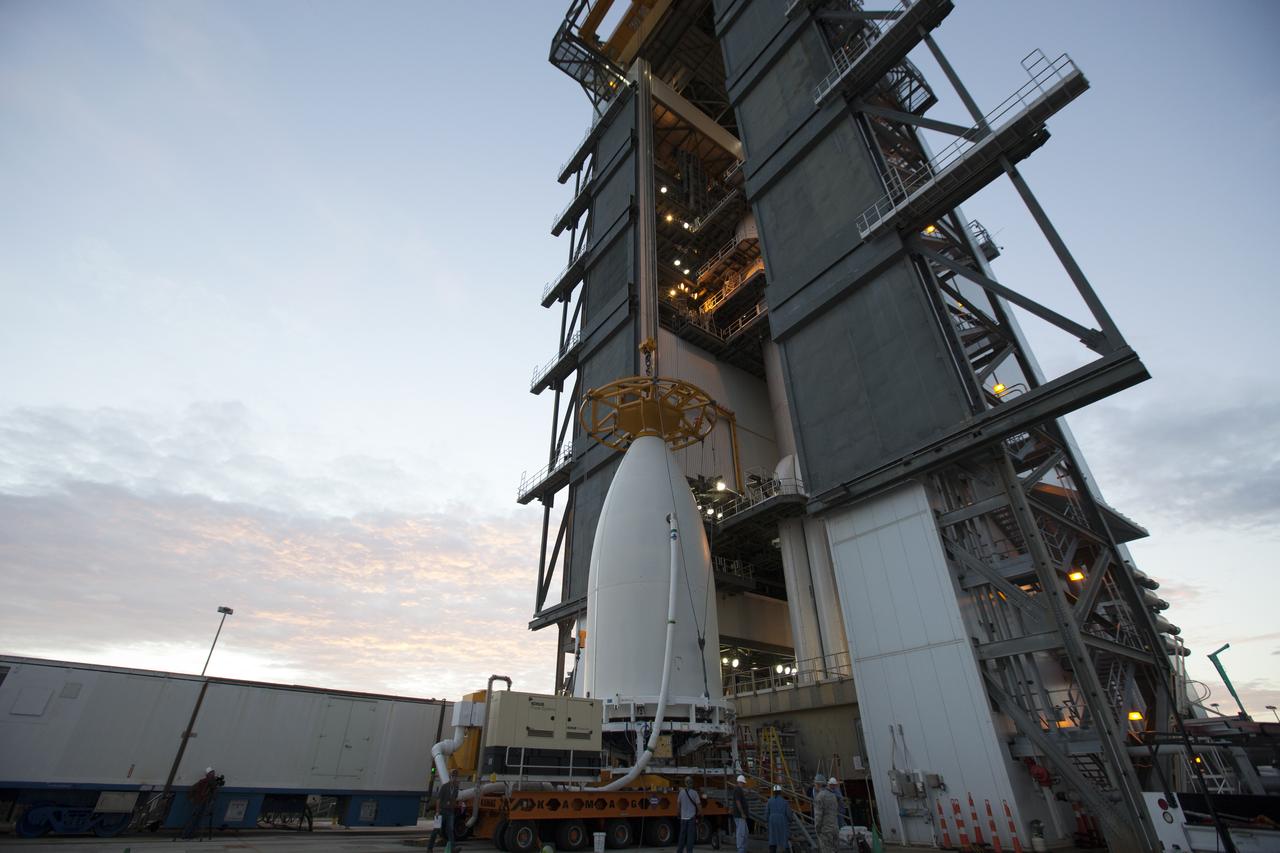

Preparations are underway to lift NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R), enclosed in its payload fairing at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. GOES-R will be mated to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V Centaur upper stage in preparation for launch in November. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
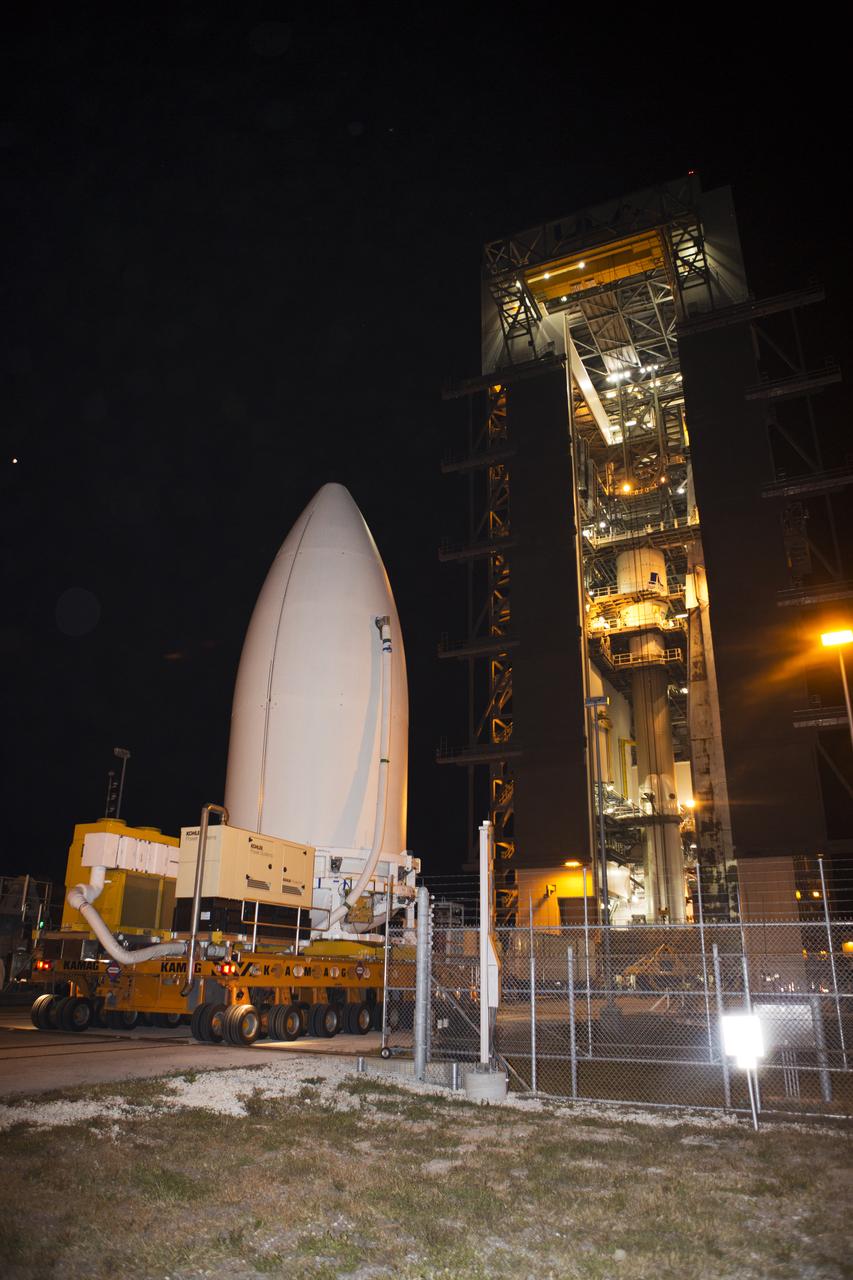

Enclosed in its payload fairing, NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) arrives at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. GOES-R will be stacked atop the United Launch Alliance Atlas V Centaur upper stage. The satellite will launch atop the Atlas V rocket in November. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
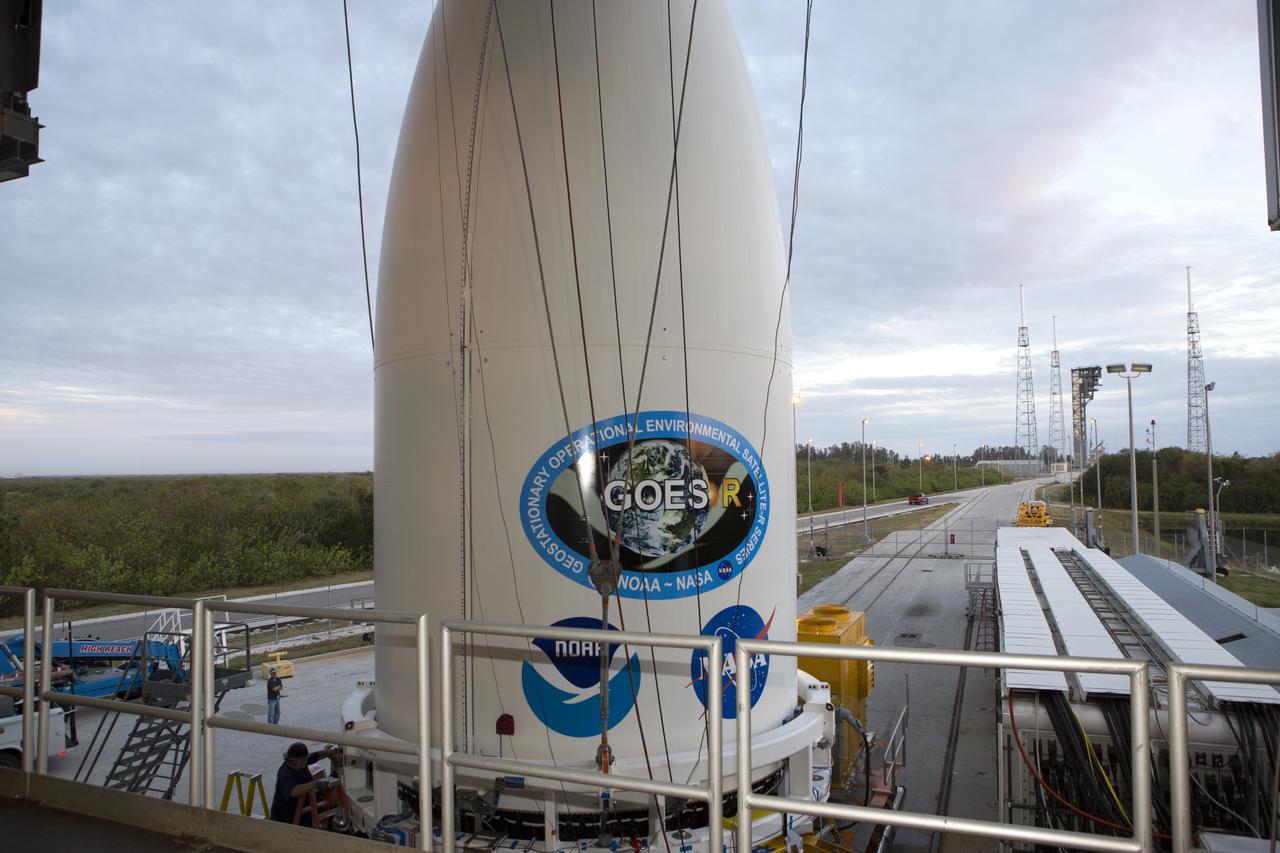

Preparations are underway to lift NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R), enclosed in its payload fairing at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. GOES-R will be mated to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V Centaur upper stage in preparation for launch in November. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
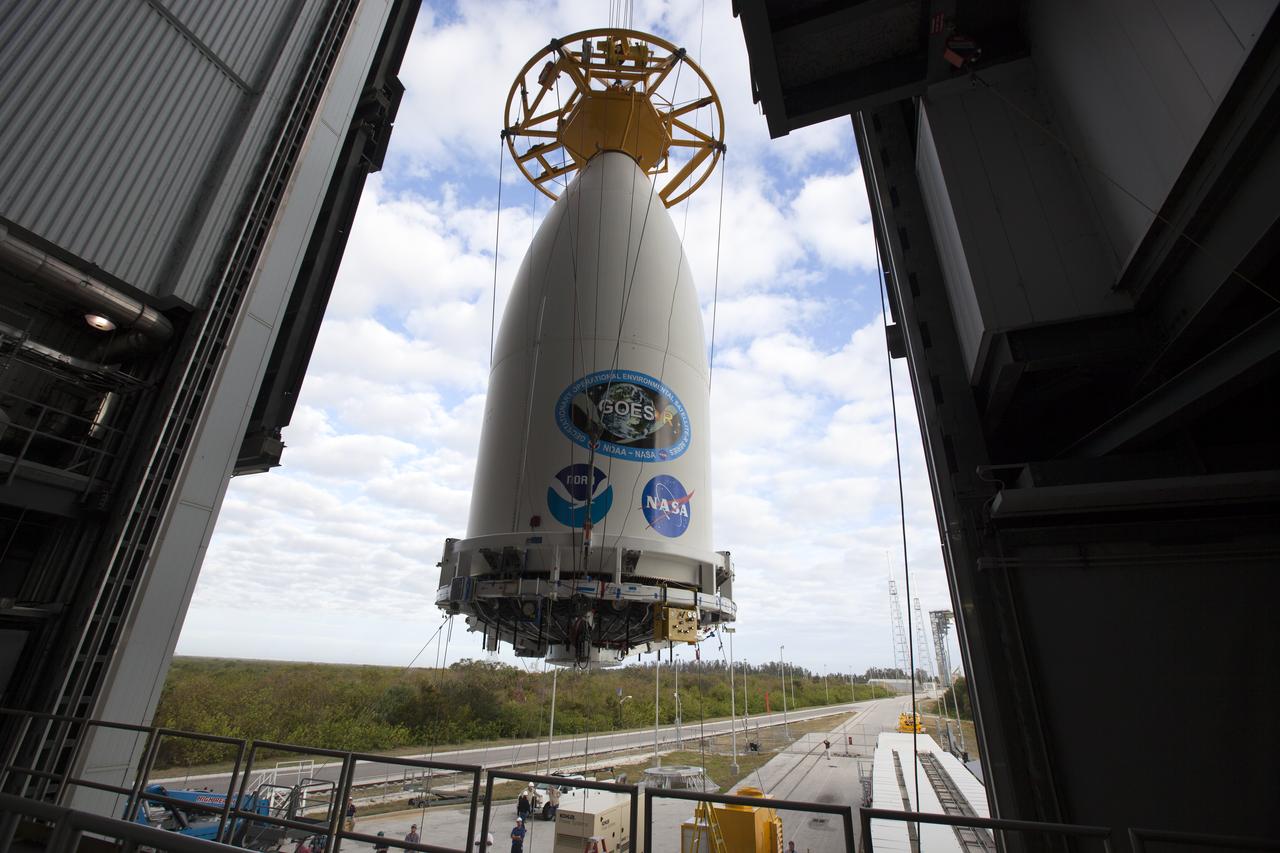

A view from high up inside the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. A crane lifts the payload fairing containing NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) for mating to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V Centaur upper stage. The satellite will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket in November. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
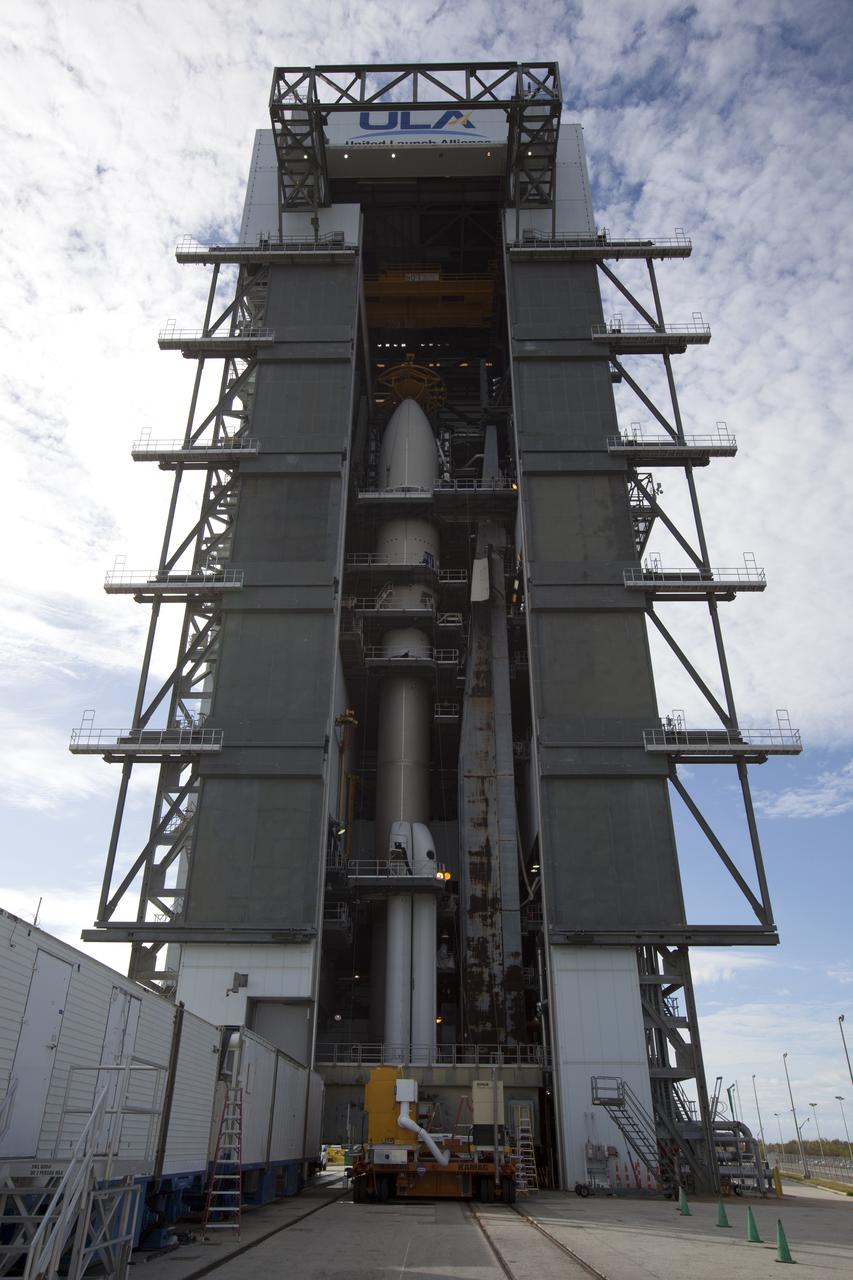

Enclosed in its payload fairing, NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) is mated to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V Centaur upper stage in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The satellite will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket in November. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
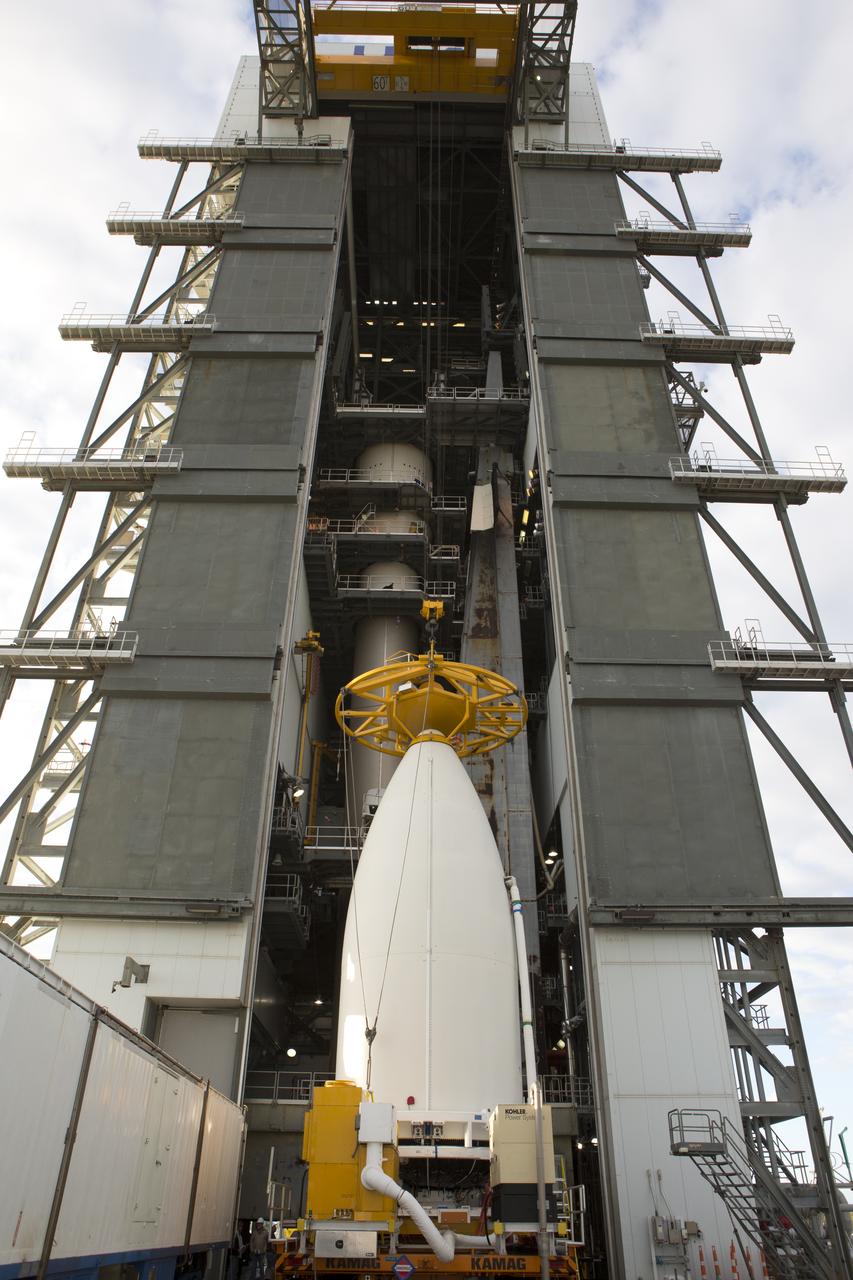

A crane begins to lift the payload fairing containing NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. GOES-R will be mated to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V Centaur upper stage in preparation for launch in November. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
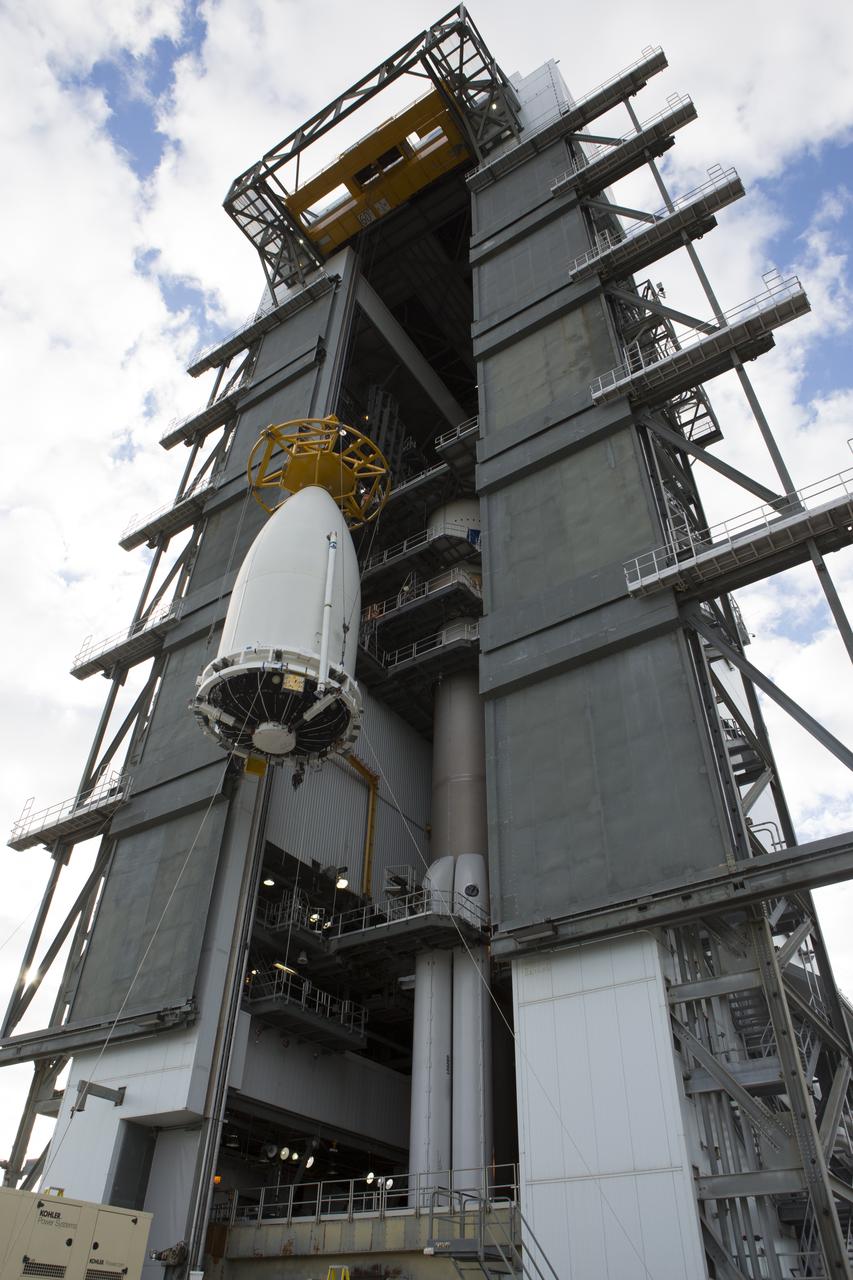

A crane is used to lift the payload fairing containing NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. GOES-R will be mated to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V Centaur upper stage in preparation for launch in November. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
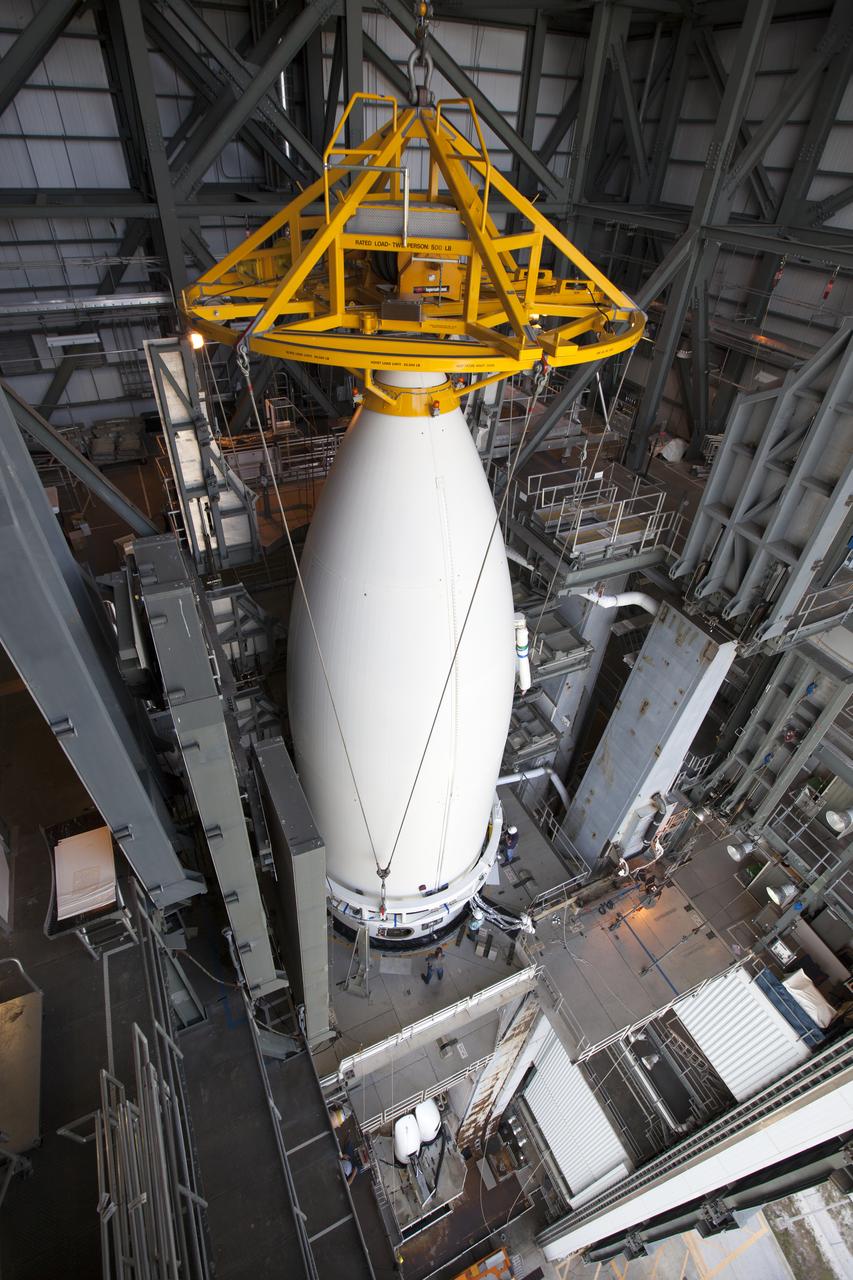

Enclosed in its payload fairing, NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) is lifted into the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. GOES-R will be mated to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V Centaur upper stage in preparation for launch aboard the rocket in November. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
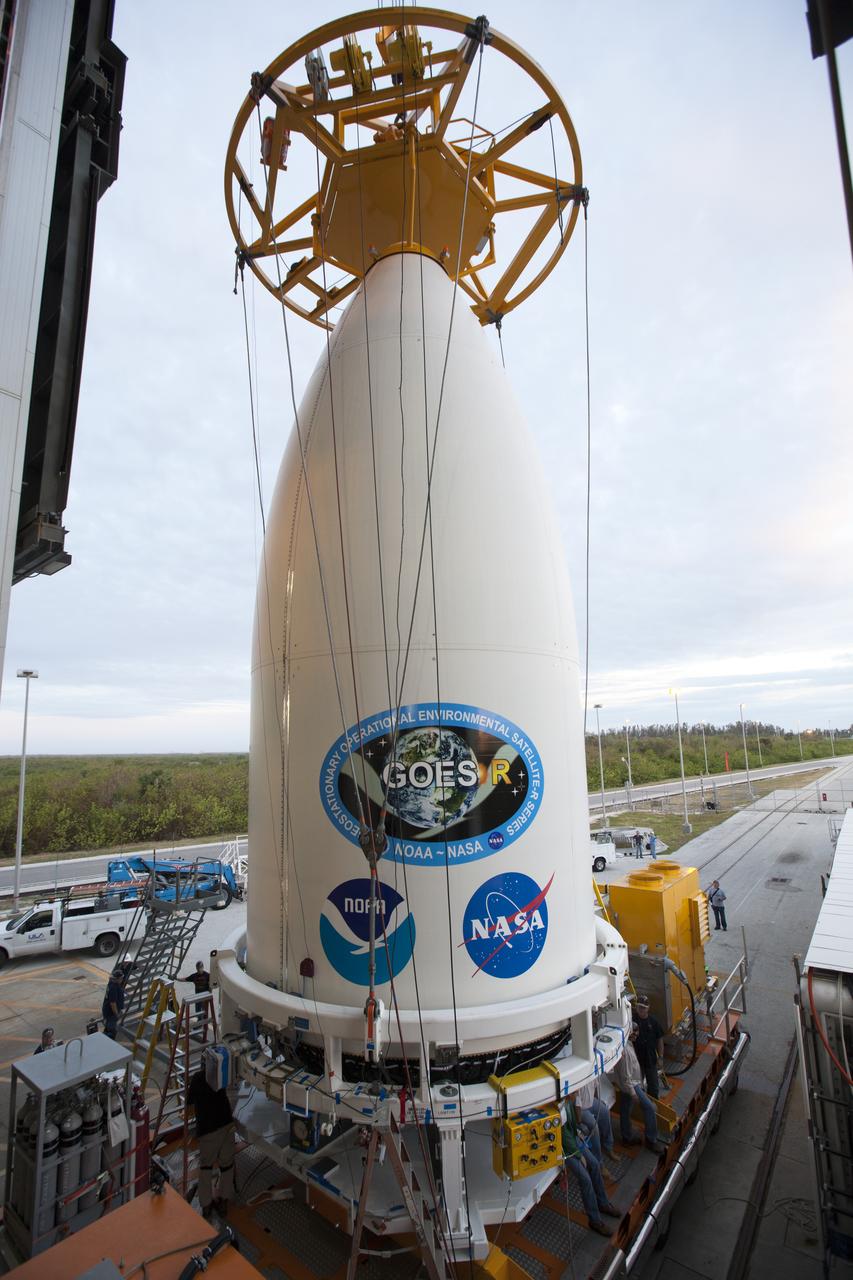

A crane has been attached to the payload fairing containing NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. GOES-R will be mated to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V Centaur upper stage in preparation for launch in November. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
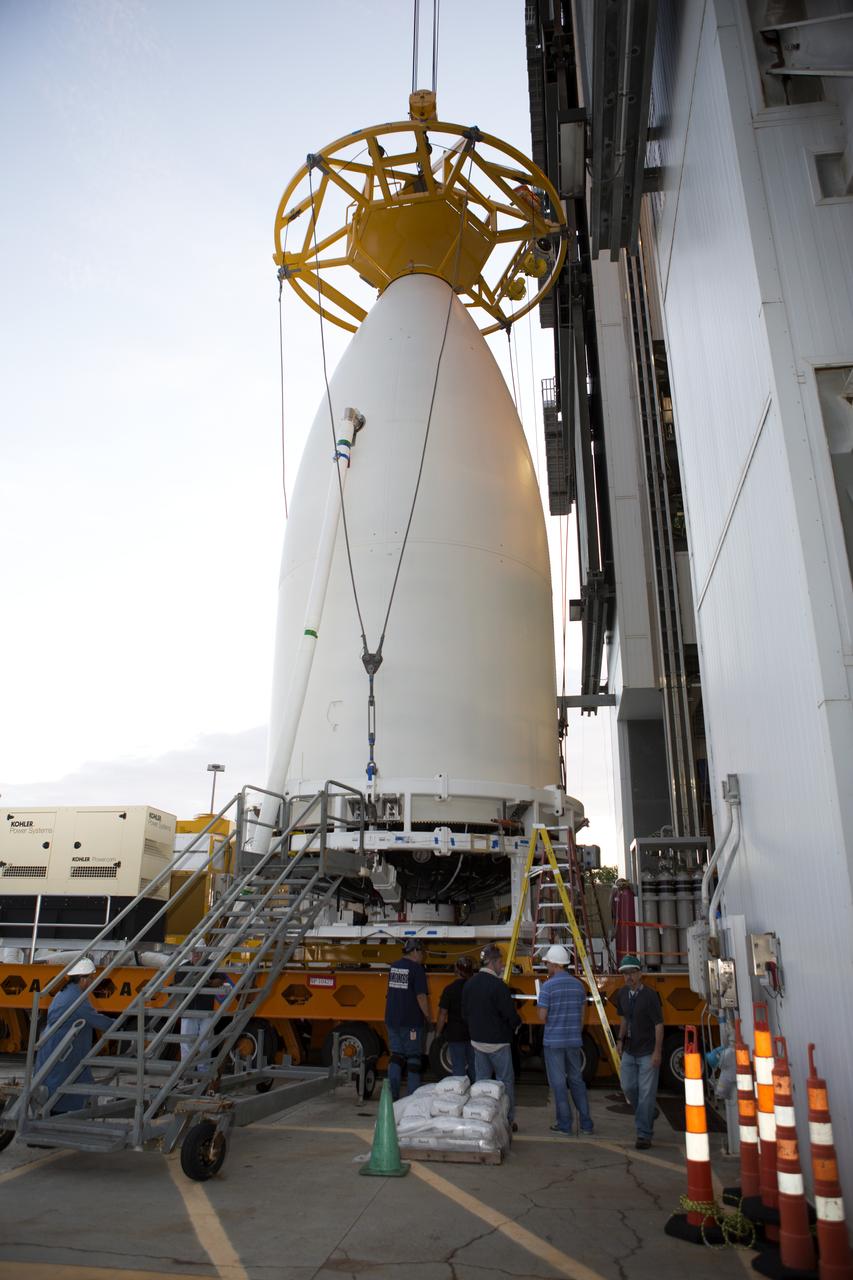

Preparations are underway to lift NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R), enclosed in its payload fairing at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. GOES-R will be mated to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V Centaur upper stage in preparation for launch in November. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
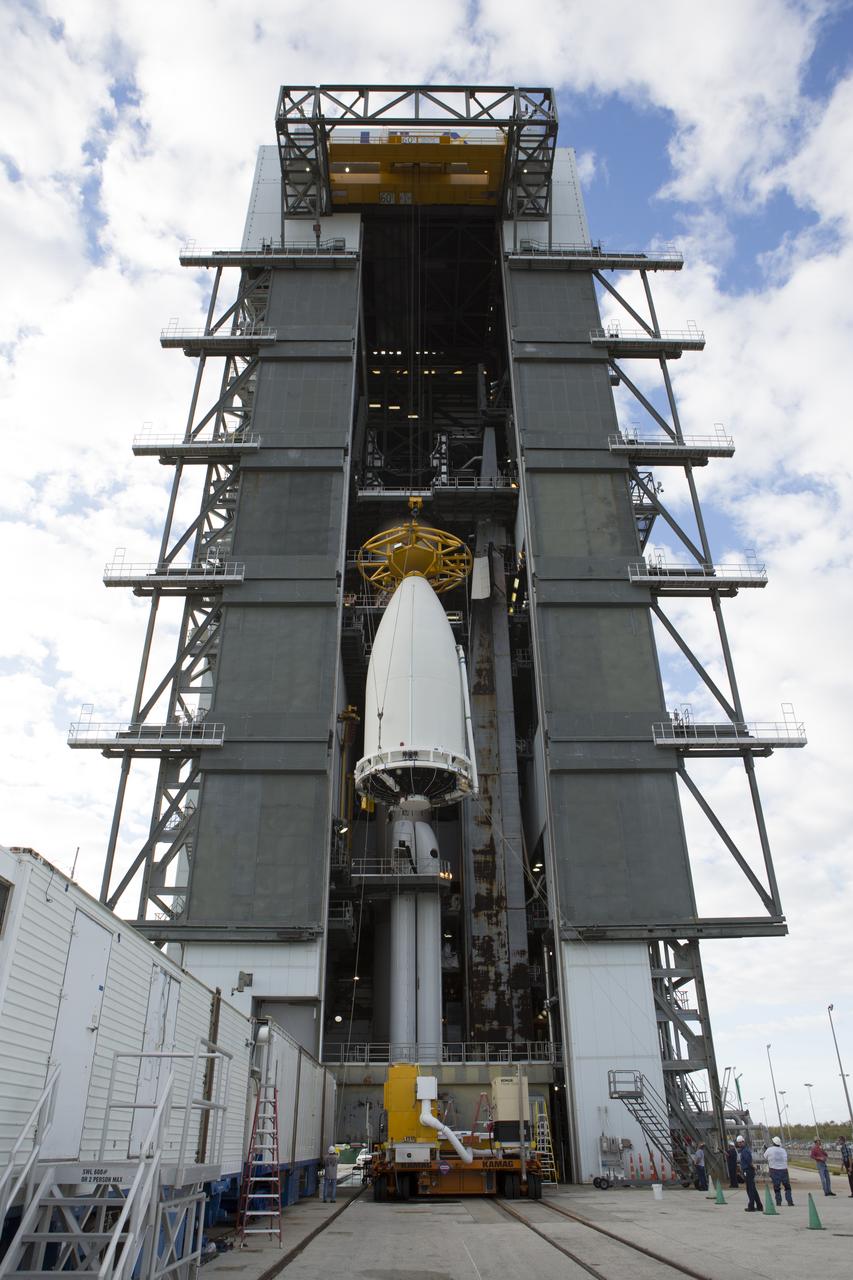

A crane is used to lift the payload fairing containing NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. GOES-R will be mated to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V Centaur upper stage in preparation for launch in November. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.

Enclosed in its payload fairing, NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) arrives at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. GOES-R will be stacked atop the United Launch Alliance Atlas V Centaur upper stage. The satellite will launch atop the Atlas V rocket in November. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.
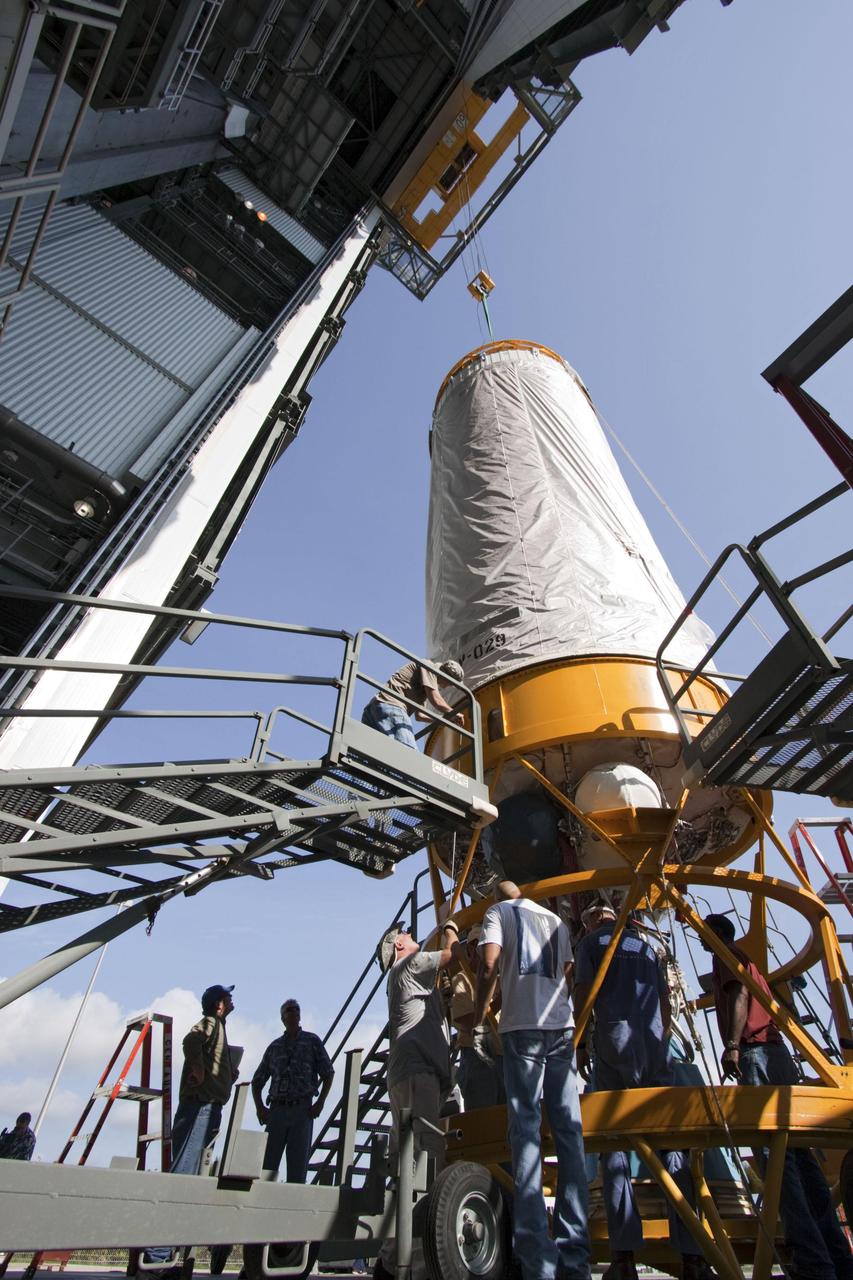

Workers guide an overhead crane as it lifts the Centaur upper stage at the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla., June 24, 2011. The Centaur is slated to launch NASA Juno spacecraft on August 5.
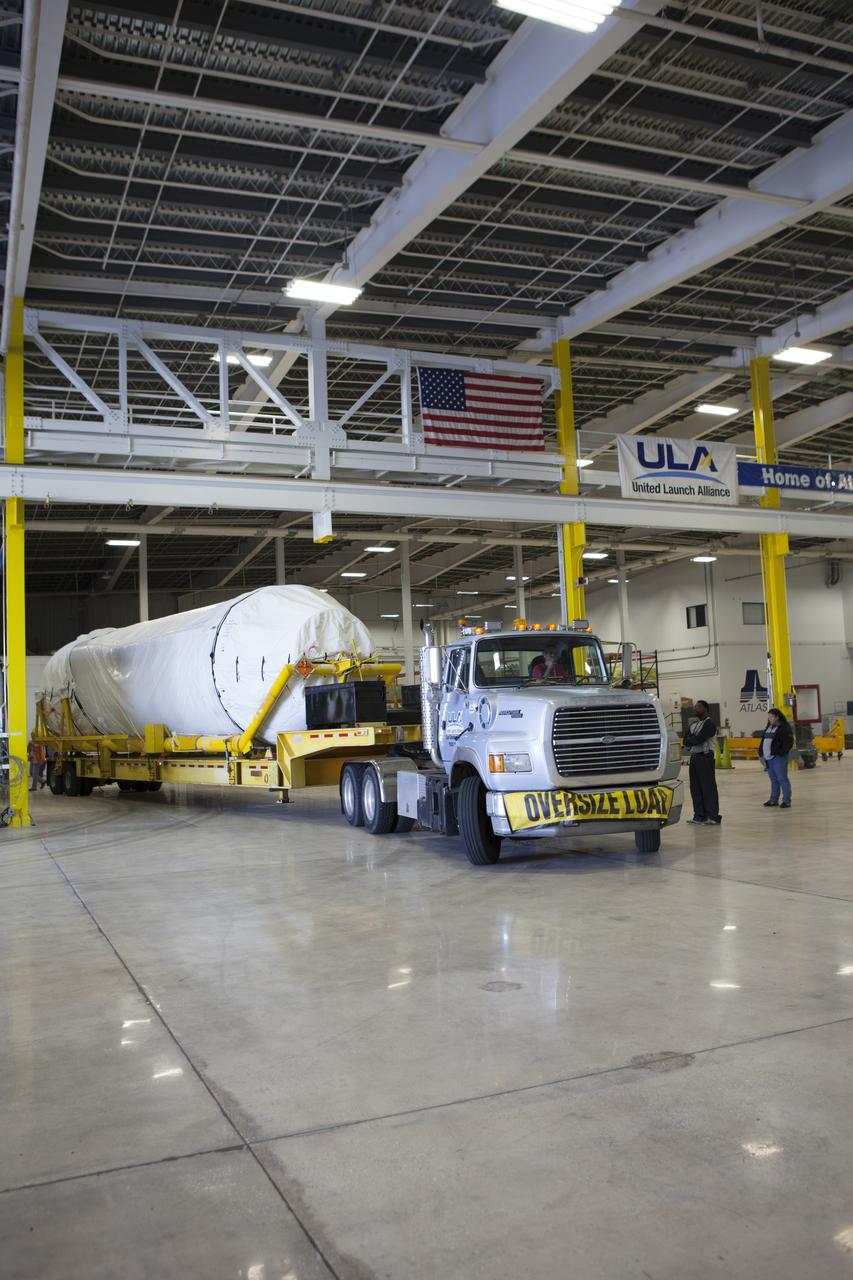

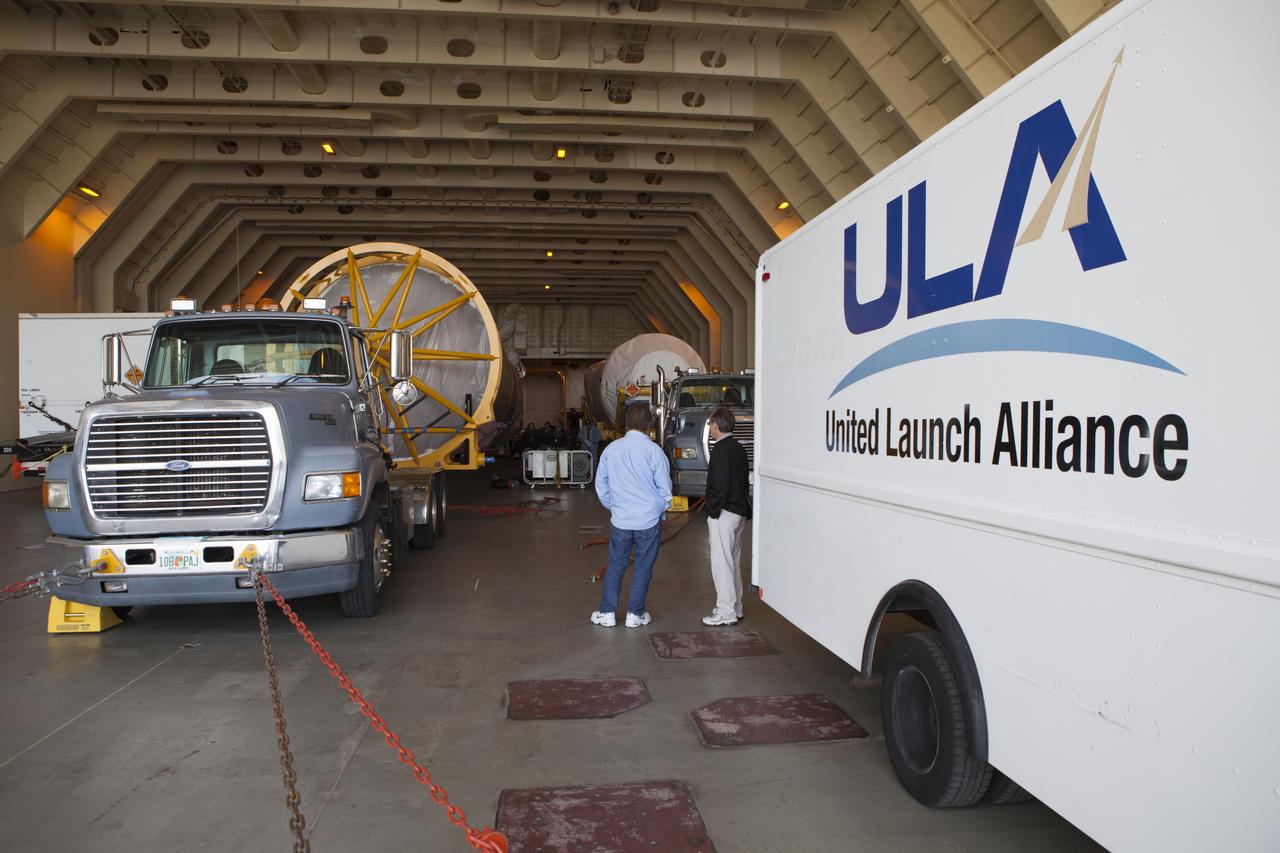
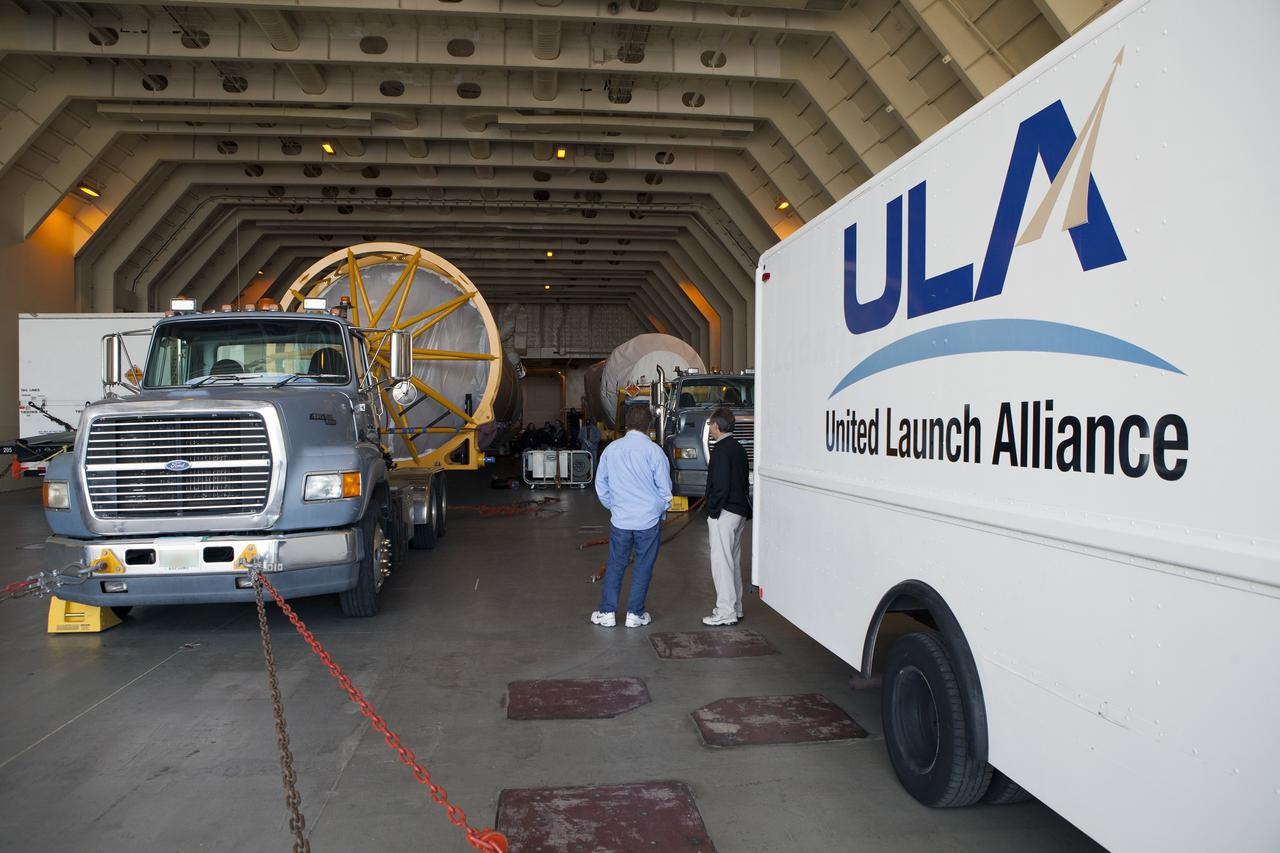
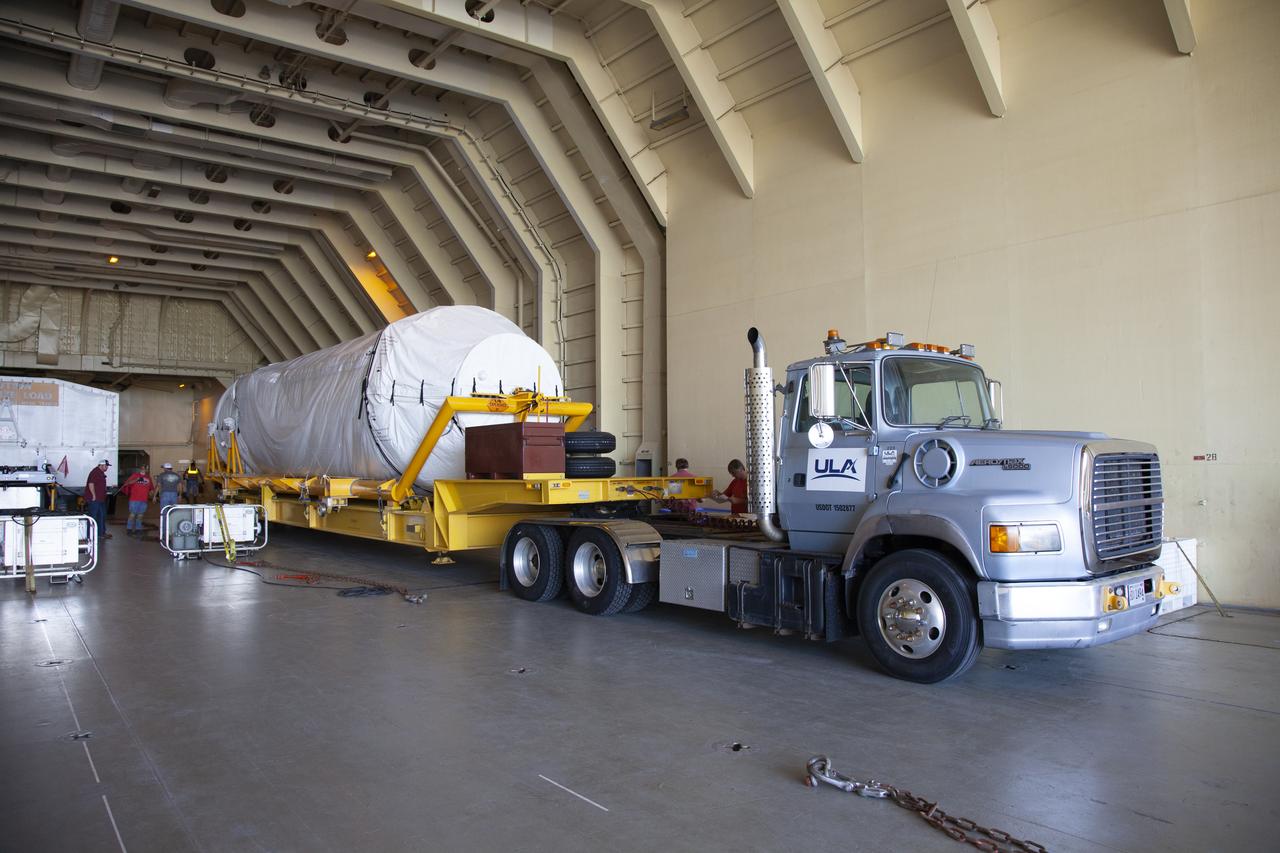
A truck positions a Centaur upper stage inside the hangar at the Atlas V Spaceflight Operations Center at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The upper stage will be used as part of the Atlas V rocket that will be used to launch NASA's Magnetospheric Multiscale mission.
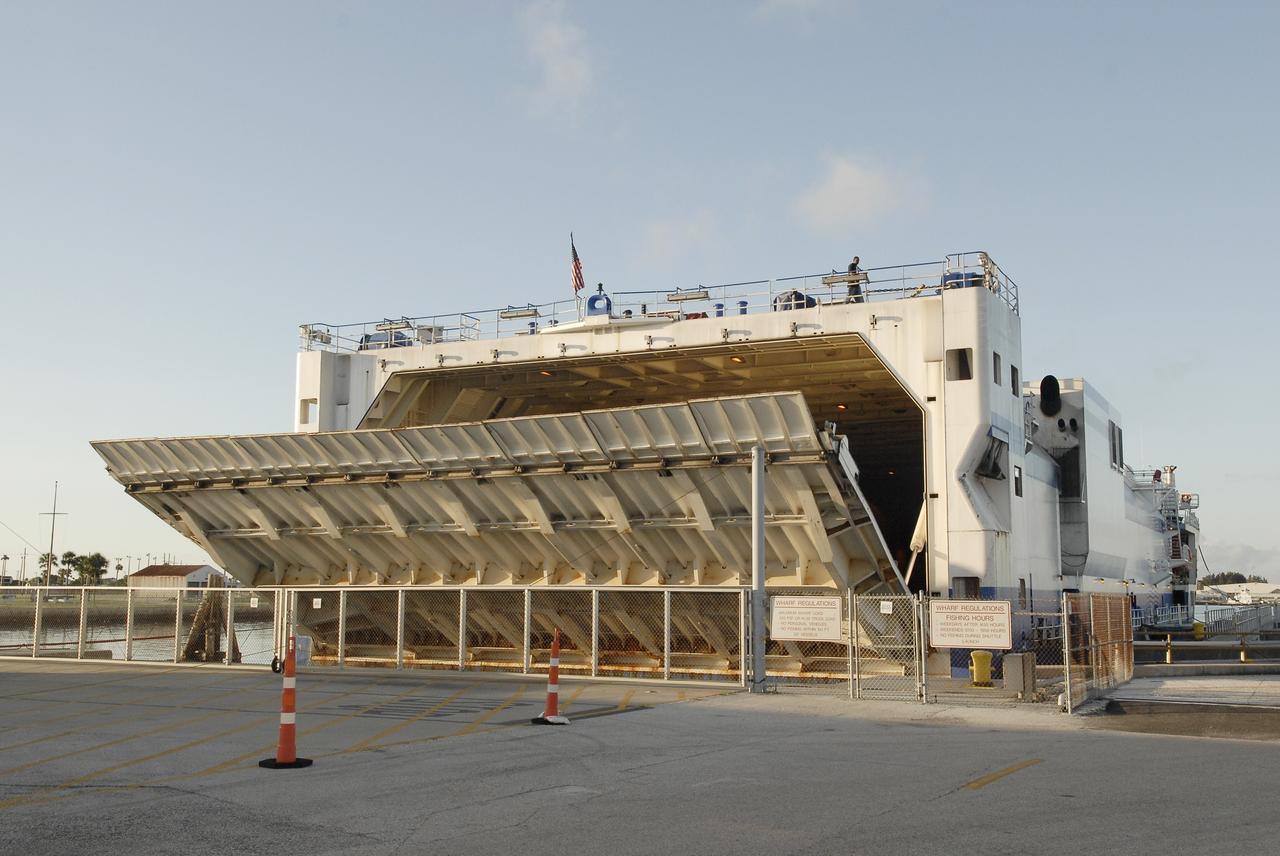

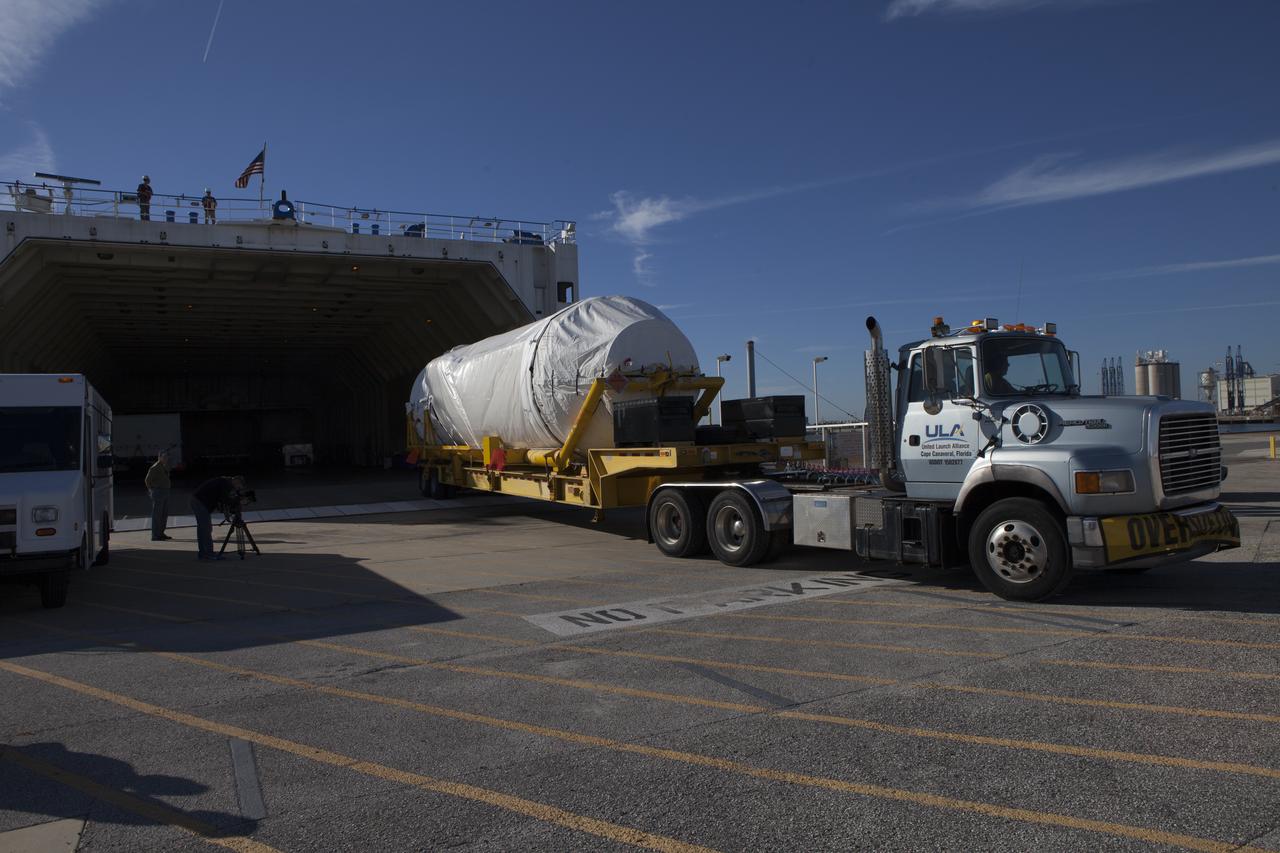
The Delta Mariner arrives at Port Canaveral carrying the Centaur upper stage destined to help launch the Radiation Belt Storm Probes, or RBSP, mission. The upper stage was removed from the ship and taken to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center, or ASOC, to begin checkout for the launch. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
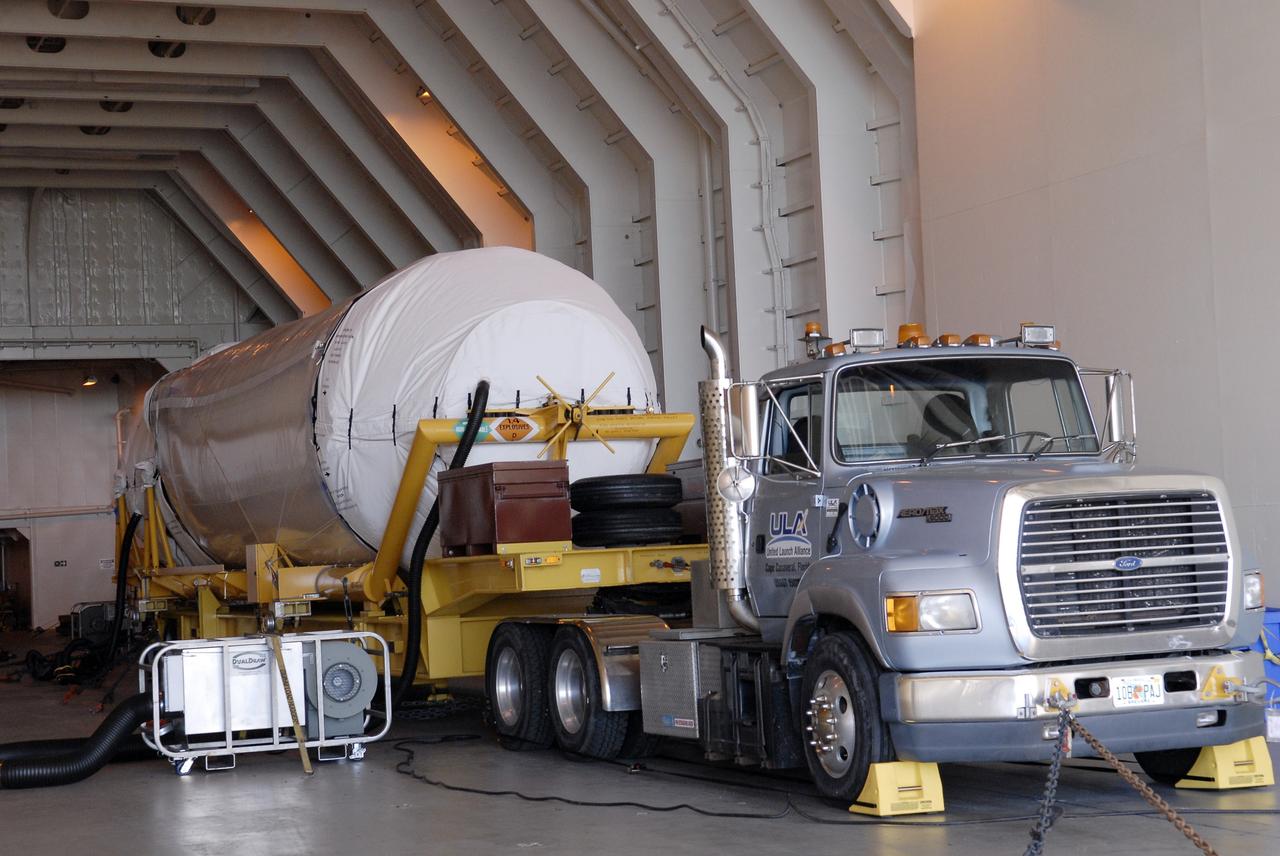

The Delta Mariner arrives at Port Canaveral carrying the Centaur upper stage destined to help launch the Radiation Belt Storm Probes, or RBSP, mission. The upper stage was removed from the ship and taken to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center, or ASOC, to begin checkout for the launch. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
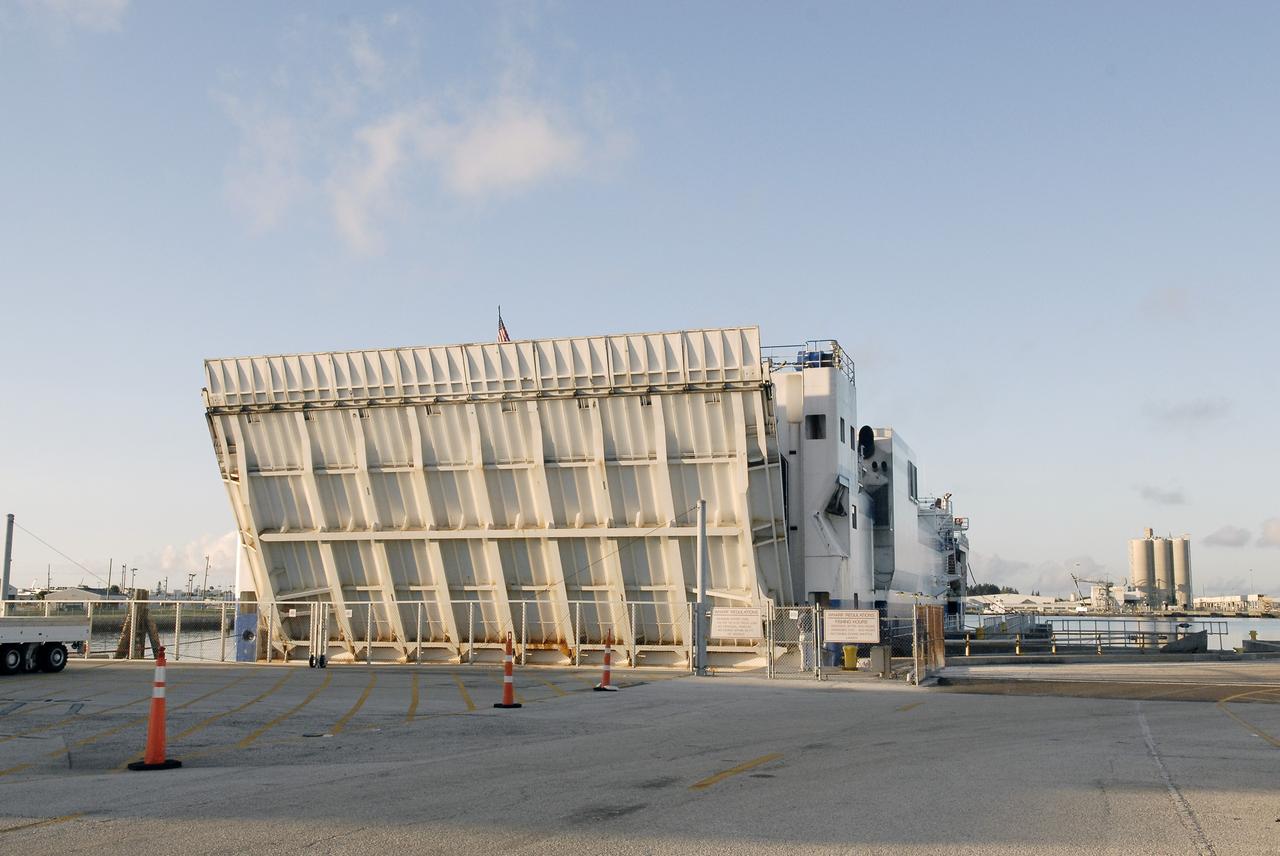

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Delta Mariner arrives at Port Canaveral carrying the Centaur upper stage destined to help launch the Radiation Belt Storm Probes, or RBSP, mission. The upper stage was removed from the ship and taken to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center, or ASOC, to begin checkout for the launch. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
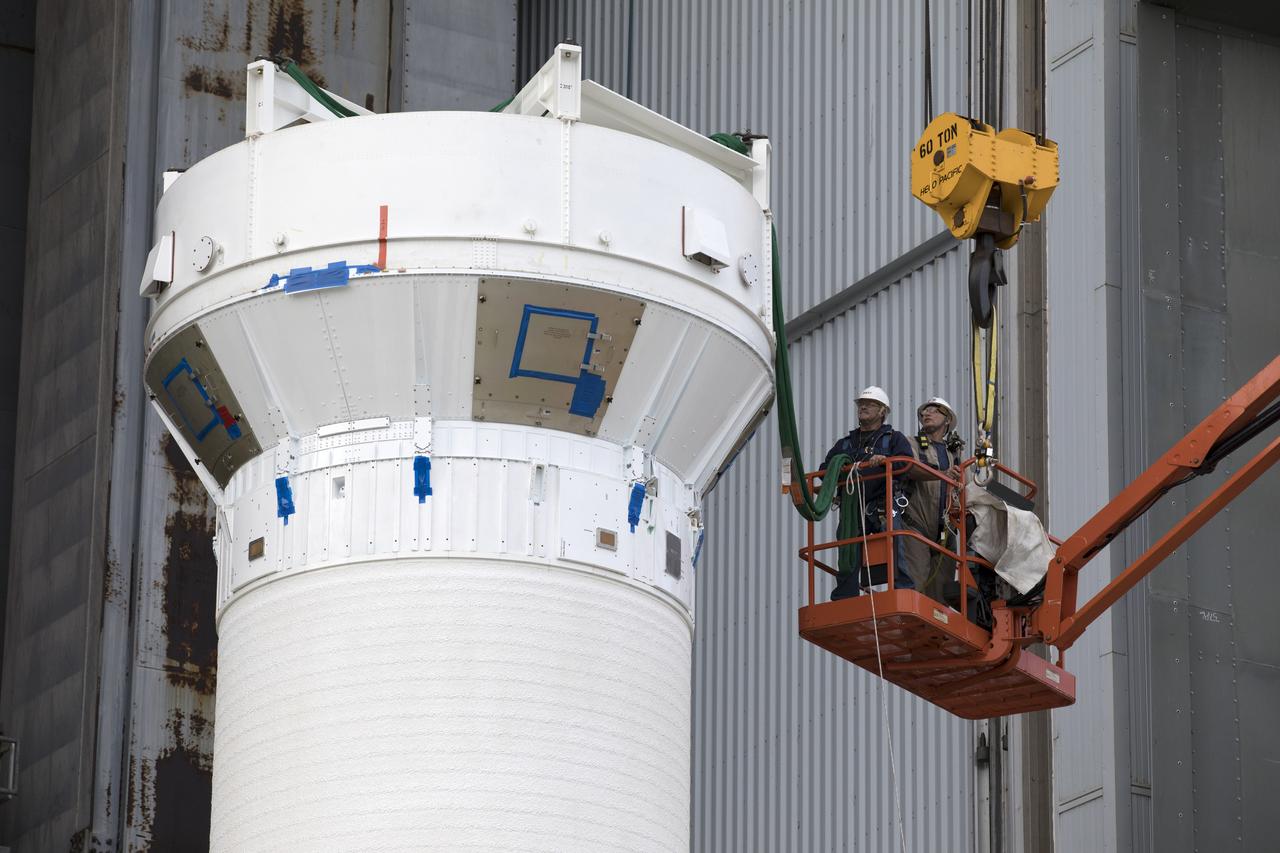

Technicians with United Launch Alliance (ULA) attach crane lines to the Centaur upper stage of the ULA Atlas V Centaur stage at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Centaur stage will be lifted and mated to the first stage booster. The rocket is being prepared for Orbital ATK's seventh commercial resupply mission, CRS-7, to the International Space Station. Orbital ATK's CYGNUS pressurized cargo module is scheduled to launch atop ULA's Atlas V rocket from Pad 41 on March 19, 2017. CYGNUS will deliver 7,600 pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
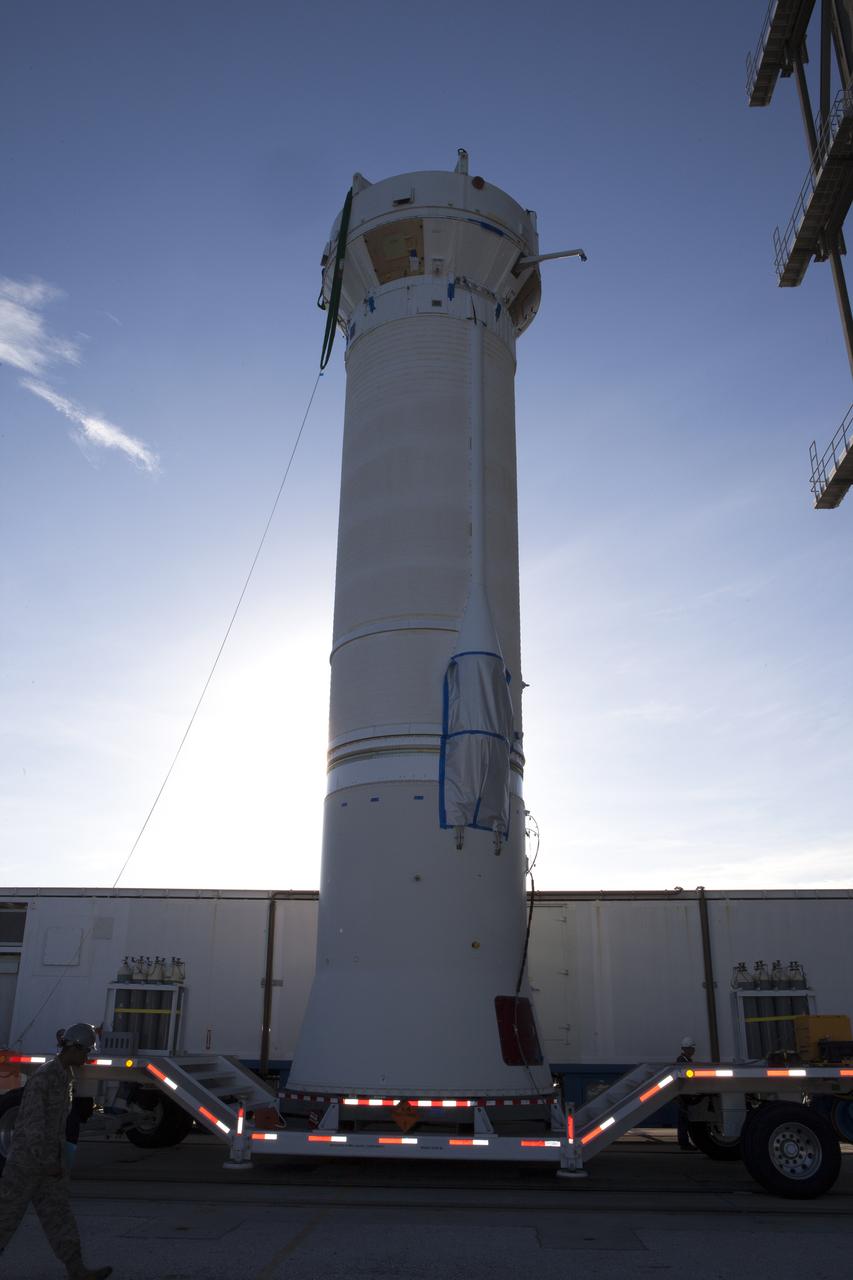

A Centaur upper stage, standing upright on a transporter, is prepared to be lifted and attached to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket first stage booster at Space Launch Complex 41 on Florida’s Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. With a Centaur upper stage, the rocket will boost NASA’s Origins, Spectral Interpretation, Resource Identification, Security-Regolith Explorer, or OSIRIS-REx spacecraft. Targeted for liftoff Sept. 8, 2016, OSIRIS-Rex will be the first U.S. mission to sample an asteroid, retrieve at least two ounces of surface material and return it to Earth for study. The asteroid, Bennu, may hold clues to the origin of the solar system and the source of water and organic molecules found on Earth.
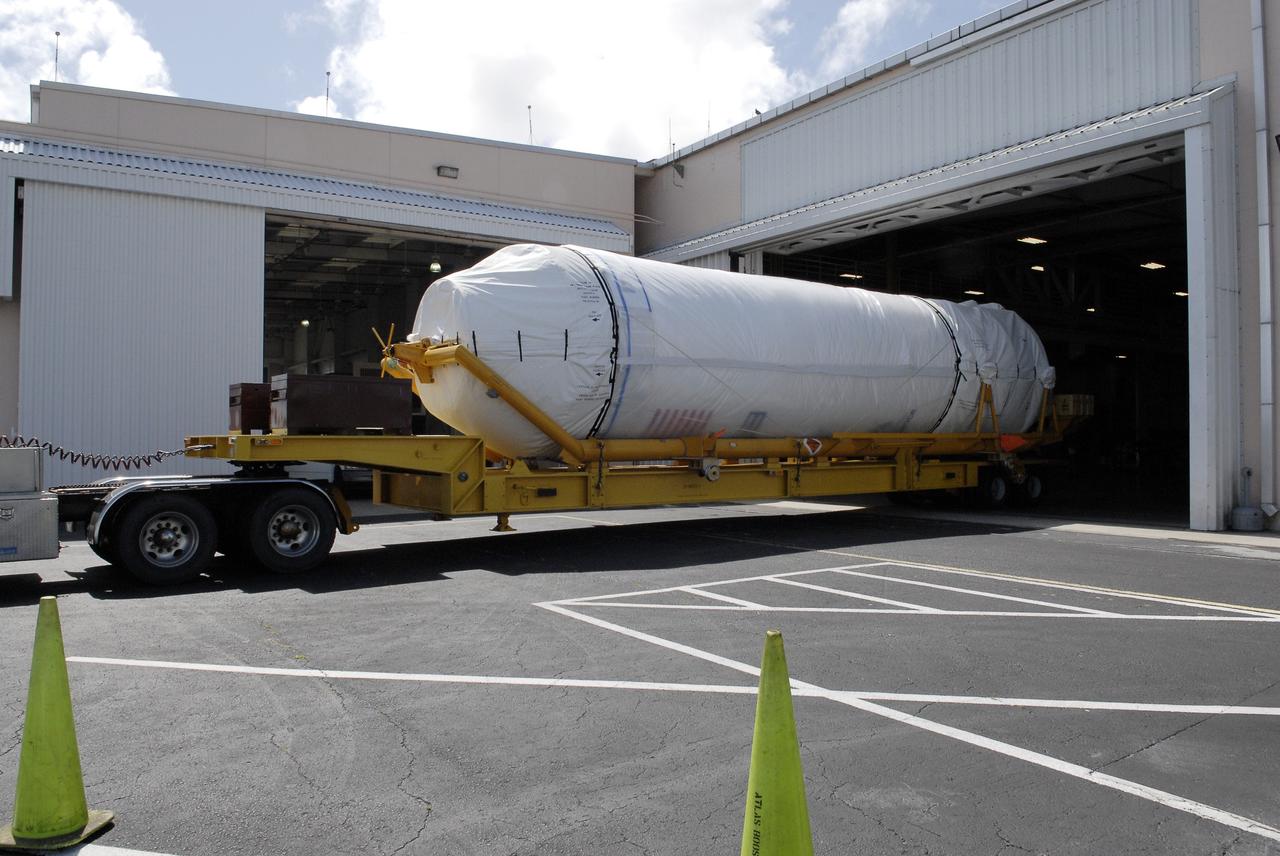

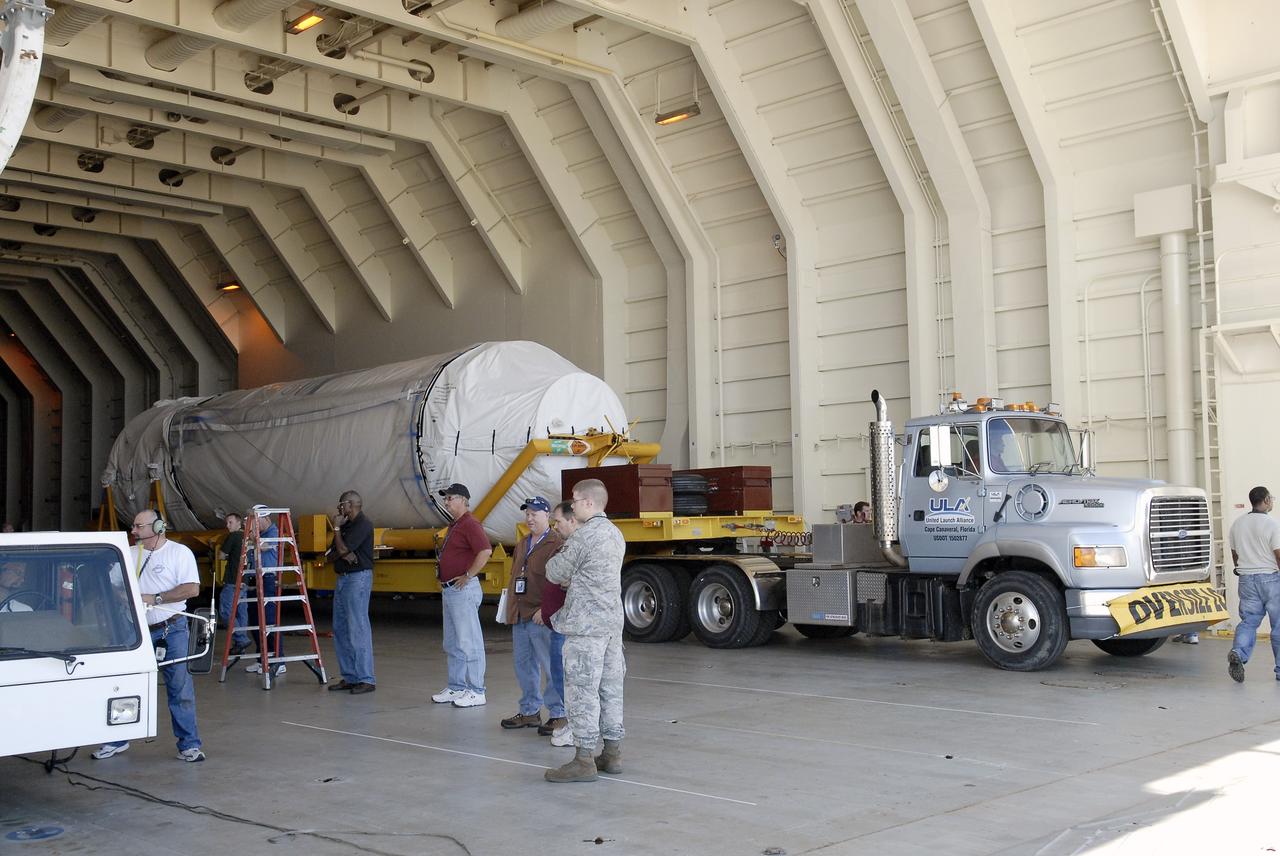
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Centaur upper stage is moved into the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center, or ASOC, to begin checkout for the launch of the Radiation Belt Storm Probes, or RBSP, mission. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
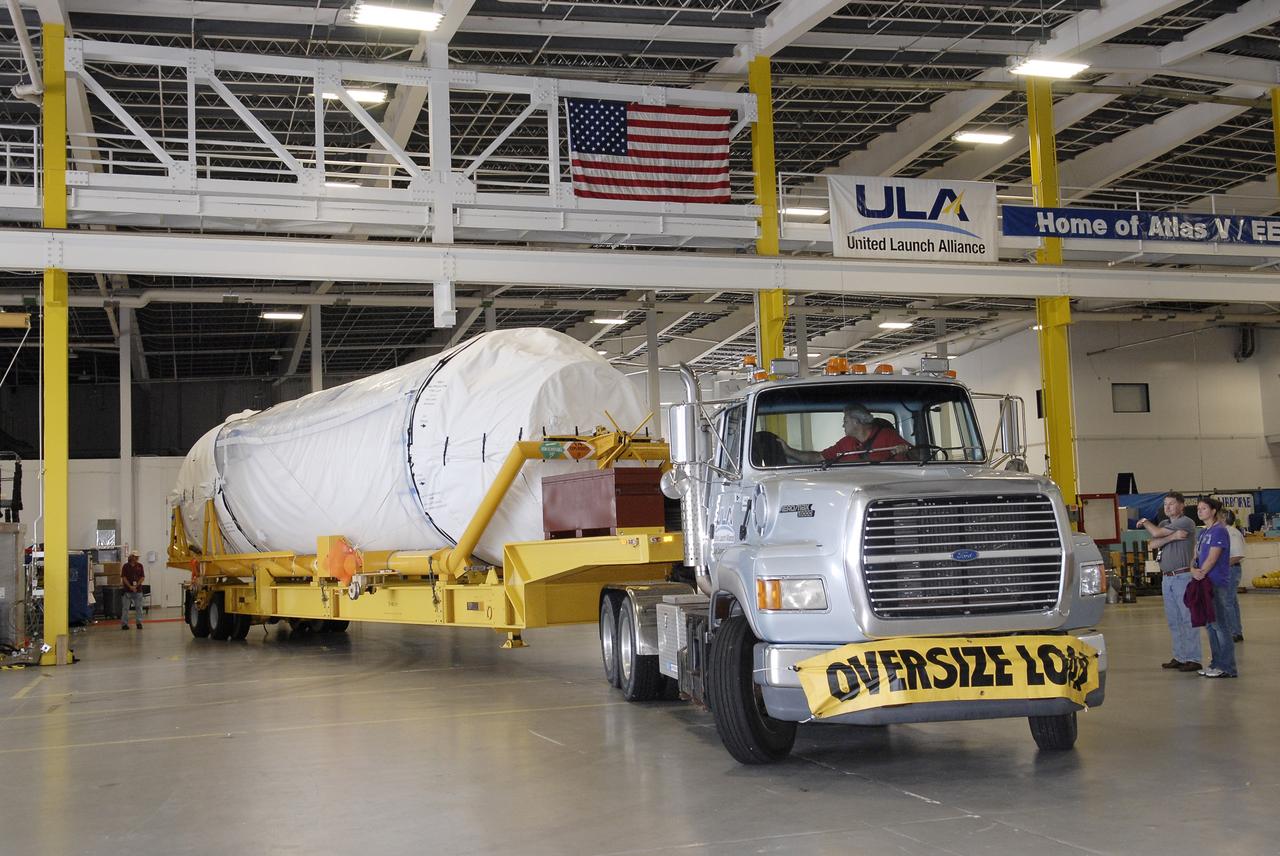

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Centaur upper stage is moved into the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center, or ASOC, to begin checkout for the launch of the Radiation Belt Storm Probes, or RBSP, mission. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser

Trucks inside the United Launch Alliance Delta Mariner prepare to transport the Atlas V rocket and Centaur upper stage that will be used to launch NASA's Magnetospheric Multiscale mission.
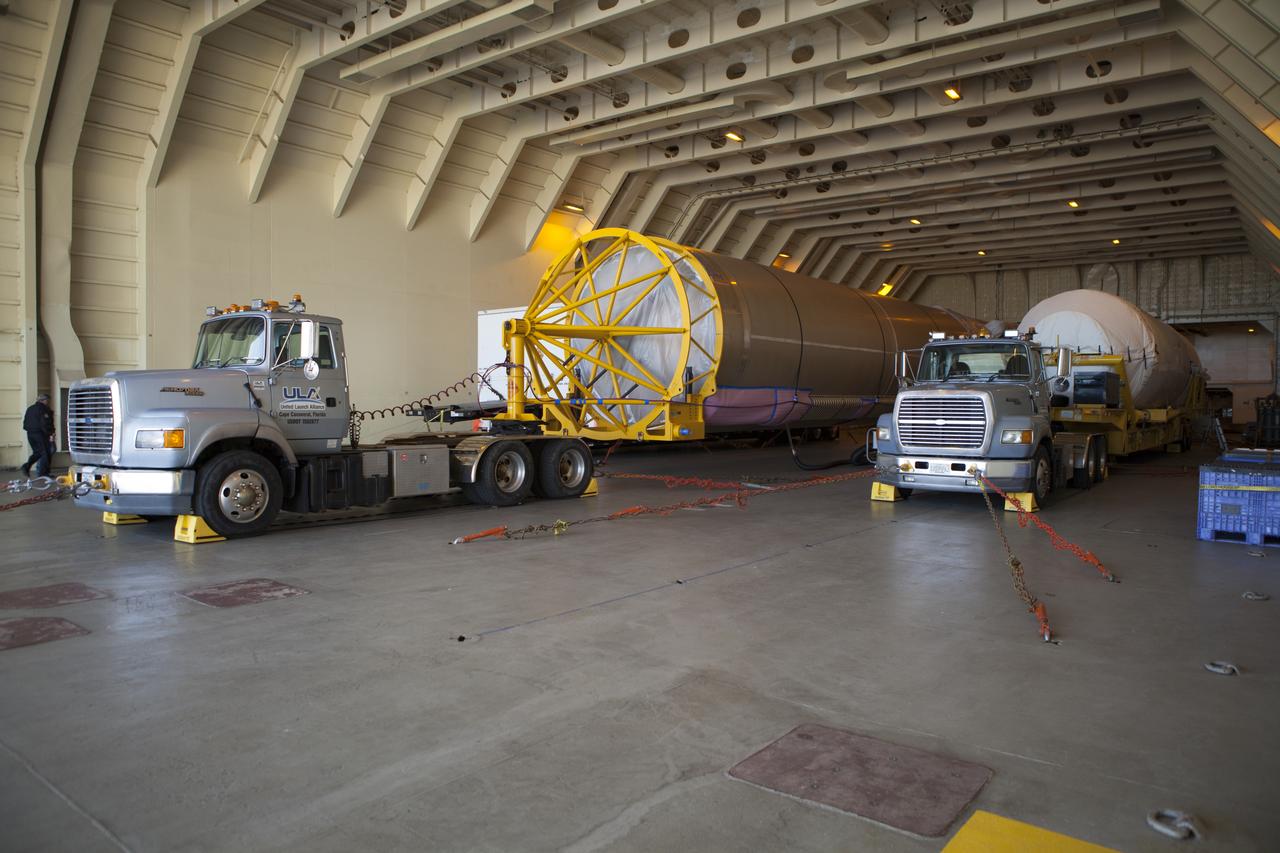

Trucks inside the United Launch Alliance Delta Mariner prepare to transport the Atlas V rocket and Centaur upper stage that will be used to launch NASA's Magnetospheric Multiscale mission.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Centaur upper stage is moved into the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center, or ASOC, to begin checkout for the launch of the Radiation Belt Storm Probes, or RBSP, mission. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
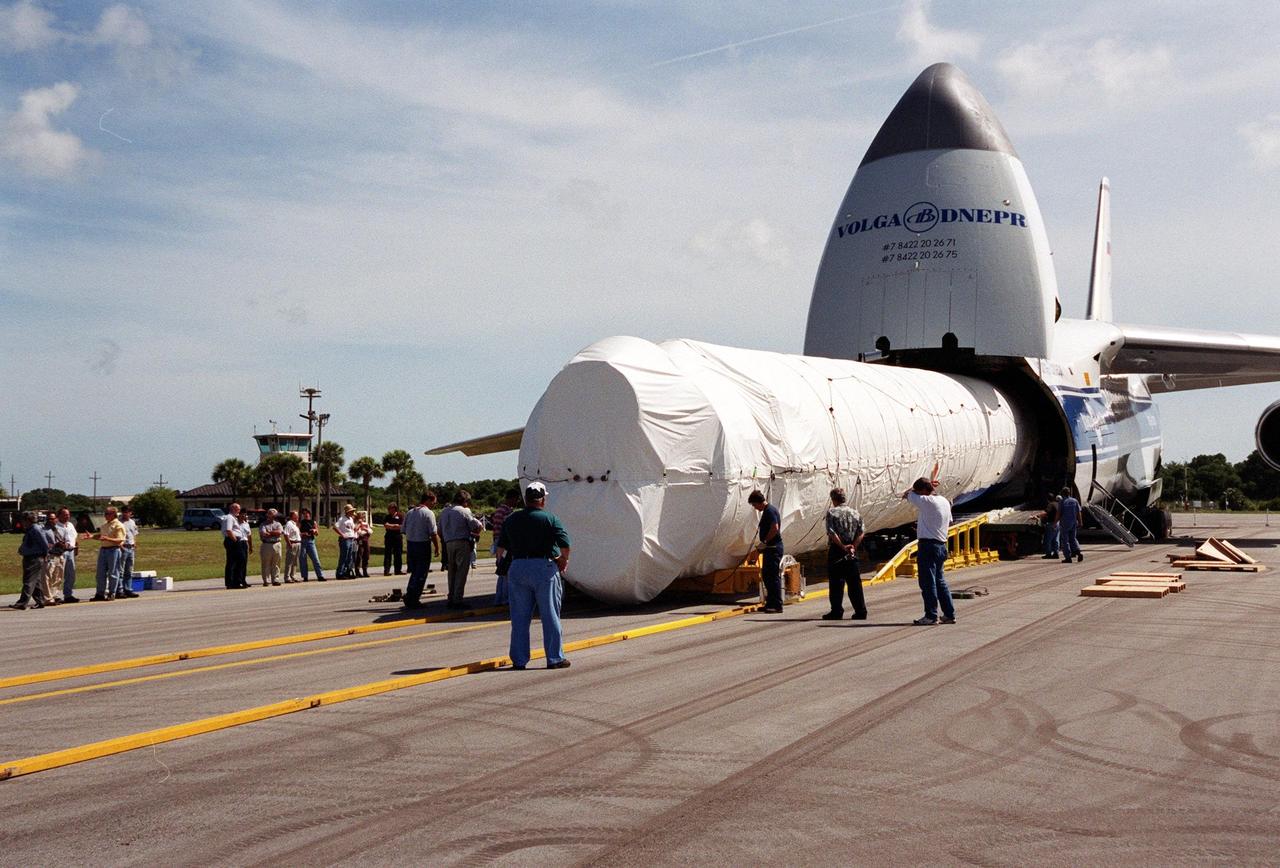

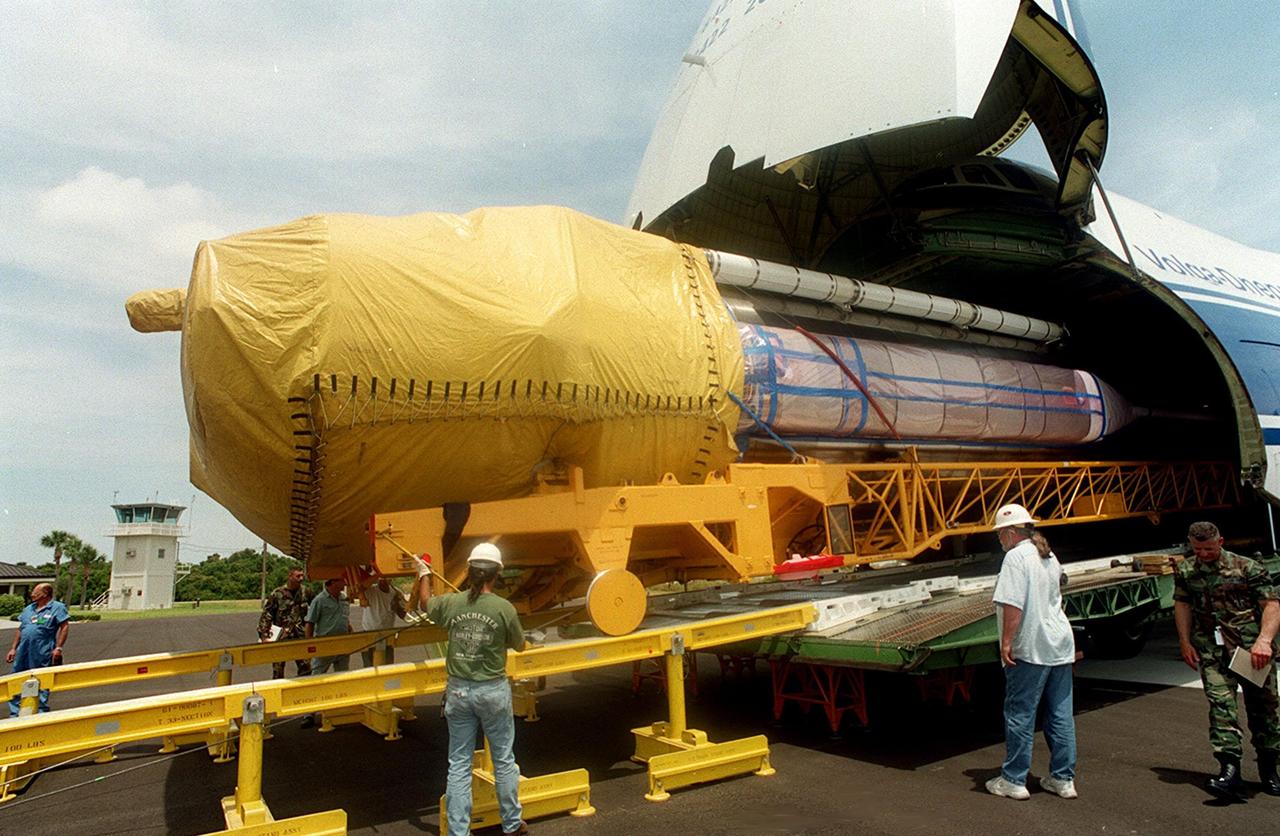
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Stages of the first Atlas V rocket are offloaded from a Russian Antonov AN-124 aircraft after their arrival at the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The Atlas V will be joined to its Centaur upper stage for testing and checkout in preparation for a May 2002 launch
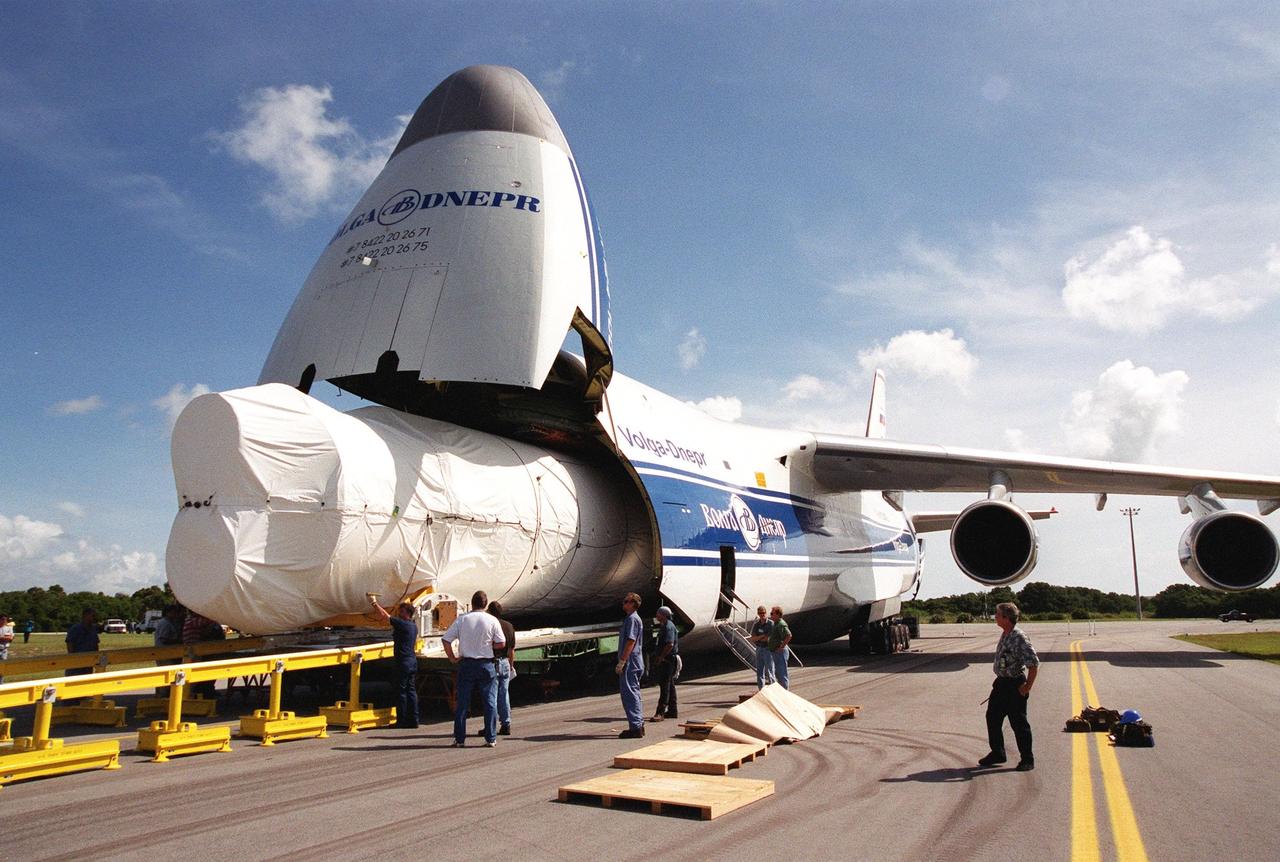

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Stages of the first Atlas V rocket are offloaded from a Russian Antonov AN-124 aircraft after their arrival at the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The booster will be joined to its Centaur upper stage for testing and checkout in preparation for launch in May 2002
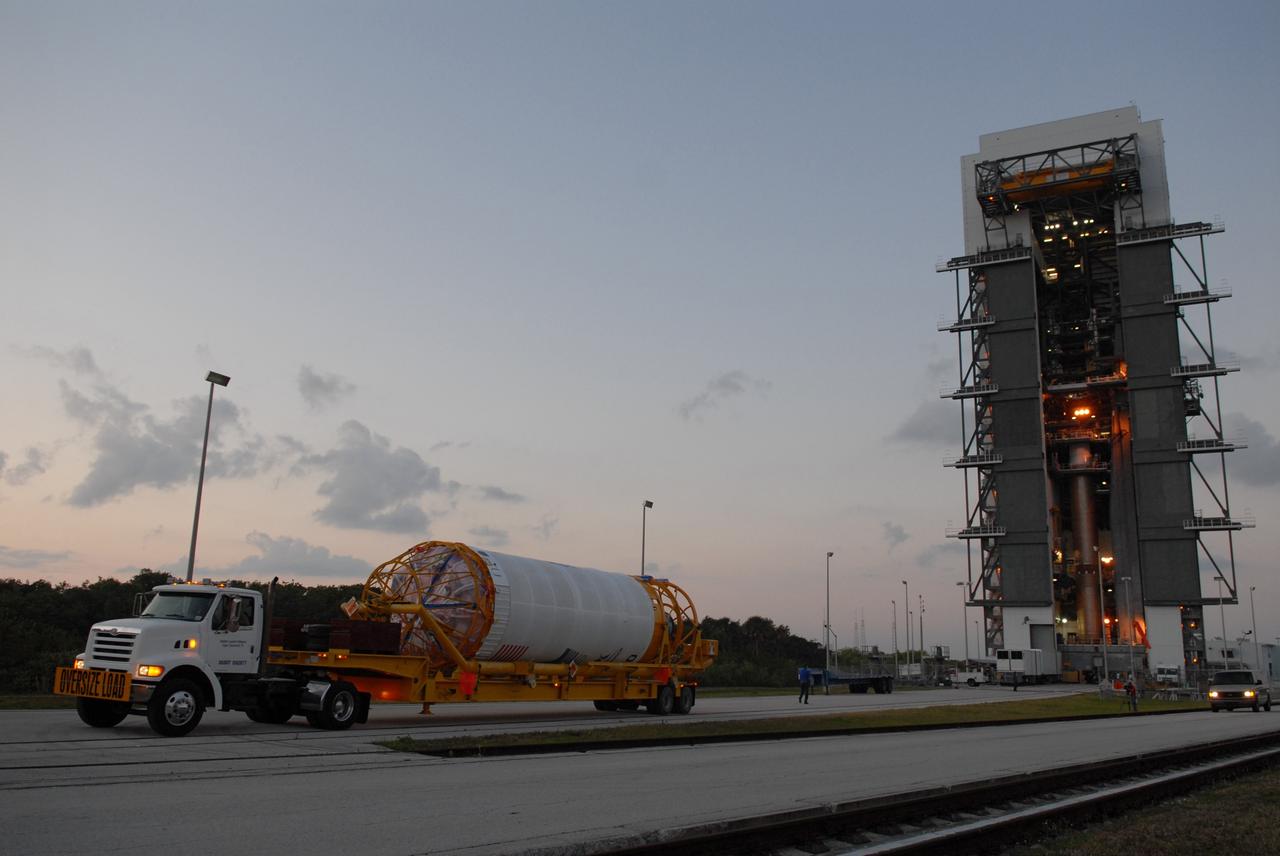

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –– The Centaur upper stage is transported to the Vertical Integration Facility near Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Complex 41, where it will be lifted onto the Atlas V first stage. The Atlas V/Centaur is the launch vehicle for NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO, and NASA's Lunar CRater Observation and Sensing Satellite, known as LCROSS. LCROSS and LRO are the first missions in NASA's plan to return humans to the moon and begin establishing a lunar outpost by 2020. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

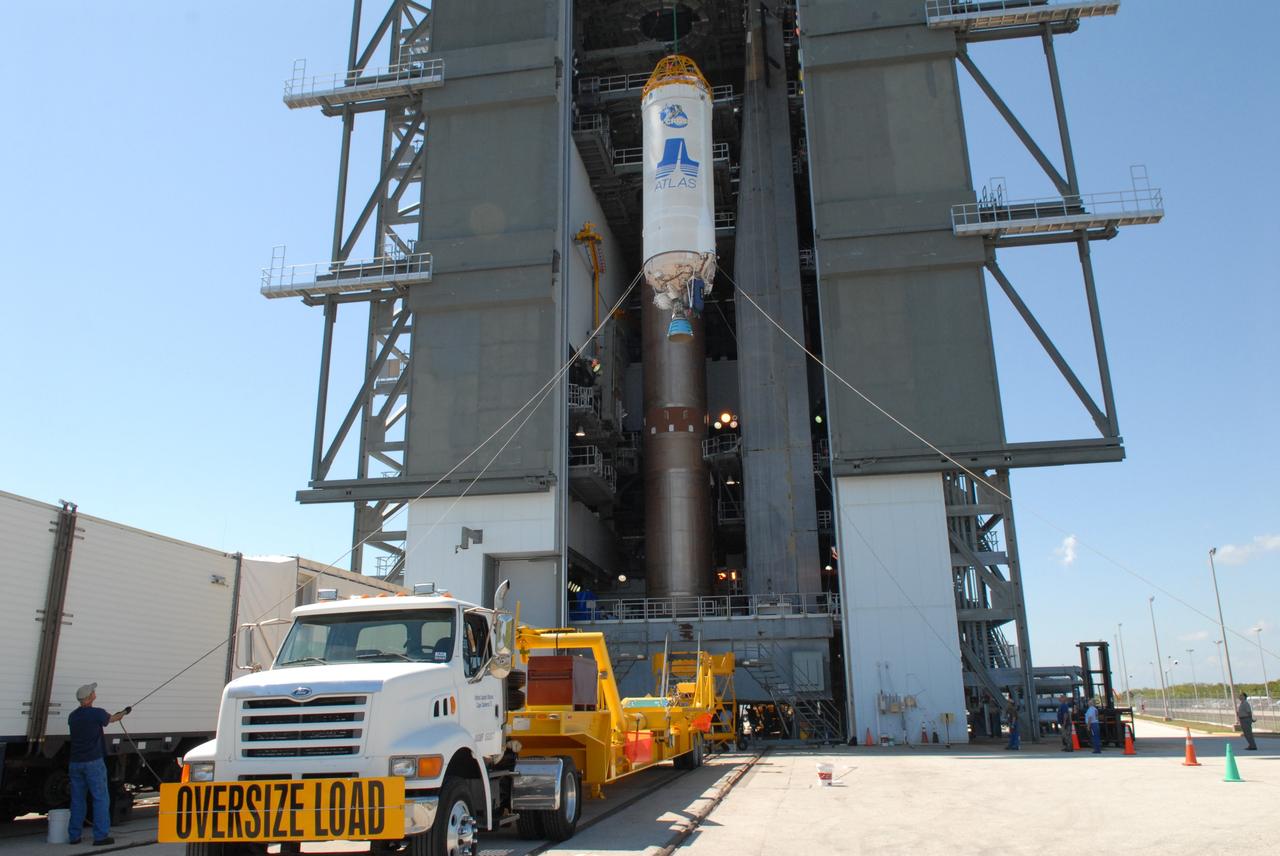
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –– On Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Complex 41, the Centaur upper stage is moved inside the Vertical Integration Facility for installation onto the Atlas V first stage, already in the tower. The Atlas V/Centaur is the launch vehicle for NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO, and NASA's Lunar CRater Observation and Sensing Satellite, known as LCROSS. LCROSS and LRO are the first missions in NASA's plan to return humans to the moon and begin establishing a lunar outpost by 2020. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
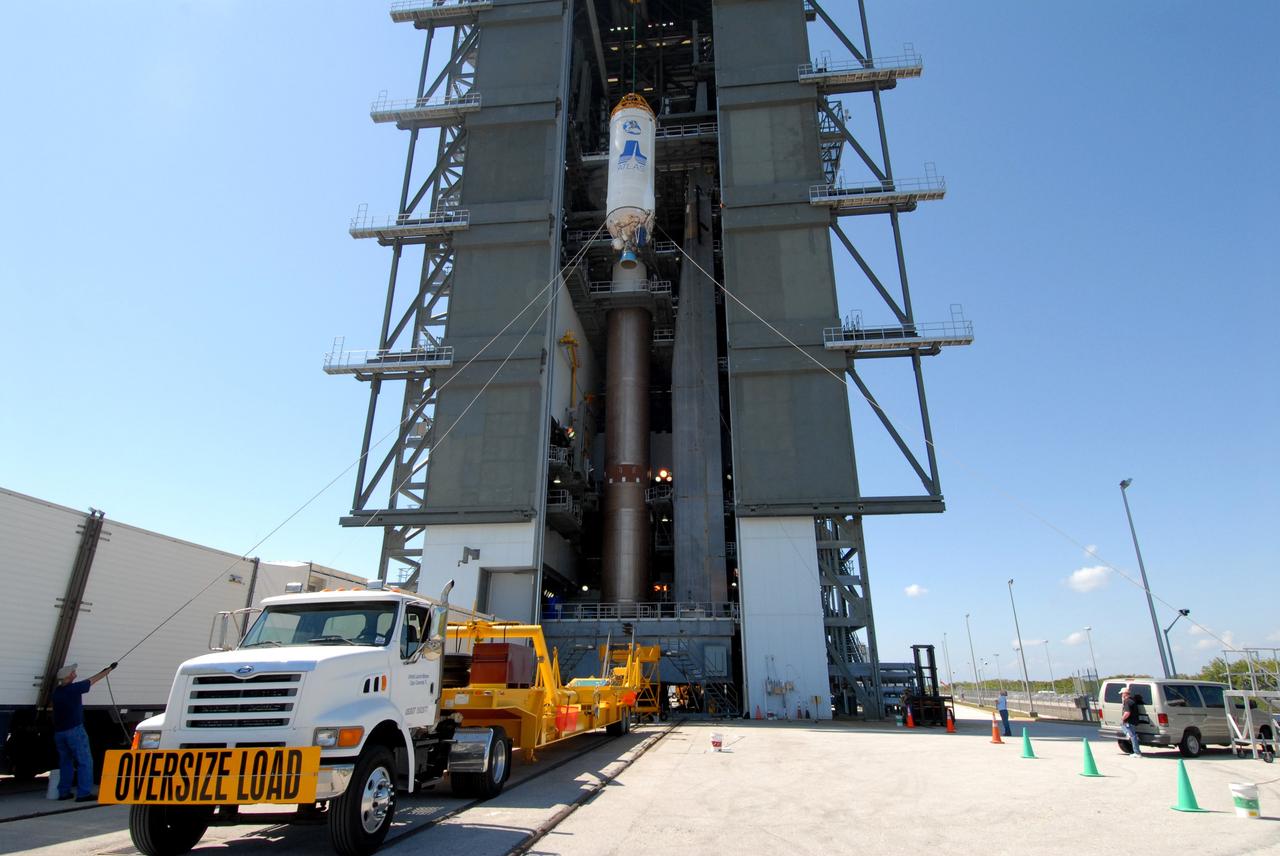

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –– On Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Complex 41, the crane lifts the Centaur upper stage into the Vertical Integration Facility for installation onto the Atlas V first stage, seen in the tower. The Atlas V/Centaur is the launch vehicle for NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO, and NASA's Lunar CRater Observation and Sensing Satellite, known as LCROSS. LCROSS and LRO are the first missions in NASA's plan to return humans to the moon and begin establishing a lunar outpost by 2020. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
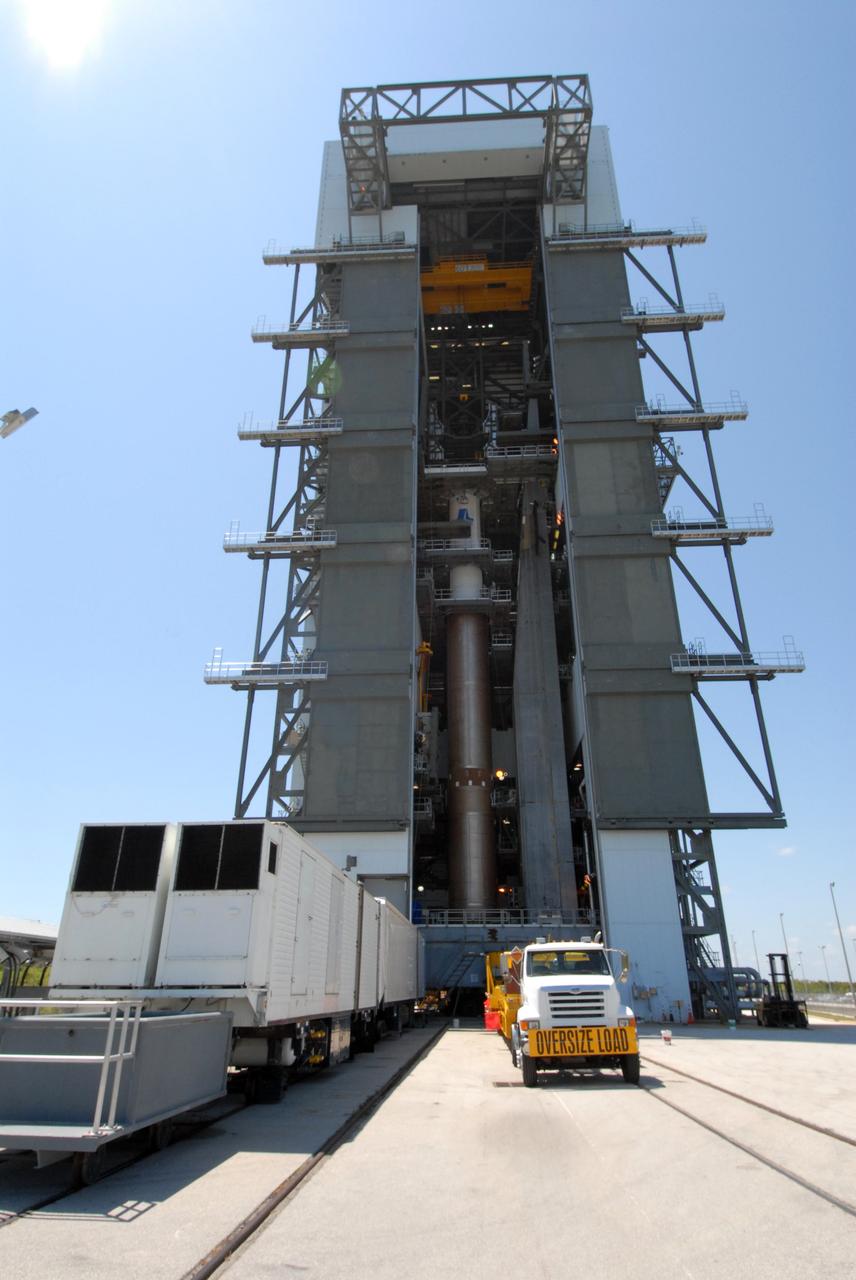

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –– On Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Complex 41, the Centaur upper stage is moved into place in the Vertical Integration Facility for installation onto the Atlas V first stage, seen below it. The Atlas V/Centaur is the launch vehicle for NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO, and NASA's Lunar CRater Observation and Sensing Satellite, known as LCROSS. LCROSS and LRO are the first missions in NASA's plan to return humans to the moon and begin establishing a lunar outpost by 2020. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
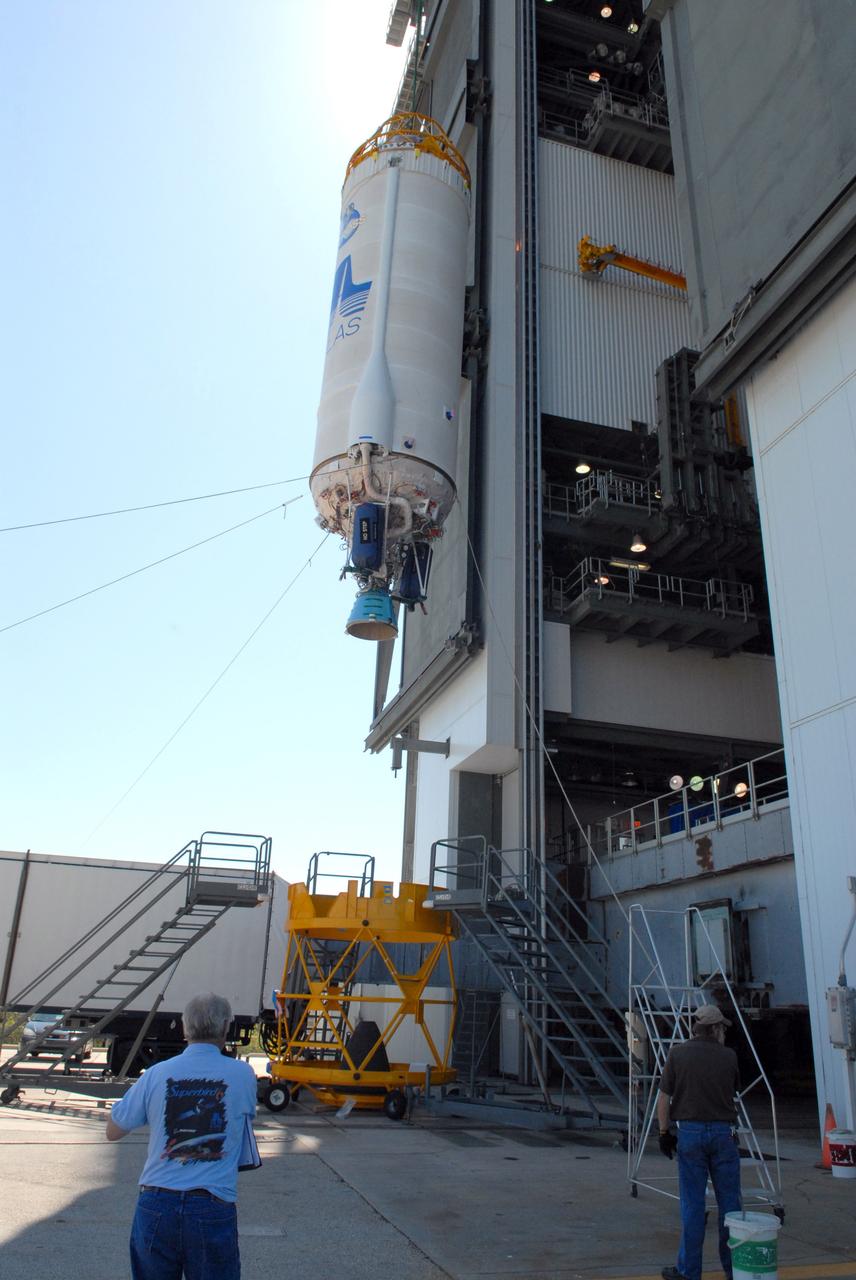

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –– On Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Complex 41, the crane lifts the Centaur upper stage into the Vertical Integration Facility for installation onto the Atlas V first stage, already in the tower. The Atlas V/Centaur is the launch vehicle for NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO, and NASA's Lunar CRater Observation and Sensing Satellite, known as LCROSS. LCROSS and LRO are the first missions in NASA's plan to return humans to the moon and begin establishing a lunar outpost by 2020. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
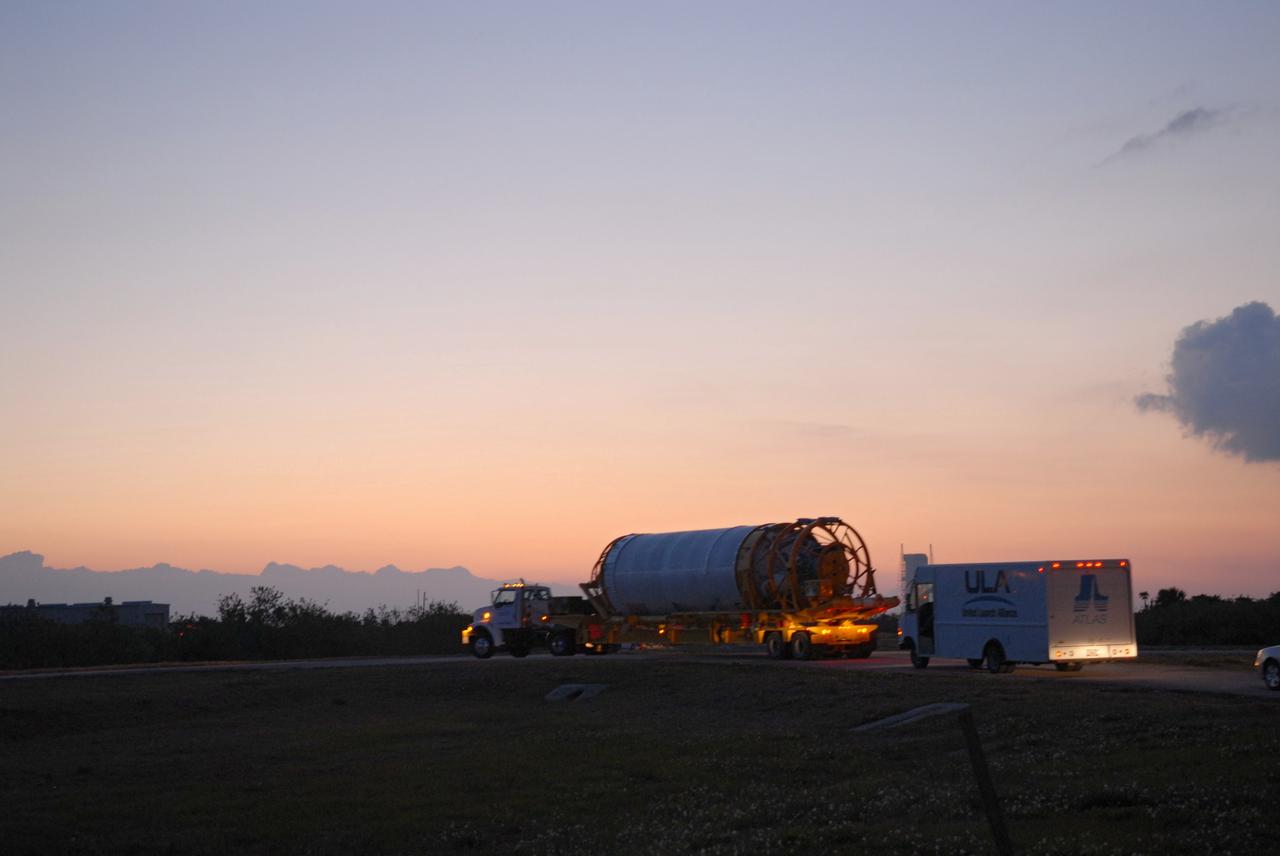

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –– The Centaur upper stage is transported to the Vertical Integration Facility near Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Complex 41, where it will be lifted onto the Atlas V first stage. The Atlas V/Centaur is the launch vehicle for NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO, and NASA's Lunar CRater Observation and Sensing Satellite, known as LCROSS. LCROSS and LRO are the first missions in NASA's plan to return humans to the moon and begin establishing a lunar outpost by 2020. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –– On Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Complex 41, the crane lifts the Centaur upper stage into the Vertical Integration Facility for installation onto the Atlas V first stage, already in the tower. The Atlas V/Centaur is the launch vehicle for NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO, and NASA's Lunar CRater Observation and Sensing Satellite, known as LCROSS. LCROSS and LRO are the first missions in NASA's plan to return humans to the moon and begin establishing a lunar outpost by 2020. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
A United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V dual engine Centaur upper stage is in ULA’s factory in Decatur, Alabama on March 29, 2019. The dual engine upper stage is being prepared for Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner Crew Flight Test. Soon the upper stage will be assembled with the first stage booster and shipped aboard the company’s Mariner cargo ship to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Starliner and the Atlas V rockets that will launch the spacecraft, are key elements of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program to restore the capability to send astronauts to the International Space Station from U.S. soil.
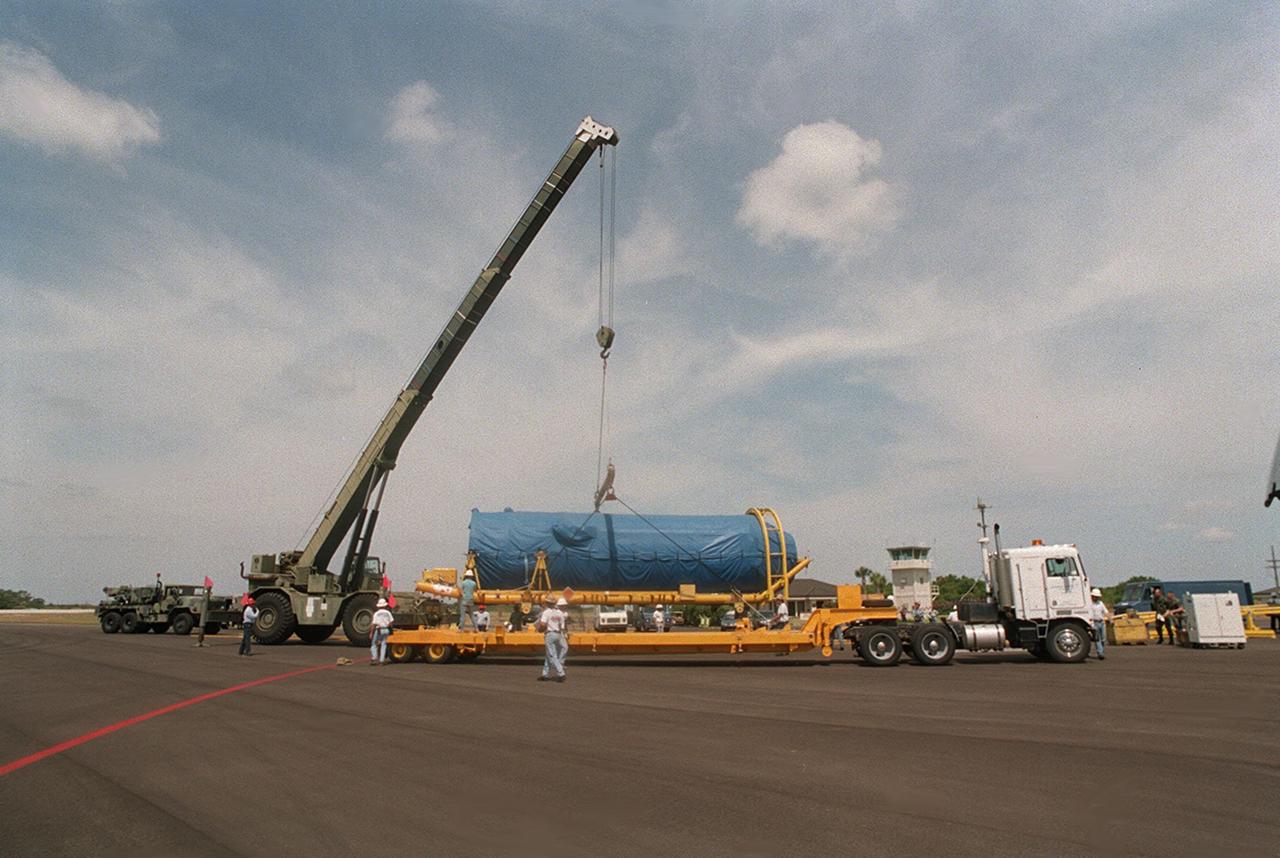

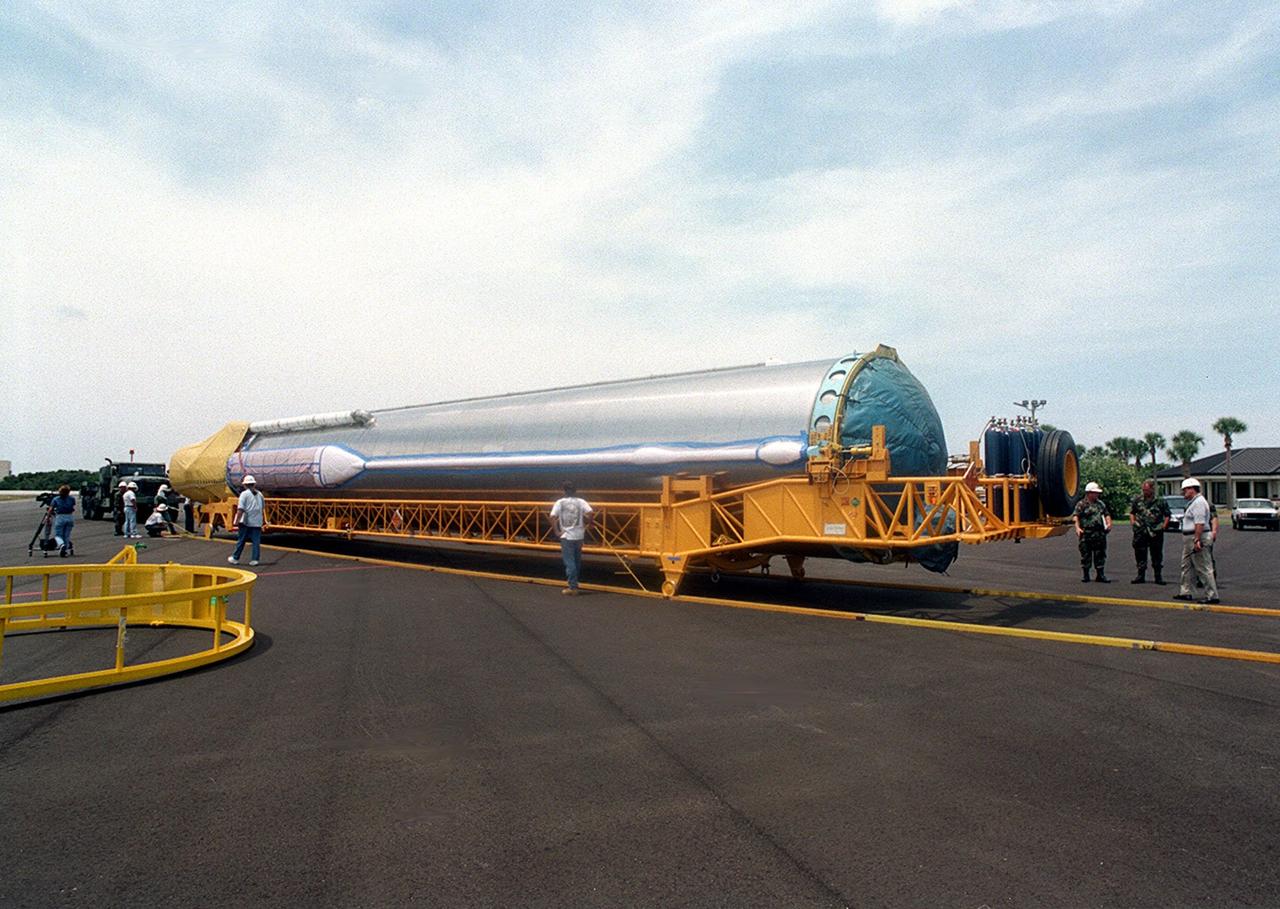
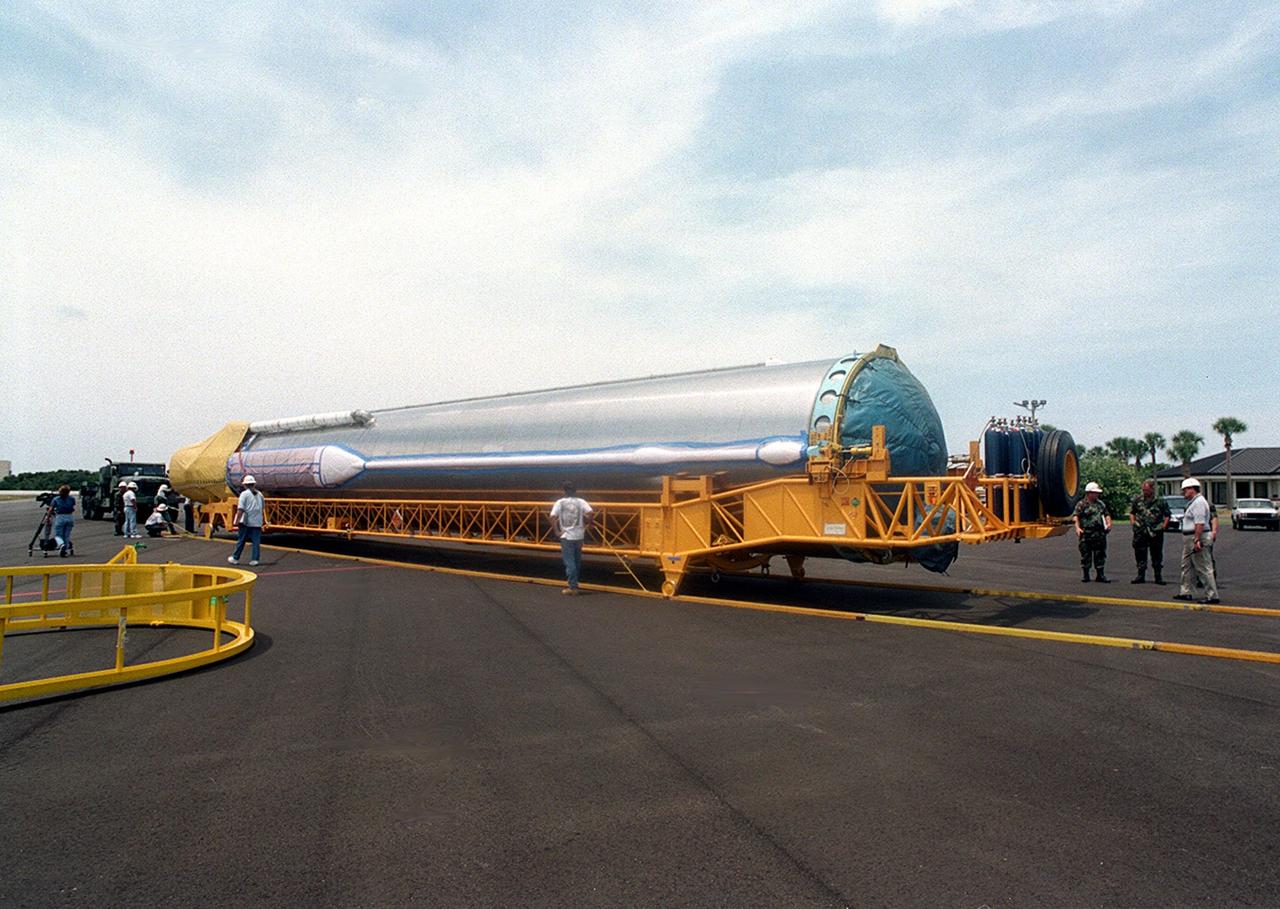
At Cape Canaveral Air Force skid strip, the Centaur upper stage is placed aboard a transporter after arriving aboard a Russian cargo plane, the Antenov 124. The Centaur will be coupled with an Atlas IIA to launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The Centaur, manufactured and operated by Lockheed Martin, is 3.05 m (10 ft) in diameter and 10.0 m (33-ft) long. It uses liquid hydrogen (LH2) and liquid oxygen (LO2) propellants
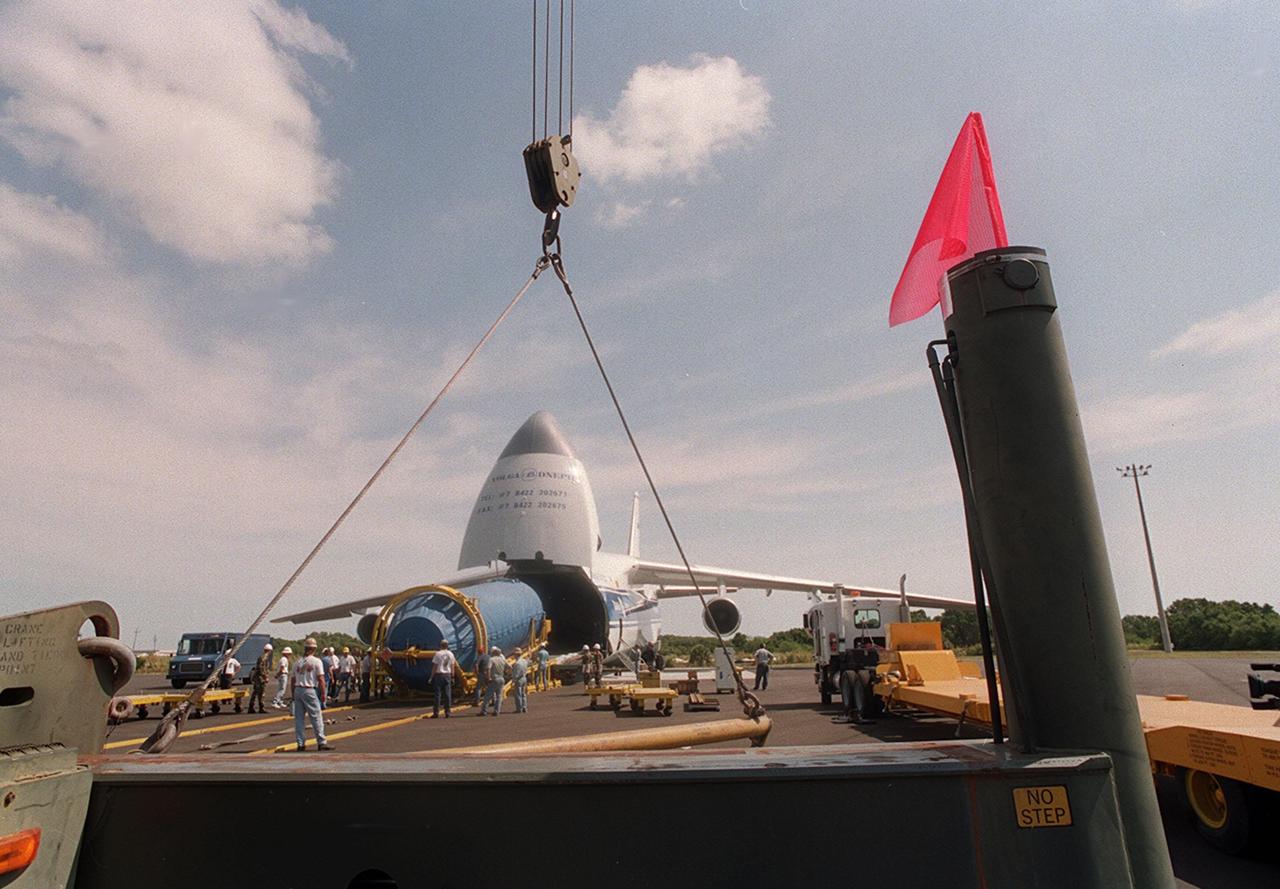

Workers at Cape Canaveral Air Force skid strip oversee the offloading of the Centaur upper stage from a Russian cargo plane, the Antenov 124. The Centaur will be coupled with an Atlas IIA to launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The Centaur, manufactured and operated by Lockheed Martin, is 3.05 m (10 ft) in diameter and 10.0 m (33-ft) long. It uses liquid hydrogen (LH2) and liquid oxygen (LO2) propellants
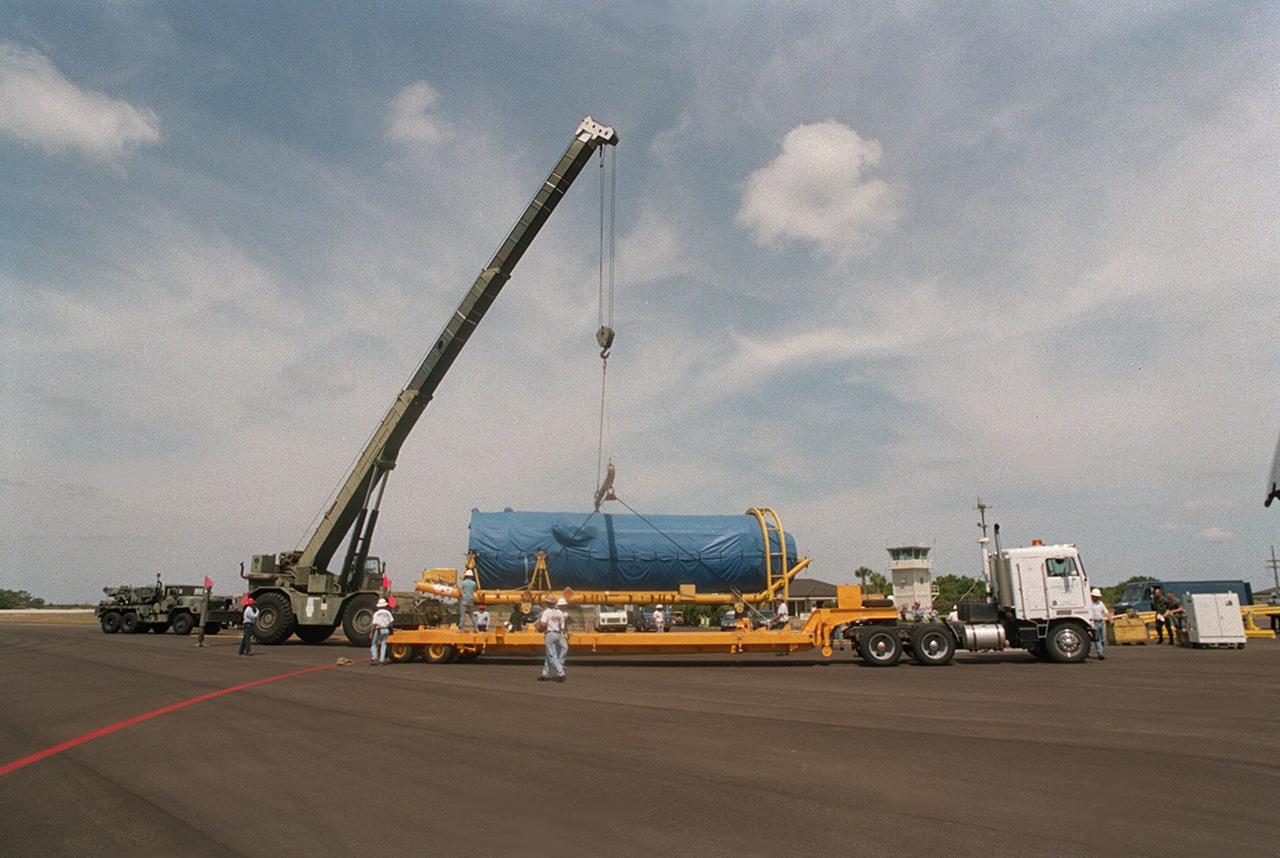

At Cape Canaveral Air Force skid strip, the Centaur upper stage is placed aboard a transporter after arriving aboard a Russian cargo plane, the Antenov 124. The Centaur will be coupled with an Atlas IIA to launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The Centaur, manufactured and operated by Lockheed Martin, is 3.05 m (10 ft) in diameter and 10.0 m (33-ft) long. It uses liquid hydrogen (LH2) and liquid oxygen (LO2) propellants
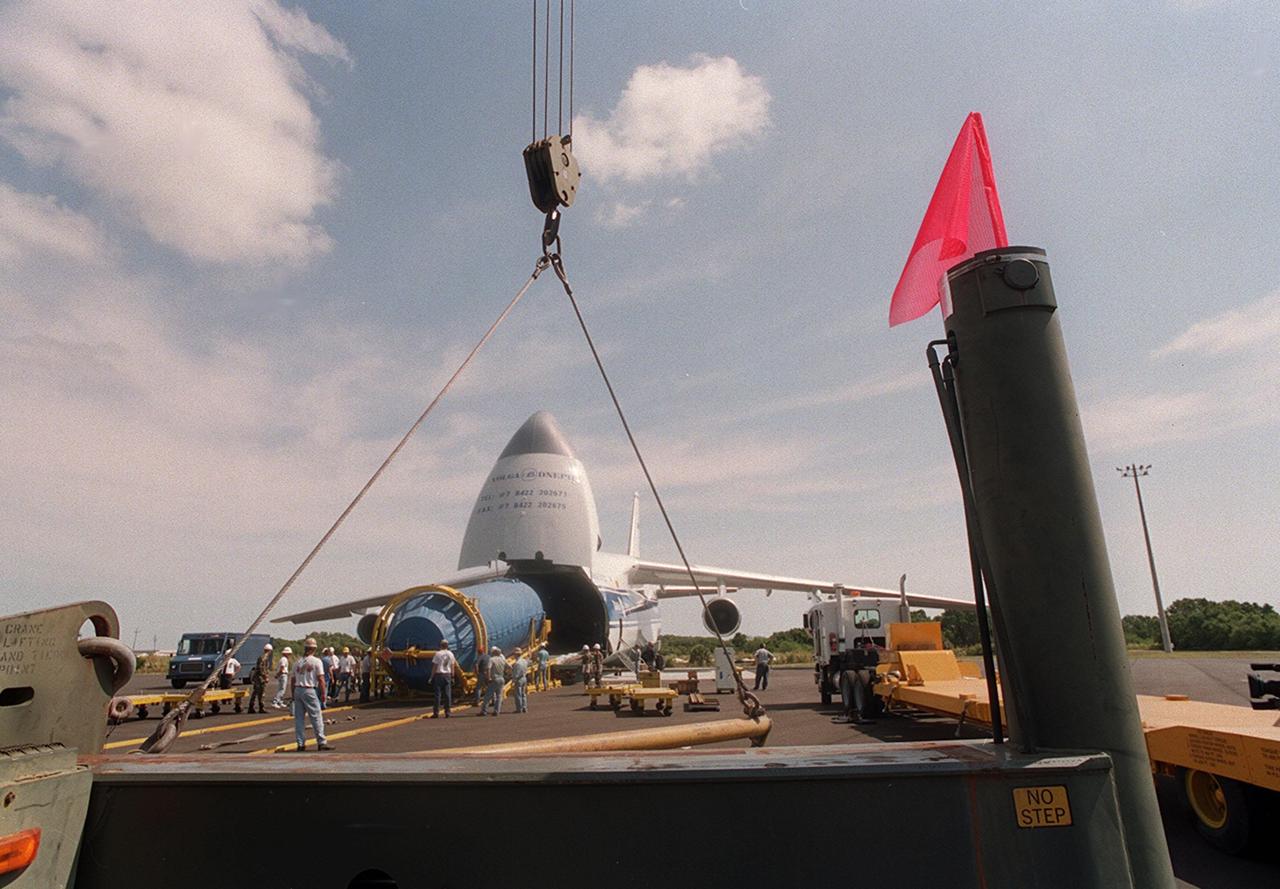

Workers at Cape Canaveral Air Force skid strip oversee the offloading of the Centaur upper stage from a Russian cargo plane, the Antenov 124. The Centaur will be coupled with an Atlas IIA to launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The Centaur, manufactured and operated by Lockheed Martin, is 3.05 m (10 ft) in diameter and 10.0 m (33-ft) long. It uses liquid hydrogen (LH2) and liquid oxygen (LO2) propellants

A Russian cargo plane, the Antenov 124, arrives at Cape Canaveral Air Force skid strip to deliver the Atlas IIA/Centaur rocket scheduled to launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Visible is the Centaur upper stage, manufactured and operated by Lockheed Martin. The Centaur vehicle is 3.05 m (10 ft) in diameter and 10.0 m (33-ft) long. It uses liquid hydrogen (LH2) and liquid oxygen (LO2) propellants
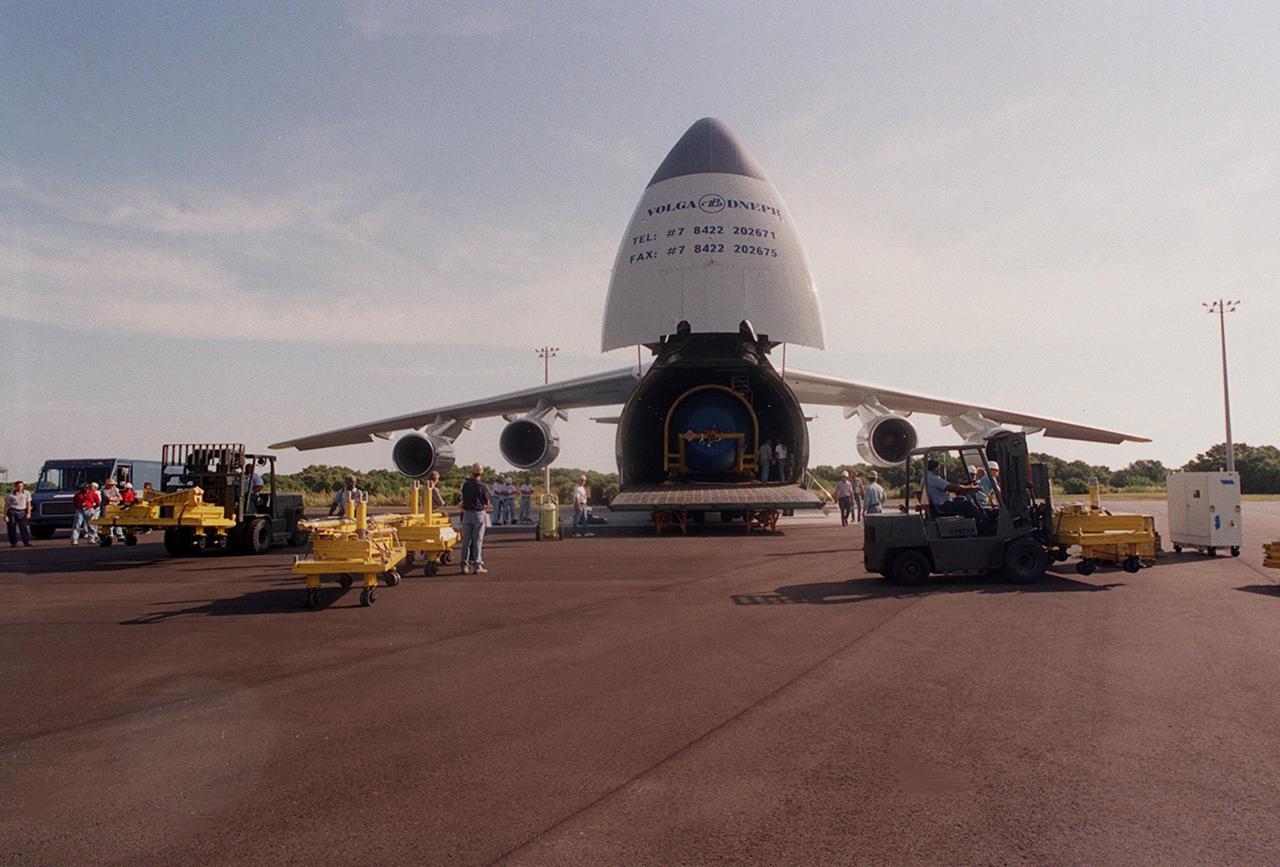

A Russian cargo plane, the Antenov 124, arrives at Cape Canaveral Air Force skid strip to deliver the Atlas IIA/Centaur rocket scheduled to launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Visible is the Centaur upper stage, manufactured and operated by Lockheed Martin. The Centaur vehicle is 3.05 m (10 ft) in diameter and 10.0 m (33-ft) long. It uses liquid hydrogen (LH2) and liquid oxygen (LO2) propellants
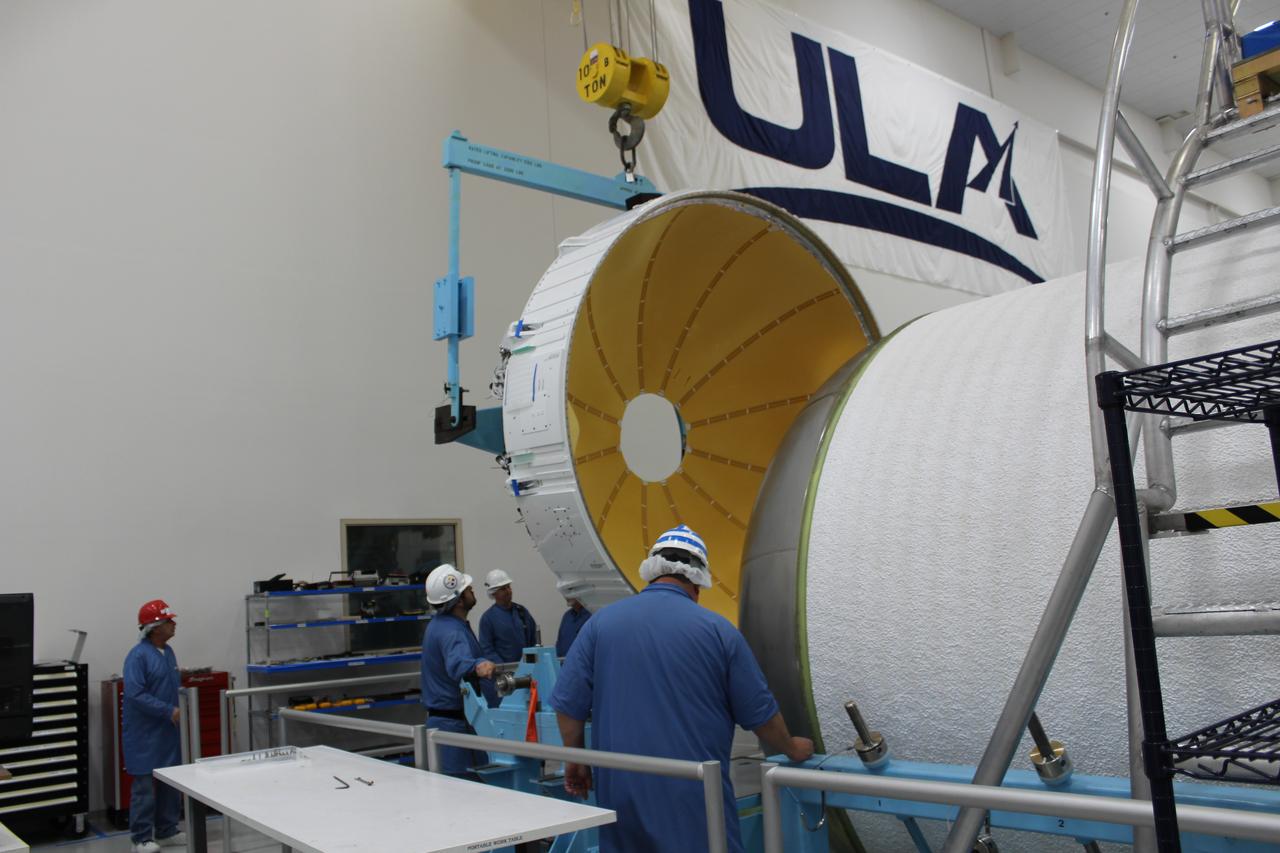

Workers assemble a United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V dual engine Centaur upper stage in ULA’s factory in Decatur, Alabama on March 29, 2019. The dual engine upper stage is being prepared for the first crew rotation mission of Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner to the International Space Station. Starliner and the Atlas V rockets that will launch the spacecraft, are key elements of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program to restore the capability to send astronauts to the space station from U.S. soil.
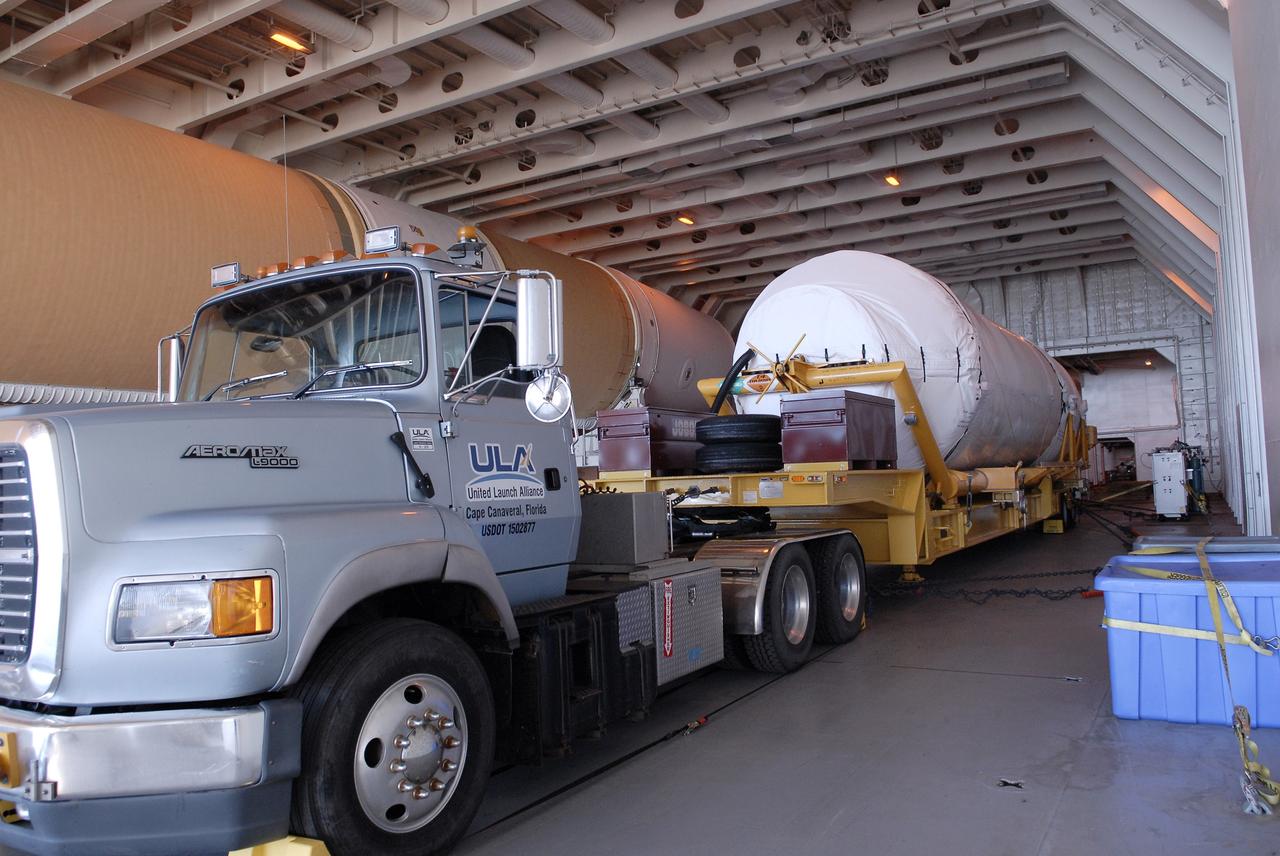

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Centaur upper stage sits on its transport trailer inside the Delta Mariner at Port Canaveral. The upper stage is destined to help launch the Radiation Belt Storm Probes, or RBSP, mission. It was removed from the ship and taken to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center, or ASOC, to begin checkout for the launch. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A truck positions a Centaur upper stage inside the hangar at the Atlas V Spaceflight Operations Center at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The upper stage will be used as part of the Atlas V rocket that will be used to launch NASA's Magnetospheric Multiscale mission. To learn about the MMS, go to http://go.nasa.gov/1GUbzxb. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
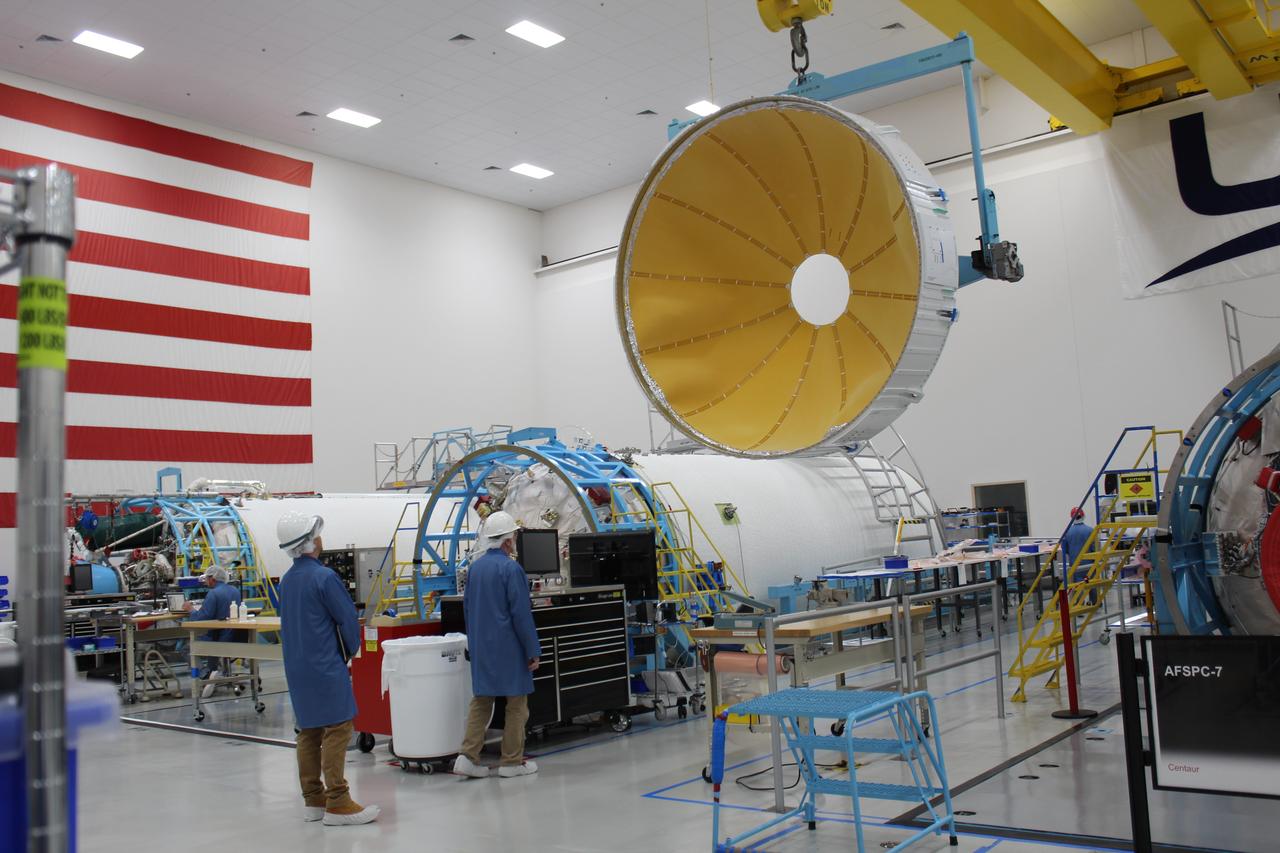

Workers assemble a United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V dual engine Centaur upper stage in ULA’s factory in Decatur, Alabama on March 29, 2019. The dual engine upper stage is being prepared for the first crew rotation mission of Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner to the International Space Station. Starliner and the Atlas V rockets that will launch the spacecraft, are key elements of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program to restore the capability to send astronauts to the space station from U.S. soil.
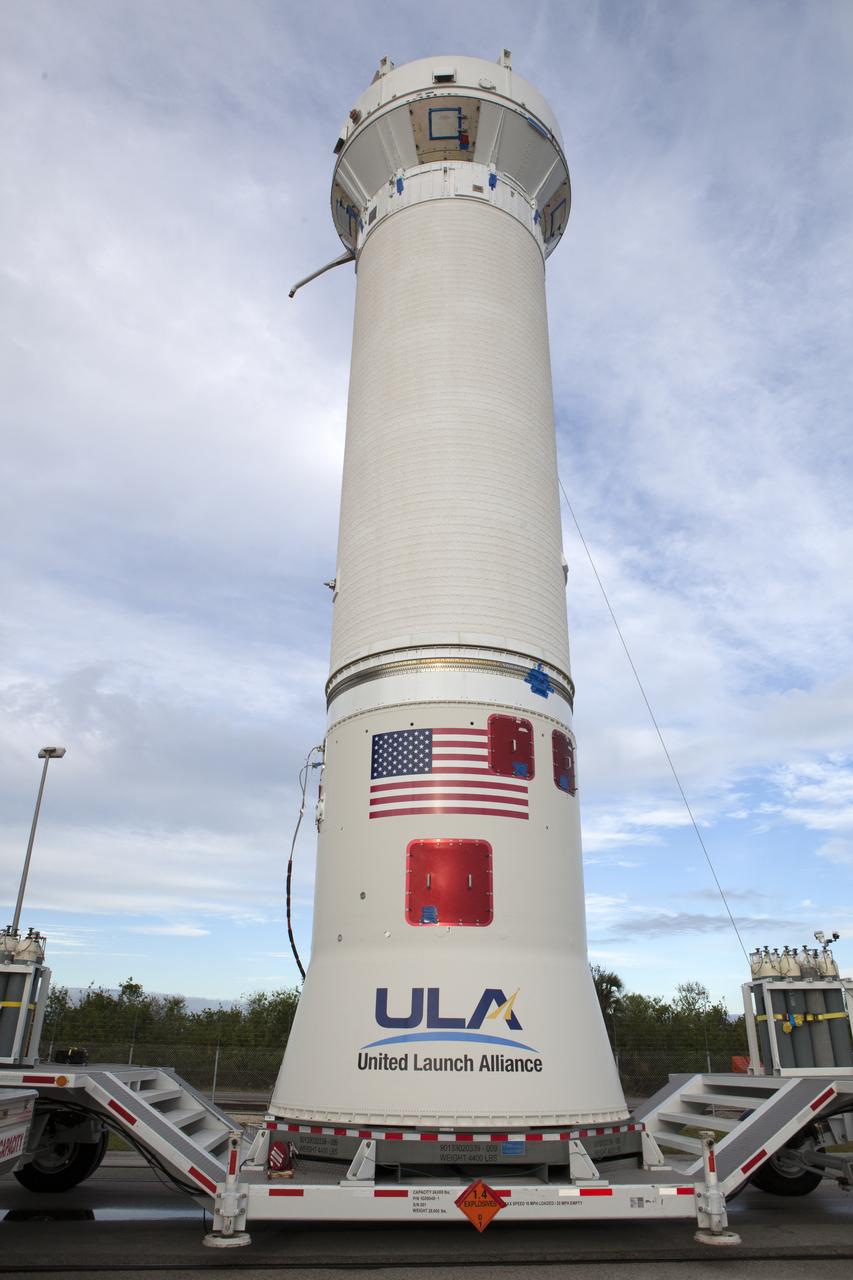

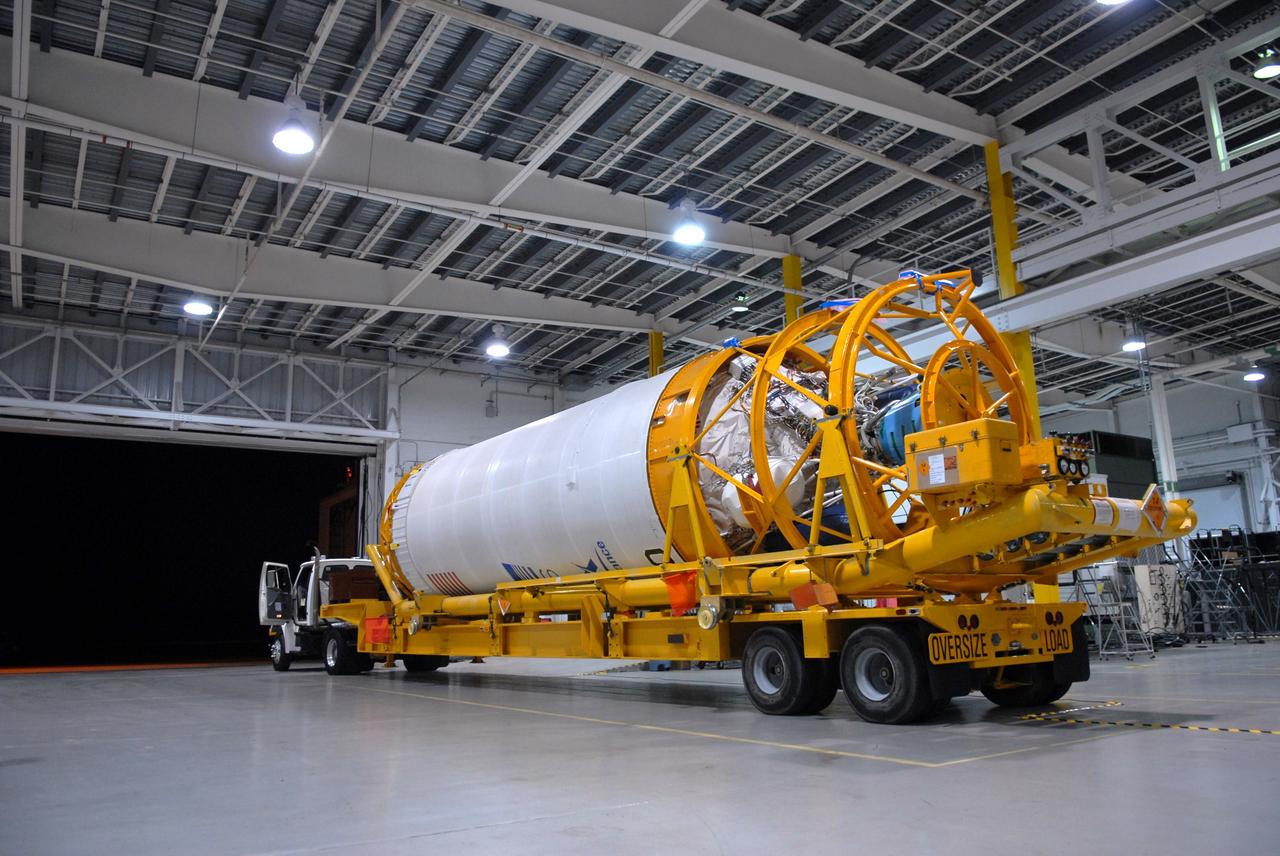
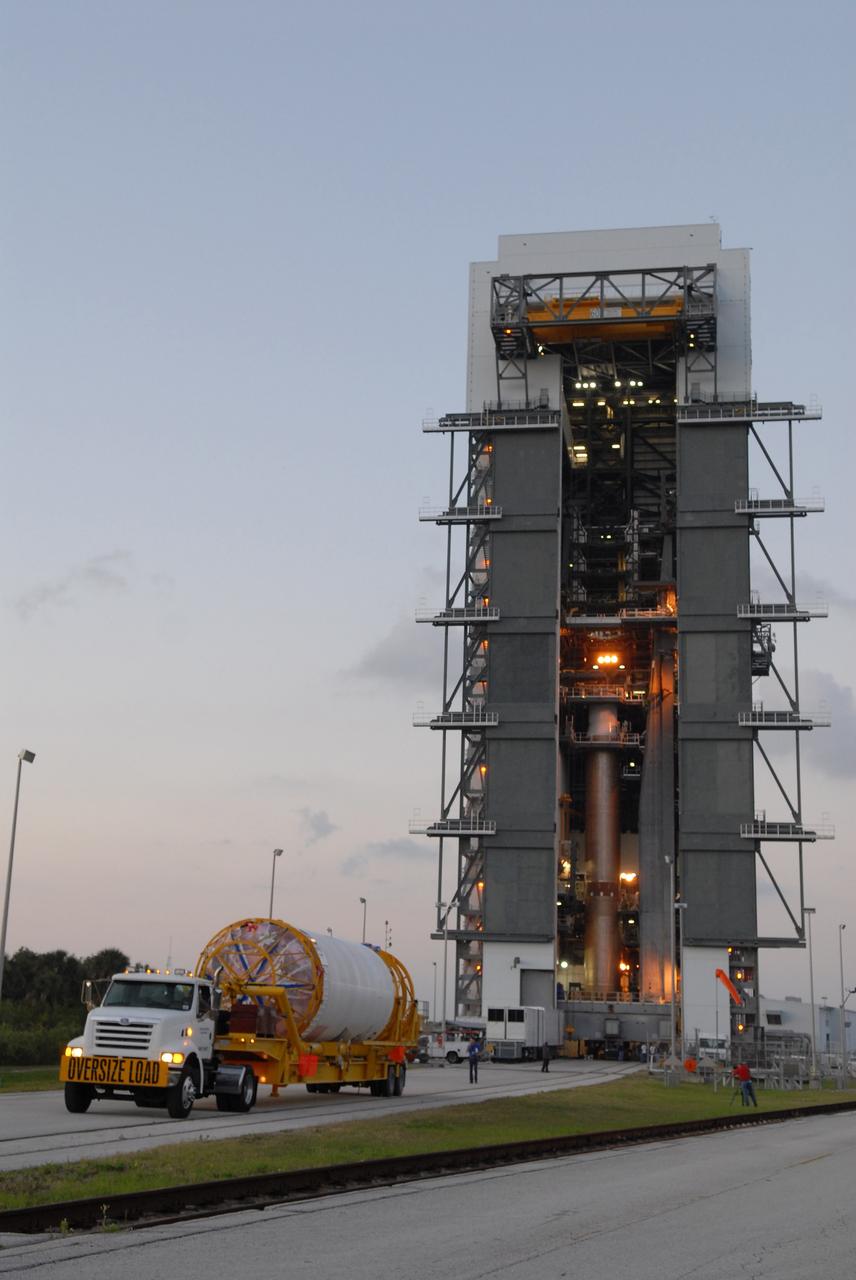
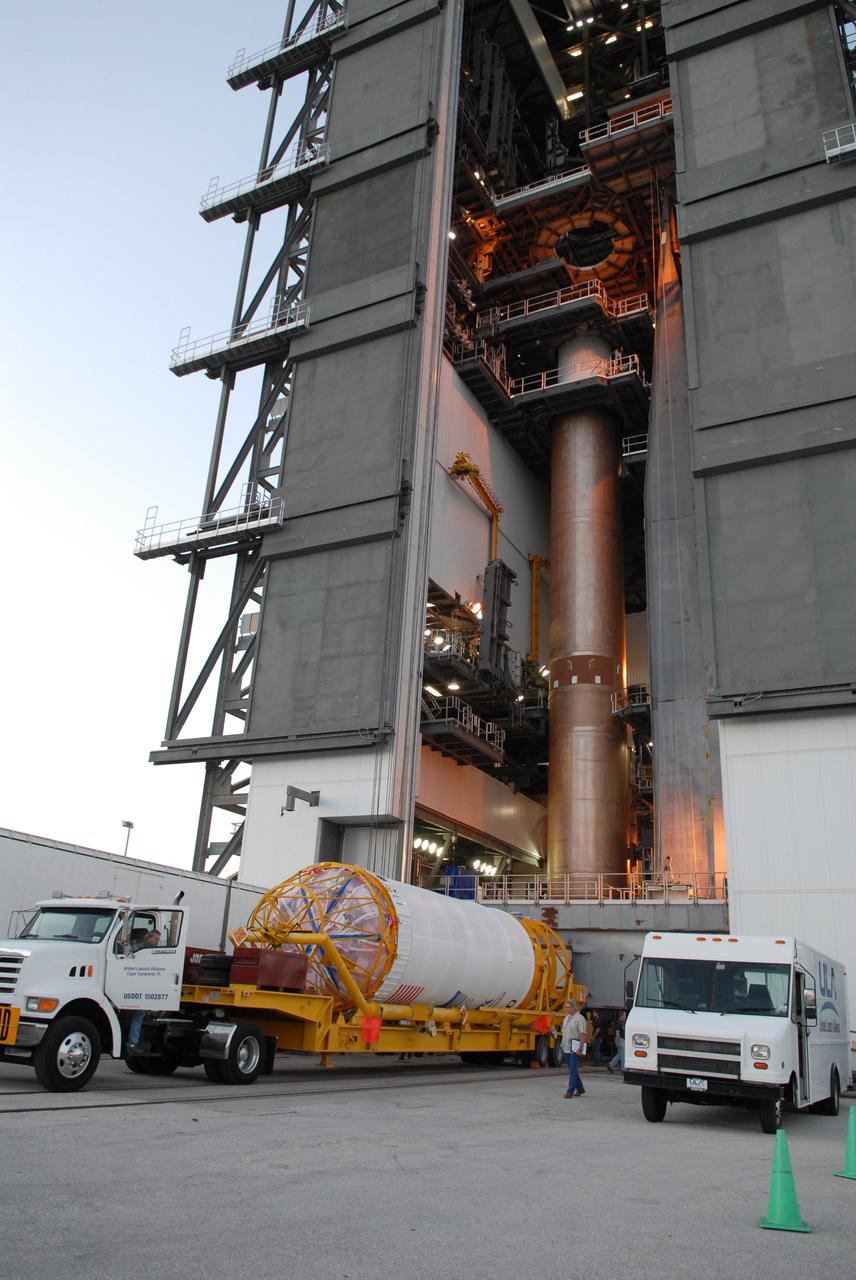
The Centaur upper stage of the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket arrives at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Centaur stage will be lifted and mated to the first stage booster. The rocket is being prepared for Orbital ATK's seventh commercial resupply mission, CRS-7, to the International Space Station. Orbital ATK's CYGNUS pressurized cargo module is scheduled to launch atop ULA's Atlas V rocket from Pad 41 on March 19, 2017. CYGNUS will deliver 7,600 pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
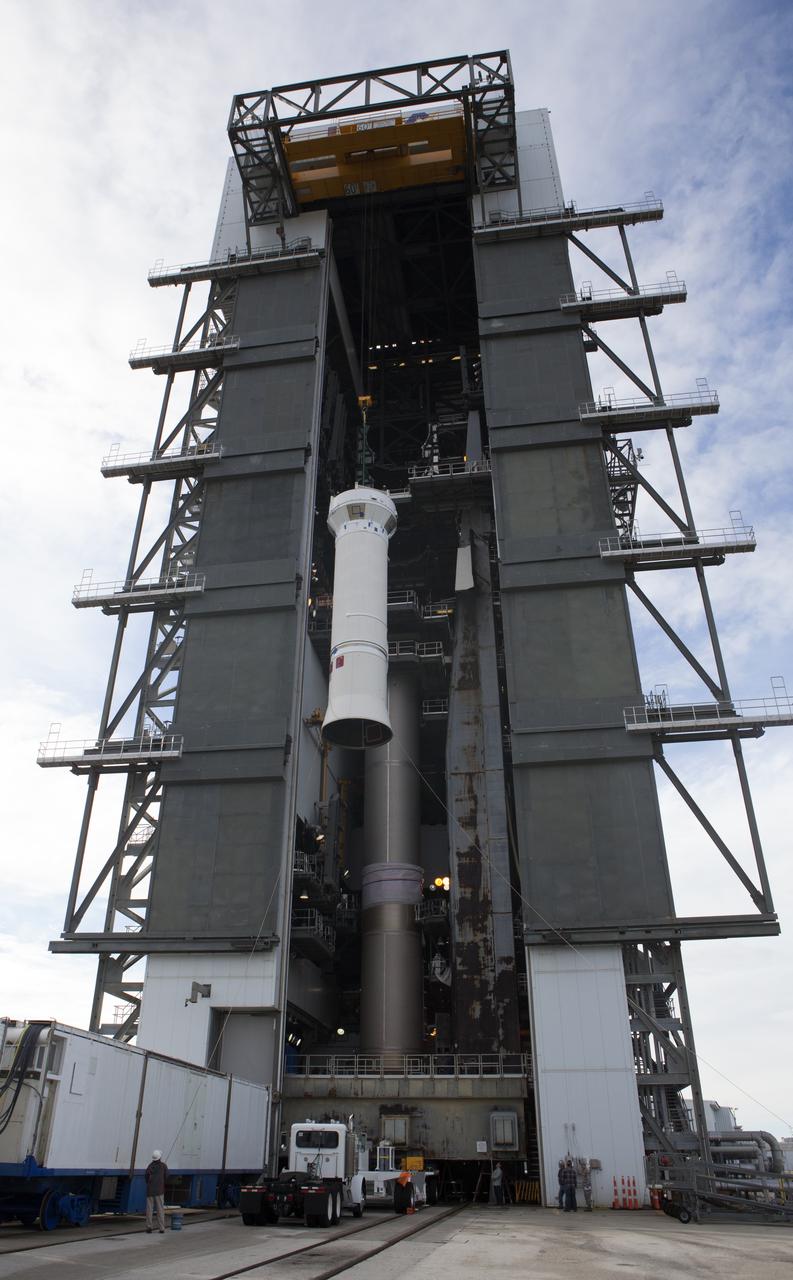

The Centaur upper stage of the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket is lifted up by crane at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Centaur stage will be lifted inside the VIF and lowered for mating to the first stage booster. The rocket is being prepared for Orbital ATK's seventh commercial resupply mission, CRS-7, to the International Space Station. Orbital ATK's CYGNUS pressurized cargo module is scheduled to launch atop ULA's Atlas V rocket from Pad 41 on March 19, 2017. CYGNUS will deliver 7,600 pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.

Technicians with United Launch Alliance (ULA) assist as a crane lifts the Centaur upper stage of the ULA Atlas V rocket up inside the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Centaur stage will be mated to the first stage booster. The rocket is being prepared for Orbital ATK's seventh commercial resupply mission, CRS-7, to the International Space Station. Orbital ATK's CYGNUS pressurized cargo module is scheduled to launch atop ULA's Atlas V rocket from Pad 41 on March 19, 2017. CYGNUS will deliver 7,600 pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
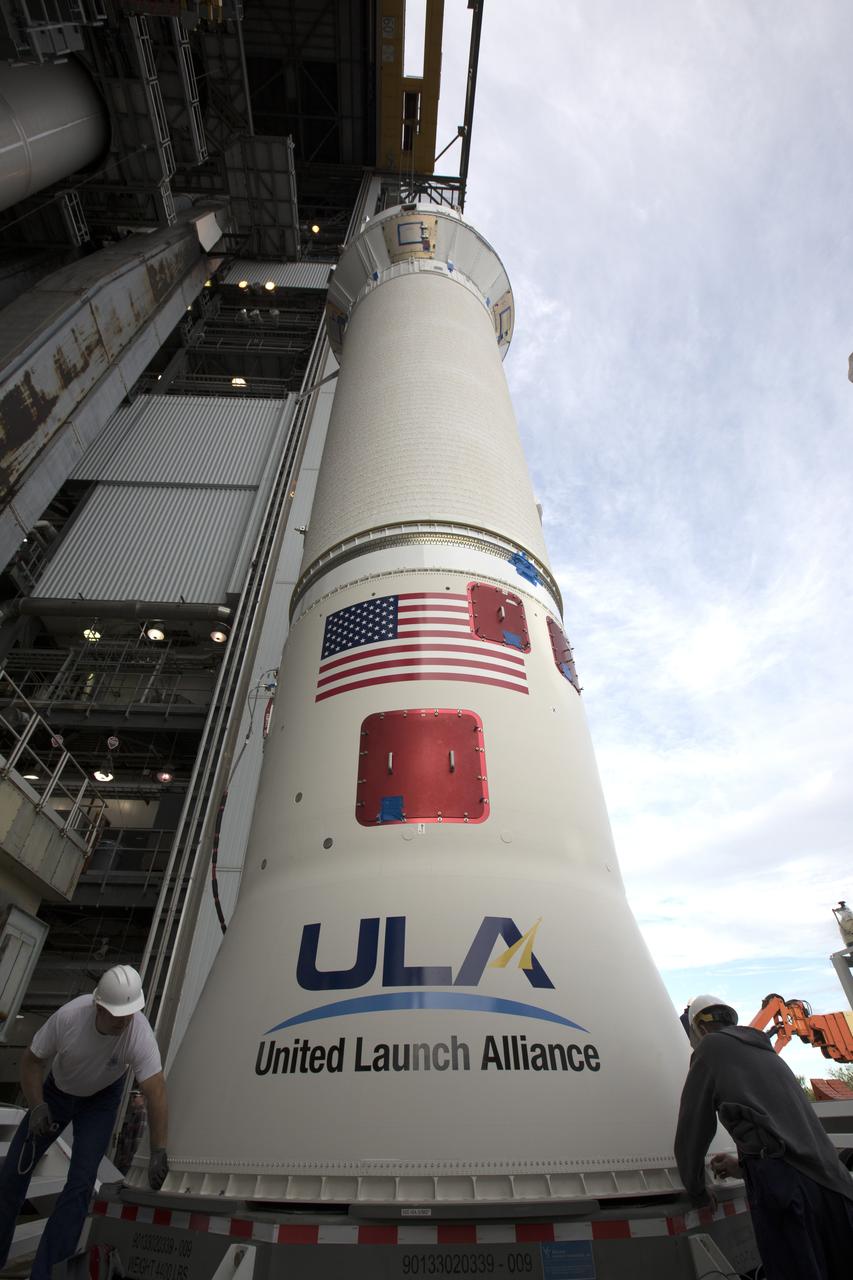

The Centaur upper stage of the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket arrives at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Centaur stage will be lifted and mated to the first stage booster. The rocket is being prepared for Orbital ATK's seventh commercial resupply mission, CRS-7, to the International Space Station. Orbital ATK's CYGNUS pressurized cargo module is scheduled to launch atop ULA's Atlas V rocket from Pad 41 on March 19, 2017. CYGNUS will deliver 7,600 of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
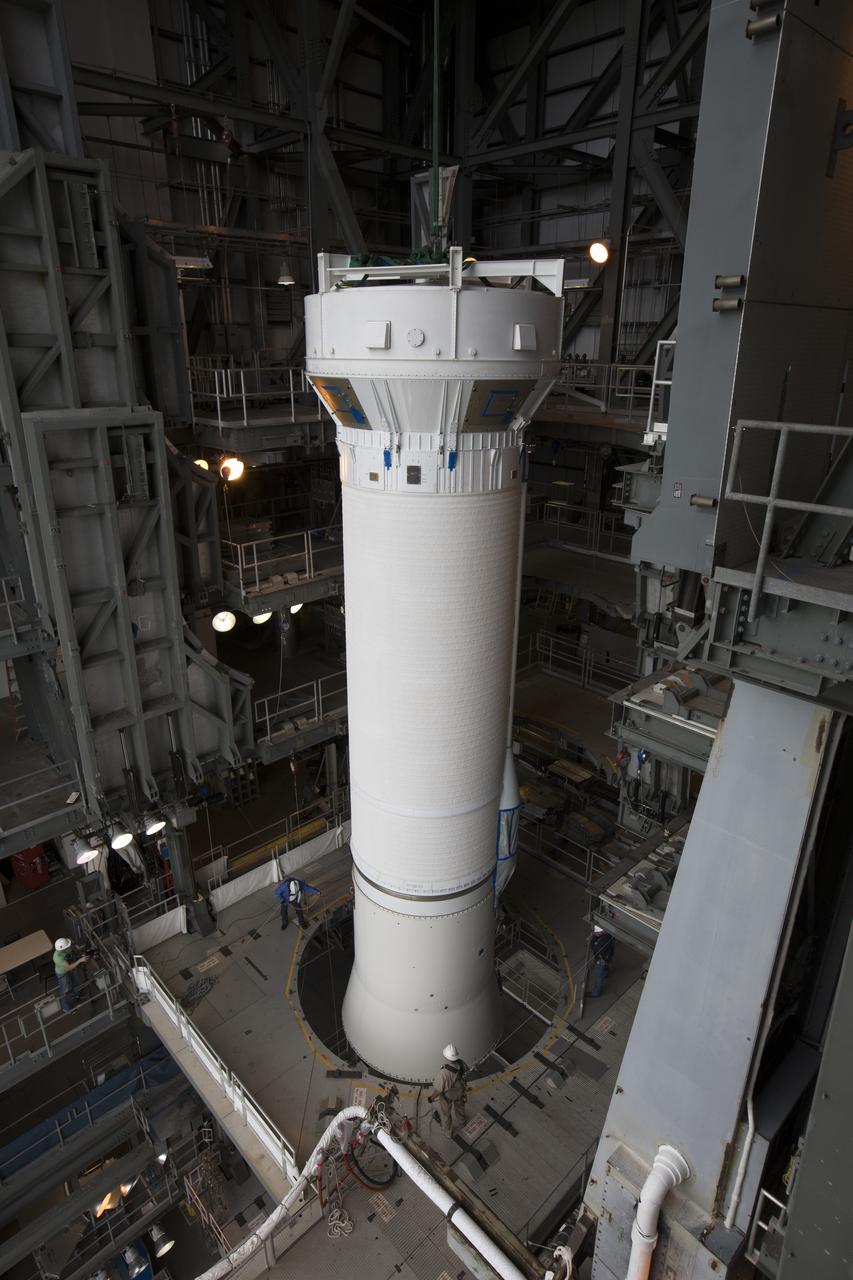

The Centaur upper stage of the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket has been lifted up inside the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Centaur stage will be lowered and mated to the first stage booster. The rocket is being prepared for Orbital ATK's seventh commercial resupply mission, CRS-7, to the International Space Station. Orbital ATK's CYGNUS pressurized cargo module is scheduled to launch atop ULA's Atlas V rocket from Pad 41 on March 19, 2017. CYGNUS will deliver 7,600 pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
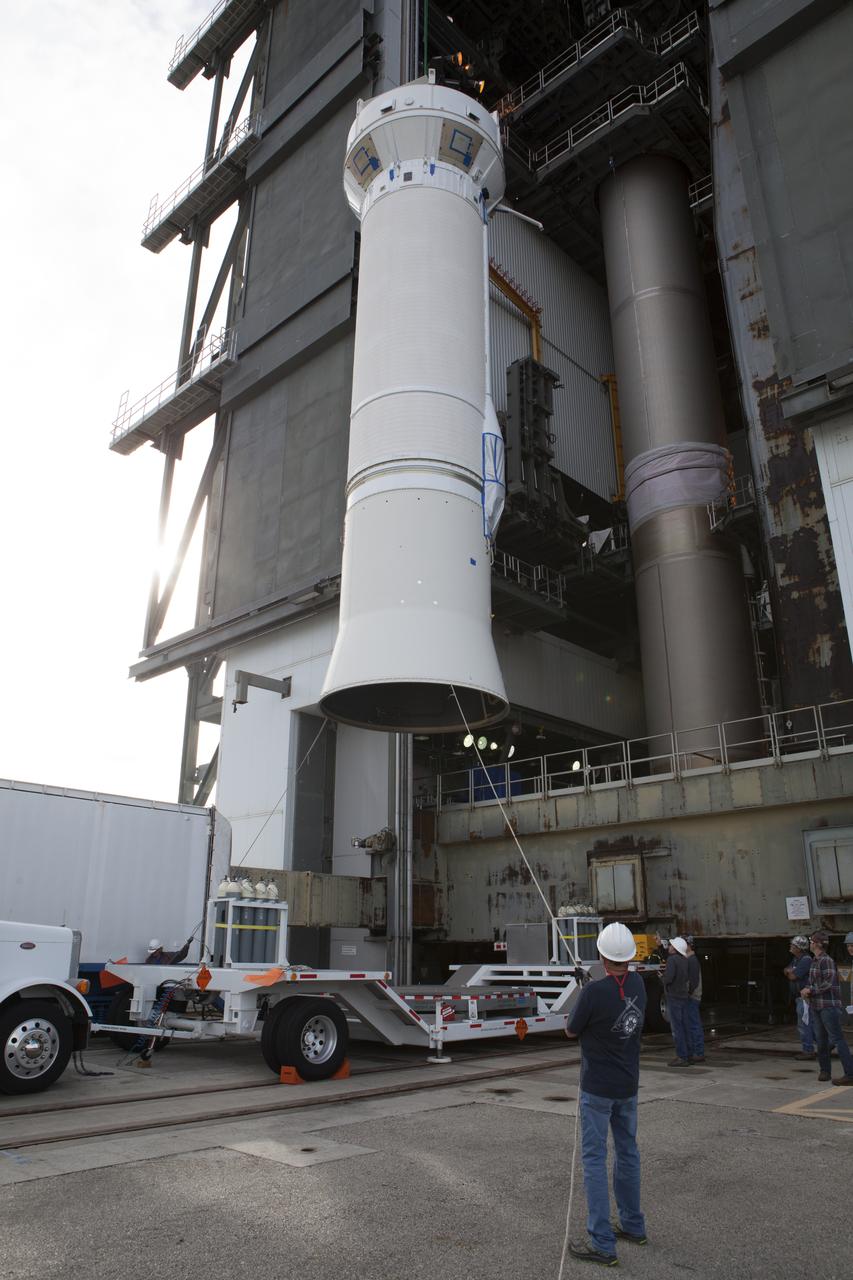

The Centaur upper stage of the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket is lifted up by crane at the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Centaur stage will be moved into the VIF, lifted up and mated to the first stage booster. The rocket is being prepared for Orbital ATK's seventh commercial resupply mission, CRS-7, to the International Space Station. Orbital ATK's CYGNUS pressurized cargo module is scheduled to launch atop ULA's Atlas V rocket from Pad 41 on March 19, 2017. CYGNUS will deliver 7,600 pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
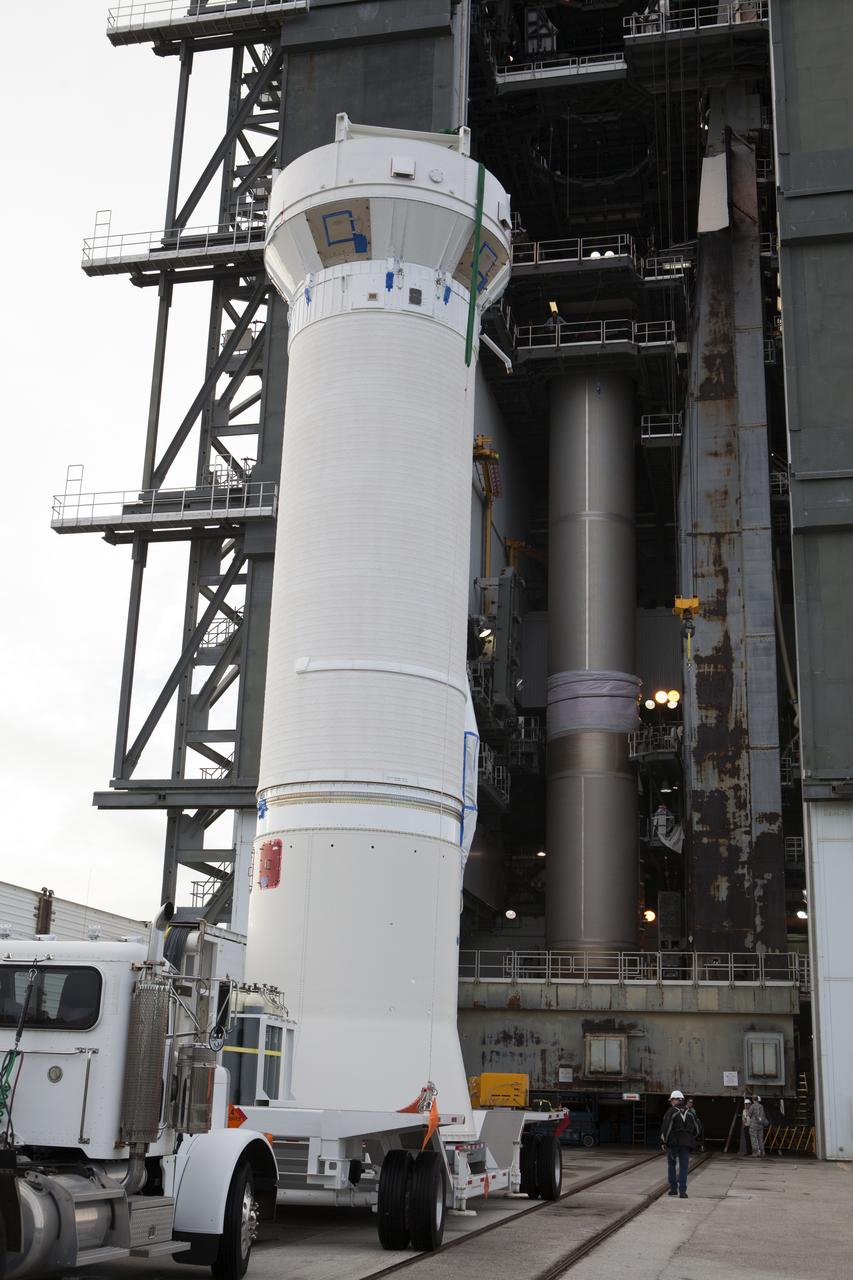

The Centaur upper stage of the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket arrives at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Centaur stage will be lifted and mated to the first stage booster. The rocket is being prepared for Orbital ATK's seventh commercial resupply mission, CRS-7, to the International Space Station. Orbital ATK's CYGNUS pressurized cargo module is scheduled to launch atop ULA's Atlas V rocket from Pad 41 on March 19, 2017. CYGNUS will deliver 7,600 pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.

Technicians with United Launch Alliance (ULA) monitor the progress as a crane lifts the Centaur upper stage of the ULA Atlas V rocket up inside the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Centaur stage will be mated to the first stage booster. The rocket is being prepared for Orbital ATK's seventh commercial resupply mission, CRS-7, to the International Space Station. Orbital ATK's CYGNUS pressurized cargo module is scheduled to launch atop ULA's Atlas V rocket from Pad 41 on March 19, 2017. CYGNUS will deliver 7,600 pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
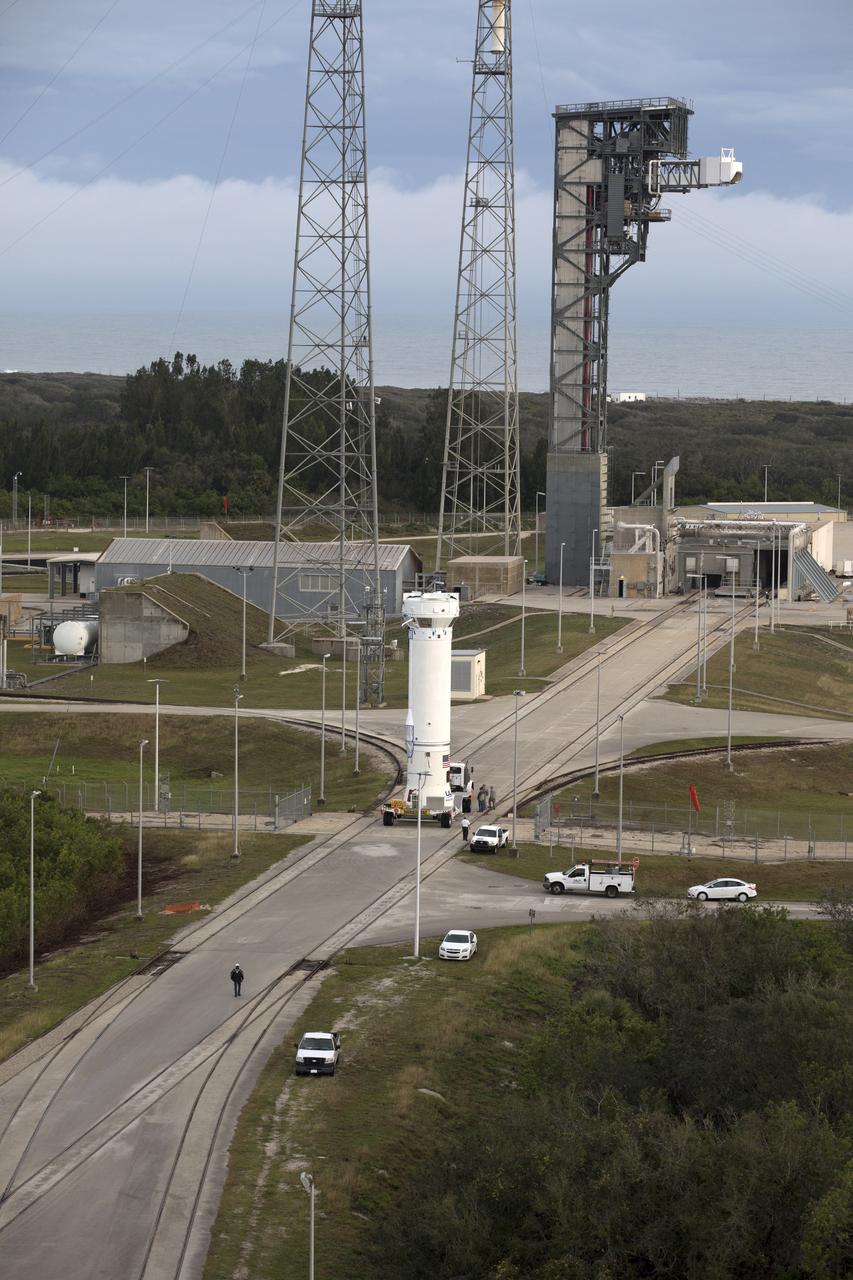

The Centaur upper stage of the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket is transported to the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Centaur stage will be lifted and mated to the first stage booster. The rocket is being prepared for Orbital ATK's seventh commercial resupply mission, CRS-7, to the International Space Station. Orbital ATK's CYGNUS pressurized cargo module is scheduled to launch atop ULA's Atlas V rocket from Pad 41 on March 19, 2017. CYGNUS will deliver 7,600 pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
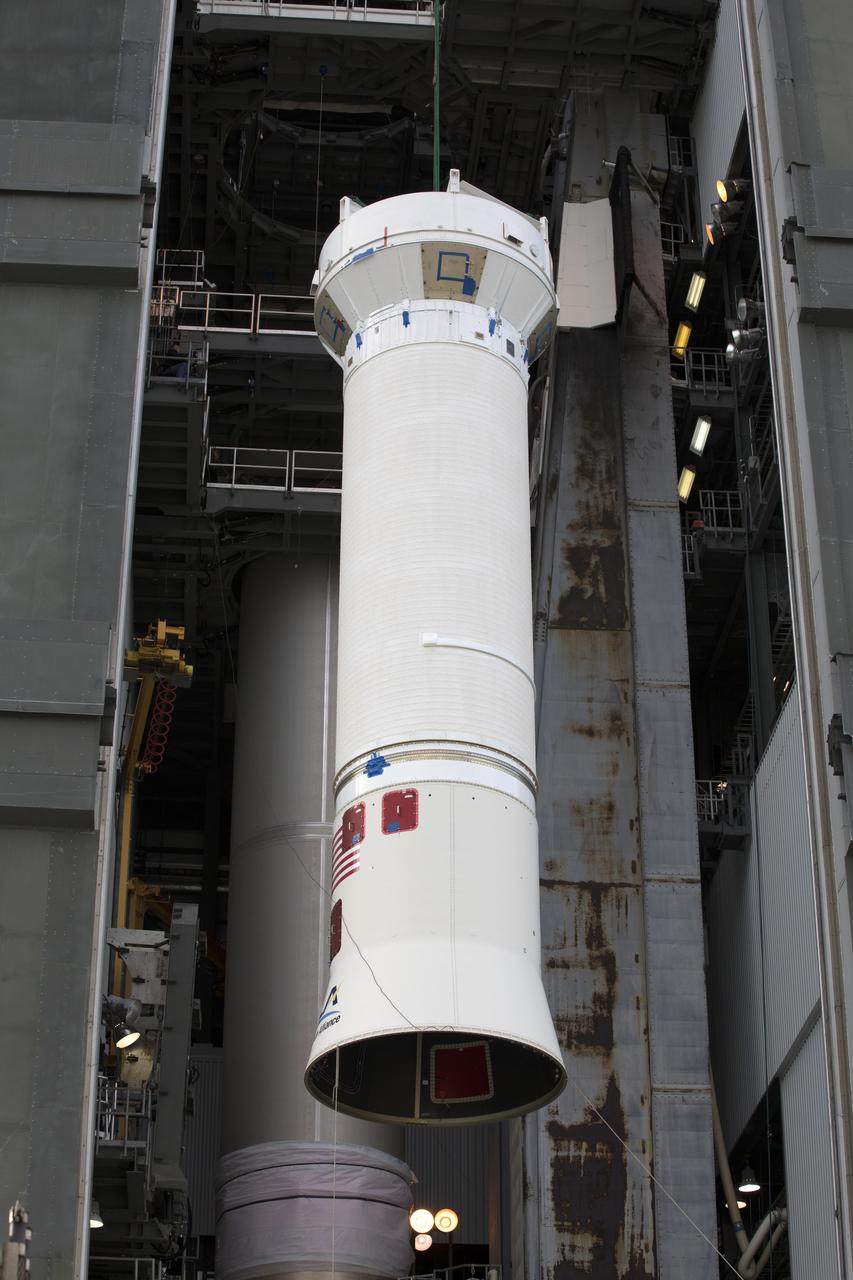

The Centaur upper stage of the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket is lifted in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Centaur stage will be mated to the first stage booster. The rocket is being prepared for Orbital ATK's seventh commercial resupply mission, CRS-7, to the International Space Station. Orbital ATK's CYGNUS pressurized cargo module is scheduled to launch atop ULA's Atlas V rocket from Pad 41 on March 19, 2017. CYGNUS will deliver 7,600 pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
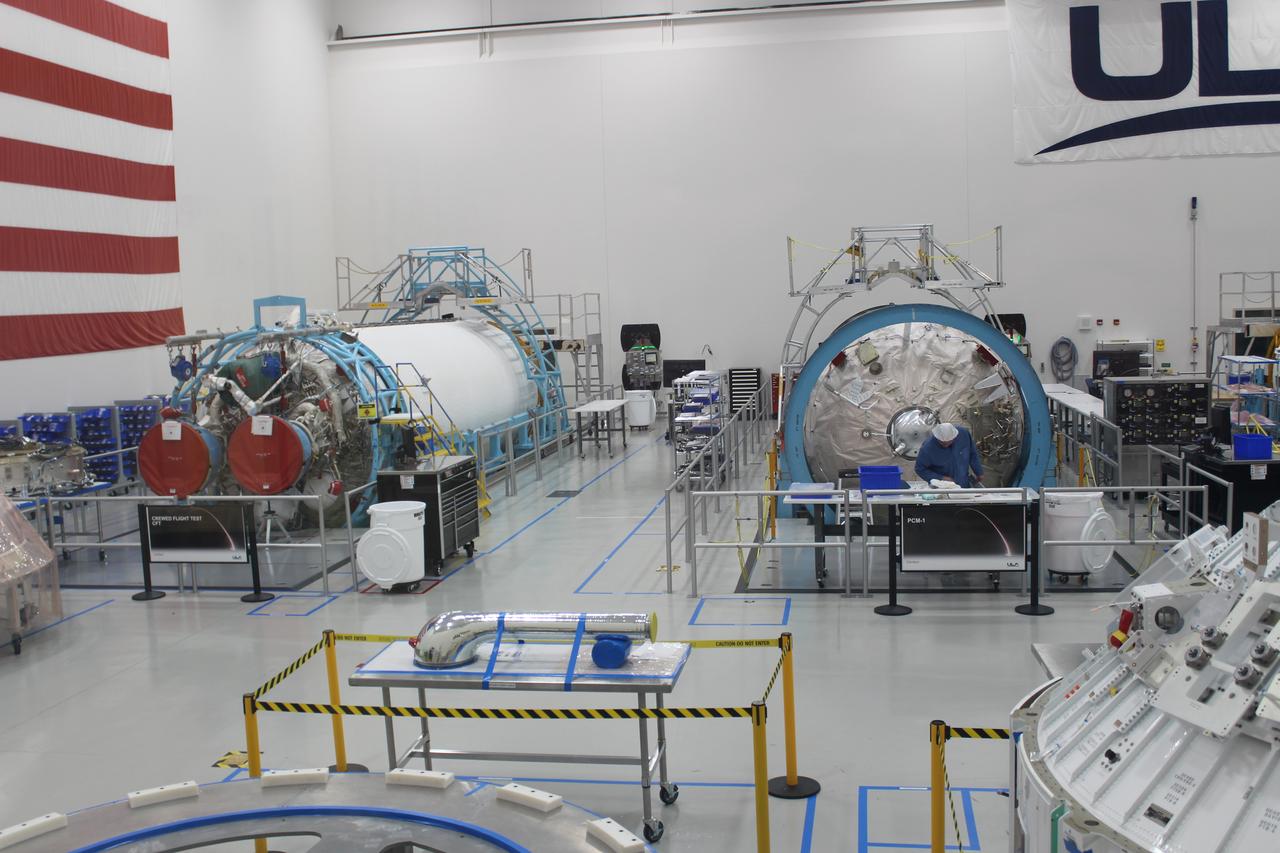

Two United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V dual engine Centaur upper stages are in production in ULA's factory in Decatur, Alabama on March 1, 2019. One is for Boeing’s Crew Flight Test on the CST-100 Starliner, and the other will be used for the first crew rotation mission on the Starliner. One of the Centaur upper stages will be assembled to the first stage booster. They will be shipped aboard the company’s Mariner cargo ship to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Starliner and the Atlas V rockets that will launch the spacecraft, are key to restoring the nation’s capability to send astronauts to the space station from U.S. soil with NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Nicole Mann, and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson will launch to the space station aboard the Starliner for the Crew Flight Test.
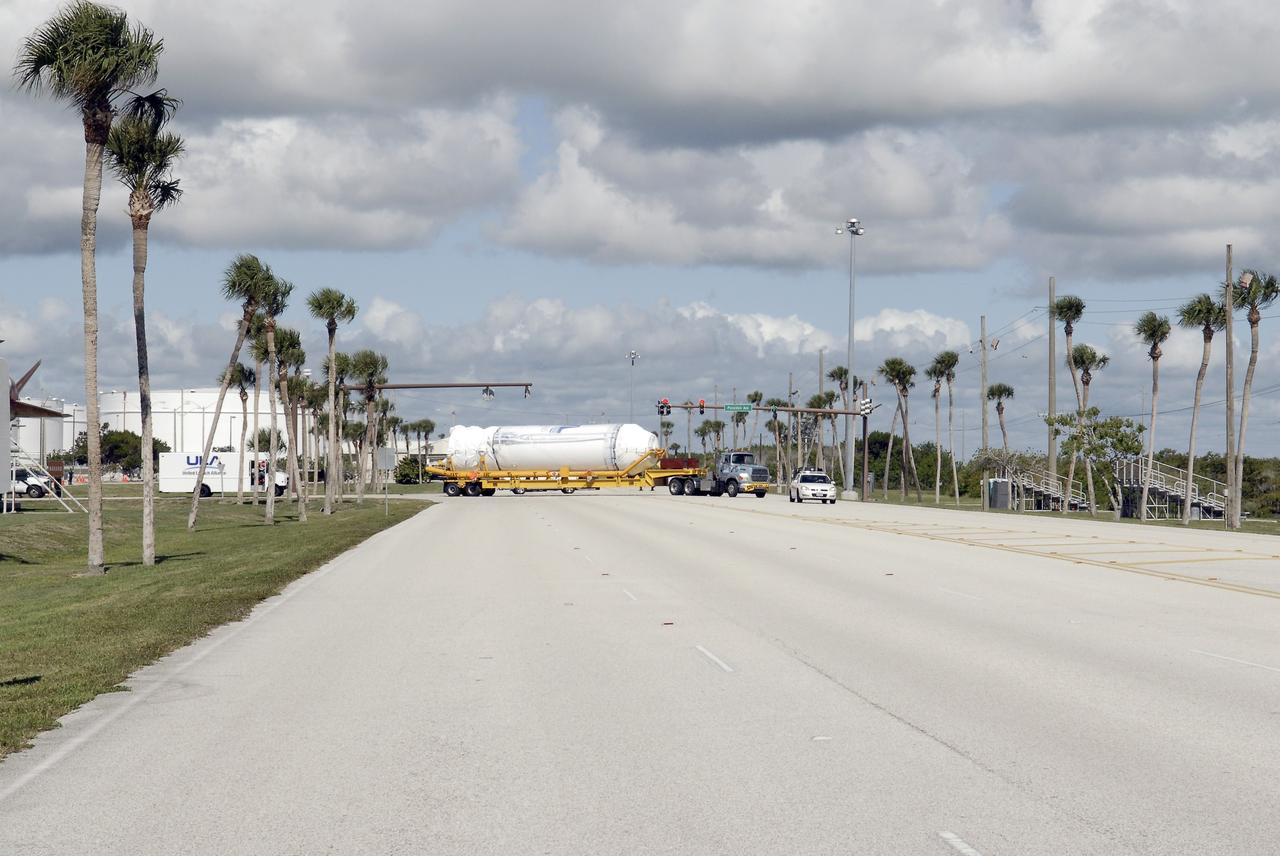

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Centaur upper stage is taken from Port Canaveral to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center, or ASOC, to begin checkout for the launch of the Radiation Belt Storm Probes, or RBSP, mission. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
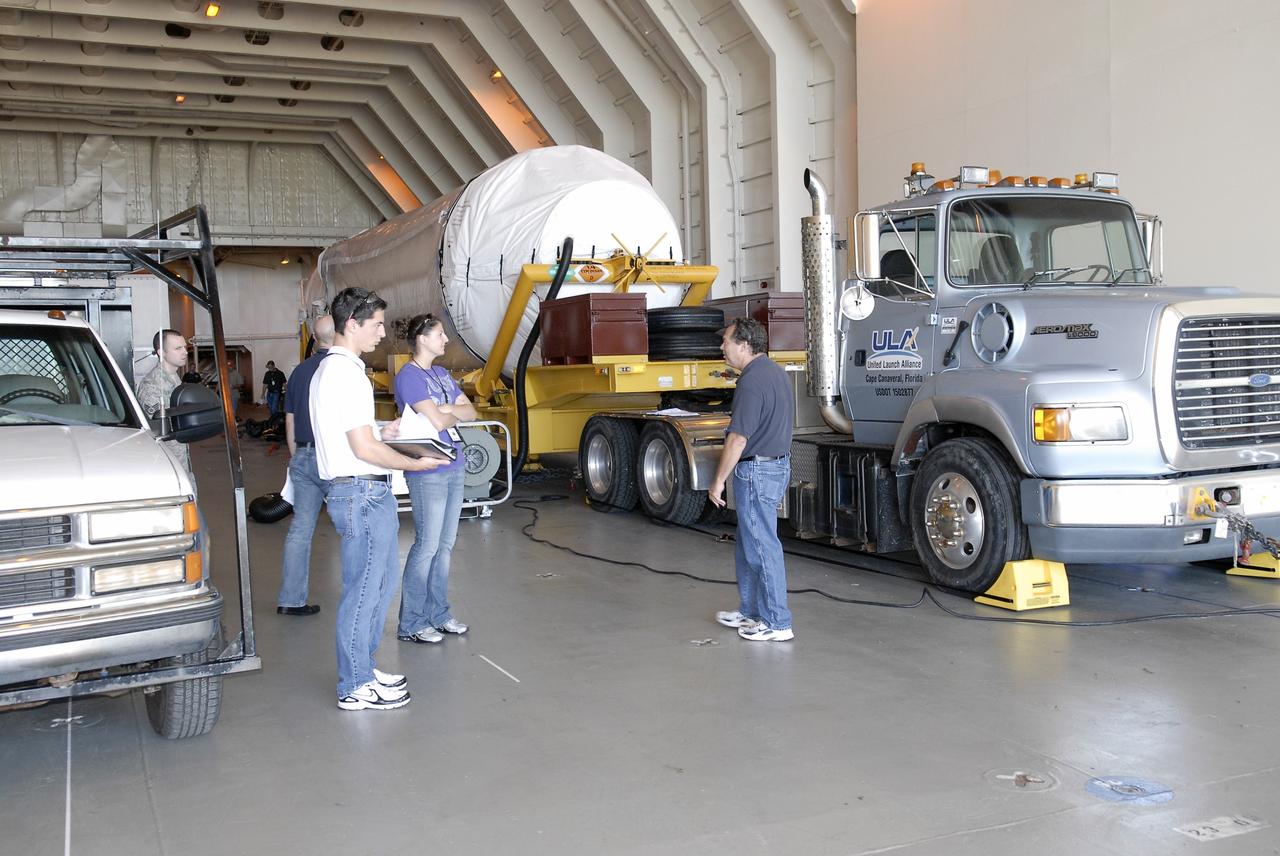

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Centaur upper stage sits on its transport trailer inside the Delta Mariner at Port Canaveral as crews prepare to move it from the ship to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center, or ASOC, to begin checkout for the launch of the Radiation Belt Storm Probes, or RBSP, mission. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
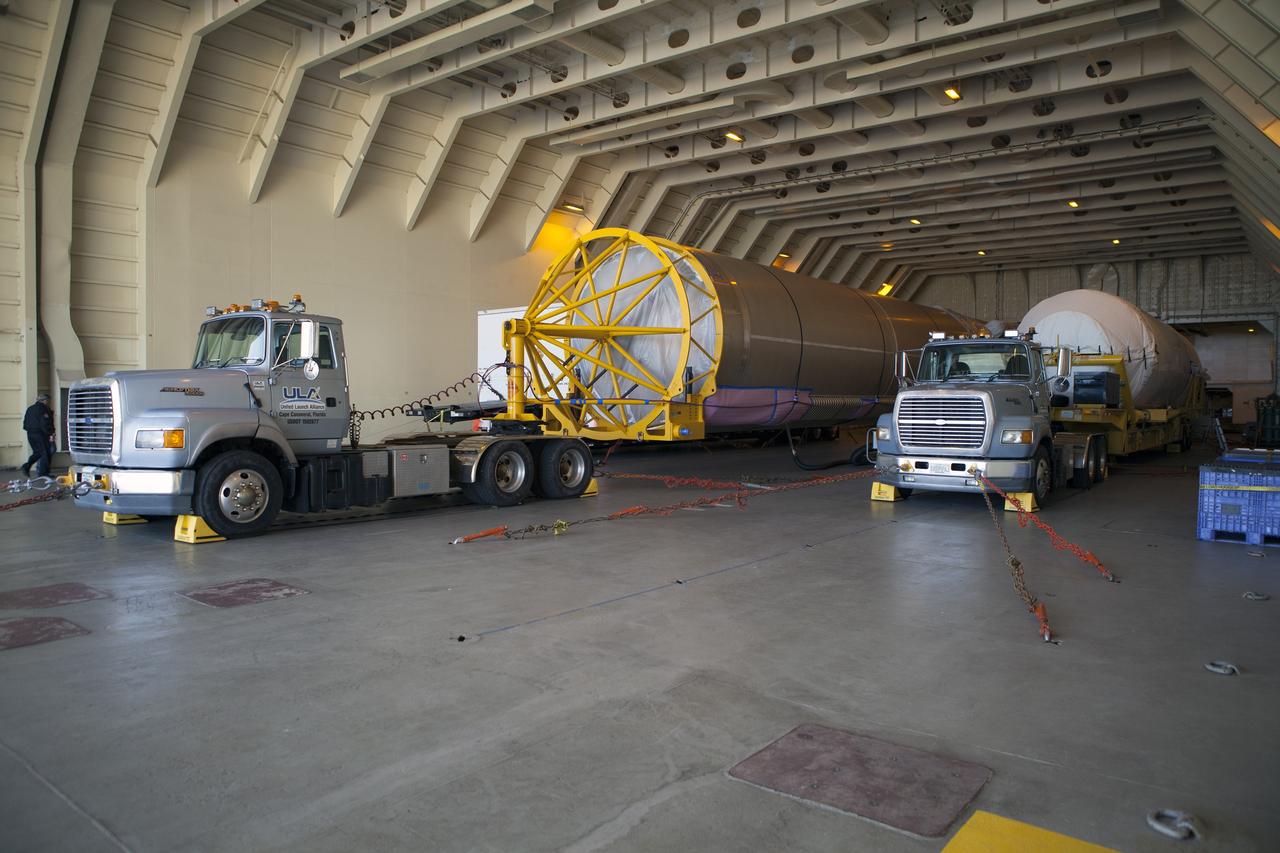

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Trucks inside the United Launch Alliance Delta Mariner prepare to transport the Atlas V rocket and Centaur upper stage that will be used to launch NASA's Magnetospheric Multiscale mission. To learn about the MMS, go to http://go.nasa.gov/1GUbzxb. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
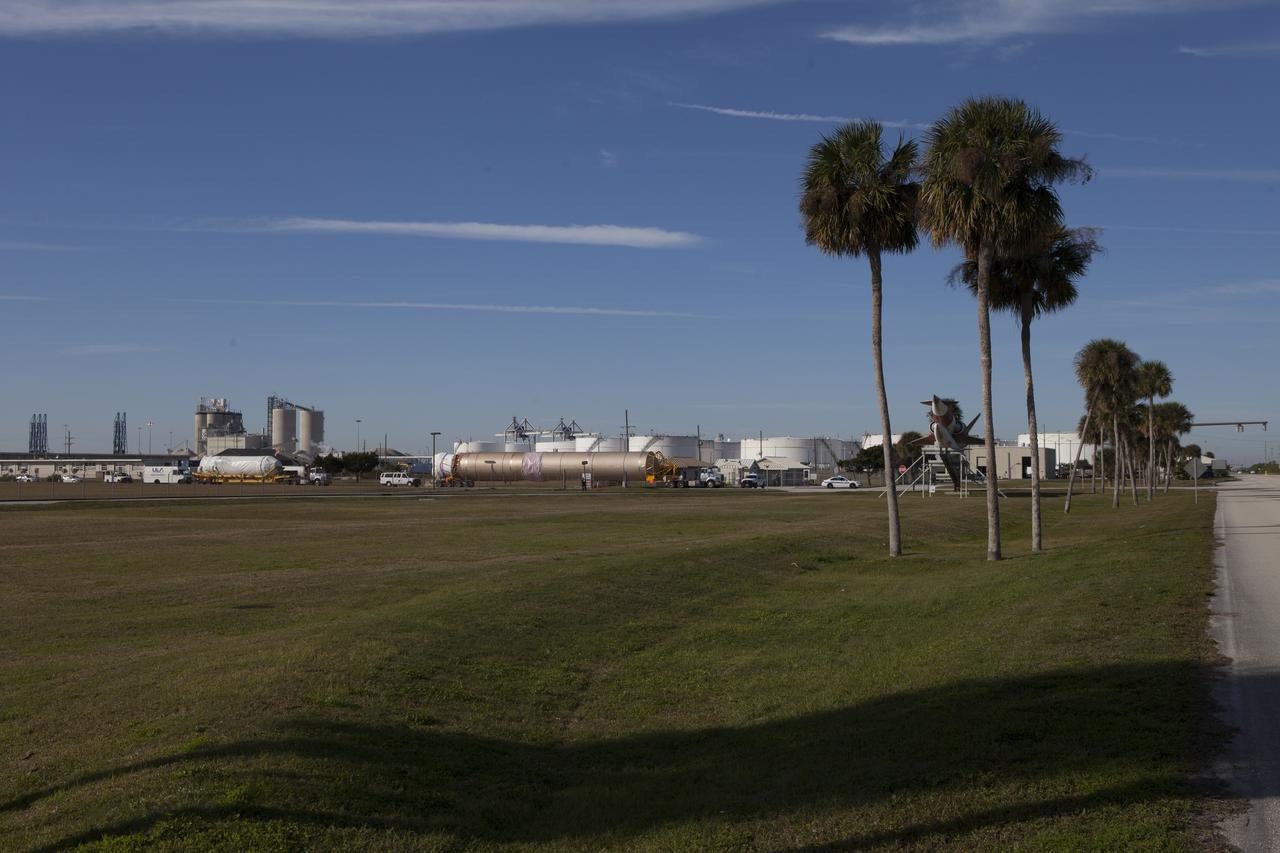

Trucks transport the Atlas V rocket and Centaur upper stage from the United Launch Alliance Delta Mariner to the Atlas V Spaceflight Operations Center at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The rocket will be used to launch NASA's Magnetospheric Multiscale mission.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Trucks inside the United Launch Alliance Delta Mariner prepare to transport the Atlas V rocket and Centaur upper stage that will be used to launch NASA's Magnetospheric Multiscale mission. To learn about the MMS, go to http://go.nasa.gov/1GUbzxb. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky

A truck begins to transport a Centaur upper stage from the United Launch Alliance Delta Mariner to the Atlas V Spaceflight Operations Center at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The rocket will be used to launch NASA's Magnetospheric Multiscale mission.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Centaur upper stage sits on its transport trailer inside the Delta Mariner at Port Canaveral as crews prepare to move it from the ship to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center, or ASOC, to begin checkout for the launch of the Radiation Belt Storm Probes, or RBSP, mission. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser

Trucks transport the Atlas V rocket and Centaur upper stage from the United Launch Alliance Delta Mariner to the Atlas V Spaceflight Operations Center at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The rocket will be used to launch NASA's Magnetospheric Multiscale mission.

After offloading of the Centaur upper stage from a Russian cargo plane, the Antenov 124, workers check the offloading of an Atlas IIA rocket. The combined Atlas IIA/Centaur will be used to launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Atlas IIA is capable of lifting payload systems weights in the 2,850 kg (6,300 lb) to 3,070 kg (6,760 lb) class to geosynchronous transfer orbit

After offloading of the Centaur upper stage from a Russian cargo plane, the Antenov 124, workers check the offloading of an Atlas IIA rocket. The combined Atlas IIA/Centaur will be used to launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Atlas IIA is capable of lifting payload systems weights in the 2,850 kg (6,300 lb) to 3,070 kg (6,760 lb) class to geosynchronous transfer orbit

After offloading of the Centaur upper stage from a Russian cargo plane, the Antenov 124, workers check the offloading of an Atlas IIA rocket. The combined Atlas IIA/Centaur will be used to launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Atlas IIA is capable of lifting payload systems weights in the 2,850 kg (6,300 lb) to 3,070 kg (6,760 lb) class to geosynchronous transfer orbit
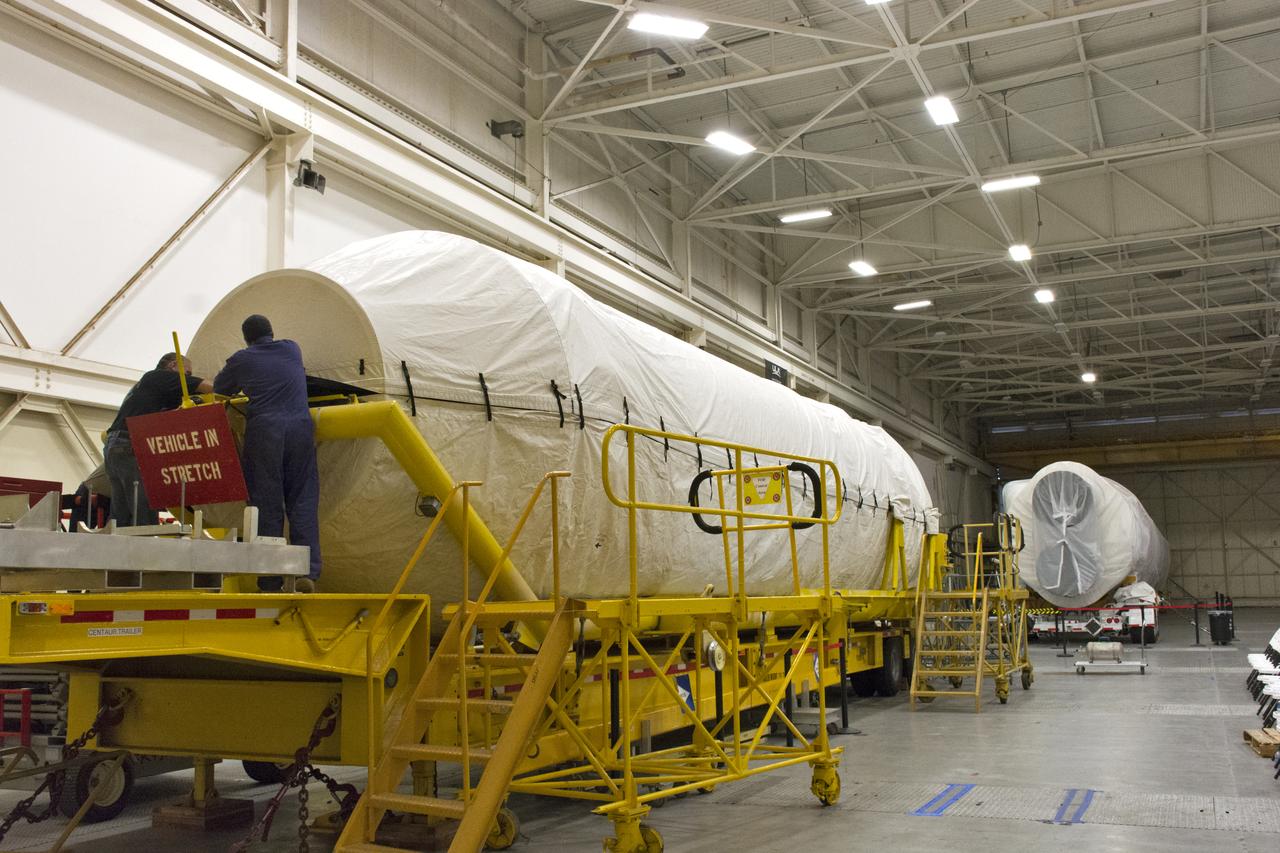

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a cover is installed on a Centaur upper stage in preparation for its transport to Space Launch Complex 3. The Centaur will be mounted atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket to boost NASA's Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, mission to land on Mars. InSight is the first mission to explore the Red Planet's deep interior. It will investigate processes that shaped the rocky planets of the inner solar system including Earth. Liftoff is scheduled for May 5, 2018.
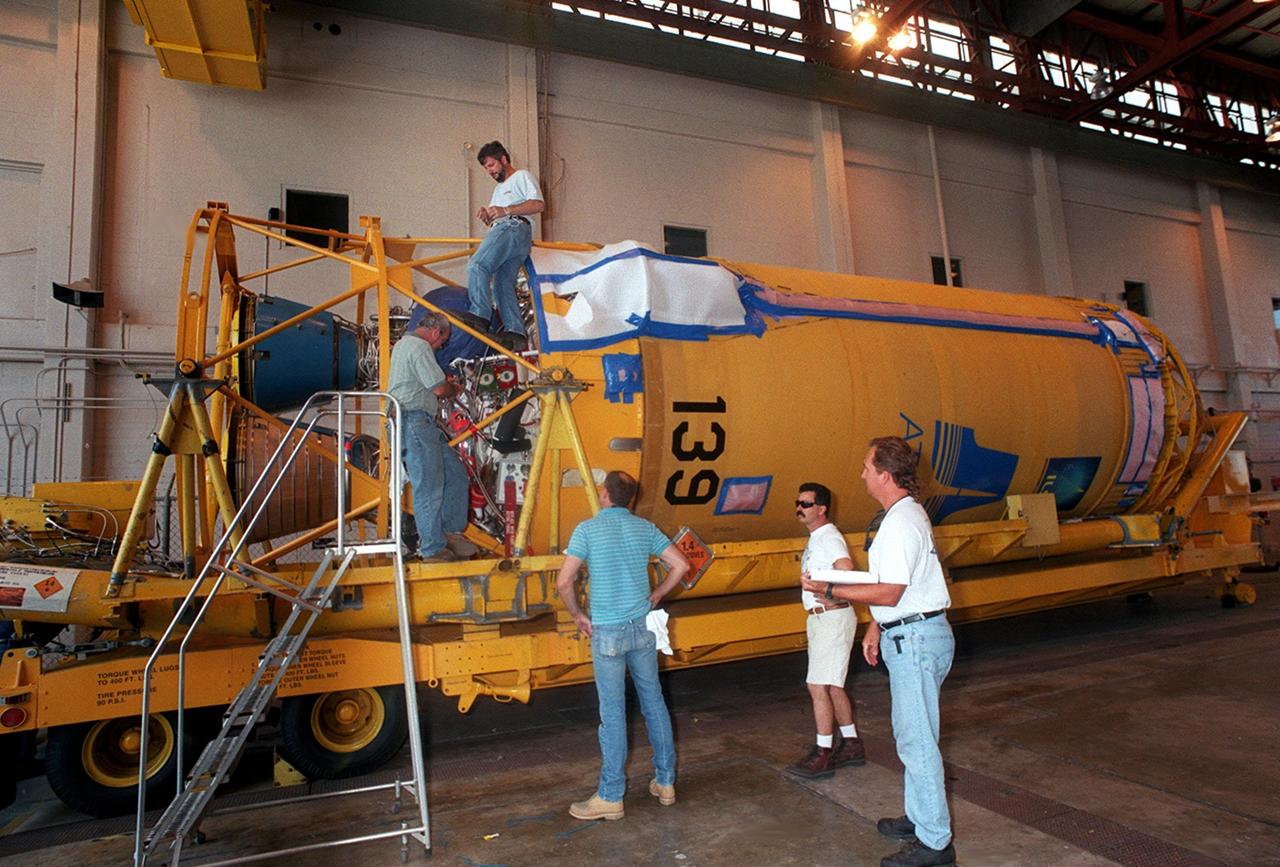

At Hangar J, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS), work is begun on the Centaur upper stage that will be used with an Atlas IIA rocket to launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from CCAFS. The Atlas/Centaur launch vehicle is manufactured and operated by Lockheed Martin. Atlas IIA is capable of lifting payload systems to geosynchronous transfer orbit
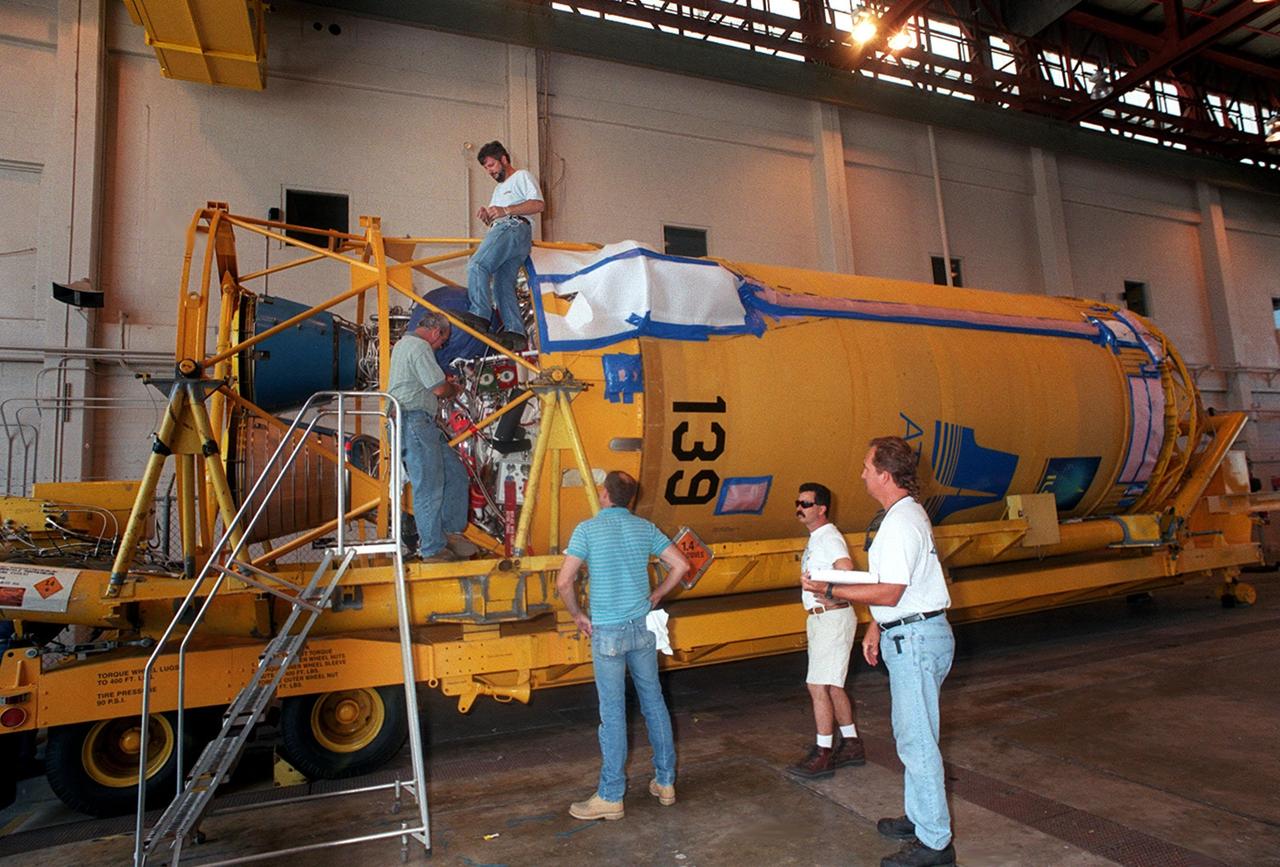

At Hangar J, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS), work is begun on the Centaur upper stage that will be used with an Atlas IIA rocket to launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from CCAFS. The Atlas/Centaur launch vehicle is manufactured and operated by Lockheed Martin. Atlas IIA is capable of lifting payload systems to geosynchronous transfer orbit
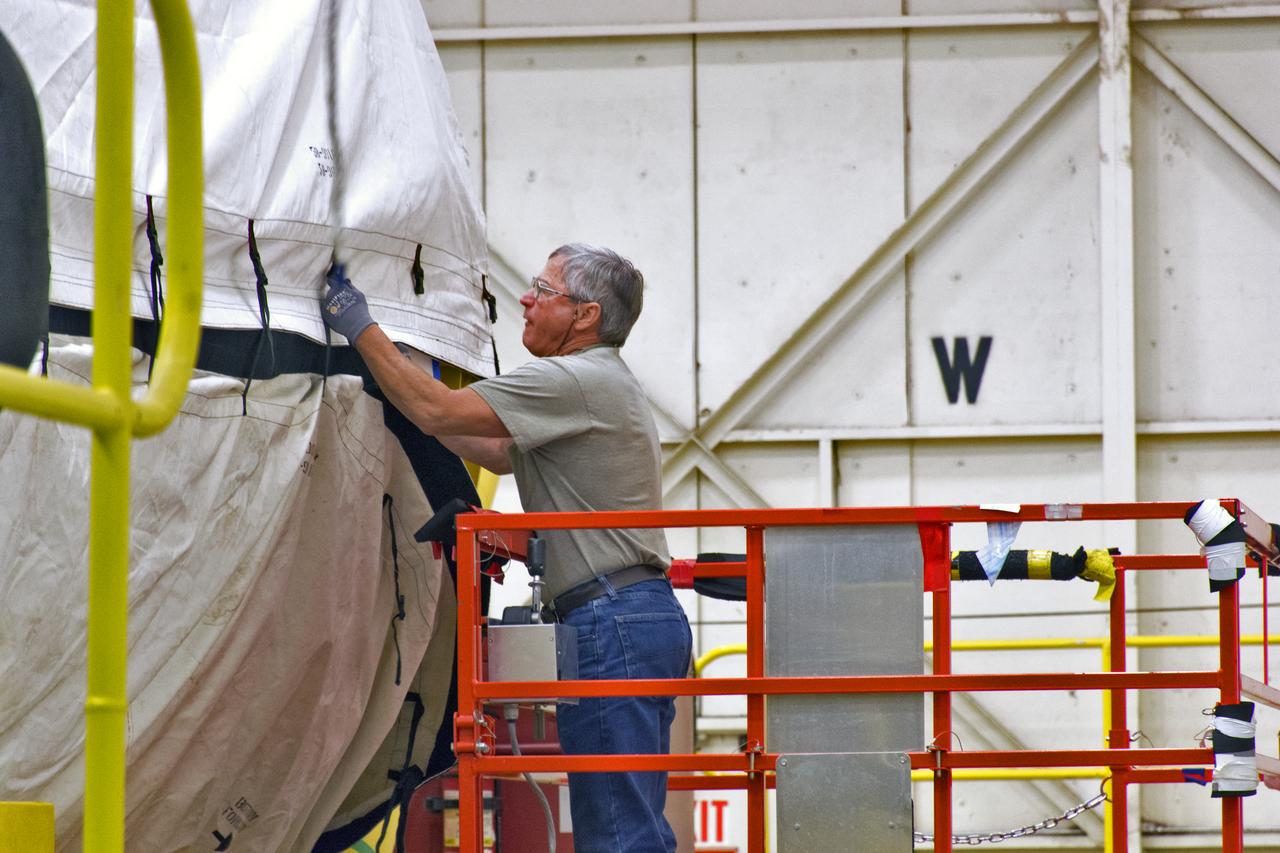

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a cover is installed on a Centaur upper stage in preparation for its transport to Space Launch Complex 3. The Centaur will be mounted atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket to boost NASA's Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, mission to land on Mars. InSight is the first mission to explore the Red Planet's deep interior. It will investigate processes that shaped the rocky planets of the inner solar system including Earth. Liftoff is scheduled for May 5, 2018.

At Hangar J, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS), work is begun on the Centaur upper stage that will be used with an Atlas IIA rocket to launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from CCAFS. The Atlas/Centaur launch vehicle is manufactured and operated by Lockheed Martin. Atlas IIA is capable of lifting payload systems to geosynchronous transfer orbit
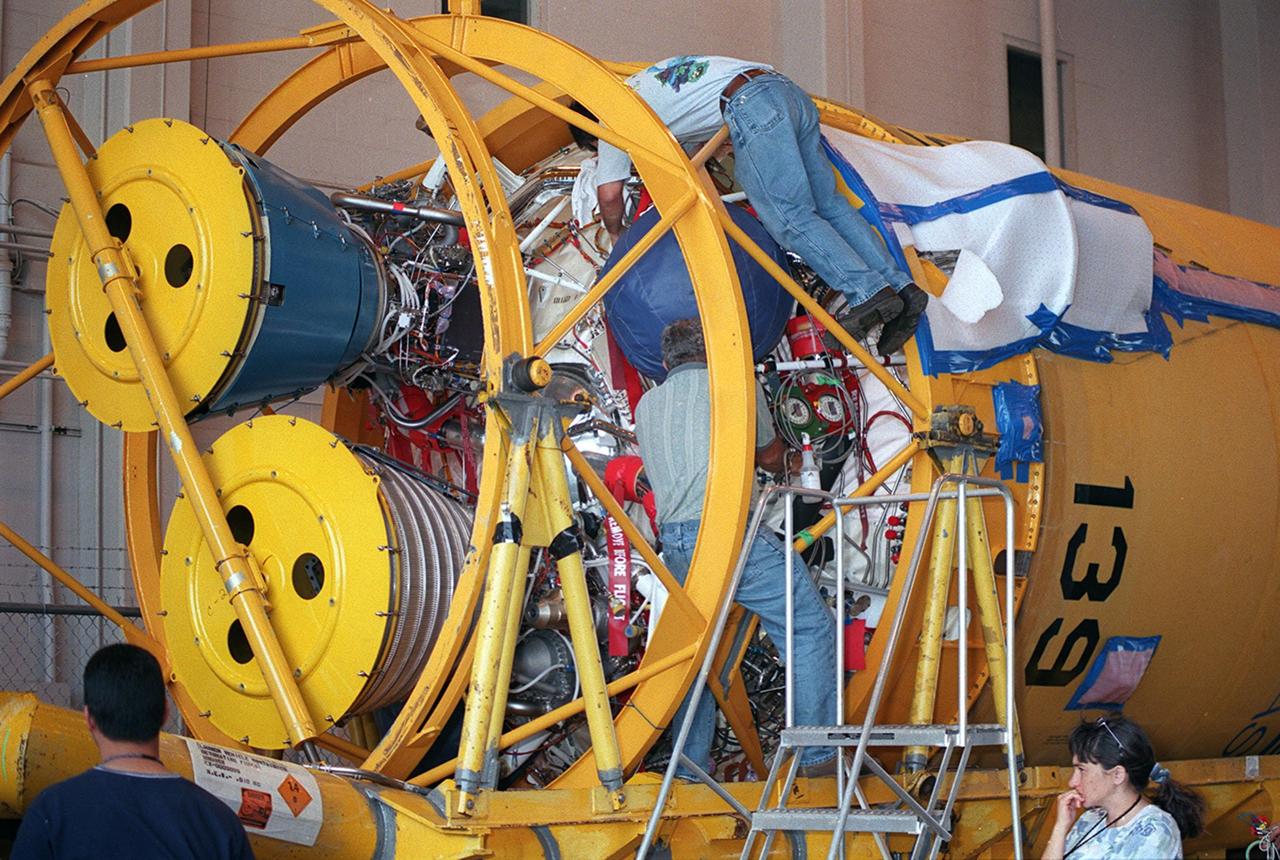

At Hangar J, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS), work is begun on the Centaur upper stage that will be used with an Atlas IIA rocket to launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from CCAFS. The Atlas/Centaur launch vehicle is manufactured and operated by Lockheed Martin. Atlas IIA is capable of lifting payload systems to geosynchronous transfer orbit
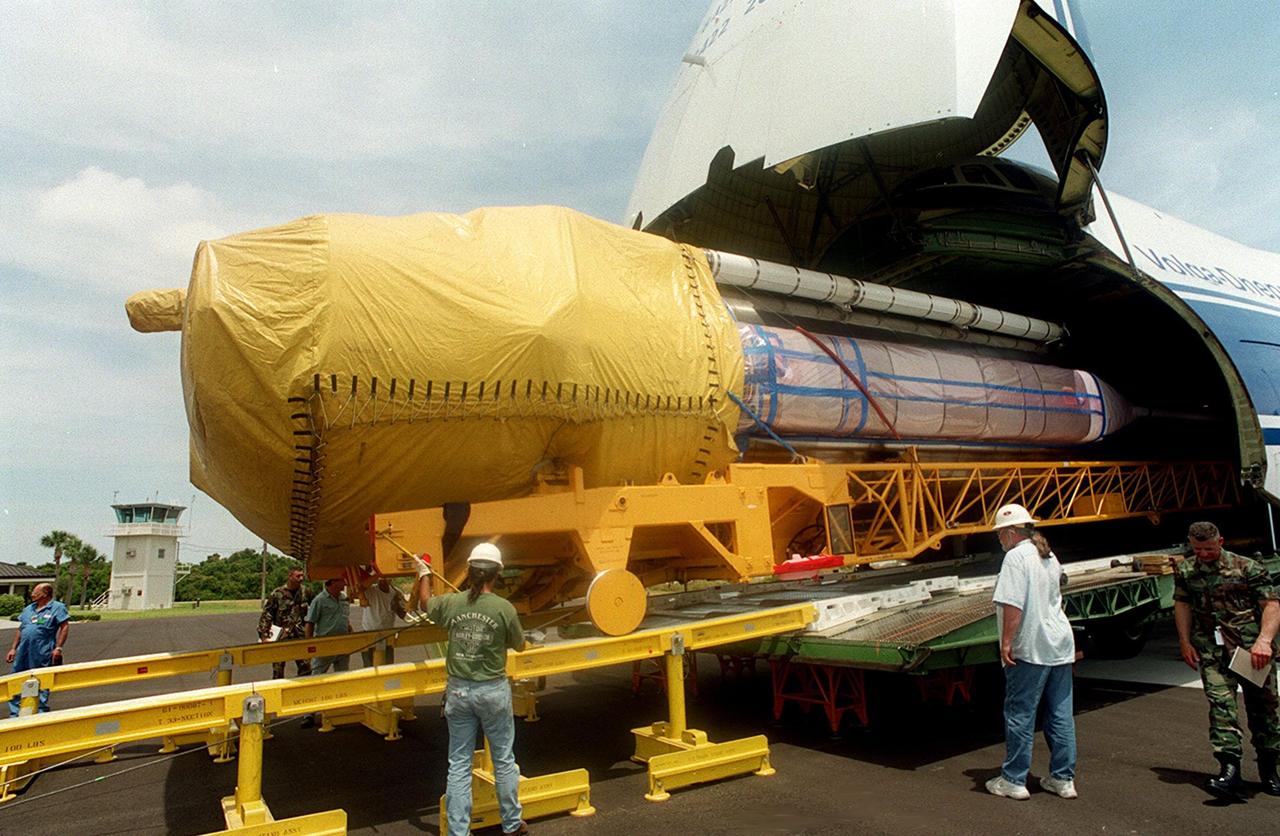

After offloading of the Centaur upper stage from a Russian cargo plane, the Antenov 124, workers check the offloading of an Atlas IIA rocket. The combined Atlas IIA/Centaur will be used to launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Atlas IIA is capable of lifting payload systems weights in the 2,850 kg (6,300 lb) to 3,070 kg (6,760 lb) class to geosynchronous transfer orbit
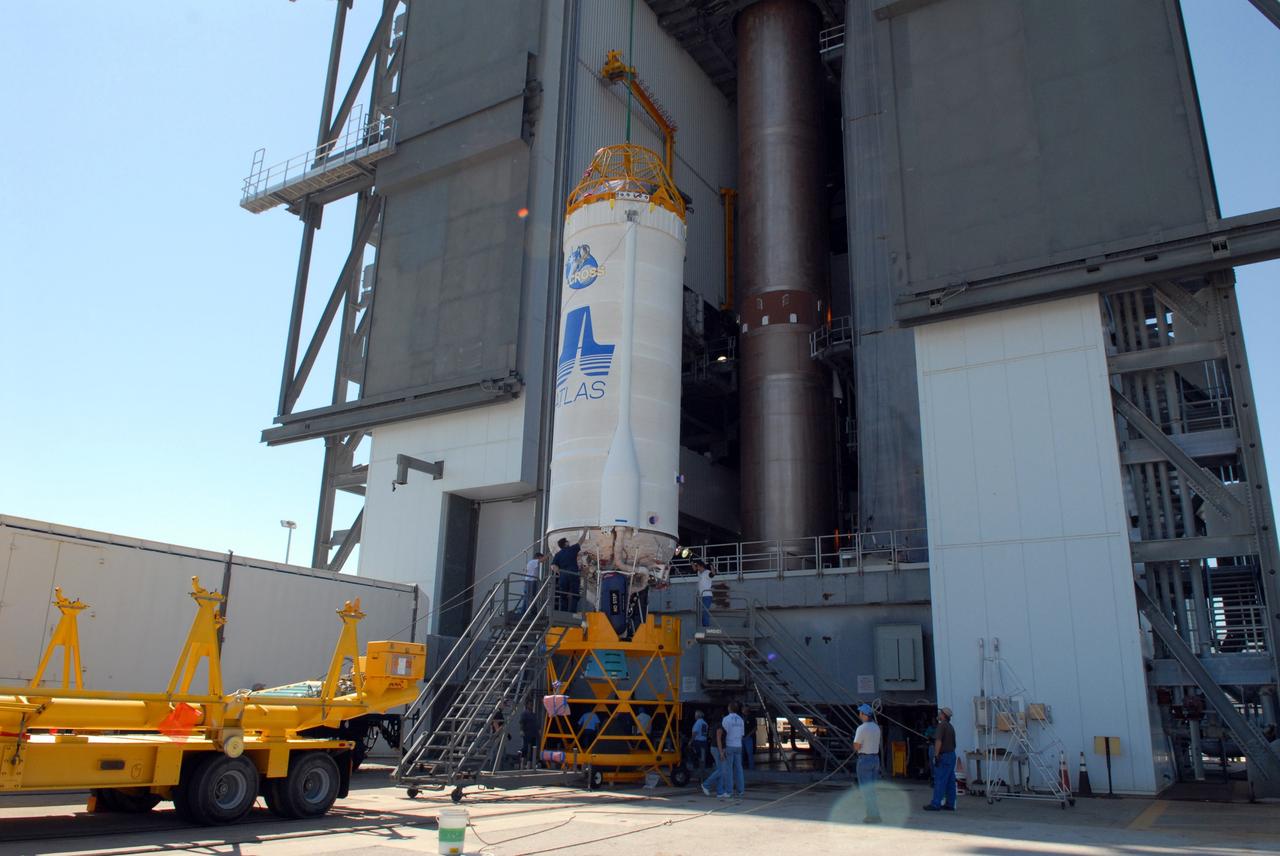

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –– On Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Complex 41, the crane begins lifting the Centaur upper stage into the Vertical Integration Facility for installation onto the Atlas V first stage, already in the tower. The Atlas V/Centaur is the launch vehicle for NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO, and NASA's Lunar CRater Observation and Sensing Satellite, known as LCROSS. LCROSS and LRO are the first missions in NASA's plan to return humans to the moon and begin establishing a lunar outpost by 2020. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
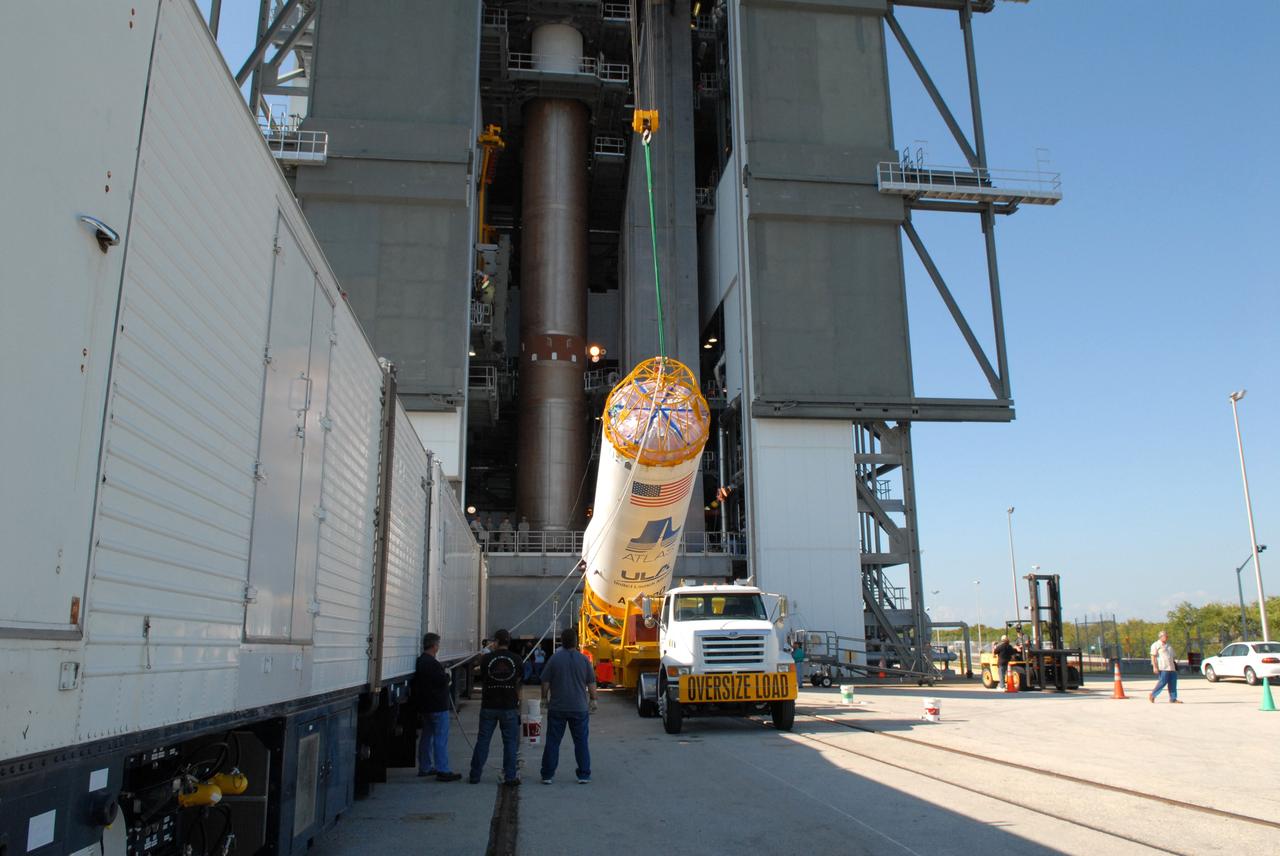

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –– On Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Complex 41, the Centaur upper stage is raised from its transporter. When it is vertical, it will be lifted into the Vertical Integration Facility for installation onto the Atlas V first stage, already in the tower. The Atlas V/Centaur is the launch vehicle for NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO, and NASA's Lunar CRater Observation and Sensing Satellite, known as LCROSS. LCROSS and LRO are the first missions in NASA's plan to return humans to the moon and begin establishing a lunar outpost by 2020. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
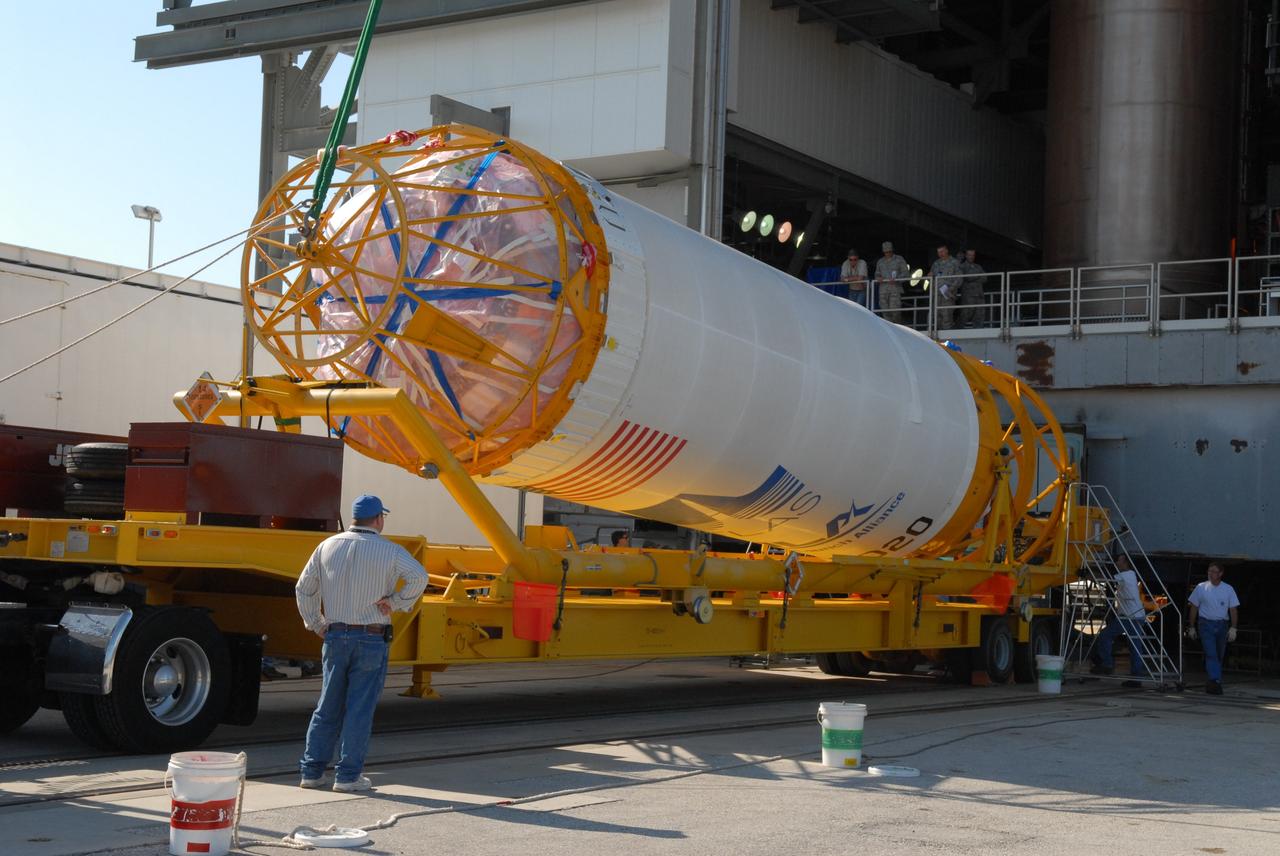

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –– On Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Complex 41, the Centaur upper stage is raised from its transporter. When it is vertical, it will be lifted into the Vertical Integration Facility for installation onto the Atlas V first stage, already in the tower. The Atlas V/Centaur is the launch vehicle for NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO, and NASA's Lunar CRater Observation and Sensing Satellite, known as LCROSS. LCROSS and LRO are the first missions in NASA's plan to return humans to the moon and begin establishing a lunar outpost by 2020. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –– On Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Complex 41, the Centaur upper stage is raised from its transporter. When it is vertical, it will be lifted into the Vertical Integration Facility for installation onto the Atlas V first stage, already in the tower. The Atlas V/Centaur is the launch vehicle for NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO, and NASA's Lunar CRater Observation and Sensing Satellite, known as LCROSS. LCROSS and LRO are the first missions in NASA's plan to return humans to the moon and begin establishing a lunar outpost by 2020. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –– On Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Complex 41, the Centaur upper stage is nearly vertical. It will be lifted into the Vertical Integration Facility for installation onto the Atlas V first stage, already in the tower. The Atlas V/Centaur is the launch vehicle for NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO, and NASA's Lunar CRater Observation and Sensing Satellite, known as LCROSS. LCROSS and LRO are the first missions in NASA's plan to return humans to the moon and begin establishing a lunar outpost by 2020. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –– The Centaur upper stage leaves the Atlas Space Operations Facility in Titusville, Fla. It is being transferred to the Vertical Integration Facility near Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Complex 41, where it will be lifted onto the Atlas V first stage. The Atlas V/Centaur is the launch vehicle for NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO, and NASA's Lunar CRater Observation and Sensing Satellite, known as LCROSS. LCROSS and LRO are the first missions in NASA's plan to return humans to the moon and begin establishing a lunar outpost by 2020. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –– The Centaur upper stage is transported to the Vertical Integration Facility near Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Complex 41, where it will be lifted onto the Atlas V first stage, already in the tower. The Atlas V/Centaur is the launch vehicle for NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO, and NASA's Lunar CRater Observation and Sensing Satellite, known as LCROSS. LCROSS and LRO are the first missions in NASA's plan to return humans to the moon and begin establishing a lunar outpost by 2020. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –– On Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Complex 41, cranes are attached to the Centaur upper stage in order to raise it to vertical. It will be lifted into the Vertical Integration Facility for installation onto the Atlas V first stage, already in the tower. The Atlas V/Centaur is the launch vehicle for NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO, and NASA's Lunar CRater Observation and Sensing Satellite, known as LCROSS. LCROSS and LRO are the first missions in NASA's plan to return humans to the moon and begin establishing a lunar outpost by 2020. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –– The Centaur upper stage arrives at the Vertical Integration Facility near Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Complex 41, where it will be lifted onto the Atlas V first stage, already in the tower. The Atlas V/Centaur is the launch vehicle for NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO, and NASA's Lunar CRater Observation and Sensing Satellite, known as LCROSS. LCROSS and LRO are the first missions in NASA's plan to return humans to the moon and begin establishing a lunar outpost by 2020. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
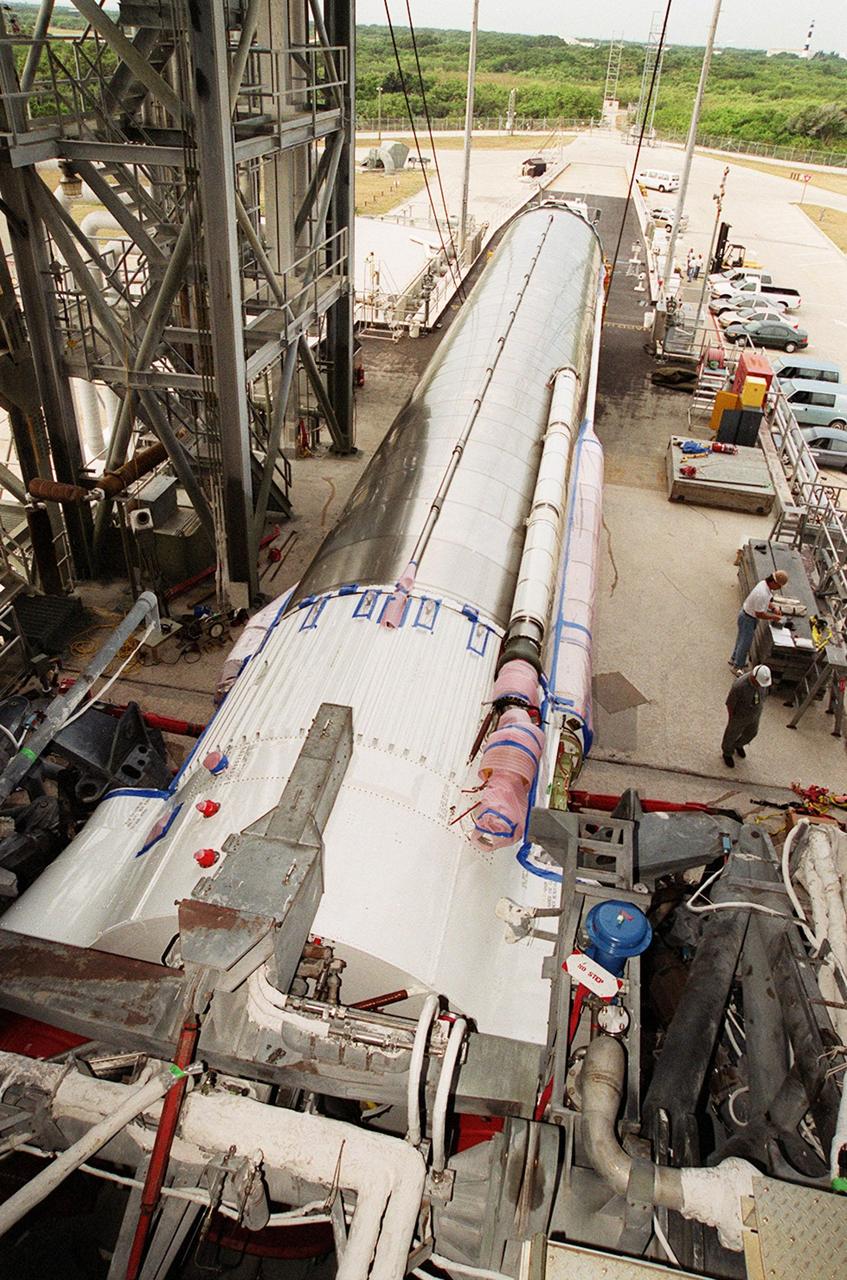

At Launch Pad 36A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the Atlas IIA rocket is ready to be lifted to vertical in the launch tower. The Atlas rocket, along with the Centaur upper stage, will launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from CCAFS. The Atlas/Centaur launch vehicle is manufactured and operated by Lockheed Martin. Atlas IIA is capable of lifting payload systems weights in the 2,850 kg (6,300 lb) to 3,070 kg (6,760 lb) class to geosynchronous transfer orbit. It is 25 m (82 ft) long and 3.05 m (10 ft) in diameter. The Centaur is 10.0 m (33-ft) long and 3.05 m (10 ft) in diameter

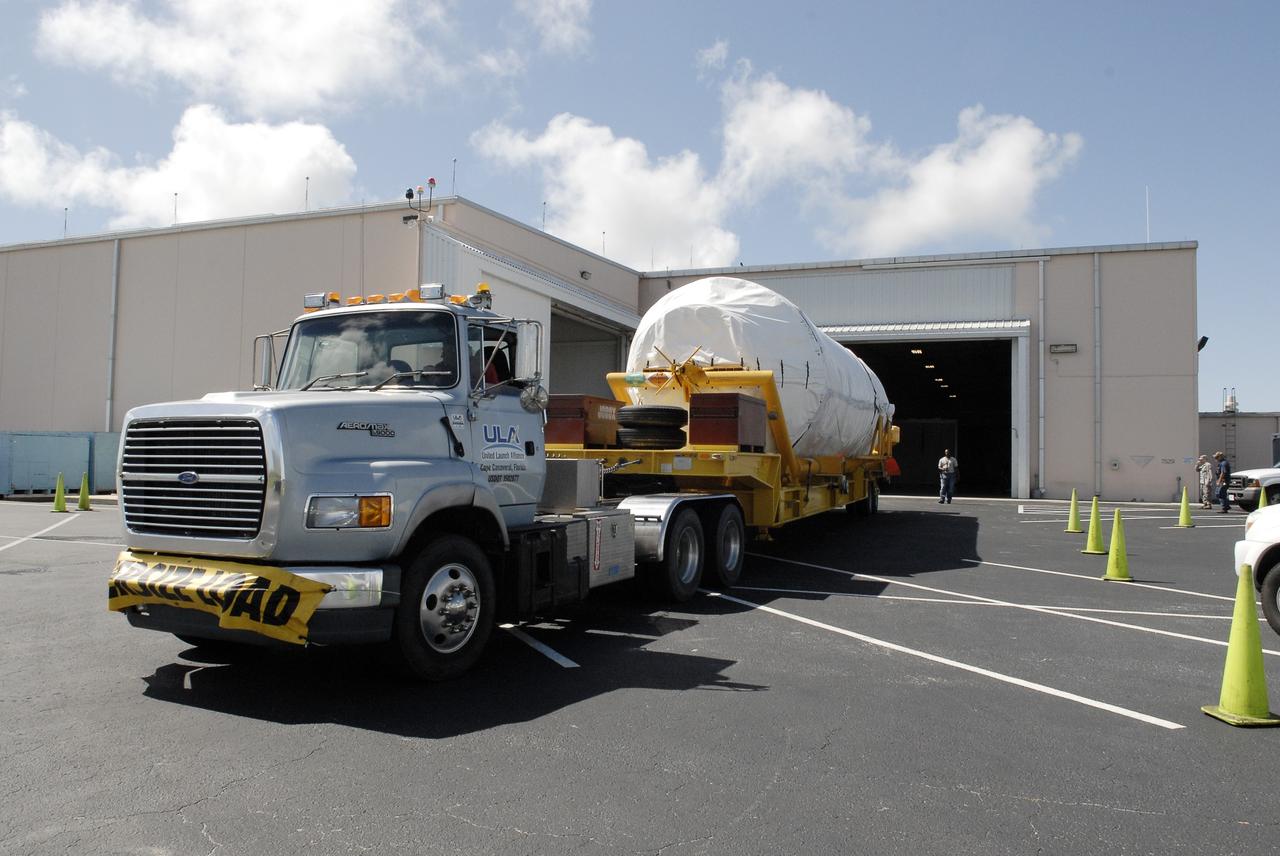
A transport truck moves a United Launch Alliance (ULA) two-engine Centaur upper stage from the company’s Mariner ship that just arrived at Port Canaveral in Florida. The Centaur will be transported to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for preliminary checkouts. Mounted atop a ULA Atlas V rocket, the Centaur will help launch a Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft on an uncrewed Orbital Flight Test from Space Launch Complex 41 at the Cape. NASA’s Commercial Crew Program will return human spaceflight launches to U.S. soil, providing safe, reliable and cost-effective access to low-Earth orbit on systems that meet our safety and mission requirements.
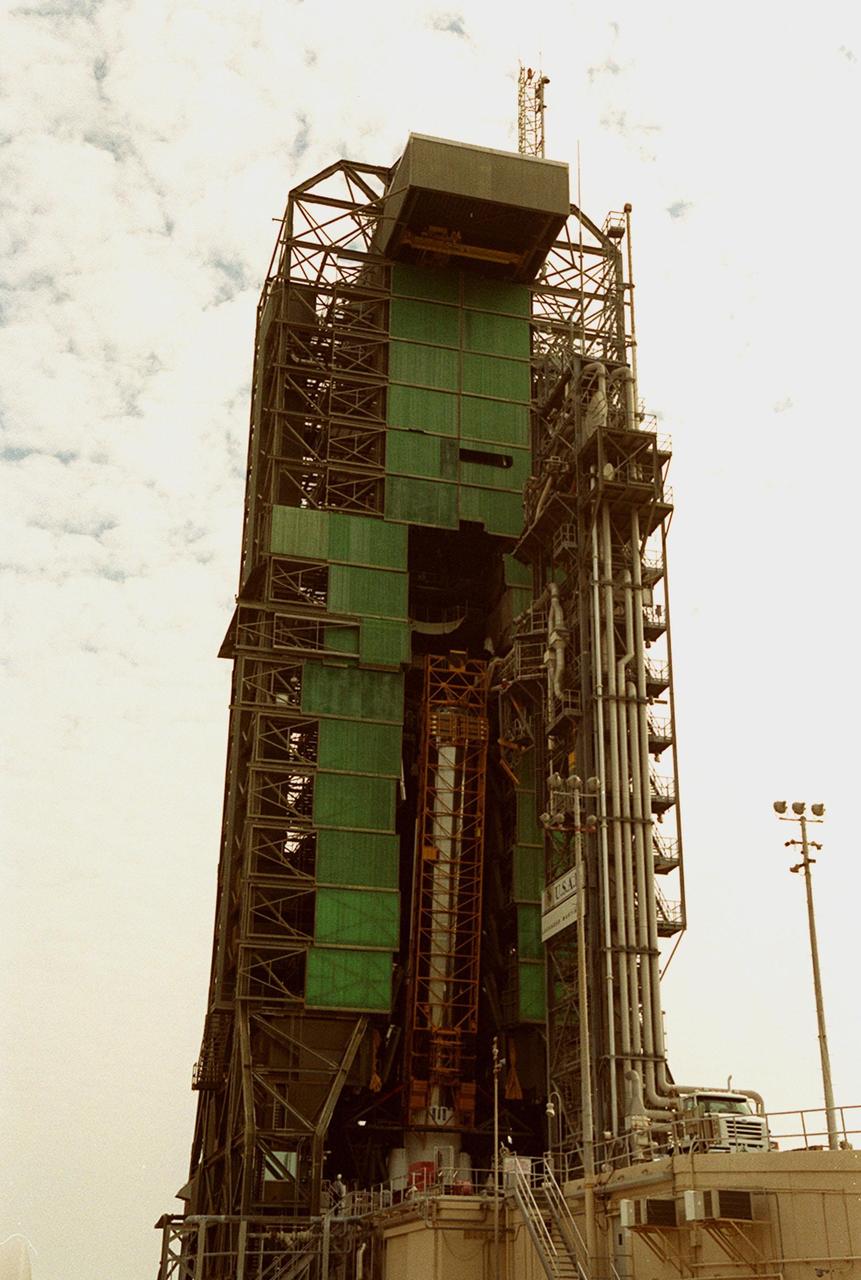

The Atlas IIA rocket is close to its vertical position in the launch tower at Launch Pad 36A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS). It will be mated with a Centaur upper stage to launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from CCAFS. The Atlas/Centaur launch vehicle is manufactured and operated by Lockheed Martin. Atlas IIA is capable of lifting payload systems weights in the 2,850 kg (6,300 lb) to 3,070 kg (6,760 lb) class to geosynchronous transfer orbit. It is 25 m (82 ft) long and 3.05 m (10 ft) in diameter. The Centaur is 10.0 m (33-ft) long and 3.05 m (10 ft) in diameter
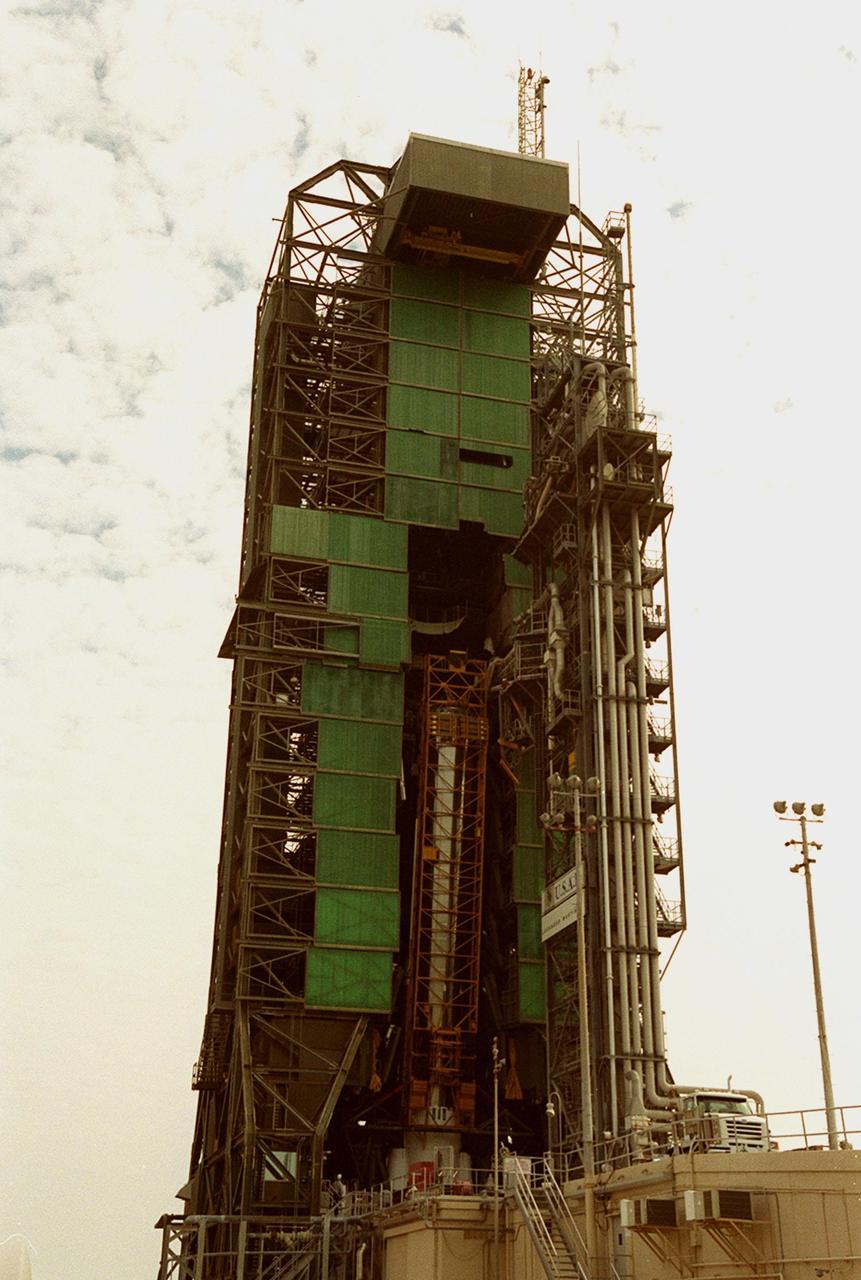

The Atlas IIA rocket is close to its vertical position in the launch tower at Launch Pad 36A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS). It will be mated with a Centaur upper stage to launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from CCAFS. The Atlas/Centaur launch vehicle is manufactured and operated by Lockheed Martin. Atlas IIA is capable of lifting payload systems weights in the 2,850 kg (6,300 lb) to 3,070 kg (6,760 lb) class to geosynchronous transfer orbit. It is 25 m (82 ft) long and 3.05 m (10 ft) in diameter. The Centaur is 10.0 m (33-ft) long and 3.05 m (10 ft) in diameter
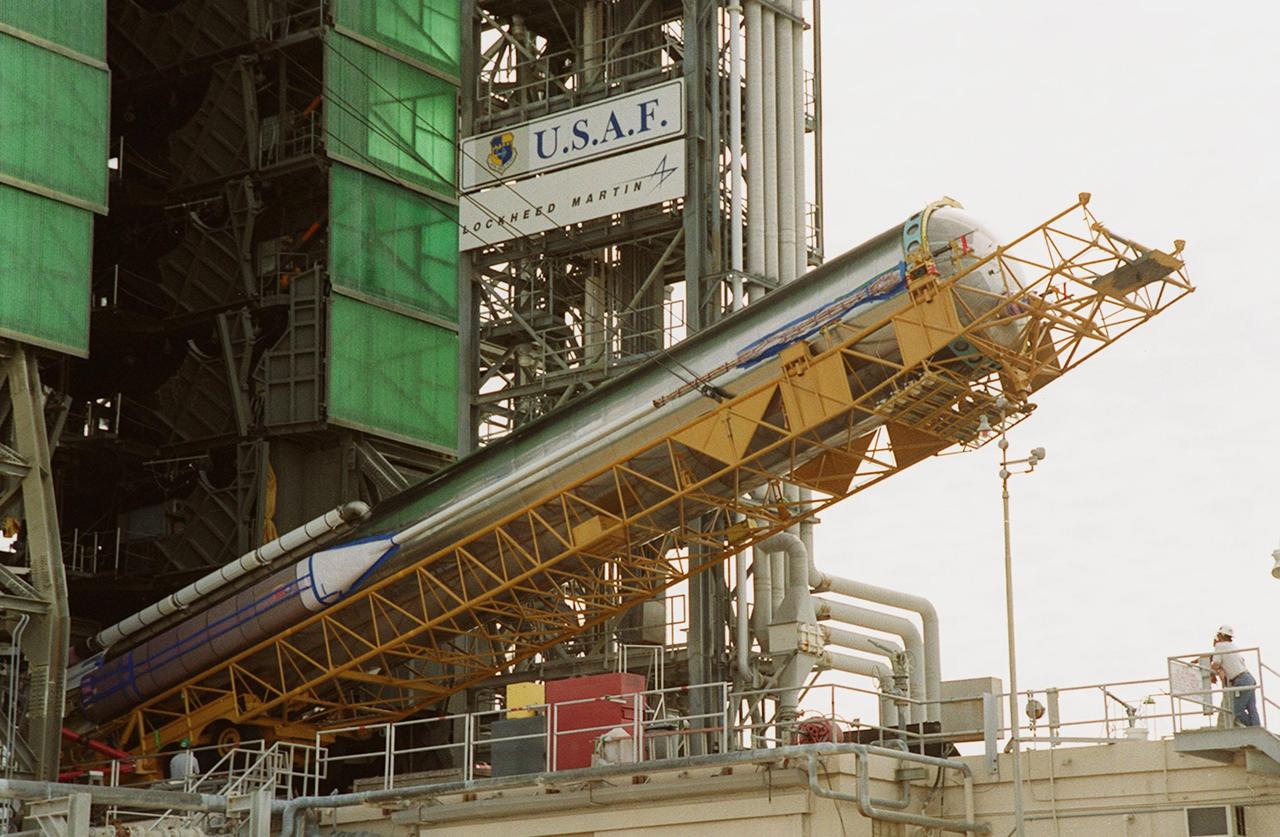

At Launch Pad 36A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the Atlas IIA rocket begins to be lifted to a vertical position at the launch tower. The Atlas rocket, along with the Centaur upper stage, will launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from CCAFS. The Atlas/Centaur launch vehicle is manufactured and operated by Lockheed Martin. Atlas IIA is capable of lifting payload systems weights in the 2,850 kg (6,300 lb) to 3,070 kg (6,760 lb) class to geosynchronous transfer orbit. It is 25 m (82 ft) long and 3.05 m (10 ft) in diameter. The Centaur is 10.0 m (33-ft) long and 3.05 m (10 ft) in diameter
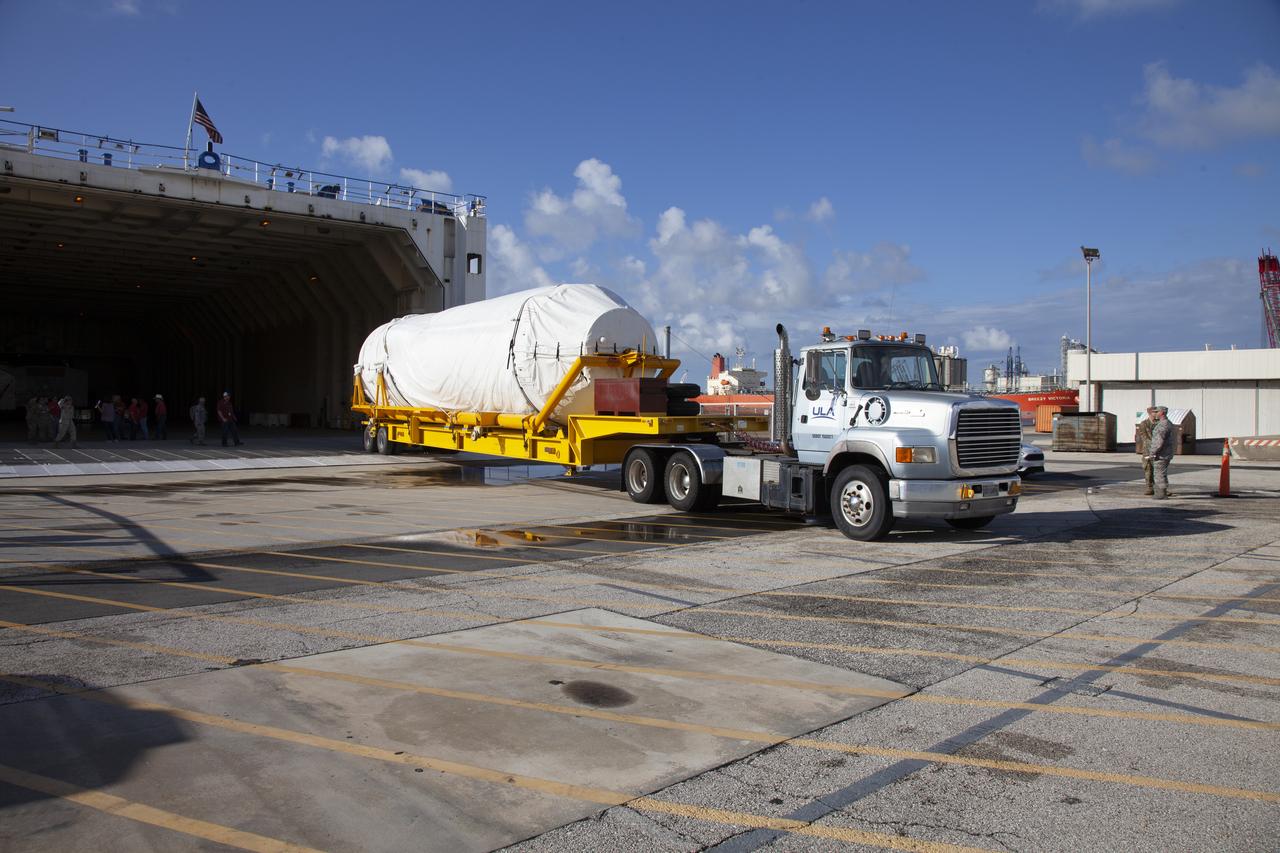

A transport truck moves a United Launch Alliance (ULA) two-engine Centaur upper stage from the company’s Mariner ship that just arrived at Port Canaveral in Florida. The Centaur will be transported to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for preliminary checkouts. Mounted atop a ULA Atlas V rocket, the Centaur will help launch a Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft on an uncrewed Orbital Flight Test from Space Launch Complex 41 at the Cape. NASA’s Commercial Crew Program will return human spaceflight launches to U.S. soil, providing safe, reliable and cost-effective access to low-Earth orbit on systems that meet our safety and mission requirements.
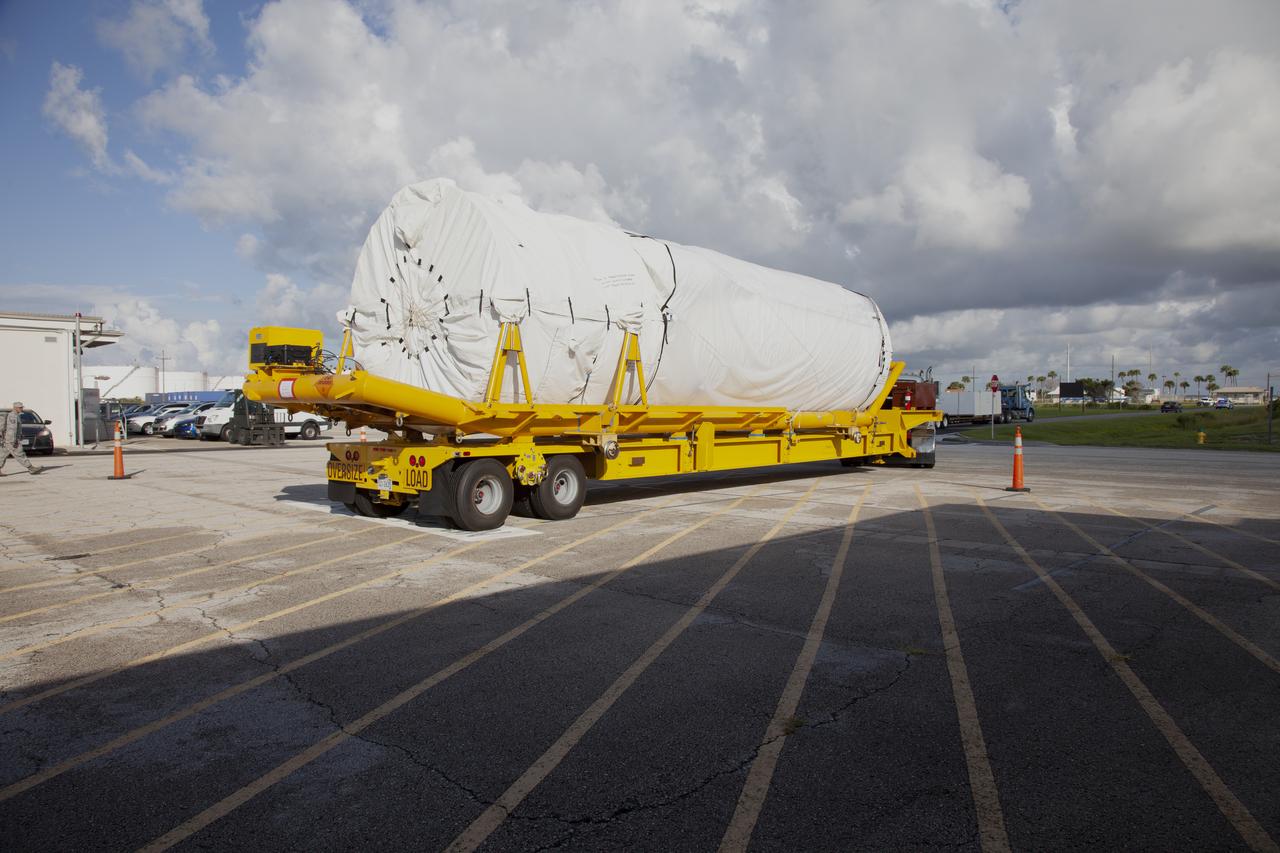

A transport truck moves a United Launch Alliance (ULA) two-engine Centaur upper stage from the company’s Mariner ship that just arrived at Port Canaveral in Florida. The Centaur will be transported to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for preliminary checkouts. Mounted atop a ULA Atlas V rocket, the Centaur will help launch a Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft on an uncrewed Orbital Flight Test from Space Launch Complex 41 at the Cape. NASA’s Commercial Crew Program will return human spaceflight launches to U.S. soil, providing safe, reliable and cost-effective access to low-Earth orbit on systems that meet our safety and mission requirements.
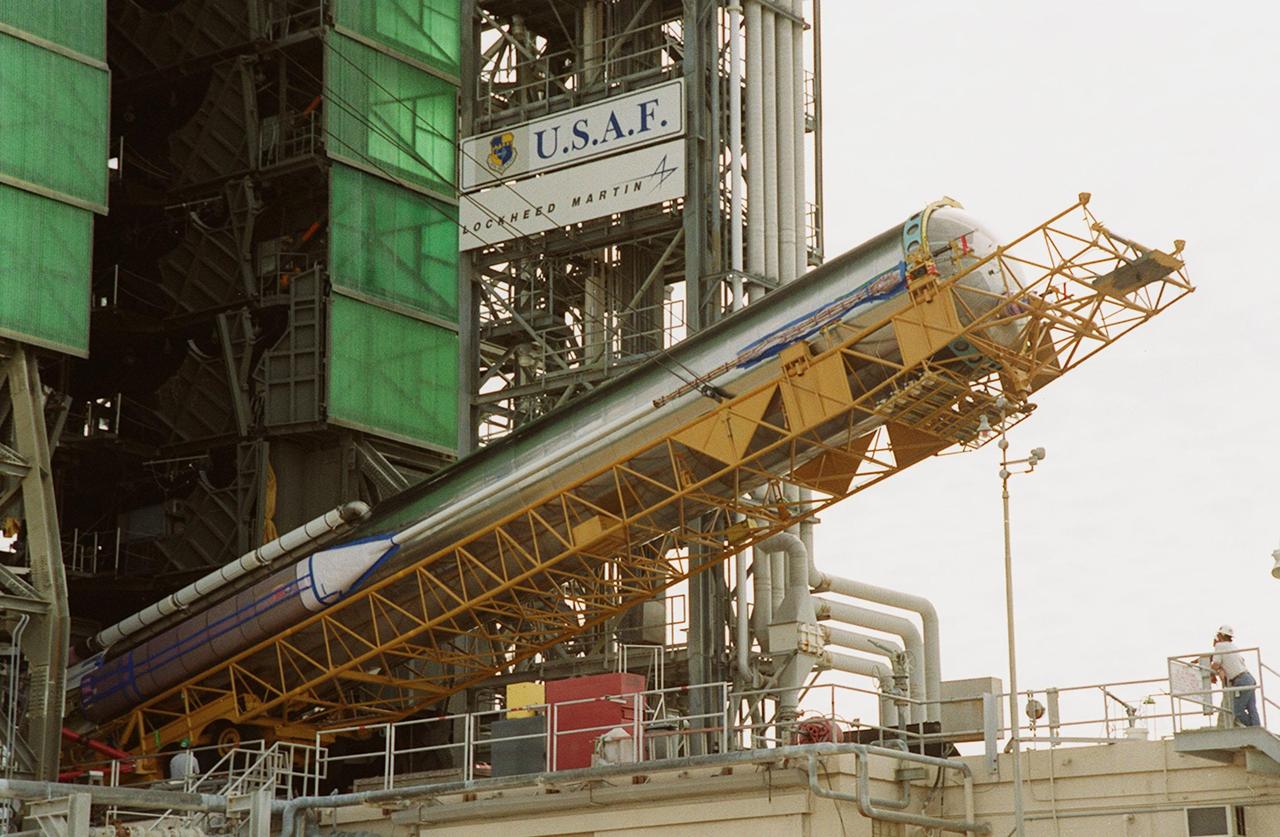

At Launch Pad 36A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the Atlas IIA rocket begins to be lifted to a vertical position at the launch tower. The Atlas rocket, along with the Centaur upper stage, will launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from CCAFS. The Atlas/Centaur launch vehicle is manufactured and operated by Lockheed Martin. Atlas IIA is capable of lifting payload systems weights in the 2,850 kg (6,300 lb) to 3,070 kg (6,760 lb) class to geosynchronous transfer orbit. It is 25 m (82 ft) long and 3.05 m (10 ft) in diameter. The Centaur is 10.0 m (33-ft) long and 3.05 m (10 ft) in diameter
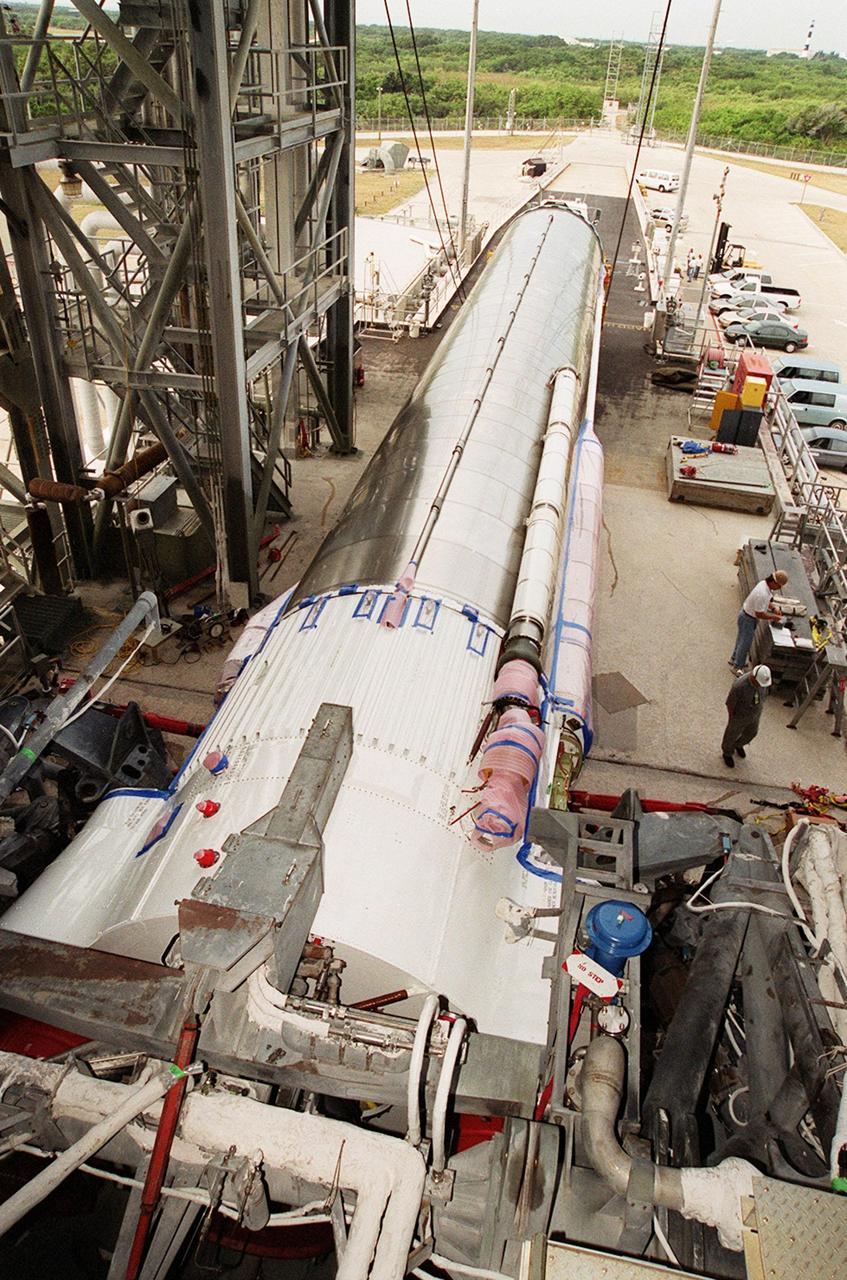

At Launch Pad 36A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the Atlas IIA rocket is ready to be lifted to vertical in the launch tower. The Atlas rocket, along with the Centaur upper stage, will launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from CCAFS. The Atlas/Centaur launch vehicle is manufactured and operated by Lockheed Martin. Atlas IIA is capable of lifting payload systems weights in the 2,850 kg (6,300 lb) to 3,070 kg (6,760 lb) class to geosynchronous transfer orbit. It is 25 m (82 ft) long and 3.05 m (10 ft) in diameter. The Centaur is 10.0 m (33-ft) long and 3.05 m (10 ft) in diameter
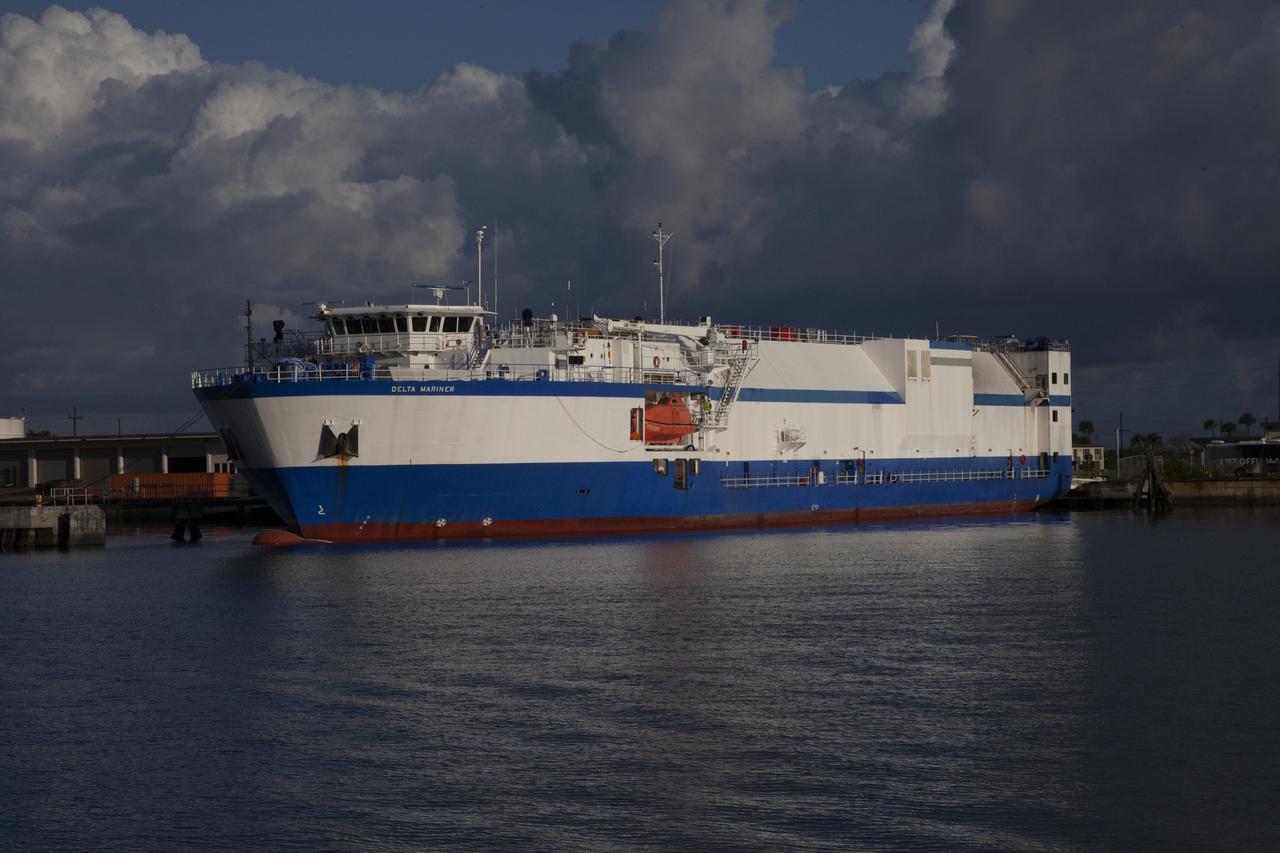

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Mariner ship arrives at Port Canaveral in Florida carrying a two-engine Centaur upper stage for the upcoming uncrewed Orbital Flight Test of a Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft. As part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program (CCP), the Starliner is part of the next generation of American spacecraft that will launch astronauts to the International Space Station. Starliner will launch early next year atop a ULA Atlas V rocket with the Centaur upper stage from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Statin. NASA’s Commercial Crew Program will return human spaceflight launches to U.S. soil, providing safe, reliable and cost-effective access to low-Earth orbit on systems that meet our safety and mission requirements.
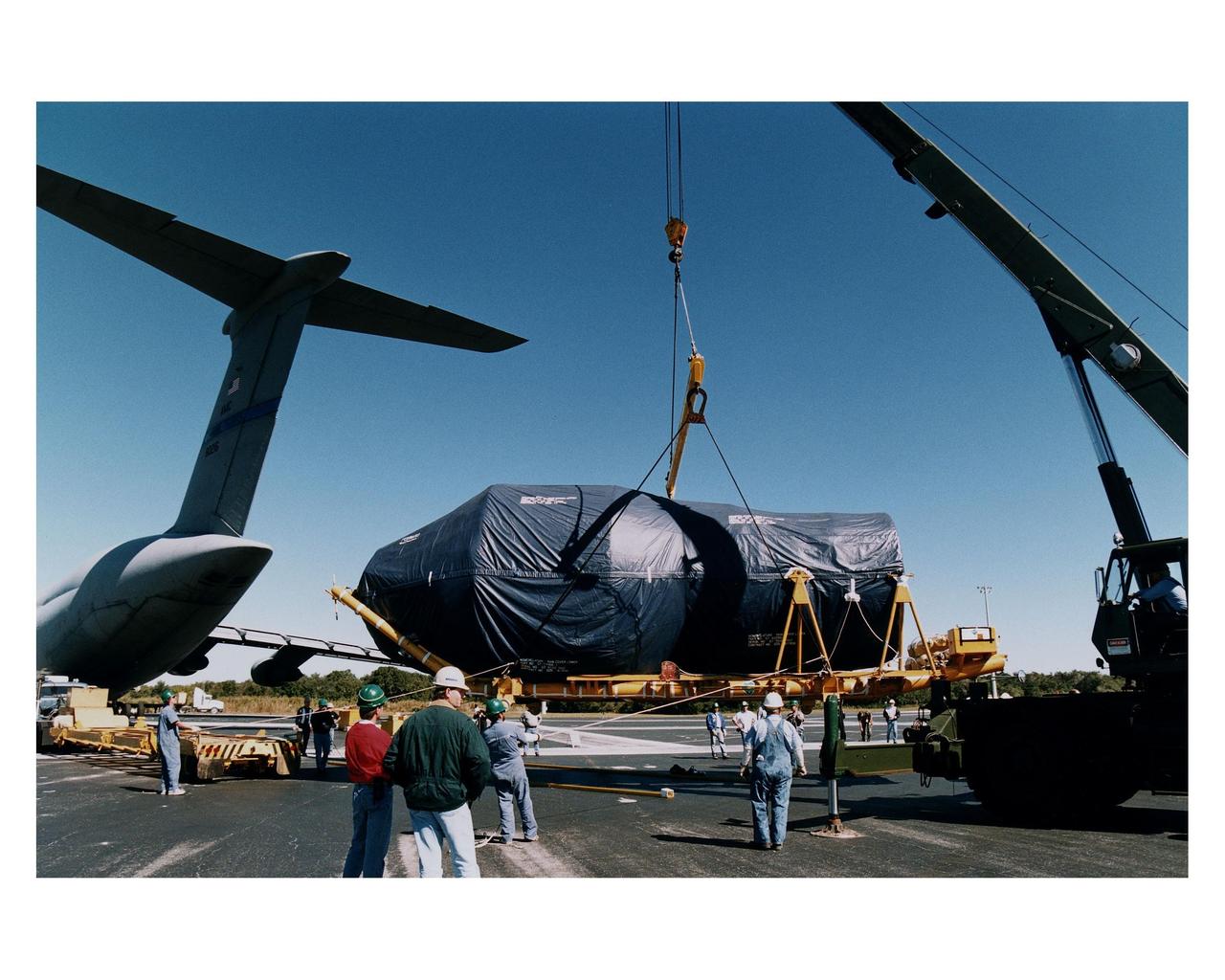

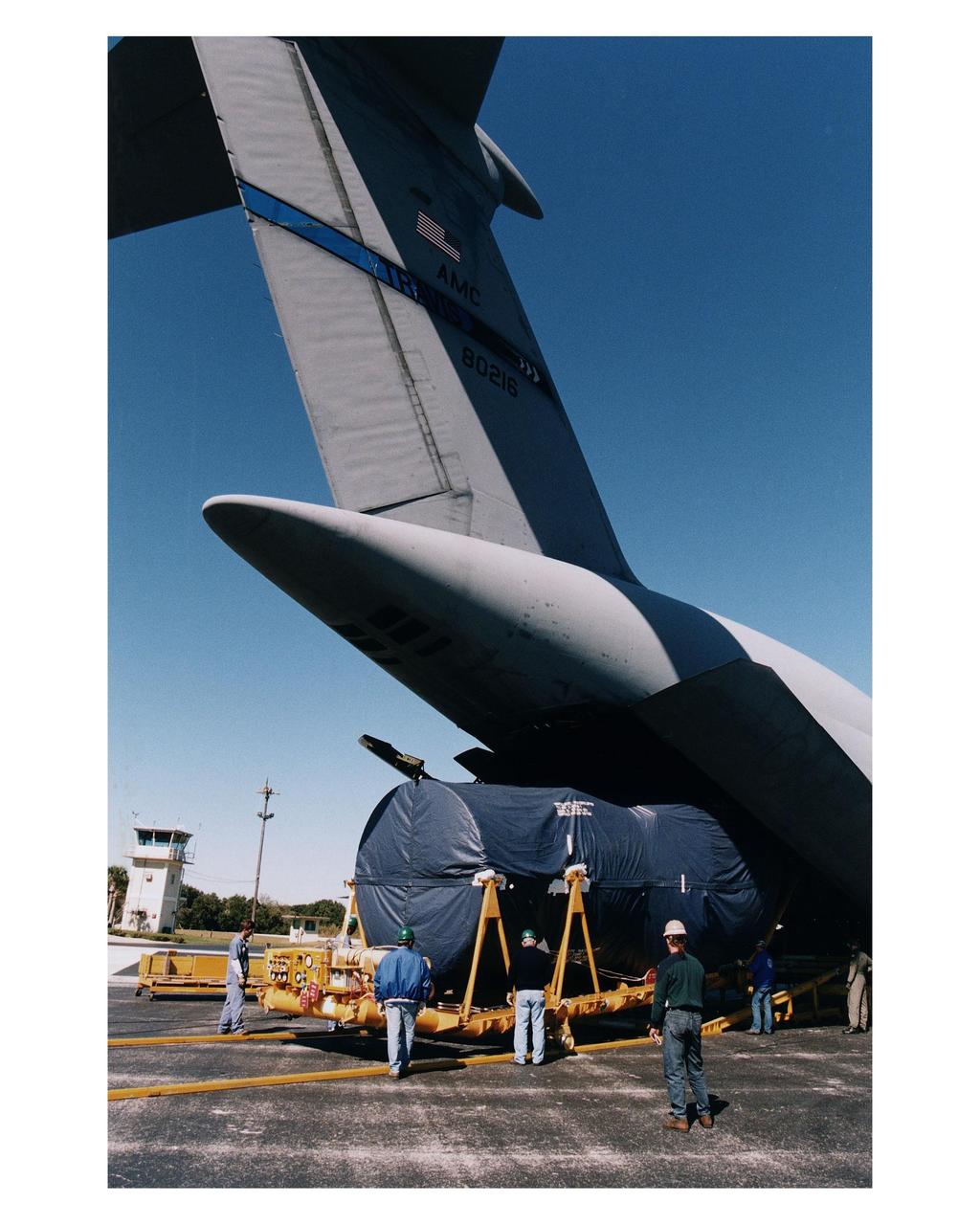
The Centaur upper stage of the Titan IV expendable launch vehicle that will propel the Cassini spacecraft to Saturn and its moon Titan is transported from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Station (CCAS) after its arrival via a jet cargo aircraft. The Titan IV is currently scheduled to lift off from Launch Pad 40 at CCAS on October 6. Once deployed from the Centaur upper stage, Cassini will conduct gravity-assist flybys of the planets Venus and Jupiter, then arrive at Saturn in July 2004. Once there, it will perform an orbital survey of Saturn and send the European Space Agency's Huygens Probe into the dense and seemingly Earthlike atmosphere of Titan. The Cassini project is managed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), Pasadena, California

The Centaur upper stage of the Titan IV expendable launch vehicle that will propel the Cassini spacecraft to Saturn and its moon Titan is transported from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Station (CCAS) after its arrival via a jet cargo aircraft. The Titan IV is currently scheduled to lift off from Launch Pad 40 at CCAS on October 6. Once deployed from the Centaur upper stage, Cassini will conduct gravity-assist flybys of the planets Venus and Jupiter, then arrive at Saturn in July 2004. Once there, it will perform an orbital survey of Saturn and send the European Space Agency's Huygens Probe into the dense and seemingly Earthlike atmosphere of Titan. The Cassini project is managed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), Pasadena, California

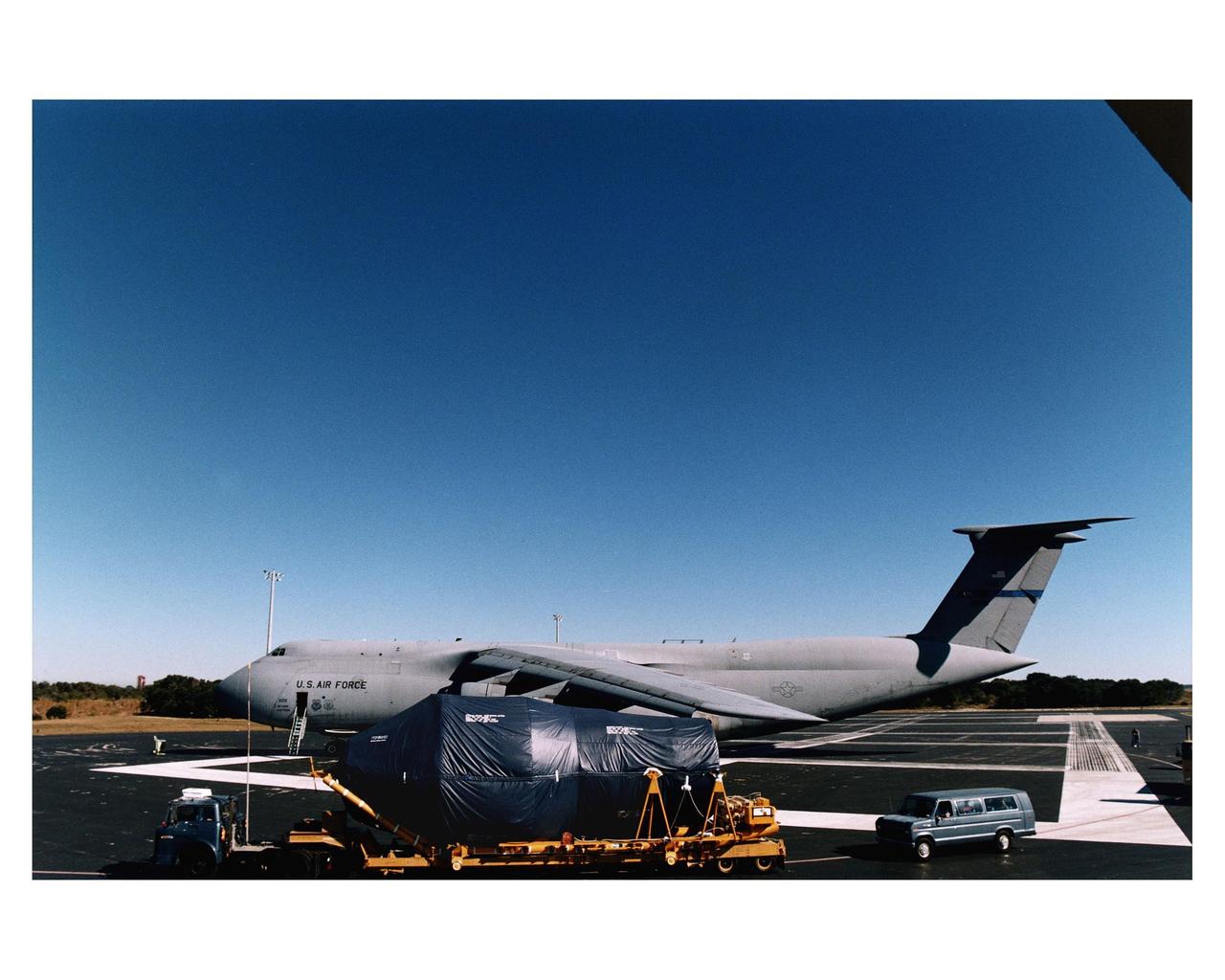
The Centaur upper stage of the Titan IV expendable launch vehicle that will propel the Cassini spacecraft to Saturn and its moon Titan is unloaded from a jet cargo aircraft at the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Station (CCAS). The Titan IV is currently scheduled to lift off from Launch Pad 40 at CCAS on October 6. Once deployed from the Centaur upper stage, Cassini will conduct gravity-assist flybys of the planets Venus and Jupiter, then arrive at Saturn in July 2004. Once there, it will perform an orbital survey of Saturn and send the European Space Agency's Huygens Probe into the dense and seemingly Earthlike atmosphere of Titan. The Cassini project is managed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), Pasadena, California
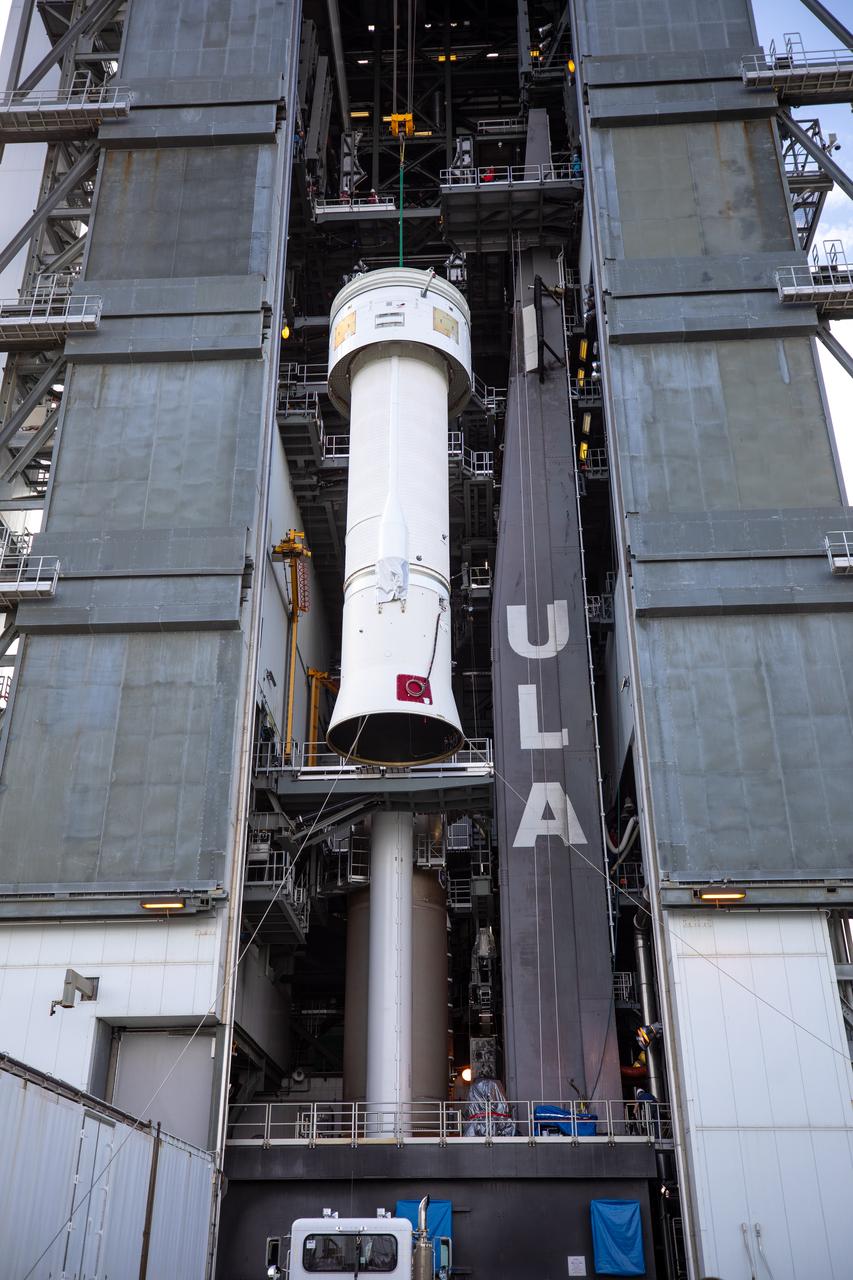

A Centaur upper stage is lifted at the Space Launch Complex 41 Vertical Integration Facility at Florida’s Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on Nov. 8, 2019, for mating to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage in preparation for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test (OFT). The uncrewed OFT mission will rendezvous and dock Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft with the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Starliner will launch atop the Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41.
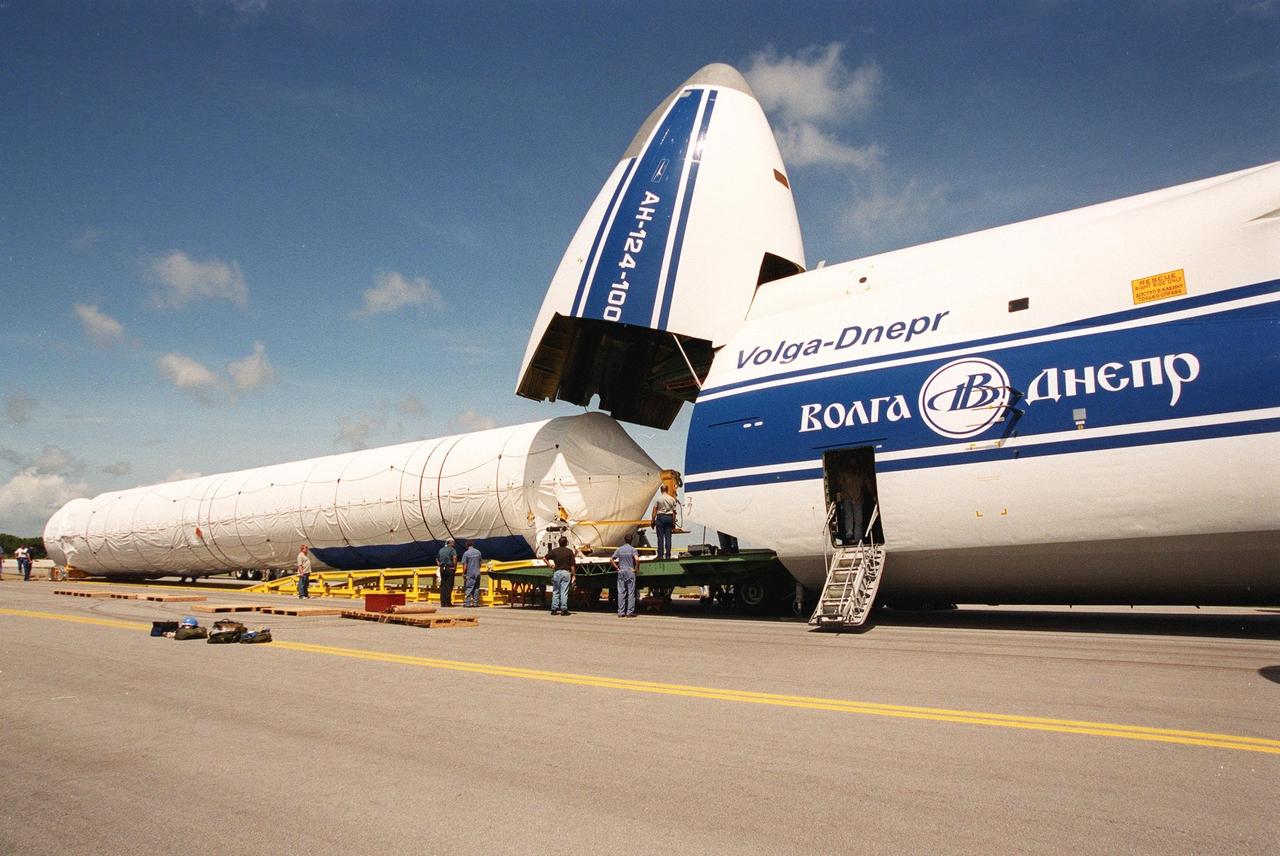

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Stages of the first Atlas V rocket are offloaded from a Russian Antonov AN-124 aircraft after their arrival at the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The Antonov AN-124 is the only carrier large enough to carry the Atlas V. The rocket will be joined to its Centaur upper stage and testing will begin in preparation for a May 2002 launch
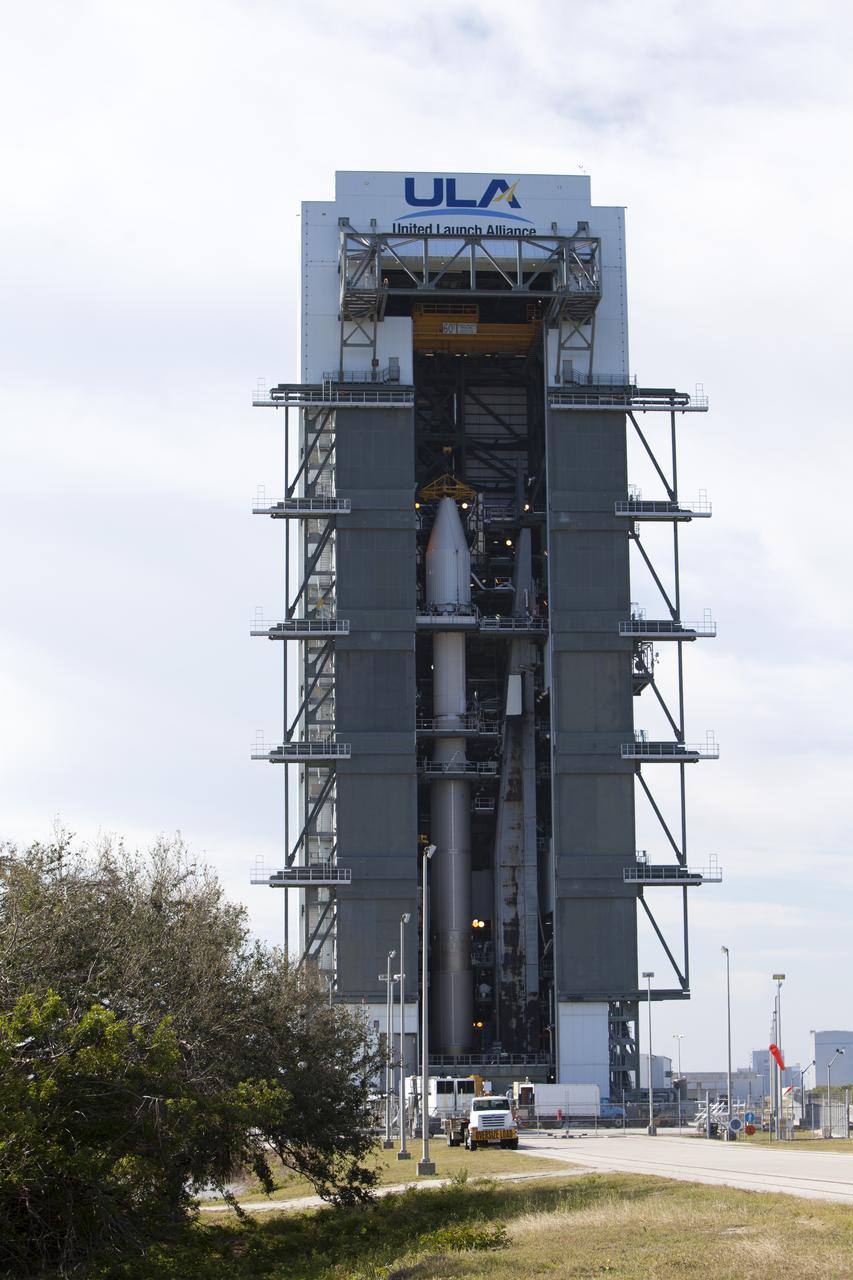

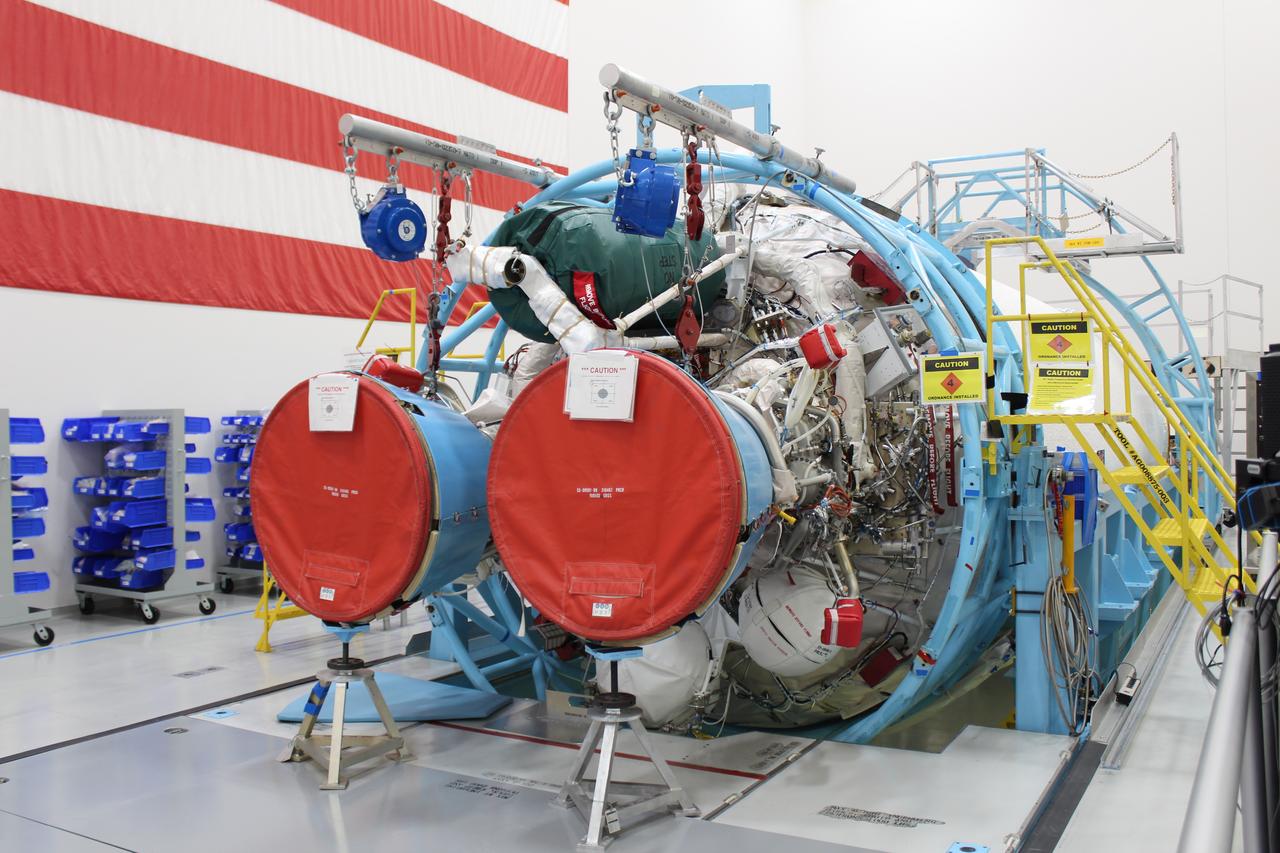
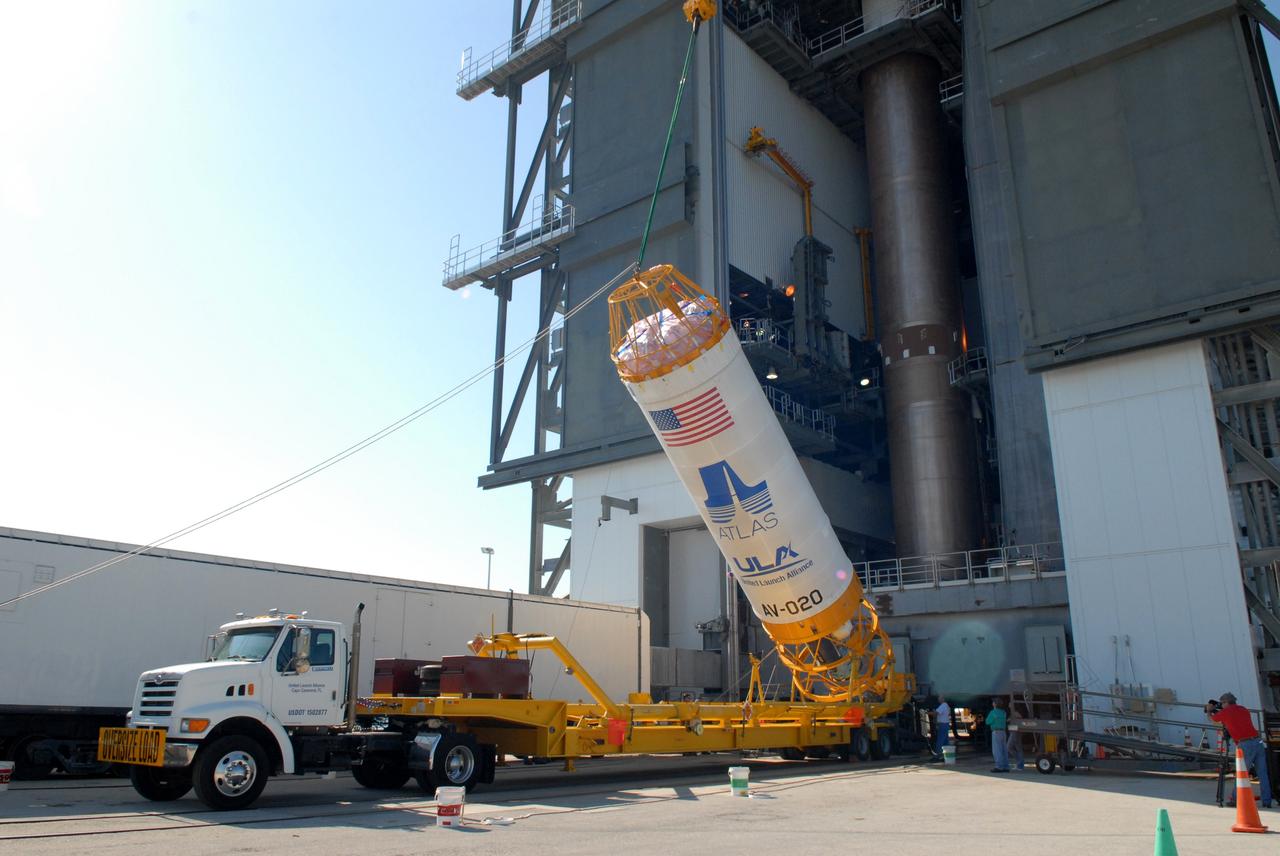
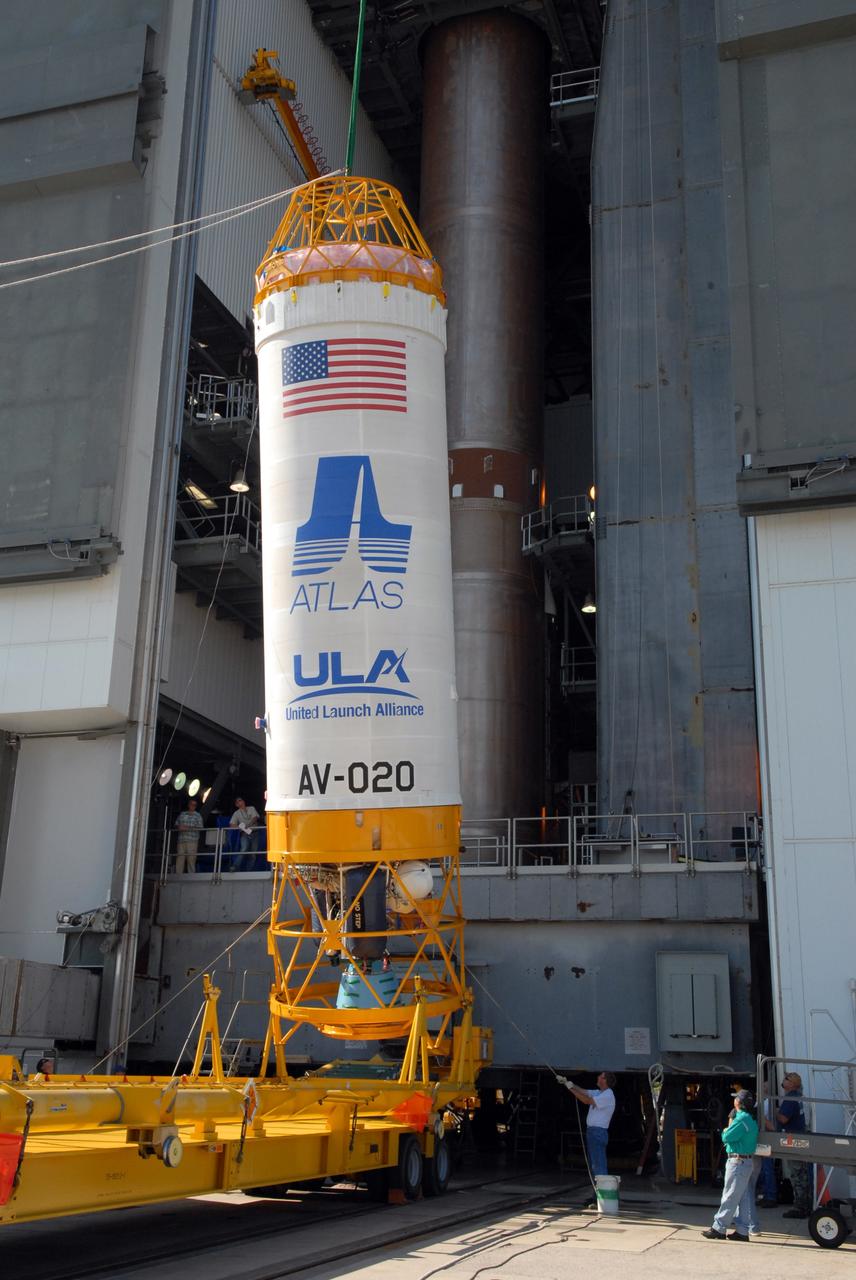
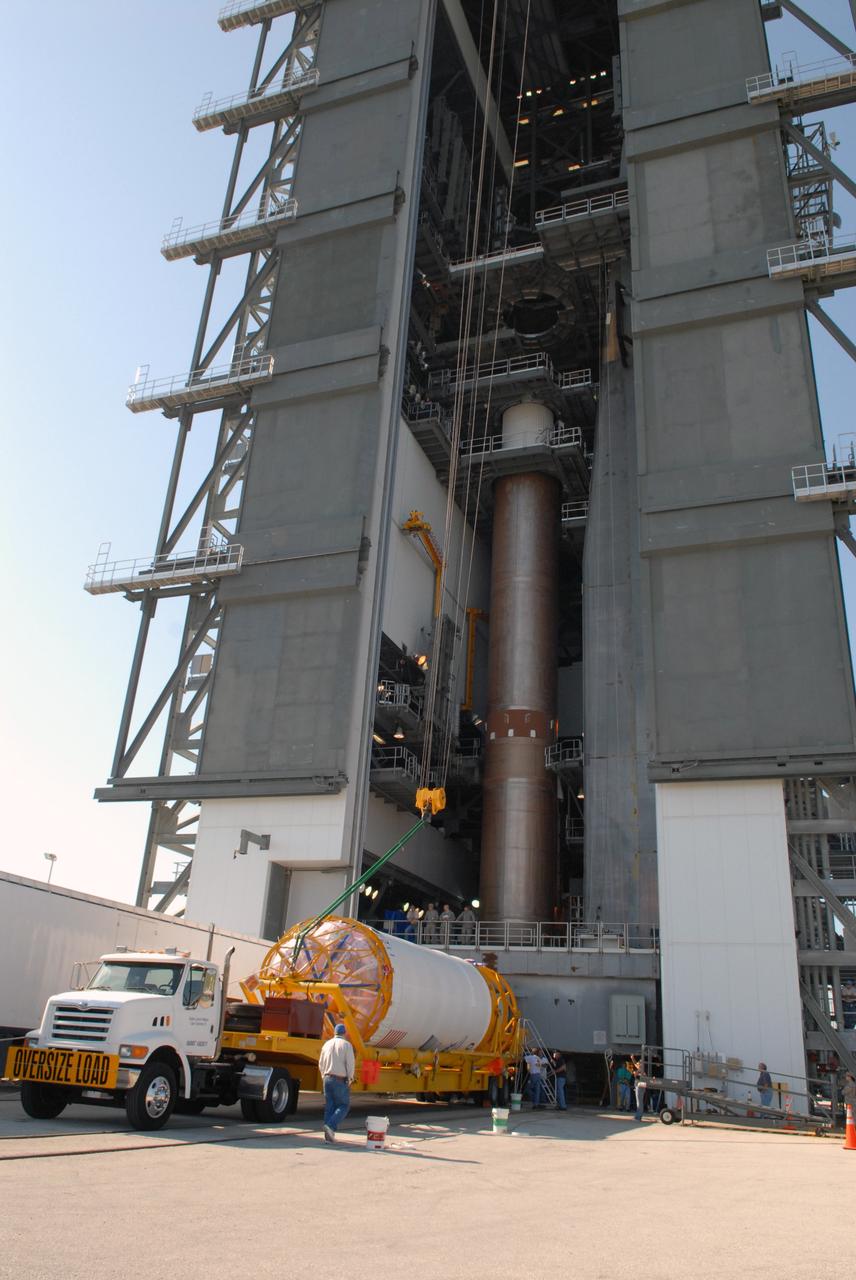
The payload fairing containing the Orbital ATK Cygnus pressurized cargo module is mated to the Centaur upper stage, or second stage, of the United Launch Alliance (ULA) rocket in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V from pad 41. Cygnus will deliver 7,600 pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
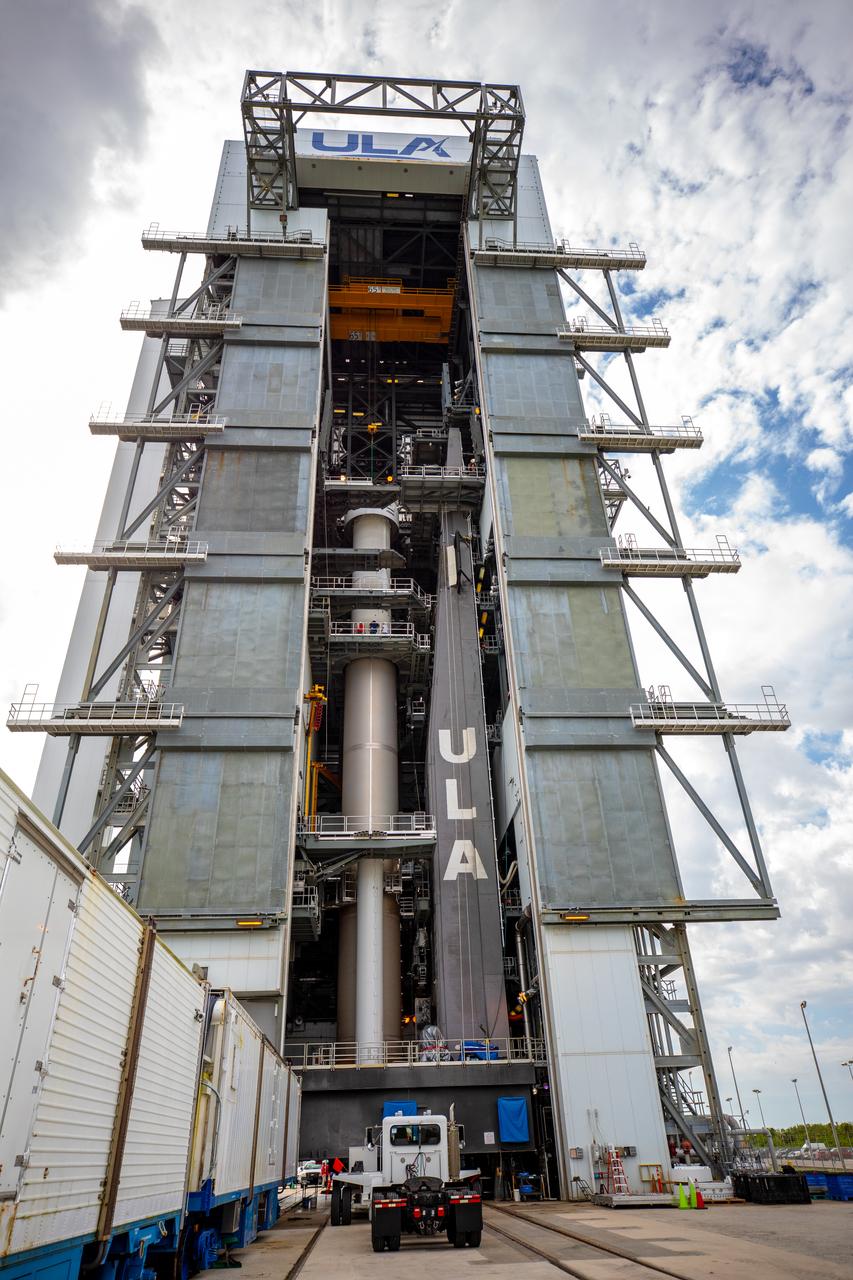

A Centaur upper stage is mated to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage inside the Space Launch Complex 41 Vertical Integration Facility at Florida’s Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on Nov. 8, 2019, in preparation for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test (OFT). The uncrewed OFT mission will rendezvous and dock Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft with the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Starliner will launch atop the Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41.
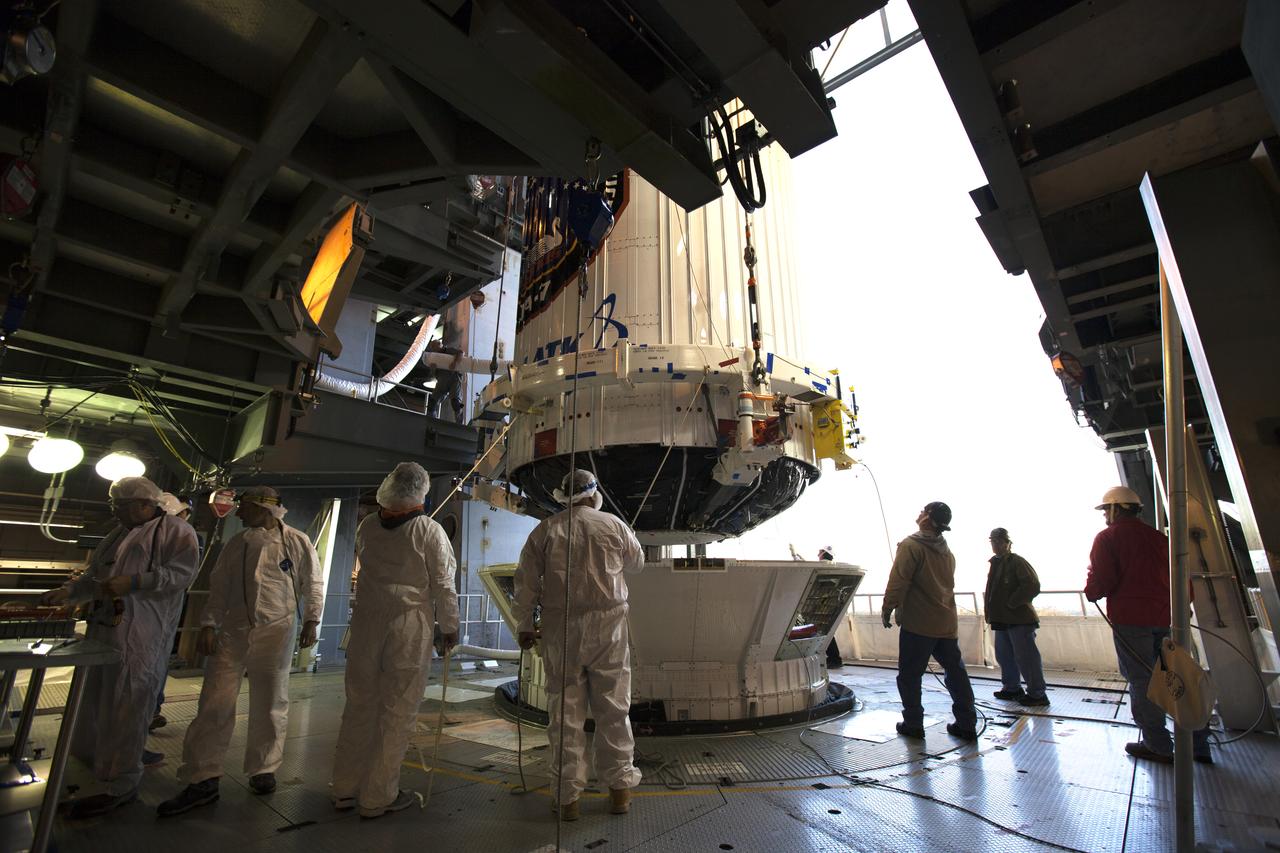

The payload fairing containing the Orbital ATK Cygnus pressurized cargo module is lowered onto the Centaur upper stage, or second stage, of the United Launch Alliance (ULA) rocket in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V from pad 41. Cygnus will deliver 7,600 pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.