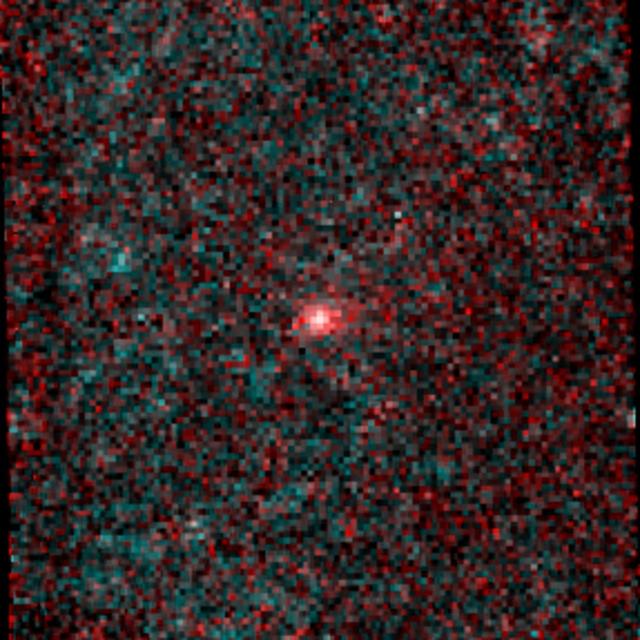

Comet NEOWISE was first observed by NASA NEOWISE spacecraft on Valentine Day, 2014. This heat-sensitive infrared image was made by combining six exposures taken by the NEOWISE mission of the newly discovered comet.
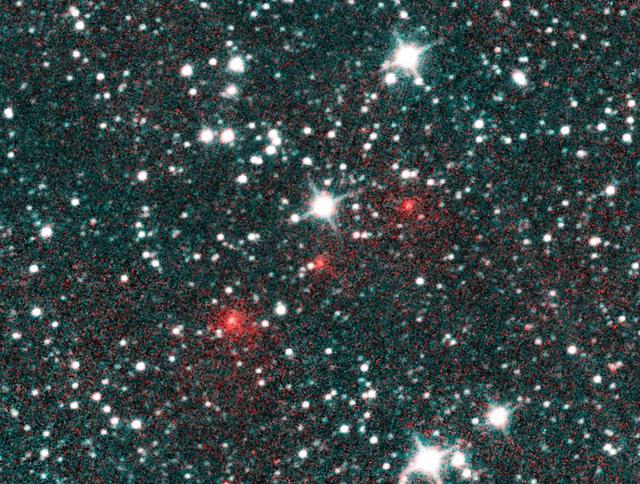

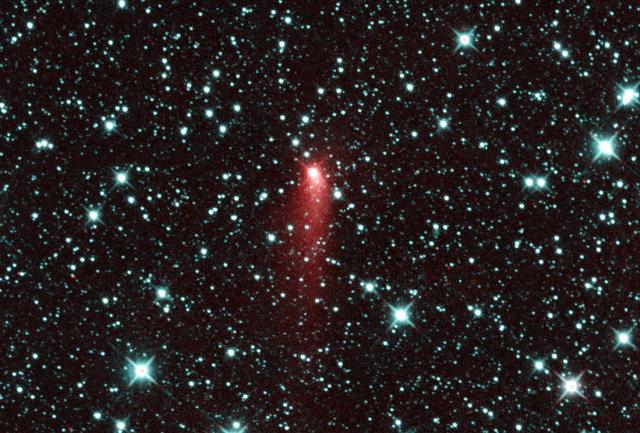
Comet C/2020 F3 NEOWISE appears as a string of fuzzy red dots in this composite of several heat-sensitive infrared images taken by NASA's Near-Earth Object Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (NEOWISE) mission on March 27, 2020. The comet was discovered using these images to track its motion across the sky against the backdrop of stationary stars and galaxies. These images have been processed such that cyan colors represent NEOWISE's 3.4-micron channel (a wavelength of light approximately seven times longer than the green light that humans see), and red colors represent the NEOWISE 4.6-micron channel. The comet's extended halo, or coma, of gas and dust was already apparent in the discovery images. The comet appears much redder than the background stars and galaxies because it is much cooler and therefore emits more light at longer wavelengths. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23792
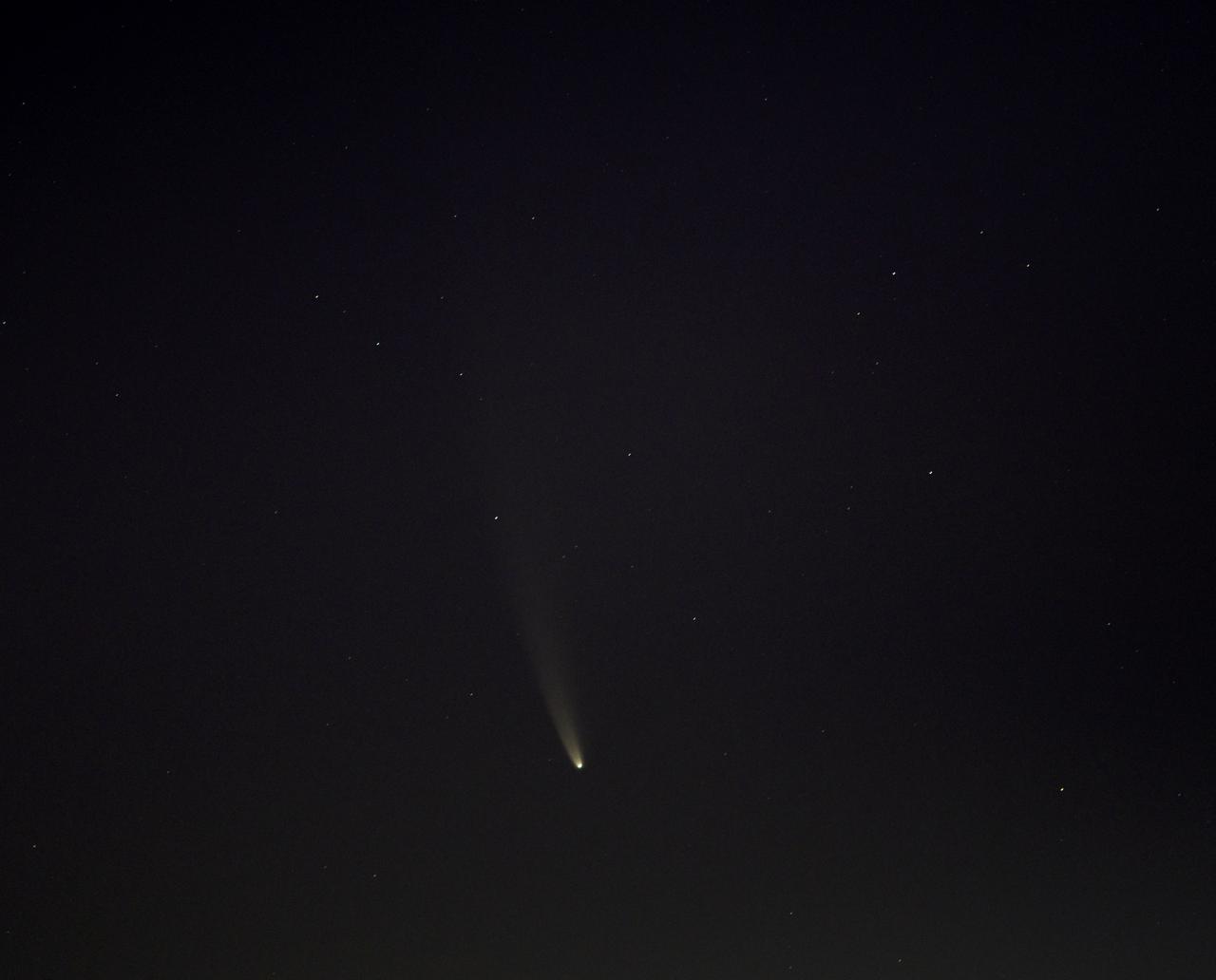

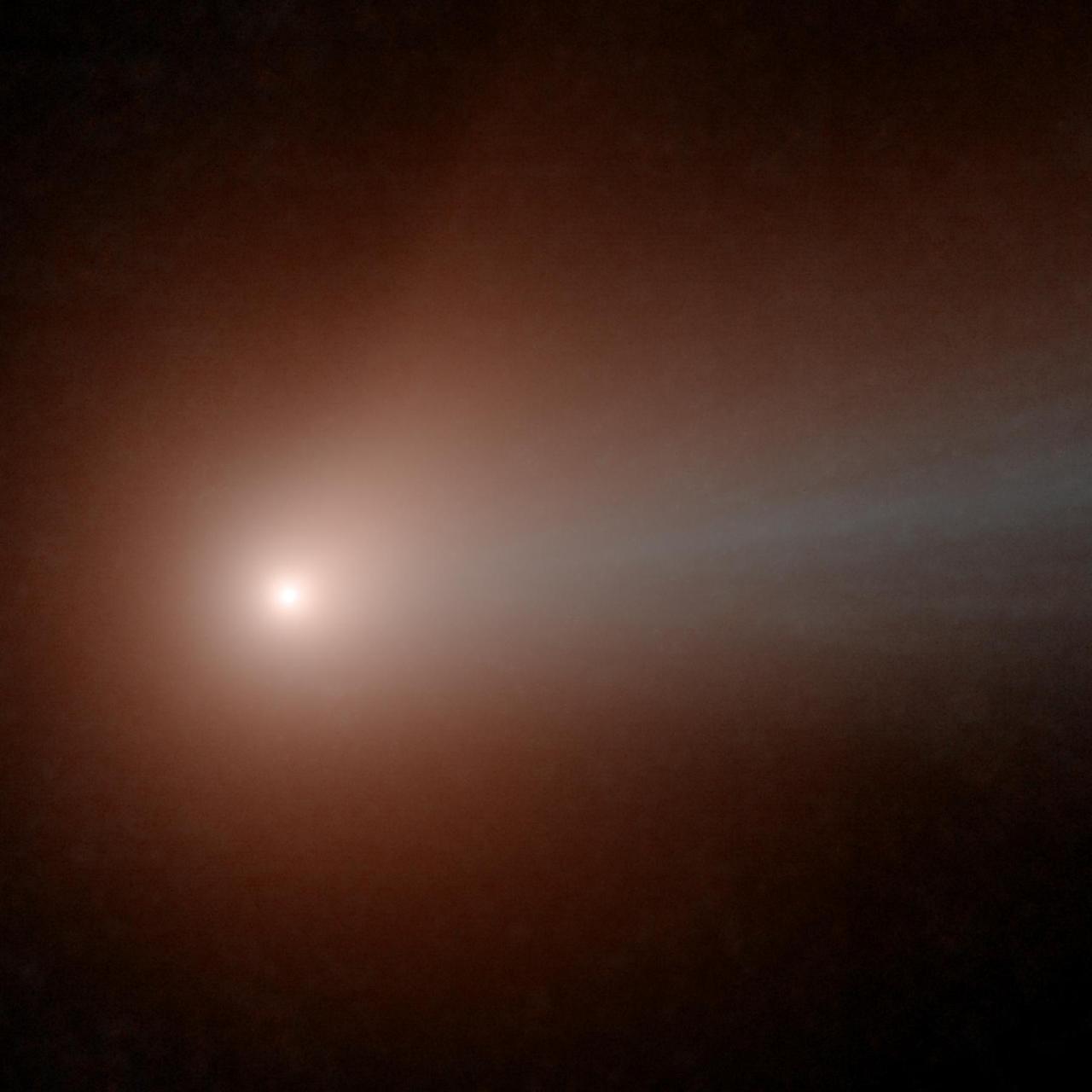
Comet NEOWISE is seen before sunrise over Washington, Sunday, July 12, 2020. The comet was discovered by NASA’s Near-Earth Object Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, or NEOWISE, on March 27. Since then, the comet — called comet C/2020 F3 NEOWISE and nicknamed comet NEOWISE — has been spotted by several NASA spacecraft, including Parker Solar Probe, NASA’s Solar and Terrestrial Relations Observatory, the ESA/NASA Solar and Heliospheric Observatory, and astronauts aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
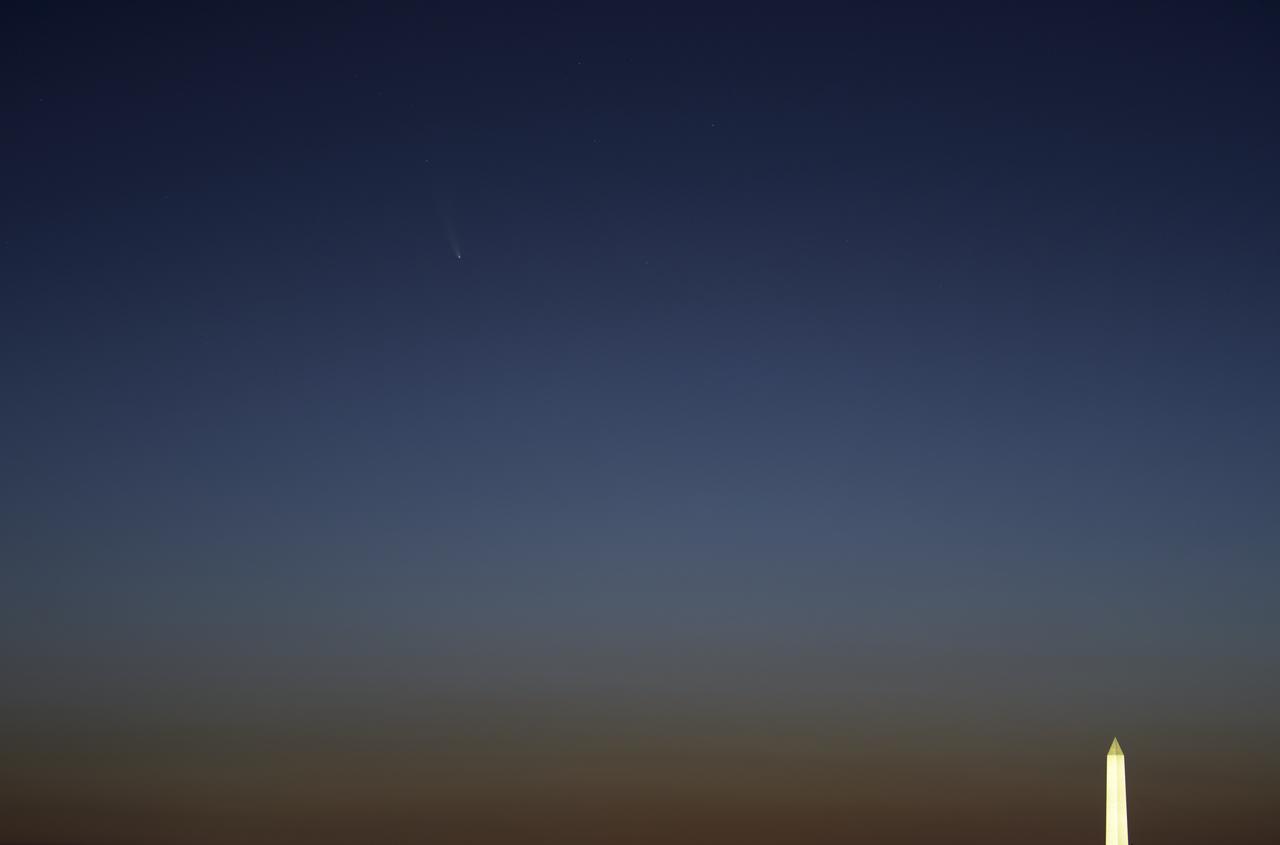

Comet NEOWISE is seen, upper left, before sunrise over Washington, Sunday, July 12, 2020. The comet was discovered by NASA’s Near-Earth Object Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, or NEOWISE, on March 27. Since then, the comet — called comet C/2020 F3 NEOWISE and nicknamed comet NEOWISE — has been spotted by several NASA spacecraft, including Parker Solar Probe, NASA’s Solar and Terrestrial Relations Observatory, the ESA/NASA Solar and Heliospheric Observatory, and astronauts aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
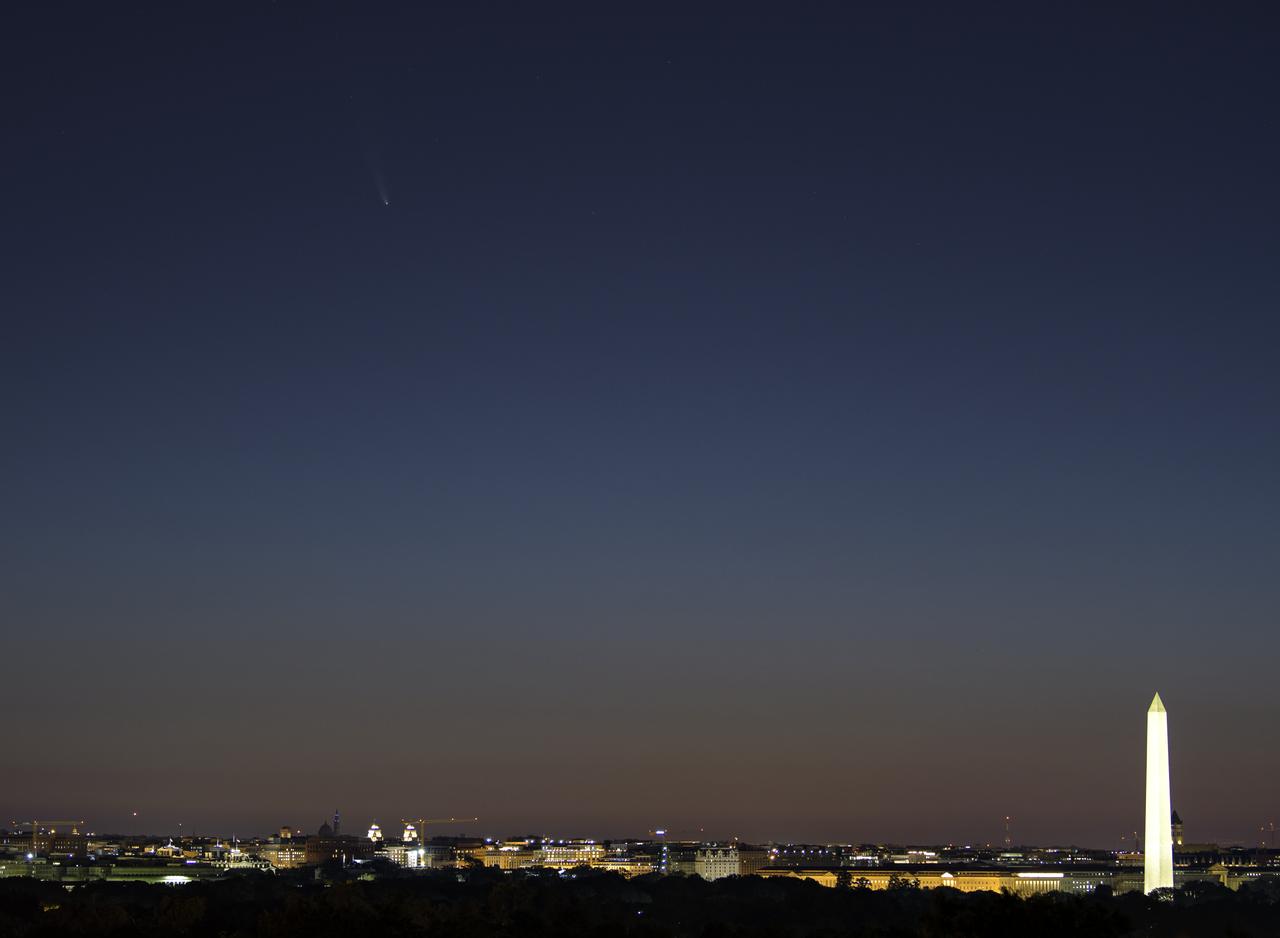

Comet NEOWISE is seen before sunrise, upper left, over Washington, Sunday, July 12, 2020. The comet was discovered by NASA’s Near-Earth Object Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, or NEOWISE, on March 27. Since then, the comet — called comet C/2020 F3 NEOWISE and nicknamed comet NEOWISE — has been spotted by several NASA spacecraft, including Parker Solar Probe, NASA’s Solar and Terrestrial Relations Observatory, the ESA/NASA Solar and Heliospheric Observatory, and astronauts aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
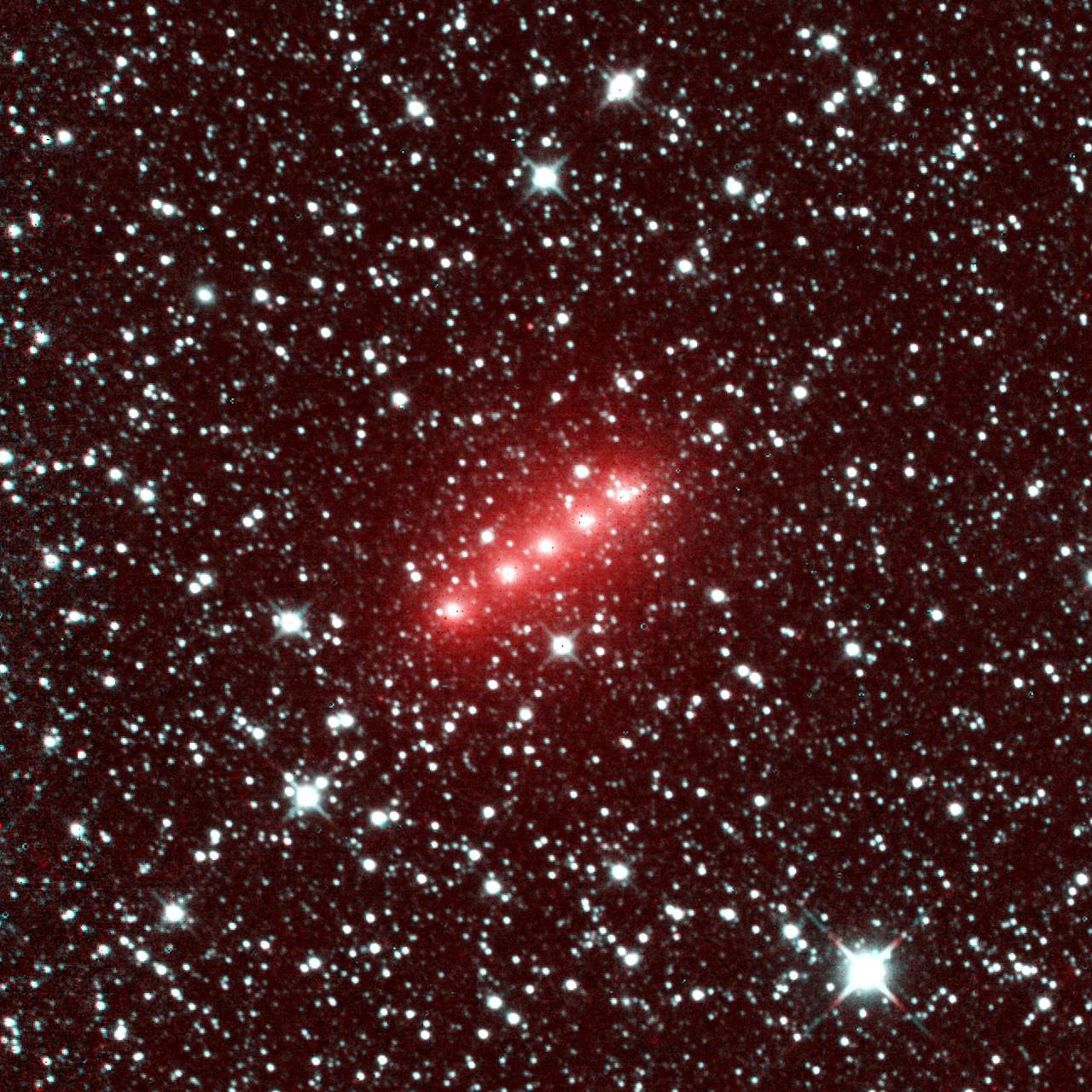

Comet C/2014 Q2 Lovejoy is one of more than 32 comets imaged by NASA NEOWISE mission from December 2013 to December 2014. This image of comet Lovejoy combines a series of observations made in November 2013.
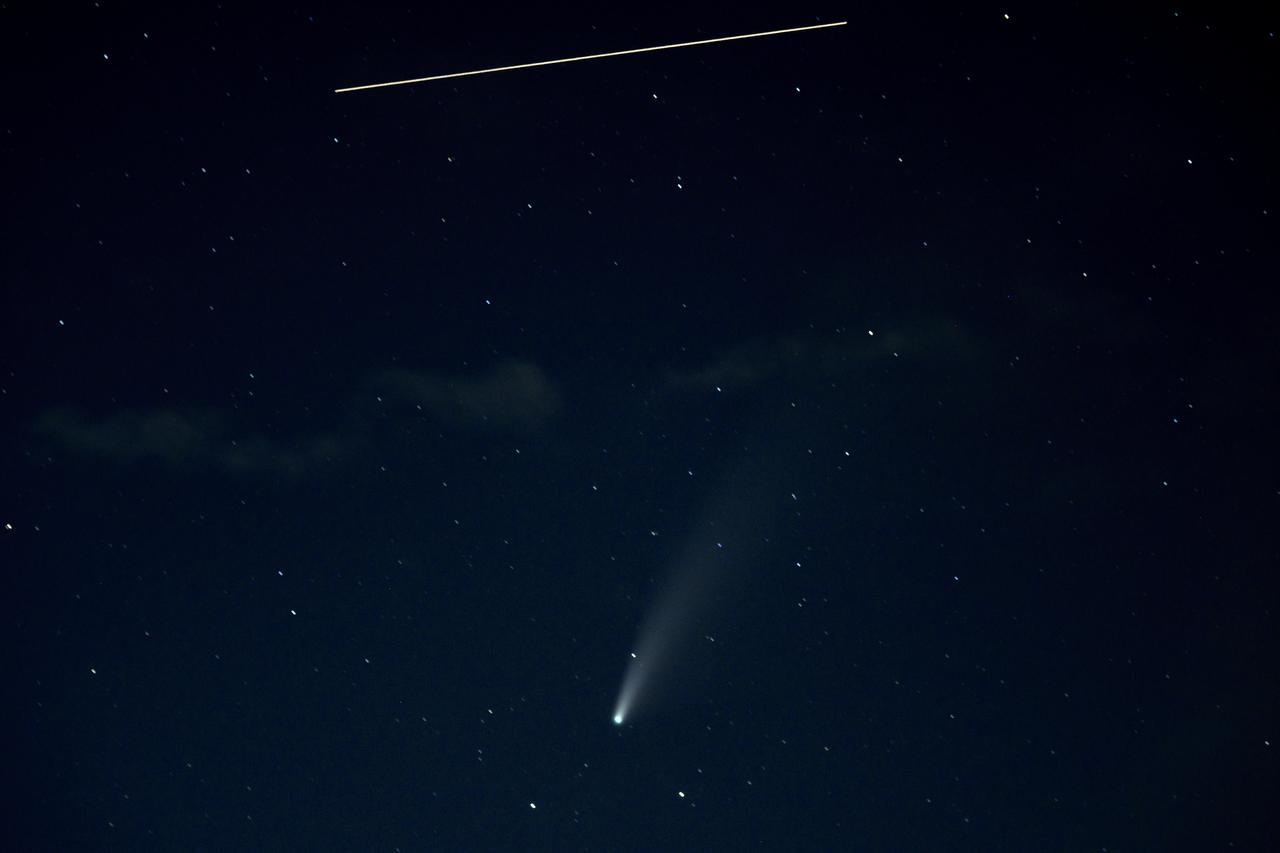

The International Space Station, with a crew of five onboard, is seen in this 10 second exposure above comet NEOWISE, Saturday, July 18, 2020 from Keys Gap, W.Va. The comet was discovered by NASA’s Near-Earth Object Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, or NEOWISE, on March 27. Since then, the comet — called comet C/2020 F3 NEOWISE and nicknamed comet NEOWISE — has been spotted by several NASA spacecraft, including Parker Solar Probe, NASA’s Solar and Terrestrial Relations Observatory, the ESA/NASA Solar and Heliospheric Observatory, and astronauts aboard the International Space Station. Onboard the International Space Station are Expedition 63 NASA astronauts Chris Cassidy, Douglas Hurley, Robert Behnken, and Roscosmos cosmonauts Anatoly Ivanishin and Ivan Vagner. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
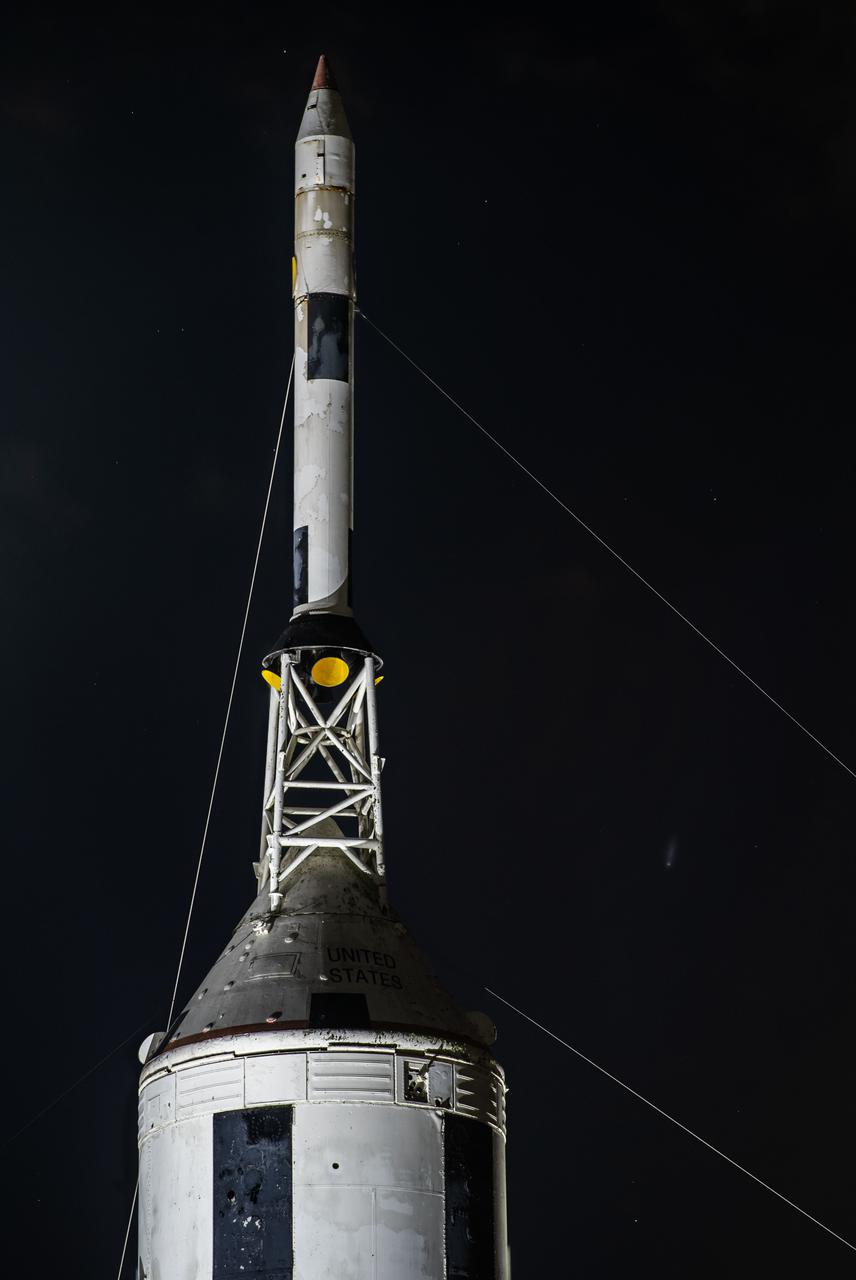

Comet NEOWISE passing over the Little Joe II rocket at NASA Johnson Space Center’s Rocket Park on July 22nd, 2020.

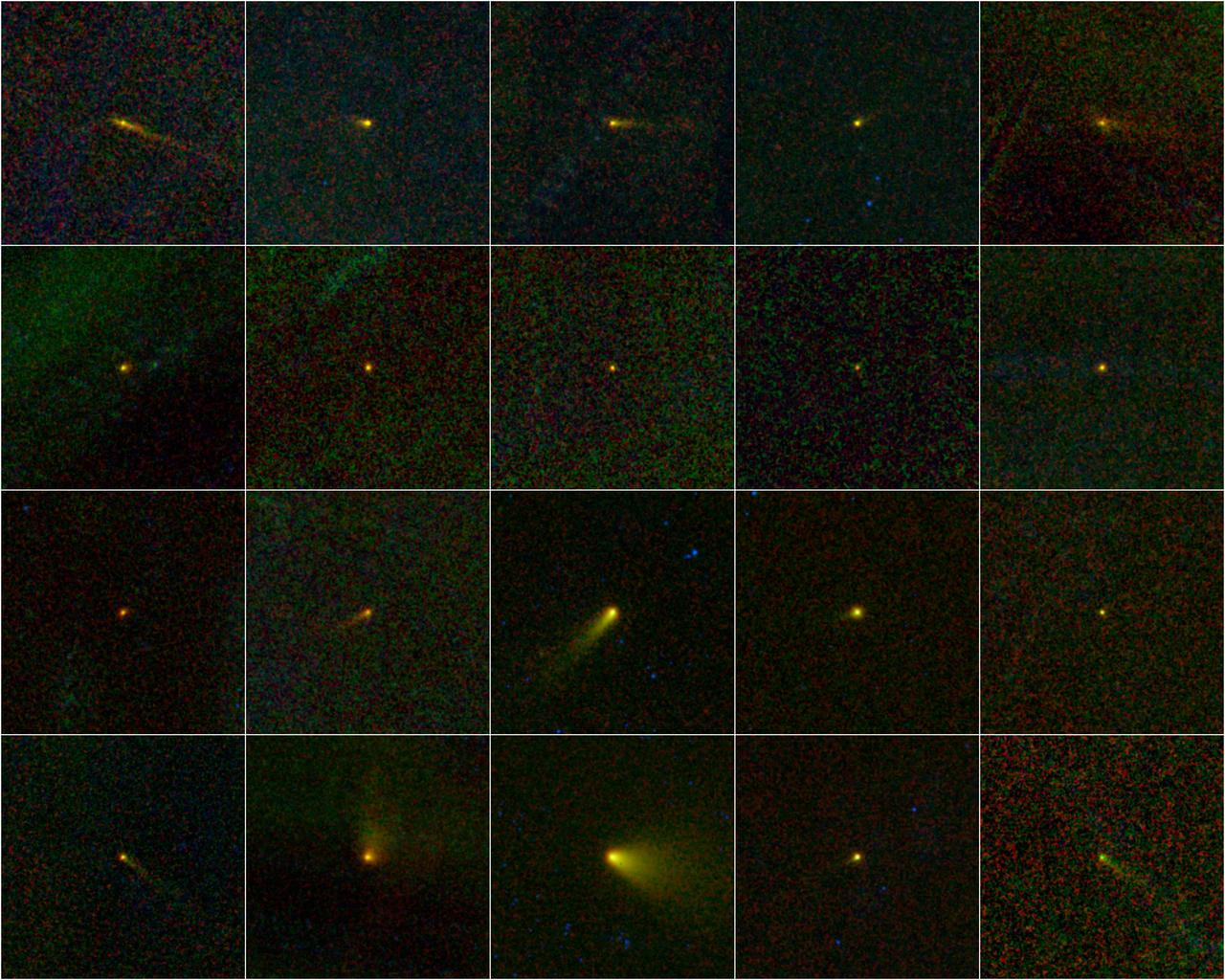
NASA NEOWISE mission captured this series of pictures of comet C/2012 K1 -- also known as comet Pan-STARRS -- as it swept across our skies on May 20, 2014.

NASA NEOWISE spotted Comet C/2013 UQ4 Catalina, appearing to be a highly active comet one day past perihelion on July 7, 2014.
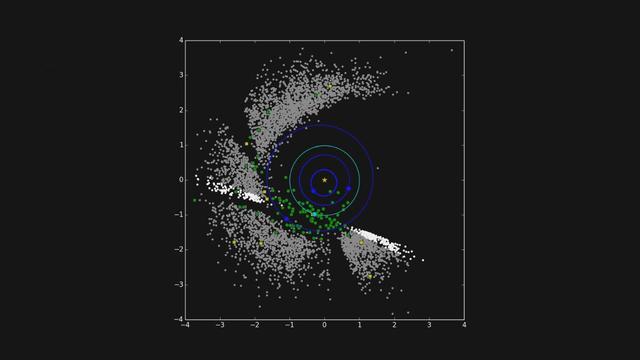
This frame from a movie shows the progression of NASA NEOWISE survey in the mission first year following its restart in December 2013. Each dot represents an asteroid or comet that the mission observed.

NASA NEOWISE spacecraft viewed comet C/2014 Q2 Lovejoy for a second time on January 30, 2015, as the comet passed through the closest point to our sun along its 14,000-year orbit, at a solar distance of 120 million miles 193 million kilometers.

Comet C/2013 UQ4 Catalina first looked like an asteroid when NASA NEOWISE team first observed it on December 31, 2013. These exposures were taken that day, when the comet was at a distance of about 2.9 AU from the sun.

NASA NEOWISE mission captured images of Comet C/2013 A1 Siding Spring. The infrared pictures reveal a comet that is active and very dusty.

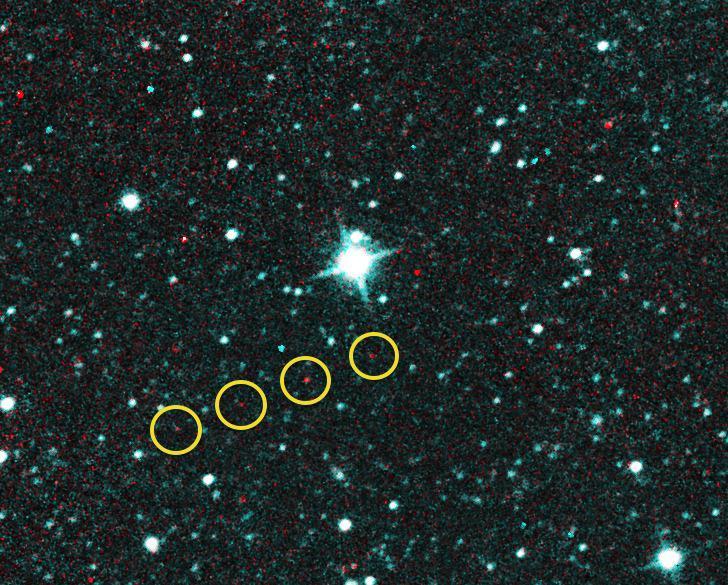
Comet C/2018 Y1 Iwamoto as imaged in multiple exposures of infrared light by the NEOWISE space telescope. The infrared images were taken on Feb. 25, 2019, when the comet was about 56 million miles, or 90 million kilometers, from Earth. C/2018 Y1 Iwamoto is a long-period comet originally from the Oort Cloud and coming in near the Sun for the first time in over 1,000 years. Appearing as a string of red dots, this comet can be seen in a series of exposures captured by the spacecraft. Infrared light detected by the 3.4-micron channel is mapped to blue and green, while light from the 4.6-micron channel is mapped to red. In this image, stars show up as blue because they are hotter, whereas the cooler dust around the comet - with a temperature near the freezing point of water - glows red. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23165
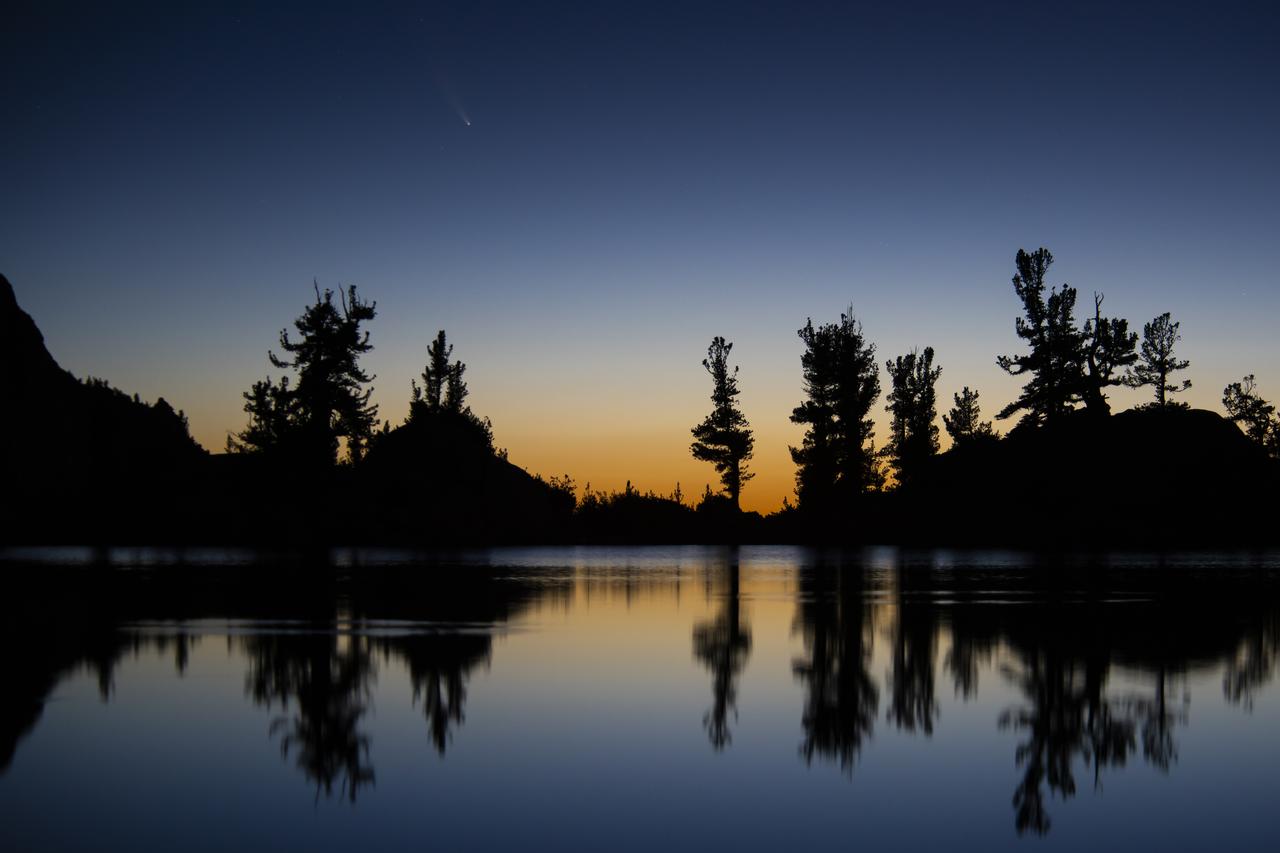

An image of the Comet C/2020 F3 NEOWISE (Comet NEOWISE) captured above the tree line of Lone Pine Lake, located on the Mount Whitney Trail in the Eastern Sierra Nevada Mountains in California. The photo was taken at 4:59 am on July 14, 2020. Visiting from the distant parts of the solar system, it’s characterized by a glowing tail and is visible during the month of July. The comet returns in 6,800 years.
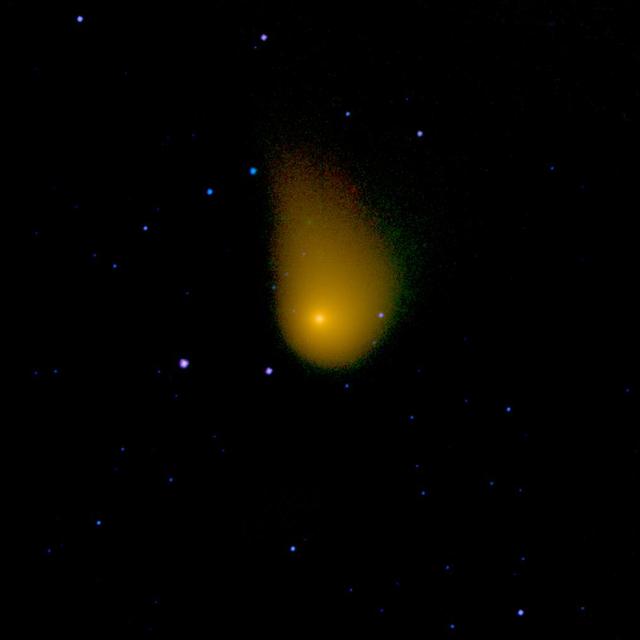
An infrared view from NASA's NEOWISE mission of the Oort cloud comet C/2006 W3 (Christensen). The spacecraft observed this comet on April 20th, 2010 as it traveled through the constellation Sagittarius. Comet Christensen was nearly 370 million miles (600 million kilometers) from Earth at the time. The image is half of a degree of the sky on each side. Infrared light with wavelengths of 3.4, 12 and 22 micron channels are mapped to blue, green, and red, respectively. The signal at these wavelengths is dominated primarily by the comet's dust thermal emission, giving it a golden hue. The WISE spacecraft was put into hibernation in 2011 upon completing its goal of surveying the entire sky in infrared light. WISE cataloged three quarters of a billion objects, including asteroids, stars and galaxies. In August 2013, NASA decided to reinstate the spacecraft on a mission to find and characterize more asteroids. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20118
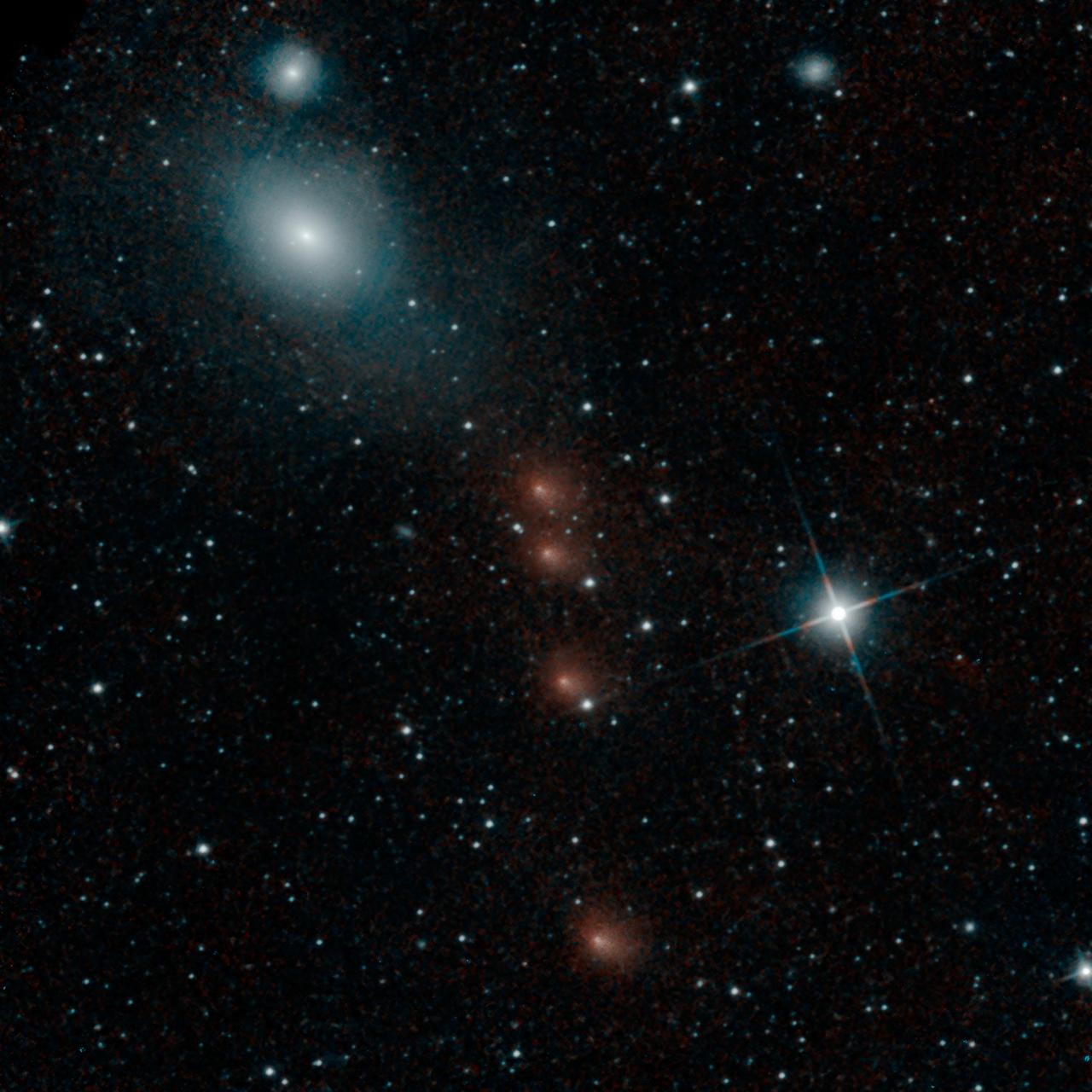

NASA NEOWISE mission detected comet C/2013 A1 Siding Spring on July 28, 2014, less than three months before this comet close flyby of Mars on Oct. 19.
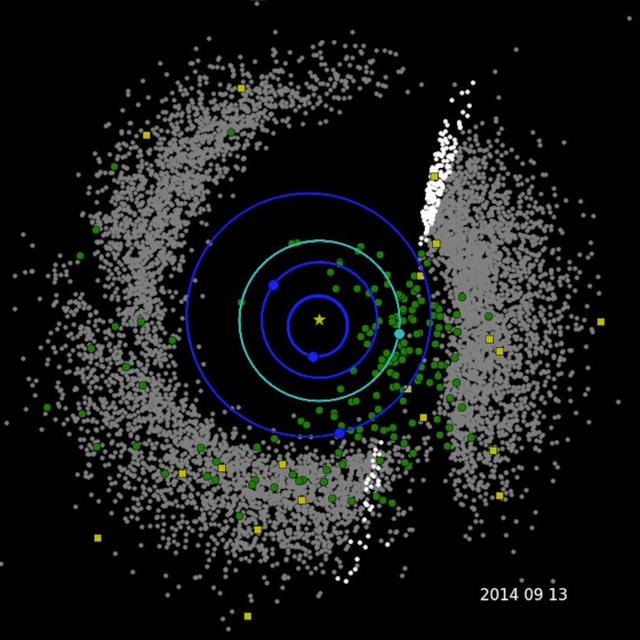
This frame from a movie shows the progression of NASA's Near-Earth Object Wide-field Survey Explorer (NEOWISE) investigation for the mission's first three years following its restart in December 2013. Green circles represent near-Earth objects (asteroids and comets that come within 1.3 astronomical units of the sun; one astronomical unit is Earth's distance from the sun). Yellow squares represent comets. Gray dots represent all other asteroids, which are mostly in the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. The orbits of Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars are shown. The spacecraft has characterized a total of 693 near-Earth objects since the mission was restarted in December 2013. Of these, 114 are new discoveries. A movie is avaiable at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21653

This artist concept shows the NASA WISE spacecraft, in its orbit around Earth. In September of 2013, engineers will attempt to bring the mission out of hibernation to hunt for more asteroids and comets in a project called NEOWISE.
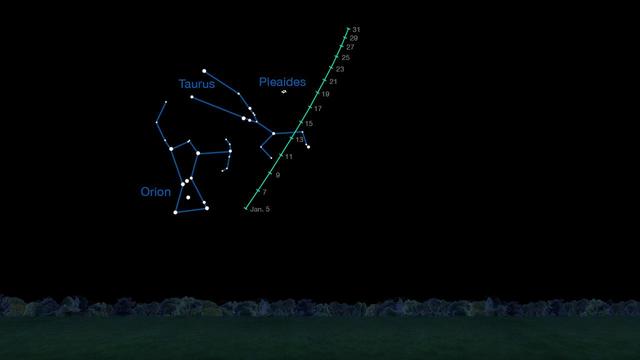
On clear nights in January 2015, comet C/2014 Q2 Lovejoy is visible in the Taurus region of the sky to observers using binoculars. This chart indicates where to look for it on different dates during the month.
During its one-year mission, NASA Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, mapped the entire sky in infrared light. Among the multitudes of astronomical bodies that have been discovered by the NEOWISE portion of the WISE mission are 20 comets.
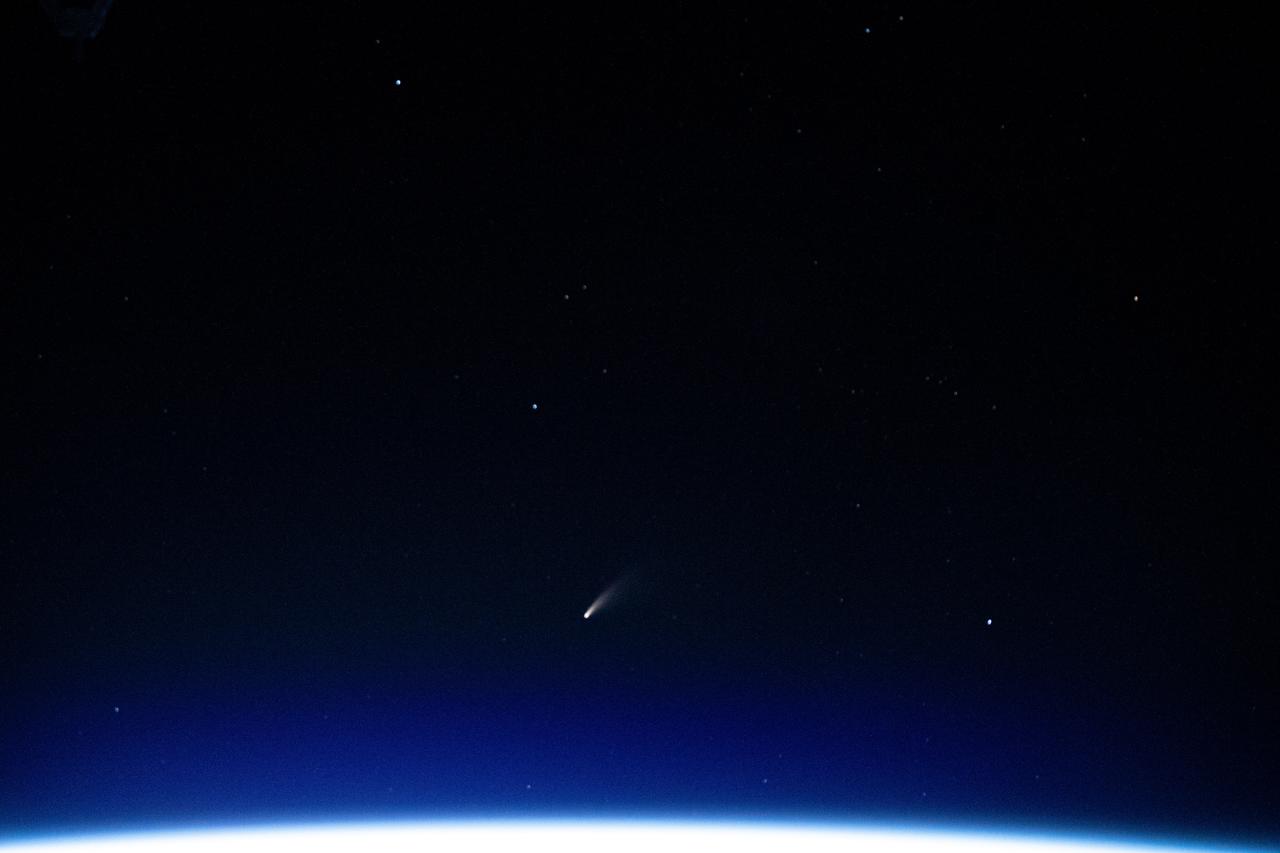

iss063e040067 (July 5, 2020) --- The tiny shooting star in the lower center of this image is Comet Neowise pictured from the International Space Station as it orbited above the Mediterranean Sea in between Tunisia and Italy.

iss063e040072 (July 5, 2020) --- The tiny shooting star in the lower center of this image is Comet Neowise pictured from the International Space Station as it orbited above the Mediterranean Sea in between Tunisia and Italy.
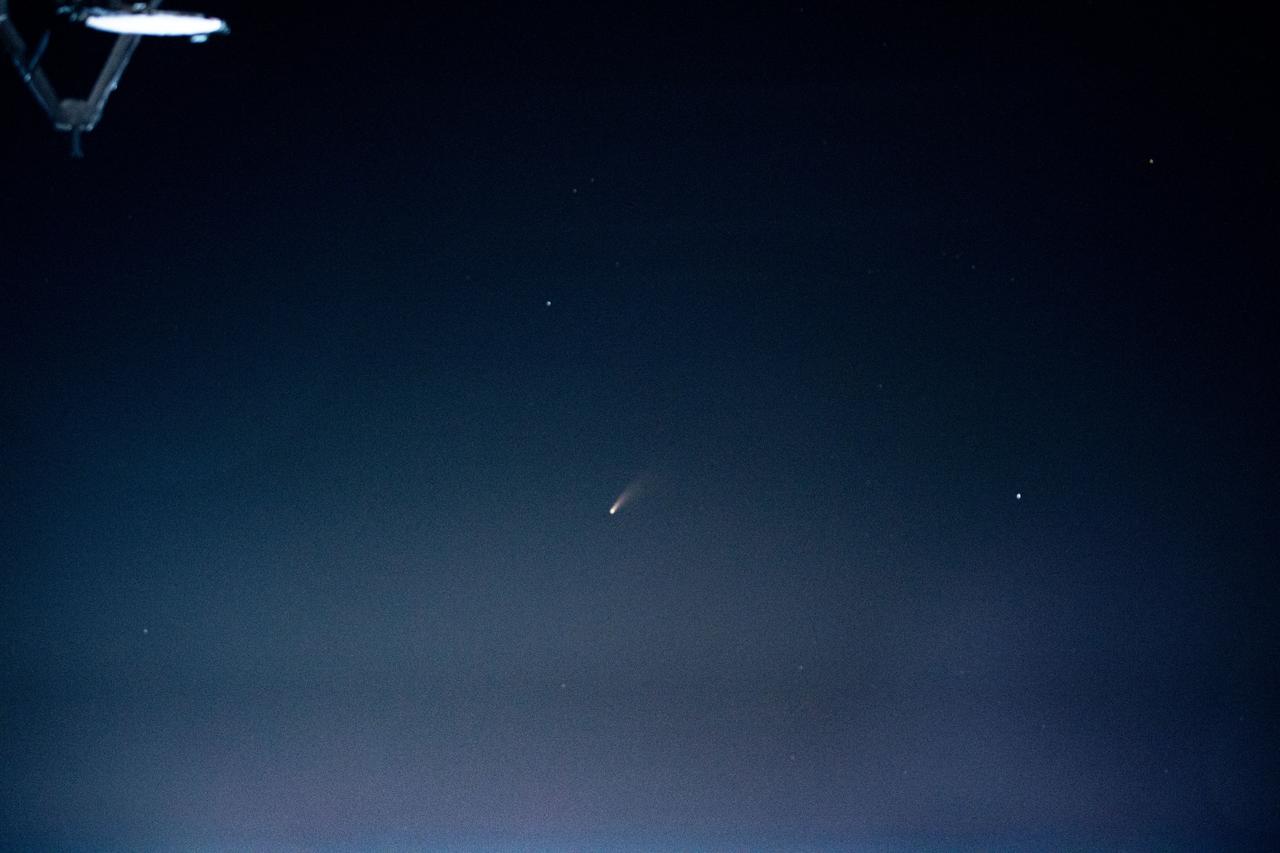

iss063e040094 (July 5, 2020) --- Comet Neowise was photographed by an Expedition 63 crew member as the International Space Station orbited above Rome, Italy, just after 1:36 a.m. local time on July 5.
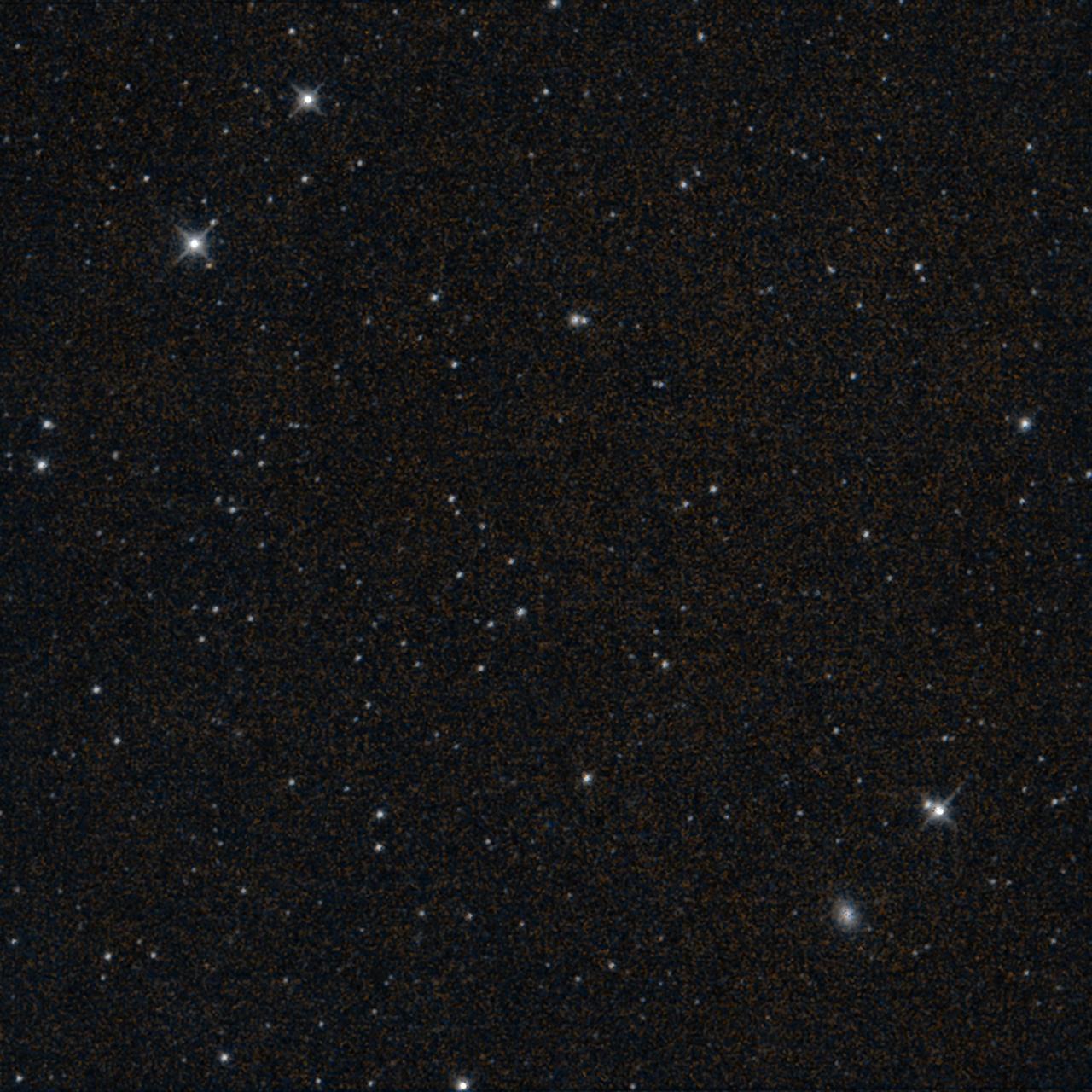

This starfield was imaged by NASA's Near-Earth Object Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (NEOWISE) moments before the mission's science survey ended at midnight on July 31, 2024. The observation shows part of Fornax, a constellation that is visible in Southern Hemisphere skies. The spacecraft's final image, which was processed by IPAC at Caltech, takes in a view about three times the width of Earth's full Moon. This infrared exposure is the space telescope's 26,886,704th, a number that includes observations captured during its WISE (Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer) mission. In addition to the stars and galaxies that appear as points of light, the spiral galaxy NGC 1339 can be seen as a fuzzy oval in the bottom right of the observation. NGC 1339 is about 64 million light-years from Earth. On Aug. 8, a week after the image was captured, project engineers commanded the spacecraft to turn its transmitter off for the last time. This concluded more than 10 years of the planetary defense mission's search for asteroids and comets, including those that could pose a threat to Earth. By repeatedly observing the sky from low Earth orbit, NEOWISE created all-sky maps featuring 1.45 million infrared measurements of more than 44,000 solar system objects. Of the 3,000-plus near-Earth objects it detected, 215 were first spotted by NEOWISE. The mission also discovered 25 new comets, including the famed comet C/2020 F3 NEOWISE. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26385

In this illustration showing NEO Surveyor, NASA's next-generation near-Earth object hunter, the spacecraft floats in an infrared starfield containing stars, star clusters, gas, and dust. More than 100 asteroids can be seen as red dots, with some of them visible in a track that shows how they were captured at different times as they marched across the sky. This starfield was observed by NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE, during its primary all-sky survey in March 2010 before it was put into hibernation a year later. In December 2013, the space telescope was reactivated to search for more asteroids as the NEOWISE mission. NASA's NEO Surveyor will build upon the successes of NEOWISE as the first space mission built specifically to find large numbers of hazardous asteroids and comets. The space telescope will launch to a region of gravitational stability between the Earth and the Sun called the L1 Lagrange point, where the spacecraft will orbit during its five-year primary mission. From this location, the space telescope will view the solar system in infrared wavelengths &ndash light that is invisible to the human eye. Because those wavelengths are mostly blocked by Earth's atmosphere, larger ground-based observatories may miss near-Earth objects that NEO Surveyor will be able to spot from space by using its modest light-collecting aperture of nearly 20 inches (50 centimeters). NEO Surveyor's cutting-edge detectors are designed to observe two heat-sensitive infrared bands that were chosen specifically so the spacecraft can track the most challenging-to-find near-Earth objects, such as dark asteroids and comets that don't reflect much visible light. In the infrared wavelengths to which NEO Surveyor is sensitive, these objects glow as they are heated by sunlight. In addition, NEO Surveyor will be able to find asteroids that approach Earth from the direction of the Sun, as well as those that lead and trail our planet's orbit, where they are typically obscured by the glare of sunlight – objects known as Earth Trojans. The mission is tasked by NASA's Planetary Science Division within the Science Mission Directorate; program oversight is provided by the PDCO, which was established in 2016 to manage the agency's ongoing efforts in planetary defense. NASA's Planetary Missions Program Office at Marshall Space Flight Center provides program management for NEO Surveyor. The project is being developed by JPL and is led by survey director Amy Mainzer at the University of Arizona. Established aerospace and engineering companies have been contracted to build the spacecraft and its instrumentation, including Ball Aerospace , Space Dynamics Laboratory, and Teledyne. The Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics at the University of Colorado, Boulder will support operations, and IPAC-Caltech in Pasadena, California, is responsible for processing survey data and producing the mission's data products. Caltech manages JPL for NASA. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25253