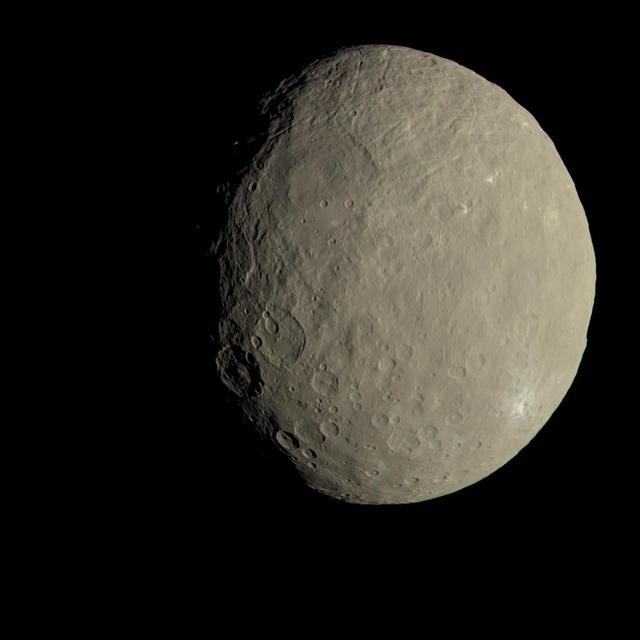

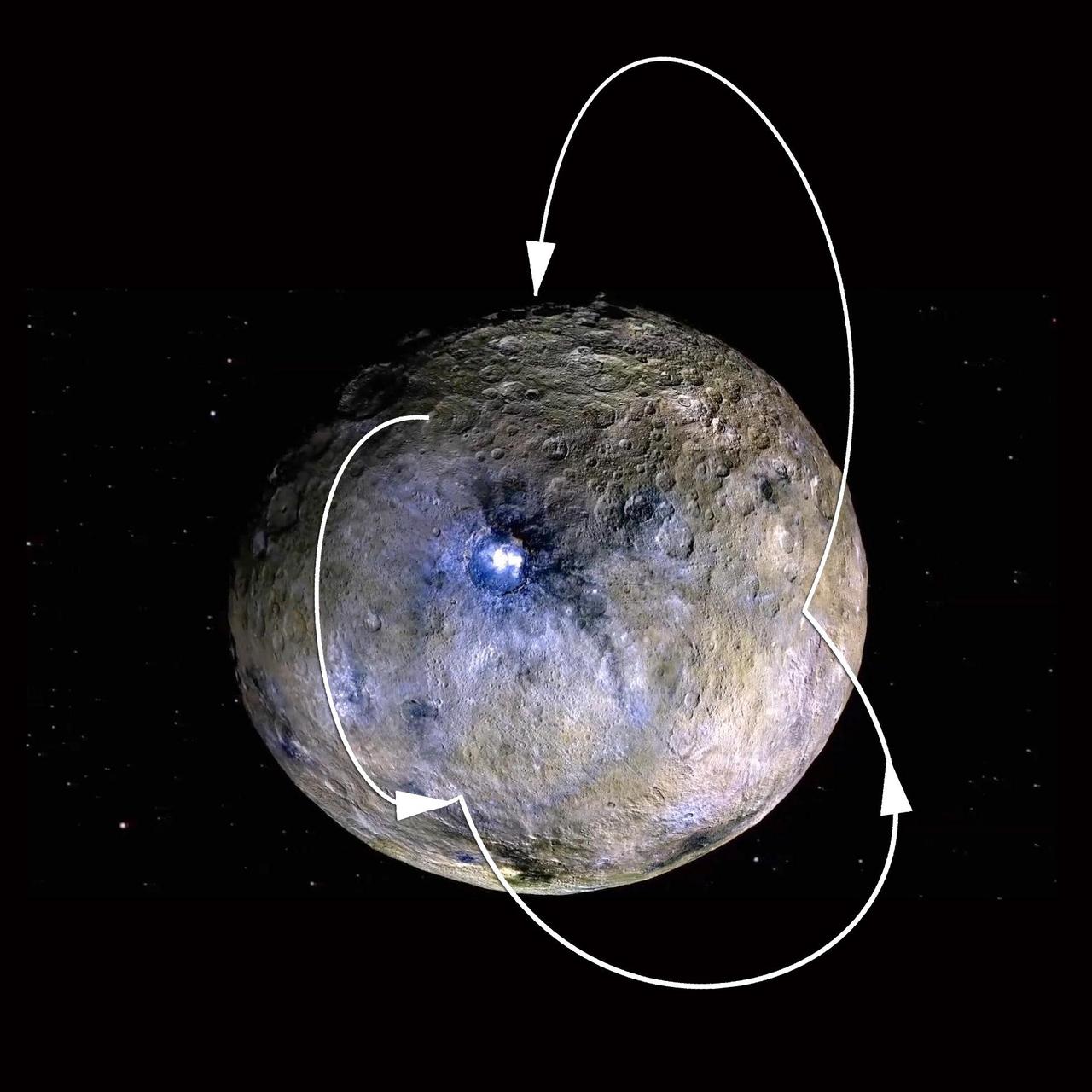
This image of Ceres approximates how the dwarf planet's colors would appear to the eye. This view of Ceres, produced by the German Aerospace Center in Berlin, combines images taken during Dawn's first science orbit in 2015 using the framing camera's red, green and blue spectral filters. The color was calculated using a reflectance spectrum, which is based on the way that Ceres reflects different wavelengths of light and the solar wavelengths that illuminate Ceres. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21079

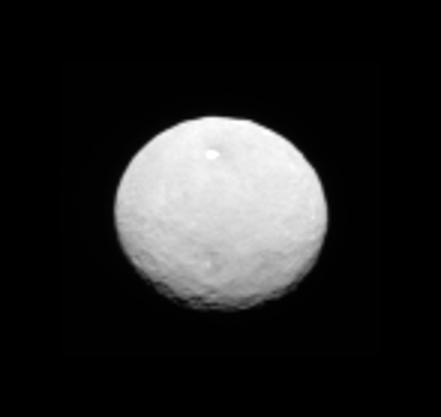
This processed image, taken Jan. 13, 2015, shows the dwarf planet Ceres as seen from the Dawn spacecraft. The image hints at craters on the surface of Ceres. Dawn framing camera took this image at 238,000 miles 383,000 kilometers from Ceres. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19167
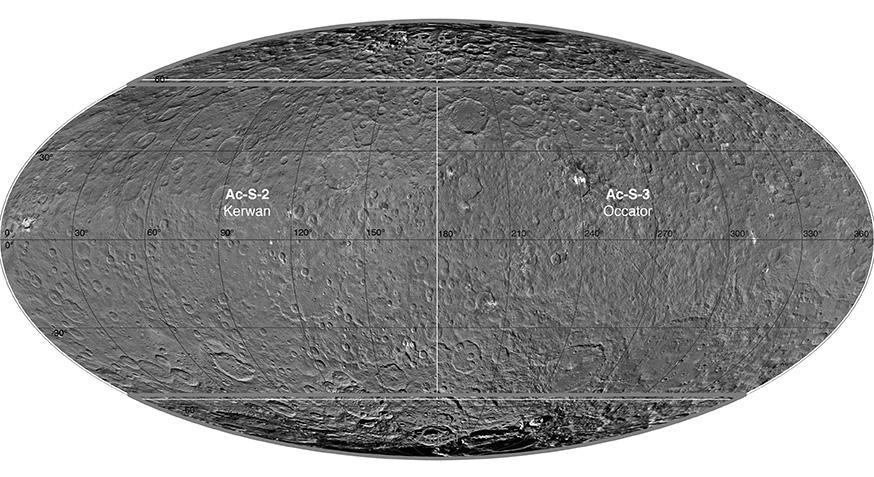

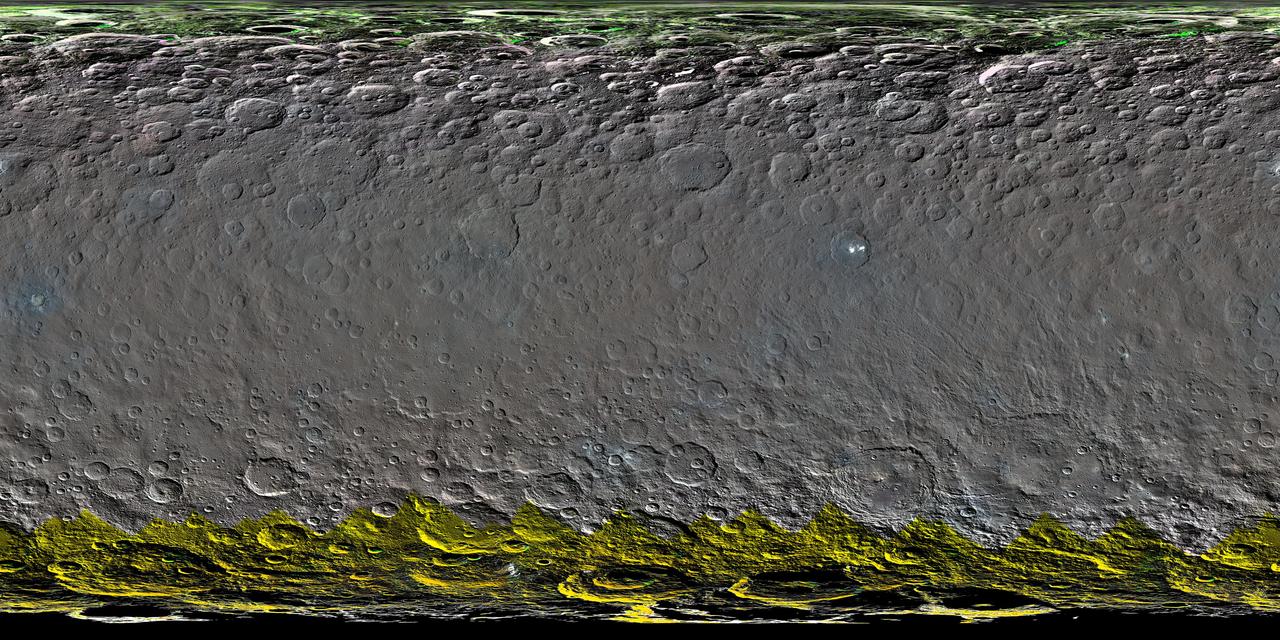
This atlas of Ceres was created using images taken by NASA Dawn spacecraft in June 2015. Researchers used 12,000 points on Ceres to construct a terrain model, which served as the basis for other maps. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20014
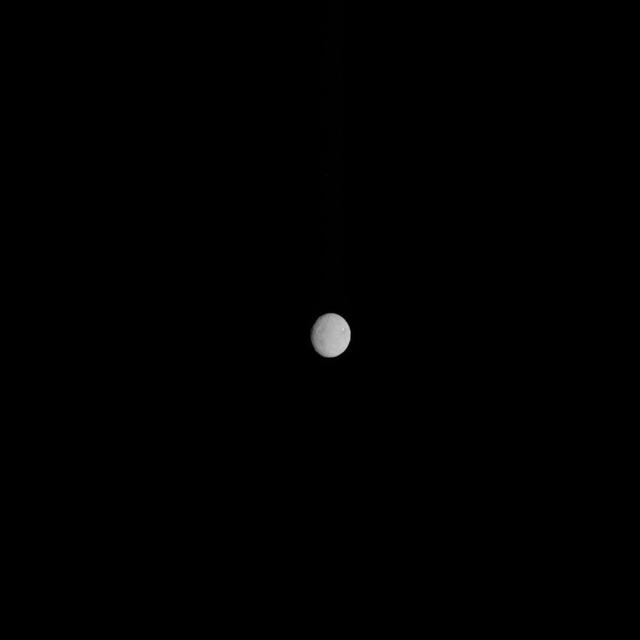

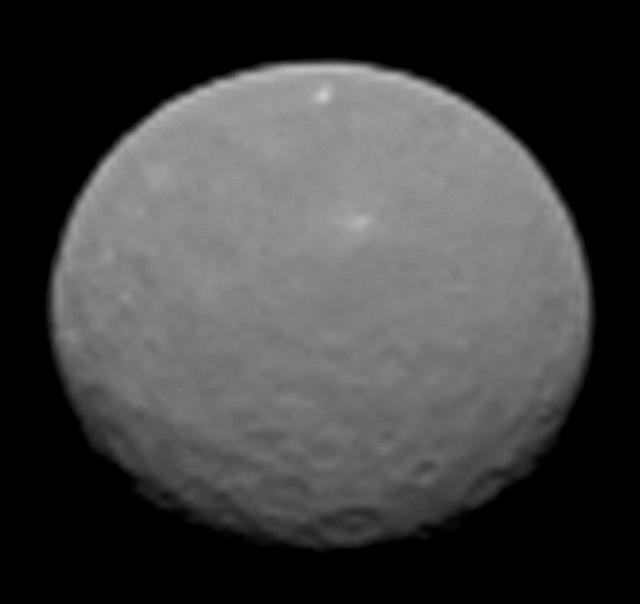
In this image, dwarf planet Ceres is seen on Feb. 4, 2015, from a distance of about 90,000 miles 145,000 kilometers. NASA Dawn spacecraft is due to arrive at Ceres on March 6, 2015. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19181
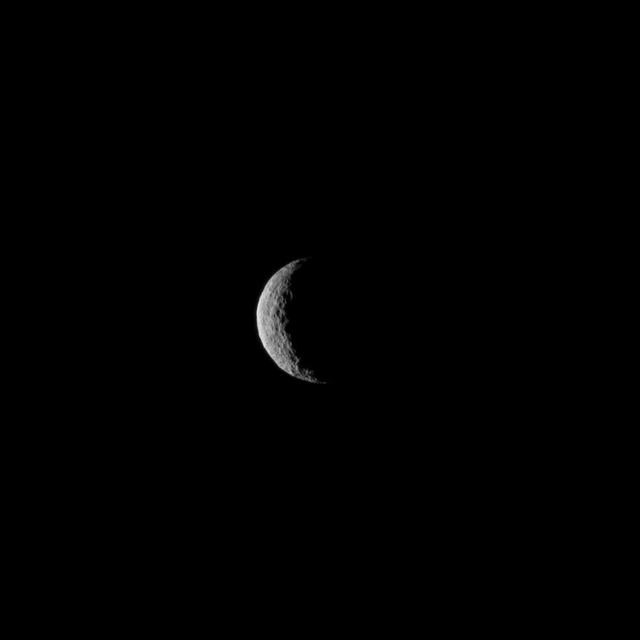

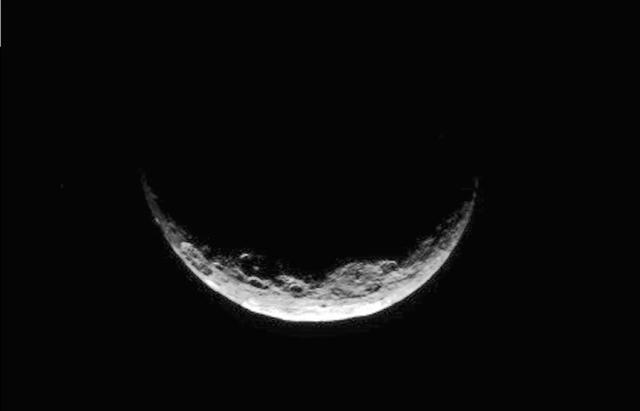
The slim crescent of Ceres smiles back as the dwarf planet awaits the arrival of an emissary from Earth. This image was taken by NASA's Dawn spacecraft on March 1, 2015, just a few days before the mission achieved orbit around the previously unexplored world. Following the image sequence in which this view was acquired, the Dawn spacecraft slipped over to the dark side -- that is, the far side of Ceres with respect to the sun. The spacecraft is slated to resume imaging of Ceres' surface in mid-April, when it once again views lit terrain on Ceres. The image was obtained at a distance of about 30,000 miles (about 48,000 kilometers) at a sun-Ceres-spacecraft angle, or phase angle, of 123 degrees. Image scale on Ceres is 1.9 miles (2.9 kilometers) per pixel. Ceres has an average diameter of about 590 miles (950 kilometers). http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19312

NASA's Dawn spacecraft has revealed many landslides on Ceres, which researchers interpret to have been shaped by a significant amount of water ice. A 2017 study in the journal Nature Geoscience classifies three types of these debris flows. Image 1 (left in the montage) shows an example of "Type I" flow features, which are relatively round and large, have thick "toes" at their ends. They look similar to rock glaciers and icy landslides on Earth. Type I landslides are mostly found at high latitudes, which is also where the most ice is thought to reside near Ceres' surface. Image 2 (center) shows an example of a "Type II" flow feature. Type II features are often thinner and longer than Type I, and are the most common type of landslide on Ceres. They appear more like the avalanches seen on Earth. Image 3 (right) shows an example of a "Type III" flow feature at Datan Crater. The study authors interpret Ceres' Type III landslides to involve melted ice, although scientists do not know if they actually contain liquid water. The authors think Type III landslides are related to impact craters, and may have formed during impact events into the ice on Ceres. The features resemble fluid material ejected from craters in the icy regions of Mars and Jupiter's moon Ganymede. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21471

This is a raw image, taken Jan. 13, 2015, showing the dwarf planet Ceres as seen from the Dawn spacecraft on its approach. Dawn framing camera took this image at 238,000 miles 383,000 kilometers from Ceres. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19166
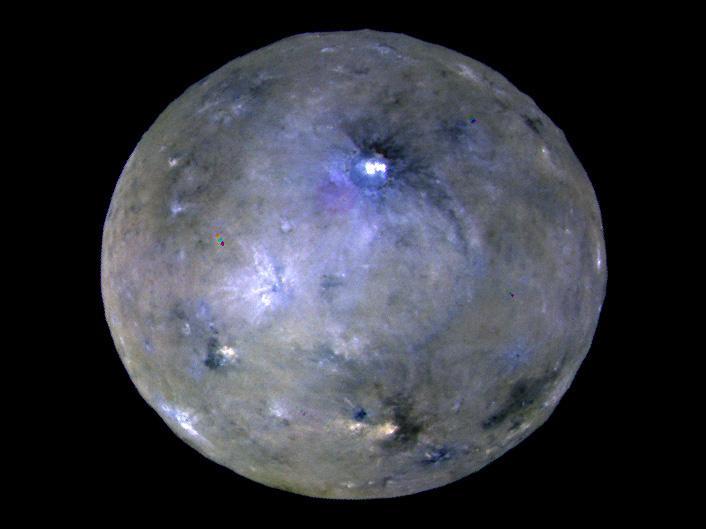
This enhanced color image of Ceres' surface was made from data obtained on April 29, 2017, when NASA's Dawn spacecraft was exactly between the sun and Ceres. Dawn's framing cameras took images of Ceres with a clear filter as well as five different color filters. Images combining these different color filter perspectives reveal fine details of Ceres' surface. For example, they emphasize the distinct compositions and textures of the material ejected from craters. The brightest region on Ceres, called Cerealia Facula, is highlighted in Occator Crater in the center of this image. Vinalia Faculae, the set of secondary bright spots in the same crater, are located to the right of Cerealia Facula. One of the darkest regions on Ceres is next to Occator, and represents ejected material from the impact that formed the crater. The ejected material forms a large arc that extends over several hundred kilometers, below the center of Ceres in this image. That material's distribution is partly determined by Ceres' rotation. Other craters also show a mixture of bright and dark regions. While the bright areas are generally identified as salt-rich material excavated from Ceres' crust, the origin of the dark material remains to be explained. It may have been excavated from a different layer within Ceres' subsurface than the rest of the ejecta blanket. Scientists will continue analyzing the color data to look for clues about the nature of the different materials on Ceres. The blueish color is generally found in association with young craters. Scientists believe the color relates to processes that occur when an impact ejects and redistributes material on the surface. The continuous bombardment of Ceres' surface by micrometeorites alters the texture of the exposed material, leading to its reddening. This image was taken altitude of about 12,000 miles (20,000 kilometers). https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21406

This frame from an animation of the dwarf planet Ceres was made by combining images taken by the Dawn spacecraft on January 25, 2015. These images of Ceres, and they represent the highest-resolution views to date of the dwarf planet. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19171

These images, from Dawn's visible and infrared mapping spectrometer (VIR), highlight two regions on Ceres containing bright spots. The top images feature a bright spot scientists have labeled "1" (located at around 4 degrees north, 8 degrees east on Ceres' surface); the bottom images feature the spot labeled "5" (located at around 20 degrees north, 240 degrees east). Spot 5 actually contains two spots, which are the brightest on Ceres. Each row shows Ceres' surface at different wavelengths. At left are images taken in visible light, close to wavelengths seen by the human eye. The center images show the same regions of Ceres in wavelengths shifted to the infrared range. The two images at right show Ceres in thermal infrared, where brighter colors represent higher temperatures. During Dawn's arrival at Ceres, VIR has been examining the relative temperatures of features on the dwarf planet's surface. Preliminary examination suggests that region 1 is cooler than the rest of Ceres' surface, but region 5 appears to be located in a region that is similar in temperature to its surroundings. The images were captured on February 19, 2015, when Dawn was nearly 29,000 miles (46,000 kilometers) from Ceres. Image scale on Ceres is about 7 miles (11 kilometers) per pixel. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19316
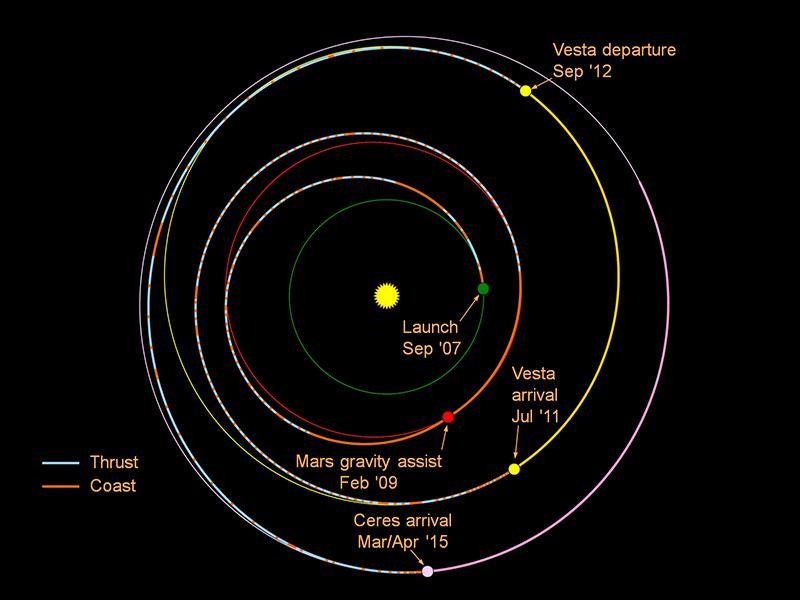
This graphic shows the planned trek of NASA Dawn spacecraft from its launch in 2007 through its arrival at the dwarf planet Ceres in early 2015.

From about three times the distance from Earth to the moon, NASA's Dawn spacecraft spies its final destination -- the dwarf planet Ceres. The resolution of this image does not yet exceed the best views of Ceres, which were obtained by the Hubble Space Telescope (see PIA10235). Nonetheless, Ceres' spherical shape is clearly revealed here. Sunlight illuminates the dwarf planet from the right, leaving a sliver of the surface in shadow at left. A zoomed-in view is provided in Figure 1, along with the original unmagnified, uncropped view. The image was taken on Dec. 1, 2014 with the Dawn spacecraft's framing camera, using a clear spectral filter. Dawn was about 740,000 miles (1.2 million kilometers) from Ceres at the time. Ceres is 590 miles (950 kilometers) across and was discovered in 1801. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19049
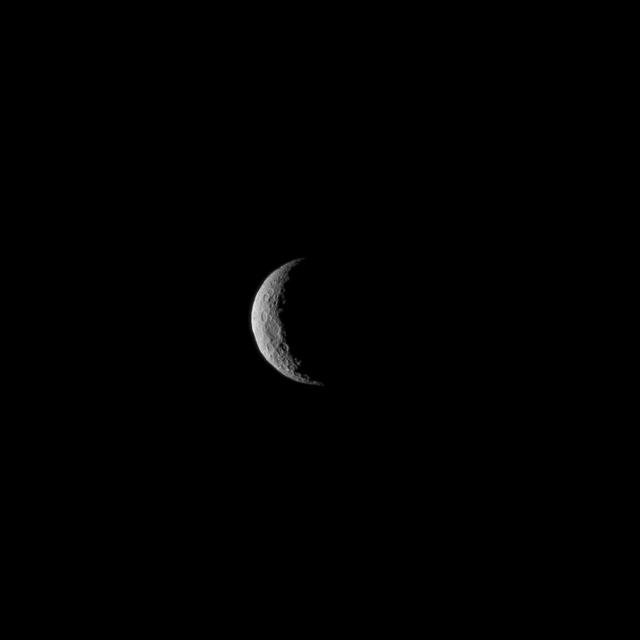

The slim crescent of Ceres smiles back as the dwarf planet awaits the arrival of an emissary from Earth. This image was taken by NASA's Dawn spacecraft on March 1, 2015, just a few days before the mission achieved orbit around the previously unexplored world. Following the image sequence in which this view was acquired, the Dawn spacecraft slipped over to the dark side -- that is, the far side of Ceres with respect to the sun. The spacecraft is slated to resume imaging of Ceres' surface in mid-April, when it once again views lit terrain on Ceres. The image was obtained at a distance of about 30,000 miles (about 48,000 kilometers) at a sun-Ceres-spacecraft angle, or phase angle, of 123 degrees. Image scale on Ceres is 1.9 miles (2.9 kilometers) per pixel. Ceres has an average diameter of about 590 miles (950 kilometers). http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19311
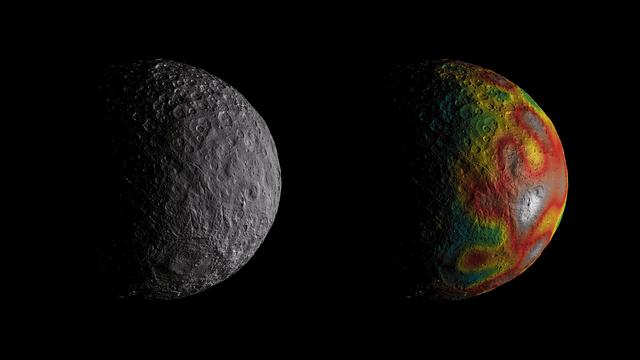
This frame from an animation shows Ceres as seen by NASA's Dawn spacecraft from its high-altitude mapping orbit at 913 miles (1,470 kilometers) above the surface. The colorful map overlaid at right shows variations in Ceres' gravity field measured by Dawn, and gives scientists hints about the dwarf planet's internal structure. Red colors indicate more positive values, corresponding to a stronger gravitational pull than expected, compared to scientists' pre-Dawn model of Ceres' internal structure; blue colors indicate more negative values, corresponding to a weaker gravitational pull. The animation was created by projecting a map of Ceres onto a rotating sphere. The image scale is about 450 feet (140 meters) per pixel. The animations are available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22083

These images of dwarf planet Ceres, processed to enhance clarity, were taken on Feb. 19, 2015, from a distance of about 29,000 miles 46,000 kilometers, by NASA Dawn spacecraft. Dawn observed Ceres completing one full rotation, lasting about nine hours. The images show the full range of different crater shapes that can be found at Ceres' surface: from shallow, flattish craters to those with peaks at their centers. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19183
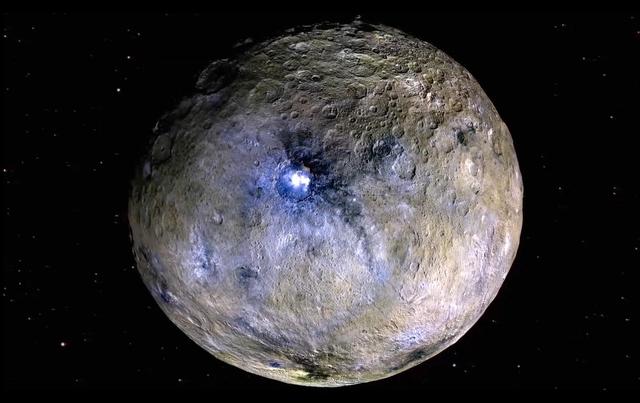

This frame from a video from NASA's Dawn mission shows dwarf planet Ceres in false-color renderings, which highlight differences in surface materials. Images were used to create a movie of Ceres rotating, followed by a flyover view of Occator Crater, home of Ceres' brightest area. A video is available at http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20182

NASA Dawn spacecraft obtained these uncropped images of dwarf planet Ceres on Feb. 19, 2015, from a distance of about 29,000 miles 46,000 kilometers. The images show the full range of different crater shapes that can be found at Ceres surface.
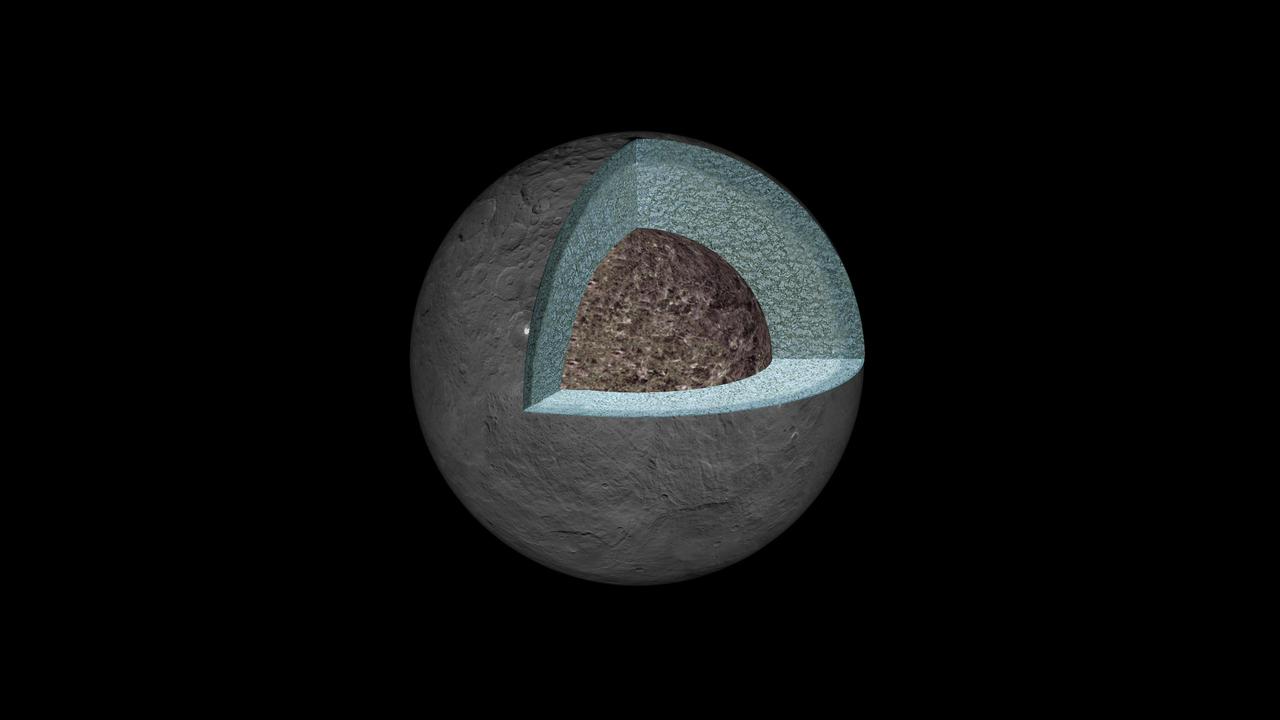
This artist's concept shows a diagram of how the inside of Ceres could be structured, based on data about the dwarf planet's gravity field from NASA's Dawn mission. Using information about Ceres' gravity and topography, scientists found that Ceres is "differentiated," which means that it has compositionally distinct layers at different depths. The densest layer is at the core, which scientists suspect is made of hydrated silicates. Above that is a volatile-rich shell, topped with a crust of mixed materials. This research teaches scientists about what internal processes could have occurred during the early history of Ceres. It appears that, during a heating phase early in the history of Ceres, water and other light materials partially separated from rock. These light materials and water then rose to the outer layer of Ceres. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20867
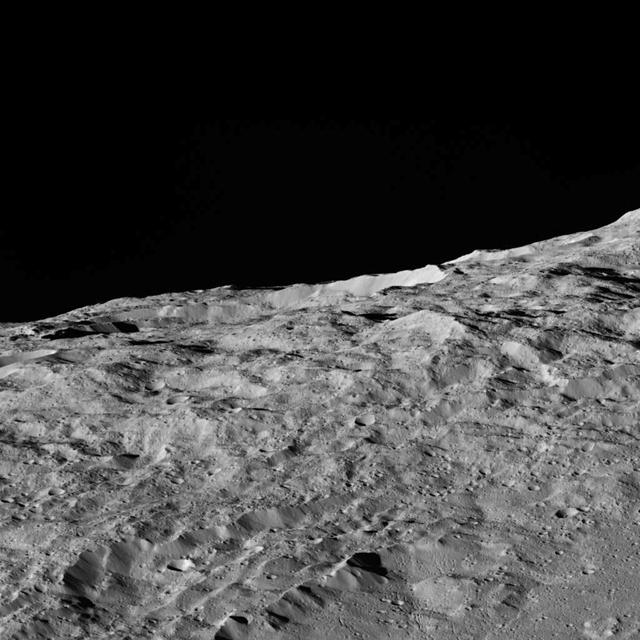

These views of Ceres, taken by NASA Dawn spacecraft on December 10, show an area in the southern part of the southern hemisphere of the dwarf planet.

This frame from an animation comes from NASA Dawn spacecraft as it observed Ceres for an hour on Jan. 13, 2015, from a distance of 238,000 miles 383,000 kilometers. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19168

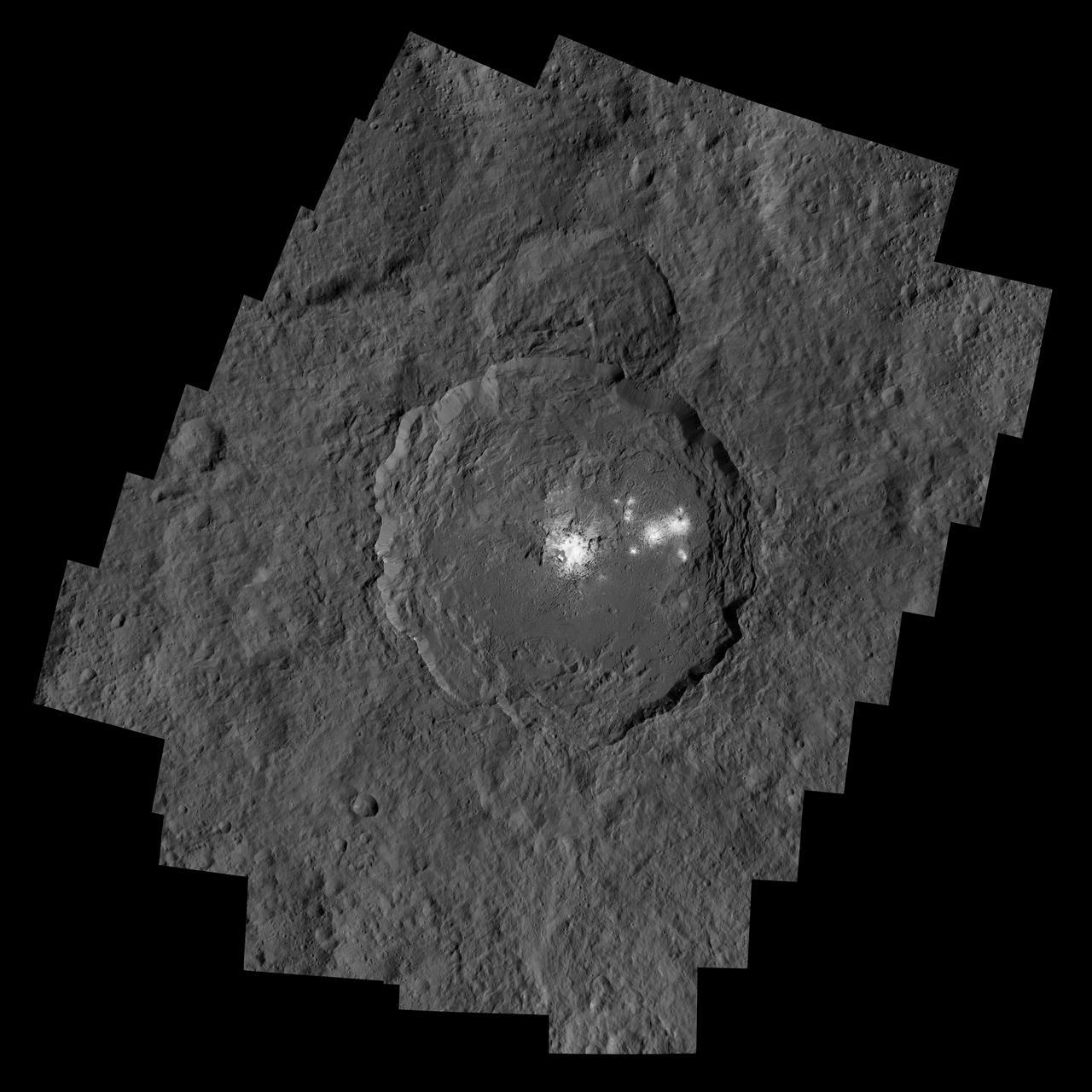
This orthographic projection shows dwarf planet Ceres as seen by NASA's Dawn spacecraft. The projection is centered on Occator Crater, home to the brightest area on Ceres. Occator is centered at 20 degrees north latitude, 239 degrees east longitude. This image was made from views Dawn took during its low-altitude mapping orbit, at about 240 miles (385 kilometers) above the surface. The image resolution is about 460 feet (140 meters) per pixel. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21906

This map from NASA's Dawn mission shows locations of bright material on dwarf planet Ceres. There are more than 300 bright areas, called "faculae," on Ceres. Scientists have divided them into four categories: bright areas on the floors of crater (red), on the rims or walls of craters (green), in the ejecta blankets of craters (blue), and on the flanks of the mountain Ahuna Mons (yellow). https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21914
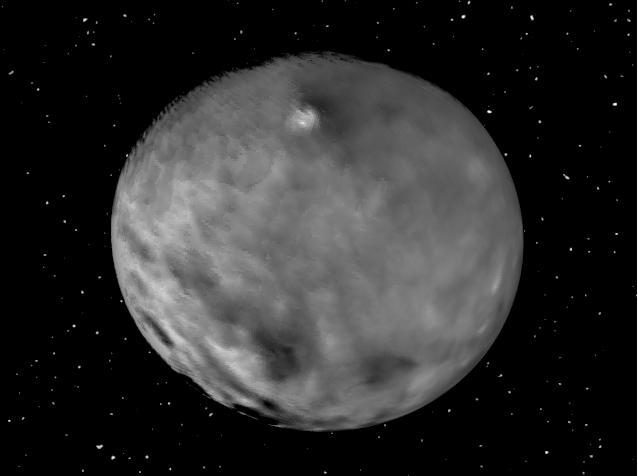

This still from an animation showcases a series of images NASA Dawn spacecraft took on approach to Ceres on Feb. 4, 2015 at a distance of about 90,000 miles 145,000 kilometers from the dwarf planet.

This still from an animation showcases a series of images NASA Dawn spacecraft took on approach to Ceres on Feb. 4, 2015 at a distance of about 90,000 miles 145,000 kilometers from the dwarf planet. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19179

This frame from an animated sequence of images shows northern terrain on the sunlit side of dwarf planet Ceres as seen by NASA Dawn spacecraft on April 14 and 15, 2015.

This image is one several images NASA Dawn spacecraft took on approach to Ceres on Feb. 4, 2015 at a distance of about 90,000 miles 145,000 kilometers from the dwarf planet. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19179
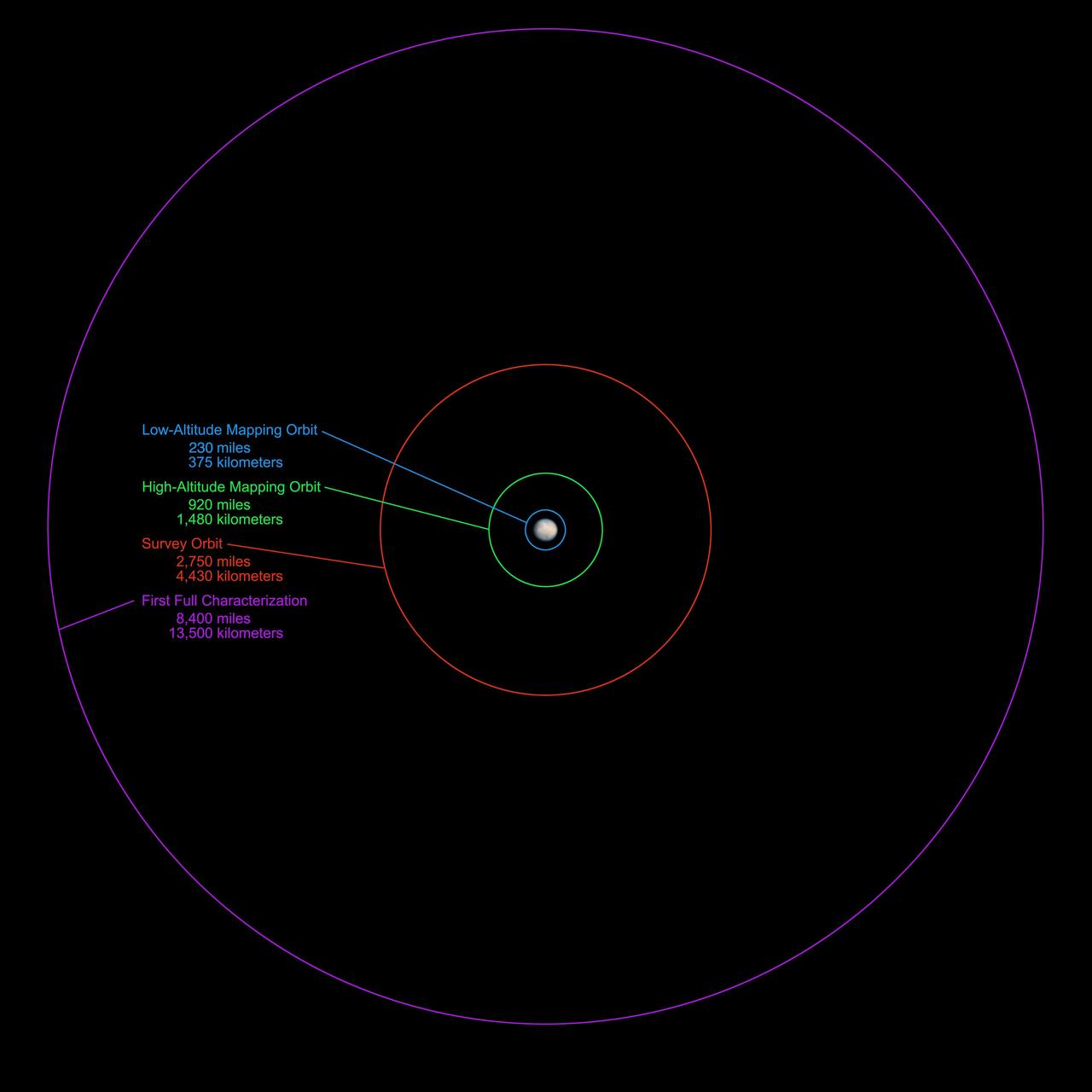
NASA Dawn spacecraft will be getting an up-close look at the dwarf planet Ceres starting in late March or the beginning of April 2015. This graphic shows the science-gathering orbits planned for the spacecraft.

This artist's rendering shows NASA's Dawn spacecraft maneuvering above Ceres with its ion propulsion system. Dawn arrived into orbit at Ceres on March 6, 2015, and continues to collect data about the mysterious and fascinating world. The mission celebrated its ninth launch anniversary on September 27, 2016. This illustration is an update to PIA18921, which was produced before Dawn had mapped Ceres' surface. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20919

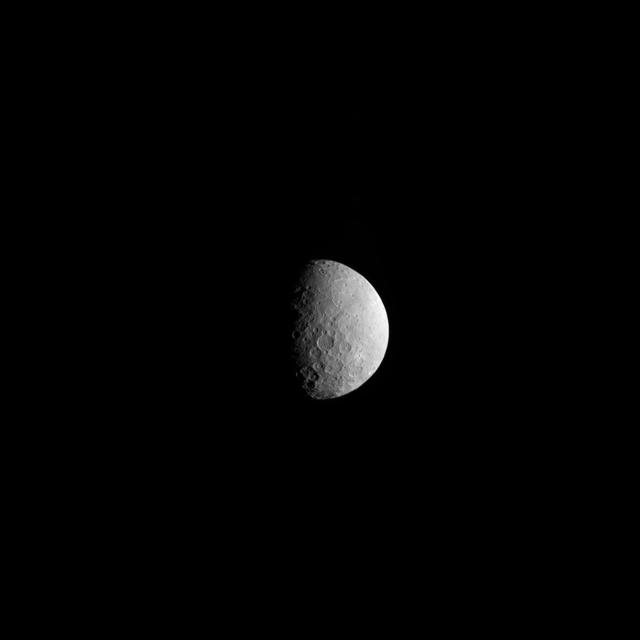
NASA's Dawn spacecraft took these images of dwarf planet Ceres from about 25,000 miles (40,000 kilometers) away on Feb. 25, 2015. Ceres appears half in shadow because of the current position of the spacecraft relative to the dwarf planet and the sun. The resolution is about 2.3 miles (3.7 kilometers) per pixel. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19310
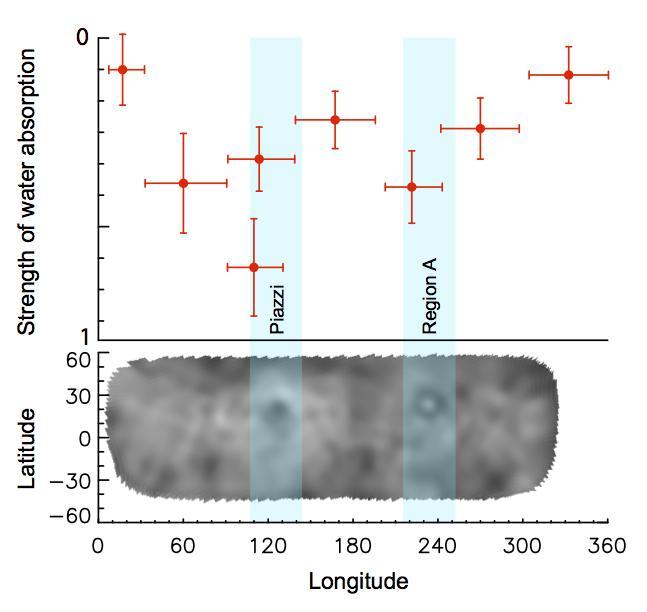
This graph shows variability in the intensity of the water absorption signal detected at Ceres by the Herschel space observatory on March 6, 2013.
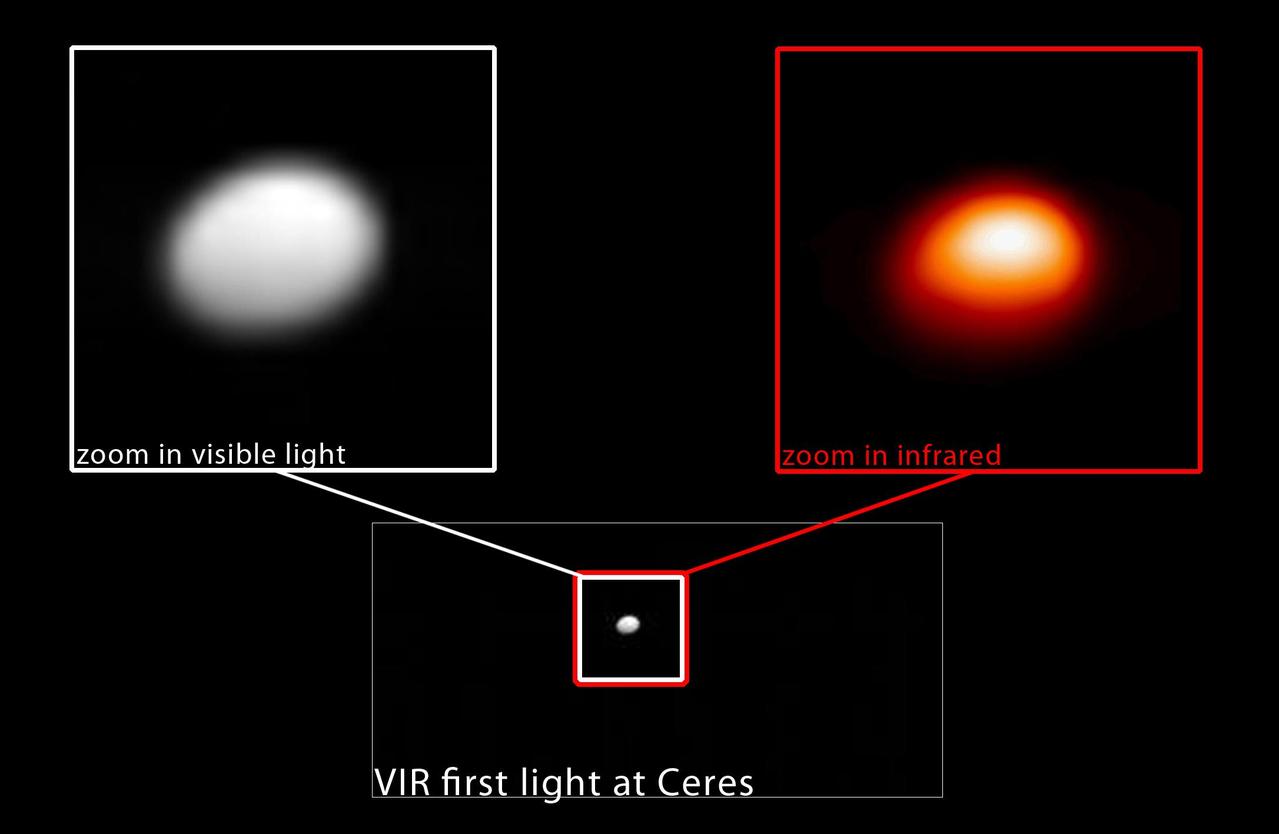
In this image, taken January 13, 2015, NASA Dawn spacecraft captures the dwarf planet Ceres in both visible and infrared light. The infrared image, right, serves as a temperature map of Ceres, where white is warmer and red is colder. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19169

NASA's Dawn spacecraft took this image of Ceres' south polar region on May 17, 2017, from an altitude of about 26,400 miles (42,500 kilometers). The image scale is about 2.5 miles (4 kilometers) per pixel. Dawn took this image to help navigators refine their measurements of the spacecraft's position in orbit. Ceres appears as a crescent as Dawn is on the night side of the dwarf planet. Zadeni Crater, which is 80 miles (128 kilometers) wide, is recognizable on the bottom left side of the crescent. The large crater seen on the right side is Urvara Crater, which is 101 miles (163 kilometers) wide. Large fractures scarring Ceres' surface can also be distinguished here. Dawn captured a similar scene (Figure 1) at higher resolution, although with a slightly different geometry, on April 26, 2015, from its RC3 orbit at an altitude of about 8,450 miles (13,600 kilometers) and an image scale of about 0.81 miles (1.3 kilometers) per pixel. The geology of Ceres' polar regions is very rough in comparison to that generally found at lower latitudes. This is because colder temperatures near the poles allow craters to hold their original shapes over longer periods of time. Features found on Ceres are named after gods and goddesses of agriculture, as well as harvest festivals, from around the world. Zadeni is named for the ancient Georgian god of bountiful harvest, while Urvara is an Indian and Iranian deity of plants and fields. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21407

NASA's Dawn spacecraft successfully observed Ceres at opposition on April 29, 2017, taking images from a position exactly between the sun and Ceres' surface. Mission specialists had carefully maneuvered Dawn into a special orbit so that the spacecraft could view Occator Crater, which contains the brightest area of Ceres, from this new perspective. A movie shows these opposition images, with contrast enhanced to highlight brightness differences. The bright spots of Occator stand out particularly well on an otherwise relatively bland surface. Dawn took these images from an altitude of about 12,000 miles (20,000 kilometers). Based on data from ground-based telescopes and spacecraft that have previously viewed planetary bodies at opposition, scientists predicted that Ceres would appear brighter from this opposition configuration. This increase in brightness, or "surge," relates the size of the grains of material on the surface, as well as how porous those materials are. The science motivation for performing these observations is further explained in the March 2017 issue of the Dawn Journal blog. A movie can be viewed at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21405
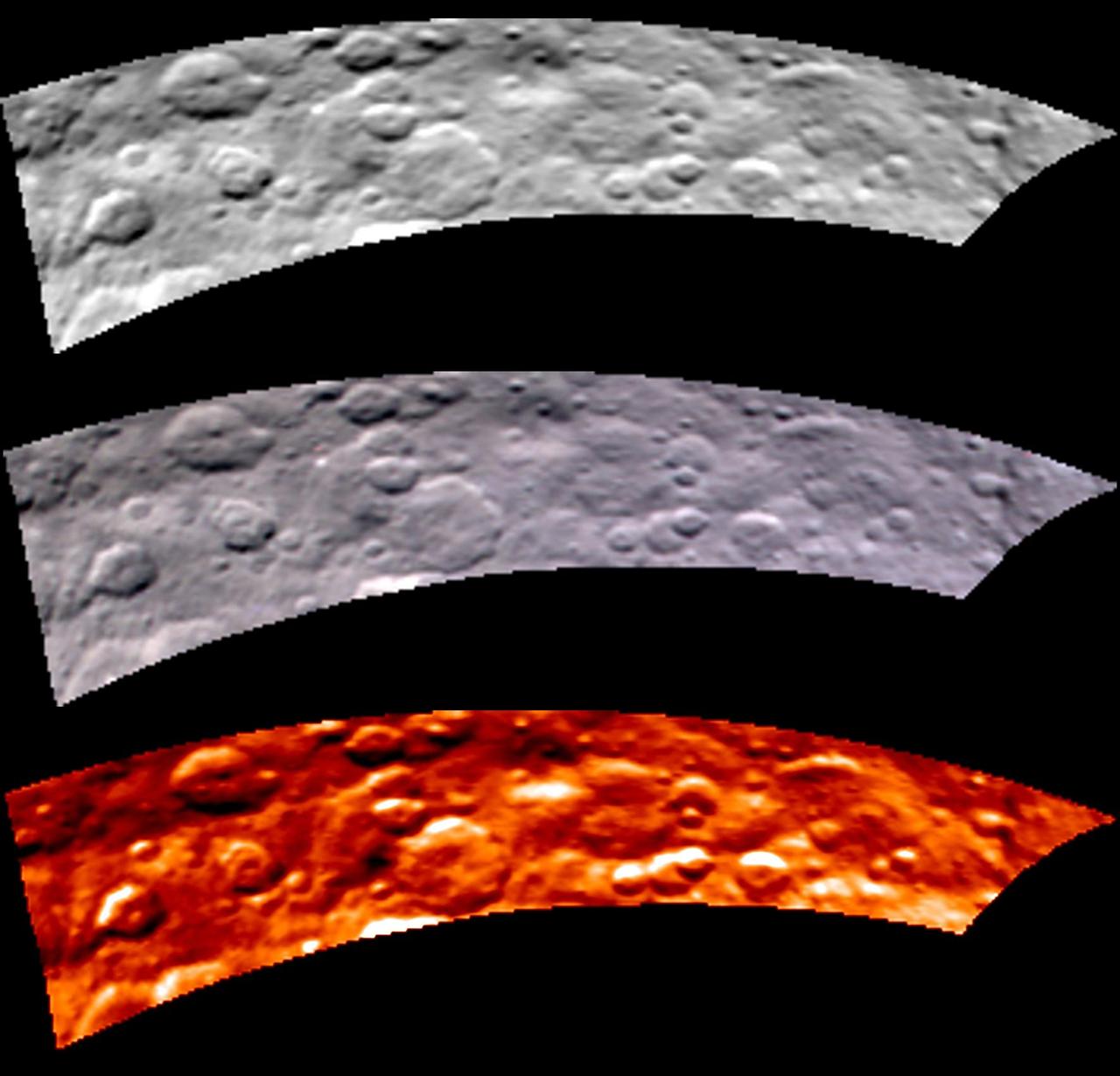
Images from Dawn's visible and infrared mapping spectrometer (VIR) show a portion of Ceres' cratered northern hemisphere, taken on May 16, 2015. From top to bottom, the views include a black-and-white image, a true-color view and a temperature image. The true-color view contains reddish dots that are image artifacts, which are not part of Ceres' surface. These images were taken at a distance of 4,500 miles (7,300 kilometers) from Ceres. They have a resolution of 1.1 miles (1.8 kilometers) per pixel. The temperature image is derived from data in the infrared light range. The lightest areas are the hottest and the darkest are the coolest. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19571

This image made with data from NASA's Dawn spacecraft shows pit chains on dwarf planet Ceres called Samhain Catenae. Scientists created this image by draping the grayscale mosaic of Ceres' surface onto the shape model of the dwarf planet. The arrows in the image point to a few of the pit chains investigated in a 2017 study in the journal Geophysical Research Letters. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22086
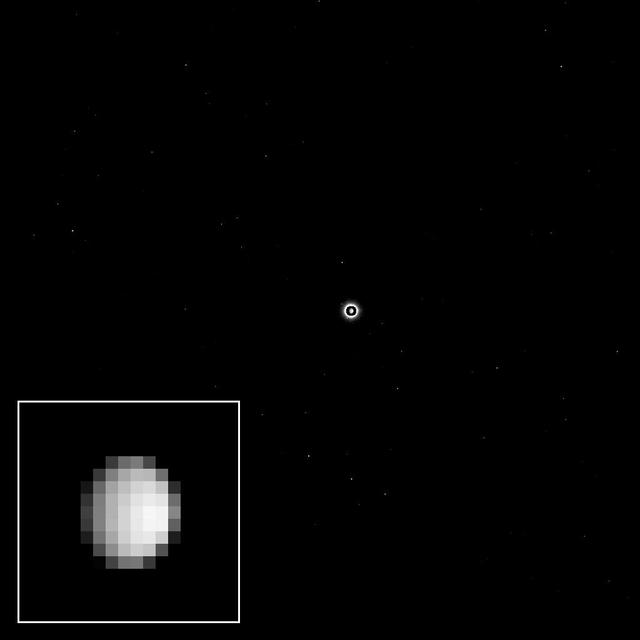

As the Dawn spacecraft flies through space toward the dwarf planet Ceres, the unexplored world appears to its camera as a bright light in the distance, full of possibility for scientific discovery. This view was acquired as part of a final calibration of the science camera before Dawn's arrival at Ceres. To accomplish this, the camera needed to take pictures of a target that appears just a few pixels across. On Dec. 1, 2014, Ceres was about nine pixels in diameter, nearly perfect for this calibration. The images provide data on very subtle optical properties of the camera that scientists will use when they analyze and interpret the details of some of the pictures returned from orbit. Ceres is the bright spot in the center of the image. Because the dwarf planet is much brighter than the stars in the background, the camera team selected a long exposure time to make the stars visible. The long exposure made Ceres appear overexposed, and exaggerated its size; this was corrected by superimposing a shorter exposure of the dwarf planet in the center of the image. A cropped, magnified view of Ceres appears in the inset image at lower left. The image was taken on Dec. 1, 2014 with the Dawn spacecraft's framing camera, using a clear spectral filter. Dawn was about 740,000 miles (1.2 million kilometers) from Ceres at the time. Ceres is 590 miles (950 kilometers) across and was discovered in 1801. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19050
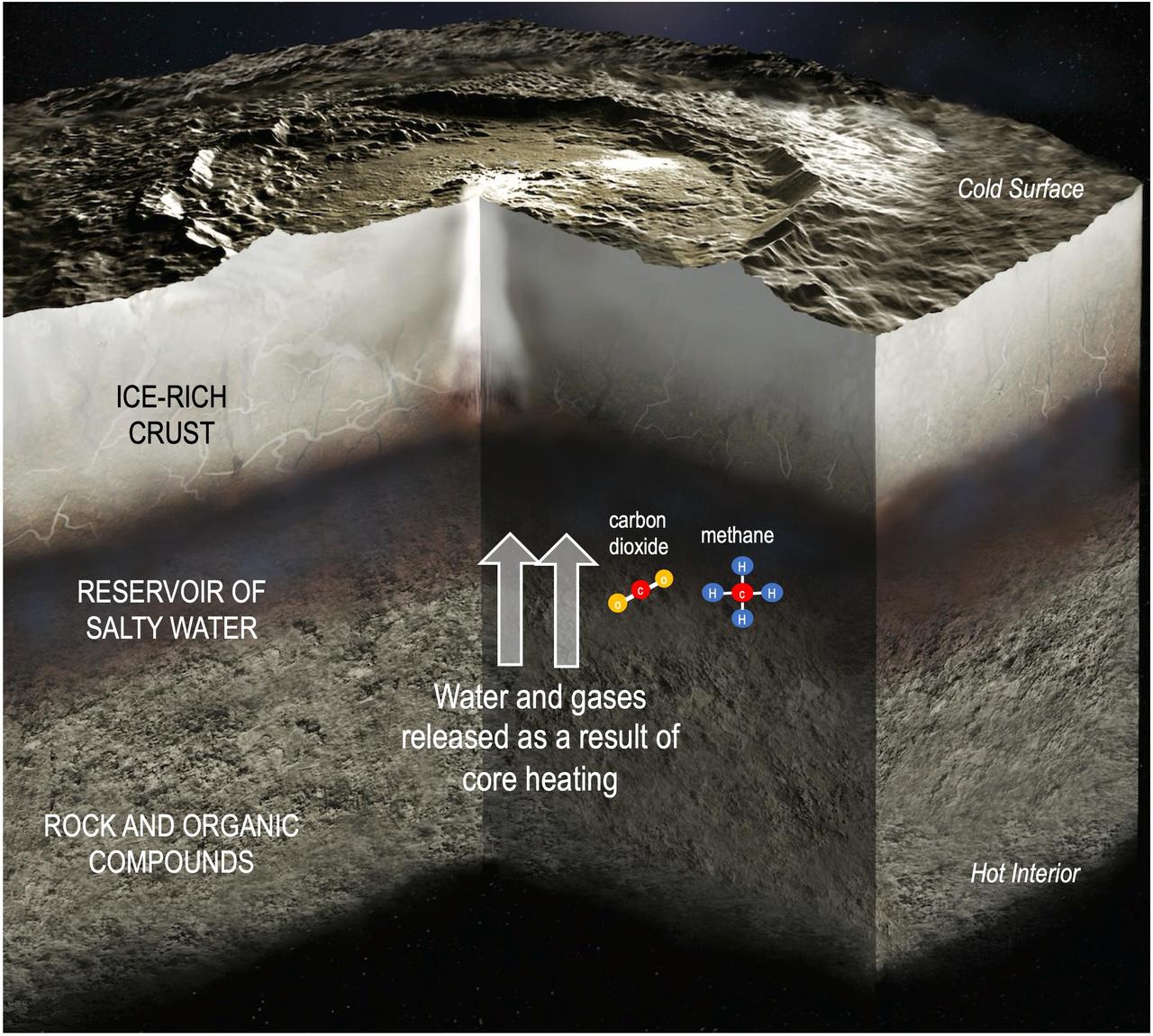
This illustration depicts the interior of dwarf planet Ceres, including the transfer of water and gases from the rocky core to a reservoir of salty water as a consequence of internal heating. A couple examples of molecules carrying chemical energy – carbon dioxide and methane – are included in the illustration. Research published in Science Advances on Aug. 20, 2025, relies on data from NASA's Dawn mission to find that chemical energy inside Ceres may have lasted long enough to fuel microbial metabolisms. Although there is no evidence that microorganisms ever existed on Ceres, the finding supports theories that this intriguing dwarf planet, which is the largest body in the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter, may have once had conditions suitable to support single-celled lifeforms. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26570
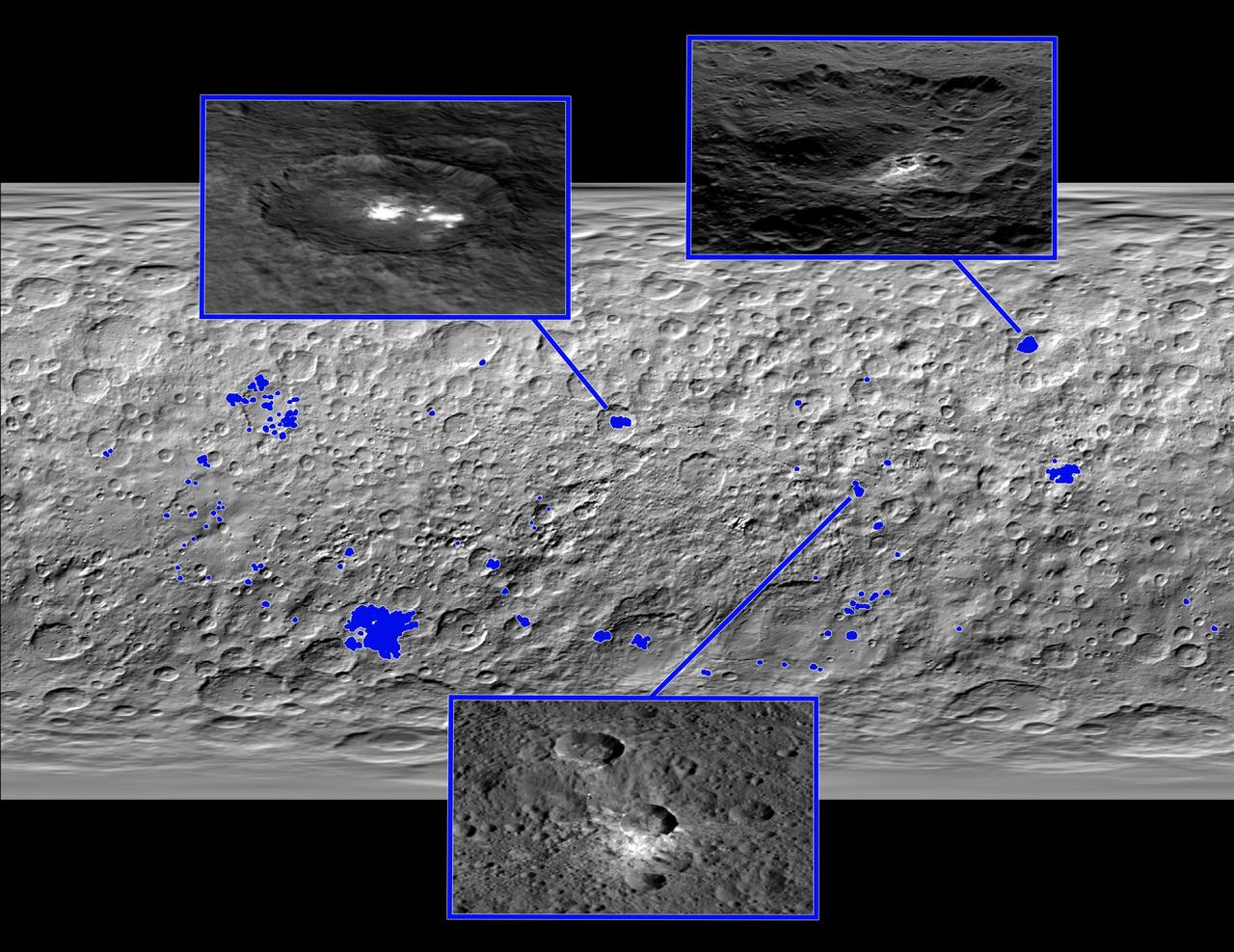
This map of Ceres, made from images taken by NASA's Dawn spacecraft, shows the locations of about 130 bright areas across the dwarf planet's surface, highlighted in blue. Most of these bright areas are associated with craters. Three insets zoom in on a few areas of interest. Occator Crater, containing the brightest area on Ceres, is shown at top left; Oxo Crater, the second-brightest feature on Ceres, is at top right. In a paper published in the Dec. 10, 2015, issue the journal Nature, Dawn mission scientists identify what they believe to be diffuse hazes at both Occator and Oxo. They believe the hazes appear when the sun shines on these craters, possibly from the sublimation of ice. A typical Ceres crater with bright material that does not appear to have remaining ice is shown at bottom. The bright material in this crater and others appears to originate from mineral salts that may have once been mixed with water ice, but dried up over time, scientists wrote in the same paper. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20183

Craters in the northern hemisphere of dwarf planet Ceres are seen in this image taken by NASA's Dawn spacecraft on June 6, 2015. This is among the first snapshots from Dawn's second mapping orbit, which is 2,700 miles (4,400 kilometers) in altitude. The resolution is 1,400 feet (410 meters) per pixel. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19570

This is a NASA Hubble Space Telescope color image of dwarf planet Ceres, the largest object in the asteroid belt. The contrast has been enhanced to reveal surface details.

NASA Dawn spacecraft captured Occator Crater, containing the brightest area on Ceres; this closeup reveals a dome in a smooth-walled pit in the bright center of the crater.

Dwarf planet Ceres is located in the main asteroid belt, between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter, as illustrated in this artist conception.

NASA's Dawn spacecraft took this picture as it reached its new orbit to observe Ceres in opposition, when Dawn is directly between the sun and the Occator Crater bright spots. Entering the very tight opposition geometry (explained here) is a major feat that requires extra checks for increased delivery accuracy. Hence, this picture was part of a series of images intended to help the navigation of the spacecraft relative to Ceres. This vantage point highlights the southern hemisphere of Ceres. Abundant polygonal craters can be seen, starting with Kerwan, Ceres' largest crater at 174 miles (280 kilometers) in diameter, in the upper right of Ceres' circular disc. Kerwan's rims appear subdued and its floor is relatively relaxed. The crater found almost in the "bullseye" of the crater is called Insitor (16 miles or 26 kilometers in diameter). The Inamahari and Homshuk craters featured here can be found at the top of the disc. Another large polygonal crater called Chaminuka (76 miles, 122 kilometers in diameter) is found toward the center. This map can be used to locate these and more features. The name "Kerwan" refers to the Hopi spirit of sprouting maize and "Chaminuka" to the Shona (Zimbabwe) spirit who provides rains in times of droughts. "Insitor" is named for the Roman agricultural deity in charge of the sowing. This picture was taken on April 17, 2017, from an altitude of about 28,000 miles (45,000 kilometers). https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21403

This artist concept shows NASA Dawn spacecraft heading toward the dwarf planet Ceres. When Dawn arrives, it will be the first spacecraft to go into orbit around two destinations in our solar system beyond Earth.

The surface of Ceres is covered with craters of many shapes and sizes, as seen in this frame from an animation of a map of the dwarf planet surface as seen by NASA Dawn spacecraft on Feb. 19, 2015.

The surface of Ceres is covered with craters of many shapes and sizes, as seen in this new mosaic of the dwarf planet comprised of images taken by NASA Dawn mission on Feb. 19, 2015 from a distance of nearly 29,000 miles 46,000 kilometers.

This is a frame from an animation showcasing a series of images NASA Dawn spacecraft took on approach to Ceres on Feb. 4, 2015 at a distance of about 90,000 miles 145,000 kilometers from the dwarf planet. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19182

This image, taken 147,000 miles 237,000 kilometers from Ceres on January 25, 2015 by NASA Dawn spacecraft, is part of a series of views representing the best look so far at the dwarf planet. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19172

NASA Dawn spacecraft flys over dwarf planet Ceres which Dawn has been orbiting for mre than a year, providing us with fascinating views of an alien world.

This image depicts the dwarf planet Ceres, as seen from the Dawn spacecraft. It was taken 147,000 miles 237,000 kilometers from Ceres on January 25, 2015, is part of a series of views representing the best look so far at the dwarf planet. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19173
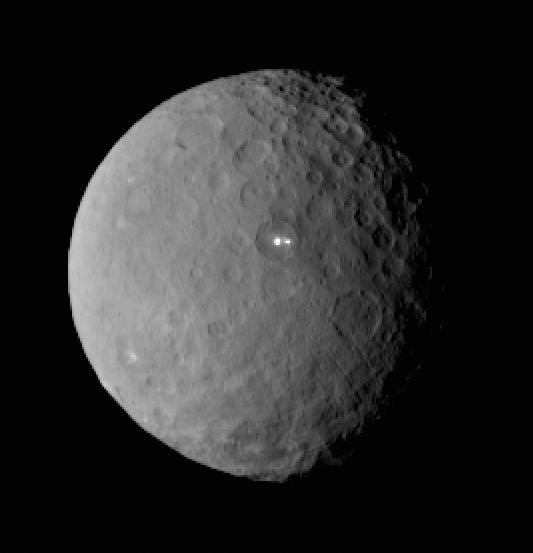

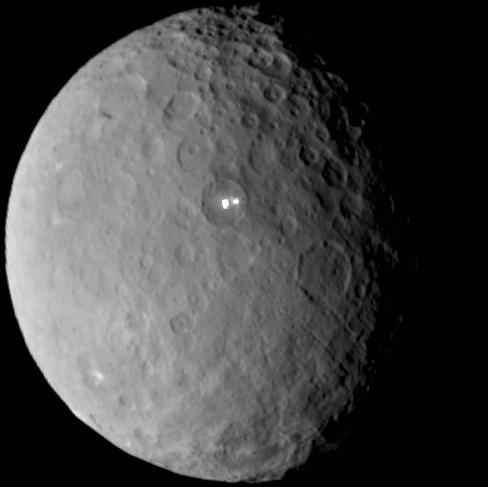
This image was taken by NASA Dawn spacecraft of dwarf planet Ceres on Feb. 19 from a distance of nearly 29,000 miles 46,000 kilometers. It shows that the brightest spot on Ceres has a dimmer companion, which apparently lies in the same basin. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19185

This map-projected view of Ceres was created from images taken by NASA's Dawn spacecraft during its high-altitude mapping orbit, in August and September, 2015. Images taken using infrared (920 nanometers), red (750 nanometers) and blue (440 nanometers) spectral filters were combined to create this false-color view. Redder colors indicate places on Ceres' surface that reflect light strongly in the infrared, while bluish colors indicate enhanced reflectivity at short (bluer) wavelengths; green indicates places where albedo, or overall brightness, is strongly enhanced. Scientists use this technique in order to highlight subtle color differences across Ceres, which would appear fairly uniform in natural color. This can provide valuable insights into the mineral composition of the surface, as well as the relative ages of surface features. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19977

This frame from an animation made of images from NASA's Dawn spacecraft shows a crater in the northern polar region of Ceres that is partly in shadow year-round. In several craters like this one, bright water ice deposits have been observed by Dawn's framing camera. This finding suggests that water ice can be stored for significant amounts of time in cold, dark craters on Ceres. Such reservoirs are called "cold traps." At less than minus 260 degrees Fahrenheit (110 Kelvin), they are so chilly that very little of the ice turns into vapor in the course of a billion years. A movie is available at http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21082

This collage shows some of the most interesting geological sites that NASA's Dawn spacecraft has revealed at dwarf planet Ceres. Images were acquired with the spacecraft's framing camera during various phases of the mission: Survey orbit at a distance of about 2,700 miles (4,400 kilometers); high-altitude mapping orbit (HAMO) at a distance of 915 miles (1,470 kilometers) from Ceres; and low-altitude mapping orbit (LAMO) at an altitude of 240 miles (385 kilometers). In the first row, from left to right: Ceres in shown in false color, roughly centered on Occator Crater, home of the brightest area on Ceres. This picture combines color images obtained by Dawn in its survey orbit. Red corresponds to a wavelength range around 980 nanometers (near infrared), green to a wavelength range around 750 nanometers (red, visible light) and blue to a wavelength range of around 430 nanometers (blue, visible light). This picture illustrates the diversity of terrains on Ceres where the bluish material points to recently emplaced material and the brownish background material is associated with older terrains. Juling Crater (12 miles, 20 kilometers in diameter) as seen in LAMO. Central coordinates are 36 degrees south latitude, 168 degrees east longitude. It is named after the Sakai/Orang Asli (Malaysia) spirit of the crops. This crater displays evidence for the presence of ice -- for example, in the form of a large flow feature seen at the top of the image. Oxo Crater (6 miles, 10 kilometers in diameter) as seen in LAMO. Center coordinates are 42 degrees north latitude, 0 degrees east longitude. It is named after the god of agriculture in Afro-Brazilian beliefs of Yoruba derivation. Oxo hosts the first site at which Dawn detected ice on Ceres, exposed by a landslide. Ahuna Mons is not only a volcano, but also the tallest mountain on Ceres. It is about 2.5 miles (4 kilometers) high and 11 miles (17 kilometers) wide. Center coordinates are 10 degrees south latitude, 316 degrees east longitude. This view combines images obtained in LAMO in blue (430 nanometers), green (750 nanometers) and infrared (980 nanometers) color filters. Ahuna is named after the Sumi tribe (Nagaland, northeastern India) traditional post-harvest thanksgiving festival. Second Row Occator Crater (57 miles, 92 kilometers across) is seen in LAMO images. Center coordinates are 20 degrees north latitude, 239 degrees east longitude. Named after the Roman agricultural deity of the harrowing. This image shows a "Type I" flow feature with a thick "toe" typical of rock glaciers and icy landslides on Earth as viewed in LAMO. The flow feature, found in Ghanan Crater (77 degrees north latitude, 31 degrees east longitude), is one of the most voluminous on Ceres. Enhanced color view of Haulani Crater (21 miles, 34 kilometers in diameter) in color observed in HAMO. Central coordinates: 6 degrees north latitude, 11 degrees east longitude. Named after the Hawaiian plant goddess. Kokopelli Crater (21 miles, 34 kilometers in diameter) seen in LAMO. Central coordinates: 18 degrees north latitude, 125 degrees east longitude. Named after the Pueblo (SW USA) fertility deity, who presides over agriculture. This crater displays a nice arrangement of scarps that likely formed when the crater partly collapsed during its formation. Third Row Central region of Occator Crater, called Cerealia Facula, seen in color. The facula -- or "bright spot" -- is about 9 miles (14 kilometers) in diameter. Center coordinates: 20 N, 240 E. Cerealia refers to the major festival in Ancient Rome that celebrates the grain goddess Ceres (8 days in mid- to late April). The view was produced by combining the highest resolution images of Occator obtained in LAMO (at image scales of 35 meters, or 115 feet, per pixel) with color images obtained in HAMO (at image scales of 135 meters, or about 440 feet, per pixel). The three images used to produce the color were taken using filters centered at 430, 750 and 980 nanometers (the last being slightly beyond the range of human vision, in the near-infrared). North part of Nar Sulcus seen in LAMO. The full feature is about 39 miles (63 km) in length and is located around 42 degrees south latitude, 280 degrees east longitude. Nar is a Azerbaijani festival of pomegranate harvest held in October-November in Goychay city, center of pomegranate cultivation in Azerbaijan. A sulcus is a set of parallel furrows or ridges. Ikapati Crater (31 miles, 50 kilometers in diameter) seen in LAMO. Central coordinates: 34 degrees north latitude, 46 degrees east longitude. Ikapati is named after the Philippine goddess of the cultivated lands. The crater has a smooth floor, probably because heat from the impact that formed Ikapati caused ice in the ground to melt, and then refreeze. This view of Ceres, taken in LAMO, shows an area located at approximately 86 degrees south longitude, 177 degrees east longitude. This part of Ceres, near the south pole, has such long shadows because, from the perspective of this location, the sun is near the horizon. At the time this image was taken, the sun was 4 degrees north of the equator. If you were standing this close to Ceres' south pole, the sun would never get high in the sky during the course of a nine-hour Cerean day. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22090
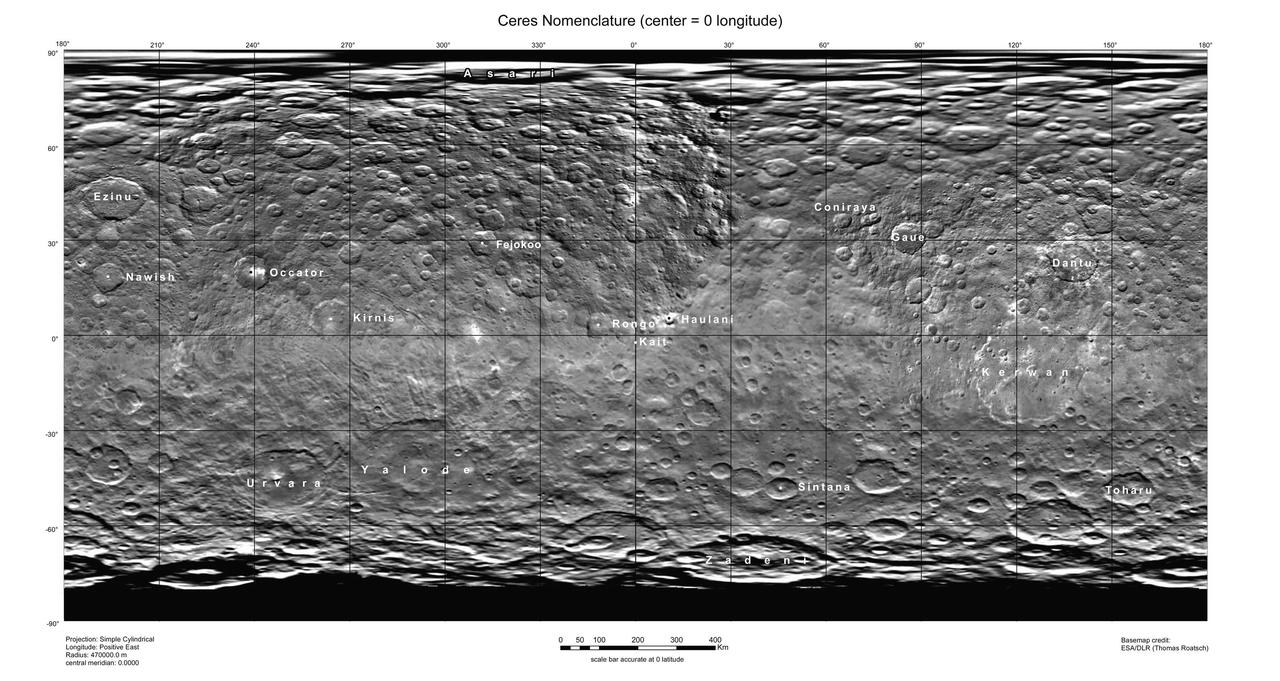
This map of Ceres, constructed from data collected by NASA's Dawn spacecraft, shows the dwarf planet's surface with features that have been named as of August 14, 2015. This is a simple cylindrical projection centered on 0 degrees east longitude, created by science team members at the German Aerospace Center (DLR). The most recently named feature is the small crater Kait, after the Hattic goddess of grain. It is a mere 0.2 miles (0.4 kilometers) across. A full list of crater names on Ceres is available at http://planetarynames.wr.usgs.gov/SearchResults%3Ftarget=CERES. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19625
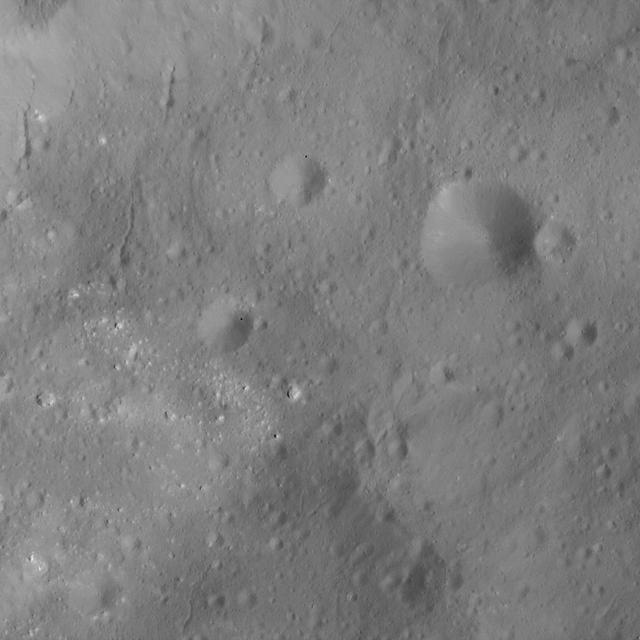

This image, obtained by NASA's Dawn spacecraft on June 9, 2018, shows subtle features on Ceres from an altitude of about 33 miles (53 kilometers). https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22523
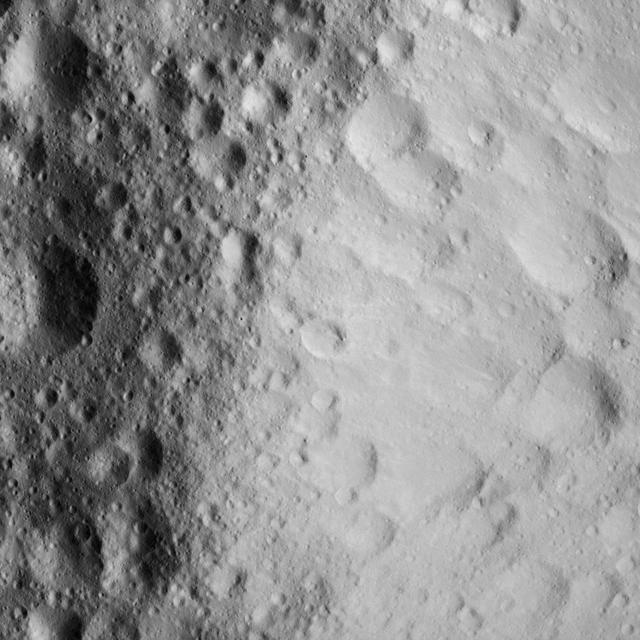

This image of a battered crater rim on Ceres was obtained by NASA's Dawn spacecraft on June 10, 2018 from an altitude of about 25 miles (40 kilometers). https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22531
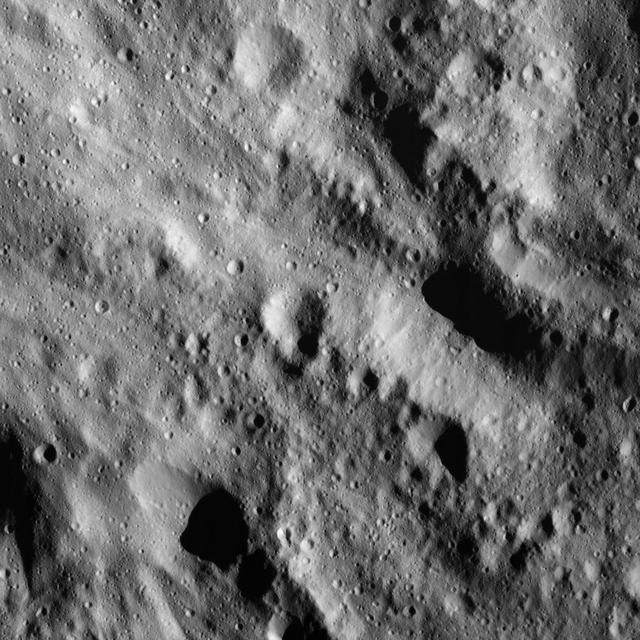

This image of smooth material on Ceres was obtained by NASA's Dawn spacecraft on June 9, 2018 from an altitude of about 41 miles (66 kilometers). https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22527
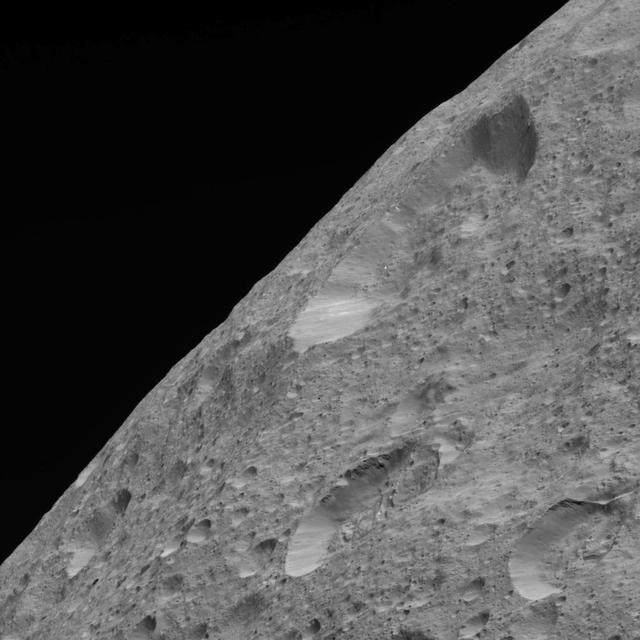

This image of Ceres' limb was obtained by NASA's Dawn spacecraft on May 30, 2018 from an altitude of about 280 miles (450 kilometers). https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22522
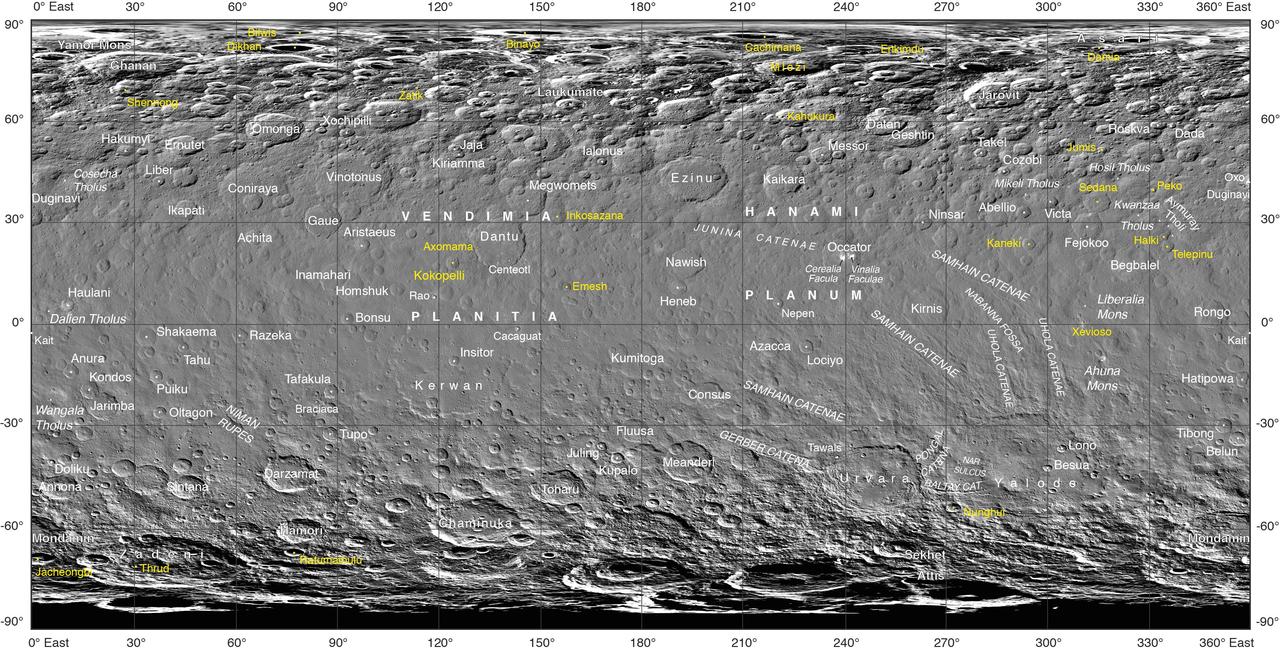
Often, the names of features on planetary bodies are connected through a specific theme -- for example, many features on the Moon have been named after famous scientists. NASA's Dawn mission, together with the International Astronomical Union, established that craters on Ceres would be named for agricultural deities from all over the world, and other features would be named for agricultural festivals. Ceres itself was named after the Roman goddess of corn and harvests by its discoverer, Giuseppe Piazzi, who spotted it with his telescope in 1801. Since March 2015, Dawn has been orbiting Ceres and sending back many intriguing images and other data about its features. Using suggestions from the Dawn team, the IAU recently approved 25 new Ceres feature names tied to theme of agricultural deities, marked in yellow on the map. Emesh Crater, for example, is named for the Sumerian god of vegetation and agriculture. Jumi is the Latvian god of fertility of the field. The newly named surface features vary in size. Thrud, for example, is a crater with a diameter of 4.8 miles (7.8 kilometers) within the larger crater Zadeni, while Mlezi has a diameter of 28 miles (42 kilometers). For more information, the characteristics of these and other features on Ceres can be found in the IAU's Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21755
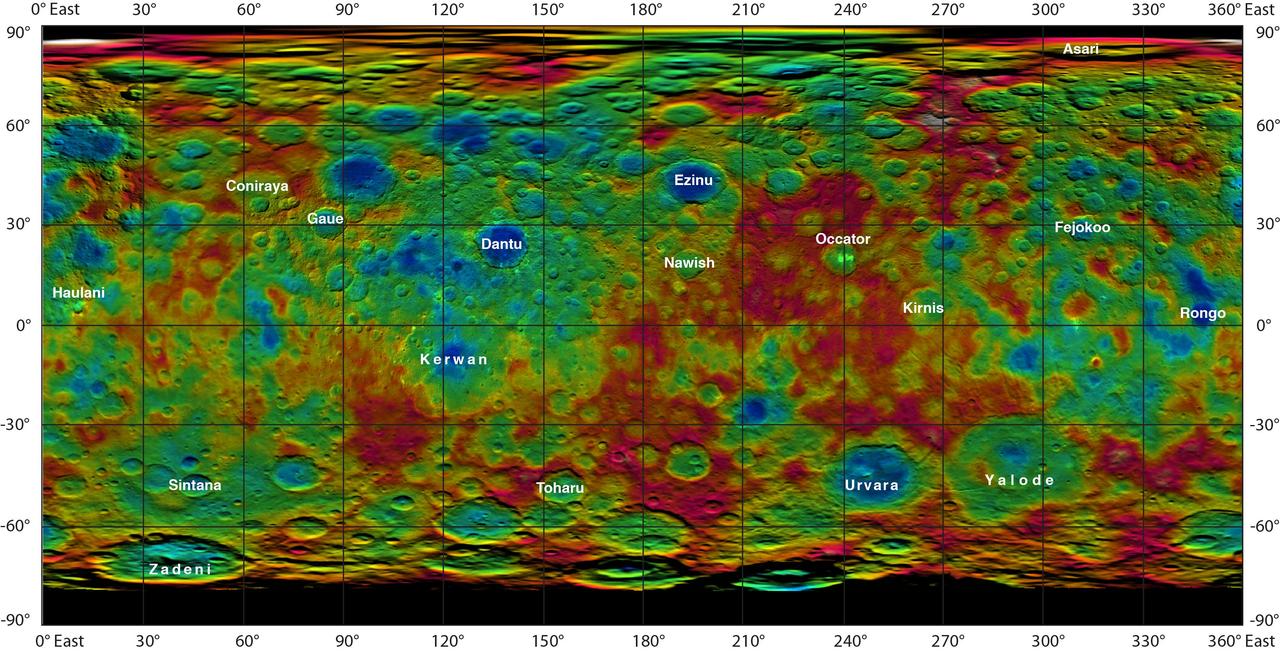
This color-coded map from NASA Dawn mission shows the highs and lows of topography on the surface of dwarf planet Ceres. It is labeled with names of features approved by the International Astronomical Union. Occator, the mysterious crater containing Ceres' mysterious bright spots, is named after the Roman agriculture deity of harrowing, a method of leveling soil. They retain their bright appearance in this map, although they are color-coded in the same green elevation of the crater floor in which they sit. The color scale extends about 5 miles (7.5 kilometers) below the surface in indigo to 5 miles (7.5 kilometers) above the surface in white. The topographic map was constructed from analyzing images from Dawn's framing camera taken from varying sun and viewing angles. The map was combined with an image mosaic of Ceres and projected as an simple cylindrical projection. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19606
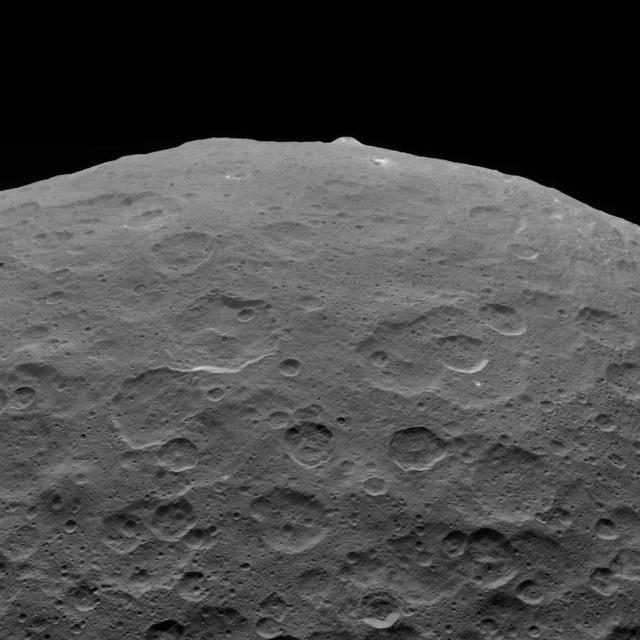

This photo of Ceres and one of its key landmarks, Ahuna Mons, was one of the last views Dawn transmitted before it depleted its remaining hydrazine and completed its mission. This view, which faces south, was captured on Sept. 1, 2018 at an altitude of 2,220 miles (3,570 kilometers) as the spacecraft was ascending in its elliptical orbit. At its lowest point, the orbit dipped down to only about 22 miles (35 kilometers), which allowed Dawn to acquire very high-resolution images in this final phase of its mission. Some of the close-up images of Ceres are shown here. Ahuna Mons is about 12 miles (20 kilometers) across and 2.5 miles (4 kilometers) high and displays sodium carbonate along its flanks. This is the most recent of a potential two dozen cryovolcanoes whose remnants are found across Ceres' surface. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22769

This frame from an animation shows a color-coded map from NASA Dawn mission revealing the highs and lows of topography on the surface of dwarf planet Ceres. The color scale extends 3.7 miles (6 kilometers) below the surface in purple to 3.7 miles (6 kilometers) above the surface in brown. The brightest features (those appearing nearly white) -- including the well-known bright spots within a crater in the northern hemisphere -- are simply reflective areas, and do not represent elevation. The topographic map was constructed from analyzing images from Dawn's framing camera taken from varying sun and viewing angles. The map was combined with an image mosaic of Ceres and projected onto a 3-D shape model of the dwarf planet to create the animation. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19605
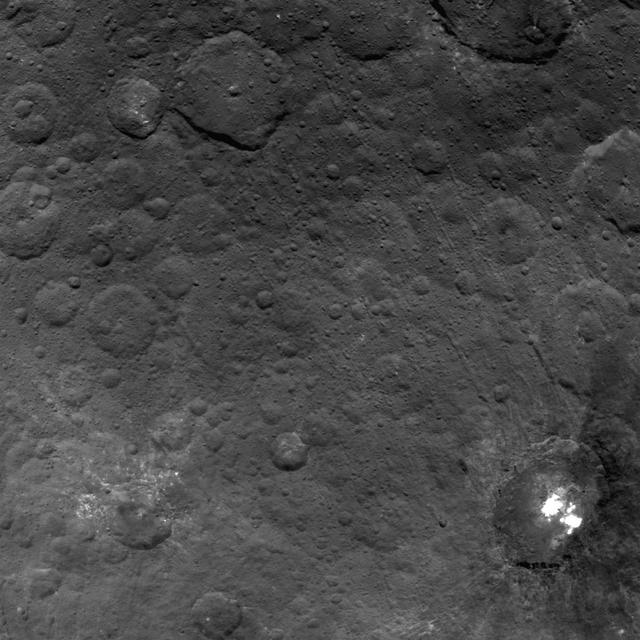

This image from NASA's Dawn spacecraft showing the northern part of Hanami Planum on Ceres honors the Japanese cherry blossom festival, or "Hanami," which is a long-standing Japanese tradition of welcoming spring. Hanami Planum is the third largest geological feature on Ceres, after Vendimia Planitia and the Samhain Catenae. It extends over 345 miles (555 kilometers). This image shows familiar features, such as Occator Crater, characterized both by bright material inside the crater and dark ejecta material outside. Several parallel linear features, called Junina Catenae, can be seen departing from Occator and extending toward the top of the image. These catenae are chains of small craters formed by the impact and scouring of material ejected when large craters are formed. Scientists were able to relate these crater chains to Urvara and Yalode. Even though these are located in the southern hemisphere, some of their ejecta could reach the northern hemisphere, thanks to Ceres' fast rotation and small size. This image was obtained by Dawn on June 15, 2015. The spacecraft was then in its survey orbit (2,700 miles, or 4,400 kilometers high), when the footprint of Dawns framing camera on Ceres surface was about 260 miles (420 kilometers). The resolution is 1,400 feet (410 meters) per pixel. The central coordinates of the picture are 14 degrees north latitude, 213 degrees east in longitude. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21921
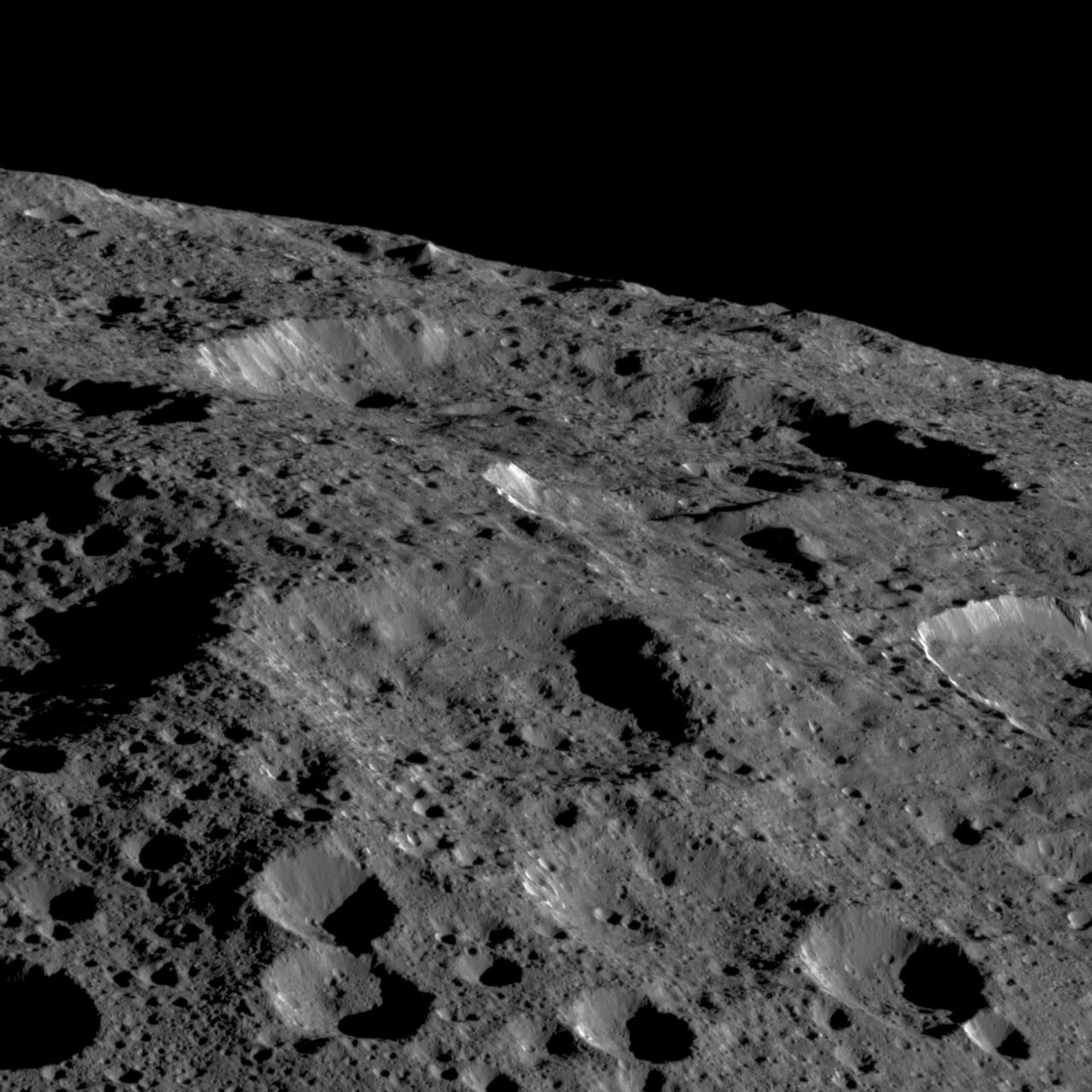

Dawn captured this view on May 19, 2018. The image shows the limb of Ceres at about 270E, 30N looking south. The spatial resolution is about 200 feet (60 meters) per pixel in the nearest parts of the image. The impact crater to the right (only partially visible) is Ninsar, named after a Sumerian goddess of plants and vegetation. It is about 25 miles (40 kilometers) in diameter. The conclusion of Dawn's mission operations was Oct. 31, 2018, when the spacecraft depleted its hydrazine used for attitude control. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23017
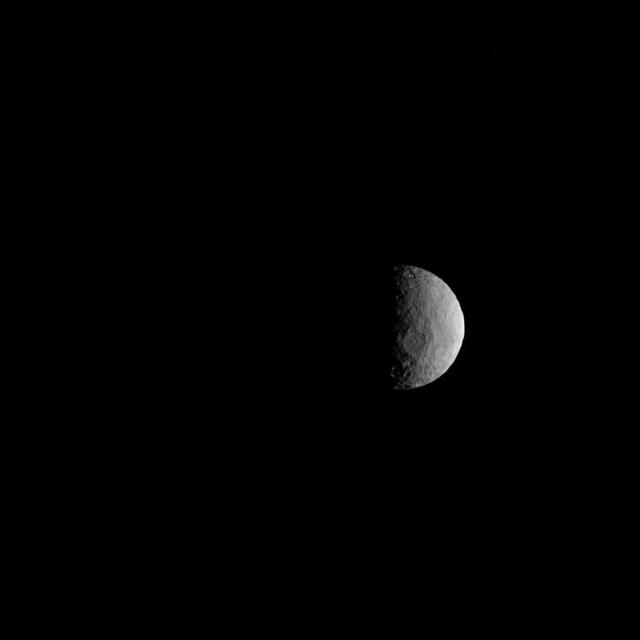

NASA's Dawn spacecraft took this picture on its way to a new orbit, at an altitude of about 30,000 miles (48,300 kilometers), as part of a series of images intended to help the navigation of the spacecraft relative to Ceres. The image was taken on March 28, 2017. Several familiar features can be identified: At the top, we see Occator Crater and its faculae (bright deposits identified as a mixture of sodium carbonate and other salts). Below center is the crater Urvara, and to the right of it, the larger crater Yalode (the third and second largest craters on Ceres, respectively). Large-scale faults called Samhain Catenae stretch from the Occator region toward the Yalode-Urvara region. The spacecraft will settle into a new orbit that will allow it to observe Ceres in opposition at the end of April 2017, when Dawn is directly between the sun and the Occator bright spots, at an altitude of about 12,400 miles (20,000 kilometers). The Dawn Journal has more details about the science expected from these observations. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21401
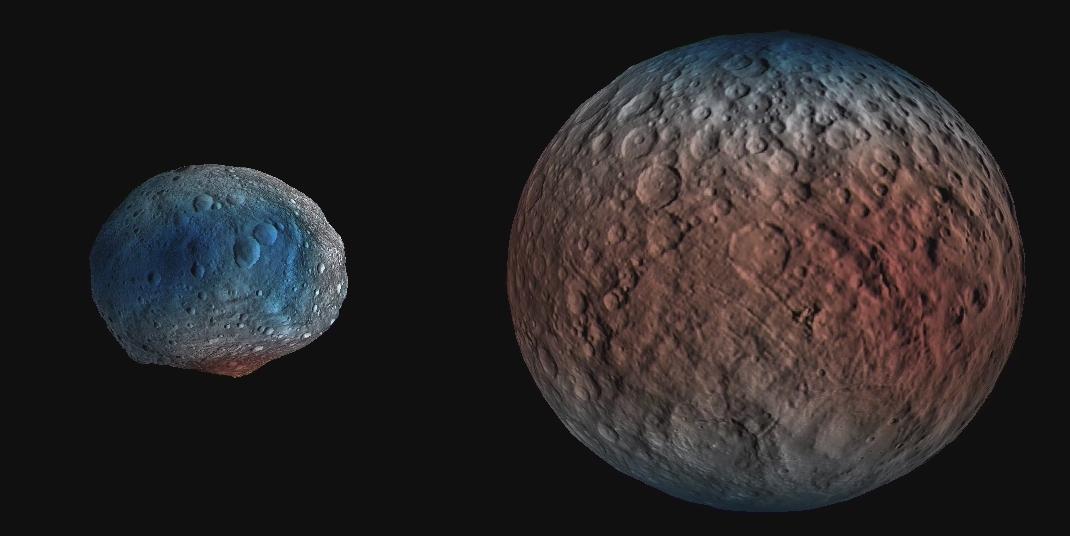
This frame from an animation shows dwarf planet Ceres overlaid with the concentration of hydrogen determined from data acquired by the gamma ray and neutron detector GRaND instrument aboard NASA Dawn spacecraft. The hydrogen is in the upper yard (or meter) of regolith, the loose surface material on Ceres. The color scale gives hydrogen content in water-equivalent units, which assumes all of the hydrogen is in the form of H2O. Blue indicates where hydrogen content is higher, near the poles, while red indicates lower content at lower latitudes. In reality, some of the hydrogen is in the form of water ice, while a portion of the hydrogen is in the form of hydrated minerals (such as OH, in serpentine group minerals). The color information is superimposed on shaded relief map for context. A second animation (Figure 2) compares the hydrogen content of Ceres' regolith with that of the giant asteroid Vesta, which Dawn orbited from 2011 to 2012. These data show Vesta is a much drier world, with a much lower percent of hydrogen in its regolith. Both maps were produced from data acquired by GRaND. Videos are available at http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21081
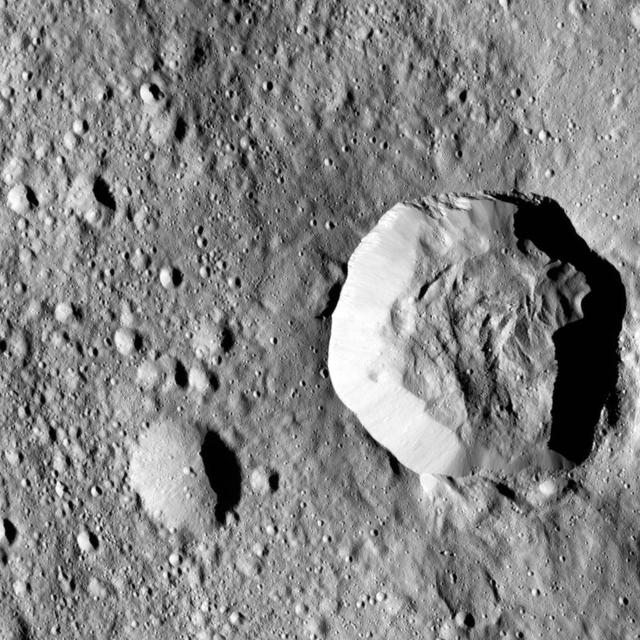
Ceres surface shows evidence for different types of flows that indicate the presence of ice in the regolith. One type of flow encircles the large impact crater at right in this image taken by NASA Dawn spacecraft. One type of flow encircles the large impact crater at right in this image. Scientists see features in this flow that indicate a low degree of internal friction within its material, meaning it was able to flow easily and far from its source. This could be due to the incorporation of a significant amount of liquid water or water vapor into the ejecta blanket. This flow also shows a large ridge along its edge (seen most clearly just to the left of the large crater). These features are commonly associated with flows on Mars called "fluidized ejecta blankets." This feature is located southwest of Kerwan crater at 40 degrees south latitude, 109 degrees east longitude. This is in the vicinity of the latitudes where Dawn's gamma ray and neutron spectrometer (GRaND) instrument sensed the presence of ice in the first meter of Ceres' regolith. The image was taken on August, 7, 2016 from an altitude of about 240 miles (390 kilometers) above Ceres. The image resolution is about 120 feet (35 meters) per pixel. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21404
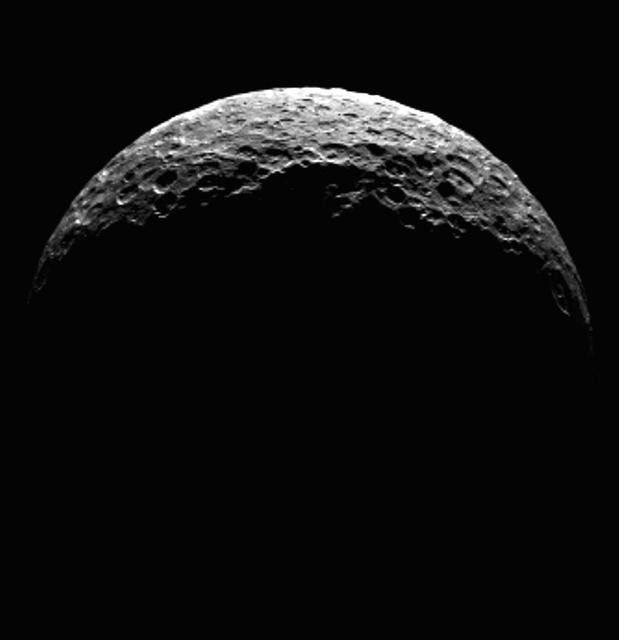

This frame from an animation shows the north pole of dwarf planet Ceres as seen by the Dawn spacecraft on April 10, 2015. Dawn was at a distance of 21,000 miles 33,000 kilometers when its framing camera took these images. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19317
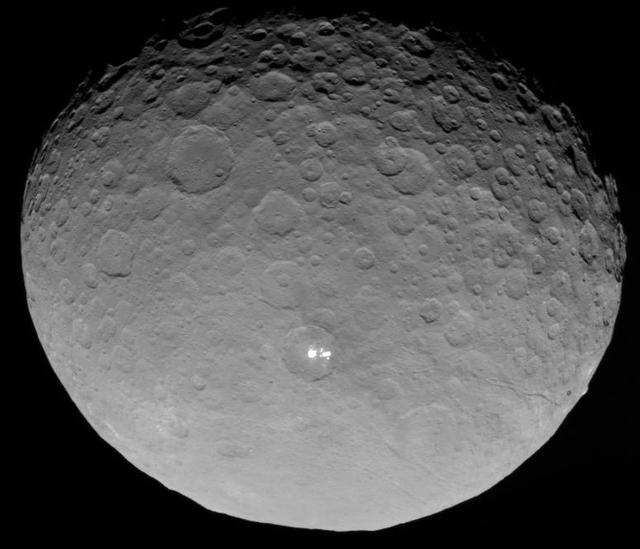

In this closest-yet view of Ceres, the brightest spots within a crater in the northern hemisphere are revealed to be composed of many smaller spots. This frame is from an animation of sequences taken by NASA Dawn spacecraft on May 4, 2015. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19547
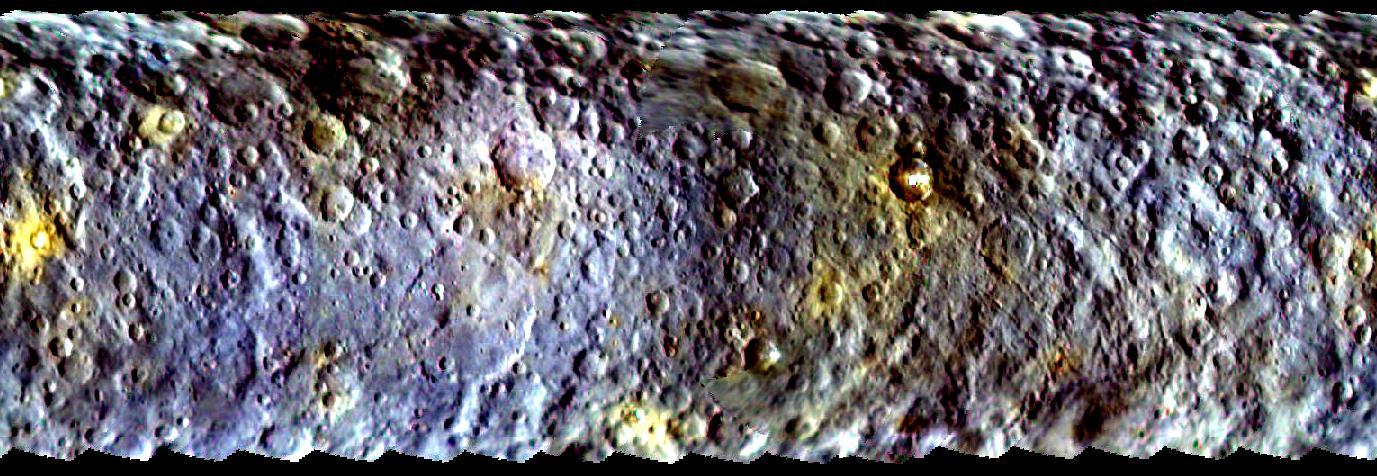
This map-projected view of Ceres was created from images taken by NASA Dawn spacecraft during its initial approach to the dwarf planet, prior to being captured into orbit in March 2015.

A large crater in the southern hemisphere of dwarf planet Ceres is seen in this image taken by NASA's Dawn spacecraft on June 6, 2015. This image shows many different surface structures associated with impacts. This is among the first snapshots from Dawn's second mapping orbit, which is 2,700 miles (4,400 kilometers) in altitude. The resolution is 1,400 feet (410 meters) per pixel. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19569

This graphic shows a theoretical path of a water molecule on Ceres. Some water molecules fall into cold, dark craters at high latitudes called "cold traps," where very little of the ice turns into vapor, even over the course of a billion years. Other water molecules that do not land in cold traps are lost to space as they hop around the dwarf planet. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21083

Ceres Haulani Crater is shown in these views from NASA Dawn spacecraft. These views reveal variations in the region brightness, mineralogy and temperature at infrared wavelengths.
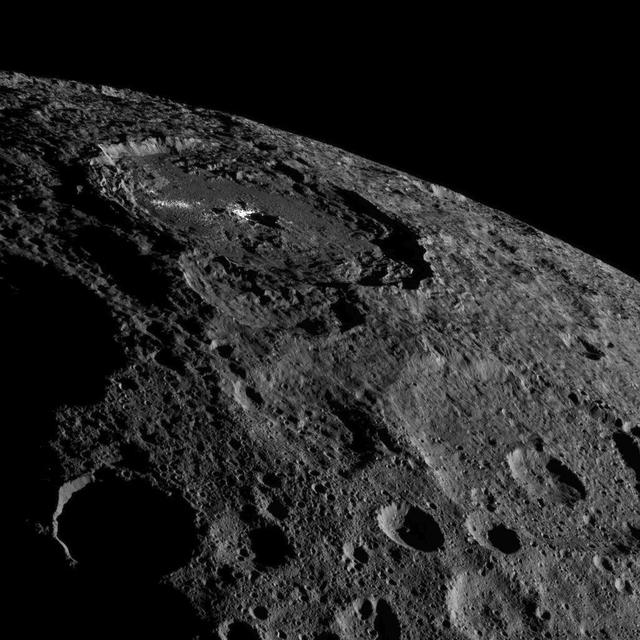

This image of the limb of dwarf planet Ceres shows a section of the northern hemisphere. Prominently featured is Occator Crater, home of Ceres' intriguing brightest areas. At 57 miles (92 kilometers) wide and 2.5 miles (4 kilometers) deep, Occator displays evidence of recent geologic activity. The latest research suggests that the bright material in this crater is comprised of salts left behind after a briny liquid emerged from below, froze and then sublimated, meaning it turned from ice into vapor. Dawn took this image on Oct. 17 from its second extended-mission science orbit (XMO2), at a distance of about 920 miles (1,480 kilometers) above the surface. The image resolution is about 460 feet (140 meters) per pixel. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21078

This photo of Ceres and the bright regions in Occator Crater was one of the last views NASA's Dawn spacecraft transmitted before it depleted its remaining hydrazine and completed its mission. This view, which faces south, was captured on Sept. 1, 2018 at an altitude of 2,340 miles (3,370 kilometers) as the spacecraft was ascending in its elliptical orbit. At its lowest point, the orbit dipped down to only about 22 miles (35 kilometers), which allowed Dawn to acquire very high-resolution images in this final phase of its mission. Some of the close-up images of Occator Crater are shown here. Occator Crater is 57 miles (92 kilometers) across and 2.5 miles (4 kilometers) deep and holds the brightest area on Ceres, Cerealia Facula in its center and Vinalia Faculae in its western side. This region has been the subject of intense interest since Dawn's approach to the dwarf planet in early 2015. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22485

Ceres rotates in this frame from a movie comprised of images taken by NASA Dawn mission during its approach to the dwarf planet. The images were taken on Feb. 19, 2015, from a distance of nearly 29,000 miles 46,000 kilometers.
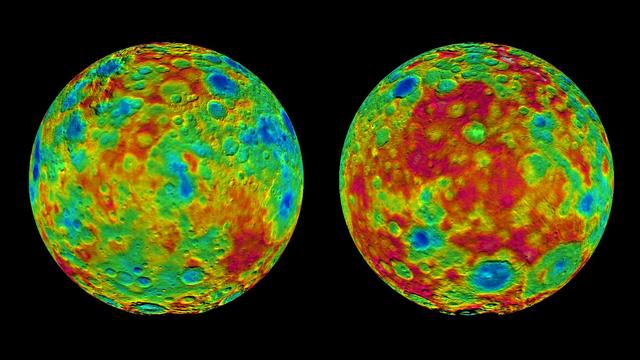
This pair of images shows color-coded maps from NASA's Dawn mission, revealing the highs and lows of topography on the surface of dwarf planet Ceres. The map at left is centered on terrain at 60 degrees east longitude; the map at right is centered on 240 degrees east longitude. The color scale extends about 5 miles (7.5 kilometers) below the surface in indigo to 5 miles (7.5 kilometers) above the surface in white. The topographic map was constructed from analyzing images from Dawn's framing camera taken from varying sun and viewing angles. The map was combined with an image mosaic of Ceres and projected as an orthographic projection. The well-known bright spots in the center of Ceres northern hemisphere in the image at right retain their bright appearance, although they are color-coded in the same green elevation of the crater floor in which they sit. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19607

This image taken by NASA's Dawn spacecraft shows Emesh, a crater on Ceres. Emesh, named after the Sumerian god of vegetation and agriculture, is 12 miles (20 kilometers) wide. Located at the edge of the Vendimia Planitia, the floor of this crater is asymmetrical with terraces distributed along the eastern rim. Additionally, this image shows many subtle linear features that are likely the surface expressions of faults. These faults play a big role in shaping Ceres' craters, leading to non-circular craters such as Emesh. To the left of Emesh in this view, a much older crater of similar size has mostly been erased by impacts and their ejecta. Dawn took this image on May 11, 2016, from its low-altitude mapping orbit, at a distance of about 240 miles (385 kilometers) above the surface. The center coordinates of this image are 11 degrees north latitude, 158 degrees east longitude. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21911
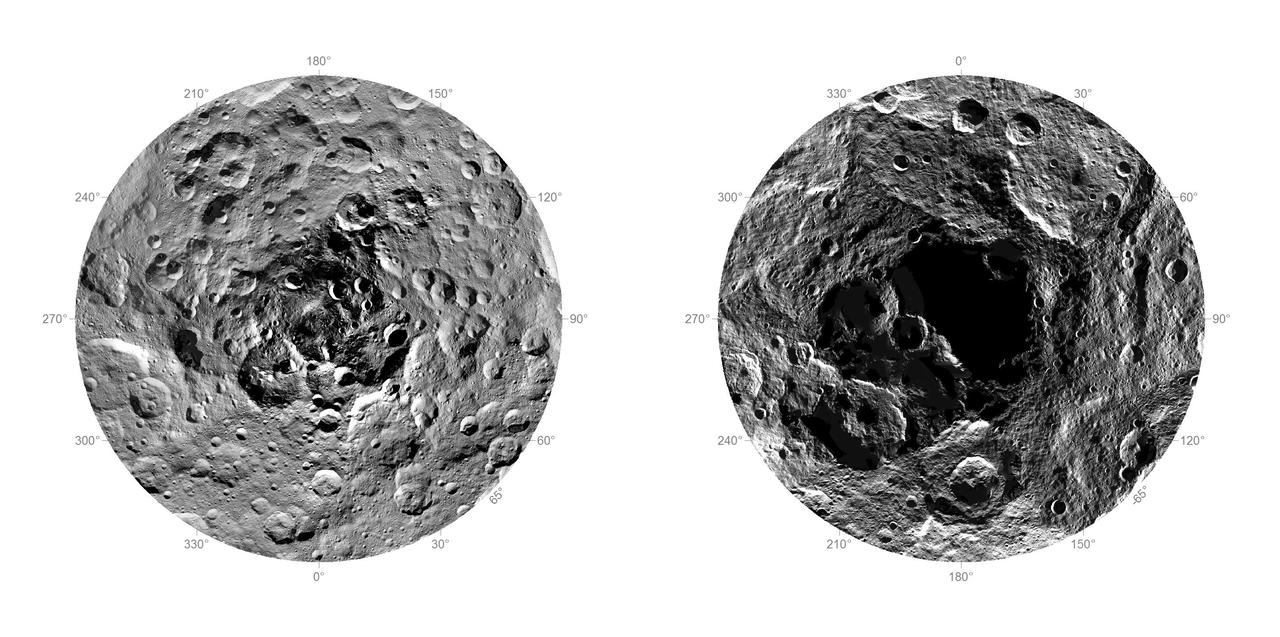
Researchers from NASA's Dawn mission have composed the first comprehensive views of the north (left) and south pole regions (right) of dwarf planet Ceres, using images obtained by the Dawn spacecraft. The images were taken between Aug. 17 and Oct. 23, 2015, from an altitude of 915 miles (1,470 kilometers). The region around the south pole appears black in this view because this area has been in shade ever since Dawn's arrival on March 6, 2015, and is therefore not visible. At the north polar region, craters Jarovit, Ghanan and Asari are visible, as well as the mountain Ysolo Mons. Near the south pole, craters Attis and Zadeni can be seen. Detailed maps of the polar regions allow researchers to study the craters in this area and compare them to those covering other parts of Ceres. Variations in shape and complexity can point to different surface compositions. In addition, the bottoms of some craters located close to the poles receive no sunlight throughout Ceres' orbit around the sun. Scientists want to investigate whether surface ice can be found there. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20126
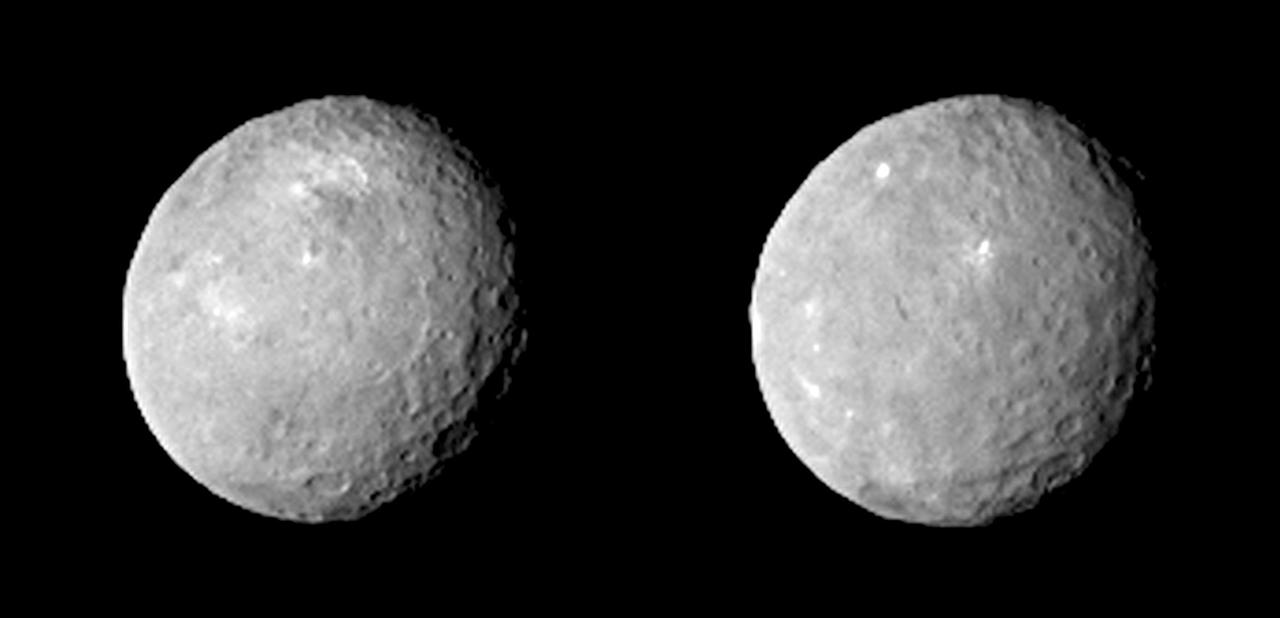

These two views of Ceres were acquired by NASA Dawn spacecraft on Feb. 12, 2015, from a distance of about 52,000 miles 83,000 kilometers as the dwarf planet rotated. The images have been magnified from their original size. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19056

NASA's Dawn Spacecraft took this image of Gaue crater, the large crater on the bottom, on Ceres. Gaue is a Germanic goddess to whom offerings are made in harvesting rye. The center of this crater is sunken in. Its diameter is 84 kilometers (52 miles). The resolution of the image is 450 feet (140 meters) per pixel. The image was taken from a distance of 915 miles (1,470 kilometers) on August 18, 2015. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19633
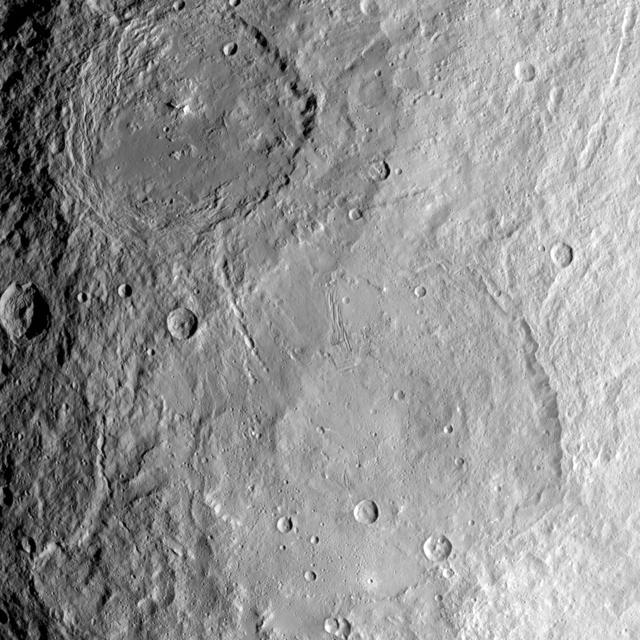

This image from NASA's Dawn spacecraft shows the large craters Urvara (top) and Yalode (bottom) on dwarf planet Ceres. These features are so big that they must be observed from high altitudes in order to fit in the frame of a single image. Urvara is (101 miles (163 kilometers) in diameter, while Yalode is 162 miles (260 kilometers) in diameter. The two giant craters were formed at different times. Yalode is almost 1 billion years older than Urvara, which is about 120 million to 140 million years old. Yalode's relatively smooth floor indicates Ceres' crust material became close to -- or even reached -- the melting temperature of ice as a consequence of the heat generated by the impact. On the other hand, the smaller Urvara has rougher terrain. This suggests Urvara had either a lower temperature increase from the impact, or a colder crust temperature at the time of the crater's formation, or a combination of the two. Indeed, Ceres' interior was warmer in the past, and has been slowly cooling as its supply of radioactive isotopes, whose decay represents Ceres' main heat source, has been decreasing over time. This picture also reveals geological details such, as the feature Nar Sulcus inside Yalode and a central peak in Urvara. Urvara is named after the Indian and Iranian deity of plants and fields. Yalode is named for the Dahomey goddess, worshipped by women at the harvest rites. This image was obtained by NASA's Dawn spacecraft on June 9, 2015. The spacecraft was then in its survey orbit (2,700 miles, 4,400 kilometers above the surface), when the footprint of Dawn's framing camera on Ceres' surface was about 260 miles (420 kilometers) across on Ceres' surface. The resolution is 1,400 feet (410 meters) per pixel. The central coordinates of the picture are 43 degrees south latitude, 278 degrees east in longitude. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21917
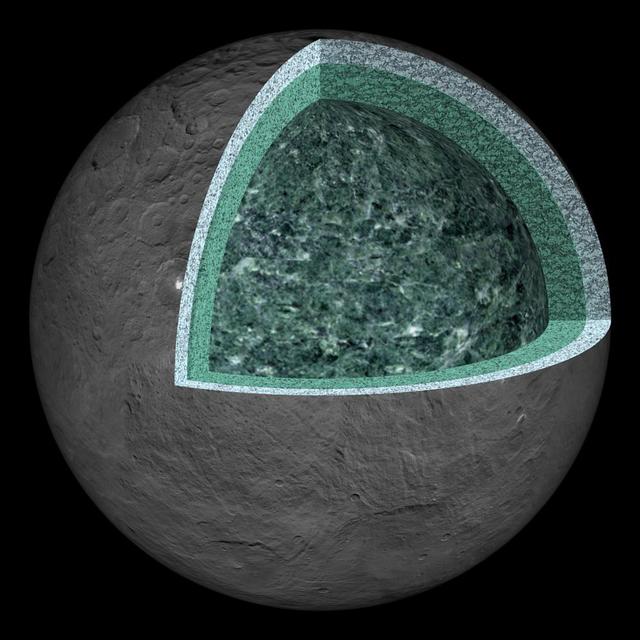
This artist's concept summarizes our understanding of how the inside of Ceres could be structured, based on the data returned by the NASA's Dawn mission. Using information about Ceres' gravity and topography, scientists found that Ceres is "differentiated," which means that it has compositionally distinct layers at different depths. The most internal layer, the "mantle" is dominated by hydrated rocks, like clays. The external layer, the 24.85-mile (40-kilometer) thick crust, is a mixture of ice, salts, and hydrated minerals. Between the two is a layer that may contain a little bit of liquid rich in salts, called brine. It extends down at least 62 miles (100 kilometers). The Dawn observations cannot "see" below about 62 miles (100 kilometers) in depth. Hence, it is not possible to tell if Ceres' deep interior contains more liquid or a core of dense material rich in metal. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22660
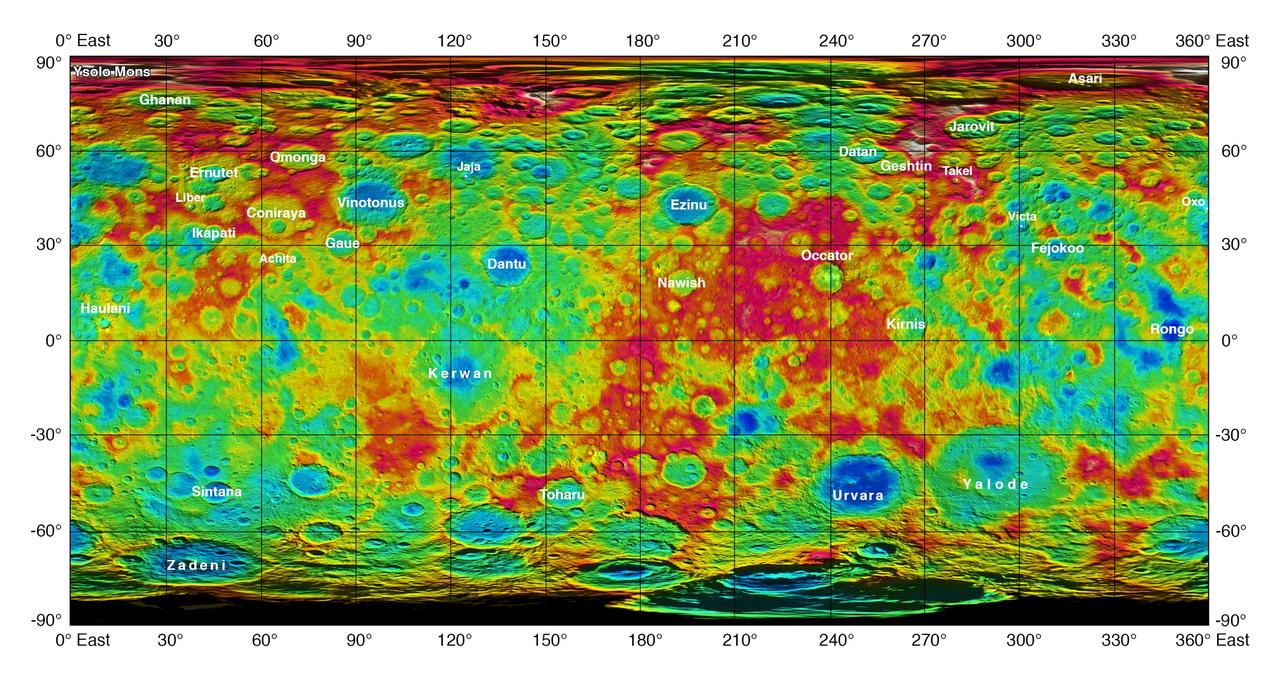
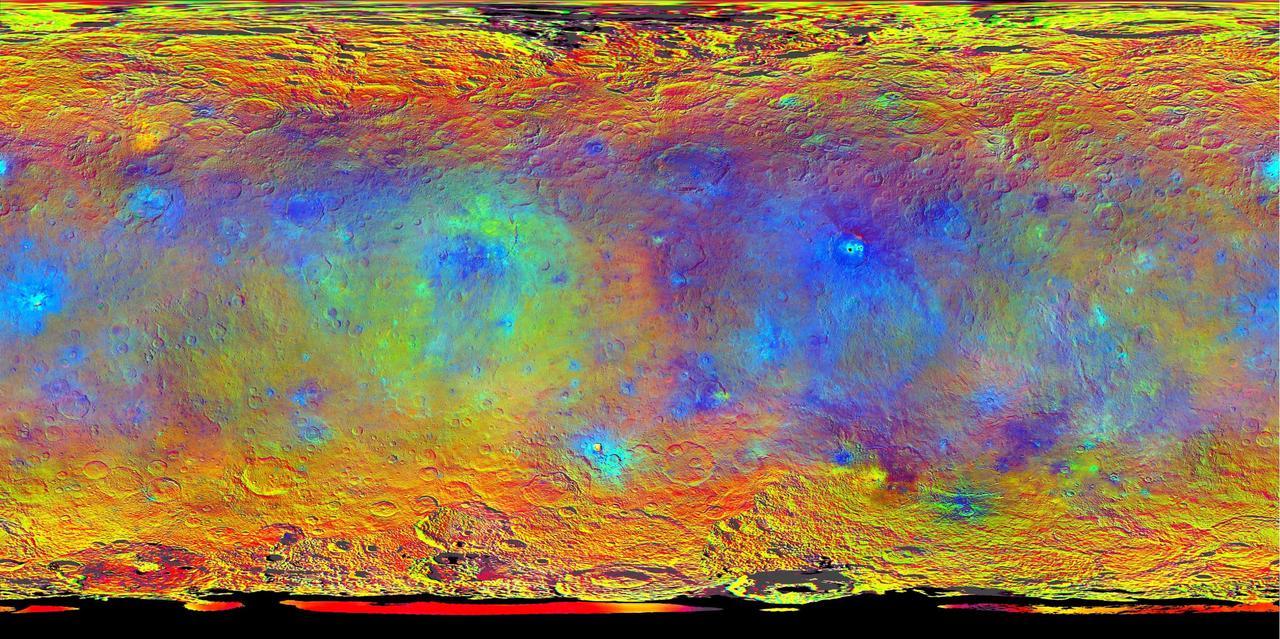
This color-coded map from NASA Dawn mission shows the highs and lows of topography on the surface of dwarf planet Ceres. It is labeled with names of features approved by the International Astronomical Union. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19974
The map is a Mercator projection and has a resolution of 460 feet 140 meters per pixel. The images used to make this map were taken from Dawn high-altitude mapping orbit HAMO, at a distance of 915 miles 1,470 kilometers from Ceres.
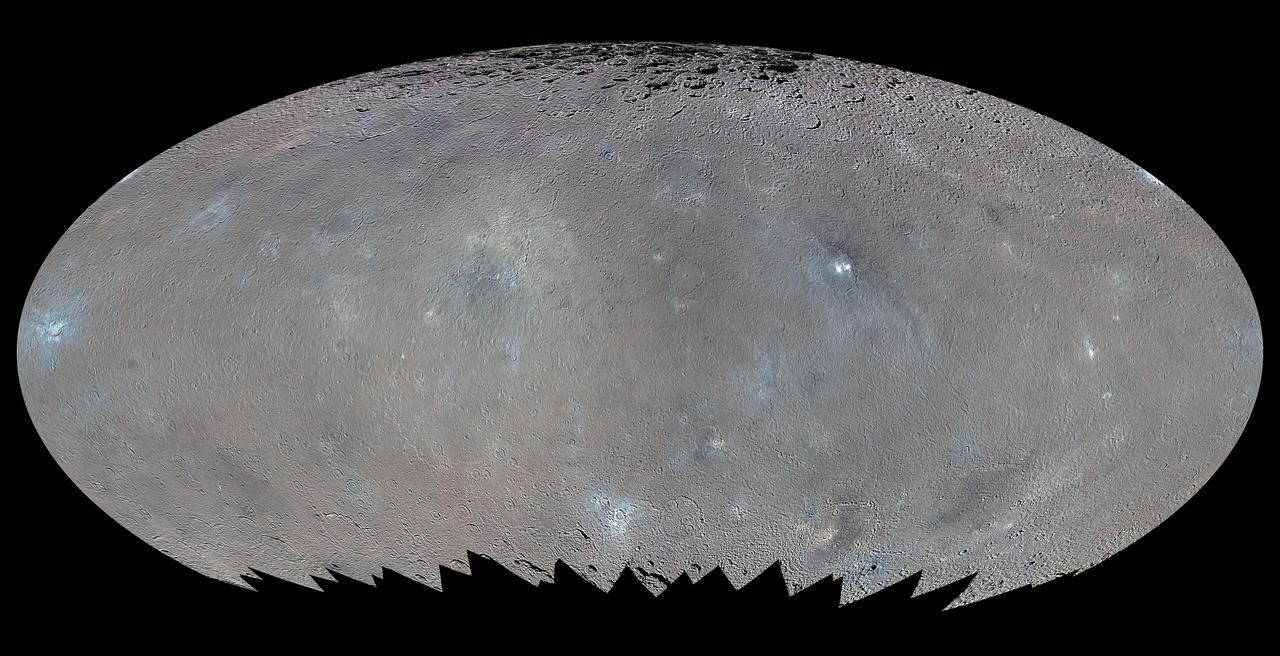

This global map elliptical map from NASA Dawn spacecraft shows the surface of Ceres in enhanced color, encompassing infrared wavelengths beyond human visual range. Some areas near the poles are black where Dawn color imaging coverage is incomplete.
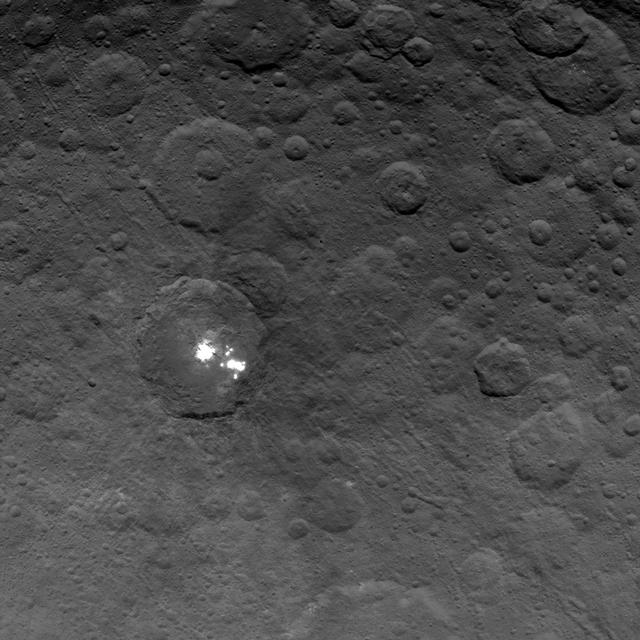

The brightest spots on dwarf planet Ceres are seen in this image taken by NASA's Dawn spacecraft on June 6, 2015. This is among the first snapshots from Dawn's second mapping orbit, which is 2,700 miles (4,400 kilometers) in altitude. The resolution is 1,400 feet (410 meters) per pixel. Scientists are still puzzled by the nature of these spots, and are considering explanations that include salt and ice. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19568
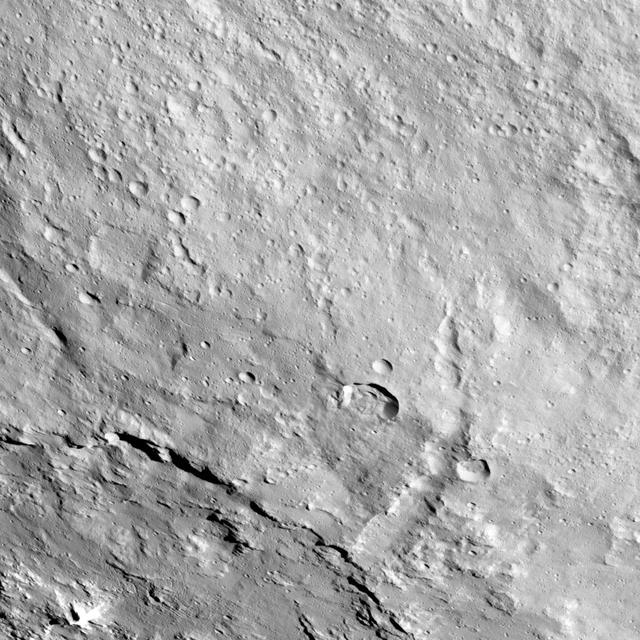

This image from NASA's Dawn spacecraft shows the northeastern rim of Urvara Crater on Ceres at lower left. To the right of the crater, the long, narrow feature that appears to jut out toward the north is called Pongal Catena, which is about 60 miles (96 km) long. Catenae are large grooves or troughs that can have various origins. They refer to chains of closely connected craters formed by a series of impacts, as found on Jupiter's moon Ganymede. They can also represent large faults created by internal forces, for example in this example found on Mars. The mechanism that formed Pongal Catena is not understood yet, but it likely formed as a consequence of the stresses generated by the large impacts that resulted in the formation of the Urvara and Yalode craters. Pongal catena is one of several types of fractures found in this region that reflect a complex history. A feature called Nar Sulcus is another example. Studying the geometry of these features and their relationships can help shed light on the nature of Ceres' subsurface. This image was obtained on September 28, 2015, from an altitude of about 915 miles (1,470 kilometers). Pongal Catena is centered at 37.4 degrees south latitude, 267.7 degrees east longitude. This feature gets its name from the Tamil (Sri Lanka and southern India) harvest festival observed in mid-January. It is a time for giving thanks to nature, and we thank Ceres for all the wonders it has offered us so far. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21408
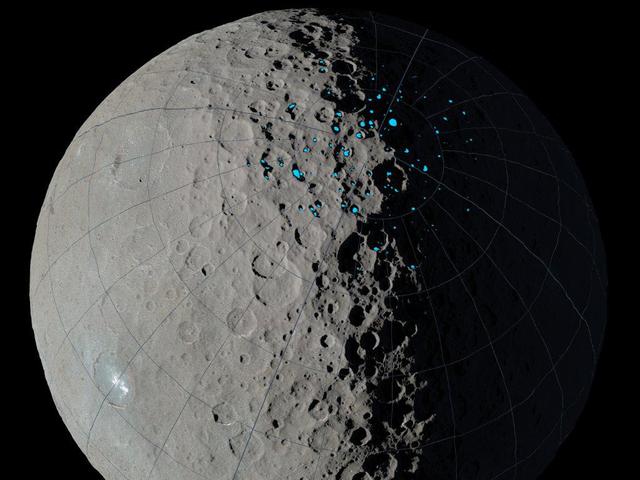

At the poles of Ceres, scientists have found craters that are permanently in shadow (indicated by blue markings). Such craters are called "cold traps" if they remain below about minus 240 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 151 degrees Celsius). These shadowed craters may have been collecting ice for billions of years because they are so cold. This image was created using data from NASA's Dawn spacecraft. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20696

This view, made using images taken by NASA's Dawn spacecraft, features a tall conical mountain on Ceres. Elevations span a range of about 5 miles (8 kilometers) from the lowest places in this region to the highest terrains. Blue represents the lowest elevation, and brown is the highest. The white streaks seen running down the side of the mountain are especially bright parts of the surface. The image was generated using two components: images of the surface taken during Dawn's High Altitude Mapping Orbit (HAMO) phase, where it viewed the surface at a resolution of about 450 feet (140 meters) per pixel, and a shape model generated using images taken at varying sun and viewing angles during Dawn's lower-resolution Survey phase. The image of the region is color-coded according to elevation, and then draped over the shape model to give this view. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19976
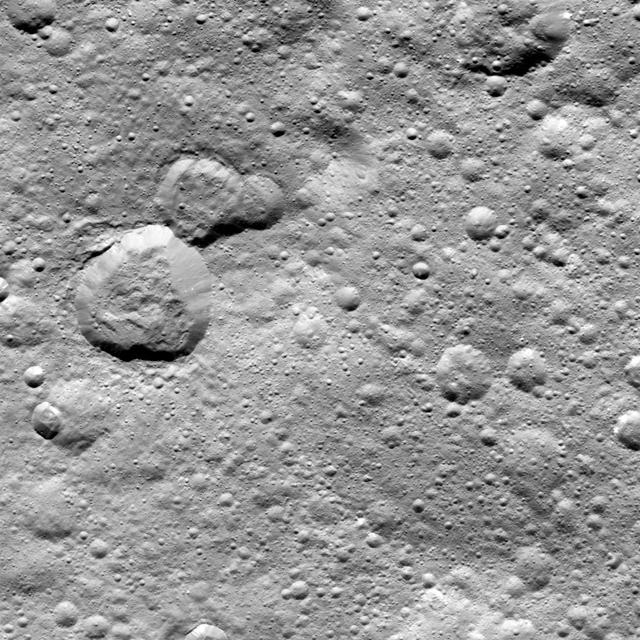

This image from NASA's Dawn spacecraft shows a group of craters, left of center, that resembles a rubber duck. Halki Crater, the "head," is 12 miles (20 kilometers) in diameter, while Telepinu Crater, the "body," is 19 miles (31 kilometers) across. They can be found in the global map of Ceres' names. The "beak" crater is unnamed. Halki and Telepinu have both been recently added to the list of official names for Ceres' geological features. They are both named after Hittite (Asia Minor) deities: the goddess of grain and the god of fertility and vegetation, respectively. Dawn acquired this picture on August 20, 2015, from its high-altitude mapping orbit at about 915 miles (1,470 kilometers) above the surface. The center coordinates of this image are 26 degrees north latitude, 339 degrees east longitude. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21909
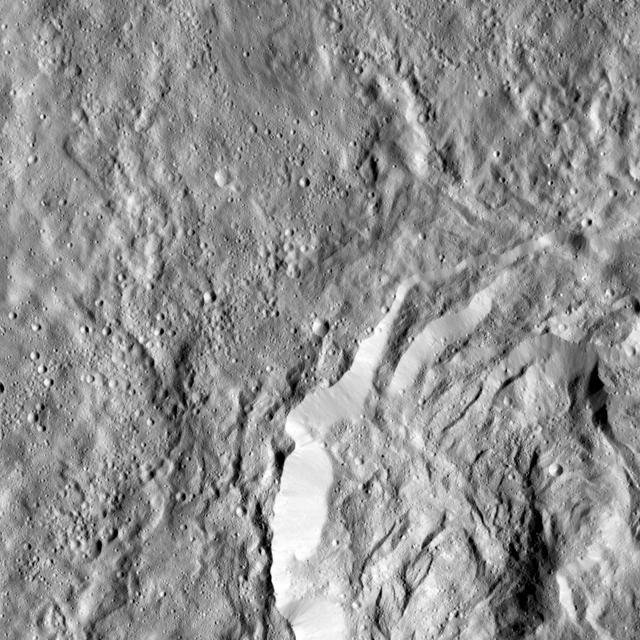

This image obtained by NASA's Dawn spacecraft shows a field of small craters next to Kokopelli Crater, seen at bottom right in this image, on dwarf planet Ceres. The small craters overlay a smooth, wavy material that represents ejecta from nearby Dantu Crater. The small craters were formed by blocks ejected in the Dantu impact event, and likely from the Kokopelli impact as well. Kokopelli is named after the fertility deity who presides over agriculture in the tradition of the Pueblo people from the southwestern United States. The crater measures 21 miles (34 kilometers) in diameter. Dawn took this image during its first extended mission on August 11, 2016, from its low-altitude mapping orbit, at about 240 miles (385 kilometers) above the surface. The center coordinates of this image are 20 degrees north latitude, 123 degrees east longitude. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21915
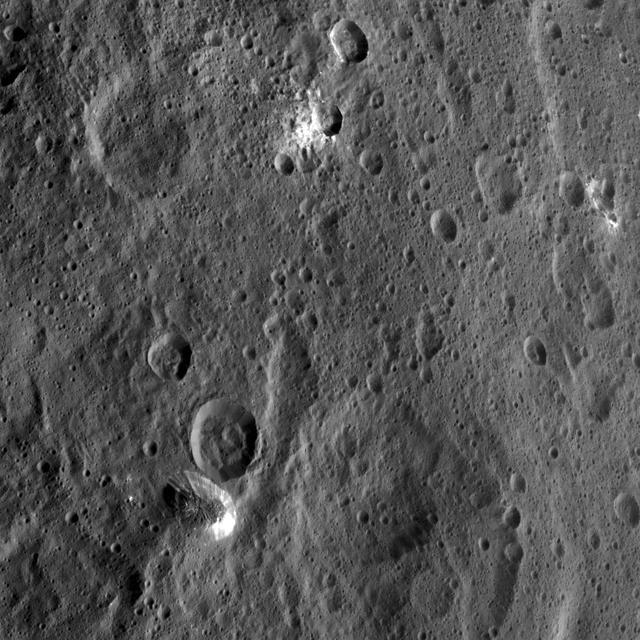

Xevioso Crater is the small (5.3 miles, 8.5 kilometers in diameter) crater associated with bright ejecta toward the top of this image, taken by NASA's Dawn spacecraft. It is one of the newly named craters on Ceres. Xevioso is located in the vicinity of Ahuna Mons, the tall, lonely mountain seen toward the bottom of the picture. Given that the small impact that formed Xevioso was able to excavate bright material, scientists suspect the material may be found at shallow depth. Its nature and relationship to other bright regions on Ceres is under analysis. The asymmetrical distribution of this bright ejecta indicates Xevioso formed via an oblique impact. Another view of Xevioso can be found here. Xevioso is named for the Fon god of thunder and fertility from the Kingdom of Dahomey, which was located in a region that is now the west African country of Benin. Dawn acquired this picture on October 15, 2015, from its high altitude mapping orbit at about 915 miles (1,470 kilometers) above the surface. The center coordinates of this image are 3.8 degrees south latitude, 314 degrees east longitude, and its resolution is 450 feet (140 meters) per pixel. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21907
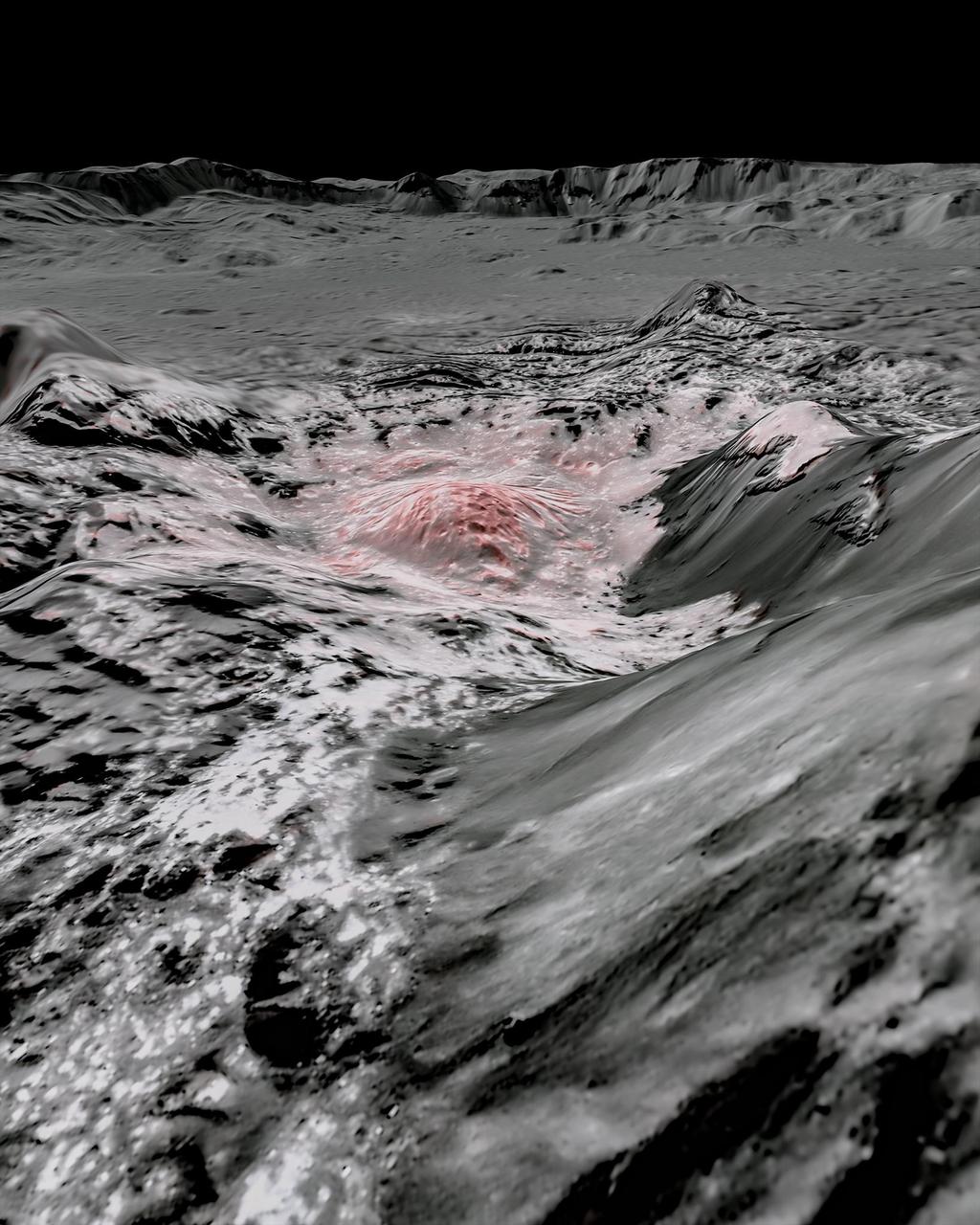
NASA's Dawn spacecraft captured pictures in visible and infrared wavelengths, which were combined to create this false-color view of a region in 57-mile-wide (92-kilometer-wide) Occator Crater on the dwarf planet Ceres (in the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter). Here, recently exposed brine, or salty liquids, in the center of the crater were pushed up from a deep reservoir below Ceres' crust. In this view, they appear reddish. In the foreground, is Cerealia Facula ("facula" means bright area), a 9-mile-wide (15-kilometer-wide) region with a composition dominated by salts. The central dome, Cerealia Tholus, is about 1.9 miles (3 kilometers) across at its base and 1,100 feet (340 meters) tall. The dome is inside a central depression about 3,000 feet (900 meters) deep. The area depicted in this scene is about 1.3 miles (2.1 kilometers) wide in the foreground, about 7 miles (11 kilometers) wide across the dome, and 35 miles (56 kilometers) wide in the background, where the crater rim rises against the black sky. The distance from the near point (at the bottom) to the far point (at the top) is about 32 miles (52 kilometers). This mosaic is made from multiple images Dawn captured during its second extended mission in 2018 from an altitude of about 22 miles (35 kilometers). Those were combined with a topographic map based on images obtained during Dawn's prime mission and first extended mission in 2016, from an altitude of about 240 miles (385 kilometers). The resolution varies from about 11 feet (3.5 meters) per pixel in the bright regions to about 115 feet (35 meters) per pixel in the background. The color data that is overlain on the topographic data was obtained during the prime mission in 2015 when the spacecraft was at an altitude of 915 miles (1470 kilometers). It has a resolution of 450 feet (140 meters) per pixel. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24021
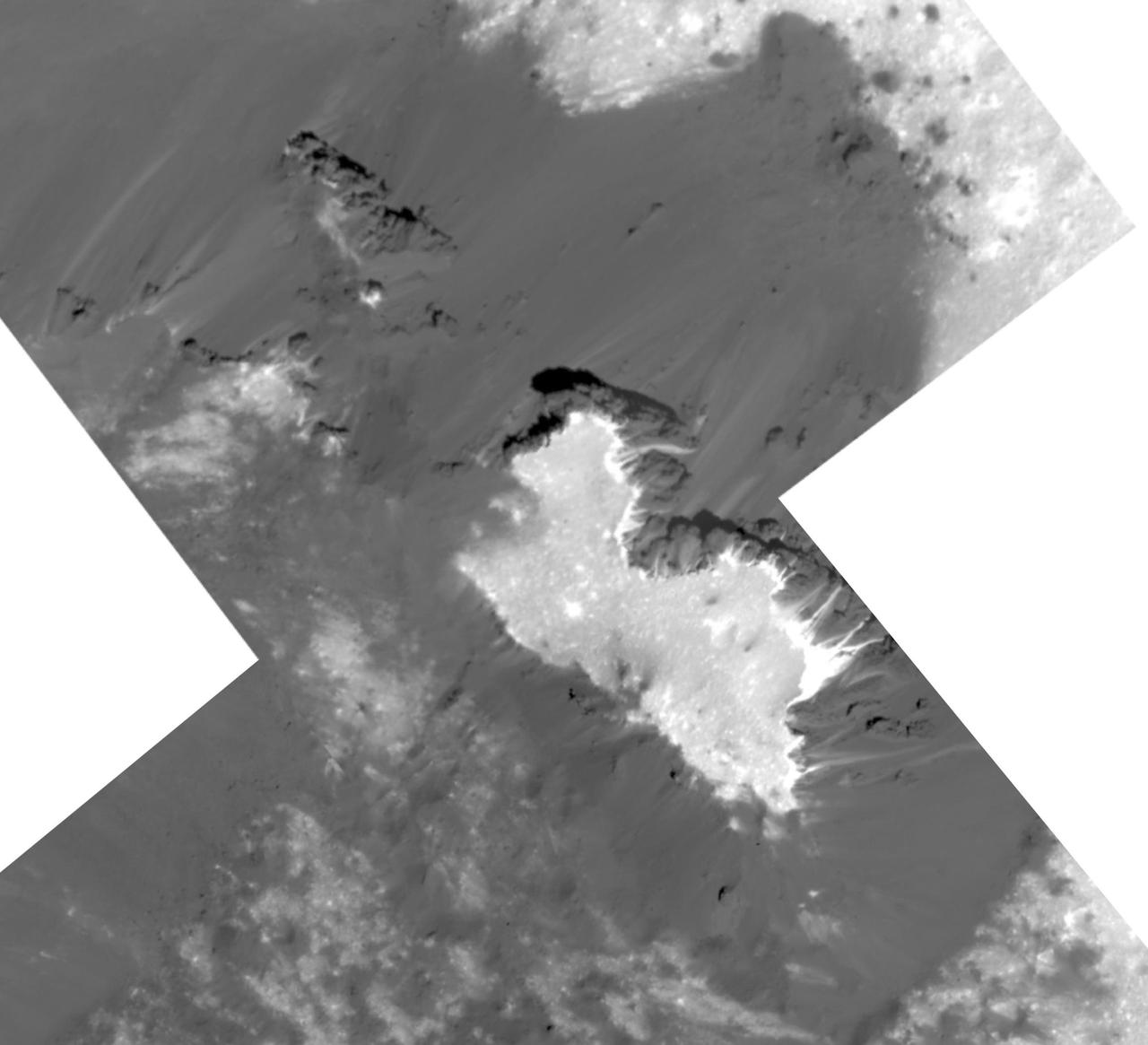
This mosaic of a prominent mound located on the western side of Cerealia Facula was obtained by NASA's Dawn spacecraft on June 22, 2018 from an altitude of about 21 miles (34 kilometers). The geometry of this feature is similar to a mesa or large butte with a flat top. It has been puzzling scientists since its discovery in the early images of the Dawn mission at Ceres. These new images reveal many details. In particular, the relationships between the bright material, mostly composed of sodium carbonate, and the dark background might hold clues about the origin of the facula. This feature is located at about 19.5 degrees north latitude and 239.2 degrees east longitude. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22477
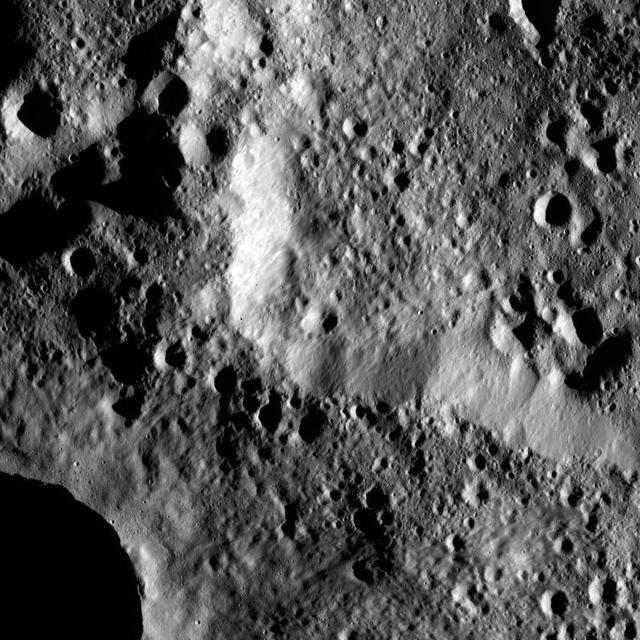

The rim of Hamori Crater on Ceres is seen in the upper right portion of this image, which was taken by NASA Dawn spacecraft. Hamori is located in the southern hemisphere of Ceres and measures 37 miles 60 kilometers wide.
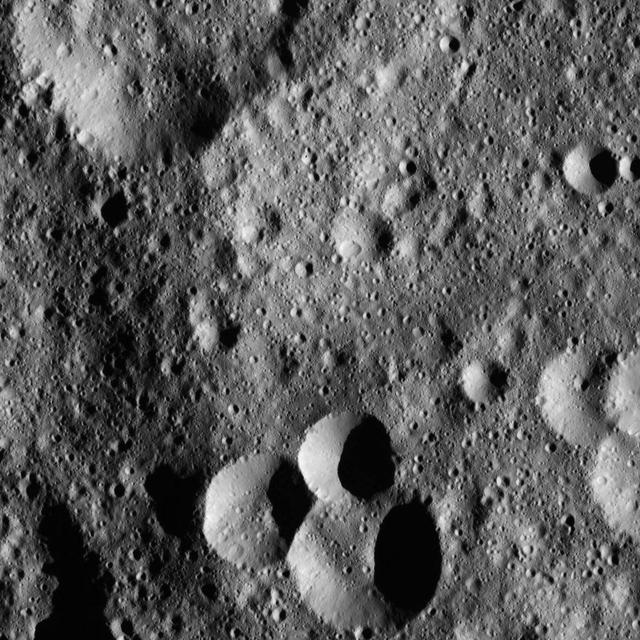

This image, taken by NASA Dawn spacecraft, shows a variety of small craters in the northern hemisphere of Ceres. The majority of Ceres images from Dawn show heavily cratered terrains such as this.
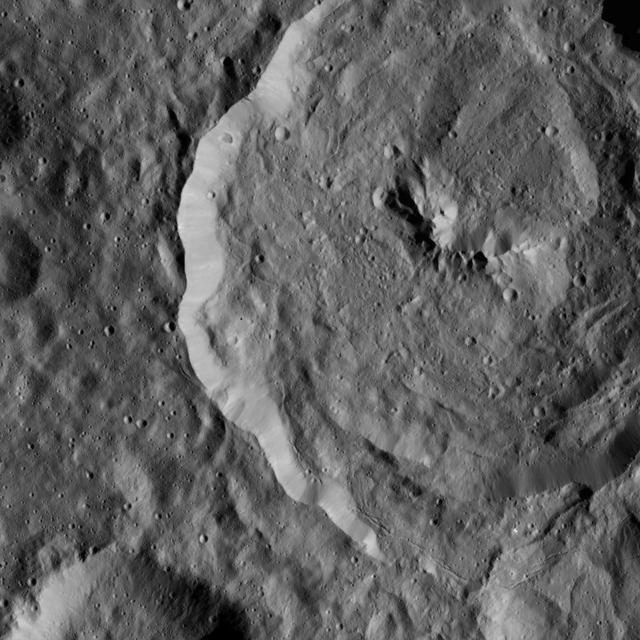

Tupo Crater on Ceres is seen in this view from NASA Dawn spacecraft. This crater, located in the southern hemisphere of Ceres, was named for the Polynesian god of turmeric. Dawn captured the scene on Dec. 24, 2015.
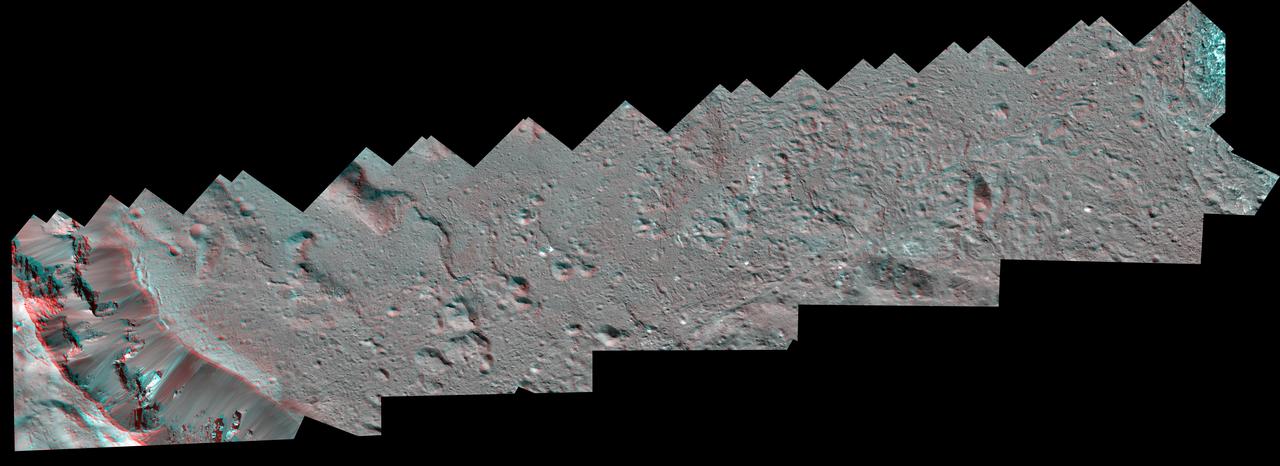

The Dawn spacecraft captured these stereo views of Occator Crater on the dwarf planet Ceres in 2018. More than 70 framing camera images were used to construct this anaglyph view (which requires red-blue stereo glasses for viewing) of the southeastern floor of the crater, including the rim at far left in this view. This area is largely covered with impact melt and features a variety of pits and low mounds, some of which are related to impact debris but others to subsurface brine seepage and deposition. The spatial resolution of the stereo images is about 11 feet (3.5 meters) per pixel. Occator Crater, named after the Roman god of the agricultural practice of harrowing, is about 57 miles (92 kilometers) in diameter. The conclusion of Dawn's mission operations was Oct. 31, 2018, when the spacecraft depleted its hydrazine used for attitude control. This image was produced by Dr. Paul Schenk at the Lunar and Planetary Institute in Houston. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24061