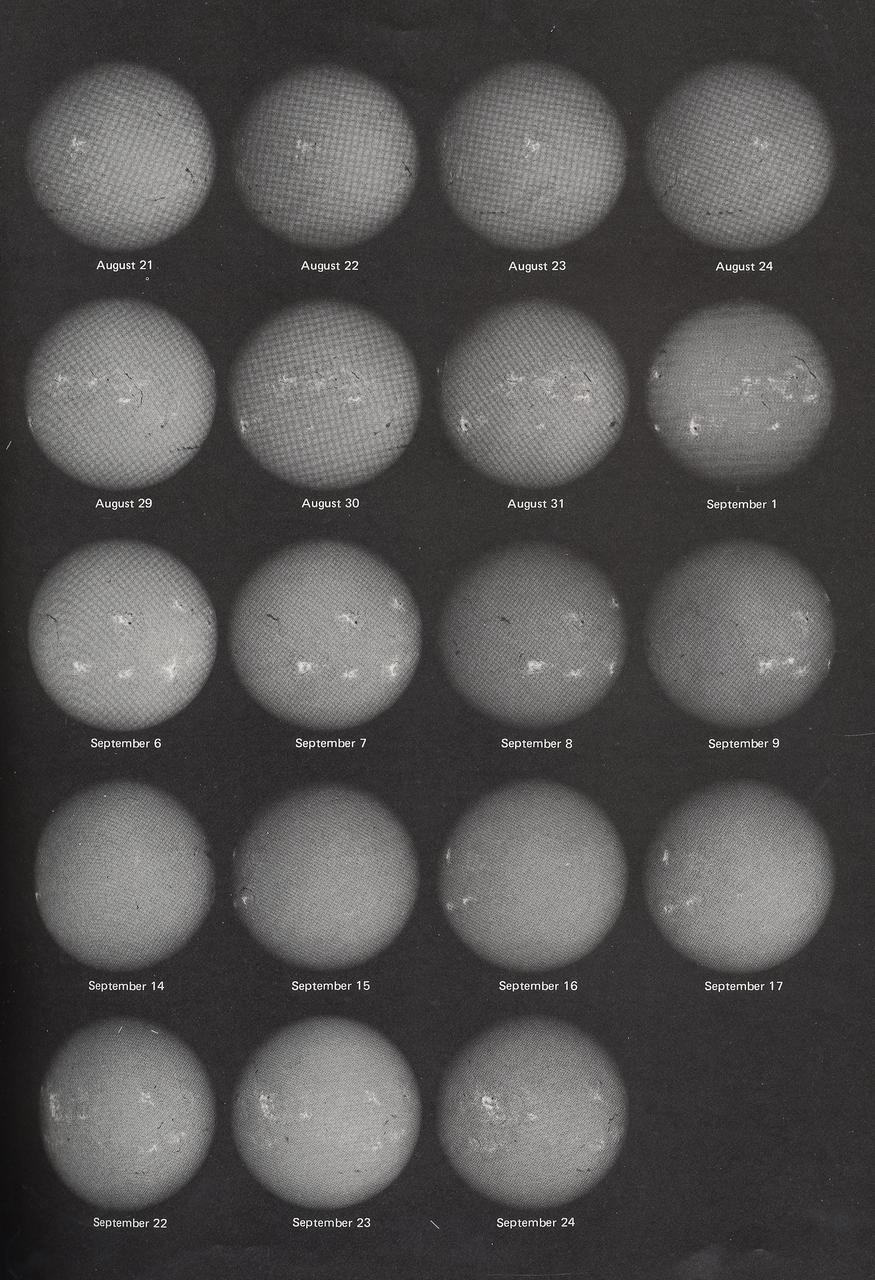
This montage shows changing faces of the Sun, recorded daily during the 59 days spent in orbit by Skylab's second crew. The Sun spun more than two full turns around its axis. Solar rotation is apparent in these daily portraits, as are real changes on the Sun. Bright features are centers of activity on the Sun. This image contains daily records from September 6, 1973 through September 24, 1973.
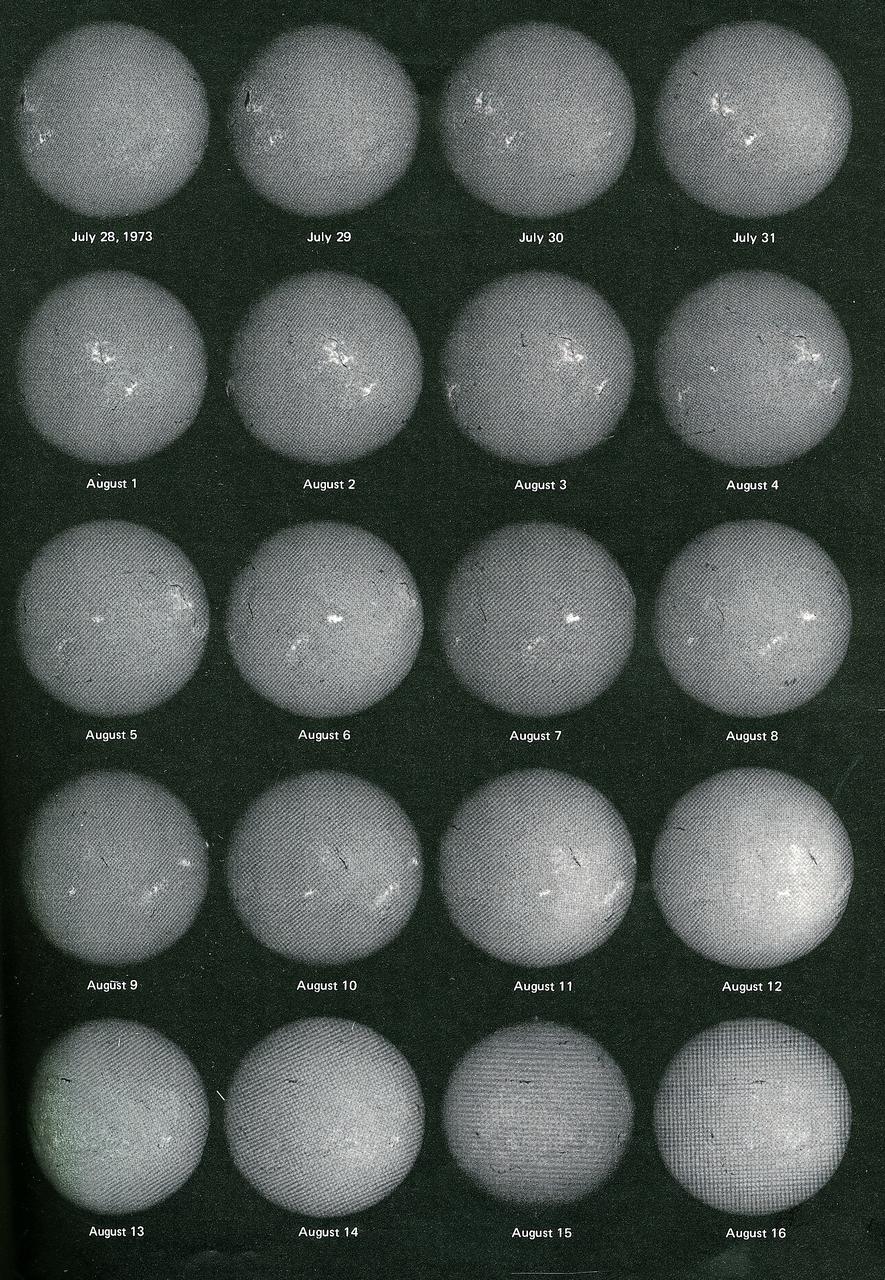
This montage shows changing faces of the Sun, recorded daily during the 59 days spent in orbit by Skylab's second crew. The Sun spun more than two full turns around its axis. Solar rotation is apparent in these daily portraits, as are real changes on the Sun. Bright features are centers of activity on the Sun. This image contains daily records from July 28, 1973 through August 16, 1973.

This montage shows changing faces of the Sun, recorded daily during the 59 days spent in orbit by Skylab's second crew. The Sun spun more than two full turns around its axis. Solar rotation is apparent in these daily portraits, as are real changes on the Sun. Bright features are centers of activity on the Sun. This image contains daily records from August 17, 1973 through September 5, 1973.

It is early springtime in the southern hemisphere of Mars in this image from NASA Mars Odyssey. The south polar cap is now illuminated by the sun and the surface can be studied as it changes with the passage of spring.
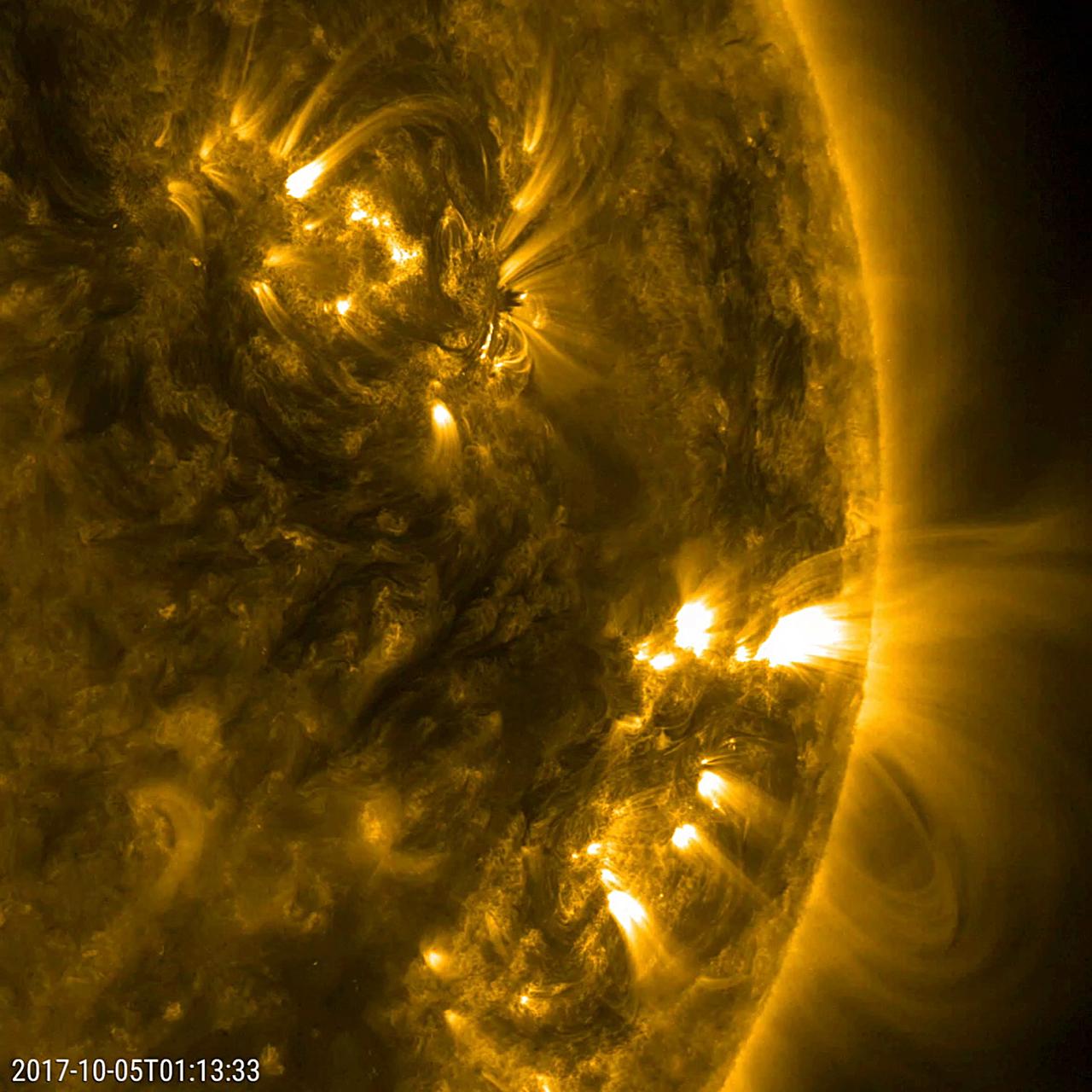

This close-up video clip shows a pair of active regions (the brighter areas) move and change as they rotate with the sun over just a 17-hour period (Oct. 4-5, 2017). They were observed in a wavelength of extreme ultraviolet light that reveals plasma heated to over a million degrees. The arches above the regions consist of charge particles spinning along and revealing magnetic field lines. Each one shows a few minor bursts of material none of them were serious. Animations are available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22039
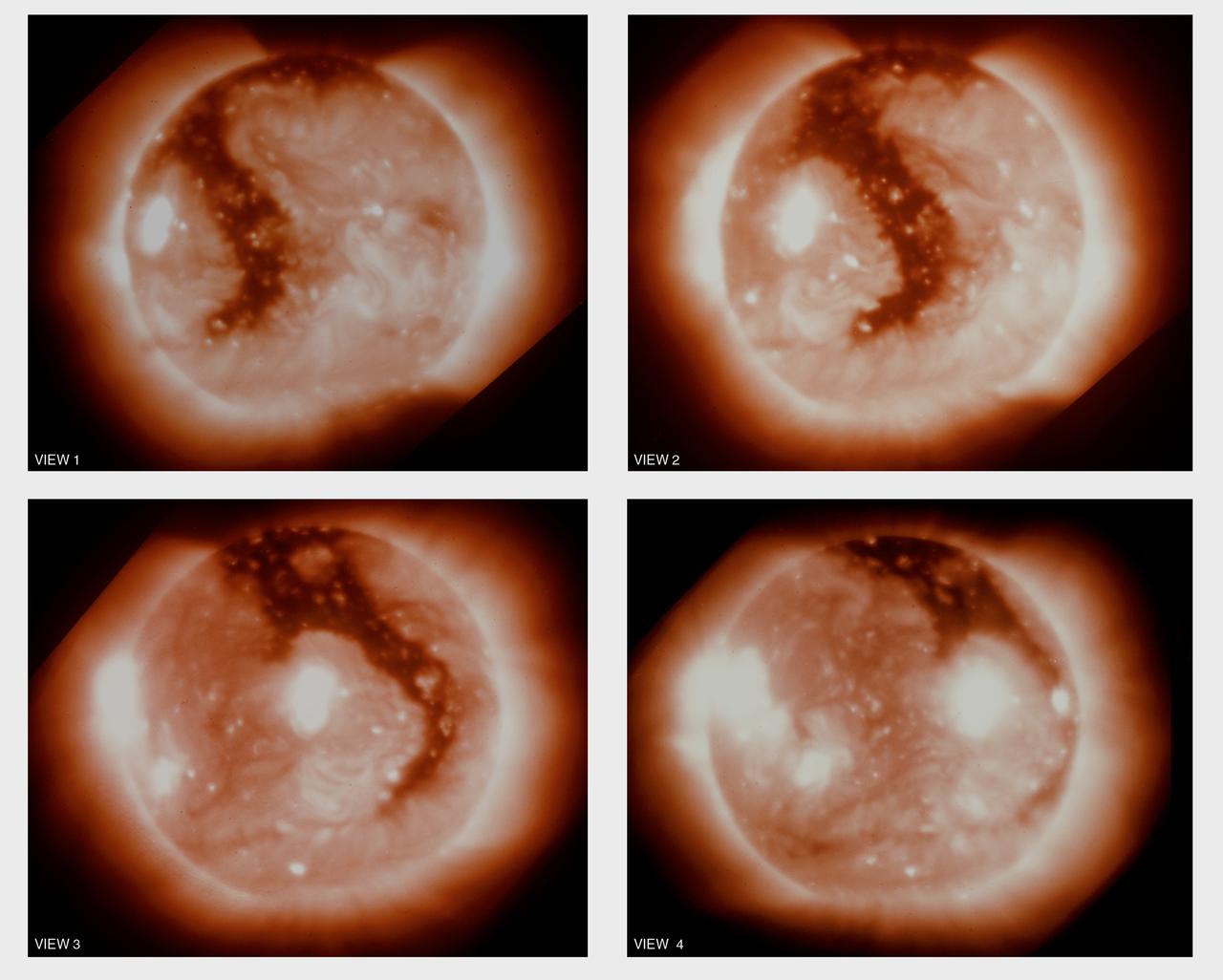
This montage is a sequence of soft x-ray photographs of the boot-shaped coronal hole rotating with the sun. The individual pictures were taken about 2 days apart by the Skylab telescope. Most of the apparent changes in this 6-day period resulted from a changing perspective. Skylab data helped demonstrate that coronal holes are sources of high-velocity streams in the solar wind. These high-velocity streams can be electrons, protons, and atomic nuclei that spray out from the Sun into interplanetary space. When the coronal hole is near the center of the Sun, as in view 2, the sprinkler is directed at Earth. These high-speed streams of solar wind distort Earth's magnetic field and disturb it's upper atmosphere.

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft atop stands vertical at Launch Complex 39A as the sun sets on Monday, Sept. 22, 2025, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft atop stands vertical at Launch Complex 39A as the sun sets on Monday, Sept. 22, 2025, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
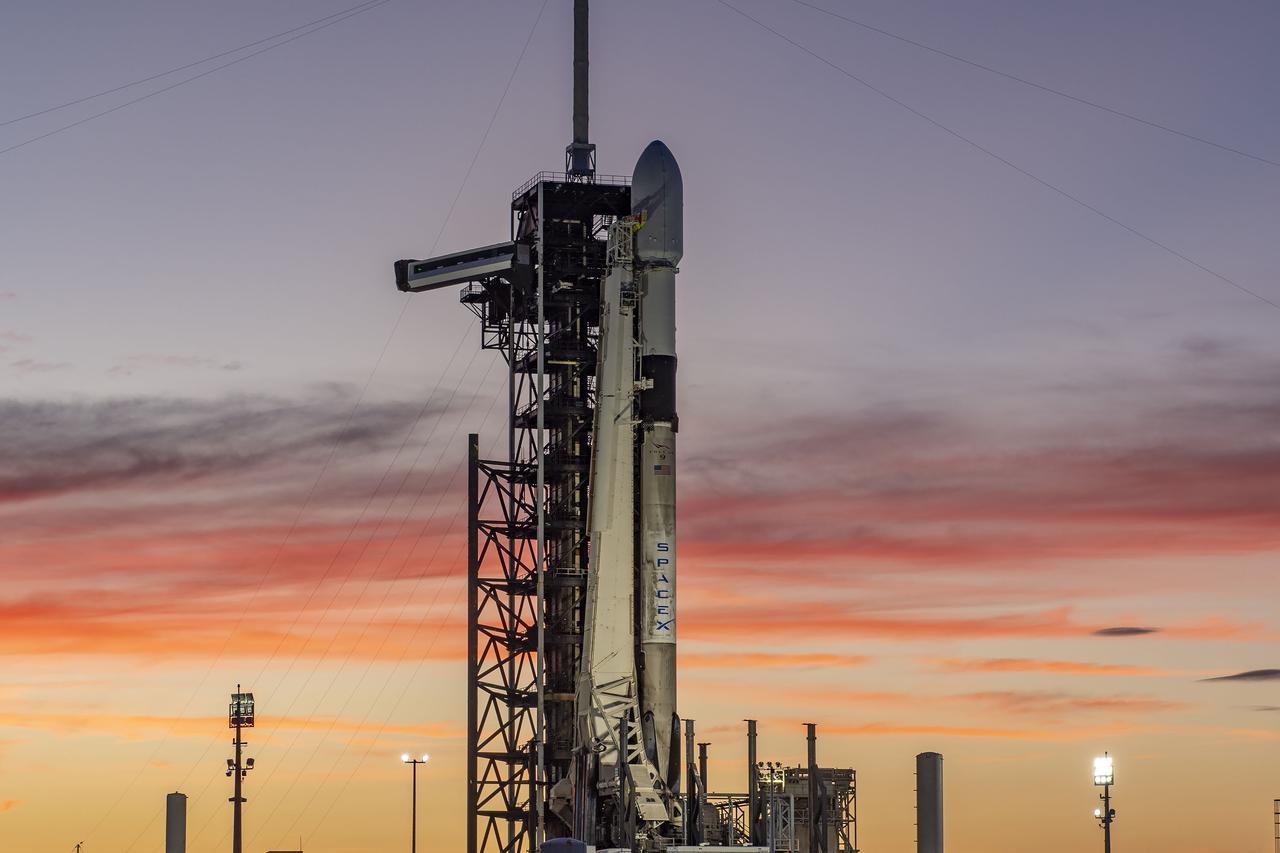

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft atop stands vertical at Launch Complex 39A as the sun sets on Monday, Sept. 22, 2025, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
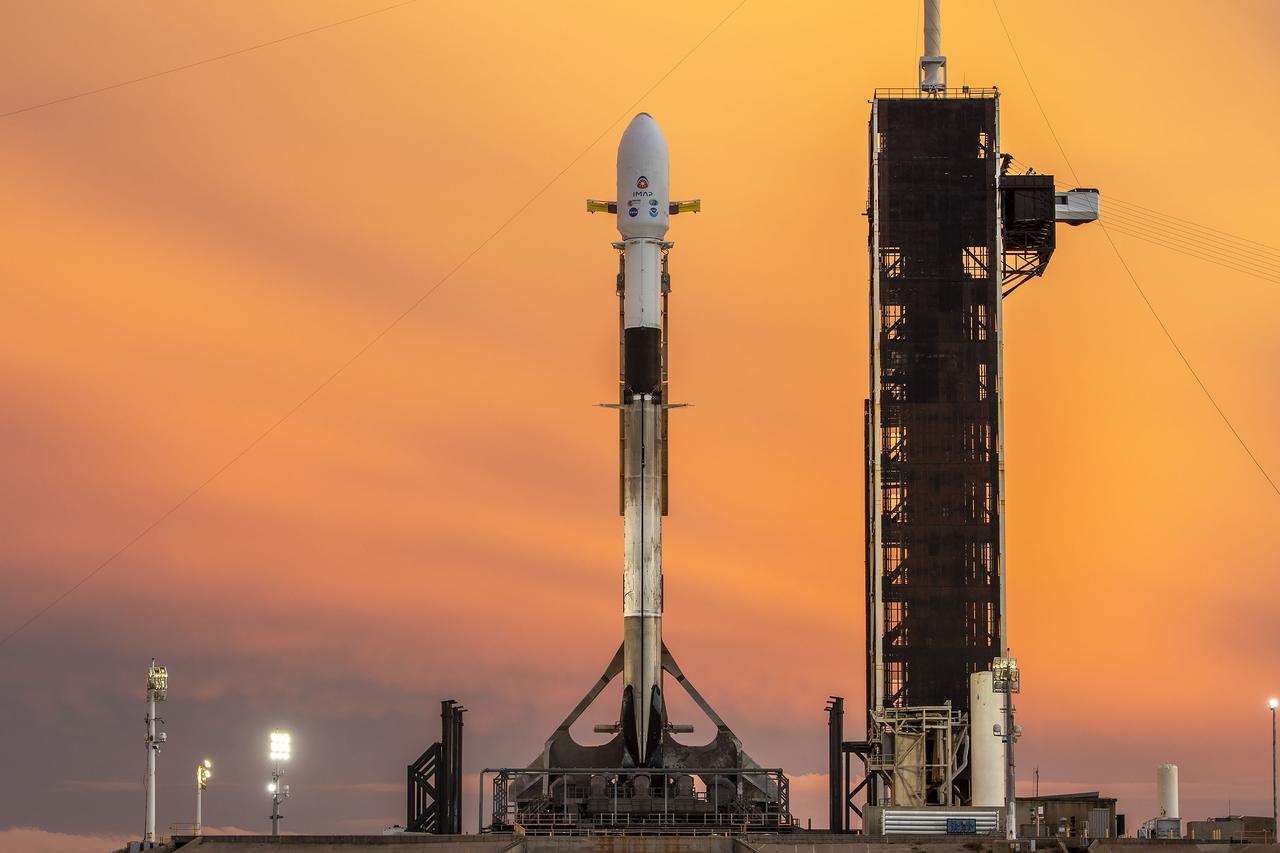

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft atop stands vertical at Launch Complex 39A as the sun sets on Monday, Sept. 22, 2025, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft atop stands vertical at Launch Complex 39A as the sun sets on Monday, Sept. 22, 2025, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.

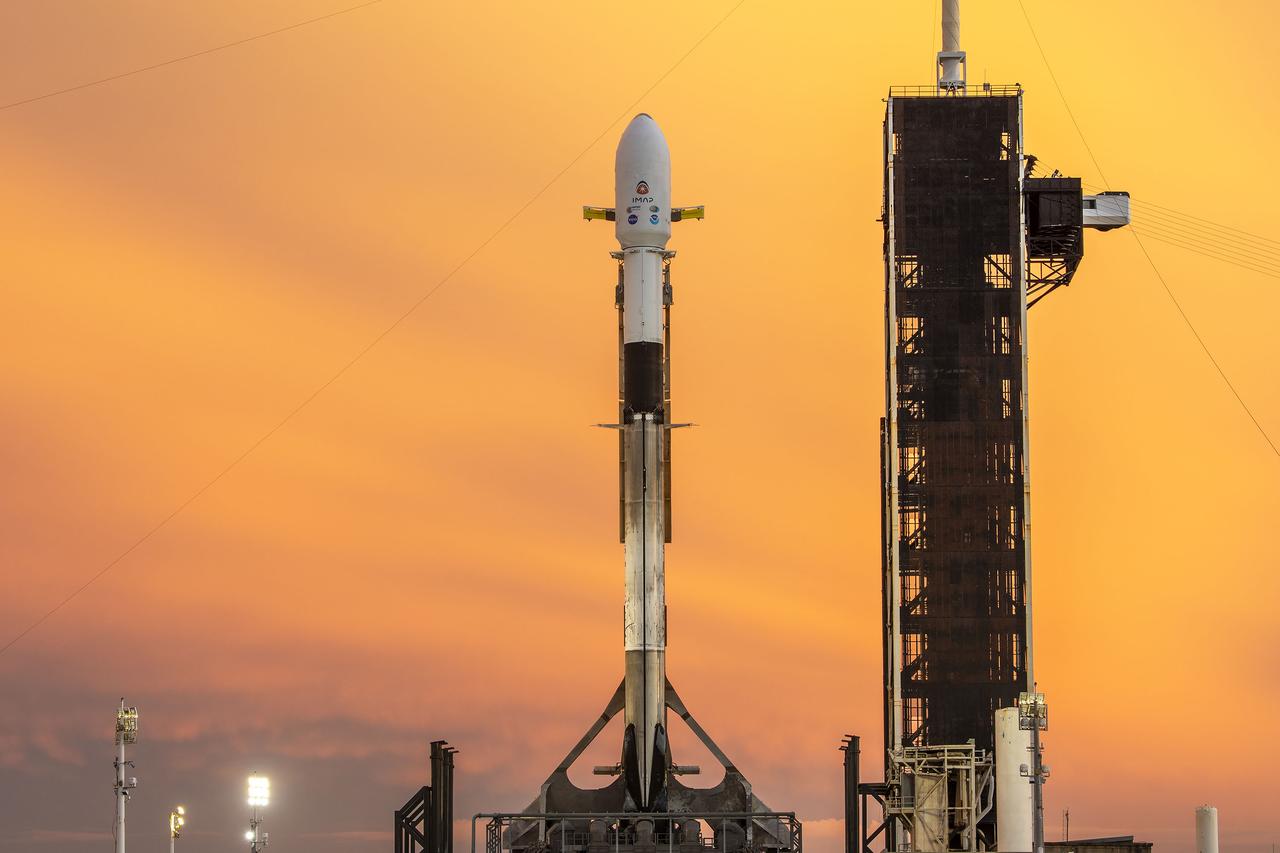
A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft atop stands vertical at Launch Complex 39A as the sun sets on Monday, Sept. 22, 2025, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
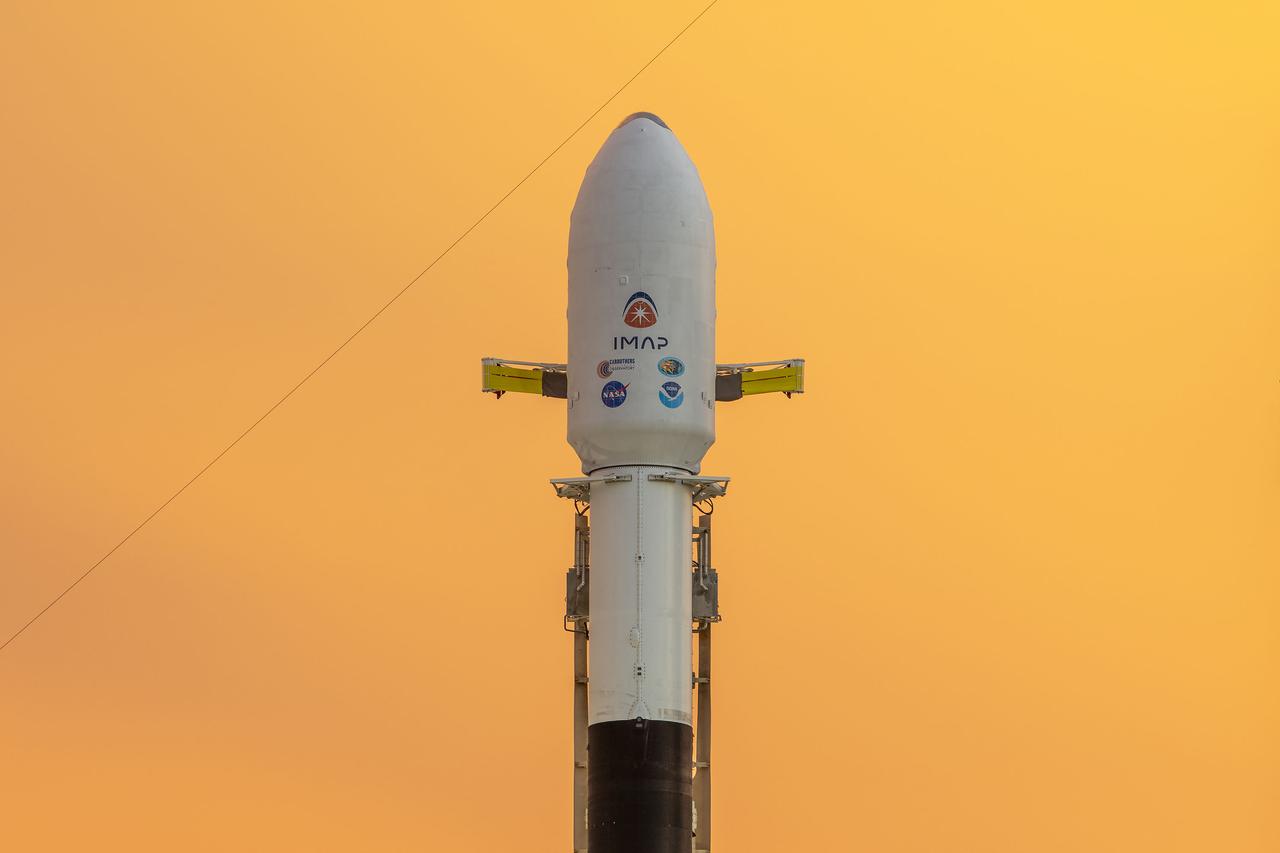

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft atop stands vertical at Launch Complex 39A as the sun sets on Monday, Sept. 22, 2025, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
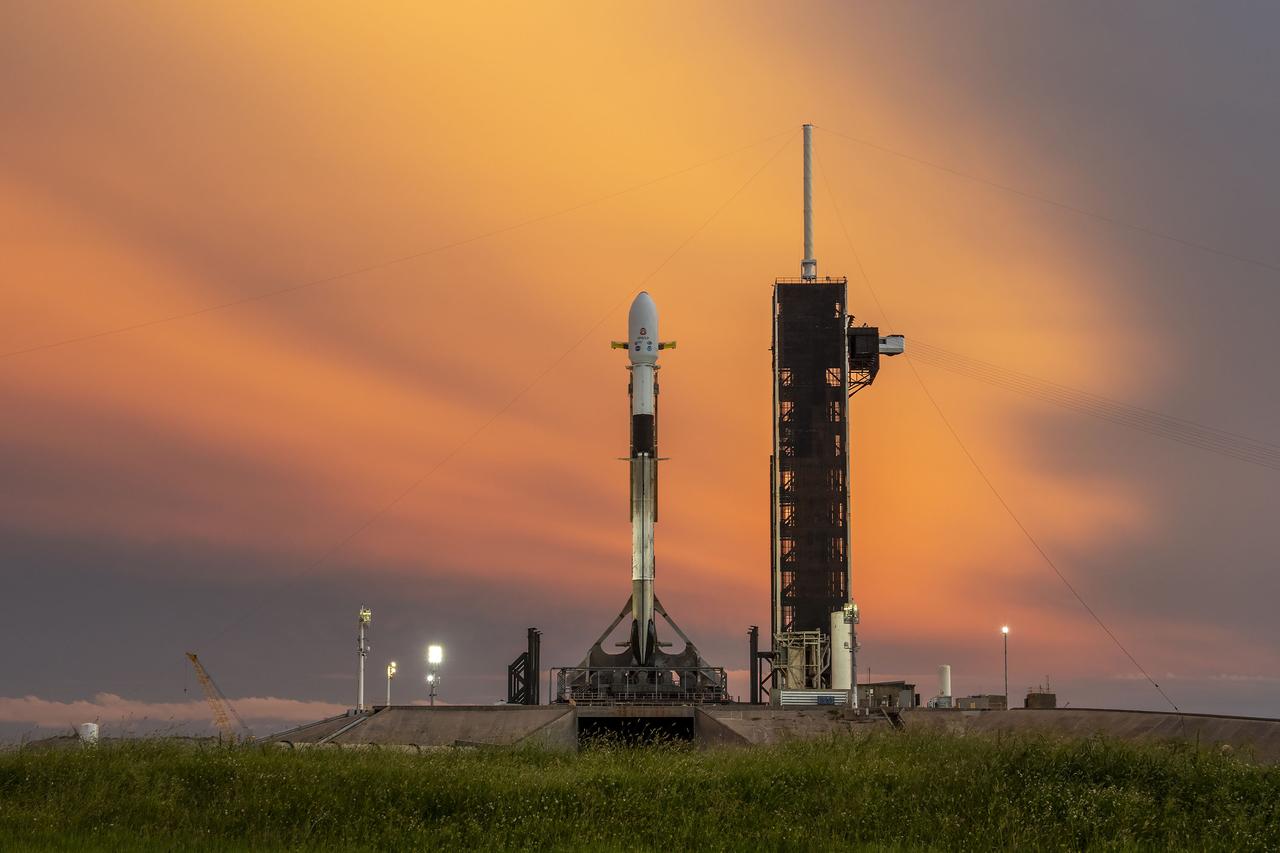

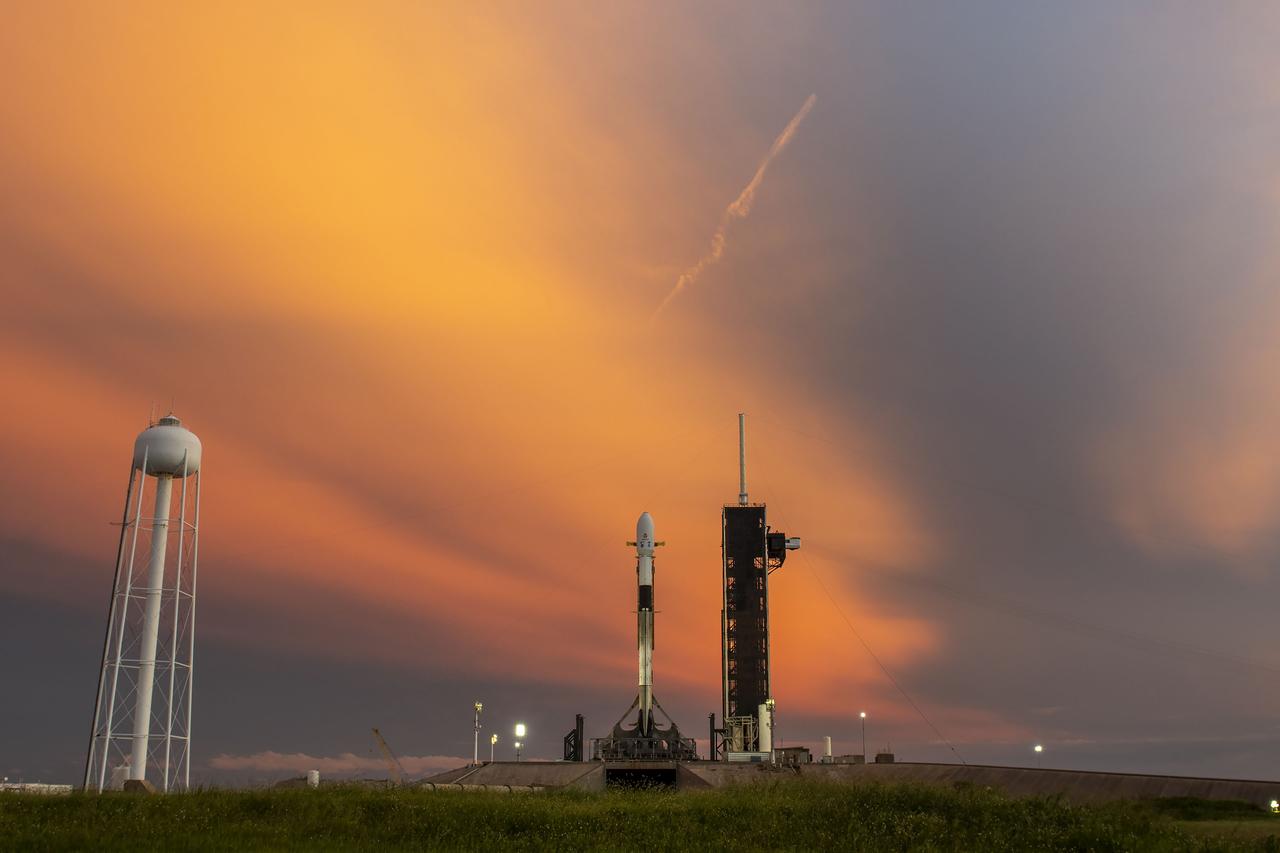
A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft atop stands vertical at Launch Complex 39A as the sun sets on Monday, Sept. 22, 2025, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
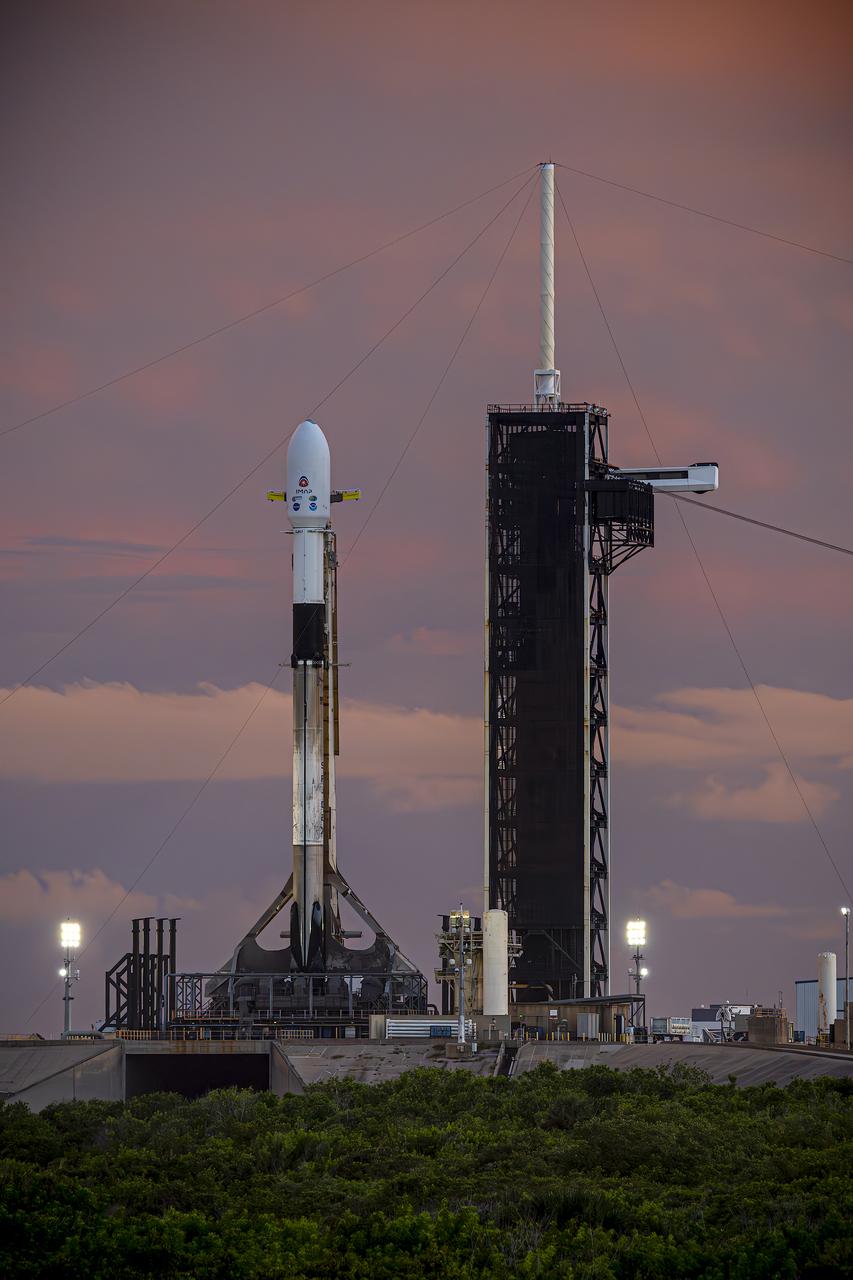

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft atop stands vertical at Launch Complex 39A as the sun sets on Monday, Sept. 22, 2025, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
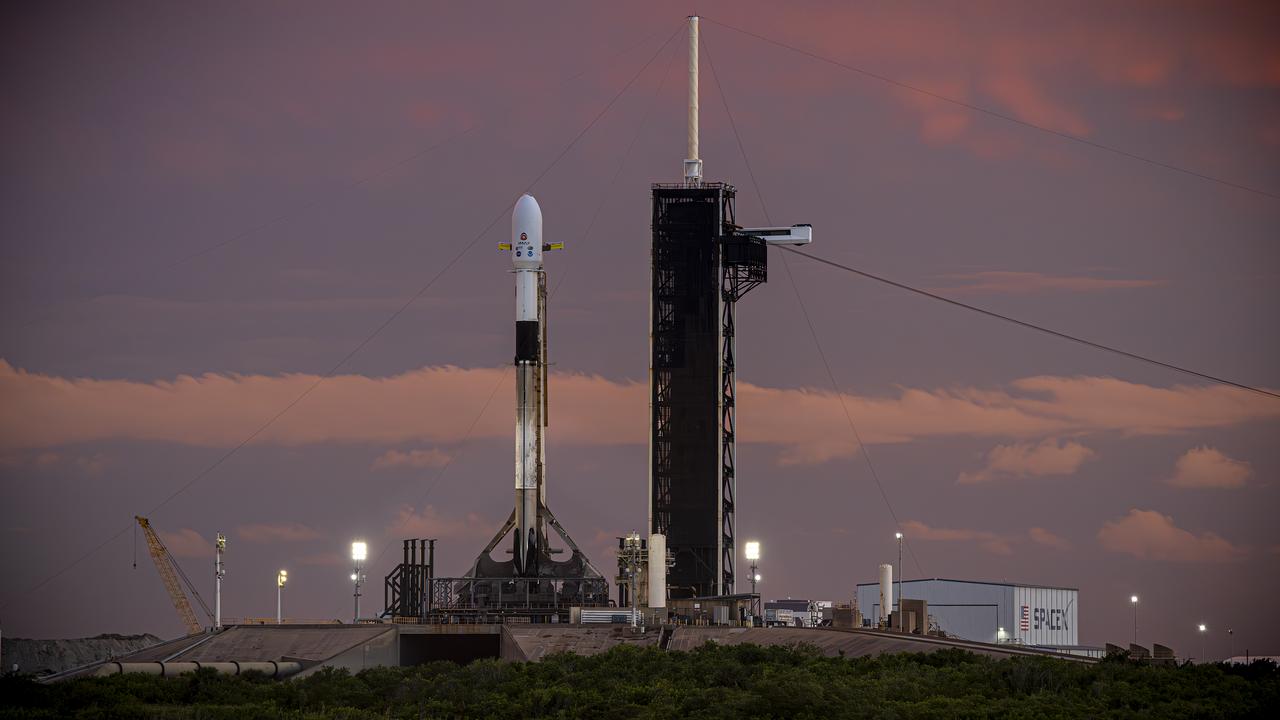

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft atop stands vertical at Launch Complex 39A as the sun sets on Monday, Sept. 22, 2025, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
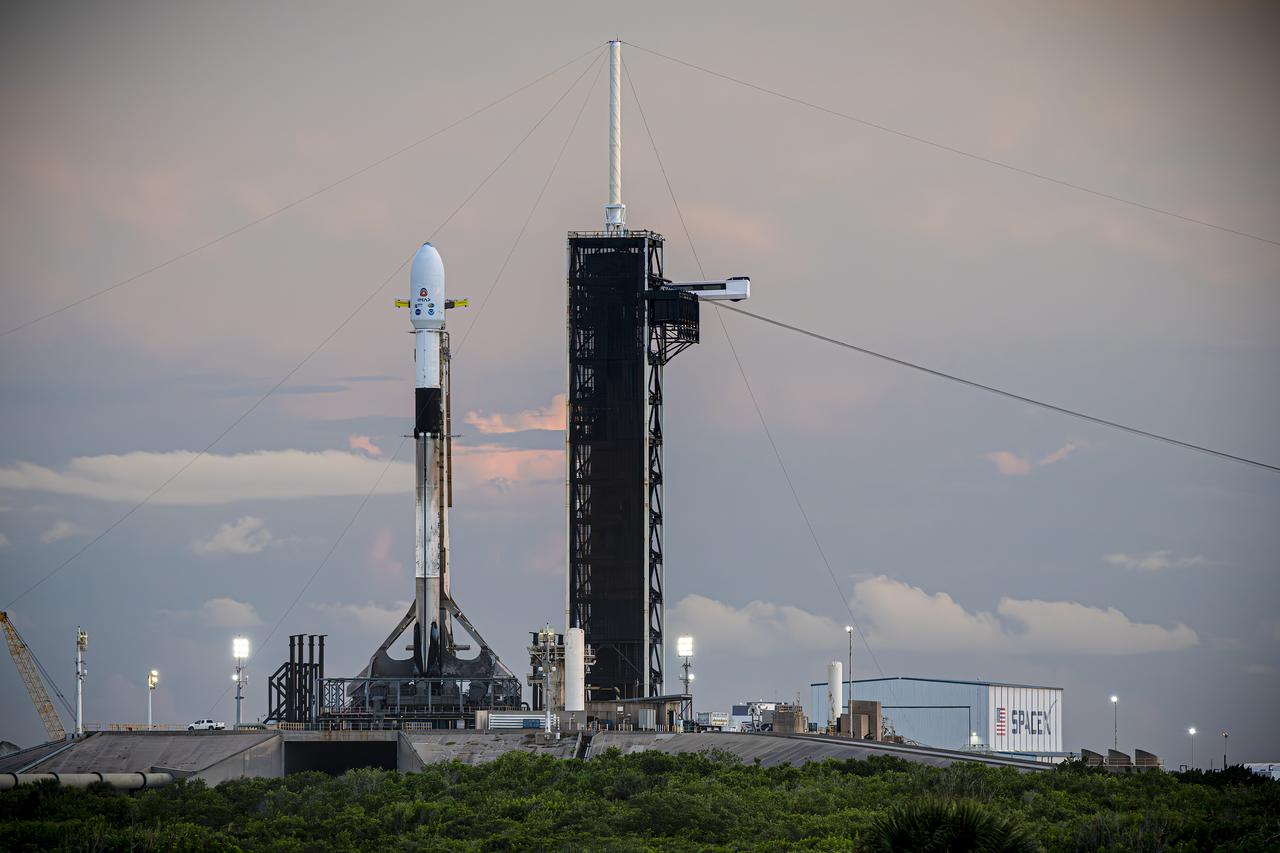

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft atop stands vertical at Launch Complex 39A as the sun sets on Monday, Sept. 22, 2025, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.

A prominence rose up above the sun, sent an arch of plasma to link up magnetically with an active region over a one-day period (Jan, 9-10, 2017). Then the flow of plasma seemed to largely change direction and head back where it came from. Finally, amidst the confused patterns of movement, it dissipated and fell away. Prominences are cooler clouds of charged particles tenuously tethered to the sun by magnetic forces. Images were taken in a wavelength of extreme ultraviolet light. Movies are available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22199
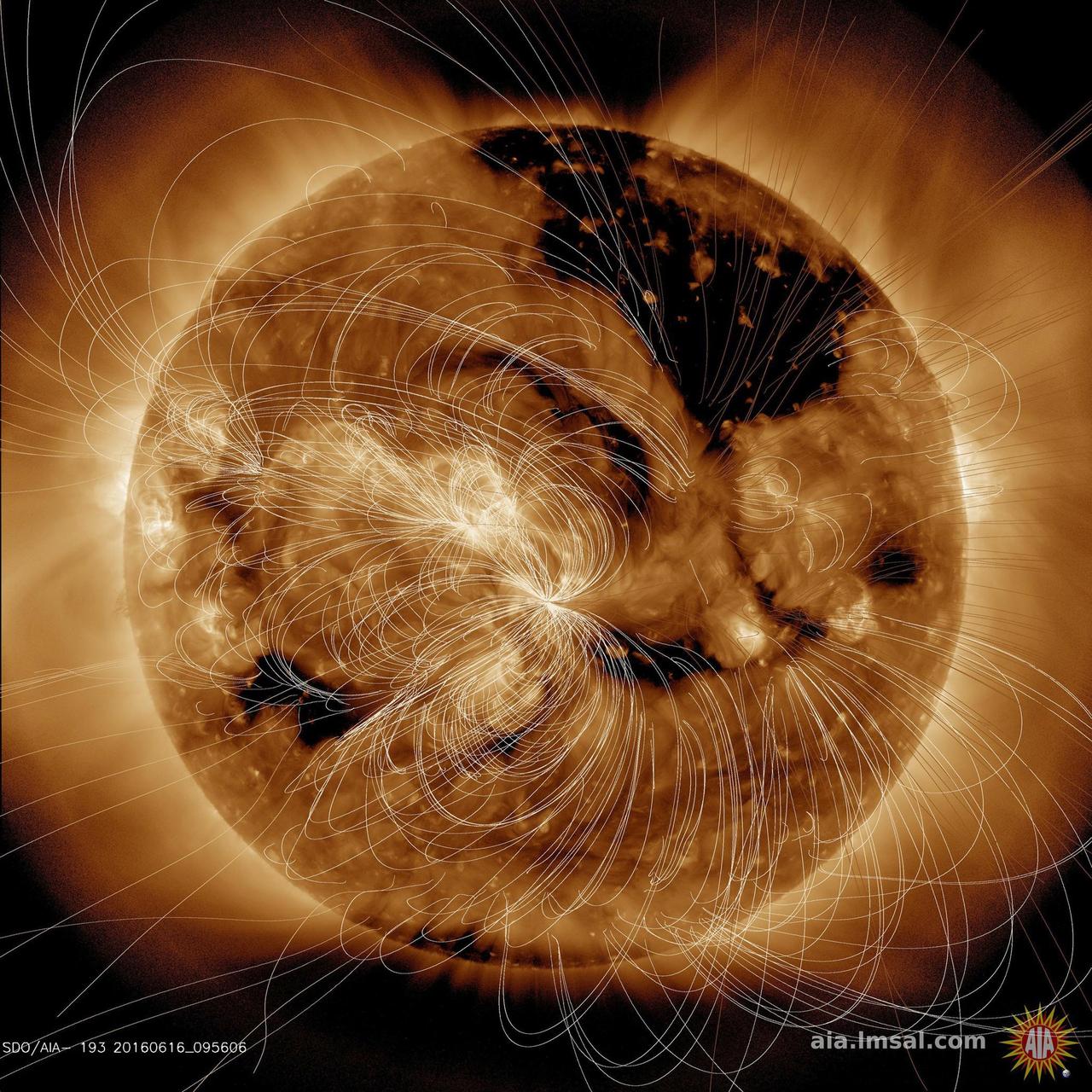
Each day NASA solar scientists produce overlays (in white lines) that show their estimation of how the magnetic field lines above the sun are configured (June16, 2016). In the video clip we show the sun in a wavelength of extreme ultraviolet light, then reveal the magnetic field line configuration in the same wavelength. Notice how the lines are tightly bundled near the lighter-toned active regions, which are magnetically intense regions. The magnetic lines from the darker areas, called coronal holes, open out into space and the extended lines show that. Our magnetically active sun is a dynamic body that changes all the time. Movie are also available at the Photojournal. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20881
![For the first time in a long time the Sun has gone an entire month without any sunspots (Feb. 1-18, 2019). To put this in context, for five years (2011-2015) surrounding the latest solar maximum in March 2014 - the period when the Sun's magnetic activity is the most intense - there were only three days without any sunspots[MH1]. What a difference! The change in the level of activity during the Sun's average 11-year solar cycle is quite dramatic. We are probably not quite at the minimum level of activity yet, but are certainly getting close. The images were taken in filtered white (visible) light. Movies available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21218](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/PIA21218/PIA21218~medium.jpg)
For the first time in a long time the Sun has gone an entire month without any sunspots (Feb. 1-18, 2019). To put this in context, for five years (2011-2015) surrounding the latest solar maximum in March 2014 - the period when the Sun's magnetic activity is the most intense - there were only three days without any sunspots[MH1]. What a difference! The change in the level of activity during the Sun's average 11-year solar cycle is quite dramatic. We are probably not quite at the minimum level of activity yet, but are certainly getting close. The images were taken in filtered white (visible) light. Movies available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21218
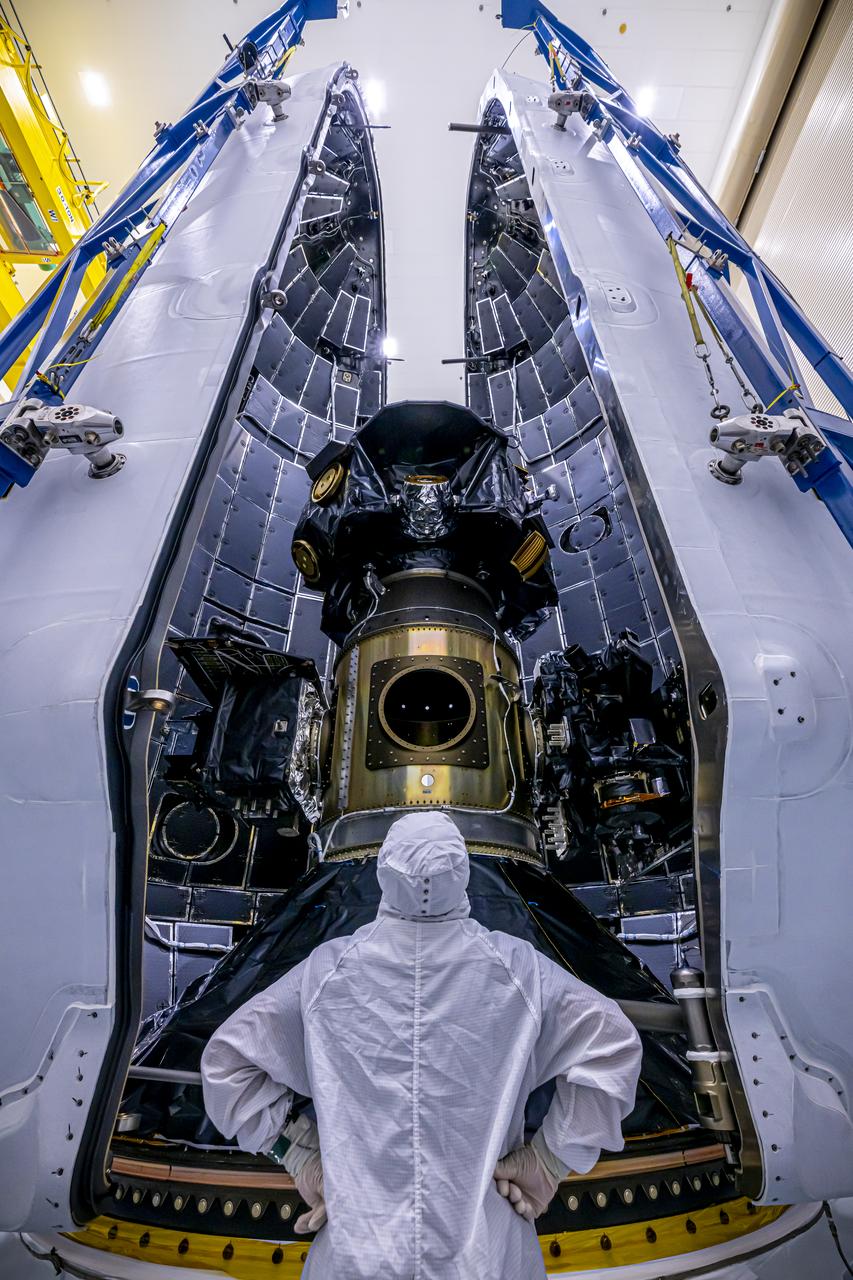

Technicians at Astrotech Space Operations Facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida encapsulate NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), along with the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft on Tuesday, Sept. 16, 2025, inside a SpaceX Falcon 9 payload fairing. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
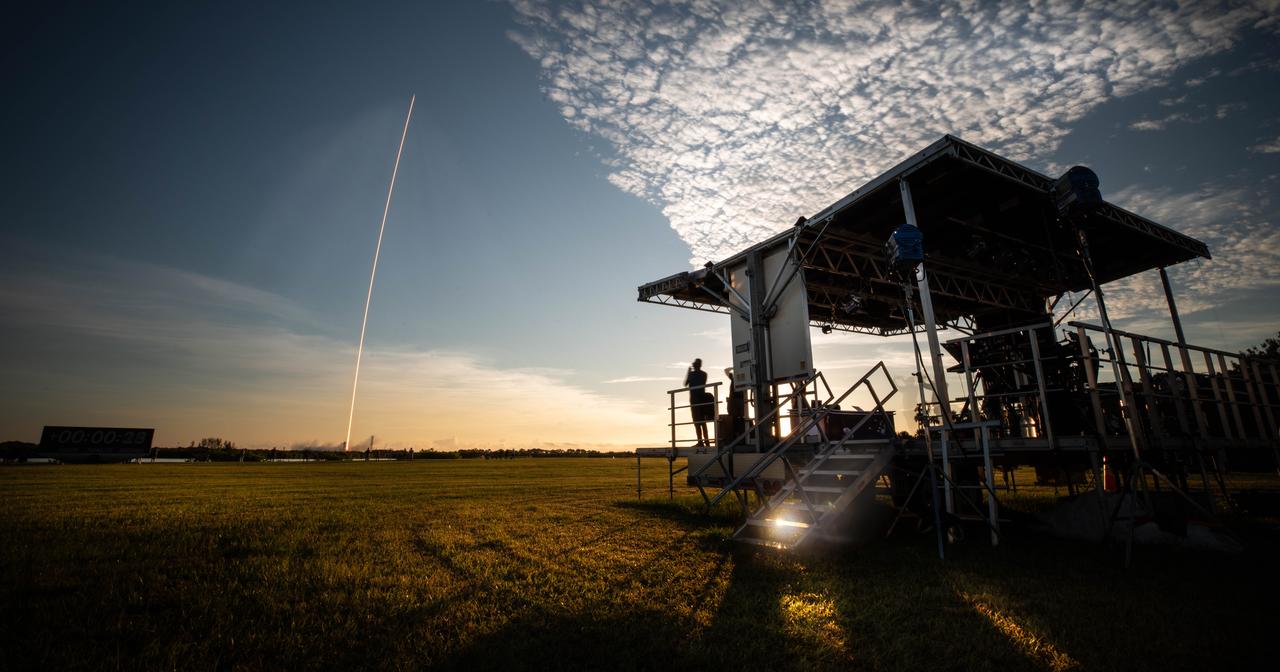

A long exposure photo shows the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft lift off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 7:30 a.m. EDT Wednesday, Sept. 24, 2025. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
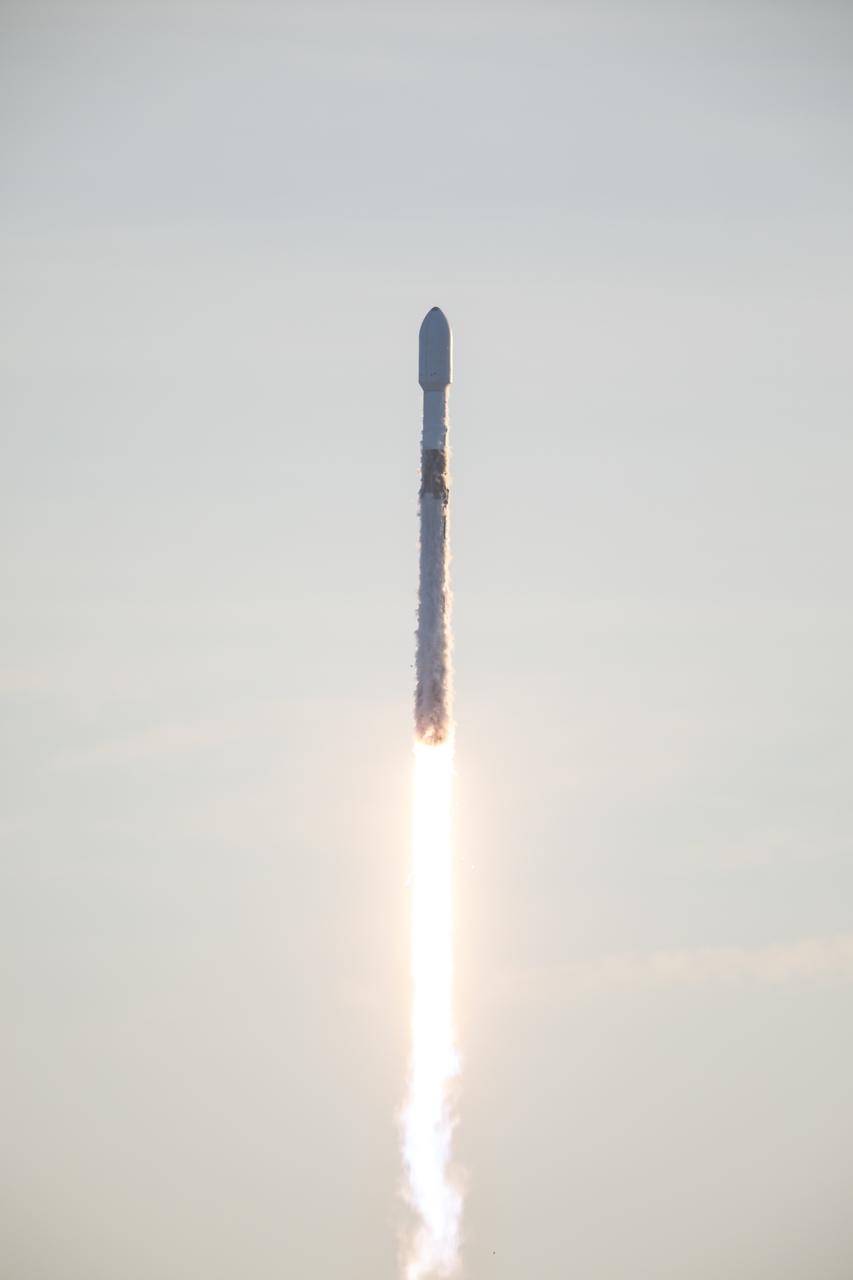

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 7:30 a.m. EDT Wednesday, Sept. 24, 2025. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
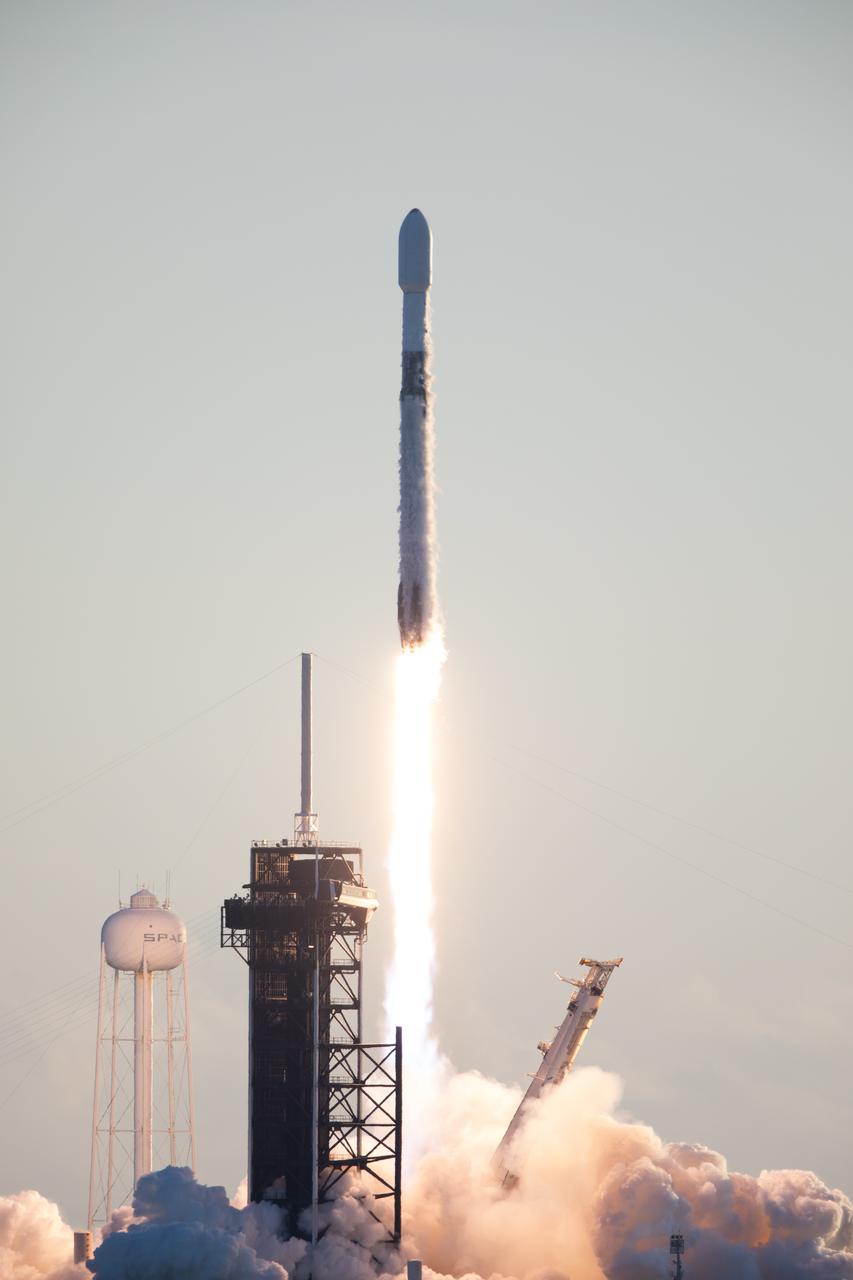

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 7:30 a.m. EDT Wednesday, Sept. 24, 2025. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
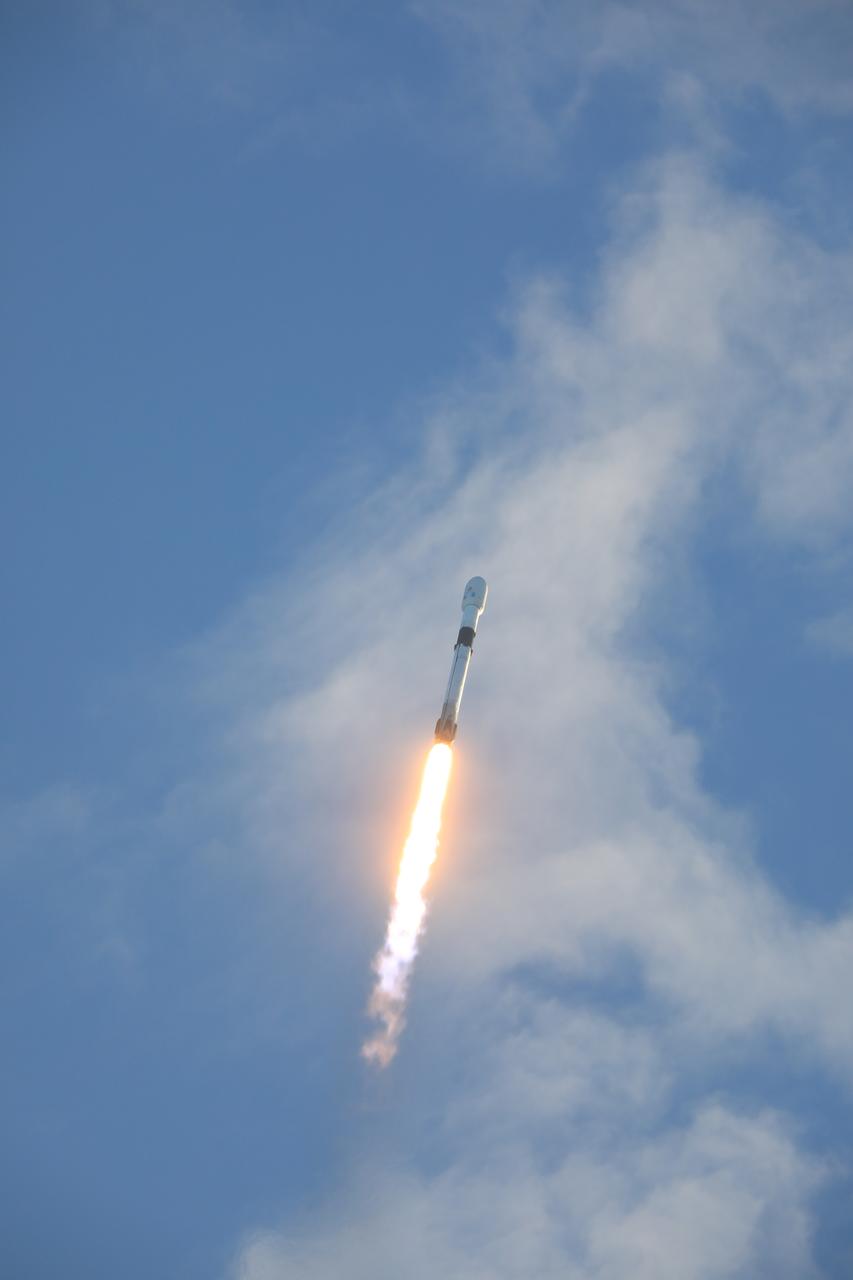

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 7:30 a.m. EDT Wednesday, Sept. 24, 2025. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
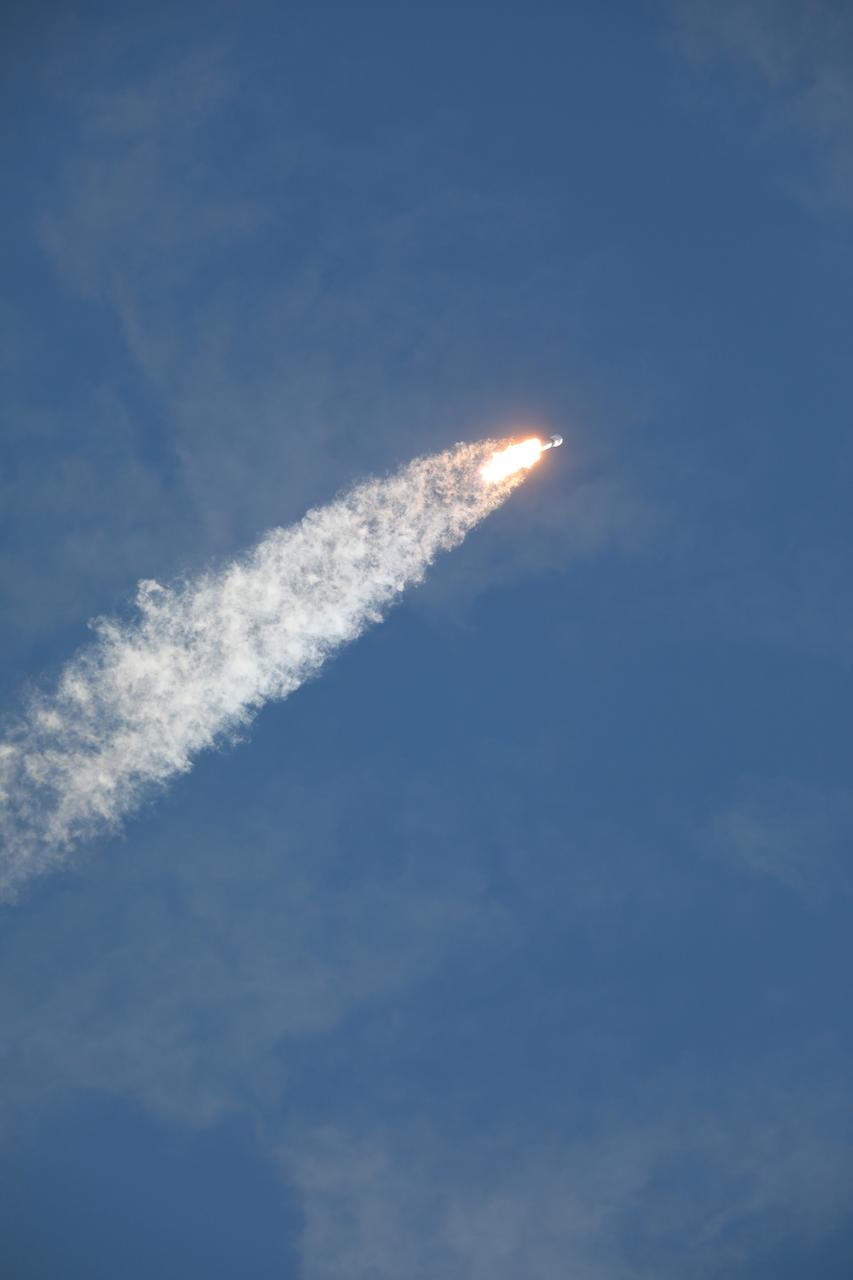

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 7:30 a.m. EDT Wednesday, Sept. 24, 2025. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
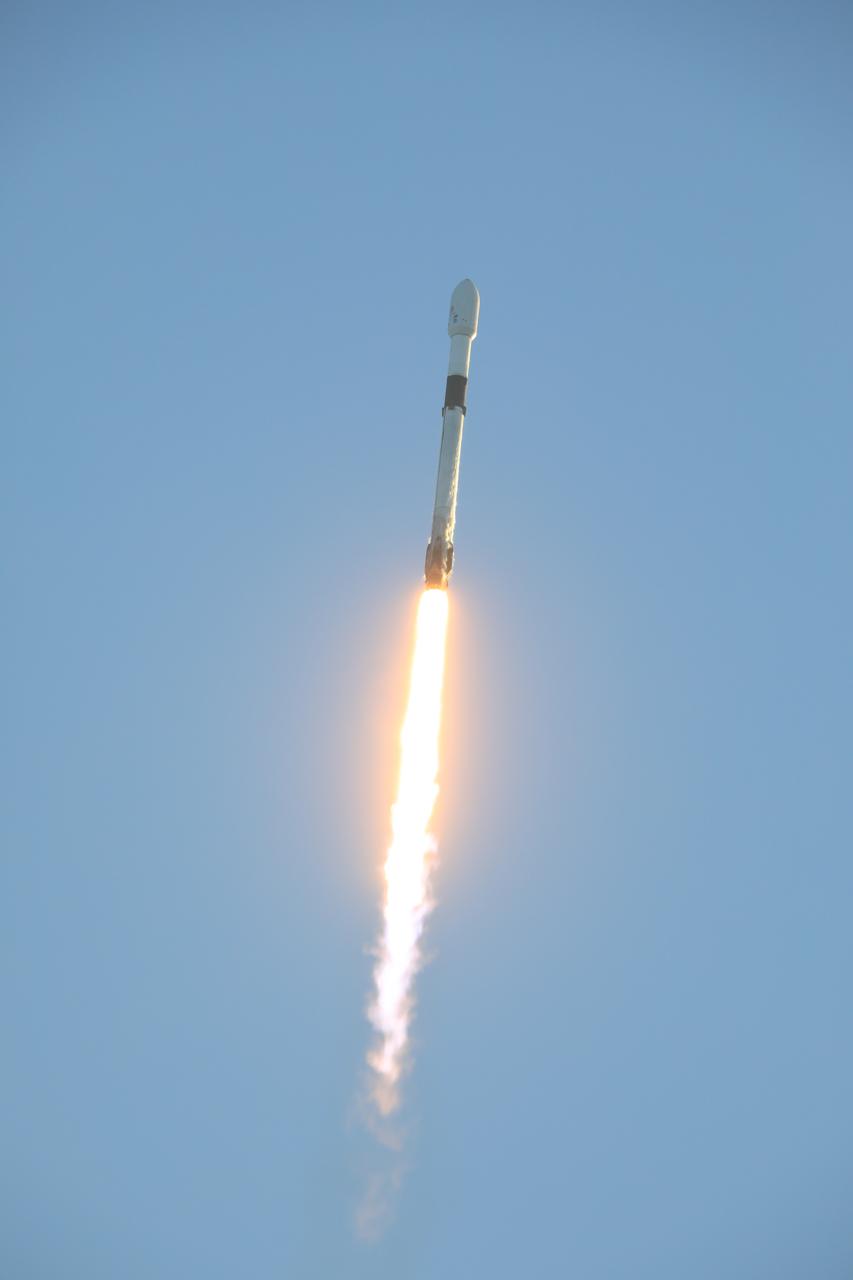

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 7:30 a.m. EDT Wednesday, Sept. 24, 2025. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
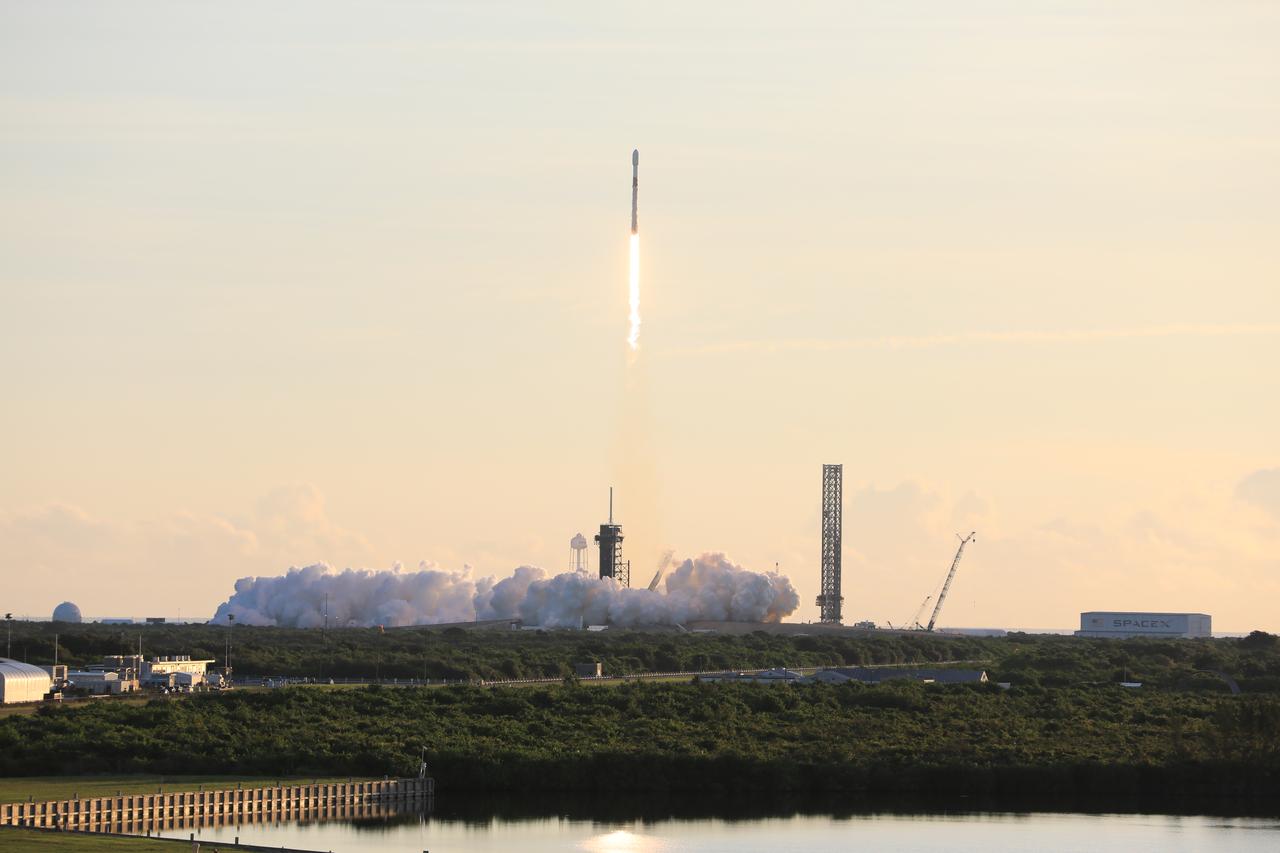

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 7:30 a.m. EDT Wednesday, Sept. 24, 2025. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
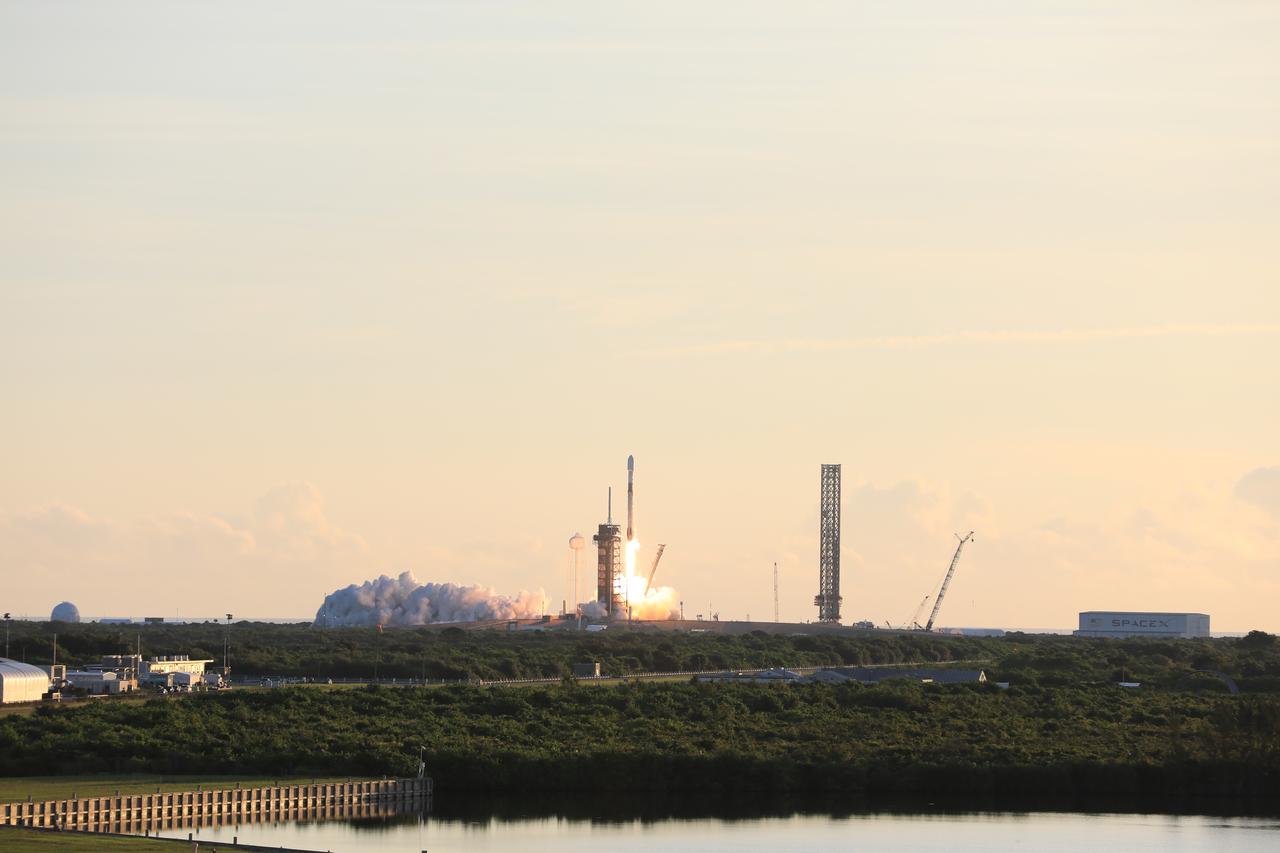

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 7:30 a.m. EDT Wednesday, Sept. 24, 2025. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
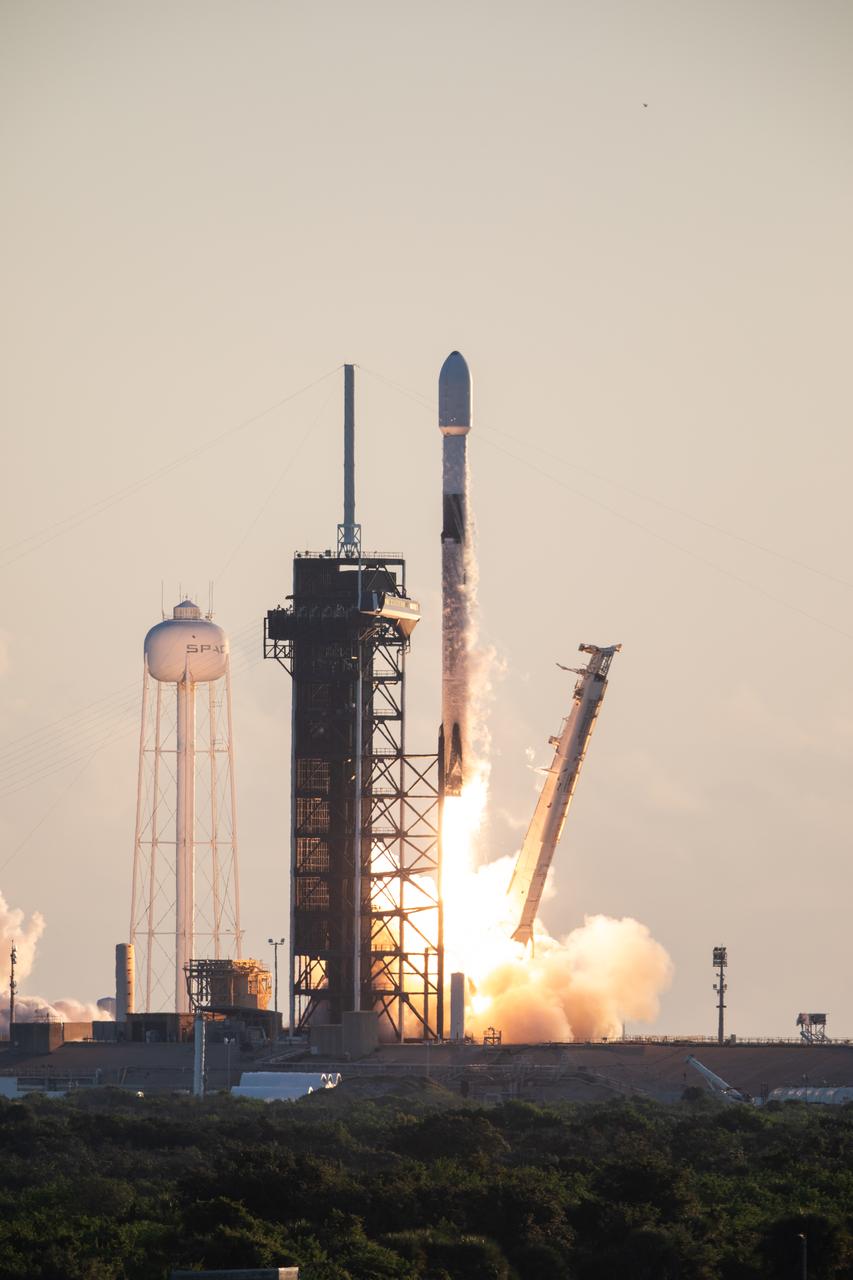

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 7:30 a.m. EDT Wednesday, Sept. 24, 2025. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
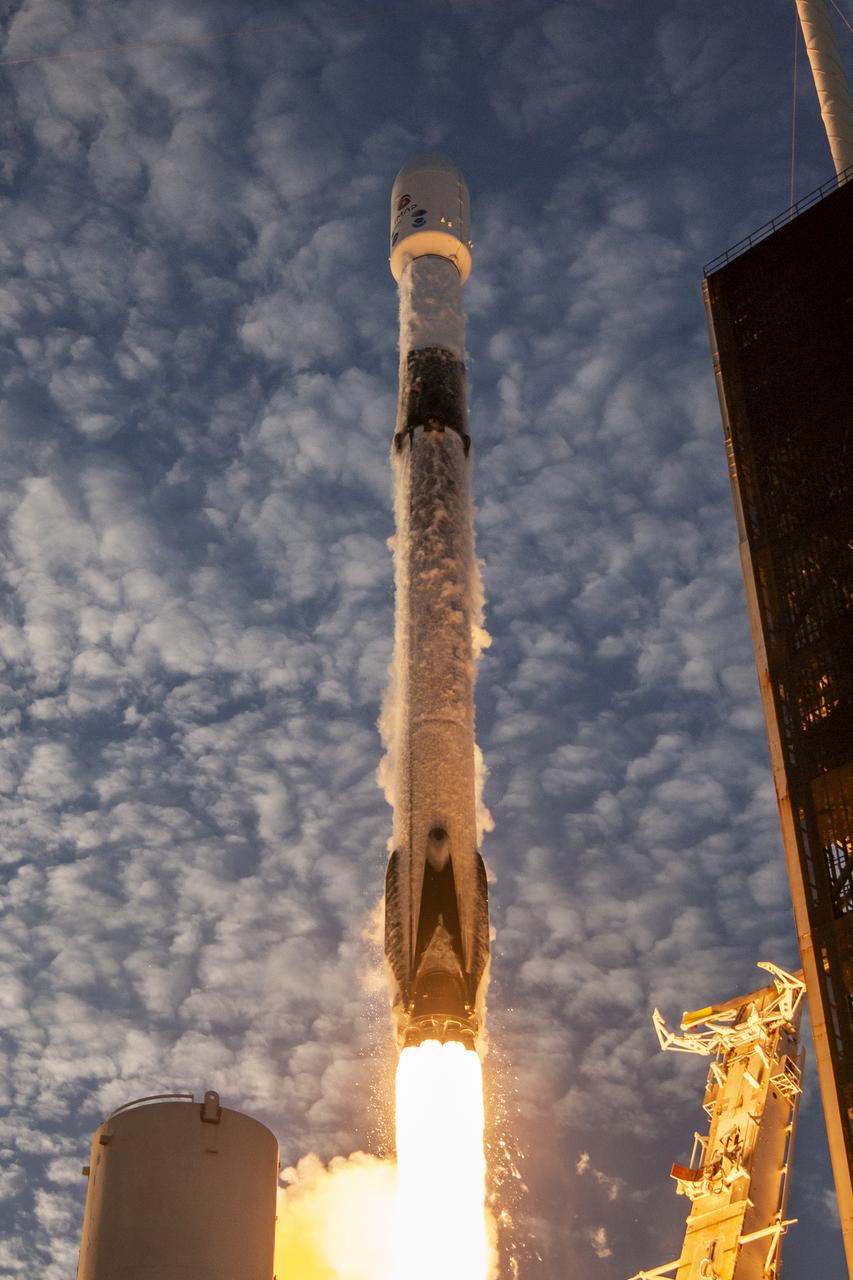

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 7:30 a.m. EDT Wednesday, Sept. 24, 2025. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
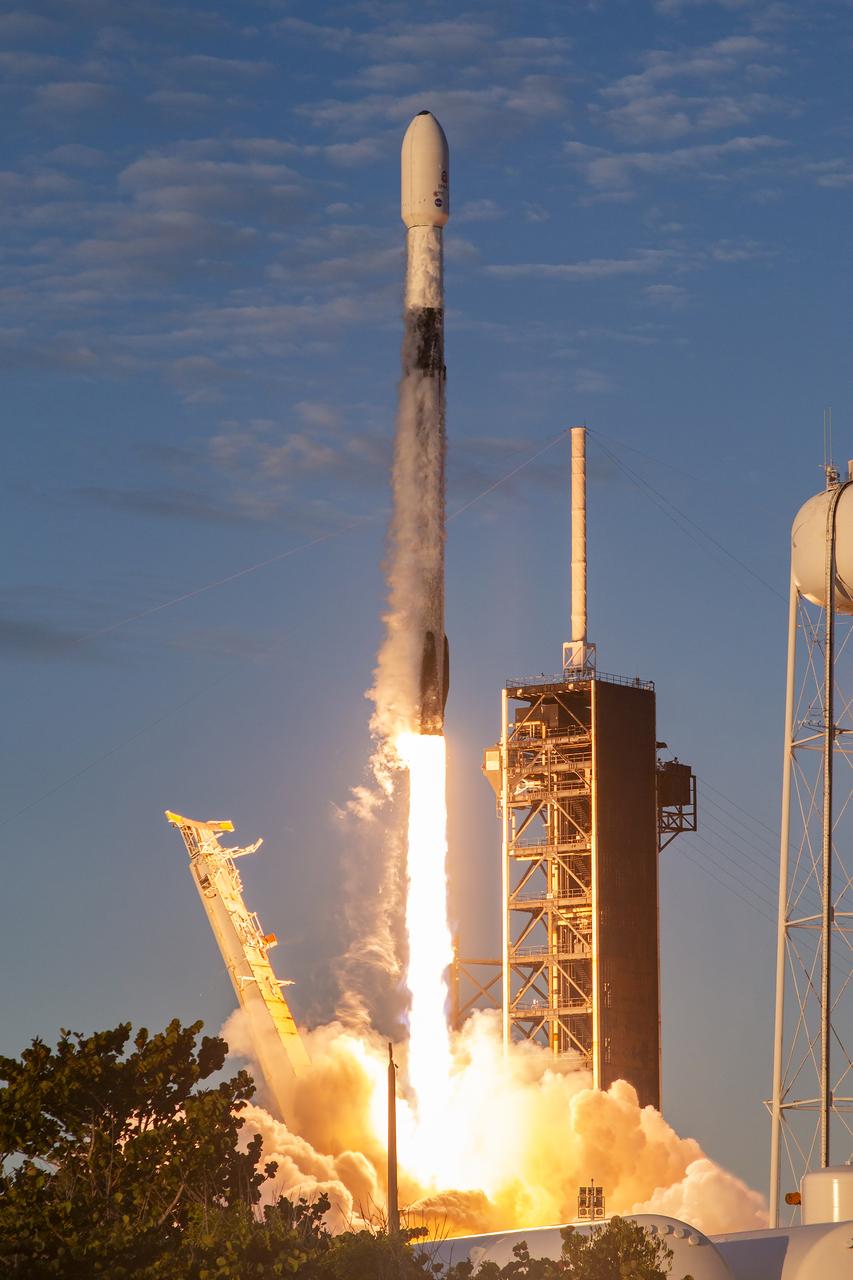

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 7:30 a.m. EDT Wednesday, Sept. 24, 2025. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
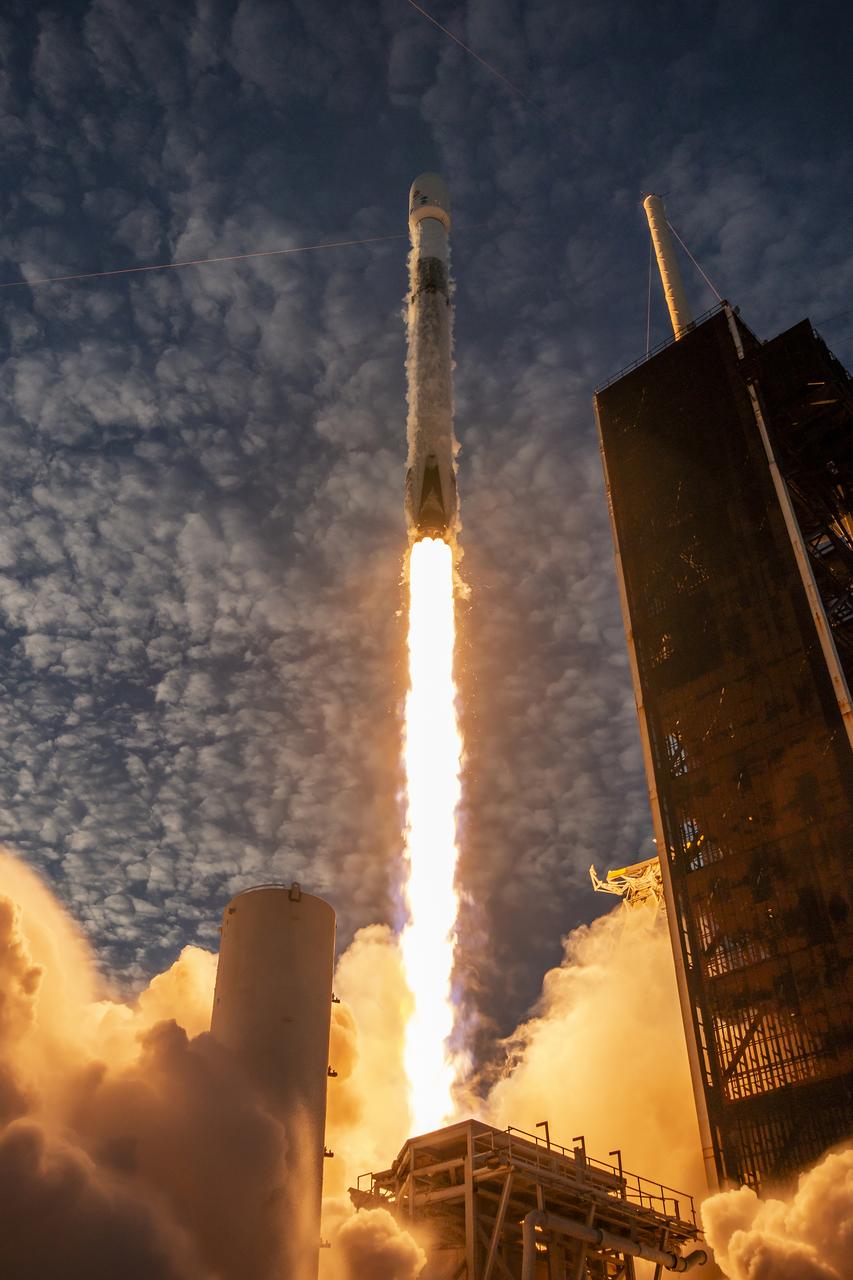

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 7:30 a.m. EDT Wednesday, Sept. 24, 2025. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
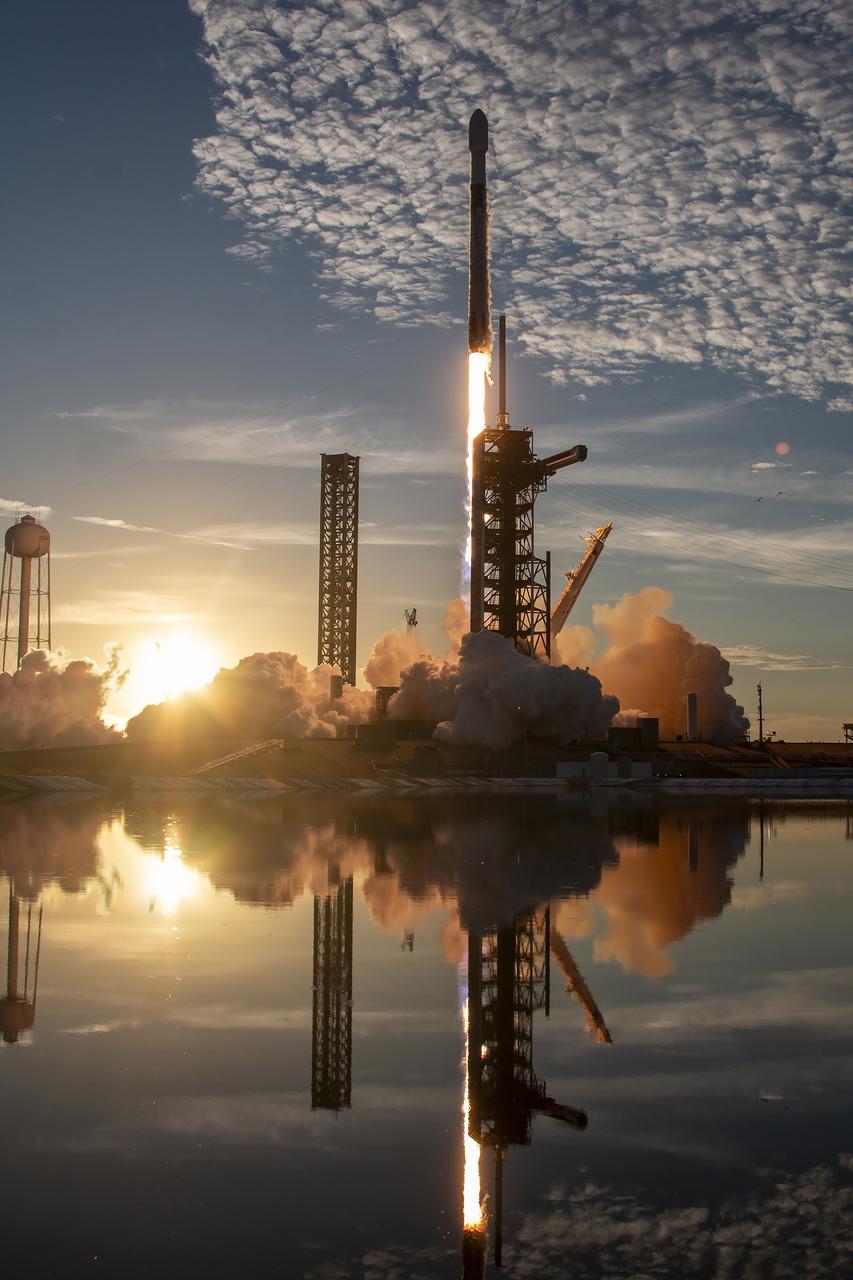

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 7:30 a.m. EDT Wednesday, Sept. 24, 2025. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
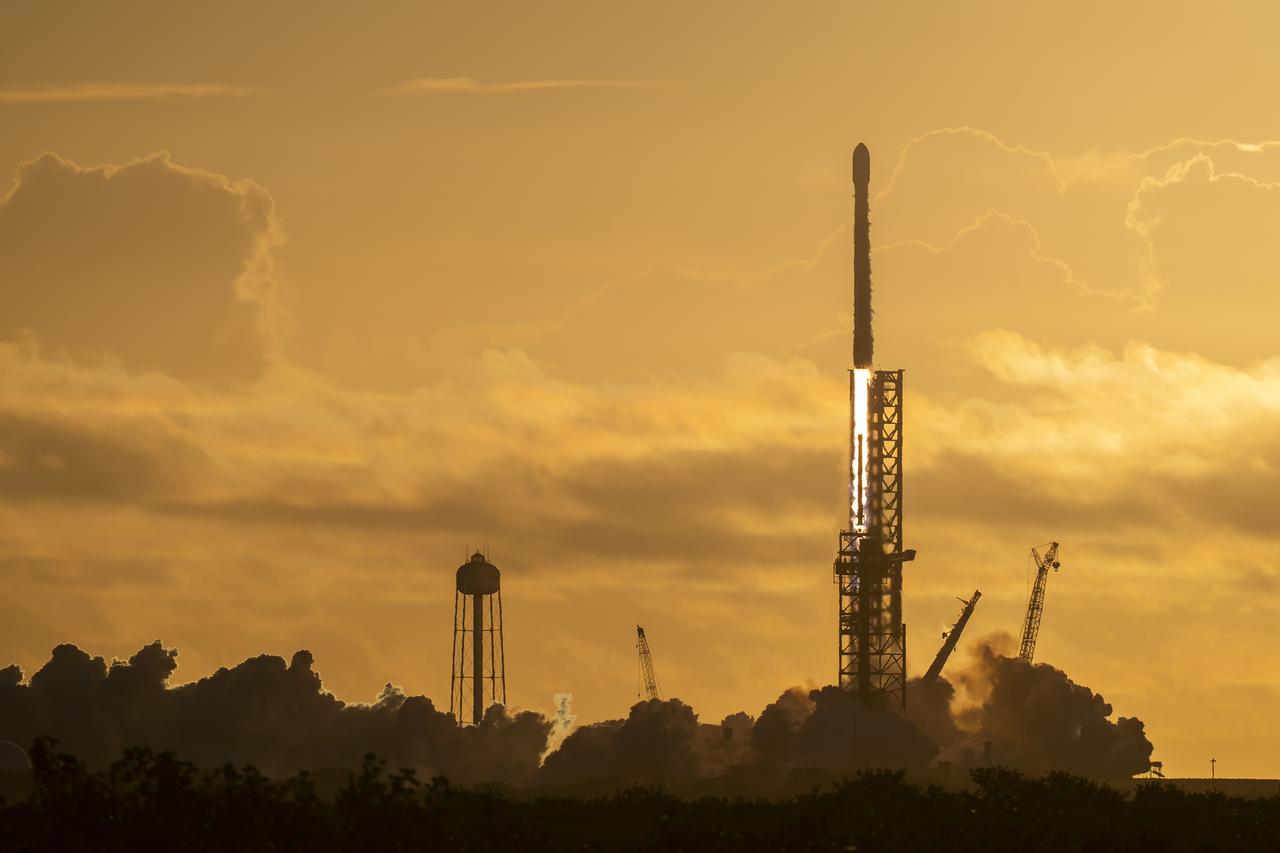

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 7:30 a.m. EDT Wednesday, Sept. 24, 2025. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
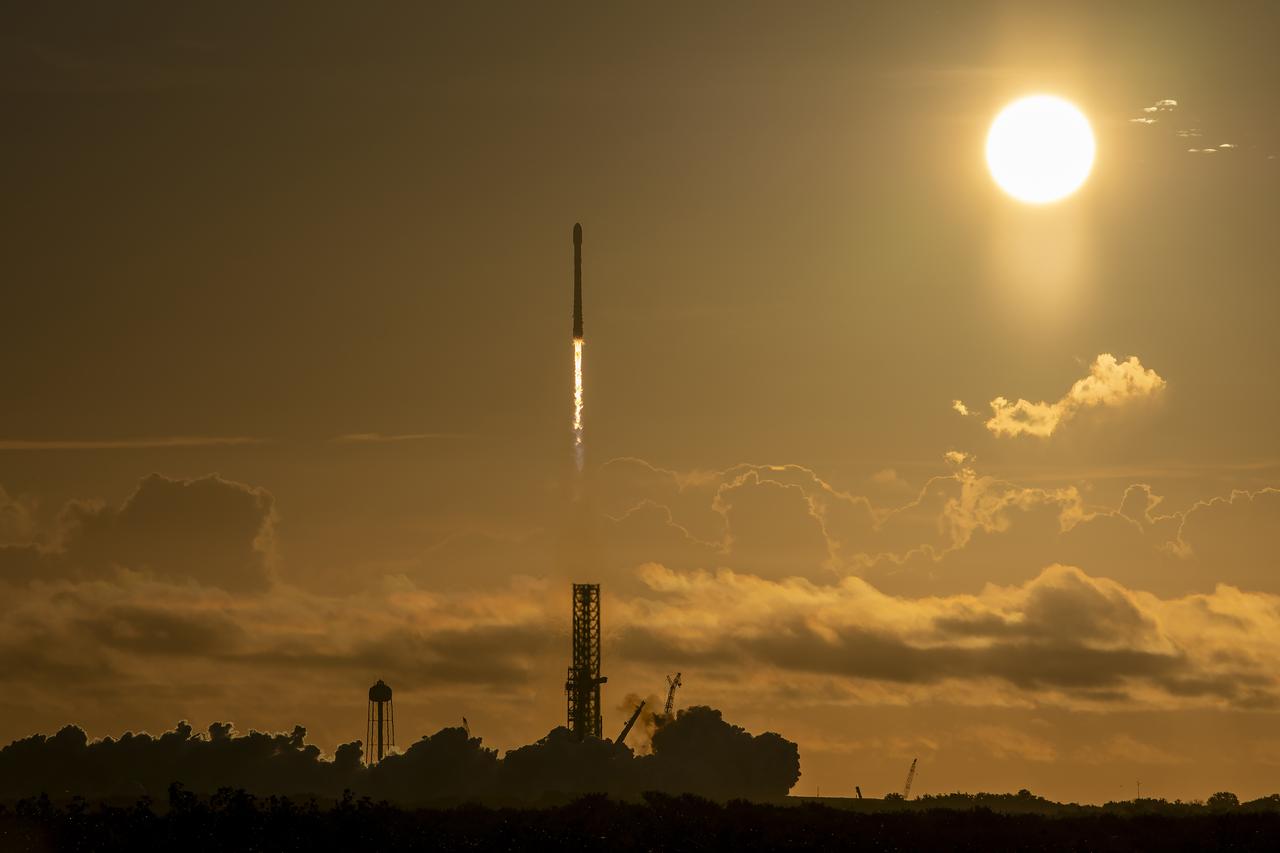

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 7:30 a.m. EDT Wednesday, Sept. 24, 2025. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
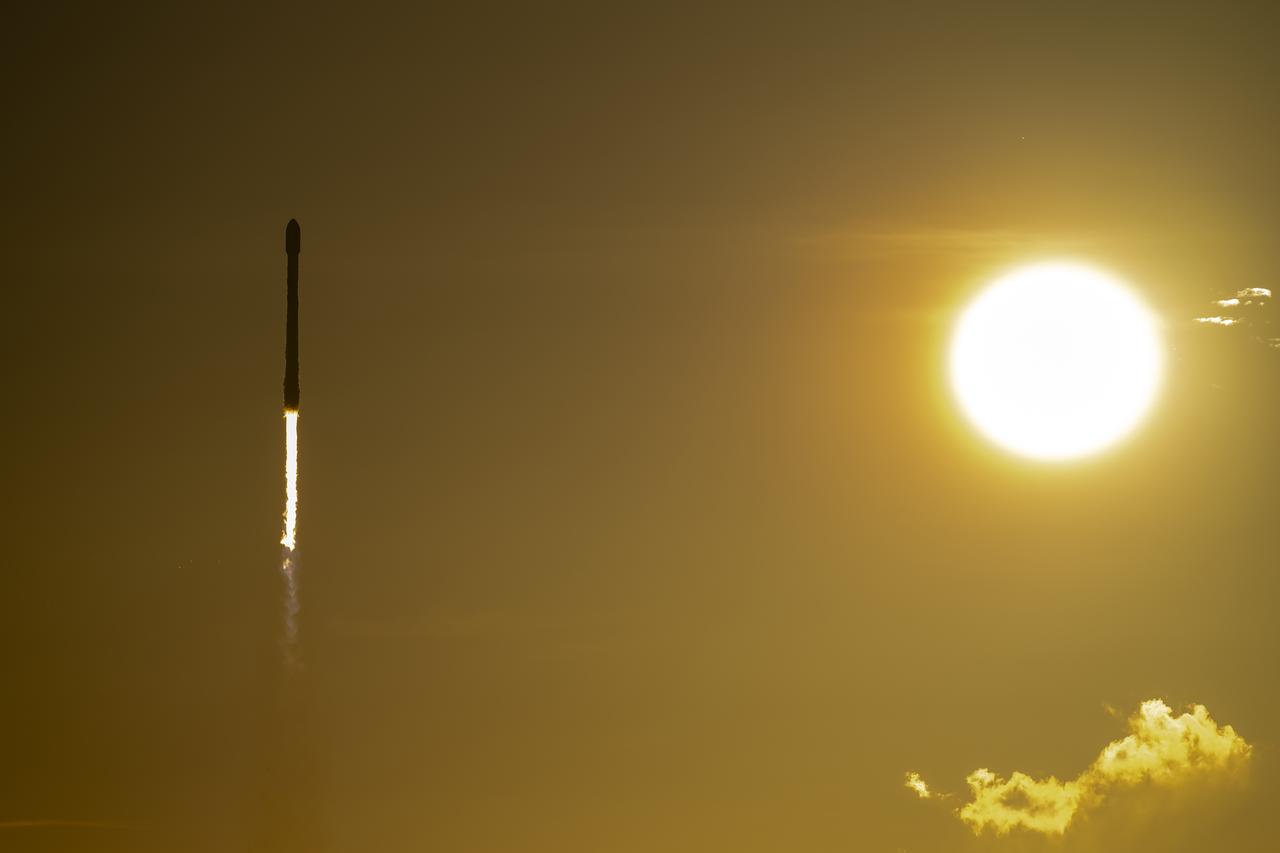

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 7:30 a.m. EDT Wednesday, Sept. 24, 2025. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
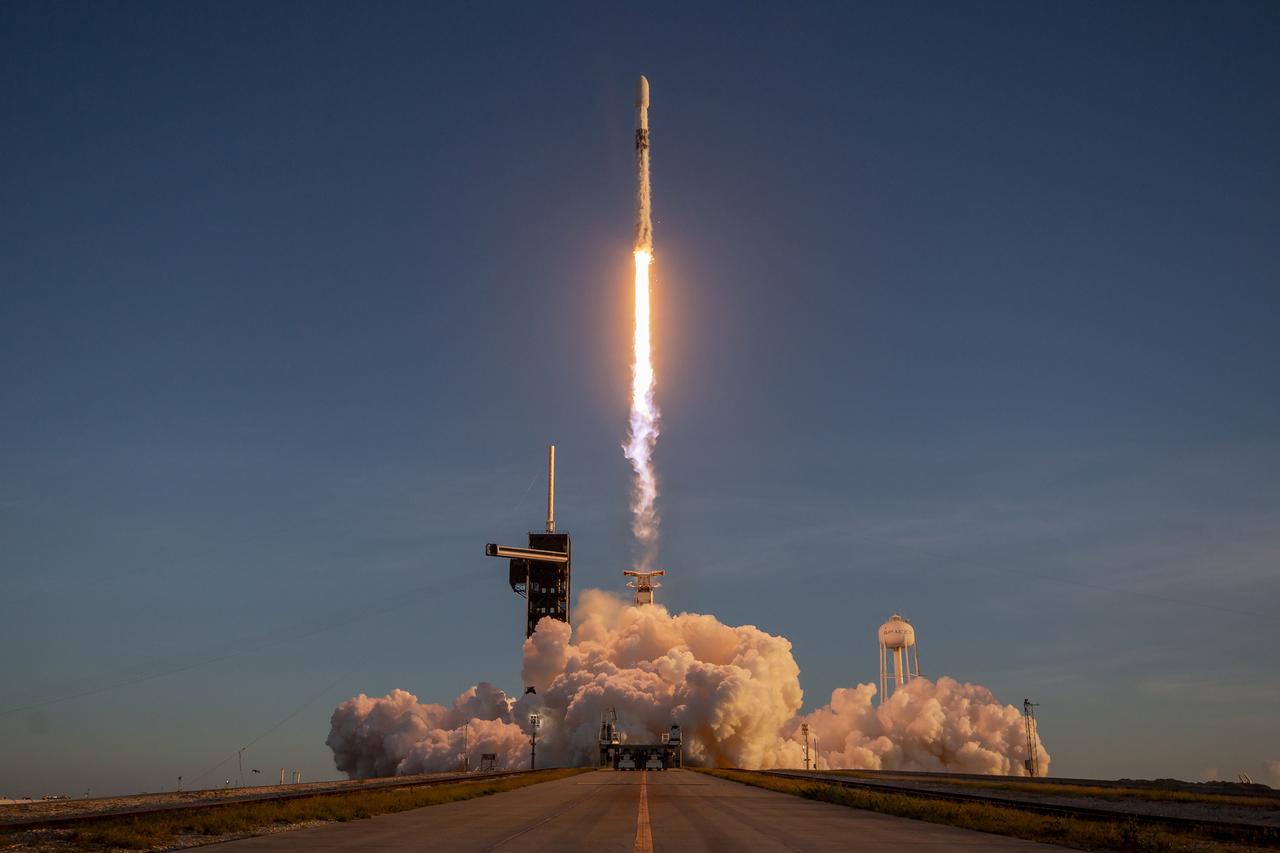

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 7:30 a.m. EDT Wednesday, Sept. 24, 2025. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 7:30 a.m. EDT Wednesday, Sept. 24, 2025. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
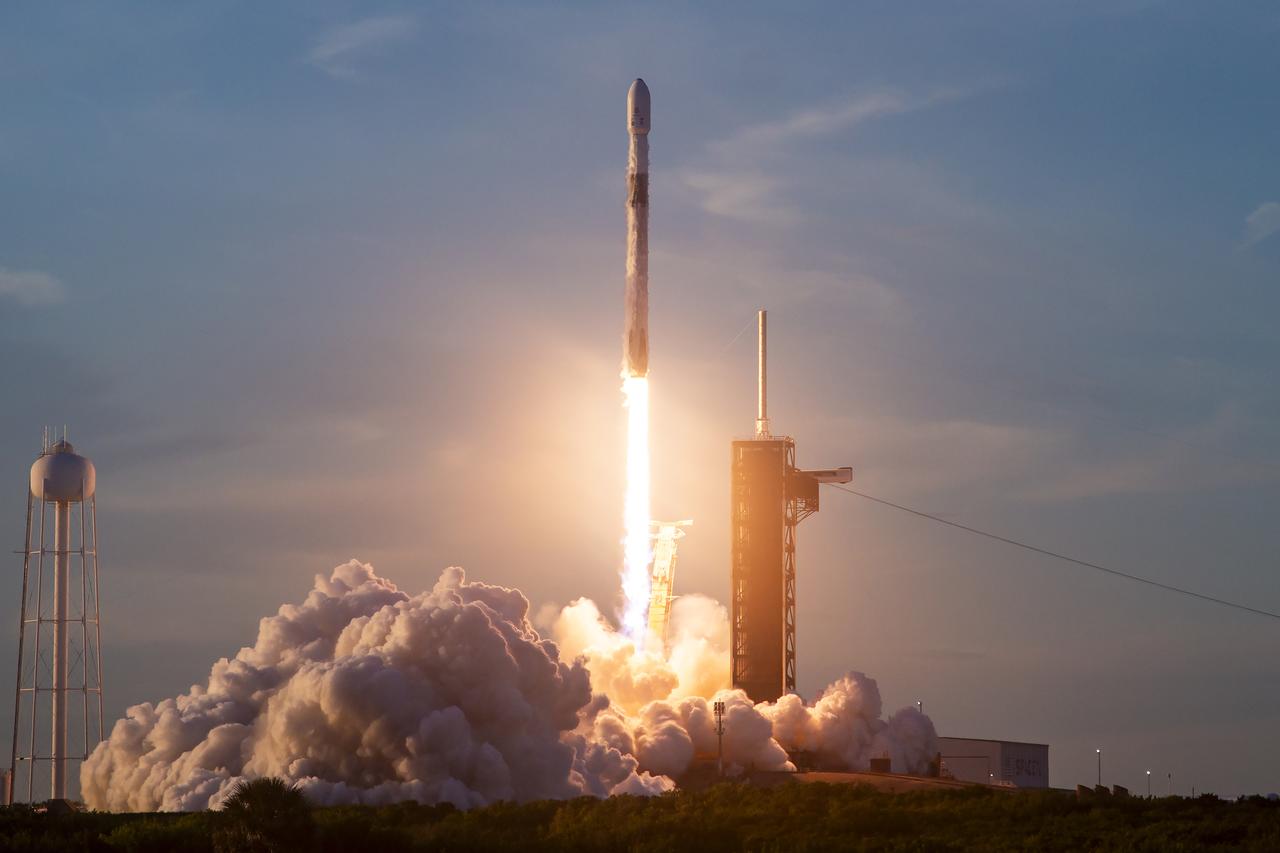

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 7:30 a.m. EDT Wednesday, Sept. 24, 2025. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
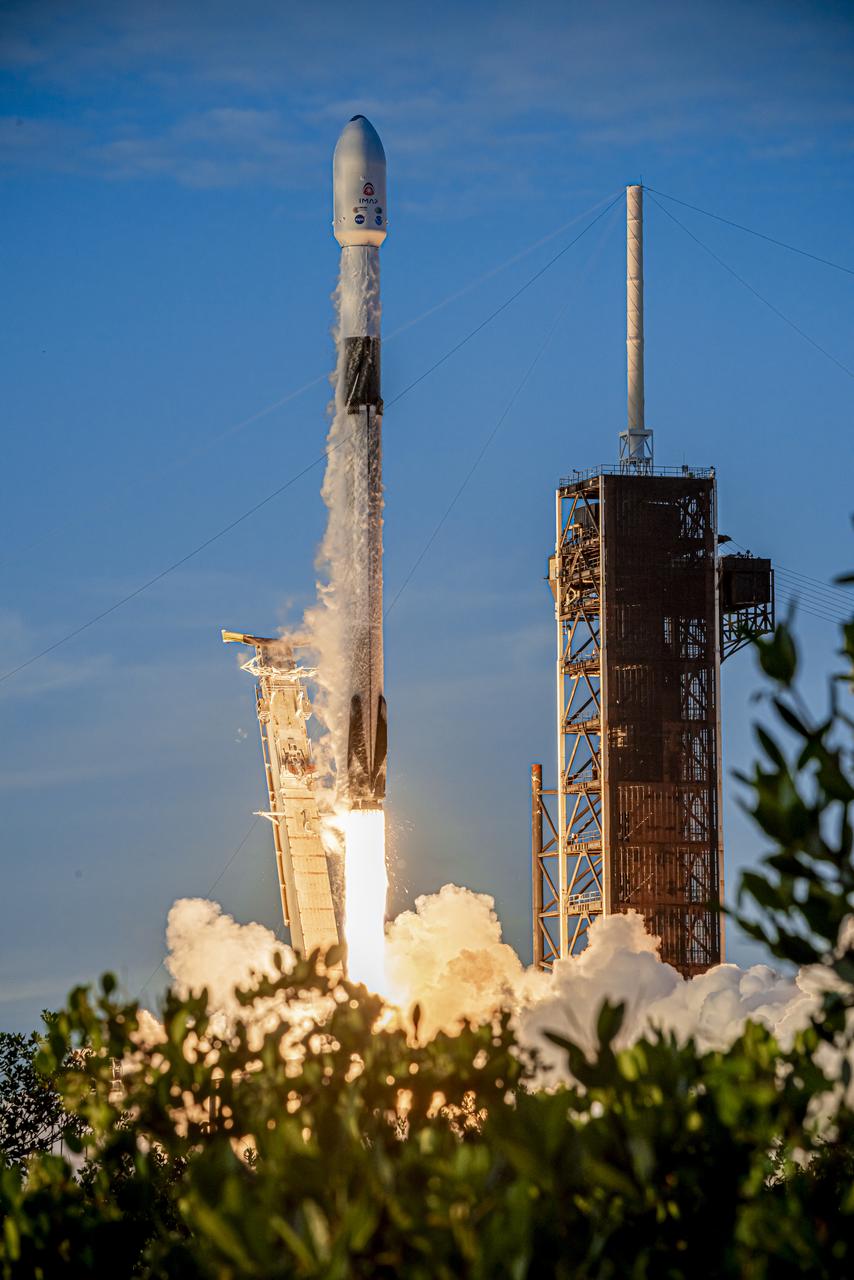

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 7:30 a.m. EDT Wednesday, Sept. 24, 2025. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
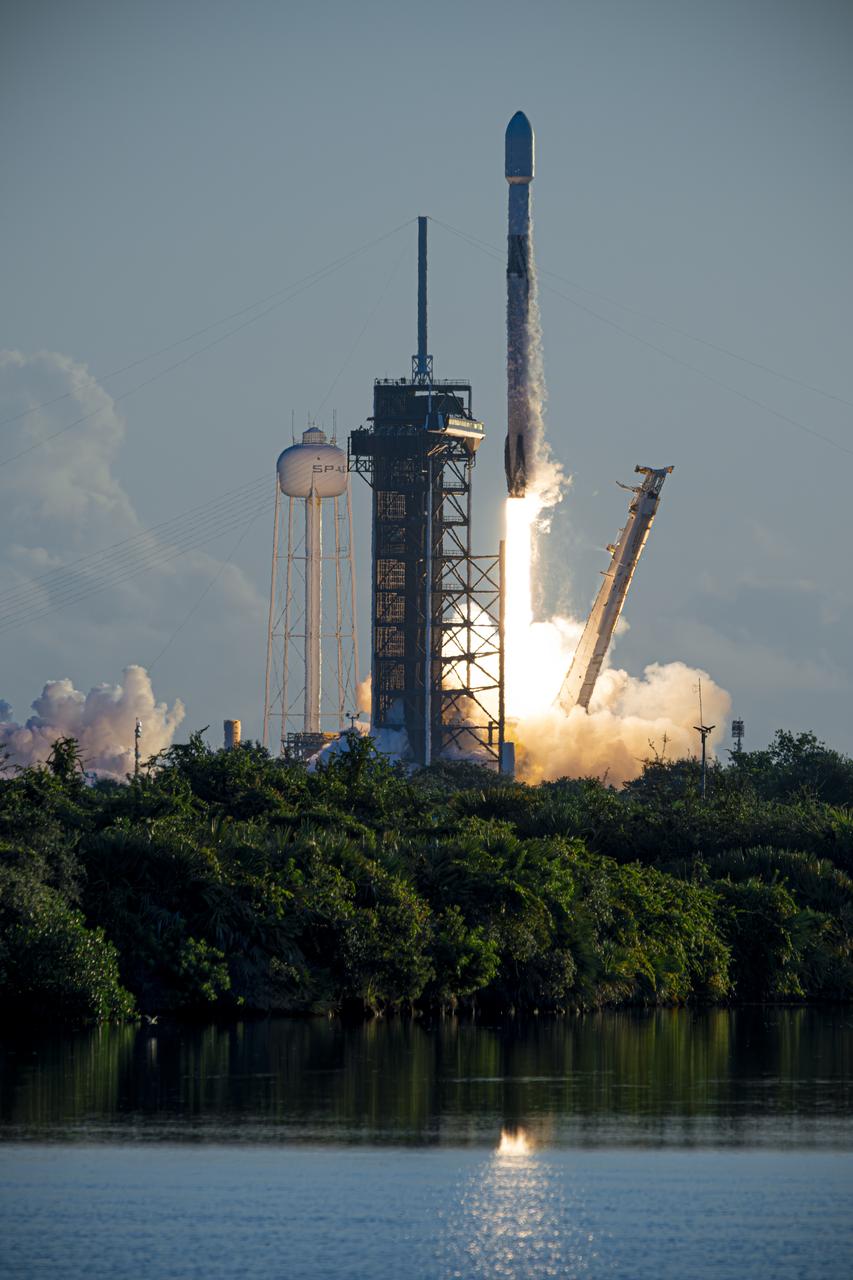

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 7:30 a.m. EDT Wednesday, Sept. 24, 2025. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
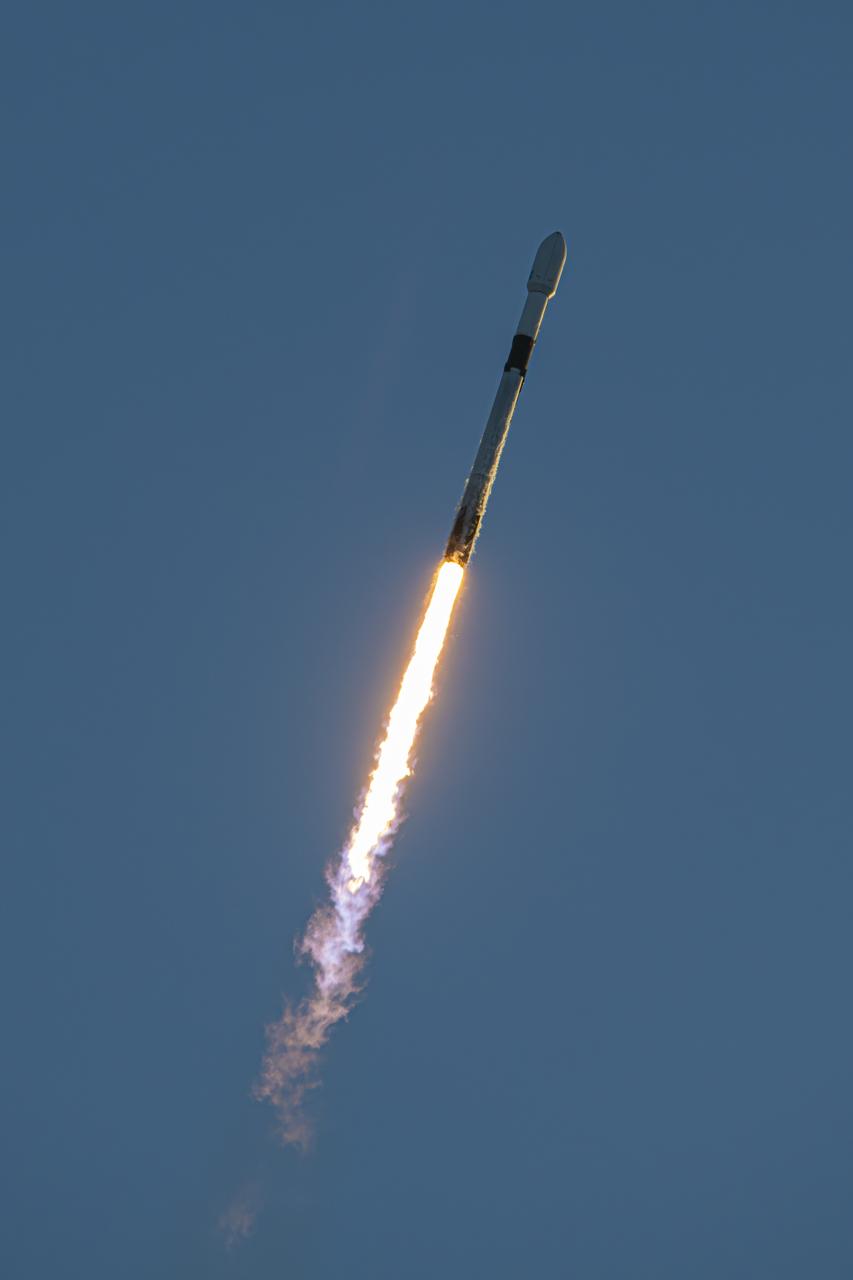

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 7:30 a.m. EDT Wednesday, Sept. 24, 2025. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
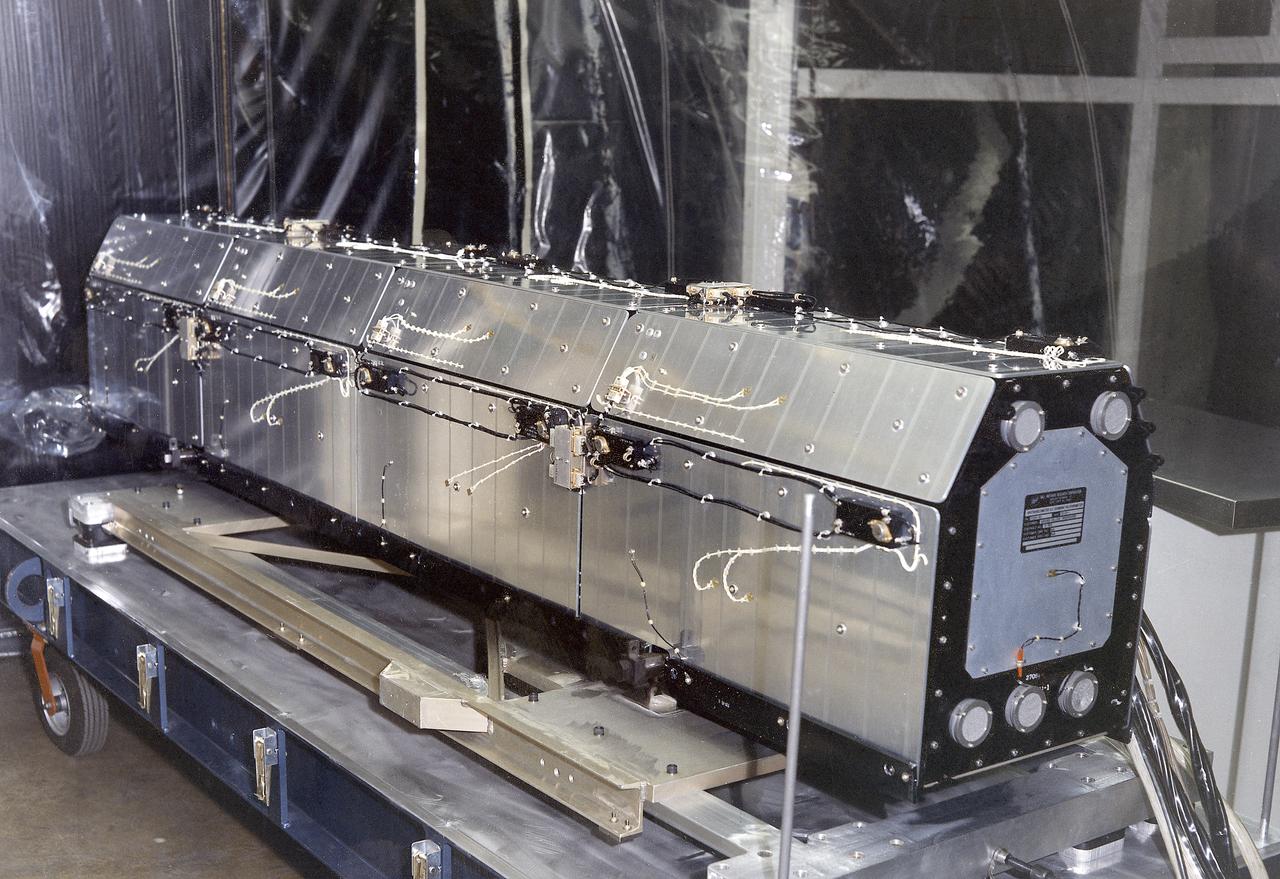
This 1970 photograph shows the flight unit for Skylab's Ultraviolet (UV) Scarning Polychromator Spectroheliometer, an Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) facility. It was designed to observe temporal changes in UV radiation emitted by the Sun's chromosphere and lower corona. The Marshall Space Flight Center had program management responsibility for the development of Skylab hardware and experiments.
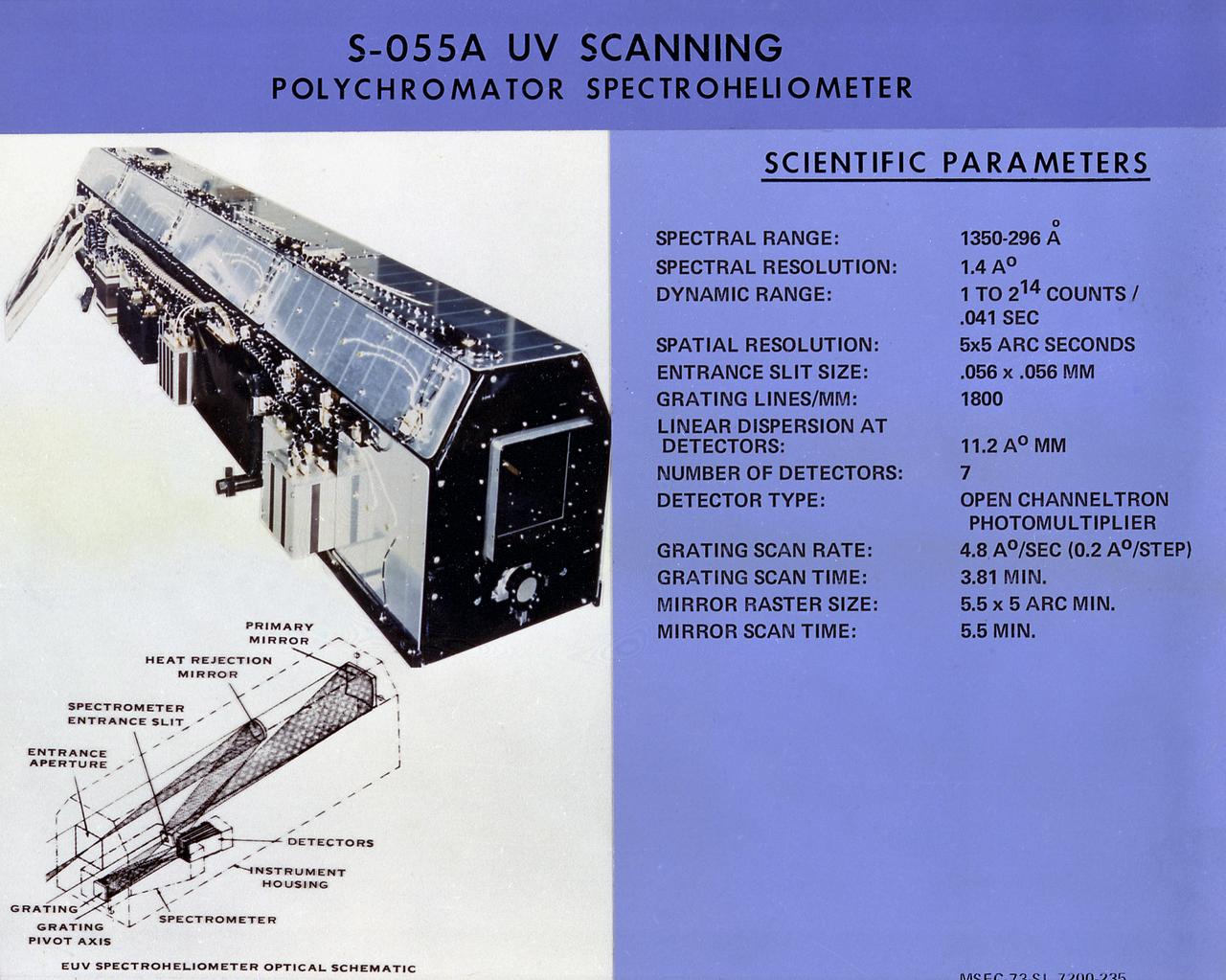
This chart describes scientific parameters of the Skylab Ultraviolet (UV) Scanning Polychromator Spectroheliometer, one the eight Apollo Telescope Mount facilities. It was designed to observe and provide temporal changes in UV radiation emitted by the Sun's chromosphere and lower corona. The Marshall Space Flight Center had program management responsibility for the development of skylab hardware and experiments.
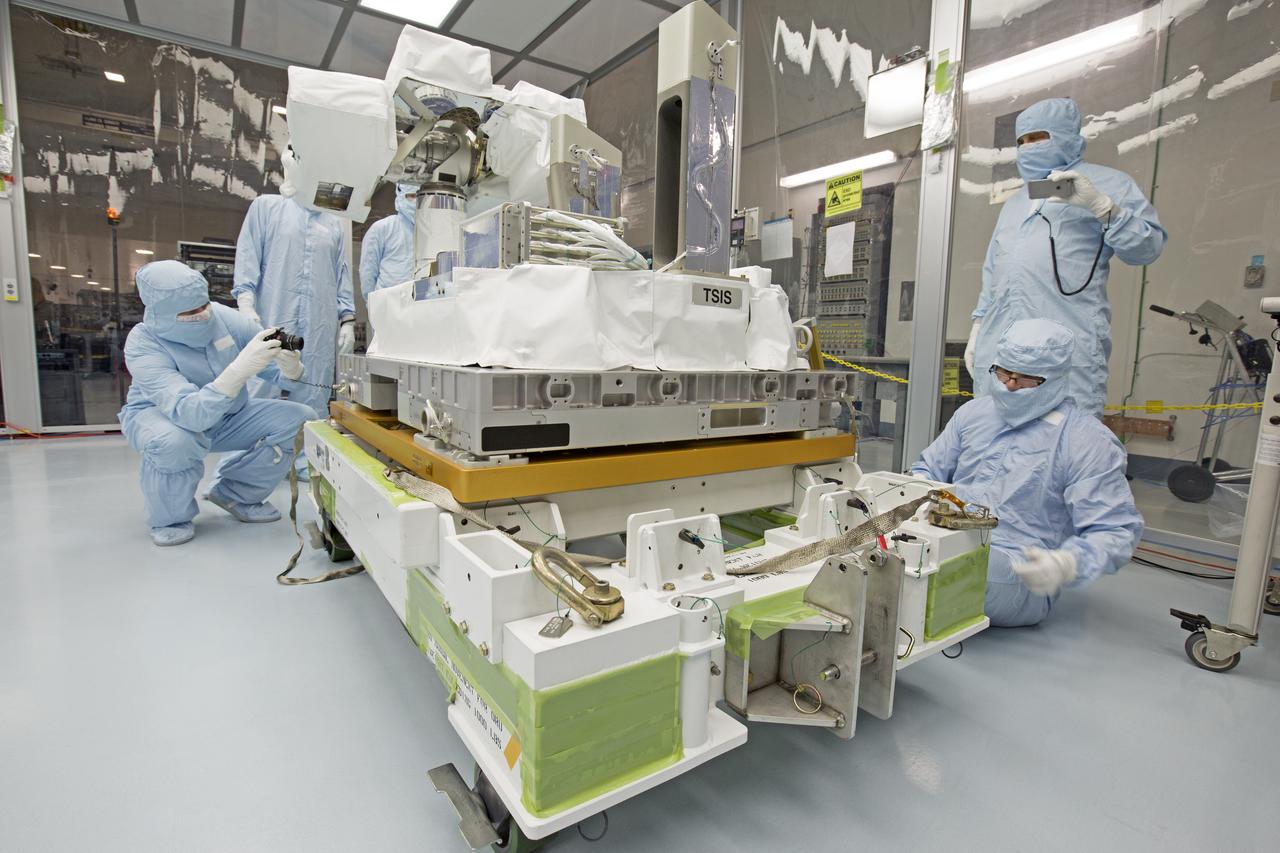

In the high bay of Kennedy Space Center's Space Station Processing Facility, Chris Hardcastle, left, of Stinger-Ghaffarian Technologies, and other payload team members performs spacewalk tool fit-checks of the integrated Total and Spectral Solar Irradiance Sensor-1 (TSIS-1) payload and the EXPRESS Pallet Adapter. TSIS-1 is designed to measure the Sun's energy input into Earth by seeing how it is distributed across different wavelengths of light. These measurements help scientists establish Earth's total energy and how our planet's atmosphere responds to changes in the Sun's energy output. TSIS-1 will launch on SpaceX's 13th commercial resupply mission to the International Space Station.
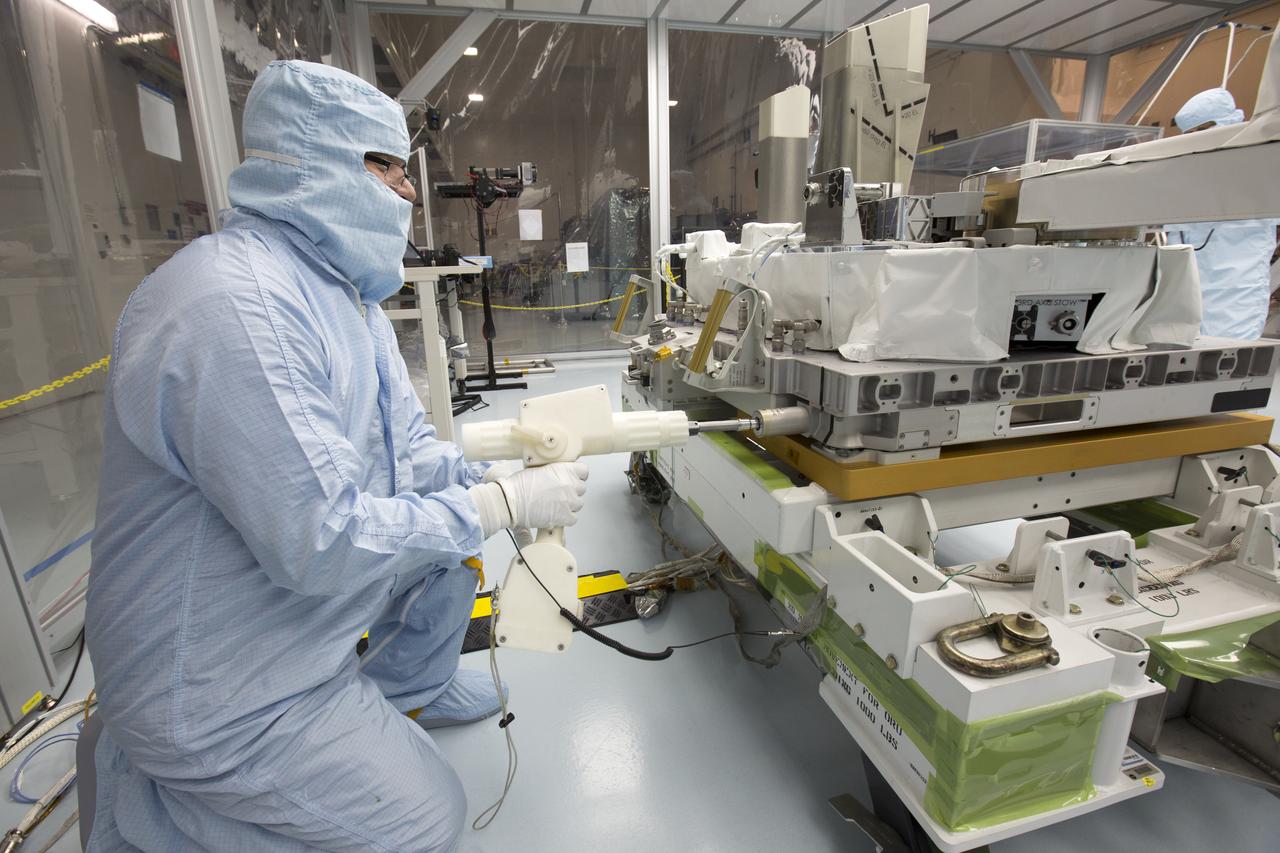

In the high bay of Kennedy Space Center's Space Station Processing Facility, Chris Hardcastle of Stinger-Ghaffarian Technologies performs spacewalk tool fit-checks of the integrated Total and Spectral Solar Irradiance Sensor-1 (TSIS-1) payload and the EXPRESS Pallet Adapter. TSIS-1 is designed to measure the Sun's energy input into Earth by seeing how it is distributed across different wavelengths of light. These measurements help scientists establish Earth's total energy and how our planet's atmosphere responds to changes in the Sun's energy output. TSIS-1 will launch on SpaceX's 13th commercial resupply mission to the International Space Station.

Designed by the mission crew members, the STS-66 emblem depicts the Space Shuttle Atlantis launching into Earth orbit to study global environmental change. The payload for the Atmospheric Laboratory for Applications and Science (ATLAS-3) and complementary experiments were part of a continuing study of the atmosphere and the Sun's influence on it. The Space Shuttle is trailed by gold plumes representing the astronaut symbol and is superimposed over Earth, much of which is visible from the flight's high inclination orbit. Sensitive instruments aboard the ATLAS pallet in the Shuttle payload bay and on the free-flying Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmospheric-Shuttle Pallet Satellite (CHRISTA-SPAS) that gazed down on Earth and toward the Sun, are illustrated by the stylized sunrise and visible spectrum.
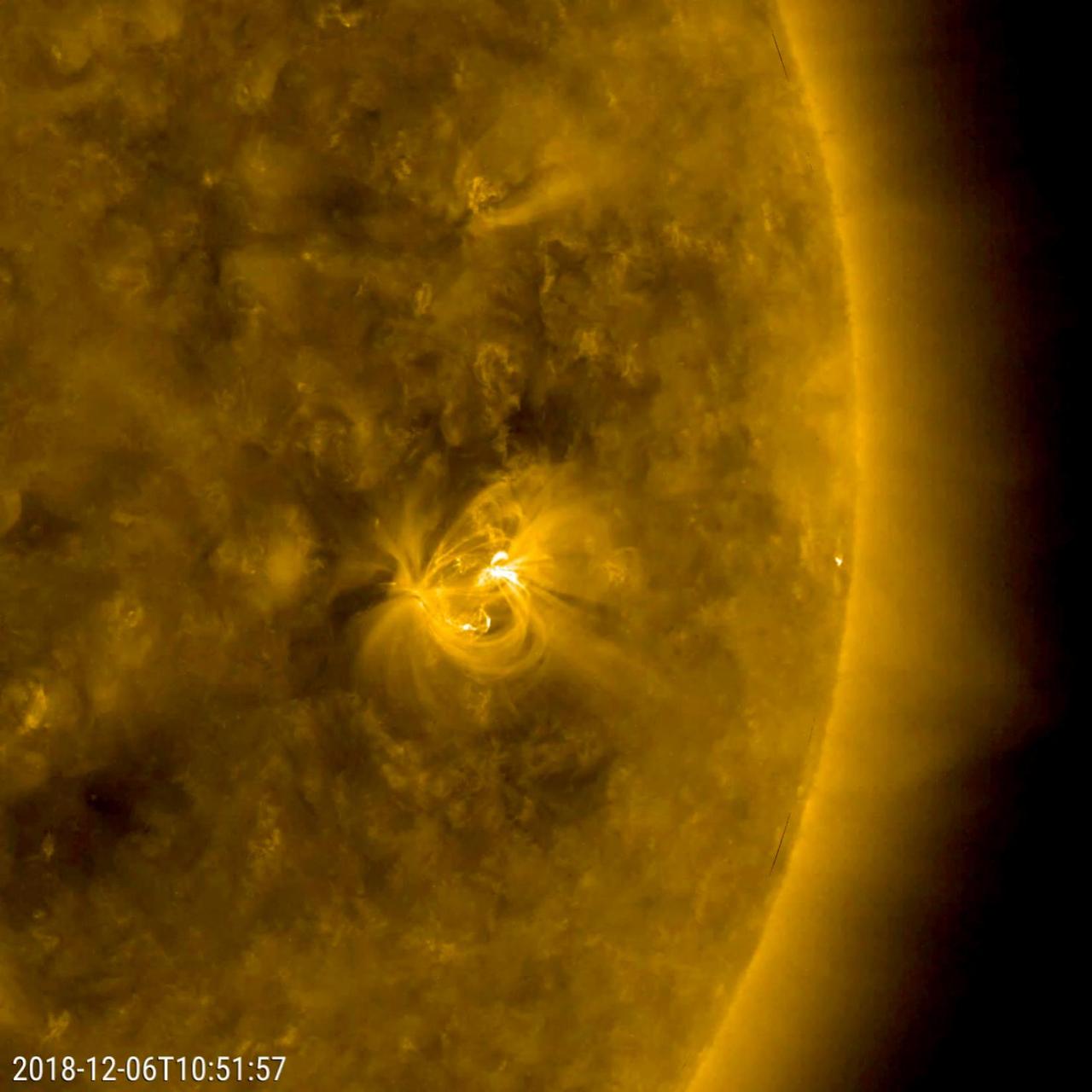
The only active region observed this week appeared on Dec. 5, 2018 and grew into an average size display of dynamic activity (Dec. 6-7, 2018). As viewed in a wavelength of extreme ultraviolet light, the region presented numerous magnetic loops of charged particles, rapidly changing their shapes and directions. As the sun is approaching its minimum level of activity in its 11 year solar cycle, we expect to see fewer and fewer active regions for quite a while. However, this active region is in the southern hemisphere of the Sun and has the North magnetic pole in the lead, so it is a sunspot of Solar Cycle 24. Movies available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21211
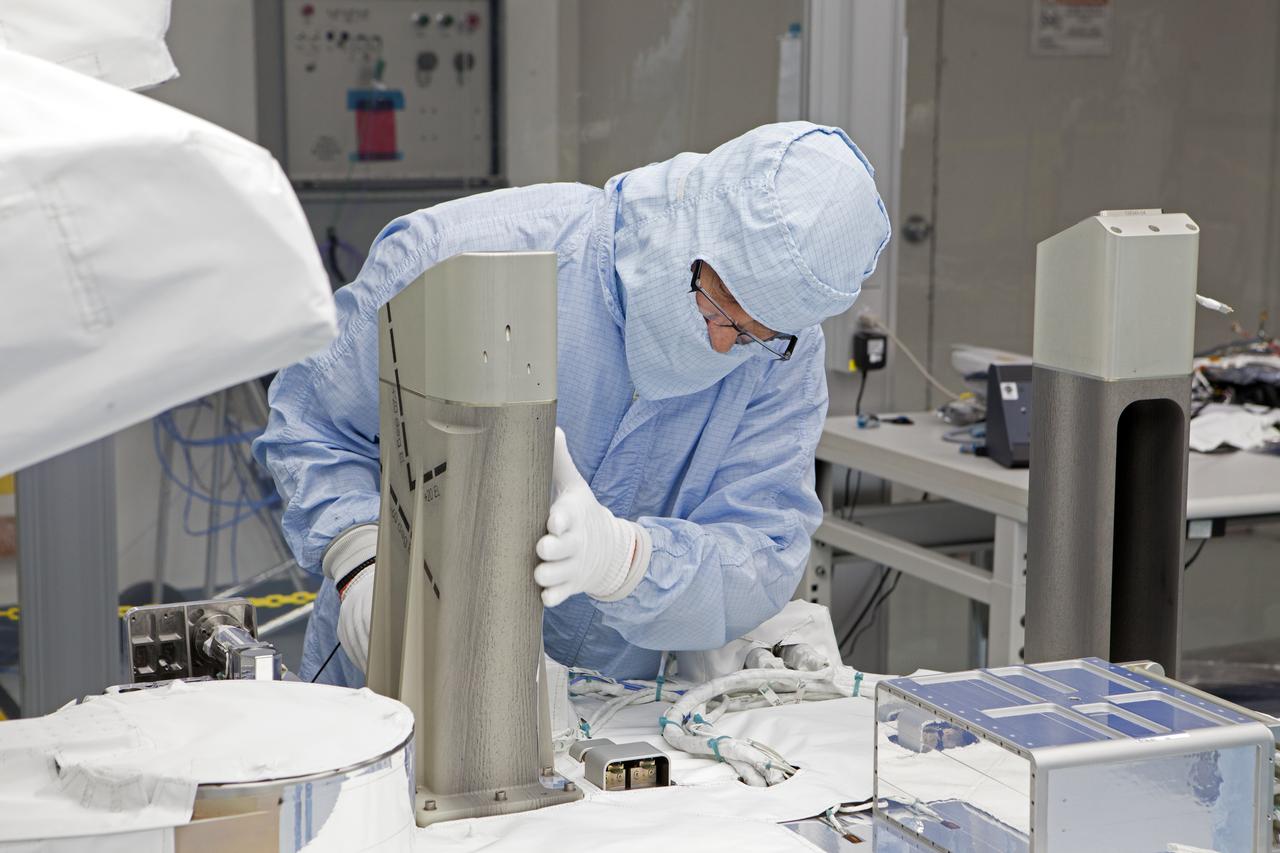

In the high bay of Kennedy Space Center's Space Station Processing Facility, Chris Hardcastle of Stinger-Ghaffarian Technologies performs a sharp edge inspection of the integrated Total and Spectral Solar Irradiance Sensor-1 (TSIS-1) payload and the EXPRESS Pallet Adapter. TSIS-1 is designed to measure the Sun's energy input into Earth by seeing how it is distributed across different wavelengths of light. These measurements help scientists establish Earth's total energy and how our planet's atmosphere responds to changes in the Sun's energy output. TSIS-1 will launch on SpaceX's 13th commercial resupply mission to the International Space Station.
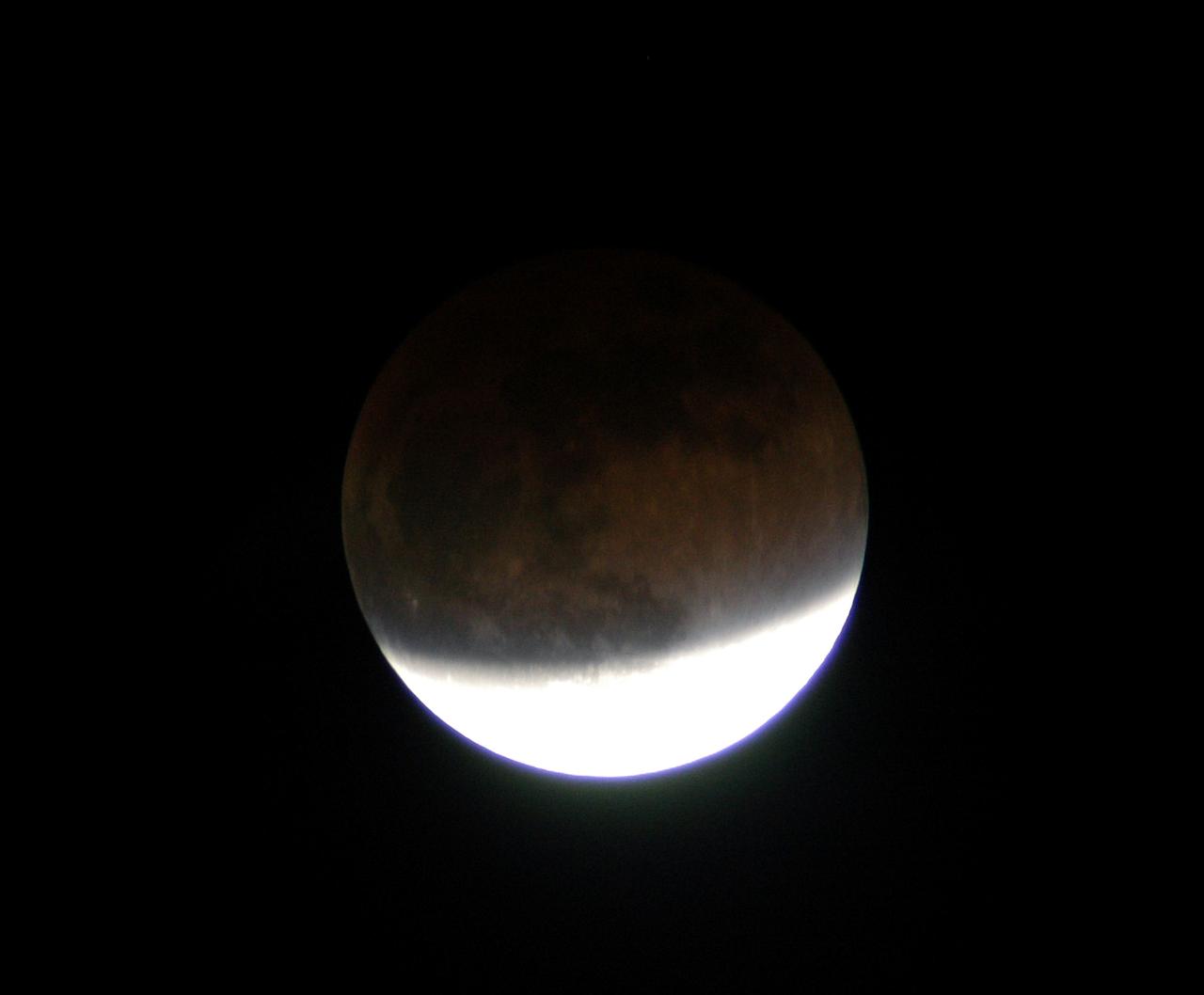

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In this lunar eclipse viewed from Merritt Island, Fla., the full moon changes color because it is being lighted slightly by sunlight passing through the Earth’s atmosphere. The earlier reddish color is fading but still somewhat visible on the darker, upper portion. Eclipses occur when the Sun, Earth and Moon line up. They are rare because the Moon usually passes above or below the imaginary line connecting Earth and the Sun. The Earth casts a shadow that the Moon can pass through - when it does, it is called a lunar eclipse.

STS041-S-001 (May 1990) --- The STS-41 crew patch, designed by the five astronaut crew members, depicts the space shuttle orbiting Earth after deployment of its primary payload - the Ulysses satellite. The orbiter is shown passing over the southeastern United States, representative of its 28-degree inclination orbit. Ulysses, the Solar Exploration Satellite, will be the fastest man-made object in the universe, traveling at 30 miles per second (over 100,000 mph) and is represented by the streaking silver teardrop passing over the sun. Ulysses' path is depicted by the bright red spiral originating from the space shuttle cargo bay. The path will extend around Jupiter where Ulysses will receive a gravitational direction change that will put it in a polar trajectory around the sun. The three-legged trajectory, extending out the payload bay, is symbolic of the astronaut logo and is in honor of those who have given their lives in the conquest of space. The five stars, four gold and one silver, represent STS-41 and each of its crew members. The NASA insignia design for space shuttle flights is reserved for use by the astronauts and for other official use as the NASA Administrator may authorize. Public availability has been approved only in the forms of illustrations by the various news media. When and if there is any change in this policy, which is not anticipated, the change will be publicly announced. Photo credit: NASA

STS066-S-001 (October 1994) --- Designed by the crew members, the STS-66 insignia depicts the space shuttle Atlantis launching into Earth orbit to study global environmental change. The payload for the Atmospheric Laboratory for Applications and Science (ATLAS-3) and complementary experiments are part of a continuing study of the atmosphere and the sun's influence on it. The space shuttle is trailed by gold plumes representing the astronaut symbol and is superimposed over Earth, much of which is visible from the flight's high inclination orbit. Sensitive instruments aboard the ATLAS pallet in the shuttle payload bay and on the free-flying Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmospheric-Shuttle Pallet Satellite (CHRISTA-SPAS) will gaze down on Earth and toward the sun, illustrated by the stylized sunrise and visible spectrum. The NASA insignia design for space shuttle flights is reserved for use by the astronauts and for other official use as the NASA Administrator may authorize. Public availability has been approved only in the forms of illustrations by the various news media. When and if there is any change in this policy, which is not anticipated, the change will be publicly announced. Photo credit: NASA

In this image, NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) observes an impact crater with associated bright deposits that at first glance give the appearance of seasonal frost or ice accumulations. MRO has an onboard spectrometer called CRISM that can distinguish between ices and other minerals. Unfortunately, there is currently no coverage of this particular spot. However, it can be deduced through several lines of evidence that this is, in fact, not ice. Just like Earth, Mars experiences seasons that change as the planet orbits the Sun. Seasonal changes are most apparent at the higher latitudes. As these regions in each hemisphere enter their respective summer seasons, the Sun rises higher in the Martian sky causing frost and ice to sublimate, and illuminate more features across the landscape. As the high latitudes of each hemisphere move toward their respective winters, the days (called "sols") grow shorter and the sun hangs low on the horizon, giving rise to prolonged periods of cold, darkness, and frost accumulation. First, it should be noted that at the time this image was taken, the Southern hemisphere is at the end of the summer season, so any frost or ice deposits have long since sublimated away. Second, numerous HiRISE images of seasonal targets show that ice accumulates on pole-facing slopes. The deposits in question are situated on a slope that faces the equator, and would not accumulate deposits of frost. Thus, it can be concluded that these exposures are light-toned mineral deposits. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21766
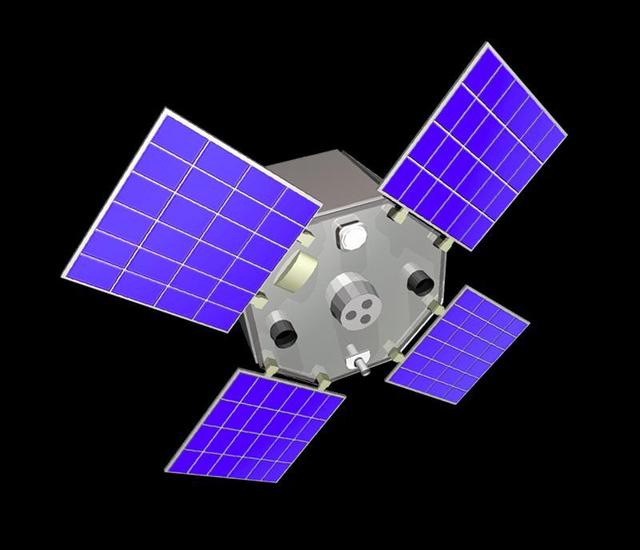

The Active Cavity Irradiance Monitor Satellite, or ACRIMSAT, mission is a climate change investigation that measures changes in how much of the sun's energy reaches Earth's atmosphere. This energy, called solar irradience, creates winds, heats the land and drives ocean currents, and therefore contains significant data that climatologists can use to improve predictions of climate change and global warming. The satellite's Active Cavity Irradiance Monitor III instrument, now in its third generation, has been used since the 1980s to study solar irradiance and its impacts on global warming. Scientists, using data from the instrument, now theorize that there is a significant correlation between solar radiation and global warming. ACRIMSAT completed its five-year primary mission in 2005 when it began operating under its extended mission. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA18157
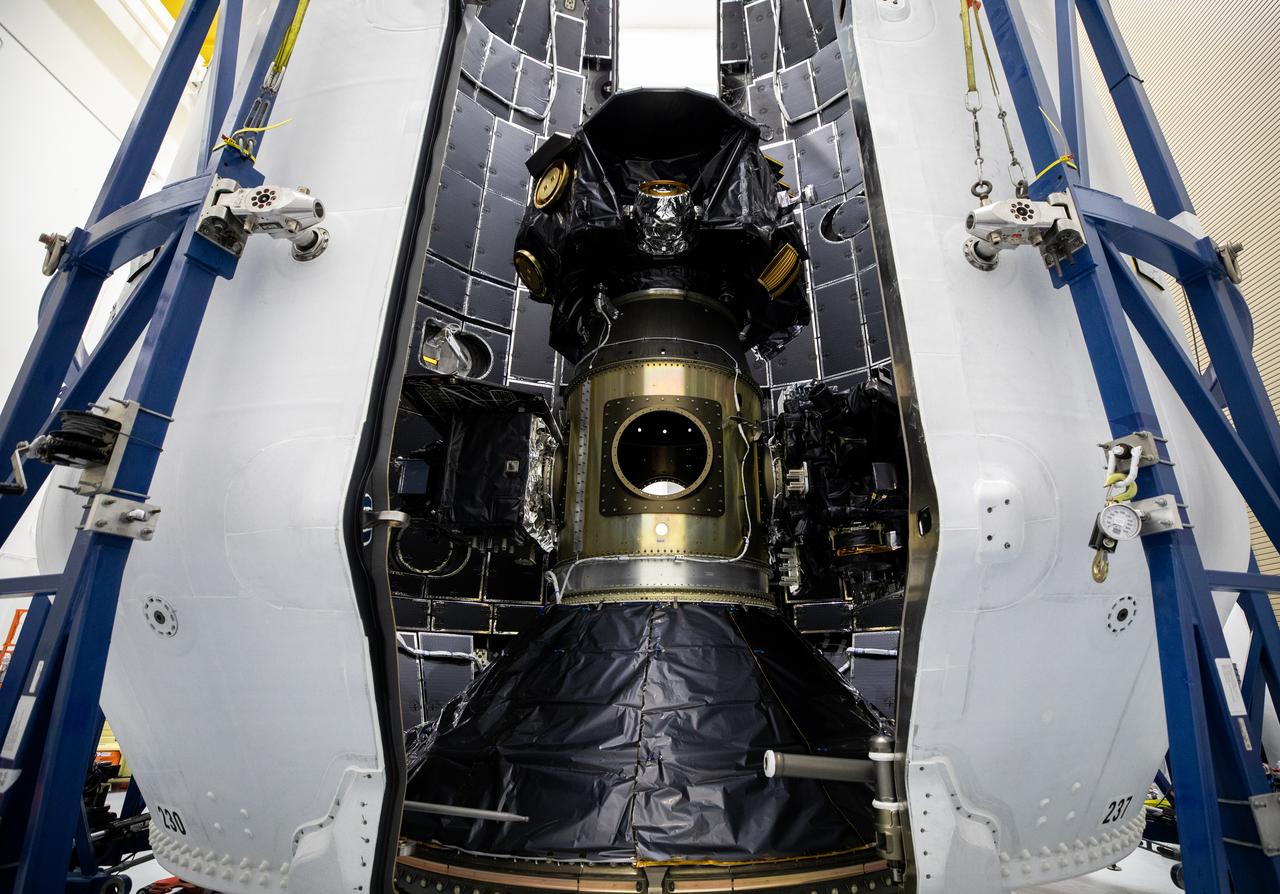

Technicians at Astrotech Space Operations Facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida encapsulate NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), along with the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft on Tuesday, Sept. 16, 2025, inside a SpaceX Falcon 9 payload fairing. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system. Liftoff of the missions on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket is targeted for 7:32 a.m. EDT, Tuesday, Sept. 23, from Launch Complex 39A at NASA Kennedy.
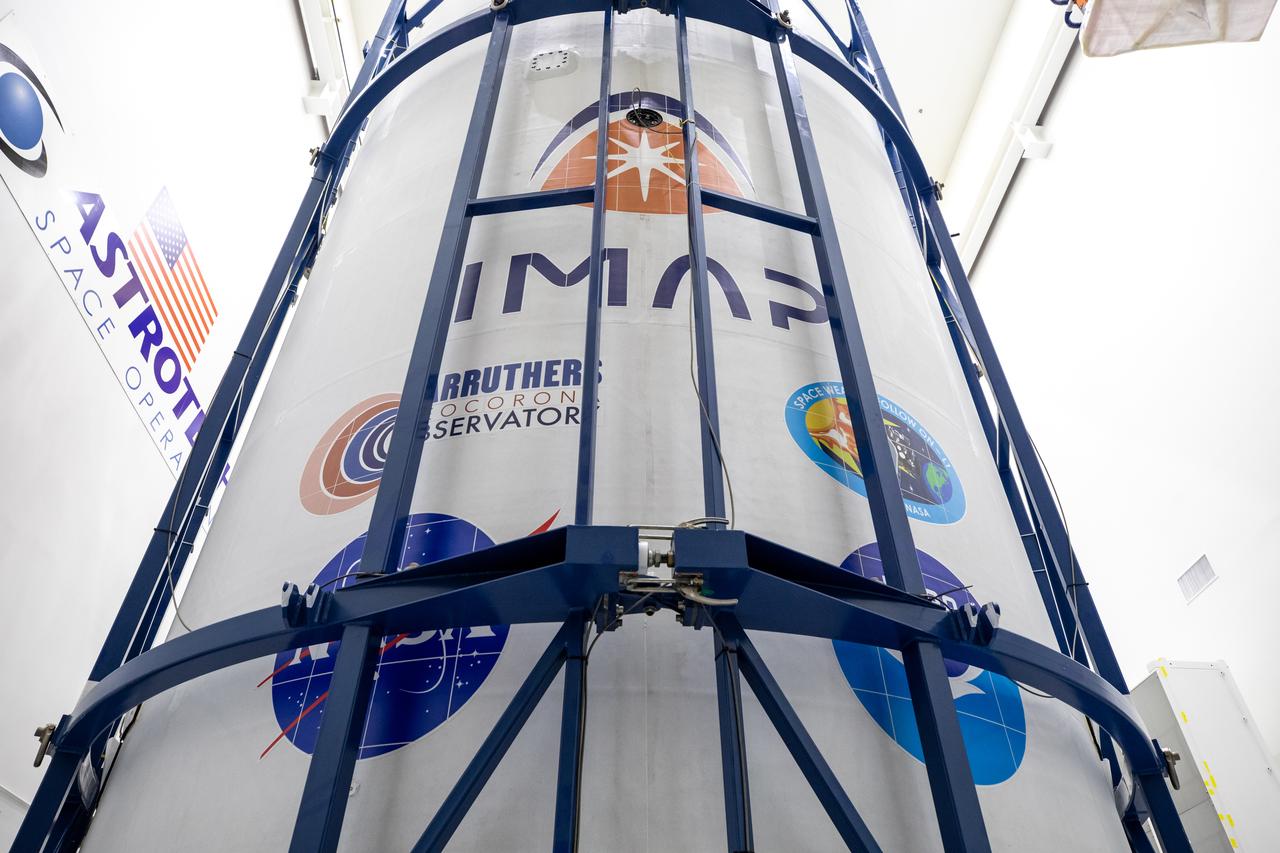

Technicians at Astrotech Space Operations Facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida encapsulate NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), along with the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft on Tuesday, Sept. 16, 2025, inside a SpaceX Falcon 9 payload fairing. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system. Liftoff of the missions on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket is targeted for 7:32 a.m. EDT, Tuesday, Sept. 23, from Launch Complex 39A at NASA Kennedy.
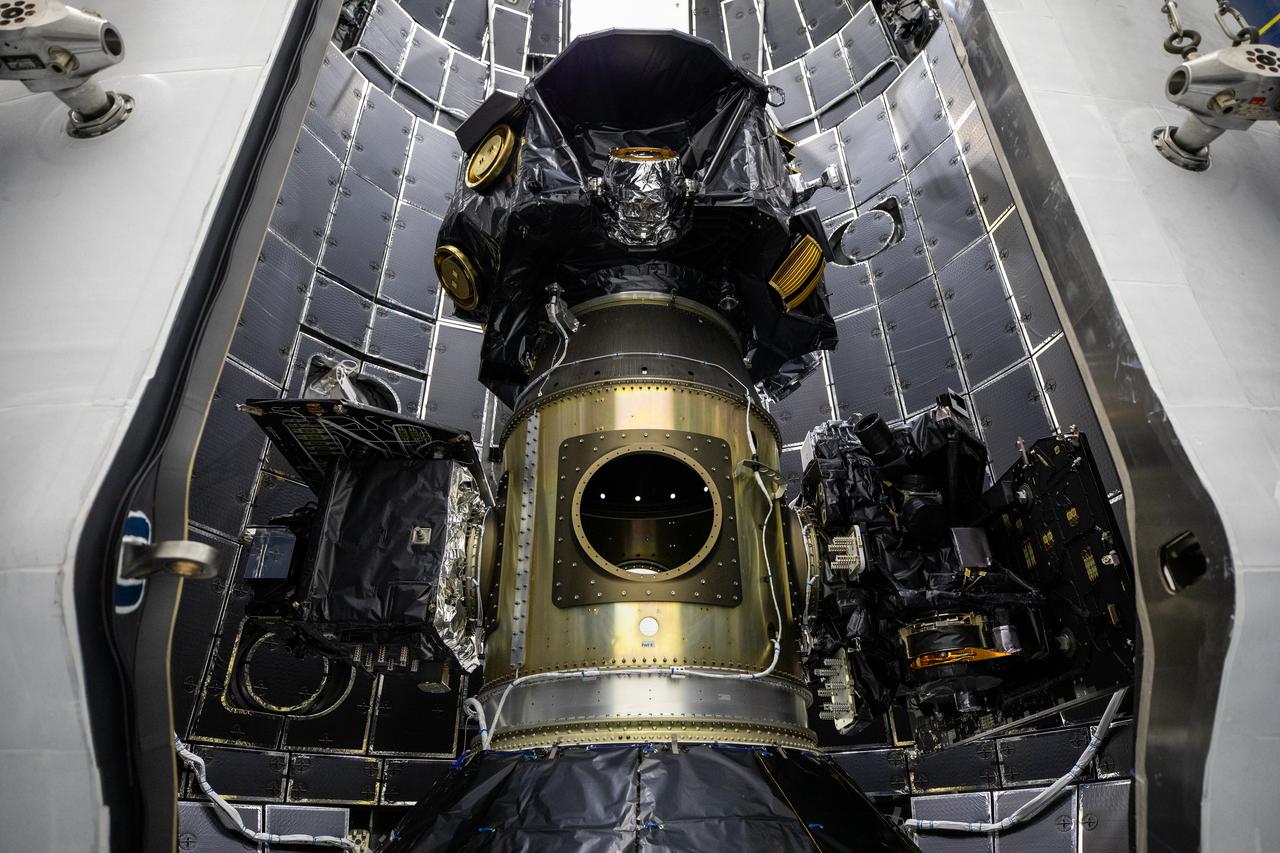

Technicians at Astrotech Space Operations Facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida encapsulate NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), along with the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft on Tuesday, Sept. 16, 2025, inside a SpaceX Falcon 9 payload fairing. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system. Liftoff of the missions on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket is targeted for 7:32 a.m. EDT, Tuesday, Sept. 23, from Launch Complex 39A at NASA Kennedy.
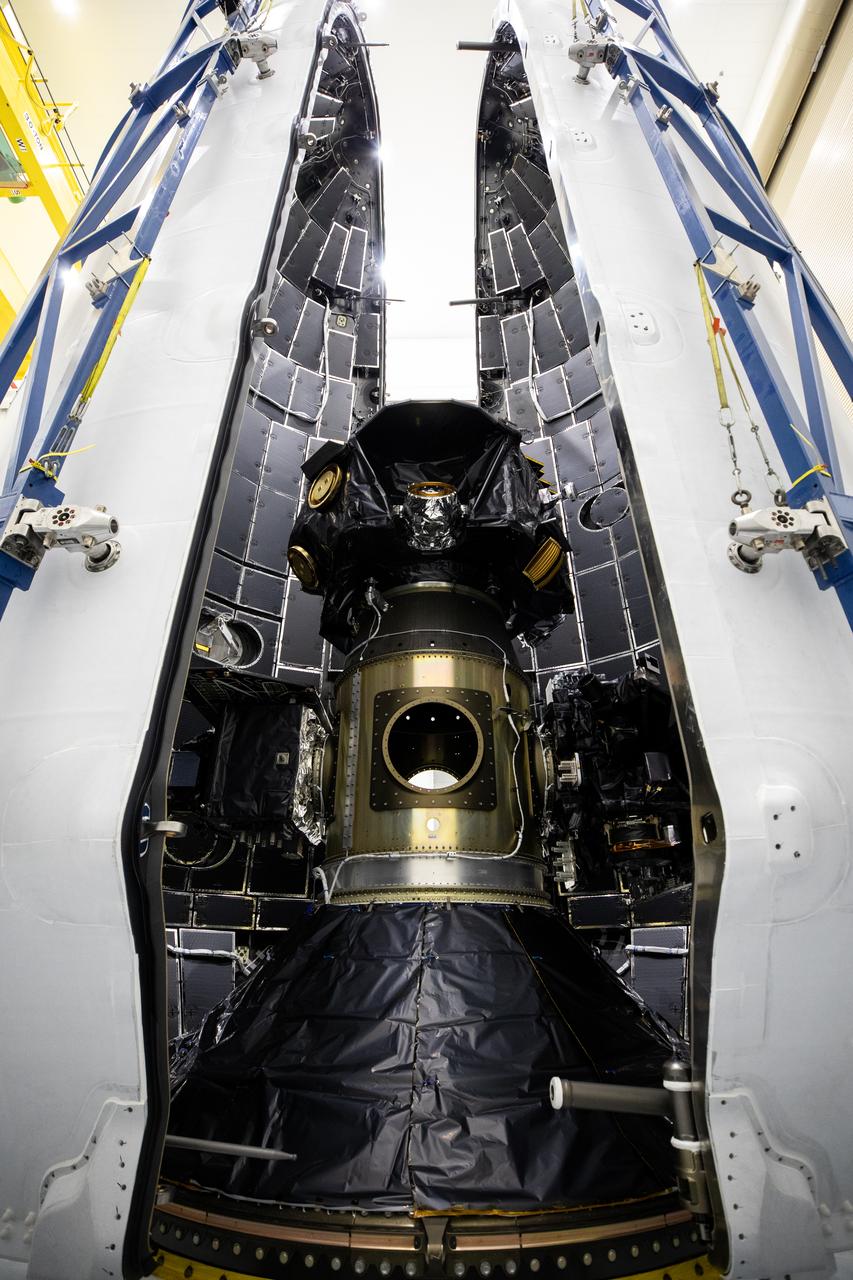

Technicians at Astrotech Space Operations Facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida encapsulate NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), along with the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft on Tuesday, Sept. 16, 2025, inside a SpaceX Falcon 9 payload fairing. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system. Liftoff of the missions on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket is targeted for 7:32 a.m. EDT, Tuesday, Sept. 23, from Launch Complex 39A at NASA Kennedy.
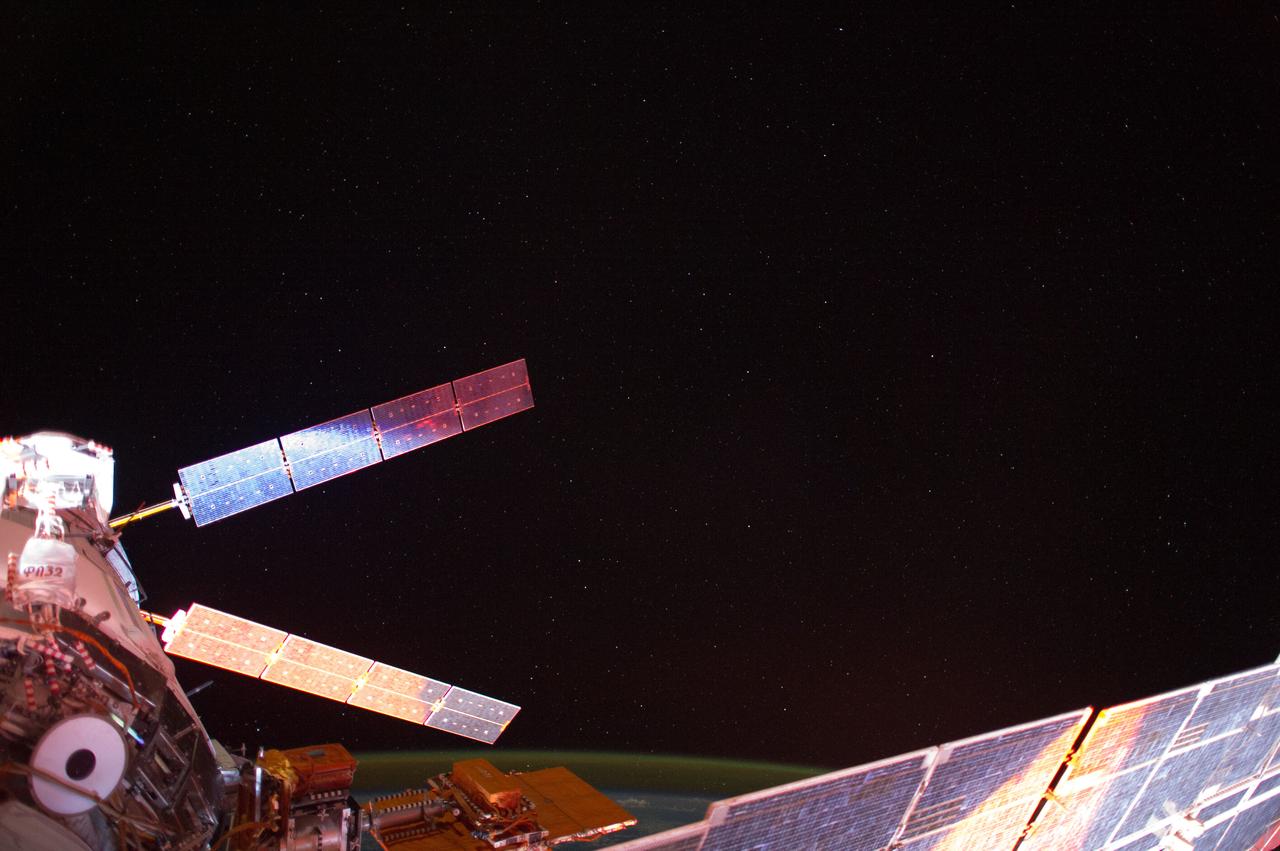

ISS041-E-013683 (13 Sept. 2014) --- Photographed with a mounted automated camera, this is one of a number of images featuring the European Space Agency?s Automated Transfer Vehicle (ATV-5 or Georges Lemaitre) docked with the International Space Station. Except for color changes, the images are almost identical. The variation in color from frame to frame is due to the camera?s response to the motion of the orbital outpost, relative to the illumination from the sun.
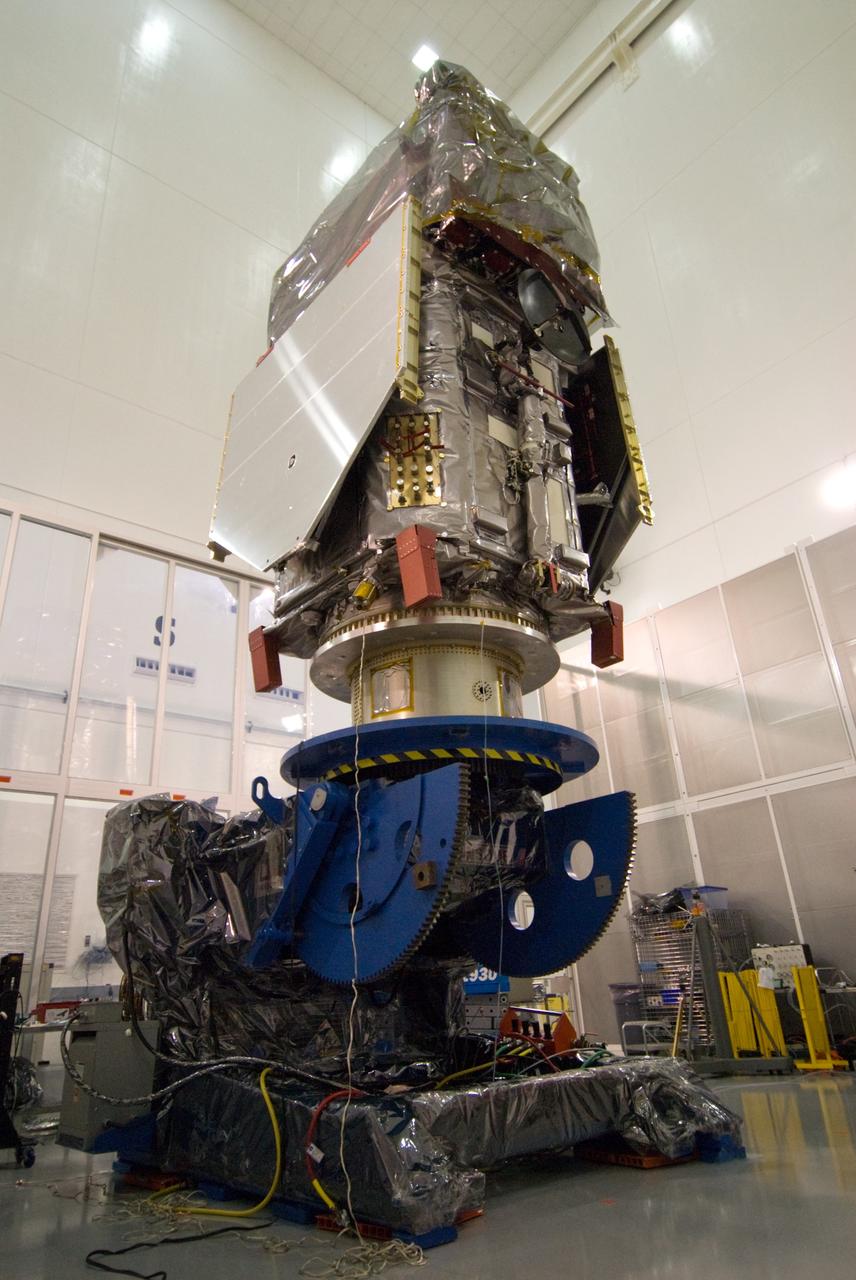

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Fla., the Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO, is vertically positioned during preparations for propulsion system testing and leak checks. SDO is the first space weather research network mission in NASA's Living With a Star Program. The spacecraft's long-term measurements will give solar scientists in-depth information about changes in the sun's magnetic field and insight into how they affect Earth. Liftoff on an Atlas V rocket is scheduled for Feb. 3, 2010. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
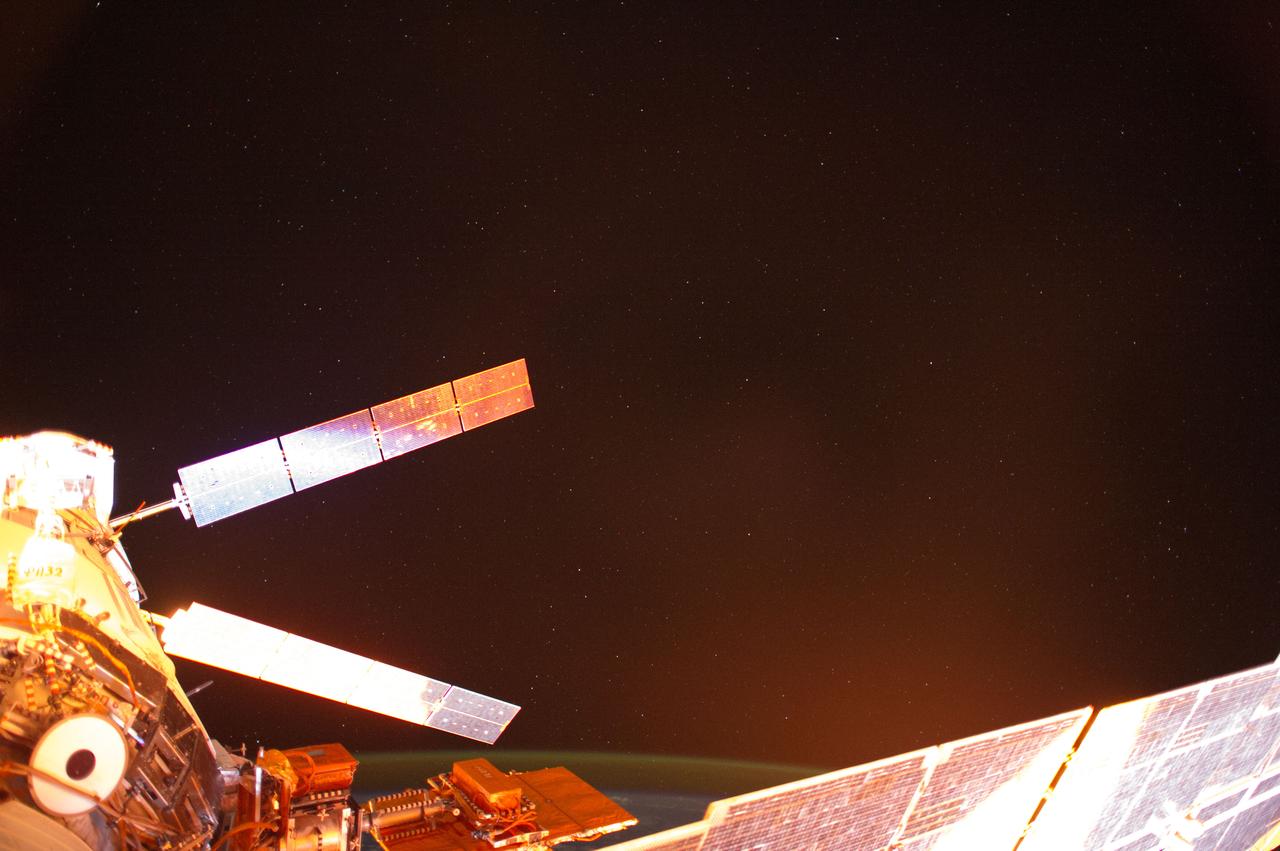

ISS041-E-013693 (13 Sept. 2014) --- Photographed with a mounted automated camera, this is one of a number of images featuring the European Space Agency?s Automated Transfer Vehicle (ATV-5 or Georges Lemaitre) docked with the International Space Station. Except for color changes, the images are almost identical. The variation in color from frame to frame is due to the camera?s response to the motion of the orbital outpost, relative to the illumination from the sun.
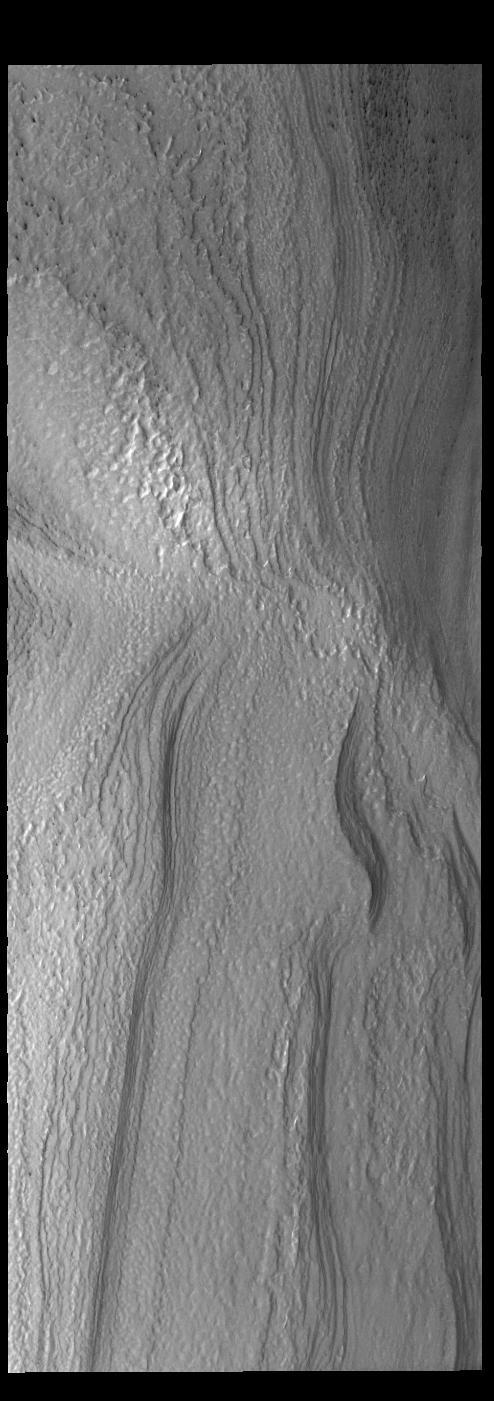

Today's VIS image shows part of the south polar cap. The sun has only just risen on the south pole. It is the start of the spring season and everything is still covered in frost. As the frost sublimates (changes from solid to gas) different surface features will become apparent. Orbit Number: 81244 Latitude: -86.5737 Longitude: 165.076 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2020-04-07 22:16 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23948

NASA Earth Science Division Director Michael Freilich shows meteorologists an AERONET sun photometer, right, and a model of the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory during a media event for the release of the Third U.S. National Climate Assessment, South Lawn of the White House in Washington, Tuesday, May 6, 2014. NASA Earth-observing satellite observations and analysis by the NASA-supported research community underlie many of the findings in the new climate change assessment. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
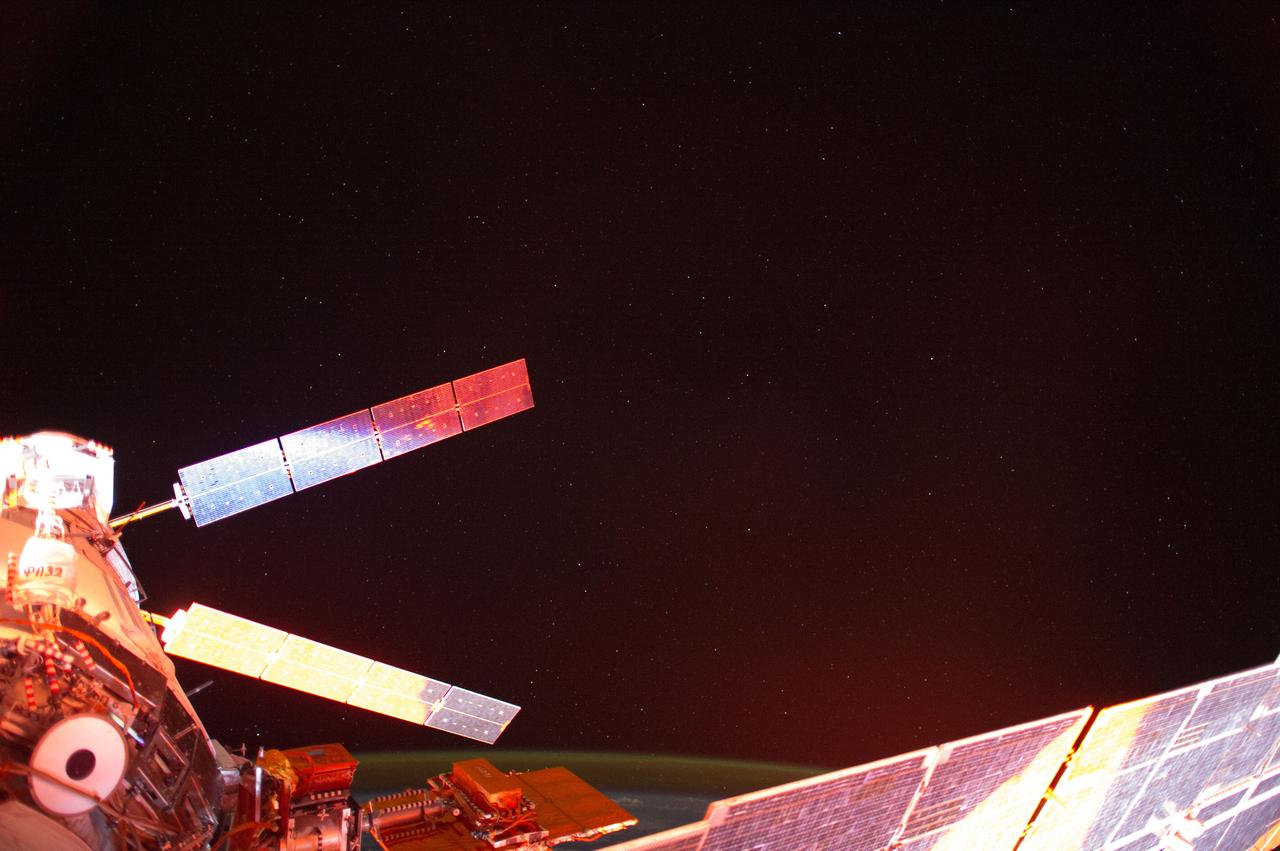

ISS041-E-013687 (13 Sept. 2014) --- Photographed with a mounted automated camera, this is one of a number of images featuring the European Space Agency?s Automated Transfer Vehicle (ATV-5 or Georges Lemaitre) docked with the International Space Station. Except for color changes, the images are almost identical. The variation in color from frame to frame is due to the camera?s response to the motion of the orbital outpost, relative to the illumination from the sun.

NASA Earth Science Division Director Michael Freilich shows meteorologists an AERONET sun photometer, right, and a model of the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Core Observatory during a media event for the release of the Third U.S. National Climate Assessment, South Lawn of the White House in Washington, Tuesday, May 6, 2014. NASA Earth-observing satellite observations and analysis by the NASA-supported research community underlie many of the findings in the new climate change assessment. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
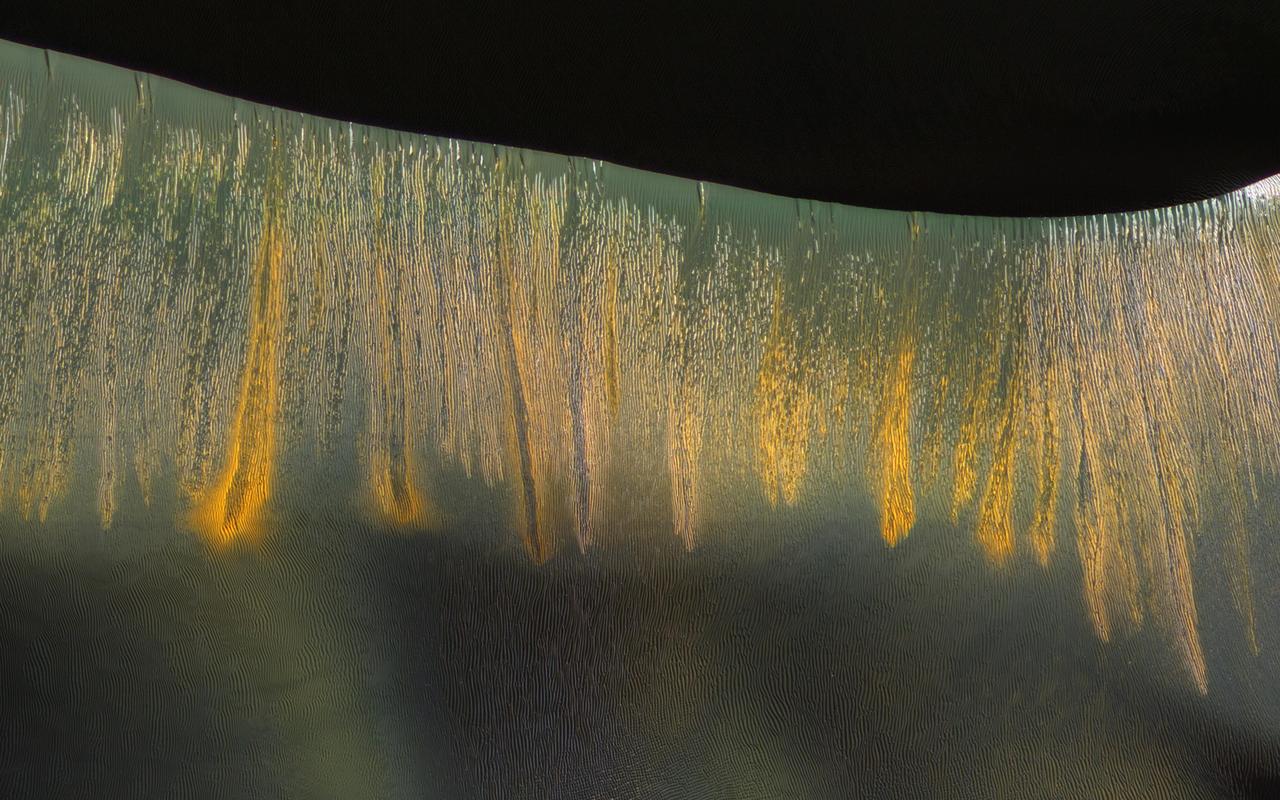
The giant sand dunes in Kaiser Crater experience gully erosion of the steep slip faces every year in late winter as the sun warms these slopes and seasonal carbon dioxide frost sublimates (meaning it changes from a solid to gas). Some of these gullies produce a variety of colors that are highlighted on the west-facing (illuminated) slopes, where the gullies appear to be glowing in the winter light. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20736

NASA image acquired May 1, 2010. As an active region rotated into view, it blew out three relatively small eruptions over about two days (Apr. 30 - May 2) as STEREO (Ahead) observed in extreme UV light. The first one was the largest and exhibited a pronounced twisting motion (shown in the still from May 1, 2010). The plasma, not far above the Sun's surface in these images, is ionized Helium heated to about 60,000 degrees. Note, too, the movement of plasma flowing along magnetic field lines that extend out beyond and loop back into the Sun's surface. Such activity occurs every day and is part of the dynamism of the changing Sun. Credit: NASA/GSFC/STEREO To learn more about STEREO go to: <a href="http://soho.nascom.nasa.gov/home.html" rel="nofollow">soho.nascom.nasa.gov/home.html</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> is home to the nation's largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe.

ISS044-S-001 (February 2014) --- This is the insignia for the Expedition 44 mission. The International Space Station is positioned in the foreground poised to study Earth, the sun and cosmos that lie beyond. Two members of the Expedition 44 crew will spend a full year on the ISS - providing valuable experience for future long duration missions into deep space. The 12 Earths represent the planet's position around the sun over the course of that year. Four of the Earths are silhouetted in sunlight representing the four month duration of Expedition 44. The nine stars in the background represent the nine individuals that will visit and work on the ISS during the course of the expedition, including the six-member crew, whose names are inscribed around the patch's border, and the three-person Soyuz "taxi" crew. The use of ellipses and circles throughout the patch reflect a theme of "completion" or "return," as investments made in this orbiting laboratory return benefit to the Earth and its inhabitants. The NASA insignia design for shuttle flights and station increments is reserved for use by the astronauts and for other official use as the NASA Administrator may authorize. Public availability has been approved only in the forms of illustrations by the various news media. When and if there is any change in this policy, which is not anticipated, the change will be publicly announced. Photo credit: NASA

S82-26315 (4 Feb. 1982) --- This is the insignia for NASA's third flight (STS-3) of the Space Transportation System's (STS) Columbia, depicted in the middle of the blue sphere against the background of the sun. The Columbia's tail, nose, and top will each be pointed at the sun for long periods to test its thermal response to extremes of temperatures. The three prominent rays represent the third STS flight. The surnames of astronauts Jack R. Lousma, commander, and C. Gordon Fullerton, pilot, flank the vehicle, and the name Columbia appears at the bottom. The spacecraft's payload bay doors are open, and the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm with an experimental payload is extended as it will be on several occasions during the actual flight, scheduled for spring of this year. The artwork was accomplished by space artist Robert C. McCall of Paradise Valley, Arizona. The NASA insignia design for space shuttle flights is reserved for use by the astronauts and for other official use as the NASA Administrator may authorize. Public availability has been approved only in the forms of illustrations by the various news media. When and if there is any change in this policy, which is not anticipated, the change will be publicly announced. Photo credit: NASA

Images acquired December 21, 2010 - September 20, 2011. To download the high res and learn more go to: <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=52248" rel="nofollow">earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=52248</a> One of the most frequently misunderstood concepts in science is the reason for Earth’s seasons. As we experience the September equinox today—anyone try to balance an egg yet?—we thought we’d offer a space-based view of what’s going on. Around 6 a.m. local time each day, the Sun, Earth, and any geosynchronous satellite form a right angle, affording a nadir (straight down) view of the terminator, where the shadows of nightfall meet the sunlight of dusk and dawn. The shape of this line between night and day varies with the seasons, which means different lengths of days and differing amounts of warming sunshine. (The line is actually a curve because the Earth is round, but satellite images only show it in two-dimensions.) The Spinning Enhanced Visible and Infrared Imager (SEVIRI) on EUMETSAT's Meteosat-9 captured these four views of the day-night terminator on December 21, 2010, and March 20, June 21, and September 20, 2011. Each image was taken at 6:12 a.m. local time. On March 20 and September 20, the terminator is a straight north-south line, and the Sun is said to sit directly above the equator. On December 21, the Sun resides directly over the Tropic of Capricorn when viewed from the ground, and sunlight spreads over more of the Southern Hemisphere. On June 21, the Sun sits above the Tropic of Cancer, spreading more sunlight in the north and turning the tables on the south. The bulge of our spherical Earth blocks sunlight from the far hemisphere at the solstices; that same curvature allows the Sun’s rays to spread over more area near the top and bottom of the globe. Of course, it is not the Sun that is moving north or south through the seasons, but a change in the orientation and angles between the Earth and its nearest star. The axis of the Earth is tilted 23.5 degrees relative to the Sun and the ecliptic plane. The axis is tilted away from the Sun at the December solstice and toward the Sun at the June solstice, spreading more and less light on each hemisphere. At the equinoxes, the tilt is at a right angle to the Sun and the light is spread evenly. The equinox and changing of the seasons occurs on September 23, 2011 at 9:05 a.m. Universal Time. (Our September image above is a few days early.) Equinox means "equal night" in Latin, capturing the idea that daytime and nighttime are equal lengths everywhere on the planet. That is true of the Sun's presence above the horizon, though it does not account for twilight, when the Sun's rays extend from beyond the horizon to illuminate our gas-filled atmosphere. <b>NASA images and animation by Robert Simmon, using data ©2010 EUMETSAT. Caption by Mike Carlowicz.</b> Instrument: Meteosat Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The covered THEMIS spacecraft is transported to Launch Complex 17 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. On Launch Pad 17-B, the spacecraft will be mated with the third stage of the Delta II rocket. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. The THEMIS mission is to investigate what causes auroras in the Earth's atmosphere to dramatically change from slowly shimmering waves of light to wildly shifting streaks of color. Discovering what causes auroras to change will provide scientists with important details on how the planet's magnetosphere works and the important Sun-Earth connection. THEMIS is scheduled to launch aboard a Delta II rocket on Feb. 15 during a window extending from 6:08 to 6:27 p.m. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers inside the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station help maneuver the upper canister away from the opening. The canister was removed from around the THEMIS spacecraft. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. The THEMIS mission is to investigate what causes auroras in the Earth's atmosphere to dramatically change from slowly shimmering waves of light to wildly shifting streaks of color. Discovering what causes auroras to change will provide scientists with important details on how the planet's magnetosphere works and the important Sun-Earth connection. THEMIS is scheduled to launch aboard a Delta II rocket on Feb. 15 during a window extending from 6:08 to 6:27 p.m. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
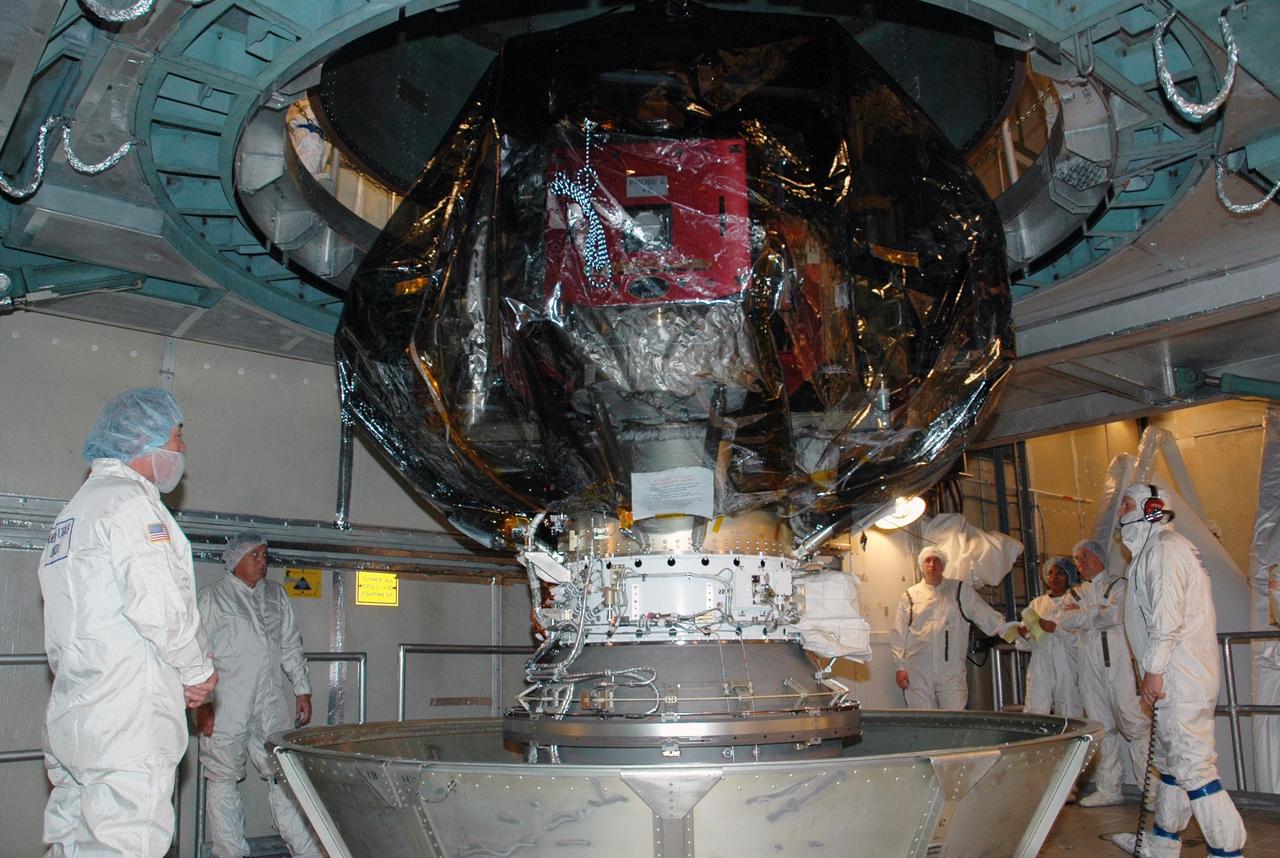

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers inside the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station watch as the upper canister is lifted away from the THEMIS spacecraft. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. The THEMIS mission is to investigate what causes auroras in the Earth's atmosphere to dramatically change from slowly shimmering waves of light to wildly shifting streaks of color. Discovering what causes auroras to change will provide scientists with important details on how the planet's magnetosphere works and the important Sun-Earth connection. THEMIS is scheduled to launch aboard a Delta II rocket on Feb. 15 during a window extending from 6:08 to 6:27 p.m. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
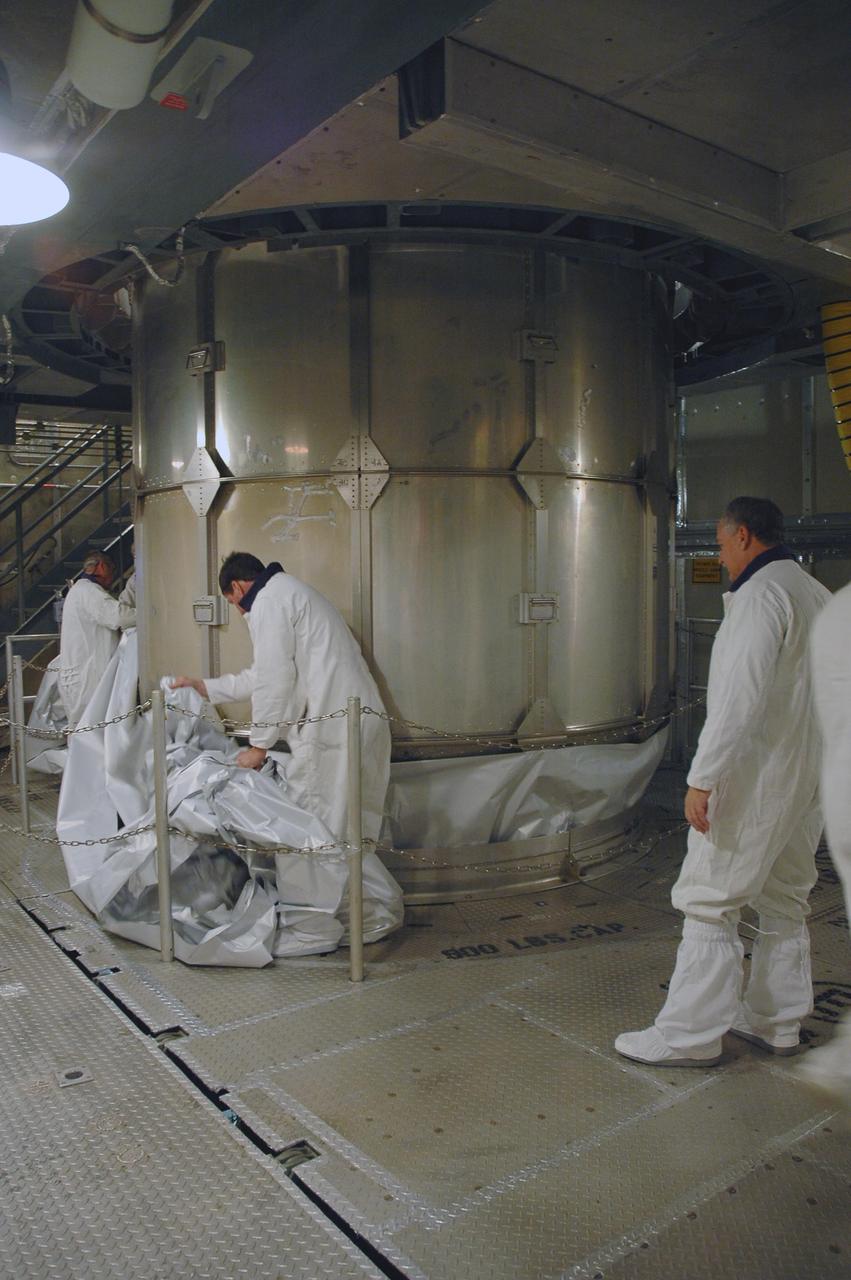

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Inside the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, workers remove the protective cover surrounding the THEMIS spacecraft. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. The THEMIS mission is to investigate what causes auroras in the Earth's atmosphere to dramatically change from slowly shimmering waves of light to wildly shifting streaks of color. Discovering what causes auroras to change will provide scientists with important details on how the planet's magnetosphere works and the important Sun-Earth connection. THEMIS is scheduled to launch aboard a Delta II rocket on Feb. 15 during a window extending from 6:08 to 6:27 p.m. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
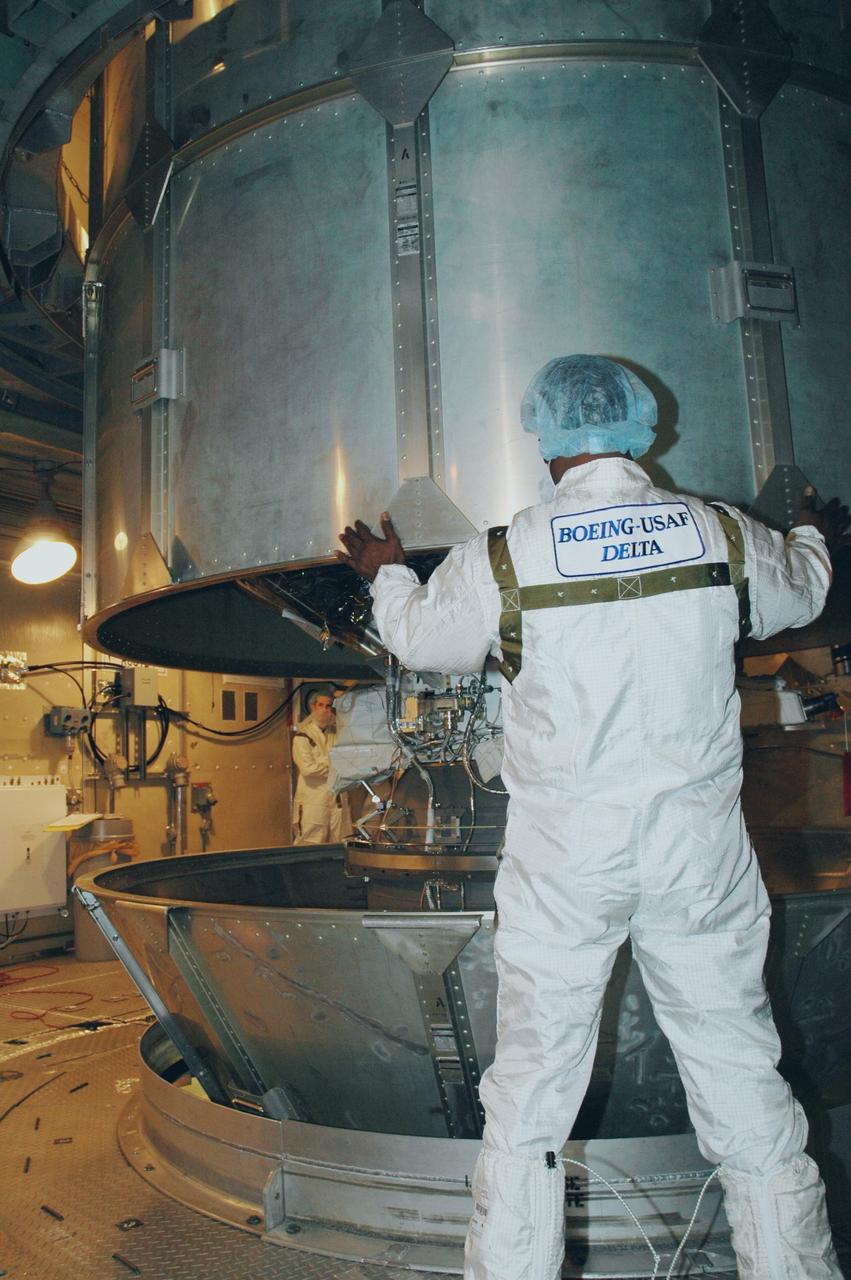

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers inside the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station maneuver the upper canister away from the THEMIS spacecraft. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. The THEMIS mission is to investigate what causes auroras in the Earth's atmosphere to dramatically change from slowly shimmering waves of light to wildly shifting streaks of color. Discovering what causes auroras to change will provide scientists with important details on how the planet's magnetosphere works and the important Sun-Earth connection. THEMIS is scheduled to launch aboard a Delta II rocket on Feb. 15 during a window extending from 6:08 to 6:27 p.m. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
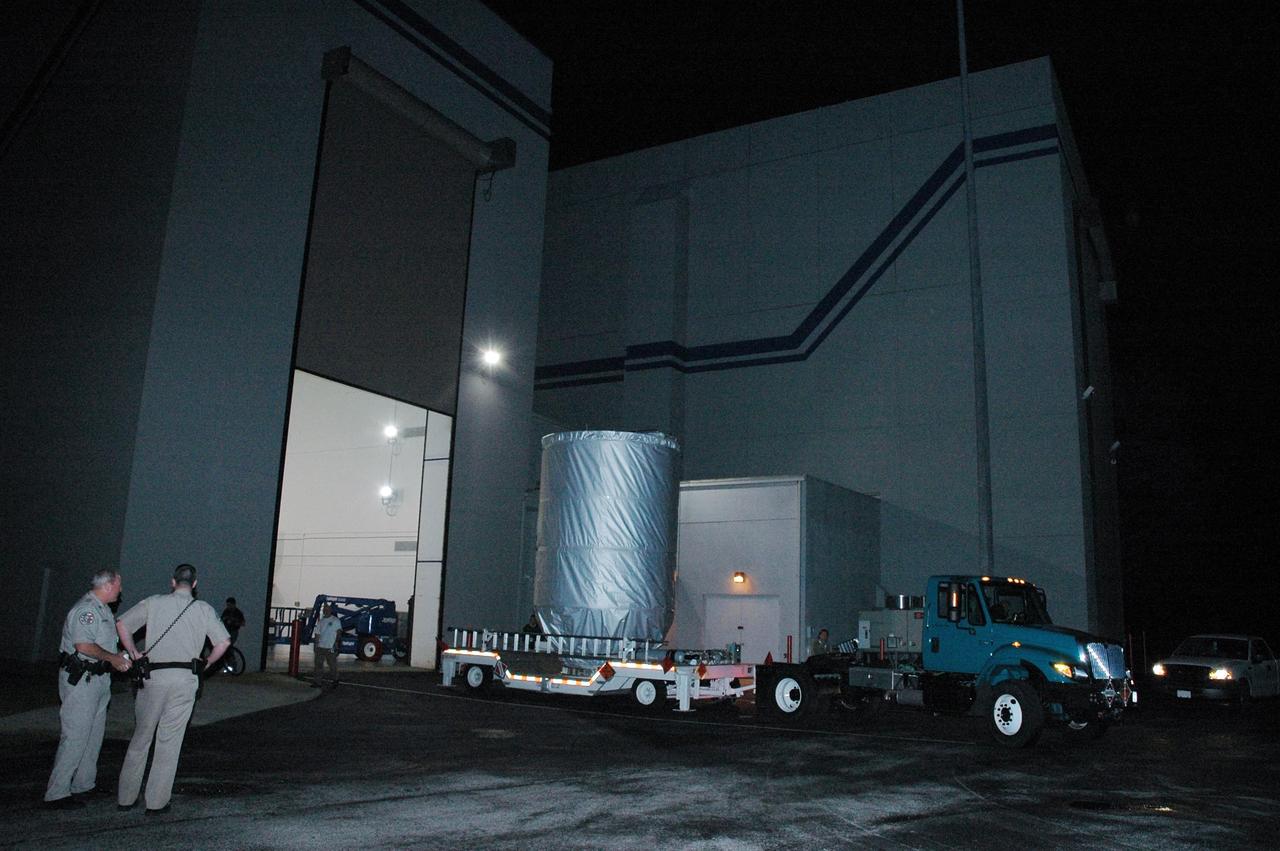

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A transport vehicle moves the covered THEMIS spacecraft away from Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., on the start of its journey to Launch Complex 17 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. On Launch Pad 17-B, the spacecraft will be mated with the third stage of the Delta II rocket. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. The THEMIS mission is to investigate what causes auroras in the Earth's atmosphere to dramatically change from slowly shimmering waves of light to wildly shifting streaks of color. Discovering what causes auroras to change will provide scientists with important details on how the planet's magnetosphere works and the important Sun-Earth connection. THEMIS is scheduled to launch aboard a Delta II rocket on Feb. 15 during a window extending from 6:08 to 6:27 p.m. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
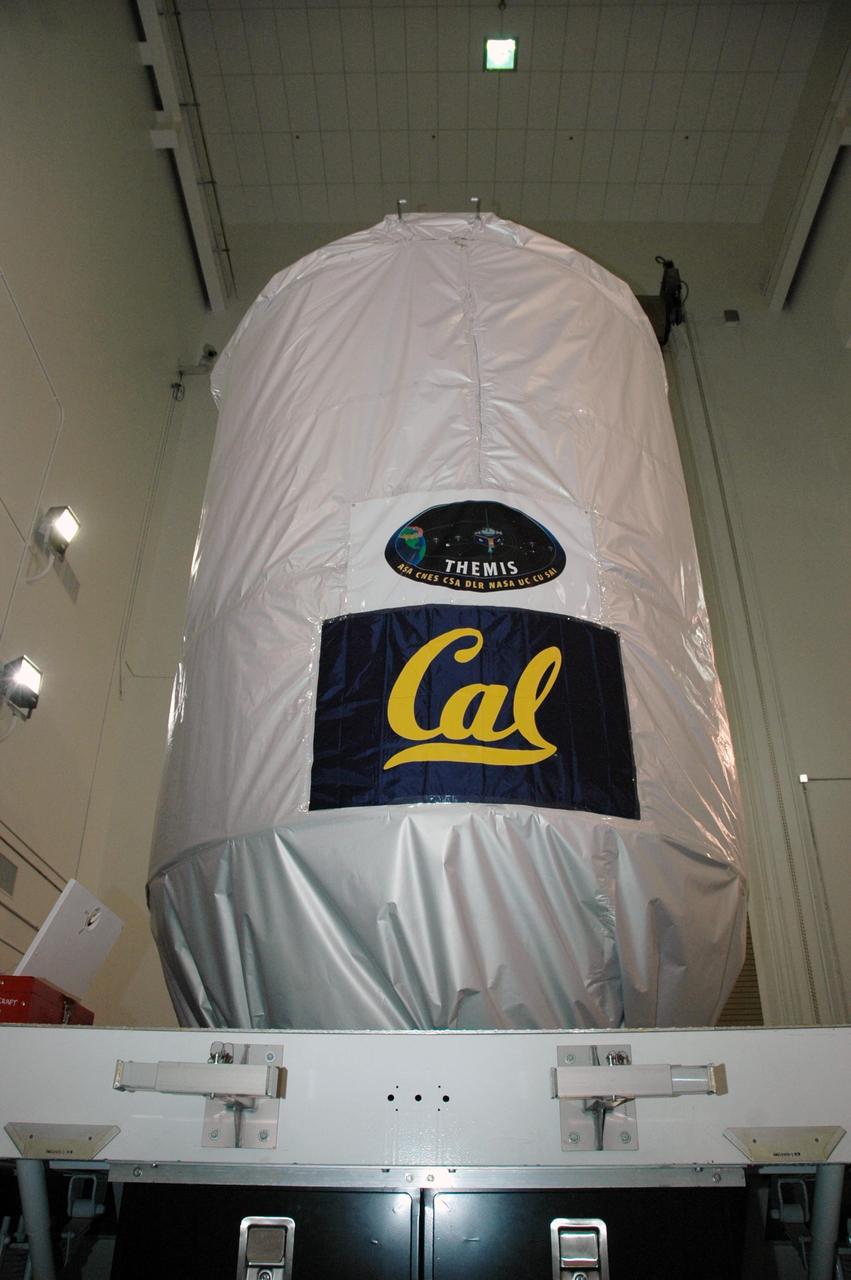

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., the THEMIS spacecraft is secure inside a protective cover for its transfer to Launch Complex 17 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. On Launch Pad 17-B, the spacecraft will be mated with the third stage of the Delta II rocket. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. The THEMIS mission is to investigate what causes auroras in the Earth's atmosphere to dramatically change from slowly shimmering waves of light to wildly shifting streaks of color. Discovering what causes auroras to change will provide scientists with important details on how the planet's magnetosphere works and the important Sun-Earth connection. THEMIS is scheduled to launch aboard a Delta II rocket on Feb. 15 during a window extending from 6:08 to 6:27 p.m. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
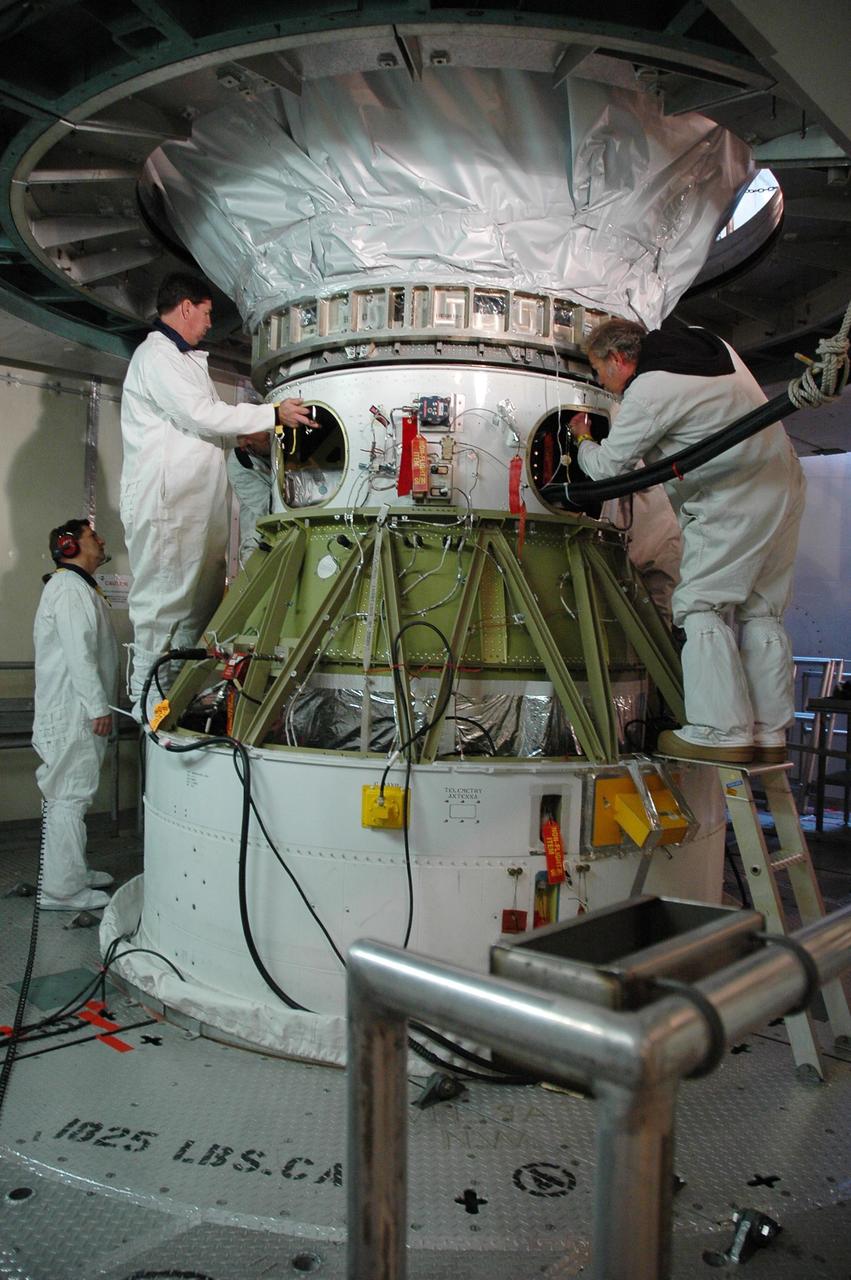

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Inside the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, workers remove the protective cover surrounding the THEMIS spacecraft. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. The THEMIS mission is to investigate what causes auroras in the Earth's atmosphere to dramatically change from slowly shimmering waves of light to wildly shifting streaks of color. Discovering what causes auroras to change will provide scientists with important details on how the planet's magnetosphere works and the important Sun-Earth connection. THEMIS is scheduled to launch aboard a Delta II rocket on Feb. 15 during a window extending from 6:08 to 6:27 p.m. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
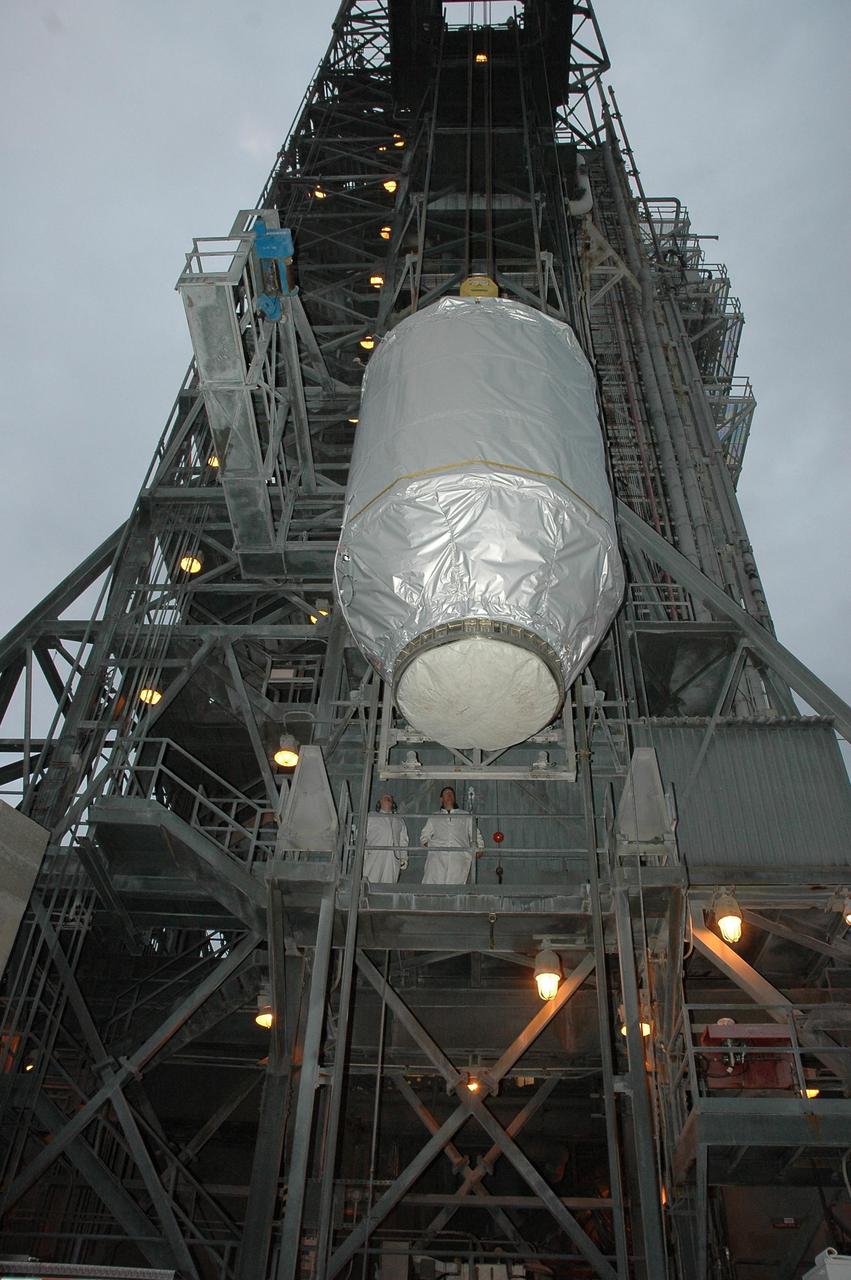

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- On Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the THEMIS spacecraft is lifted up alongside the mobile service tower. Once inside, THEMIS will be encapsulated and mated with the third stage of the Delta II rocket. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. The THEMIS mission is to investigate what causes auroras in the Earth's atmosphere to dramatically change from slowly shimmering waves of light to wildly shifting streaks of color. Discovering what causes auroras to change will provide scientists with important details on how the planet's magnetosphere works and the important Sun-Earth connection. THEMIS is scheduled to launch aboard a Delta II rocket on Feb. 15 during a window extending from 6:08 to 6:27 p.m. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
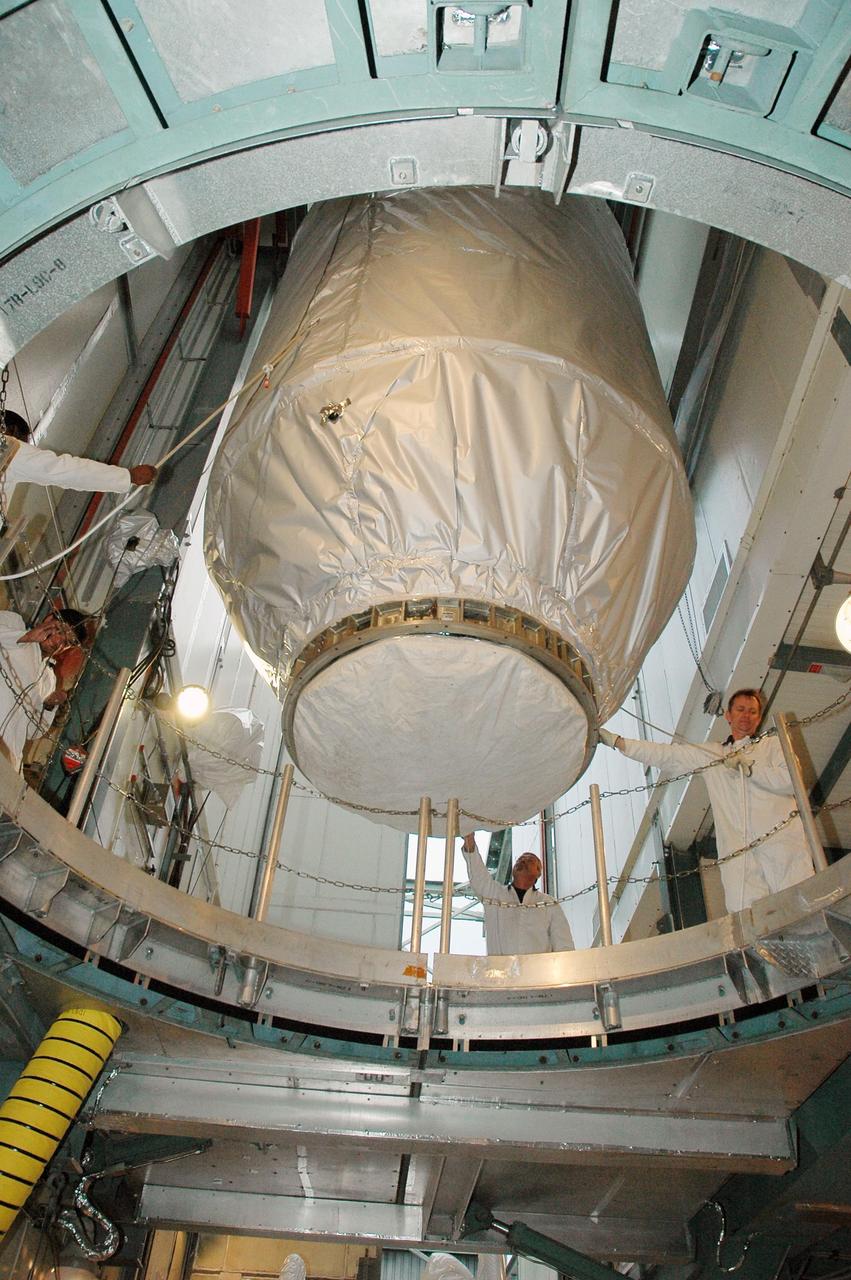

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the upper level of the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, workers help maneuver the THEMIS spacecraft into place. They will next remove the protective cover before encapsulating and mating the spacecraft with the third stage of the Delta II rocket. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. The THEMIS mission is to investigate what causes auroras in the Earth's atmosphere to dramatically change from slowly shimmering waves of light to wildly shifting streaks of color. Discovering what causes auroras to change will provide scientists with important details on how the planet's magnetosphere works and the important Sun-Earth connection. THEMIS is scheduled to launch aboard a Delta II rocket on Feb. 15 during a window extending from 6:08 to 6:27 p.m. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
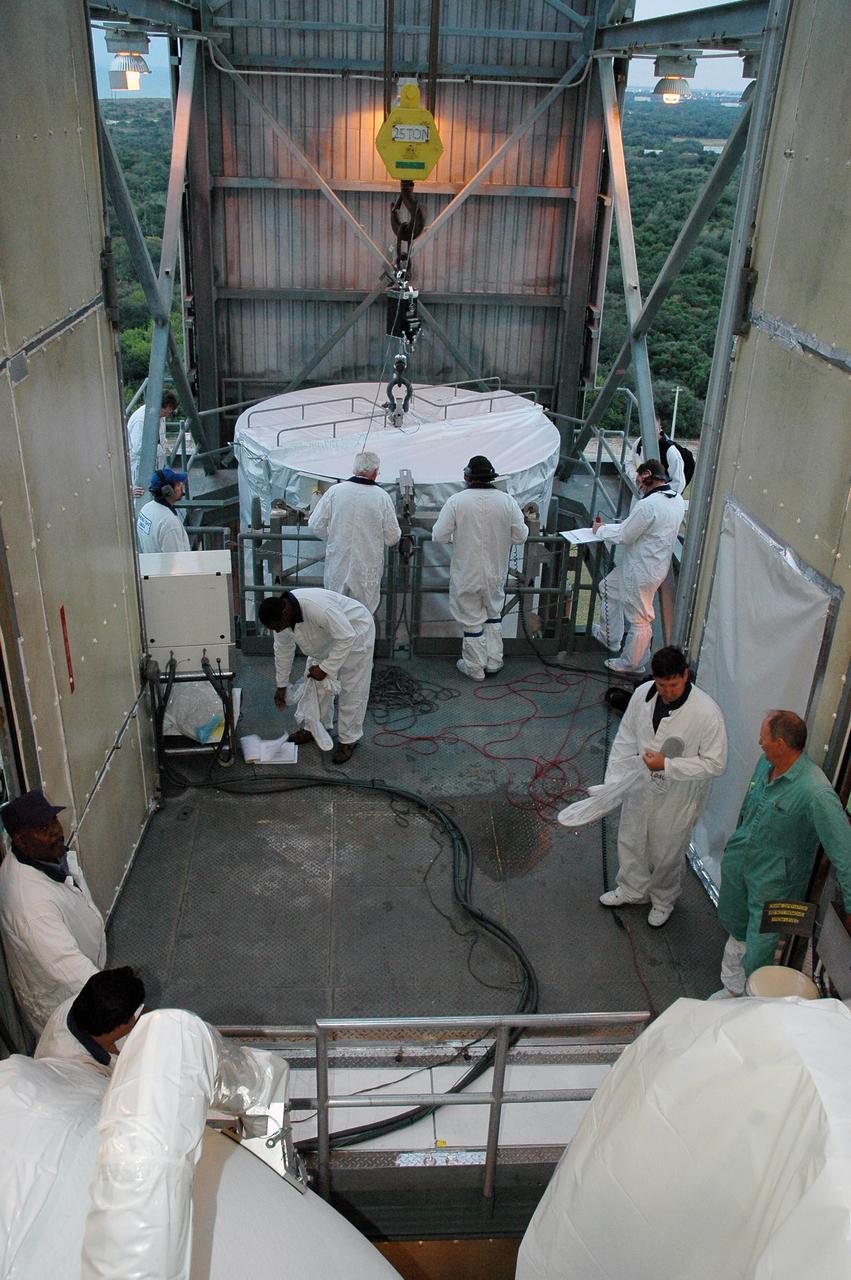

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the upper level of the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, workers wait for the THEMIS spacecraft (background) to be lifted and moved inside. THEMIS will then be encapsulated and mated with the third stage of the Delta II rocket. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. The THEMIS mission is to investigate what causes auroras in the Earth's atmosphere to dramatically change from slowly shimmering waves of light to wildly shifting streaks of color. Discovering what causes auroras to change will provide scientists with important details on how the planet's magnetosphere works and the important Sun-Earth connection. THEMIS is scheduled to launch aboard a Delta II rocket on Feb. 15 during a window extending from 6:08 to 6:27 p.m. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
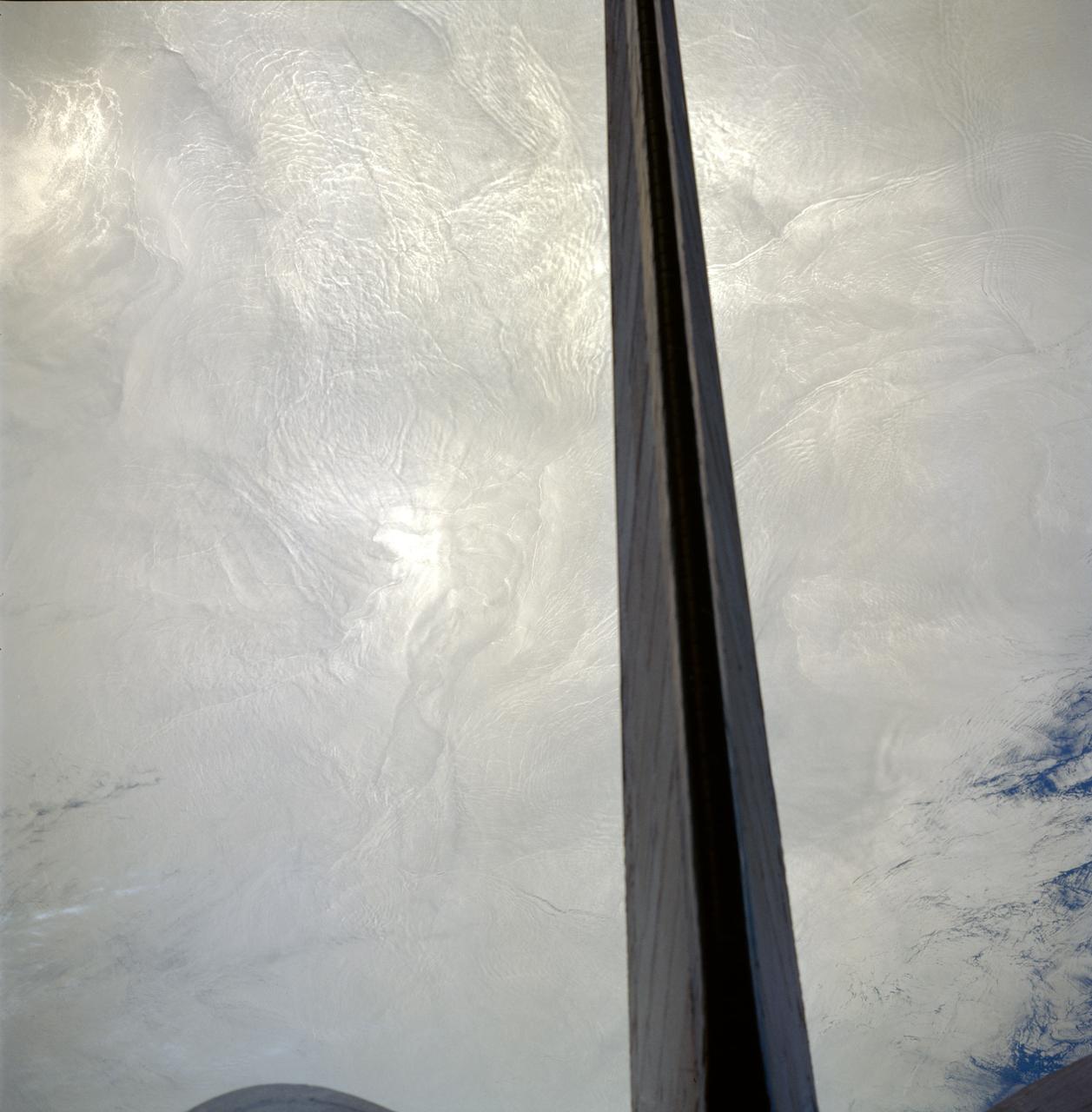

STS091-713-061 (2-12 June 1998) --- The vertical stabilizer of the Space Shuttle Discovery runs through this Atlantic Ocean image made from its crew cabin. Many sets of internal waves are seen in the 70mm frame traveling through an area off the Atlantic coast of Nova Scotia, Canada. There are seven sets that run perpendicular to each other. Internal waves are tidally induced and travel below the surface of the ocean along a density change which occurs often around 150 feet deep. According to NASA scientists studying the STS-91 collection, the waves are visible because, as the wave action smoothes out the smaller waves on the surface, the manner in which the sun is reflected is changed.
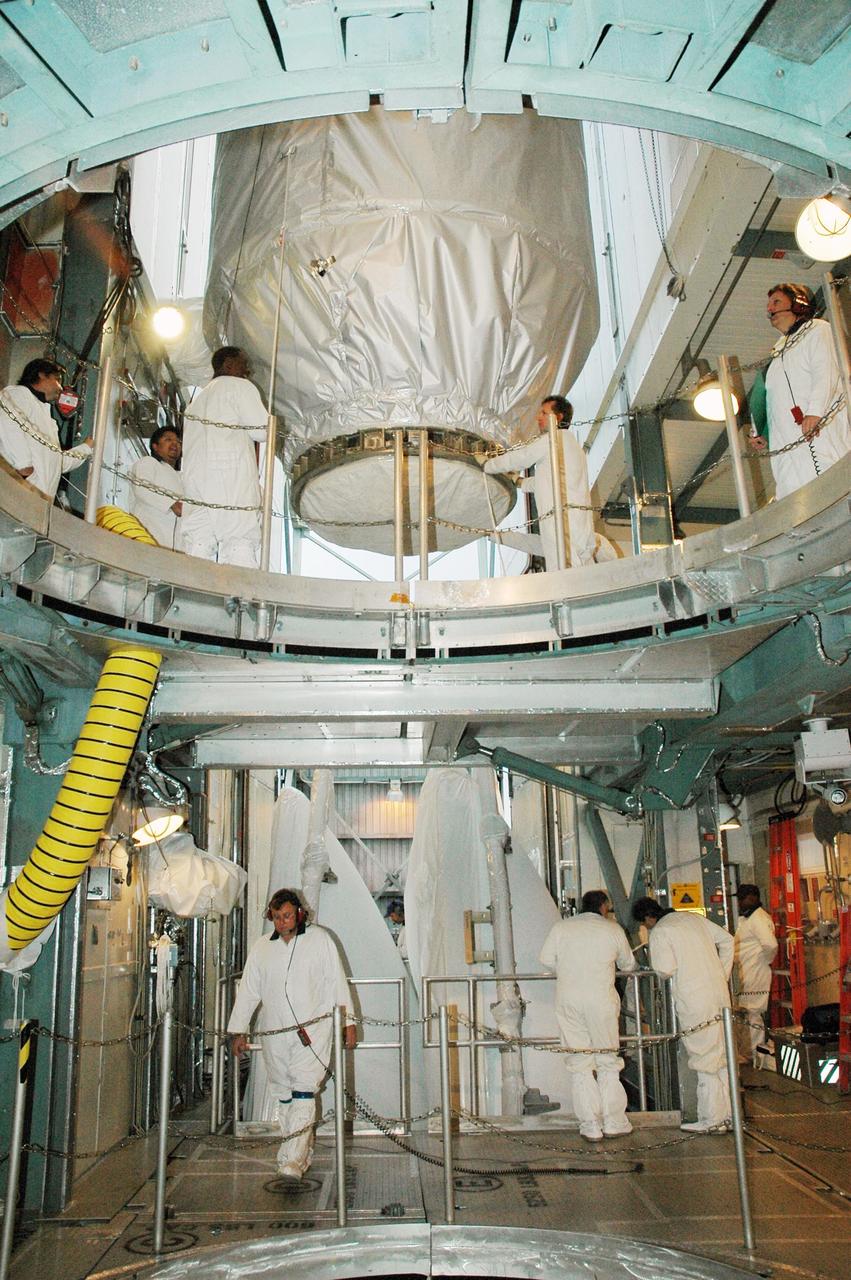

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the upper level of the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, workers help maneuver the THEMIS spacecraft into place. They will next remove the protective cover before encapsulating and mating the spacecraft with the third stage of the Delta II rocket. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. The THEMIS mission is to investigate what causes auroras in the Earth's atmosphere to dramatically change from slowly shimmering waves of light to wildly shifting streaks of color. Discovering what causes auroras to change will provide scientists with important details on how the planet's magnetosphere works and the important Sun-Earth connection. THEMIS is scheduled to launch aboard a Delta II rocket on Feb. 15 during a window extending from 6:08 to 6:27 p.m. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
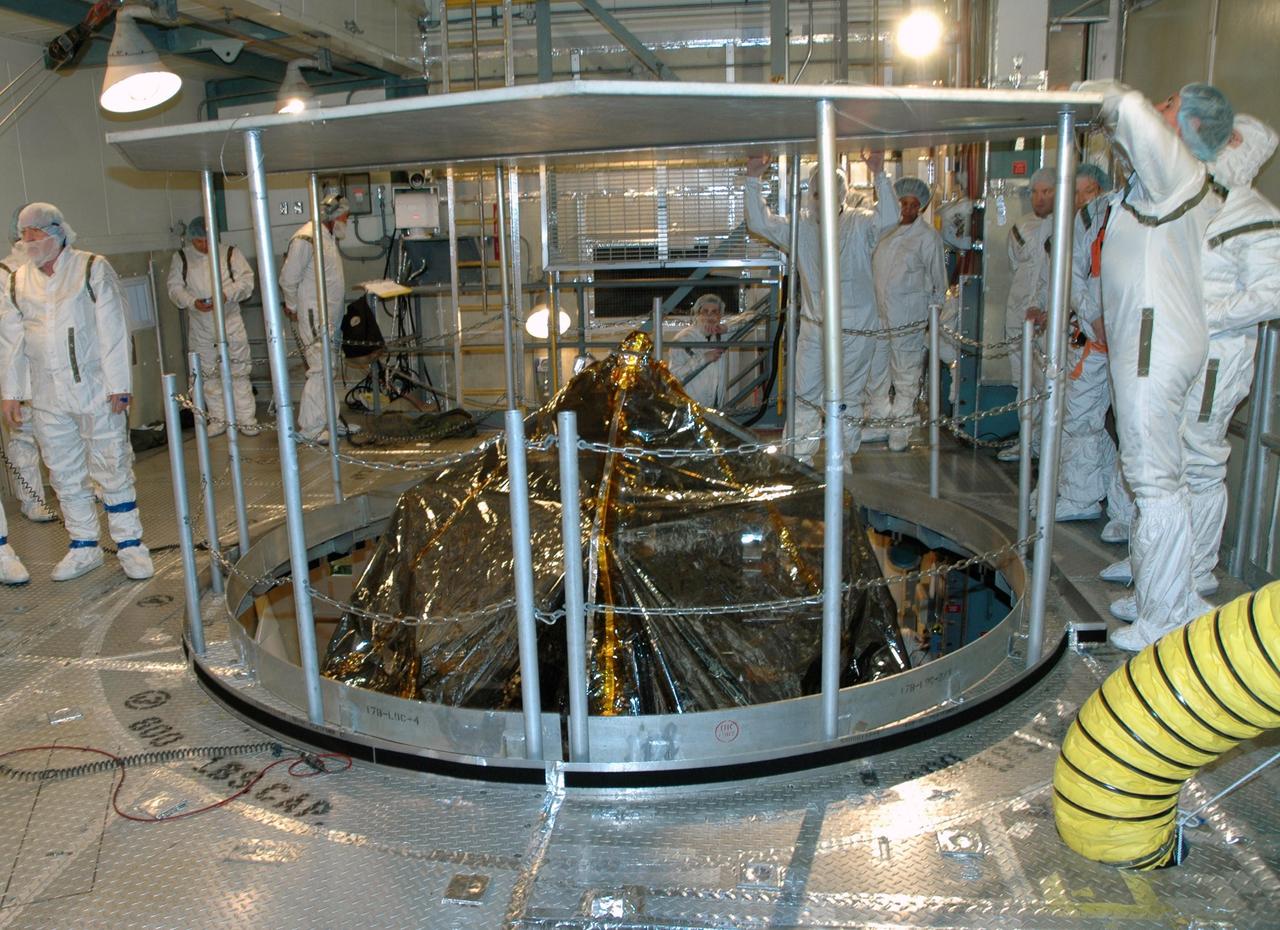

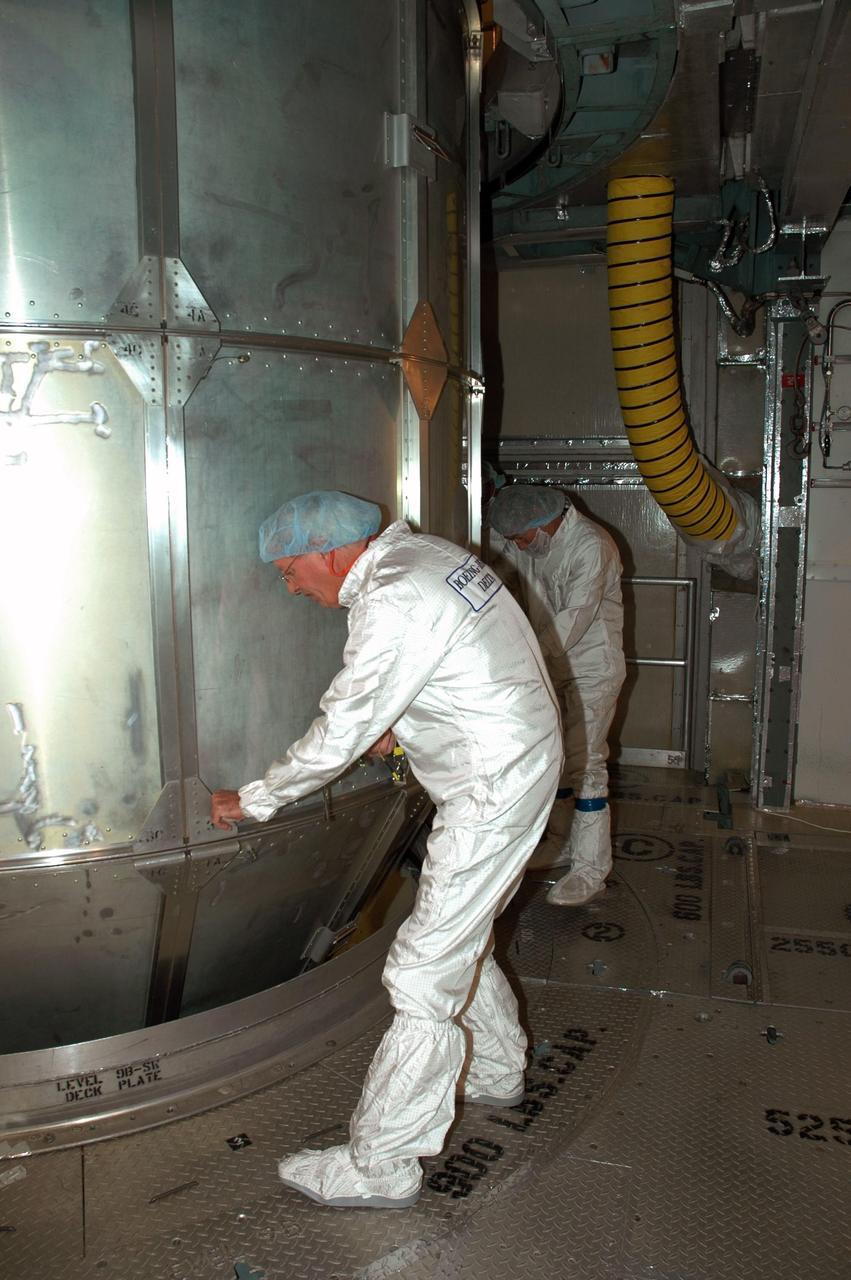
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Inside the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, workers erect a protective screen above the THEMIS spacecraft to preserve a clean-room environment. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. The THEMIS mission is to investigate what causes auroras in the Earth's atmosphere to dramatically change from slowly shimmering waves of light to wildly shifting streaks of color. Discovering what causes auroras to change will provide scientists with important details on how the planet's magnetosphere works and the important Sun-Earth connection. THEMIS is scheduled to launch aboard a Delta II rocket on Feb. 15 during a window extending from 6:08 to 6:27 p.m. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
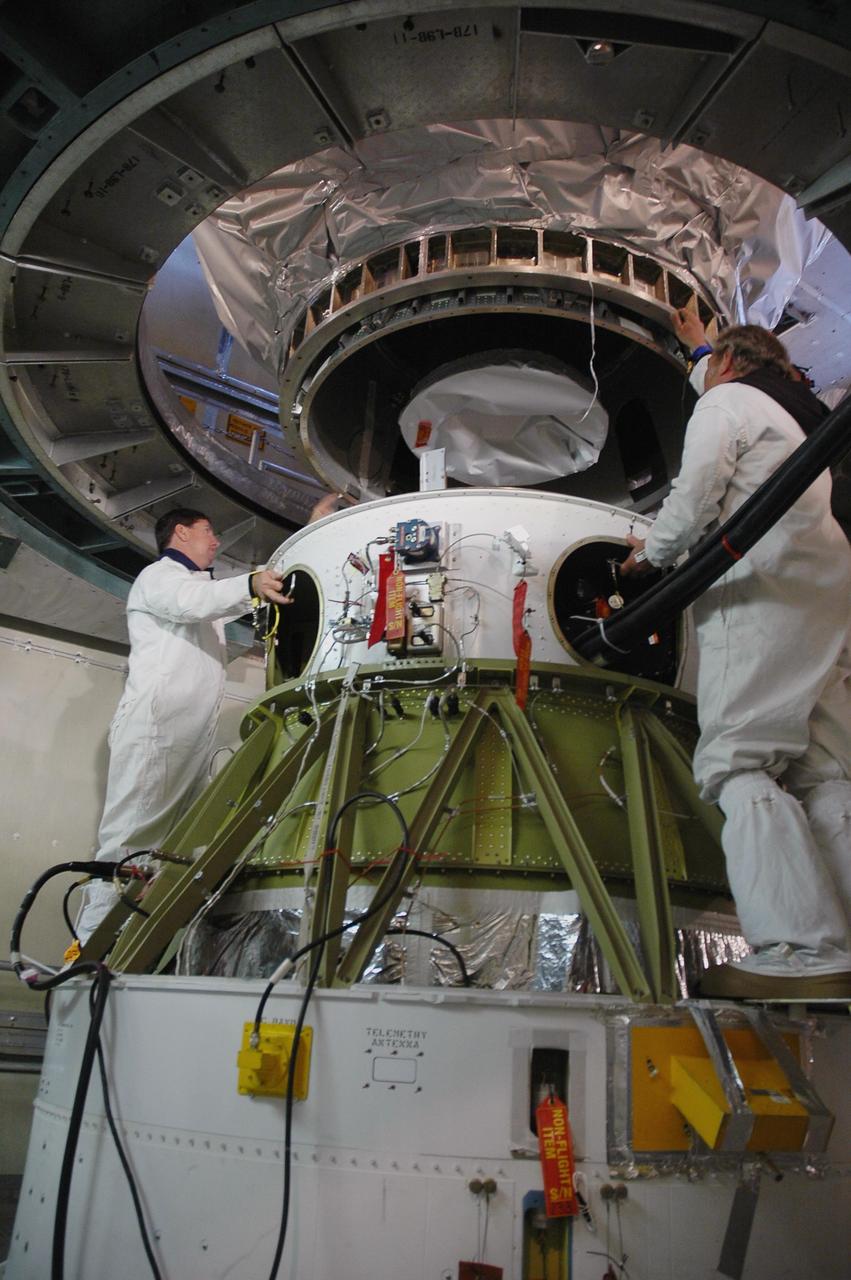

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Inside the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, workers remove the protective cover surrounding the THEMIS spacecraft. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. The THEMIS mission is to investigate what causes auroras in the Earth's atmosphere to dramatically change from slowly shimmering waves of light to wildly shifting streaks of color. Discovering what causes auroras to change will provide scientists with important details on how the planet's magnetosphere works and the important Sun-Earth connection. THEMIS is scheduled to launch aboard a Delta II rocket on Feb. 15 during a window extending from 6:08 to 6:27 p.m. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
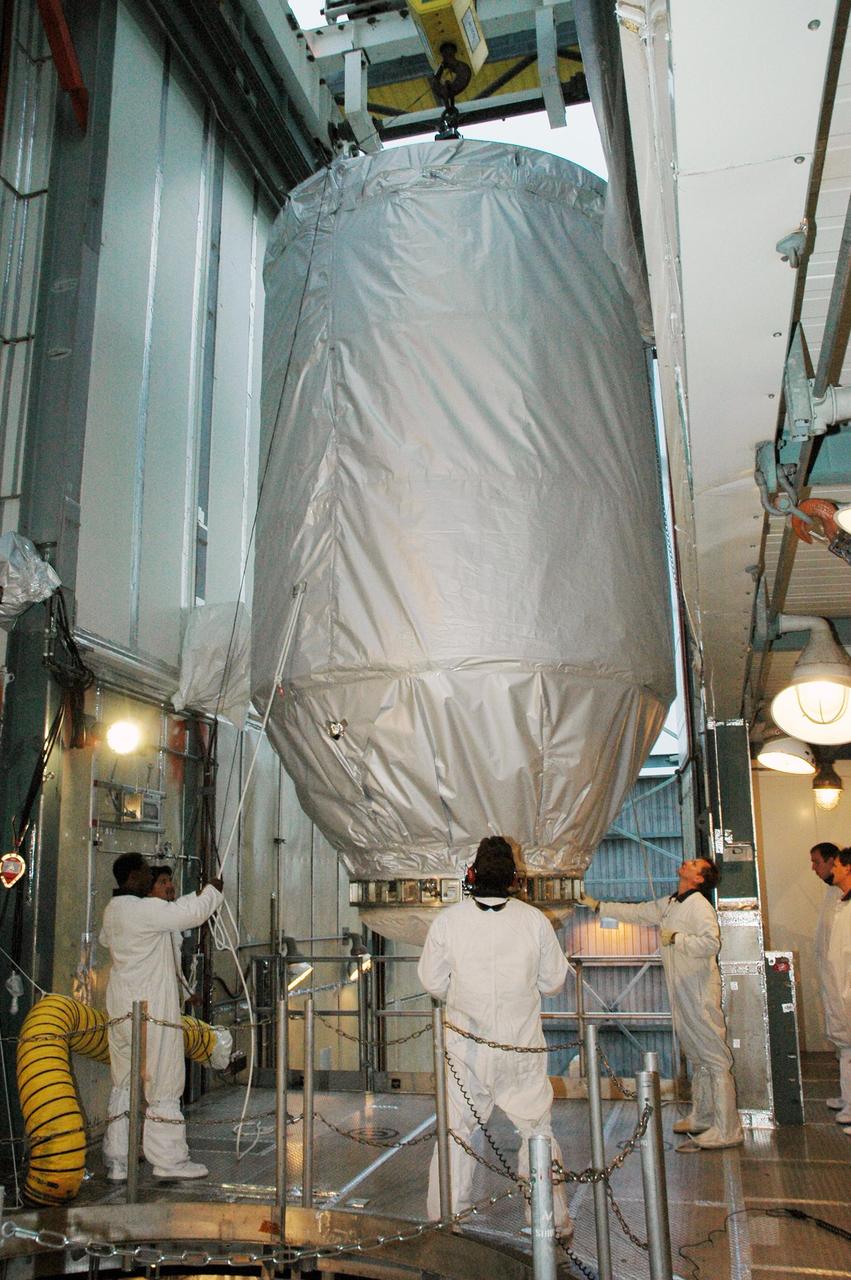

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the upper level of the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, workers help maneuver the THEMIS spacecraft inside. THEMIS will then be encapsulated and mated with the third stage of the Delta II rocket. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. The THEMIS mission is to investigate what causes auroras in the Earth's atmosphere to dramatically change from slowly shimmering waves of light to wildly shifting streaks of color. Discovering what causes auroras to change will provide scientists with important details on how the planet's magnetosphere works and the important Sun-Earth connection. THEMIS is scheduled to launch aboard a Delta II rocket on Feb. 15 during a window extending from 6:08 to 6:27 p.m. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
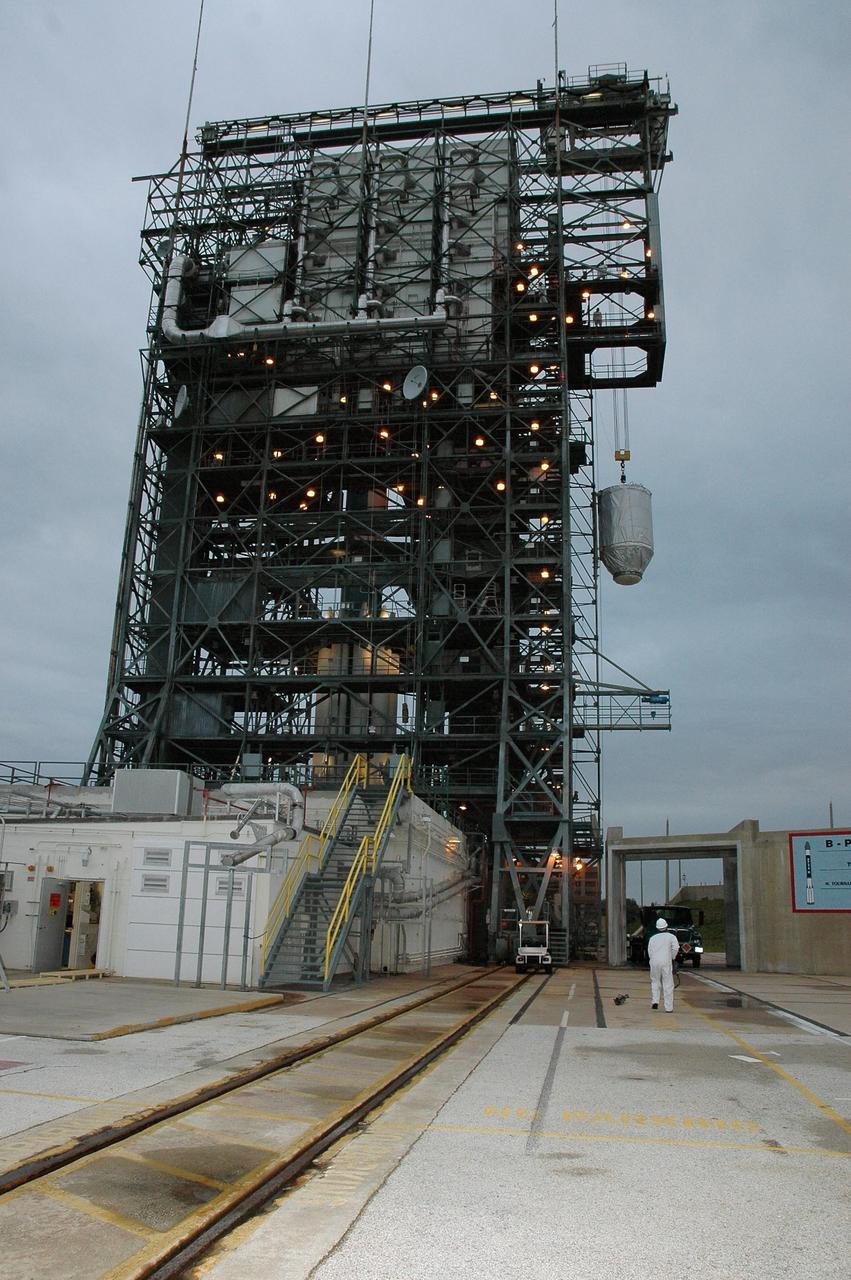

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- On Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the THEMIS spacecraft is lifted up alongside the mobile service tower. Once inside, THEMIS will be encapsulated and mated with the third stage of the Delta II rocket. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. The THEMIS mission is to investigate what causes auroras in the Earth's atmosphere to dramatically change from slowly shimmering waves of light to wildly shifting streaks of color. Discovering what causes auroras to change will provide scientists with important details on how the planet's magnetosphere works and the important Sun-Earth connection. THEMIS is scheduled to launch aboard a Delta II rocket on Feb. 15 during a window extending from 6:08 to 6:27 p.m. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers inside the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station prepare to remove the canister surrounding the THEMIS spacecraft. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. The THEMIS mission is to investigate what causes auroras in the Earth's atmosphere to dramatically change from slowly shimmering waves of light to wildly shifting streaks of color. Discovering what causes auroras to change will provide scientists with important details on how the planet's magnetosphere works and the important Sun-Earth connection. THEMIS is scheduled to launch aboard a Delta II rocket on Feb. 15 during a window extending from 6:08 to 6:27 p.m. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
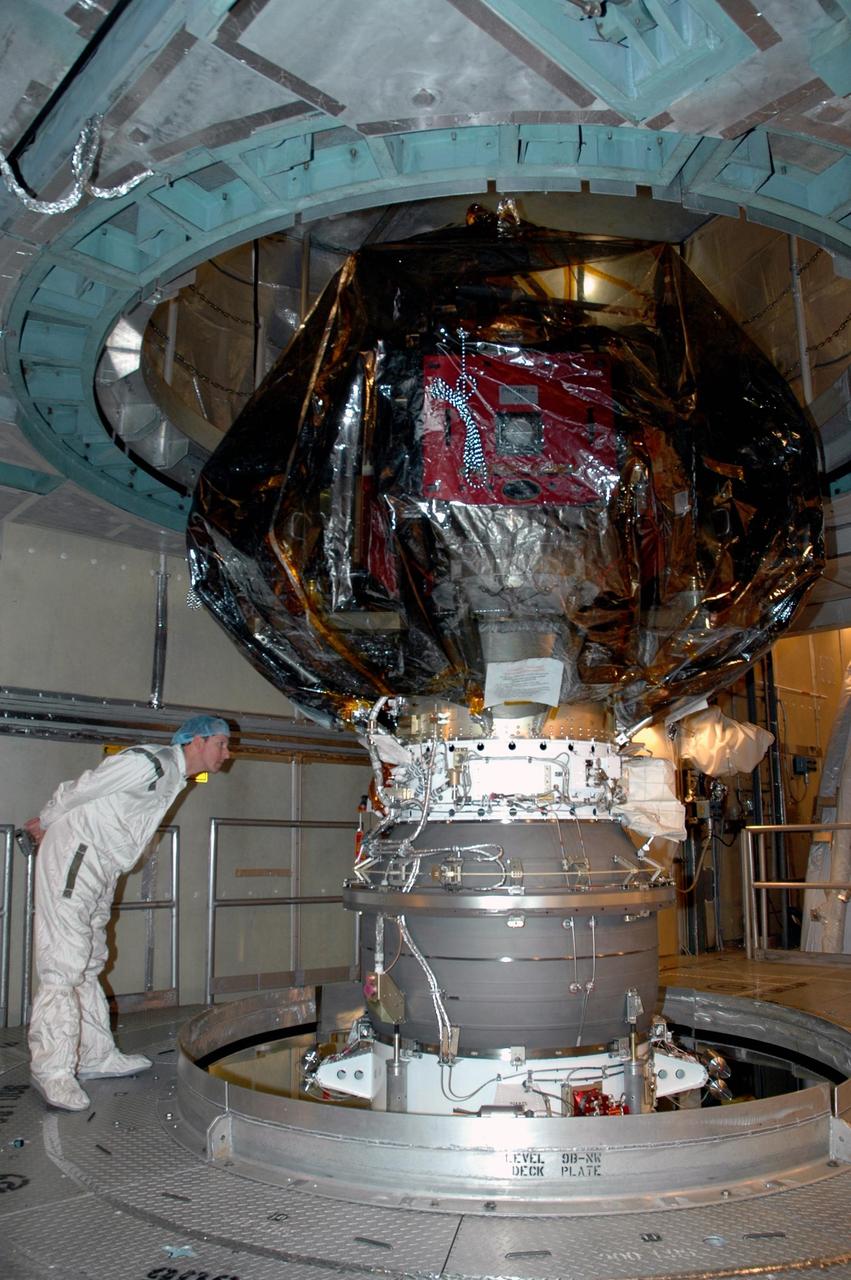

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A worker inside the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station examines the Delta II upper stage booster mated to the THEMIS spacecraft above. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. The THEMIS mission is to investigate what causes auroras in the Earth's atmosphere to dramatically change from slowly shimmering waves of light to wildly shifting streaks of color. Discovering what causes auroras to change will provide scientists with important details on how the planet's magnetosphere works and the important Sun-Earth connection. THEMIS is scheduled to launch aboard a Delta II rocket on Feb. 15 during a window extending from 6:08 to 6:27 p.m. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
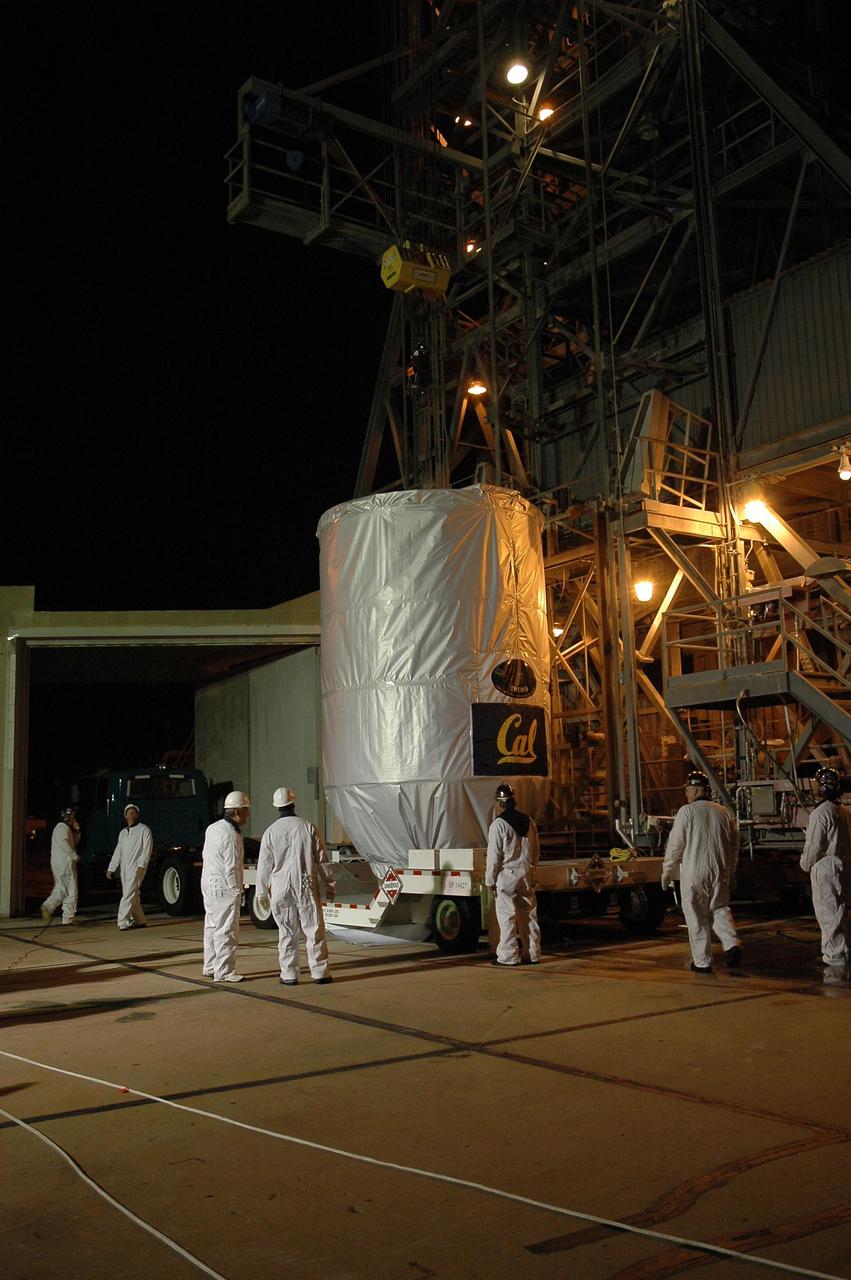

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The THEMIS spacecraft arrives on Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The spacecraft will be lifted into the mobile service tower and, after encapsulation, mated with the third stage of the Delta II rocket. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. The THEMIS mission is to investigate what causes auroras in the Earth's atmosphere to dramatically change from slowly shimmering waves of light to wildly shifting streaks of color. Discovering what causes auroras to change will provide scientists with important details on how the planet's magnetosphere works and the important Sun-Earth connection. THEMIS is scheduled to launch aboard a Delta II rocket on Feb. 15 during a window extending from 6:08 to 6:27 p.m. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
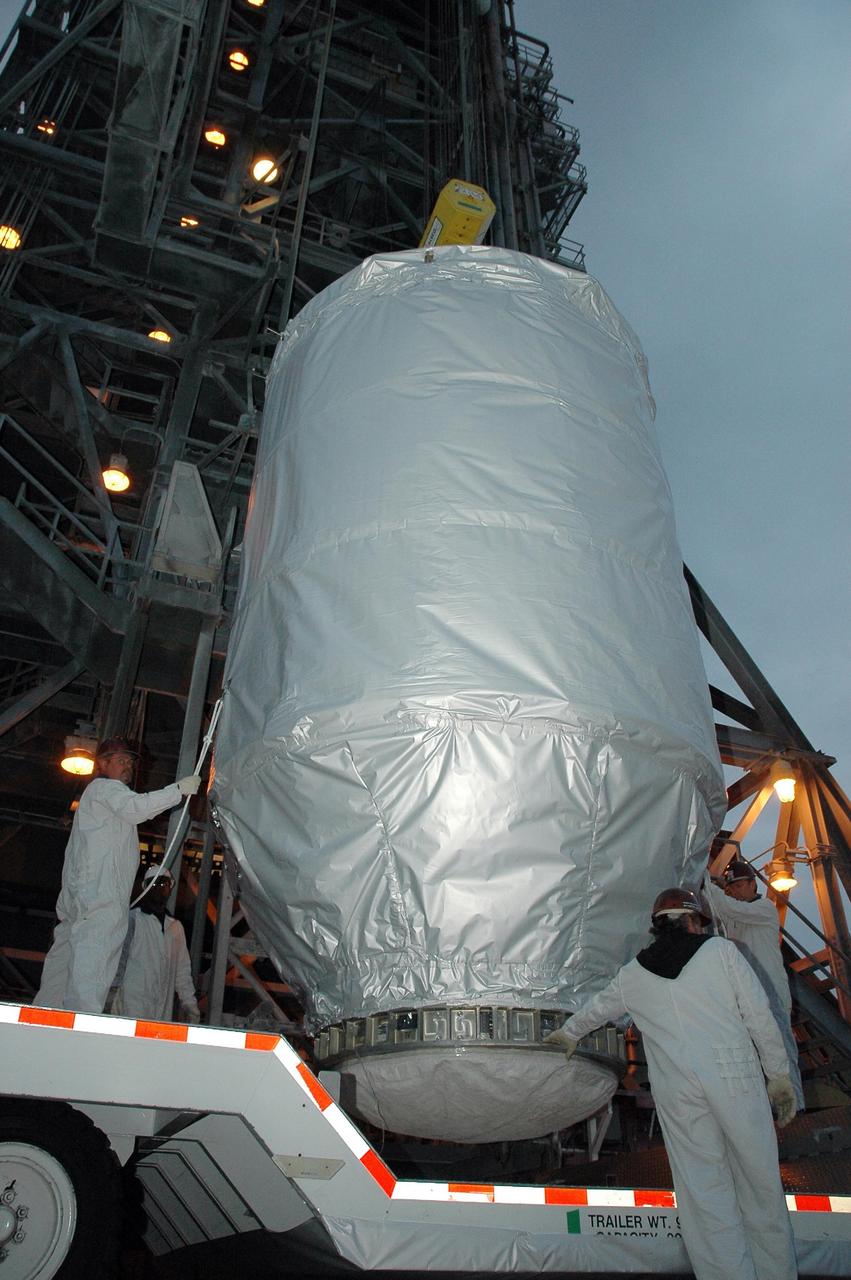

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- On Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, technicians stand by as the THEMIS spacecraft is lifted off its transporter. The spacecraft will be lifted into the mobile service tower and, after encapsulation, mated with the third stage of the Delta II rocket. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. The THEMIS mission is to investigate what causes auroras in the Earth's atmosphere to dramatically change from slowly shimmering waves of light to wildly shifting streaks of color. Discovering what causes auroras to change will provide scientists with important details on how the planet's magnetosphere works and the important Sun-Earth connection. THEMIS is scheduled to launch aboard a Delta II rocket on Feb. 15 during a window extending from 6:08 to 6:27 p.m. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller

In the high bay of Kennedy Space Center's Space Station Processing Facility, Chris Hardcastle, center, of Stinger-Ghaffarian Technologies performs a sharp edge inspection of the integrated Total and Spectral Solar Irradiance Sensor-1 (TSIS-1) payload and the EXPRESS Pallet Adapter. Hardcastle is joined by Dwayne Swieter, left, and Norm Perish, right, TSIS-1 payload team members from the Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics, a Research Institute at the University of Colorado (Boulder). TSIS-1 is designed to measure the Sun's energy input into Earth by seeing how it is distributed across different wavelengths of light. These measurements help scientists establish Earth's total energy and how our planet's atmosphere responds to changes in the Sun's energy output. TSIS-1 will launch on SpaceX's 13th commercial resupply mission to the International Space Station.
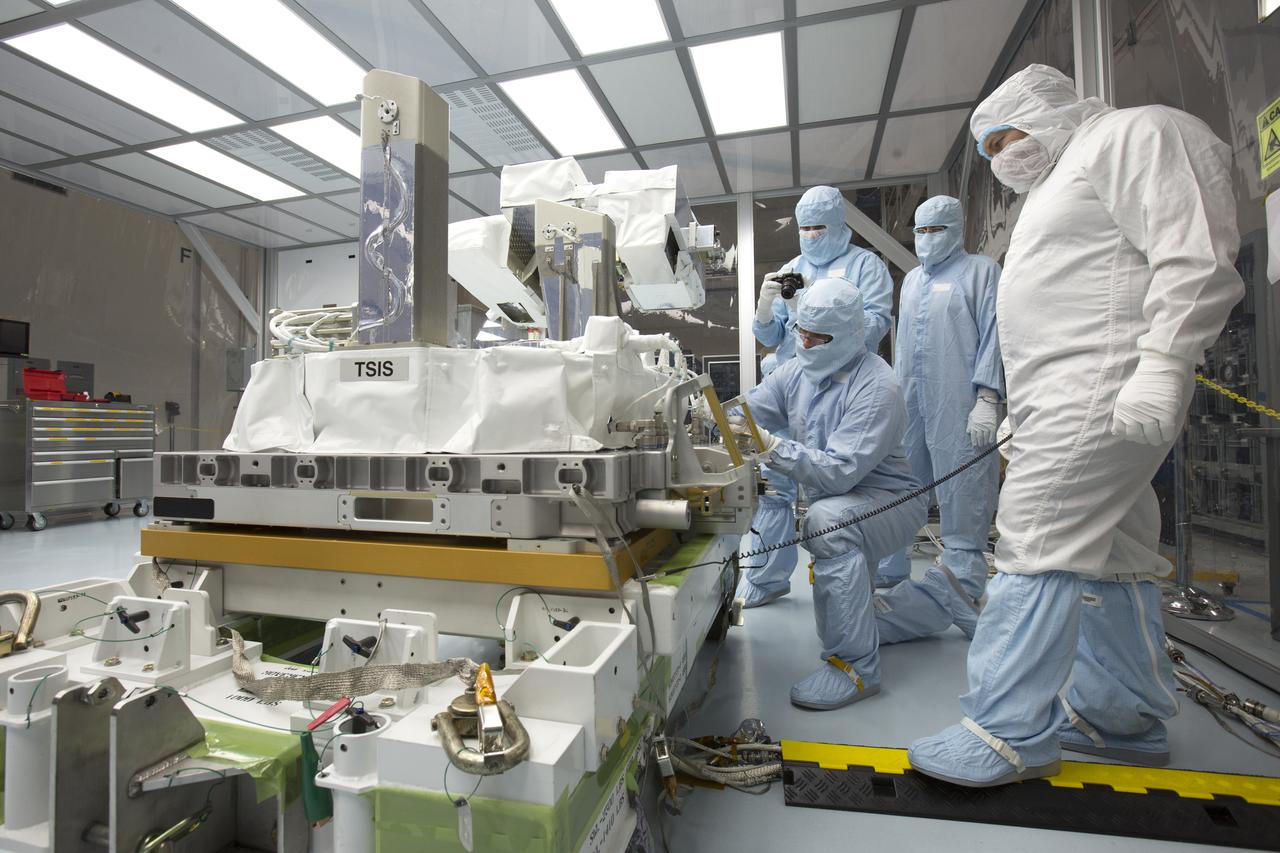

In the high bay of Kennedy Space Center's Space Station Processing Facility, Chris Hardcastle, left, of Stinger-Ghaffarian Technologies applies crew preference tape to the integrated Total and Spectral Solar Irradiance Sensor-1 (TSIS-1) payload and the EXPRESS Pallet Adapter. Hardcastle is joined by TSIS-1 payload team members from the Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics, a Research Institute at the University of Colorado (Boulder). Standing from left to right are Tom Patton, Greg Ucker and Norm Perish. TSIS-1 is designed to measure the Sun's energy input into Earth by seeing how it is distributed across different wavelengths of light. These measurements help scientists establish Earth's total energy and how our planet's atmosphere responds to changes in the Sun's energy output. TSIS-1 will launch on SpaceX's 13th commercial resupply mission to the International Space Station.
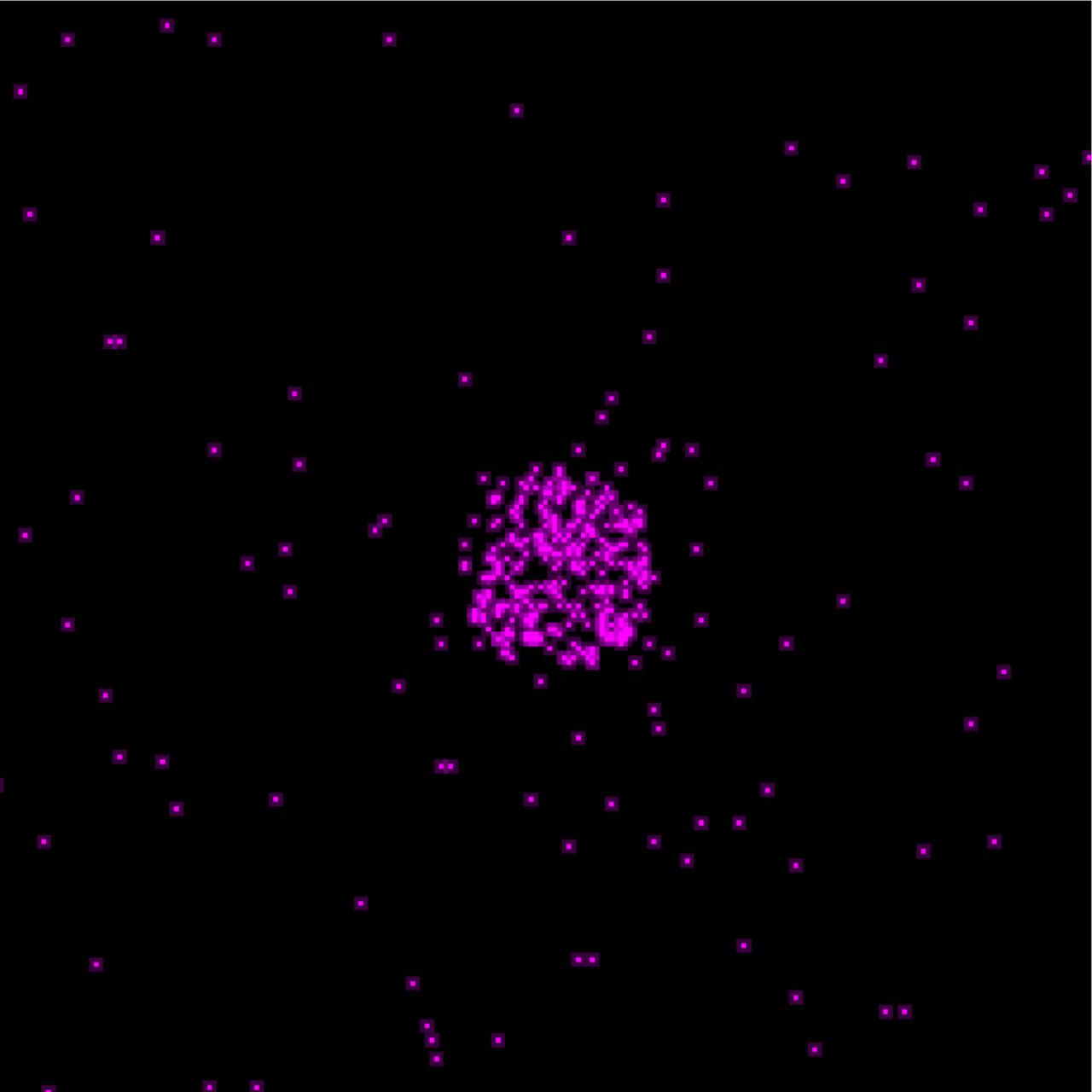
Giving scientists their first look, Chandra observed x-rays produced by fluorescent radiation from oxygen atoms of the Sun in the sparse upper atmosphere of Mars, about 120 kilometers (75 miles) above its surface. The x-ray power detected from the Martian atmosphere is very small, amounting to only 4 megawatts, comparable to the x-ray power of about ten thousand medical x-ray machines. At the time of the Chandra observation, a huge dust storm developed on Mars that covered about one hemisphere, later to cover the entire planet. This hemisphere rotated out of view over the 9-hour observation, but no change was observed in the x-ray intensity indicating that the dust storm did not affect the upper atmosphere. Scientists also observed a halo of x-rays extending out to 7,000 kilometers above the surface of Mars believed to be produced by collisions of ions racing away from the Sun (the solar wind).

In the high bay of Kennedy Space Center's Space Station Processing Facility, Chris Hardcastle, right, of Stinger-Ghaffarian Technologies performs a sharp edge inspection of the integrated Total and Spectral Solar Irradiance Sensor-1 (TSIS-1) payload and the EXPRESS Pallet Adapter. Hardcastle is joined by Norm Perish, left, a TSIS-1 payload team member from the Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics, a Research Institute at the University of Colorado (Boulder). TSIS-1 is designed to measure the Sun's energy input into Earth by seeing how it is distributed across different wavelengths of light. These measurements help scientists establish Earth's total energy and how our planet's atmosphere responds to changes in the Sun's energy output. TSIS-1 will launch on SpaceX's 13th commercial resupply mission to the International Space Station.
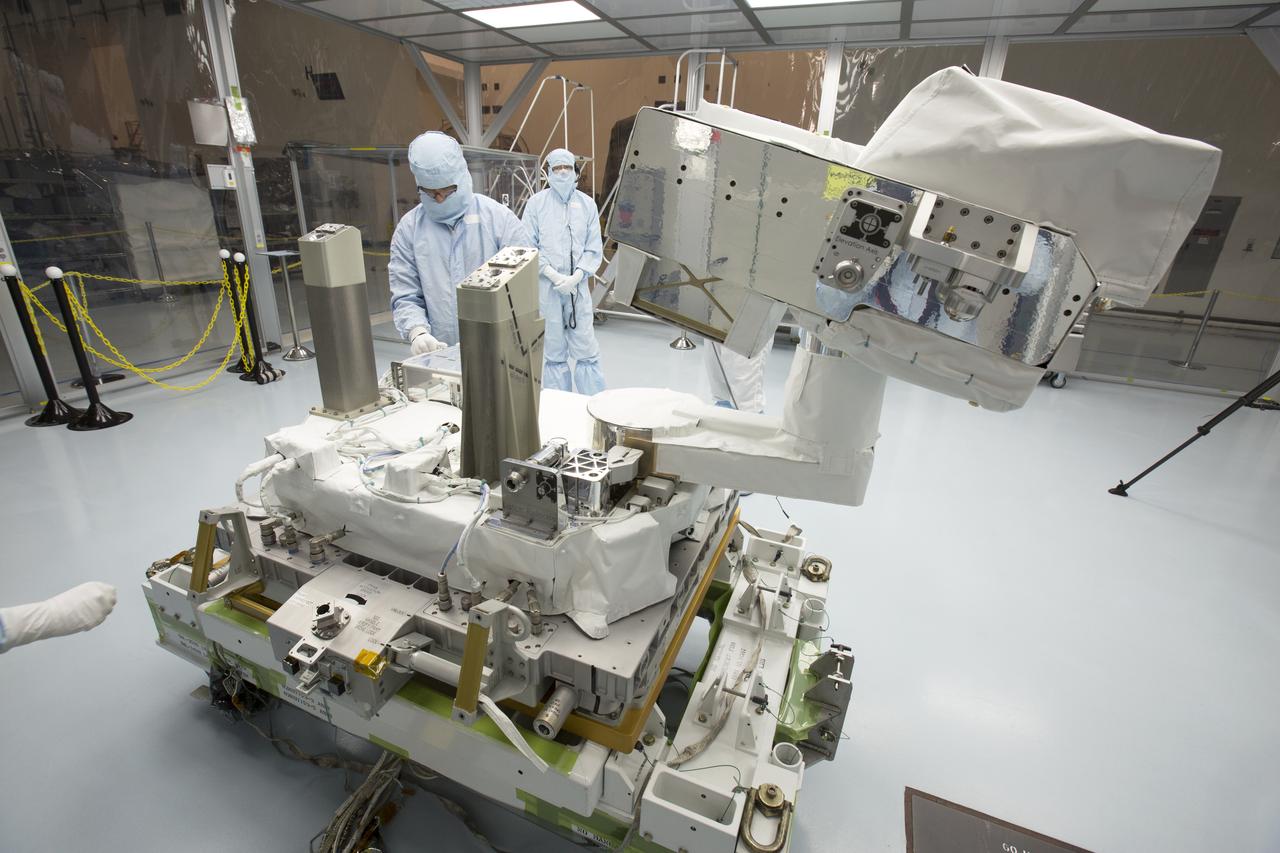

In the high bay of Kennedy Space Center's Space Station Processing Facility, Chris Hardcastle, left, of Stinger-Ghaffarian Technologies performs a sharp edge inspection of the integrated Total and Spectral Solar Irradiance Sensor-1 (TSIS-1) payload and the EXPRESS Pallet Adapter. Hardcastle is joined by Dwayne Swieter, right, a TSIS-1 payload team member from the Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics, a Research Institute at the University of Colorado (Boulder). TSIS-1 is designed to measure the Sun's energy input into Earth by seeing how it is distributed across different wavelengths of light. These measurements help scientists establish Earth's total energy and how our planet's atmosphere responds to changes in the Sun's energy output. TSIS-1 will launch on SpaceX's 13th commercial resupply mission to the International Space Station.
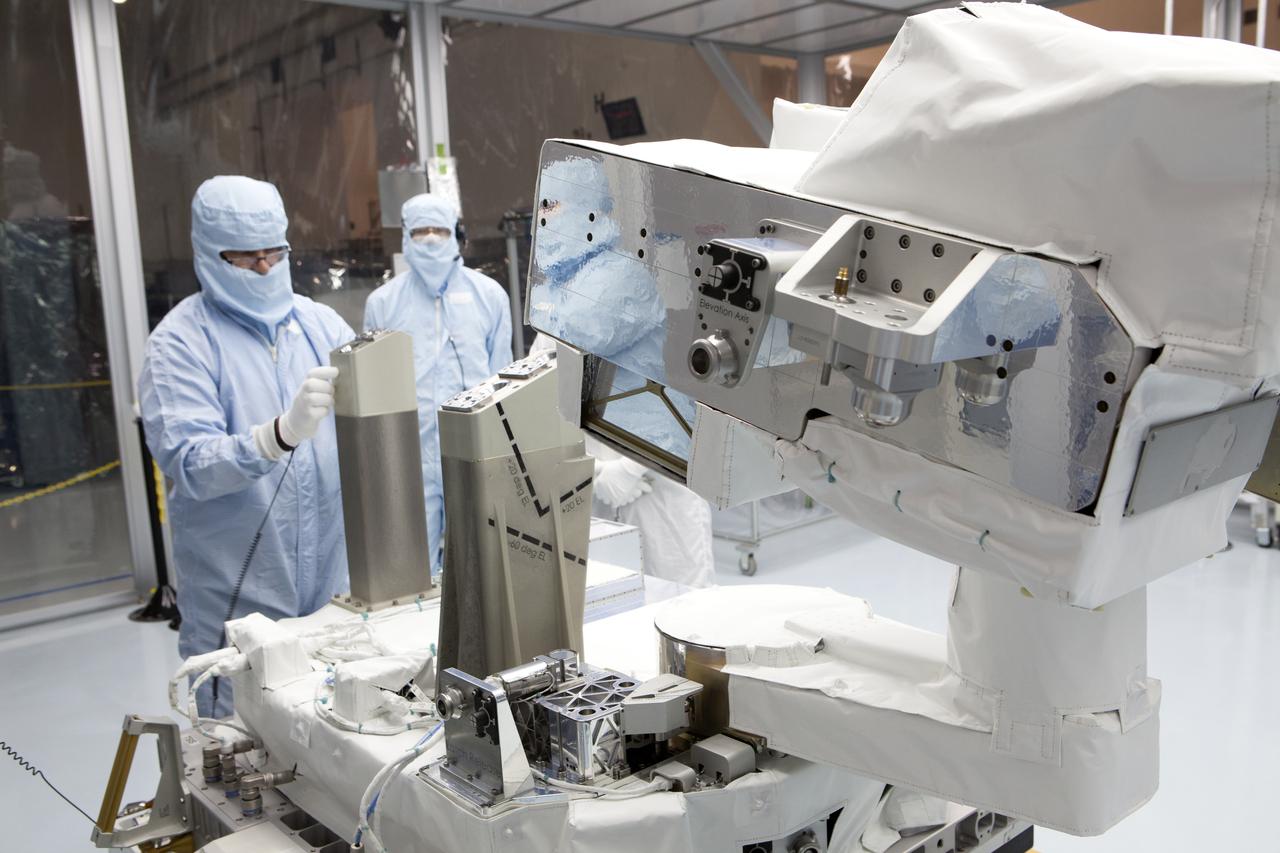

In the high bay of Kennedy Space Center's Space Station Processing Facility, Chris Hardcastle, left, of Stinger-Ghaffarian Technologies performs a sharp edge inspection of the integrated Total and Spectral Solar Irradiance Sensor-1 (TSIS-1) payload and the EXPRESS Pallet Adapter. Hardcastle is joined by Dwayne Swieter, right, a TSIS-1 payload team member from the Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics, a Research Institute at the University of Colorado (Boulder). TSIS-1 is designed to measure the Sun's energy input into Earth by seeing how it is distributed across different wavelengths of light. These measurements help scientists establish Earth's total energy and how our planet's atmosphere responds to changes in the Sun's energy output. TSIS-1 will launch on SpaceX's 13th commercial resupply mission to the International Space Station.
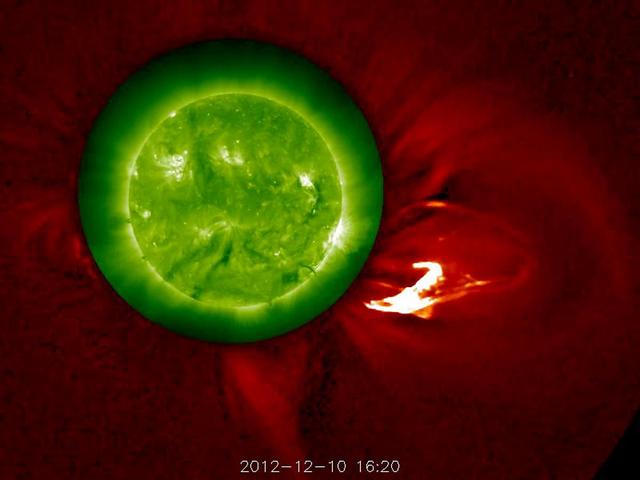

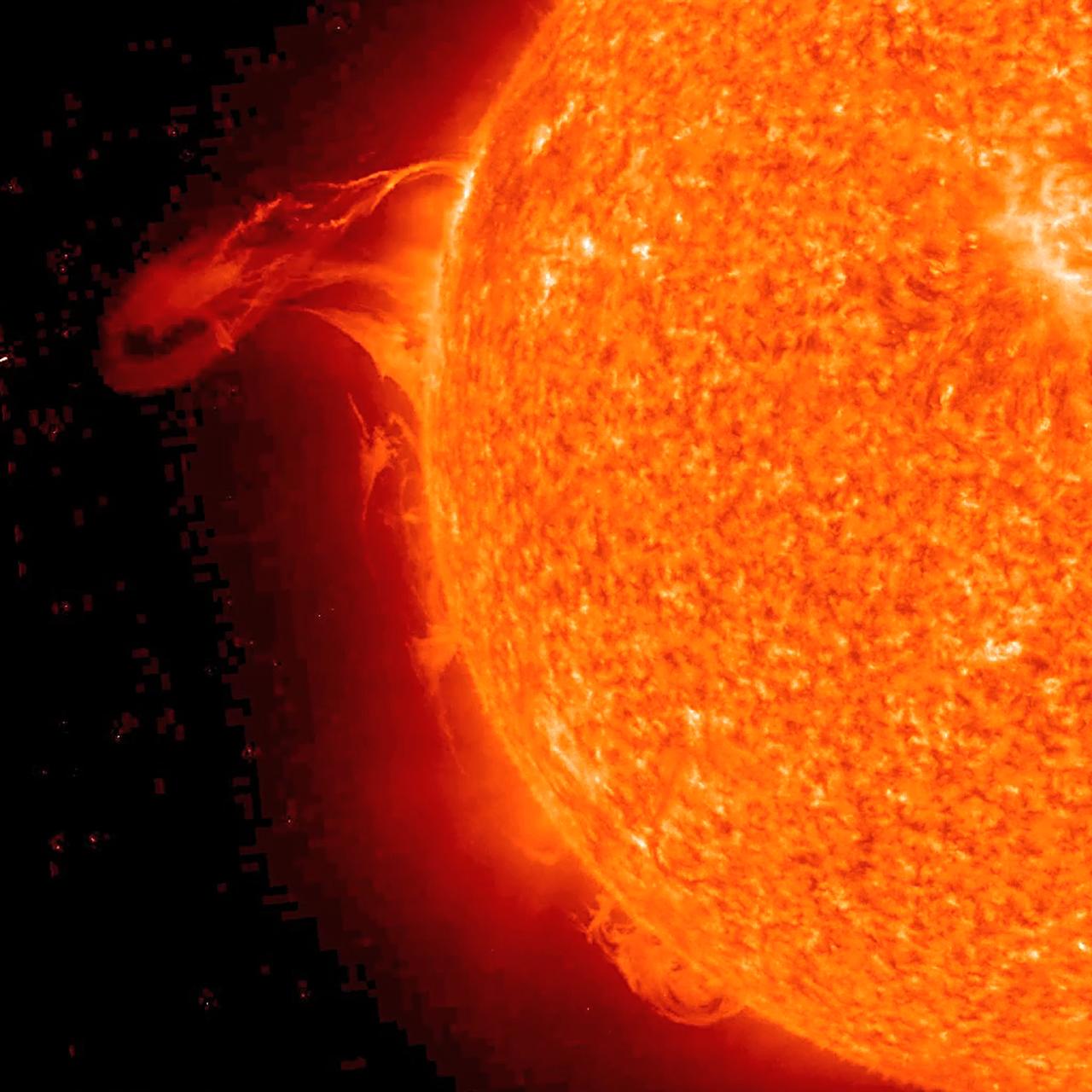
The Sun blows a robust prominence out into space (Dec. 10, 2102). The outer image, from the STEREO-A's COR1 coronagraph, has been changed from green to red to complement the green Sun image, taken in extreme UV light. The movie covers six hours of activity. Kind of Christmassy looking, isn't it? Some of the prominence falls back towards the sun, although the disturbance as a whole continues out into the solar system. Credit: NASA/GSFC/STEREO <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., workers ensure the smooth rotation of NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO. After rotation, the SDO will be moved to a work stand. SDO is the first space weather research network mission in NASA's Living With a Star Program. The spacecraft's long-term measurements will give solar scientists in-depth information about changes in the sun's magnetic field and insight into how they affect Earth. In preparation for its anticipated November launch, engineers will perform a battery of comprehensive tests to ensure SDO can withstand the stresses and vibrations of the launch itself, as well as what it will encounter in the space environment after launch. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston