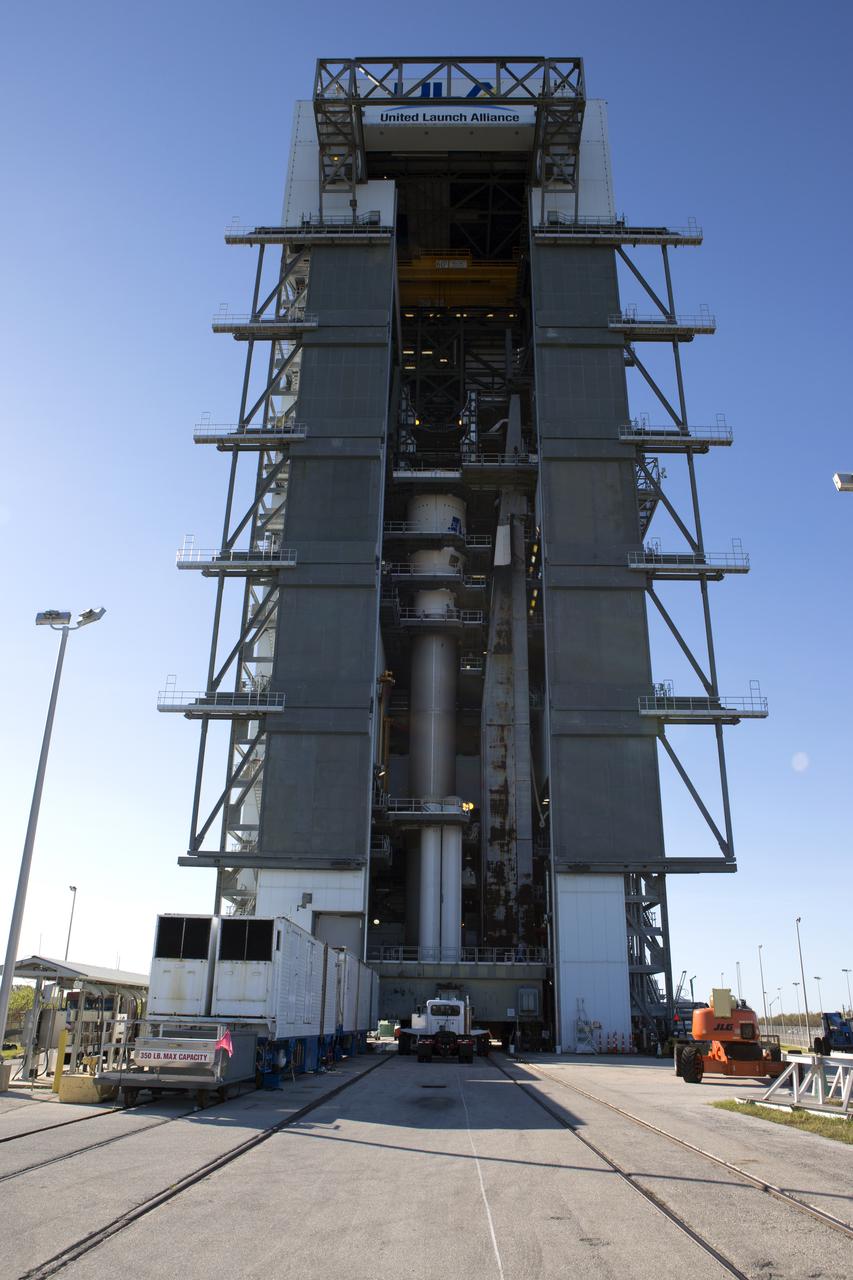

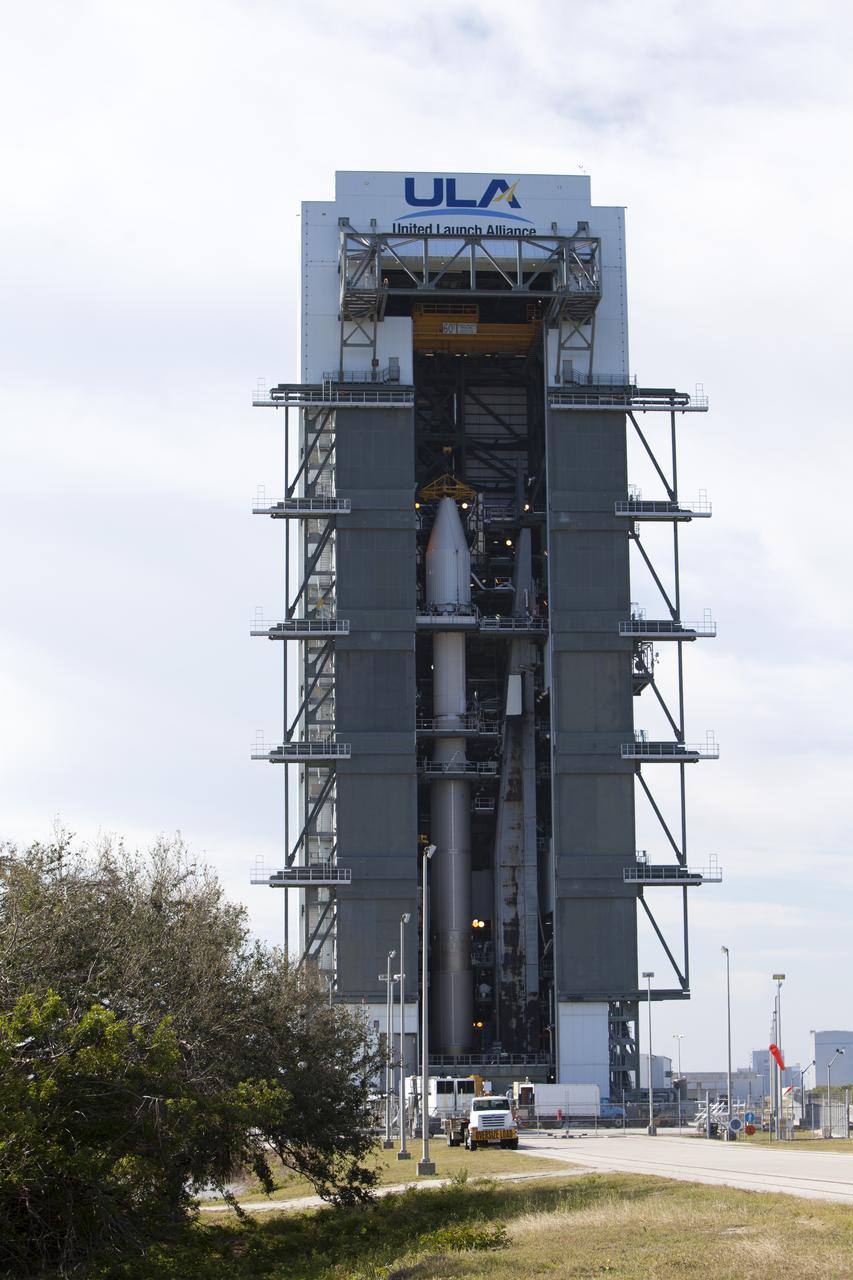
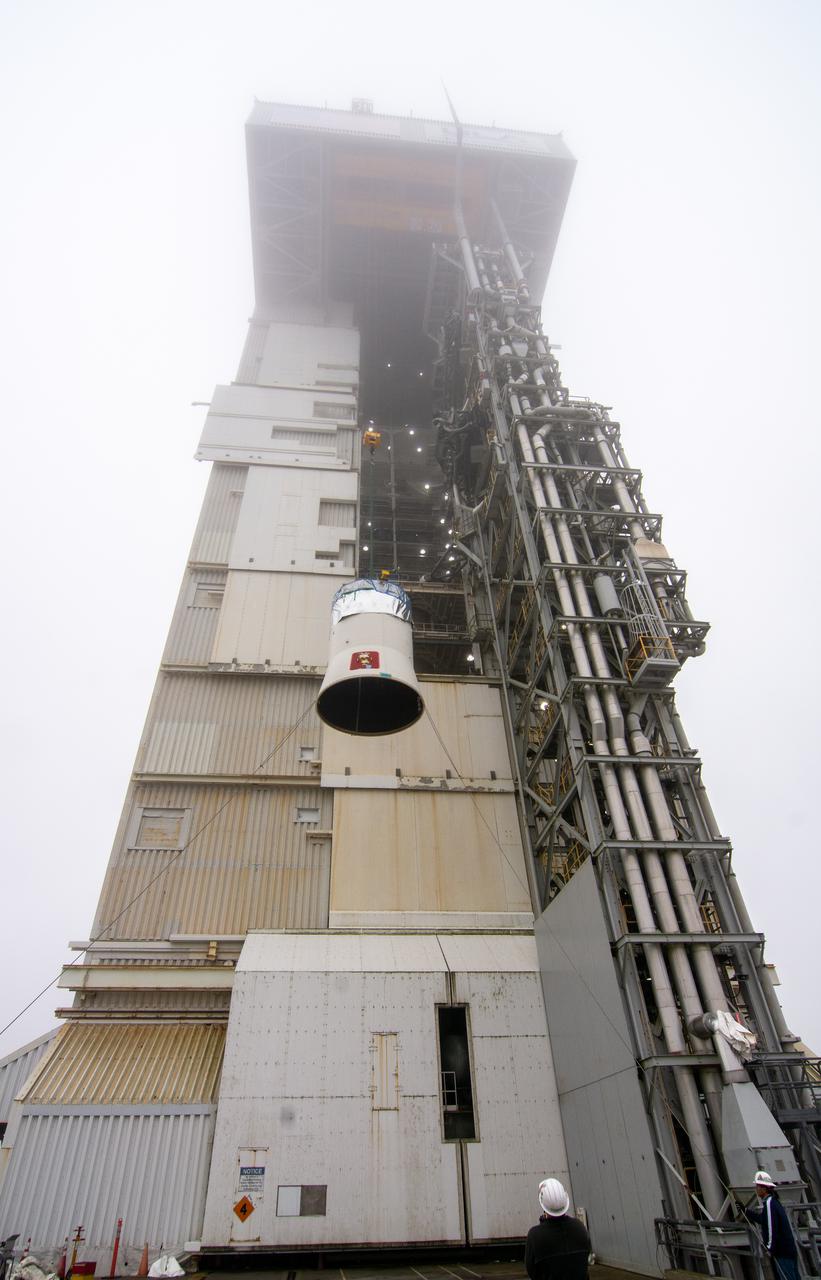
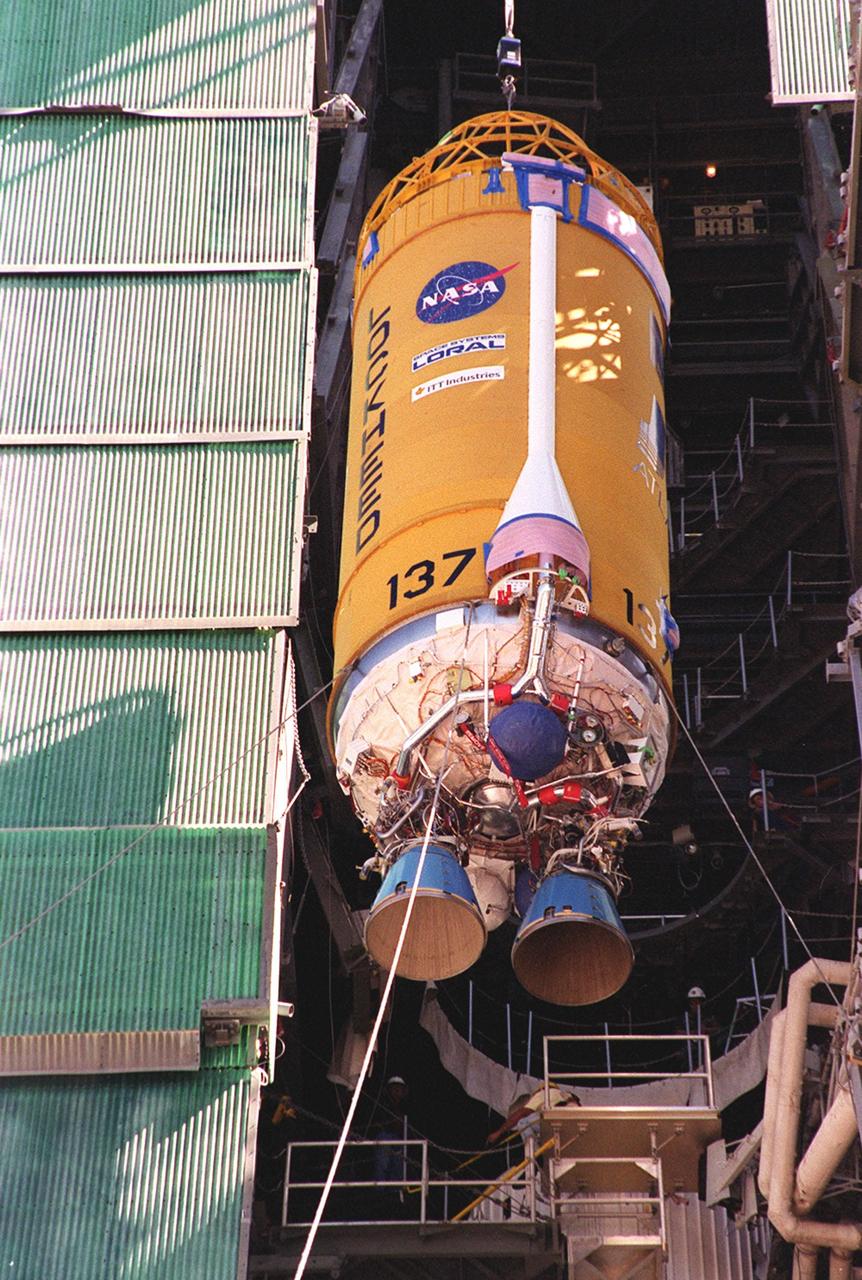
Operations are underway to stack the United Launch Alliance Atlas V Centaur second stage onto the first stage in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket in November. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
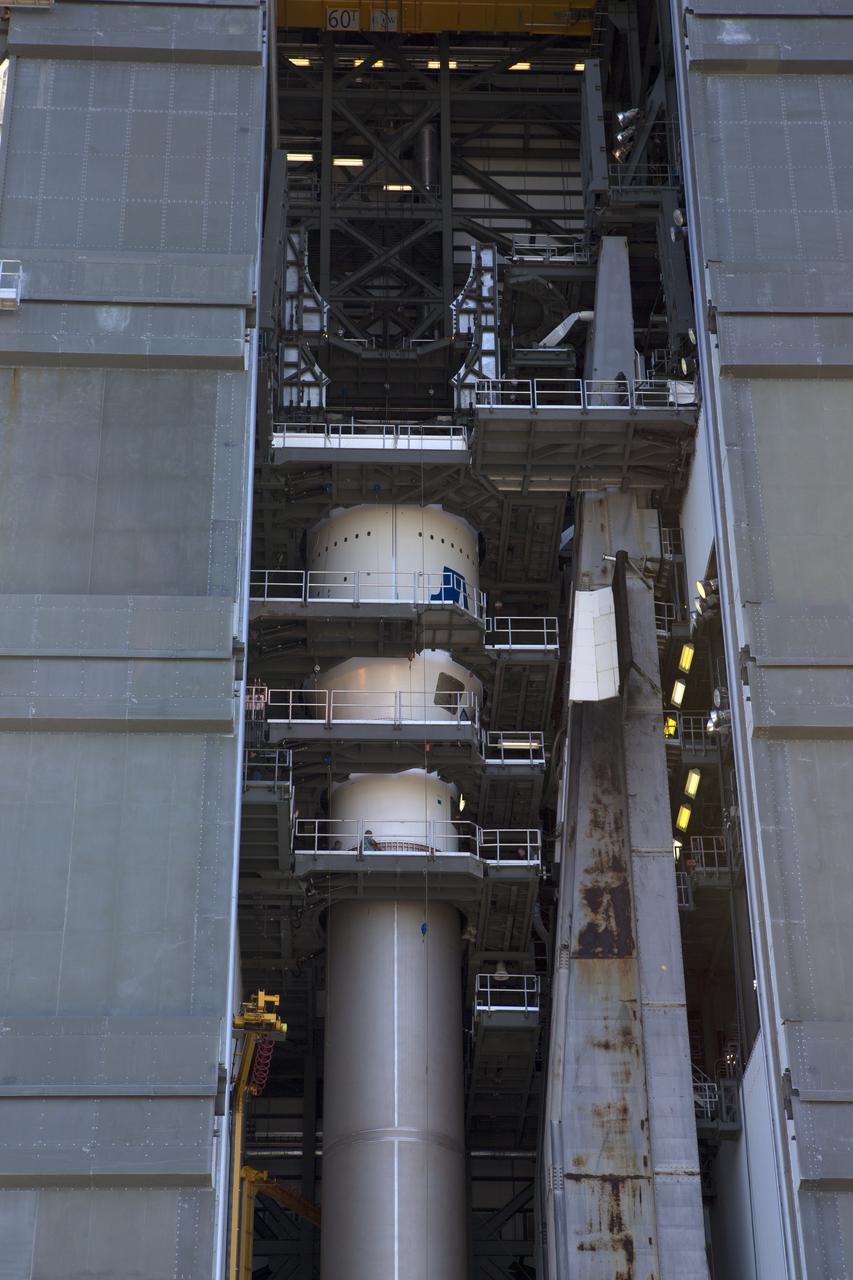

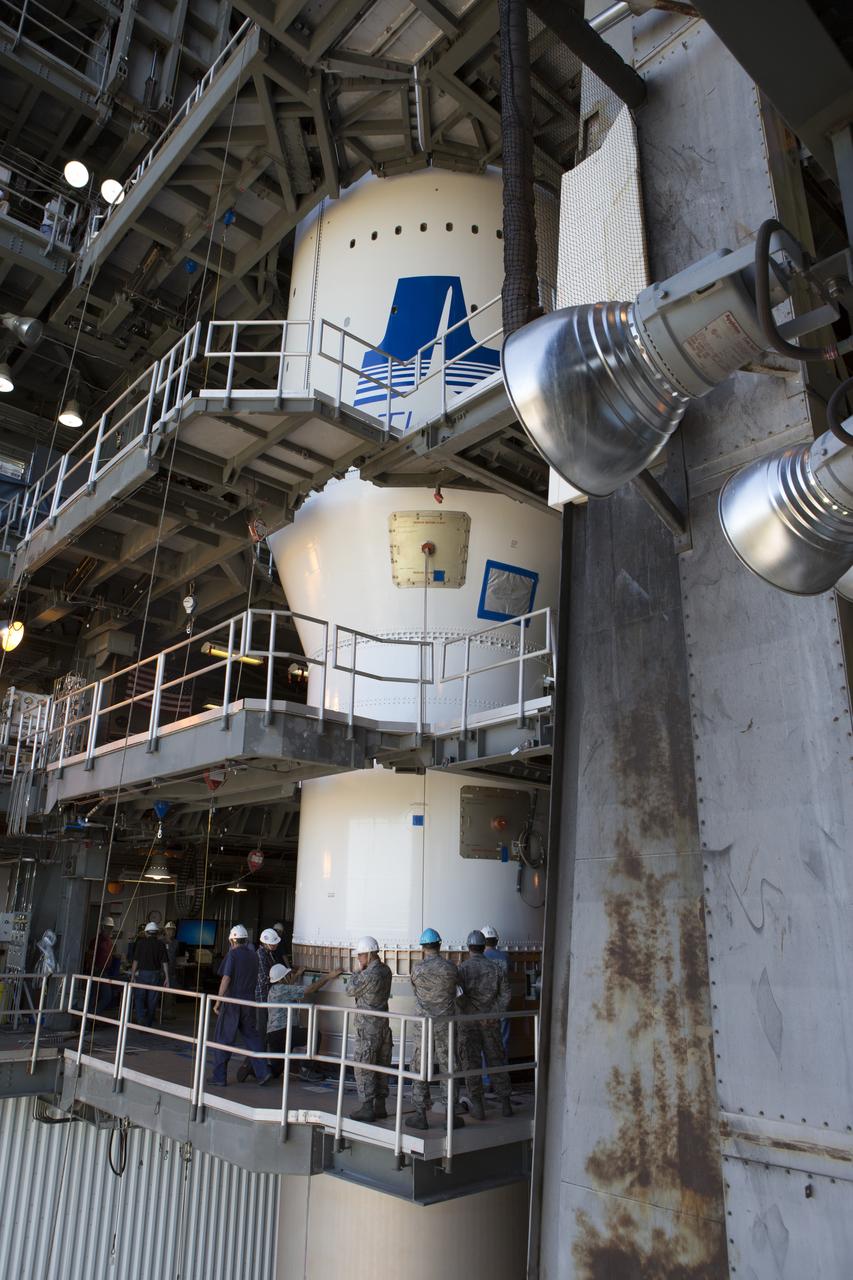
The United Launch Alliance Atlas V Centaur second stage has been mated to the first stage in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket in November. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.

Operations are underway to stack the United Launch Alliance Atlas V Centaur second stage onto the first stage in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket in November. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
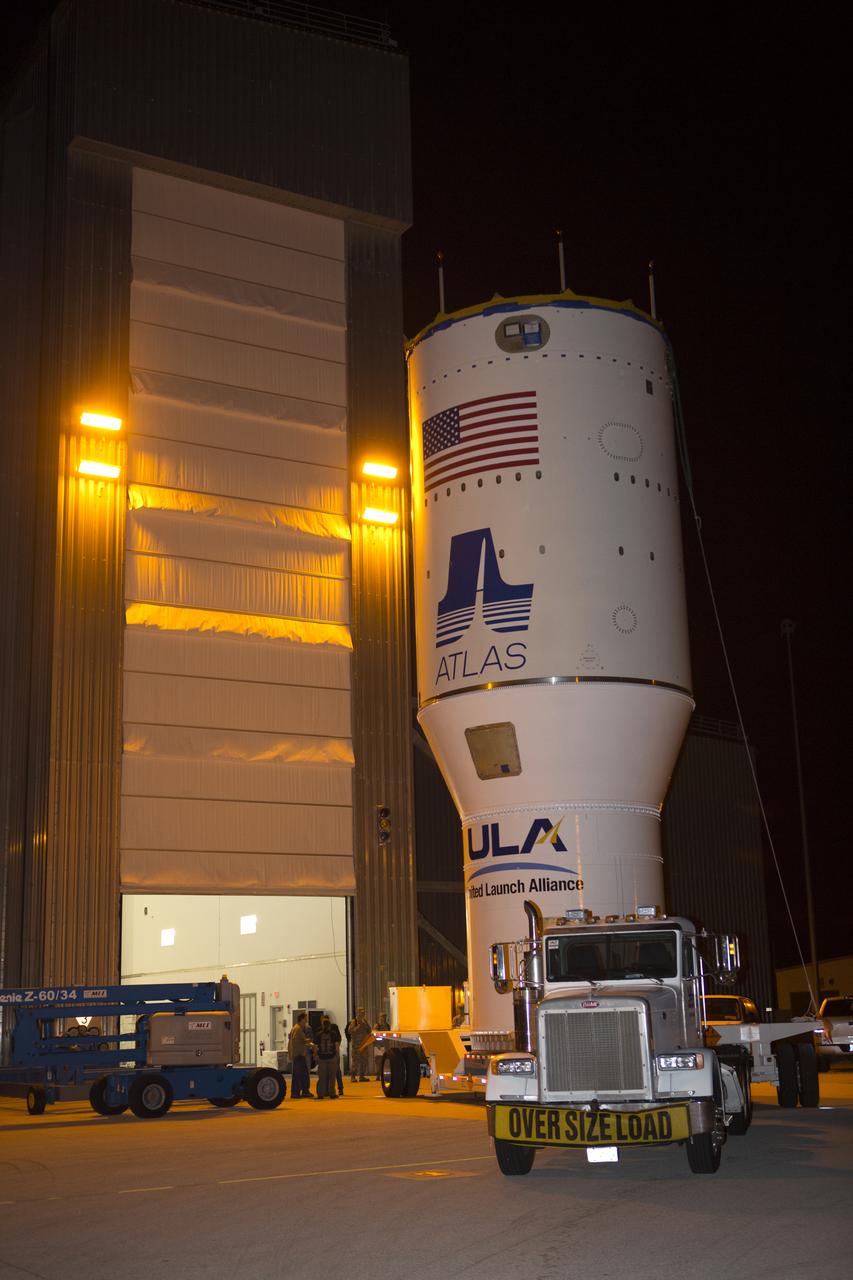

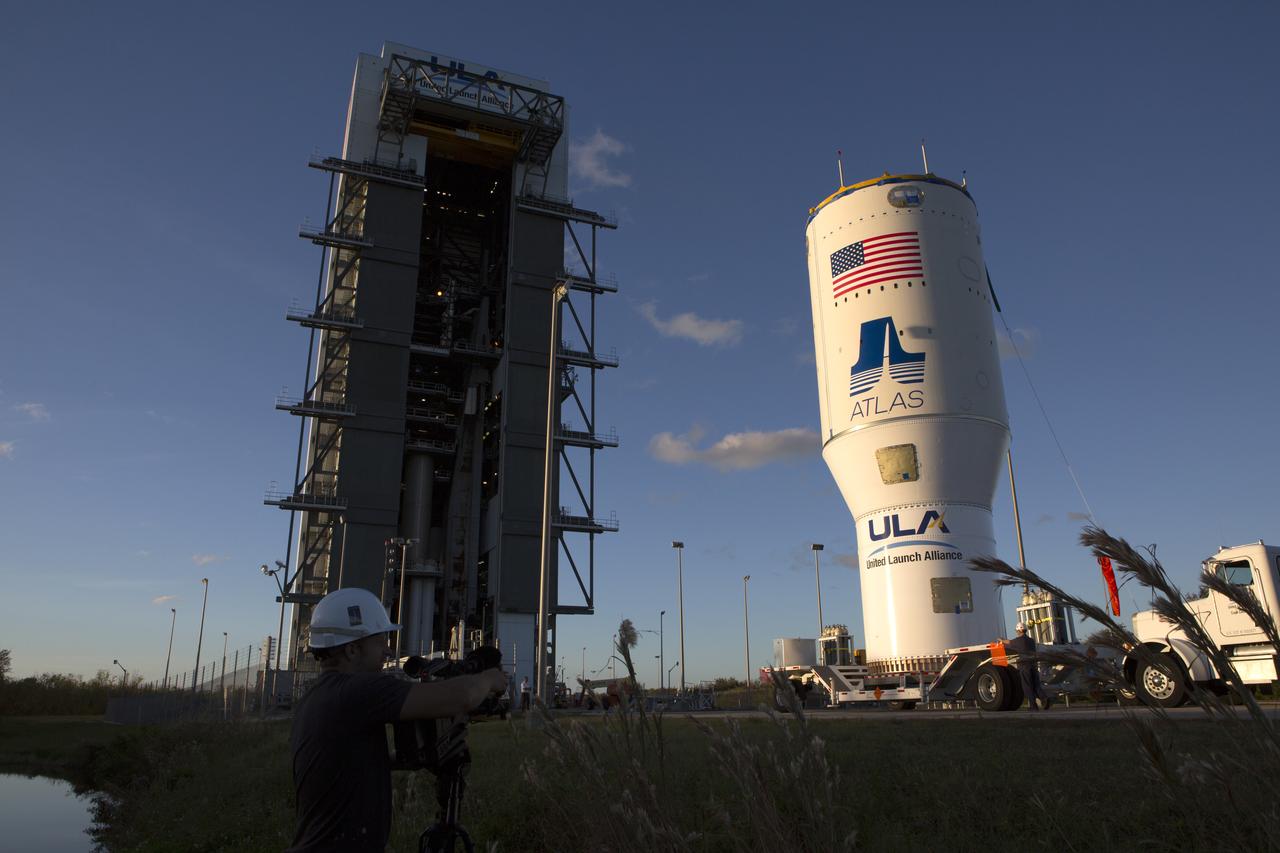
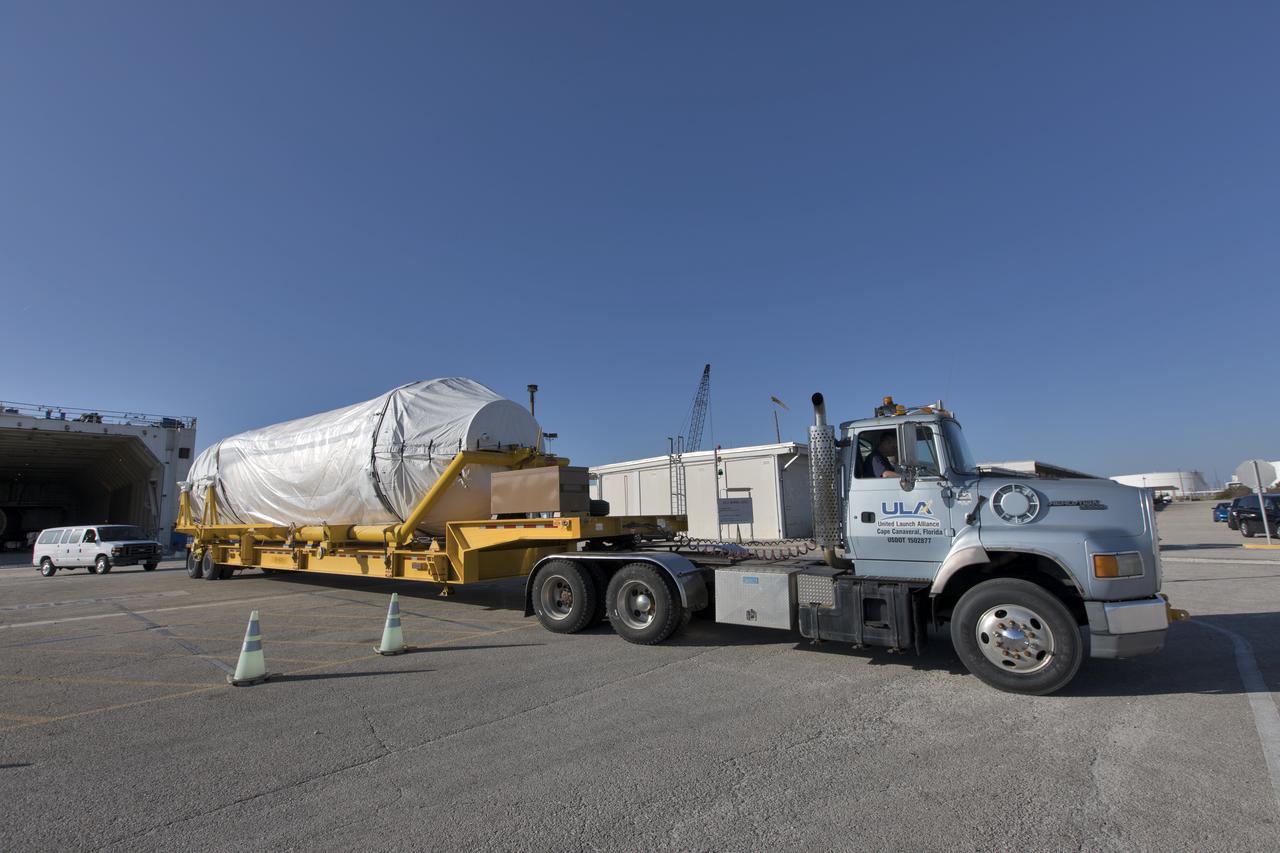
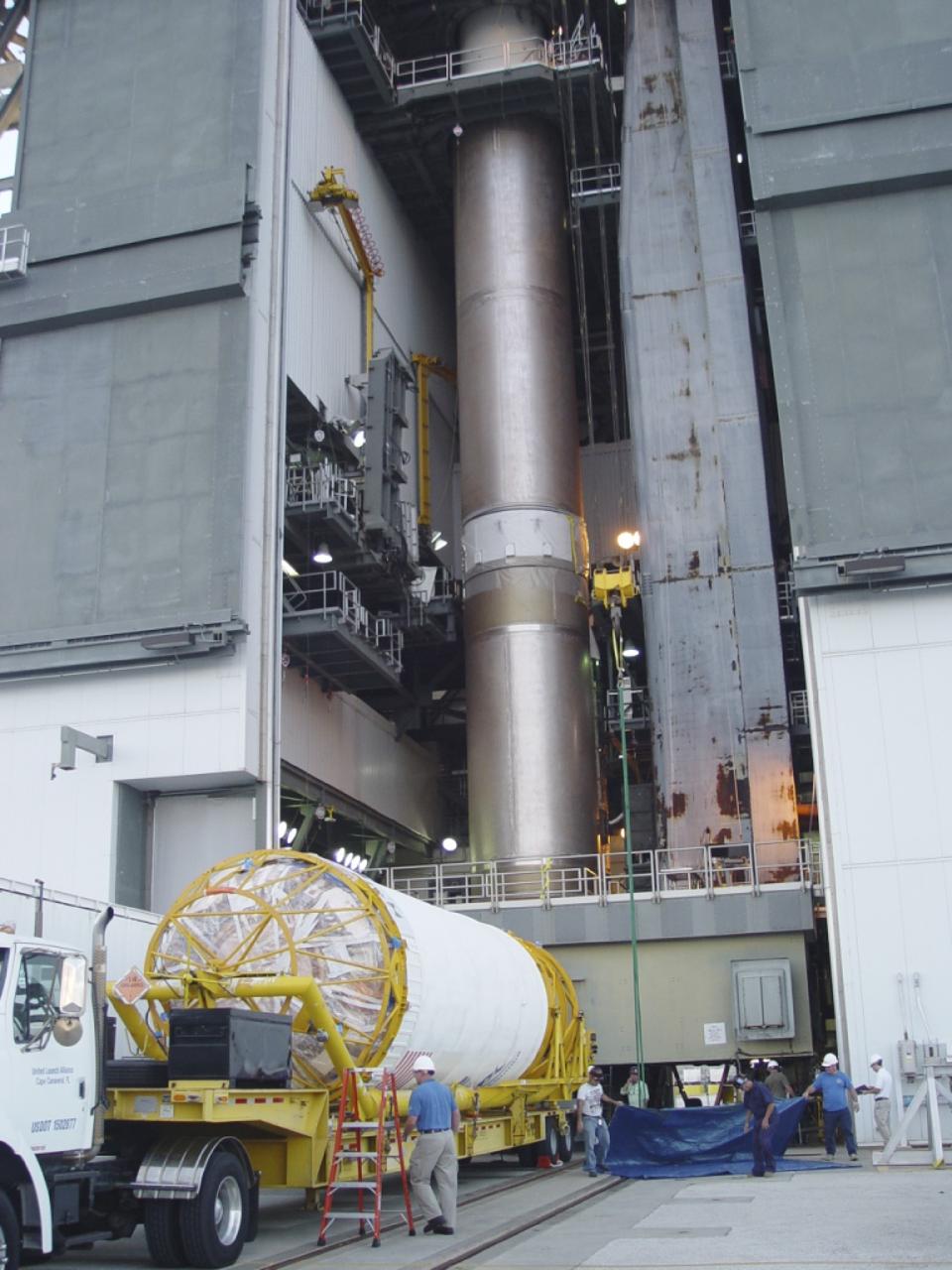
The United Launch Alliance Atlas V Centaur second stage departs the Launch Vehicle Integration Facility aboard a transport trailer for delivery to the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket in November. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
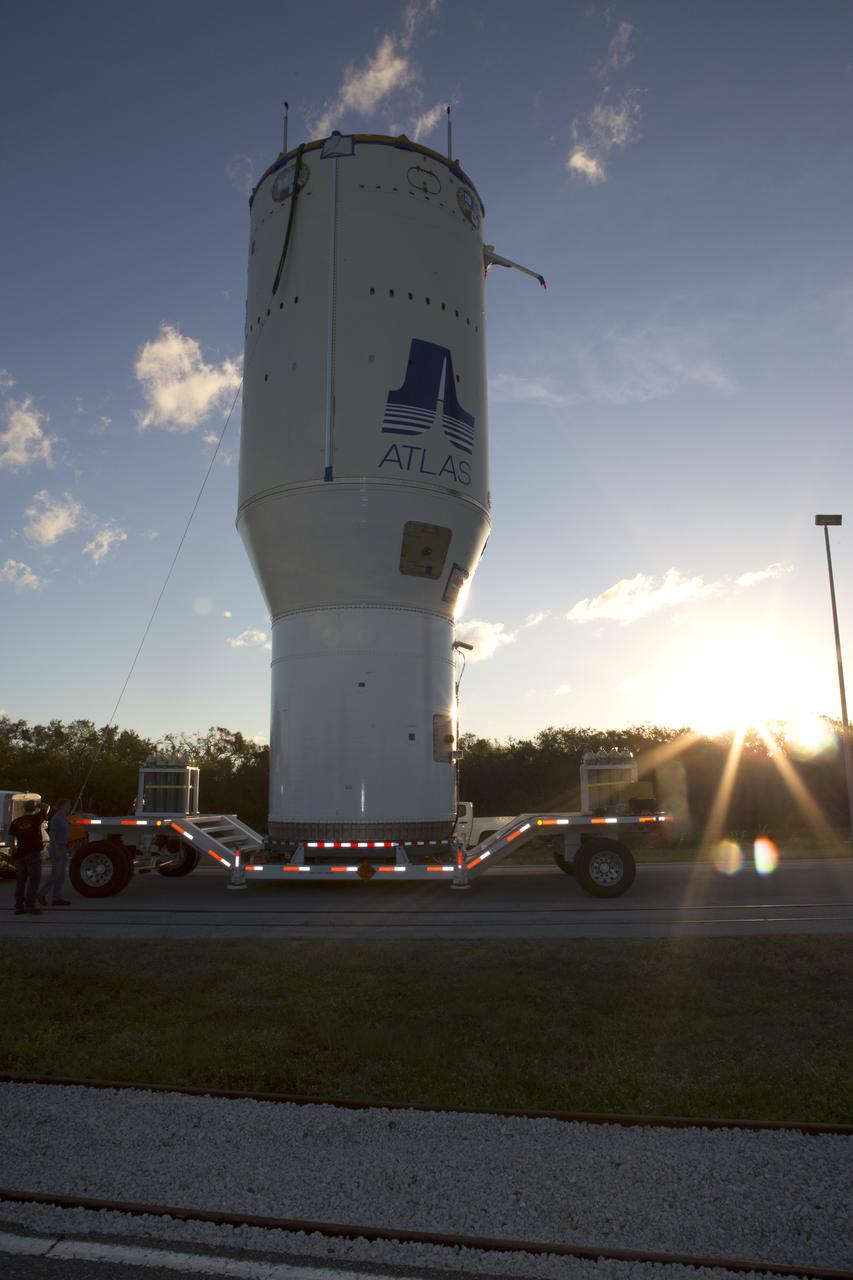

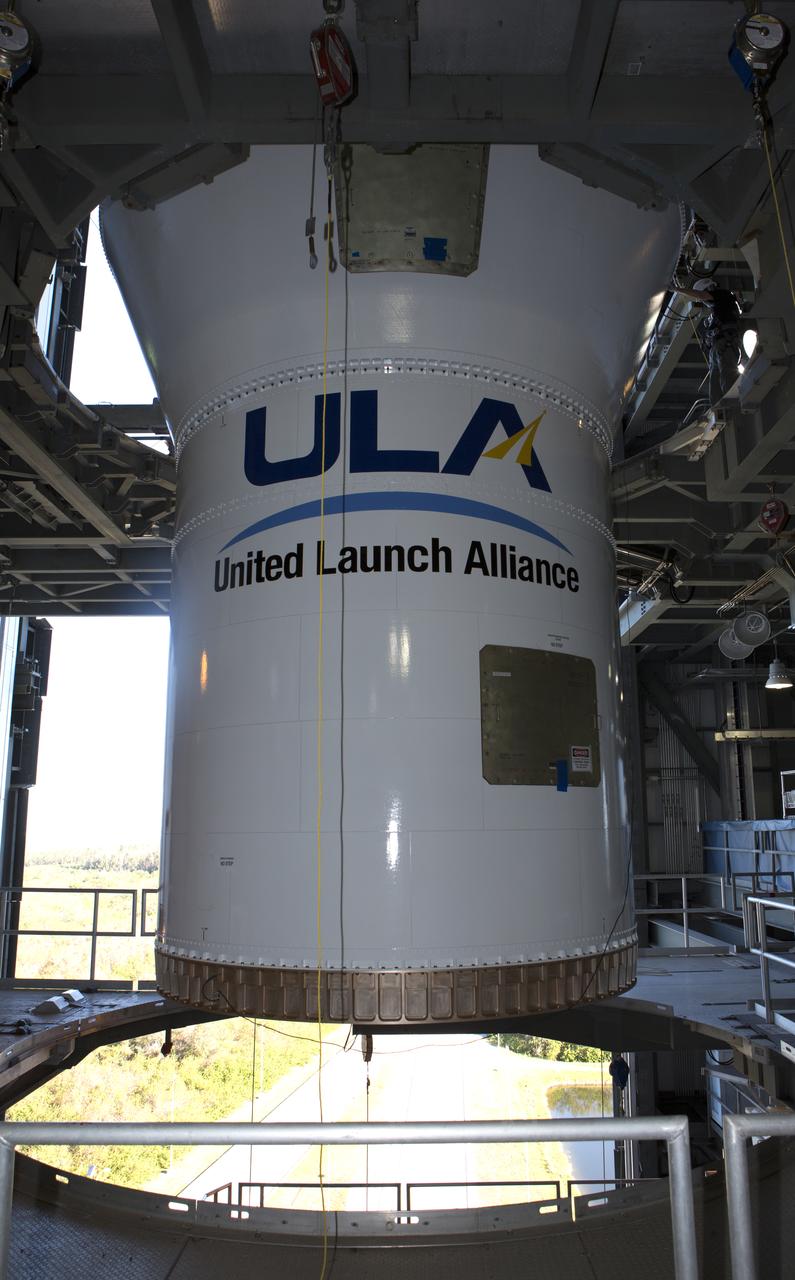
The United Launch Alliance Atlas V Centaur second stage is on a transport trailer for delivery to the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket in November. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
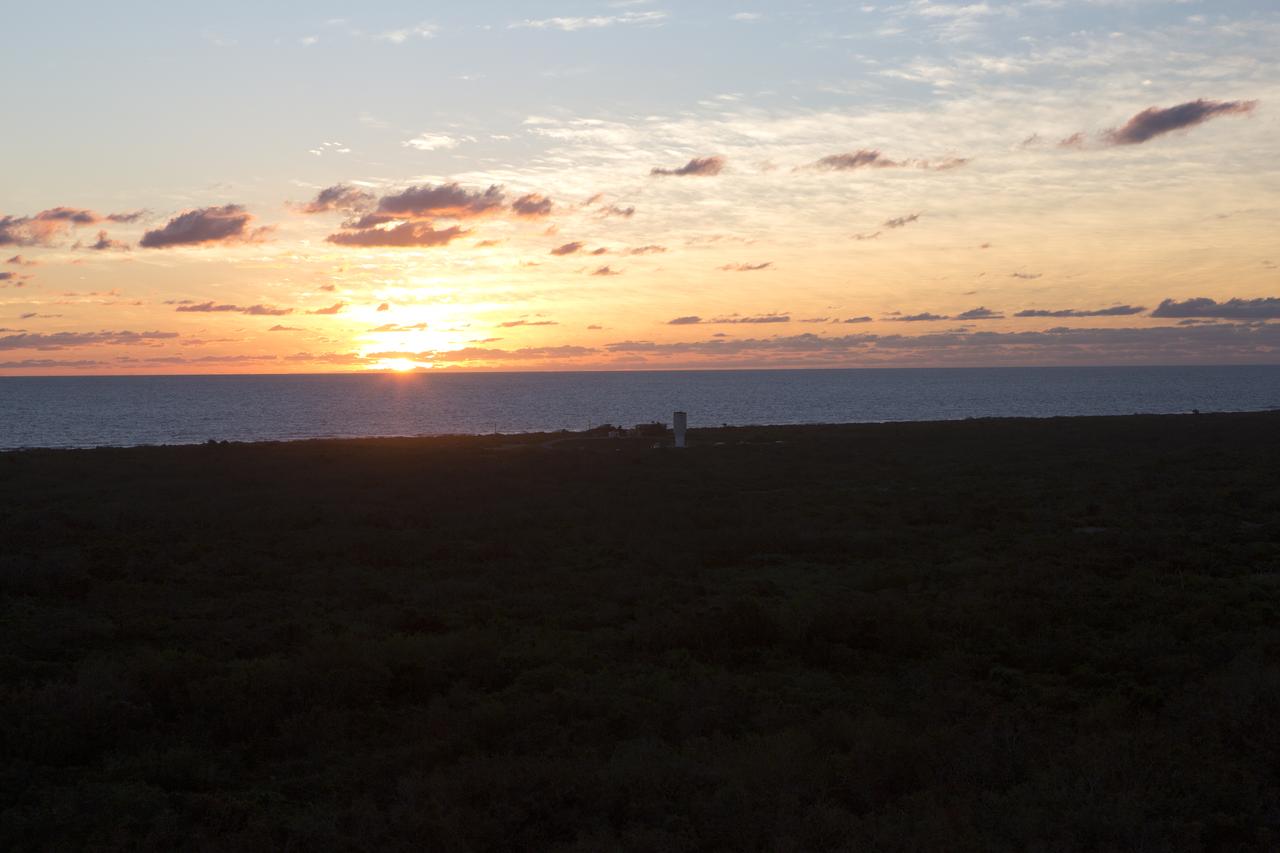

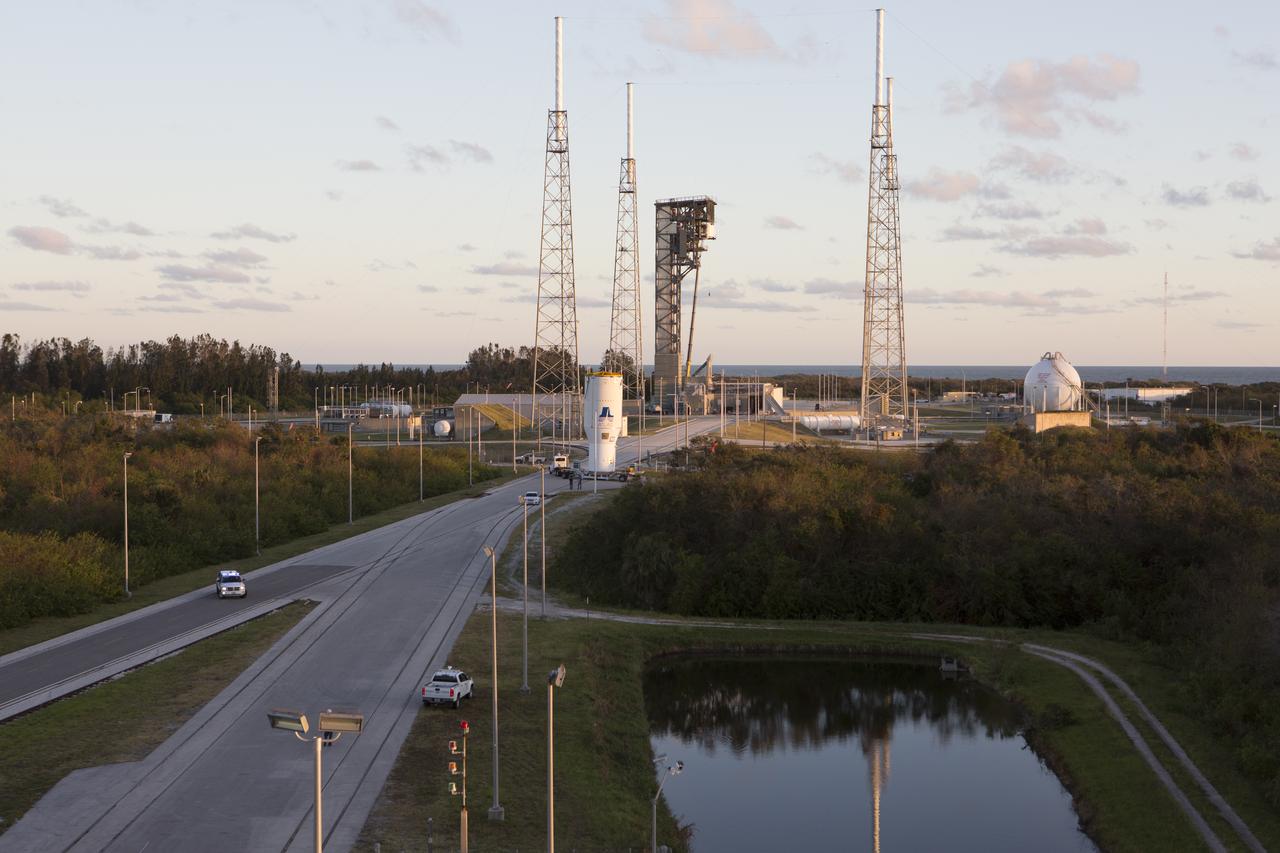
A colorful sunrise fills the early morning sky as the United Launch Alliance Atlas V Centaur second stage is transported along the beach road to the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket in November. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
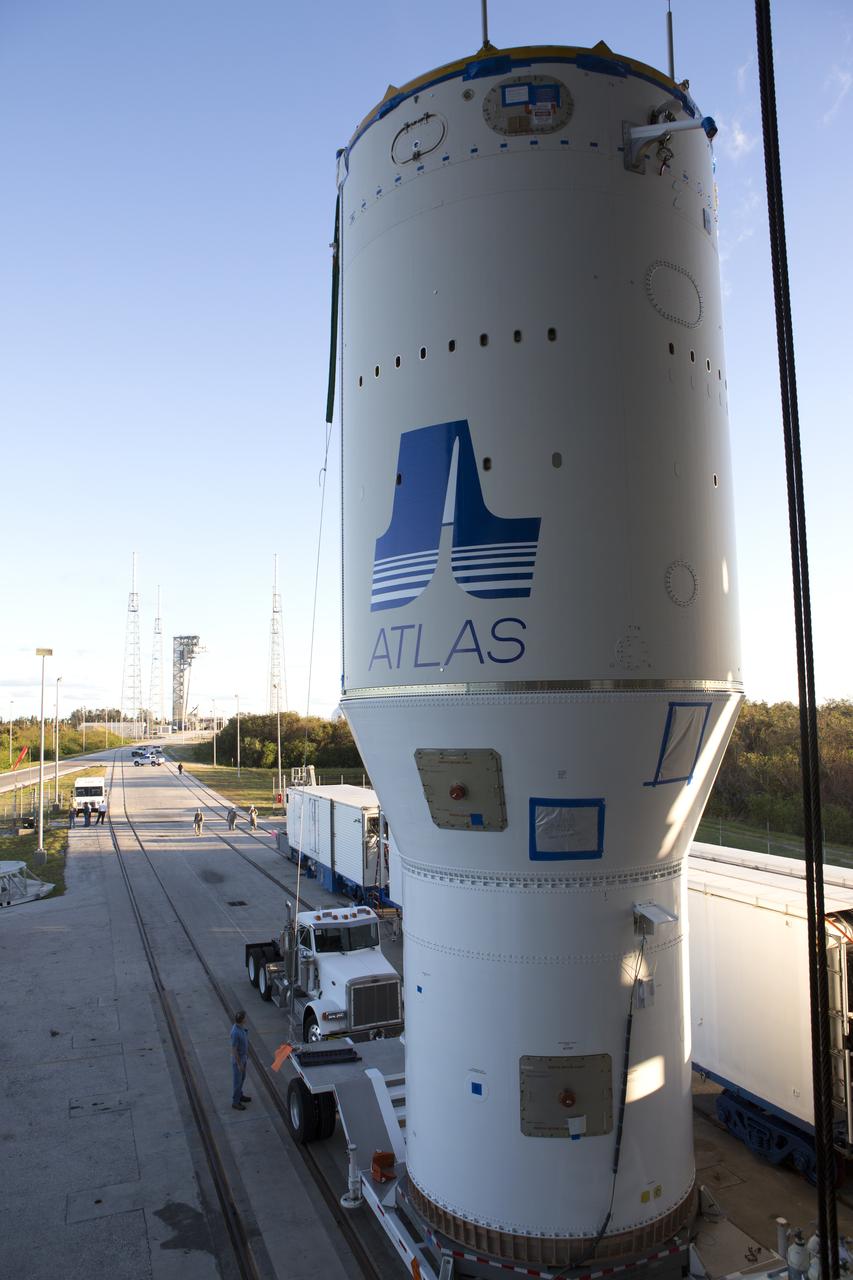

A close-up view of the United Launch Alliance Atlas V Centaur second stage as it travels to the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket in November. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
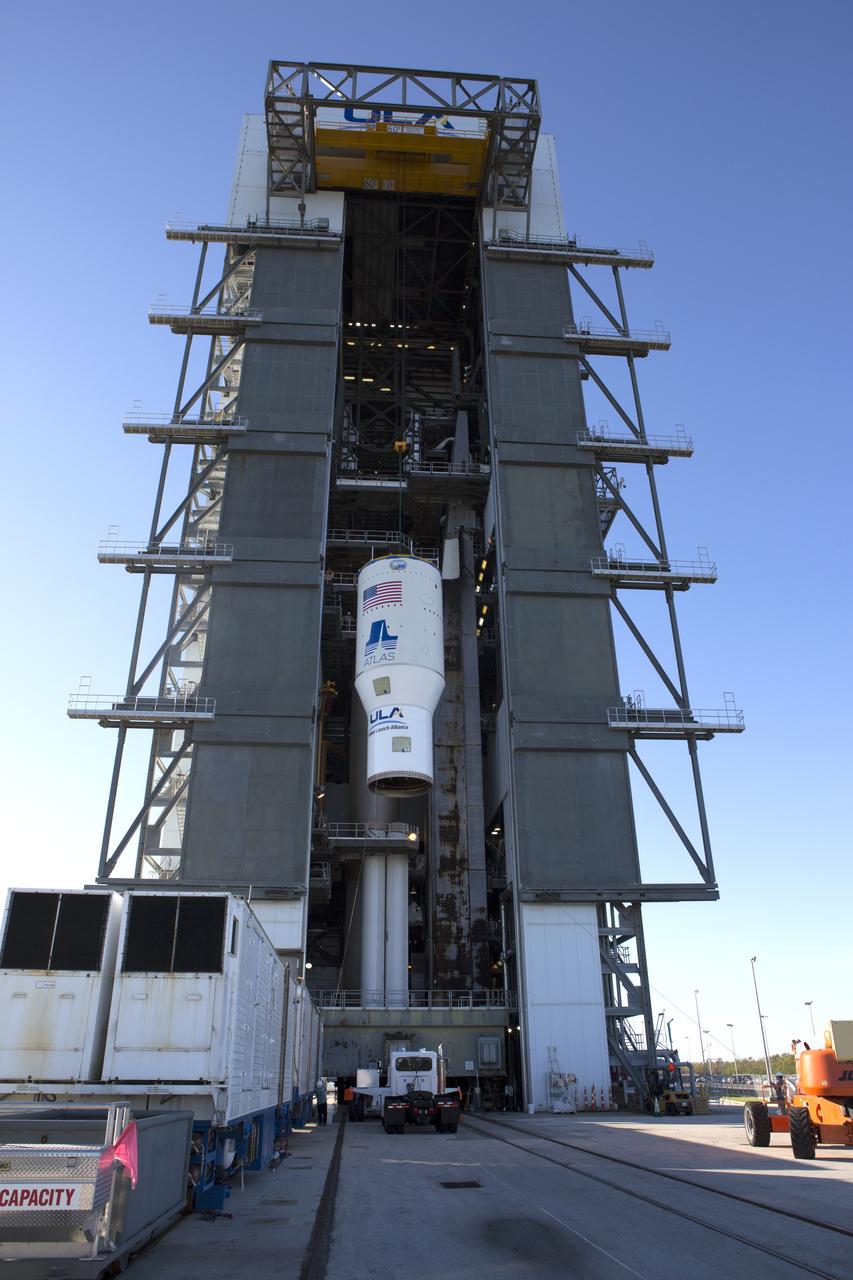

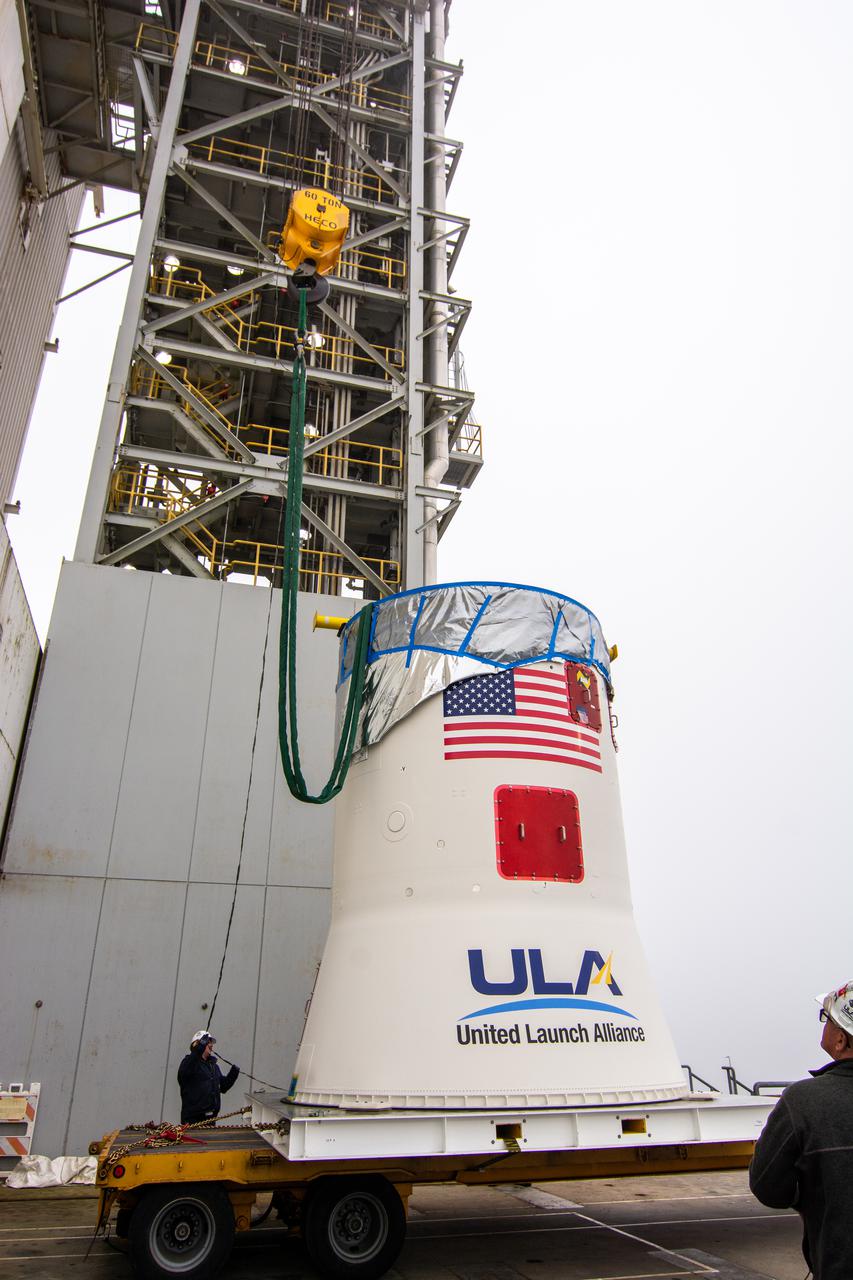
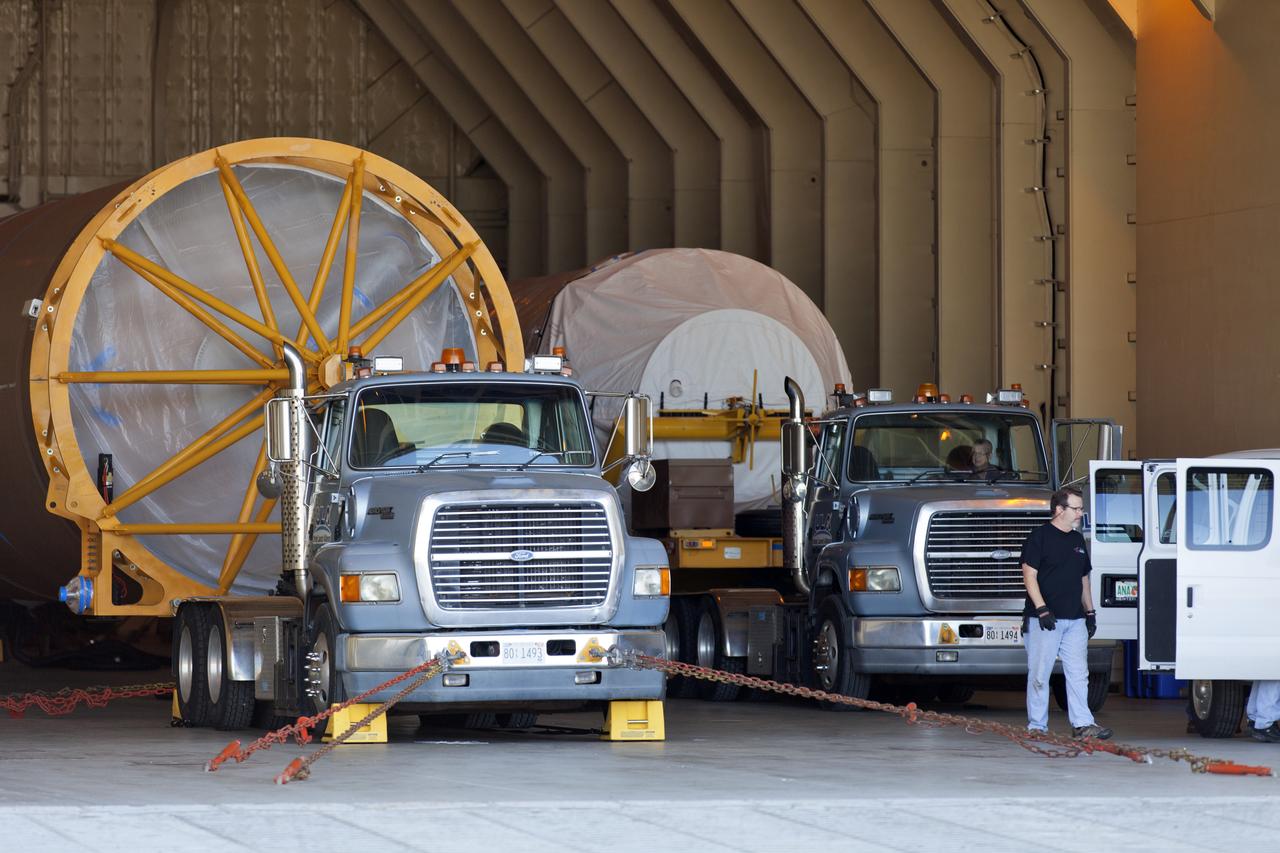
The United Launch Alliance Atlas V Centaur second stage is lifted up by crane for transfer into Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket in November. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.

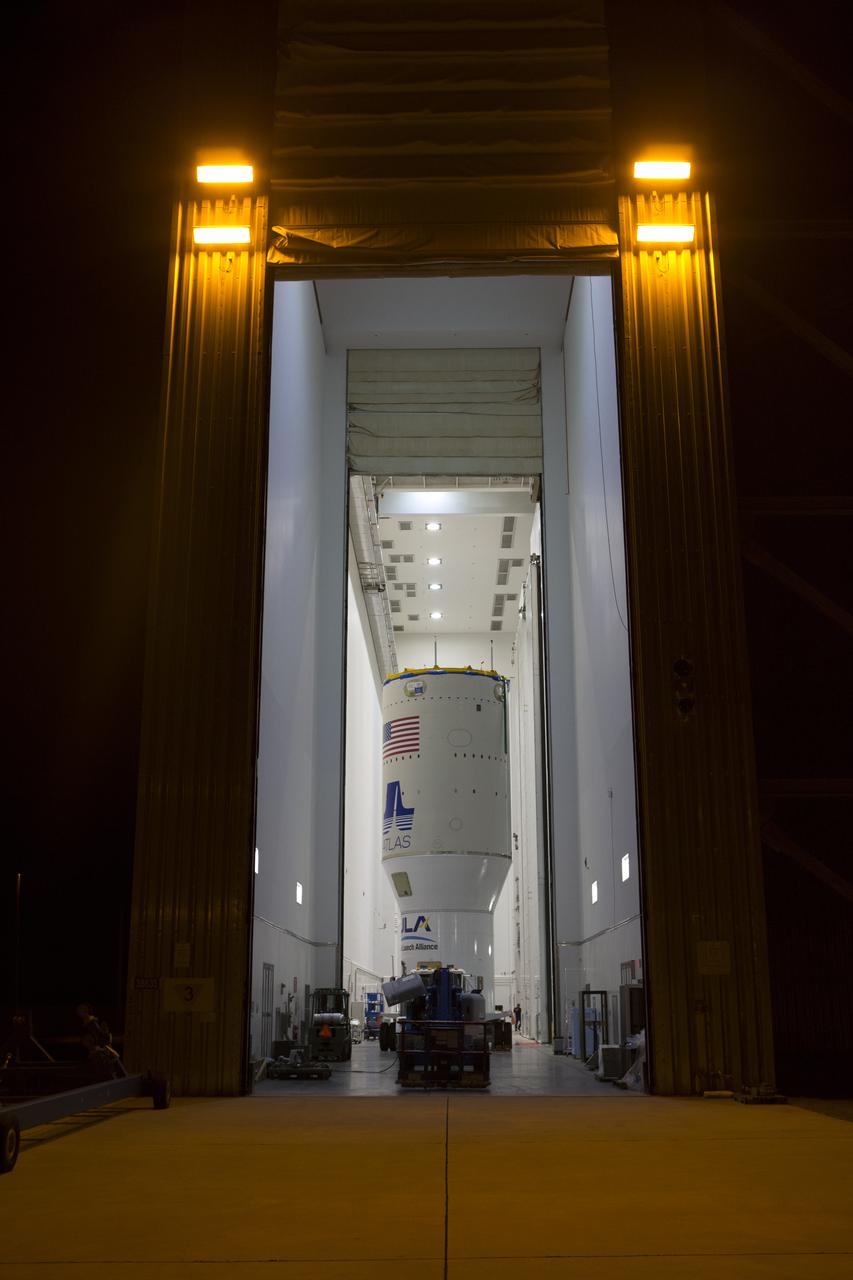
The United Launch Alliance Atlas V Centaur second stage is on its way to the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket in November. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V Centaur second stage emerges from the Launch Vehicle Integration Facility aboard a transport trailer for delivery to the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket in November. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V Centaur second stage has been lifted up and transferred into the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket in November. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.

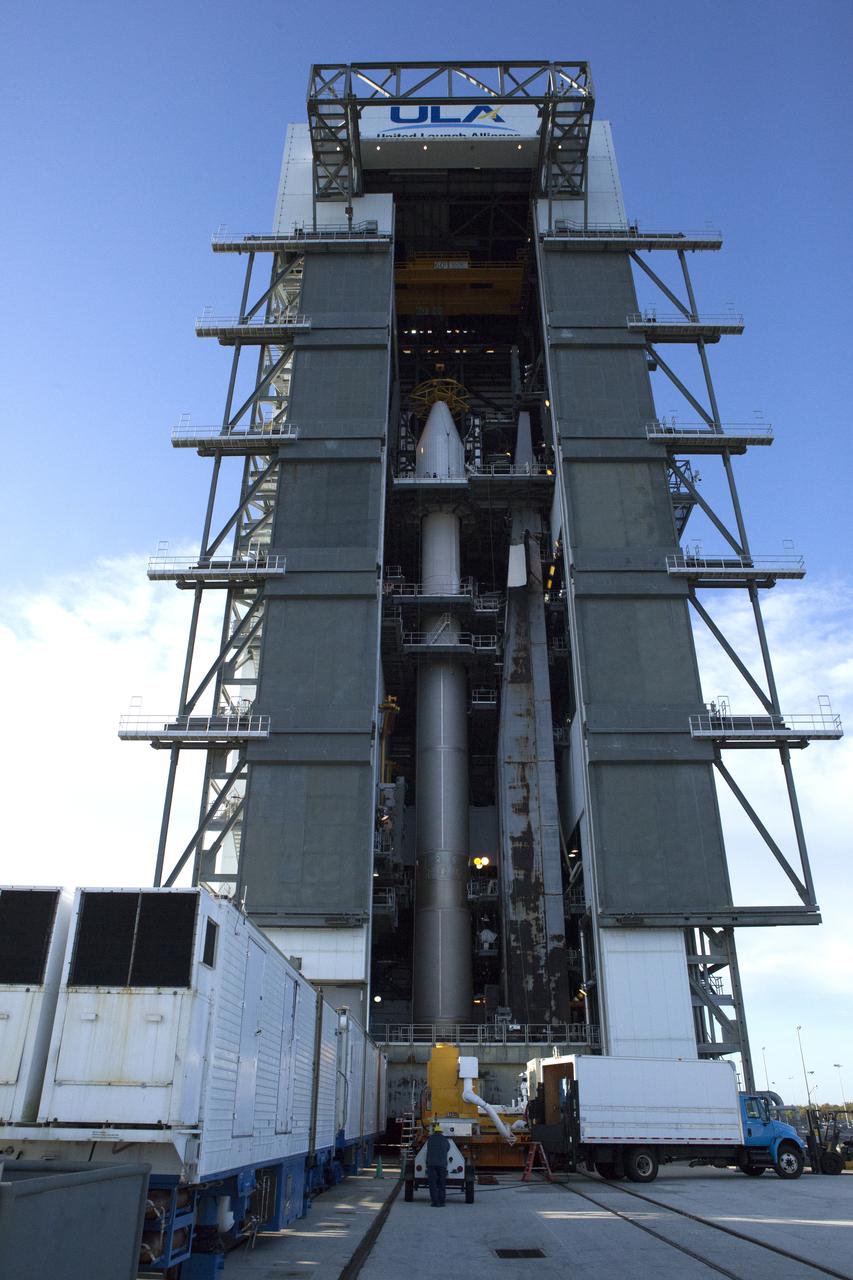
The United Launch Alliance Atlas V Centaur second stage arrives at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket in November. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
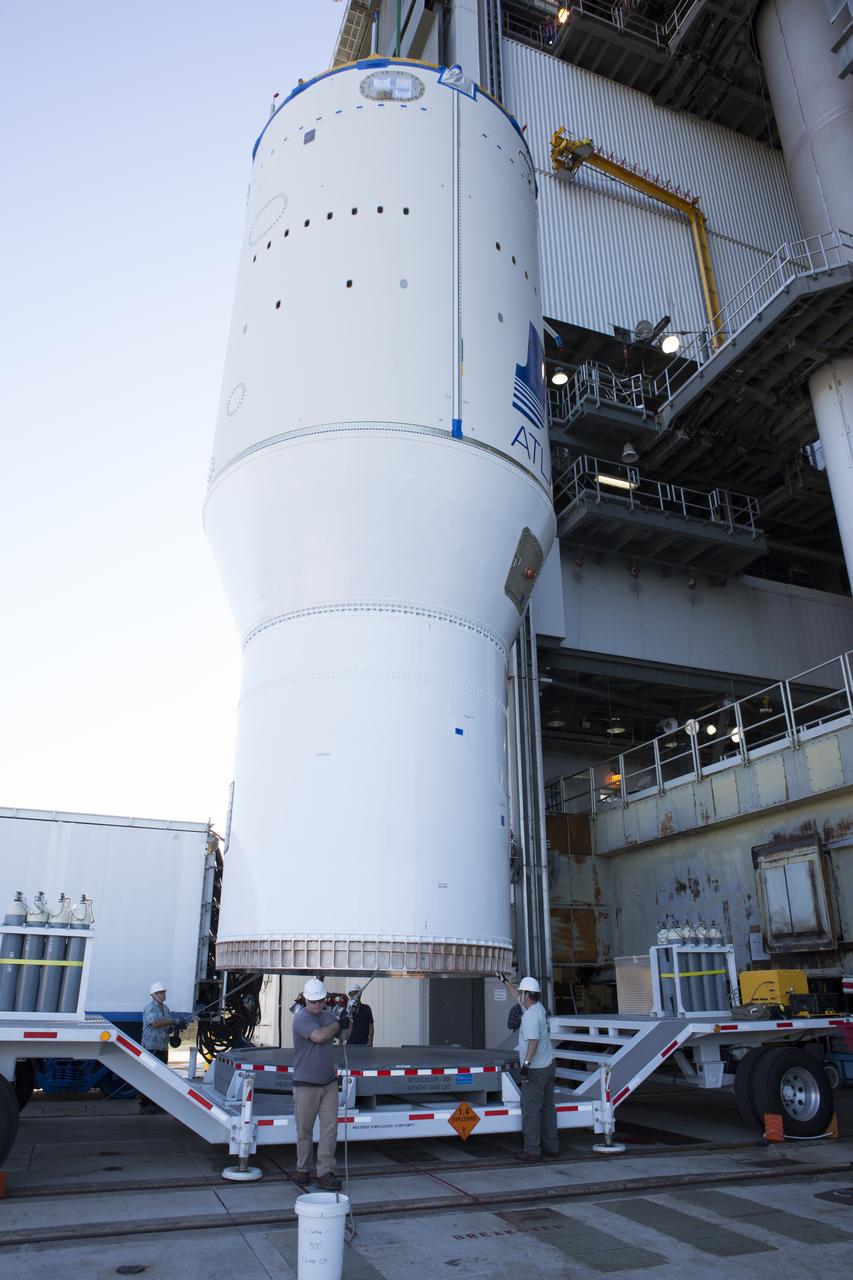

United Launch Alliance team members assist as operation begin to lift the Atlas V Centaur second stage into the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket in November. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
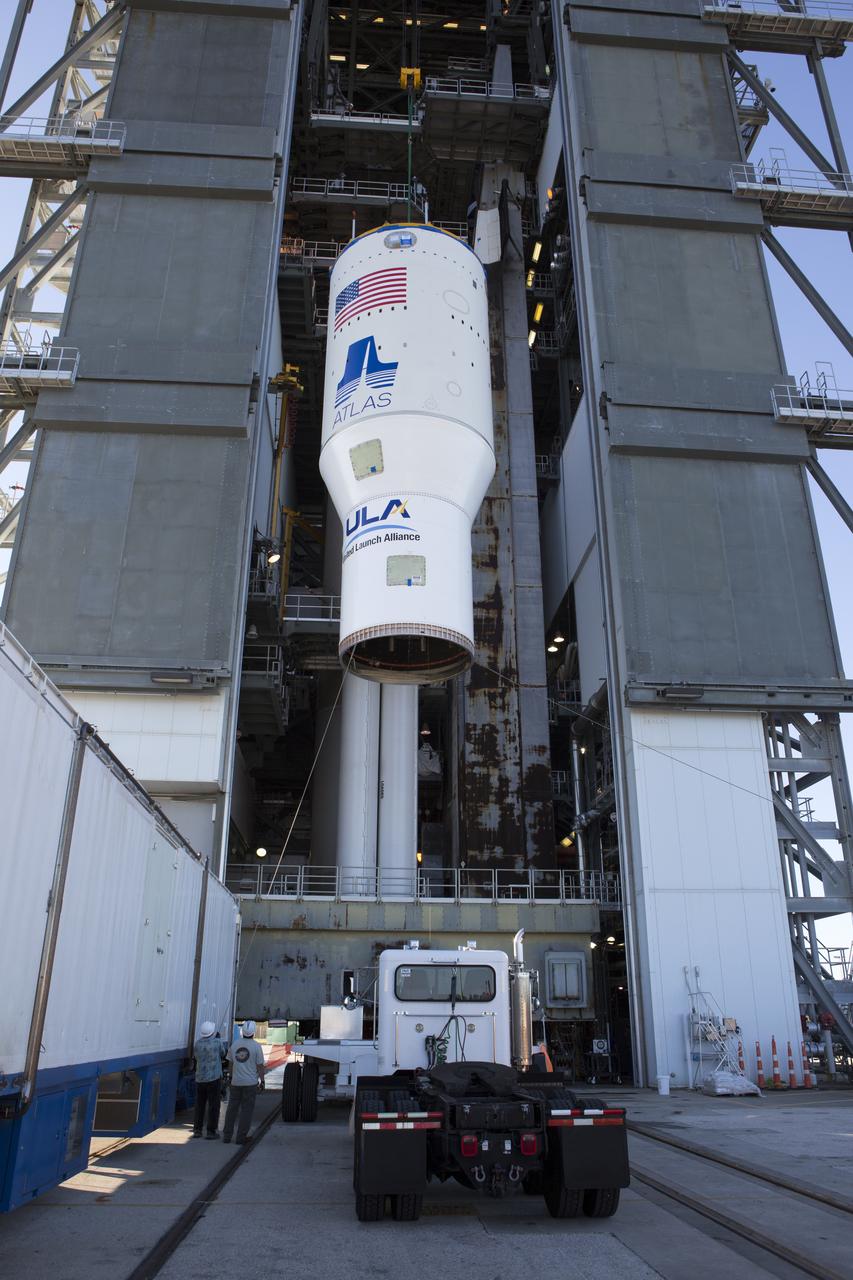

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V Centaur second stage is lifted up for transfer into the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket in November. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
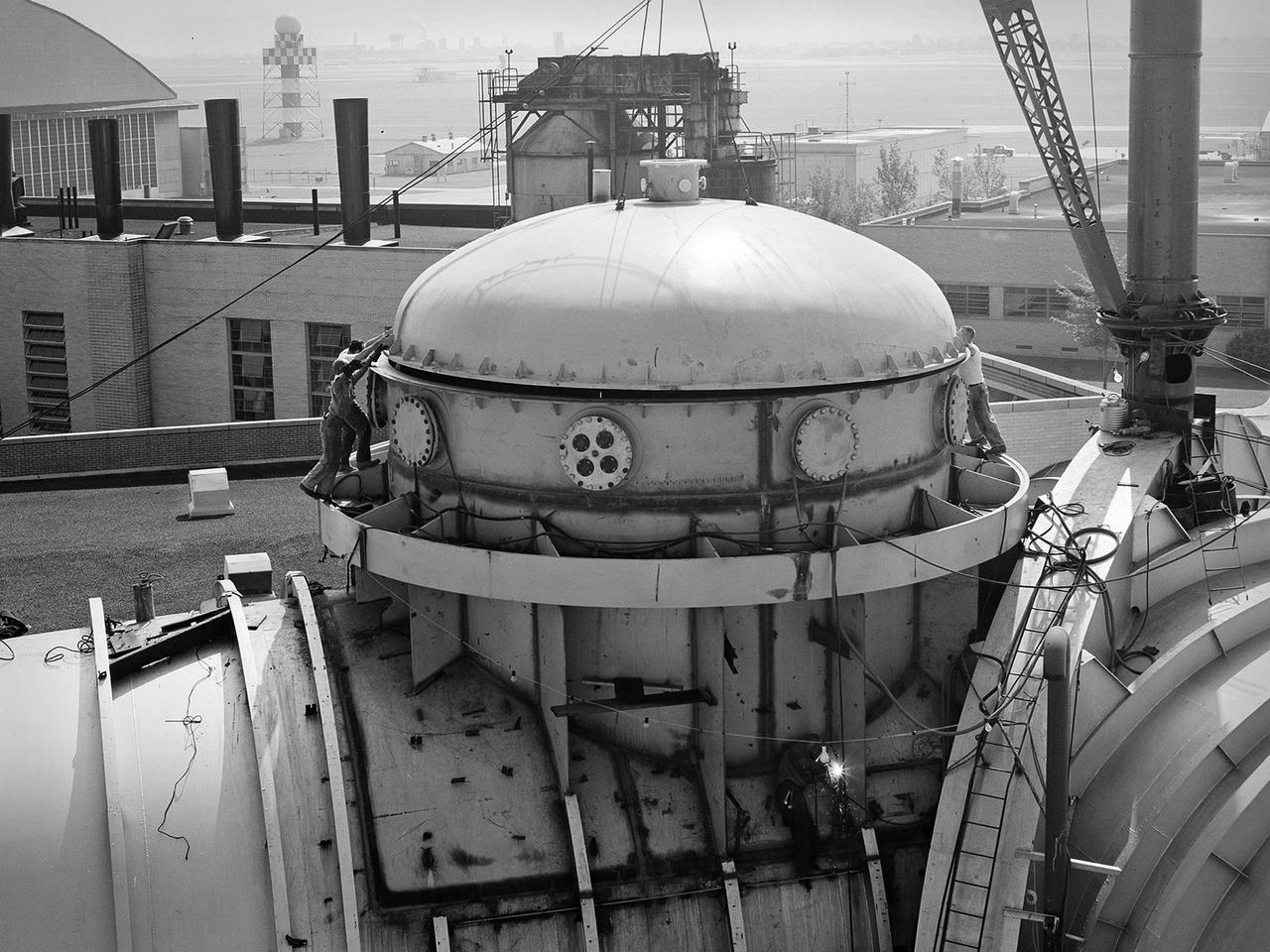

This 22.5-foot-diameter domed lid was added to the Space Power Chambers to allow the vertical installation of a Centaur second-stage rocket into the vacuum tank at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. The lid could be removed using a crane so that the Centaur could be lowered into the chamber. After a year of additional construction, the new dome and extension were completed in September 1963. The feature became the facility’s distinctive attribute. The modifications to the facility began two years earlier, however. In 1961, NASA Lewis management decided to convert the Altitude Wind Tunnel into two large test chambers and later renamed it the Space Power Chambers. The conversion included the removal of the tunnel’s internal components and the insertion of bulkheads to seal off the new chambers within the tunnel. The 100-foot-long vacuum tank was created in the east leg of the tunnel, which was 31 feet in diameter at one end and 27 feet in diameter at the other. With the transfer of the Centaur second-stage rocket program to NASA Lewis in October 1962, the newly completed Space Power Chambers facility had to be modified to accommodate the space vehicle. The goal of the test engineers was to subject the Centaur to long durations in conditions that would replicate those encountered during its missions in space. The facility was used for a variety of tests on the Centaur second-stage rocket until the early 1970s.
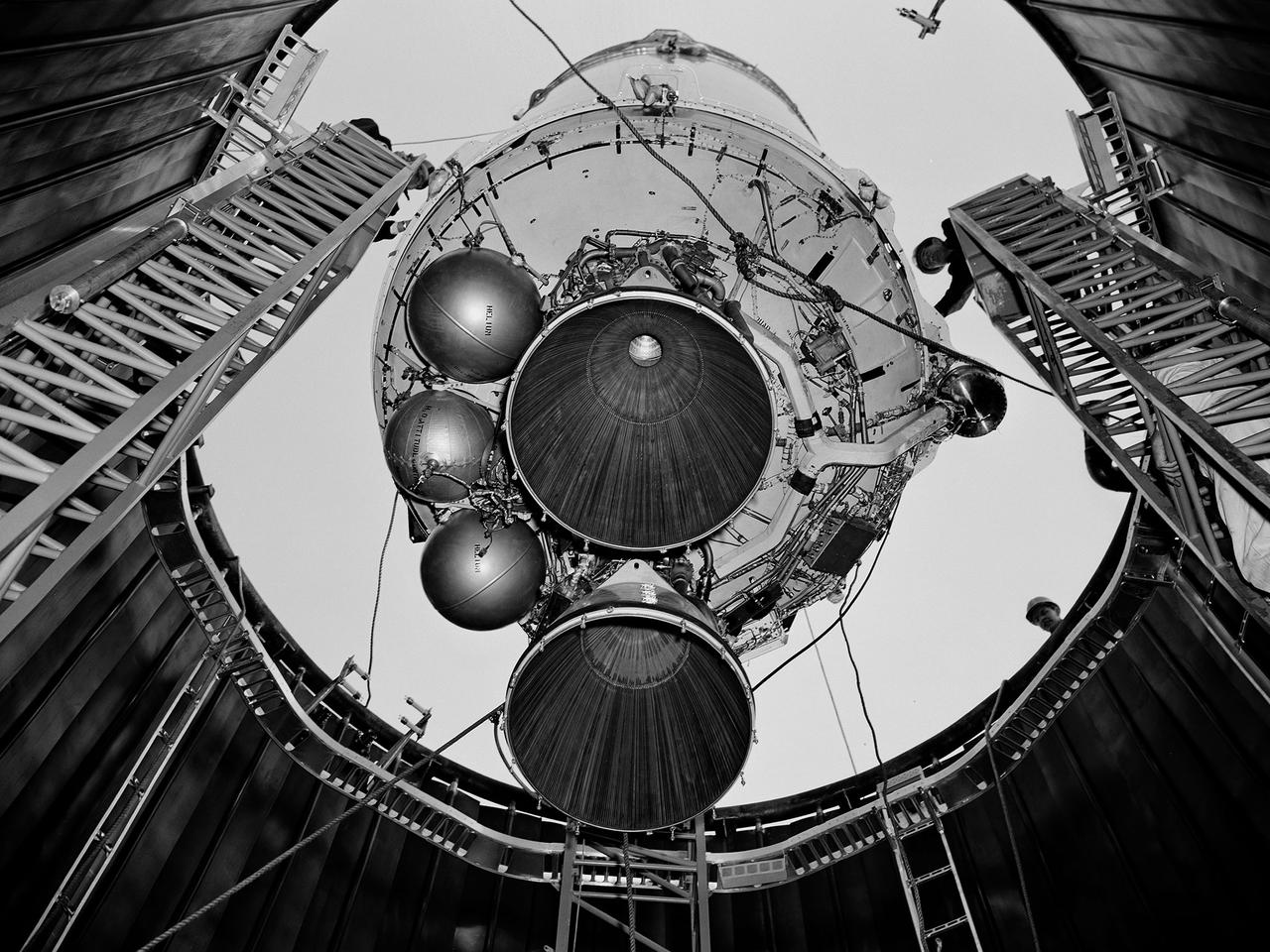

A Centaur second-stage rocket is lowered into the vacuum tank inside the Space Power Chambers at NASA’s Lewis Research Center. Centaur was to be paired with an Atlas booster to send the Surveyor spacecraft to the moon as a precursor to the Apollo landings. Lewis was assigned responsibility for the Centaur Program after the failure of its first developmental flight in May 1962. Lewis’ Altitude Wind Tunnel was converted into two large test chambers—the Space Power Chambers. The facility’s vacuum chamber, seen here, allowed the Centaur to be stood up vertically and subjected to atmospheric conditions-- pressures, temperature, and radiation--similar to those it would encounter in space. The Centaur for these tests was delivered to Cleveland in a C‒130 aircraft on September 27, 1963. The rocket was set up in the facility’s high bay where Lewis technicians and General Dynamics consultants updated its flight systems to match the upcoming Atlas-Centaur‒4 mission. Months were spent reharnessing the Centaur’s electronics, learning about the systems, and being taught how to handle flight hardware. By early spring 1964, the extensive setup of both the spacecraft and the chamber was finally completed. On March 19 the Centaur was rolled out from the shop, hoisted high into the air by a crane, and lowered into the waiting space tank. Researchers were able to verify that the Centaur’s electronics and electrical systems functioned reliably in a space environment.

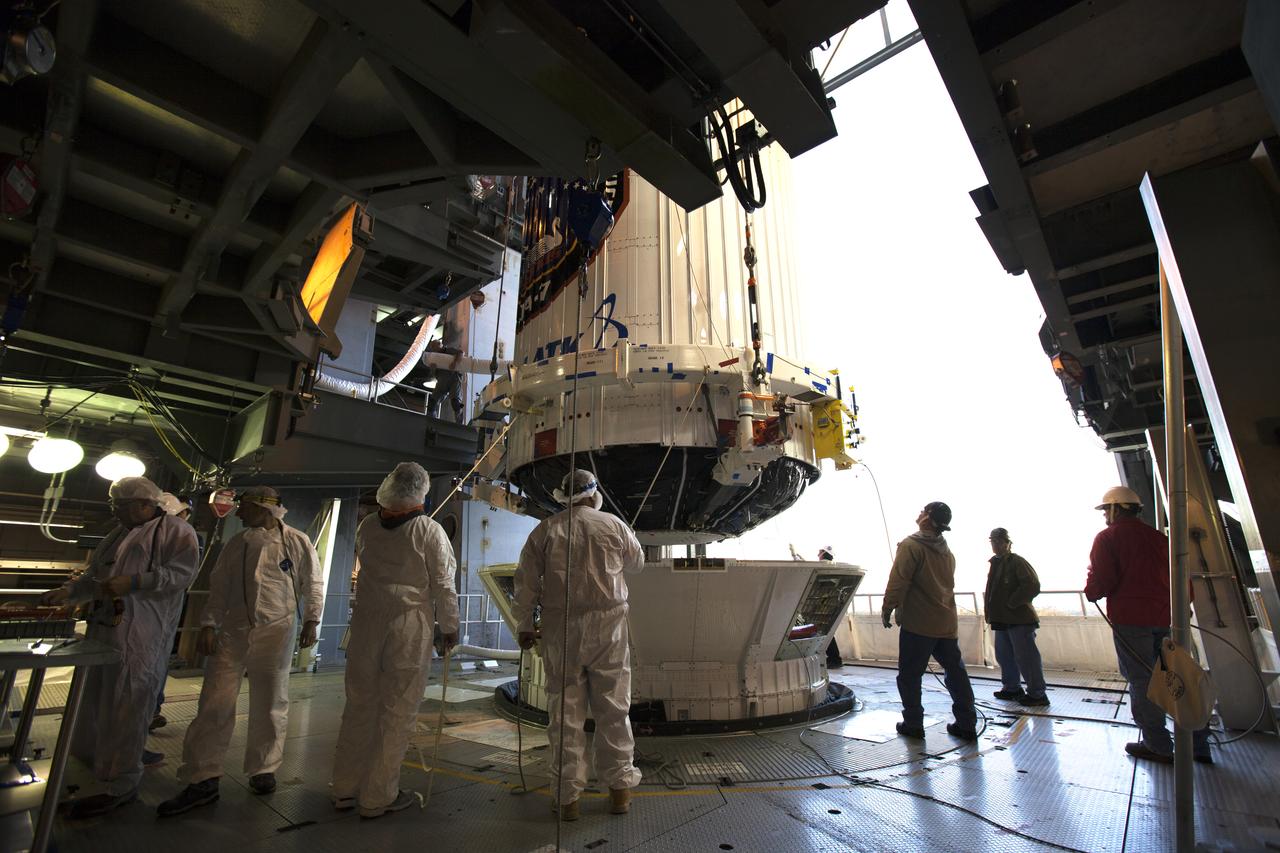
The payload fairing containing the Orbital ATK Cygnus pressurized cargo module is mated to the Centaur upper stage, or second stage, of the United Launch Alliance (ULA) rocket in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V from pad 41. Cygnus will deliver 7,600 pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.

The payload fairing containing the Orbital ATK Cygnus pressurized cargo module is lowered onto the Centaur upper stage, or second stage, of the United Launch Alliance (ULA) rocket in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V from pad 41. Cygnus will deliver 7,600 pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
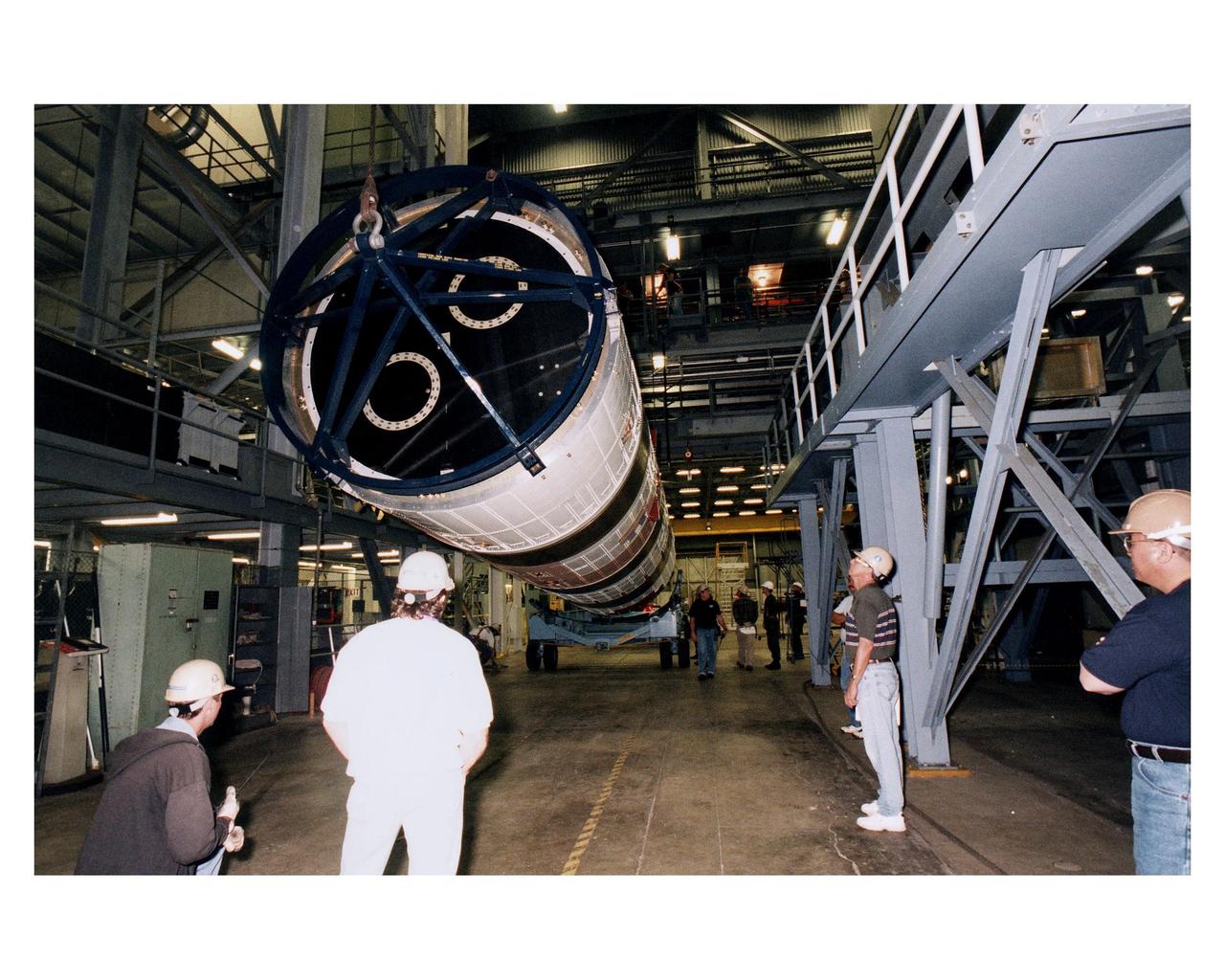

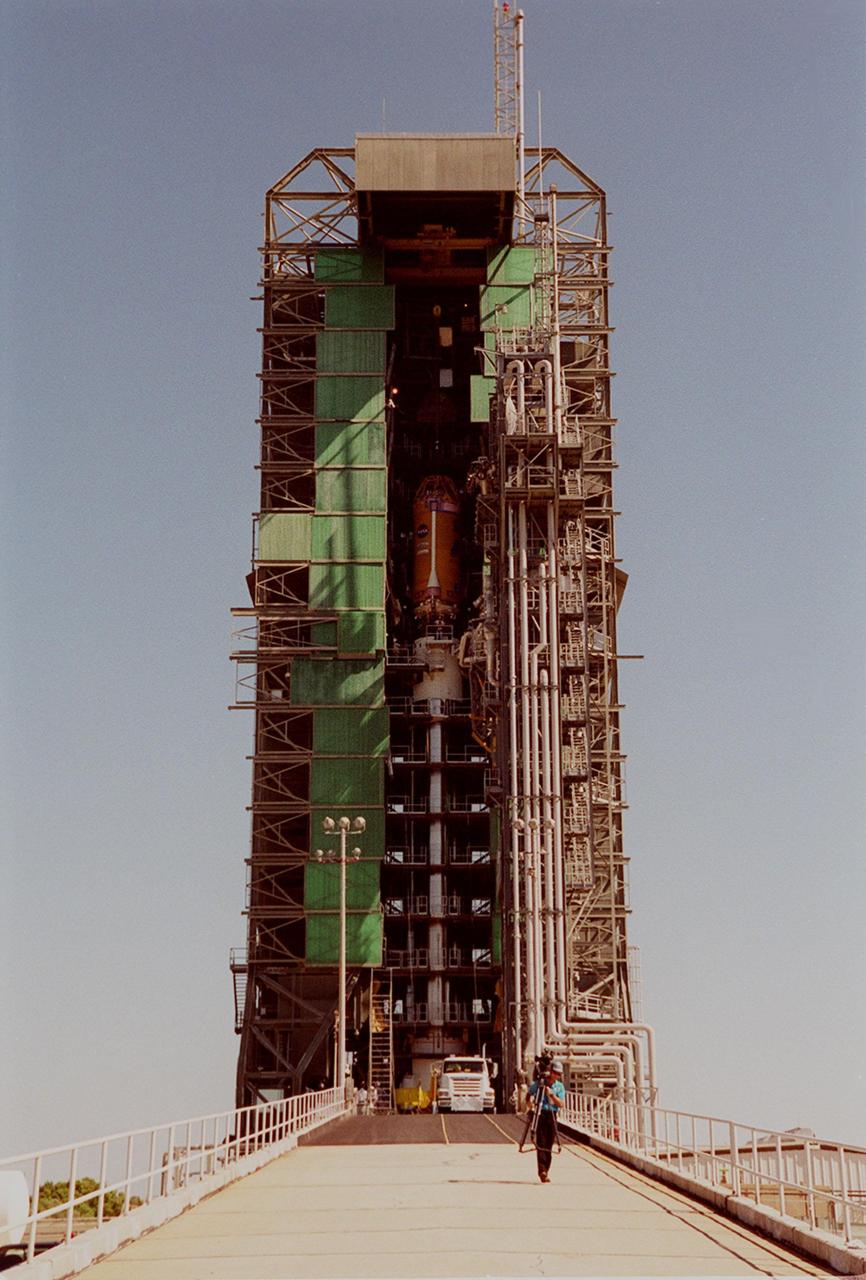
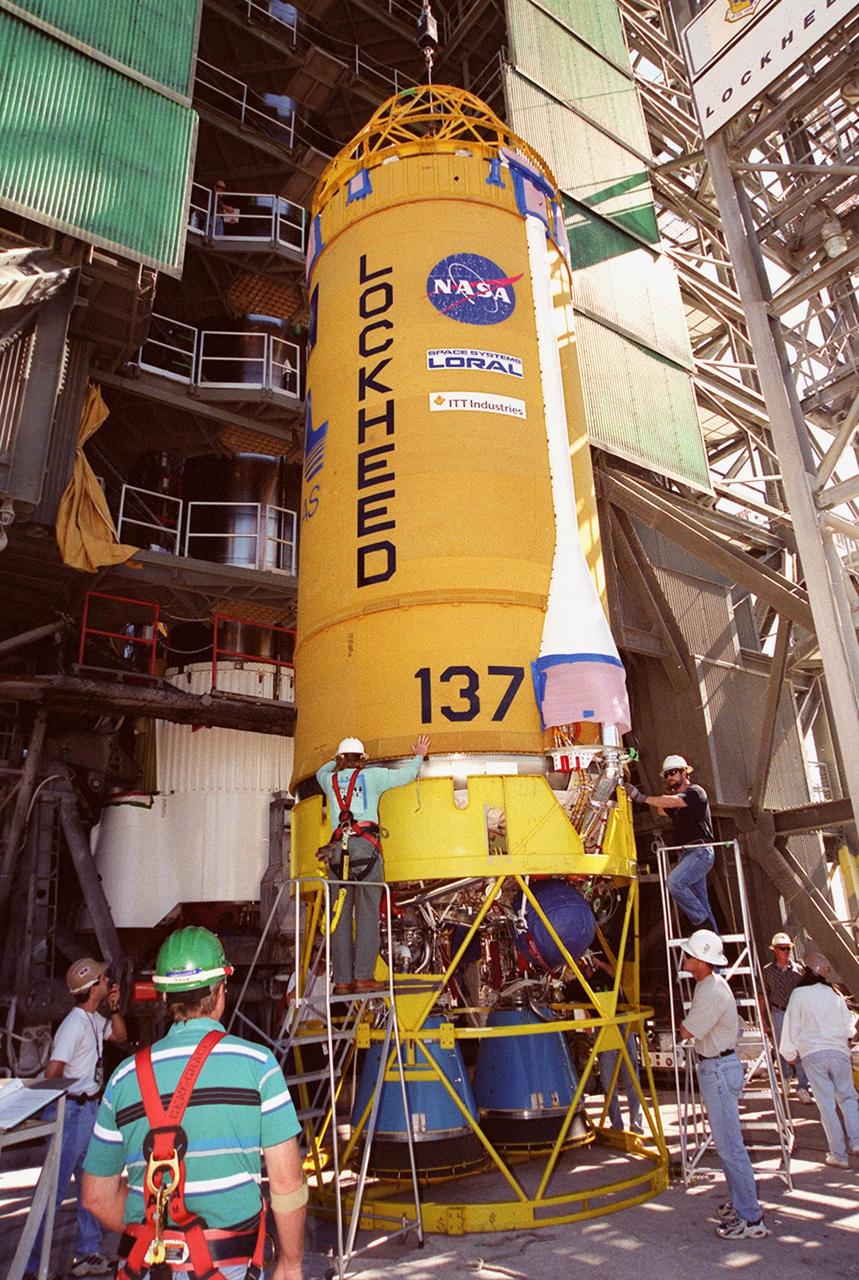
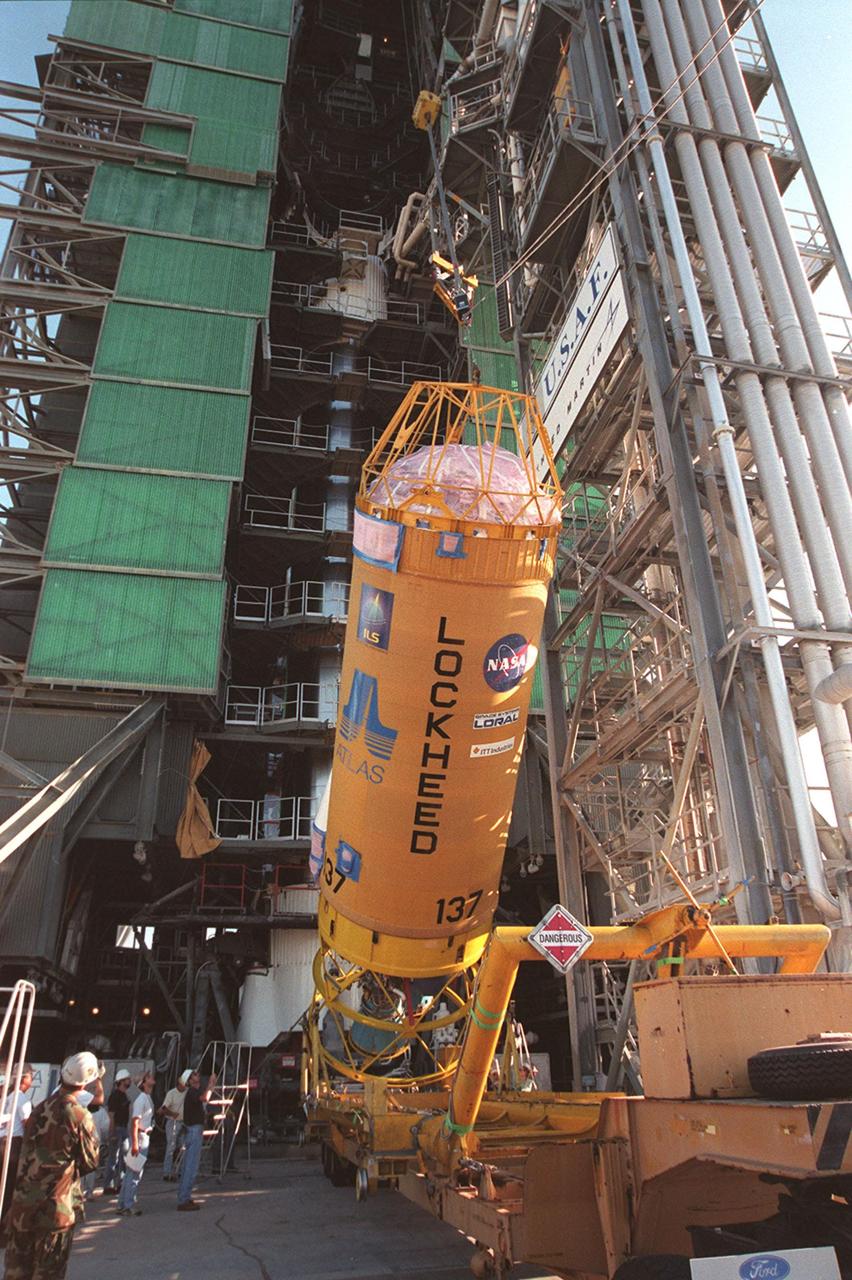
Lockheed Martin technicians and engineers in the Vertical Integration Building prepare to hoist the second stage of a Titan IV/Centaur expendable launch vehicle into a vertical position where it can lifted and mated to the first stage of the rocket. The Titan IVB rocket is the newest version of America's most powerful unmanned rocket. This rocket will be used for the Cassini mission to Saturn. The Cassini launch is targeted for October 6 from Launch Complex 40, Cape Canaveral Air Station

The payload fairing containing the Orbital ATK Cygnus pressurized cargo module is mated to the Centaur upper stage, or second stage, of the United Launch Alliance (ULA) rocket in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V from pad 41. Cygnus will deliver 7,600 pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
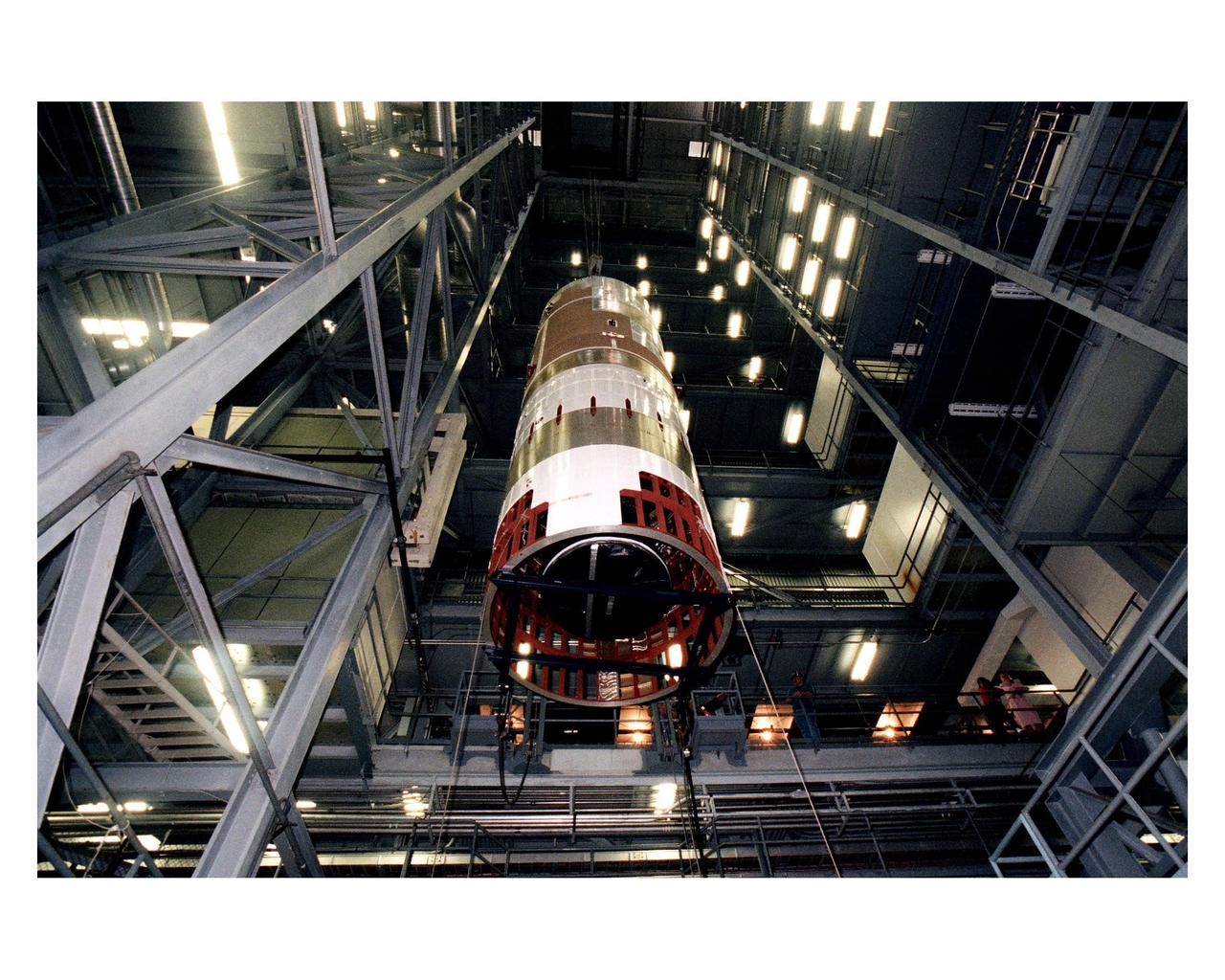

The second stage of a Titan IV/Centaur expendable launch vehicle is suspended in the Vertical Integration Building before being moved into position for mating to the first stage. The Titan IVB rocket is the newest version of America's most powerful unmanned rocket. This rocket will be used for the Cassini mission to Saturn. The Cassini launch is targeted for October 6 from Launch Complex 40, Cape Canaveral Air Station
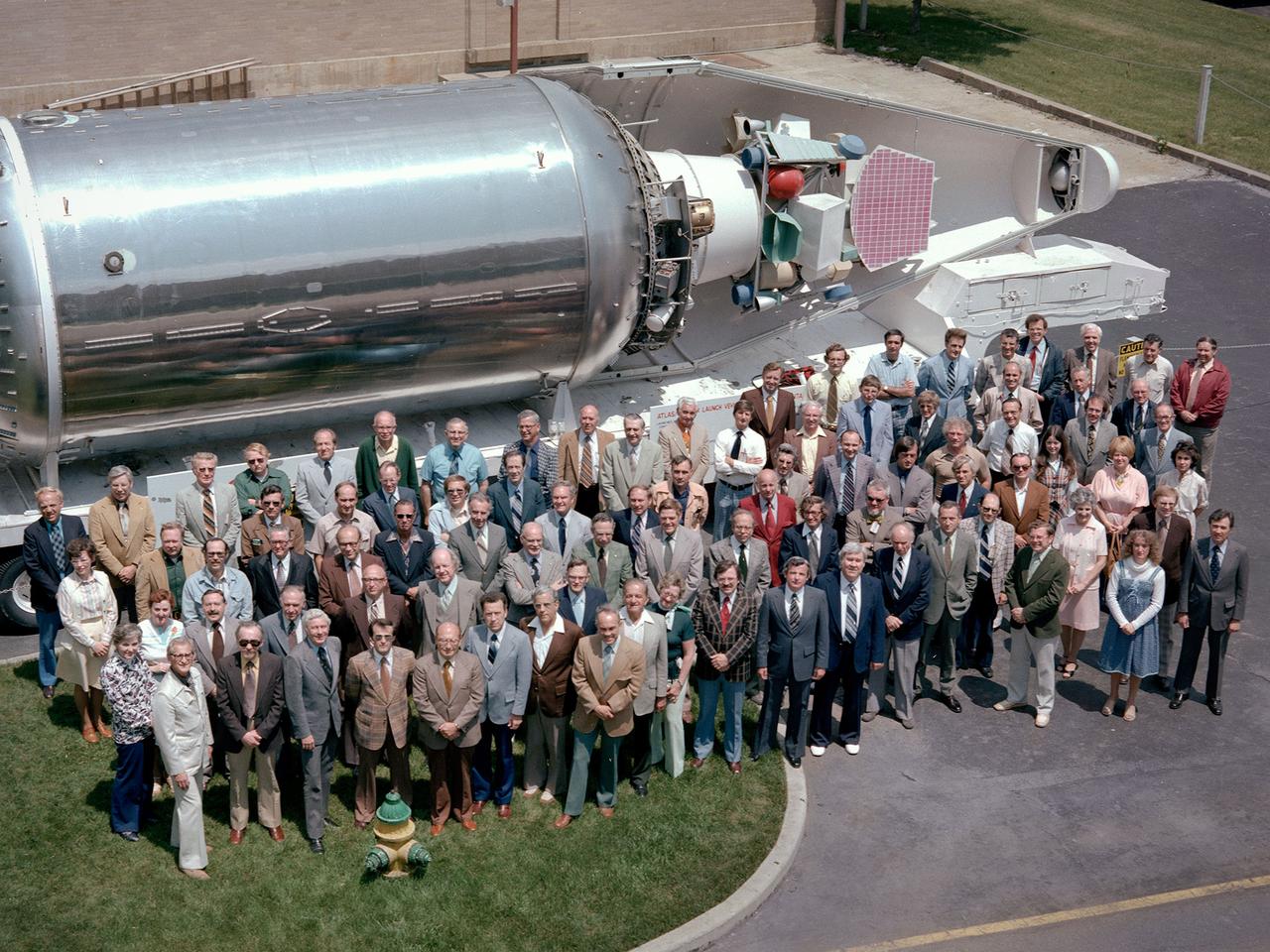

The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center’s Launch Vehicle Directorate in front of a full-scale model of the Centaur second-stage rocket. The photograph was taken to mark Centaur’s fiftieth launch. NASA Lewis managed the Centaur Program since 1962. At that time, the only prior launch attempt ended in failure. Lewis improved the spacecraft and tested it extensively throughout the early 1960s. In May 1966 an Atlas-Centaur sent the Surveyor spacecraft to the moon. It was the first successful soft landing on another planet. The Launch Vehicles Division was formed in 1969 to handle the increasing number of Centaur launches. The Lewis team became experts at integrating the payload with the Centaur and calculating proper trajectories for the missions. Centaur’s first 50 missions included Orbiting Astronomical Observatories, the Mariner 6 and 7 flybys of Mars, Mariner 9 which was the first spacecraft to orbit around another planet, the Pioneer 10 and 11 missions to the outer solar system, the Mariner 10 flyby of Venus and Mercury, the Viking 1 and 2 Mars landers, Voyagers 1 and 2 missions to Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune, and the Pioneer 12 and 13 flights to Venus.
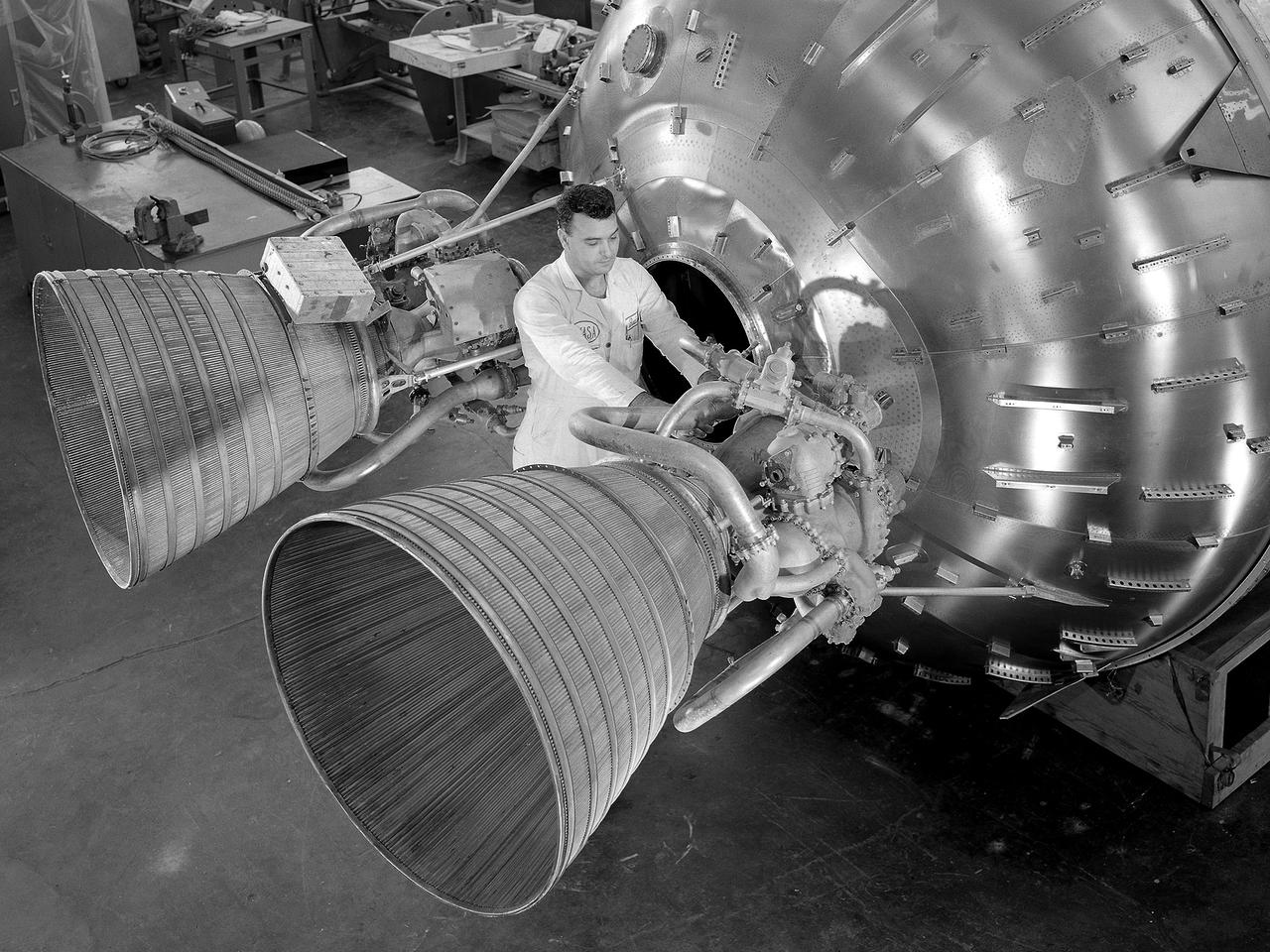
A researcher prepares a Centaur 6A second-stage rocket for a series of tests in the Space Power Chambers’ vacuum tank at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. Lewis was assigned oversight of the Centaur Program in the fall of 1962. Prior to that, Centaur’s only launch had failed shortly after liftoff. Lewis engineers undertook an expansive effort to quickly resolve Centaur’s problems and prepare it for its planned missions to send Surveyor spacecraft to land on the moon. For one test program, a complete Centaur vehicle was lowered into the vacuum chamber at the Space Power Chambers to verify that its electronics and electrical systems functioned reliably in a space environment. At the time, electronic malfunctions were one of the most likely causes of failures in space. Studying these systems during long soaks inside the space tank helped the Lewis team calibrate them and facilitate the monitoring of the spacecraft during an actual flight. The Centaur for the tests was delivered to Cleveland in a C-130 aircraft on September 27, 1963. The rocket was set up in the facility’s high bay where Lewis technicians and General Dynamics consultants updated its flight systems to match the upcoming Atlas-Centaur-4 mission, as seen in this photograph.
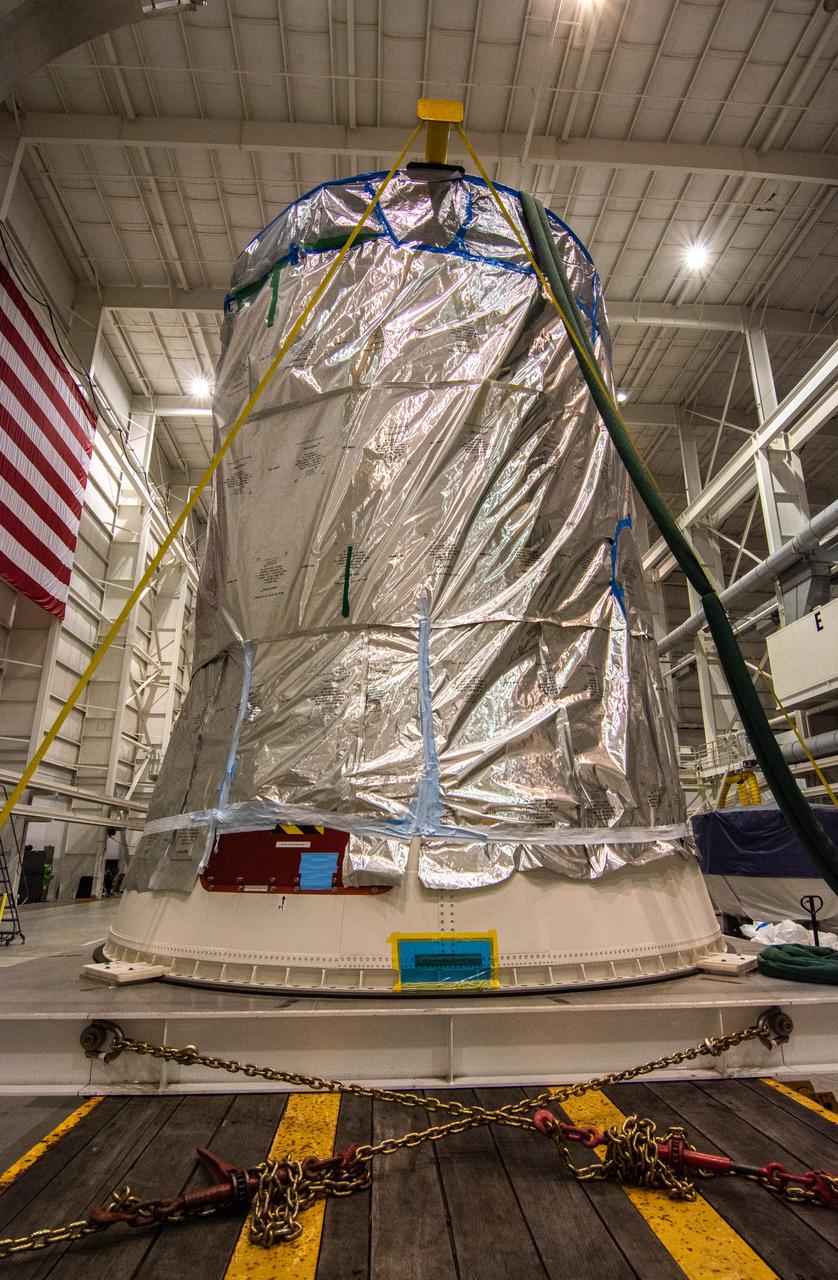

Preparations are underway to lift the interstage and assembly second stage adapters for the United Alliance Atlas V Centaur second stage for NASA’s Landsat 9 mission at Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, on July 14, 2021. The adapters will be stacked atop the Centaur second stage in the Vertical Integration Facility near the launch pad. The Landsat 9 mission will launch atop the Atlas V rocket from Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multiuser spaceport. The Landsat 9 satellite will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.

Preparations are underway to lift the interstage and assembly second stage adapters for the United Alliance Atlas V Centaur second stage for NASA’s Landsat 9 mission at Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, on July 14, 2021. The adapters will be stacked atop the Centaur second stage in the Vertical Integration Facility near the launch pad. The Landsat 9 mission will launch atop the Atlas V rocket from Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multiuser spaceport. The Landsat 9 satellite will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.

The interstage and assembly second stage adapters for the United Alliance Atlas V Centaur second stage for NASA’s Landsat 9 mission are lifted by crane at Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, on July 14, 2021. The adapters will be stacked atop the Centaur second stage in the Vertical Integration Facility near the launch pad. The Landsat 9 mission will launch atop the Atlas V rocket from Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multiuser spaceport. The Landsat 9 satellite will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.

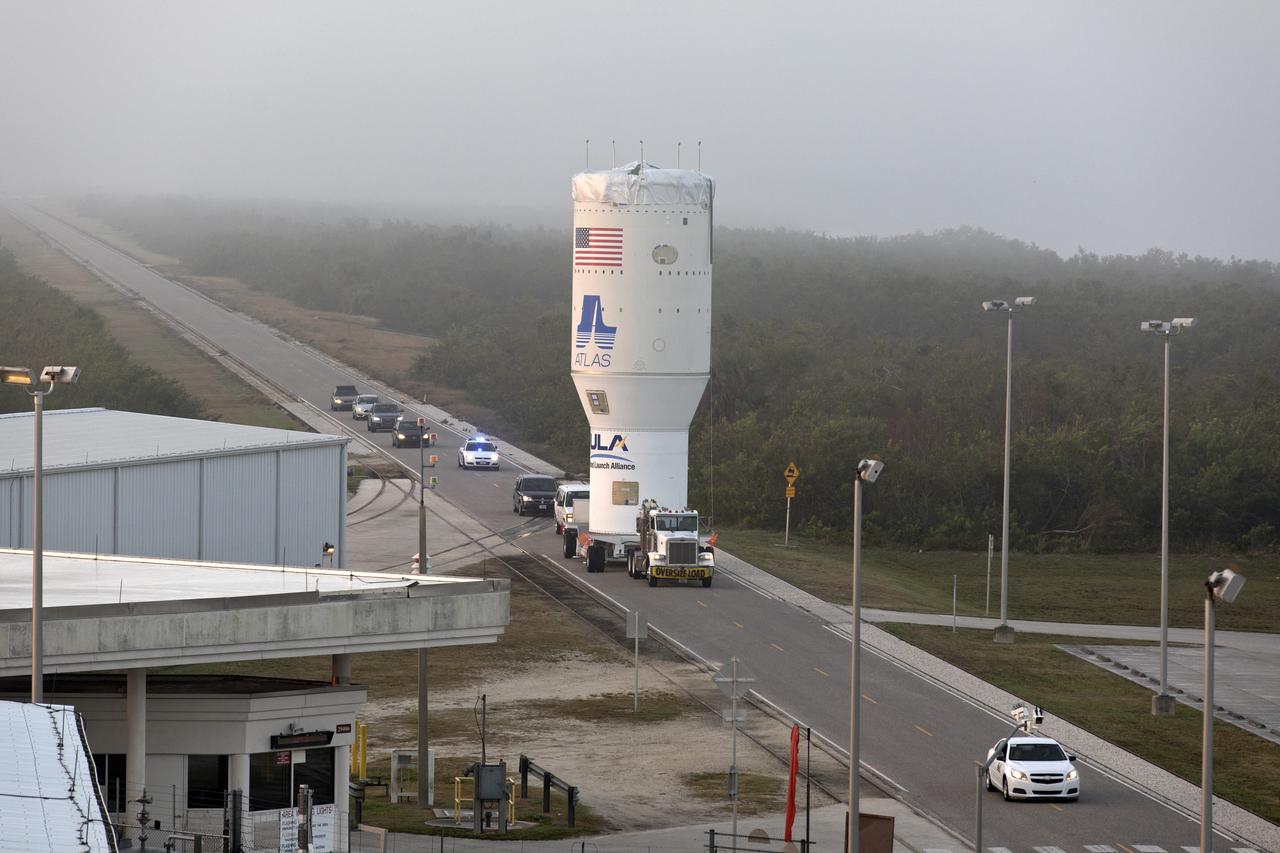
The Centaur upper stage that will help launch NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S, or GOES-S, arrives at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Centaur will be mated to a United Launch Alliance Atlas V booster. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites that will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018.

The Centaur upper stage that will help launch NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S, or GOES-S, arrives at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Centaur will be mated to a United Launch Alliance Atlas V booster. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites that will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018.
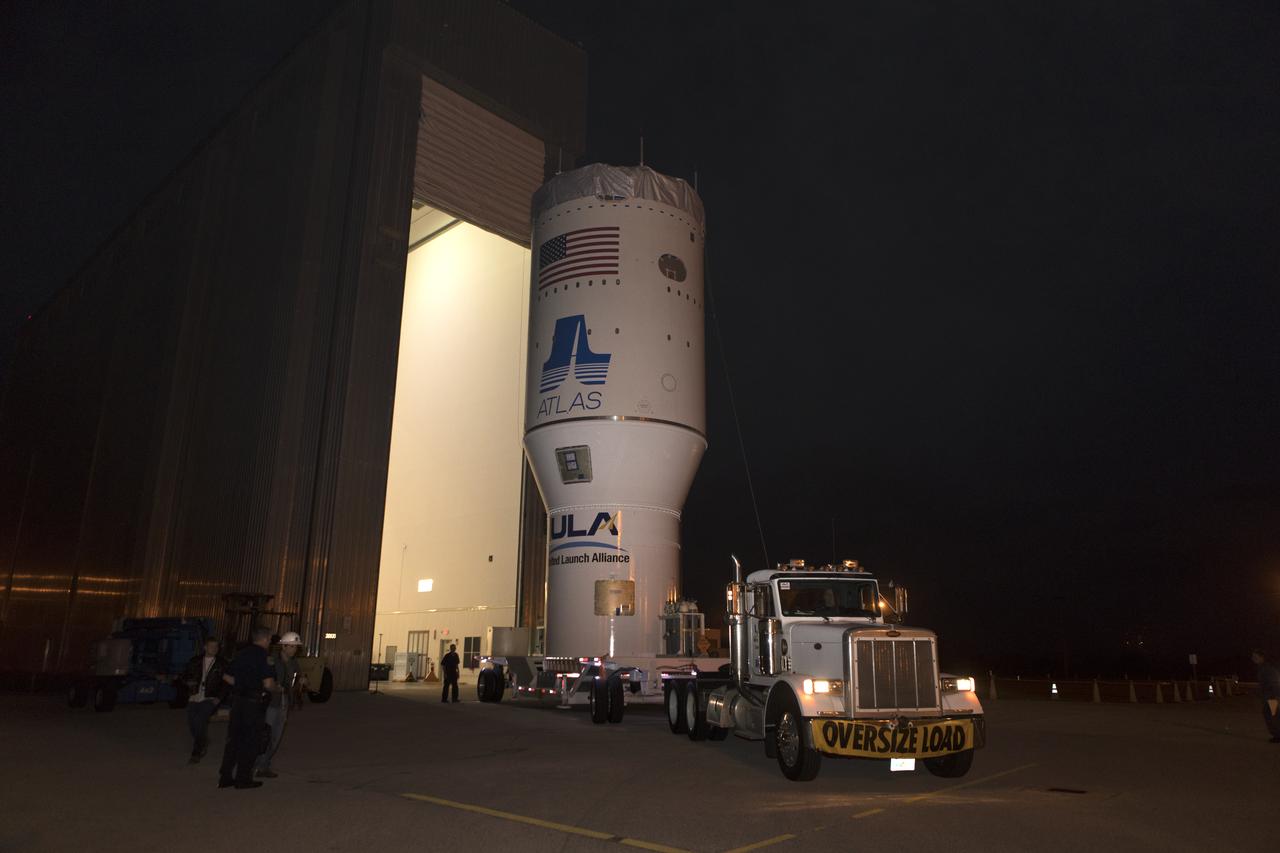

The Centaur upper stage that will help launch NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S, or GOES-S, departs the Delta Operations Center for the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Centaur then will be mated to a United Launch Alliance Atlas V booster. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites that will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018.
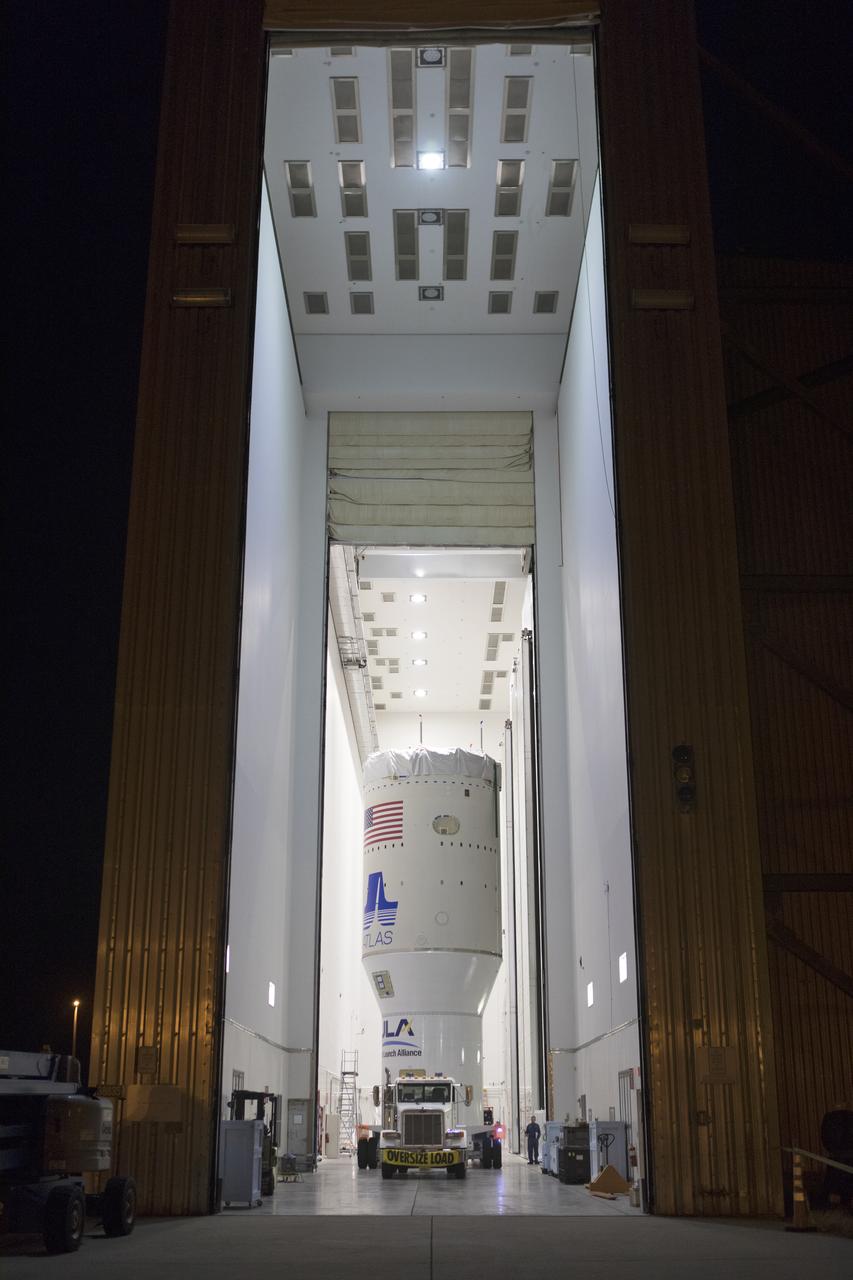

The Centaur upper stage that will help launch NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S, or GOES-S, departs the Delta Operations Center for the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Centaur then will be mated to a United Launch Alliance Atlas V booster. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites that will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018.
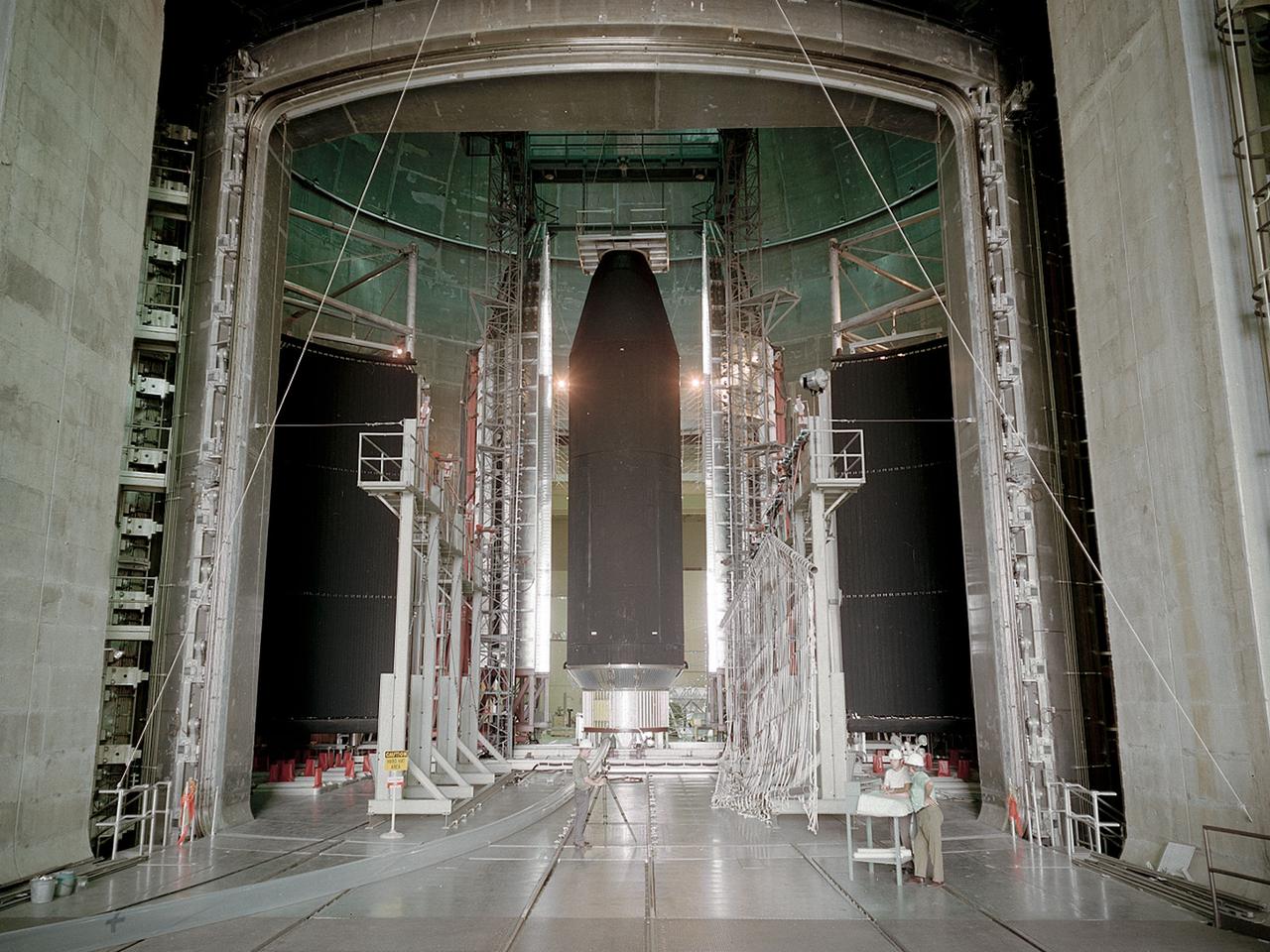

The Centaur Standard Shroud prepared for a jettison test in the Space Power Facility at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration’s (NASA) Plum Brook Station. In the late 1960s NASA engineers were planning the ambitious new Viking mission to send two rover vehicles to the surface of Mars. The Viking rovers were the heaviest payloads ever attempted by the Centaur second-stage rocket. Each Viking was over three times the weight of the Atlas-Centaur’s previous heaviest payload. Consequently, NASA engineers sought to mate the Centaur with the more powerful Titan III booster for the launches. General Dynamics created a new version of the Centaur, D-1T, specifically for Titan. The D-1T’s most significant modification was a completely new shroud designed by Lockheed, called the Centaur Standard Shroud. The conical two-piece covering encapsulated the payload to protect it against adverse conditions and improve the aerodynamics as the launch vehicle passed through the atmosphere. The shroud would be jettisoned when the vehicle reached the edge of space. A string of tests were conducted in Plum Brook’s Nuclear Rocket Dynamics and Control Facility (B-3) during 1973 and 1974. The new shroud performed flawlessly during the actual Viking launches in 1975. Viking 1 and 2 operated on the Martian surface until November 1982 and April 1980, respectively.
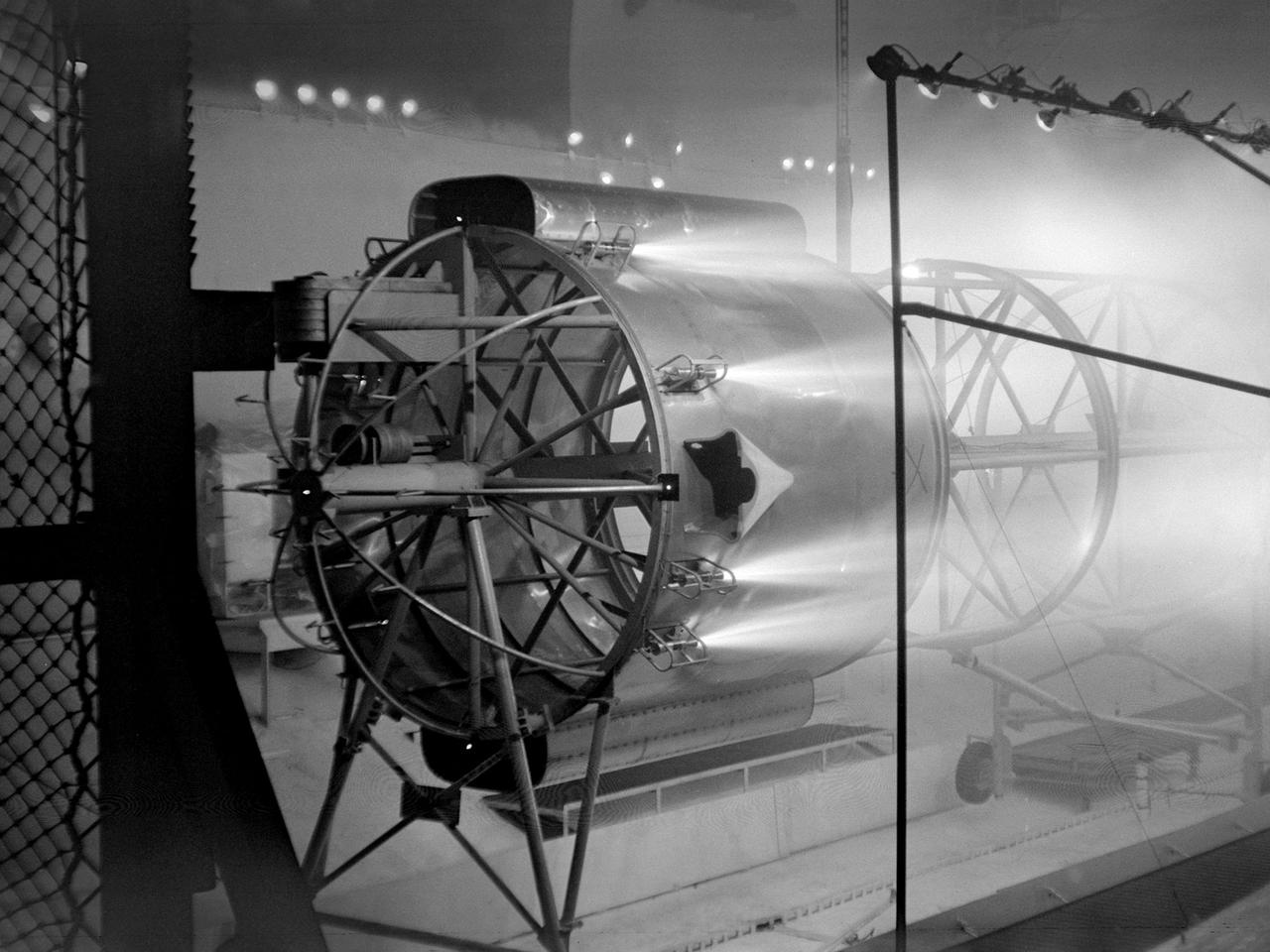

An Atlas/Centaur mass model undergoes a separation test inside the Space Power Chambers at NASA Lewis Research Center. Lewis was in the midst of an extensive effort to prepare the Centaur second-stage rocket for its missions to send the Surveyor spacecraft to the moon as a precursor to the Apollo missions. As part of these preparations, Lewis management decided to convert its Altitude Wind Tunnel into two large test chambers—the Space Power Chambers. The conversion included the removal of the tunnel’s internal components and the insertion of bulkheads to seal off the new chambers within the tunnel. One chamber could simulate conditions found at 100 miles altitude, while this larger chamber simulated the upper atmosphere. In this test series, researchers wanted to verify that the vehicle’s retrorockets would properly separate the Centaur from the Atlas. The model was suspended horizontally on a trolley system inside chamber. A net was hung at one end to catch the jettisoned Atlas model. The chamber atmosphere was reduced to a pressure altitude of 100,000 feet, and high-speed cameras were synchronized to the ignition of the retrorockets. The simulated Centaur is seen here jettisoning from the Atlas out of view to the right. The study resulted in a new jettison method that would significantly reduce the separation time and thus minimize the danger of collision between the two stages during separation.
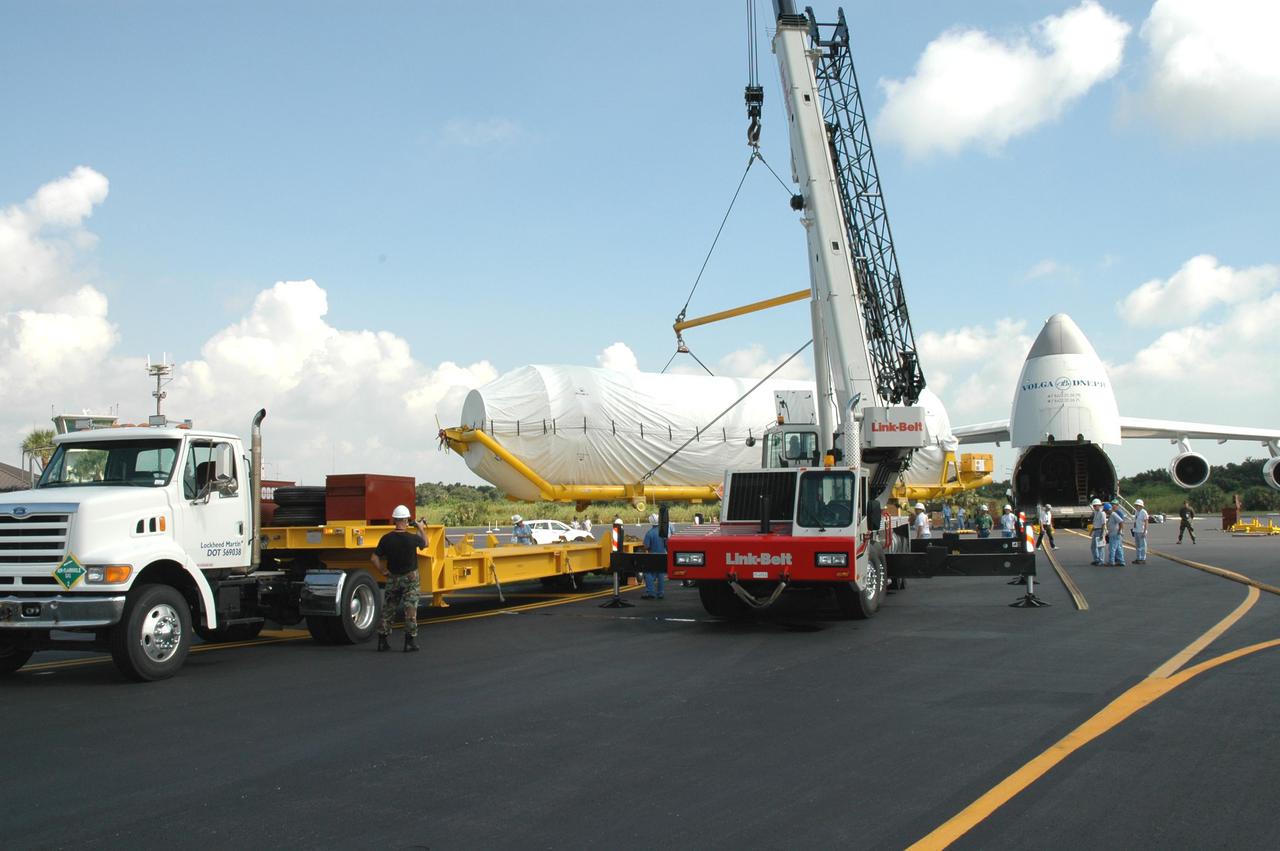

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At the Skid Strip on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS), a crane lifts the second stage Centaur onto the back of a transporter trailer. The Centaur is the upper stage of the Atlas V configuration that will launch the New Horizons spacecraft from Launch Complex 41 at CCAFS. New Horizons is designed to help us understand worlds at the edge of our solar system by making the first reconnaissance of Pluto and Charon - a 'double planet' and the last planet in our solar system to be visited by spacecraft. The mission will then visit one or more objects in the Kuiper Belt region beyond Neptune. New Horizons is scheduled to launch in January 2006, swing past Jupiter for a gravity boost and scientific studies in February or March 2007, and reach Pluto and its moon, Charon, in July 2015.
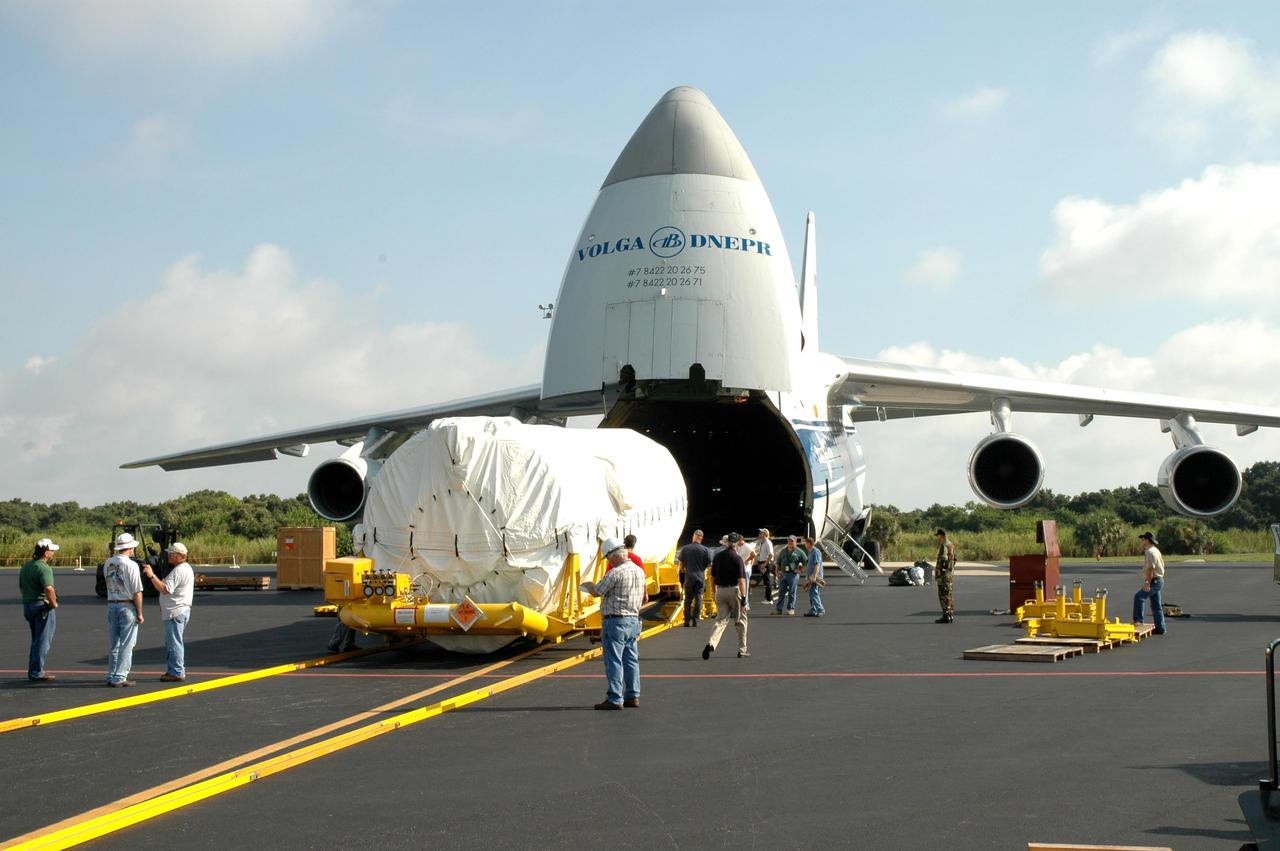

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At the Skid Strip on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS), the second stage Centaur has been offloaded from a Russian air cargo plane. The Centaur is the upper stage of the Atlas V configuration that will launch the New Horizons spacecraft from Launch Complex 41 at CCAFS. New Horizons is designed to help us understand worlds at the edge of our solar system by making the first reconnaissance of Pluto and Charon - a 'double planet' and the last planet in our solar system to be visited by spacecraft. The mission will then visit one or more objects in the Kuiper Belt region beyond Neptune. New Horizons is scheduled to launch in January 2006, swing past Jupiter for a gravity boost and scientific studies in February or March 2007, and reach Pluto and its moon, Charon, in July 2015.
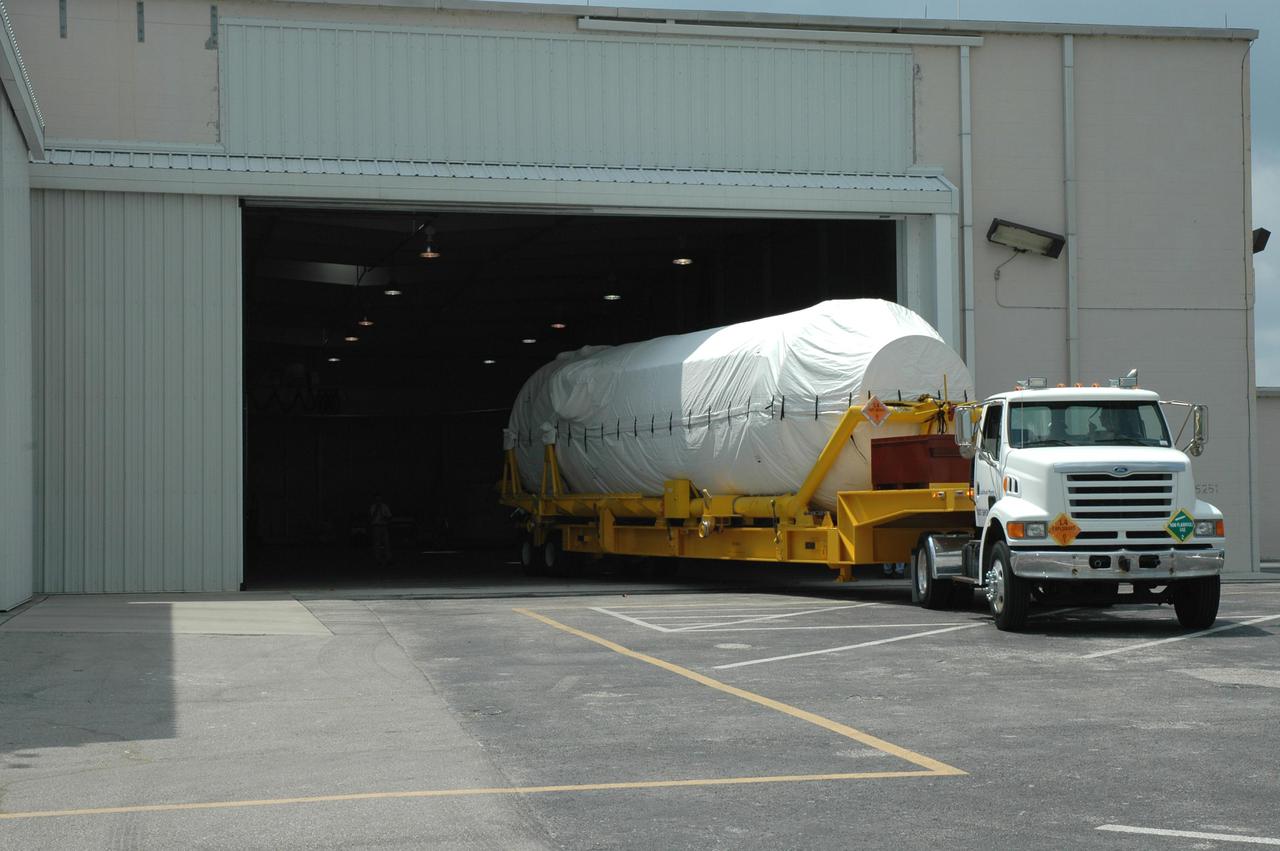

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The truck transporting the second stage Centaur backs into the Atlas Space Operations Center on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS). The Centaur is the upper stage of the Atlas V configuration that will launch the New Horizons spacecraft from Launch Complex 41 at CCAFS. New Horizons is designed to help us understand worlds at the edge of our solar system by making the first reconnaissance of Pluto and Charon - a 'double planet' and the last planet in our solar system to be visited by spacecraft. The mission will then visit one or more objects in the Kuiper Belt region beyond Neptune. New Horizons is scheduled to launch in January 2006, swing past Jupiter for a gravity boost and scientific studies in February or March 2007, and reach Pluto and its moon, Charon, in July 2015.
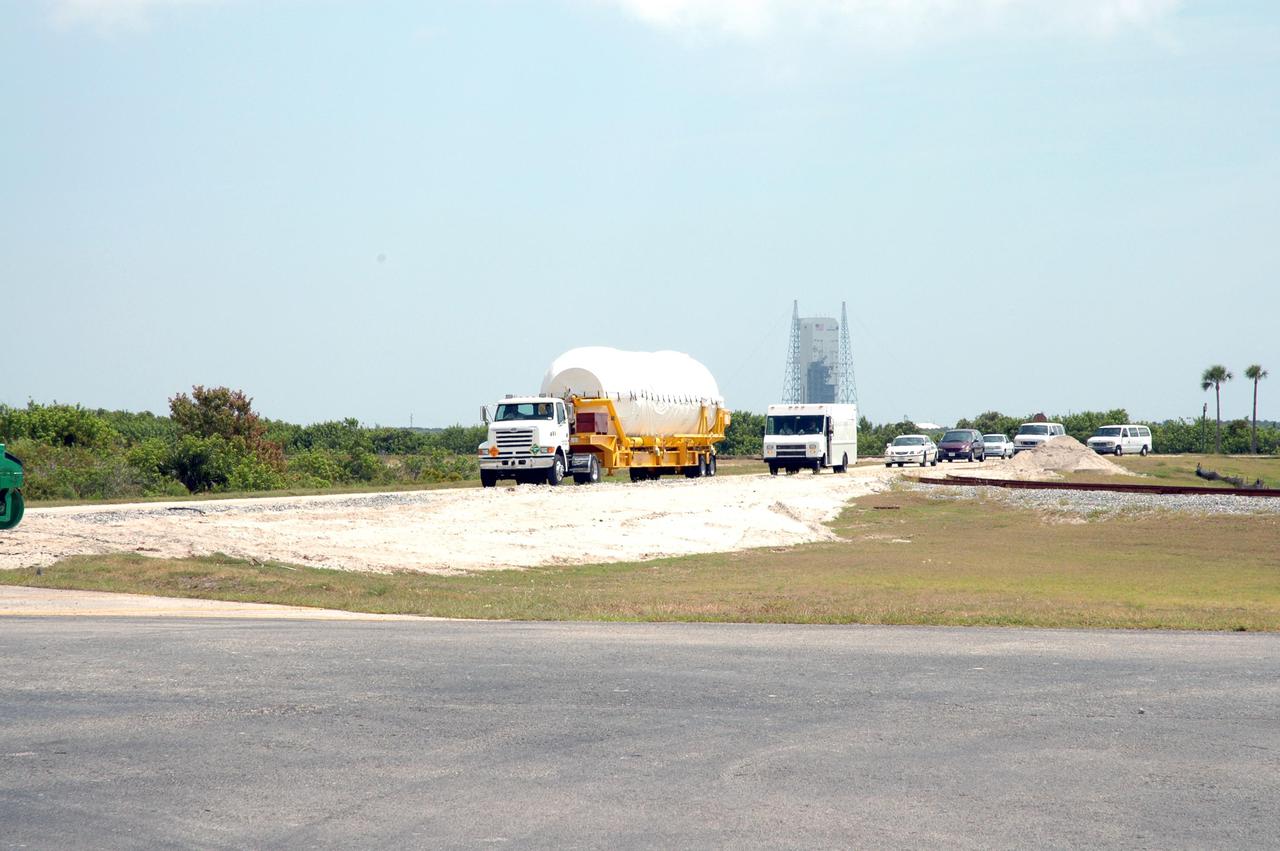

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The truck transporting the second stage Centaur drives away from the Skid Strip on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) to its destination - the Atlas Space Operations Center. The Centaur is the upper stage of the Atlas V configuration that will launch the New Horizons spacecraft from Launch Complex 41 at CCAFS. New Horizons is designed to help us understand worlds at the edge of our solar system by making the first reconnaissance of Pluto and Charon - a 'double planet' and the last planet in our solar system to be visited by spacecraft. The mission will then visit one or more objects in the Kuiper Belt region beyond Neptune. New Horizons is scheduled to launch in January 2006, swing past Jupiter for a gravity boost and scientific studies in February or March 2007, and reach Pluto and its moon, Charon, in July 2015.
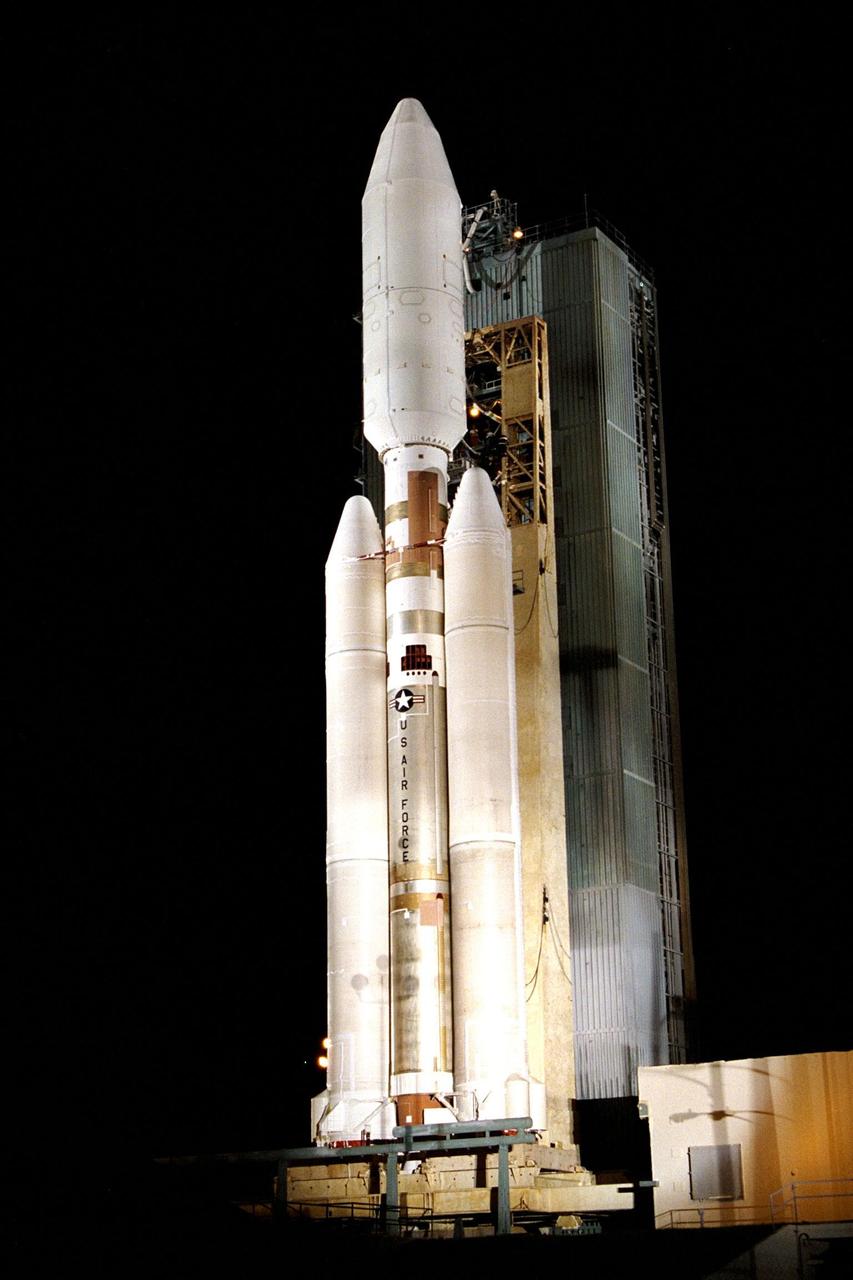

At Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Station, the Mobile Service Tower has been retracted away from the Titan IVB/Centaur carrying the Cassini spacecraft and its attached Huygens probe. This is the second launch attempt for the Saturn-bound mission; a first try Oct. 13 was scrubbed primarily due to concerns about upper level wind conditions. Liftoff Oct. 15 is set to occur during a launch window opening at 4:43 a.m. EDT and extending until 7:03 a.m. Clearly visible in this view are the 66-foot-tall, 17-foot-wide payload fairing atop the vehicle, in which Cassini and the attached Centaur stage are encased, the two-stage liquid propellant core vehicle, and the twin 112-foot long solid rocket motor upgrades (SRMUs) straddling the core vehicle. It is the SRMUs which ignite first to begin the launch sequence
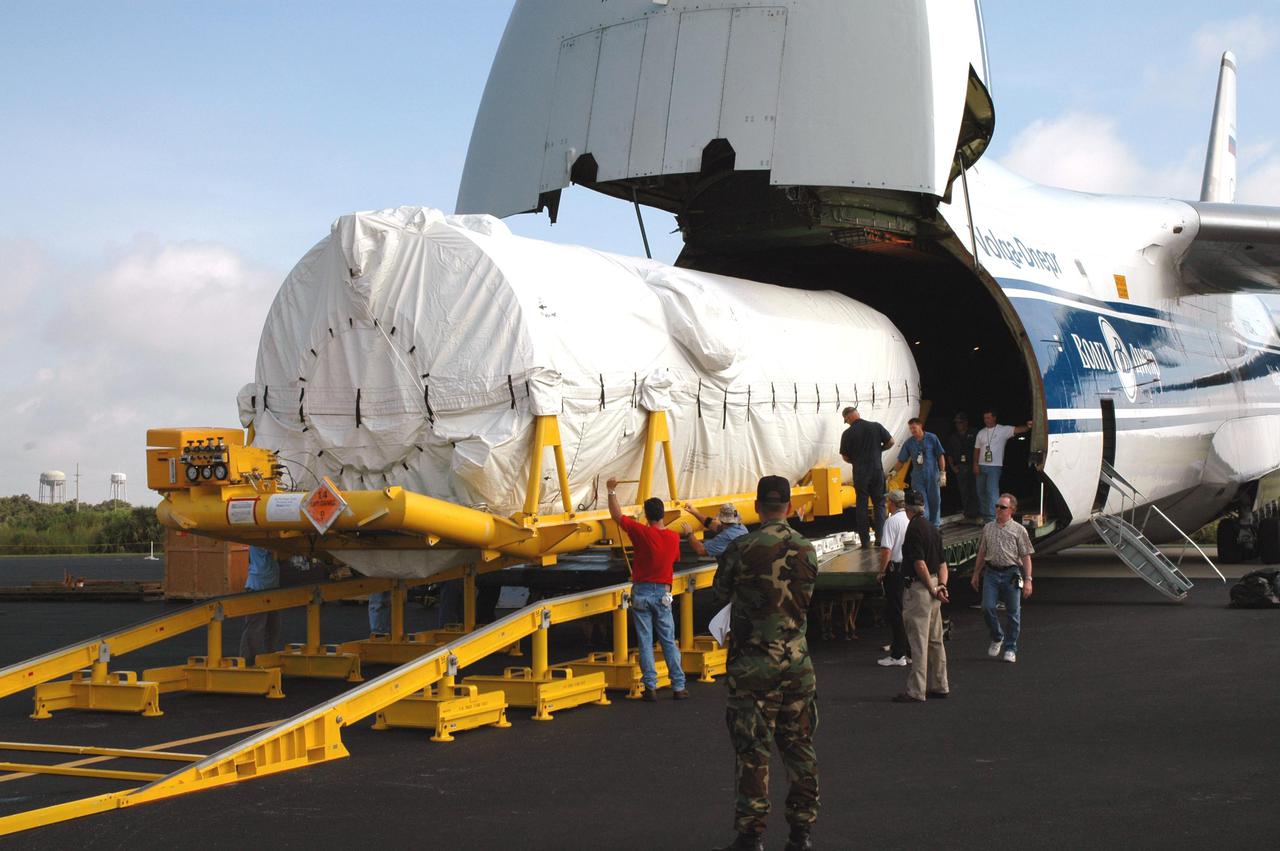

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At the Skid Strip on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS), the second stage Centaur is offloaded from a Russian air cargo plane. The Centaur is the upper stage of the Atlas V configuration that will launch the New Horizons spacecraft from Launch Complex 41 at CCAFS. New Horizons is designed to help us understand worlds at the edge of our solar system by making the first reconnaissance of Pluto and Charon - a 'double planet' and the last planet in our solar system to be visited by spacecraft. The mission will then visit one or more objects in the Kuiper Belt region beyond Neptune. New Horizons is scheduled to launch in January 2006, swing past Jupiter for a gravity boost and scientific studies in February or March 2007, and reach Pluto and its moon, Charon, in July 2015.
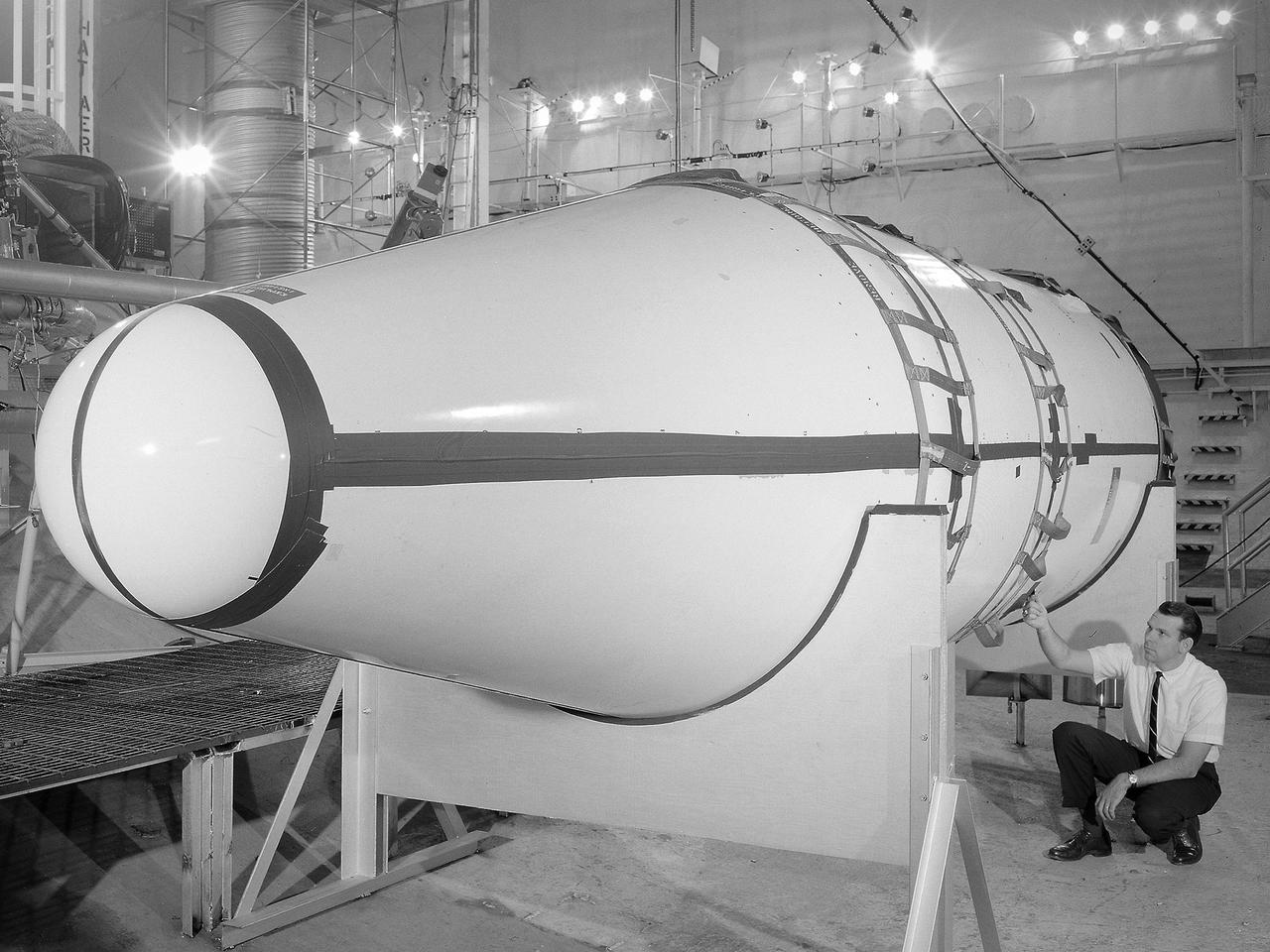
Setup of a Surveyor/Atlas/Centaur shroud in the Space Power Chambers for a leak test at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. Centaur was a 15,000-pound thrust second-stage rocket designed for the military in 1957 and 1958 by General Dynamics. It was the first major rocket to use the liquid hydrogen technology developed by Lewis in the 1950s. The Centaur Program suffered numerous problems before being transferred to Lewis in 1962. Several test facilities at Lewis’ main campus and Plum Brook Station were built or modified specifically for Centaur, including the Space Power Chambers. In 1961, NASA Lewis management decided to convert its Altitude Wind Tunnel into two large test chambers and later renamed it the Space Power Chambers. The conversion, which took over 2 years, included the removal of the tunnel’s internal components and insertion of bulkheads to seal off the new chambers. The larger chamber, seen here, could simulate altitudes of 100,000 feet. It was used for Centaur shroud separation and propellant management studies until the early 1970s. The leak test in this photograph was likely an attempt to verify that the shroud’s honeycomb shell did not seep any of its internal air when the chamber was evacuated to pressures similar to those found in the upper atmosphere.
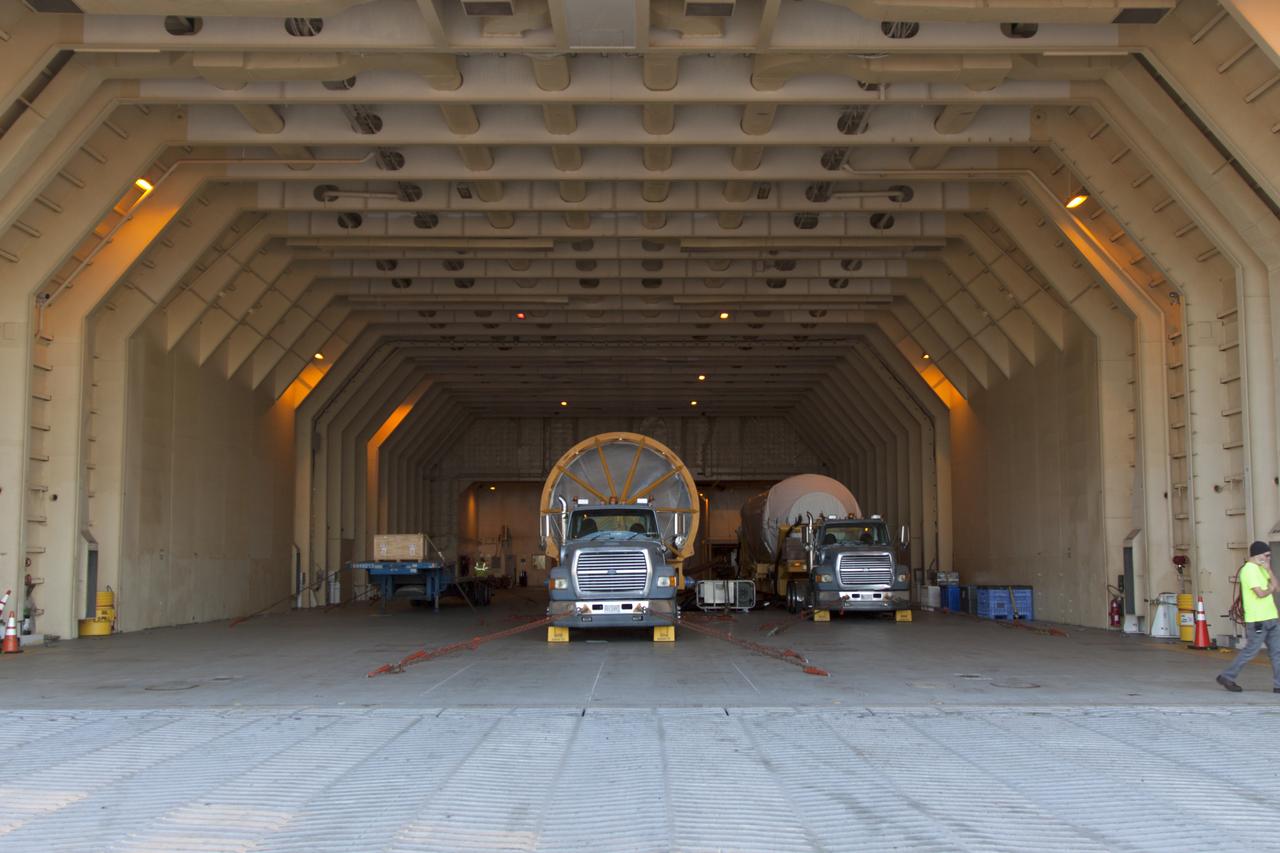

Preparations are underway to offload the United Launch Alliance Atlas V booster and Centaur stage for NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) from the Mariner transport ship at the Army Wharf at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. They will be transported to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center near Space Launch Complex 41 at CCAFS. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The satellite is slated to launch aboard the Atlas V rocket March 1.
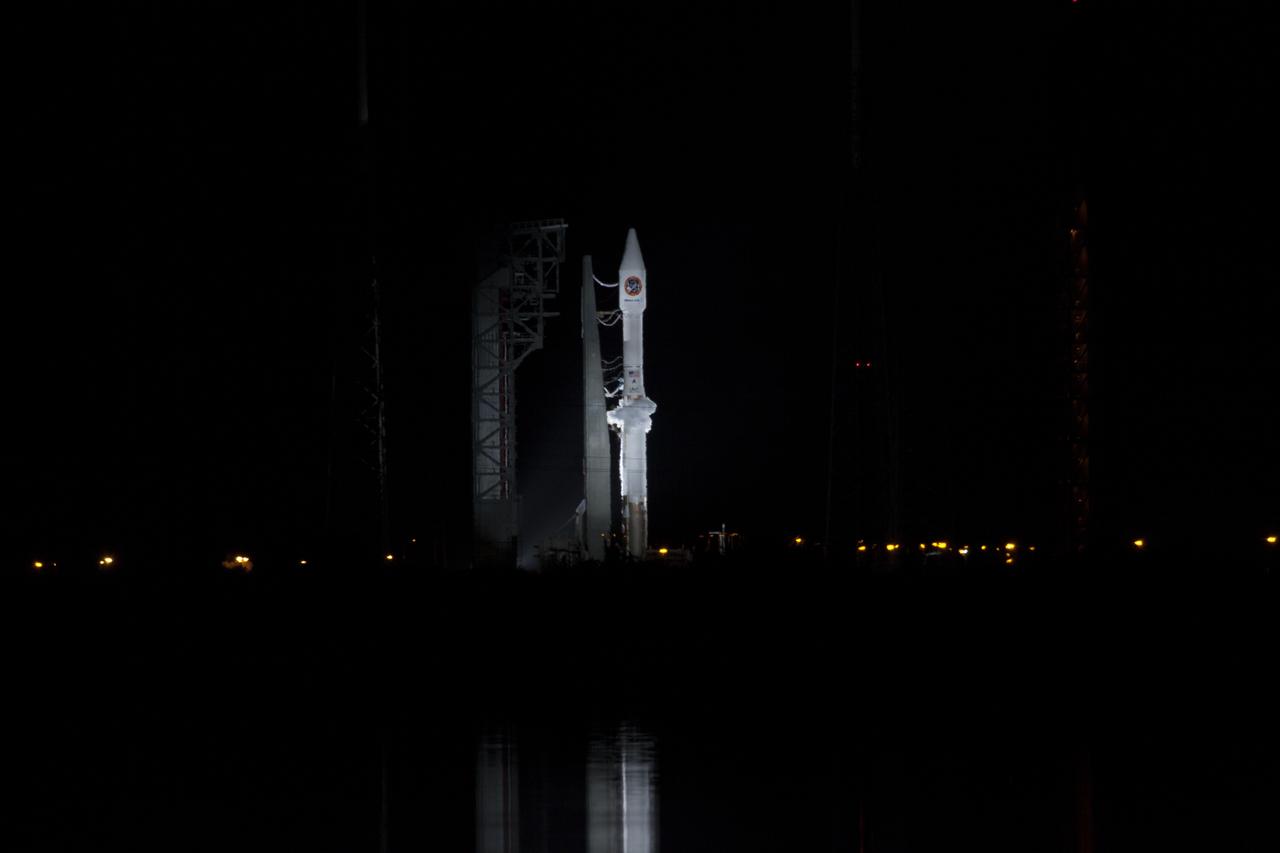

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 41, a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with a single-engine Centaur upper stage stands ready to boost an Orbital ATK Cygnus spacecraft on a resupply mission to the International Space Station. Science payloads include the second generation of a portable onboard printer to demonstrate three-dimensional printing, an instrument for first space-based observations of the chemical composition of meteors entering Earth’s atmosphere and an experiment to study how fires burn in microgravity.

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V booster and Centaur stage for NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) are offloaded from the Mariner transport ship at the Army Wharf at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. They will be transported to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center near Space Launch Complex 41 at CCAFS. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The satellite is slated to launch aboard the Atlas V rocket March 1.
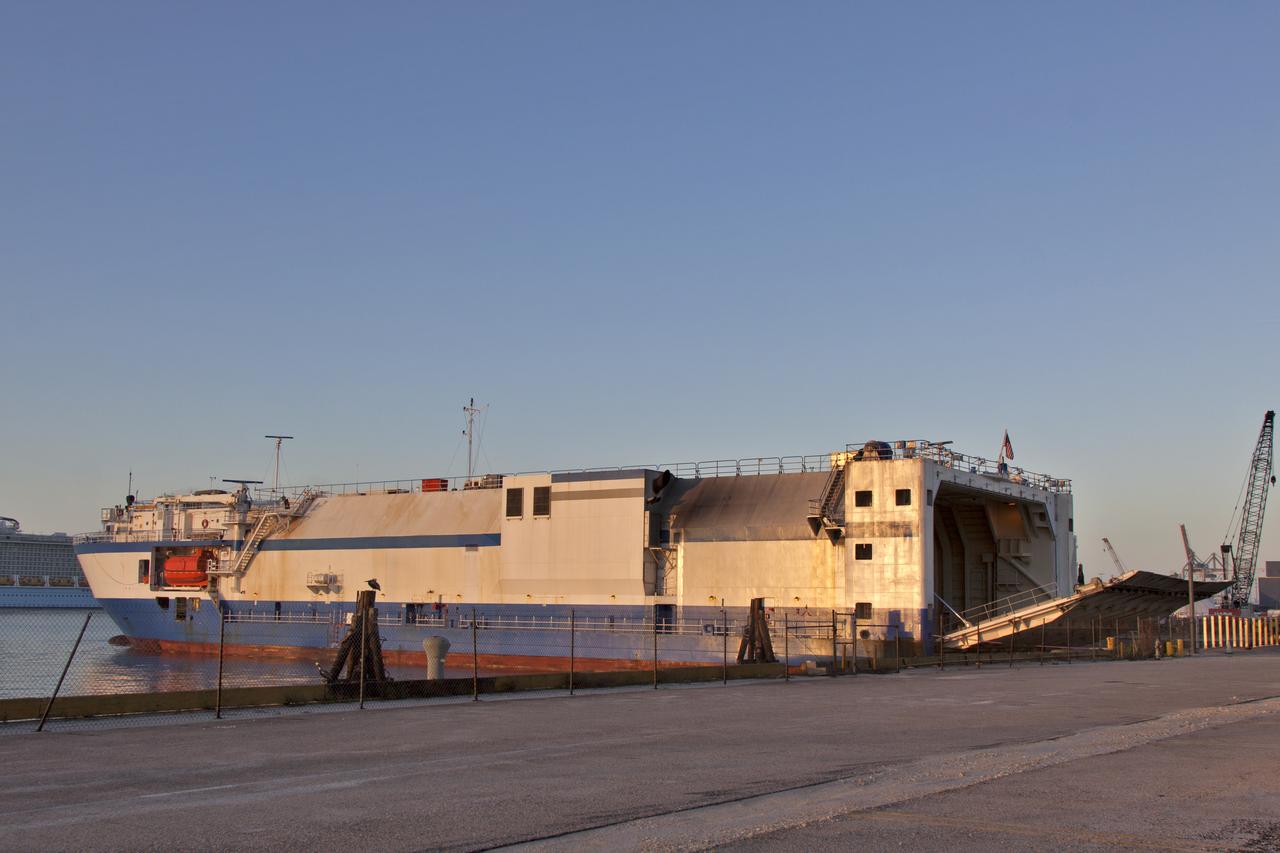

The Mariner transport ship arrives at the Army Wharf at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, carrying the United Launch Alliance Atlas V booster and Centaur stage for NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S). They will be offloaded and transported to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center near Space Launch Complex 41 at CCAFS. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The satellite is slated to launch aboard the Atlas V rocket March 1.

Preparations are underway to offload the United Launch Alliance Atlas V booster and Centaur stage for NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) from the Mariner transport ship at the Army Wharf at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. They will be transported to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center near Space Launch Complex 41 at CCAFS. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The satellite is slated to launch aboard the Atlas V rocket March 1.

At launch pad 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, lifting of the second stage of an Atlas II/Centaur rocket in the launch gantry is completed. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the GOES-L satellite, part of the NOAA National Weather Service system in weather imagery and atmospheric sounding information. The primary objective of the GOES-L is to provide a full capability satellite in an on-orbit storage condition, to assure NOAA continuity in services from a two-satellite constellation. Launch services are being provided by the 45th Space Wing
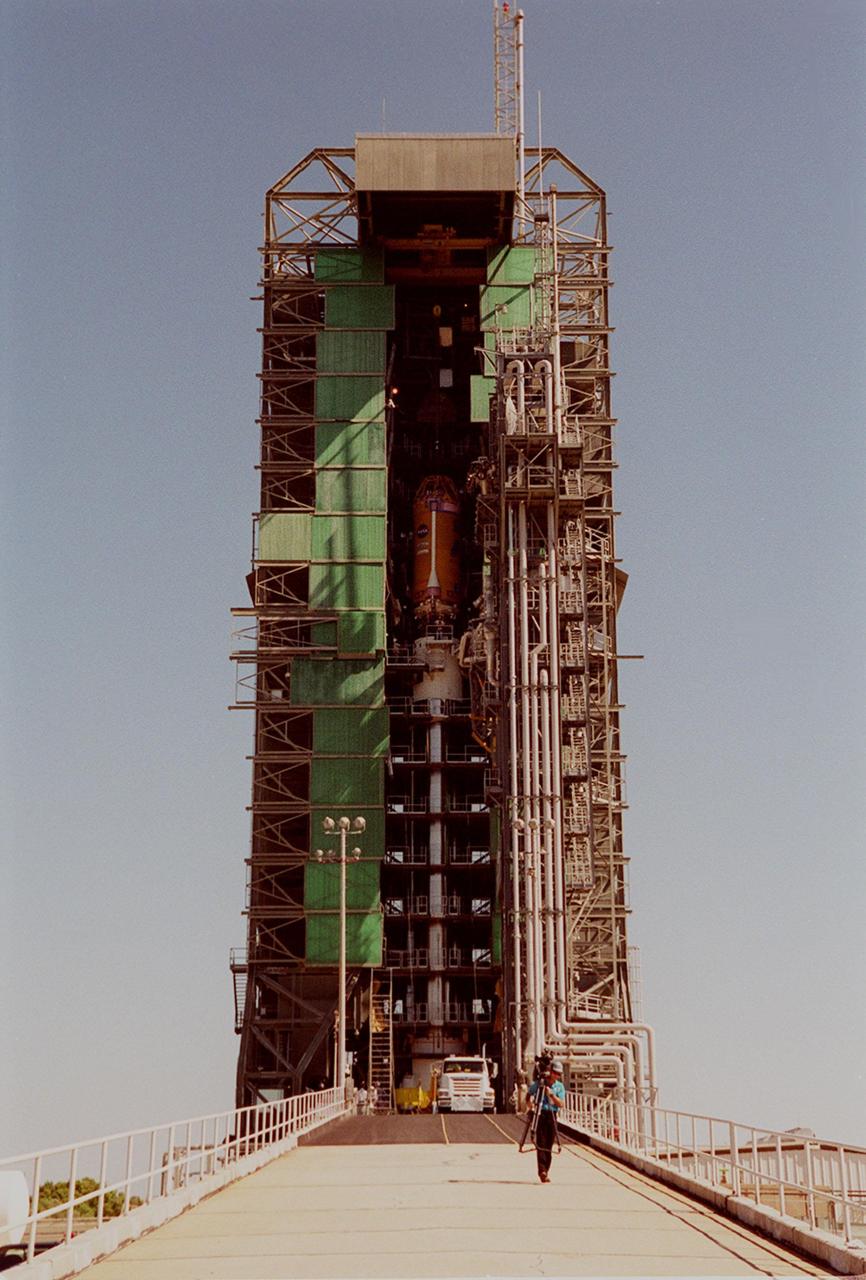

At launch pad 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, lifting of the second stage of an Atlas II/Centaur rocket in the launch gantry is completed. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the GOES-L satellite, part of the NOAA National Weather Service system in weather imagery and atmospheric sounding information. The primary objective of the GOES-L is to provide a full capability satellite in an on-orbit storage condition, to assure NOAA continuity in services from a two-satellite constellation. Launch services are being provided by the 45th Space Wing

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 41, a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with a single-engine Centaur upper stage stands ready to boost an Orbital ATK Cygnus spacecraft on a resupply mission to the International Space Station. Science payloads include the second generation of a portable onboard printer to demonstrate three-dimensional printing, an instrument for first space-based observations of the chemical composition of meteors entering Earth’s atmosphere and an experiment to study how fires burn in microgravity.
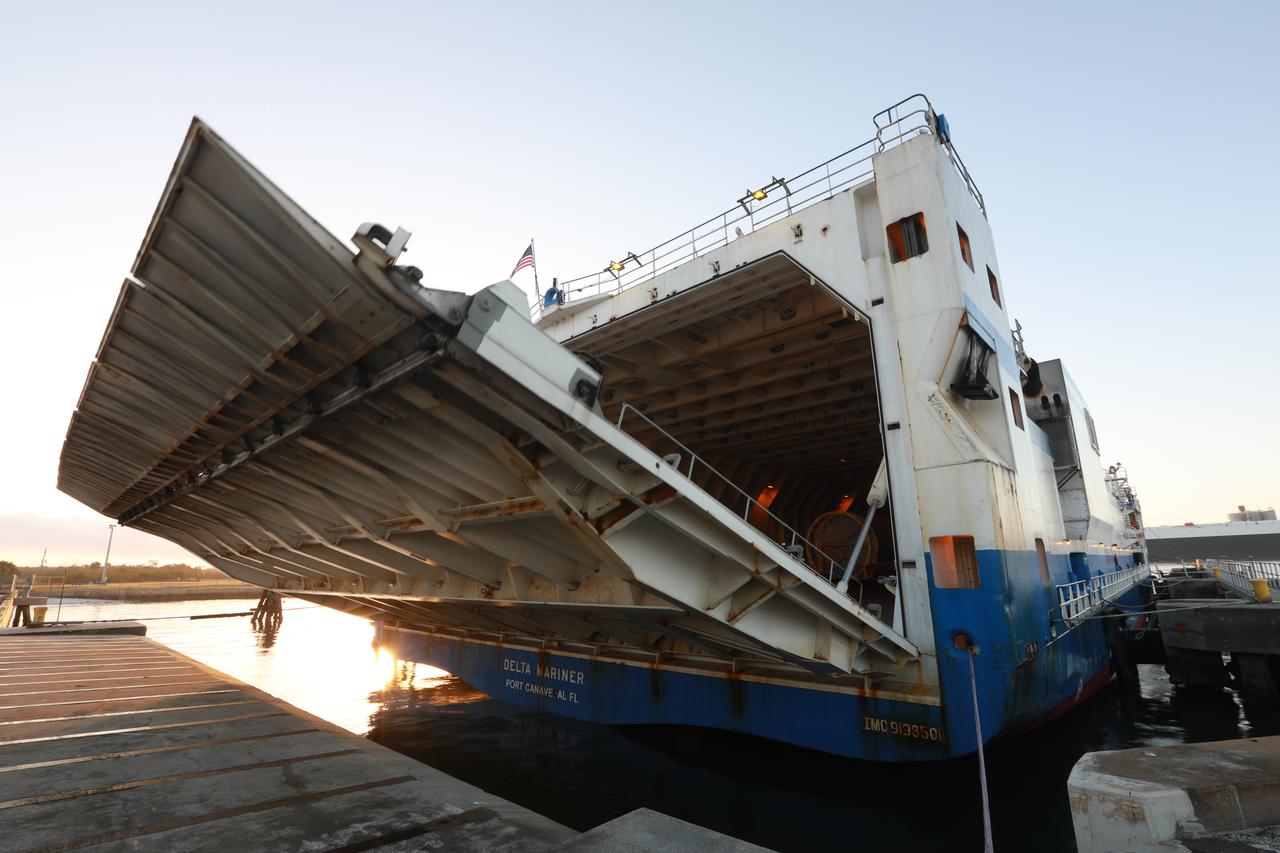

The Mariner transport ship arrives at the Army Wharf at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, carrying the United Launch Alliance Atlas V booster and Centaur stage for NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S). They will be offloaded and transported to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center near Space Launch Complex 41 at CCAFS. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The satellite is slated to launch aboard the Atlas V rocket March 1.
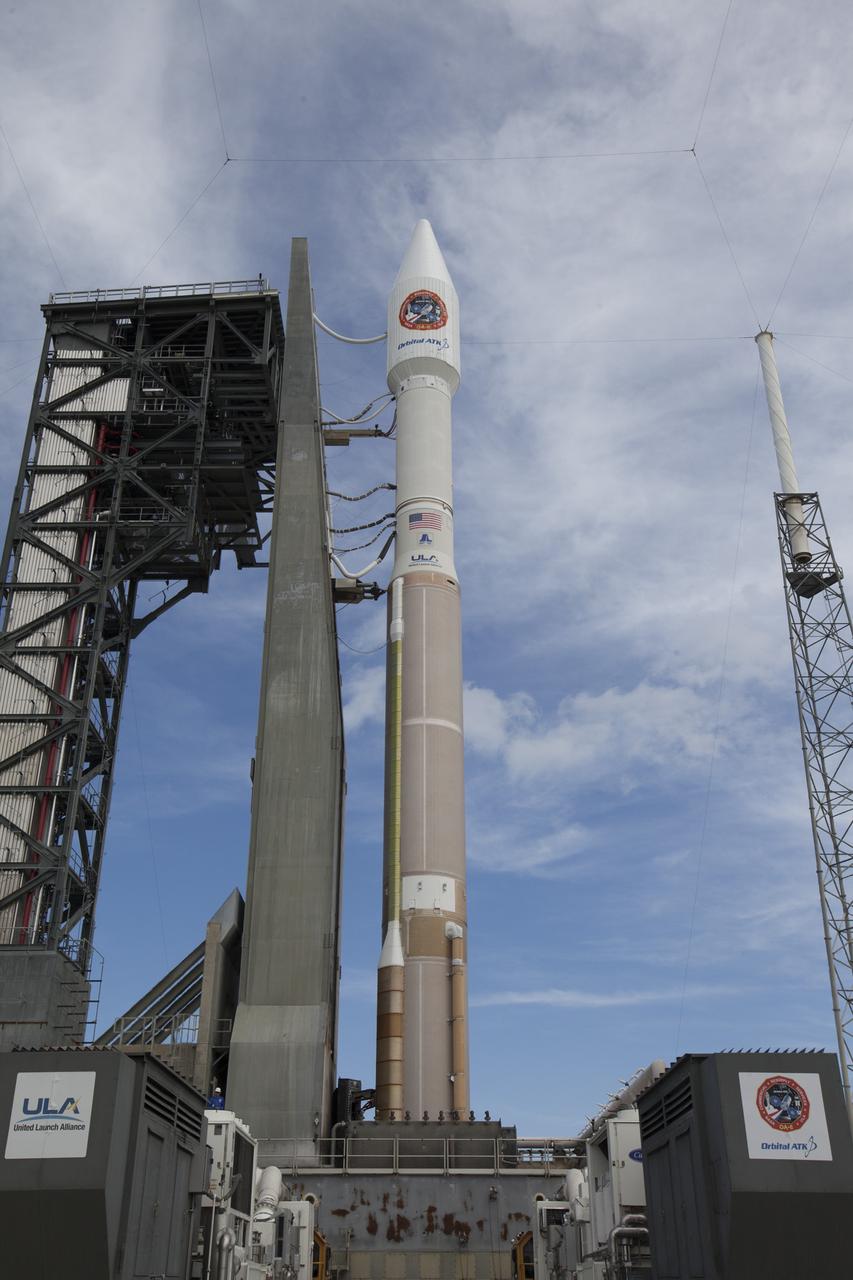

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 41, a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with a single-engine Centaur upper stage stands ready to boost an Orbital ATK Cygnus spacecraft on a resupply mission to the International Space Station. Science payloads include the second generation of a portable onboard printer to demonstrate three-dimensional printing, an instrument for first space-based observations of the chemical composition of meteors entering Earth’s atmosphere and an experiment to study how fires burn in microgravity.
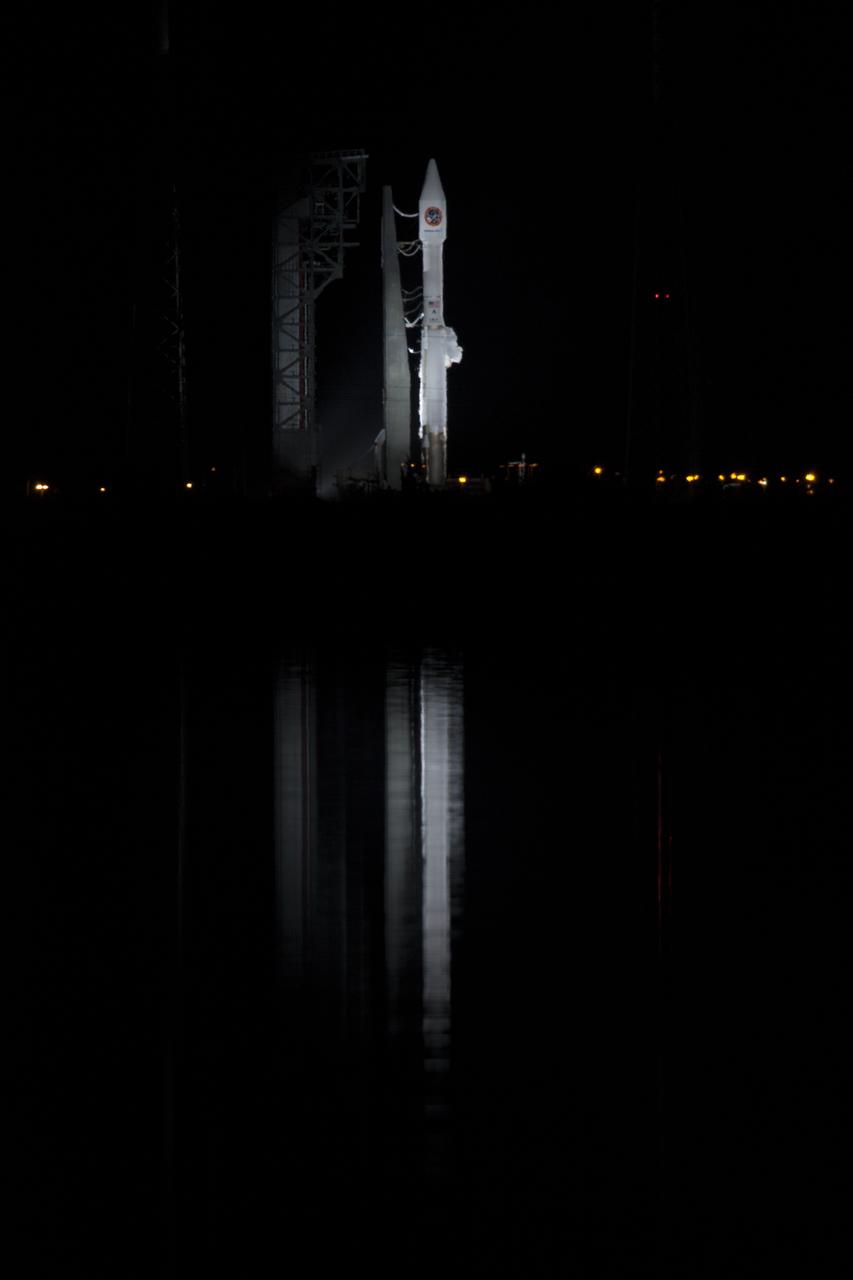

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 41, a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with a single-engine Centaur upper stage stands ready to boost an Orbital ATK Cygnus spacecraft on a resupply mission to the International Space Station. Science payloads include the second generation of a portable onboard printer to demonstrate three-dimensional printing, an instrument for first space-based observations of the chemical composition of meteors entering Earth’s atmosphere and an experiment to study how fires burn in microgravity.

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 41, a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with a single-engine Centaur upper stage stands ready to boost an Orbital ATK Cygnus spacecraft on a resupply mission to the International Space Station. Science payloads include the second generation of a portable onboard printer to demonstrate three-dimensional printing, an instrument for first space-based observations of the chemical composition of meteors entering Earth’s atmosphere and an experiment to study how fires burn in microgravity.
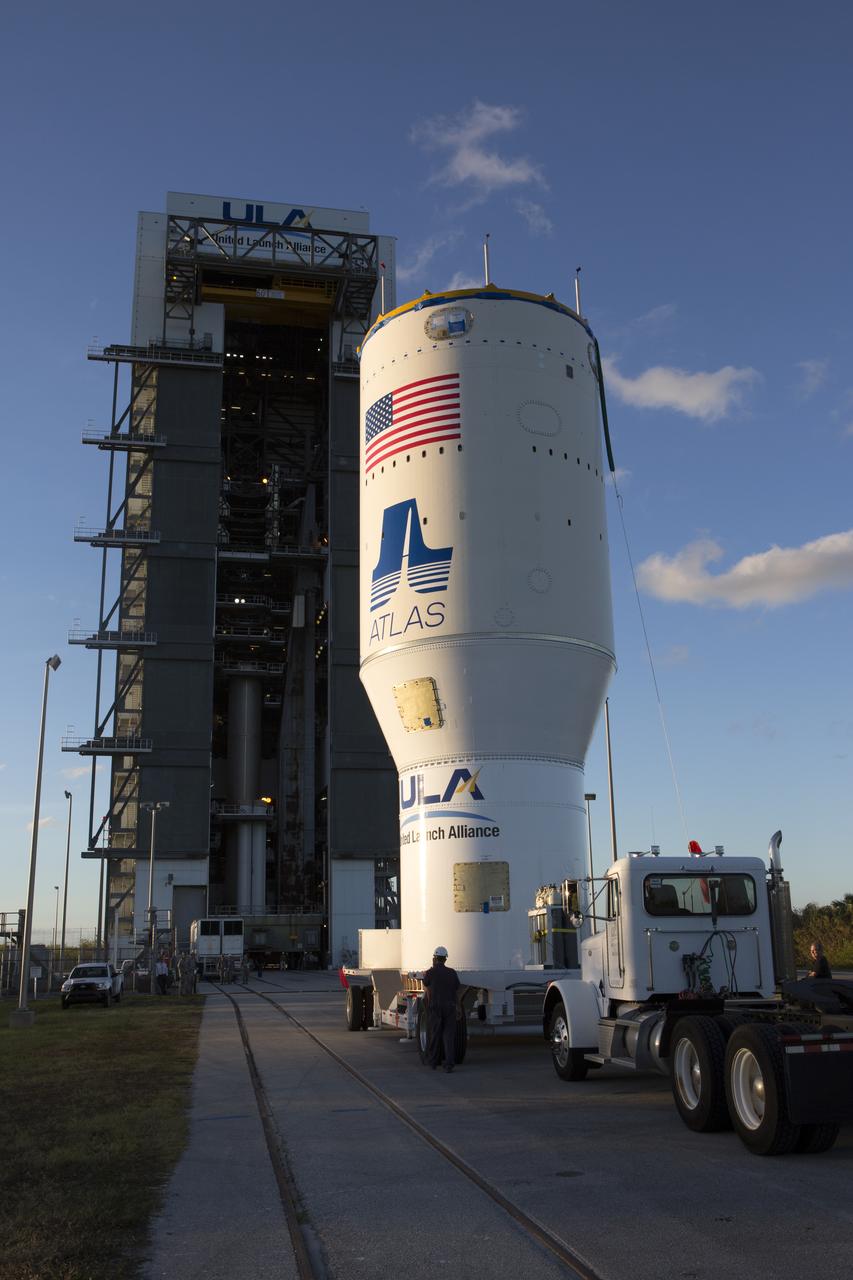

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V Centaur second stage arrives at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket in November. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
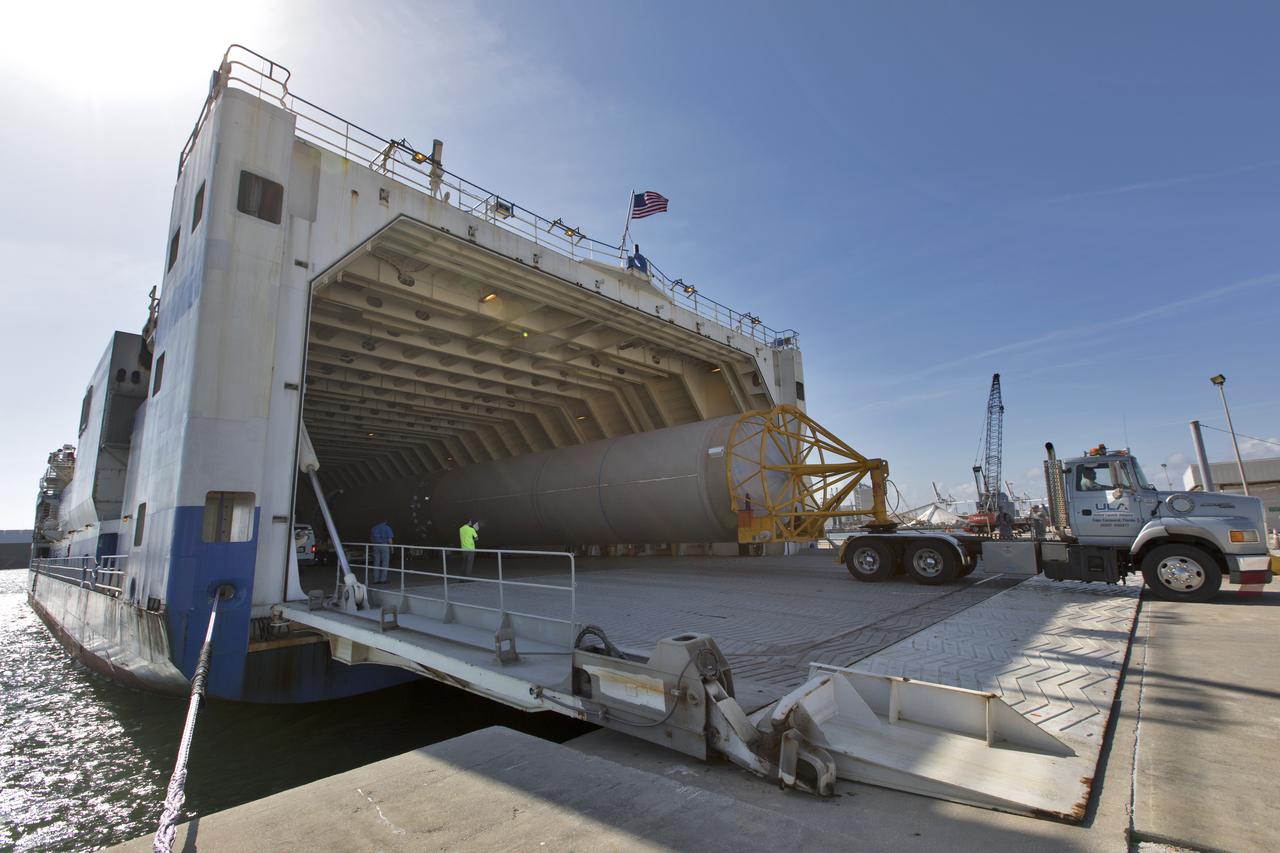

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V booster and Centaur stage for NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) are offloaded from the Mariner transport ship at the Army Wharf at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. They will be transported to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center near Space Launch Complex 41 at CCAFS. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The satellite is slated to launch aboard the Atlas V rocket March 1.
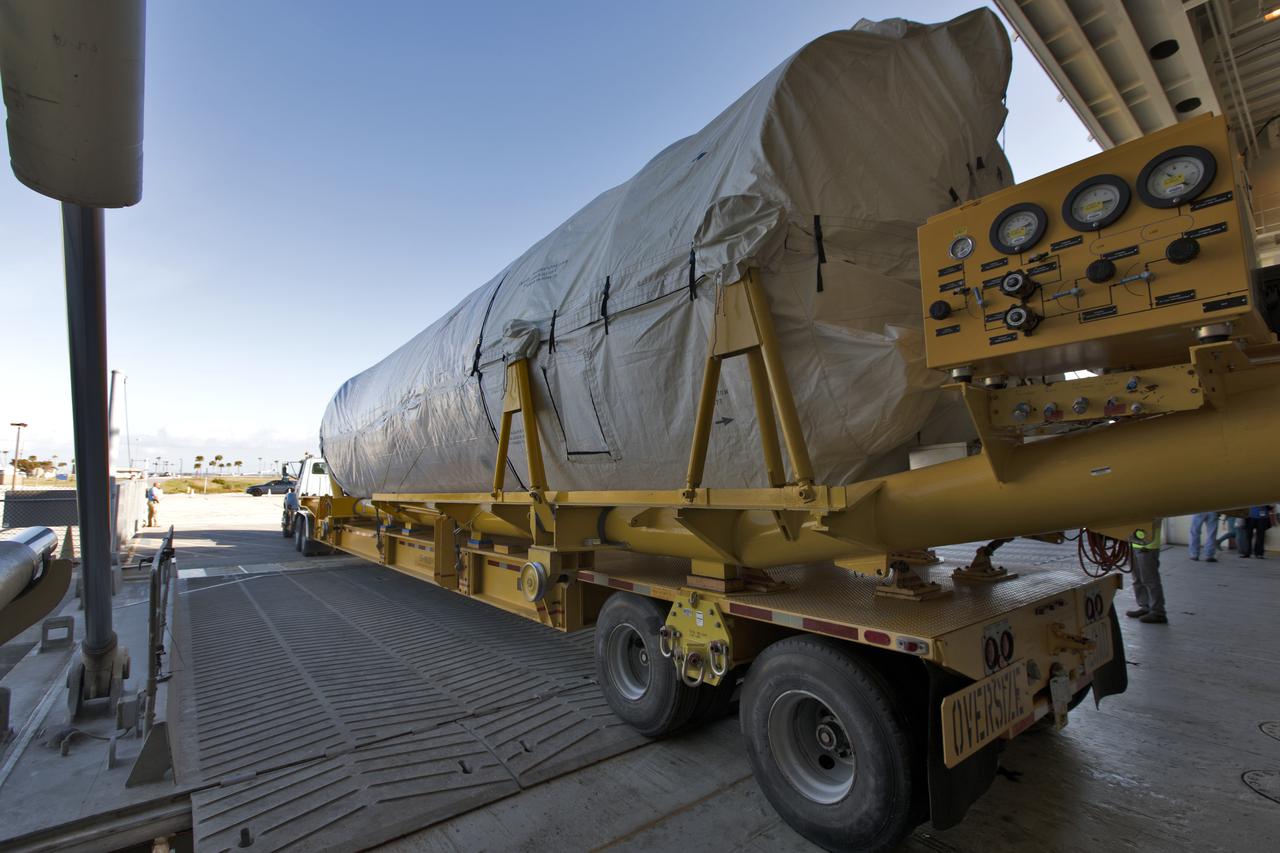

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V booster and Centaur stage for NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) are offloaded from the Mariner transport ship at the Army Wharf at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. They will be transported to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center near Space Launch Complex 41 at CCAFS. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The satellite is slated to launch aboard the Atlas V rocket March 1.
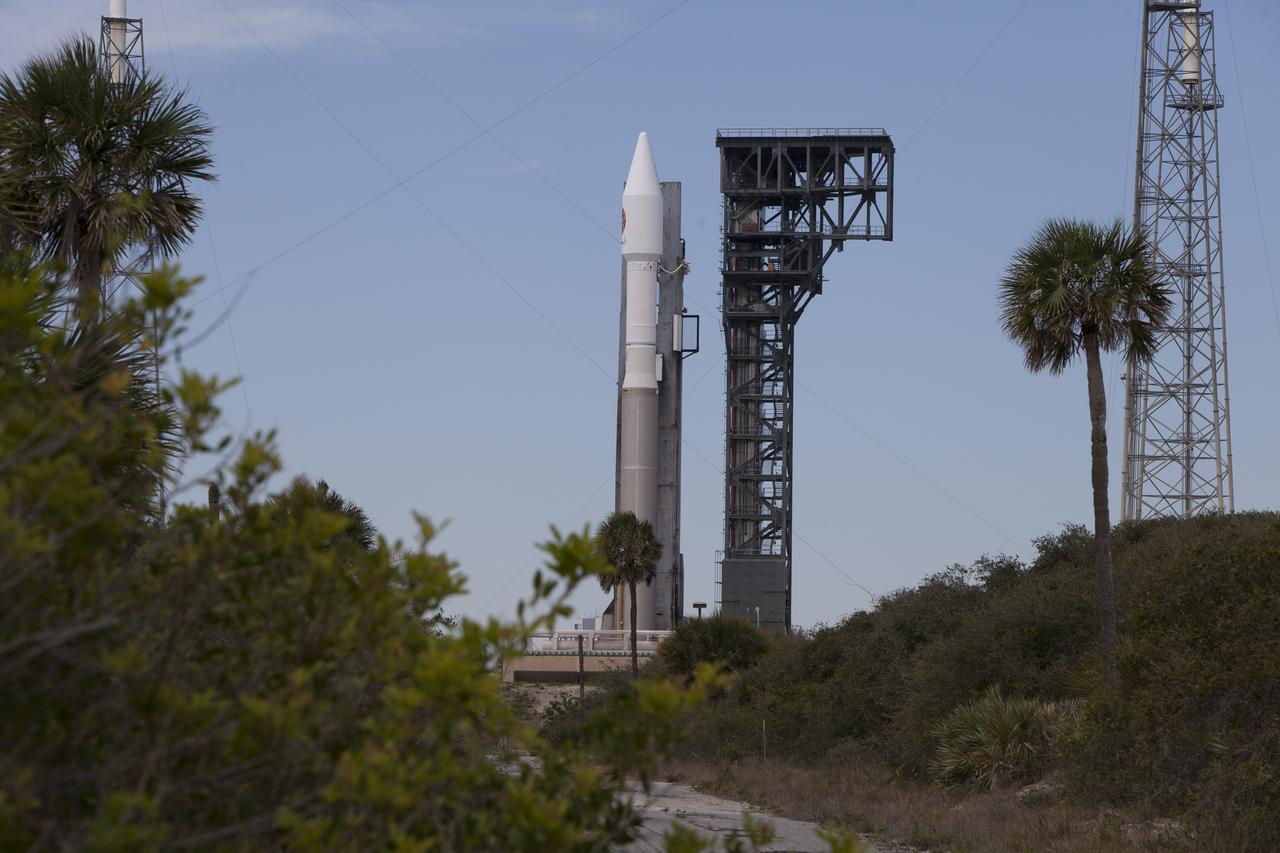

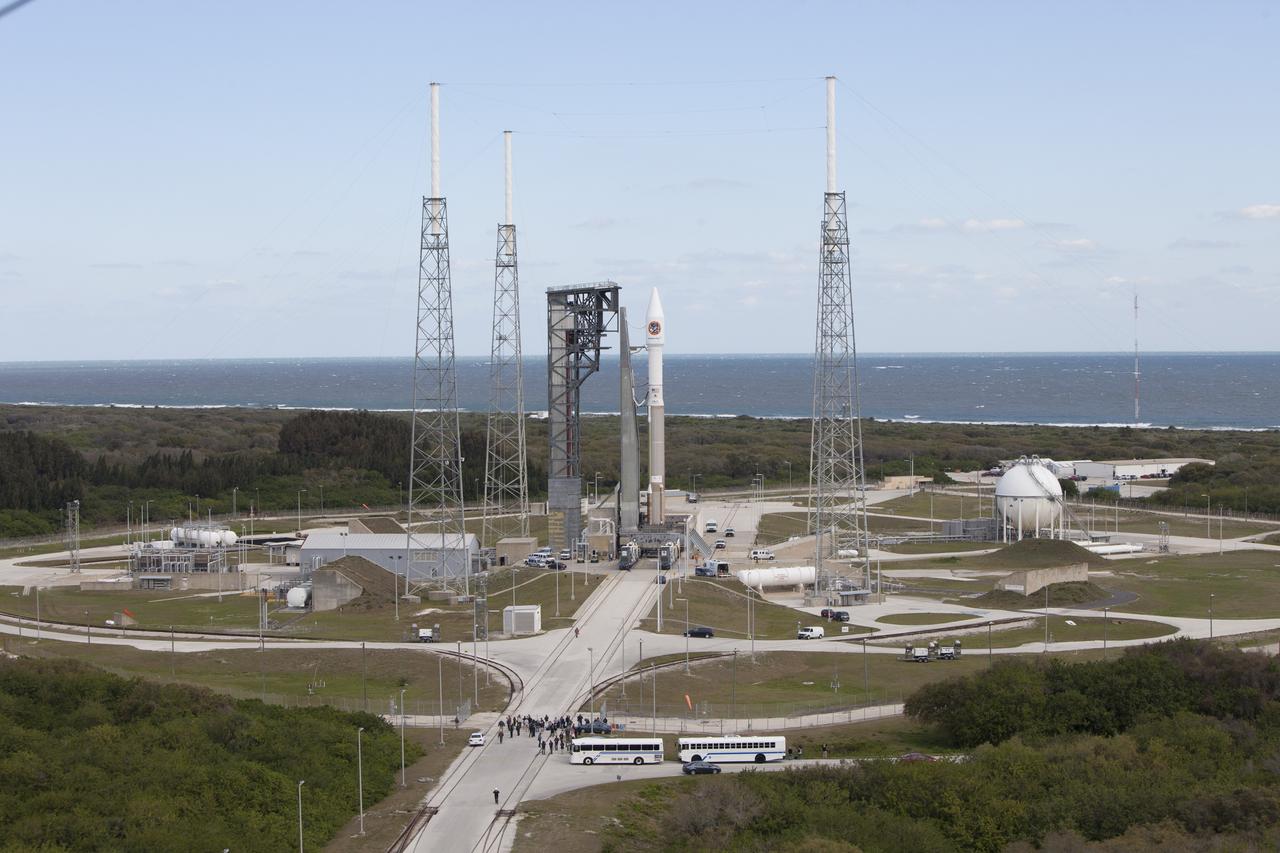
At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 41, a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with a single-engine Centaur upper stage stands ready to boost an Orbital ATK Cygnus spacecraft on a resupply mission to the International Space Station. Science payloads include the second generation of a portable onboard printer to demonstrate three-dimensional printing, an instrument for first space-based observations of the chemical composition of meteors entering Earth’s atmosphere and an experiment to study how fires burn in microgravity.
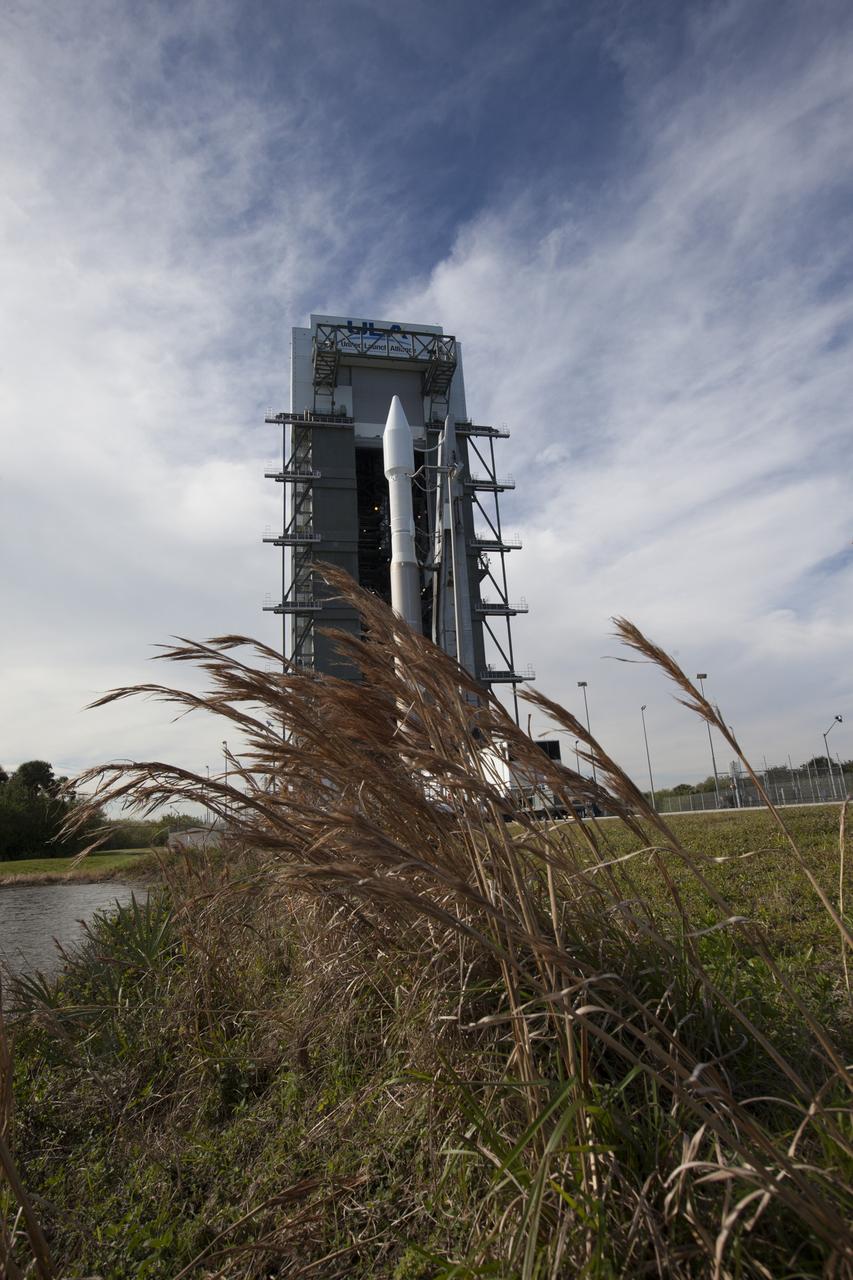

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 41, a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with a single-engine Centaur upper stage stands ready to boost an Orbital ATK Cygnus spacecraft on a resupply mission to the International Space Station. Science payloads include the second generation of a portable onboard printer to demonstrate three-dimensional printing, an instrument for first space-based observations of the chemical composition of meteors entering Earth’s atmosphere and an experiment to study how fires burn in microgravity.
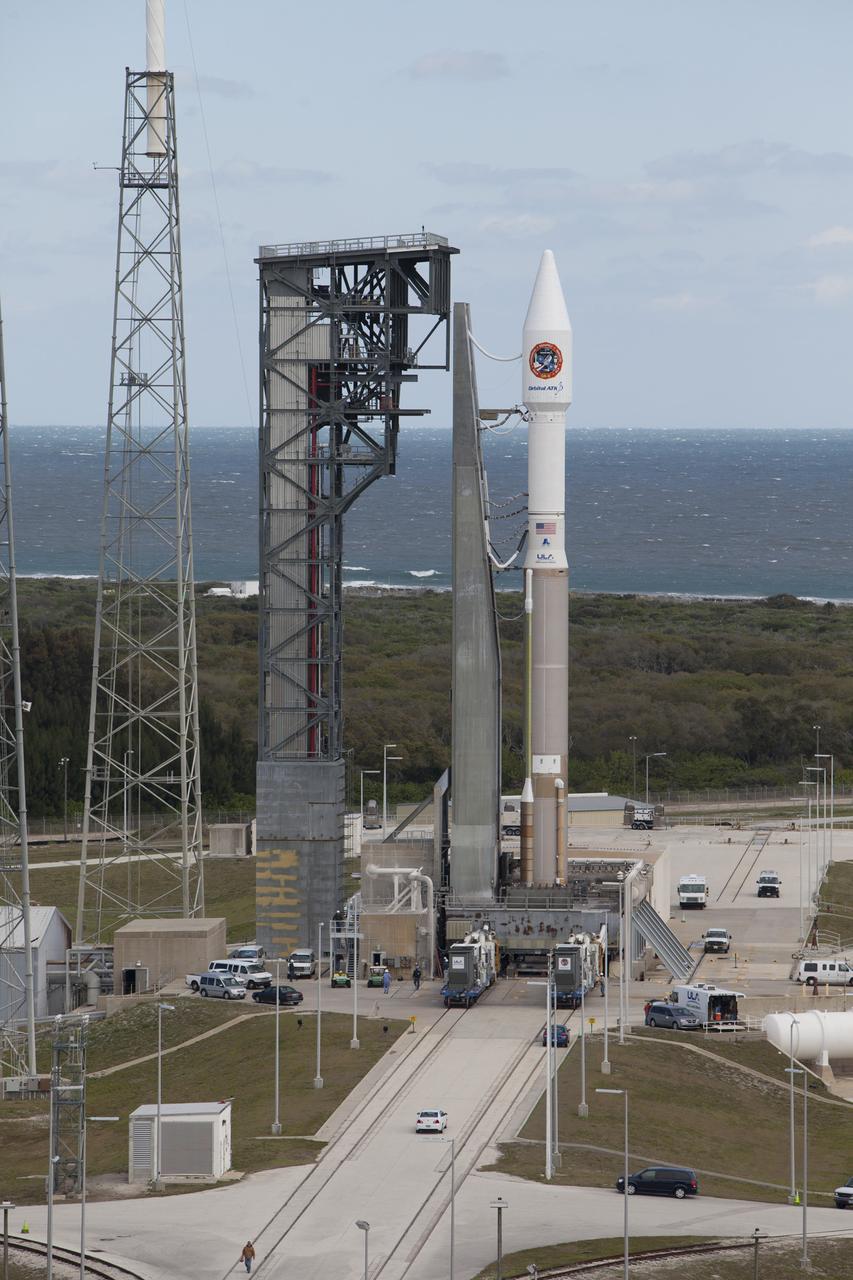

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 41, a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with a single-engine Centaur upper stage stands ready to boost an Orbital ATK Cygnus spacecraft on a resupply mission to the International Space Station. Science payloads include the second generation of a portable onboard printer to demonstrate three-dimensional printing, an instrument for first space-based observations of the chemical composition of meteors entering Earth’s atmosphere and an experiment to study how fires burn in microgravity.
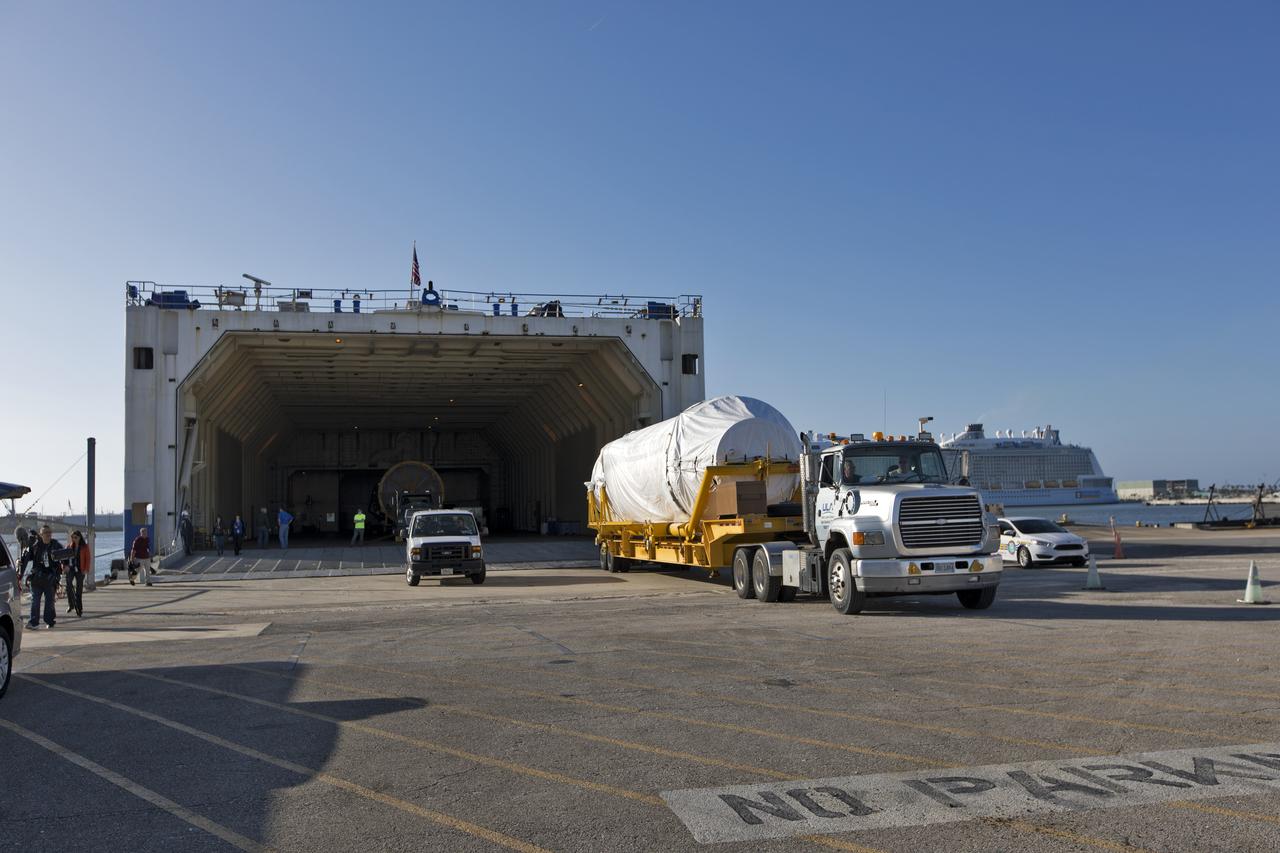

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V booster and Centaur stage for NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) are offloaded from the Mariner transport ship at the Army Wharf at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. They will be transported to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center near Space Launch Complex 41 at CCAFS. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The satellite is slated to launch aboard the Atlas V rocket March 1.
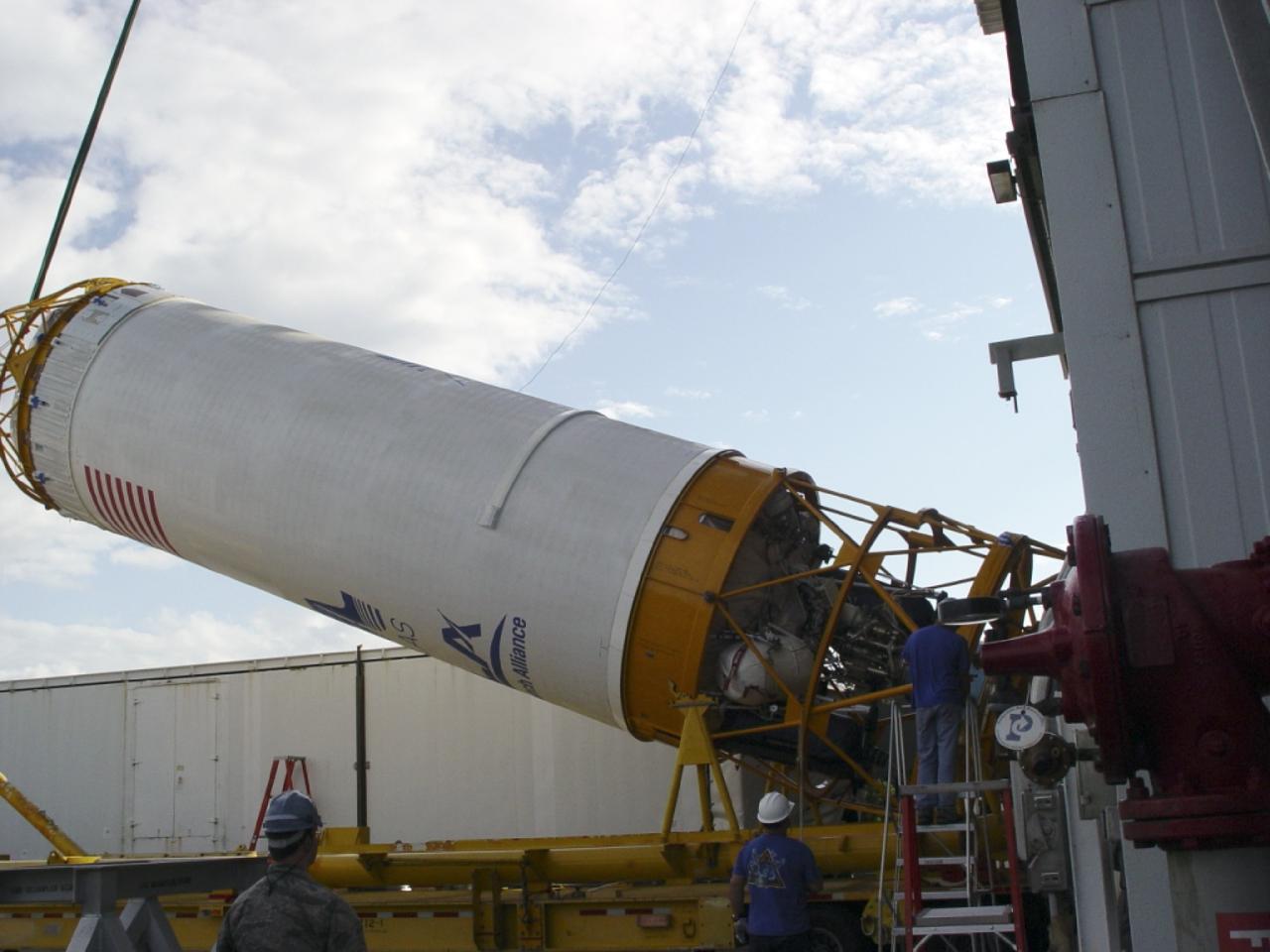

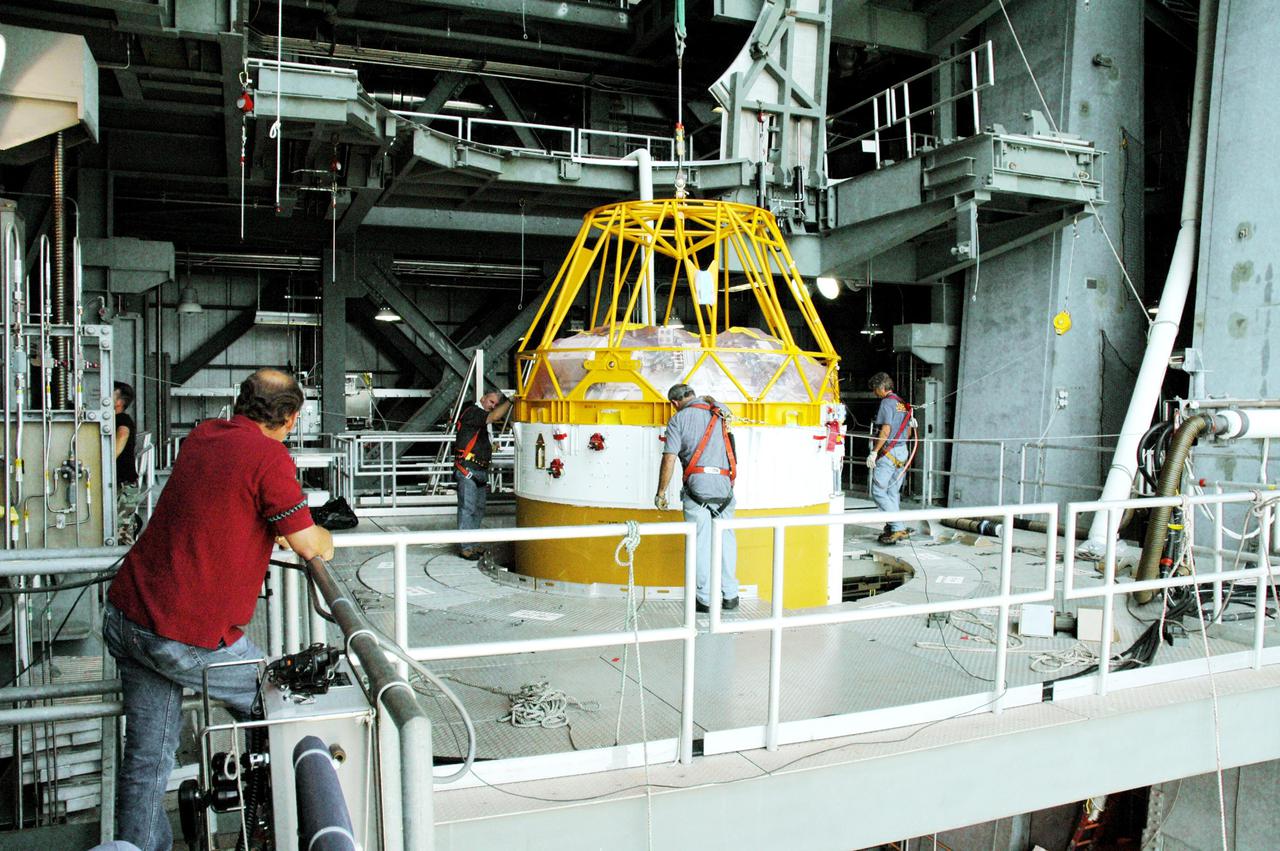
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the United Launch Alliance Centaur second stage is lifted for stacking atop its Atlas V first stage at Launch Pad 41 in preparation for the Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution, or MAVEN, mission. MAVEN is being prepared for its scheduled launch on Nov 18, 2013 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Positioned in an orbit above the Red Planet, MAVEN will study the upper atmosphere of Mars in unprecedented detail. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/maven/main/index.html Photo credit: United Launch Alliance
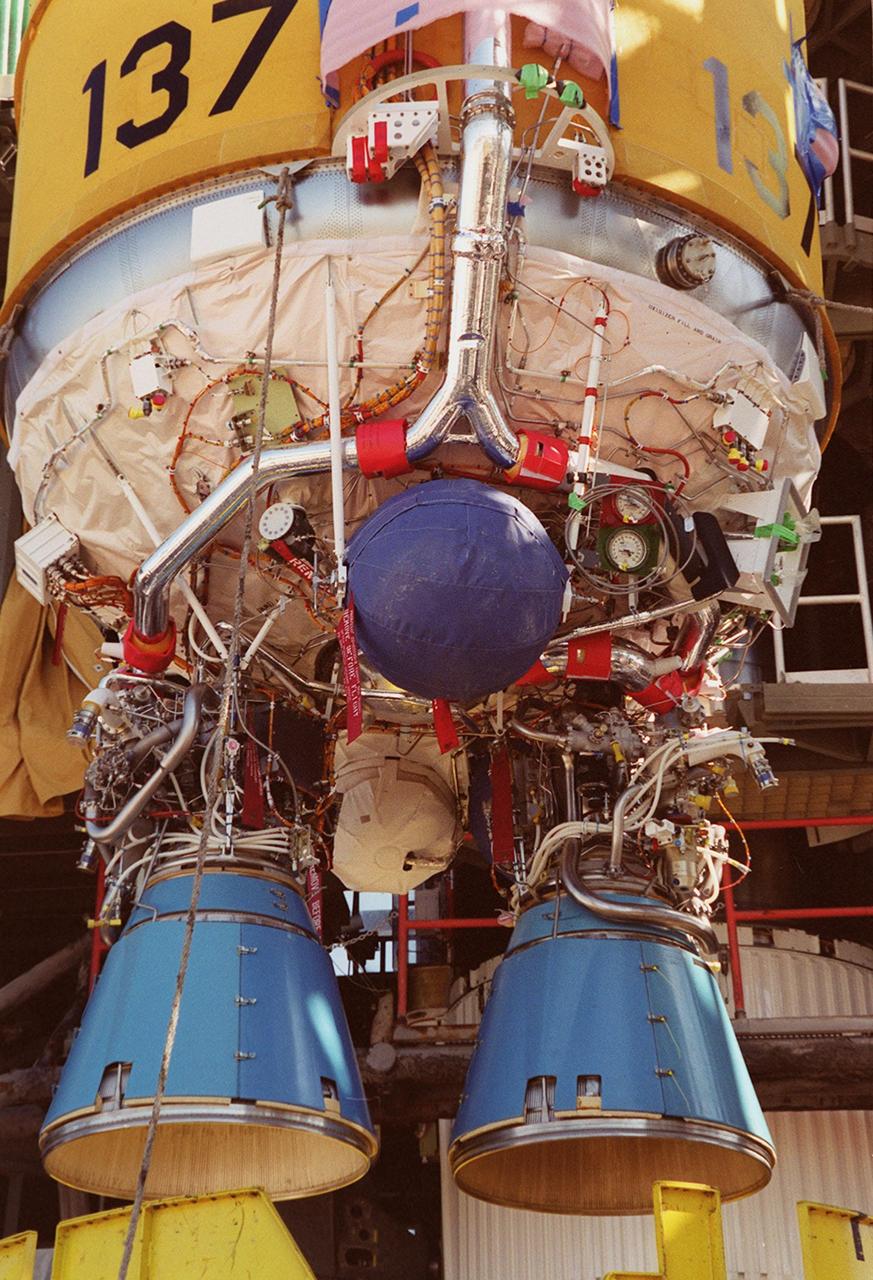
At launch pad 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the second stage of an Atlas II/Centaur rocket is lifted up the gantry (behind it) for mating with the first stage. Atlas II is designed to launch payloads into low earth orbit, geosynchronous transfer orbit or geosynchronous orbit. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the GOES-L satellite, part of the NOAA National Weather Service system in weather imagery and atmospheric sounding information. The primary objective of the GOES-L is to provide a full capability satellite in an on-orbit storage condition, to assure NOAA continuity in services from a two-satellite constellation. Launch services are being provided by the 45th Space Wing

United Launch Alliance (ULA) technicians monitor the progress as the payload fairing containing the Orbital ATK Cygnus pressurized cargo module is lowered onto the Centaur upper stage, or second stage, of the ULA Atlas V rocket in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V from pad 41. Cygnus will deliver 7,600 pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
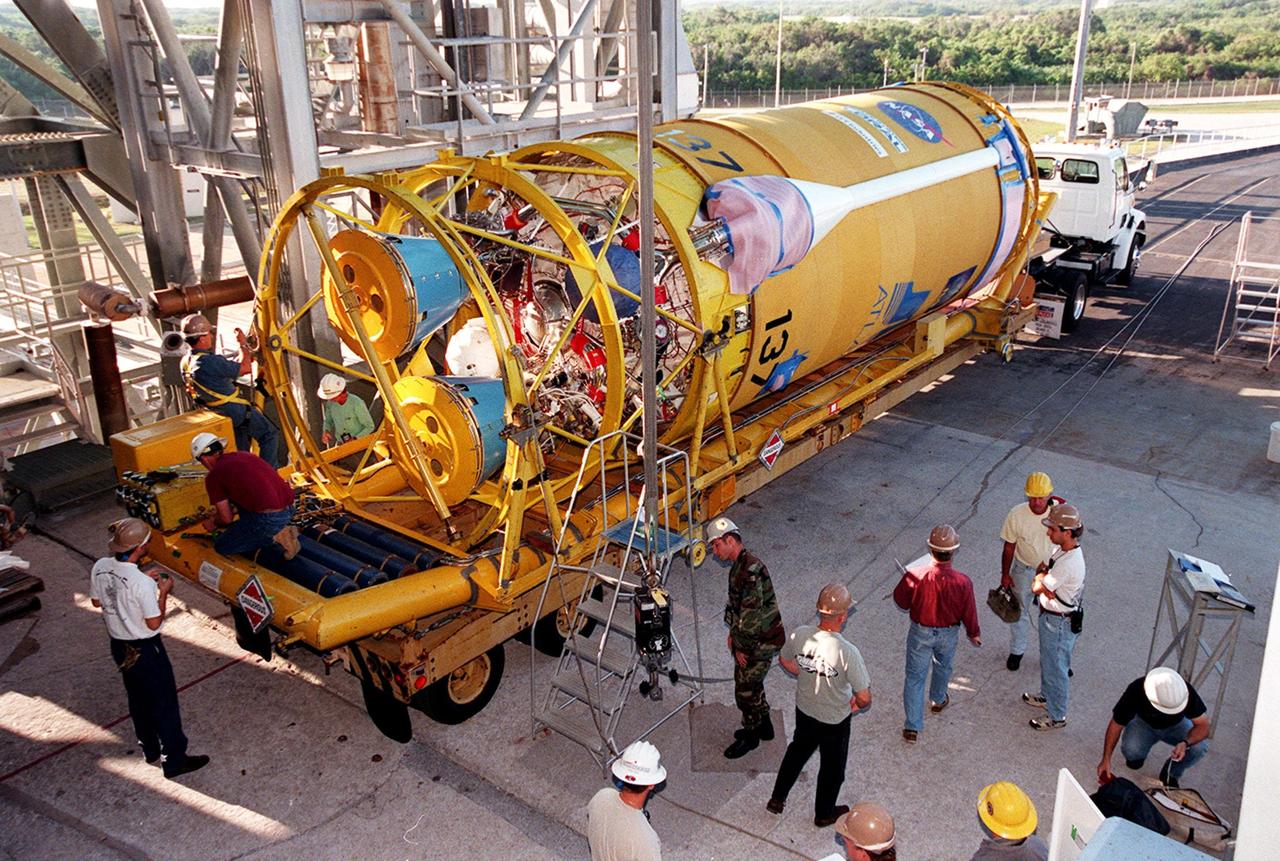

The second stage of an Atlas II/Centaur rocket arrives on pad 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, for mating with the first stage. Atlas II is designed to launch payloads into low earth orbit, geosynchronous transfer orbit or geosynchronous orbit. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the GOES-L satellite, part of the NOAA National Weather Service system in weather imagery and atmospheric sounding information. The primary objective of the GOES-L is to provide a full capability satellite in an on-orbit storage condition, to assure NOAA continuity in services from a two-satellite constellation. Launch services are being provided by the 45th Space Wing
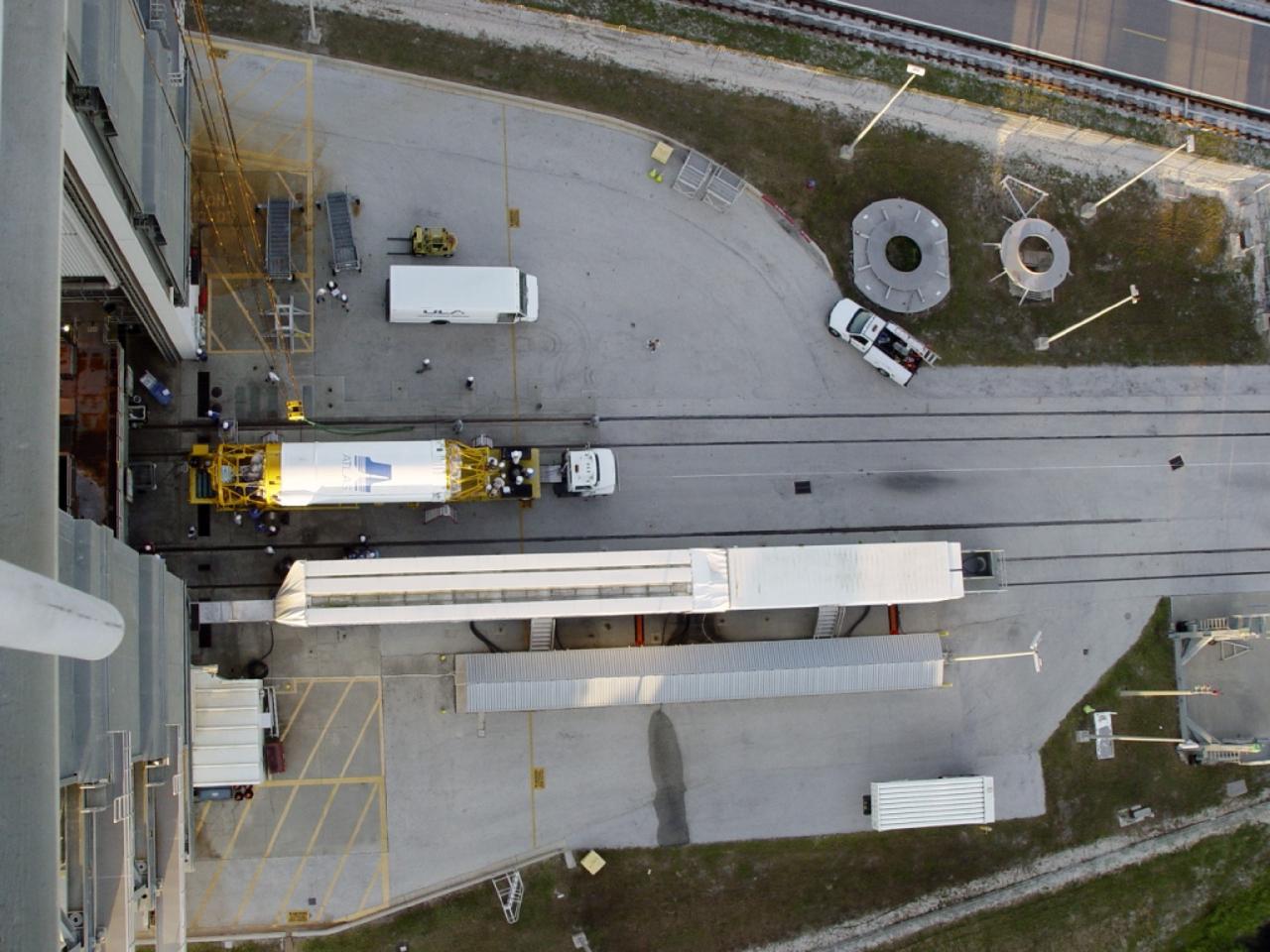

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In this overhead view at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the United Launch Alliance Centaur second stage is prepared for stacking atop the Atlas V first stage at Launch Pad 41 in preparation for the Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution, or MAVEN, mission. MAVEN is being prepared for its scheduled launch on Nov 18, 2013 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Positioned in an orbit above the Red Planet, MAVEN will study the upper atmosphere of Mars in unprecedented detail. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/maven/main/index.html Photo credit: United Launch Alliance
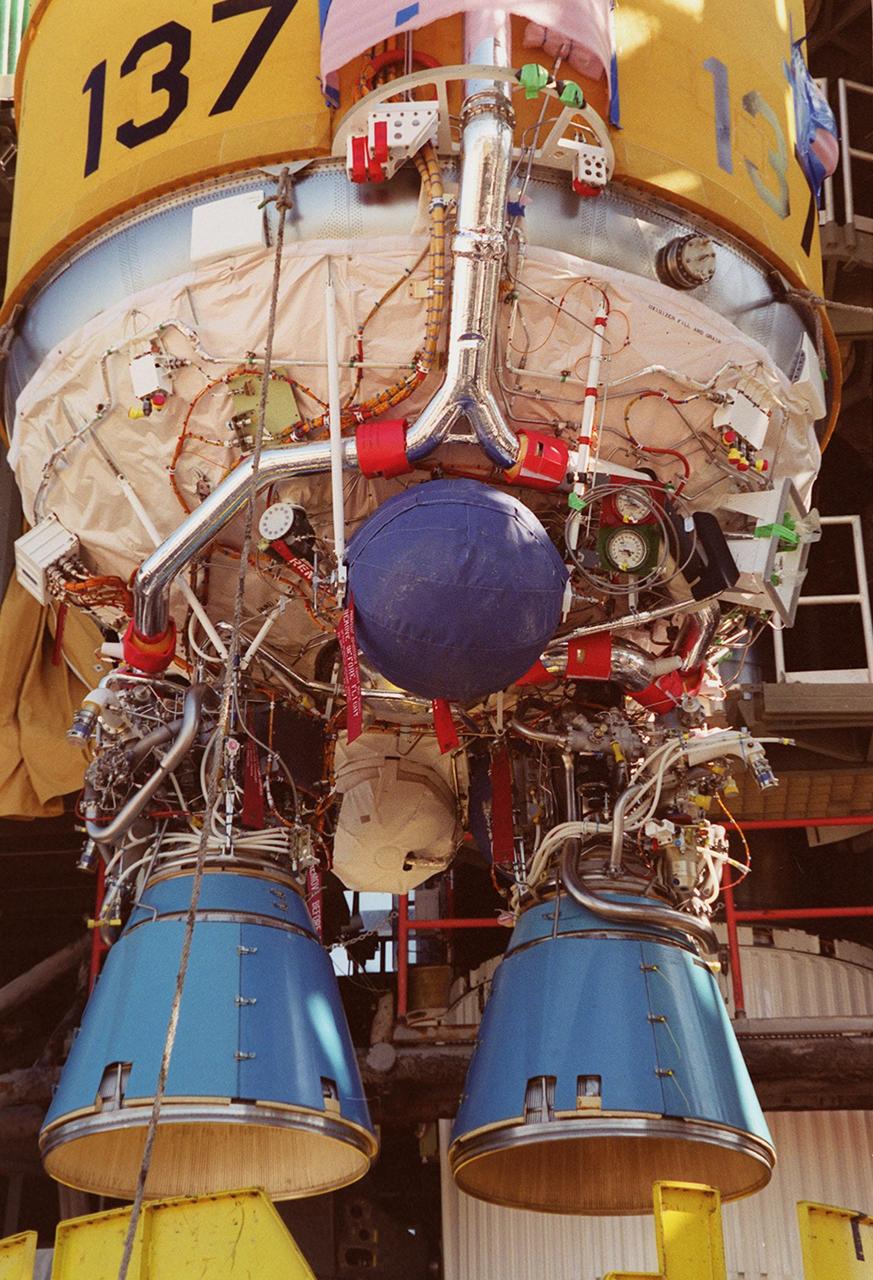
At launch pad 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the second stage of an Atlas II/Centaur rocket is lifted up the gantry (behind it) for mating with the first stage. Atlas II is designed to launch payloads into low earth orbit, geosynchronous transfer orbit or geosynchronous orbit. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the GOES-L satellite, part of the NOAA National Weather Service system in weather imagery and atmospheric sounding information. The primary objective of the GOES-L is to provide a full capability satellite in an on-orbit storage condition, to assure NOAA continuity in services from a two-satellite constellation. Launch services are being provided by the 45th Space Wing

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the United Launch Alliance Centaur second stage is prepared for stacking atop the Atlas V first stage at Launch Pad 41 in preparation for the Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution, or MAVEN, mission. MAVEN is being prepared for its scheduled launch on Nov 18, 2013 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Positioned in an orbit above the Red Planet, MAVEN will study the upper atmosphere of Mars in unprecedented detail. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/maven/main/index.html Photo credit: United Launch Alliance

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the United Launch Alliance Centaur second stage is prepared for stacking atop the Atlas V first stage at Launch Pad 41 in preparation for the Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution, or MAVEN, mission. MAVEN is being prepared for its scheduled launch on Nov 18, 2013 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Positioned in an orbit above the Red Planet, MAVEN will study the upper atmosphere of Mars in unprecedented detail. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/maven/main/index.html Photo credit: United Launch Alliance

At launch pad 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, workers check over the second stage of an Atlas II/Centaur rocket before it is lifted up the gantry (behind it) for mating with the first stage. Atlas II is designed to launch payloads into low earth orbit, geosynchronous transfer orbit or geosynchronous orbit. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the GOES-L satellite, part of the NOAA National Weather Service system in weather imagery and atmospheric sounding information. The primary objective of the GOES-L is to provide a full capability satellite in an on-orbit storage condition, to assure NOAA continuity in services from a two-satellite constellation. Launch services are being provided by the 45th Space Wing

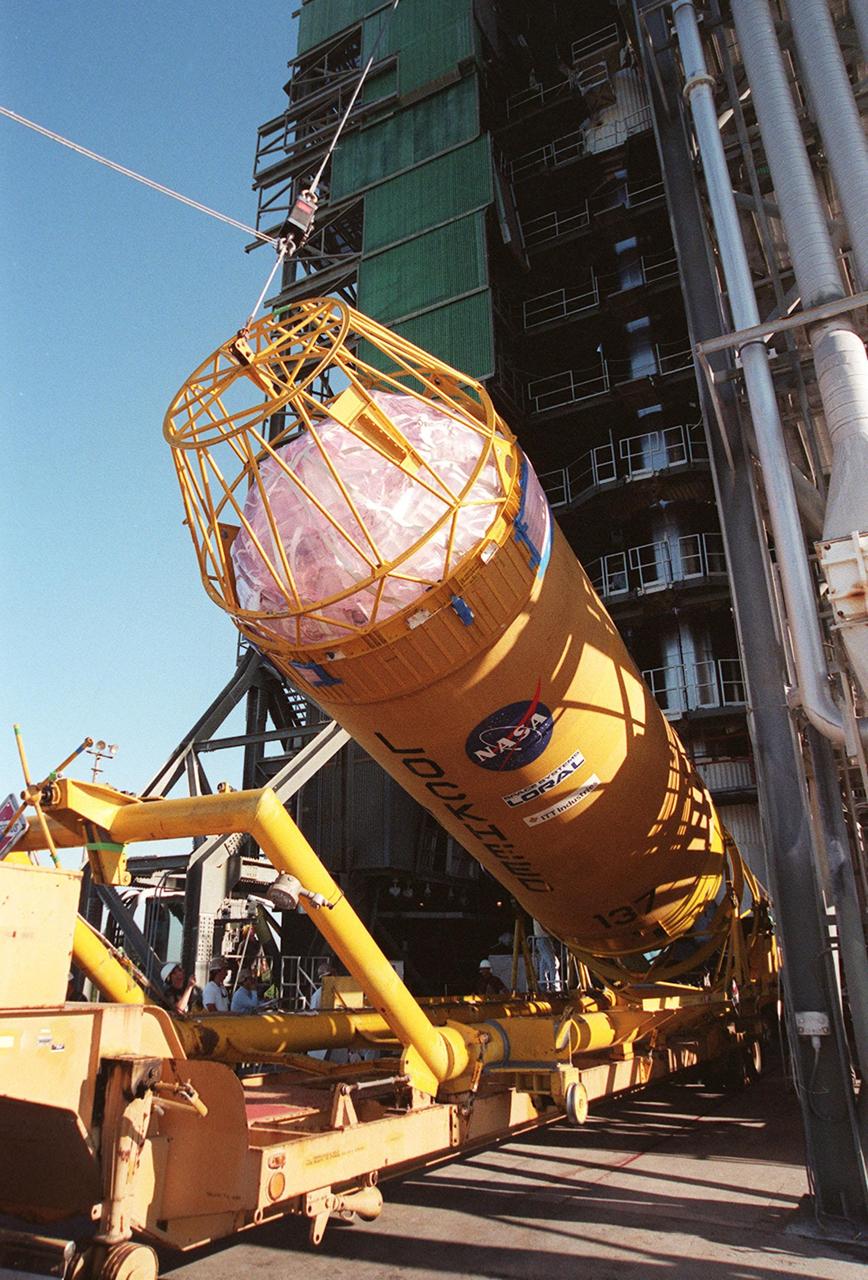
The second stage of an Atlas II/Centaur rocket is raised to a vertical position in front of the gantry on pad 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, for mating with the first stage. Atlas II is designed to launch payloads into low earth orbit, geosynchronous transfer orbit or geosynchronous orbit. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the GOES-L satellite, part of the NOAA National Weather Service system in weather imagery and atmospheric sounding information. The primary objective of the GOES-L is to provide a full capability satellite in an on-orbit storage condition, to assure NOAA continuity in services from a two-satellite constellation. Launch services are being provided by the 45th Space Wing

The second stage of an Atlas II/Centaur rocket arrives on pad 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, for mating with the first stage. Atlas II is designed to launch payloads into low earth orbit, geosynchronous transfer orbit or geosynchronous orbit. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the GOES-L satellite, part of the NOAA National Weather Service system in weather imagery and atmospheric sounding information. The primary objective of the GOES-L is to provide a full capability satellite in an on-orbit storage condition, to assure NOAA continuity in services from a two-satellite constellation. Launch services are being provided by the 45th Space Wing
At launch pad 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, cables help guide the second stage of an Atlas II/Centaur rocket as it is lifted up the gantry (behind it) for mating with the first stage. Atlas II is designed to launch payloads into low earth orbit, geosynchronous transfer orbit or geosynchronous orbit. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the GOES-L satellite, part of the NOAA National Weather Service system in weather imagery and atmospheric sounding information. The primary objective of the GOES-L is to provide a full capability satellite in an on-orbit storage condition, to assure NOAA continuity in services from a two-satellite constellation. Launch services are being provided by the 45th Space Wing
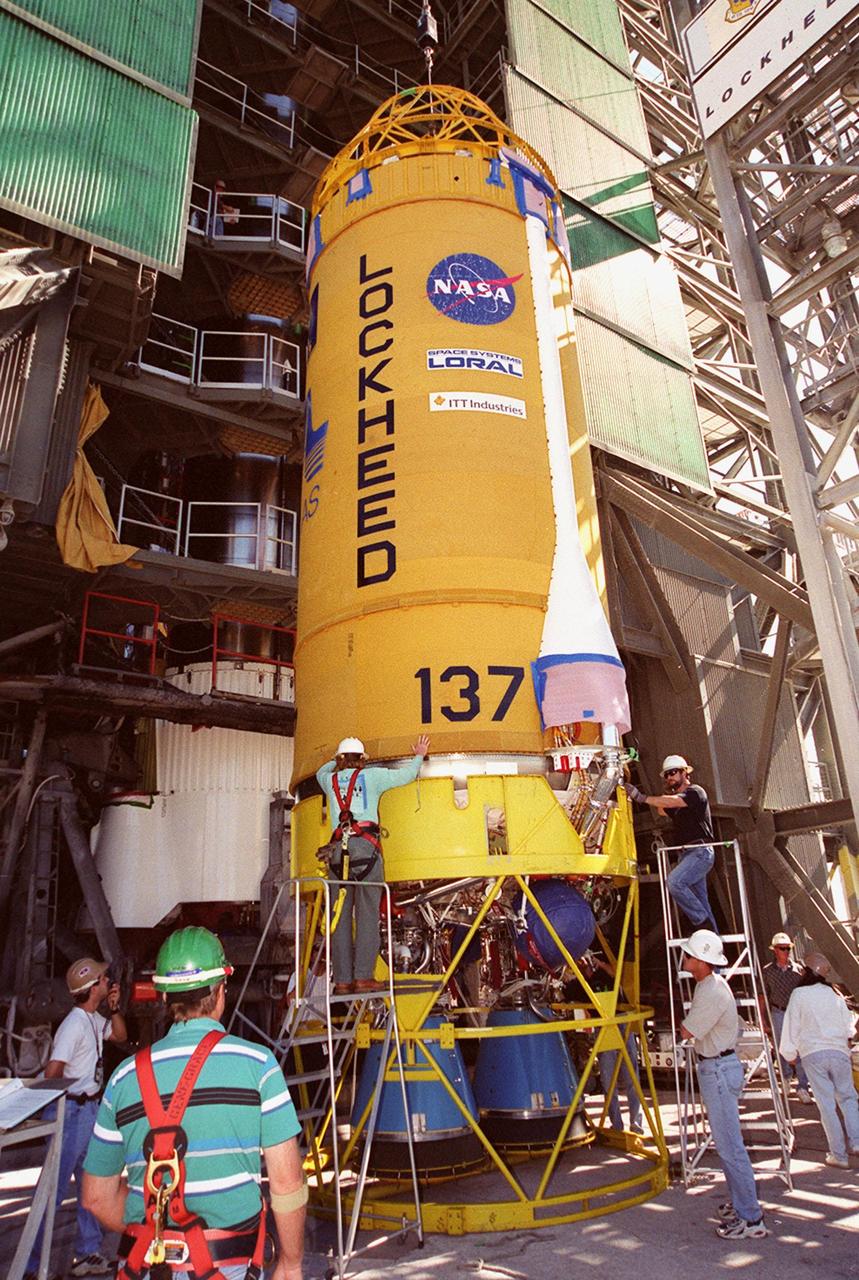

At launch pad 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, workers check over the second stage of an Atlas II/Centaur rocket before it is lifted up the gantry (behind it) for mating with the first stage. Atlas II is designed to launch payloads into low earth orbit, geosynchronous transfer orbit or geosynchronous orbit. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the GOES-L satellite, part of the NOAA National Weather Service system in weather imagery and atmospheric sounding information. The primary objective of the GOES-L is to provide a full capability satellite in an on-orbit storage condition, to assure NOAA continuity in services from a two-satellite constellation. Launch services are being provided by the 45th Space Wing

The second stage of an Atlas II/Centaur rocket is raised to a vertical position in front of the gantry on pad 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, for mating with the first stage. Atlas II is designed to launch payloads into low earth orbit, geosynchronous transfer orbit or geosynchronous orbit. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the GOES-L satellite, part of the NOAA National Weather Service system in weather imagery and atmospheric sounding information. The primary objective of the GOES-L is to provide a full capability satellite in an on-orbit storage condition, to assure NOAA continuity in services from a two-satellite constellation. Launch services are being provided by the 45th Space Wing
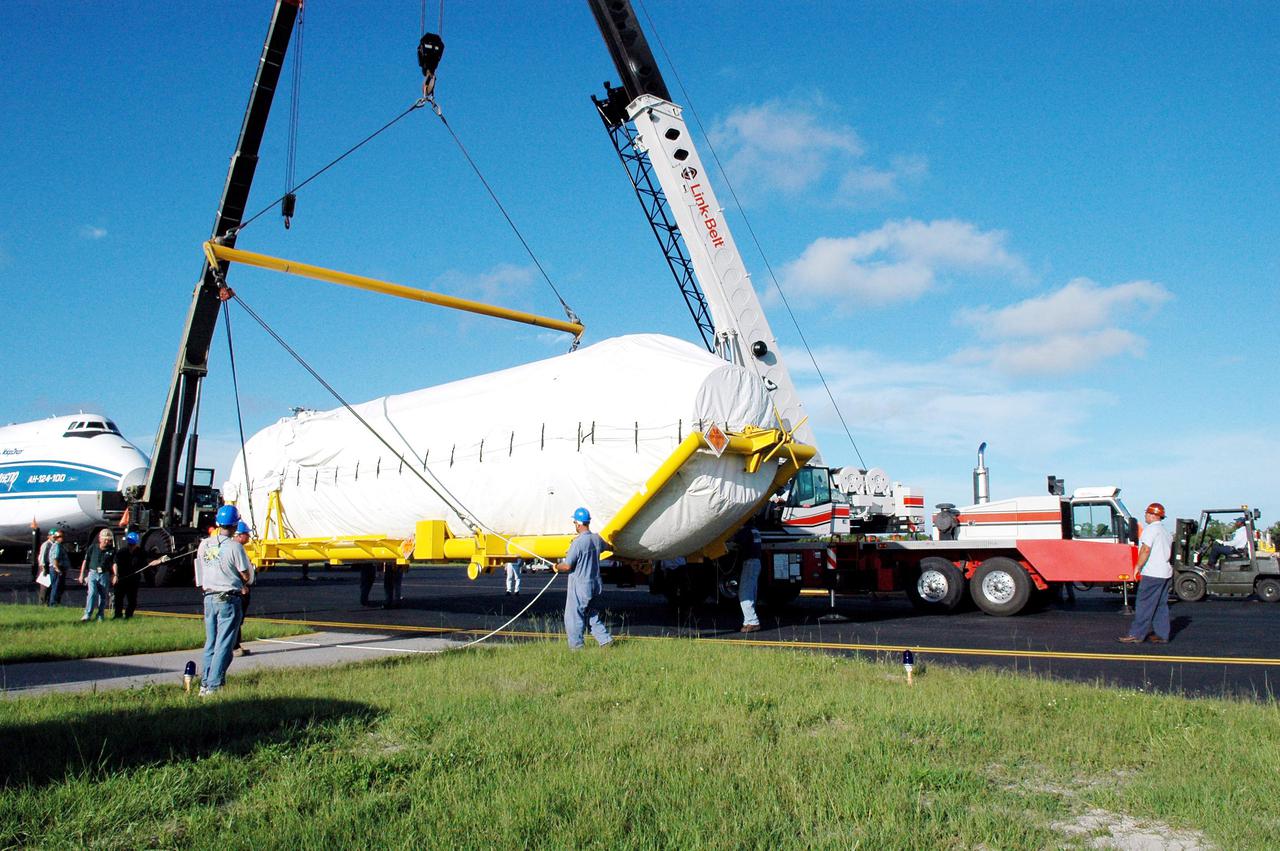

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station Skid Strip, a large crane is attached to the offloaded second stage Centaur (Block I) to lift and place it on a flat bed truck. The Centaur arrived on a Russian Antonov AH-124-100 cargo airplane. The Centaur upper stage will be mated with the Lockheed Martin Atlas V, designated AV-007, that is the launch vehicle for the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). The MRO is designed for a series of global mapping, regional survey and targeted observations from a near-polar, low-altitude Mars orbit. These observations will be unprecedented in terms of the spatial resolution and coverage achieved by the orbiter’s instruments as they observe the atmosphere and surface of Mars while probing its shallow subsurface as part of a “follow the water” strategy. The orbiter is undergoing environmental tests in facilities at Lockheed Martin Space Systems in Denver, Colo., and is on schedule for a launch window that begins Aug. 10. Launch will be from Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.

The interstage and assembly second stage adapters for the United Alliance Centaur Atlas V for NASA’s Landsat 9 mission are lifted by crane from a flatbed truck at Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, on July 14, 2021. The adapters will be stacked atop the Centaur second stage in the Vertical Integration Facility near the launch pad. The Landsat 9 mission will launch atop the Atlas V rocket from Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multiuser spaceport. The Landsat 9 satellite will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.
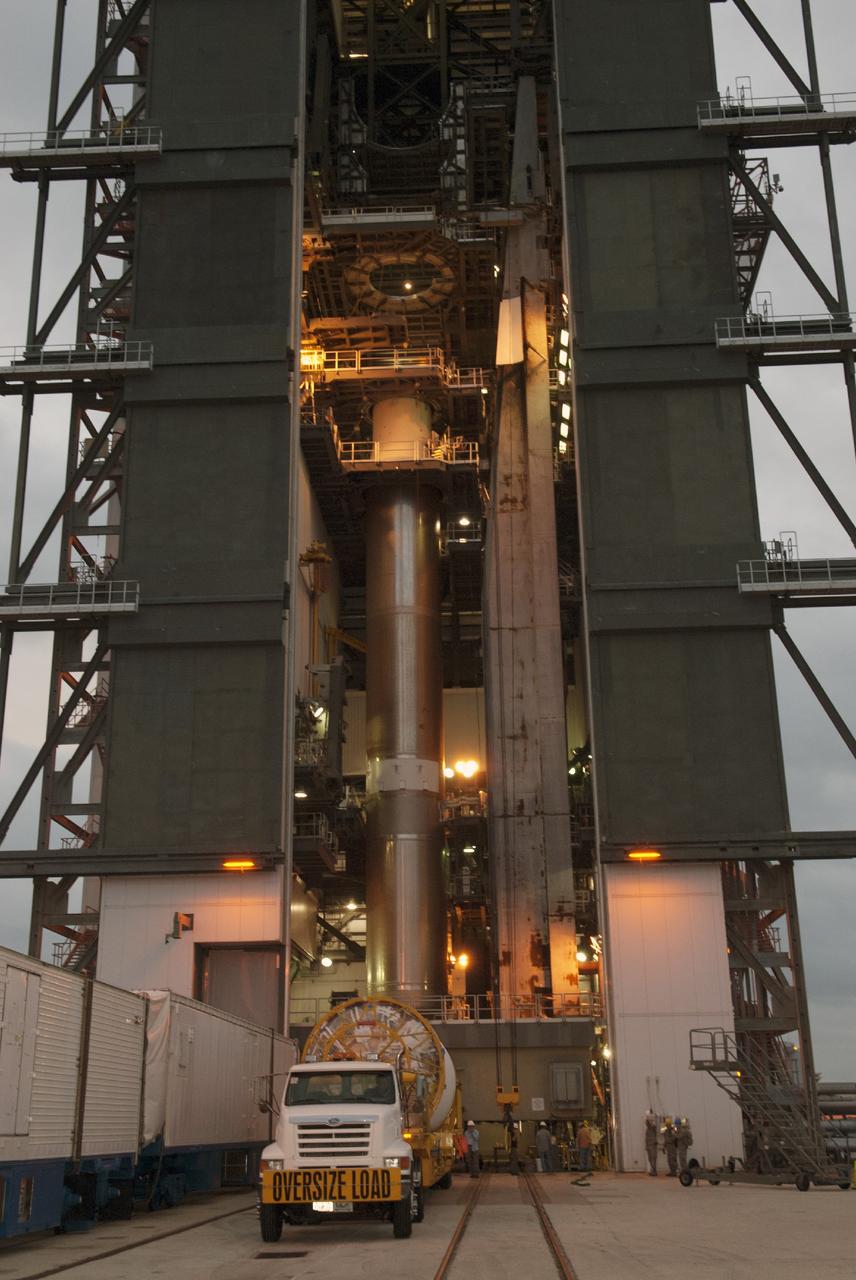

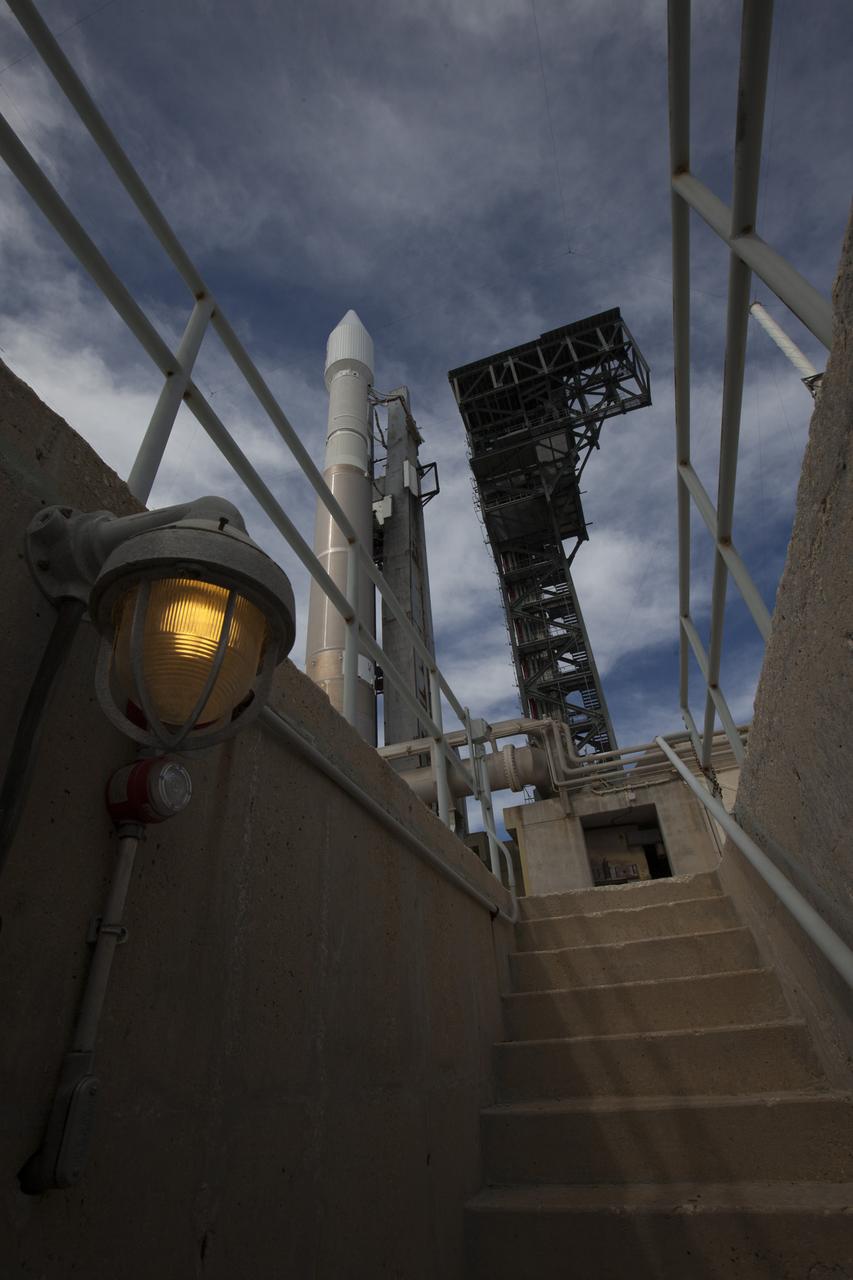
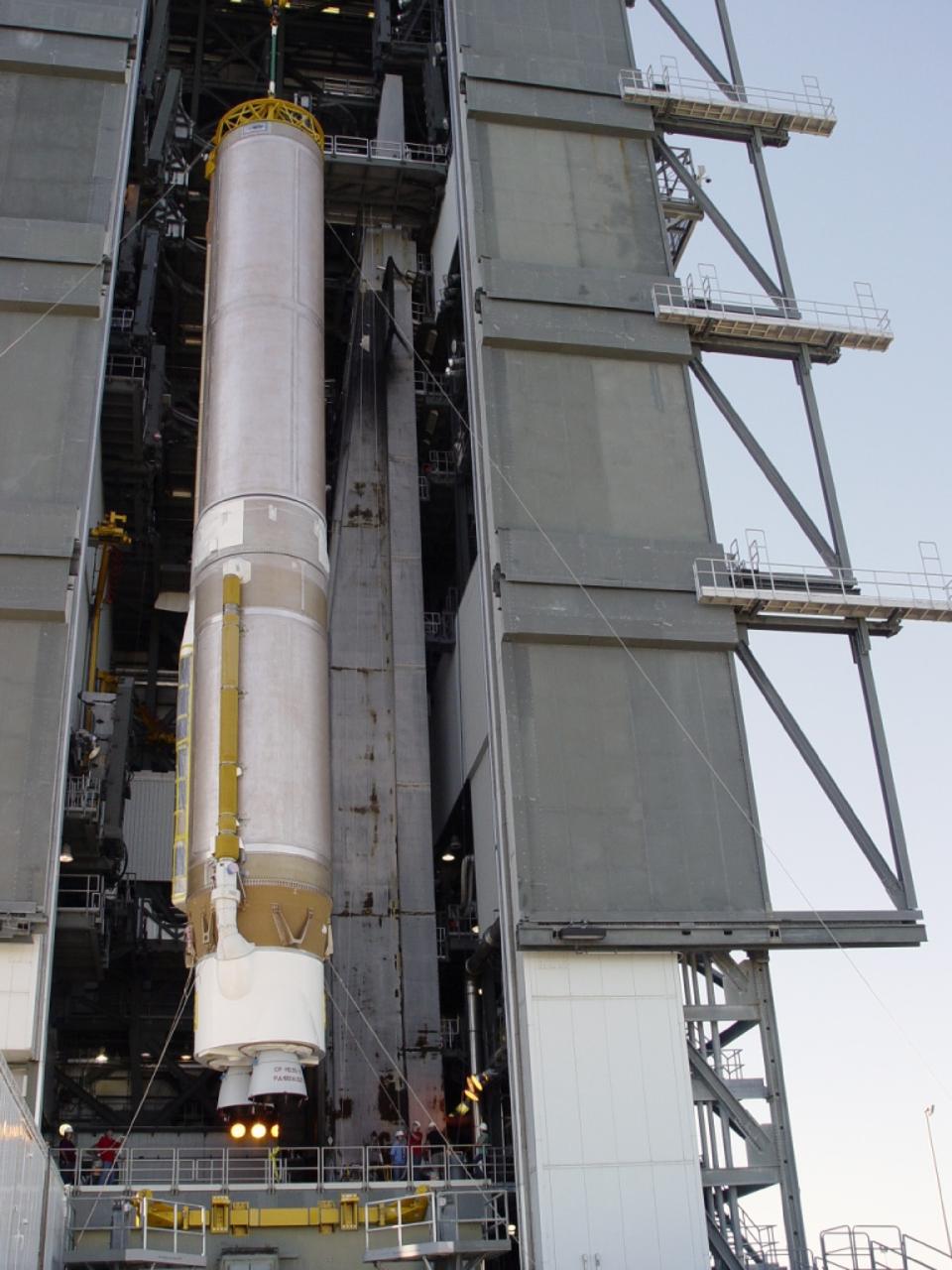
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The United Launch Alliance Centaur second stage that will help boost the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, or TDRS-L, spacecraft into orbit arrives at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Complex 41. It will be lifted and mounted atop the Atlas V first stage already in position inside the Vertical Integration Facility. TDRS-L is the second of three next-generation satellites designed to ensure vital operational continuity for the NASA Space Network. It is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 41 atop an Atlas V rocket in January 2014. The current Tracking and Data Relay Satellite system consists of eight in-orbit satellites distributed to provide near continuous information relay service to missions such as the Hubble Space Telescope and International Space Station. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/content/tracking-and-data-relay-satellite-tdrs/ Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
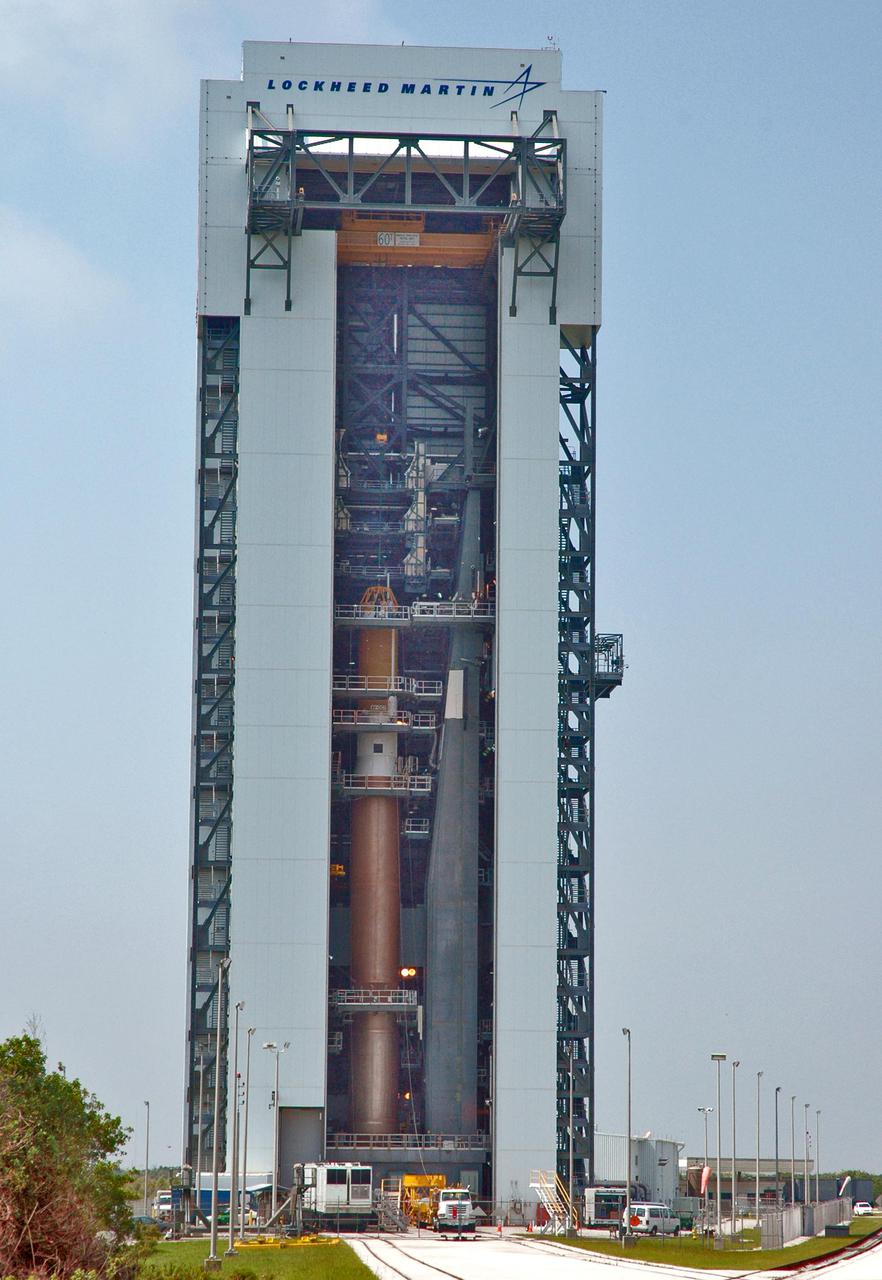

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Inside the launch tower on Launch Pad 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the upper end of the Lockheed Martin Centaur second stage is being lowered through an opening toward the Atlas V below. The Centaur will be mated with the Atlas V. The Atlas V_Centaur is the launch vehicle for the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). The MRO is designed for a series of global mapping, regional survey and targeted observations from a near-polar, low-altitude Mars orbit. These observations will be unprecedented in terms of the spatial resolution and coverage achieved by the orbiter’s instruments as they observe the atmosphere and surface of Mars while probing its shallow subsurface as part of a “follow the water” strategy. The launch window for the MRO begins Aug. 10.
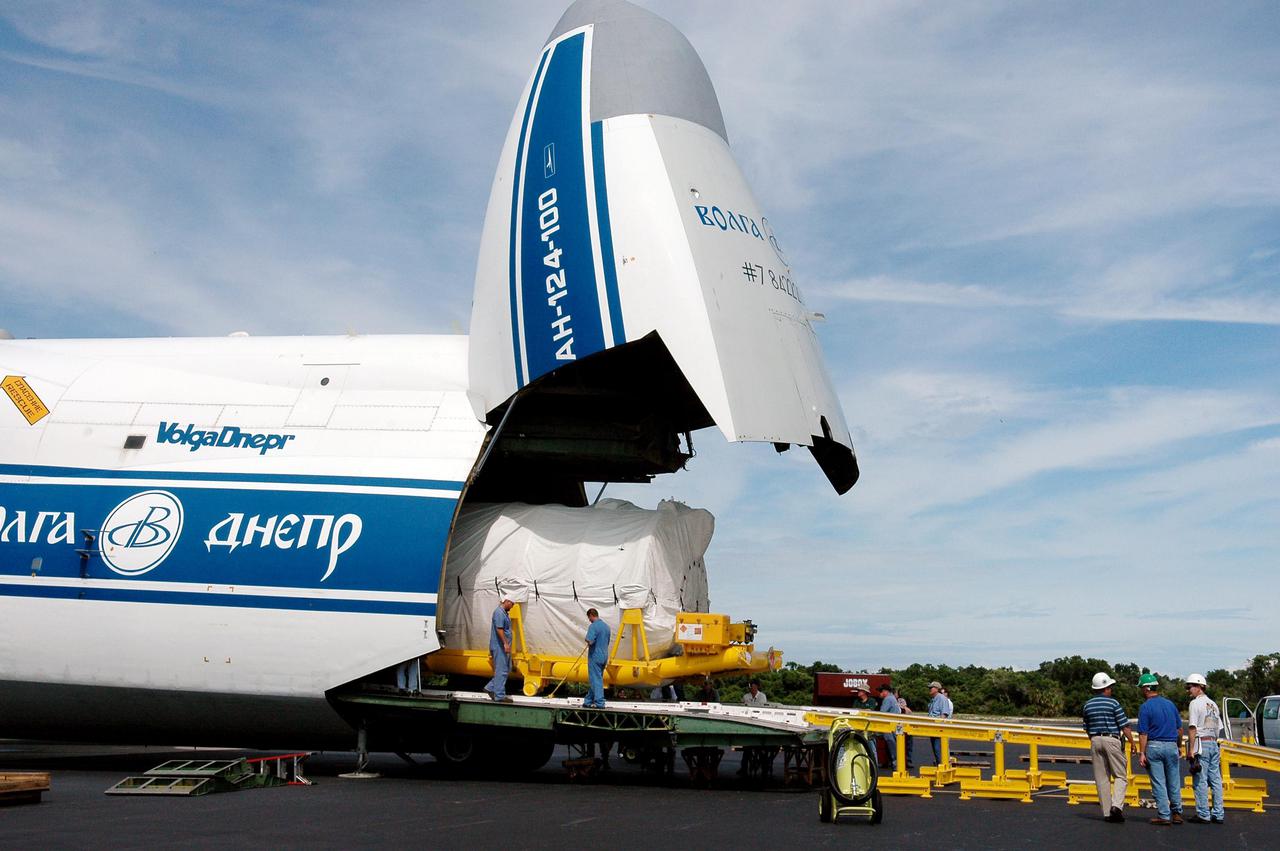

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station Skid Strip, a second stage Centaur (Block I) is rolled out of a Russian Antonov AH-124-100 cargo airplane. The Centaur will be mated with the Lockheed Martin Atlas V, designated AV-007, that is the launch vehicle for the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). The MRO is designed for a series of global mapping, regional survey and targeted observations from a near-polar, low-altitude Mars orbit. These observations will be unprecedented in terms of the spatial resolution and coverage achieved by the orbiter’s instruments as they observe the atmosphere and surface of Mars while probing its shallow subsurface as part of a “follow the water” strategy. The orbiter is undergoing environmental tests in facilities at Lockheed Martin Space Systems in Denver, Colo., and is on schedule for a launch window that begins Aug. 10. Launch will be from Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Inside the launch tower on Launch Pad 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the lower end of the Lockheed Martin Centaur second stage is being lowered through an opening toward the Atlas V below. The Centaur will be mated with the Atlas V. The Atlas V_Centaur is the launch vehicle for the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). The MRO is designed for a series of global mapping, regional survey and targeted observations from a near-polar, low-altitude Mars orbit. These observations will be unprecedented in terms of the spatial resolution and coverage achieved by the orbiter’s instruments as they observe the atmosphere and surface of Mars while probing its shallow subsurface as part of a “follow the water” strategy. The launch window for the MRO begins Aug. 10.
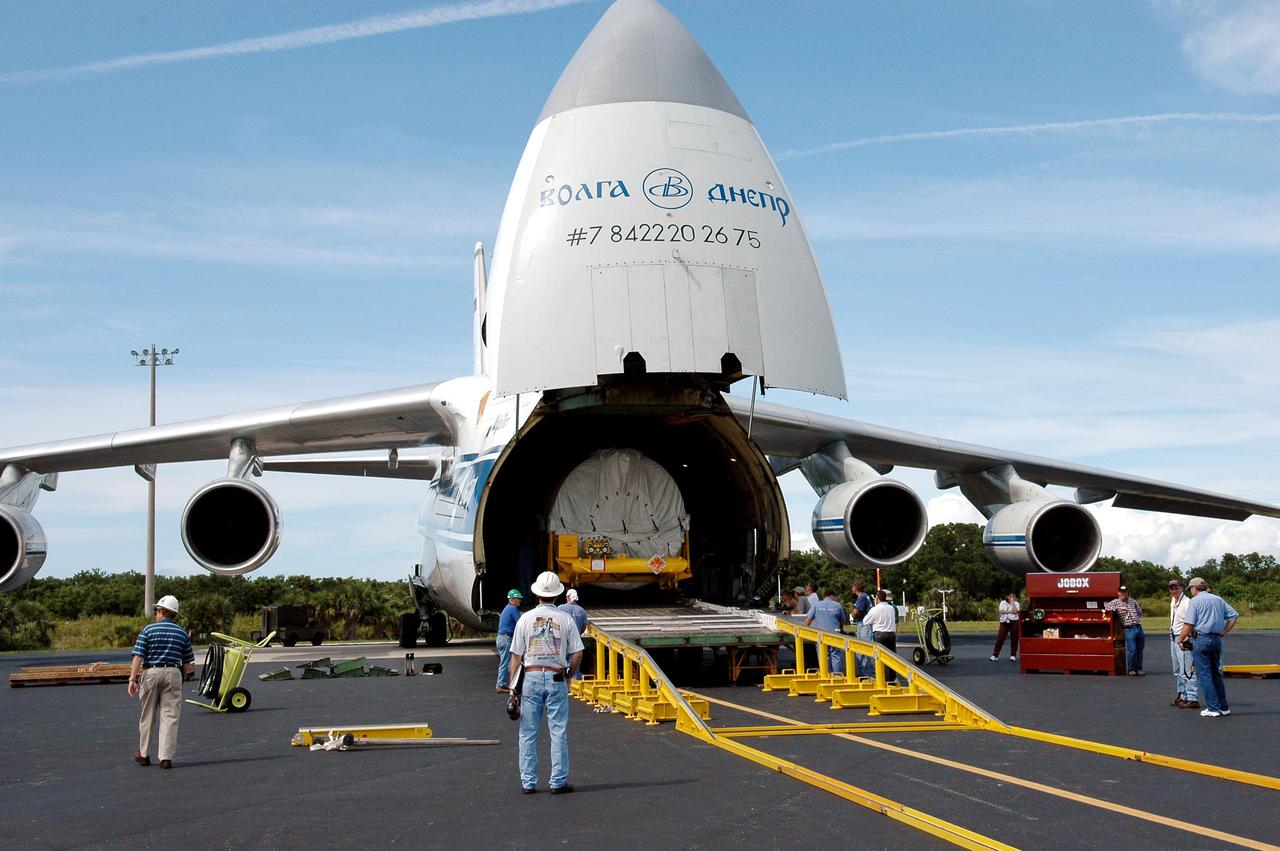

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station Skid Strip, a second stage Centaur (Block I) is ready to be offloaded from a Russian Antonov AH-124-100 cargo airplane. The Centaur will be mated with the Lockheed Martin Atlas V, designated AV-007, that is the launch vehicle for the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). The MRO is designed for a series of global mapping, regional survey and targeted observations from a near-polar, low-altitude Mars orbit. These observations will be unprecedented in terms of the spatial resolution and coverage achieved by the orbiter’s instruments as they observe the atmosphere and surface of Mars while probing its shallow subsurface as part of a “follow the water” strategy. The orbiter is undergoing environmental tests in facilities at Lockheed Martin Space Systems in Denver, Colo., and is on schedule for a launch window that begins Aug. 10. Launch will be from Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
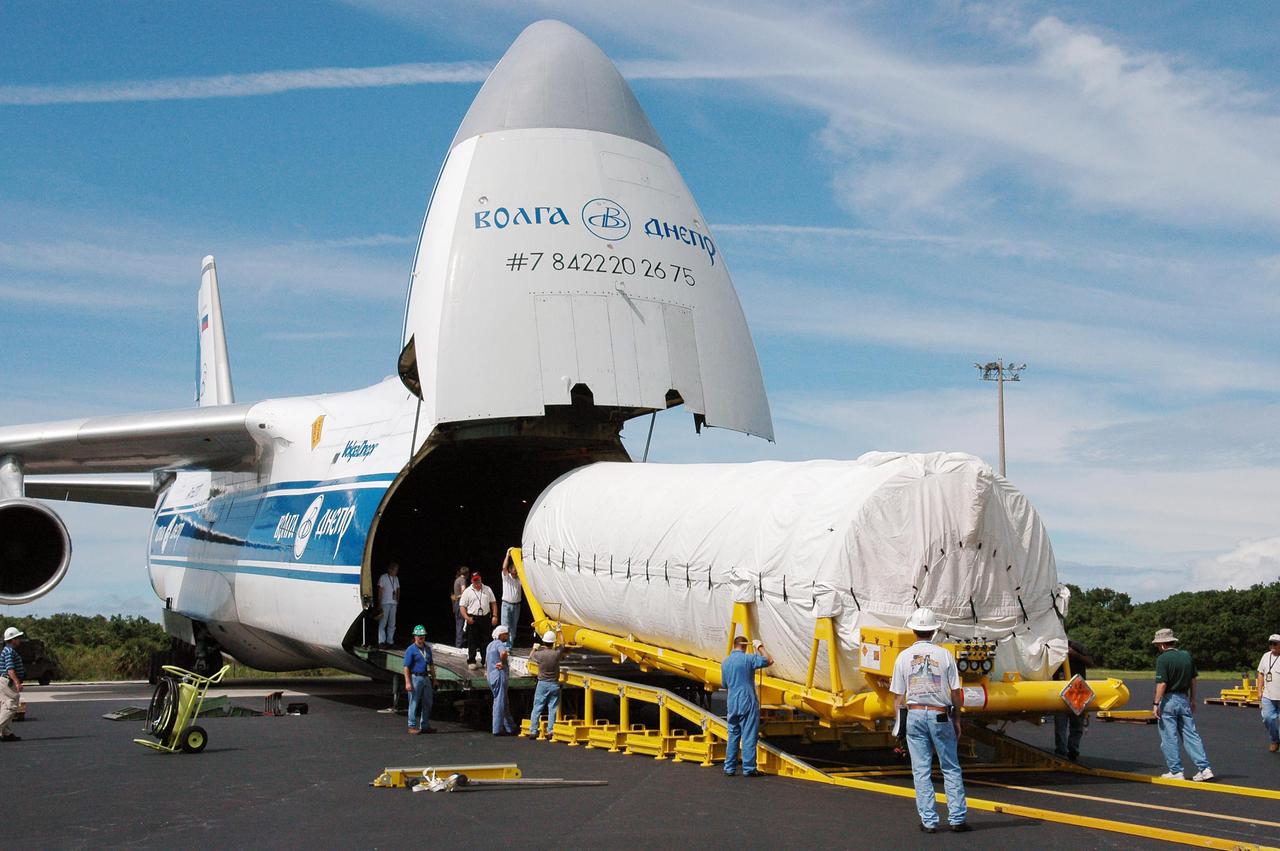

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station Skid Strip, a second stage Centaur (Block I) is rolled out of a Russian Antonov AH-124-100 cargo airplane. The Centaur will be mated with the Lockheed Martin Atlas V, designated AV-007, that is the launch vehicle for the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). The MRO is designed for a series of global mapping, regional survey and targeted observations from a near-polar, low-altitude Mars orbit. These observations will be unprecedented in terms of the spatial resolution and coverage achieved by the orbiter’s instruments as they observe the atmosphere and surface of Mars while probing its shallow subsurface as part of a “follow the water” strategy. The orbiter is undergoing environmental tests in facilities at Lockheed Martin Space Systems in Denver, Colo., and is on schedule for a launch window that begins Aug. 10. Launch will be from Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In front of the mobile service tower on Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the Lockheed Martin Atlas V Centaur stage is raised off the transporter. Once vertical, the Centaur, the second stage of the launch vehicle for the New Horizons spacecraft, will be lifted up the tower and mated with the waiting first stage, seen at left. New Horizons will make the first reconnaissance of Pluto and its moon, Charon - a "double planet" and the last planet in our solar system to be visited by spacecraft. As it approaches Pluto, the spacecraft will look for ultraviolet emission from Pluto's atmosphere and make the best global maps of Pluto and Charon in green, blue, red and a special wavelength that is sensitive to methane frost on the surface. It will also take spectral maps in the near infrared, telling the science team about Pluto's and Charon's surface compositions and locations and temperatures of these materials. When the spacecraft is closest to Pluto or its moon, it will take close-up pictures in both visible and near-infrared wavelengths. The mission will then visit one or more objects in the Kuiper Belt region beyond Neptune. New Horizons is scheduled to launch in January 2006, swing past Jupiter for a gravity boost and scientific studies in February or March 2007, and reach Pluto and Charon in July 2015.
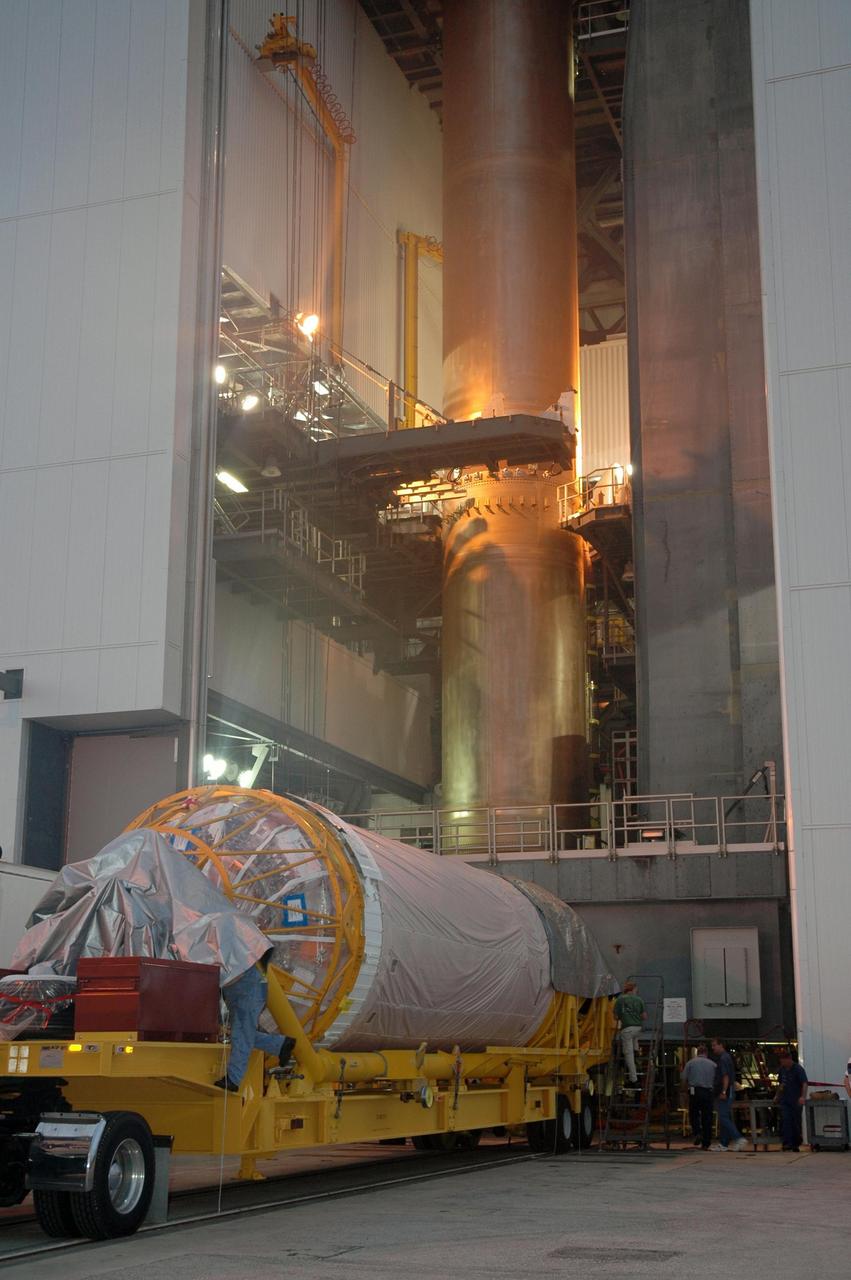

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Lockheed Martin Atlas V Centaur stage arrives at the mobile service tower on Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Centaur is the second stage of the launch vehicle for the New Horizons spacecraft. Seen in the tower is the first stage. New Horizons will make the first reconnaissance of Pluto and its moon, Charon - a "double planet" and the last planet in our solar system to be visited by spacecraft. As it approaches Pluto, the spacecraft will look for ultraviolet emission from Pluto's atmosphere and make the best global maps of Pluto and Charon in green, blue, red and a special wavelength that is sensitive to methane frost on the surface. It will also take spectral maps in the near infrared, telling the science team about Pluto's and Charon's surface compositions and locations and temperatures of these materials. When the spacecraft is closest to Pluto or its moon, it will take close-up pictures in both visible and near-infrared wavelengths. The mission will then visit one or more objects in the Kuiper Belt region beyond Neptune. New Horizons is scheduled to launch in January 2006, swing past Jupiter for a gravity boost and scientific studies in February or March 2007, and reach Pluto and Charon in July 2015.
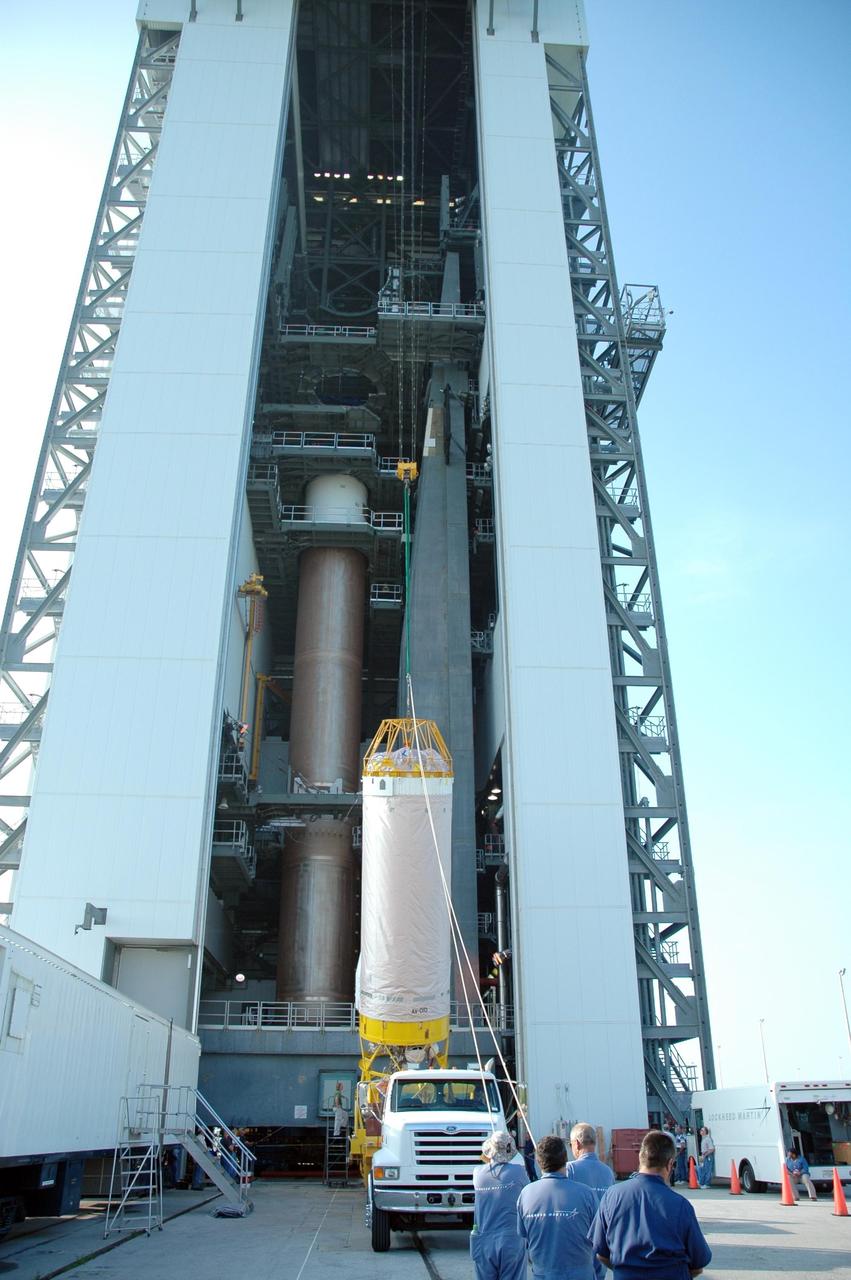

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In front of the mobile service tower on Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, workers complete the raising of the Lockheed Martin Atlas V Centaur stage to a vertical position. The second stage of the launch vehicle for the New Horizons spacecraft, the Centaur will be mated with the waiting first stage, seen behind it at left. New Horizons will make the first reconnaissance of Pluto and its moon, Charon - a "double planet" and the last planet in our solar system to be visited by spacecraft. As it approaches Pluto, the spacecraft will look for ultraviolet emission from Pluto's atmosphere and make the best global maps of Pluto and Charon in green, blue, red and a special wavelength that is sensitive to methane frost on the surface. It will also take spectral maps in the near infrared, telling the science team about Pluto's and Charon's surface compositions and locations and temperatures of these materials. When the spacecraft is closest to Pluto or its moon, it will take close-up pictures in both visible and near-infrared wavelengths. The mission will then visit one or more objects in the Kuiper Belt region beyond Neptune. New Horizons is scheduled to launch in January 2006, swing past Jupiter for a gravity boost and scientific studies in February or March 2007, and reach Pluto and Charon in July 2015.
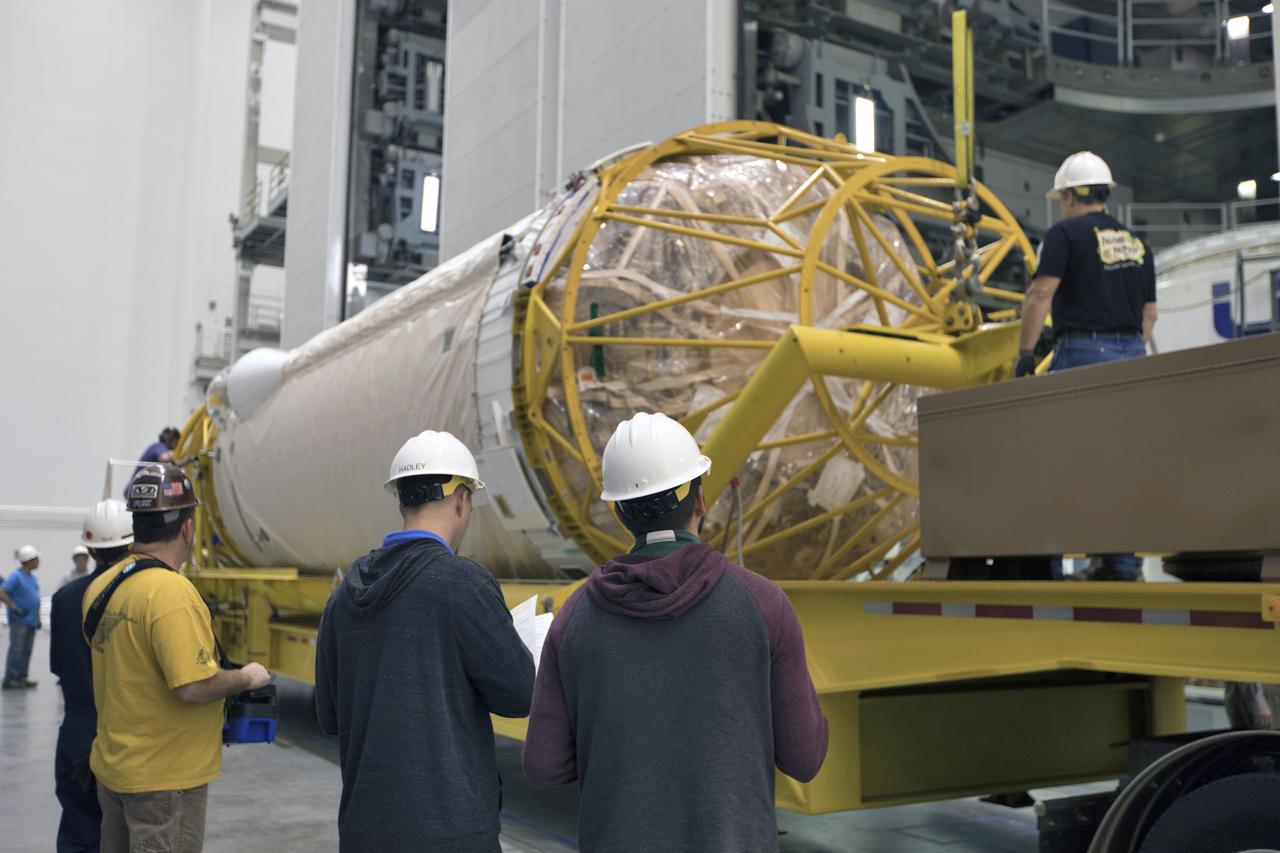

Under the watchful eyes of technicians and engineers, the Centaur upper stage that will help launch NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S, or GOES-S, arrives inside the Delta Operations Center at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for further processing. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.
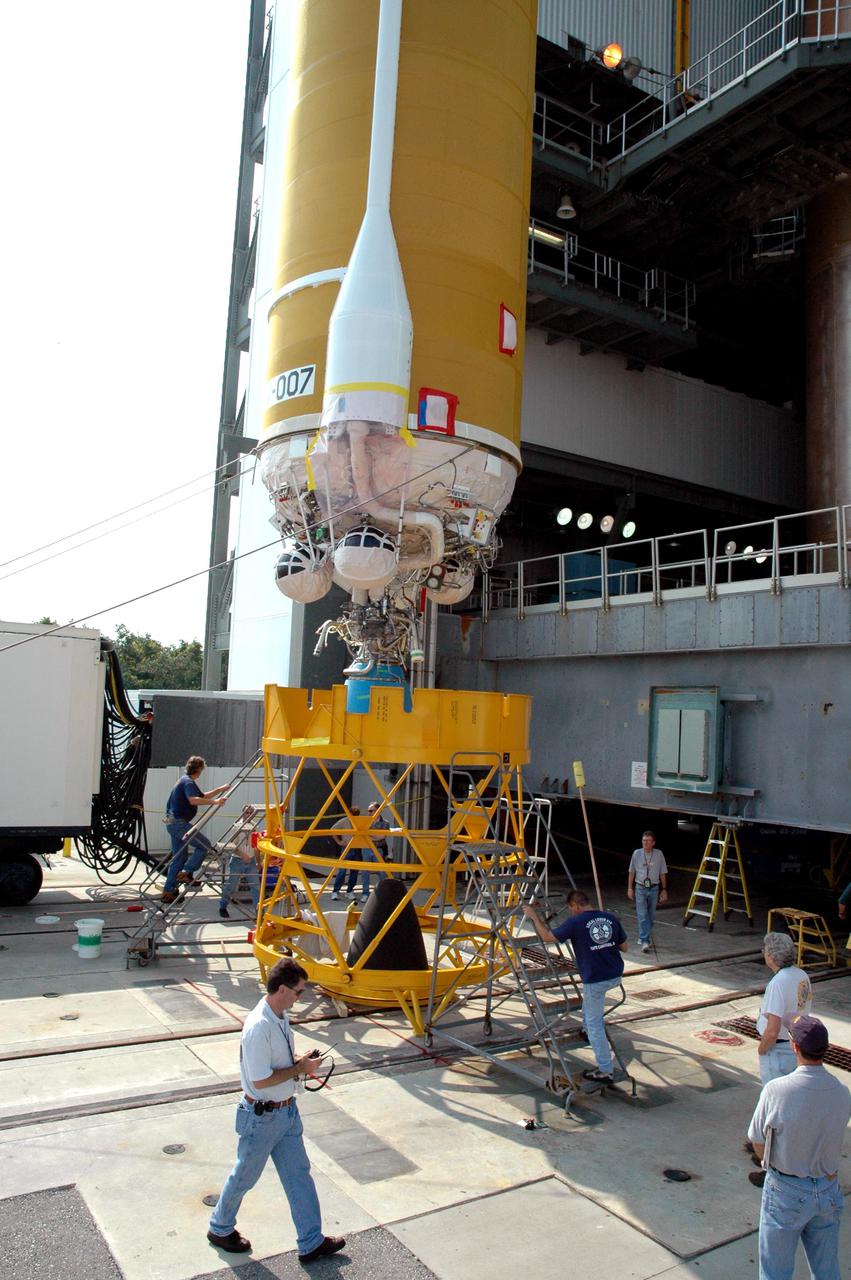

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At the Vertical Integration Facility on Launch Pad 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the Lockheed Martin Centaur second stage is ready for lifting into the launch tower where it will be mated with the Atlas V already there. The Atlas V_Centaur is the launch vehicle for the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). The MRO is designed for a series of global mapping, regional survey and targeted observations from a near-polar, low-altitude Mars orbit. These observations will be unprecedented in terms of the spatial resolution and coverage achieved by the orbiter’s instruments as they observe the atmosphere and surface of Mars while probing its shallow subsurface as part of a “follow the water” strategy. The launch window for the MRO begins Aug. 10.
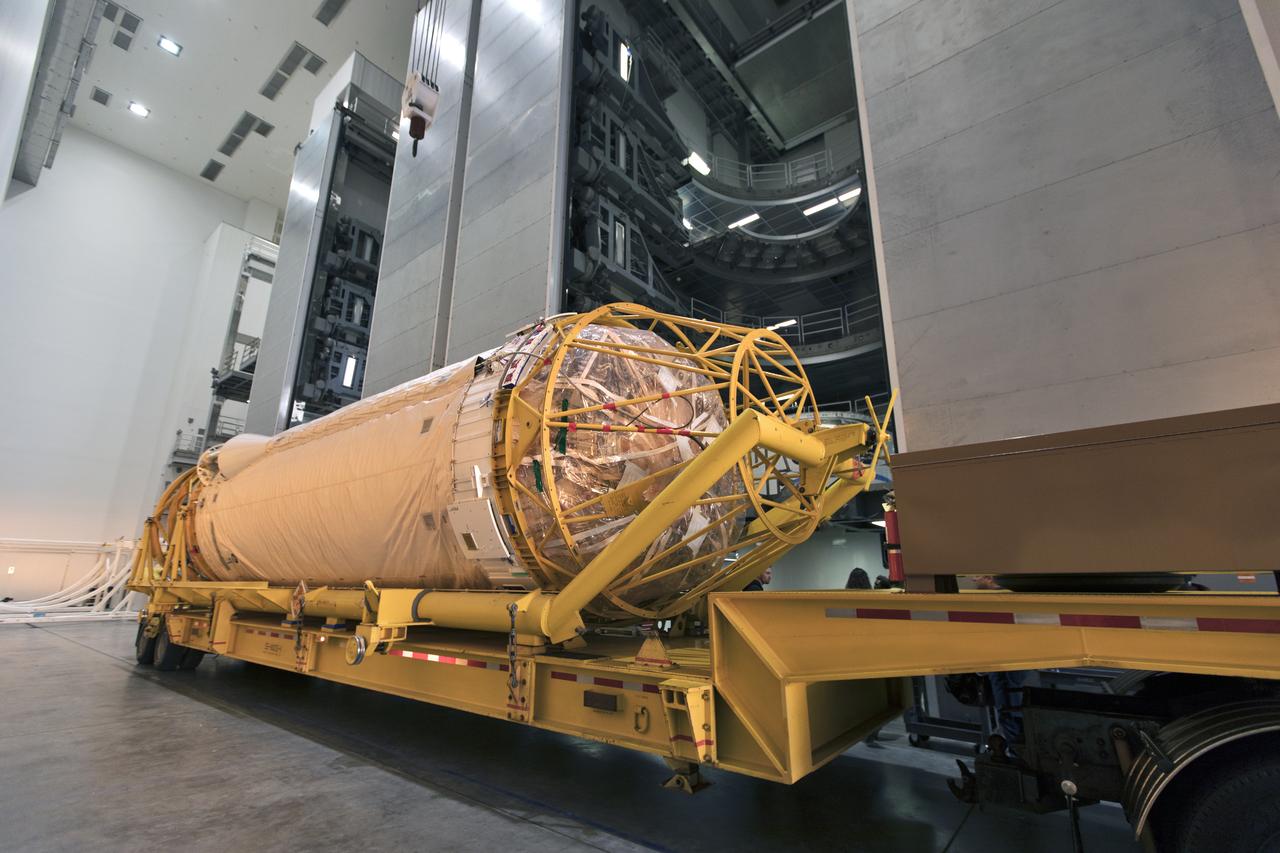

The Centaur upper stage that will help launch NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S, or GOES-S, arrives inside the Delta Operations Center at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for further processing. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.
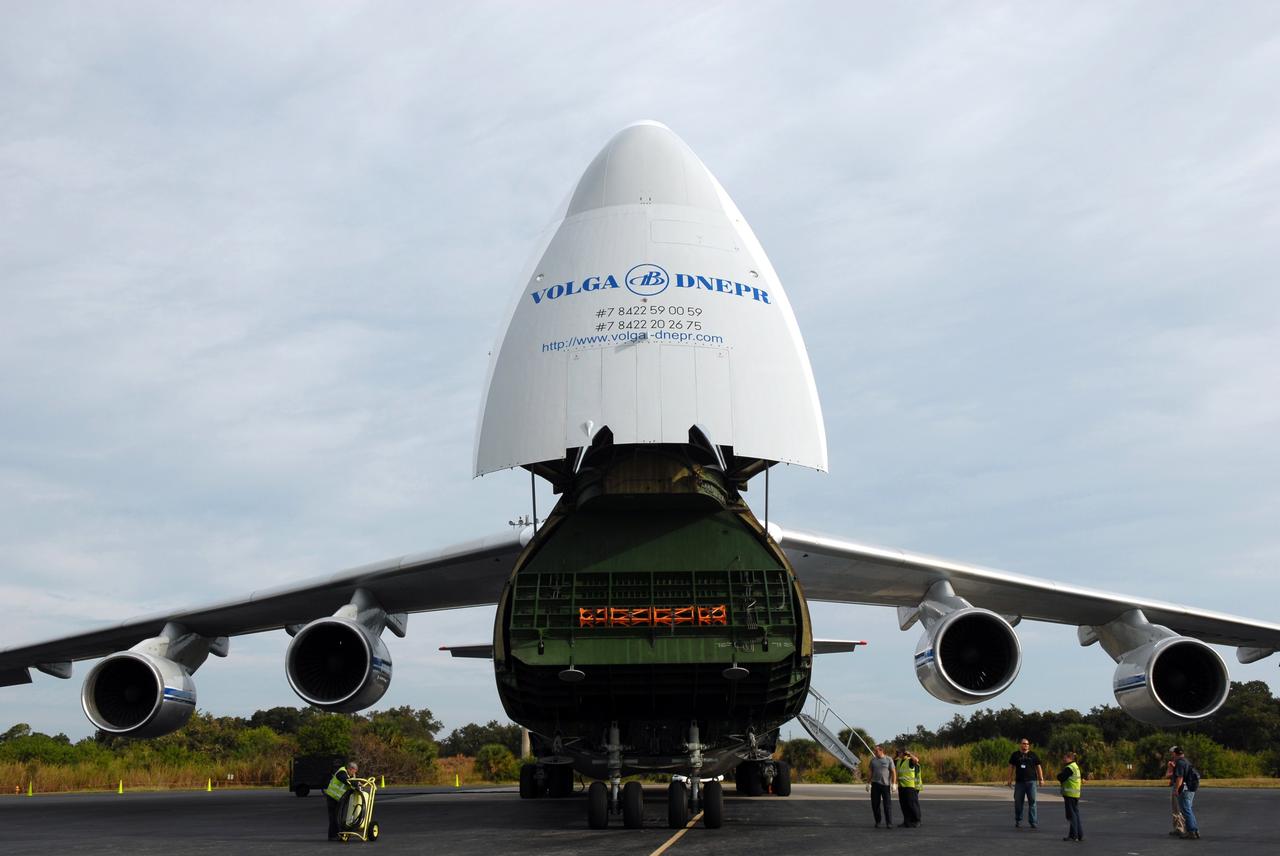

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Skid Strip on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, a Volga-Dnepr Antonov AN-124-100, a Ukranian/Russian aircraft, delivers the Centaur second stage for the Atlas V rocket slated to launch NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO. SDO is the first space weather research network mission in NASA's Living With a Star Program. The spacecraft's long-term measurements will give solar scientists in-depth information about changes in the sun's magnetic field and insight into how they affect Earth. Liftoff on the United Launch Alliance Atlas V is scheduled for Feb. 3, 2010. For information on SDO, visit http://www.nasa.gov/sdo. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
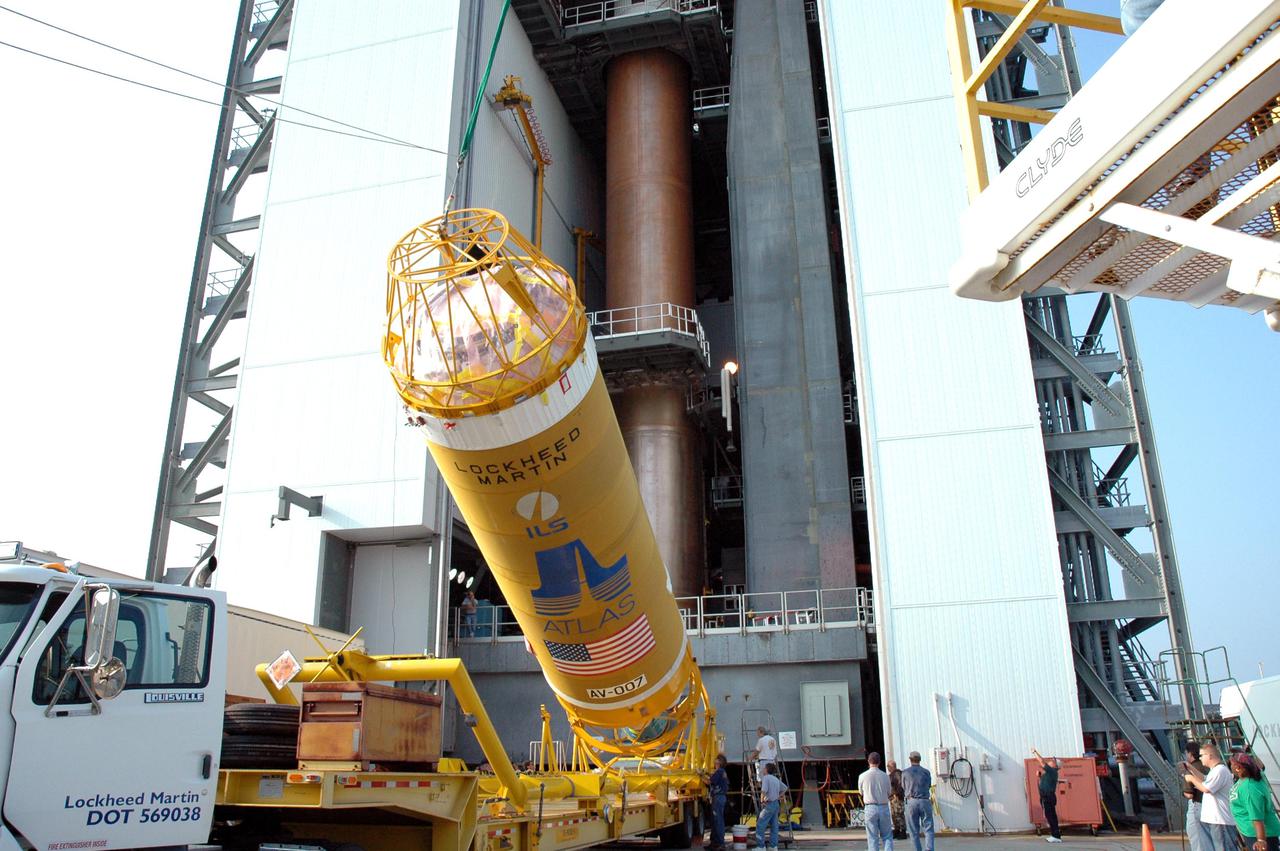

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At the Vertical Integration Facility on Launch Pad 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the Lockheed Martin Centaur second stage is being raised to a vertical position for lifting into the launch tower and mating with the Atlas V already there. The MRO is designed for a series of global mapping, regional survey and targeted observations from a near-polar, low-altitude Mars orbit. These observations will be unprecedented in terms of the spatial resolution and coverage achieved by the orbiter’s instruments as they observe the atmosphere and surface of Mars while probing its shallow subsurface as part of a “follow the water” strategy. The launch window for the MRO begins Aug. 10.
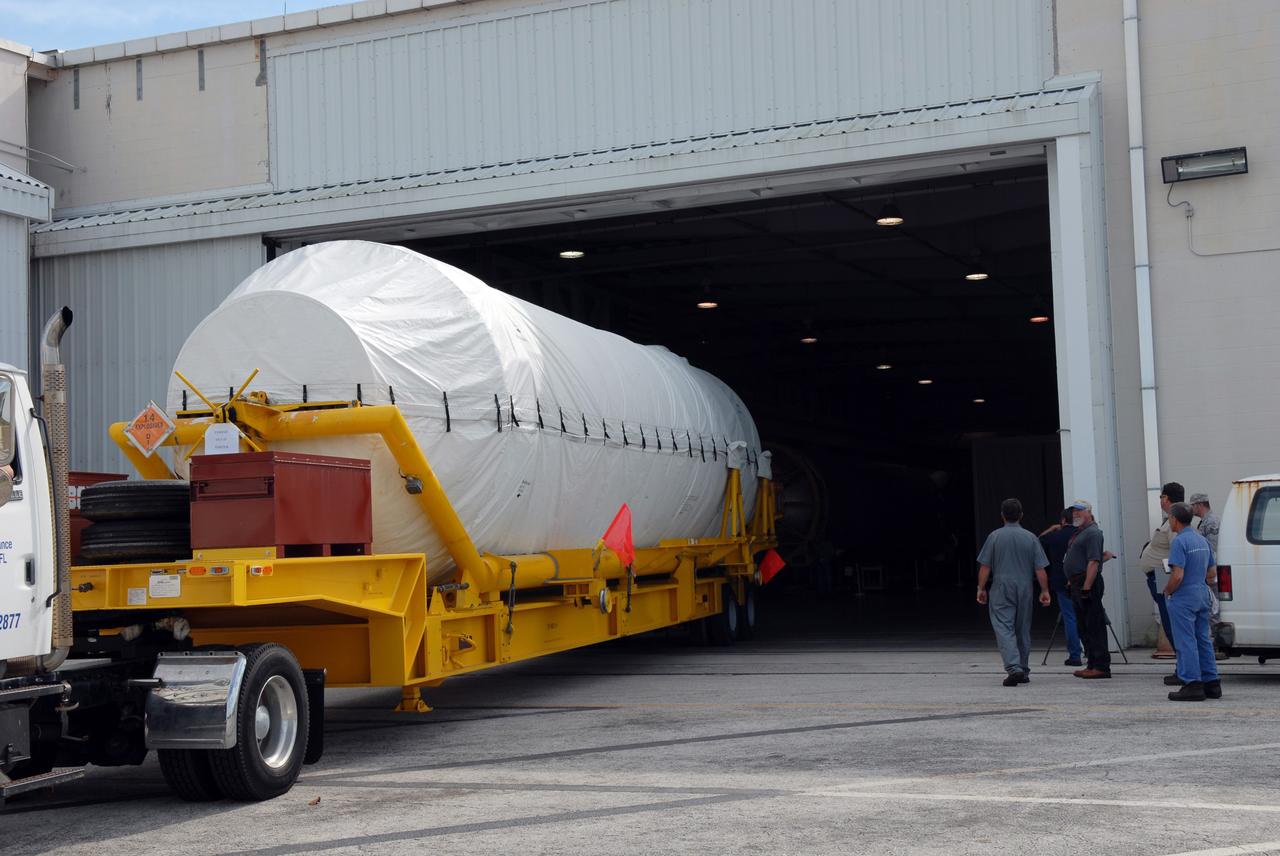

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Centaur second stage for the Atlas V rocket slated to launch NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO, is moved into the hangar at the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. SDO is the first space weather research network mission in NASA's Living With a Star Program. The spacecraft's long-term measurements will give solar scientists in-depth information about changes in the sun's magnetic field and insight into how they affect Earth. Liftoff on the United Launch Alliance Atlas V is scheduled for Feb. 3, 2010. For information on SDO, visit http://www.nasa.gov/sdo. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
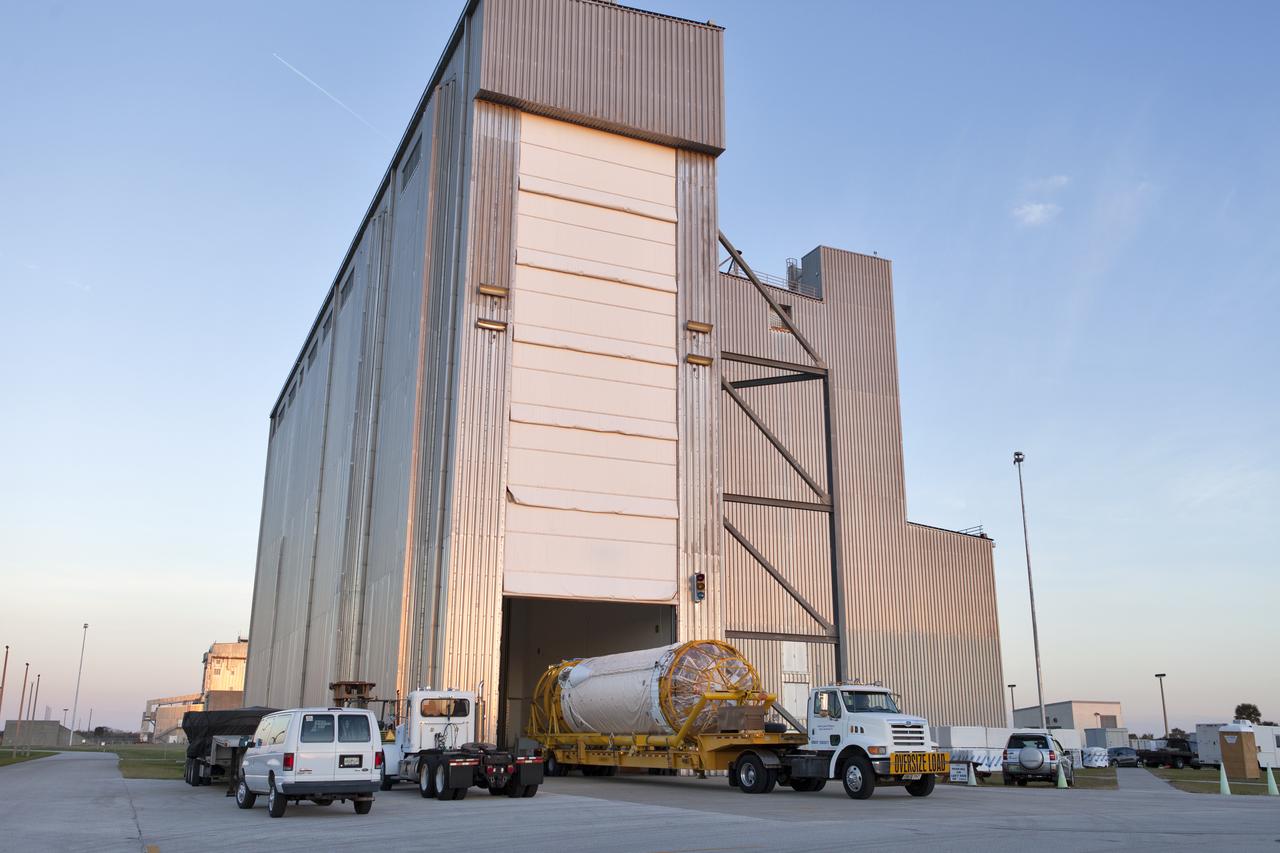

The Centaur upper stage that will help launch NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S, or GOES-S, arrives at the Delta Operations Center at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for further processing. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.
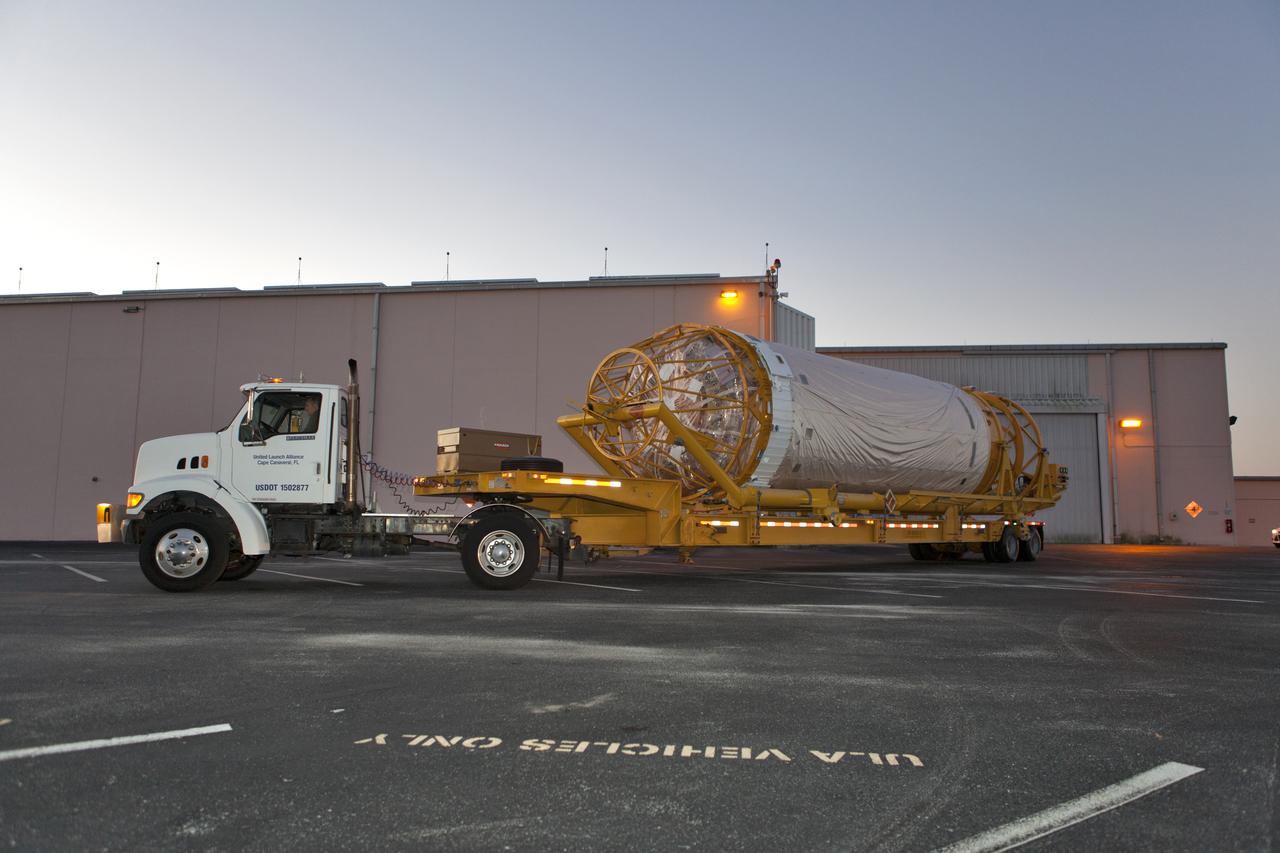

The Centaur upper stage that will help launch NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S, or GOES-S, is being transported from the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station to the Delta Operations Center for further processing. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.
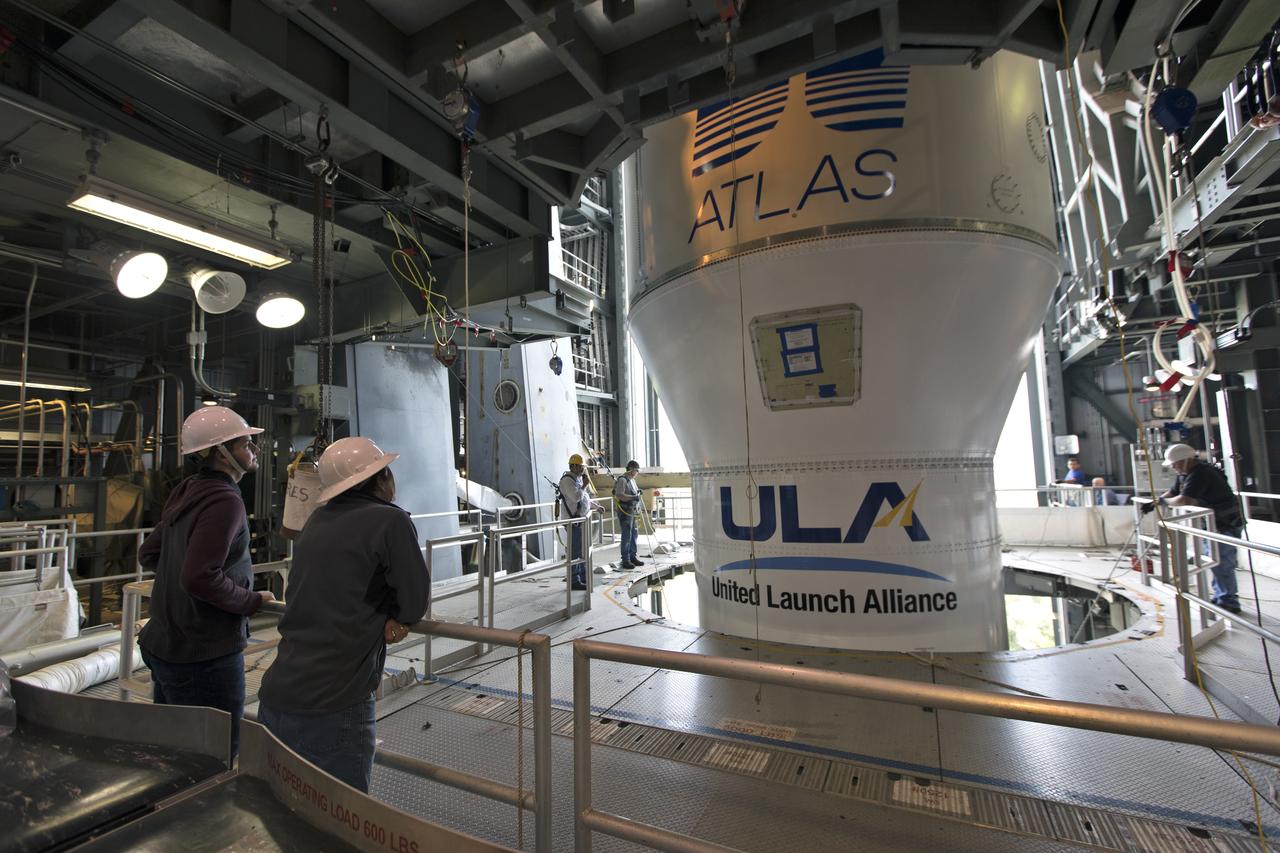

At the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, technicians and engineers monitor progress as a Centaur upper stage is mated to a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket that will boost NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S, or GOES-S, to orbit. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites that will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018.
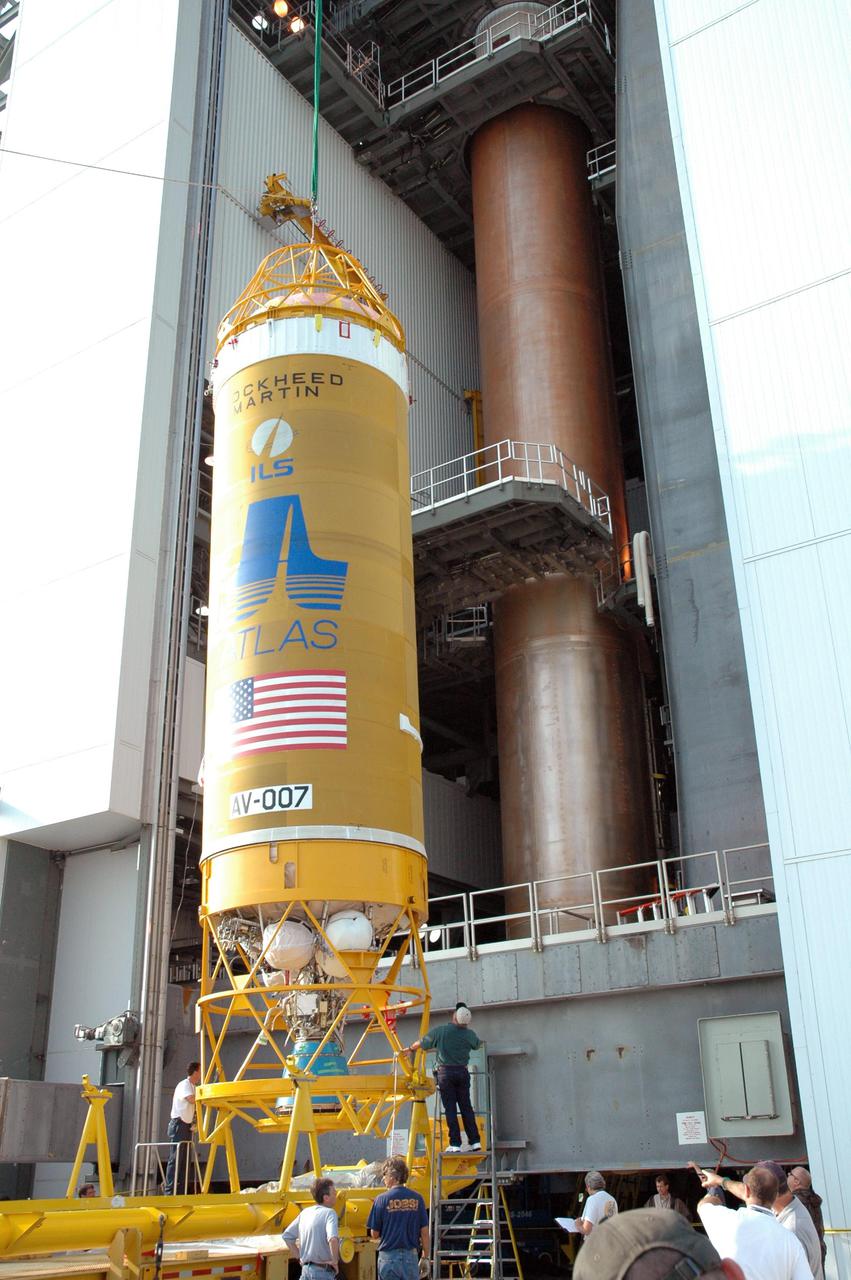

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At the Vertical Integration Facility on Launch Pad 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the Lockheed Martin Centaur second stage is positioned vertically to be lifted into the launch tower where it will be mated with the Atlas V already there. The Atlas V_Centaur is the launch vehicle for the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). The MRO is designed for a series of global mapping, regional survey and targeted observations from a near-polar, low-altitude Mars orbit. These observations will be unprecedented in terms of the spatial resolution and coverage achieved by the orbiter’s instruments as they observe the atmosphere and surface of Mars while probing its shallow subsurface as part of a “follow the water” strategy. The launch window for the MRO begins Aug. 10.
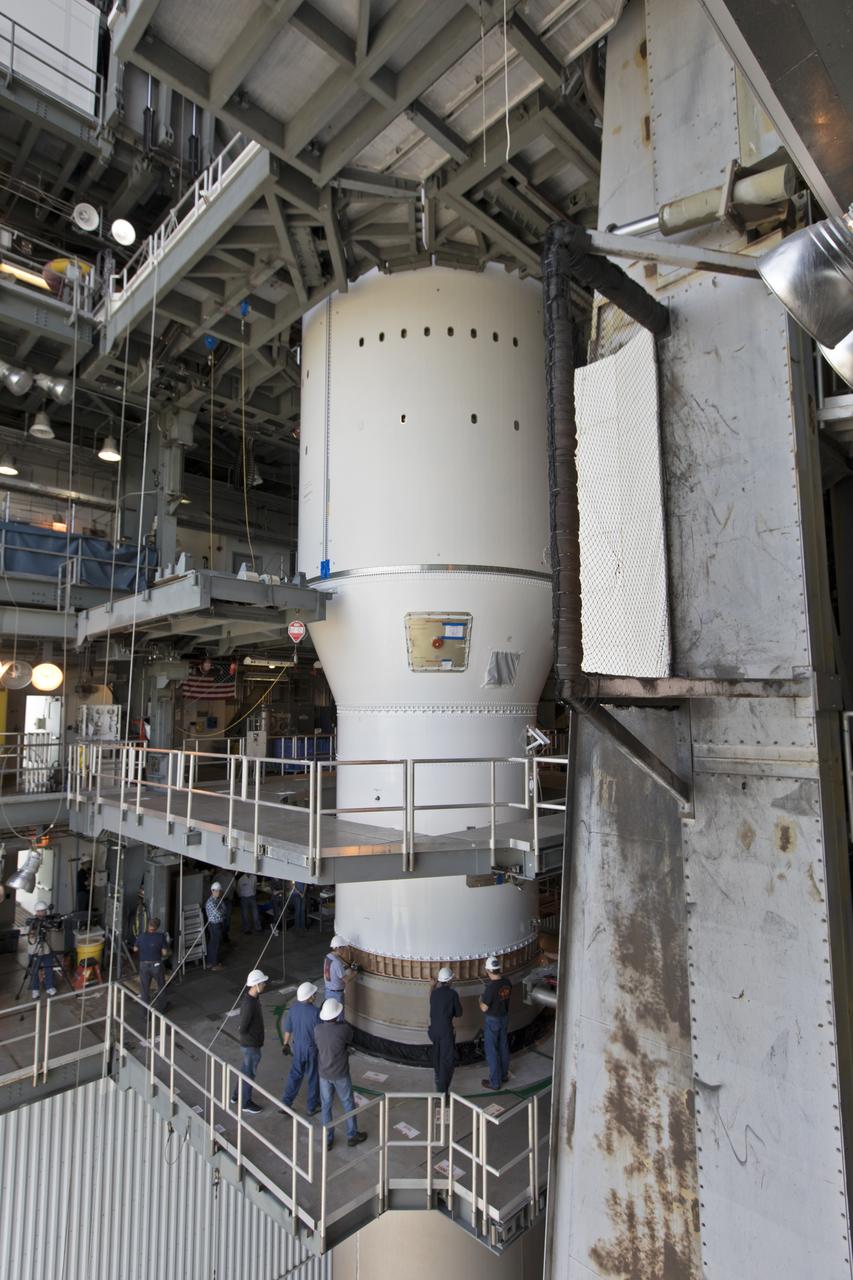

At the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, a Centaur upper stage is mated to a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket that will boost NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S, or GOES-S, to orbit. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites that will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018.

Workers at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station watch as the second stage of an Atlas II/Centaur rocket is raised to a vertical position in front of the gantry on pad 36-A. Atlas II is designed to launch payloads into low earth orbit, geosynchronous transfer orbit or geosynchronous orbit. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the GOES-L satellite, part of the NOAA National Weather Service system in weather imagery and atmospheric sounding information. The primary objective of the GOES-L is to provide a full capability satellite in an on-orbit storage condition, to assure NOAA continuity in services from a two-satellite constellation. Launch services are being provided by the 45th Space Wing
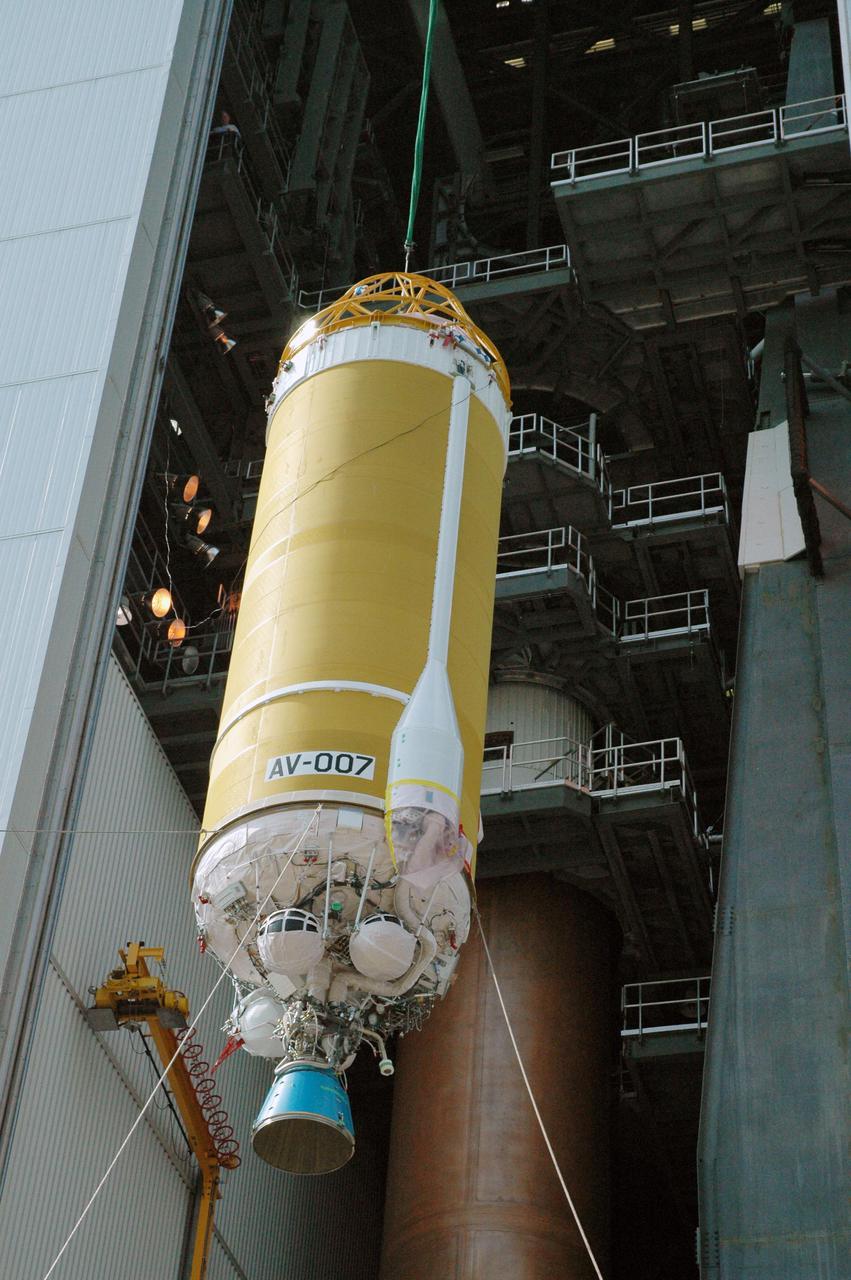

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At the Vertical Integration Facility on Launch Pad 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the Lockheed Martin Centaur second stage is lifted into the launch tower where it will be mated with the Atlas V already there. The Atlas V_Centaur is the launch vehicle for the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). The MRO is designed for a series of global mapping, regional survey and targeted observations from a near-polar, low-altitude Mars orbit. These observations will be unprecedented in terms of the spatial resolution and coverage achieved by the orbiter’s instruments as they observe the atmosphere and surface of Mars while probing its shallow subsurface as part of a “follow the water” strategy. The launch window for the MRO begins Aug. 10.
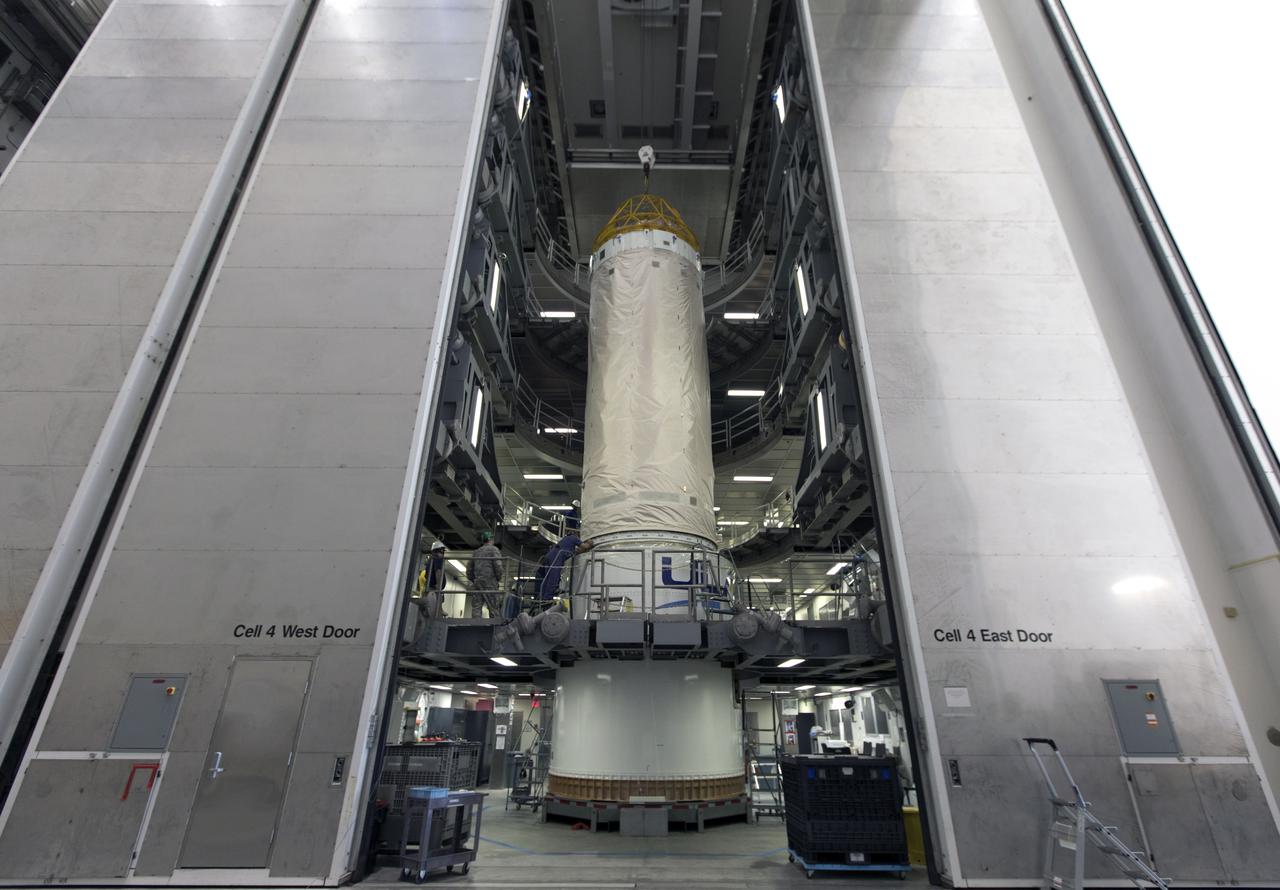

The Centaur upper stage that will help launch NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S, or GOES-S, has been positioned in at test cell inside the Delta Operations Center at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for further processing. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.
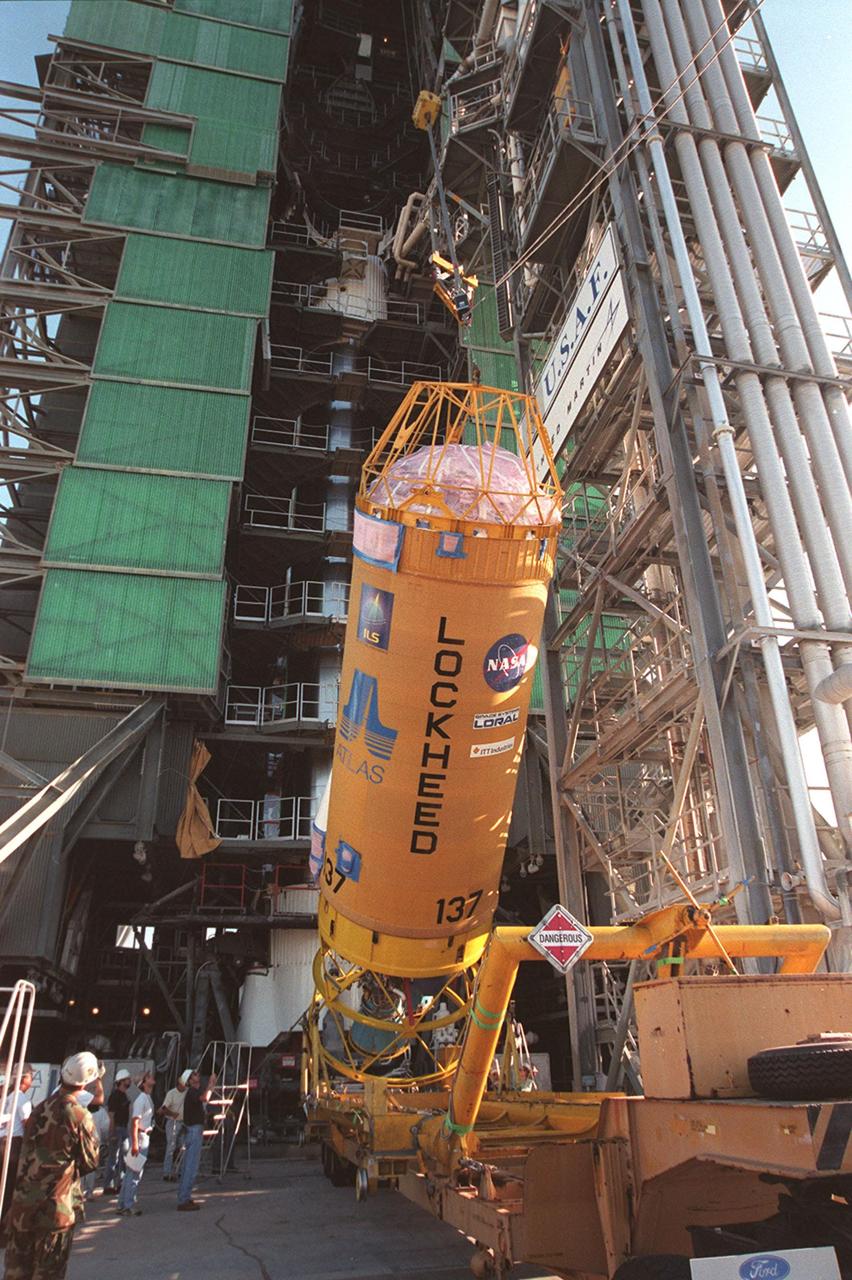

Workers at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station watch as the second stage of an Atlas II/Centaur rocket is raised to a vertical position in front of the gantry on pad 36-A. Atlas II is designed to launch payloads into low earth orbit, geosynchronous transfer orbit or geosynchronous orbit. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the GOES-L satellite, part of the NOAA National Weather Service system in weather imagery and atmospheric sounding information. The primary objective of the GOES-L is to provide a full capability satellite in an on-orbit storage condition, to assure NOAA continuity in services from a two-satellite constellation. Launch services are being provided by the 45th Space Wing
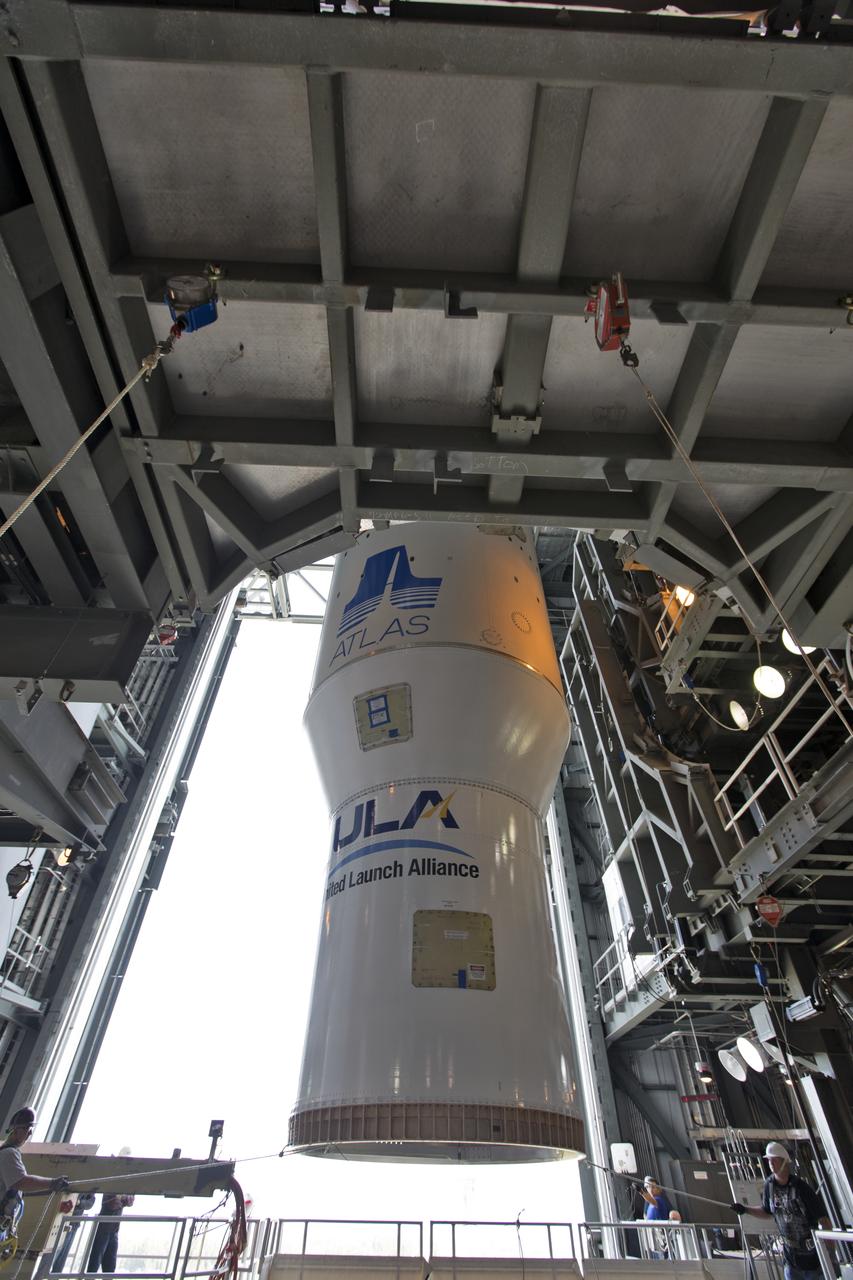

At the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, a crane lifts a Centaur upper stage for mating to a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket that will boost NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S, or GOES-S, to orbit. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites that will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018.
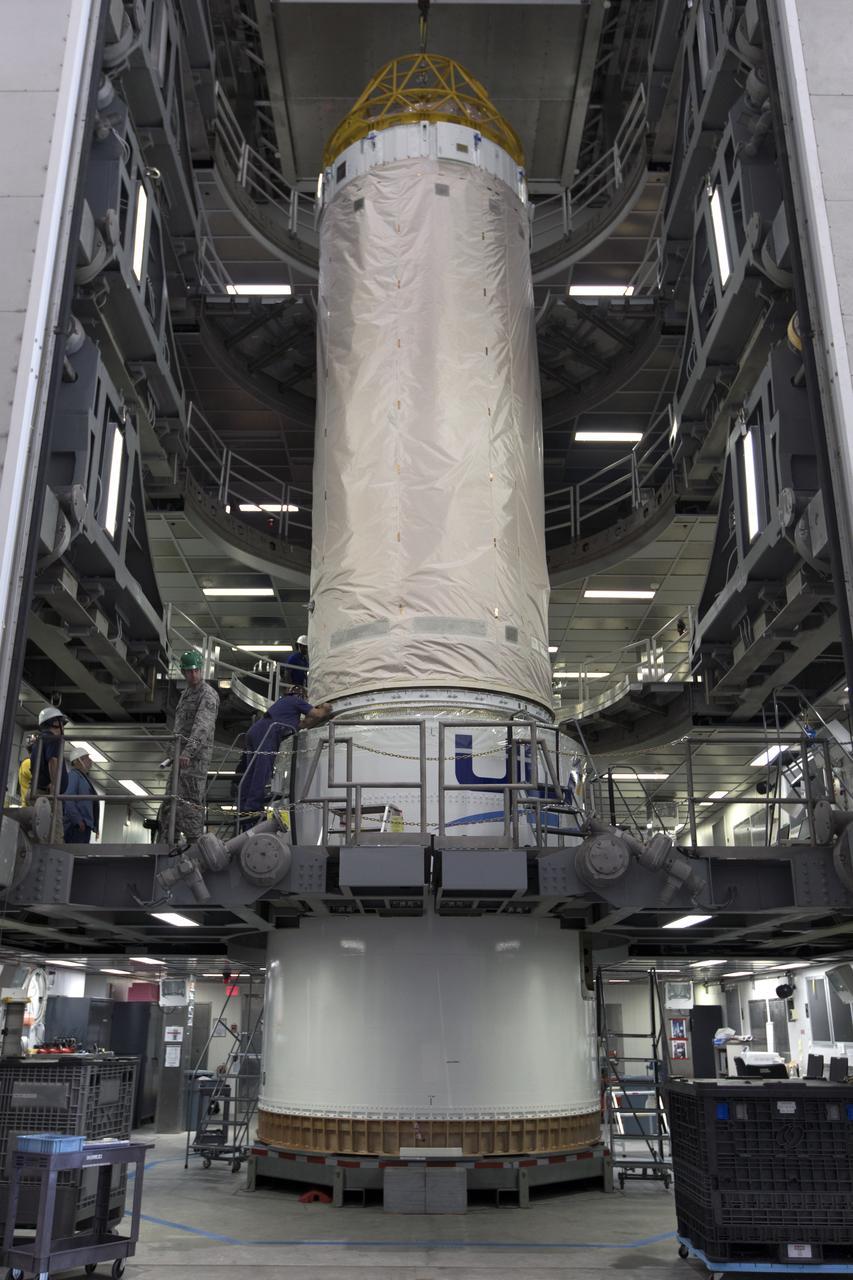

The Centaur upper stage that will help launch NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S, or GOES-S, has been positioned in at test cell inside the Delta Operations Center at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for further processing. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.