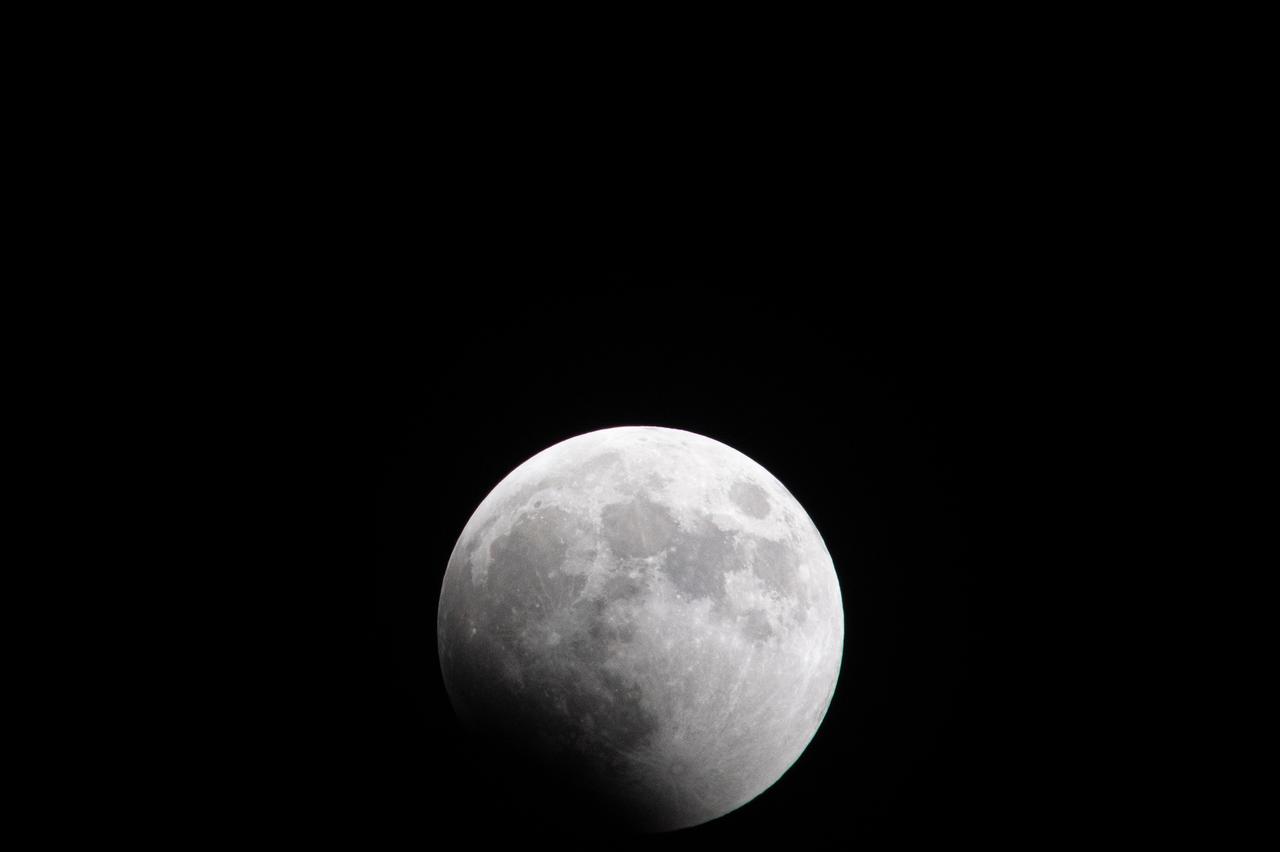

Blood Moon/Lunar Eclipse on March 14th, 2025 seen from Brookpark, OH at NASA Glenn Research Center.. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Cochran)
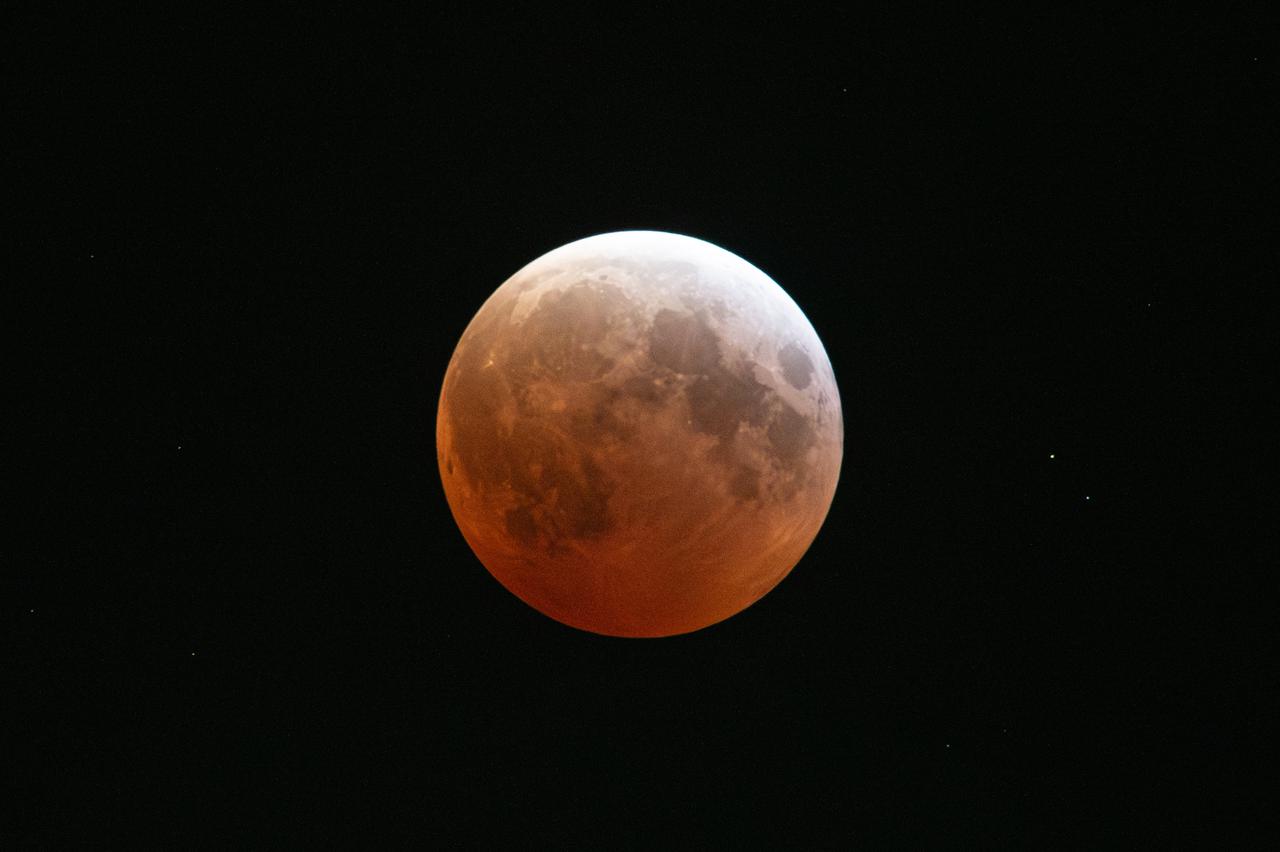

Blood Moon/Lunar Eclipse on March 14th, 2025 seen from Brookpark, OH at NASA Glenn Research Center.. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Cochran)
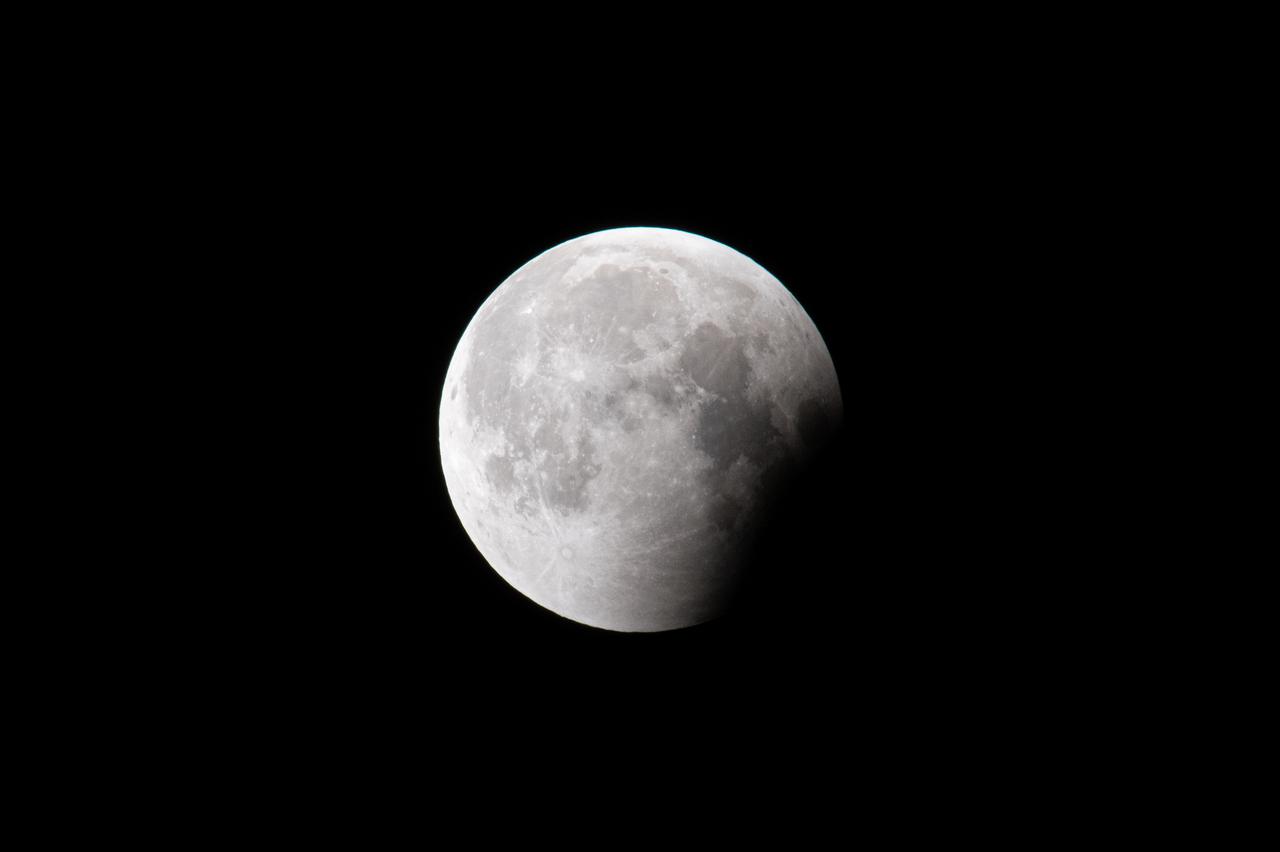

Blood Moon/Lunar Eclipse on March 14th, 2025 seen from Brookpark, OH at NASA Glenn Research Center.. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Cochran)
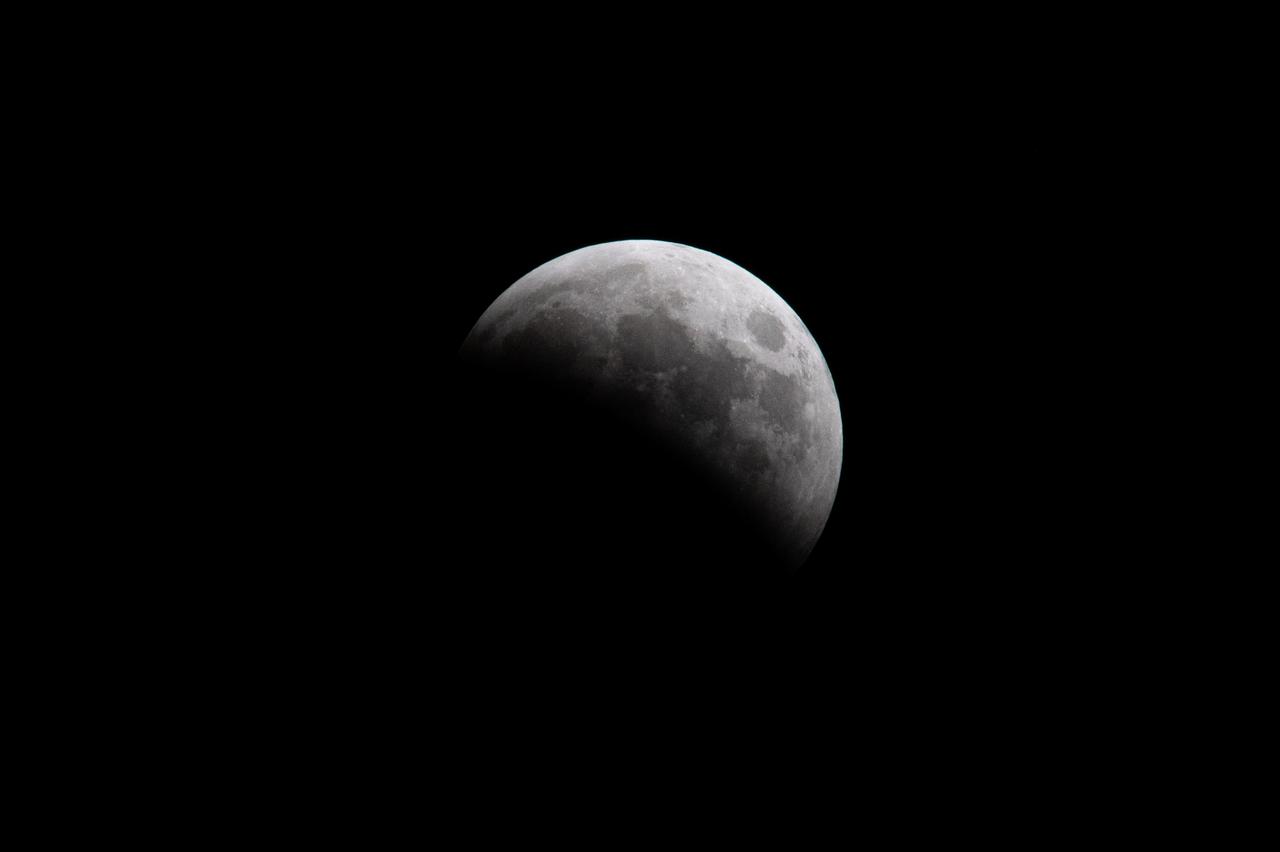

Blood Moon/Lunar Eclipse on March 14th, 2025 seen from Brookpark, OH at NASA Glenn Research Center.. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Cochran)
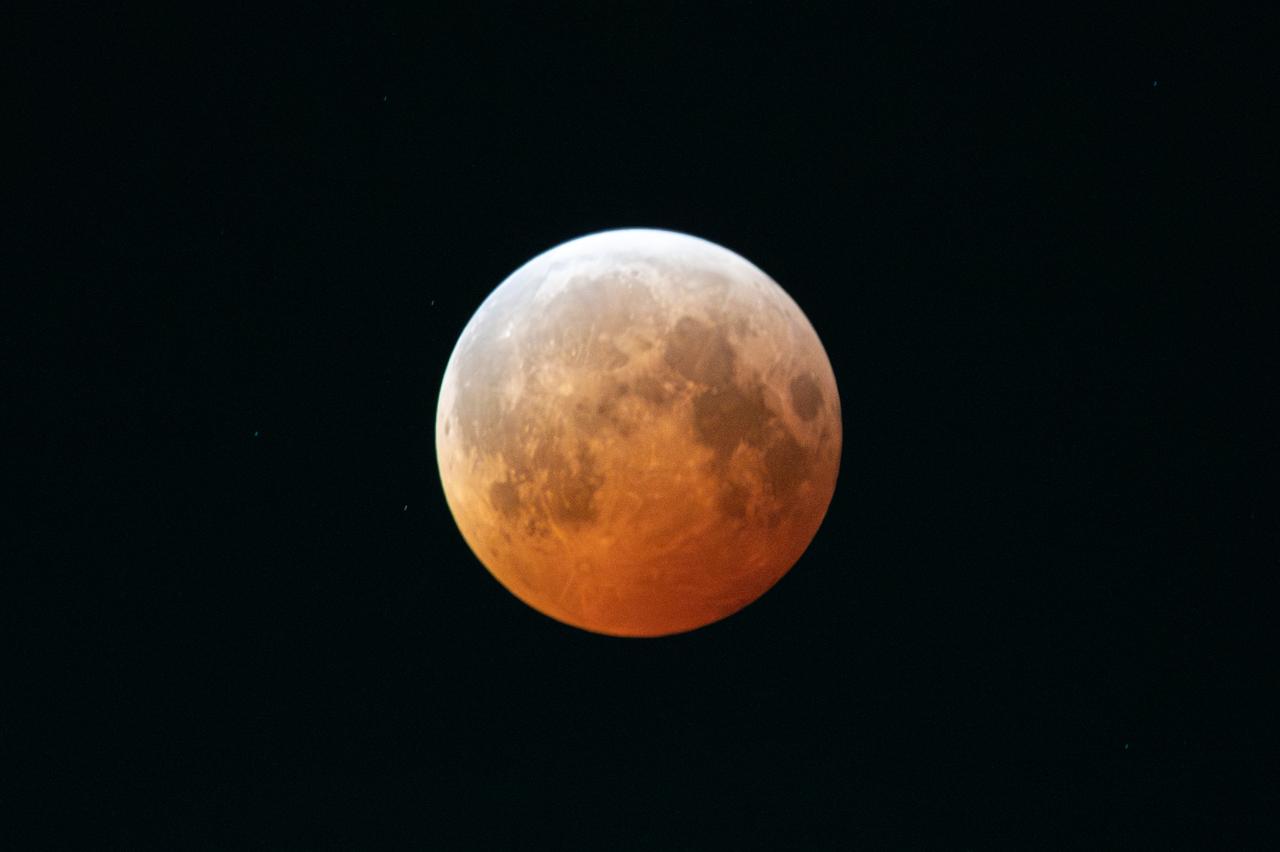

Blood Moon/Lunar Eclipse on March 14th, 2025 seen from Brookpark, OH at NASA Glenn Research Center.. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Cochran)
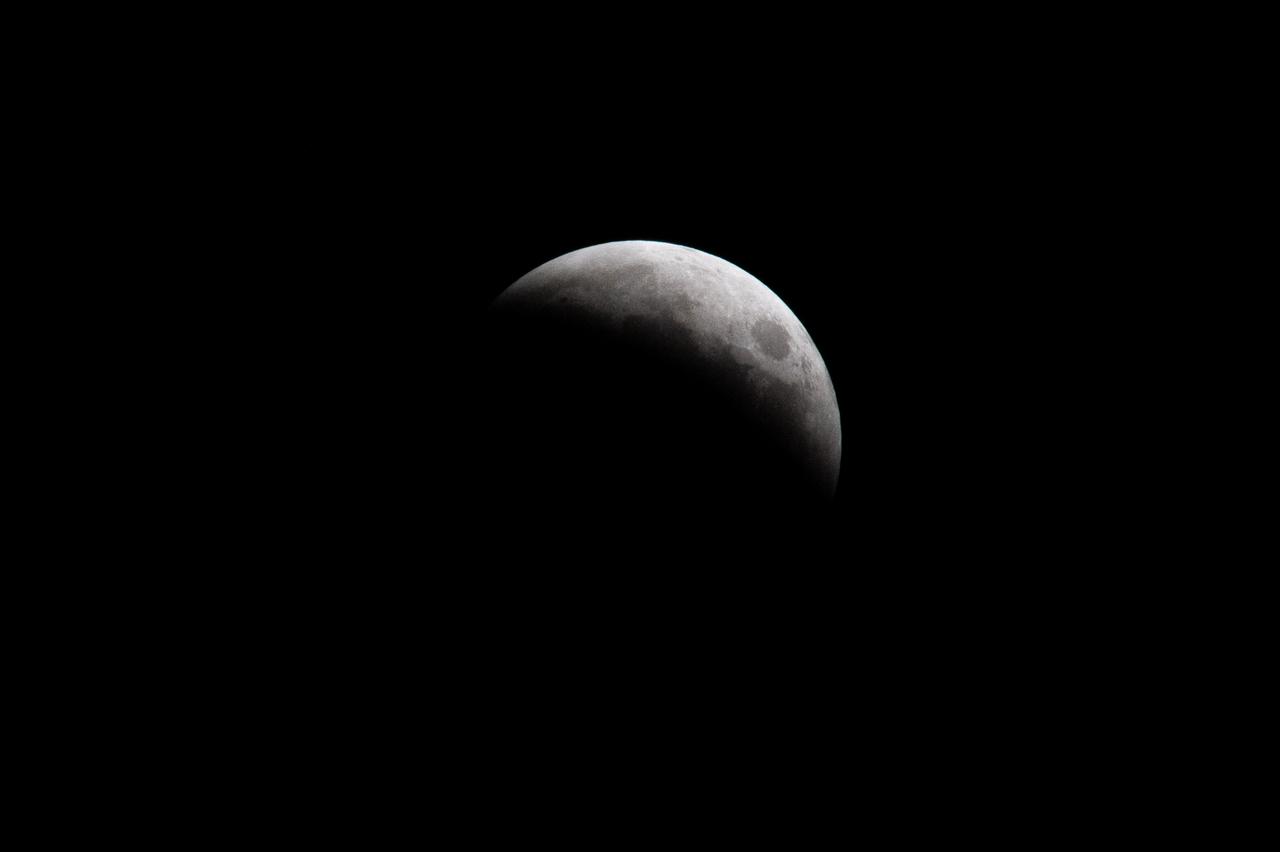

Blood Moon/Lunar Eclipse on March 14th, 2025 seen from Brookpark, OH at NASA Glenn Research Center.. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Cochran)
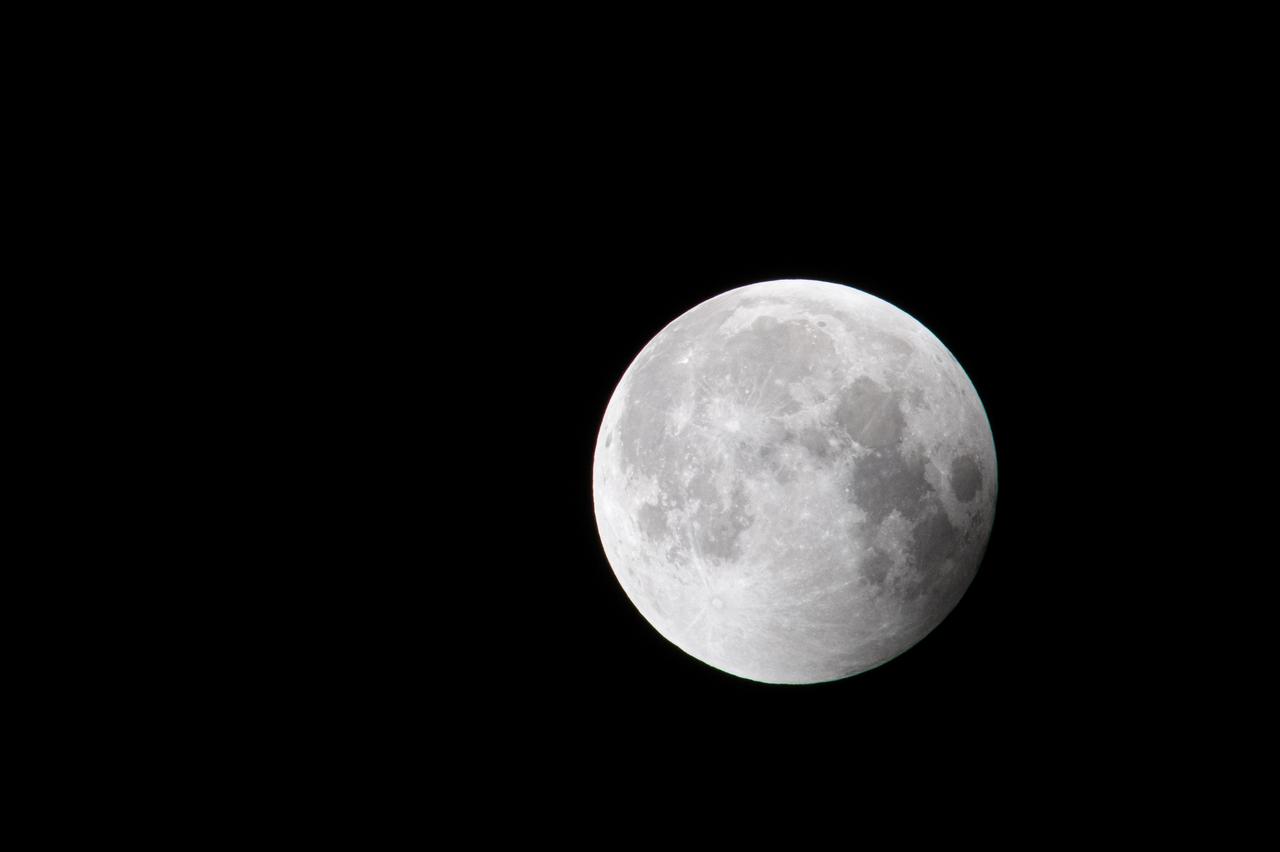

Blood Moon/Lunar Eclipse on March 14th, 2025 seen from Brookpark, OH at NASA Glenn Research Center.. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Cochran)
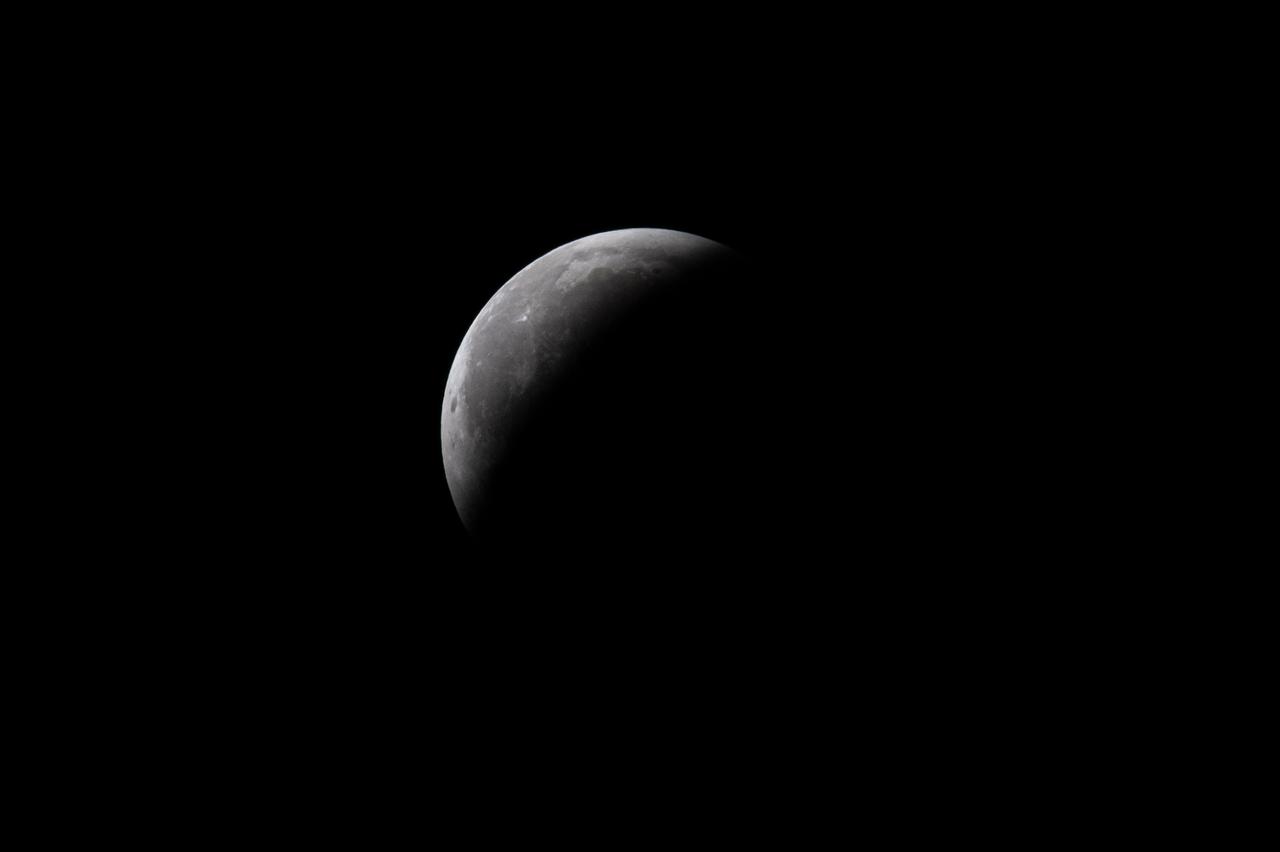

Blood Moon/Lunar Eclipse on March 14th, 2025 seen from Brookpark, OH at NASA Glenn Research Center.. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Cochran)
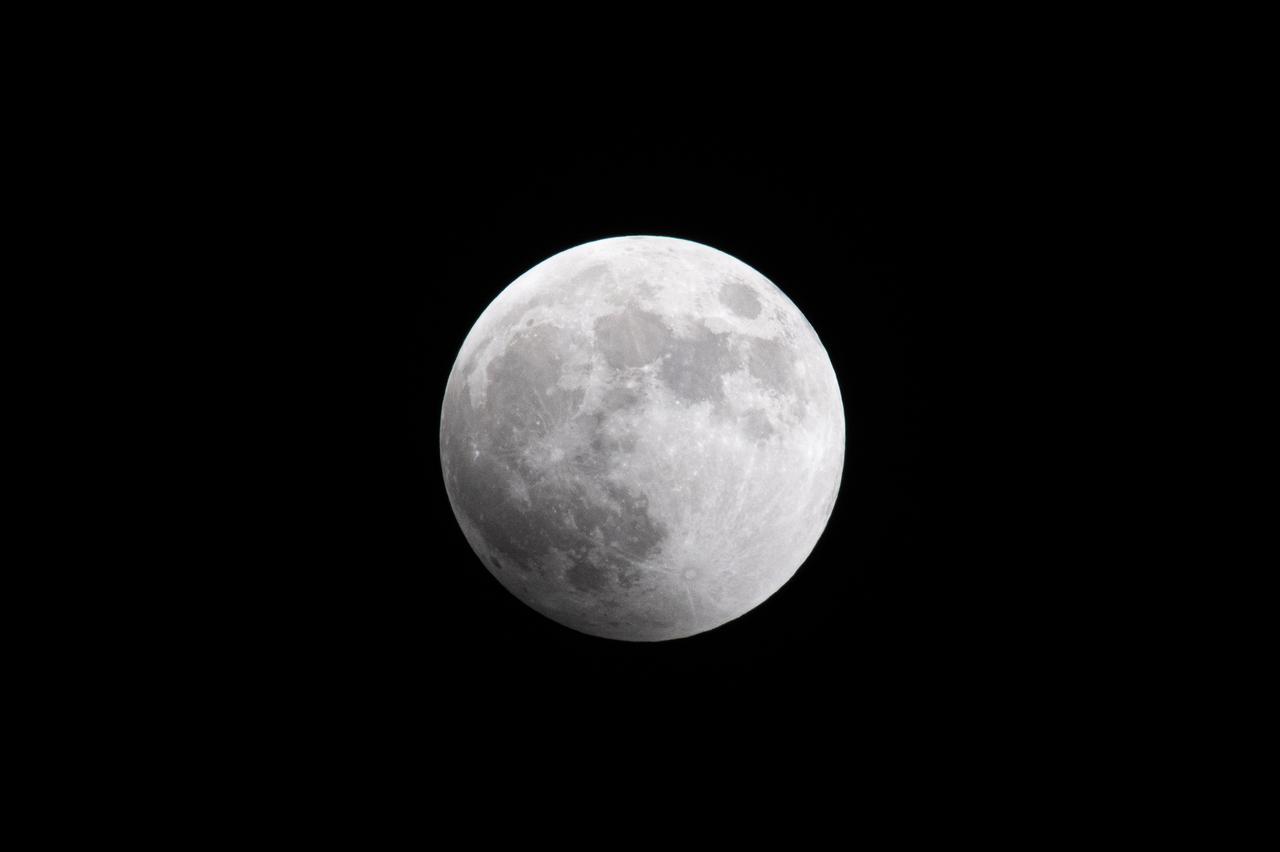

Blood Moon/Lunar Eclipse on March 14th, 2025 seen from Brookpark, OH at NASA Glenn Research Center.. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Cochran)
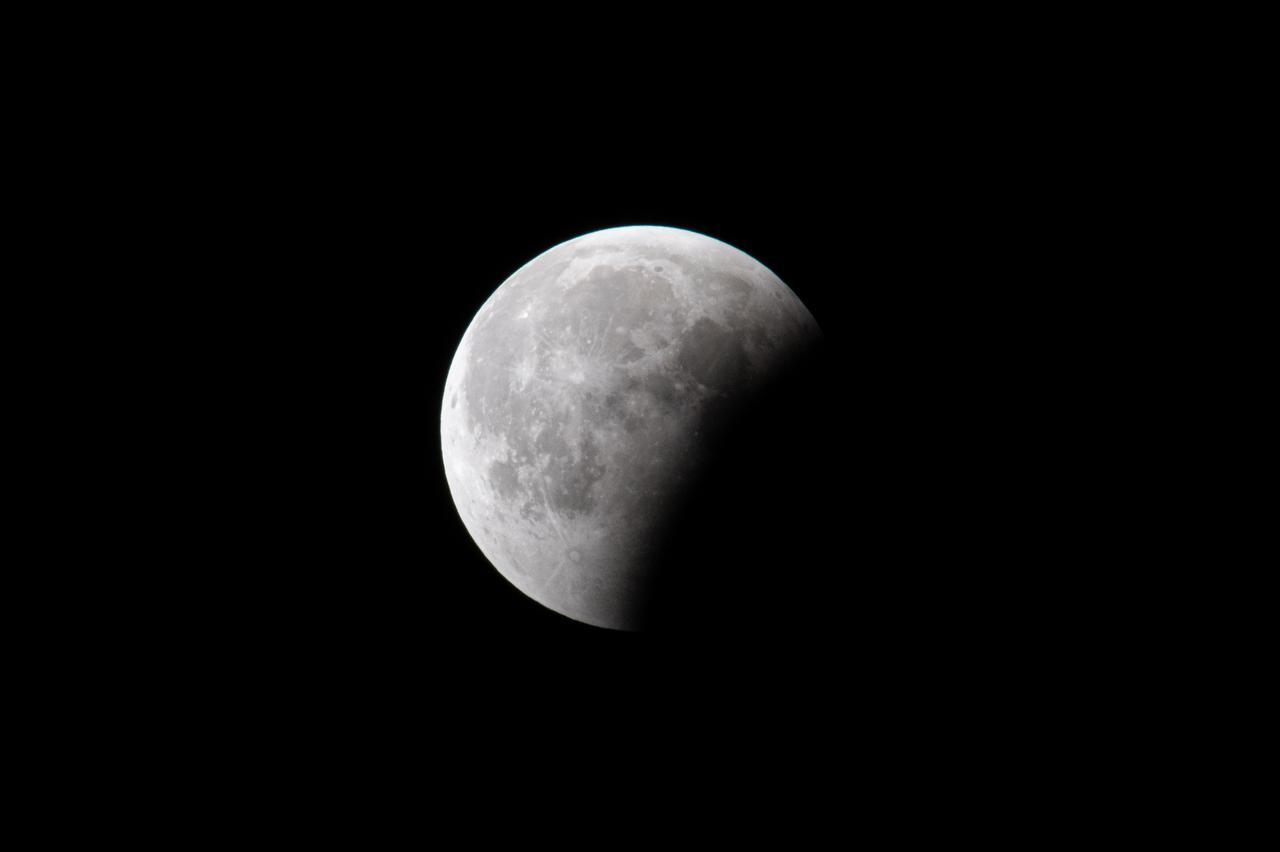

Blood Moon/Lunar Eclipse on March 14th, 2025 seen from Brookpark, OH at NASA Glenn Research Center.. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Cochran)
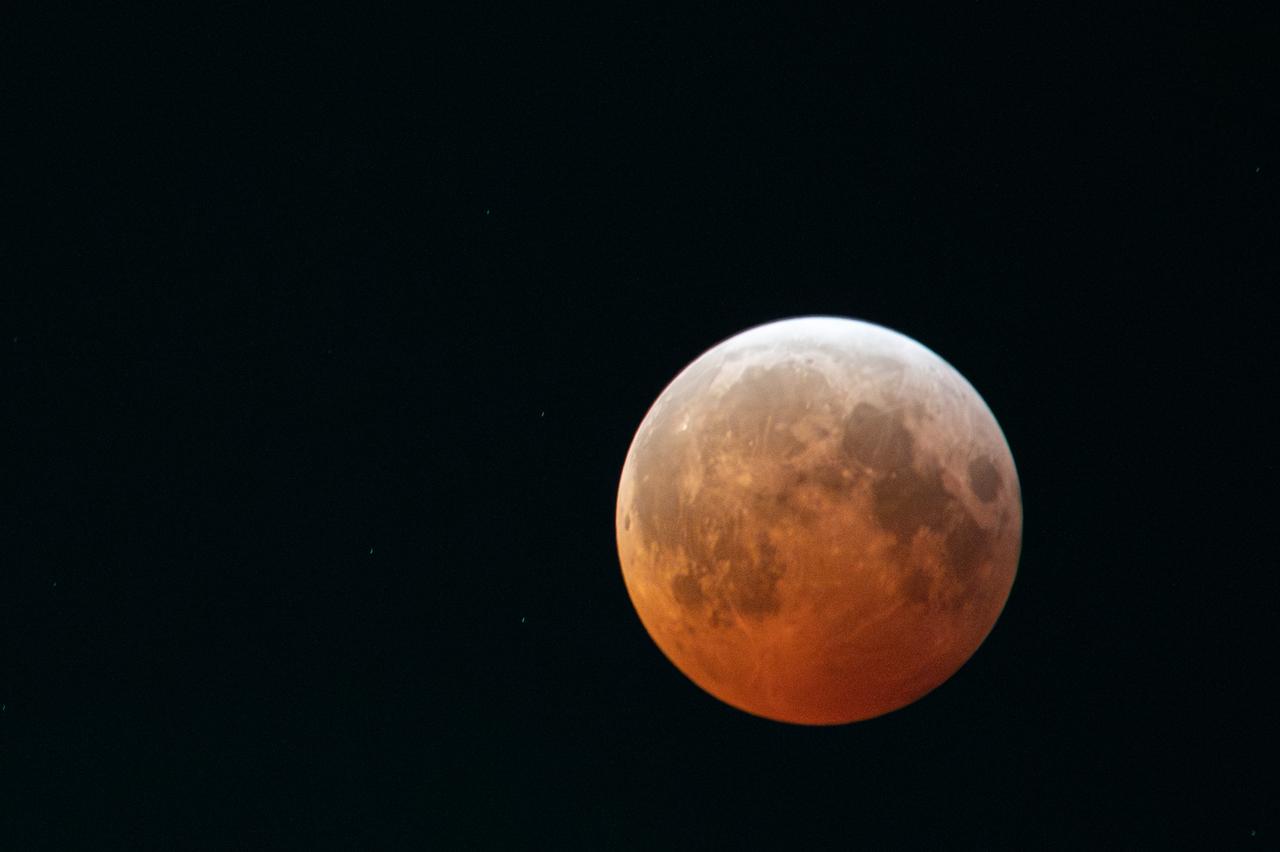

Blood Moon/Lunar Eclipse on March 14th, 2025 seen from Brookpark, OH at NASA Glenn Research Center.. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Cochran)
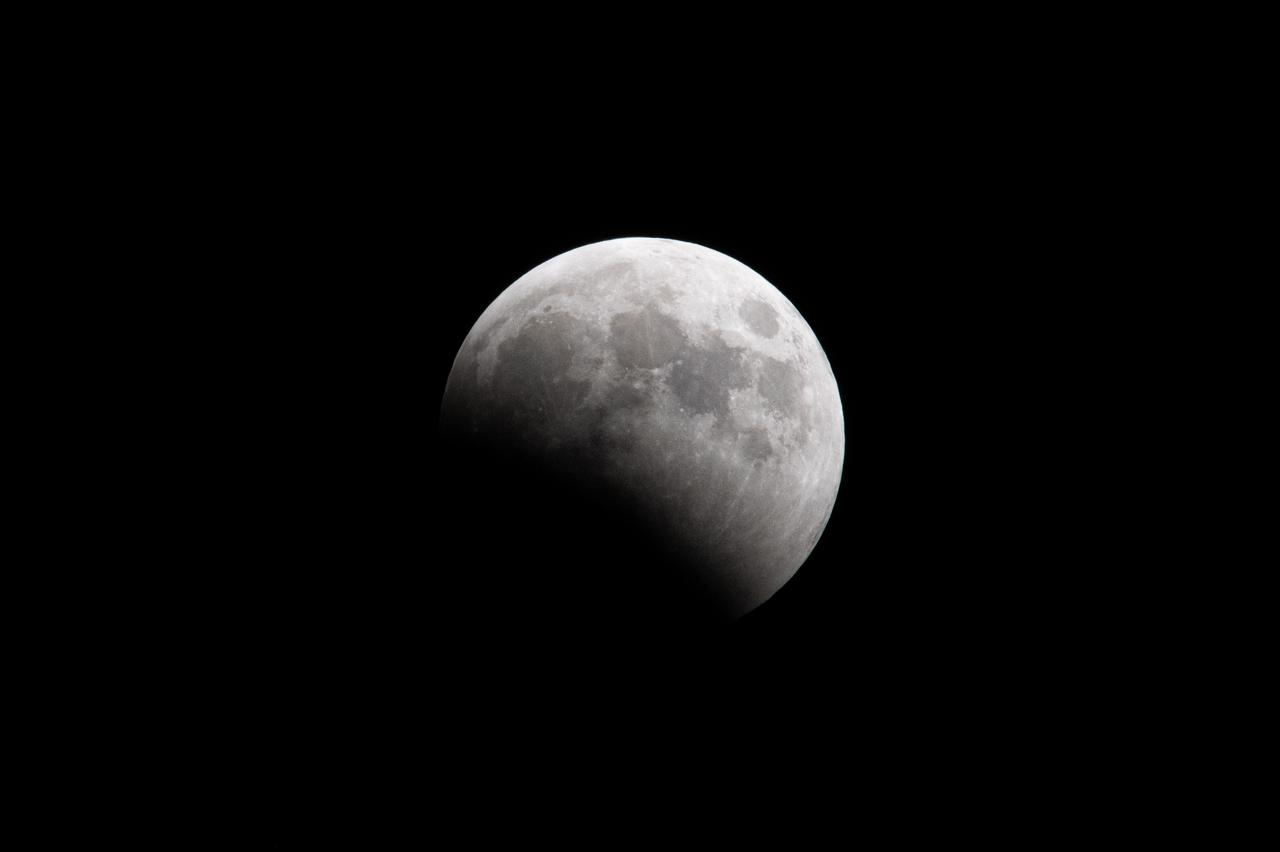

Blood Moon/Lunar Eclipse on March 14th, 2025 seen from Brookpark, OH at NASA Glenn Research Center.. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Cochran)

Blood Moon/Lunar Eclipse on March 14th, 2025 seen from Brookpark, OH at NASA Glenn Research Center.. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Cochran)
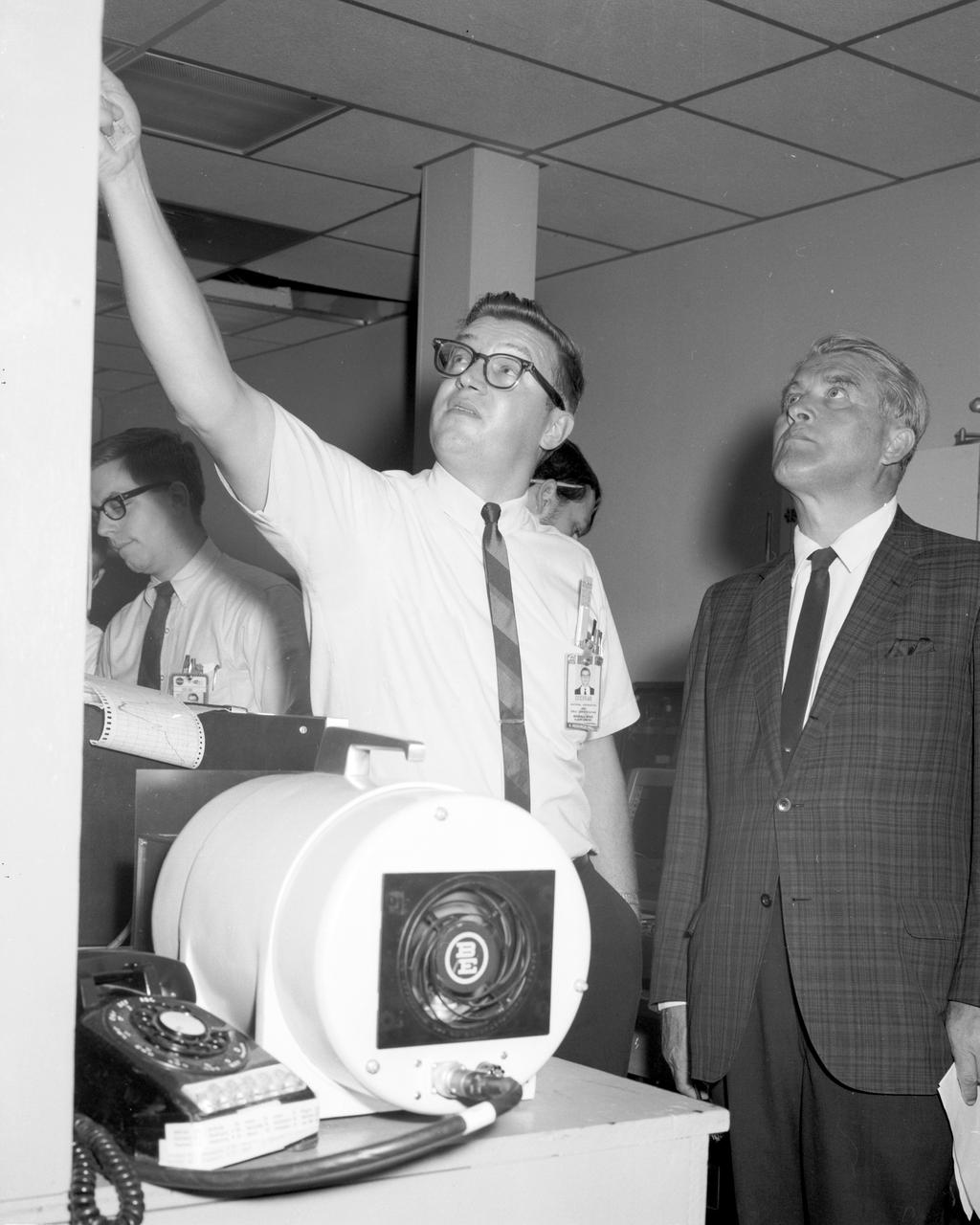

Charles Cochran charts the progress of a test being conducted in Marshall Space Flight Center’s (MSFC) Space Sciences Laboratory for center director, Dr. Wernher von Braun.
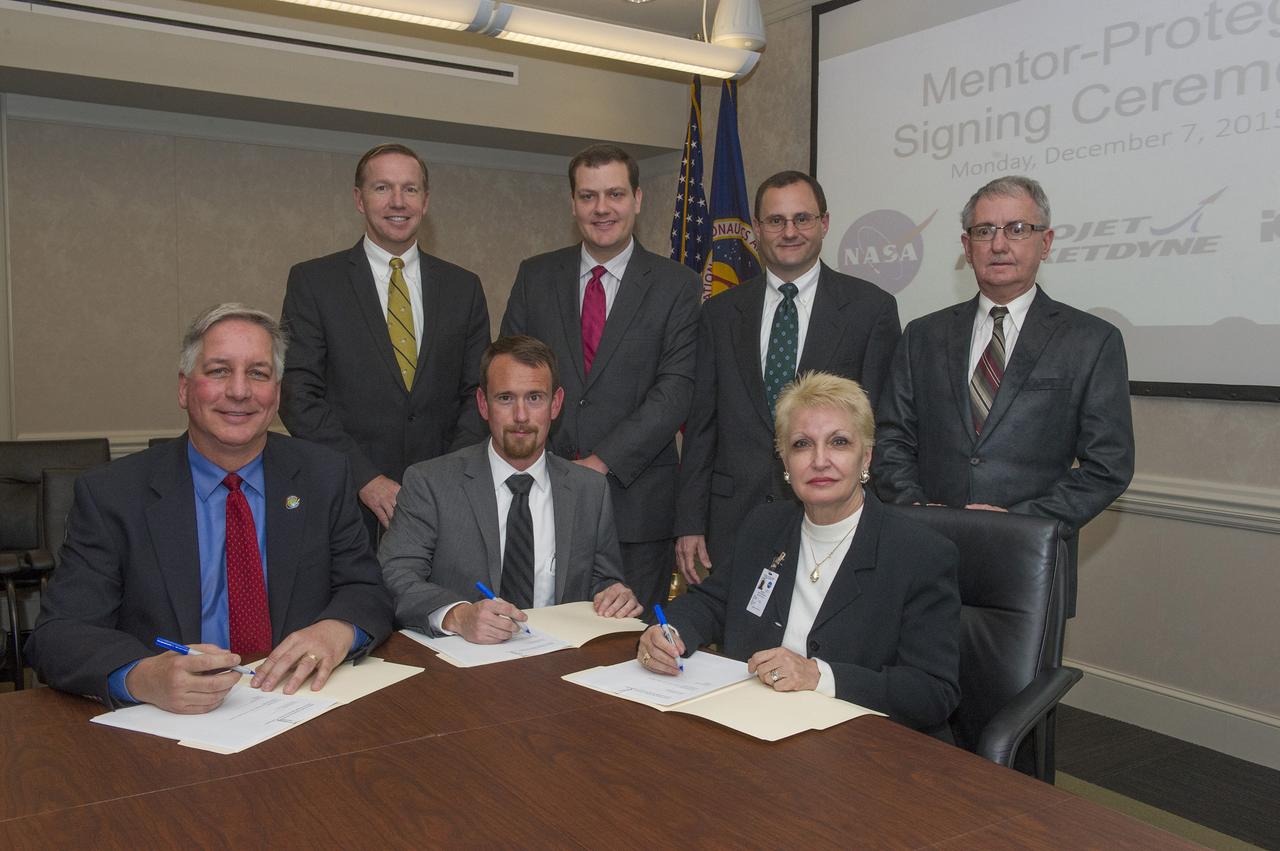

MENTOR PROTÉGÉ AGREEMENT SIGNING CEREMONY, DECEMBER 7, 2015 L TO R STANDING: STEVE MILEY, TYLER COCHRAN, STEVE WOFFORD, DAVID BROCK (ALL NASA) L TO R SEATED: DANIEL ADAMSKI (AEROJET ROCKETDYNE), JOE MCCOLLISTER (NASA), EDWINA CIOFFI (ICO RALLY)

Dr. Anita Cochran, Assistant Director, McDonald Observatory at the University of Texas-Austin, speaks during a symposium commemorating a quarter-century of comet discoveries, Friday, Sept. 10, 2010, in the Knight studio at the Newseum in Washington. The International Sun-Earth Explorer-3 (ISEE-3) spacecraft flew past the comet Giacobini-Zinner on Sept. 11, 1985 which established a foundation of discoveries that continue today. Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers)

This composite photo made up of 11 images of shows the Blood Moon and the phases of the Lunar Eclipse on March 14th, 2025 seen from Brookpark, OH at NASA Glenn Research Center.. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Cochran)
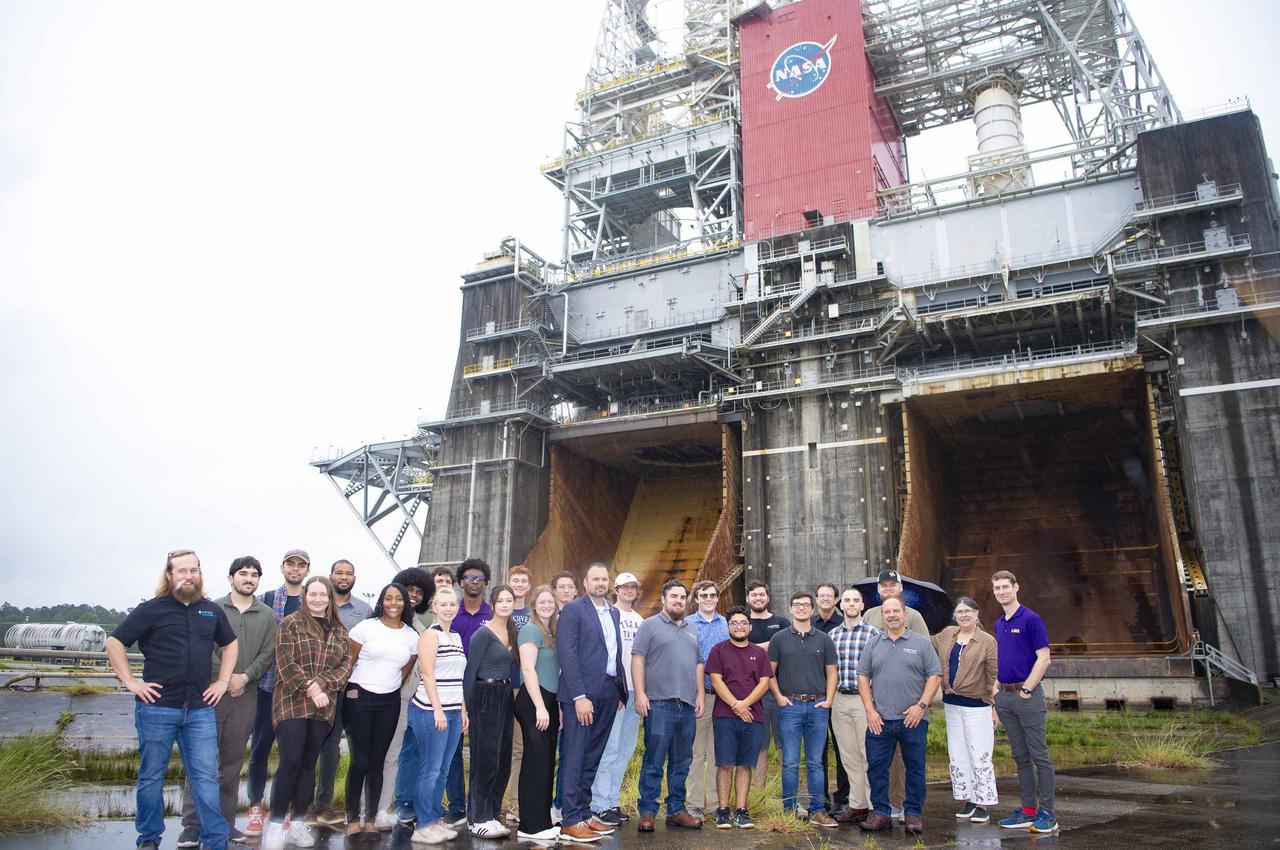

Members of the Society for the Advancement of Material and Process Engineering at Louisiana State University stand at the Thad Cochran Test Stand during a visit to NASA Stennis on Oct. 4. The Thad Cochran Test Stand (B-2) is where future Green Run testing of NASA’s exploration upper stage will take place ahead of future Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond. The mission of the Society for the Advancement of Material and Process Engineering at LSU is to provide enhanced educational opportunities by delivering information on new and advanced materials and processing technology.
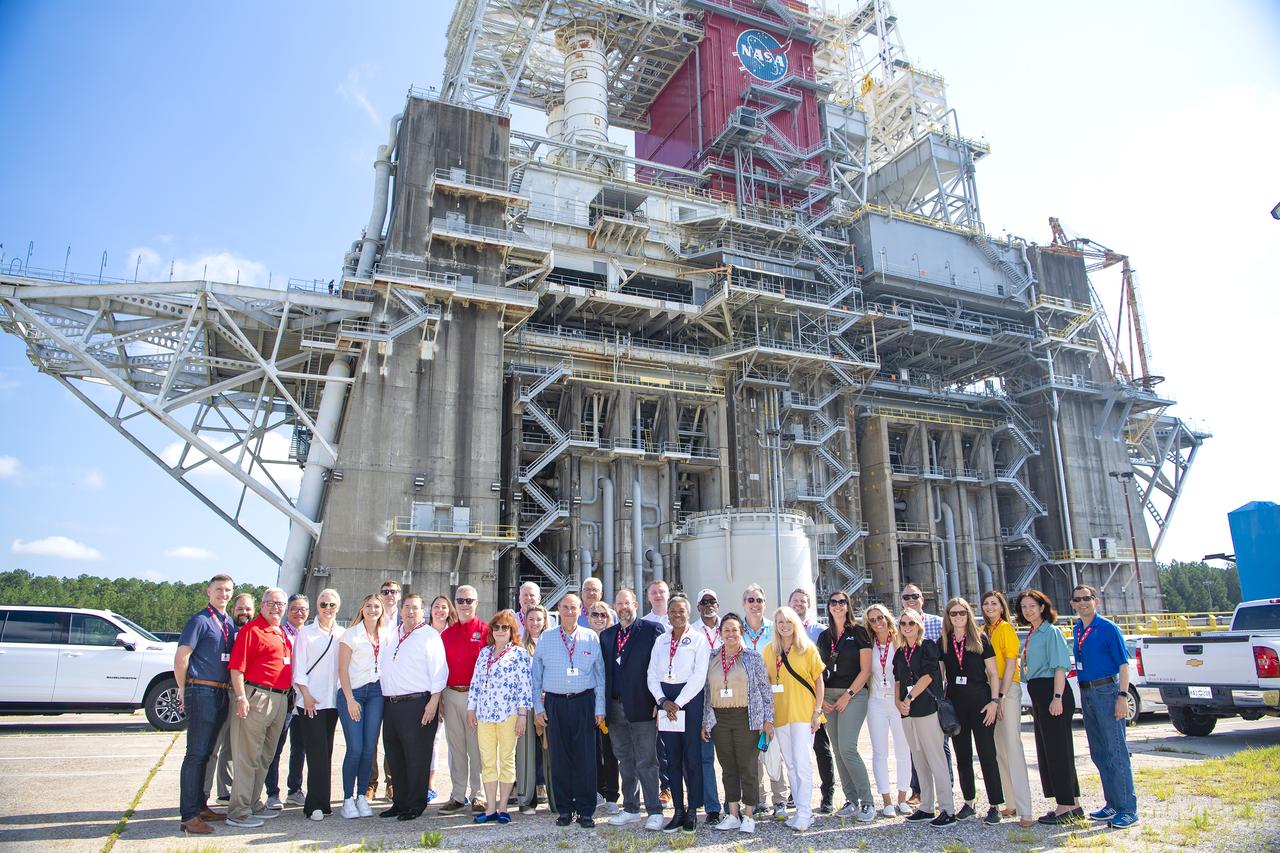

Members of the Aerospace States Association stand at the Thad Cochran Test Stand on June 25 during a visit to NASA’s Stennis Space Center. The group came to the south Mississippi NASA center during the Aerospace States Association conference in New Orleans June 24-27. NASA Stennis will use the Thad Cochran Test Stand (B-2) to test the exploration upper stage, a more powerful second stage to send the Orion spacecraft to deep space on NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket, ahead of its expected flight on the Artemis IV mission.
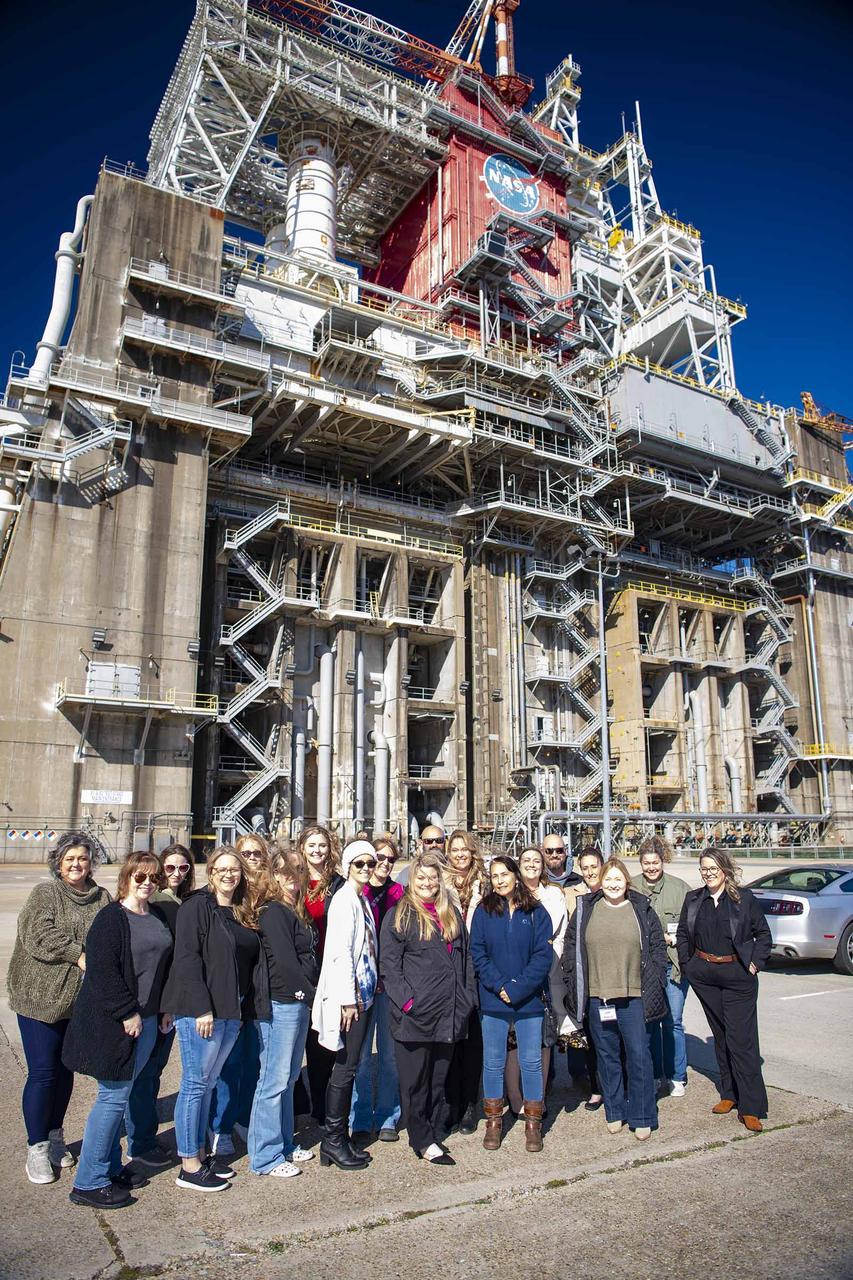

The Pearl River County Leadership Class visits the Thad Cochran Test Stand (B-1/B-2) during a NASA Stennis tour on Feb. 20. NASA Stennis is at the front end of the critical path for the future of human deep space exploration through NASA’s Artemis campaign. The B-2 side of the Thad Cochran Test Stand is undergoing preparations for exploration upper stage testing. The upper stage is scheduled to undergo Green Run tests of its integrated systems before its first flight on the Artemis IV mission. The test series will culminate with a hot fire of the stage’s four RL10 engines, just as during an actual mission.
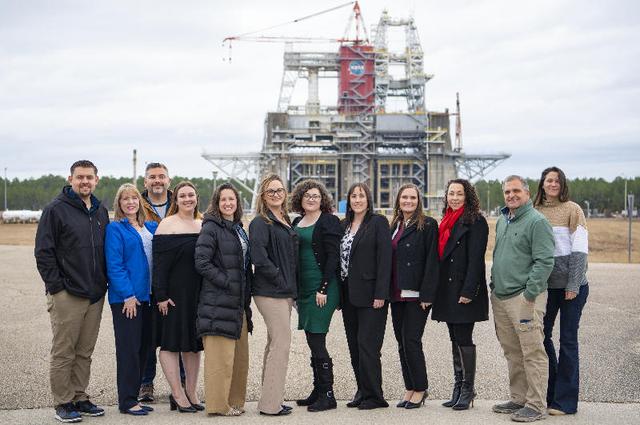

The Pearl River County Leadership Class stands in front of the Thad Cochran Test Stand during a NASA Stennis site tour on Jan. 18. The group learned about the RS-25 engine certification test series underway for future flights of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket and preparations for Green Run testing at the Thad Cochran Test Stand (B-2) for NASA’s Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) in support of the Artemis program. EUS is expected to fly on the Artemis IV mission. Prior to that time, it will undergo a series of integrated systems tests to demonstrate it is ready to fly. Through Artemis, NASA will send the first woman and first person of color to the Moon. The agency will use what is learned on and around the Moon to take the next giant leap – sending astronauts to Mars.
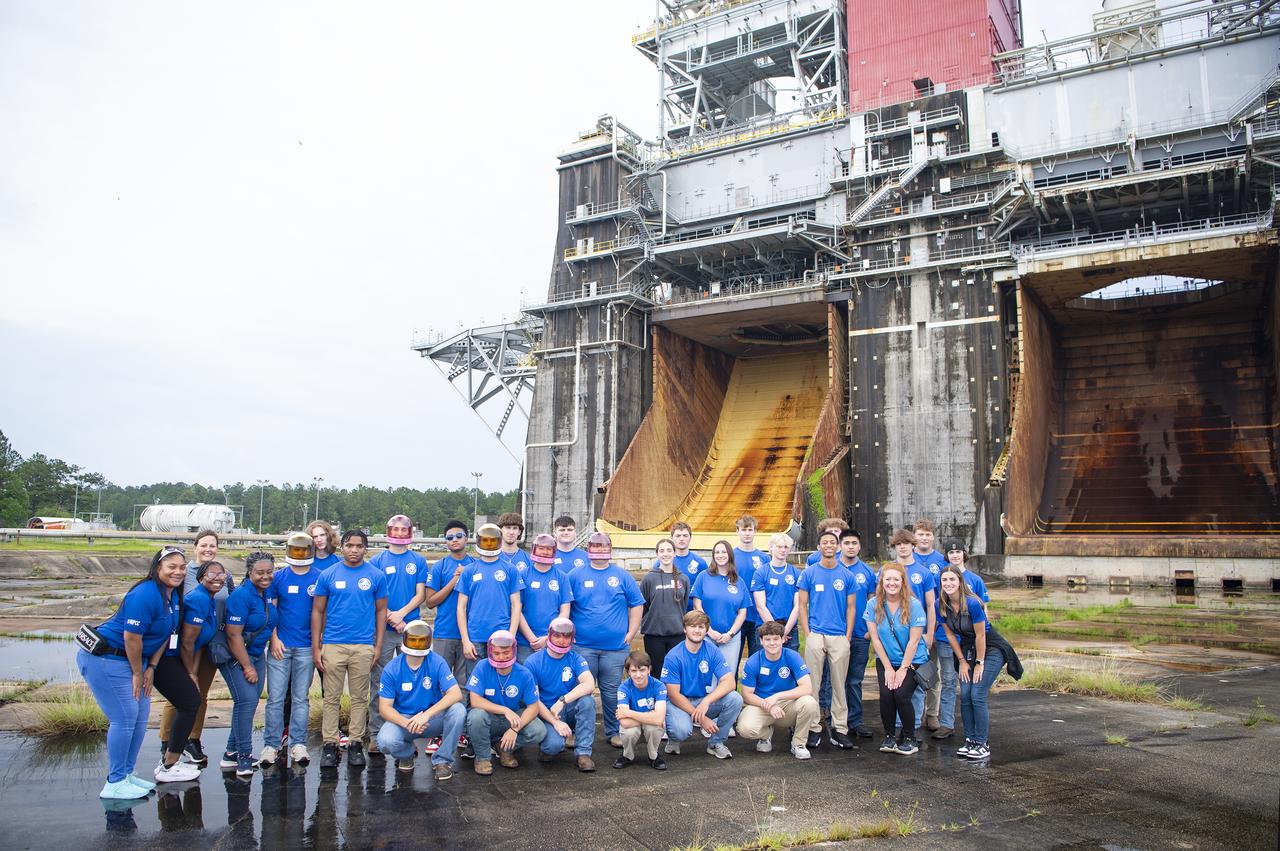

Rising high school juniors and seniors from Ascension Parish, Louisiana, visit the Thad Cochran Test Stand on June 6 during a tour of NASA’s Stennis Space Center. The students are part of the week-long BASF Tech Academy, in coordination with River Parishes Community College, where participants learn about technical careers and education. NASA Stennis is preparing the test stand to test the exploration upper stage, which will fly on future SLS (Space Launch System) missions as NASA continues its mission of exploring the secrets of the universe for the benefit of all. The upper stage is being built at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans as a more powerful second stage to send the Orion spacecraft to deep space. It is expected to fly on the Artemis IV mission. Before that, it will be installed on the Thad Cochran Test Stand (B-2) at NASA Stennis to undergo a series of Green Run tests of its integrated systems to demonstrate it is ready to fly.
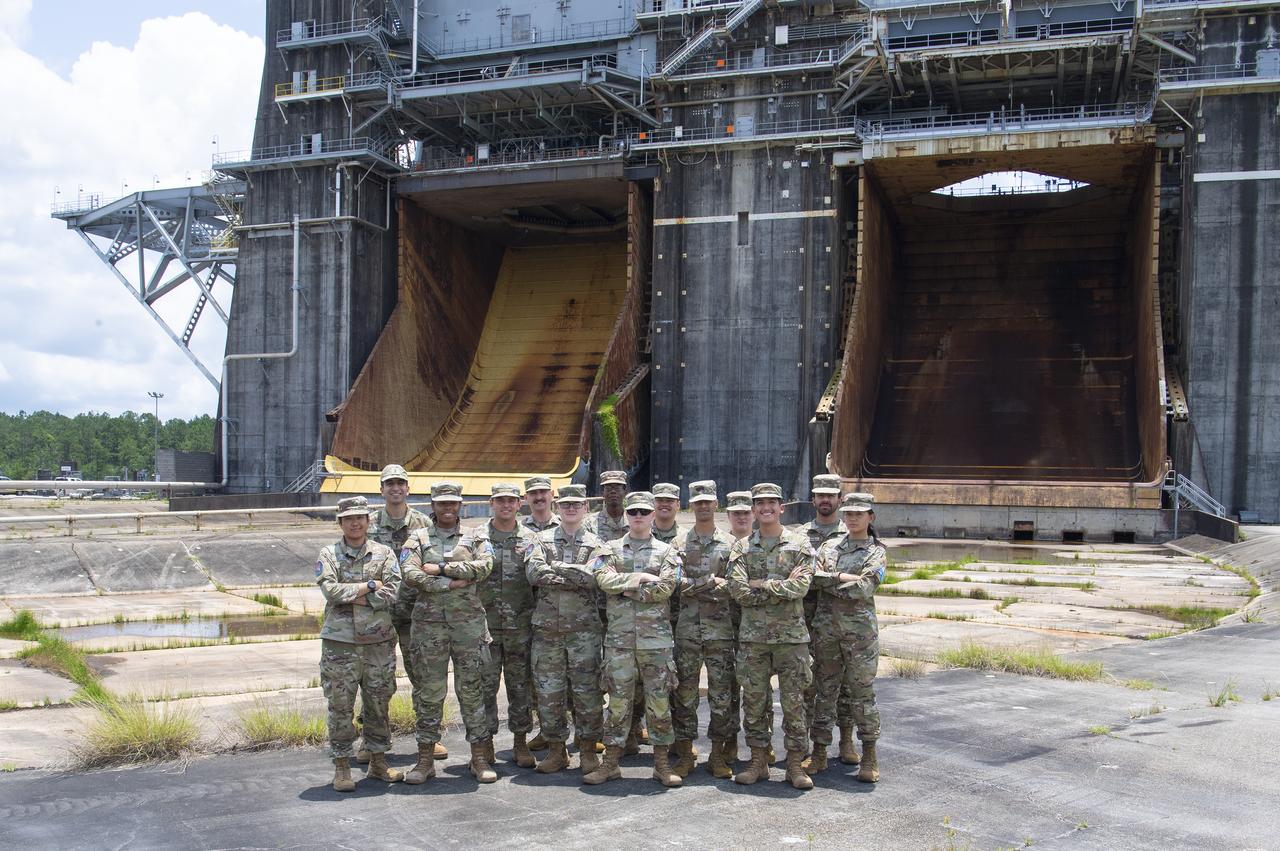

United States Space Force training students and professors stand at the Thad Cochran Test Stand on June 4 during a tour of NASA’s Stennis Space Center. NASA Stennis is preparing the test stand to test the exploration upper stage, which will fly on future SLS (Space Launch System) missions as NASA continues its mission of exploring the secrets of the universe for the benefit of all. The upper stage is being built at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans as a more powerful second stage to send the Orion spacecraft to deep space. It is expected to fly on the Artemis IV mission. Before that, it will be installed on the Thad Cochran Test Stand (B-2) at NASA Stennis to undergo a series of Green Run tests of its integrated systems to demonstrate it is ready to fly. The Space Force, established in 2019, organizes, trains, and equips personnel to protect U.S. and allied interests in space and to provide space capabilities to the joint forces.
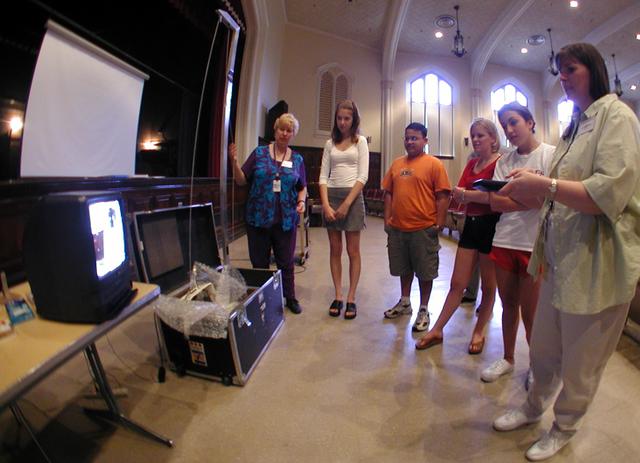

Marshall Space Flight Center employees visited DuPont Manual High School in Louisville, Kentucky. NASA's Mini Drop Tower was used to demonstrate free fall and a presentation was given on microgravity and the science performed in a microgravity environment. The visit coincided with the Pan-Pacific Basin Workshop on Microgravity Sciences held in Pasadena, California. Materials engineer Chris Cochrane explains the operation of the mini-drop tower. This image is from a digital still camera; higher resolution is not available.
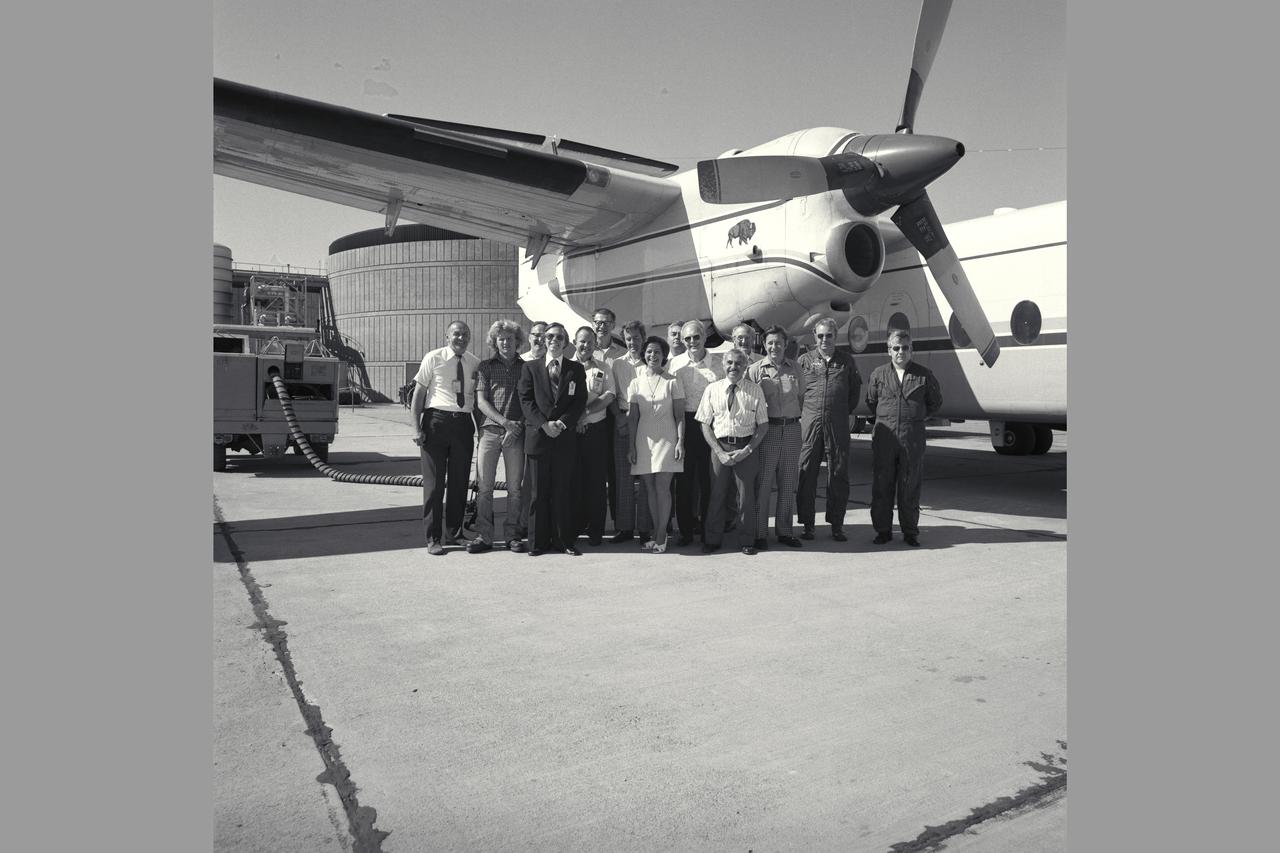

NASA SUPPORT GROUP (QSRA PROJECT TEAM). L-R: John Cochrane, Robert Price, Howard Tuner, Mike Shovlin, Dennis Riddle, Al Boissevain, Dennis Brown, Patty Beck, John Weyers, Bob McCracken, Peter Patterakis, Jack Ratcliff, Al Kass, Bob Innis, Tom Twiggs (Boeing). Note: Used in publication in Flight Research at Ames; 57 Years of Development and Validation of Aeronautical Technology NASA SP-1998-3300 fig. 111

Students from DuPont Manual High School in Louisville, Kentucky participated in a video-teleconference during the Pan-Pacific Basin Workshop on Microgravity Sciences held in Pasadena, California. The event originated at the California Science Center in Los Angeles. The DuPont Manual students patched in to the event through the distance learning lab at the Louisville Science Center. Education coordinator Twila Schneider (left) of Infinity Technology and NASA materials engineer Chris Cochrane prepare students for the on-line workshop. This image is from a digital still camera; higher resolution is not available.
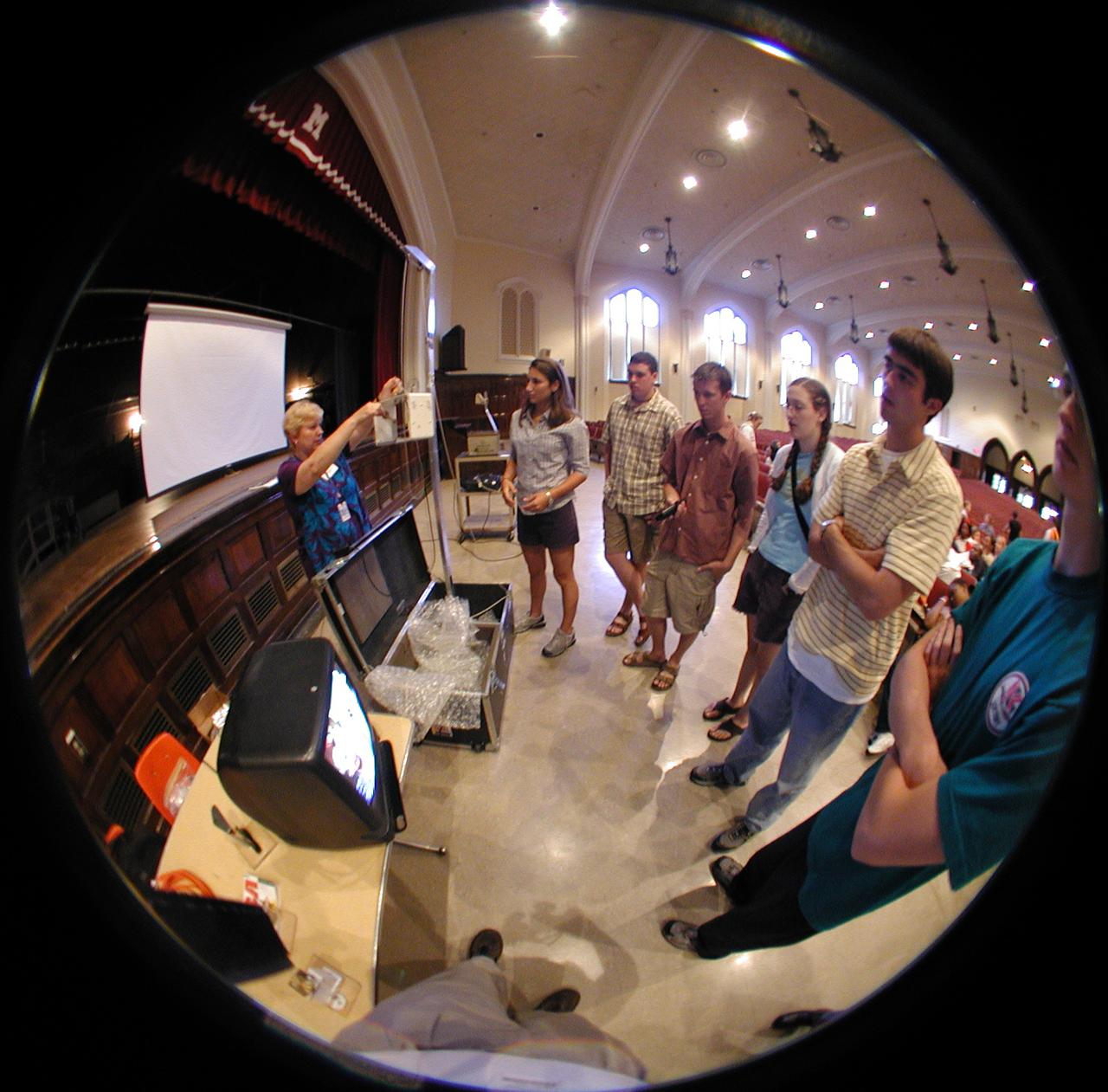

Marshall Space Flight Center employees visited DuPont Manual High School in Louisville, Kentucky. NASA's Mini Drop Tower was used to demonstrate free fall and a presentation was given on microgravity and the science performed in a microgravity environment. The visit coincided with the Pan-Pacific Basin Workshop on Microgravity Sciences held in Pasadena, California. Materials engineer Chris Cochrane explains the operation of the mini-drop tower. This image is from a digital still camera; higher resolution is not available.
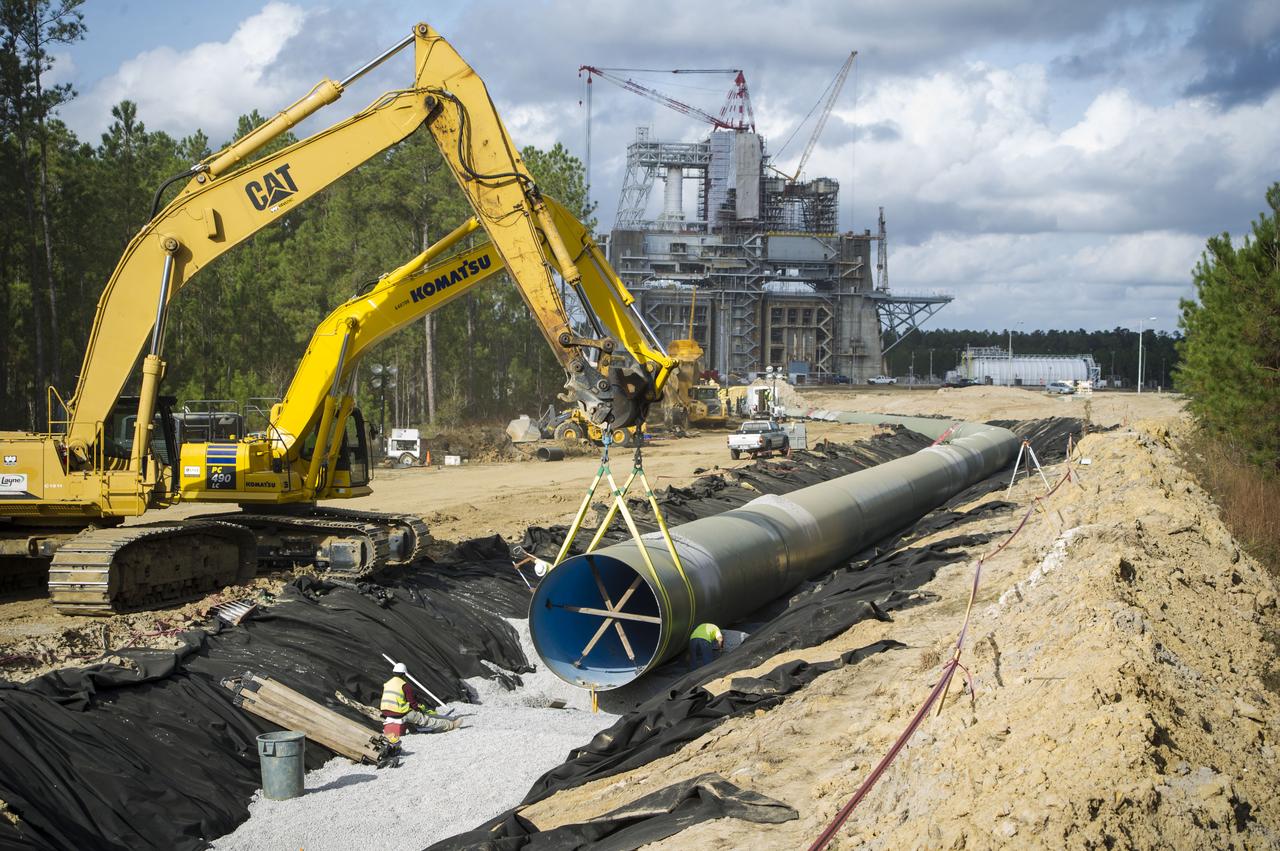

Water piping is installed near the Thad Cochran Test Stand (B-1/B-2) at NASA’s Stennis Space Center in December 2014. The project to replace and upgrade the center’s high pressure industrial water system was a key milestone in preparations to test the SLS (Space Launch System) core stage ahead of the successful Artemis I launch.
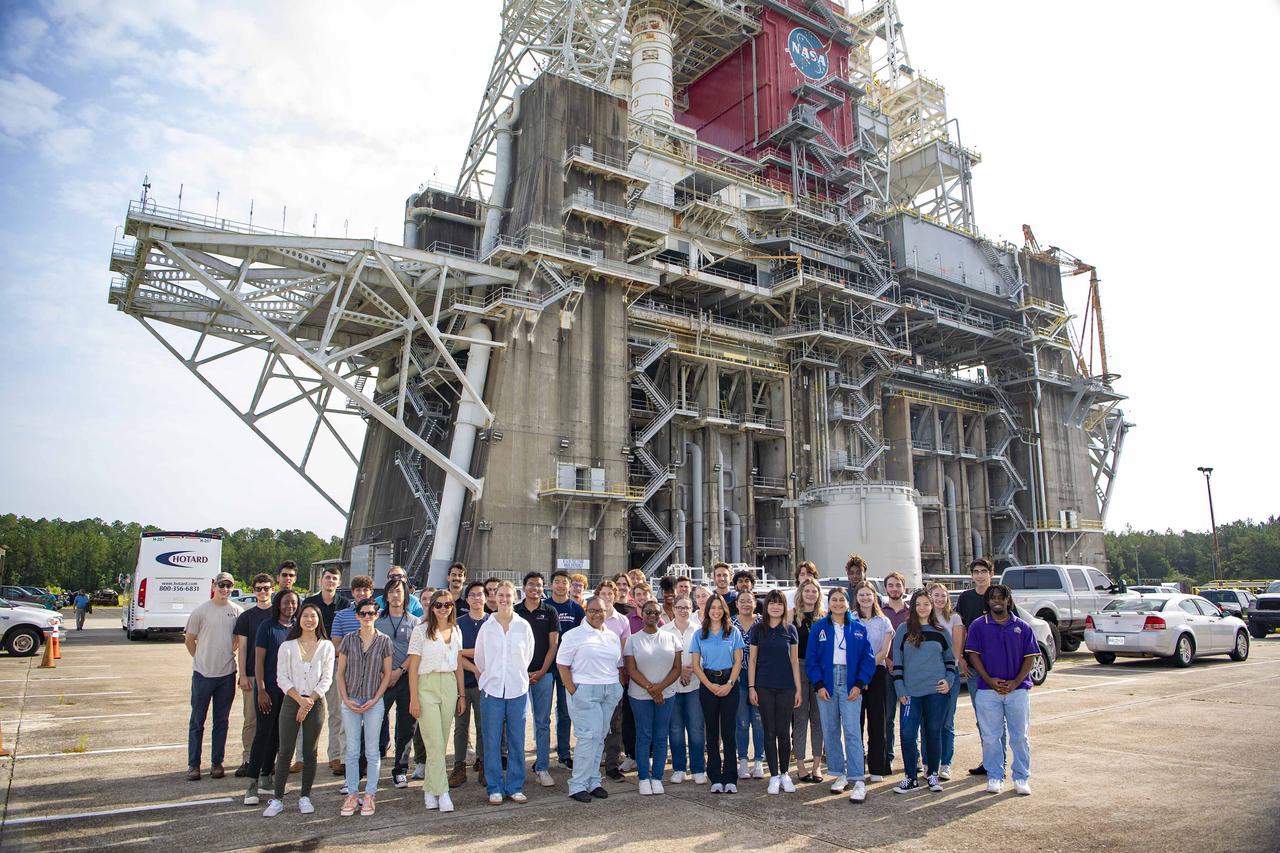

Interns at NASA Stennis visit the Thad Cochran Test Stand (B-1/B-2) on July 25 during a test complex tour on National Intern Day. As NASA continues to progress with the Artemis campaign, students across the nation are invited to join the journey. NASA’s internships aim to inspire the Artemis Generation to pursue STEM careers across the nation.
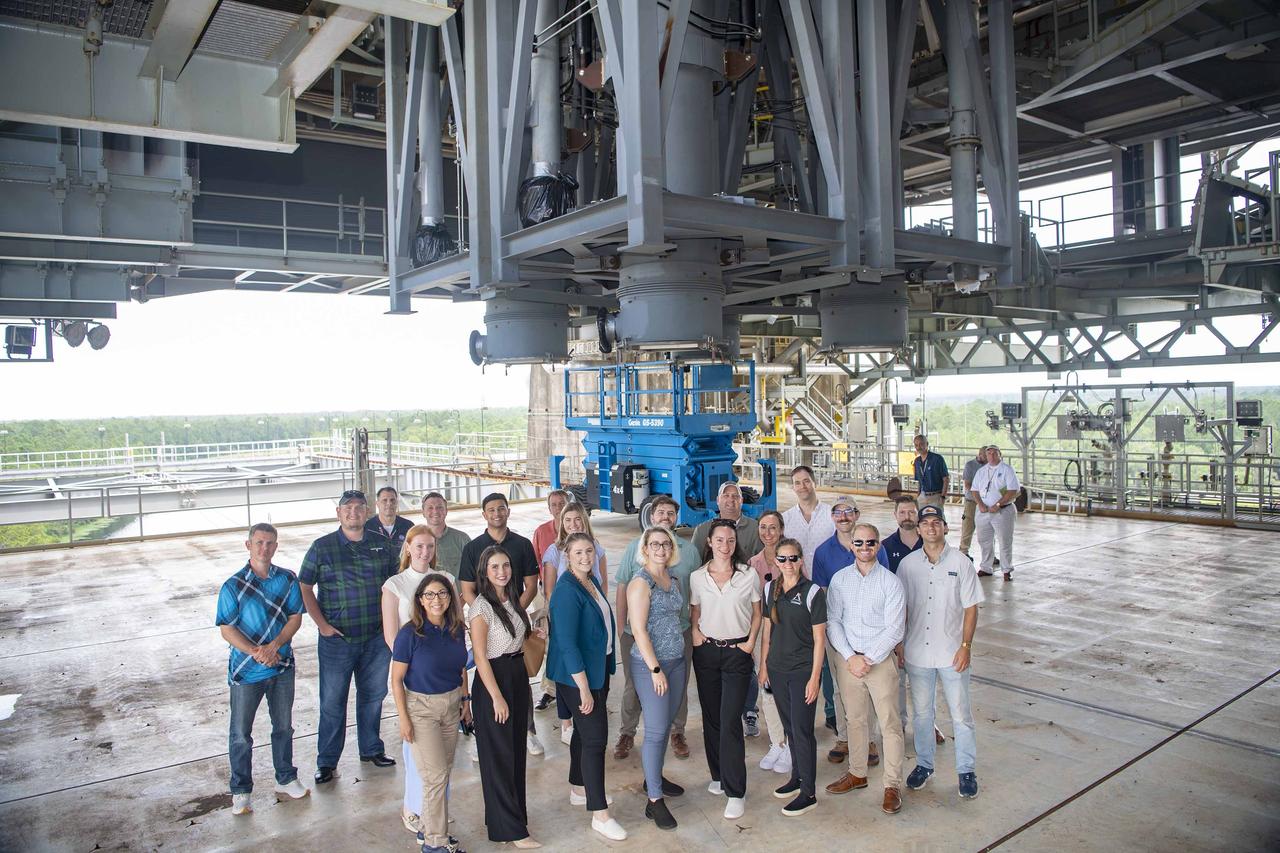

Congressional staff delegates representing eight states (Alabama, California, Colorado, Illinois, Louisiana, Maryland, New Jersey, and New York), along with NASA and U.S. Air Force representatives, tour the Thad Cochran Test Stand (B-2) at NASA Stennis on July 16. The visit provided an opportunity for the group to learn about propulsion test work carried out onsite by NASA and commercial companies.
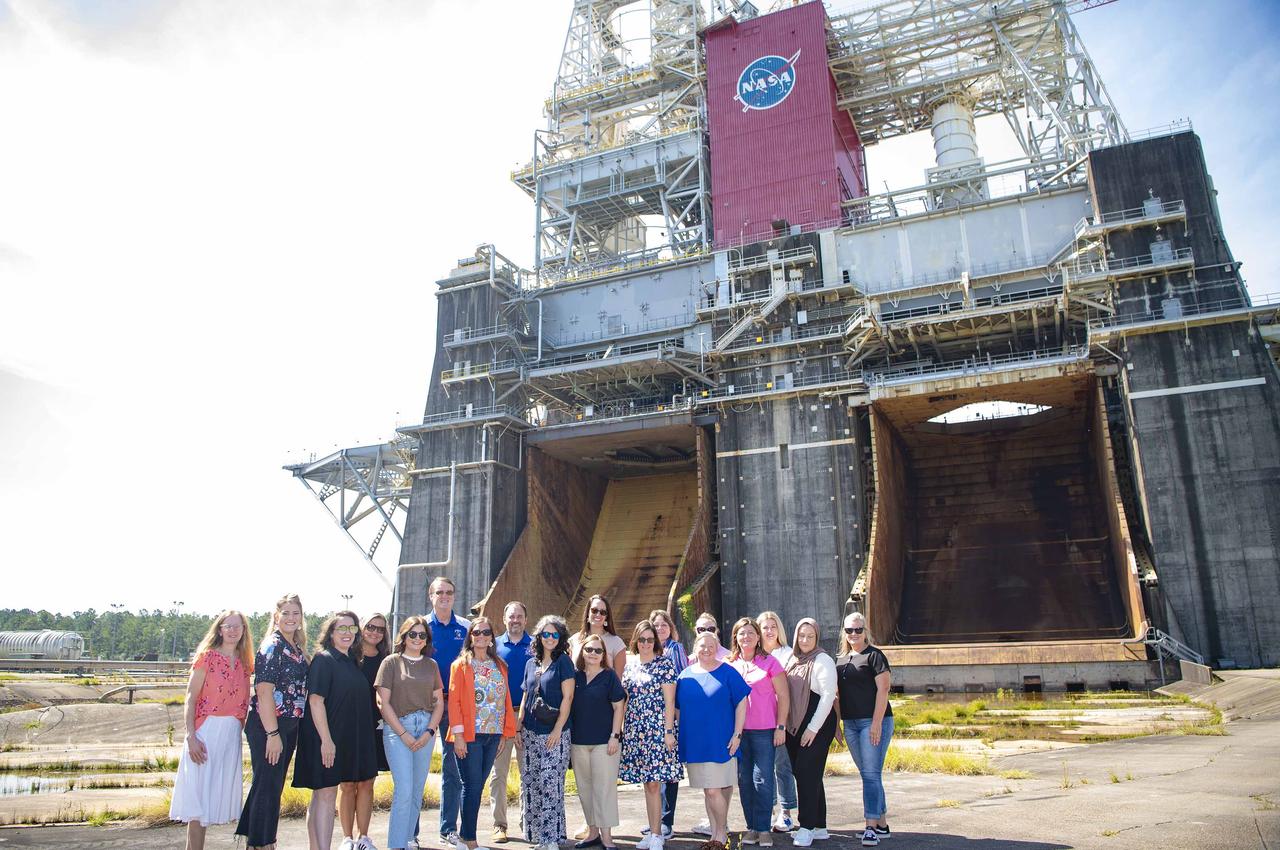

Pearl River County Elementary School leaders visit the Thad Cochran Test Stand (B-1/B-2) during a NASA Stennis tour on July 15. The school leaders received an overview of work conducted at NASA Stennis, including how the south Mississippi site is contributing to NASA’s return to the Moon through the Artemis campaign by testing engines and stages to help power the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket.

Marshall Space Flight Center employees visited DuPont Manual High School in Louisville, Kentucky. NASA's Mini Drop Tower was used to demonstrate free fall and a presentation was given on microgravity and the science performed in a microgravity environment. The visit coincided with the Pan-Pacific Basin Workshop on Microgravity Sciences held in Pasadena, California. Materials engineer Chris Cochrane explains the basics of microgravity research. This image is from a digital still camera; higher resolution is not available.

Representatives of NASA’s Space Flight Awareness Program are shown at the Thad Cochran Test Stand (B-1/B-2) on Sept. 25. The Space Flight Awareness program manager and working group had its annual meeting this year at NASA’s Stennis Space Center to review plans for 2025. NASA’s Space Flight Awareness Program recognizes outstanding job performances and contributions by civil servants and contract employees and focuses on excellence in quality and safety in support of human space flight.
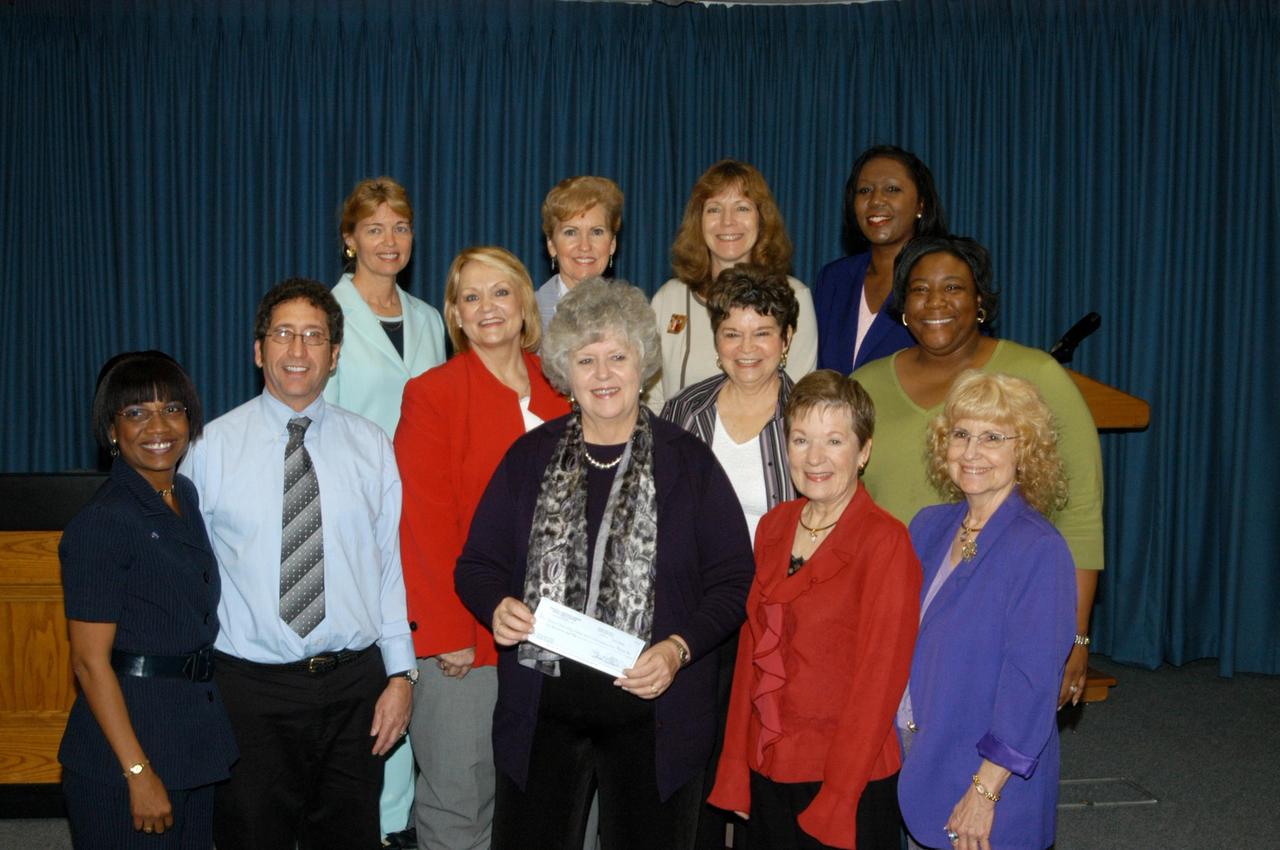

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Kieta Osteen-Cochrane (front center), executive director of the Institute for Business Training and Community Education at Brevard Community College, holds the check donated to BCC's WENDI program by the Federally Employed Women-Space Coast Chapter at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. The ceremony was held at Kennedy. Gathered for the presentation were (front row, left to right) Helen Kane, Richard Belton, Sandra Eliason, Osteen-Cochrane, Jean Grenville, Arden Belt, Charmel Anderson and Carolyn Burnham; (back row) Kathy Roberts, Connie Dobrin, Patty Boatman and Purvette Bryant. Eliason is president of FEW. The FEW scholarship committee, chaired by Helen Kane, and the chapter’s Board of Directors, recently voted to contribute their educational scholarship money for 2006 to the WENDI program. This donation amounts to $6,000. FEW organizes and sponsors conferences and seminars on issues pertinent to women that have benefited not only their members and women at Kennedy Space Center, but throughout all of Brevard.
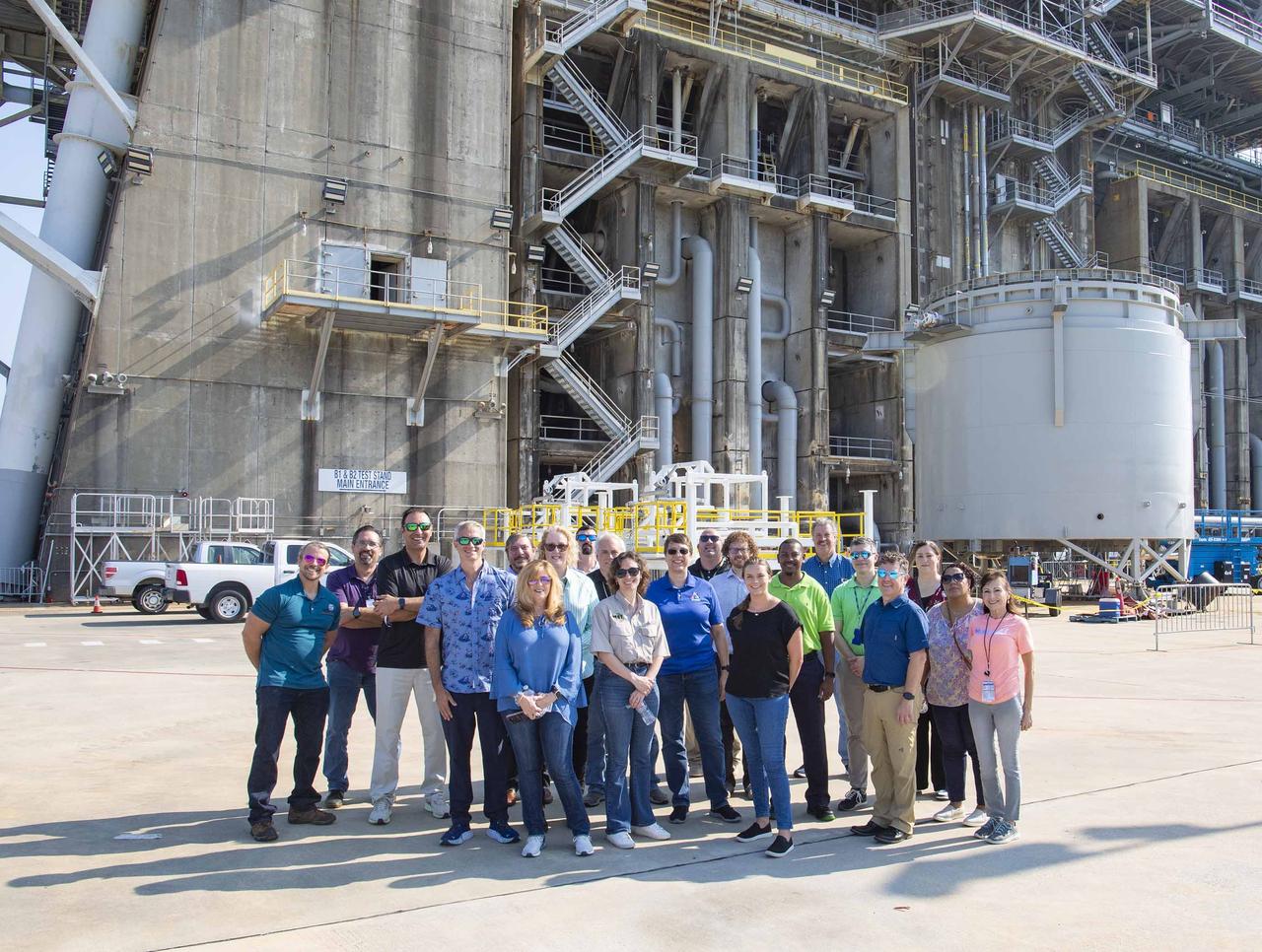

NASA and contractor representatives working with NASA’s Rocket Propulsion Test Program Office stand at the base of the Thad Cochran Test Stand during a tour of the test complex on Aug. 15 at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The program office hosted a Risk Workshop and Program Management Review meeting at NASA Stennis on Aug. 13-15. The representatives are from NASA Stennis; NASA’s Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky, Ohio; NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans; NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama; NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia; and NASA Headquarters in Washington. NASA Stennis is preparing the Thad Cochran Test Stand (B-2) to test the exploration upper stage, which will fly on future SLS (Space Launch System) missions as NASA continues its mission of exploring the secrets of the universe for the benefit of all. The upper stage is being built at NASA Michoud as a more powerful second stage to send the Orion spacecraft to deep space. It is expected to fly on the Artemis IV mission. Before that, it will be installed on the test stand at NASA Stennis to undergo a series of Green Run tests of its integrated systems to demonstrate it is ready to fly.
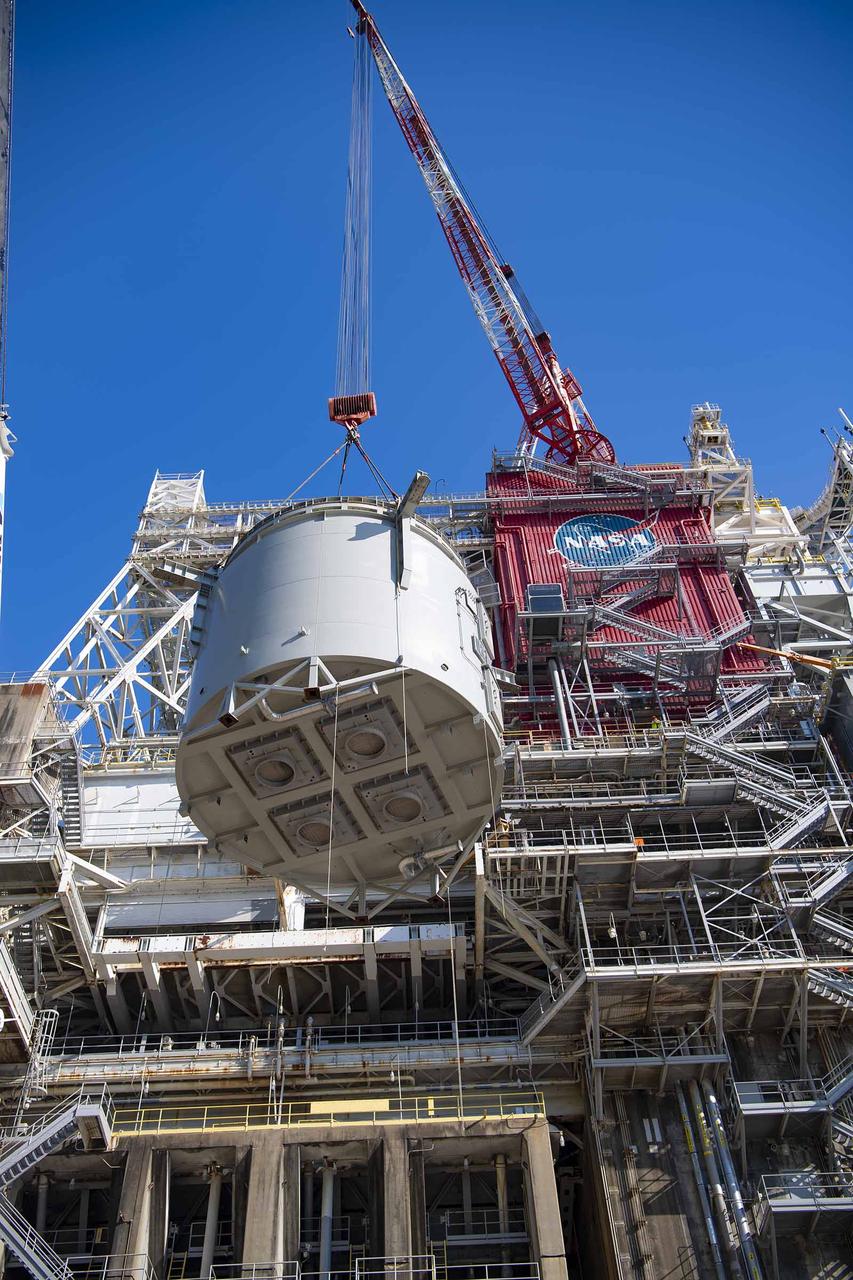

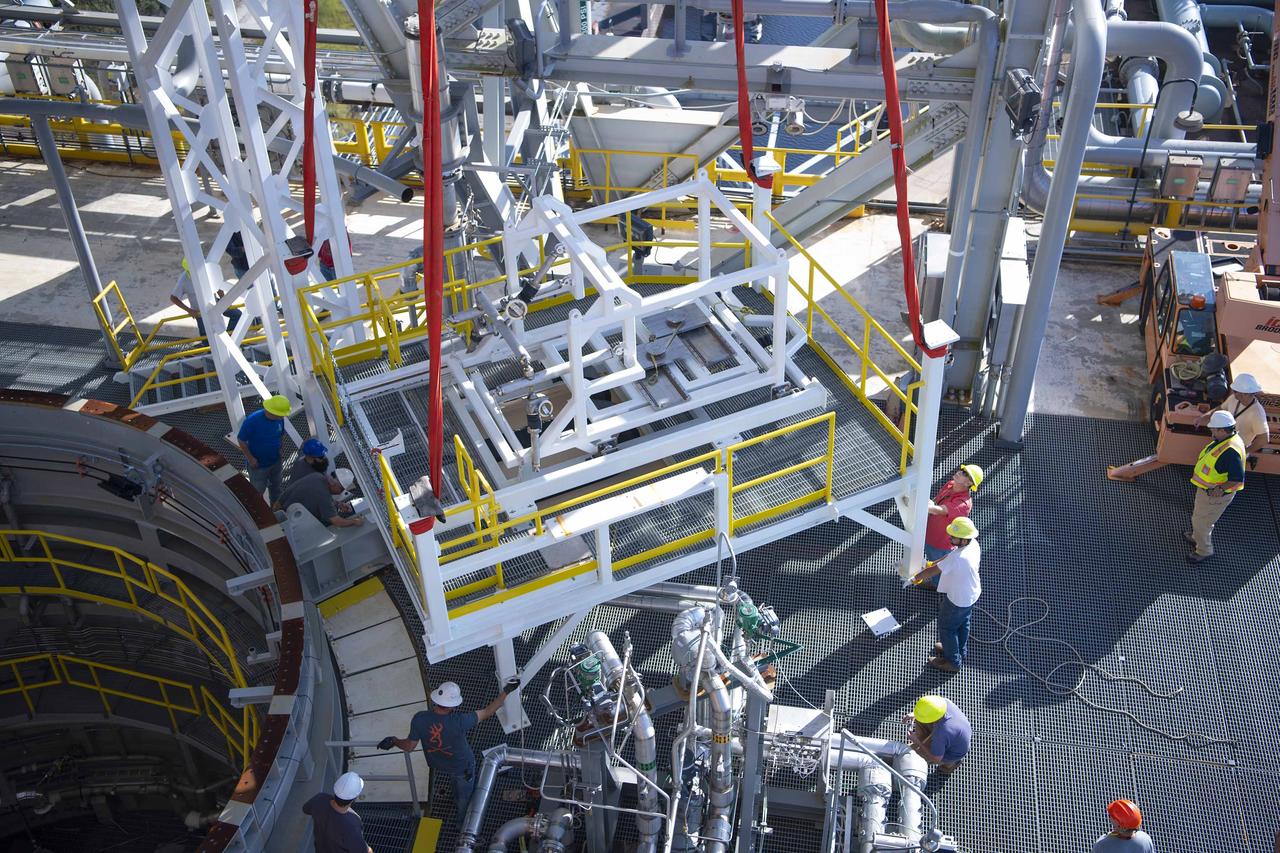
Teams at NASA’s Stennis Space Center complete a safe lift and install of an interstage simulator unit needed for future testing of NASA’s exploration upper stage (EUS) in the B-2 position of the Thad Cochran Test Stand. The lift and install, completed over a two-week period that began Oct. 10, marks a milestone for testing the new SLS (Space Launch System) rocket stage that will fly on future Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond. The EUS will undergo a series of Green Run tests of its integrated systems prior to its first flight. During testing, the interstage simulator component will function like the SLS interstage section that helps protect the upper stage during Artemis launches.
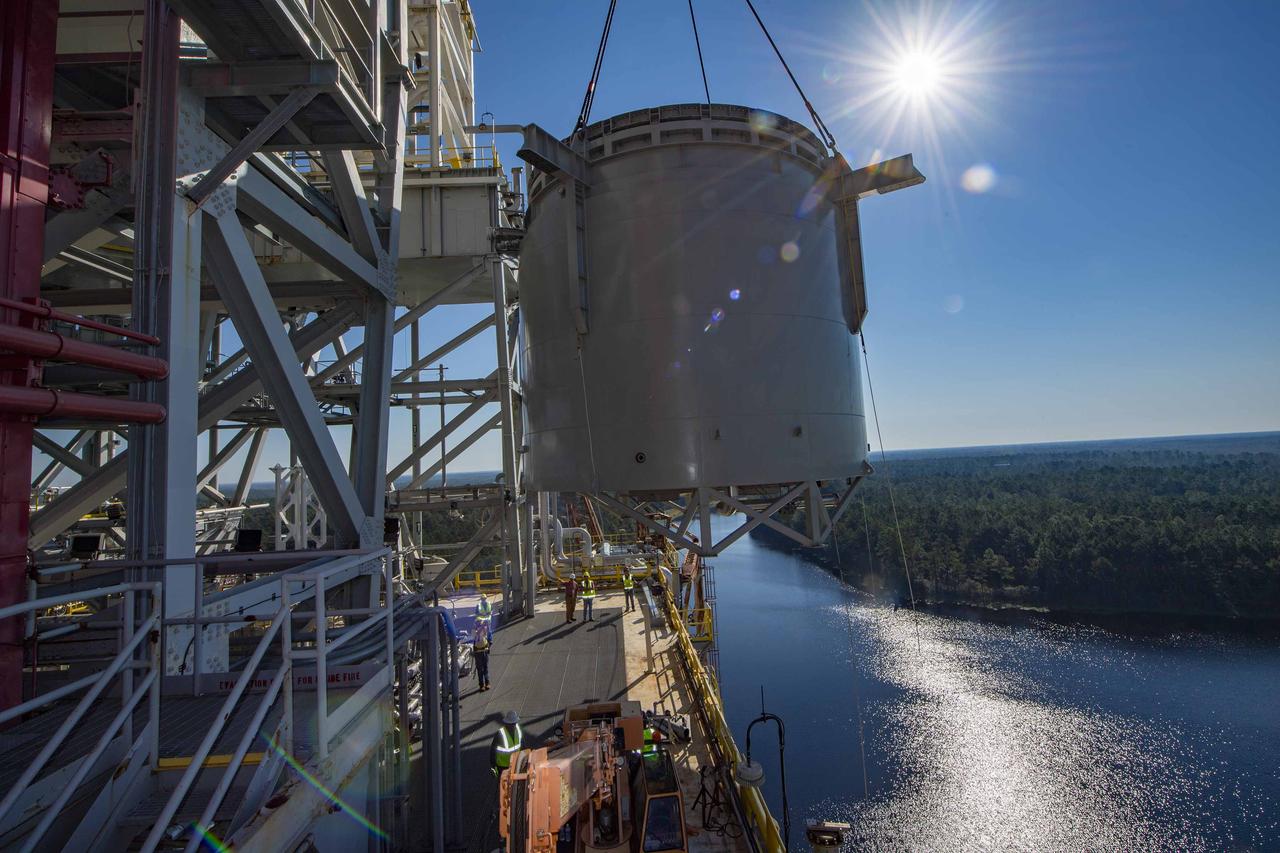

Teams at NASA’s Stennis Space Center complete a safe lift and install of an interstage simulator unit needed for future testing of NASA’s exploration upper stage (EUS) in the B-2 position of the Thad Cochran Test Stand. The lift and install, completed over a two-week period that began Oct. 10, marks a milestone for testing the new SLS (Space Launch System) rocket stage that will fly on future Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond. The EUS will undergo a series of Green Run tests of its integrated systems prior to its first flight. During testing, the interstage simulator component will function like the SLS interstage section that helps protect the upper stage during Artemis launches.
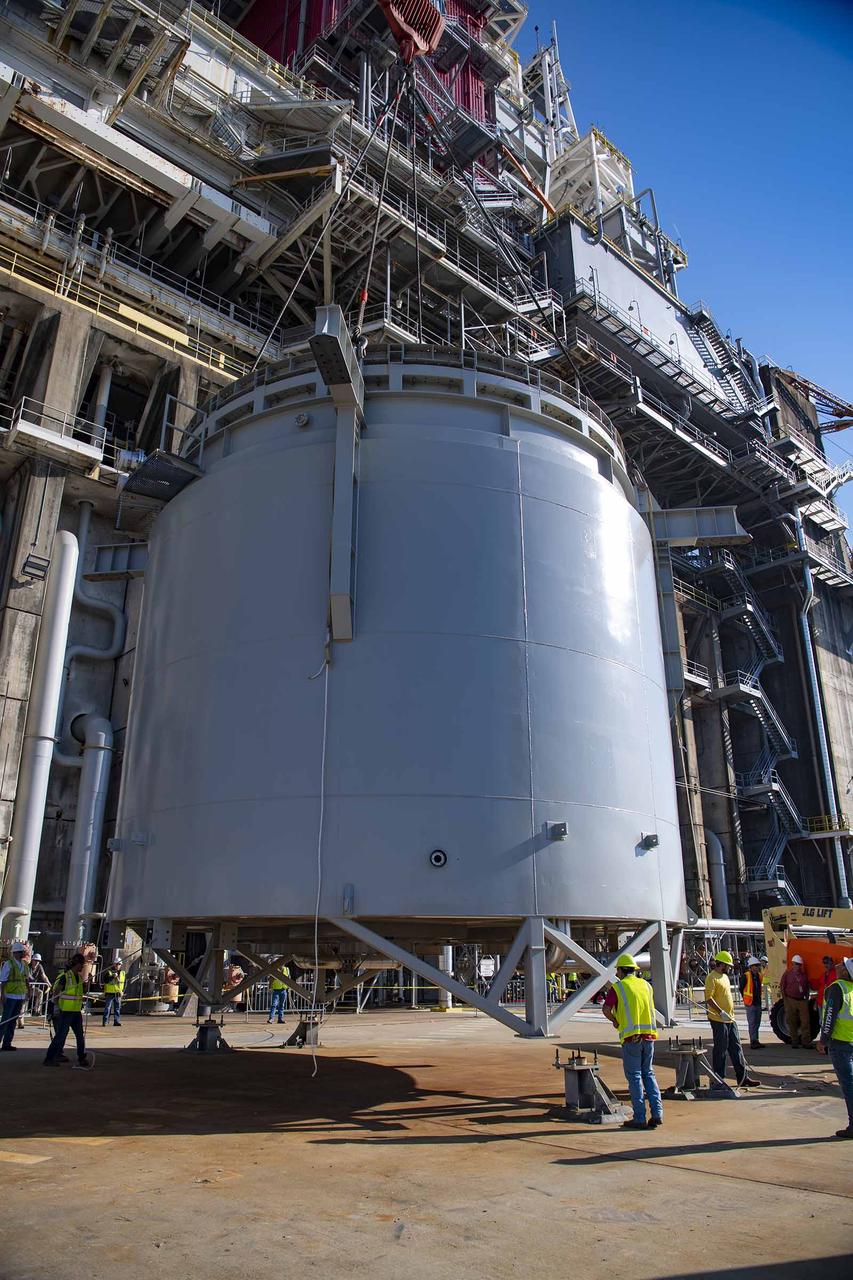

Teams at NASA’s Stennis Space Center complete a safe lift and install of an interstage simulator unit needed for future testing of NASA’s exploration upper stage (EUS) in the B-2 position of the Thad Cochran Test Stand. The lift and install, completed over a two-week period that began Oct. 10, marks a milestone for testing the new SLS (Space Launch System) rocket stage that will fly on future Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond. The EUS will undergo a series of Green Run tests of its integrated systems prior to its first flight. During testing, the interstage simulator component will function like the SLS interstage section that helps protect the upper stage during Artemis launches.
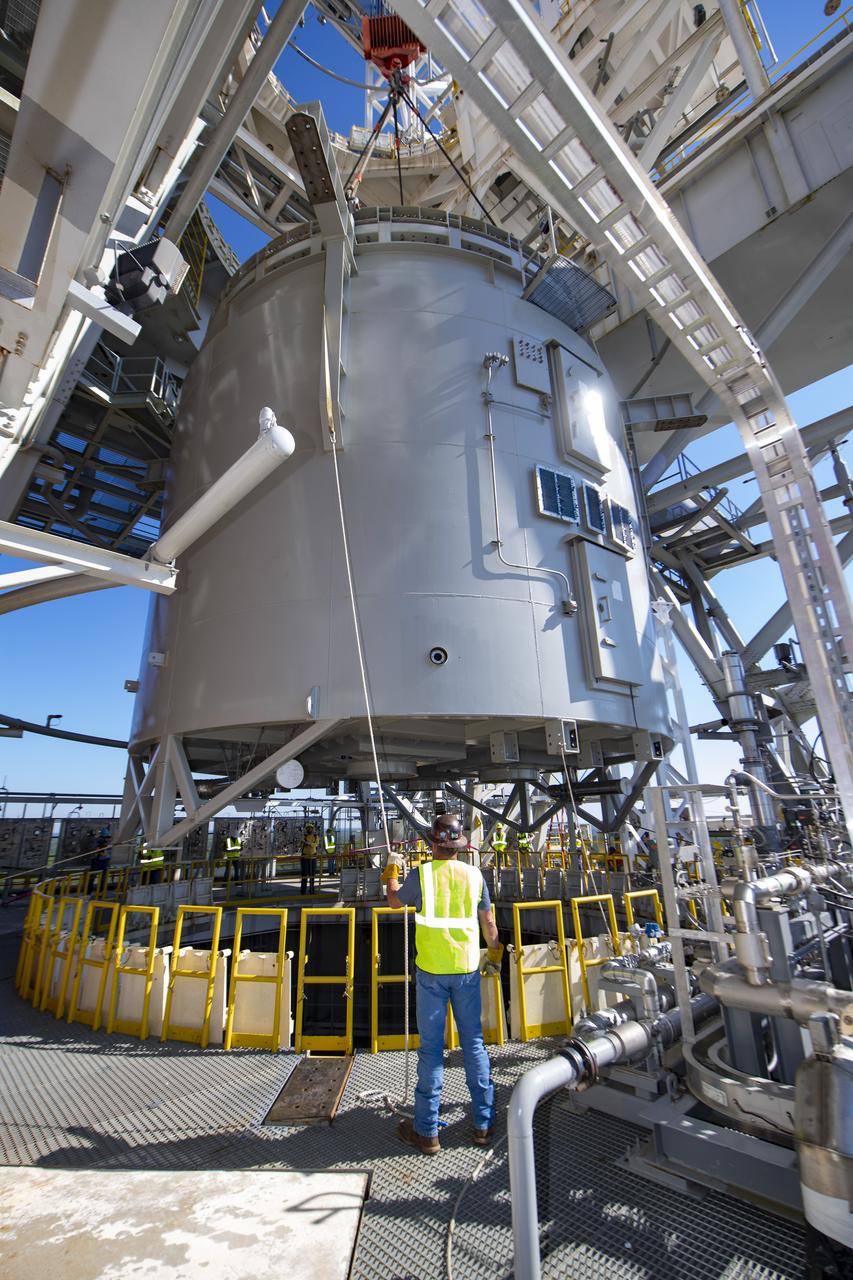

Teams at NASA’s Stennis Space Center complete a safe lift and install of an interstage simulator unit needed for future testing of NASA’s exploration upper stage (EUS) in the B-2 position of the Thad Cochran Test Stand. The lift and install, completed over a two-week period that began Oct. 10, marks a milestone for testing the new SLS (Space Launch System) rocket stage that will fly on future Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond. The EUS will undergo a series of Green Run tests of its integrated systems prior to its first flight. During testing, the interstage simulator component will function like the SLS interstage section that helps protect the upper stage during Artemis launches.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Kieta Osteen-Cochrane (left), executive director of the Institute for Business Training and Community Education at Brevard Community College, accepts a check for the WENDI program from Sandra Eliason, president of the Federally Employed Women-Space Coast Chapter at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. The FEW scholarship committee, chaired by Helen Kane, and the chapter’s Board of Directors, recently voted to contribute their educational scholarship money for 2006 to the WENDI program. This donation amounts to $6,000. FEW organizes and sponsors conferences and seminars on issues pertinent to women that have benefited not only their members and women at Kennedy Space Center, but throughout all of Brevard. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton

Members of the Florida A&M University Program of Excellence in STEM attend a presentation June 21 during a visit to NASA’s Stennis Space Center. The NASA Office of STEM Engagement provided information on grants and student activities during the presentation about NASA Stennis and the work conducted at the unique federal city. The group also visited the Thad Cochran Test Stand and Relativity Space test complex during a site tour. The Program of Excellence in STEM summer academy aims to enhance student knowledge of opportunities in the fields of science, technology, engineering, and mathematics.
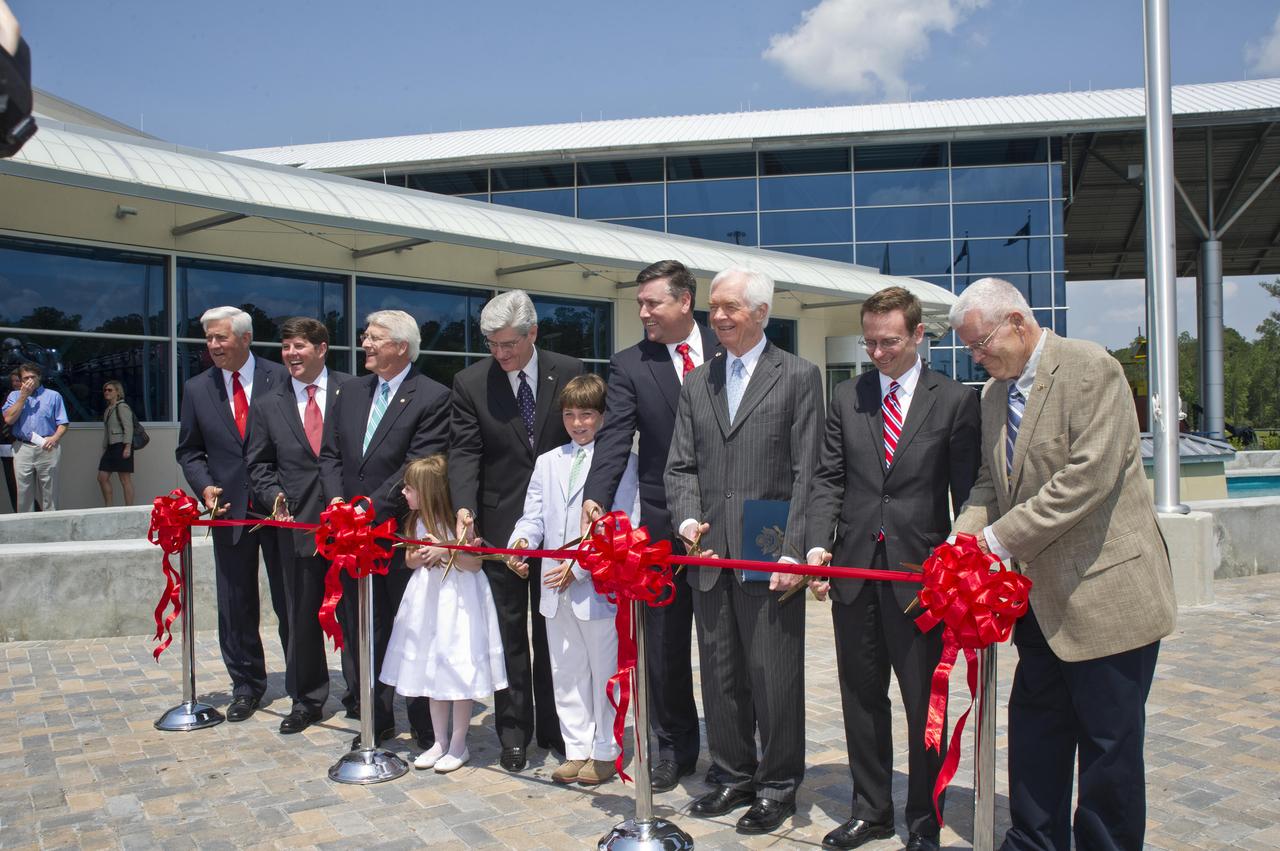

Ceremony participants prepare to cut the ribbon on the INFINITY at NASA Stennis Space Center facility April 11, 2012. Participating in the ceremony were (l to r): Gulfport Mayor and INFINITY Science Center Inc. Chairman George Schloegel; U.S. Rep. Steven Palazzo, R-Miss.; U.S. Sen. Roger Wicker, R-Miss.; Roy S. Estess granddaughter Lauren McKay; Mississippi Gov. Phil Bryant; Leo Seal Jr. grandson Leo Seal IV; Stennis Director Patrick Scheuermann; U.S. Sen. Thad Cochran, R-Miss.; NASA Chief of Staff David Radzanowski; and Apollo 13 astronaut and INFINITY Science Center Inc. Vice Chairman Fred Haise.
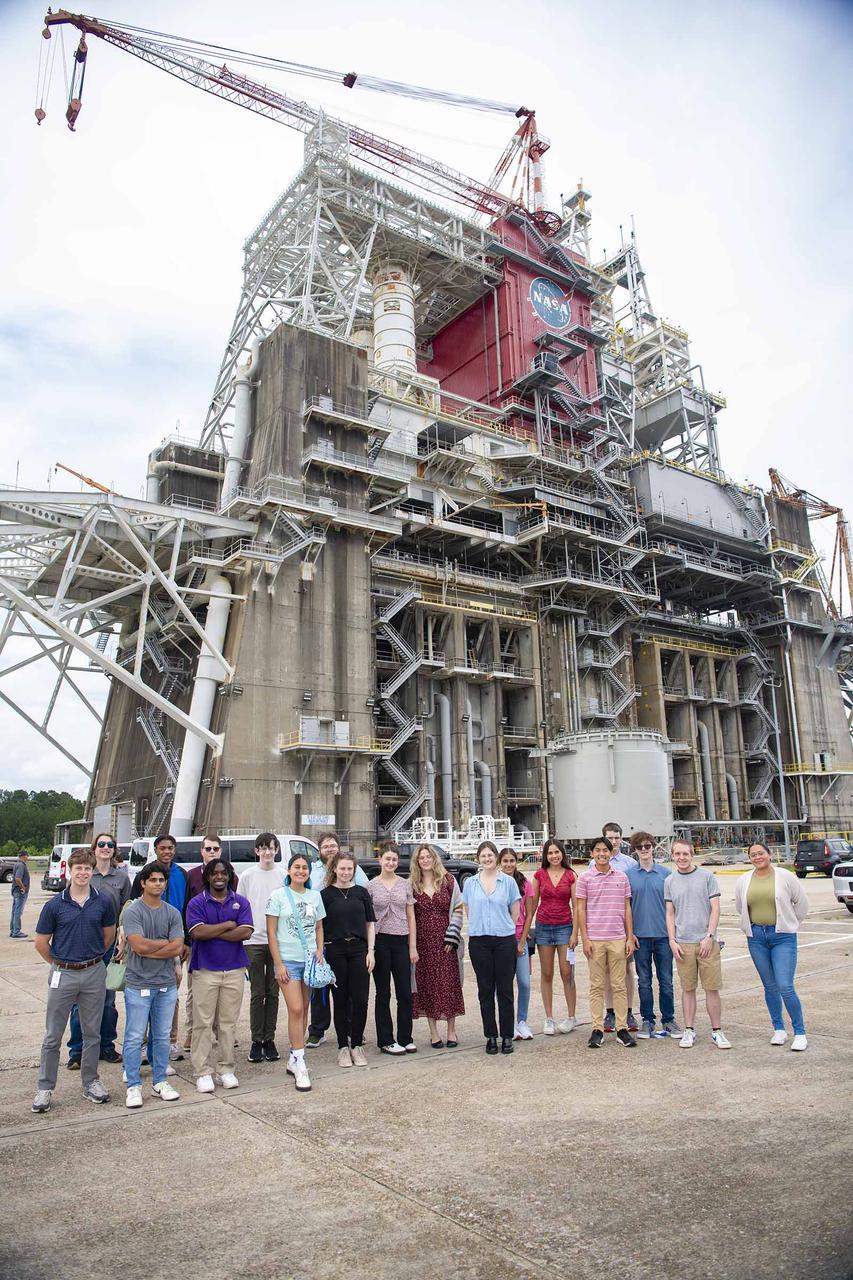

Summer interns with the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory stand in front of the Thad Cochran Test Stand (B-1/B-2) on July 10. NASA Stennis crews are preparing the B-2 side of the stand for future testing of NASA’s exploration upper stage. The more powerful second stage is expected to fly on NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for Artemis IV. The Naval Research Laboratory interns visited the stand during an afternoon tour of NASA Stennis. The Naval Research Laboratory is a tenant of the NASA Stennis federal city, where it provides advanced scientific capabilities required to bolster the nation’s position of global naval leadership.
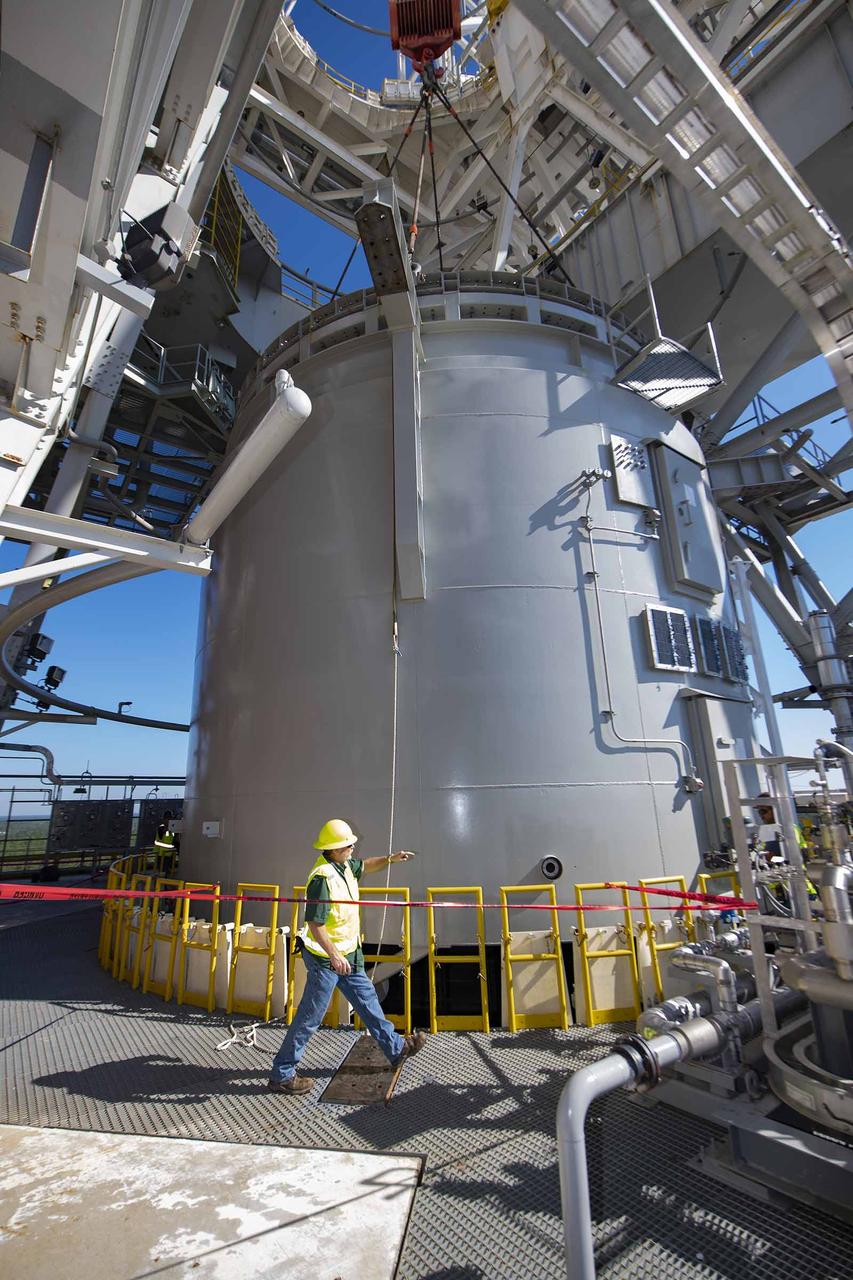

Teams at NASA’s Stennis Space Center complete a safe lift and install of an interstage simulator unit needed for future testing of NASA’s exploration upper stage (EUS) in the B-2 position of the Thad Cochran Test Stand. The lift and install, completed over a two-week period that began Oct. 10, marks a milestone for testing the new SLS (Space Launch System) rocket stage that will fly on future Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond. The EUS will undergo a series of Green Run tests of its integrated systems prior to its first flight. During testing, the interstage simulator component will function like the SLS interstage section that helps protect the upper stage during Artemis launches.
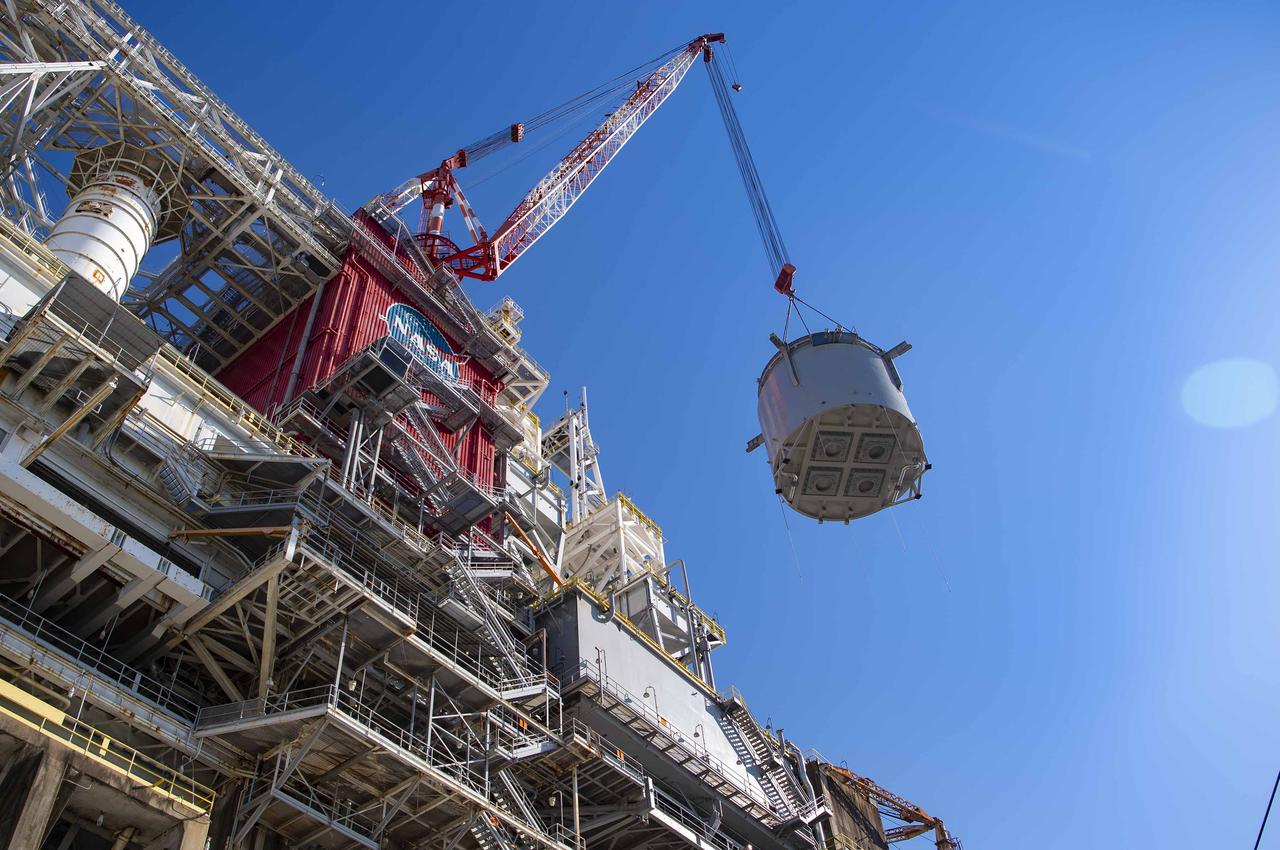

Teams at NASA’s Stennis Space Center complete a safe lift and install of an interstage simulator unit needed for future testing of NASA’s exploration upper stage (EUS) in the B-2 position of the Thad Cochran Test Stand. The lift and install, completed over a two-week period that began Oct. 10, marks a milestone for testing the new SLS (Space Launch System) rocket stage that will fly on future Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond. The EUS will undergo a series of Green Run tests of its integrated systems prior to its first flight. During testing, the interstage simulator component will function like the SLS interstage section that helps protect the upper stage during Artemis launches.
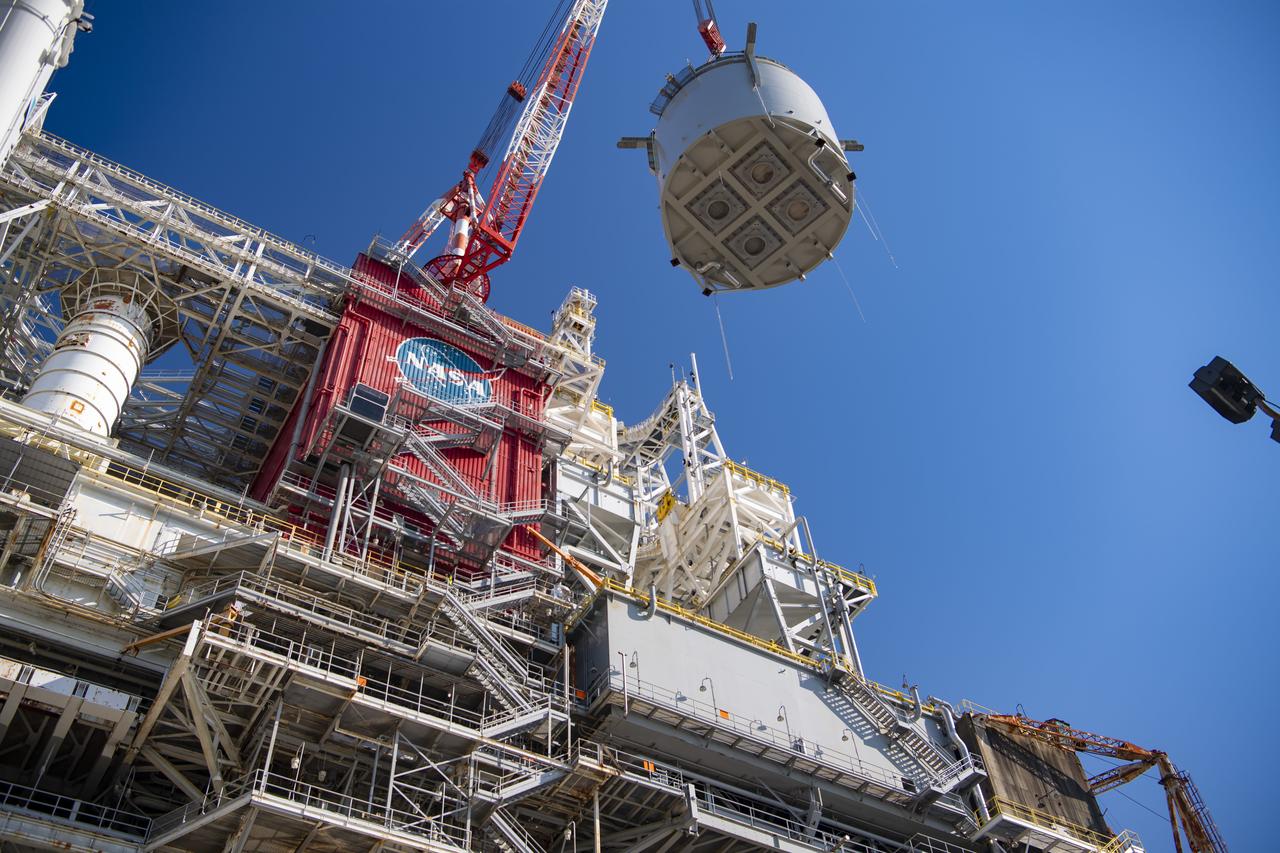

Teams at NASA’s Stennis Space Center complete a safe lift and install of an interstage simulator unit needed for future testing of NASA’s exploration upper stage (EUS) in the B-2 position of the Thad Cochran Test Stand. The lift and install, completed over a two-week period that began Oct. 10, marks a milestone for testing the new SLS (Space Launch System) rocket stage that will fly on future Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond. The EUS will undergo a series of Green Run tests of its integrated systems prior to its first flight. During testing, the interstage simulator component will function like the SLS interstage section that helps protect the upper stage during Artemis launches.
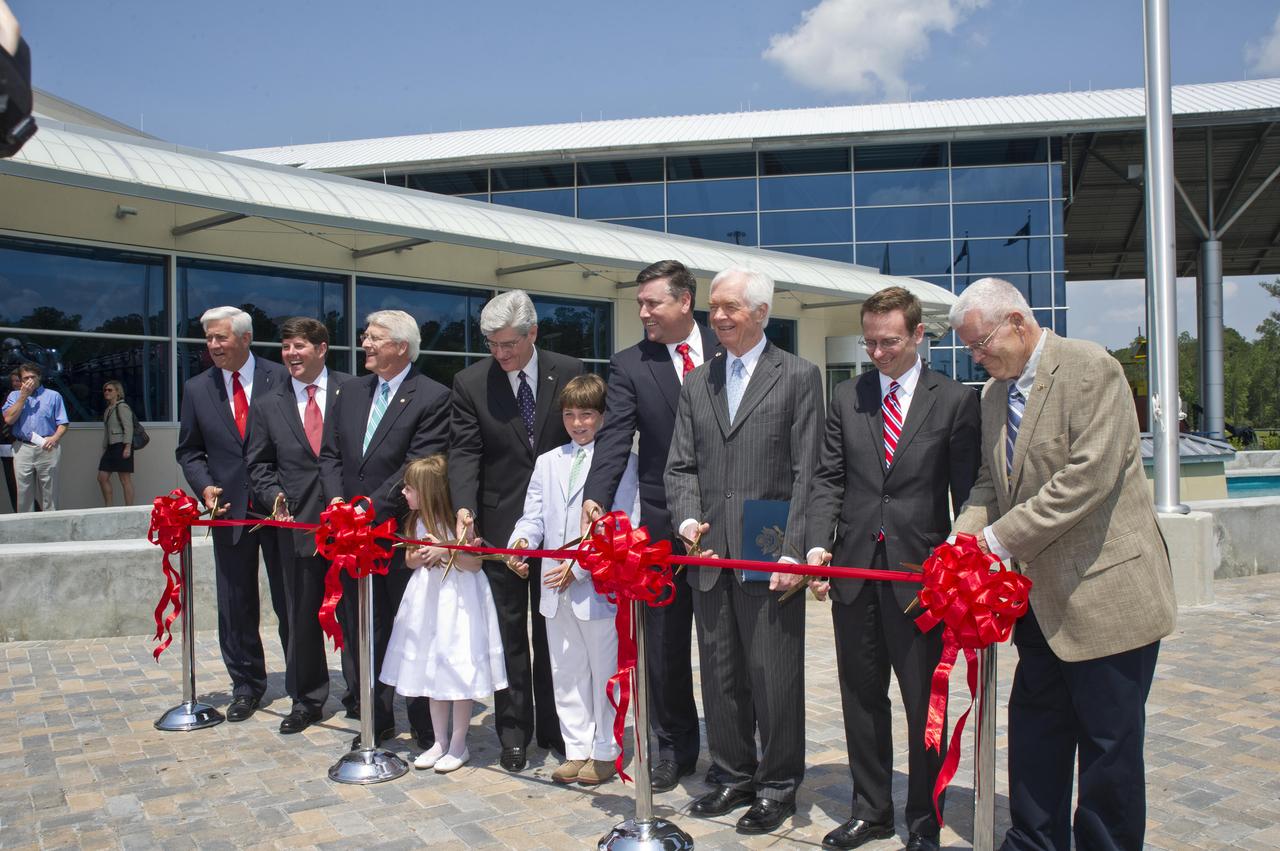

Ceremony participants prepare to cut the ribbon on the INFINITY at NASA Stennis Space Center facility April 11, 2012. Participating in the ceremony were (l to r): Gulfport Mayor and INFINITY Science Center Inc. Chairman George Schloegel; U.S. Rep. Steven Palazzo, R-Miss.; U.S. Sen. Roger Wicker, R-Miss.; Roy S. Estess granddaughter Lauren McKay; Mississippi Gov. Phil Bryant; Leo Seal Jr. grandson Leo Seal IV; Stennis Director Patrick Scheuermann; U.S. Sen. Thad Cochran, R-Miss.; NASA Chief of Staff David Radzanowski; and Apollo 13 astronaut and INFINITY Science Center Inc. Vice Chairman Fred Haise.

Teams at NASA’s Stennis Space Center complete a safe lift and install of an interstage simulator unit needed for future testing of NASA’s exploration upper stage (EUS) in the B-2 position of the Thad Cochran Test Stand. The lift and install, completed over a two-week period that began Oct. 10, marks a milestone for testing the new SLS (Space Launch System) rocket stage that will fly on future Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond. The EUS will undergo a series of Green Run tests of its integrated systems prior to its first flight. During testing, the interstage simulator component will function like the SLS interstage section that helps protect the upper stage during Artemis launches.
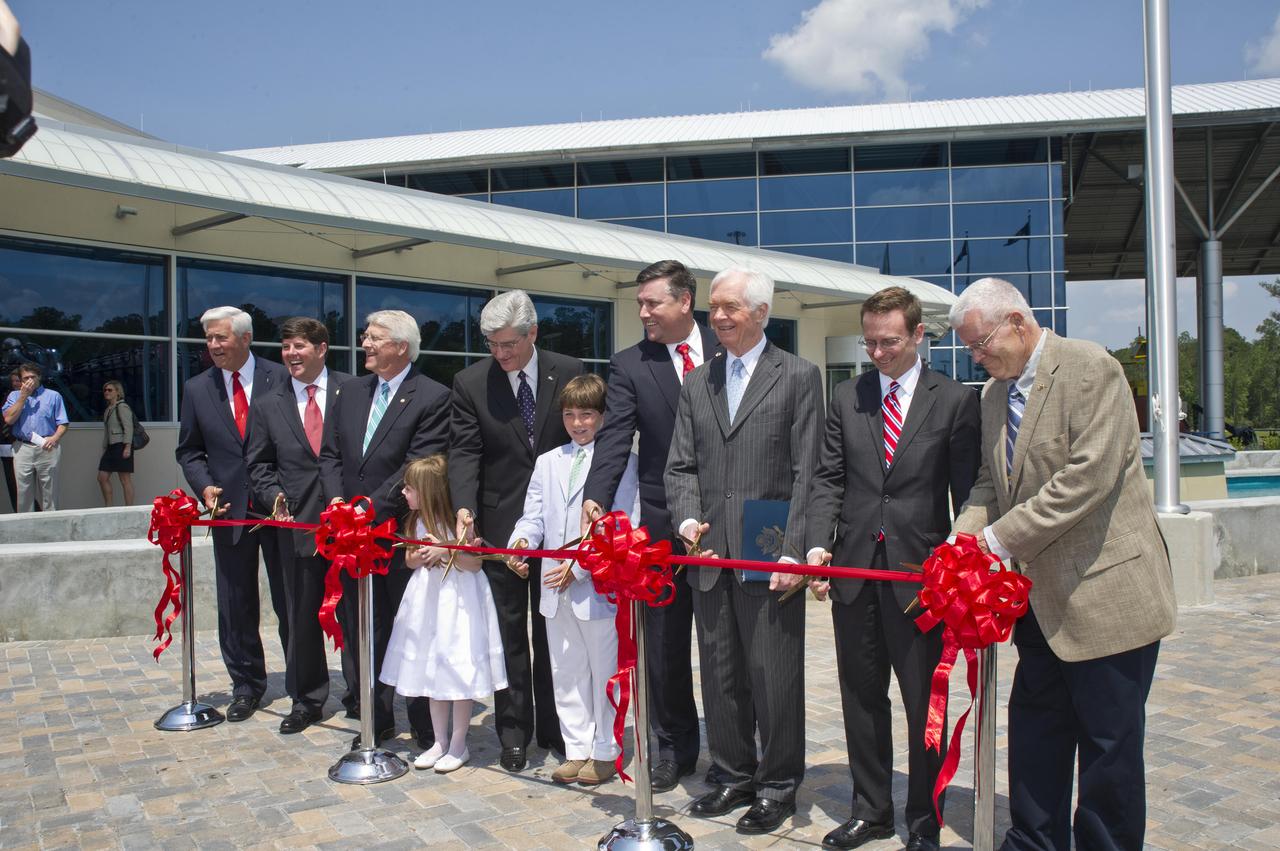

Ceremony participants prepare to cut the ribbon on the INFINITY at NASA Stennis Space Center facility April 11, 2012. Participating in the ceremony were (l to r): Gulfport Mayor and INFINITY Science Center Inc. Chairman George Schloegel; U.S. Rep. Steven Palazzo, R-Miss.; U.S. Sen. Roger Wicker, R-Miss.; Roy S. Estess granddaughter Lauren McKay; Mississippi Gov. Phil Bryant; Leo Seal Jr. grandson Leo Seal IV; Stennis Director Patrick Scheuermann; U.S. Sen. Thad Cochran, R-Miss.; NASA Chief of Staff David Radzanowski; and Apollo 13 astronaut and INFINITY Science Center Inc. Vice Chairman Fred Haise.
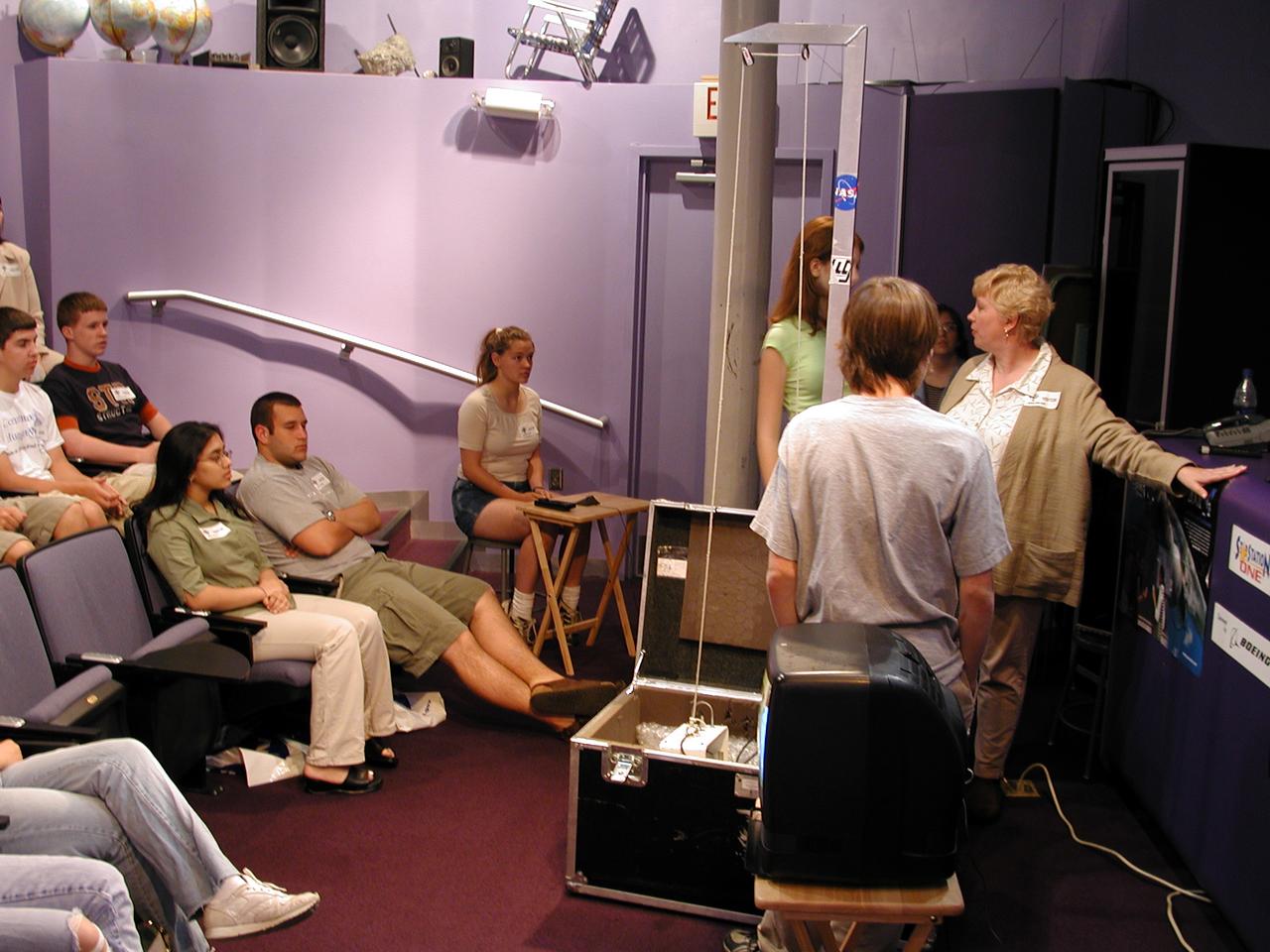

Suzarne Nichols (12th grade) from DuPont Manual High School in Louisville, Kentucky, asks a question of on of the on-line lecturers during the Pan-Pacific Basin Workshop on Microgravity Sciences held in Pasadena, California. The event originated at the California Science Center in Los Angeles. The DuPont Manual students patched in to the event through the distance learning lab at the Louisville Science Center. NASA materials engineer Chris Cochrane prepare students for the on-line workshop helps two students prepare a drop demonstration. This image is from a digital still camera; higher resolution is not available.

Teams at NASA’s Stennis Space Center complete a safe lift and install of an interstage simulator unit needed for future testing of NASA’s exploration upper stage (EUS) in the B-2 position of the Thad Cochran Test Stand. The lift and install, completed over a two-week period that began Oct. 10, marks a milestone for testing the new SLS (Space Launch System) rocket stage that will fly on future Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond. The EUS will undergo a series of Green Run tests of its integrated systems prior to its first flight. During testing, the interstage simulator component will function like the SLS interstage section that helps protect the upper stage during Artemis launches.
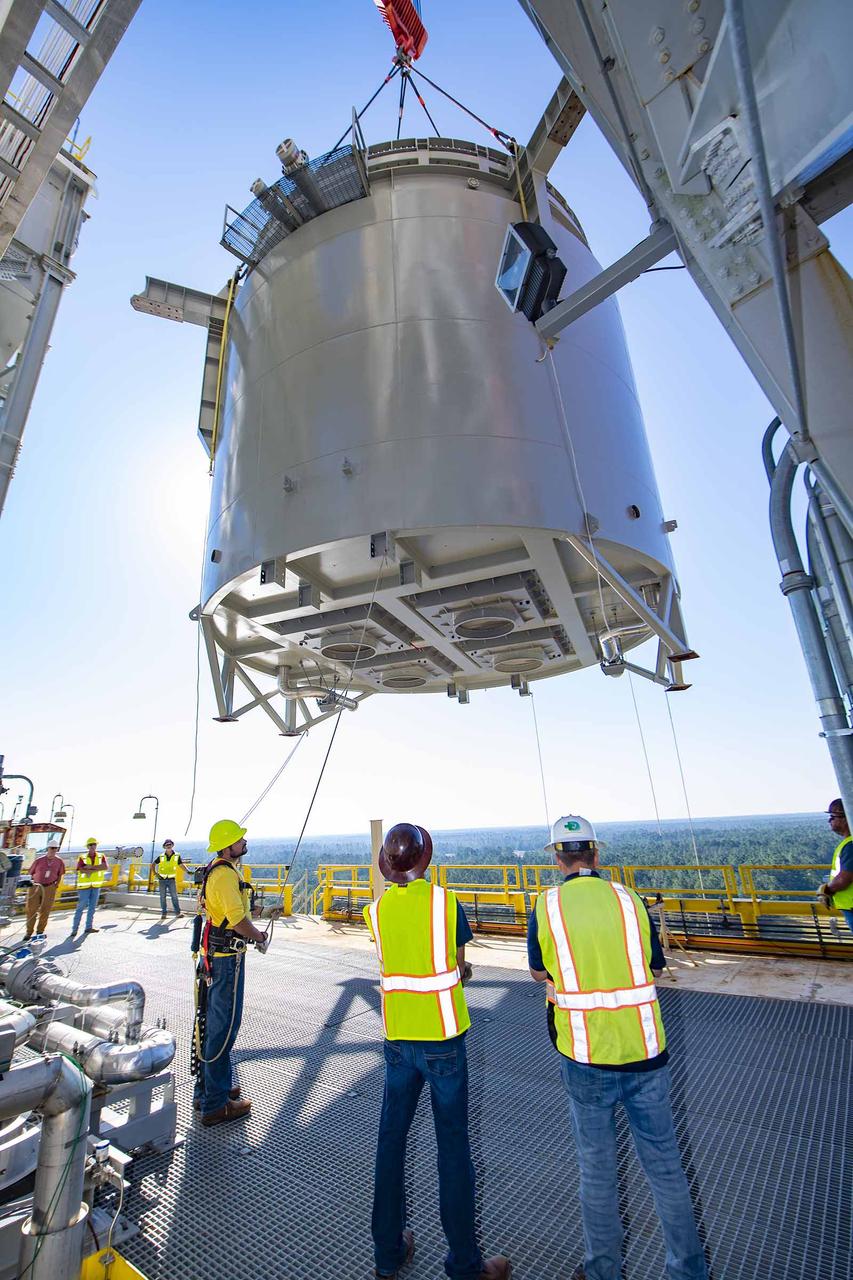

Teams at NASA’s Stennis Space Center complete a safe lift and install of an interstage simulator unit needed for future testing of NASA’s exploration upper stage (EUS) in the B-2 position of the Thad Cochran Test Stand. The lift and install, completed over a two-week period that began Oct. 10, marks a milestone for testing the new SLS (Space Launch System) rocket stage that will fly on future Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond. The EUS will undergo a series of Green Run tests of its integrated systems prior to its first flight. During testing, the interstage simulator component will function like the SLS interstage section that helps protect the upper stage during Artemis launches.
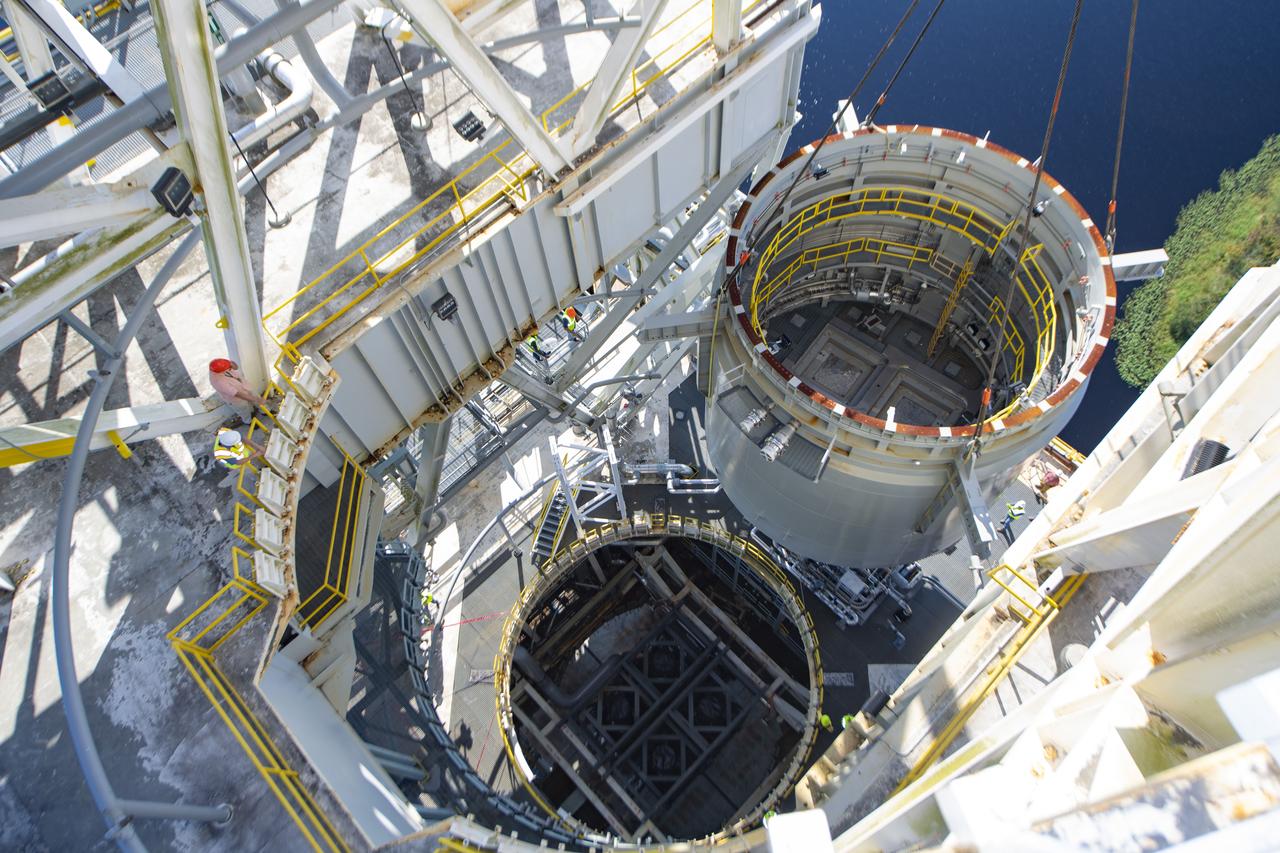

Teams at NASA’s Stennis Space Center complete a safe lift and install of an interstage simulator unit needed for future testing of NASA’s exploration upper stage (EUS) in the B-2 position of the Thad Cochran Test Stand. The lift and install, completed over a two-week period that began Oct. 10, marks a milestone for testing the new SLS (Space Launch System) rocket stage that will fly on future Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond. The EUS will undergo a series of Green Run tests of its integrated systems prior to its first flight. During testing, the interstage simulator component will function like the SLS interstage section that helps protect the upper stage during Artemis launches.
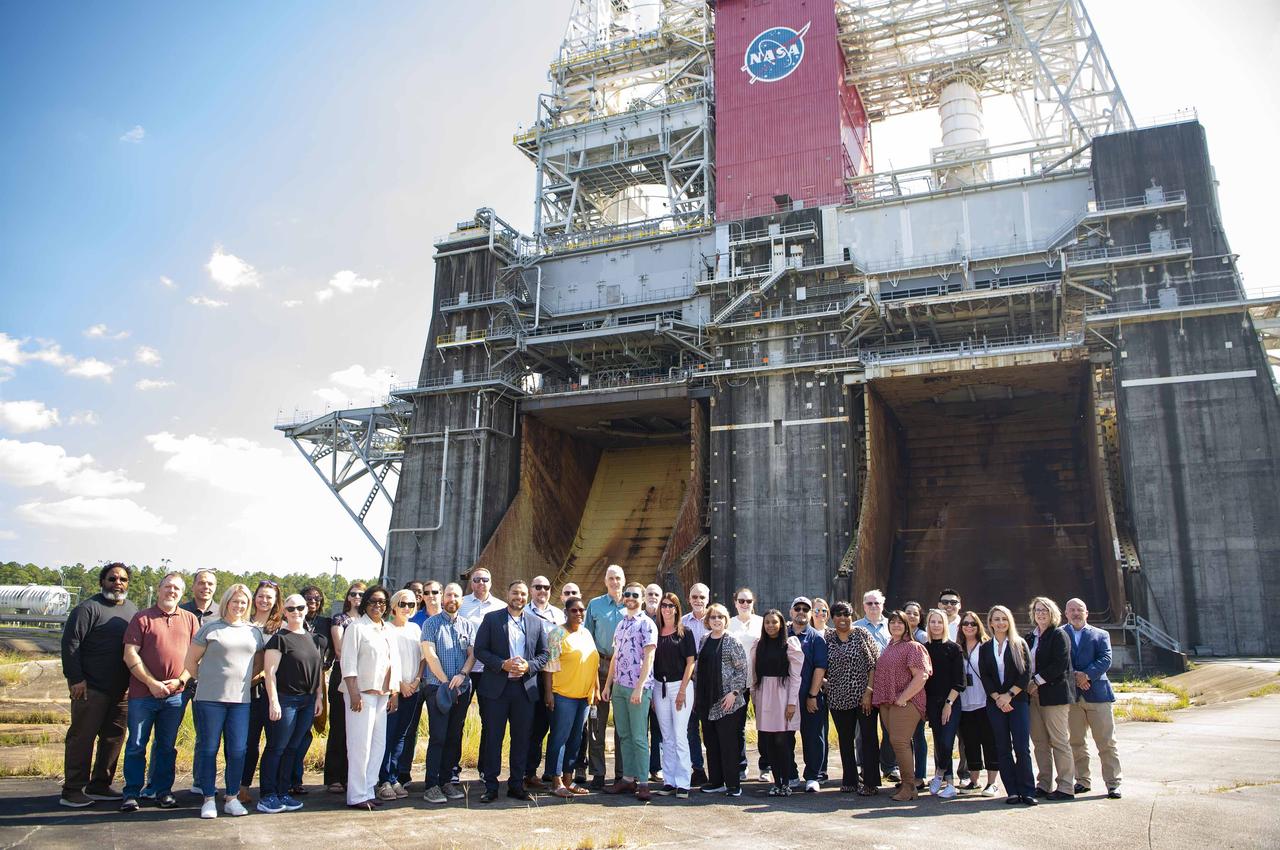

The NASA Office of the Chief Information Officer Integrated Design and Assurance Systems team are shown at the Thad Cochran Test Stand (B-1/B-2) during a tour of NASA Stennis on Oct. 9. To accomplish NASA’s vision, the agency depends heavily on many things and information technology is key among them. Information technology capabilities enable NASA’s discoveries, allow sharing of mission data, improve workforce productivity, and increase mission quality, resilience, and cost-effectiveness. To enable success for NASA’s mission portfolio, the Office of the Chief Information Officer goals are to deliver great customer experiences; achieve consistent operational excellence; transform NASA through information and technology; and ensure proactive, resilient cybersecurity – all delivered by an exceptional team.

Cookbook author and culinary content creator Caroline Davis, popularly known as Mississippi Kween, and her family enjoy touring facilities and learning about NASA Stennis and its frontline work during a site visit Dec. 18. Davis, husband Joe, and children Zeke and Zoey, met with NASA Stennis leadership before touring the L3Harris (formerly Aerojet Rocketdyne) Engine Assembly Facility, Thad Cochran Test Stand, Autonomous Systems Laboratory, and the NASA Stennis rocket engine garden. The tour highlighted the NASA Stennis story and how the south Mississippi NASA center has the ingredients for a recipe that accelerates the exploration and commercialization of space, innovates to benefit NASA and industry, and leverages assets to stimulate the economy.
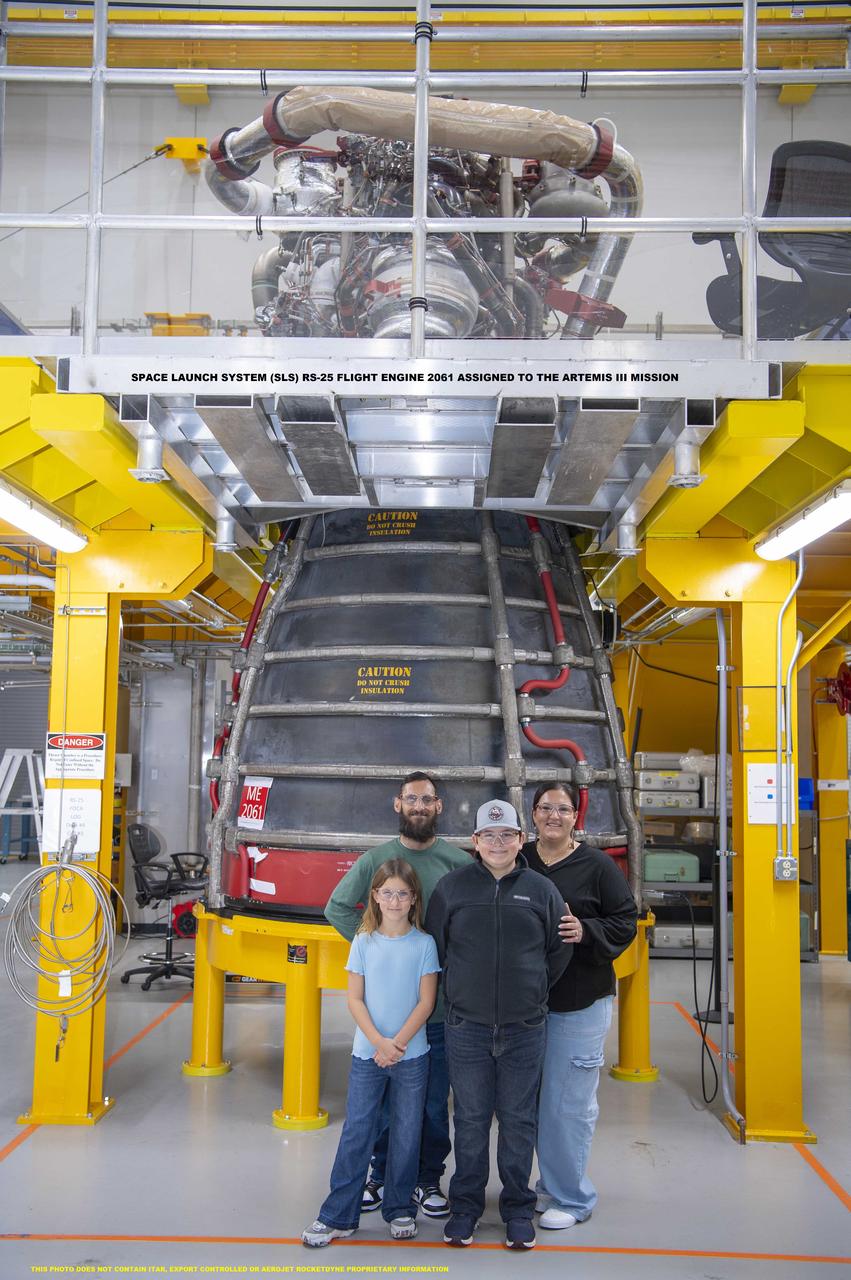

Cookbook author and culinary content creator Caroline Davis, popularly known as Mississippi Kween, and her family enjoy touring facilities and learning about NASA Stennis and its frontline work during a site visit Dec. 18. Davis, husband Joe, and children Zeke and Zoey, met with NASA Stennis leadership before touring the L3Harris (formerly Aerojet Rocketdyne) Engine Assembly Facility, Thad Cochran Test Stand, Autonomous Systems Laboratory, and the NASA Stennis rocket engine garden. The tour highlighted the NASA Stennis story and how the south Mississippi NASA center has the ingredients for a recipe that accelerates the exploration and commercialization of space, innovates to benefit NASA and industry, and leverages assets to stimulate the economy.
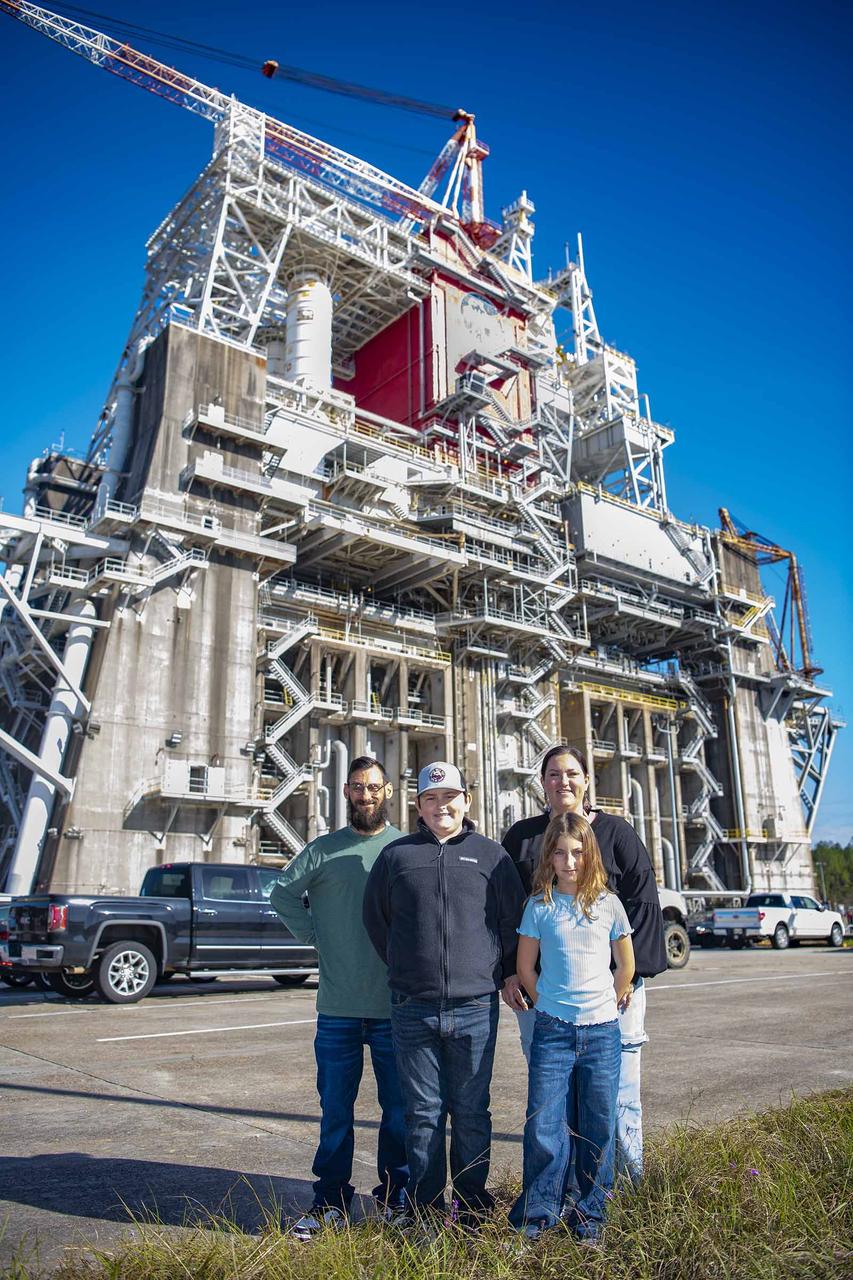

Cookbook author and culinary content creator Caroline Davis, popularly known as Mississippi Kween, and her family enjoy touring facilities and learning about NASA Stennis and its frontline work during a site visit Dec. 18. Davis, husband Joe, and children Zeke and Zoey, met with NASA Stennis leadership before touring the L3Harris (formerly Aerojet Rocketdyne) Engine Assembly Facility, Thad Cochran Test Stand, Autonomous Systems Laboratory, and the NASA Stennis rocket engine garden. The tour highlighted the NASA Stennis story and how the south Mississippi NASA center has the ingredients for a recipe that accelerates the exploration and commercialization of space, innovates to benefit NASA and industry, and leverages assets to stimulate the economy.
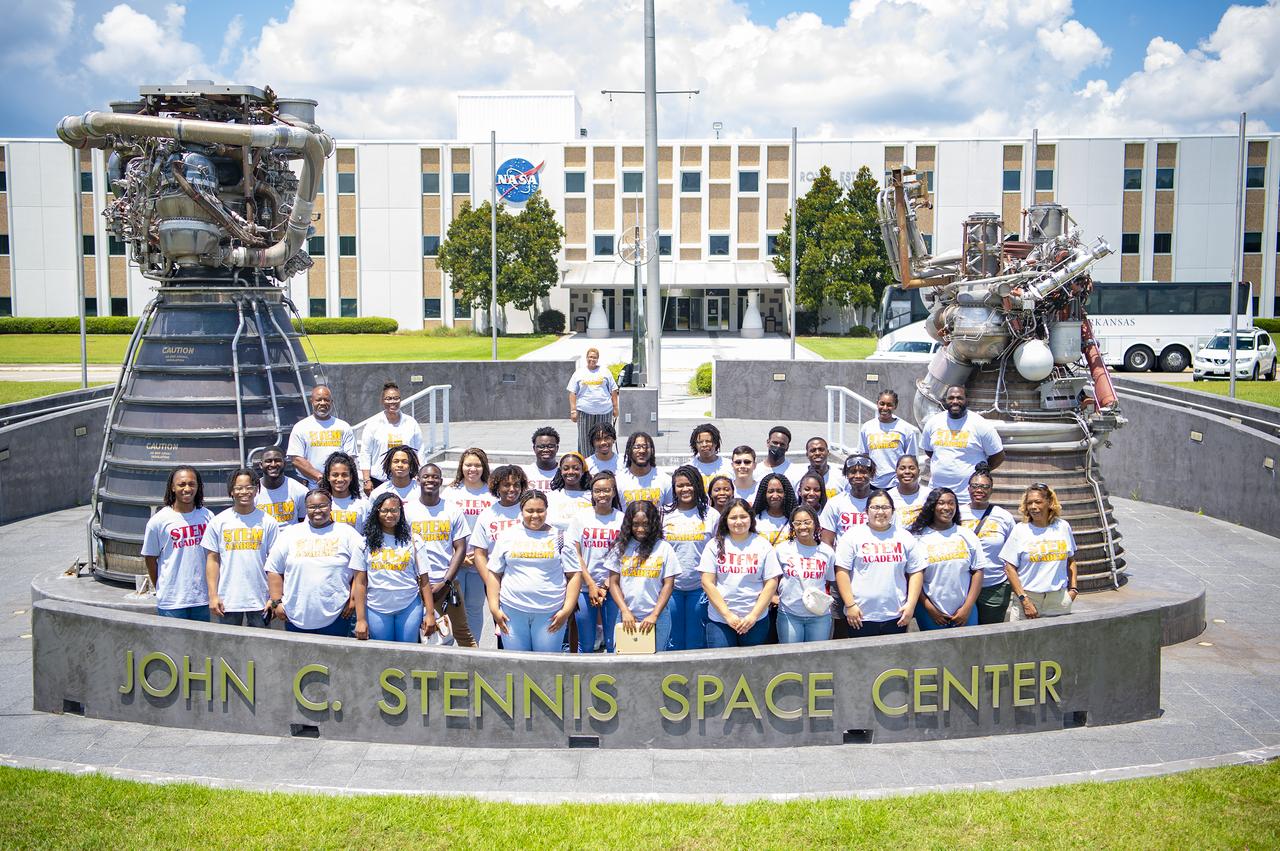

Participants in the University of Arkansas at Pine Bluff STEM (science, technology, engineering and mathematics) Summer Institute stand in front of the Roy Estess Building at NASA’s Stennis Space Center during a site tour on June 25. The students viewed multiple areas of the federal city, including a visit to the Thad Cochran Test Stand, where students learned about NASA Stennis’ role in the Artemis campaign. NASA is going back to the Moon for scientific discovery, economic benefits, and inspiration for a new generation of explorers: the Artemis Generation. The agency will use what is learned on and around the Moon to take the next giant leap – sending astronauts to Mars. The Arkansas at Pine Bluff STEM program started in 2003 and is designed to help increase the number and diversity of well-prepared STEM graduates.
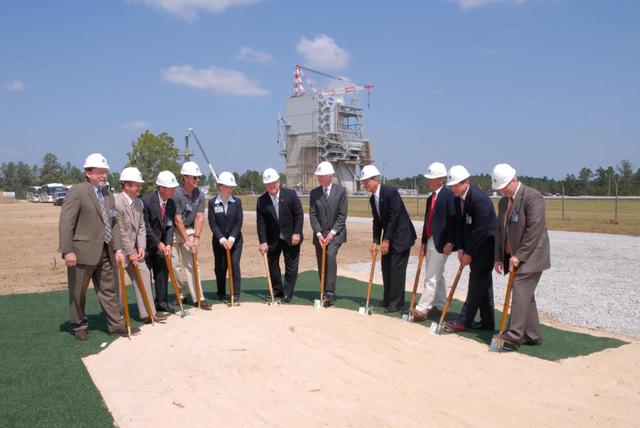

NASA officials and government leaders participated in a groundbreaking event for a new rocket engine test stand at NASA's Stennis Space Center, Miss. Pictured (left to right) are Deputy Associate Administrator for Exploration Systems Doug Cooke, Pratt & Whitney Rocketdyne President Jim Maser, Stennis Space Center Director Richard Gilbrech, NASA Associate Administrator for Exploration Systems Scott Horowitz, NASA Deputy Administrator Shana Dale, Mississippi Gov. Haley Barbour, Sen. Thad Cochran, Sen. Trent Lott, Rep. Gene Taylor, SSC's Deputy Director Gene Goldman, and SSC's A-3 Project Manager Lonnie Dutreix. Stennis' A-3 Test Stand will provide altitude testing for NASA's developing J-2X engine. That engine will power the upper stages of NASA's Ares I and Ares V rockets. A-3 is the first large test stand to be built at SSC since the site's inception in the 1960s.

Cookbook author and culinary content creator Caroline Davis, popularly known as Mississippi Kween, and her family enjoy touring facilities and learning about NASA Stennis and its frontline work during a site visit Dec. 18. Davis, husband Joe, and children Zeke and Zoey, met with NASA Stennis leadership before touring the L3Harris (formerly Aerojet Rocketdyne) Engine Assembly Facility, Thad Cochran Test Stand, Autonomous Systems Laboratory, and the NASA Stennis rocket engine garden. The tour highlighted the NASA Stennis story and how the south Mississippi NASA center has the ingredients for a recipe that accelerates the exploration and commercialization of space, innovates to benefit NASA and industry, and leverages assets to stimulate the economy.
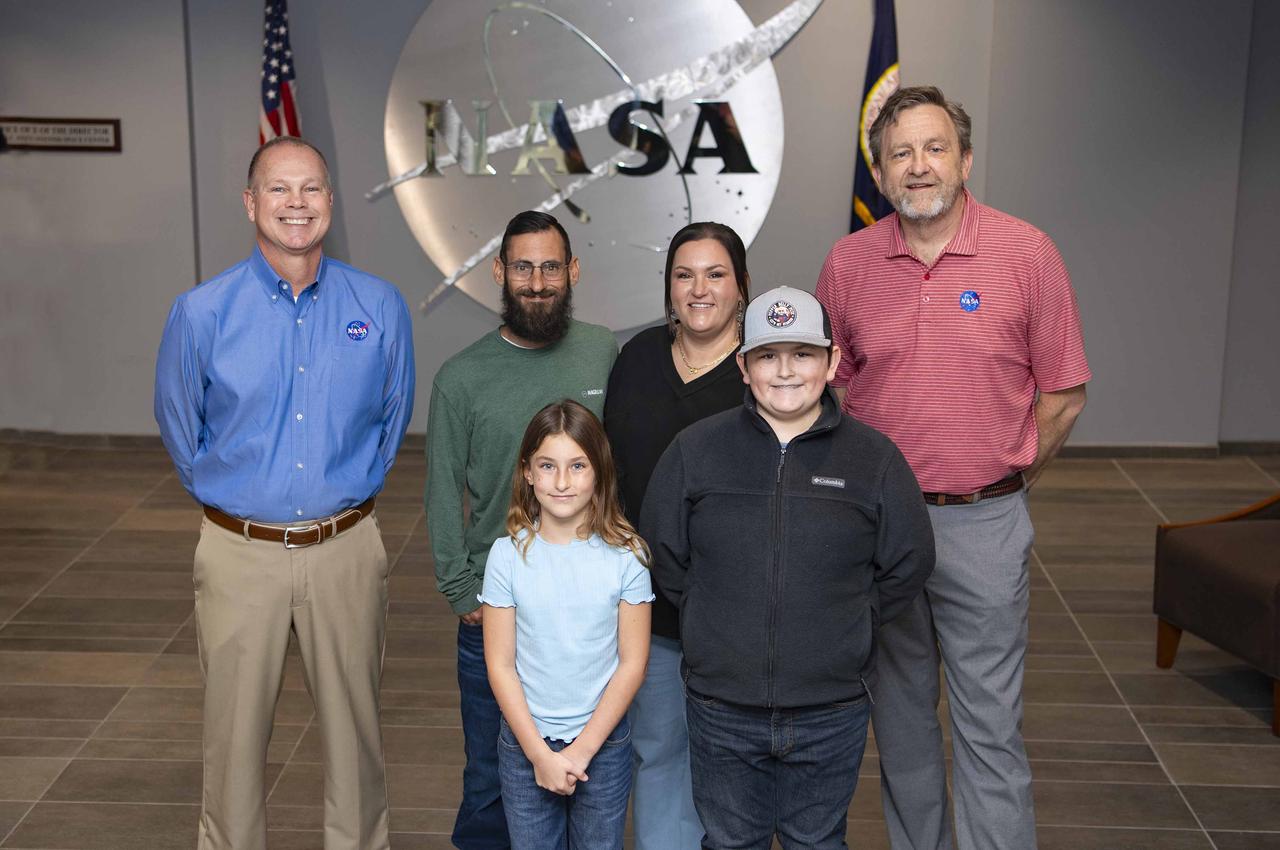

Cookbook author and culinary content creator Caroline Davis, popularly known as Mississippi Kween, and her family enjoy touring facilities and learning about NASA Stennis and its frontline work during a site visit Dec. 18. Davis, husband Joe, and children Zeke and Zoey, met with NASA Stennis leadership before touring the L3Harris (formerly Aerojet Rocketdyne) Engine Assembly Facility, Thad Cochran Test Stand, Autonomous Systems Laboratory, and the NASA Stennis rocket engine garden. The tour highlighted the NASA Stennis story and how the south Mississippi NASA center has the ingredients for a recipe that accelerates the exploration and commercialization of space, innovates to benefit NASA and industry, and leverages assets to stimulate the economy.
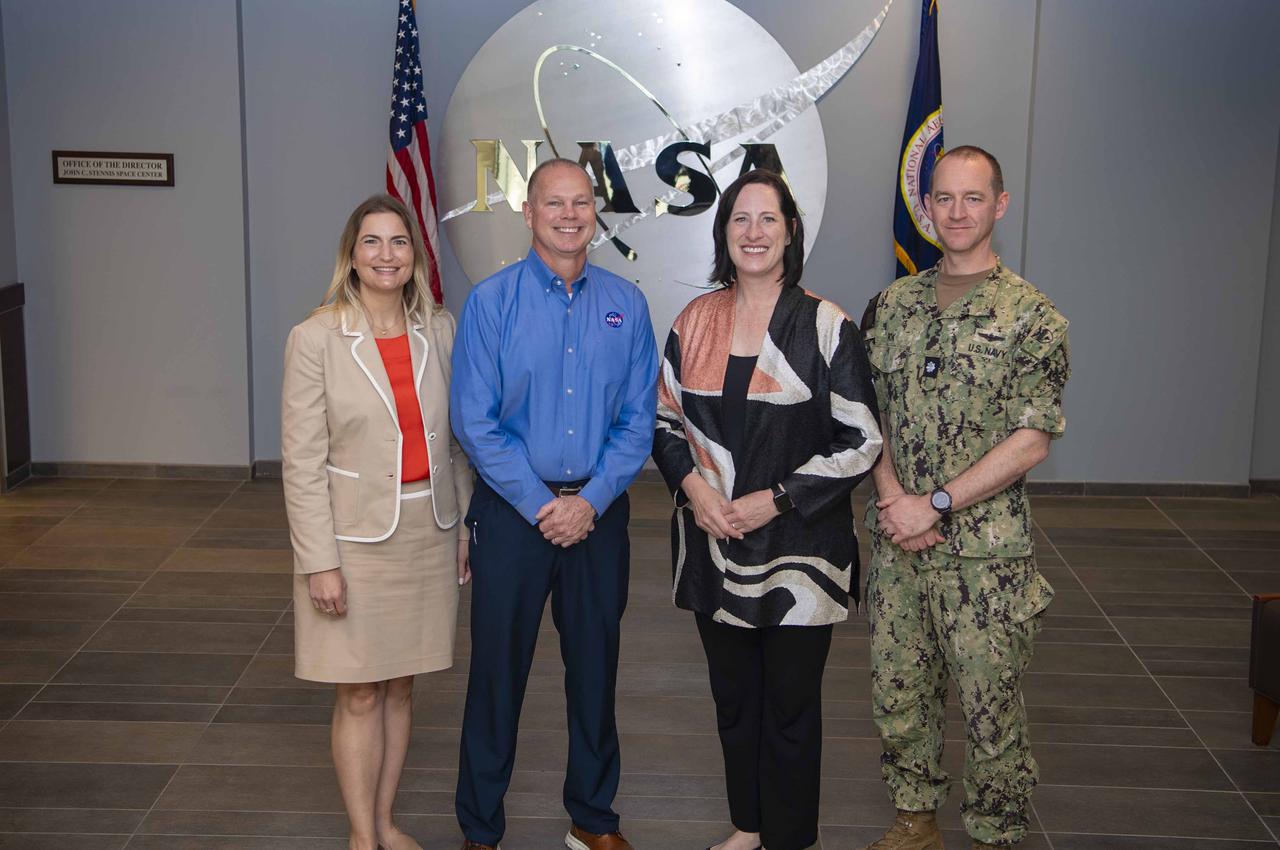

Heide Fulton, U.S. Ambassador to the Oriental Republic of Uruguay, visits NASA Stennis on Oct. 8 to meet with site leadership and tour test complex facilities. During her visit, Fulton met with NASA Stennis Director John Bailey and other leaders of the center and the NASA Shared Services Center located onsite. She also toured the rocket propulsion test complex, visiting the B-2 side of the Thad Cochran Test Stand, where she was briefed by B-2 Stand Director Ryan Roberts about NASA Stennis testing for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket and NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond. Uruguay is one of 45 nations who have signed the Artemis Accords, which establish a practical set of principles to guide space exploration cooperation among nations. The country became the 36th nation to sign the Artemis Accords during a Washington, D.C. ceremony in February. Ambassador Fulton was joined on the visit by Cmdr. Brendan Rok, chief of the U.S. Navy Office of Defense Cooperation at the U.S. Embassy in Montevideo, Uruguay; and Leah Thorstenson, foreign policy advisor with the U.S. Marines Corps. Forces South.
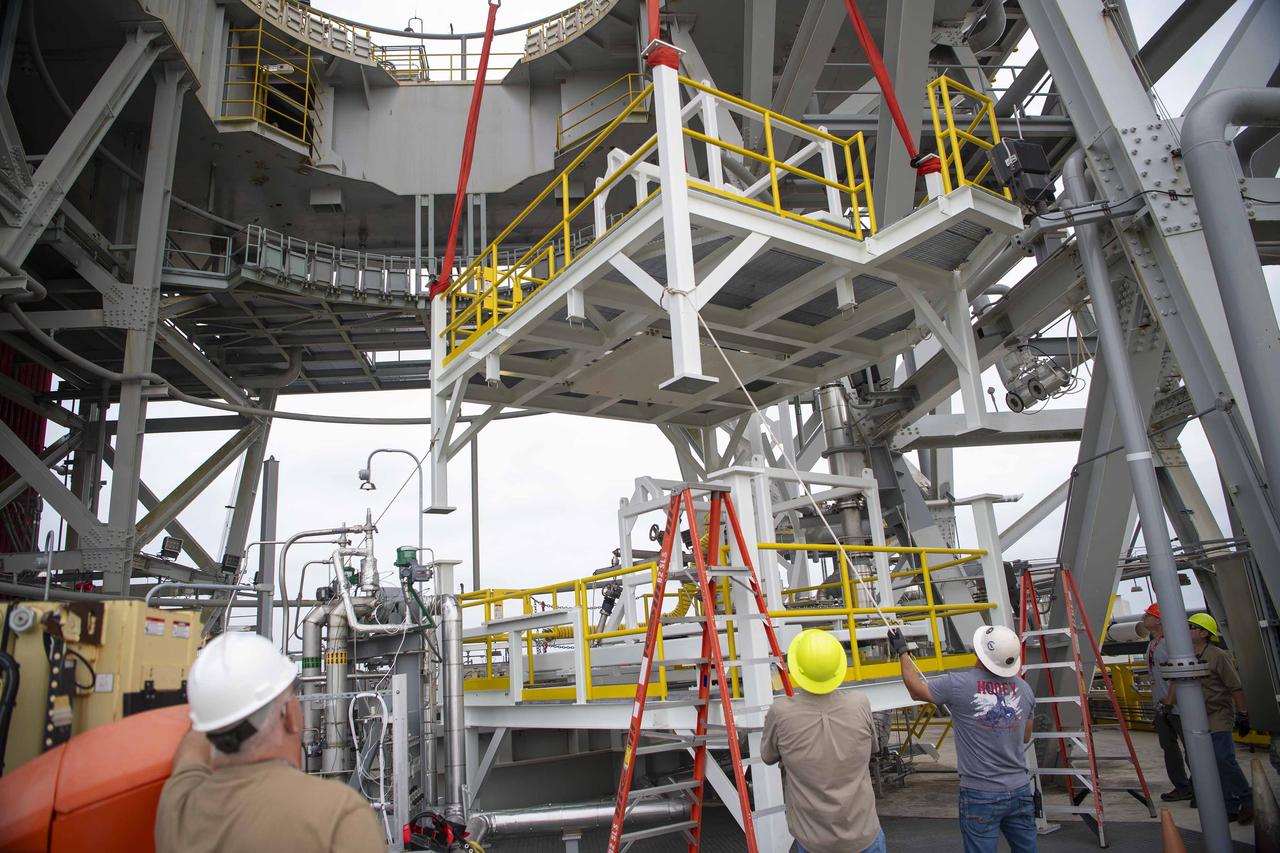

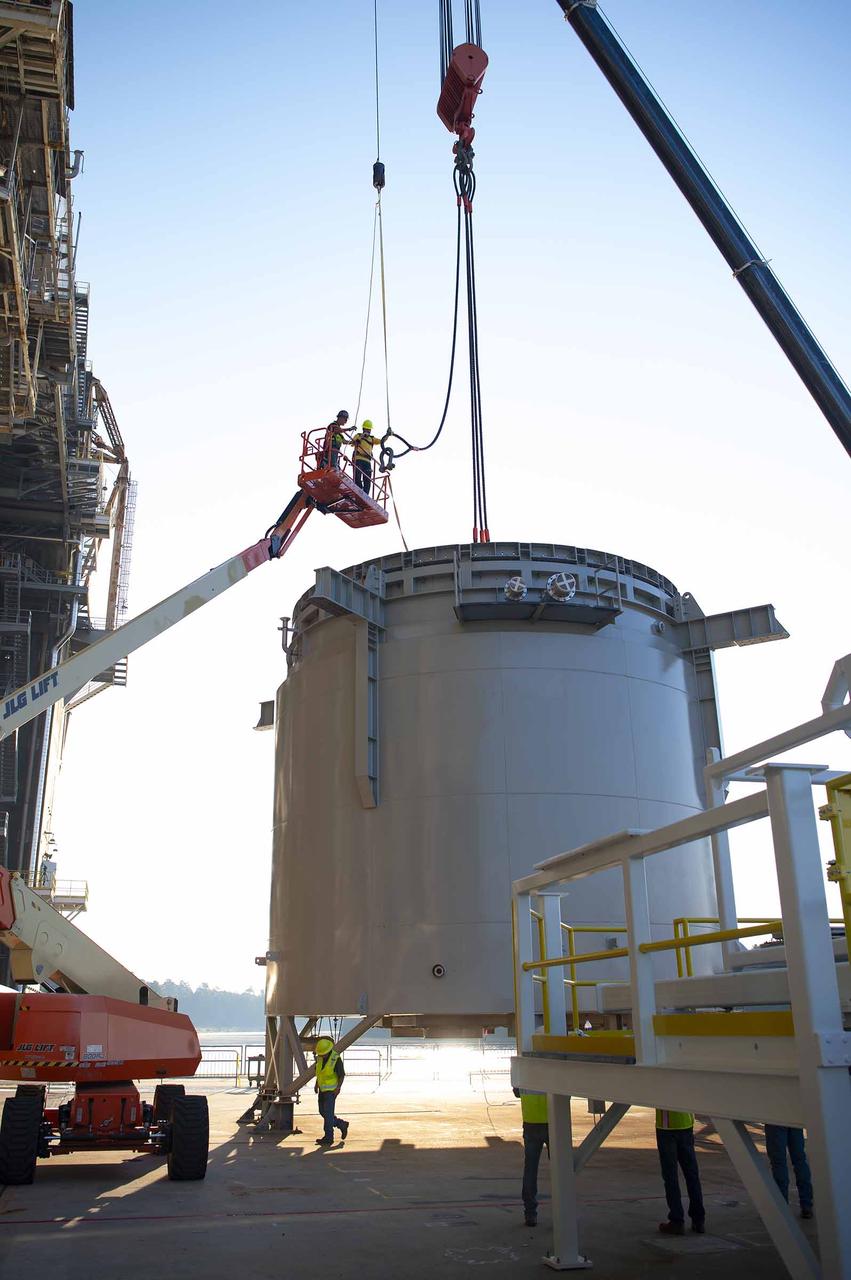
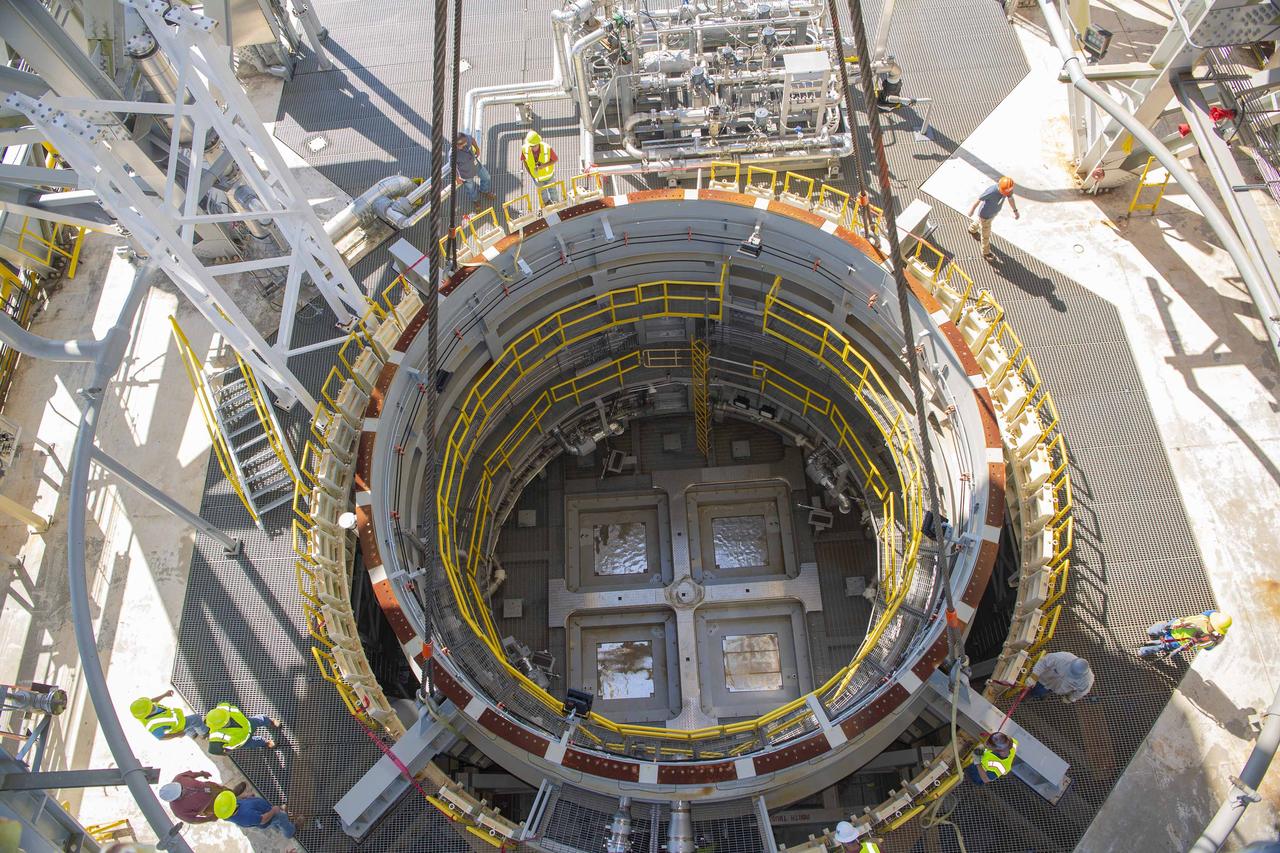
A pair of umbilical support structures needed for future testing of NASA’s exploration upper stage (EUS) were installed in the B-2 position of the Thad Cochran Test Stand on Oct. 30-31 at NASA’s Stennis Space Center. The support structures arrived from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans via the unique NASA Stennis seven-and-a-half-mile canal system in 2023. Since then, crews have prepared the structures that will align with the EUS unit for installation. In addition to helping secure the unit in place during hot fire testing, the umbilical support structures are where the command, control, and data electrical connections are mated to connect the ground systems to the vehicle systems, as well as most the commodity connections such as liquid hydrogen, liquid oxygen, hydrogen vent, helium bottle fill pressure, and purges. Prior to its initial flight, the EUS unit will undergo a series of so-called Green Run tests at NASA Stennis to ensure all systems are ready to go. The test series will culminate with a hot fire of the stage’s four RL10 engines, made by Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company and lead SLS engines contractor. The new upper stage will enable NASA to carry larger payloads on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond.
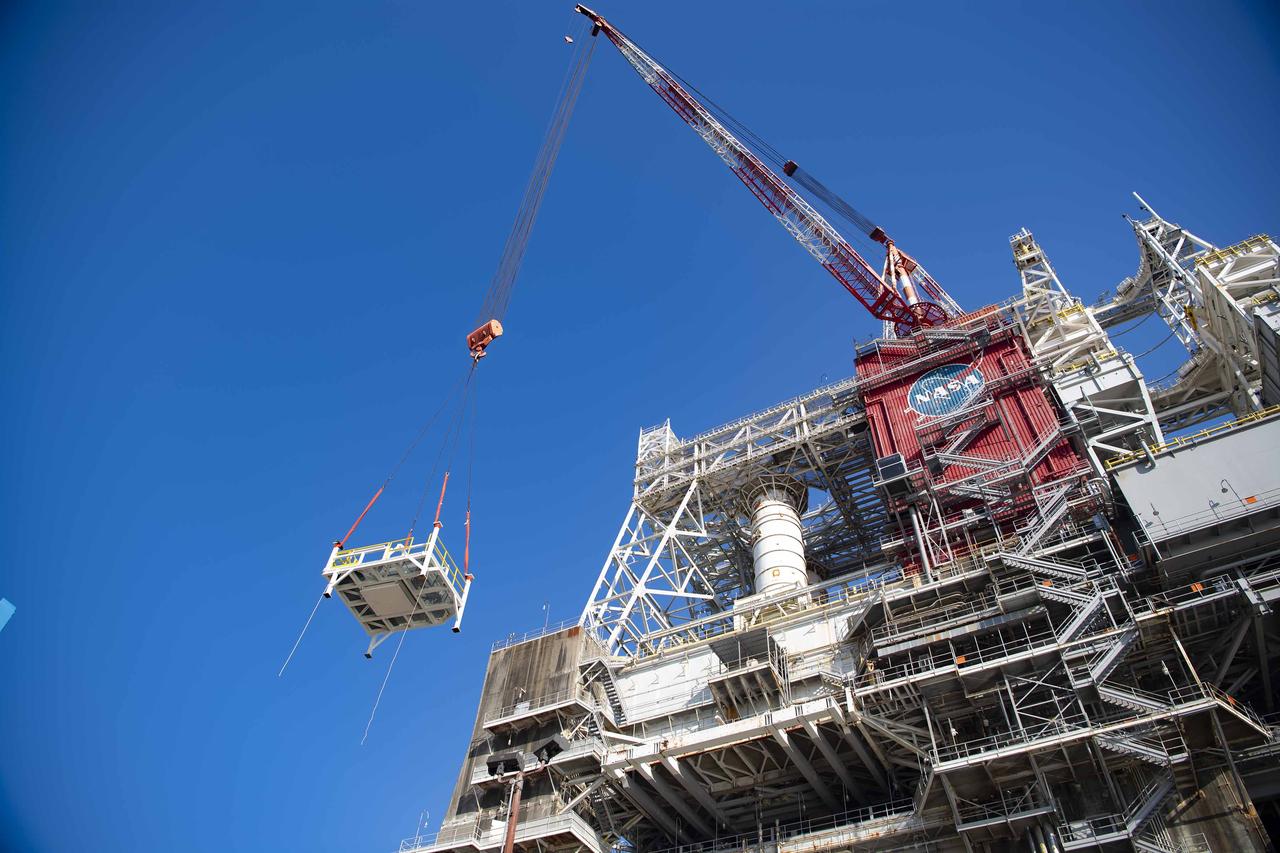

A pair of umbilical support structures needed for future testing of NASA’s exploration upper stage (EUS) were installed in the B-2 position of the Thad Cochran Test Stand on Oct. 30-31 at NASA’s Stennis Space Center. The support structures arrived from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans via the unique NASA Stennis seven-and-a-half-mile canal system in 2023. Since then, crews have prepared the structures that will align with the EUS unit for installation. In addition to helping secure the unit in place during hot fire testing, the umbilical support structures are where the command, control, and data electrical connections are mated to connect the ground systems to the vehicle systems, as well as most the commodity connections such as liquid hydrogen, liquid oxygen, hydrogen vent, helium bottle fill pressure, and purges. Prior to its initial flight, the EUS unit will undergo a series of so-called Green Run tests at NASA Stennis to ensure all systems are ready to go. The test series will culminate with a hot fire of the stage’s four RL10 engines, made by Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company and lead SLS engines contractor. The new upper stage will enable NASA to carry larger payloads on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond.
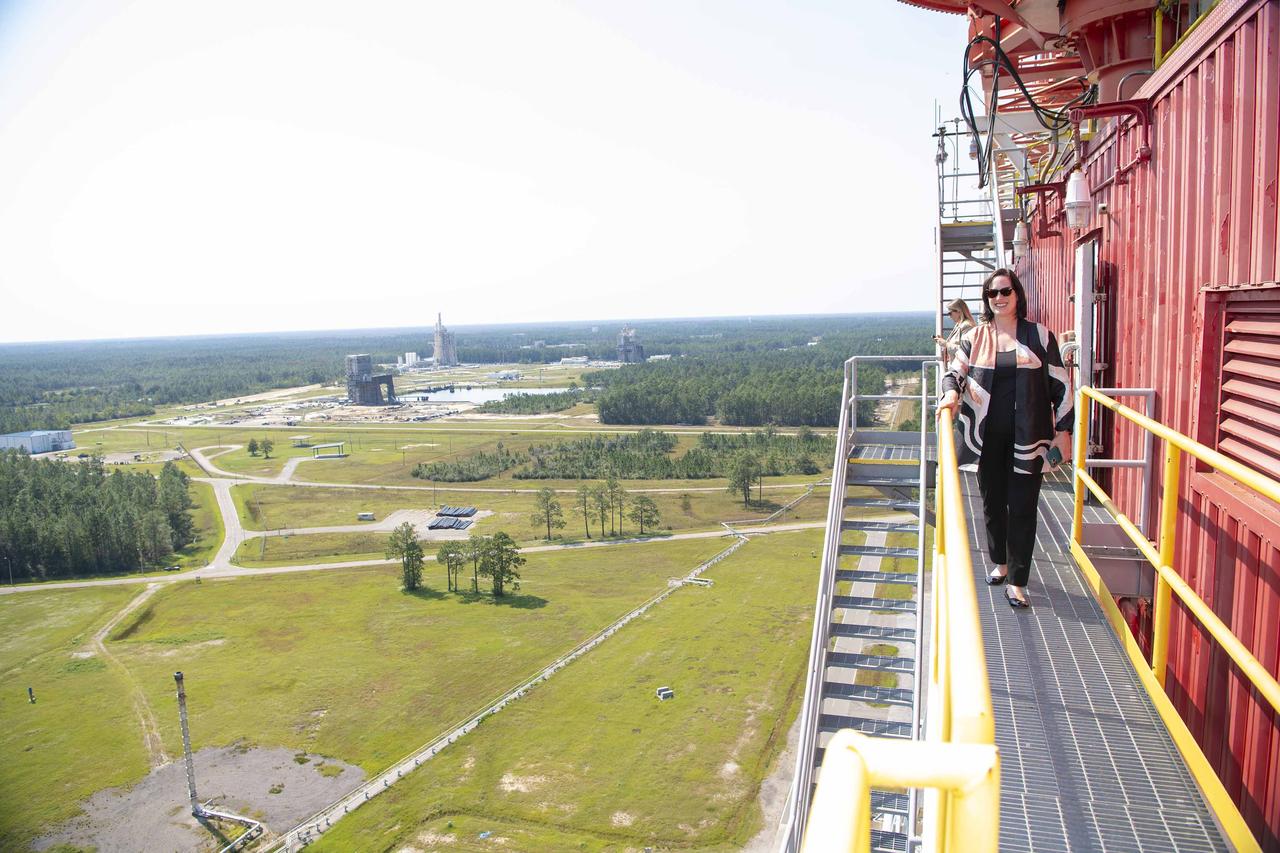

Heide Fulton, U.S. Ambassador to the Oriental Republic of Uruguay, visits NASA Stennis on Oct. 8 to meet with site leadership and tour test complex facilities. During her visit, Fulton met with NASA Stennis Director John Bailey and other leaders of the center and the NASA Shared Services Center located onsite. She also toured the rocket propulsion test complex, visiting the B-2 side of the Thad Cochran Test Stand, where she was briefed by B-2 Stand Director Ryan Roberts about NASA Stennis testing for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket and NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond. Uruguay is one of 45 nations who have signed the Artemis Accords, which establish a practical set of principles to guide space exploration cooperation among nations. The country became the 36th nation to sign the Artemis Accords during a Washington, D.C. ceremony in February. Ambassador Fulton was joined on the visit by Cmdr. Brendan Rok, chief of the U.S. Navy Office of Defense Cooperation at the U.S. Embassy in Montevideo, Uruguay; and Leah Thorstenson, foreign policy advisor with the U.S. Marines Corps. Forces South.
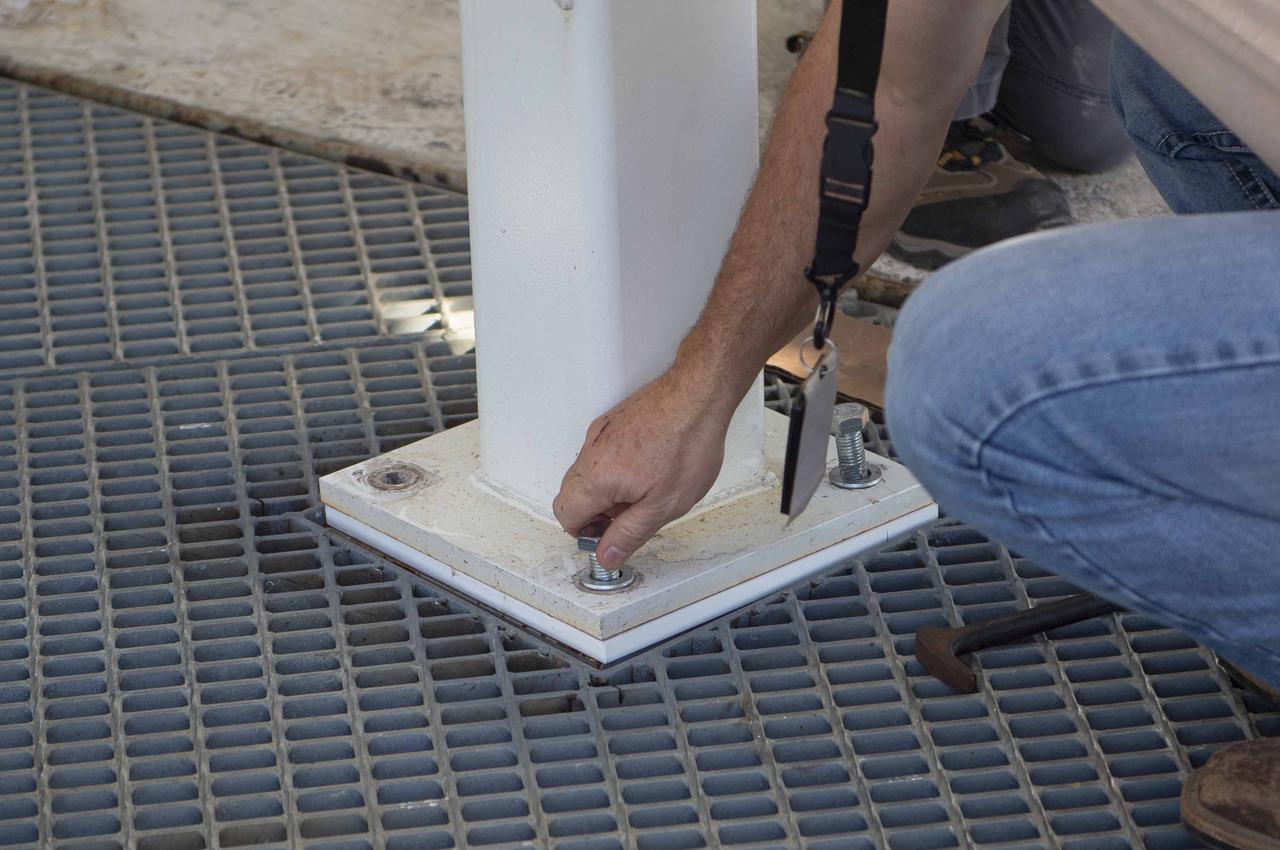

A pair of umbilical support structures needed for future testing of NASA’s exploration upper stage (EUS) were installed in the B-2 position of the Thad Cochran Test Stand on Oct. 30-31 at NASA’s Stennis Space Center. The support structures arrived from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans via the unique NASA Stennis seven-and-a-half-mile canal system in 2023. Since then, crews have prepared the structures that will align with the EUS unit for installation. In addition to helping secure the unit in place during hot fire testing, the umbilical support structures are where the command, control, and data electrical connections are mated to connect the ground systems to the vehicle systems, as well as most the commodity connections such as liquid hydrogen, liquid oxygen, hydrogen vent, helium bottle fill pressure, and purges. Prior to its initial flight, the EUS unit will undergo a series of so-called Green Run tests at NASA Stennis to ensure all systems are ready to go. The test series will culminate with a hot fire of the stage’s four RL10 engines, made by Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company and lead SLS engines contractor. The new upper stage will enable NASA to carry larger payloads on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond.
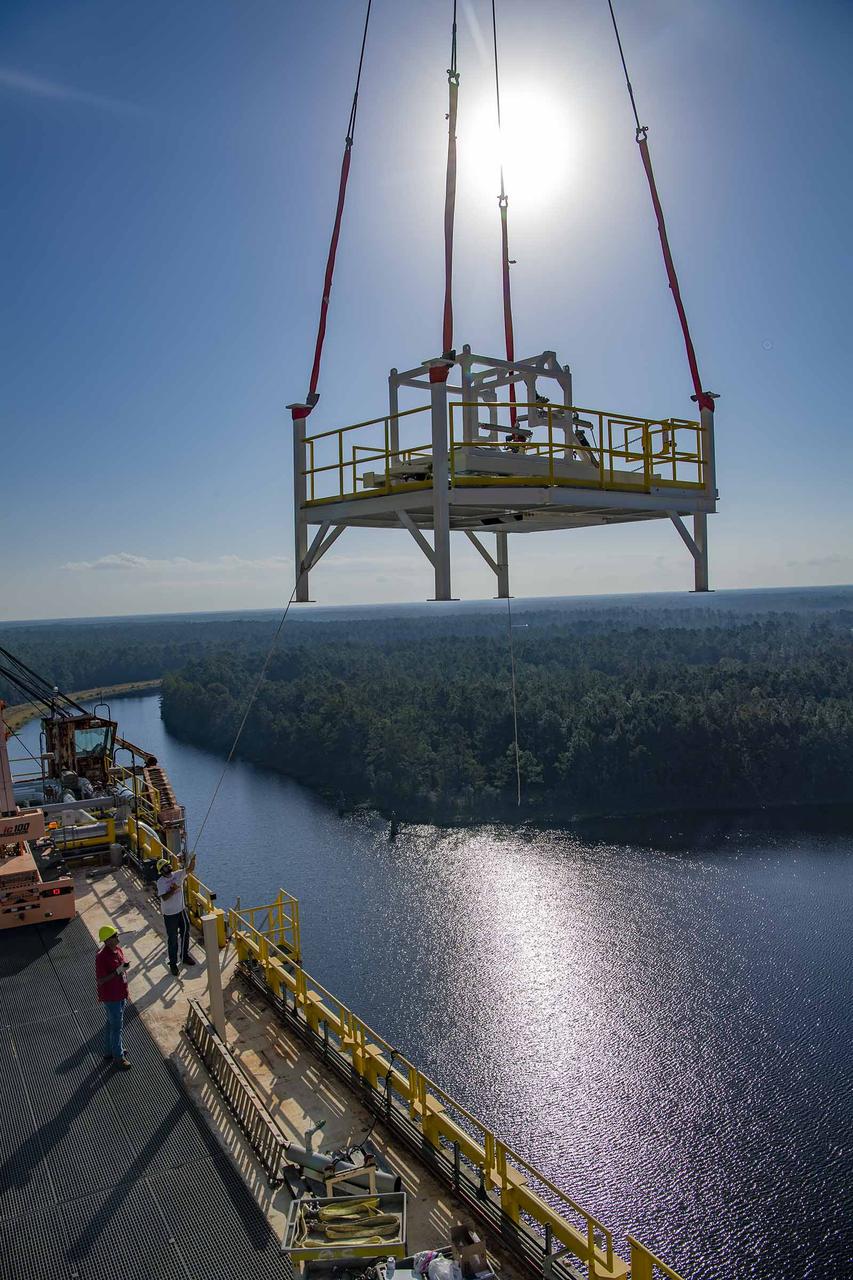

A pair of umbilical support structures needed for future testing of NASA’s exploration upper stage (EUS) were installed in the B-2 position of the Thad Cochran Test Stand on Oct. 30-31 at NASA’s Stennis Space Center. The support structures arrived from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans via the unique NASA Stennis seven-and-a-half-mile canal system in 2023. Since then, crews have prepared the structures that will align with the EUS unit for installation. In addition to helping secure the unit in place during hot fire testing, the umbilical support structures are where the command, control, and data electrical connections are mated to connect the ground systems to the vehicle systems, as well as most the commodity connections such as liquid hydrogen, liquid oxygen, hydrogen vent, helium bottle fill pressure, and purges. Prior to its initial flight, the EUS unit will undergo a series of so-called Green Run tests at NASA Stennis to ensure all systems are ready to go. The test series will culminate with a hot fire of the stage’s four RL10 engines, made by Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company and lead SLS engines contractor. The new upper stage will enable NASA to carry larger payloads on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond.

Afognak Native Corporation Board of Director members and Alutiiq, LLC executives stand at the Thad Cochran Test Stand (B-1/B-2) during a visit to NASA’s Stennis Space Center on Sept. 19. The board members and executives visited the site to learn about laboratory services provided by Alutiiq Essential Services at NASA Stennis since 2020. Afognak is an Alaskan corporation focused on serving the needs of its native Alaskan people. Alutiiq, LLC operates as a subsidiary of the corporation to provide a variety of services to federal entities. Alutiiq Essential Services operates as a subsidiary of Alutiiq, LLC. Shown at the test stand during the Sept. 19 visit are, left to right: Ian Neumann, Alutiiq executive; John Monaccio, Alutiiq Essential Services president; Autumn Sellers, Alutiiq executive; Loretta Nelson, director; Marci Orth, director; Wade Hall, director; Shane Mendel, Alutiiq Essential Services program manager at NASA Stennis; Erik Olsen, director; Alan Hines, Alutiiq Essential Services executive.

A pair of umbilical support structures needed for future testing of NASA’s exploration upper stage (EUS) were installed in the B-2 position of the Thad Cochran Test Stand on Oct. 30-31 at NASA’s Stennis Space Center. The support structures arrived from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans via the unique NASA Stennis seven-and-a-half-mile canal system in 2023. Since then, crews have prepared the structures that will align with the EUS unit for installation. In addition to helping secure the unit in place during hot fire testing, the umbilical support structures are where the command, control, and data electrical connections are mated to connect the ground systems to the vehicle systems, as well as most the commodity connections such as liquid hydrogen, liquid oxygen, hydrogen vent, helium bottle fill pressure, and purges. Prior to its initial flight, the EUS unit will undergo a series of so-called Green Run tests at NASA Stennis to ensure all systems are ready to go. The test series will culminate with a hot fire of the stage’s four RL10 engines, made by Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company and lead SLS engines contractor. The new upper stage will enable NASA to carry larger payloads on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond.
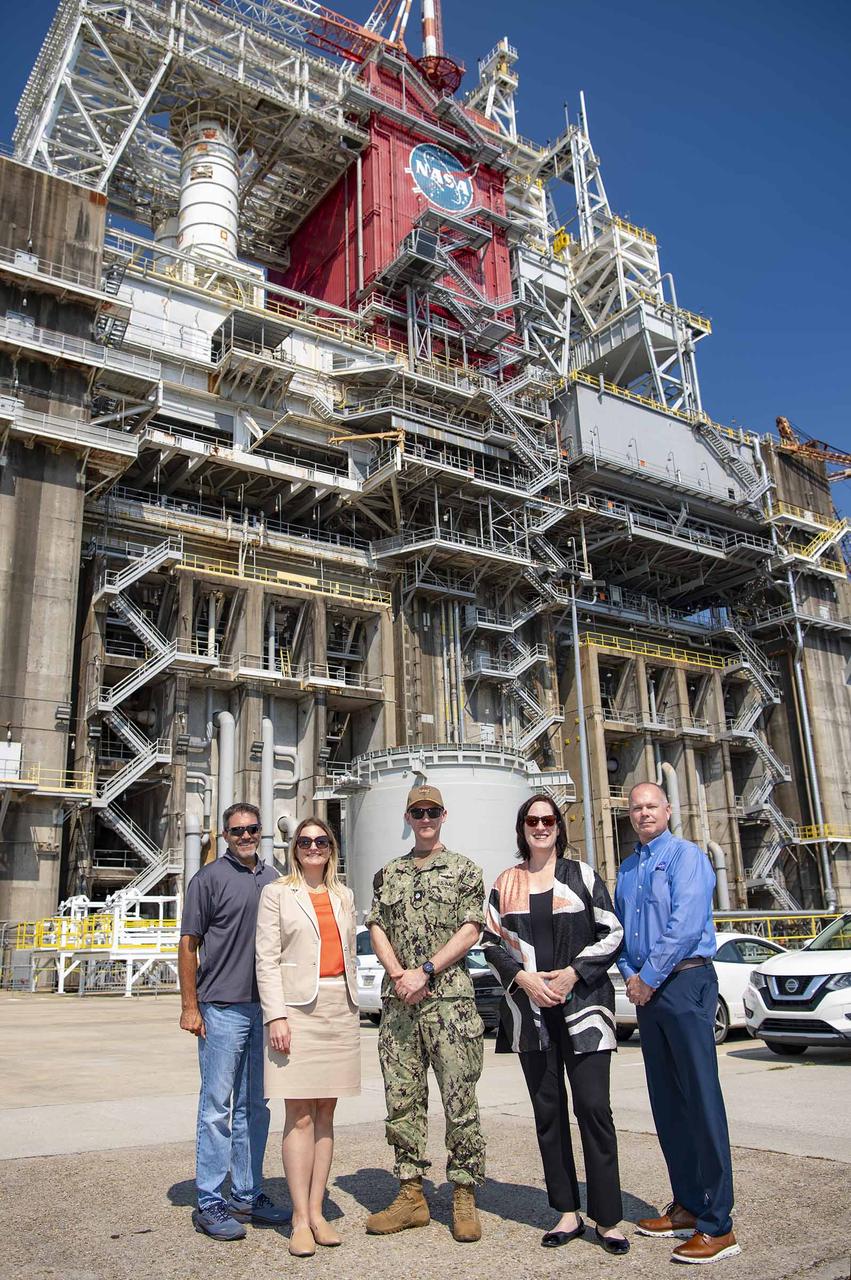

Heide Fulton, U.S. Ambassador to the Oriental Republic of Uruguay, visits NASA Stennis on Oct. 8 to meet with site leadership and tour test complex facilities. During her visit, Fulton met with NASA Stennis Director John Bailey and other leaders of the center and the NASA Shared Services Center located onsite. She also toured the rocket propulsion test complex, visiting the B-2 side of the Thad Cochran Test Stand, where she was briefed by B-2 Stand Director Ryan Roberts about NASA Stennis testing for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket and NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond. Uruguay is one of 45 nations who have signed the Artemis Accords, which establish a practical set of principles to guide space exploration cooperation among nations. The country became the 36th nation to sign the Artemis Accords during a Washington, D.C. ceremony in February. Ambassador Fulton was joined on the visit by Cmdr. Brendan Rok, chief of the U.S. Navy Office of Defense Cooperation at the U.S. Embassy in Montevideo, Uruguay; and Leah Thorstenson, foreign policy advisor with the U.S. Marines Corps. Forces South.
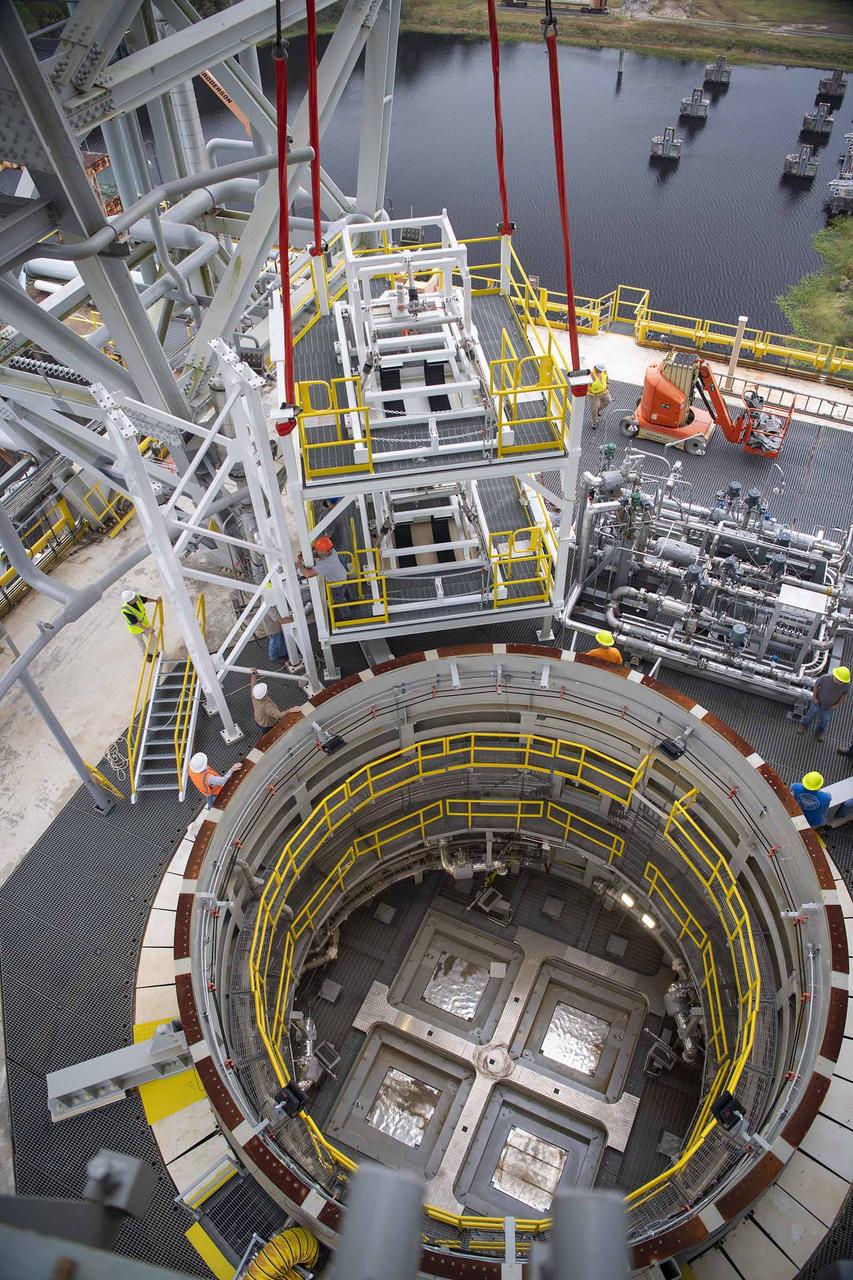
A pair of umbilical support structures needed for future testing of NASA’s exploration upper stage (EUS) were installed in the B-2 position of the Thad Cochran Test Stand on Oct. 30-31 at NASA’s Stennis Space Center. The support structures arrived from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans via the unique NASA Stennis seven-and-a-half-mile canal system in 2023. Since then, crews have prepared the structures that will align with the EUS unit for installation. In addition to helping secure the unit in place during hot fire testing, the umbilical support structures are where the command, control, and data electrical connections are mated to connect the ground systems to the vehicle systems, as well as most the commodity connections such as liquid hydrogen, liquid oxygen, hydrogen vent, helium bottle fill pressure, and purges. Prior to its initial flight, the EUS unit will undergo a series of so-called Green Run tests at NASA Stennis to ensure all systems are ready to go. The test series will culminate with a hot fire of the stage’s four RL10 engines, made by Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company and lead SLS engines contractor. The new upper stage will enable NASA to carry larger payloads on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond.
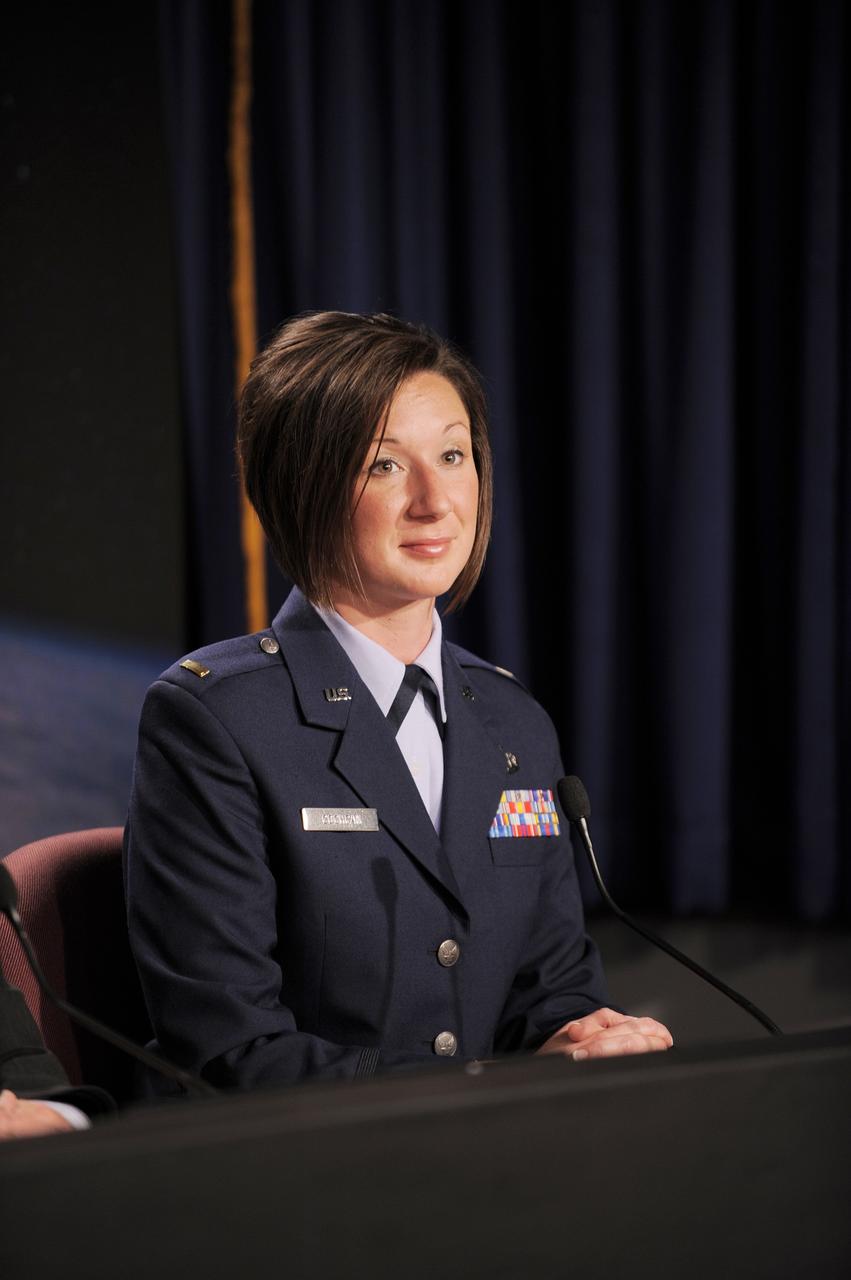

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- 2nd Lt. Lisa Cochran, launch weather officer, 30th Operations Support Squadron, Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif., participates in the prelaunch news conference at Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif., for NASA’s National Polar-orbiting Operational Environmental Satellite System Preparatory Project (NPP) spacecraft. NPP represents a critical first step in building the next-generation of Earth-observing satellites. NPP will carry the first of the new sensors developed for this satellite fleet, now known as the Joint Polar Satellite System (JPSS), to be launched in 2016. NPP is the bridge between NASA's Earth Observing System (EOS) satellites and the forthcoming series of JPSS satellites. The mission will test key technologies and instruments for the JPSS missions. NPP is targeted to launch Oct. 28 from Space Launch Complex-2 aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/NPP. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB
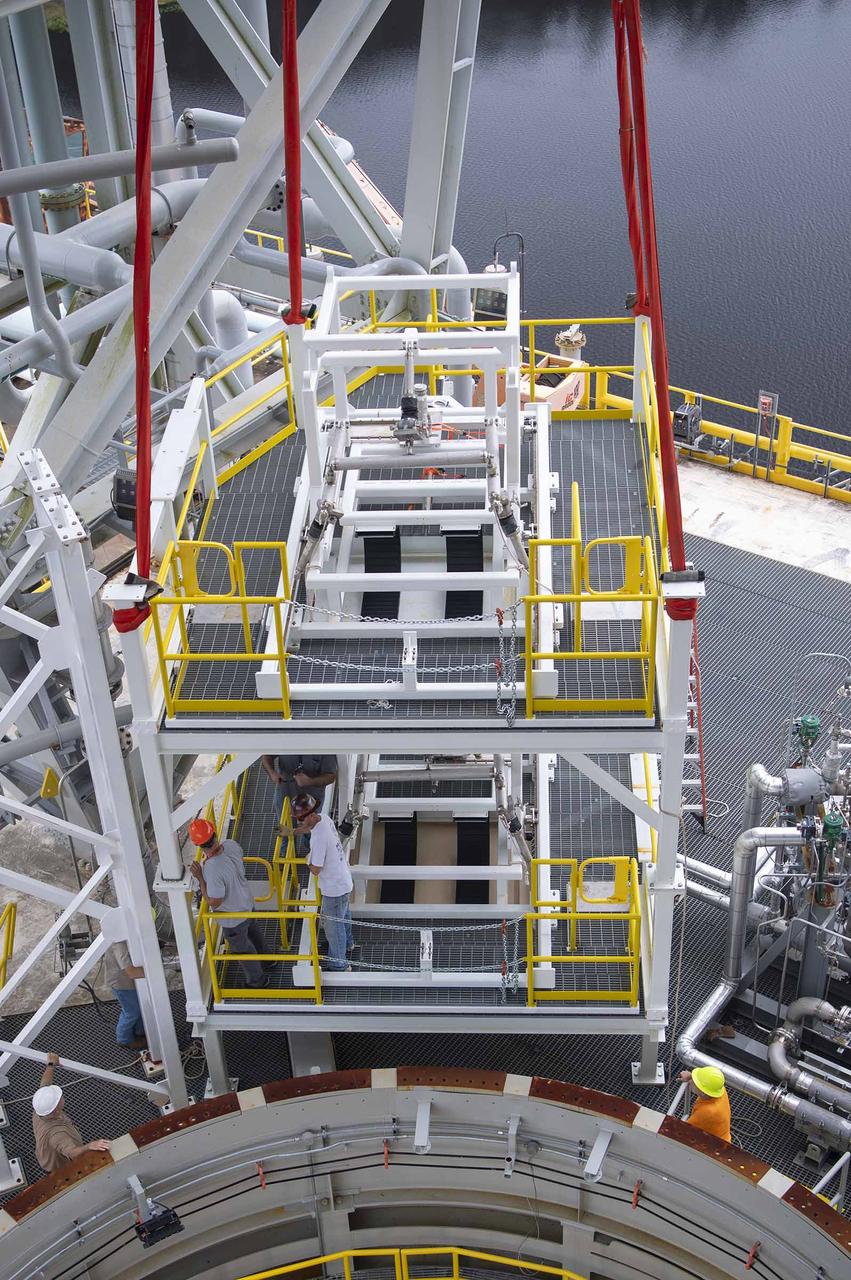

A pair of umbilical support structures needed for future testing of NASA’s exploration upper stage (EUS) were installed in the B-2 position of the Thad Cochran Test Stand on Oct. 30-31 at NASA’s Stennis Space Center. The support structures arrived from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans via the unique NASA Stennis seven-and-a-half-mile canal system in 2023. Since then, crews have prepared the structures that will align with the EUS unit for installation. In addition to helping secure the unit in place during hot fire testing, the umbilical support structures are where the command, control, and data electrical connections are mated to connect the ground systems to the vehicle systems, as well as most the commodity connections such as liquid hydrogen, liquid oxygen, hydrogen vent, helium bottle fill pressure, and purges. Prior to its initial flight, the EUS unit will undergo a series of so-called Green Run tests at NASA Stennis to ensure all systems are ready to go. The test series will culminate with a hot fire of the stage’s four RL10 engines, made by Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company and lead SLS engines contractor. The new upper stage will enable NASA to carry larger payloads on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond.
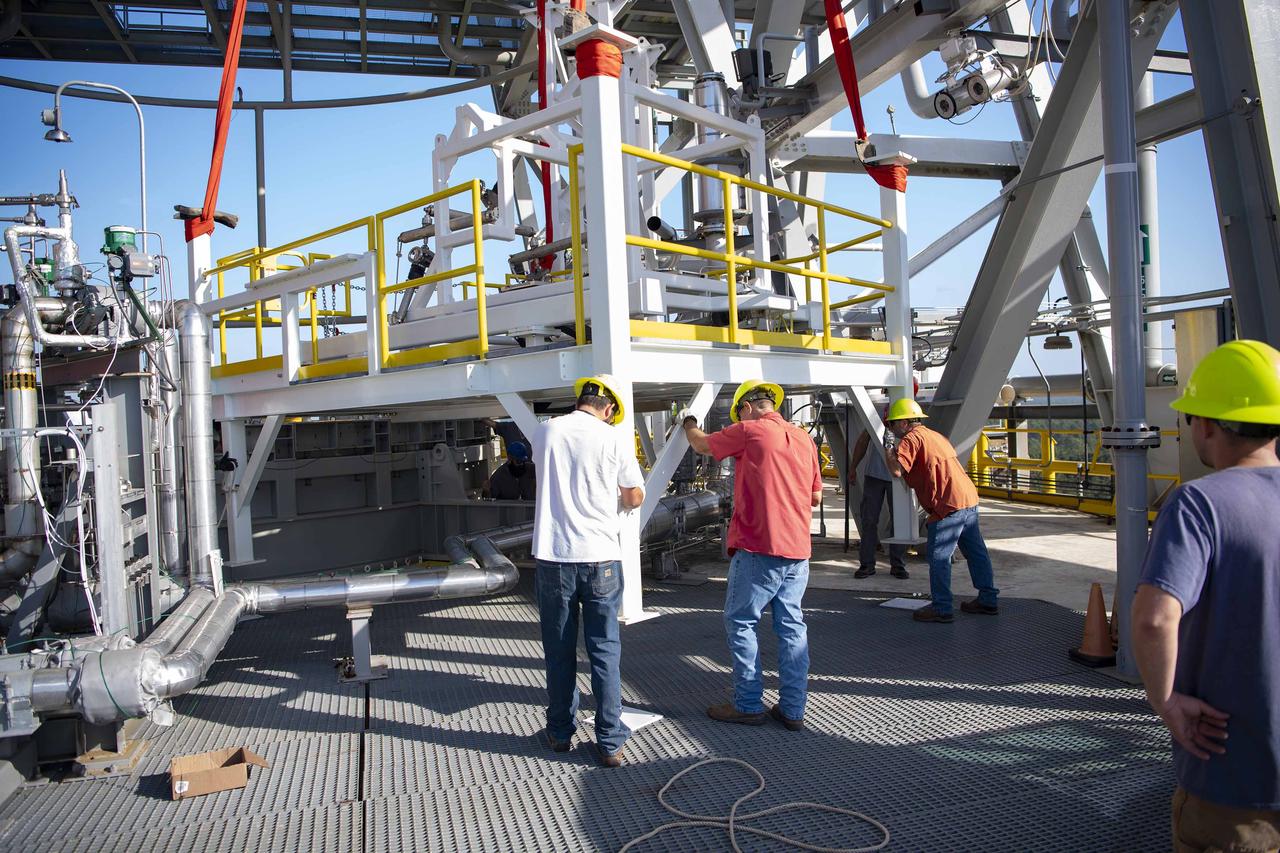

A pair of umbilical support structures needed for future testing of NASA’s exploration upper stage (EUS) were installed in the B-2 position of the Thad Cochran Test Stand on Oct. 30-31 at NASA’s Stennis Space Center. The support structures arrived from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans via the unique NASA Stennis seven-and-a-half-mile canal system in 2023. Since then, crews have prepared the structures that will align with the EUS unit for installation. In addition to helping secure the unit in place during hot fire testing, the umbilical support structures are where the command, control, and data electrical connections are mated to connect the ground systems to the vehicle systems, as well as most the commodity connections such as liquid hydrogen, liquid oxygen, hydrogen vent, helium bottle fill pressure, and purges. Prior to its initial flight, the EUS unit will undergo a series of so-called Green Run tests at NASA Stennis to ensure all systems are ready to go. The test series will culminate with a hot fire of the stage’s four RL10 engines, made by Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company and lead SLS engines contractor. The new upper stage will enable NASA to carry larger payloads on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond.
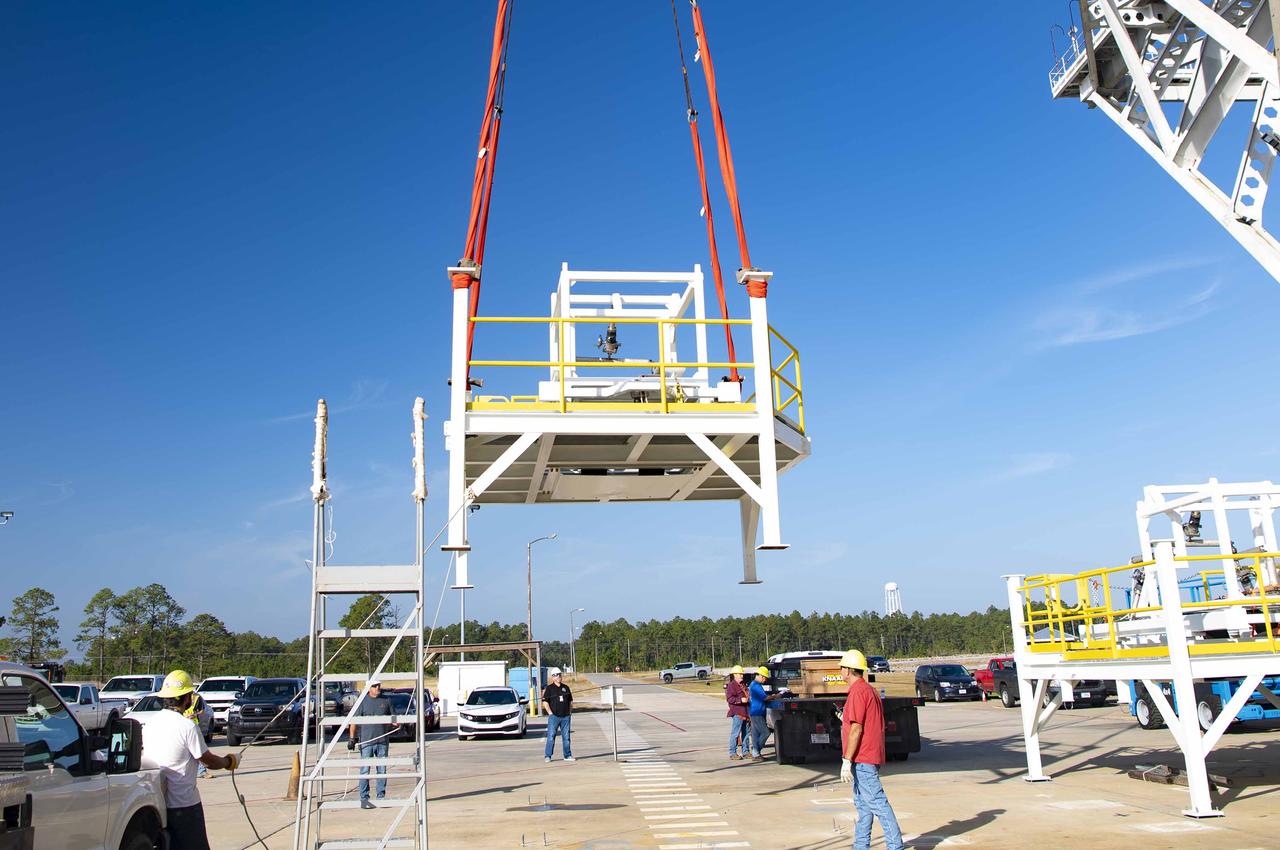

A pair of umbilical support structures needed for future testing of NASA’s exploration upper stage (EUS) were installed in the B-2 position of the Thad Cochran Test Stand on Oct. 30-31 at NASA’s Stennis Space Center. The support structures arrived from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans via the unique NASA Stennis seven-and-a-half-mile canal system in 2023. Since then, crews have prepared the structures that will align with the EUS unit for installation. In addition to helping secure the unit in place during hot fire testing, the umbilical support structures are where the command, control, and data electrical connections are mated to connect the ground systems to the vehicle systems, as well as most the commodity connections such as liquid hydrogen, liquid oxygen, hydrogen vent, helium bottle fill pressure, and purges. Prior to its initial flight, the EUS unit will undergo a series of so-called Green Run tests at NASA Stennis to ensure all systems are ready to go. The test series will culminate with a hot fire of the stage’s four RL10 engines, made by Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company and lead SLS engines contractor. The new upper stage will enable NASA to carry larger payloads on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond.
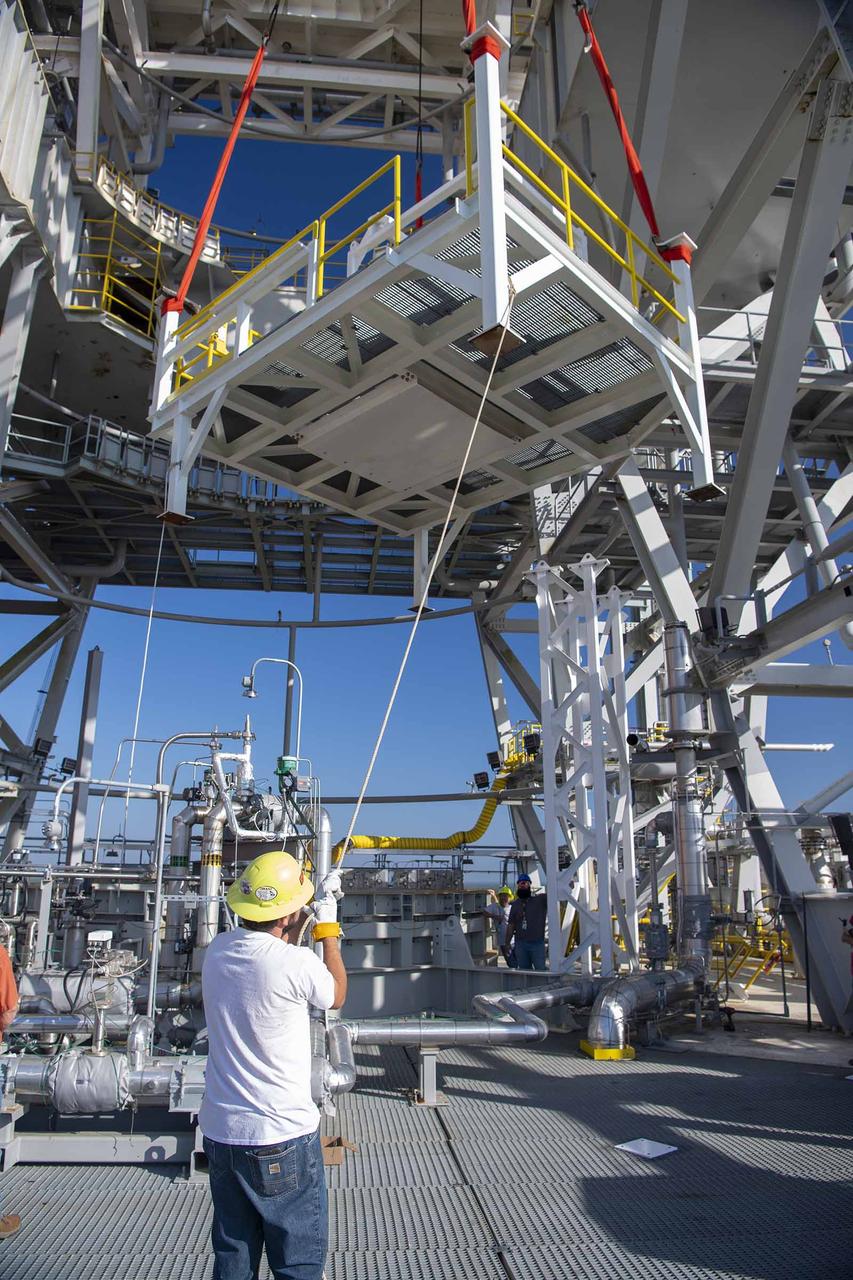

A pair of umbilical support structures needed for future testing of NASA’s exploration upper stage (EUS) were installed in the B-2 position of the Thad Cochran Test Stand on Oct. 30-31 at NASA’s Stennis Space Center. The support structures arrived from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans via the unique NASA Stennis seven-and-a-half-mile canal system in 2023. Since then, crews have prepared the structures that will align with the EUS unit for installation. In addition to helping secure the unit in place during hot fire testing, the umbilical support structures are where the command, control, and data electrical connections are mated to connect the ground systems to the vehicle systems, as well as most the commodity connections such as liquid hydrogen, liquid oxygen, hydrogen vent, helium bottle fill pressure, and purges. Prior to its initial flight, the EUS unit will undergo a series of so-called Green Run tests at NASA Stennis to ensure all systems are ready to go. The test series will culminate with a hot fire of the stage’s four RL10 engines, made by Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company and lead SLS engines contractor. The new upper stage will enable NASA to carry larger payloads on Artemis missions to the Moon and beyond.
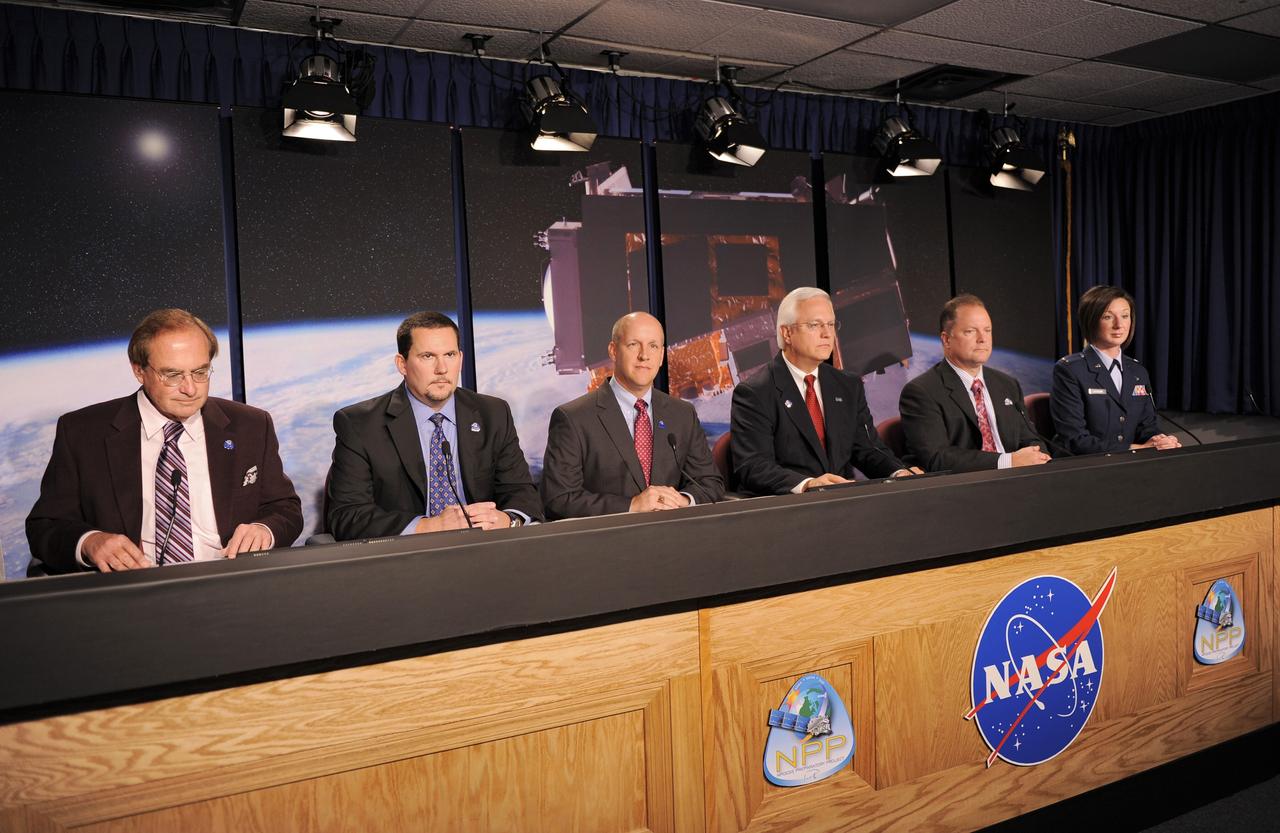

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- Participants in the prelaunch news conference for NASA’s National Polar-orbiting Operational Environmental Satellite System Preparatory Project (NPP) spacecraft prepare to address members of the news media gathered at Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. Panelists are, from left, George Diller, NASA launch commentator, Andrew Carson, NPP program executive, NASA Headquarters, Tim Dunn, NASA launch director, Kennedy Space Center, Vernon Thorp, program manager, NASA missions, United Launch Alliance, Ken Schwer, NPP project manager, Goddard Space Flight Center, and 2nd Lt. Lisa Cochran, launch weather officer, 30th Operations Support Squadron, Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. NPP represents a critical first step in building the next-generation of Earth-observing satellites. NPP will carry the first of the new sensors developed for this satellite fleet, now known as the Joint Polar Satellite System (JPSS), to be launched in 2016. NPP is the bridge between NASA's Earth Observing System (EOS) satellites and the forthcoming series of JPSS satellites. The mission will test key technologies and instruments for the JPSS missions. NPP is targeted to launch Oct. 28 from Space Launch Complex-2 aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/NPP. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB