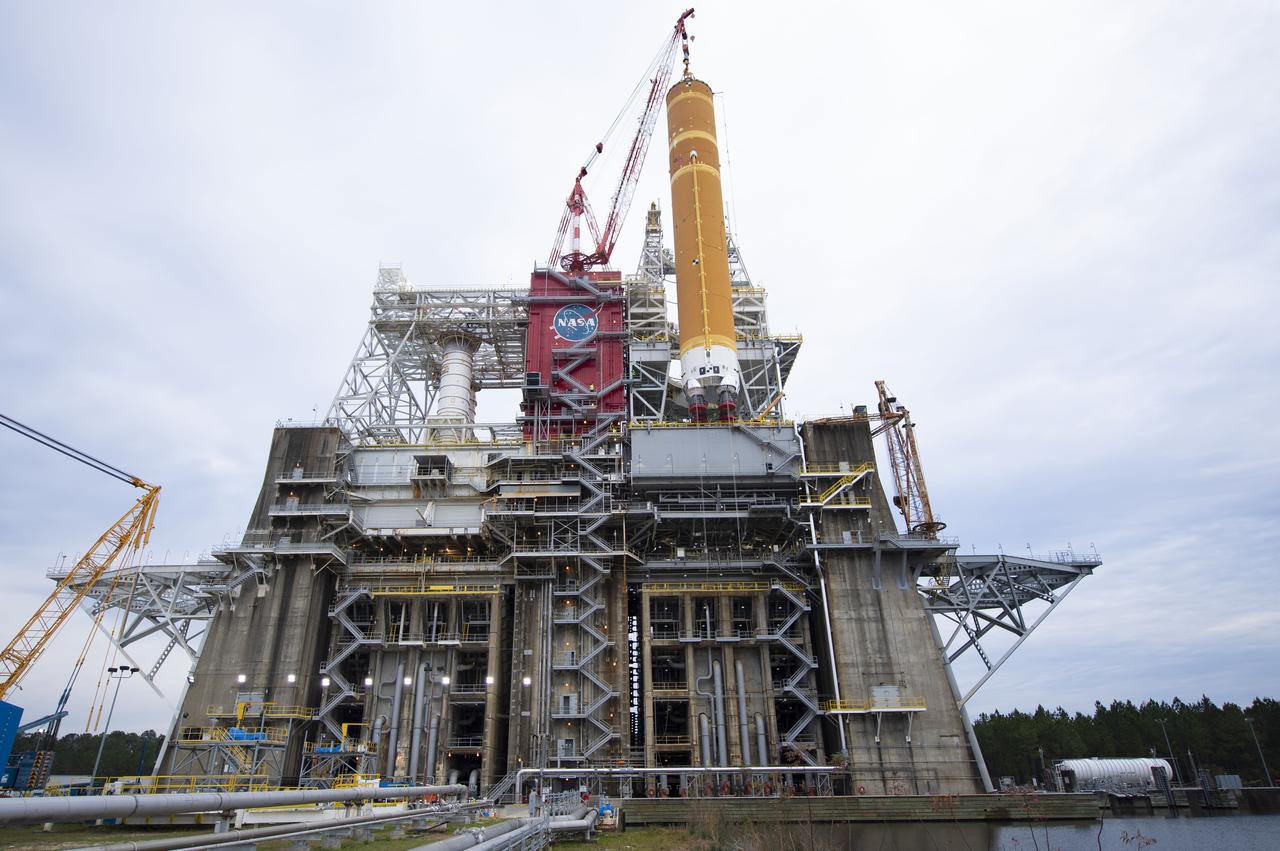

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.
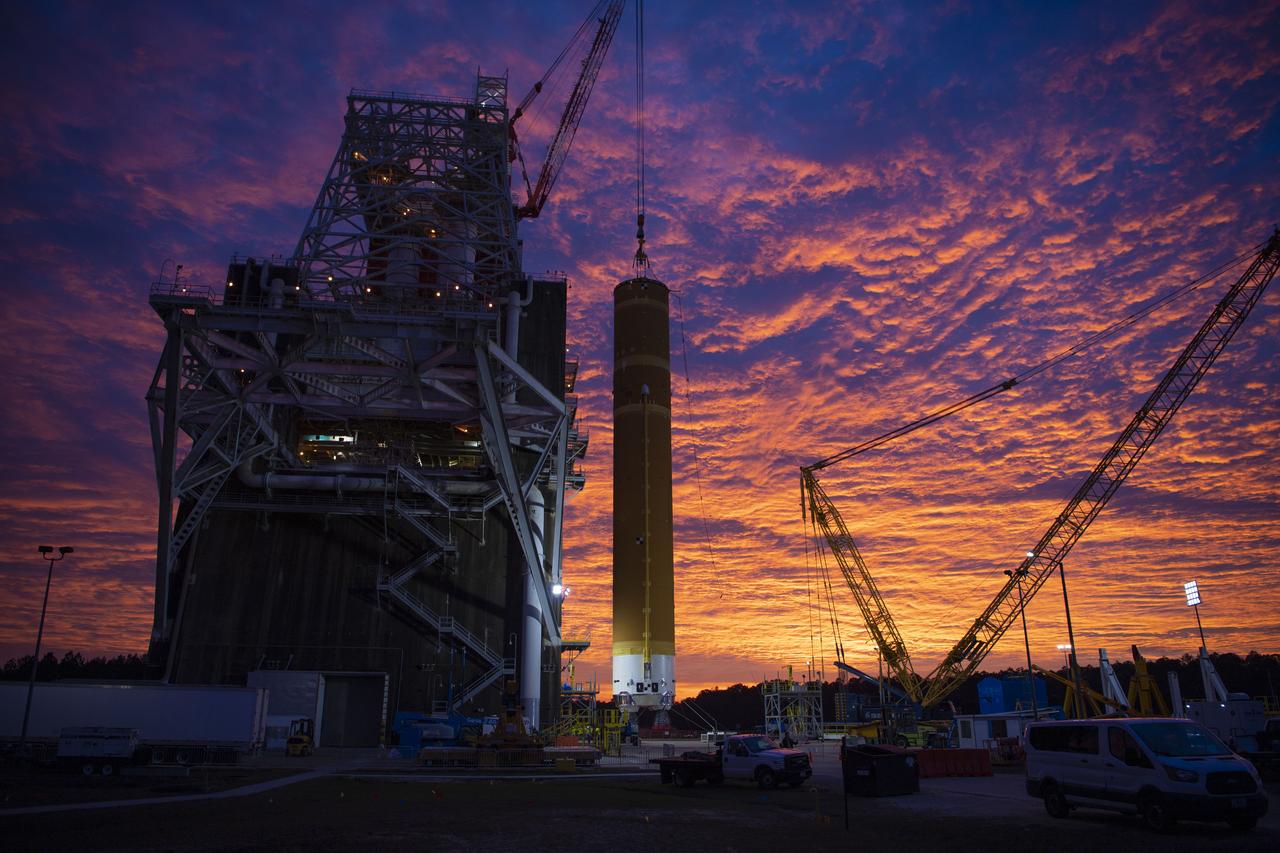

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.
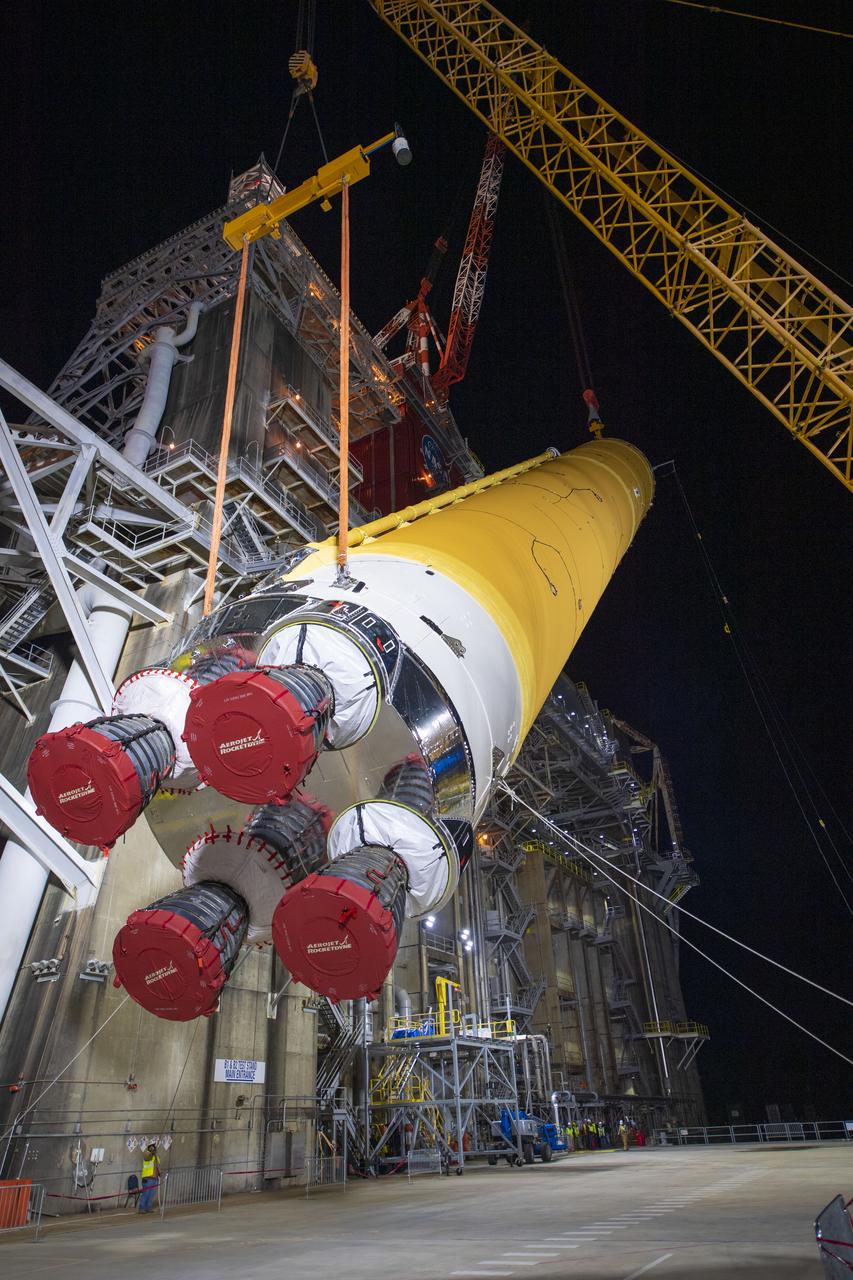

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.
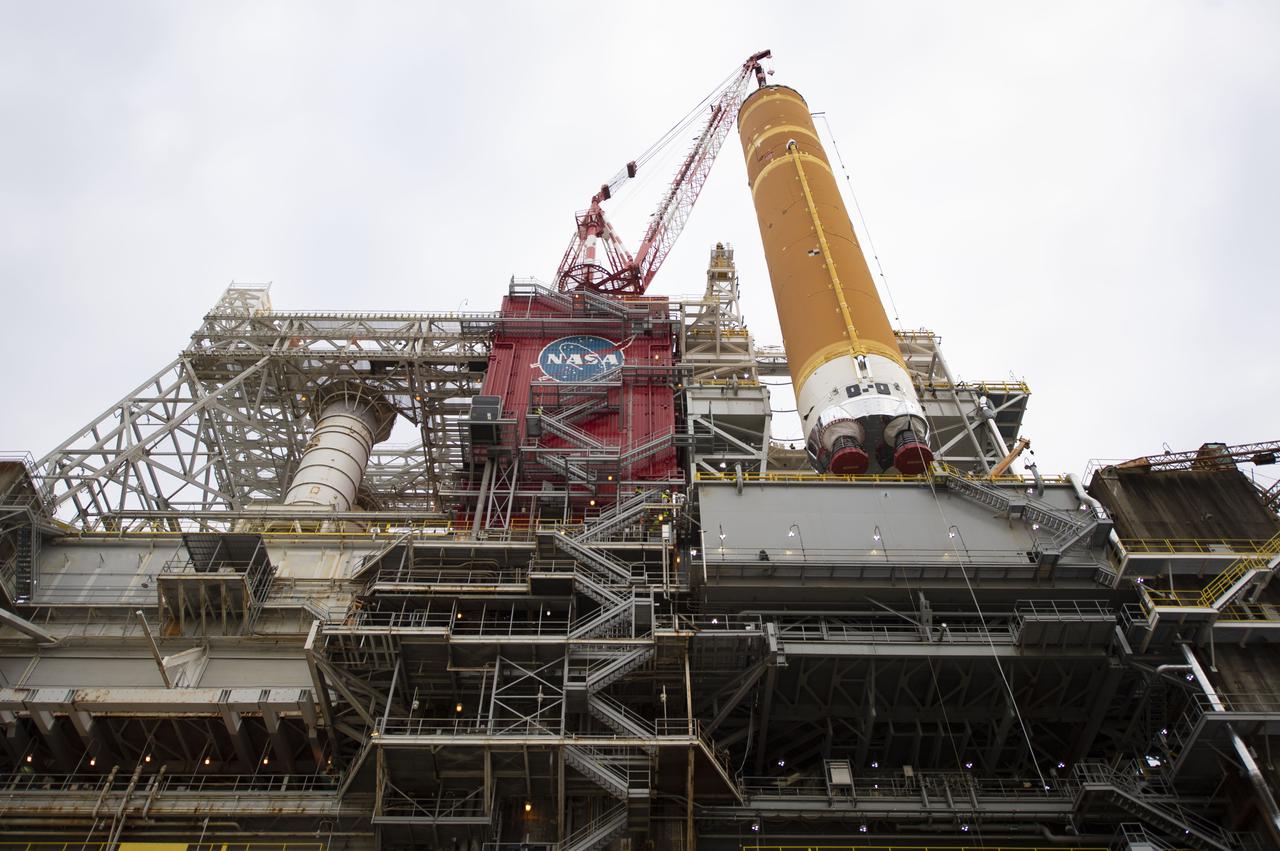

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.
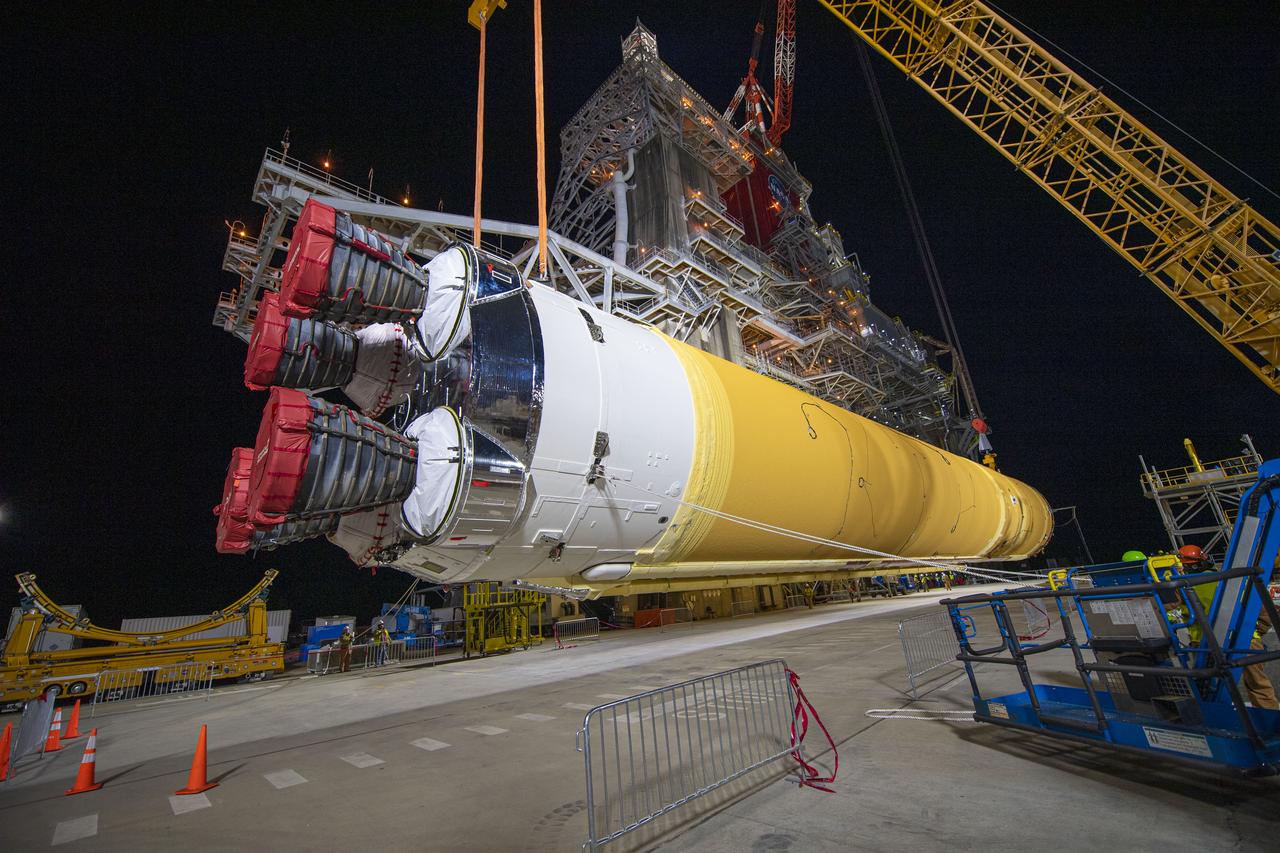

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.
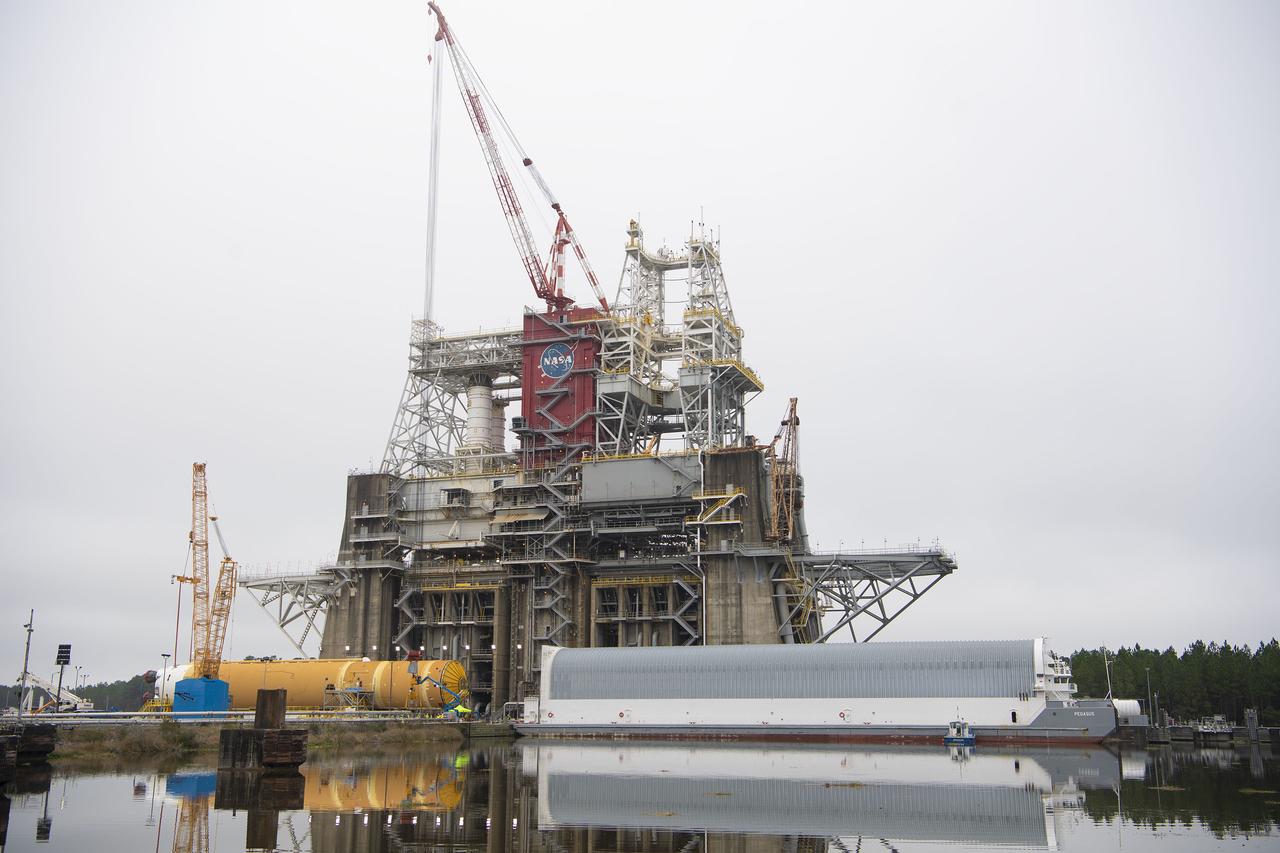

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.
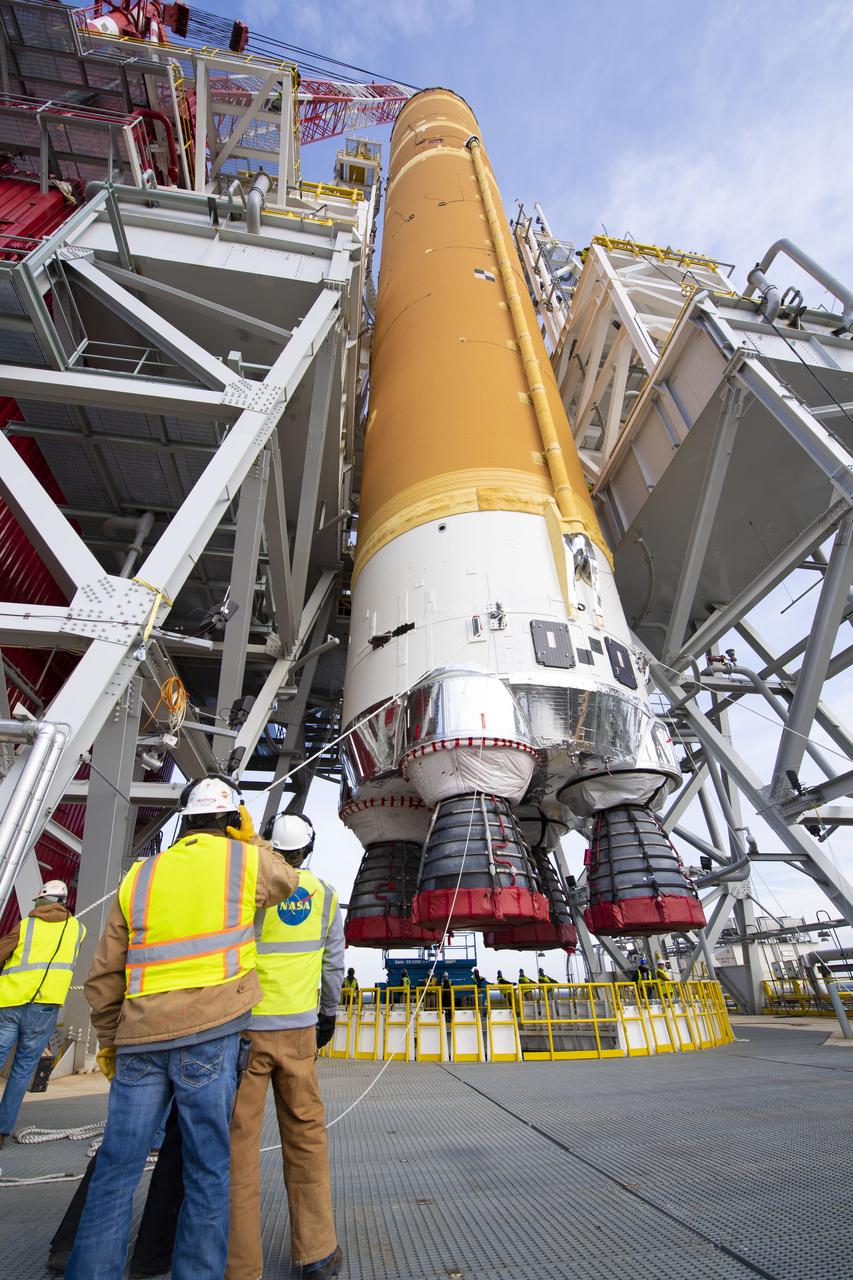

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.
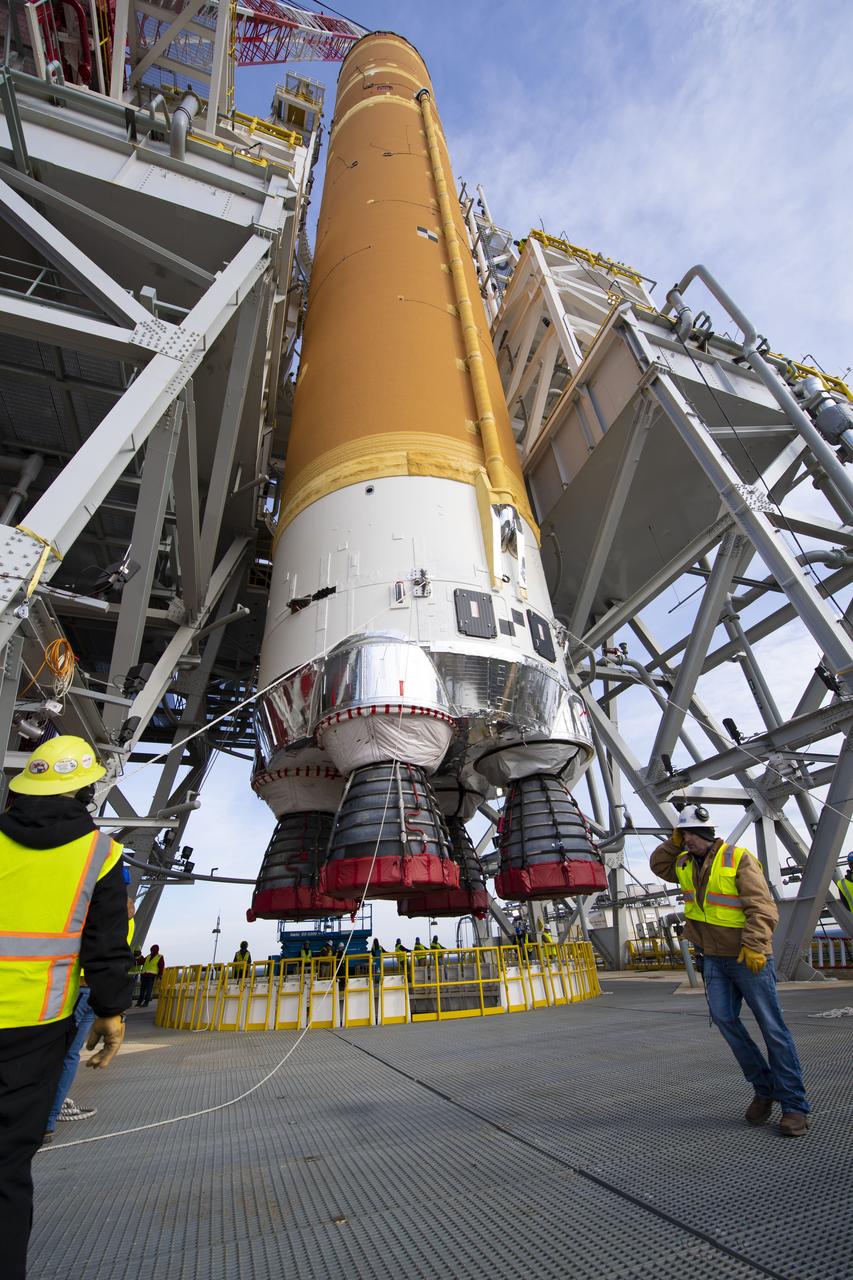

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.
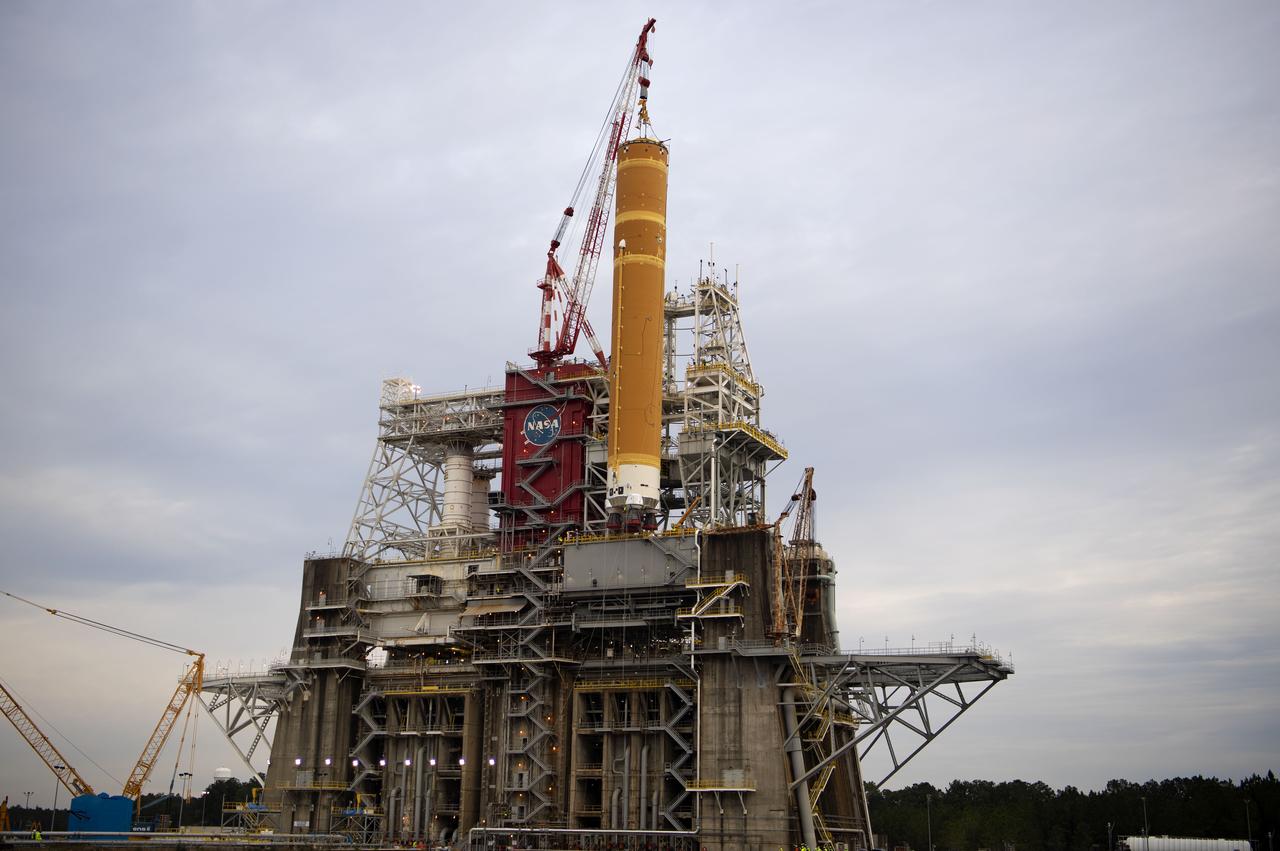

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.
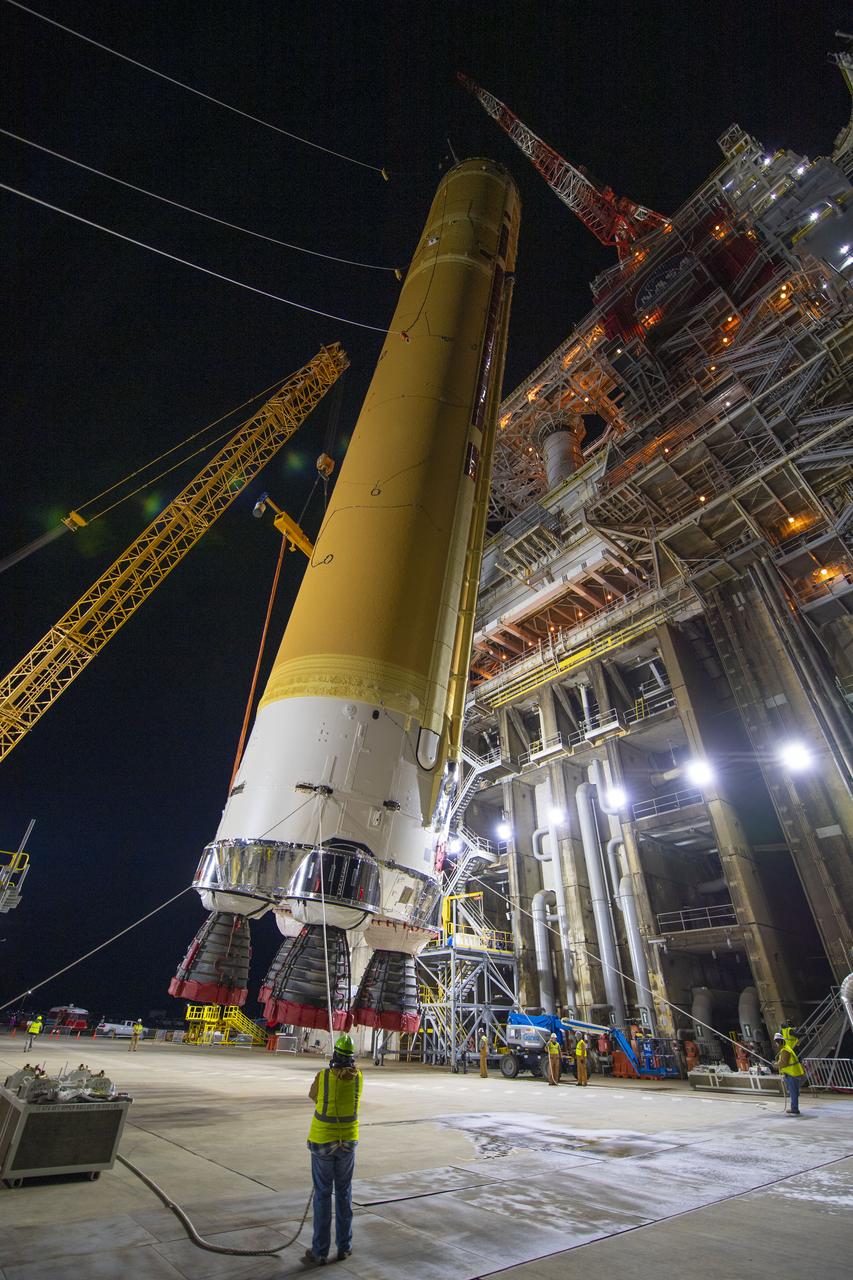

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.
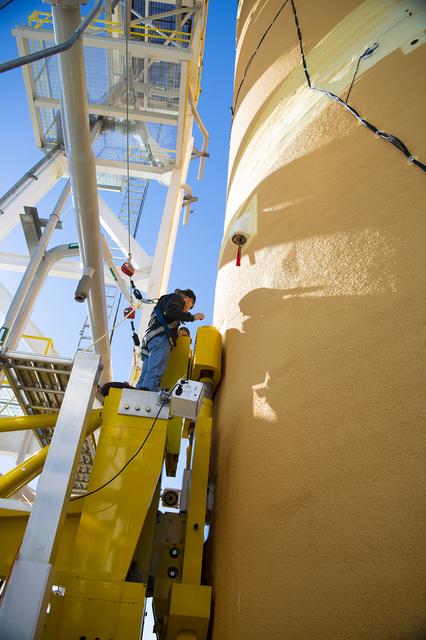

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.
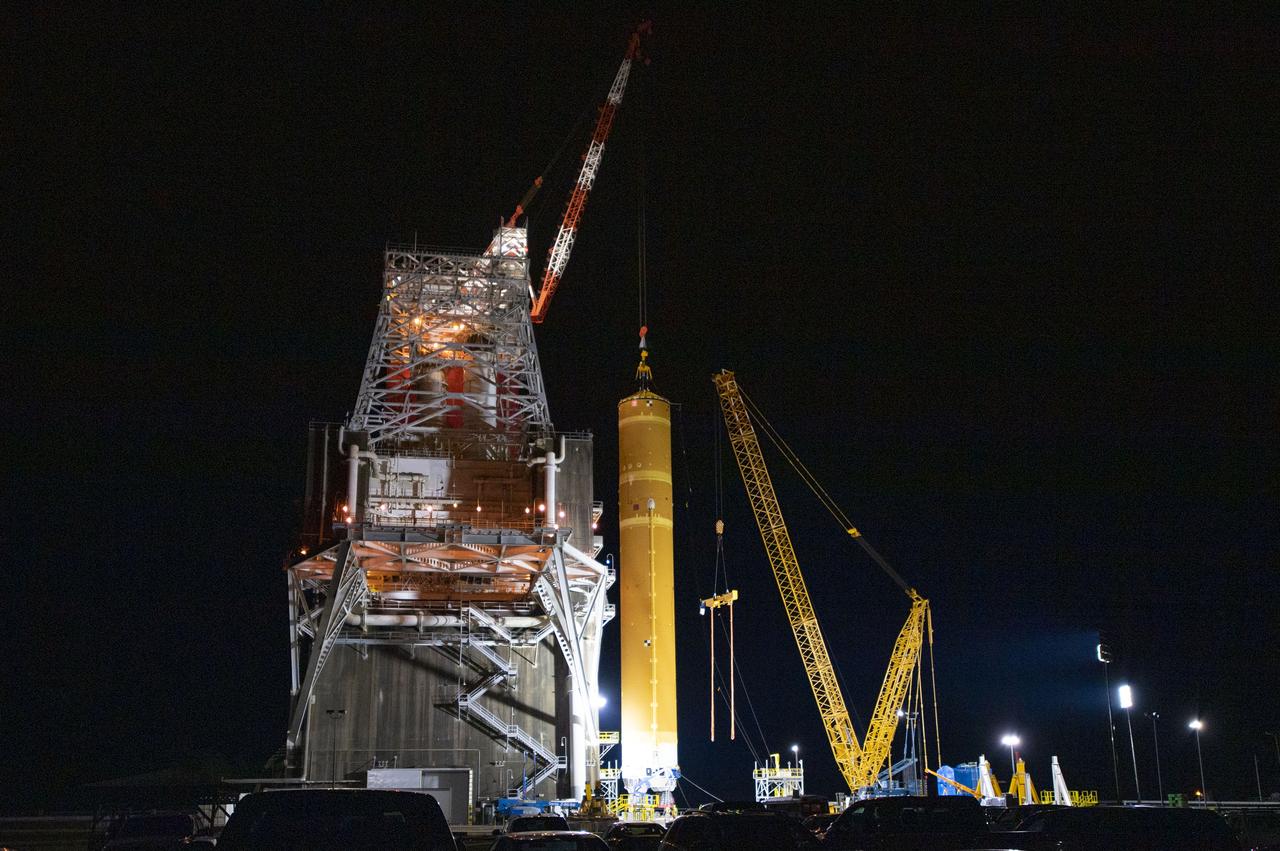

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.
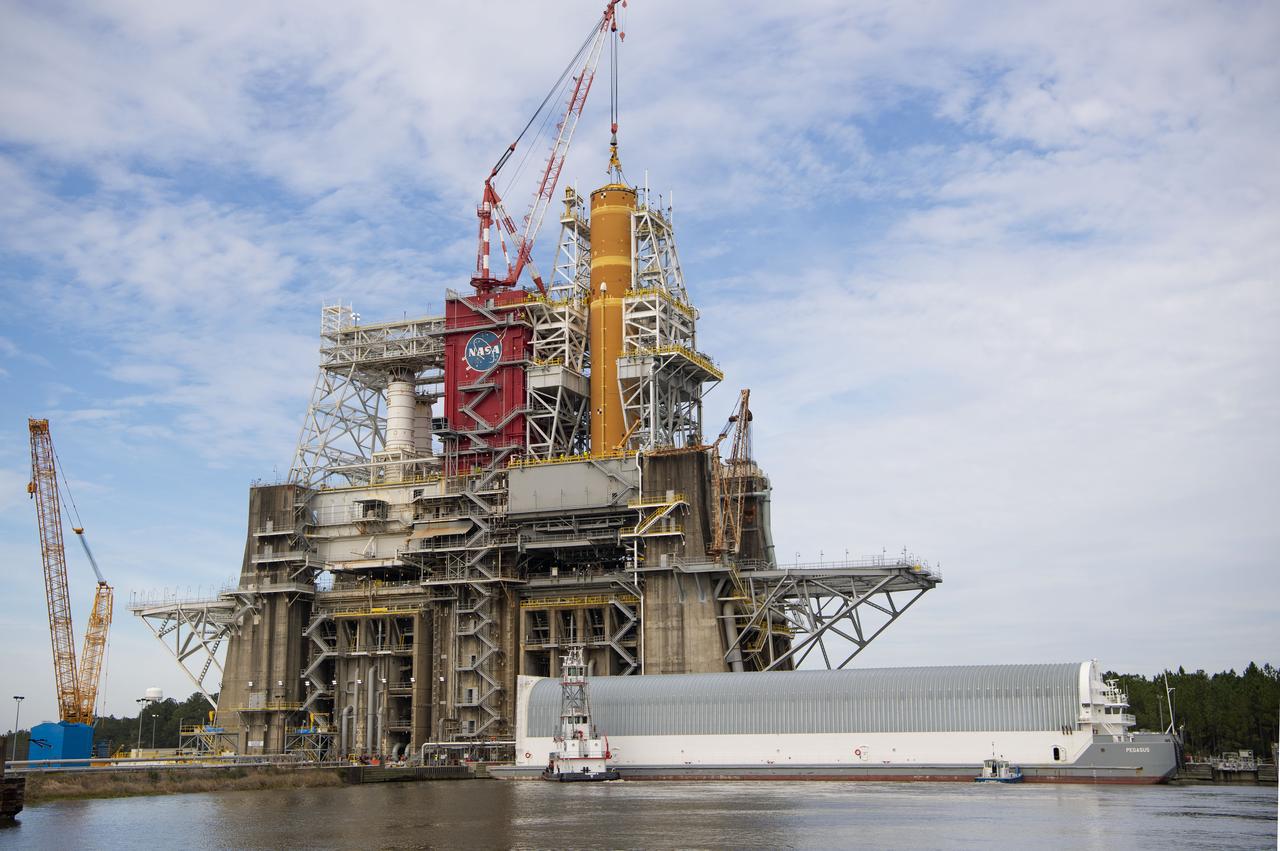

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.
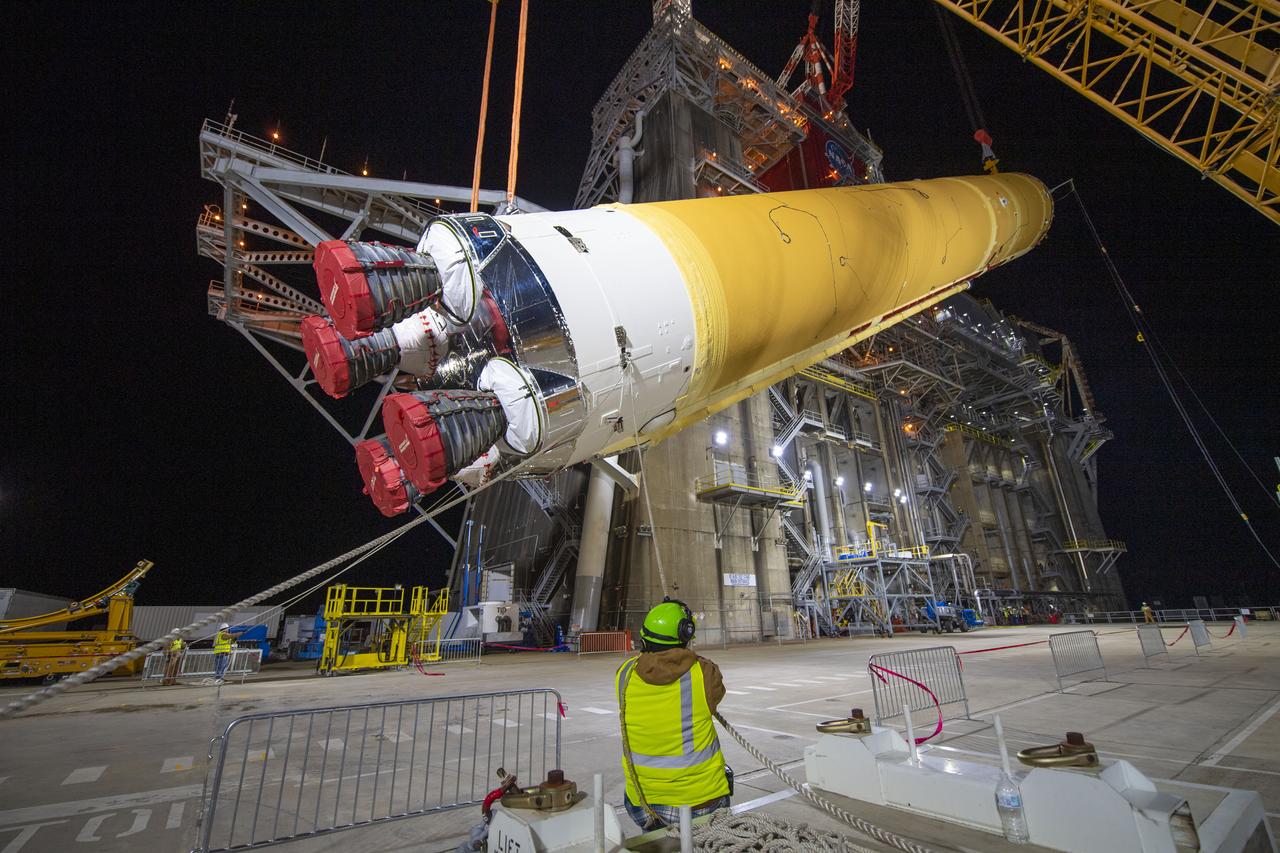

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.
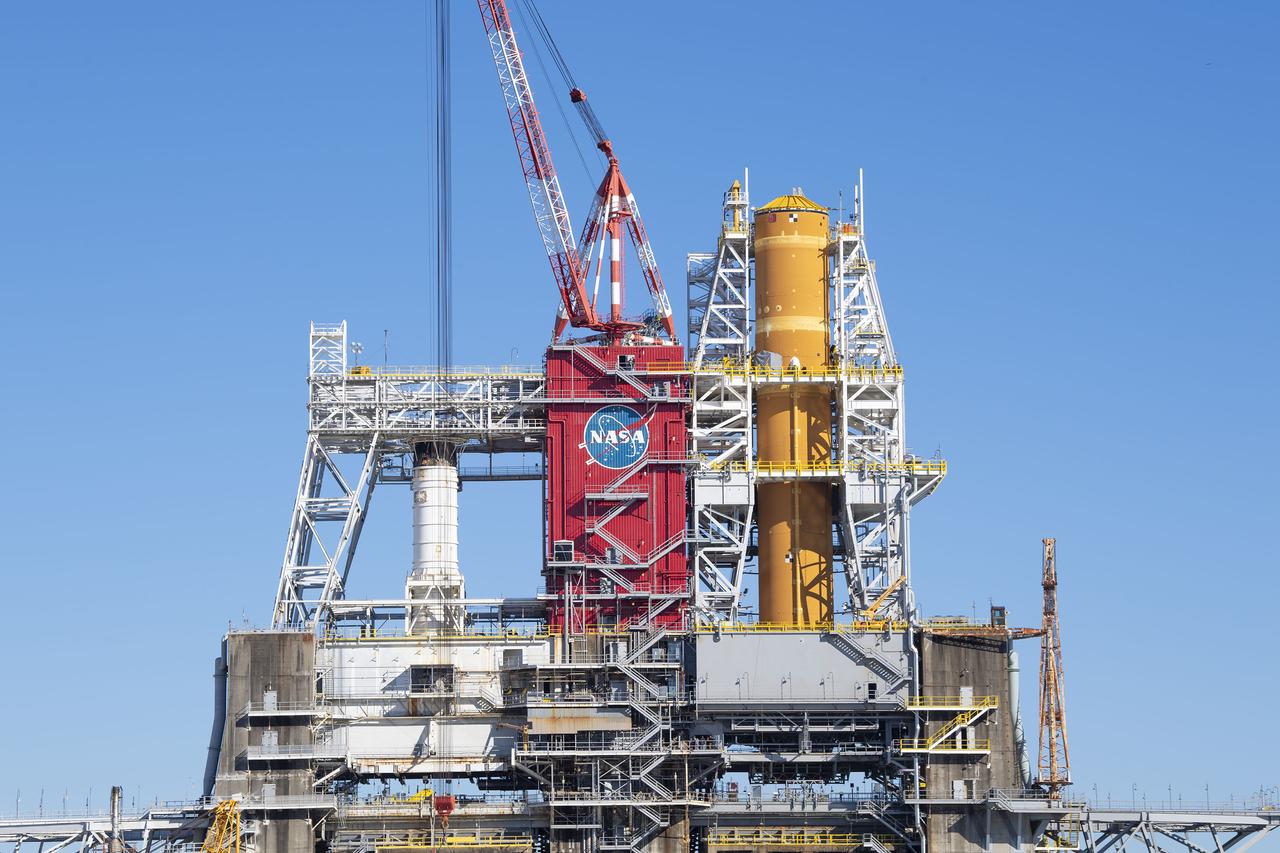

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.
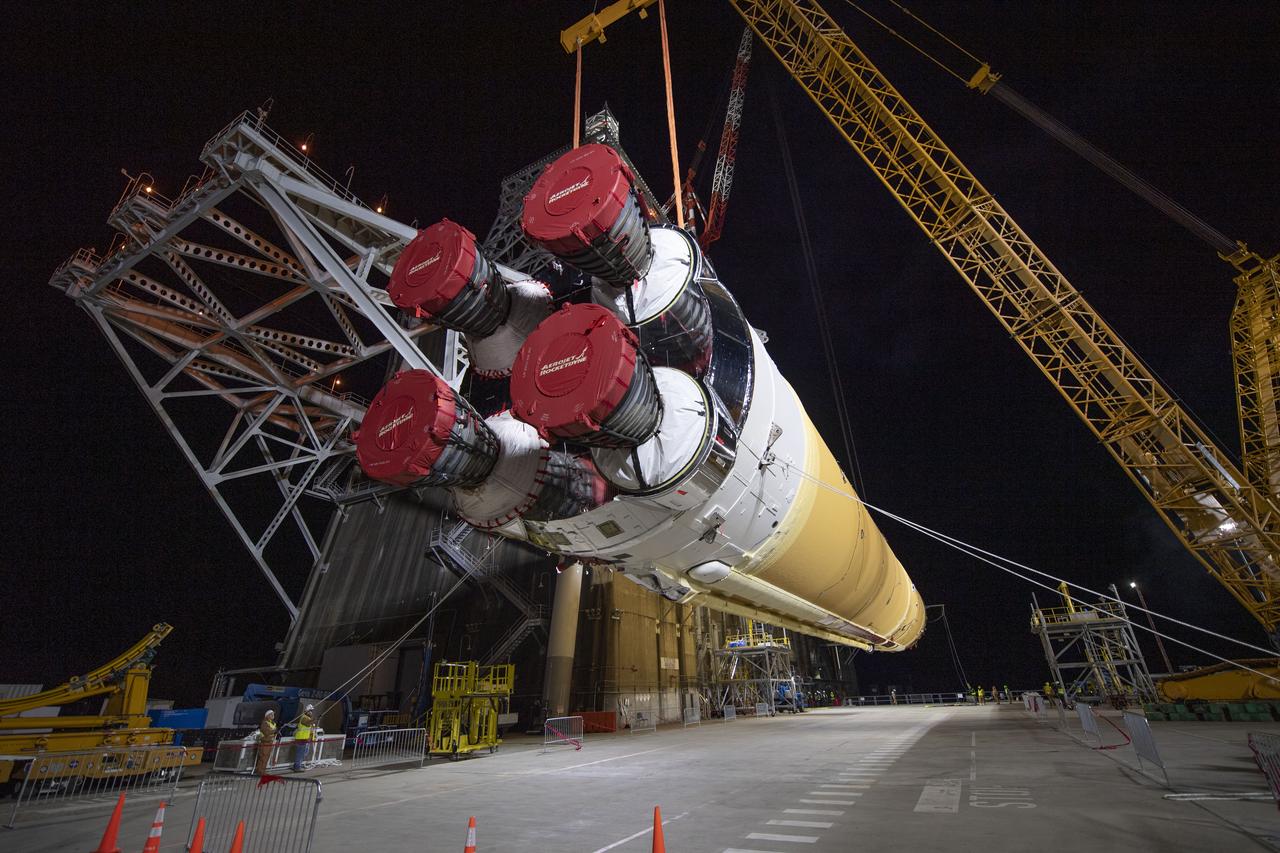

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.
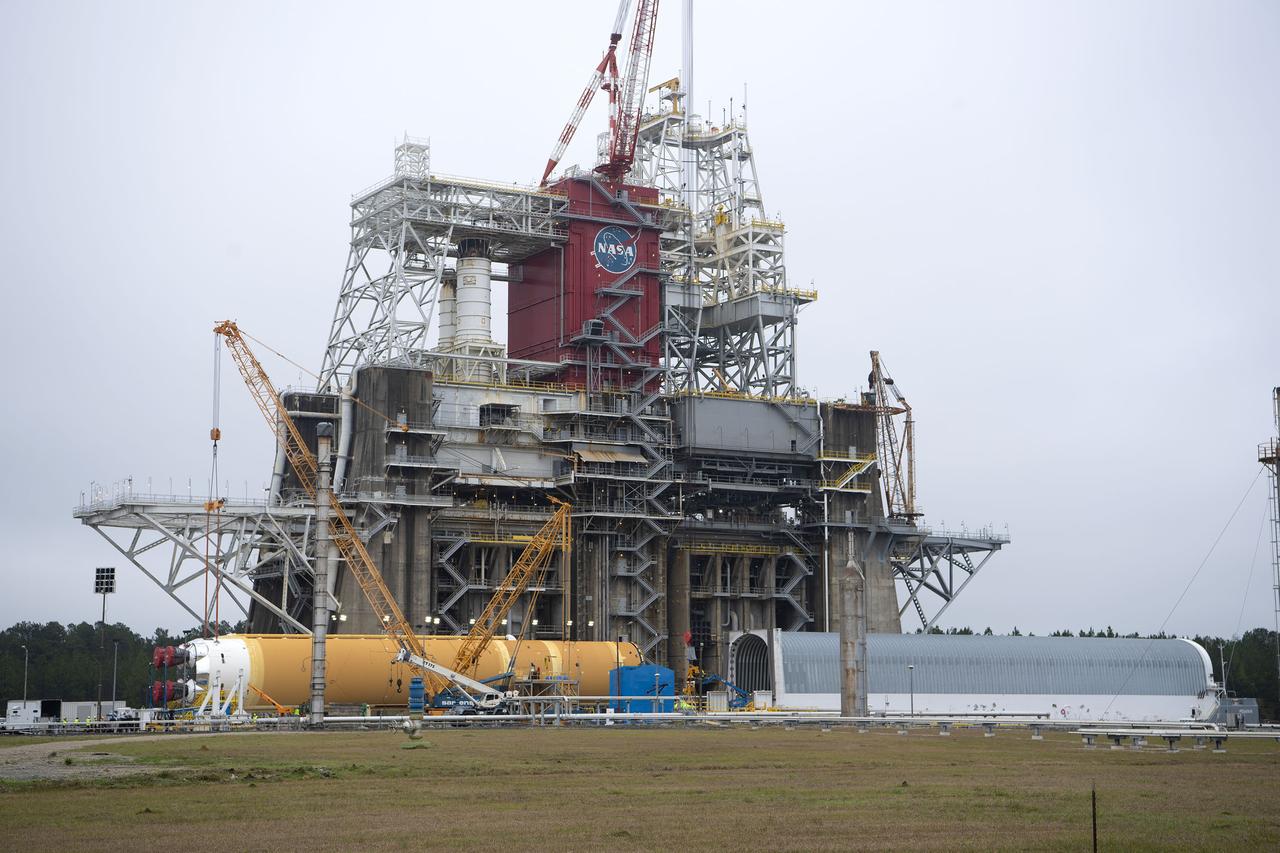

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.
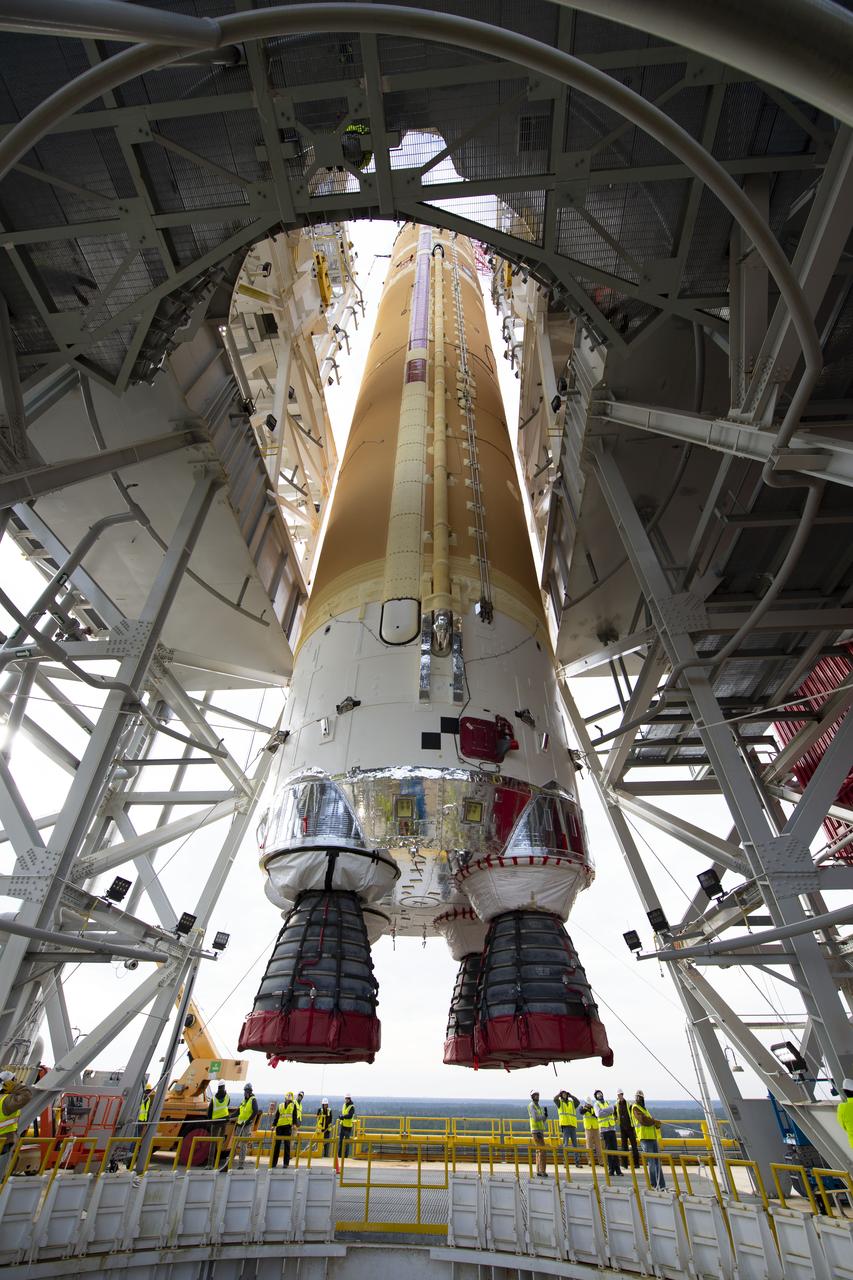

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.
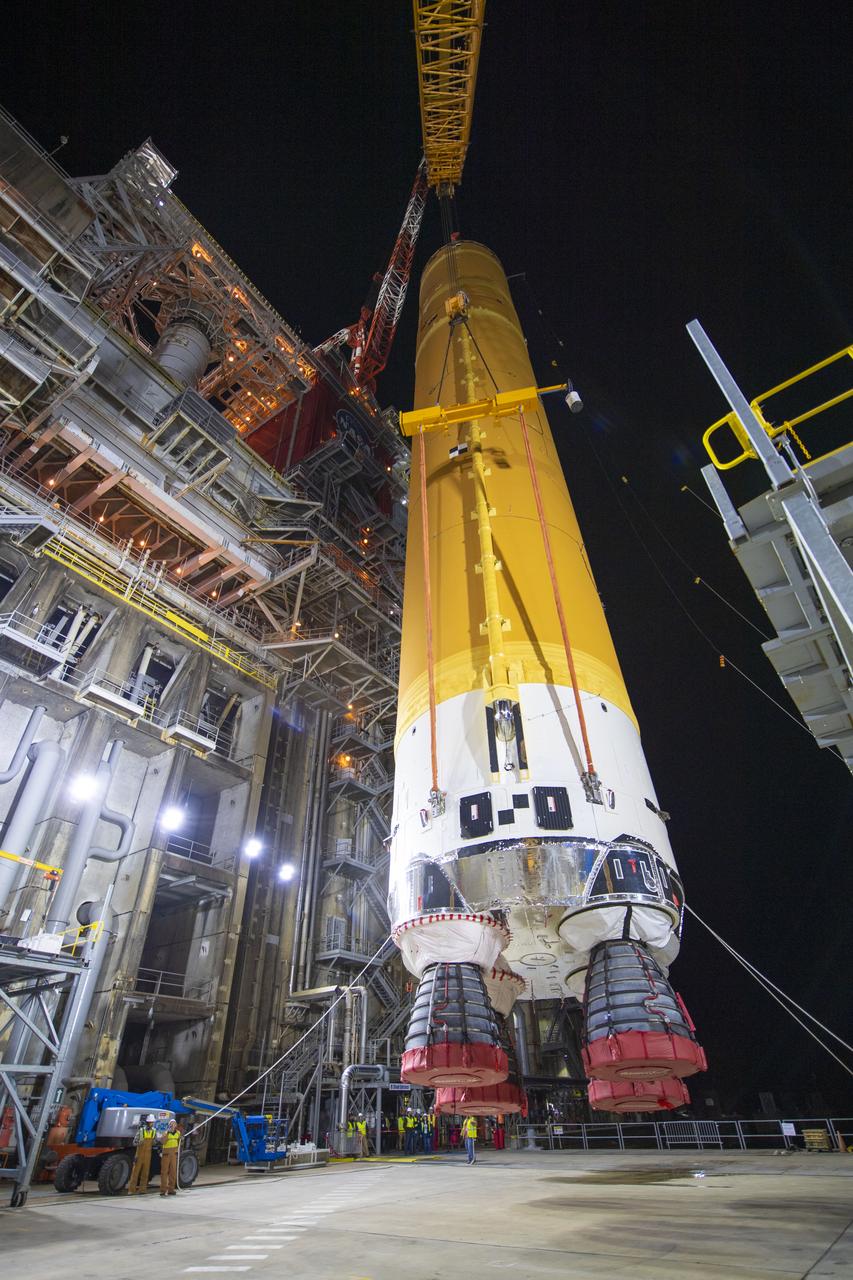

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.
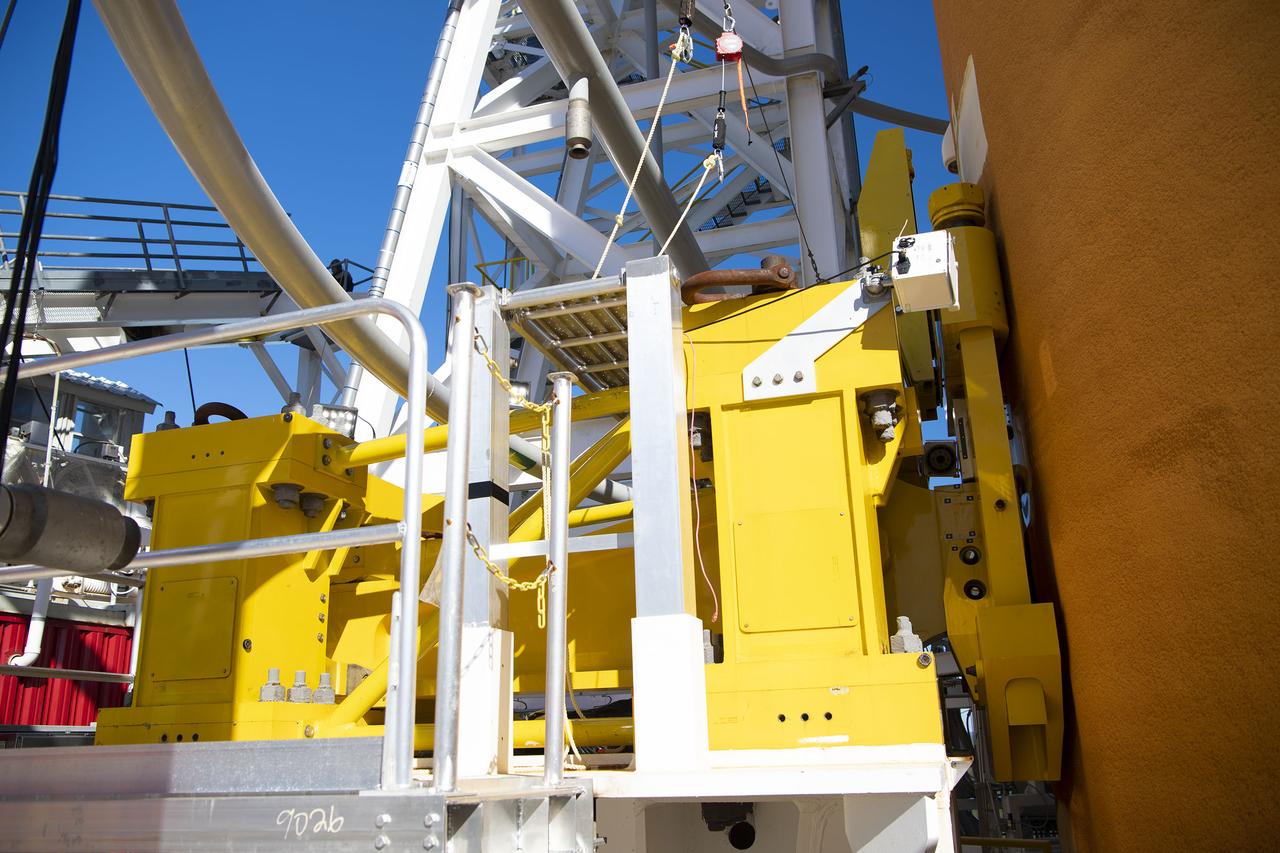

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.
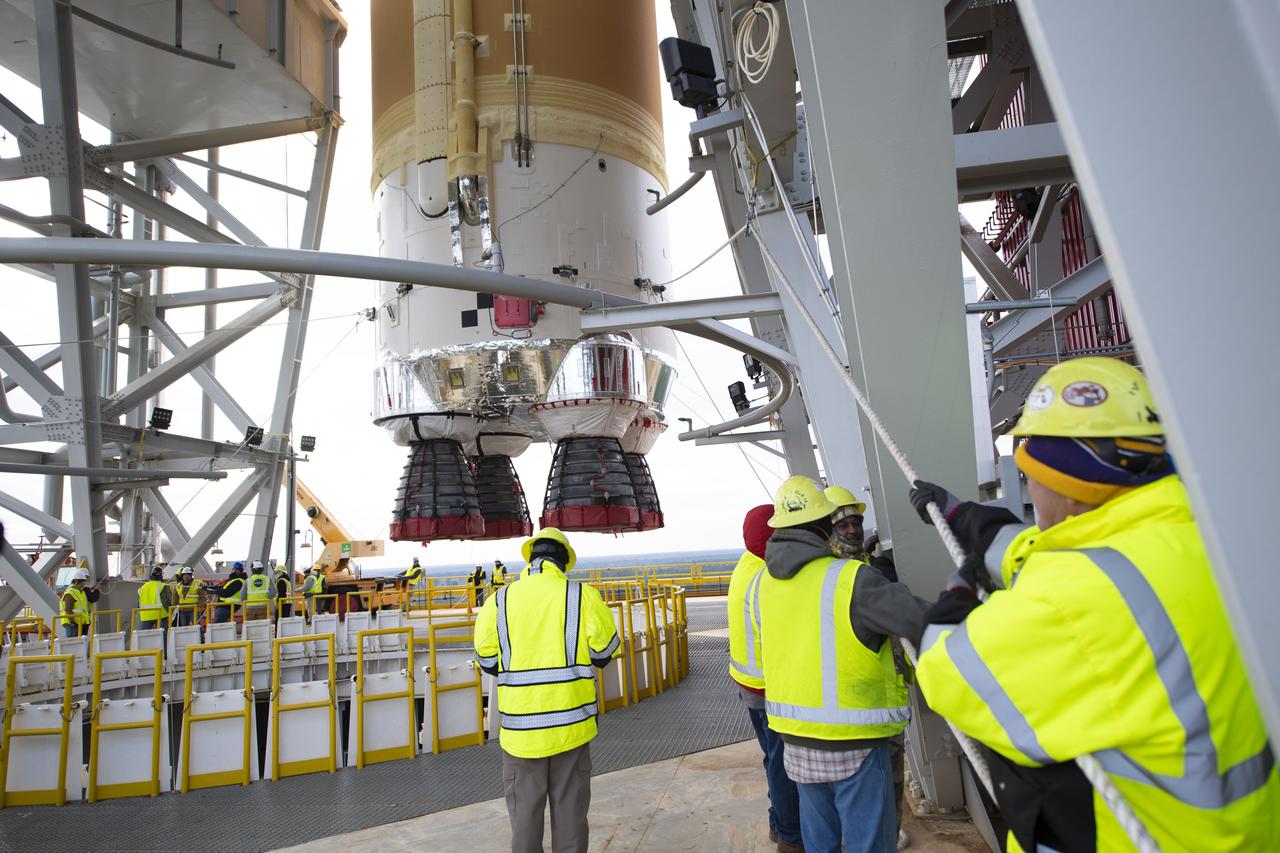

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.
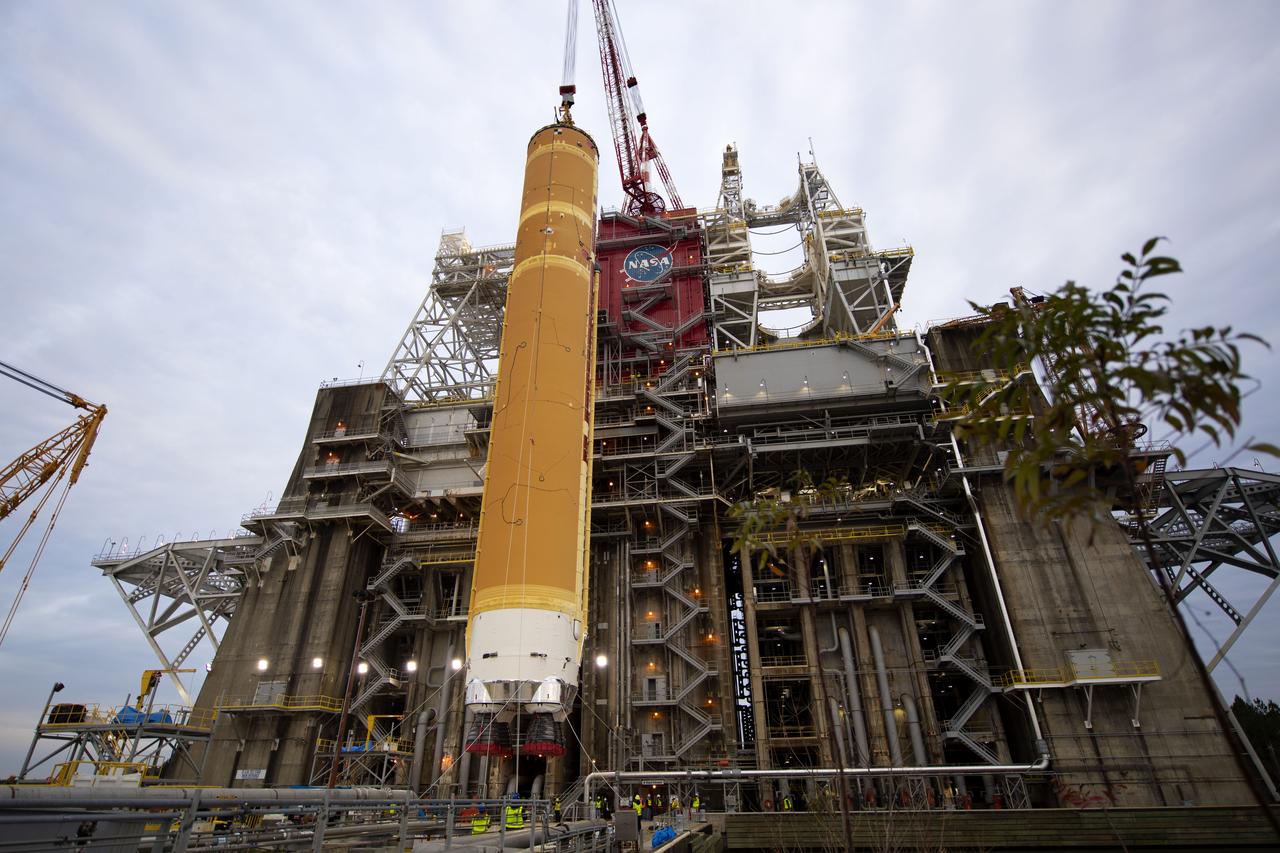

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.
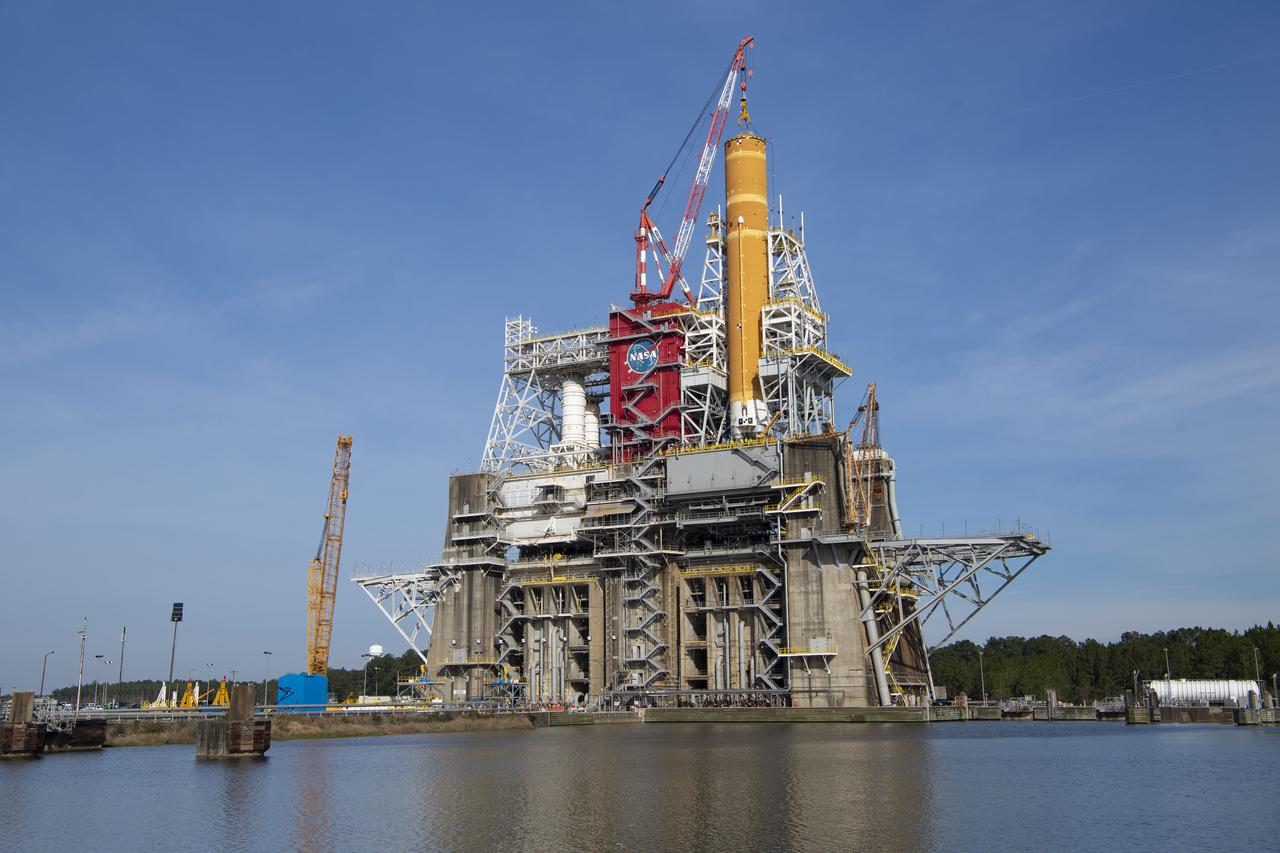

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.
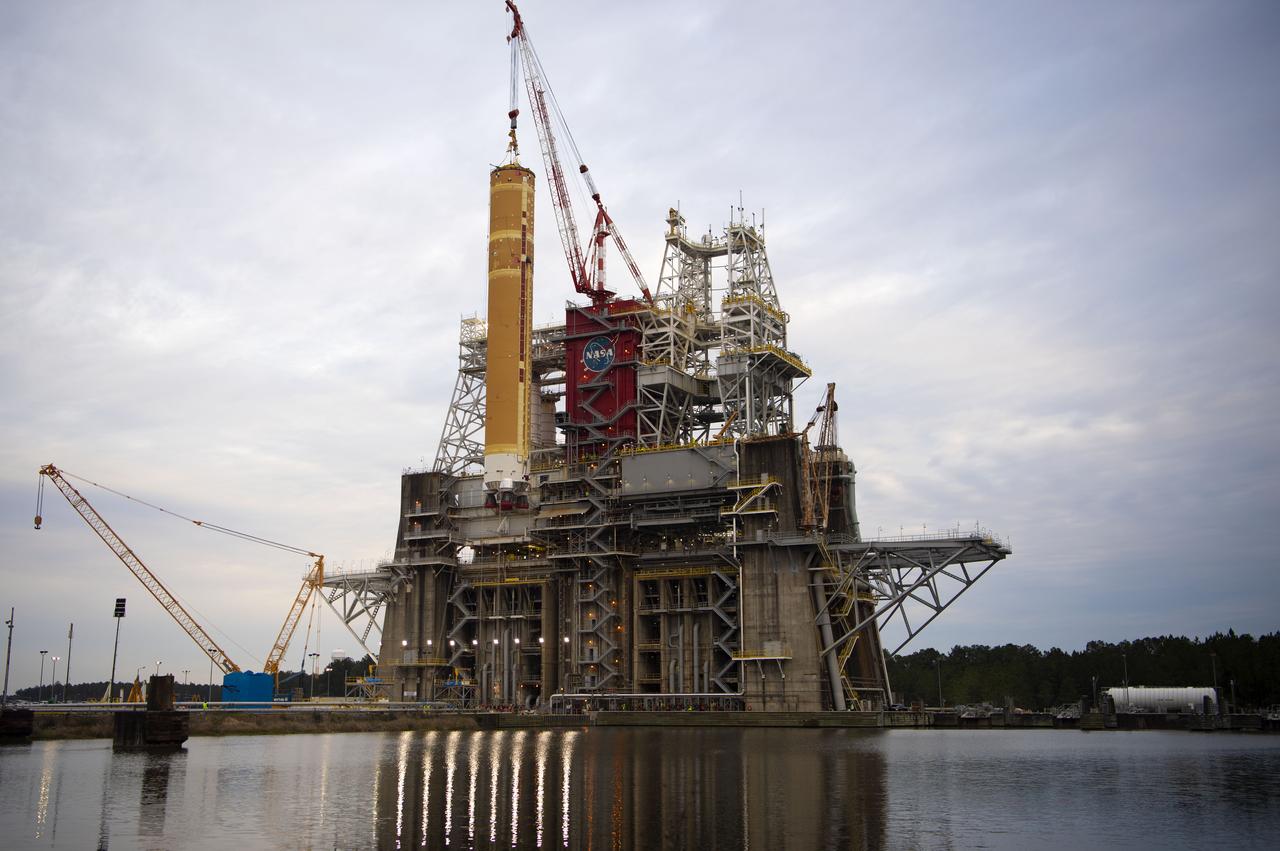

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.
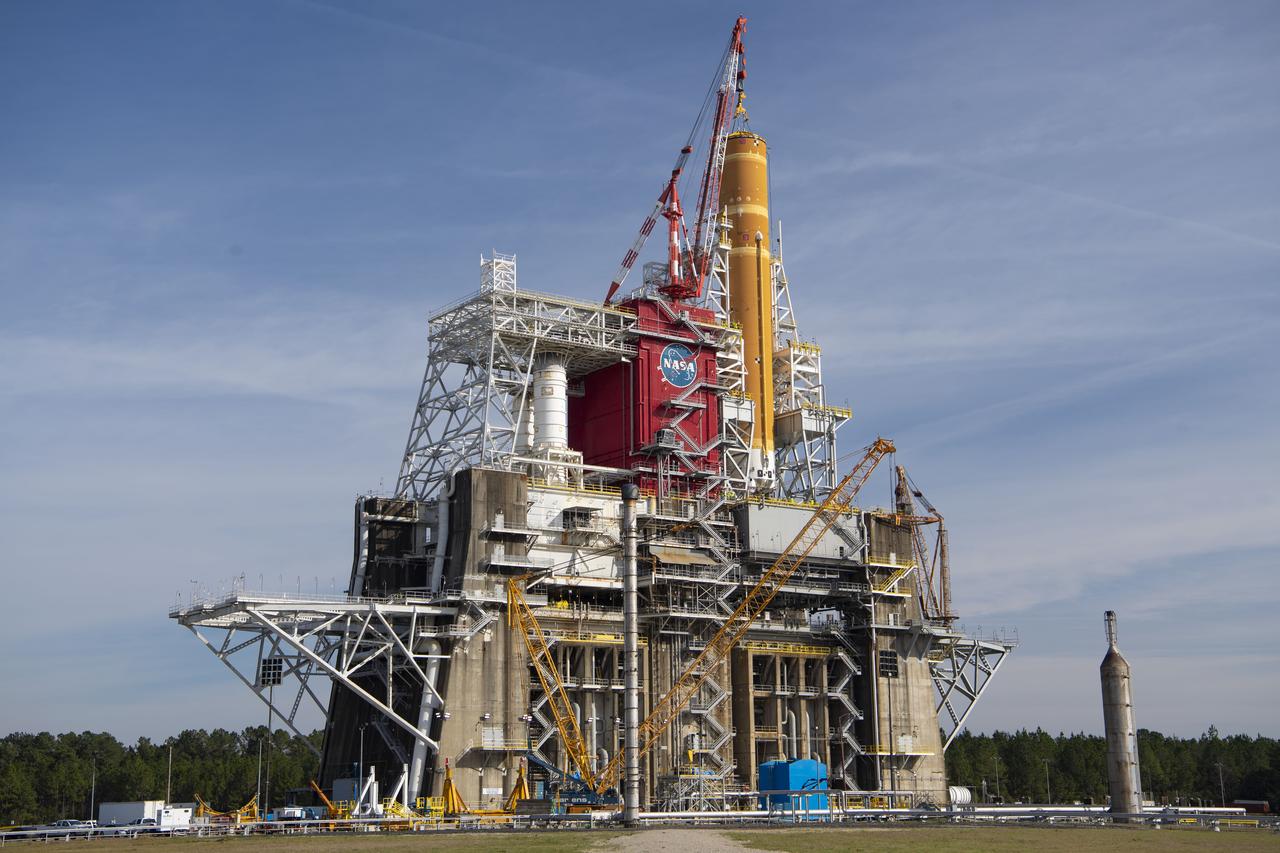

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.
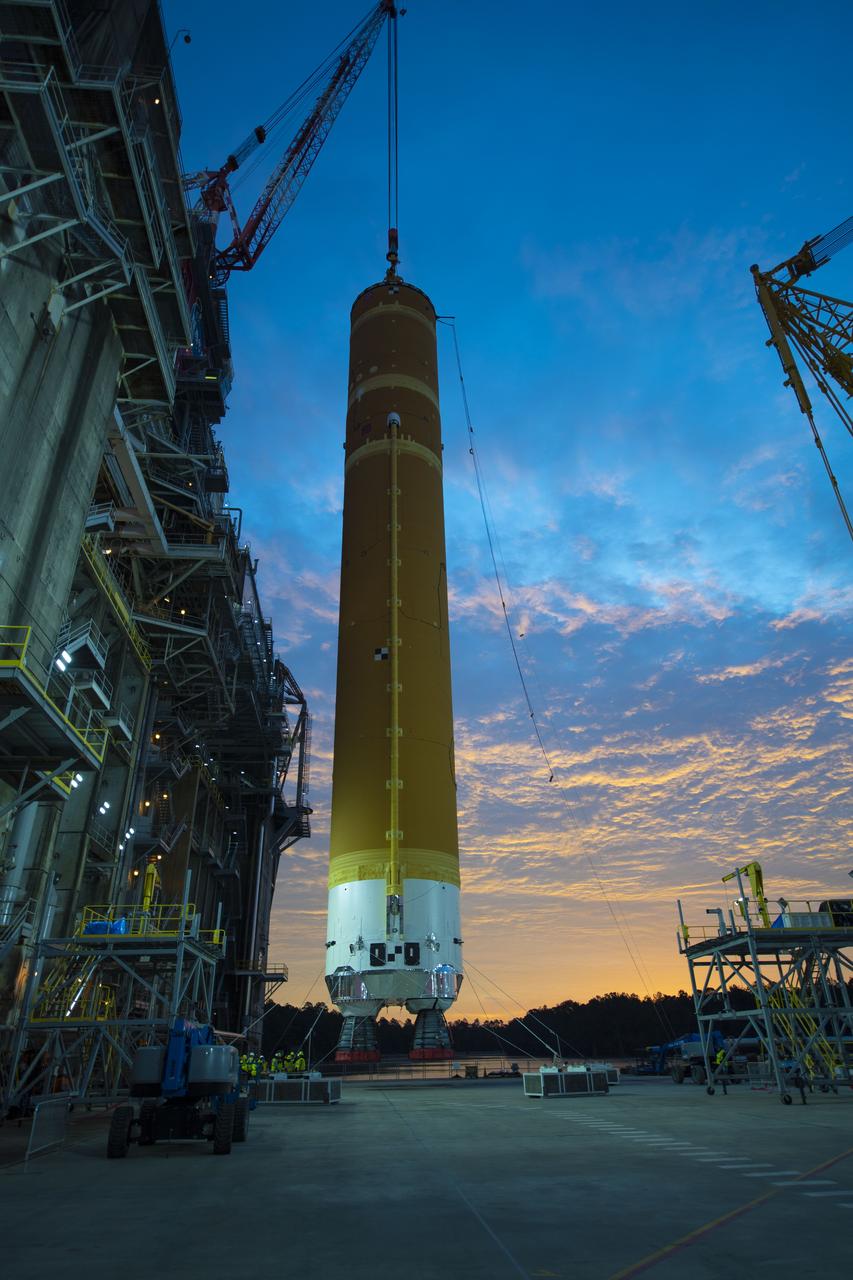

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.
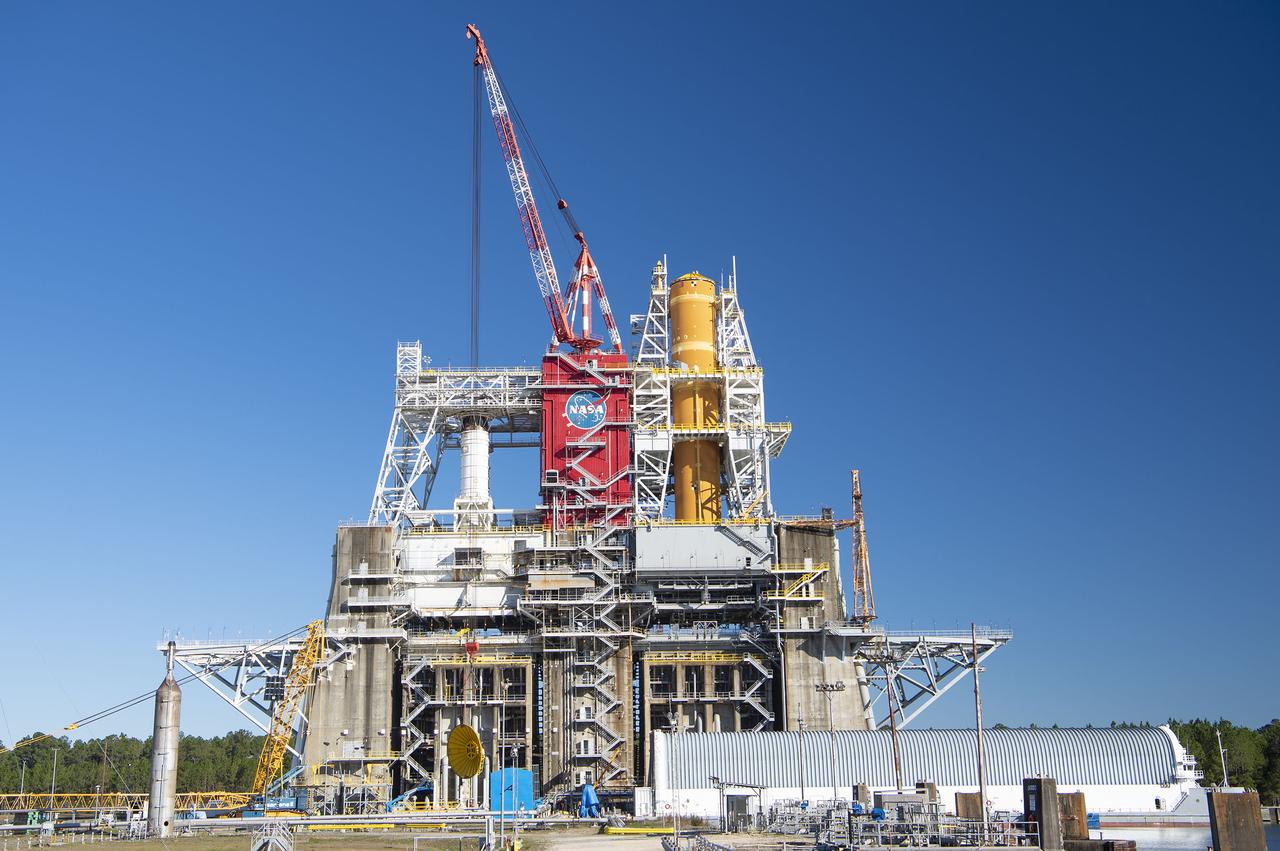

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.
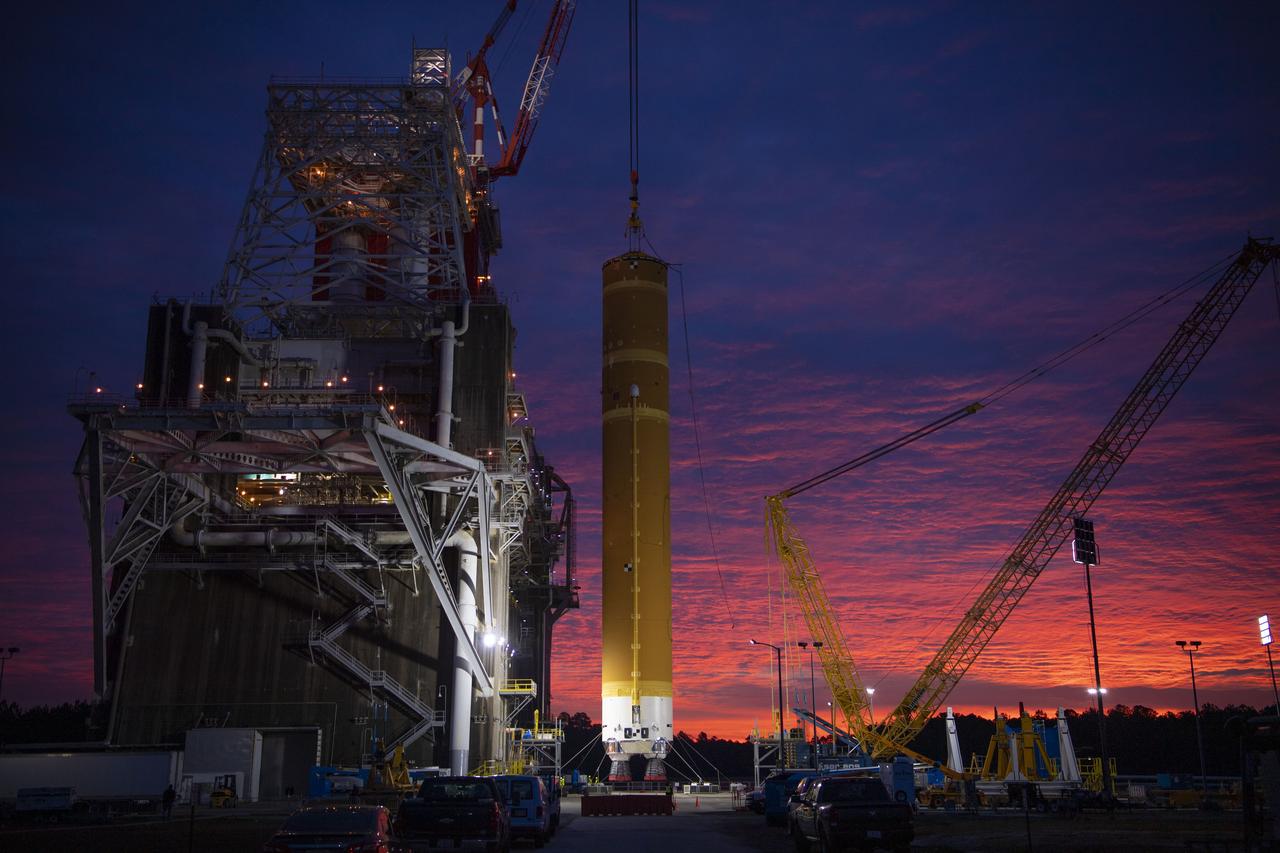

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.
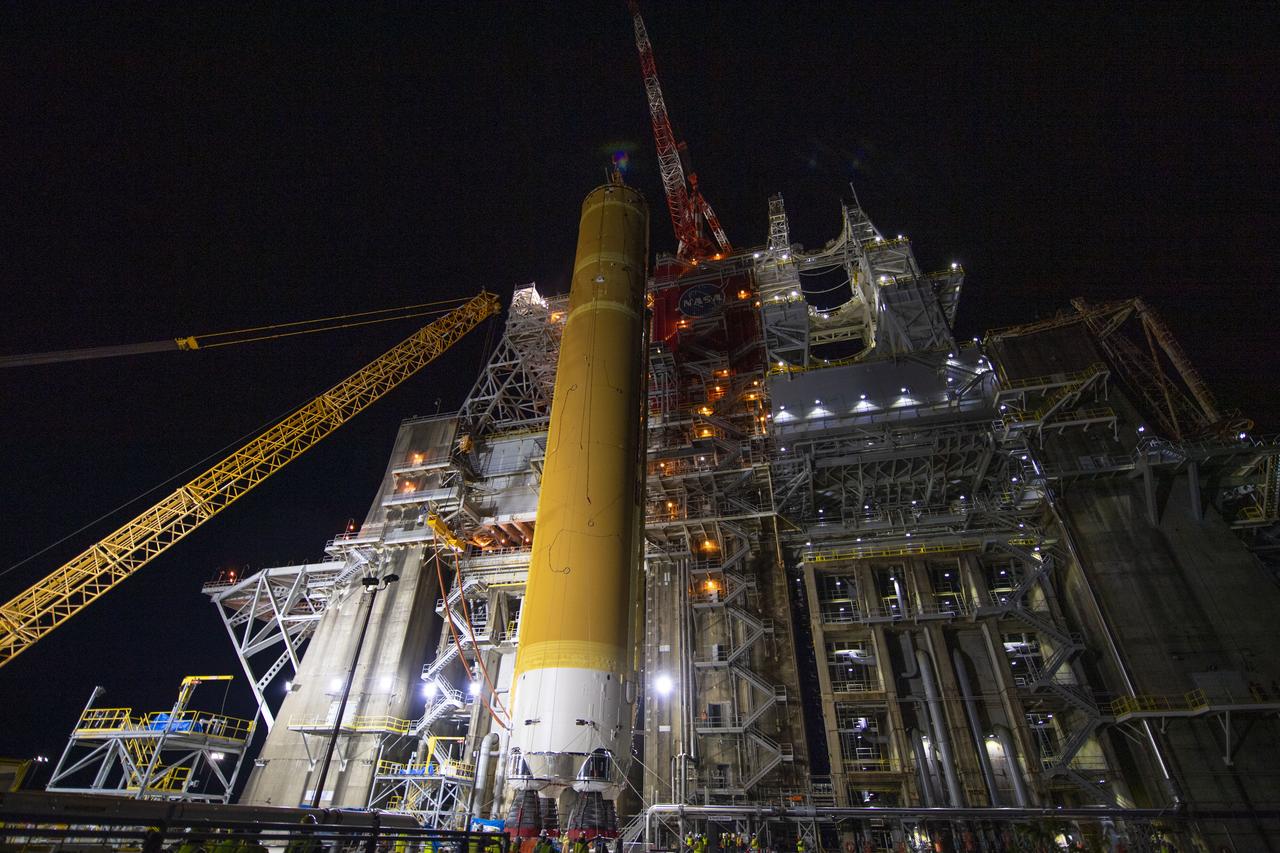

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.
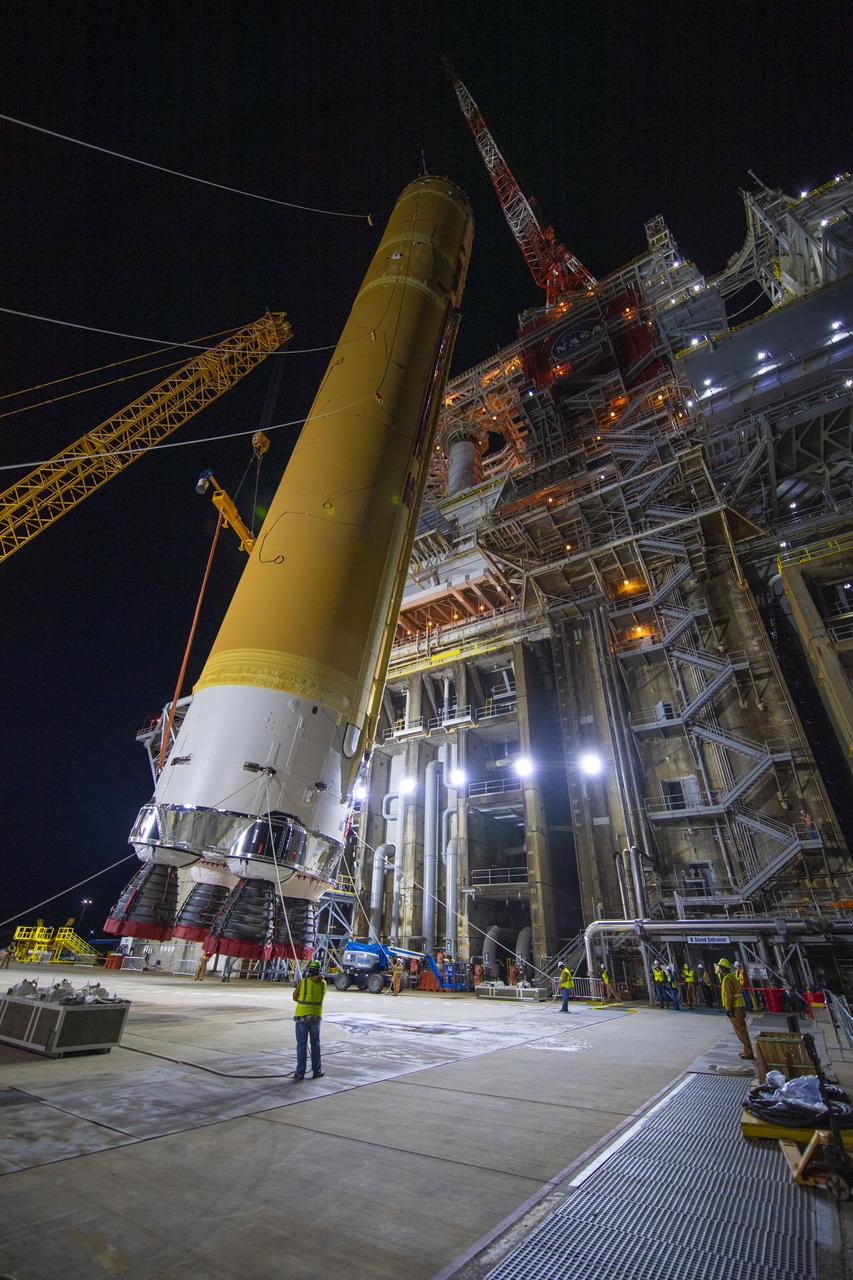

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.
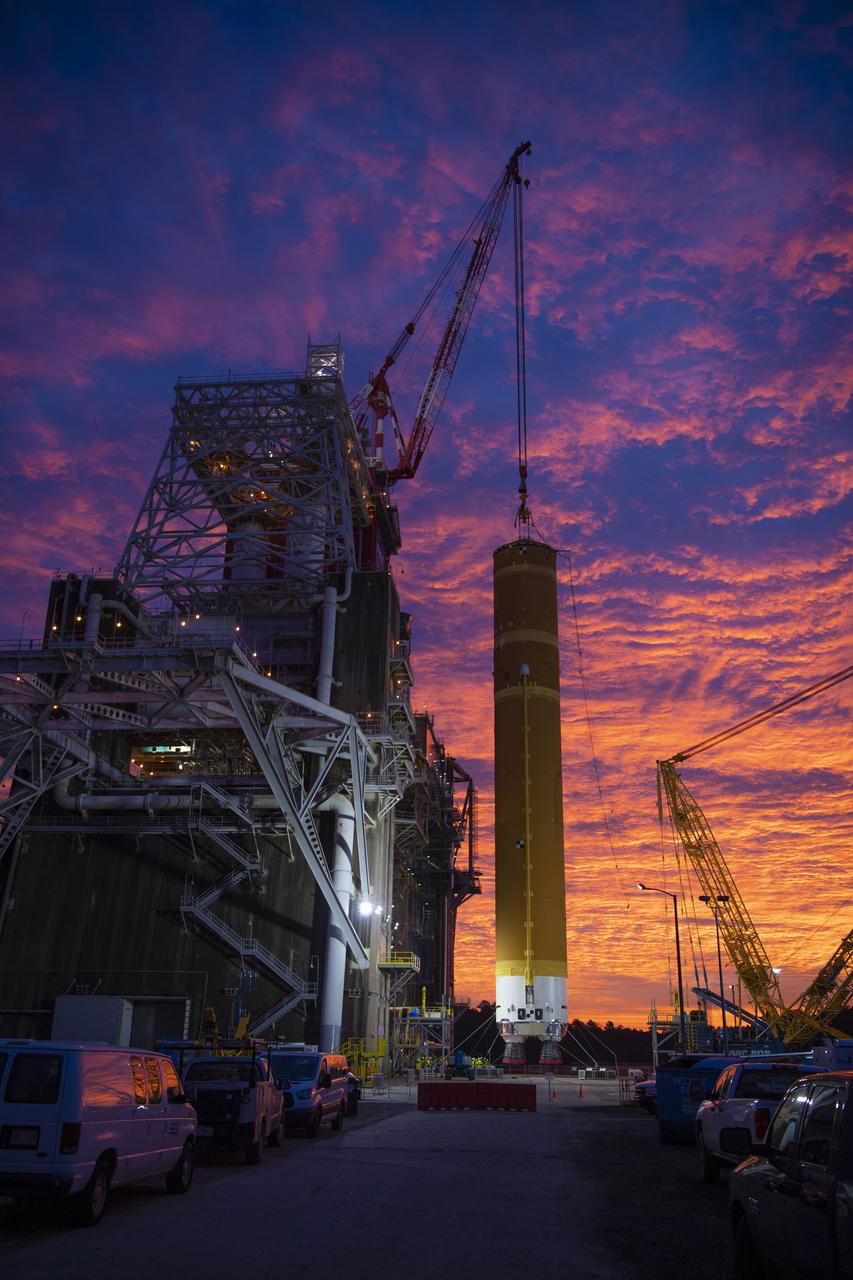

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.
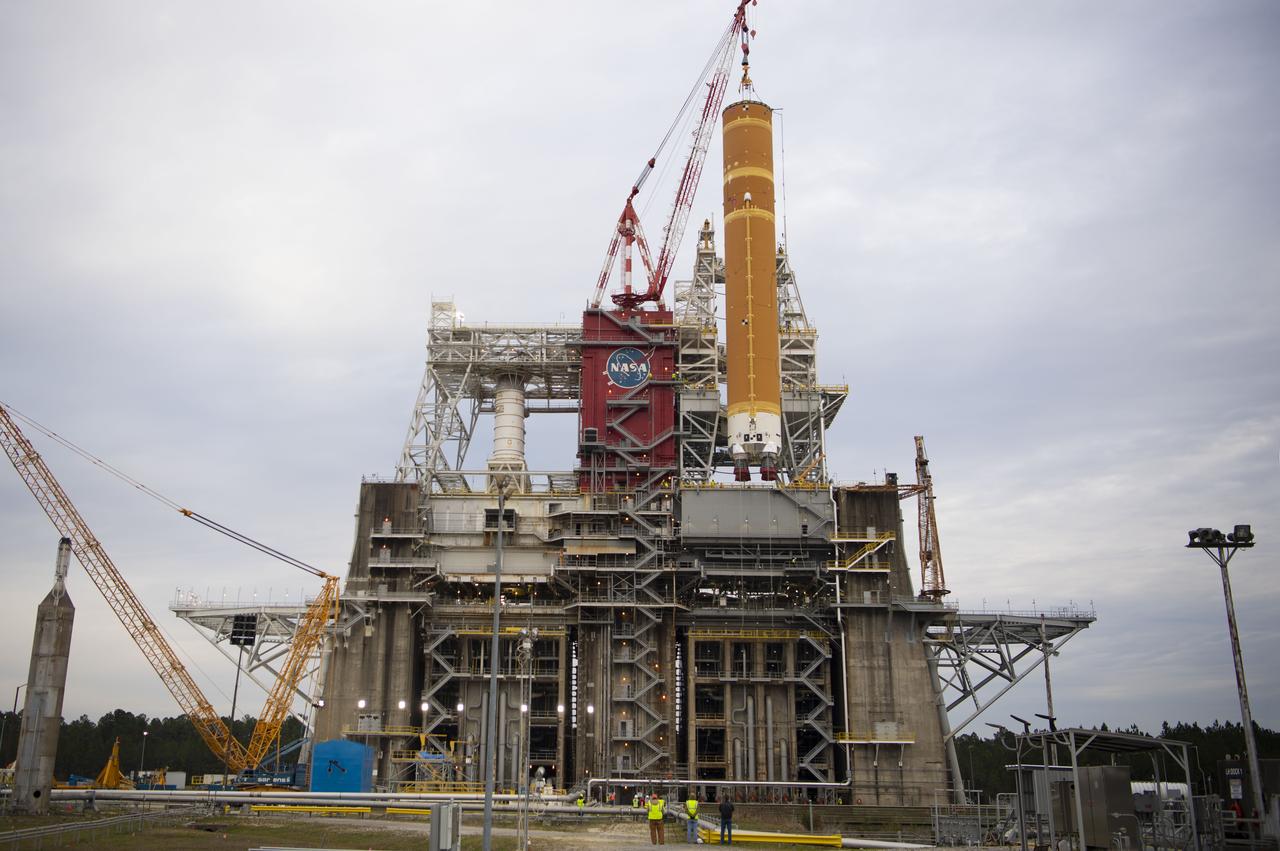

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.
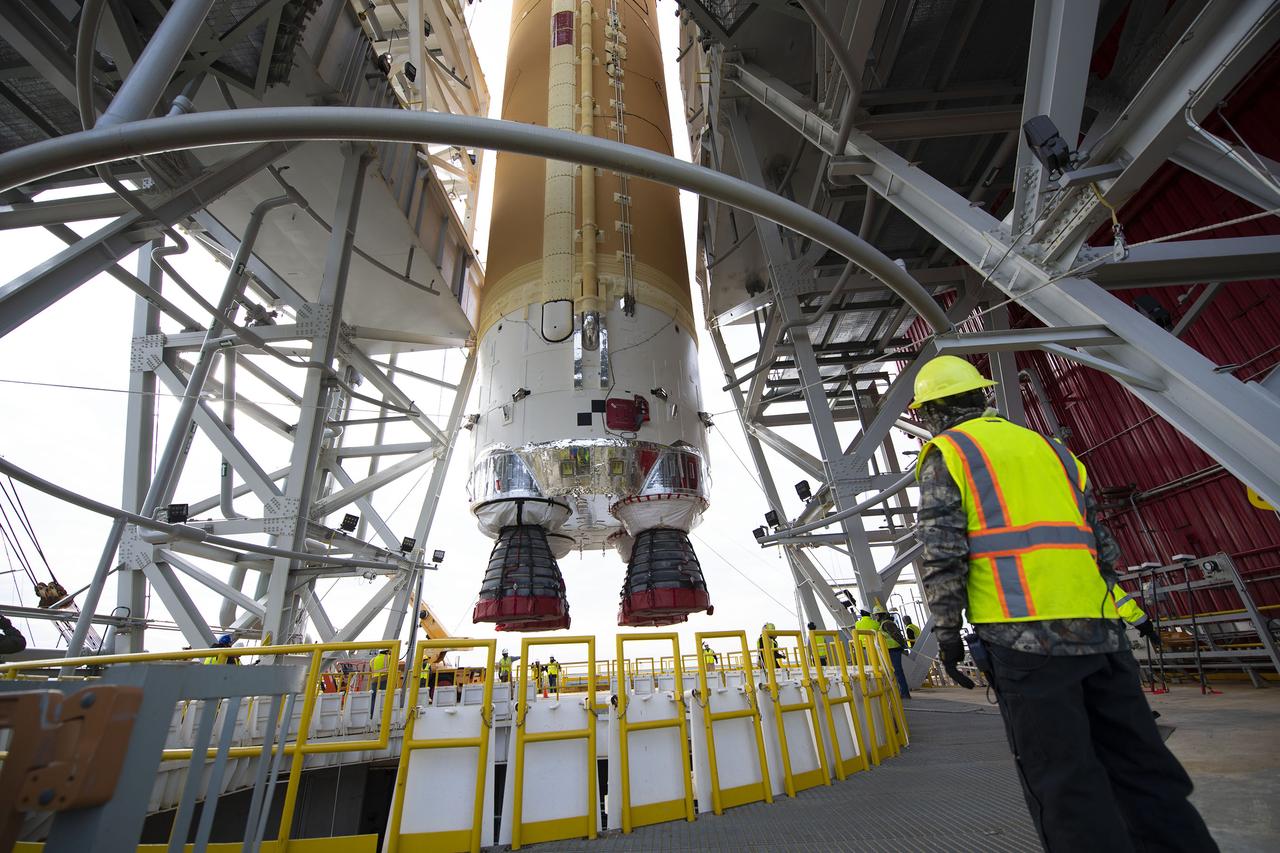

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.
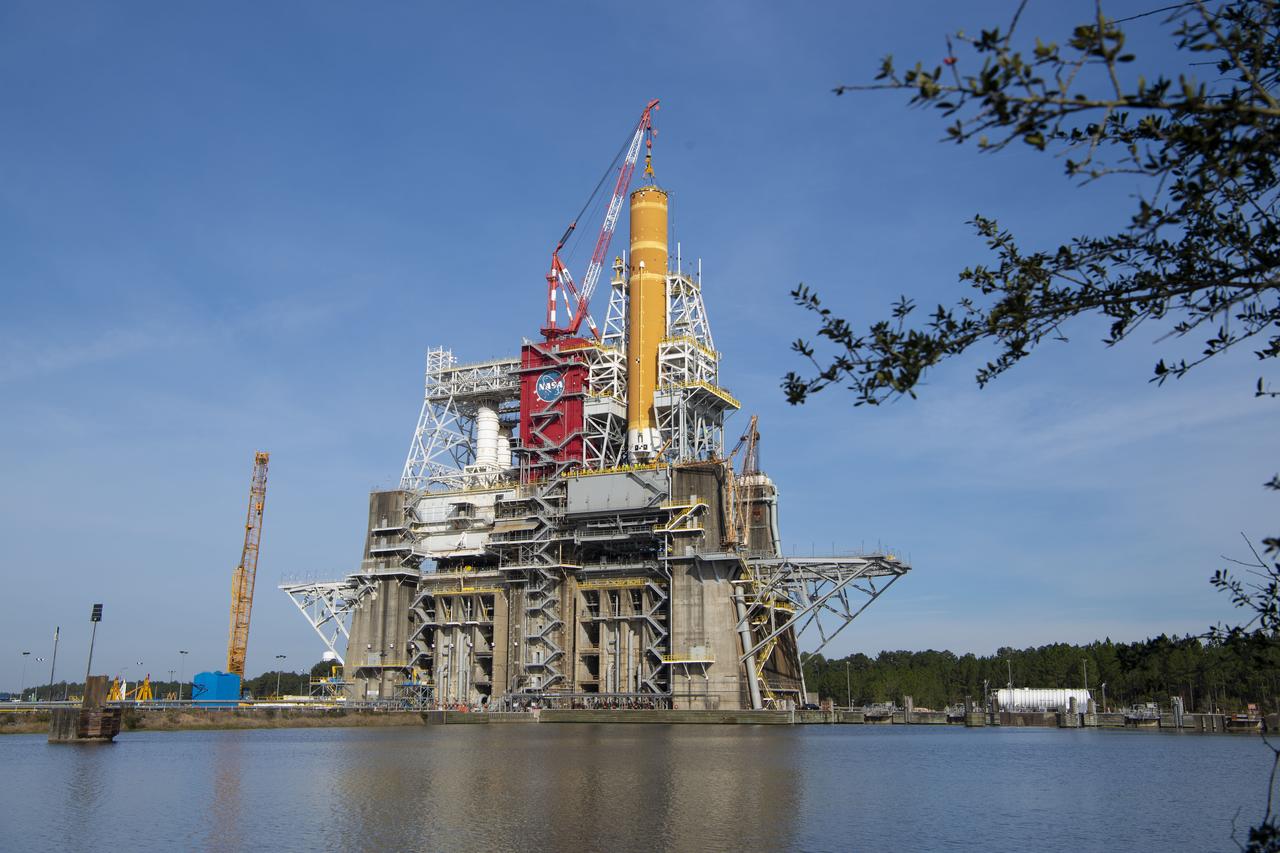

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.
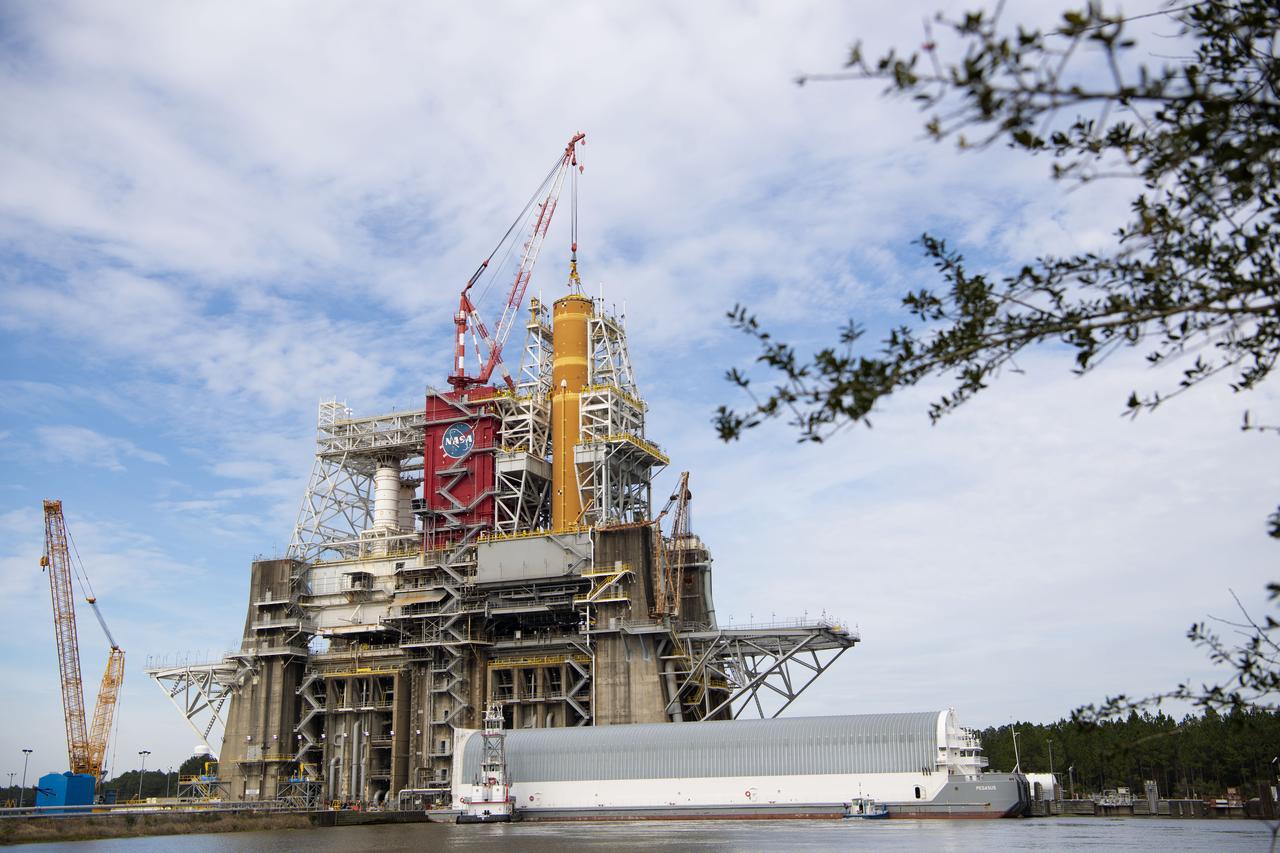

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.
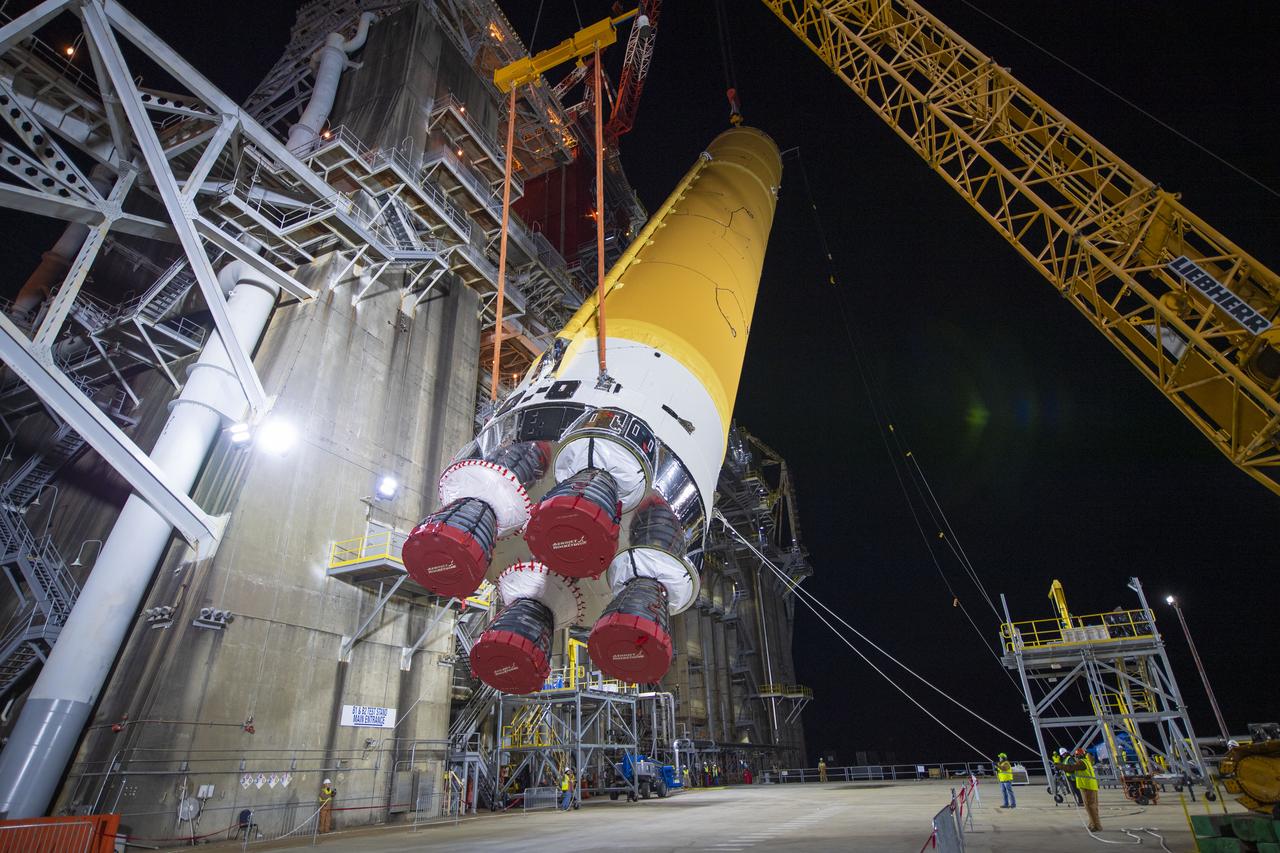

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.
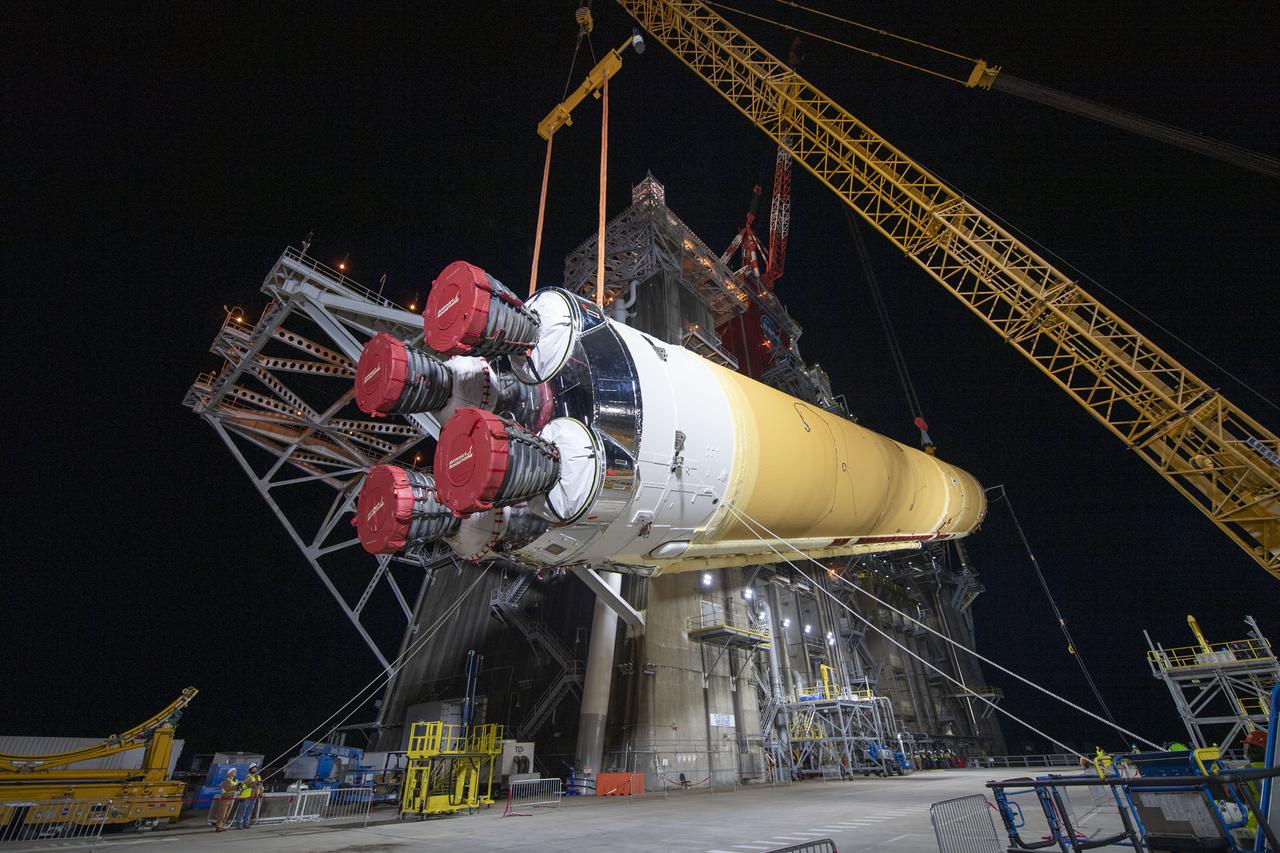

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.
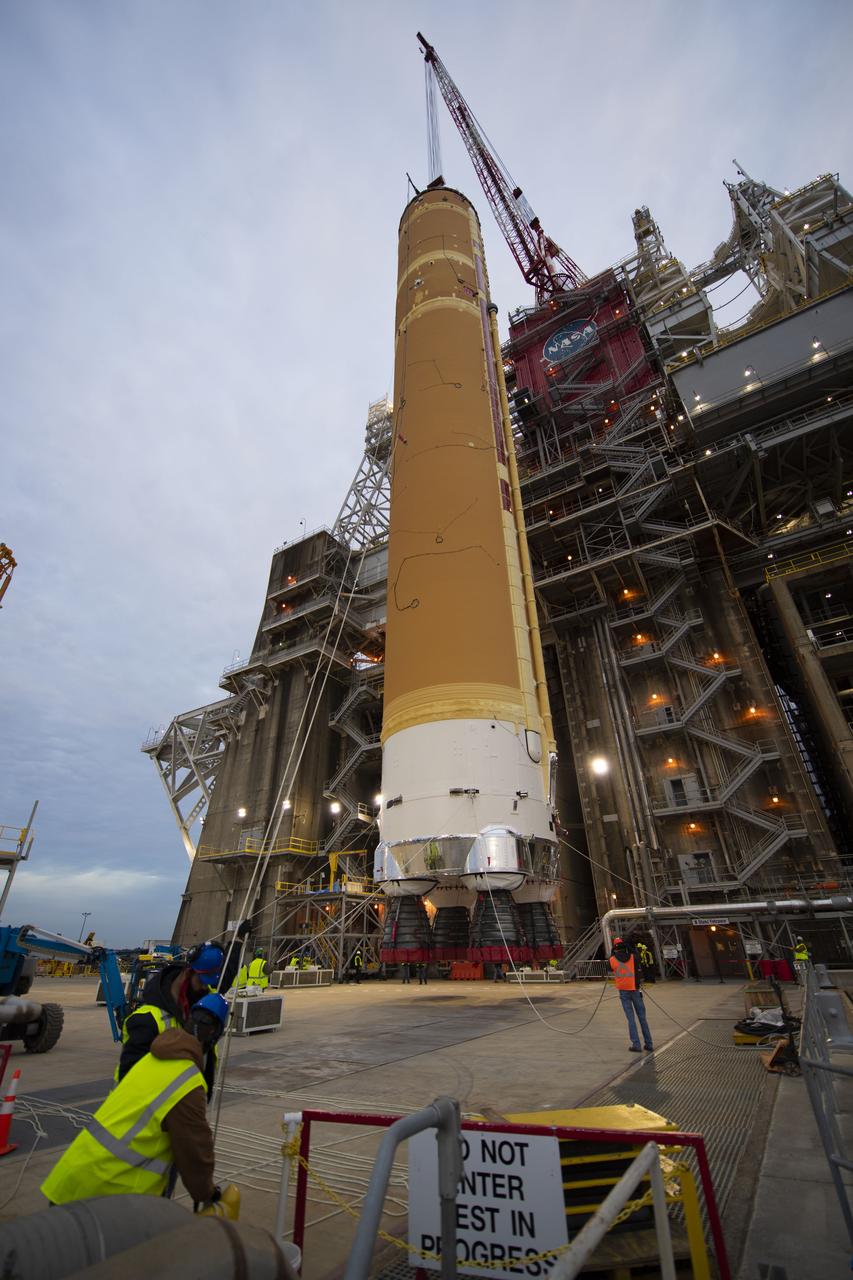

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.
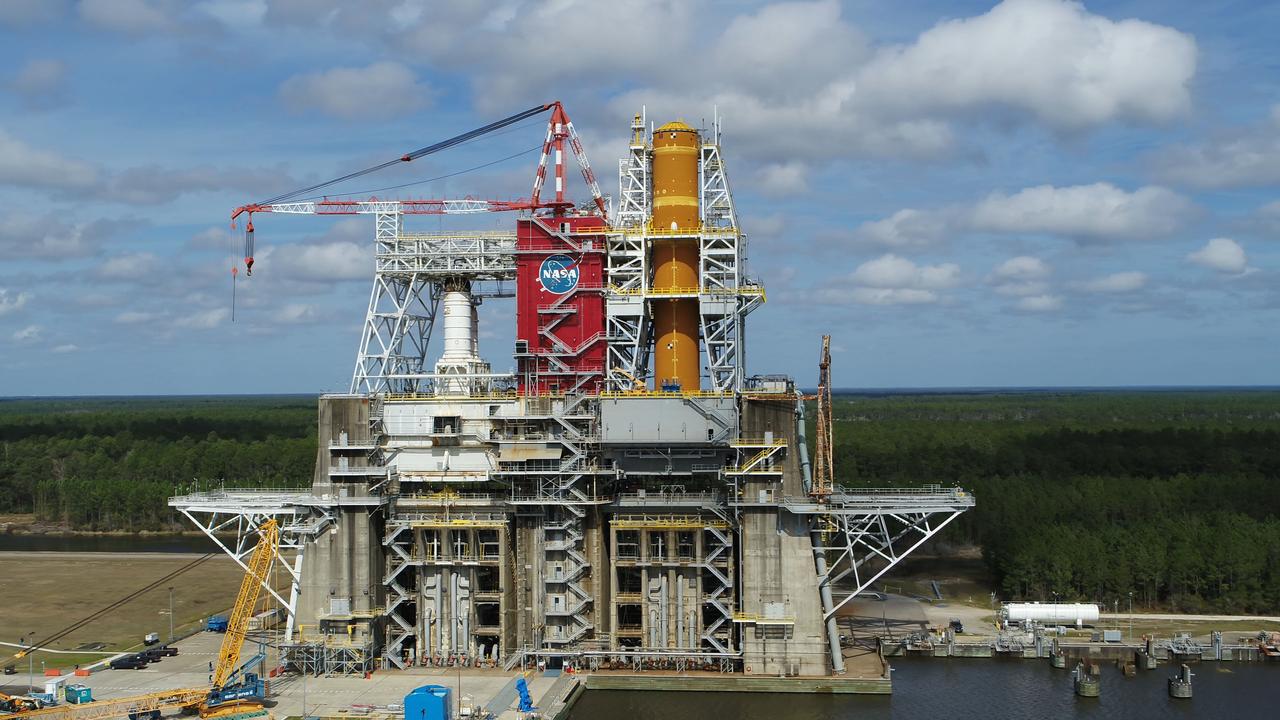
A NASA drone photo offers a bird’s-eye view of the B-2 Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center with the first flight core stage for NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) installed for Green Run testing. The SLS core stage is undergoing a series of tests on its integrated systems prior to its use on the Artemis I mission. NASA is building SLS to return humans, including the first woman, to the Moon as part of the Artemis program and to prepare for eventual missions to Mars. The Green Run series at Stennis culminates with a hot fire of the core stage’s four RS-25 engines, just as during an actual launch.
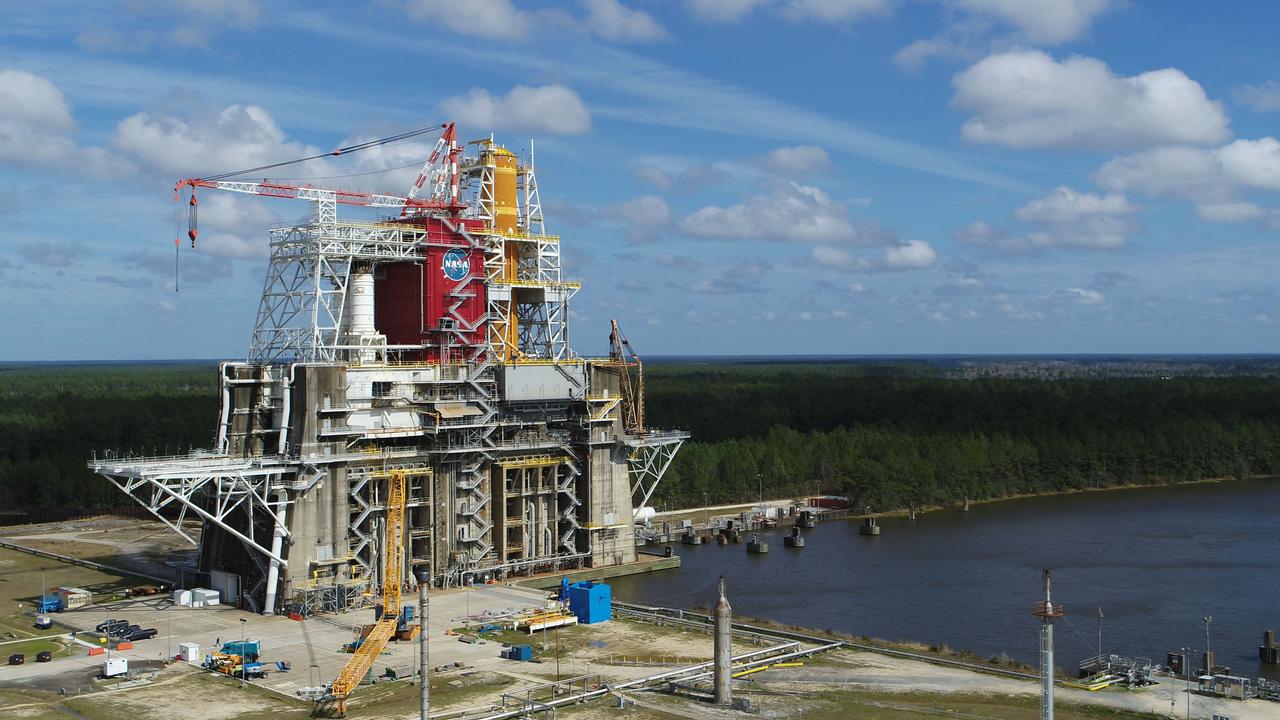

A NASA drone photo offers a bird’s-eye view of the B-2 Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center with the first flight core stage for NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) installed for Green Run testing. The SLS core stage is undergoing a series of tests on its integrated systems prior to its use on the Artemis I mission. NASA is building SLS to return humans, including the first woman, to the Moon as part of the Artemis program and to prepare for eventual missions to Mars. The Green Run series at Stennis culminates with a hot fire of the core stage’s four RS-25 engines, just as during an actual launch.
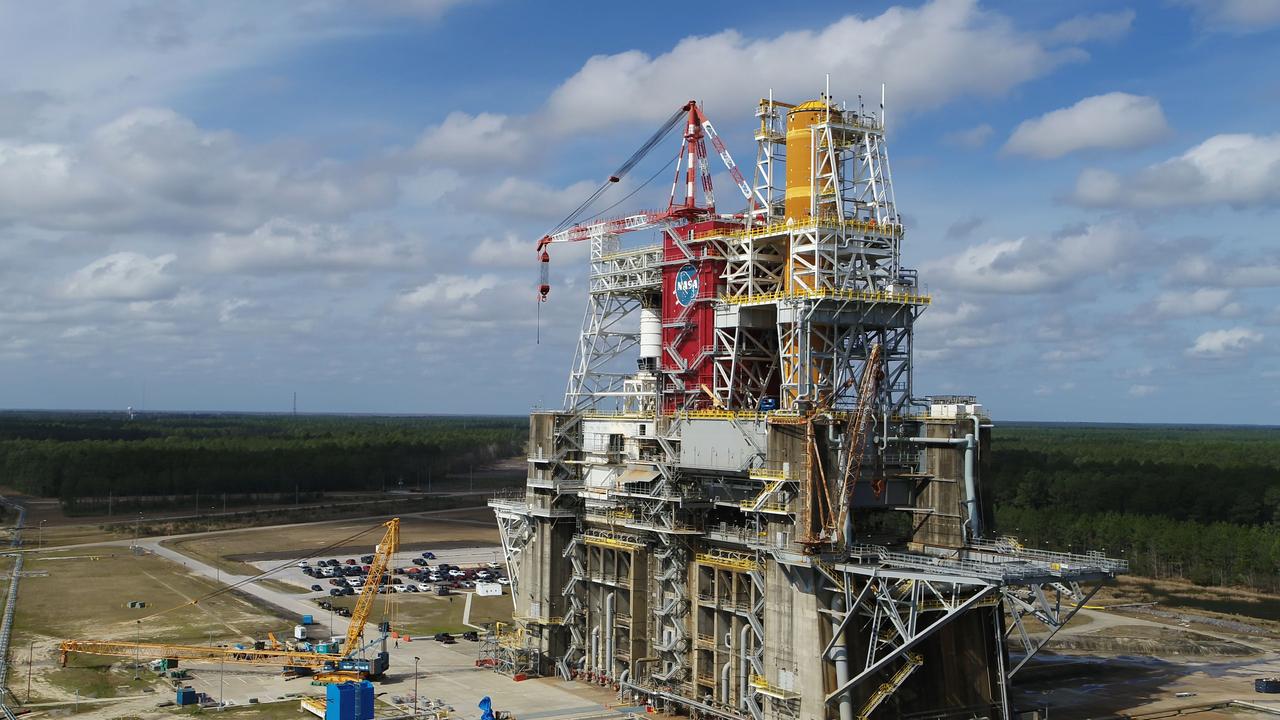

A NASA drone photo offers a bird’s-eye view of the B-2 Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center with the first flight core stage for NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) installed for Green Run testing. The SLS core stage is undergoing a series of tests on its integrated systems prior to its use on the Artemis I mission. NASA is building SLS to return humans, including the first woman, to the Moon as part of the Artemis program and to prepare for eventual missions to Mars. The Green Run series at Stennis culminates with a hot fire of the core stage’s four RS-25 engines, just as during an actual launch.
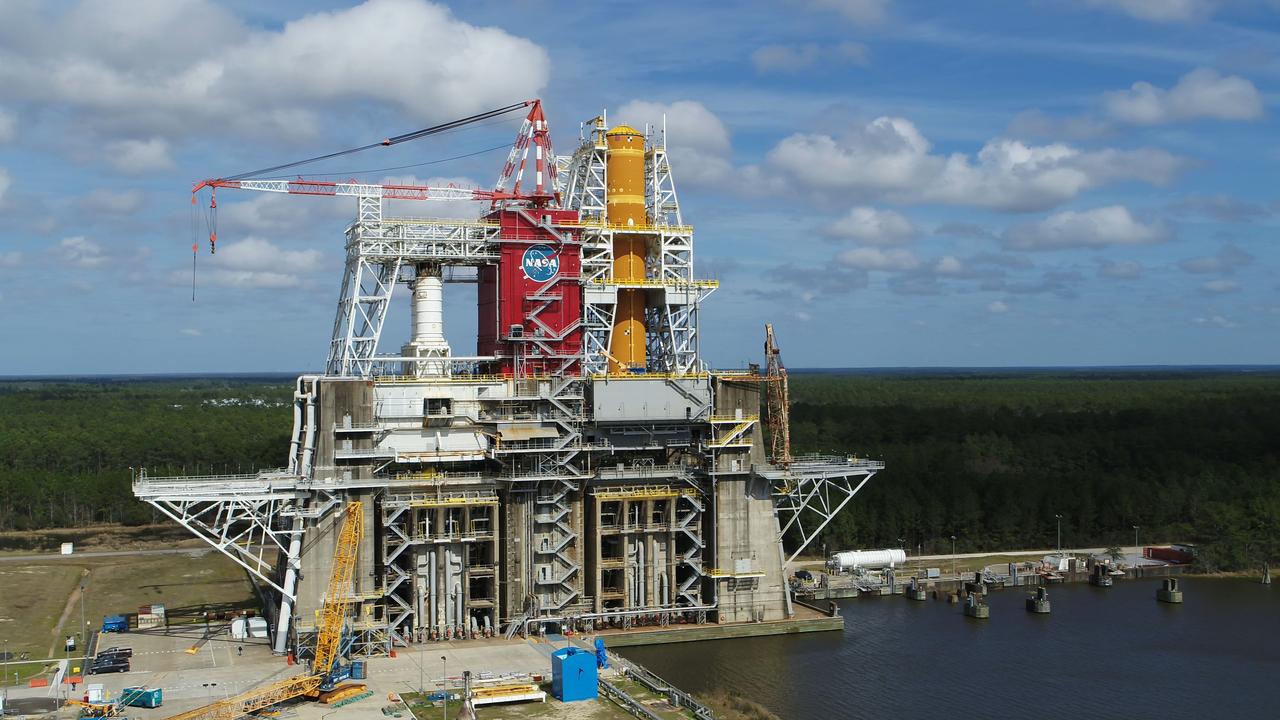

A NASA drone photo offers a bird’s-eye view of the B-2 Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center with the first flight core stage for NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) installed for Green Run testing. The SLS core stage is undergoing a series of tests on its integrated systems prior to its use on the Artemis I mission. NASA is building SLS to return humans, including the first woman, to the Moon as part of the Artemis program and to prepare for eventual missions to Mars. The Green Run series at Stennis culminates with a hot fire of the core stage’s four RS-25 engines, just as during an actual launch.
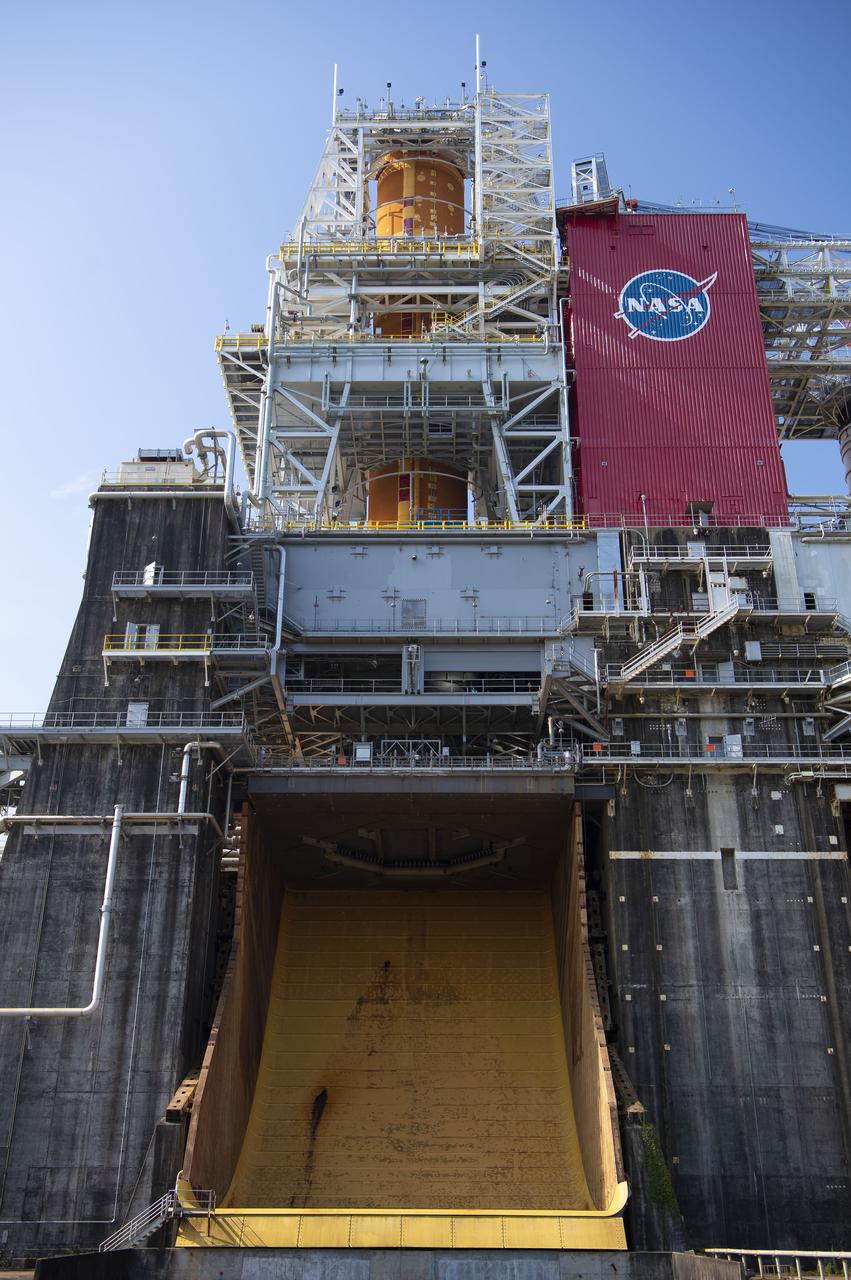

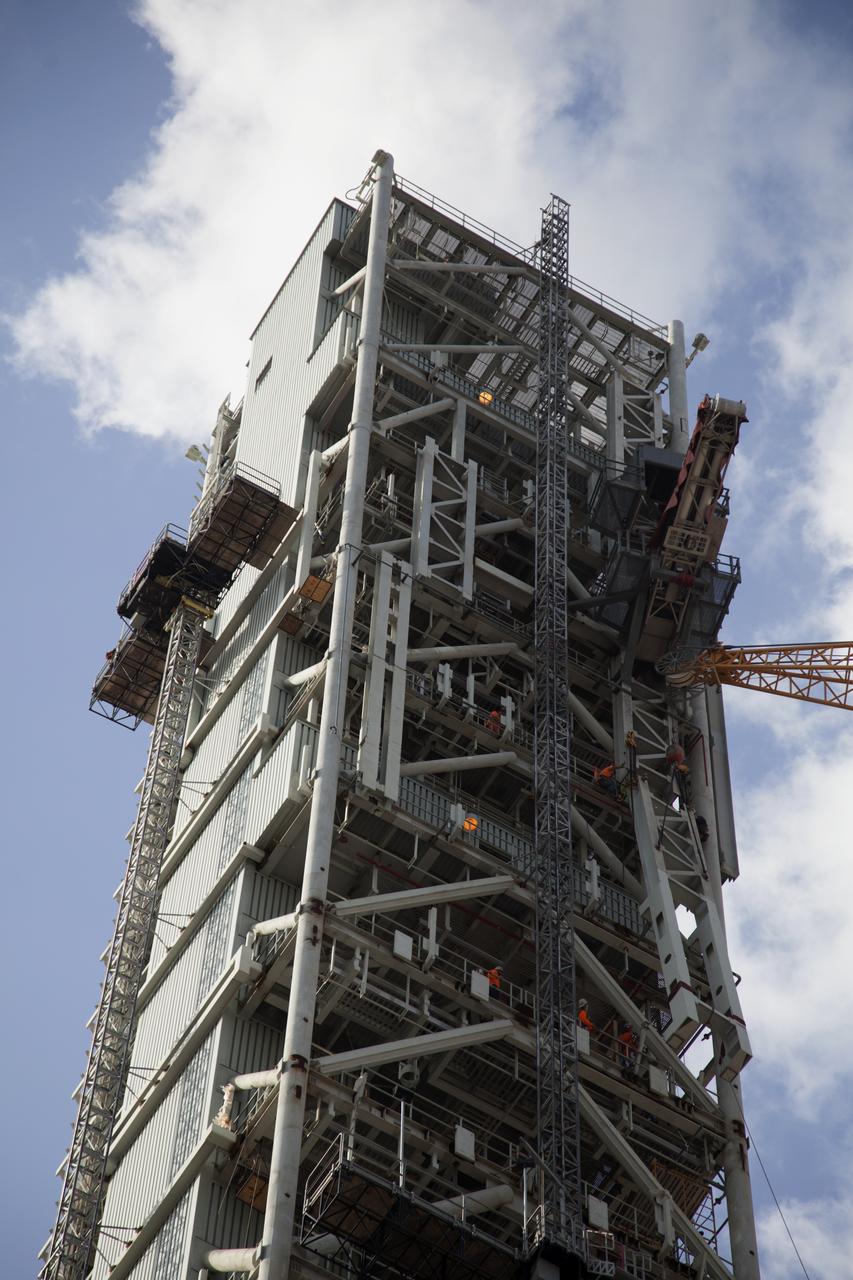
A photo from the north (flame trench) side of the B-2 Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center shows the first flight core stage for NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket installed for Green Run testing. The SLS core stage was transported to Stennis in January to begin Green Run testing prior to its use on the Artemis I mission. NASA is building SLS to return humans, including the first woman, to the Moon as part of the Artemis program and to prepare for eventual missions to Mars. At Stennis, the SLS core stage will undergo a series of tests on its integrated systems, culminating with a hot fire of its four RS-25 engines, just as during an actual launch.
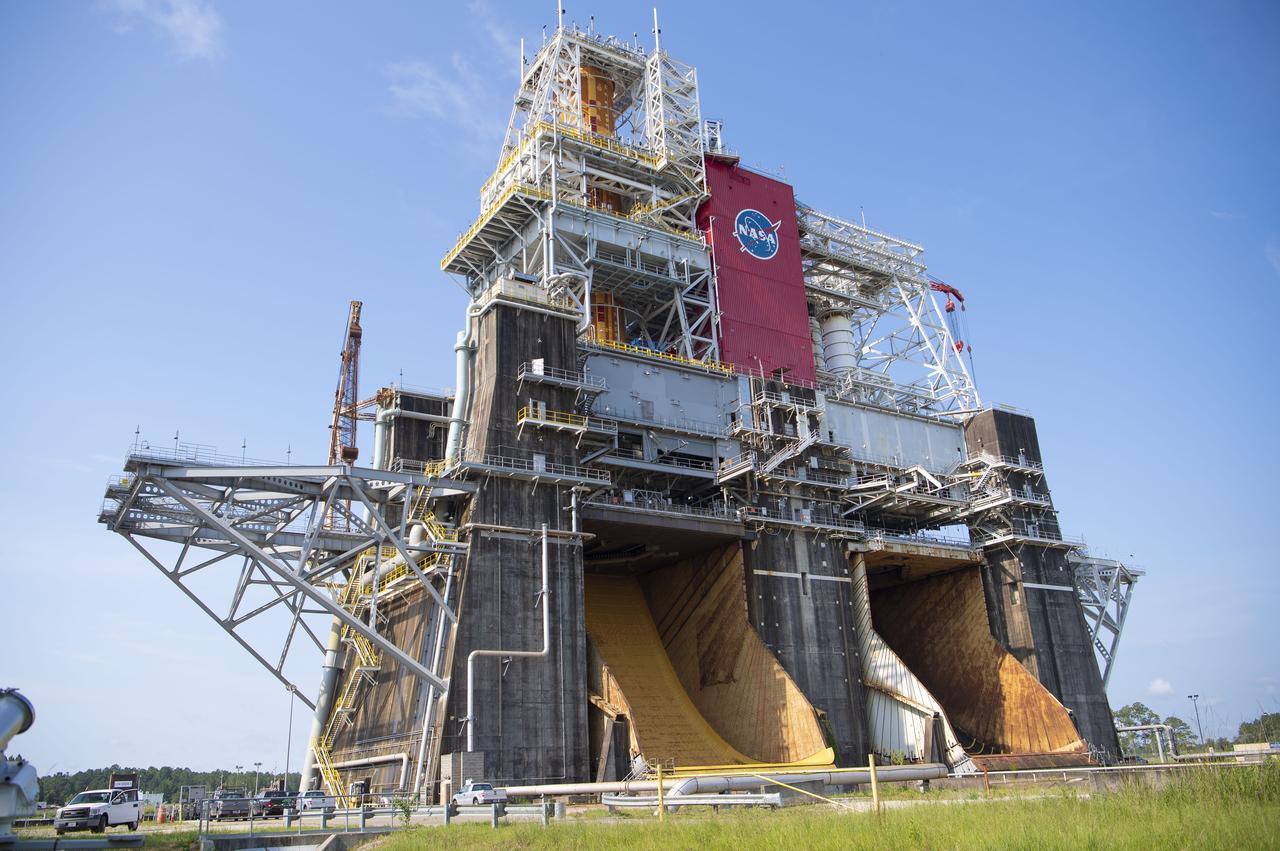

A photo from the north (flame trench) side of the B-2 Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center shows the first flight core stage for NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket installed for Green Run testing. The SLS core stage was transported to Stennis in January to begin Green Run testing prior to its use on the Artemis I mission. NASA is building SLS to return humans, including the first woman, to the Moon as part of the Artemis program and to prepare for eventual missions to Mars. At Stennis, the SLS core stage will undergo a series of tests on its integrated systems, culminating with a hot fire of its four RS-25 engines, just as during an actual launch.
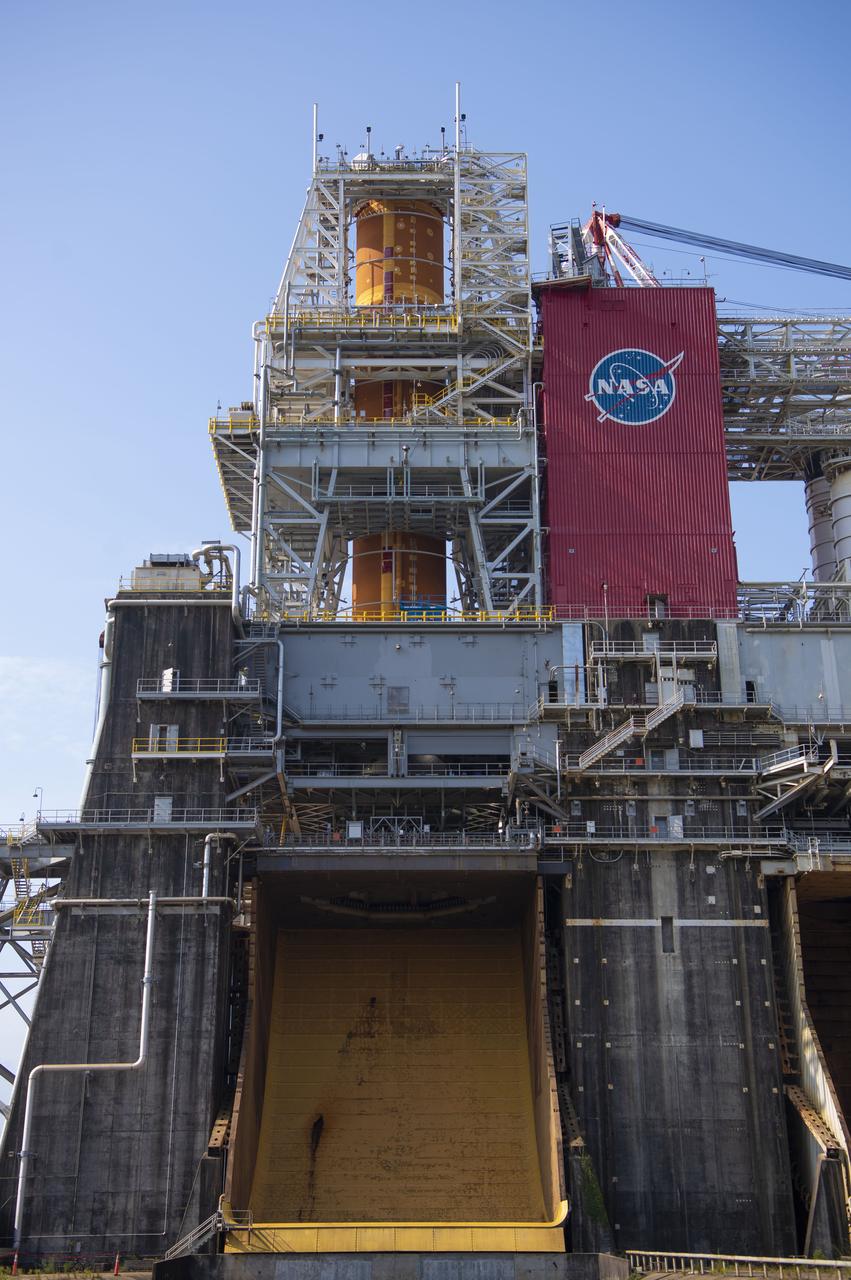

A photo from the north (flame trench) side of the B-2 Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center shows the first flight core stage for NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket installed for Green Run testing. The SLS core stage was transported to Stennis in January to begin Green Run testing prior to its use on the Artemis I mission. NASA is building SLS to return humans, including the first woman, to the Moon as part of the Artemis program and to prepare for eventual missions to Mars. At Stennis, the SLS core stage will undergo a series of tests on its integrated systems, culminating with a hot fire of its four RS-25 engines, just as during an actual launch.
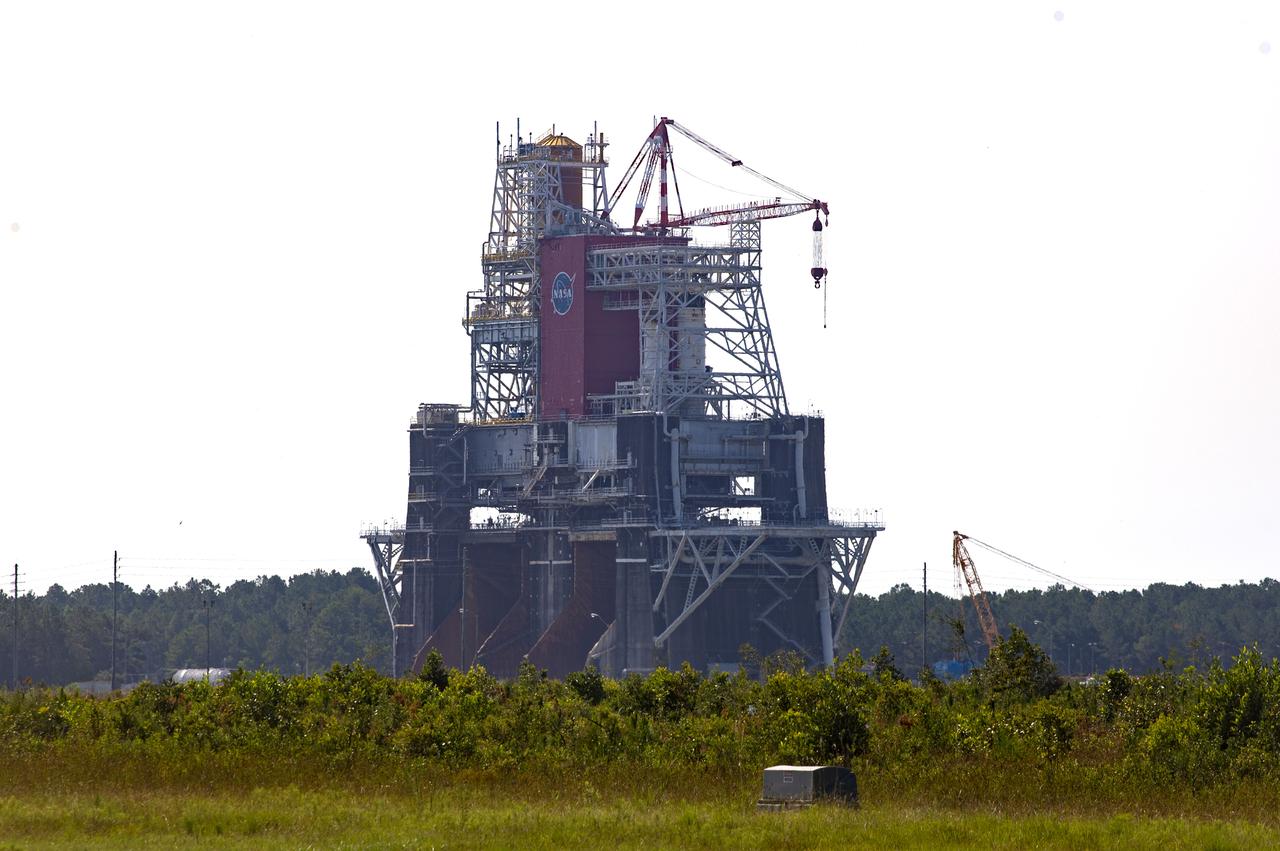

A photo from the north (flame trench) side of the B-2 Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center shows the first flight core stage for NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket installed for Green Run testing. The SLS core stage was transported to Stennis in January to begin Green Run testing prior to its use on the Artemis I mission. NASA is building SLS to return humans, including the first woman, to the Moon as part of the Artemis program and to prepare for eventual missions to Mars. At Stennis, the SLS core stage will undergo a series of tests on its integrated systems, culminating with a hot fire of its four RS-25 engines, just as during an actual launch.
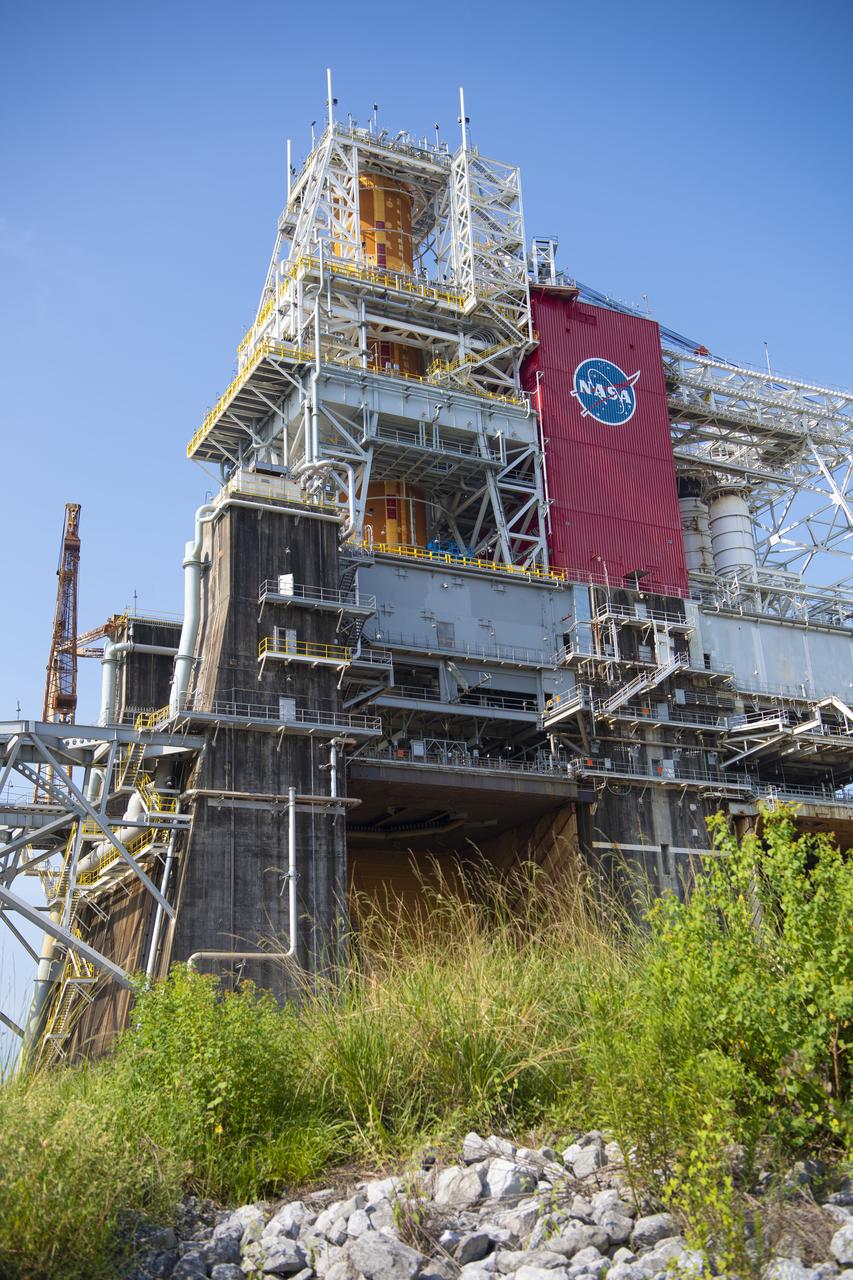

A photo from the north (flame trench) side of the B-2 Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center shows the first flight core stage for NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket installed for Green Run testing. The SLS core stage was transported to Stennis in January to begin Green Run testing prior to its use on the Artemis I mission. NASA is building SLS to return humans, including the first woman, to the Moon as part of the Artemis program and to prepare for eventual missions to Mars. At Stennis, the SLS core stage will undergo a series of tests on its integrated systems, culminating with a hot fire of its four RS-25 engines, just as during an actual launch.
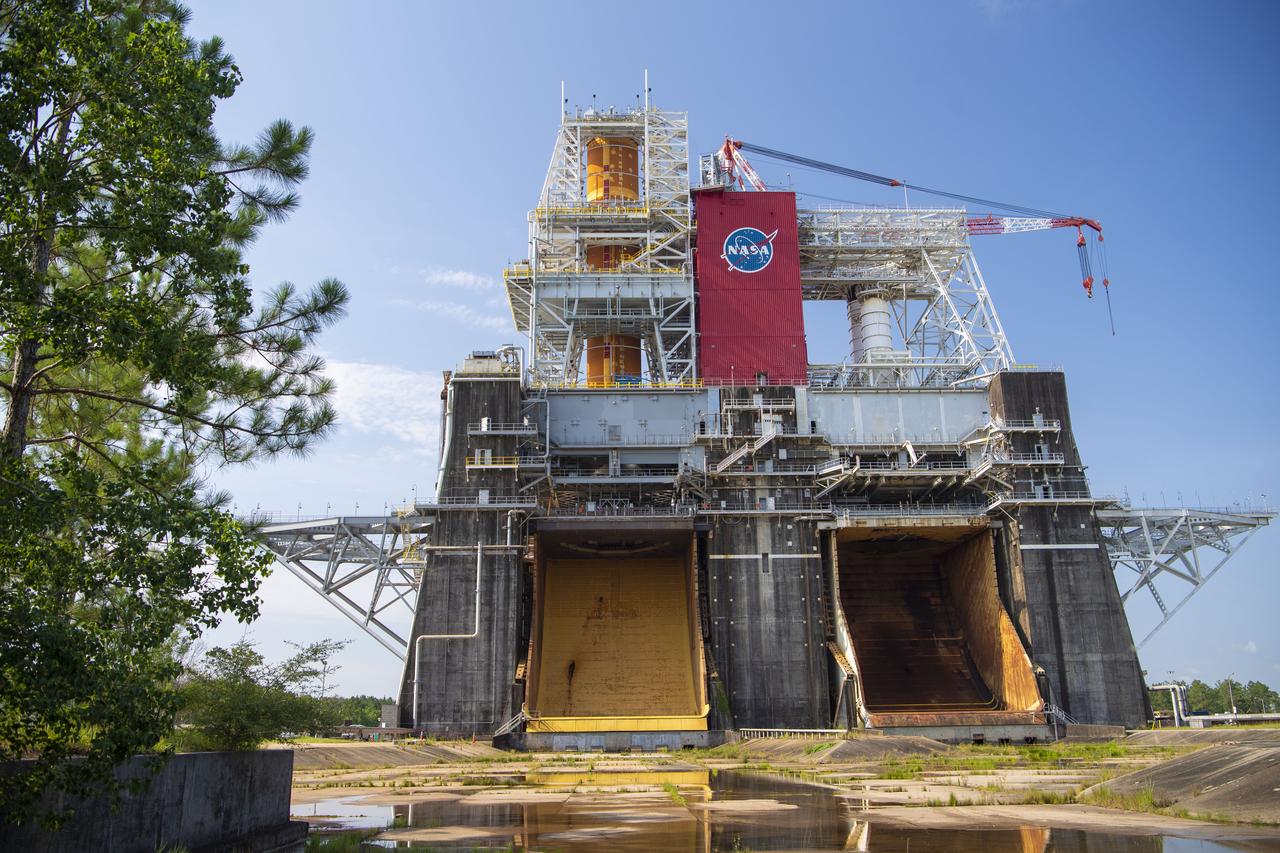

A photo from the north (flame trench) side of the B-2 Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center shows the first flight core stage for NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket installed for Green Run testing. The SLS core stage was transported to Stennis in January to begin Green Run testing prior to its use on the Artemis I mission. NASA is building SLS to return humans, including the first woman, to the Moon as part of the Artemis program and to prepare for eventual missions to Mars. At Stennis, the SLS core stage will undergo a series of tests on its integrated systems, culminating with a hot fire of its four RS-25 engines, just as during an actual launch.
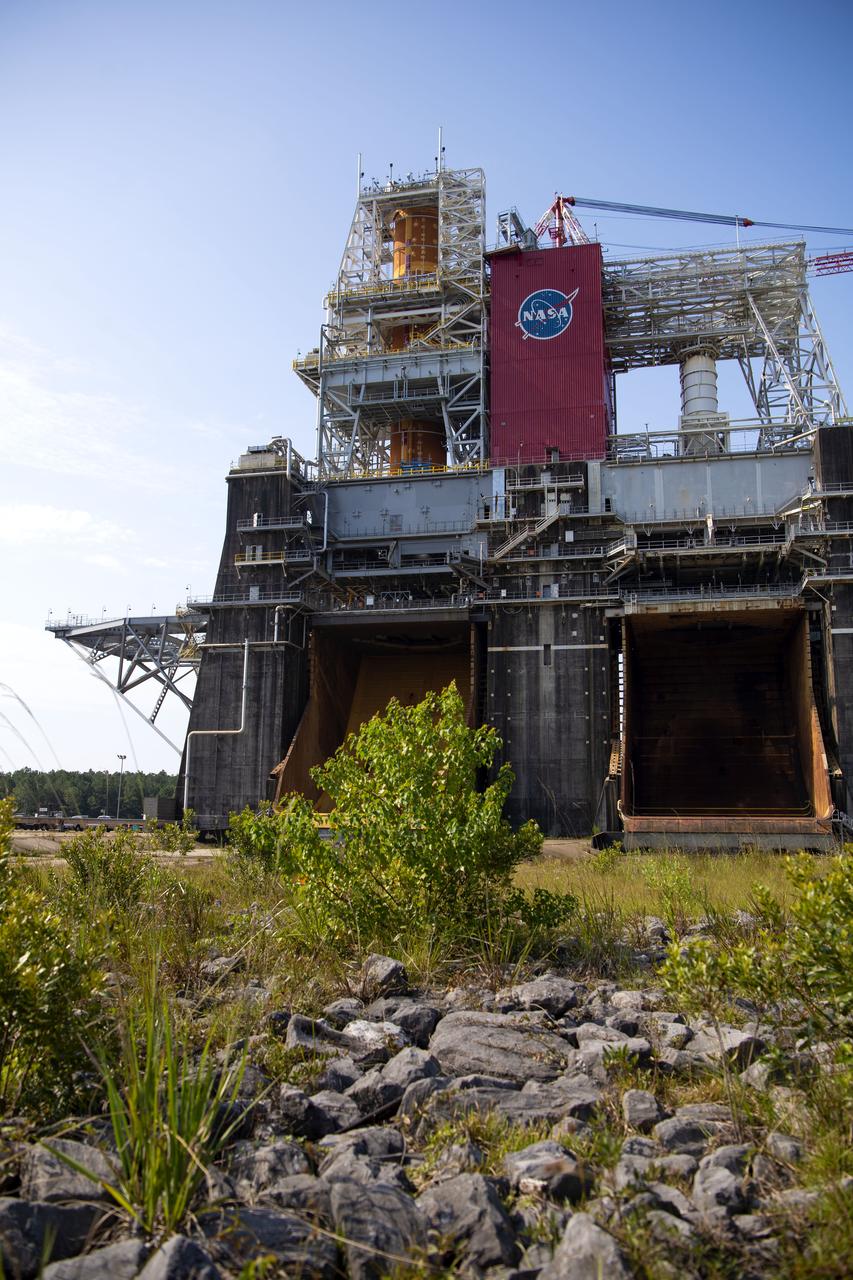

A photo from the north (flame trench) side of the B-2 Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center shows the first flight core stage for NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket installed for Green Run testing. The SLS core stage was transported to Stennis in January to begin Green Run testing prior to its use on the Artemis I mission. NASA is building SLS to return humans, including the first woman, to the Moon as part of the Artemis program and to prepare for eventual missions to Mars. At Stennis, the SLS core stage will undergo a series of tests on its integrated systems, culminating with a hot fire of its four RS-25 engines, just as during an actual launch.
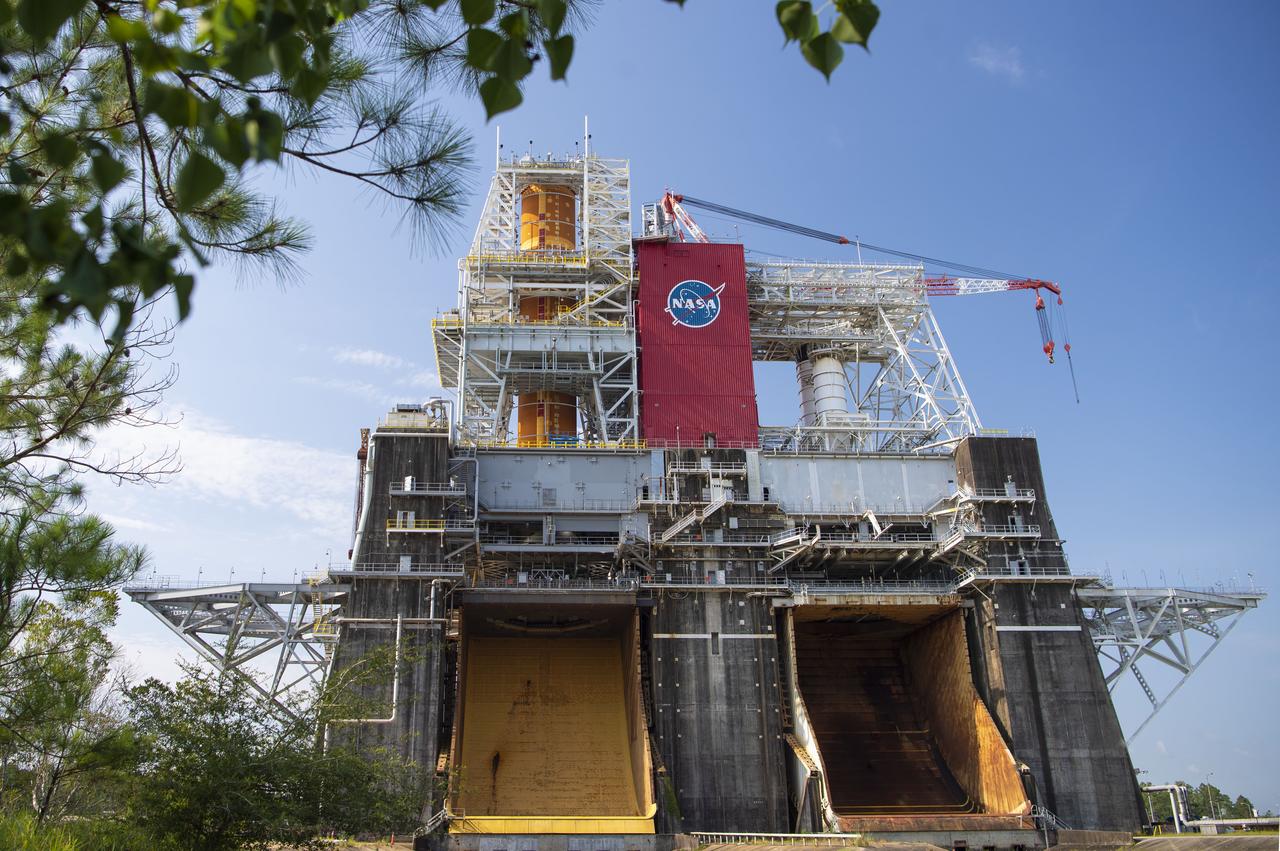

A photo from the north (flame trench) side of the B-2 Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center shows the first flight core stage for NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket installed for Green Run testing. The SLS core stage was transported to Stennis in January to begin Green Run testing prior to its use on the Artemis I mission. NASA is building SLS to return humans, including the first woman, to the Moon as part of the Artemis program and to prepare for eventual missions to Mars. At Stennis, the SLS core stage will undergo a series of tests on its integrated systems, culminating with a hot fire of its four RS-25 engines, just as during an actual launch.
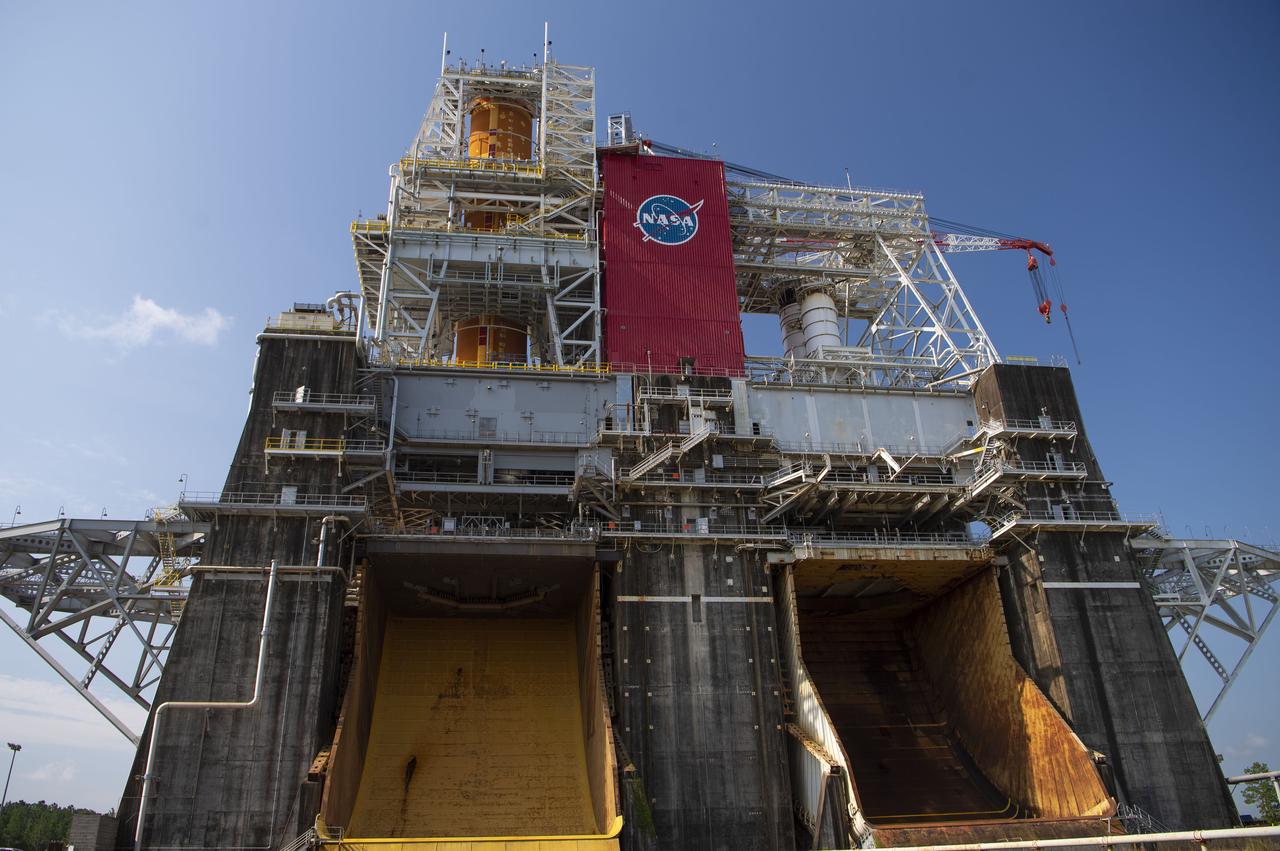

A photo from the north (flame trench) side of the B-2 Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center shows the first flight core stage for NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket installed for Green Run testing. The SLS core stage was transported to Stennis in January to begin Green Run testing prior to its use on the Artemis I mission. NASA is building SLS to return humans, including the first woman, to the Moon as part of the Artemis program and to prepare for eventual missions to Mars. At Stennis, the SLS core stage will undergo a series of tests on its integrated systems, culminating with a hot fire of its four RS-25 engines, just as during an actual launch.
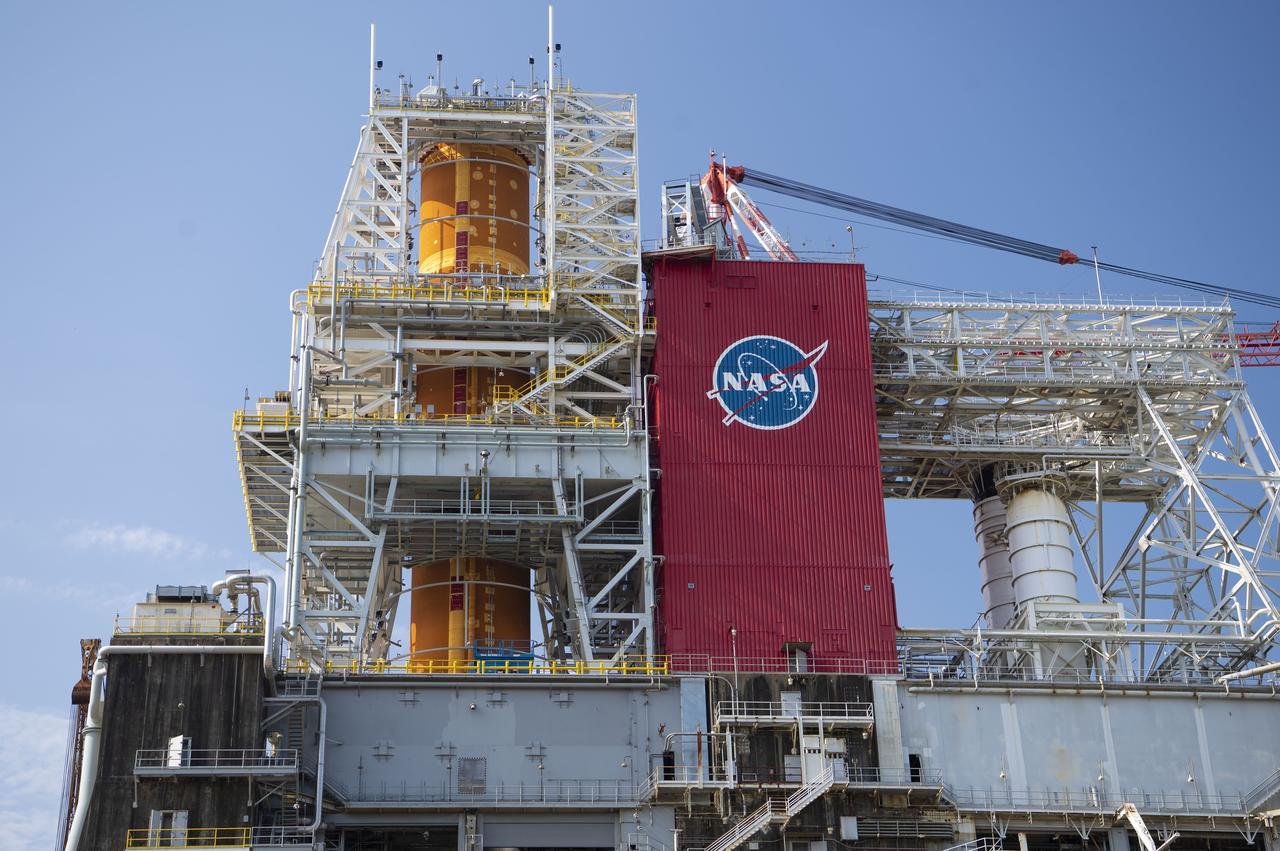

A photo from the north (flame trench) side of the B-2 Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center shows the first flight core stage for NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket installed for Green Run testing. The SLS core stage was transported to Stennis in January to begin Green Run testing prior to its use on the Artemis I mission. NASA is building SLS to return humans, including the first woman, to the Moon as part of the Artemis program and to prepare for eventual missions to Mars. At Stennis, the SLS core stage will undergo a series of tests on its integrated systems, culminating with a hot fire of its four RS-25 engines, just as during an actual launch.
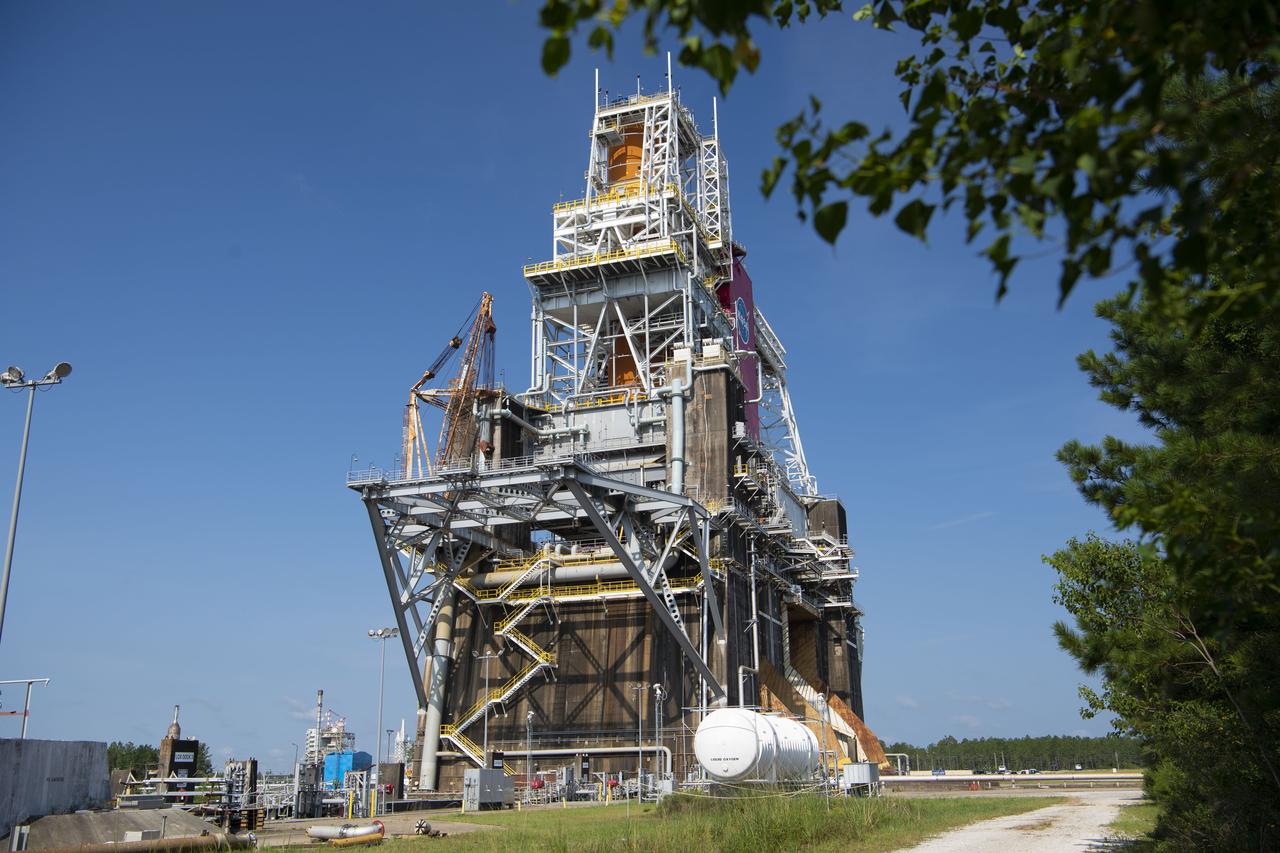

A photo from the north (flame trench) side of the B-2 Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center shows the first flight core stage for NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket installed for Green Run testing. The SLS core stage was transported to Stennis in January to begin Green Run testing prior to its use on the Artemis I mission. NASA is building SLS to return humans, including the first woman, to the Moon as part of the Artemis program and to prepare for eventual missions to Mars. At Stennis, the SLS core stage will undergo a series of tests on its integrated systems, culminating with a hot fire of its four RS-25 engines, just as during an actual launch.
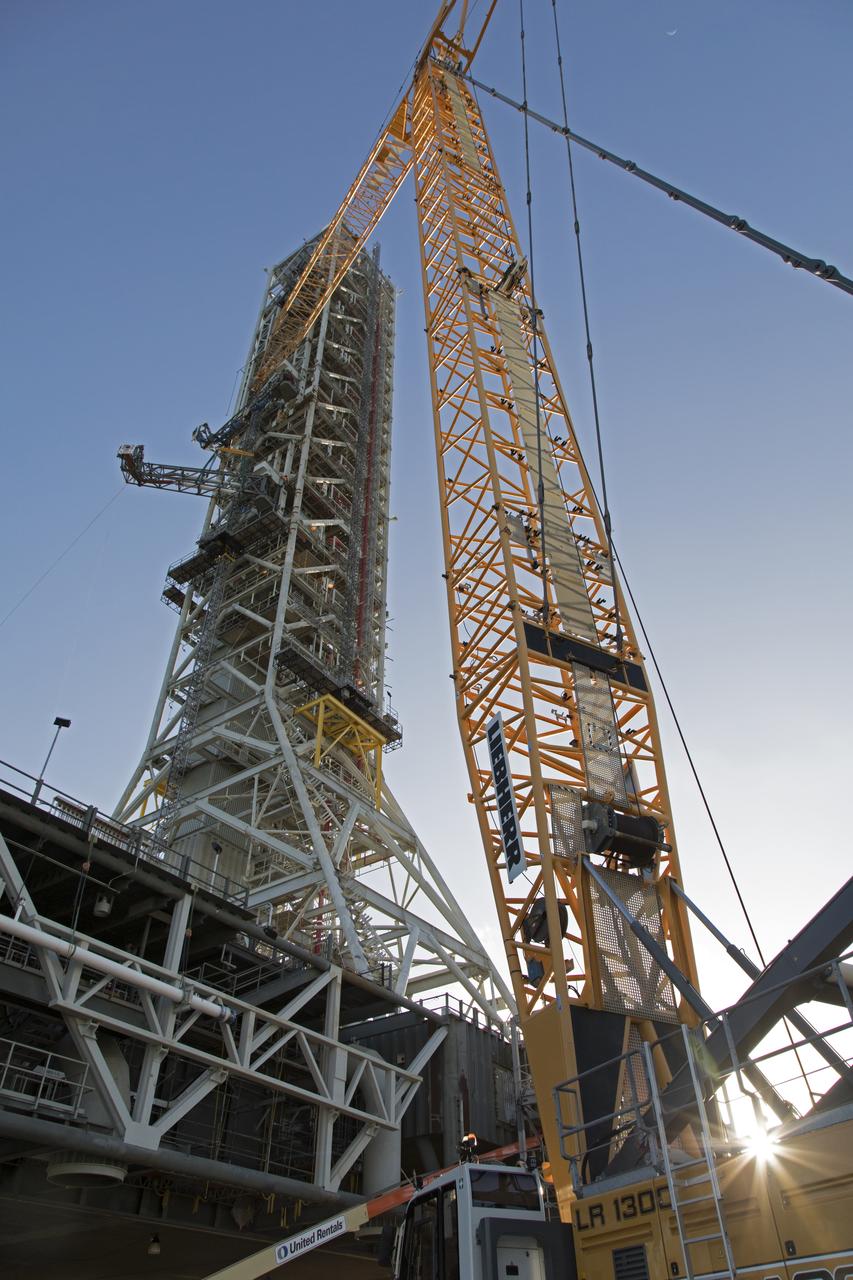

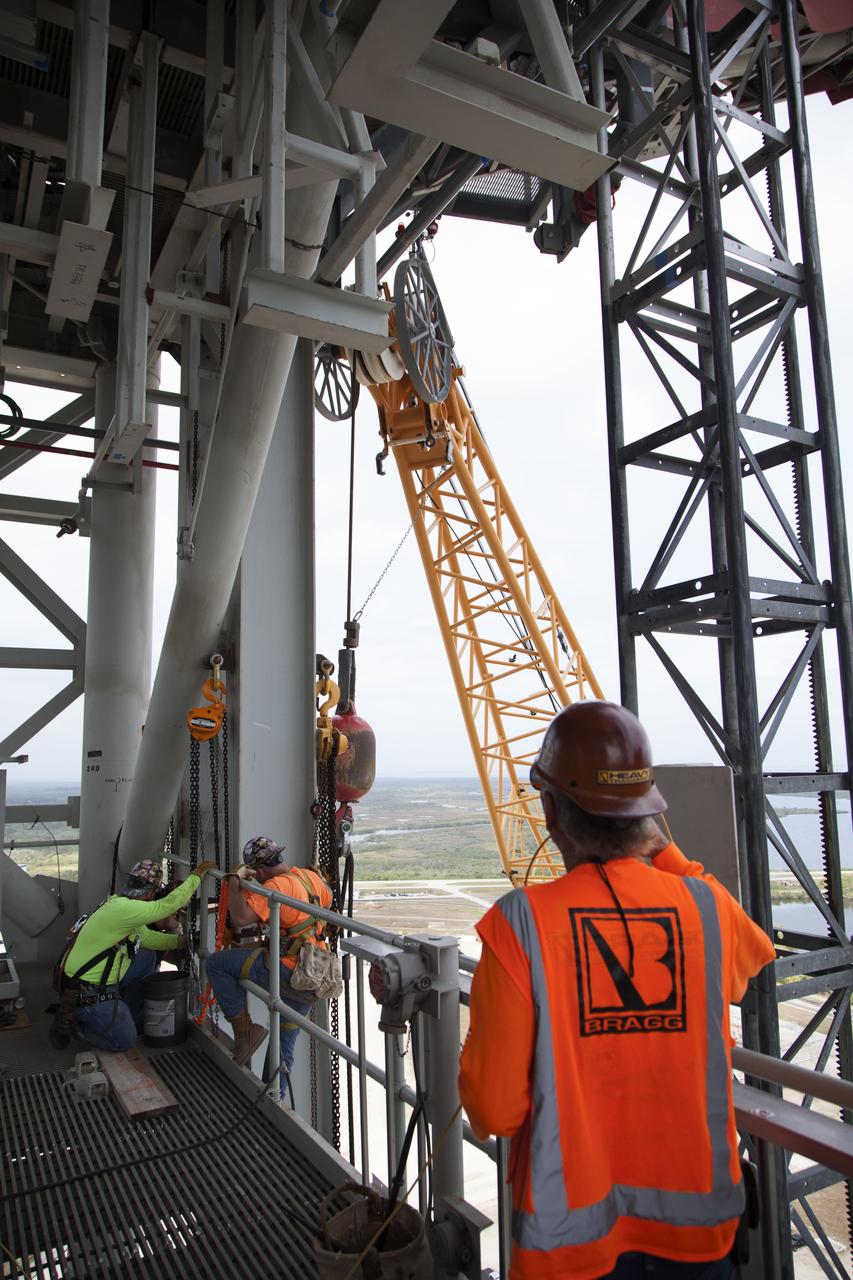
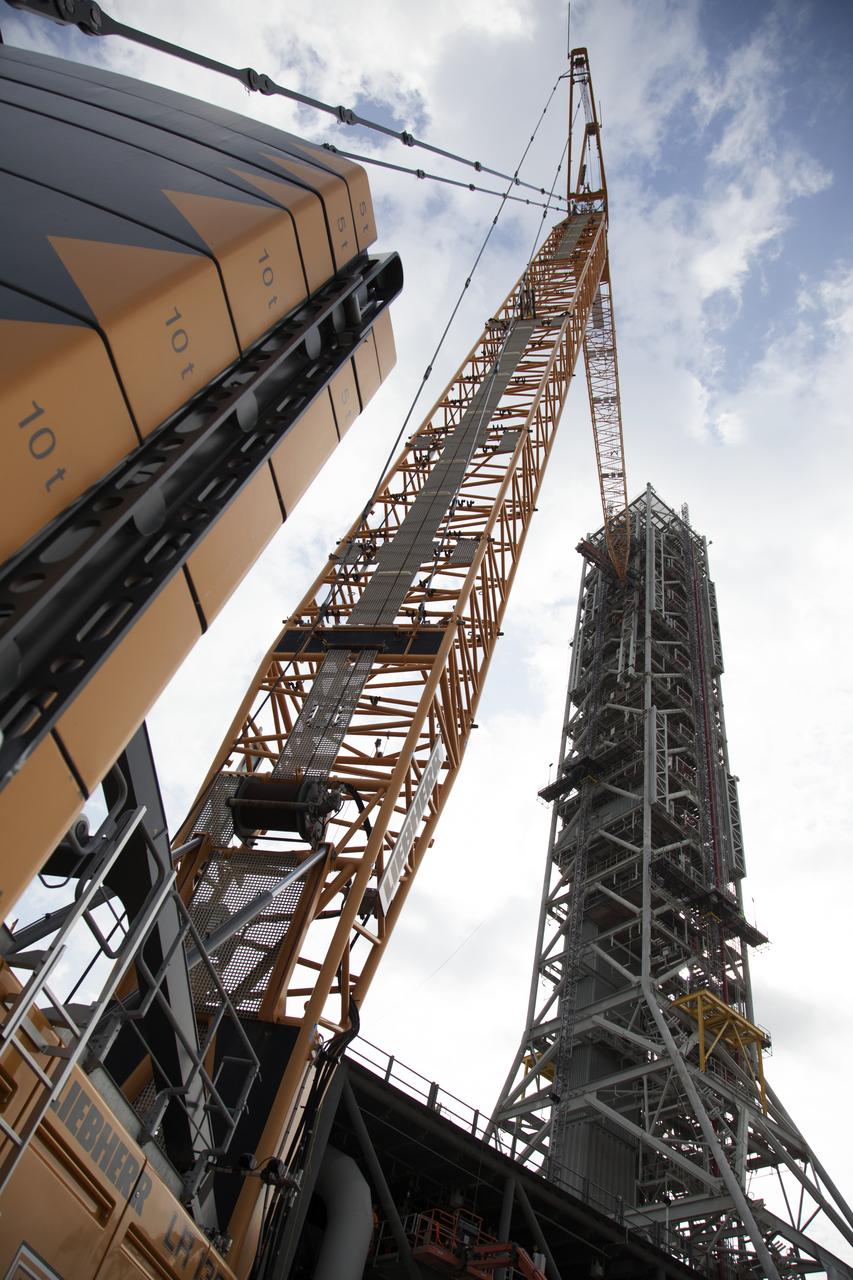
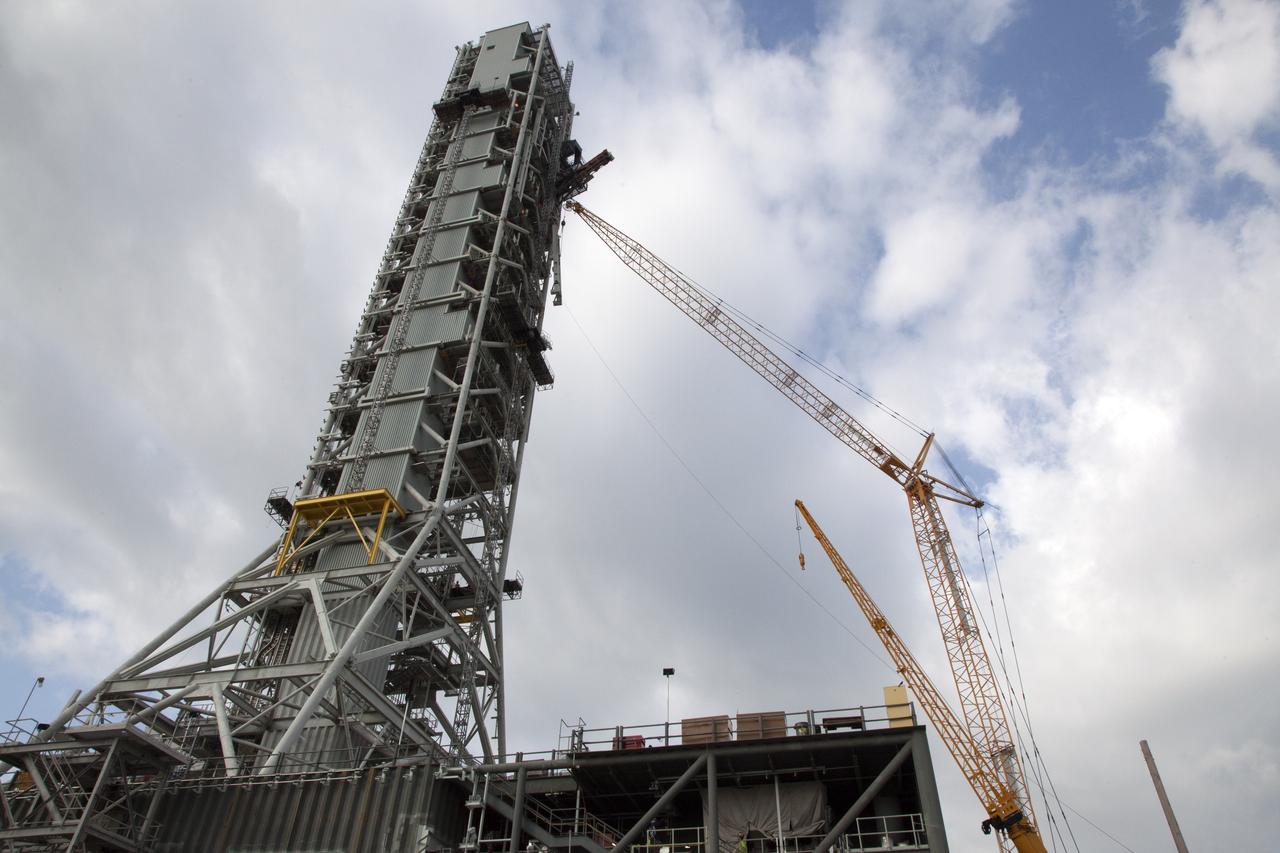
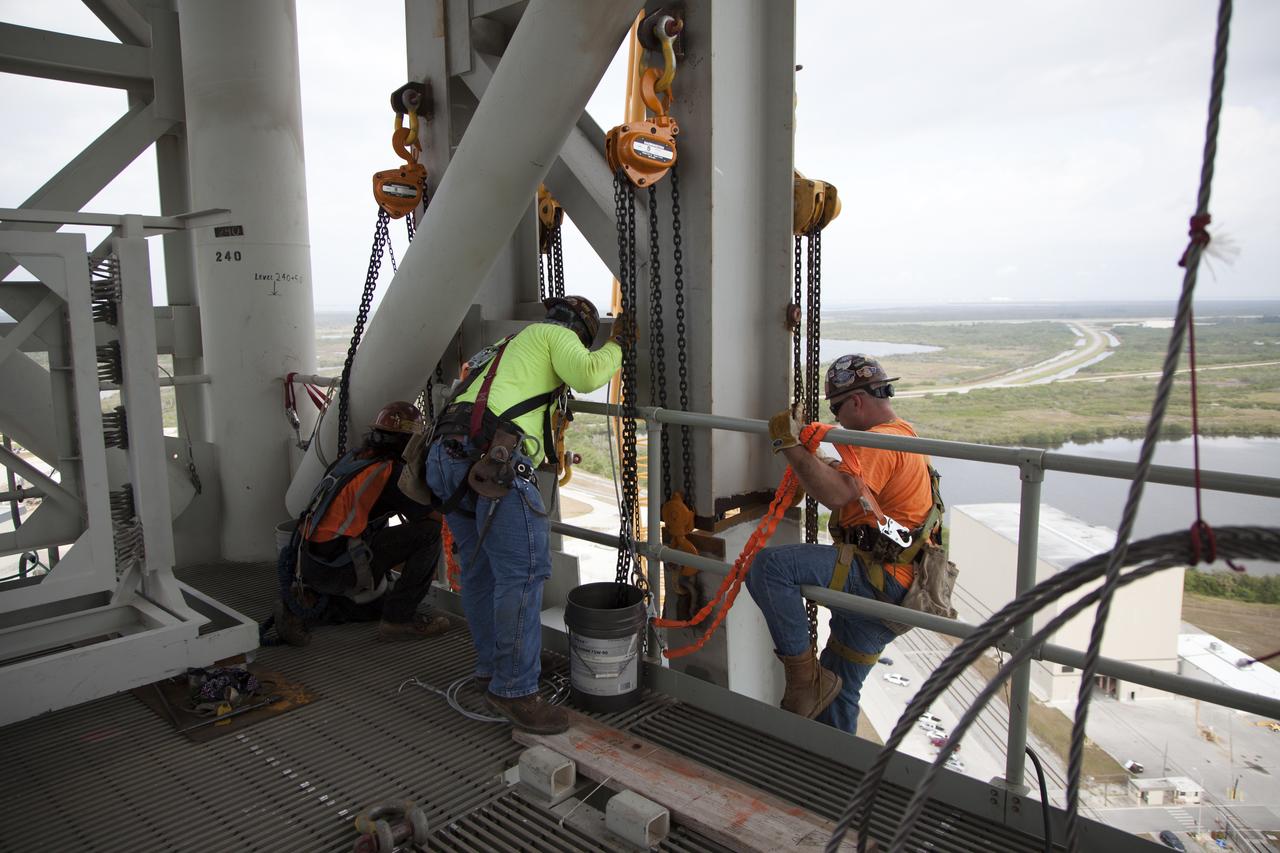
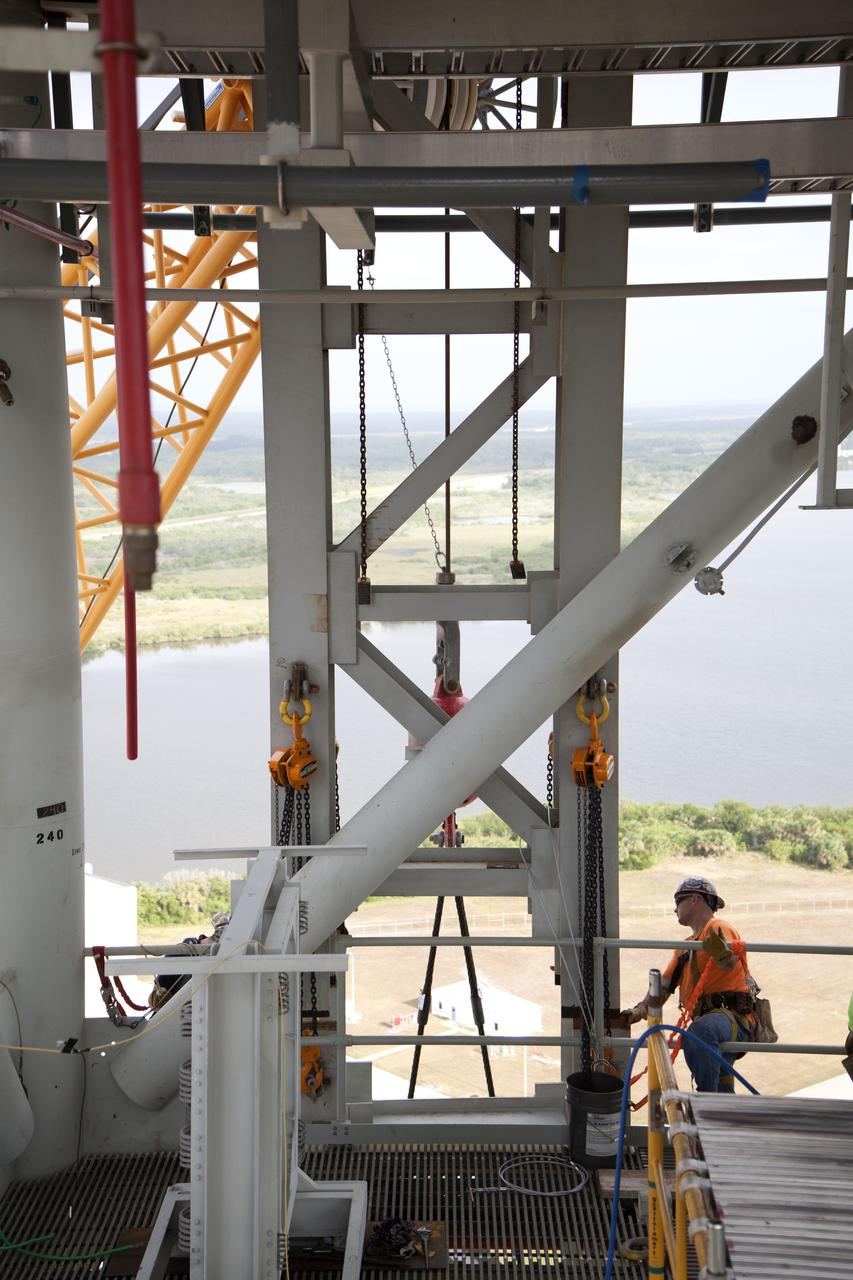
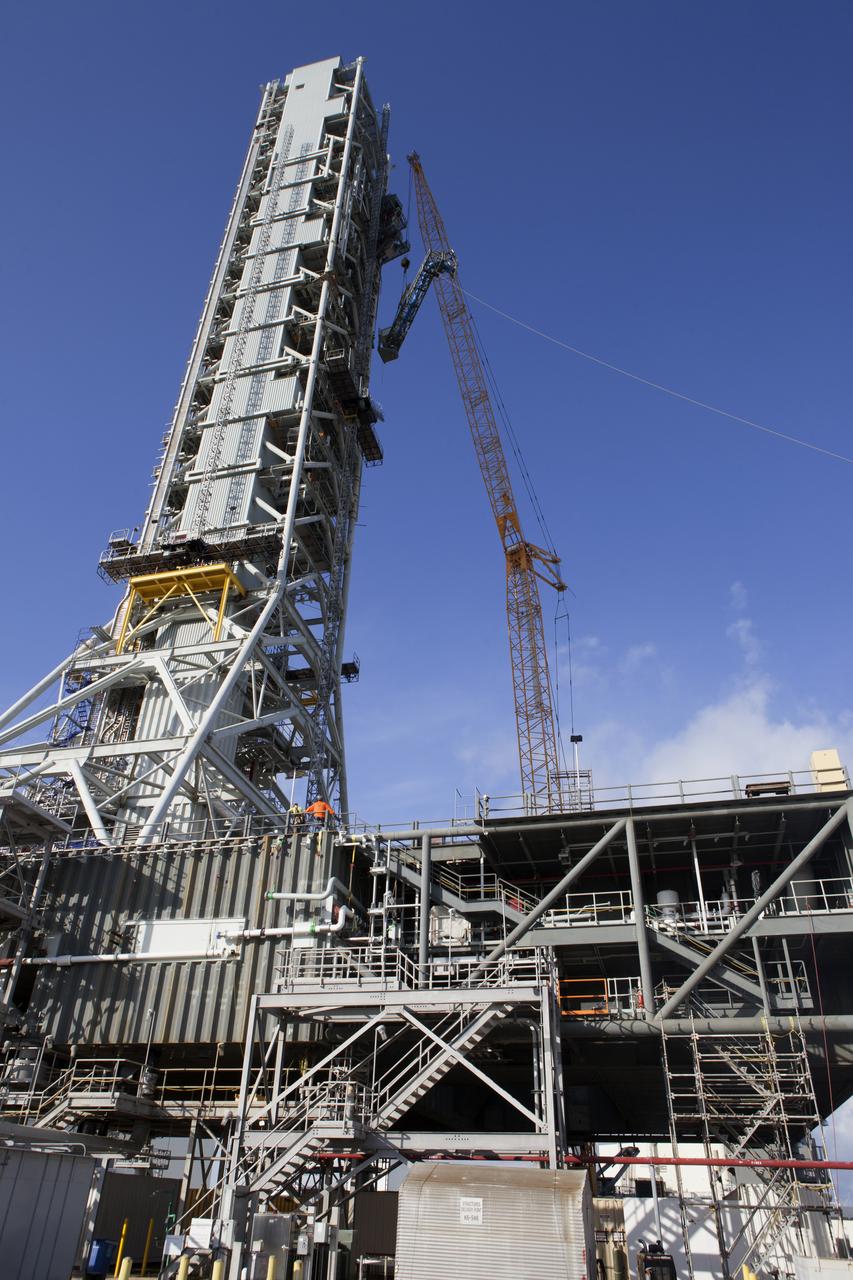
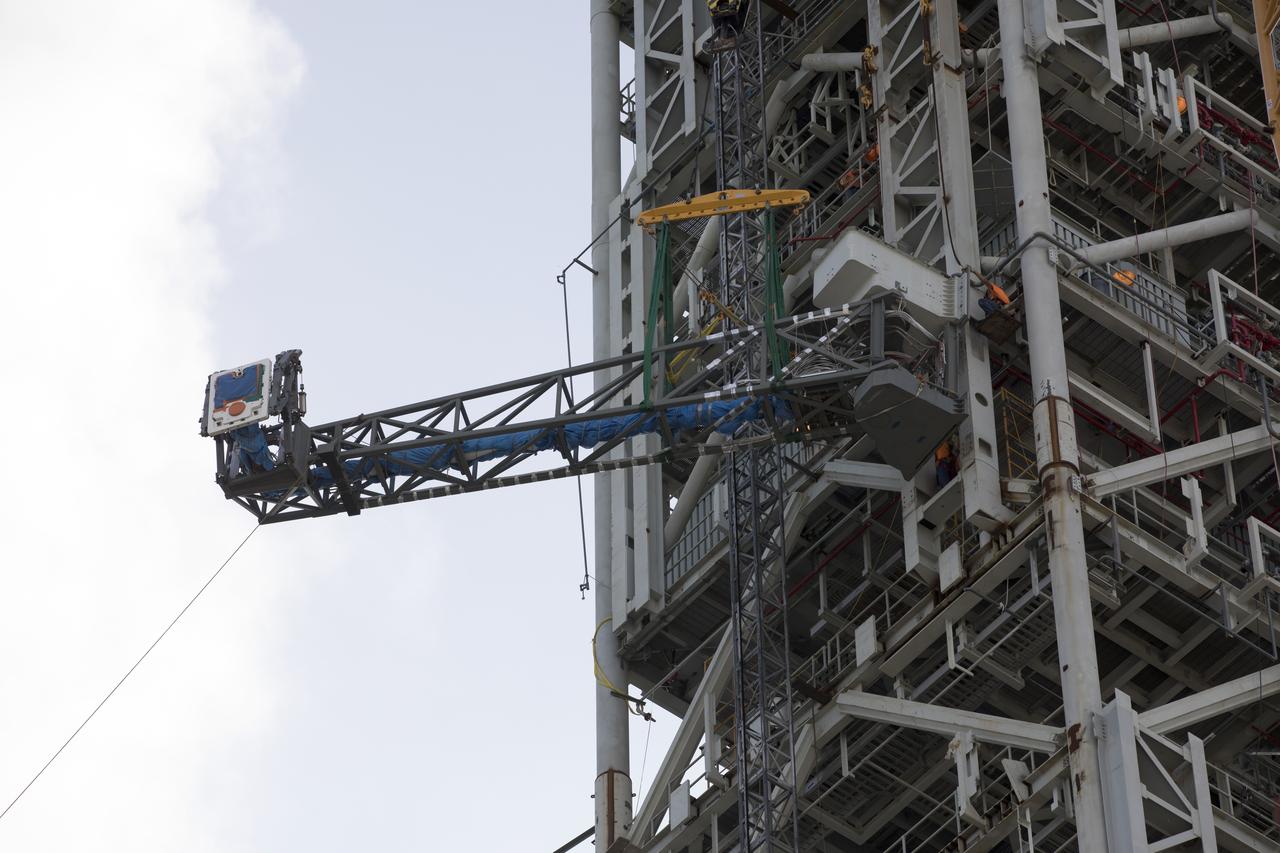
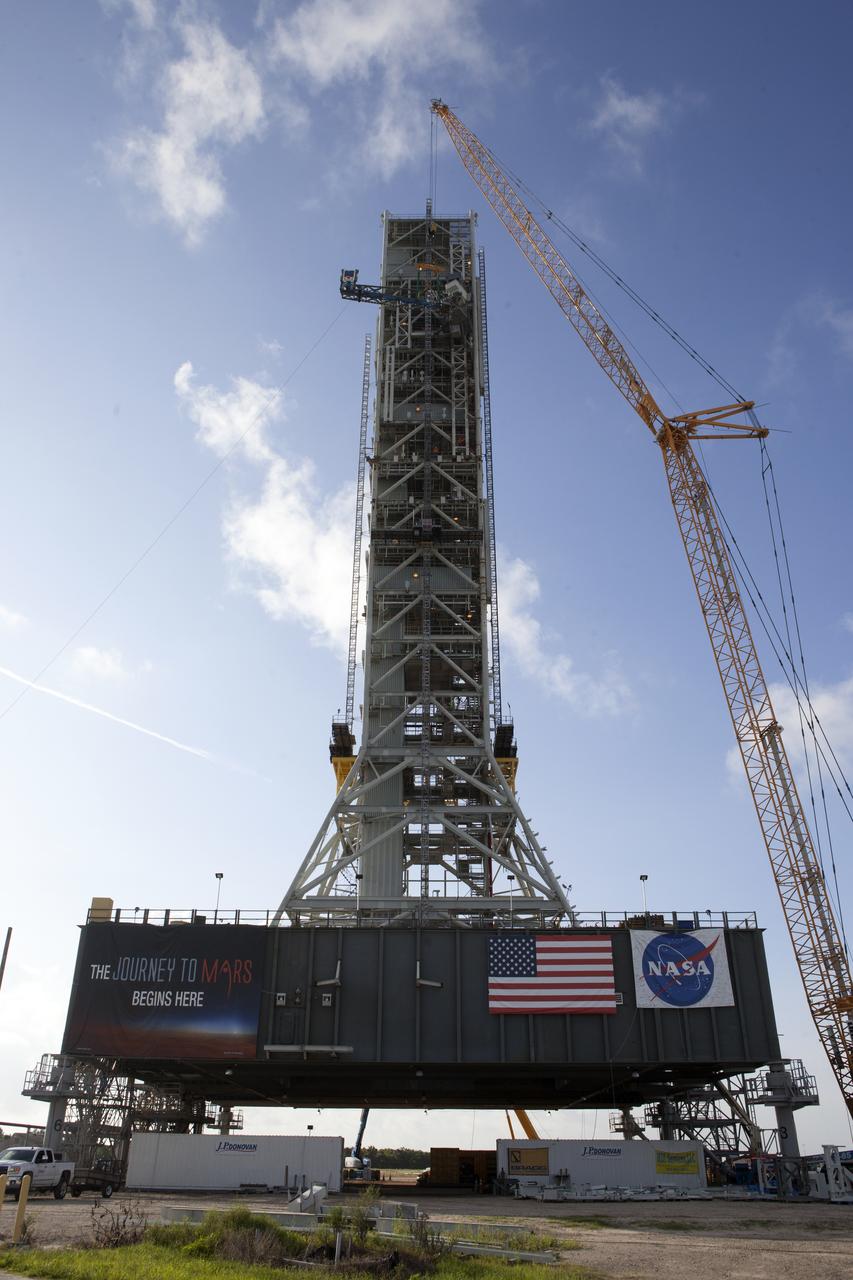
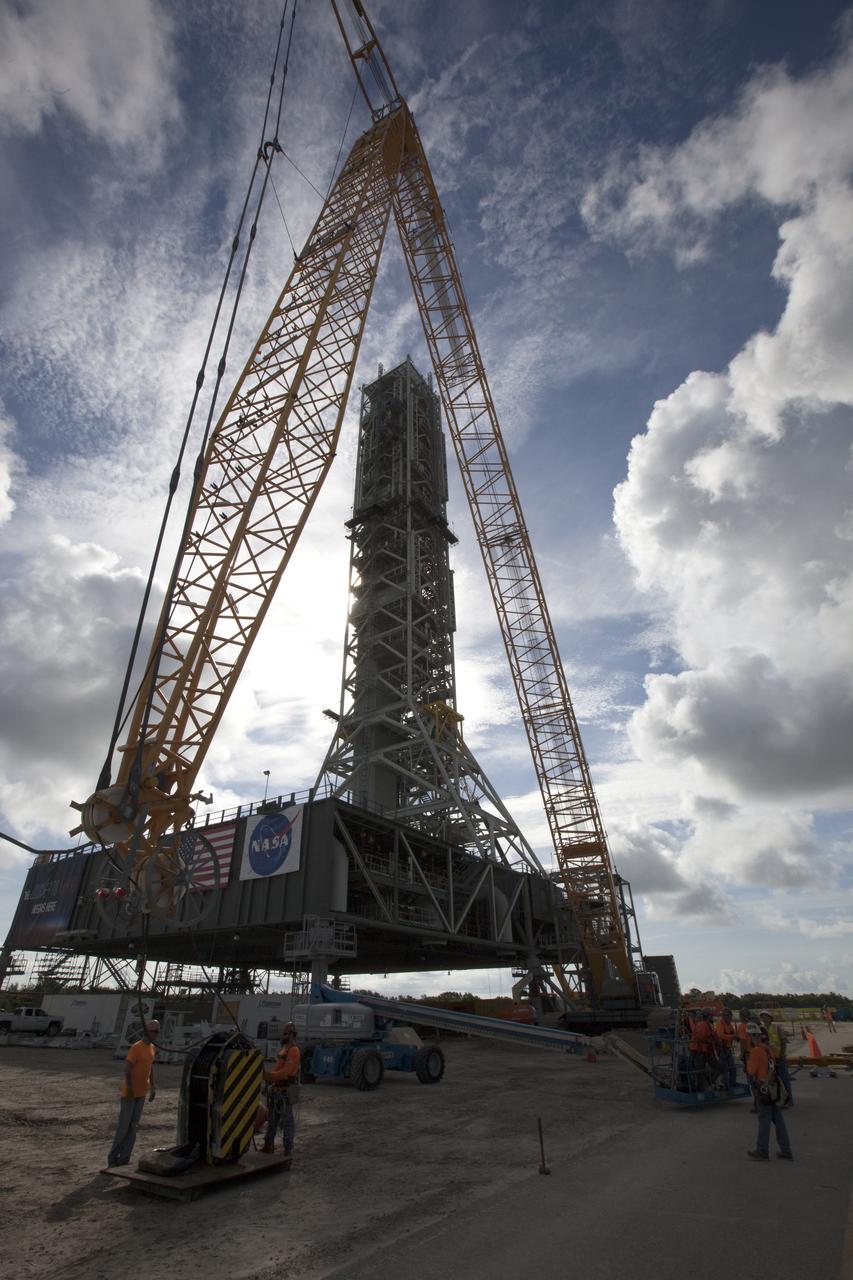
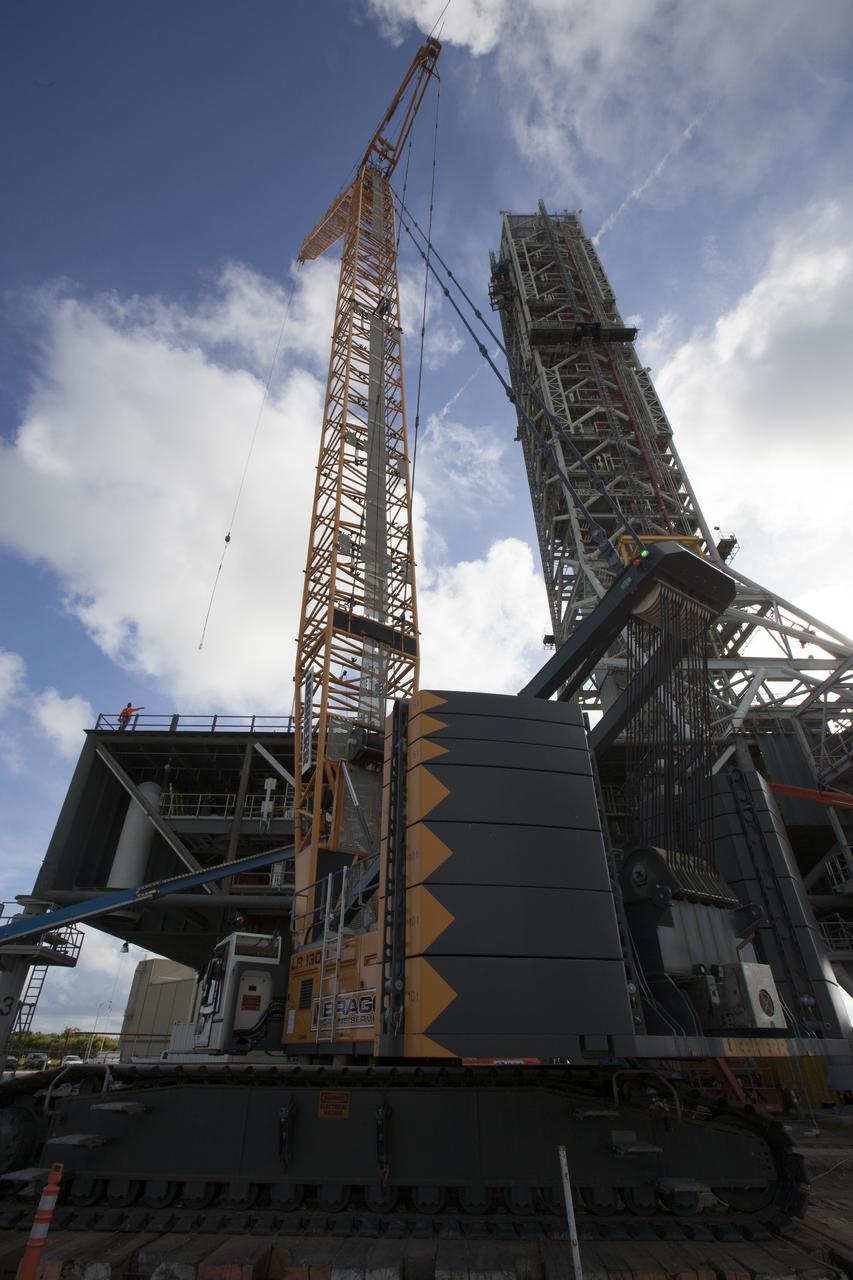
High up on the mobile launcher (ML) tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, construction workers assist as a crane moves the Core Stage Inter-tank Umbilical (CSITU) into place for a fit check of the attachment hardware. The CSITU will be located at about the 140-foot level of the ML tower. The umbilical will be lowered down and installed permanently on the ML at a later date. The CSITU is a swing-arm umbilical that will connect to the Space Launch System core stage inter-tank. It will provide conditioned air, pressurized gases and power and data connection to the core stage. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.
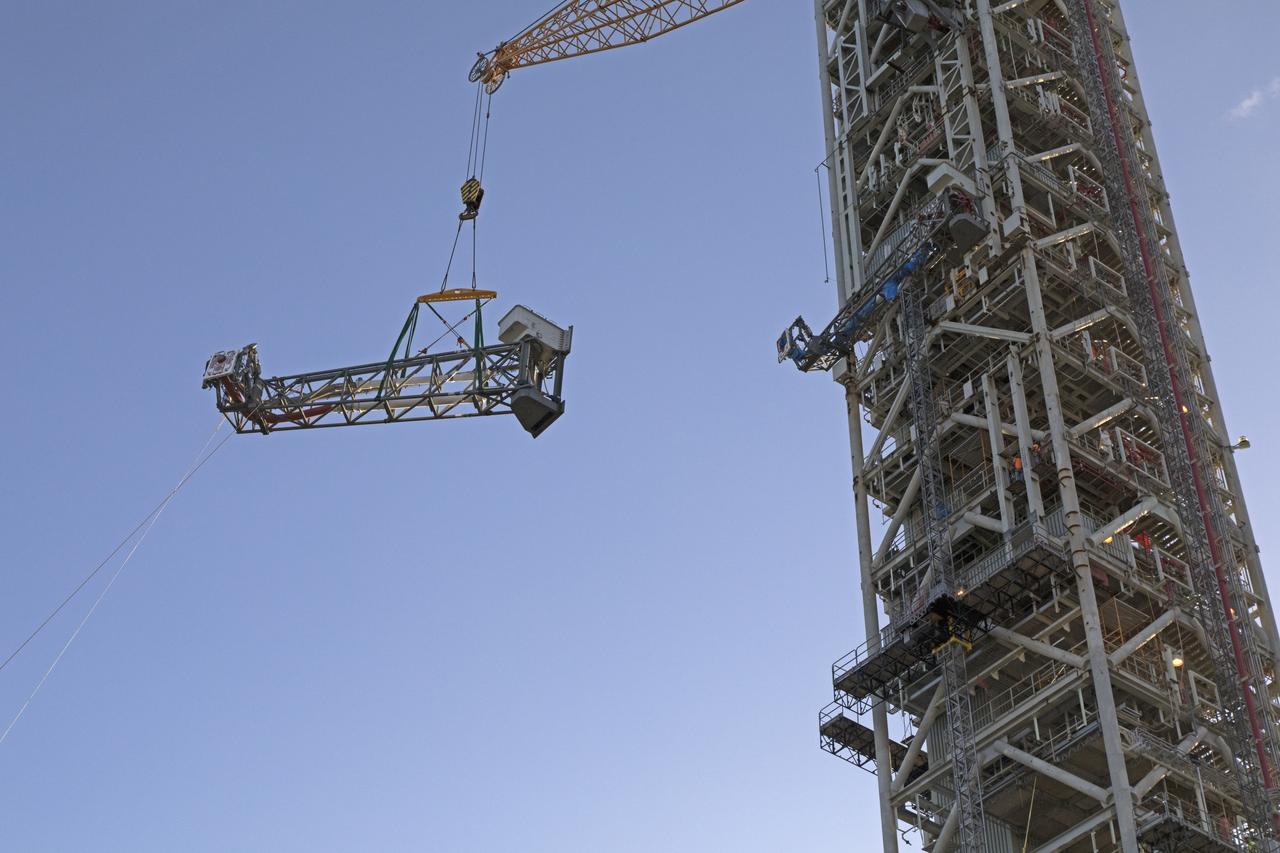

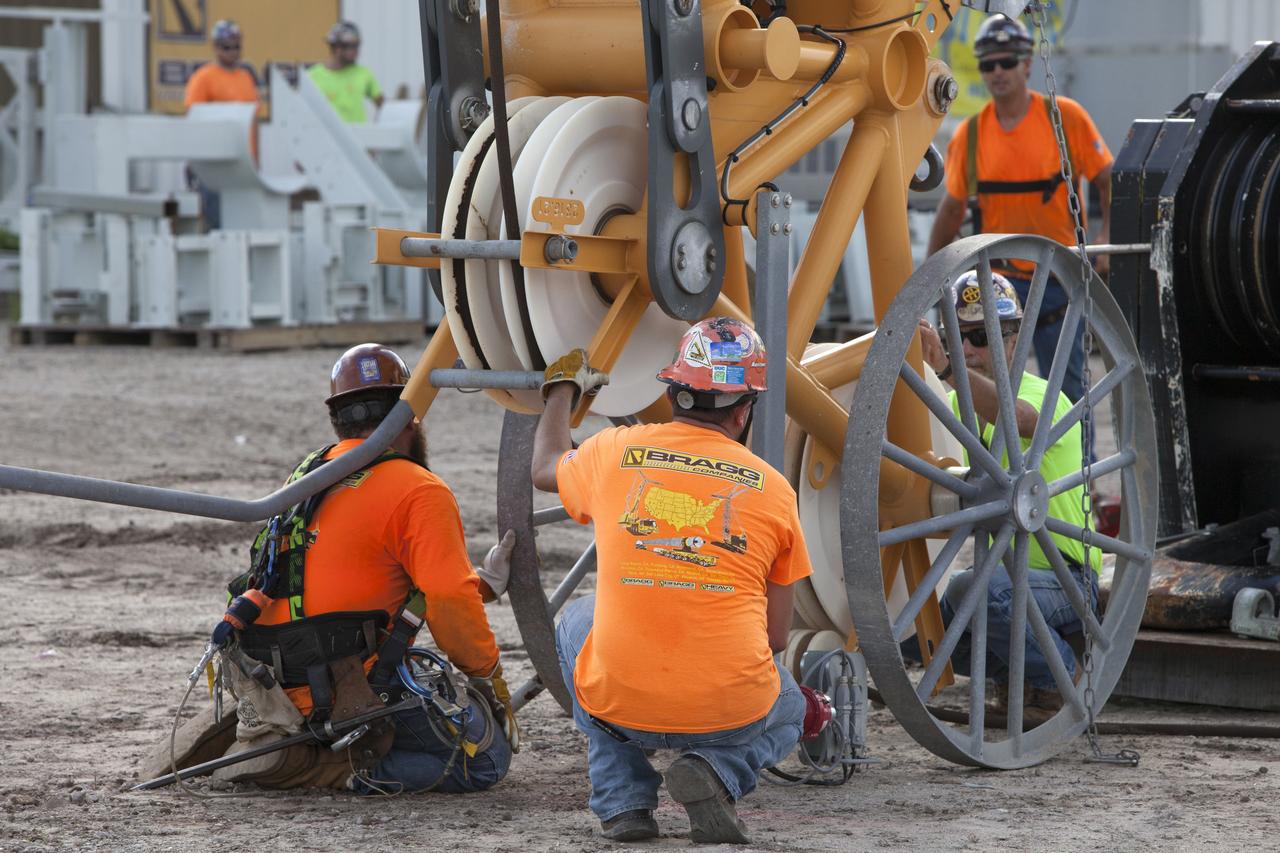
A heavy-lift crane and rigging are used to lift the Core Stage Inter-tank Umbilical (CSITU) up to about the 140-foot level of the mobile launcher (ML) tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The CSITU will be moved into place for a fit check of the attachment hardware. The umbilical will be lowered down and installed permanently on the ML at a later date. The CSITU is a swing-arm umbilical that will connect to the Space Launch System core stage inter-tank. It will provide conditioned air, pressurized gases and power and data connection to the core stage. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.

A heavy-lift crane moves the Core Stage Inter-tank Umbilical (CSITU) up to about the 140-foot level of the mobile launcher (ML) tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The CSITU is moved into place for a fit check of the attachment hardware. The umbilical will be lowered down and installed permanently on the ML at a later date. The CSITU is a swing-arm umbilical that will connect to the Space Launch System core stage inter-tank. It will provide conditioned air, pressurized gases and power and data connection to the core stage. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.

A heavy-lift crane and rigging are used to lift the Core Stage Inter-tank Umbilical (CSITU) up to about the 140-foot level of the mobile launcher (ML) tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The CSITU will be moved into place for a fit check of the attachment hardware. The umbilical will be lowered down and installed permanently on the ML at a later date. The CSITU is a swing-arm umbilical that will connect to the Space Launch System core stage inter-tank. It will provide conditioned air, pressurized gases and power and data connection to the core stage. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.
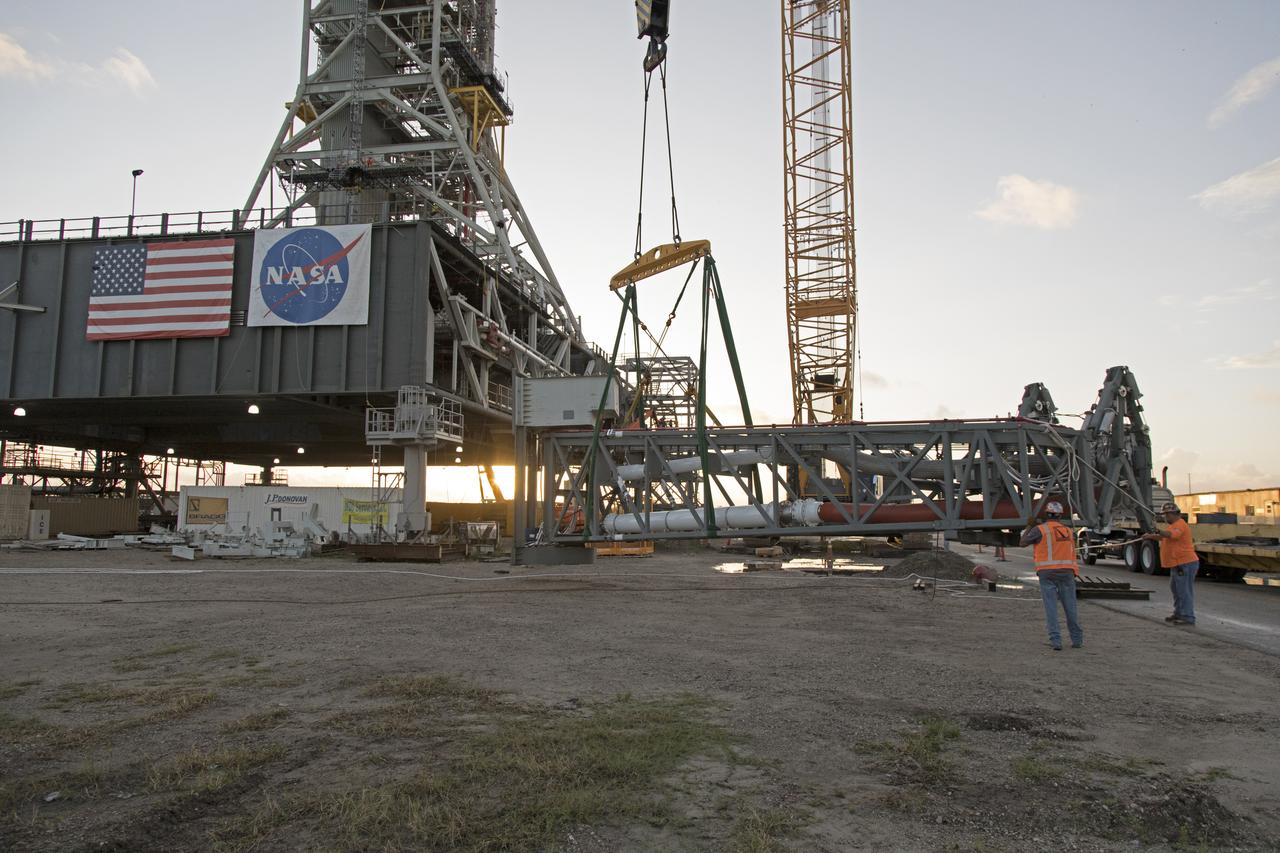

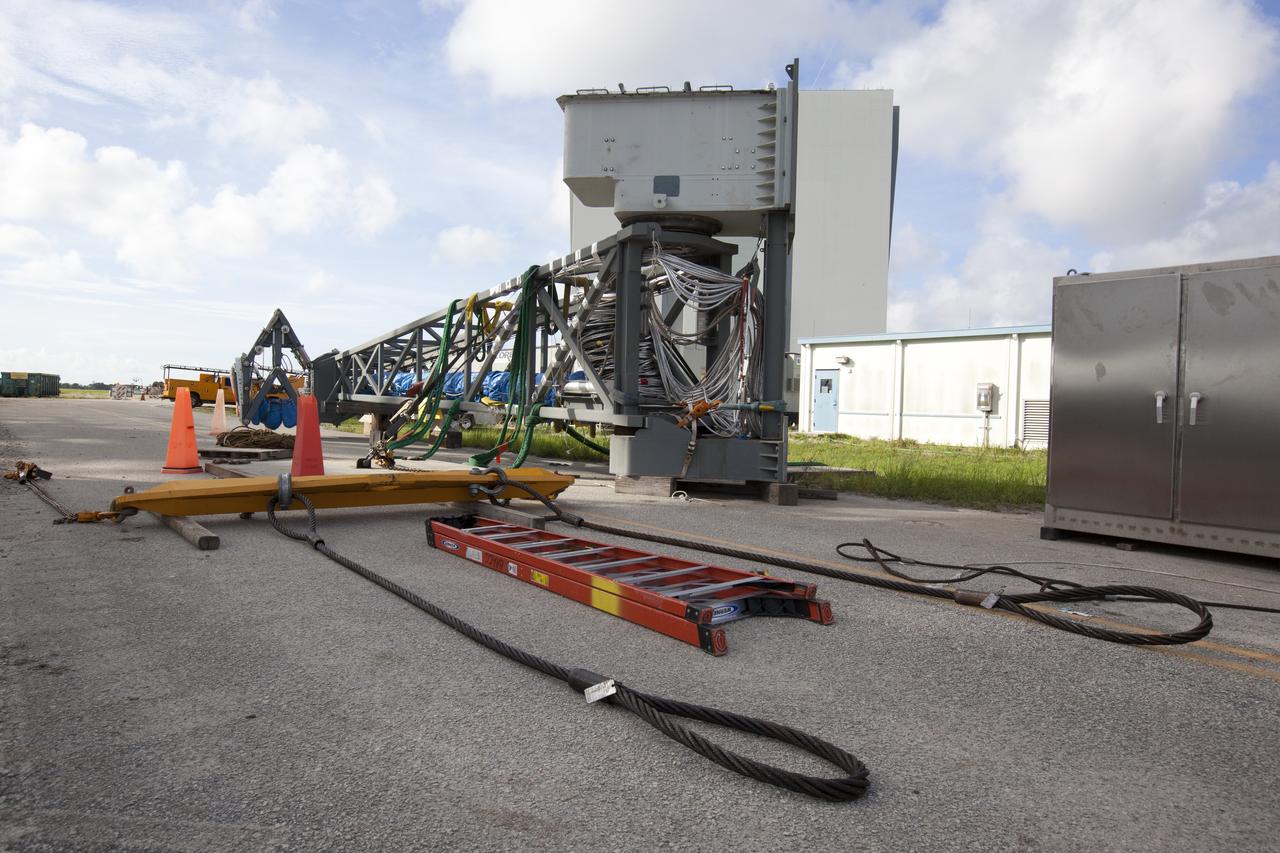
A heavy-lift crane has been attached to the Core Stage Inter-tank Umbilical (CSITU) to lift it up from a flatbed truck near the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The CSITU will be lifted up to about the 140-foot level of the mobile launcher (ML) tower for a fit check of the attachment hardware. It will be lowered down and installed permanently on the ML at a later date. The CSITU is a swing-arm umbilical that will connect to the Space Launch System core stage inter-tank. It will provide conditioned air, pressurized gases and power and data connection to the core stage. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.
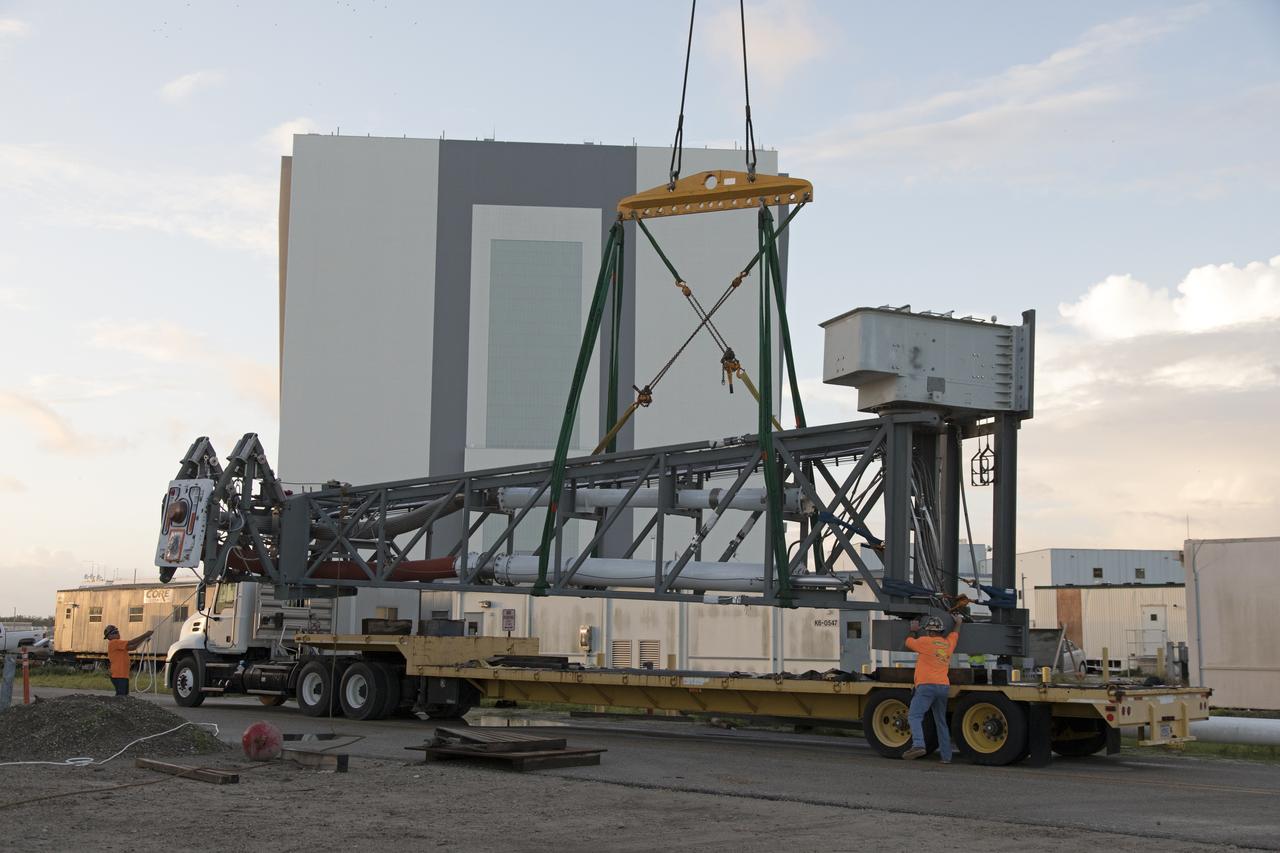

A heavy-lift crane has been attached to the Core Stage Inter-tank Umbilical (CSITU) to lift it up from a flatbed truck near the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The CSITU will be lifted up to about the 140-foot level of the mobile launcher (ML) tower for a fit check of the attachment hardware. It will be lowered down and installed permanently on the ML at a later date. The CSITU is a swing-arm umbilical that will connect to the Space Launch System core stage inter-tank. It will provide conditioned air, pressurized gases and power and data connection to the core stage. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.
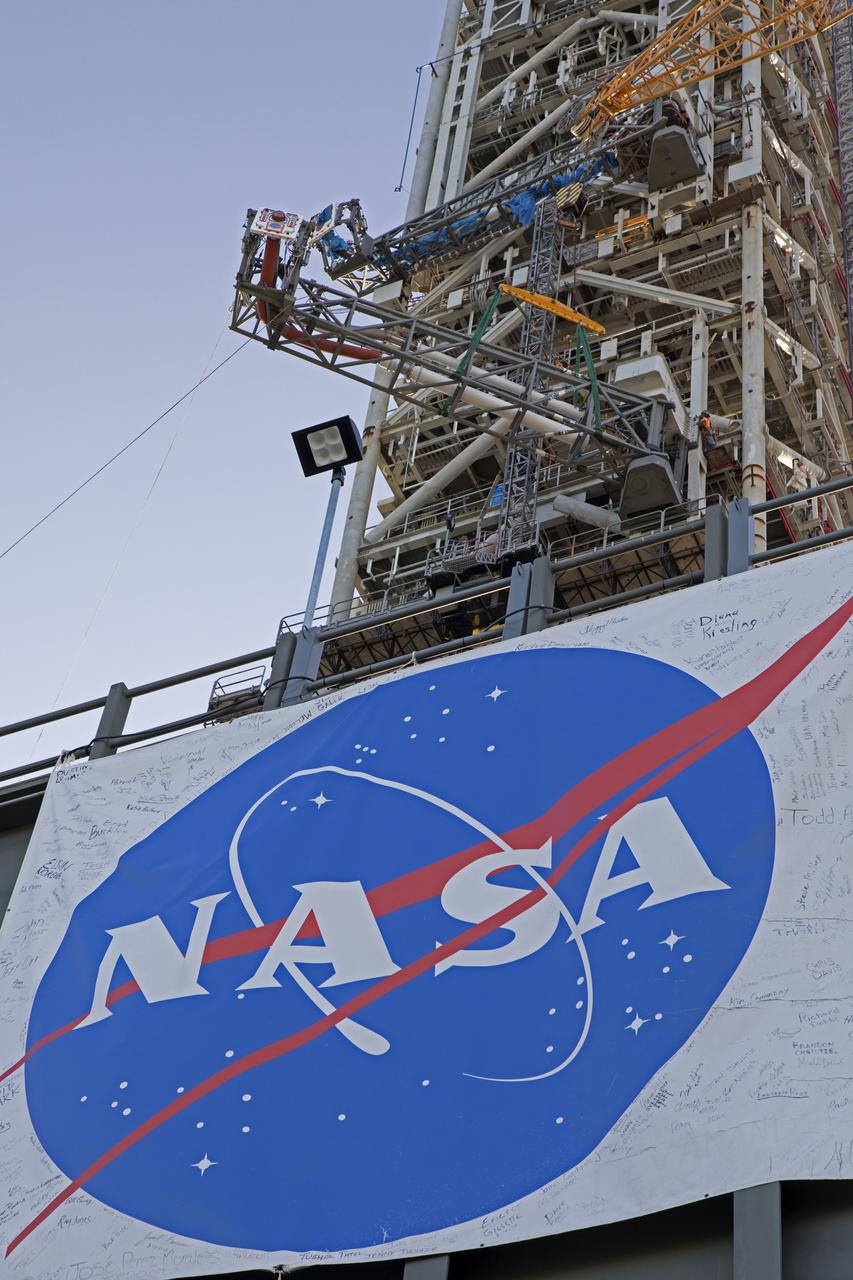

A heavy-lift crane moves the Core Stage Inter-tank Umbilical (CSITU) up to about the 140-foot level of the mobile launcher (ML) tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The CSITU is moved into place for a fit check of the attachment hardware. The umbilical will be lowered down and installed permanently on the ML at a later date. The CSITU is a swing-arm umbilical that will connect to the Space Launch System core stage inter-tank. It will provide conditioned air, pressurized gases and power and data connection to the core stage. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.
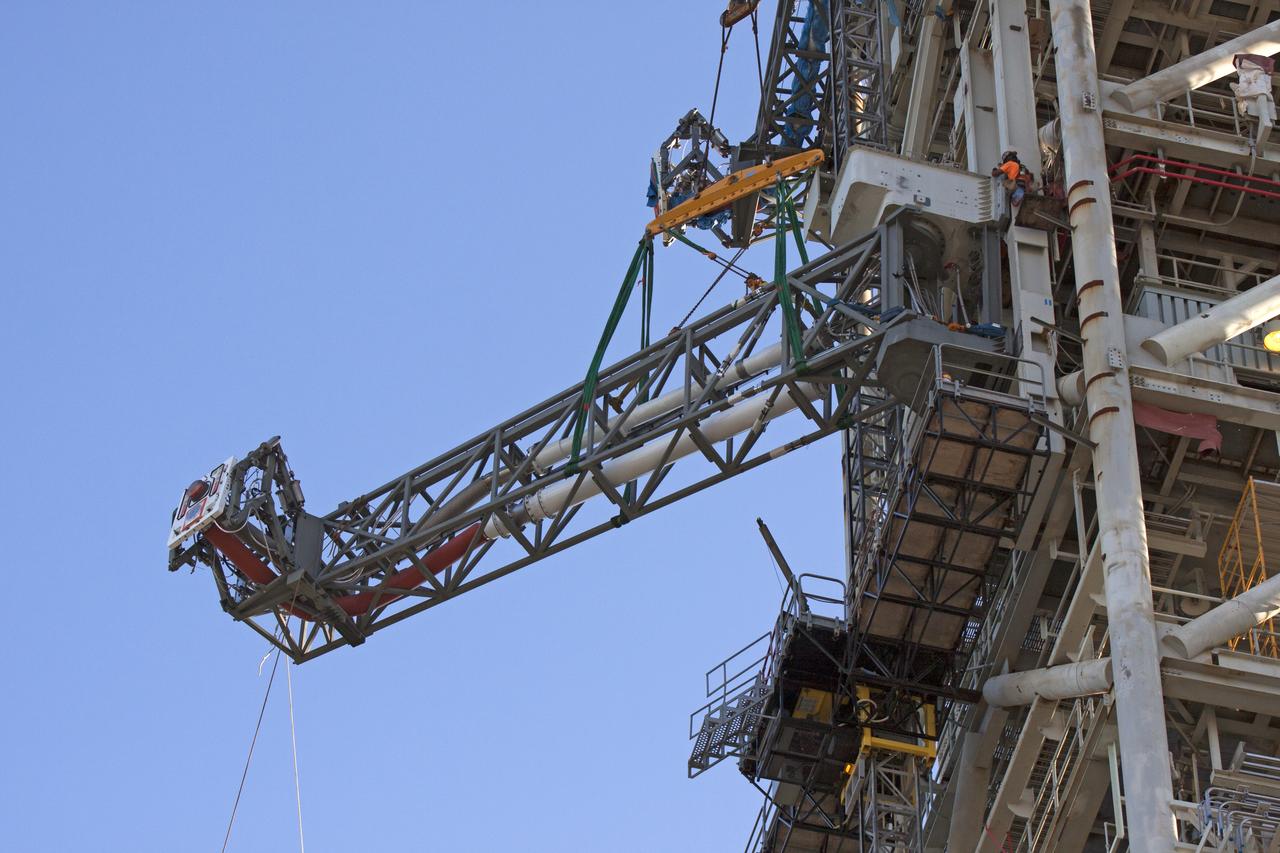

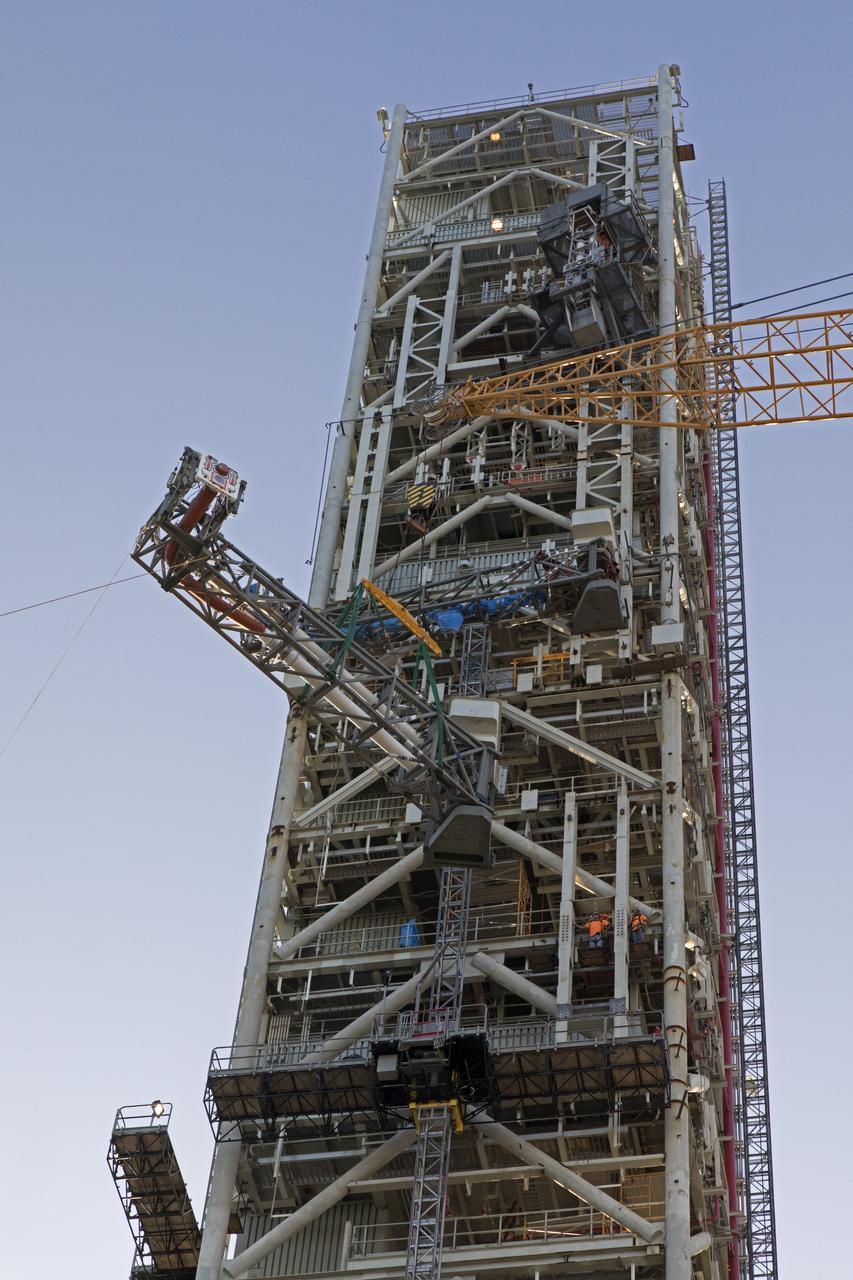
High up on the mobile launcher (ML) tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, construction workers assist as a crane moves the Core Stage Inter-tank Umbilical (CSITU) into place for a fit check of the attachment hardware. The CSITU will be located at about the 140-foot level of the ML tower. The umbilical will be lowered down and installed permanently on the ML at a later date. The CSITU is a swing-arm umbilical that will connect to the Space Launch System core stage inter-tank. It will provide conditioned air, pressurized gases and power and data connection to the core stage. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.
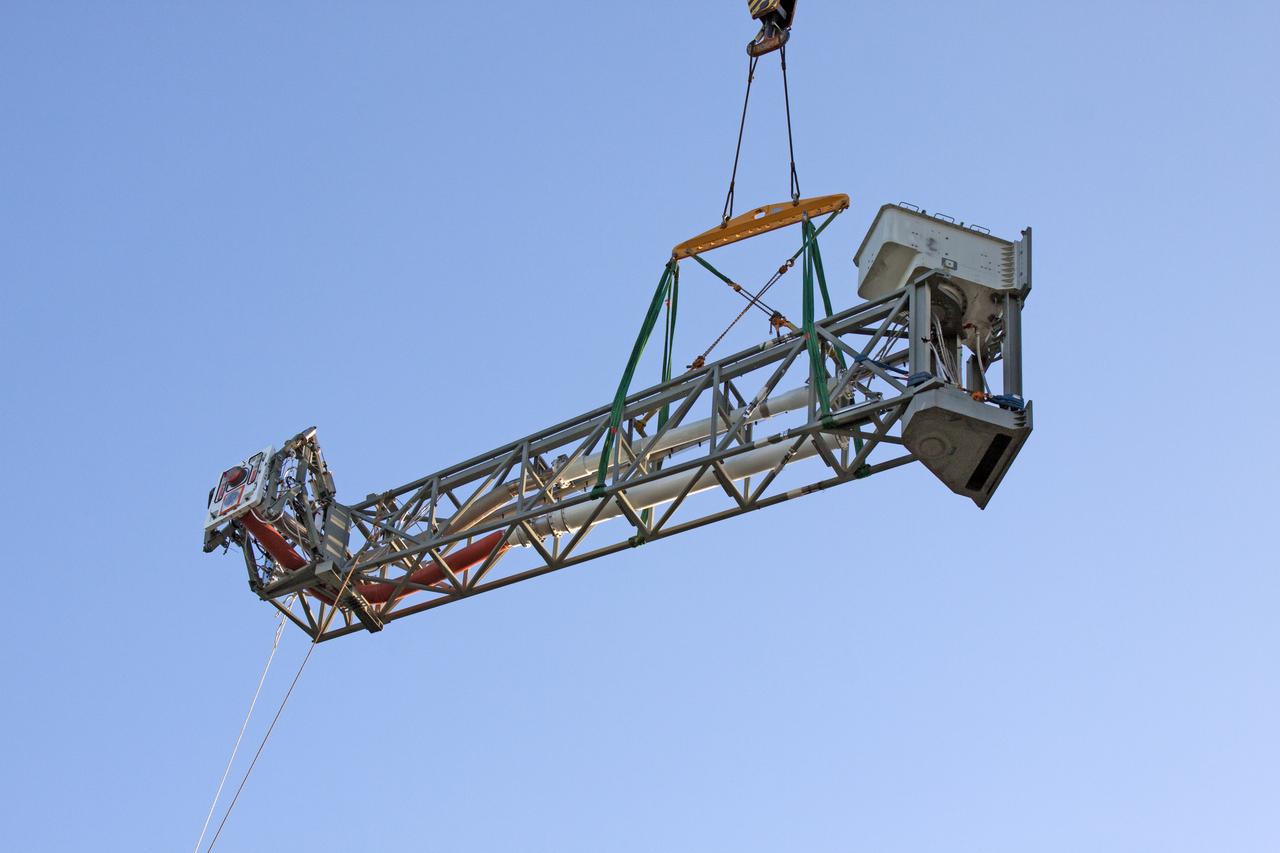

Seeming to hang in midair, the Core Stage Inter-tank Umbilical (CSITU) is lifted by crane and rigging up to about the 140-foot level of the mobile launcher (ML) tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The CSITU will be moved into place for a fit check of the attachment hardware. The umbilical will be lowered down and installed permanently on the ML at a later date. The CSITU is a swing-arm umbilical that will connect to the Space Launch System core stage inter-tank. It will provide conditioned air, pressurized gases and power and data connection to the core stage. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.
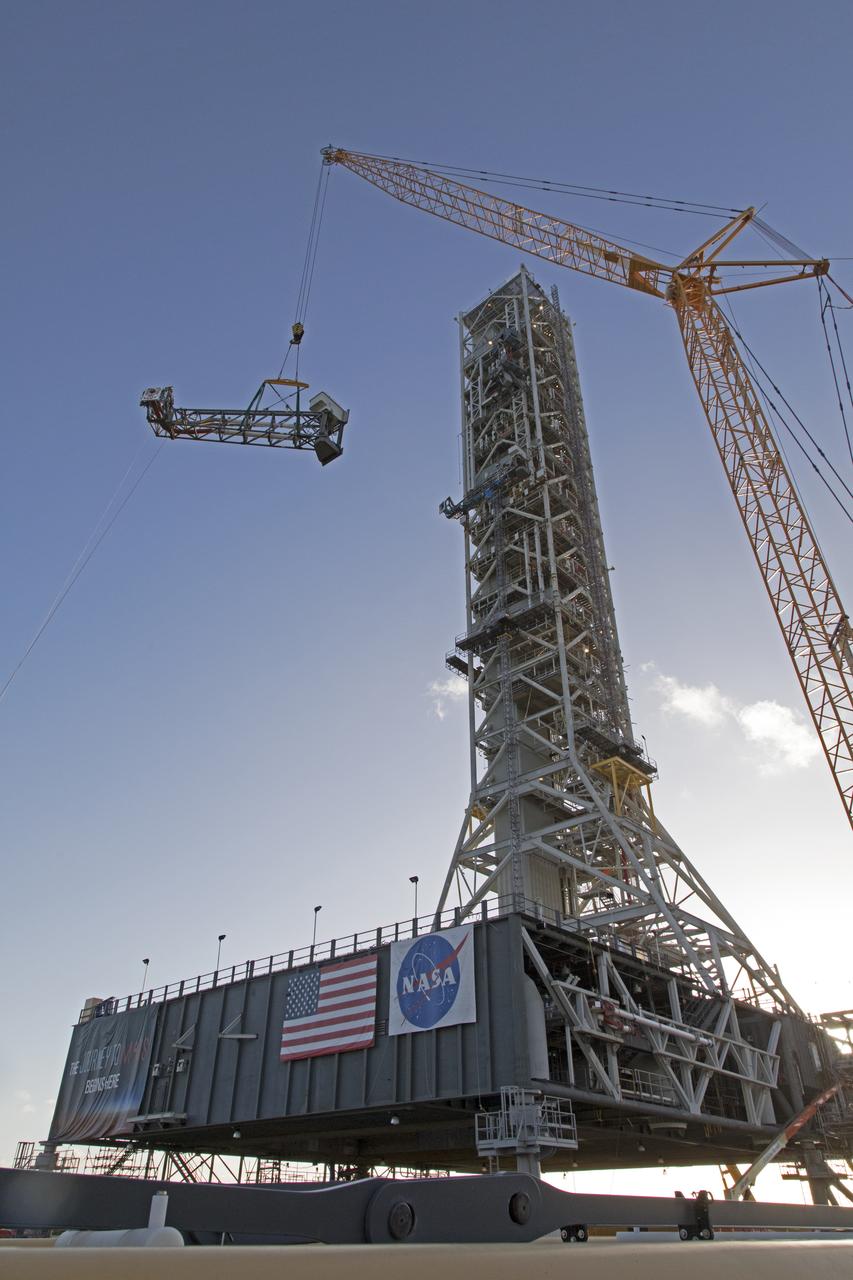

A heavy-lift crane and rigging are used to lift the Core Stage Inter-tank Umbilical (CSITU) up to about the 140-foot level of the mobile launcher (ML) tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The CSITU will be moved into place for a fit check of the attachment hardware. The umbilical will be lowered down and installed permanently on the ML at a later date. The CSITU is a swing-arm umbilical that will connect to the Space Launch System core stage inter-tank. It will provide conditioned air, pressurized gases and power and data connection to the core stage. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.
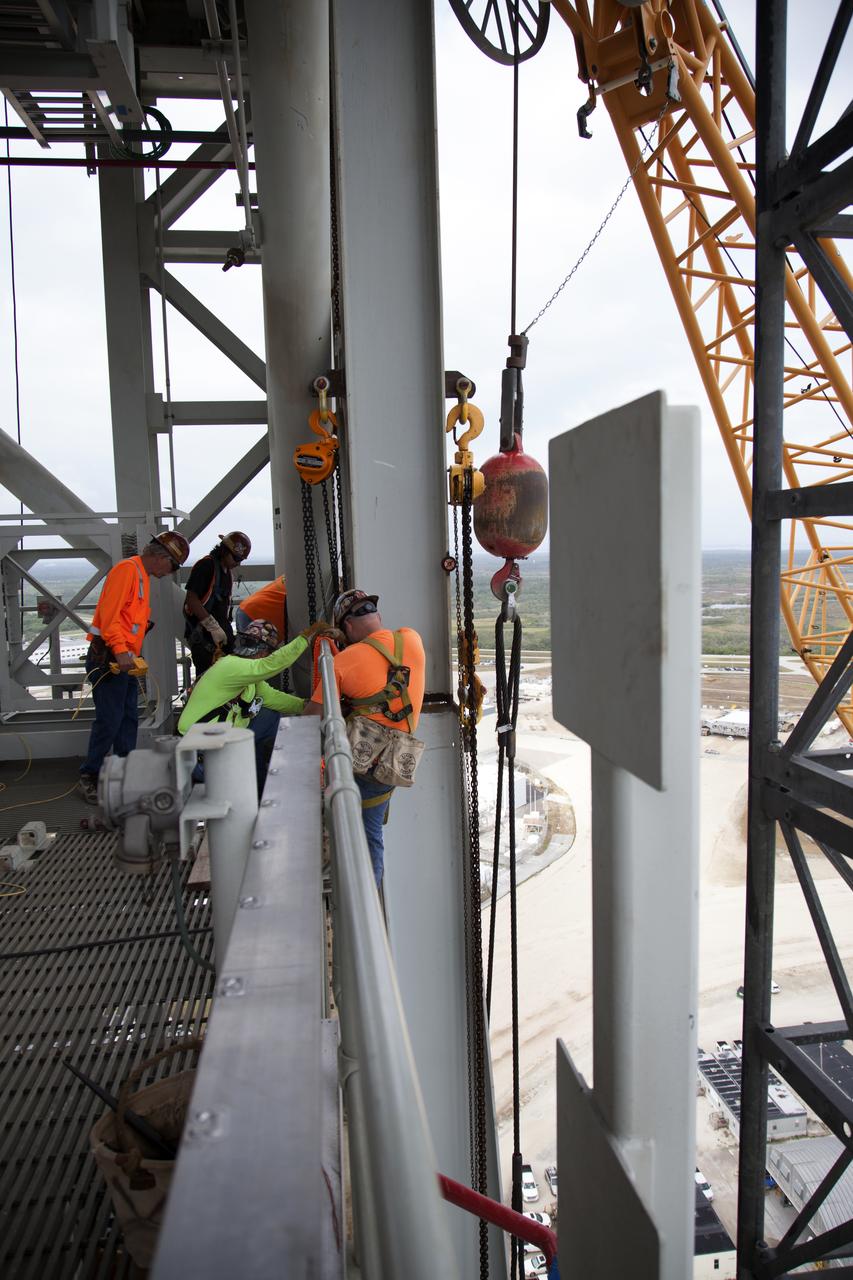

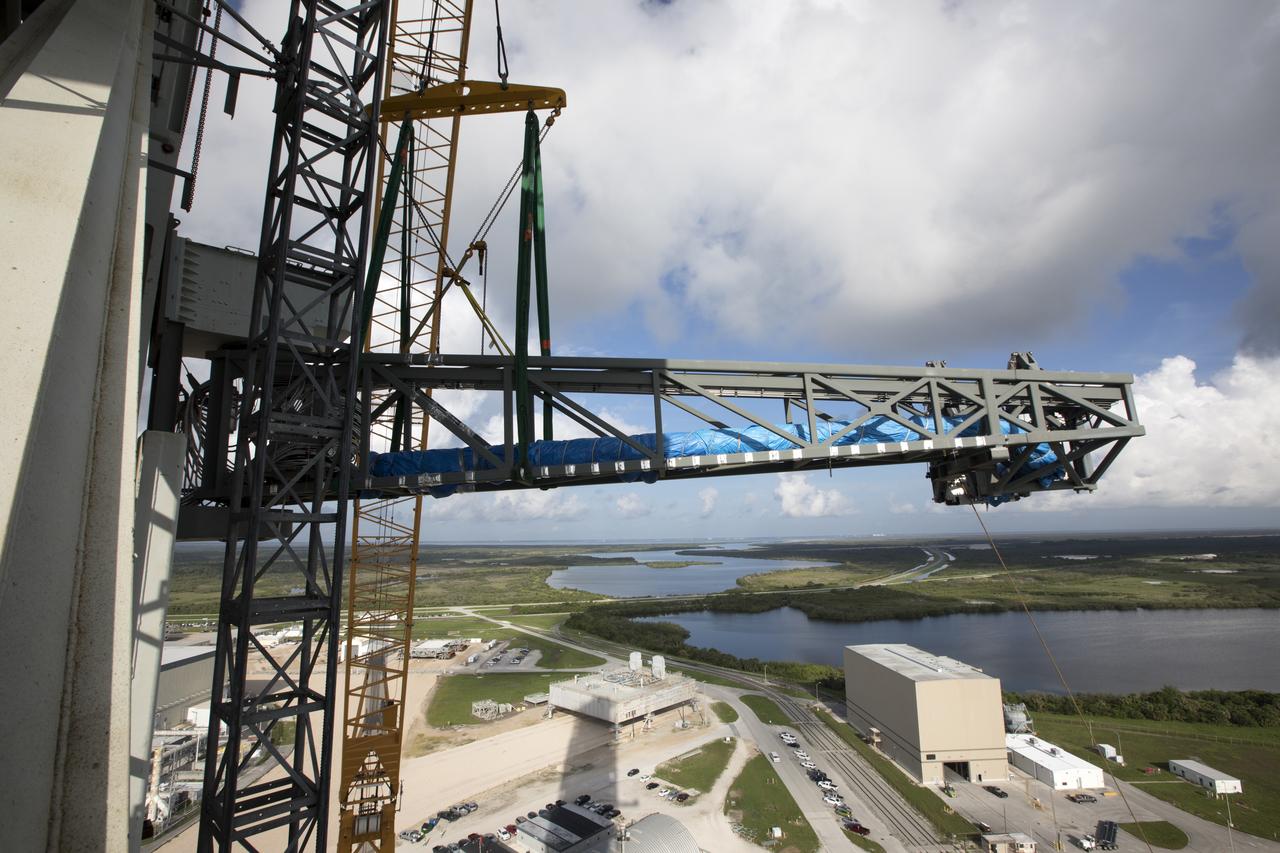
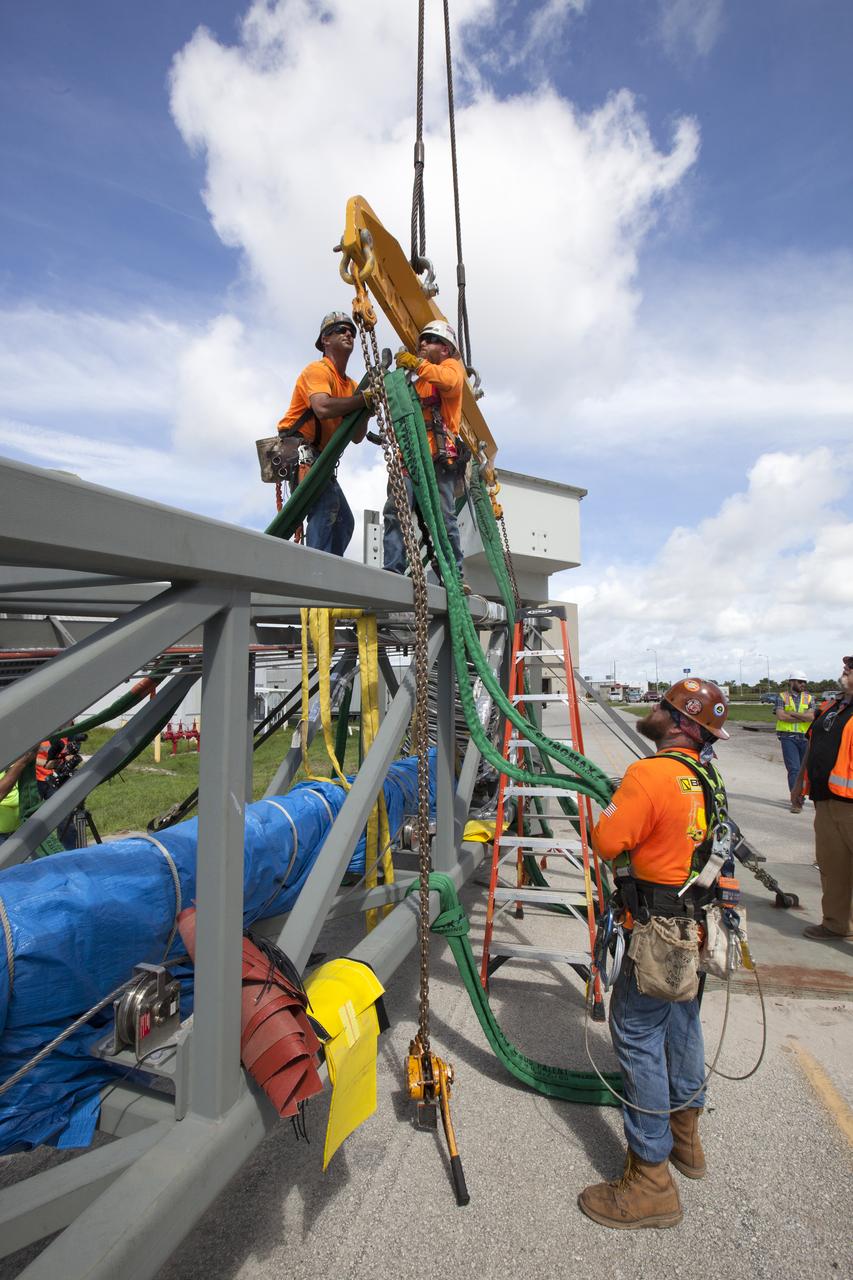
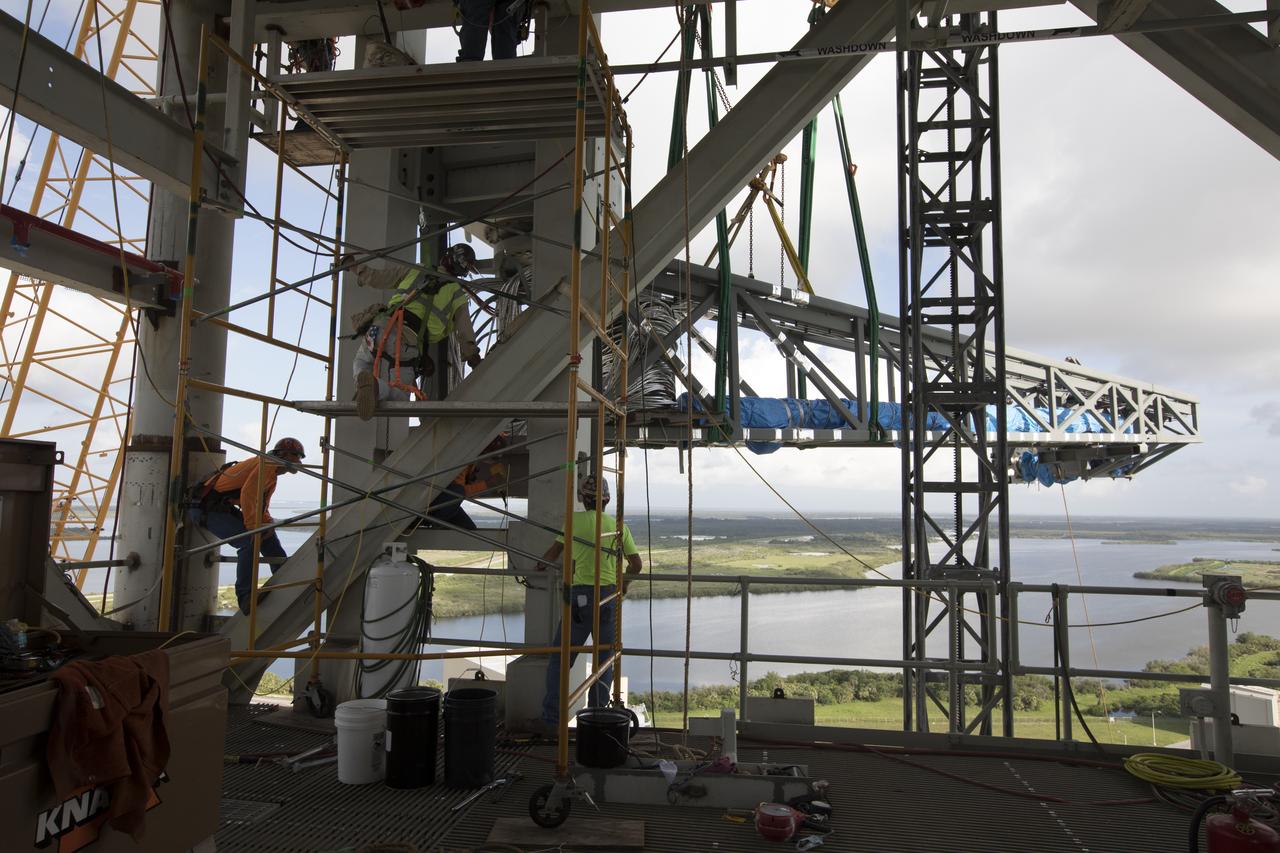
Construction workers assist as a crane lifts the Core Stage Forward Skirt Umbilical into position for installation on the mobile launcher tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals that will connect to the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The CSFSU will be located at about the 180-foot level on the tower, above the liquid oxygen tank. The CSFSU is an umbilical that will swing into position to provide connections to the core stage forward skirt of the SLS rocket, and then swing away before launch. Its main purpose is to provide conditioned air/GN2 to the SLS core stage forward skirt cavity. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.

Cranes and rigging are being used to lift up the Core Stage Forward Skirt Umbilical (CSFSU) for installation on the mobile launcher tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals that will connect to the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The CSFSU will be located at about the 180-foot level on the tower, above the liquid oxygen tank. The CSFSU is an umbilical that will swing into position to provide connections to the core stage forward skirt of the SLS rocket, and then swing away before launch. Its main purpose is to provide conditioned air/GN2 to the SLS core stage forward skirt cavity. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.
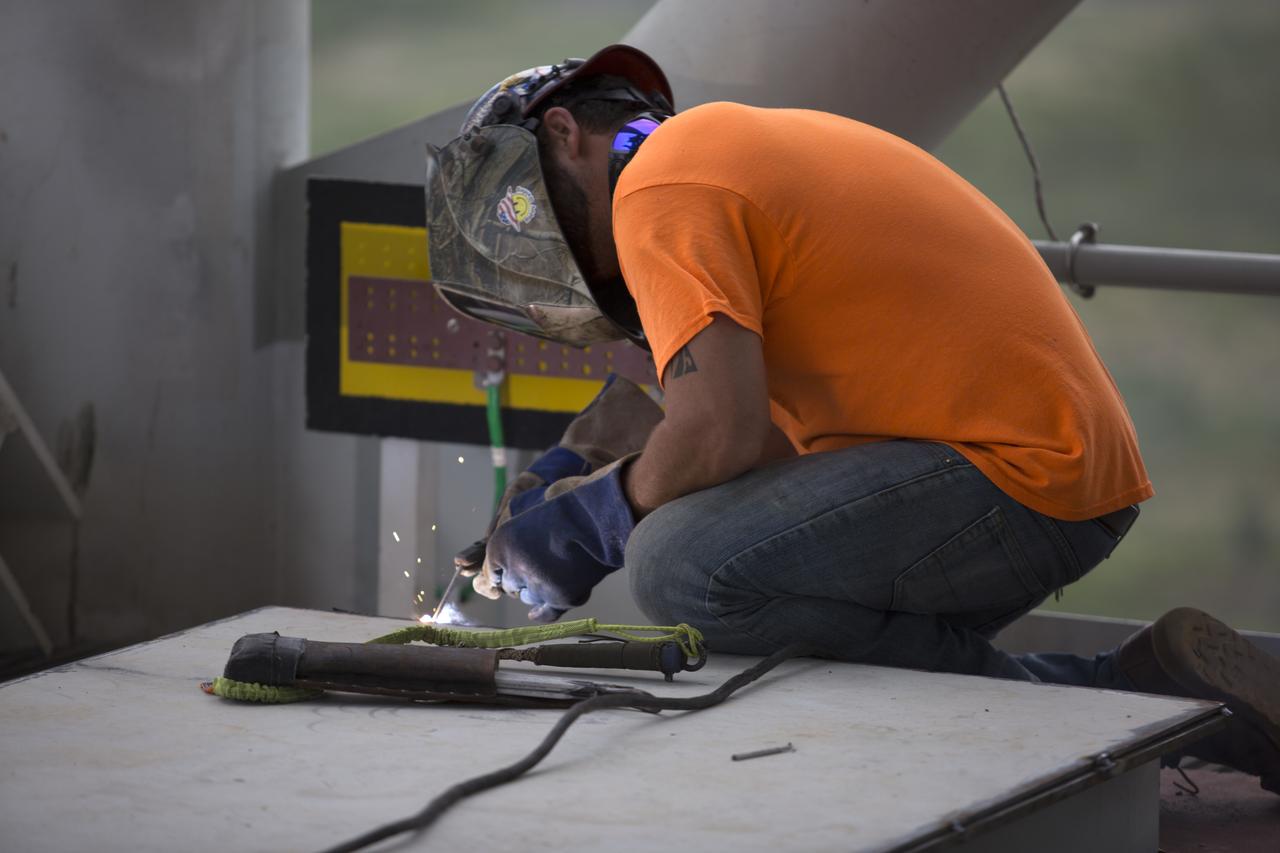

A construction worker welds a metal part during installation of the Core Stage Forward Skirt Umbilical on the mobile launcher tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals that will connect to the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The CSFSU will be located at about the 180-foot level on the tower, above the liquid oxygen tank. The CSFSU is an umbilical that will swing into position to provide connections to the core stage forward skirt of the SLS rocket, and then swing away before launch. Its main purpose is to provide conditioned air/GN2 to the SLS core stage forward skirt cavity. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.

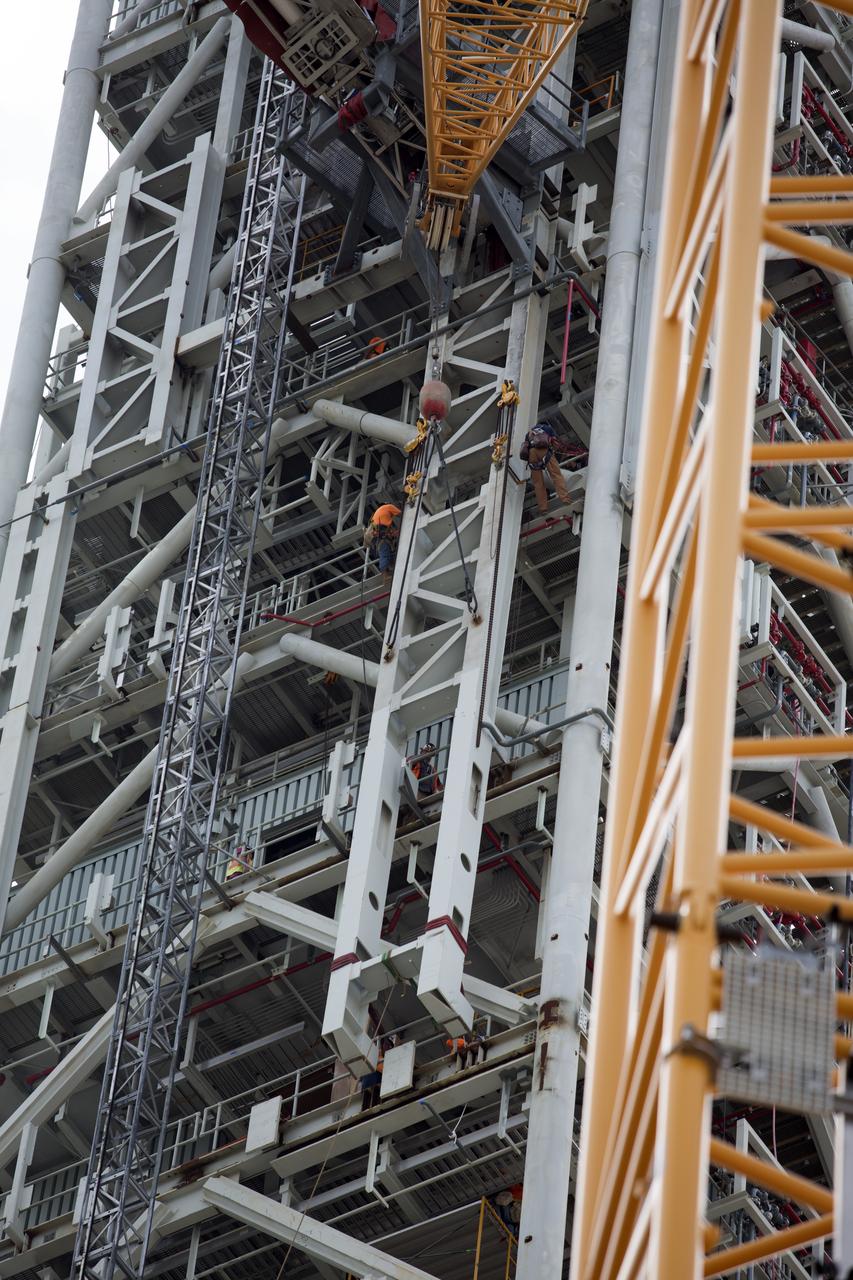
A crane has been attached to the Core Stage Forward Skirt Umbilical (CSFSU) to lift it up for installation on the mobile launcher tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals that will connect to the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The CSFSU will be located at about the 180-foot level on the tower, above the liquid oxygen tank. The CSFSU is an umbilical that will swing into position to provide connections to the core stage forward skirt of the SLS rocket, and then swing away before launch. Its main purpose is to provide conditioned air/GN2 to the SLS core stage forward skirt cavity. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.

Construction workers assist as a crane lifts the Core Stage Forward Skirt Umbilical into position for installation on the mobile launcher tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals that will connect to the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The CSFSU will be located at about the 180-foot level on the tower, above the liquid oxygen tank. The CSFSU is an umbilical that will swing into position to provide connections to the core stage forward skirt of the SLS rocket, and then swing away before launch. Its main purpose is to provide conditioned air/GN2 to the SLS core stage forward skirt cavity. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.
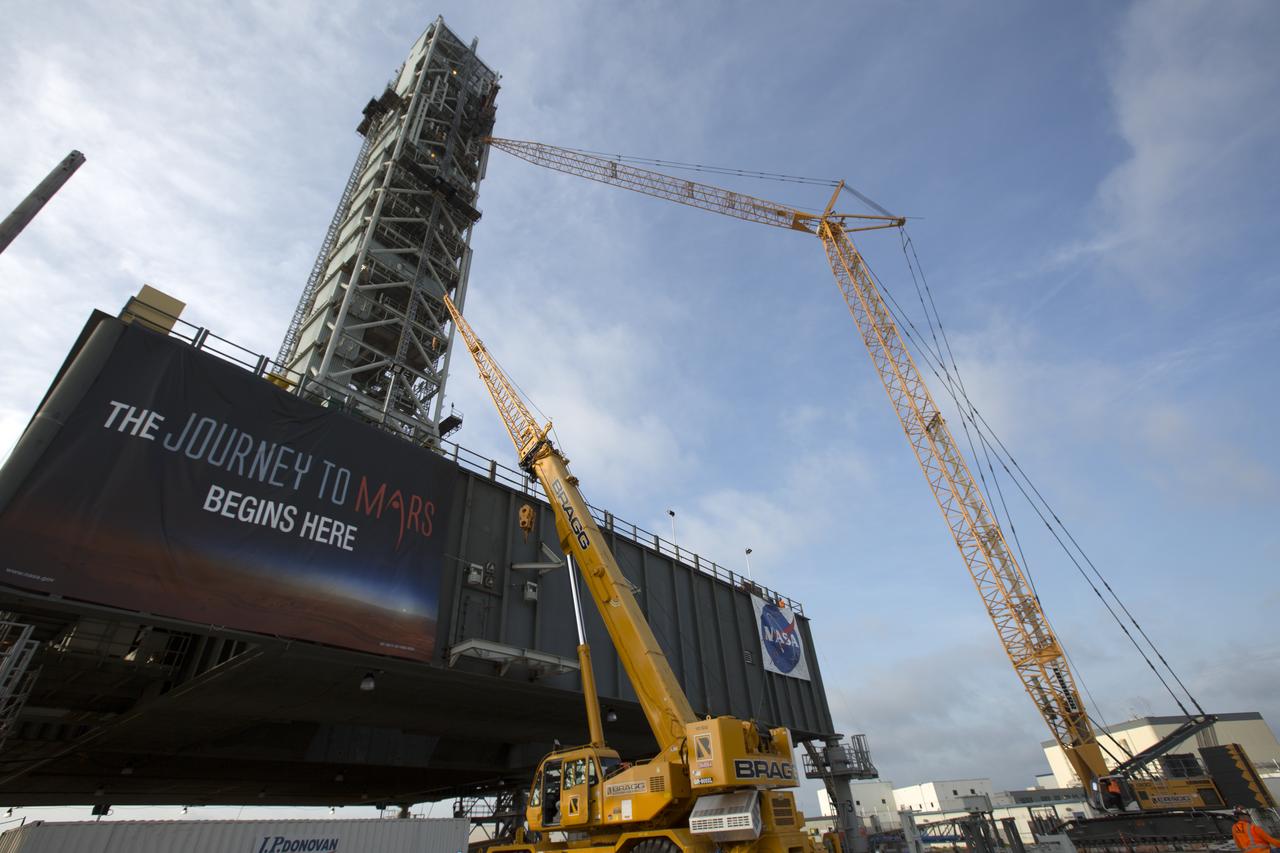

Cranes and rigging are being used to lift up the Core Stage Forward Skirt Umbilical (CSFSU) for installation on the mobile launcher tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals that will connect to the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The CSFSU will be located at about the 180-foot level on the tower, above the liquid oxygen tank. The CSFSU is an umbilical that will swing into position to provide connections to the core stage forward skirt of the SLS rocket, and then swing away before launch. Its main purpose is to provide conditioned air/GN2 to the SLS core stage forward skirt cavity. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.

Construction workers assist as a crane lifts the Core Stage Forward Skirt Umbilical up for installation on the mobile launcher tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals that will connect to the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The CSFSU will be located at about the 180-foot level on the tower, above the liquid oxygen tank. The CSFSU is an umbilical that will swing into position to provide connections to the core stage forward skirt of the SLS rocket, and then swing away before launch. Its main purpose is to provide conditioned air/GN2 to the SLS core stage forward skirt cavity. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.

Cranes and rigging are being used to lift up the Core Stage Forward Skirt Umbilical (CSFSU) for installation on the mobile launcher tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals that will connect to the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The CSFSU will be located at about the 180-foot level on the tower, above the liquid oxygen tank. The CSFSU is an umbilical that will swing into position to provide connections to the core stage forward skirt of the SLS rocket, and then swing away before launch. Its main purpose is to provide conditioned air/GN2 to the SLS core stage forward skirt cavity. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.

Cranes and rigging are being used to lift the Core Stage Forward Skirt Umbilical (CSFSU) into position for installation on the mobile launcher tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals that will connect to the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The CSFSU will be located at about the 180-foot level on the tower, above the liquid oxygen tank. The CSFSU is an umbilical that will swing into position to provide connections to the core stage forward skirt of the SLS rocket, and then swing away before launch. Its main purpose is to provide conditioned air/GN2 to the SLS core stage forward skirt cavity. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.

Cranes and rigging are being used to lift up the Core Stage Forward Skirt Umbilical (CSFSU) for installation on the mobile launcher tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals that will connect to the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The CSFSU will be located at about the 180-foot level on the tower, above the liquid oxygen tank. The CSFSU is an umbilical that will swing into position to provide connections to the core stage forward skirt of the SLS rocket, and then swing away before launch. Its main purpose is to provide conditioned air/GN2 to the SLS core stage forward skirt cavity. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.

Construction workers assist as a crane lifts the Core Stage Forward Skirt Umbilical up for installation on the mobile launcher tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals that will connect to the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The CSFSU will be located at about the 180-foot level on the tower, above the liquid oxygen tank. The CSFSU is an umbilical that will swing into position to provide connections to the core stage forward skirt of the SLS rocket, and then swing away before launch. Its main purpose is to provide conditioned air/GN2 to the SLS core stage forward skirt cavity. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.
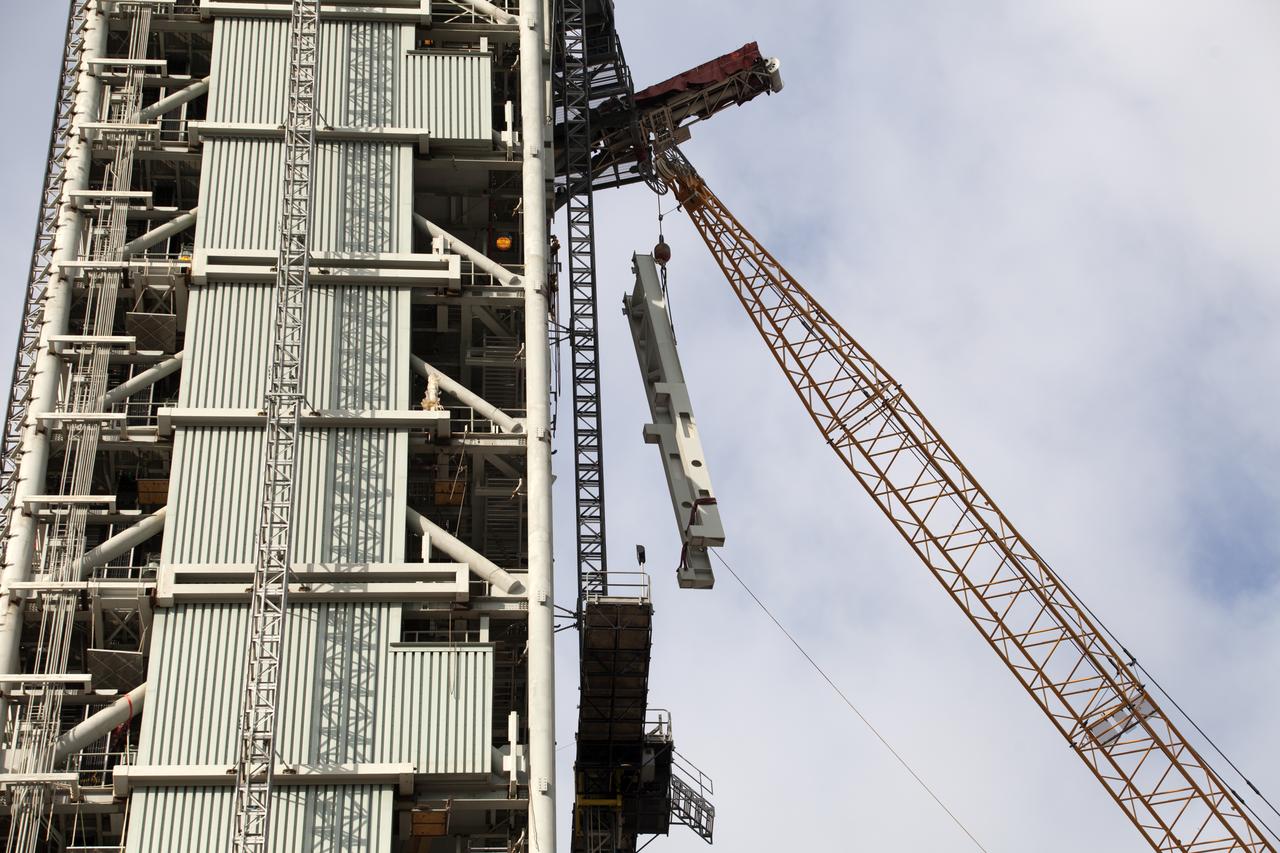

Cranes and rigging are being used to lift up the Core Stage Forward Skirt Umbilical (CSFSU) for installation on the mobile launcher tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals that will connect to the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The CSFSU will be located at about the 180-foot level on the tower, above the liquid oxygen tank. The CSFSU is an umbilical that will swing into position to provide connections to the core stage forward skirt of the SLS rocket, and then swing away before launch. Its main purpose is to provide conditioned air/GN2 to the SLS core stage forward skirt cavity. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.

Construction workers assist as a crane lifts the Core Stage Forward Skirt Umbilical up for installation on the mobile launcher tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals that will connect to the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The CSFSU will be located at about the 180-foot level on the tower, above the liquid oxygen tank. The CSFSU is an umbilical that will swing into position to provide connections to the core stage forward skirt of the SLS rocket, and then swing away before launch. Its main purpose is to provide conditioned air/GN2 to the SLS core stage forward skirt cavity. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.
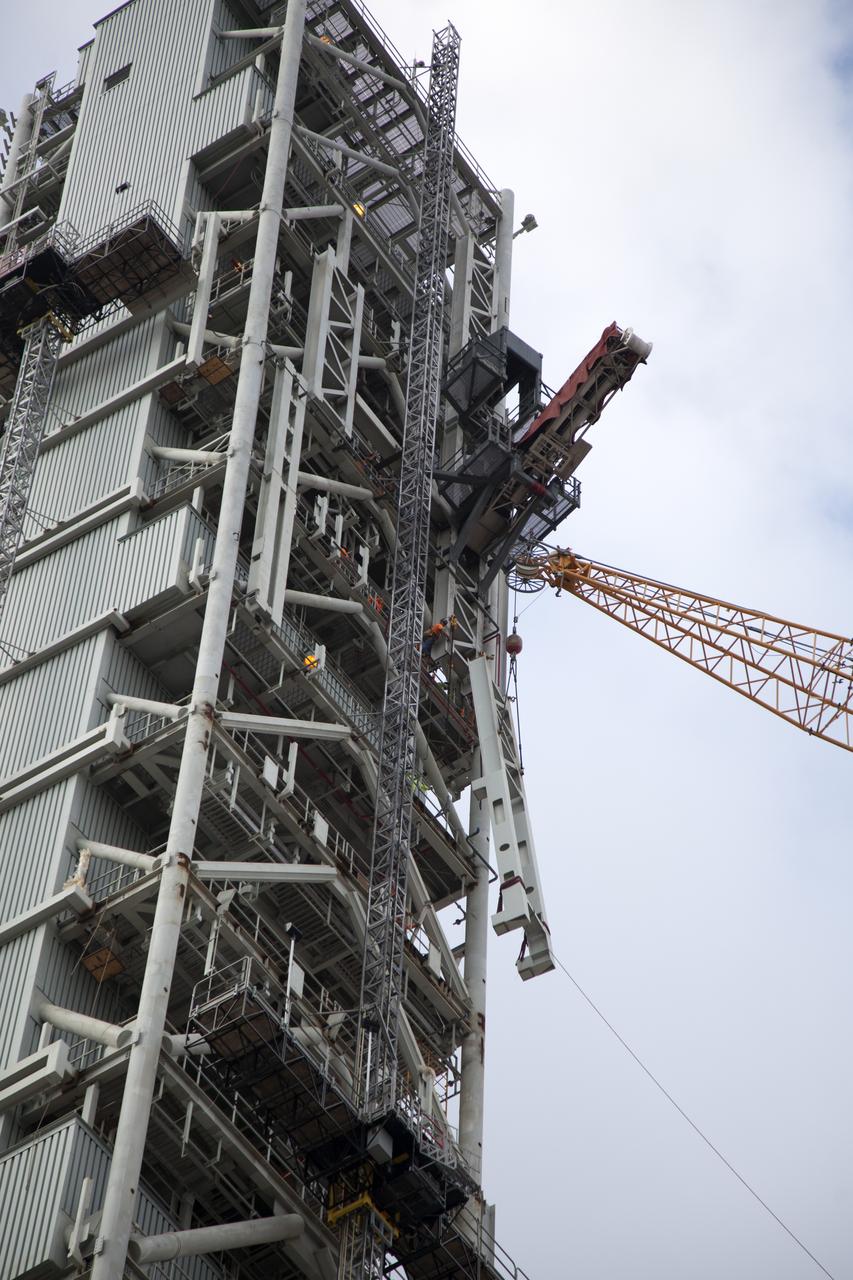

Seeming to hang in midair, the Core Stage Forward Skirt Umbilical (CSFSU) is lifted high up by crane for installation on the mobile launcher tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals that will connect to the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The CSFSU will be located at about the 180-foot level on the tower, above the liquid oxygen tank. The CSFSU is an umbilical that will swing into position to provide connections to the core stage forward skirt of the SLS rocket, and then swing away before launch. Its main purpose is to provide conditioned air/GN2 to the SLS core stage forward skirt cavity. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.
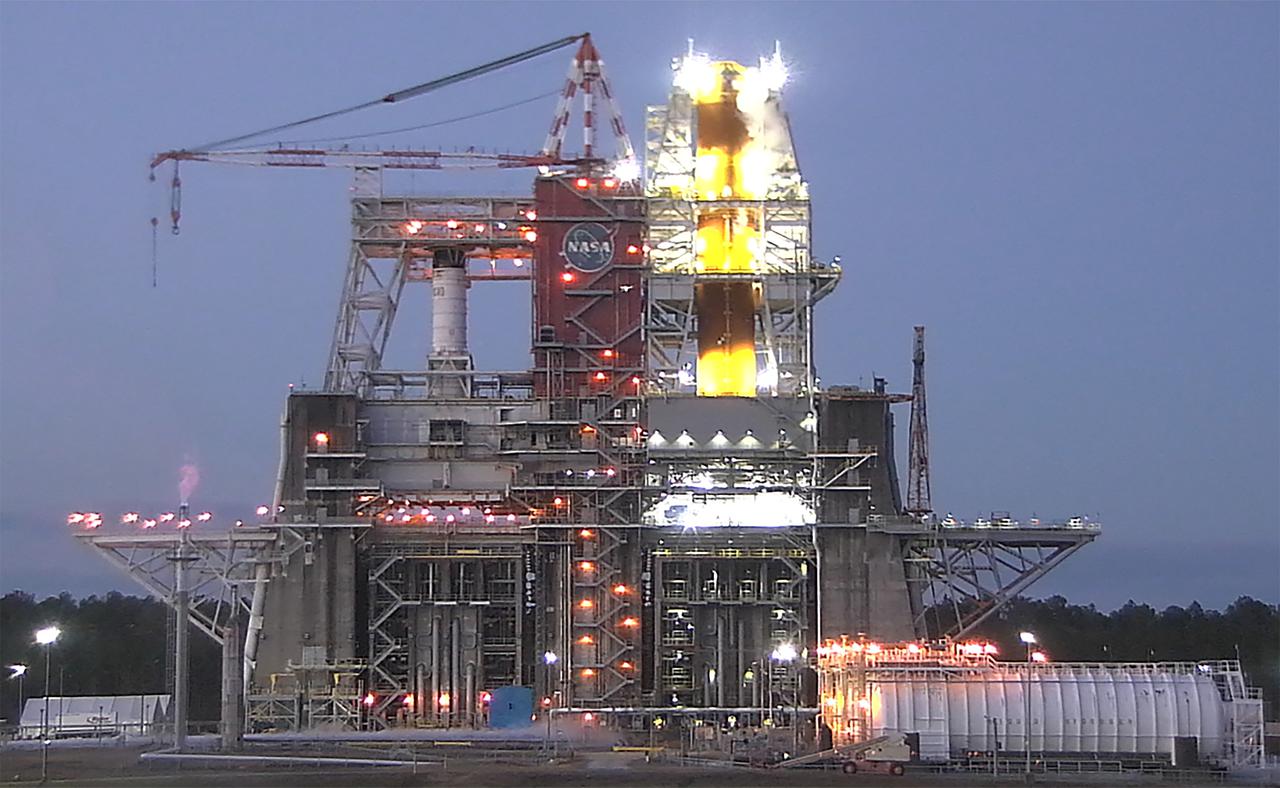

Operators at the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, conducted a wet dress rehearsal for the hot fire test of the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System on Dec. 21, 2020. In this image, liquid oxygen can be seen venting near the top of the installed core stage. Following the wet dress rehearsal, operators will conduct a full hot fire test of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines. The hot fire will conclude a series of eight Green Run tests of all core stage systems before it is transported to Kennedy Space Center for launch on the Artemis I mission.
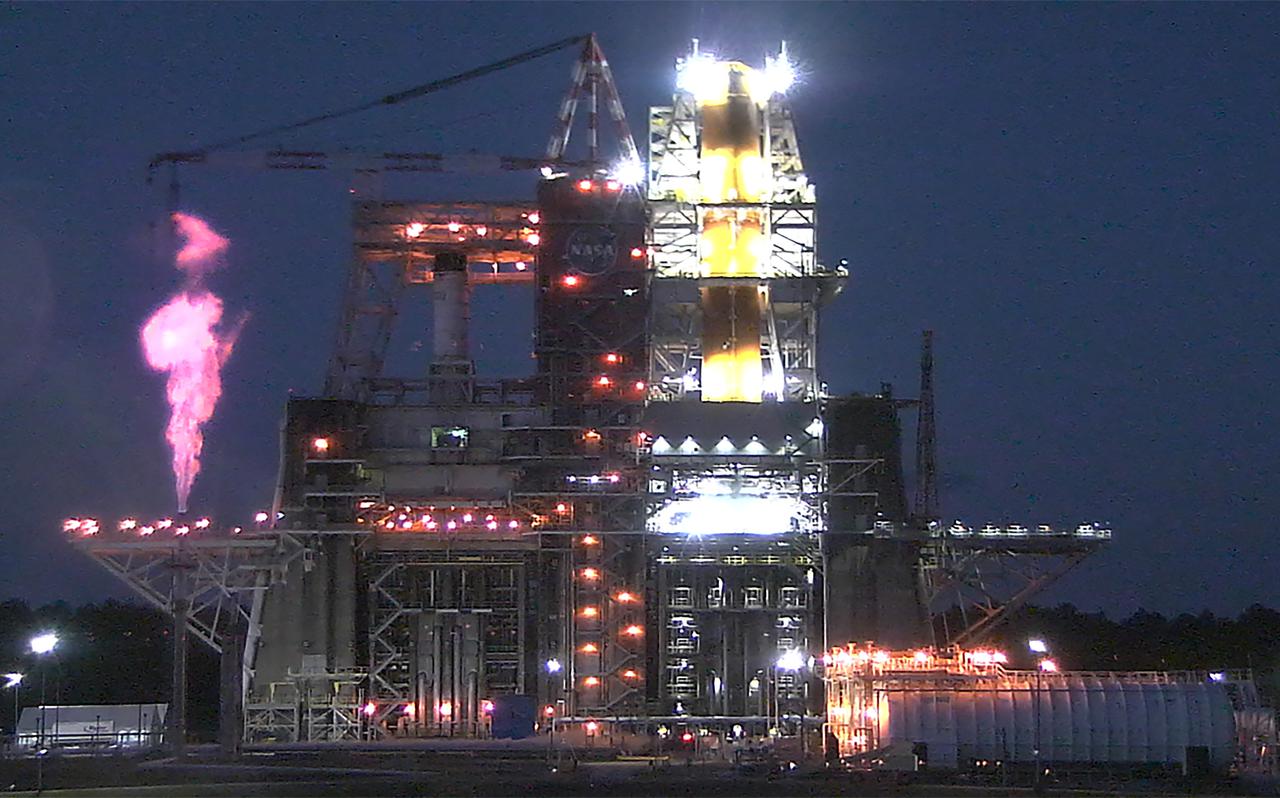

Operators at the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, conducted a wet dress rehearsal for the hot fire test of the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System on Dec. 21, 2020. In this image, liquid oxygen can be seen venting near the top of the installed core stage. Following the wet dress rehearsal, operators will conduct a full hot fire test of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines. The hot fire will conclude a series of eight Green Run tests of all core stage systems before it is transported to Kennedy Space Center for launch on the Artemis I mission.
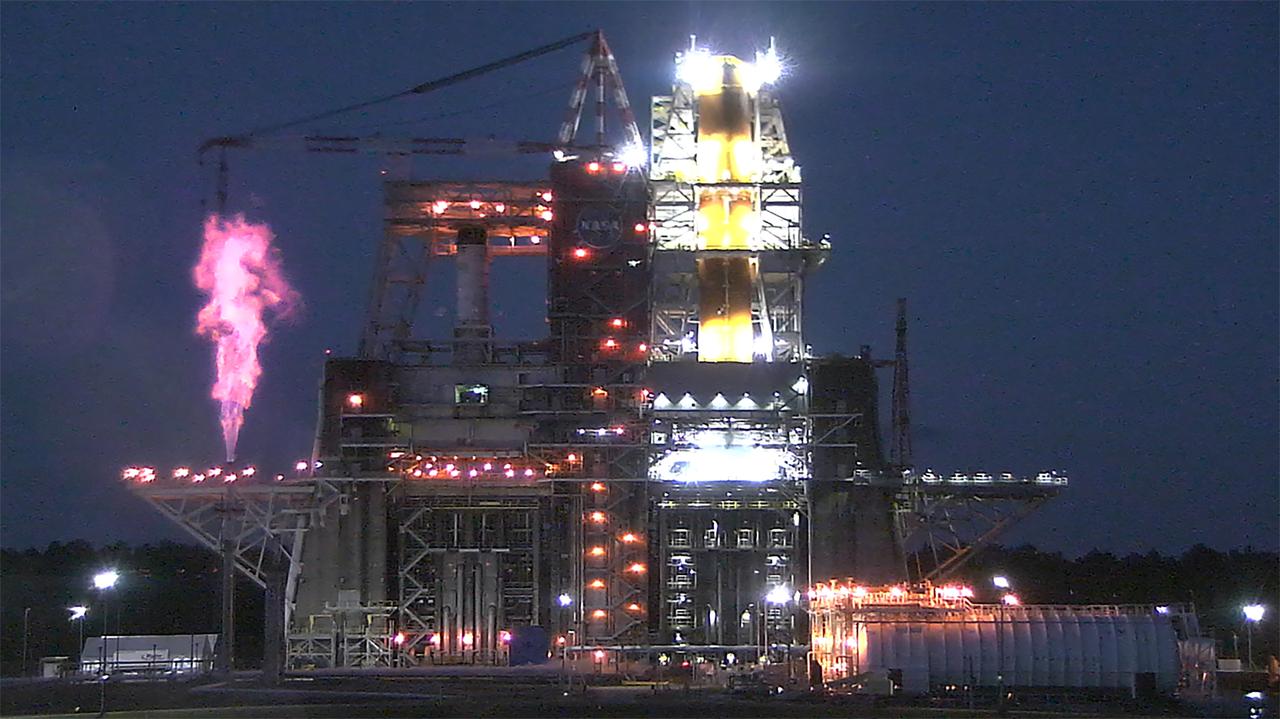

Operators at the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, conducted a wet dress rehearsal for the hot fire test of the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System on Dec. 21, 2020. In this image, liquid oxygen can be seen venting near the top of the installed core stage. Following the wet dress rehearsal, operators will conduct a full hot fire test of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines. The hot fire will conclude a series of eight Green Run tests of all core stage systems before it is transported to Kennedy Space Center for launch on the Artemis I mission.

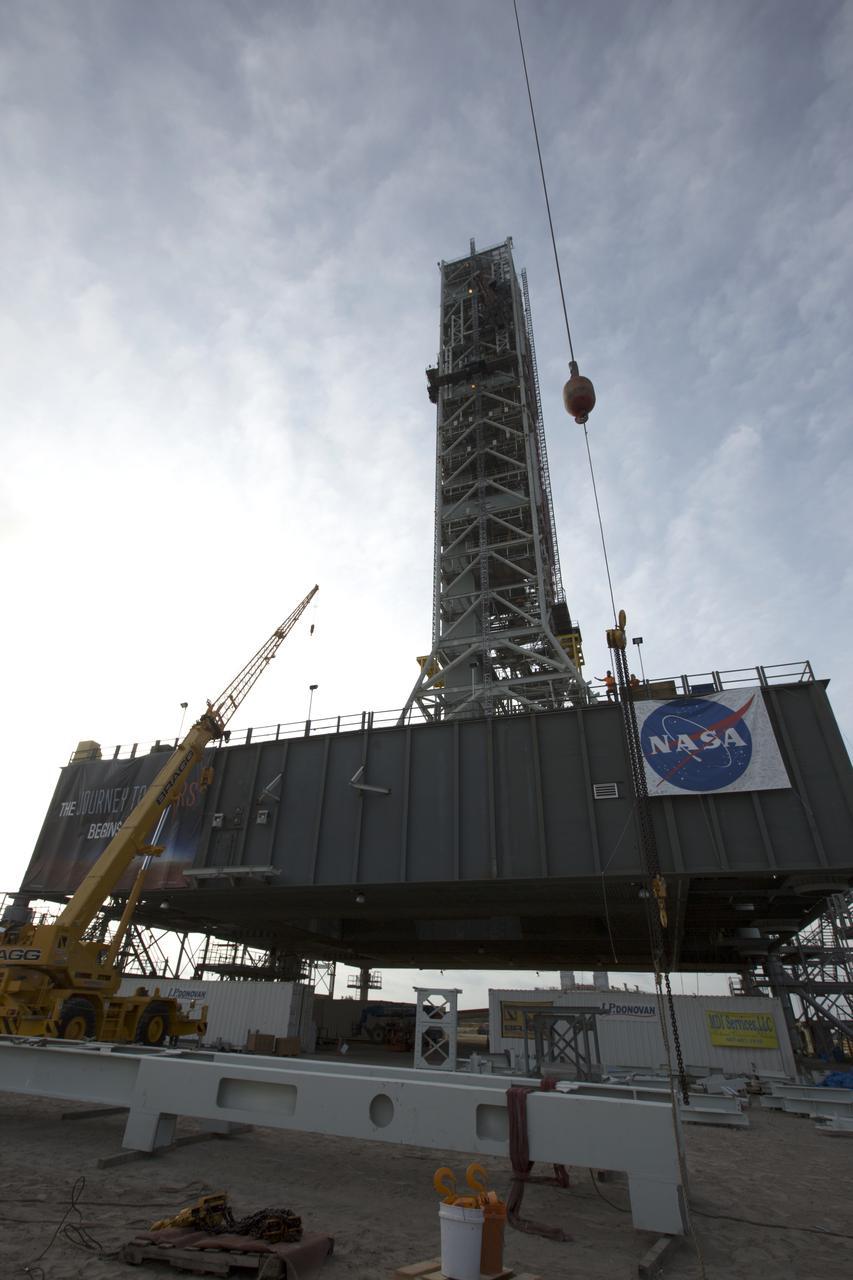
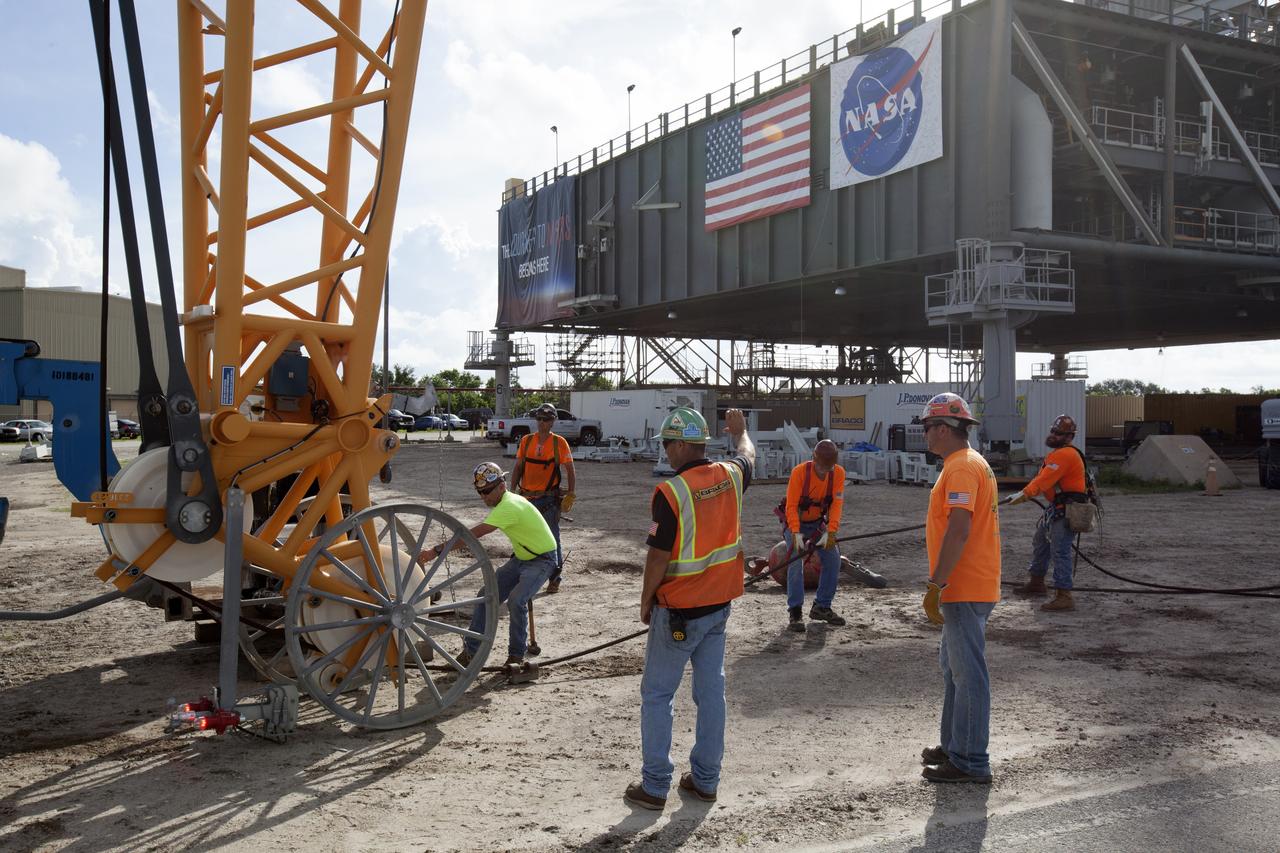
Just north of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane lifts the core stage forward skirt umbilical for installation onto the mobile launcher. The mobile launcher is designed to support the assembly, testing and check-out of the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and the Orion spacecraft.

Just north of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the core stage forward skirt umbilical is installed on the mobile launcher. The mobile launcher is designed to support the assembly, testing and check-out of the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and the Orion spacecraft.

Just north of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians prepare a crane to lift the core stage forward skirt umbilical for installation onto the mobile launcher. The mobile launcher is designed to support the assembly, testing and check-out of the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and the Orion spacecraft.

Just north of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians prepare a crane to lift the core stage forward skirt umbilical for installation onto the mobile launcher. The mobile launcher is designed to support the assembly, testing and check-out of the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and the Orion spacecraft.

Just north of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the core stage forward skirt umbilical is installed on the mobile launcher. The mobile launcher is designed to support the assembly, testing and check-out of the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and the Orion spacecraft.

Just north of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the core stage forward skirt umbilical is prepped and rigged for installation onto the mobile launcher. The mobile launcher is designed to support the assembly, testing and check-out of the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and the Orion spacecraft.

Just north of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians prepare a crane to lift the core stage forward skirt umbilical (CSFSU) for installation onto the mobile launcher. The mobile launcher is designed to support the assembly, testing and check-out of the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and the Orion spacecraft.

Just north of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane is prepared to lift the core stage forward skirt umbilical for installation onto the mobile launcher. The mobile launcher is designed to support the assembly, testing and check-out of the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and the Orion spacecraft.

Just north of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane lifts the core stage forward skirt umbilical for installation onto the mobile launcher. The mobile launcher is designed to support the assembly, testing and check-out of the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and the Orion spacecraft.

Just north of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane is prepared to lift the core stage forward skirt umbilical for installation onto the mobile launcher. The mobile launcher is designed to support the assembly, testing and check-out of the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and the Orion spacecraft.

Just north of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane is prepared to lift the core stage forward skirt umbilical) for installation onto the mobile launcher. The mobile launcher is designed to support the assembly, testing and check-out of the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and the Orion spacecraft.

Just north of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians install the core stage forward skirt umbilical on the mobile launcher. The mobile launcher is designed to support the assembly, testing and check-out of the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and the Orion spacecraft.
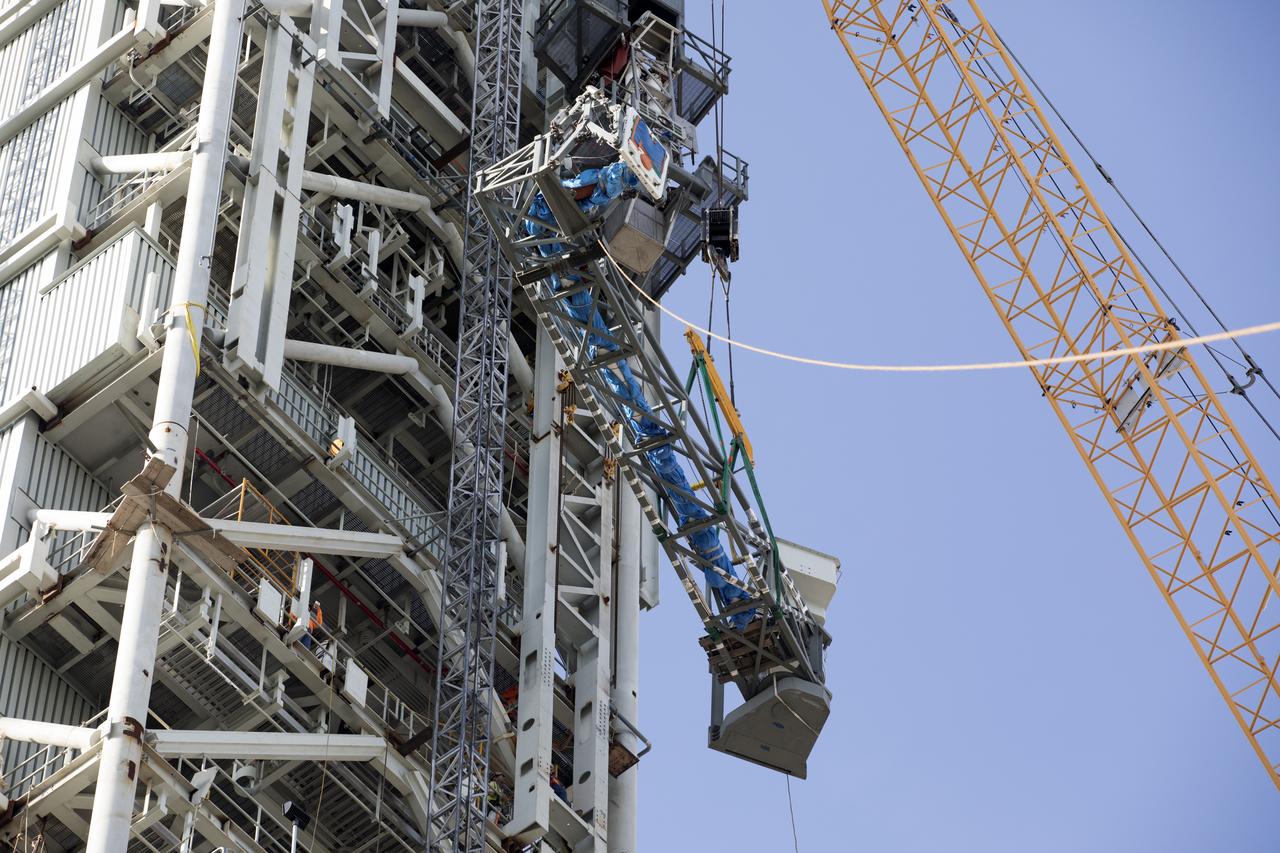

Just north of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the core stage forward skirt umbilical is installed on the mobile launcher. The mobile launcher is designed to support the assembly, testing and check-out of the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and the Orion spacecraft.
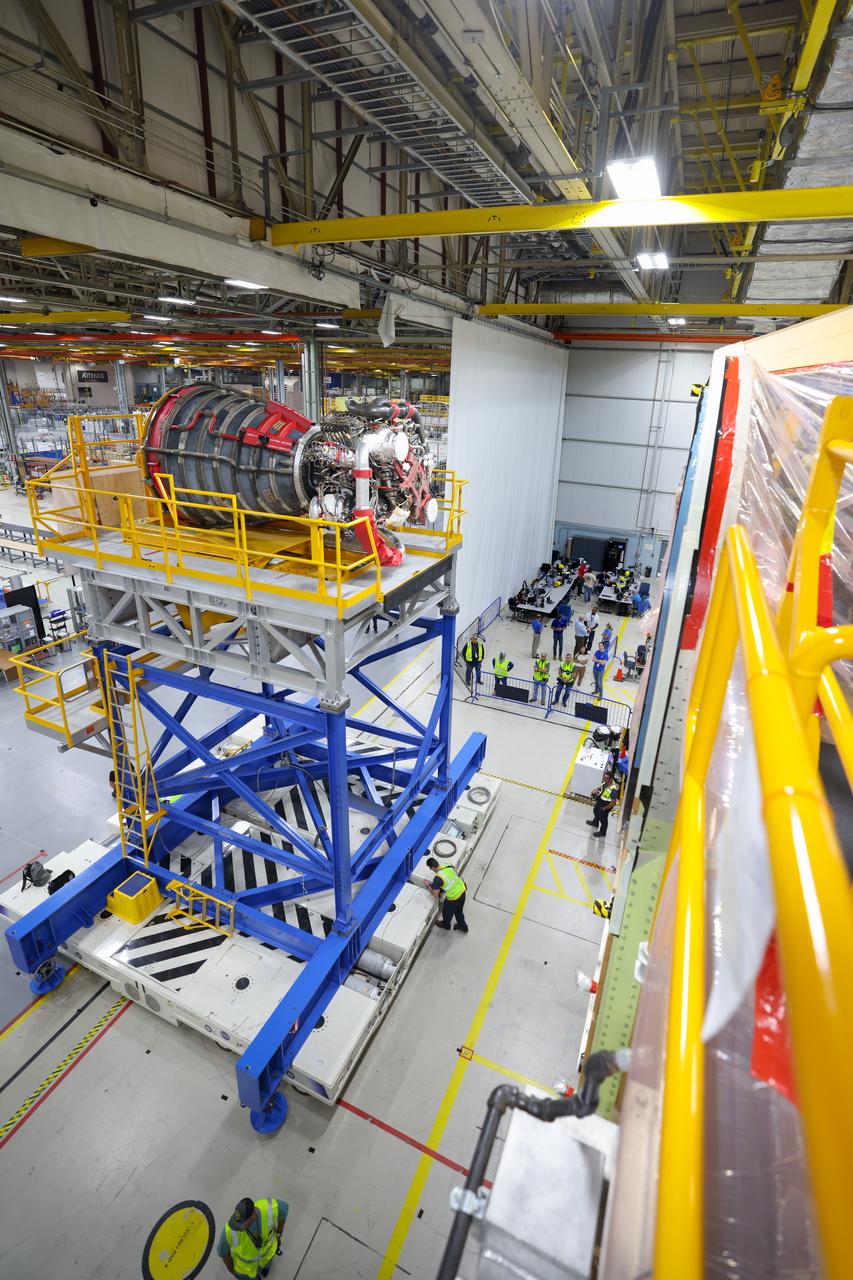

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans have installed the first of four RS-25 engines on the core stage of the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket that will help power NASA’s first crewed Artemis mission to the Moon. The Sept. 11 engine installation follows the joining of all five major structures that make up the SLS core stage earlier this spring. NASA, lead RS-25 engines contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3 Harris Technologies company, and Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, will continue integrating the remaining three engines into the stage and installing the propulsion and electrical systems within the structure. All four RS-25 engines are located at the base of the core stage within the engine section. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.
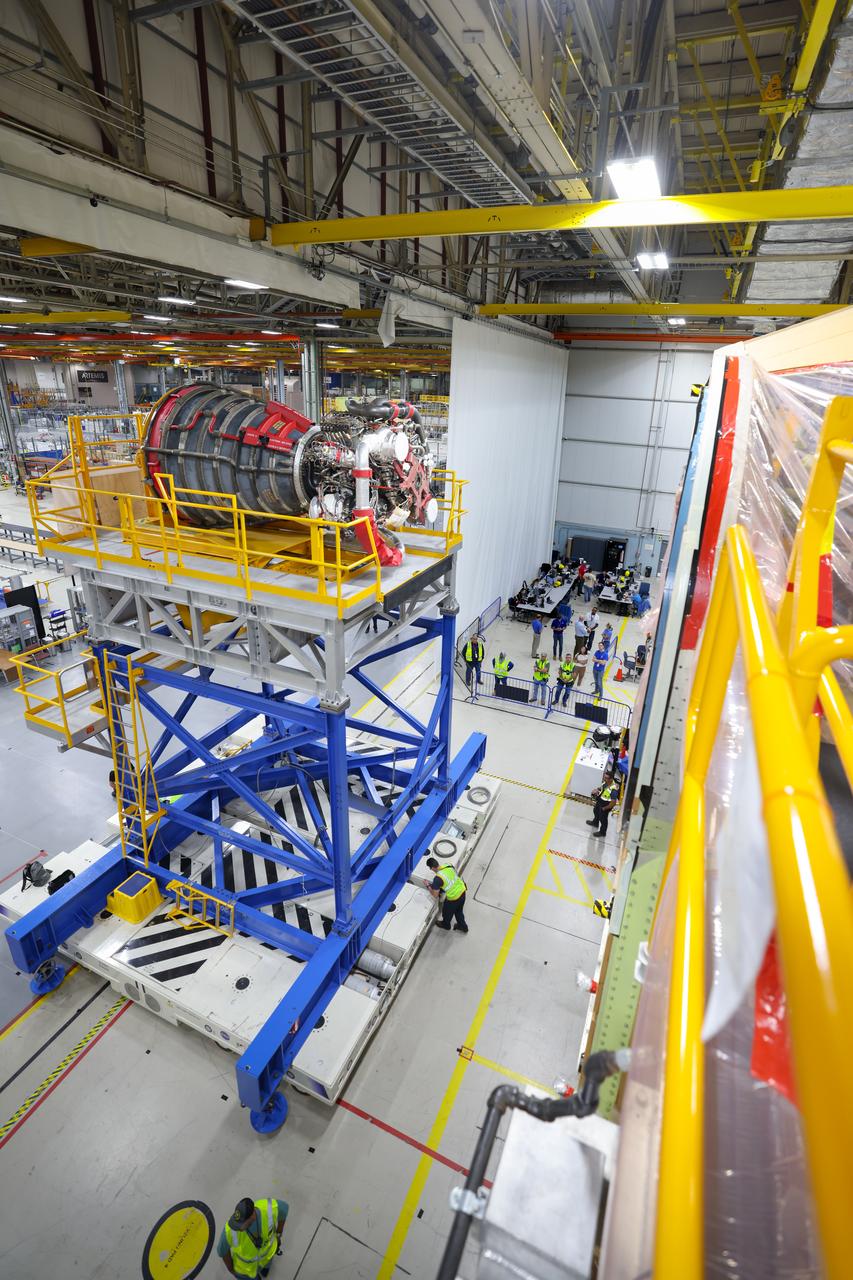

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans have installed the first of four RS-25 engines on the core stage of the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket that will help power NASA’s first crewed Artemis mission to the Moon. The Sept. 11 engine installation follows the joining of all five major structures that make up the SLS core stage earlier this spring. NASA, lead RS-25 engines contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3 Harris Technologies company, and Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, will continue integrating the remaining three engines into the stage and installing the propulsion and electrical systems within the structure. All four RS-25 engines are located at the base of the core stage within the engine section. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.