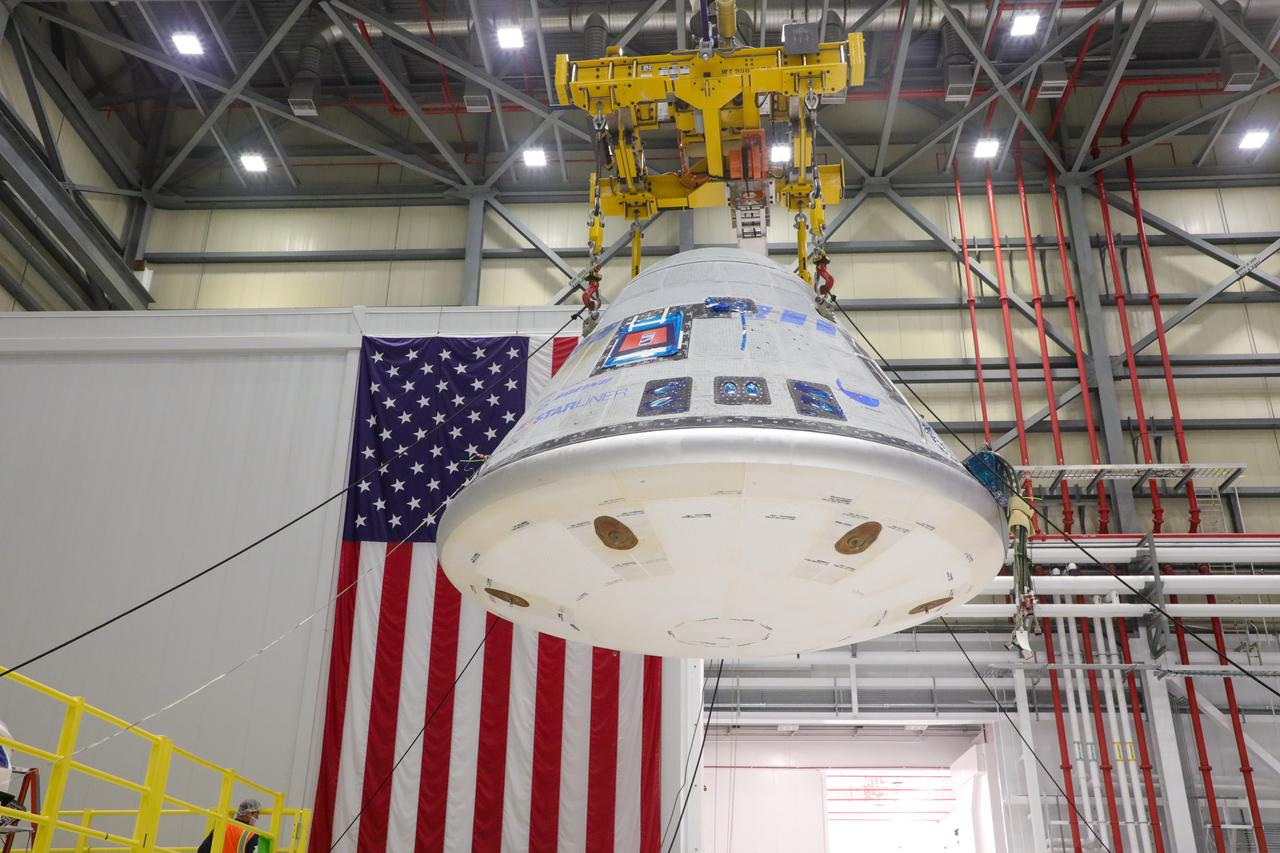

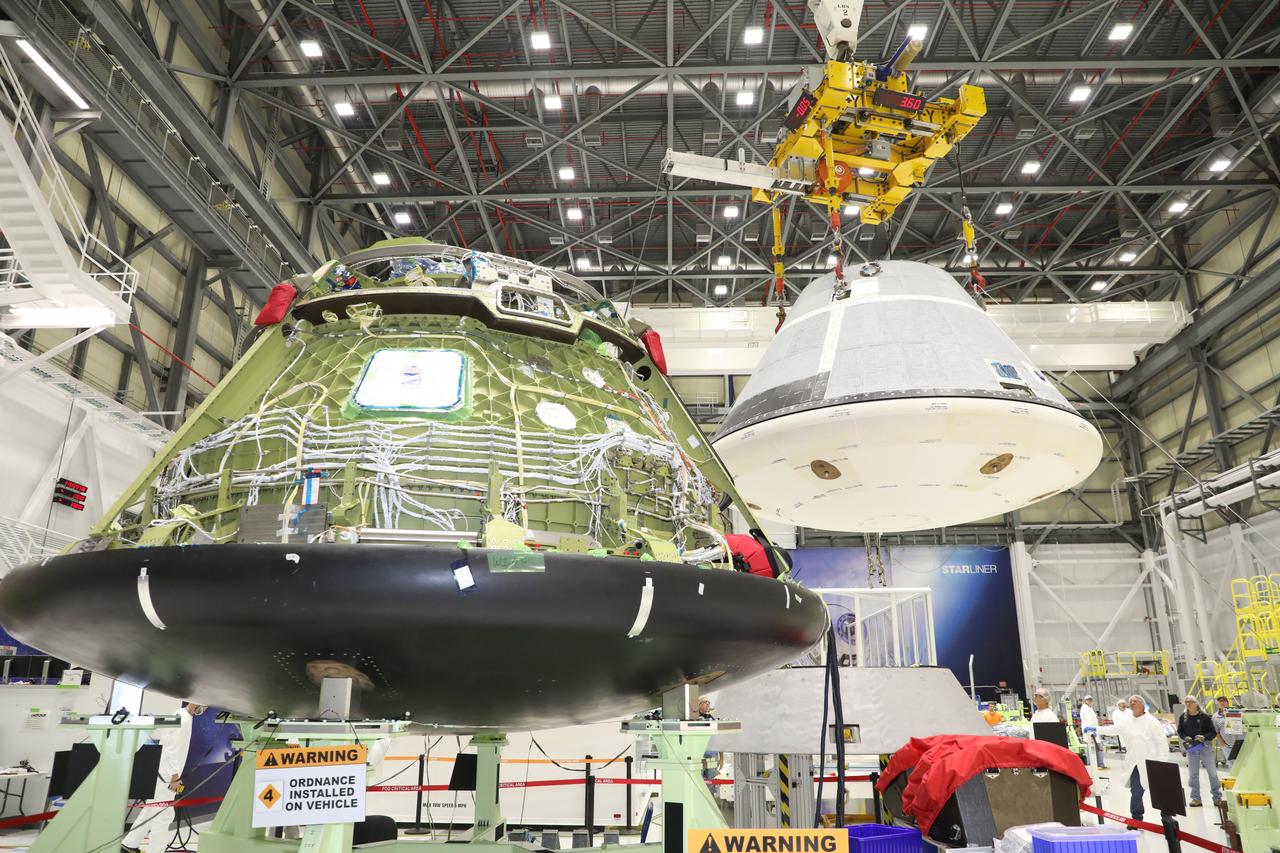
The Starliner crew module is hoisted in Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility on Jan. 19, 2023 before being mated to a new service module for NASA’s Boeing Crew Flight Test.
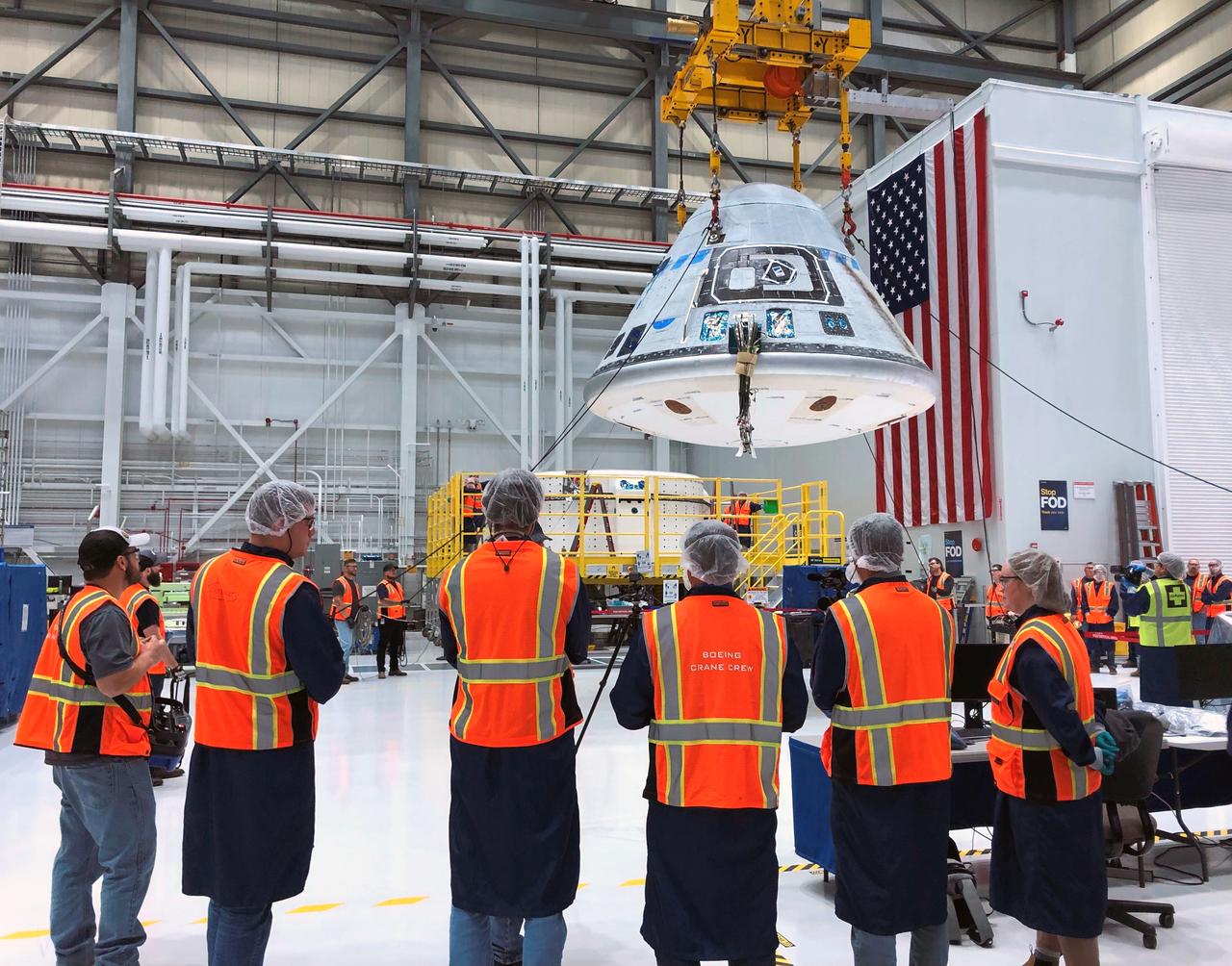

The Starliner team, including the crane crew, monitors the lift of the crew module on Jan. 19, 2023, at Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility before it is mated onto the new service module ahead of NASA’s Boeing Crew Flight Test.
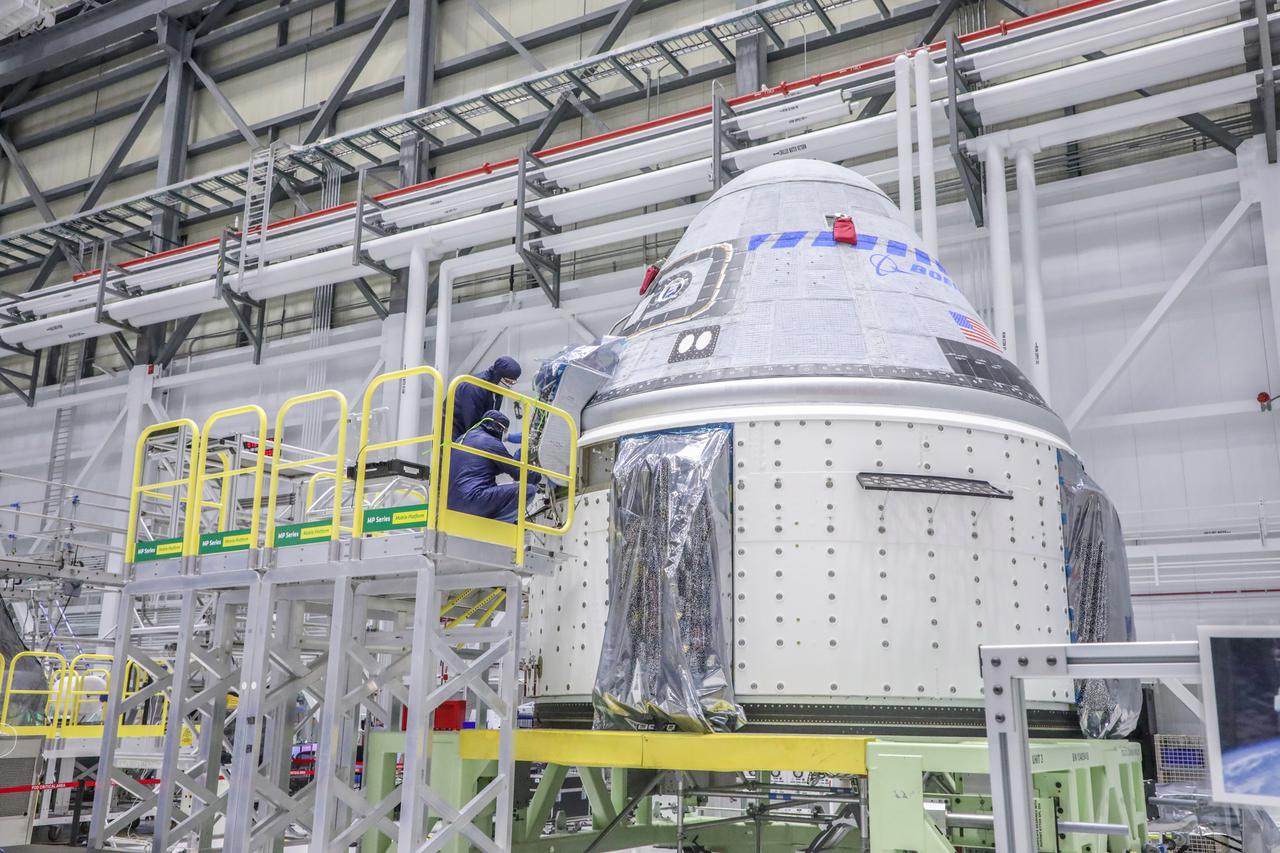

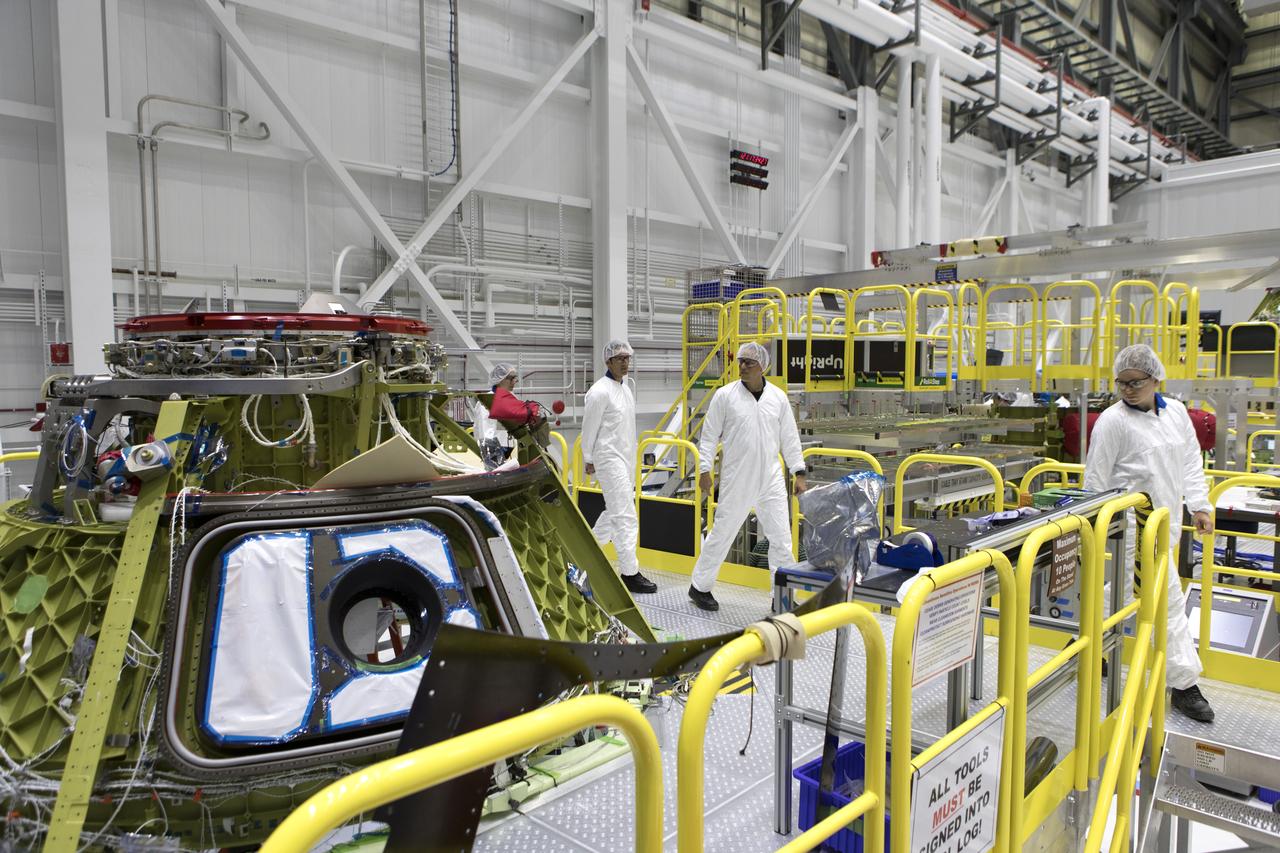
Starliner technicians work on the Orbital Flight Test-2 spacecraft in the high bay of Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 13, 2022.

NASA astronaut Barry "Butch" Wilmore, center, tours Boeing's Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility (C3PF) on Oct. 25, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Boeing's CST-100 Starliner will launch on its first uncrewed flight test on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. The Starliner is being developed and manufactured in partnership with NASA's Commercial Crew Program to return human spaceflight capabilities to the U.S.

NASA astronaut Barry "Butch" Wilmore, at left, tours Boeing's Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility (C3PF) on Oct. 25, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Boeing's CST-100 Starliner will launch on its first uncrewed flight test on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. The Starliner is being developed and manufactured in partnership with NASA's Commercial Crew Program to return human spaceflight capabilities to the U.S.
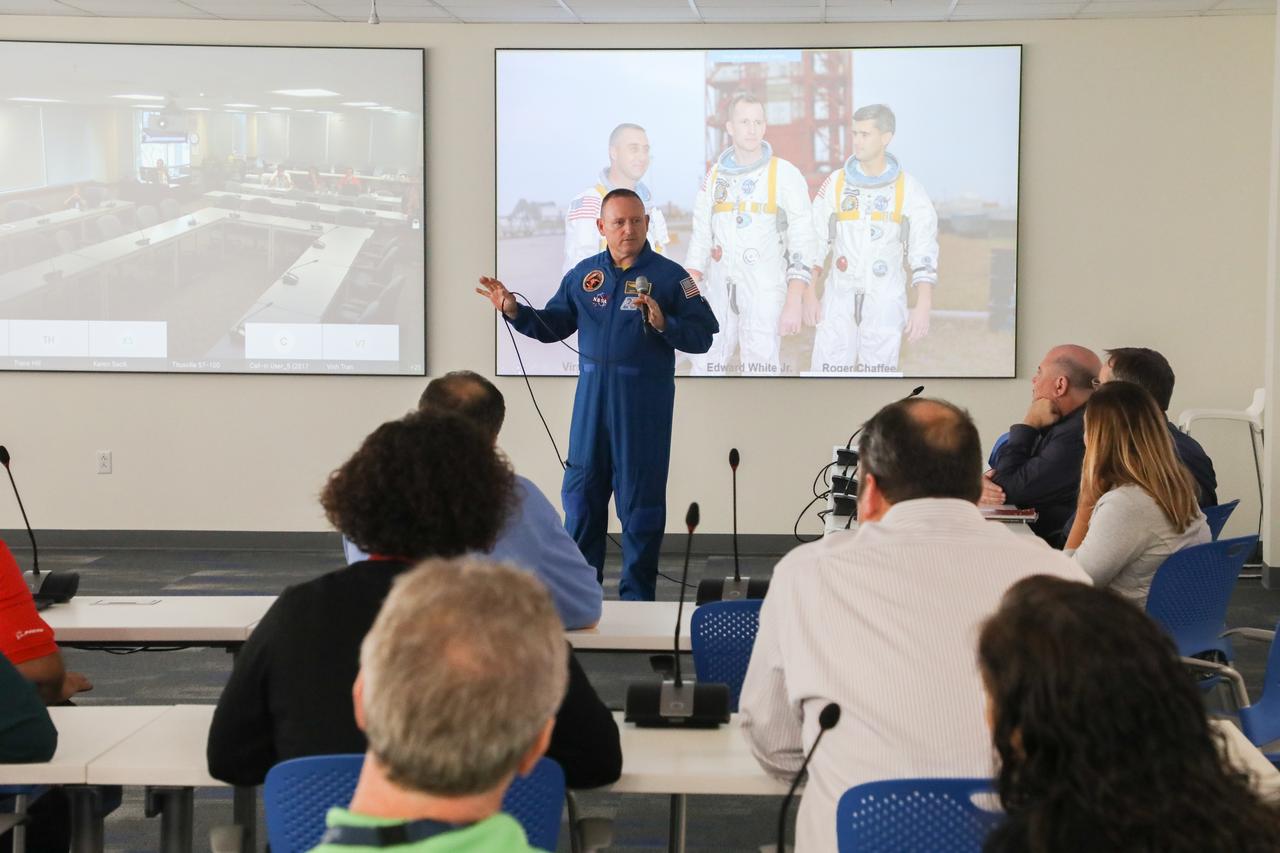

NASA astronaut Barry "Butch" Wilmore, speaks to workers during a tour of Boeing's Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility (C3PF) on Oct. 25, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Boeing's CST-100 Starliner will launch on its first uncrewed flight test on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. The Starliner is being developed and manufactured in partnership with NASA's Commercial Crew Program to return human spaceflight capabilities to the U.S.
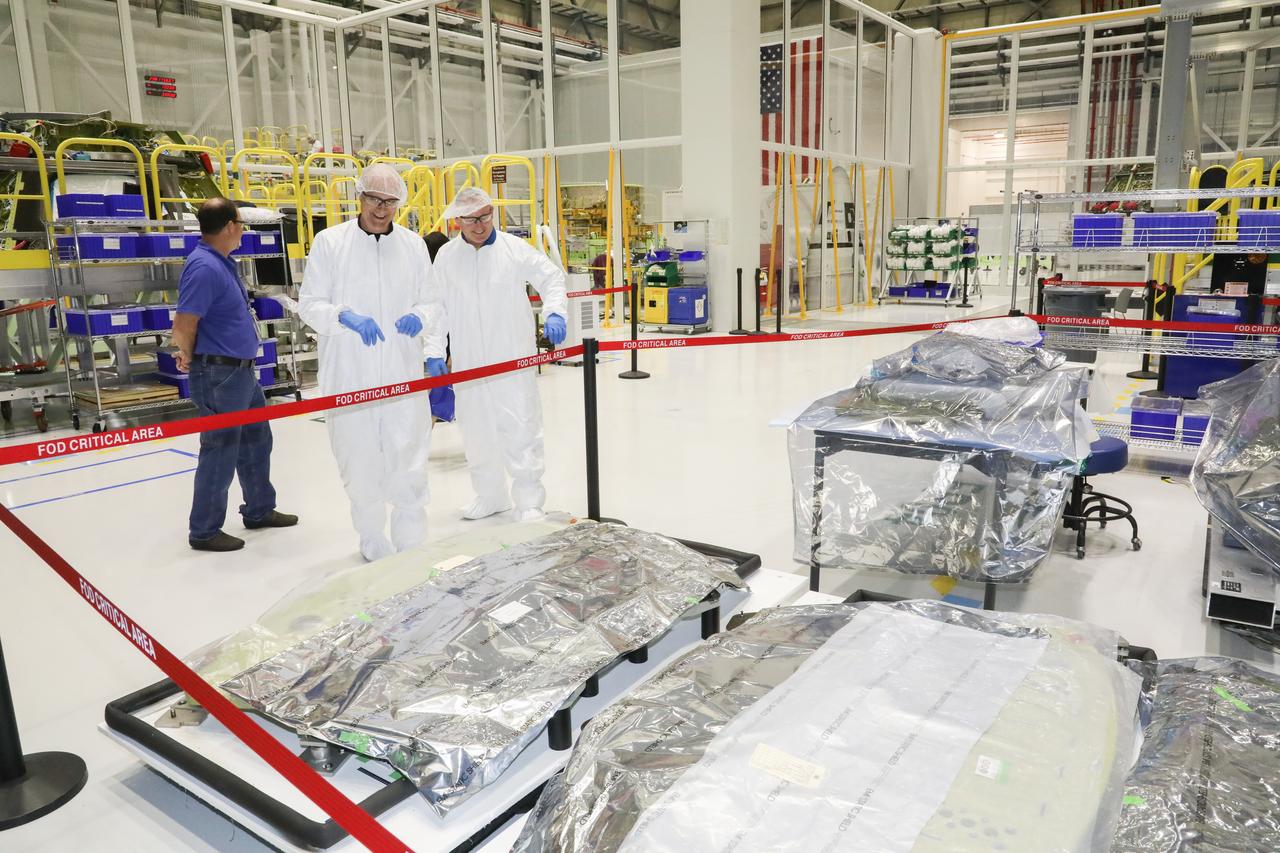

NASA astronaut Barry "Butch" Wilmore, center, tours Boeing's Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility (C3PF) on Oct. 25, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Boeing's CST-100 Starliner will launch on its first uncrewed flight test on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. The Starliner is being developed and manufactured in partnership with NASA's Commercial Crew Program to return human spaceflight capabilities to the U.S.

NASA astronaut Barry "Butch" Wilmore, at left, tours Boeing's Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility (C3PF) on Oct. 25, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Boeing's CST-100 Starliner will launch on its first uncrewed flight test on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. The Starliner is being developed and manufactured in partnership with NASA's Commercial Crew Program to return human spaceflight capabilities to the U.S.
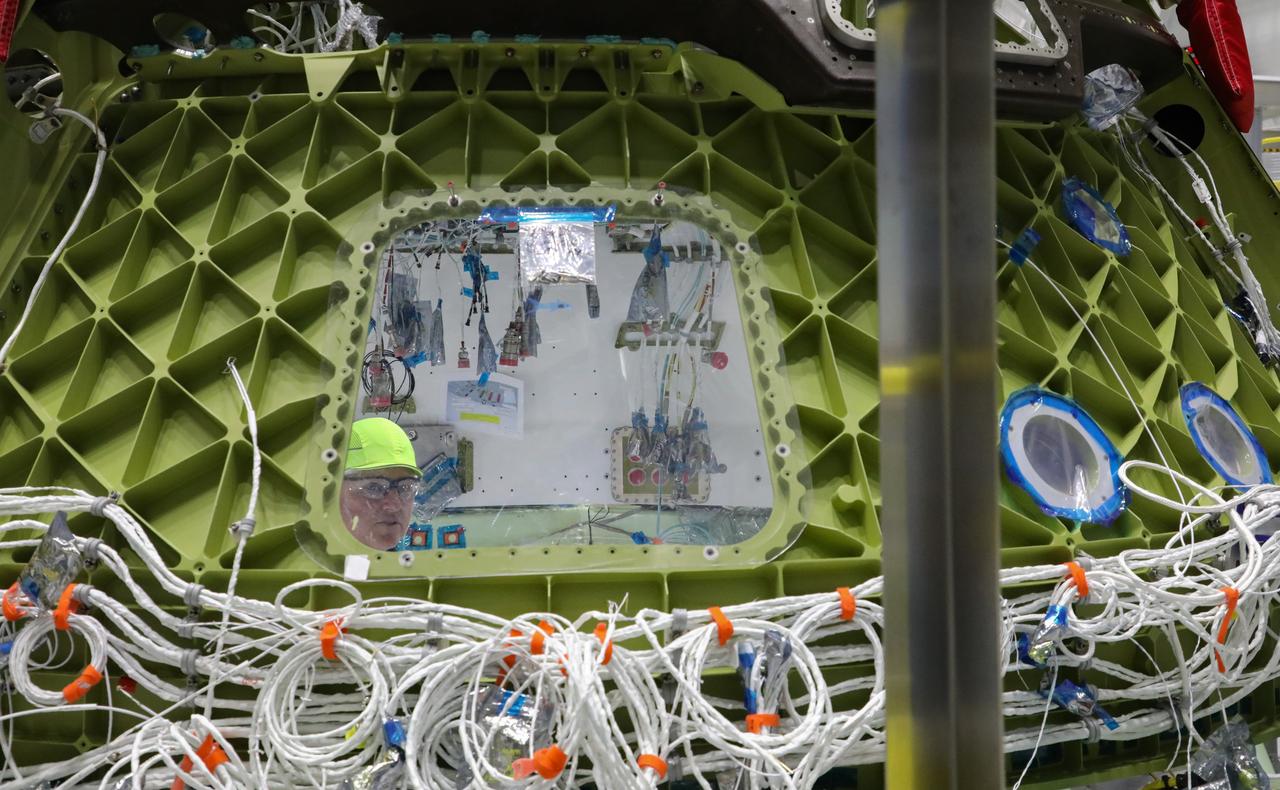

NASA astronaut Barry "Butch" Wilmore, center, tours Boeing's Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility (C3PF) on Oct. 25, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Wilmore is looking over Boeing's CST-100 Starliner that will launch on its first uncrewed flight test on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. The Starliner is being developed and manufactured in partnership with NASA's Commercial Crew Program to return human spaceflight capabilities to the U.S.
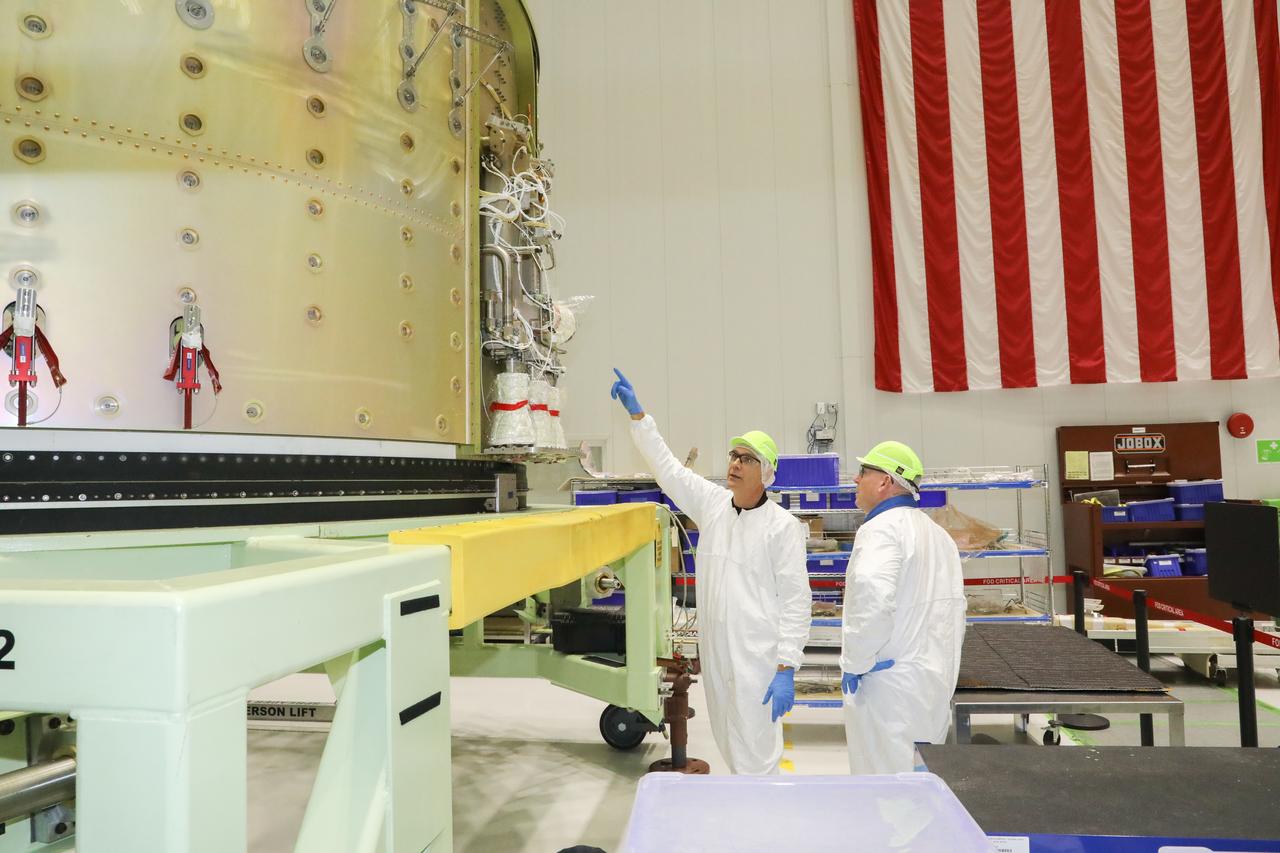

NASA astronaut Barry "Butch" Wilmore, at right, tours Boeing's Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility (C3PF) on Oct. 25, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Boeing's CST-100 Starliner will launch on its first uncrewed flight test on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. The Starliner is being developed and manufactured in partnership with NASA's Commercial Crew Program to return human spaceflight capabilities to the U.S.

Seen in the foreground inside the Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility (C3PF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 11, 2018, the spacecraft destined to fly astronauts to the International Space Station in Boeing's Crew Flight Test (CFT) is prepared for transport to the company's testing facilities in El Segundo, California. The company's CST-100 Starliner will be undergoing a series of environmental tests designed to simulate what the spacecraft will experience during different stages of flight as part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program (CCP). The agency's CCP will return human spaceflight launches to U.S. soil, providing safe, reliable and cost-effective access to low-Earth orbit on systems that meet our safety and mission requirements.
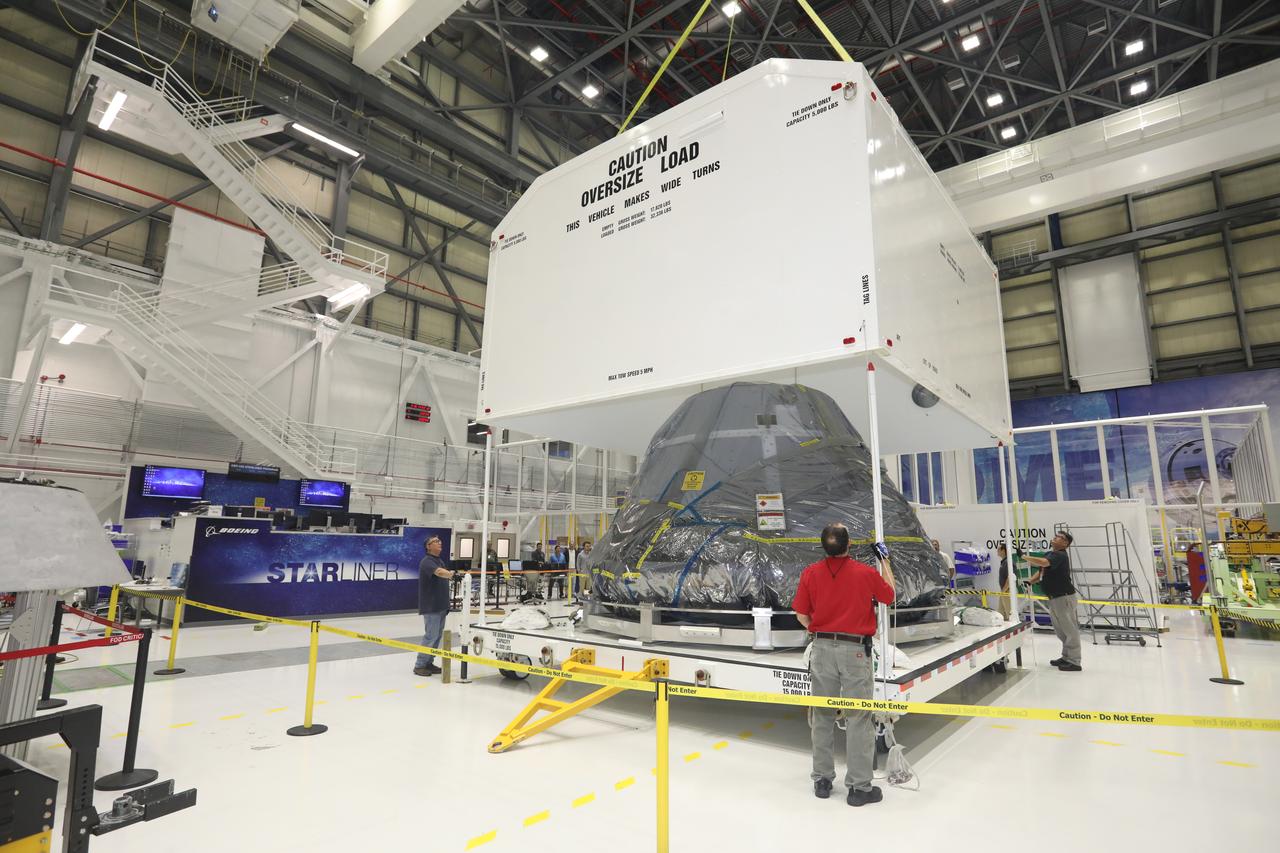

Inside the Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility (C3PF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 11, 2018, the spacecraft destined to fly astronauts to the International Space Station in Boeing's Crew Flight Test (CFT) is crated in preparation for transport to the company's testing facilities in El Segundo, California. The company's CST-100 Starliner will be undergoing a series of environmental tests designed to simulate what the spacecraft will experience during different stages of flight as part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program (CCP). The agency's CCP will return human spaceflight launches to U.S. soil, providing safe, reliable and cost-effective access to low-Earth orbit on systems that meet our safety and mission requirements.

Inside the Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility (C3PF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 11, 2018, the spacecraft destined to fly astronauts to the International Space Station in Boeing's Crew Flight Test (CFT) is prepared for transport to the company's testing facilities in El Segundo, California. The company's CST-100 Starliner will be undergoing a series of environmental tests designed to simulate what the spacecraft will experience during different stages of flight as part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program (CCP). The agency's CCP will return human spaceflight launches to U.S. soil, providing safe, reliable and cost-effective access to low-Earth orbit on systems that meet our safety and mission requirements.

Inside the Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility (C3PF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 11, 2018, the spacecraft destined to fly astronauts to the International Space Station in Boeing's Crew Flight Test (CFT) is prepared for transport to the company's testing facilities in El Segundo, California. The company's CST-100 Starliner will be undergoing a series of environmental tests designed to simulate what the spacecraft will experience during different stages of flight as part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program (CCP). The agency's CCP will return human spaceflight launches to U.S. soil, providing safe, reliable and cost-effective access to low-Earth orbit on systems that meet our safety and mission requirements.
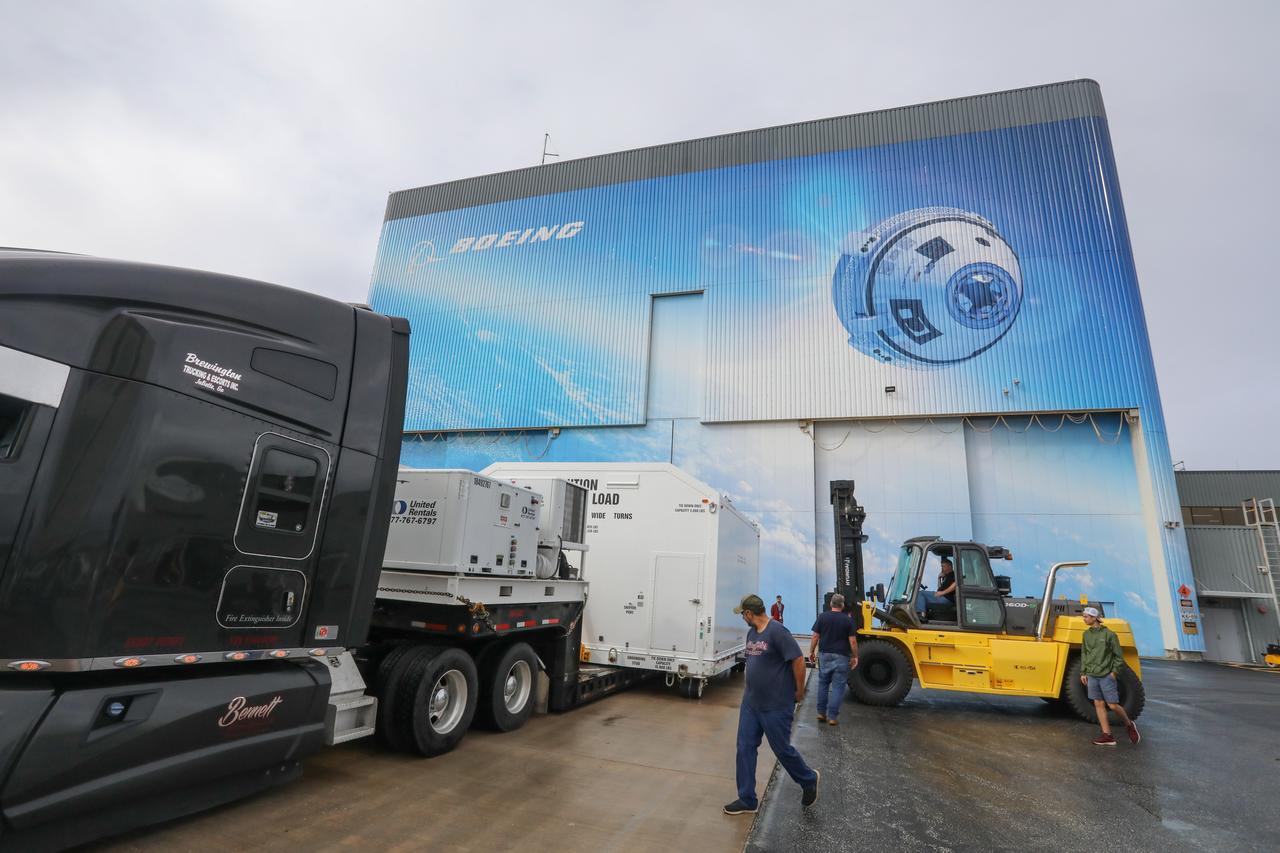

On Nov. 12, 2018, the crated spacecraft destined to fly astronauts to the International Space Station in Boeing's Crew Flight Test (CFT) departs the Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility (C3PF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida in preparation for transport to the company's testing facilities in El Segundo, California. The company's CST-100 Starliner will be undergoing a series of environmental tests designed to simulate what the spacecraft will experience during different stages of flight as part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program (CCP). The agency's CCP will return human spaceflight launches to U.S. soil, providing safe, reliable and cost-effective access to low-Earth orbit on systems that meet our safety and mission requirements.
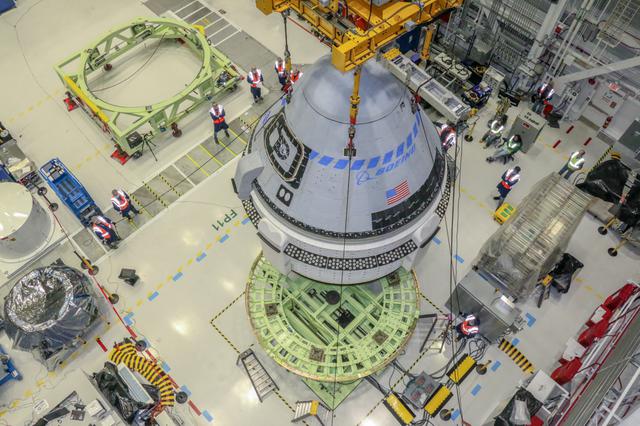

Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner undergoes weight and center of gravity checks in the Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 13, 2021. The operations are in preparation for the company’s second Orbital Flight Test (OFT-2), as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.
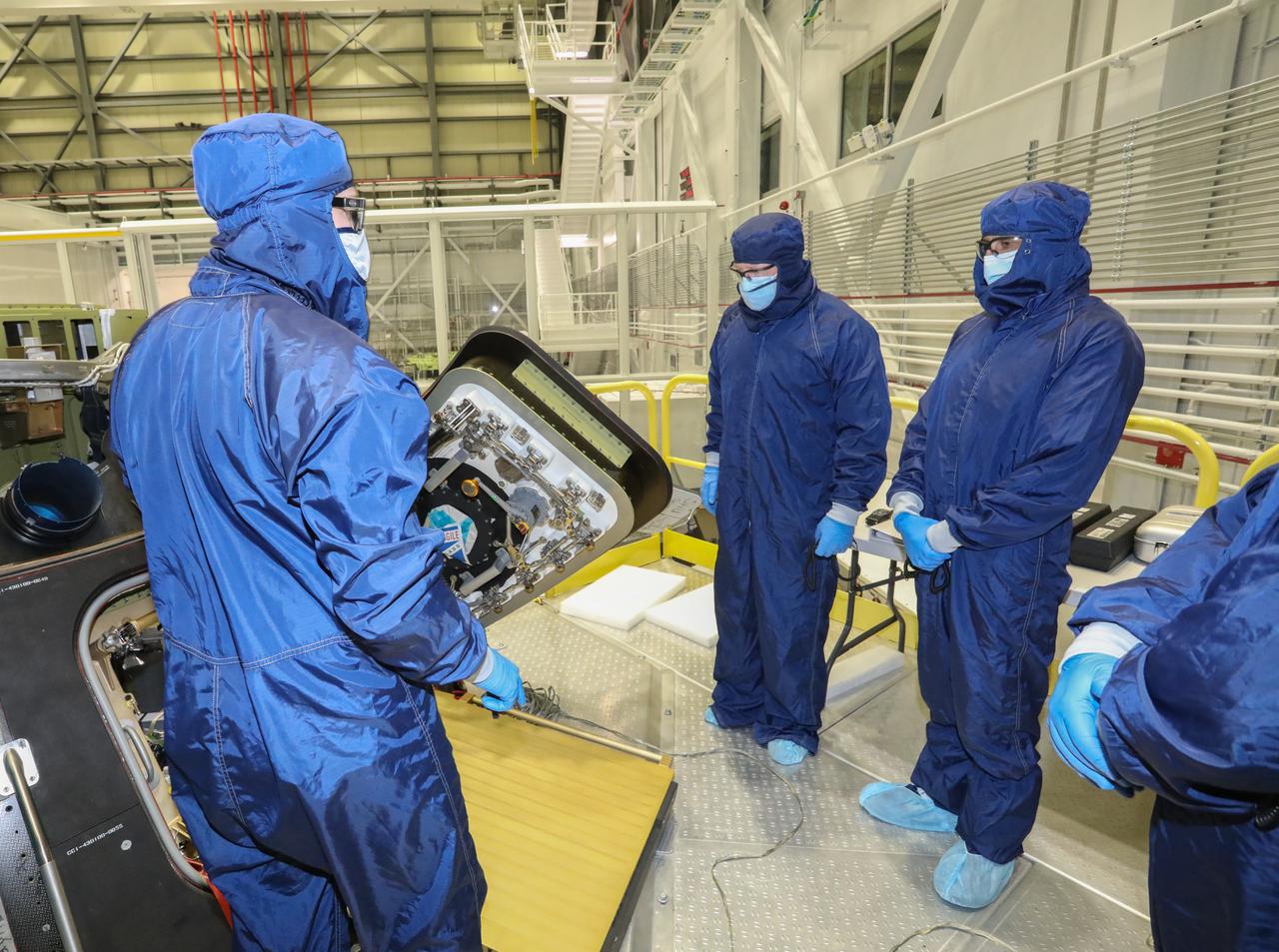

NASA astronauts Barry “Butch” Wilmore and Sunita "Suni" Williams visit the Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 17, 2020. The astronauts are at Kennedy to prepare for their flights to the International Space Station on Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner, as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. Wilmore and Williams will command the Crew Flight Test and the Starliner-1 mission, respectively.

NASA astronauts Barry “Butch” Wilmore, left, and Sunita "Suni" Williams visit the Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 17, 2020. The astronauts are at Kennedy to prepare for their flights to the International Space Station on Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner, as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. Wilmore and Williams will command the Crew Flight Test and the Starliner-1 mission, respectively.
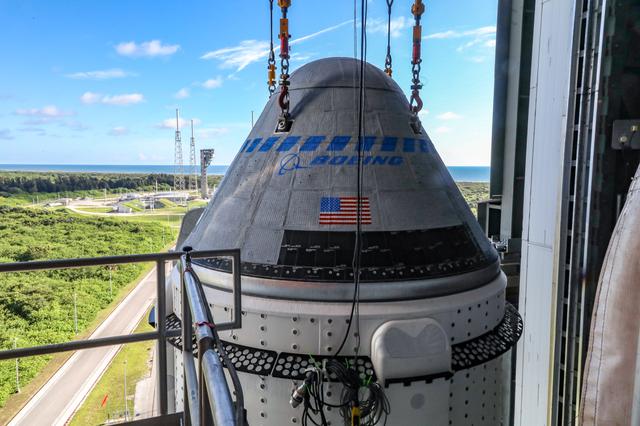

The Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft is secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on July 17, 2021. Starliner will launch on the Atlas V for Boeing’s second Orbital Flight Test (OFT-2) for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.
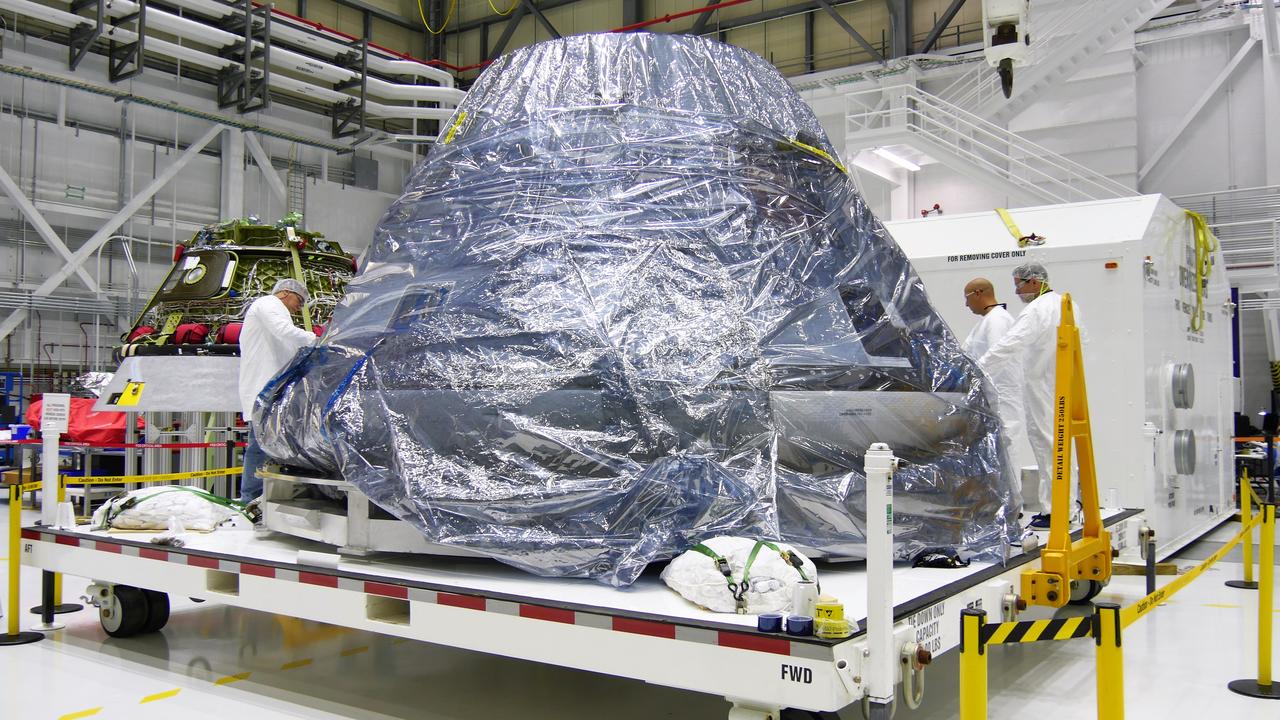

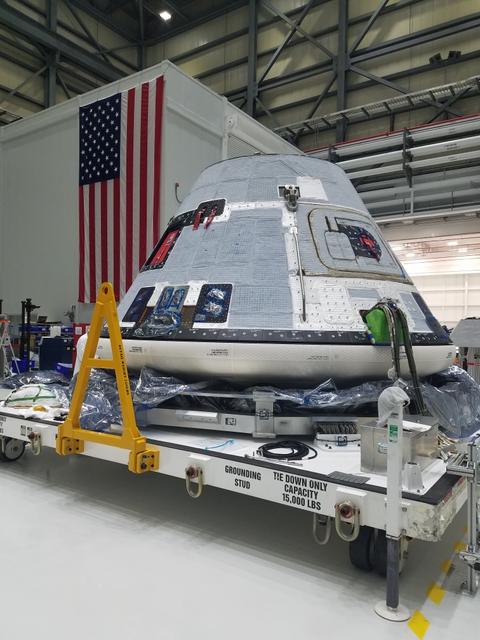
The spacecraft destined to fly astronauts to the International Space Station in Boeing's Crew Flight Test (CFT) is seen Inside the Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility (C3PF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 12, 2018. It is surrounded by protective wrapping in preparation for transport to Boeing's testing facilities in El Segundo, California. The company's CST-100 Starliner will be undergoing a series of environmental tests designed to simulate what the spacecraft will experience during different stages of flight as part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program (CCP). The agency's CCP will return human spaceflight launches to U.S. soil, providing safe, reliable and cost-effective access to low-Earth orbit on systems that meet our safety and mission requirements.
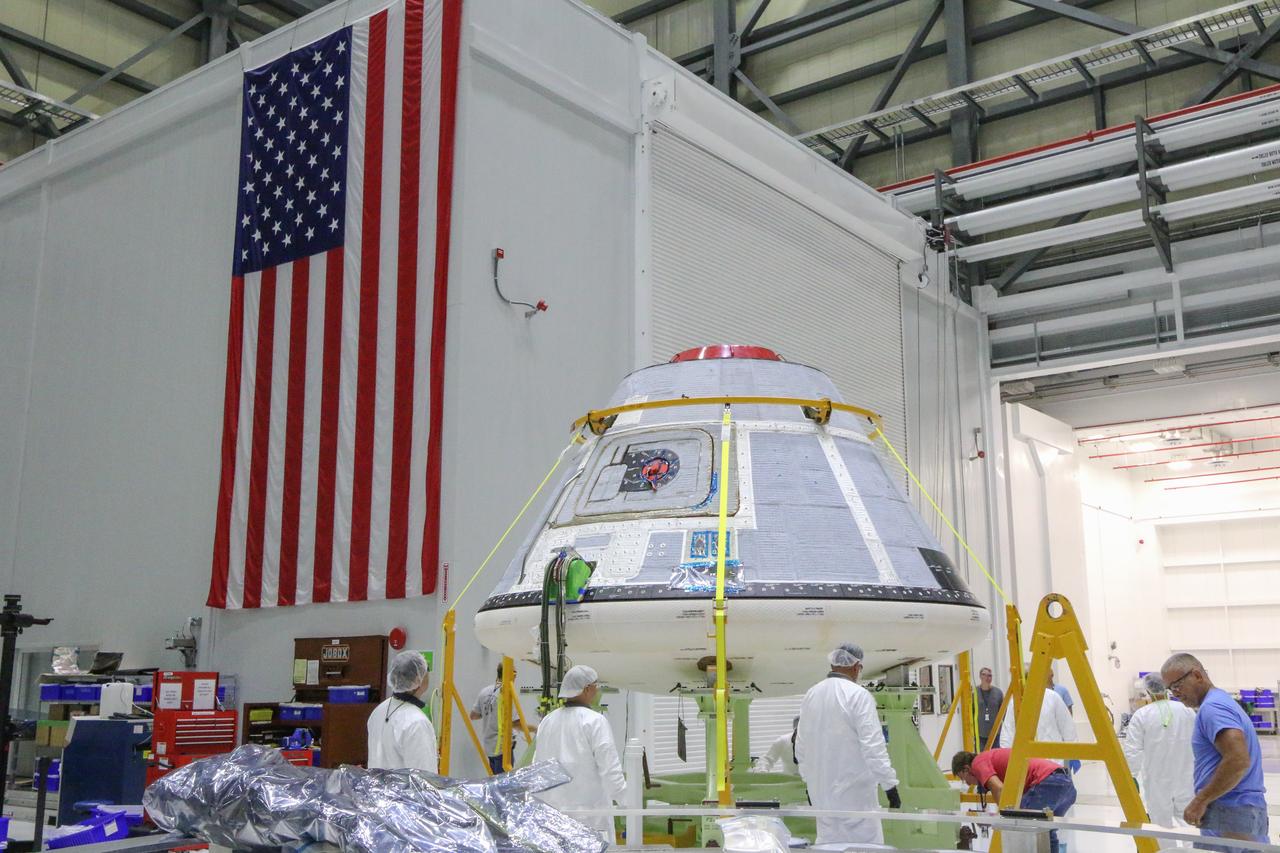

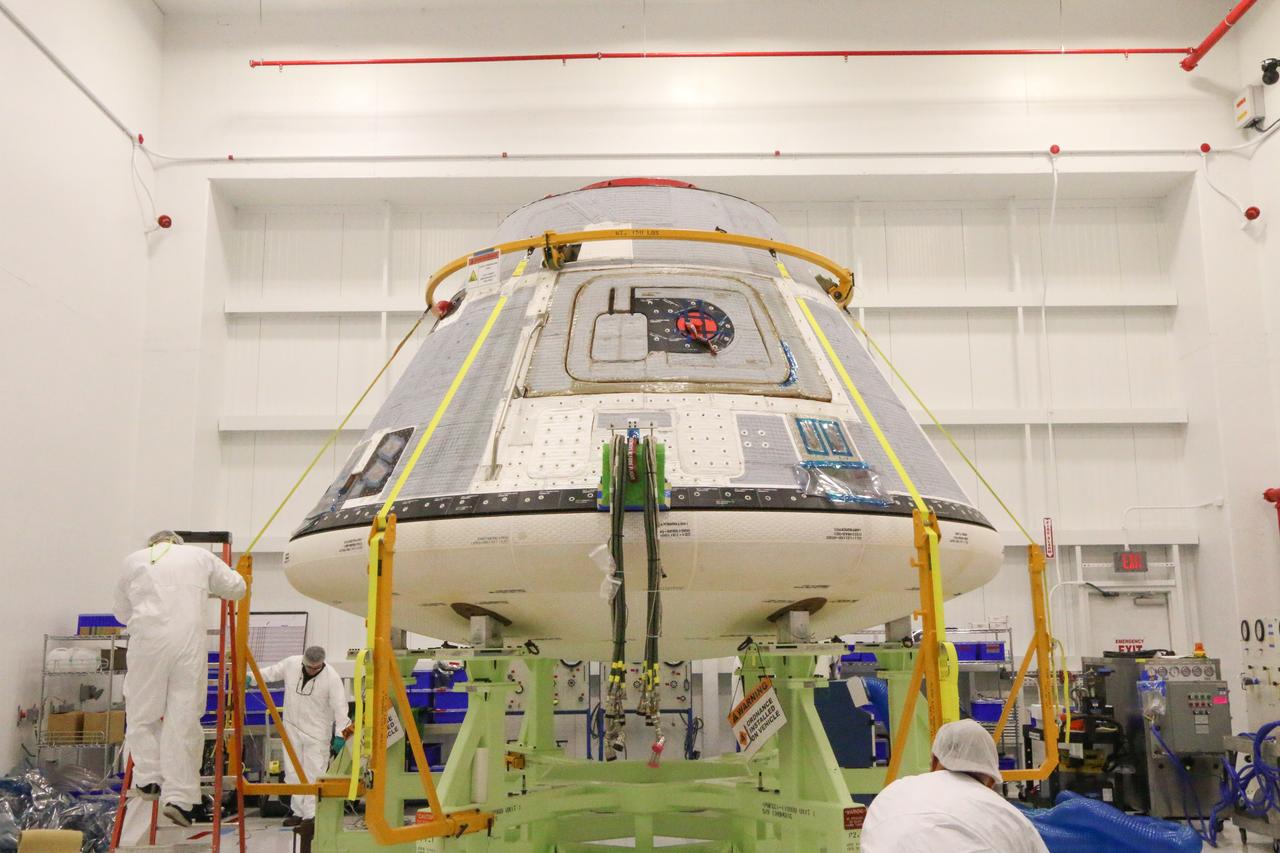
On Nov. 12, 2018, inside the Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility (C3PF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians and engineers prepare the company's CST-100 Starliner for transport to the company's testing facilities in El Segundo, California. The spacecraft is destined to fly astronauts to the International Space Station in Boeing's Crew Flight Test (CFT) as part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program (CCP). The Starliner will be undergoing a series of environmental tests designed to simulate what the spacecraft will experience during different stages of flight. The agency's CCP will return human spaceflight launches to U.S. soil, providing safe, reliable and cost-effective access to low-Earth orbit on systems that meet our safety and mission requirements.

On Nov. 12, 2018, inside the Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility (C3PF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians and engineers prepare the company's CST-100 Starliner for transport to the company's testing facilities in El Segundo, California. The spacecraft is destined to fly astronauts to the International Space Station in Boeing's Crew Flight Test (CFT) as part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program (CCP). The Starliner will be undergoing a series of environmental tests designed to simulate what the spacecraft will experience during different stages of flight. The agency's CCP will return human spaceflight launches to U.S. soil, providing safe, reliable and cost-effective access to low-Earth orbit on systems that meet our safety and mission requirements.
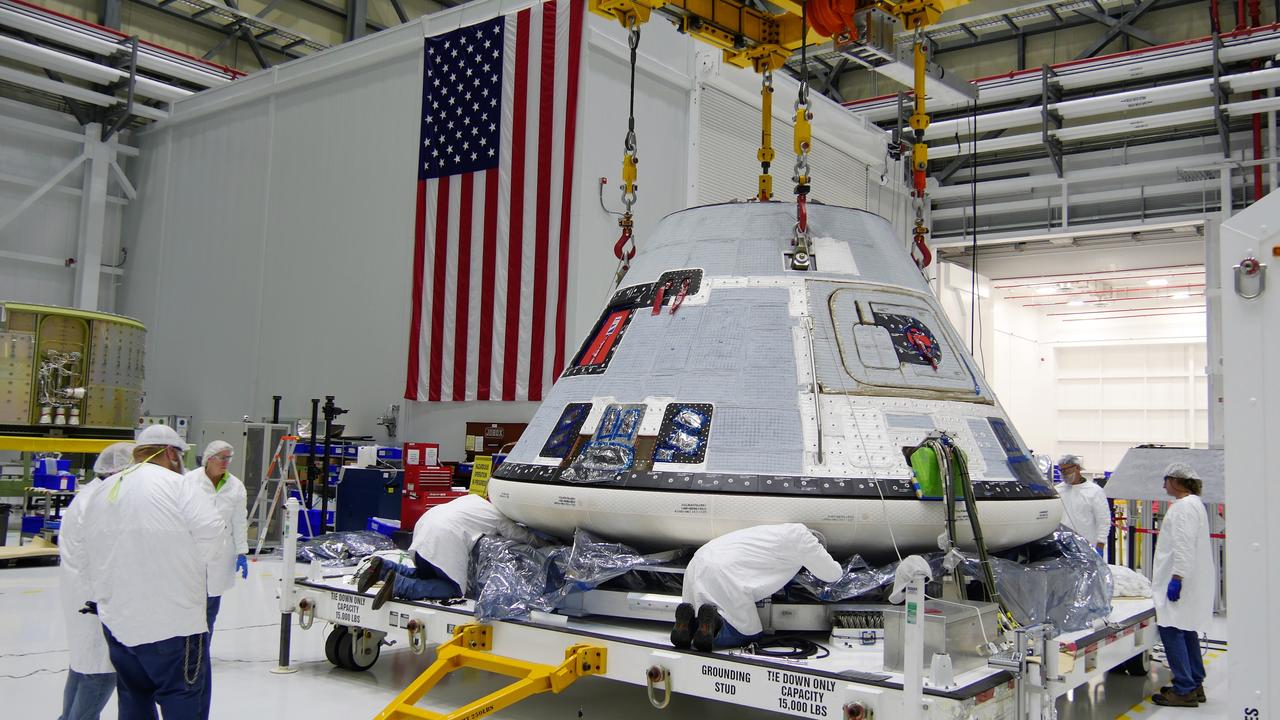

On Nov. 12, 2018, inside the Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility (C3PF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians and engineers prepare Boeing's CST-100 Starliner for transport to the company's testing facilities in El Segundo, California. The spacecraft is destined to fly astronauts to the International Space Station in Boeing's Crew Flight Test (CFT) as part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program (CCP). The Starliner will be undergoing a series of environmental tests designed to simulate what the spacecraft will experience during different stages of flight. The agency's CCP will return human spaceflight launches to U.S. soil, providing safe, reliable and cost-effective access to low-Earth orbit on systems that meet our safety and mission requirements.
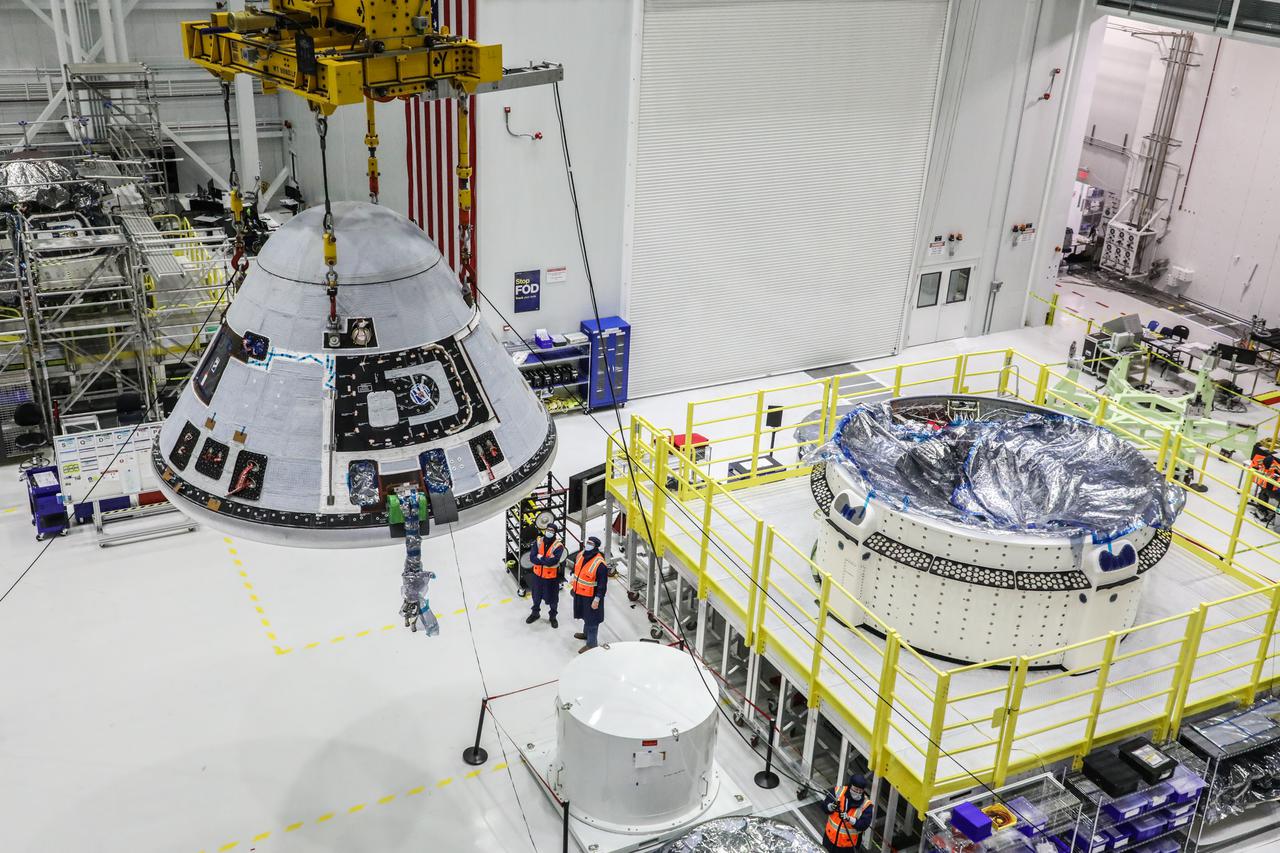

Boeing’s Starliner crew module is hoisted and moves past the service module in the Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Jan. 13, 2021, prior to the weight and center of gravity test. The crew module and service module will soon be mated, making the spacecraft complete for the company’s second Orbital Flight Test (OFT-2) for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. OFT-2 is a critical developmental milestone on the company’s path toward flying crew missions for NASA.
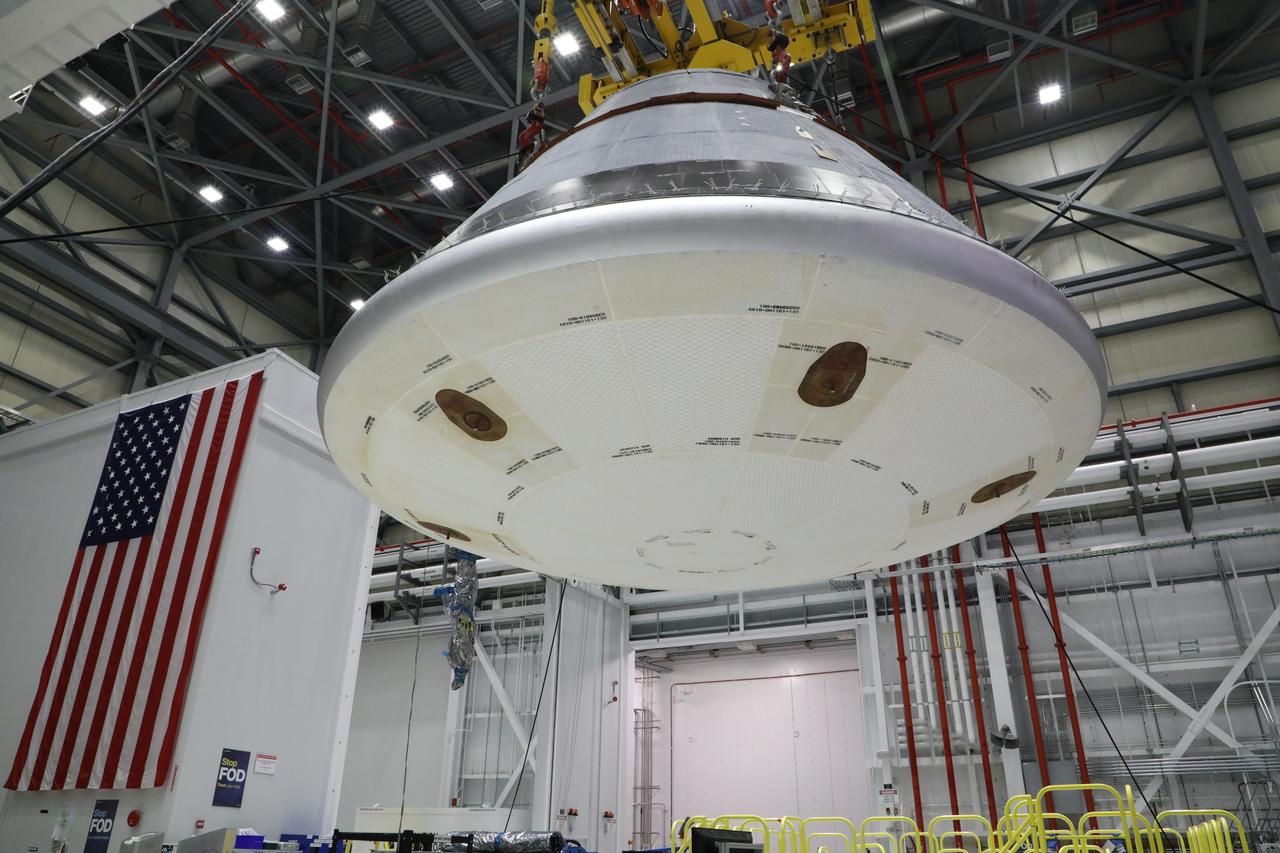

The Boeing Starliner crew module is hoisted across the Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 14, 2021, to be mated with the service module. The Starliner spacecraft is being prepared for Boeing’s second Orbital Flight Test (OFT-2). As part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program, OFT-2 is a critical developmental milestone on the company’s path to fly crew missions for NASA.
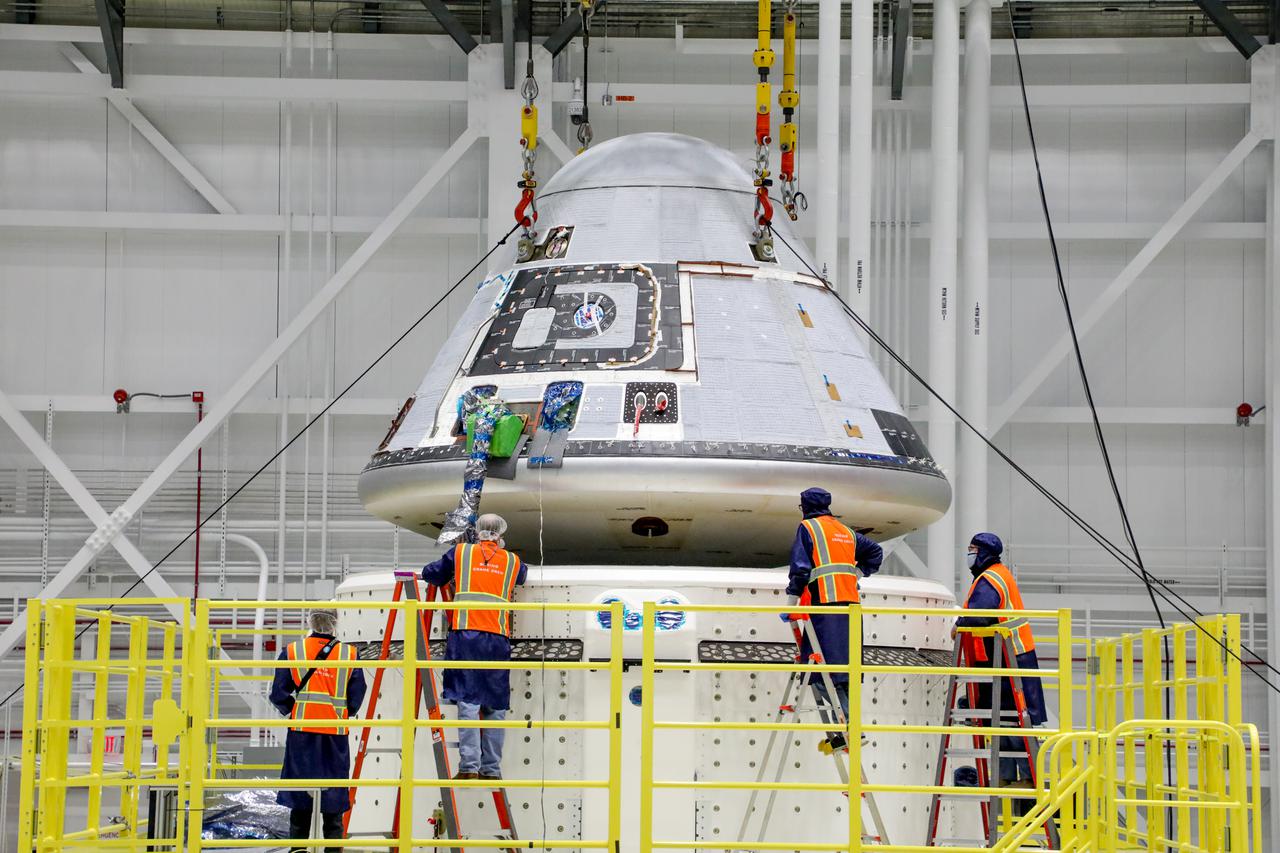

Technicians observe Boeing’s Starliner crew module being placed on top of the service module in the Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 14, 2021. The Starliner spacecraft is being prepared for Boeing’s second Orbital Flight Test (OFT-2). As part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program, OFT-2 is a critical developmental milestone on the company’s path to fly crew missions for NASA.
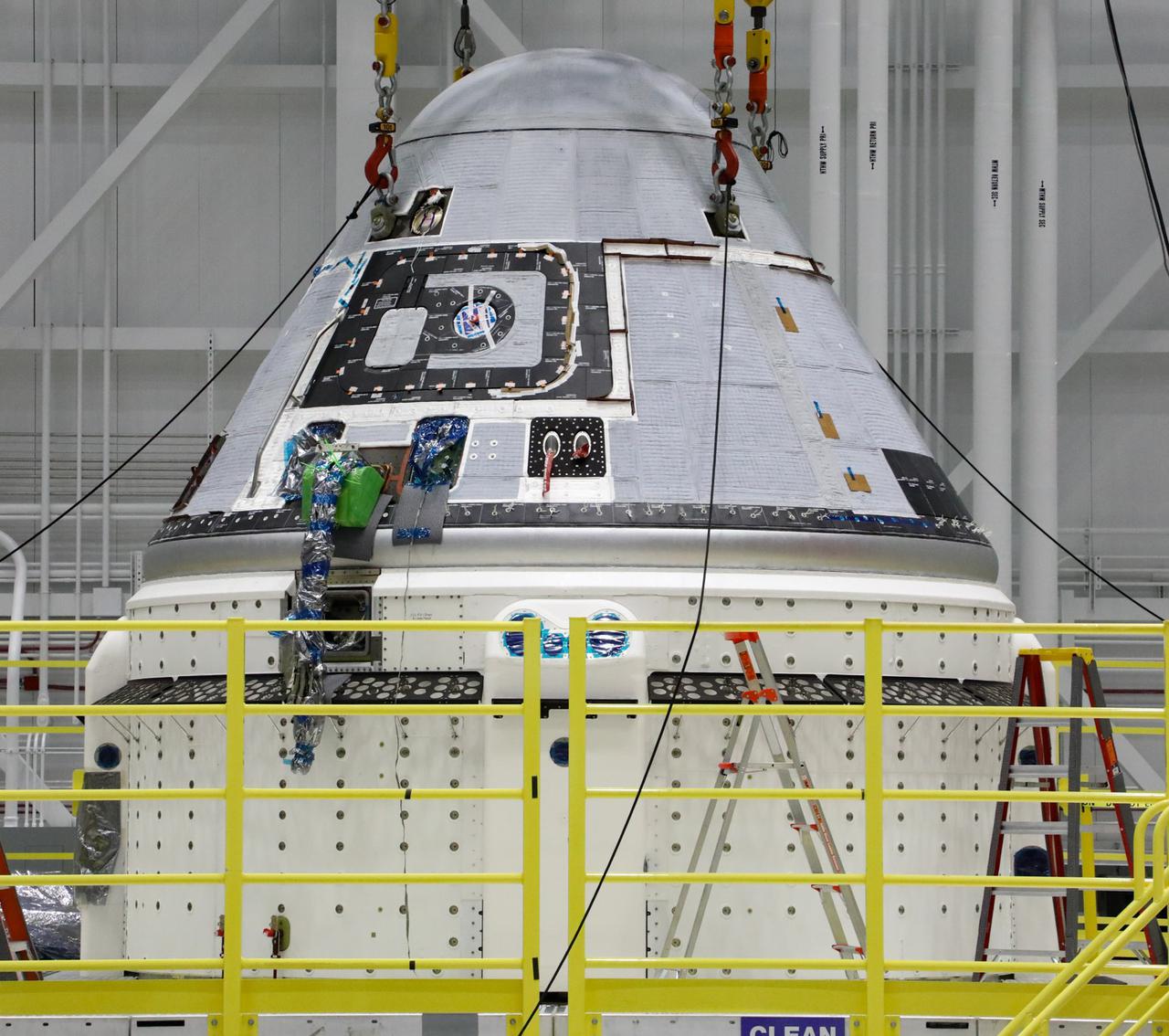

The completed Boeing Starliner vehicle for the second Orbital Flight Test (OFT-2) is seen in the Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida following the mating of the crew module and service module on Jan. 14, 2021. As part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program, OFT-2 is a critical developmental milestone on the company’s path to fly crew missions for NASA.
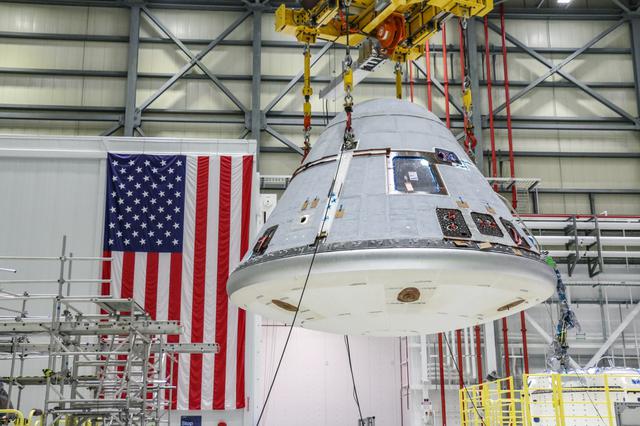

Boeing’s Starliner crew module for the company’s second Orbital Flight Test (OFT-2) is lifted Wednesday, Jan. 13, 2021, in the Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida prior to the vehicle having a weight and center of gravity test. OFT-2 is a critical developmental milestone on the company’s path toward flying crew missions for NASA, as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program.
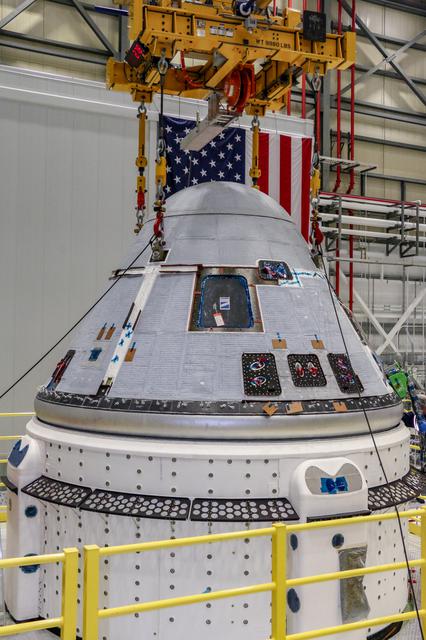

The completed Boeing Starliner vehicle for the second Orbital Flight Test (OFT-2) is seen in the Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida following the mating of the crew module and service module on Jan. 14, 2021. As part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program, OFT-2 is a critical developmental milestone on the company’s path to fly crew missions for NASA.
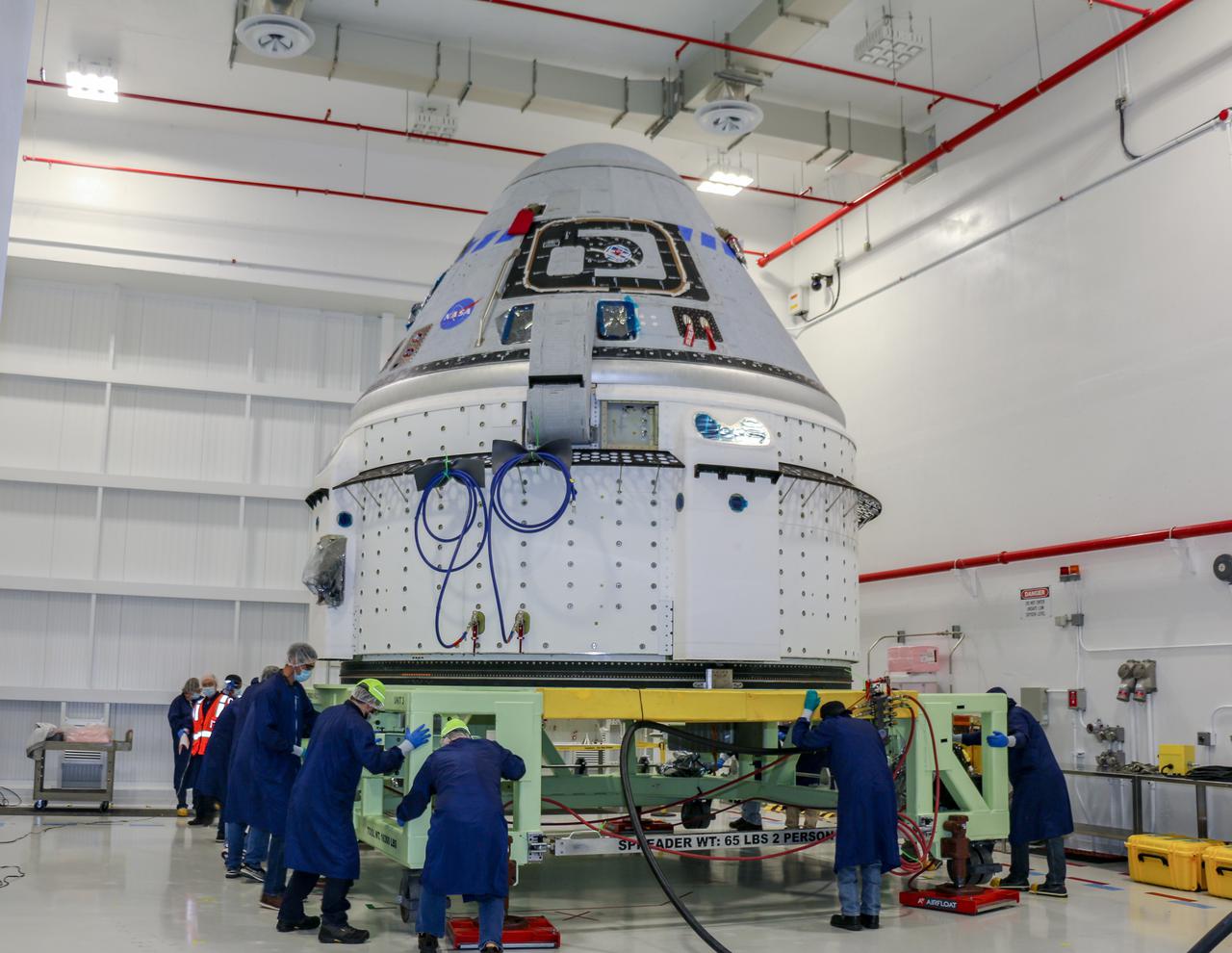

Technicians prepare Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner for the company’s Orbital Flight Test-2 (OFT-2) in the Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 2. Part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program, OFT-2 is a critical developmental milestone on the company’s path to fly crew missions for NASA.
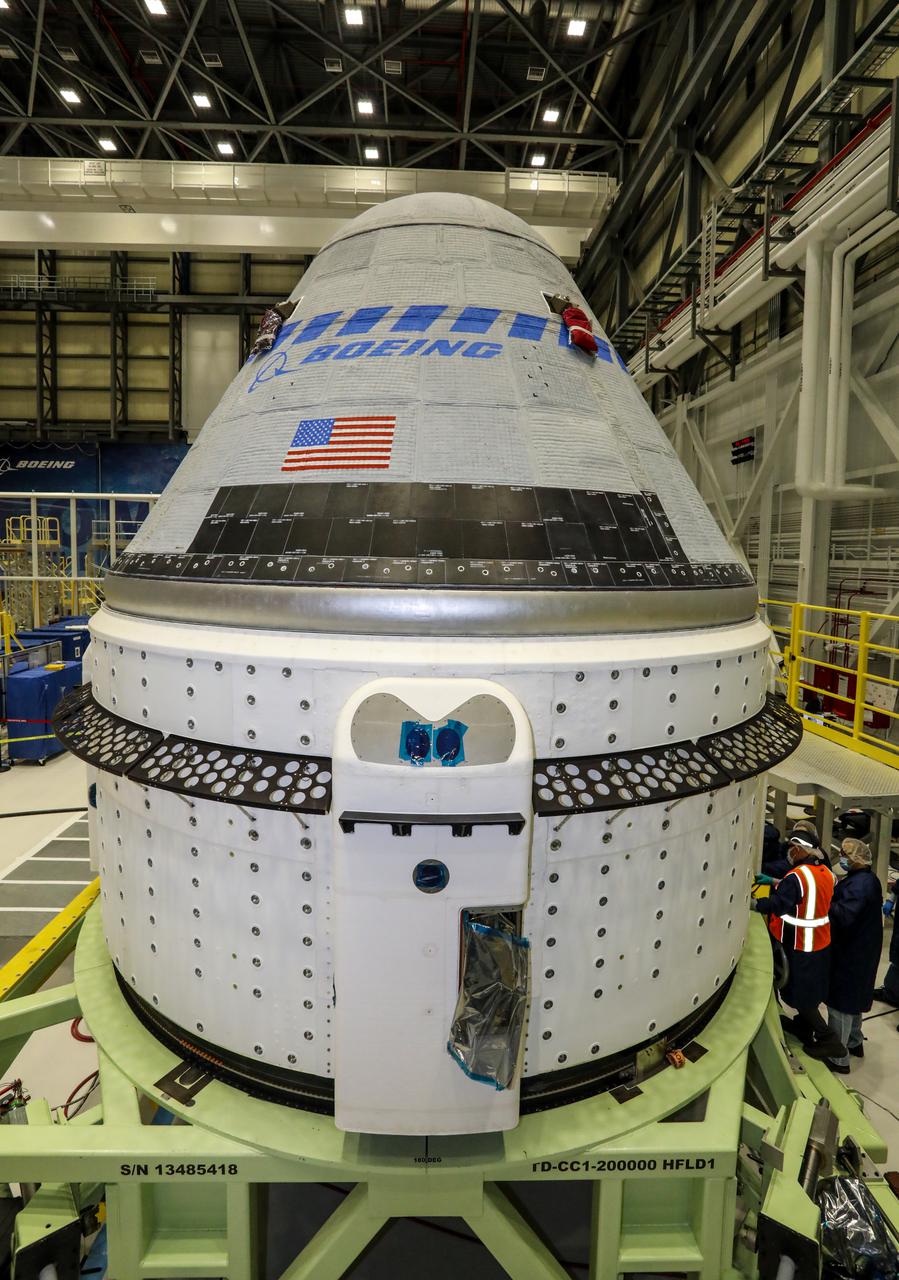

The Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft to be flown on Orbital Flight Test-2 (OFT-2) is seen in the Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 2. Part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program, OFT-2 is a critical developmental milestone on the company’s path to fly crew missions for NASA.
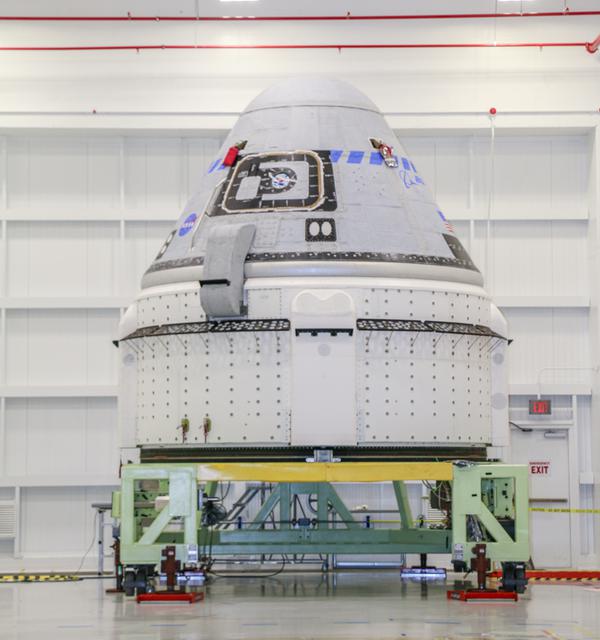

The Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft to be flown on Orbital Flight Test-2 (OFT-2) is seen in the Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 12, 2021. Part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program, OFT-2 is a critical developmental milestone on the company’s path to fly crew missions for NASA.
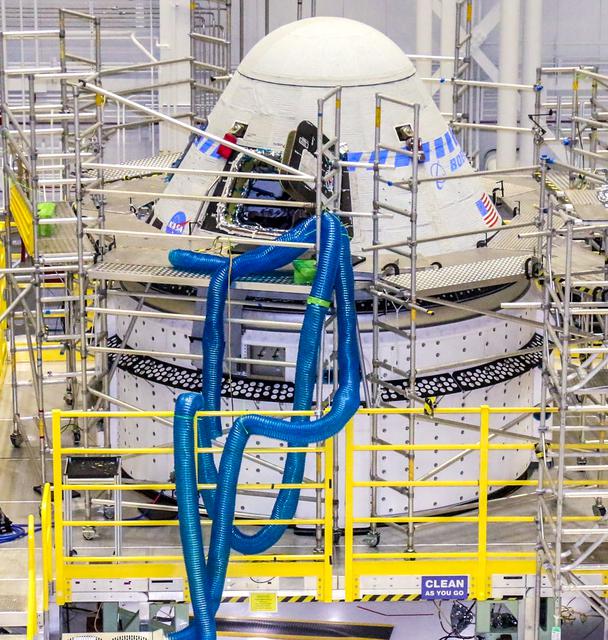

Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft undergoes preparations for the company’s Orbital Flight Test-2 (OFT-2) in the Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Wednesday, April 28, 2021. As part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, OFT-2 is a critical developmental milestone on Boeing’s path to fly crew missions for NASA.
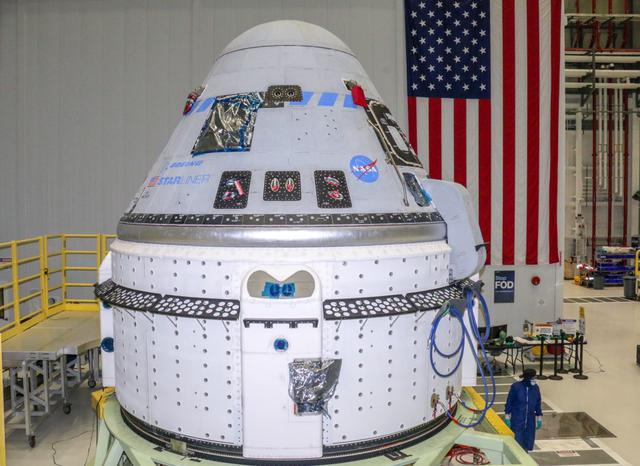
The Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft to be flown on Orbital Flight Test-2 (OFT-2) is seen in the Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 2. Part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program, OFT-2 is a critical developmental milestone on the company’s path to fly crew missions for NASA.
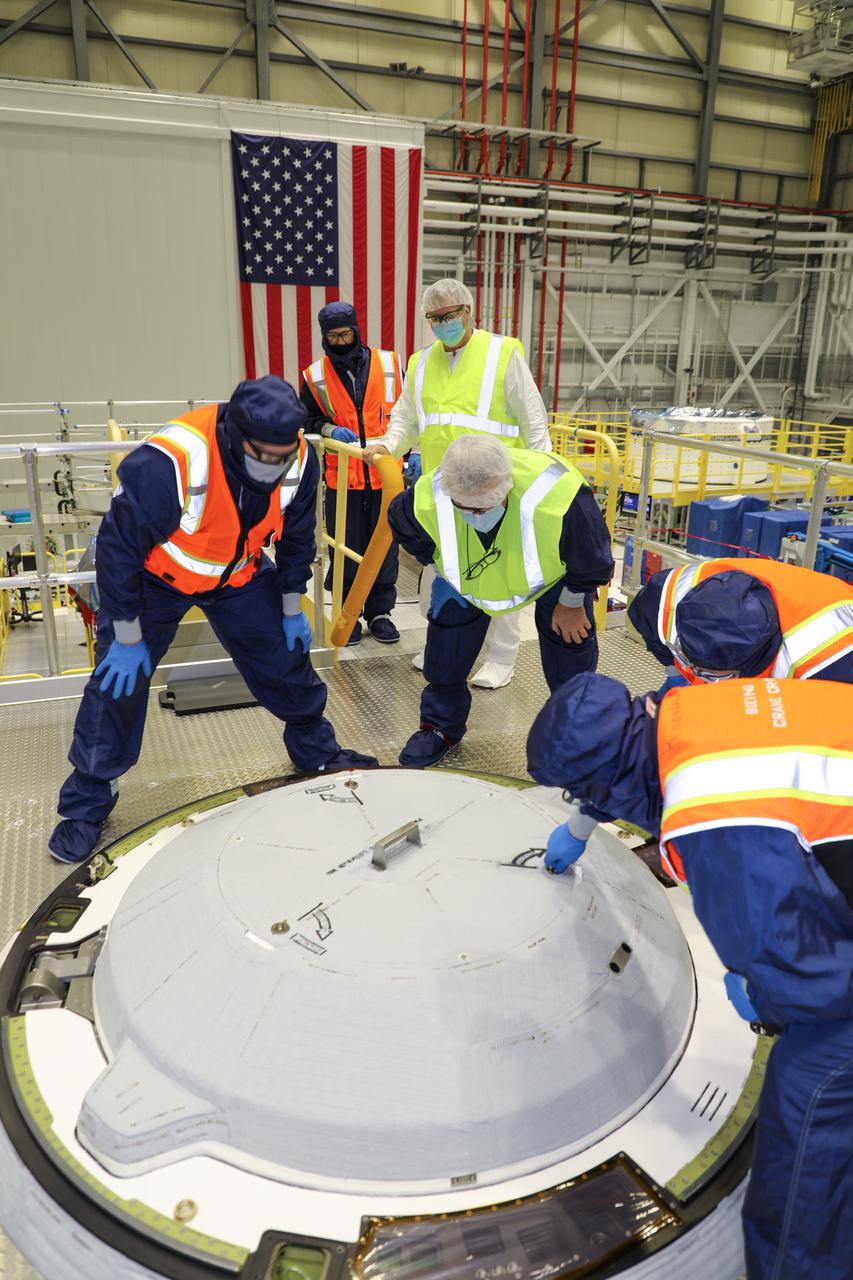

Technicians work on the NASA Docking System (NDS) hatch installation in the Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 2, 2021. The NDS cover was installed on Boeing’s Starliner spacecraft in preparation for the company’s second Orbital Flight Test (OFT-2), as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The cover is designed to protect the components that connect the spacecraft to the International Space Station.
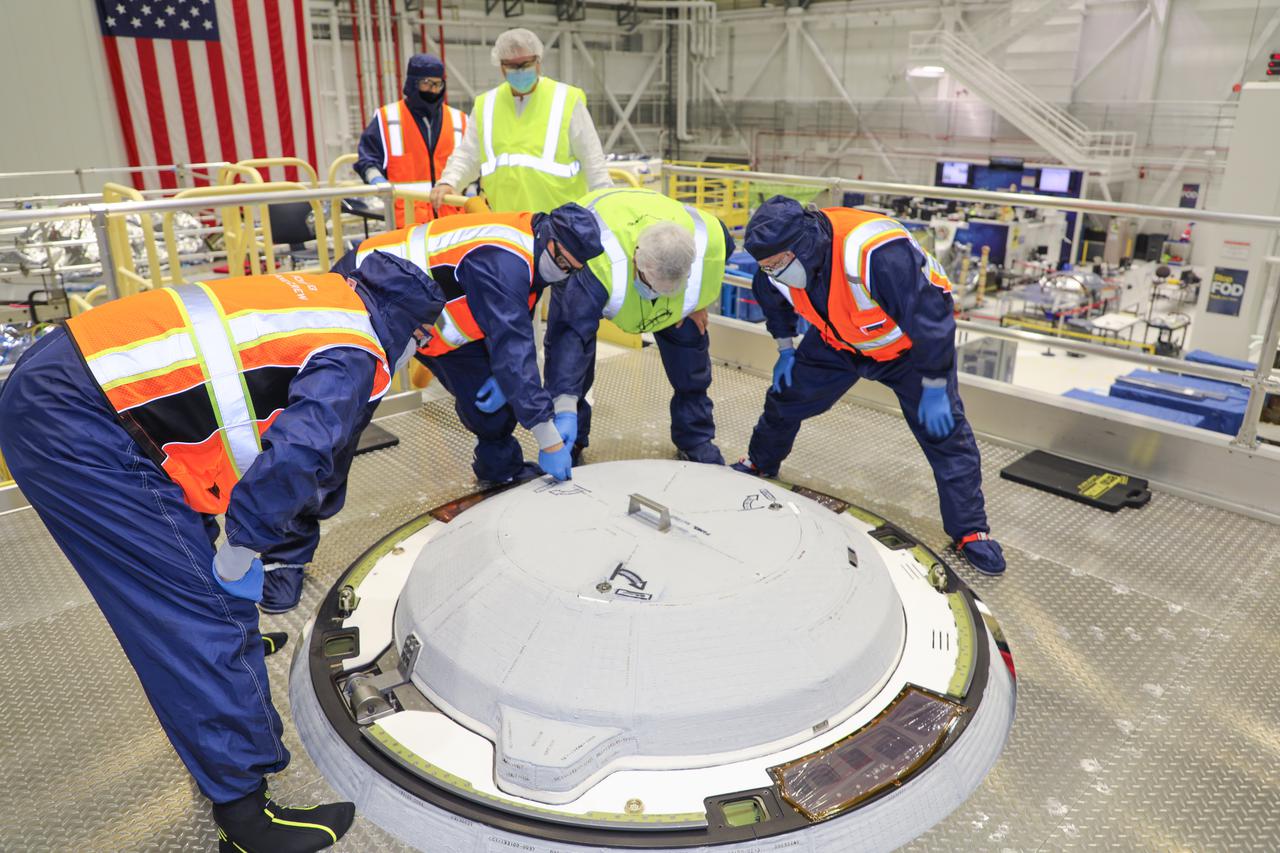

Technicians work on the NASA Docking System (NDS) cover hatch installation in the Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 2, 2021. The NDS cover was installed on Boeing’s Starliner spacecraft in preparation for the company’s second Orbital Flight Test (OFT-2), as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The cover is designed to protect the components that connect the spacecraft to the International Space Station.
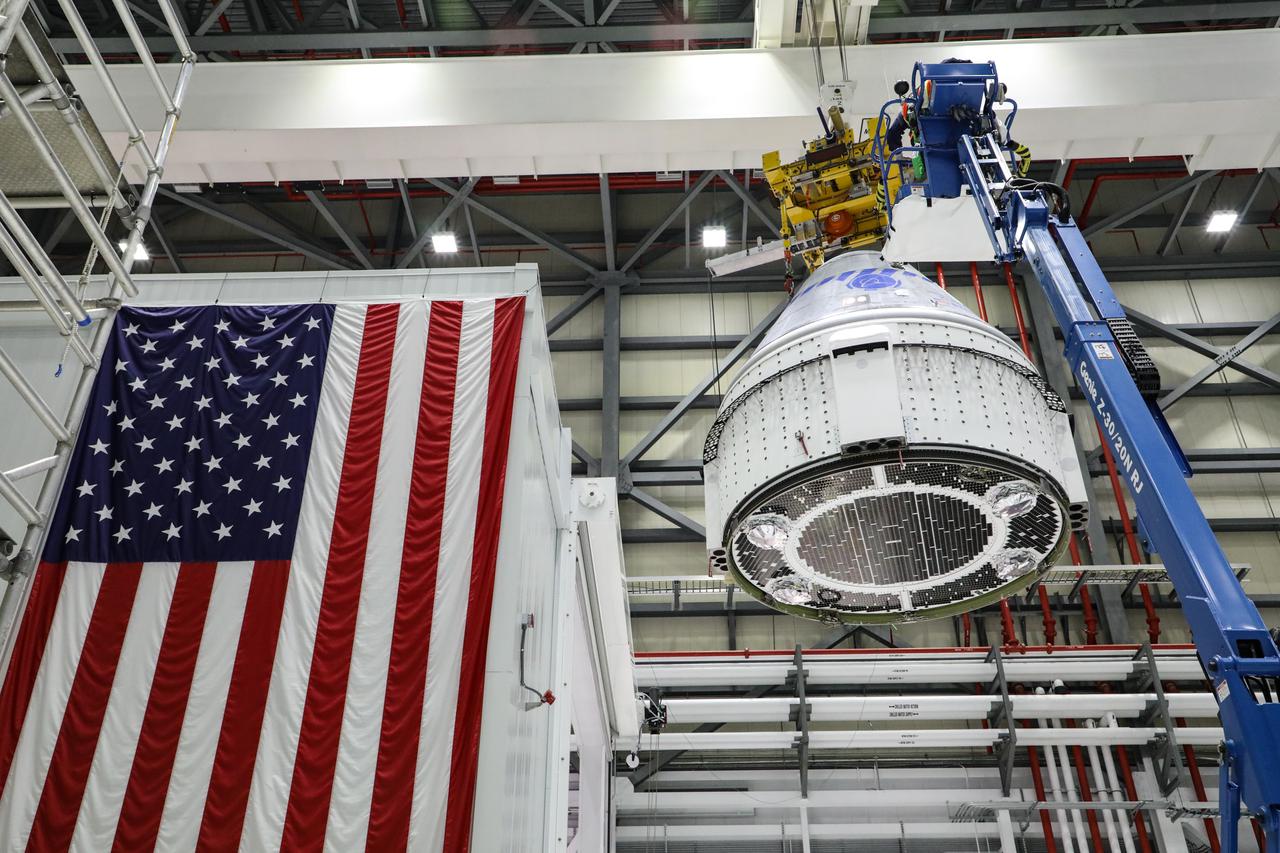

On July 13, 2021, inside the Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft moved from Hazardous Processing Area to the Weight and Center of Gravity machine and then transferred to the KMAG. The operations are in preparation for the company’s second Orbital Flight Test (OFT-2), as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.
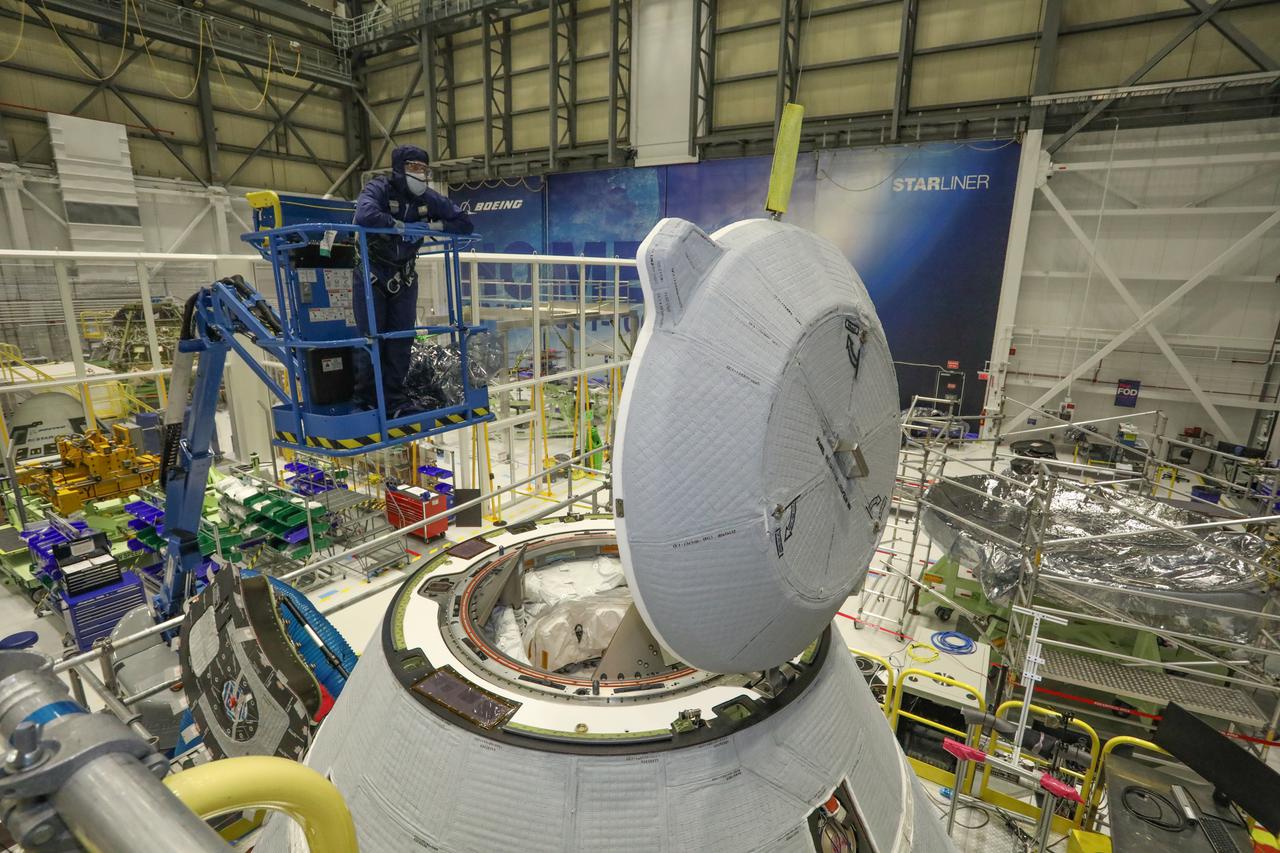

A technician observes the functional test of the NASA Docking System (NDS) cover in the Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 2, 2021. The test was conducted in preparation for Boeing’s second Orbital Flight Test (OFT-2), as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The cover is designed to protect the components that connect the spacecraft to the International Space Station.
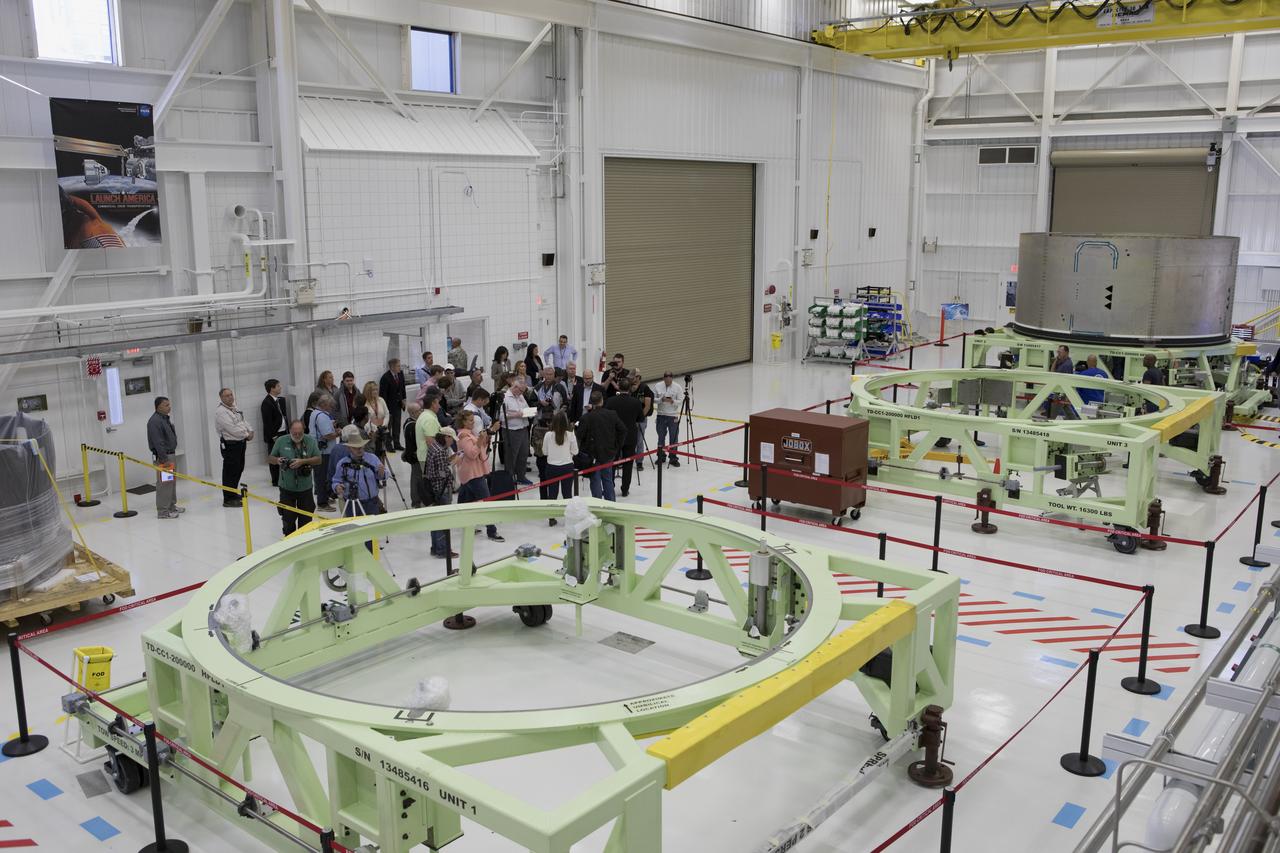

Inside Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida members of the news media view work platforms that will be used in manufacturing Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft for flight tests and crew rotation missions to the International Space Station as part of the agency's Commercial Crew Program.
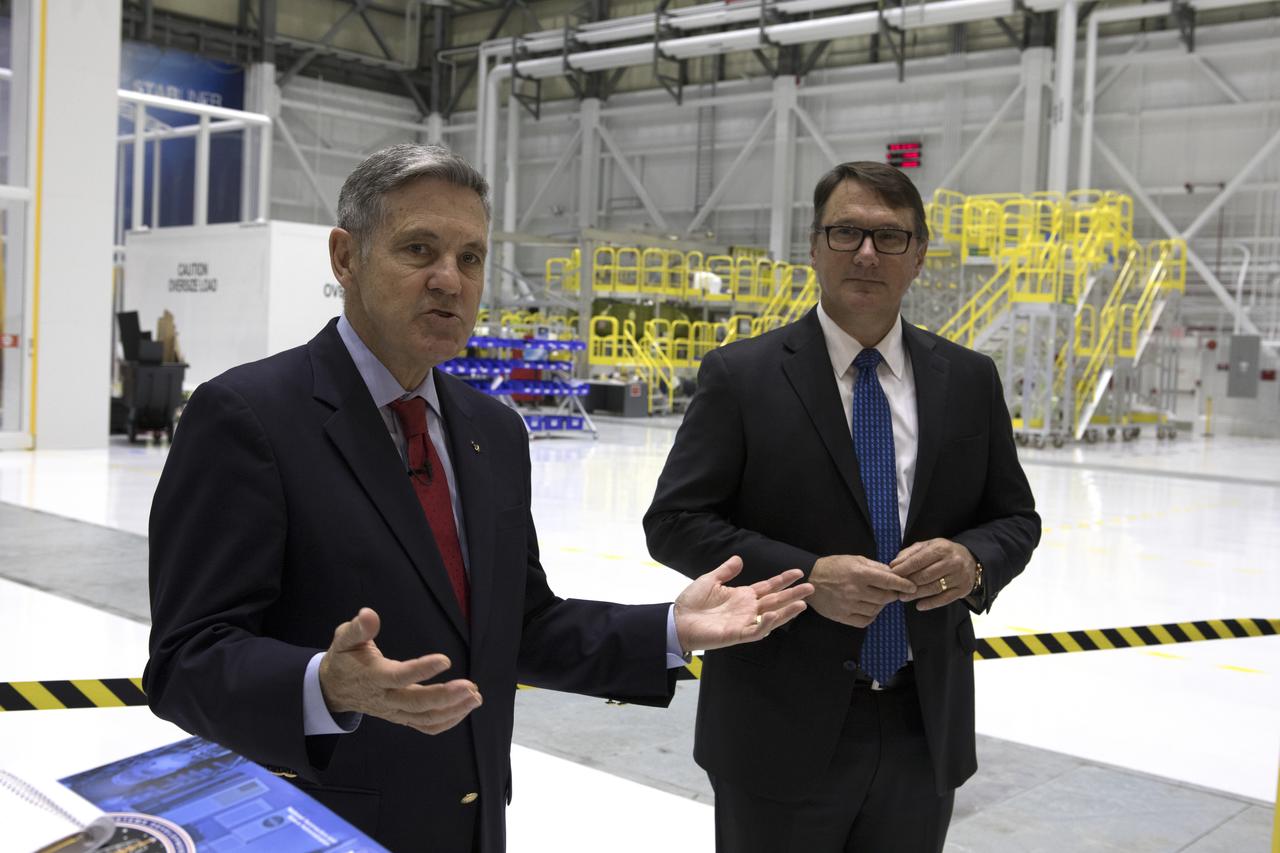

Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana, left, and John Mulholland, Boeing vice president and program manager for Commercial Programs, speak to members of the news media inside the Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at the Florida spaceport. The facility will be used in manufacturing Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft for flight tests and crew rotation missions to the International Space Station as part of the agency's Commercial Crew Program.
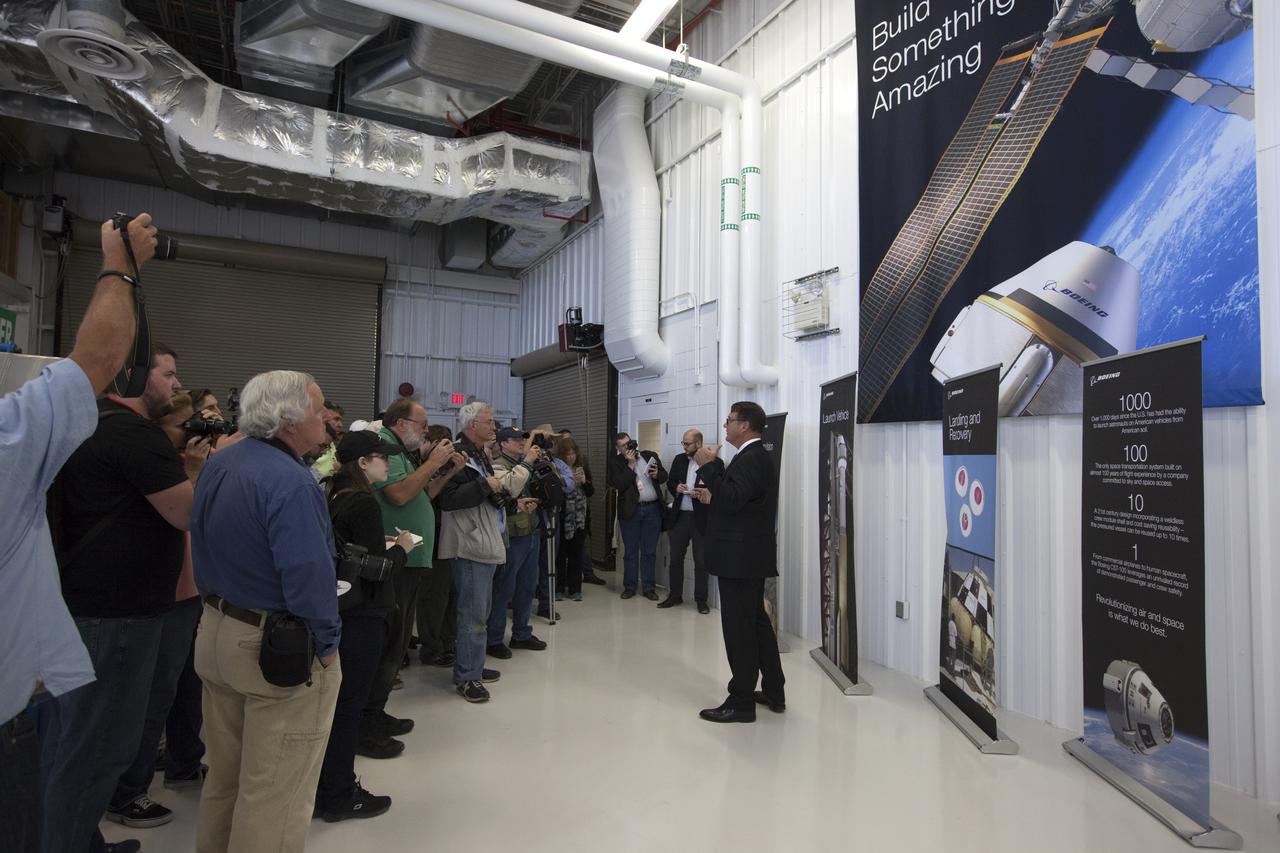

John Mulholland, Boeing vice president and program manager for Commercial Programs, speaks to members of the news media inside the Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at the Florida spaceport. The facility will be used in manufacturing Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft for flight tests and crew rotation missions to the International Space Station as part of the agency's Commercial Crew Program.
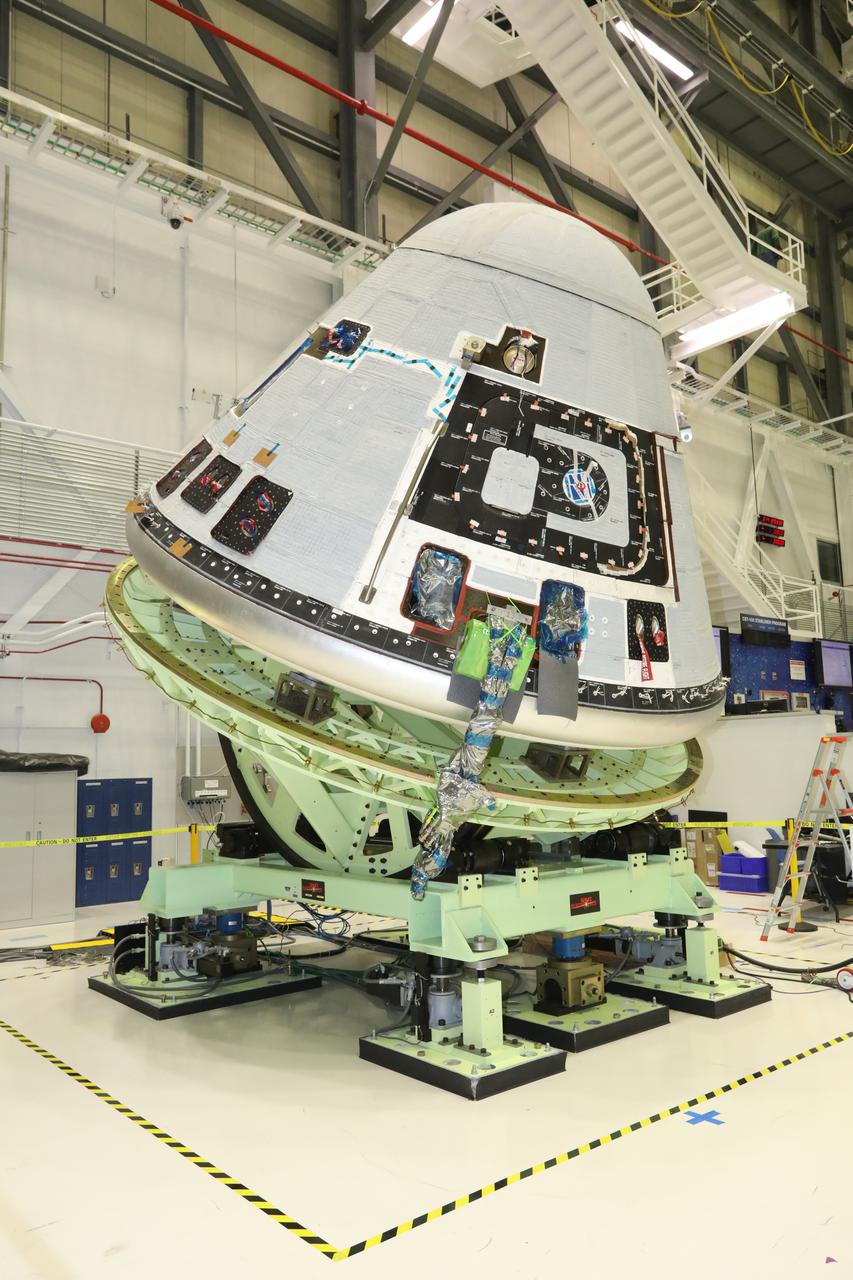

Boeing’s Starliner crew module is weighed in the Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 14, 2021, in preparation for the company’s second Orbital Flight Test (OFT-2), as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.. The Weight and Center of Gravity test measures the weight and balance of the spacecraft to ensure optimal performance during launch and re-entry. The test helps to validate parameters required for launching on United Launch Alliance’s Atlas V rocket, docking to the International Space Station and for navigation of the vehicle, among others.
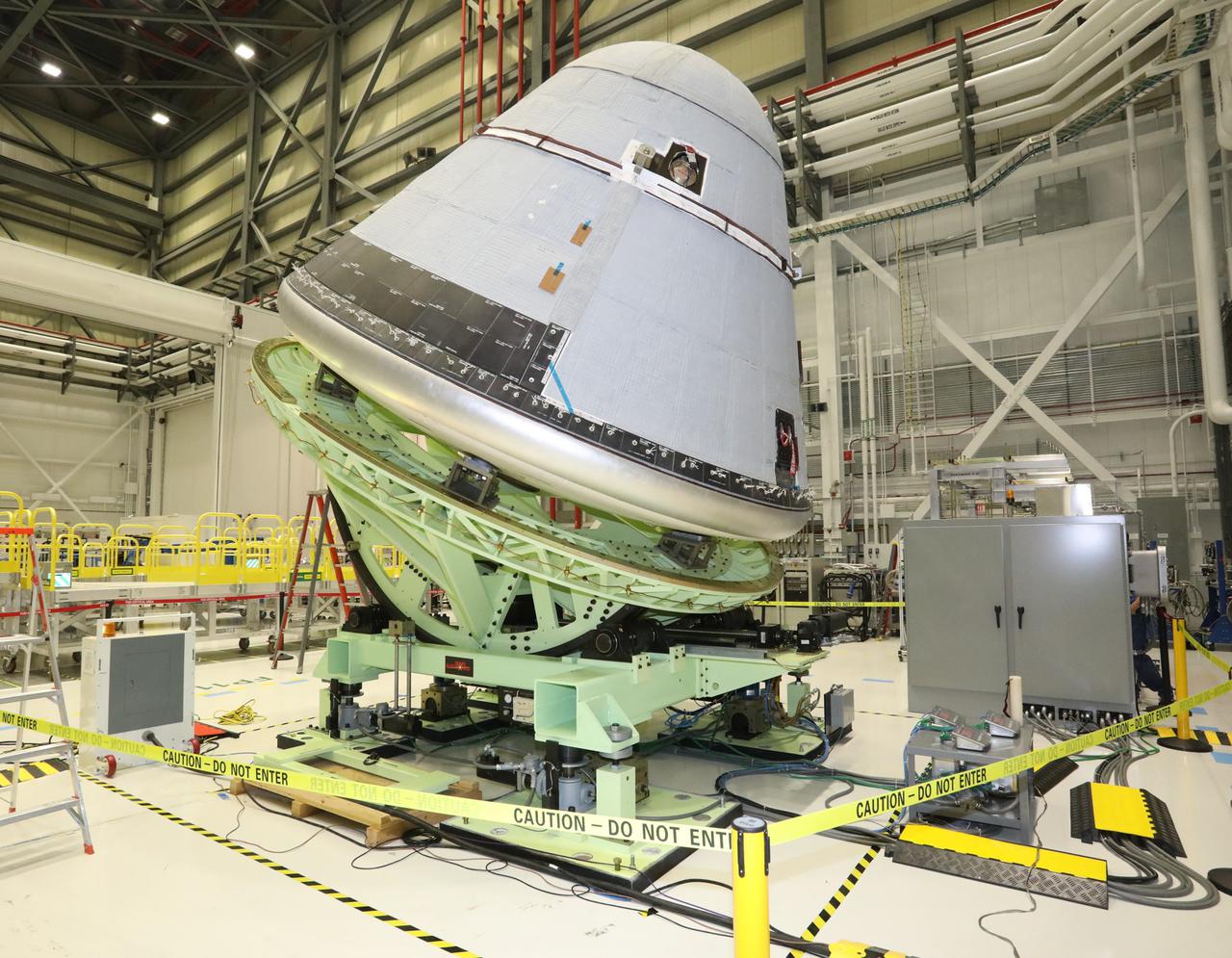

Boeing’s Starliner crew module is weighed in the Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 14, 2021, in preparation for the company’s second Orbital Flight Test (OFT-2), as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.. The Weight and Center of Gravity test measures the weight and balance of the spacecraft to ensure optimal performance during launch and re-entry. The test helps to validate parameters required for launching on United Launch Alliance’s Atlas V rocket, docking to the International Space Station and for navigation of the vehicle, among others.
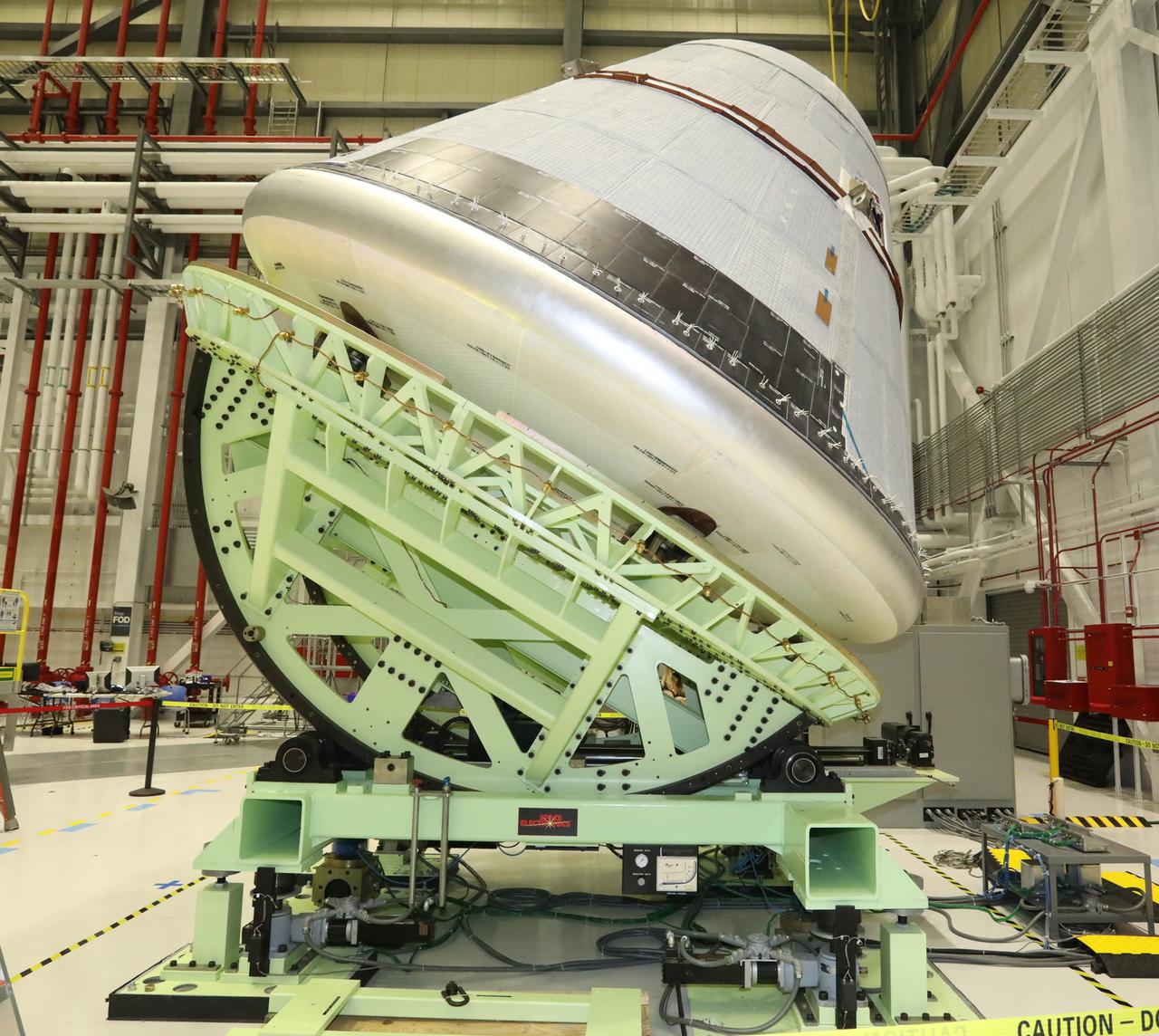

Boeing’s Starliner crew module is weighed in the Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 14, 2021, in preparation for the company’s second Orbital Flight Test (OFT-2), as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.. The Weight and Center of Gravity test measures the weight and balance of the spacecraft to ensure optimal performance during launch and re-entry. The test helps to validate parameters required for launching on United Launch Alliance’s Atlas V rocket, docking to the International Space Station and for navigation of the vehicle, among others.
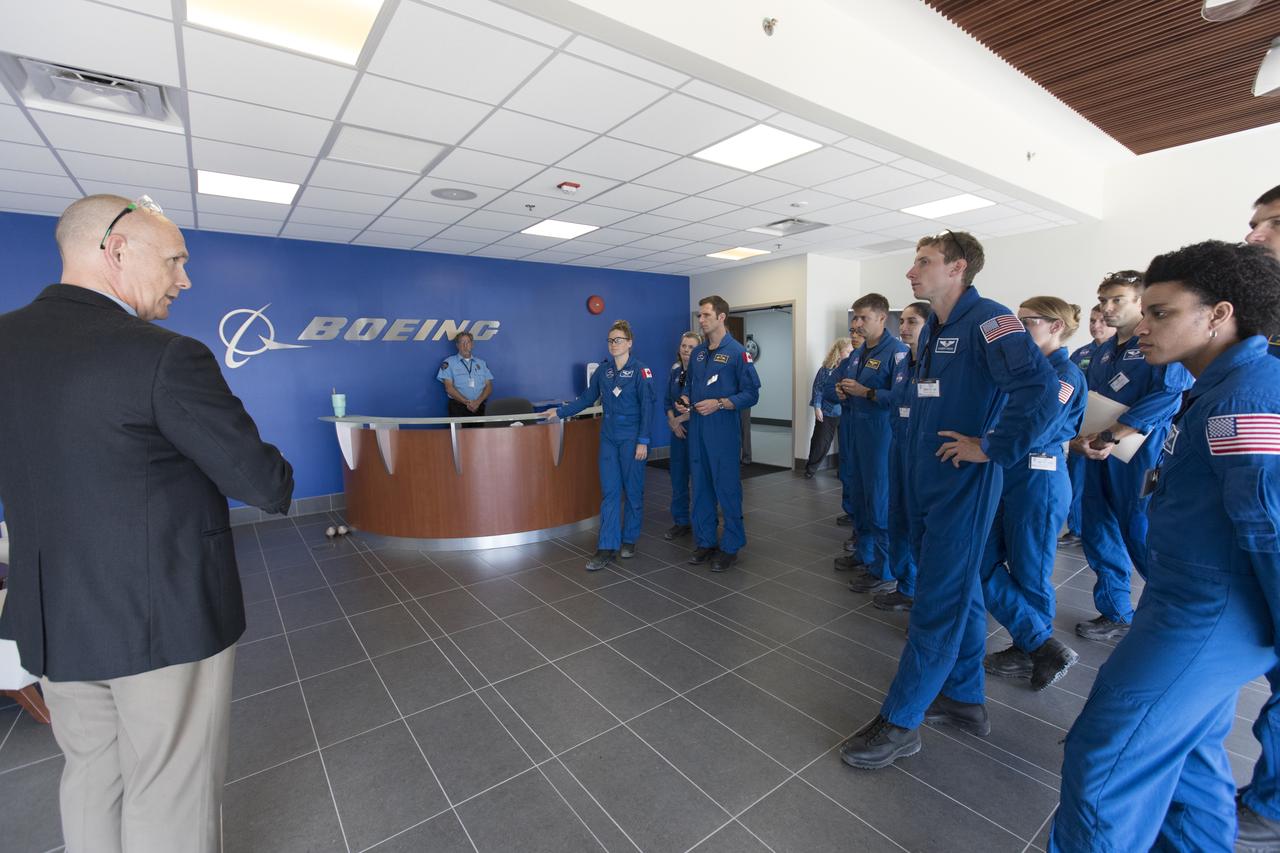

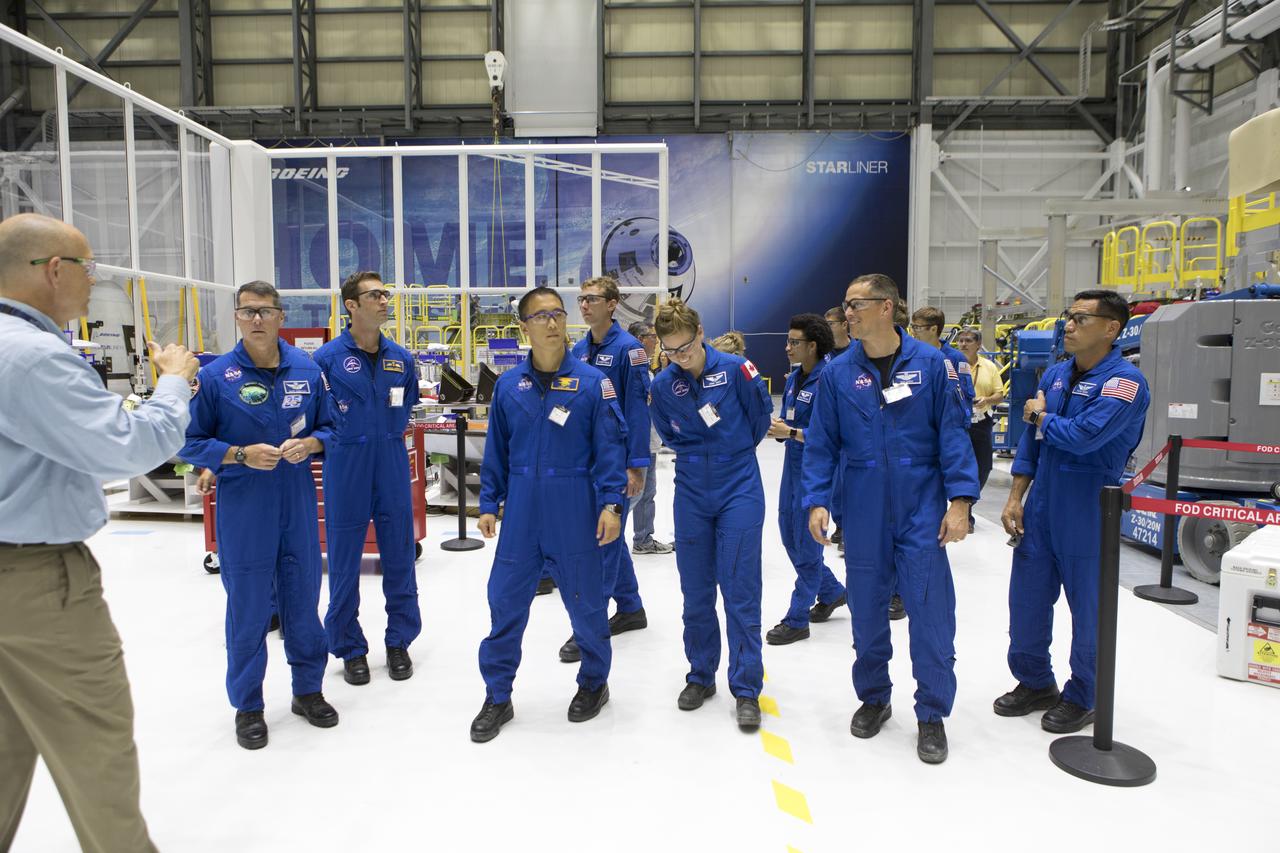
The 2017 class of astronaut candidates arrive at Boeing's Commercial Crew and Cargo Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 1. They are at the center for a familiarization tour of facilities, including the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay; the Launch Control Center, Launch Complex 39B, and the Vehicle Assembly Building. They also toured United Launch Alliance's Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, and SpaceX's Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy. The candidates will spend about two years getting to know the space station systems and learning how to spacewalk, speak Russian, control the International Space Station's robotic arm and fly T-38s, before they're eligible to be assigned to a mission.

The 2017 class of astronaut candidates tour Boeing's Commercial Crew and Cargo Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 1. They are at the center for a familiarization tour of facilities, including the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay; the Launch Control Center, Launch Complex 39B, and the Vehicle Assembly Building. They also toured United Launch Alliance's Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, and SpaceX's Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy. The candidates will spend about two years getting to know the space station systems and learning how to spacewalk, speak Russian, control the International Space Station's robotic arm and fly T-38s, before they're eligible to be assigned to a mission.
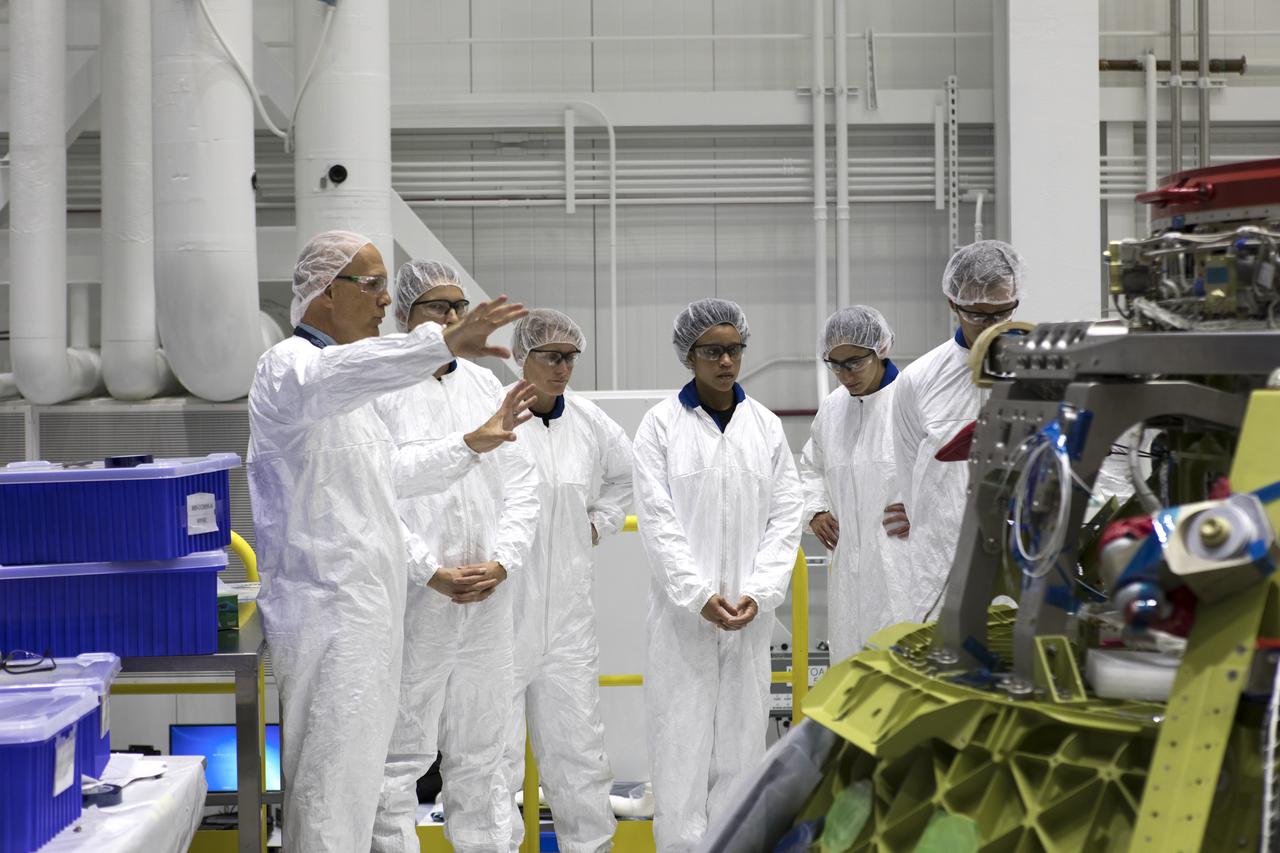

The 2017 class of astronaut candidates tour Boeing's Commercial Crew and Cargo Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 1. They are at the center for a familiarization tour of facilities, including the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay; the Launch Control Center, Launch Complex 39B, and the Vehicle Assembly Building. They also toured United Launch Alliance's Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, and SpaceX's Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy. The candidates will spend about two years getting to know the space station systems and learning how to spacewalk, speak Russian, control the International Space Station's robotic arm and fly T-38s, before they're eligible to be assigned to a mission.

The 2017 class of astronaut candidates tour Boeing's Commercial Crew and Cargo Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 1. They are at the center for a familiarization tour of facilities, including the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay; the Launch Control Center, Launch Complex 39B, and the Vehicle Assembly Building. They also toured United Launch Alliance's Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, and SpaceX's Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy. The candidates will spend about two years getting to know the space station systems and learning how to spacewalk, speak Russian, control the International Space Station's robotic arm and fly T-38s, before they're eligible to be assigned to a mission.
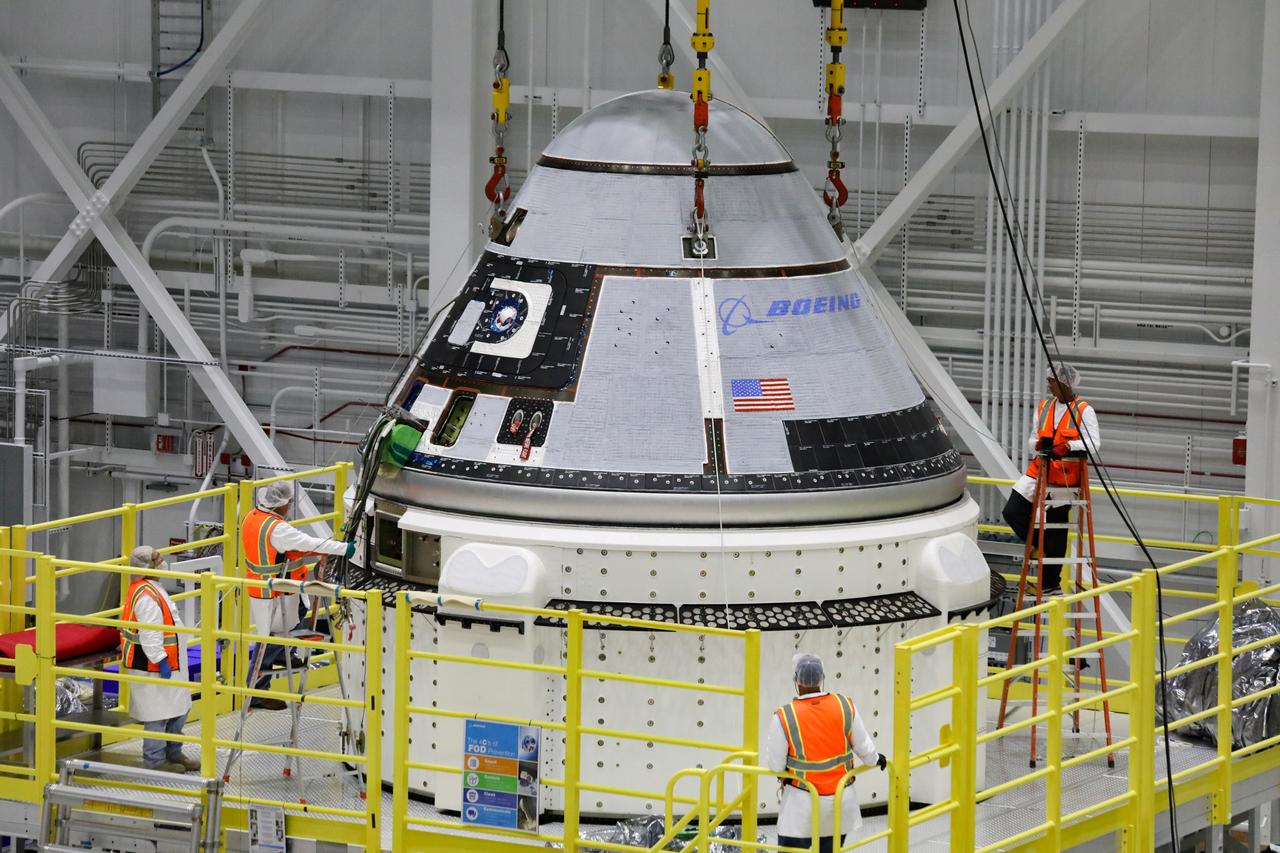

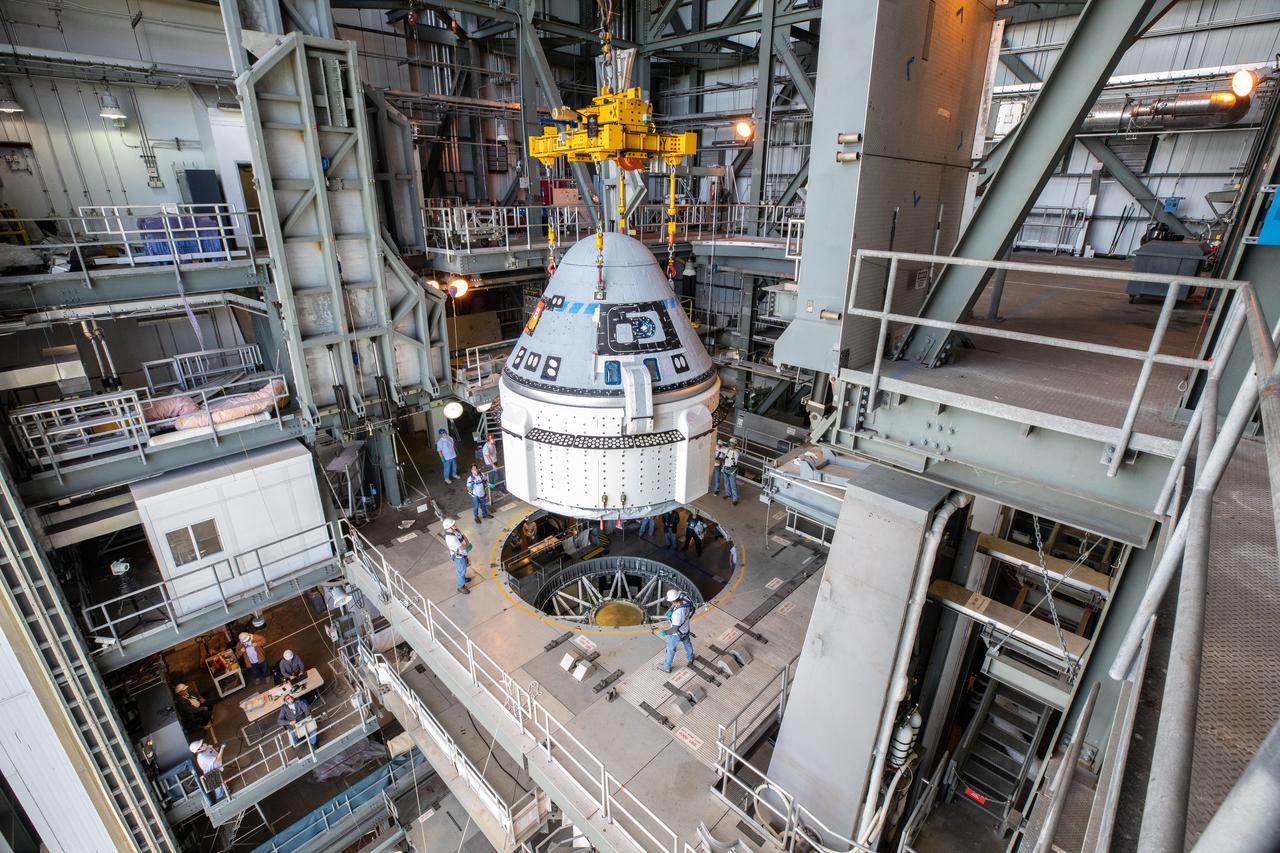
The crew module of Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft is lifted onto its service module on Oct. 16, 2019, inside the Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility (C3PF) at Kennedy Space Center in Florida ahead of the company's Orbital Flight Test to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program.
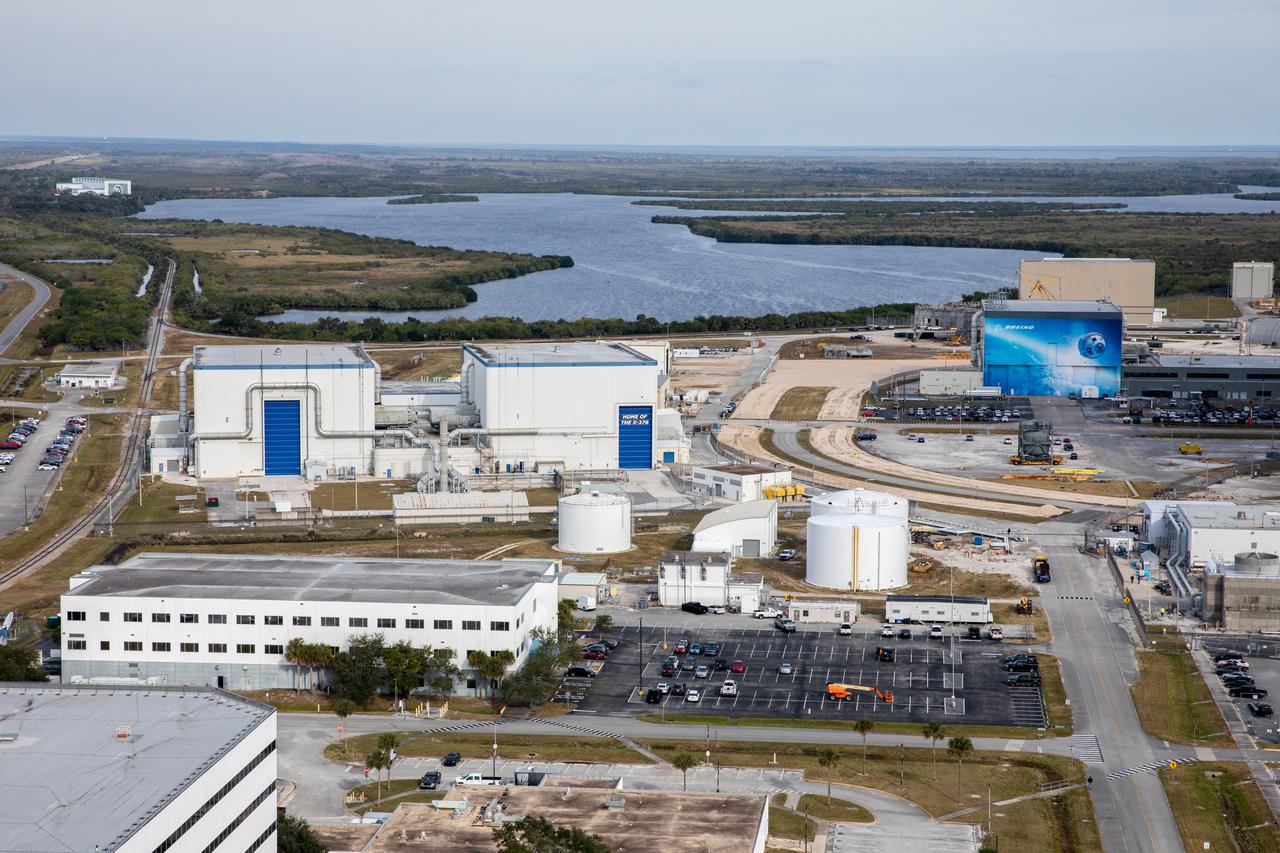

An aerial view of several processing facilities at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 13, 2021. In view at right is Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility.
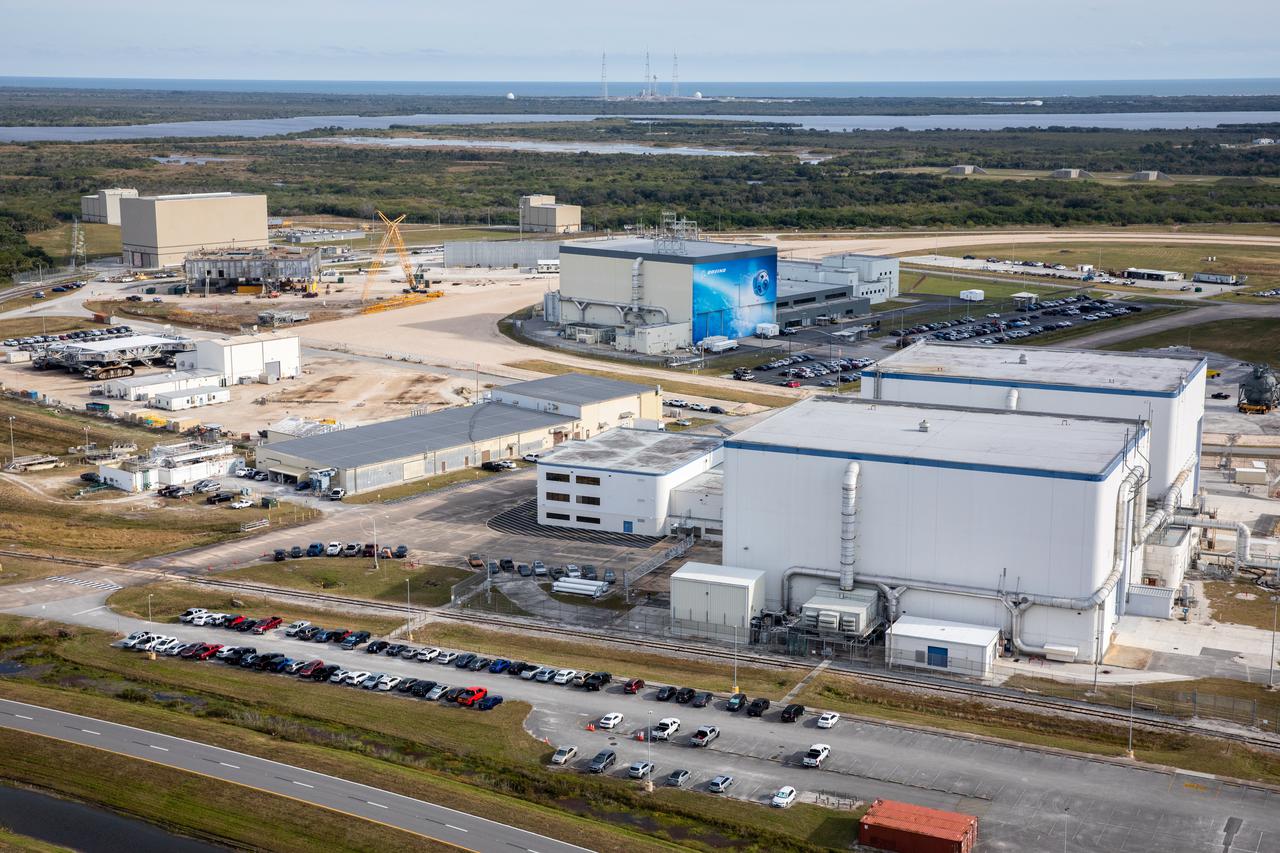

An aerial view of several processing facilities at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 13, 2021. In view in the background is Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility.
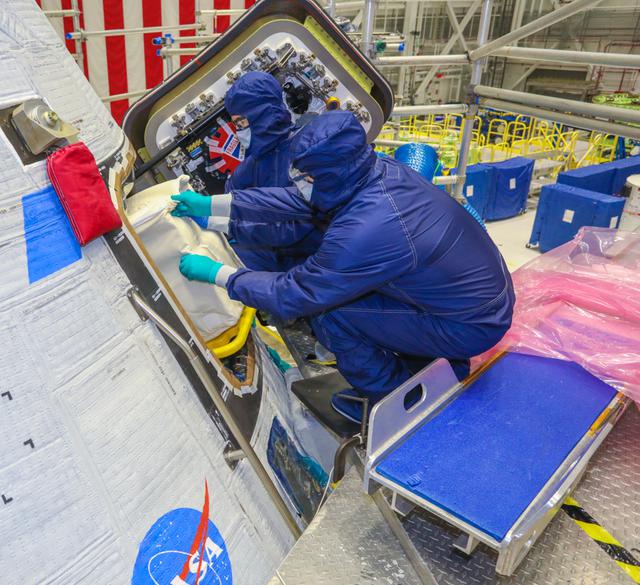

Technicians place cargo inside Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner ahead of Orbital Flight Test-2 (OFT-2) in the Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 28, 2021. Part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program, OFT-2 is a critical developmental milestone on the company’s path to fly crew missions for NASA.
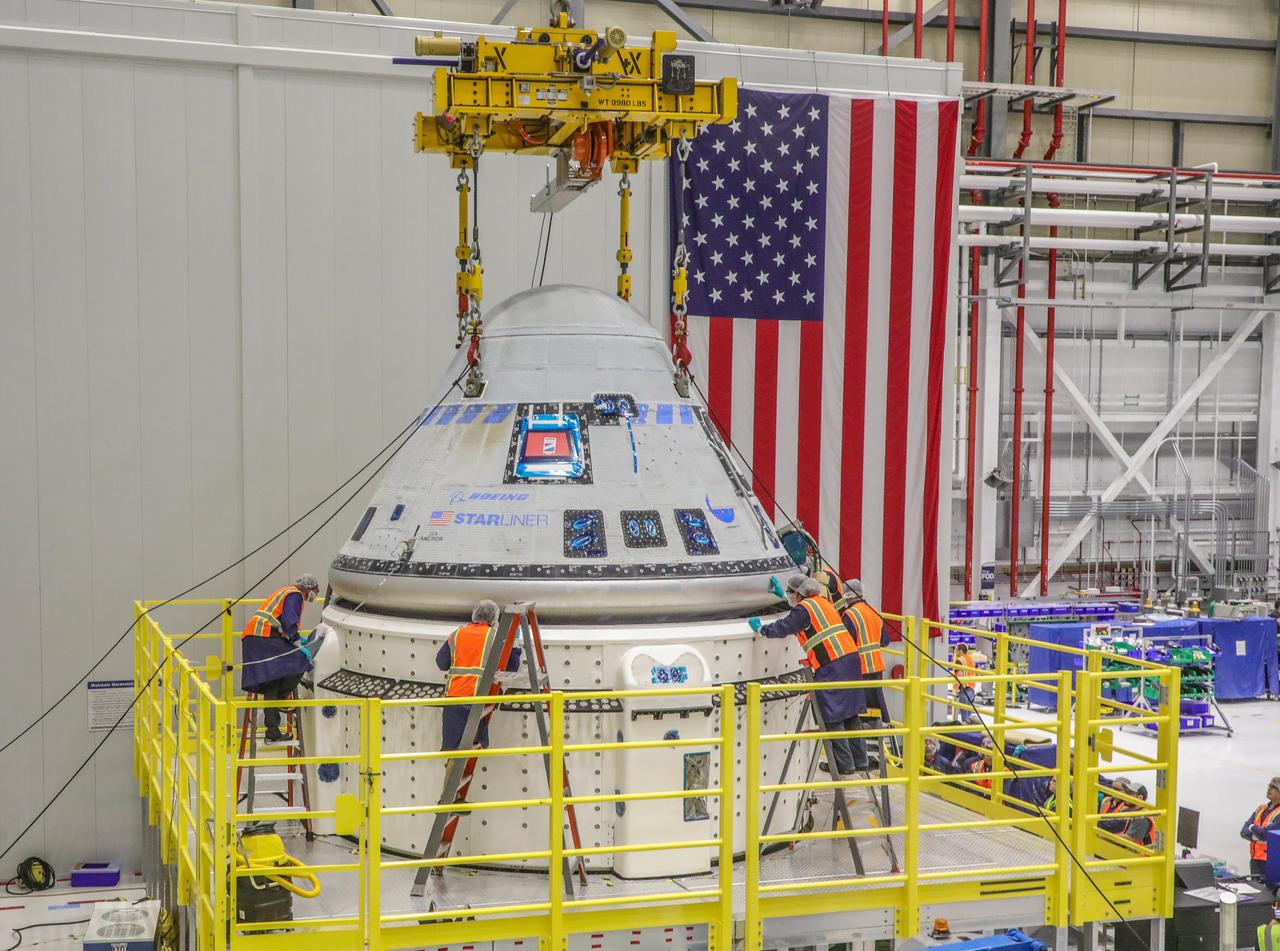

The Starliner team works to finalize the mate of the crew module and new service module for NASA's Boeing Crew Flight Test that will take NASA astronauts Barry “Butch” Wilmore and Sunita “Suni” Williams to and from the International Space Station.
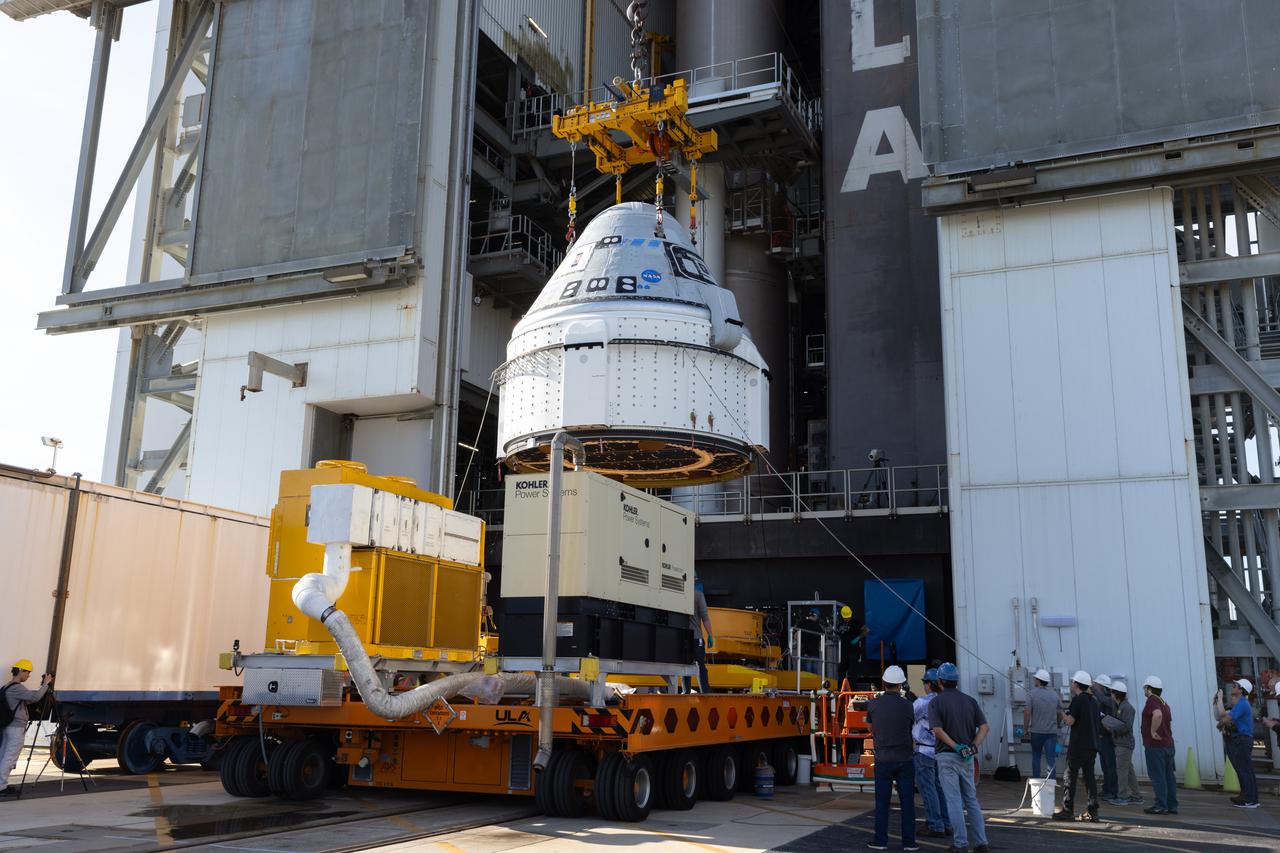

The Boeing Starliner spacecraft is lifted at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Tuesday, April 16, 2024. Starliner will be secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for NASA’s Boeing Crew Flight Test to the International Space Station for the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing's Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.
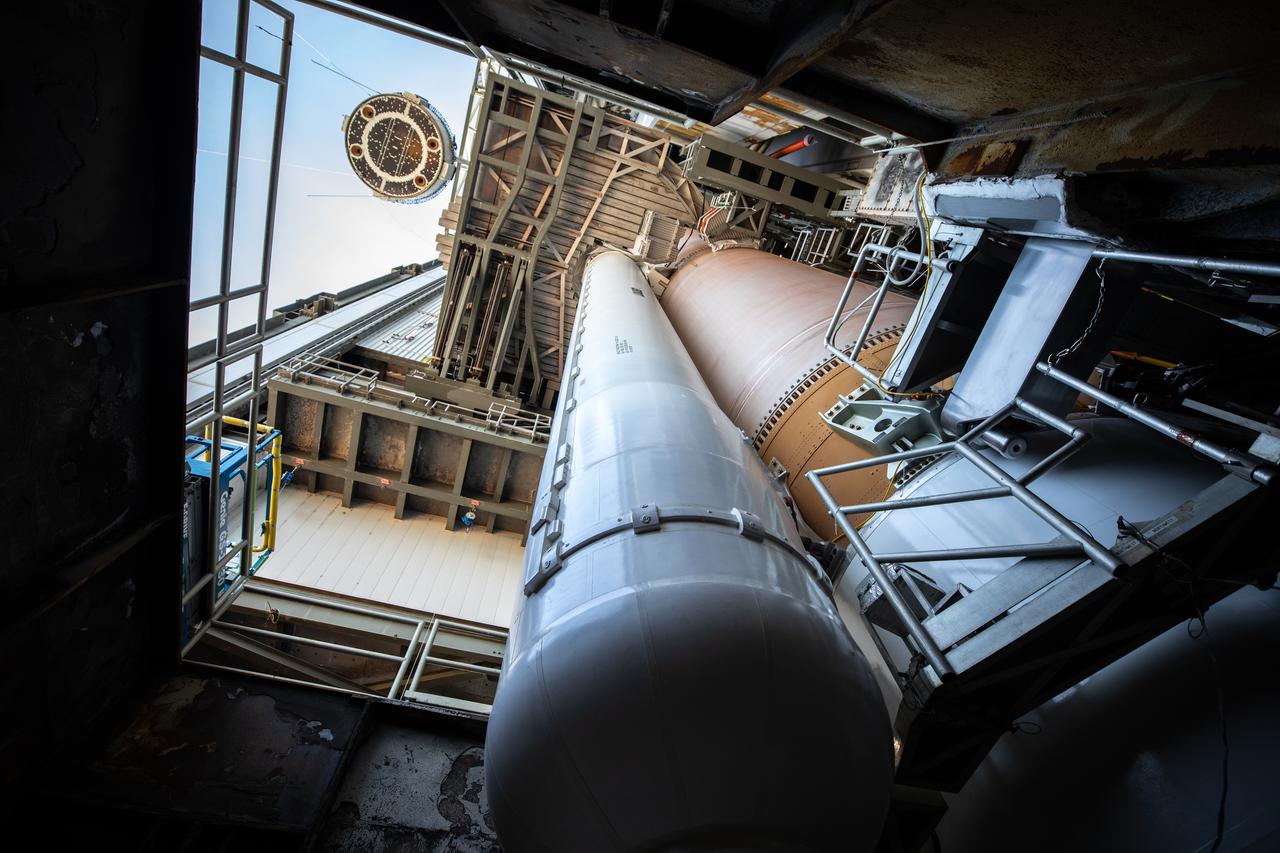

The Boeing Starliner spacecraft is lifted at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Tuesday, April 16, 2024. Starliner will be secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for NASA’s Boeing Crew Flight Test to the International Space Station for the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing's Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.
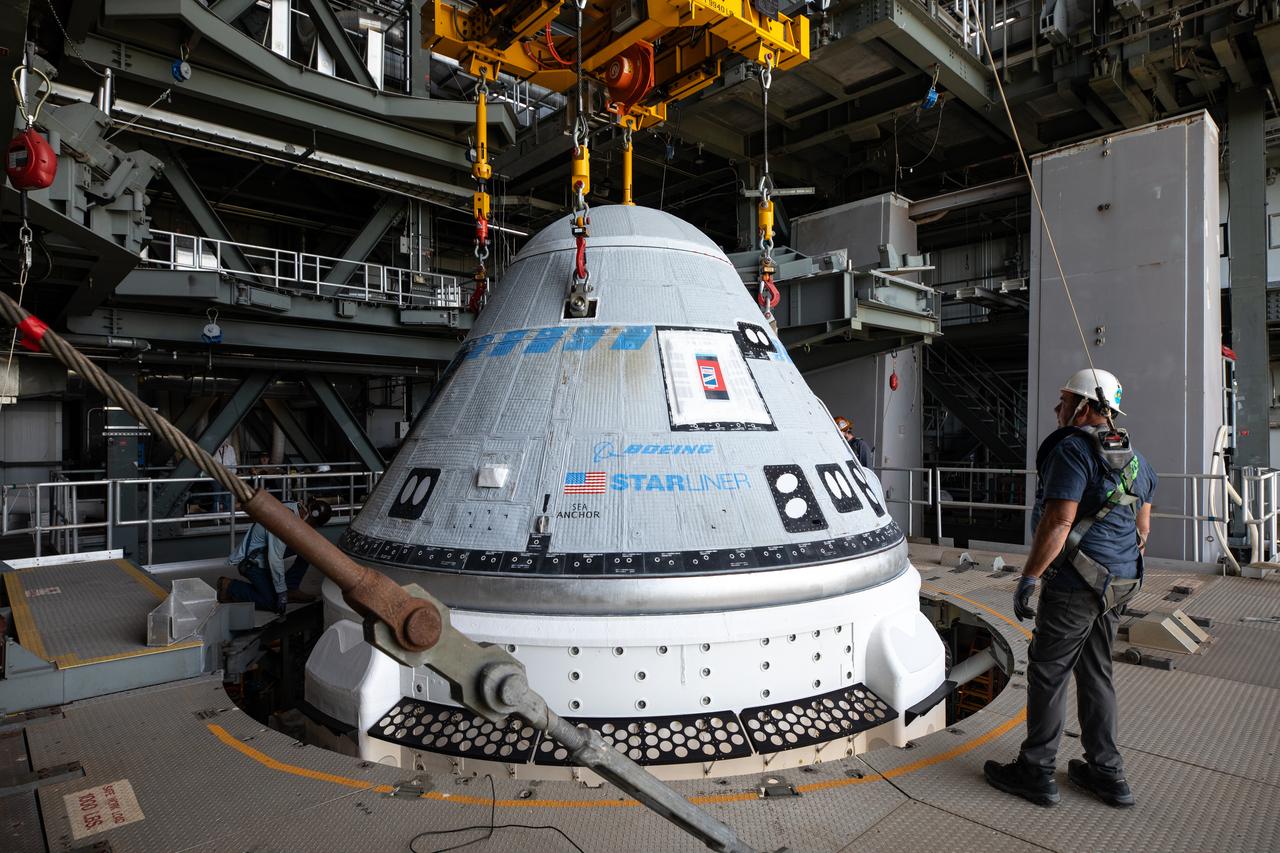

The Boeing Starliner spacecraft is lifted at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Tuesday, April 16, 2024. Starliner will be secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for NASA’s Boeing Crew Flight Test to the International Space Station for the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing's Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.
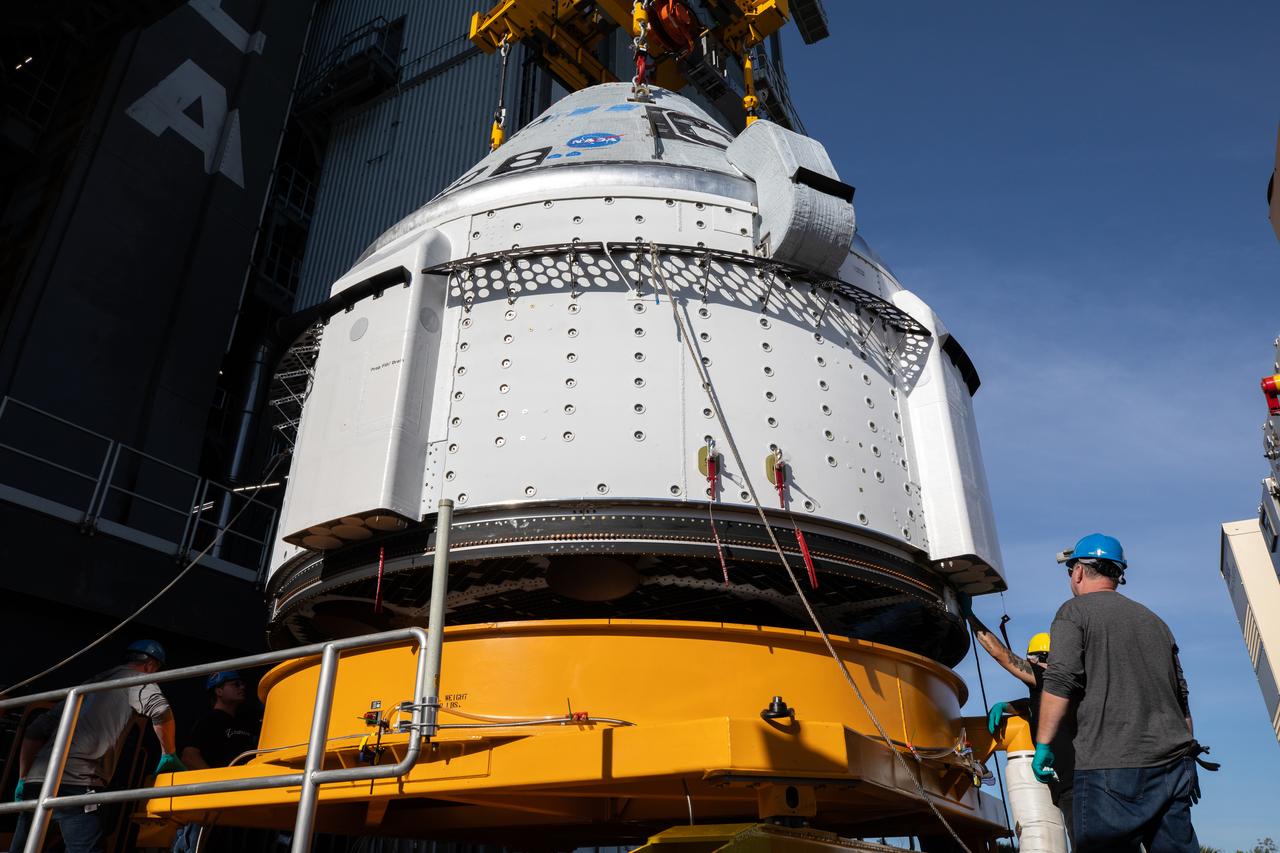

The Boeing Starliner spacecraft is lifted at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Tuesday, April 16, 2024. Starliner will be secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for NASA’s Boeing Crew Flight Test to the International Space Station for the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing's Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.
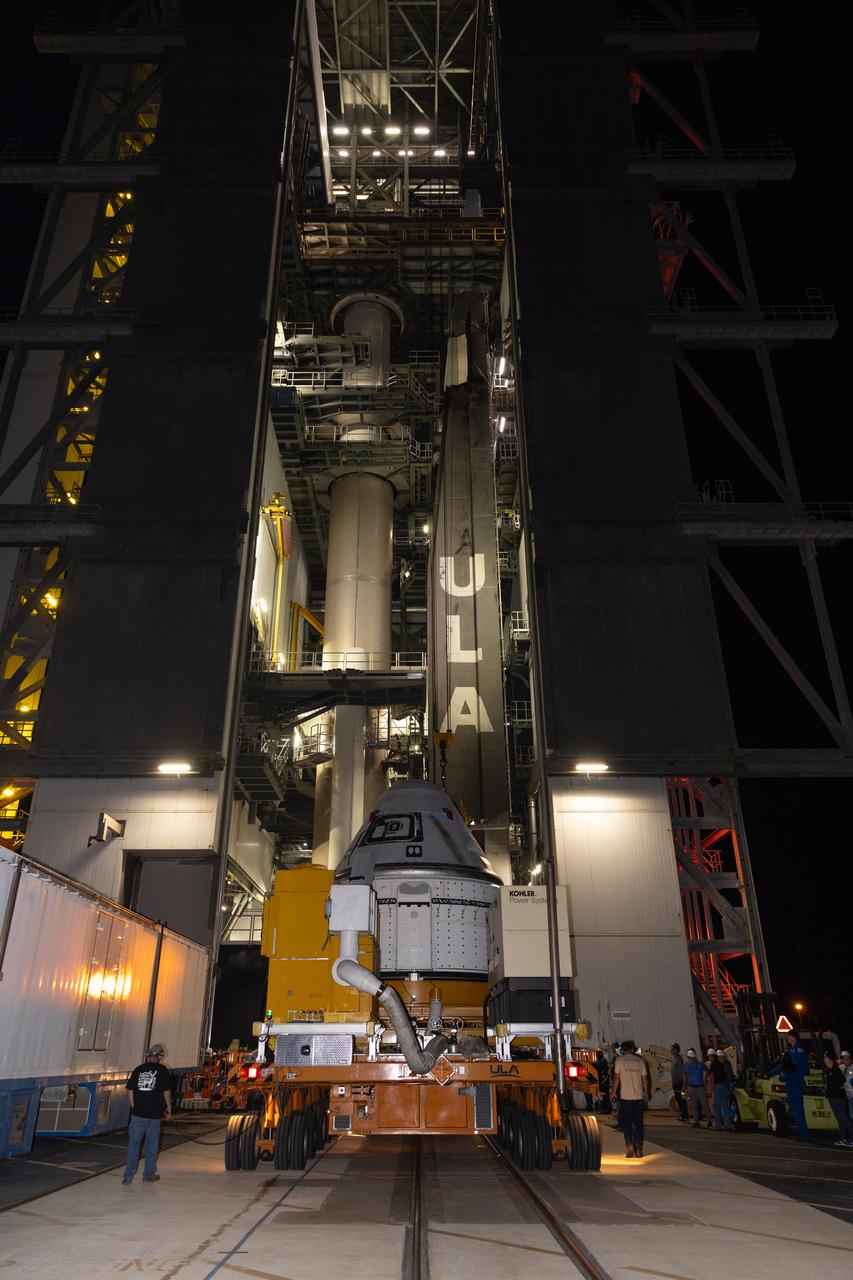

Boeing’s Starliner spacecraft arrives at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Tuesday, April 16, 2024. Starliner will be secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for NASA’s Boeing Crew Flight Test to the International Space Station for the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.
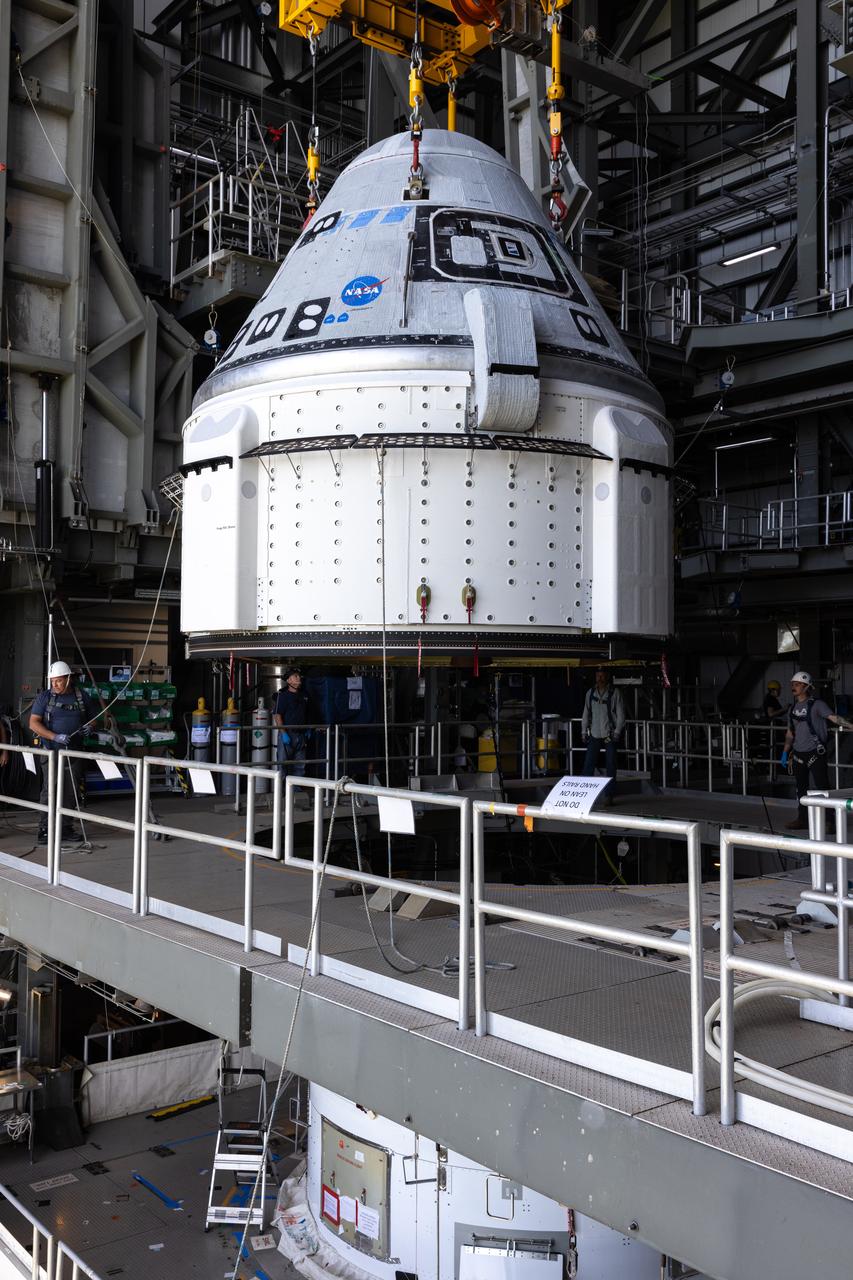

The Boeing Starliner spacecraft is lifted at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Tuesday, April 16, 2024. Starliner will be secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for NASA’s Boeing Crew Flight Test to the International Space Station for the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing's Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.
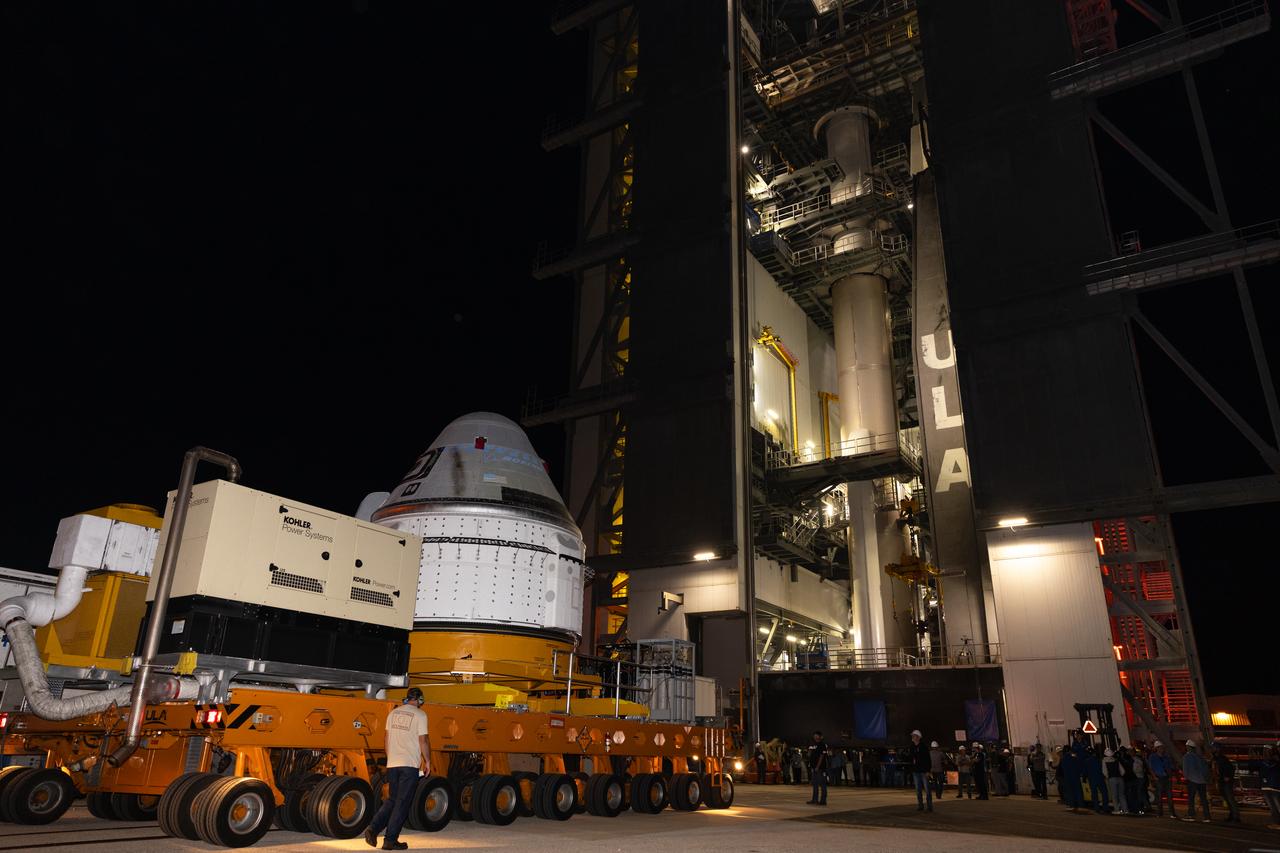

Boeing’s Starliner spacecraft arrives at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Tuesday, April 16, 2024. Starliner will be secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for NASA’s Boeing Crew Flight Test to the International Space Station for the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.
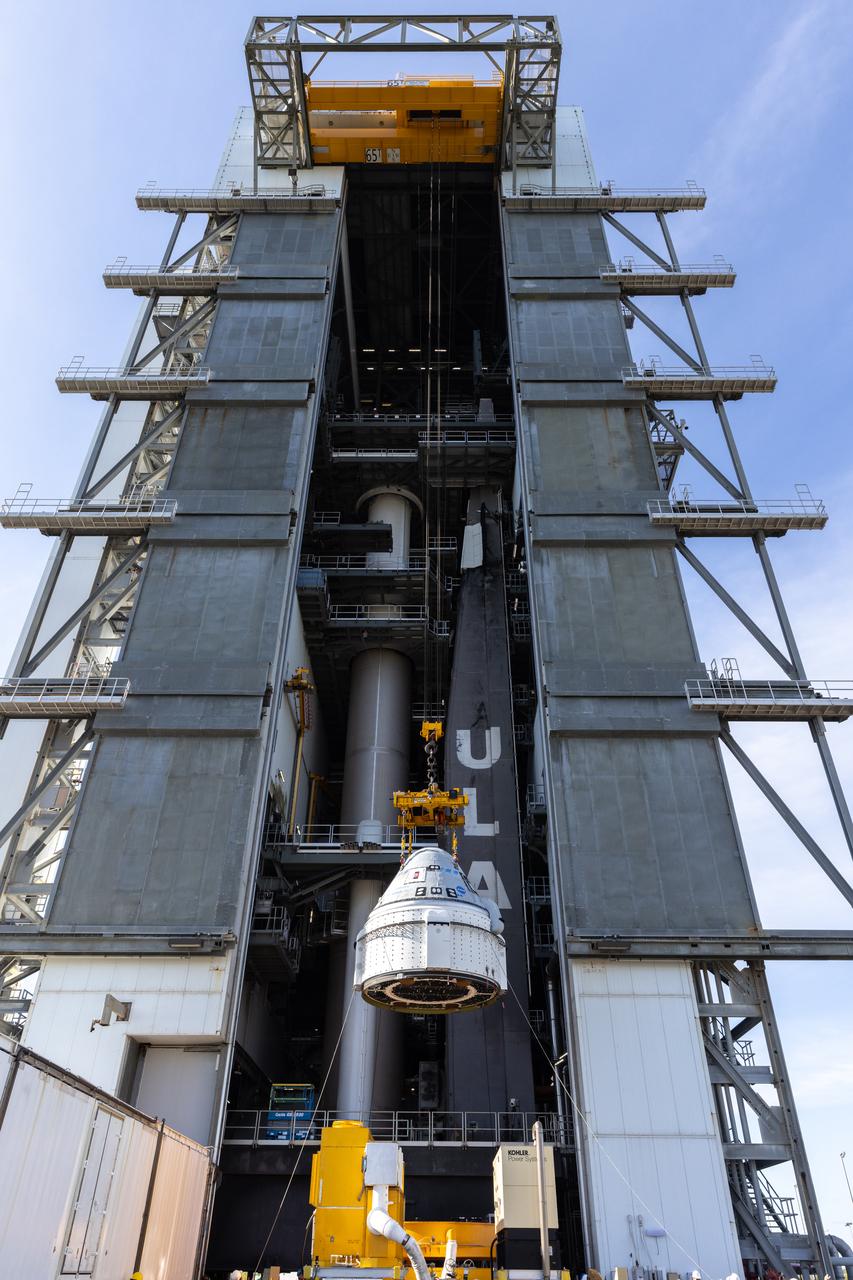

The Boeing Starliner spacecraft is lifted at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Tuesday, April 16, 2024. Starliner will be secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for NASA’s Boeing Crew Flight Test to the International Space Station for the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing's Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.
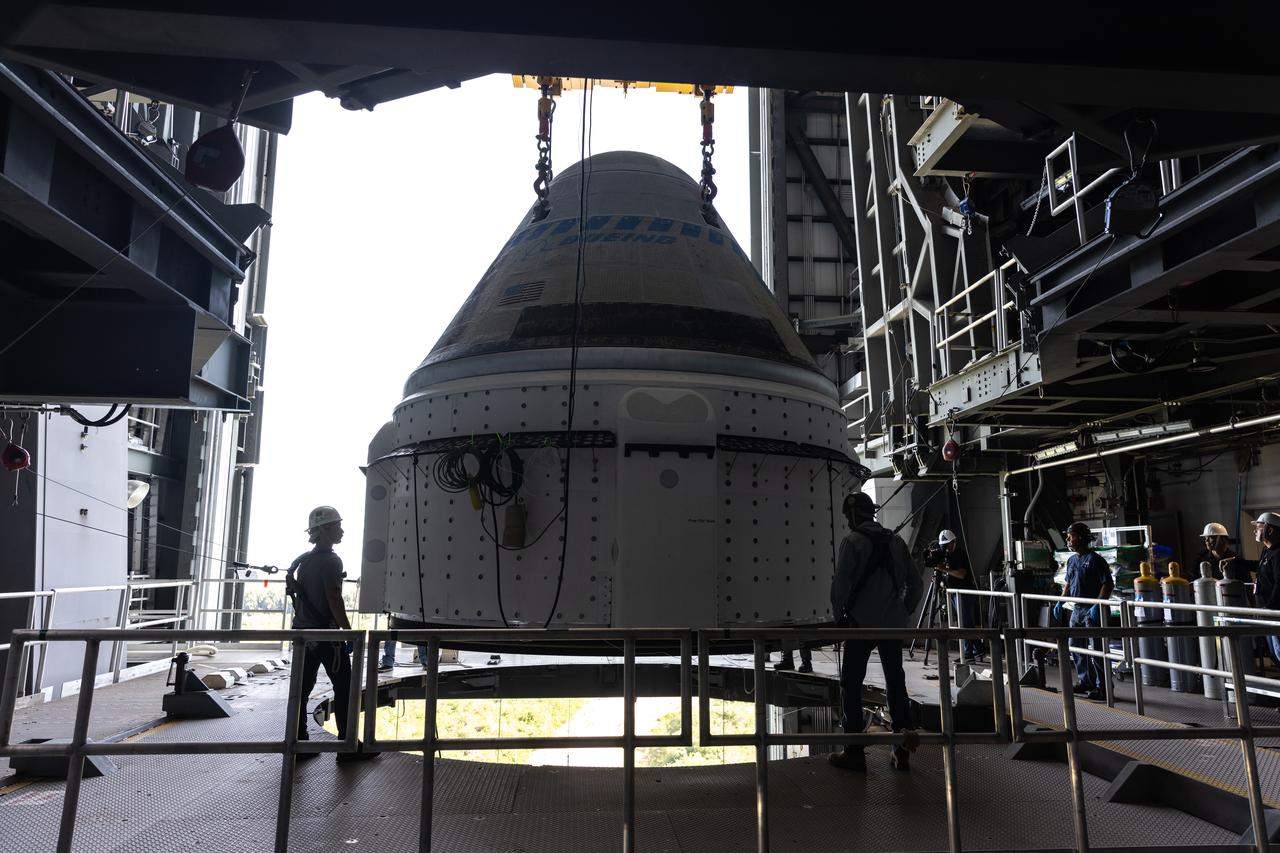

The Boeing Starliner spacecraft is lifted at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Tuesday, April 16, 2024. Starliner will be secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for NASA’s Boeing Crew Flight Test to the International Space Station for the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing's Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.
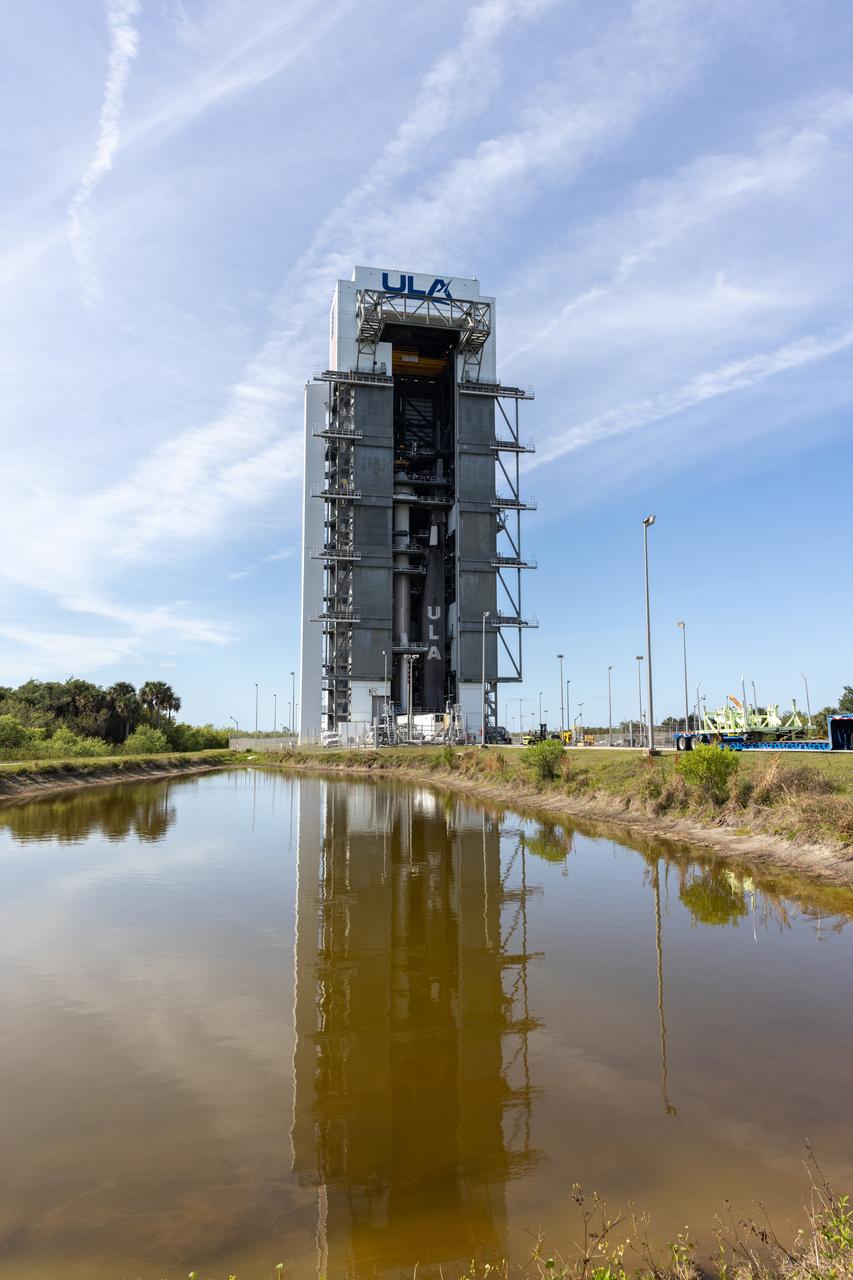

The Boeing Starliner spacecraft is lifted at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Tuesday, April 16, 2024. Starliner will be secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for NASA’s Boeing Crew Flight Test to the International Space Station for the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing's Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.
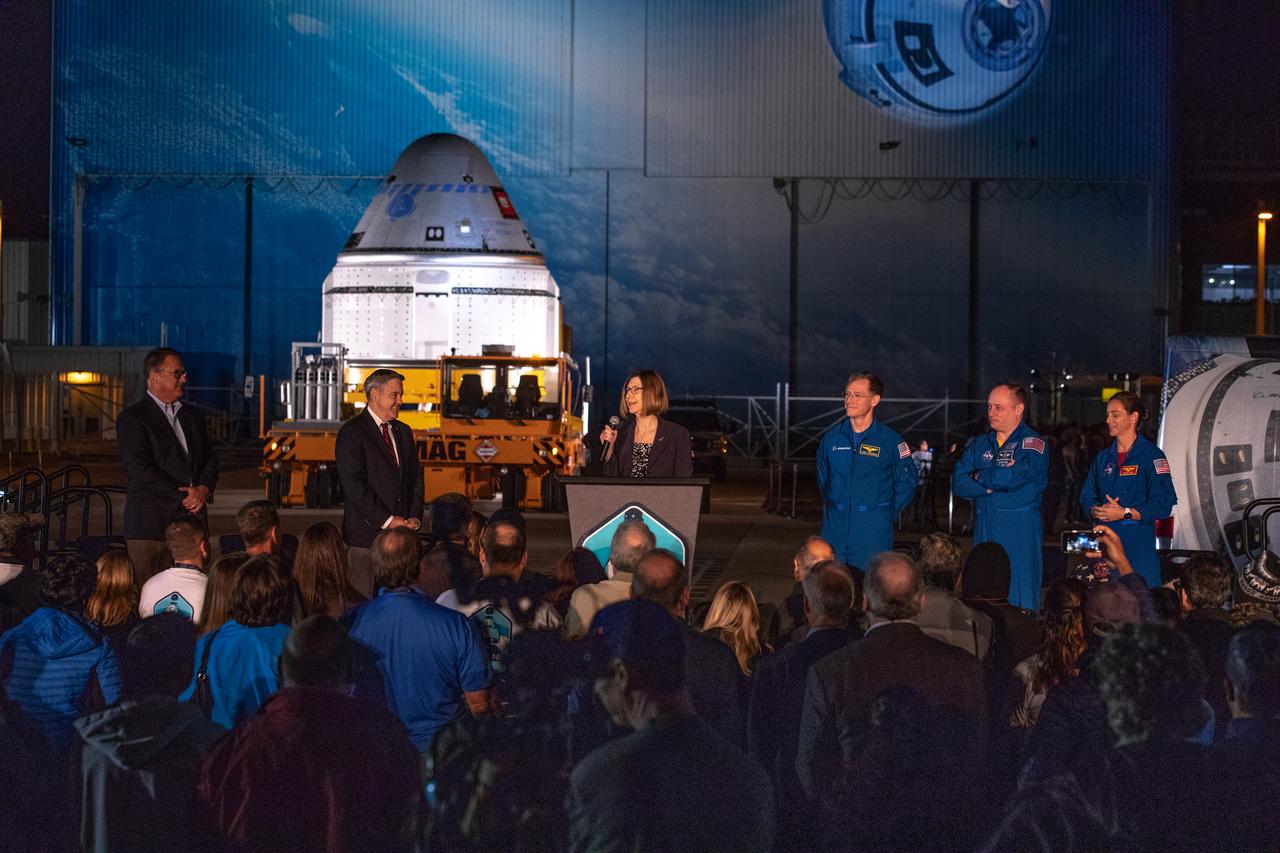

Kathy Lueders, program manager, NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, speaks during the Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft rollout from the company’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 21, 2019. Starliner will make the trip to Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station where it will be secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.
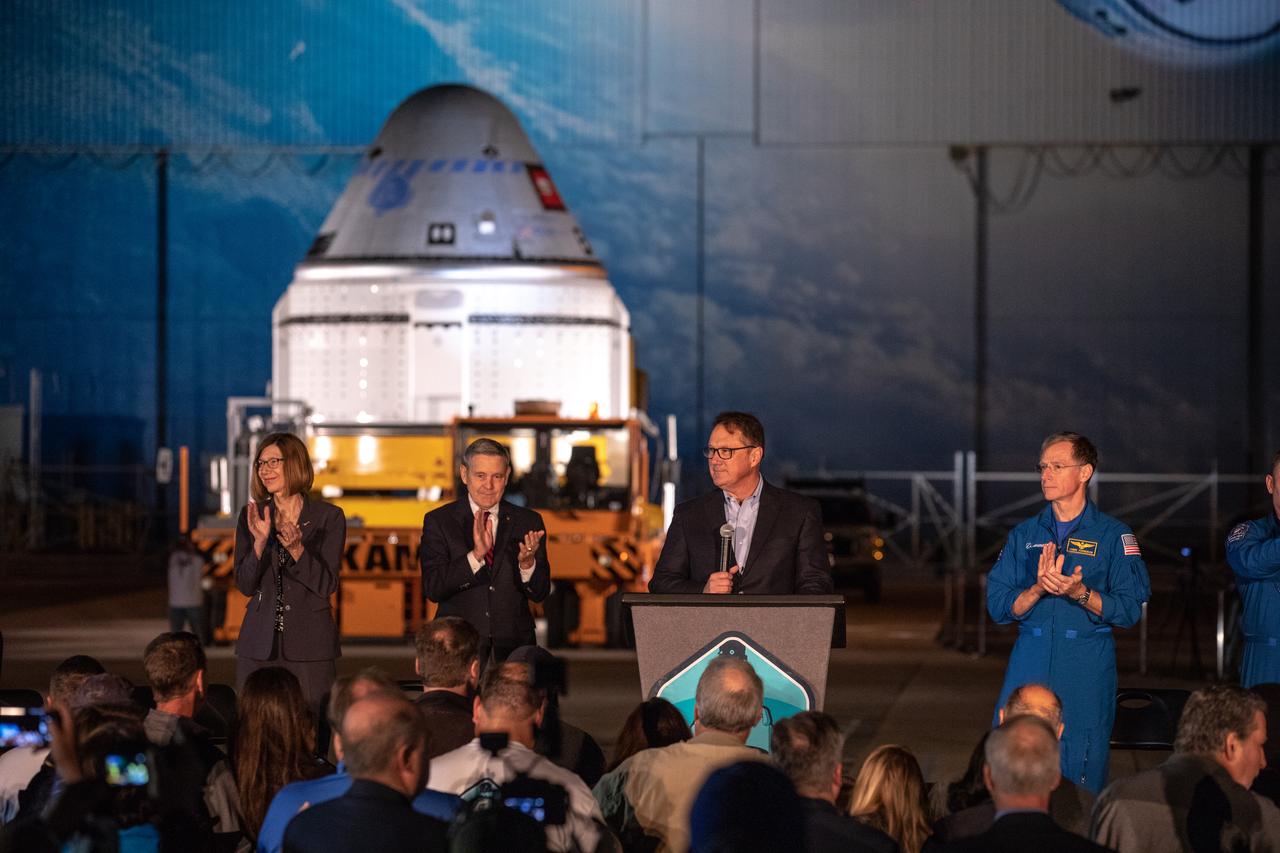

John Mulholland, Boeing vice president and program manager, Commercial Crew Program, speaks during the Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft rollout from the company’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 21, 2019. Starliner will make the trip to Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station where it will be secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.
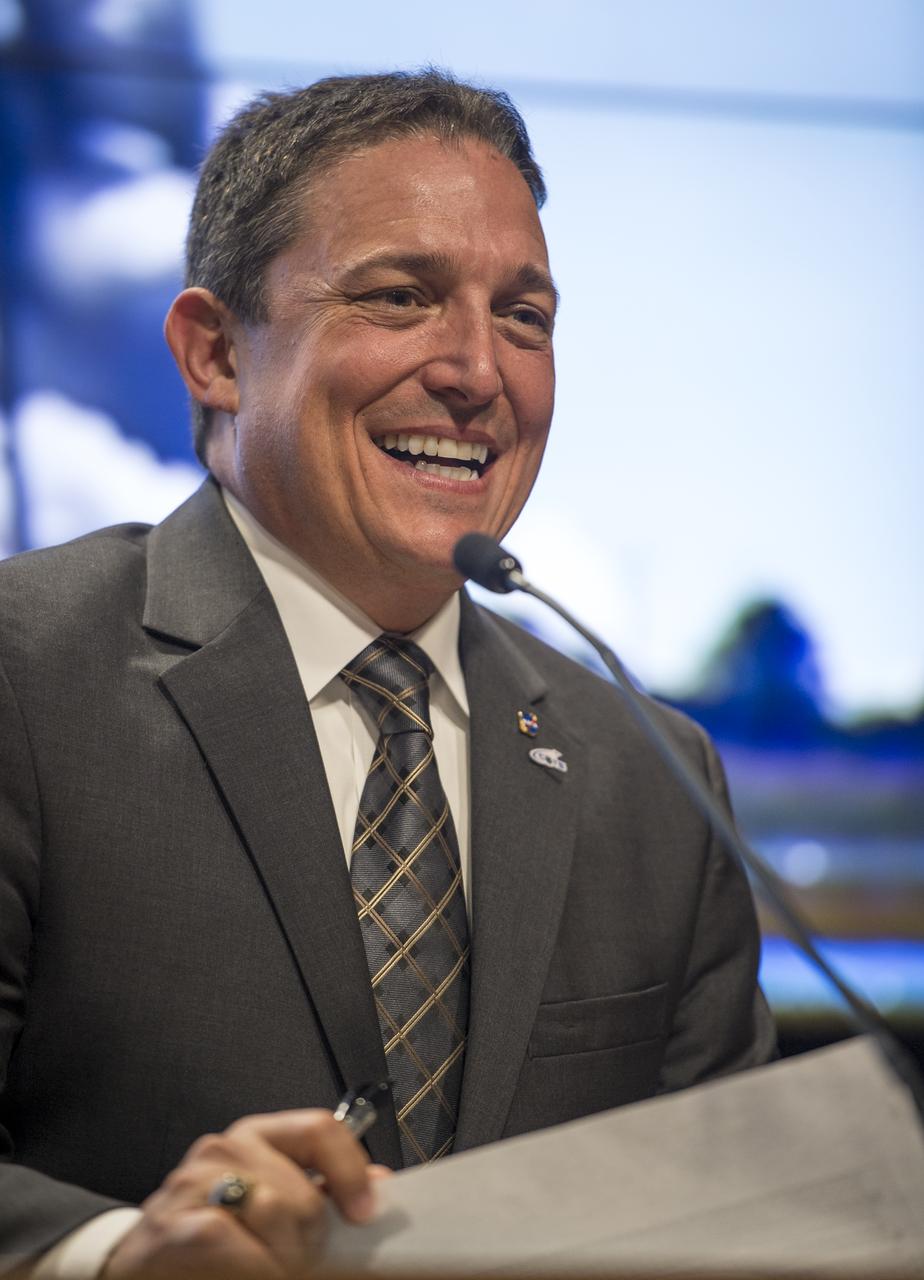

Alan Lindenmoyer, program manager, NASA's Commercial Crew and Cargo Program, talks during a press conference held after the successful launch of the Orbital Sciences Corporation Antares rocket, with the Cygnus cargo spacecraft aboard, Wednesday, Sept. 18, 2013, NASA Wallops Flight Facility, Virginia. Cygnus is on its way to rendezvous with the space station. The spacecraft will deliver about 1,300 pounds (589 kilograms) of cargo, including food and clothing, to the Expedition 37 crew. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
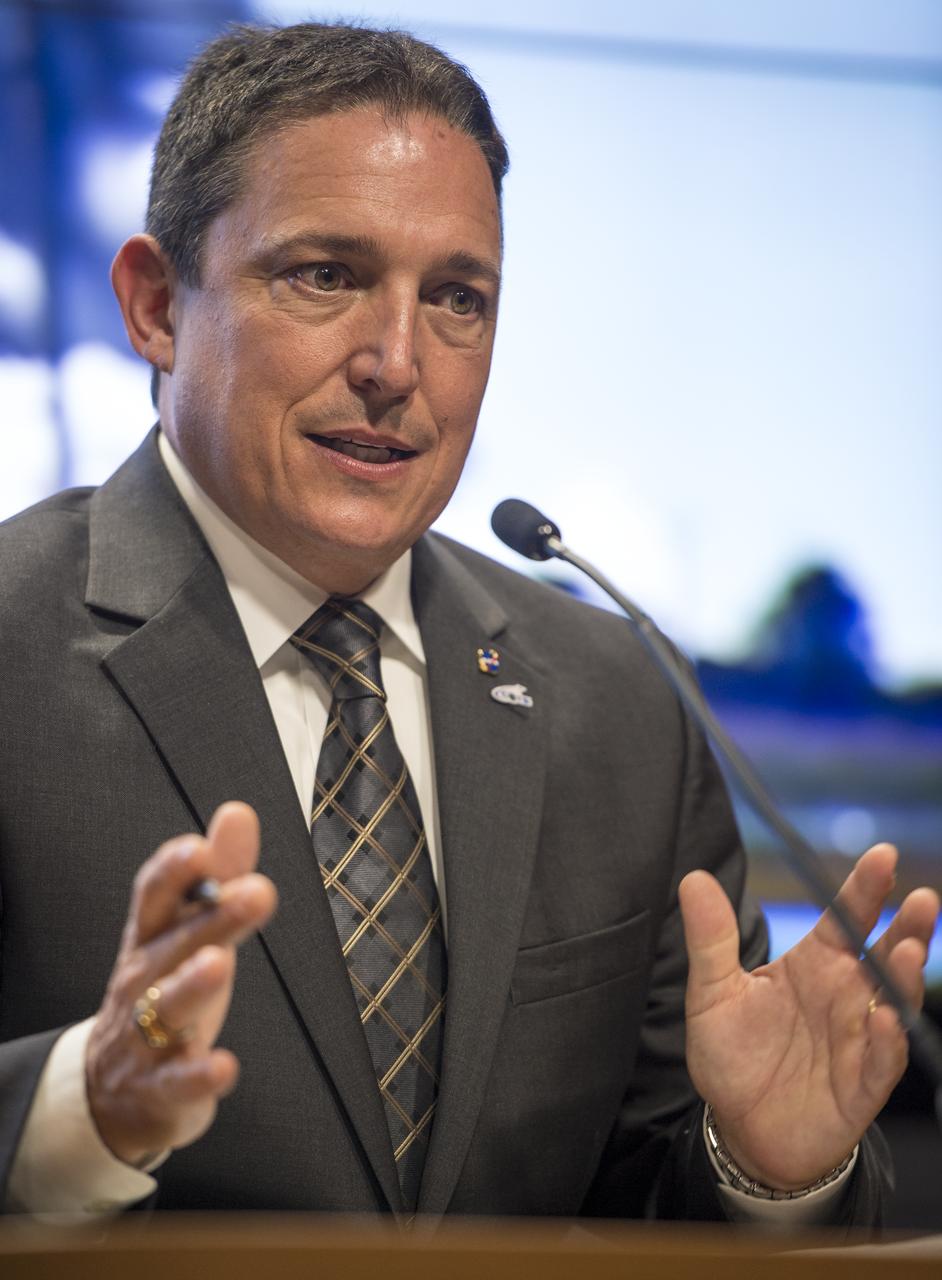

Alan Lindenmoyer, program manager, NASA's Commercial Crew and Cargo Program, talks during a press conference held after the successful launch of the Orbital Sciences Corporation Antares rocket, with the Cygnus cargo spacecraft aboard, Wednesday, Sept. 18, 2013, NASA Wallops Flight Facility, Virginia. Cygnus is on its way to rendezvous with the space station. The spacecraft will deliver about 1,300 pounds (589 kilograms) of cargo, including food and clothing, to the Expedition 37 crew. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
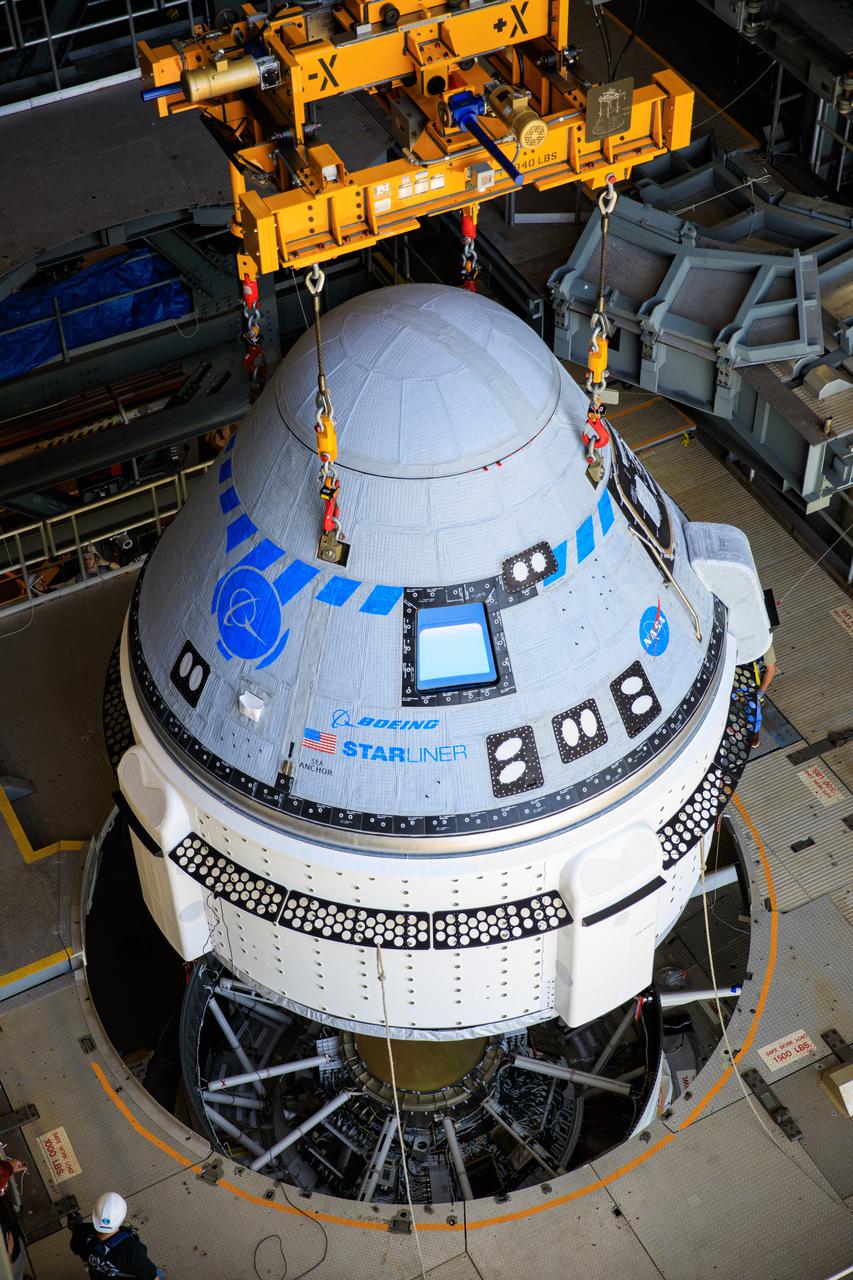

The Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft is lifted at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex-41 at Florida's Cape Canaveral Space Force Station on May 4th, 2022. Starliner will be secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for Boeing's second Orbital Flight Test (OFT-2) to the International Space Station for NASA's Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing's Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.
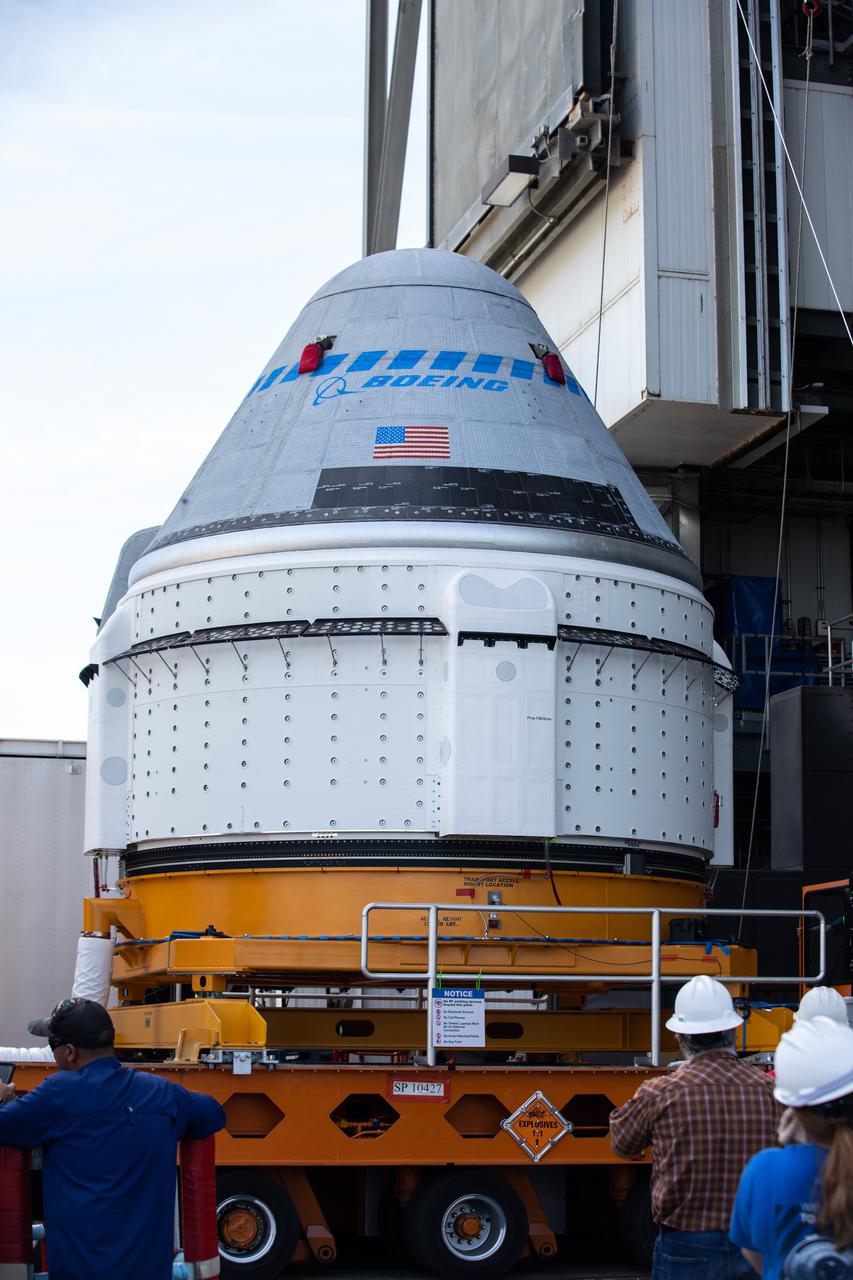

Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft arrives at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on May 4, 2022. Starliner will be secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for Boeing’s second Orbital Flight Test (OFT-2) to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.
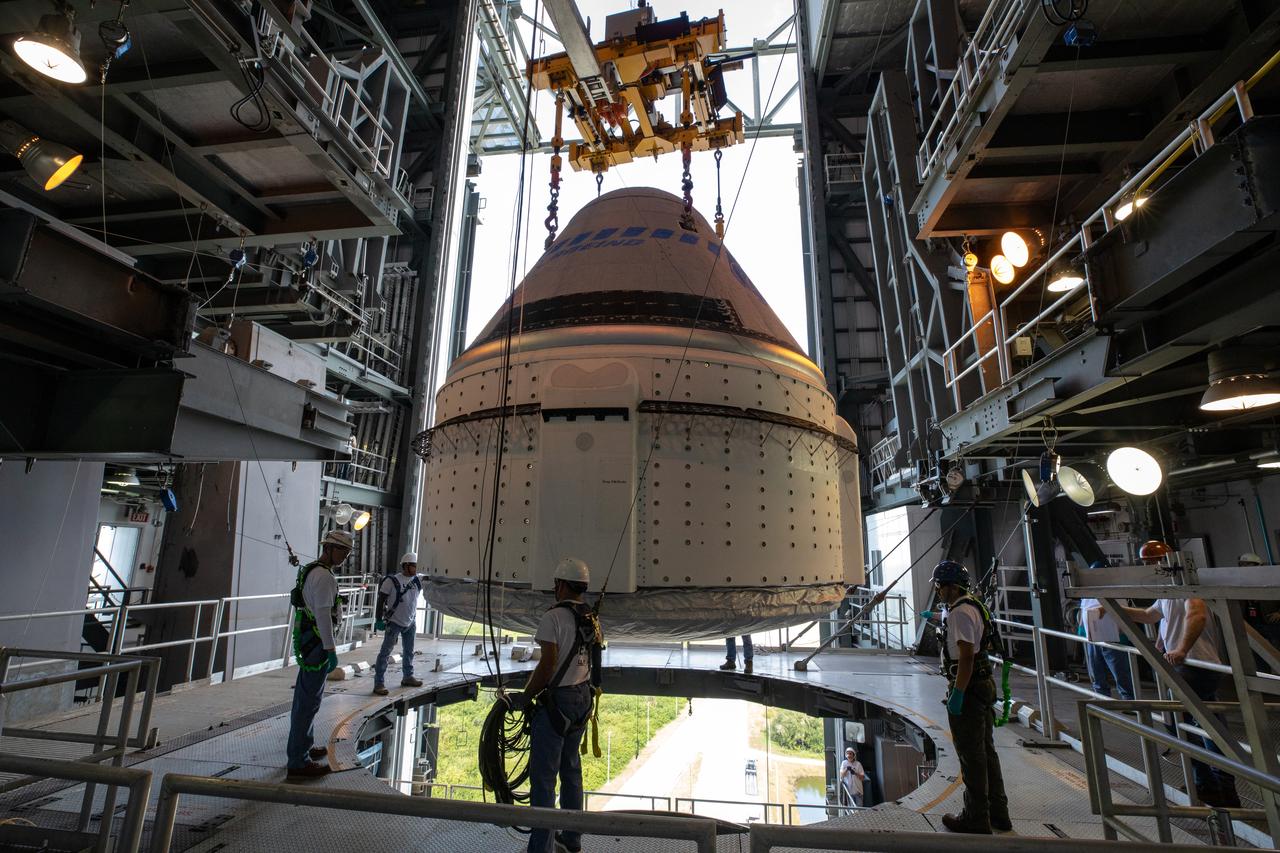

The Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft is guided into position above a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Florida’s Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on Nov. 21, 2019. Starliner will be secured atop the rocket for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.
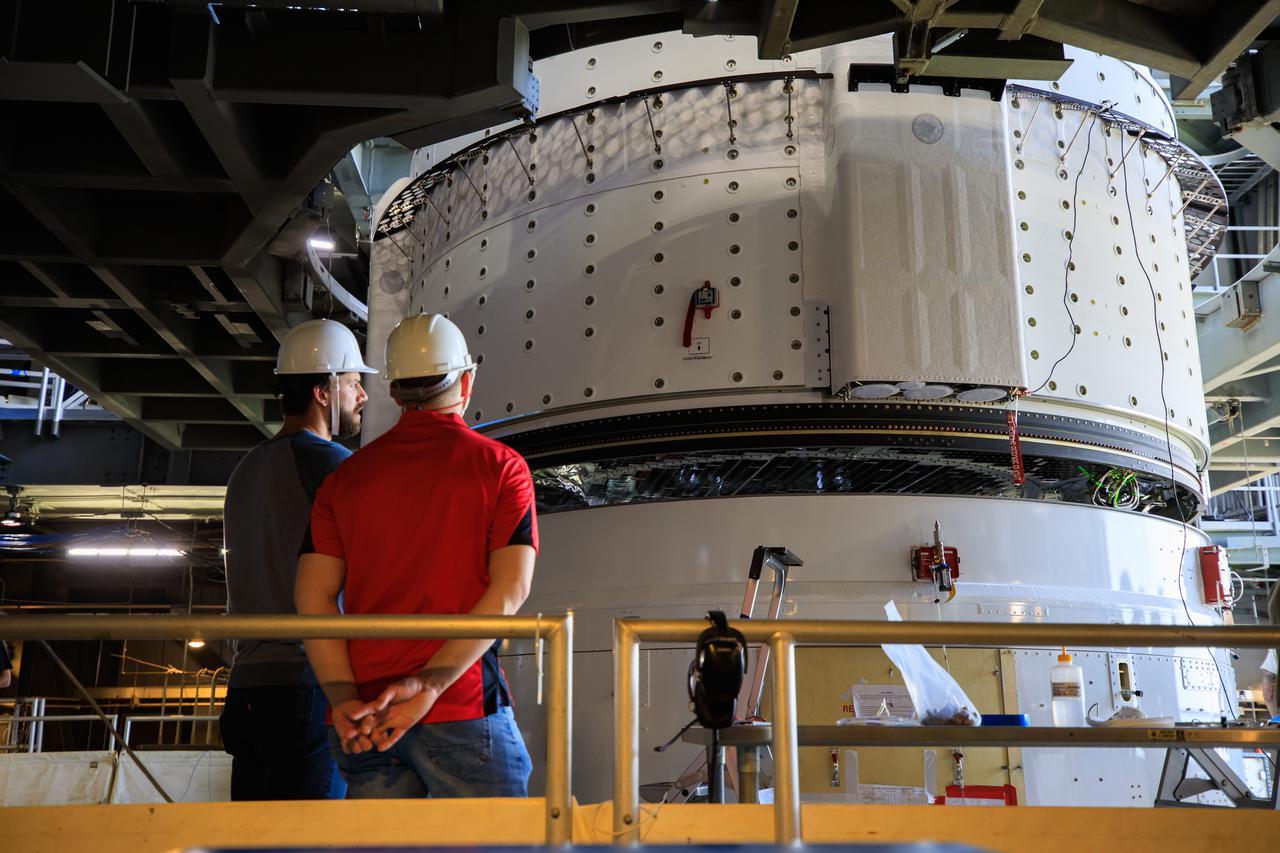
The Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft is lifted at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex-41 at Florida's Cape Canaveral Space Force Station on May 4th, 2022. Starliner will be secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for Boeing's second Orbital Flight Test (OFT-2) to the International Space Station for NASA's Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing's Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.
The Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft is lifted at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex-41 at Florida's Cape Canaveral Space Force Station on May 4th, 2022. Starliner will be secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for Boeing's second Orbital Flight Test (OFT-2) to the International Space Station for NASA's Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing's Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.
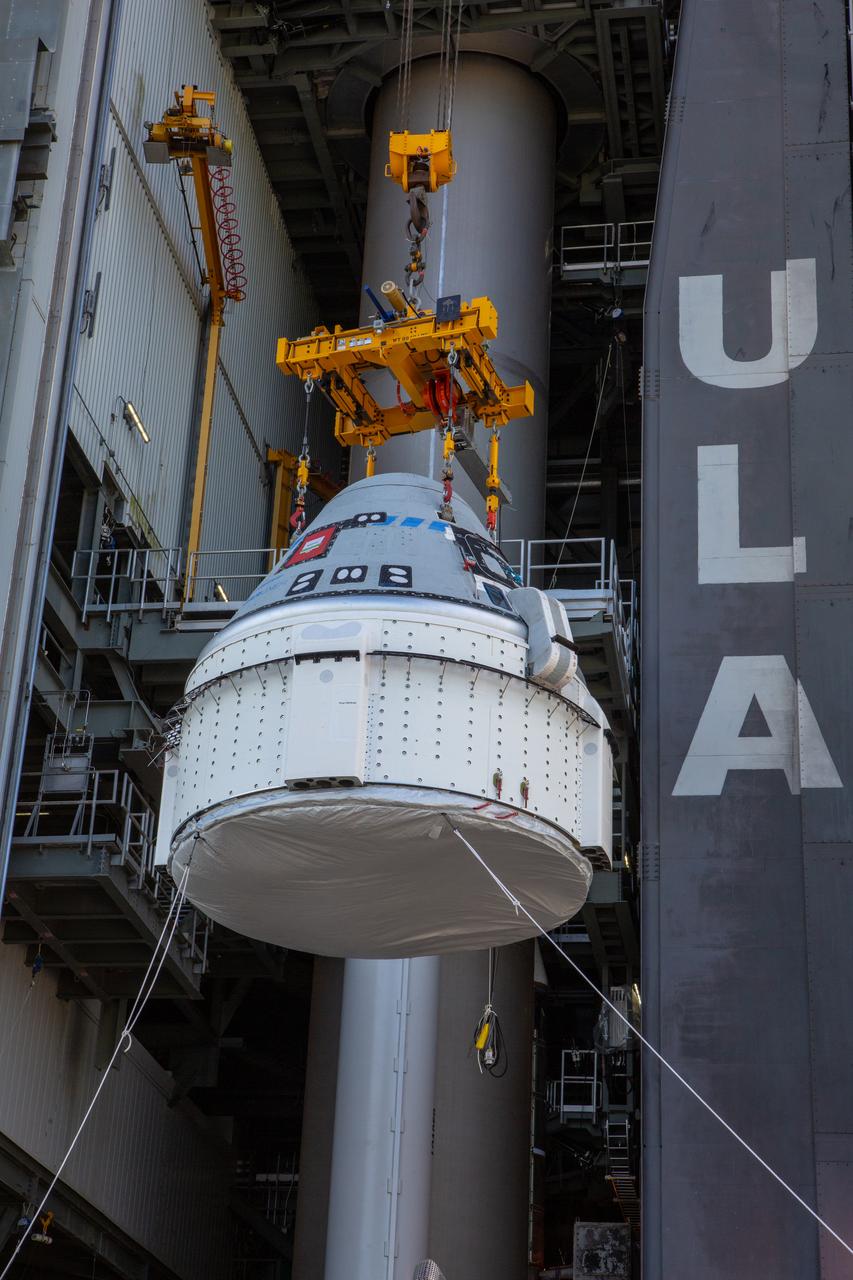

The Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft is lifted at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Florida’s Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on Nov. 21, 2019. Starliner will be secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.
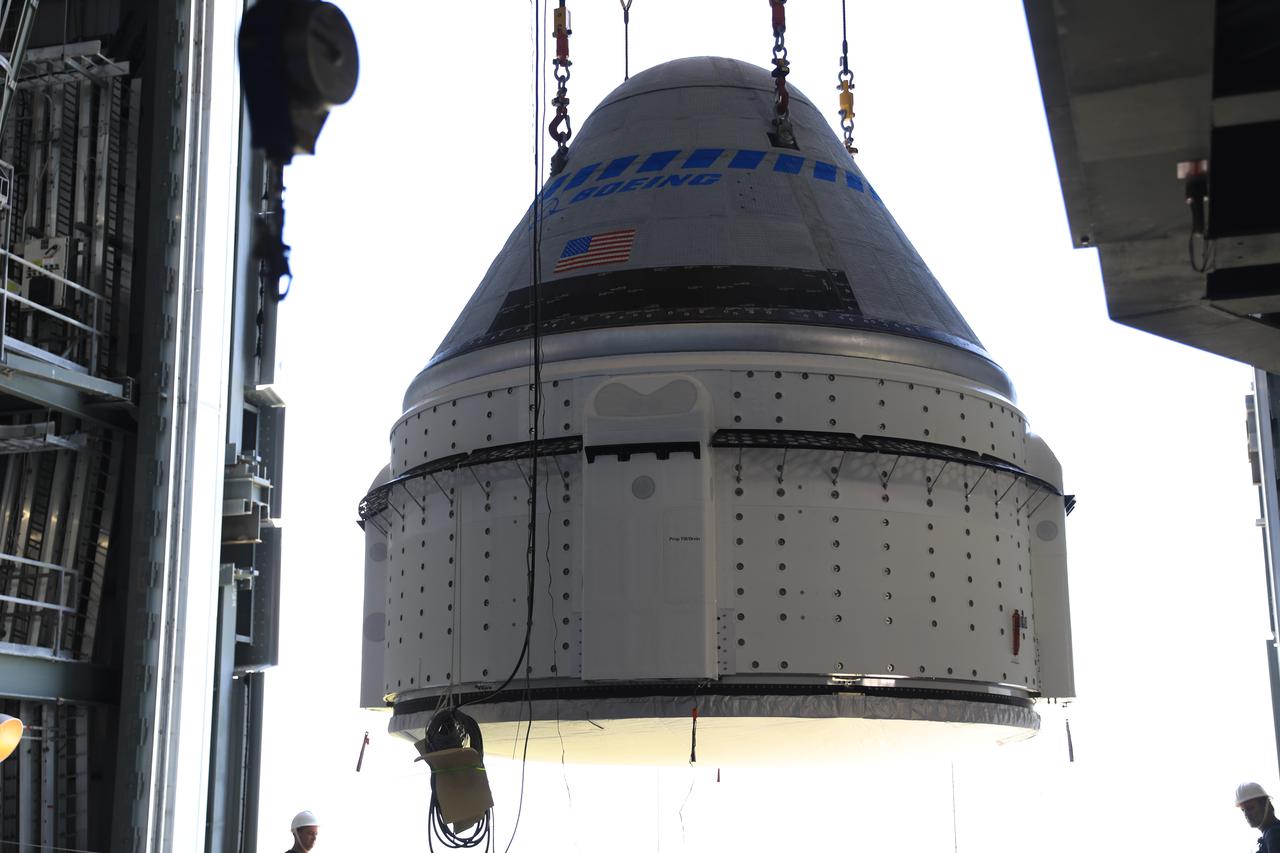

The Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft is lifted at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex-41 at Florida’s Cape Canaveral Space Force Station on May 4, 2022. Starliner will be secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for Boeing’s second Orbital Flight Test (OFT-2) to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.
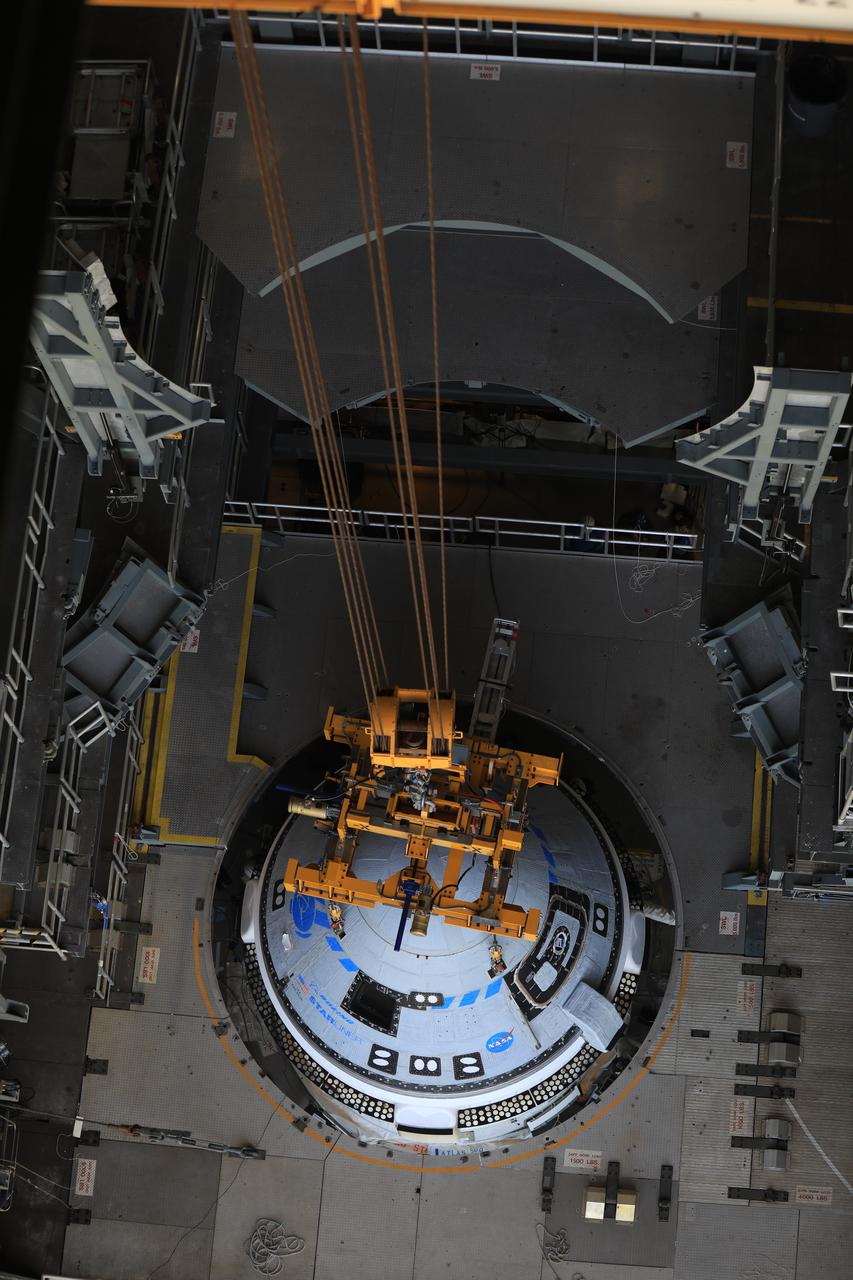
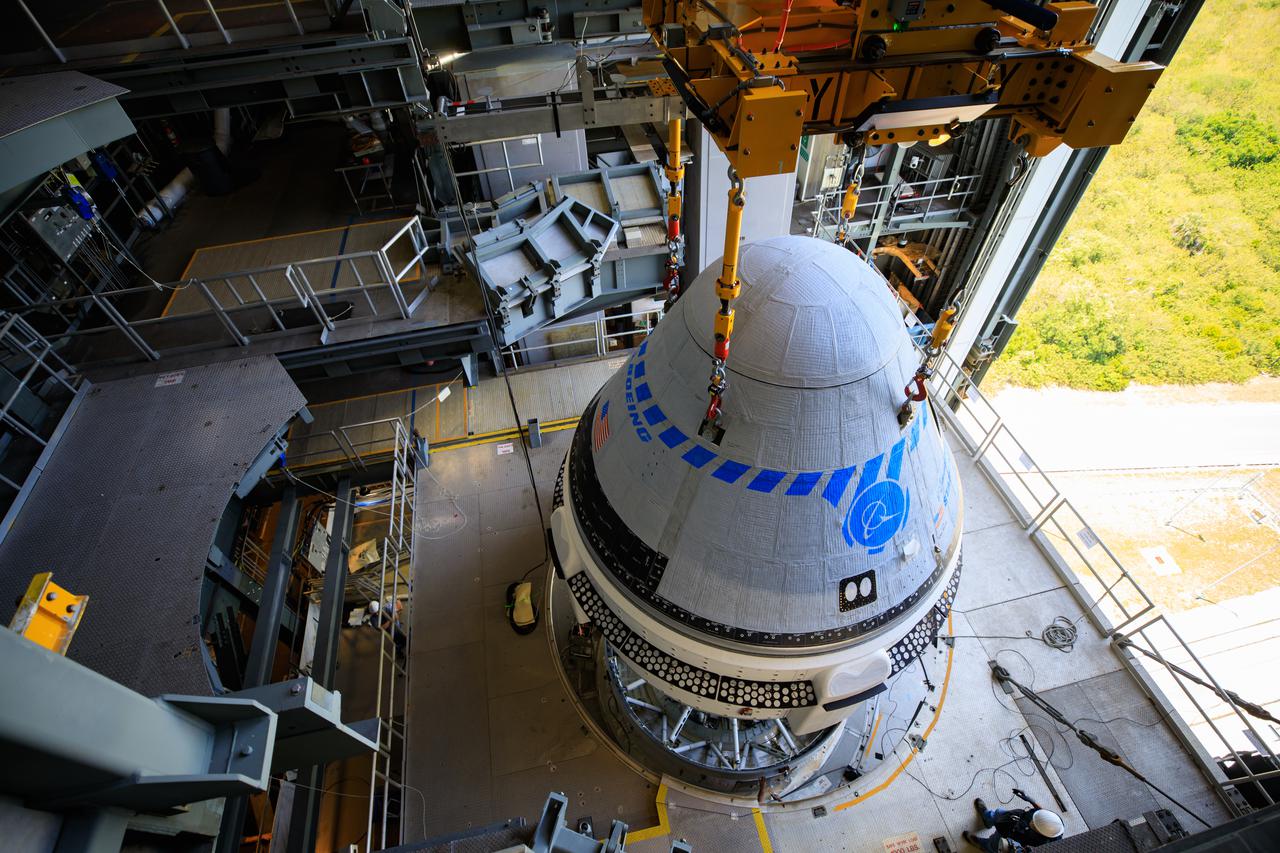
The Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft is lifted at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex-41 at Florida’s Cape Canaveral Space Force Station on May 4, 2022. Starliner will be secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for Boeing’s second Orbital Flight Test (OFT-2) to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.
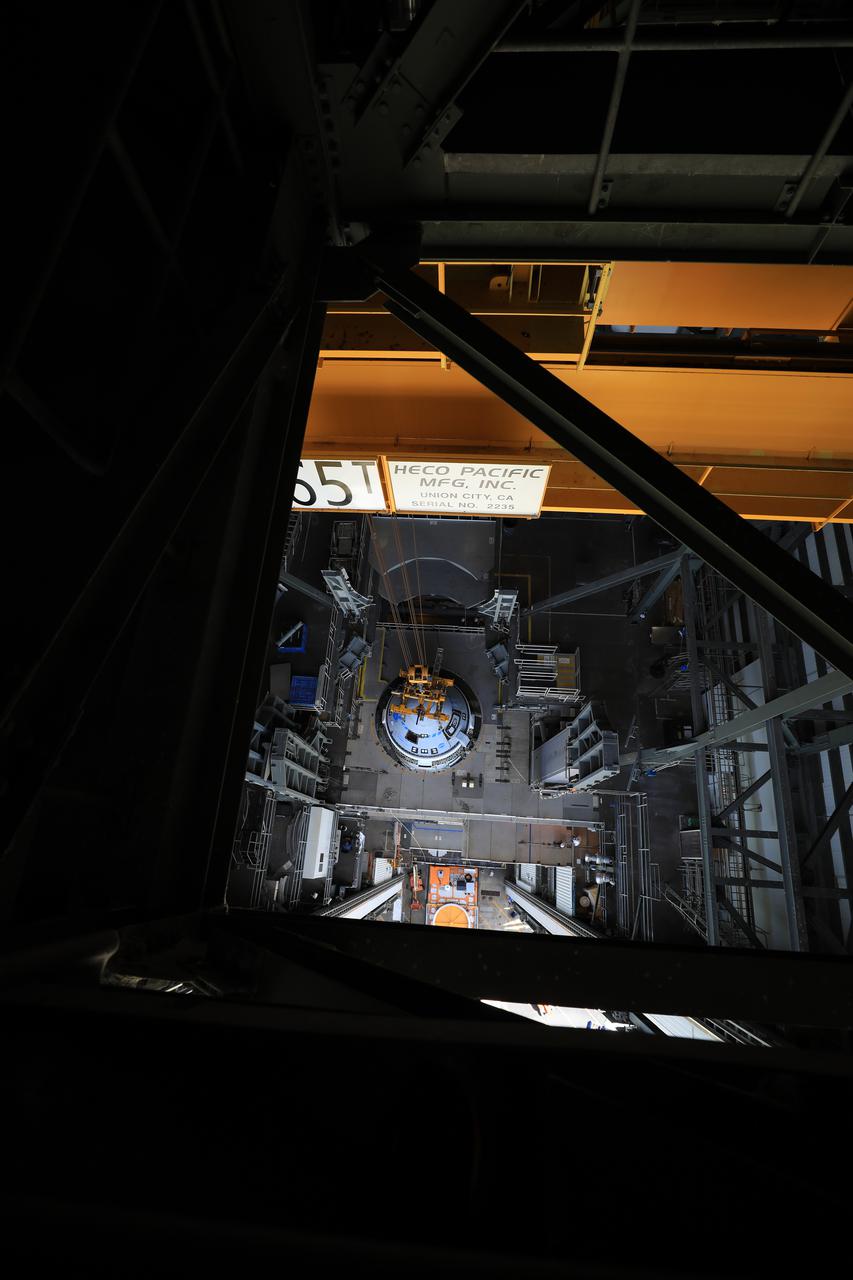

The Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft is lifted at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex-41 at Florida’s Cape Canaveral Space Force Station on May 4, 2022. Starliner will be secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for Boeing’s second Orbital Flight Test (OFT-2) to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.
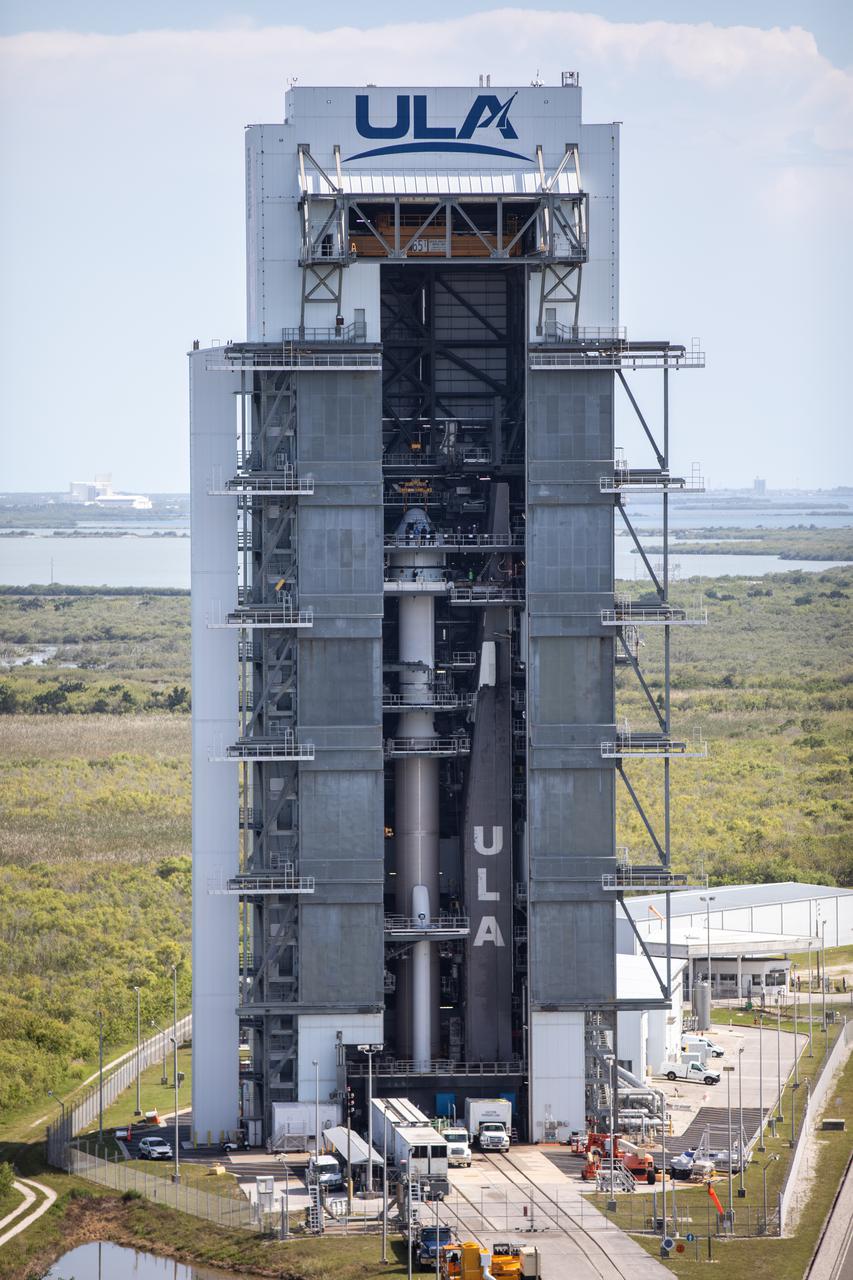

The Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft is lifted at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex-41 at Florida’s Cape Canaveral Space Force Station on May 4, 2022. Starliner will be secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for Boeing’s second Orbital Flight Test (OFT-2) to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.
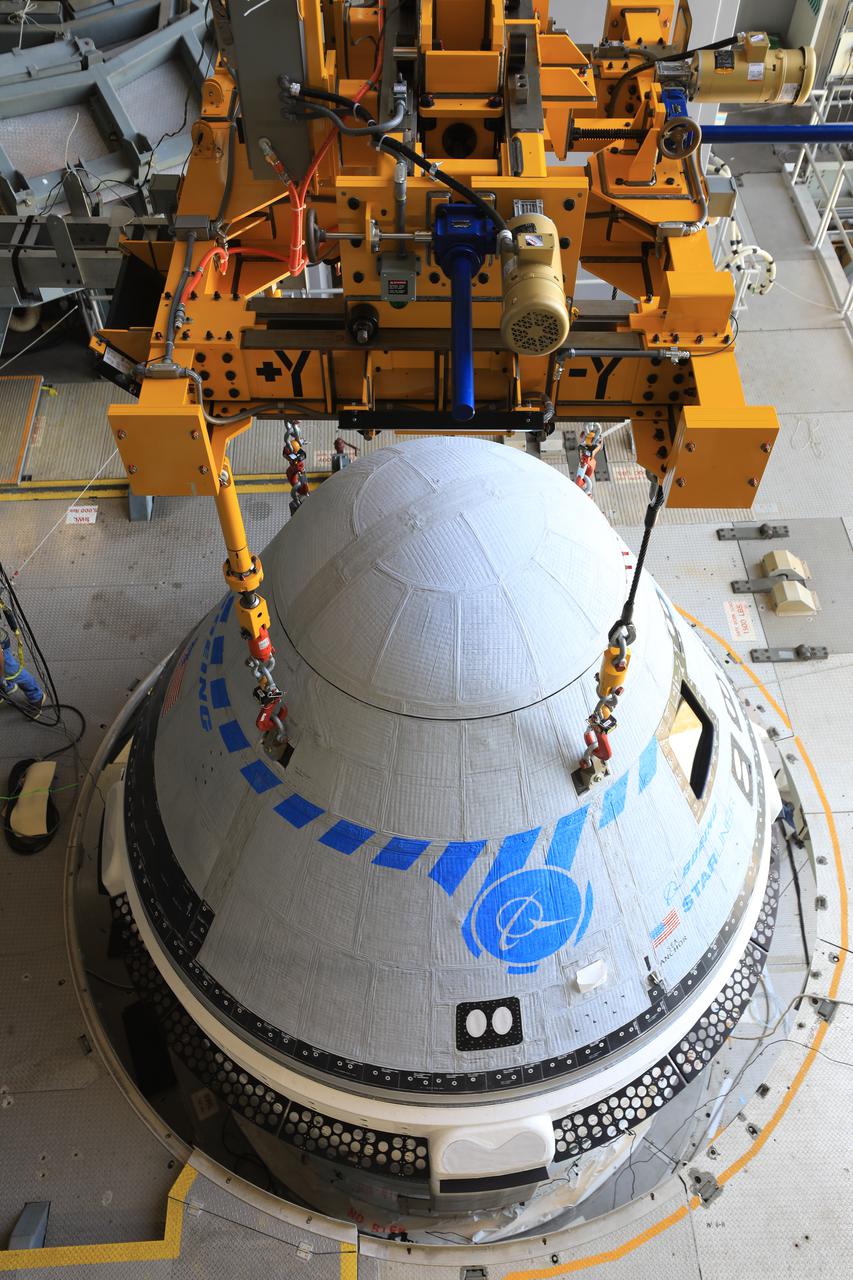

The Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft is lifted at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex-41 at Florida’s Cape Canaveral Space Force Station on May 4, 2022. Starliner will be secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for Boeing’s second Orbital Flight Test (OFT-2) to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.
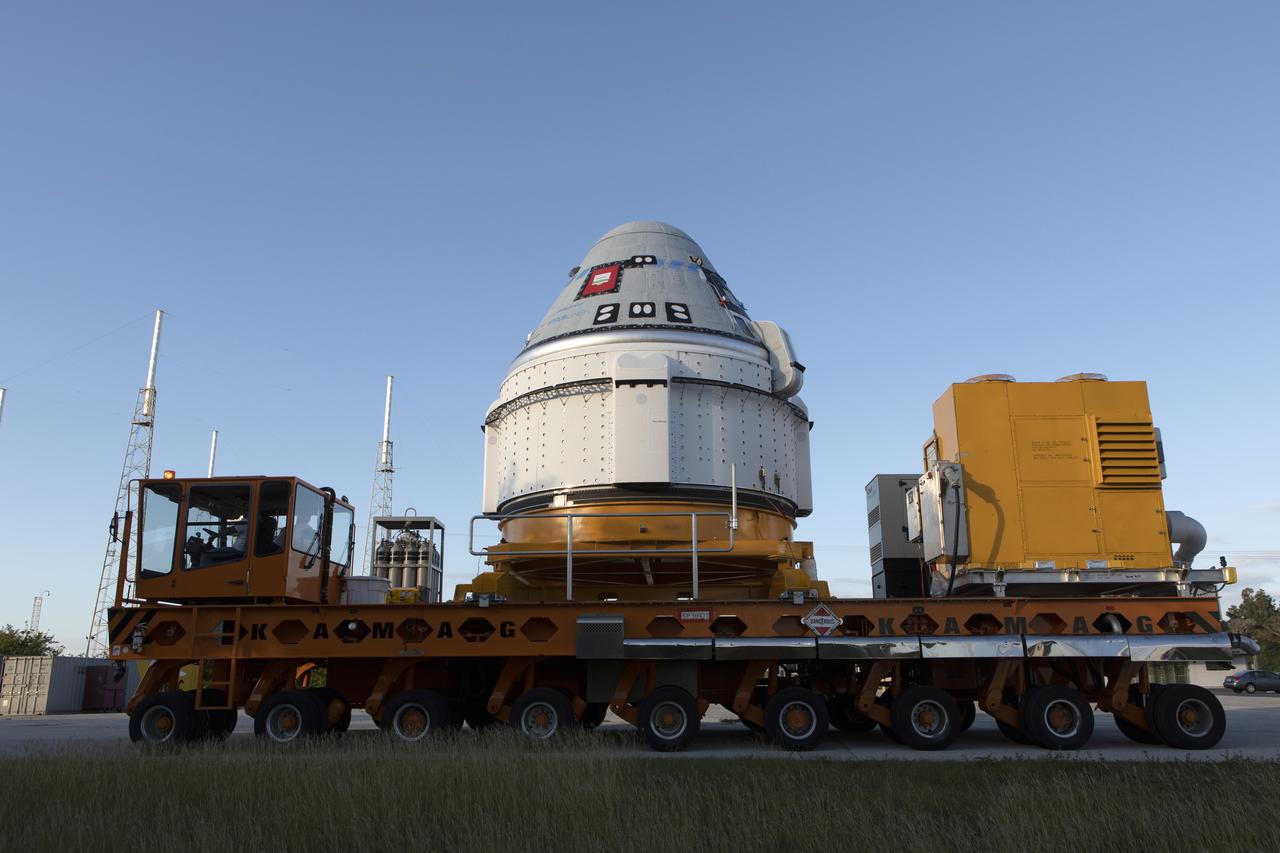

The Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft arrives at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Nov. 21, 2019. Starliner will be secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.
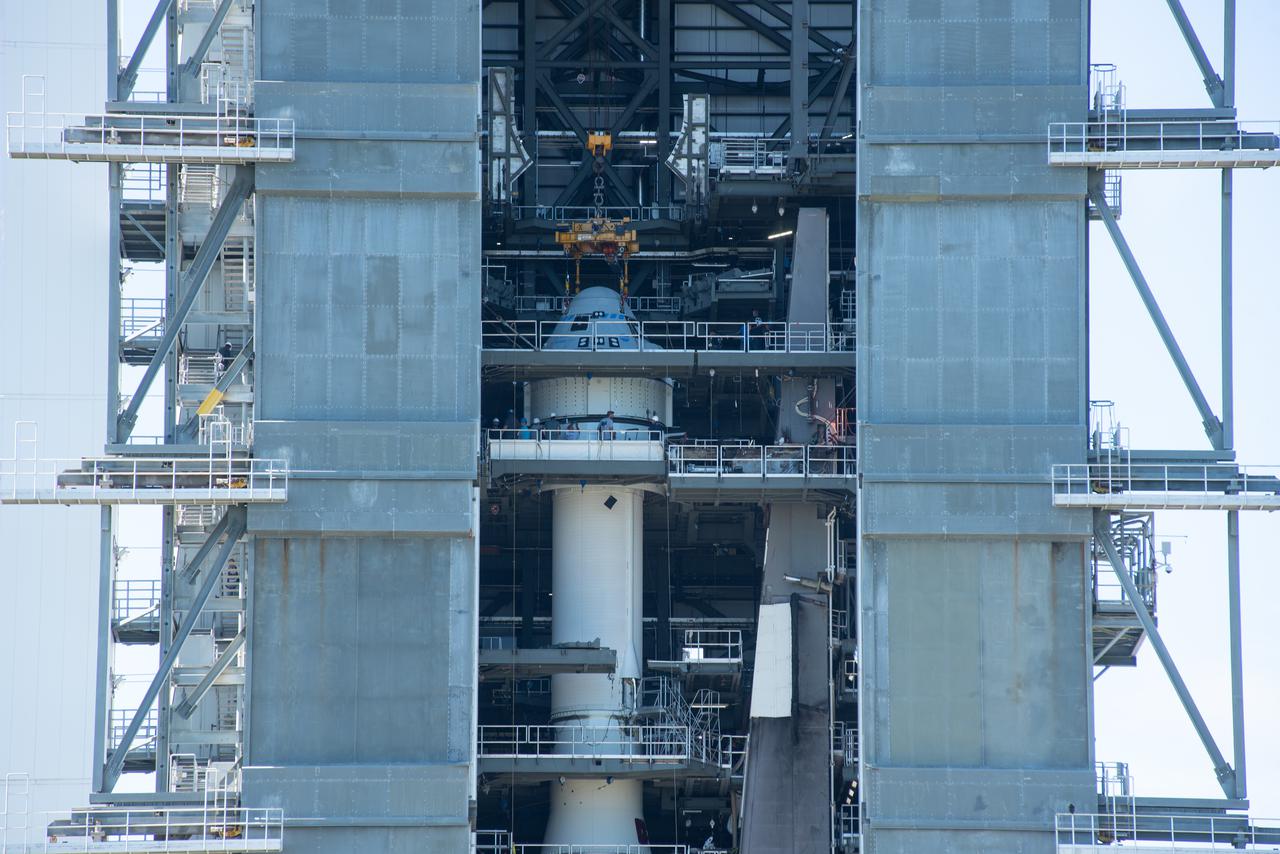
Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft is secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex-41 at Florida’s Cape Canaveral Space Force Station on July 17, 2021. Starliner will launch on the Atlas V for Boeing’s second Orbital Flight Test (OFT-2) for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.
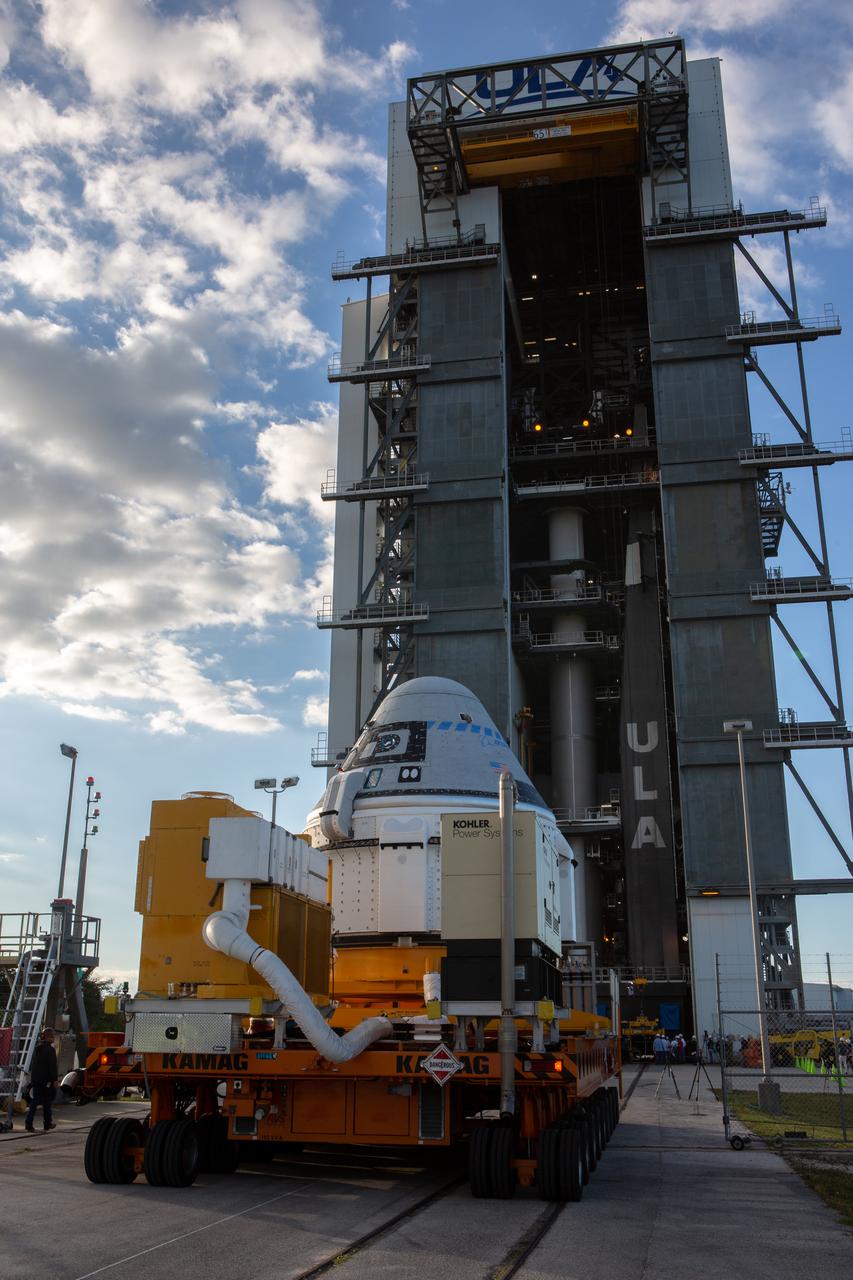

The Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft arrives at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Florida’s Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on Nov. 21, 2019. Starliner will be secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.
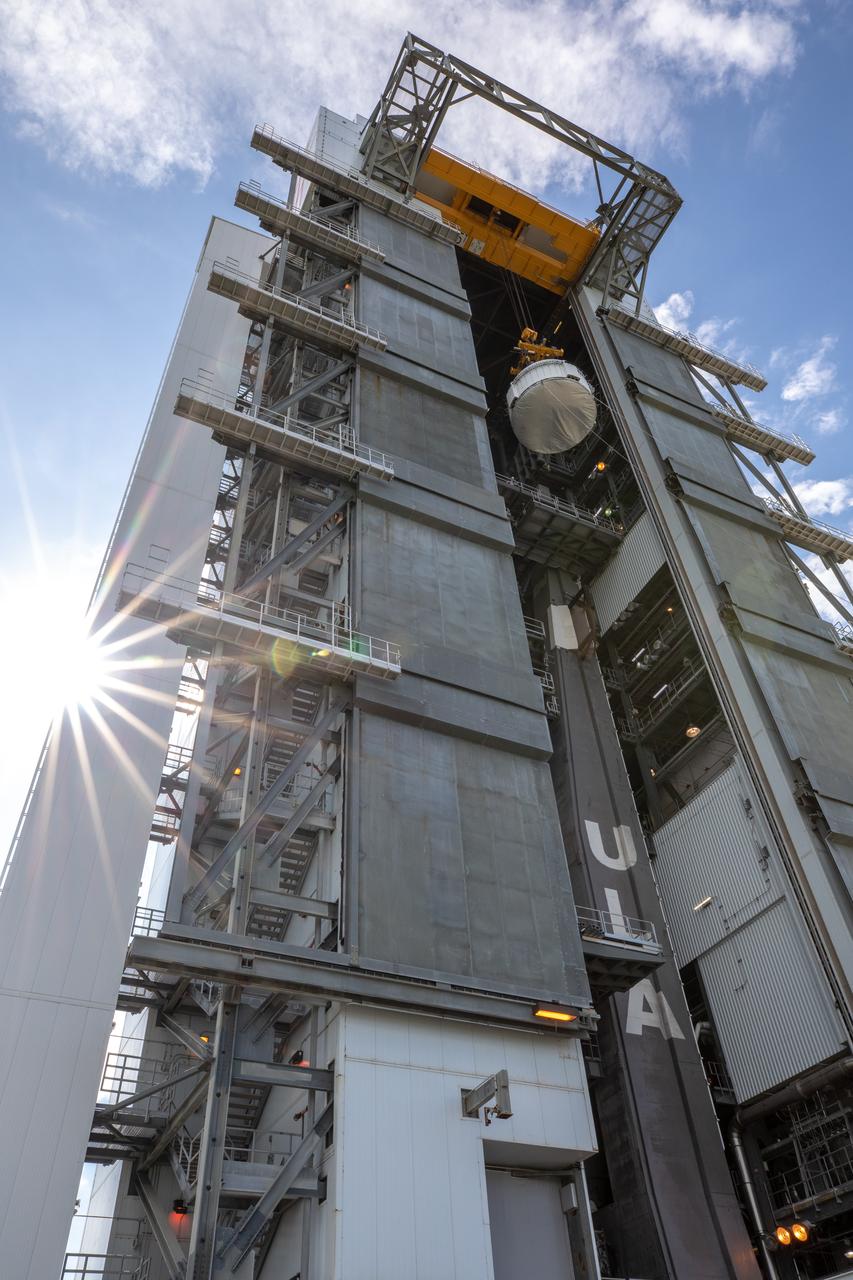

The Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft is lifted at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Florida’s Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on Nov. 21, 2019. Starliner will be secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.
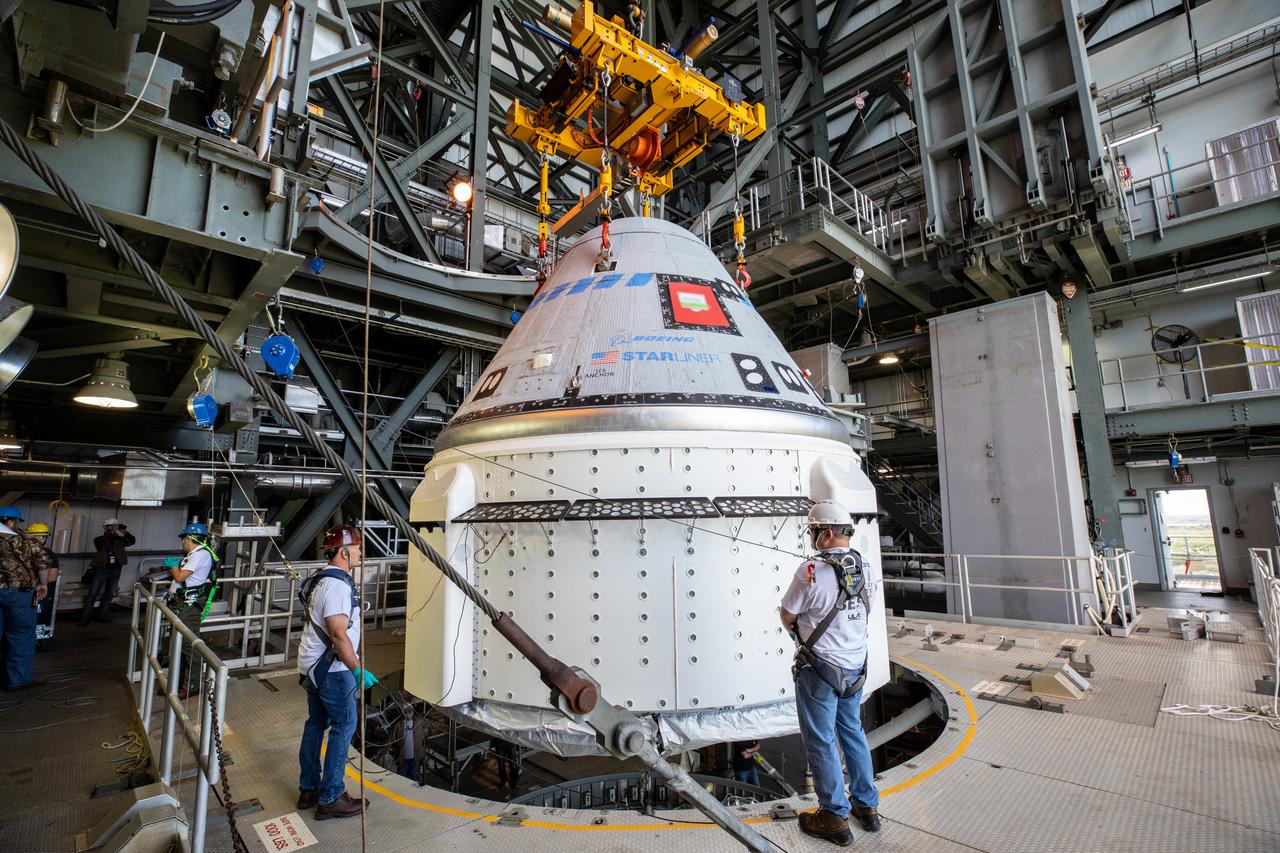

The Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft is secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Florida’s Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on Nov. 21, 2019. Starliner will launch on the Atlas V for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.
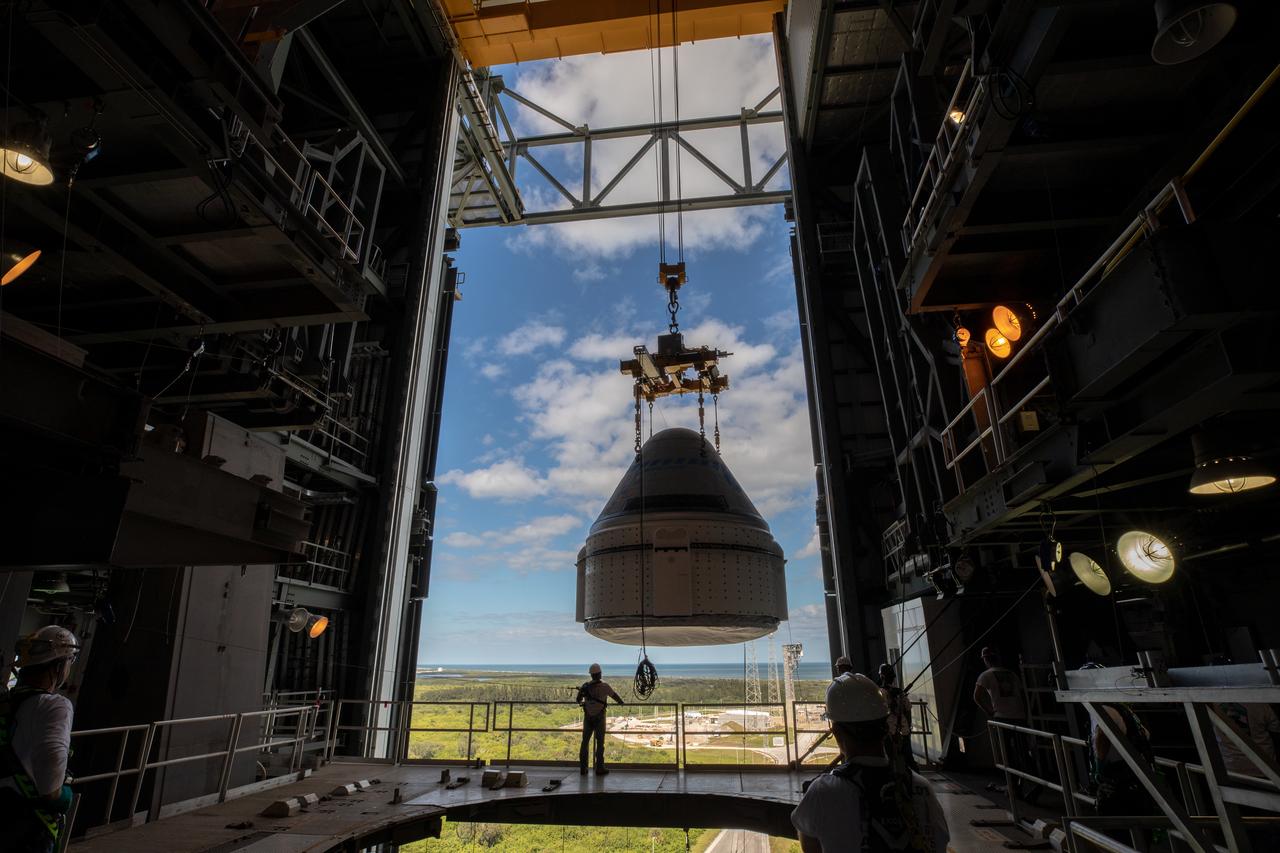

The Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft is guided into position above a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Florida’s Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on Nov. 21, 2019. Starliner will be secured atop the rocket for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.

The Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft is guided into position above a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Florida’s Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on Nov. 21, 2019. Starliner will be secured atop the rocket for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.
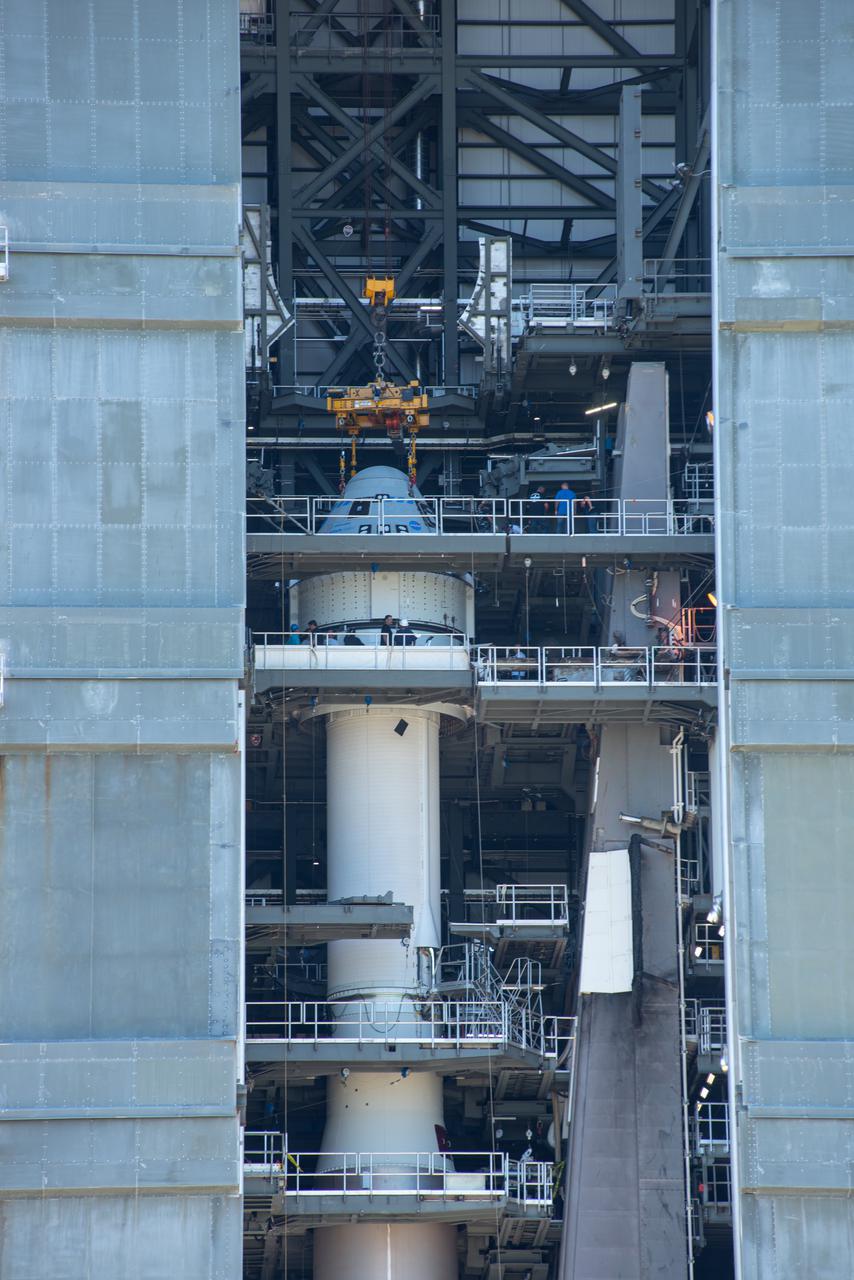

Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft is secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex-41 at Florida’s Cape Canaveral Space Force Station on July 17, 2021. Starliner will launch on the Atlas V for Boeing’s second Orbital Flight Test (OFT-2) for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.
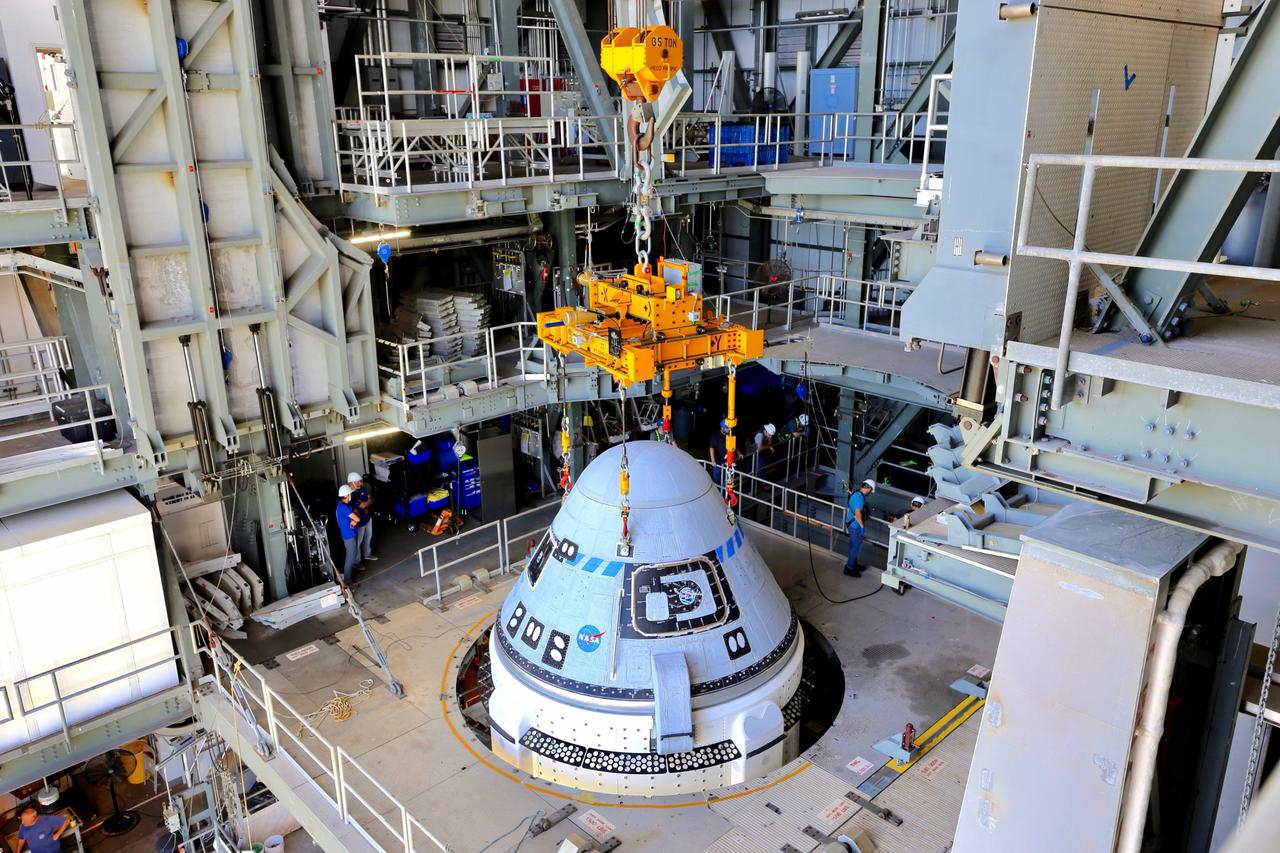

Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft is secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex-41 at Florida’s Cape Canaveral Space Force Station on July 17, 2021. Starliner will launch on the Atlas V for Boeing’s second Orbital Flight Test (OFT-2) for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.
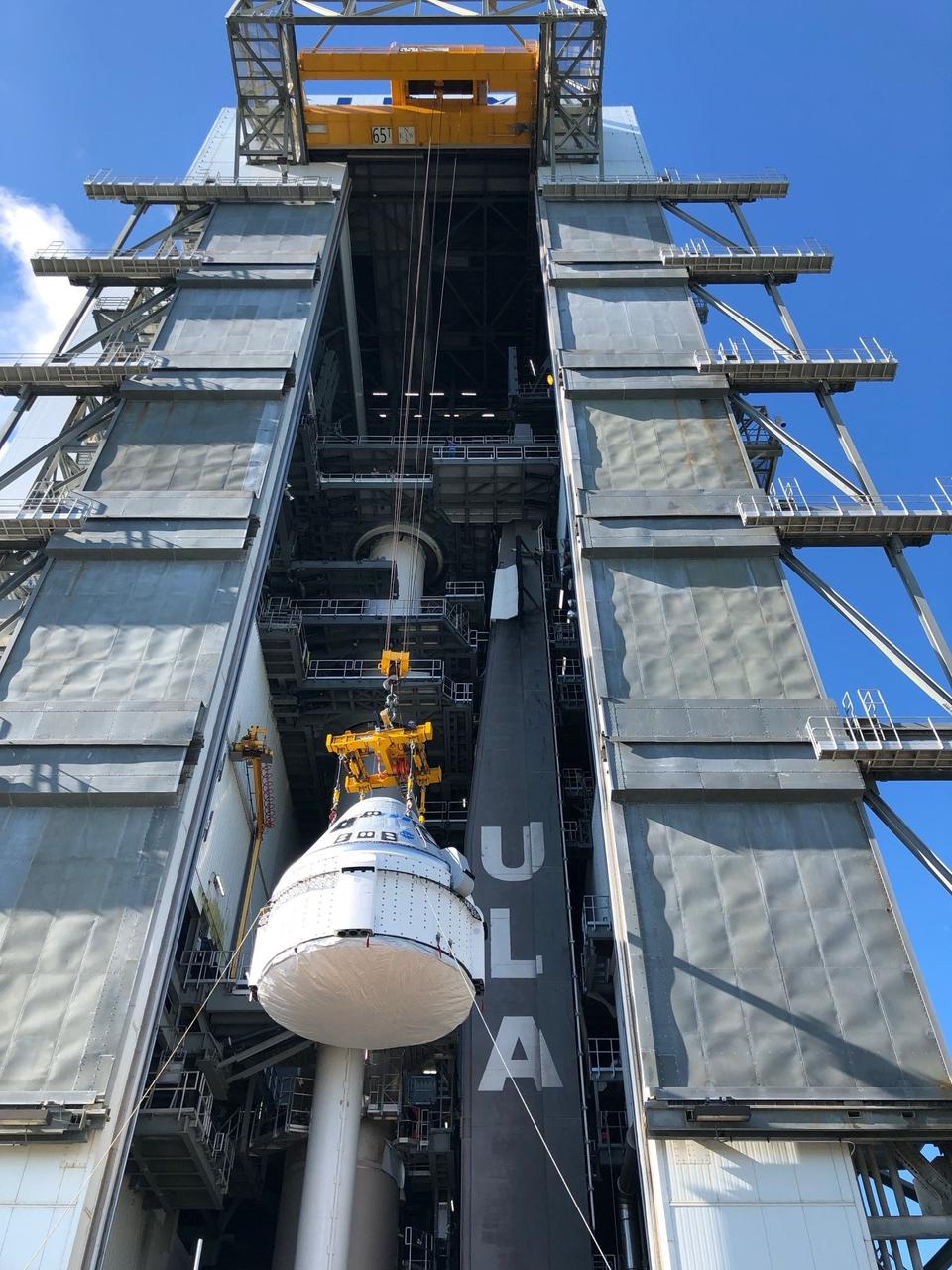

Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft is lifted at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex-41 at Florida’s Cape Canaveral Space Force Station on July 17, 2021. Starliner will be secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.
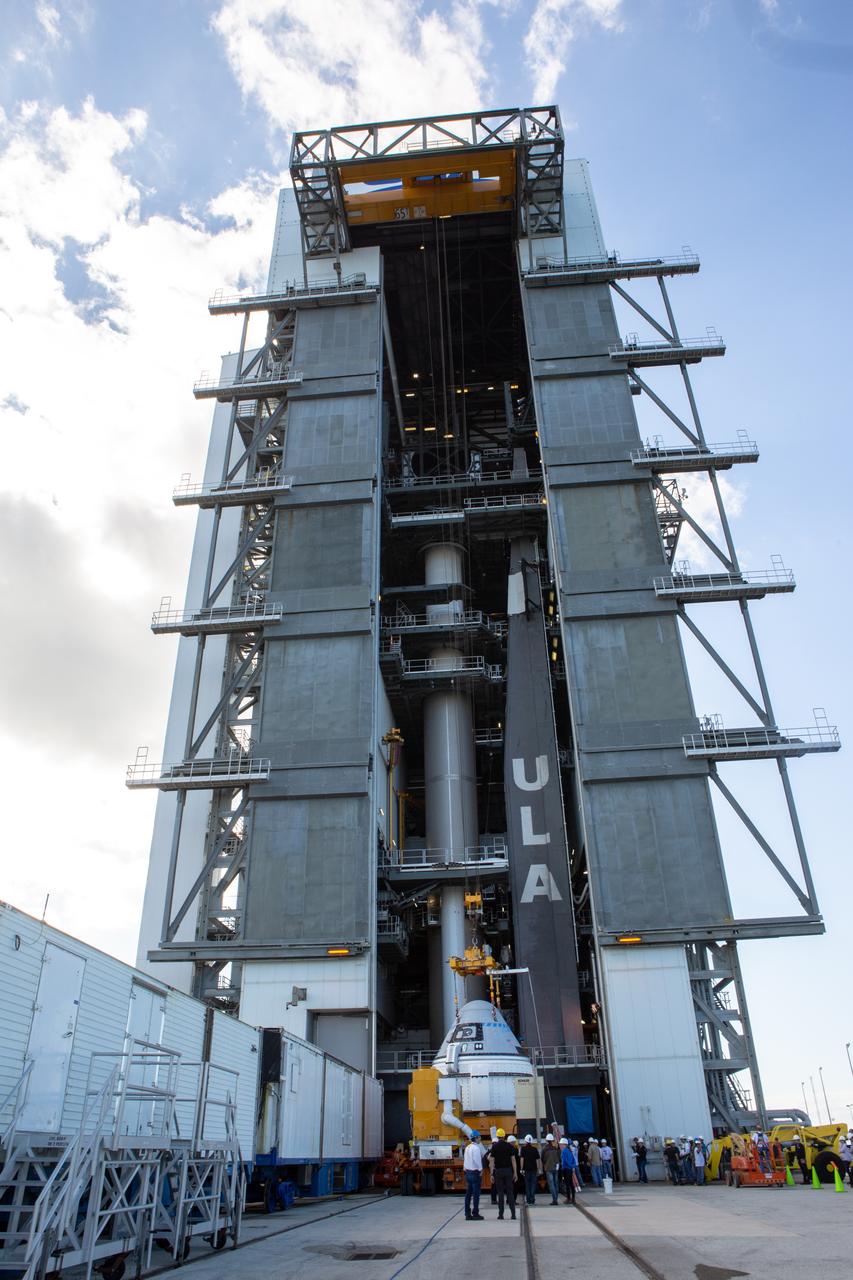
The Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft is lifted at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Florida’s Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on Nov. 21, 2019. Starliner will be secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.
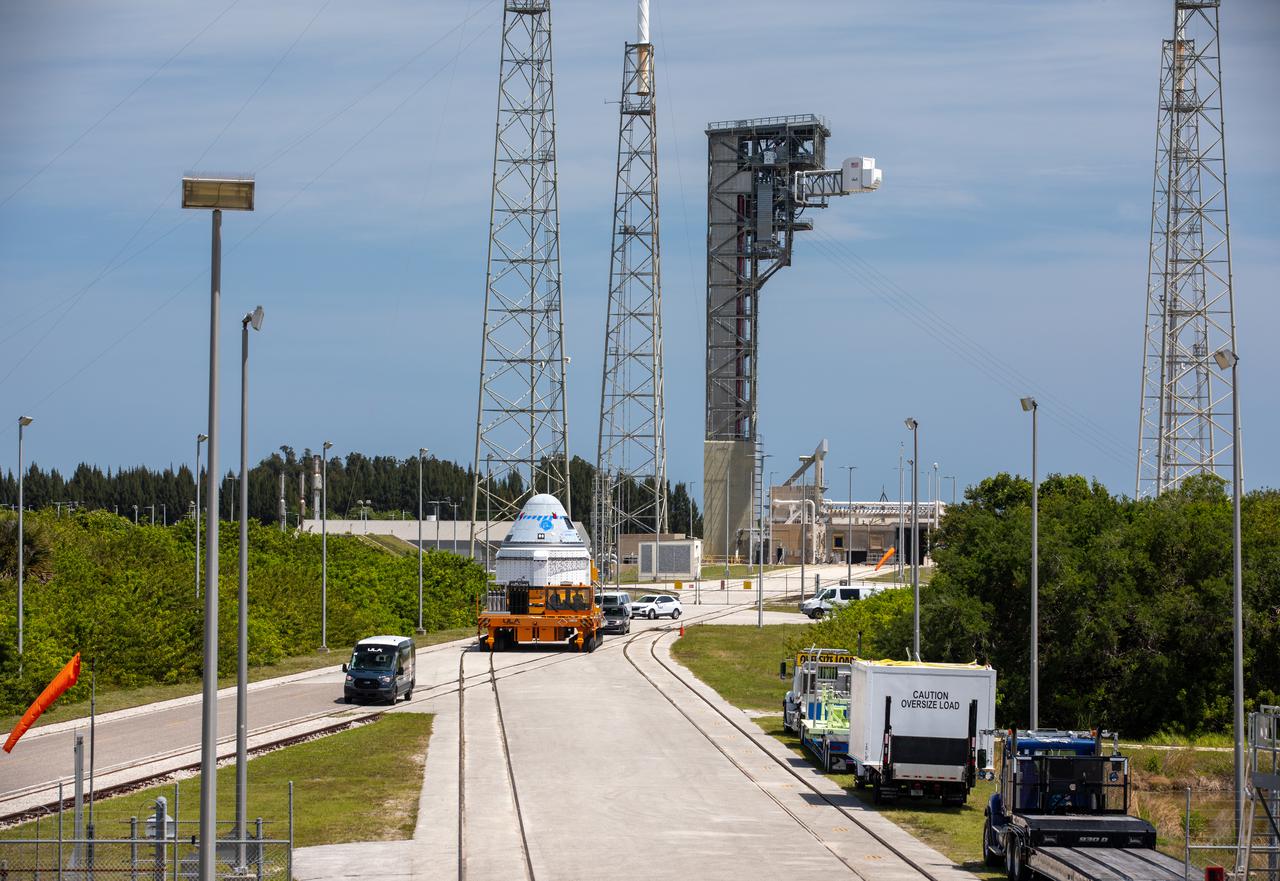

Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft rolls out from the company’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 4, 2022. The spacecraft will make the trip to the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station where it will be secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for Boeing’s second Orbital Flight Test (OFT-2) to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.
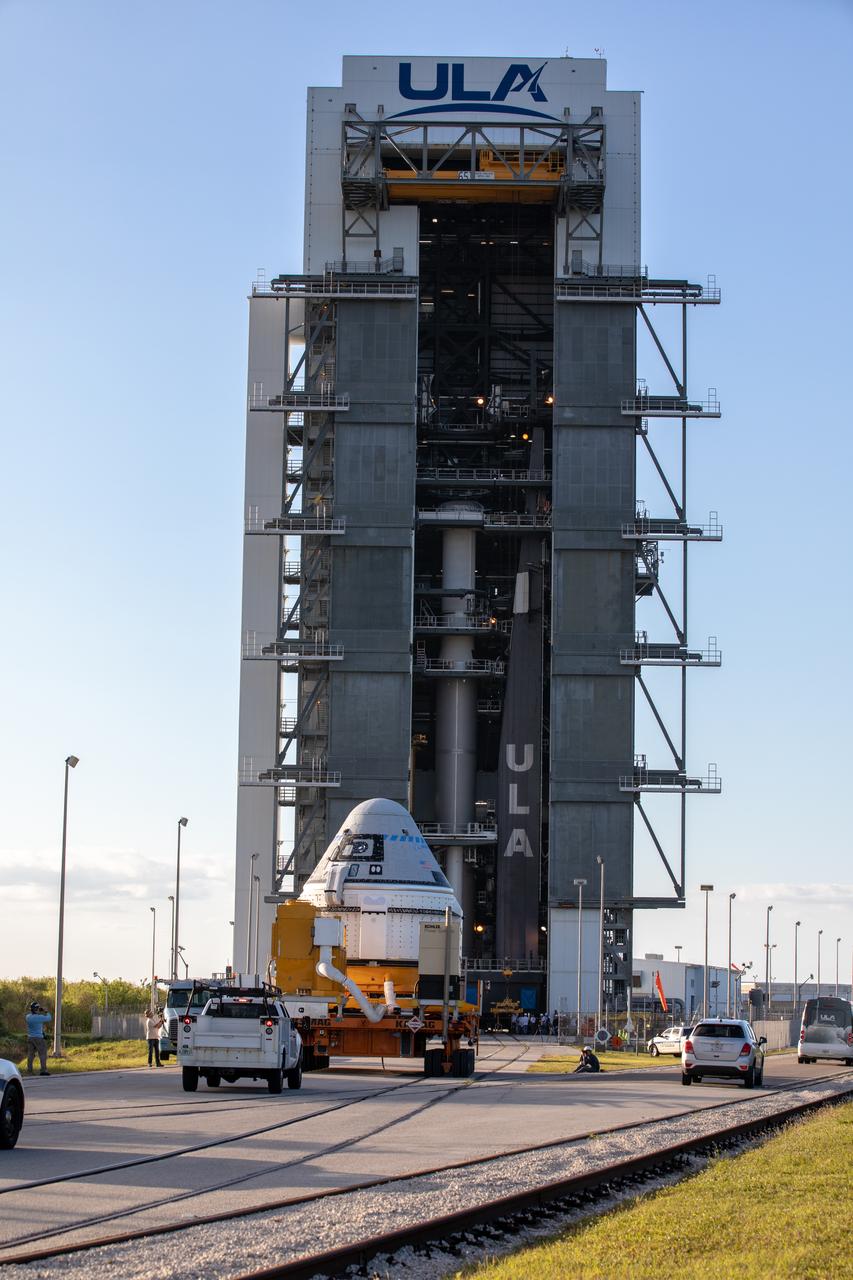

The Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft arrives at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Nov. 21, 2019. Starliner will be secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.
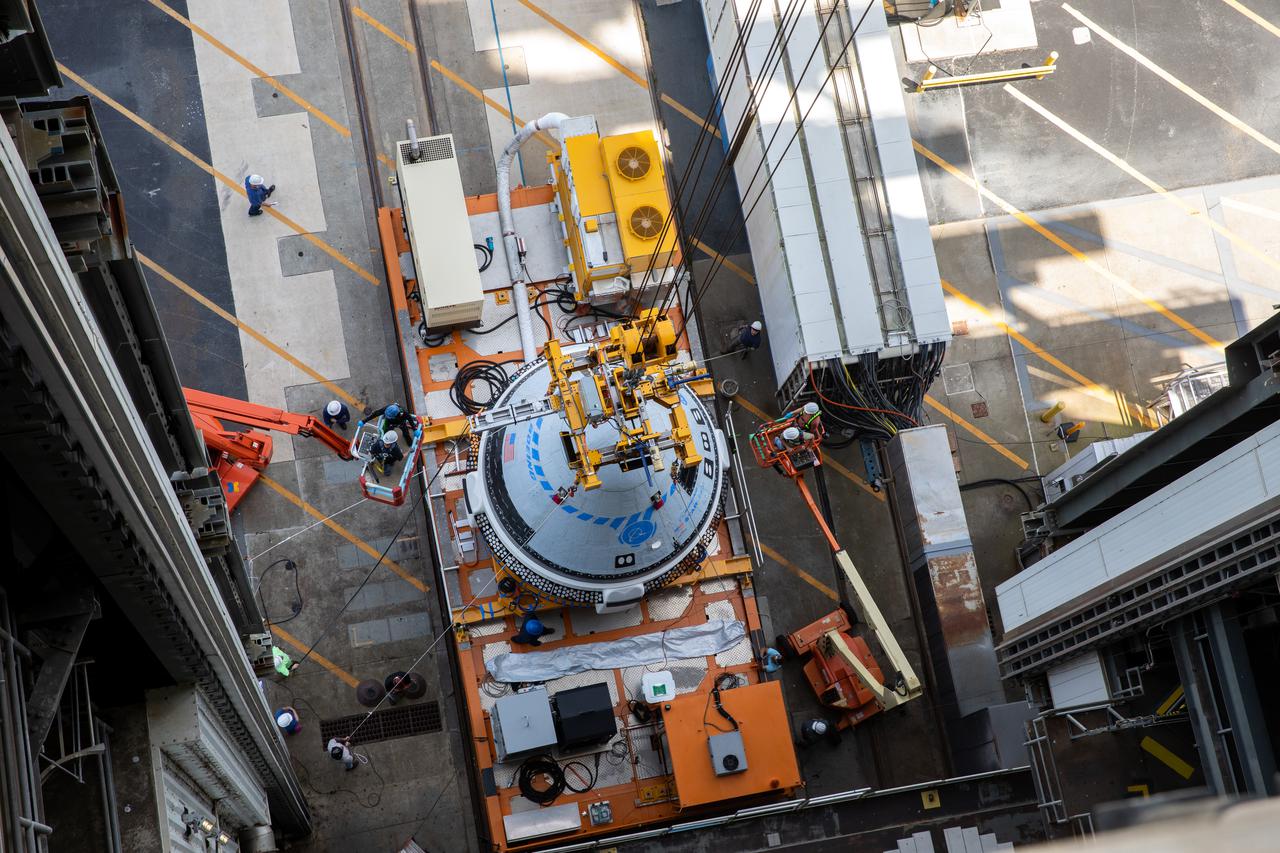
The Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft is lifted at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex-41 at Florida’s Cape Canaveral Space Force Station on May 4, 2022. Starliner will be secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for Boeing’s second Orbital Flight Test (OFT-2) to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.
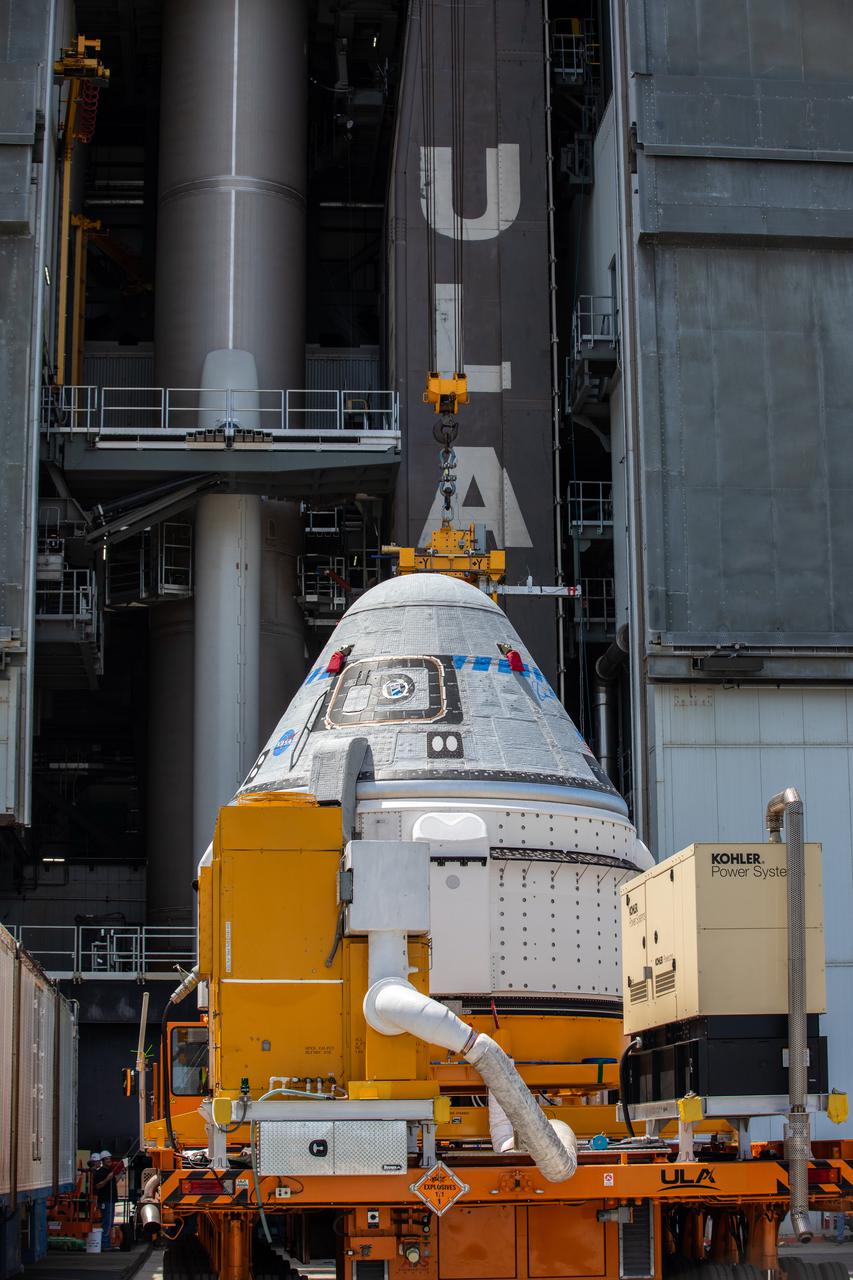

Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft arrives at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on May 4, 2022. Starliner will be secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for Boeing’s second Orbital Flight Test (OFT-2) to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.
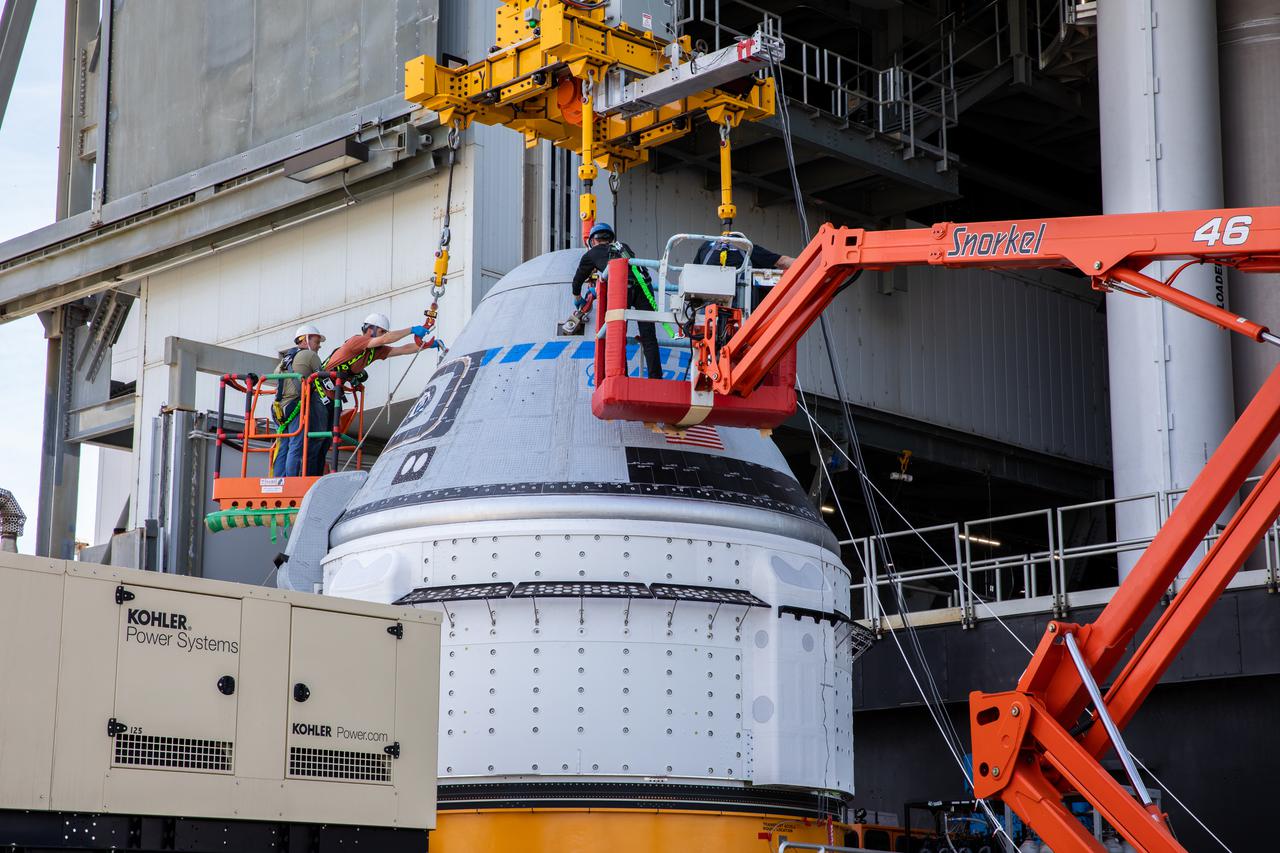
The Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft is lifted at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex-41 at Florida’s Cape Canaveral Space Force Station on May 4, 2022. Starliner will be secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for Boeing’s second Orbital Flight Test (OFT-2) to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.
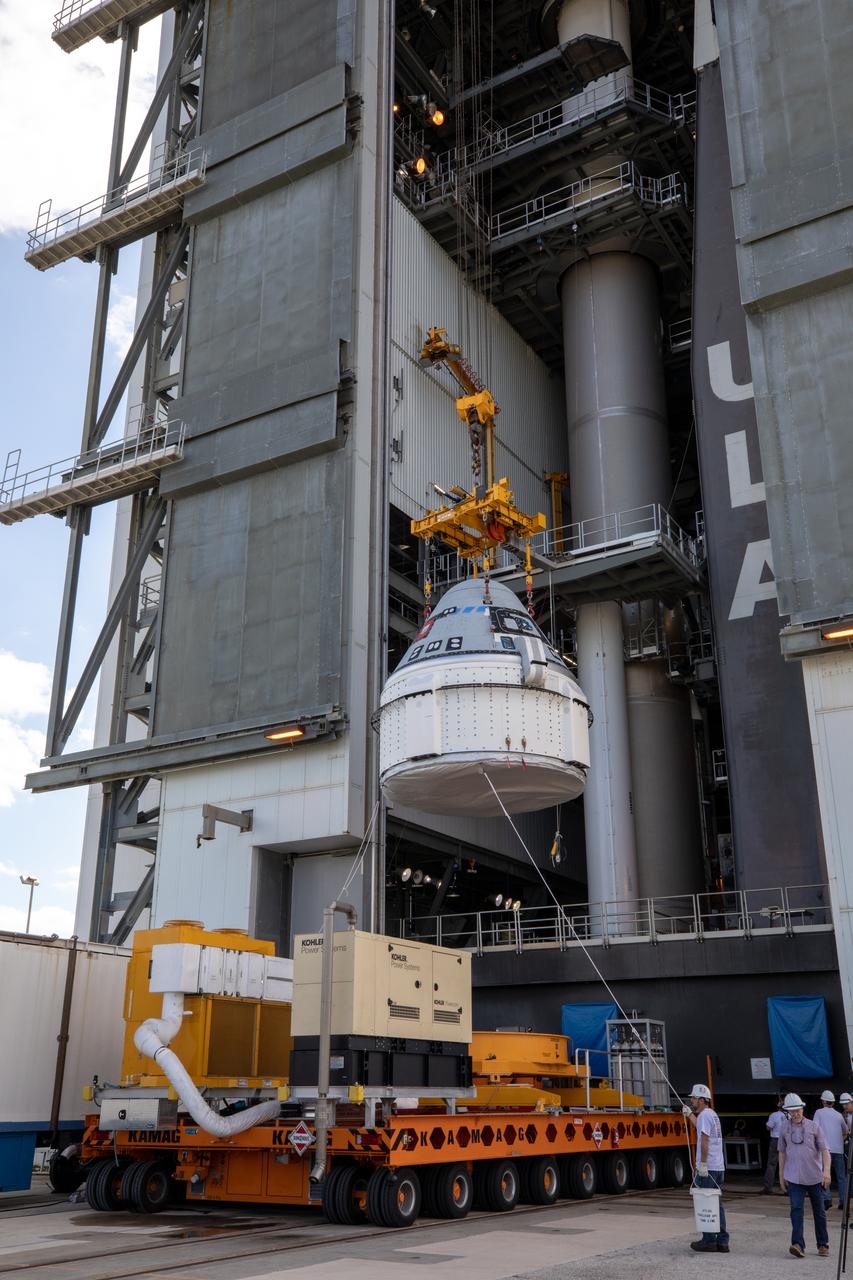

The Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft is lifted at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Florida’s Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on Nov. 21, 2019. Starliner will be secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.
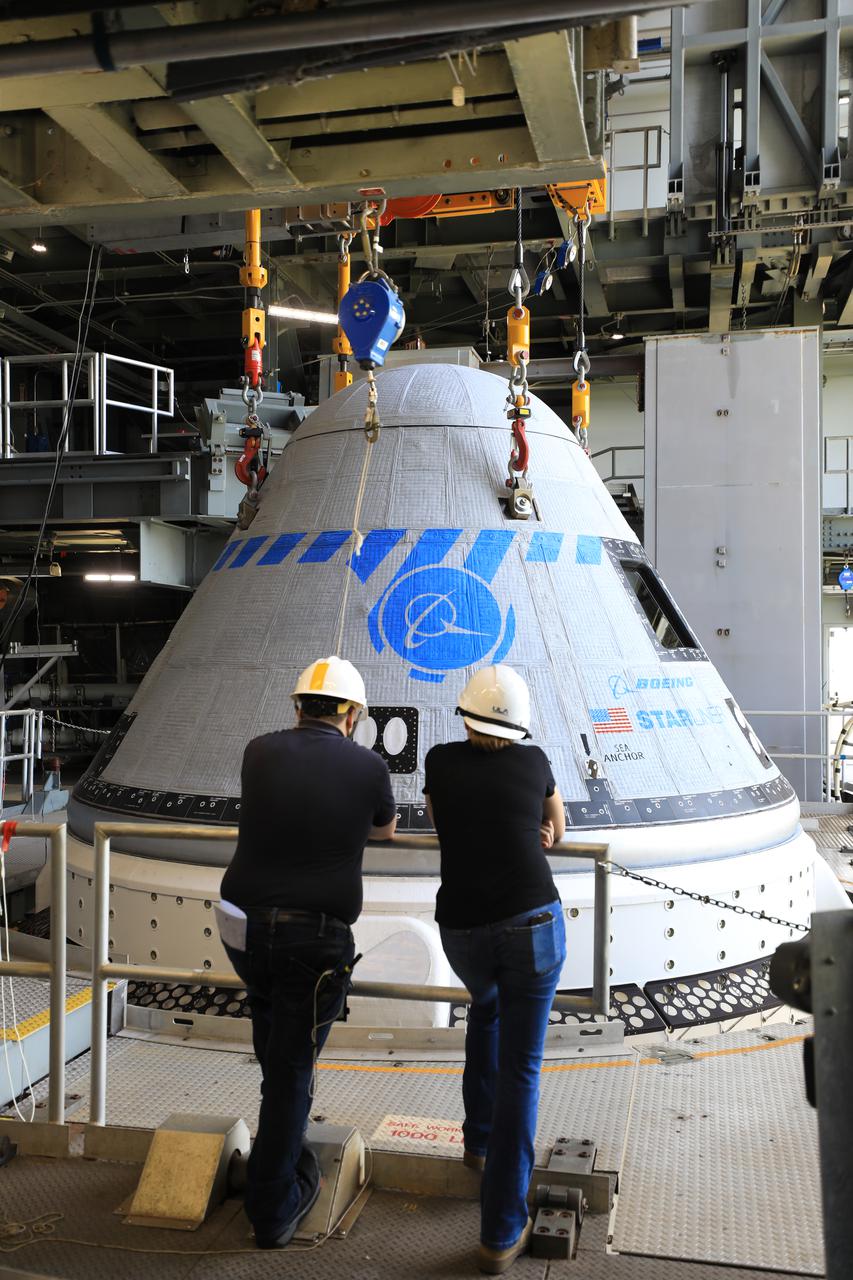

The Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft is lifted at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex-41 at Florida’s Cape Canaveral Space Force Station on May 4, 2022. Starliner will be secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for Boeing’s second Orbital Flight Test (OFT-2) to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.
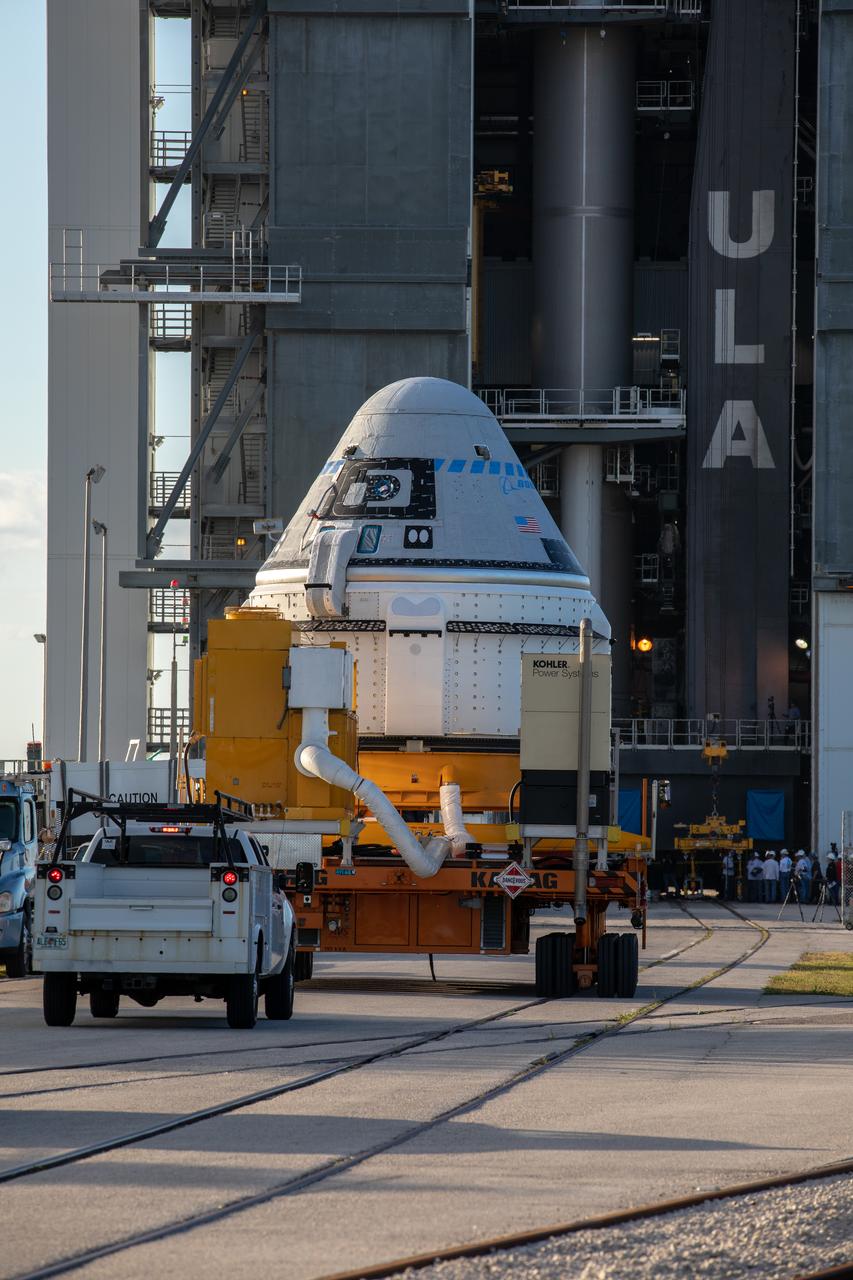

The Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft arrives at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Nov. 21, 2019. Starliner will be secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.
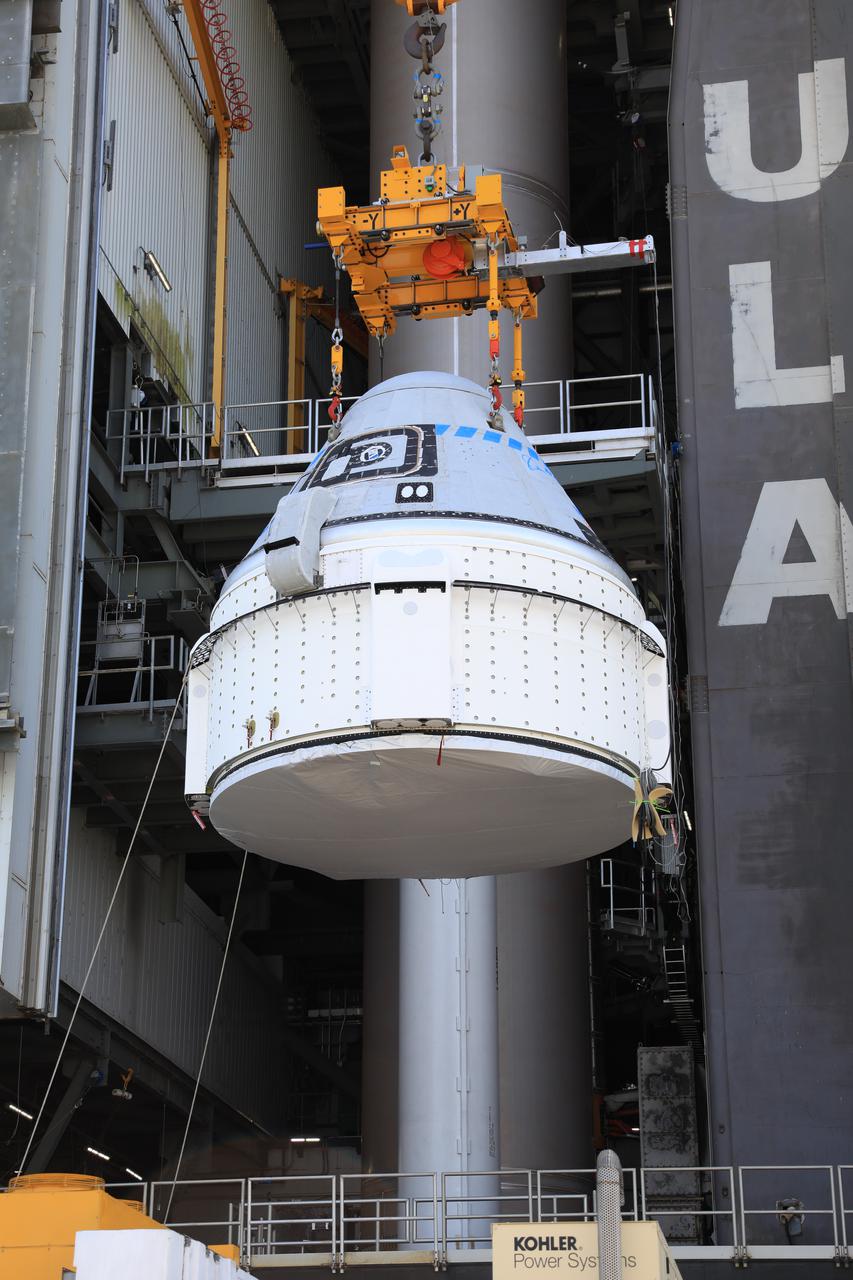

The Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft is lifted at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex-41 at Florida’s Cape Canaveral Space Force Station on May 4, 2022. Starliner will be secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for Boeing’s second Orbital Flight Test (OFT-2) to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.
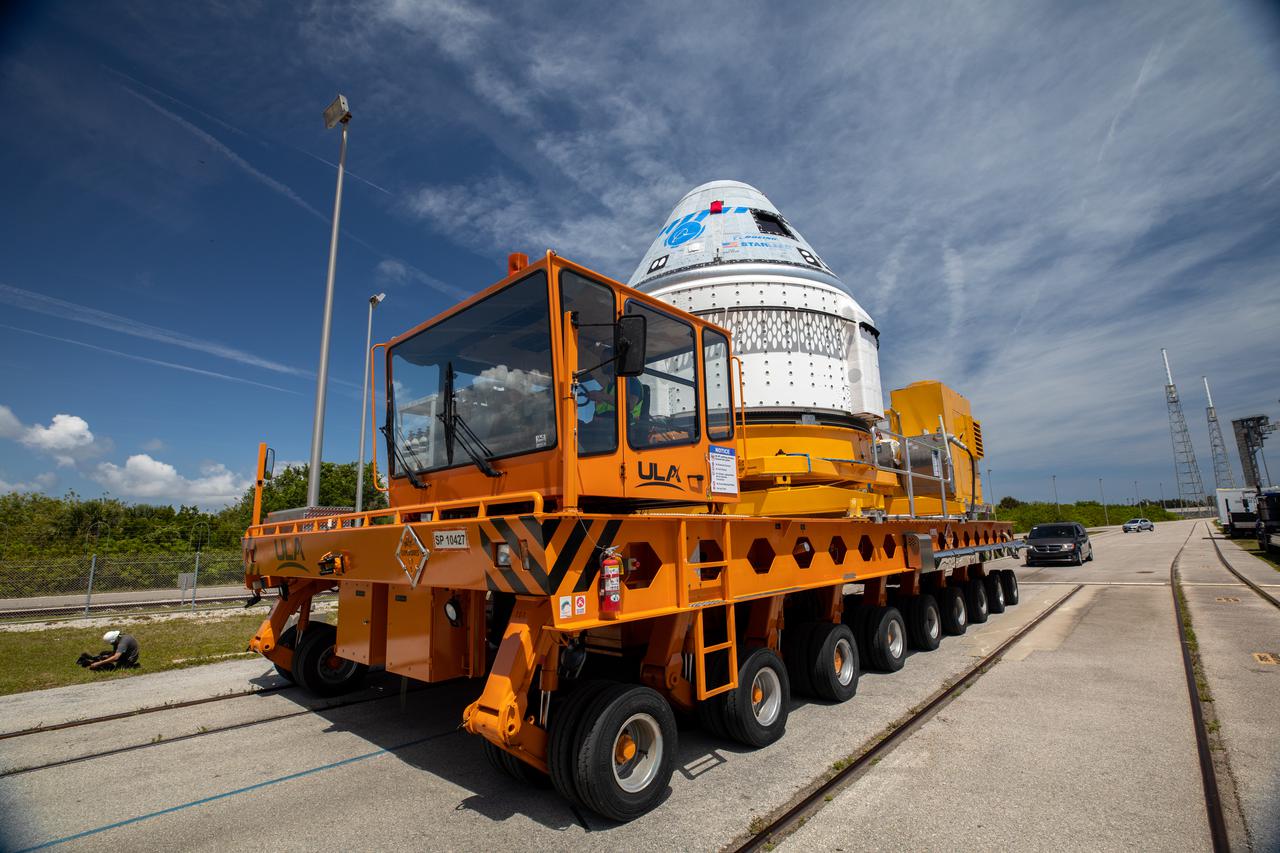

Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft rolls out from the company’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 4, 2022. The spacecraft will make the trip to the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station where it will be secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for Boeing’s second Orbital Flight Test (OFT-2) to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.
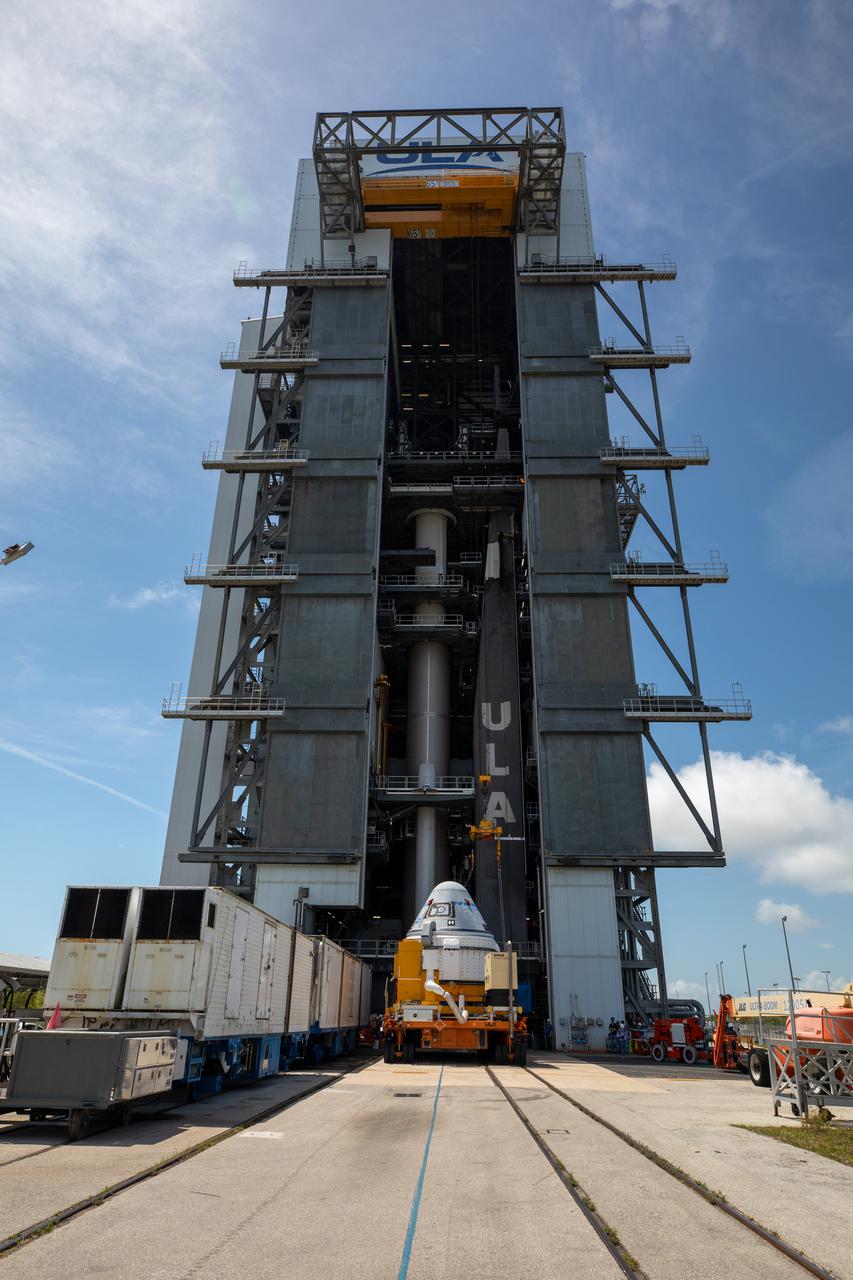

Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft arrives at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on May 4, 2022. Starliner will be secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for Boeing’s second Orbital Flight Test (OFT-2) to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.