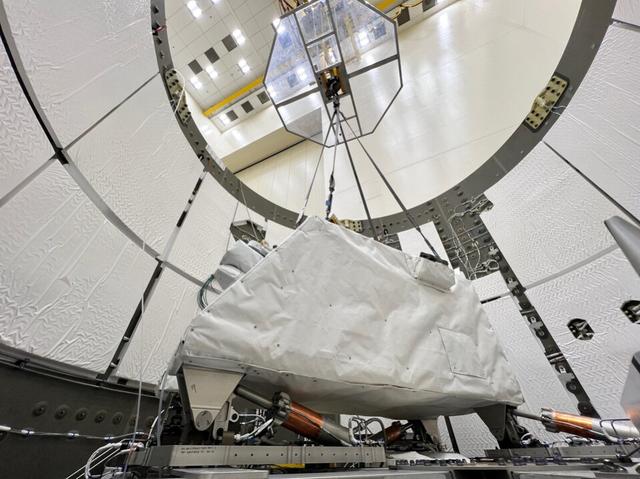

The Integrated LCRD Low Earth Orbit User Modem and Amplifier Terminal (ILLUMA-T) has been loaded into Dragon’s unpressurized spacecraft trunk. SpaceX will deliver the payload to the International Space Station during its 29th commercial resupply services mission. Launch is targeted for Sunday, Nov. 5 at 10:01 p.m. EST.

NASA announces the agency’s five-part plan to open the International Space Station to expanded commercial and marketing activities and private astronaut missions to the station and enable additional commercial destinations in low-Earth orbit, Friday, June 7, 2019 at the Nasdaq MarketSite in New York City. NASA will continue to maintain human presence and research in low-Earth orbit, and the long-term goal is to achieve a robust economy from which NASA can purchase services at a lower cost. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
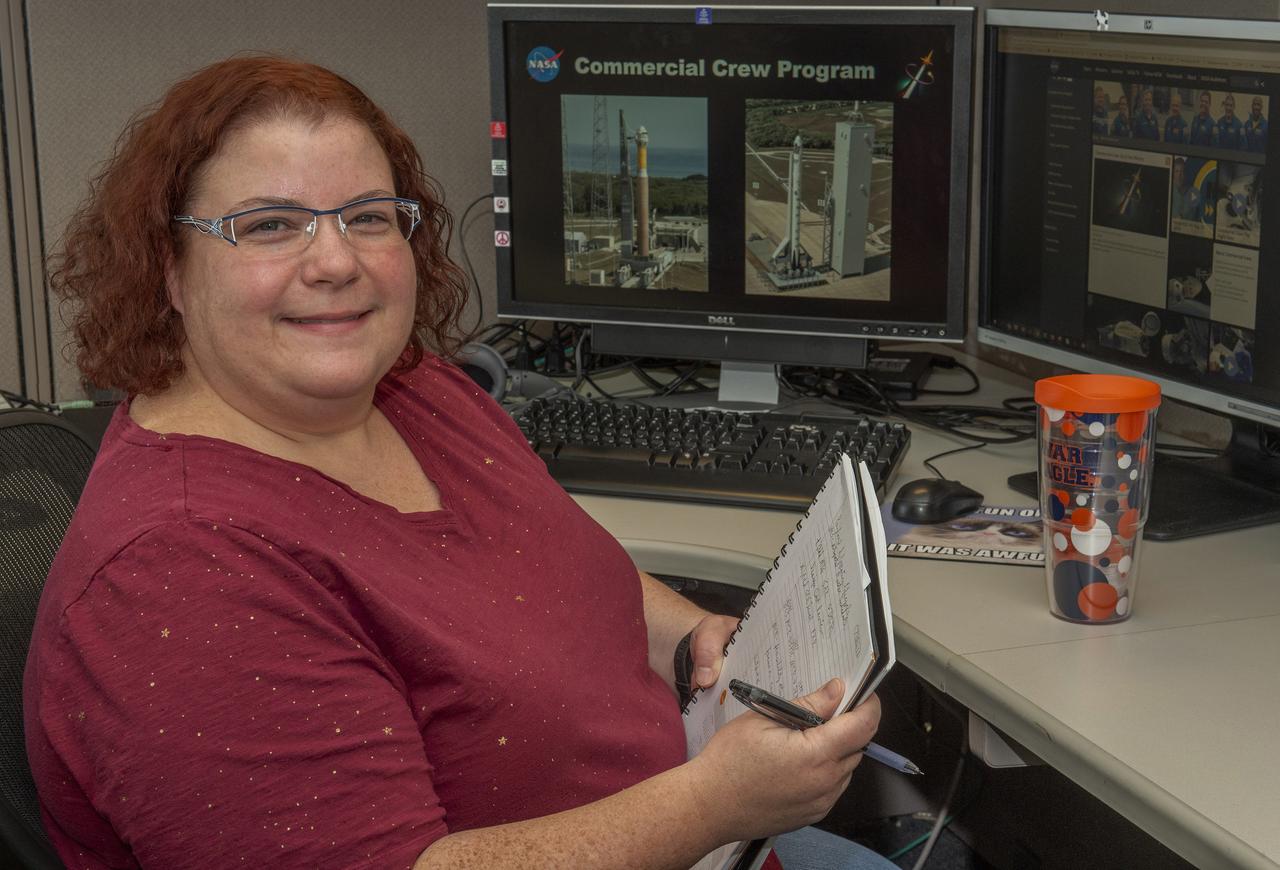

Miranda Holton is the Main Propulsion Systems (MPS) Subsystem Manager for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The goal of the Commercial Crew Program is to have safe, reliable and cost-effective access to and from the International Space Station and foster commercial access to other potential low-Earth orbit destinations.

NASA International Space Station Deputy Director Robyn Gatens answers questions during a briefing where NASA announced the agency’s five-part plan to open the International Space Station to expanded commercial and marketing activities and private astronaut missions to the station and enable additional commercial destinations in low-Earth orbit, Friday, June 7, 2019 at the Nasdaq MarketSite in New York City. NASA will continue to maintain human presence and research in low-Earth orbit, and the long-term goal is to achieve a robust economy from which NASA can purchase services at a lower cost. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA astronaut Christina Koch onboard the International Space Station gives remarks in a video during a briefing where NASA announced the agency’s five-part plan to open the International Space Station to expanded commercial and marketing activities and private astronaut missions to the station and enable additional commercial destinations in low-Earth orbit, Friday, June 7, 2019 at the Nasdaq MarketSite in New York City. NASA will continue to maintain human presence and research in low-Earth orbit, and the long-term goal is to achieve a robust economy from which NASA can purchase services at a lower cost. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Chief Financial Officer Jeff DeWit gives remarks during a briefing where NASA announced the agency’s five-part plan to open the International Space Station to expanded commercial and marketing activities and private astronaut missions to the station and enable additional commercial destinations in low-Earth orbit, Friday, June 7, 2019 at the Nasdaq MarketSite in New York City. NASA will continue to maintain human presence and research in low-Earth orbit, and the long-term goal is to achieve a robust economy from which NASA can purchase services at a lower cost. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Public Affairs Officer Stephanie Schierholz moderates a briefing where NASA announced the agency’s five-part plan to open the International Space Station to expanded commercial and marketing activities and private astronaut missions to the station and enable additional commercial destinations in low-Earth orbit, Friday, June 7, 2019 at the Nasdaq MarketSite in New York City. NASA will continue to maintain human presence and research in low-Earth orbit, and the long-term goal is to achieve a robust economy from which NASA can purchase services at a lower cost. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

The Nasdaq MarketSite tower displays a congratulatory message to NASA as the agency announces a five-part plan to open the International Space Station to expanded commercial and marketing activities and private astronaut missions to the station and enable additional commercial destinations in low-Earth orbit, Friday, June 7, 2019 at Nasdaq MarketSite in New York City. NASA will continue to maintain human presence and research in low-Earth orbit, and the long-term goal is to achieve a robust economy from which NASA can purchase services at a lower cost. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Associate Administrator for the Human Exploration and Operations Directorate William Gerstenmaier gives remarks during a briefing where NASA announced the agency’s five-part plan to open the International Space Station to expanded commercial and marketing activities and private astronaut missions to the station and enable additional commercial destinations in low-Earth orbit, Friday, June 7, 2019 at the Nasdaq MarketSite in New York City. NASA will continue to maintain human presence and research in low-Earth orbit, and the long-term goal is to achieve a robust economy from which NASA can purchase services at a lower cost. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At a news conference NASA officials and industry partners discuss progress of the agency's Commercial Crew Program. Among those participating in the briefing is Phil McAlister, NASA Commercial Spaceflight Development director. Through CCP, NASA is facilitating the development of U.S. commercial crew space transportation capabilities to achieve safe, reliable and cost-effective access to and from low-Earth orbit for potential future government and commercial customers. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At a news conference NASA officials and industry partners discuss progress of the agency's Commercial Crew Program. Among those participating in the briefing is Ed Mango, NASA Commercial Crew Program manager. Through CCP, NASA is facilitating the development of U.S. commercial crew space transportation capabilities to achieve safe, reliable and cost-effective access to and from low-Earth orbit for potential future government and commercial customers. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
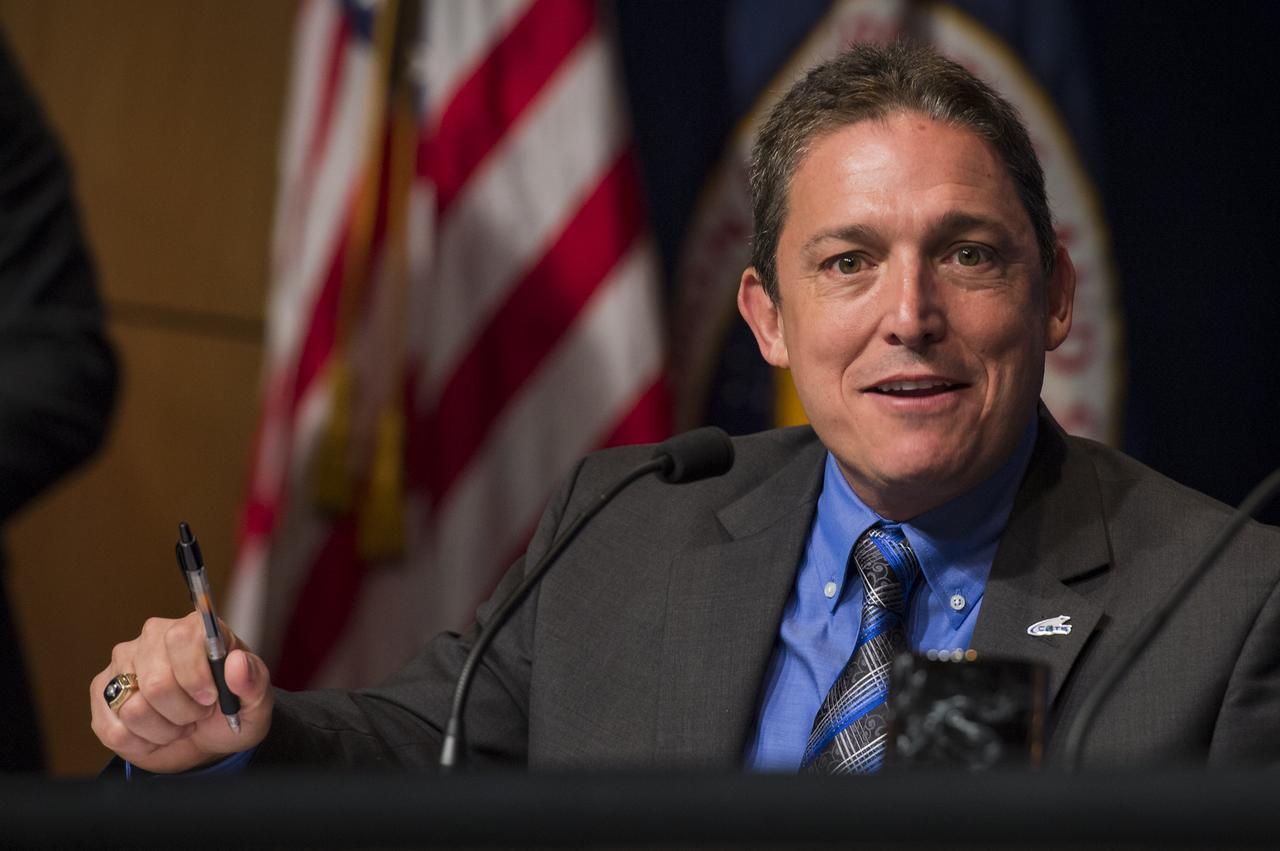

Alan Lindenmoyer, Manager of Commercial Crew and Cargo Program at NASA, delivers remarks panel discussion on the Commercial Orbital Transportation Services (COTS) initiative at NASA Headquarters in Washington on Wednesday, November 13, 2013. Through COTS, NASA's partners Space Exploration Technologies Corp. (SpaceX) and Orbital Sciences Corp., developed new U.S. rockets and spacecraft, launched from U.S. soil, capable of transporting cargo to low-Earth orbit and the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jay Westcott)
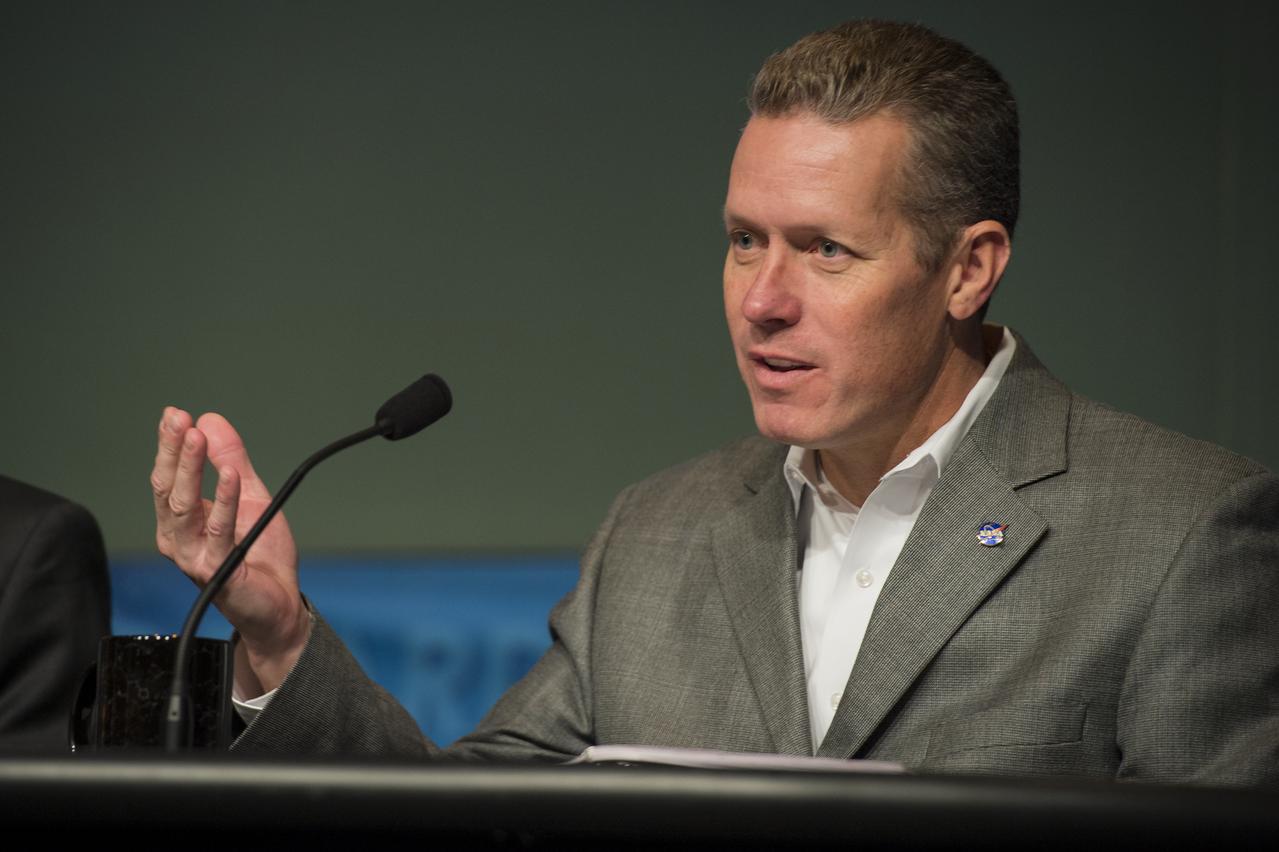

Phil McAlister, Director of Commercial Spaceflight Development at NASA, delivers remarks panel discussion on the Commercial Orbital Transportation Services (COTS) initiative at NASA Headquarters in Washington on Wednesday, November 13, 2013. Through COTS, NASA's partners Space Exploration Technologies Corp. (SpaceX) and Orbital Sciences Corp., developed new U.S. rockets and spacecraft, launched from U.S. soil, capable of transporting cargo to low-Earth orbit and the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jay Westcott)

A Nasdaq moderator, center, talks with NASA Director of Commercial Spaceflight Development Phil McAlister, left, ISS National Lab Vice President and Chief Operating Officer Ken Shields, NASA Advisory Council Regulatory and Policy Committee Chair Mike Gold, and NASA Deputy Chief Financial Officer for Integration Doug Comstock, right, during a live social media event shortly after NASA announced a five-part plan to open the International Space Station to expanded commercial and marketing activities and private astronaut missions to the station and enable additional commercial destinations in low-Earth orbit, Friday, June 7, 2019 at the Nasdaq MarketSite in New York City. NASA will continue to maintain human presence and research in low-Earth orbit, and the long-term goal is to achieve a robust economy from which NASA can purchase services at a lower cost. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

A Nasdaq moderator, center, talks with NASA Director of Commercial Spaceflight Development Phil McAlister, left, ISS National Lab Vice President and Chief Operating Officer Ken Shields, NASA Advisory Council Regulatory and Policy Committee Chair Mike Gold, and NASA Deputy Chief Financial Officer for Integration Doug Comstock, right, during a live social media event shortly after NASA announced a five-part plan to open the International Space Station to expanded commercial and marketing activities and private astronaut missions to the station and enable additional commercial destinations in low-Earth orbit, Friday, June 7, 2019 at the Nasdaq MarketSite in New York City. NASA will continue to maintain human presence and research in low-Earth orbit, and the long-term goal is to achieve a robust economy from which NASA can purchase services at a lower cost. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
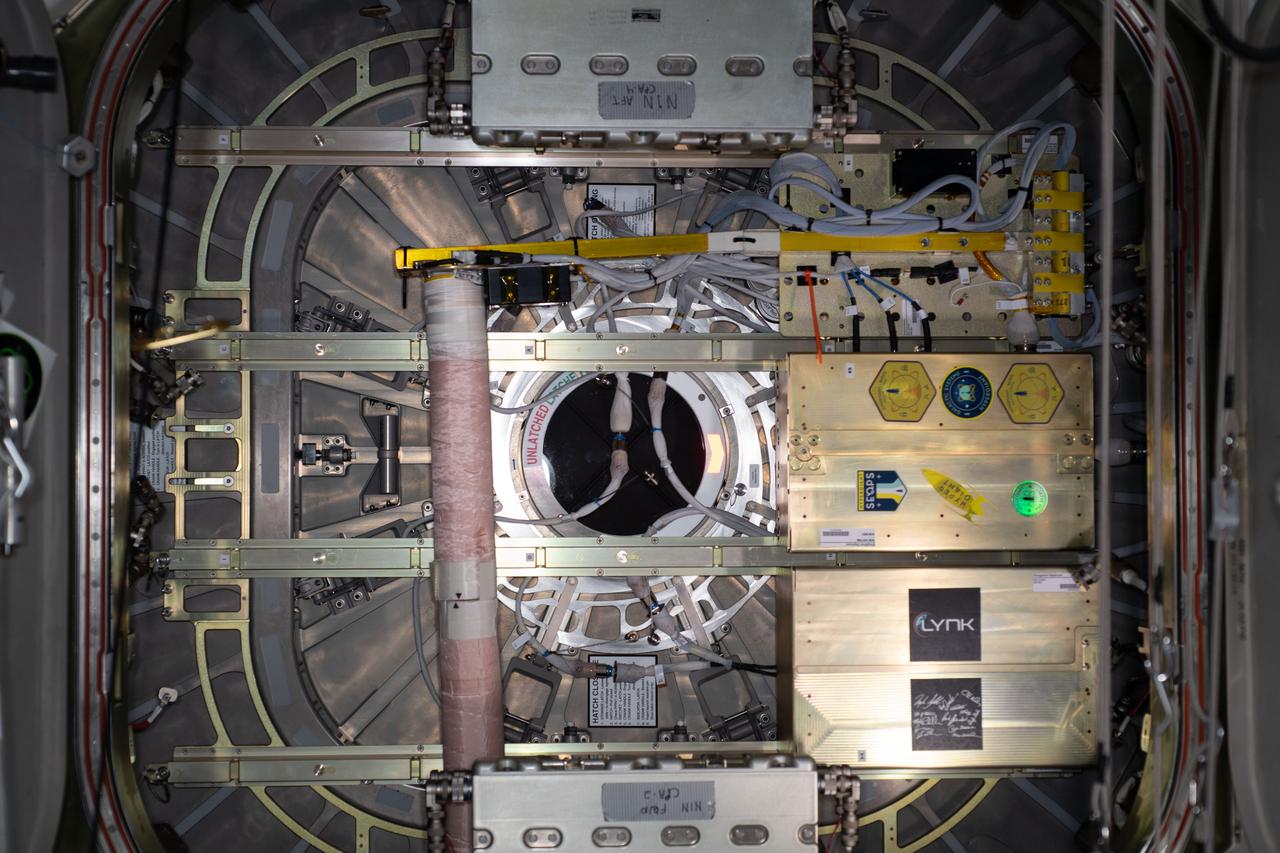
iss063e010534 (5/10/2020) --- A view from the Unity module aboard the International Space Station (ISS) of the Northrop Grumman NG-13 hatch. Attached to the hatch is the SlingShot small satellite deployer loaded with two CubeSats that will be deployed into Earth orbit after Cygnus departs the orbiting lab on May 11, 2020. The SEOPS-UbiquitiLink investigation furthers demonstrates the premise that small satellites/nano satellites can perform vital communications missions and provide valuable communications services. The SEOPS-WIDAR investigation demonstrates technologies that increase the utility of low-cost microsatellites, contributing to the increased commercialization of the International Space Station and low-Earth orbit.
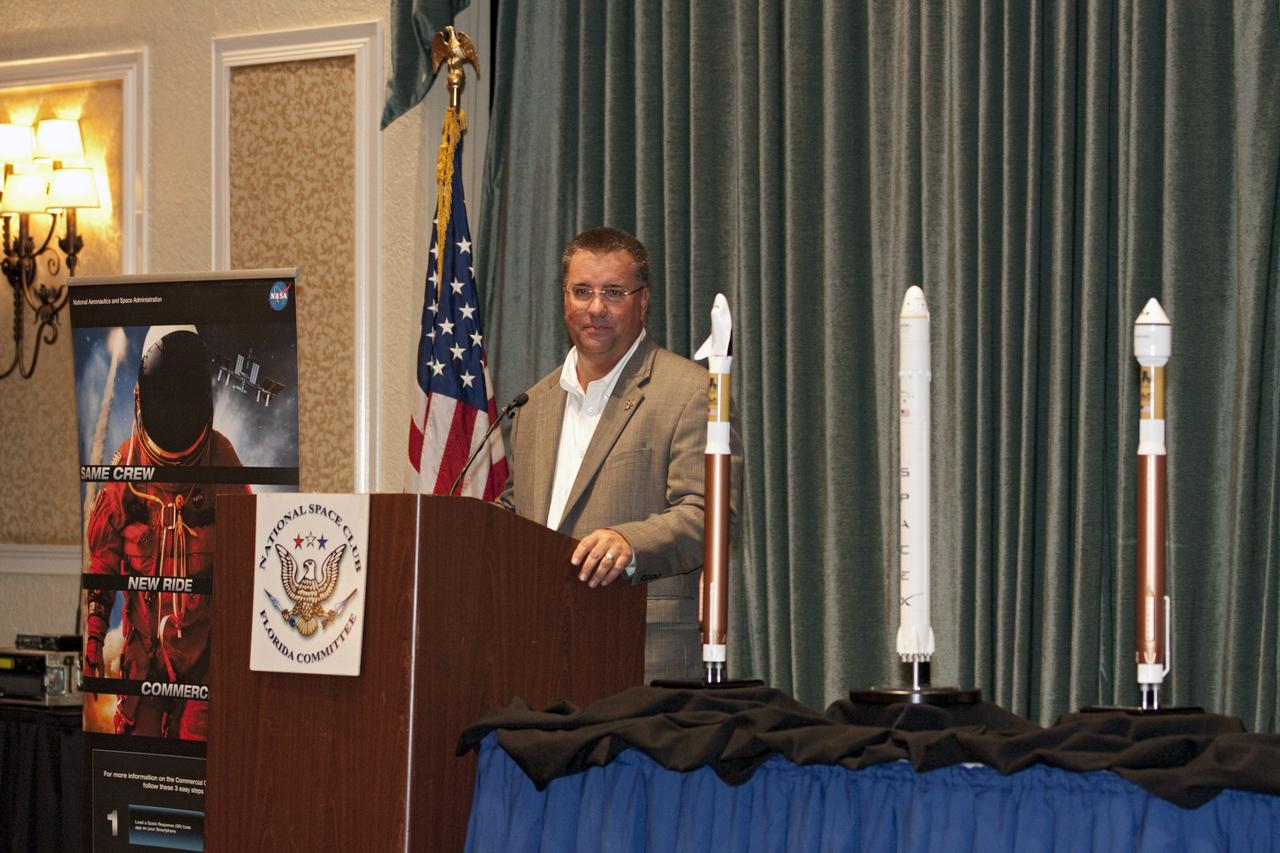

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the National Space Club Florida Committee's August luncheon at the Radisson Resort at the Port in Cape Canaveral, Fla., NASA Commercial Crew Program Manager Ed Mango discusses the innovative steps the agency is taking with industry partners to develop the next U.S. space transportation capability to and from low Earth orbit, which will eventually be available for use by the U.S. government and other commercial customers. To learn more about the Commercial Crew Program, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At a news conference NASA officials and industry partners discuss progress of the agency's Commercial Crew Program. Among those participating in the briefing is Rob Meyerson, Blue Origin president and program manager. Through CCP, NASA is facilitating the development of U.S. commercial crew space transportation capabilities to achieve safe, reliable and cost-effective access to and from low-Earth orbit for potential future government and commercial customers. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the National Space Club Florida Committee's August luncheon at the Radisson Resort at the Port in Cape Canaveral, Fla., NASA Commercial Crew Program Manager Ed Mango discusses the innovative steps the agency is taking with industry partners to develop the next U.S. space transportation capability to and from low Earth orbit, which will eventually be available for use by the U.S. government and other commercial customers. To learn more about the Commercial Crew Program, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the National Space Club Florida Committee's August luncheon at the Radisson Resort at the Port in Cape Canaveral, Fla., NASA Commercial Crew Program Manager Ed Mango discusses the innovative steps the agency is taking with industry partners to develop the next U.S. space transportation capability to and from low Earth orbit, which will eventually be available for use by the U.S. government and other commercial customers. To learn more about the Commercial Crew Program, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the National Space Club Florida Committee's August luncheon at the Radisson Resort at the Port in Cape Canaveral, Fla., NASA Commercial Crew Program Manager Ed Mango discusses the innovative steps the agency is taking with industry partners to develop the next U.S. space transportation capability to and from low Earth orbit, which will eventually be available for use by the U.S. government and other commercial customers. To learn more about the Commercial Crew Program, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett
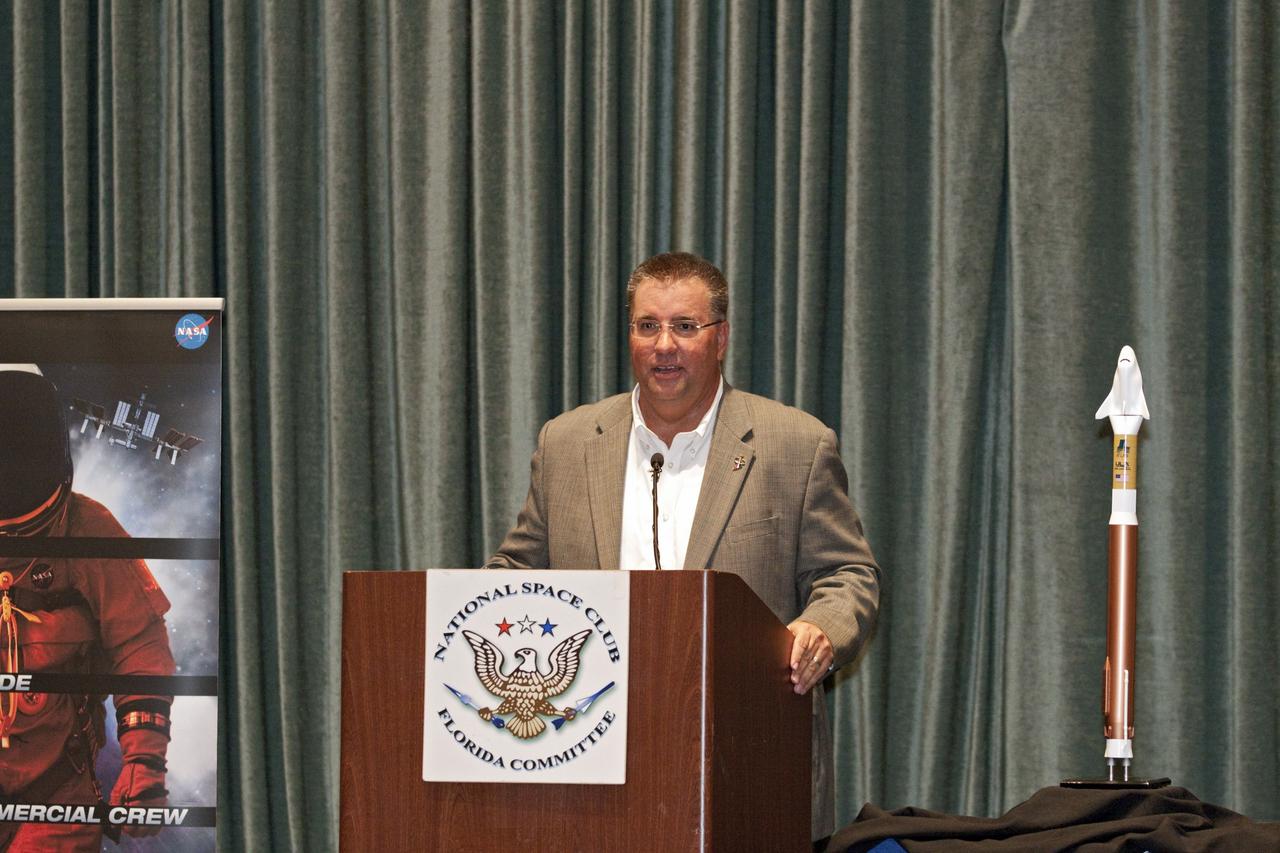

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the National Space Club Florida Committee's August luncheon at the Radisson Resort at the Port in Cape Canaveral, Fla., NASA Commercial Crew Program Manager Ed Mango discusses the innovative steps the agency is taking with industry partners to develop the next U.S. space transportation capability to and from low Earth orbit, which will eventually be available for use by the U.S. government and other commercial customers. To learn more about the Commercial Crew Program, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett
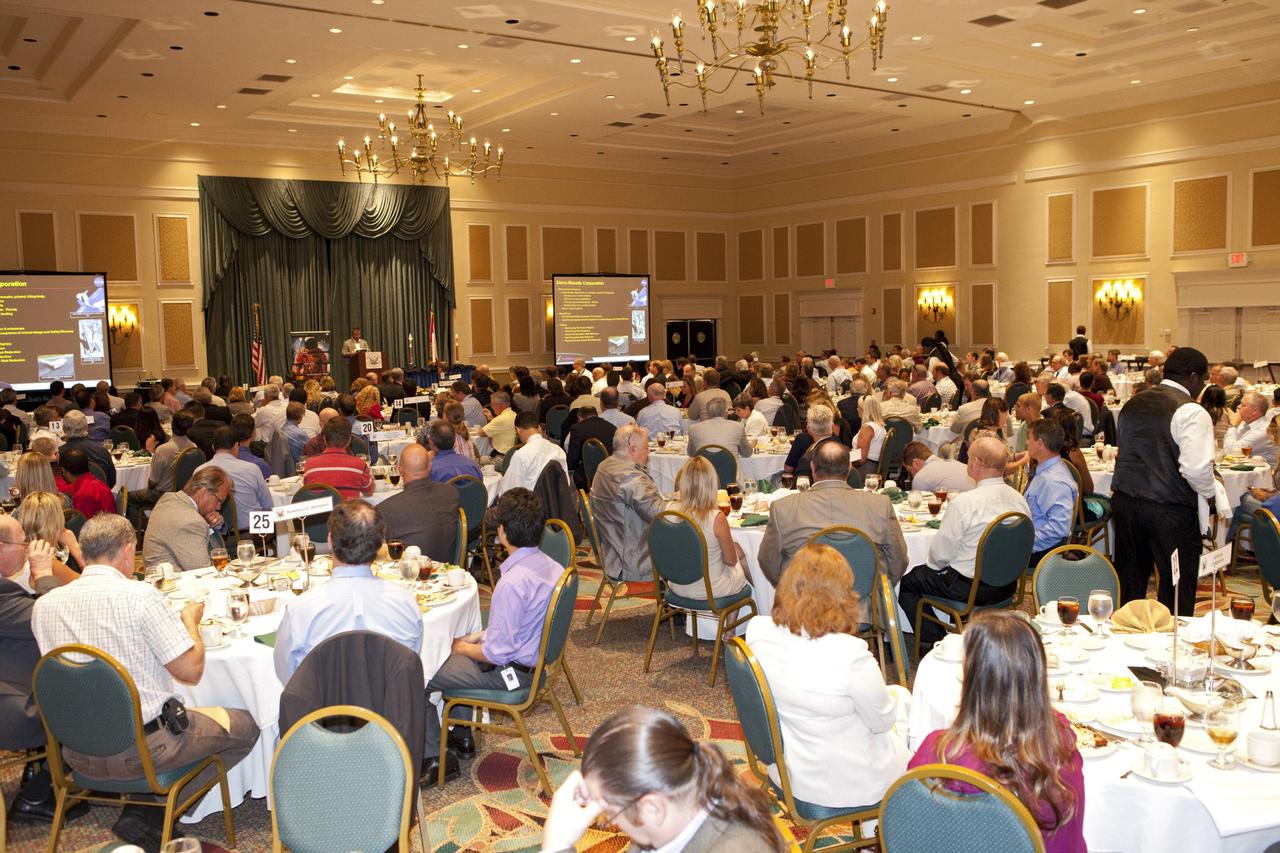

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the National Space Club Florida Committee's August luncheon at the Radisson Resort at the Port in Cape Canaveral, Fla., NASA Commercial Crew Program Manager Ed Mango discusses the innovative steps the agency is taking with industry partners to develop the next U.S. space transportation capability to and from low Earth orbit, which will eventually be available for use by the U.S. government and other commercial customers. To learn more about the Commercial Crew Program, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett
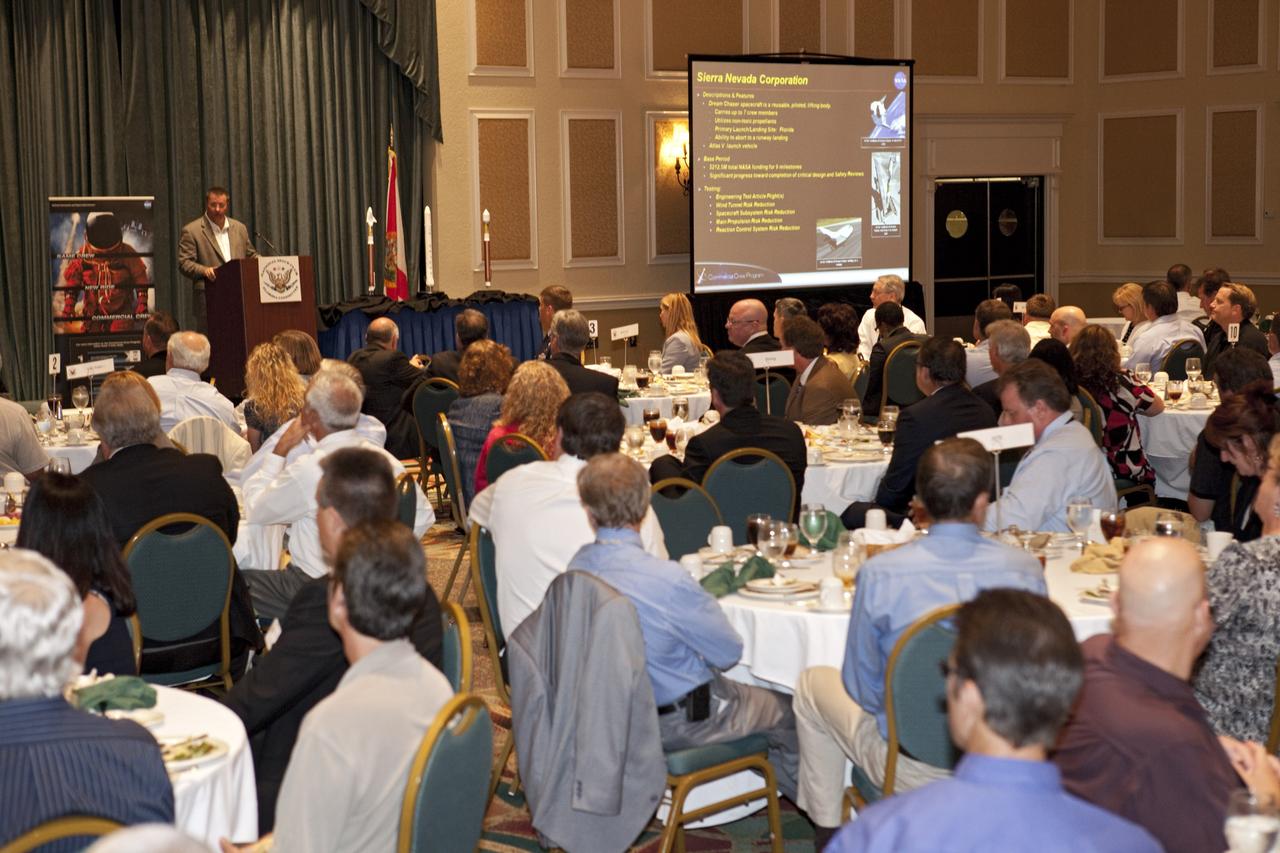

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the National Space Club Florida Committee's August luncheon at the Radisson Resort at the Port in Cape Canaveral, Fla., NASA Commercial Crew Program Manager Ed Mango discusses the innovative steps the agency is taking with industry partners to develop the next U.S. space transportation capability to and from low Earth orbit, which will eventually be available for use by the U.S. government and other commercial customers. To learn more about the Commercial Crew Program, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- This is an artist's conception of NASA's Commercial Crew Program or CCP, logo and low Earth orbit. The program is entering its third phase of development, called Commercial Crew integrated Capability, or CCiCap, to propel America's next human space transportation system to low Earth orbit forward. Operating under funded Space Act Agreements, or SAAs, The Boeing Co. of Houston, Sierra Nevada Corp., or SNC, Space Systems of Louisville, Colo., and Space Exploration Technologies, or SpaceX, of Hawthorne, Calif., will spend the next 21 months completing their designs, conducting critical risk reduction testing on their spacecraft and launch vehicles, and showcasing how they would operate and manage missions from launch through orbit and landing, setting the stage for future demonstration missions. To learn more about CCP, which is based at Kennedy and supported by NASA's Johnson Space Center in Houston, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA/Matthew Young

NASA Associate Administrator for the Human Exploration and Operations Directorate William Gerstenmaier, left, NASA Chief Financial Officer Jeff DeWit, center, and NASA International Space Station Deputy Director Robyn Gatens announce the agency’s five-part plan to open the International Space Station to expanded commercial and marketing activities and private astronaut missions to the station and enable additional commercial destinations in low-Earth orbit, Friday, June 7, 2019 at the Nasdaq MarketSite in New York City. NASA will continue to maintain human presence and research in low-Earth orbit, and the long-term goal is to achieve a robust economy from which NASA can purchase services at a lower cost. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

A Nasdaq moderator, center, talks with NanoRacks CEO Jeff Manber, left, NASA Manager of the International Space Station Research Office Marybeth Edeen, AlphaSpace Founder and Chairman Stephanie Murphy, and Made in Space Vice President of Advanced Programs and Concepts Justin Kugler, right, during a live social media event shortly after NASA announced a five-part plan to open the International Space Station to expanded commercial and marketing activities and private astronaut missions to the station and enable additional commercial destinations in low-Earth orbit, Friday, June 7, 2019 at the Nasdaq MarketSite in New York City. NASA will continue to maintain human presence and research in low-Earth orbit, and the long-term goal is to achieve a robust economy from which NASA can purchase services at a lower cost. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
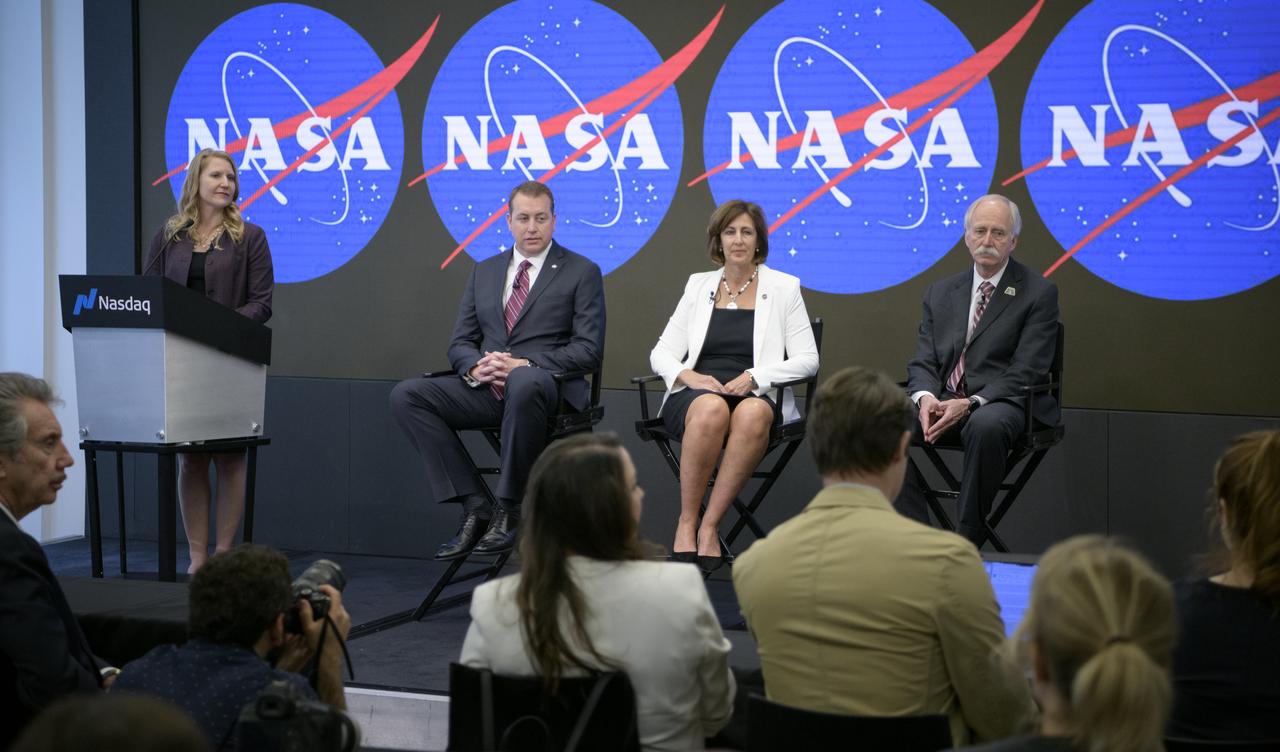

NASA Public Affairs Officer Stephanie Schierholz, standing left, moderates a media briefing with NASA Chief Financial Officer Jeff DeWit, left, NASA International Space Station Deputy Director Robyn Gatens, center, and NASA Associate Administrator for the Human Exploration and Operations Directorate William Gerstenmaier where they announced the agency’s five-part plan to open the International Space Station to expanded commercial and marketing activities and private astronaut missions to the station and enable additional commercial destinations in low-Earth orbit, Friday, June 7, 2019 at the Nasdaq MarketSite in New York City. NASA will continue to maintain human presence and research in low-Earth orbit, and the long-term goal is to achieve a robust economy from which NASA can purchase services at a lower cost. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
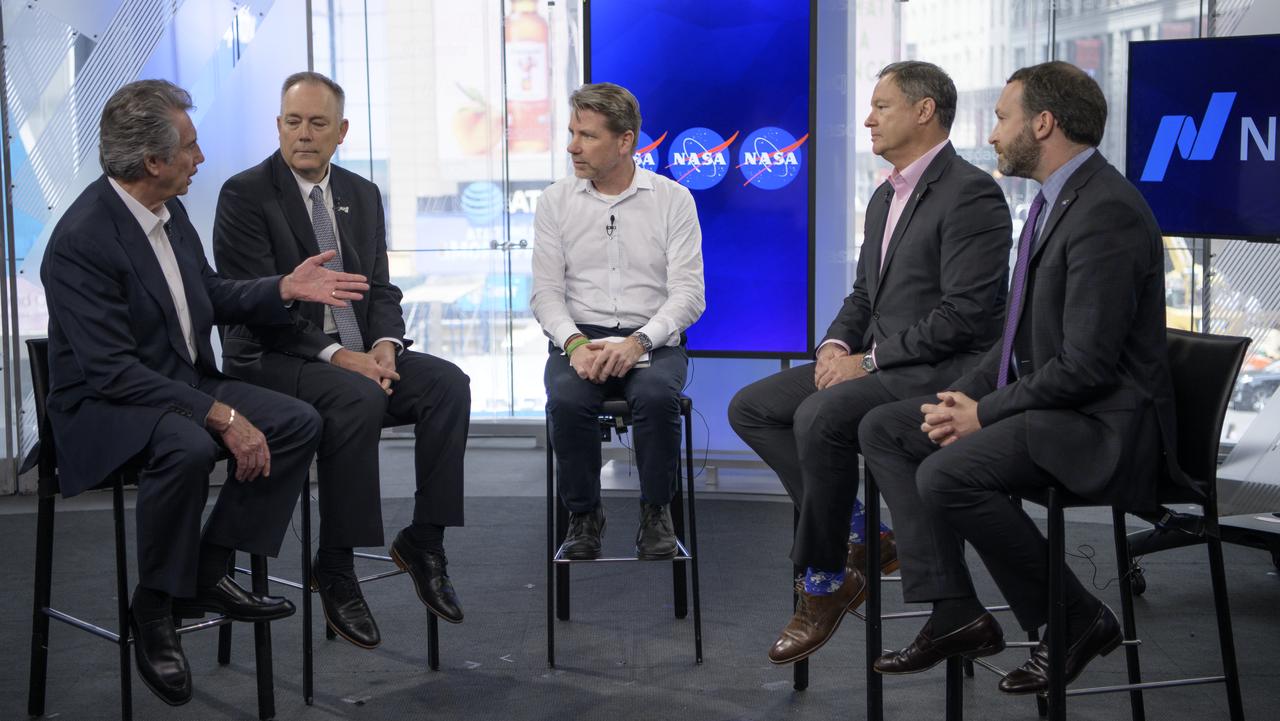

A Nasdaq moderator, center, talks with Bigelow Aerospace, LLC Founder and President Robert Bigelow, left, Boeing Global Sales and Marketing, Space Exploration, Kevin Foley, Axiom Vice President of Business Development Michael Lopez-Alegria, and NASA Senior Economic Advisor Alex MacDonald, right, during a live social media event shortly after NASA announced a five-part plan to open the International Space Station to expanded commercial and marketing activities and private astronaut missions to the station and enable additional commercial destinations in low-Earth orbit, Friday, June 7, 2019 at the Nasdaq MarketSite in New York City. NASA will continue to maintain human presence and research in low-Earth orbit, and the long-term goal is to achieve a robust economy from which NASA can purchase services at a lower cost. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Commercial Crew Program: The Commercial Crew Program at Kennedy Space Center is leading NASA’s efforts to develop the next United States capability for crew transportation and rescue services to and from the International Space Station ISS and other low Earth orbit destinations by the middle of the decade. The outcome of this capability is expected to stimulate and expand the U.S. space transportation industry. Poster designed by Kennedy Space Center Graphics Department/Greg Lee. Credit: NASA
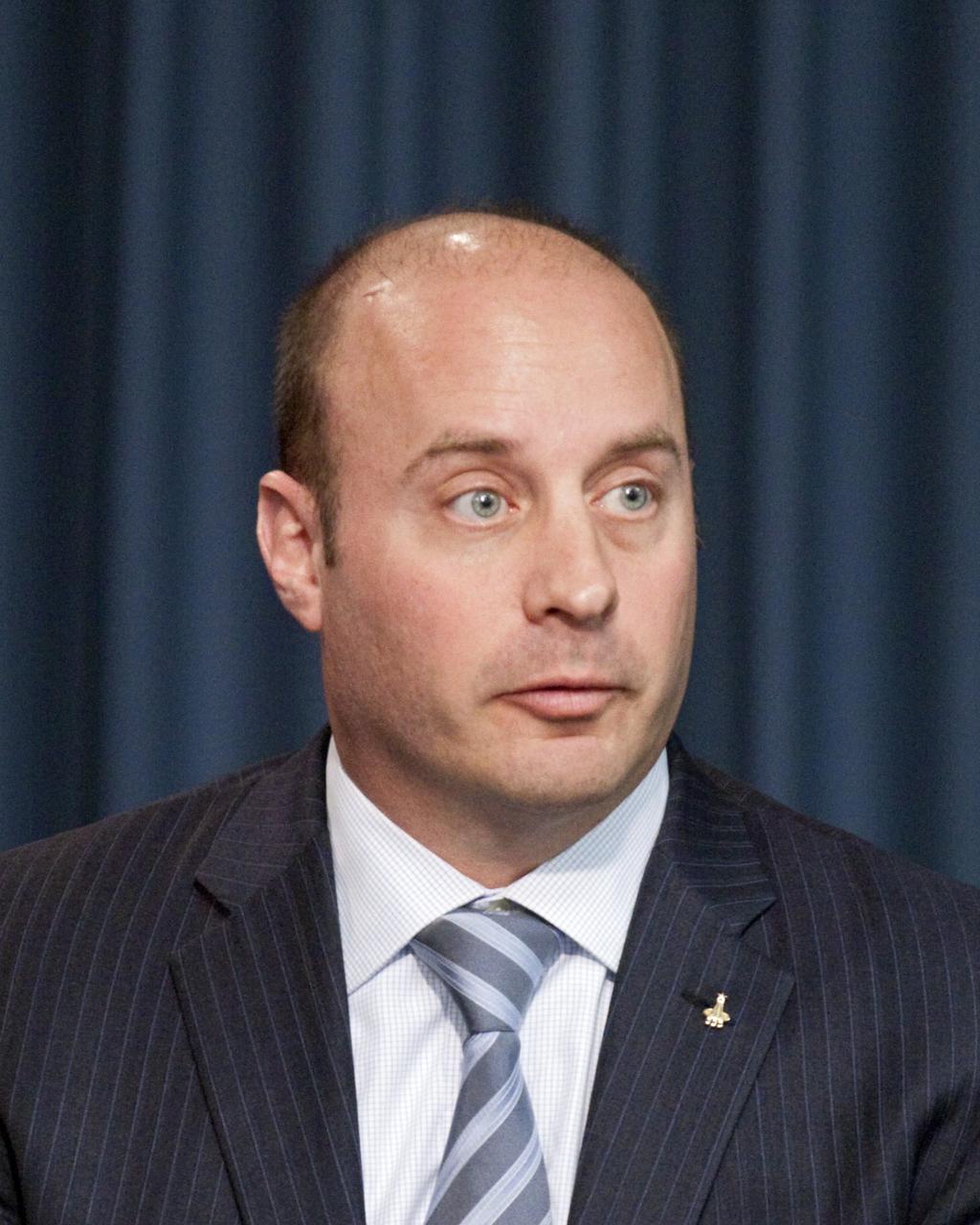

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At a news conference NASA officials and industry partners discuss progress of the agency's Commercial Crew Program. Among those participating in the briefing is Garrett Reisman, Space Exploration Technologies SpaceX Commercial Crew project manager. Through CCP, NASA is facilitating the development of U.S. commercial crew space transportation capabilities to achieve safe, reliable and cost-effective access to and from low-Earth orbit for potential future government and commercial customers. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
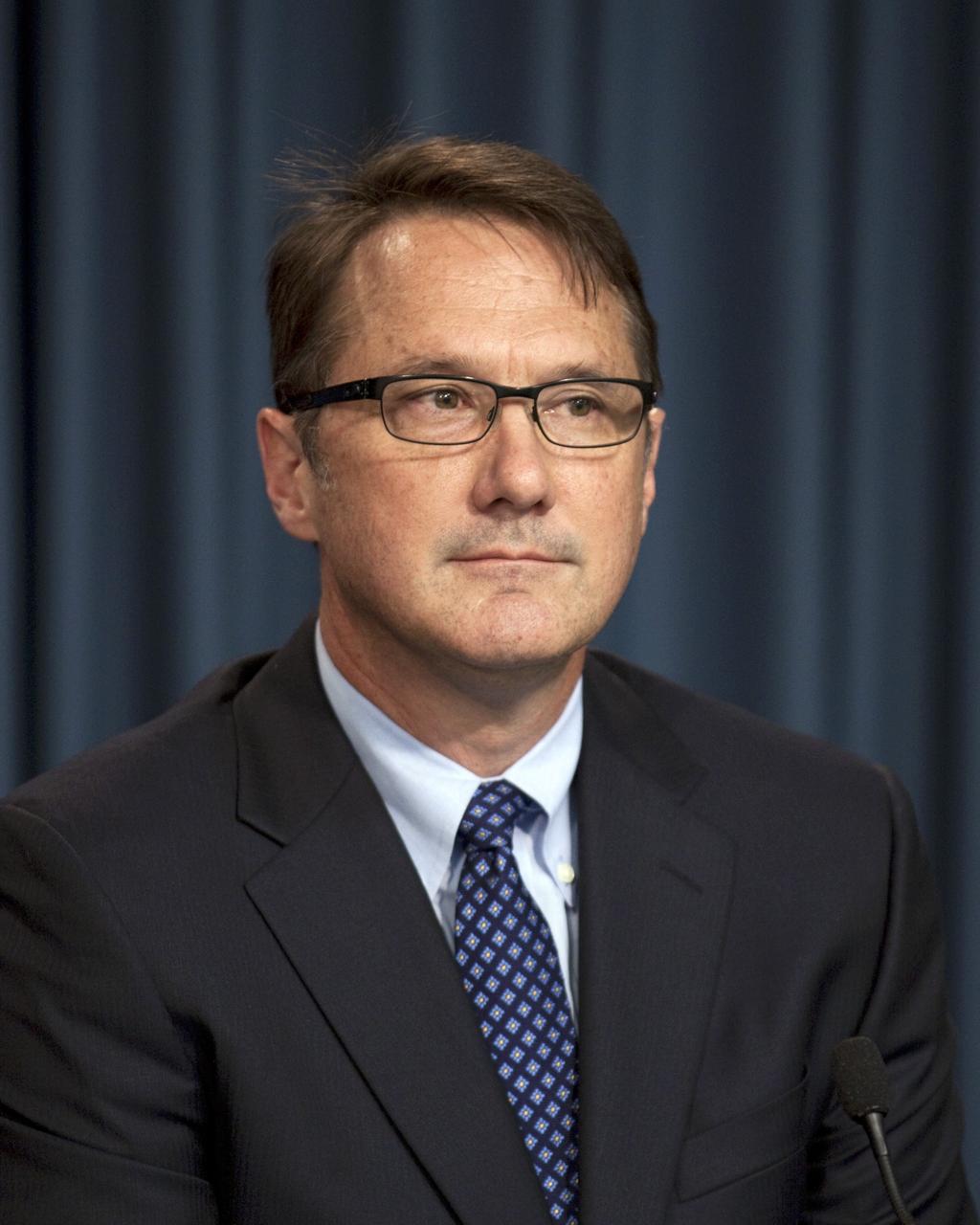

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At a news conference NASA officials and industry partners discuss progress of the agency's Commercial Crew Program. Among those participating in the briefing is John Mulholland, The Boeing Company Commercial Programs Space Exploration vice president and program manager. Through CCP, NASA is facilitating the development of U.S. commercial crew space transportation capabilities to achieve safe, reliable and cost-effective access to and from low-Earth orbit for potential future government and commercial customers. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
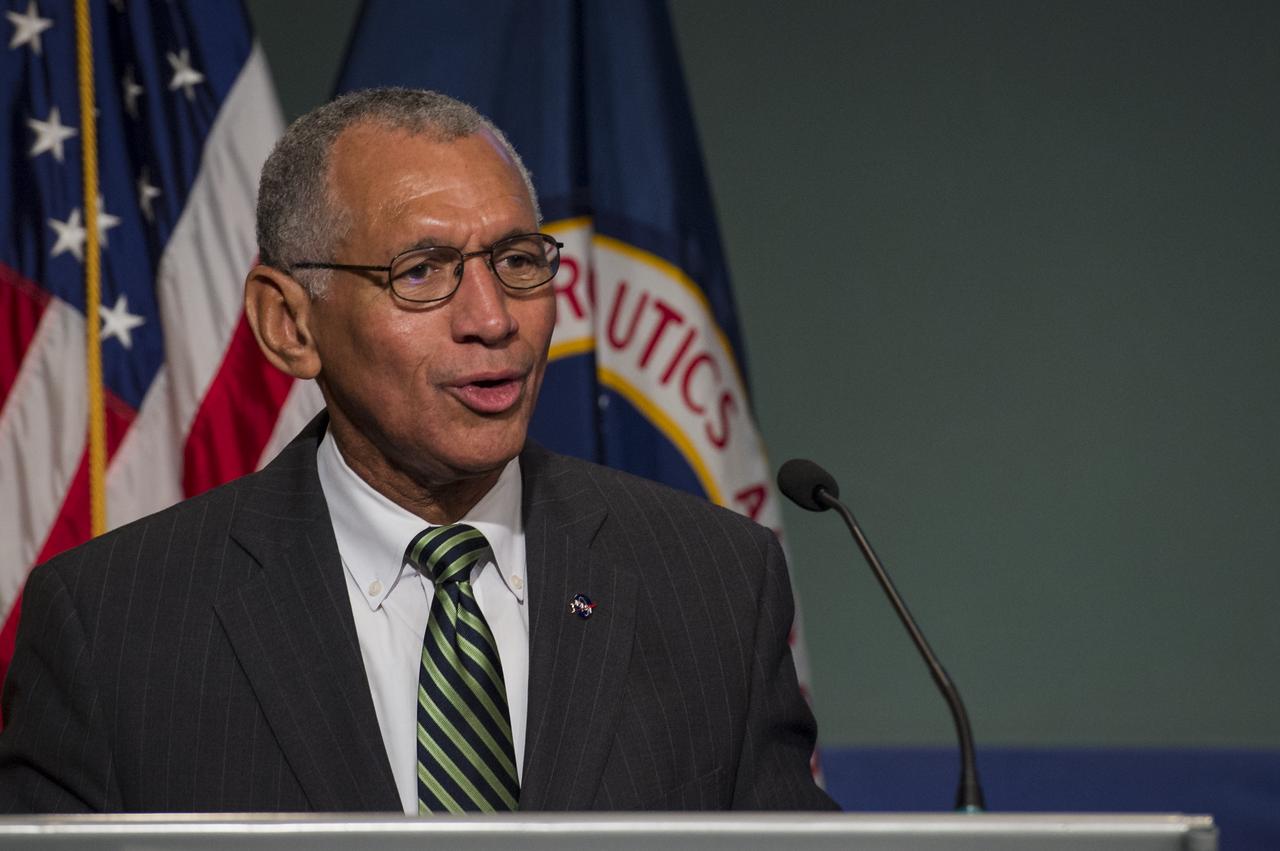

NASA Administrator Charles Bolden delivers remarks before a panel discussion on the Commercial Orbital Transportation Services (COTS) initiative at NASA Headquarters in Washington on Wednesday, November 13, 2013. Through COTS, NASA's partners Space Exploration Technologies Corp. (SpaceX) and Orbital Sciences Corp., developed new U.S. rockets and spacecraft, launched from U.S. soil, capable of transporting cargo to low-Earth orbit and the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jay Westcott)

NASA Administrator Charles Bolden delivers remarks before a panel discussion on the Commercial Orbital Transportation Services (COTS) initiative at NASA Headquarters in Washington on Wednesday, November 13, 2013. Through COTS, NASA's partners Space Exploration Technologies Corp. (SpaceX) and Orbital Sciences Corp., developed new U.S. rockets and spacecraft, launched from U.S. soil, capable of transporting cargo to low-Earth orbit and the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jay Westcott)
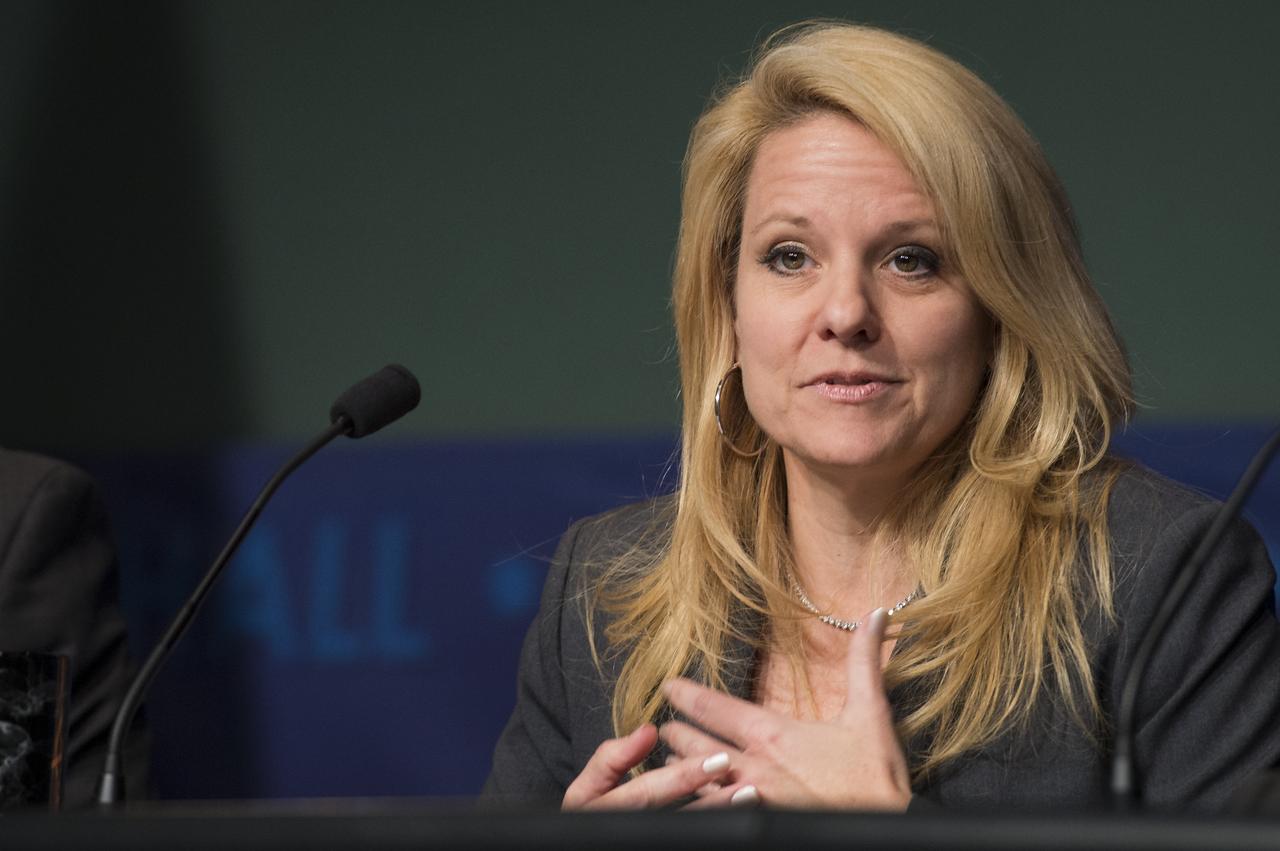

Gwynne Shotwell, President of SpaceX, delivers remarks panel discussion on the Commercial Orbital Transportation Services (COTS) initiative at NASA Headquarters in Washington on Wednesday, November 13, 2013. Through COTS, NASA's partners Space Exploration Technologies Corp. (SpaceX) and Orbital Sciences Corp., developed new U.S. rockets and spacecraft, launched from U.S. soil, capable of transporting cargo to low-Earth orbit and the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jay Westcott)
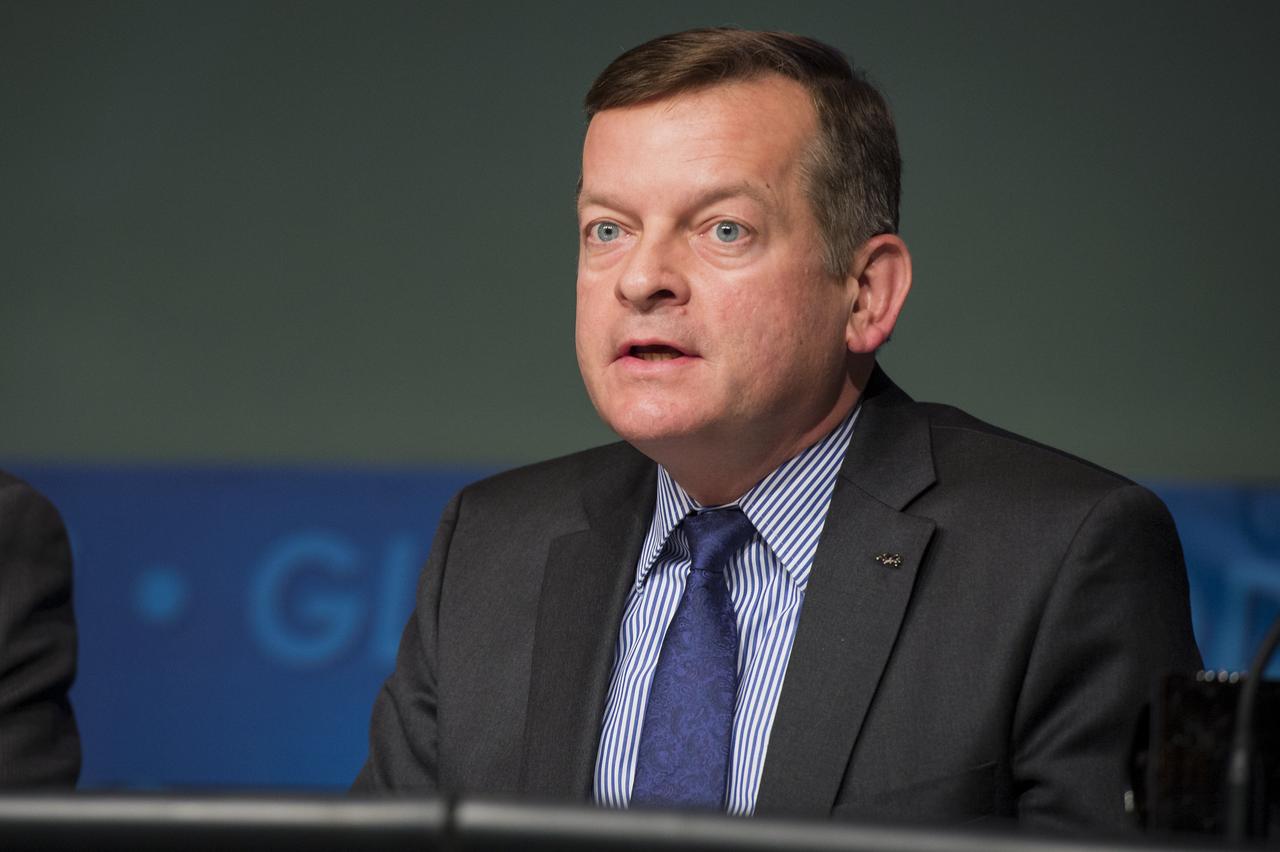

Frank Slazer, Vice President of Space Systems, Aerospace Industries Association, delivers remarks panel discussion on the Commercial Orbital Transportation Services (COTS) initiative at NASA Headquarters in Washington on Wednesday, November 13, 2013. Through COTS, NASA's partners Space Exploration Technologies Corp. (SpaceX) and Orbital Sciences Corp., developed new U.S. rockets and spacecraft, launched from U.S. soil, capable of transporting cargo to low-Earth orbit and the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jay Westcott)
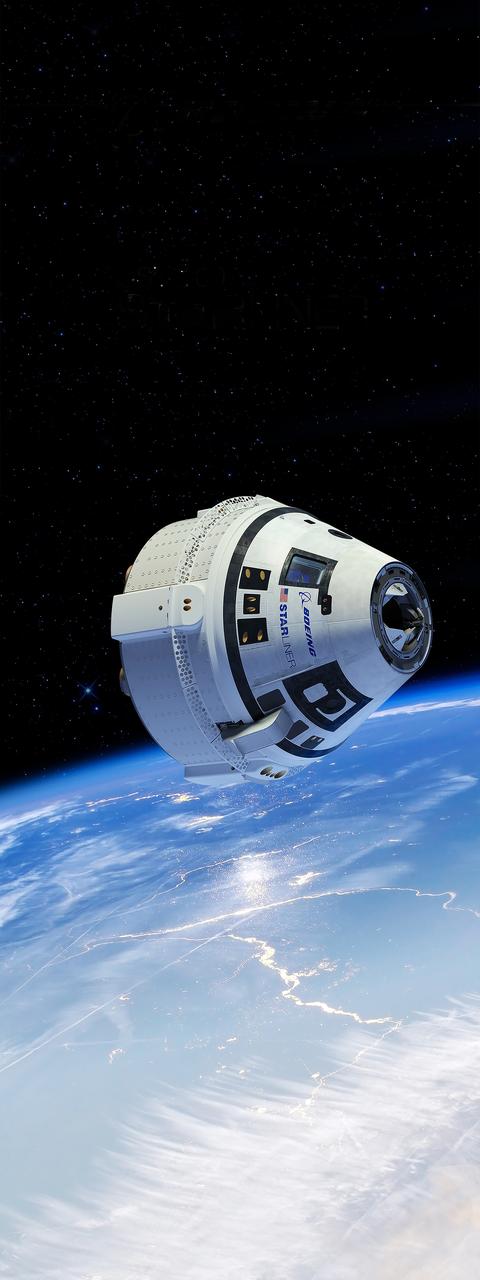

In this illustration, a Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft is shown in low-Earth orbit. NASA is partnering with Boeing and SpaceX to build a new generation of human-rated spacecraft capable of taking astronauts to the International Space Station and expanding research opportunities in orbit. Boeing's upcoming Orbital Flight Test is part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Transportation Capability contract with the goal of returning human spaceflight launch capabilities to the United States.
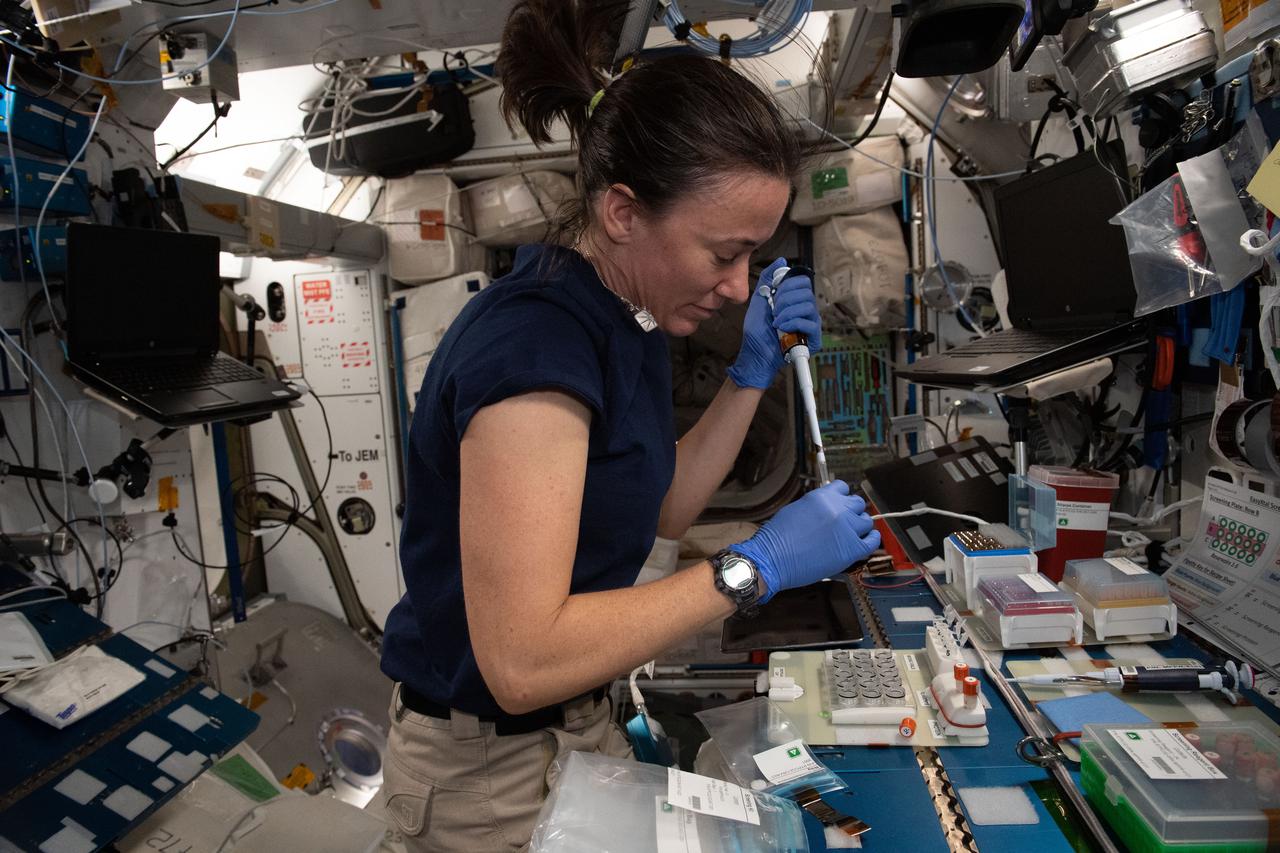

iss065e085491 (June 3, 2021) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 65 Flight Engineer Megan McArthur loads protein crystallography plates with protein solutions for the Real-time Protein Crystal Growth experiment. The biotechnology study demonstrates new methods for producing high-quality protein crystals in microgravity. Results may help identify new targets and develop better drugs to treat a variety of diseases on Earth and advance the commercialization of low-Earth orbit.
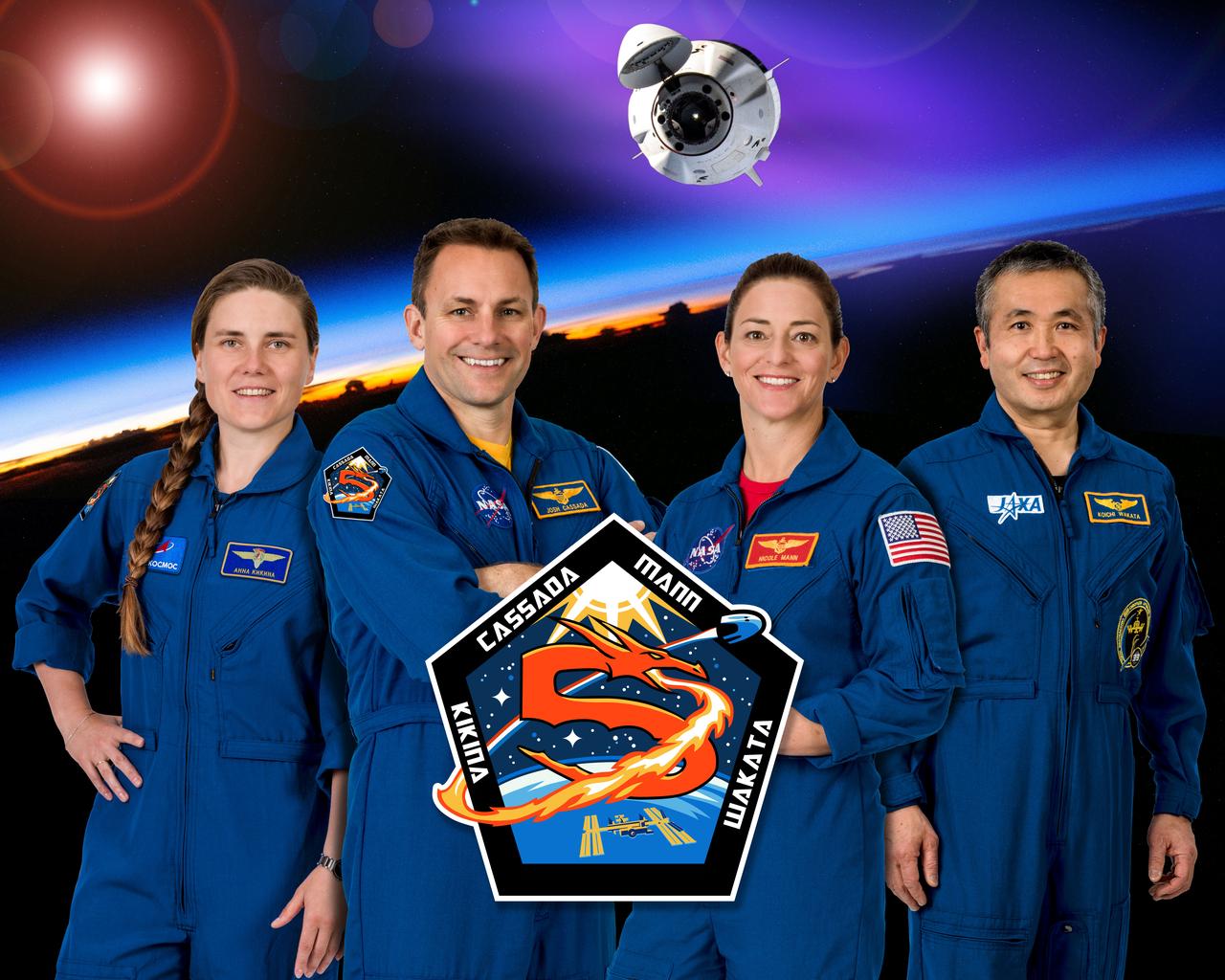

A fire-breathing, five-shaped dragon propels the Crew Dragon spacecraft of NASA's SpaceX Crew-5 mission beyond the confines of a pentagon’s outline and into low-Earth orbit. As the spacecraft ascends above the Earth’s atmosphere and its crew of courageous explorers embarks on their expedition aboard the International Space Station, the dragon’s fire transitions to the colors of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program representing the unrelenting efforts of the many teams who have met this challenge with unparalleled determination. The sun shines its light on this international team as they bravely pursue.

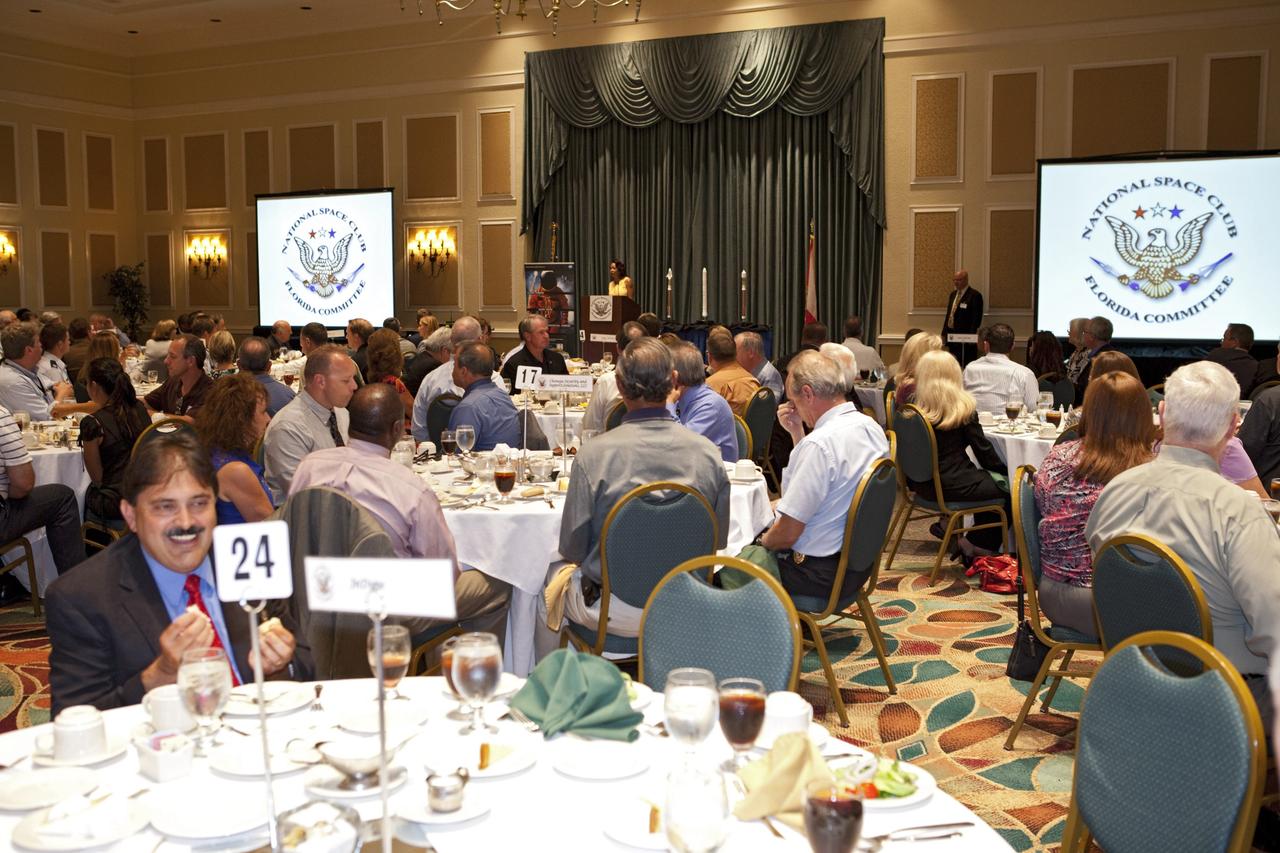
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Attendees of the National Space Club Florida Committee's August luncheon gather at the Radisson Resort at the Port in Cape Canaveral, Fla. NASA Commercial Crew Program Manager Ed Mango was the guest speaker, discussing the innovative steps the agency is taking with industry partners to develop the next U.S. space transportation capability to and from low Earth orbit, which will eventually be available for use by the U.S. government and other commercial customers. To learn more about the Commercial Crew Program, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- National Space Club Florida Committee Chair Steve Griffin, left, Florida's Lt. Gov. Jennifer Carroll, and NASA Commercial Crew Program Manager Ed Mango pose for a photo at the club's August luncheon at the Radisson Resort at the Port in Cape Canaveral, Fla. Mango was the event's guest speaker, discussing the innovative steps the agency is taking with industry partners to develop the next U.S. space transportation capability to and from low Earth orbit, which will eventually be available for use by the U.S. government and other commercial customers. To learn more about the Commercial Crew Program, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett
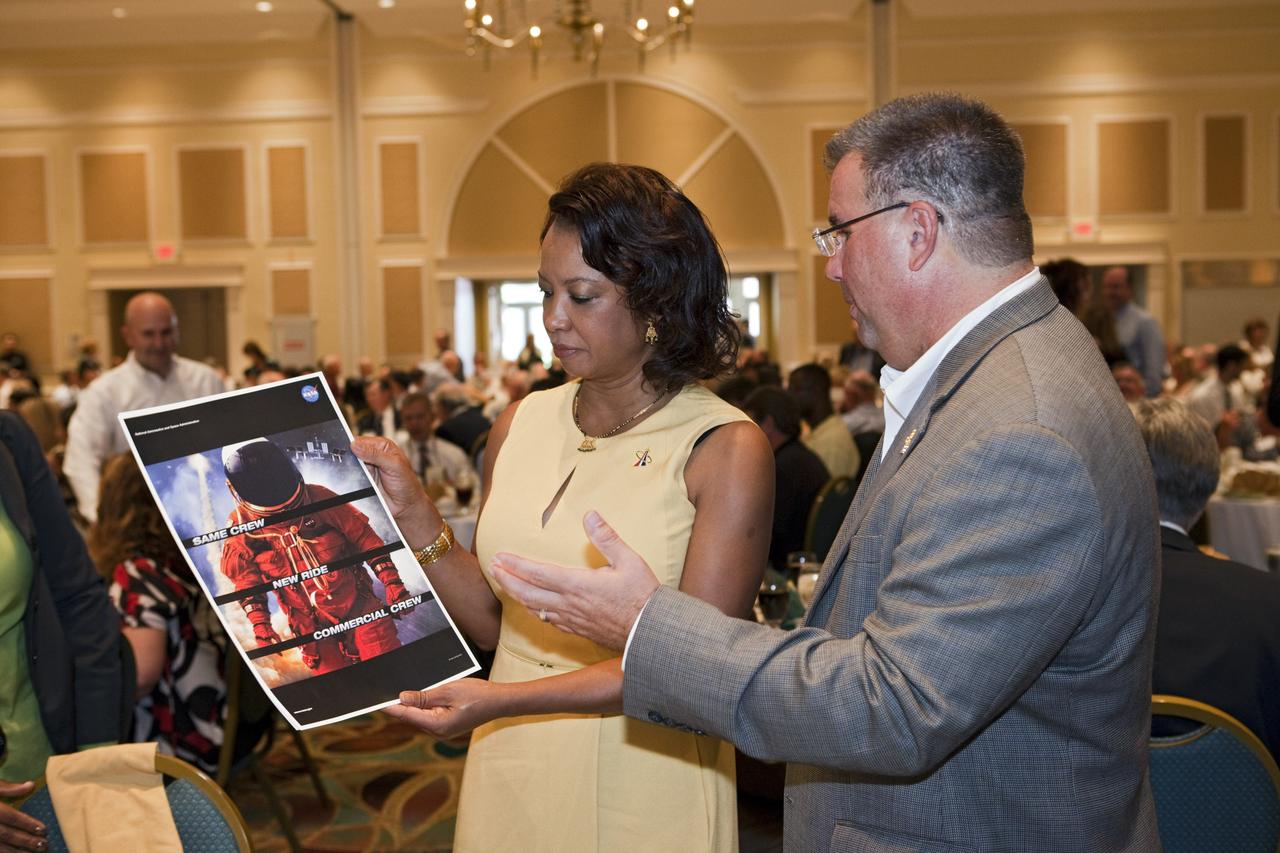

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA Commercial Crew Program Manager Ed Mango, right, shows Florida's Lt. Gov. Jennifer Carroll the program's "Same Crew, New Ride" poster at the National Space Club Florida Committee's August luncheon at the Radisson Resort at the Port in Cape Canaveral, Fla. Mango was the event's guest speaker, discussing the innovative steps the agency is taking with industry partners to develop the next U.S. space transportation capability to and from low Earth orbit, which will eventually be available for use by the U.S. government and other commercial customers. To learn more about the Commercial Crew Program, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett
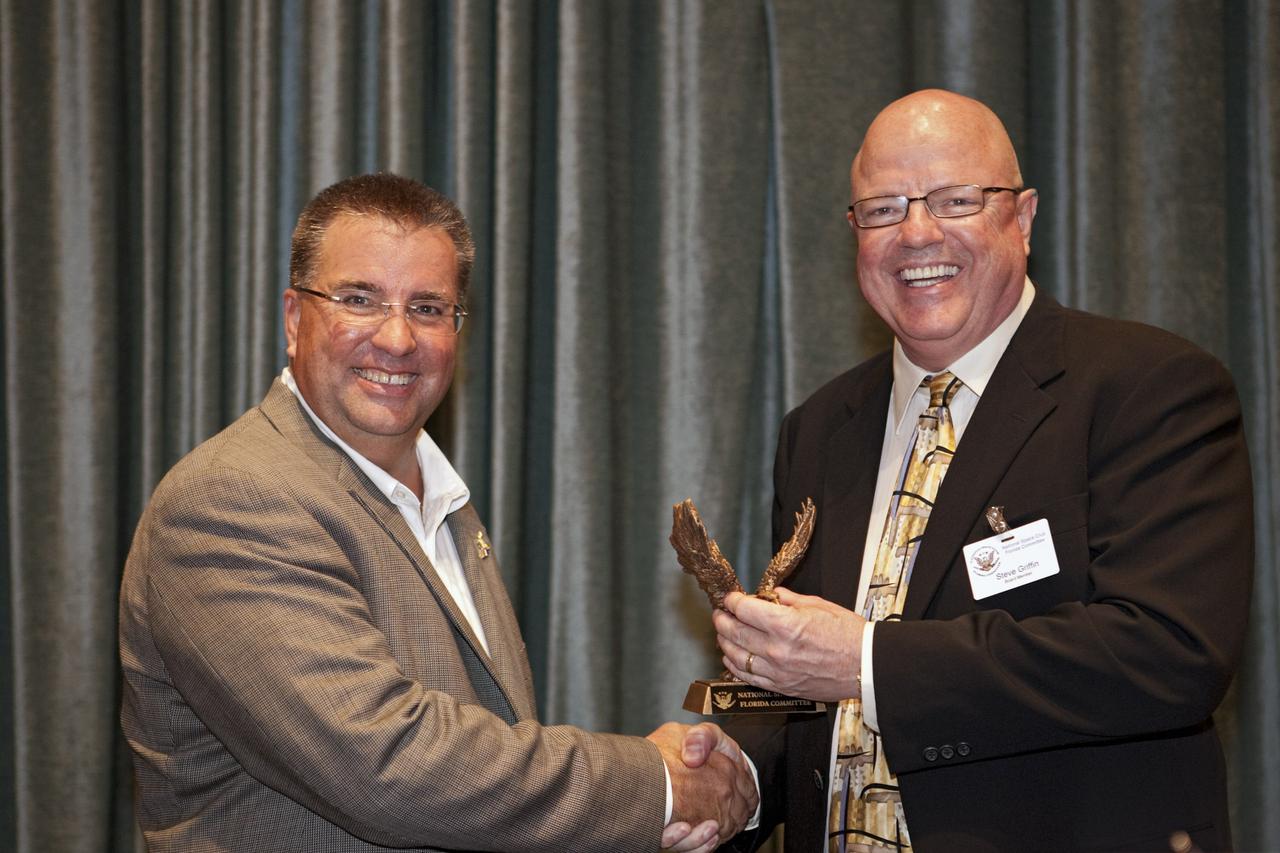

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- National Space Club Florida Committee Chair Steve Griffin presents NASA Commercial Crew Program Manager Ed Mango with an eagle statue during the club's August luncheon at the Radisson Resort at the Port in Cape Canaveral, Fla. Mango was the event's guest speaker, discussing the innovative steps the agency is taking with industry partners to develop the next U.S. space transportation capability to and from low Earth orbit, which will eventually be available for use by the U.S. government and other commercial customers. To learn more about the Commercial Crew Program, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Florida's Lt. Gov. Jennifer Carroll talks about the positive impact the aerospace industry has on the state of Florida during the National Space Club Florida Committee's August luncheon at the Radisson Resort at the Port in Cape Canaveral, Fla. NASA Commercial Crew Program Manager Ed Mango also discussed the innovative steps the agency is taking with industry partners to develop the next U.S. space transportation capability to and from low Earth orbit, which will eventually be available for use by the U.S. government and other commercial customers. To learn more about the Commercial Crew Program, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Florida's Lt. Gov. Jennifer Carroll, left, and NASA Commercial Crew Program Manager Ed Mango pose for a photo at the National Space Club Florida Committee's August luncheon at the Radisson Resort at the Port in Cape Canaveral, Fla. Mango was the event's guest speaker, discussing the innovative steps the agency is taking with industry partners to develop the next U.S. space transportation capability to and from low Earth orbit, which will eventually be available for use by the U.S. government and other commercial customers. To learn more about the Commercial Crew Program, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- National Space Club Florida Committee Chair Steve Griffin welcomes attendees of the club's August luncheon at the Radisson Resort at the Port in Cape Canaveral, Fla. NASA Commercial Crew Program Manager Ed Mango was the event's guest speaker, discussing the innovative steps the agency is taking with industry partners to develop the next U.S. space transportation capability to and from low Earth orbit, which will eventually be available for use by the U.S. government and other commercial customers. To learn more about the Commercial Crew Program, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Florida's Lt. Gov. Jennifer Carroll talks about the positive impact the aerospace industry has on the state of Florida during the National Space Club Florida Committee's August luncheon at the Radisson Resort at the Port in Cape Canaveral, Fla. NASA Commercial Crew Program Manager Ed Mango also discussed the innovative steps the agency is taking with industry partners to develop the next U.S. space transportation capability to and from low Earth orbit, which will eventually be available for use by the U.S. government and other commercial customers. To learn more about the Commercial Crew Program, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett
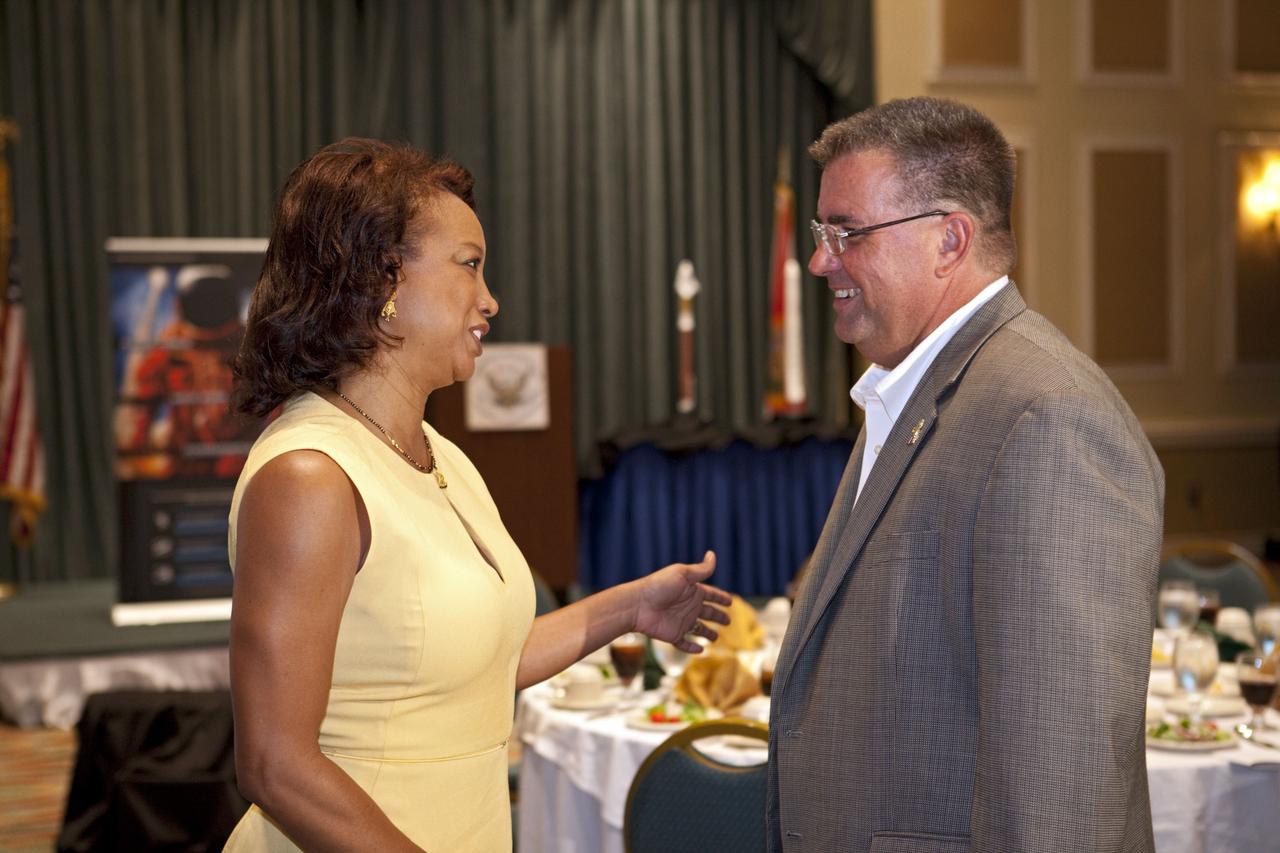

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Florida's Lt. Gov. Jennifer Carroll, left, and NASA Commercial Crew Program Manager Ed Mango discuss the future of human spaceflight at the National Space Club Florida Committee's August luncheon at the Radisson Resort at the Port in Cape Canaveral, Fla. Mango was the event's guest speaker, discussing the innovative steps the agency is taking with industry partners to develop the next U.S. space transportation capability to and from low Earth orbit, which will eventually be available for use by the U.S. government and other commercial customers. To learn more about the Commercial Crew Program, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Florida's Lt. Gov. Jennifer Carroll talks about the positive impact the aerospace industry has on the state of Florida during the National Space Club Florida Committee's August luncheon at the Radisson Resort at the Port in Cape Canaveral, Fla. NASA Commercial Crew Program Manager Ed Mango also discussed the innovative steps the agency is taking with industry partners to develop the next U.S. space transportation capability to and from low Earth orbit, which will eventually be available for use by the U.S. government and other commercial customers. To learn more about the Commercial Crew Program, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett
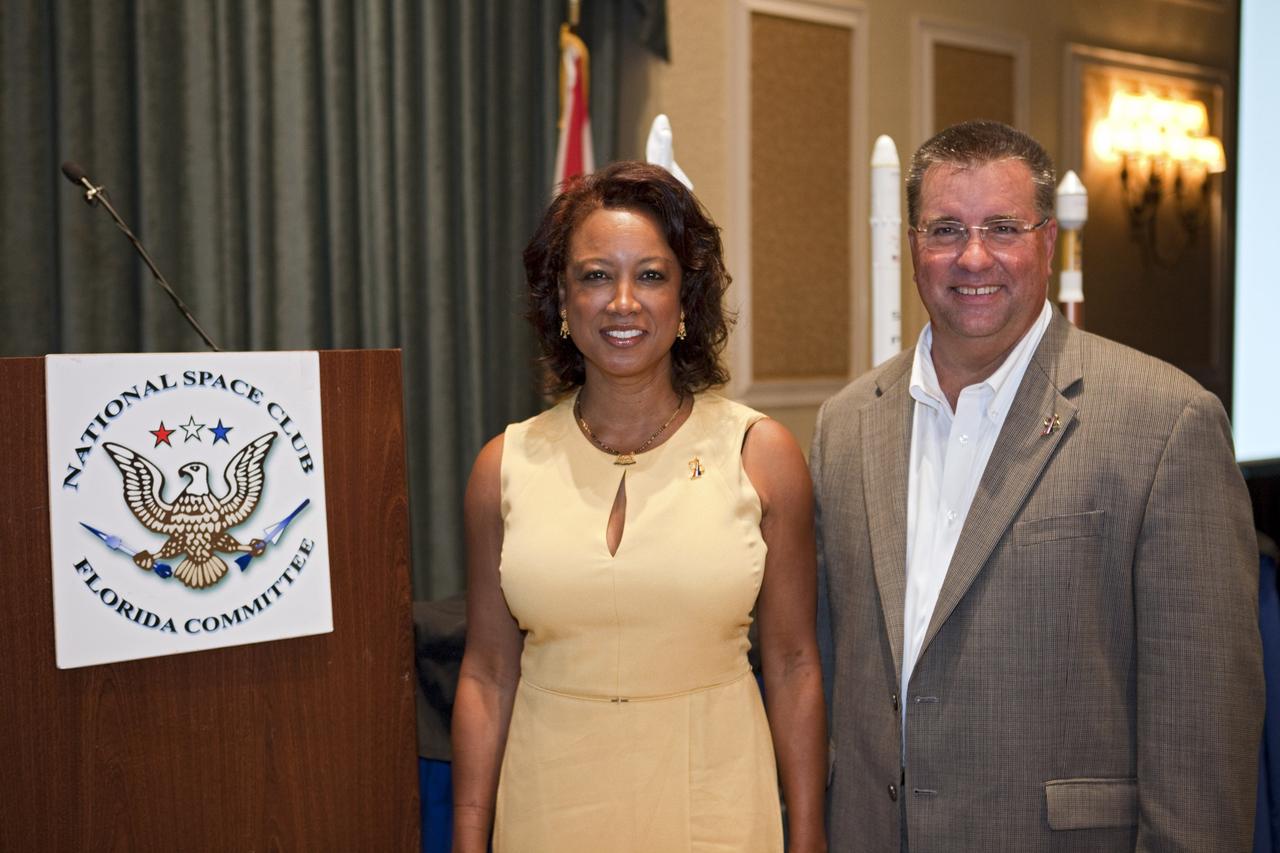

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Florida's Lt. Gov. Jennifer Carroll, left, and NASA Commercial Crew Program Manager Ed Mango pose for a photo at the National Space Club Florida Committee's August luncheon at the Radisson Resort at the Port in Cape Canaveral, Fla. Mango was the event's guest speaker, discussing the innovative steps the agency is taking with industry partners to develop the next U.S. space transportation capability to and from low Earth orbit, which will eventually be available for use by the U.S. government and other commercial customers. To learn more about the Commercial Crew Program, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett
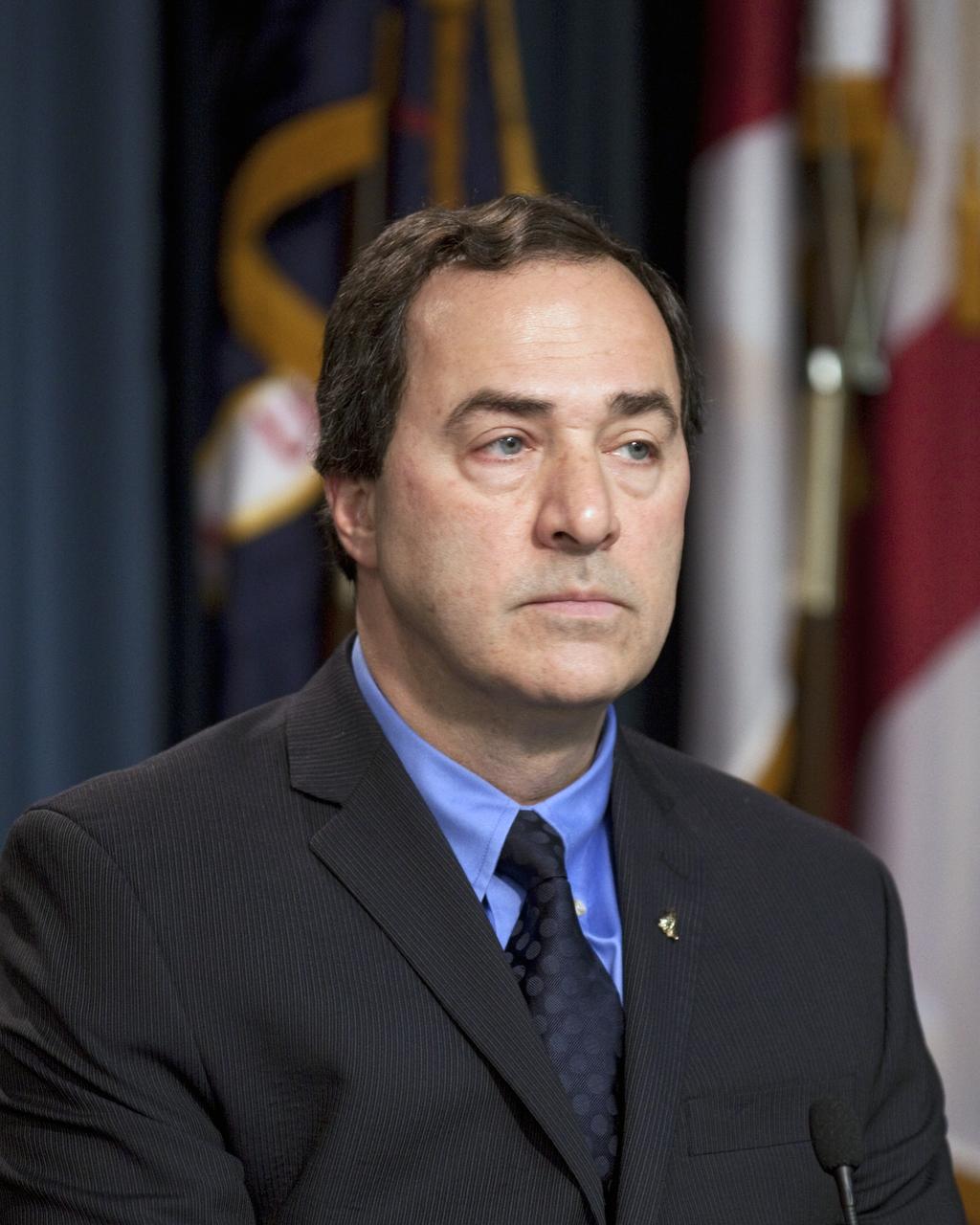

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At a news conference NASA officials and industry partners discuss progress of the agency's Commercial Crew Program. Among those participating in the briefing is Mark Sirangelo, Sierra Nevada Corp. vice president and SNC Space Systems chairman. Through CCP, NASA is facilitating the development of U.S. commercial crew space transportation capabilities to achieve safe, reliable and cost-effective access to and from low-Earth orbit for potential future government and commercial customers. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
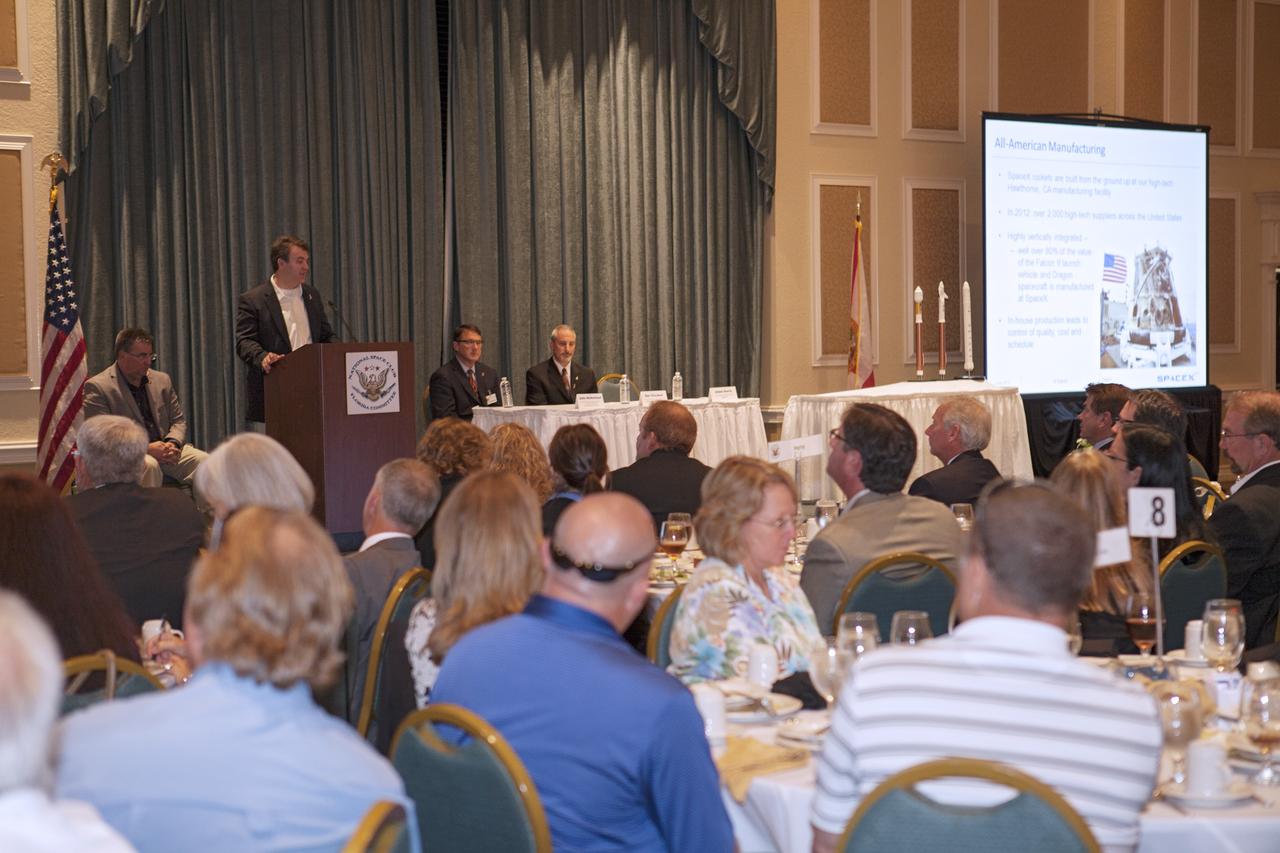

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Adam Harris, vice president of government sales for Space Exploration Technologies, or SpaceX, speaks to a crowd of spaceflight enthusiasts at the National Space Club Florida Committee's June meeting near the Kennedy Space Center. Harris was joined at the Radisson Resort at the Port in Cape Canaveral, Fla., by Ed Mango, manager of NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, left, and representatives from The Boeing Company and Sierra Nevada Corporation, or SNC. All three CCP partner are planning to increase their commercial activities on Florida’s space coast to send astronauts to low-Earth orbit. To learn more about the Commercial Crew Program, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett

In this illustration, a SpaceX Crew Dragon spacecraft is shown in low-Earth orbit. NASA is partnering with Boeing and SpaceX to build a new generation of human-rated spacecraft capable of taking astronauts to the International Space Station and expanding research opportunities in orbit. SpaceX's upcoming Demo-1 flight test is part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Transportation Capability contract with the goal of returning human spaceflight launch capabilities to the United States.
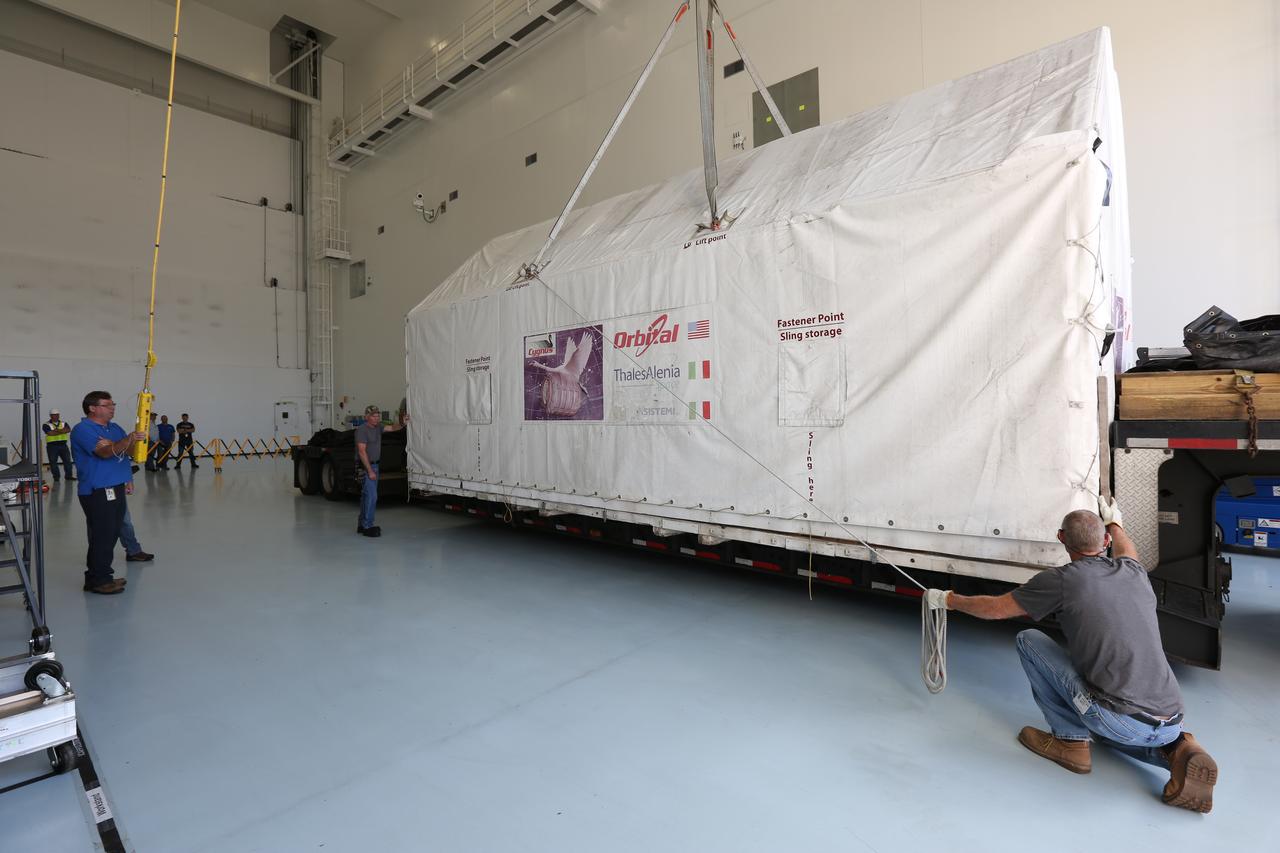

Sealed in its shipping container, the ground support equipment for the Orbital ATK OA-7 commercial resupply services mission was moved inside the low bay of the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 with the Cygnus cargo module will lift off atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station will deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials that improve life on Earth and drive progress toward future space exploration.

Inside the Space Station Processing Facility low bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians use a crane to lift the cover off ground support equipment for the Orbital ATK OA-7 commercial resupply services mission. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 with the Cygnus cargo module will lift off atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station will deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials that improve life on Earth and drive progress toward future space exploration.
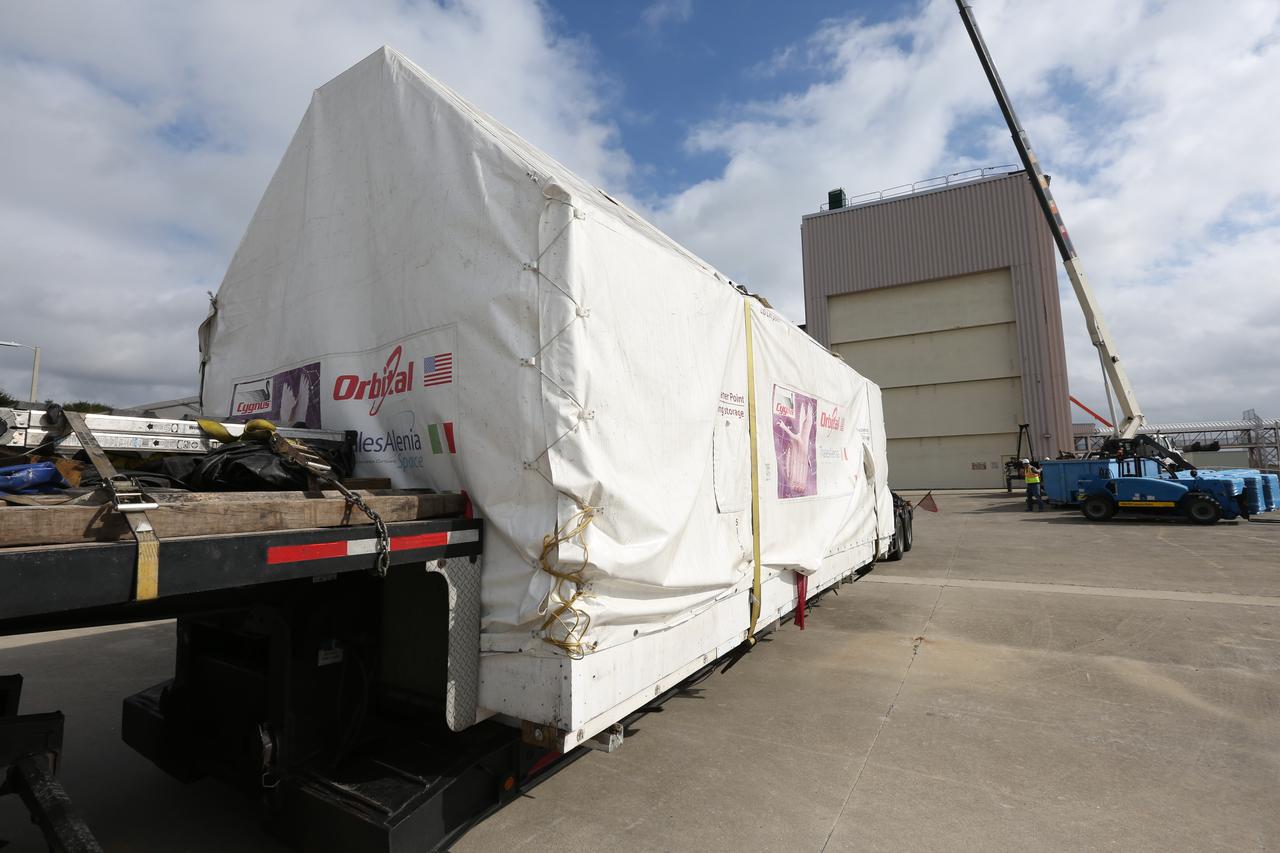

Sealed in its shipping container, the ground support equipment for the Orbital ATK OA-7 commercial resupply services mission has arrived at the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The container will be moved inside the low bay of the facility. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 with the Cygnus cargo module will lift off atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station will deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials that improve life on Earth and drive progress toward future space exploration.

Sealed in its shipping container, the ground support equipment for the Orbital ATK OA-7 commercial resupply services mission has arrived at the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The container will be moved inside the low bay of the facility. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 with the Cygnus cargo module will lift off atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station will deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials that improve life on Earth and drive progress toward future space exploration.
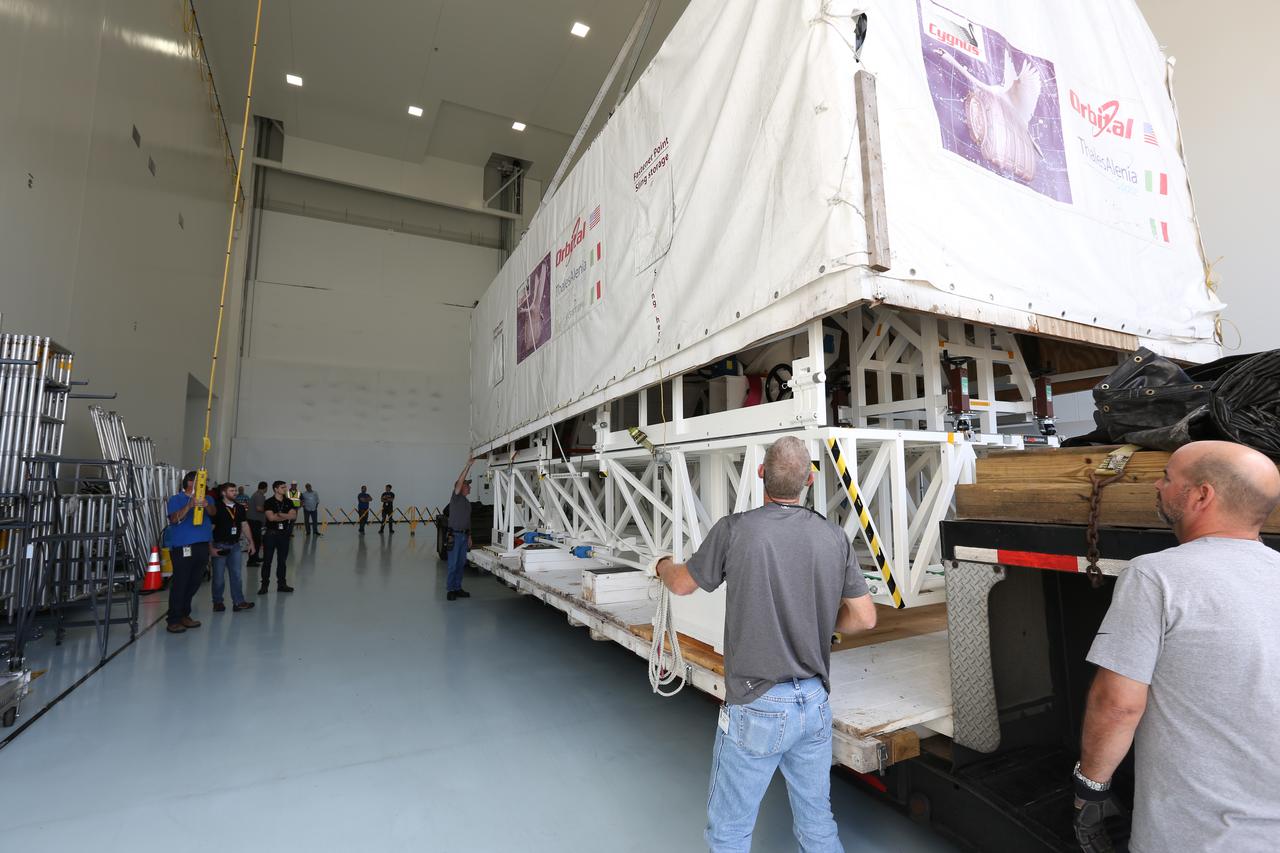

Inside the Space Station Processing Facility low bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians use a crane to lift the cover off ground support equipment for the Orbital ATK OA-7 commercial resupply services mission. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 with the Cygnus cargo module will lift off atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station will deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials that improve life on Earth and drive progress toward future space exploration.
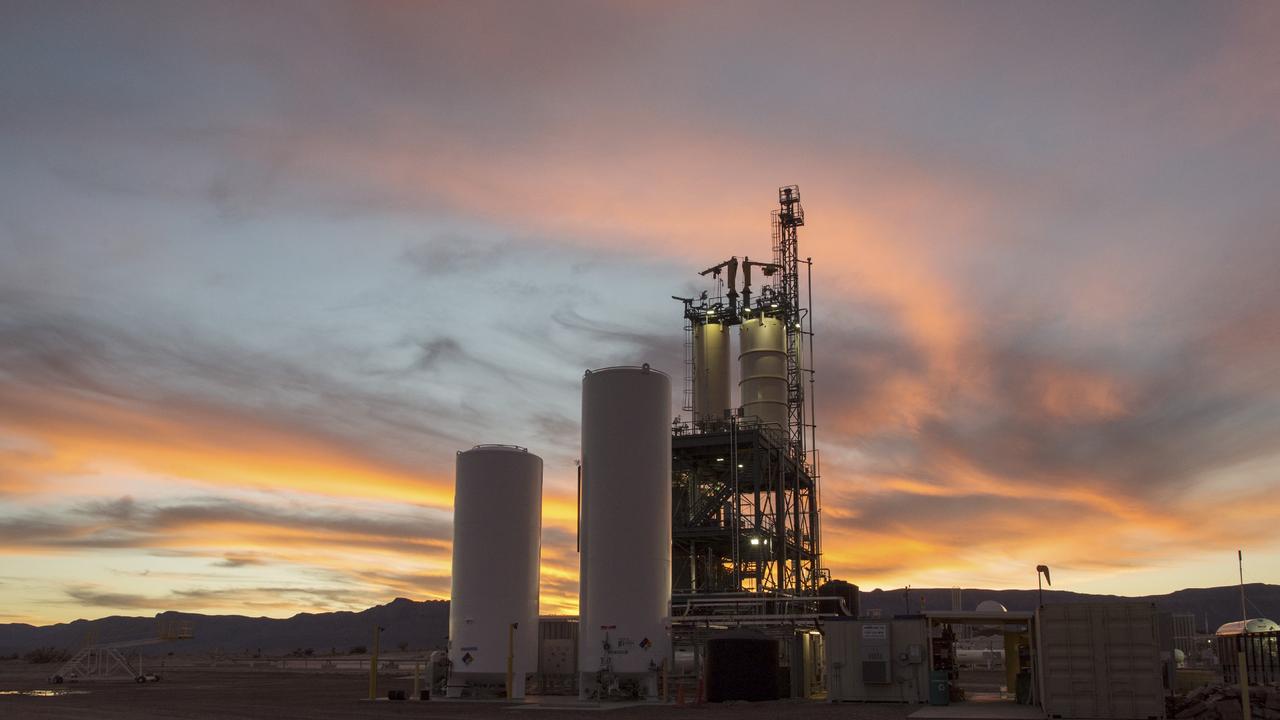

VAN HORN, Texas – The sun sets over a test stand at Blue Origin’s West Texas facility. The company used this test stand to fire its powerful new hydrogen- and oxygen-fueled American rocket engine, the BE-3, on Nov. 20. The BE-3 fired at full power for more than two minutes to simulate a launch, then paused for about four minutes, mimicking a coast through space before it re-ignited for a brief final burn. The last phase of the test covered the work the engine could perform in landing the booster back softly on Earth. Blue Origin, a partner of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, is developing its Orbital Launch Vehicle, which could eventually be used to launch the company's Space Vehicle into orbit to transport crew and cargo to low-Earth orbit. CCP is aiding in the innovation and development of American-led commercial capabilities for crew transportation and rescue services to and from the station and other low-Earth orbit destinations by the end of 2017. For information about CCP, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: NASA/Lauren Harnett
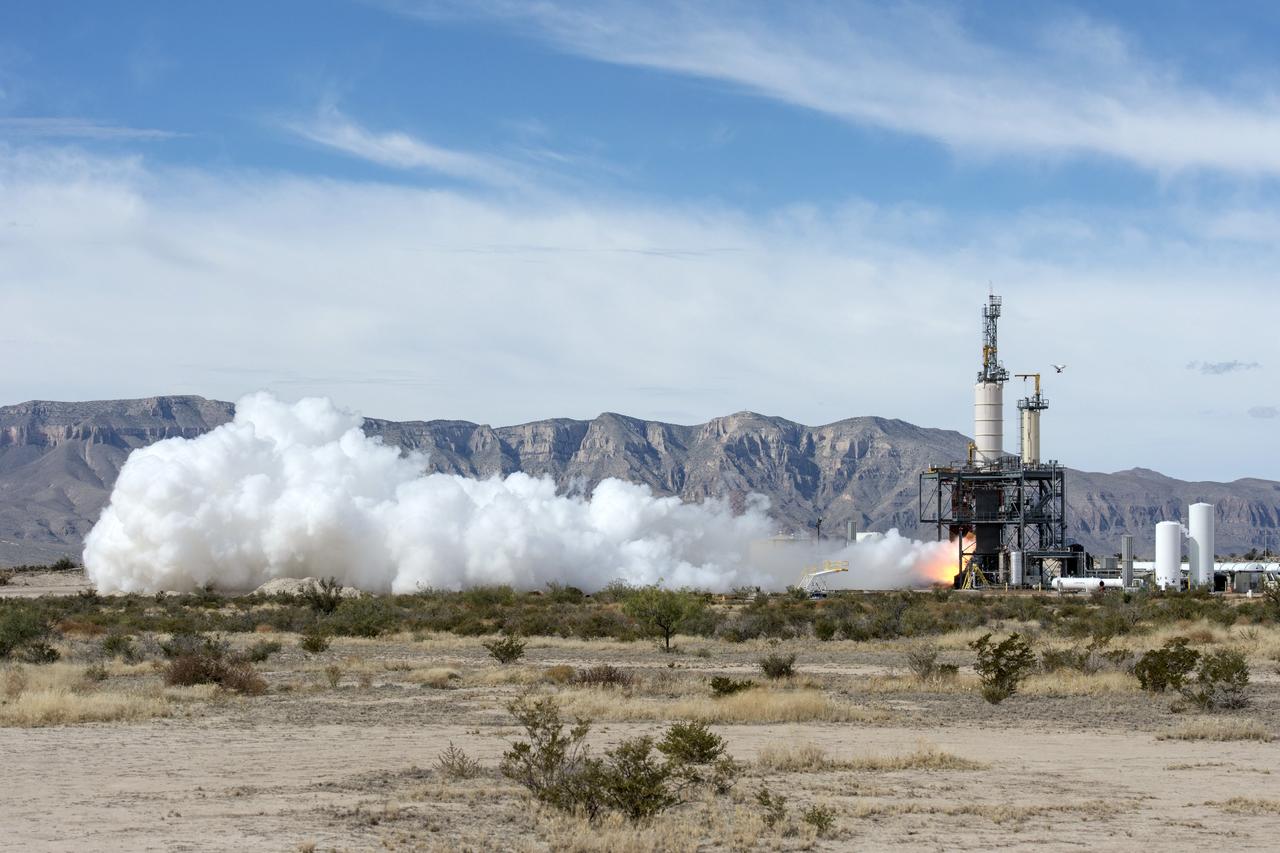

VAN HORN, Texas – Blue Origin test fires a powerful new hydrogen- and oxygen-fueled American rocket engine at the company's West Texas facility. During the test, the BE-3 engine fired at full power for more than two minutes to simulate a launch, then paused for about four minutes, mimicking a coast through space before it re-ignited for a brief final burn. The last phase of the test covered the work the engine could perform in landing the booster back softly on Earth. Blue Origin, a partner of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, is developing its Orbital Launch Vehicle, which could eventually be used to launch the company's Space Vehicle into orbit to transport crew and cargo to low-Earth orbit. CCP is aiding in the innovation and development of American-led commercial capabilities for crew transportation and rescue services to and from the station and other low-Earth orbit destinations by the end of 2017. For information about CCP, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: NASA/Lauren Harnett
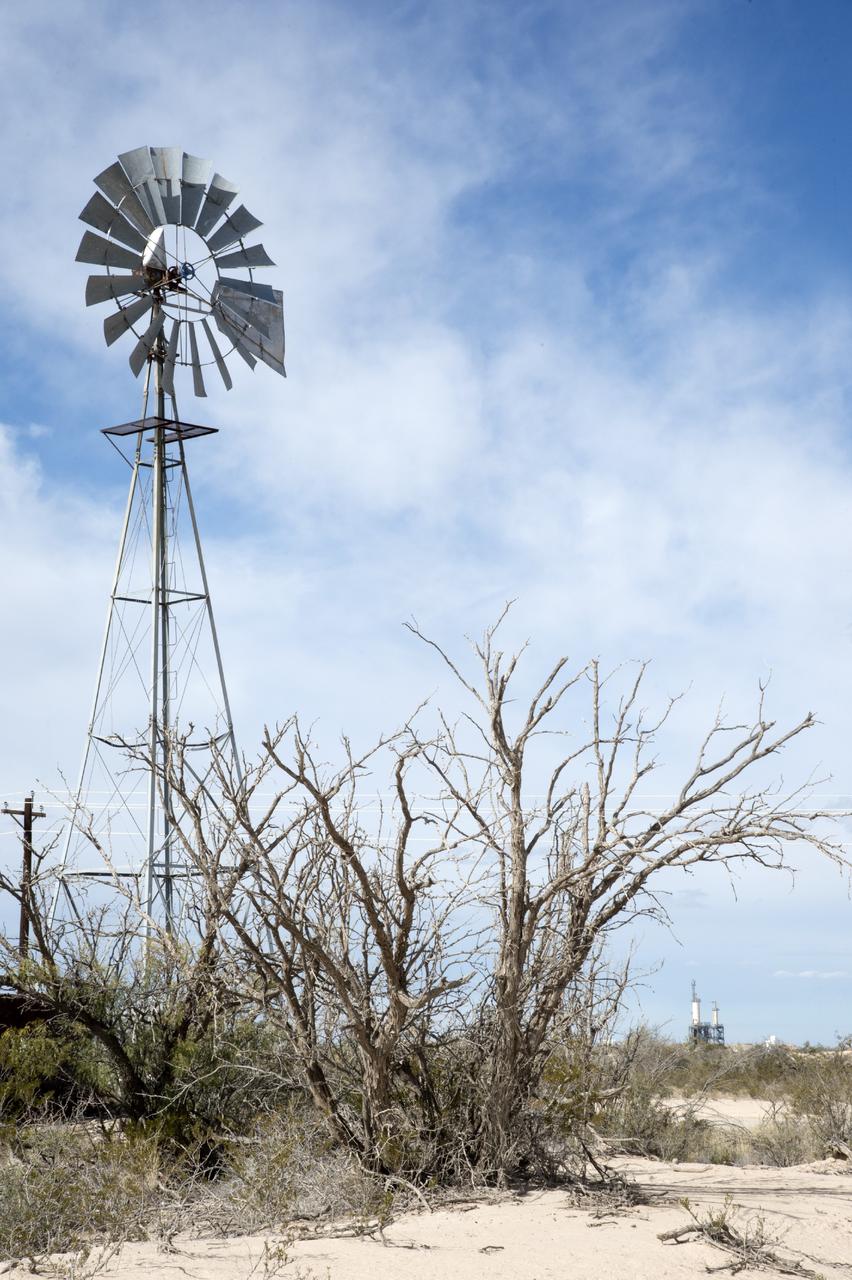

VAN HORN, Texas – Blue Origin’s test stand, back right, is framed by a wind mill at the company’s West Texas facility. The company used this test stand to fire its powerful new hydrogen- and oxygen-fueled American rocket engine, the BE-3. The engine fired at full power for more than two minutes to simulate a launch, then paused for about four minutes, mimicking a coast through space before it re-ignited for a brief final burn. The last phase of the test covered the work the engine could perform in landing the booster back softly on Earth. Blue Origin, a partner of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, is developing its Orbital Launch Vehicle, which could eventually be used to launch the company's Space Vehicle into orbit to transport crew and cargo to low-Earth orbit. CCP is aiding in the innovation and development of American-led commercial capabilities for crew transportation and rescue services to and from the station and other low-Earth orbit destinations by the end of 2017. For information about CCP, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: NASA/Lauren Harnett
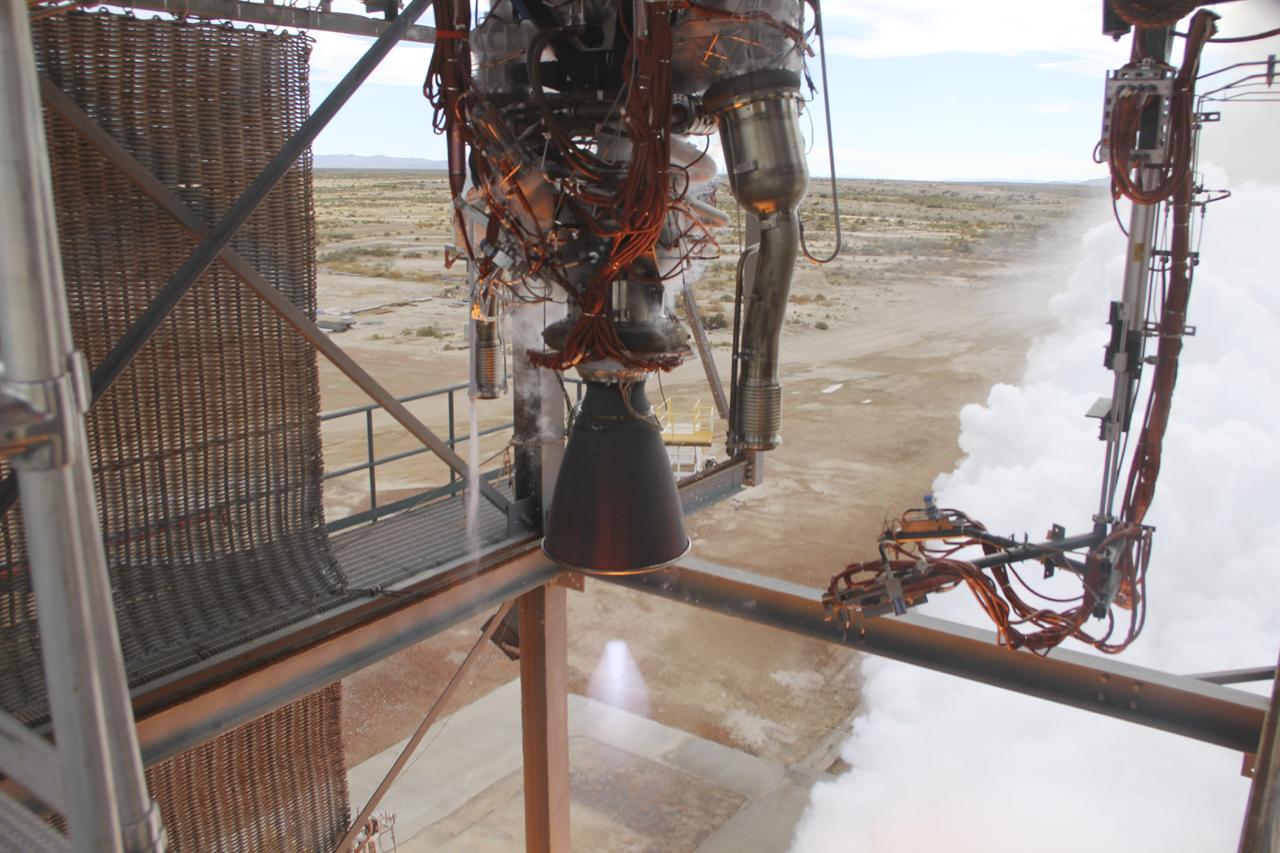
VAN HORN, Texas – Blue Origin test fires a powerful new hydrogen- and oxygen-fueled American rocket engine at the company's West Texas facility. During the test, the BE-3 engine fired at full power for more than two minutes to simulate a launch, then paused for about four minutes, mimicking a coast through space before it re-ignited for a brief final burn. The last phase of the test covered the work the engine could perform in landing the booster back softly on Earth. Blue Origin, a partner of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, is developing its Orbital Launch Vehicle, which could eventually be used to launch the company's Space Vehicle into orbit to transport crew and cargo to low-Earth orbit. CCP is aiding in the innovation and development of American-led commercial capabilities for crew transportation and rescue services to and from the station and other low-Earth orbit destinations by the end of 2017. For information about CCP, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: Blue Origin

L-R: Alan Lindenmoyer, Manager of Commercial Crew and Cargo Program, NASA; Gwynne Shotwell, President, SpaceX; Frank Culbertson, Executive Vice President and General Manager, Orbital Sciences Advanced Programs Group; Frank Slazer, Vice President of Space Systems, Aerospace Industries Association and Phil McAlister, Director of Commercial Spaceflight Development at NASA, participate in a panel discussion on the Commercial Orbital Transportation Services (COTS) initiative at NASA Headquarters in Washington on Wednesday, November 13, 2013. Through COTS, NASA's partners Space Exploration Technologies Corp. (SpaceX) and Orbital Sciences Corp., developed new U.S. rockets and spacecraft, launched from U.S. soil, capable of transporting cargo to low-Earth orbit and the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jay Westcott)
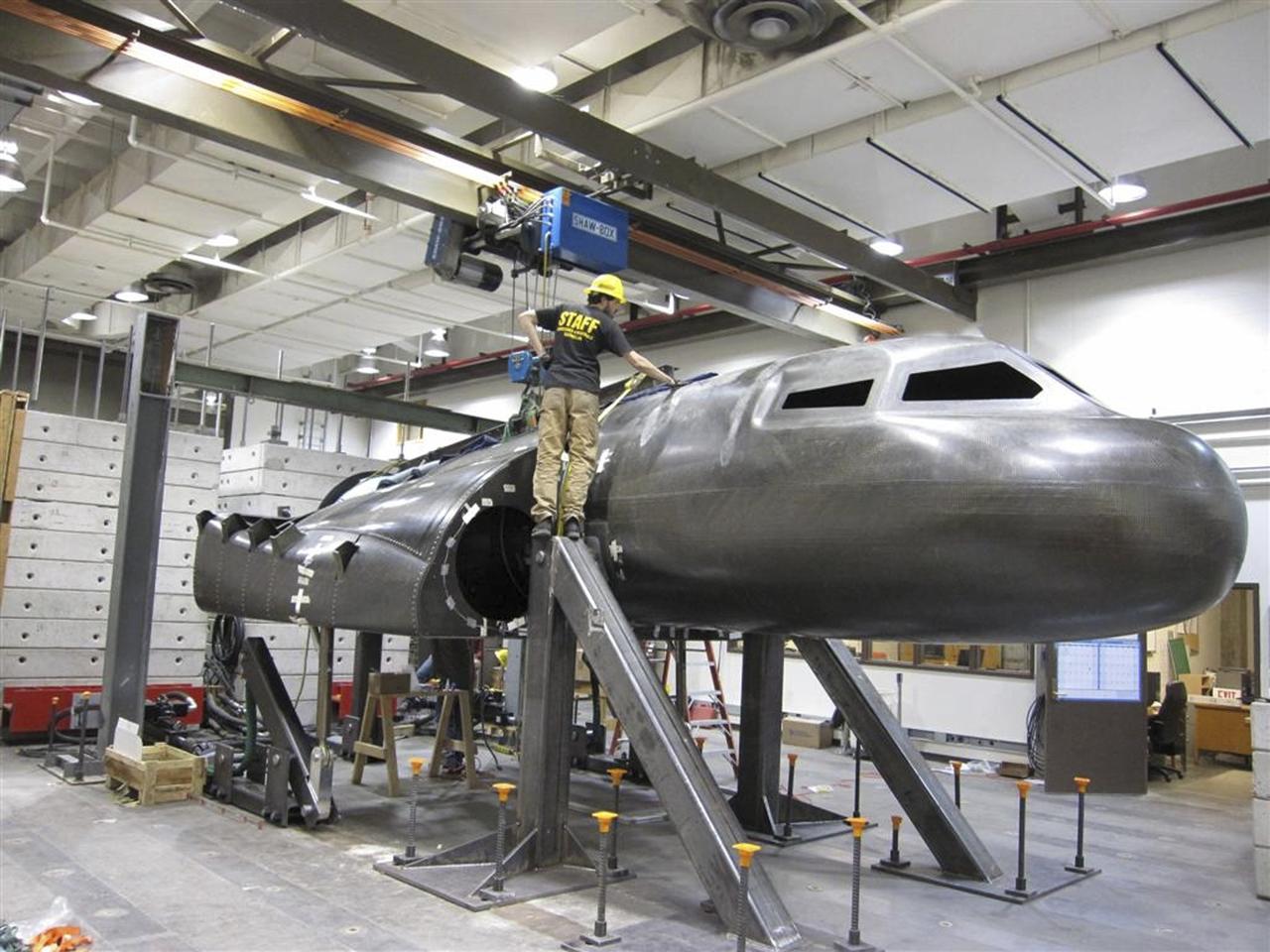

BOULDER, Colo. – A Sierra Nevada Corp. team member examines the company's structural test article for the Dream Chaser spacecraft in the University of Colorado at Boulder’s Facility for Advanced Spatial Technology. The university is one of Sierra Nevada’s partners on the design and development of the Dream Chaser orbital crew vehicle. Dream Chaser is one of five systems NASA invested in during Commercial Crew Development Round 1 CCDev1 activities in order to aid in the innovation and development of American-led commercial capabilities for crew transportation and rescue services to and from the International Space Station and other low Earth orbit destinations. In 2011, NASA's Commercial Crew Program CCP entered into another funded Space Act Agreement with Sierra Nevada for the second round of commercial crew development CCDev2) so the company could further develop its Dream Chaser spacecraft for NASA transportation services. For information about CCP, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: Sierra Nevada Corp.
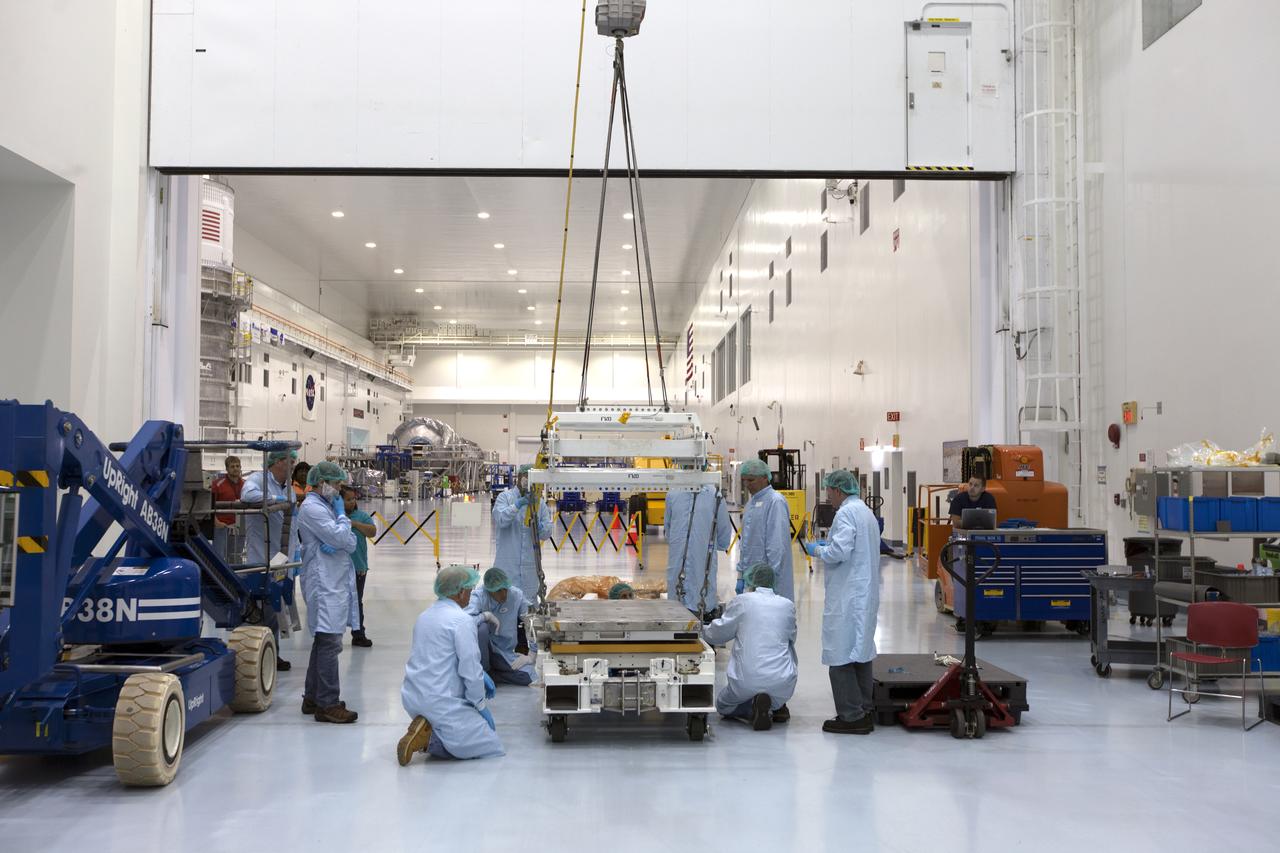

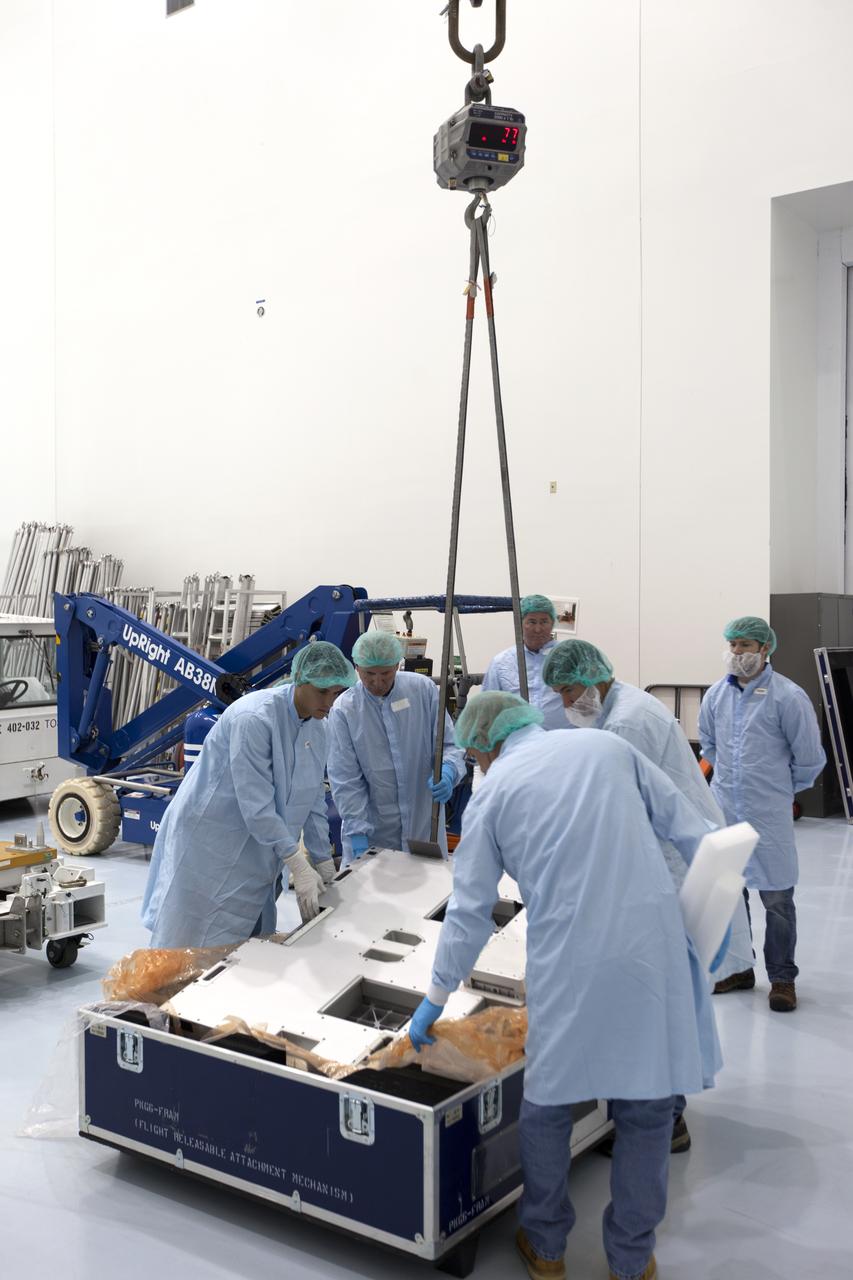
The Materials International Space Station Experiment-Flight Facility, or MISSE-FF, hardware arrived at the Space Station Processing Facility low bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Technicians assist as one of the components is lowered onto another MISSE component. MISSE will be used to test various materials and computing elements on the exterior of the space station. They will be exposed to the harsh environment of low-Earth orbit, including to a vacuum, atomic oxygen, ultraviolet radiation, direct sunlight and extreme heat and cold. The experiment will provide a better understanding of material durability, from coatings to electronic sensors, which could be applied to future spacecraft designs. MISSE will be delivered to the space station on a future commercial resupply mission.
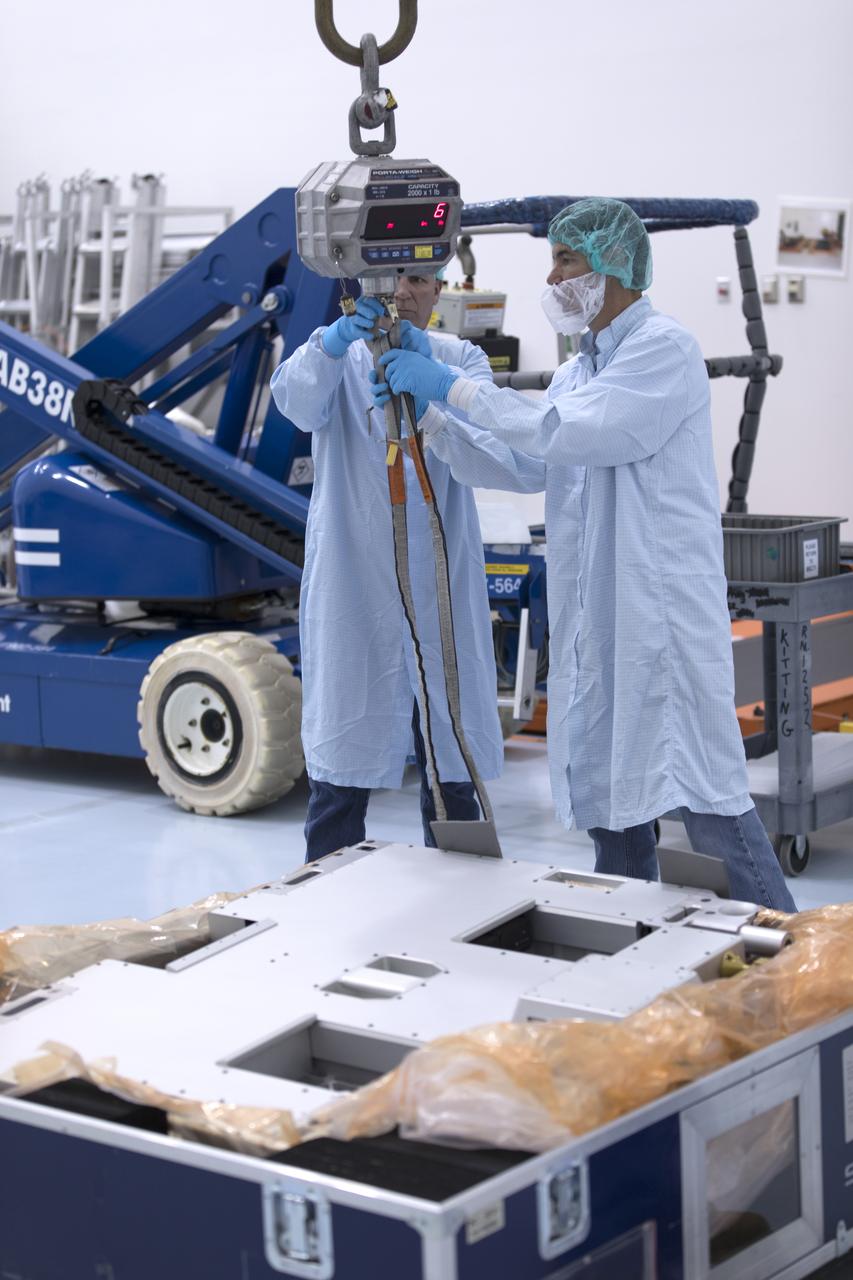

The Materials International Space Station Experiment-Flight Facility, or MISSE-FF, hardware arrived at the Space Station Processing Facility low bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Technicians work to attach a crane to MISSE for lifting out of its shipping container. MISSE will be used to test various materials and computing elements on the exterior of the space station. They will be exposed to the harsh environment of low-Earth orbit, including to a vacuum, atomic oxygen, ultraviolet radiation, direct sunlight and extreme heat and cold. The experiment will provide a better understanding of material durability, from coatings to electronic sensors, which could be applied to future spacecraft designs. MISSE will be delivered to the space station on a future commercial resupply mission.
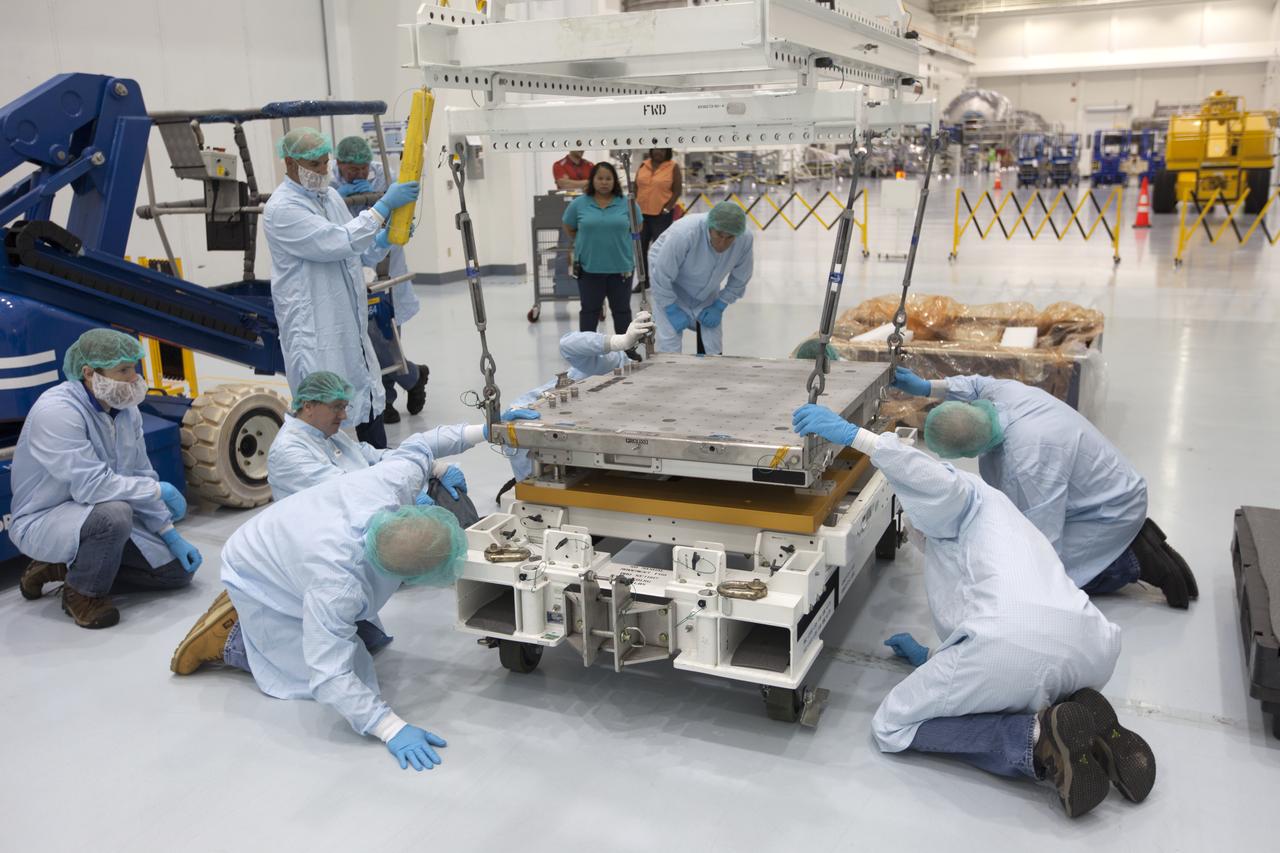

The Materials International Space Station Experiment-Flight Facility, or MISSE-FF, hardware arrived at the Space Station Processing Facility low bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Technicians assist as one of the components is lowered onto another MISSE component. MISSE will be used to test various materials and computing elements on the exterior of the space station. They will be exposed to the harsh environment of low-Earth orbit, including to a vacuum, atomic oxygen, ultraviolet radiation, direct sunlight and extreme heat and cold. The experiment will provide a better understanding of material durability, from coatings to electronic sensors, which could be applied to future spacecraft designs. MISSE will be delivered to the space station on a future commercial resupply mission.
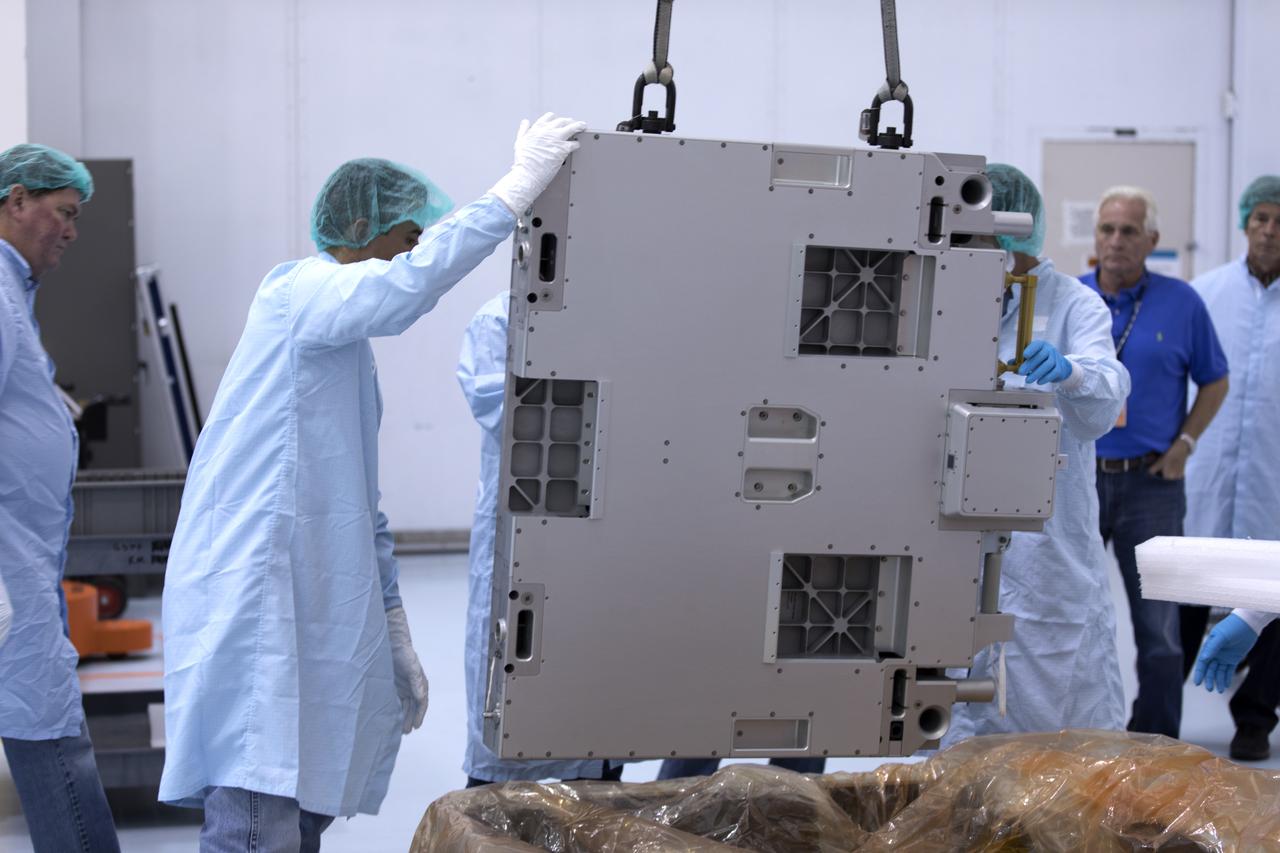

The Materials International Space Station Experiment-Flight Facility, or MISSE-FF, hardware arrived at the Space Station Processing Facility low bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Technicians assist as a crane is used to lift MISSE out of its shipping container. MISSE will be used to test various materials and computing elements on the exterior of the space station. They will be exposed to the harsh environment of low-Earth orbit, including to a vacuum, atomic oxygen, ultraviolet radiation, direct sunlight and extreme heat and cold. The experiment will provide a better understanding of material durability, from coatings to electronic sensors, which could be applied to future spacecraft designs. MISSE will be delivered to the space station on a future commercial resupply mission.
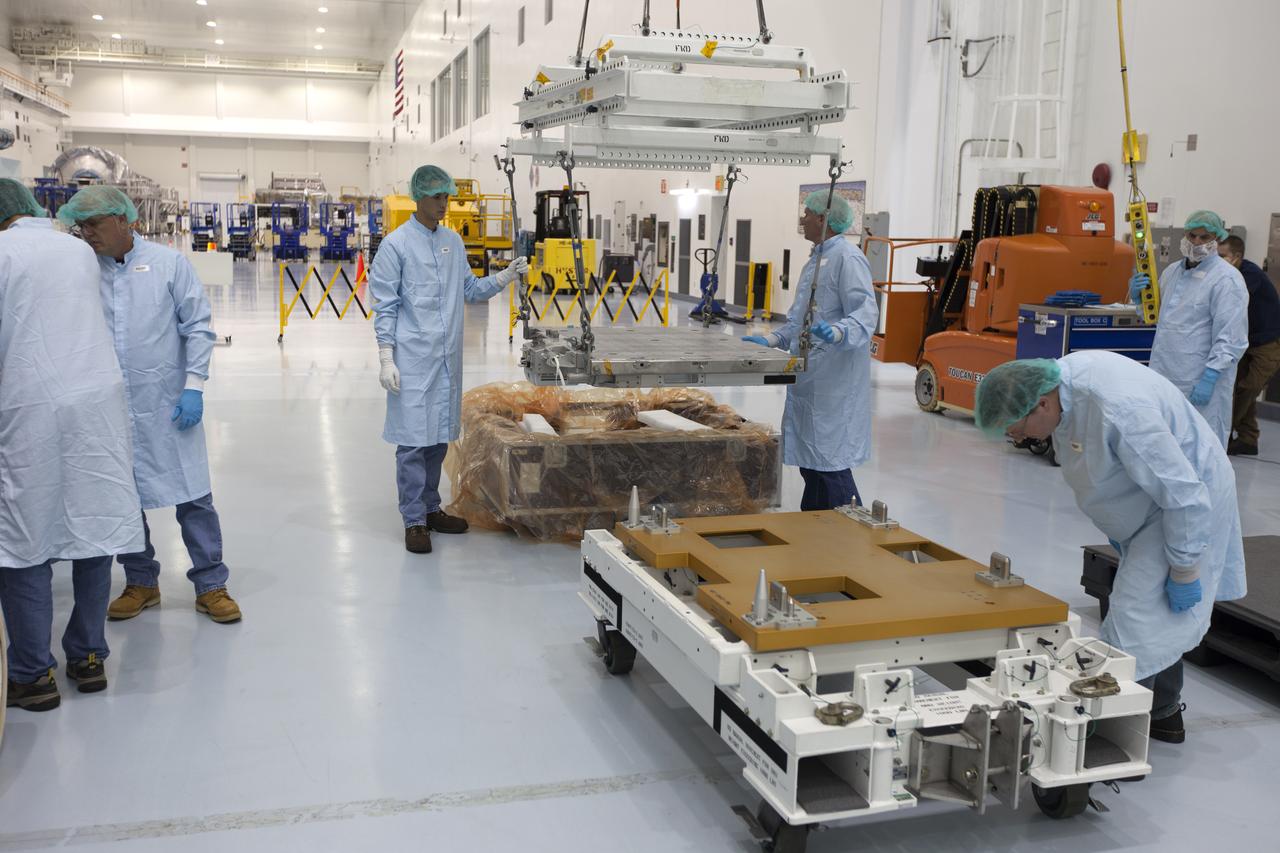

The Materials International Space Station Experiment-Flight Facility, or MISSE-FF, hardware arrived at the Space Station Processing Facility low bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Technicians assist as MISSE is lifted by crane from its shipping container. MISSE will be used to test various materials and computing elements on the exterior of the space station. They will be exposed to the harsh environment of low-Earth orbit, including to a vacuum, atomic oxygen, ultraviolet radiation, direct sunlight and extreme heat and cold. The experiment will provide a better understanding of material durability, from coatings to electronic sensors, which could be applied to future spacecraft designs. MISSE will be delivered to the space station on a future commercial resupply mission.
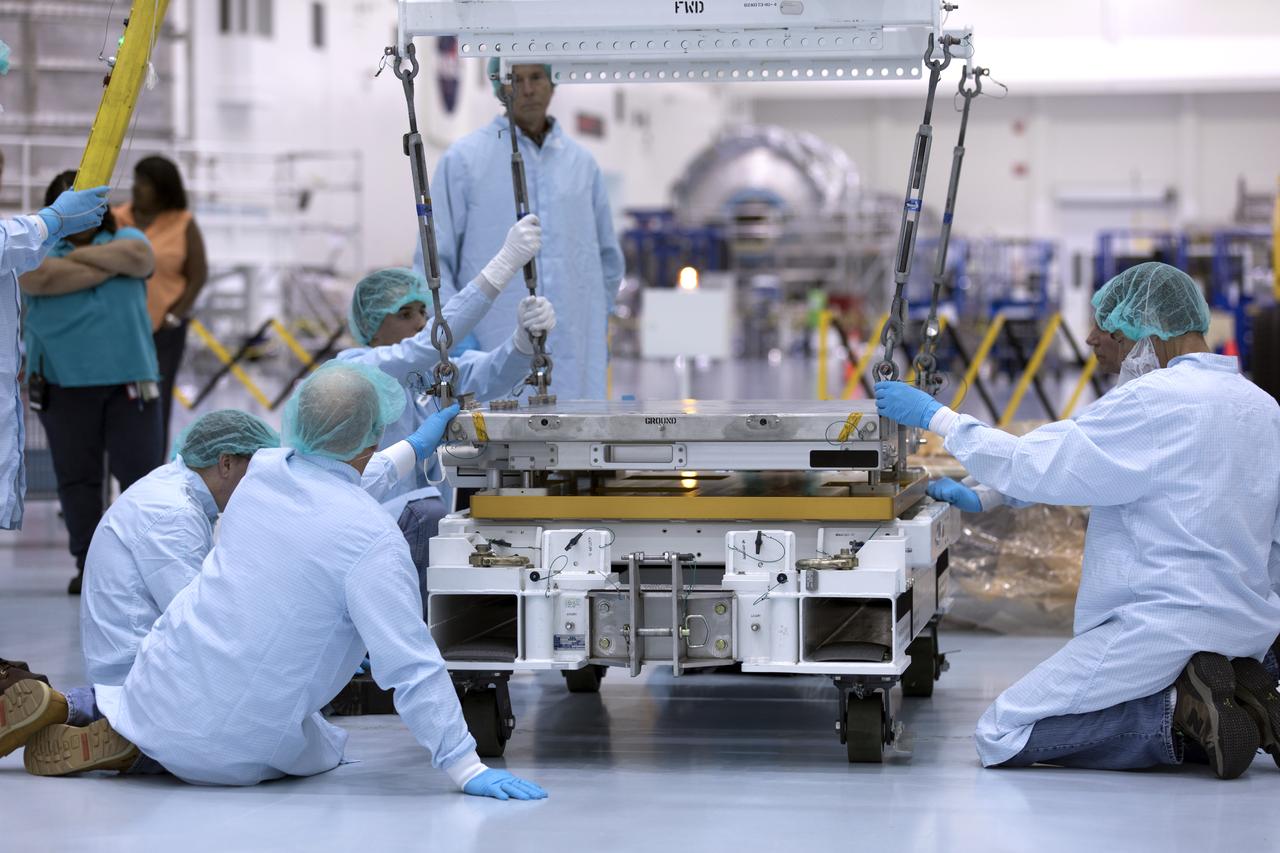

The Materials International Space Station Experiment-Flight Facility, or MISSE-FF, hardware arrived at the Space Station Processing Facility low bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Technicians assist as one of the components is lowered and secured onto another MISSE component. MISSE will be used to test various materials and computing elements on the exterior of the space station. They will be exposed to the harsh environment of low-Earth orbit, including to a vacuum, atomic oxygen, ultraviolet radiation, direct sunlight and extreme heat and cold. The experiment will provide a better understanding of material durability, from coatings to electronic sensors, which could be applied to future spacecraft designs. MISSE will be delivered to the space station on a future commercial resupply mission.
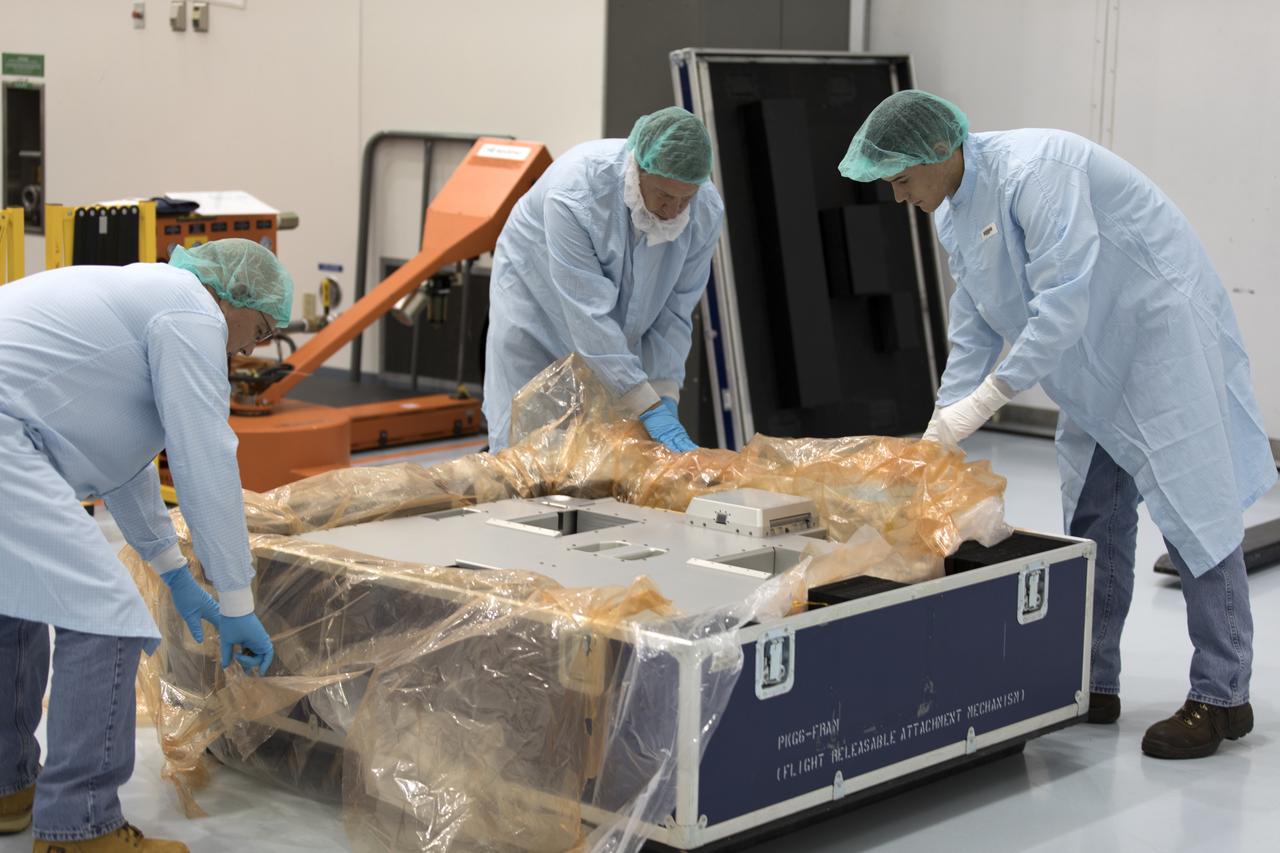

The Materials International Space Station Experiment-Flight Facility, or MISSE-FF, hardware arrived at the Space Station Processing Facility low bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. MISSE will be unpacked for integration and processing. MISSE will be used to test various materials and computing elements on the exterior of the space station. They will be exposed to the harsh environment of low-Earth orbit, including to a vacuum, atomic oxygen, ultraviolet radiation, direct sunlight and extreme heat and cold. The experiment will provide a better understanding of material durability, from coatings to electronic sensors, which could be applied to future spacecraft designs. MISSE will be delivered to the space station on a future commercial resupply mission.
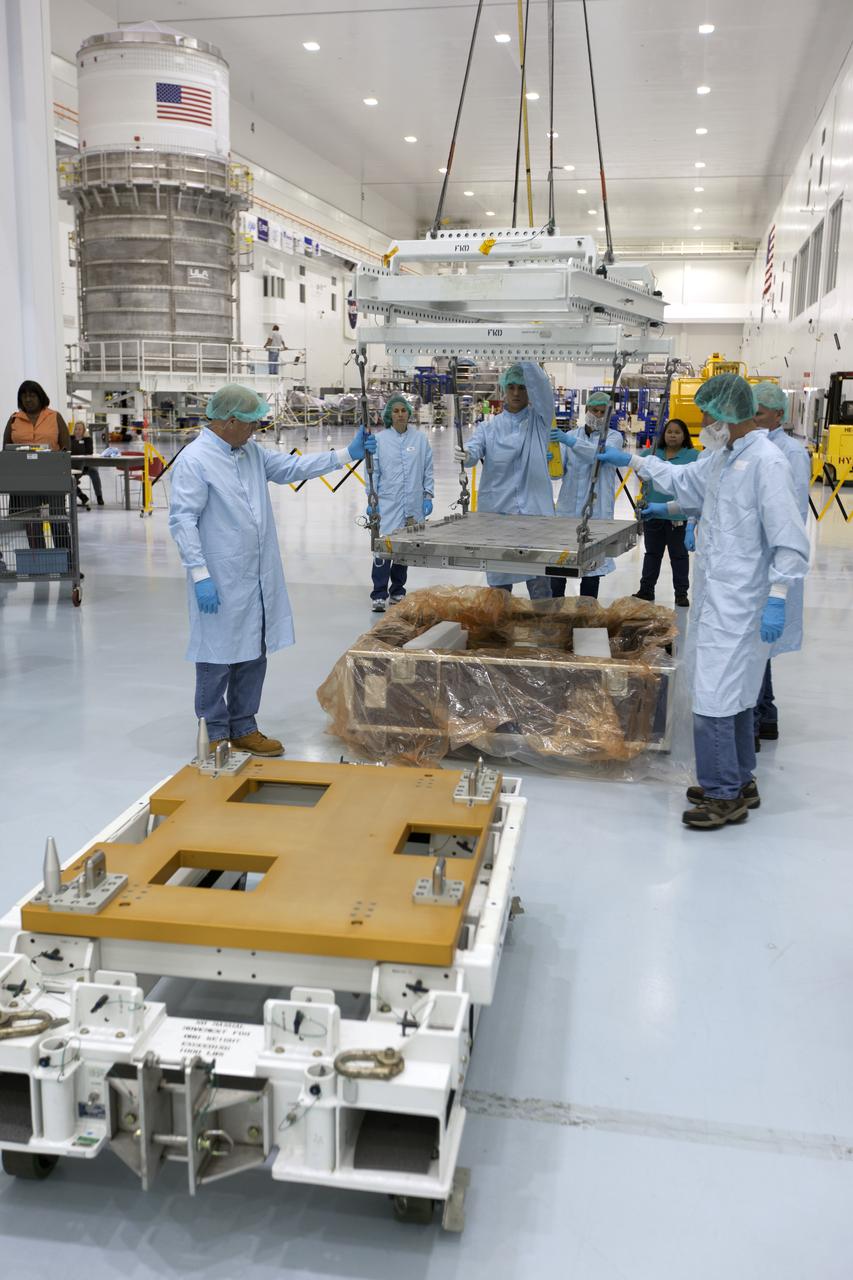

The Materials International Space Station Experiment-Flight Facility, or MISSE-FF, hardware arrived at the Space Station Processing Facility low bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Technicians assist as MISSE is lifted by crane from its shipping container. MISSE will be used to test various materials and computing elements on the exterior of the space station. They will be exposed to the harsh environment of low-Earth orbit, including to a vacuum, atomic oxygen, ultraviolet radiation, direct sunlight and extreme heat and cold. The experiment will provide a better understanding of material durability, from coatings to electronic sensors, which could be applied to future spacecraft designs. MISSE will be delivered to the space station on a future commercial resupply mission.

The Materials International Space Station Experiment-Flight Facility, or MISSE-FF, hardware arrived at the Space Station Processing Facility low bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Technicians attach a crane to MISSE for lifting out of its shipping container. MISSE will be used to test various materials and computing elements on the exterior of the space station. They will be exposed to the harsh environment of low-Earth orbit, including to a vacuum, atomic oxygen, ultraviolet radiation, direct sunlight and extreme heat and cold. The experiment will provide a better understanding of material durability, from coatings to electronic sensors, which could be applied to future spacecraft designs. MISSE will be delivered to the space station on a future commercial resupply mission.
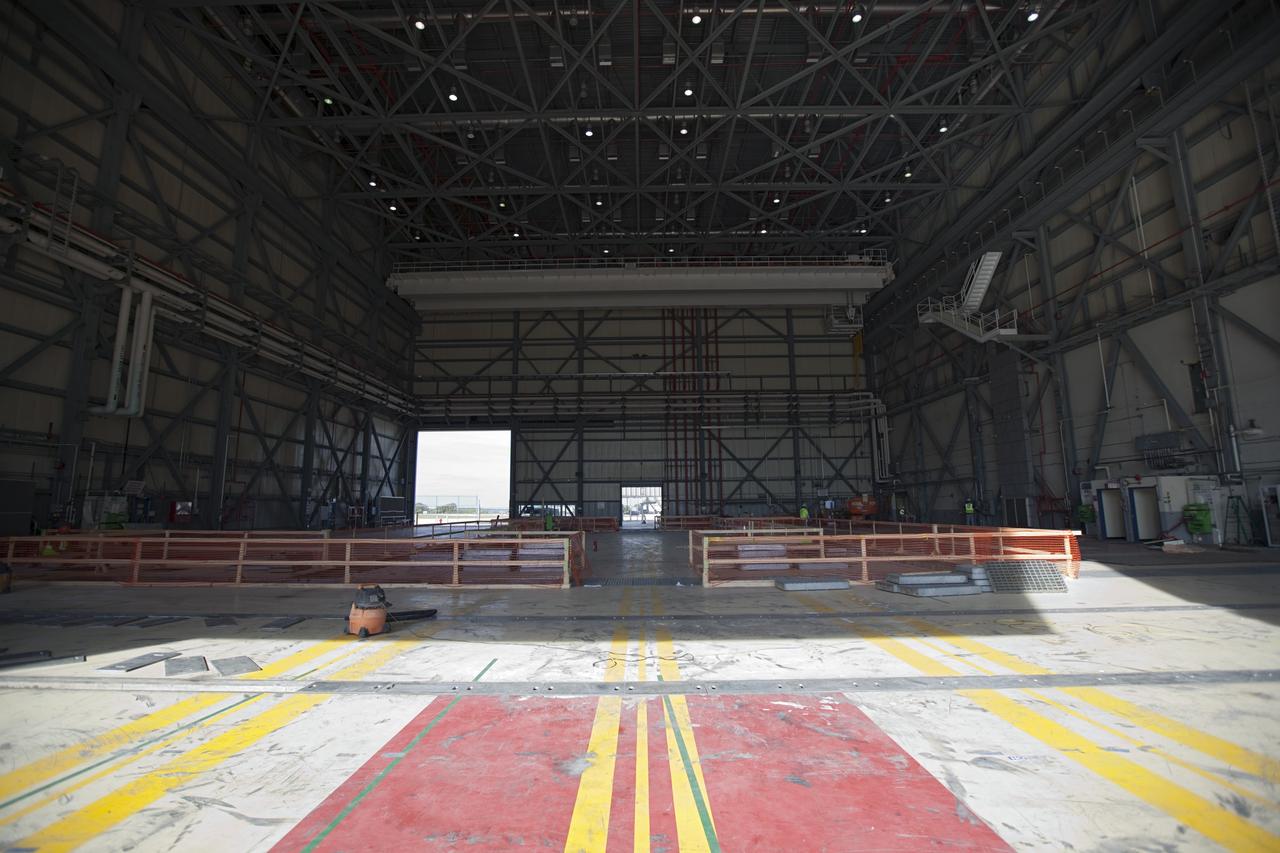

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility, or C3PF, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida is going through major renovations to support the manufacturing of The Boeing Company's CST-100 spacecraft. Known throughout the space shuttle era as Orbiter Processing Facilty-3, or OPF-3, the facility's orbiter-specific platforms were removed recently to make room for a clean-floor factory-like facility. The modernization will allow Boeing to process its new fleet of low-Earth-orbit bound spacecraft, which is under development in collaboration with NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP. Boeing is leasing the excess government facility for next-generation commercial activities through a land-use agreement with Space Florida. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: Dimitri Gerondidakis
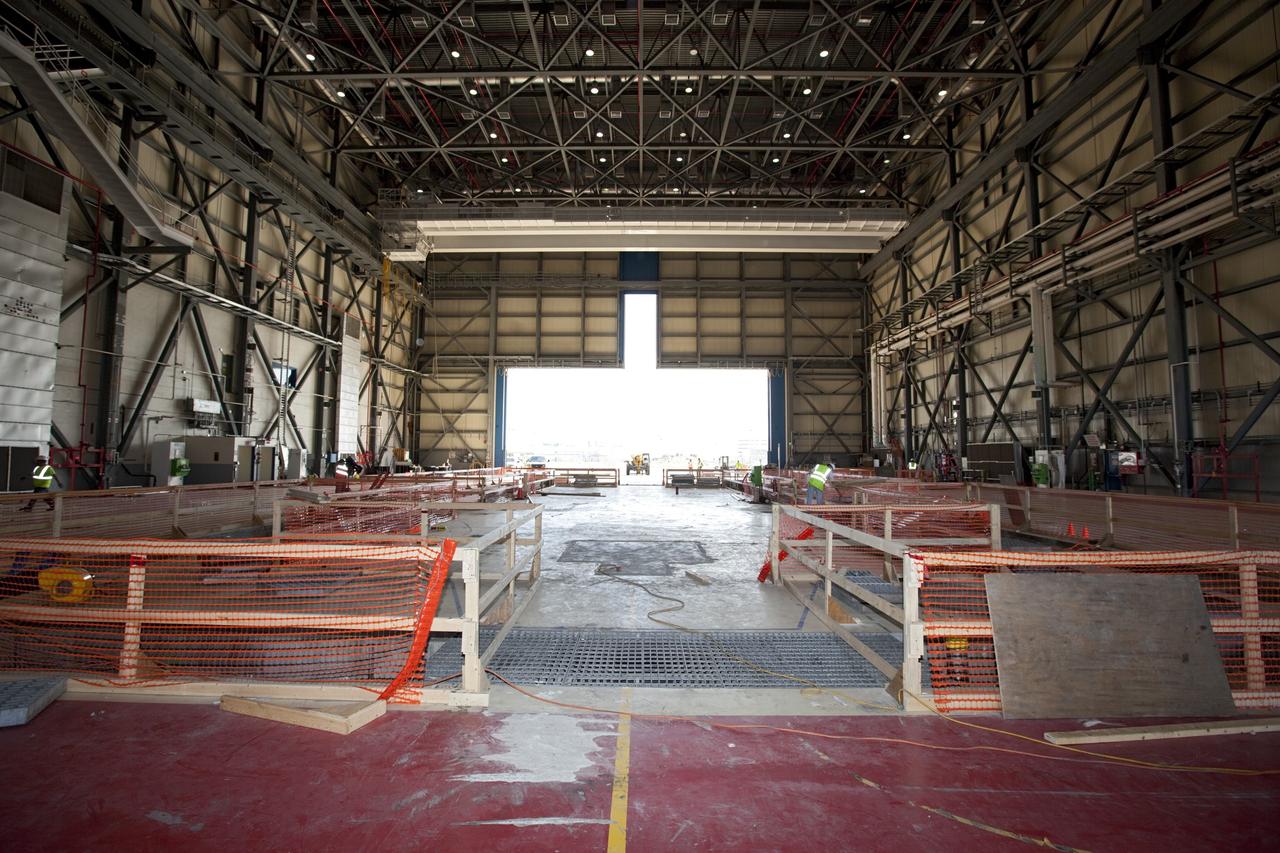

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility, or C3PF, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida is going through major renovations to support the manufacturing of The Boeing Company's CST-100 spacecraft. Known throughout the space shuttle era as Orbiter Processing Facilty-3, or OPF-3, the facility's orbiter-specific platforms were removed recently to make room for a clean-floor factory-like facility. The modernization will allow Boeing to process its new fleet of low-Earth-orbit bound spacecraft, which is under development in collaboration with NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP. Boeing is leasing the excess government facility for next-generation commercial activities through a land-use agreement with Space Florida. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: Dimitri Gerondidakis
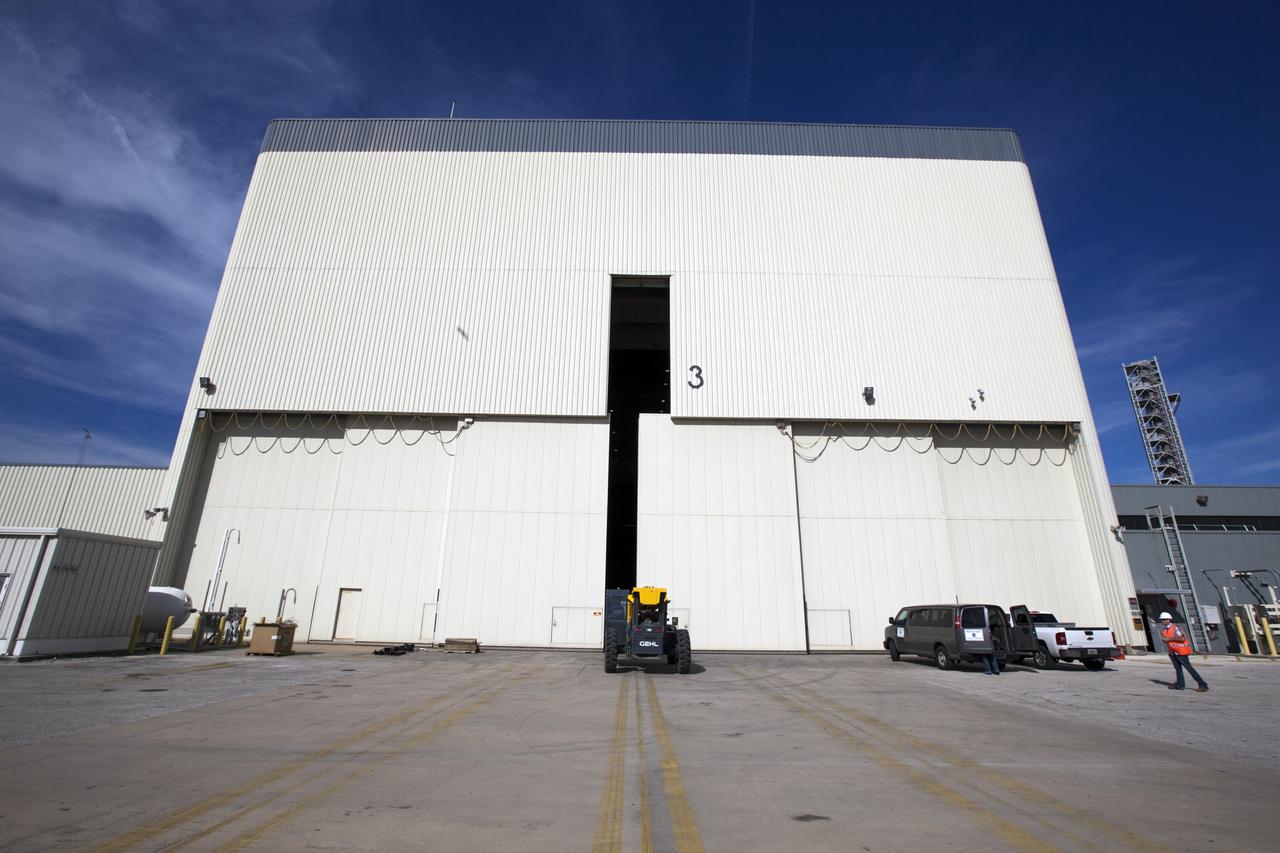

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility, or C3PF, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida is going through major renovations to support the manufacturing of The Boeing Company's CST-100 spacecraft. Known throughout the space shuttle era as Orbiter Processing Facilty-3, or OPF-3, the facility's orbiter-specific platforms were removed recently to make room for a clean-floor factory-like facility. The modernization will allow Boeing to process its new fleet of low-Earth-orbit bound spacecraft, which is under development in collaboration with NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP. Boeing is leasing the excess government facility for next-generation commercial activities through a land-use agreement with Space Florida. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: Dimitri Gerondidakis
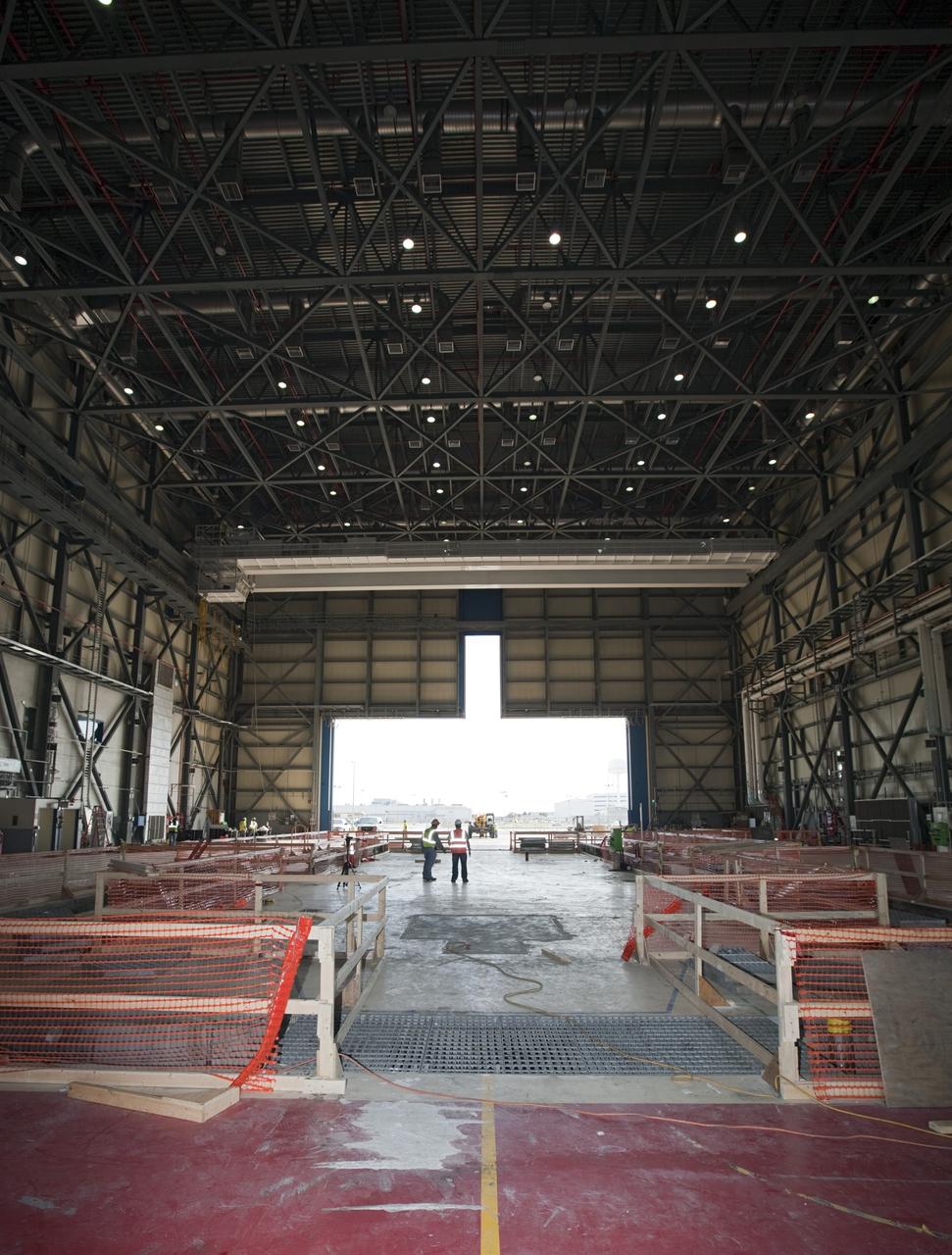

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility, or C3PF, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida is going through major renovations to support the manufacturing of The Boeing Company's CST-100 spacecraft. Known throughout the space shuttle era as Orbiter Processing Facilty-3, or OPF-3, the facility's orbiter-specific platforms were removed recently to make room for a clean-floor factory-like facility. The modernization will allow Boeing to process its new fleet of low-Earth-orbit bound spacecraft, which is under development in collaboration with NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP. Boeing is leasing the excess government facility for next-generation commercial activities through a land-use agreement with Space Florida. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: Dimitri Gerondidakis
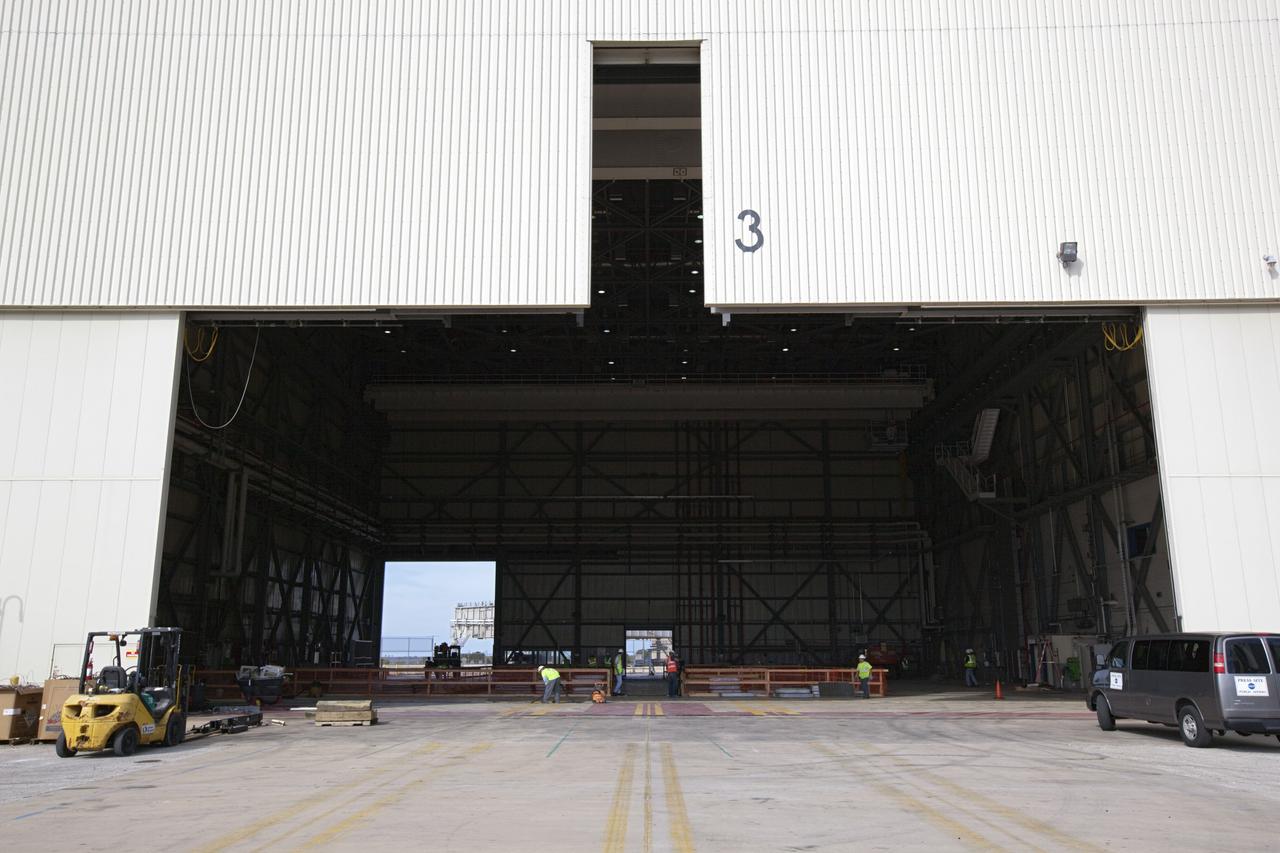

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility, or C3PF, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida is going through major renovations to support the manufacturing of The Boeing Company's CST-100 spacecraft. Known throughout the space shuttle era as Orbiter Processing Facilty-3, or OPF-3, the facility's orbiter-specific platforms were removed recently to make room for a clean-floor factory-like facility. The modernization will allow Boeing to process its new fleet of low-Earth-orbit bound spacecraft, which is under development in collaboration with NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP. Boeing is leasing the excess government facility for next-generation commercial activities through a land-use agreement with Space Florida. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: Dimitri Gerondidakis
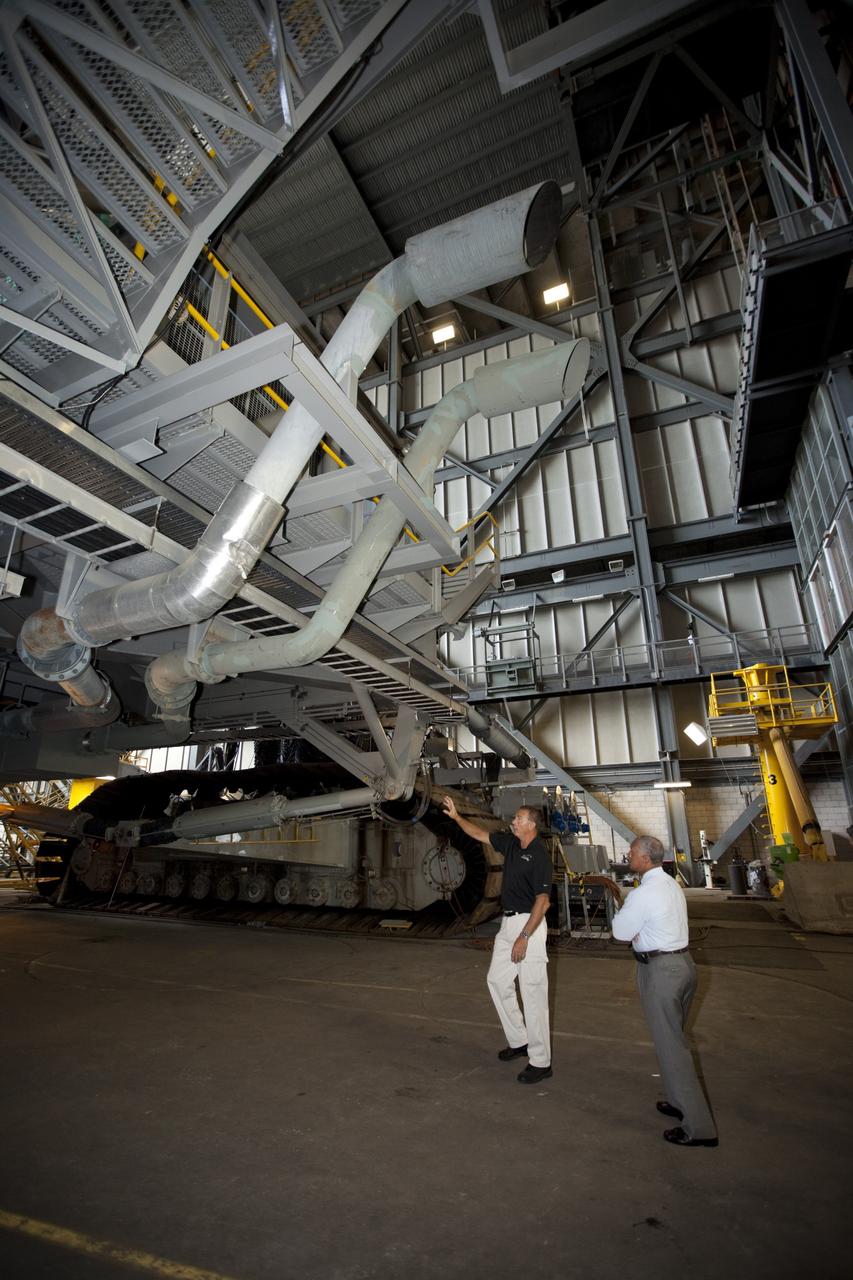

Cape Canaveral, Fla. -- NASA Administrator Charlie Bolden sees firsthand how Kennedy Space Center is transitioning to a spaceport of the future as Kennedy's Mike Parrish explains the upcoming use of the crawler-transporter, which has carried space vehicles to the launch pad since the Apollo Program. NASA is working with U.S. industry partners to develop commercial spaceflight capabilities to low Earth orbit as the agency also is developing the Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle MPCV and the Space Launch System SLS, a crew capsule and heavy-lift rocket to provide an entirely new capability for human exploration. Designed to be flexible for launching spacecraft for crew and cargo missions, SLS and Orion MPCV will expand human presence beyond low Earth orbit and enable new missions of exploration across the solar system. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
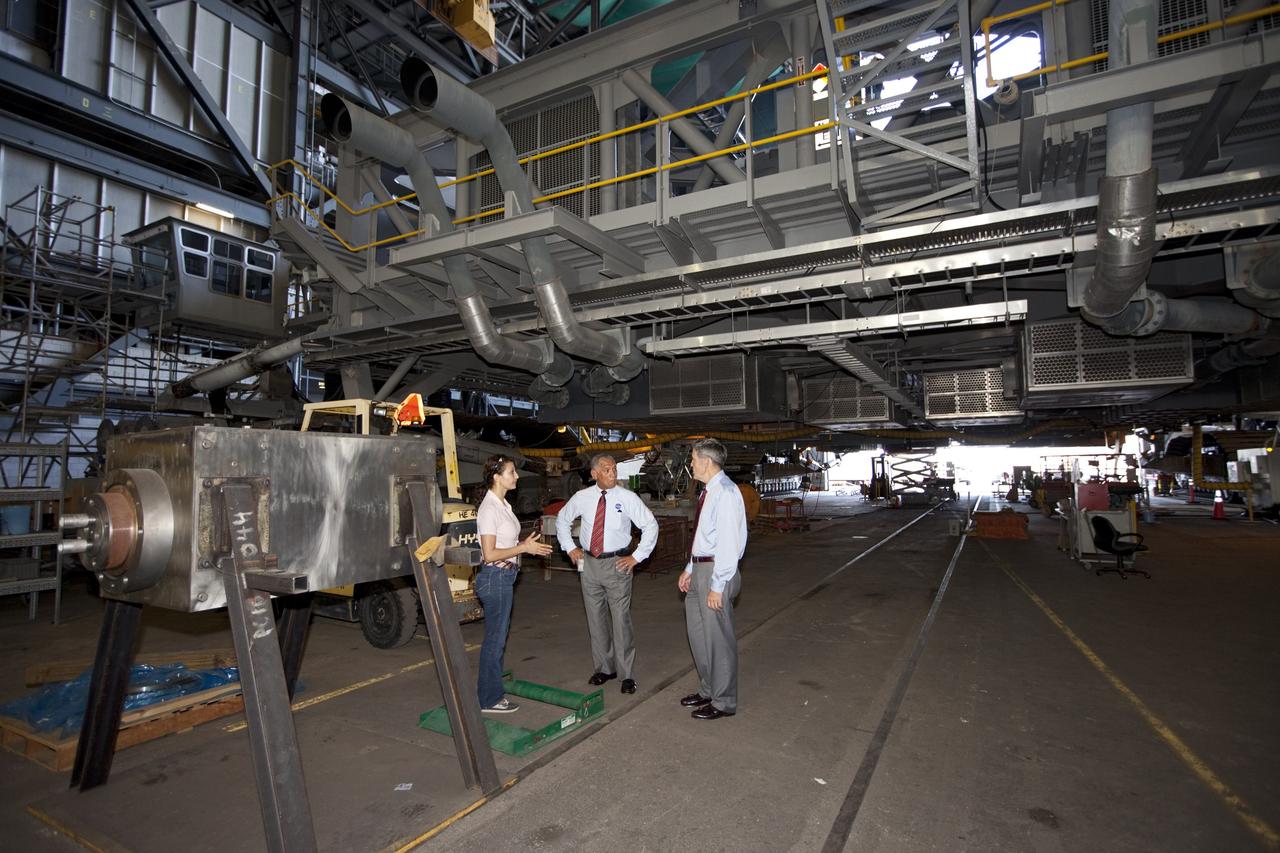

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA Administrator Charlie Bolden, accompanied by Center Director Bob Cabana, sees firsthand how NASA's Kennedy Space Center is transiting to a spaceport of the future as Kennedy's Mary Hanna explains the upcoming uses for the crawler-transporter that has carried space vehicles to the launch pad since the Apollo Program. NASA is working with U.S. industry partners to develop commercial spaceflight capabilities to low Earth orbit as the agency also is developing the Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle MPCV and the Space Launch System SLS, a crew capsule and heavy-lift rocket to provide an entirely new capability for human exploration. Designed to be flexible for launching spacecraft for crew and cargo missions, SLS and Orion MPCV will expand human presence beyond low Earth orbit and enable new missions of exploration across the solar system. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
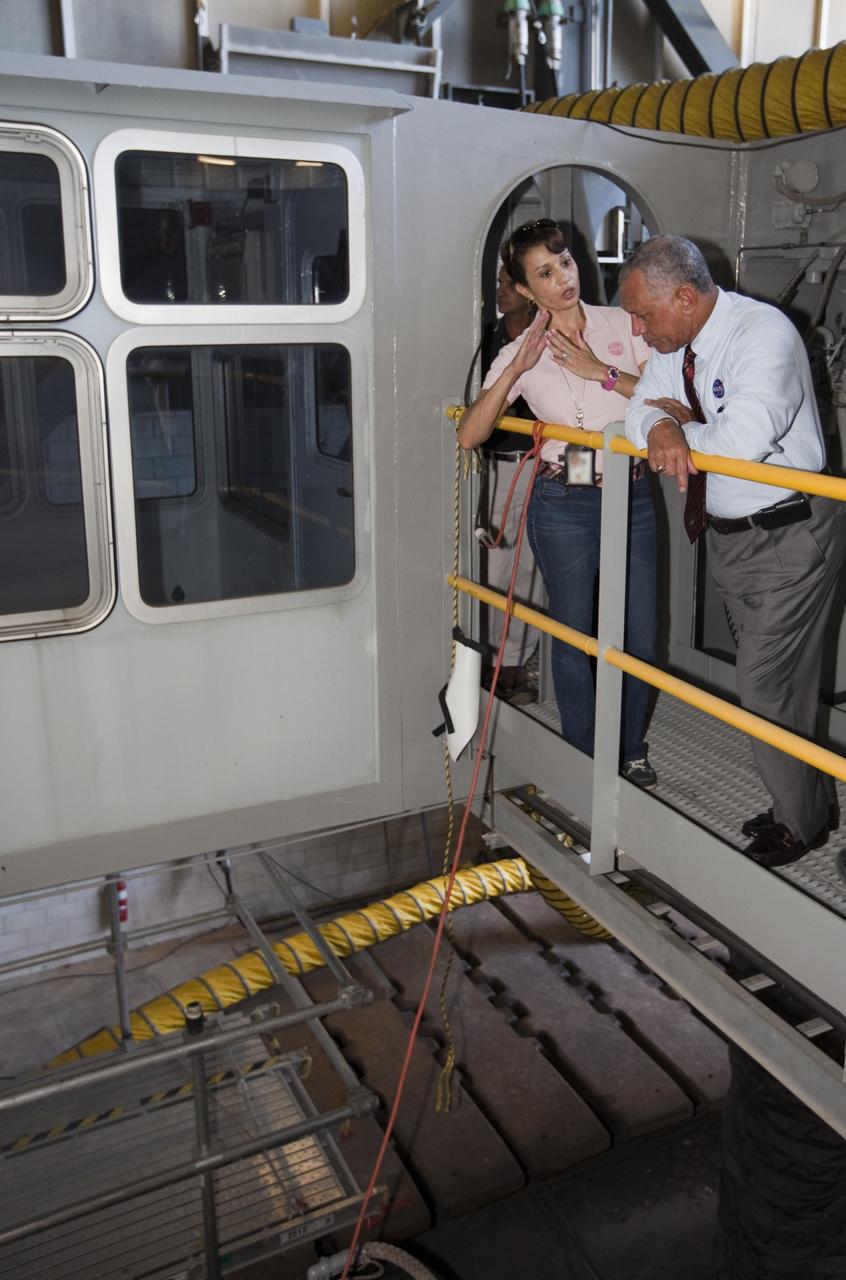

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA Administrator Charlie Bolden sees firsthand how Kennedy Space Center is transitioning to a spaceport of the future as Kennedy's Mary Hanna explains the upcoming use of the crawler-transporter, which has carried space vehicles to the launch pad since the Apollo Program. NASA is working with U.S. industry partners to develop commercial spaceflight capabilities to low Earth orbit as the agency also is developing the Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle MPCV and the Space Launch System SLS, a crew capsule and heavy-lift rocket to provide an entirely new capability for human exploration. Designed to be flexible for launching spacecraft for crew and cargo missions, SLS and Orion MPCV will expand human presence beyond low Earth orbit and enable new missions of exploration across the solar system. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
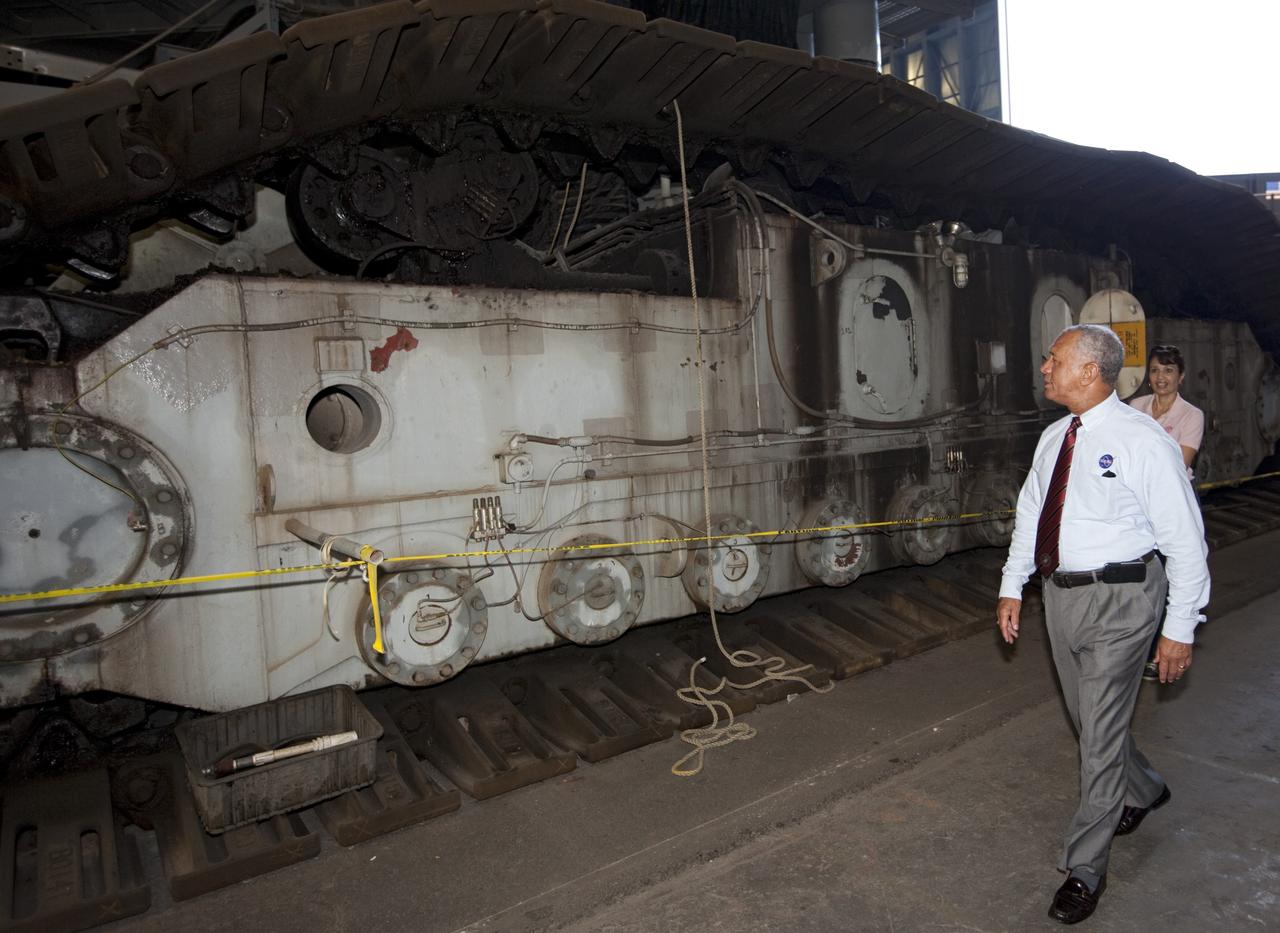

Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. -- NASA Administrator Charlie Bolden sees firsthand how NASA's Kennedy Space Center is transiting to a spaceport of the future as he gets a close look at the crawler-transporter that has carried space vehicles to the launch pad since the Apollo Program. NASA is working with U.S. industry partners to develop commercial spaceflight capabilities to low Earth orbit as the agency also is developing the Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle MPCV and the Space Launch System SLS, a crew capsule and heavy-lift rocket to provide an entirely new capability for human exploration. Designed to be flexible for launching spacecraft for crew and cargo missions, SLS and Orion MPCV will expand human presence beyond low Earth orbit and enable new missions of exploration across the solar system. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
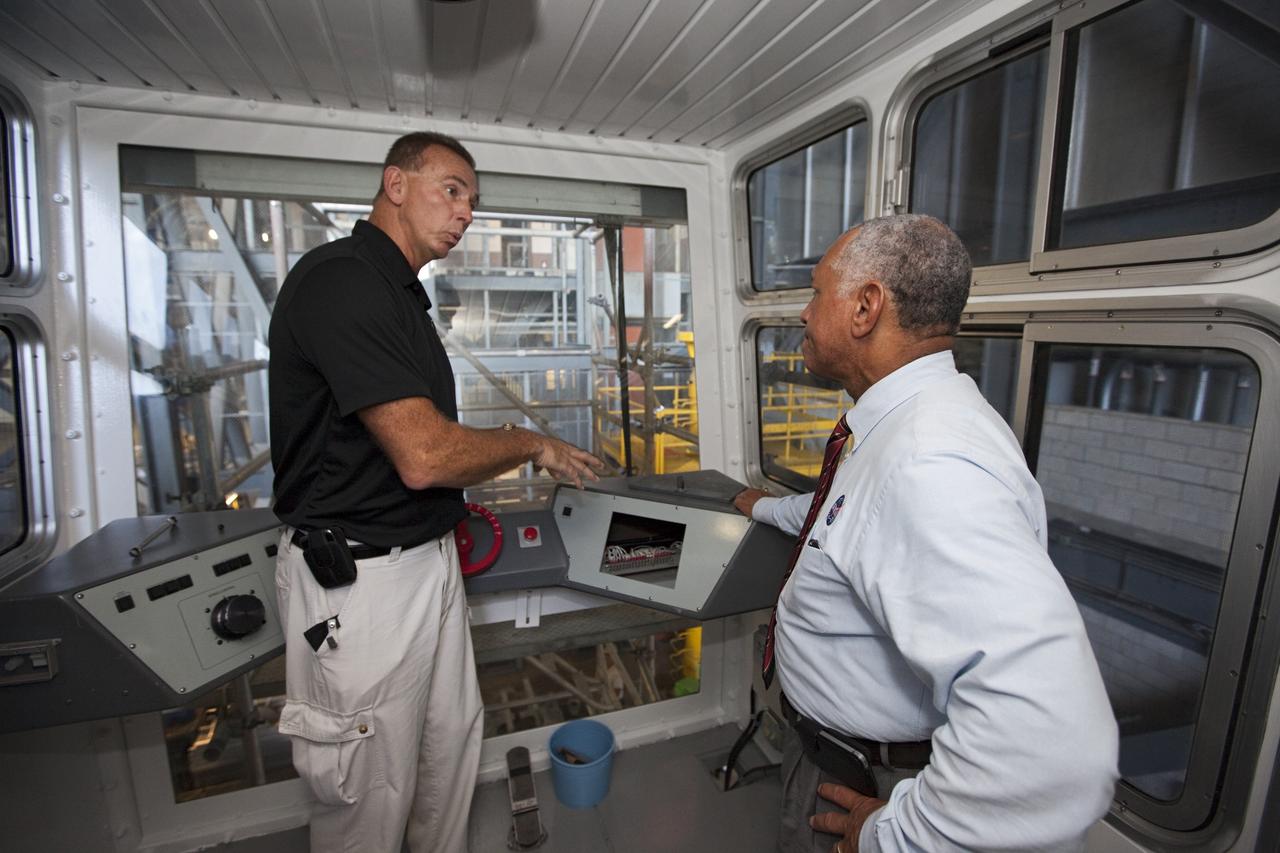

Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. -- NASA Administrator Charlie Bolden sees firsthand how Kennedy Space Center is transitioning to a spaceport of the future as Kennedy's Mike Parrish explains the upcoming use of the crawler-transporter, which has carried space vehicles to the launch pad since the Apollo Program. NASA is working with U.S. industry partners to develop commercial spaceflight capabilities to low Earth orbit as the agency also is developing the Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle MPCV and the Space Launch System SLS, a crew capsule and heavy-lift rocket to provide an entirely new capability for human exploration. Designed to be flexible for launching spacecraft for crew and cargo missions, SLS and Orion MPCV will expand human presence beyond low Earth orbit and enable new missions of exploration across the solar system. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. -- NASA Administrator Charlie Bolden, accompanied by Center Director Bob Cabana, sees firsthand how NASA's Kennedy Space Center is transiting to a spaceport of the future as Kennedy's Mike Parrish explains the upcoming uses for the crawler-transporter that has carried space vehicles to the launch pad since the Apollo Program. NASA is working with U.S. industry partners to develop commercial spaceflight capabilities to low Earth orbit as the agency also is developing the Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle MPCV and the Space Launch System SLS, a crew capsule and heavy-lift rocket to provide an entirely new capability for human exploration. Designed to be flexible for launching spacecraft for crew and cargo missions, SLS and Orion MPCV will expand human presence beyond low Earth orbit and enable new missions of exploration across the solar system. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

HOUSTON -- JSC-2013-E076054 -- NASA Administrator Charlie Bolden, left, talks to The Boeing Company's Vice President and Program Manager of Commercial Programs John Mulholland, center, and Director of Crew and Mission Operations Chris Ferguson at the company's Houston Product Support Center near Johnson Space Center. Boeing showcased its work on a fully outfitted test version of the CST-100 spacecraft to Bolden and Johnson management. Boeing's CST-100 is designed to transport a mix of crew and cargo to low-Earth-orbit destinations. Boeing is one of three aerospace industry partners working with NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, during the Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative, which is intended to make commercial human spaceflight services available for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: NASA/James Blair

HOUSTON - JSC2013e068290 - Kathy Lueders, NASA deputy manager for the Commercial Crew Program, addresses the media before the unveiling of a CST-100 mock-up at the company's Houston Product Support Center. This test version is optimized to support five crew members and will allow the company to evaluate crew safety, interfaces, communications, maneuverability and ergonomics. Boeing's CST-100 is being designed to transport crew members or a mix of crew and cargo to low-Earth-orbit destinations. The evaluation is part of the ongoing work supporting Boeing's funded Space Act Agreement with NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, during the agency's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative. CCiCap is intended to make commercial human spaceflight services available for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP, visit http://www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: NASA/Robert Markowitz

EDWARDS, Calif. – ED13-0142-16: Mounted securely on a flatbed trailer, Sierra Nevada Corporation, or SNC, Space Systems' Dream Chaser engineering test article arrives at Hangar 4826 at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center on Edwards Air Force Base, Calif., in the morning. One of three low-Earth orbit space access vehicles being developed under NASA's Commercial Crew Program, the Dream Chaser will undergo ground and approach-and-landing flight tests at NASA Dryden during the next several months. SNC is one of three companies working with NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, during the agency's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative, which is intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov_commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA_Tom Tschida
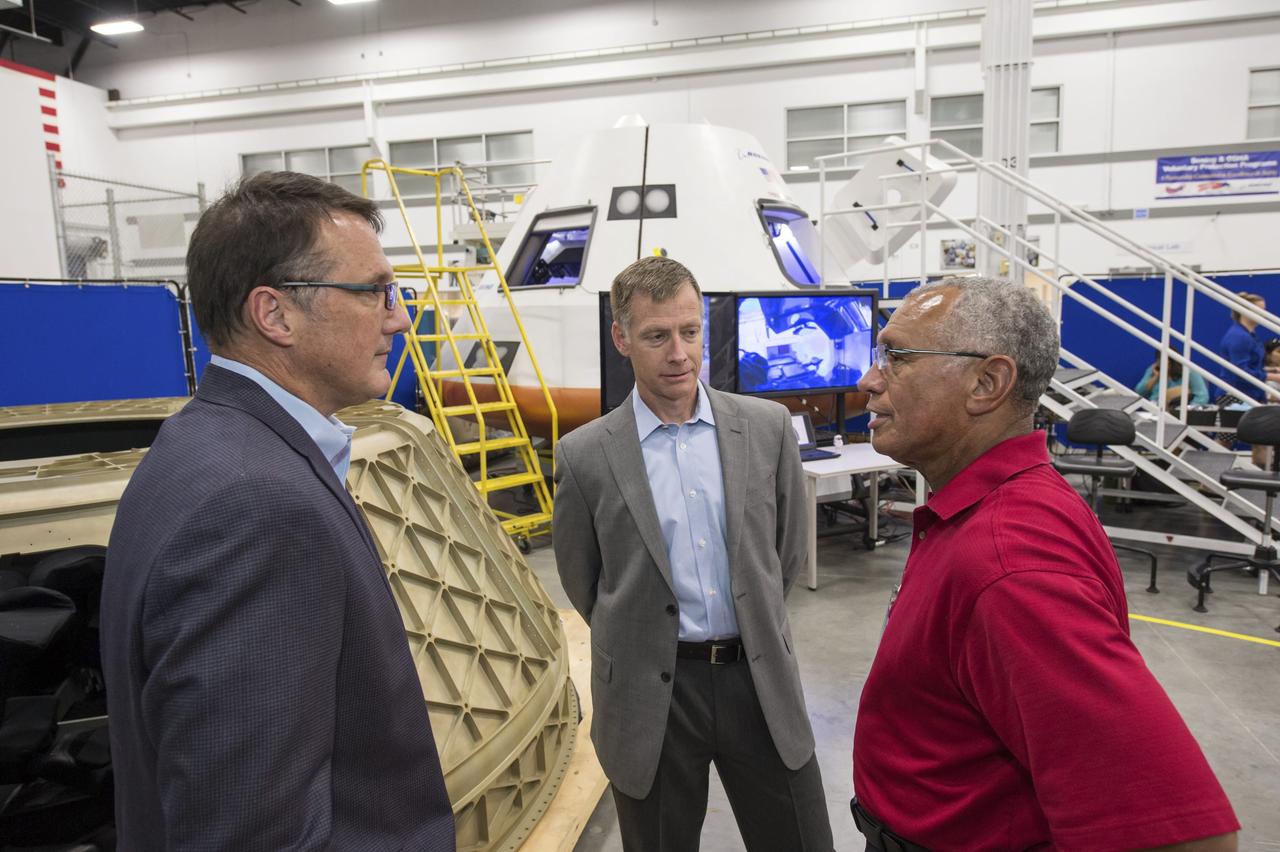

HOUSTON -- JSC-2013-E076048 -- NASA Administrator Charlie Bolden, right, talks to The Boeing Company's Vice President and Program Manager of Commercial Programs John Mulholland, left, and Director of Crew and Mission Operations Chris Ferguson at the company's Houston Product Support Center near Johnson Space Center. Boeing showcased its work on a fully outfitted test version of the CST-100 spacecraft to Bolden and Johnson management. Boeing's CST-100 is designed to transport a mix of crew and cargo to low-Earth-orbit destinations. Boeing is one of three aerospace industry partners working with NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, during the Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative, which is intended to make commercial human spaceflight services available for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: NASA/James Blair
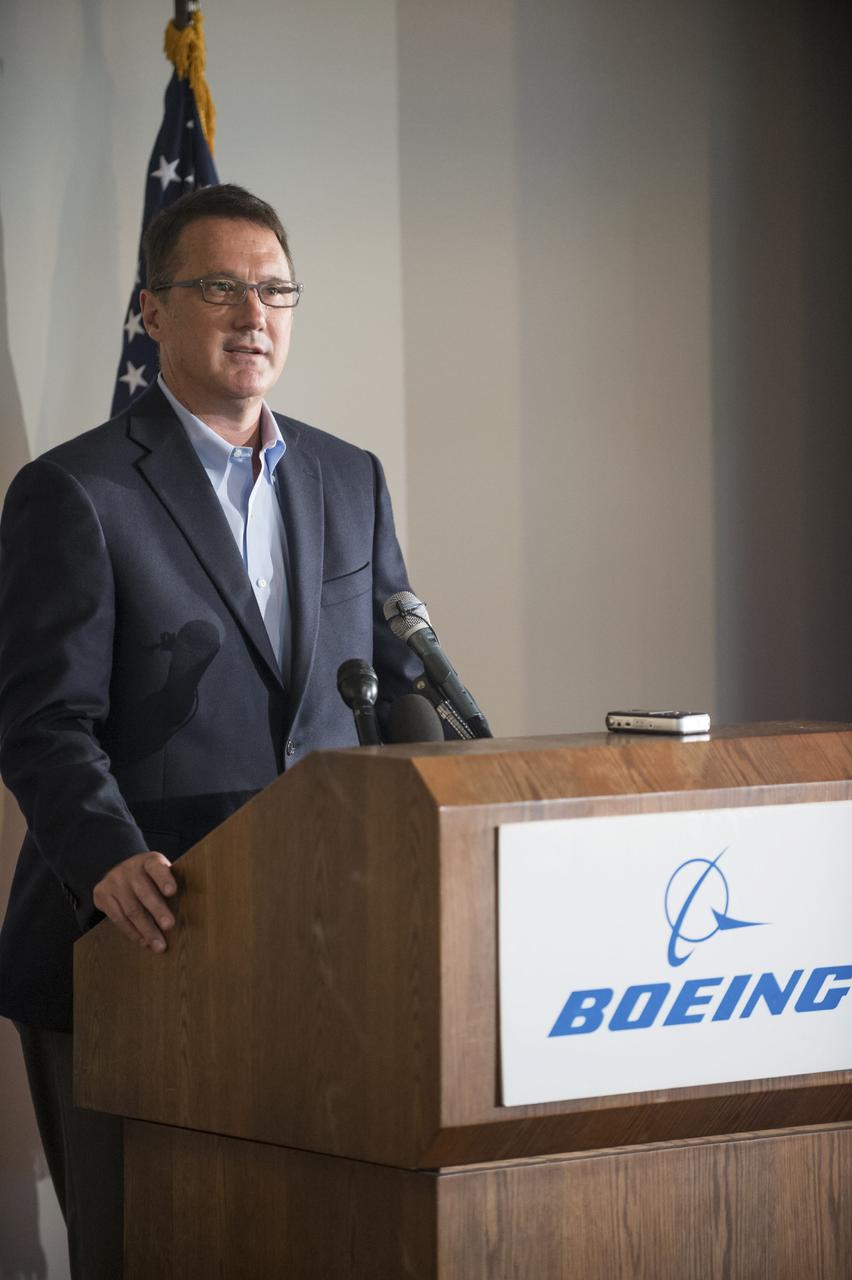

HOUSTON - JSC2013e068296 - John Mulholland, vice president and program manager, Commercial Crew, for The Boeing Company, addresses the media before the unveiling of a CST-100 mock-up at the company's Houston Product Support Center. This test version is optimized to support five crew members and will allow the company to evaluate crew safety, interfaces, communications, maneuverability and ergonomics. Boeing's CST-100 is being designed to transport crew members or a mix of crew and cargo to low-Earth-orbit destinations. The evaluation is part of the ongoing work supporting Boeing's funded Space Act Agreement with NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, during the agency's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative. CCiCap is intended to make commercial human spaceflight services available for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP, visit http://www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: NASA/Robert Markowitz
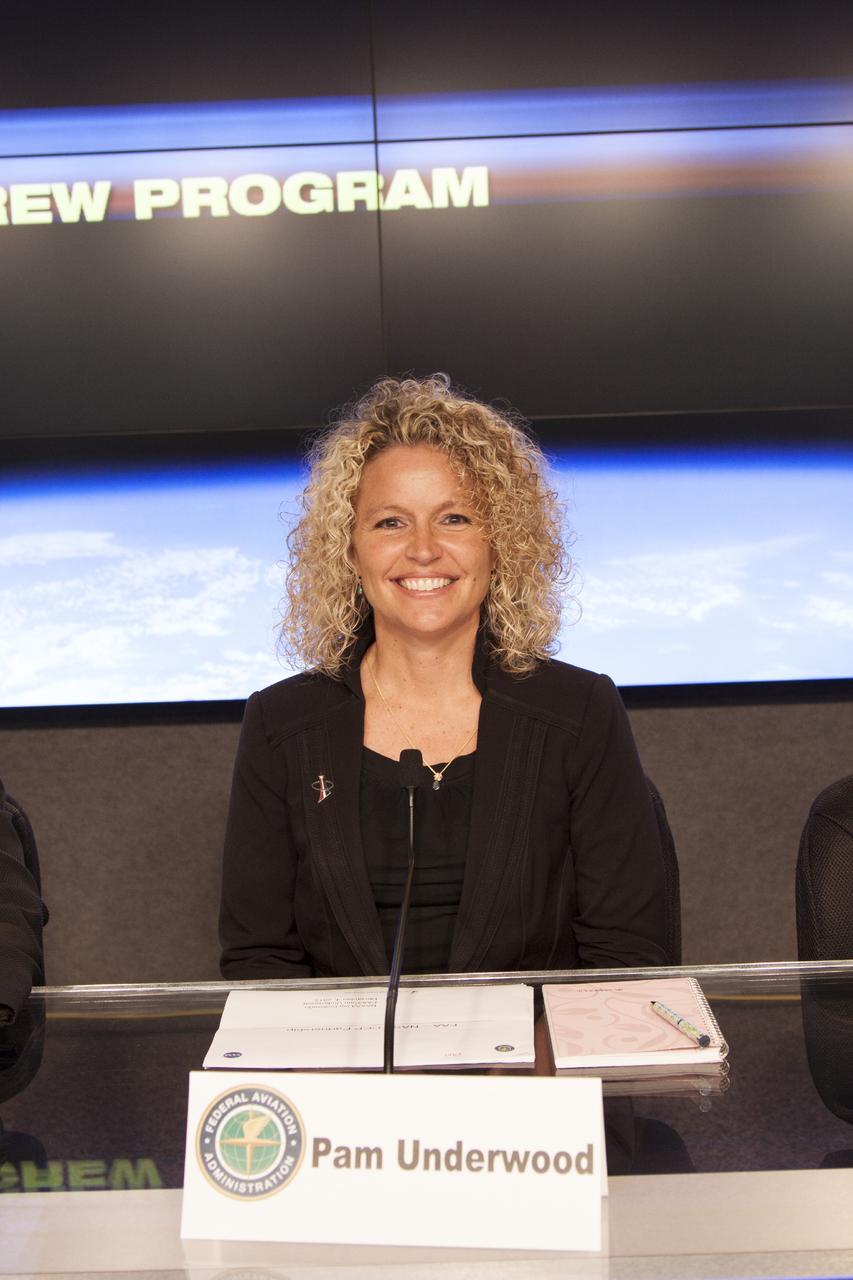

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Pam Underwood of the Federal Aviation Administration's Office of Commercial Transportation and a panelist of the Commercial Crew Transportation Capability, or CCtCap, Pre-Proposal Conference, is seen before the start of an industry conference inside the Television Auditorium at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The conference was held following the Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, request for proposals from commercial companies for a development and certification contract under CCtCap. The contract will provide a finish line for the agency following more than four years of development work by CCP and American aerospace companies. CCtCap is the second phase of a two-phase certification plan for privately built and operated integrated crew transportation systems. CCP’s goal is to aid in the development of commercial capabilities for crew transportation and rescue services to and from the International Space Station and other low-Earth orbit destinations by the end of 2017. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Lisa Colloredo, associate program manager of NASA's Commercial Crew Program and a panelist of the Commercial Crew Transportation Capability, or CCtCap, Pre-Proposal Conference, is seen before the start of an industry conference inside the Television Auditorium at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The conference was held following the Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, request for proposals from commercial companies for a development and certification contract under CCtCap. The contract will provide a finish line for the agency following more than four years of development work by CCP and American aerospace companies. CCtCap is the second phase of a two-phase certification plan for privately built and operated integrated crew transportation systems. CCP’s goal is to aid in the development of commercial capabilities for crew transportation and rescue services to and from the International Space Station and other low-Earth orbit destinations by the end of 2017. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
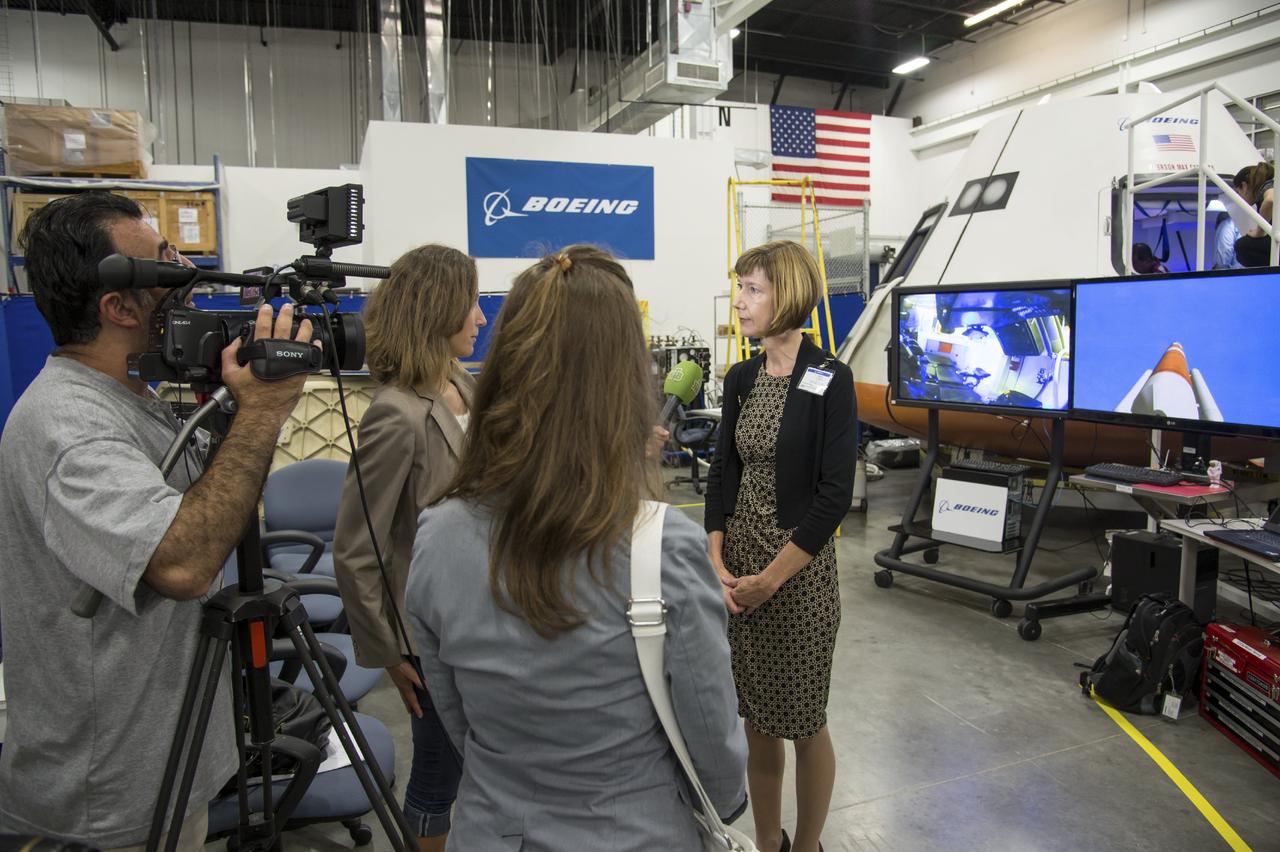

HOUSTON - JSC2013e068324 - Kathy Lueders, NASA deputy manager for the Commercial Crew Program, is interviewed by the media during the unveiling of a CST-100 mock-up at the company's Houston Product Support Center. This test version is optimized to support five crew members and will allow the company to evaluate crew safety, interfaces, communications, maneuverability and ergonomics. Boeing's CST-100 is being designed to transport crew members or a mix of crew and cargo to low-Earth-orbit destinations. The evaluation is part of the ongoing work supporting Boeing's funded Space Act Agreement with NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, during the agency's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative. CCiCap is intended to make commercial human spaceflight services available for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP, visit http://www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: NASA/Robert Markowitz
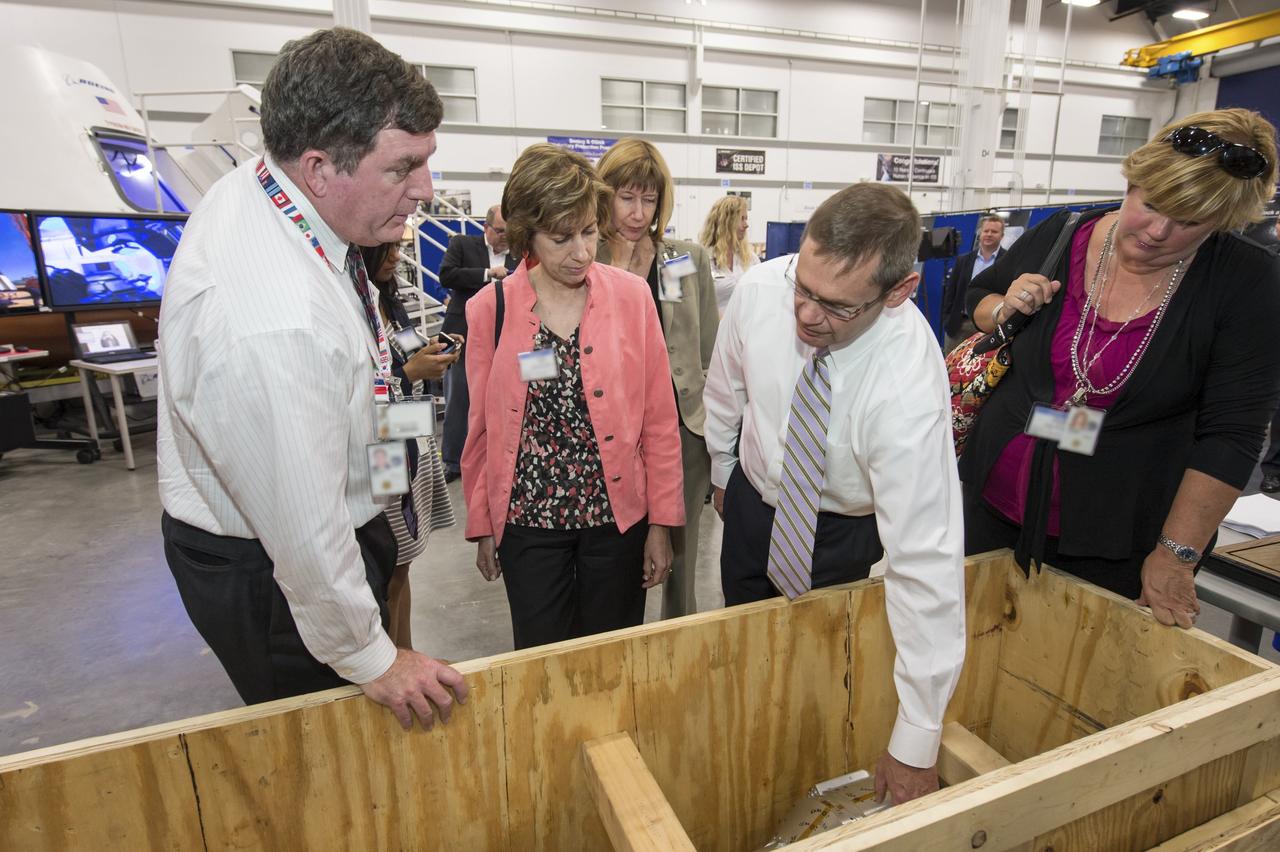

HOUSTON -- JSC-2013-E076043 -- John Elbon, The Boeing Company's vice president of Space Exploration, second right, shows off a wind tunnel model of the CST-100 spacecraft to Johnson Space Center management at the company's Houston Product Support Center. From left, are Kirk Shireman, Johnson's deputy director, Ellen Ochoa, Johnson's director, Kathy Lueders, deputy director of NASA's Commercial Crew Program, Elbon, and Melanie Saunders, Johnson's associate director. Boeing's CST-100 is designed to transport a mix of crew and cargo to low-Earth-orbit destinations. Boeing is one of three aerospace industry partners working with NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, during the Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative, which is intended to make commercial human spaceflight services available for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: NASA/James Blair
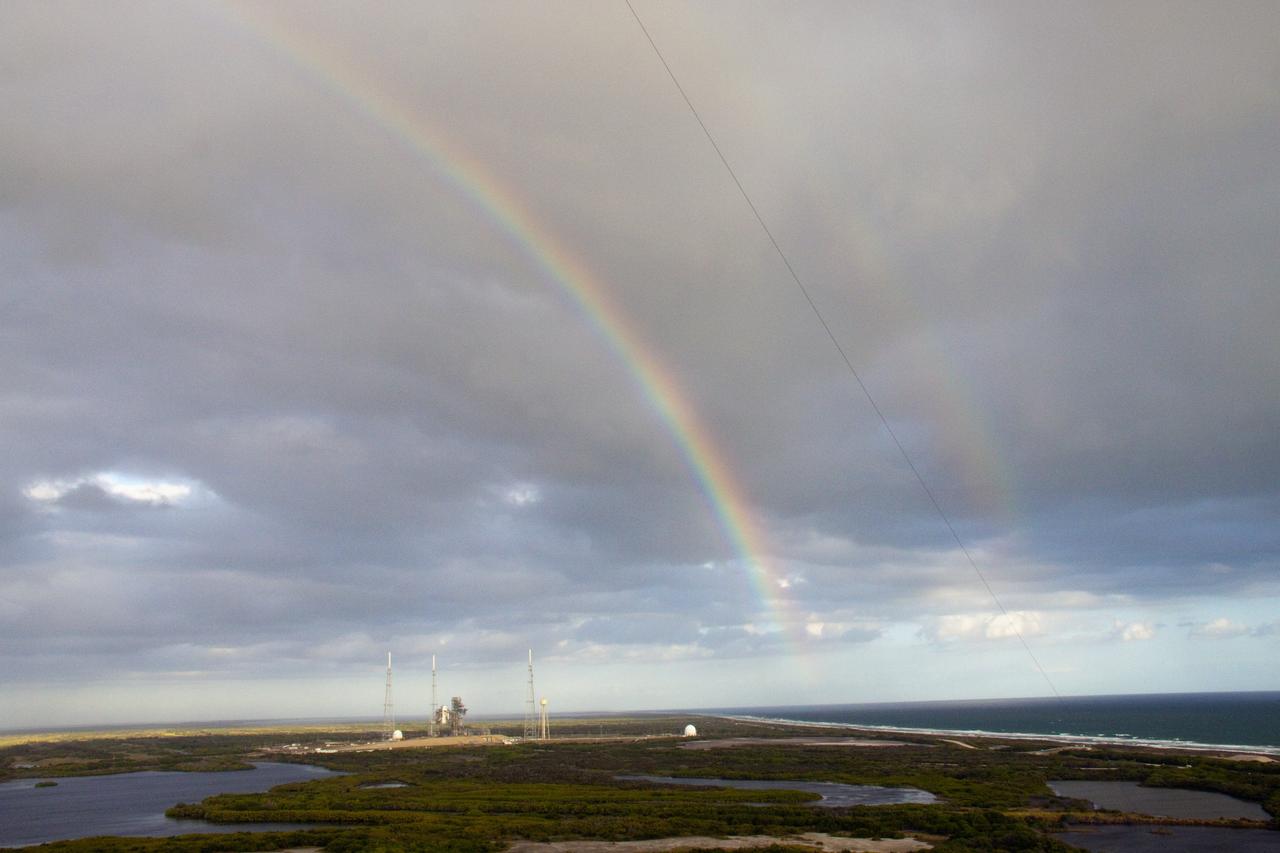

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, two rainbows appear between Launch Pad 39B and Launch Pad 39A. Pad B, seen here, is morphing to support a commercial space program with multiple customers, multiple providers and multiple systems that will take Americans to the International Space Station and other low Earth orbit destinations. For information on NASA's future plans, visit www.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
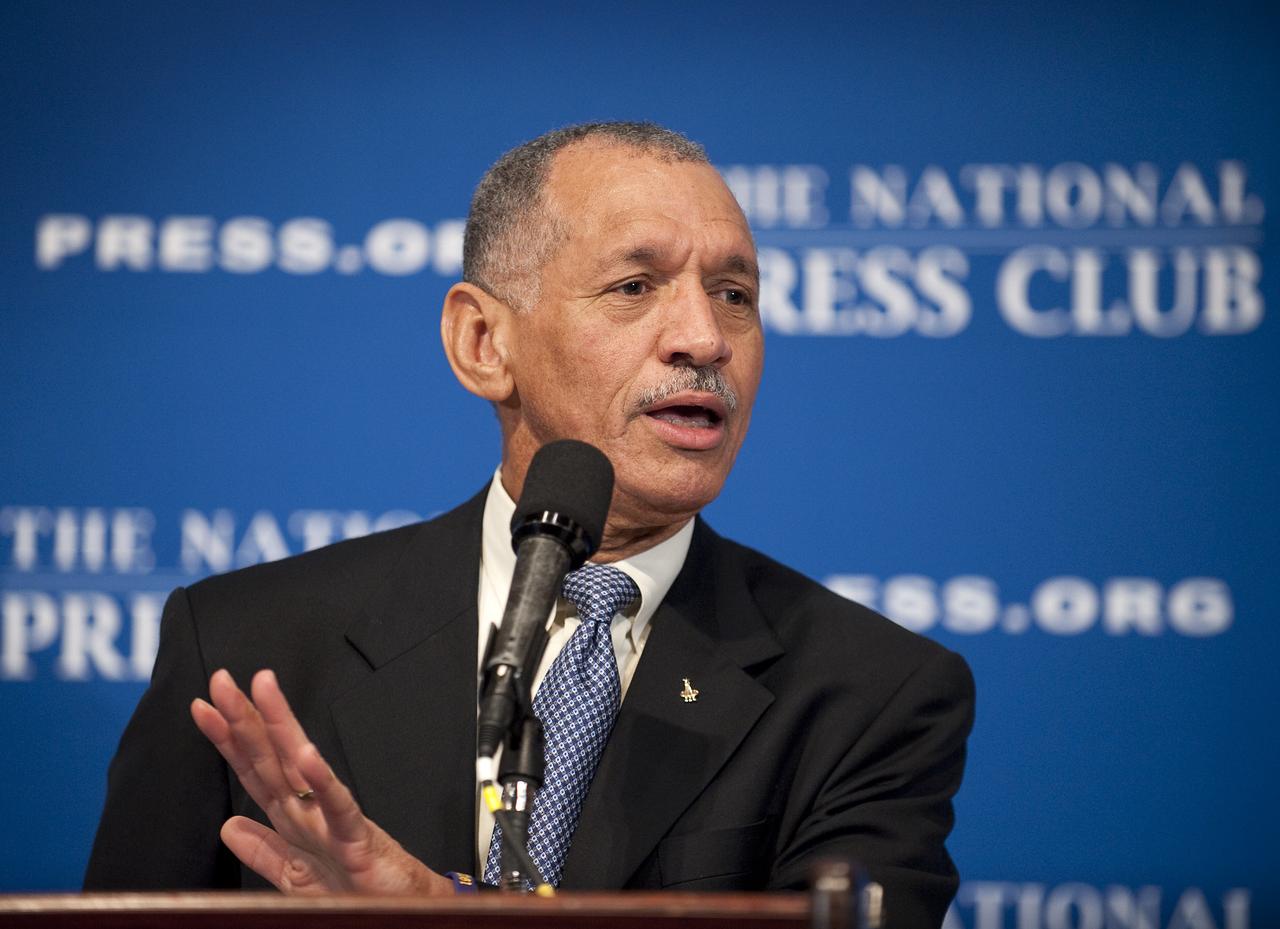

NASA Administrator Charles Bolden speaks during a press conference, Tuesday, Feb. 2, 2010, at the National Press Club in Washington, where it was announced that NASA has awarded $50 million through funded agreements to further the commercial sector's capability to support transport of crew to and from low Earth orbit. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
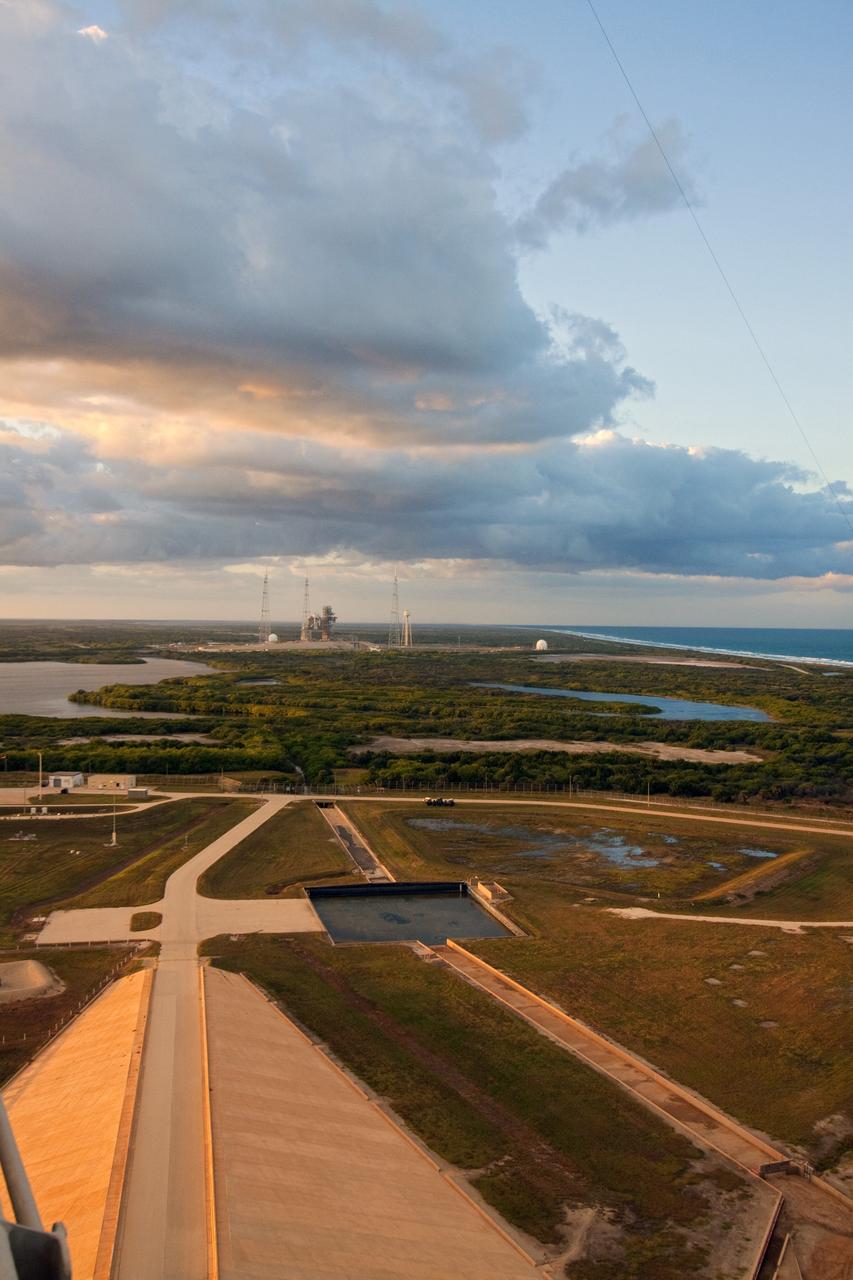

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Launch Pad 39B is seen from Launch Pad 39A. Pad B is morphing to support a commercial space program with multiple customers, multiple providers and multiple systems that will take Americans to the International Space Station and other low Earth orbit destinations. For information on NASA's future plans, visit www.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

NASA Administrator Charles Bolden, left, and Assistant to the President for Science and Technology and Director of the White House Office of Science and Technology Policy Dr. John P. Holdren are seen during a press conference, Tuesday, Feb. 2, 2010, at the National Press Club in Washington, where it was announced that NASA has awarded $50 million through funded agreements to further the commercial sector's capability to support transport of crew to and from low Earth orbit. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
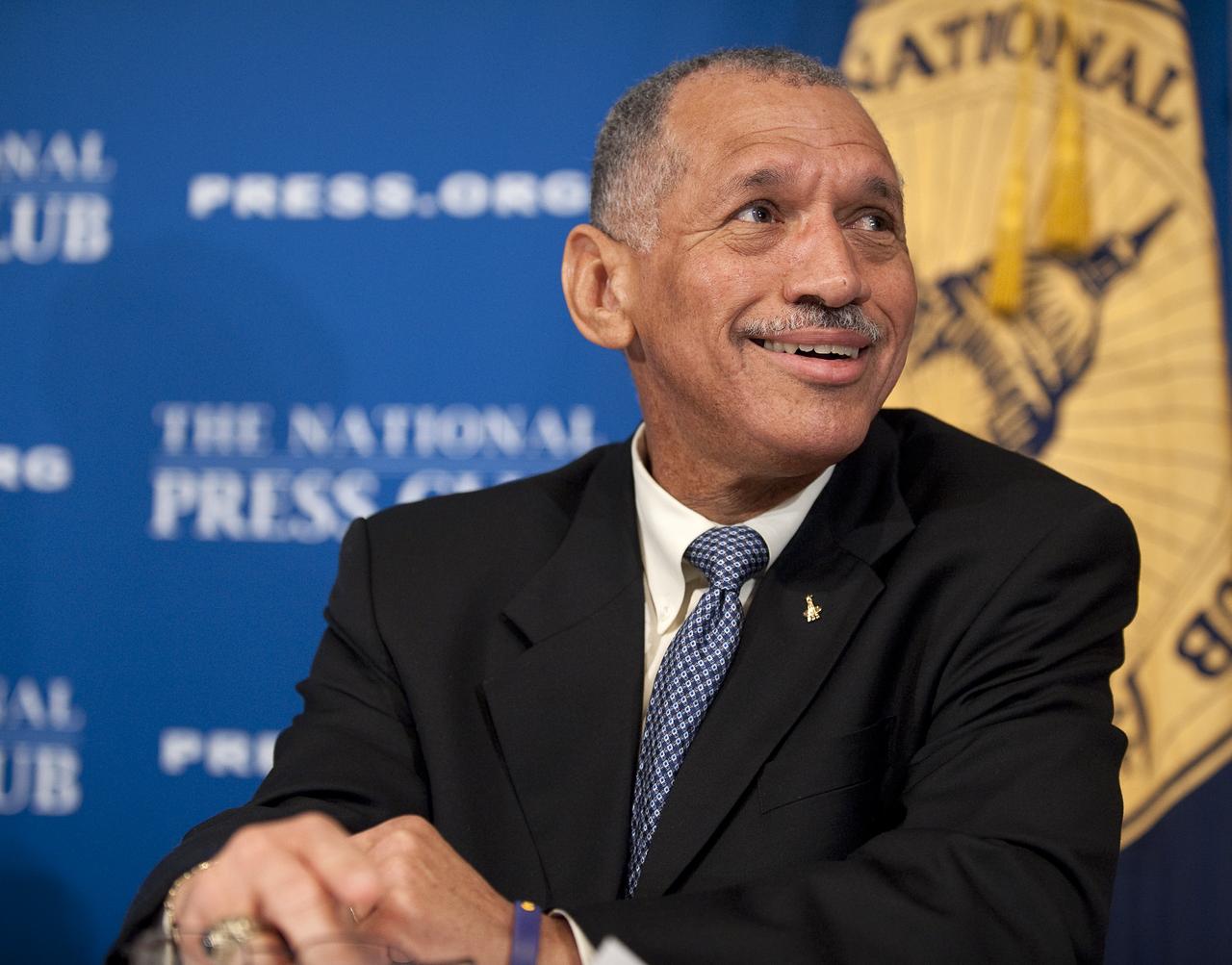

NASA Administrator Charles Bolden listens to his introduction by Assistant to the President for Science and Technology and Director of the White House Office of Science and Technology Policy Dr. John P. Holdren during a press conference, Tuesday, Feb. 2, 2010, at the National Press Club in Washington, where it was announced that NASA has awarded $50 million through funded agreements to further the commercial sector's capability to support transport of crew to and from low Earth orbit. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
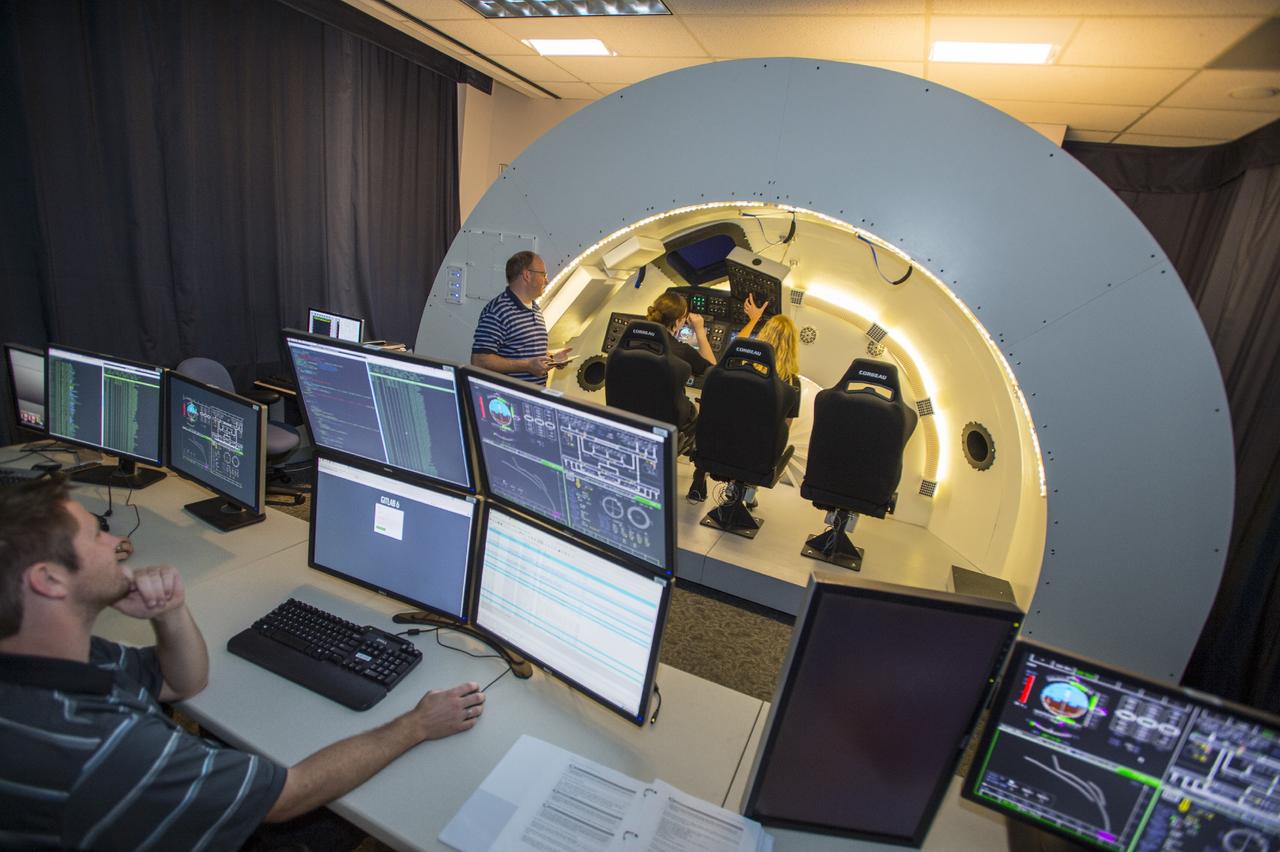

HOUSTON – Engineers and managers work inside a simulator of The Boeing Company's CST-100 spacecraft during evaluations of potential designs and software functions in a room at the company's Houston location. The CST-100 is under development in partnership between the company and NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP. The spacecraft is designed to fly to low-Earth orbit and potentially dock with the International Space Station. Photo credit: The Boeing Company
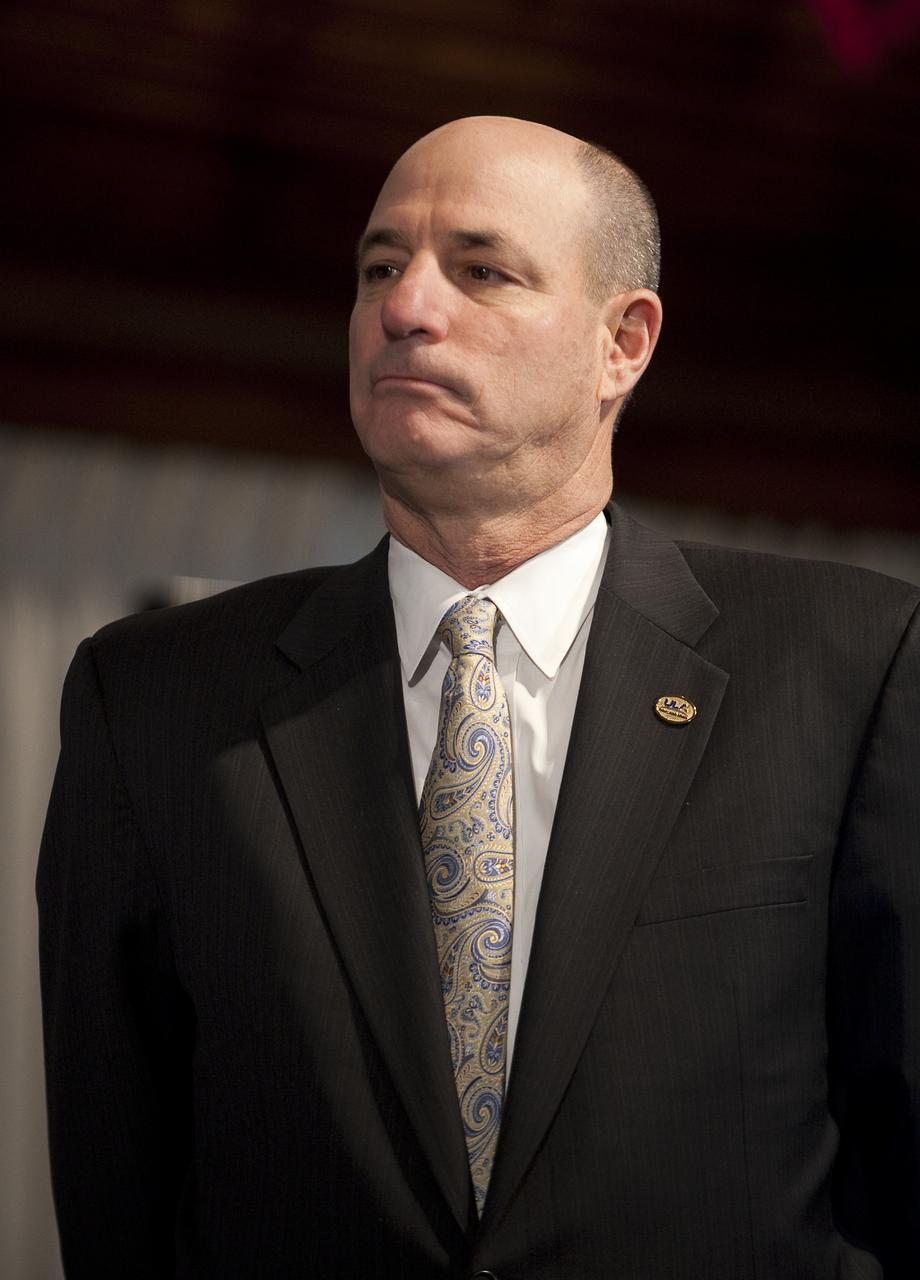

Mike Gass, President and Chief Executive, United Launch Alliance is seen during a press conference, Tuesday, Feb. 2, 2010, at the National Press Club in Washington, where it was announced that NASA has awarded $50 million through funded agreements to further the commercial sector's capability to support transport of crew to and from low Earth orbit. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)