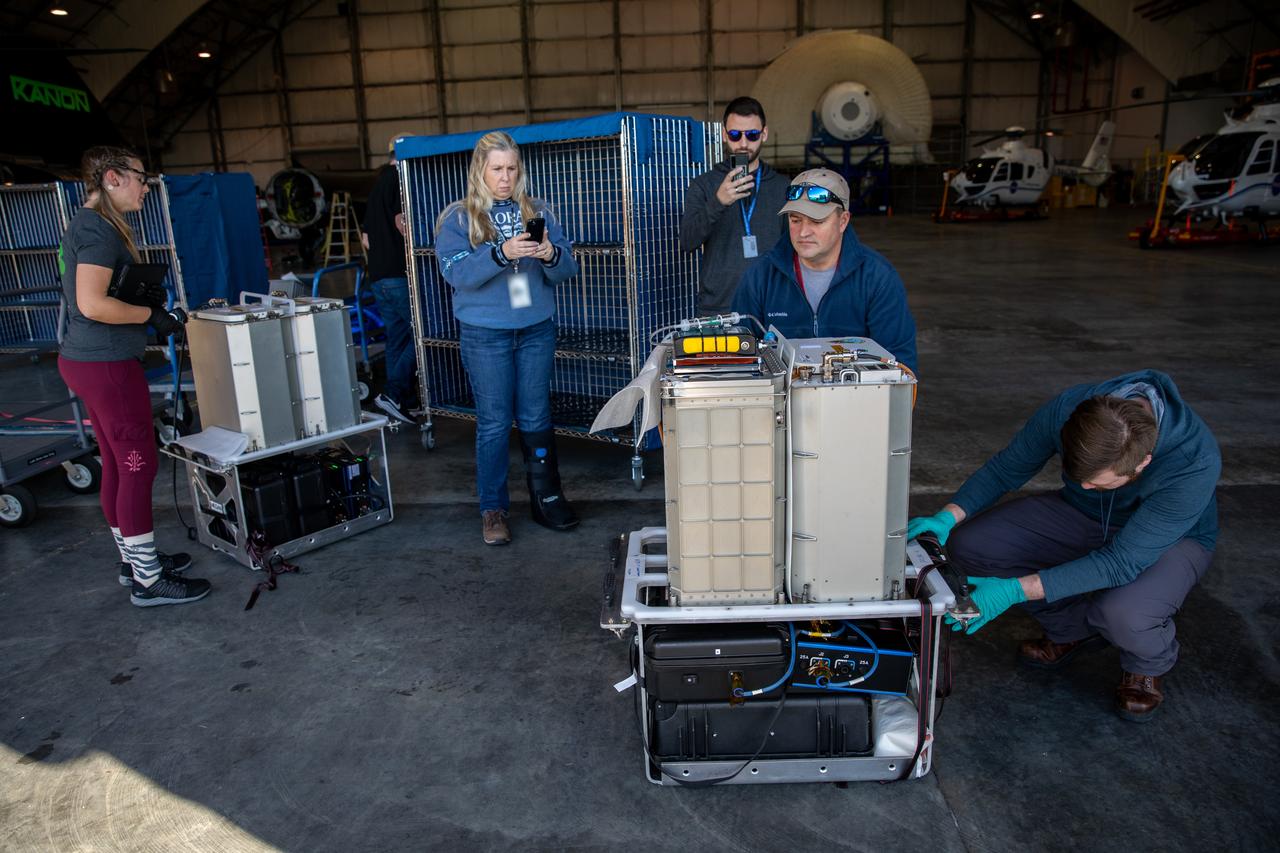

Technicians at the Launch and Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida receive scientific research samples for processing at the spaceport’s Space Station Processing Facility on Jan. 11, 2023. The experiments returned to Earth on SpaceX's 26th commercial resupply services mission, which launched from Kennedy’s Pad 39A at 2:20 p.m. EST on Nov. 26, 2022, making its successful parachute-assisted splashdown west of Tampa in the Gulf of Mexico, at 5:19 a.m. EST on Jan. 11. The SpaceX cargo Dragon returned approximately 4,400 pounds of scientific experiments and other cargo from the International Space Station. Splashing down off the coast of Florida enables quick transportation of the experiments, allowing SpaceX to retrieve Dragon and offload time-sensitive research cargo to pack on an Airbus H225 helicopter for delivery to Kennedy just hours later. Some of the scientific investigations that Dragon returned include those on deep space radiation protection, hydroponic and aeroponic plants, and bioprospecting, which is identifying plants and animals that may contain substances with potential for use as drugs, biochemicals, and more.
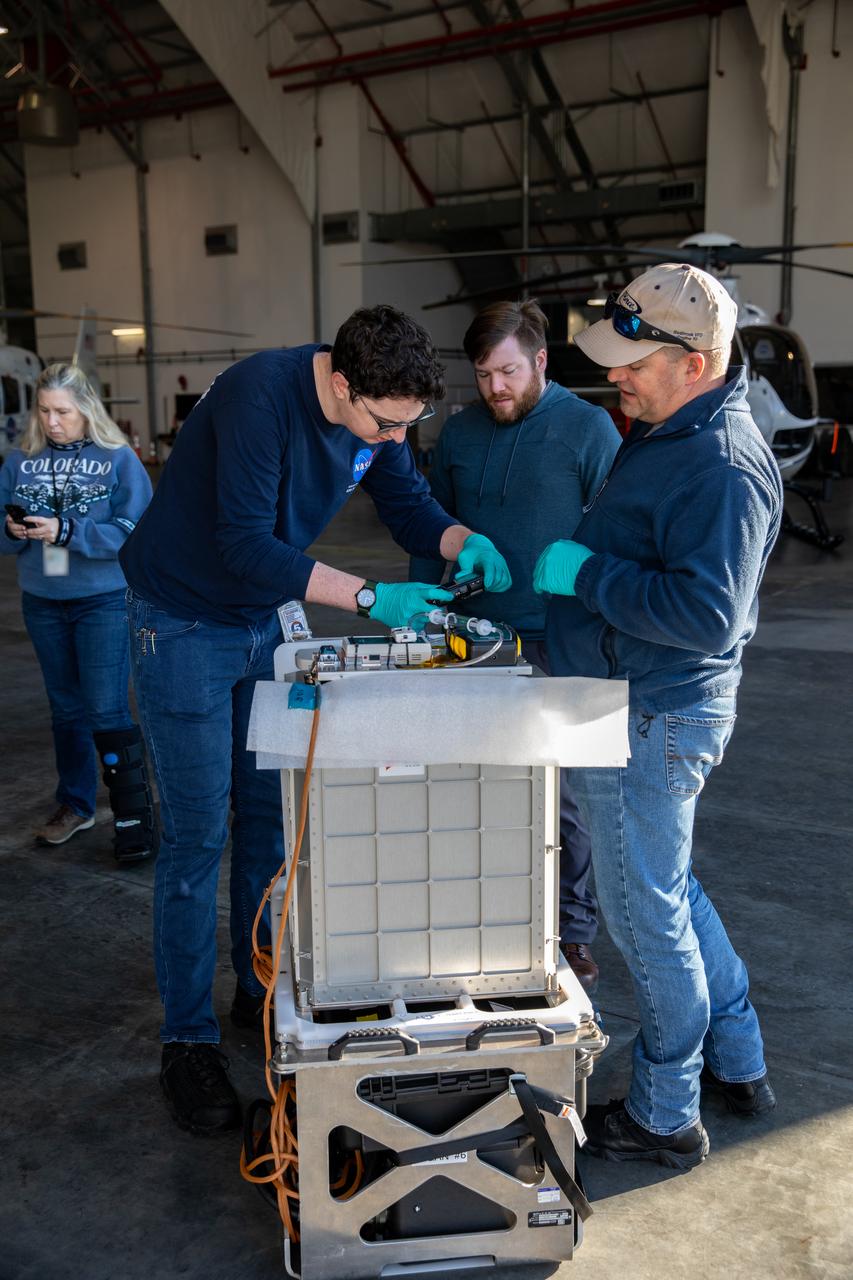

Technicians at the Launch and Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida receive scientific research samples for processing at the spaceport’s Space Station Processing Facility on Jan. 11, 2023. The experiments returned to Earth on SpaceX's 26th commercial resupply services mission, which launched from Kennedy’s Pad 39A at 2:20 p.m. EST on Nov. 26, 2022, making its successful parachute-assisted splashdown west of Tampa in the Gulf of Mexico, at 5:19 a.m. EST on Jan. 11. The SpaceX cargo Dragon returned approximately 4,400 pounds of scientific experiments and other cargo from the International Space Station. Splashing down off the coast of Florida enables quick transportation of the experiments, allowing SpaceX to retrieve Dragon and offload time-sensitive research cargo to pack on an Airbus H225 helicopter for delivery to Kennedy just hours later. Some of the scientific investigations that Dragon returned include those on deep space radiation protection, hydroponic and aeroponic plants, and bioprospecting, which is identifying plants and animals that may contain substances with potential for use as drugs, biochemicals, and more.

An Airbus H225 helicopter lands at the Launch and Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 11, 2023, delivering scientific research samples for processing at the spaceport’s Space Station Processing Facility. The experiments returned to Earth on SpaceX's 26th commercial resupply services mission, which launched from Kennedy’s Pad 39A at 2:20 p.m. EST on Nov. 26, 2022, making its successful parachute-assisted splashdown west of Tampa in the Gulf of Mexico at 5:19 a.m. EST on Jan. 11. The SpaceX cargo Dragon returned approximately 4,400 pounds of scientific experiments and other cargo from the International Space Station. Splashing down off the coast of Florida enables quick transportation of the experiments, allowing SpaceX to retrieve Dragon and offload time-sensitive research cargo to pack on an Airbus H225 helicopter for delivery to Kennedy just hours later. Some of the scientific investigations that Dragon returned include those on deep space radiation protection, hydroponic and aeroponic plants, and bioprospecting, which is identifying plants and animals that may contain substances with potential for use as drugs, biochemicals, and more.
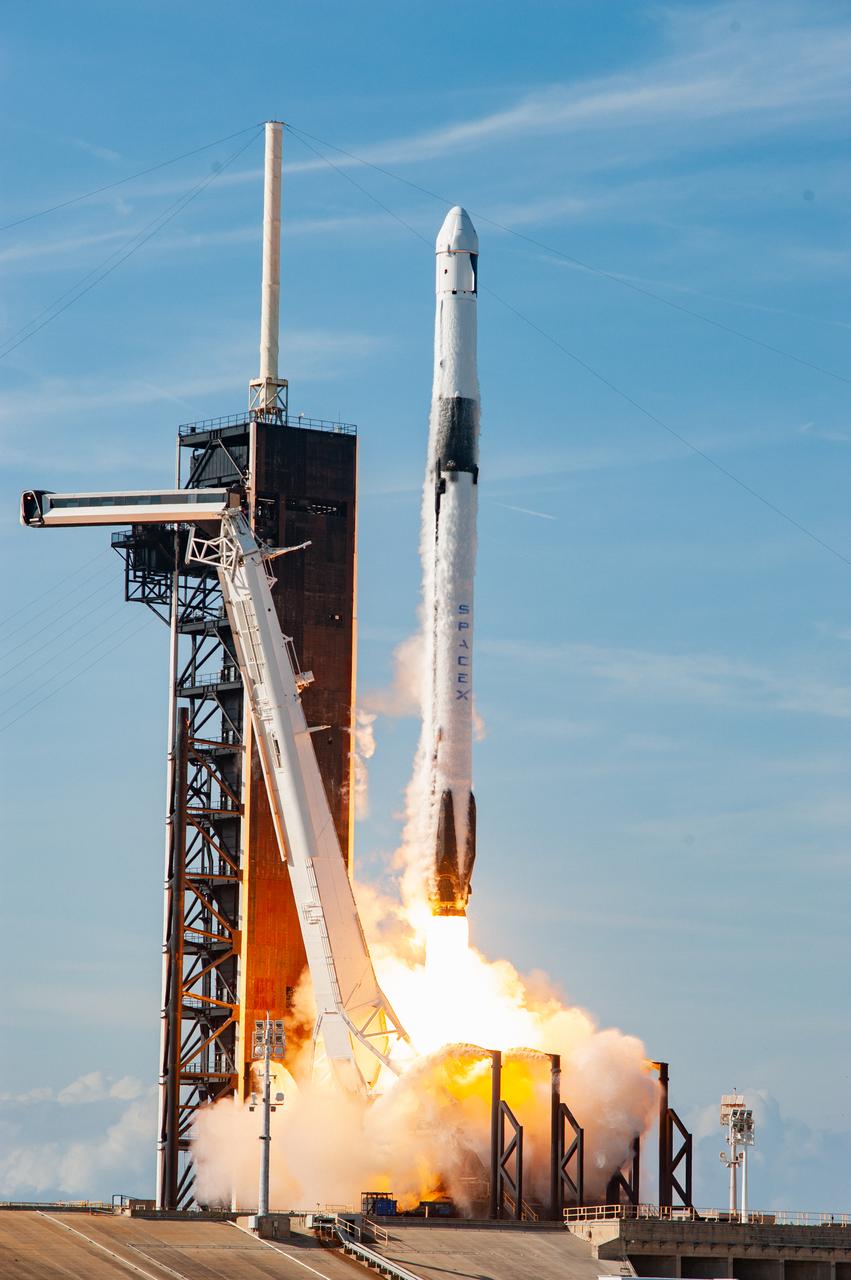

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Dragon cargo spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 26, 2022, on the company’s 26th commercial resupply services mission for the agency to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 2:20 p.m. EST. Dragon will deliver more than 7,700 pounds of cargo, including a variety of NASA investigations, supplies, and equipment to the crew aboard the space station, including the next pair of ISS Roll Out Solar Arrays (iROSAs). The spacecraft is expected to spend about a month attached to the orbiting outpost before it returns to Earth with research and return cargo, splashing down off the coast of Florida.

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket soars upward after its liftoff from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 26, 2022, on the company’s 26th Commercial Resupply Services mission for the agency to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo spacecraft will deliver about 7,700 pounds of science and research, supplies, and equipment to the crew aboard the space station, including the next pair of ISS Roll Out Solar Arrays (iROSAs). The spacecraft is expected to spend about a month attached to the orbiting outpost before it returns to Earth with research and return cargo, splashing down off the coast of Florida.
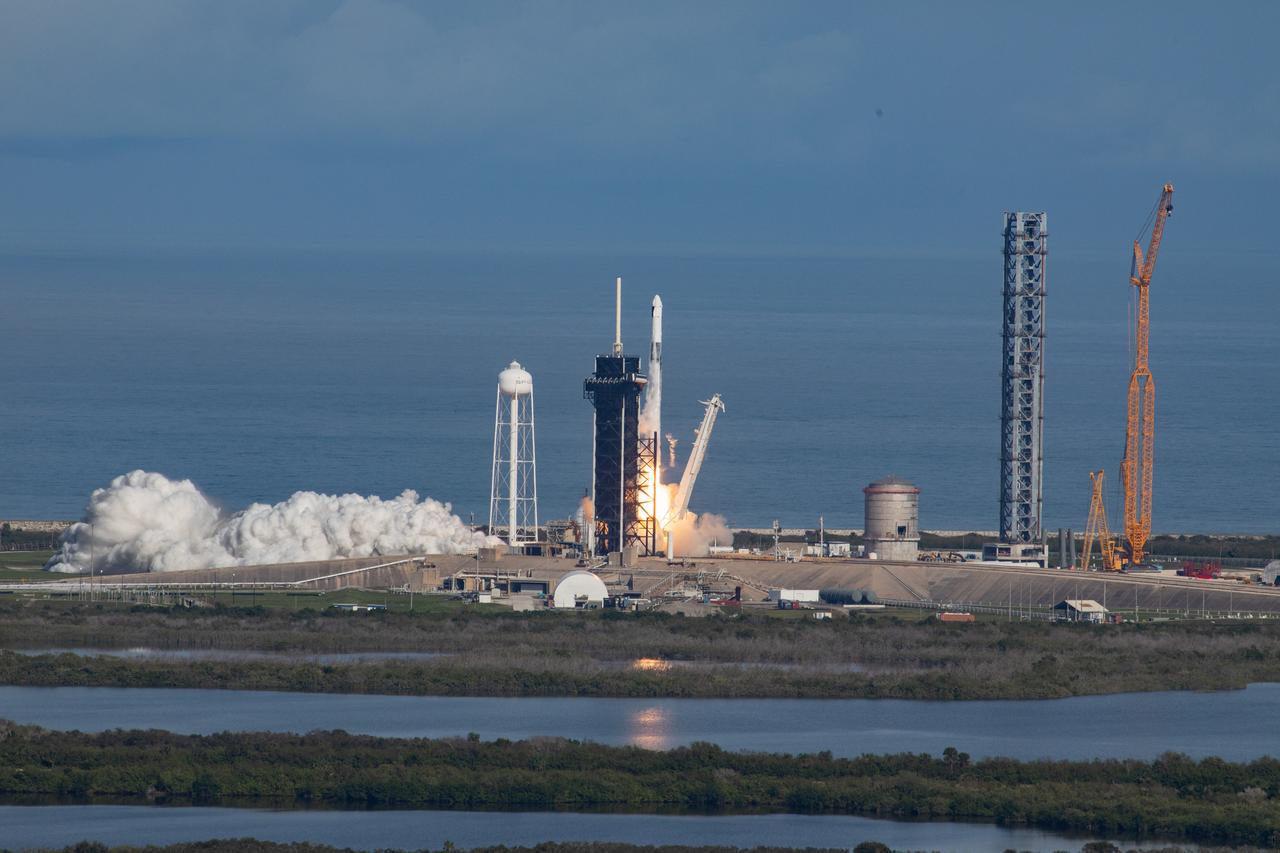

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Dragon cargo spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 26, 2022, on the company’s 26th commercial resupply services mission for the agency to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 2:20 p.m. EST. Dragon will deliver more than 7,700 pounds of cargo, including a variety of NASA investigations, supplies, and equipment to the crew aboard the space station, including the next pair of ISS Roll Out Solar Arrays (iROSAs). The spacecraft is expected to spend about a month attached to the orbiting outpost before it returns to Earth with research and return cargo, splashing down off the coast of Florida.
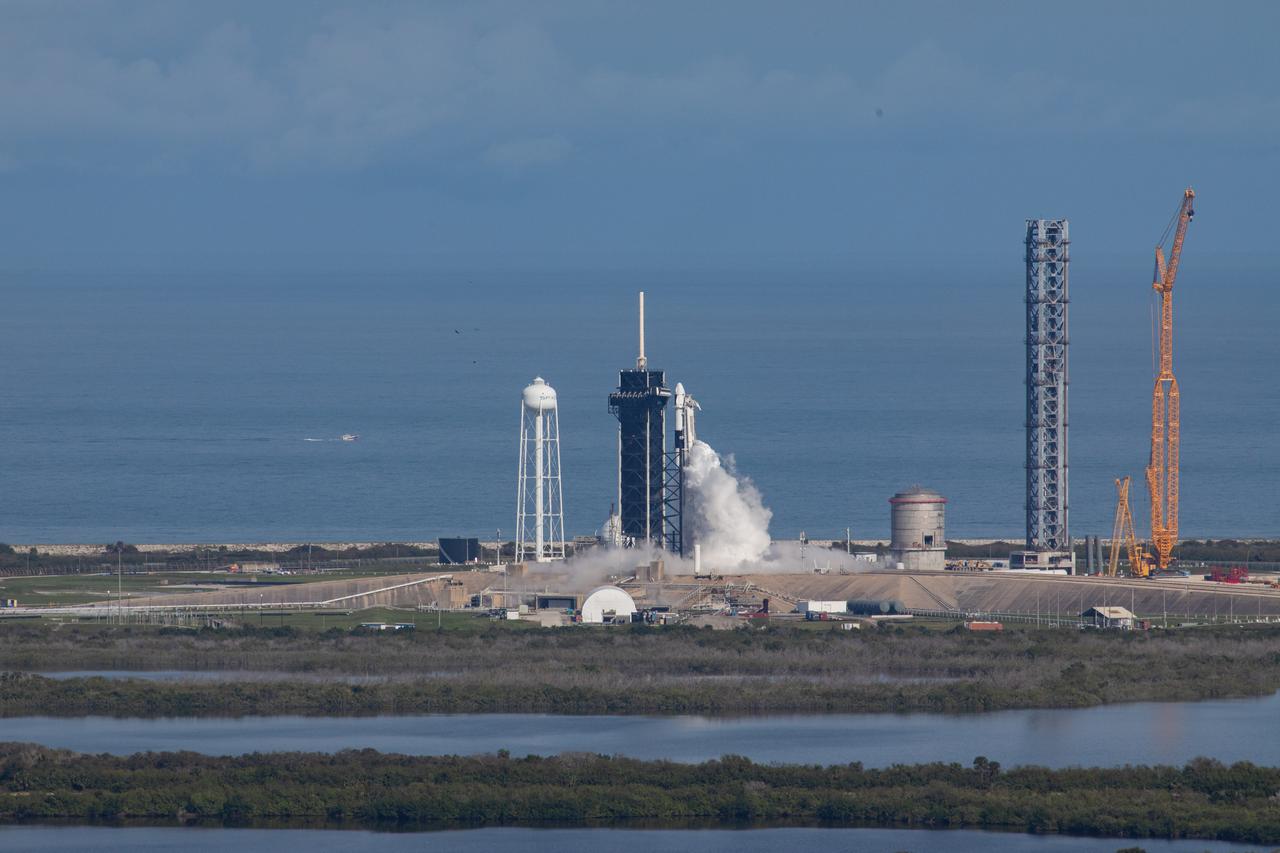

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Dragon cargo spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 26, 2022, on the company’s 26th commercial resupply services mission for the agency to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 2:20 p.m. EST. Dragon will deliver more than 7,700 pounds of cargo, including a variety of NASA investigations, supplies, and equipment to the crew aboard the space station, including the next pair of ISS Roll Out Solar Arrays (iROSAs). The spacecraft is expected to spend about a month attached to the orbiting outpost before it returns to Earth with research and return cargo, splashing down off the coast of Florida.
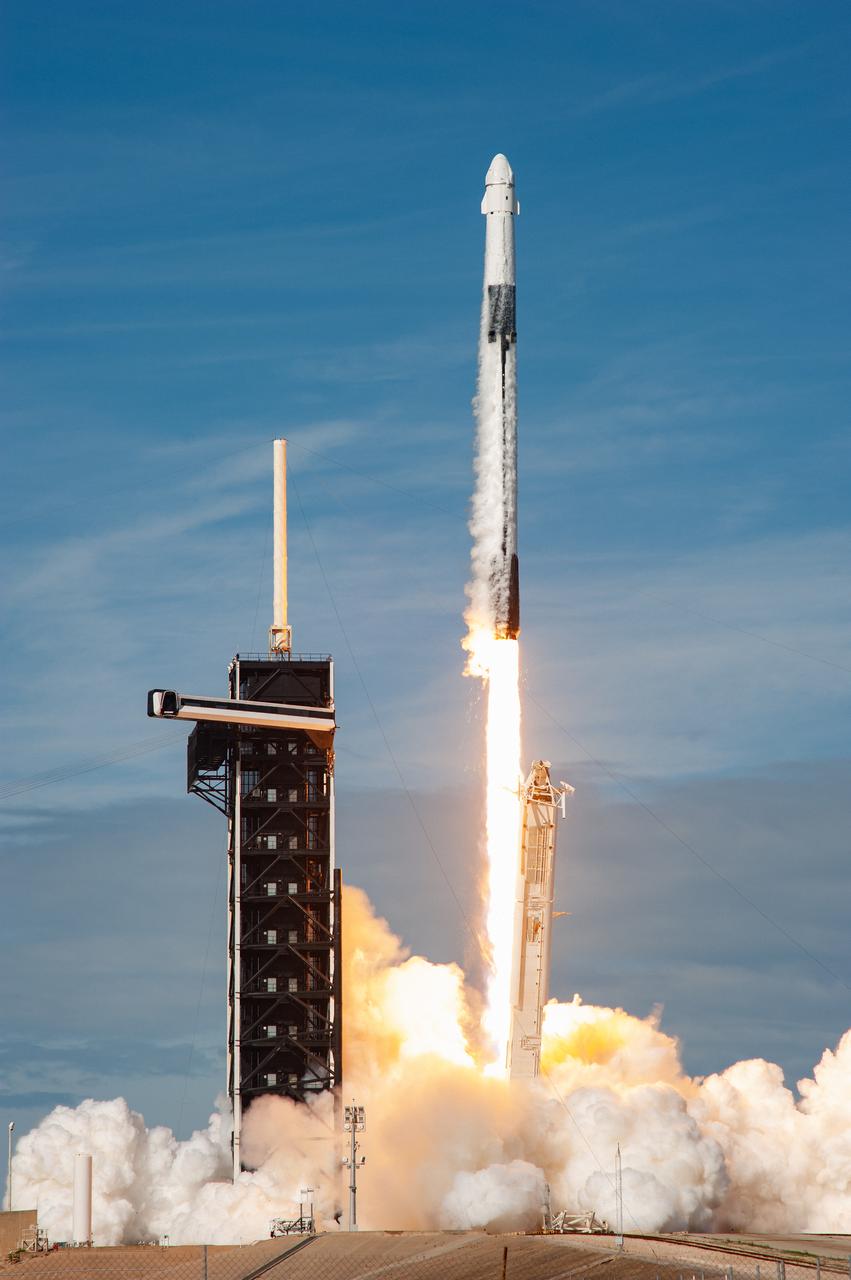

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Dragon cargo spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 26, 2022, on the company’s 26th commercial resupply services mission for the agency to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 2:20 p.m. EST. Dragon will deliver more than 7,700 pounds of cargo, including a variety of NASA investigations, supplies, and equipment to the crew aboard the space station, including the next pair of ISS Roll Out Solar Arrays (iROSAs). The spacecraft is expected to spend about a month attached to the orbiting outpost before it returns to Earth with research and return cargo, splashing down off the coast of Florida.
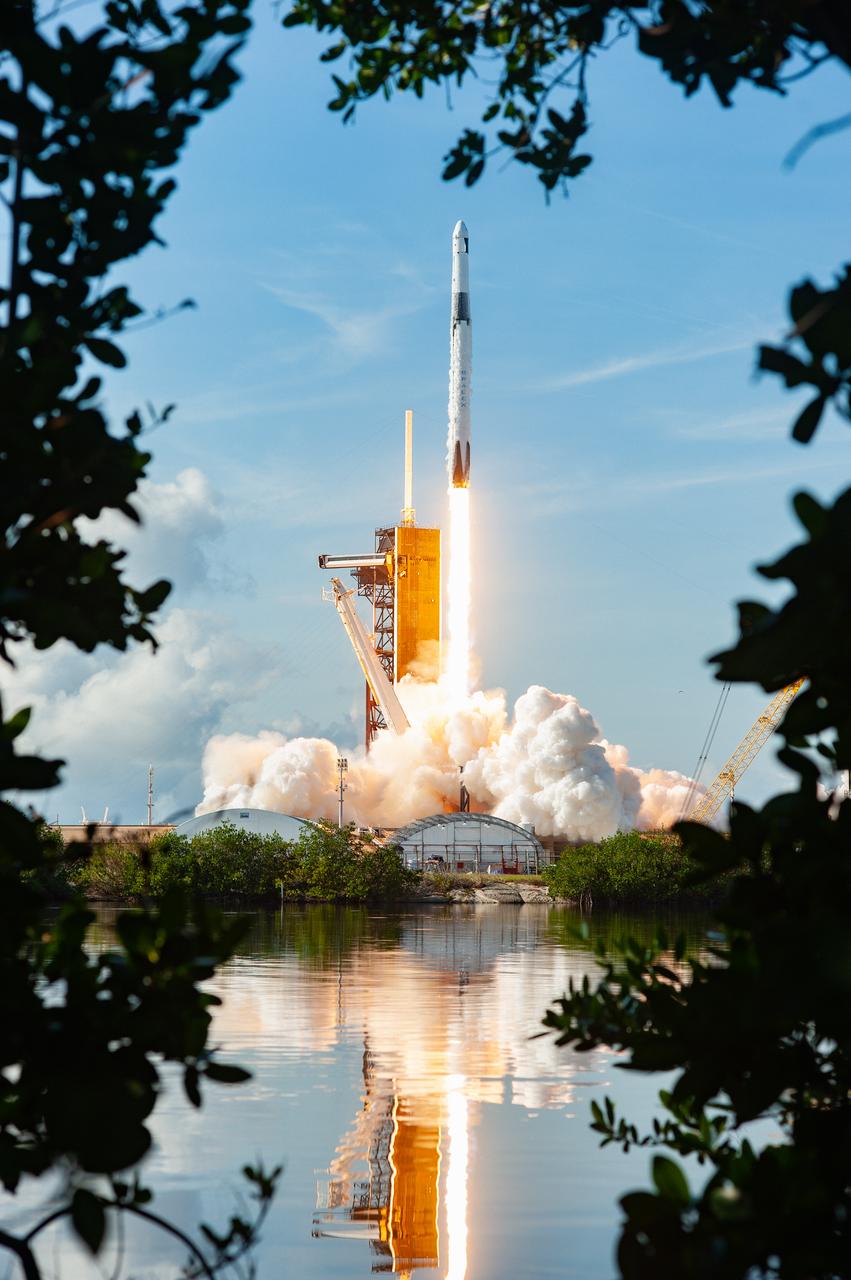

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Dragon cargo spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 26, 2022, on the company’s 26th commercial resupply services mission for the agency to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 2:20 p.m. EST. Dragon will deliver more than 7,700 pounds of cargo, including a variety of NASA investigations, supplies, and equipment to the crew aboard the space station, including the next pair of ISS Roll Out Solar Arrays (iROSAs). The spacecraft is expected to spend about a month attached to the orbiting outpost before it returns to Earth with research and return cargo, splashing down off the coast of Florida.
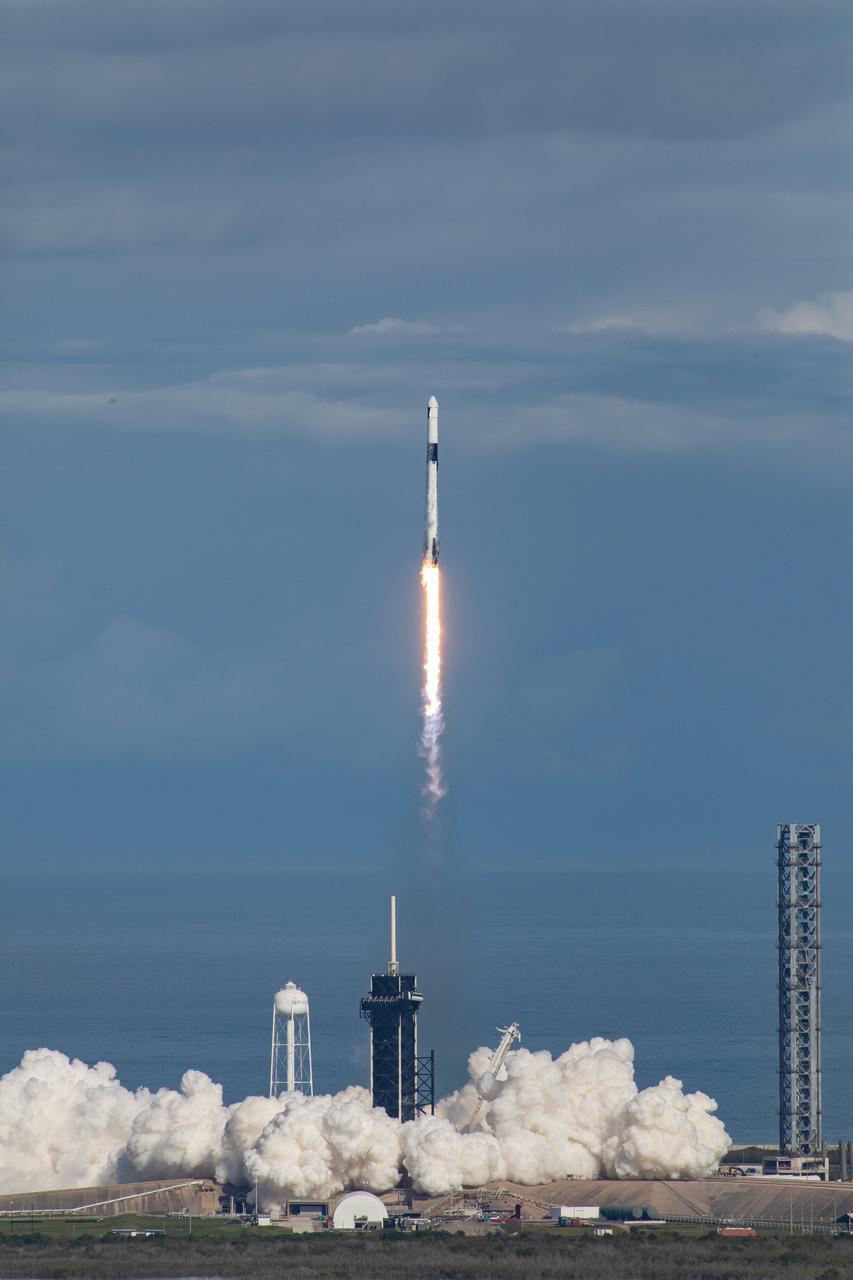

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Dragon cargo spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 26, 2022, on the company’s 26th commercial resupply services mission for the agency to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 2:20 p.m. EST. Dragon will deliver more than 7,700 pounds of cargo, including a variety of NASA investigations, supplies, and equipment to the crew aboard the space station, including the next pair of ISS Roll Out Solar Arrays (iROSAs). The spacecraft is expected to spend about a month attached to the orbiting outpost before it returns to Earth with research and return cargo, splashing down off the coast of Florida.
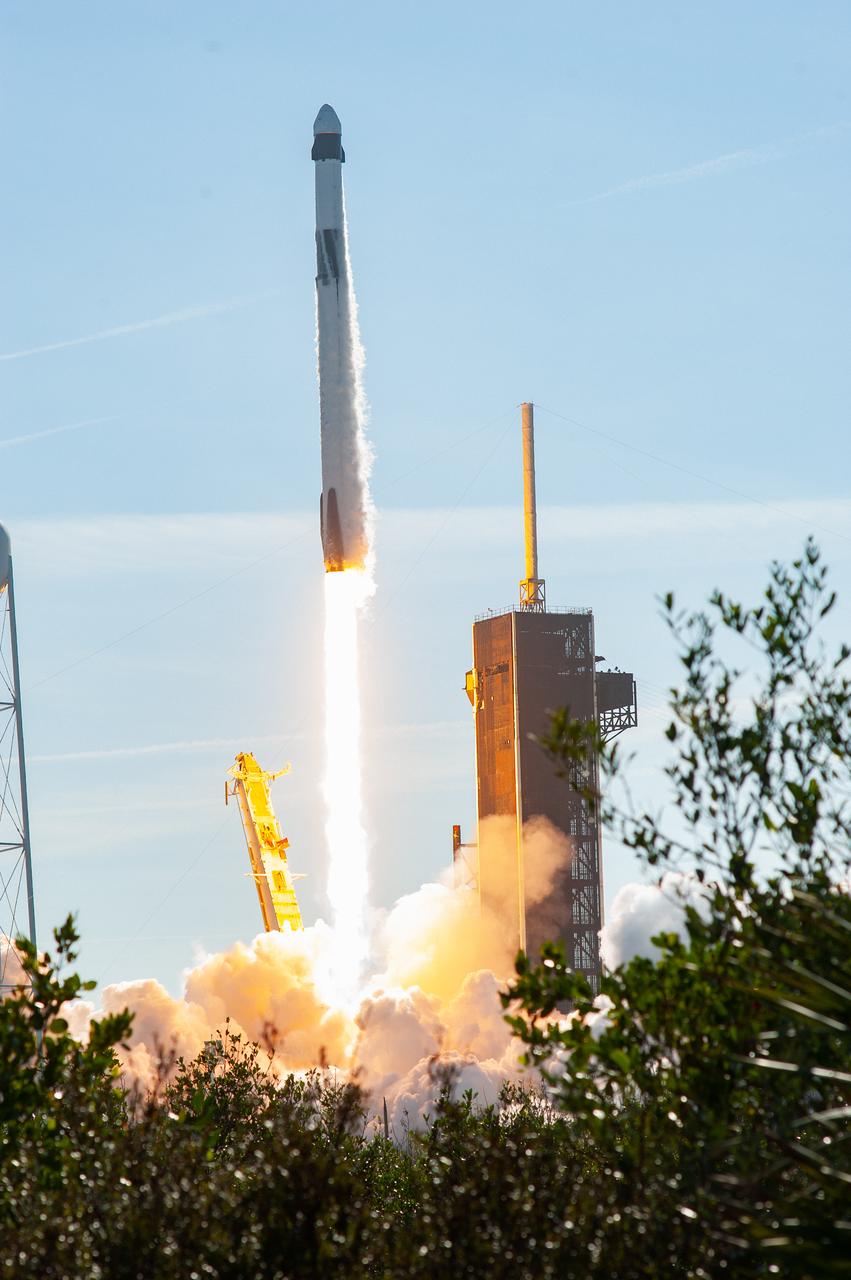

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Dragon cargo spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 26, 2022, on the company’s 26th commercial resupply services mission for the agency to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 2:20 p.m. EST. Dragon will deliver more than 7,700 pounds of cargo, including a variety of NASA investigations, supplies, and equipment to the crew aboard the space station, including the next pair of ISS Roll Out Solar Arrays (iROSAs). The spacecraft is expected to spend about a month attached to the orbiting outpost before it returns to Earth with research and return cargo, splashing down off the coast of Florida.
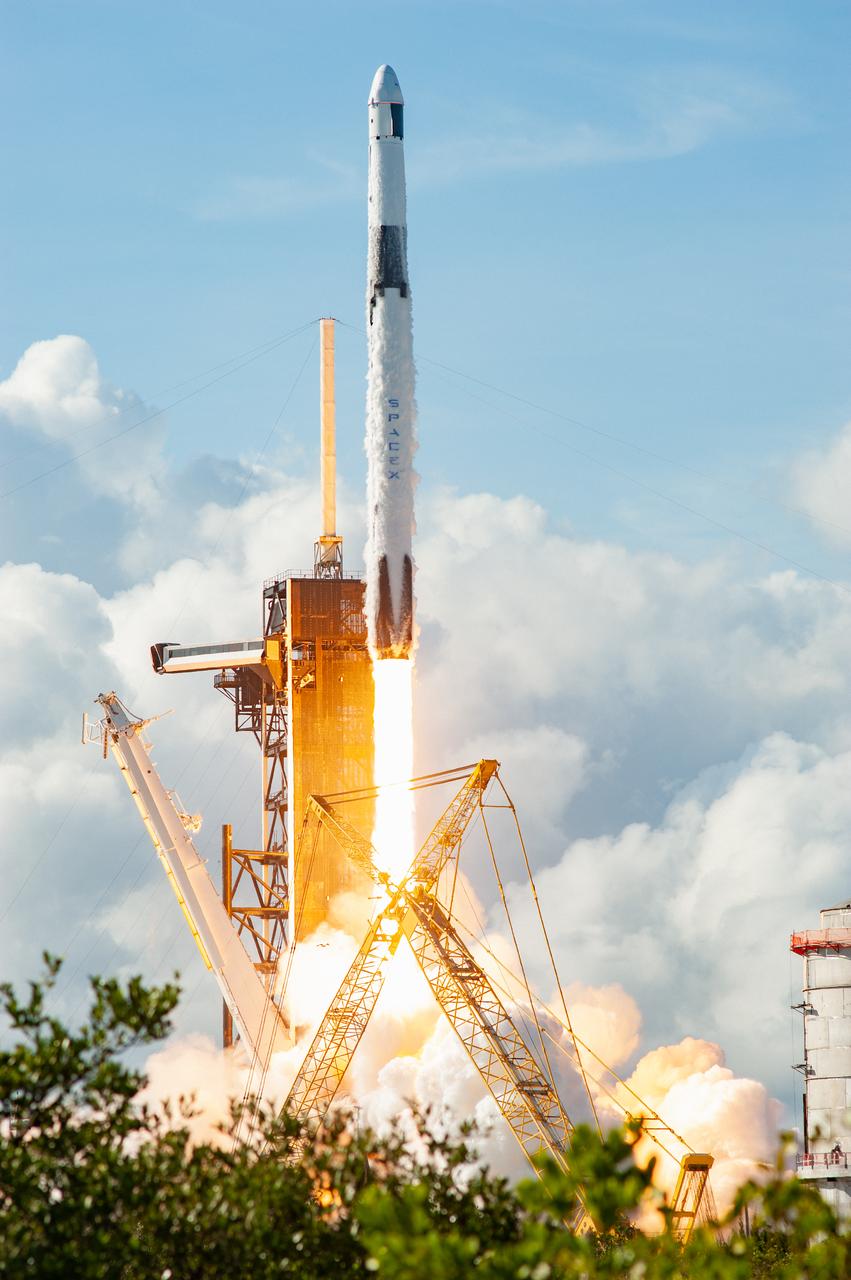

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Dragon cargo spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 26, 2022, on the company’s 26th commercial resupply services mission for the agency to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 2:20 p.m. EST. Dragon will deliver more than 7,700 pounds of cargo, including a variety of NASA investigations, supplies, and equipment to the crew aboard the space station, including the next pair of ISS Roll Out Solar Arrays (iROSAs). The spacecraft is expected to spend about a month attached to the orbiting outpost before it returns to Earth with research and return cargo, splashing down off the coast of Florida.
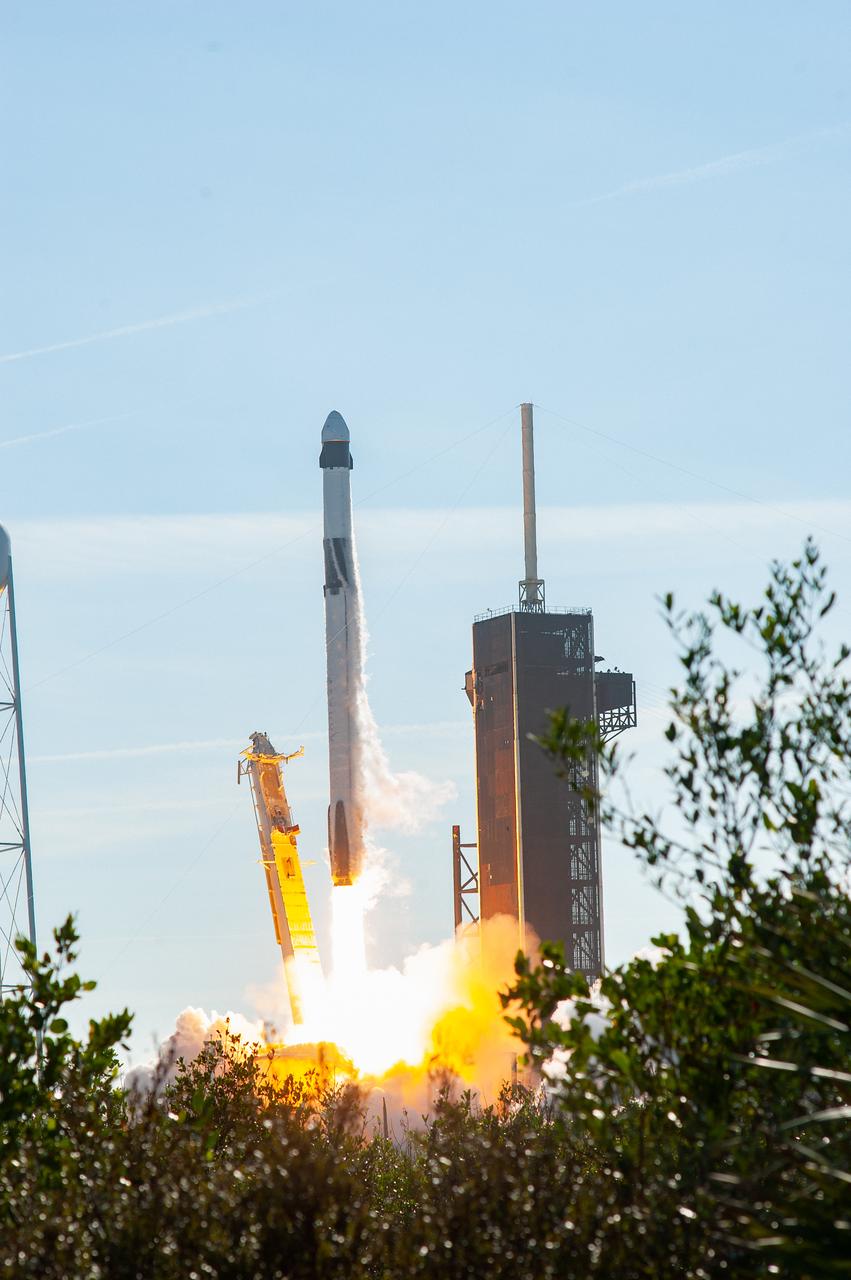

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Dragon cargo spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 26, 2022, on the company’s 26th commercial resupply services mission for the agency to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 2:20 p.m. EST. Dragon will deliver more than 7,700 pounds of cargo, including a variety of NASA investigations, supplies, and equipment to the crew aboard the space station, including the next pair of ISS Roll Out Solar Arrays (iROSAs). The spacecraft is expected to spend about a month attached to the orbiting outpost before it returns to Earth with research and return cargo, splashing down off the coast of Florida.
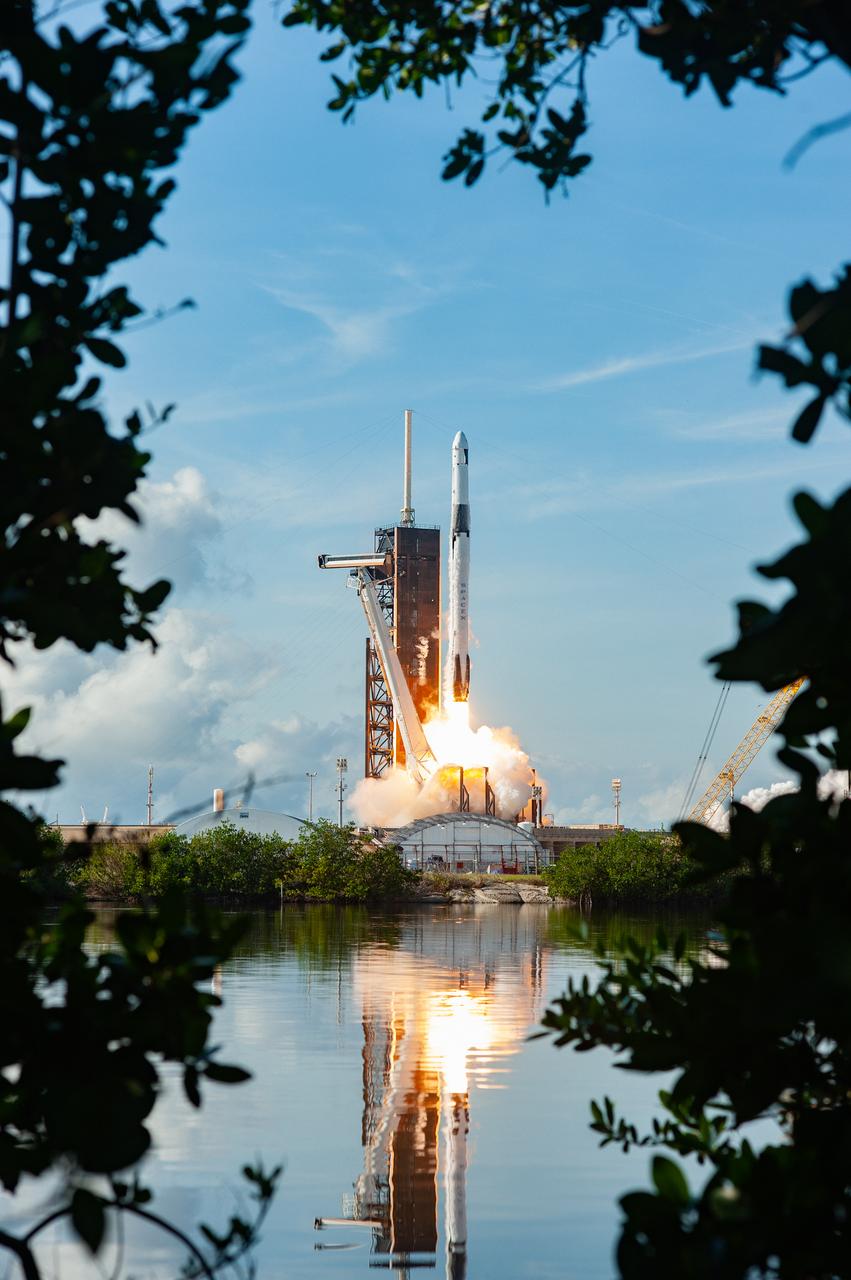

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Dragon cargo spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 26, 2022, on the company’s 26th commercial resupply services mission for the agency to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 2:20 p.m. EST. Dragon will deliver more than 7,700 pounds of cargo, including a variety of NASA investigations, supplies, and equipment to the crew aboard the space station, including the next pair of ISS Roll Out Solar Arrays (iROSAs). The spacecraft is expected to spend about a month attached to the orbiting outpost before it returns to Earth with research and return cargo, splashing down off the coast of Florida.
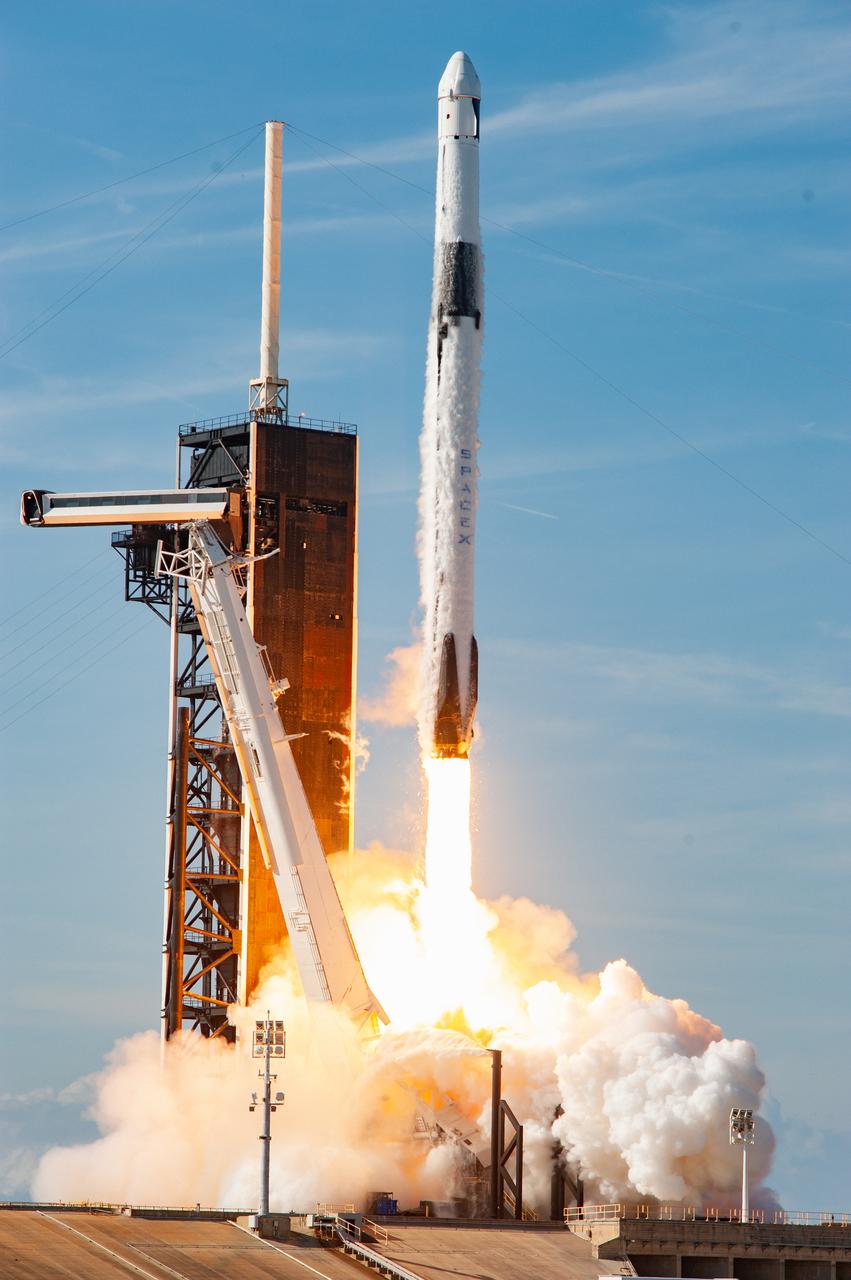

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Dragon cargo spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 26, 2022, on the company’s 26th commercial resupply services mission for the agency to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 2:20 p.m. EST. Dragon will deliver more than 7,700 pounds of cargo, including a variety of NASA investigations, supplies, and equipment to the crew aboard the space station, including the next pair of ISS Roll Out Solar Arrays (iROSAs). The spacecraft is expected to spend about a month attached to the orbiting outpost before it returns to Earth with research and return cargo, splashing down off the coast of Florida.

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket soars upward after its liftoff from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 26, 2022, on the company’s 26th Commercial Resupply Services mission for the agency to the International Space Station. The Dragon cargo spacecraft will deliver about 7,700 pounds of science and research, supplies, and equipment to the crew aboard the space station, including the next pair of ISS Roll Out Solar Arrays (iROSAs). The spacecraft is expected to spend about a month attached to the orbiting outpost before it returns to Earth with research and return cargo, splashing down off the coast of Florida.
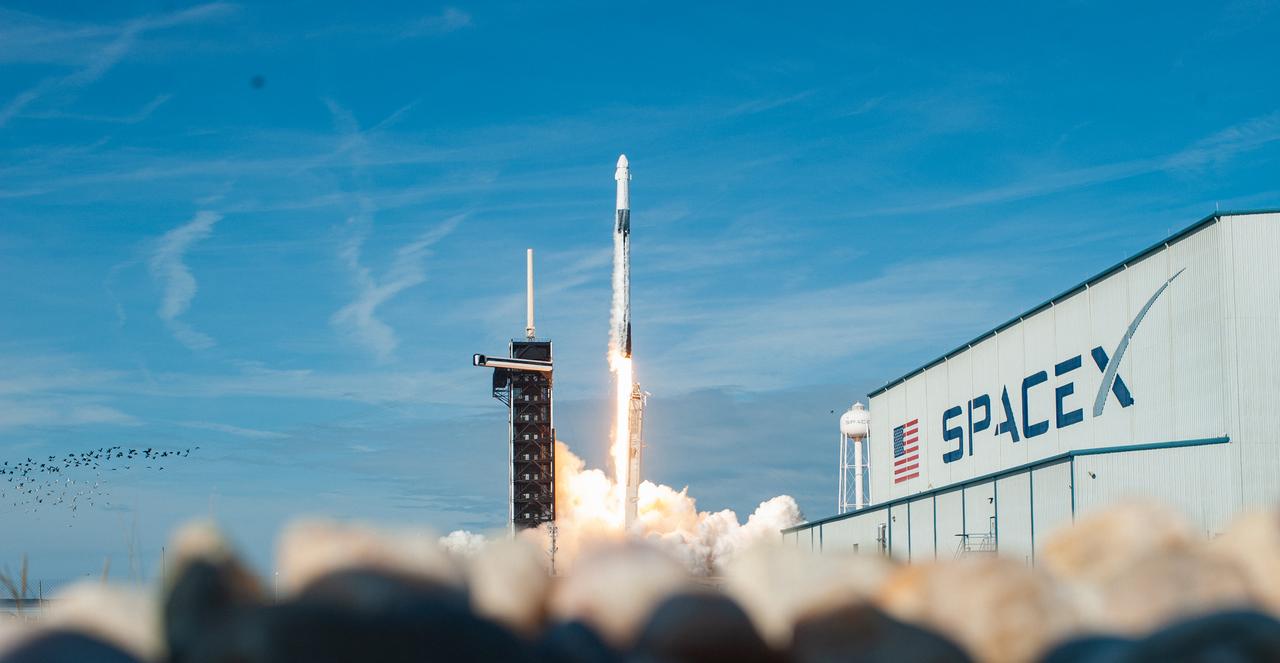

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Dragon cargo spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 26, 2022, on the company’s 26th commercial resupply services mission for the agency to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 2:20 p.m. EST. Dragon will deliver more than 7,700 pounds of cargo, including a variety of NASA investigations, supplies, and equipment to the crew aboard the space station, including the next pair of ISS Roll Out Solar Arrays (iROSAs). The spacecraft is expected to spend about a month attached to the orbiting outpost before it returns to Earth with research and return cargo, splashing down off the coast of Florida.
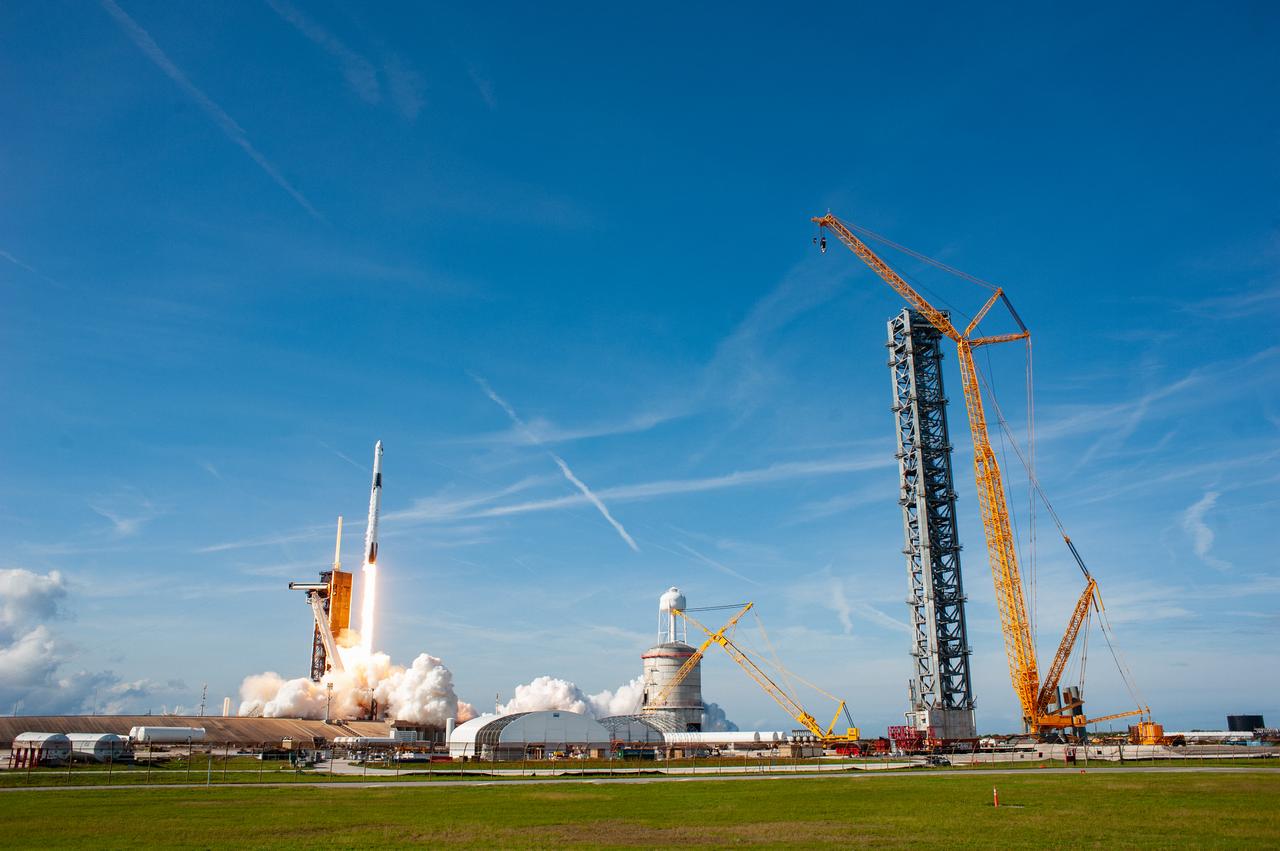

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Dragon cargo spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 26, 2022, on the company’s 26th commercial resupply services mission for the agency to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 2:20 p.m. EST. Dragon will deliver more than 7,700 pounds of cargo, including a variety of NASA investigations, supplies, and equipment to the crew aboard the space station, including the next pair of ISS Roll Out Solar Arrays (iROSAs). The spacecraft is expected to spend about a month attached to the orbiting outpost before it returns to Earth with research and return cargo, splashing down off the coast of Florida.
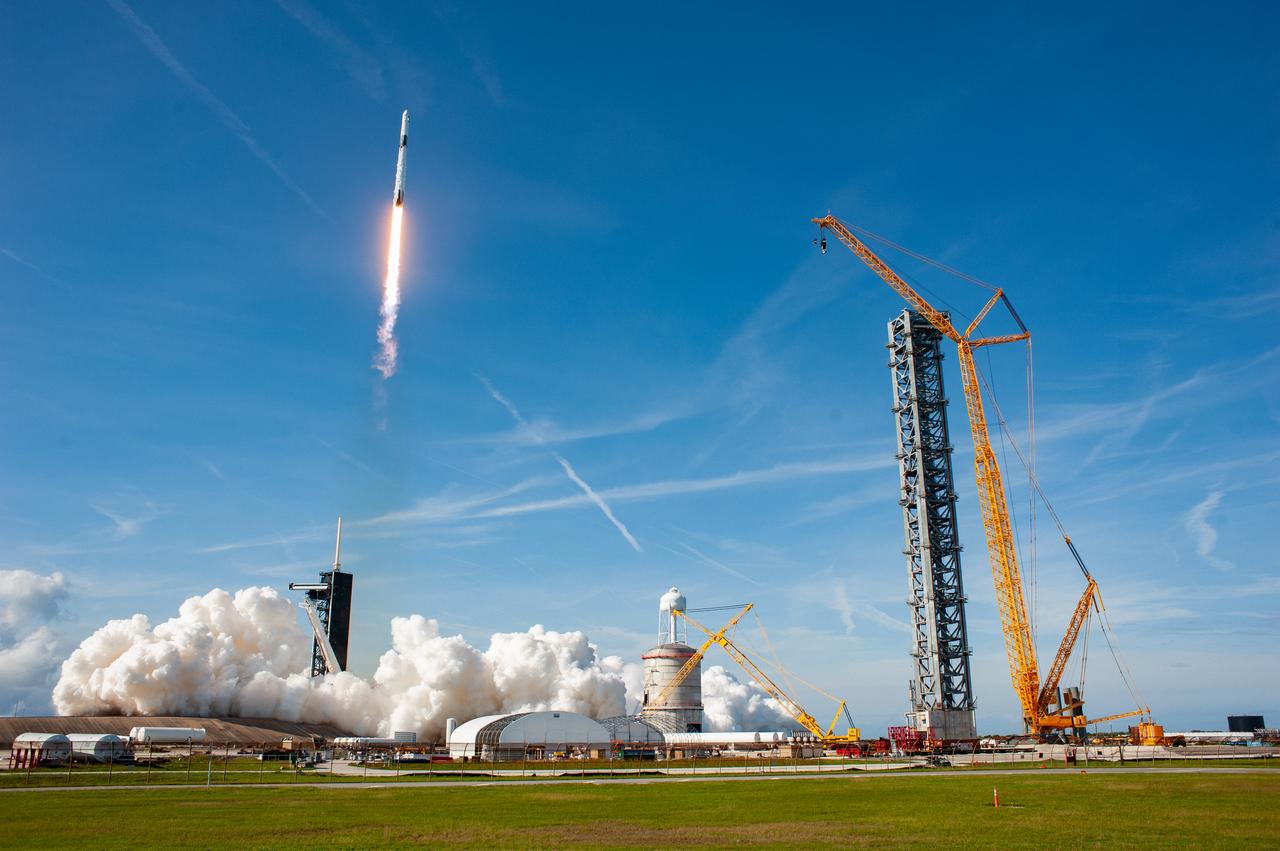

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Dragon cargo spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 26, 2022, on the company’s 26th commercial resupply services mission for the agency to the International Space Station. Liftoff was at 2:20 p.m. EST. Dragon will deliver more than 7,700 pounds of cargo, including a variety of NASA investigations, supplies, and equipment to the crew aboard the space station, including the next pair of ISS Roll Out Solar Arrays (iROSAs). The spacecraft is expected to spend about a month attached to the orbiting outpost before it returns to Earth with research and return cargo, splashing down off the coast of Florida.
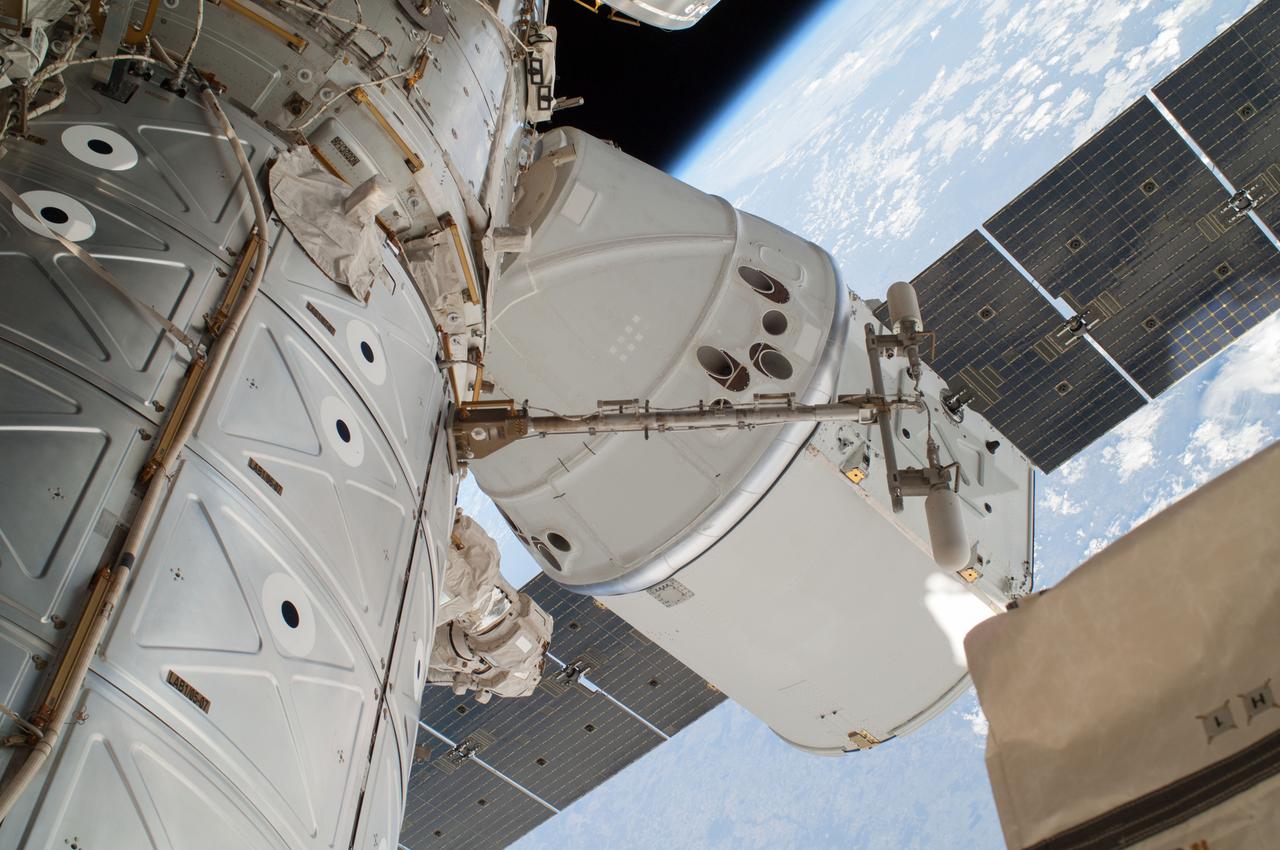

View of the SpaceX Dragon Commercial Resupply Services-3 (CRS-3) spacecraft and portions of the Destiny U.S. Laboratory and Harmony Node 2 taken against a backdrop of Earth and space by Extravehicular crewmember 1 (EV1) during Extravehicular Activity 26 (EVA 26).

ISS047e021823 (03/26/2016) --- The Orbital ATK Cygnus cargo ship is seen on final approach to the International Space Station. The vehicle was captured at 6:51 a.m. EDT March 26 using the space station's Canadarm2 robotic arm by Expedition 47 Commander Tim Kopra. The unmanned cargo craft was then bolted to the Earth-facing port on the Unity module at 10:52 a.m. Orbital ATK’s fifth cargo delivery flight under its Commercial Resupply Services contract delivered over 7,700 pounds of cargo and included equipment to support some 250 experiments during Expeditions 47 and 48.
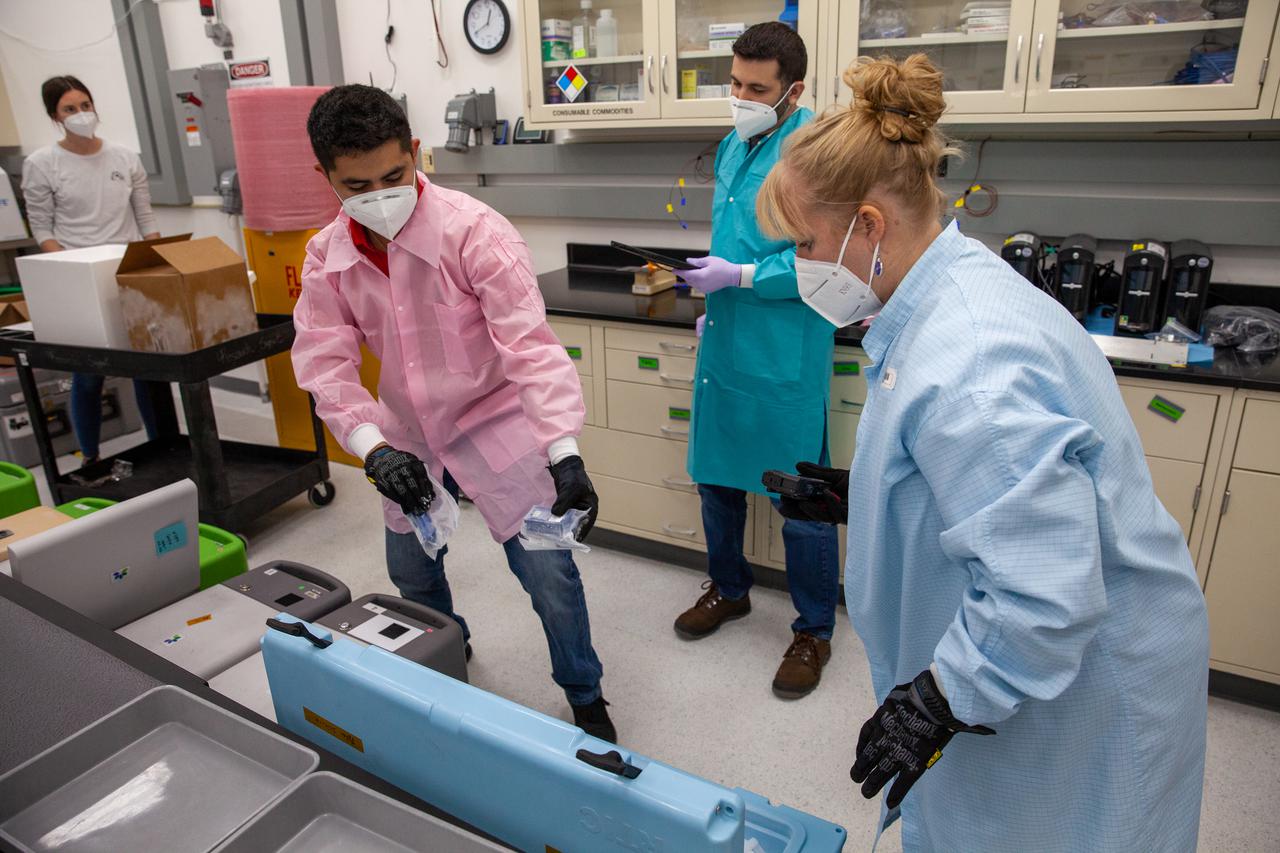

Members of the cold stowage team unpack science experiments inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 14, 2021. The experiments returned to Earth on SpaceX’s 21st commercial resupply services mission (CRS-21). Making its successful parachute-assisted splashdown west of Tampa off the Florida coast, at 8:26 p.m. EST on Jan. 13, the SpaceX cargo Dragon returned more than 4,400 pounds of scientific experiments and other cargo from the International Space Station. After splashdown, SpaceX loaded Dragon aboard their Go Navigator recovery ship and packed an Airbus H225 helicopter with the time-sensitive research cargo for delivery to Kennedy. The upgraded cargo Dragon capsule also boasts double the powered locker capacity to preserve science samples, allowing for a significant increase in the research that can be carried back to Earth.
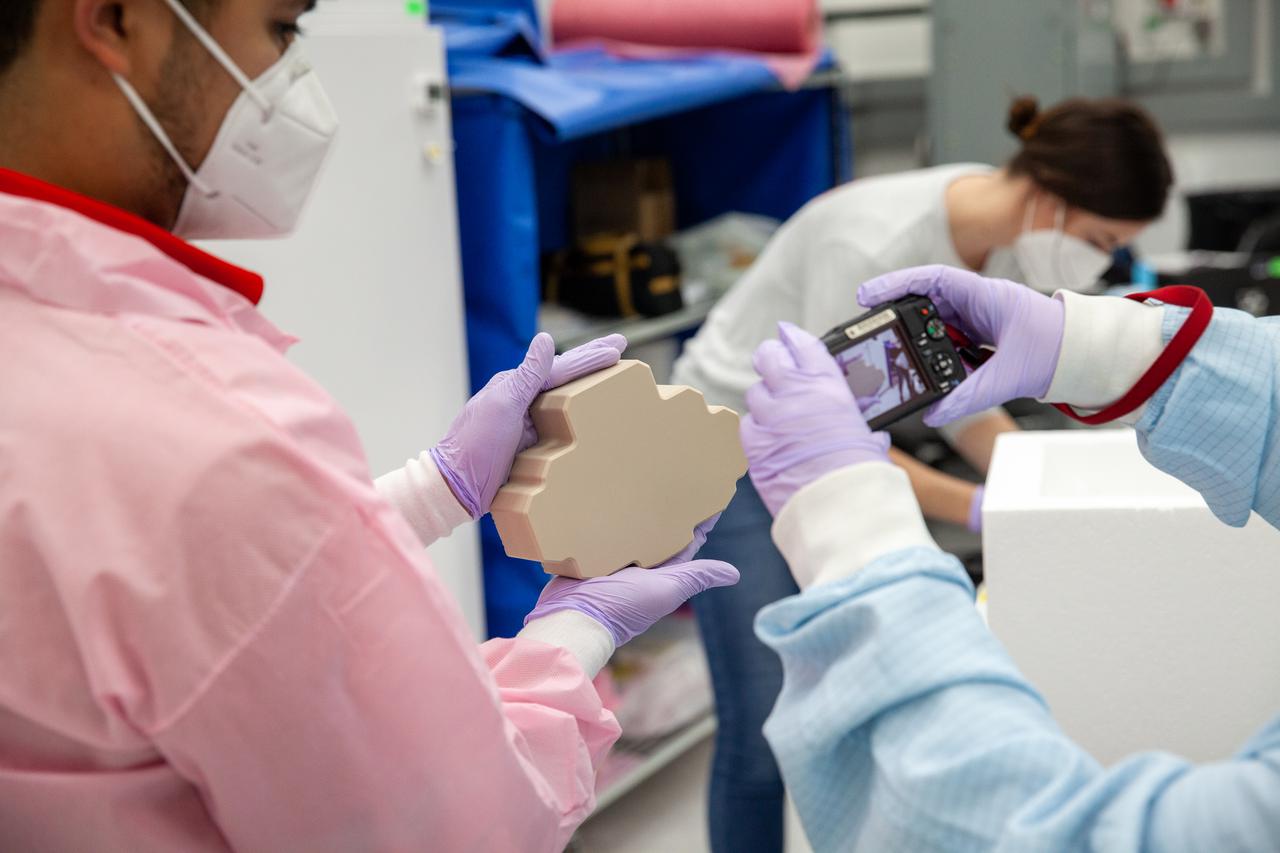

Members of the cold stowage team unpack science experiments inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 14, 2021. The experiments returned to Earth on SpaceX’s 21st commercial resupply services mission (CRS-21). Making its successful parachute-assisted splashdown west of Tampa off the Florida coast, at 8:26 p.m. EST on Jan. 13, the SpaceX cargo Dragon returned more than 4,400 pounds of scientific experiments and other cargo from the International Space Station. After splashdown, SpaceX loaded Dragon aboard their Go Navigator recovery ship and packed an Airbus H225 helicopter with the time-sensitive research cargo for delivery to Kennedy. The upgraded cargo Dragon capsule also boasts double the powered locker capacity to preserve science samples, allowing for a significant increase in the research that can be carried back to Earth.
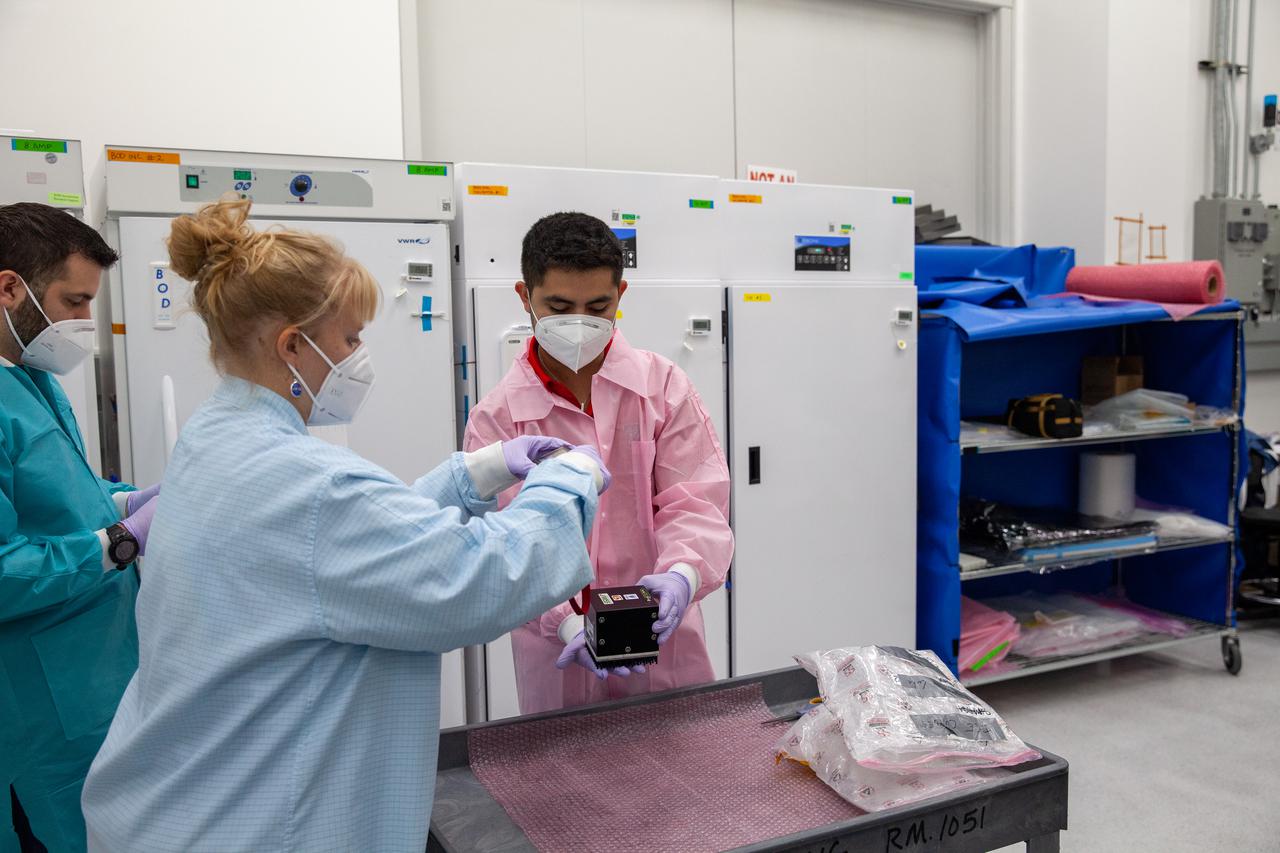

Members of the cold stowage team unpack science experiments inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 14, 2021. The experiments returned to Earth on SpaceX’s 21st commercial resupply services mission (CRS-21). Making its successful parachute-assisted splashdown west of Tampa off the Florida coast, at 8:26 p.m. EST on Jan. 13, the SpaceX cargo Dragon returned more than 4,400 pounds of scientific experiments and other cargo from the International Space Station. After splashdown, SpaceX loaded Dragon aboard their Go Navigator recovery ship and packed an Airbus H225 helicopter with the time-sensitive research cargo for delivery to Kennedy. The upgraded cargo Dragon capsule also boasts double the powered locker capacity to preserve science samples, allowing for a significant increase in the research that can be carried back to Earth.
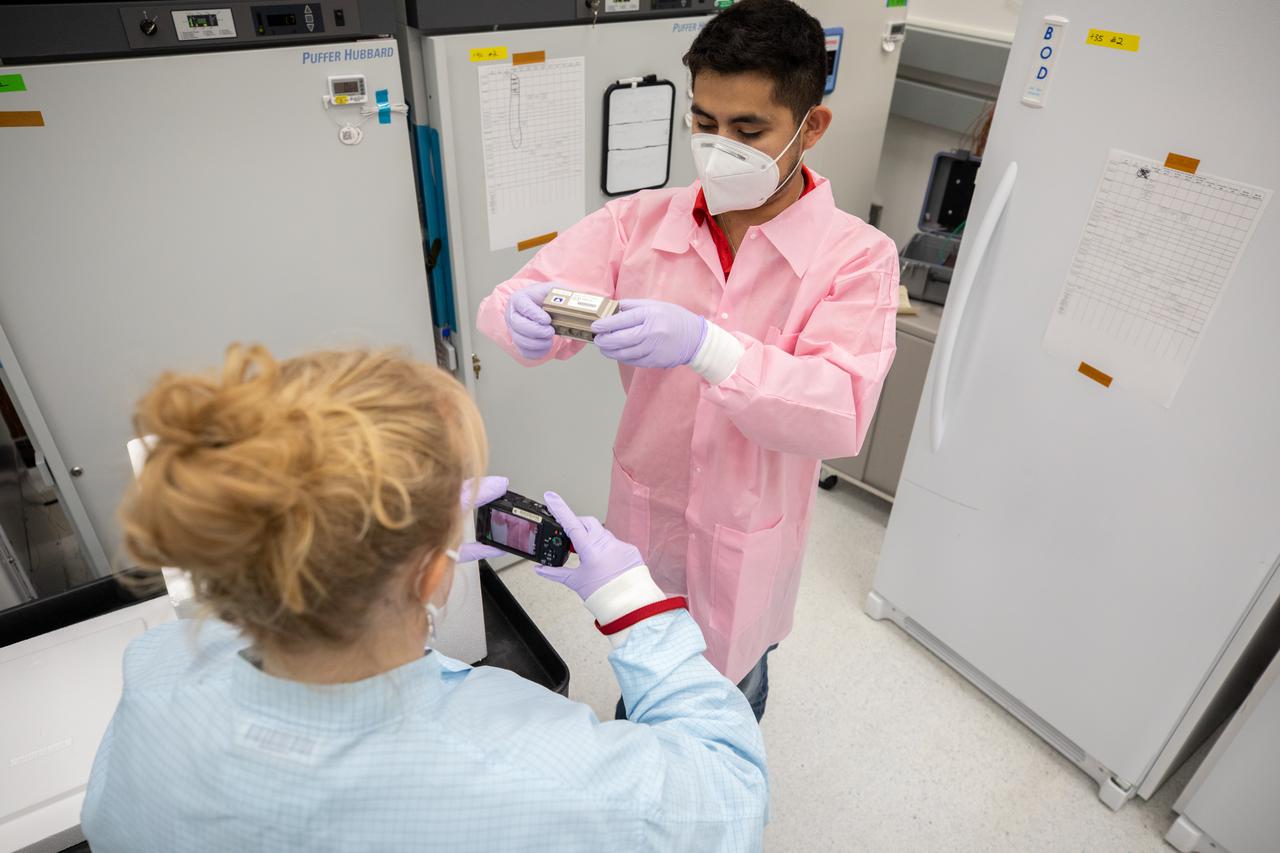
Members of the cold stowage team unpack science experiments inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 14, 2021. The experiments returned to Earth on SpaceX’s 21st commercial resupply services mission (CRS-21). Making its successful parachute-assisted splashdown west of Tampa off the Florida coast, at 8:26 p.m. EST on Jan. 13, the SpaceX cargo Dragon returned more than 4,400 pounds of scientific experiments and other cargo from the International Space Station. After splashdown, SpaceX loaded Dragon aboard their Go Navigator recovery ship and packed an Airbus H225 helicopter with the time-sensitive research cargo for delivery to Kennedy. The upgraded cargo Dragon capsule also boasts double the powered locker capacity to preserve science samples, allowing for a significant increase in the research that can be carried back to Earth.
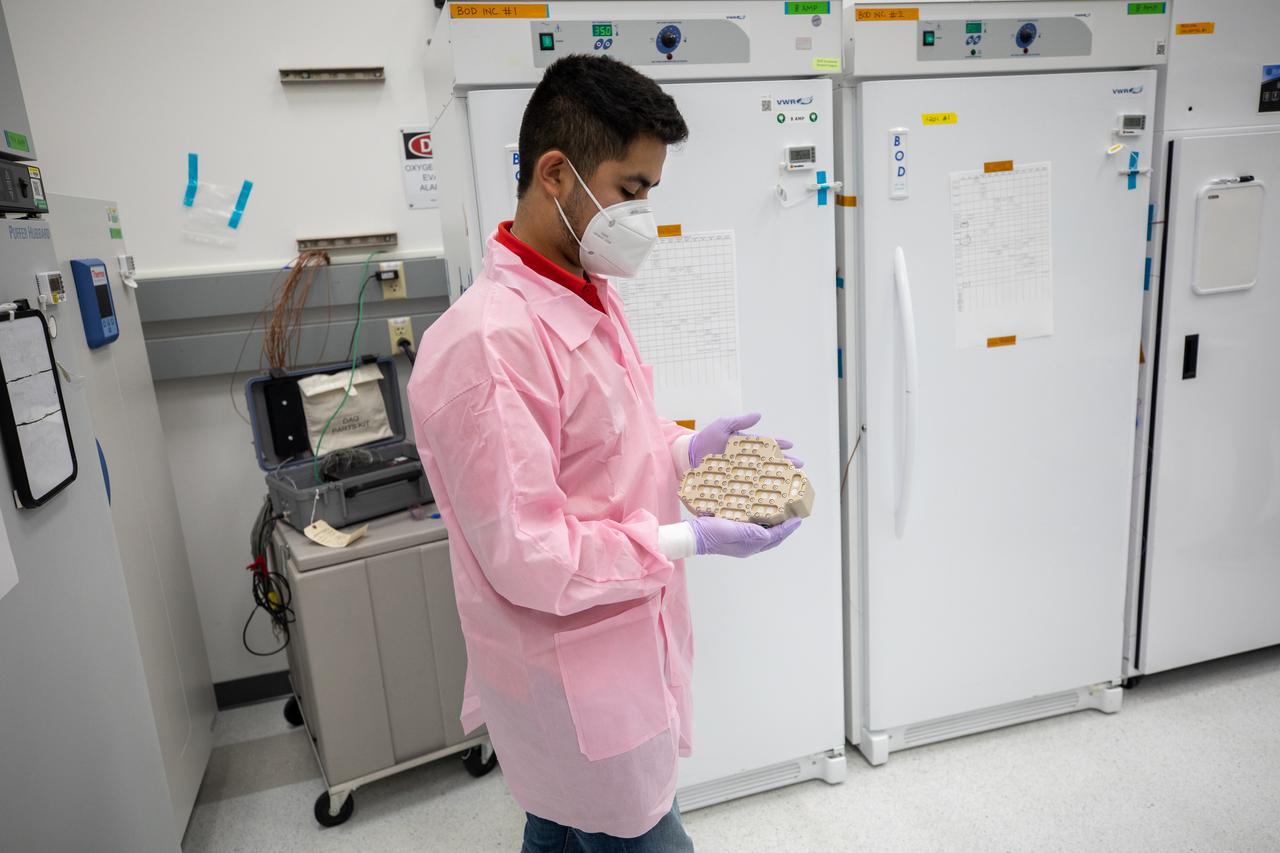

A member of the cold stowage team unpacks science experiments inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 14, 2021. The experiments returned to Earth on SpaceX’s 21st commercial resupply services mission (CRS-21). Making its successful parachute-assisted splashdown west of Tampa off the Florida coast, at 8:26 p.m. EST on Jan. 13, the SpaceX cargo Dragon returned more than 4,400 pounds of scientific experiments and other cargo from the International Space Station. After splashdown, SpaceX loaded Dragon aboard their Go Navigator recovery ship and packed an Airbus H225 helicopter with the time-sensitive research cargo for delivery to Kennedy. The upgraded cargo Dragon capsule also boasts double the powered locker capacity to preserve science samples, allowing for a significant increase in the research that can be carried back to Earth.
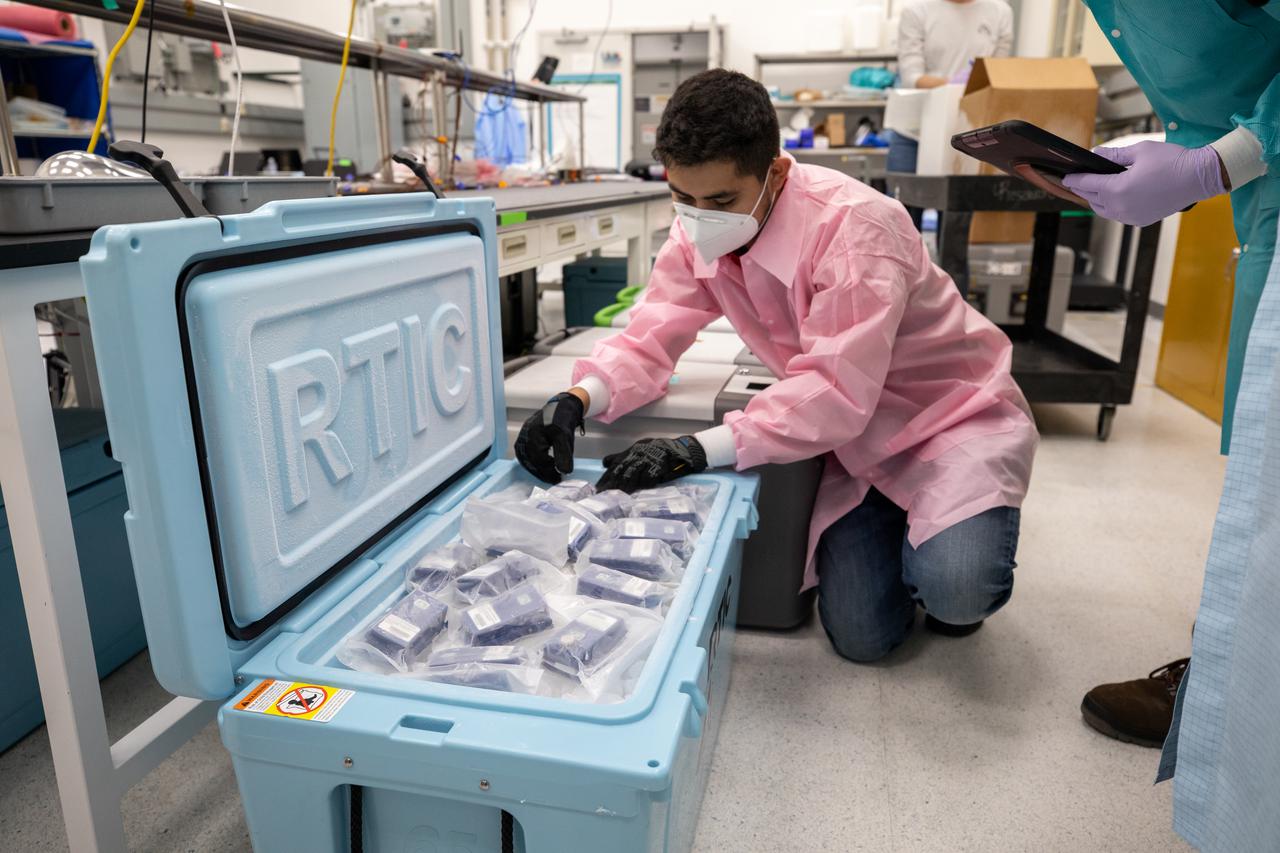

Members of the cold stowage team unpack science experiments inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 14, 2021. The experiments returned to Earth on SpaceX’s 21st commercial resupply services mission (CRS-21). Making its successful parachute-assisted splashdown west of Tampa off the Florida coast, at 8:26 p.m. EST on Jan. 13, the SpaceX cargo Dragon returned more than 4,400 pounds of scientific experiments and other cargo from the International Space Station. After splashdown, SpaceX loaded Dragon aboard their Go Navigator recovery ship and packed an Airbus H225 helicopter with the time-sensitive research cargo for delivery to Kennedy. The upgraded cargo Dragon capsule also boasts double the powered locker capacity to preserve science samples, allowing for a significant increase in the research that can be carried back to Earth.
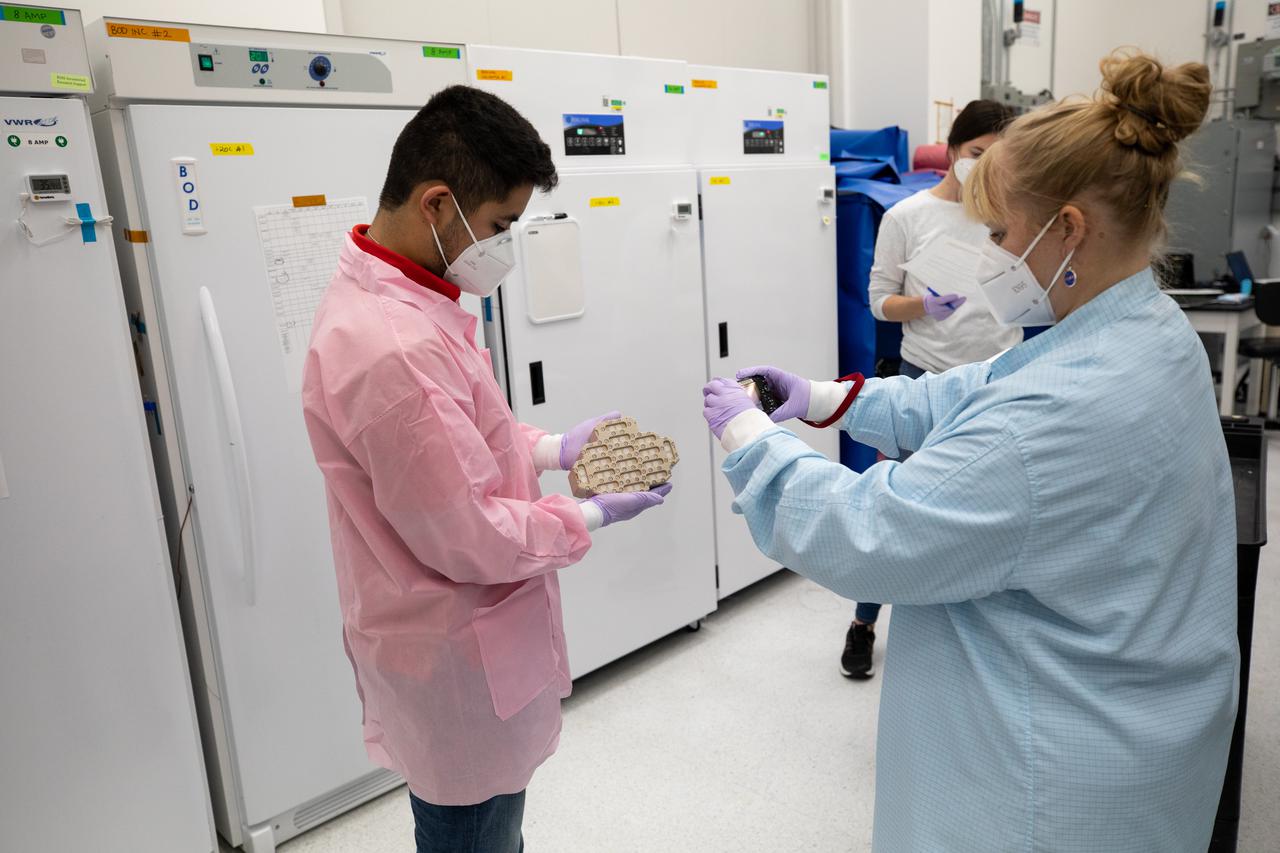

Members of the cold stowage team unpack science experiments inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 14, 2021. The experiments returned to Earth on SpaceX’s 21st commercial resupply services mission (CRS-21). Making its successful parachute-assisted splashdown west of Tampa off the Florida coast, at 8:26 p.m. EST on Jan. 13, the SpaceX cargo Dragon returned more than 4,400 pounds of scientific experiments and other cargo from the International Space Station. After splashdown, SpaceX loaded Dragon aboard their Go Navigator recovery ship and packed an Airbus H225 helicopter with the time-sensitive research cargo for delivery to Kennedy. The upgraded cargo Dragon capsule also boasts double the powered locker capacity to preserve science samples, allowing for a significant increase in the research that can be carried back to Earth.
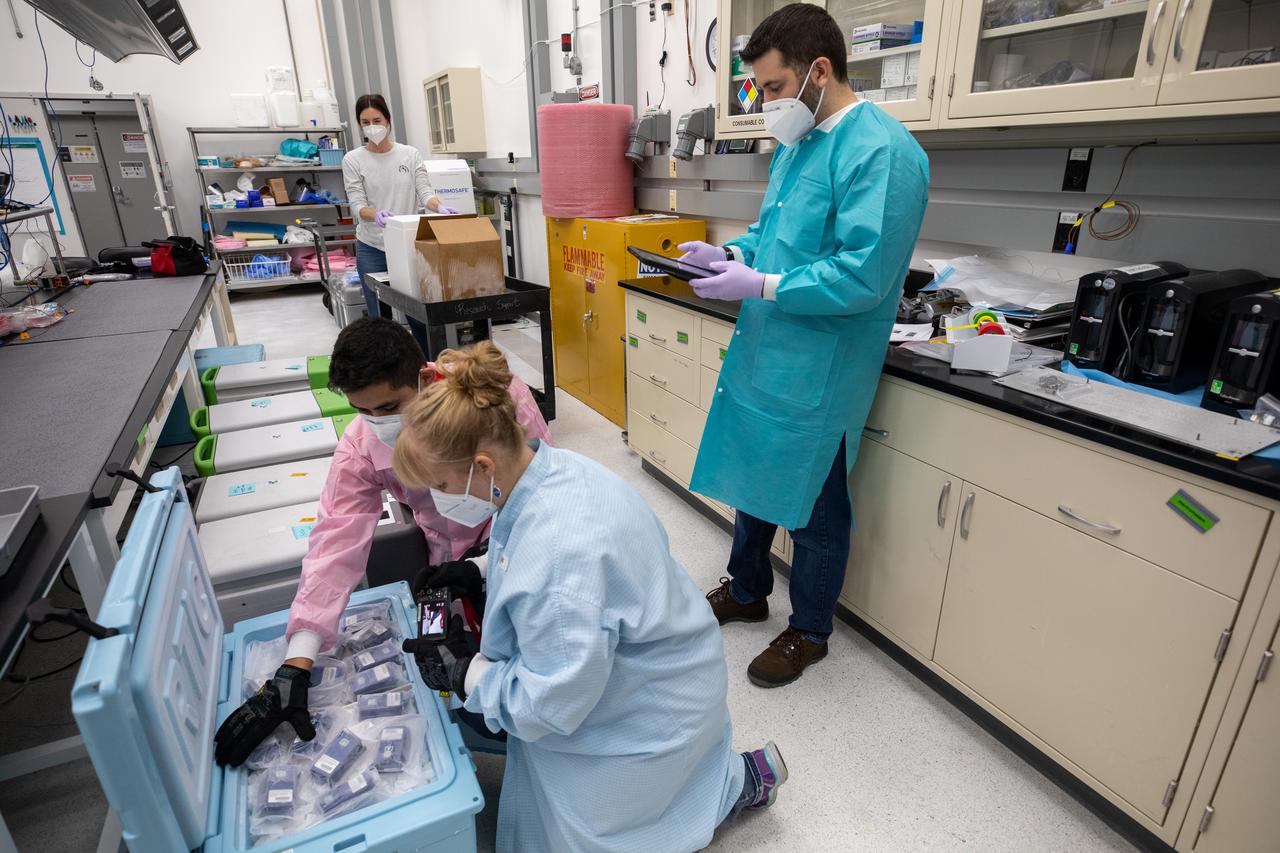

Members of the cold stowage team unpack science experiments inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 14, 2021. The experiments returned to Earth on SpaceX’s 21st commercial resupply services mission (CRS-21). Making its successful parachute-assisted splashdown west of Tampa off the Florida coast, at 8:26 p.m. EST on Jan. 13, the SpaceX cargo Dragon returned more than 4,400 pounds of scientific experiments and other cargo from the International Space Station. After splashdown, SpaceX loaded Dragon aboard their Go Navigator recovery ship and packed an Airbus H225 helicopter with the time-sensitive research cargo for delivery to Kennedy. The upgraded cargo Dragon capsule also boasts double the powered locker capacity to preserve science samples, allowing for a significant increase in the research that can be carried back to Earth.
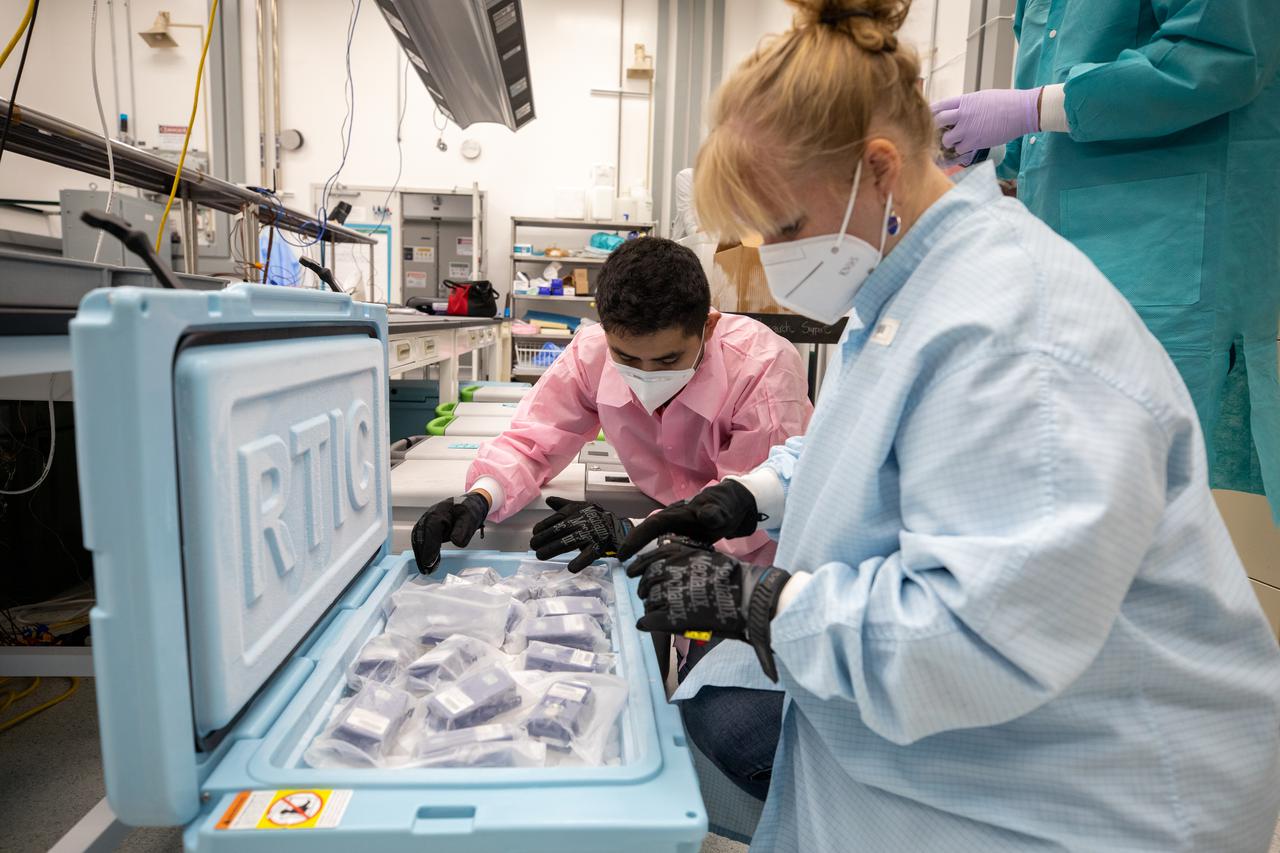

Members of the cold stowage team unpack science experiments inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 14, 2021. The experiments returned to Earth on SpaceX’s 21st commercial resupply services mission (CRS-21). Making its successful parachute-assisted splashdown west of Tampa off the Florida coast, at 8:26 p.m. EST on Jan. 13, the SpaceX cargo Dragon returned more than 4,400 pounds of scientific experiments and other cargo from the International Space Station. After splashdown, SpaceX loaded Dragon aboard their Go Navigator recovery ship and packed an Airbus H225 helicopter with the time-sensitive research cargo for delivery to Kennedy. The upgraded cargo Dragon capsule also boasts double the powered locker capacity to preserve science samples, allowing for a significant increase in the research that can be carried back to Earth.
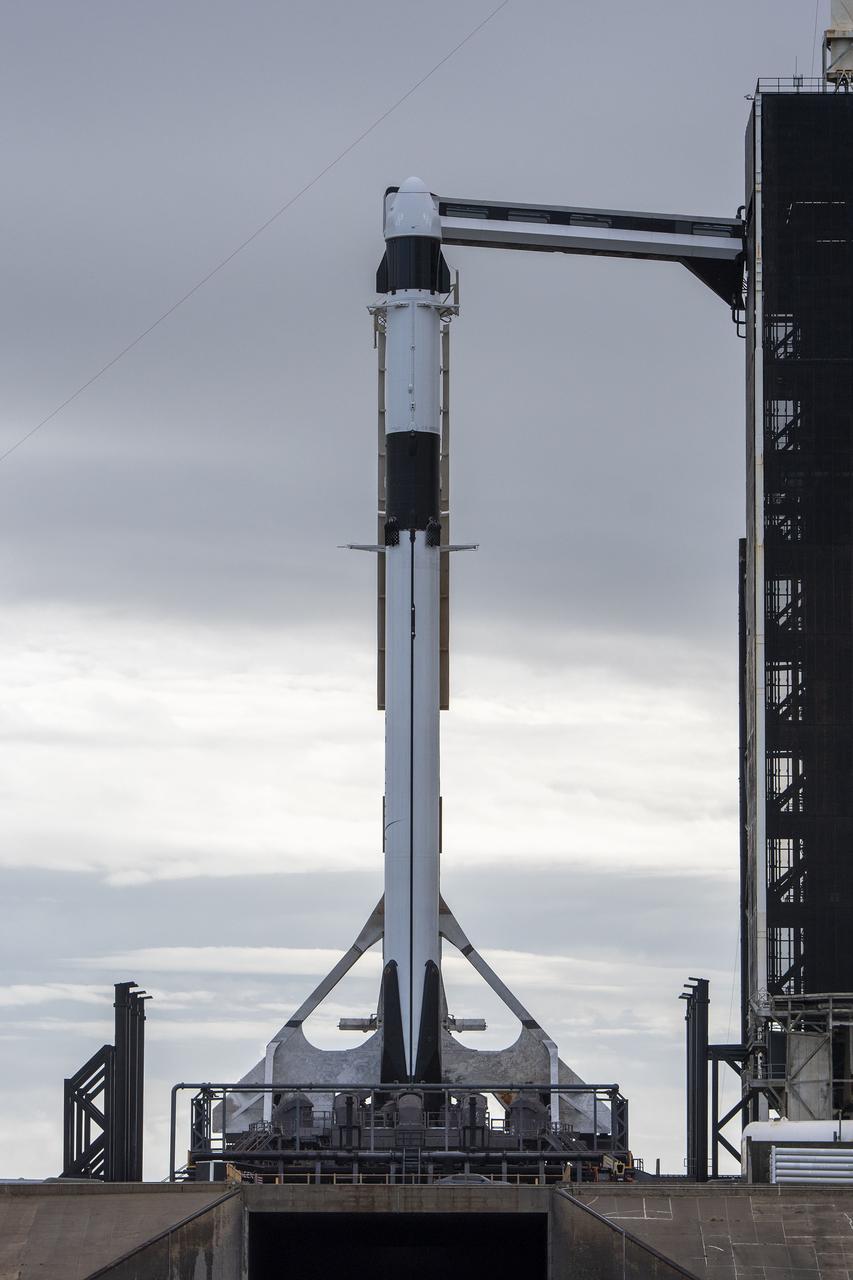

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, with the company’s Dragon cargo spacecraft atop, is raised to a vertical position at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39A on Nov. 21, 2022, in preparation for the 26th commercial resupply services launch to the International Space Station. The mission will deliver new science investigations, supplies, and equipment to the crew aboard the space station, including the next pair of ISS Roll Out Solar Arrays (iROSAs). Liftoff is scheduled for 3:54 p.m. EST on Monday, Nov. 22, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A.
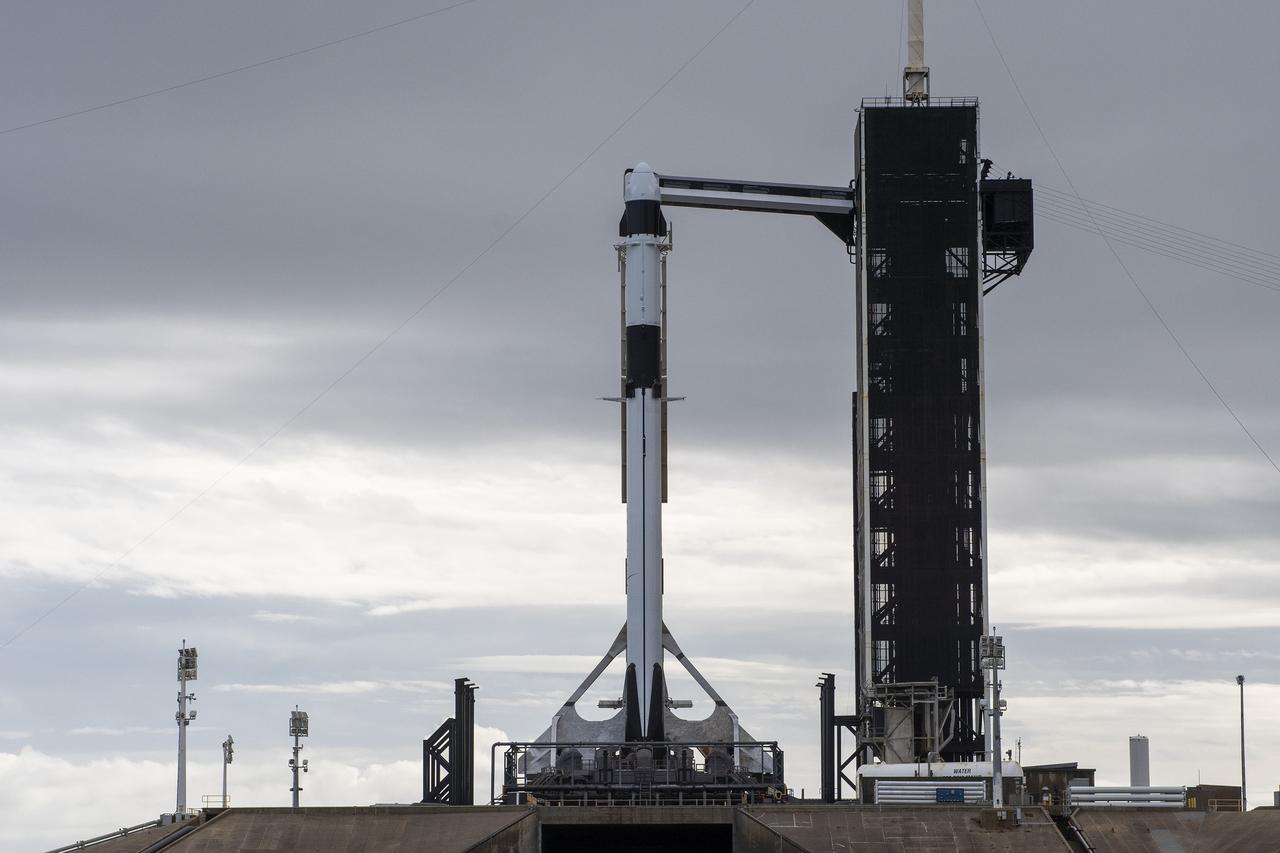

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, with the company’s Dragon cargo spacecraft atop, is raised to a vertical position at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39A on Nov. 21, 2022, in preparation for the 26th commercial resupply services launch to the International Space Station. The mission will deliver new science investigations, supplies, and equipment to the crew aboard the space station, including the next pair of ISS Roll Out Solar Arrays (iROSAs). Liftoff is scheduled for 3:54 p.m. EST on Monday, Nov. 22, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A.
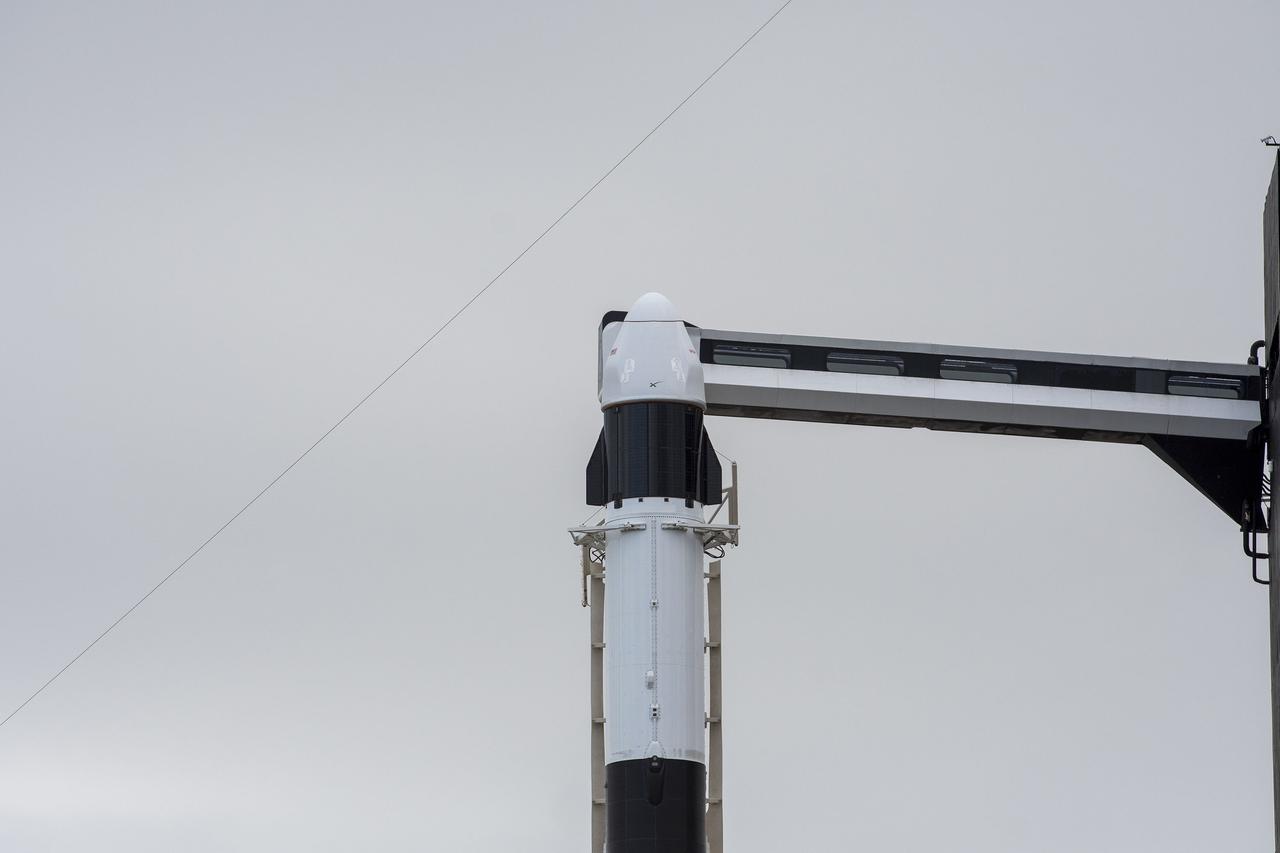

Seen here is the SpaceX Dragon cargo spacecraft atop the company’s Falcon 9 rocket after being raised to a vertical position at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 21, 2022, in preparation for the 26th commercial resupply services launch to the International Space Station. The mission will deliver new science investigations, supplies, and equipment to the crew aboard the space station, including the next pair of ISS Roll Out Solar Arrays (iROSAs). Liftoff is scheduled for 3:54 p.m. EST on Monday, Nov. 22, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A.