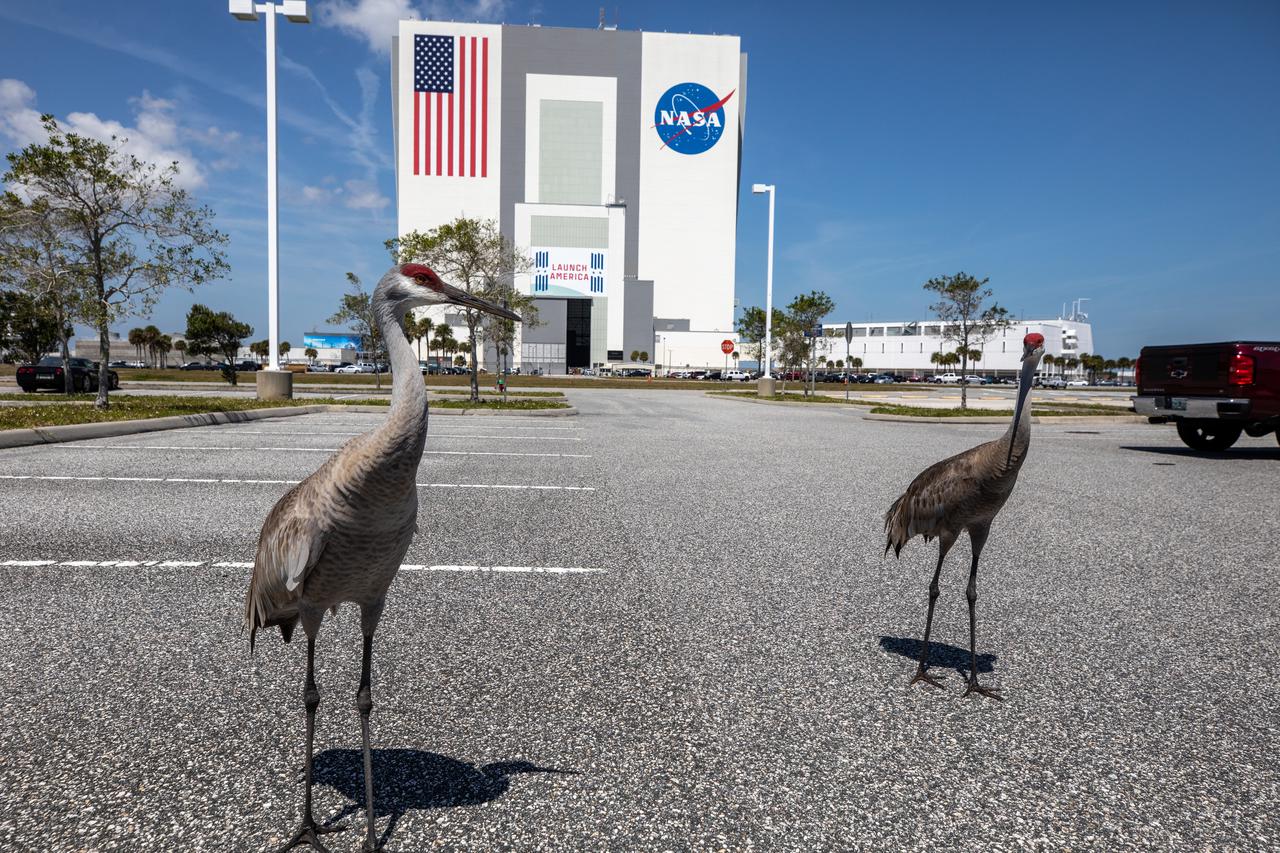

A pair of sandhill cranes explore a paved parking area near the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 24, 2021. Kennedy shares space with the Merritt Island National Wildlife refuge, which is home to more than 1,000 species of plants, 117 species of fish, 68 amphibians and reptiles, 330 birds, and 31 different mammals. The refuge provides a favorable environment for the cranes as it contains shallow freshwater habitats for nesting, along with a variety of vegetation and prey to feed on.
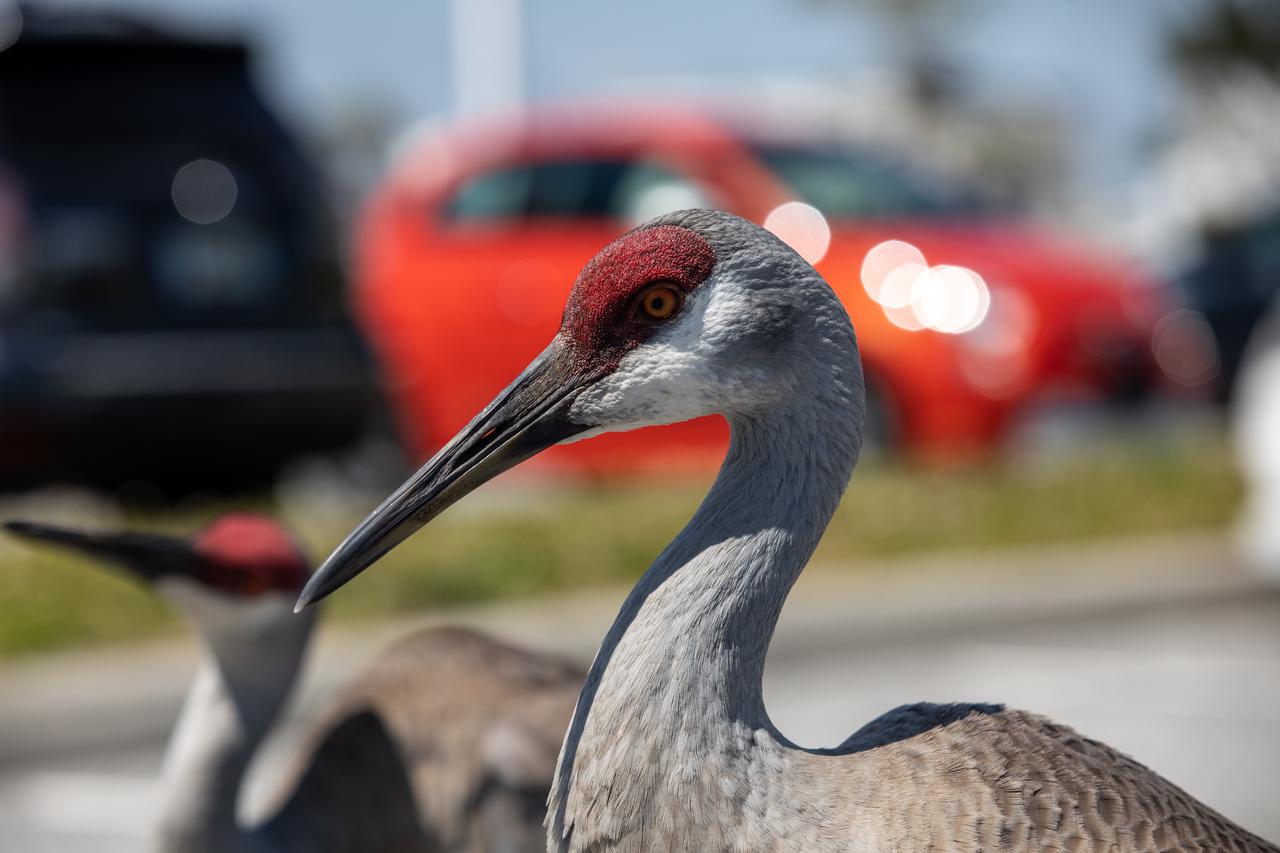

A pair of sandhill cranes explore a paved parking area at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 24, 2021. Kennedy shares space with the Merritt Island National Wildlife refuge, which is home to more than 1,000 species of plants, 117 species of fish, 68 amphibians and reptiles, 330 birds, and 31 different mammals. The refuge provides a favorable environment for the cranes as it contains shallow freshwater habitats for nesting, along with a variety of vegetation and prey to feed on.

A sandhill crane explores a paved parking area near the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 24, 2021. Kennedy shares space with the Merritt Island National Wildlife refuge, which is home to more than 1,000 species of plants, 117 species of fish, 68 amphibians and reptiles, 330 birds, and 31 different mammals. The refuge provides a favorable environment for sandhill cranes as it contains shallow freshwater habitats for nesting, along with a variety of vegetation and prey to feed on.
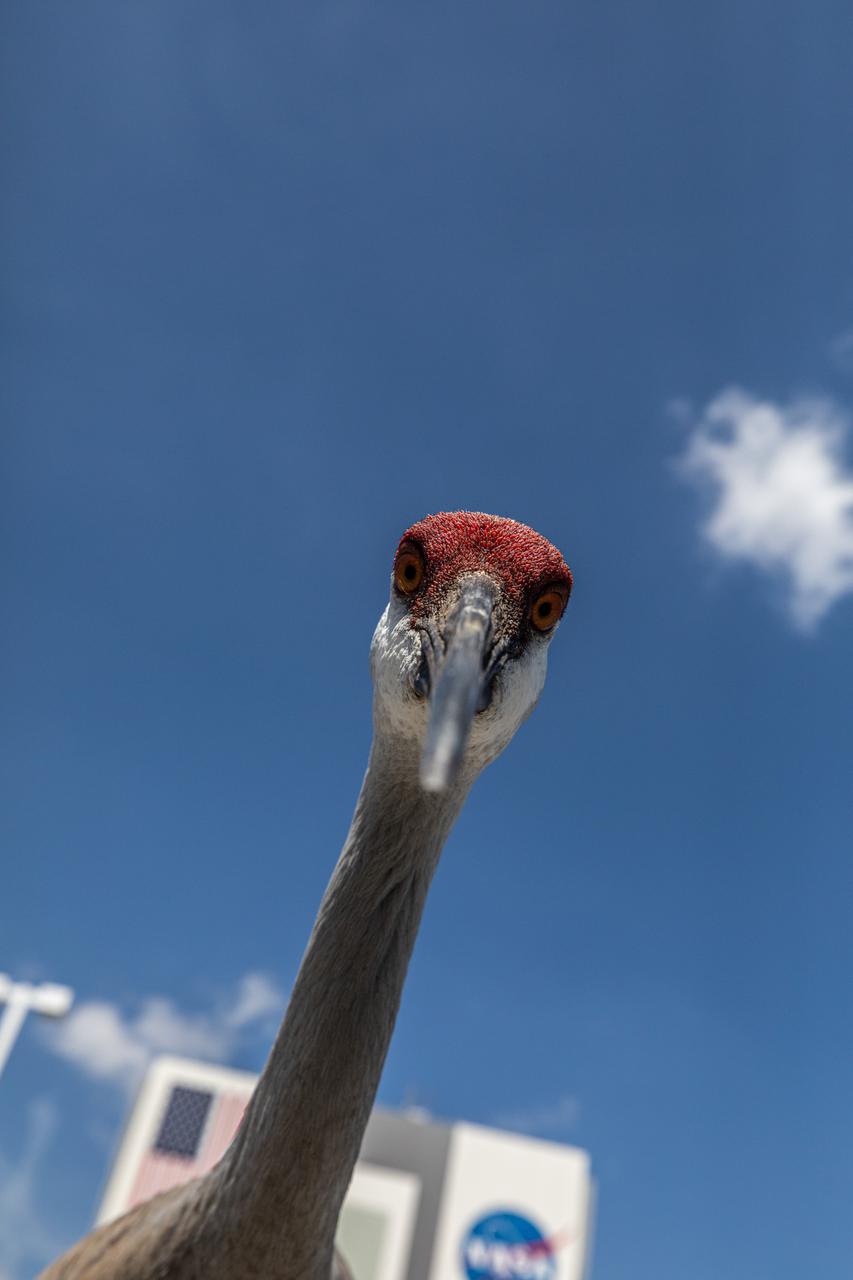

An inquisitive sandhill crane approaches the photographer near the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 24, 2021. Kennedy shares space with the Merritt Island National Wildlife refuge, which is home to more than 1,000 species of plants, 117 species of fish, 68 amphibians and reptiles, 330 birds, and 31 different mammals. The refuge provides a favorable environment for sandhill cranes as it contains shallow freshwater habitats for nesting, along with a variety of vegetation and prey to feed on.
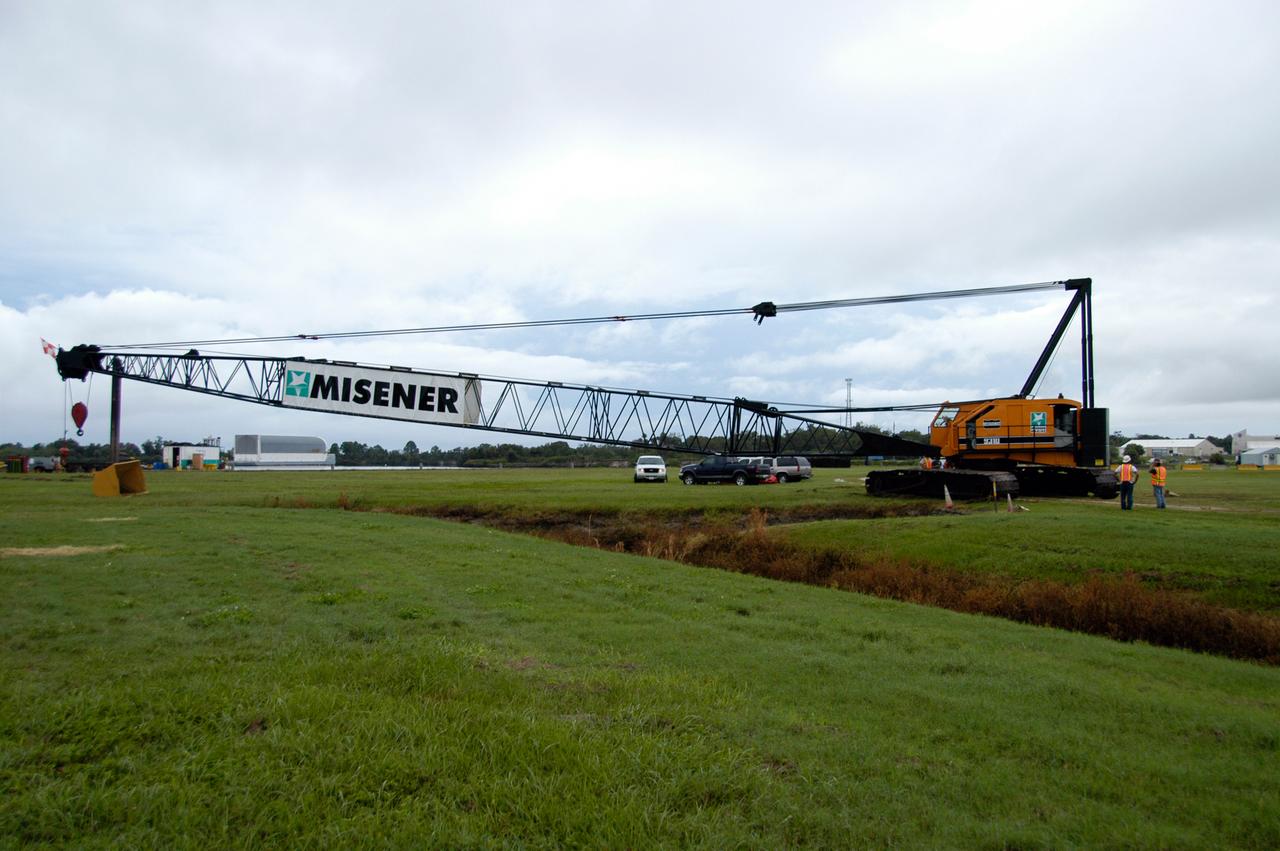

A large crawler crane begins moving away from the turn basin at the Launch Complex 39 Area on NASA's Kennedy Space Center. The crane with its 70-foot boom will be moved to Launch Pad 39B and used to construct a new lightning protection system for the Constellation Program and Ares/Orion launches. Pad B will be the site of the first Ares vehicle launch, including Ares I-X which is scheduled for April 2009.
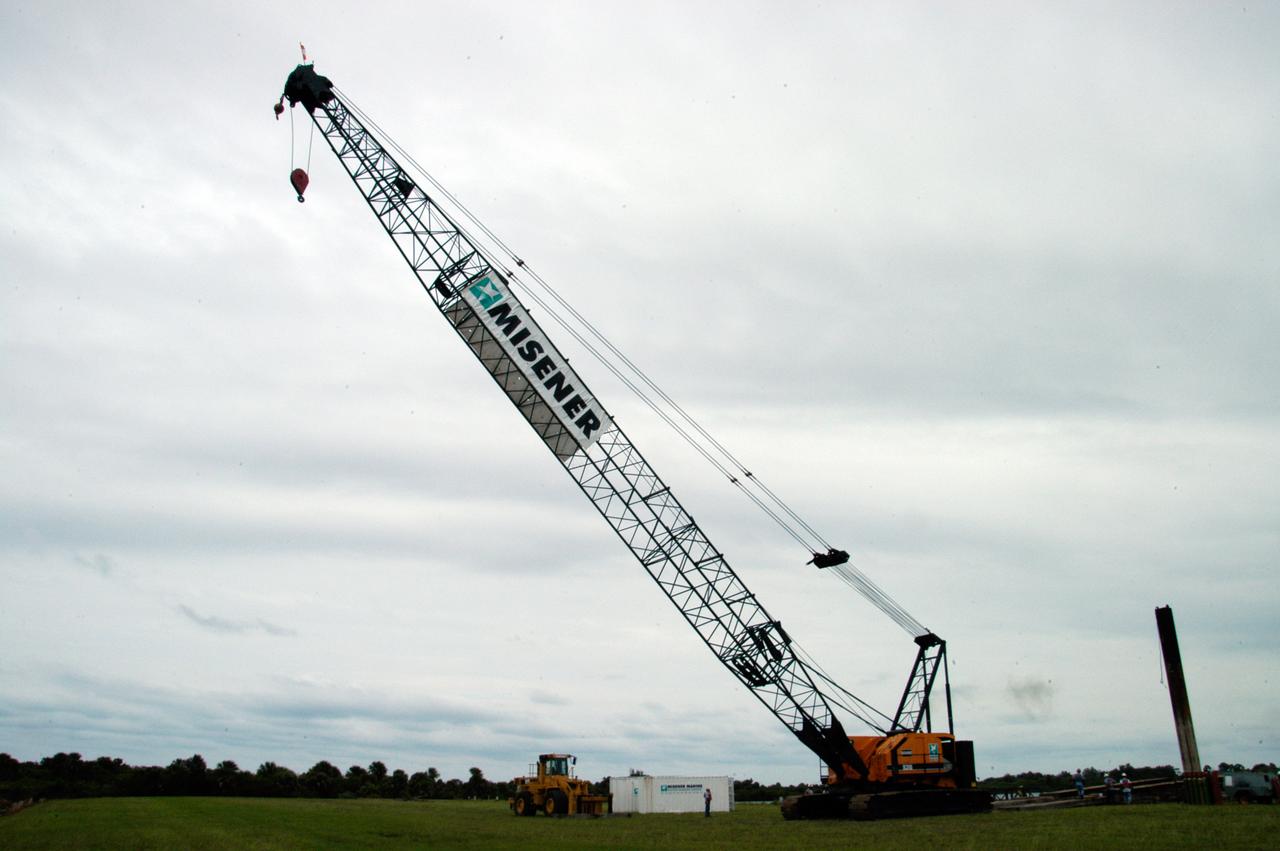

A large crawler crane begins moving away from the turn basin at the Launch Complex 39 Area on NASA's Kennedy Space Center. The crane with its 70-foot boom will be moved to Launch Pad 39B and used to construct a new lightning protection system for the Constellation Program and Ares/Orion launches. Pad B will be the site of the first Ares vehicle launch, including Ares I-X which is scheduled for April 2009.
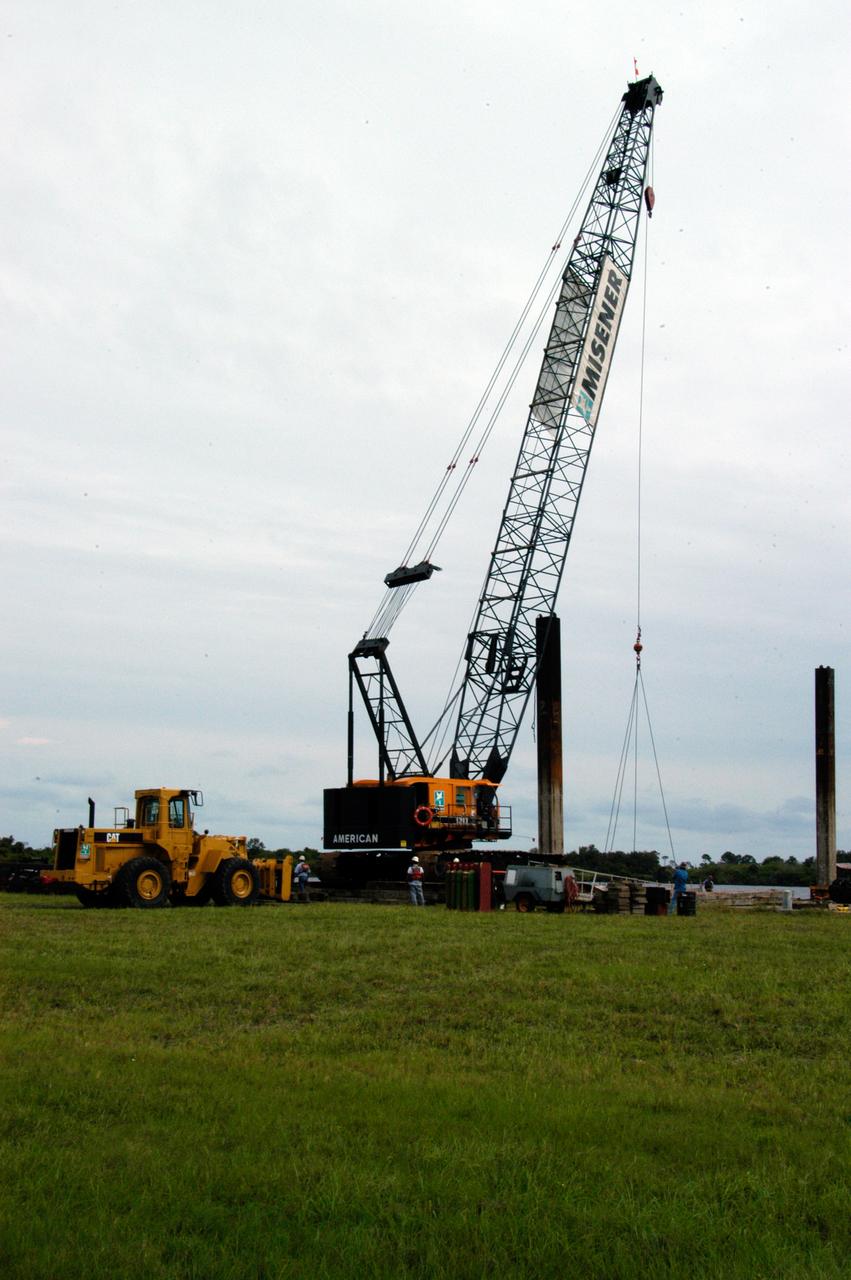

A large crawler crane arrives at the turn basin at the Launch Complex 39 Area on NASA's Kennedy Space Center. The crane with its 70-foot boom will be moved to Launch Pad 39B and used to construct a new lightning protection system for the Constellation Program and Ares/Orion launches. Pad B will be the site of the first Ares vehicle launch, including Ares I-X which is scheduled for April 2009.
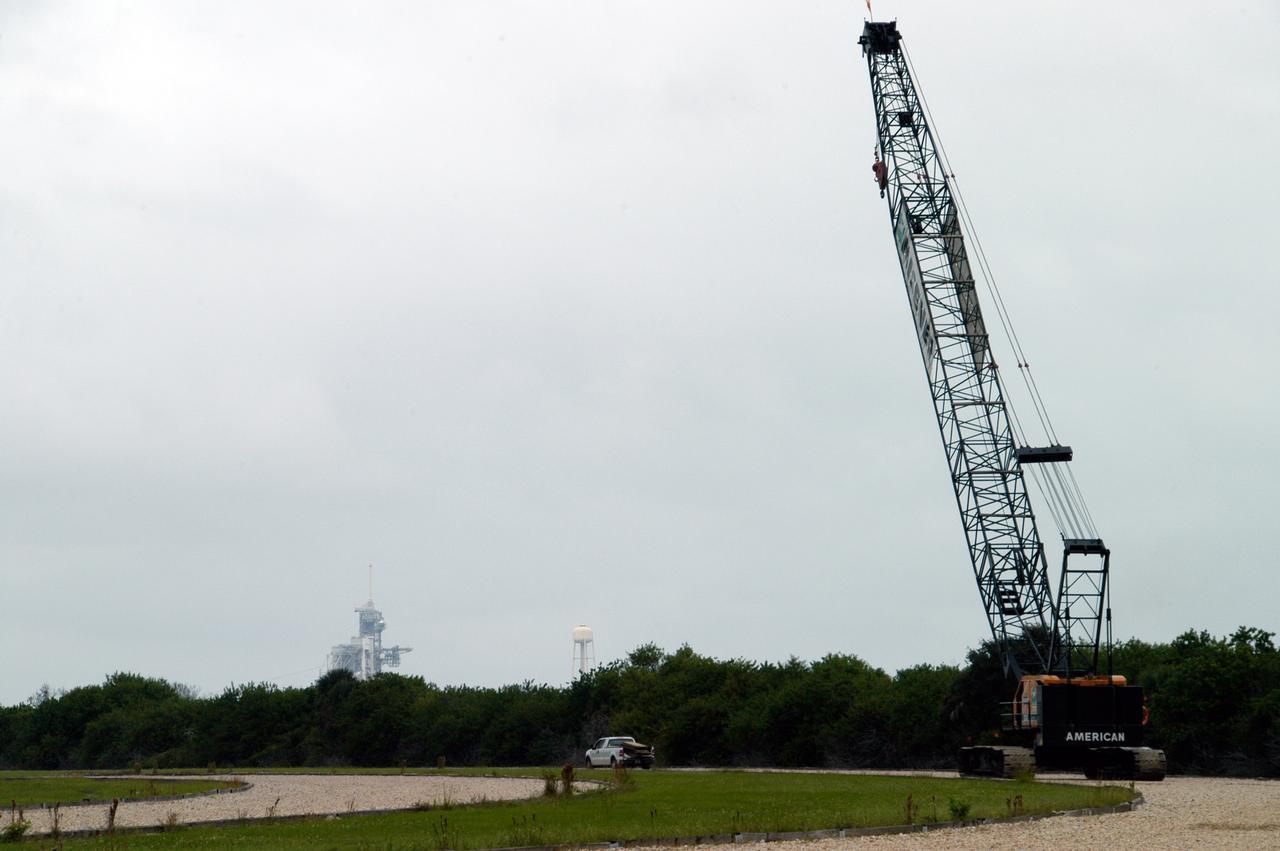

A large crawler crane traveling long one of the crawlerway tracks makes the turn toward Launch Pad 39B. The crane with its 70-foot boom will be used to construct a new lightning protection system for the Constellation Program and Ares/Orion launches. Pad B will be the site of the first Ares vehicle launch, including Ares I-X which is scheduled for April 2009.

A large crawler crane arrives at the turn basin at the Launch Complex 39 Area on NASA's Kennedy Space Center. The crane with its 70-foot boom will be moved to Launch Pad 39B and used to construct a new lightning protection system for the Constellation Program and Ares/Orion launches. Pad B will be the site of the first Ares vehicle launch, including Ares I-X which is scheduled for April 2009.
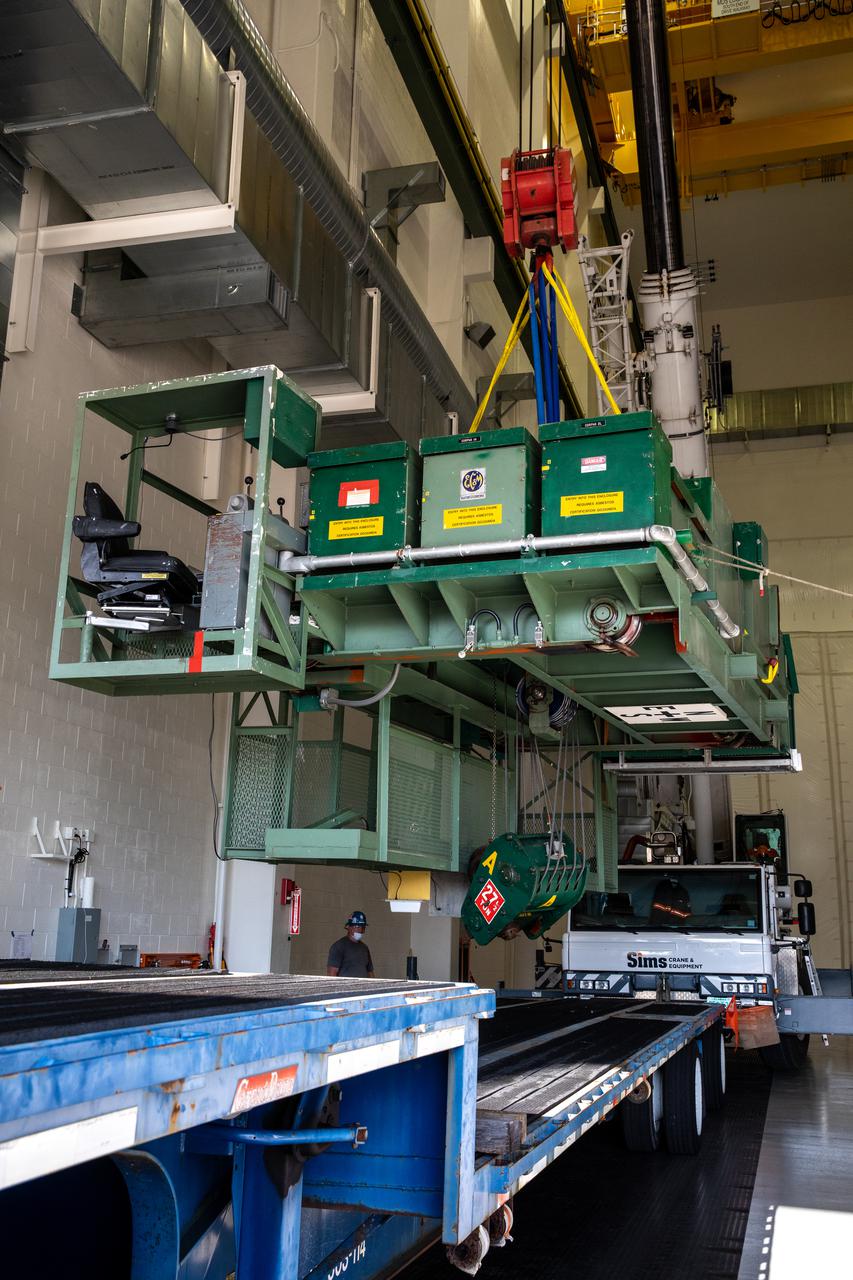

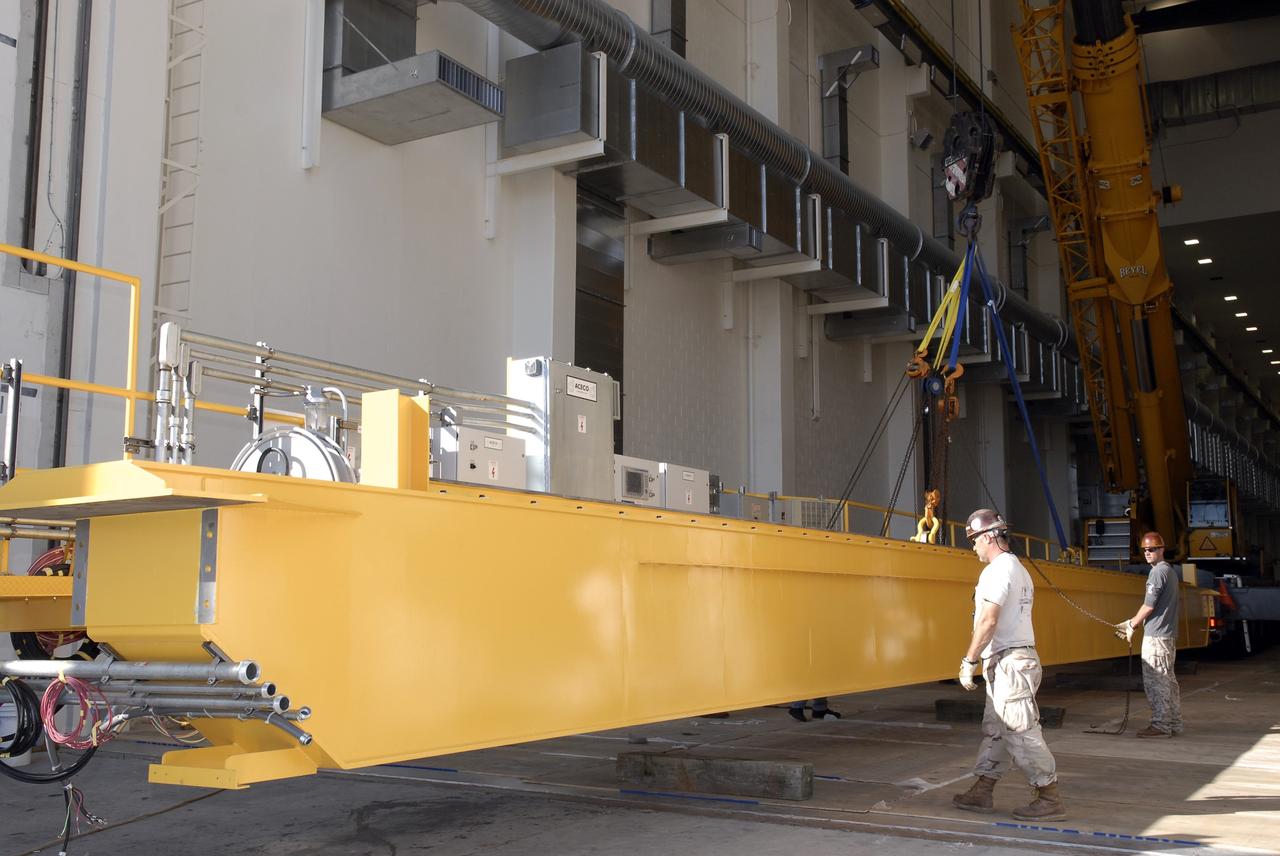
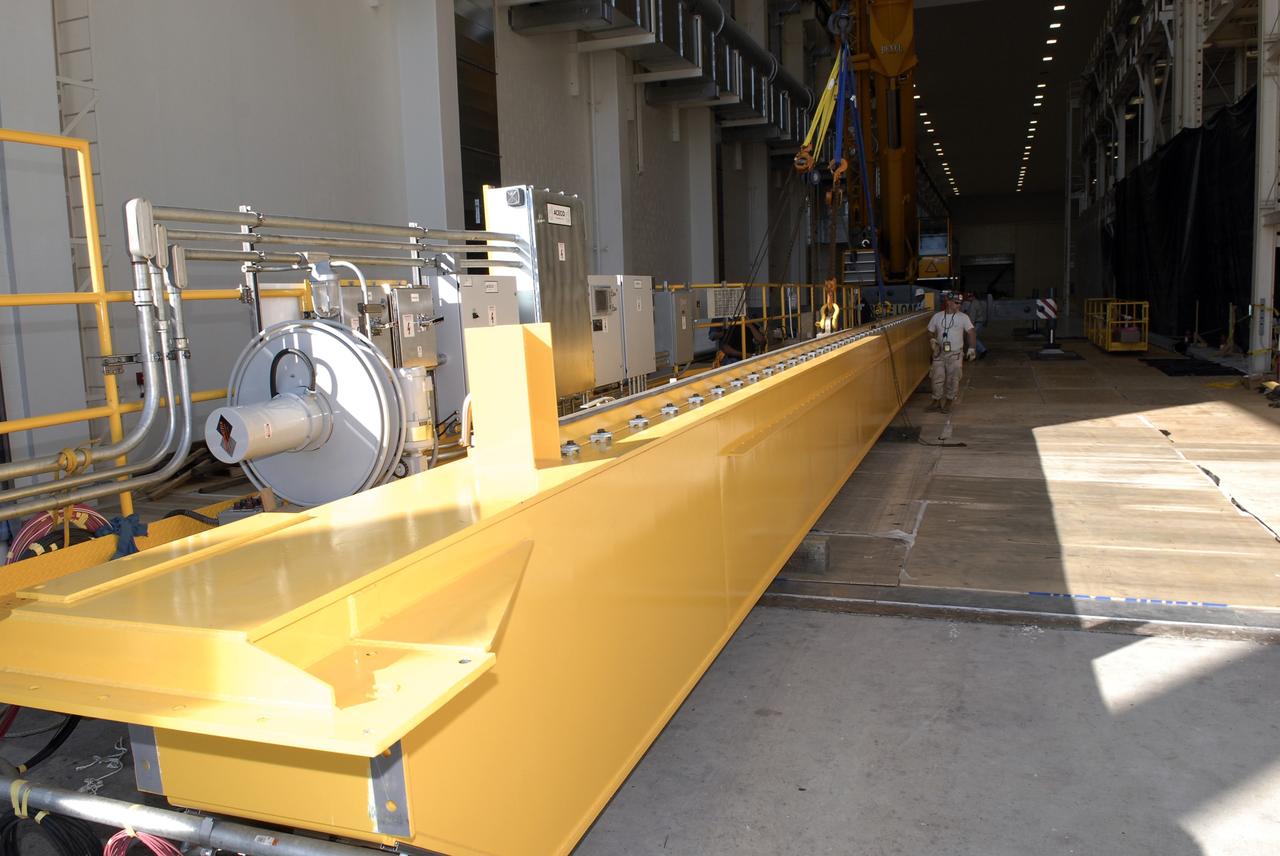
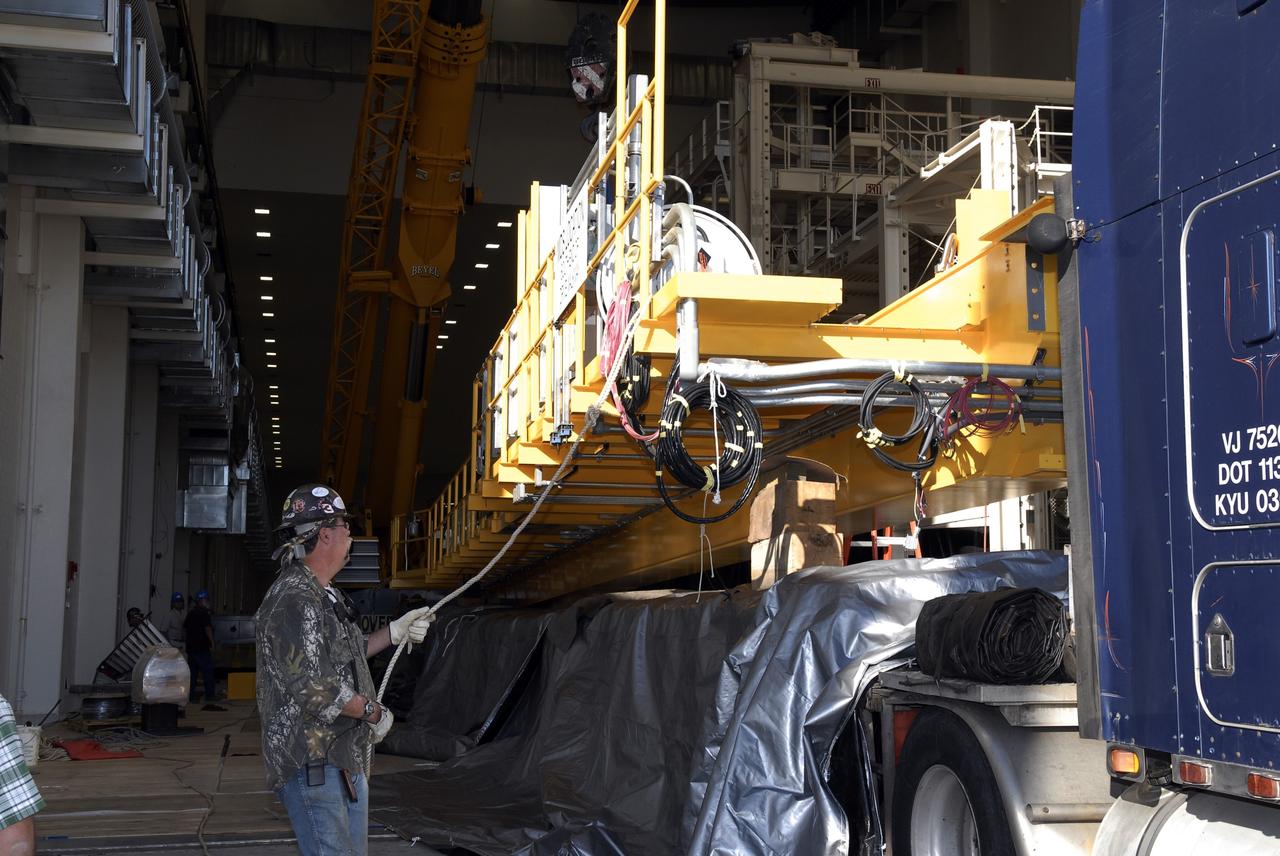
Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a new overhead crane was installed, while the old Lypta 2.5-ton crane is lowered by crane on March 15, 2021. The new overhead crane will be used to process Orion for the agency’s first crewed mission, Artemis II. Teams from American Crane and Equipment Corp. are replacing the Lypta crane with the new Artemis-rated 30-ton crane. The new crane has enhanced controls and additional safety features that will allow for micro movements to within 1/100th of an inch. Operators will use the crane to lift Orion once the crew and service modules are mated.
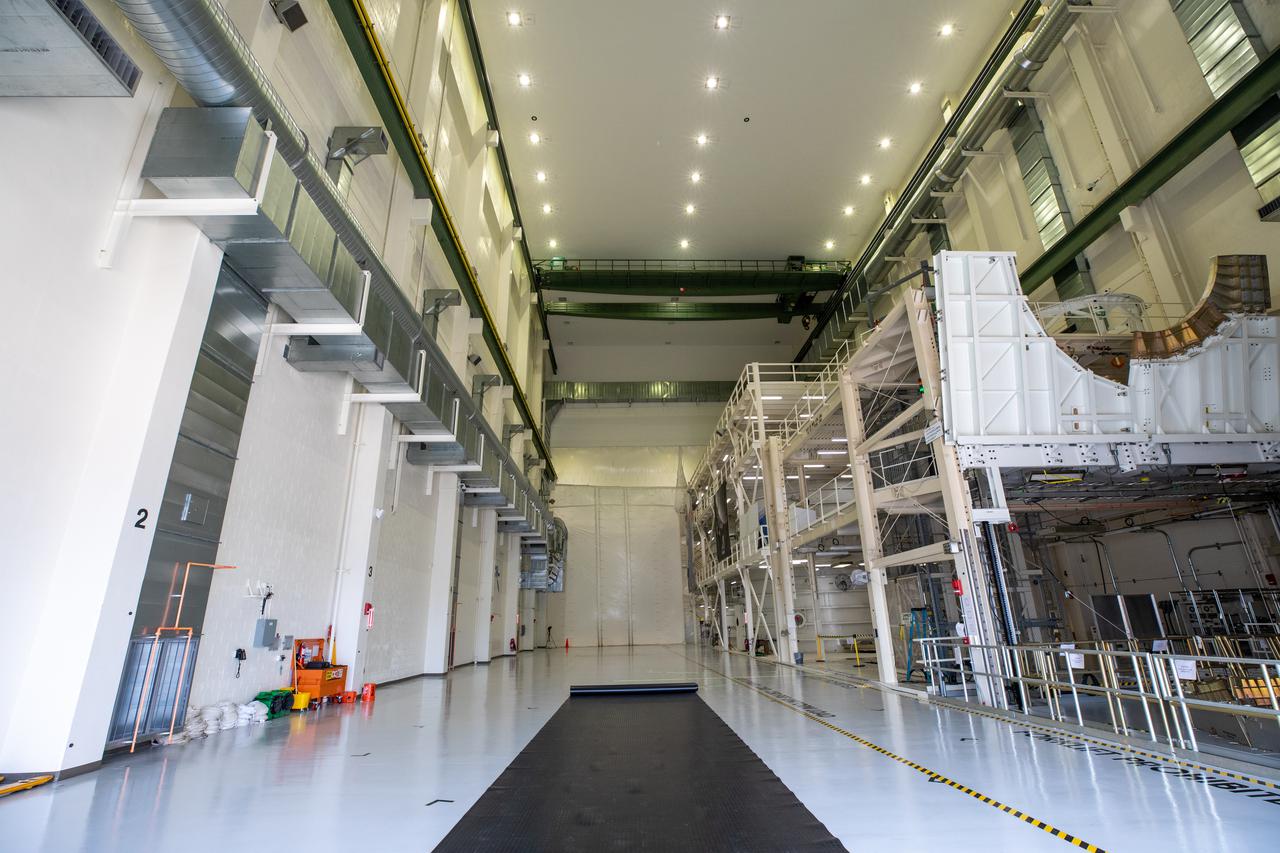

The high bay inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is being readied on March 3, 2021, for installation of a new crane. The new overhead crane will be used to process Orion beginning with the agency’s first crewed mission, Artemis II. Teams from American Crane and Equipment Corp. replaced the Lypta 27.5-ton crane (pictured) with the new Artemis-rated 30-ton crane. The new crane will have enhanced controls and additional safety features that will allow for micro movements to within 1/100th of an inch. Operators will use the crane to lift Orion once the crew and service modules are mated.

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, installation of a new overhead crane is in progress on March 15, 2021. The previous Lypta 2.5-ton crane is lowered by crane to the floor. It will be used to process Orion beginning with the agency’s first crewed mission, Artemis II. Teams from American Crane and Equipment Corp. are replacing the Lypta crane with the new Artemis-rated 30-ton crane. The hardware has enhanced controls and additional safety features that will allow for micro movements to within 1/100th of an inch. Operators will use the crane to lift Orion once the crew and service modules are mated.
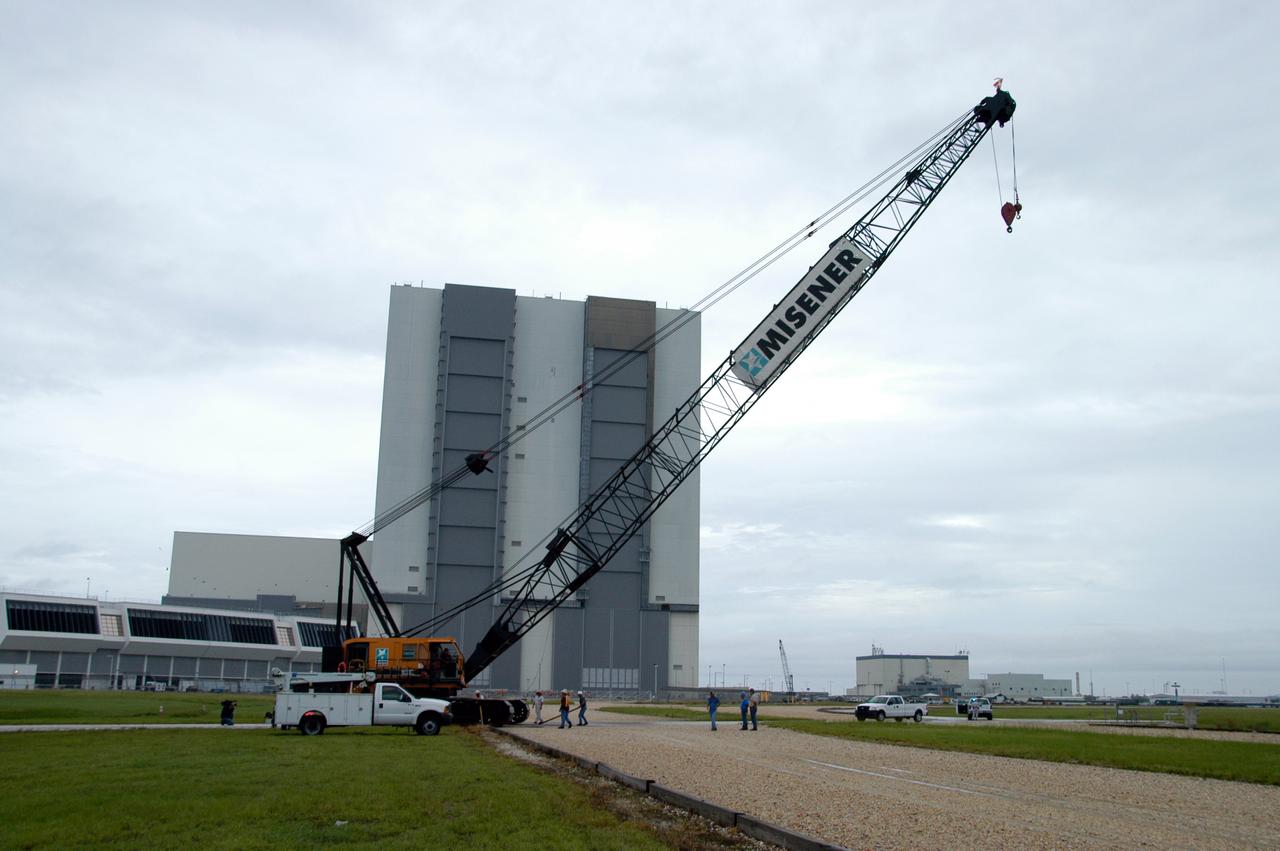

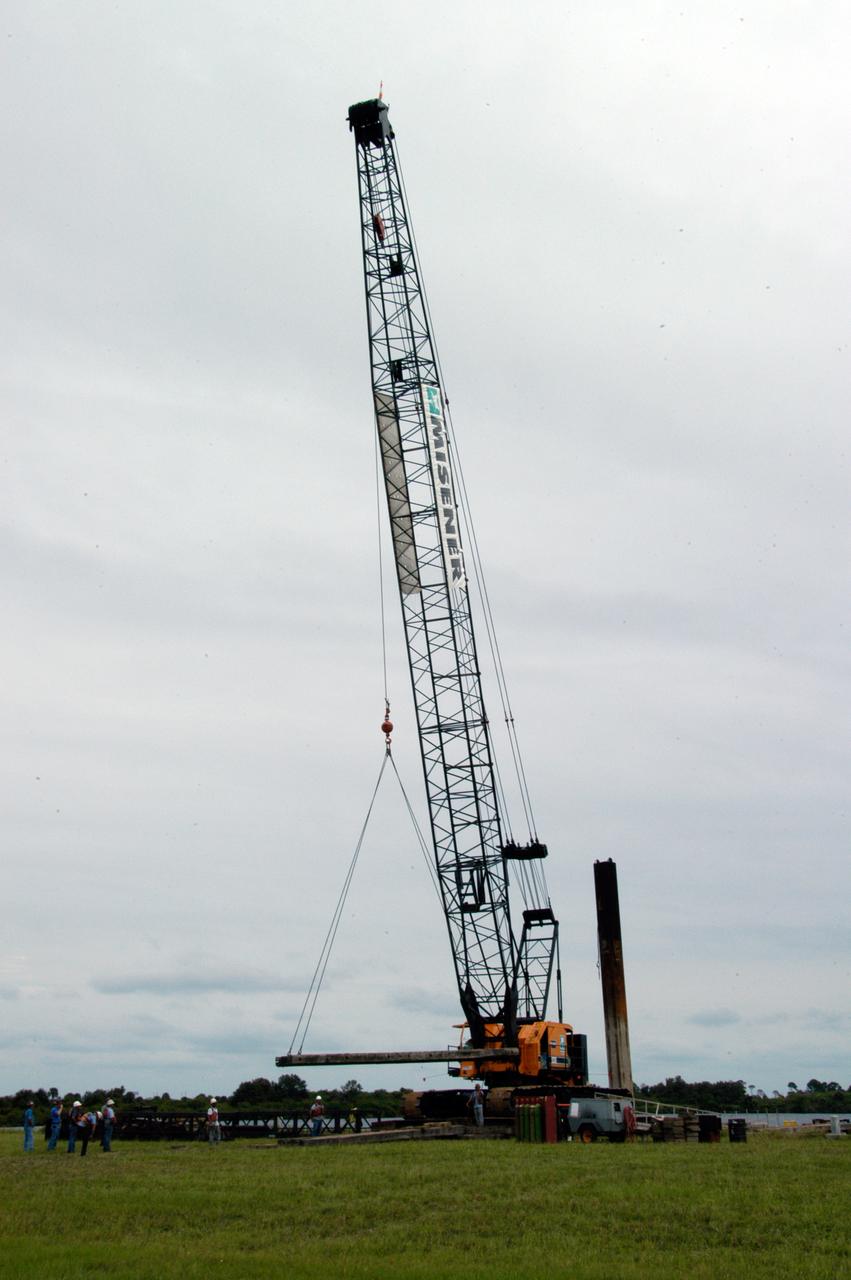
A large crawler crane moves past the Vehicle Assembly Building on its way to Launch Pad 39B. The crane with its 70-foot boom will be used to construct a new lightning protection system for the Constellation Program and Ares/Orion launches. Pad B will be the site of the first Ares vehicle launch, including Ares I-X which is scheduled for April 2009.

A large crawler crane travels along one of the crawlerway tracks on its way to Launch Pad 39B. The crane with its 70-foot boom will be used to construct a new lightning protection system for the Constellation Program and Ares/Orion launches. Pad B will be the site of the first Ares vehicle launch, including Ares I-X which is scheduled for April 2009.
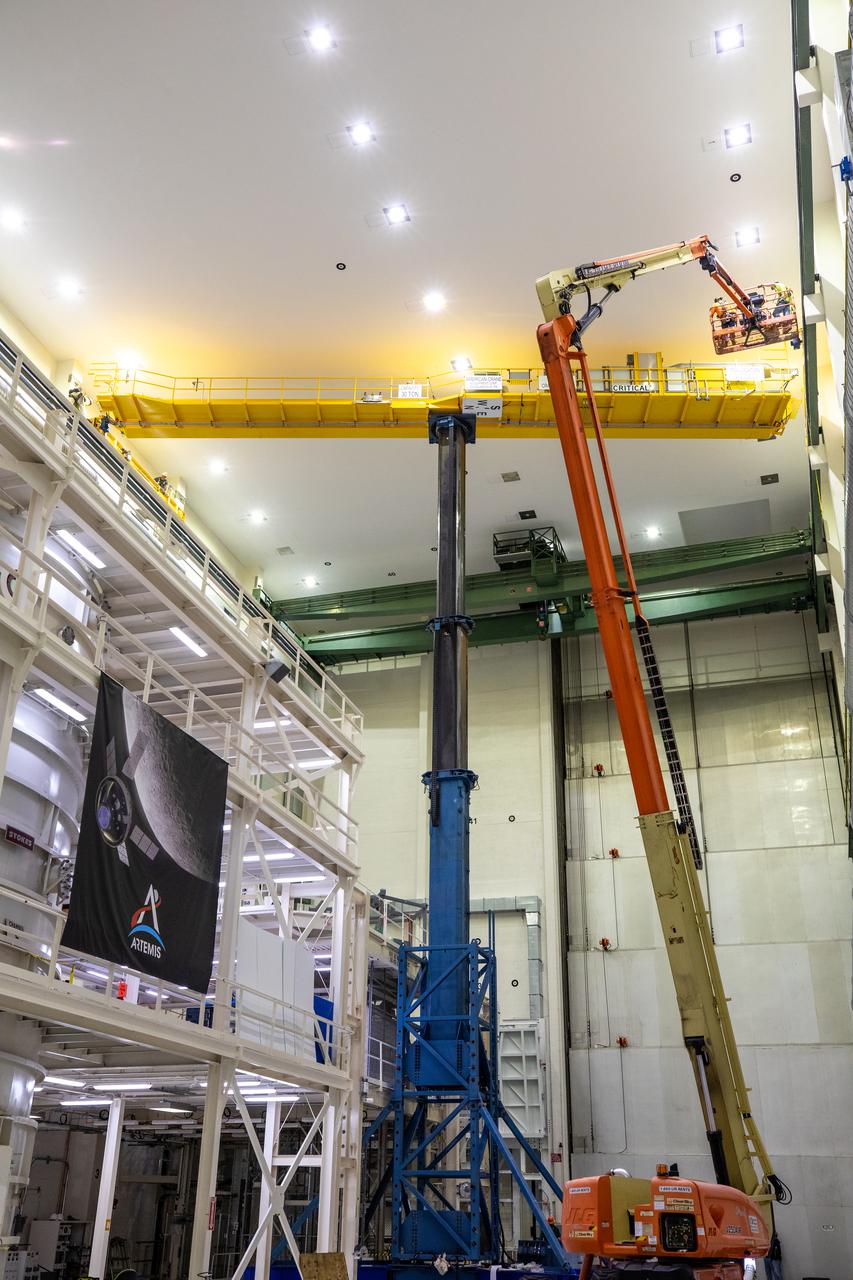

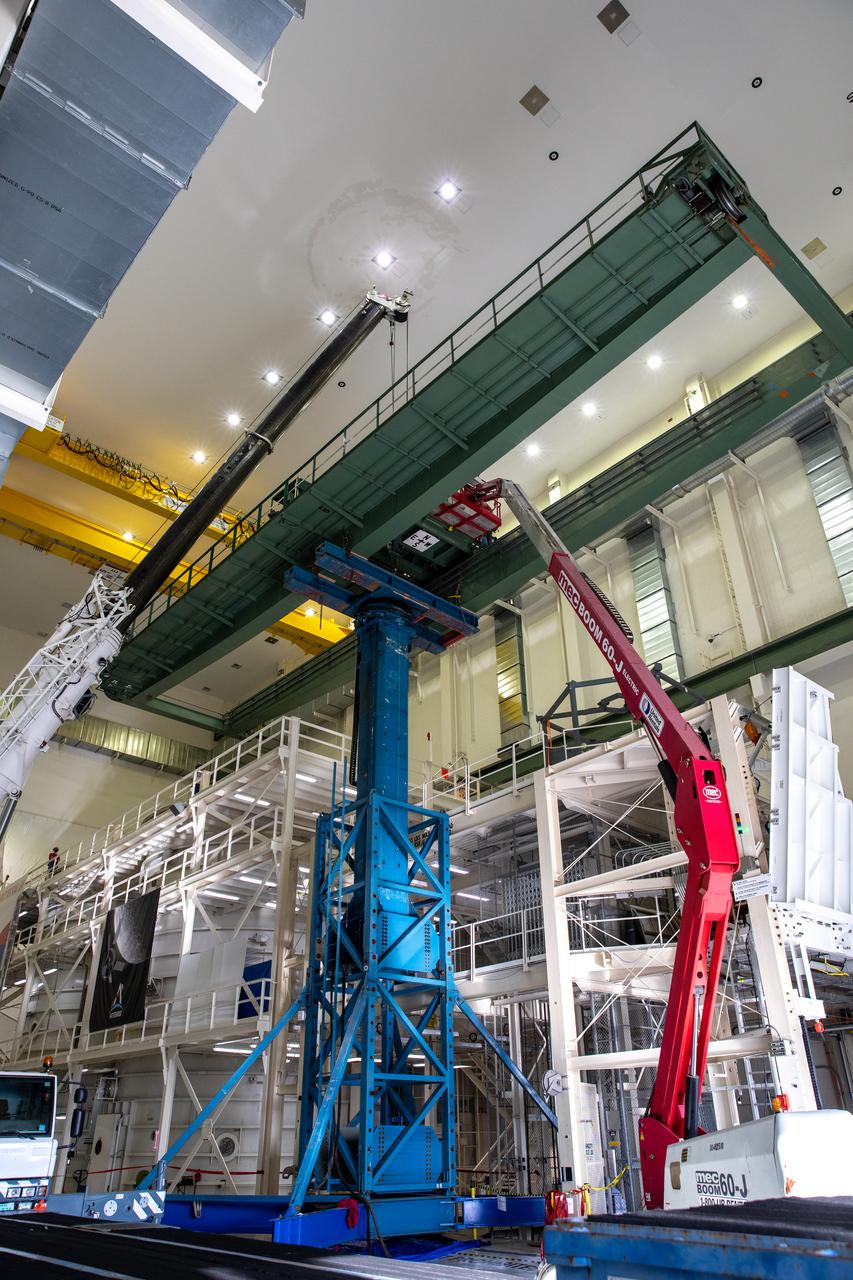
Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a new overhead crane is being installed on March 10, 2021. The new hardware will be used to process Orion beginning with the agency’s first crewed mission, Artemis II. Teams from American Crane and Equipment Corp. are replacing the Lypta 27.5-ton crane with the new Artemis-rated 30-ton crane. The new crane has enhanced controls and additional safety features that will allow for micro movements to within 1/100th of an inch. Operators will use the crane to lift Orion once the crew and service modules are mated.
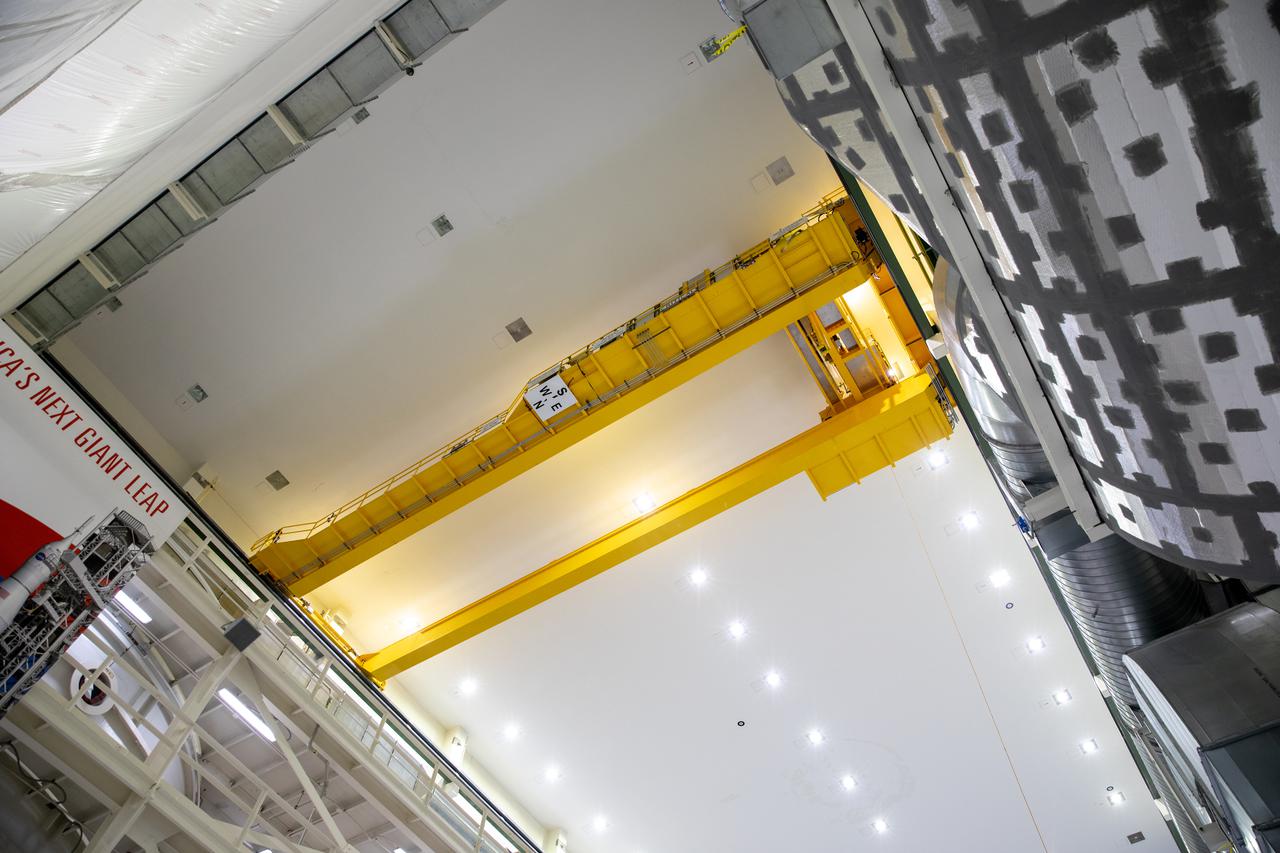

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, installation of a new overhead crane is completed on March 17, 2021. The new hardware will be used to process Orion beginning with the agency’s first crewed mission, Artemis II. Teams from American Crane and Equipment Corp. replaced the Lypta 27.5-ton crane with the new Artemis-rated 30-ton crane. The new crane has enhanced controls and additional safety features that will allow for micro movements to within 1/100th of an inch. Operators will use the crane to lift Orion once the crew and service modules are mated.
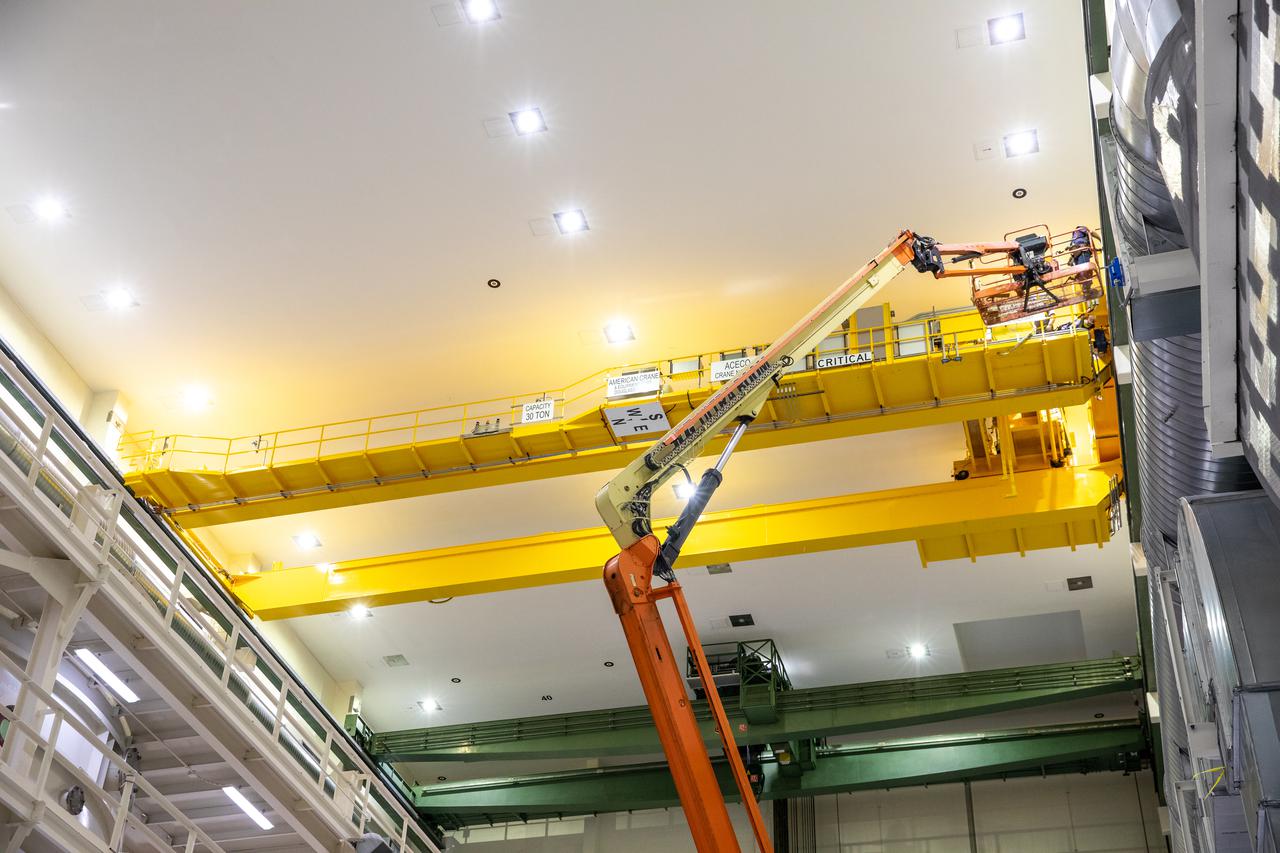

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a new overhead crane is being installed on March 10, 2021. The new hardware will be used to process Orion beginning with the agency’s first crewed mission, Artemis II. Teams from American Crane and Equipment Corp. are replacing the Lypta 27.5-ton crane with the new Artemis-rated 30-ton crane. The new crane has enhanced controls and additional safety features that will allow for micro movements to within 1/100th of an inch. Operators will use the crane to lift Orion once the crew and service modules are mated.

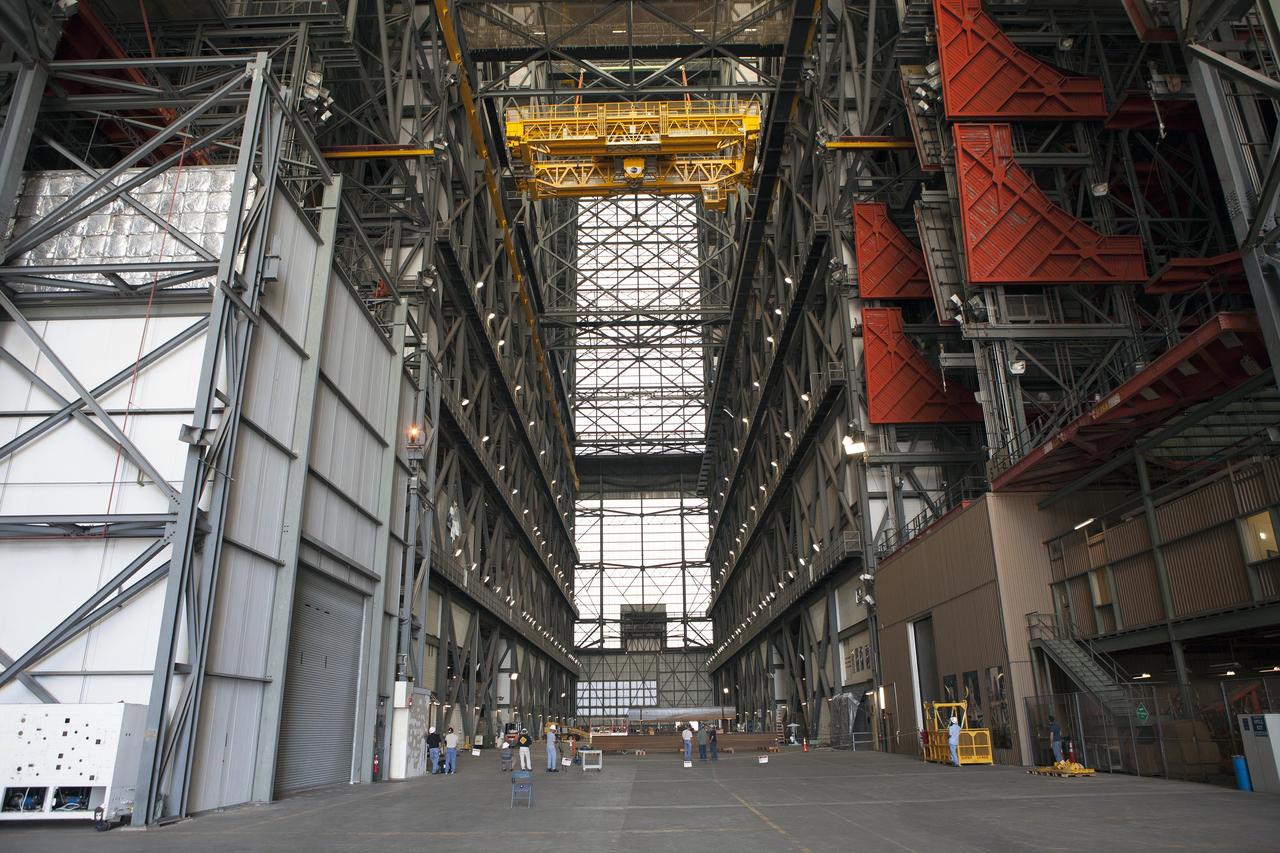
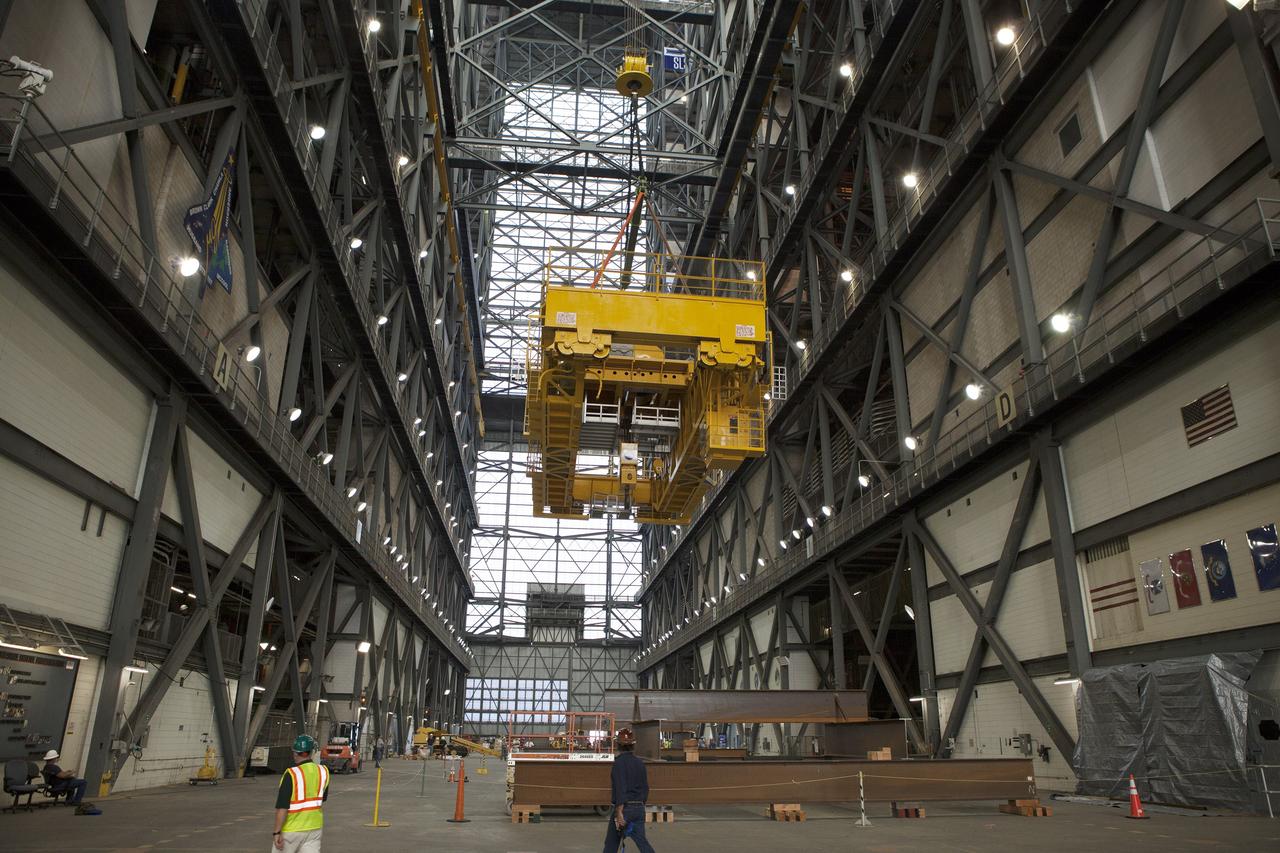
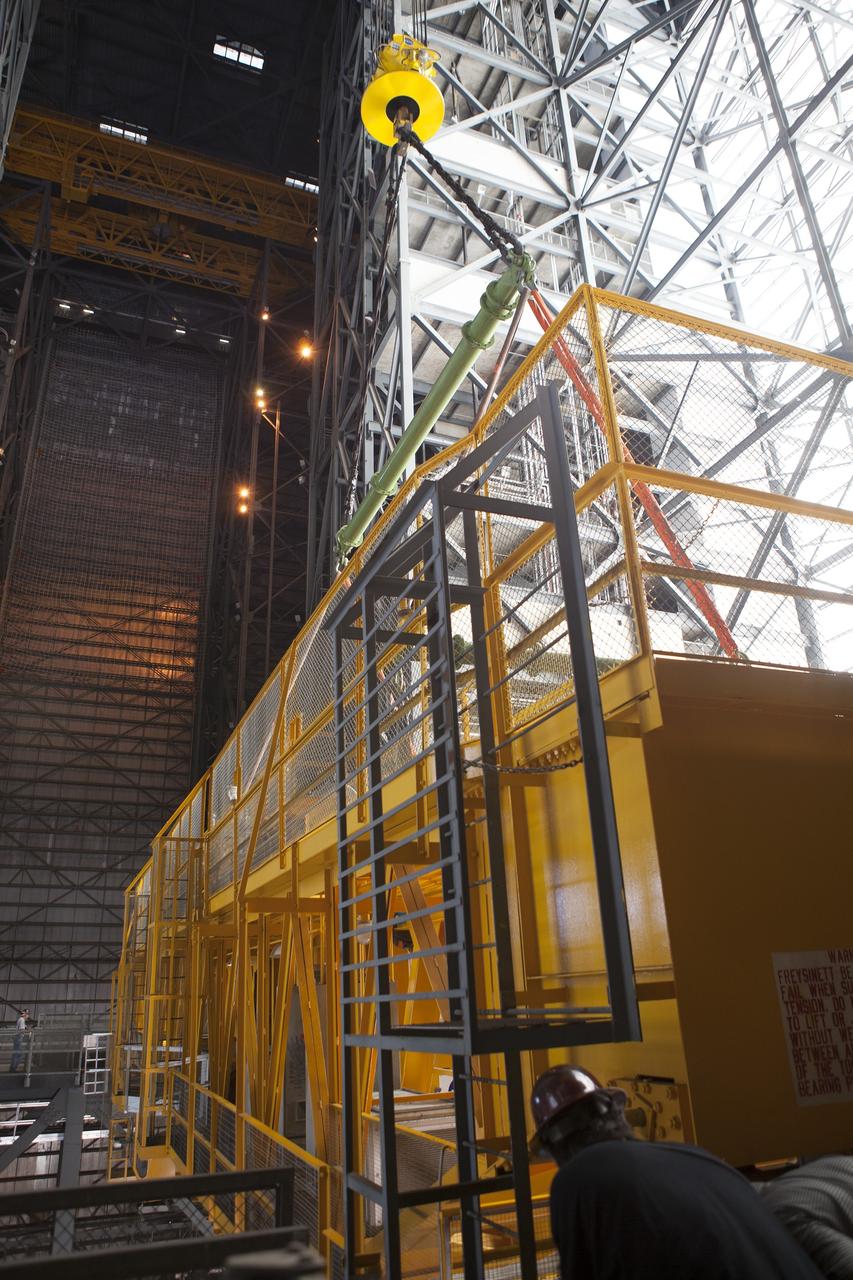
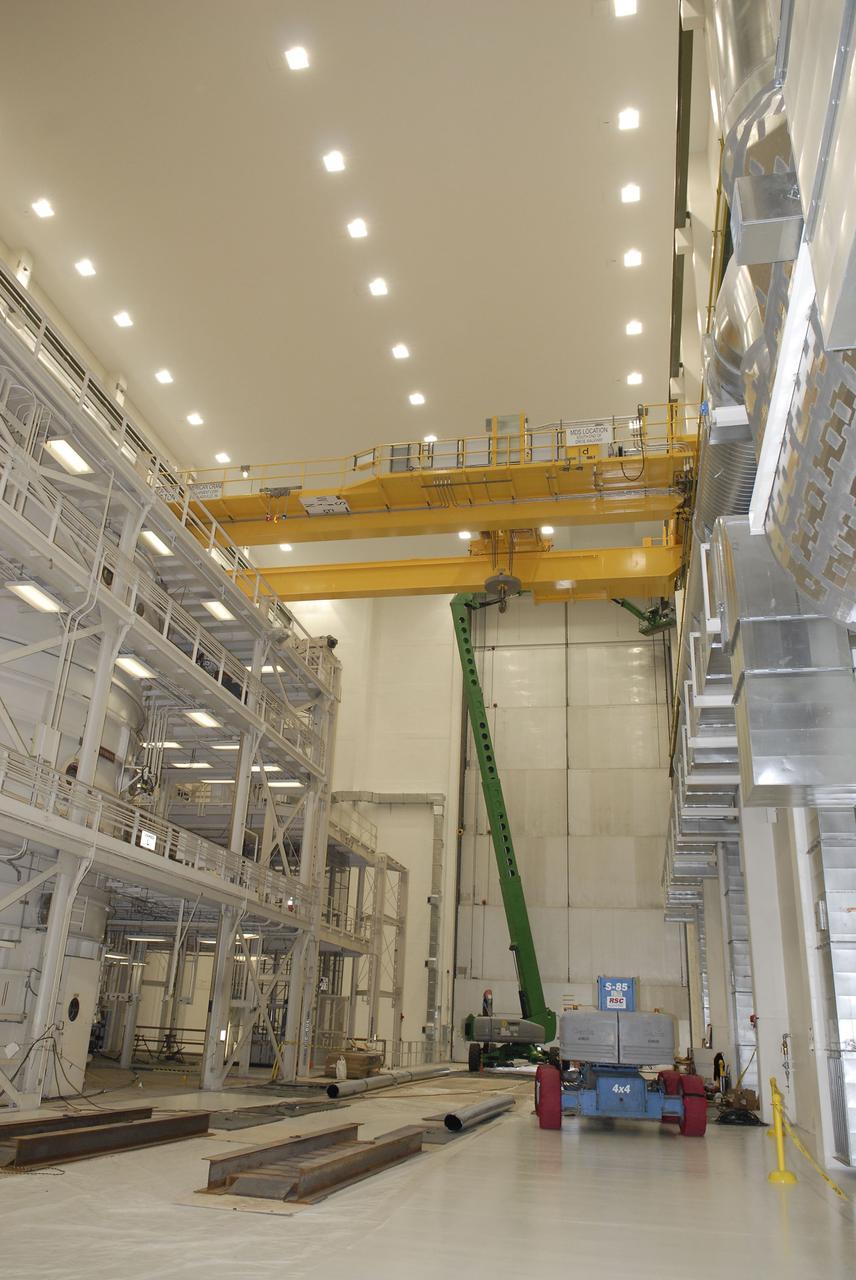
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the 175-ton crane is being lowered by crane onto steel stands on the transfer aisle floor. The crane was lowered from Level 16. In view at right is the cab that is used to control the crane. Upgrades to the crane's 45-year-old controls will be performed in order to improve reliability, precision and safety. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to the VAB. The crane will be upgraded so that it can support lifting needs for NASA and other exploration vehicles, including the agency's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
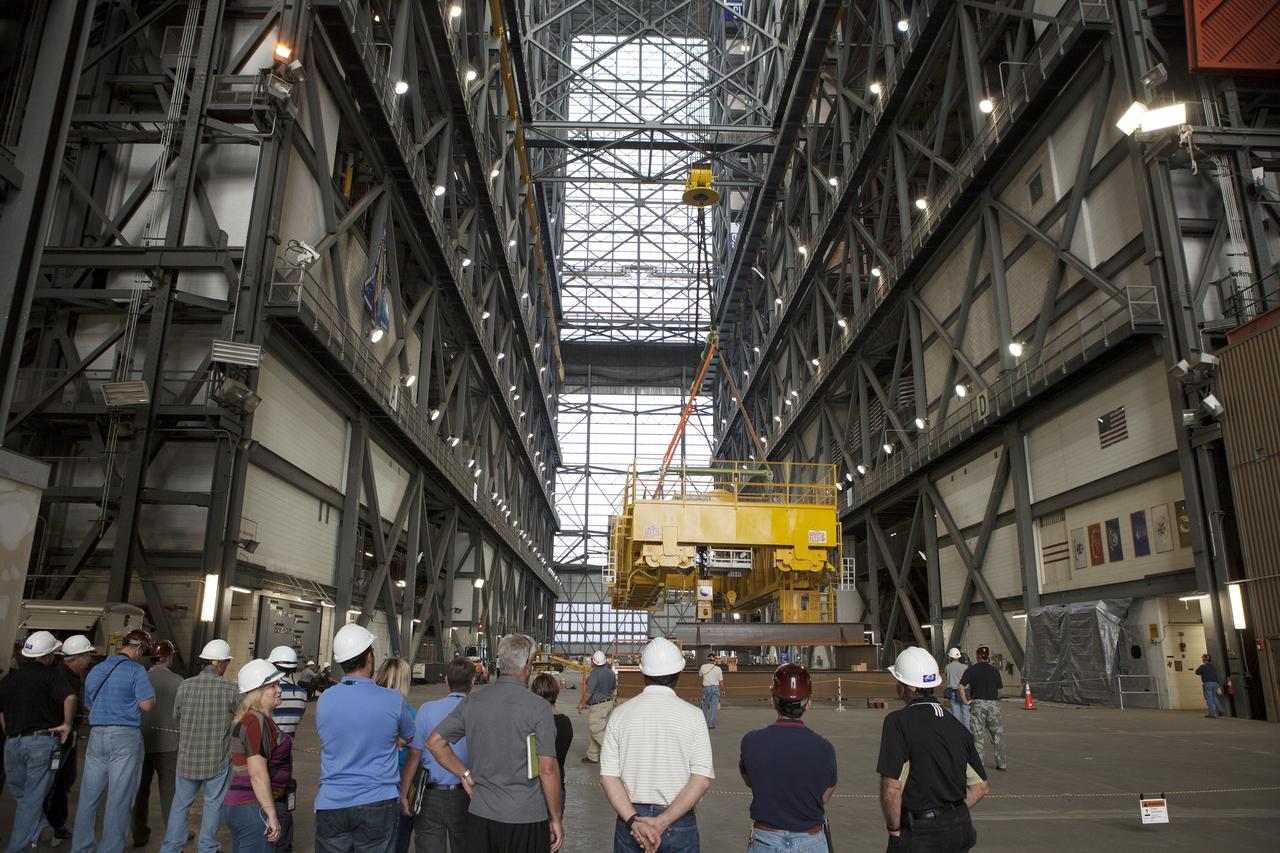

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, NASA, contractor and construction workers watch as a crane lowers the 175-ton crane toward the floor of the transfer aisle. The crane was turned to make it easier to lower it from Level 16. Upgrades to the crane's 45-year-old controls will be performed in order to improve reliability, precision and safety. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to the VAB. The crane will be upgraded so that it can support lifting needs for NASA and other exploration vehicles, including the agency's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
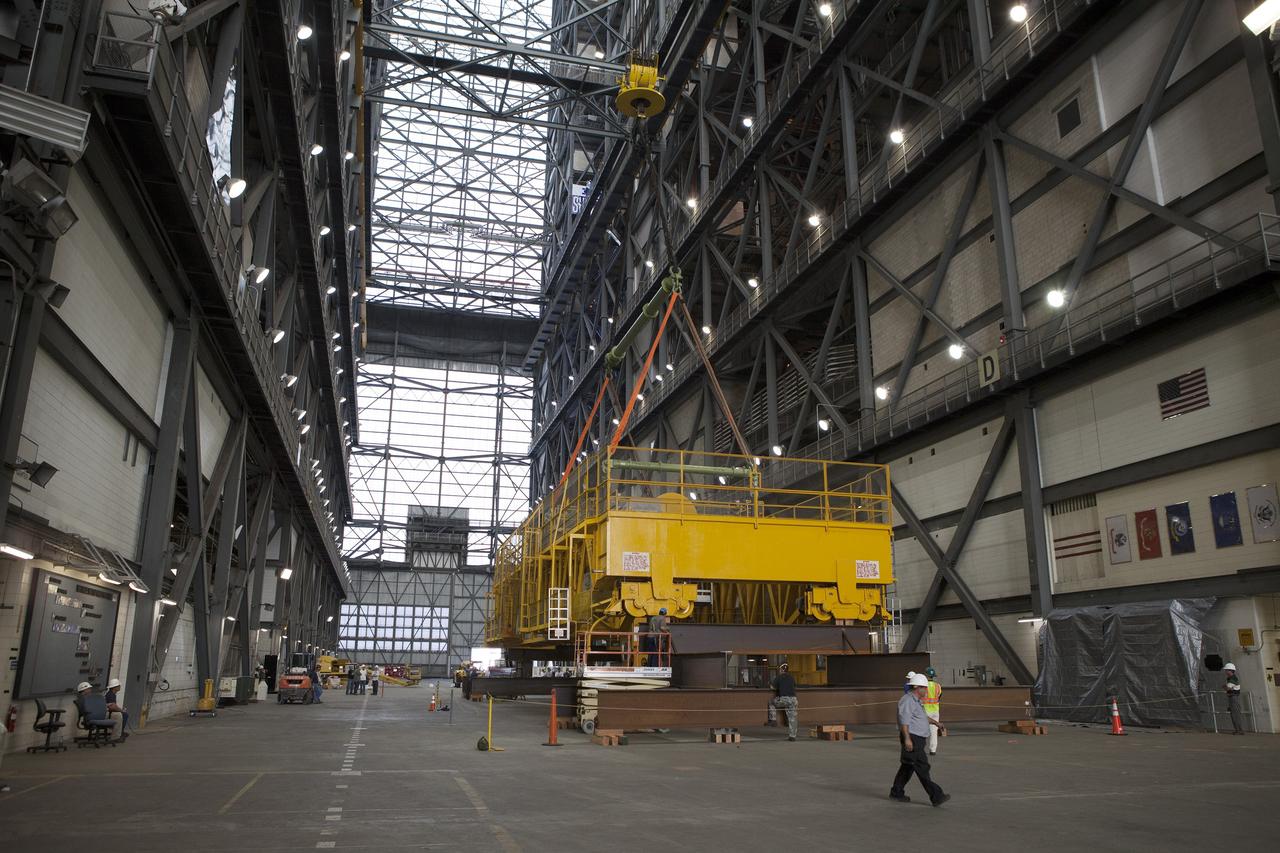

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the 175-ton crane has been lowered by crane onto steel stands on the transfer aisle floor. The crane was lowered from Level 16. Upgrades to the crane's 45-year-old controls will be performed in order to improve reliability, precision and safety. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to the VAB. The crane will be upgraded so that it can support lifting needs for NASA and other exploration vehicles, including the agency's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
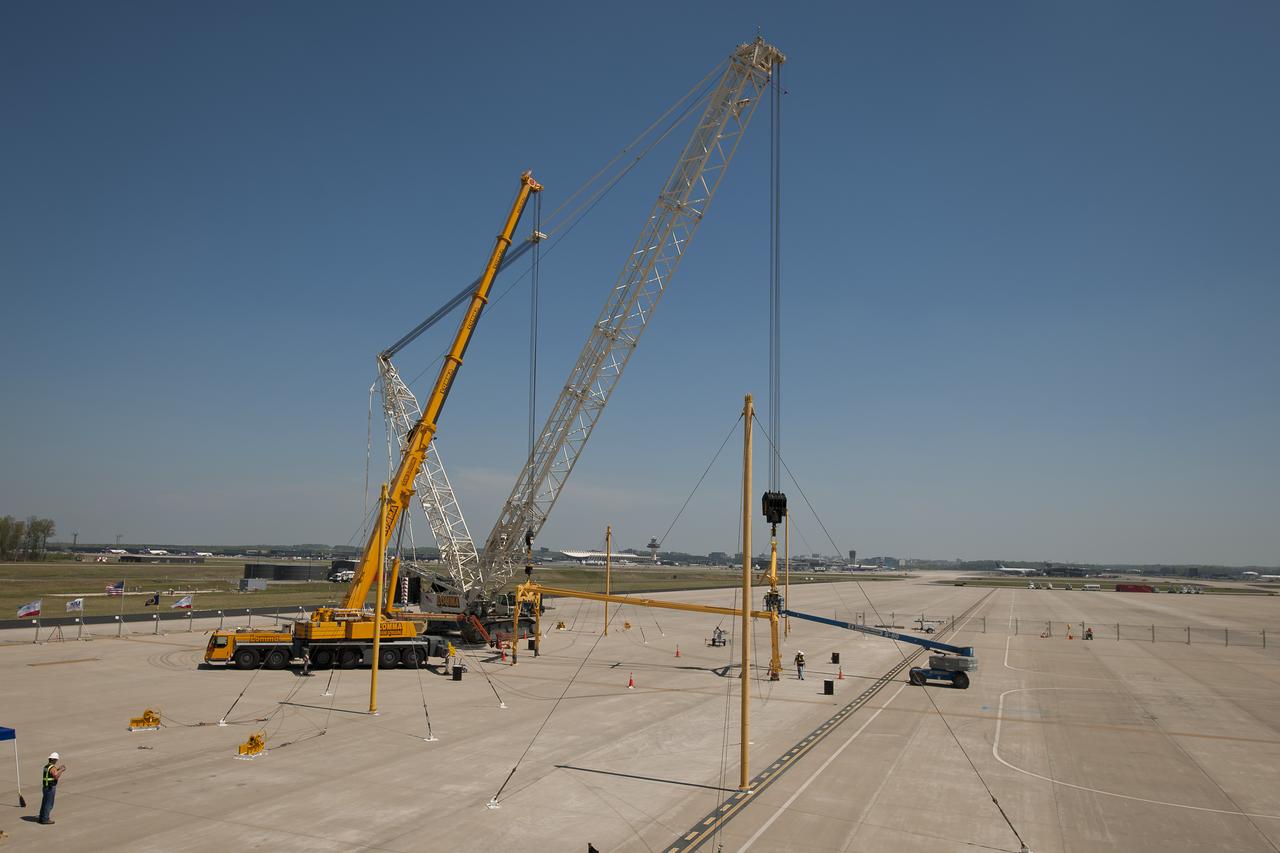

Workers use two cranes to position the sling that will be used to demate the space shuttle Discovery, Monday, April 16, 2012, at the Apron W area of Washington Dulles international Airport in Sterling, Va. The sling will be used to demate the space shuttle Discovery from the 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft (SCA) once it arrives. Discovery, the first orbiter retired from NASA’s shuttle fleet, completed 39 missions, spent 365 days in space, orbited the Earth 5,830 times, and traveled 148,221,675 miles. NASA will transfer Discovery to the National Air and Space Museum to begin its new mission to commemorate past achievements in space and to educate and inspire future generations of explorers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
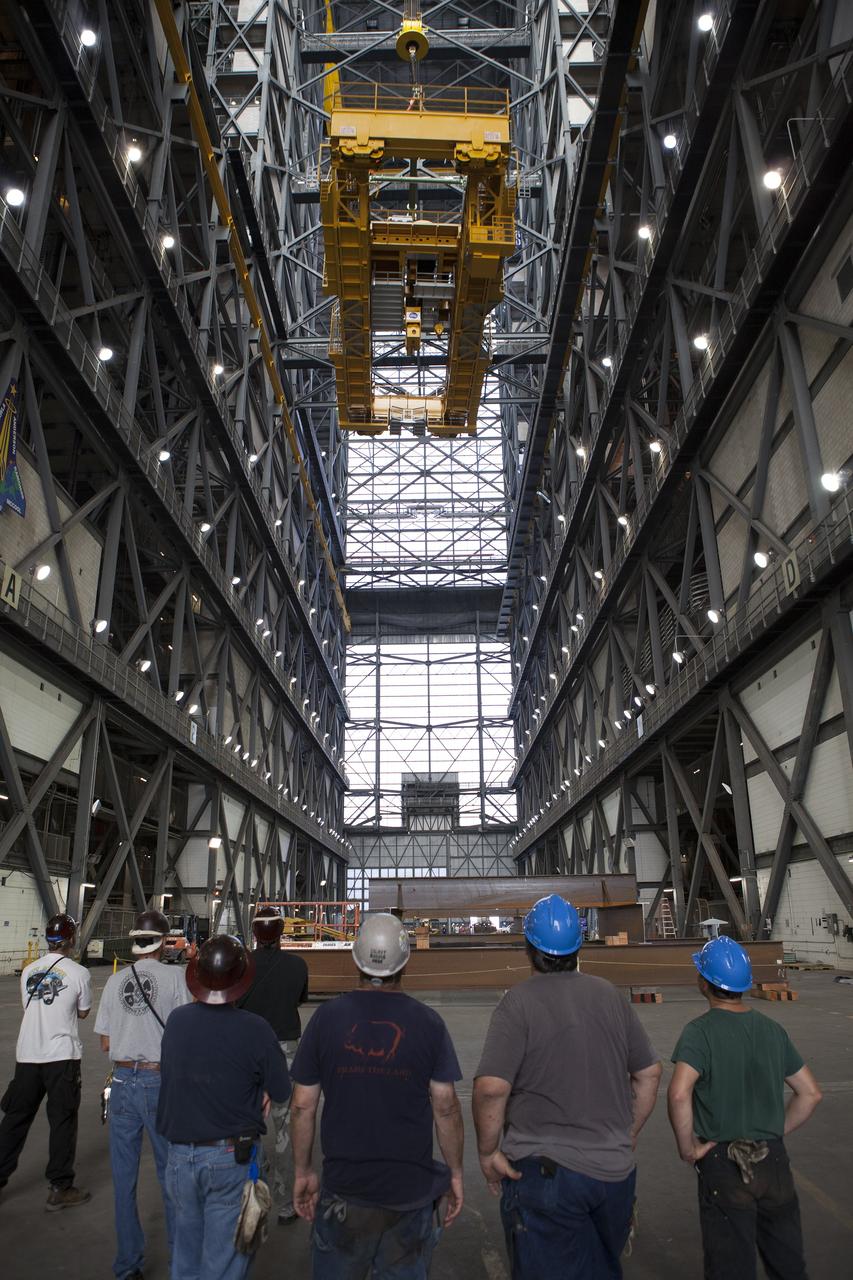

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, construction workers watch as the 175-ton crane is lowered by crane from Level 16 down to the transfer aisle floor. Upgrades to the crane's 45-year-old controls will be performed in order to improve reliability, precision and safety. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to the VAB. The crane will be upgraded so that it can support lifting needs for NASA and other exploration vehicles, including the agency's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
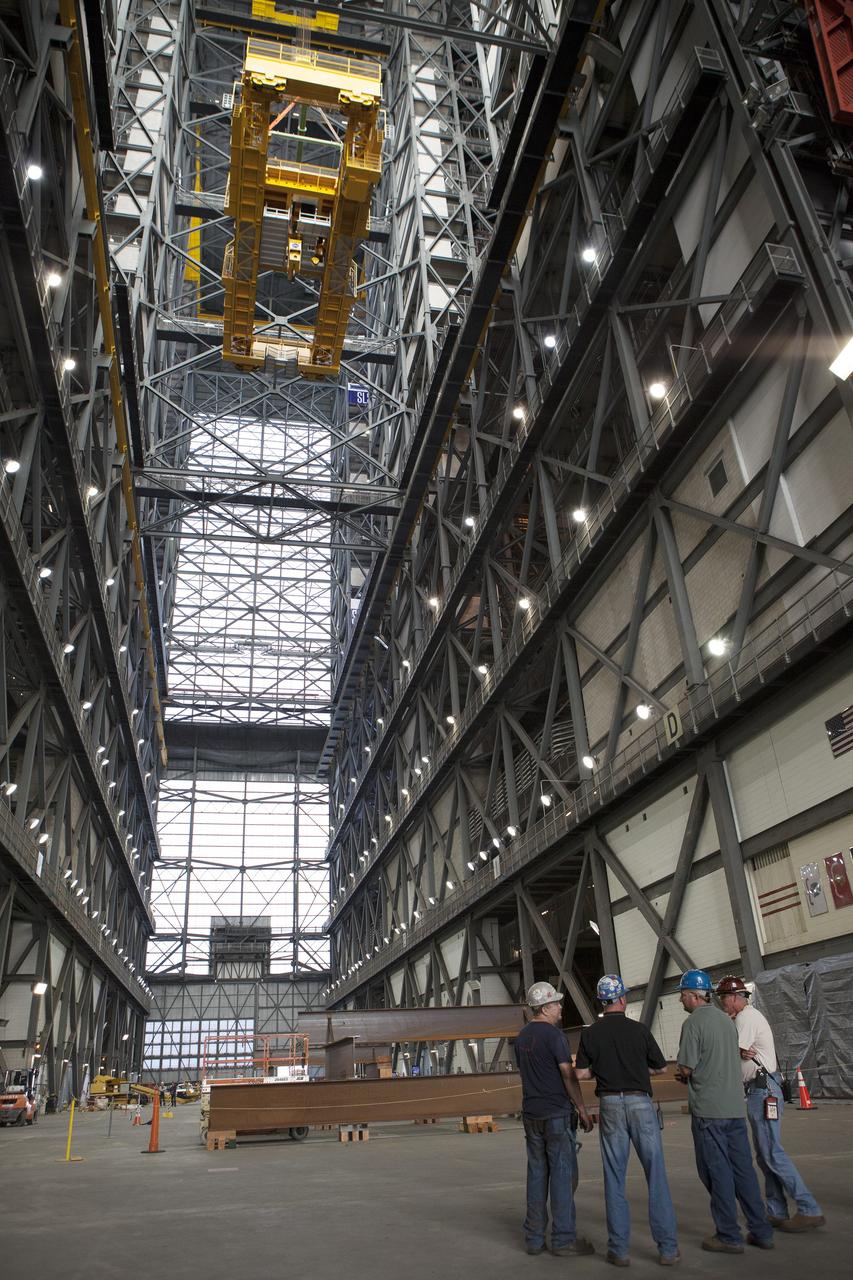

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the 175-ton crane has been turned as it is lowered by crane from Level 16 down to the transfer aisle floor. Upgrades to the crane's 45-year-old controls will be performed in order to improve reliability, precision and safety. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to the VAB. The crane will be upgraded so that it can support lifting needs for NASA and other exploration vehicles, including the agency's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
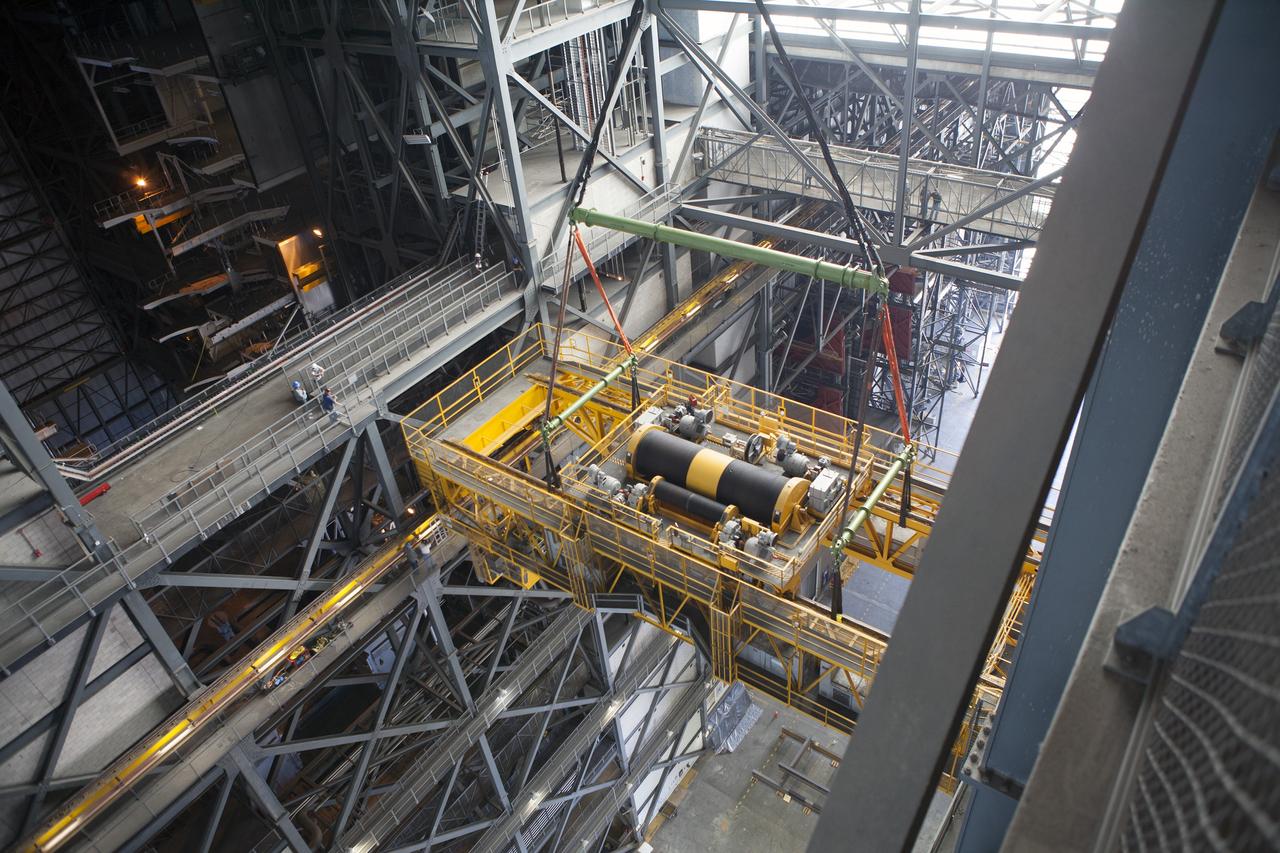

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a view from above shows a crane being used to lower the 175-ton crane. The crane is being lowered from Level 16 down to the transfer aisle floor to perform upgrades to its 45-year-old controls in order to improve reliability, precision and safety. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to the VAB. The crane will be upgraded so that it can support lifting needs for NASA and other exploration vehicles, including the agency's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
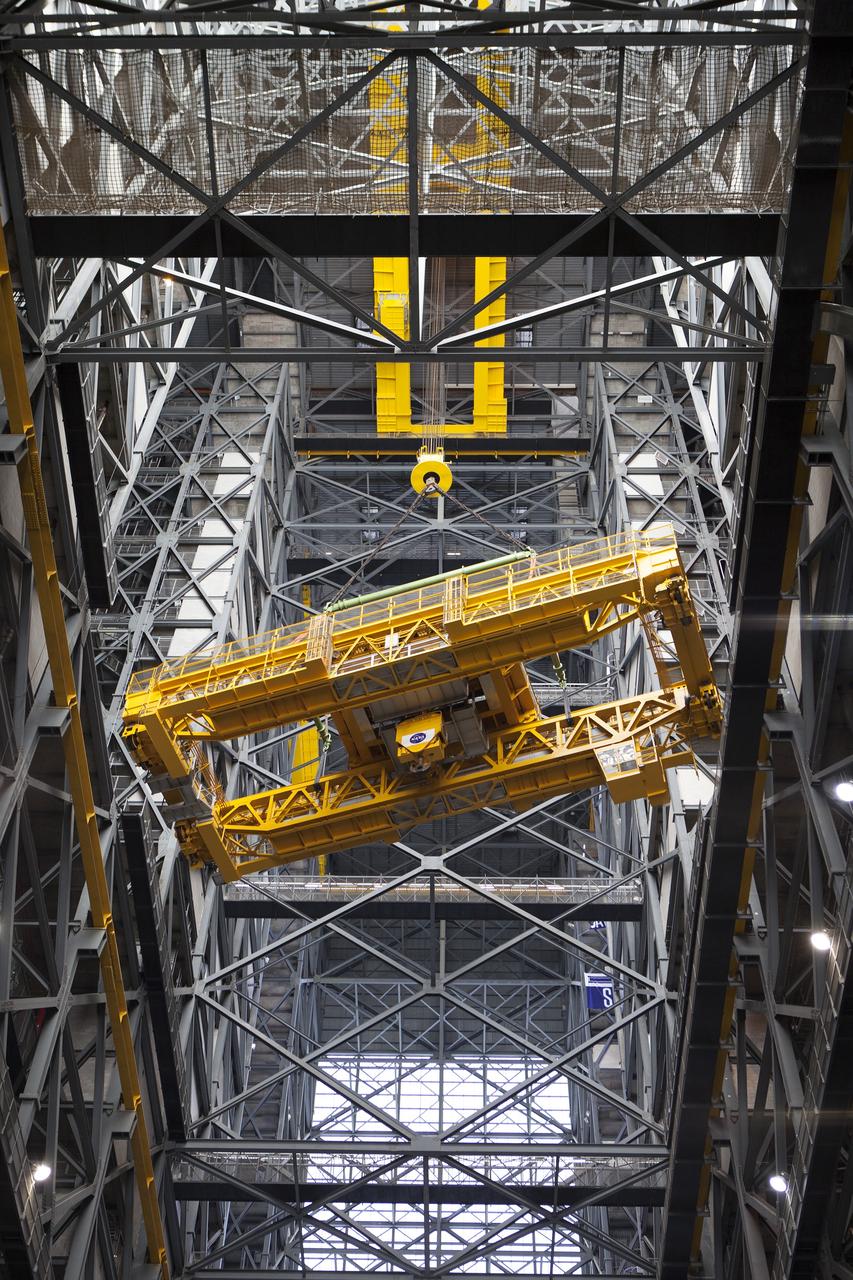

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the 175-ton crane is being turned as it is lowered by crane from Level 16 down to the transfer aisle floor. Upgrades to the crane's 45-year-old controls will be performed in order to improve reliability, precision and safety. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to the VAB. The crane will be upgraded so that it can support lifting needs for NASA and other exploration vehicles, including the agency's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
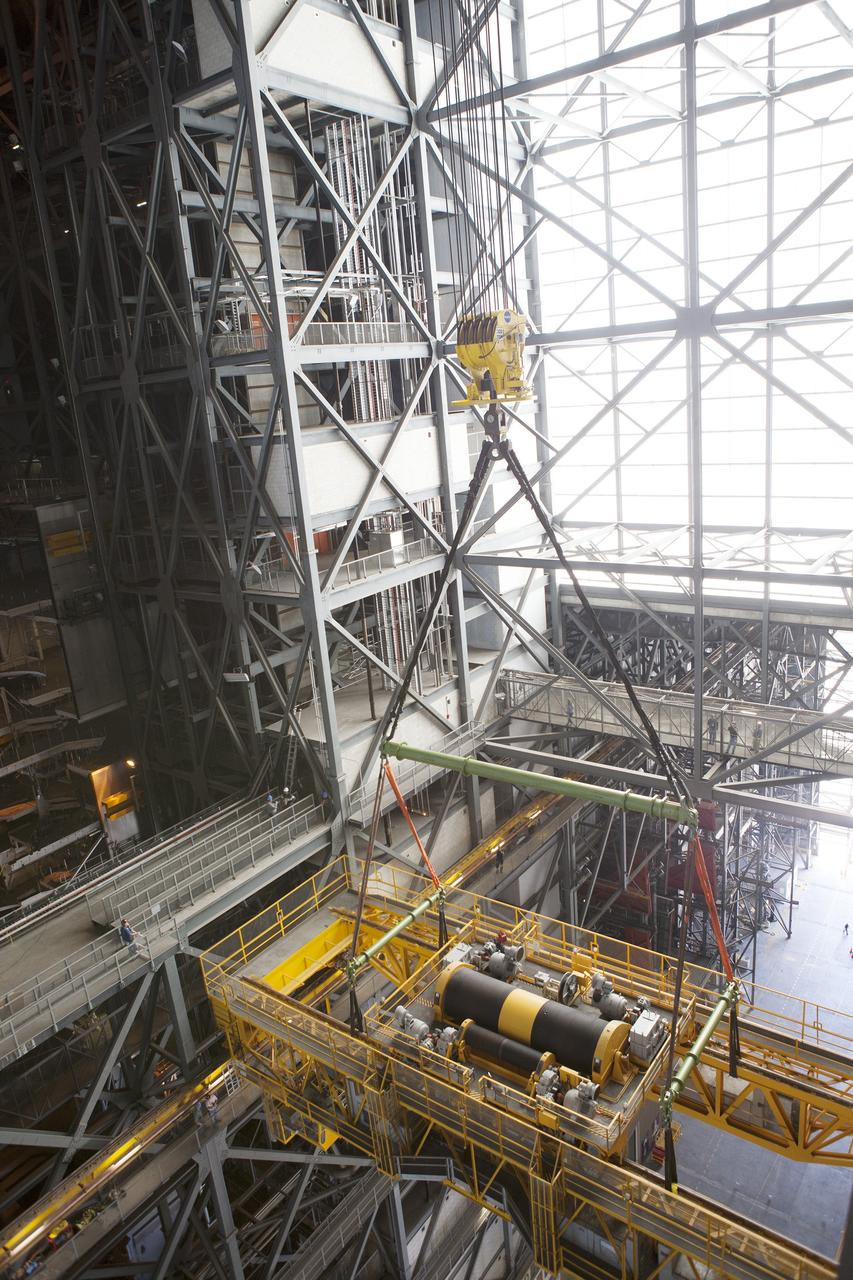

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a view from above shows a crane being used to lower the 175-ton crane. The crane is being lowered from Level 16 down to the transfer aisle floor to perform upgrades to its 45-year-old controls in order to improve reliability, precision and safety. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to the VAB. The crane will be upgraded so that it can support lifting needs for NASA and other exploration vehicles, including the agency's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
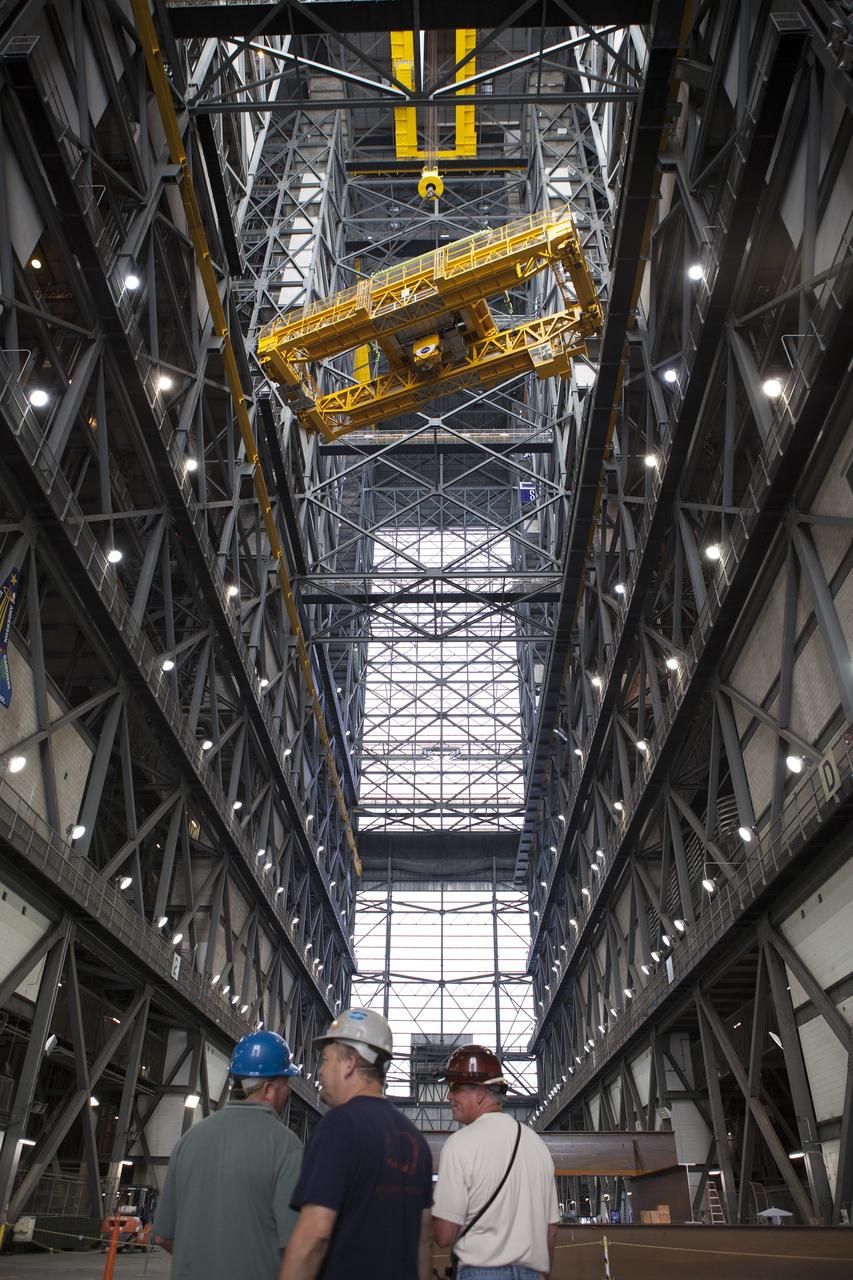

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the 175-ton crane is being turned as it is lowered by crane from Level 16 down to the transfer aisle floor. Upgrades to the crane's 45-year-old controls will be performed in order to improve reliability, precision and safety. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to the VAB. The crane will be upgraded so that it can support lifting needs for NASA and other exploration vehicles, including the agency's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
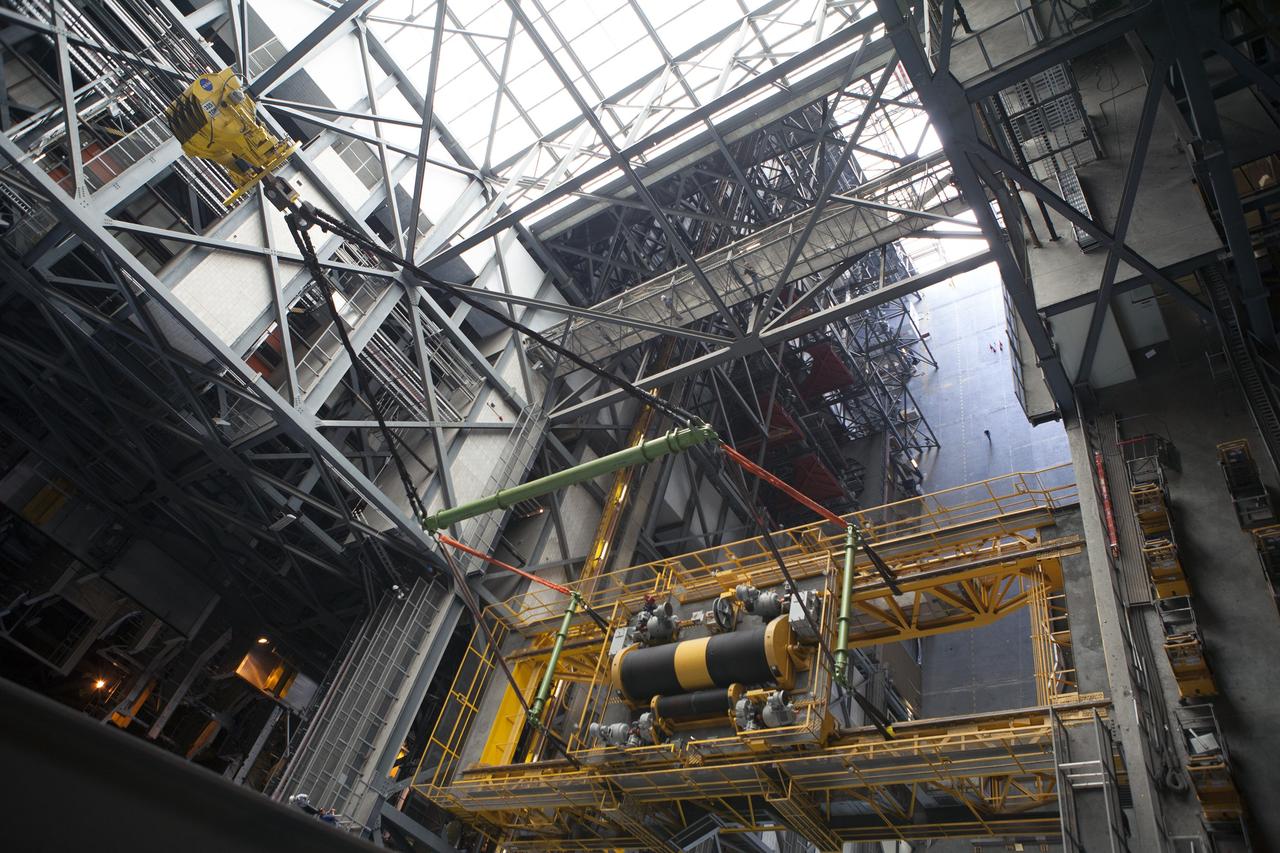

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a view from above shows a crane being used to lower the 175-ton crane. The crane is being lowered from Level 16 down to the transfer aisle floor to perform upgrades to its 45-year-old controls in order to improve reliability, precision and safety. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to the VAB. The crane will be upgraded so that it can support lifting needs for NASA and other exploration vehicles, including the agency's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
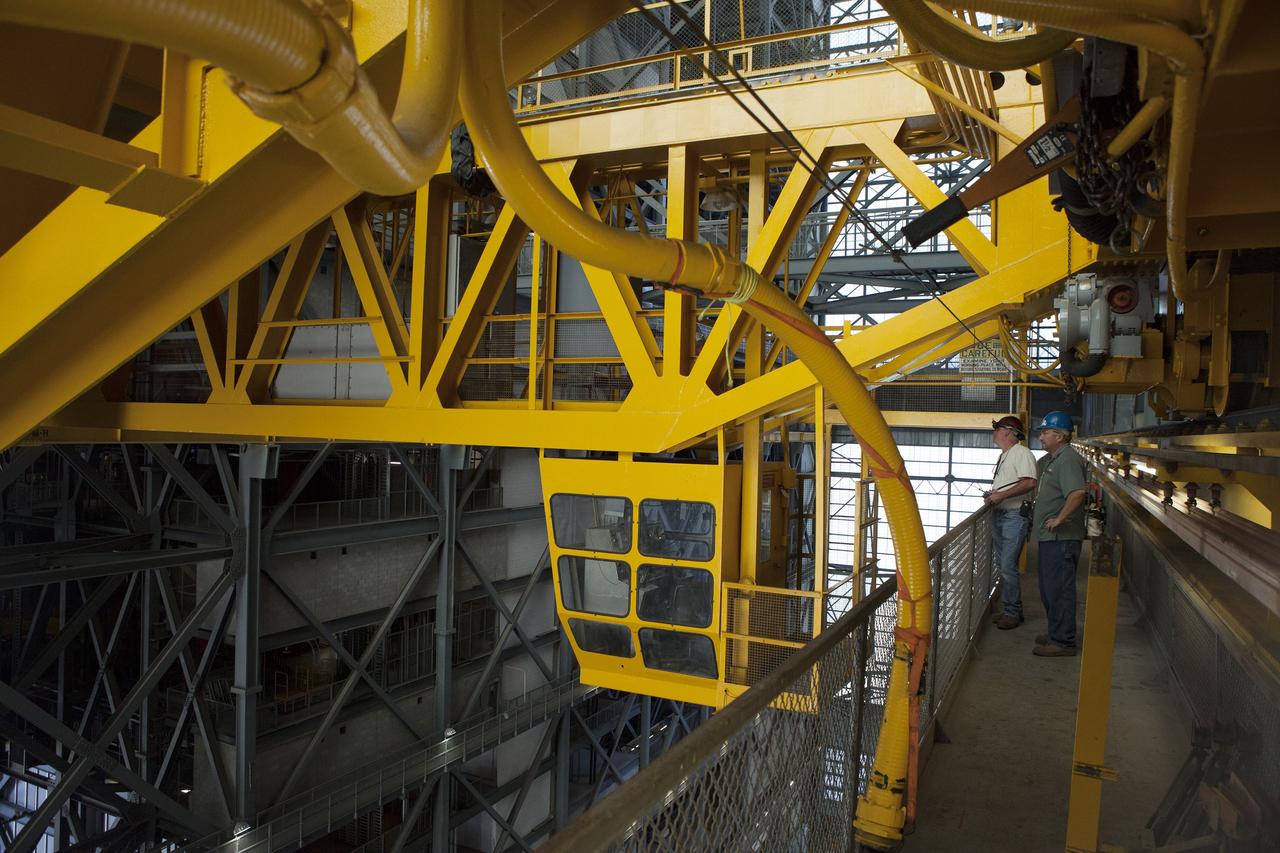

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, preparations are underway to lower the 175-ton crane. In view is the cab that is used to control the crane. The crane is being lowered from Level 16 down to the floor of the transfer aisle to perform upgrades to its 45-year-old controls in order to improve reliability, precision and safety. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to the VAB. The crane will be upgraded so that it can support lifting needs for NASA and other exploration vehicles, including the agency's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
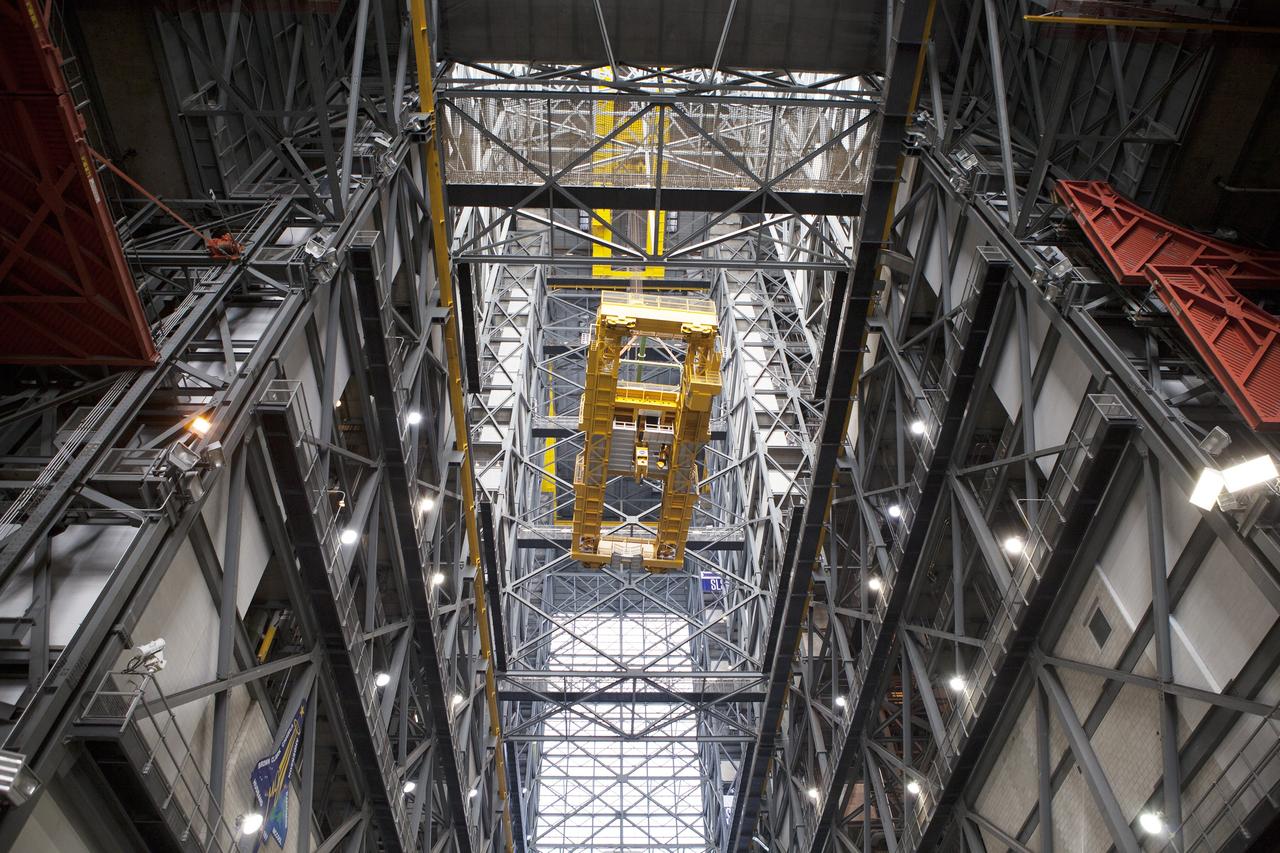

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the 175-ton crane has been turned as it is lowered by crane from Level 16 down to the transfer aisle floor. Upgrades to the crane's 45-year-old controls will be performed in order to improve reliability, precision and safety. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to the VAB. The crane will be upgraded so that it can support lifting needs for NASA and other exploration vehicles, including the agency's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
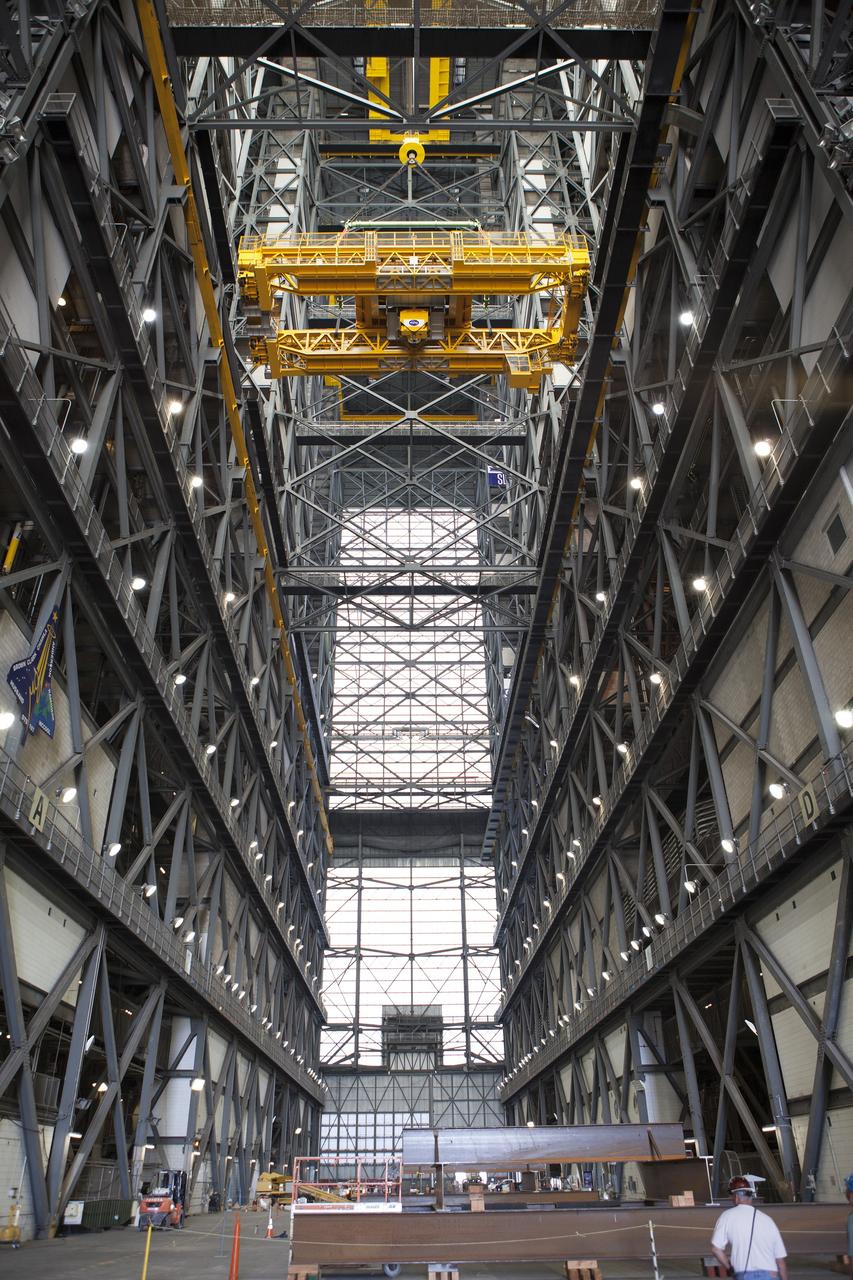

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane is being used to lower the 175-ton crane from Level 16 down to the transfer aisle floor. Upgrades to the crane's 45-year-old controls will be performed in order to improve reliability, precision and safety. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to the VAB. The crane will be upgraded so that it can support lifting needs for NASA and other exploration vehicles, including the agency's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane is being used to lower the 175-ton crane from Level 16 down to the transfer aisle floor. Upgrades to the crane's 45-year-old controls will be performed in order to improve reliability, precision and safety. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to the VAB. The crane will be upgraded so that it can support lifting needs for NASA and other exploration vehicles, including the agency's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the 175-ton crane is lowered closer to the transfer aisle floor. The crane was turned to make it easier to lower it from Level 16. Upgrades to the crane's 45-year-old controls will be performed in order to improve reliability, precision and safety. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to the VAB. The crane will be upgraded so that it can support lifting needs for NASA and other exploration vehicles, including the agency's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane is being used to lower the 175-ton crane from Level 16 down to the transfer aisle floor. Upgrades to the crane's 45-year-old controls will be performed in order to improve reliability, precision and safety. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to the VAB. The crane will be upgraded so that it can support lifting needs for NASA and other exploration vehicles, including the agency's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
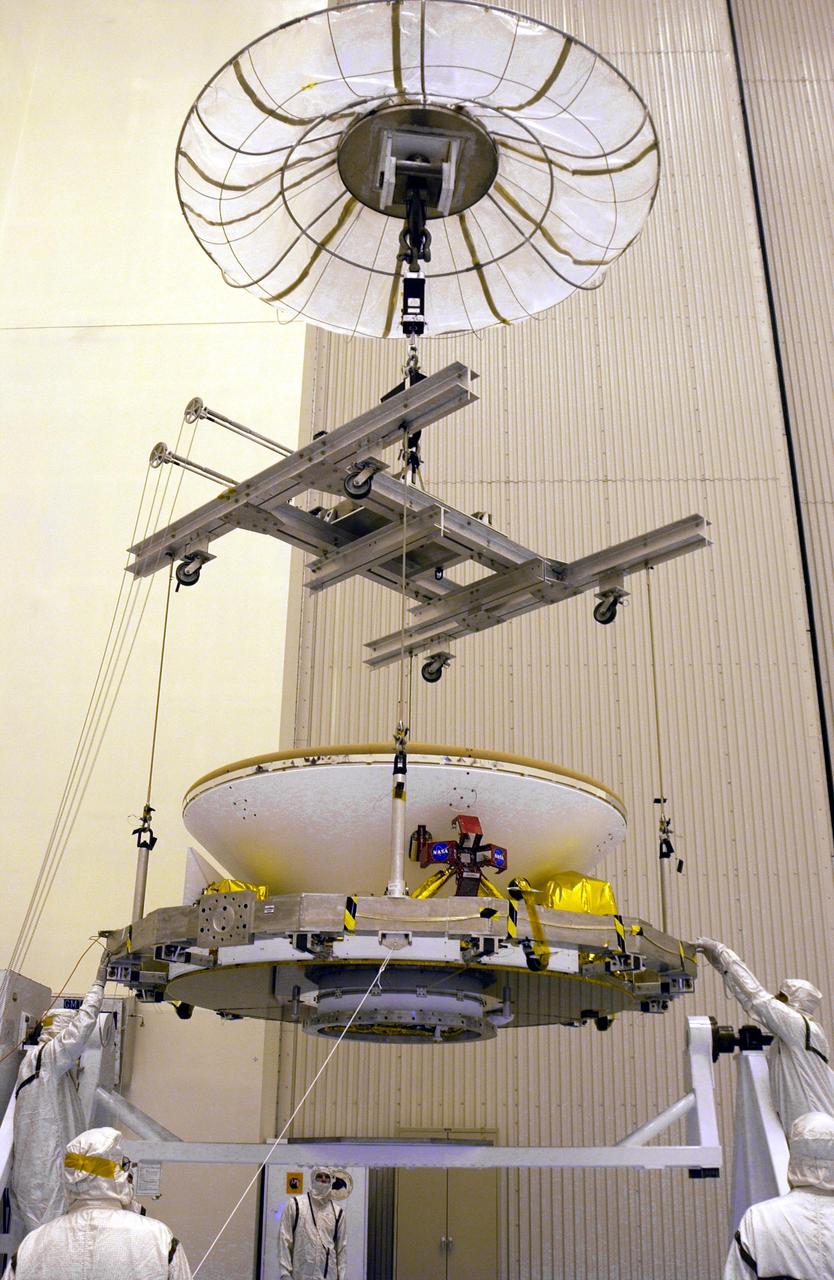

In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility, an overhead crane lowers the Mars Exploration Rover MER aeroshell toward a rotation stand.

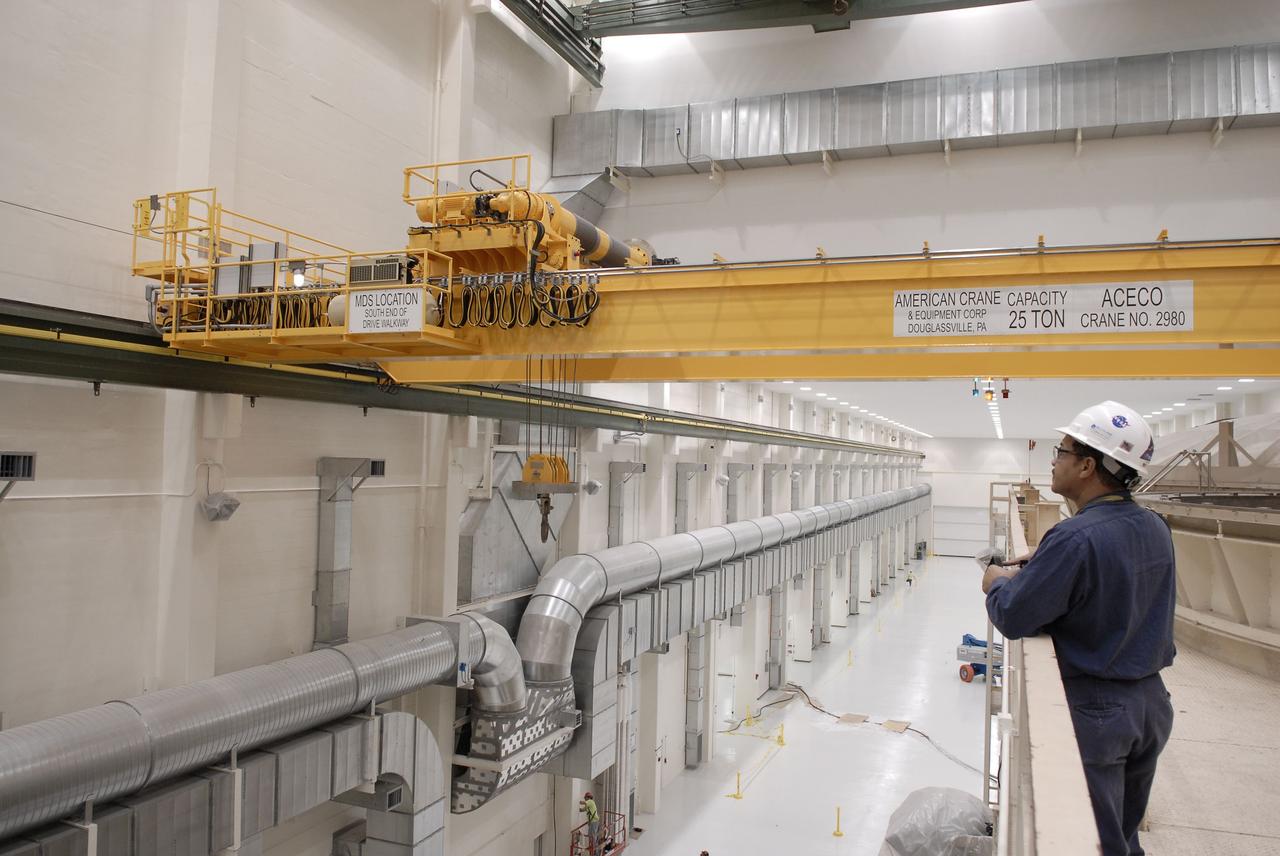
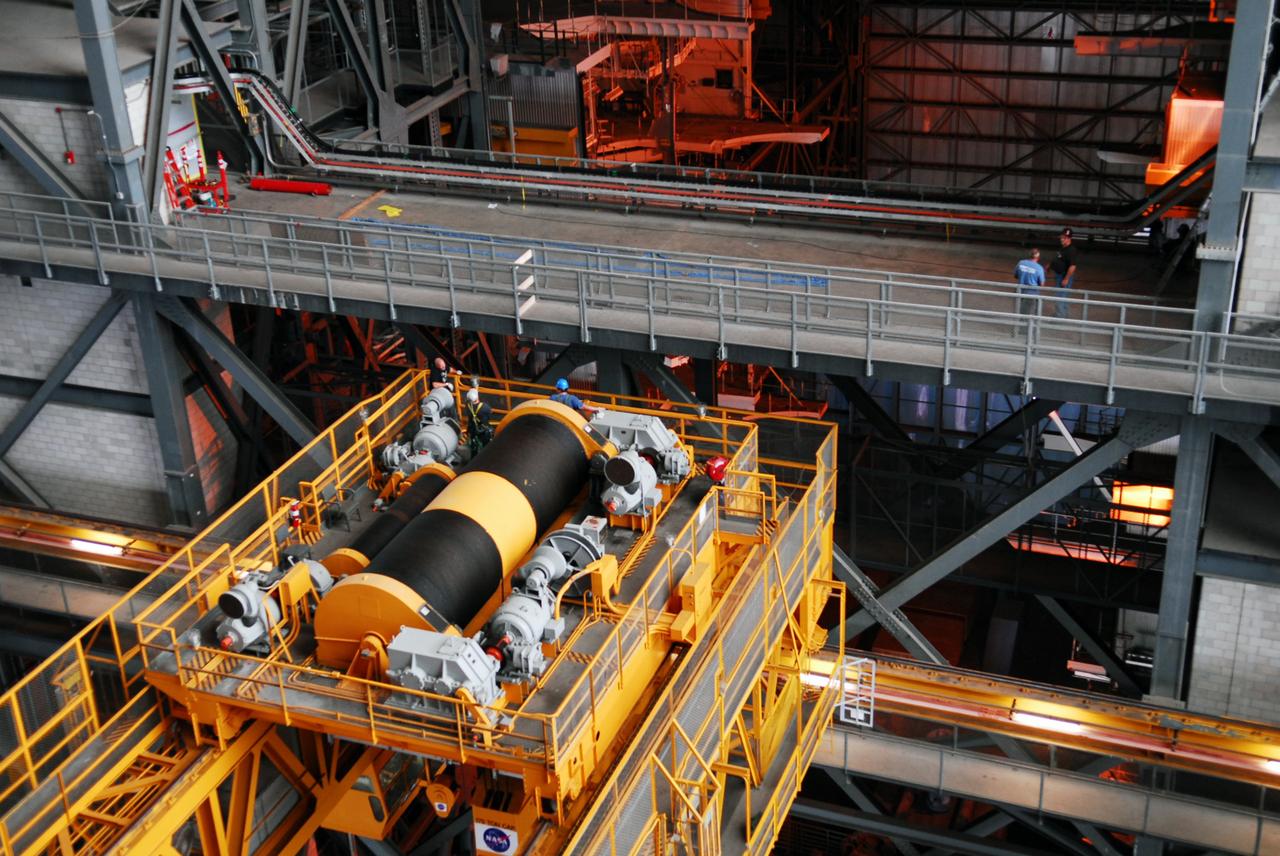
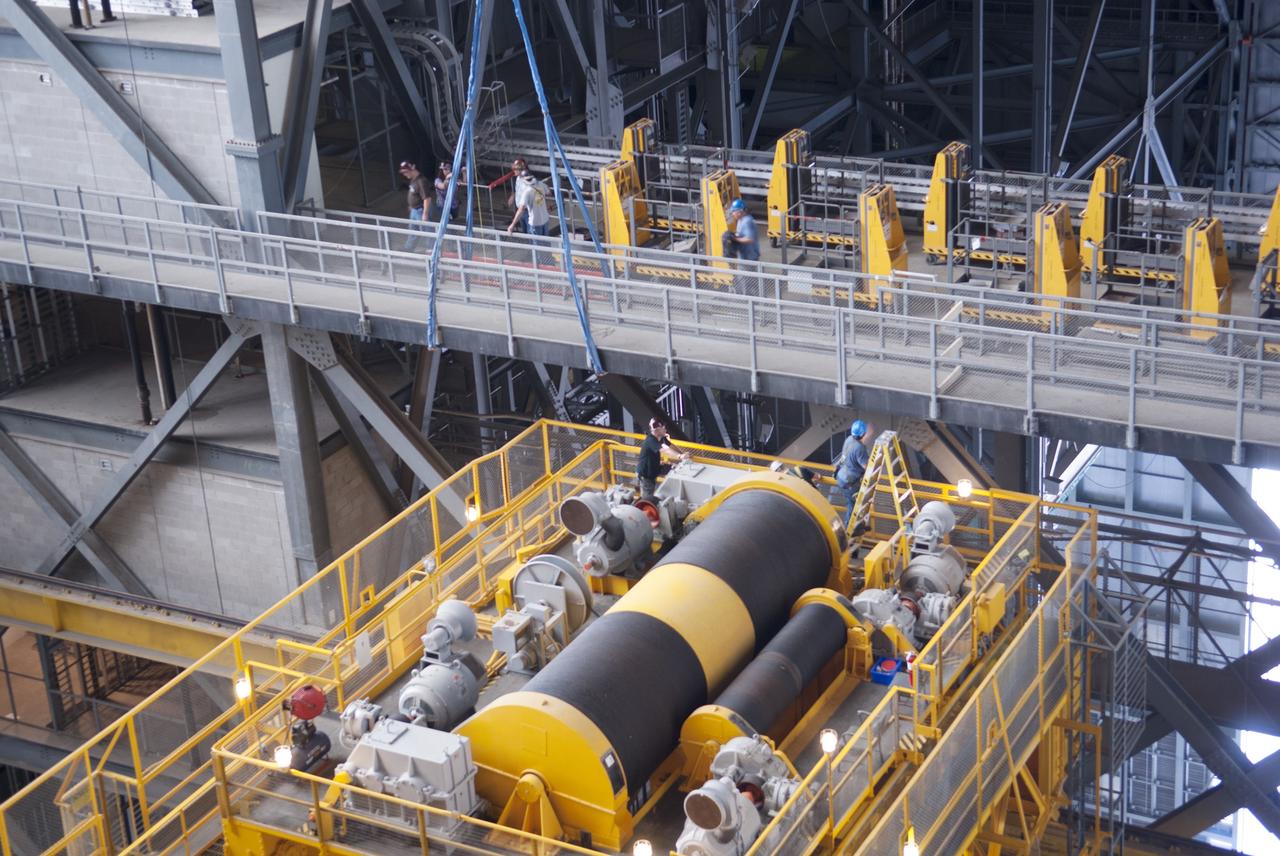
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Segments of a crane are lowered onto the floor of the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The new O&C low-bay crane is a 25-ton overhead bridge crane built for Lockheed Martin and Space Florida by American Crane and Equipment Corporation in Douglasville, Pa. The crane has a bridge span of 78’-2” and a hook height of 48’-10”. The crane will be used for lifting and moving flight hardware, fixtures and equipment in support of the Orion spacecraft manufacturing. Part of NASA's Constellation Program, the Orion spacecraft will return humans to the moon and prepare for future voyages to Mars and other destinations in our solar system. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Segments of a new crane are tested inside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The new O&C low-bay crane is a 25-ton overhead bridge crane built for Lockheed Martin and Space Florida by American Crane and Equipment Corporation in Douglasville, Pa. The crane has a bridge span of 78’-2” and a hook height of 48’-10”. The crane will be used for lifting and moving flight hardware, fixtures and equipment in support of the Orion spacecraft manufacturing. Part of NASA's Constellation Program, the Orion spacecraft will return humans to the moon and prepare for future voyages to Mars and other destinations in our solar system. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Segments of a crane are moved into the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The new O&C low-bay crane is a 25-ton overhead bridge crane built for Lockheed Martin and Space Florida by American Crane and Equipment Corporation in Douglasville, Pa. The crane has a bridge span of 78’-2” and a hook height of 48’-10”. The crane will be used for lifting and moving flight hardware, fixtures and equipment in support of the Orion spacecraft manufacturing. Part of NASA's Constellation Program, the Orion spacecraft will return humans to the moon and prepare for future voyages to Mars and other destinations in our solar system. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Segments of a crane arrive at the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The new O&C low-bay crane is a 25-ton overhead bridge crane built for Lockheed Martin and Space Florida by American Crane and Equipment Corporation in Douglasville, Pa. The crane has a bridge span of 78’-2” and a hook height of 48’-10”. The crane will be used for lifting and moving flight hardware, fixtures and equipment in support of the Orion spacecraft manufacturing. Part of NASA's Constellation Program, the Orion spacecraft will return humans to the moon and prepare for future voyages to Mars and other destinations in our solar system. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
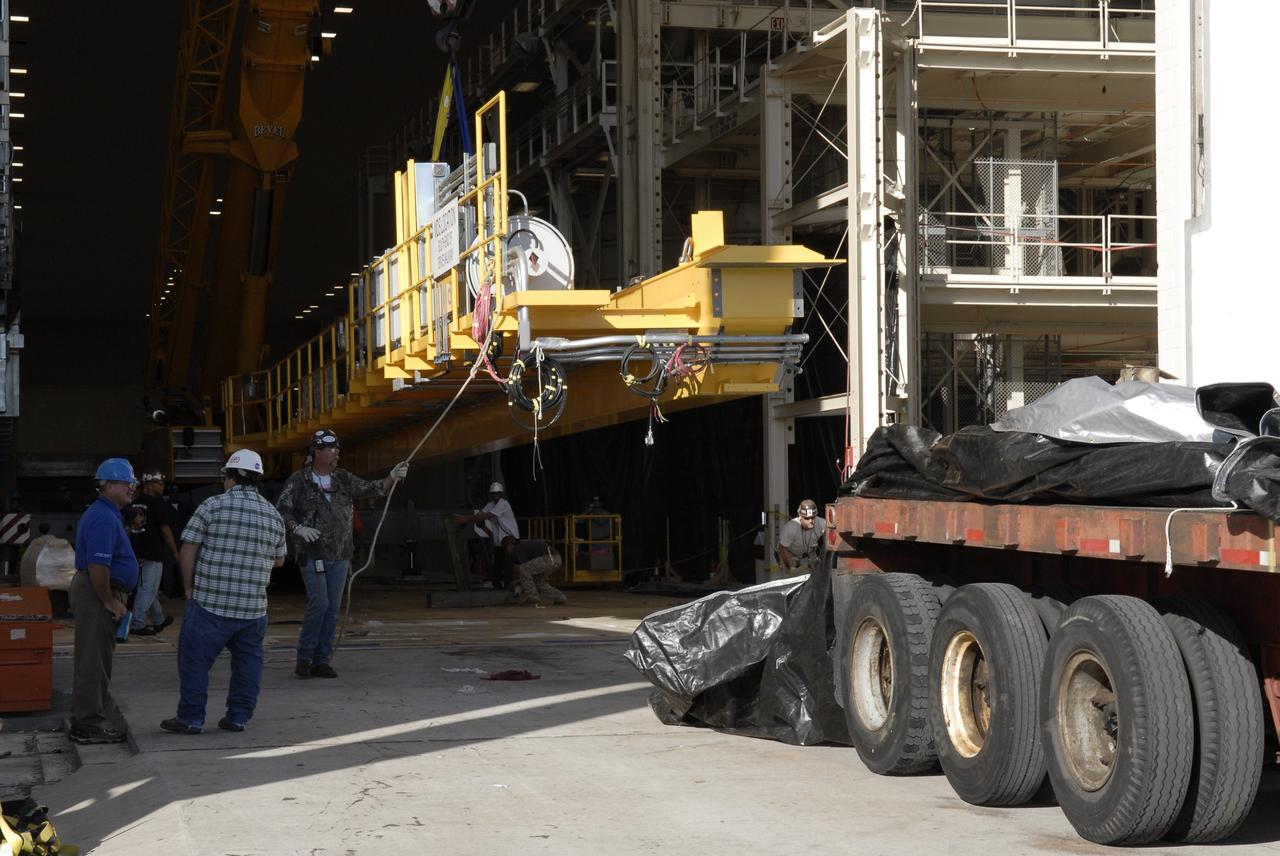

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Segments of a crane are being offloaded at the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The new O&C low-bay crane is a 25-ton overhead bridge crane built for Lockheed Martin and Space Florida by American Crane and Equipment Corporation in Douglasville, Pa. The crane has a bridge span of 78’-2” and a hook height of 48’-10”. The crane will be used for lifting and moving flight hardware, fixtures and equipment in support of the Orion spacecraft manufacturing. Part of NASA's Constellation Program, the Orion spacecraft will return humans to the moon and prepare for future voyages to Mars and other destinations in our solar system. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
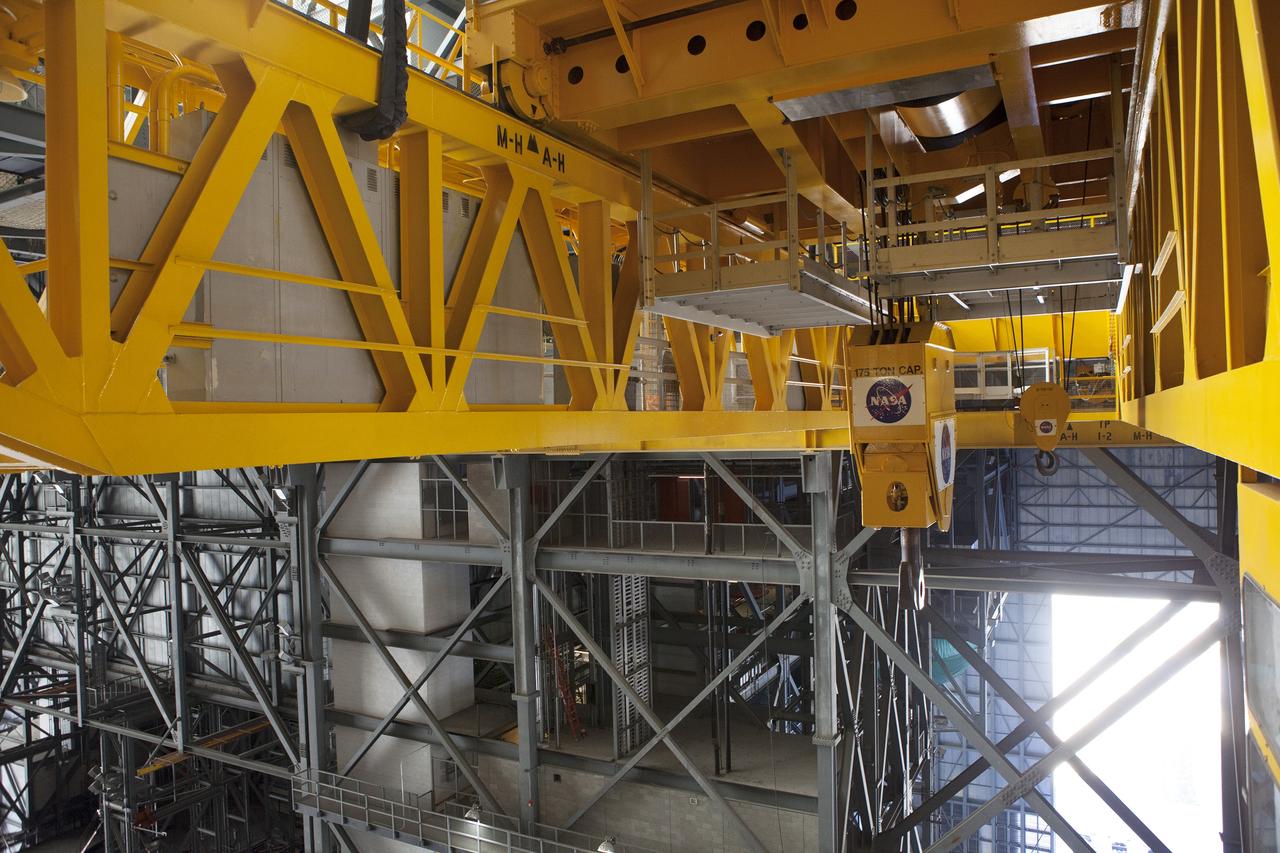

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, preparations are underway to lower the 175-ton crane. The crane is being lowered from Level 16 down to the floor of the transfer aisle to perform upgrades to its 45-year-old controls in order to improve reliability, precision and safety. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to the VAB. The crane will be upgraded so that it can support lifting needs for NASA and other exploration vehicles, including the agency's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
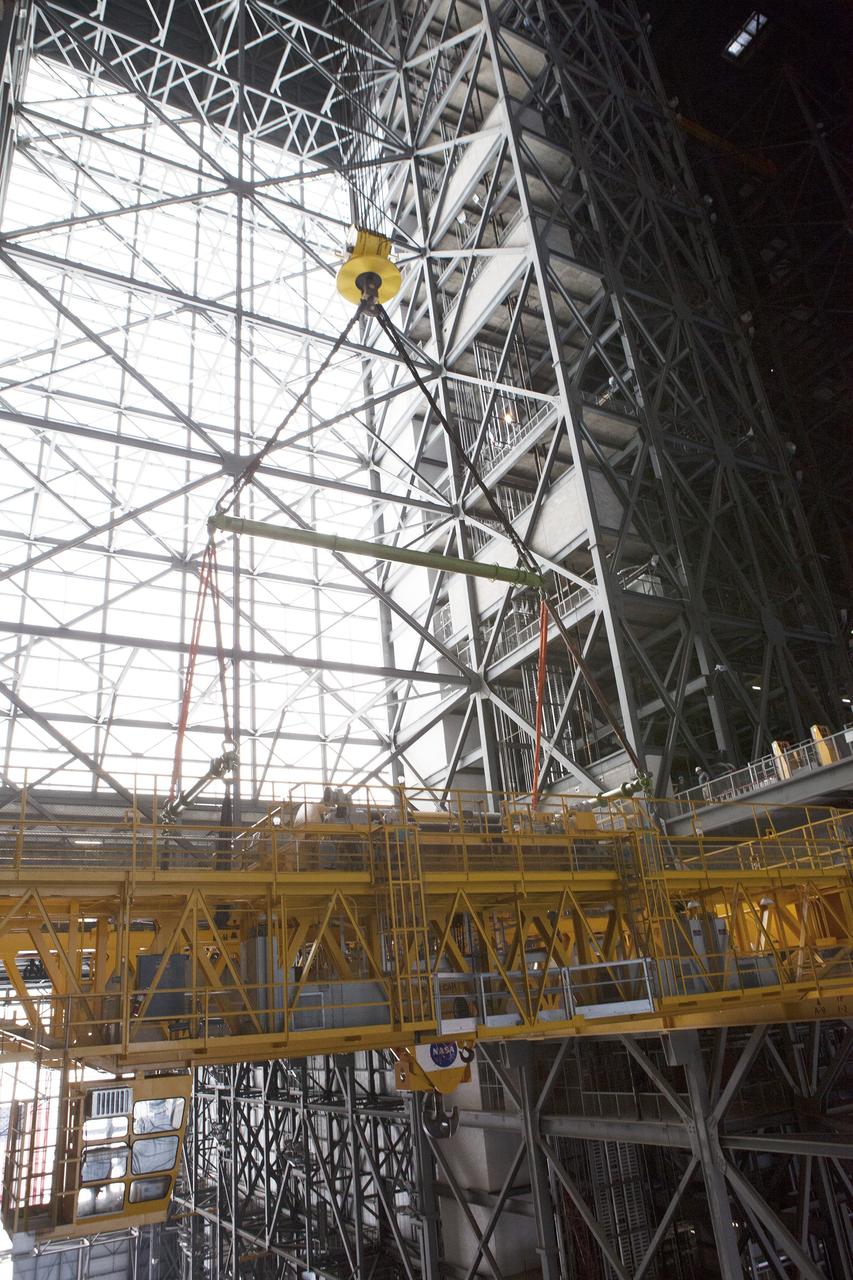

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, preparations are underway to lower the 175-ton crane. The crane is being lowered from Level 16 down to the floor of the transfer aisle to perform upgrades to its 45-year-old controls in order to improve reliability, precision and safety. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to the VAB. The crane will be upgraded so that it can support lifting needs for NASA and other exploration vehicles, including the agency's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the 175-ton crane is being lowered from Level 16 down to the transfer aisle floor. Upgrades to the crane's 45-year-old controls will be performed in order to improve reliability, precision and safety. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to the VAB. The crane will be upgraded so that it can support lifting needs for NASA and other exploration vehicles, including the agency's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
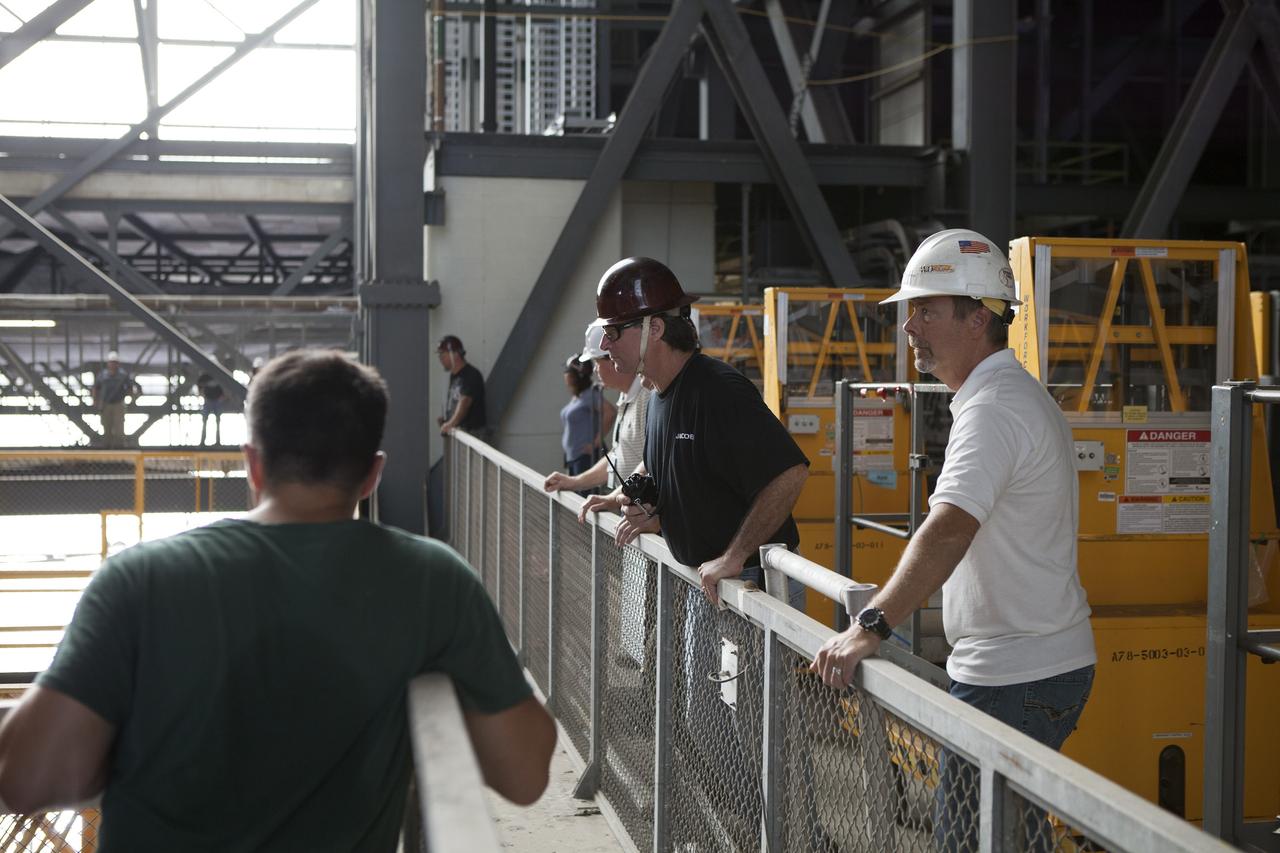

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, NASA and contractor workers monitor the progress as the 175-ton crane is being lowered from Level 16 down to the transfer aisle floor. Upgrades to the crane's 45-year-old controls will be performed in order to improve reliability, precision and safety. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to the VAB. The crane will be upgraded so that it can support lifting needs for NASA and other exploration vehicles, including the agency's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
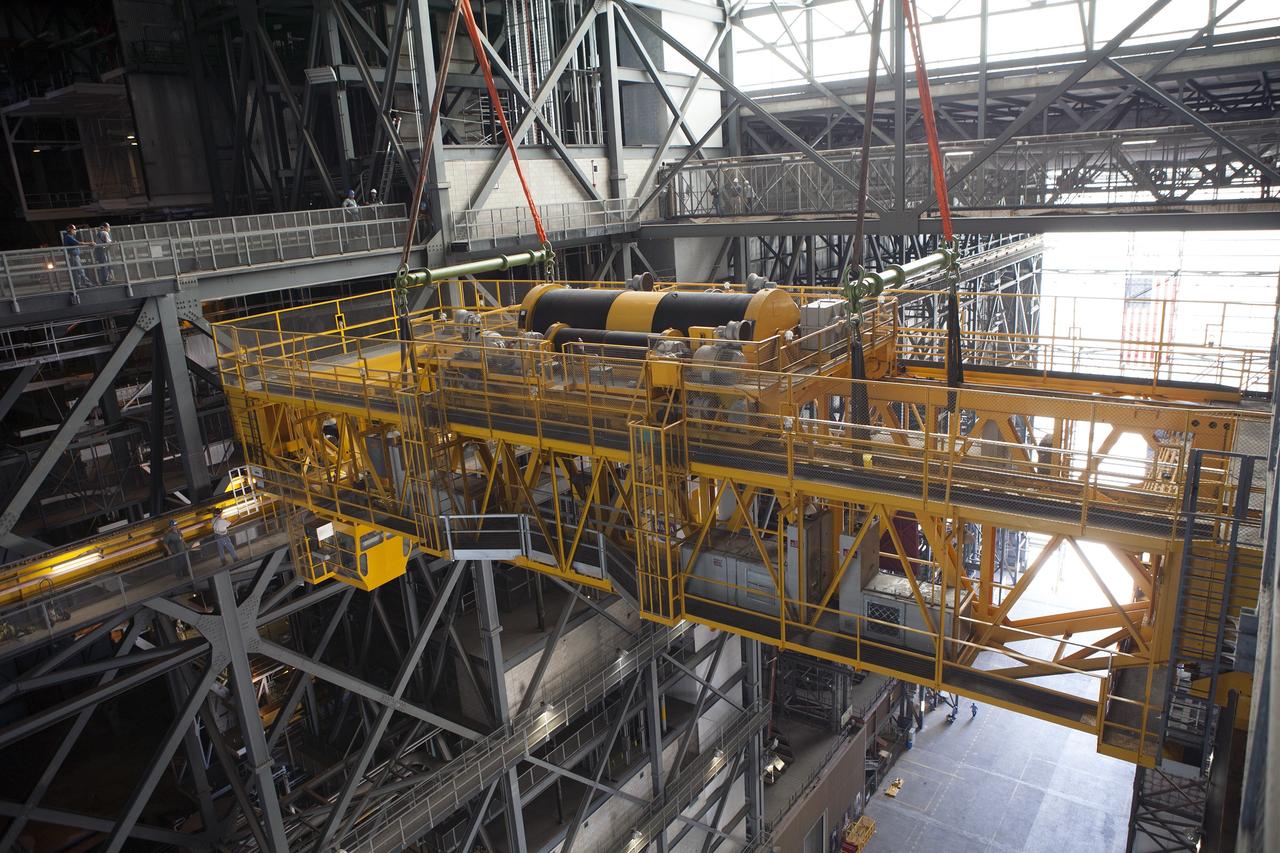

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the 175-ton crane is being lowered from Level 16 down to the transfer aisle floor. Upgrades to the crane's 45-year-old controls will be performed in order to improve reliability, precision and safety. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to the VAB. The crane will be upgraded so that it can support lifting needs for NASA and other exploration vehicles, including the agency's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Motion of the segments of a new crane is tested inside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The new O&C low-bay crane is a 25-ton overhead bridge crane built for Lockheed Martin and Space Florida by American Crane and Equipment Corporation in Douglasville, Pa. The crane has a bridge span of 78’-2” and a hook height of 48’-10”. The crane will be used for lifting and moving flight hardware, fixtures and equipment in support of the Orion spacecraft manufacturing. Part of NASA's Constellation Program, the Orion spacecraft will return humans to the moon and prepare for future voyages to Mars and other destinations in our solar system. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
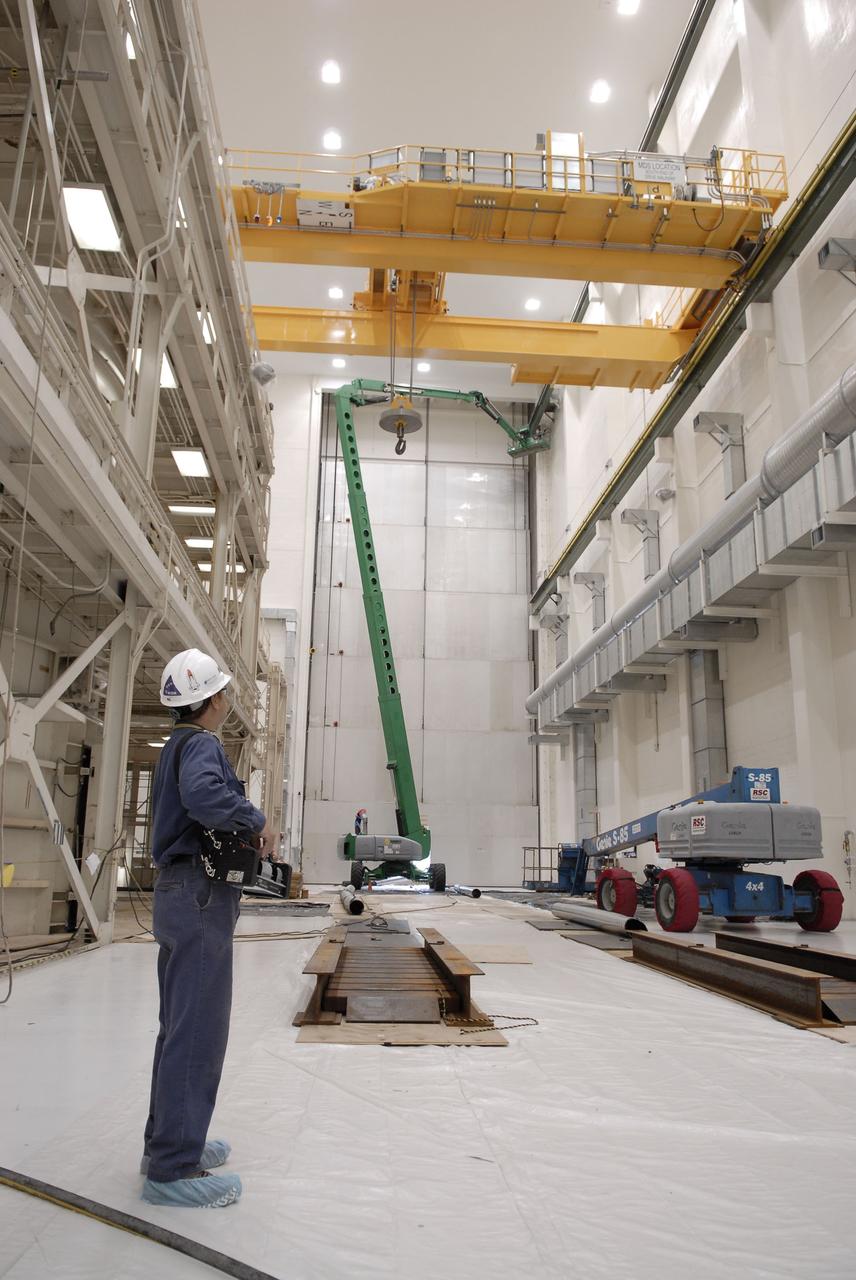

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Movement of the hook from a new crane are is tested inside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The new O&C low-bay crane is a 25-ton overhead bridge crane built for Lockheed Martin and Space Florida by American Crane and Equipment Corporation in Douglasville, Pa. The crane has a bridge span of 78’-2” and a hook height of 48’-10”. The crane will be used for lifting and moving flight hardware, fixtures and equipment in support of the Orion spacecraft manufacturing. Part of NASA's Constellation Program, the Orion spacecraft will return humans to the moon and prepare for future voyages to Mars and other destinations in our solar system. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
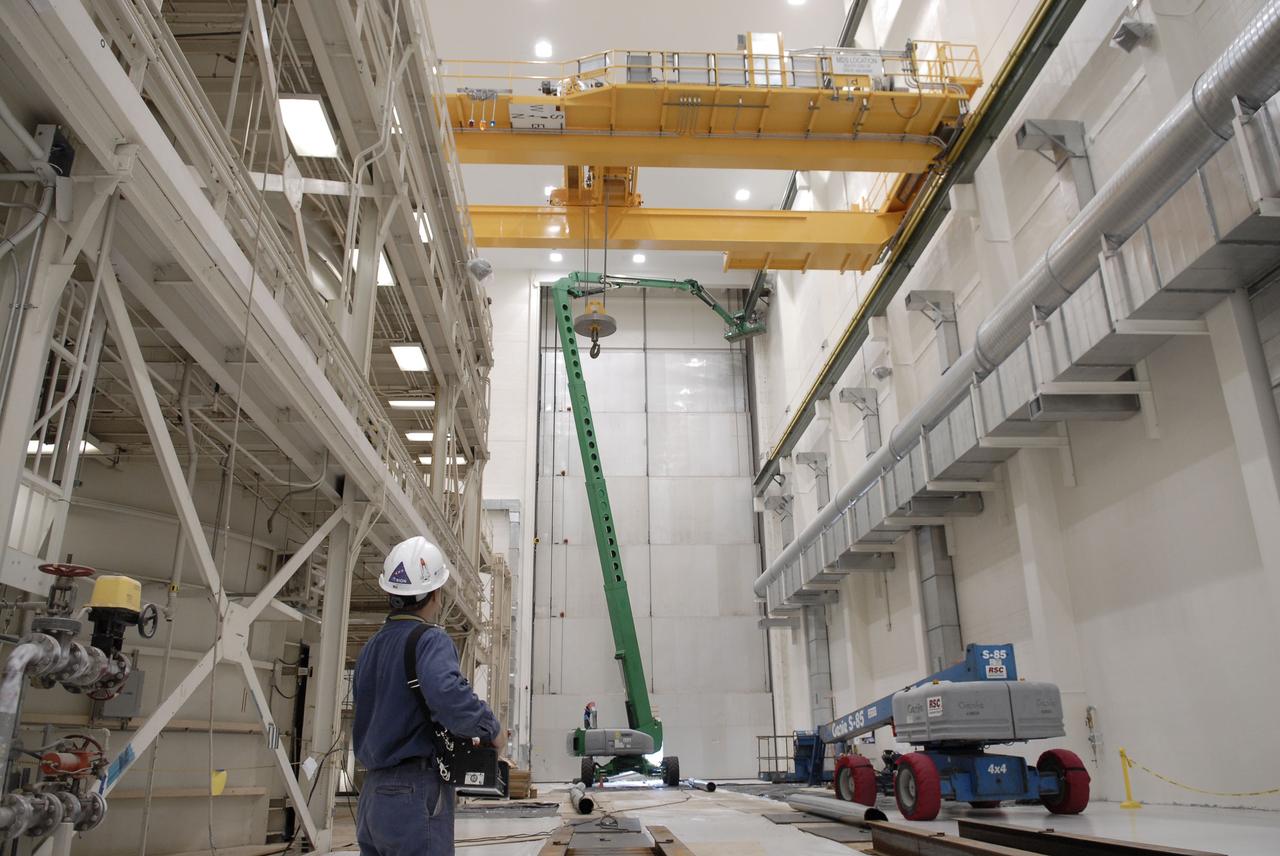

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Motion of the segments of a new crane is tested inside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The new O&C low-bay crane is a 25-ton overhead bridge crane built for Lockheed Martin and Space Florida by American Crane and Equipment Corporation in Douglasville, Pa. The crane has a bridge span of 78’-2” and a hook height of 48’-10”. The crane will be used for lifting and moving flight hardware, fixtures and equipment in support of the Orion spacecraft manufacturing. Part of NASA's Constellation Program, the Orion spacecraft will return humans to the moon and prepare for future voyages to Mars and other destinations in our solar system. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
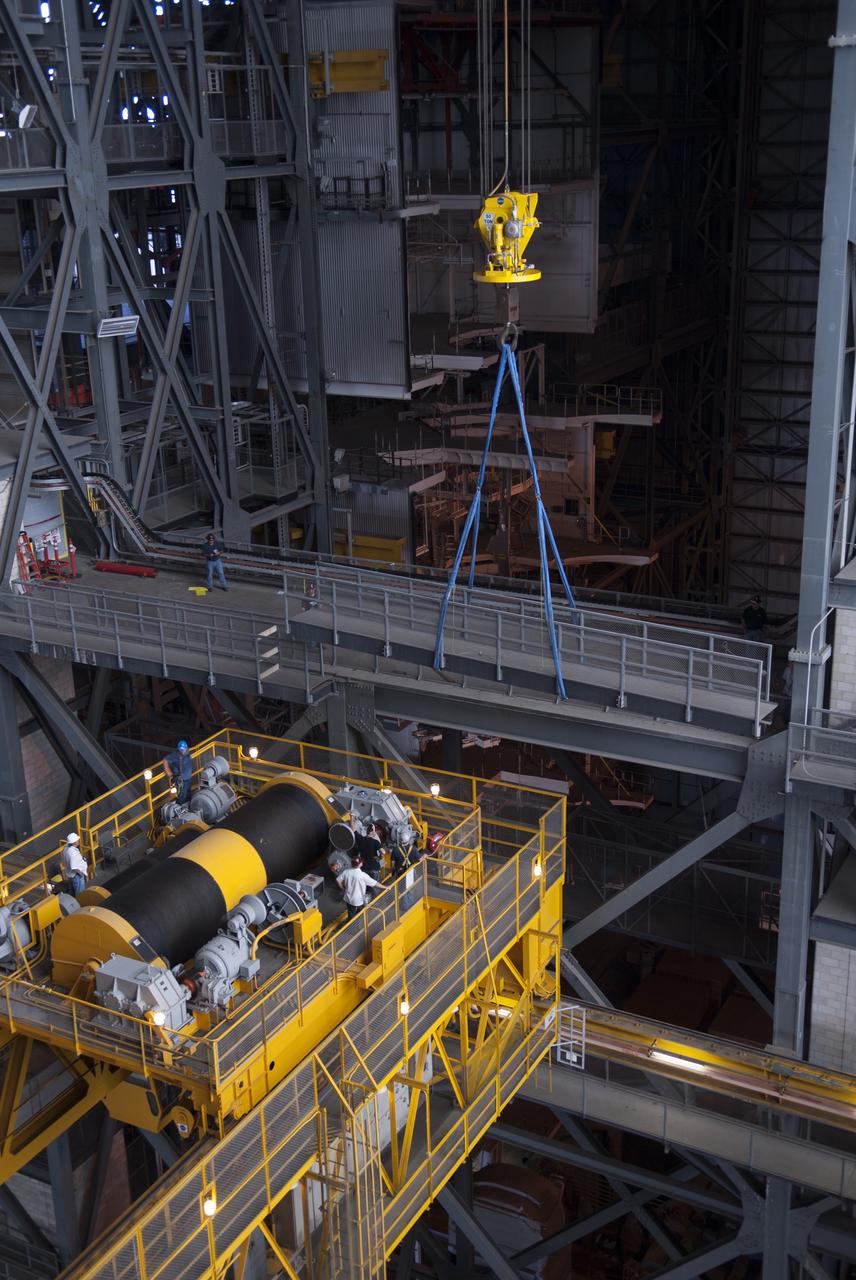

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane is used to lift up a portion of the catwalk on the east side of Level 16. The catwalk is being removed to allow room for the removal of the 175-ton crane that is situated above the transfer aisle. The crane will be lowered to the floor to perform upgrades to its 45-year-old controls in order to improve reliability, precision and safety. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to the VAB. The crane will be upgraded so that it can support lifting needs for NASA and other exploration vehicles, including the agency's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
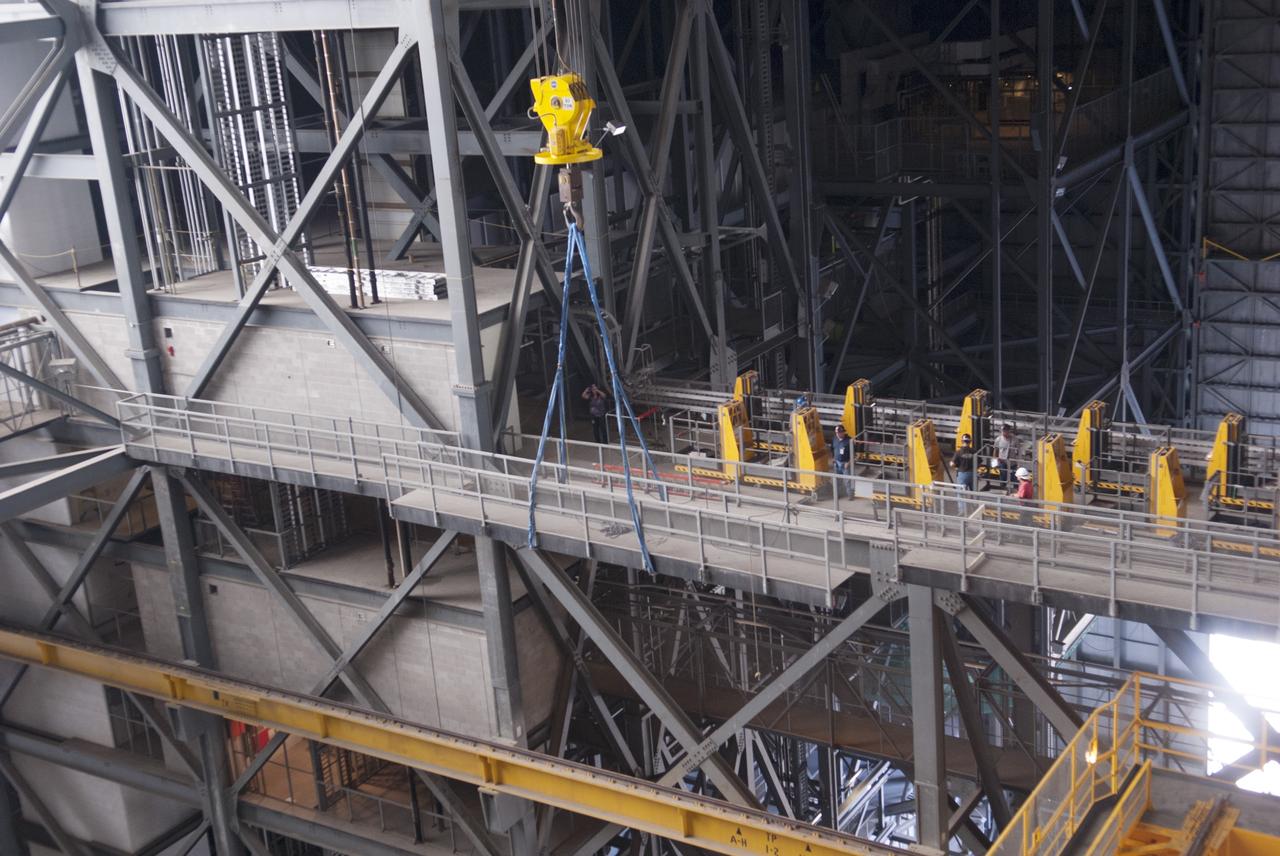

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane is used to remove a portion of the catwalk on the west side of Level 16. The catwalk is being removed to allow room for the removal of the 175-ton crane that is situated above the transfer aisle. The crane will be lowered to the floor to perform upgrades to its 45-year-old controls in order to improve reliability, precision and safety. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to the VAB. The crane will be upgraded so that it can support lifting needs for NASA and other exploration vehicles, including the agency's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
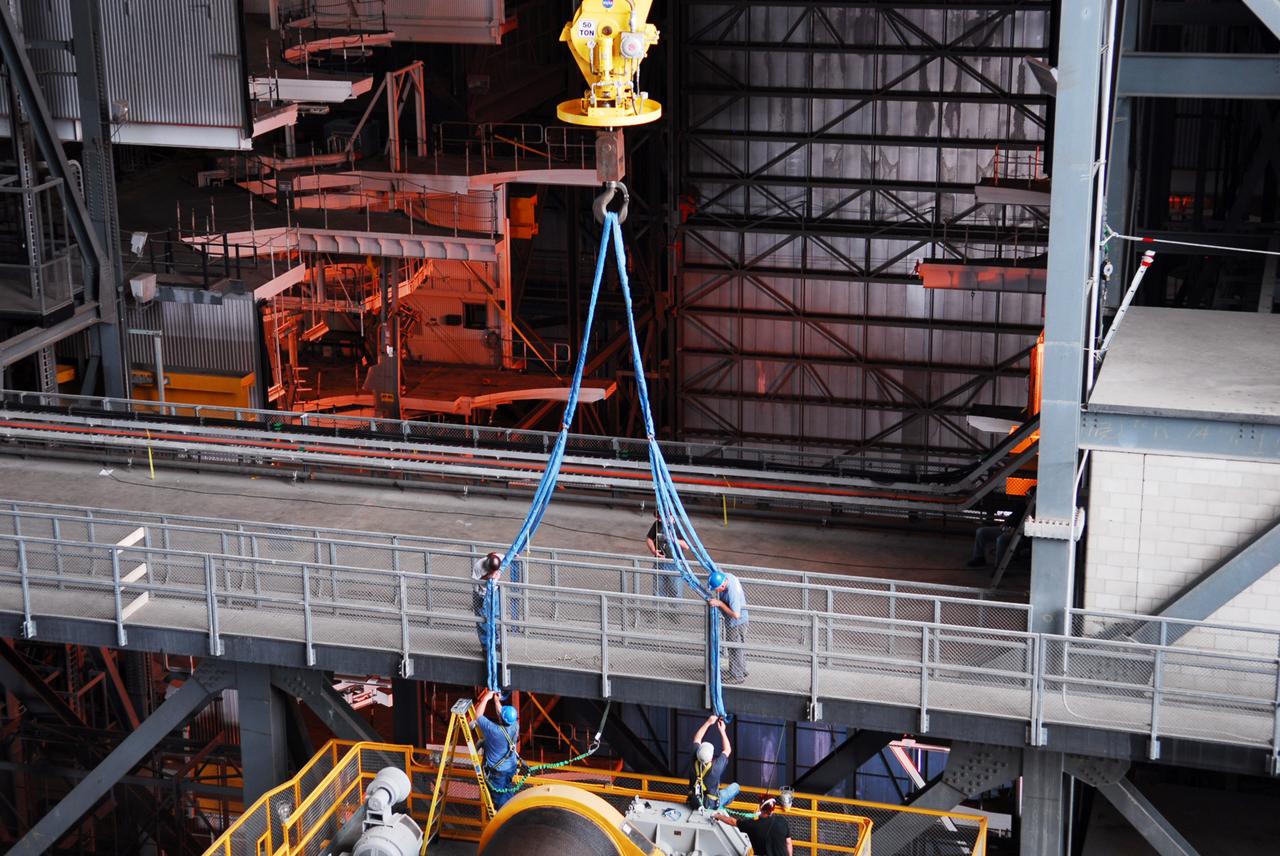

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers have secured a crane to a portion of the catwalk on the east side of Level 16. The catwalk will be removed to allow room for the removal of the 175-ton crane that is situated above the transfer aisle. The crane will be lowered to the floor to perform upgrades to its 45-year-old controls in order to improve reliability, precision and safety. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to the VAB. The crane will be upgraded so that it can support lifting needs for NASA and other exploration vehicles, including the agency's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
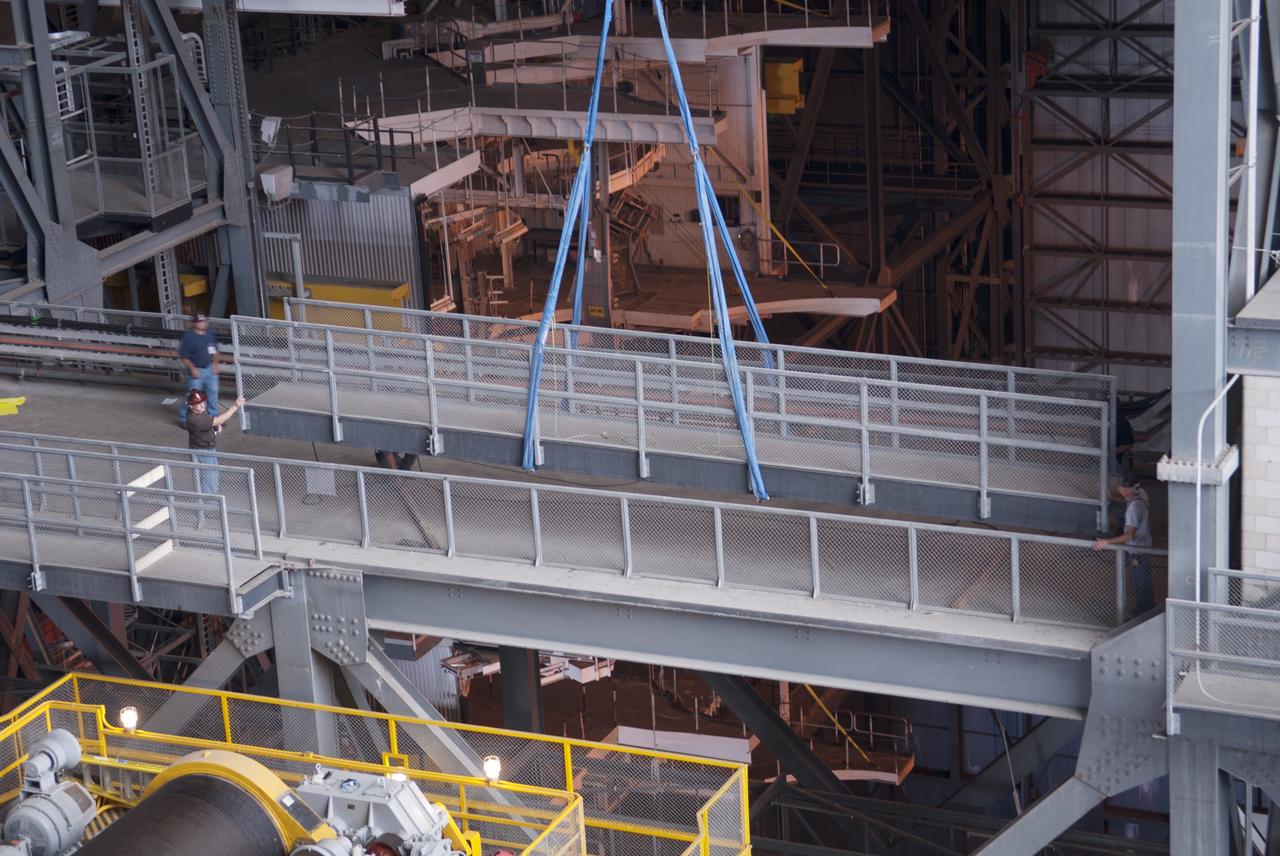

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers monitor the progress as a crane lifts up a portion of the catwalk on the east side of Level 16. The catwalk is being removed to allow room for the removal of the 175-ton crane that is situated above the transfer aisle. The crane will be lowered to the floor to perform upgrades to its 45-year-old controls in order to improve reliability, precision and safety. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to the VAB. The crane will be upgraded so that it can support lifting needs for NASA and other exploration vehicles, including the agency's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
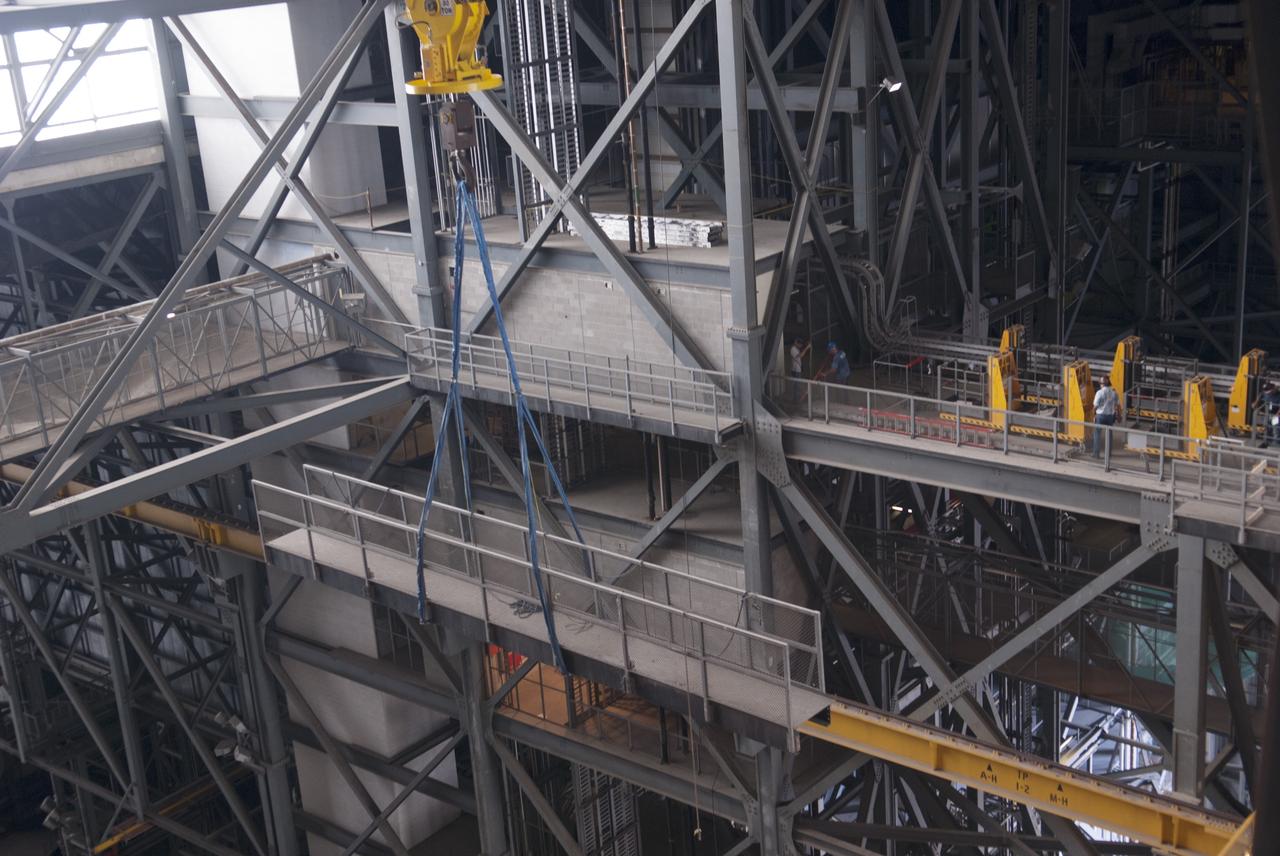

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a portion of the catwalk on the west side of Level 16 has been removed by crane and is being moved over the east side for storage. The catwalk was removed to allow room for the removal of the 175-ton crane that is situated above the transfer aisle. The crane will be lowered to the floor to perform upgrades to its 45-year-old controls in order to improve reliability, precision and safety. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to the VAB. The crane will be upgraded so that it can support lifting needs for NASA and other exploration vehicles, including the agency's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, portions of the catwalks on the east and west sides of Level 16 have been removed by crane and are being placed on the east side for storage. The catwalks were removed to allow room for the removal of the 175-ton crane that is situated above the transfer aisle. The crane will be lowered to the floor to perform upgrades to its 45-year-old controls in order to improve reliability, precision and safety. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to the VAB. The crane will be upgraded so that it can support lifting needs for NASA and other exploration vehicles, including the agency's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

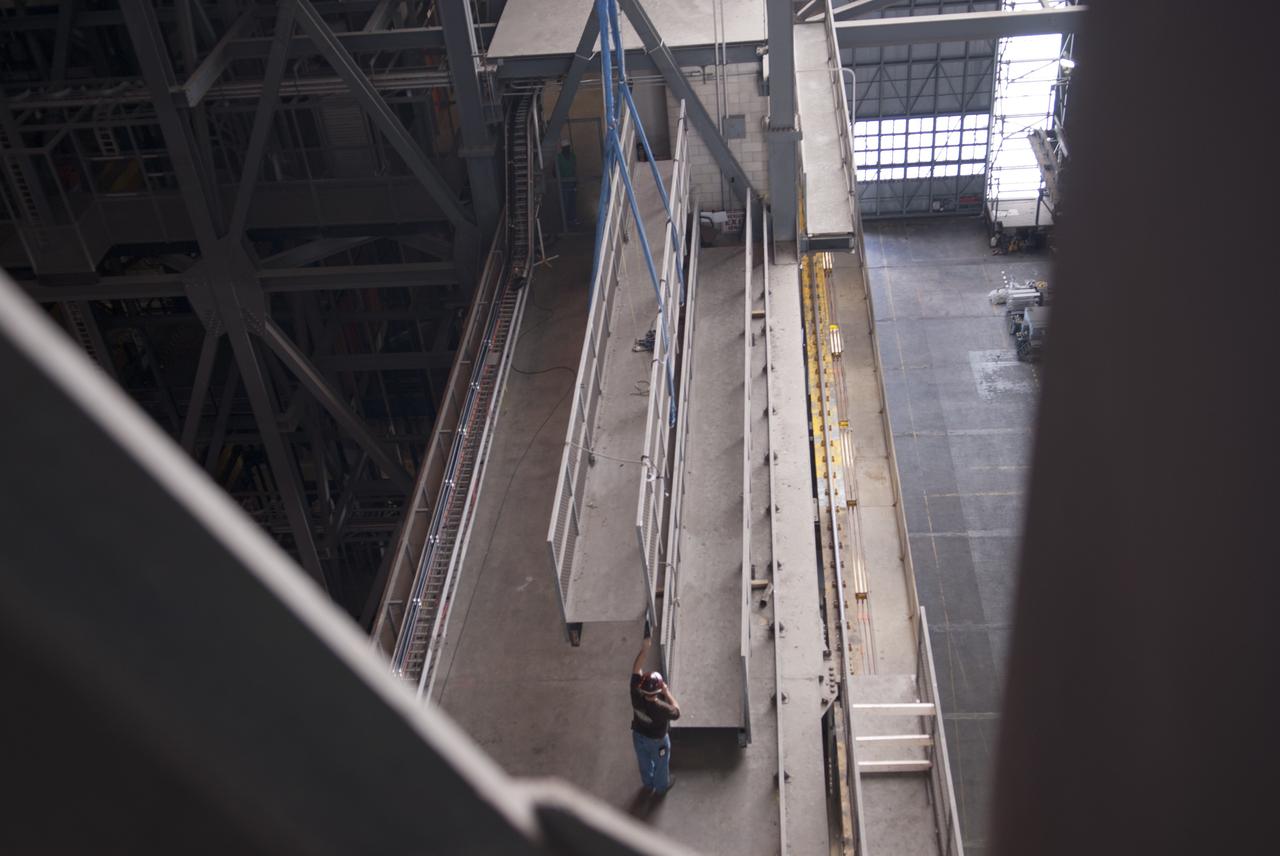
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, preparations are underway to remove a portion of the catwalk on the east side of Level 16 to allow room for the removal of the 175-ton crane that is situated above the transfer aisle. The crane will be lowered to the floor to perform upgrades to its 45-year-old controls in order to improve reliability, precision and safety. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to the VAB. The crane will be upgraded so that it can support lifting needs for NASA and other exploration vehicles, including the agency's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, preparations are underway to remove a portion of the catwalk on the west side of Level 16. The catwalk is being removed to allow room for the removal of the 175-ton crane that is situated above the transfer aisle. The crane will be lowered to the floor to perform upgrades to its 45-year-old controls in order to improve reliability, precision and safety. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to the VAB. The crane will be upgraded so that it can support lifting needs for NASA and other exploration vehicles, including the agency's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
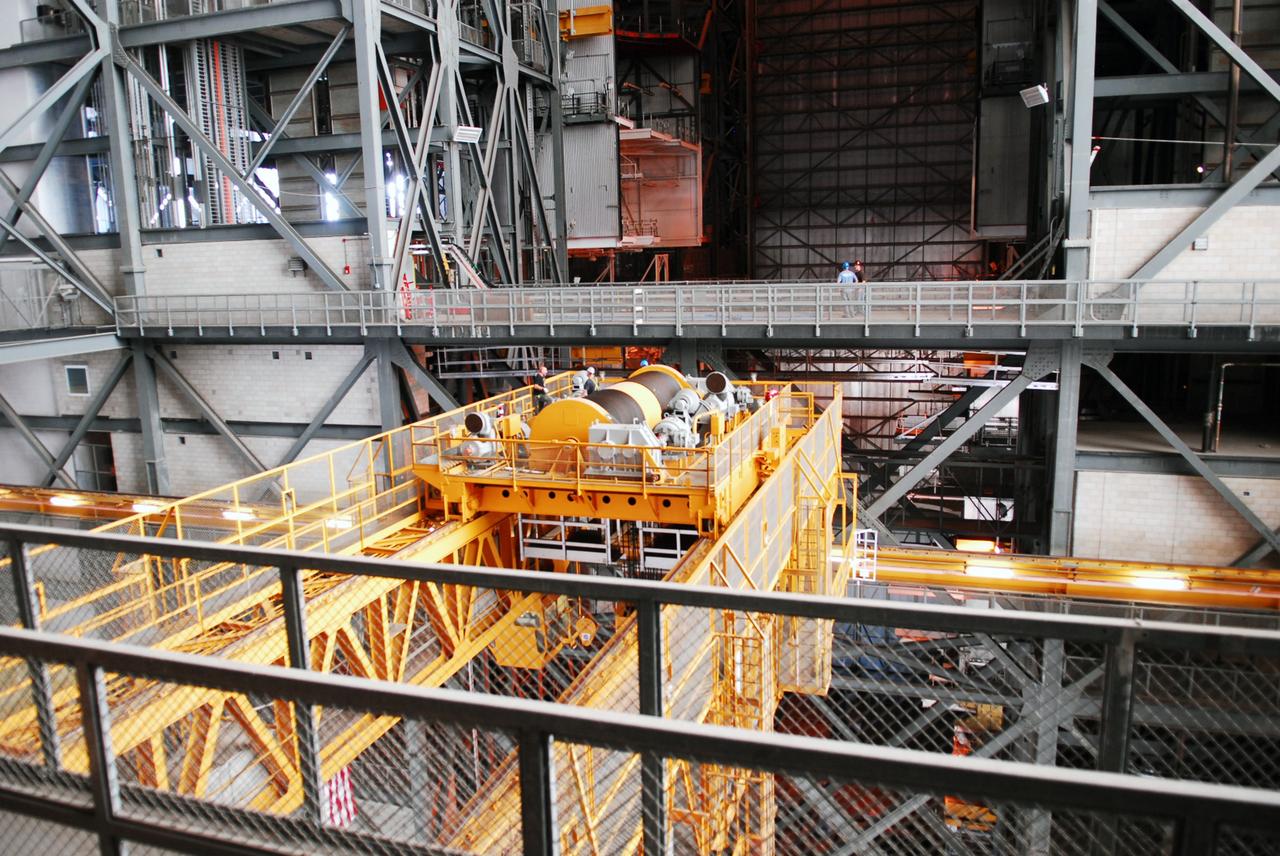

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, preparations are underway to remove a portion of the catwalk on the east side of Level 16 to allow room for the removal of the 175-ton crane that is situated above the transfer aisle. The crane will be lowered to the floor to perform upgrades to its 45-year-old controls in order to improve reliability, precision and safety. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to the VAB. The crane will be upgraded so that it can support lifting needs for NASA and other exploration vehicles, including the agency's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
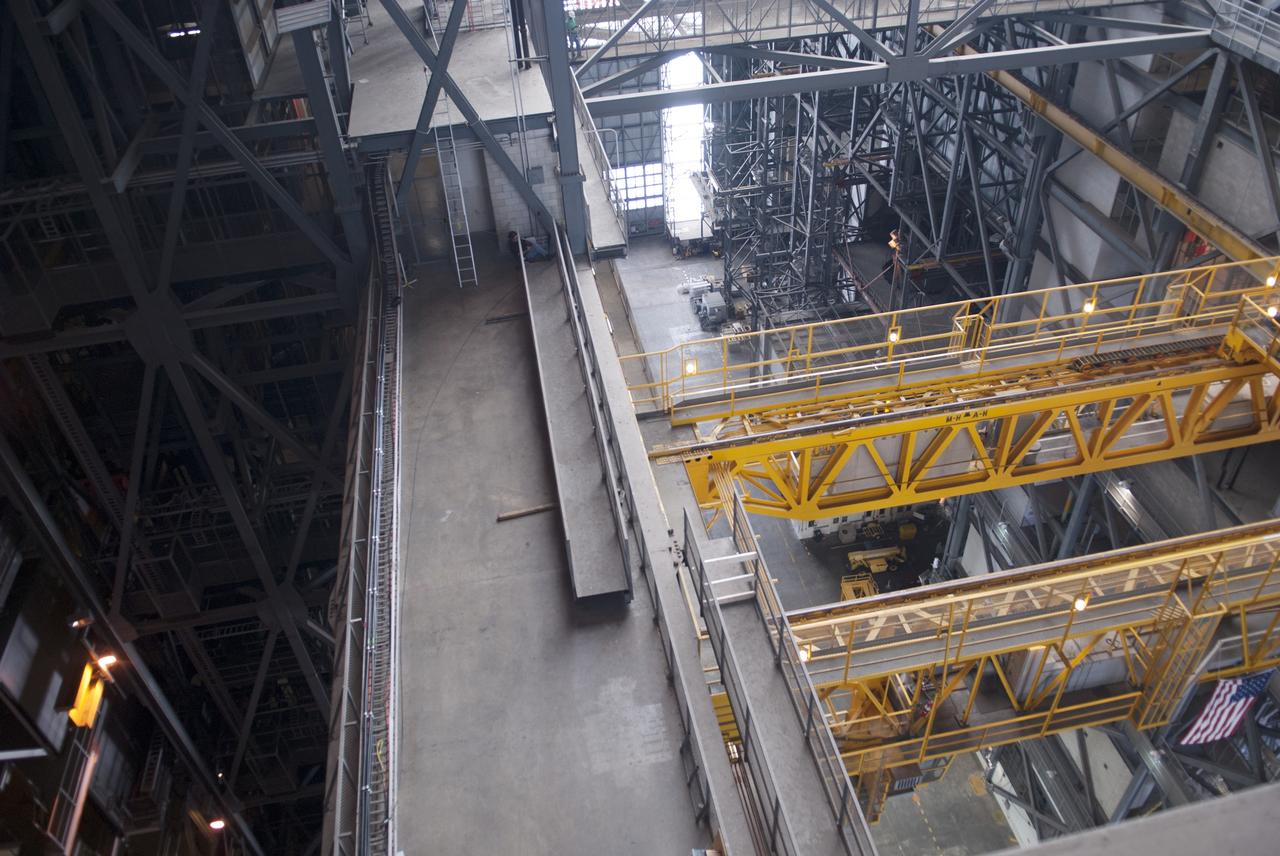

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a portion of the catwalk on the east side of Level 16 has been removed to allow room for the removal of the 175-ton crane that is situated above the transfer aisle. The crane will be lowered to the floor to perform upgrades to its 45-year-old controls in order to improve reliability, precision and safety. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to the VAB. The crane will be upgraded so that it can support lifting needs for NASA and other exploration vehicles, including the agency's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
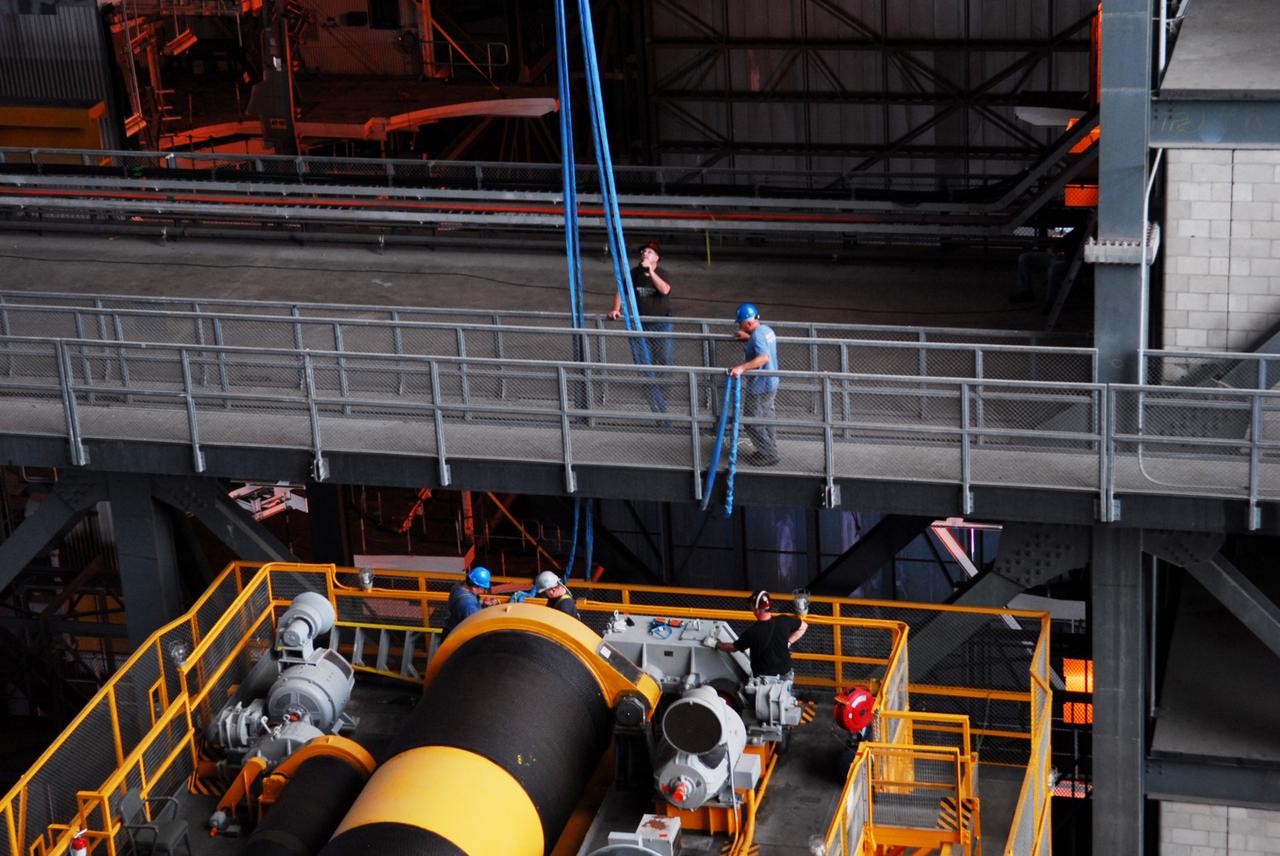

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, preparations are underway to remove a portion of the catwalk on the east side of Level 16 to allow room for the removal of the 175-ton crane that is situated above the transfer aisle. The crane will be lowered to the floor to perform upgrades to its 45-year-old controls in order to improve reliability, precision and safety. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to the VAB. The crane will be upgraded so that it can support lifting needs for NASA and other exploration vehicles, including the agency's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
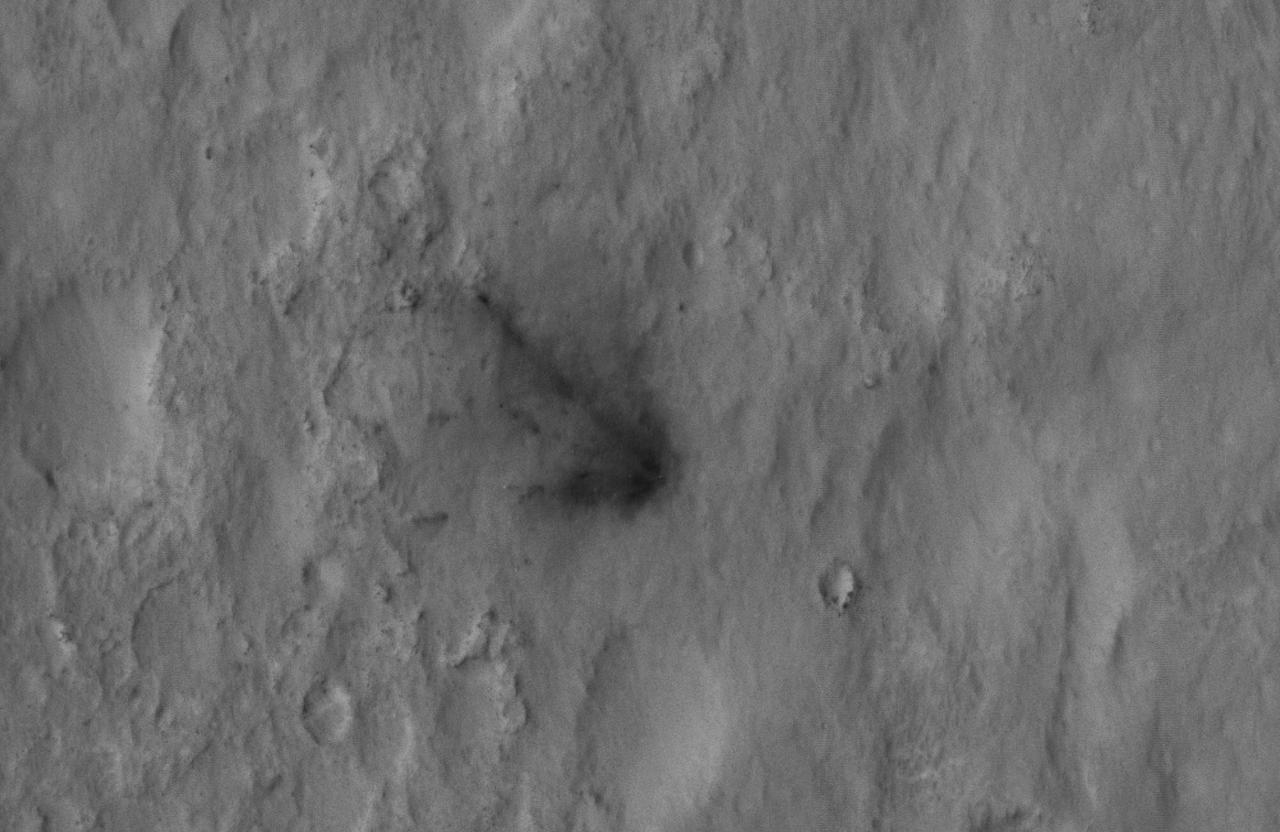

This close-up view captured by NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter shows darkened radial jets caused by the impact of Curiosity sky crane, which helped deliver the rover to the surface of Mars.
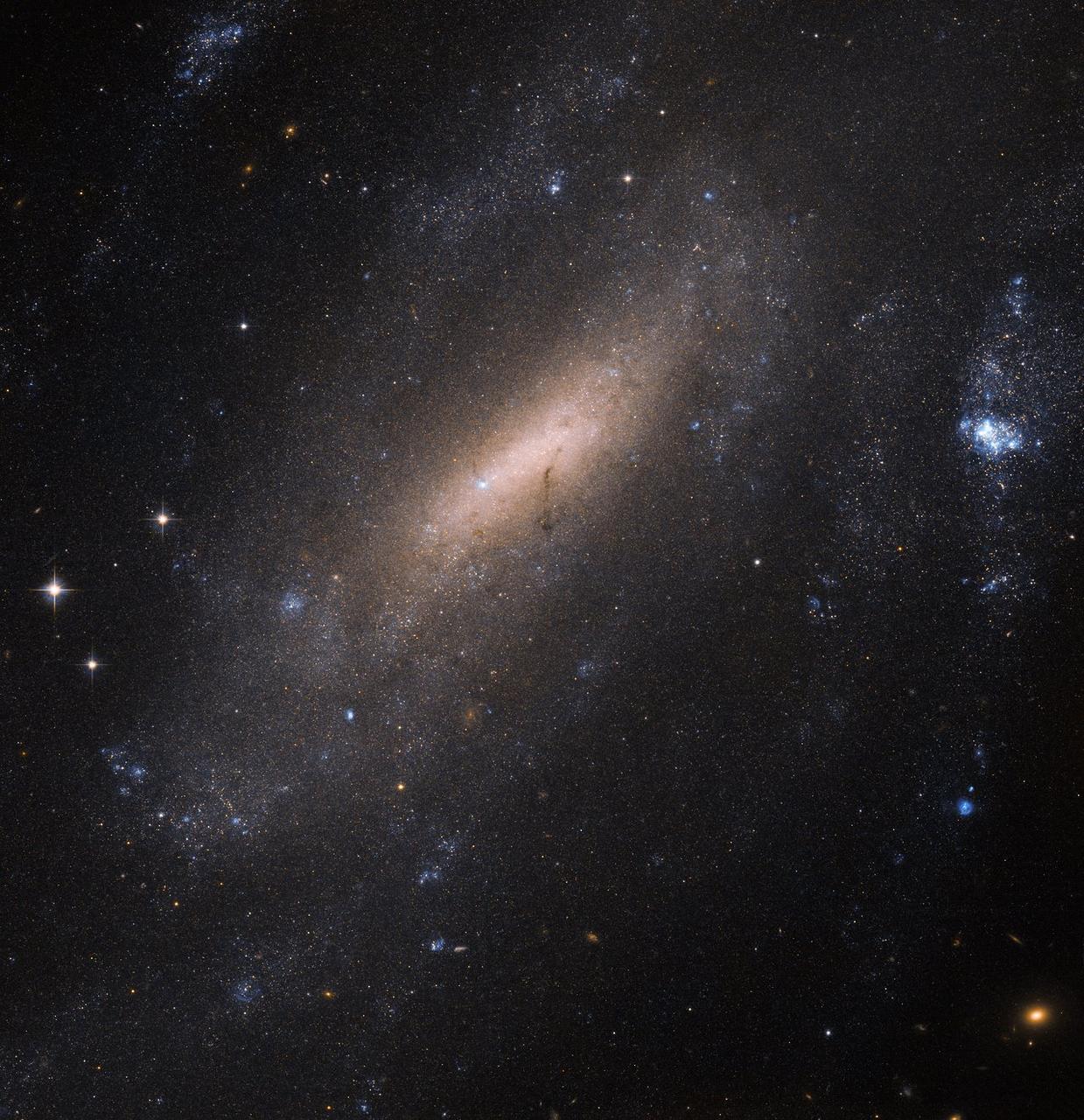

In 1900, astronomer Joseph Lunt made a discovery: Peering through a telescope at Cape Town Observatory, the British–South African scientist spotted this beautiful sight in the southern constellation of Grus (The Crane): a barred spiral galaxy now named IC 5201. Over a century later, the galaxy is still of interest to astronomers. For this image, the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope used its Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS) to produce a beautiful and intricate image of the galaxy. Hubble’s ACS can resolve individual stars within other galaxies, making it an invaluable tool to explore how various populations of stars sprang to life, evolved, and died throughout the cosmos. IC 5201 sits over 40 million light-years away from us. As with two thirds of all the spirals we see in the Universe — including the Milky Way — the galaxy has a bar of stars slicing through its center. Credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
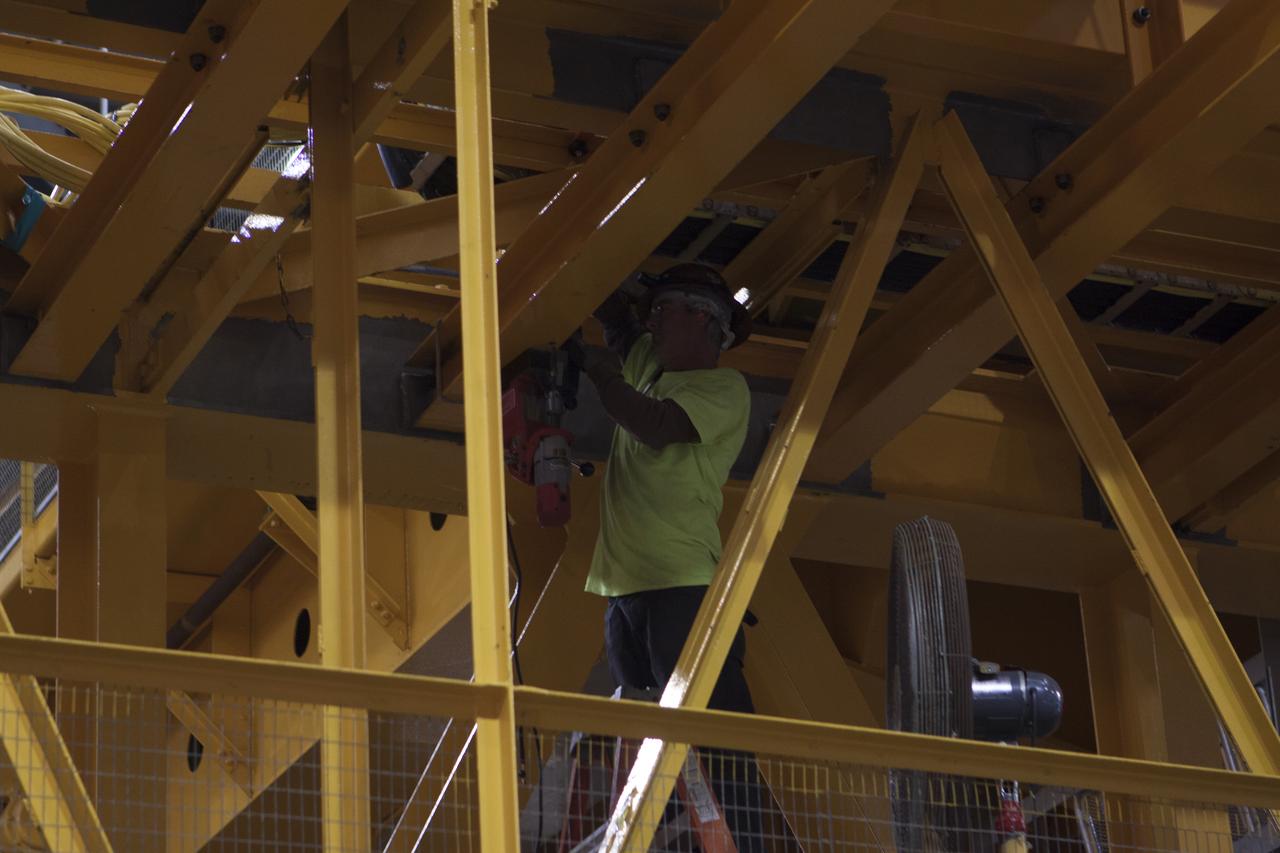

Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a construction worker continues with refurbishment and upgrades to the 175-ton crane on the ground floor of the transfer aisle. The crane's 45-year-old controls are being upgraded to improve reliability, precision and safety. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to the crane so that it can support lifting needs for NASA and other exploration vehicles, including the agency's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft.
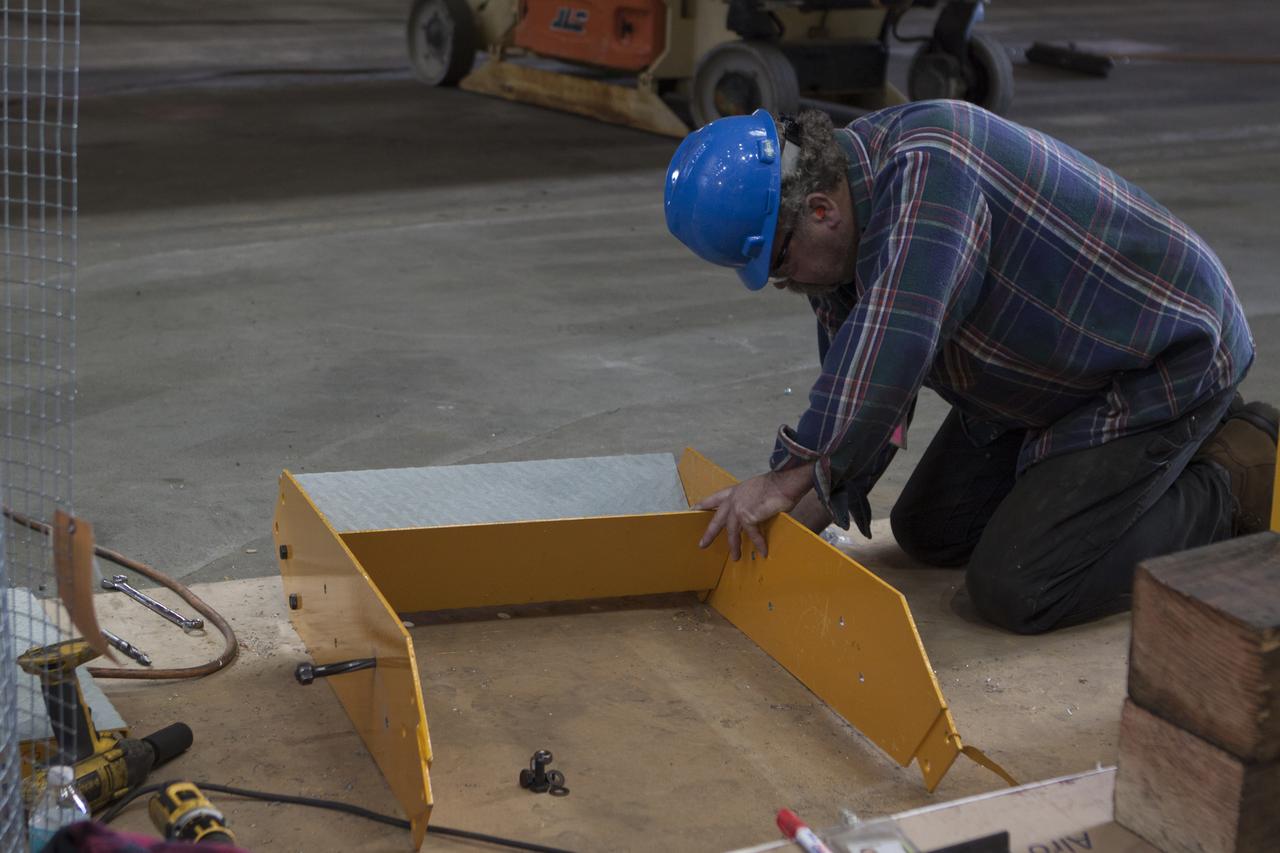

Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a construction worker continues with refurbishment and upgrades to parts of the 175-ton crane on the ground floor of the transfer aisle. The crane's 45-year-old controls are being upgraded to improve reliability, precision and safety. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to the crane so that it can support lifting needs for NASA and other exploration vehicles, including the agency's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft.
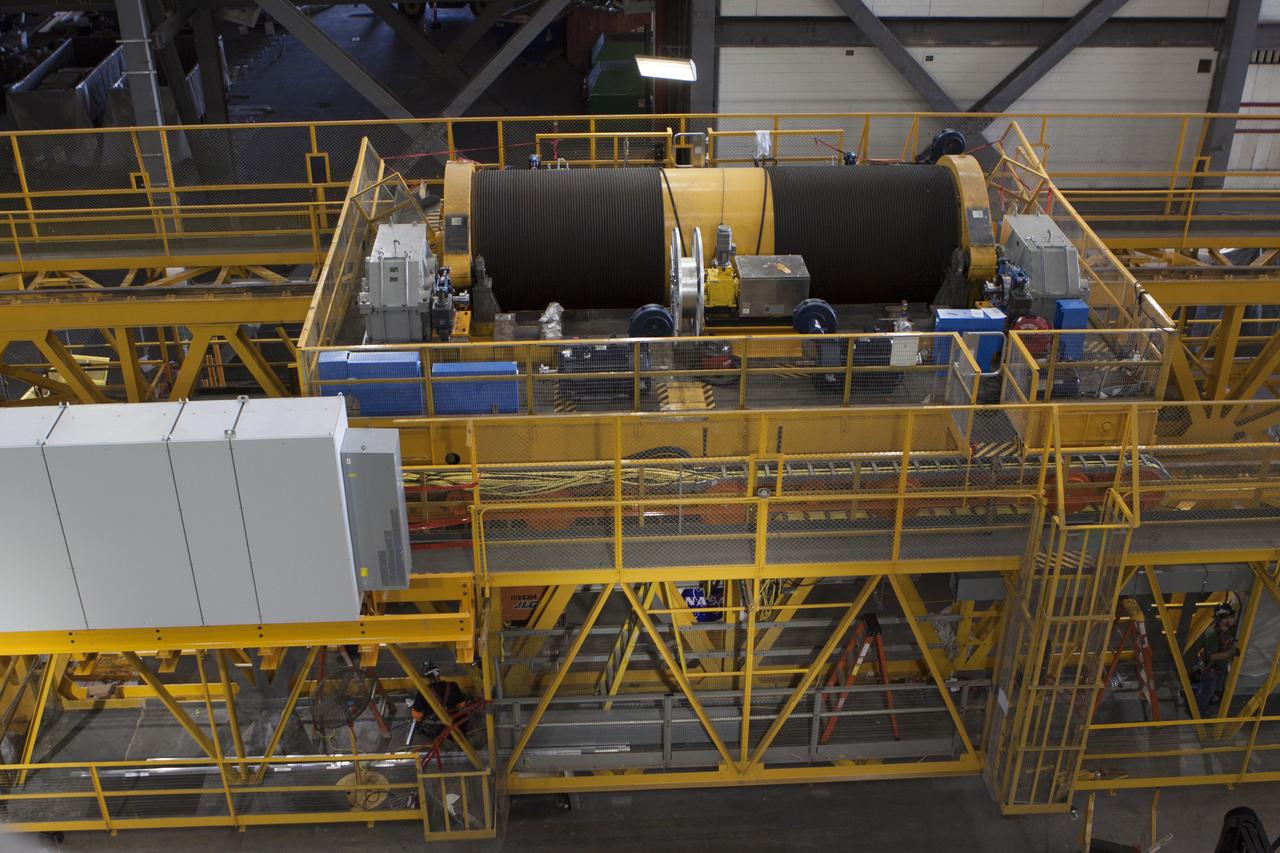

A view from above inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, shows the 175-ton crane on the ground floor of the transfer aisle. The crane's 45-year-old controls are being upgraded to improve reliability, precision and safety. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to the crane so that it can support lifting needs for NASA and other exploration vehicles, including the agency's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft.
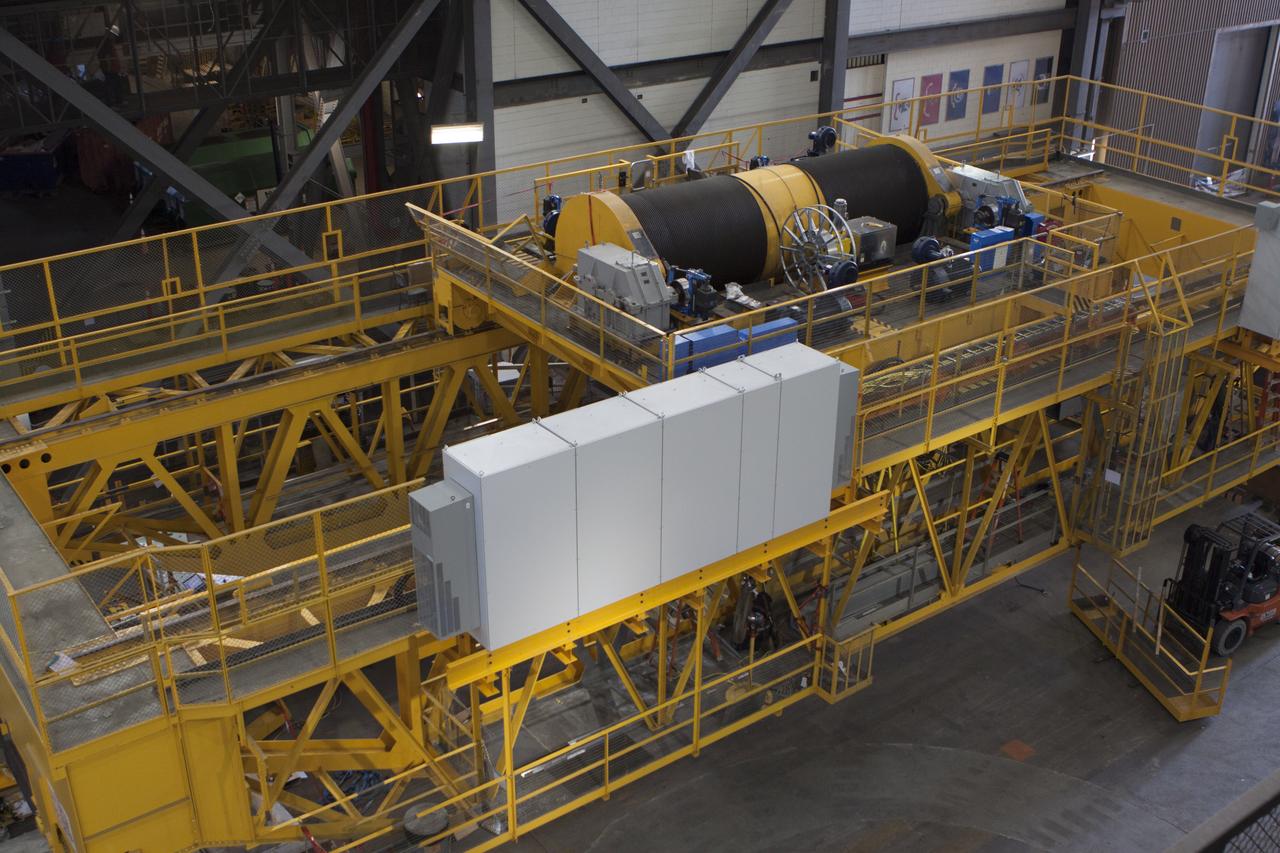

A view from above inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, shows the 175-ton crane on the ground floor of the transfer aisle. The crane's 45-year-old controls are being upgraded to improve reliability, precision and safety. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to the crane so that it can support lifting needs for NASA and other exploration vehicles, including the agency's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft.
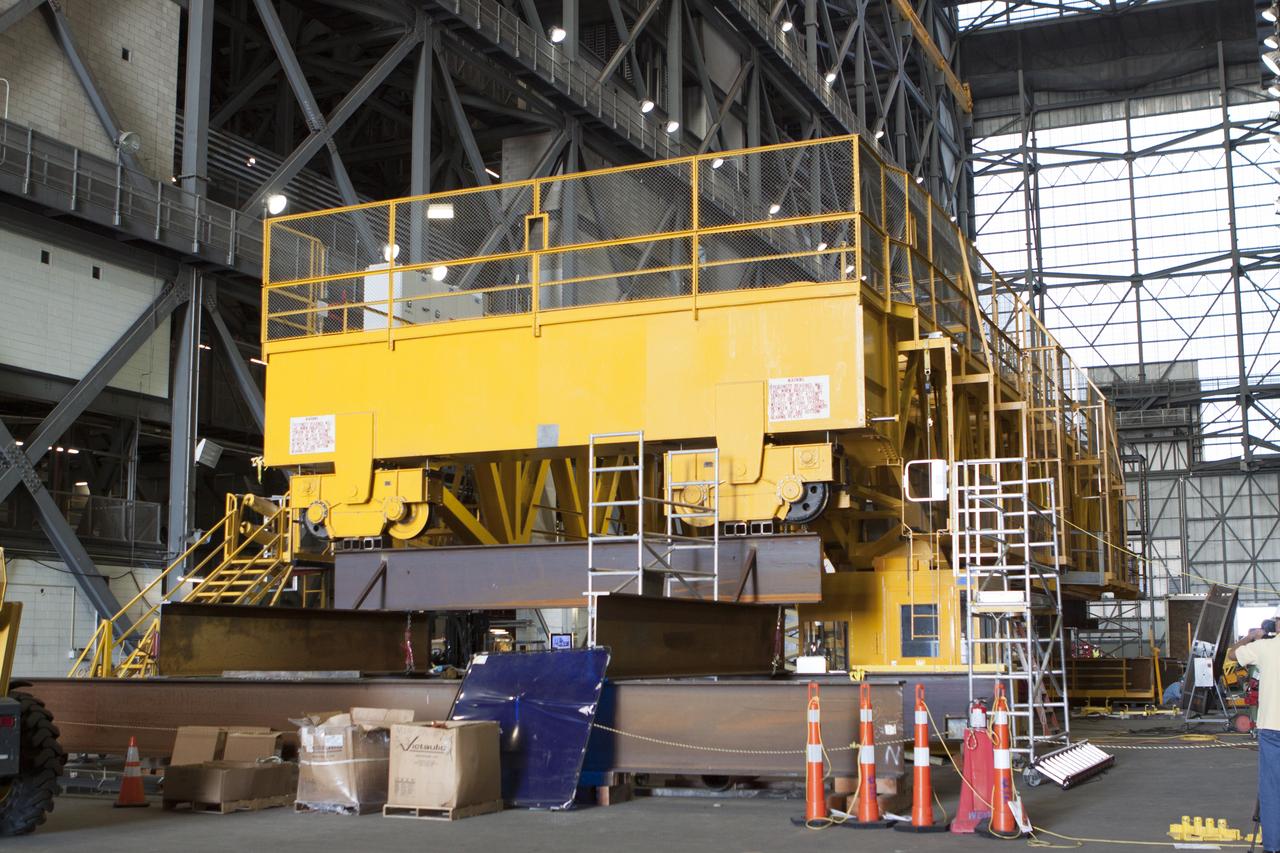

Upgrades and modifications continue on the 175-ton crane on the ground floor of the transfer aisle inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The crane's 45-year-old controls are being upgraded to improve reliability, precision and safety. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to the crane so that it can support lifting needs for NASA and other exploration vehicles, including the agency's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft.
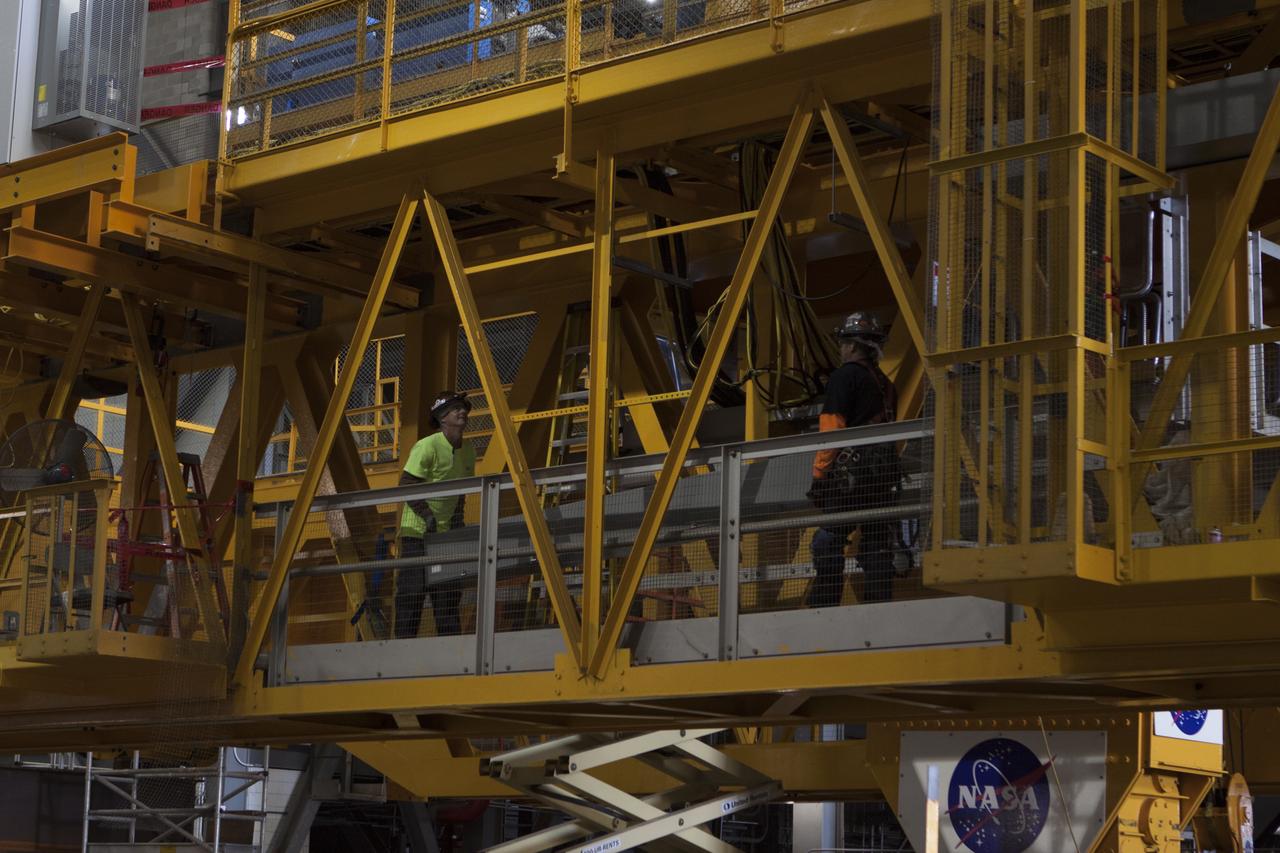

Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, construction workers continue with refurbishment and upgrades to the 175-ton crane on the ground floor of the transfer aisle. The crane's 45-year-old controls are being upgraded to improve reliability, precision and safety. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to the crane so that it can support lifting needs for NASA and other exploration vehicles, including the agency's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft.
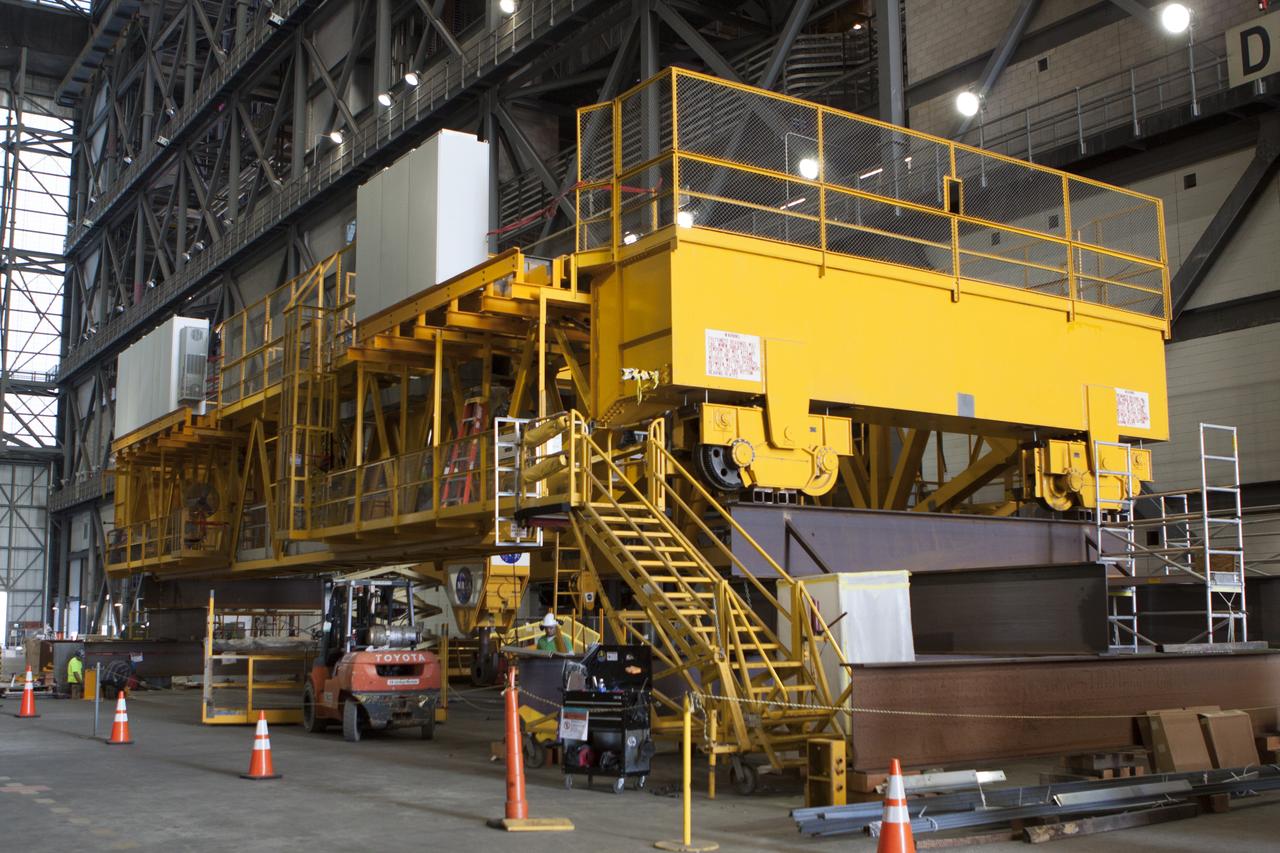

Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, refurbishment and upgrades to the 175-ton crane are under way on the ground floor of the transfer aisle. The crane's 45-year-old controls are being upgraded to improve reliability, precision and safety. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to the crane so that it can support lifting needs for NASA and other exploration vehicles, including the agency's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft.

After a rocket-powered descent stage, also known as the sky crane, delivered NASA Curiosity rover to Mars on Aug. 5 PDT Aug. 6 EDT, 2012, it flew away and fell to the surface.

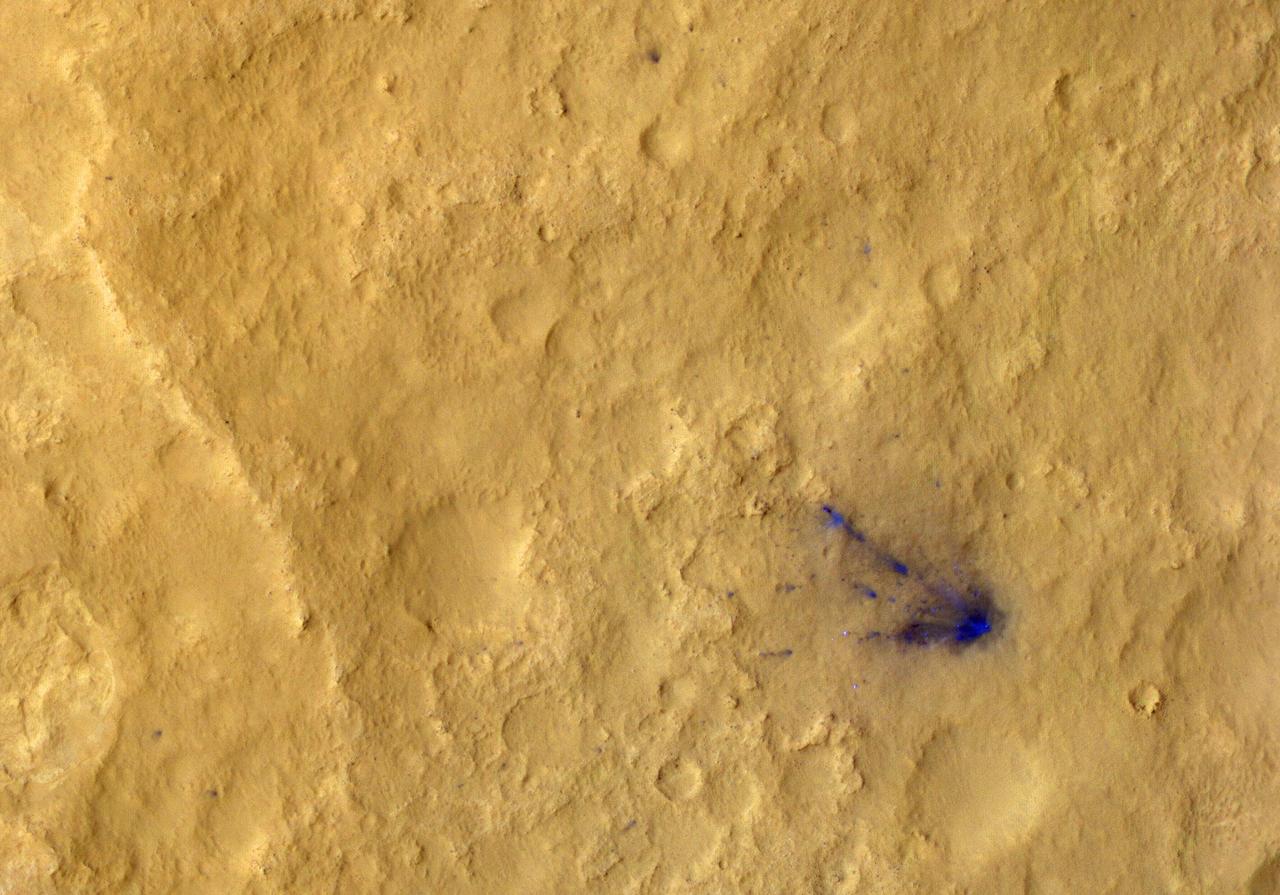
This photo mosaic shows the scour mark, dubbed Goulburn, left by the thrusters on the sky crane that helped lower NASA Curiosity rover to the Red Planet.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A view from above inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, shows the 175-ton crane on the ground floor of the transfer aisle. The crane's 45-year-old controls are being upgraded to improve reliability, precision and safety. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to the crane so that it can support lifting needs for NASA and other exploration vehicles, including the agency's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Upgrades and modifications continue on the 175-ton crane on the ground floor of the transfer aisle inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The crane's 45-year-old controls are being upgraded to improve reliability, precision and safety. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to the crane so that it can support lifting needs for NASA and other exploration vehicles, including the agency's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
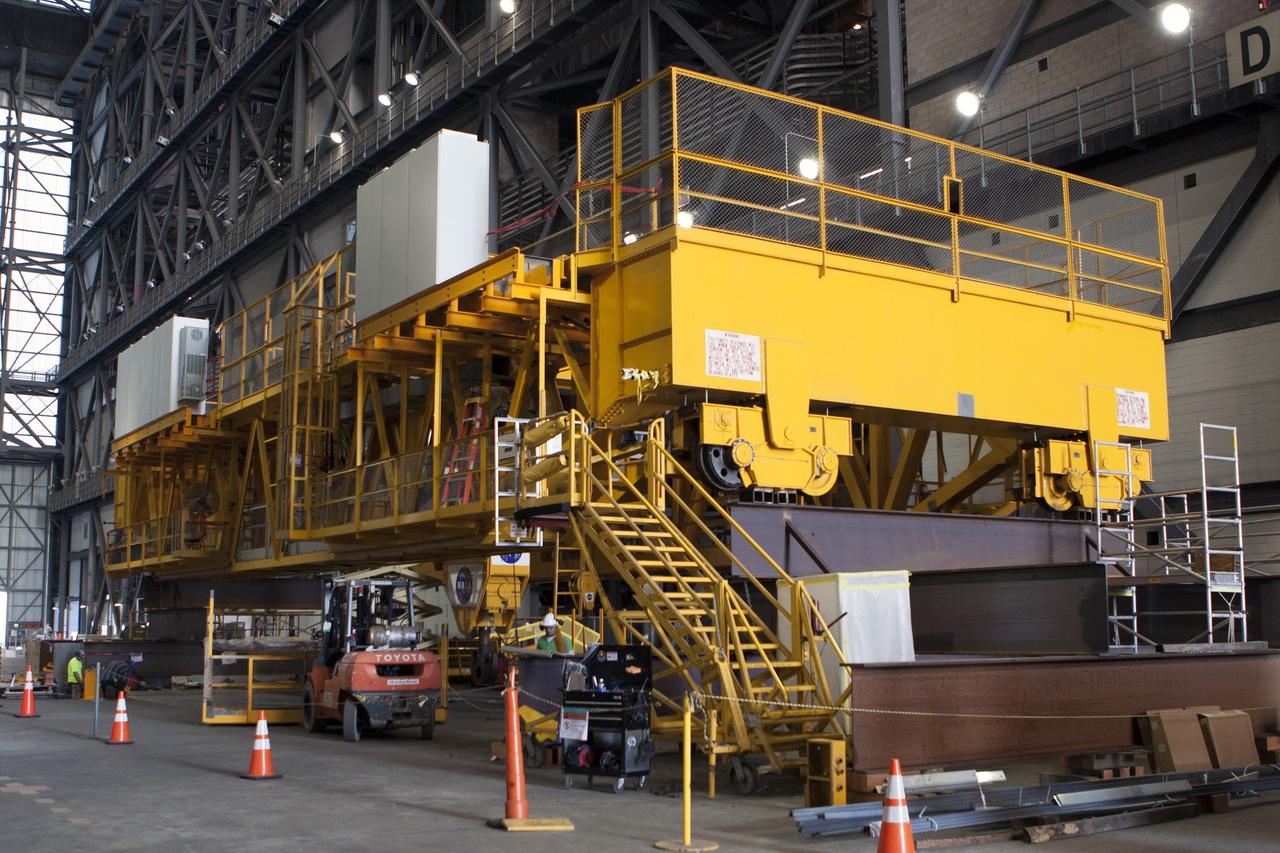

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, refurbishment and upgrades to the 175-ton crane are under way on the ground floor of the transfer aisle. The crane's 45-year-old controls are being upgraded to improve reliability, precision and safety. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to the crane so that it can support lifting needs for NASA and other exploration vehicles, including the agency's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
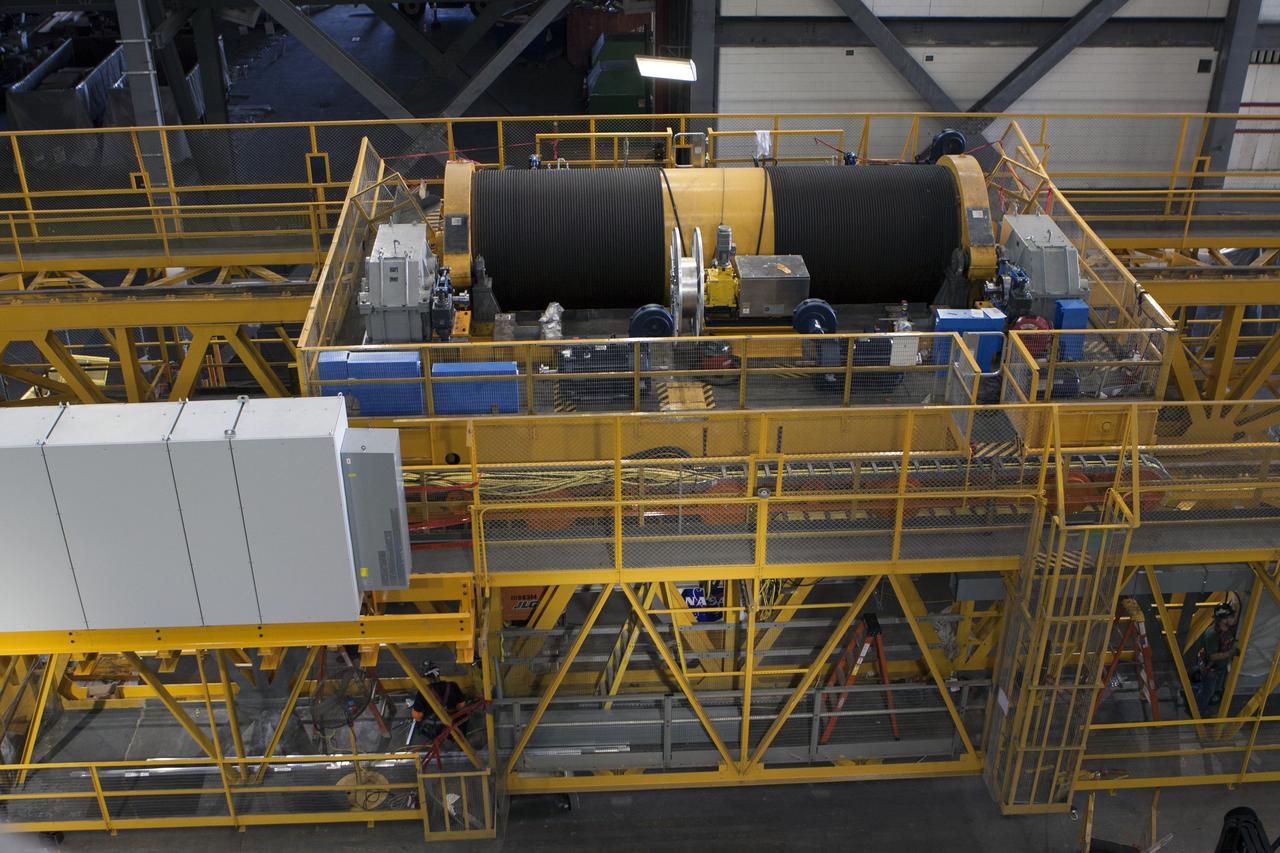

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A view from above inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, shows the 175-ton crane on the ground floor of the transfer aisle. The crane's 45-year-old controls are being upgraded to improve reliability, precision and safety. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to the crane so that it can support lifting needs for NASA and other exploration vehicles, including the agency's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
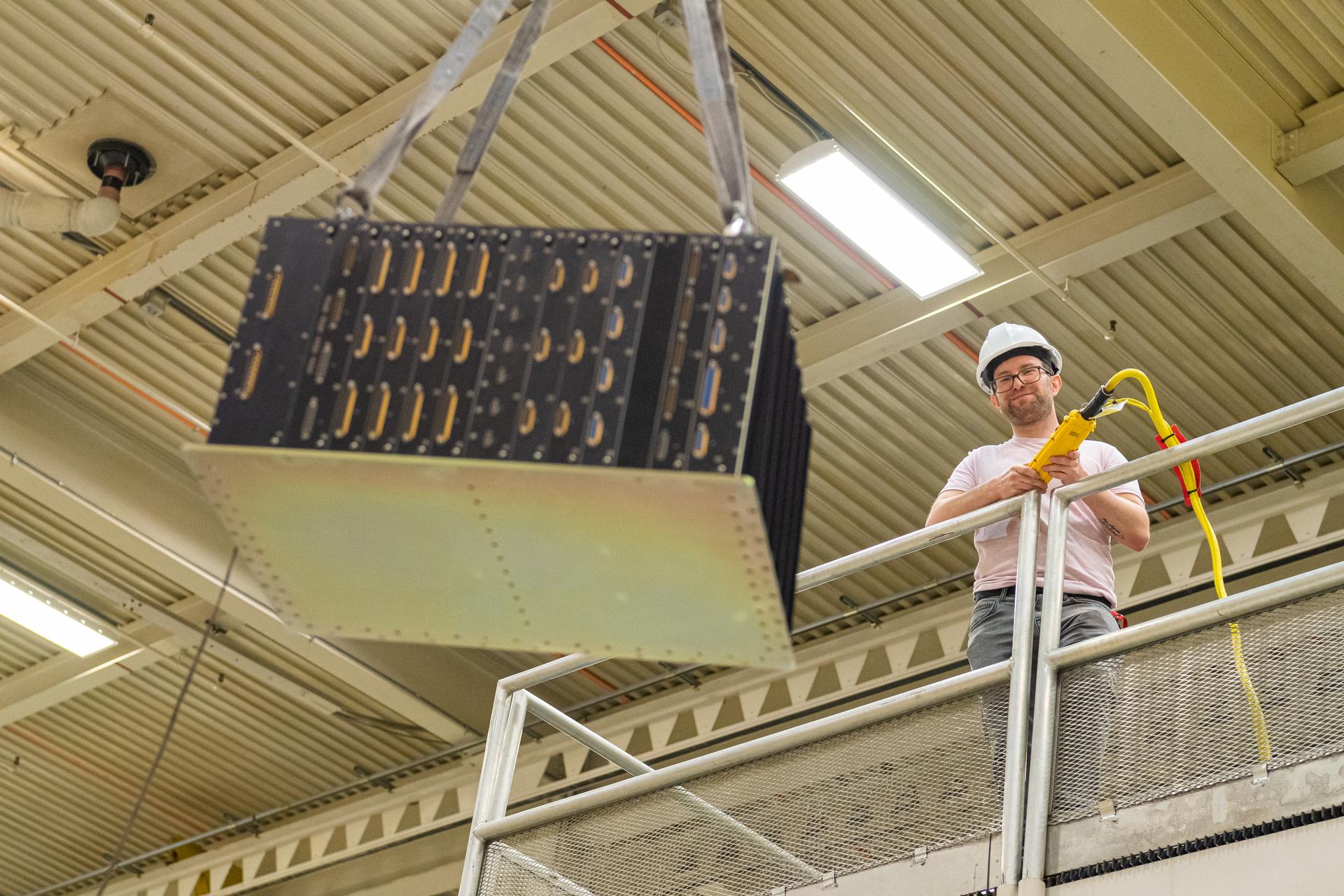

Mechanical engineering and integration technician Seth Alton crane lifts the OSAM-1 power supply unit into the thermal vacuum chamber at Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt Md., April 12, 2023. This photo has been reviewed by OSAM1 project management and the Export Control Office and is released for public view. NASA/Mike Guinto
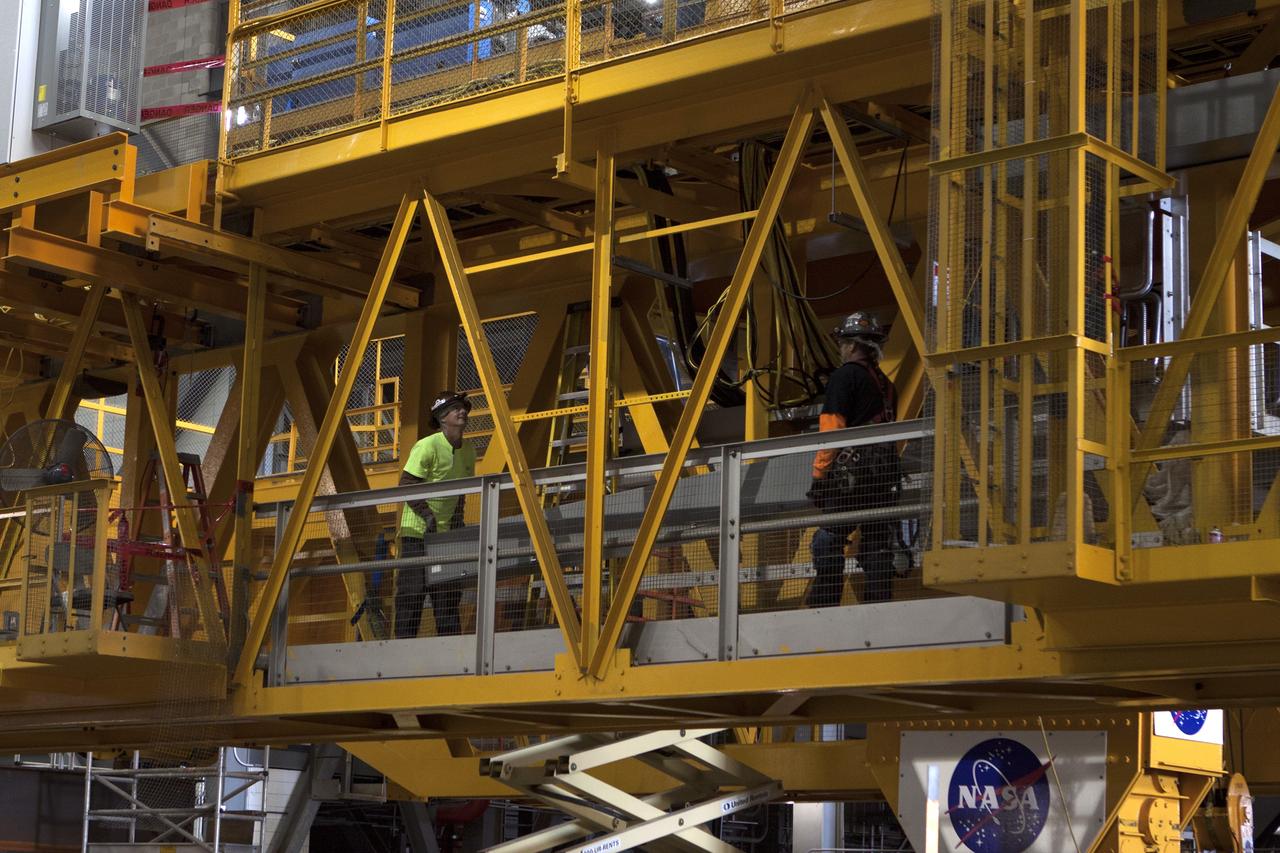

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, construction workers continue with refurbishment and upgrades to the 175-ton crane on the ground floor of the transfer aisle. The crane's 45-year-old controls are being upgraded to improve reliability, precision and safety. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to the crane so that it can support lifting needs for NASA and other exploration vehicles, including the agency's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
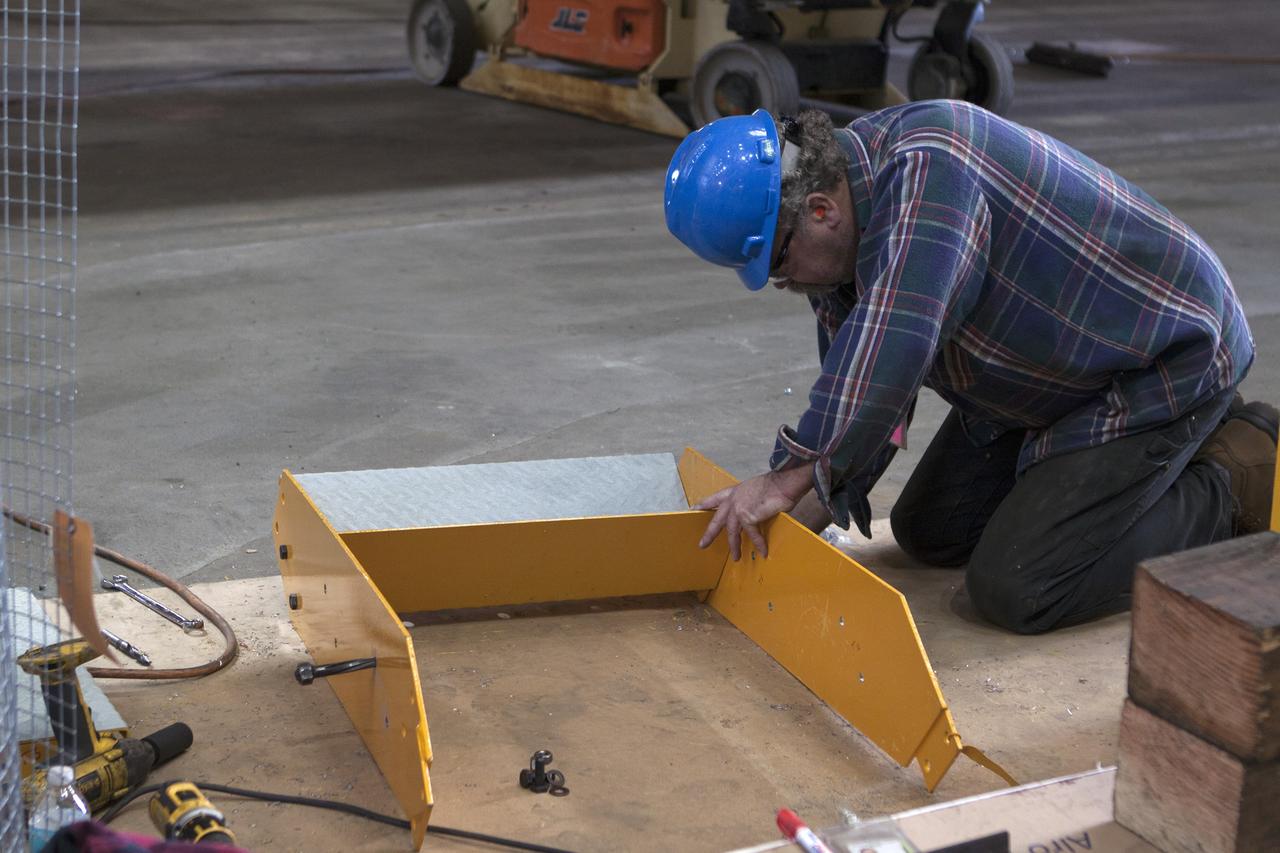

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a construction worker continues with refurbishment and upgrades to parts of the 175-ton crane on the ground floor of the transfer aisle. The crane's 45-year-old controls are being upgraded to improve reliability, precision and safety. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to the crane so that it can support lifting needs for NASA and other exploration vehicles, including the agency's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
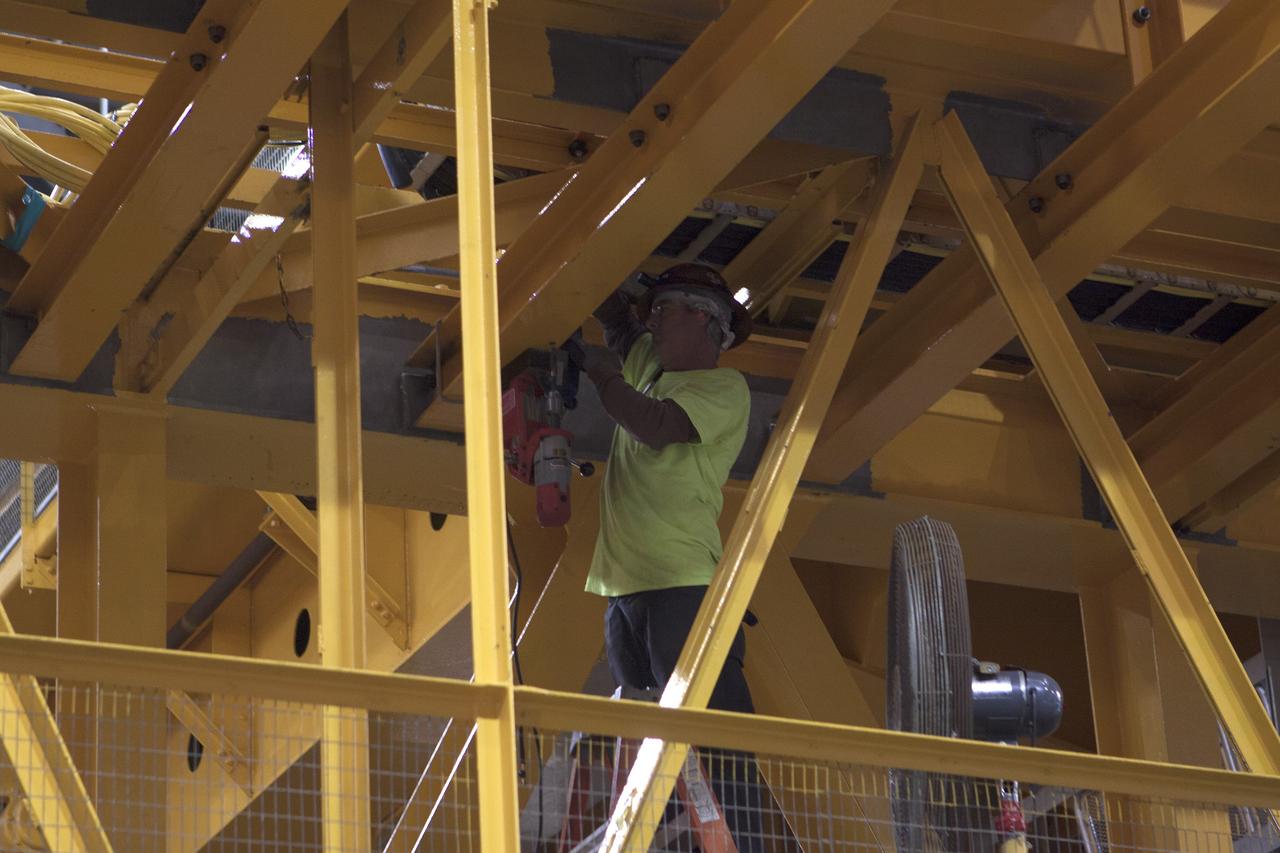

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a construction worker continues with refurbishment and upgrades to the 175-ton crane on the ground floor of the transfer aisle. The crane's 45-year-old controls are being upgraded to improve reliability, precision and safety. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to the crane so that it can support lifting needs for NASA and other exploration vehicles, including the agency's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
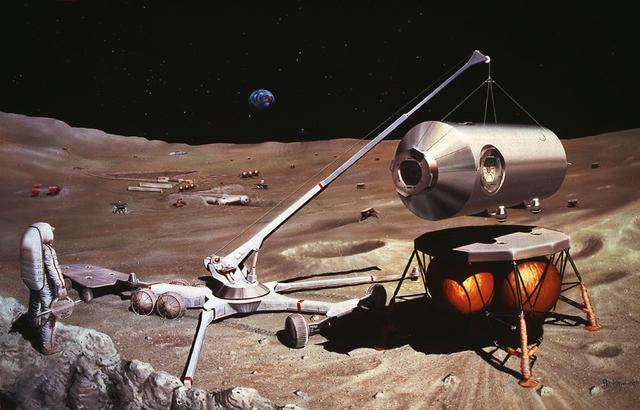

Artist Pat Rawlings' conception of the different types of machinery that will likely be needed in the future: Lunar Crane
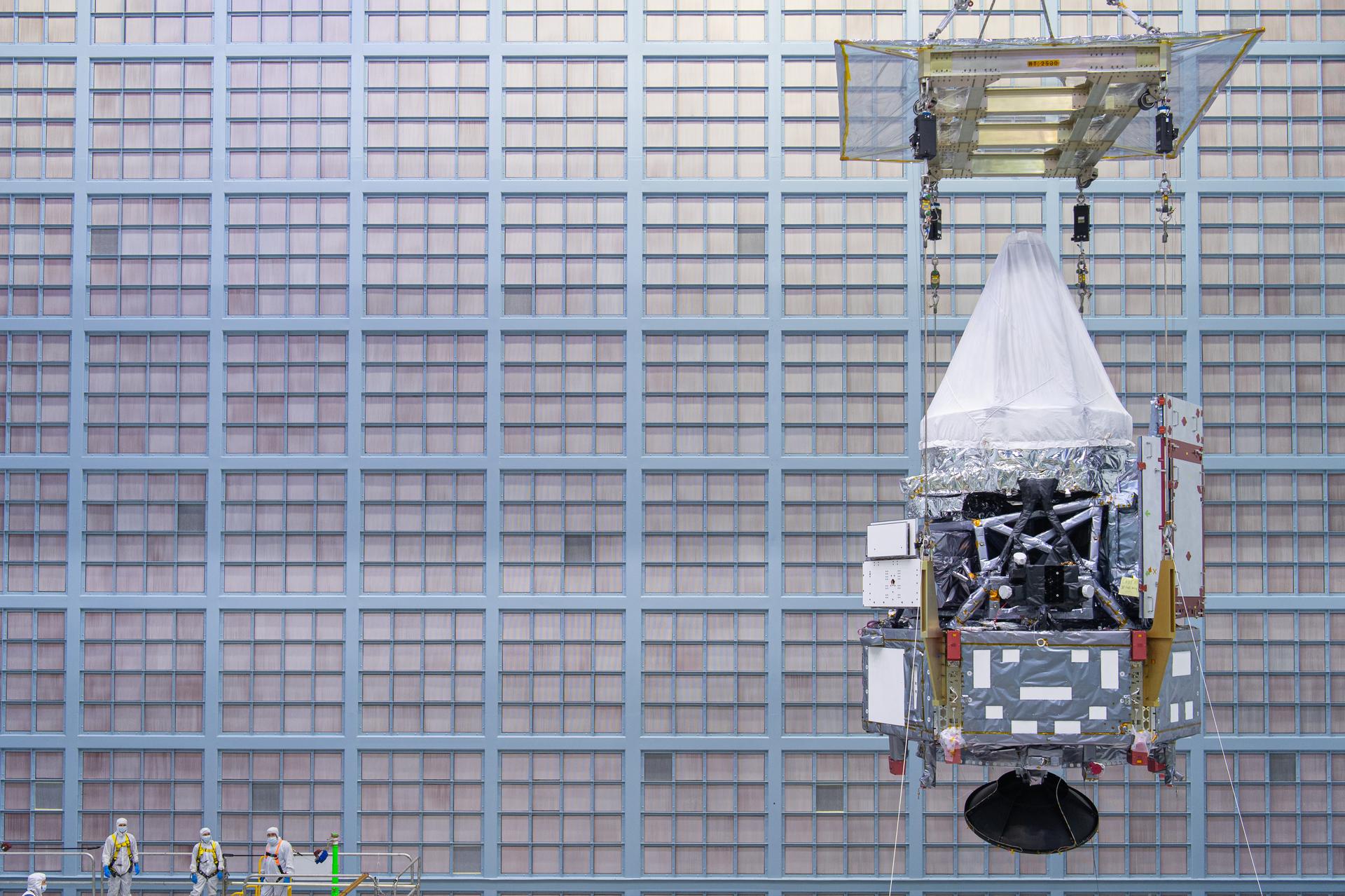
The Roman Space Telescope's Spacecraft Bus and Integrated Payload Assembly is crane lifted inside the cleanroom at Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt Md., June 12, 2025. This photo has been approved for public release. NASA/Mike Guinto
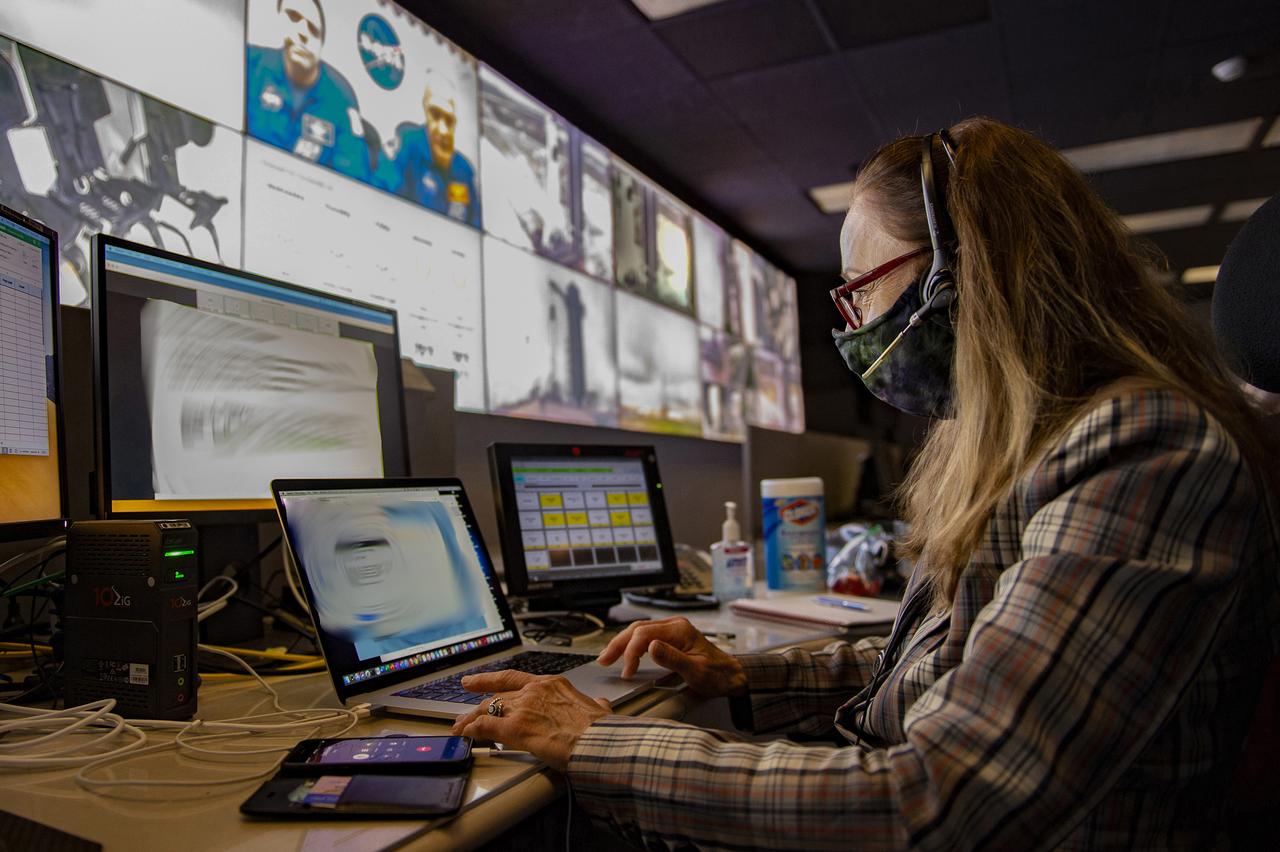

Deborah Crane andTeams at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center help monitor launch conditions for the Demo-2 mission from the Huntsville Operations Support Center, HOSC.

Deborah Crane and Teams at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center help monitor launch conditions for the Demo-2 mission from the Huntsville Operations Support Center, HOSC.
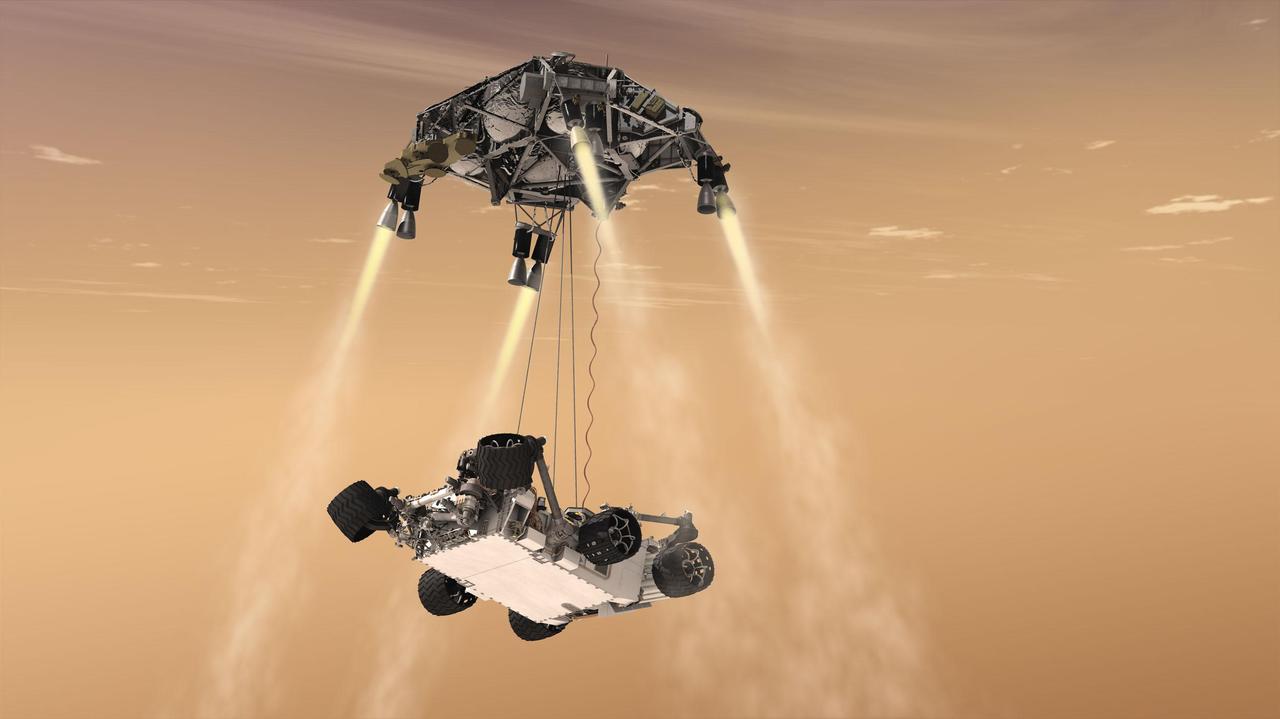

This artist concept shows the sky crane maneuver during the descent of NASA Curiosity rover to the Martian surface. The sheer size of the rover over one ton, or 900 kilograms would preclude it from taking advantage of an airbag-assisted landing.
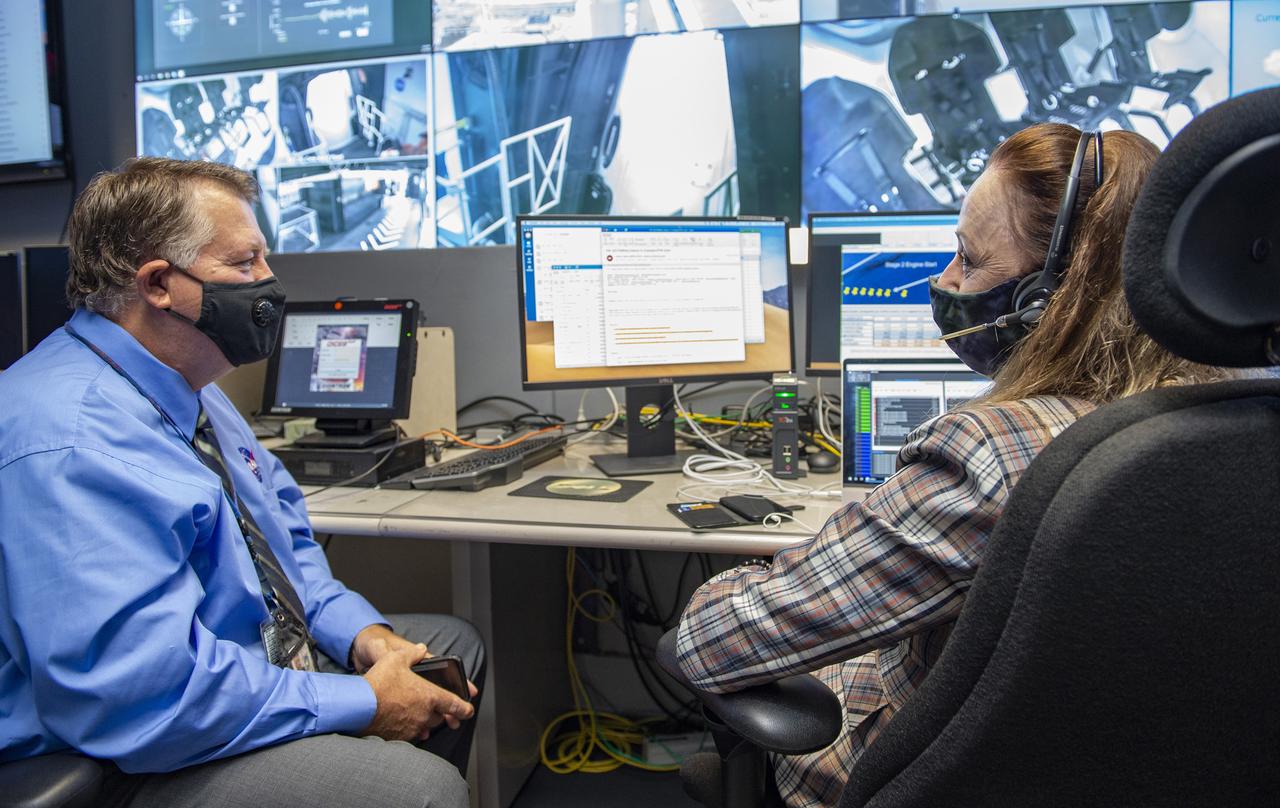

Preston Jones, Deborah Crane, and teams at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center help monitor launch conditions for the Demo-2 mission from the Huntsville Operations Support Center, HOSC.
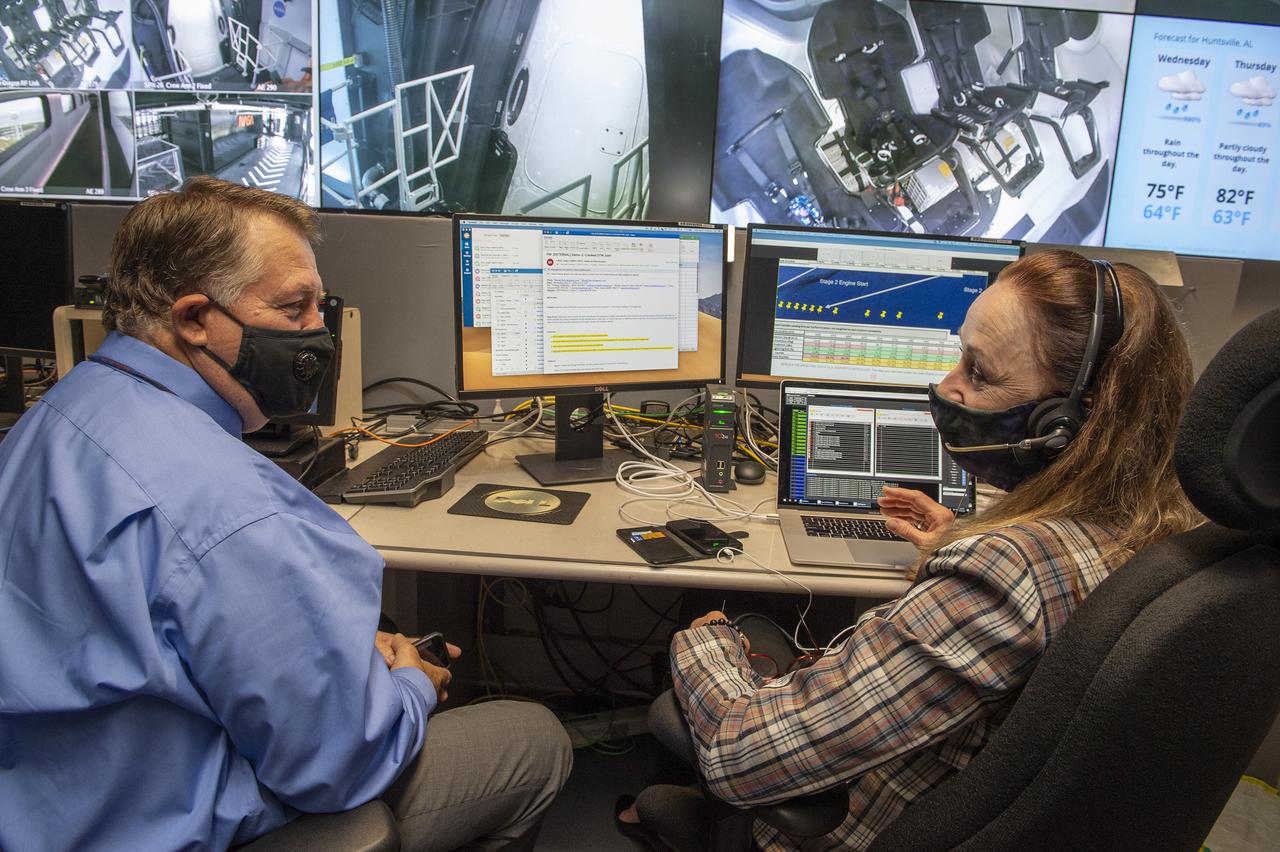

Preston Jones, Deborah Crane, and teams at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center help monitor launch conditions for the Demo-2 mission from the Huntsville Operations Support Center, HOSC.
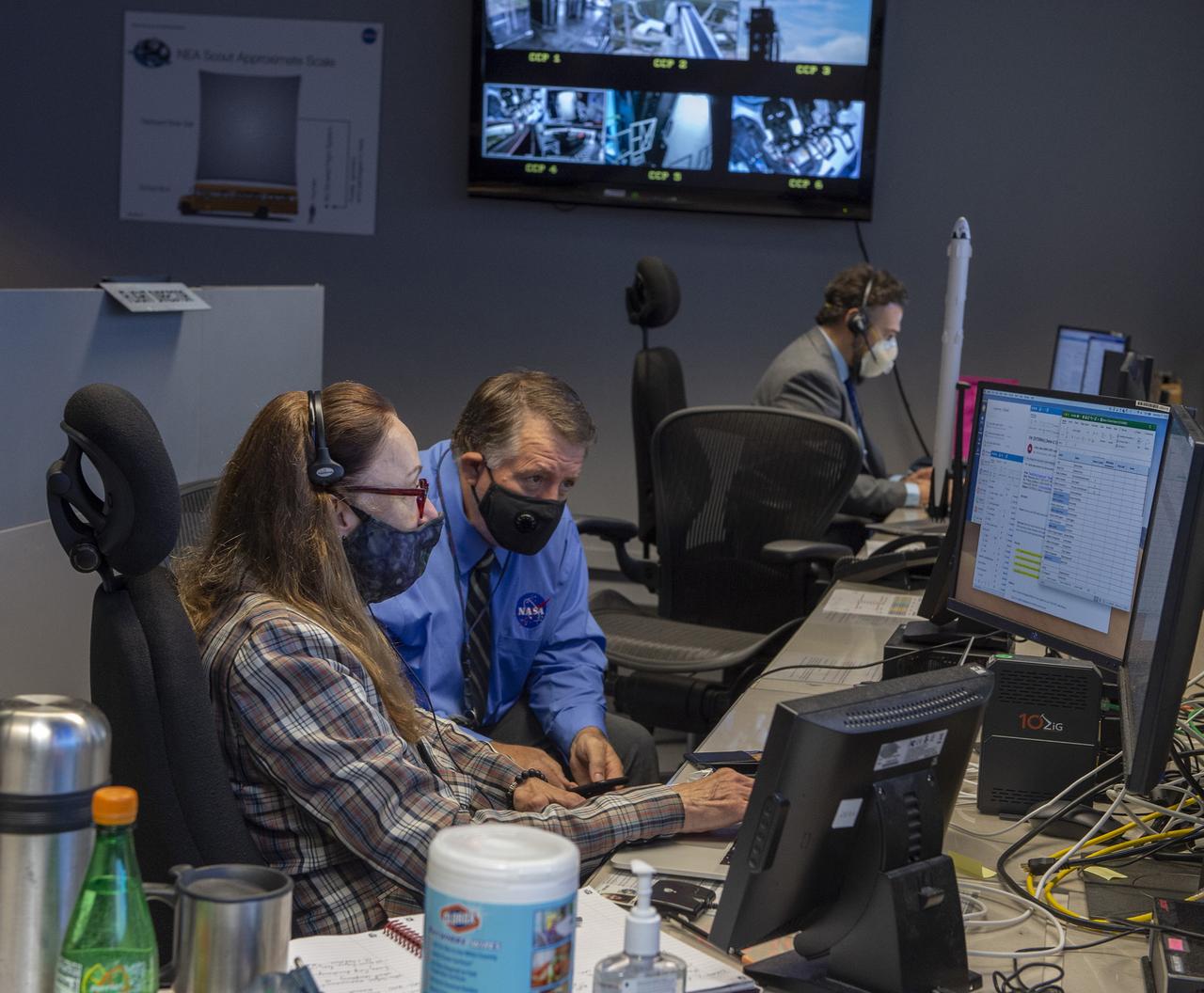

Preston Jones, Deborah Crane, Adam Butt, and teams at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center help monitor launch conditions for the Demo-2 mission from the Huntsville Operations Support Center, HOSC.
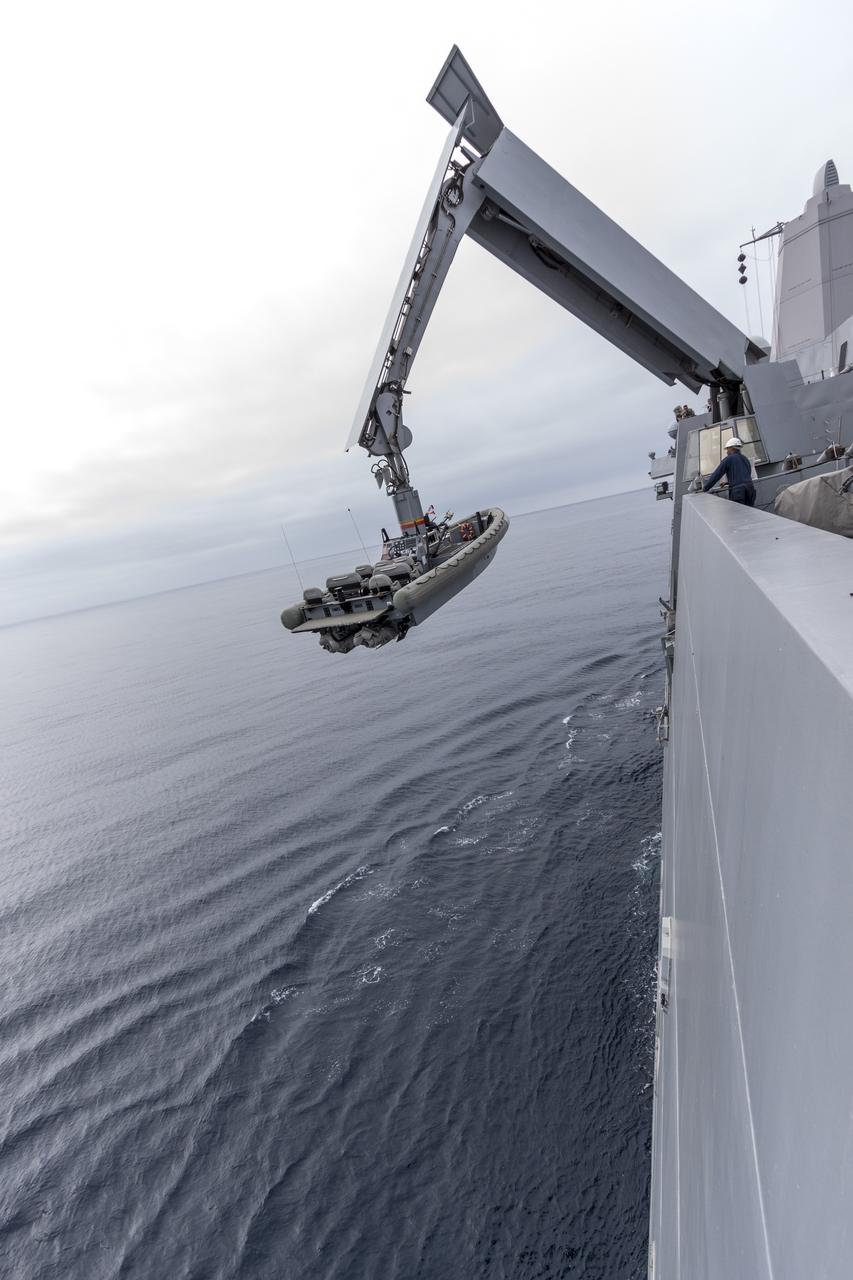

SAN DIEGO, Calif. – The USS San Diego heads out to sea with the Orion boilerplate test vehicle and other hardware in its well deck for an underway recovery test. A crane is used to lower a rigid hull inflatable boat into the water. About 100 miles offshore, NASA and the U.S. Navy conducted tests to prepare for recovery of the Orion crew module, forward bay cover and parachutes on its return from a deep space mission. The underway recovery test will allow the teams to demonstrate and evaluate the recovery processes, procedures, hardware and personnel in open waters. During the testing, the tether lines were unable to support the tension caused by crew module motion that was driven by wave turbulence in the well deck of the ship. NASA and the U.S. Navy are reviewing the testing data collected to evaluate the next steps. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program conducted the underway recovery tests. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
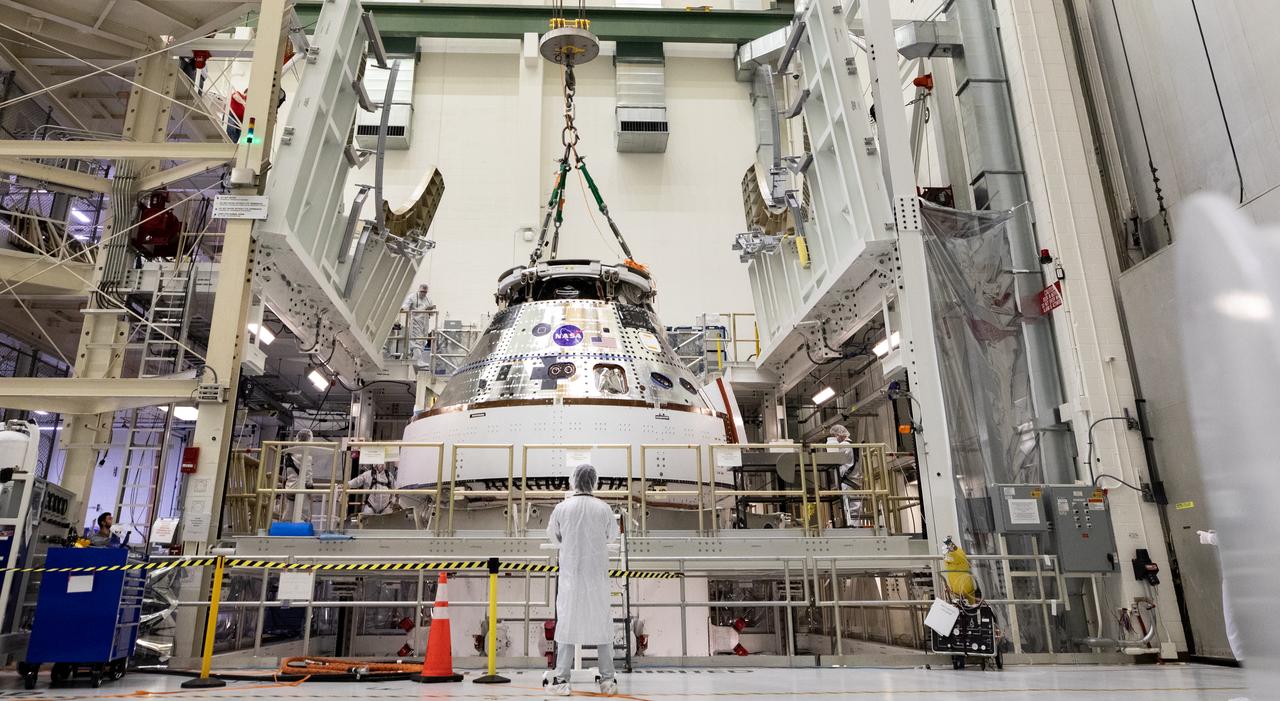

Technicians with NASA and Lockheed Martin operate a 30-ton crane to move NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft out of the Final Assembly and System Testing cell inside the Neil A. Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Saturday, Feb. 22, 2025. The move prepares for the upcoming installation of four solar array wings and spacecraft adapter jettison fairings for the agency’s first crewed flight test under the Artemis campaign.
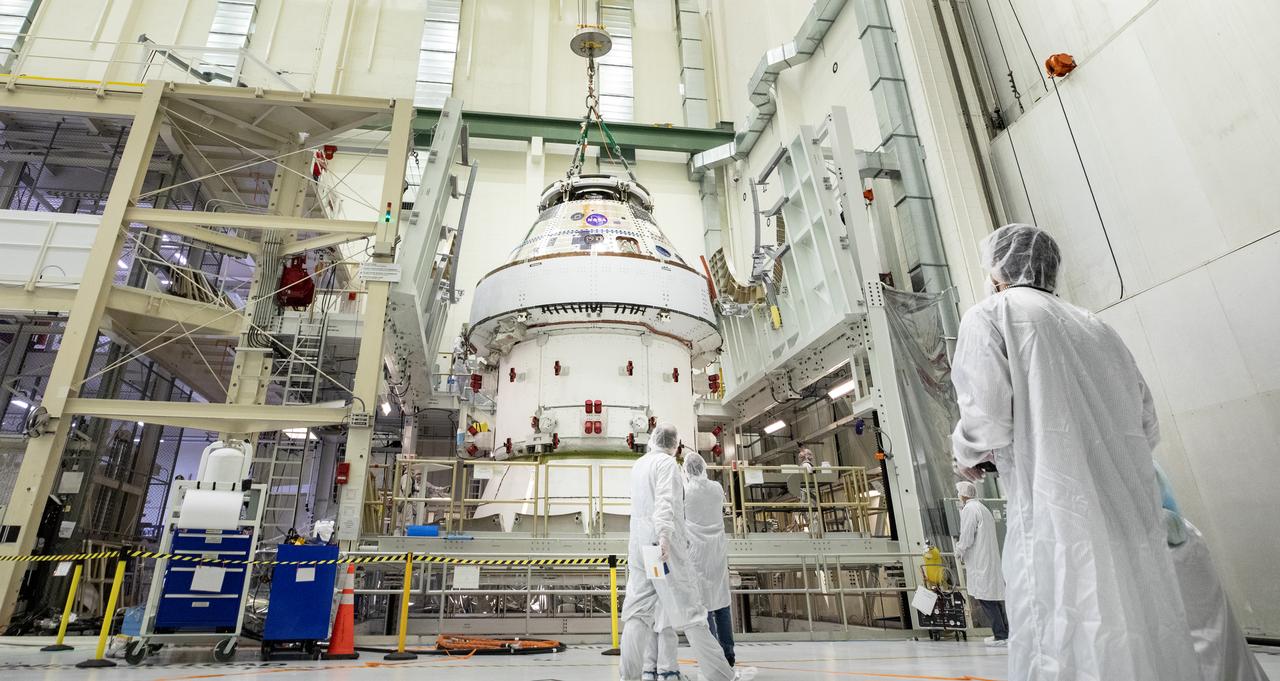

Technicians with NASA and Lockheed Martin operate a 30-ton crane to move NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft out of the Final Assembly and System Testing cell inside the Neil A. Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Saturday, Feb. 22, 2025. The move prepares for the upcoming installation of four solar array wings and spacecraft adapter jettison fairings for the agency’s first crewed flight test under the Artemis campaign.

Technicians with NASA and Lockheed Martin operate a 30-ton crane to move NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft out of the Final Assembly and System Testing cell inside the Neil A. Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Saturday, Feb. 22, 2025. The move prepares for the upcoming installation of four solar array wings and spacecraft adapter jettison fairings for the agency’s first crewed flight test under the Artemis campaign.
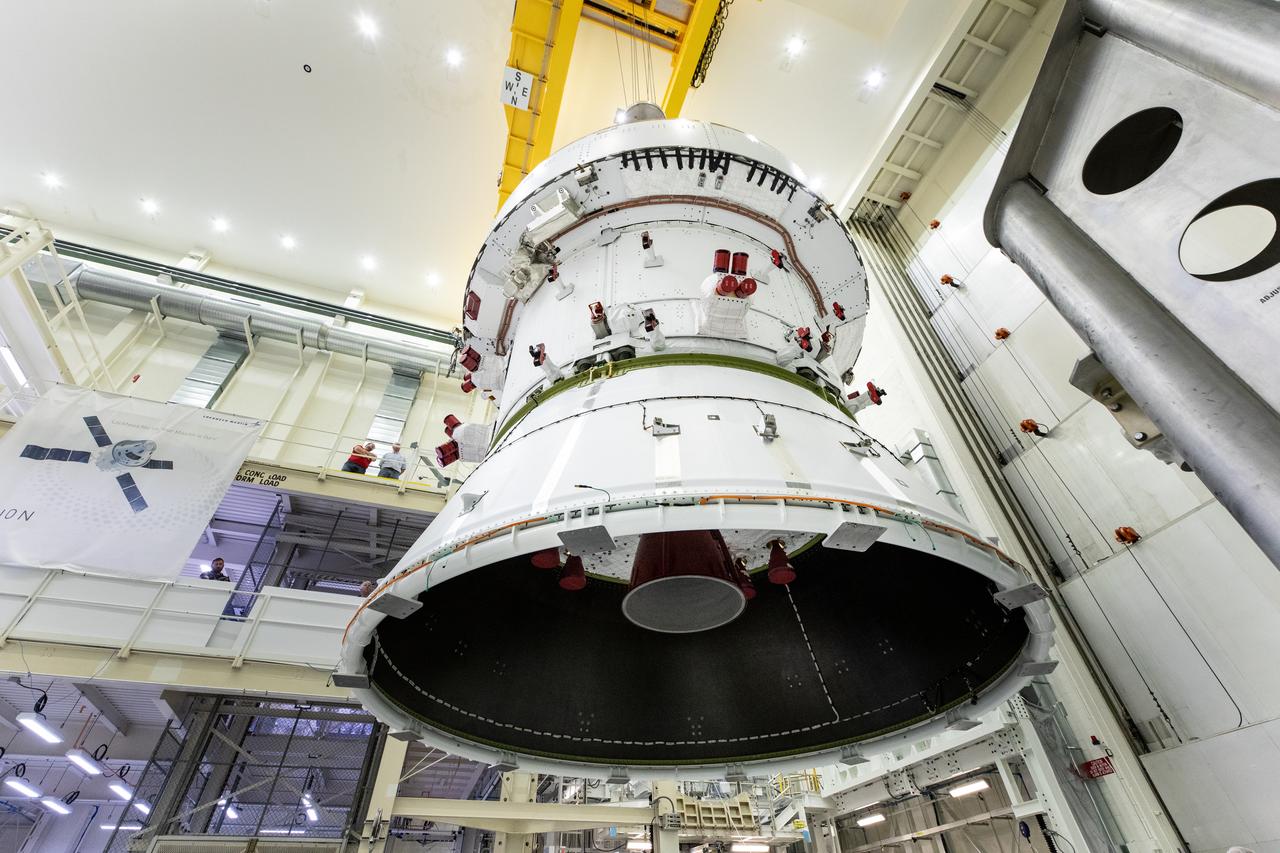

Technicians with NASA and Lockheed Martin operate a 30-ton crane to move NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft out of the Final Assembly and System Testing cell inside the Neil A. Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Saturday, Feb. 22, 2025. The move prepares for the upcoming installation of four solar array wings and spacecraft adapter jettison fairings for the agency’s first crewed flight test under the Artemis campaign.
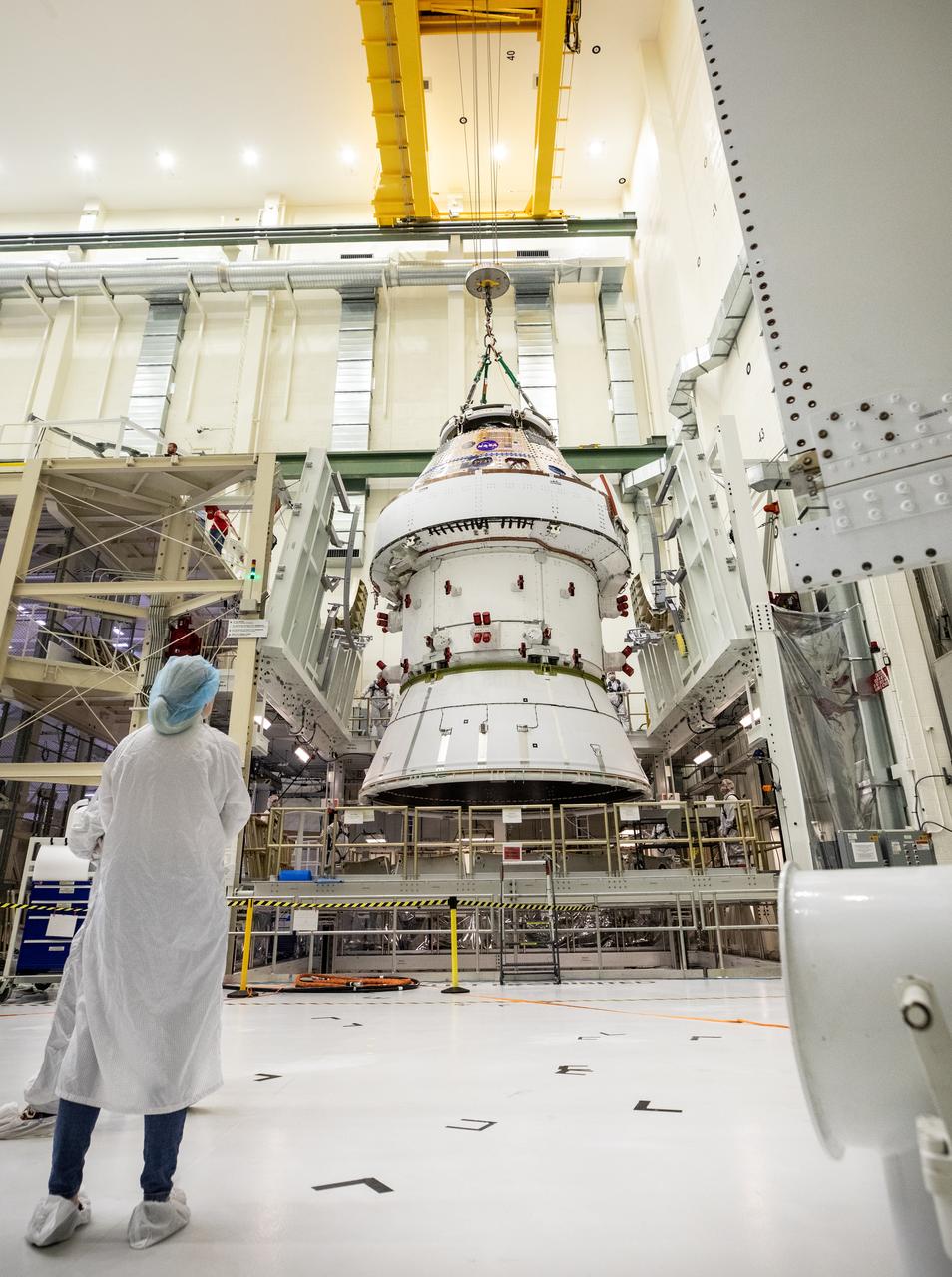

Technicians with NASA and Lockheed Martin operate a 30-ton crane to move NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft out of the Final Assembly and System Testing cell inside the Neil A. Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Saturday, Feb. 22, 2025. The move prepares for the upcoming installation of four solar array wings and spacecraft adapter jettison fairings for the agency’s first crewed flight test under the Artemis campaign.
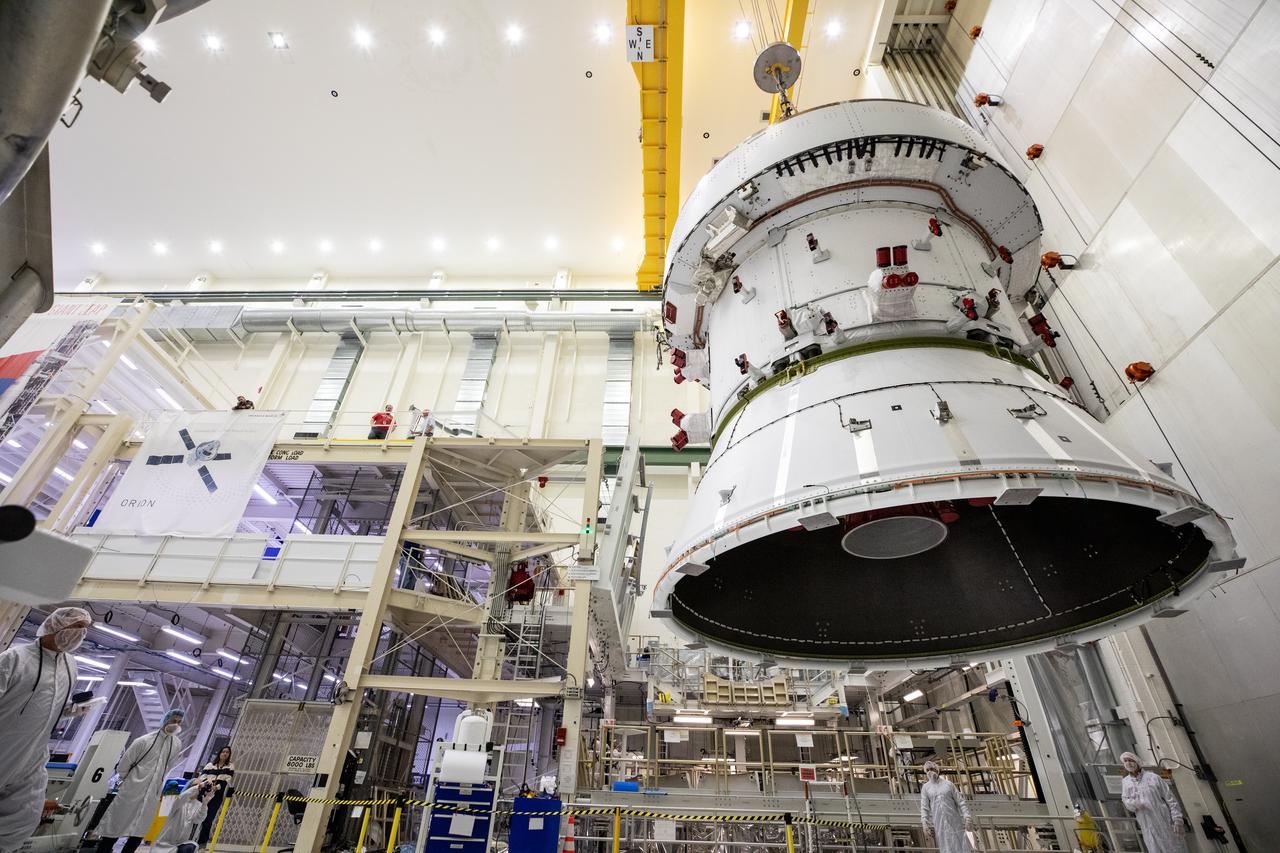

Technicians with NASA and Lockheed Martin operate a 30-ton crane to move NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft out of the Final Assembly and System Testing cell inside the Neil A. Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Saturday, Feb. 22, 2025. The move prepares for the upcoming installation of four solar array wings and spacecraft adapter jettison fairings for the agency’s first crewed flight test under the Artemis campaign.
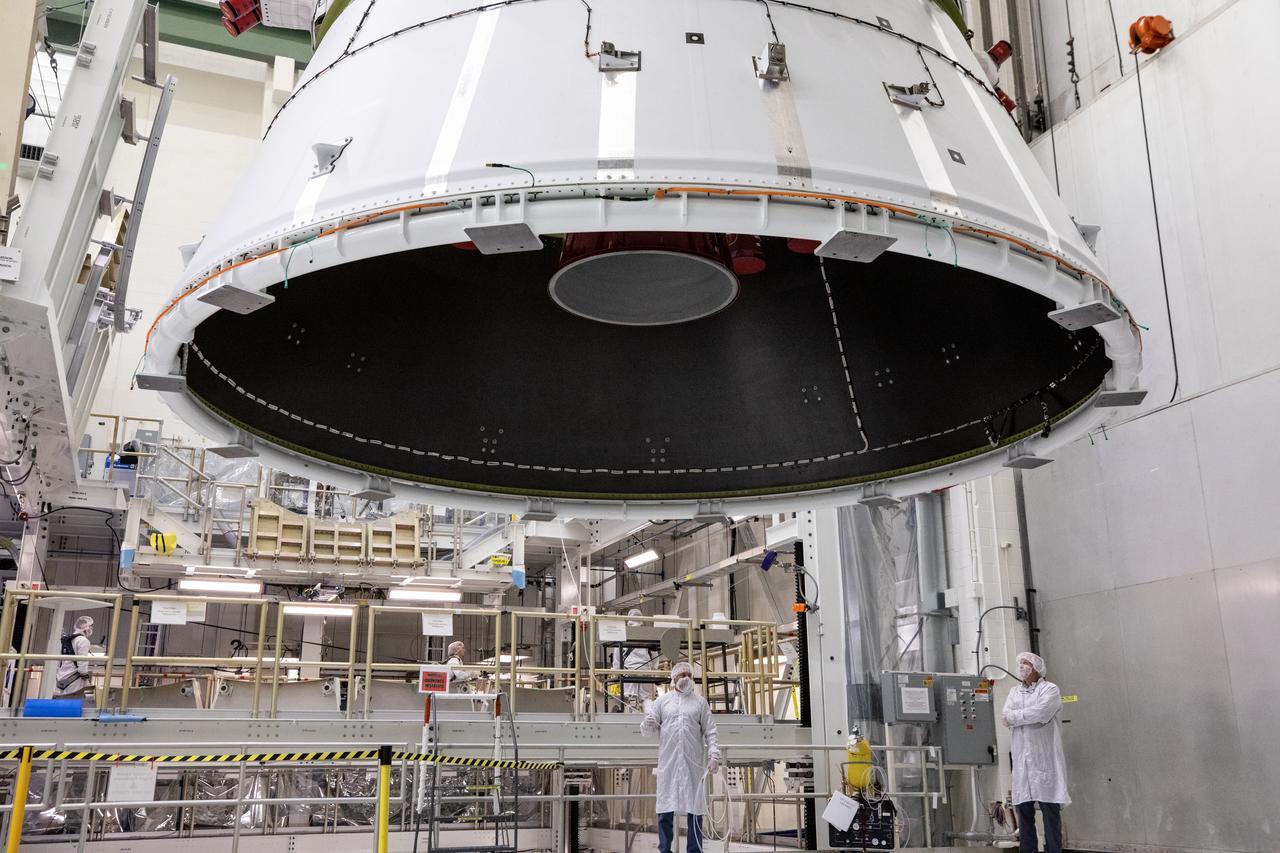

Technicians with NASA and Lockheed Martin operate a 30-ton crane to move NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft out of the Final Assembly and System Testing cell inside the Neil A. Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Saturday, Feb. 22, 2025. The move prepares for the upcoming installation of four solar array wings and spacecraft adapter jettison fairings for the agency’s first crewed flight test under the Artemis campaign.
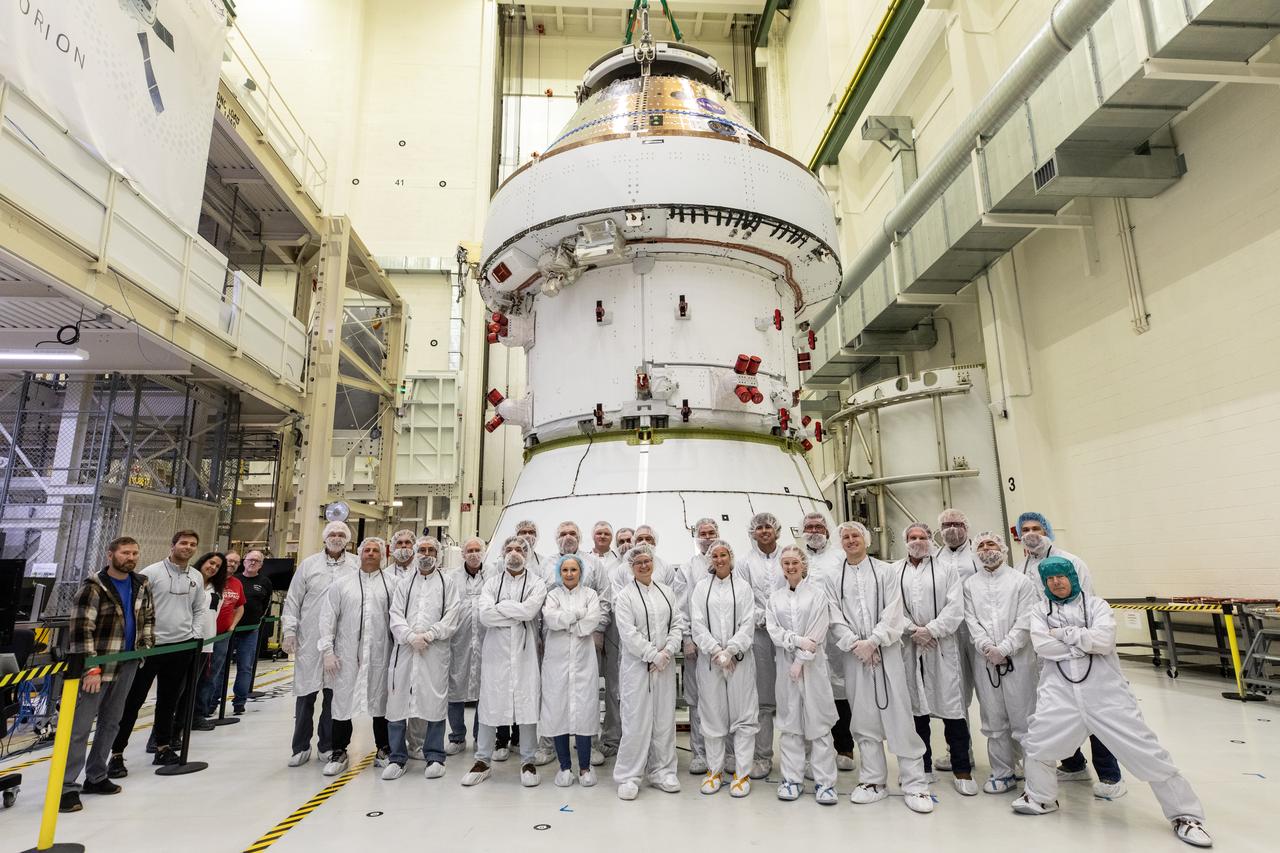

Crews with NASA and Lockheed Martin pose for a photo in front of NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft inside the Neil A. Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Saturday, Feb. 22, 2025. Technicians operated a 30-ton crane to move the spacecraft from the Final Assembly and System Testing cell to prepare for upcoming installation of four solar array wings and spacecraft adapter jettison fairings for the agency’s first crewed flight test under the Artemis campaign.
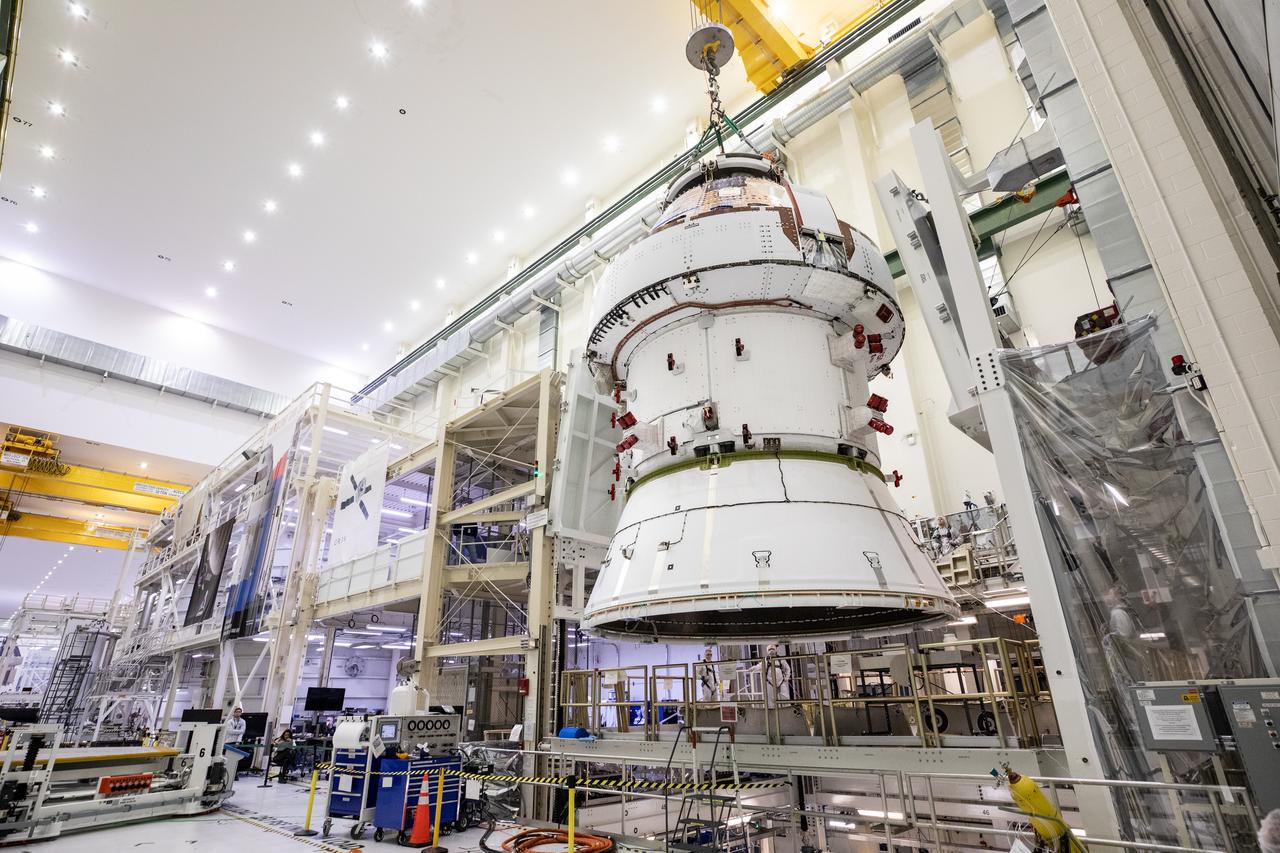

Technicians with NASA and Lockheed Martin operate a 30-ton crane to move NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft out of the Final Assembly and System Testing cell inside the Neil A. Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Saturday, Feb. 22, 2025. The move prepares for the upcoming installation of four solar array wings and spacecraft adapter jettison fairings for the agency’s first crewed flight test under the Artemis campaign.
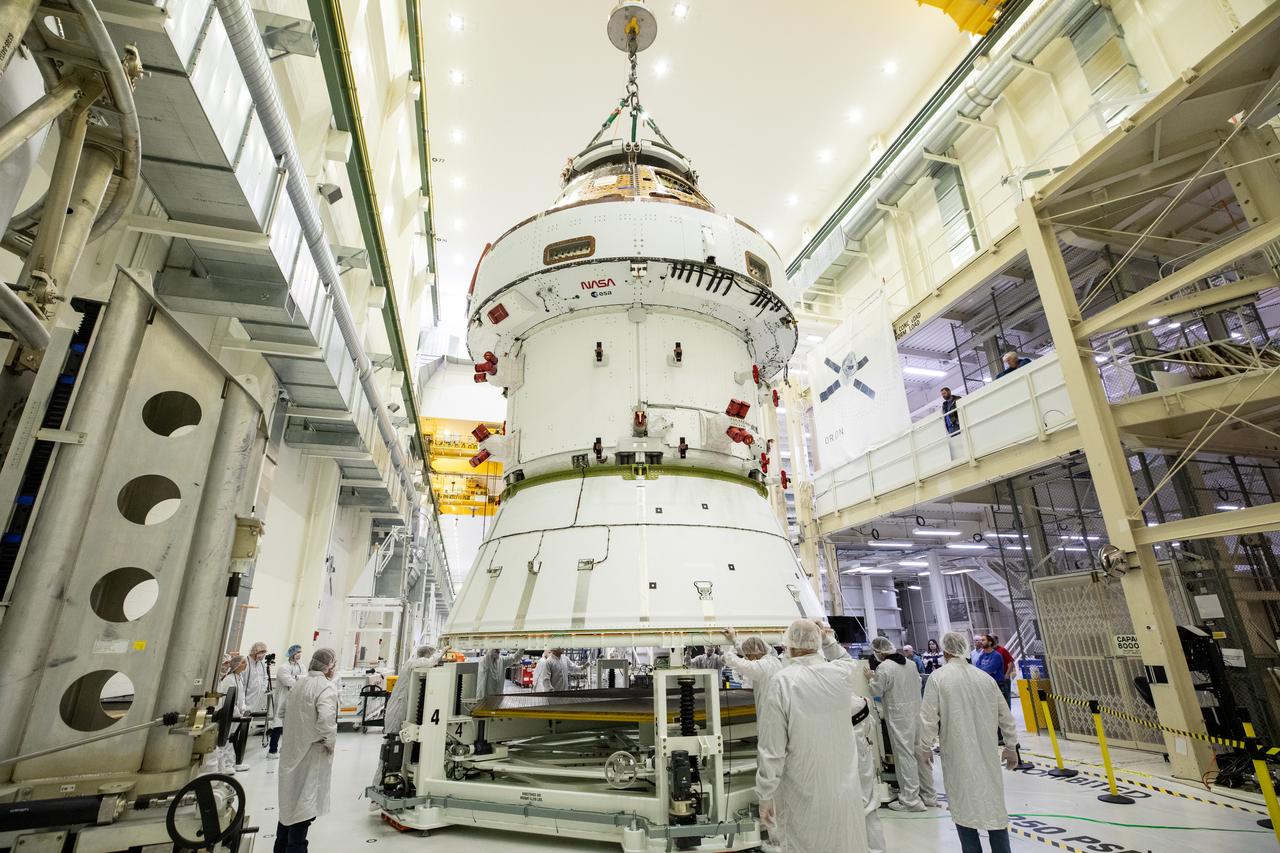

Technicians with NASA and Lockheed Martin operate a 30-ton crane to move NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft out of the Final Assembly and System Testing cell inside the Neil A. Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Saturday, Feb. 22, 2025. The move prepares for the upcoming installation of four solar array wings and spacecraft adapter jettison fairings for the agency’s first crewed flight test under the Artemis campaign.
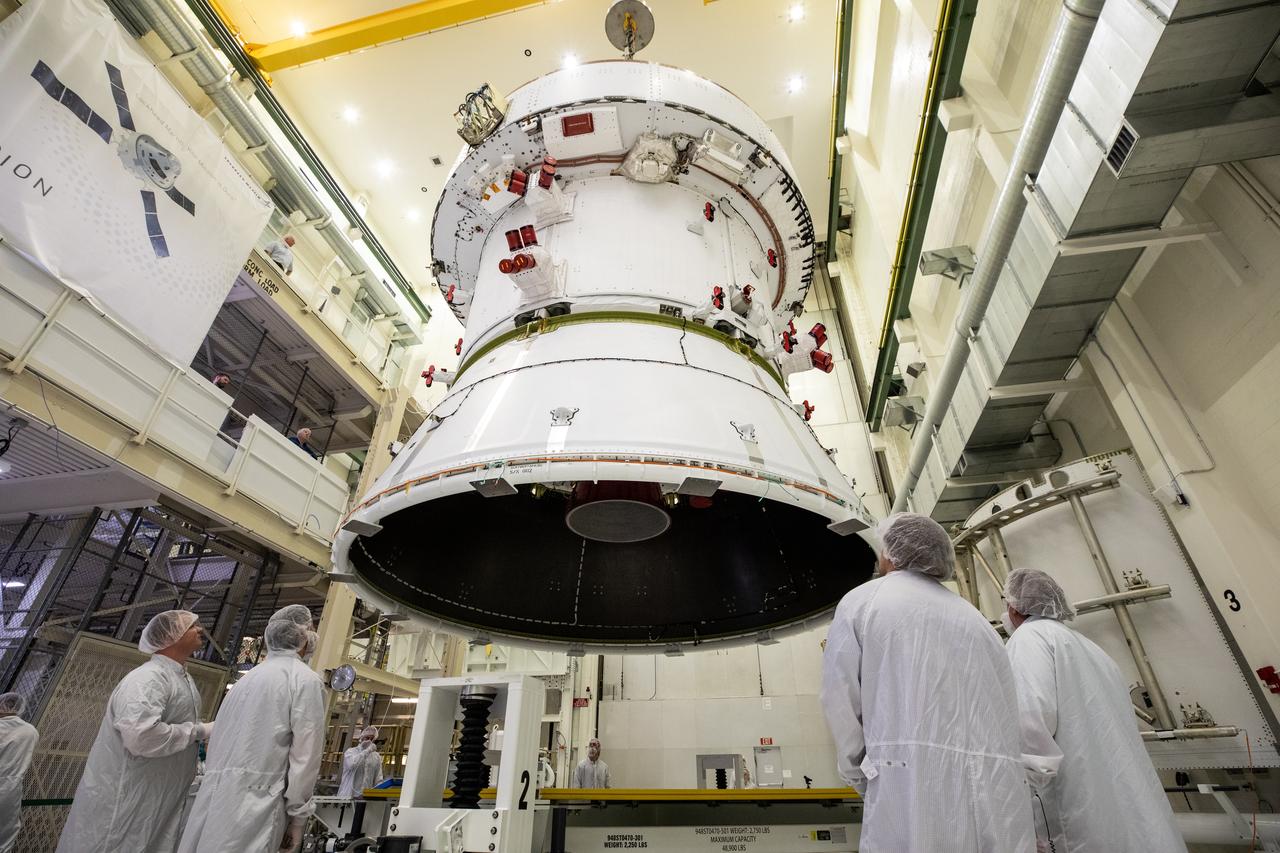

Technicians with NASA and Lockheed Martin operate a 30-ton crane to move NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft out of the Final Assembly and System Testing cell inside the Neil A. Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Saturday, Feb. 22, 2025. The move prepares for the upcoming installation of four solar array wings and spacecraft adapter jettison fairings for the agency’s first crewed flight test under the Artemis campaign.
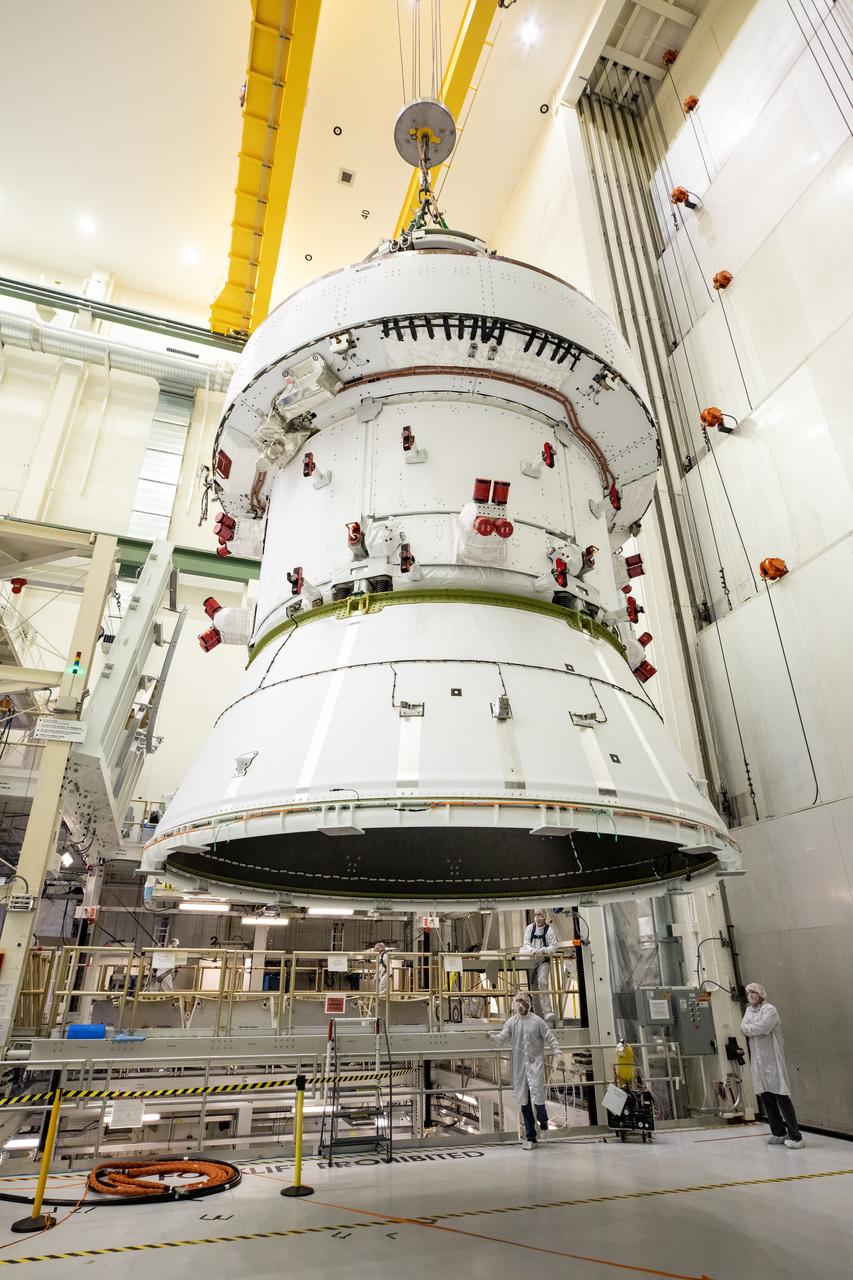

Technicians with NASA and Lockheed Martin operate a 30-ton crane to move NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft out of the Final Assembly and System Testing cell inside the Neil A. Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Saturday, Feb. 22, 2025. The move prepares for the upcoming installation of four solar array wings and spacecraft adapter jettison fairings for the agency’s first crewed flight test under the Artemis campaign.
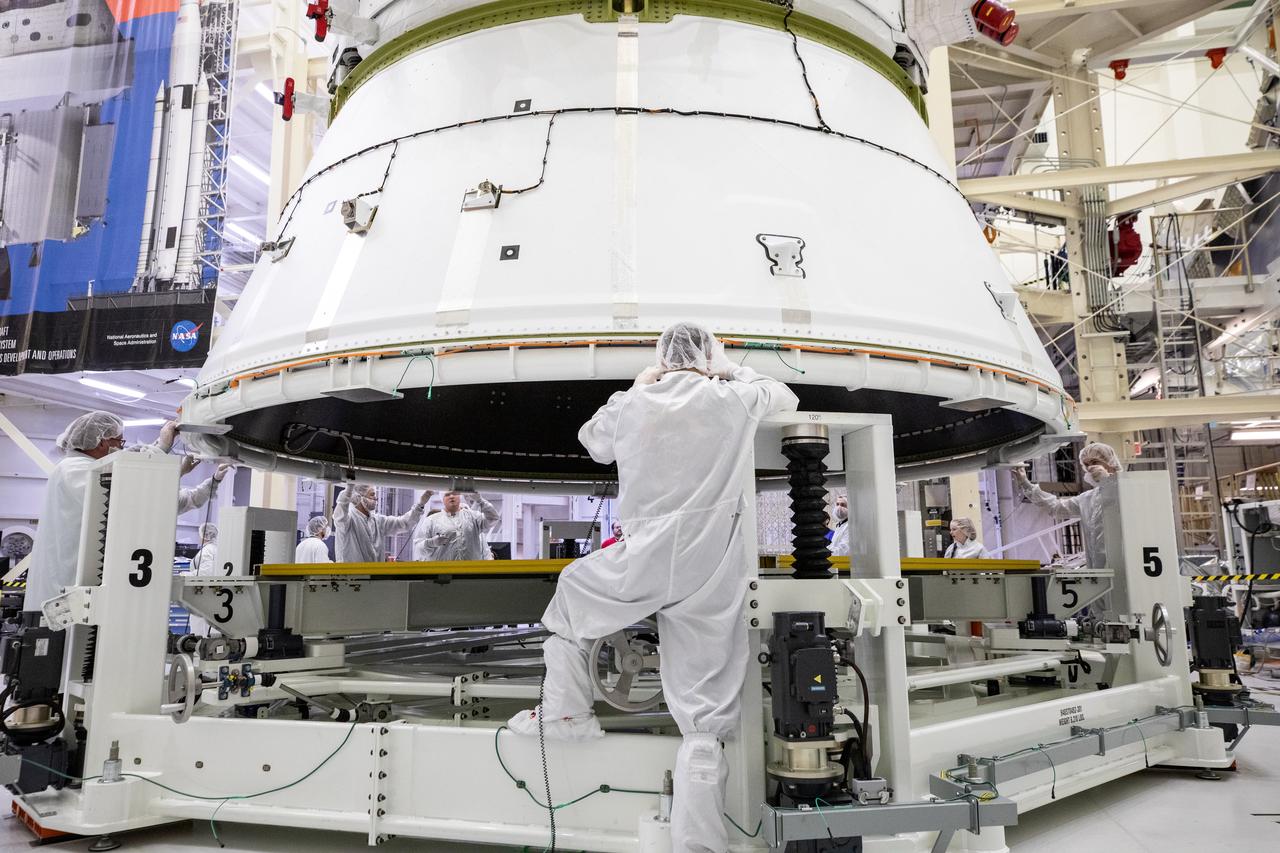

Technicians with NASA and Lockheed Martin operate a 30-ton crane to move NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft out of the Final Assembly and System Testing cell inside the Neil A. Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Saturday, Feb. 22, 2025. The move prepares for the upcoming installation of four solar array wings and spacecraft adapter jettison fairings for the agency’s first crewed flight test under the Artemis campaign.