
A star field in the constellation Cepheus is a composite of two 600-second exposures by the Framing Camera acquired during tests on December 3, 2007.
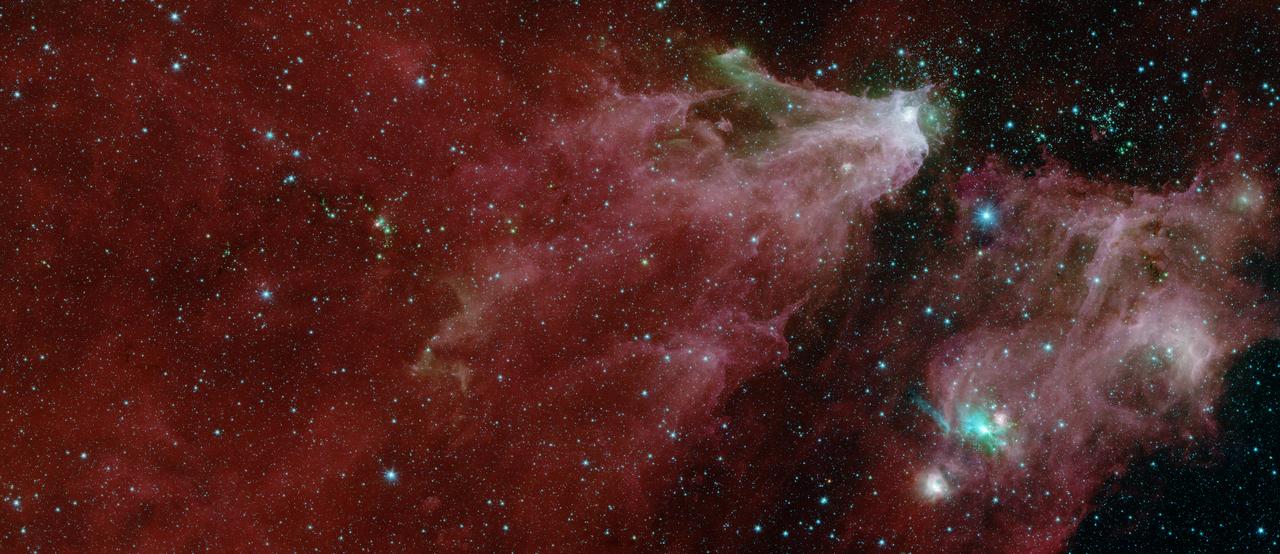

This image shows data from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope, from the IRAC instrument, with colors corresponding to wavelengths of 3.6, 4.5, 5.8 and 8.0 µm (shown as blue, green, orange and red). The grand red delta filling most of the image is a far-away nebula, or a cloud of gas and dust. A second nebula is located in the lower right portion of the image. Within the first nebula, on the left side of this image, a dark filament runs horizontally through the green cloud. A smattering of baby stars (the red and yellow dots) appear inside it. Known as Cepheus C, the area is a particularly dense concentration of gas and dust where infant stars form. This region is called Cepheus C because it lies in the constellation Cepheus, which can be found near the constellation Cassiopeia. Cepheus-C is about 6 light years long, and lies about 40 light-years from the bright spot at the tip of the nebula. Two features identified in the annotated image are visible only in the multi-instrument version of the image, found here. The first is V374 Ceph in the larger nebula. The second is the "runaway star" in the smaller nebula. A second star cluster is located just above the second large nebula on the right side of the image. Known as Cepheus B, the cluster sits within a few thousand light-years of our Sun. A study of this region using Spitzer found that the dramatic collection is about 4 million to 5 million years old — slightly older than those in Cepheus C. Also found in the second nebula is a small cluster of newborn stars that illuminates the dense cloud of gas and dust where they formed. It appears as a bright teal splash. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23127

This image was compiled using data from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope using the Infrared Array Camera (IRAC) and the Multiband Imaging Photometer (MIPS) during Spitzer's "cold" mission, before the spacecraft's liquid helium coolant ran out in 2009. The colors correspond with IRAC wavelengths of 3.6 microns (blue), 4.5 microns (cyan) and 8 microns (green), and 24 microns (red) from the MIPS instrument. The green-and-orange delta filling most of this image is a nebula, or a cloud of gas and dust. This region formed from a much larger cloud of gas and dust that has been carved away by radiation from stars. The bright region at the tip of the nebula is dust that has been heated by the stars' radiation, which creates the surrounding red glow. The white color is the combination of four colors (blue, green, orange and red), each representing a different wavelength of infrared light, which is invisible to human eyes. The massive stars illuminating this region belong to a star cluster that extends above the white spot. On the left side of this image, a dark filament runs horizontally through the green cloud. A smattering of baby stars (the red and yellow dots) appear inside it. Known as Cepheus C, the area is a particularly dense concentration of gas and dust where infant stars form. This region is called Cepheus C because it lies in the constellation Cepheus, which can be found near the constellation Cassiopeia. Cepheus-C is about 6 light-years long, and lies about 40 light-years from the bright spot at the tip of the nebula. The small, red hourglass shape just below Cepheus C is V374 Ceph. Astronomers studying this massive star have speculated that it might be surrounded by a nearly edge-on disk of dark, dusty material. The dark cones extending to the right and left of the star are a shadow of that disk. The smaller nebula on the right side of the image includes a blue star crowned by a small, red arc of light. This "runaway star" is plowing through the gas and dust at a rapid clip, creating a shock wave or "bow shock" in front of itself. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23126
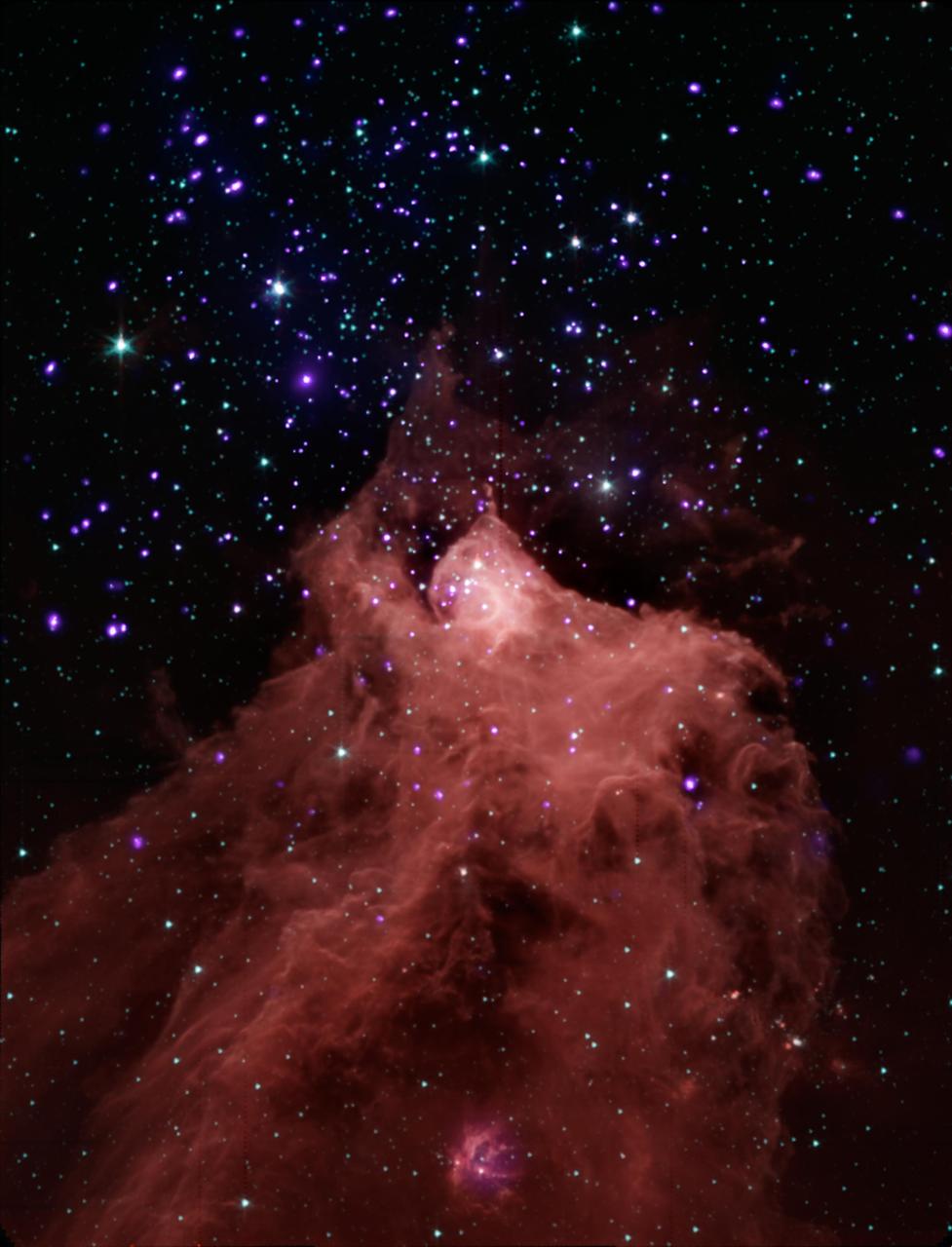

This composite image, combining data from NASA Chandra X-ray Observatory and Spitzer Space Telescope shows the star-forming cloud Cepheus B, located in our Milky Way galaxy about 2,400 light years from Earth

SCI2016_0006: Map of Cepheus E emphasizing the jets of material flowing to the upper left and lower right from the protostar. The protostar itself is the central yellow-red 'blob" in the colored background map of hydrogen emission made at a wavelength of 4.5 microns by the Spitzer infrared space telescope. The contour curves show the strength of emission from cool carbon monoxide gas measured by the Plateau de Bure radio telescope located in the French Alps. Lefloch et al. used GREAT on SOFIA to measure the amount and velocity of hot carbon monoxide gas at multiple positions along both "wings" of the outflow jet. Credit: Lefloch et al. 2015 Figure 1

In the quest to better understand the birth of stars and the formation of new worlds, astronomers have used NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope to examine the massive stars contained in a cloudy region called Sharpless 140. This cloud is a fascinating microcosm of a star-forming region since it exhibits, within a relatively small area, all of the classic manifestations of stellar birth. Sharpless 140 lies almost 3000 light-years from Earth in the constellation Cepheus. At its heart is a cluster of three deeply embedded young stars, which are each several thousand times brighter than the Sun. Though they are strikingly visible in this image from Spitzer's infrared array camera, they are completely obscured in visible light, buried within the core of the surrounding dust cloud. The extreme youth of at least one of these stars is indicated by the presence of a stream of gas moving at high velocities. Such outflows are signatures of the processes surrounding a star that is still gobbling up material as part of its formation. The bright red bowl, or arc, seen in this image traces the outer surface of the dense dust cloud encasing the young stars. This arc is made up primarily of organic compounds called polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, which glow on the surface of the cloud. Ultraviolet light from a nearby bright star outside of the image is "eating away" at these molecules. Eventually, this light will destroy the dust envelope and the masked young stars will emerge. This false-color image was taken on Oct. 11, 2003 and is composed of photographs obtained at four wavelengths: 3.6 microns (blue), 4.5 microns (green), 5.8 microns (orange) and 8 microns (red). http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA05878
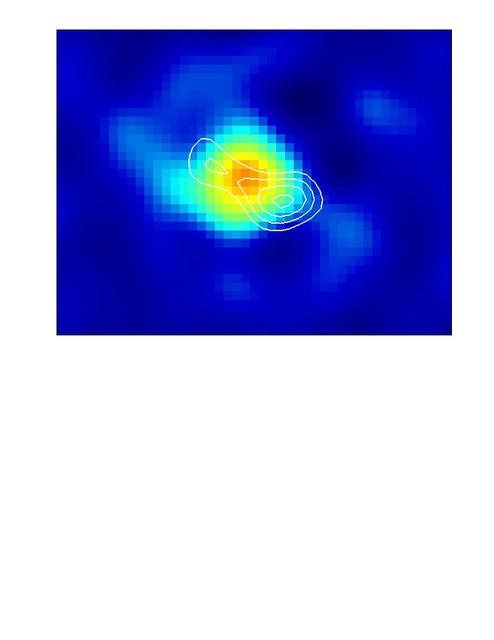
These observations of interstellar dark cloud L1157, are located in the Cepheus constellation. The multi-colored area shows a dust disk surrounding a newborn star.
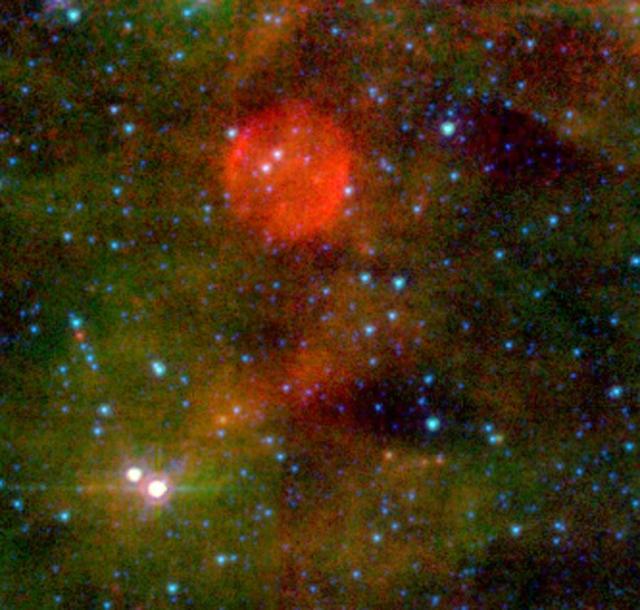

NASA Spitzer Space Telescope caught a glimpse of the Cepheus constellation, thirty thousand light-years away; astronomers think theyve found a massive star whose death barely made a peep.
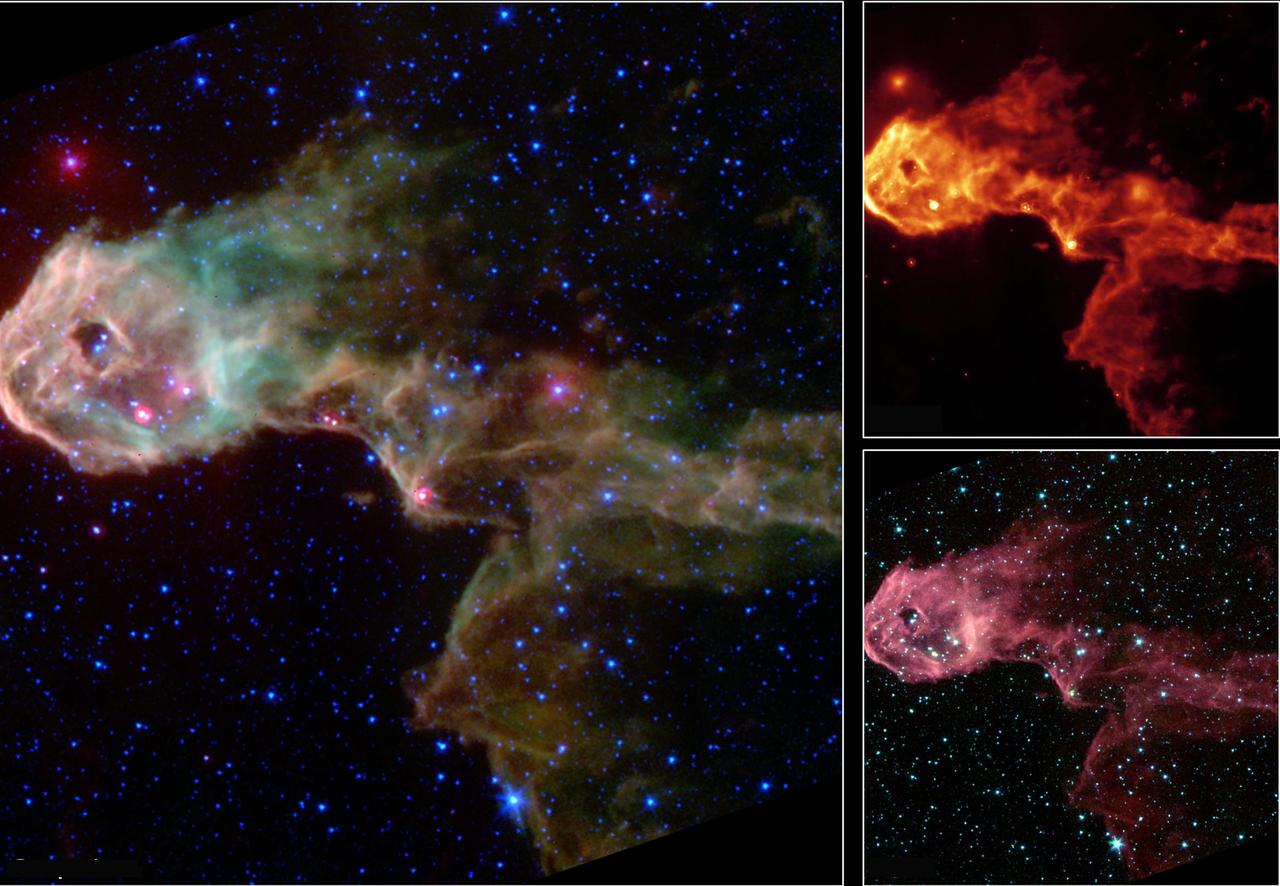

This archival image from 2003 captured by NASA Spitzer Space Telescope captured the Elephant Trunk Nebula, an elongated dark globule within the emission nebula IC 1396 in the constellation of Cepheus.
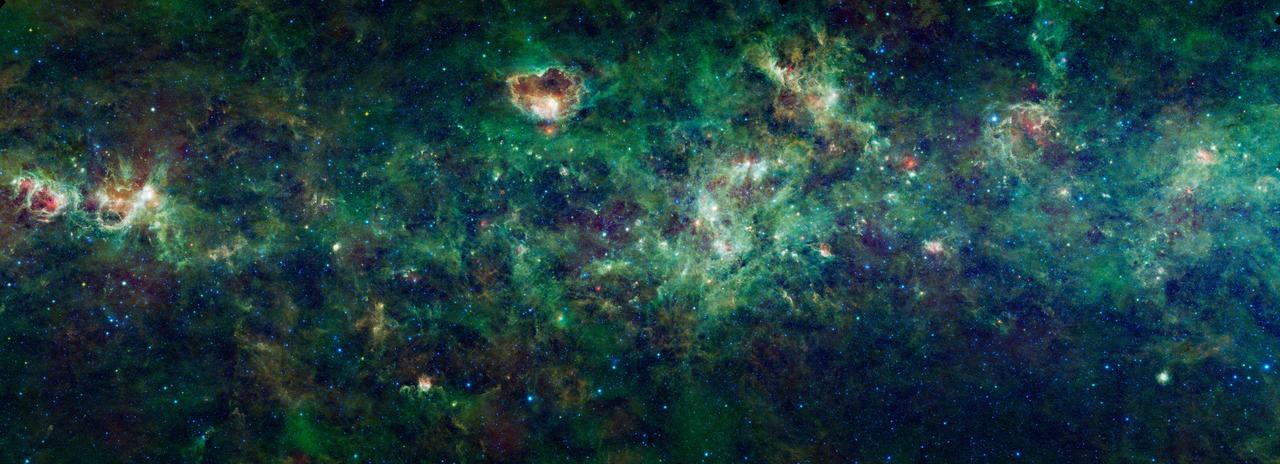

This enormous section of the Milky Way galaxy is a mosaic of images from NASA Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer. The constellations Cassiopeia and Cepheus are featured in this 1,000-square degree expanse.
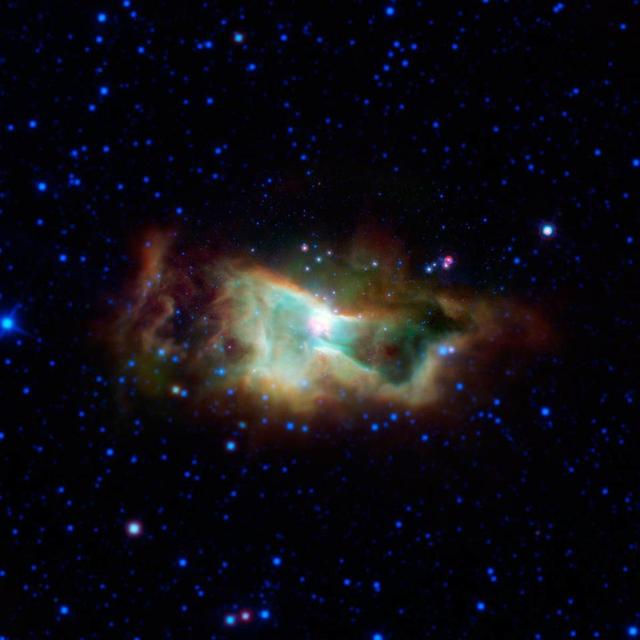

This cloud of glowing gas is the Iris nebula, also called NGC 7023.as seen in infrared light by NASA Spitzer Space Telescope. It lies 1,300 light-years away in the Cepheus constellation.
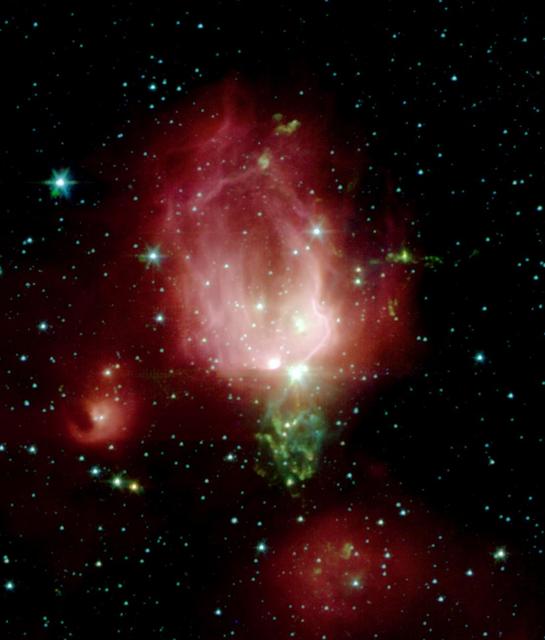

A cluster of newborn stars herald their birth in this interstellar Valentine Day commemorative picture obtained with NASA Spitzer Space Telescope. These bright young stars are found in a rosebud-shaped and rose-colored nebulosity known as NGC 7129. The star cluster and its associated nebula are located at a distance of 3300 light-years in the constellation Cepheus. A recent census of the cluster reveals the presence of 130 young stars. The stars formed from a massive cloud of gas and dust that contains enough raw materials to create a thousand Sun-like stars. In a process that astronomers still poorly understand, fragments of this molecular cloud became so cold and dense that they collapsed into stars. Most stars in our Milky Way galaxy are thought to form in such clusters. The Spitzer Space Telescope image was obtained with an infrared array camera that is sensitive to invisible infrared light at wavelengths that are about ten times longer than visible light. In this four-color composite, emission at 3.6 microns is depicted in blue, 4.5 microns in green, 5.8 microns in orange, and 8.0 microns in red. The image covers a region that is about one quarter the size of the full moon. As in any nursery, mayhem reigns. Within the astronomically brief period of a million years, the stars have managed to blow a large, irregular bubble in the molecular cloud that once enveloped them like a cocoon. The rosy pink hue is produced by glowing dust grains on the surface of the bubble being heated by the intense light from the embedded young stars. Upon absorbing ultraviolet and visible-light photons produced by the stars, the surrounding dust grains are heated and re-emit the energy at the longer infrared wavelengths observed by Spitzer. The reddish colors trace the distribution of molecular material thought to be rich in hydrocarbons. The cold molecular cloud outside the bubble is mostly invisible in these images. However, three very young stars near the center of the image are sending jets of supersonic gas into the cloud. The impact of these jets heats molecules of carbon monoxide in the cloud, producing the intricate green nebulosity that forms the stem of the rosebud. Not all stars are formed in clusters. Away from the main nebula and its young cluster are two smaller nebulae, to the left and bottom of the central 'rosebud,'each containing a stellar nursery with only a few young stars. Astronomers believe that our own Sun may have formed billions of years ago in a cluster similar to NGC 7129. Once the radiation from new cluster stars destroys the surrounding placental material, the stars begin to slowly drift apart. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA05266
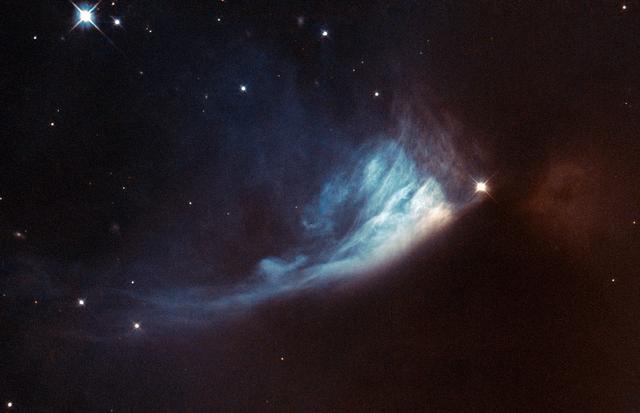

The Universe is rarely static, although the timescales involved can be very long. Since modern astronomical observations began we have been observing the birthplaces of new stars and planets, searching for and studying the subtle changes that help us to figure out what is happening within. The bright spot located at the edge of the bluish fan-shaped structure in this Hubble image is a young star called V* PV Cephei, or PV Cep. It is a favorite target for amateur astronomers because the fan-shaped nebulosity, known as GM 1-29 or Gyulbudaghian’s Nebula, changes over a timescale of months. The brightness of the star has also varied over time. Images of PV Cep taken in 1952 showed a nebulous streak, similar to a comet’s tail. However, this had vanished when new images of the star were obtained some twenty-five years later. Instead, the blue fan-shaped nebula had appeared. Twenty-five years is a very short period on cosmic timescales, so astronomers think that the mysterious streak may have been a temporary phenomenon, such as the remnants of a massive stellar flare — similar to the solar flares we are used to seeing in the solar system. At the same time as this was happening, the star itself was brightening. This provided the light to illuminate the newly formed fan-shaped nebula. This brightening might be related to the start of the hydrogen-burning phase of the star, which would mean that it was reaching maturity. PV Cep is thought to be surrounded by a disc of gas and dust, which would stop light from escaping in all directions. The fan-like appearance is therefore probably a result of starlight escaping from the dust disc and projecting onto the nebula. PV Cep is located in the northern constellation of Cepheus at a distance of over 1600 light-years from Earth. European Space Agency/NASA Hubble <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>