
The U.S. Coast Guard Cutter Healy encountered only small patches of sea ice in the Chukchi Sea during the final days collecting ocean data for the 2011 ICESCAPE mission. The ICESCAPE mission, or "Impacts of Climate on Ecosystems and Chemistry of the Arctic Pacific Environment," is a NASA shipborne investigation to study how changing conditions in the Arctic affect the ocean's chemistry and ecosystems. The bulk of the research took place in the Beaufort and Chukchi seas in summer 2010 and 2011. Credit: NASA/Kathryn Hansen <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

The terrain for the scientific work conducted by ICESCAPE scientists on July 4, 2010, is Arctic sea ice and melt ponds in the Chukchi Sea. The five-week field mission is dedicated to sampling the physical, chemical and biological characteristics of the ocean and sea ice. Impacts of Climate change on the Eco-Systems and Chemistry of the Arctic Pacific Environment (ICESCAPE) is a multi-year NASA shipborne project. The bulk of the research will take place in the Beaufort and Chukchi Sea’s in summer of 2010 and fall of 2011. Photo Credit: (NASA/Kathryn Hansen)

Scientists on the sea ice in the Chukchi Sea off the north coast of Alaska disperse equipment on July 4, 2010, as they prepare to collect data on and below the ice. The research is part of NASA's ICESCAPE mission onboard the U.S. Coast Guard icebreaker Healy to sample the physical, chemical and biological characteristics of the ocean and sea ice. Impacts of Climate change on the Eco-Systems and Chemistry of the Arctic Pacific Environment (ICESCAPE) is a multi-year NASA shipborne project. The bulk of the research will take place in the Beaufort and Chukchi Sea’s in summer of 2010 and fall of 2011. Photo Credit: (NASA/Kathryn Hansen)

Clark University student Christie Wood lowers a water sampler into a borehole on July 4, 2010, to collect water samples from below the Arctic sea ice off the north coast of Alaska. The research is part of NASA's ICESCAPE oceanographic mission to sample the physical, chemical and biological characteristics of the ocean and sea ice. Impacts of Climate change on the Eco-Systems and Chemistry of the Arctic Pacific Environment (ICESCAPE) is a multi-year NASA shipborne project. The bulk of the research will take place in the Beaufort and Chukchi Sea’s in summer of 2010 and fall of 2011. Photo Credit: (NASA/Kathryn Hansen)

Clark University's Luke Trusel works amid sea ice in the Chukchi Sea on July 9, 2010, and logs the depths at which measurements are collected below the ice. The research is part of NASA's ICESCAPE mission to sample the physical, chemical and biological characteristics of the ocean and sea ice. Impacts of Climate change on the Eco-Systems and Chemistry of the Arctic Pacific Environment (ICESCAPE) is a multi-year NASA shipborne project. The bulk of the research will take place in the Beaufort and Chukchi Sea’s in summer of 2010 and fall of 2011. Photo Credit: (NASA/Kathryn Hansen)

Teams of scientists set up equipment on sea ice not far from the U.S. Coast Guard icebreaker Healy in the Chukchi Sea on July 4, 2010, where they spent the day collecting data. The research is part of NASA's ICESCAPE oceanographic mission to sample the physical, chemical and biological characteristics of the ocean and sea ice. Impacts of Climate change on the Eco-Systems and Chemistry of the Arctic Pacific Environment (ICESCAPE) is a multi-year NASA shipborne project. The bulk of the research will take place in the Beaufort and Chukchi Sea’s in summer of 2010 and fall of 2011. Photo Credit: (NASA/Kathryn Hansen)

Scientists and Coast Guard swimmers test the integrity a melt pond on sea ice in the Chukchi Sea on July 9, 2010, before drilling holes through which instruments can be deployed to collect data. The research is part of NASA's ICESCAPE mission onboard the U.S. Coast Guard icebreaker Healy to sample the physical, chemical and biological characteristics of the ocean and sea ice. Impacts of Climate change on the Eco-Systems and Chemistry of the Arctic Pacific Environment (ICESCAPE) is a multi-year NASA shipborne project. The bulk of the research will take place in the Beaufort and Chukchi Sea’s in summer of 2010 and fall of 2011. Photo Credit: (NASA/Kathryn Hansen)

Dartmouth College's Chris Polashenski cuts a block of ice from below a melt pond on sea ice in the Chukchi Sea on July 9, 2010, for analysis upon return from the mission. The research is part of NASA's ICESCAPE mission onboard the U.S. Coast Guard icebreaker Healy to sample the physical, chemical and biological characteristics of the ocean and sea ice. Impacts of Climate change on the Eco-Systems and Chemistry of the Arctic Pacific Environment (ICESCAPE) is a multi-year NASA shipborne project. The bulk of the research will take place in the Beaufort and Chukchi Sea’s in summer of 2010 and fall of 2011. Photo Credit: (NASA/Kathryn Hansen)

Benny Hopson from the Barrow (Alaska) Arctic Science Consortium drills a core sample from sea ice in the Chukchi Sea on July 4, 2010. The core is sliced up into puck-sized sections and stored onboard the U.S. Coast Guard Healy for analysis in the ship's lab. Impacts of Climate change on the Eco-Systems and Chemistry of the Arctic Pacific Environment (ICESCAPE) is a multi-year NASA shipborne project. The bulk of the research will take place in the Beaufort and Chukchi Sea’s in summer of 2010 and fall of 2011. Photo Credit: (NASA/Kathryn Hansen)

Clark University's Karen Frey and Luke Trusel work amid sea ice in the Chukchi Sea on July 4, 2010, setting up an instrument that measures the optical properties of melt ponds. The research is part of NASA's ICESCAPE mission to sample the physical, chemical and biological characteristics of the ocean and sea ice. Impacts of Climate change on the Eco-Systems and Chemistry of the Arctic Pacific Environment (ICESCAPE) is a multi-year NASA shipborne project. The bulk of the research will take place in the Beaufort and Chukchi Sea’s in summer of 2010 and fall of 2011. Photo Credit: (NASA/Kathryn Hansen)

In northestern Siberia, along the Chukchi Sea, and 100 kilometers west of Mys Shmidta, significant evidence of mining is visible in this ASTER image. The numerous small waste piles and small ponds point to dredging operations, most likely for gold. The image was acquired July 15, 2011, covers an area of 27.8 by 36.4 kilometers, and is located at 69.3 degrees north, 178.5 degrees east. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22672
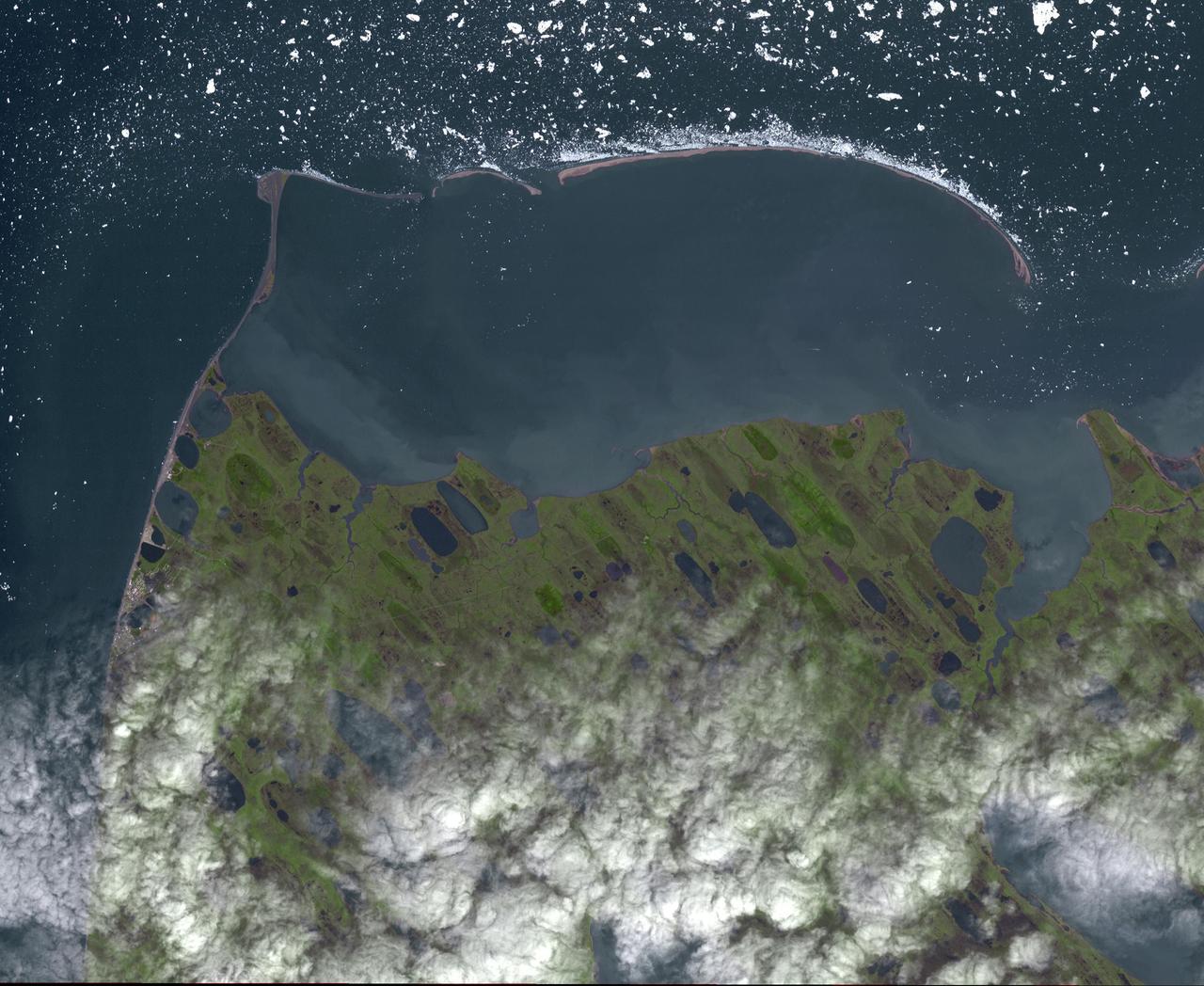
Point Barrow or Nuvuk, Alaska is the northernmost point of all territory of the United States. It also marks the limit between the Chukchi Sea to the west, and the Beaufort Sea to the east. Archaeological evidence indicates that Point Barrow was occupied about 500 CE, probably as hunting camps for whales. The image covers an area of 32 by 38 km, was acquired July 29, 2015, and is located at 71.6 degrees north, 156.45 degrees west. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19775
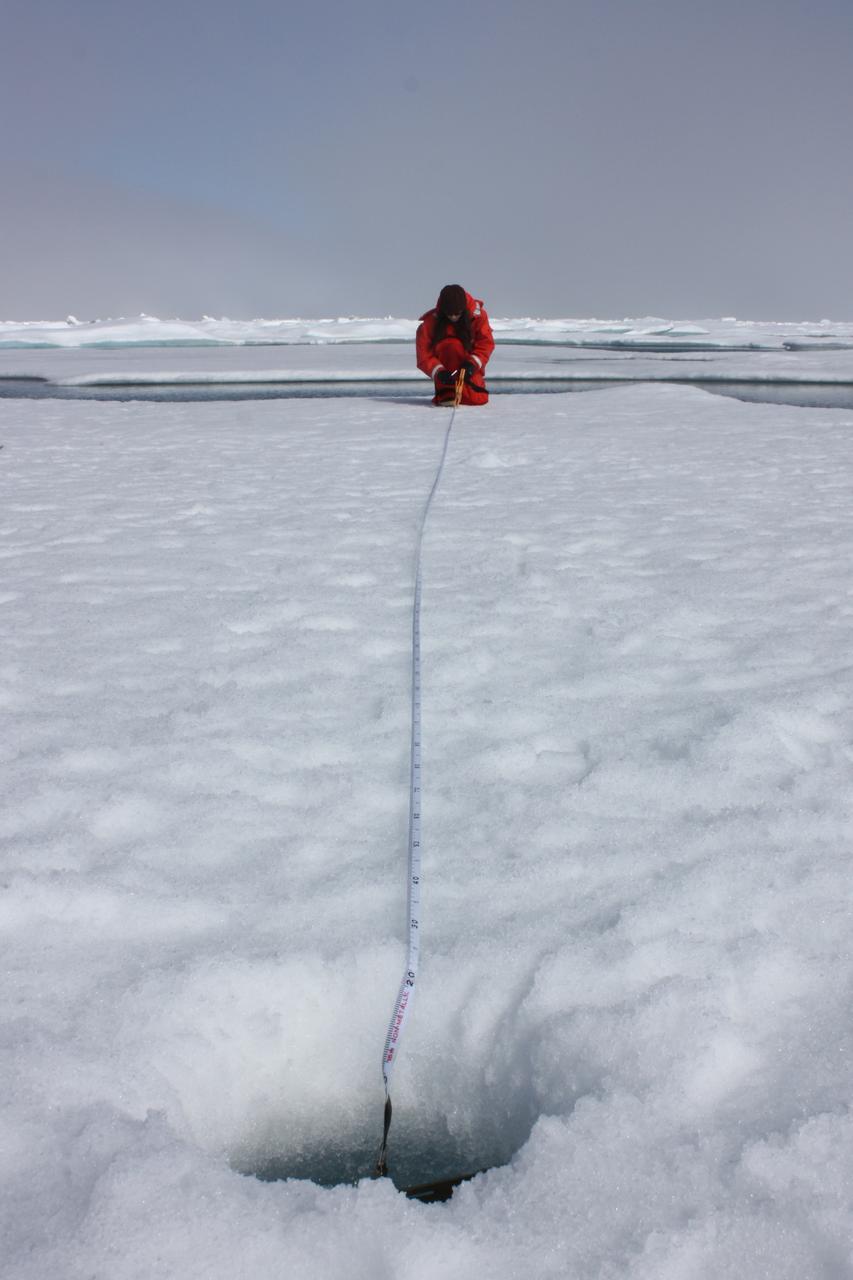

On July 10, 2011, Melinda Webster of University of Washington mapped the locations where measurements were collected during the 2011 ICESCAPE mission's fourth sea ice station in the Chukchi Sea. The ICESCAPE mission, or "Impacts of Climate on Ecosystems and Chemistry of the Arctic Pacific Environment," is a NASA shipborne investigation to study how changing conditions in the Arctic affect the ocean's chemistry and ecosystems. The bulk of the research took place in the Beaufort and Chukchi seas in summer 2010 and 2011. Credit: NASA/Kathryn Hansen <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
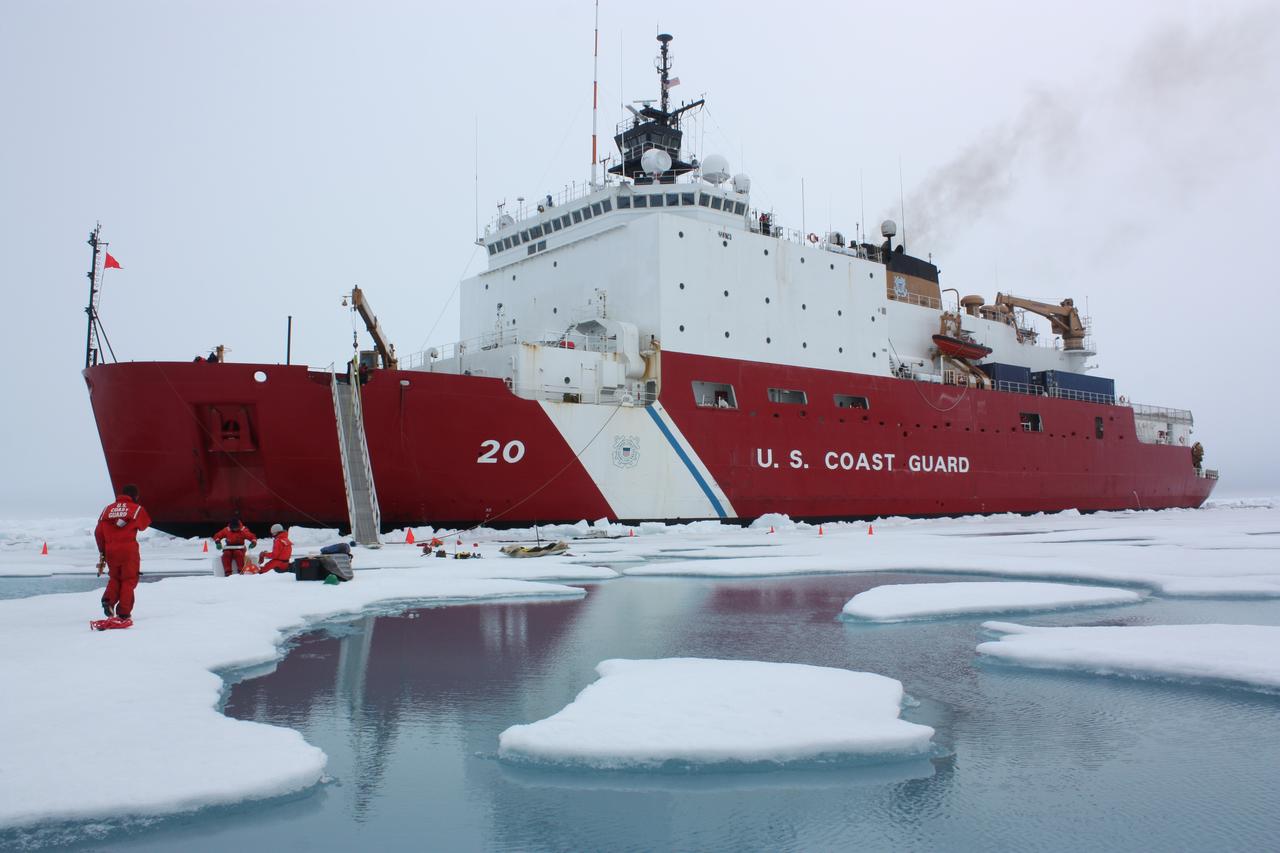

On July 6, 2011, the U.S. Coast Guard Cutter Healy parked in an ice floe for the 2011 ICESCAPE mission's third ice station in the Chukchi Sea. The ICESCAPE mission, or "Impacts of Climate on Ecosystems and Chemistry of the Arctic Pacific Environment," is a NASA shipborne investigation to study how changing conditions in the Arctic affect the ocean's chemistry and ecosystems. The bulk of the research took place in the Beaufort and Chukchi seas in summer 2010 and 2011. Credit: NASA/Kathryn Hansen <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
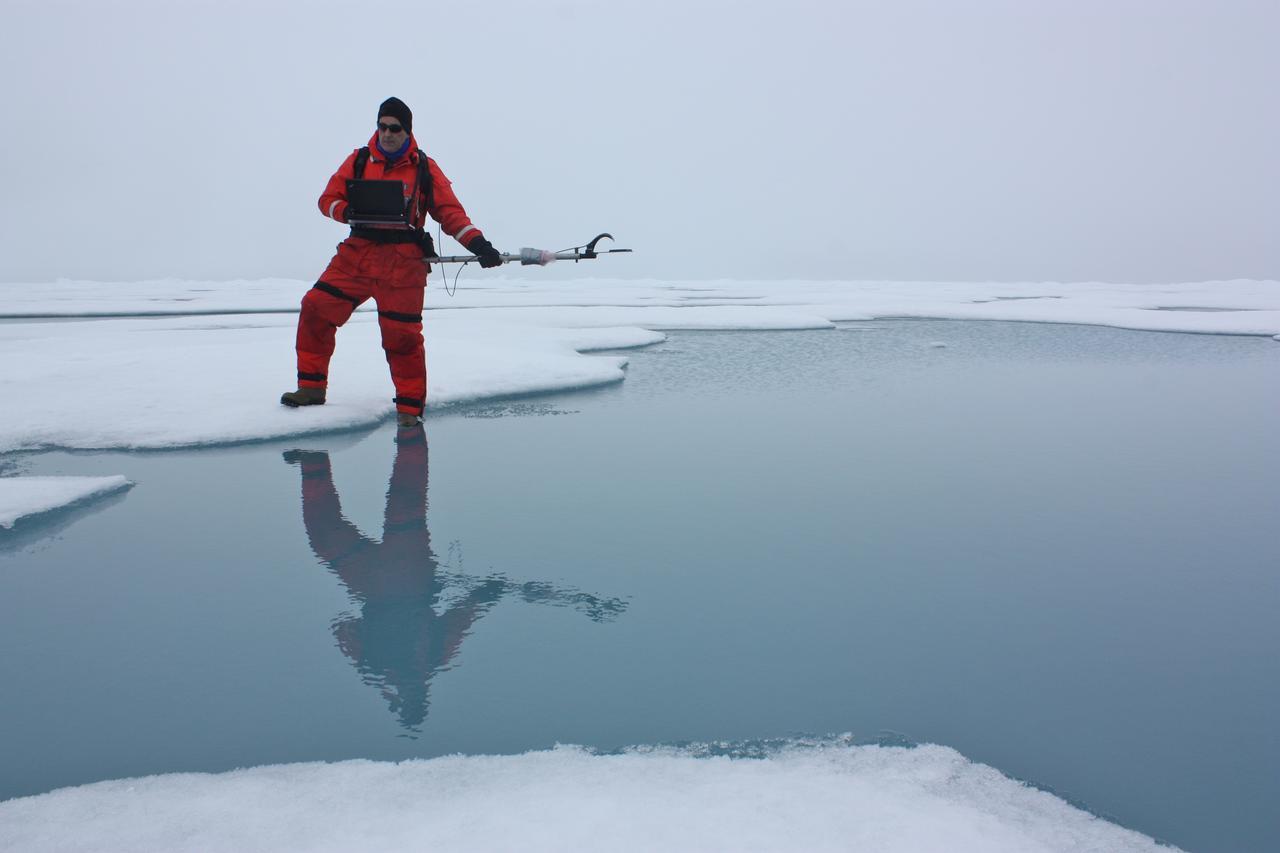

On July 6, 2011, Don Perovich, of Cold Regions Research and Engineering Laboratory, used a spectroradiometer to measure the amount of sunlight reflected from the surface of ice and melt ponds in the Chukchi Sea. The ICESCAPE mission, or "Impacts of Climate on Ecosystems and Chemistry of the Arctic Pacific Environment," is a NASA shipborne investigation to study how changing conditions in the Arctic affect the ocean's chemistry and ecosystems. The bulk of the research took place in the Beaufort and Chukchi seas in summer 2010 and 2011. Credit: NASA/Kathryn Hansen <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
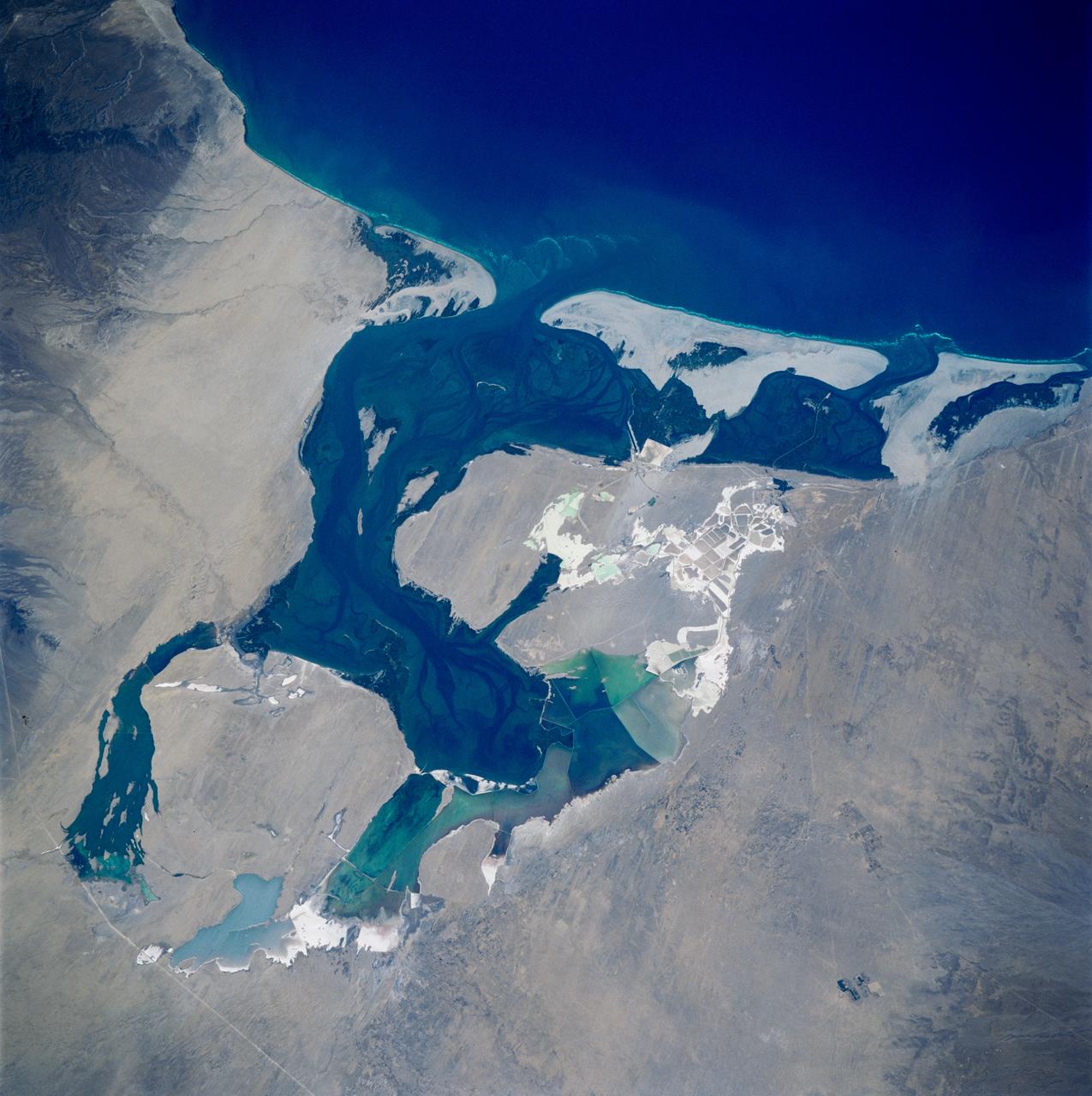

STS083-749-084 (4-8 April 1997) --- Laguna Oja De Liebre, Baja, gray whale breeding ground Laguna Oja De Liebre, Baja (Scammons Lagoon) is located on the west coast in the plains of the central Baja. This lagoon and others like it along the Baja coast are used for breeding grounds for the gray whale. One group of gray whales inhabits the Sea of Okhotsk in summer, migrating south in winter then breed off southern Korea. The other summers in the Bering and Chukchi seas and travels south to winter breeding grounds along the coast of Baja California. The gray whale was hunted almost to extinction by 1925 but was placed under complete international protection and since the 1940s has increased in numbers. The white grids seen in the photo are commercial salt ponds.
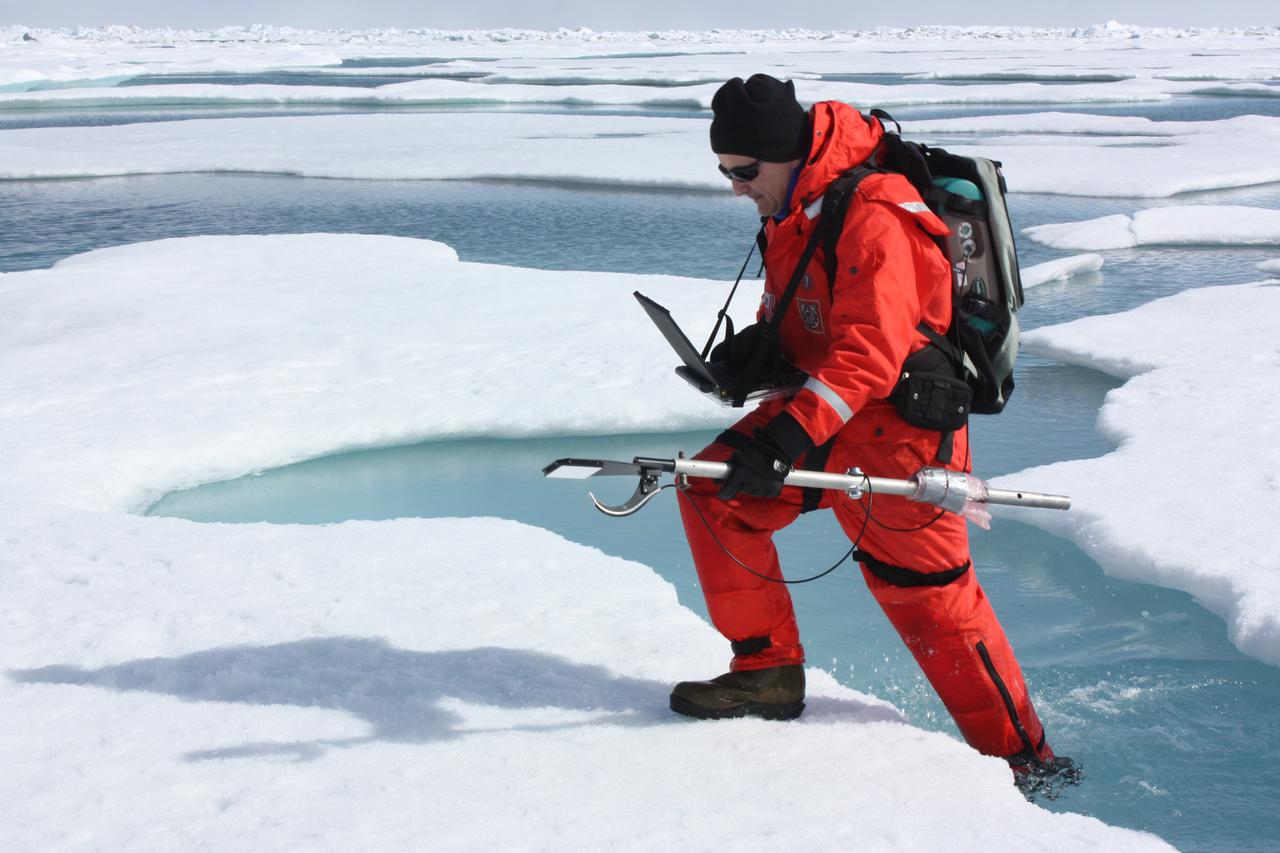

On July 10, 2011, Don Perovich, of Cold Regions Research and Engineering Laboratory, maneuvered through melt ponds collecting optical data along the way to get a sense of the amount of sunlight reflected from sea ice and melt ponds in the Chukchi Sea. The ICESCAPE mission, or "Impacts of Climate on Ecosystems and Chemistry of the Arctic Pacific Environment," is a NASA shipborne investigation to study how changing conditions in the Arctic affect the ocean's chemistry and ecosystems. The bulk of the research took place in the Beaufort and Chukchi seas in summer 2010 and 2011. Credit: NASA/Kathryn Hansen <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
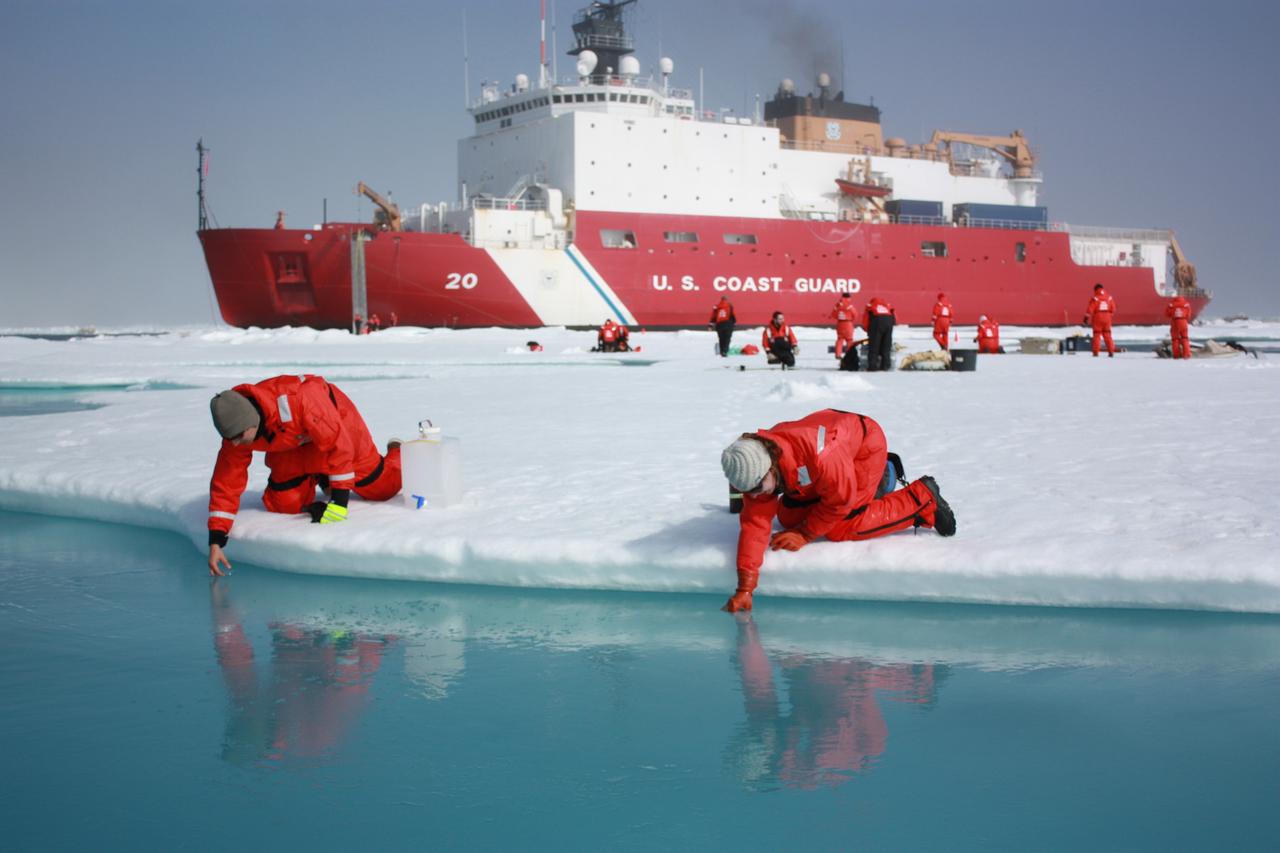

On July 10, 2011, Jens Ehn of Scripps Institution of Oceanography (left), and Christie Wood of Clark University (right), scooped water from melt ponds on sea ice in the Chukchi Sea. The water was later analyzed from the Healy's onboard science lab. The ICESCAPE mission, or "Impacts of Climate on Ecosystems and Chemistry of the Arctic Pacific Environment," is a NASA shipborne investigation to study how changing conditions in the Arctic affect the ocean's chemistry and ecosystems. The bulk of the research took place in the Beaufort and Chukchi seas in summer 2010 and 2011. Credit: NASA/Kathryn Hansen <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
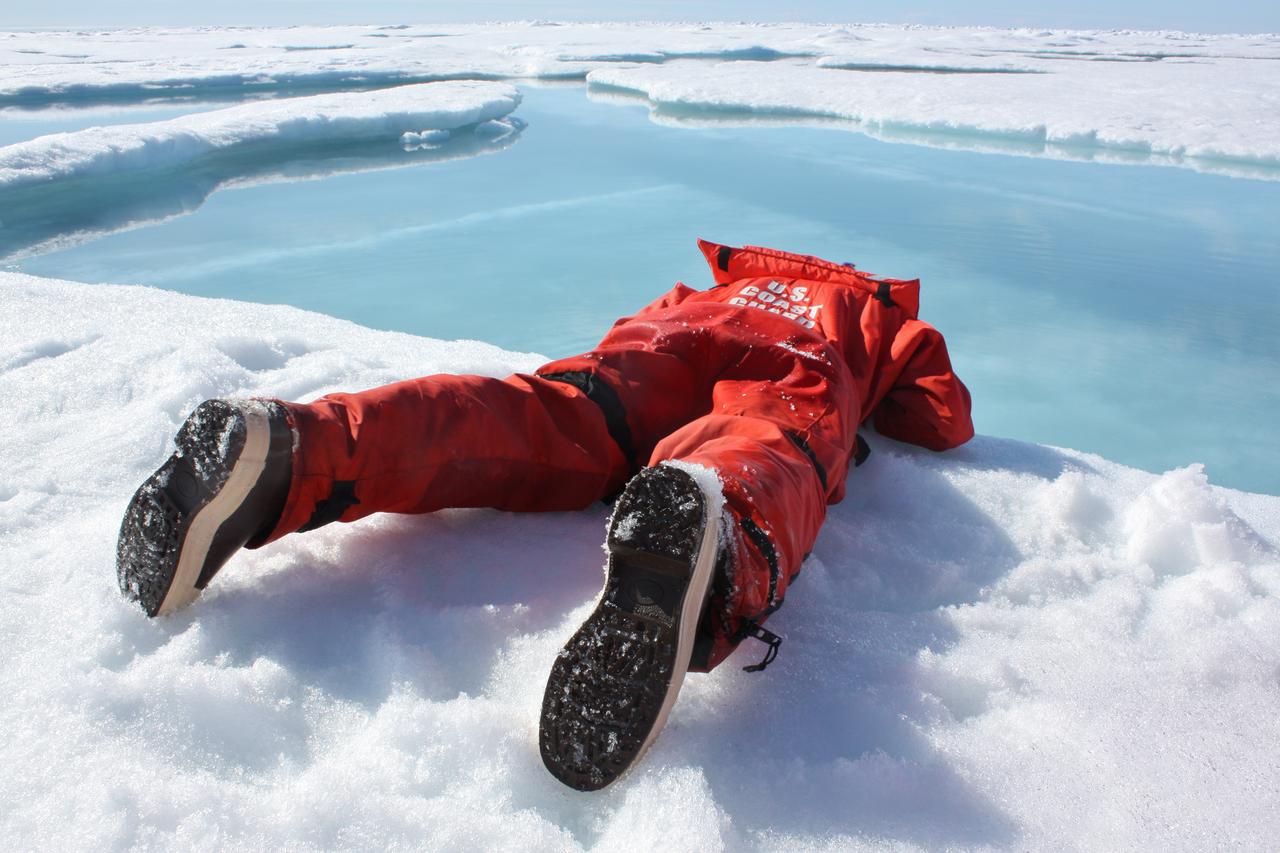

On July 19, 2011, Zachary Brown of Stanford University sipped freshwater from a melt pond on sea ice in the Arctic ocean. The ICESCAPE mission, or "Impacts of Climate on Ecosystems and Chemistry of the Arctic Pacific Environment," is a NASA shipborne investigation to study how changing conditions in the Arctic affect the ocean's chemistry and ecosystems. The bulk of the research took place in the Beaufort and Chukchi seas in summer 2010 and 2011. Credit: NASA/Kathryn Hansen <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

On July 18, 2011, Melinda Webster of University of Washington, calculated distances between sampling locations during the 2011 ICESCAPE mission's eighth sea ice station in the Arctic Ocean. The ICESCAPE mission, or "Impacts of Climate on Ecosystems and Chemistry of the Arctic Pacific Environment," is a NASA shipborne investigation to study how changing conditions in the Arctic affect the ocean's chemistry and ecosystems. The bulk of the research took place in the Beaufort and Chukchi seas in summer 2010 and 2011. Credit: NASA/Kathryn Hansen <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
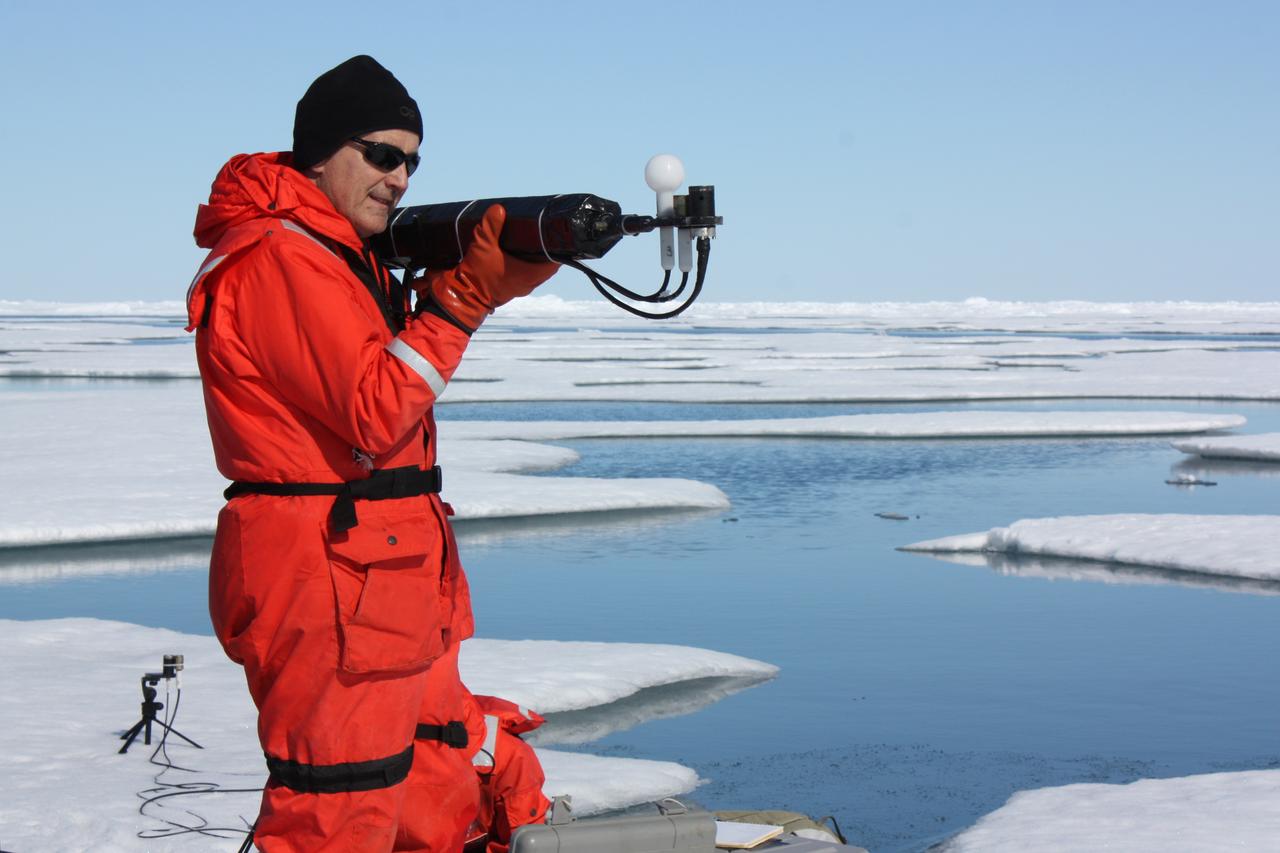

On July 13, 2011, Don Perovich, of Cold Regions Research and Engineering Laboratory, measured the light that drives photosynthesis at the sixth sea ice station of the 2011 ICESCAPE mission. The ICESCAPE mission, or "Impacts of Climate on Ecosystems and Chemistry of the Arctic Pacific Environment," is a NASA shipborne investigation to study how changing conditions in the Arctic affect the ocean's chemistry and ecosystems. The bulk of the research took place in the Beaufort and Chukchi seas in summer 2010 and 2011. Credit: NASA/Kathryn Hansen <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

On February 4, 2014 the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) flying aboard NASA’s Aqua satellite captured a true-color image of sea ice off of western Alaska. In this true-color image, the snow and ice covered land appears bright white while the floating sea ice appears a duller grayish-white. Snow over the land is drier, and reflects more light back to the instrument, accounting for the very bright color. Ice overlying oceans contains more water, and increasing water decreases reflectivity of ice, resulting in duller colors. Thinner ice is also duller. The ocean waters are tinted with green, likely due to a combination of sediment and phytoplankton. Alaska lies to the east in this image, and Russia to the west. The Bering Strait, covered with ice, lies between to two. South of the Bering Strait, the waters are known as the Bering Sea. To the north lies the Chukchi Sea. The bright white island south of the Bering Strait is St. Lawrence Island. Home to just over 1200 people, the windswept island belongs to the United States, but sits closer to Russia than to Alaska. To the southeast of the island a dark area, loosely covered with floating sea ice, marks a persistent polynya – an area of open water surrounded by more frozen sea ice. Due to the prevailing winds, which blow the sea ice away from the coast in this location, the area rarely completely freezes. The ice-covered areas in this image, as well as the Beaufort Sea, to the north, are critical areas for the survival of the ringed seal, a threatened species. The seals use the sea ice, including ice caves, to rear their young, and use the free-floating sea ice for molting, raising the young and breeding. In December 2014, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) proposed that much of this region be set aside as critical, protected habitat for the ringed seal. Credit: NASA/GSFC/Jeff Schmaltz/MODIS Land Rapid Response Team <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
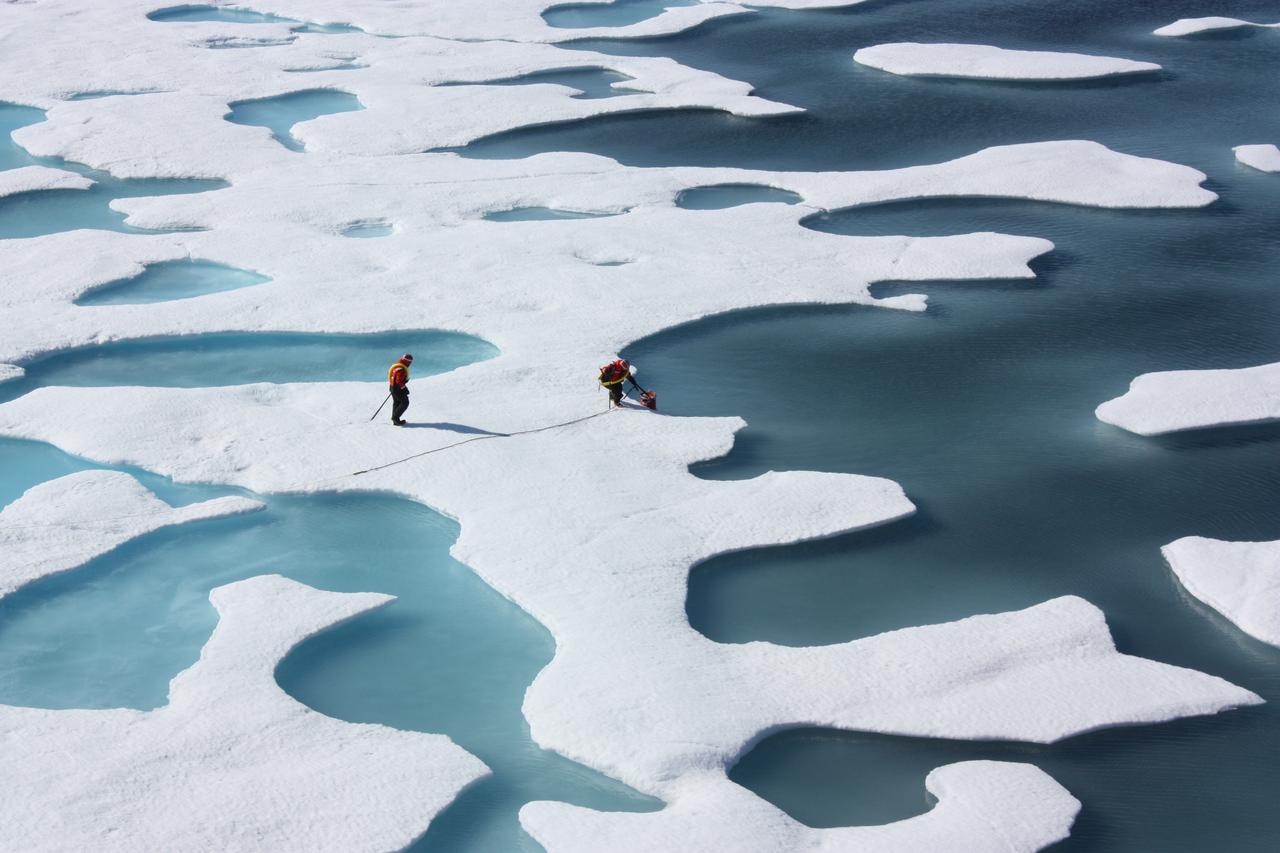

On July 12, 2011, crew from the U.S. Coast Guard Cutter Healy retrieved a canister dropped by parachute from a C-130, which brought supplies for some mid-mission fixes. The ICESCAPE mission, or "Impacts of Climate on Ecosystems and Chemistry of the Arctic Pacific Environment," is a NASA shipborne investigation to study how changing conditions in the Arctic affect the ocean's chemistry and ecosystems. The bulk of the research took place in the Beaufort and Chukchi seas in summer 2010 and 2011. Credit: NASA/Kathryn Hansen <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
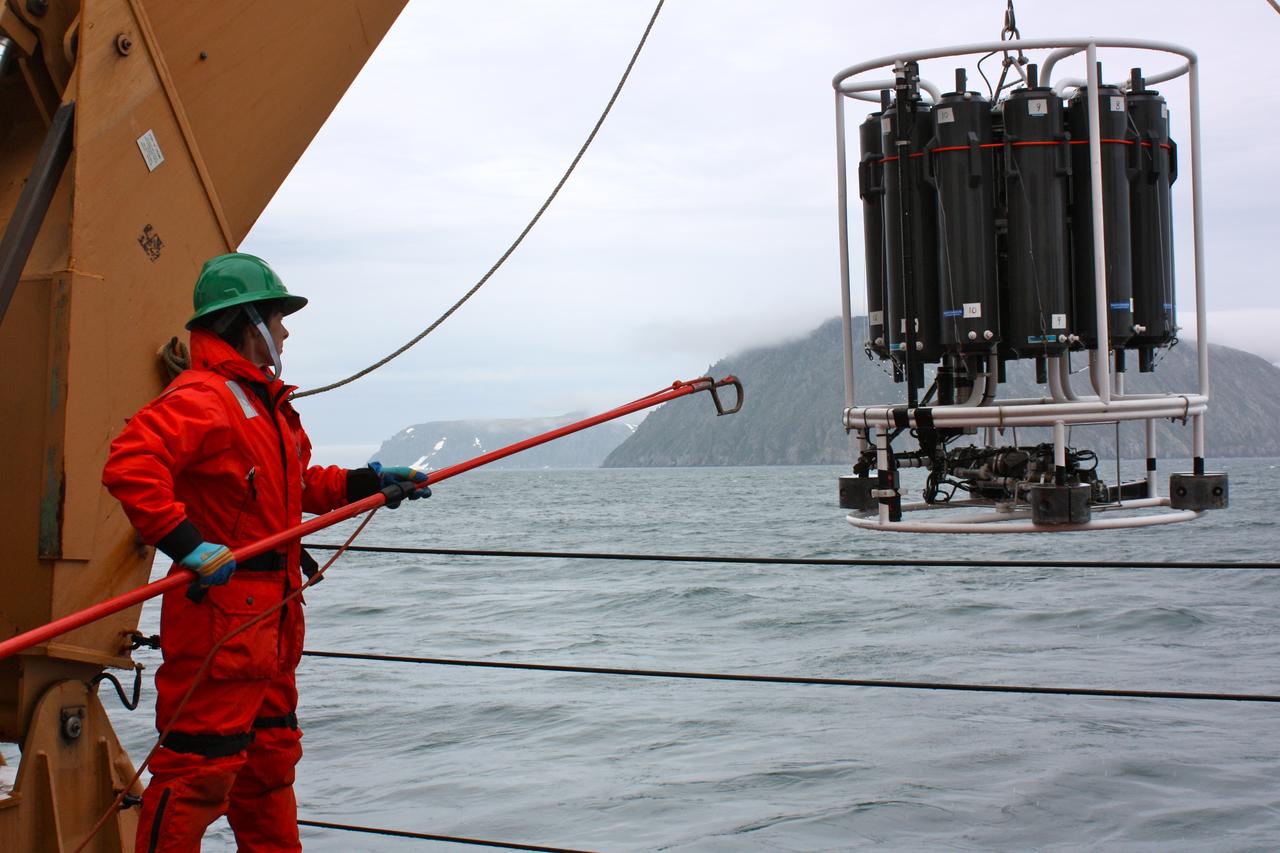

On June 28, 2011, Holley Kelly, a teacher from Farragut High School, helped retrieve the CTD/Rosette ensemble from the Bering Strait, east of the Diomede Islands. The ICESCAPE mission, or "Impacts of Climate on Ecosystems and Chemistry of the Arctic Pacific Environment," is a NASA shipborne investigation to study how changing conditions in the Arctic affect the ocean's chemistry and ecosystems. The bulk of the research took place in the Beaufort and Chukchi seas in summer 2010 and 2011. Credit: NASA/Kathryn Hansen <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
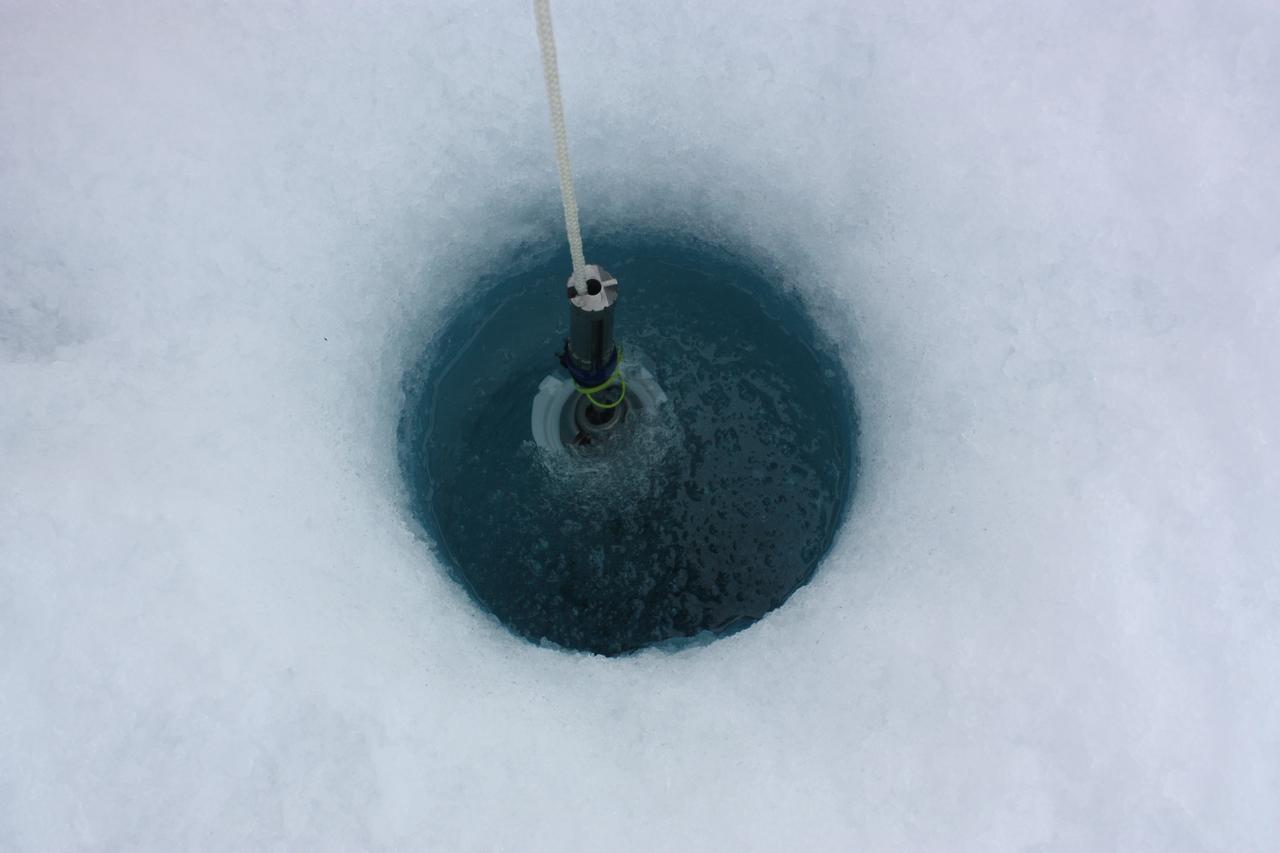

On July 6, 2011, ICESCAPE scientists lowered optical instruments through a hole at the bottom of a melt pond, to study the waters underneath the ice. The ICESCAPE mission, or "Impacts of Climate on Ecosystems and Chemistry of the Arctic Pacific Environment," is a NASA shipborne investigation to study how changing conditions in the Arctic affect the ocean's chemistry and ecosystems. The bulk of the research took place in the Beaufort and Chukchi seas in summer 2010 and 2011. Credit: NASA/Kathryn Hansen <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
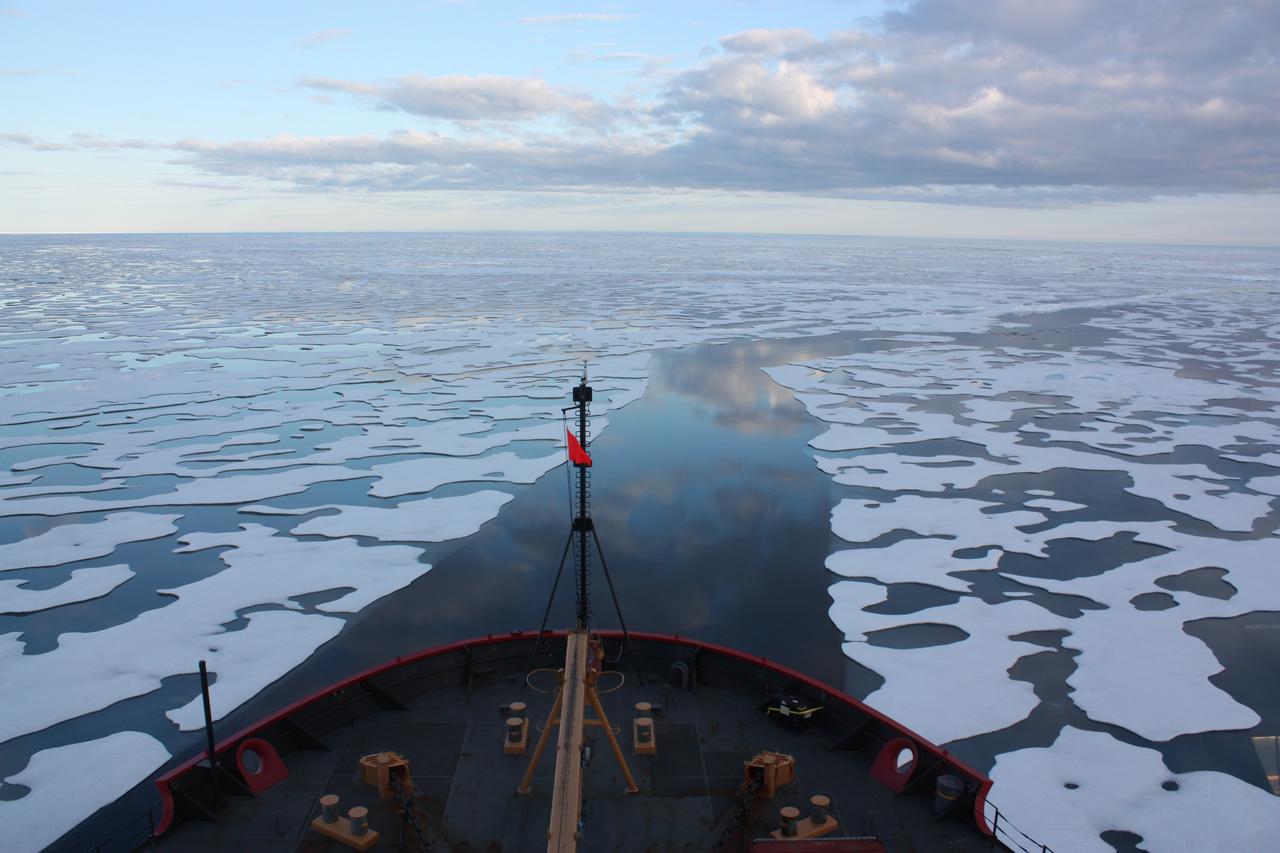

Scientists on board the U.S. Coast Guard Cutter Healy in the Beaufort Sea, northeast of Barrow, Alaska, finished collecting the mission¹s sea ice data and cruised south on July 20, 2011, through thin ice and ultimately into the open ocean. The ICESCAPE mission, or "Impacts of Climate on Ecosystems and Chemistry of the Arctic Pacific Environment," is a NASA shipborne investigation to study how changing conditions in the Arctic affect the ocean's chemistry and ecosystems. The bulk of the research took place in the Beaufort and Chukchi seas in summer 2010 and 2011. Credit: NASA/Kathryn Hansen Credit: NASA/Kathryn Hansen <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
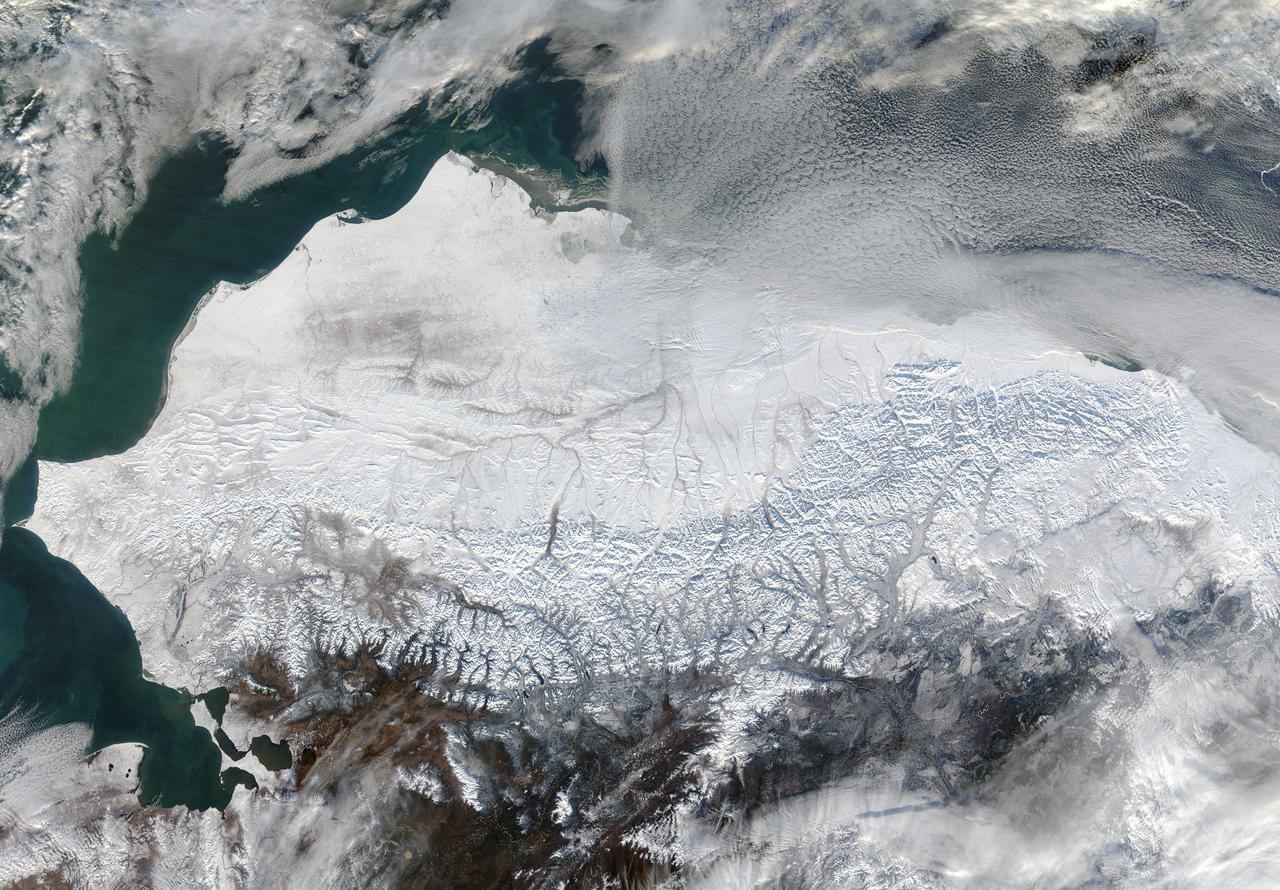

As autumn colors moved across much of the lower forty-eight states in mid-October 2015, winter weather had already arrived in Alaska. The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) aboard NASA’s Terra satellite captured this true-color image of the icy scene on October 16 as it passed over the region. Point Barrow, the northern-most location in the United States sits between the Chukchi Sea (west) and the Beaufort Sea on the east. The rugged peaks of the Brooks Range can be seen along the southern section of the image. North of the Brooks Range the land is almost entirely covered with snow; to the south the tan and browns visible between snow marks uncovered land. Sea ice lies over the waters near the coasts of much of Alaska’s North Slope, especially east of Point Barrow. White cloud banks are notable in the northeast and southeast sections of the image. Credit: NASA/GSFC/Jeff Schmaltz/MODIS Land Rapid Response Team <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

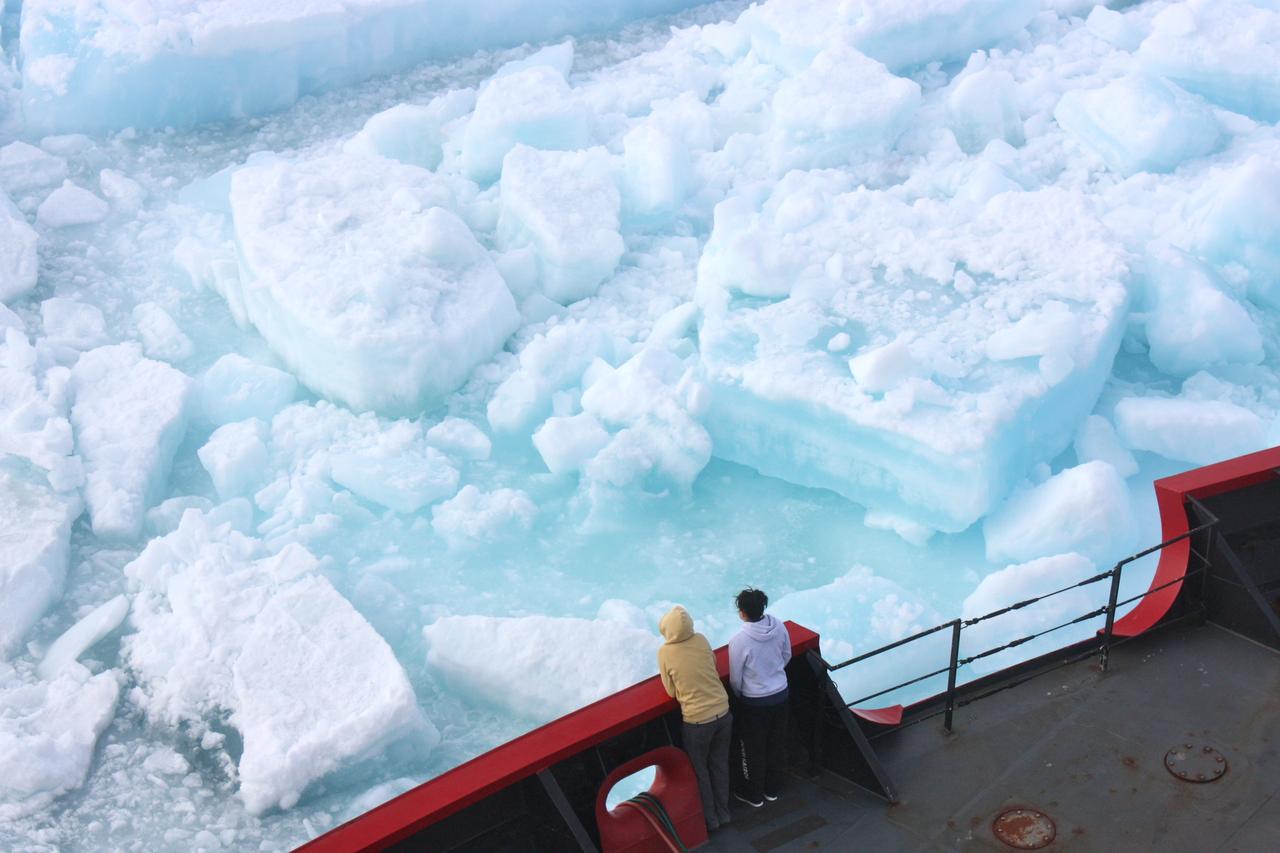
On July 20, the U.S. Coast Guard Cutter Healy steamed south in the Arctic Ocean toward the edge of the sea ice. The ICESCAPE mission, or "Impacts of Climate on Ecosystems and Chemistry of the Arctic Pacific Environment," is NASA's two-year shipborne investigation to study how changing conditions in the Arctic affect the ocean's chemistry and ecosystems. The bulk of the research takes place in the Beaufort and Chukchi seas in summer 2010 and 2011. Credit: NASA/Kathryn Hansen For updates on the five-week ICESCAPE voyage, visit the mission blog at: go.usa.gov/WwU <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

ICESCAPE scientists watched from the deck of the Healy as it cut a path through thick multiyear ice on July 6, 2011. Cutting the path is key for getting researchers to remote research sites amid the sea ice. Credit: NASA/Kathryn Hansen The ICESCAPE mission, or "Impacts of Climate on Ecosystems and Chemistry of the Arctic Pacific Environment," is a NASA shipborne investigation to study how changing conditions in the Arctic affect the ocean's chemistry and ecosystems. The bulk of the research took place in the Beaufort and Chukchi seas in summer 2010 and 2011. Credit: NASA/Kathryn Hansen <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
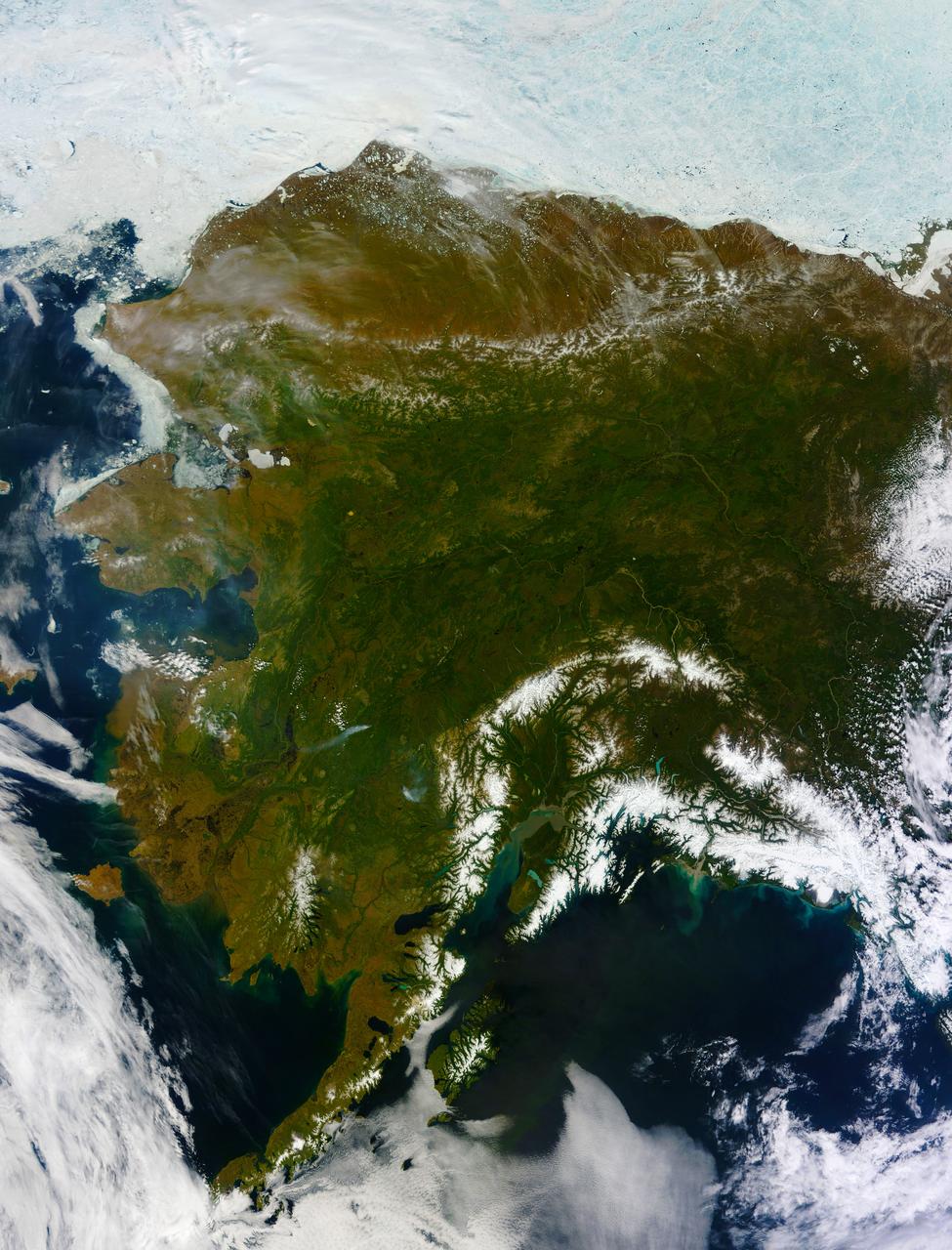

On most days, relentless rivers of clouds wash over Alaska, obscuring most of the state’s 6,640 miles (10,690 kilometers) of coastline and 586,000 square miles (1,518,000 square kilometers) of land. The south coast of Alaska even has the dubious distinction of being the cloudiest region of the United States, with some locations averaging more than 340 cloudy days per year. That was certainly not the case on June 17, 2013, the date that the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on NASA’s Terra satellite acquired this rare, nearly cloud-free view of the state. The absence of clouds exposed a striking tapestry of water, ice, land, forests, and even wildfires. Snow-covered mountains such as the Alaska Range and Chugach Mountains were visible in southern Alaska, while the arc of mountains that make up the Brooks Range dominated the northern part of the state. The Yukon River—the longest in Alaska and the third longest in the United States—wound its way through the green boreal forests that inhabit the interior of the state. Plumes of sediment and glacial dust poured into the Gulf of Alaska from the Copper River. And Iliamna Lake, the largest in Alaska, was ice free. The same ridge of high pressure that cleared Alaska’s skies also brought stifling temperatures to many areas accustomed to chilly June days. Talkeetna, a town about 100 miles north of Anchorage, saw temperatures reach 96°F (36°C) on June 17. Other towns in southern Alaska set all-time record highs, including Cordova, Valez, and Seward. The high temperatures also helped fuel wildfires and hastened the breakup of sea ice in the Chukchi Sea. NASA image courtesy Jeff Schmaltz, LANCE MODIS Rapid Response Team at NASA GSFC. Caption by Adam Voiland. Instrument: Terra - MODIS More info: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/102MAEj" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/102MAEj</a> Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
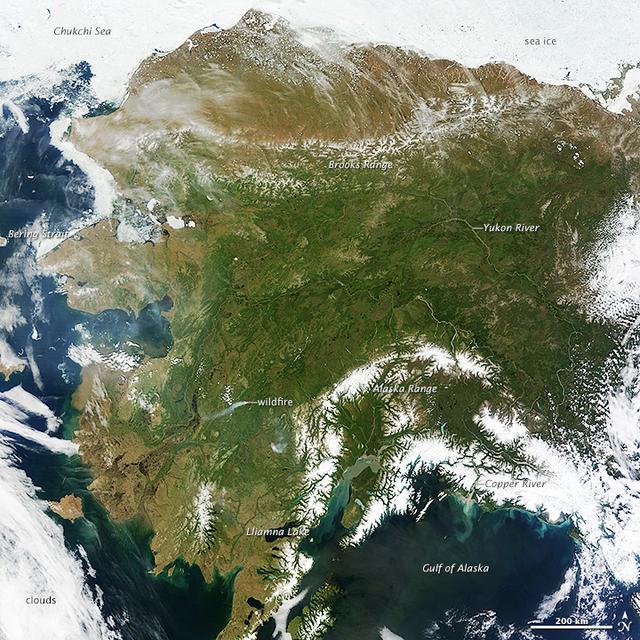
On most days, relentless rivers of clouds wash over Alaska, obscuring most of the state’s 6,640 miles (10,690 kilometers) of coastline and 586,000 square miles (1,518,000 square kilometers) of land. The south coast of Alaska even has the dubious distinction of being the cloudiest region of the United States, with some locations averaging more than 340 cloudy days per year. That was certainly not the case on June 17, 2013, the date that the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on NASA’s Terra satellite acquired this rare, nearly cloud-free view of the state. The absence of clouds exposed a striking tapestry of water, ice, land, forests, and even wildfires. Snow-covered mountains such as the Alaska Range and Chugach Mountains were visible in southern Alaska, while the arc of mountains that make up the Brooks Range dominated the northern part of the state. The Yukon River—the longest in Alaska and the third longest in the United States—wound its way through the green boreal forests that inhabit the interior of the state. Plumes of sediment and glacial dust poured into the Gulf of Alaska from the Copper River. And Iliamna Lake, the largest in Alaska, was ice free. The same ridge of high pressure that cleared Alaska’s skies also brought stifling temperatures to many areas accustomed to chilly June days. Talkeetna, a town about 100 miles north of Anchorage, saw temperatures reach 96°F (36°C) on June 17. Other towns in southern Alaska set all-time record highs, including Cordova, Valez, and Seward. The high temperatures also helped fuel wildfires and hastened the breakup of sea ice in the Chukchi Sea. NASA image courtesy Jeff Schmaltz, LANCE MODIS Rapid Response Team at NASA GSFC. Caption by Adam Voiland. Instrument: Terra - MODIS More info: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/102MAEj" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/102MAEj</a> Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

On July 12, 2011, crew from the U.S. Coast Guard Cutter Healy retrieved a canister dropped by parachute from a C-130, which brought supplies for some mid-mission fixes. The ICESCAPE mission, or "Impacts of Climate on Ecosystems and Chemistry of the Arctic Pacific Environment," is NASA's two-year shipborne investigation to study how changing conditions in the Arctic affect the ocean's chemistry and ecosystems. The bulk of the research takes place in the Beaufort and Chukchi seas in summer 2010 and 2011. Credit: NASA/Kathryn Hansen For updates on the five-week ICESCAPE voyage, visit the mission blog at: go.usa.gov/WwU <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>