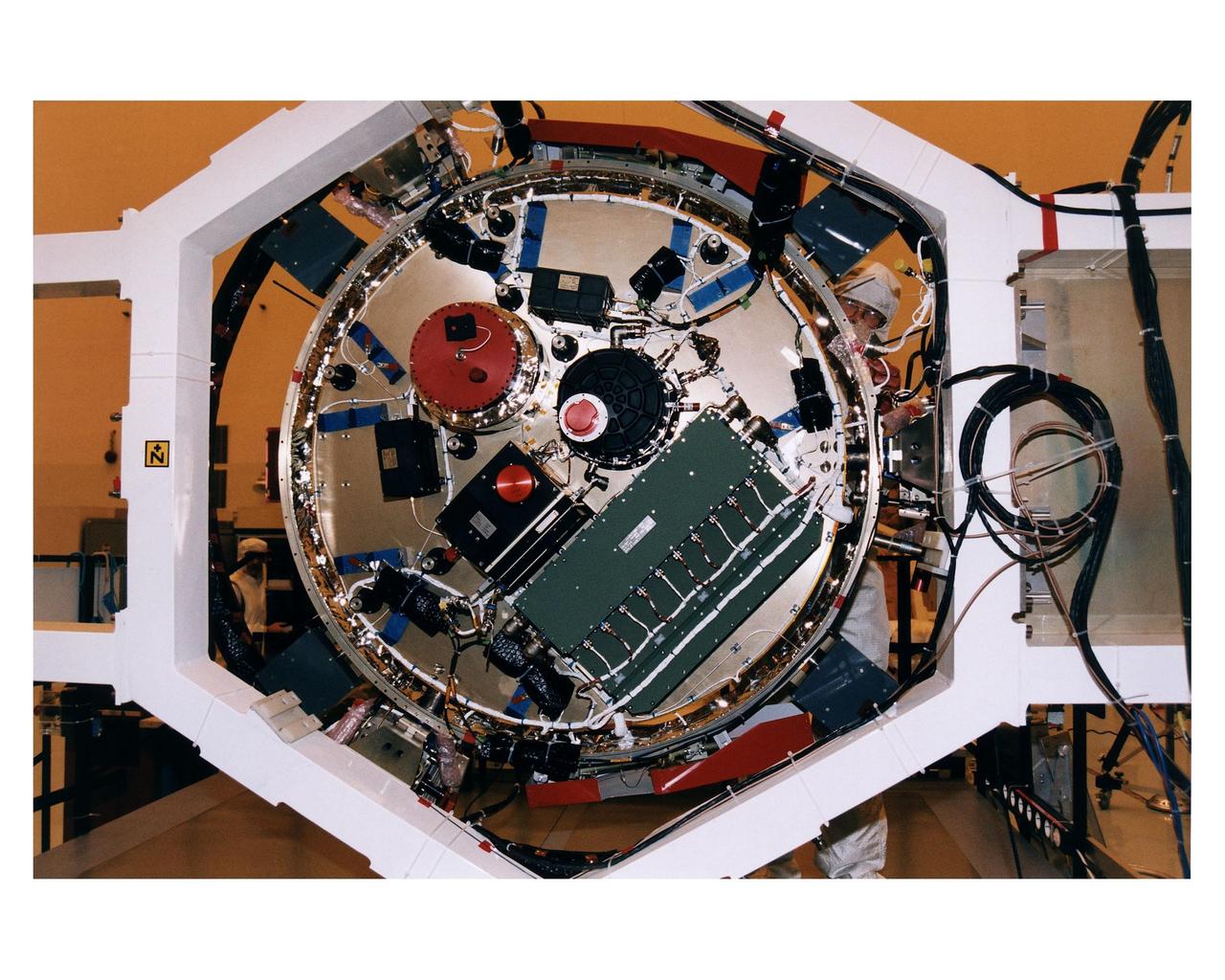
A worker in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) stands behind the bottom side of the experiment platform for the Huygens probe that will accompany the Cassini orbiter to Saturn during prelaunch processing testing and integration in that facility. The Huygens probe and the Cassini orbiter being processed at KSC are the two primary components of the Cassini spacecraft, which will be launched on a Titan IVB/Centaur expendable launch vehicle from Cape Canaveral Air Station. Cassini will explore Saturn, its rings and moons for four years. The Huygens probe, designed and developed for the European Space Agency (ESA), will be deployed from the orbiter to study the clouds, atmosphere and surface of Saturn’s largest moon, Titan. The orbiter was designed and assembled at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California. Following postflight inspections, integration of the 12 science instruments not already installed on the orbiter will be completed. Then, the parabolic high-gain antenna and the propulsion module will be mated to the orbiter, followed by the Huygens probe, which will complete spacecraft integration. The Cassini mission is targeted for an Oct. 6 launch to begin its 6.7-year journey to the Saturnian system. Arrival at the planet is expected to occur around July 1, 2004

Cassini has sighted Prometheus and Pandora, the two F-ring-shepherding moons whose unpredictable orbits both fascinate scientists and wreak havoc on the F ring. Prometheus (102 kilometers, or 63 miles across) is visible left of center in the image, inside the F ring. Pandora (84 kilometers, or 52 miles across) appears above center, outside the ring. The dark shadow cast by the planet stretches more than halfway across the A ring, the outermost main ring. The mottled pattern appearing in the dark regions of the image is 'noise' in the signal recorded by the camera system, which has subsequently been magnified by the image processing. The F ring is a narrow, ribbon-like structure, with a width seen in this geometry equivalent to a few kilometers. The two small, irregularly shaped moons exert a gravitational influence on particles that make up the F ring, confining it and possibly leading to the formation of clumps, strands and other structures observed there. Pandora prevents the F ring from spreading outward and Prometheus prevents it from spreading inward. However, their interaction with the ring is complex and not fully understood. The shepherds are also known to be responsible for many of the observed structures in Saturn's A ring. The moons, which were discovered in images returned by the Voyager 1 spacecraft in 1980, are in chaotic orbits--their orbits can change unpredictably when the moons get very close to each other. This strange behavior was first noticed in ground-based and Hubble Space Telescope observations in 1995, when the rings were seen nearly edge-on from Earth and the usual glare of the rings was reduced, making the satellites more readily visible than usual. The positions of both satellites at that time were different than expected based on Voyager data. One of the goals for the Cassini-Huygens mission is to derive more precise orbits for Prometheus and Pandora. Seeing how their orbits change over the duration of the mission will help to determine their masses, which in turn will help constrain models of their interiors and provide a more complete understanding of their effect on the rings. This narrow angle camera image was snapped through the broadband green spectral filter, centered at 568 nanometers, on March 10, 2004, when the spacecraft was 55.5 million kilometers (34.5 million miles) from the planet. Image scale is approximately 333 kilometers (207 miles) per pixel. Contrast has been greatly enhanced, and the image has been magnified to aid visibility of the moons as well as structure in the rings. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA05387
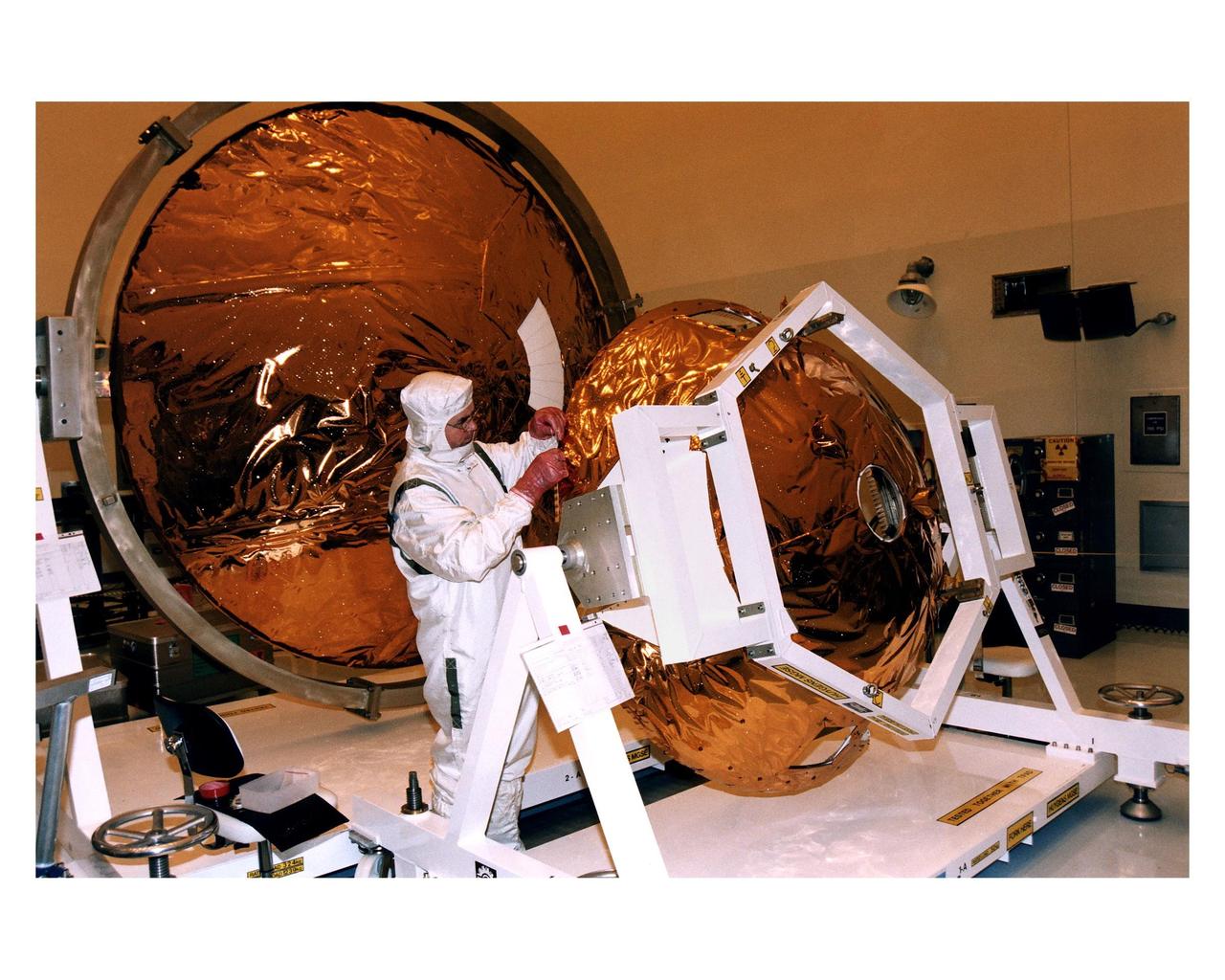

An employee in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) sews thermal insulation material on the front heat shield of the Huygens probe during prelaunch processing testing and integration in that facility, with the probe’s back cover in the background. The Huygens probe and the Cassini orbiter being processed at KSC are the two primary components of the Cassini spacecraft, which will be launched on a Titan IVB/Centaur expendable launch vehicle from Cape Canaveral Air Station. Cassini will explore Saturn, its rings and moons for four years. The Huygens probe, designed and developed for the European Space Agency (ESA), will be deployed from the orbiter to study the clouds, atmosphere and surface of Saturn’s largest moon, Titan. The orbiter was designed and assembled at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California. Following postflight inspections, integration of the 12 science instruments not already installed on the orbiter will be completed. Then, the parabolic high-gain antenna and the propulsion module will be mated to the orbiter, followed by the Huygens probe, which will complete spacecraft integration. The Cassini mission is targeted for an Oct. 6 launch to begin its 6.7-year journey to the Saturnian system. Arrival at the planet is expected to occur around July 1, 2004
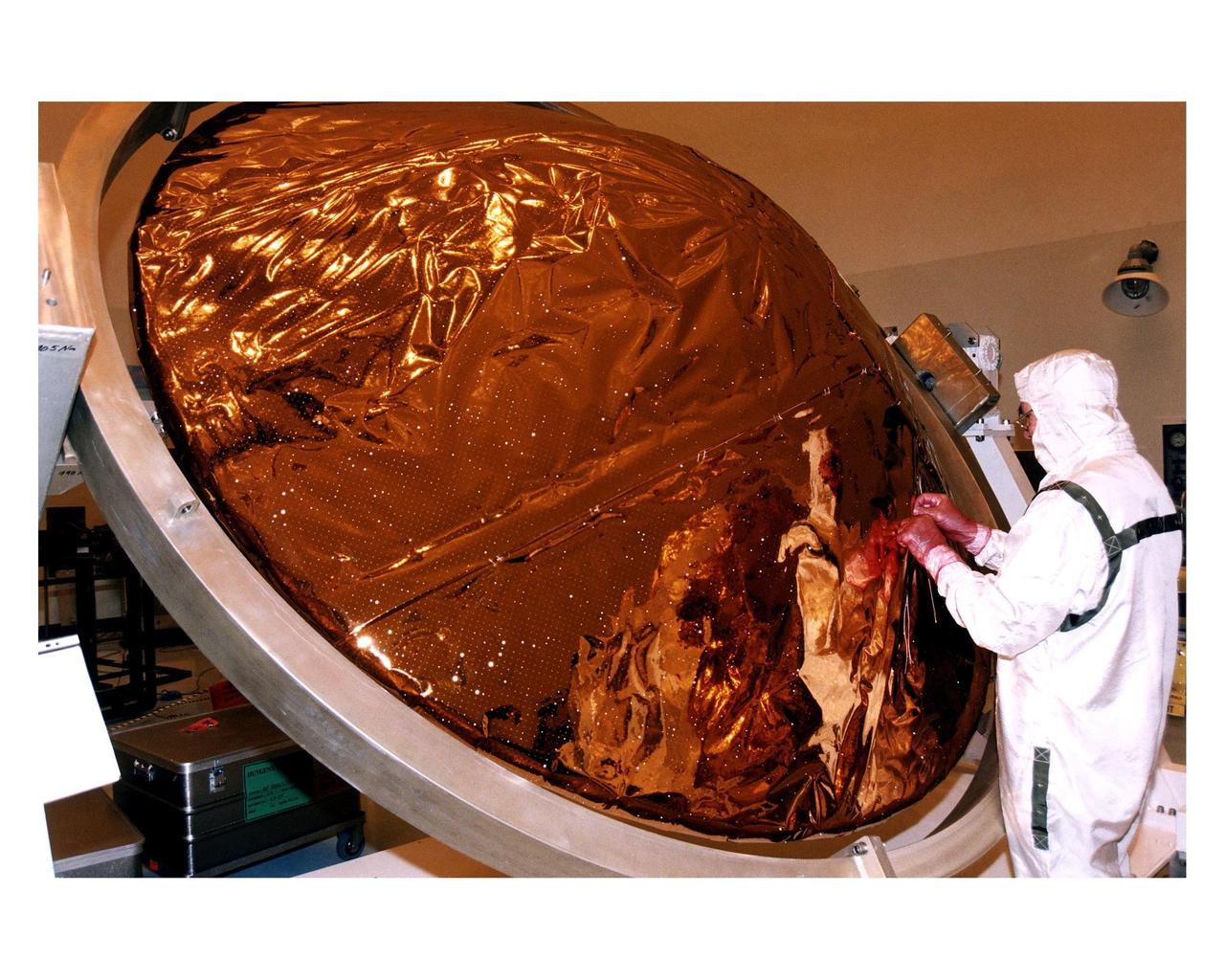
An employee in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) sews thermal insulation material on the back cover and heat shield of the Huygens probe during prelaunch processing, testing and integration in that facility. The Huygens probe and the Cassini orbiter being processed at KSC are the two primary components of the Cassini spacecraft, which will be launched on a Titan IVB/Centaur expendable launch vehicle from Cape Canaveral Air Station. Cassini will explore Saturn, its rings and moons for four years. The Huygens probe, designed and developed for the European Space Agency (ESA), will be deployed from the orbiter to study the clouds, atmosphere and surface of Saturn’s largest moon, Titan. The orbiter was designed and assembled at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California. Following postflight inspections, integration of the 12 science instruments not already installed on the orbiter will be completed. Then, the parabolic high-gain antenna and the propulsion module will be mated to the orbiter, followed by the Huygens probe, which will complete spacecraft integration. The Cassini mission is targeted for an Oct. 6 launch to begin its 6.7-year journey to the Saturnian system. Arrival at the planet is expected to occur around July 1, 2004
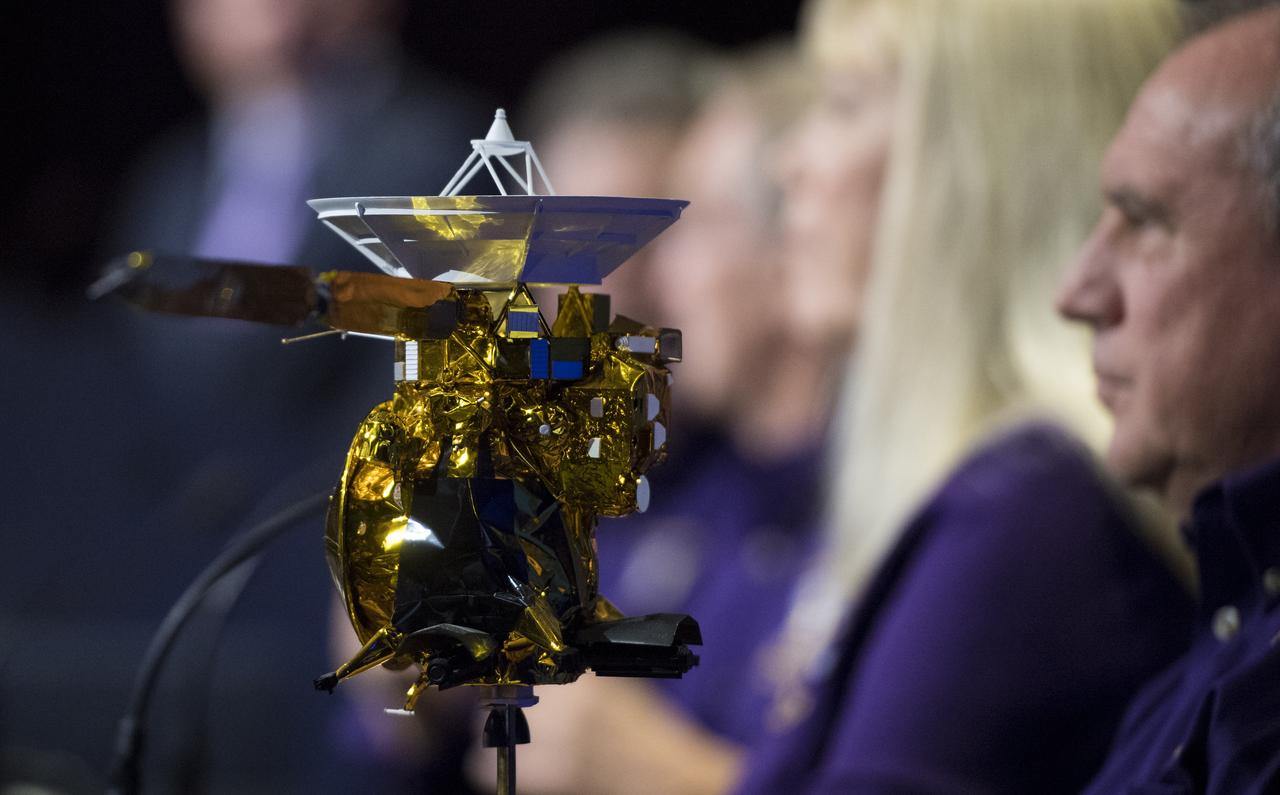
A model of the Cassini-Huygens spacecraft is seen during a press conference previewing Cassini's End of Mission, Wednesday, Sept. 13, 2017 at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. Since its arrival in 2004, the Cassini-Huygens mission has been a discovery machine, revolutionizing our knowledge of the Saturn system and captivating us with data and images never before obtained with such detail and clarity. On Sept. 15, 2017, operators will deliberately plunge the spacecraft into Saturn, as Cassini gathered science until the end. The “plunge” ensures Saturn’s moons will remain pristine for future exploration. During Cassini’s final days, mission team members from all around the world gathered at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, to celebrate the achievements of this historic mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

A model of the Cassini-Huygens spacecraft is seen in the von Kármán Auditorium during a press conference previewing Cassini's End of Mission, Wednesday, Sept. 13, 2017 at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. Since its arrival in 2004, the Cassini-Huygens mission has been a discovery machine, revolutionizing our knowledge of the Saturn system and captivating us with data and images never before obtained with such detail and clarity. On Sept. 15, 2017, operators will deliberately plunge the spacecraft into Saturn, as Cassini gathered science until the end. The “plunge” ensures Saturn’s moons will remain pristine for future exploration. During Cassini’s final days, mission team members from all around the world gathered at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, to celebrate the achievements of this historic mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
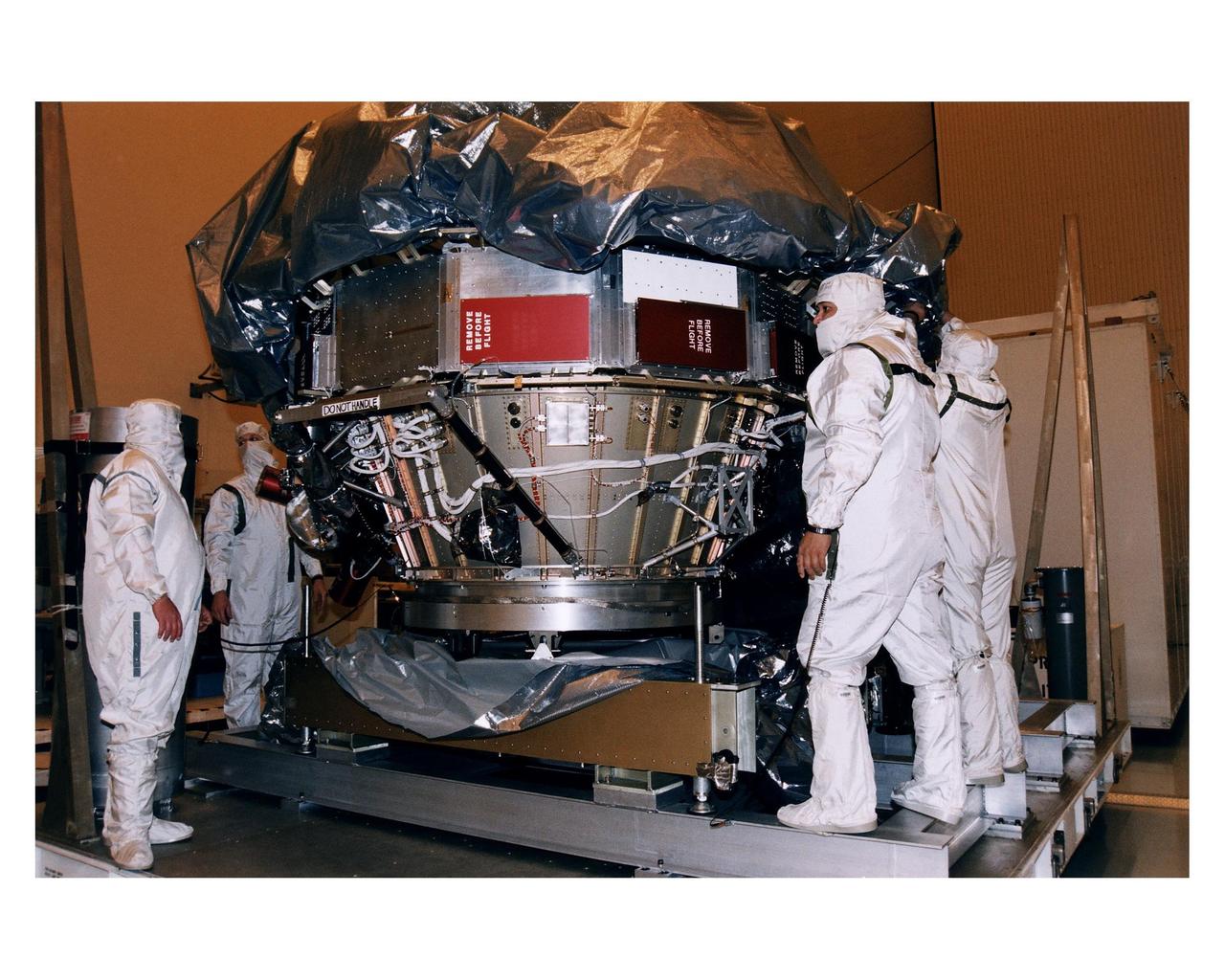

Workers in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) stand around the upper experiment module and base of the Cassini orbiter during prelaunch processing, testing and integration in that facility. The Cassini orbiter and Huygens probe being processed at KSC are the two primary components of the Cassini spacecraft, which will be launched on a Titan IVB/Centaur expendable launch vehicle from Cape Canaveral Air Station. Cassini will explore Saturn, its rings and moons for four years. The Huygens probe, designed and developed for the European Space Agency (ESA), will be deployed from the orbiter to study the clouds, atmosphere and surface of Saturn’s largest moon, Titan. The orbiter was designed and assembled at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California. Following postflight inspections, integration of the 12 science instruments not already installed on the orbiter will be completed. Then, the parabolic high-gain antenna and the propulsion module will be mated to the orbiter, followed by the Huygens probe, which will complete spacecraft integration. The Cassini mission is targeted for an Oct. 6 launch to begin its 6.7-year journey to the Saturnian system. Arrival at the planet is expected to occur around July 1, 2004
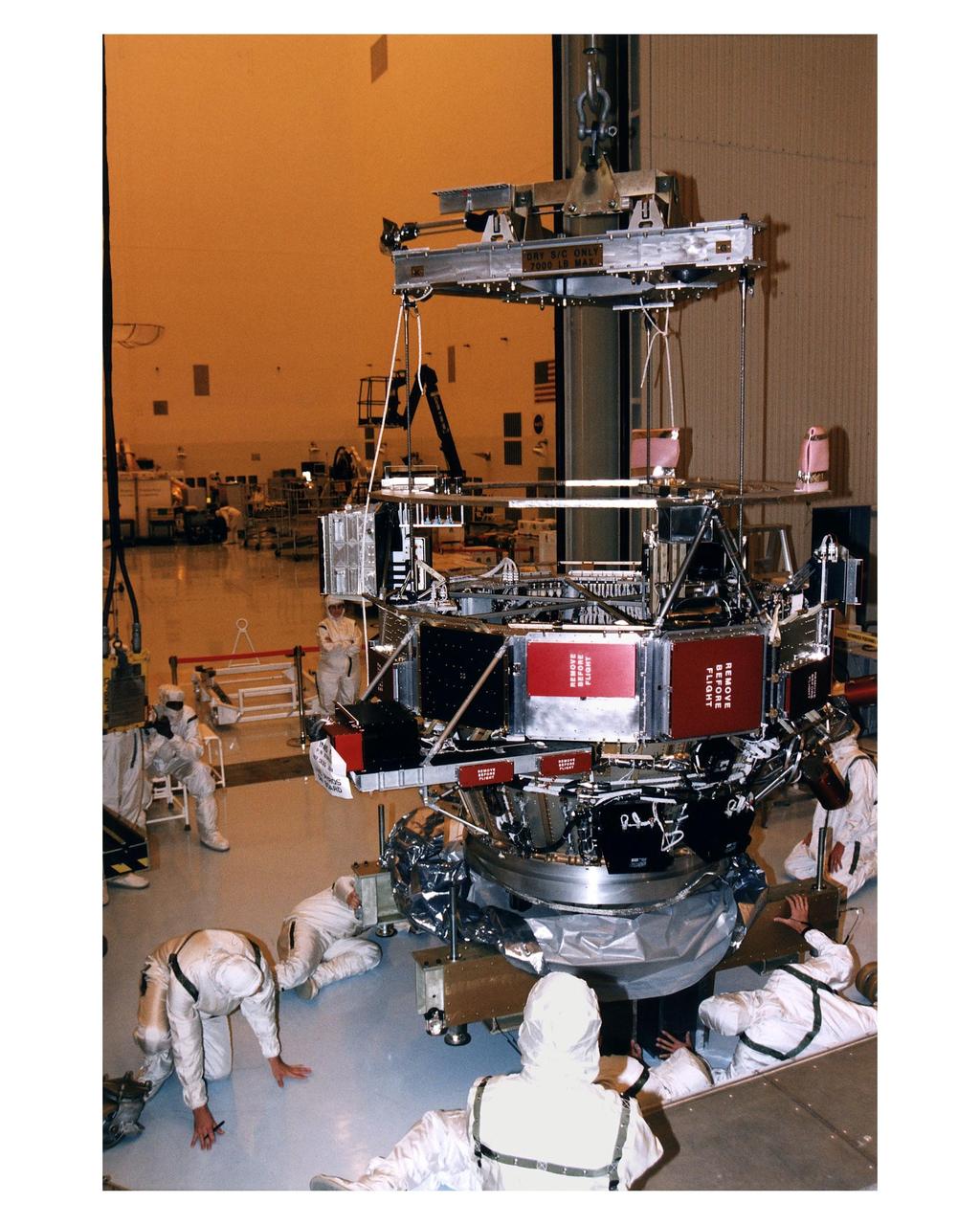
Employees in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) lower the upper experiment module and base of the Cassini orbiter onto a work stand during prelaunch processing, testing and integration work in that facility. The Cassini orbiter and Huygens probe being processed at KSC are the two primary components of the Cassini spacecraft, which will be launched on a Titan IVB/Centaur expendable launch vehicle from Cape Canaveral Air Station. Cassini will explore Saturn, its rings and moons for four years. The Huygens probe, designed and developed for the European Space Agency (ESA), will be deployed from the orbiter to study the clouds, atmosphere and surface of Saturn’s largest moon, Titan. The orbiter was designed and assembled at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California. Following postflight inspections, integration of the 12 science instruments not already installed on the orbiter will be completed. Then, the parabolic high-gain antenna and the propulsion module will be mated to the orbiter, followed by the Huygens probe, which will complete spacecraft integration. The Cassini mission is targeted for an Oct. 6 launch to begin its 6.7-year journey to the Saturnian system. Arrival at the planet is expected to occur around July 1, 2004
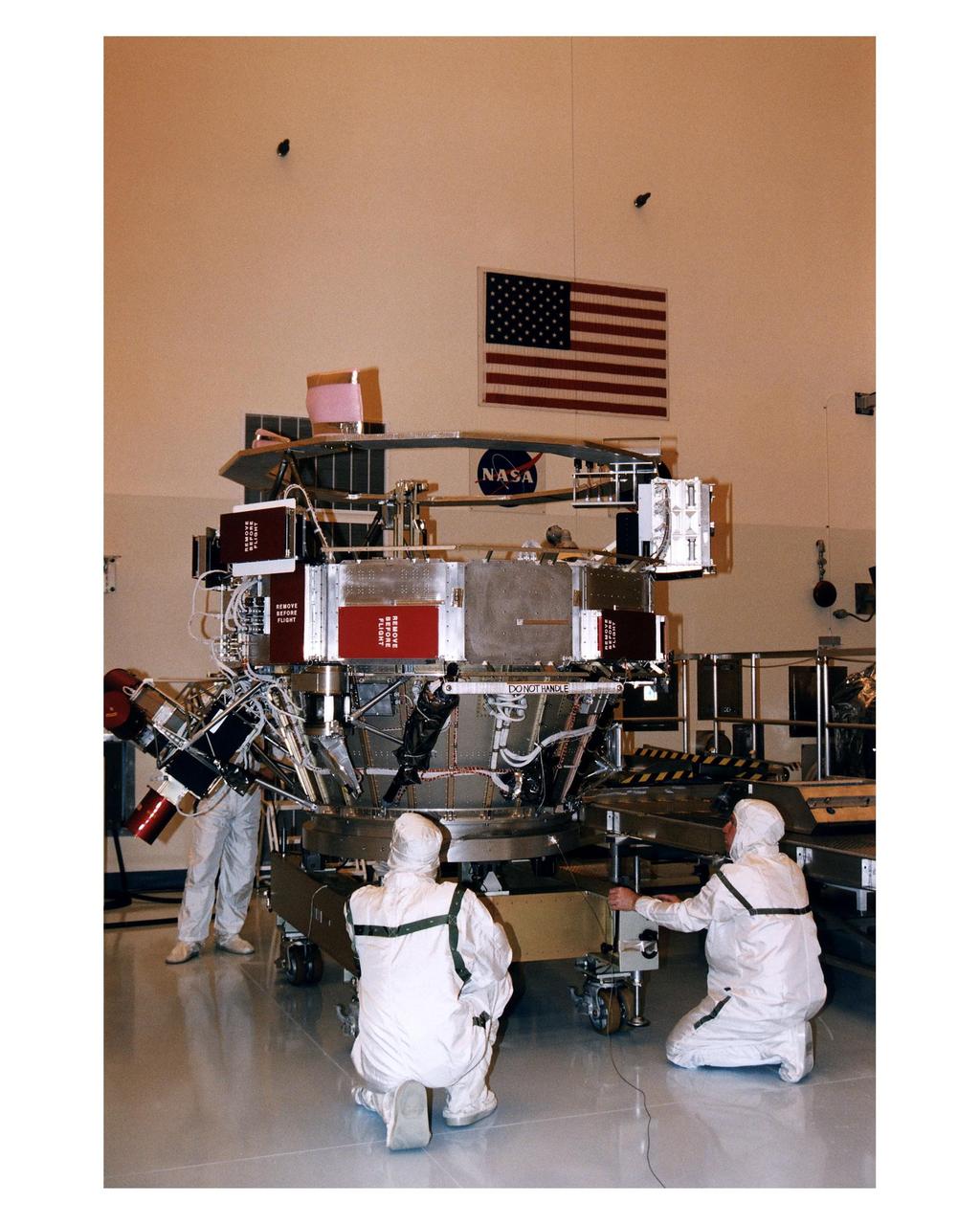

Workers in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) perform checkouts of the upper experiment module and base of the Cassini orbiter during prelaunch processing, testing and integration in that facility. The Cassini orbiter and Huygens probe being processed at KSC are the two primary components of the Cassini spacecraft, which will be launched on a Titan IVB/Centaur expendable launch vehicle from Cape Canaveral Air Station. Cassini will explore Saturn, its rings and moons for four years. The Huygens probe, designed and developed for the European Space Agency (ESA), will be deployed from the orbiter to study the clouds, atmosphere and surface of Saturn’s largest moon, Titan. The orbiter was designed and assembled at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California. Following postflight inspections, integration of the 12 science instruments not already installed on the orbiter will be completed. Then, the parabolic high-gain antenna and the propulsion module will be mated to the orbiter, followed by the Huygens probe, which will complete spacecraft integration. The Cassini mission is targeted for an Oct. 6 launch to begin its 6.7-year journey to the Saturnian system. Arrival at the planet is expected to occur around July 1, 2004
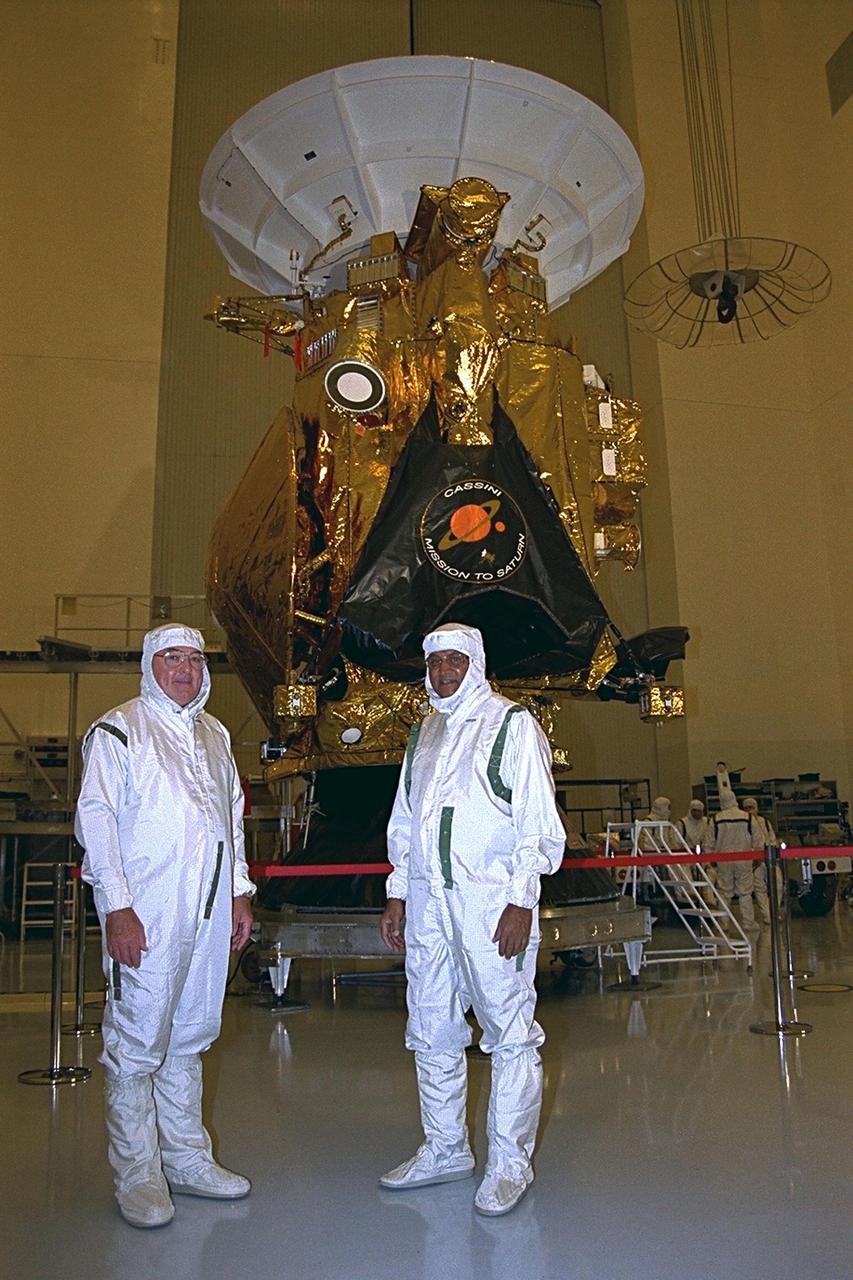

Richard Spehalski, program manager of the Cassini mission, and Hamid Hassan, the European Space Agency Huygens project manager, stand in front of the Cassini spacecraft in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF). The Cassini spacecraft is scheduled to launch on an Air Force Titan IV/Centaur launch vehicle on Oct. 6, 1997. It is destined to arrive at Saturn in July 2004, to study Saturn, its rings, moons and magnetic environment for a four-year period. The Cassini project is managed for NASA by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif
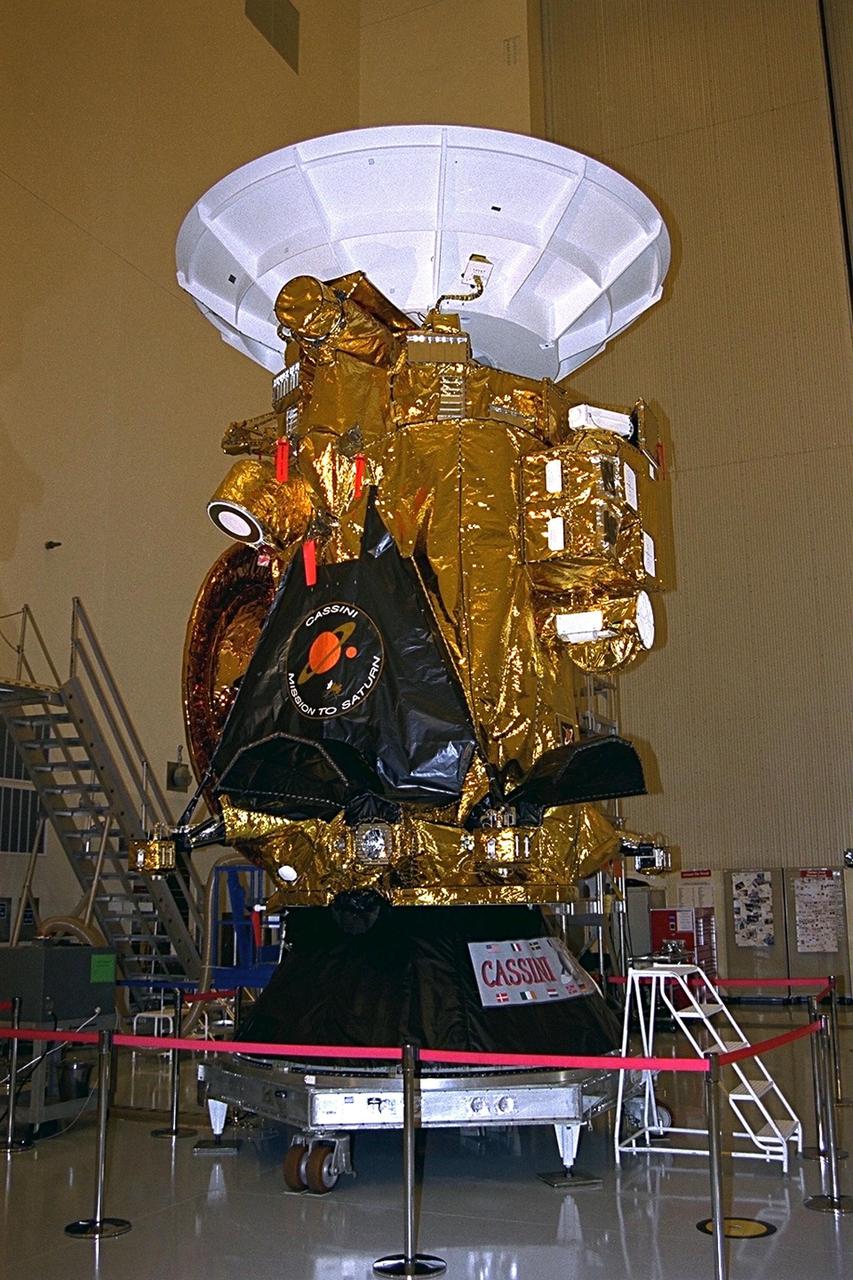
The Cassini spacecraft is on view for the media in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at Kennedy Space Center, Florida. The two-story-tall spacecraft, scheduled for launch on an Air Force Titan IV/Centaur launch vehicle on Oct. 6, is destined to arrive at Saturn in July 2004, where it will orbit and study Saturn, its rings, moons and magnetic environment in detail over a four-year period. Cassini carries a scientific probe called Huygens, provided by the European Space Agency. Huygens will be released from the main Cassini spacecraft and parachute through the atmosphere of Saturn's most intriguing moon, Titan, which is thought to chemically resemble a very cold version of Earth's environment before life began. The Cassini mission is managed for NASA by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology
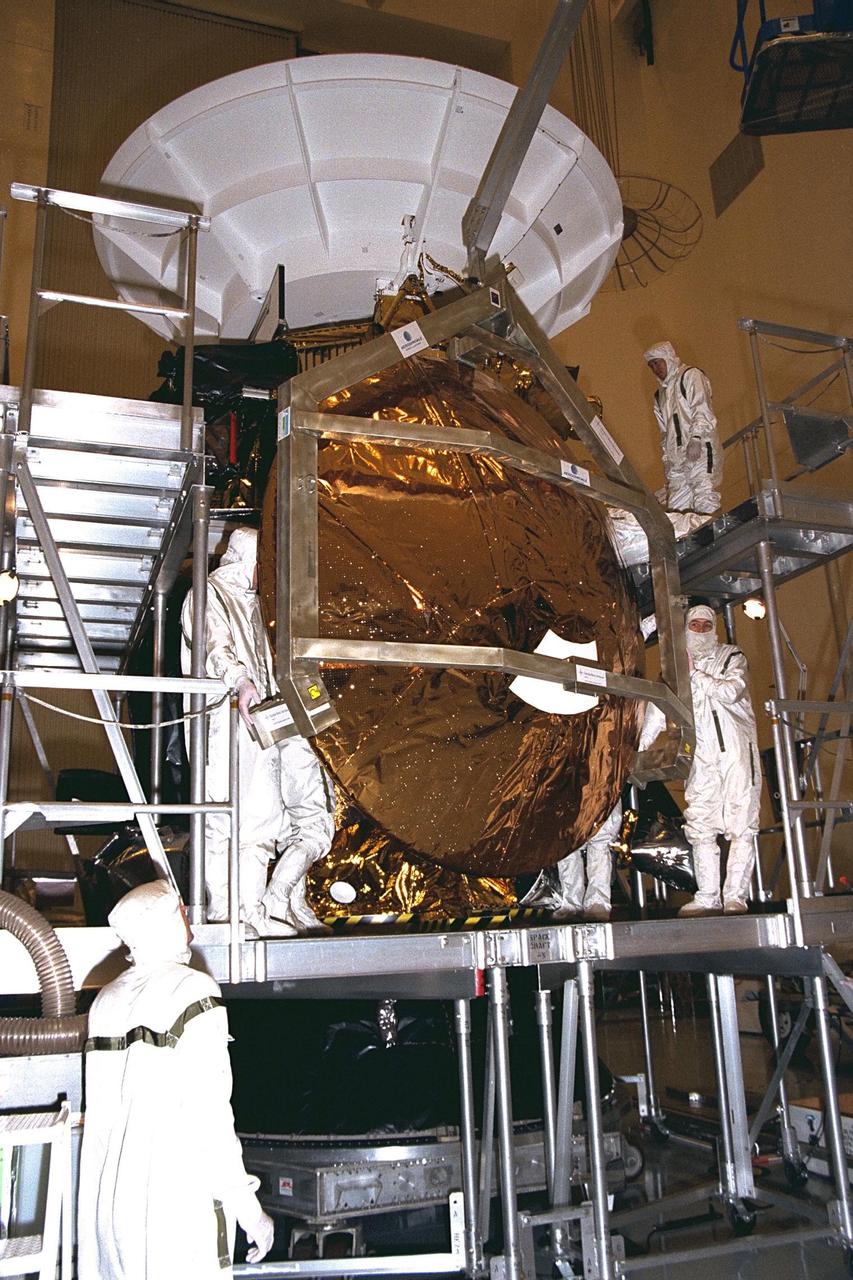

Workers remove the Huygens probe from the Cassini spacecraft in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at KSC. The spacecraft was returned to the PHSF after damage to thermal insulation was discovered inside Huygens from an abnormally high flow of conditioned air. Further internal inspection, insulation repair and a cleaning of the probe are now required. Mission managers are targeting a mid-October launch date after Cassini returns to the pad and is once again placed atop its Titan IVB expendable launch vehicle at Launch Pad 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Station
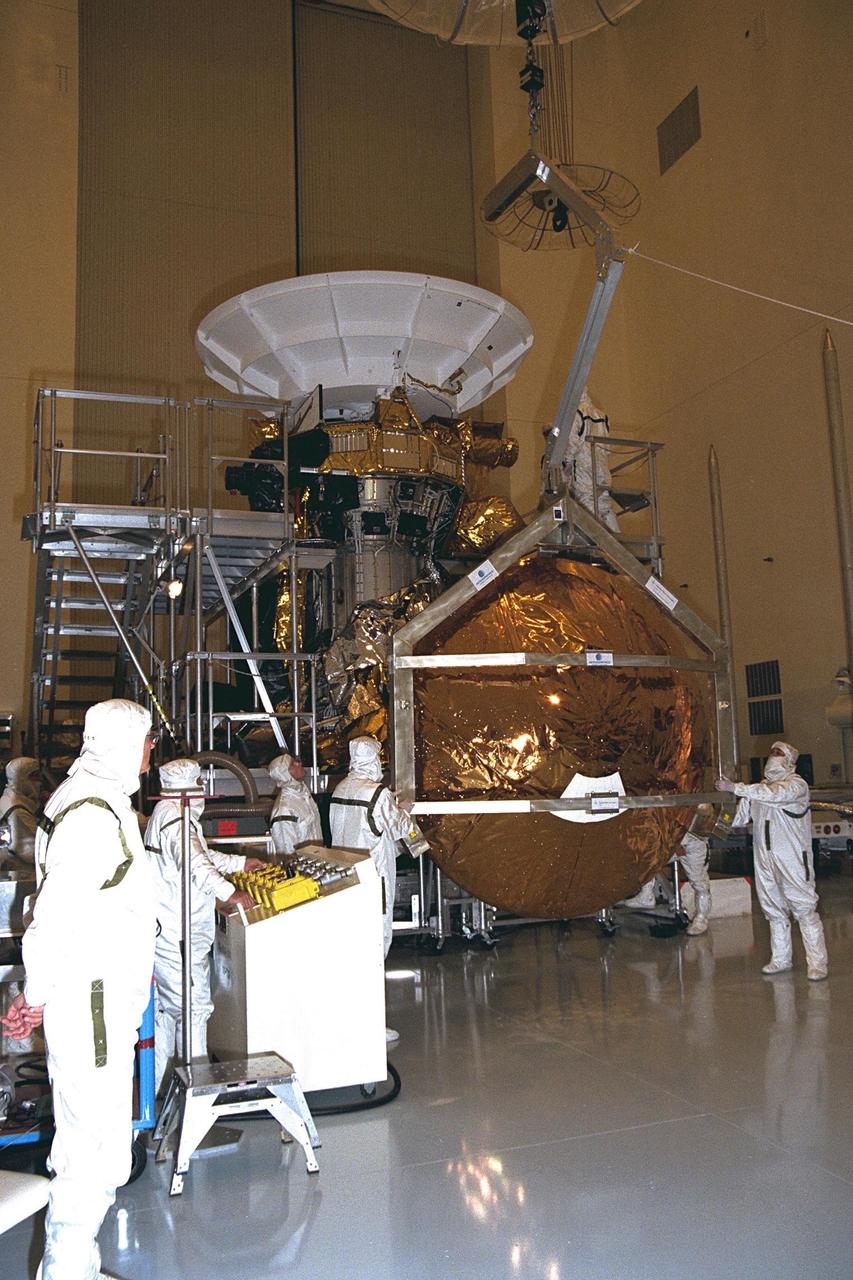

Workers remove the Huygens probe from the Cassini spacecraft in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at KSC. The spacecraft was returned to the PHSF after damage to thermal insulation was discovered inside Huygens from an abnormally high flow of conditioned air. Further internal inspection, insulation repair and a cleaning of the probe are now required. Mission managers are targeting a mid-October launch date after Cassini returns to the pad and is once again placed atop its Titan IVB expendable launch vehicle at Launch Pad 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Station
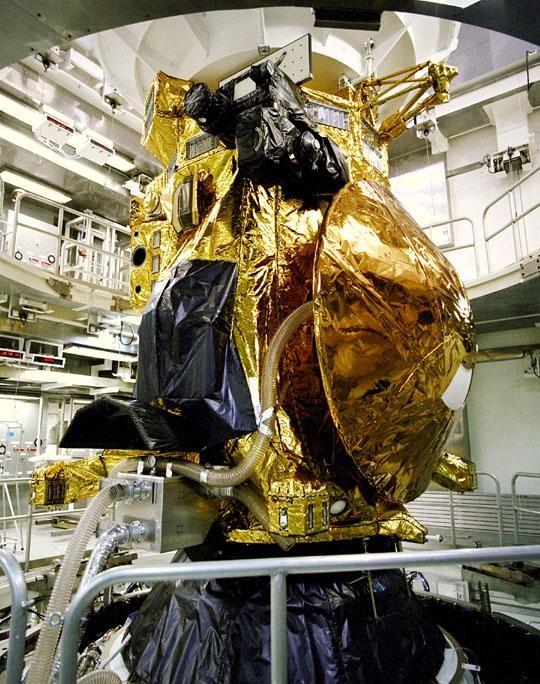

The Cassini spacecraft, with the Huygens probe seen on the right in this photo, sits atop a Titan IVB expendable launch vehicle at Launch Pad 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Station, where it awaits placement of its payload fairing to protect Cassini during launch. Instruments mounted on the Huygens probe, which was developed by the European Space Agency (ESA), will receive atmospheric and surface data on Saturn’s main moon, Titan, to send back to Earth as part of the mission. A four-year, close-up study of the Saturnian system, the mission is scheduled for launch from Cape Canaveral Air Station in mid-October
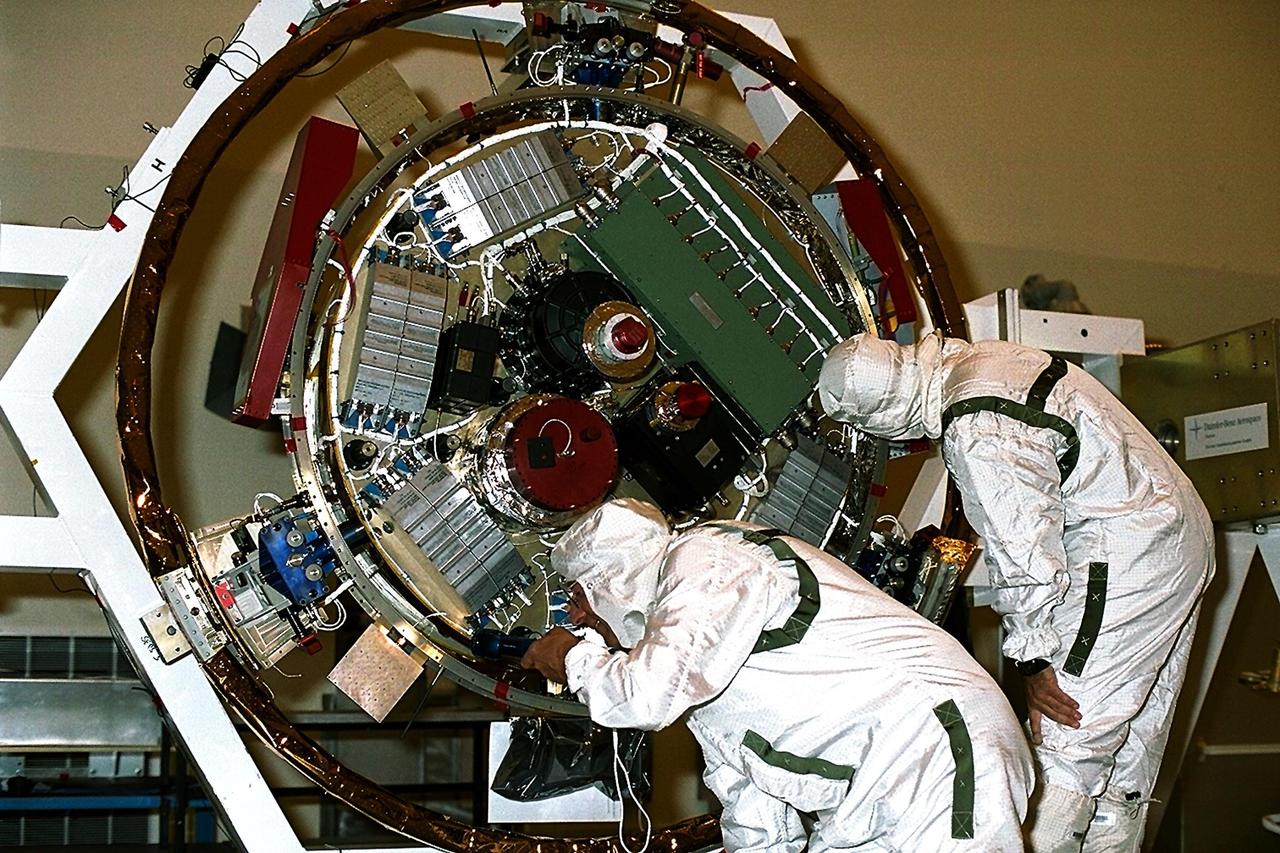
Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) workers examine the Huygens probe after removal from the Cassini spacecraft in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at KSC. The spacecraft was returned to the PHSF after damage to thermal insulation was discovered inside Huygens from an abnormally high flow of conditioned air. Internal inspection, insulation repair and a cleaning of the probe were required. Mission managers are targeting a mid-October launch date after Cassini returns to the pad and is once again placed atop its Titan IVB expendable launch vehicle at Launch Pad 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Station
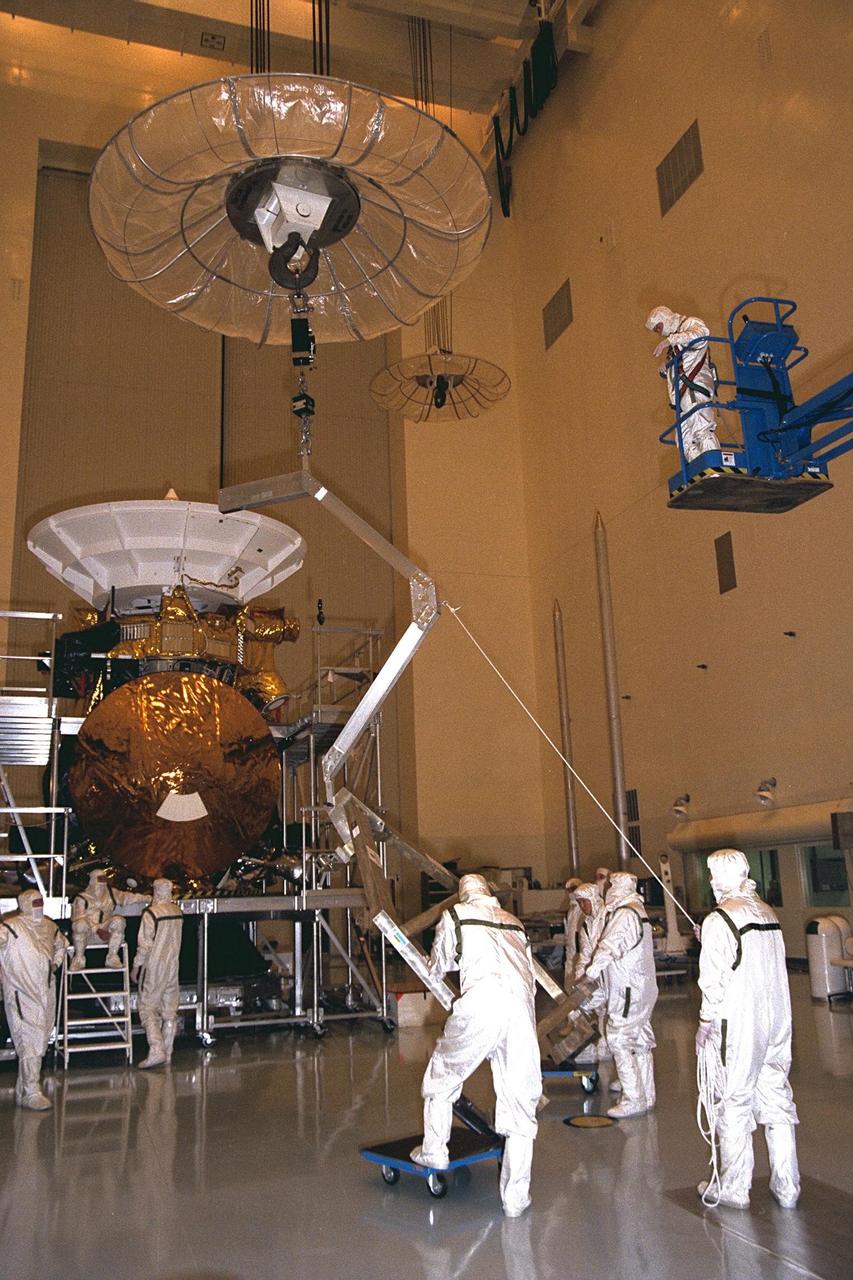

Workers remove the Huygens probe from the Cassini spacecraft in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at KSC. The spacecraft was returned to the PHSF after damage to thermal insulation was discovered inside Huygens from an abnormally high flow of conditioned air. Further internal inspection, insulation repair and a cleaning of the probe are now required. Mission managers are targeting a mid-October launch date after Cassini returns to the pad and is once again placed atop its Titan IVB expendable launch vehicle at Launch Pad 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Station
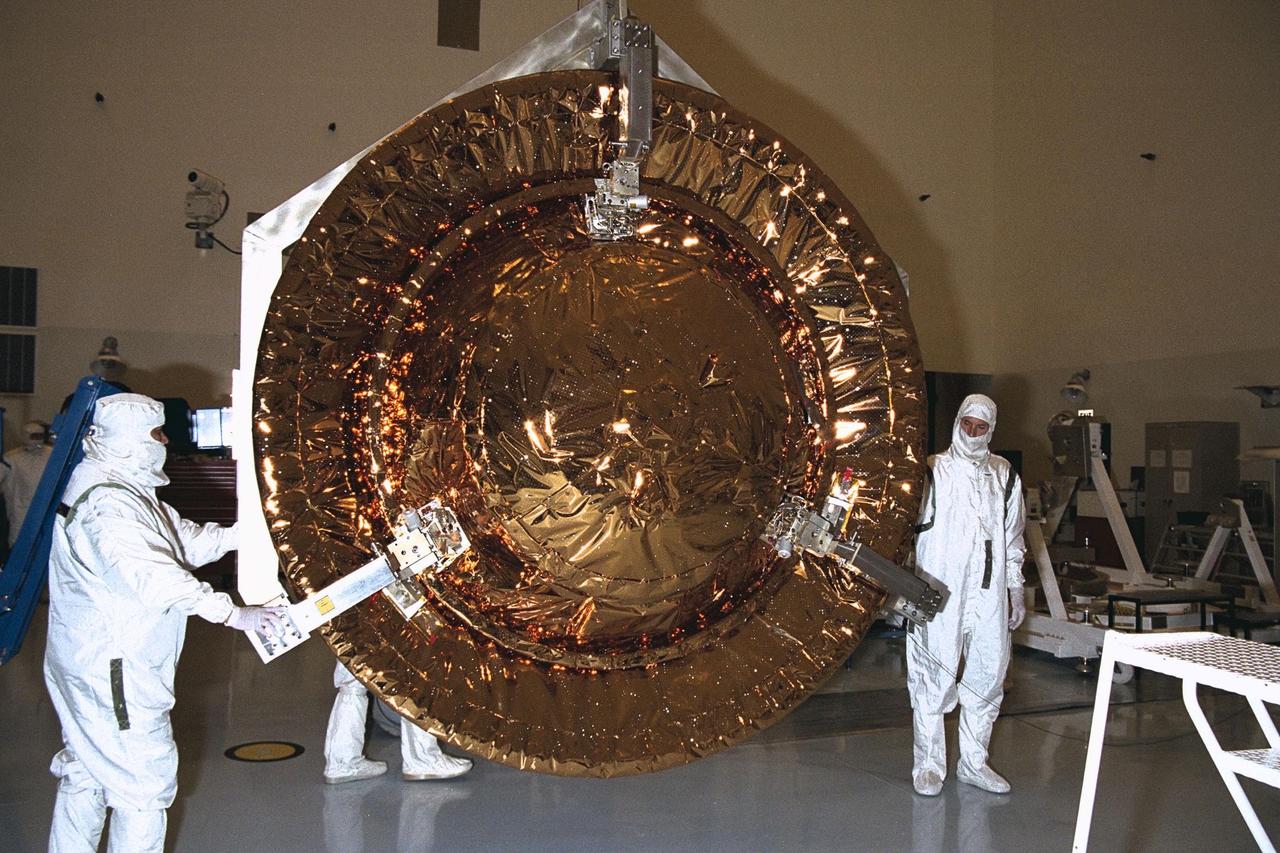
Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) workers remove the Huygens probe from the Cassini spacecraft in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at KSC. The spacecraft was returned to the PHSF after damage to thermal insulation was discovered inside Huygens from an abnormally high flow of conditioned air. Further internal inspection, insulation repair and a cleaning of the probe are now required. Mission managers are targeting a mid-October launch date after Cassini returns to the pad and is once again placed atop its Titan IVB expendable launch vehicle at Launch Pad 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Station

Workers begin unloading the Cassini orbiter from a U.S. Air Force C-17 air cargo plane after its <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/release/1997/66-97.htm">arrival</a> at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility from Edwards Air Force Base, California. The orbiter and the Huygens probe already being processed at KSC are the two primary components of the Cassini spacecraft, which will be launched on a Titan IVB/Centaur expendable launch vehicle from Cape Canaveral Air Station. Cassini will explore Saturn, its rings and moons for four years. The Huygens probe, designed and developed for the European Space Agency (ESA), will be deployed from the orbiter to study the clouds, atmosphere and surface of Saturn’s largest moon, Titan. The orbiter was designed and assembled at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California. Following postflight inspections, integration of the 12 science instruments not already installed on the orbiter will be completed. Then, the parabolic high-gain antenna and the propulsion module will be mated to the orbiter, followed by the Huygens probe, which will complete spacecraft integration. The Cassini mission is targeted for an Oct. 6 launch to begin its 6.7-year journey to the Saturnian system. Arrival at the planet is expected to occur around July 1, 2004
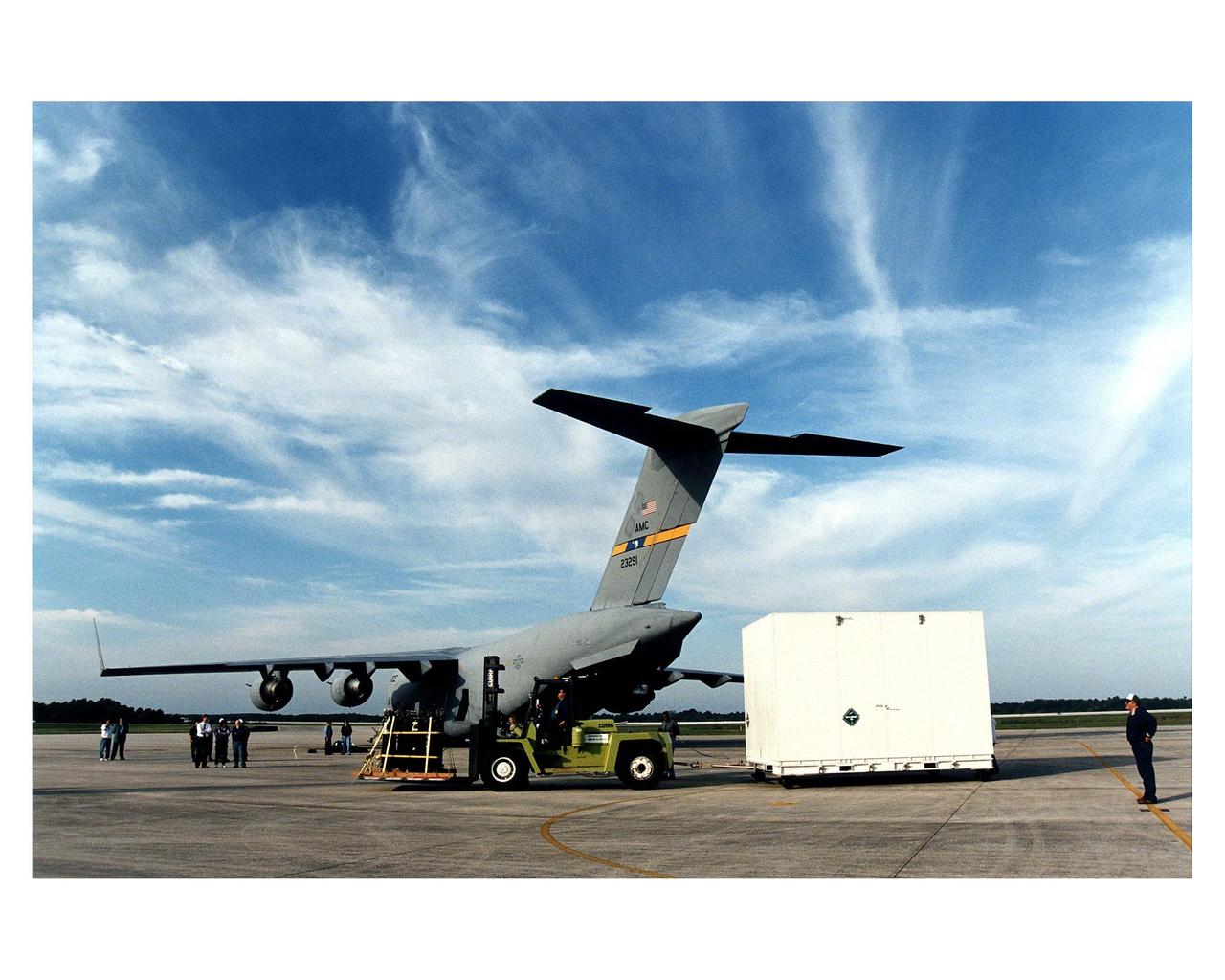

Workers prepare to tow away the large container with the Cassini orbiter from KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility. The orbiter <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/release/1997/66-97.htm">just arrived</a> on the U.S. Air Force C-17 air cargo plane, shown here, from Edwards Air Force Base, California. The orbiter and the Huygens probe already being processed at KSC are the two primary components of the Cassini spacecraft, which will be launched on a Titan IVB/Centaur expendable launch vehicle from Cape Canaveral Air Station. Cassini will explore Saturn, its rings and moons for four years. The Huygens probe, designed and developed for the European Space Agency (ESA), will be deployed from the orbiter to study the clouds, atmosphere and surface of Saturn’s largest moon, Titan. The orbiter was designed and assembled at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California. Following postflight inspections, integration of the 12 science instruments not already installed on the orbiter will be completed. Then, the parabolic high-gain antenna and the propulsion module will be mated to the orbiter, followed by the Huygens probe, which will complete spacecraft integration. The Cassini mission is targeted for an Oct. 6 launch to begin its 6.7-year journey to the Saturnian system. Arrival at the planet is expected to occur around July 1, 2004
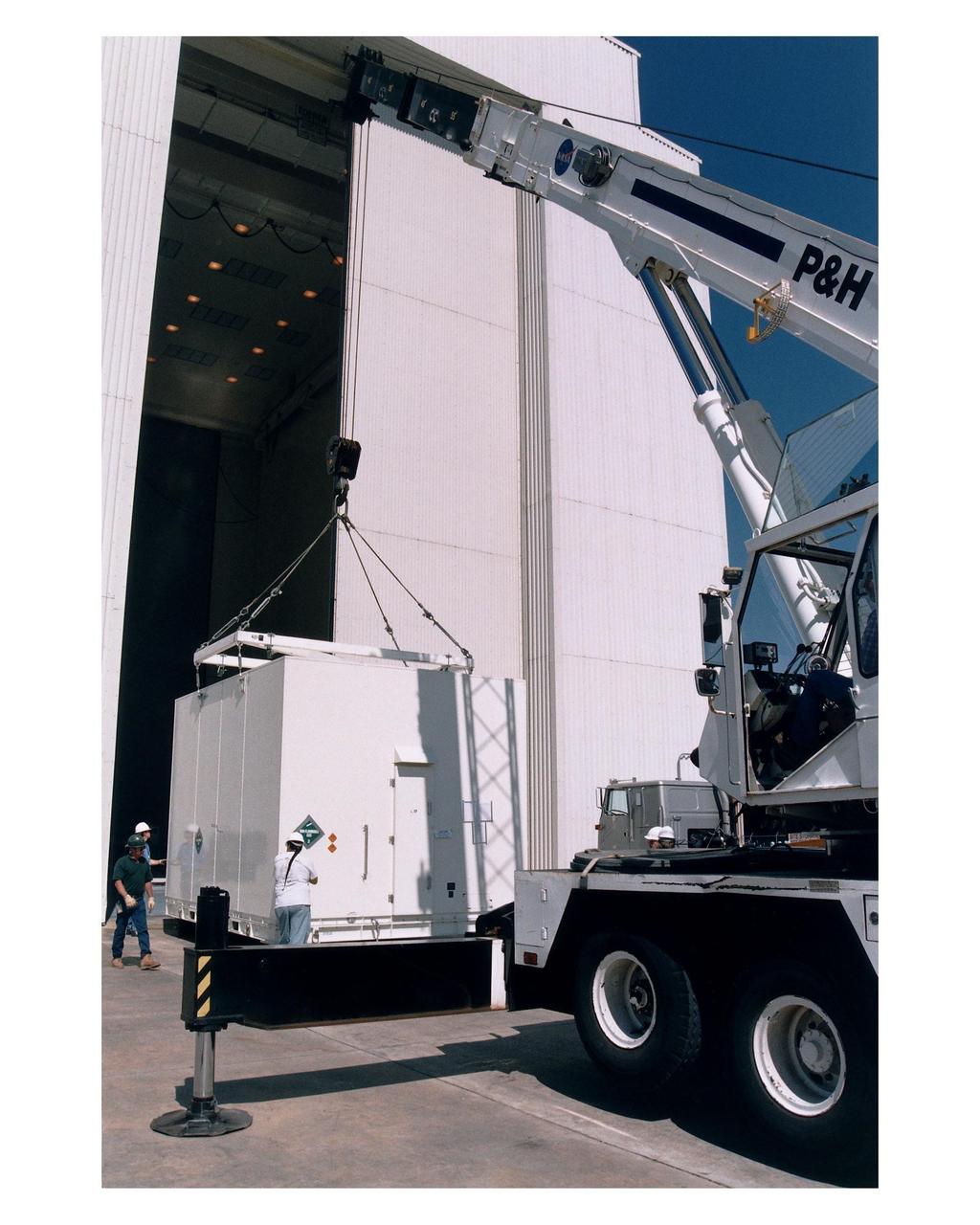

Workers prepare to move the shipping container with the Cassini orbiter inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) for prelaunch processing, testing and integration. The <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/release/1997/66-97.htm">orbiter arrived</a> at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility in a U.S. Air Force C-17 air cargo plane from Edwards Air Force Base, California. The orbiter and the Huygens probe already being processed at KSC are the two primary components of the Cassini spacecraft, which will be launched on a Titan IVB/Centaur expendable launch vehicle from Cape Canaveral Air Station. Cassini will explore Saturn, its rings and moons for four years. The Huygens probe, designed and developed for the European Space Agency (ESA), will be deployed from the orbiter to study the clouds, atmosphere and surface of Saturn’s largest moon, Titan. The orbiter was designed and assembled at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California. Following postflight inspections, integration of the 12 science instruments not already installed on the orbiter will be completed. Then, the parabolic high-gain antenna and the propulsion module will be mated to the orbiter, followed by the Huygens probe, which will complete spacecraft integration. The Cassini mission is targeted for an Oct. 6 launch to begin its 6.7-year journey to the Saturnian system. Arrival at the planet is expected to occur around July 1, 2004
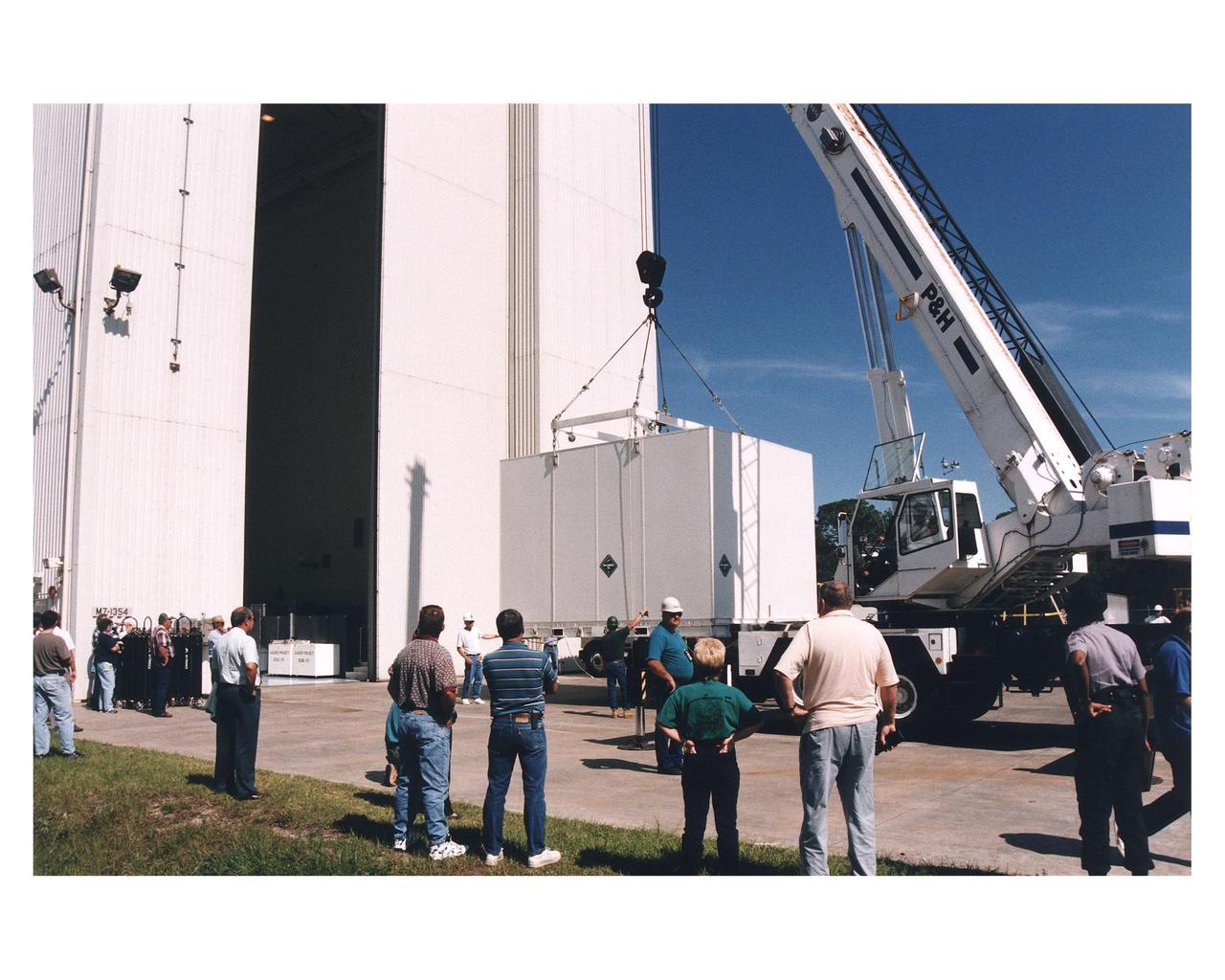

Workers prepare to move the shipping container with the Cassini orbiter inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) for prelaunch processing, testing and integration. The <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/release/1997/66-97.htm">orbiter arrived</a> at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility in a U.S. Air Force C-17 air cargo plane from Edwards Air Force Base, California. The orbiter and the Huygens probe already being processed at KSC are the two primary components of the Cassini spacecraft, which will be launched on a Titan IVB/Centaur expendable launch vehicle from Cape Canaveral Air Station. Cassini will explore Saturn, its rings and moons for four years. The Huygens probe, designed and developed for the European Space Agency (ESA), will be deployed from the orbiter to study the clouds, atmosphere and surface of Saturn’s largest moon, Titan. The orbiter was designed and assembled at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California. Following postflight inspections, integration of the 12 science instruments not already installed on the orbiter will be completed. Then, the parabolic high-gain antenna and the propulsion module will be mated to the orbiter, followed by the Huygens probe, which will complete spacecraft integration. The Cassini mission is targeted for an Oct. 6 launch to begin its 6.7-year journey to the Saturnian system. Arrival at the planet is expected to occur around July 1, 2004
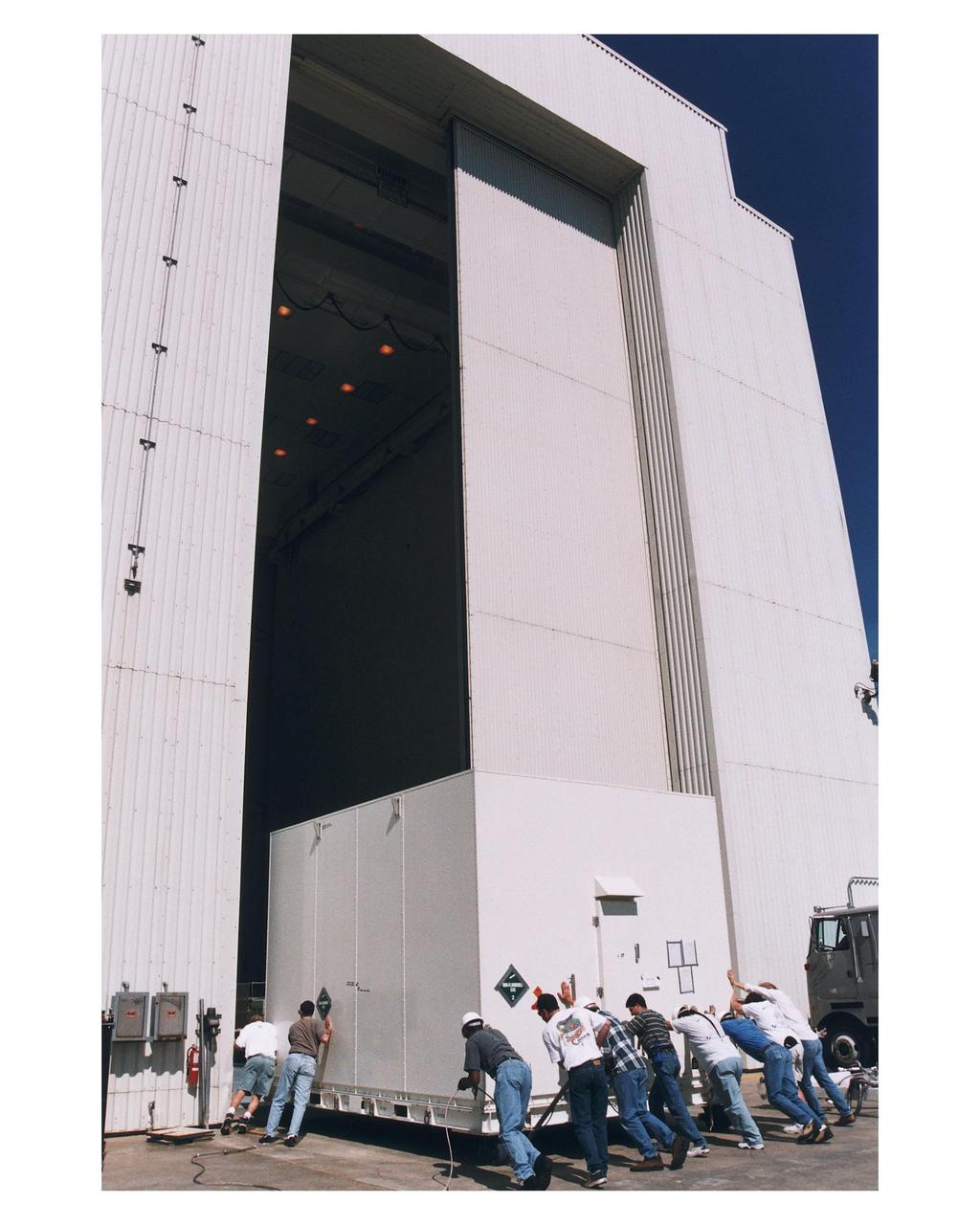

Workers prepare to move the shipping container with the Cassini orbiter inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) for prelaunch processing, testing and integration. The <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/release/1997/66-97.htm">orbiter arrived</a> at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility in a U.S. Air Force C-17 air cargo plane from Edwards Air Force Base, California. The orbiter and the Huygens probe already being processed at KSC are the two primary components of the Cassini spacecraft, which will be launched on a Titan IVB/Centaur expendable launch vehicle from Cape Canaveral Air Station. Cassini will explore Saturn, its rings and moons for four years. The Huygens probe, designed and developed for the European Space Agency (ESA), will be deployed from the orbiter to study the clouds, atmosphere and surface of Saturn’s largest moon, Titan. The orbiter was designed and assembled at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California. Following postflight inspections, integration of the 12 science instruments not already installed on the orbiter will be completed. Then, the parabolic high-gain antenna and the propulsion module will be mated to the orbiter, followed by the Huygens probe, which will complete spacecraft integration. The Cassini mission is targeted for an Oct. 6 launch to begin its 6.7-year journey to the Saturnian system. Arrival at the planet is expected to occur around July 1, 2004
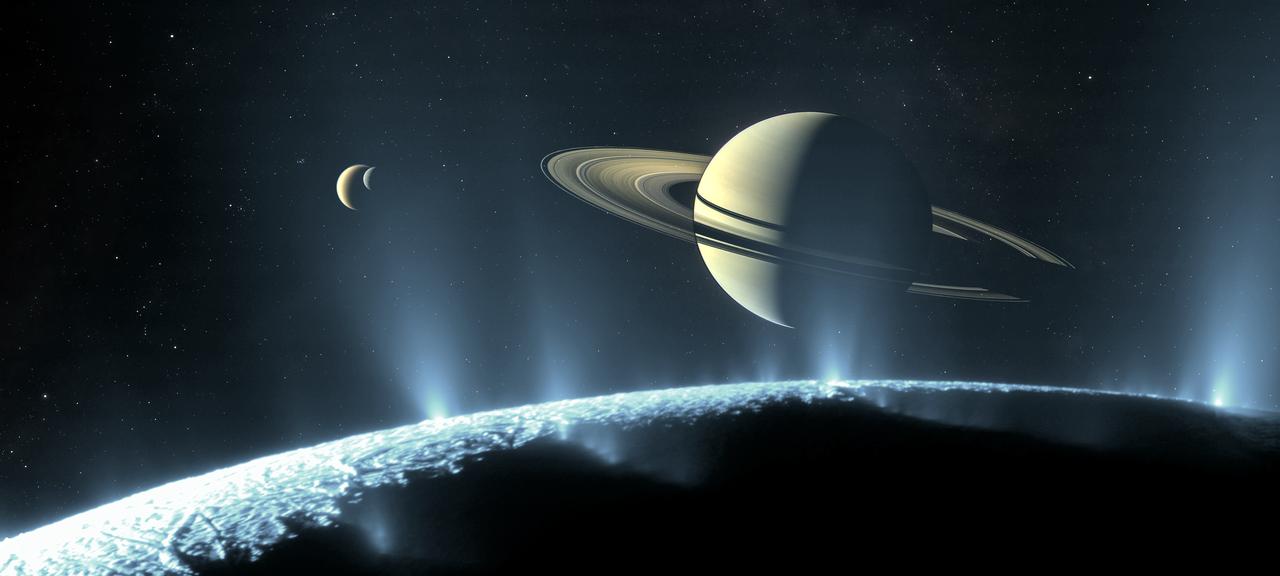

Saturn has long inspired astronomers, from Galileo’s first glimpse of its rings in 1610 to the last pictures taken by the Cassini spacecraft as it descended toward the planet’s atmosphere in 2017. But after four centuries of observing Saturn with telescopes, robotic flybys and orbiters, what might it look like to visit in person and witness the jewel of the solar system rising above one of its many natural satellites? Here we imagine the scene. Gazing over the south pole of the small moon Enceladus, geysers burst forth from cracks in the ice, scattering sunlight and forming a luminous veil around Saturn. In the distance, the large moons Rhea (right) and Titan (left) make their rounds of the gas giant’s far side. These bodies were discovered in the 17th century by astronomers Giovanni Domenico Cassini and Christiaan Huygens – the namesakes of the Cassini-Huygens mission, which explored the Saturn system from 2004 to 2017. The wealth of data and imagery returned by Cassini-Huygens vastly improved our understanding of the ringed planet and paved the way for future exploration.

Workers offload the shipping container with the Cassini orbiter from what looks like a giant shark mouth, but is really an Air Force C-17 air cargo plane which <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/release/1997/66-97.htm">just landed</a> at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility from Edwards Air Force Base, California. The orbiter and the Huygens probe already being processed at KSC are the two primary components of the Cassini spacecraft, which will be launched on a Titan IVB/Centaur expendable launch vehicle from Cape Canaveral Air Station. Cassini will explore Saturn, its rings and moons for four years. The Huygens probe, designed and developed for the European Space Agency (ESA), will be deployed from the orbiter to study the clouds, atmosphere and surface of Saturn’s largest moon, Titan. The orbiter was designed and assembled at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California. Following postflight inspections, integration of the 12 science instruments not already installed on the orbiter will be completed. Then, the parabolic high-gain antenna and the propulsion module will be mated to the orbiter, followed by the Huygens probe, which will complete spacecraft integration. The Cassini mission is targeted for an Oct. 6 launch to begin its 6.7-year journey to the Saturnian system. Arrival at the planet is expected to occur around July 1, 2004

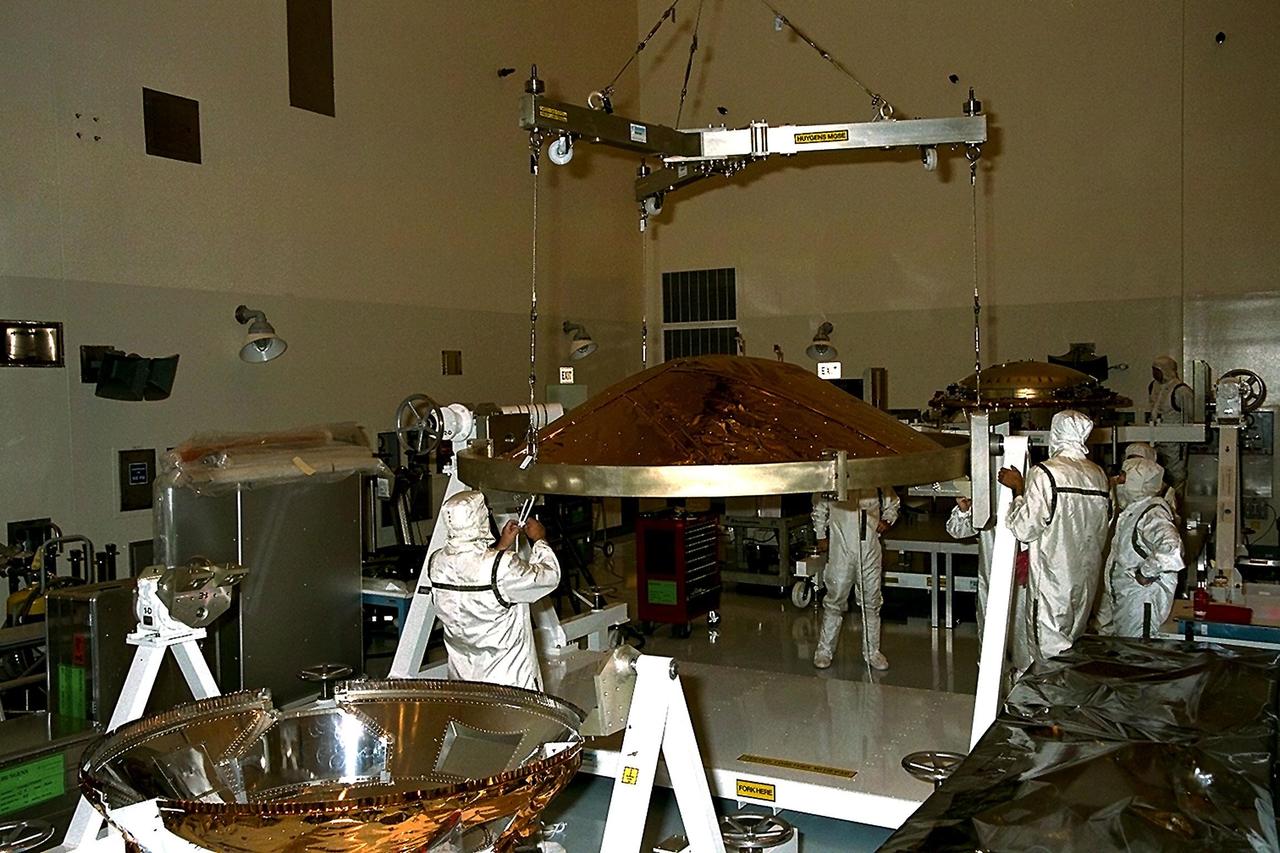
Dornier Satelliten Systeme (DSS) workers place the back cover of the Huygens probe under its front heat shield in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at KSC. The spacecraft was returned to the PHSF after damage to thermal insulation was discovered inside Huygens from an abnormally high flow of conditioned air. Internal inspection, insulation repair and a cleaning of the probe were required. Mission managers are targeting a mid-October launch date after the Cassini spacecraft, aboard which Huygens will be launched, returns to the pad and is once again placed atop its Titan IVB expendable launch vehicle at Launch Pad 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Station

Dornier Satelliten Systeme (DSS) workers place the back cover of the Huygens probe under its front heat shield in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at KSC. The spacecraft was returned to the PHSF after damage to thermal insulation was discovered inside Huygens from an abnormally high flow of conditioned air. Internal inspection, insulation repair and a cleaning of the probe were required. Mission managers are targeting a mid-October launch date after the Cassini spacecraft, aboard which Huygens will be launched, returns to the pad and is once again placed atop its Titan IVB expendable launch vehicle at Launch Pad 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Station

Dornier Satelliten Systeme (DSS) workers lift the front heat shield of the Huygens probe in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at KSC. The spacecraft was returned to the PHSF after damage to thermal insulation was discovered inside Huygens from an abnormally high flow of conditioned air. Internal inspection, insulation repair and a cleaning of the probe were required. Mission managers are targeting a mid-October launch date after the Cassini spacecraft, aboard which Huygens will be launched, returns to the pad and is once again placed atop its Titan IVB expendable launch vehicle at Launch Pad 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Station
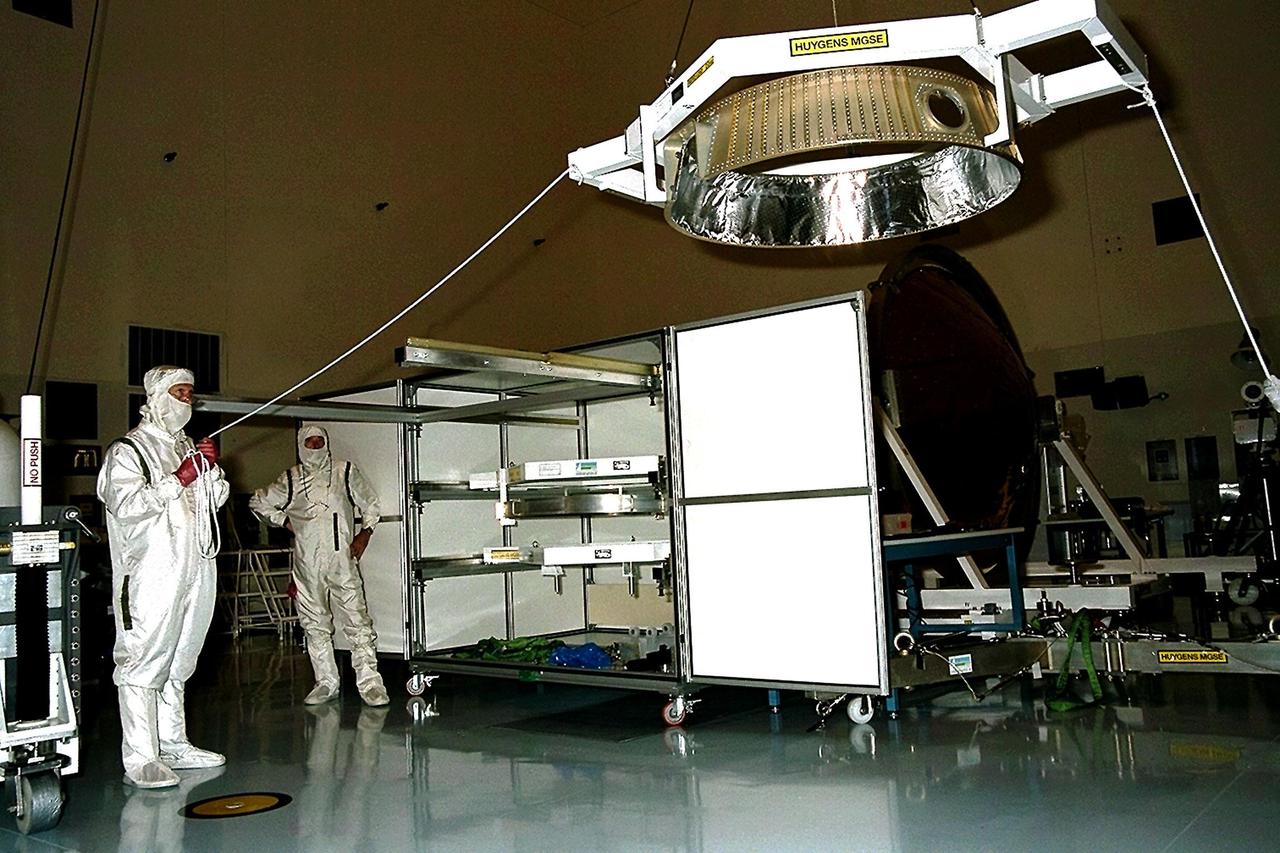

Dornier Satelliten Systeme (DSS) workers lift part of the Huygens probe aft cover assembly in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at KSC. The spacecraft was returned to the PHSF after damage to thermal insulation was discovered inside Huygens from an abnormally high flow of conditioned air. Internal inspection, insulation repair and a cleaning of the probe were required. Mission managers are targeting a mid-October launch date after the Cassini spacecraft, aboard which Huygens will be launched, returns to the pad and is once again placed atop its Titan IVB expendable launch vehicle at Launch Pad 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Station
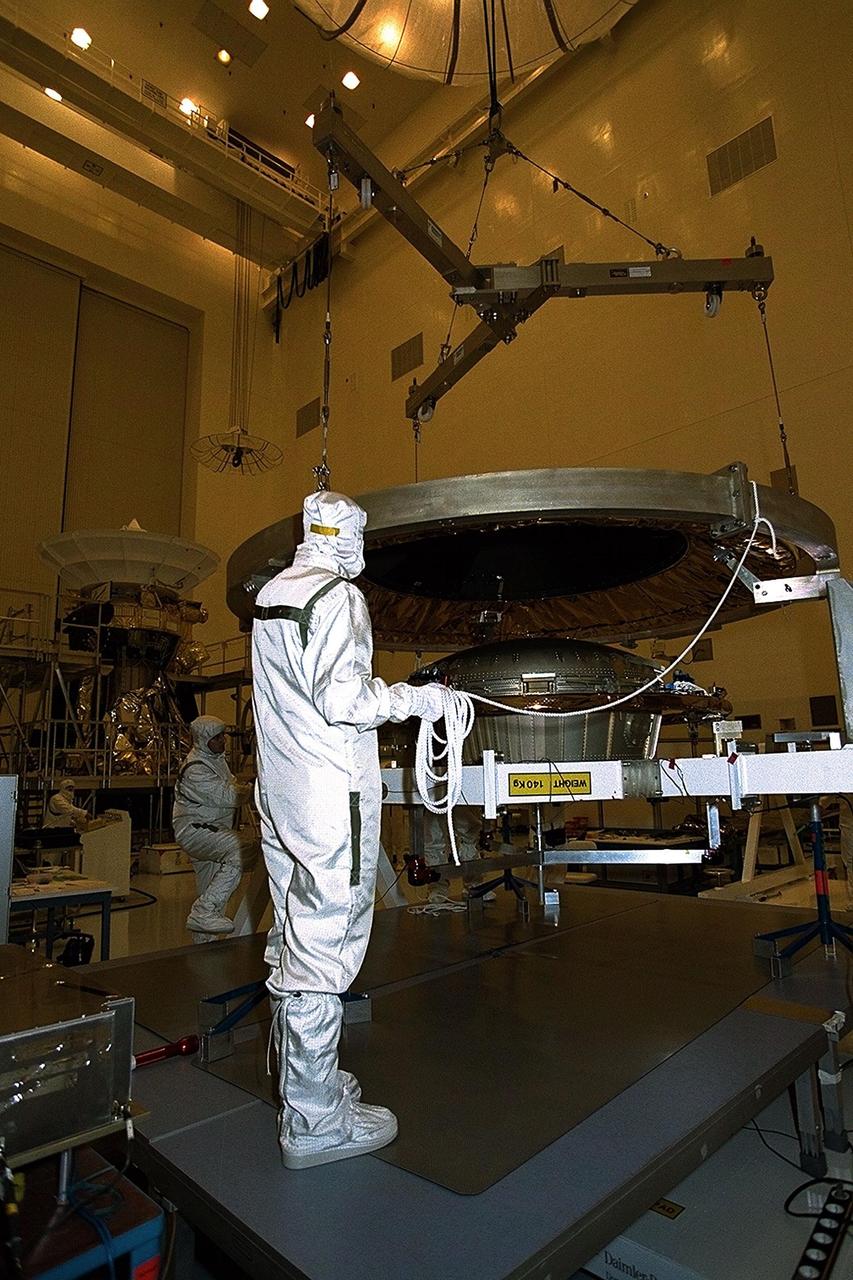

Dornier Satelliten Systeme (DSS) workers lift the heat shield of the Huygens probe in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at KSC. The spacecraft was returned to the PHSF after damage to thermal insulation was discovered inside Huygens from an abnormally high flow of conditioned air. Internal inspection, insulation repair and a cleaning of the probe were required. Mission managers are targeting a mid-October launch date after the Cassini spacecraft, aboard which Huygens will be launched, returns to the pad and is once again placed atop its Titan IVB expendable launch vehicle at Launch Pad 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Station

Dornier Satelliten Systeme (DSS) workers lift the heat shield of the Huygens probe in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at KSC. The spacecraft was returned to the PHSF after damage to thermal insulation was discovered inside Huygens from an abnormally high flow of conditioned air. Internal inspection, insulation repair and a cleaning of the probe were required. Mission managers are targeting a mid-October launch date after the Cassini spacecraft, aboard which Huygens will be launched, returns to the pad and is once again placed atop its Titan IVB expendable launch vehicle at Launch Pad 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Station
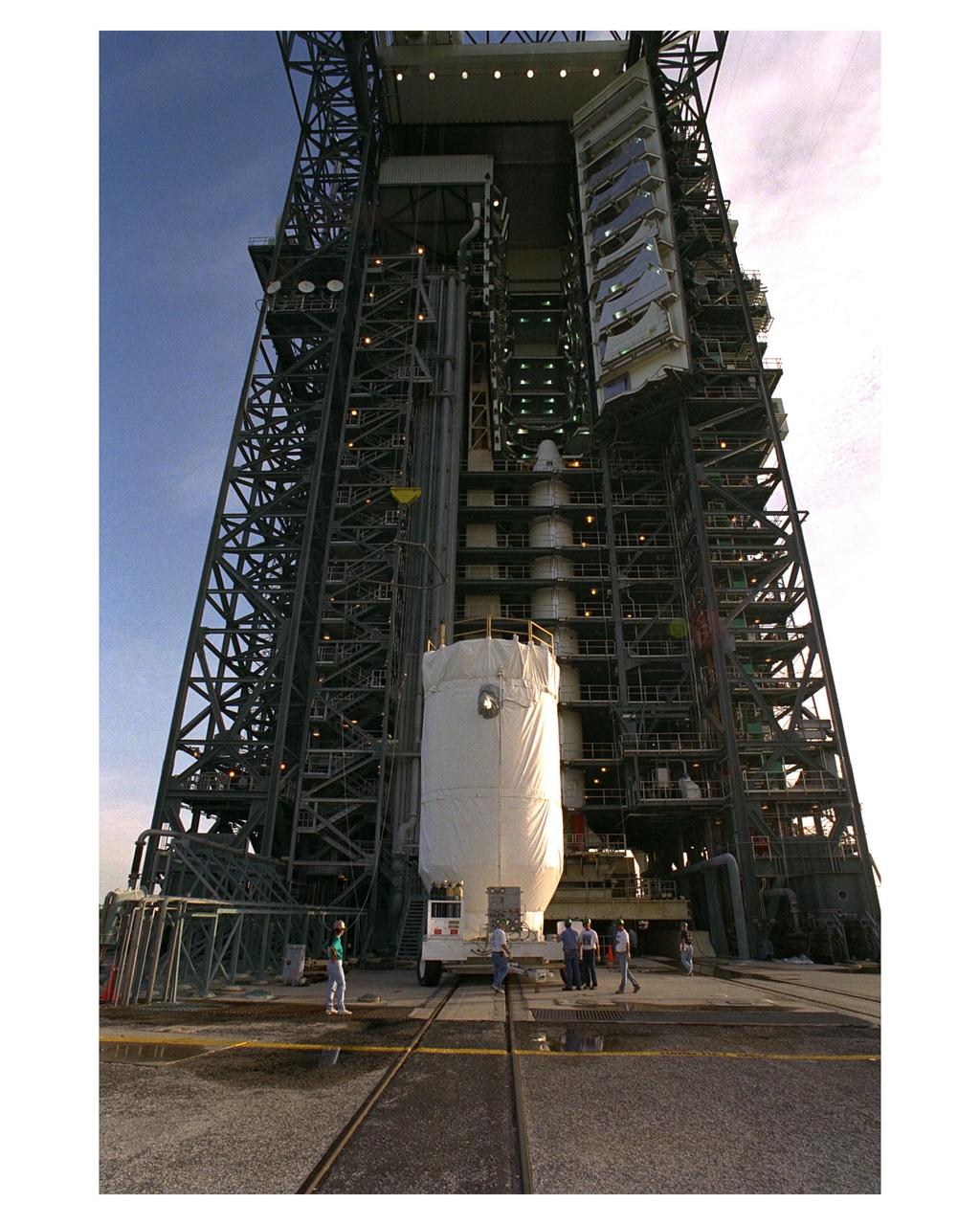

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A Centaur upper stage is prepared for hoisting at Launch Pad 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Station to be mated with the Titan IV expendable launch vehicle that will propel the Cassini spacecraft and the European Space Agency's Huygens probe to Saturn and its moon Titan. Cassini will explore Saturn, its rings and moons for four years. The Huygens probe, designed and developed for the European Space Agency (ESA), will be deployed from the orbiter to study the clouds, atmosphere and surface of Saturn's largest moon, Titan. The orbiter was designed and assembled at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California. The Cassini mission is targeted for an October 6 launch to begin its 6.7-year journey to the Saturnian system. Arrival at the planet is expected to occur around July 1, 2004.
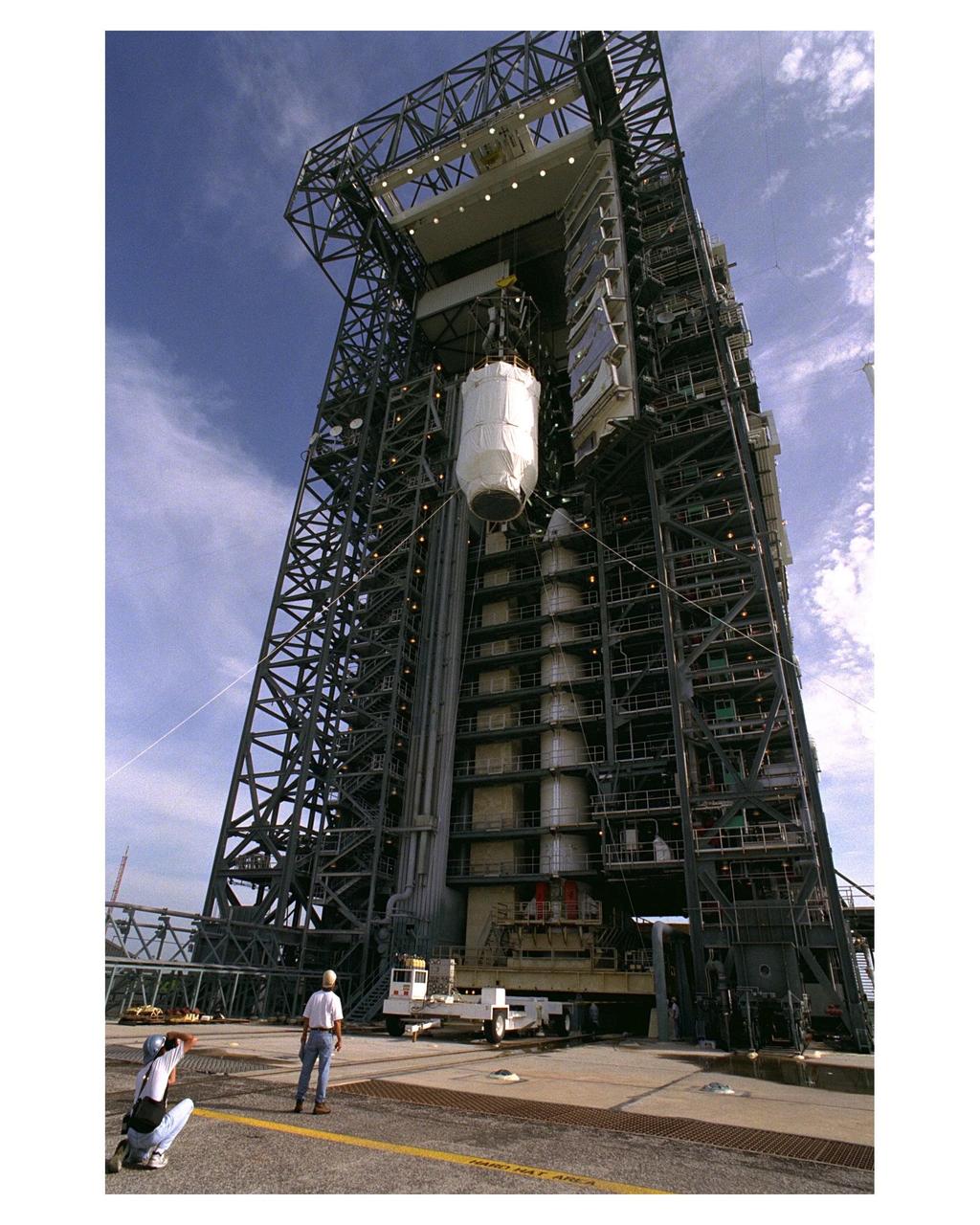

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A Centaur upper stage is hoisted at Launch Pad 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Station for mating with the Titan IV expendable launch vehicle that will propel the Cassini spacecraft and the European Space Agency's Huygens probe to Saturn and its moon Titan. Cassini will explore Saturn, its rings and moons for four years. The Huygens probe, designed and developed for the European Space Agency (ESA), will be deployed from the orbiter to study the clouds, atmosphere and surface of Saturn's largest moon, Titan. The orbiter was designed and assembled at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California. The Cassini mission is targeted for an October 6 launch to begin its 6.7-year journey to the Saturnian system. Arrival at the planet is expected to occur around July 1, 2004.
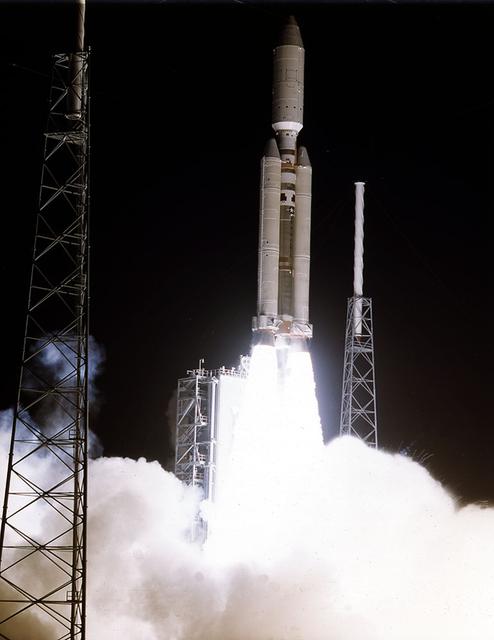

The 7-year journey to Saturn began with the liftoff of a Titan IVB/Centaur carrying the Cassini orbiter and its attached Huygens probe. After a 2.2-billion mile journey that included two swingbys of Venus and one of Earth to gain additional velocity, the two-story tall spacecraft will arrive at Saturn in July 2004. The orbiter will circle the planet for 4 years, its compliment of 12 scientific instruments gathering data about Saturn's atmosphere, rings and magnetosphere, and conducting close-up observations of the Saturnian moons. Huygens, with a separate suite of 6 science instruments, will separate from Cassini to fly on a ballistic trajectory toward Titan, the only celestial body besides Earth to have an atmosphere rich in nitrogen. Scientists are eager to study further this chemical similarity in hopes of learning more about the origins of our own planet Earth. Huygens will provide the first direct sampling of Titan's atmospheric chemistry and the first detailed photographs of its surface. The Cassini mission is an international effort involving NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA), and the Italian Space Agency, Agenzia Spaziale Italiana (ASI).
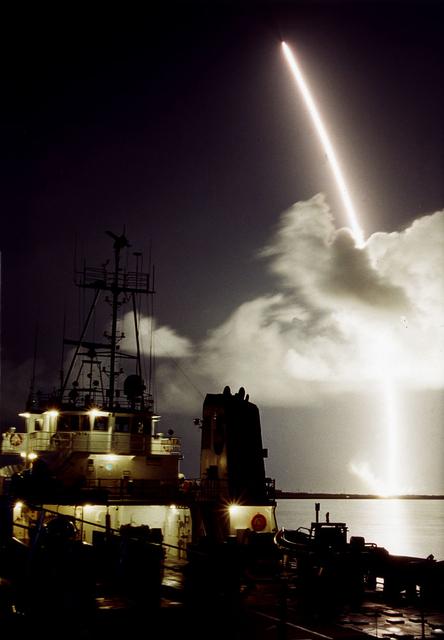

The 7-year journey to Saturn began with the liftoff of a Titan IVB/ Centaur carrying the Cassini orbiter and its attached Huygens probe. After a 2.2-billion mile journey that included two swingbys of Venus and one of the Earth to gain additional velocity, the two-story tall spacecraft will arrive at Saturn in July 2004. The orbiter will circle the planet for 4 years, its compliment of 12 scientific instruments gathering data about Saturn's atmosphere, rings and magnetosphere and conducting close-up observations of Saturnian moons. Huygens, with a separate suite of 6 science instruments, will separate from Cassini to fly on a ballistic trajectory toward Titan, the only celestial body besides Earth to have an atmosphere rich in nitrogen. Scientists are eager to study further this chemical similarity in hopes of learning more about the origins of our own planet Earth. Huygens will provide the first direct sampling of Titan's atmospheric chemistry and the first detailed photographs of its surface. The Cassini mission is an International effort involving NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA), and the Italian Space Agency, Agenzia Spaziale Italiana (ASI).

Cassini project scientist at JPL, Linda Spilker is seen during a press conference held after the end of the Cassini mission, Friday, Sept. 15, 2017 at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. Since its arrival in 2004, the Cassini-Huygens mission has been a discovery machine, revolutionizing our knowledge of the Saturn system and captivating us with data and images never before obtained with such detail and clarity. On Sept. 15, 2017, operators deliberately plunged the spacecraft into Saturn, as Cassini gathered science until the end. Loss of contact with the Cassini spacecraft occurred at 7:55 a.m. EDT (4:55 a.m. PDT). The “plunge” ensures Saturn’s moons will remain pristine for future exploration. During Cassini’s final days, mission team members from all around the world gathered at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, to celebrate the achievements of this historic mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
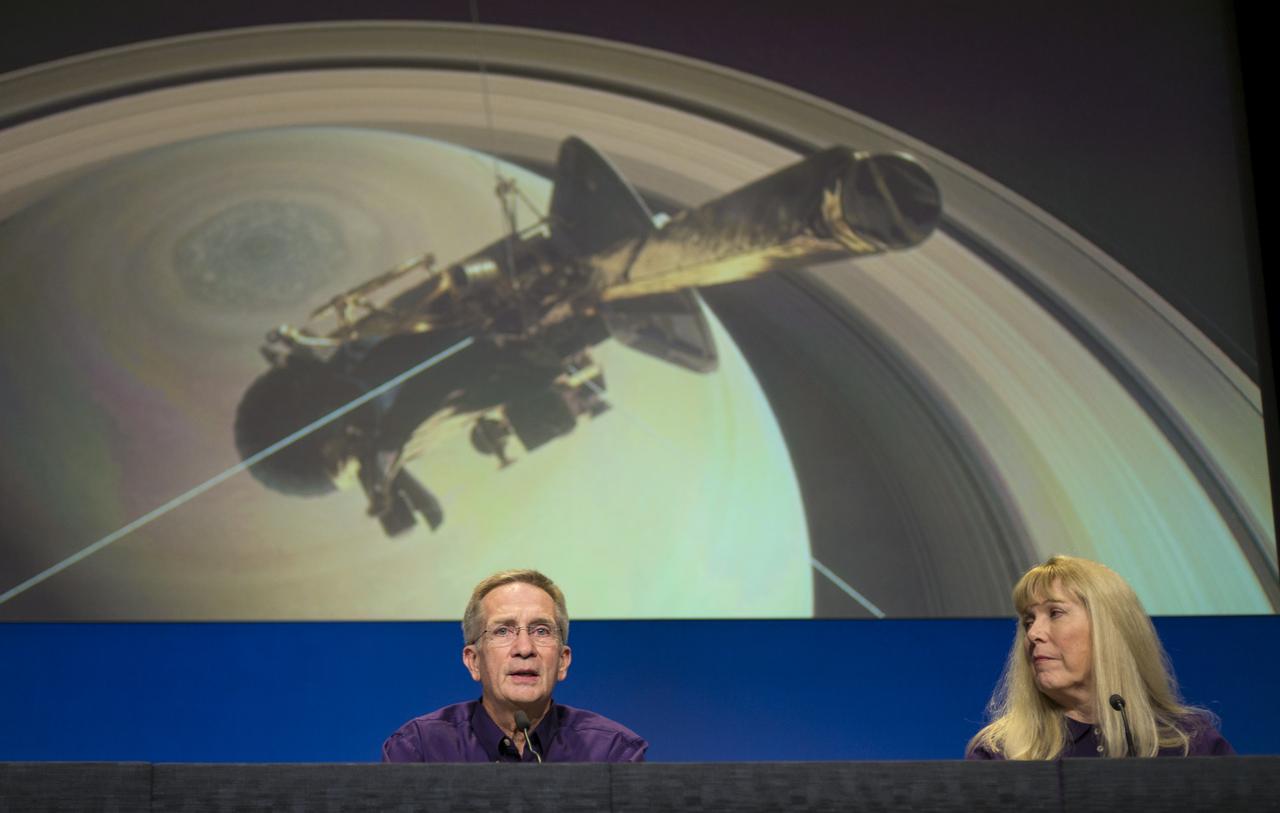

Cassini project scientist at JPL, Linda Spilker, right, looks on as Cassini program manager at JPL, Earl Maize speaks during a press conference previewing Cassini's End of Mission, Wednesday, Sept. 13, 2017 at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. Since its arrival in 2004, the Cassini-Huygens mission has been a discovery machine, revolutionizing our knowledge of the Saturn system and captivating us with data and images never before obtained with such detail and clarity. On Sept. 15, 2017, operators will deliberately plunge the spacecraft into Saturn, as Cassini gathered science until the end. The “plunge” ensures Saturn’s moons will remain pristine for future exploration. During Cassini’s final days, mission team members from all around the world gathered at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, to celebrate the achievements of this historic mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
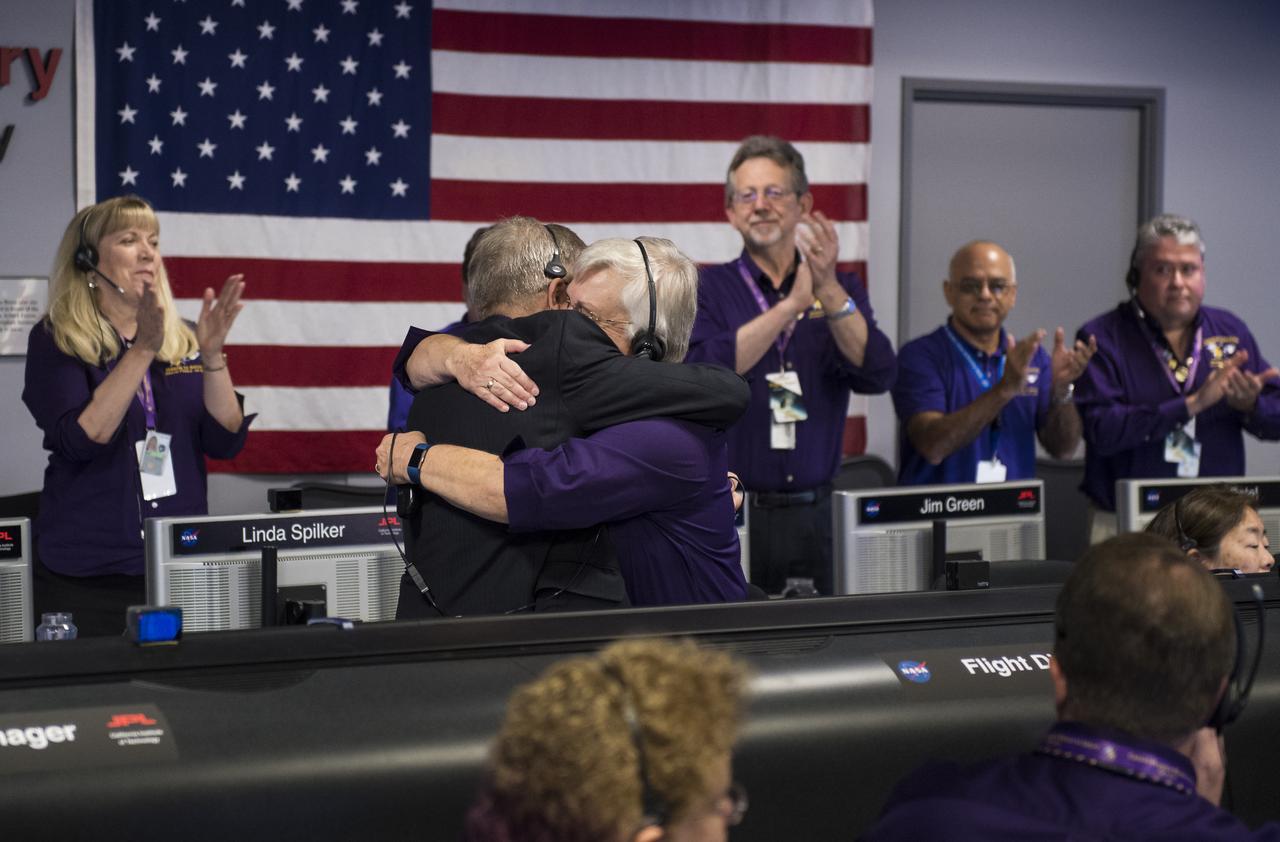

Cassini program manager at JPL, Earl Maize, left, and spacecraft operations team manager for the Cassini mission at Saturn, Julie Webster, right, embrace after the Cassini spacecraft plunged into Saturn, Friday, Sept. 15, 2017 at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. Since its arrival in 2004, the Cassini-Huygens mission has been a discovery machine, revolutionizing our knowledge of the Saturn system and captivating us with data and images never before obtained with such detail and clarity. On Sept. 15, 2017, operators will deliberately plunge the spacecraft into Saturn, as Cassini gathered science until the end. The “plunge” ensures Saturn’s moons will remain pristine for future exploration. During Cassini’s final days, mission team members from all around the world gathered at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, to celebrate the achievements of this historic mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
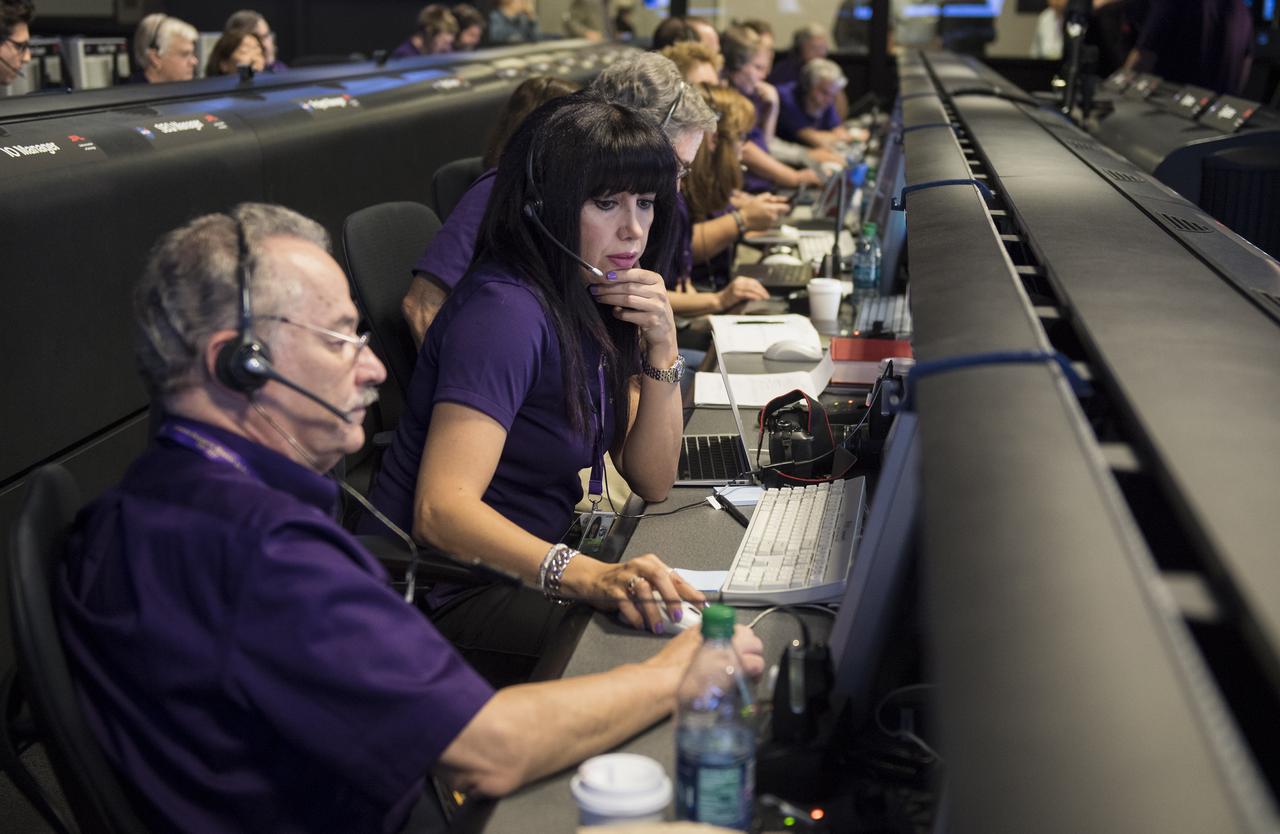

Aseel Anabtawi, of Cassini's radio science team, monitors her console in mission control during Cassini's final plunge into Saturn, Friday, Sept. 15, 2017 at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. Since its arrival in 2004, the Cassini-Huygens mission has been a discovery machine, revolutionizing our knowledge of the Saturn system and captivating us with data and images never before obtained with such detail and clarity. On Sept. 15, 2017, operators deliberately plunged the spacecraft into Saturn, as Cassini gathered science until the end. Loss of contact with the Cassini spacecraft occurred at 7:55 a.m. EDT (4:55 a.m. PDT). The “plunge” ensures Saturn’s moons will remain pristine for future exploration. During Cassini’s final days, mission team members from all around the world gathered at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, to celebrate the achievements of this historic mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
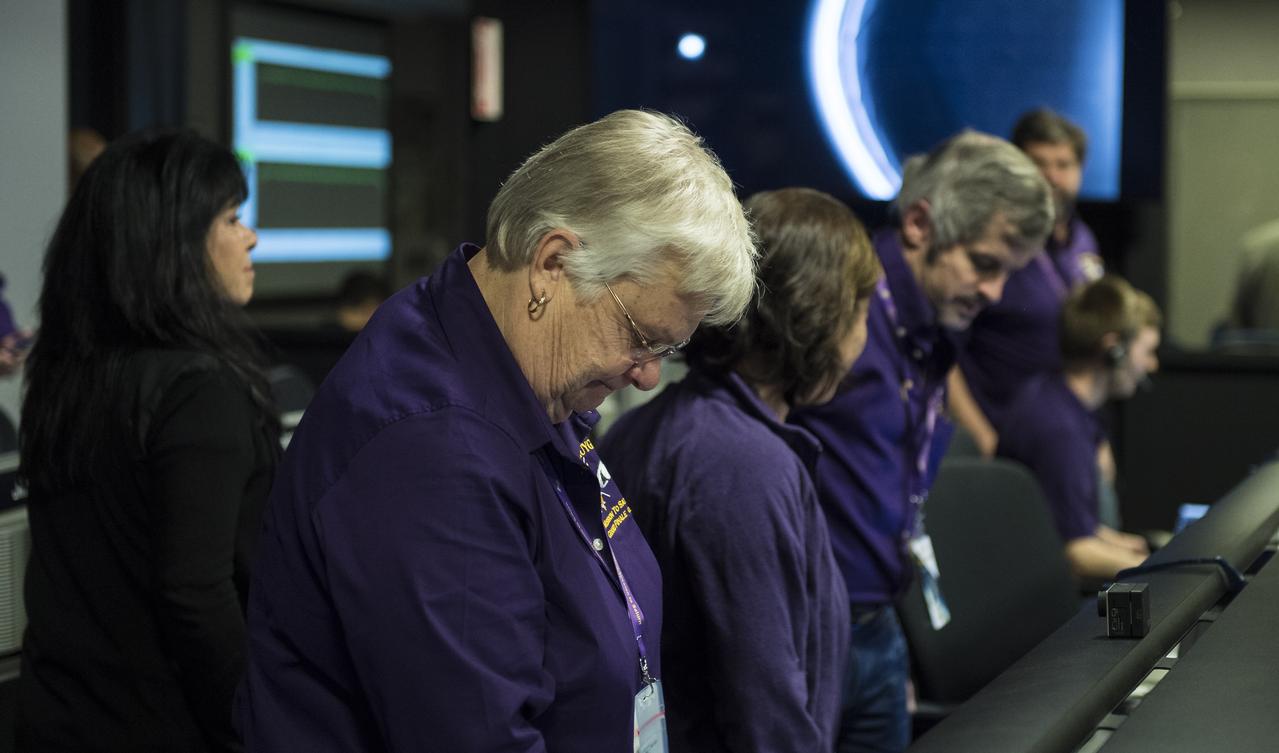

Spacecraft operations team manager for the Cassini mission at Saturn, Julie Webster is seen after the end of the Cassini mission, Friday, Sept. 15, 2017 at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. Since its arrival in 2004, the Cassini-Huygens mission has been a discovery machine, revolutionizing our knowledge of the Saturn system and captivating us with data and images never before obtained with such detail and clarity. On Sept. 15, 2017, operators deliberately plunged the spacecraft into Saturn, as Cassini gathered science until the end. Loss of contact with the Cassini spacecraft occurred at 7:55 a.m. EDT (4:55 a.m. PDT). The “plunge” ensures Saturn’s moons will remain pristine for future exploration. During Cassini’s final days, mission team members from all around the world gathered at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, to celebrate the achievements of this historic mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
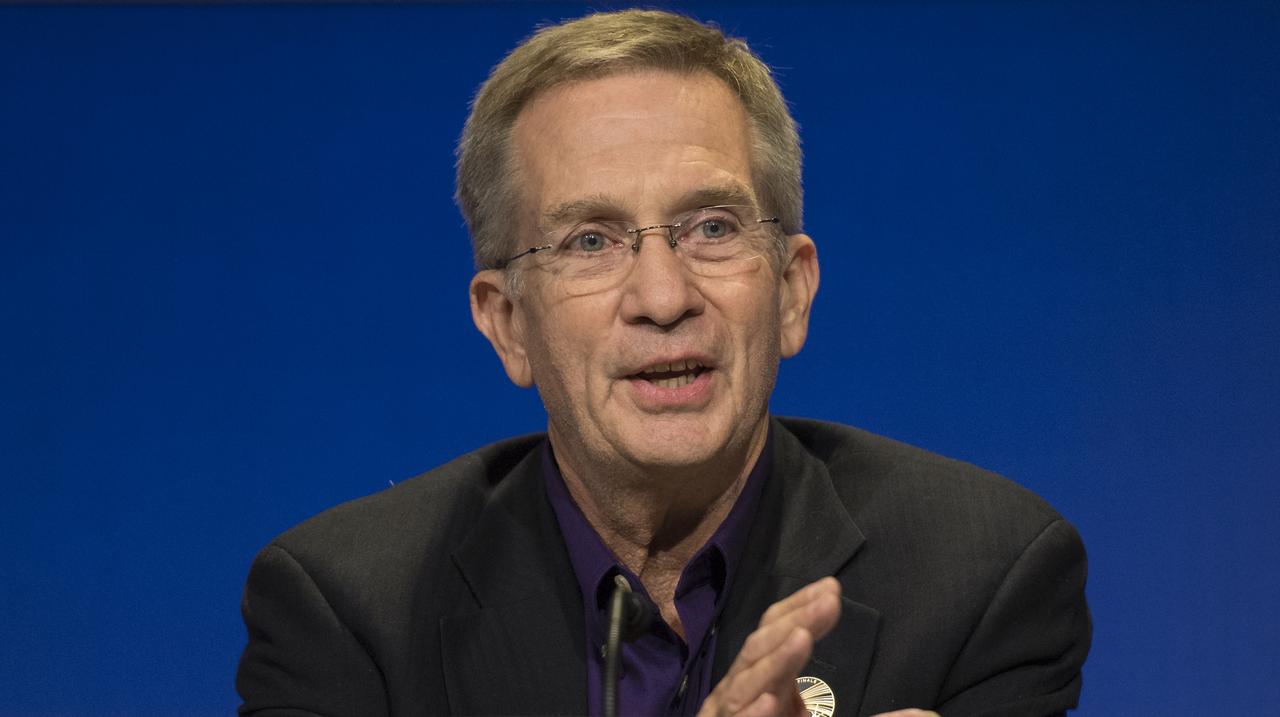

Cassini program manager at JPL, Earl Maize speaks during a press conference held after the end of the Cassini mission, Friday, Sept. 15, 2017 at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. Since its arrival in 2004, the Cassini-Huygens mission has been a discovery machine, revolutionizing our knowledge of the Saturn system and captivating us with data and images never before obtained with such detail and clarity. On Sept. 15, 2017, operators deliberately plunged the spacecraft into Saturn, as Cassini gathered science until the end. Loss of contact with the Cassini spacecraft occurred at 7:55 a.m. EDT (4:55 a.m. PDT). The “plunge” ensures Saturn’s moons will remain pristine for future exploration. During Cassini’s final days, mission team members from all around the world gathered at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, to celebrate the achievements of this historic mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
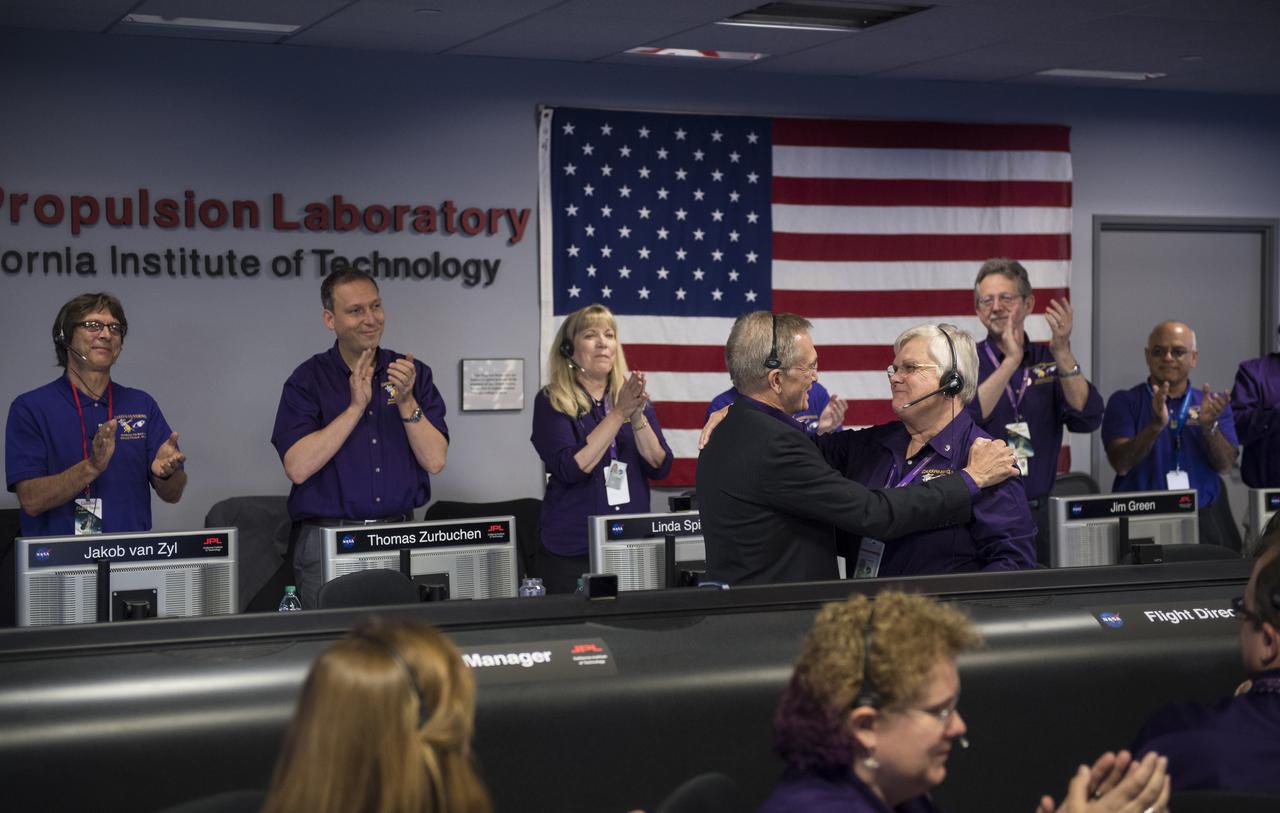

Cassini program manager at JPL, Earl Maize, left, and spacecraft operations team manager for the Cassini mission at Saturn, Julie Webster, right, embrace after the Cassini spacecraft plunged into Saturn, Friday, Sept. 15, 2017 at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. Since its arrival in 2004, the Cassini-Huygens mission has been a discovery machine, revolutionizing our knowledge of the Saturn system and captivating us with data and images never before obtained with such detail and clarity. On Sept. 15, 2017, operators will deliberately plunge the spacecraft into Saturn, as Cassini gathered science until the end. The “plunge” ensures Saturn’s moons will remain pristine for future exploration. During Cassini’s final days, mission team members from all around the world gathered at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, to celebrate the achievements of this historic mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
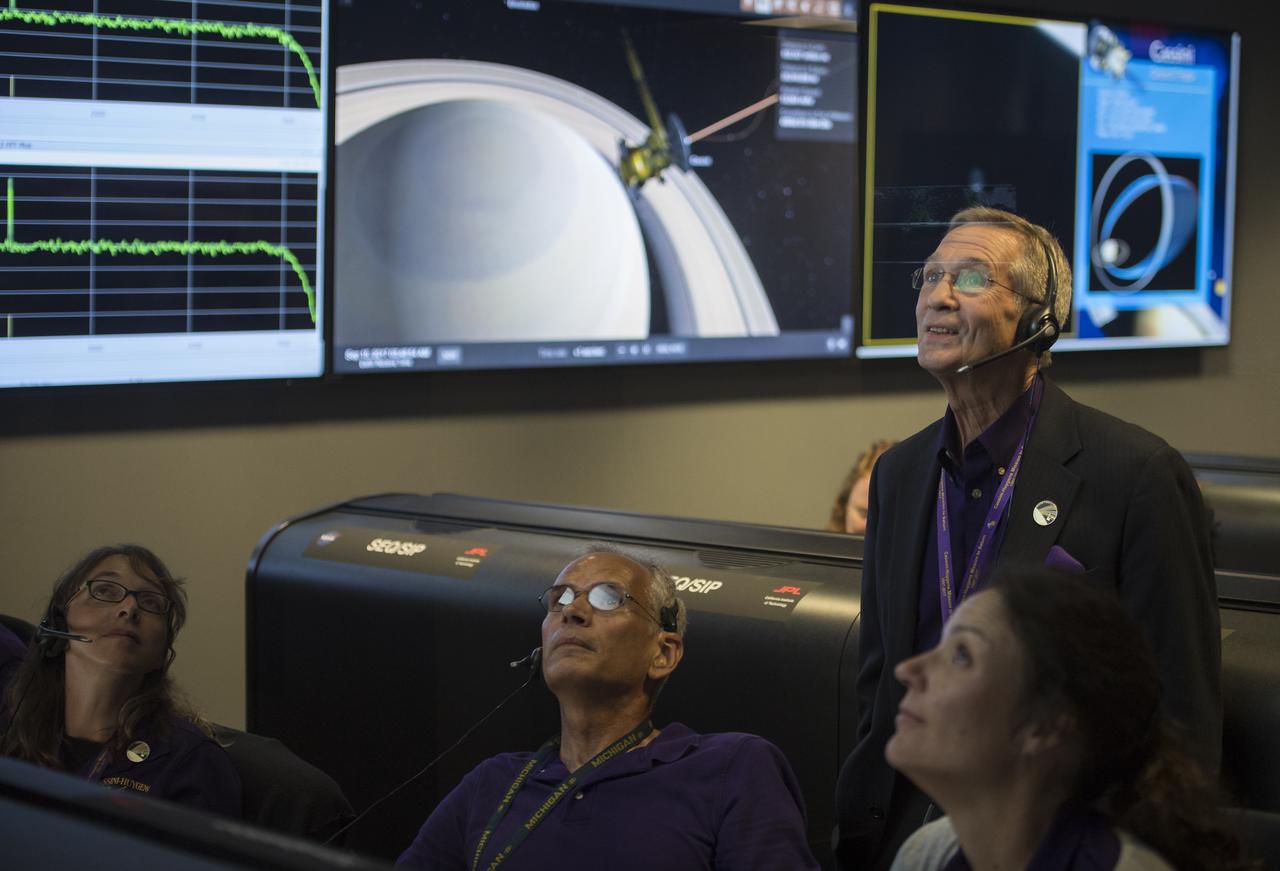

Cassini program manager at JPL, Earl Maize, standing, watches telemetry come in from Cassini with Julie Bellerose, left, Duane Roth, second from left, and Mar Vaquero of the Cassini navigation team in the mission control room, Friday, Sept. 15, 2017 at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. Since its arrival in 2004, the Cassini-Huygens mission has been a discovery machine, revolutionizing our knowledge of the Saturn system and captivating us with data and images never before obtained with such detail and clarity. On Sept. 15, 2017, operators deliberately plunged the spacecraft into Saturn, as Cassini gathered science until the end. The “plunge” ensures Saturn’s moons will remain pristine for future exploration. During Cassini’s final days, mission team members from all around the world gathered at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, to celebrate the achievements of this historic mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
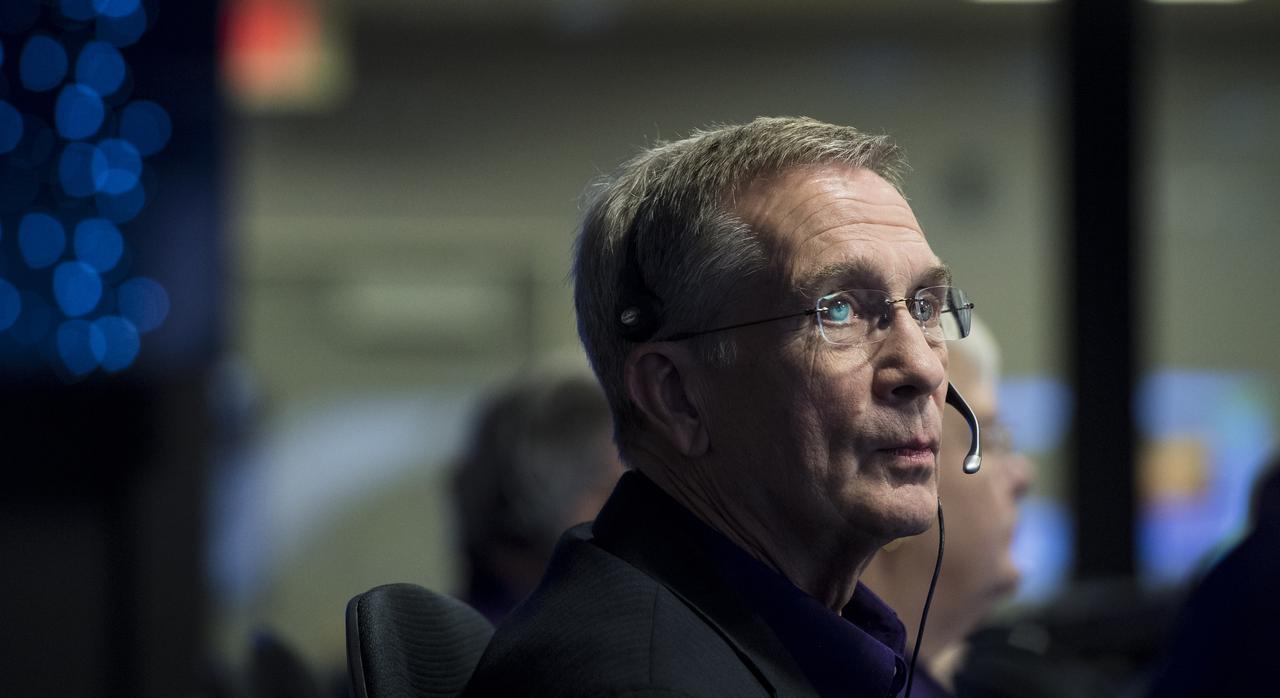

Cassini program manager at JPL, Earl Maize, is seen in mission control as he monitors the Cassini spacecraft, Friday, Sept. 15, 2017 at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. Since its arrival in 2004, the Cassini-Huygens mission has been a discovery machine, revolutionizing our knowledge of the Saturn system and captivating us with data and images never before obtained with such detail and clarity. On Sept. 15, 2017, operators deliberately plunged the spacecraft into Saturn, as Cassini gathered science until the end. Loss of contact with the Cassini spacecraft occurred at 7:55 a.m. EDT (4:55 a.m. PDT). The “plunge” ensures Saturn’s moons will remain pristine for future exploration. During Cassini’s final days, mission team members from all around the world gathered at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, to celebrate the achievements of this historic mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
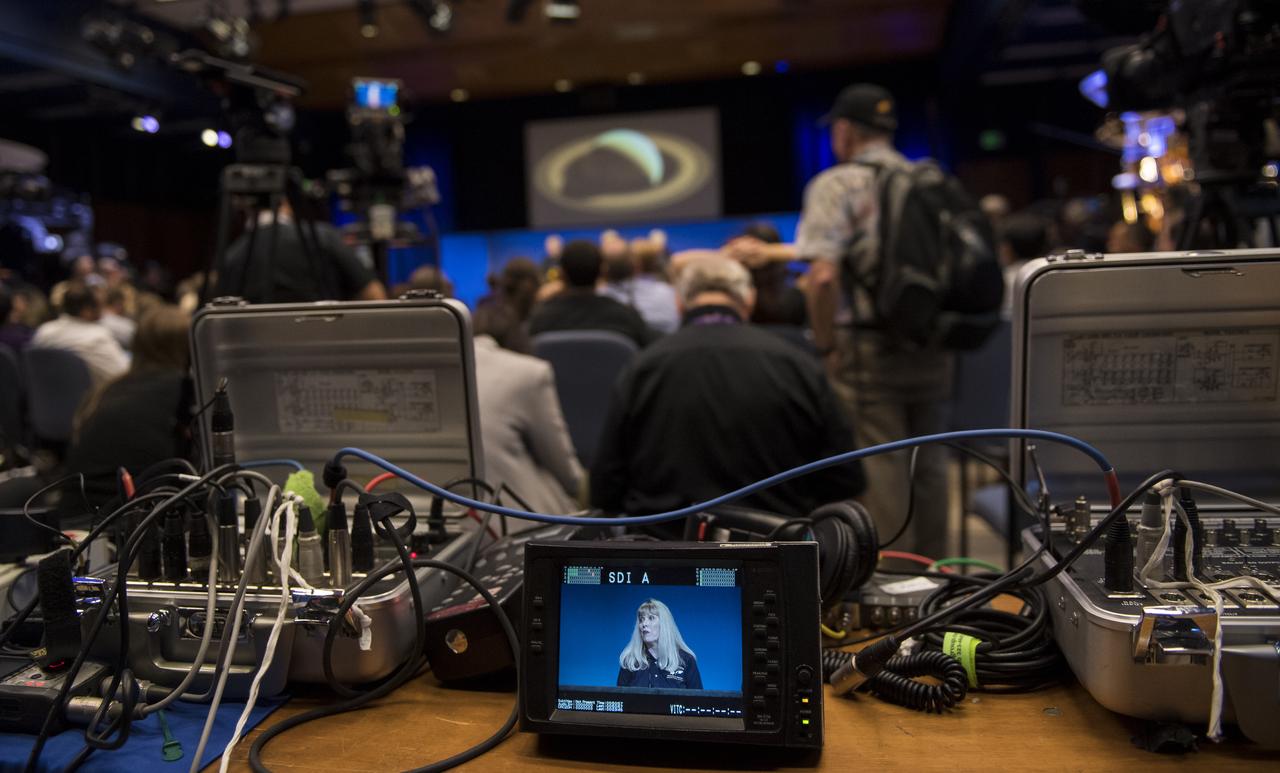

Cassini project scientist at JPL, Linda Spilker is seen on a monitor during a press conference held after the end of the Cassini mission, Friday, Sept. 15, 2017 at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. Since its arrival in 2004, the Cassini-Huygens mission has been a discovery machine, revolutionizing our knowledge of the Saturn system and captivating us with data and images never before obtained with such detail and clarity. On Sept. 15, 2017, operators deliberately plunged the spacecraft into Saturn, as Cassini gathered science until the end. Loss of contact with the Cassini spacecraft occurred at 7:55 a.m. EDT (4:55 a.m. PDT). The “plunge” ensures Saturn’s moons will remain pristine for future exploration. During Cassini’s final days, mission team members from all around the world gathered at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, to celebrate the achievements of this historic mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
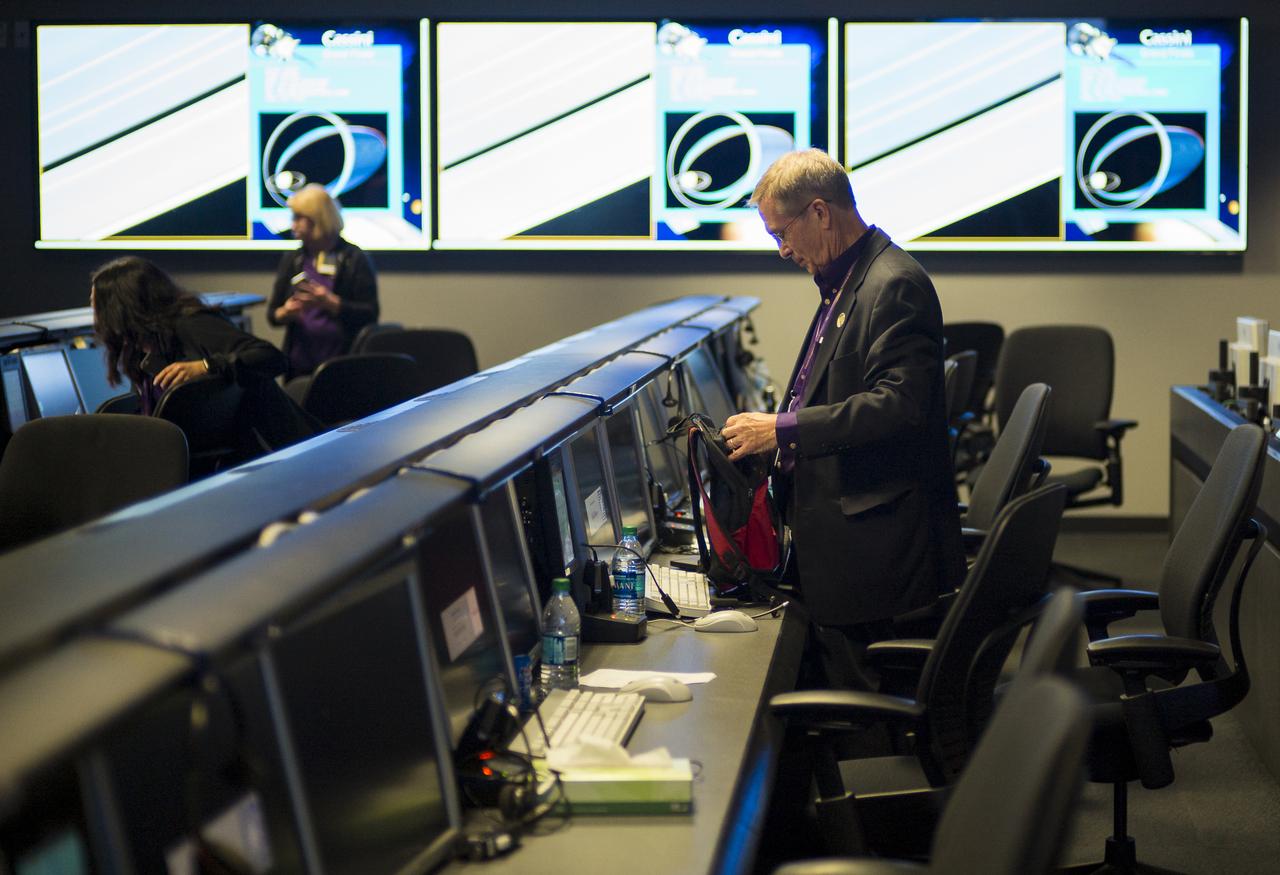

Cassini program manager at JPL, Earl Maize packs up his workspace in mission control after the end of the Cassini mission, Friday, Sept. 15, 2017 at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. Since its arrival in 2004, the Cassini-Huygens mission has been a discovery machine, revolutionizing our knowledge of the Saturn system and captivating us with data and images never before obtained with such detail and clarity. On Sept. 15, 2017, operators deliberately plunged the spacecraft into Saturn, as Cassini gathered science until the end. Loss of contact with the Cassini spacecraft occurred at 7:55 a.m. EDT (4:55 a.m. PDT). The “plunge” ensures Saturn’s moons will remain pristine for future exploration. During Cassini’s final days, mission team members from all around the world gathered at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, to celebrate the achievements of this historic mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
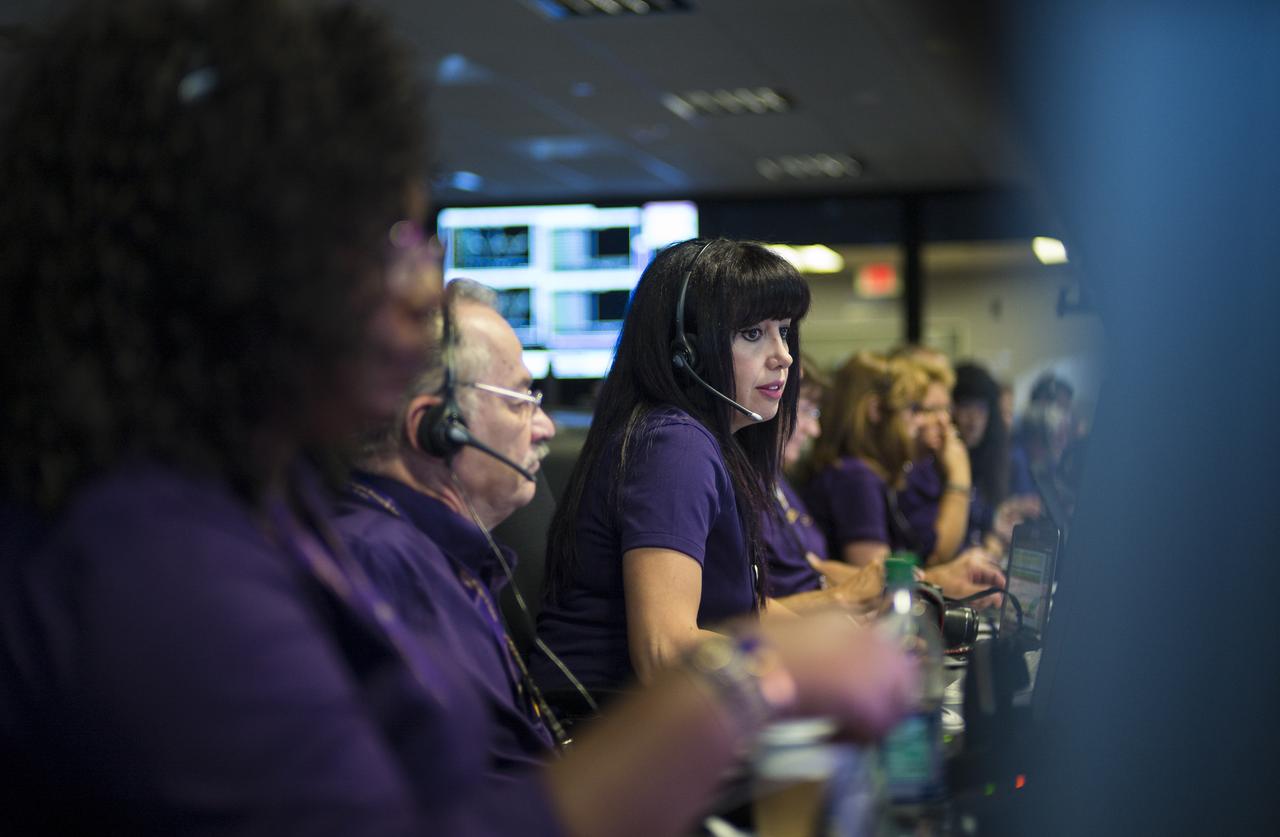

Aseel Anabtawi, of Cassini's radio science team, monitors her console in mission control during Cassini's final plunge into Saturn, Friday, Sept. 15, 2017 at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. Since its arrival in 2004, the Cassini-Huygens mission has been a discovery machine, revolutionizing our knowledge of the Saturn system and captivating us with data and images never before obtained with such detail and clarity. On Sept. 15, 2017, operators deliberately plunged the spacecraft into Saturn, as Cassini gathered science until the end. Loss of contact with the Cassini spacecraft occurred at 7:55 a.m. EDT (4:55 a.m. PDT). The “plunge” ensures Saturn’s moons will remain pristine for future exploration. During Cassini’s final days, mission team members from all around the world gathered at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, to celebrate the achievements of this historic mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
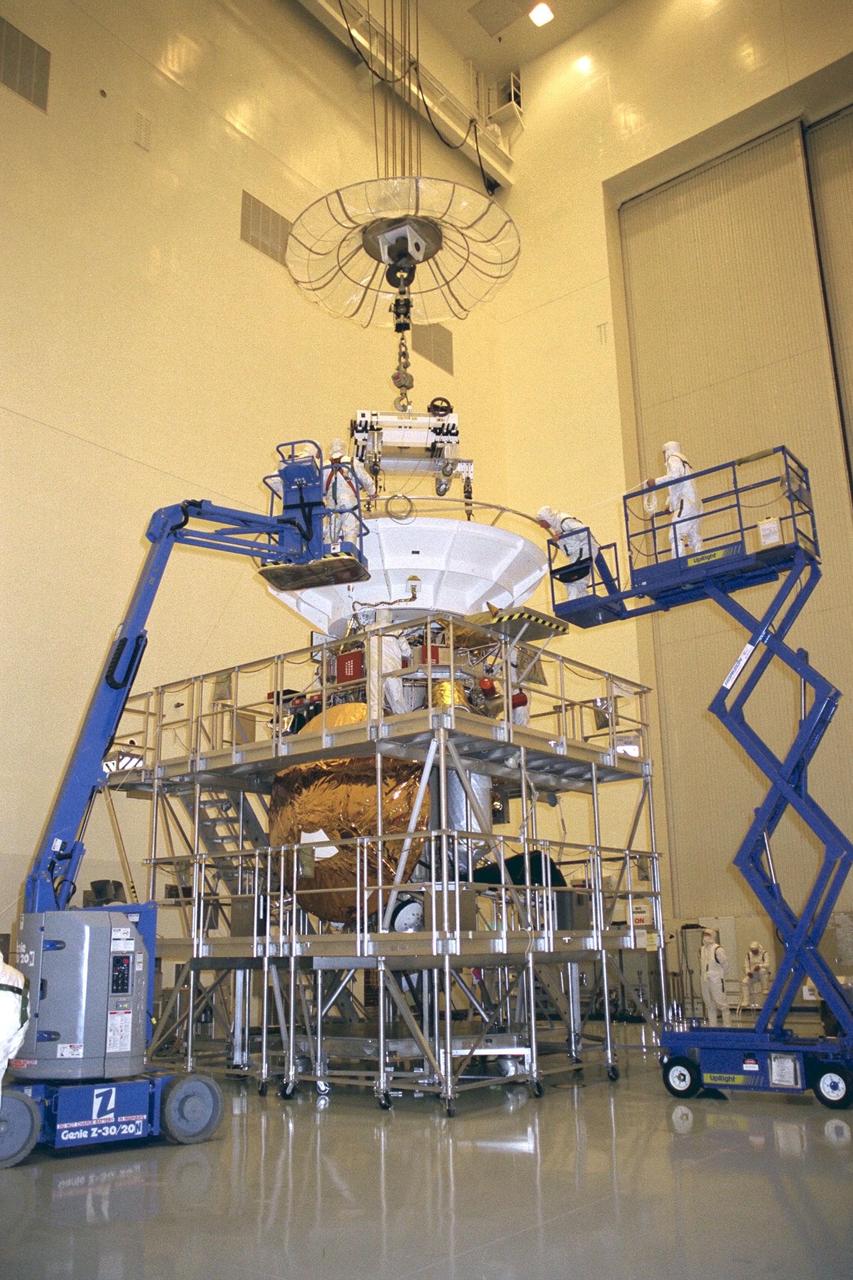

Flight mechanics from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Pasadena, Calif., work on the lifting fixture that picks up the Cassini spacecraft in KSC’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility. The orbiter alone weighs about 4,750 pounds (2,150 kilograms). At launch, the combined orbiter, Huygens probe, launch vehicle adapter, and propellants will weigh about 12,346 pounds (5,600 kilograms). Scheduled for launch in October, the Cassini mission, a joint US-European four-year orbital surveillance of Saturn's atmosphere and magnetosphere, its rings, and its moons, seeks insight into the origins and evolution of the early solar system. JPL is managing the Cassini project for NASA
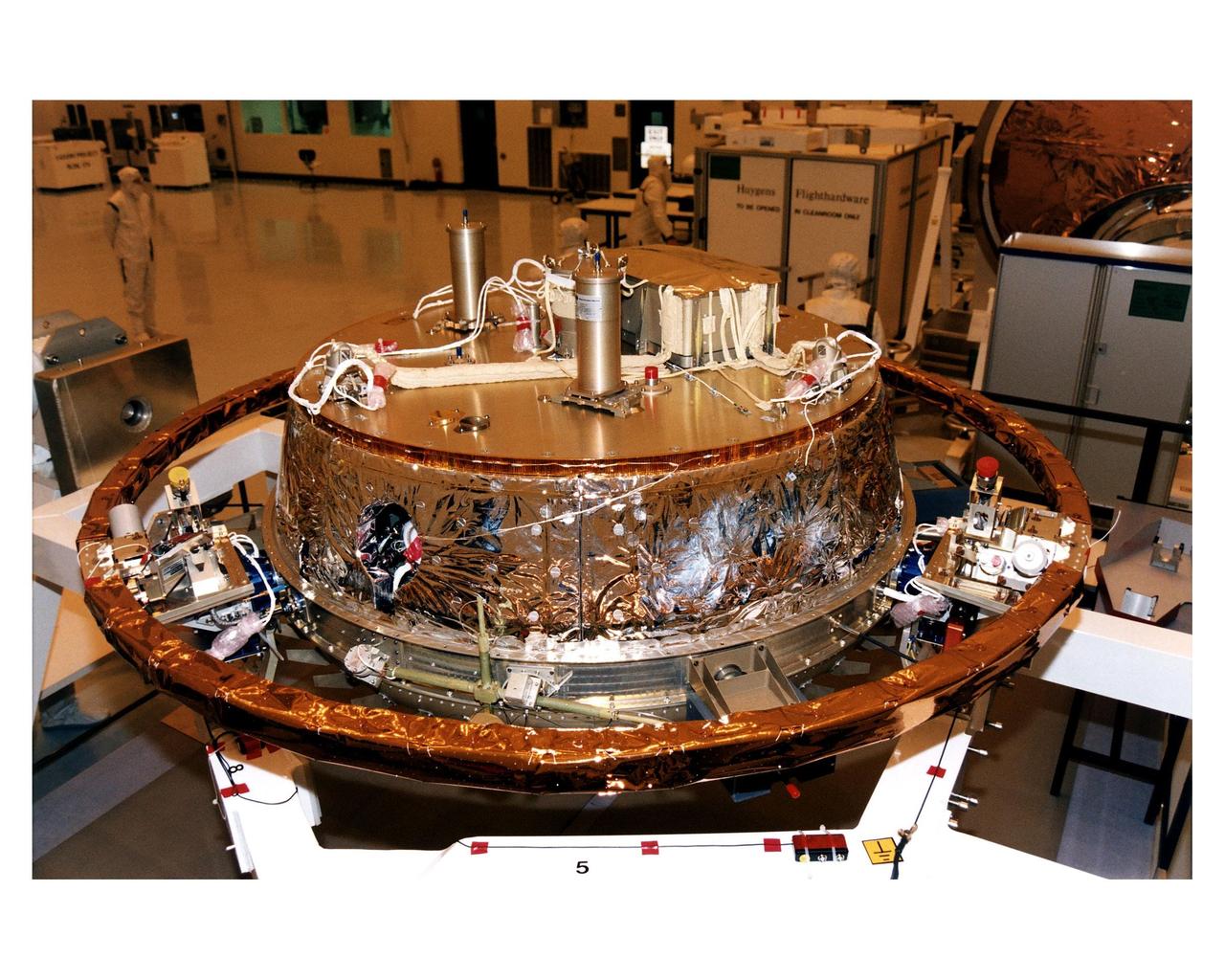
The descent module of the Titan-bound Huygens probe undergoes preflight processing on a support structure in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF). The probe will study the clouds, atmosphere and surface of Saturn's moon, Titan, as part of the Cassini mission to the Saturnian system. The cylinders on the top of the probe contain antennas; the small square box has a parachute. The probe will detach from the Cassini orbiter after arrival at Saturn in 2004 to slowly descend through Titan's atmosphere to the surface of the Saturn moon. The Cassini launch on a Titan IVB/Centaur expendable launch vehicle is scheduled for October 6 from Cape Canaveral Air Station
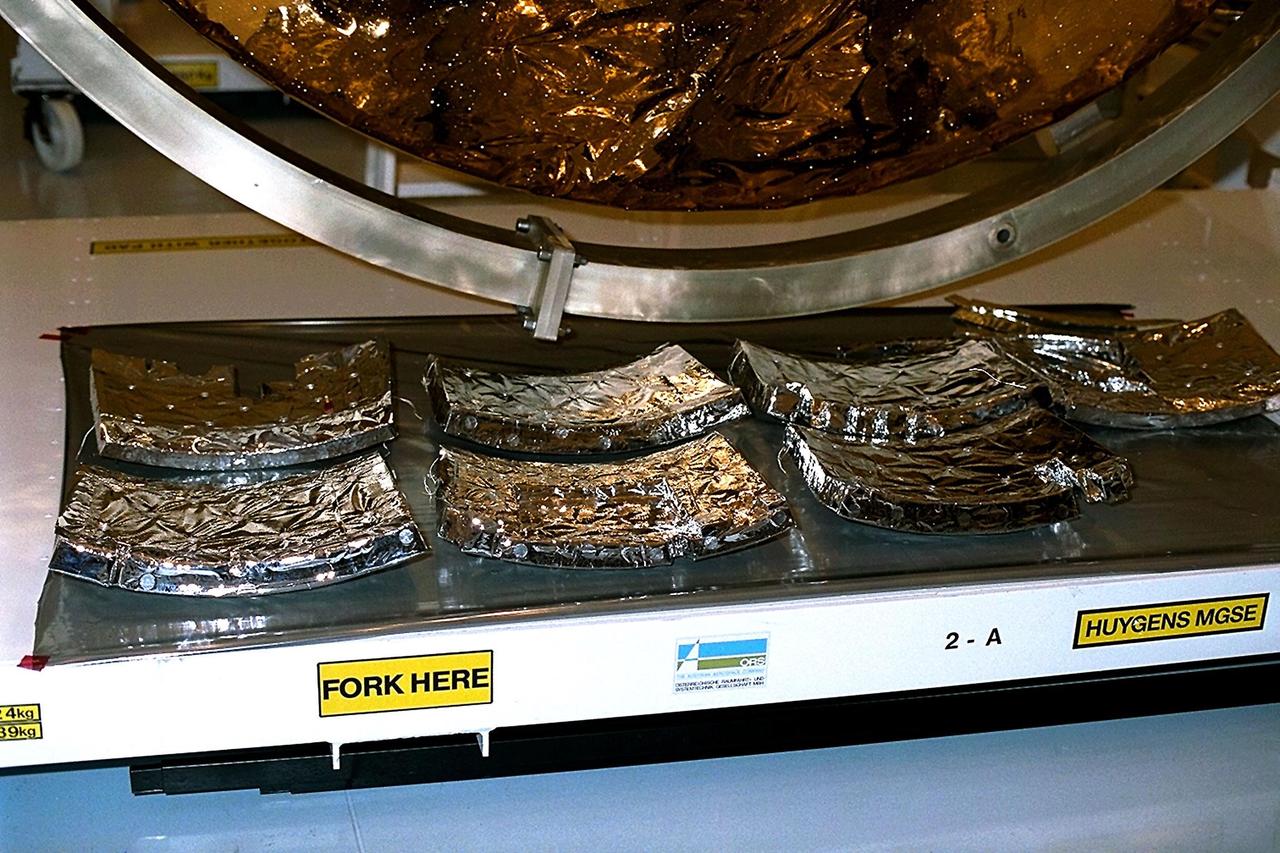

Pieces of the Huygens probe internal insulating foam await inspection after removal from the probe in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at KSC. The spacecraft was returned to the PHSF after damage to thermal insulation was discovered inside Huygens from an abnormally high flow of conditioned air. Internal inspection, insulation repair and a cleaning of the probe were required. Mission managers are targeting a mid-October launch date after Cassini returns to the pad and is once again placed atop its Titan IVB expendable launch vehicle at Launch Pad 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Station

Cassini program manager at JPL, Earl Maize speaks during a press conference previewing Cassini's End of Mission, Wednesday, Sept. 13, 2017 at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. Since its arrival in 2004, the Cassini-Huygens mission has been a discovery machine, revolutionizing our knowledge of the Saturn system and captivating us with data and images never before obtained with such detail and clarity. On Sept. 15, 2017, operators will deliberately plunge the spacecraft into Saturn, as Cassini gathered science until the end. The “plunge” ensures Saturn’s moons will remain pristine for future exploration. During Cassini’s final days, mission team members from all around the world gathered at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, to celebrate the achievements of this historic mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Italian Space Agency (ASI) representative, Enrico Flamini, is introduced during a press conference held after the end of the Cassini mission, Friday, Sept. 15, 2017 at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. Since its arrival in 2004, the Cassini-Huygens mission has been a discovery machine, revolutionizing our knowledge of the Saturn system and captivating us with data and images never before obtained with such detail and clarity. On Sept. 15, 2017, operators deliberately plunged the spacecraft into Saturn, as Cassini gathered science until the end. Loss of contact with the Cassini spacecraft occurred at 7:55 a.m. EDT (4:55 a.m. PDT). The “plunge” ensures Saturn’s moons will remain pristine for future exploration. During Cassini’s final days, mission team members from all around the world gathered at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, to celebrate the achievements of this historic mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
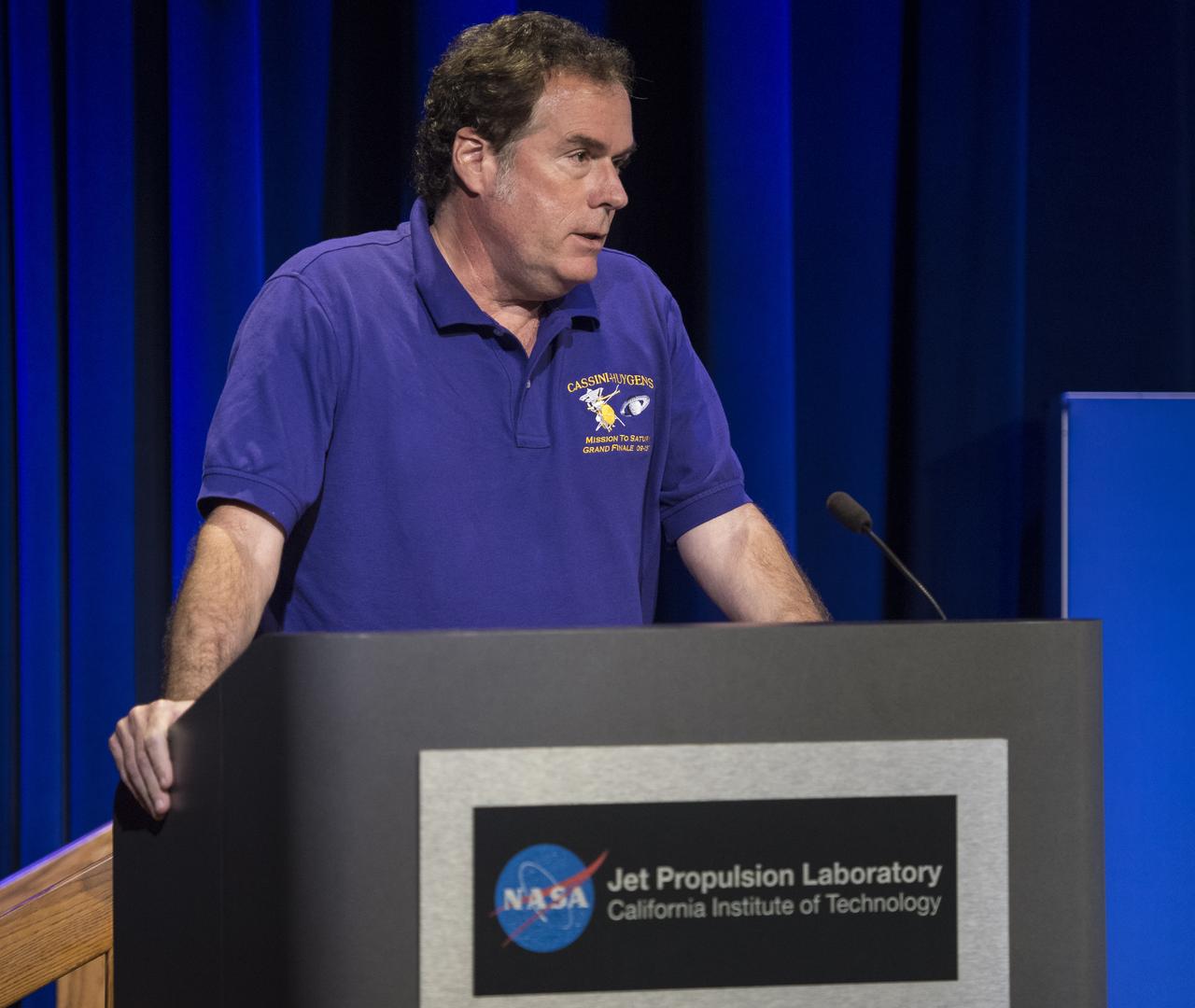

Director of NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Michael Watkins speaks during a press conference held after the end of the Cassini mission, Friday, Sept. 15, 2017 at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. Since its arrival in 2004, the Cassini-Huygens mission has been a discovery machine, revolutionizing our knowledge of the Saturn system and captivating us with data and images never before obtained with such detail and clarity. On Sept. 15, 2017, operators deliberately plunged the spacecraft into Saturn, as Cassini gathered science until the end. Loss of contact with the Cassini spacecraft occurred at 7:55 a.m. EDT (4:55 a.m. PDT). The “plunge” ensures Saturn’s moons will remain pristine for future exploration. During Cassini’s final days, mission team members from all around the world gathered at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, to celebrate the achievements of this historic mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
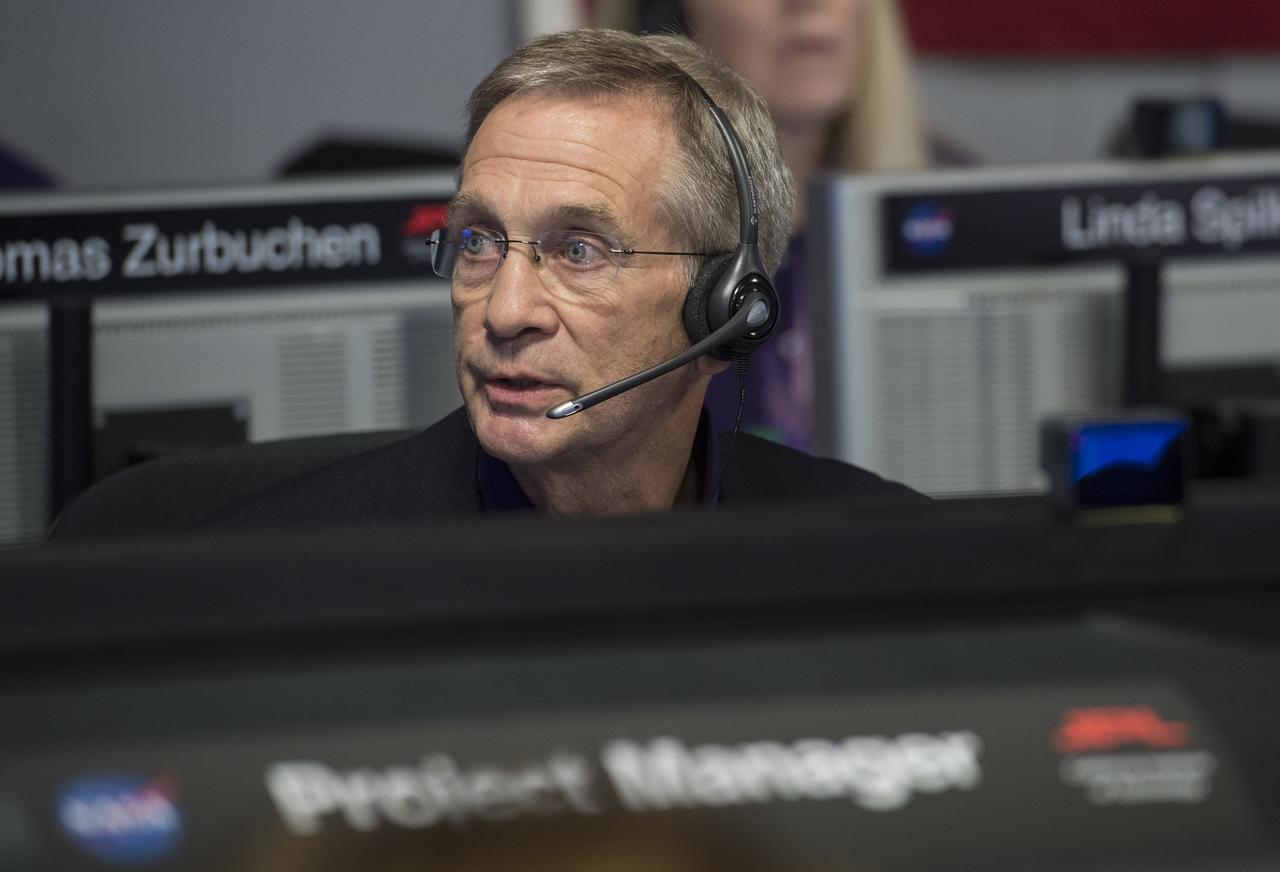

Cassini program manager at JPL, Earl Maize, center row, calls out the end of the Cassini mission, Friday, Sept. 15, 2017 at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. Since its arrival in 2004, the Cassini-Huygens mission has been a discovery machine, revolutionizing our knowledge of the Saturn system and captivating us with data and images never before obtained with such detail and clarity. On Sept. 15, 2017, operators deliberately plunged the spacecraft into Saturn, as Cassini gathered science until the end. The “plunge” ensures Saturn’s moons will remain pristine for future exploration. During Cassini’s final days, mission team members from all around the world gathered at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, to celebrate the achievements of this historic mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
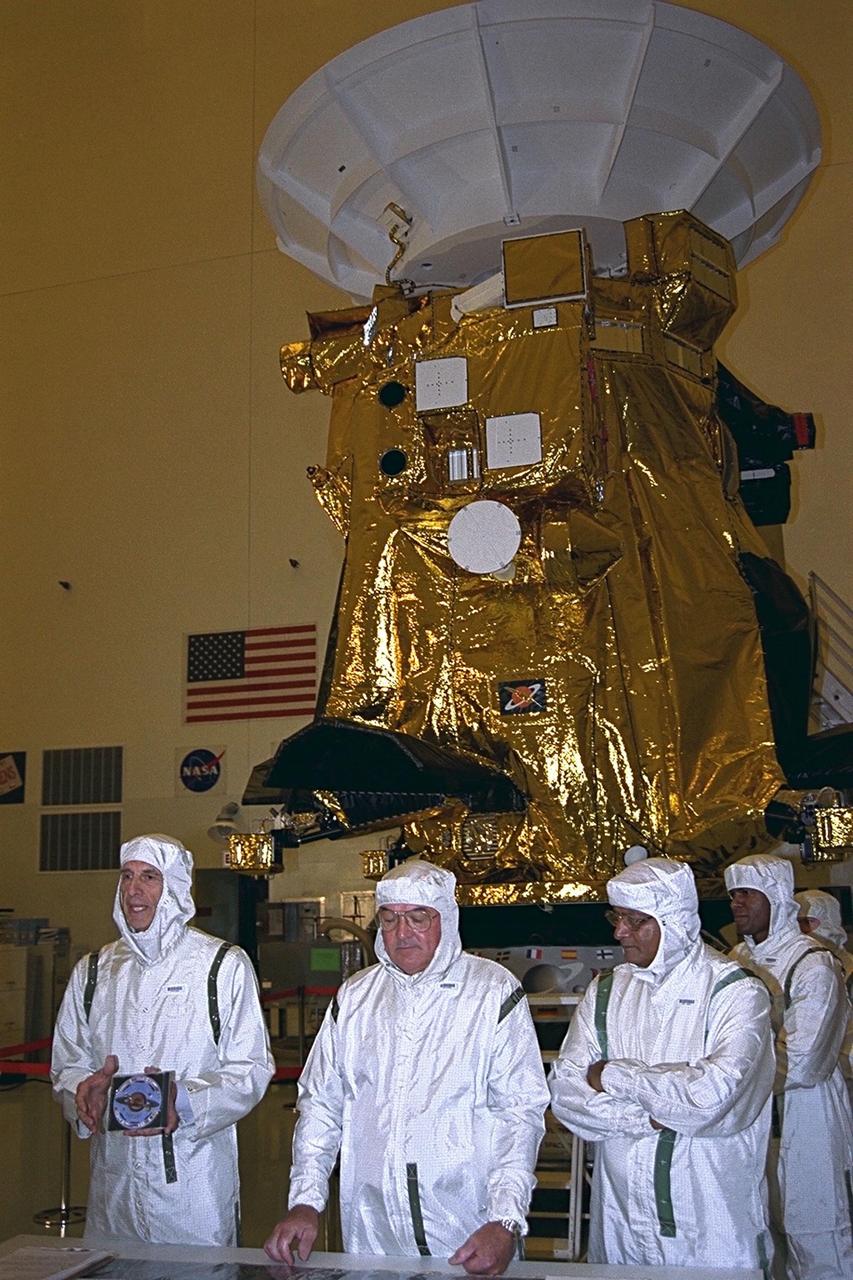

In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF), Charley Kohlhase, Cassini's science and mission design manager, who oversaw the development of the Digital Video Disk (DVD), discusses it with members of the press. To Kohlhase's left are Richard J. Spehalski, Cassini project manager, and Hamid Hassan, the European Space Agancy Huygens manager. Kohlhase holds the high-tech data disk that will be installed on the Cassini spacecraft. More than 616,400 signatures from 81 countries around the world are on the disk. The Cassini spacecraft is being prepared for launch on Oct. 6, 1997. It will be launched on an Air Force Titan IV/Centaur launch vehicle on an international scientific mission to the planet Saturn. It is destined to arrive at Saturn in July 2004. The Cassini mission is managed for NASA's Office of Space Science, Washington, D.C., by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif
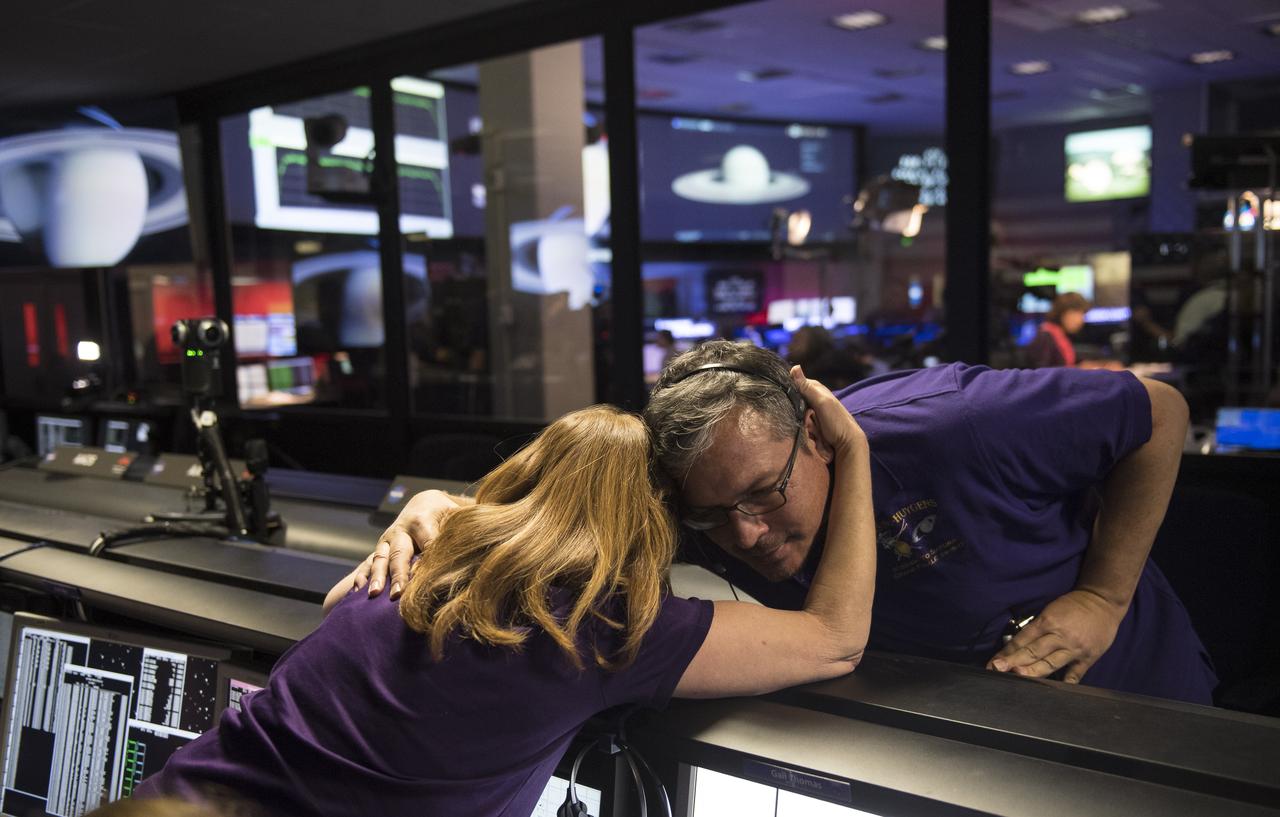

Cassini team members embrace after the spacecraft was deliberately plunged into Saturn, Friday, Sept. 15, 2017 at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. Since its arrival in 2004, the Cassini-Huygens mission has been a discovery machine, revolutionizing our knowledge of the Saturn system and captivating us with data and images never before obtained with such detail and clarity. On Sept. 15, 2017, operators deliberately plunged the spacecraft into Saturn, as Cassini gathered science until the end. Loss of contact with the Cassini spacecraft occurred at 7:55 a.m. EDT (4:55 a.m. PDT) The “plunge” ensures Saturn’s moons will remain pristine for future exploration. During Cassini’s final days, mission team members from all around the world gathered at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, to celebrate the achievements of this historic mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
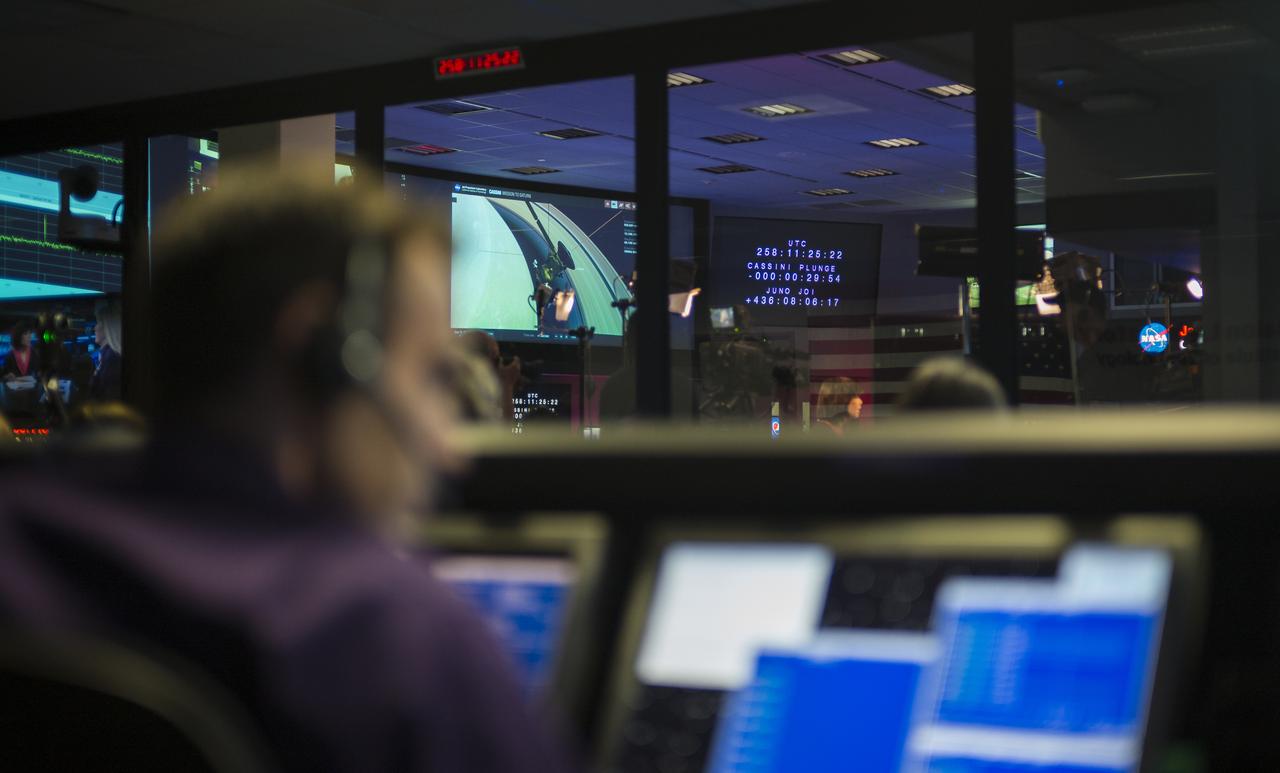

A monitor in mission control shows the time remaining until Cassini makes its final plunge into Saturn, Friday, Sept. 15, 2017 at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. Since its arrival in 2004, the Cassini-Huygens mission has been a discovery machine, revolutionizing our knowledge of the Saturn system and captivating us with data and images never before obtained with such detail and clarity. On Sept. 15, 2017, operators deliberately plunged the spacecraft into Saturn, as Cassini gathered science until the end. Loss of contact with the Cassini spacecraft occurred at 7:55 a.m. EDT (4:55 a.m. PDT). The “plunge” ensures Saturn’s moons will remain pristine for future exploration. During Cassini’s final days, mission team members from all around the world gathered at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, to celebrate the achievements of this historic mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
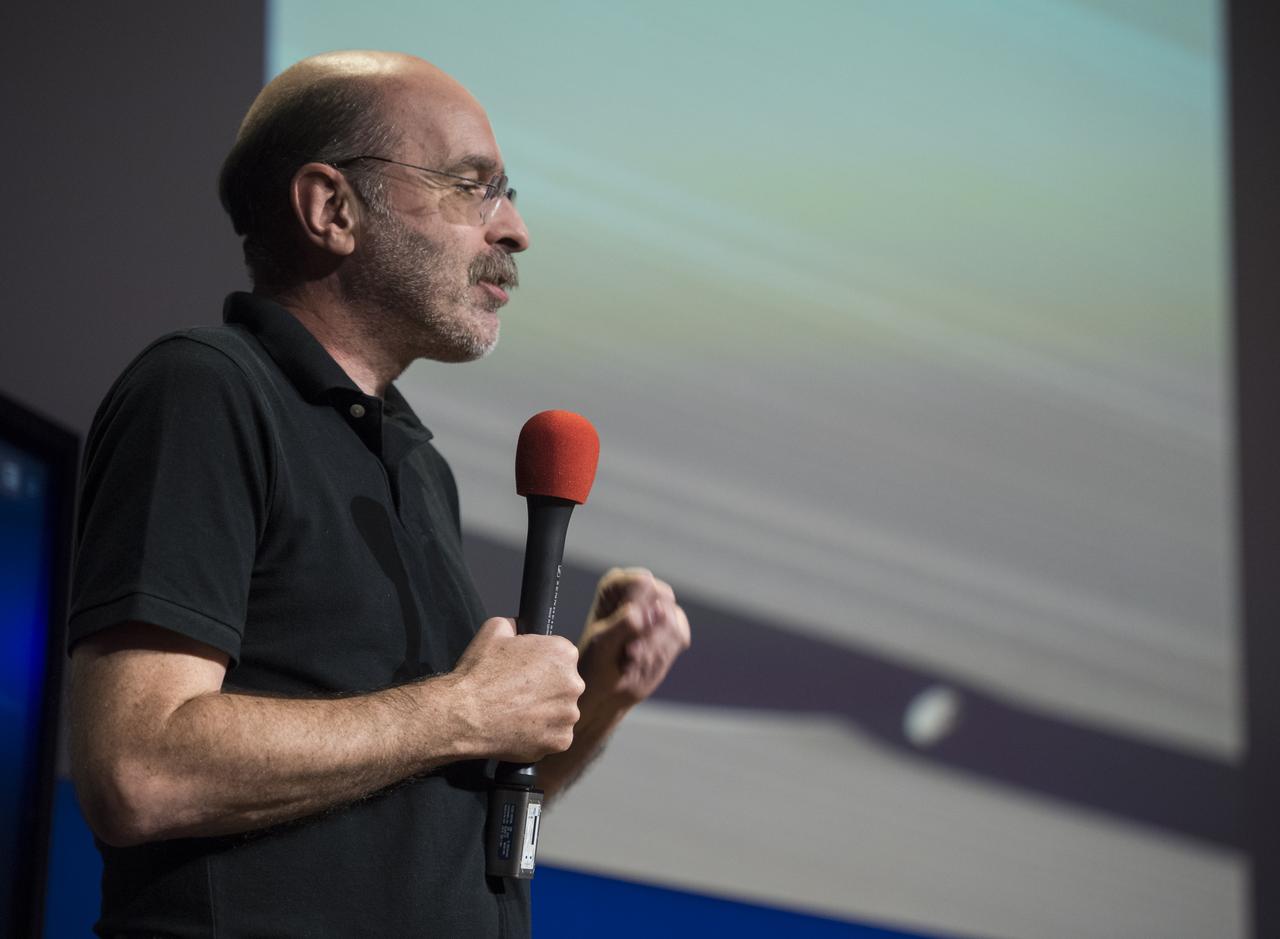

Cassini imaging science subsystem (ISS) team associate Mike Evans speaks with Cassini NASA Social attendees, Thursday, Sept. 14, 2017 at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. Since its arrival in 2004, the Cassini-Huygens mission has been a discovery machine, revolutionizing our knowledge of the Saturn system and captivating us with data and images never before obtained with such detail and clarity. On Sept. 15, 2017, operators will deliberately plunge the spacecraft into Saturn, as Cassini gathered science until the end. The “plunge” ensures Saturn’s moons will remain pristine for future exploration. During Cassini’s final days, mission team members from all around the world gathered at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, to celebrate the achievements of this historic mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
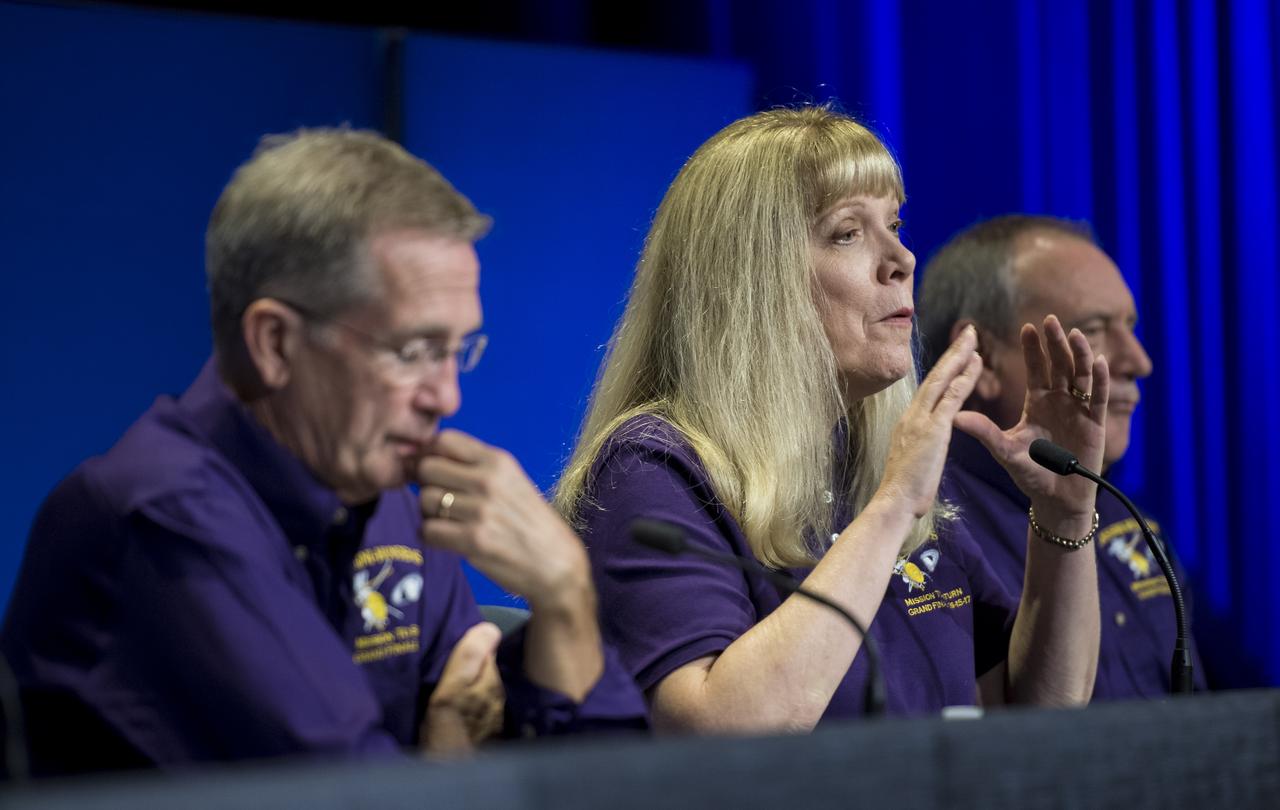

Cassini project scientist at JPL, Linda Spilker answers questions from members of the media during a press conference previewing Cassini's End of Mission, Wednesday, Sept. 13, 2017 at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. Since its arrival in 2004, the Cassini-Huygens mission has been a discovery machine, revolutionizing our knowledge of the Saturn system and captivating us with data and images never before obtained with such detail and clarity. On Sept. 15, 2017, operators will deliberately plunge the spacecraft into Saturn, as Cassini gathered science until the end. The “plunge” ensures Saturn’s moons will remain pristine for future exploration. During Cassini’s final days, mission team members from all around the world gathered at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, to celebrate the achievements of this historic mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Cassini program manager at JPL, Earl Maize, watches monitors in mission control of the Space Flight Operations Center as the Cassini spacecraft begins downlink data through NASA's Deep Space Network, Thursday, Sept. 14, 2017 at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. Since its arrival in 2004, the Cassini-Huygens mission has been a discovery machine, revolutionizing our knowledge of the Saturn system and captivating us with data and images never before obtained with such detail and clarity. On Sept. 15, 2017, operators will deliberately plunge the spacecraft into Saturn, as Cassini gathered science until the end. The “plunge” ensures Saturn’s moons will remain pristine for future exploration. During Cassini’s final days, mission team members from all around the world gathered at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, to celebrate the achievements of this historic mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

A computer screen in mission control displays mission elapsed time for Cassini minutes after the spacecraft plunged into Saturn's atmosphere, Friday, Sept. 15, 2017 at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. Since its arrival in 2004, the Cassini-Huygens mission has been a discovery machine, revolutionizing our knowledge of the Saturn system and captivating us with data and images never before obtained with such detail and clarity. On Sept. 15, 2017, operators will deliberately plunge the spacecraft into Saturn, as Cassini gathered science until the end. Loss of contact with the Cassini spacecraft occurred at 7:55 a.m. EDT (4:55 a.m. PDT). The “plunge” ensures Saturn’s moons will remain pristine for future exploration. During Cassini’s final days, mission team members from all around the world gathered at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, to celebrate the achievements of this historic mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
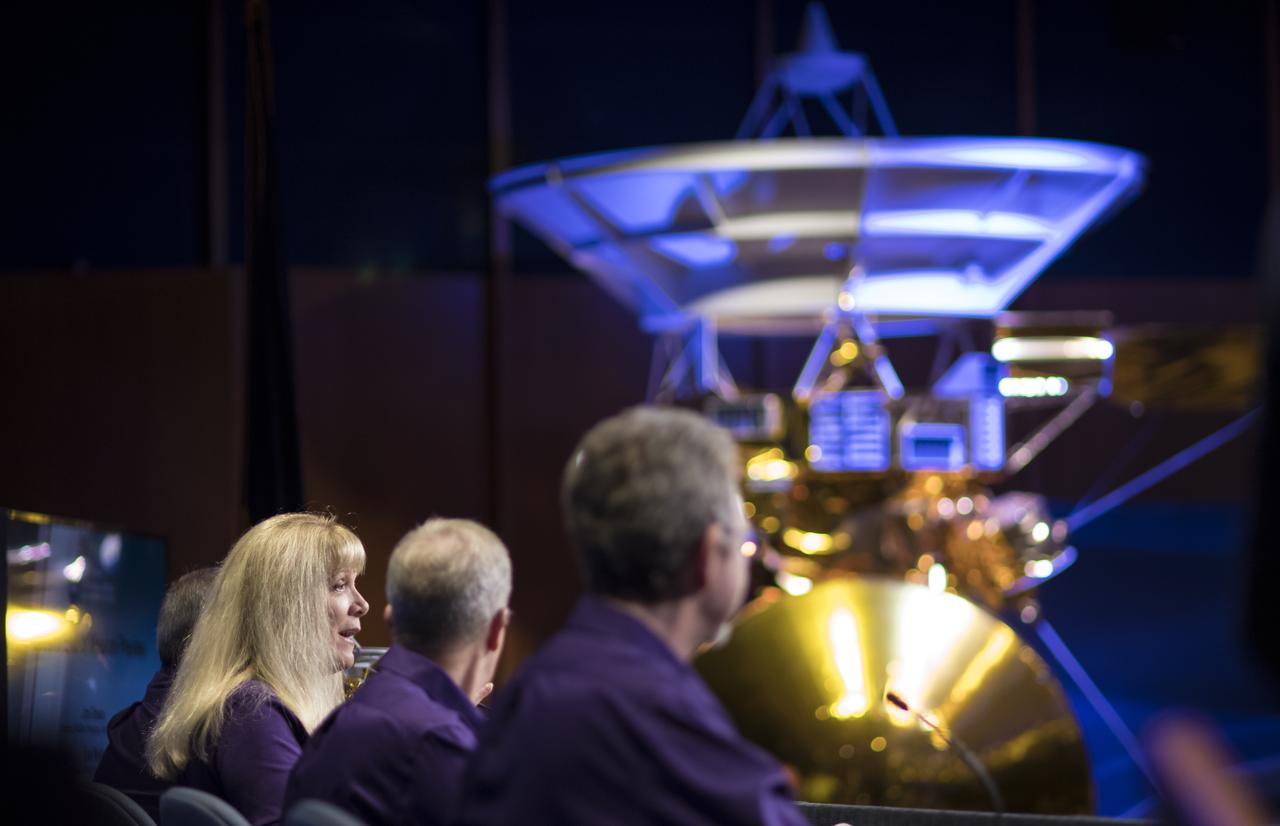

Cassini project scientist at JPL, Linda Spilker answers questions from members of the media during a press conference previewing Cassini's End of Mission, Wednesday, Sept. 13, 2017 at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. Since its arrival in 2004, the Cassini-Huygens mission has been a discovery machine, revolutionizing our knowledge of the Saturn system and captivating us with data and images never before obtained with such detail and clarity. On Sept. 15, 2017, operators will deliberately plunge the spacecraft into Saturn, as Cassini gathered science until the end. The “plunge” ensures Saturn’s moons will remain pristine for future exploration. During Cassini’s final days, mission team members from all around the world gathered at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, to celebrate the achievements of this historic mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
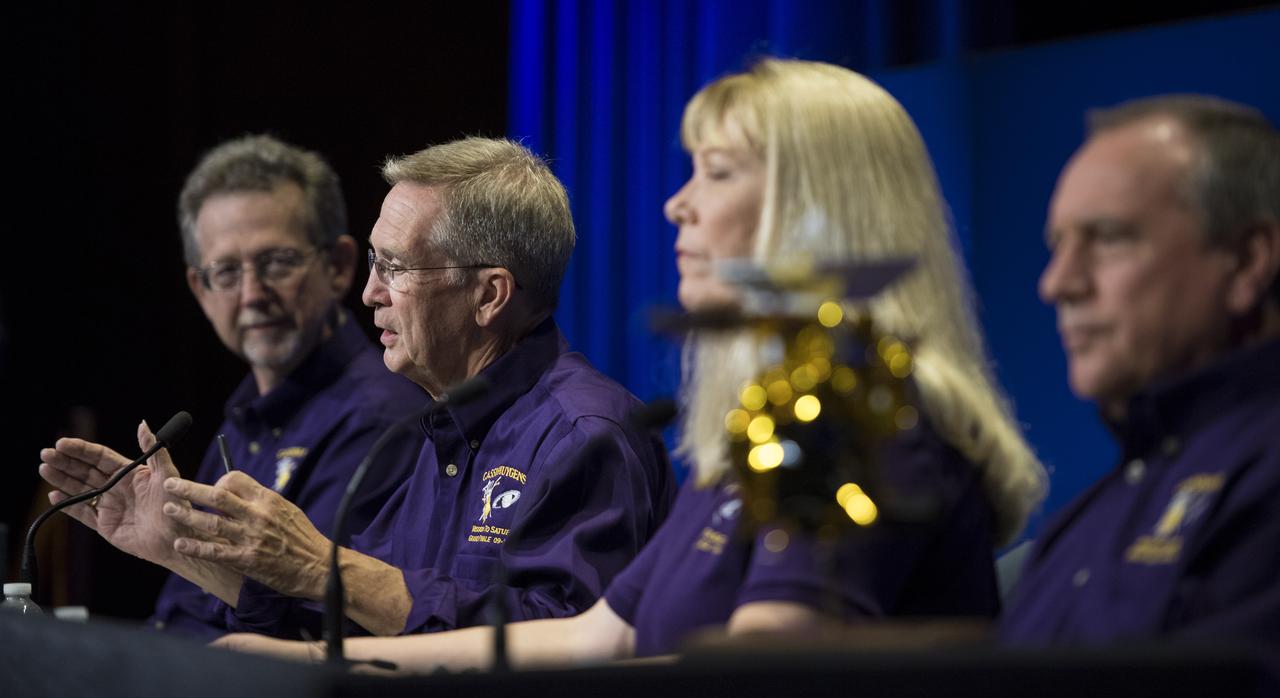

Cassini program manager at JPL, Earl Maize, speaks during a press conference previewing Cassini's End of Mission, Wednesday, Sept. 13, 2017 at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. Since its arrival in 2004, the Cassini-Huygens mission has been a discovery machine, revolutionizing our knowledge of the Saturn system and captivating us with data and images never before obtained with such detail and clarity. On Sept. 15, 2017, operators will deliberately plunge the spacecraft into Saturn, as Cassini gathered science until the end. The “plunge” ensures Saturn’s moons will remain pristine for future exploration. During Cassini’s final days, mission team members from all around the world gathered at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, to celebrate the achievements of this historic mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Cassini imaging science subsystem (ISS) team associate Mike Evans discusses an image of Saturn's moon Daphnis with Cassini NASA Social attendees, Thursday, Sept. 14, 2017 at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. Since its arrival in 2004, the Cassini-Huygens mission has been a discovery machine, revolutionizing our knowledge of the Saturn system and captivating us with data and images never before obtained with such detail and clarity. On Sept. 15, 2017, operators will deliberately plunge the spacecraft into Saturn, as Cassini gathered science until the end. The “plunge” ensures Saturn’s moons will remain pristine for future exploration. During Cassini’s final days, mission team members from all around the world gathered at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, to celebrate the achievements of this historic mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
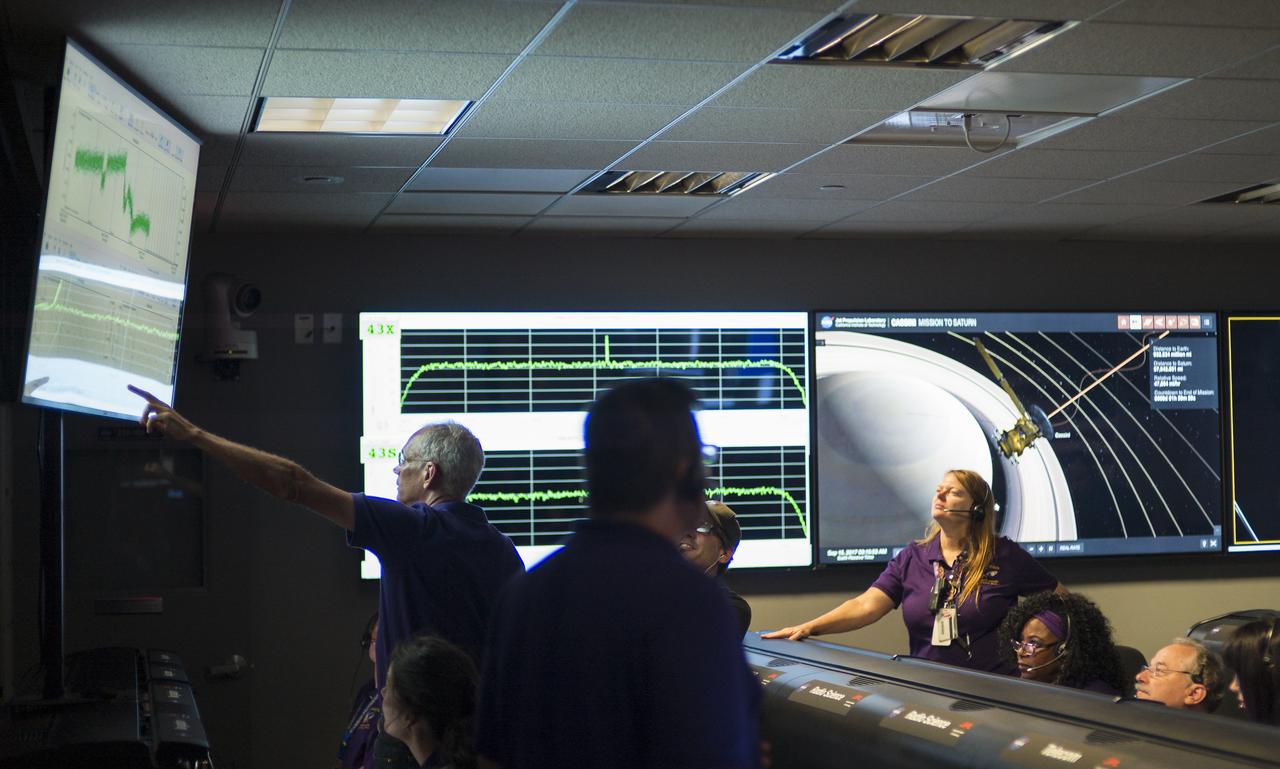

Cassini team members monitor data from the spacecraft as it makes its final plunge into Saturn, Friday, Sept. 15, 2017 at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. Since its arrival in 2004, the Cassini-Huygens mission has been a discovery machine, revolutionizing our knowledge of the Saturn system and captivating us with data and images never before obtained with such detail and clarity. On Sept. 15, 2017, operators deliberately plunged the spacecraft into Saturn, as Cassini gathered science until the end. Loss of contact with the Cassini spacecraft occurred at 7:55 a.m. EDT (4:55 a.m. PDT). The “plunge” ensures Saturn’s moons will remain pristine for future exploration. During Cassini’s final days, mission team members from all around the world gathered at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, to celebrate the achievements of this historic mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)