
The blue dots in this field of galaxies, known as the COSMOS field, show galaxies that contain supermassive black holes emitting high-energy X-rays. The black holes were detected by NASA's Nuclear Spectroscopic Array, or NuSTAR, which spotted 32 such black holes in this field and has observed hundreds across the whole sky so far. The other colored dots are galaxies that host black holes emitting lower-energy X-rays, and were spotted by NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory. Chandra data show X-rays with energies between 0.5 to 7 kiloelectron volts, while NuSTAR data show X-rays between 8 to 24 kiloelectron volts. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20865
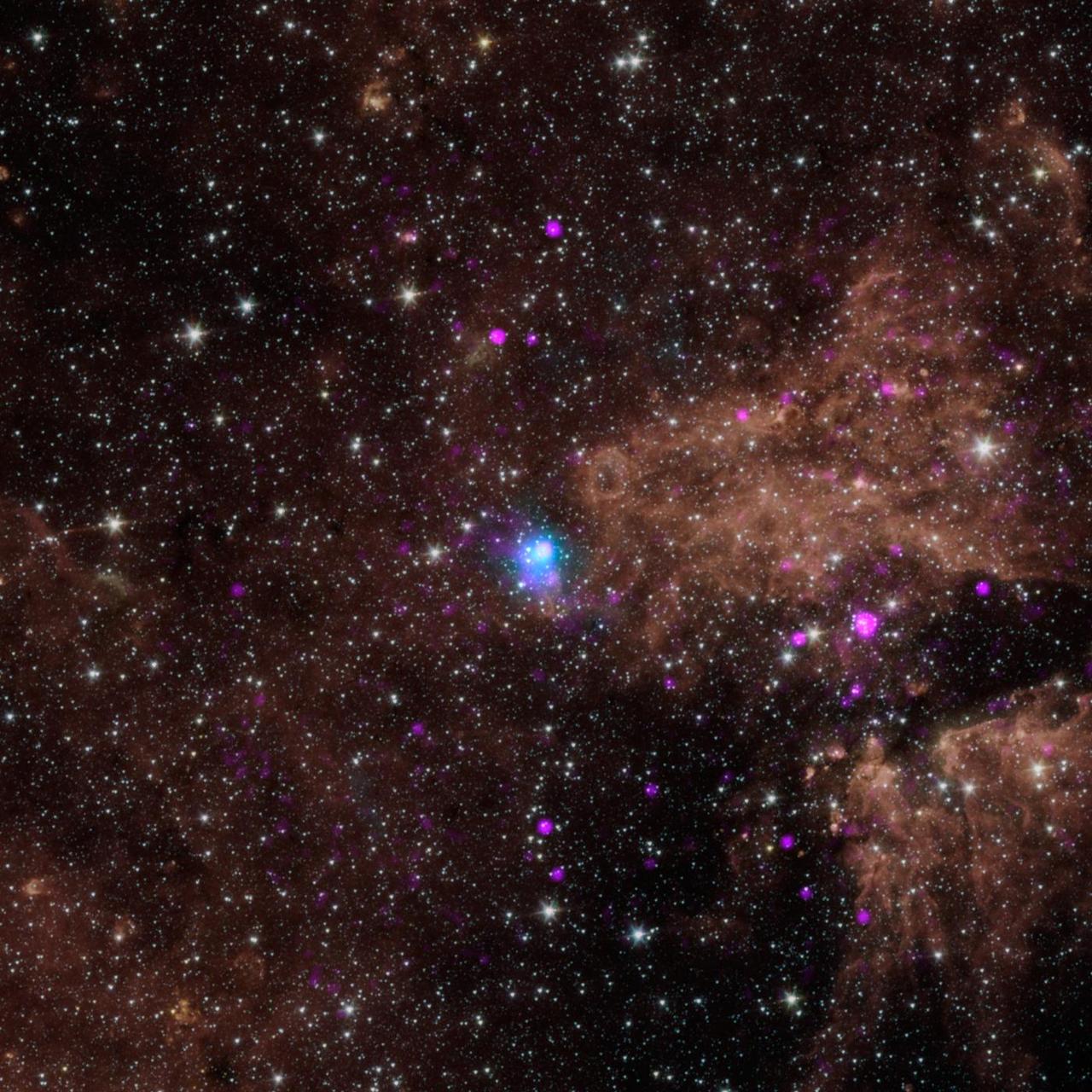

The blue dot in this image marks the spot of an energetic pulsar -- the magnetic, spinning core of star that blew up in a supernova explosion. NASA NuSTAR discovered the pulsar by identifying its telltale pulse.
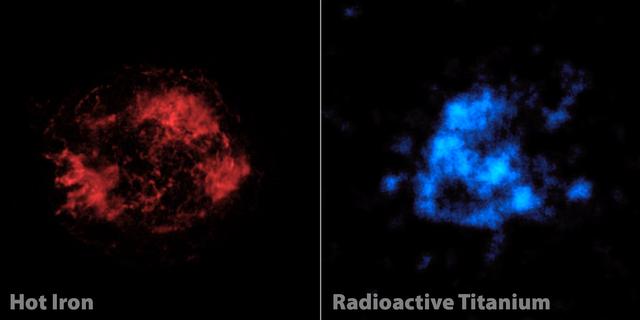
When astronomers first looked at images of a supernova remnant called Cassiopeia A, captured by NASA NuSTAR. The mystery of Cassiopeia A Cas A, a massive star that exploded in a supernova more than 11,000 years ago continues to confound scientists.
NASA NuSTAR has, for the first time, imaged the radioactive guts of a supernova remnant, the leftover remains of a star that exploded. The NuSTAR data are blue, and show high-energy X-rays.
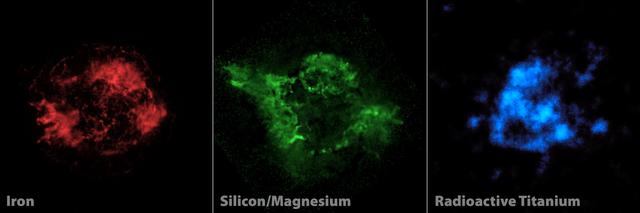
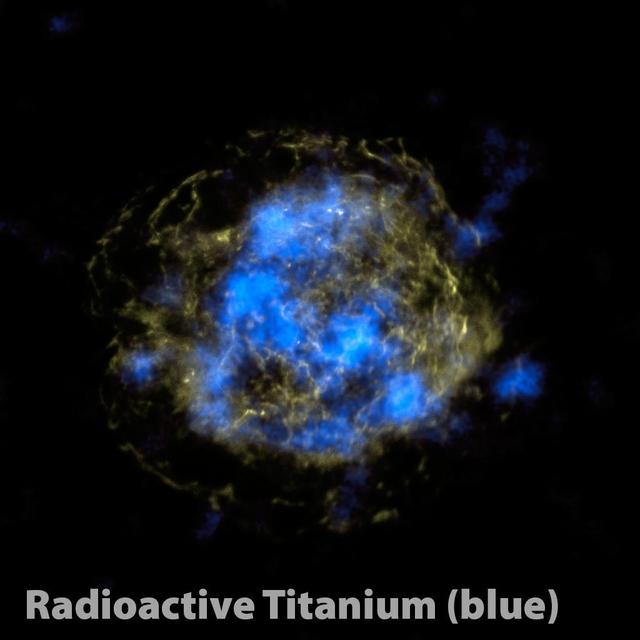
NASA NuSTAR is complementing previous observations of the Cassiopeia A supernova remnant red and green by providing the first maps of radioactive material forged in the fiery explosion blue.
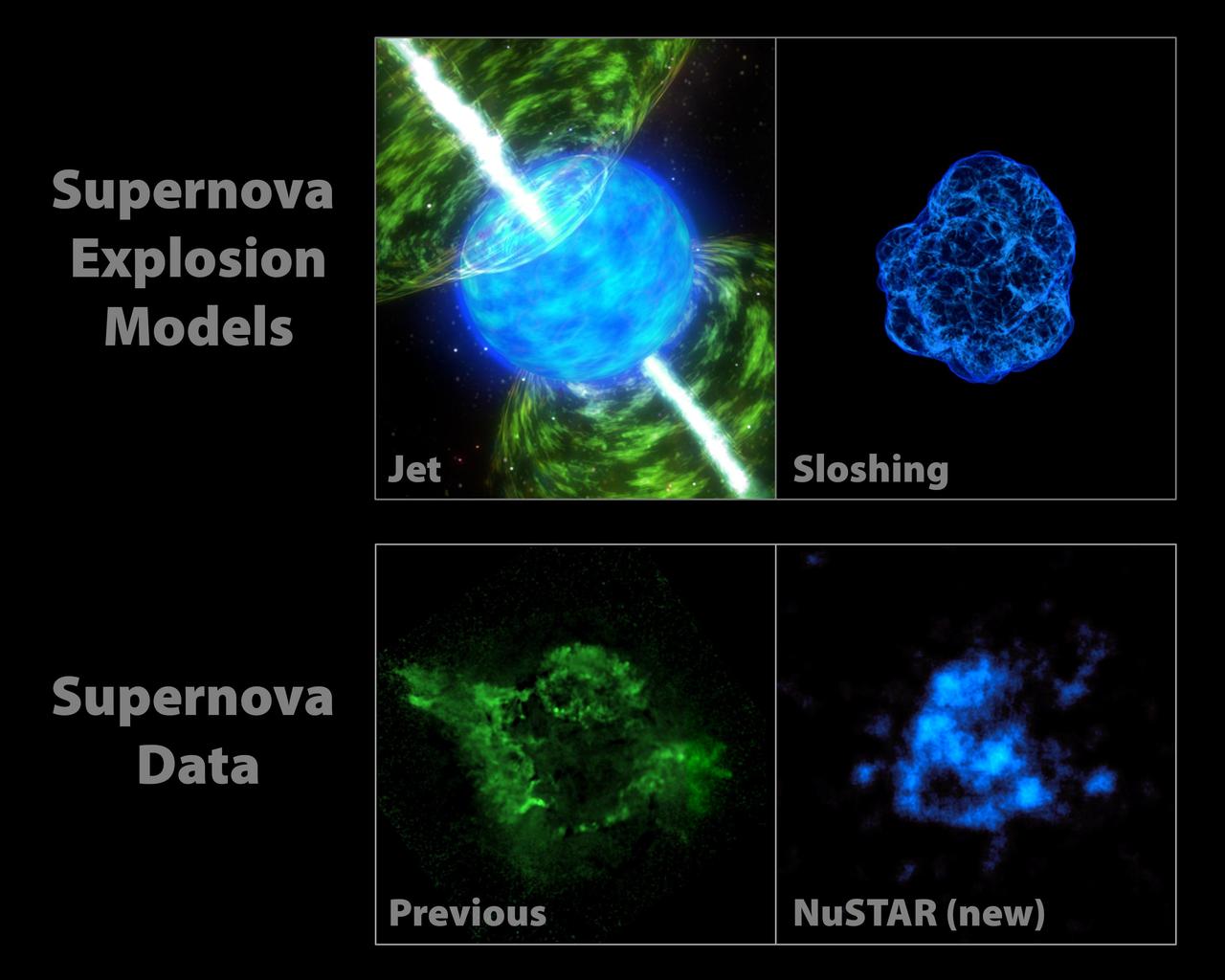
The images at the top of this graphic represent two popular models describing how stars blast apart. The models point to different triggers of the explosion. Jet-driven models are illustrated with an artist concept shown at left.
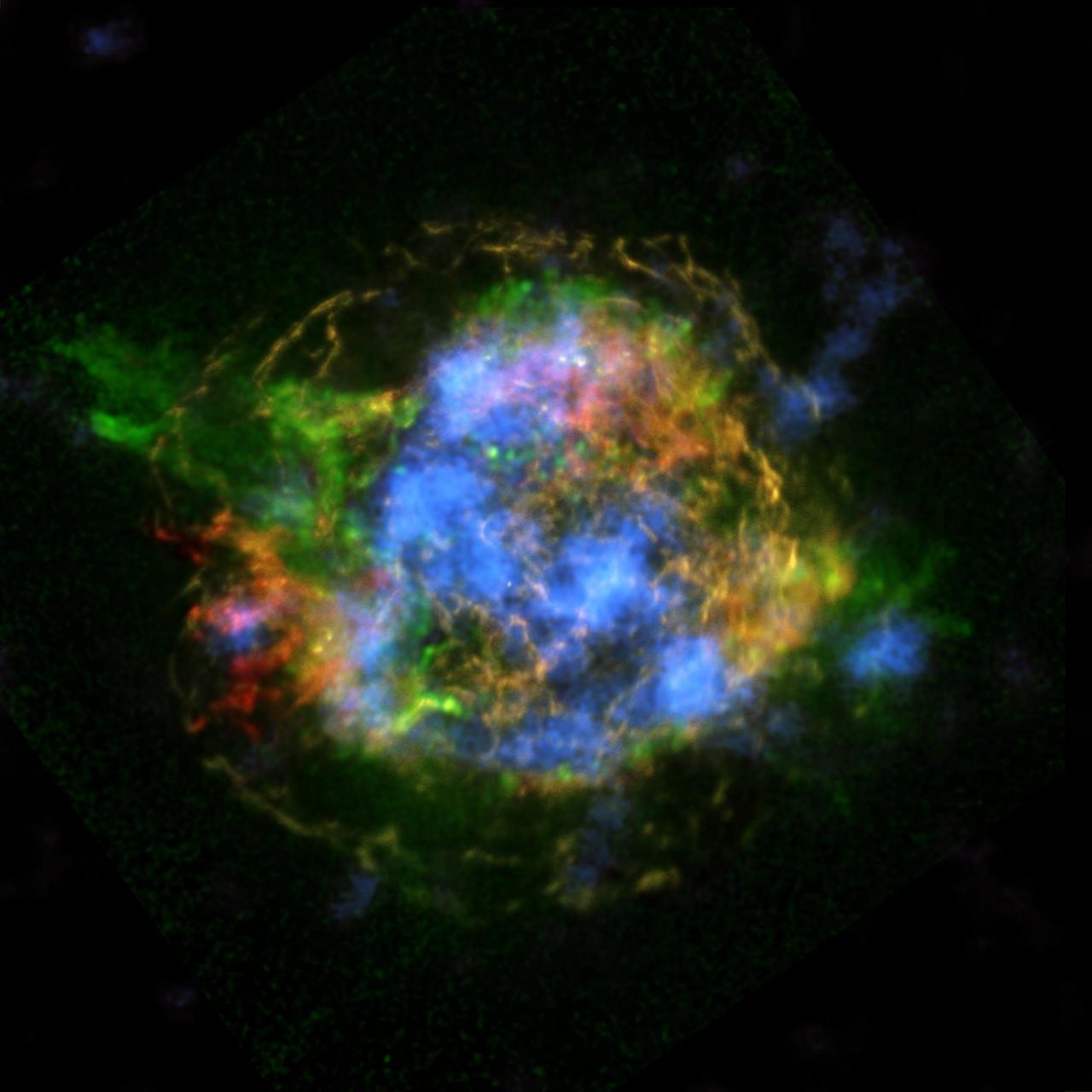
This is the first map of radioactivity in a supernova remnant, the blown-out bits and pieces of a massive star that exploded. The blue color shows radioactive material mapped in high-energy X-rays using NASA NuSTAR.

A massive star left, which has created elements as heavy as iron in its interior, blows up in a tremendous explosion middle, scattering its outer layers in a structure called a supernova remnant right.
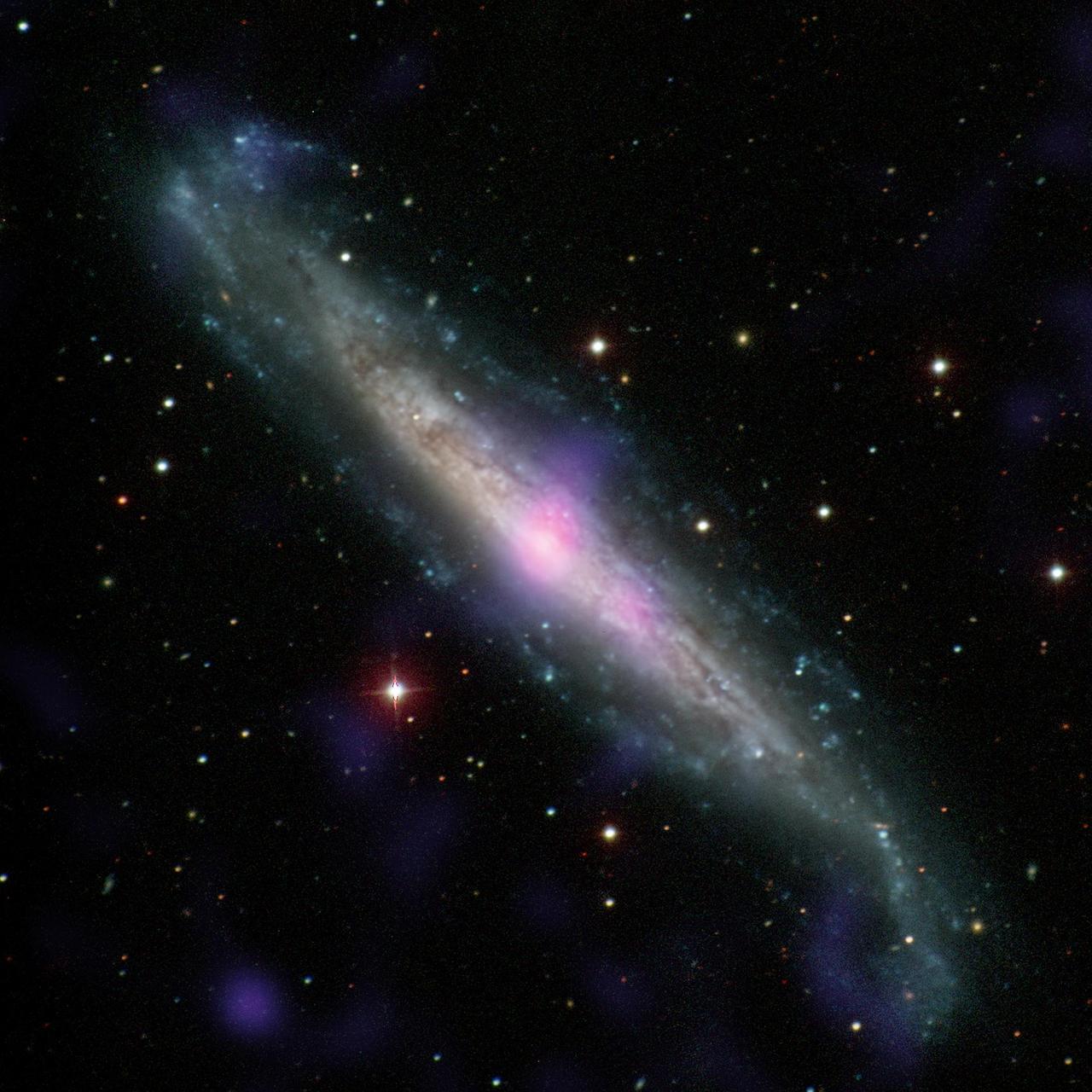

NGC 1448, a galaxy with an active galactic nucleus, is seen in this image combining data from the Carnegie-Irvine Galaxy Survey in the optical range and NuSTAR in the X-ray range. This galaxy contains an example of a supermassive black hole hidden by gas and dust. X-ray emissions from NGC 1448, as seen by NuSTAR and Chandra, suggests for the first time that, like IC 3639 in PIA21087, there must be a thick layer of gas and dust hiding the active black hole in this galaxy from our line of sight. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21086

The blue dots in this field of galaxies, known as the COSMOS field, show galaxies that contain supermassive black holes emitting high-energy X-rays. The black holes were detected by NASA's Nuclear Spectroscopic Array, or NuSTAR, which spotted 32 such black holes in this field and has observed hundreds across the whole sky so far. The other colored dots are galaxies that host black holes emitting lower-energy X-rays, and were spotted by NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory. Chandra data show X-rays with energies between 0.5 to 7 kiloelectron volts, while NuSTAR data show X-rays between 8 to 24 kiloelectron volts. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20865
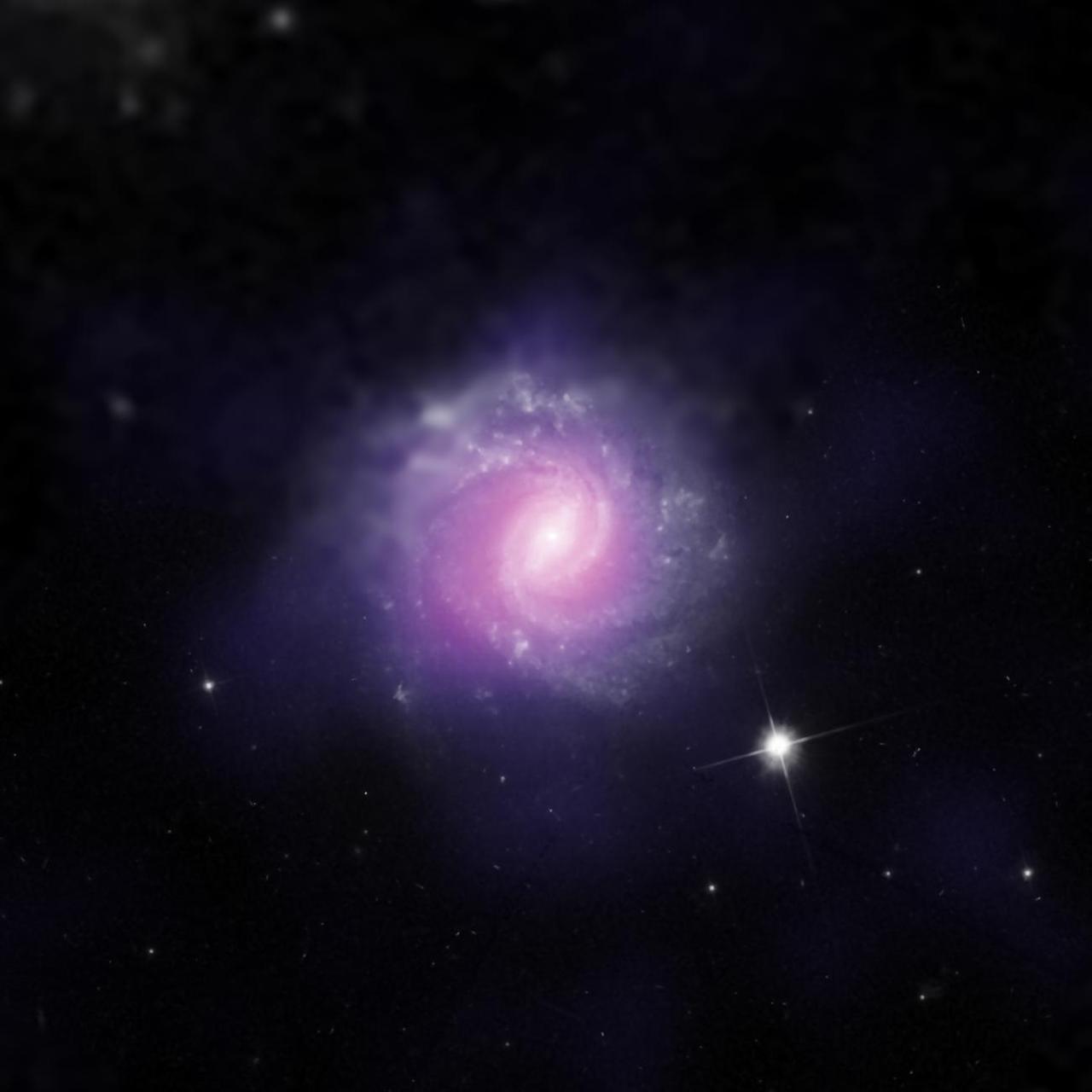

IC 3639, a galaxy with an active galactic nucleus, is seen in this image combining data from the Hubble Space Telescope and the European Southern Observatory. This galaxy contains an example of a supermassive black hole hidden by gas and dust. Researchers analyzed NuSTAR data from this object and compared them with previous observations from NASA's Chandra X-Ray Observatory and the Japanese-led Suzaku satellite. The findings from NuSTAR, which is more sensitive to higher energy X-rays than these observatories, confirm the nature of IC 3639 as an active galactic nucleus that is heavily obscured, and intrinsically much brighter than observed. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21087
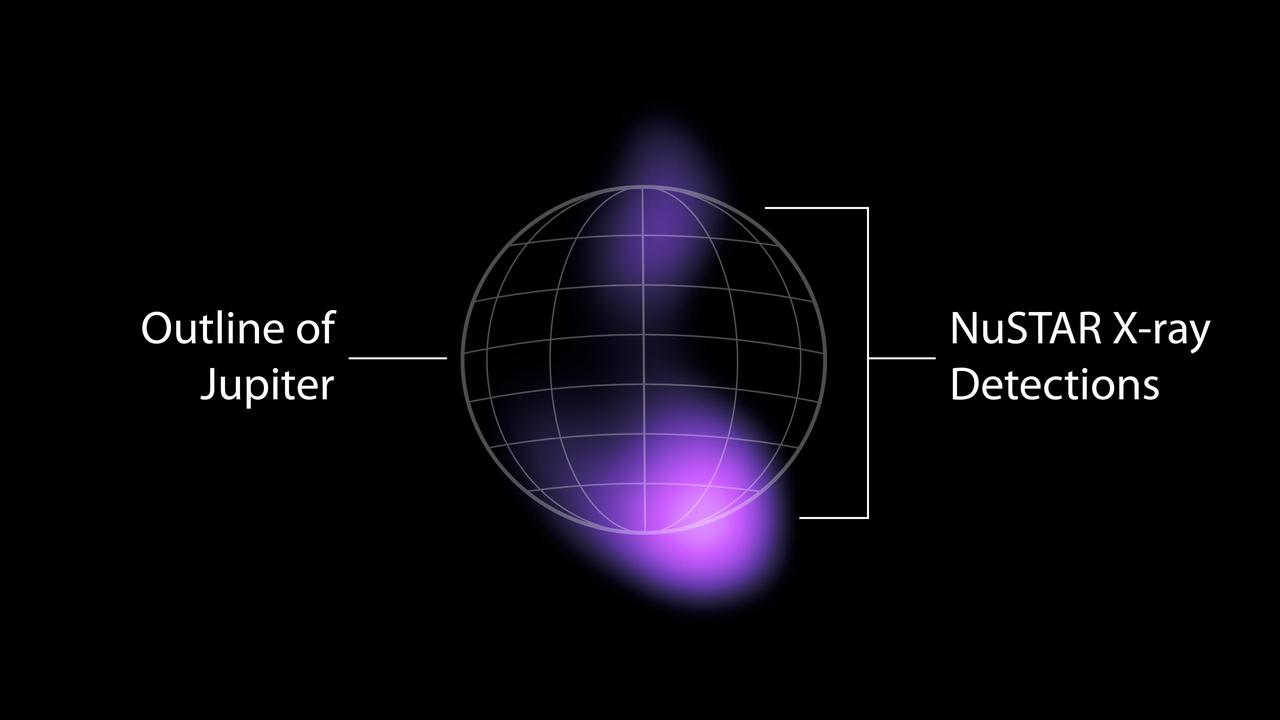
The areas where high-energy X-rays were detected by NASA's NuSTAR (Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array) from the auroras near Jupiter's north and south poles are shown in purple in this graphic. The emissions are the highest-energy light ever seen at Jupiter and the highest-energy light ever detected from a planet in our solar system other than Earth. The light comes from accelerated electrons colliding with the atmosphere. NuSTAR cannot pinpoint the source of the light with high precision, but can only find that it is coming from somewhere in the purple-colored regions. X-rays are a form of light, but with much higher energies and shorter wavelengths than the visible light human eyes can see. NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory and the ESA (European Space Agency) XMM-Newton observatory have both studied X-rays from Jupiter's auroras – produced when volcanos on Jupiter's moon Io shower the planet with ions (atoms stripped of their electrons). Jupiter's powerful magnetic field accelerates the particles and funnels them toward the planet's poles, where they collide with its atmosphere and release energy in the form of light, including X-rays. Electrons from Io are also accelerated by the planet's magnetic field, according to observations by the Jovian Auroral Distributions Experiment (JADE) and Jupiter Energetic-particle Detector Instrument (JEDI) on NASA's Juno spacecraft, which arrived at Jupiter in 2016. Researchers suspected that those electrons should produce even higher-energy X-rays than those observed by Chandra and XMM-Newton, and the NuSTAR detections confirm that hypothesis. The high-energy X-rays are relatively faint, and required a week of NuSTAR observations to detect. Scientists have detected X-rays in Earth's auroras with even higher energies than what NuSTAR saw at Jupiter, but those emissions can only be spotted by small satellites or high-altitude balloons that get extremely close to the locations in the atmosphere that generate those X-rays. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25131
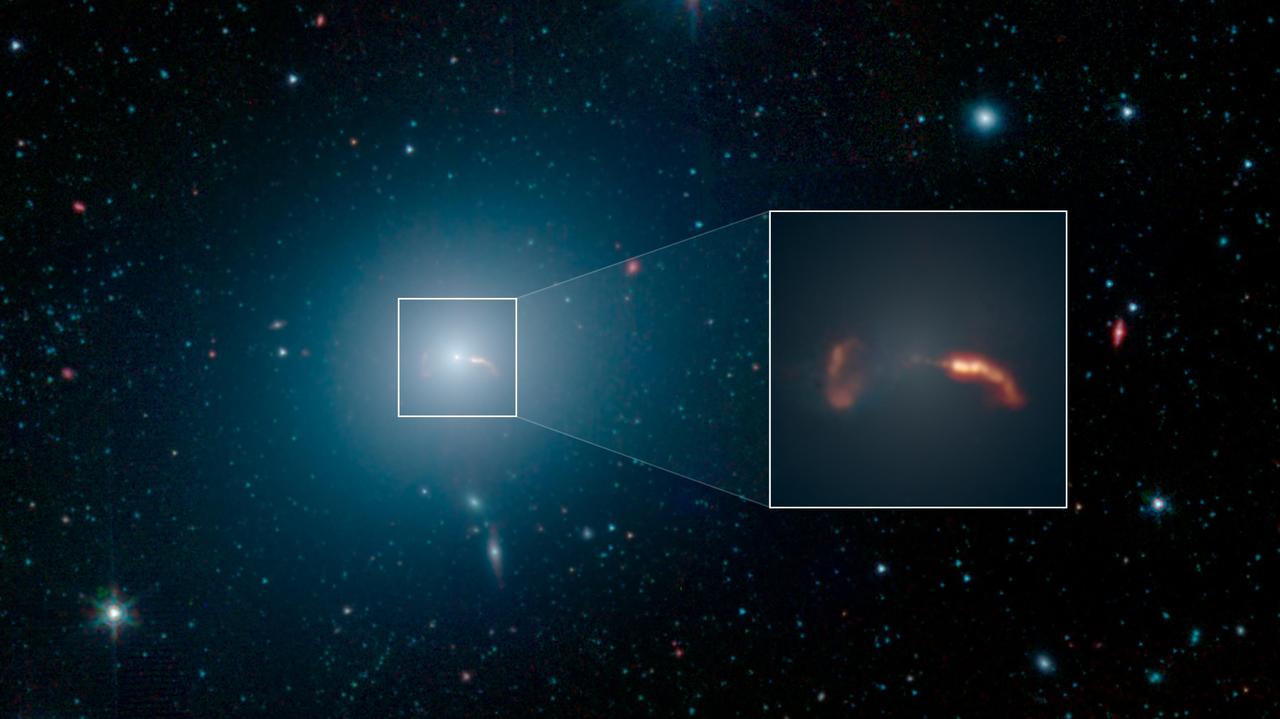

This image from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope shows the elliptical galaxy Messier 87 (M87), the home galaxy of the supermassive black hole recently imaged by the Event Horizon Telescope (EHT). Spitzer's infrared view shows a faint trace of a jet of material spewing to the right of the galaxy - a feature that was previously one key indicator that a supermassive black hole lived at the galaxy's center. More prominent in the image is the shockwave created by that jet. The inset in the image below shows a close-up view of the shockwave on the right side of the galaxy, as well as the shockwave from a second jet traveling to the left of the galaxy. Located about 55 million light-years from Earth, M87 has been a subject of astronomical study for more than 100 years and has been imaged by many NASA observatories, including the Hubble Space Telescope, the Chandra X-ray Observatory and NuSTAR. In 1918, astronomer Heber Curtis first noticed "a curious straight ray" extending from the galaxy's center. This bright jet (which appears to extend to the right of the galaxy) is visible in multiple wavelengths of light, from radio waves through X-rays. The jet is produced by a disk of material spinning rapidly around the black hole, and spewing in opposite directions away from the galaxy. When the particles in the jet impact the interstellar medium (the sparse material filling the space between stars in M87), they create a shockwave that radiates in infrared and radio wavelengths of light, but not visible light. The jet on the right is traveling almost directly toward Earth, and its brightness is amplified due to its high speed in our direction. But the jet's trajectory is just slightly offset from our line of sight with the galaxy, so we can still see some of the length of the jet. The shockwave begins around the point where the jet appears to curve down, highlighting the regions where the fast-moving particles are colliding with gas in the galaxy and slowing down. There is also a second jet on the left that is moving so rapidly away from us it is rendered invisible at all wavelengths. But the shockwave it creates in the interstellar medium can still be seen here. In the Spitzer image, the shockwave is on the left side of the galaxy and looks like an inverted letter "C." Scientists are still striving for a solid theoretical understanding of how inflowing gas around black holes creates outflowing jets. Infrared light at wavelengths of 3.6 and 4.5 microns are rendered in blue and green, showing the distribution of stars, while dust features that glow brightly at 8.0 microns are shown in red. The image was taken during Spitzer's initial "cold" mission. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23122

This is a Hubble Space Telescope composite image of a supernova explosion designated SN 2014J in the galaxy M82. At a distance of approximately 11.5 million light-years from Earth it is the closest supernova of its type discovered in the past few decades. The explosion is categorized as a Type Ia supernova, which is theorized to be triggered in binary systems consisting of a white dwarf and another star — which could be a second white dwarf, a star like our sun, or a giant star. Astronomers using a ground-based telescope discovered the explosion on January 21, 2014. This Hubble photograph was taken on January 31, as the supernova approached its peak brightness. The Hubble data are expected to help astronomers refine distance measurements to Type Ia supernovae. In addition, the observations could yield insights into what kind of stars were involved in the explosion. Hubble’s ultraviolet-light sensitivity will allow astronomers to probe the environment around the site of the supernova explosion and in the interstellar medium of the host galaxy. Because of their consistent peak brightness, Type Ia supernovae are among the best tools to measure distances in the universe. They were fundamental to the 1998 discovery of the mysterious acceleration of the expanding universe. A hypothesized repulsive force, called dark energy, is thought to cause the acceleration. Among the other major NASA space-based observatories used in the M82 viewing campaign are Spitzer Space Telescope, Chandra X-ray Observatory, Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR), Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope, Swift Gamma Ray Burst Explorer, and the Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA). Image Credit: NASA, ESA, A. Goobar (Stockholm University), and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA) <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>