
Alexander Blanchard, a chemistry doctoral student at Florida State University and graduate student at Marshall this summer, conducts analysis in a Marshall laboratory on the Chemical Gardens experiment, which is growing delicate crystalline structures in solution in the microgravity environment on the space station. Researchers hope the study could yield practical benefits for bioremediation and other "green" commercial applications.
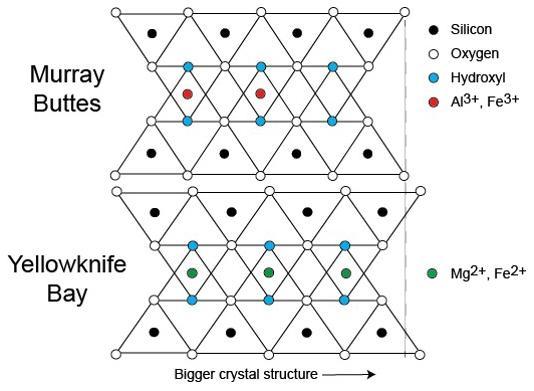
This diagram illustrates how the dimensions of clay minerals' crystal structure are affected by which ions are present in the composition of the mineral. Different clay minerals were identified this way at two sites in Mars' Gale Crater: "Murray Buttes" and "Yellowknife Bay." In otherwise identical clay minerals, a composition that includes aluminum and ferric iron ions (red dots) results in slightly smaller crystalline unit cells than one that instead includes magnesium and ferrous iron ions (green dots). Ferric iron is more highly oxidized than ferrous iron. Crystalline cell units are the basic repeating building blocks that define minerals. X-ray diffraction analysis, a capability of the Chemistry and Mineralogy (CheMin) instrument on NASA's Curiosity Mars rover, identifies minerals from their crystalline structure. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21148
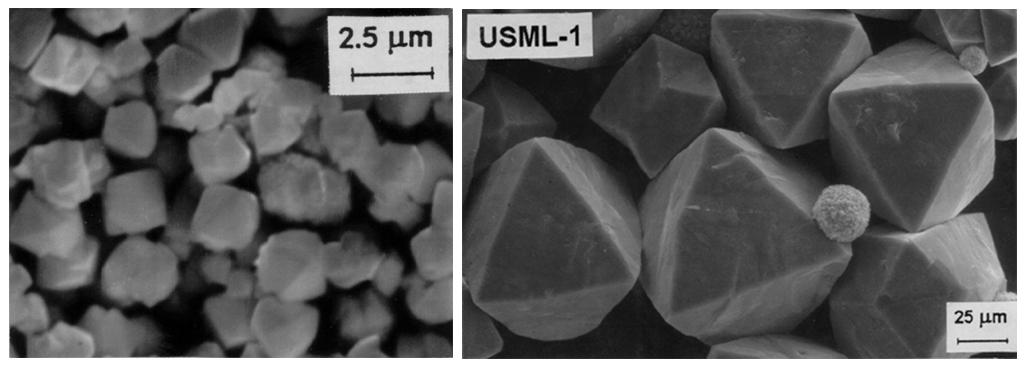
Zeolites are crystalline aluminosilicates that have complex framework structures. However, there are several features of zeolite crystals that make unequivocal structure determinations difficult. The acquisition of reliable structural information on zeolites is greatly facilitated by the availability of high-quality specimens. For structure determinations by conventional diffraction techniques, large single-crystal specimens are essential. Alternatively, structural determinations by powder profile refinement methods relax the constraints on crystal size, but still require materials with a high degree of crystalline perfection. Studies conducted at CAMMP (Center for Advanced Microgravity Materials Processing) have demonstrated that microgravity processing can produce larger crystal sizes and fewer structural defects relative to terrestrial crystal growth. Principal Investigator: Dr. Albert Sacco
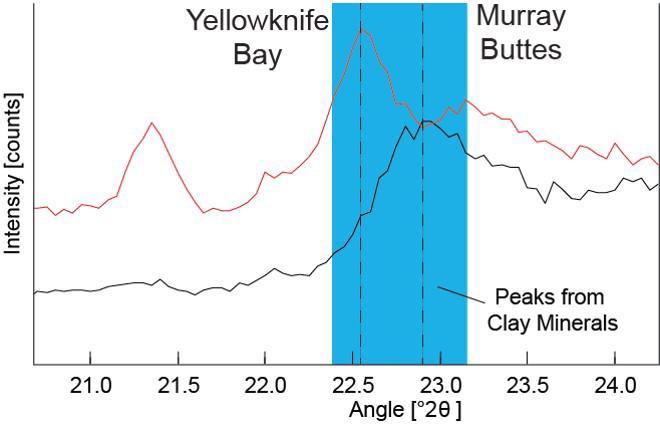
Data graphed here from the Chemistry and Camera (CheMin) instrument on NASA's Mars Curiosity rover show a difference between clay minerals in powder drilled from mudstone outcrops at two locations in Mars' Gale Crater: "Yellowknife Bay" and "Murray Buttes." CheMin's X-ray diffraction analysis reveals information about the crystalline structure of minerals in the rock. The intensity peaks marked with dotted vertical lines in this chart indicate that the crystalline structure of the two sites' clay minerals differs. The difference can be tied to a compositional difference in the clay minerals, as depicted in a diagram at PIA21148. The Yellowknife Bay site is on the floor of Gale Crater. The Murray Buttes site is on lower Mount Sharp, the layered mound in the center of the crater. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21147

iss062e014345 (2-16-2020) --- A view of NASA astronaut Jessica Meir configuring the Light Microscopy Module (LMM) for the Advanced Colloids Experiment-Temperature-4 (ACE-T-4) science run in the Destiny module aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Introducing disorder to a crystalline system in a controlled way can form glass. Advanced Colloids Experiment-Temperature-4 (ACE-T-4) examines the transition of an ordered crystal to a disordered glass to determine how increasing disorder affects structural and dynamic properties
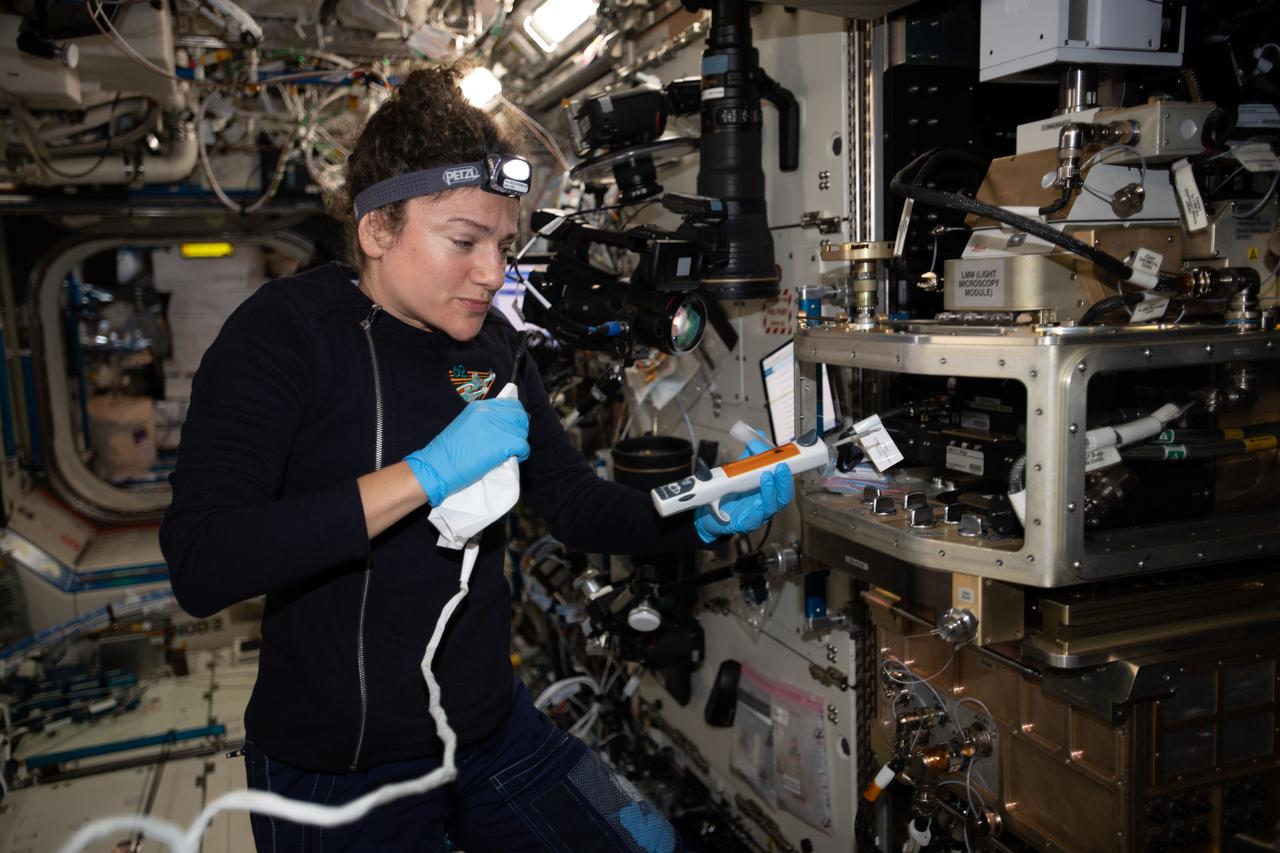

iss062e014349 (Feb. 16, 2020) --- A view of NASA astronaut Jessica Meir configuring the Light Microscopy Module (LMM) for the Advanced Colloids Experiment-Temperature-4 (ACE-T-4) science in the Destiny module aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Introducing disorder to a crystalline system in a controlled way can form glass. Advanced Colloids Experiment-Temperature-4 (ACE-T-4) examines the transition of an ordered crystal to a disordered glass to determine how increasing disorder affects structural and dynamic properties.
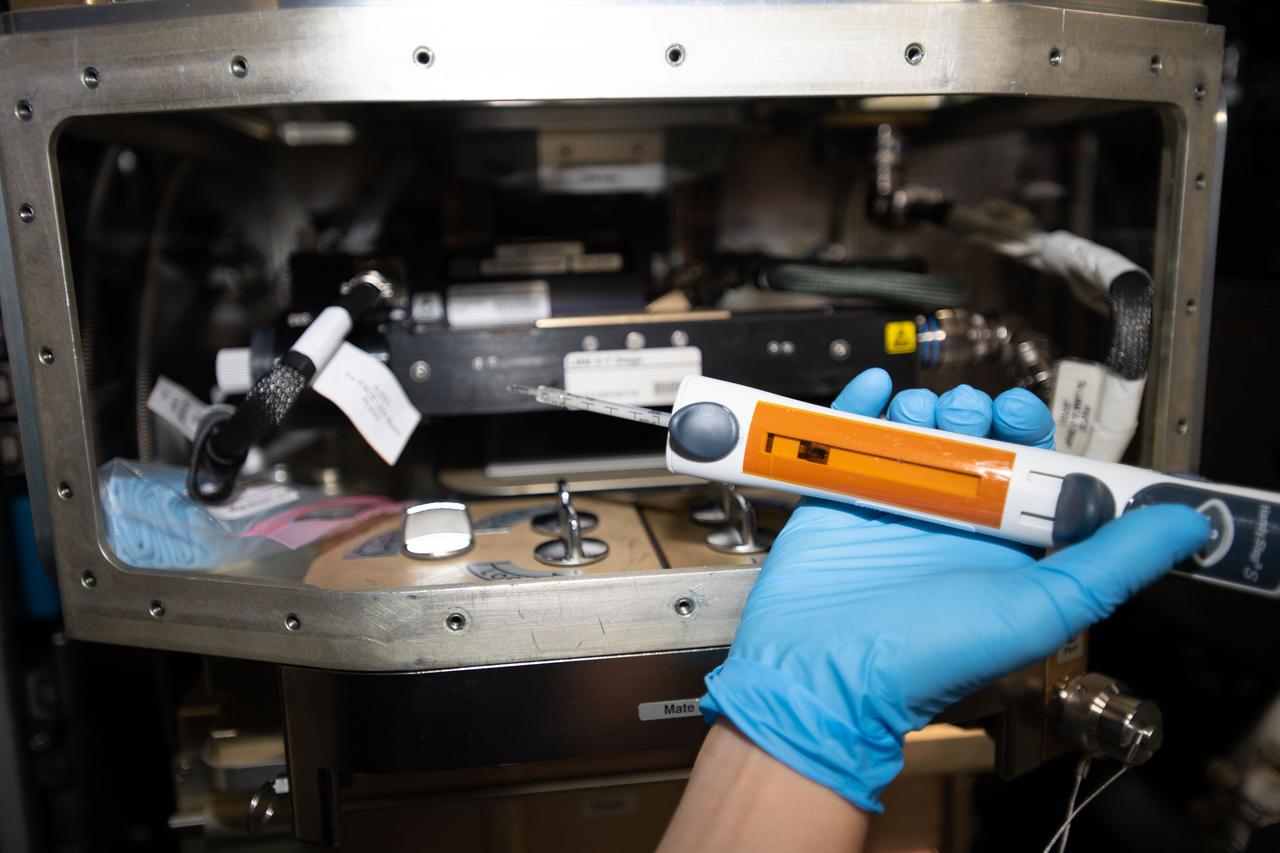

iss062e014342 (2-16-2020) --- A view of NASA astronaut Jessica Meir configuring the Light Microscopy Module (LMM) for the Advanced Colloids Experiment-Temperature-4 (ACE-T-4) science run in the Destiny module aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Introducing disorder to a crystalline system in a controlled way can form glass. Advanced Colloids Experiment-Temperature-4 (ACE-T-4) examines the transition of an ordered crystal to a disordered glass to determine how increasing disorder affects structural and dynamic properties
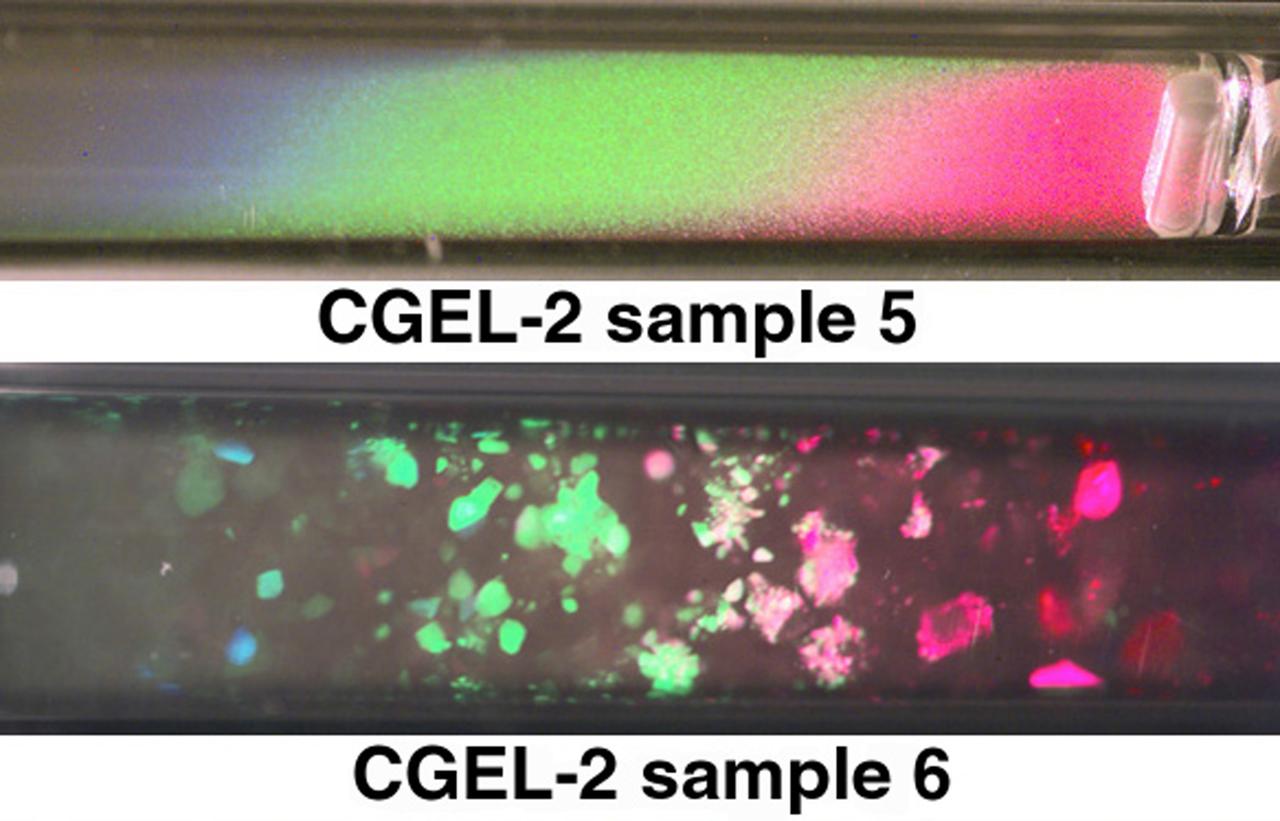
These are images of CGEL-2 samples taken during STS-95. They show binary colloidal suspensions that have formed ordered crystalline structures in microgravity. In sample 5, there are more particles therefore, many, many crystallites (small crystals) form. In sample 6, there are less particles therefore, the particles are far apart and few, much larger crystallites form. The white object in the right corner of sample 5 is the stir bar used to mix the sample at the begirning of the mission.
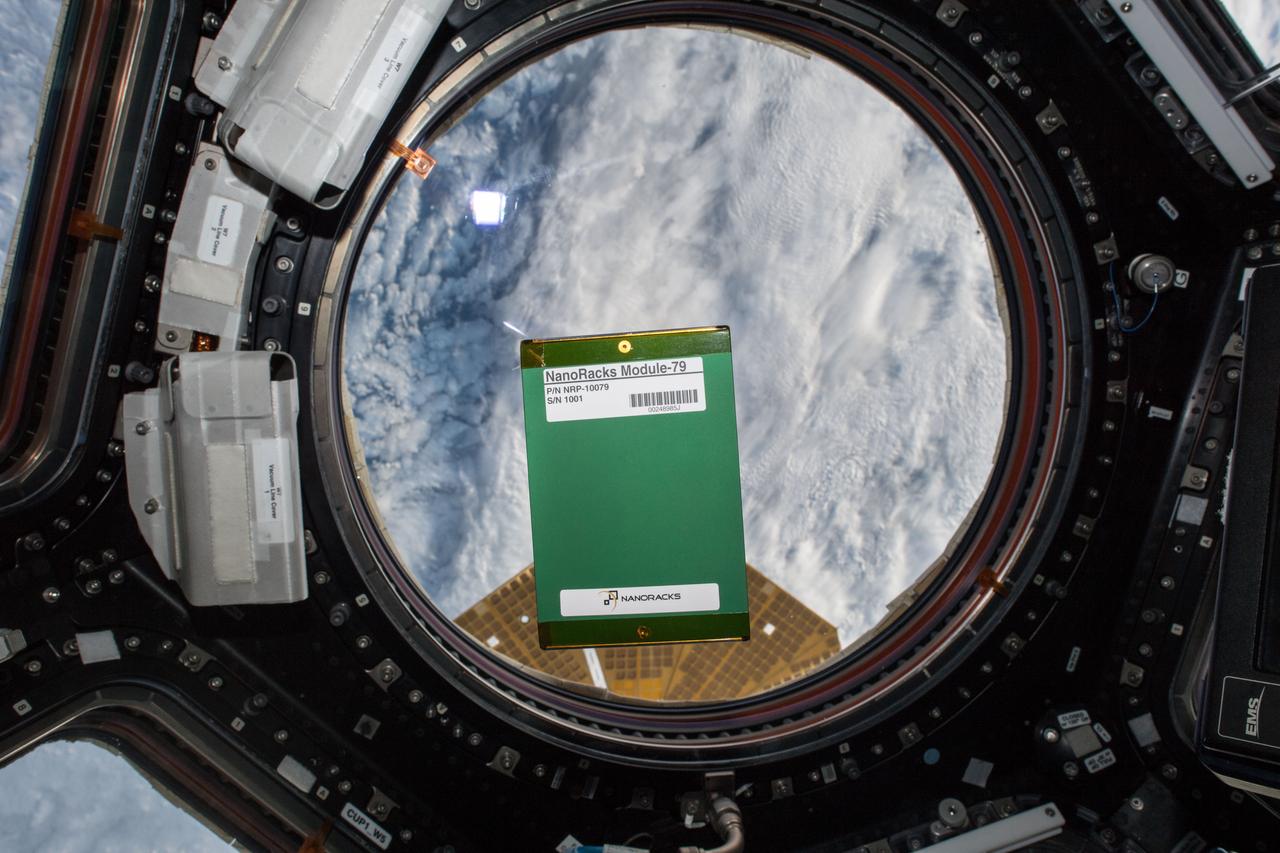

iss056e078370 (6/7/2018) --- Photo of the QUANTUM experiment floating in front of Window 7 in the Cupola module. Earth is in the background. QUANTUM observes the effects of entropy outside of the Earth’s atmosphere. Materials with tight, intense crystalline structures are exposed to a space environment to observe even small changes and differences between materials aboard the International Space Station (ISS) and those on Earth.

iss056e078371 (6/7/2018) --- Photo of the QUANTUM experiment floating in front of Window 7 in the Cupola module. Earth is in the background. QUANTUM observes the effects of entropy outside of the Earth’s atmosphere. Materials with tight, intense crystalline structures are exposed to a space environment to observe even small changes and differences between materials aboard the International Space Station (ISS) and those on Earth.
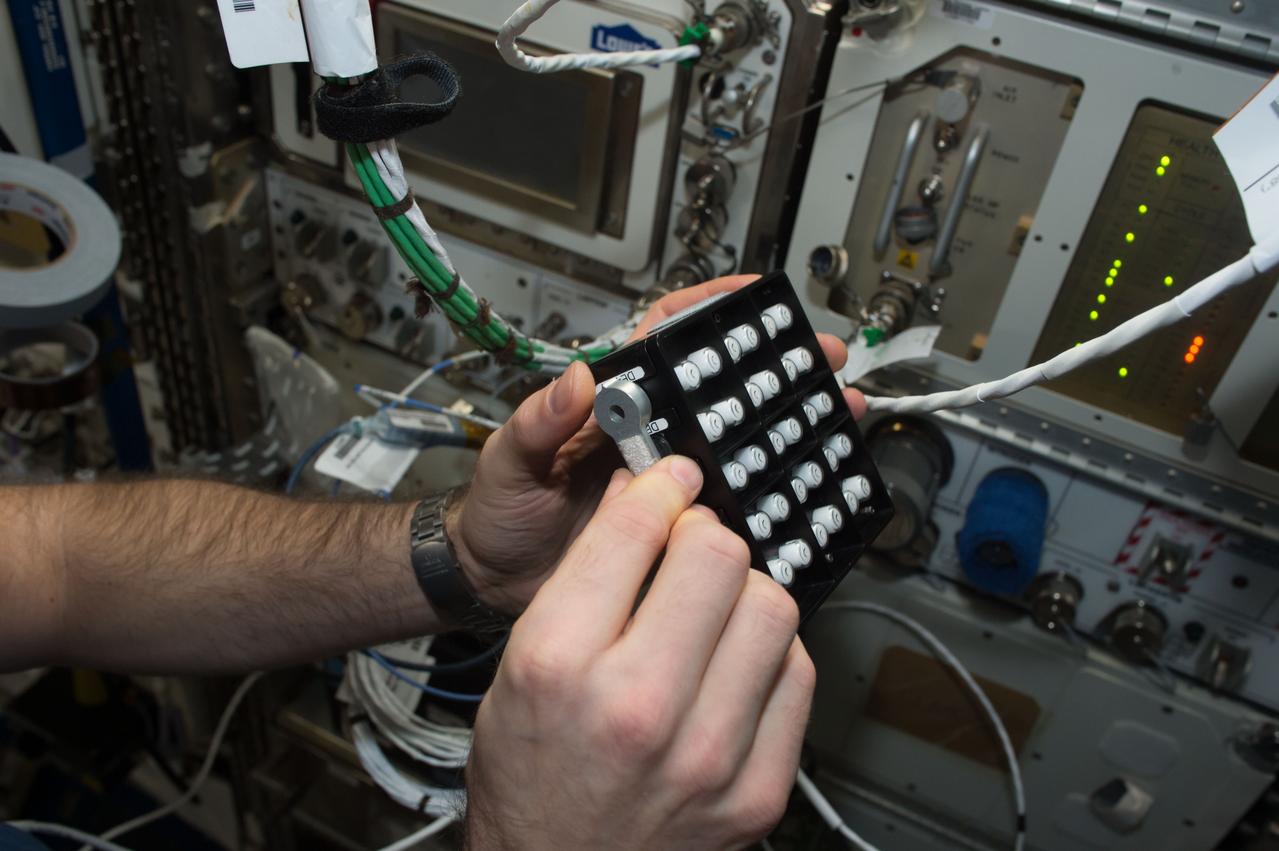

iss050e058807 (3/17/2017) --- A view of European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Thomas Pesquet, during Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) -5 hardware deactivation and stow, from Microgravity Experiment Research Locker Incubator (MERLIN) on Expedite the Processing of Experiments to the Space Station (EXPRESS) Rack 5. The Microgravity Growth of Crystalline Monoclonal Antibodies for Pharmaceutical Applications (CASIS-PCG-5) investigation crystallizes a monoclonal antibody developed by Merck Research Labs. Microgravity enables the growth of extremely high-quality crystals, which allow scientists to study the proteins’ structure, improve drug delivery, manufacturing, and developing better methods for storing these biological molecules.
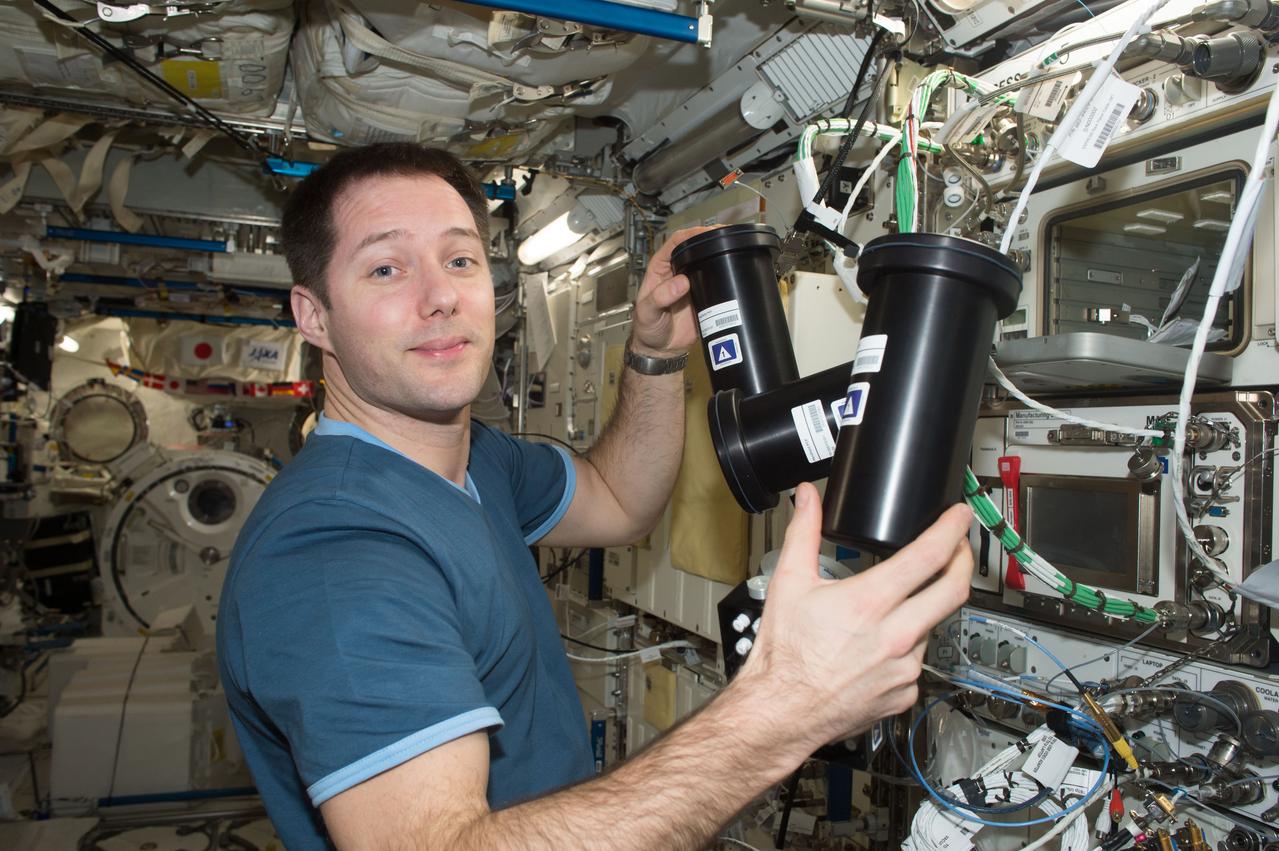

iss050e058812 (3/17/2017) --- A view of European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Thomas Pesquet, during Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) -5 hardware deactivation and stow, from Microgravity Experiment Research Locker Incubator (MERLIN) on Expedite the Processing of Experiments to the Space Station (EXPRESS) Rack 5. The Microgravity Growth of Crystalline Monoclonal Antibodies for Pharmaceutical Applications (CASIS-PCG-5) investigation crystallizes a monoclonal antibody developed by Merck Research Labs. Microgravity enables the growth of extremely high-quality crystals, which allow scientists to study the proteins’ structure, improve drug delivery, manufacturing, and developing better methods for storing these biological molecules.
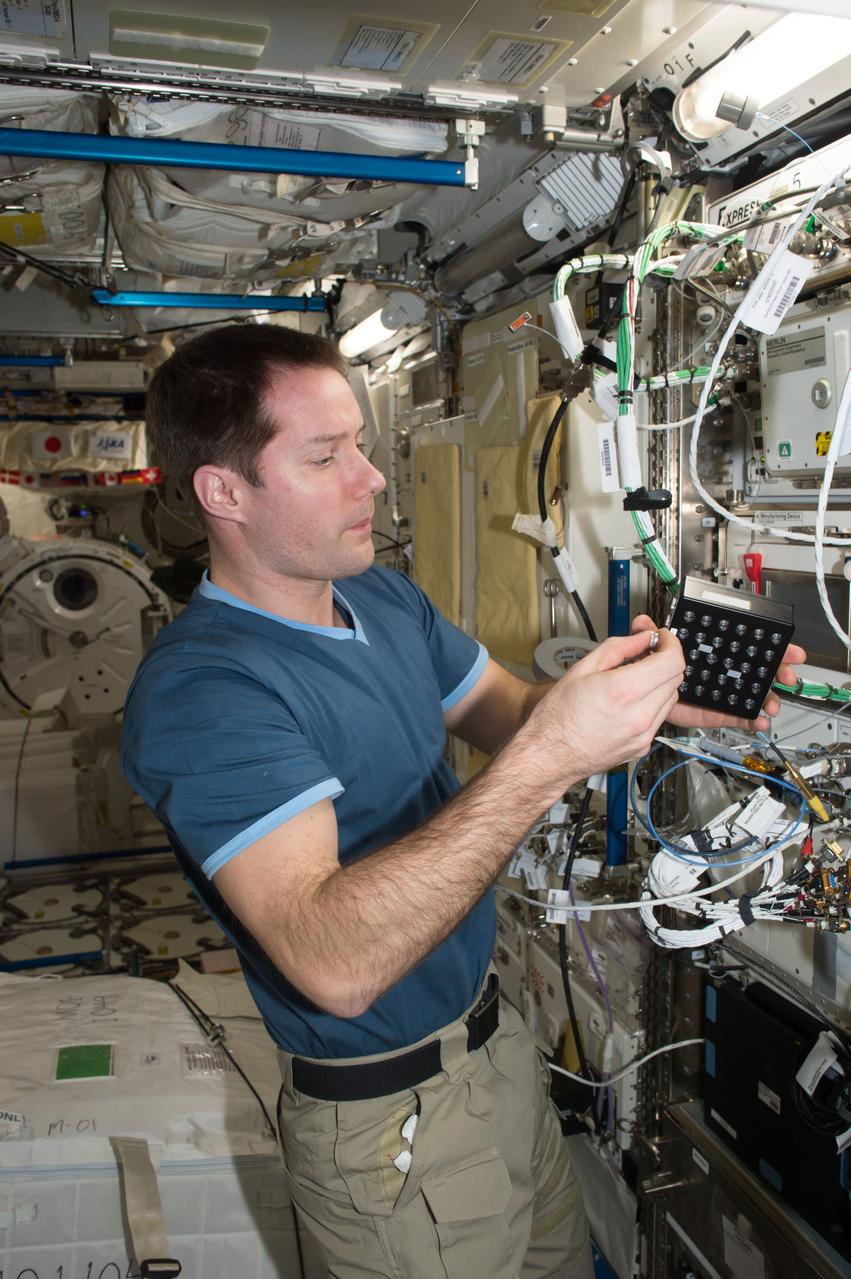

iss050e058802 (3/17/2017) --- A view of European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Thomas Pesquet, during Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) -5 hardware deactivation and stow, from Microgravity Experiment Research Locker Incubator (MERLIN) on Expedite the Processing of Experiments to the Space Station (EXPRESS) Rack 5. The Microgravity Growth of Crystalline Monoclonal Antibodies for Pharmaceutical Applications (CASIS-PCG-5) investigation crystallizes a monoclonal antibody developed by Merck Research Labs. Microgravity enables the growth of extremely high-quality crystals, which allow scientists to study the proteins’ structure, improve drug delivery, manufacturing, and developing better methods for storing these biological molecules.
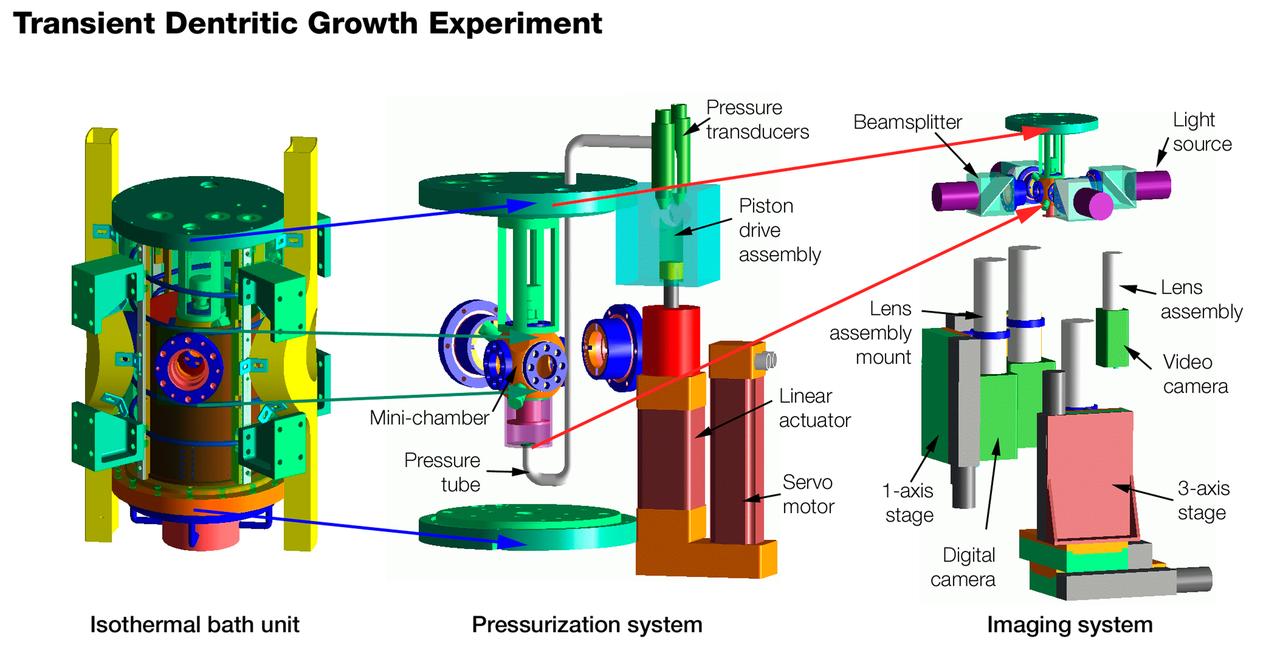
The Transient Dendritic Solidification Experiment (TDSE) is being developed as a candidate for flight aboard the International Space Station. TDSE will study the growth of dendrites (treelike crystalline structures) in a transparent material (succinonitrile or SCN) that mimics the behavior or widely used iron-based metals. Basic work by three Space Shuttle missions of the Isothermal Dendritic Growth Experiment (IDGE) is yielding new insights into virtually all industrially relevant metal and alloy forming operations. The TDSE is similar to IDGE, but will maintain a constant temperature while varying pressure on the dendrites. Shown here is an exploded view of major elements of the TDSE. A similar view is availble without labels. The principal investigator is Matthew Koss of College of the Holy Cross in Worcester, MA. Photo credit: NASA/Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC)
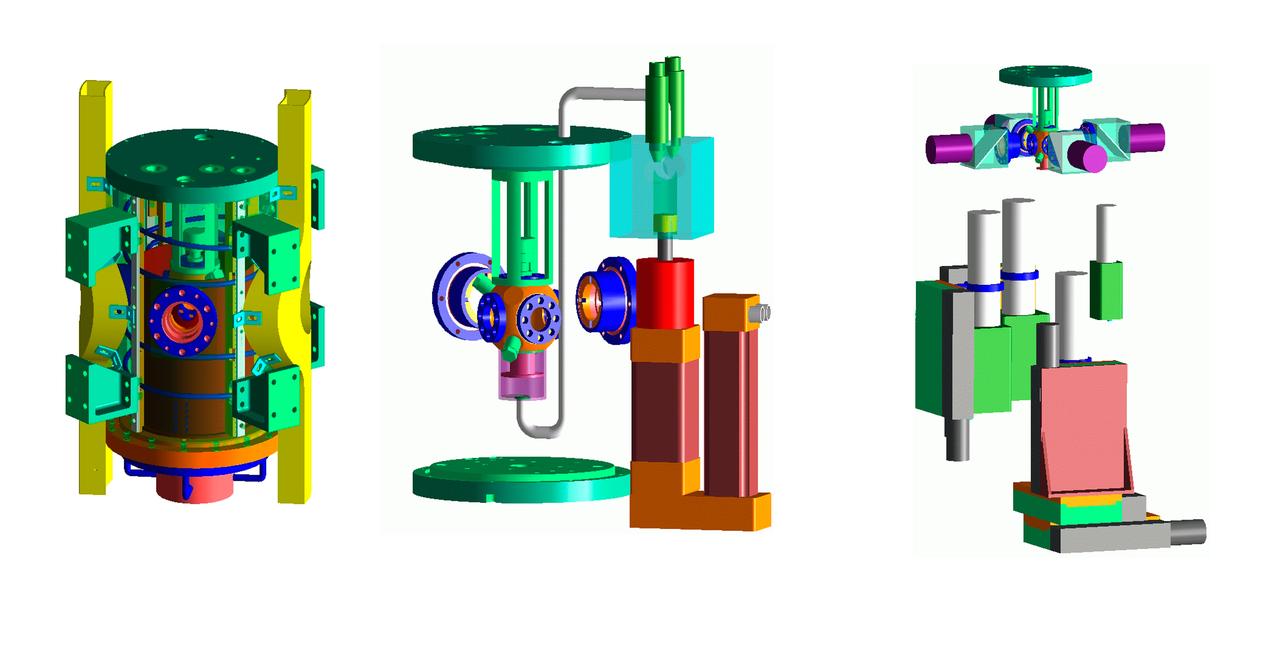
The Transient Dendritic Solidification Expepriment (TDSE) is being developed as a candidate for flight aboard the International Space Station. TDSE will study the growth of dendrites (treelike crystalline structures) in a transparent material (succinonitrile or SCN) that mimics the behavior of widely used iron-based metals. Basic work by three Space Shuttle missions of the Isothermal Dendritic Growth Expepriment (IDGE) is yielding new insights into virtually all industrially relevant metal and alloy forming operations. The TDSE is similar to IDGE, but will maintain a constant temperature while varying pressure on the dendrites. Shown here is an exploded view of major elements of TDSE. A similar view is available with labels. The principal investigator is Matthew Koss of College of the Holy Cross in Worcester, MA. Photo credit: NASA/Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC)
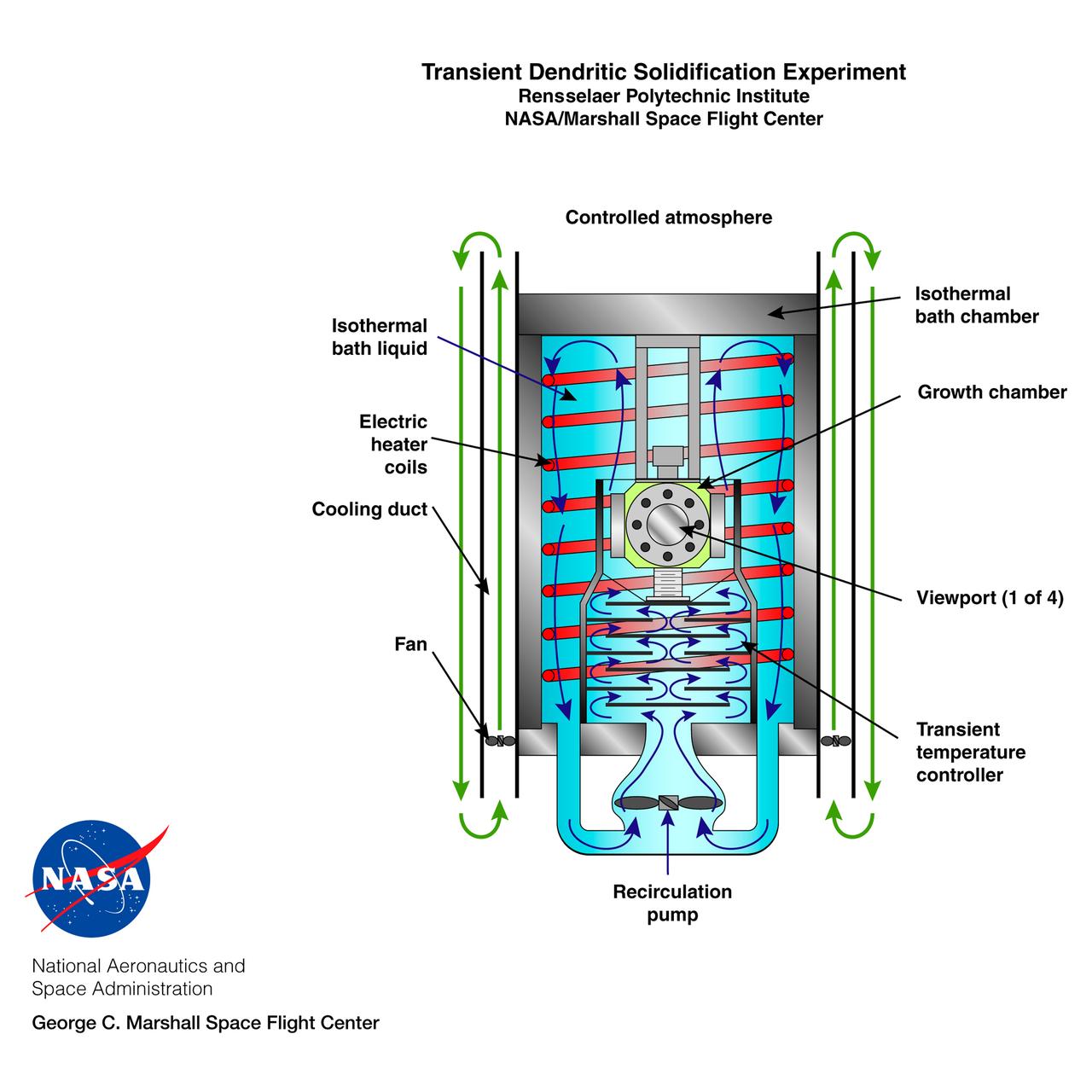
The Transient Dentritic Solidification Experiment (TDSE) is being developed as a candidate for flight aboard the International Space Station. TDSE will study the growth of dentrites (treelike crystalline structures) in a transparent material (succinonitrile or SCN) that mimics the behavior of widely used iron-based metals. Basic work by three Space Shuttle flights (STS-62, STS-75, and STS-87) of the Isothermal Dendritic Growth Experiment (IDGE) is yielding new insights into virtually all industrially relevant metal and alloy forming operations. The TDSE is similar to IDGE, but will maintain a constant temperature while varying pressure on the dentrites. Shown here is a cutaway of the isothermal bath containing its growth cell at the heart of the TDSE. The principal investigator is Matthew Koss of College of the Holy Cross in Worcester, MA. Note: an Acrobat PDF version is available from http://microgravity.nasa.gov/gallery
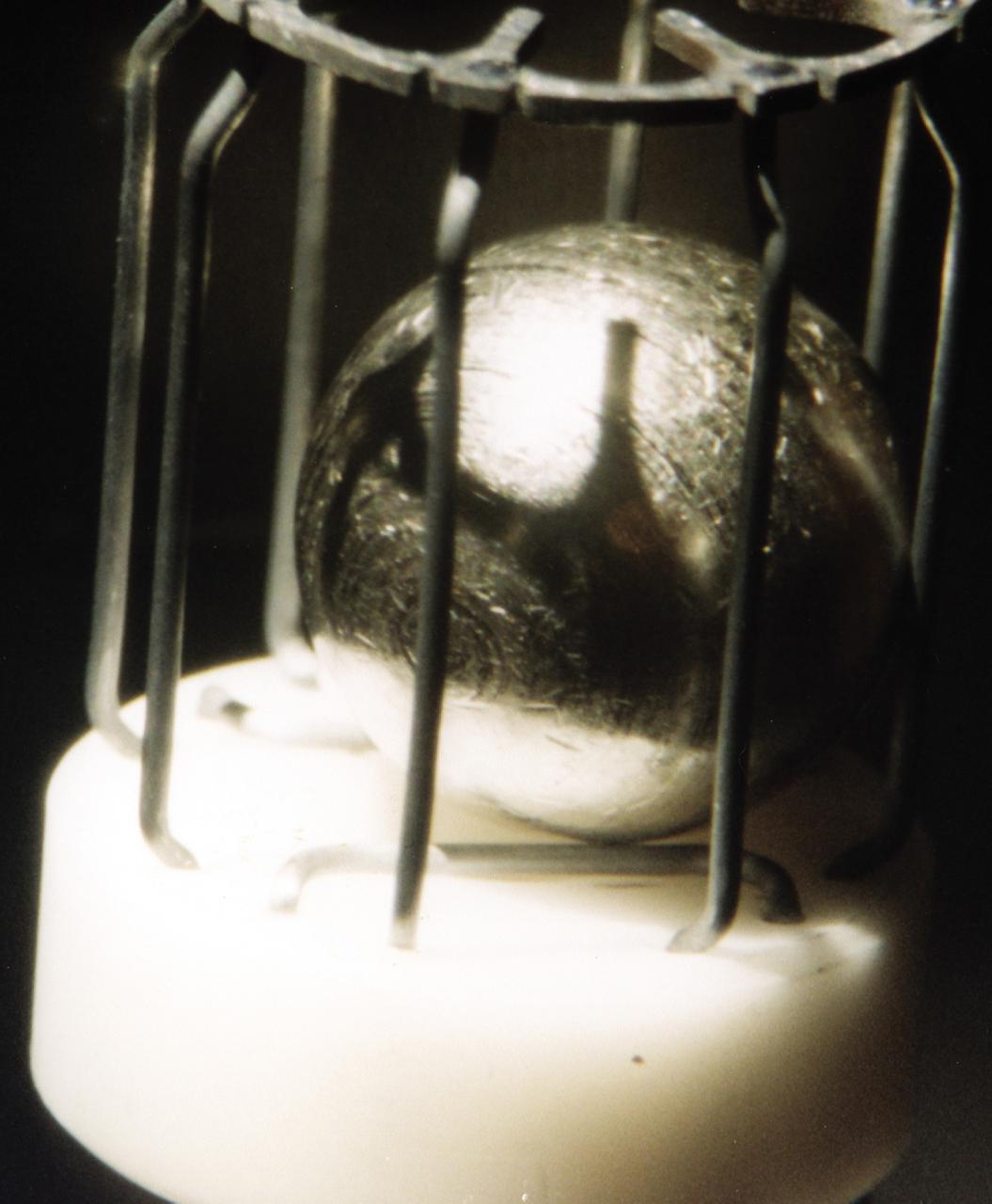
This metal sample, which is approximately 1 cm in diameter, is typical of the metals that were studied using the German designed electromagnetic containerless processing facility. The series of experiments that use this device is known as TEMPUS which is the acronym that stands for the German Tiegelfreies Elektromanetisches Prozessieren Unter Schwerelosigkeit. Most of the TEMPUS experiments focused on various aspects of undercooling liquid metal and alloys. Undercooling is the process of melting a material and then cooling it to a temperature that is below its normal freezing or solidification point. The TEMPUS experiments that used the metal cages as shown in the photograph, often studied bulk metallic glass, a solid material with no crystalline structures. We study metals and alloys not only to build things in space, but to improve things that are made on Earth. Metals and alloys are everywhere around us; in our automobiles, in the engines of aircraft, in our power-plants, and elsewhere. Despite their presence in everyday life, there are many scientific aspects of metals that we do not understand.
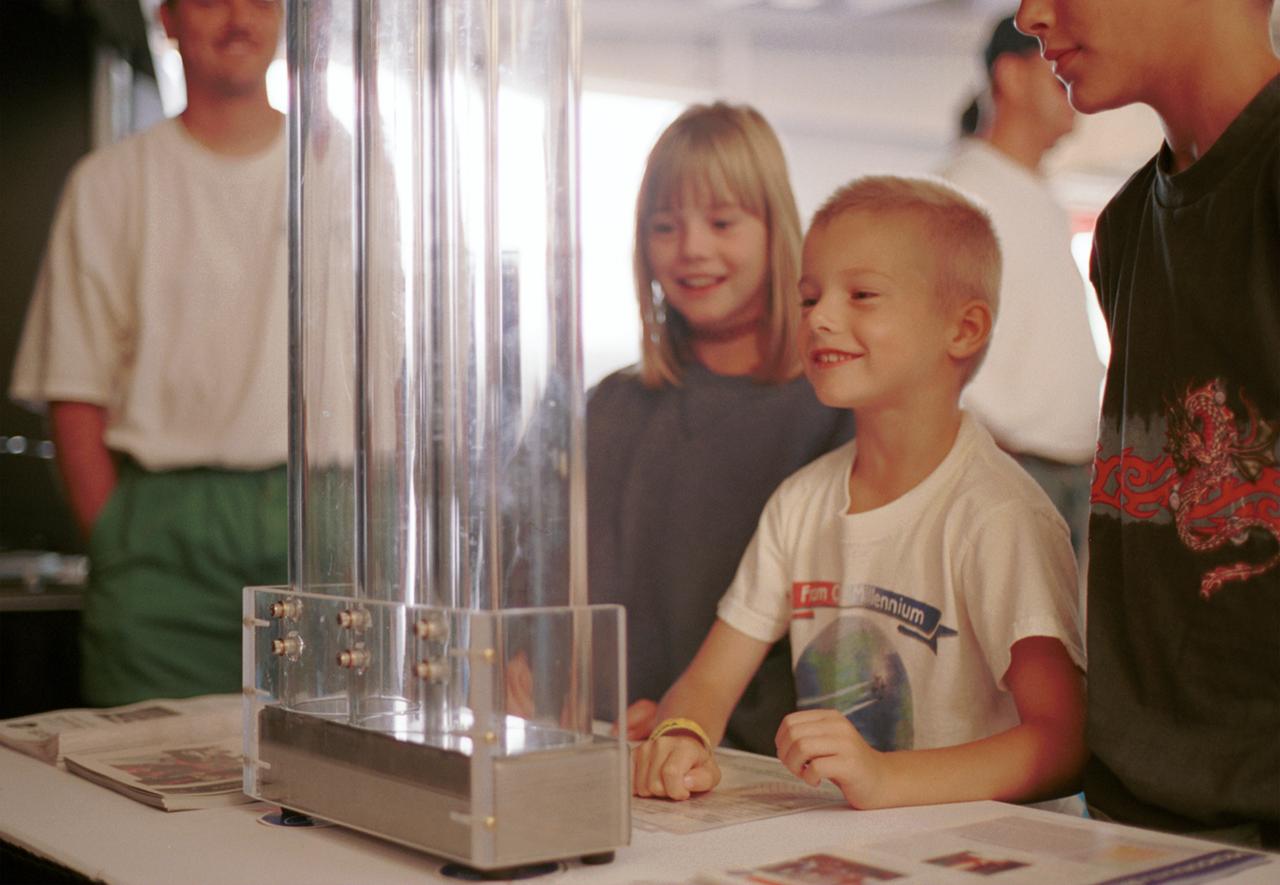

An entranced youngster watches a demonstration of the enhanced resilience of undercooled metal alloys as compared to conventional alloys. Steel bearings are dropped onto plates made of steel, titanium alloy, and zirconium liquid metal alloy, so-called because its molecular structure is amorphous and not crystalline. The bearing on the liquid metal plate bounces for a minute or more longer than on the other plates. Experiments aboard the Space Shuttle helped scientists refine their understanding of the physical properties of certain metal alloys when undercooled (i.e., kept liquid below their normal solidification temperature). This new knowledge then allowed scientists to modify a terrestrial production method so they can now make limited quantities marketed under the Liquid Metal trademark. The exhibit was a part of the NASA outreach activity at AirVenture 2000 sponsored by the Experimental Aircraft Association in Oshkosh, WI.

S89-44076 (November 1989) --- The STS-32 patch, designed by the five crew members for the scheduled December 1989 space mission, depicts the space shuttle orbiter rendezvousing with the Long Duration Exposure Facility (LDEF) satellite from above. The Syncom satellite is successfully deployed and on its way to geosynchronous orbit. Five stars have been arranged so that three are one side of the orbiter and two on the other to form the number 32. The seven major rays of the sun are in remembrance of the crew members for STS51-L. In preparation for the first Extended Duration Orbiter (EDO) missions, STS-32 will conduct a number of medical and middeck scientific experiments. The caduceus on the left represents the medical experiments, and the crystalline structure on the right represents the materials science. The crew is comprised of astronauts Daniel C. Brandenstein, James D. Wetherbee, Bonnie J. Dunbar, Marsha S. Ivins and G. David Low. The NASA insignia design for space shuttle flights is reserved for use by the astronauts and for other official use as the NASA Administrator may authorize. Public availability has been approved only in the form of illustrations by the various news media. When and if there is any change in this policy, which is not anticipated, it will be publicly announced. Photo credit: NASA
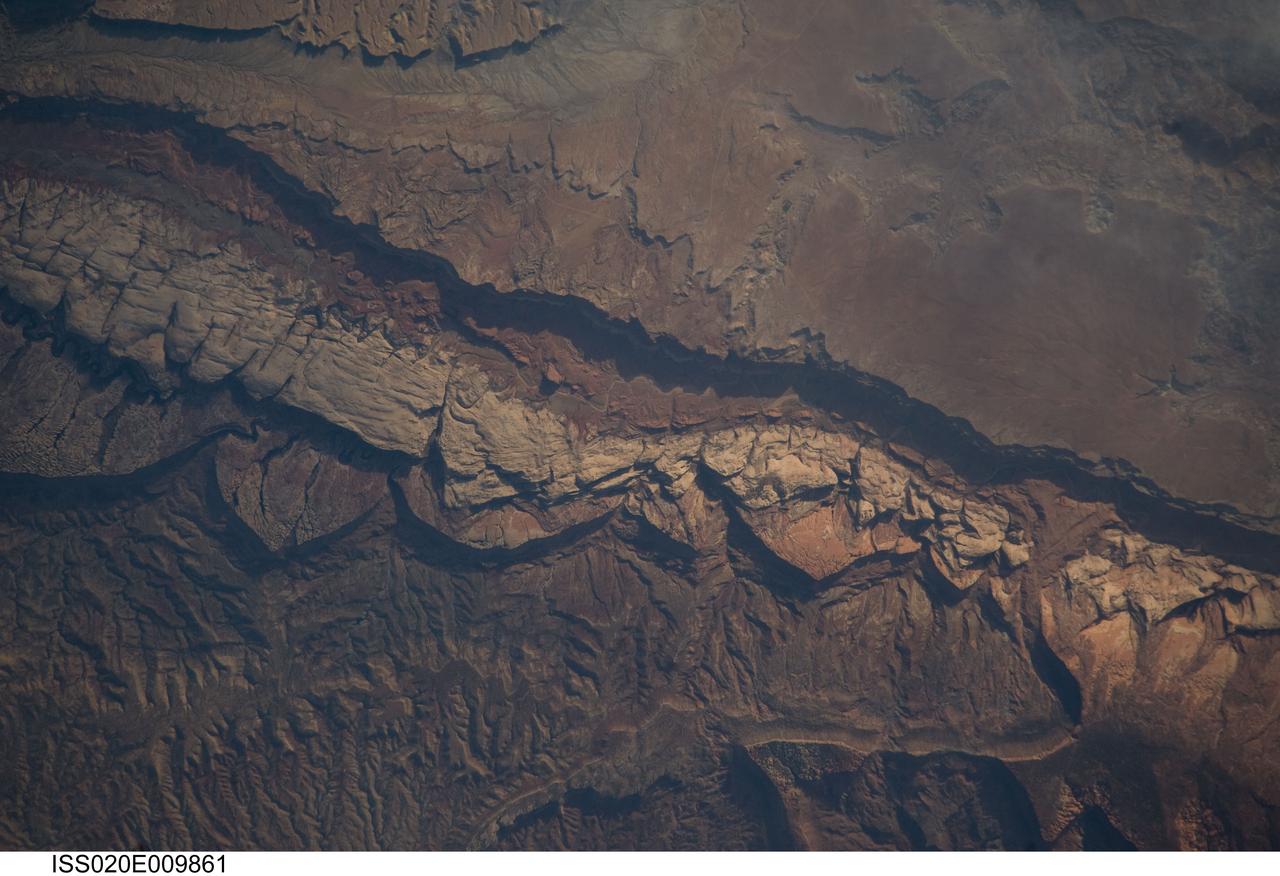

ISS020-E-009861 (14 June 2009) --- Big Thompson Mesa in the Capitol Reef National Park, Utah is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 20 crew member on the International Space Station. This detailed photograph depicts a portion of Big Thompson Mesa located near the southern end of Capitol Reef National Park. Capitol Reef National Park is located on the Colorado Plateau, a physiographic and geologic province that comprises the adjacent quarters of Arizona, Colorado, New Mexico and Utah. Big Thompson Mesa (upper right) is part of a large feature known as the Waterpocket Fold. The Fold is a geologic structure called a monocline, characterized by generally flat-laying sedimentary rock layers with a steep and highly localized flexure– much like a carpet runner draped over a stair step. Monoclines on the Colorado Plateau are thought to be the result of faulting of stratigraphically lower and more brittle crystalline rocks; while the crystalline rocks were broken into raised or lowered blocks, the overlaying, less brittle sedimentary rocks were flexed without breaking. According to scientists, the portion of the Waterpocket Fold illustrated in this image includes layered rocks formed during the Mesozoic Era (approximately 250 – 65 million years ago) – the oldest layers are at the bottom of the sequence (and also, in this view, the image), with each successive layer younger than the preceding one going upwards in the sequence. Not all of the units present are clearly visible, but some of the major units can be easily distinguished. The bottom half of the image includes the oldest rocks in the view: dark brown and dark green Moenkopi (Trm) and Chinle (Trc) Formations. At center, two strikingly colored units are visible – light red to orange Wingate Sandstone (Jw) and white Navajo Sandstone (Jn). A topographic bench above these units includes reddish brown to brown Carmel Formation (Jc) and Entrada Sandstone (Je). The top of the cliff face above this bench - Big Thompson Mesa - is comprised of brown Dakota Sandstone (Kd). Scientists believe this sequence represents more than 100 million years of deposition. Much younger Quaternary (2.0 million to approximately 10,000 years old) deposits are also present in the view. A regional view of Capitol Reef National Park and the Waterpocket Fold is available here. The area shown in this view is located approximately 65 kilometers to the southeast of Fruita, UT near the southern end of Capitol Reef National Park.