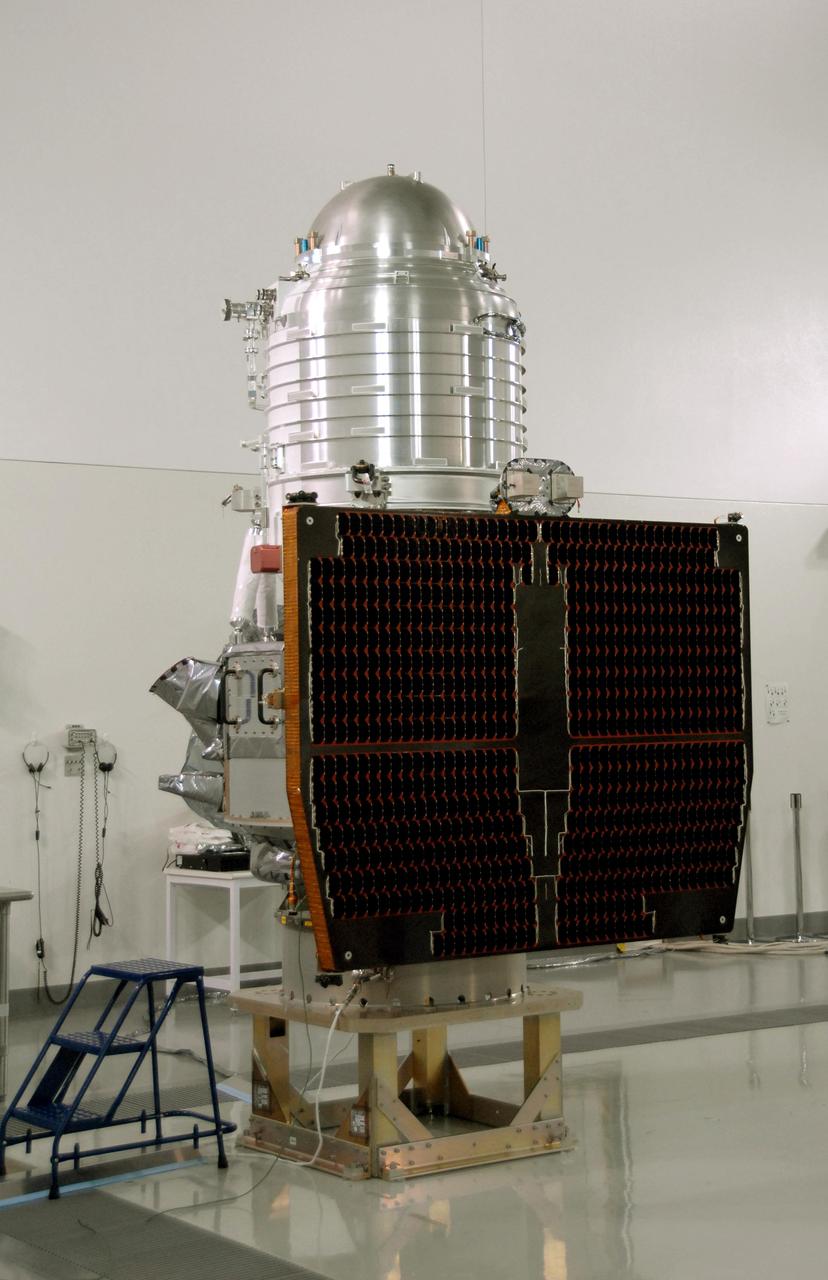

NASA Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE, spacecraft sits on the test stand after connection to the conical adapter.
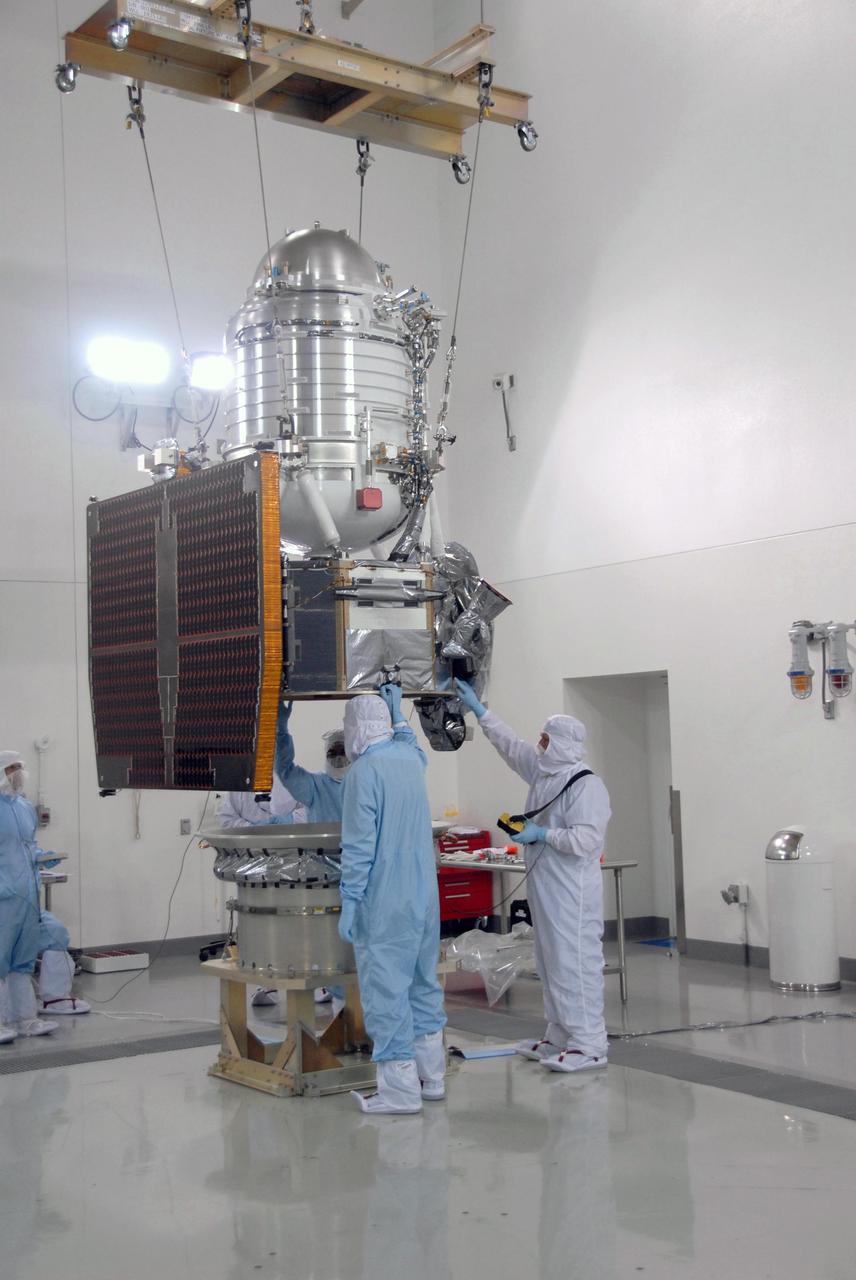

At Vandenberg Air Force Base Astrotech processing facility in California, NASA Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE, spacecraft is lowered toward the flight conical adapter and test stand.
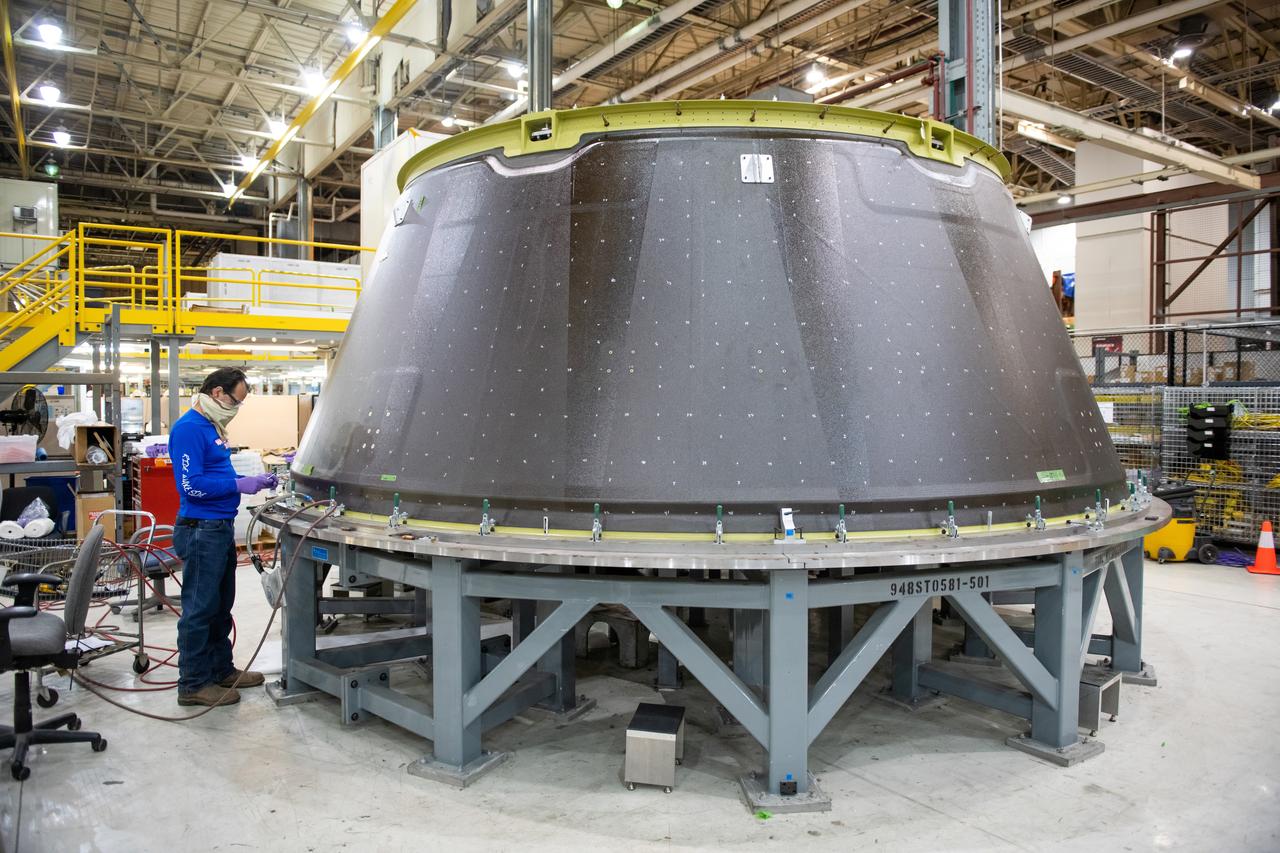

This week, NASA is taking preliminary steps to resume @NASA_SLS core stage production. Limited crews will return to #NASAMichoud to perform critical work essential to the agency's #Artemis program and our return to the Moon.
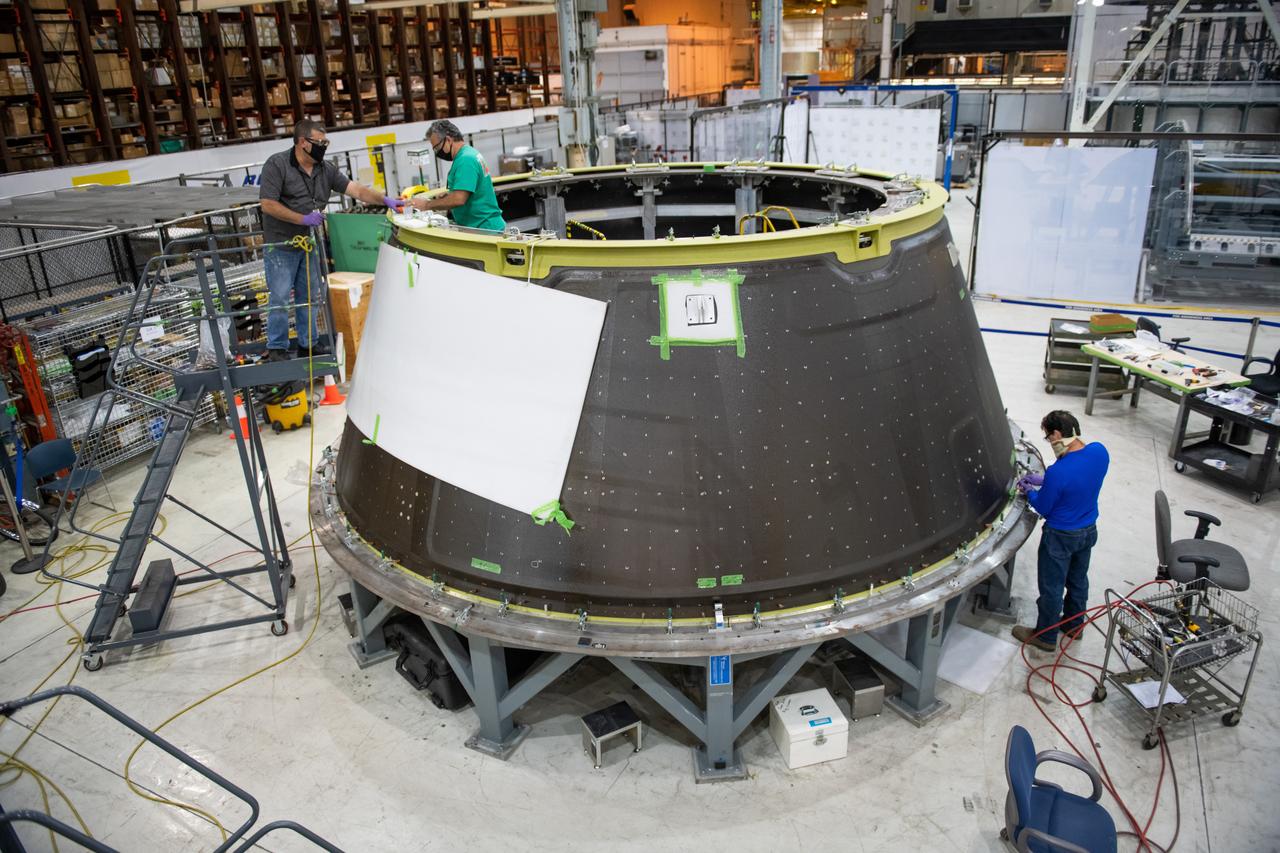

This week, NASA is taking preliminary steps to resume @NASA_SLS core stage production. Limited crews will return to #NASAMichoud to perform critical work essential to the agency's #Artemis program and our return to the Moon.
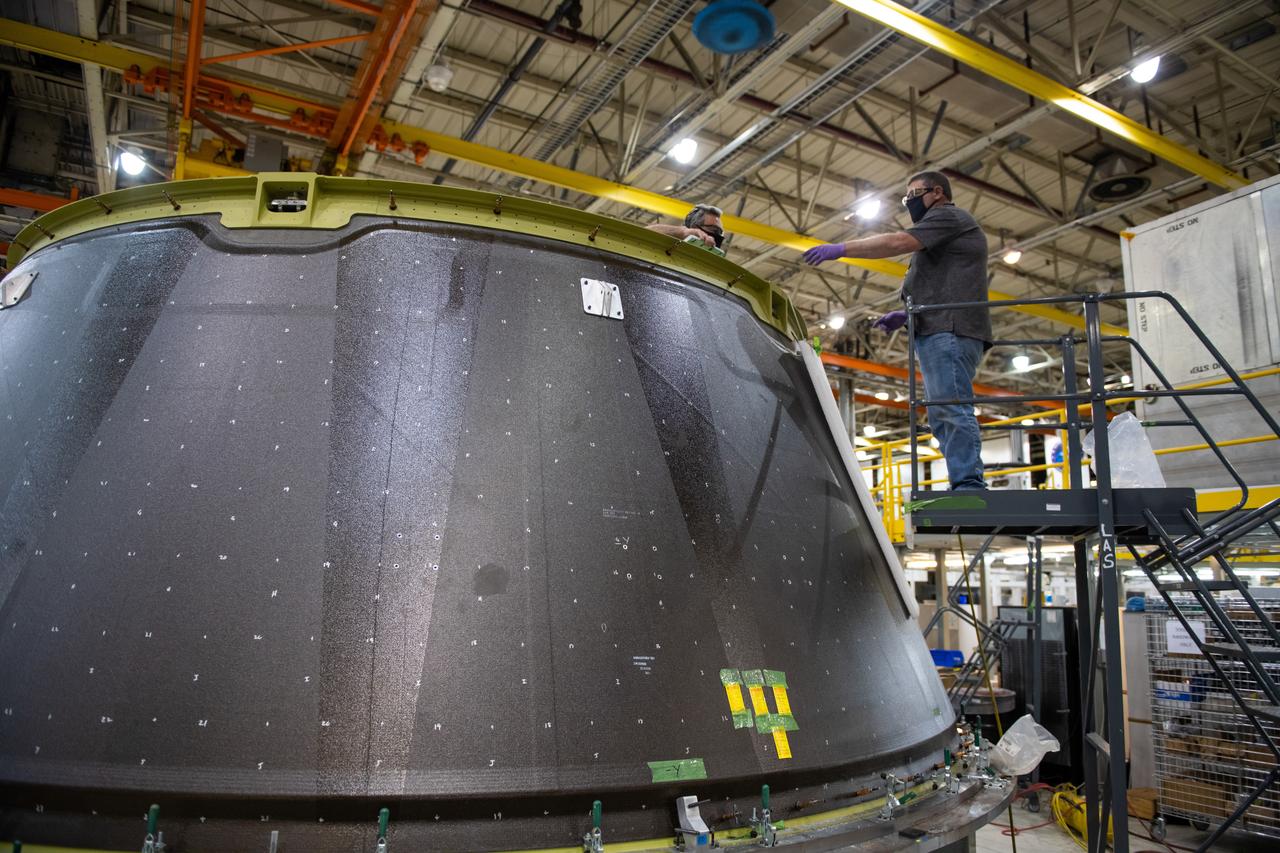

This week, NASA is taking preliminary steps to resume @NASA_SLS core stage production. Limited crews will return to #NASAMichoud to perform critical work essential to the agency's #Artemis program and our return to the Moon.
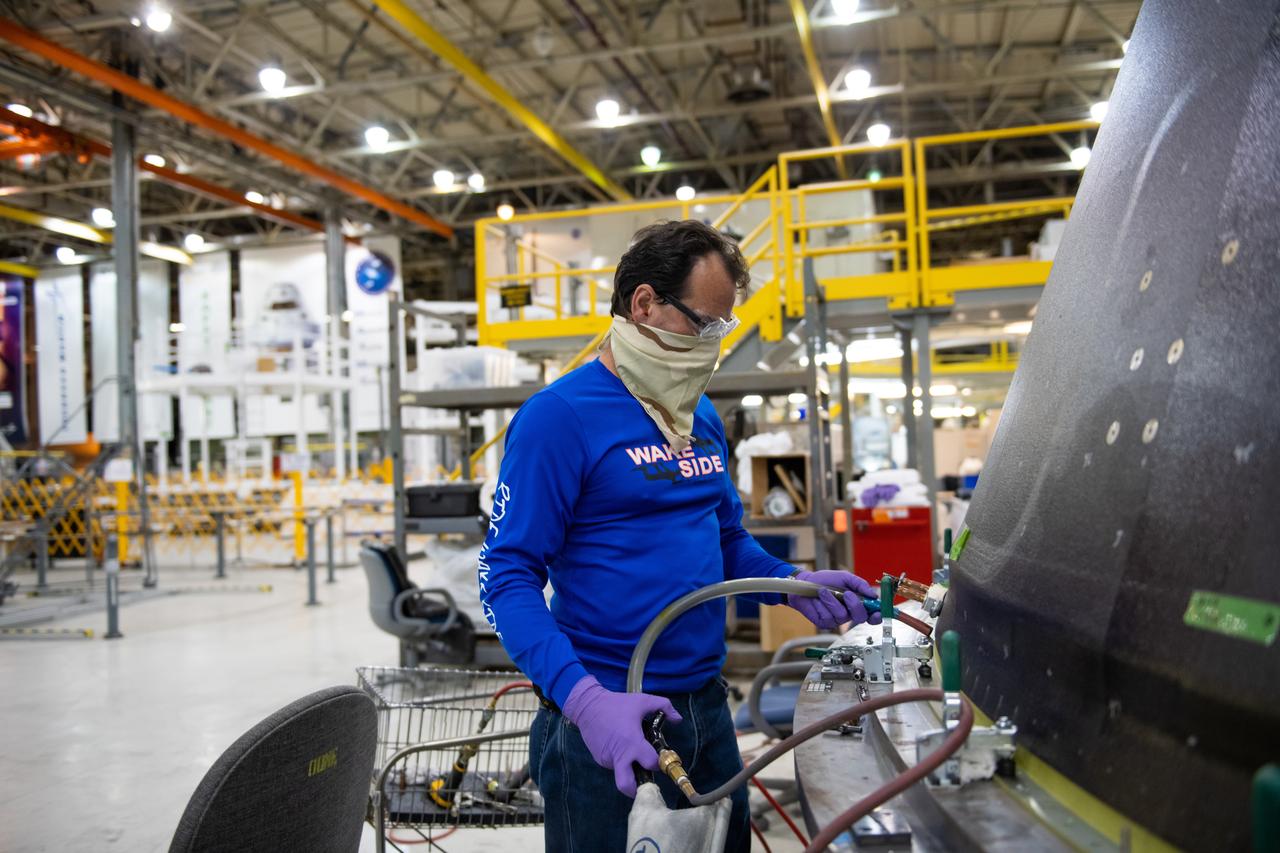

This week, NASA is taking preliminary steps to resume @NASA_SLS core stage production. Limited crews will return to #NASAMichoud to perform critical work essential to the agency's #Artemis program and our return to the Moon.
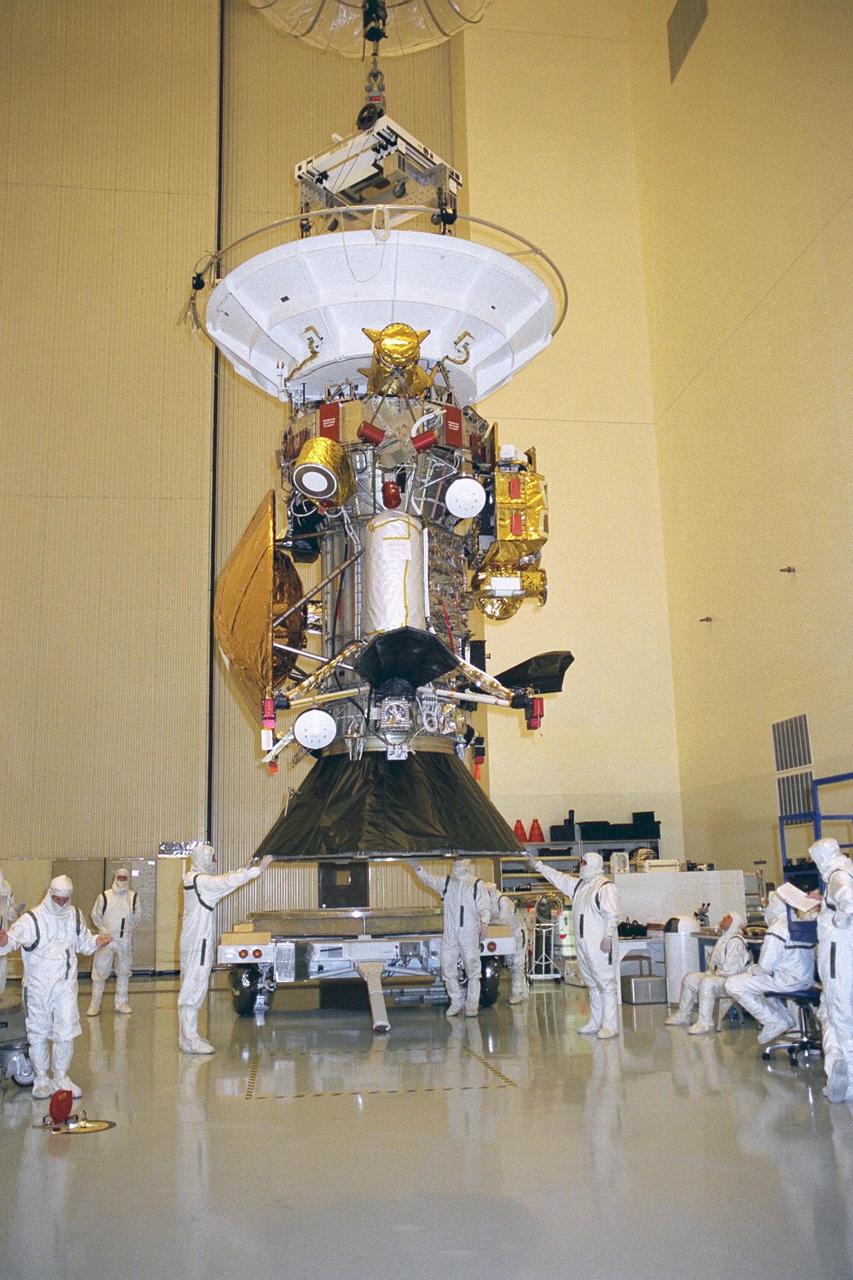

Flight mechanics from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Pasadena, Calif., lift the Cassini spacecraft along with its launch vehicle adapter in KSC’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility. The black conical-shaped adapter seen at the bottom of the spacecraft will later be mated to a Titan IV/Centaur expendable launch vehicle that will lift Cassini into space. Scheduled for launch in October, the Cassini mission seeks insight into the origins and evolution of the early solar system. Scientific instruments carried aboard the spacecraft will study Saturn’s atmosphere, magnetic field, rings, and several moons. JPL is managing the Cassini project for NASA
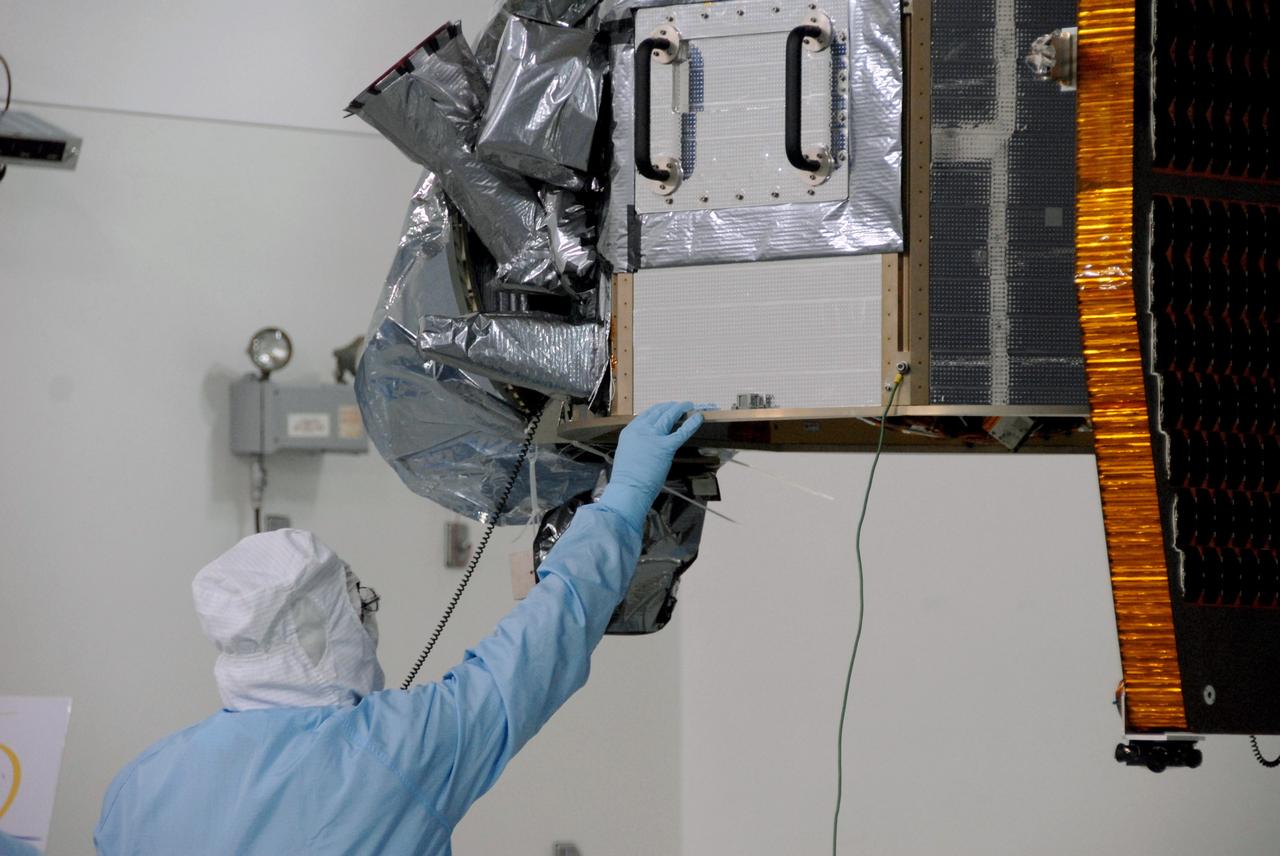

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base's Astrotech processing facility in California, technicians help guide NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE, spacecraft to the flight conical adapter and test stand. The satellite will survey the entire sky at infrared wavelengths, creating a cosmic clearinghouse of hundreds of millions of objects, which will be catalogued, providing a vast storehouse of knowledge about the solar system, the Milky Way, and the universe. Launch is scheduled no earlier than Dec. 7. Photo credit: NASA/Doug Kolkow
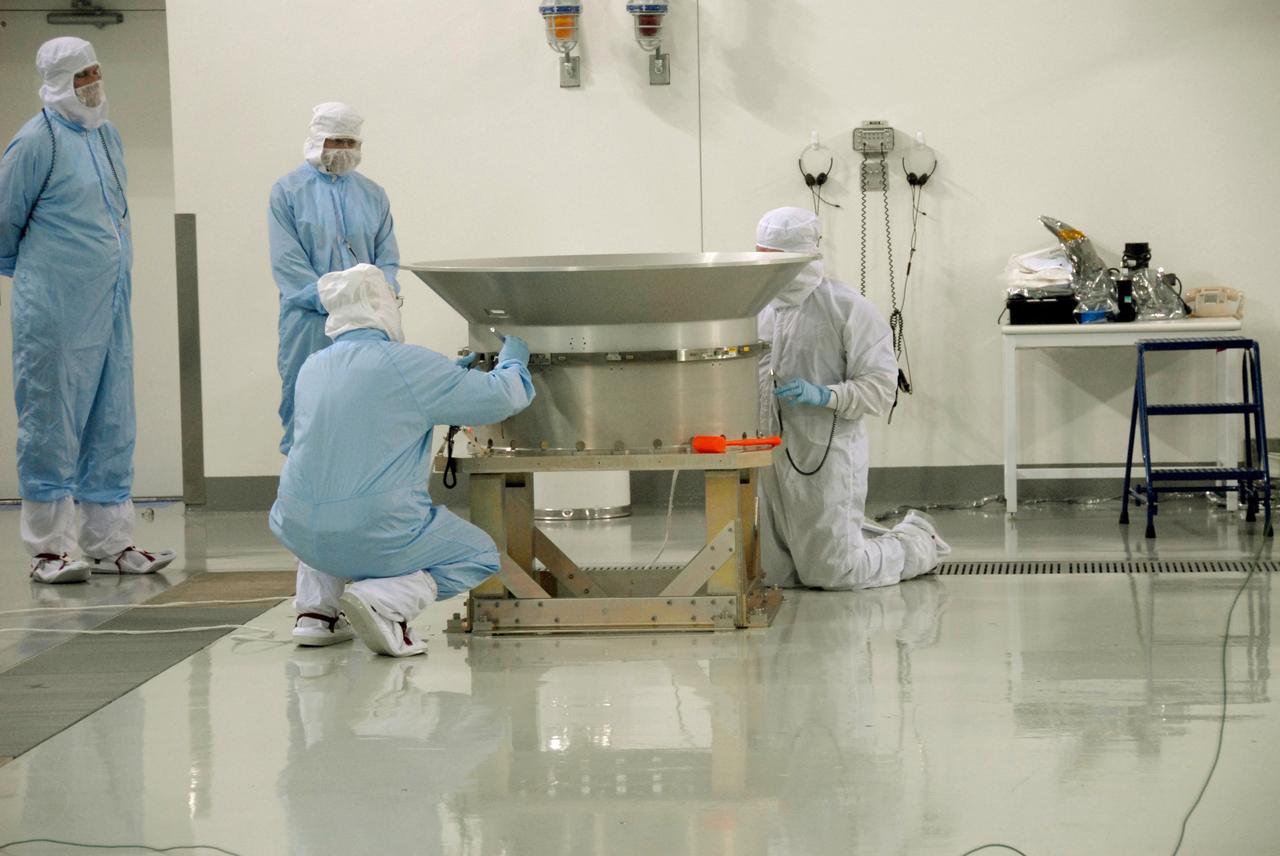

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base's Astrotech processing facility in California, technicians prepare to mate the flight conical adapter and soft ride to the test payload attach fitting clampband on the spacecraft test stand. The satellite will survey the entire sky at infrared wavelengths, creating a cosmic clearinghouse of hundreds of millions of objects, which will be catalogued, providing a vast storehouse of knowledge about the solar system, the Milky Way, and the universe. Launch is scheduled no earlier than Dec. 7. Photo credit: NASA/Doug Kolkow
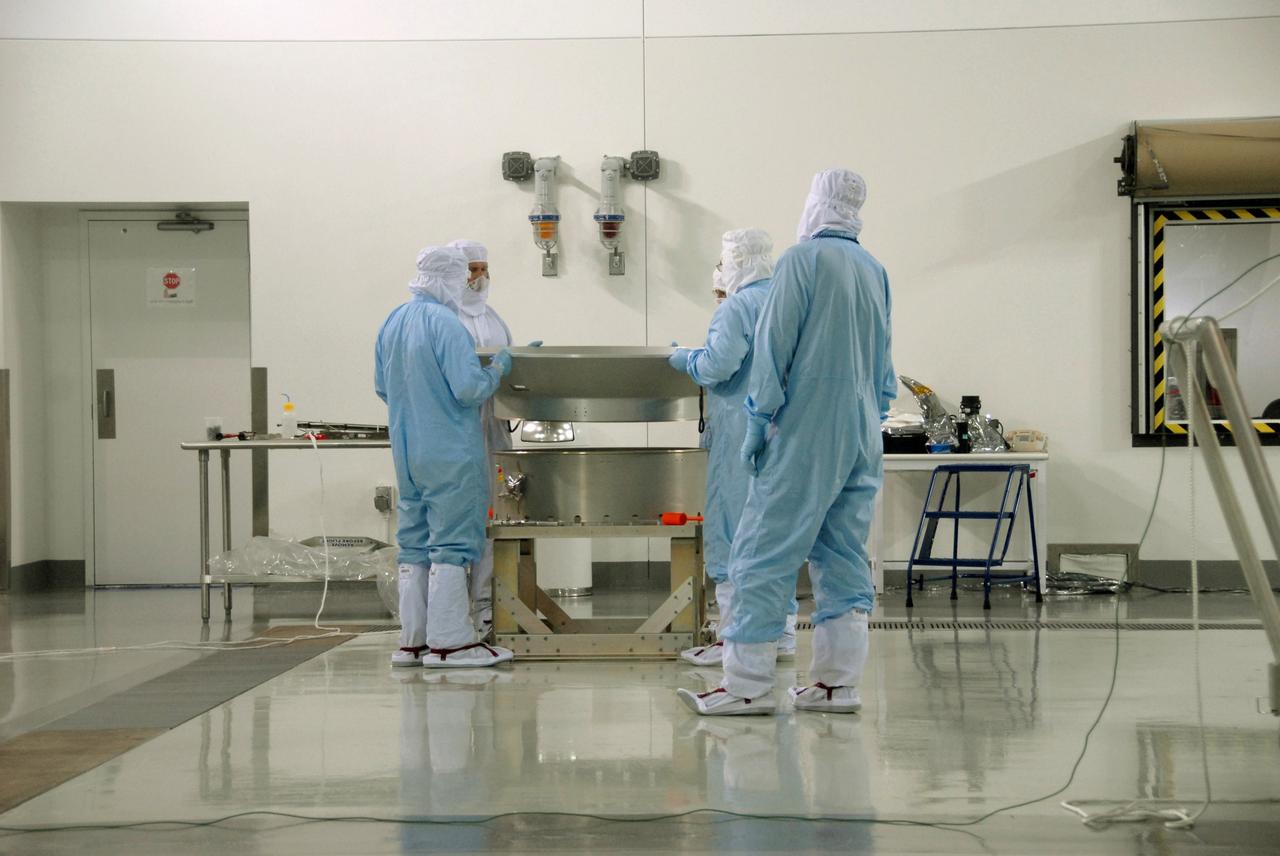

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base's Astrotech processing facility in California, technicians prepare to mate the flight conical adapter and soft ride to the test payload attach fitting clampband on the spacecraft test stand. The satellite will survey the entire sky at infrared wavelengths, creating a cosmic clearinghouse of hundreds of millions of objects, which will be catalogued, providing a vast storehouse of knowledge about the solar system, the Milky Way, and the universe. Launch is scheduled no earlier than Dec. 7. Photo credit: NASA/Doug Kolkow
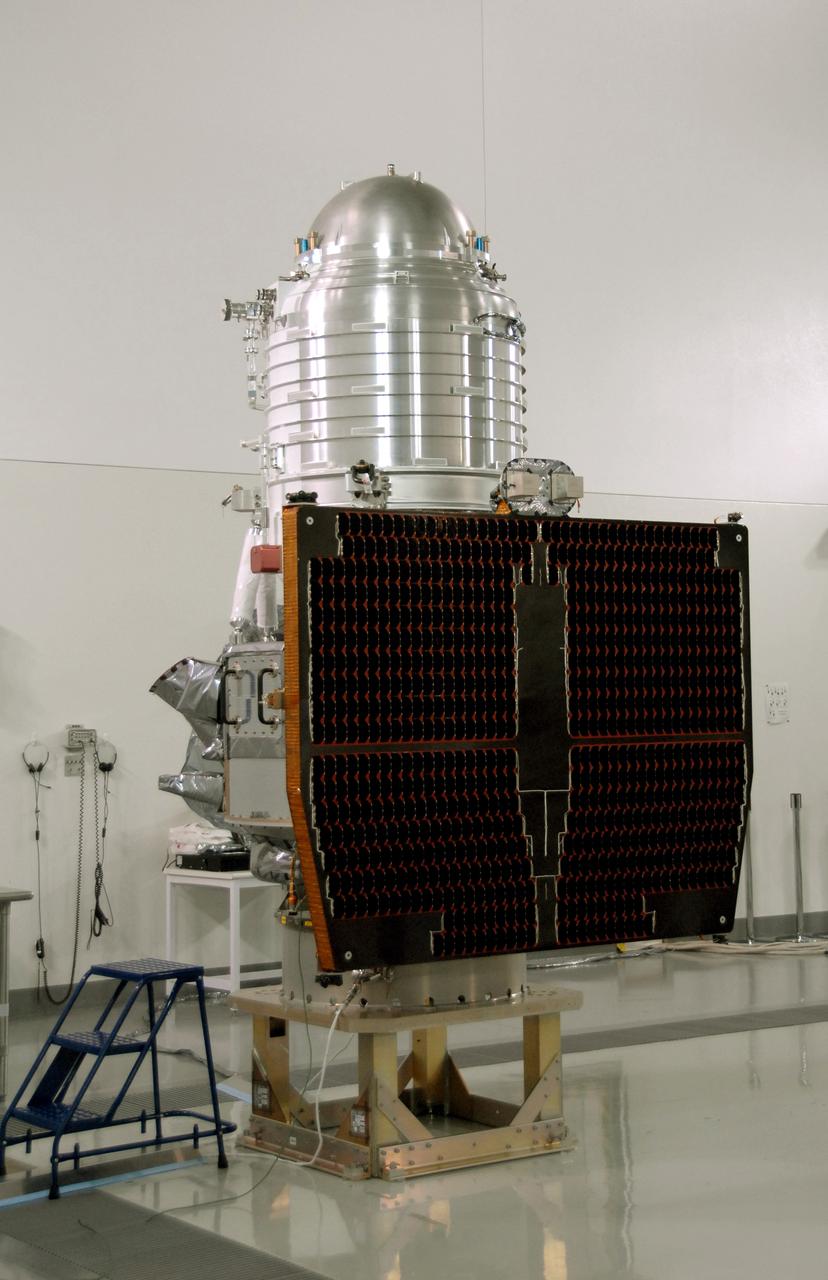

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base's Astrotech processing facility in California, NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE, spacecraft sits on the test stand after connection to the conical adapter. The satellite will survey the entire sky at infrared wavelengths, creating a cosmic clearinghouse of hundreds of millions of objects, which will be catalogued, providing a vast storehouse of knowledge about the solar system, the Milky Way, and the universe. Launch is scheduled no earlier than Dec. 7. Photo credit: NASA/Doug Kolkow
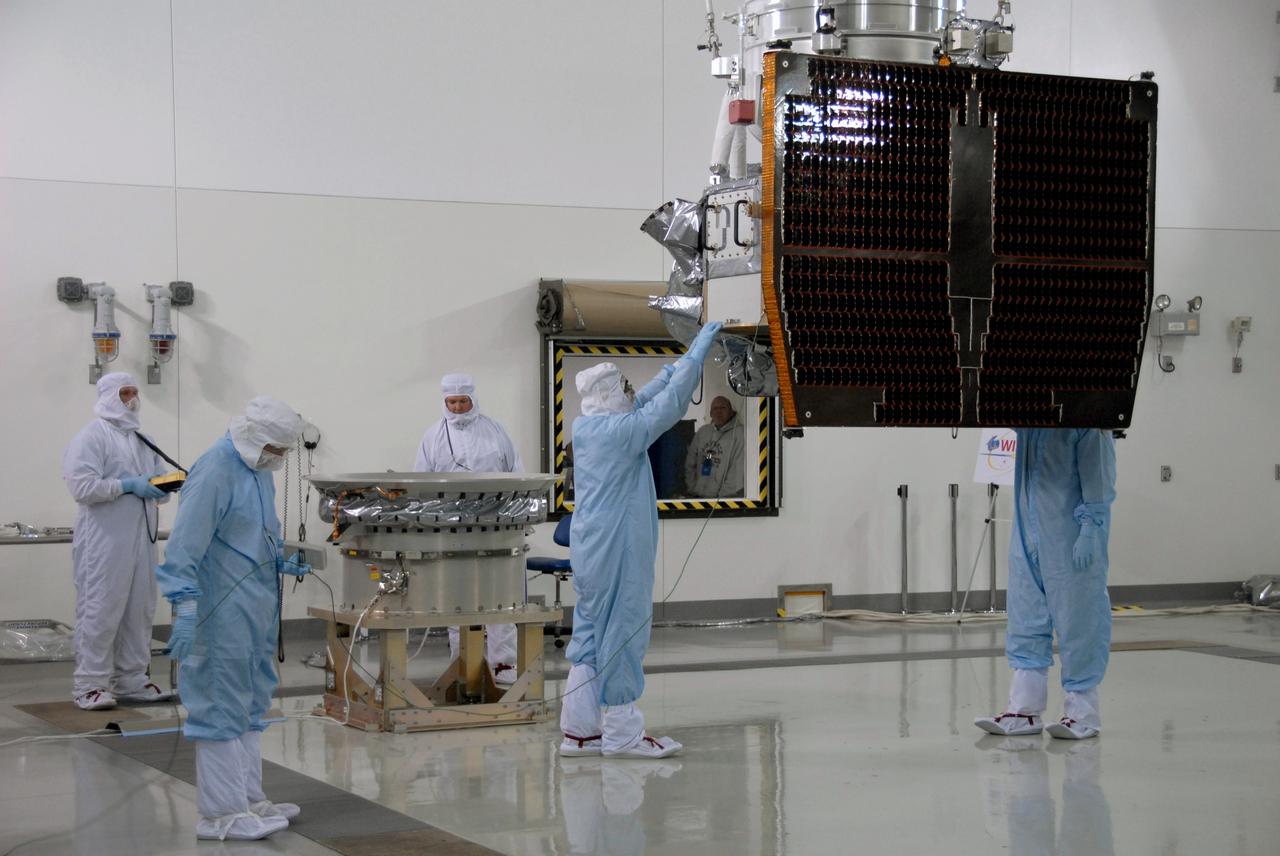

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base's Astrotech processing facility in California, technicians help guide NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE, spacecraft to the flight conical adapter and test stand. The satellite will survey the entire sky at infrared wavelengths, creating a cosmic clearinghouse of hundreds of millions of objects, which will be catalogued, providing a vast storehouse of knowledge about the solar system, the Milky Way, and the universe. Launch is scheduled no earlier than Dec. 7. Photo credit: NASA/Doug Kolkow
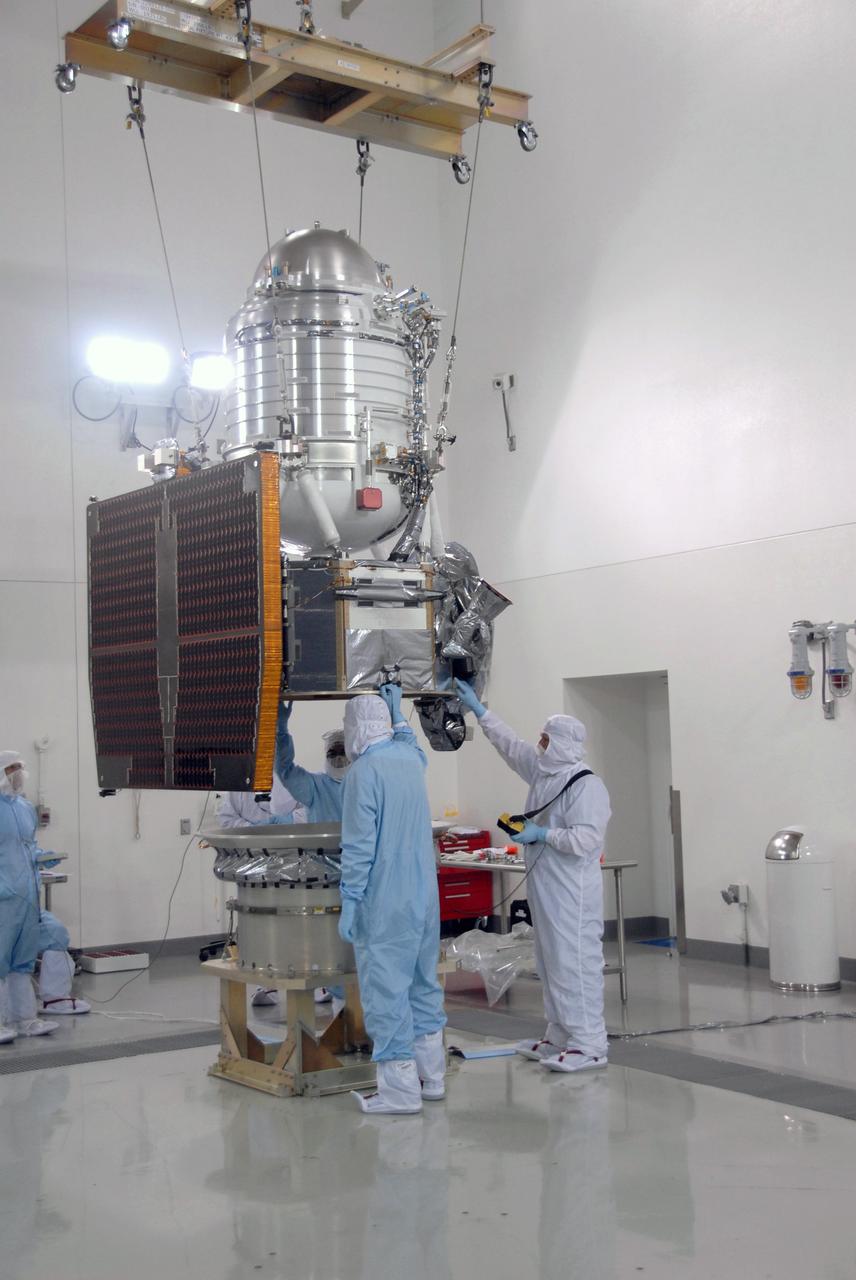

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base's Astrotech processing facility in California, NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE, spacecraft is lowered toward the flight conical adapter and test stand. The satellite will survey the entire sky at infrared wavelengths, creating a cosmic clearinghouse of hundreds of millions of objects, which will be catalogued, providing a vast storehouse of knowledge about the solar system, the Milky Way, and the universe. Launch is scheduled no earlier than Dec. 7. Photo credit: NASA/Doug Kolkow
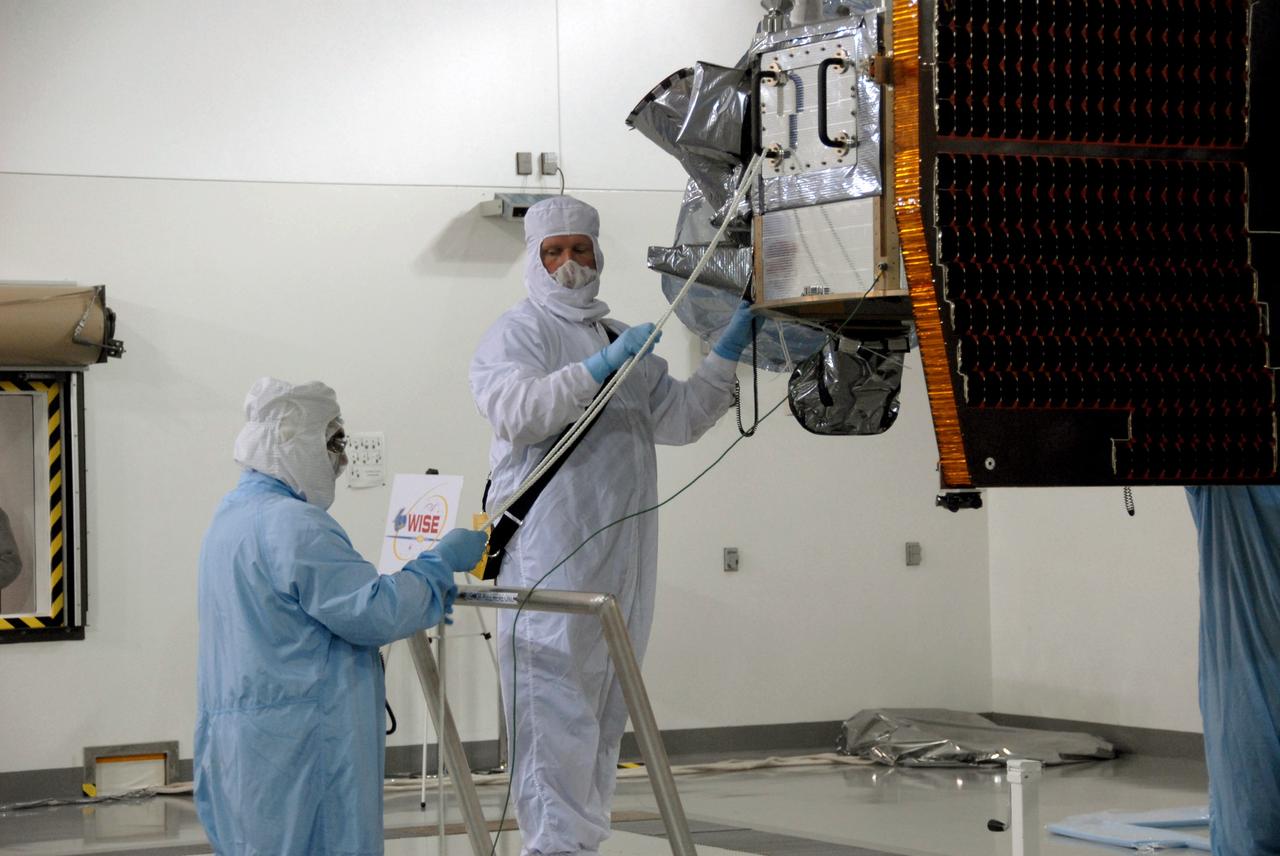

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base's Astrotech processing facility in California, technicians help guide NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE, spacecraft to the flight conical adapter and test stand. The satellite will survey the entire sky at infrared wavelengths, creating a cosmic clearinghouse of hundreds of millions of objects, which will be catalogued, providing a vast storehouse of knowledge about the solar system, the Milky Way, and the universe. Launch is scheduled no earlier than Dec. 7. Photo credit: NASA/Doug Kolkow

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base's Astrotech processing facility in California, NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE, spacecraft is being moved to the flight conical adapter and test stand. The satellite will survey the entire sky at infrared wavelengths, creating a cosmic clearinghouse of hundreds of millions of objects, which will be catalogued, providing a vast storehouse of knowledge about the solar system, the Milky Way, and the universe. Launch is scheduled no earlier than Dec. 7. Photo credit: NASA/Doug Kolkow
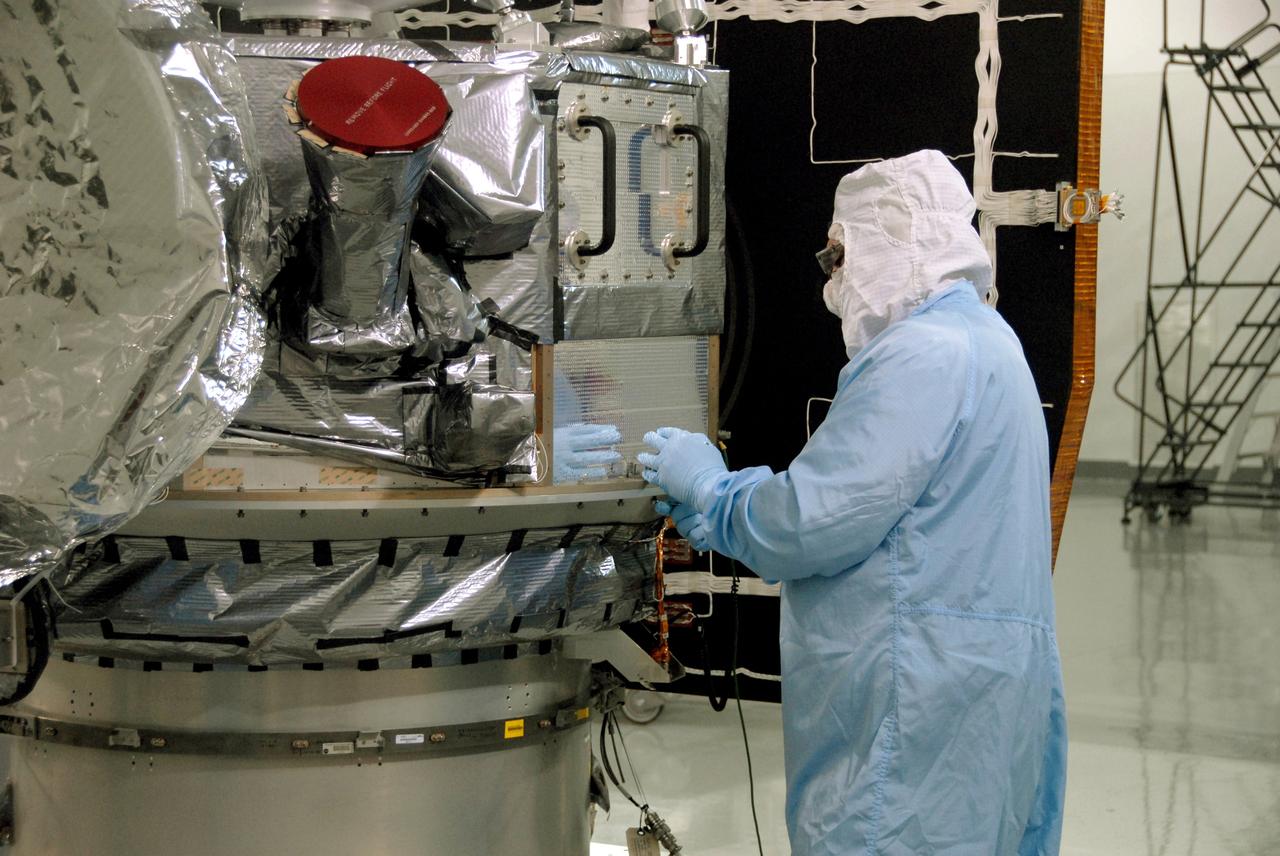

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base's Astrotech processing facility in California, a technician fastens NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE, spacecraft onto the flight conical adapter and test stand. The satellite will survey the entire sky at infrared wavelengths, creating a cosmic clearinghouse of hundreds of millions of objects, which will be catalogued, providing a vast storehouse of knowledge about the solar system, the Milky Way, and the universe. Launch is scheduled no earlier than Dec. 7. Photo credit: NASA/Doug Kolkow
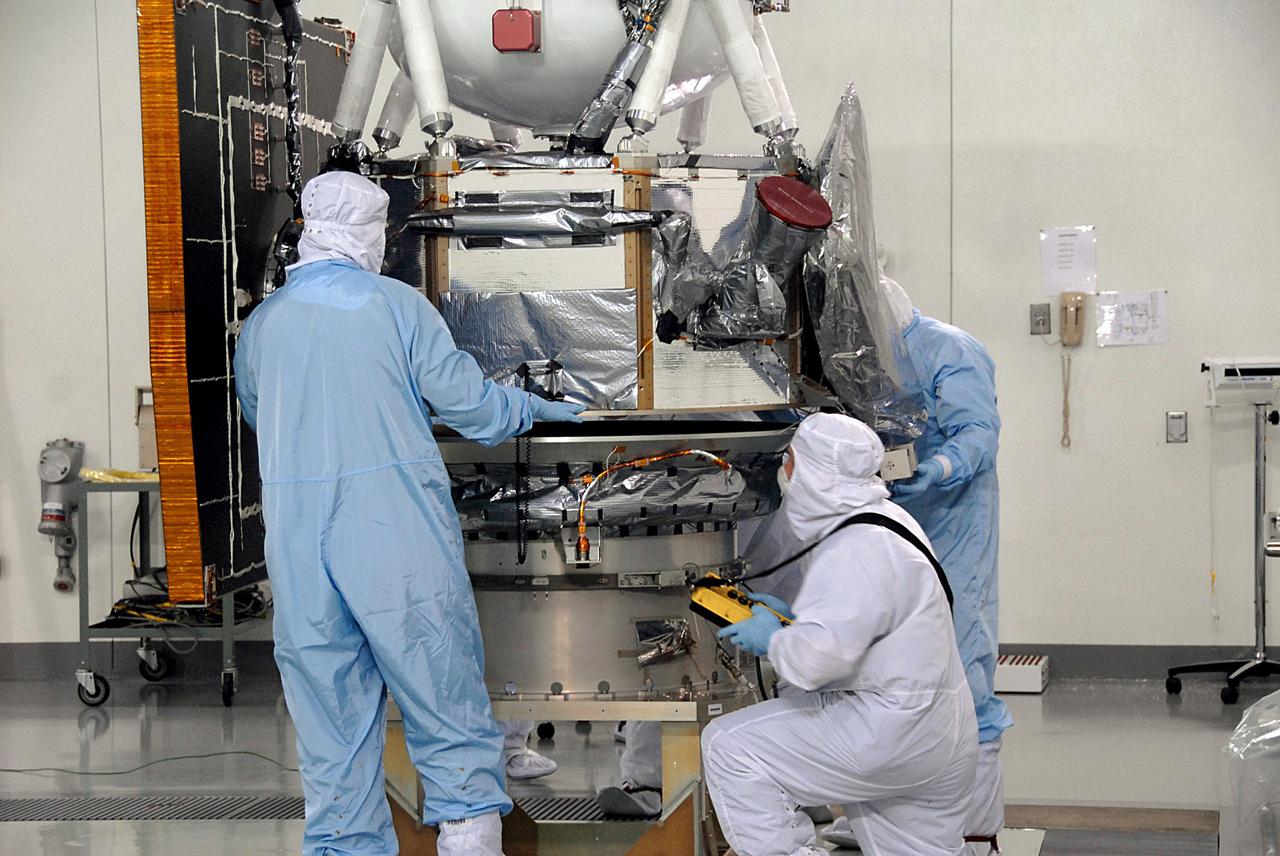

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base's Astrotech processing facility in California, NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE, spacecraft is lowered onto the flight conical adapter and test stand. The satellite will survey the entire sky at infrared wavelengths, creating a cosmic clearinghouse of hundreds of millions of objects, which will be catalogued, providing a vast storehouse of knowledge about the solar system, the Milky Way, and the universe. Launch is scheduled no earlier than Dec. 7. Photo credit: NASA/Doug Kolkow
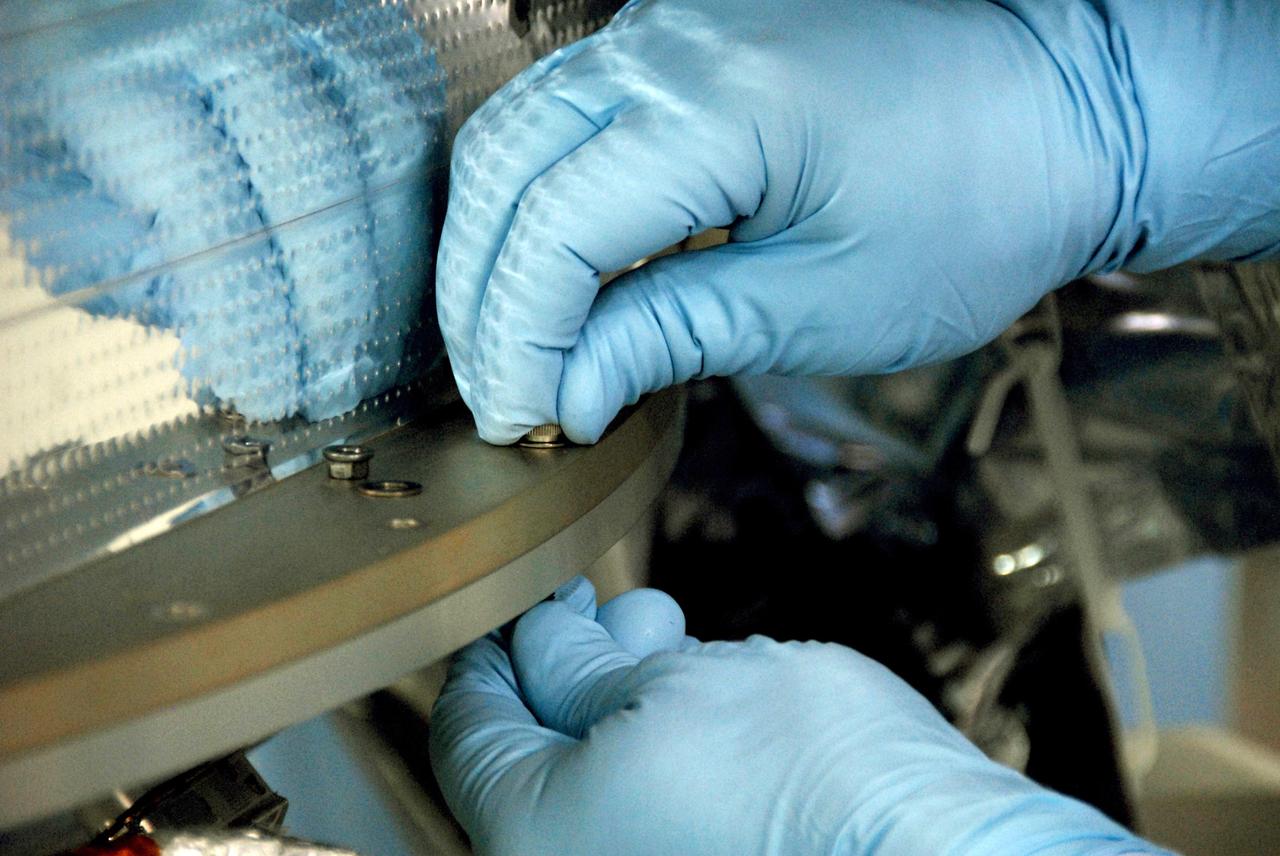

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base's Astrotech processing facility in California, a technician fastens NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE, spacecraft onto the flight conical adapter and test stand. The satellite will survey the entire sky at infrared wavelengths, creating a cosmic clearinghouse of hundreds of millions of objects, which will be catalogued, providing a vast storehouse of knowledge about the solar system, the Milky Way, and the universe. Launch is scheduled no earlier than Dec. 7. Photo credit: NASA/Doug Kolkow
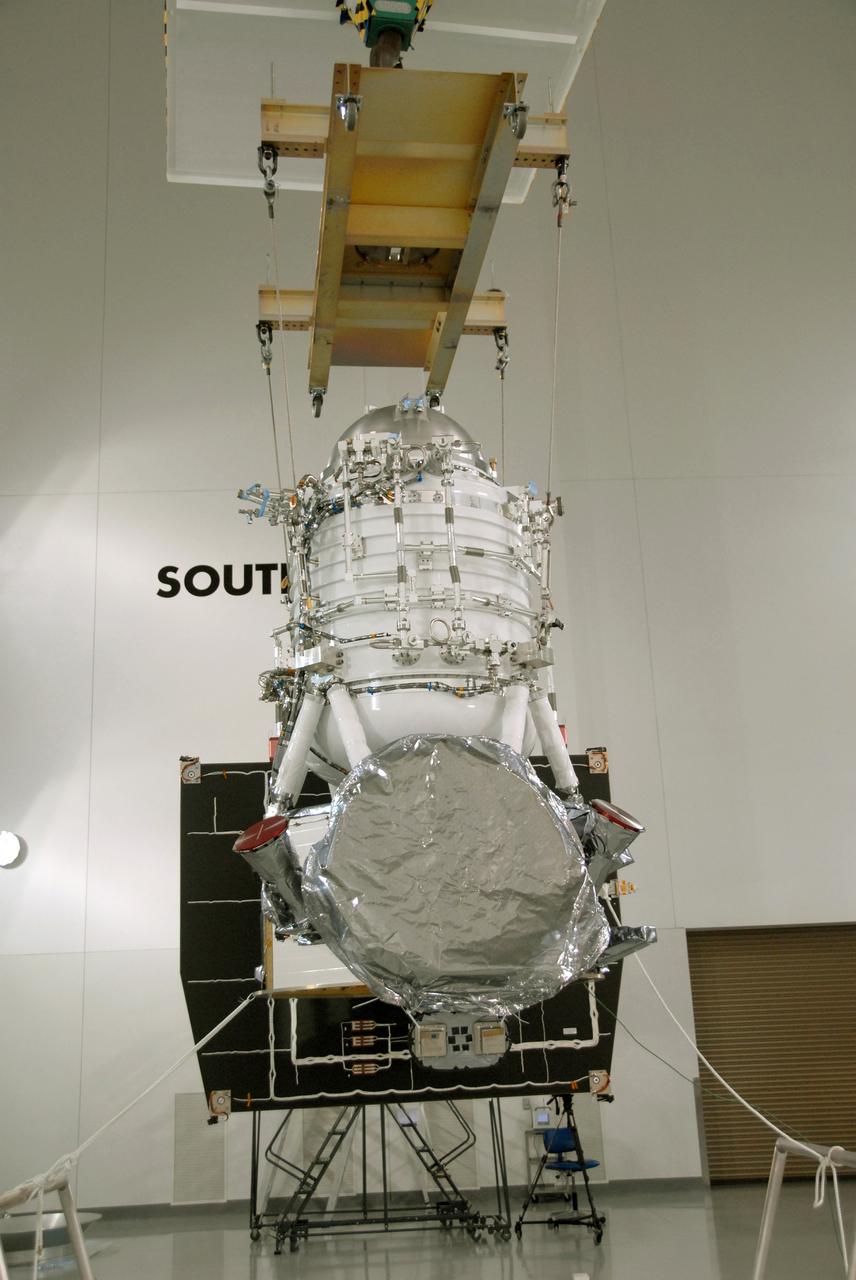
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base's Astrotech processing facility in California, NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE, spacecraft is being moved to the flight conical adapter and test stand. The satellite will survey the entire sky at infrared wavelengths, creating a cosmic clearinghouse of hundreds of millions of objects, which will be catalogued, providing a vast storehouse of knowledge about the solar system, the Milky Way, and the universe. Launch is scheduled no earlier than Dec. 7. Photo credit: NASA/Doug Kolkow
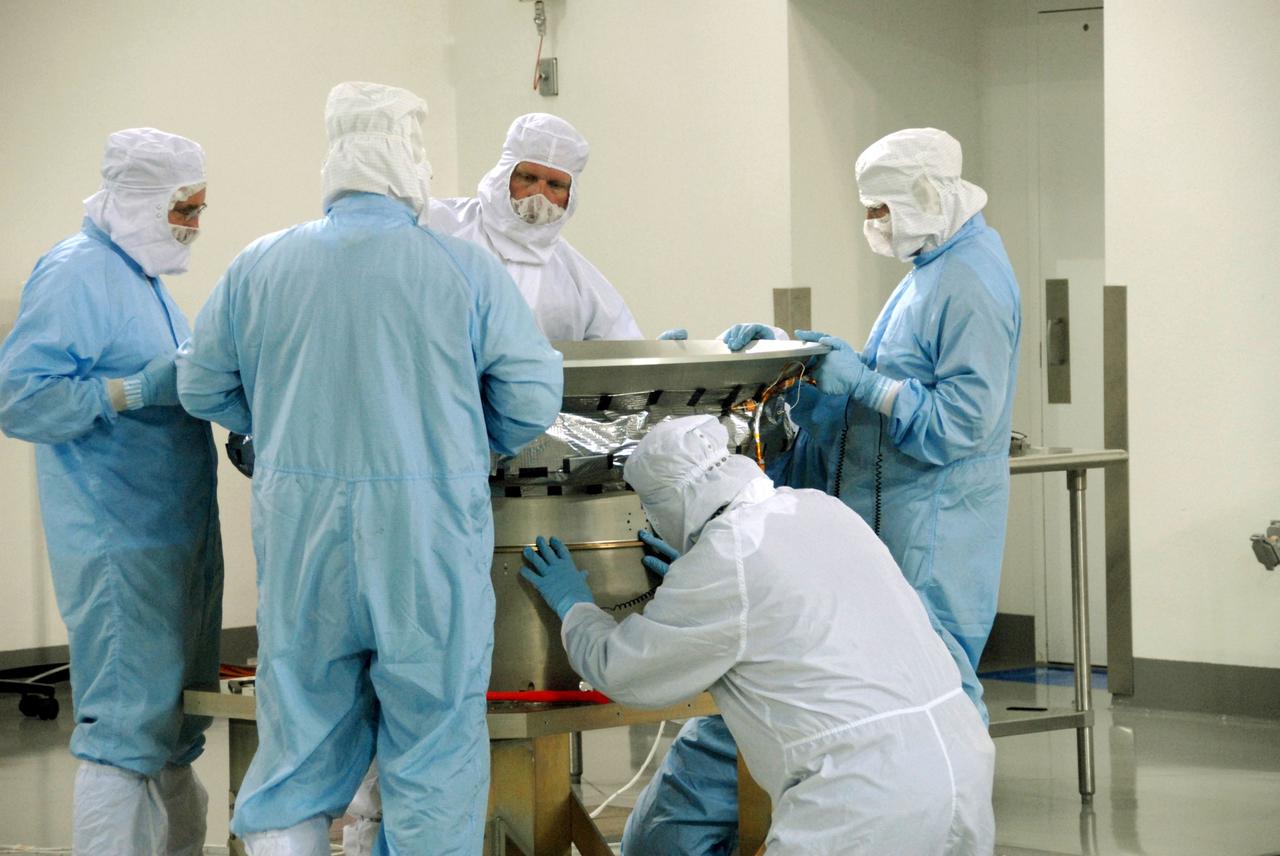

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base's Astrotech processing facility in California, technicians working on NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE, spacecraft mate the flight conical adapter and soft ride to the test payload attach fitting clampband on the spacecraft test stand. The satellite will survey the entire sky at infrared wavelengths, creating a cosmic clearinghouse of hundreds of millions of objects, which will be catalogued, providing a vast storehouse of knowledge about the solar system, the Milky Way, and the universe. Launch is scheduled no earlier than Dec. 7. Photo credit: NASA/Doug Kolkow
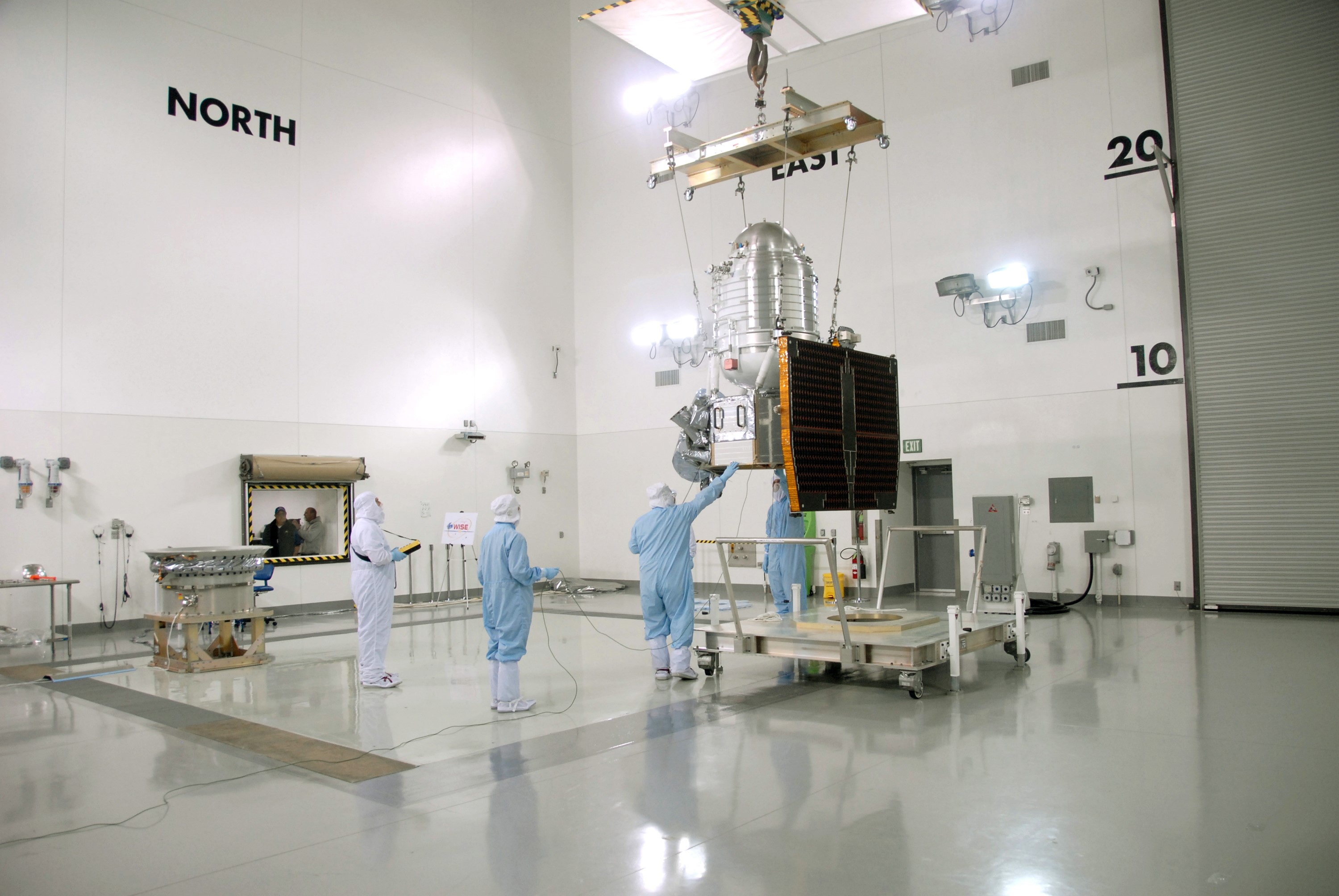

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base's Astrotech processing facility in California, technicians help guide NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE, spacecraft to the flight conical adapter and test stand, at far left. The satellite will survey the entire sky at infrared wavelengths, creating a cosmic clearinghouse of hundreds of millions of objects, which will be catalogued, providing a vast storehouse of knowledge about the solar system, the Milky Way, and the universe. Launch is scheduled no earlier than Dec. 7. Photo credit: NASA/Doug Kolkow
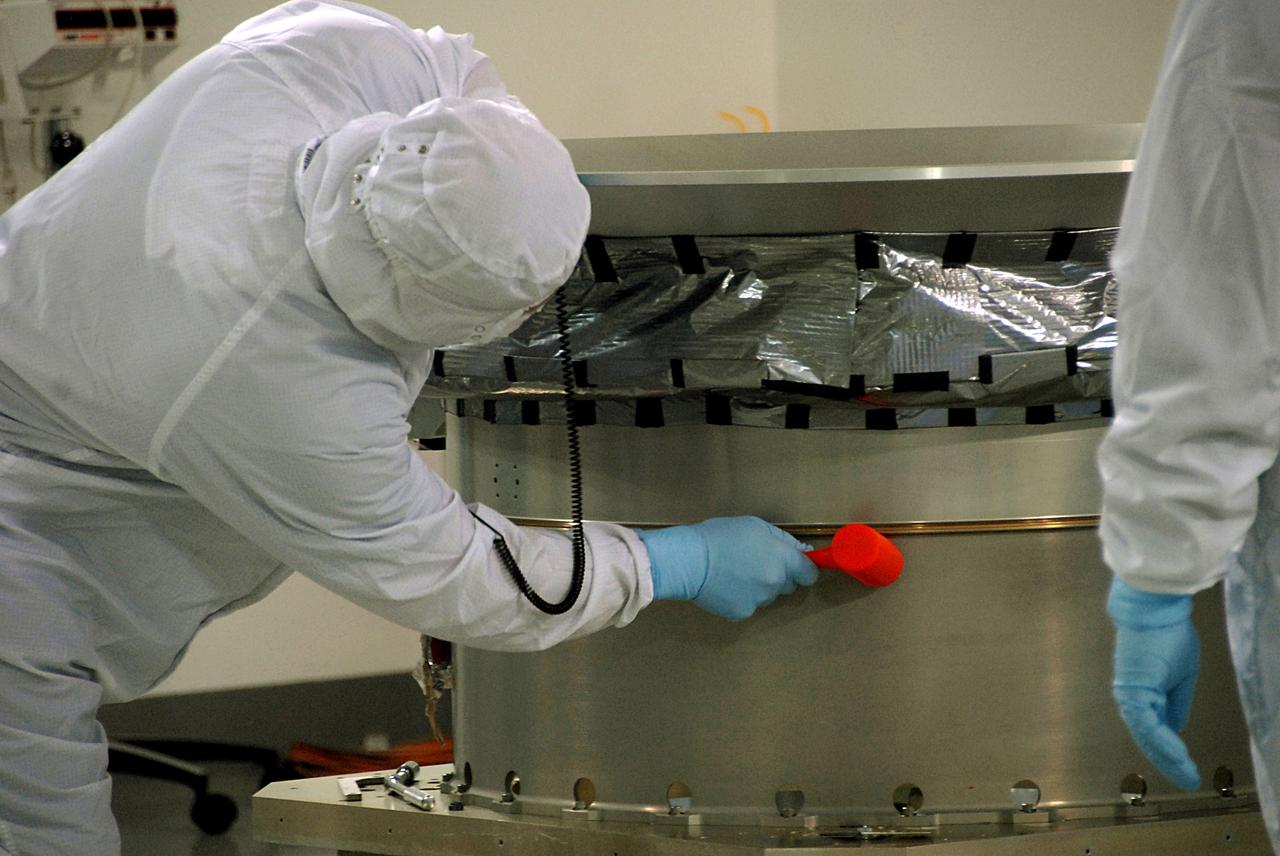

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base's Astrotech processing facility in California, a technician working on NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE, spacecraft uses a dead blow hammer to seat the clampband on the test payload attach fitting to complete the mating with the conical adapter. The satellite will survey the entire sky at infrared wavelengths, creating a cosmic clearinghouse of hundreds of millions of objects, which will be catalogued, providing a vast storehouse of knowledge about the solar system, the Milky Way, and the universe. Launch is scheduled no earlier than Dec. 7. Photo credit: NASA/Doug Kolkow
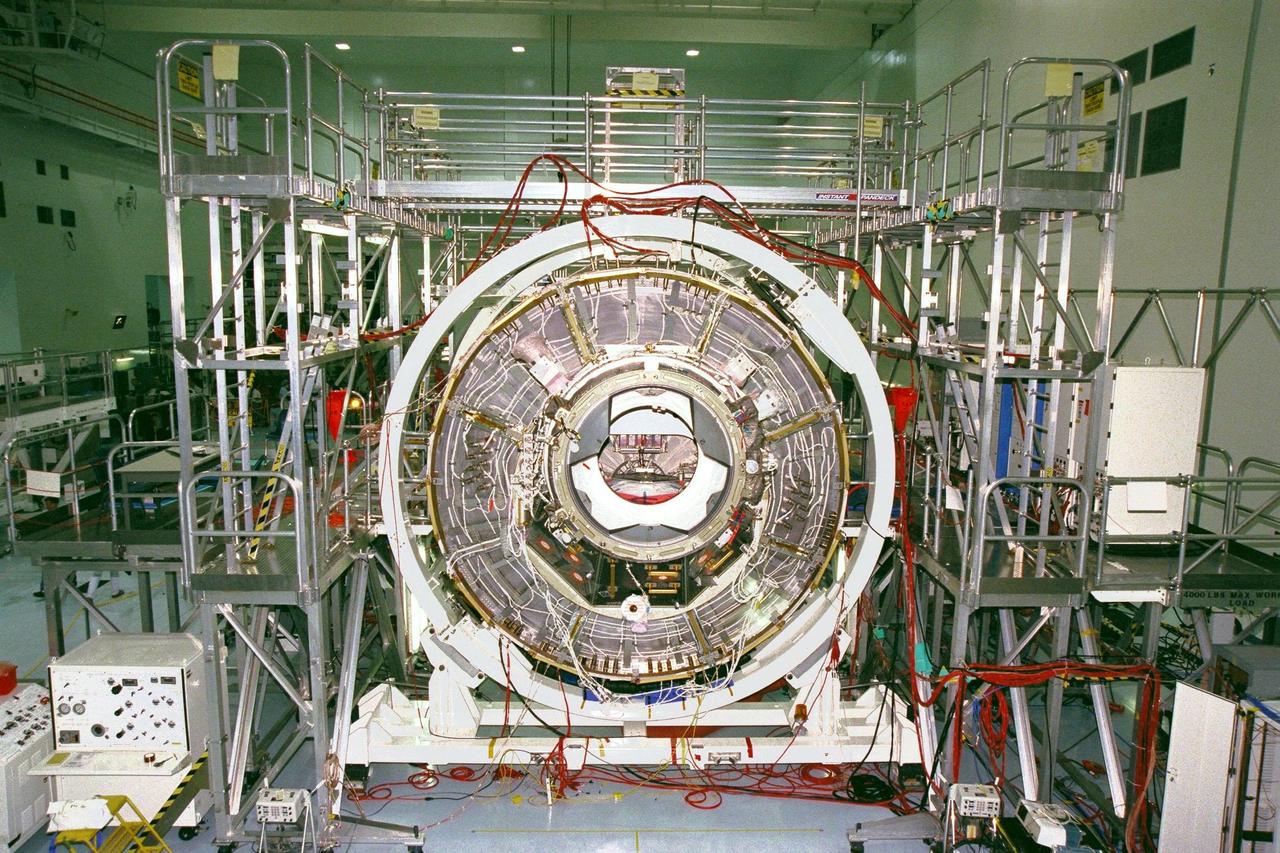

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The International Space Station's (ISS) Unity node, with Pressurized Mating Adapter (PMA)-2 attached, awaits further processing in the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF). The Unity node is the first element of the ISS to be manufactured in the United States and is currently scheduled to lift off aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour on STS-88 later this year. Unity has two PMAs attached to it now that this mate is completed. PMAs are conical docking adapters which will allow the docking systems used by the Space Shuttle and by Russian modules to attach to the node's hatches and berthing mechanisms. Once in orbit, Unity, which has six hatches, will be mated with the already orbiting Control Module and will eventually provide attachment points for the U.S. laboratory module; Node 3; an early exterior framework or truss for the station; an airlock; and a multi-windowed cupola. The Control Module, or Functional Cargo Block, is a U.S.-funded and Russian-built component that will be launched aboard a Russian rocket from Kazakstan
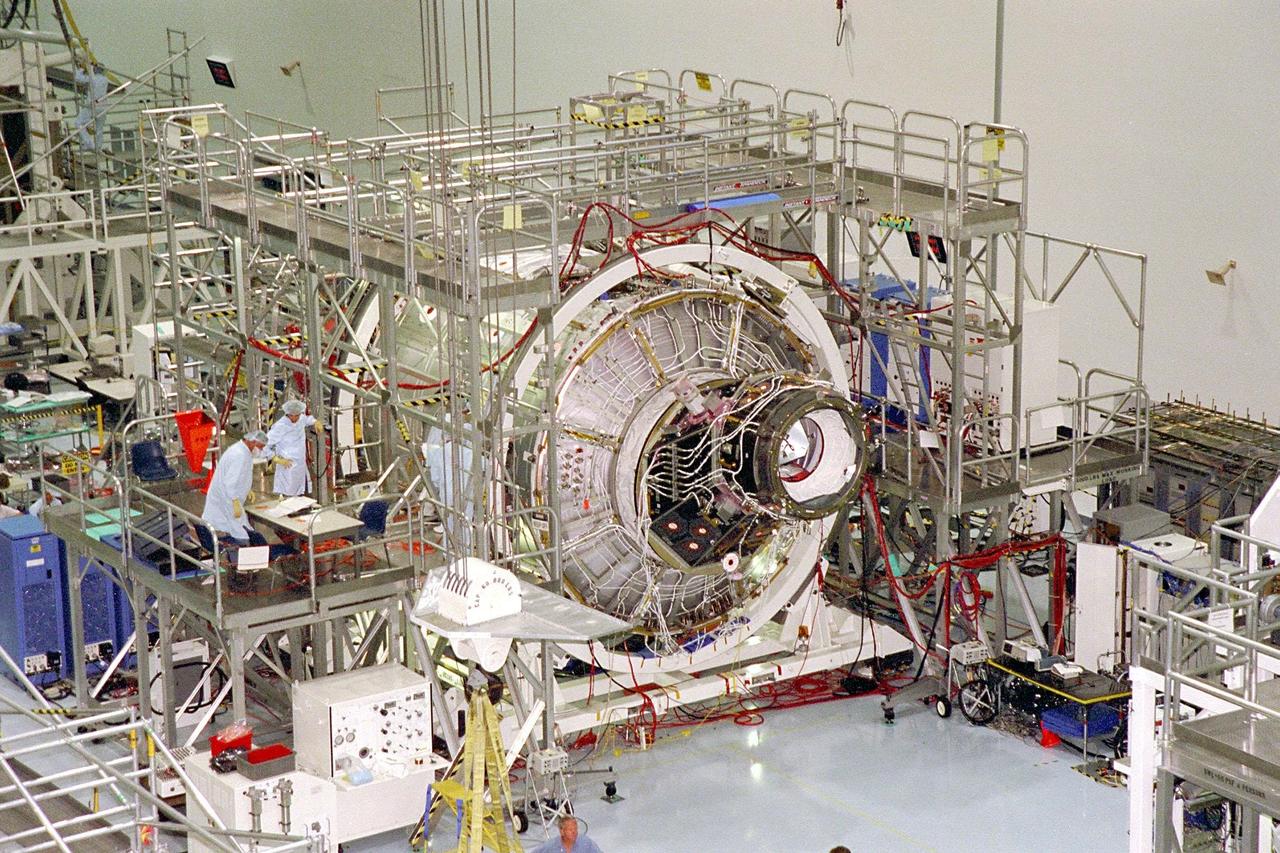
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The International Space Station's (ISS) Unity node, with Pressurized Mating Adapter (PMA)-2 attached, awaits further processing by Boeing technicians in its workstand in the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF). The Unity node is the first element of the ISS to be manufactured in the United States and is currently scheduled to lift off aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour on STS-88 later this year. Unity has two PMAs attached to it now that this mate is completed. PMAs are conical docking adapters which will allow the docking systems used by the Space Shuttle and by Russian modules to attach to the node's hatches and berthing mechanisms. Once in orbit, Unity, which has six hatches, will be mated with the already orbiting Control Module and will eventually provide attachment points for the U.S. laboratory module; Node 3; an early exterior framework or truss for the station; an airlock; and a multi-windowed cupola. The Control Module, or Functional Cargo Block, is a U.S.-funded and Russian-built component that will be launched aboard a Russian rocket from Kazakstan
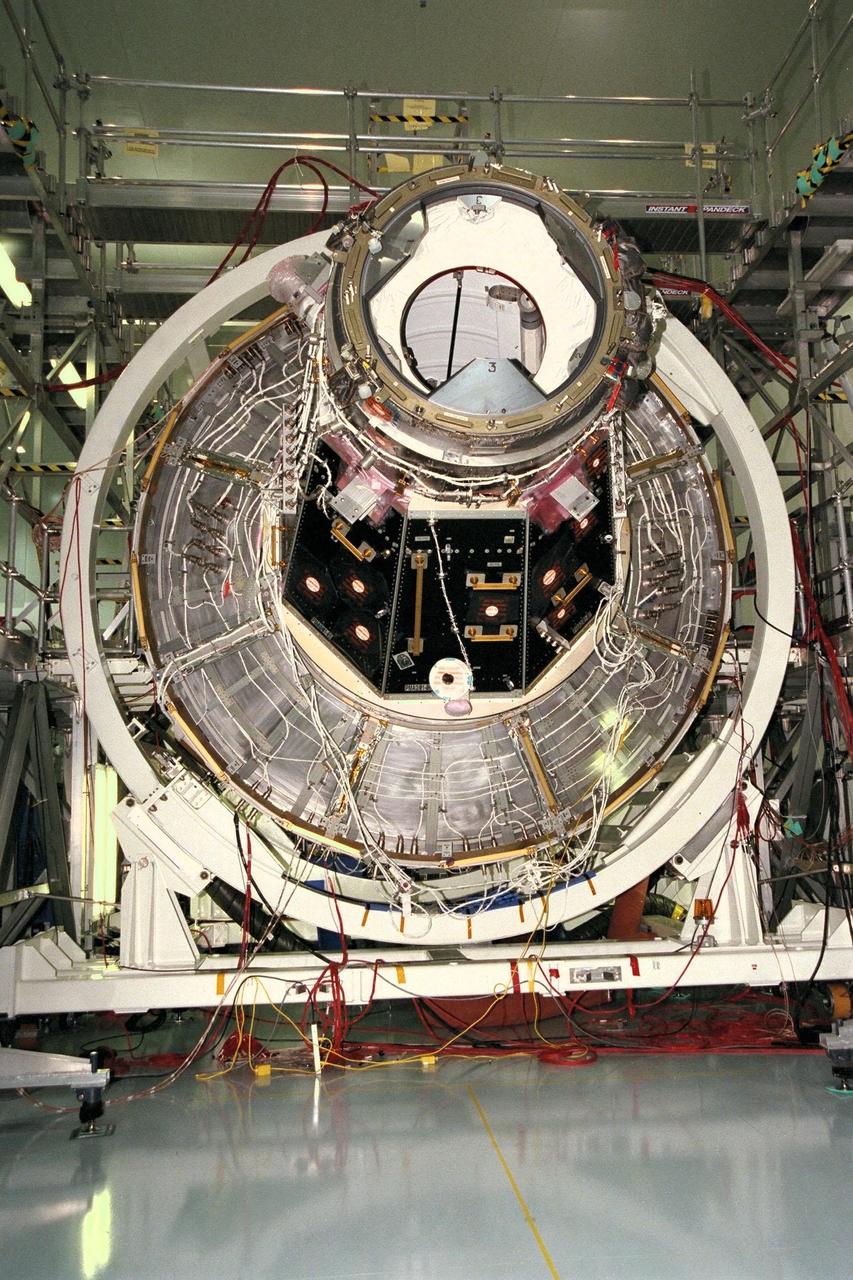

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The International Space Station's (ISS) Unity node, with Pressurized Mating Adapter (PMA)-2 attached, awaits further processing in the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF). The Unity node is the first element of the ISS to be manufactured in the United States and is currently scheduled to lift off aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour on STS-88 later this year. Unity has two PMAs attached to it now that this mate is completed. PMAs are conical docking adapters which will allow the docking systems used by the Space Shuttle and by Russian modules to attach to the node's hatches and berthing mechanisms. Once in orbit, Unity, which has six hatches, will be mated with the already orbiting Control Module and will eventually provide attachment points for the U.S. laboratory module; Node 3; an early exterior framework or truss for the station; an airlock; and a multi-windowed cupola. The Control Module, or Functional Cargo Block, is a U.S.-funded and Russian-built component that will be launched aboard a Russian rocket from Kazakstan
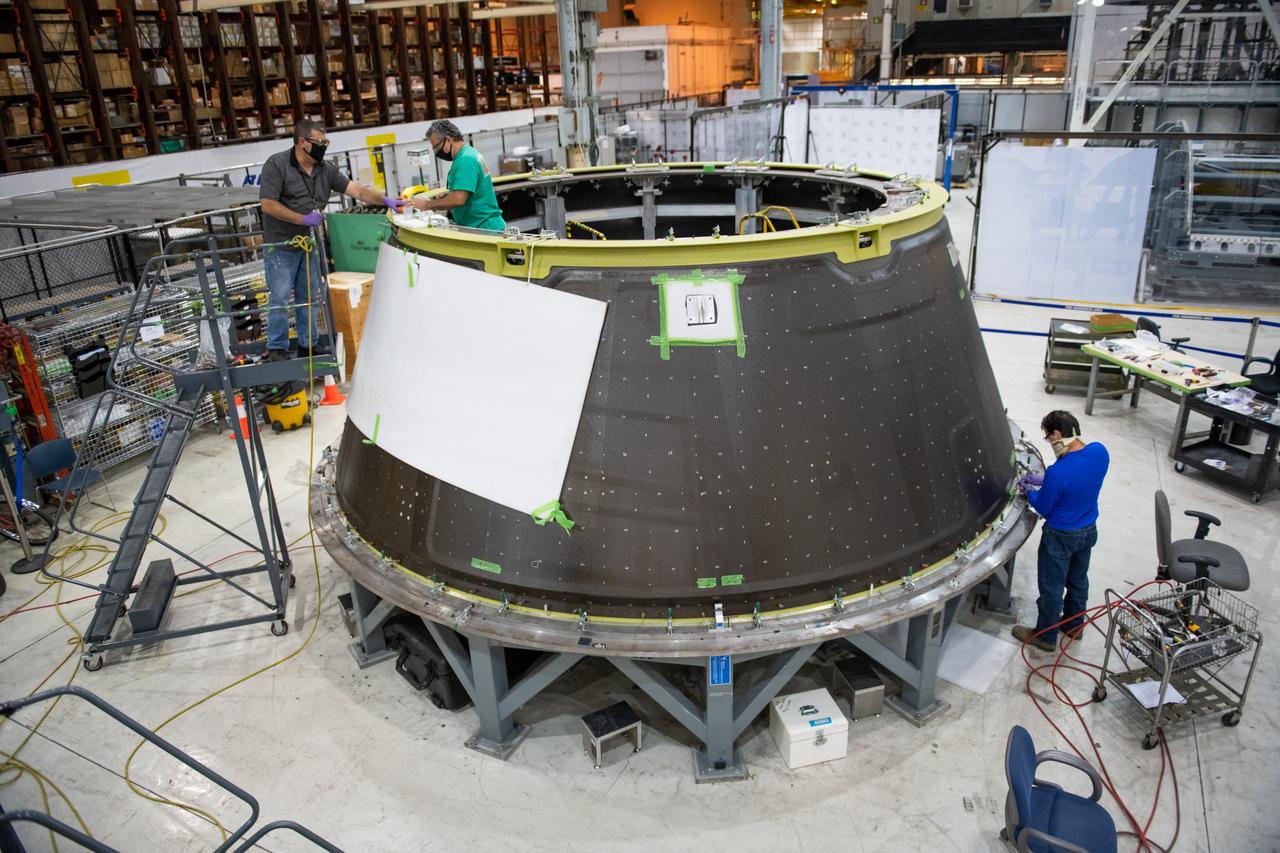

Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.
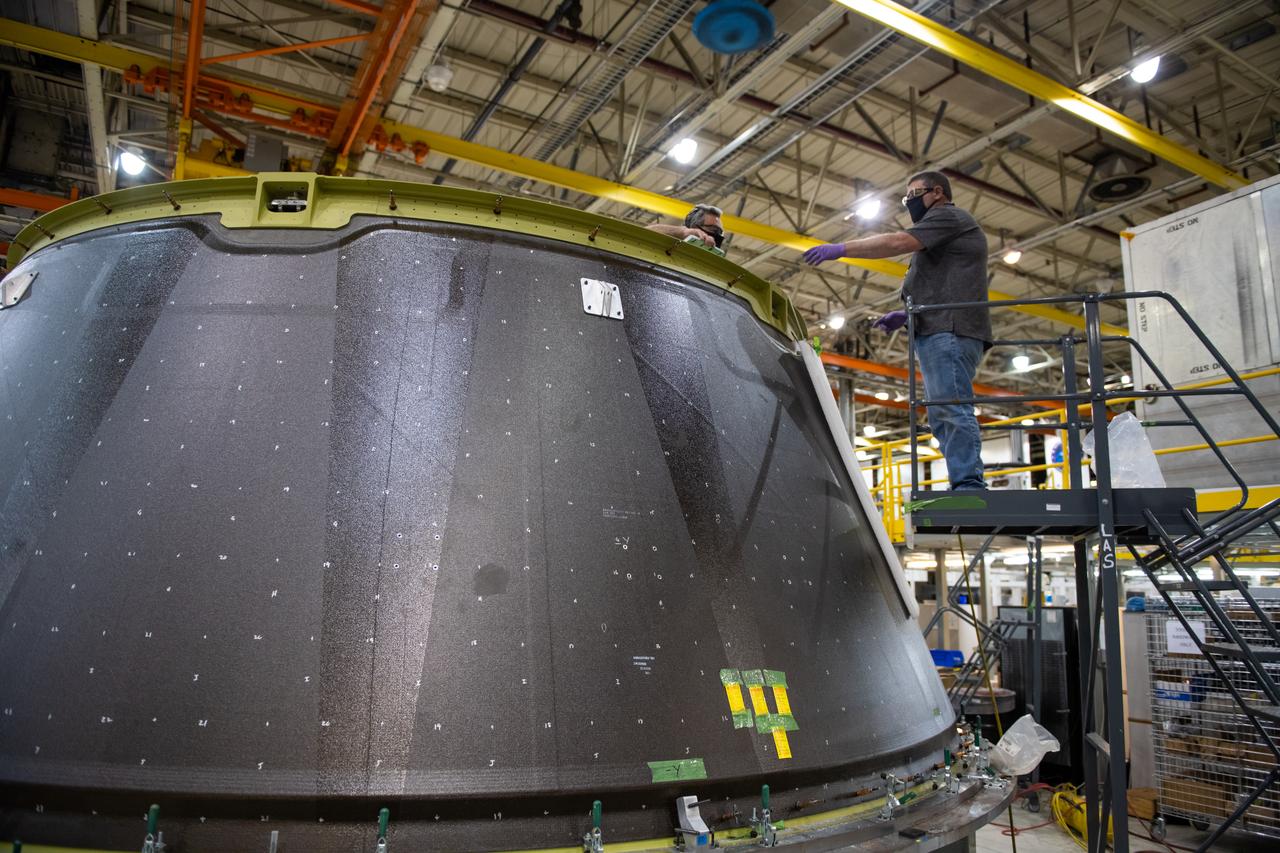

Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.
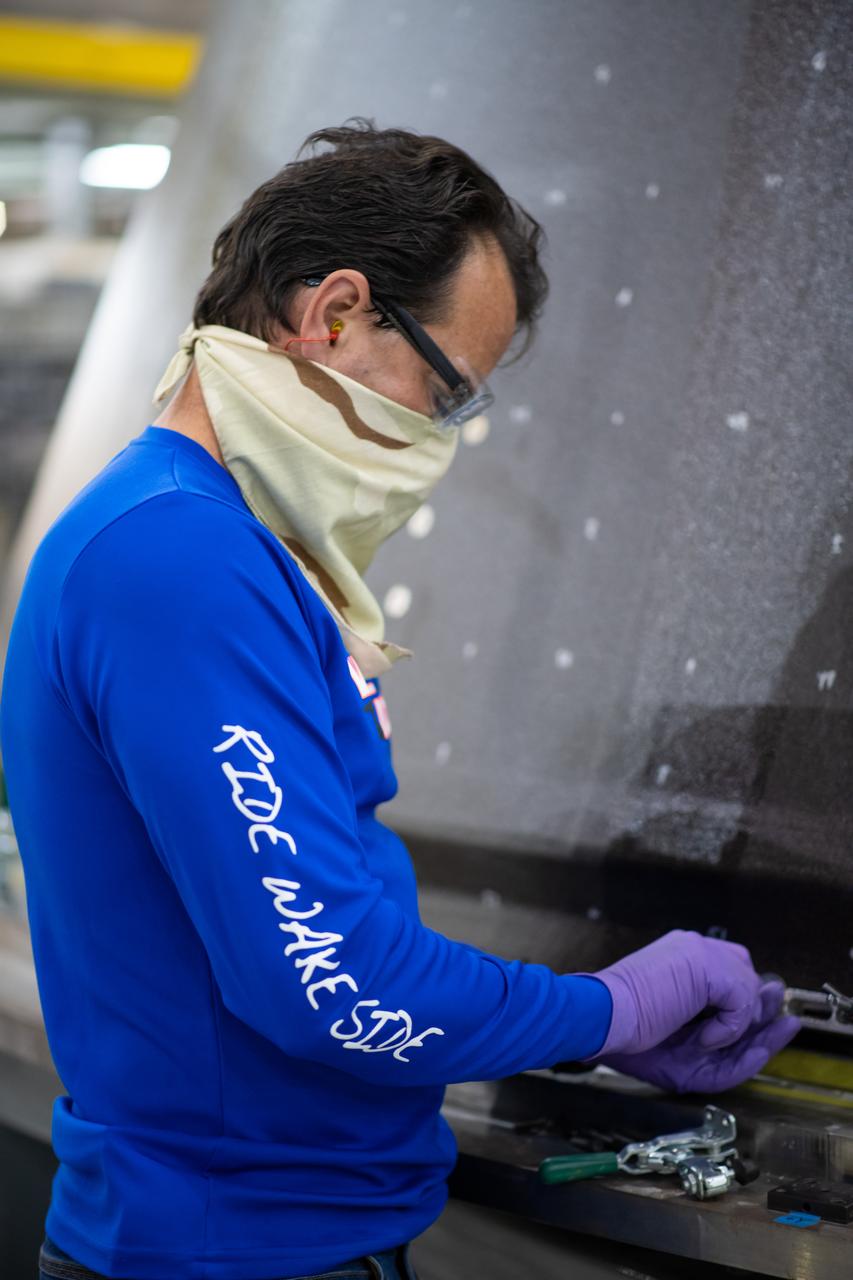

Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.
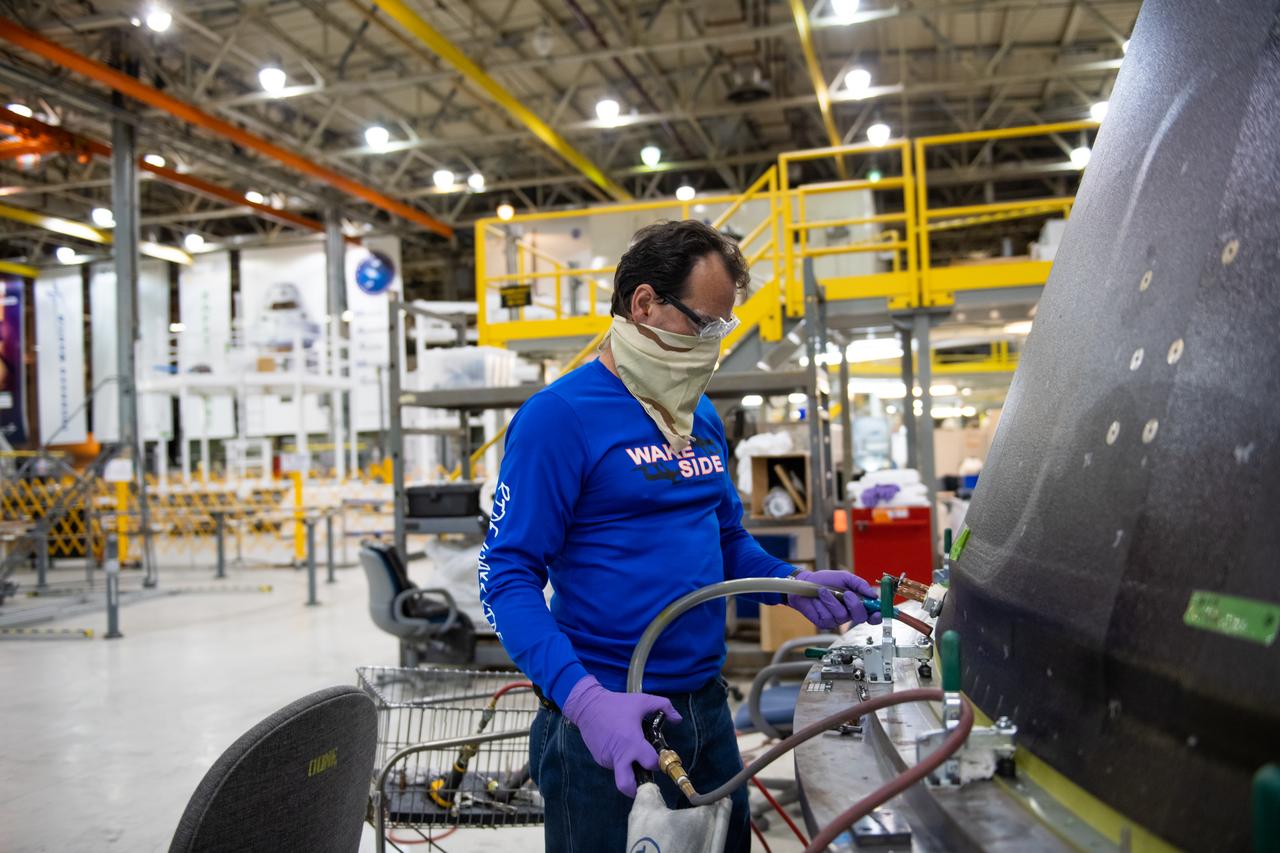

Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.
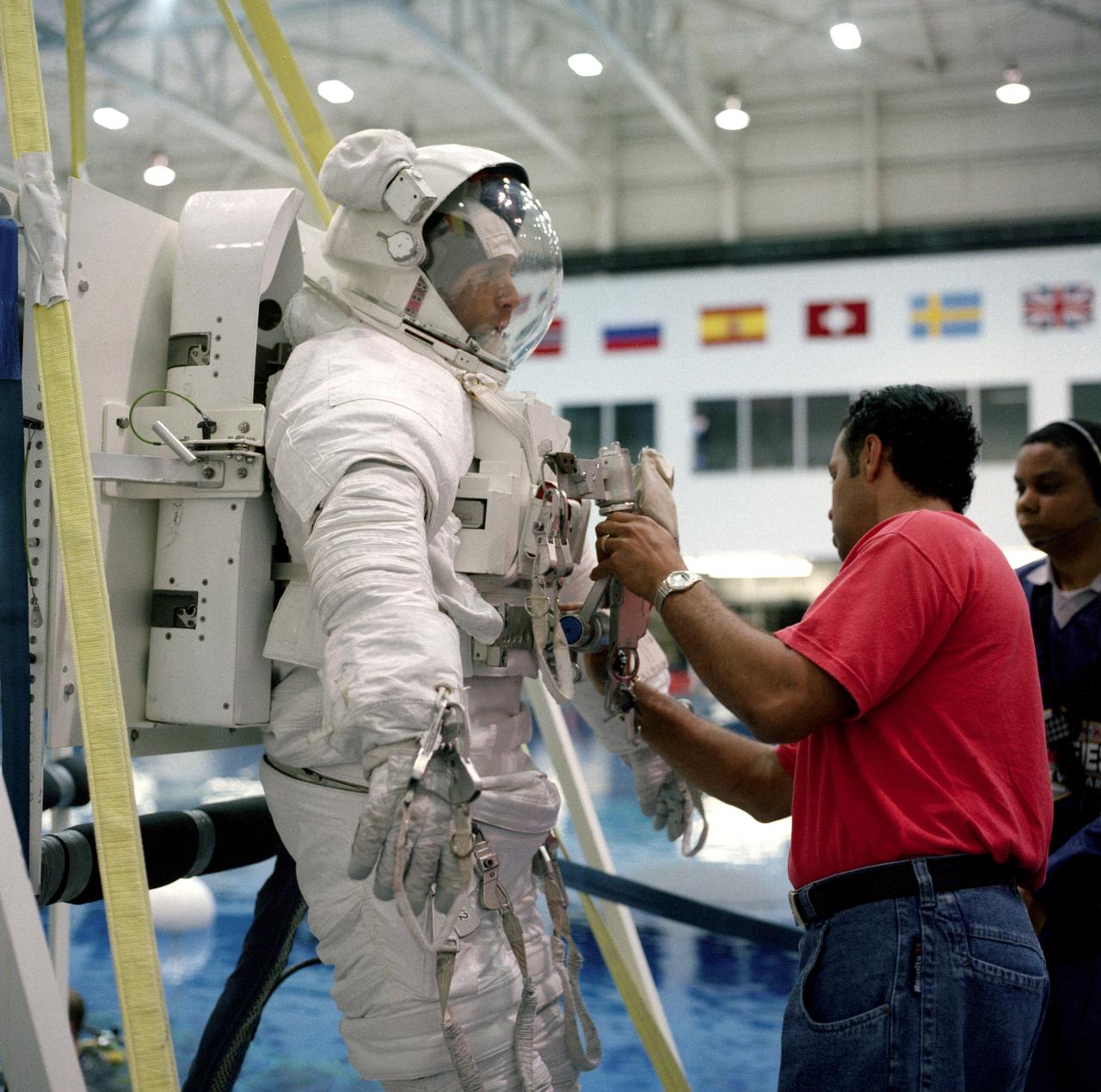

S98-09040 (June 1998) --- Astronaut James H. Newman, mission specialist, gets final touches on the training version of his Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU) space suit prior to being submerged in the waters of the Neutral Buoyancy Laboratory (NBL) at the Johnson Space Center (JSC). The two assigned space walkers -- Newman and Jerry L. Ross -- shared the platform as it was lowered into the water where the pair moments later were training with full-scale mockups of the International Space Station (ISS) hardware with which they'll be working in space. One of those elements will be the Functional Cargo Block (FGB), which will have been launched a couple of weeks prior to STS-88. Once the FGB is captured using the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) of the Space Shuttle Endeavour, astronaut Nancy J. Currie, mission specialist, will maneuver the robot arm to dock the FGB to the conical mating adapter at the top of Node 1, to be carried in the Space Shuttle's cargo bay. In ensuing days, three Extravehicular Activity?s (EVA) by Ross and Newman will be performed to make power, data and utility connections between the two modules.
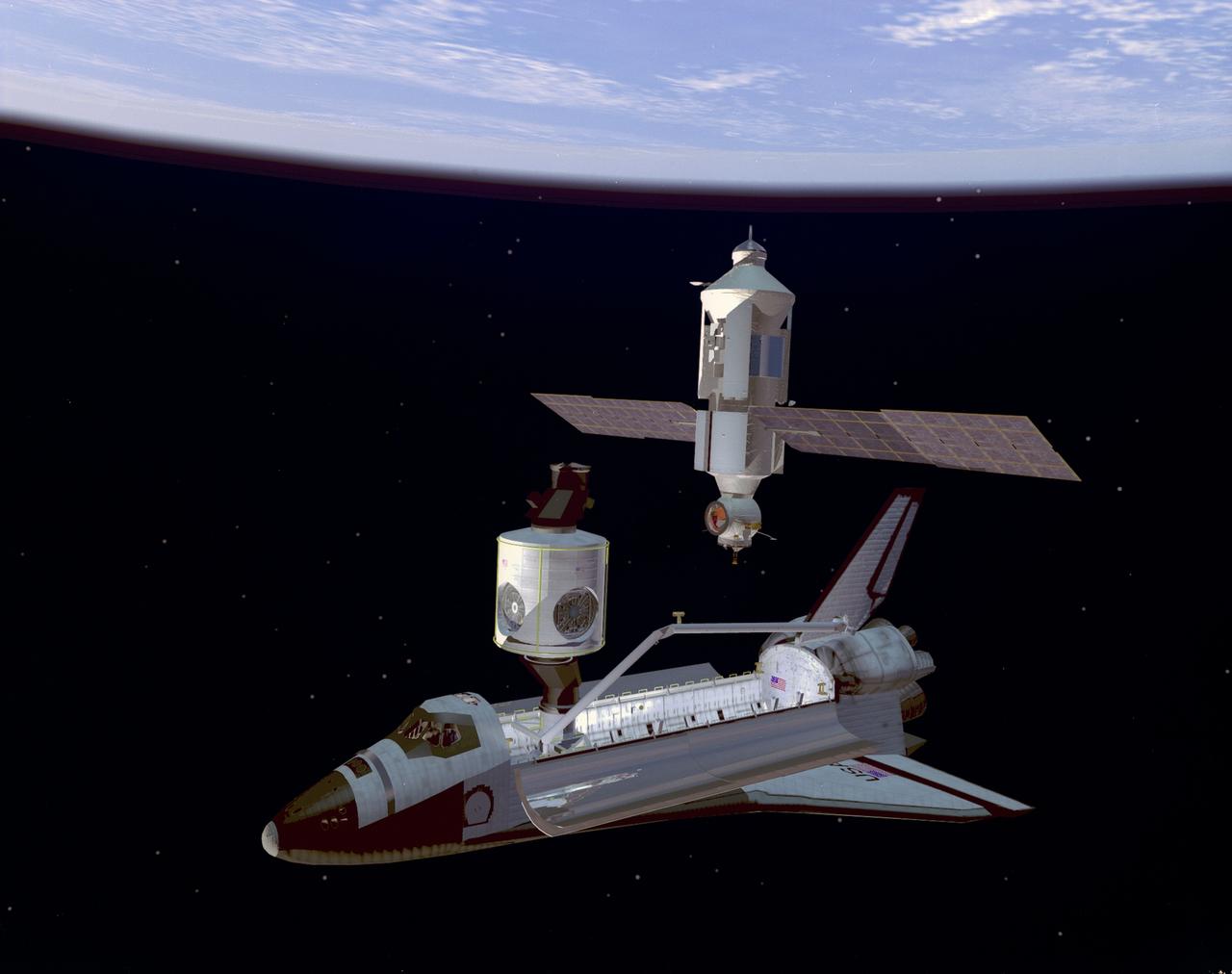

S98-04904 (21 July 1997) --- The Space Shuttle Endeavour prepares to capture the Functional Cargo Block (FGB) using the shuttle's mechanical arm in this artist's depiction of the first Space Shuttle assembly flight for the International Space Station (ISS), mission STS-88 scheduled to launch in December 1998. The shuttle will carry the first United States-built component for the station, a connecting module called Node 1 or Unity, and attach it to the already orbiting FGB, which supplies early electrical power and propulsion. The FGB, Zarya, will have been launched about two weeks earlier on a Russian Proton rocket from the Baikonur Cosmodrome, Kazahkstan. Once the FGB is captured using the mechanical arm, astronaut Nancy J. Currie will maneuver the arm to dock the FGB to the conical mating adapter at the top of Node 1 in the Shuttle's cargo bay. In ensuing days, three Extravehicular Activity?s (EVA) by astronauts Jerry L. Ross and James H. Newman will be performed to make power, data and utility connections between the two modules.
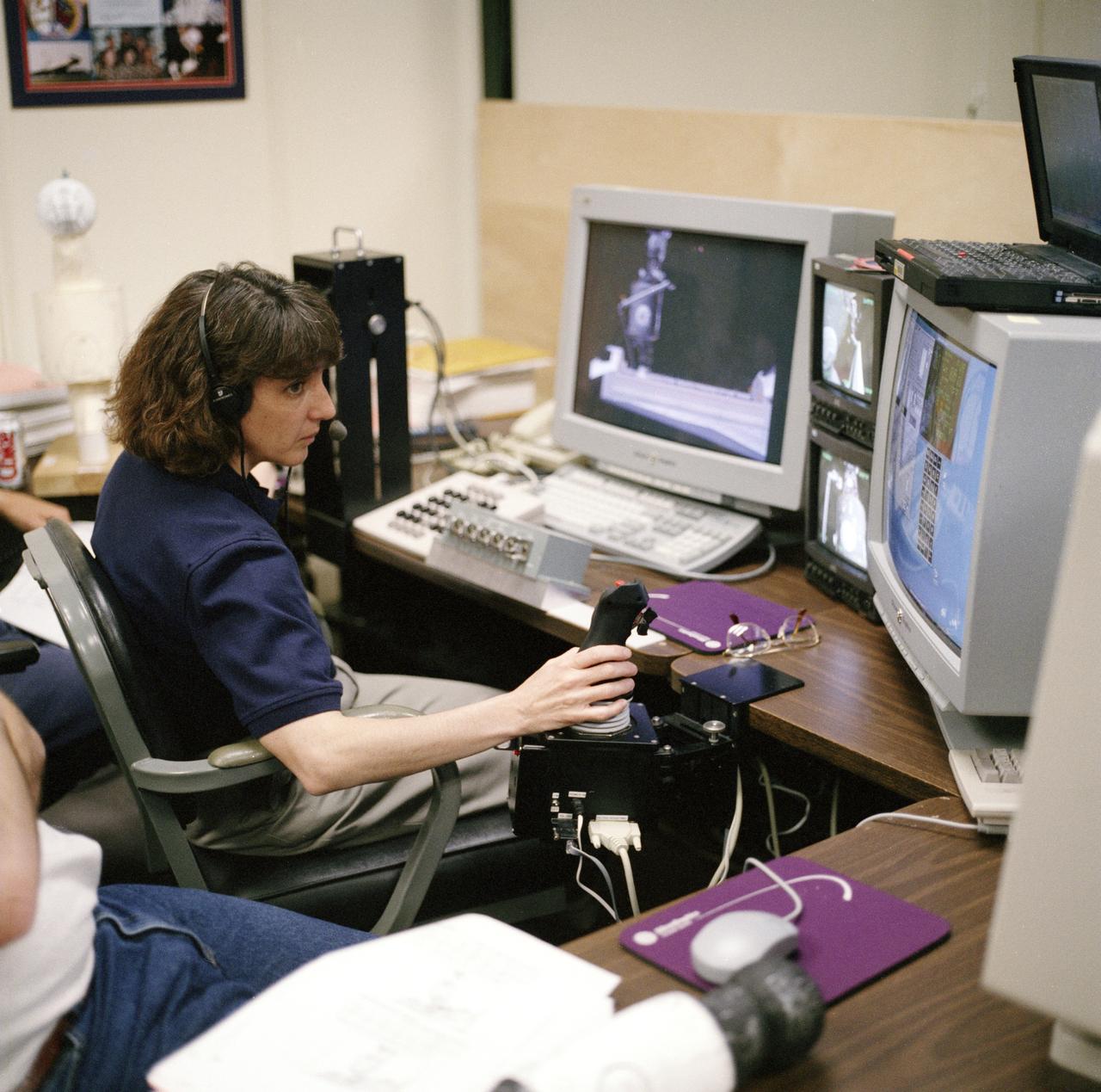

S98-05075 (8 Apr. 1998) --- Astronaut Nancy J. Currie, assigned as a mission specialist for the mission, uses hardware in the virtual reality lab at the Johnson Space Center (JSC) to train for her duties aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour. This type computer interface paired with virtual reality training hardware for the assigned space-walking astronauts -- in this case, Jerry L. Ross and James H. Newman -- helps to prepare the entire team for dealing with International Space Station (ISS) elements. One of those elements will be the Functional Cargo Block (FGB), which will have been launched a couple of weeks prior to STS-88. Once the FGB is captured using the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) of the Endeavour, Currie will maneuver the robot arm to dock the FGB to the conical mating adapter at the top of Node 1, to be carried in the Endeavour?s cargo bay. In ensuing days, three Extravehicular Activity?s (EVA) by Ross and Newman will be performed to make power, data and utility connections between the two modules.
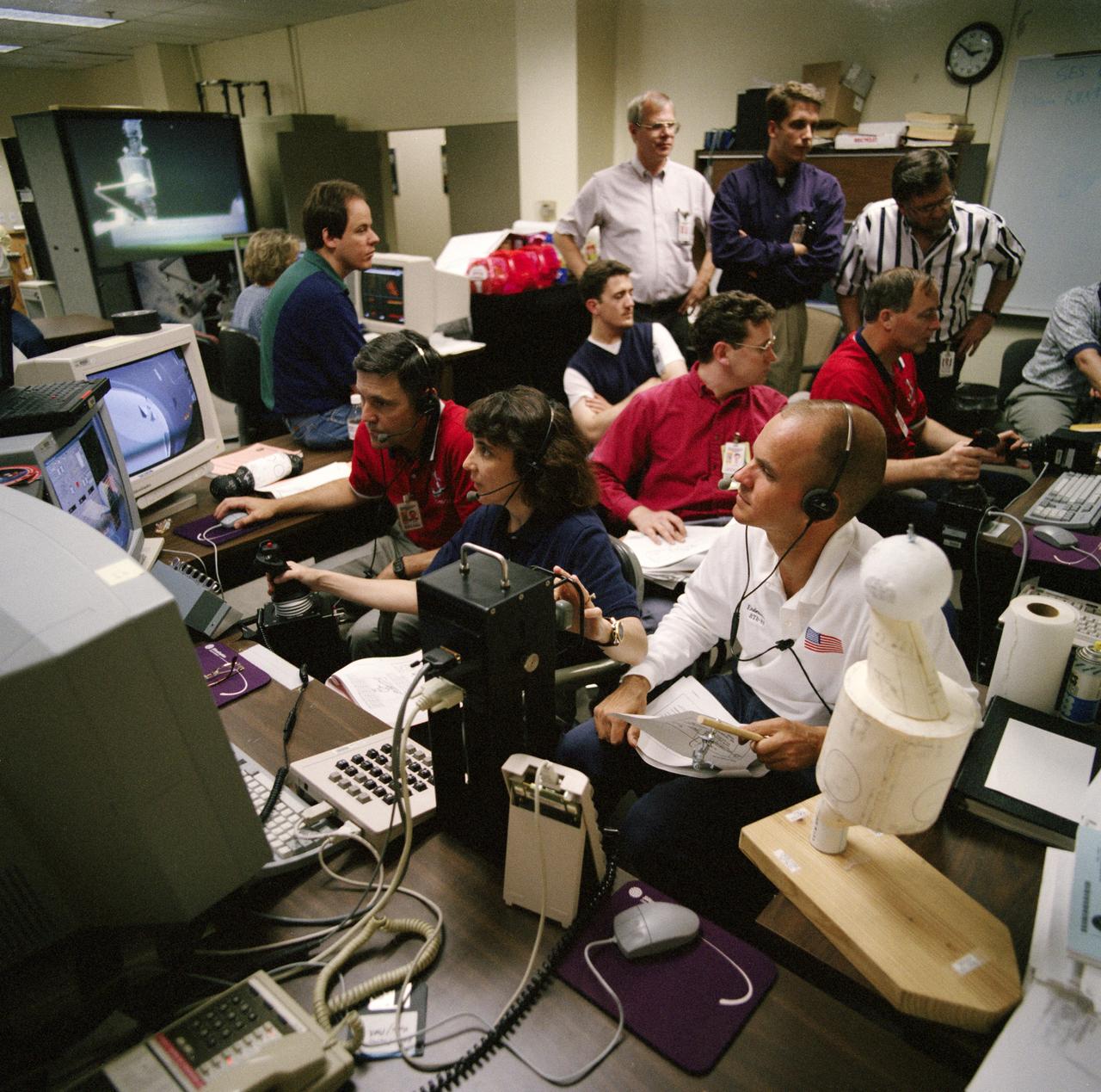

S98-05077 (8 Apr. 1998) --- With crew mates looking on, astronaut Nancy J. Currie, mission specialist, uses hardware in the virtual reality lab at the Johnson Space Center (JSC) to train for her duties aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour. She is flanked by astronaut Robert Cabana (left), commander; and Frederick W. Sturckow (right), pilot. This type computer interface paired with virtual reality training hardware for the assigned space-walking astronauts -- Jerry L. Ross and James H. Newman -- helps to prepare the entire team for dealing with International Space Station (ISS) elements. One of those elements will be the Functional Cargo Block (FGB), which will have been launched a couple of weeks prior to STS-88. Once the FGB is captured using the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) of the Endeavour, Currie will maneuver the robot arm to dock the FGB to the conical mating adapter at the top of Node 1, to be carried in the Endeavour's cargo bay. In ensuing days, three Extravehicular Activity?s (EVA) by Ross and Newman will be performed to make power, data and utility connections between the two modules. Looking on is Scott A. Bleisath (behind Currie), with the EVA Systems Group at JSC.
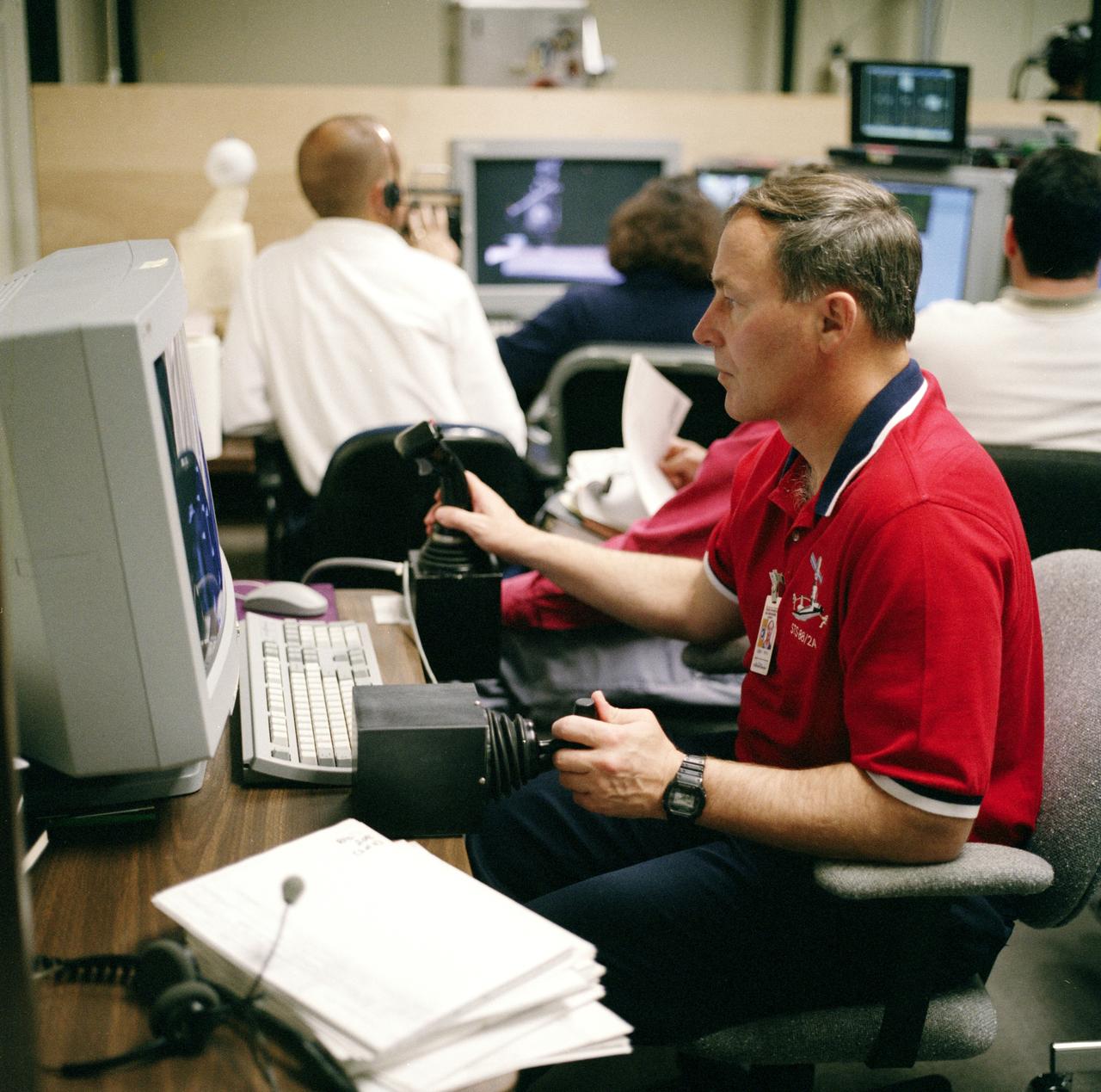

S98-05074 (8 Apr. 1998) --- Astronaut Jerry L. Ross, assigned as a mission specialist for the mission, uses special gear and software to train for his duties aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour. This type virtual reality training supplements practice for each of the assigned space-walking astronauts -- Ross and James H. Newman -- during which they wear a helmet and special gloves to look at computer displays simulating actual movements around the various locations on the early International Space Station (ISS) hardware with which they'll be working. One of those elements will be the Functional Cargo Block (FGB), which will have been launched a couple of weeks prior to STS-88. Once the FGB is captured using the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) of the Endeavour, astronaut Nancy J. Currie will maneuver the robot arm to dock the FGB to the conical mating adapter at the top of Node 1, to be carried in the Shuttle's cargo bay. In ensuing days, three space walks by Ross and Newman will be performed to make power, data and utility connections between the two modules. Currie also uses this same lab to train for her RMS controlling duties.
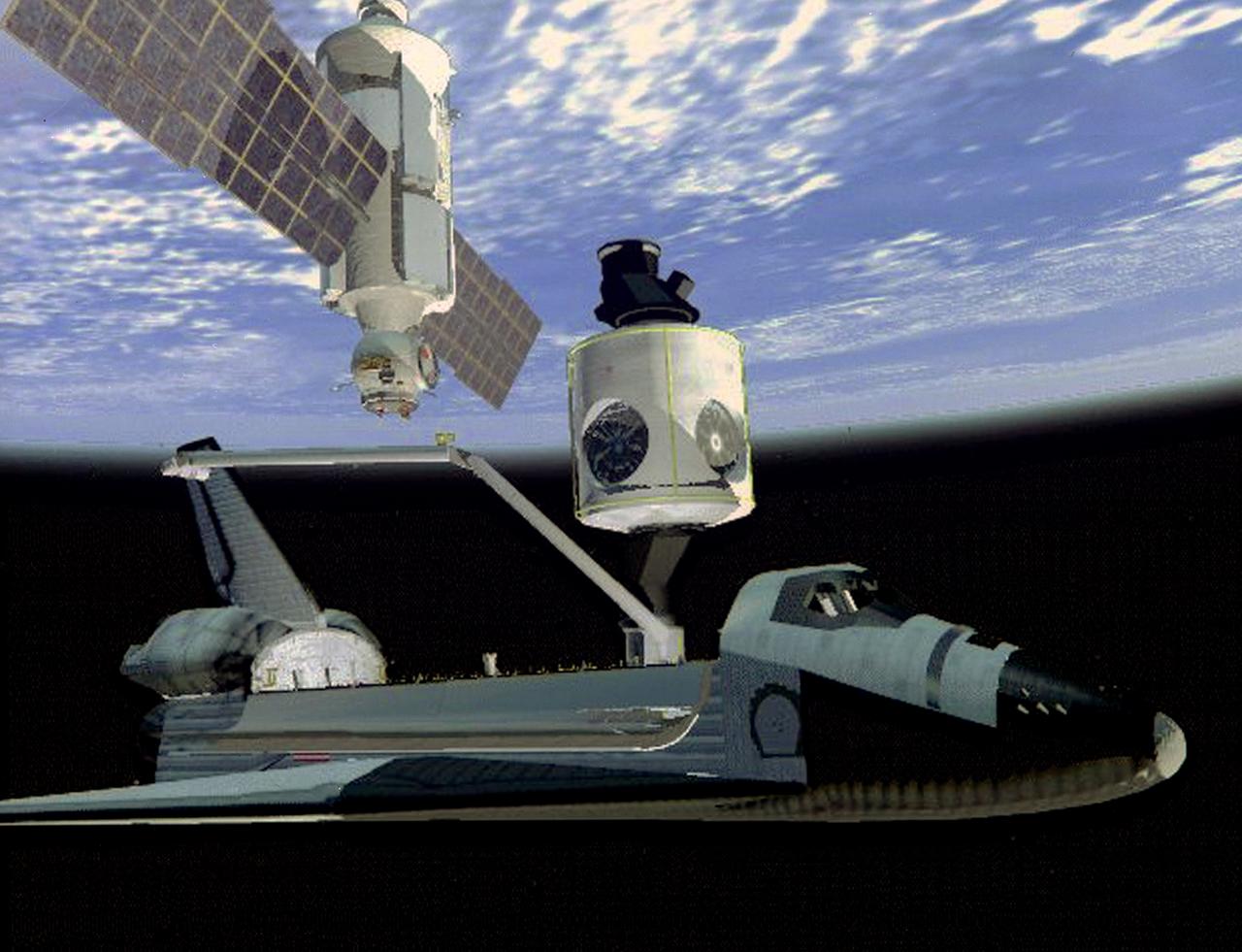

S98-09020 (21 July 1997) --- The Space Shuttle Endeavour prepares to capture the Functional Cargo Block (FGB) using the shuttle's mechanical arm in this artist's depiction of the first Space Shuttle assembly flight for the International Space Station (ISS), mission STS-88 scheduled to launch in July 1998. The shuttle will carry the first United States-built component for the station, a connecting module called Node 1, and attach it to the already orbiting FGB, which supplies early electrical power and propulsion. The FGB will have been launched about two weeks earlier on a Russian Proton rocket from the Baikonur Cosmodrome, Kazahkstan. Once the FGB is captured using the mechanical arm, astronaut Nancy J. Currie will maneuver the arm to dock the FGB to the conical mating adapter at the top of Node 1 in the Shuttle's cargo bay. In ensuing days, three Extravehicular Activity?s (EVA) by astronauts Jerry L. Ross and James H. Newman will be performed to make power, data and utility connections between the two modules.
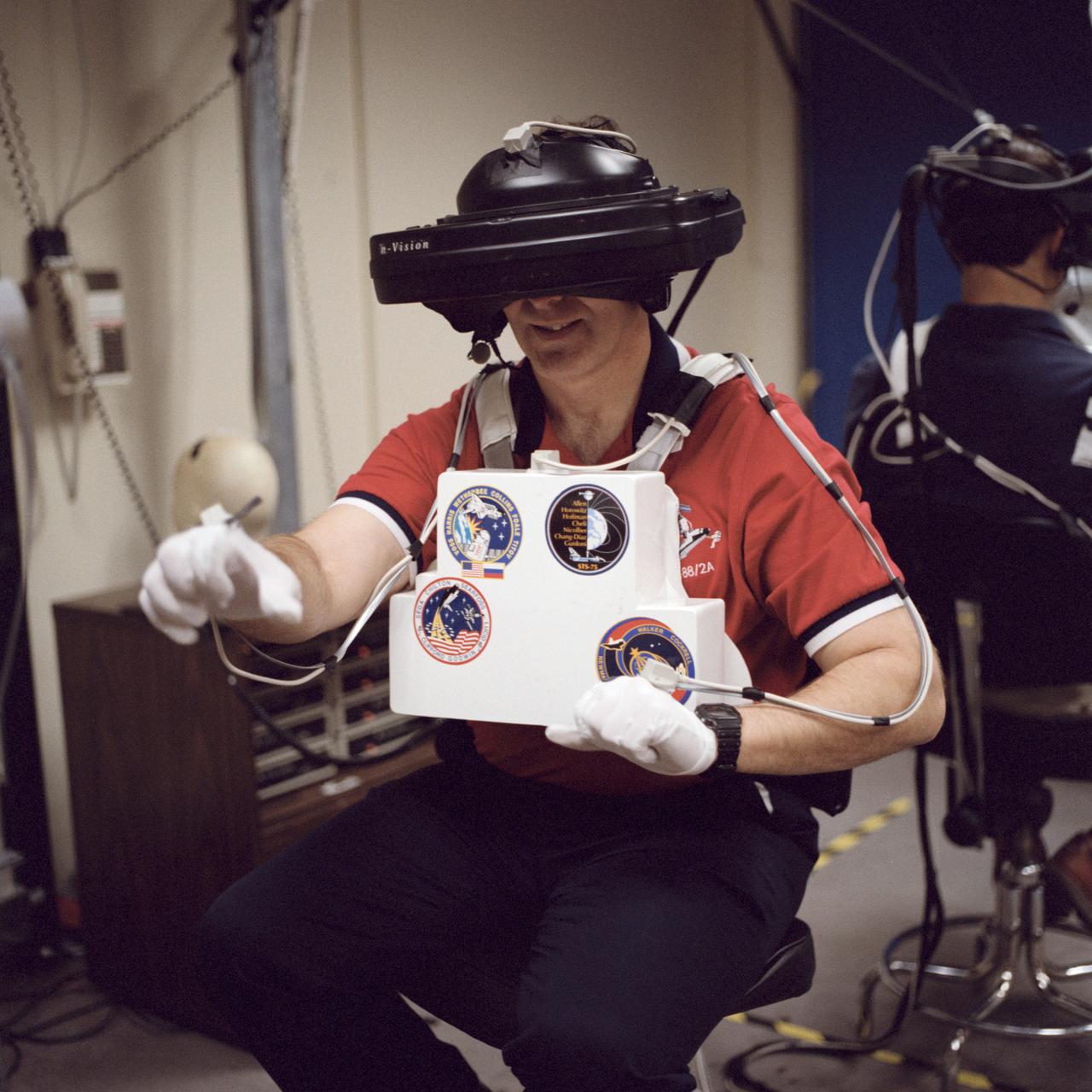

S98-05079 (8 Apr. 1998) --- Astronaut Jerry L. Ross, assigned as a mission specialist for the mission, uses specialized gear to train for his duties aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour. This type virtual reality training allows each of the assigned Extravehicular Activity (EVA) astronauts -- Ross and James H. Newman -- to wear a helmet and special gloves to look at computer displays simulating actual movements around the various locations on the International Space Station (ISS) hardware with which they'll be working. One of those elements will be the Functional Cargo Block (FGB), which will have been launched a couple of weeks prior to STS-88. Once the FGB is captured using the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) of the Endeavour, astronaut Nancy J. Currie will maneuver the robot arm to dock the FGB to the conical mating adapter at the top of Node 1, to be carried in the Shuttle's cargo bay. In ensuing days, three EVA space walks by Ross and Newman will be performed to make power, data and utility connections between the two modules. Currie also uses this same lab to train for her RMS controlling duties.
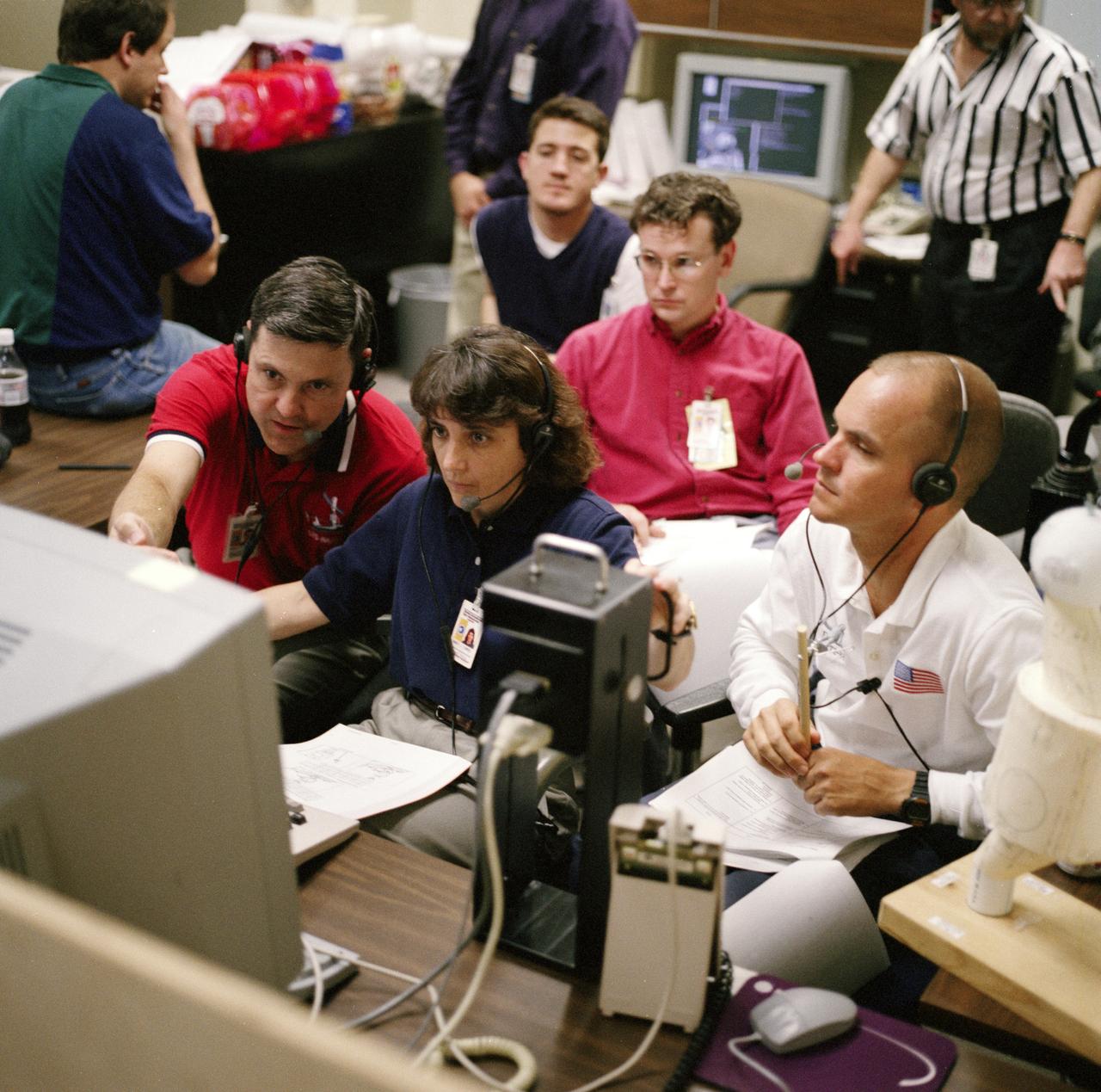

S98-05078 (8 Apr. 1998) --- With crew mates looking on, astronaut Nancy J. Currie, mission specialist, uses hardware in the virtual reality lab at the Johnson Space Center (JSC) to train for her duties aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour. She is flanked by astronaut Robert Cabana (left), commander; and Frederick W. Sturckow (right), pilot. This type computer interface paired with virtual reality training hardware for the assigned space-walking astronauts -- Jerry L. Ross and James H. Newman -- helps to prepare the entire team for dealing with International Space Station (ISS) elements. One of those elements will be the Functional Cargo Block (FGB), which will have been launched a couple of weeks prior to STS-88. Once the FGB is captured using the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) of the Endeavour, Currie will maneuver the robot arm to dock the FGB to the conical mating adapter at the top of Node 1, to be carried in the Endeavour's cargo bay. In ensuing days, three Extravehicular Activity?s (EVA) by Ross and Newman will be performed to make power, data and utility connections between the two modules. Looking on is Scott A. Bleisath (behind Currie), with the EVA Systems Group at JSC.
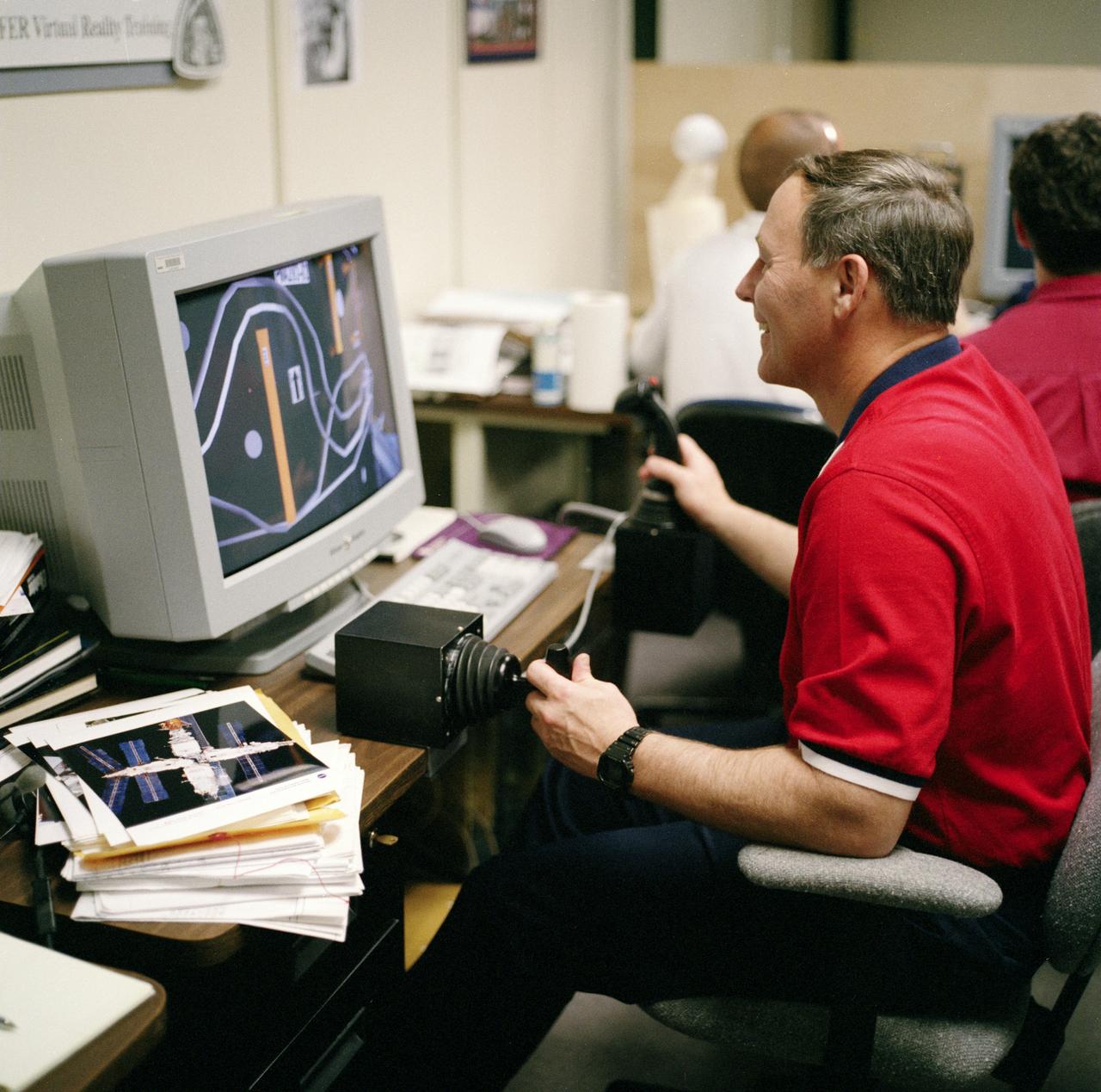

S98-05076 (8 Apr. 1998) --- Astronaut Jerry L. Ross, assigned as a mission specialist for the mission, uses special gear and software to train for his duties aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour. This type virtual reality training supplements practice for each of the assigned space-walking astronauts -- Ross and James H. Newman -- during which they wear a helmet and special gloves to look at computer displays simulating actual movements around the various locations on the early International Space Station (ISS) hardware with which they'll be working. One of those elements will be the Functional Cargo Block (FGB), which will have been launched a couple of weeks prior to STS-88. Once the FGB is captured using the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) of the Endeavour, astronaut Nancy J. Currie will maneuver the robot arm to dock the FGB to the conical mating adapter at the top of Node 1, to be carried in the Shuttle's cargo bay. In ensuing days, three space walks by Ross and Newman will be performed to make power, data and utility connections between the two modules. Currie also uses this same lab to train for her RMS controlling duties.