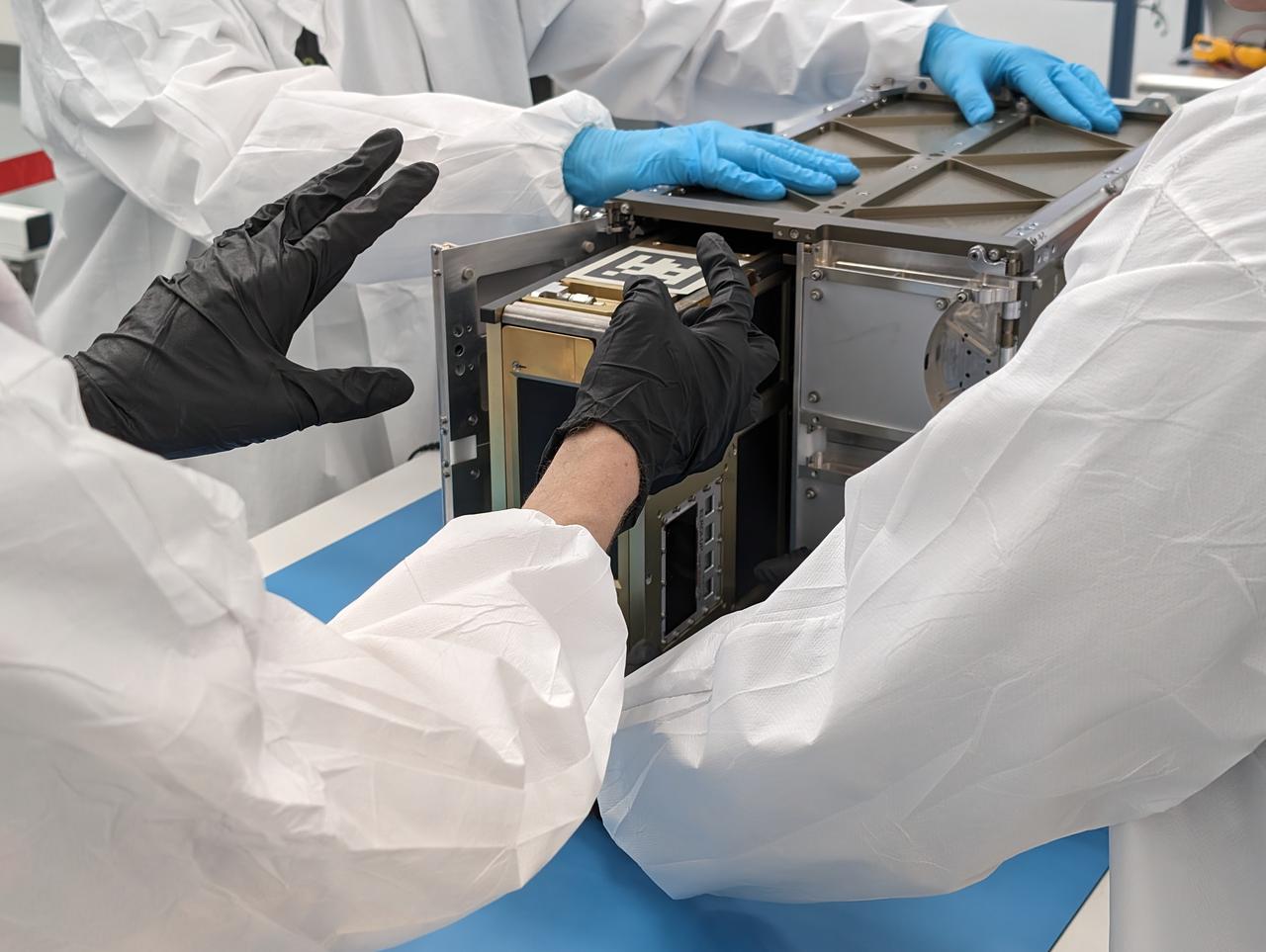

A NASA engineer installs the agency’s CubeSat R5 Spacecraft 4 (R5-S4) into the dispenser at Firefly Aerospace's Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base, California on Wednesday, April 24, 2024. The spacecraft will soon be integrated for launch aboard the company’s Alpha rocket, as part of launch services provided for NASA's CubeSat Launch Initiative and Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 43 mission in support of the agency ’s Venture-Class Launch Services Demonstration 2 contract.
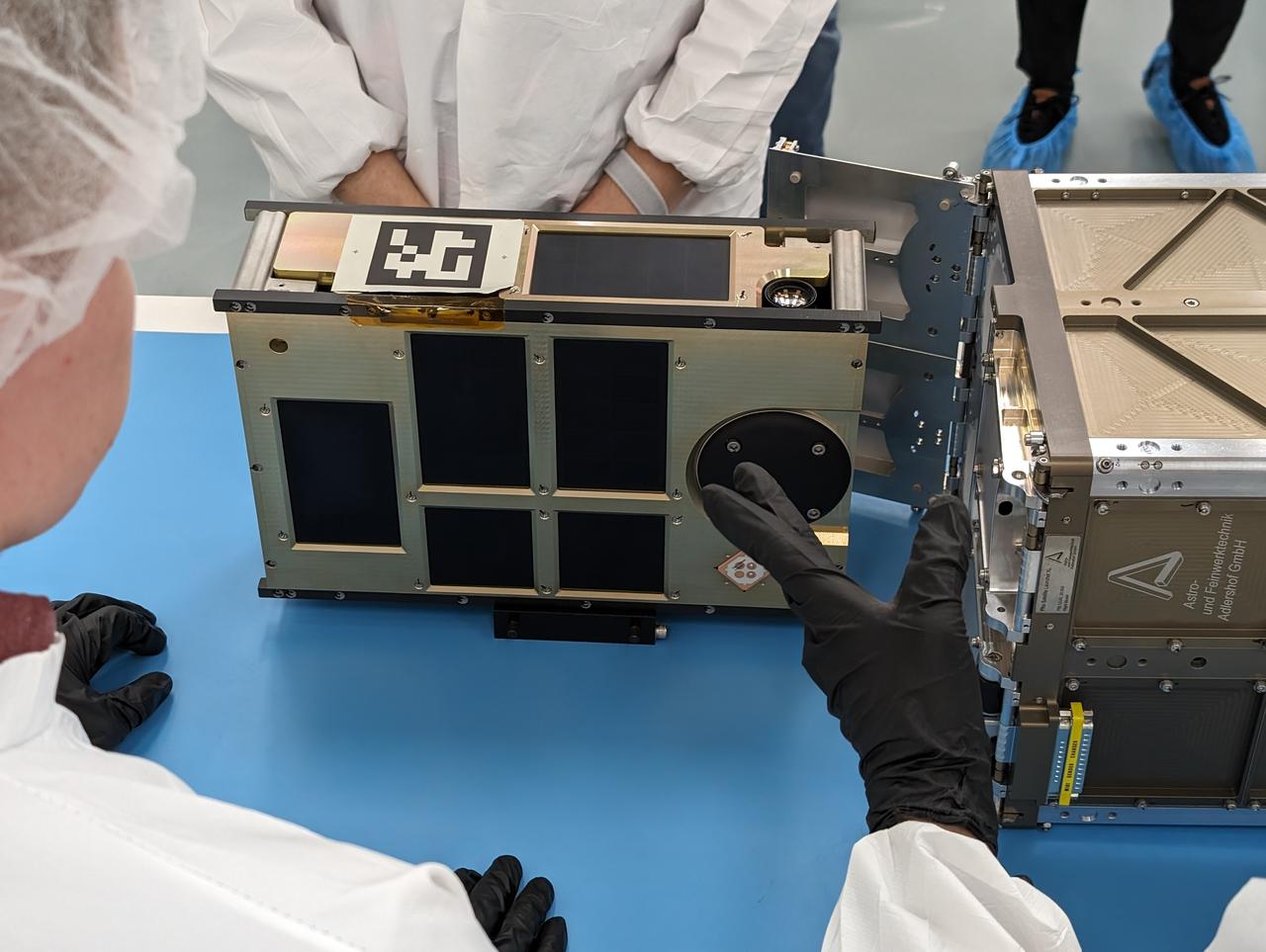

NASA and Firefly Aerospace engineers review the integration plan for the agency’s CubeSat R5 Spacecraft 4 (R5-S4) at Firefly Aerospace’s Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base, California on Wednesday, April 24, 2024. The spacecraft will soon be integrated for launch aboard the company’s Alpha rocket, as part of launch services provided for NASA's CubeSat Launch Initiative and Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 43 mission in support of the agency ’s Venture-Class Launch Services Demonstration 2 contract.

A Satellite for Optimal Control and Imaging (SOC-i) CubeSat awaits integration at Firefly’s Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base, California on Thursday, June 6, 2024. SOC-i, along with several other CubeSats, will launch to space on an Alpha rocket during NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellites (ELaNa) 43 mission as part of the agency’s CubeSat Launch Initiative and Firefly’s Venture-Class Launch Services Demonstration 2 contract.

NASA’s TechEdSat-11 (TES-11) CubeSat awaits integration at Firefly’s Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base, California on Saturday, June 8, 2024. Serenity, along with several other CubeSats, will launch to space on an Alpha rocket during NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellites (ELaNa) 43 mission as part of the agency’s CubeSat Launch Initiative and Firefly’s Venture-Class Launch Services Demonstration 2 contract.
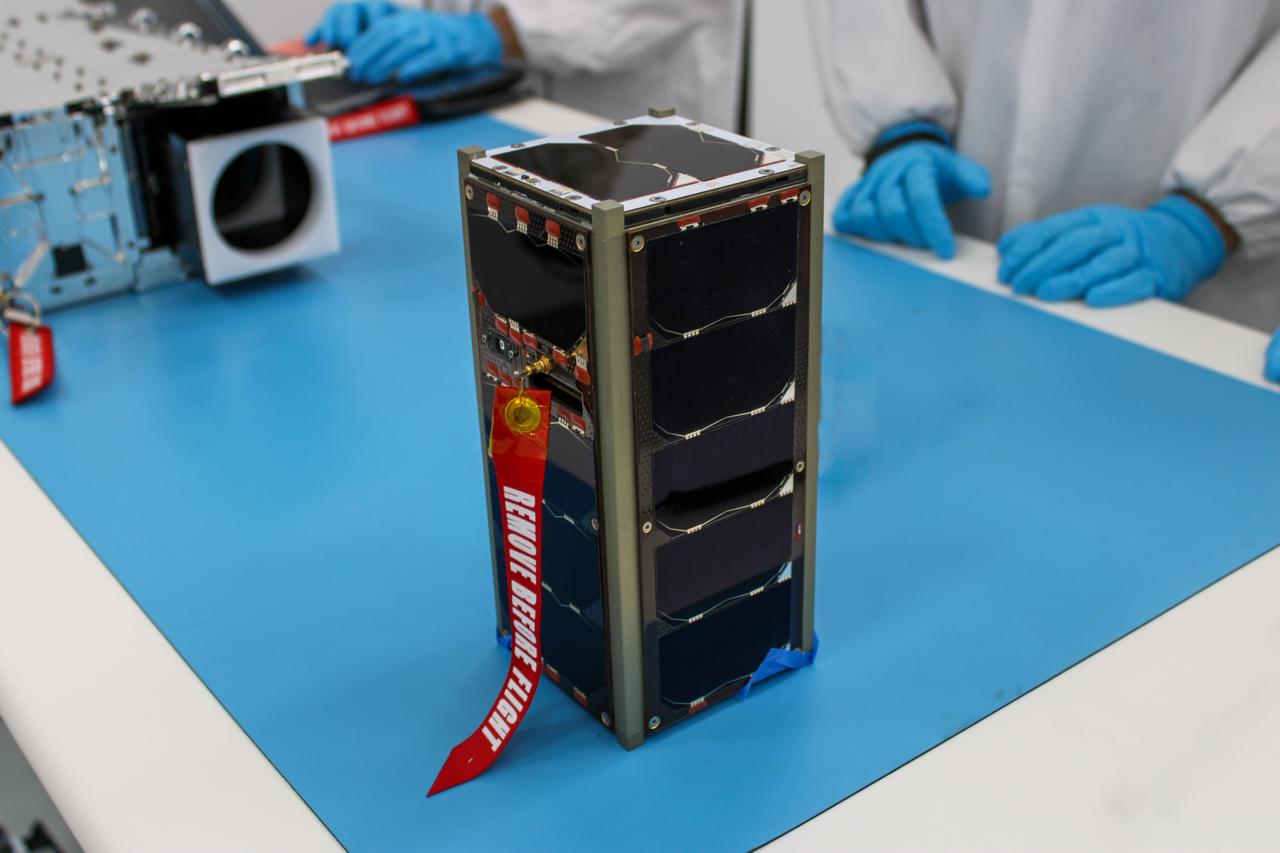

A Satellite for Optimal Control and Imaging (SOC-i) CubeSat awaits integration at Firefly’s Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base, California on Thursday, June 6, 2024. SOC-i, along with several other CubeSats, will launch to space on an Alpha rocket during NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellites (ELaNa) 43 mission as part of the agency’s CubeSat Launch Initiative and Firefly’s Venture-Class Launch Services Demonstration 2 contract.
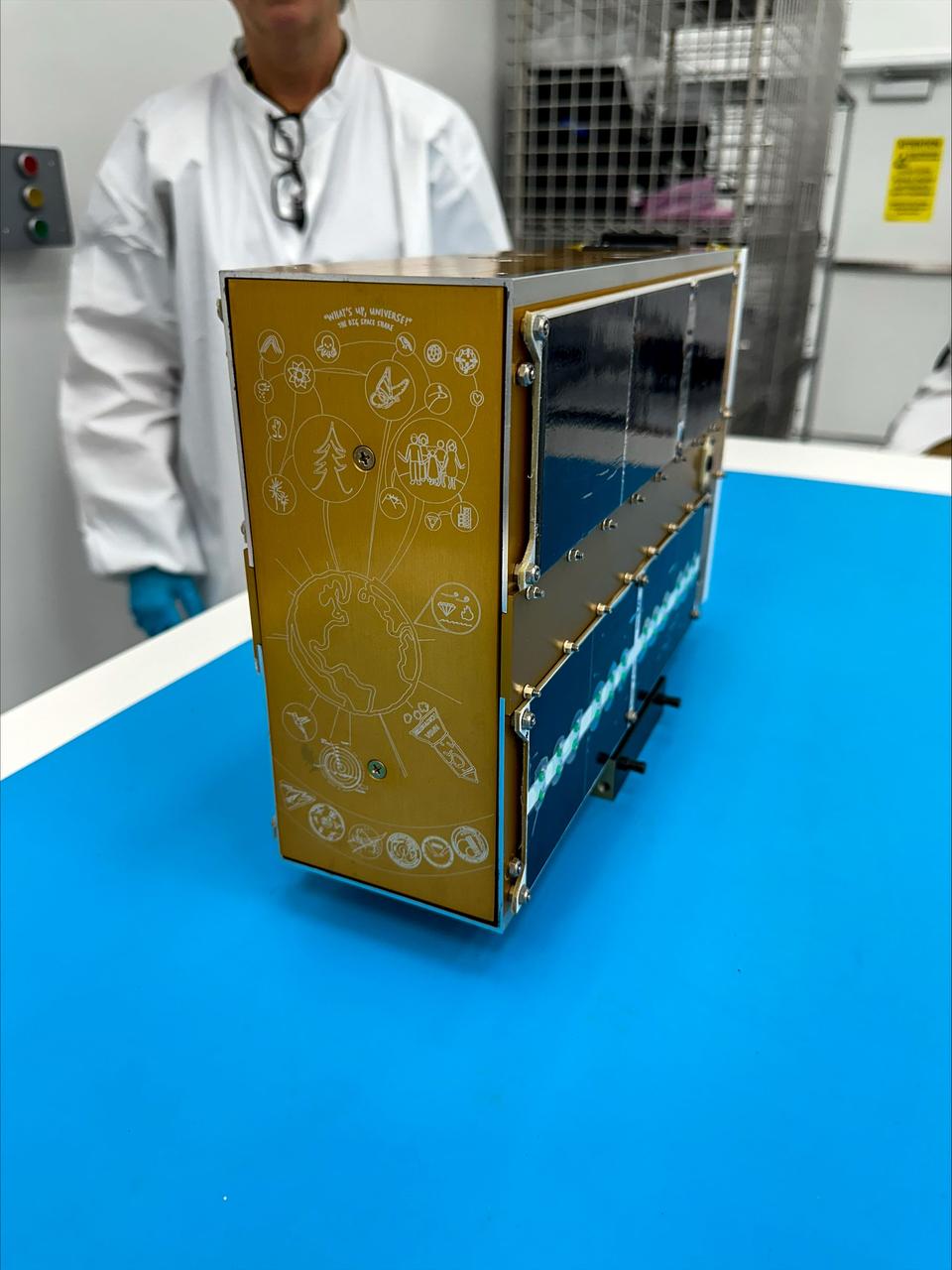

NASA’s TechEdSat-11 (TES-11) CubeSat awaits integration at Firefly’s Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base, California on Saturday, June 8, 2024. Serenity, along with several other CubeSats, will launch to space on an Alpha rocket during NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellites (ELaNa) 43 mission as part of the agency’s CubeSat Launch Initiative and Firefly’s Venture-Class Launch Services Demonstration 2 contract.
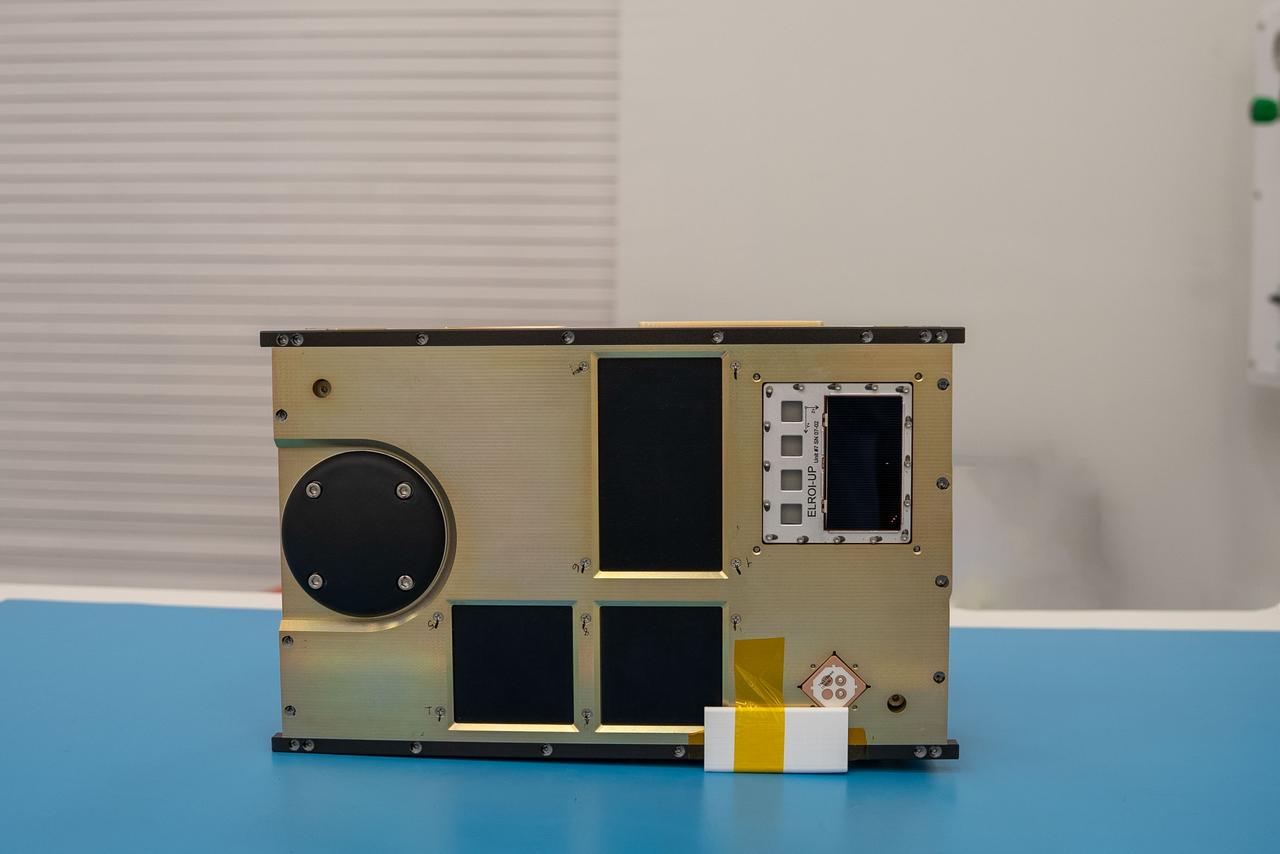

NASA’s CubeSat R5 Spacecraft 4 (R5-S4) awaits integration at Firefly’s Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base, California on Wednesday, April 24, 2024. R5-S4, along with several other CubeSats, will launch to space on an Alpha rocket during NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellites (ELaNa) 43 mission as part of the agency’s CubeSat Launch Initiative and Firefly’s Venture-Class Launch Services Demonstration 2 contract.
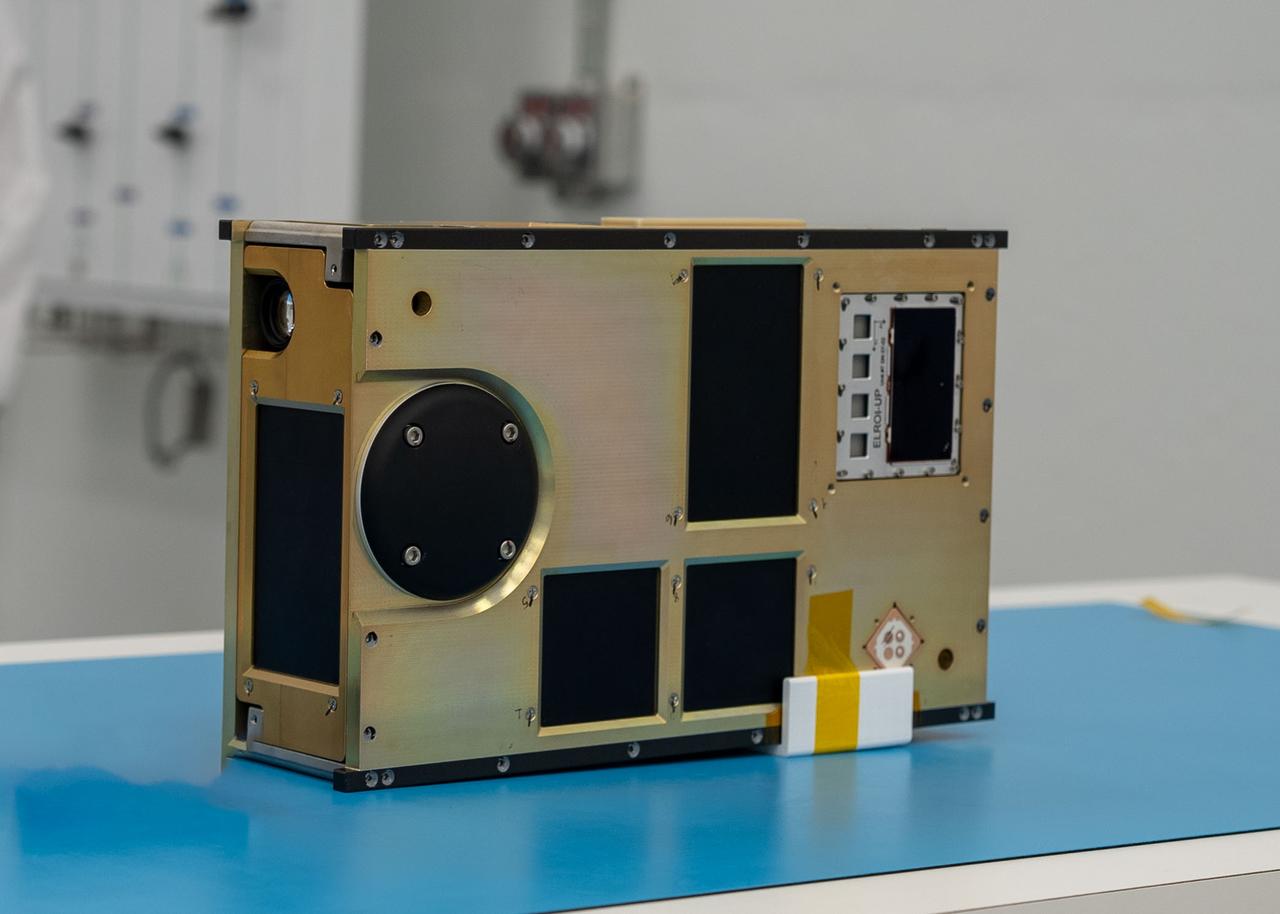

NASA’s CubeSat R5 Spacecraft 4 (R5-S4) awaits integration at Firefly’s Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base, California on Wednesday, April 24, 2024. R5-S4, along with several other CubeSats, will launch to space on an Alpha rocket during NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellites (ELaNa) 43 mission as part of the agency’s CubeSat Launch Initiative and Firefly’s Venture-Class Launch Services Demonstration 2 contract.
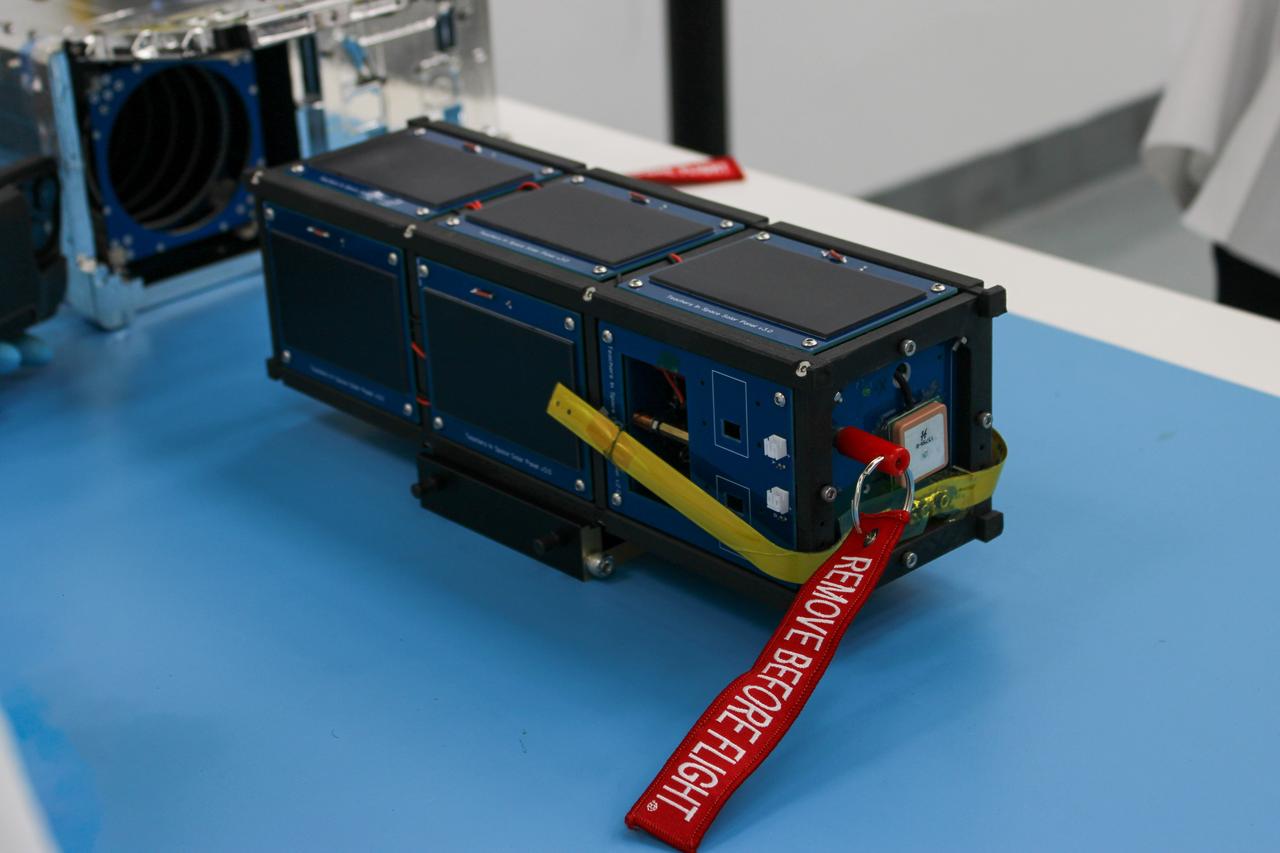
Serenity, a 3U CubeSat, awaits integration at Firefly’s Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base, California on Friday, June 7, 2024. Serenity, along with several other CubeSats, will launch to space on an Alpha rocket during NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellites (ELaNa) 43 mission as part of the agency’s CubeSat Launch Initiative and Firefly’s Venture-Class Launch Services Demonstration 2 contract.
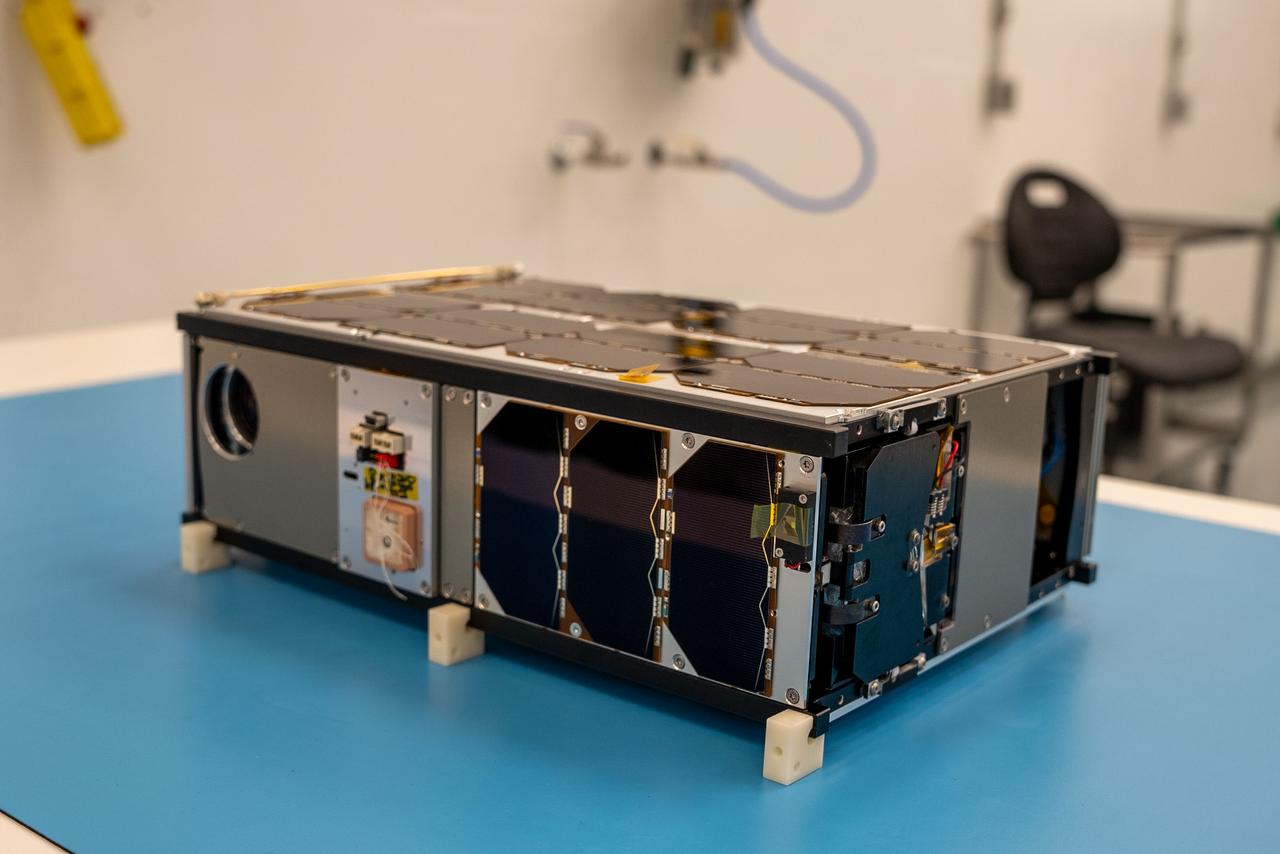
A CubeSat named CatSat from the University of Arizona awaits integration at Firefly’s Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base, California on Thursday, April 25, 2024. CatSat, along with several other CubeSats, will launch to space on an Alpha rocket during NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellites (ELaNa) 43 mission as part of the agency’s CubeSat Launch Initiative and Firefly’s Venture-Class Launch Services Demonstration 2 contract.
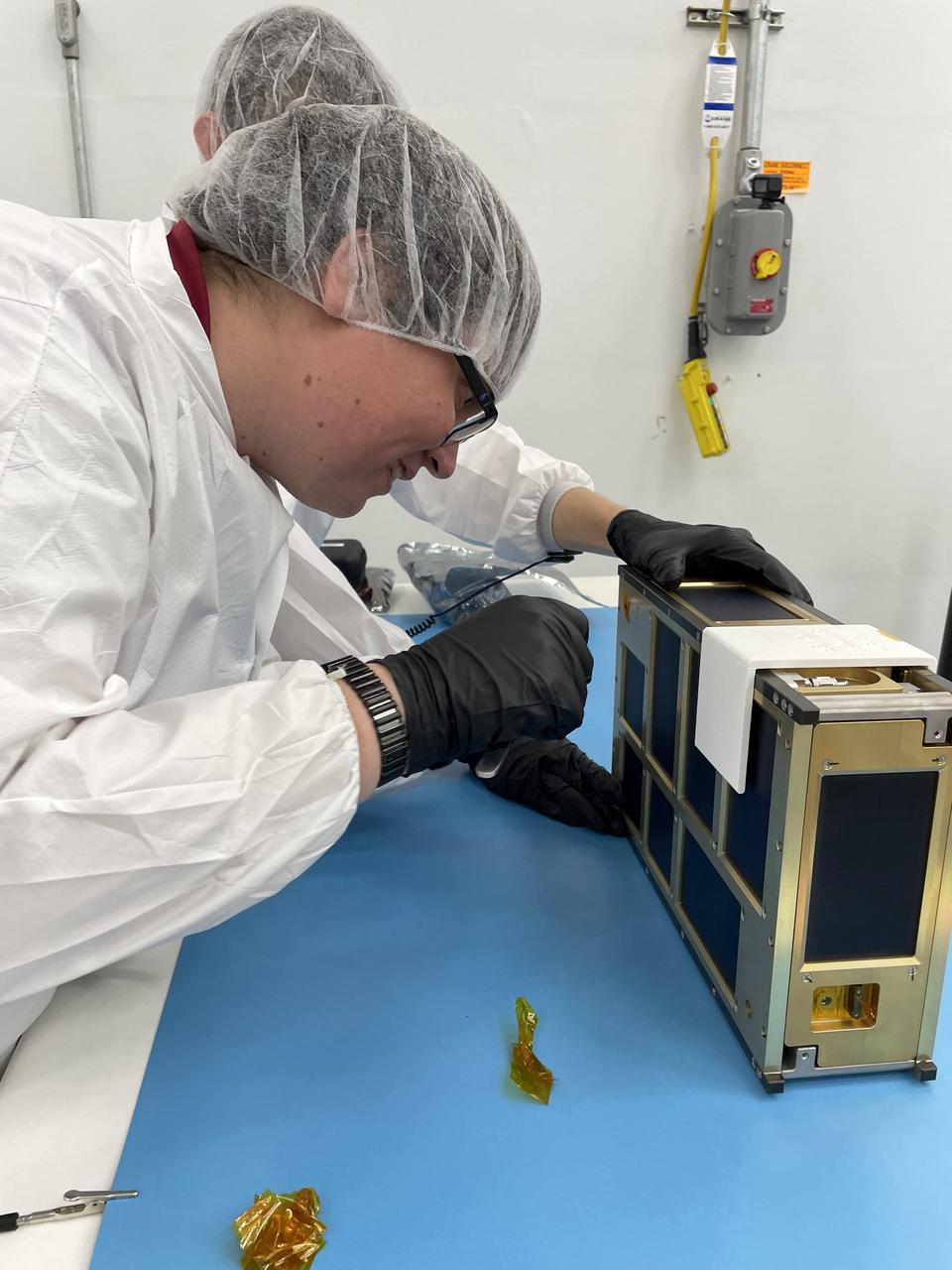

NASA engineer Jacob Nunez-Kearny removes the foreign object debris (FOD) cover from the propulsion system on the agency’s CubeSat R5 Spacecraft 4 (R5-S4) at Firefly Aerospace’s Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base, California on Wednesday, April 24, 2024. The spacecraft will soon be integrated for launch aboard the company’s Alpha rocket, as part of launch services provided for NASA's CubeSat Launch Initiative and Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 43 mission in support of the agency ’s Venture-Class Launch Services Demonstration 2 contract .
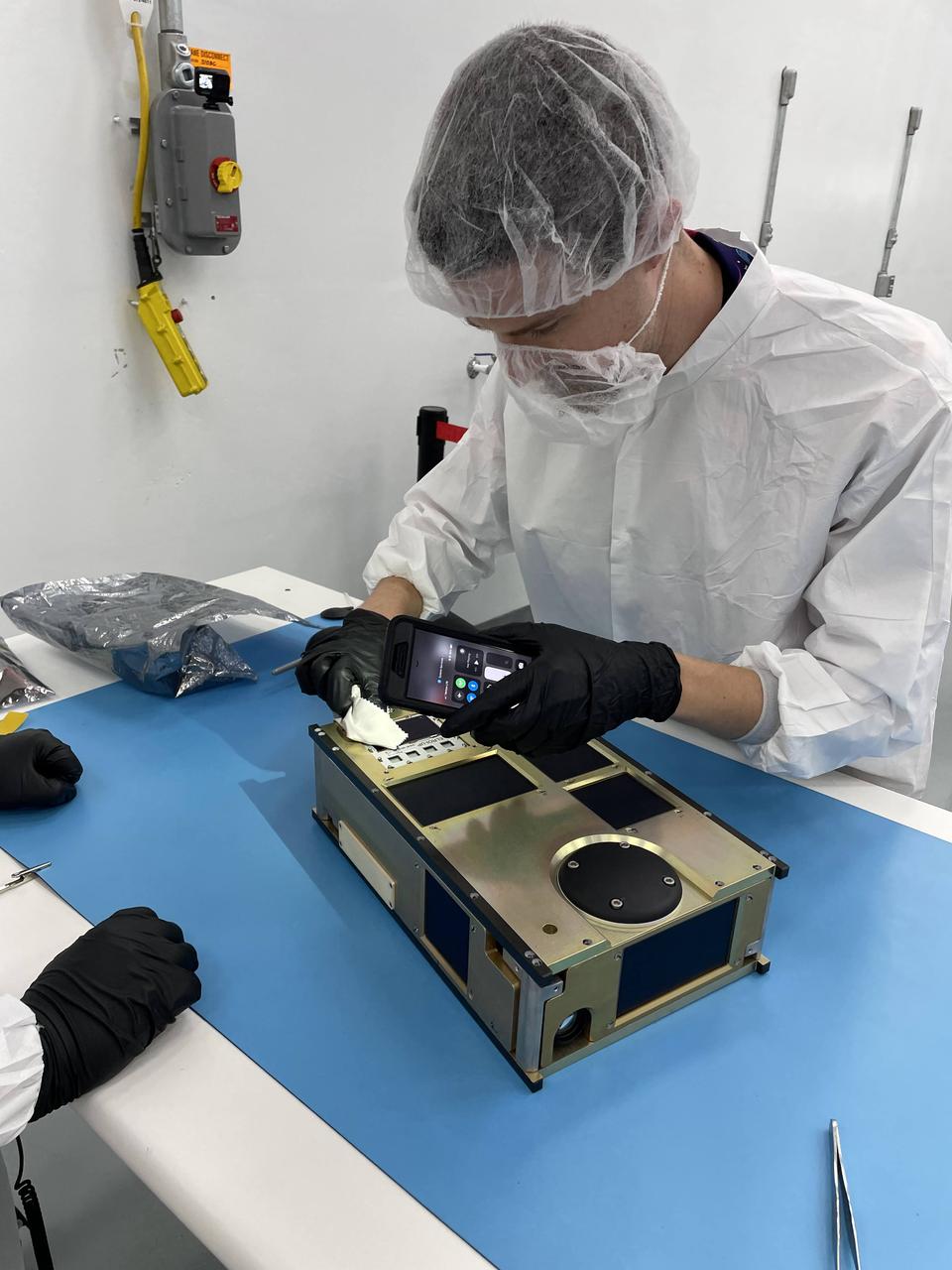

NASA engineer Sam Pedrotty performs final cleaning of Los Alamos National Laboratory’s (LANL’s) Extremely Low Resource Optical Identifier (ELROI) on the agency’s CubeSat R5 Spacecraft 4 (R5-S4) at Firefly Aerospace’s Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base, California on Wednesday, April 24, 2024. The spacecraft will soon be integrated for launch aboard the company’s Alpha rocket, as part of launch services provided for NASA's CubeSat Launch Initiative and Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 43 mission in support of the agency ’s Venture-Class Launch Services Demonstration 2 contract.

From left, Firefly mission manager Marcy Mabry observes NASA engineer James Berck install the agency’s CubeSat R5 Spacecraft 4 (R5-S4) into the dispenser at Firefly Aerospace’s Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base, California on Wednesday, April 24, 2024. The spacecraft will soon be integrated for launch aboard the company’s Alpha rocket, as part of launch services provided for NASA's CubeSat Launch Initiative and Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 43 mission in support of the agency ’s Venture-Class Launch Services Demonstration 2 contract.
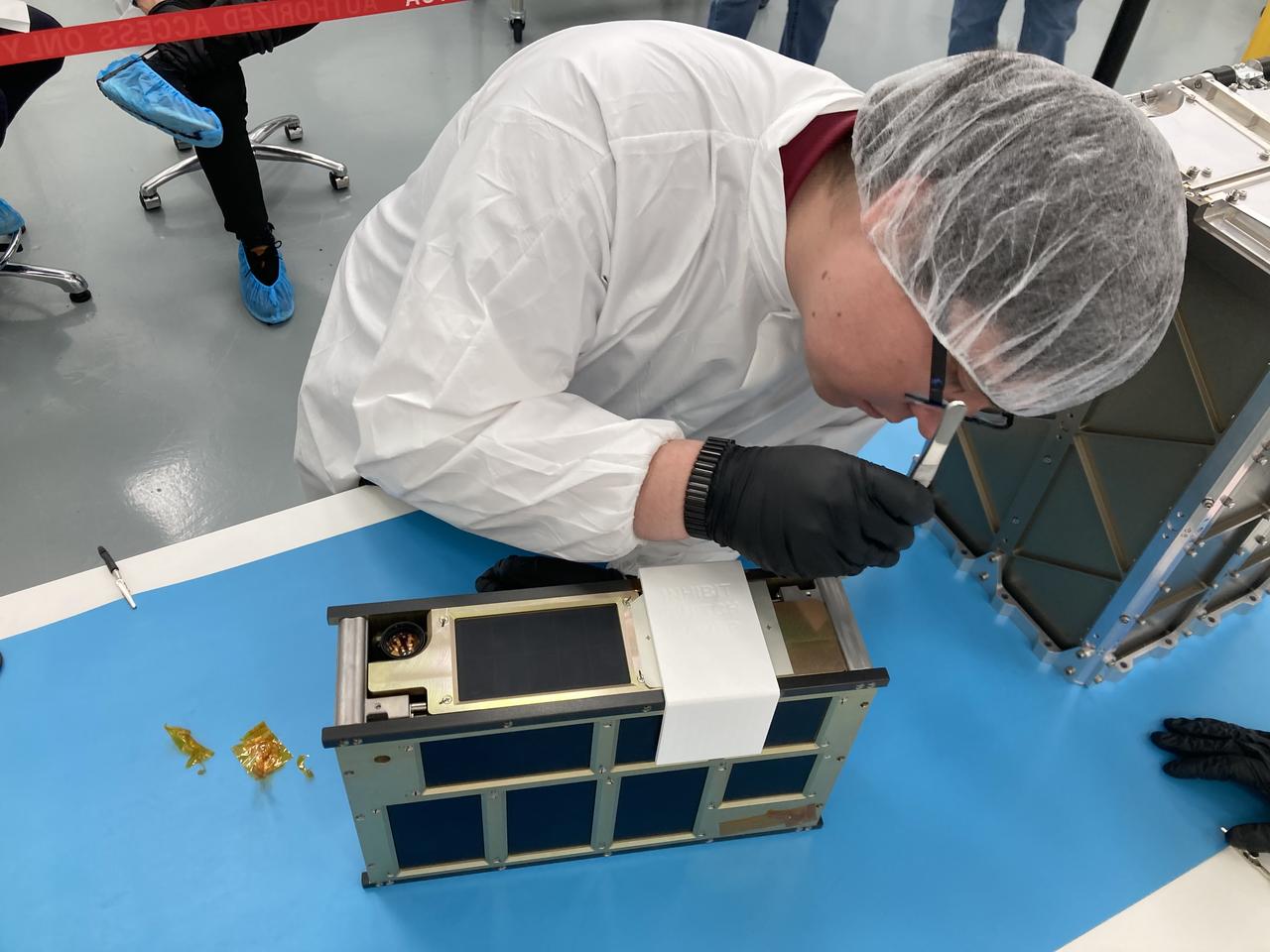

NASA engineer Jacob Nunez-Kearny removes foreign object debris (FOD) cover from the propulsion system on the agency’s CubeSat R5 Spacecraft 4 (R5-S4) at Firefly Aerospace’s Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base, California on Wednesday, April 24, 2024. The spacecraft will soon be integrated for launch aboard the company’s Alpha rocket, as part of launch services provided for NASA's CubeSat Launch Initiative and Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 43 mission in support of the agency ’s Venture-Class Launch Services Demonstration 2 contract.
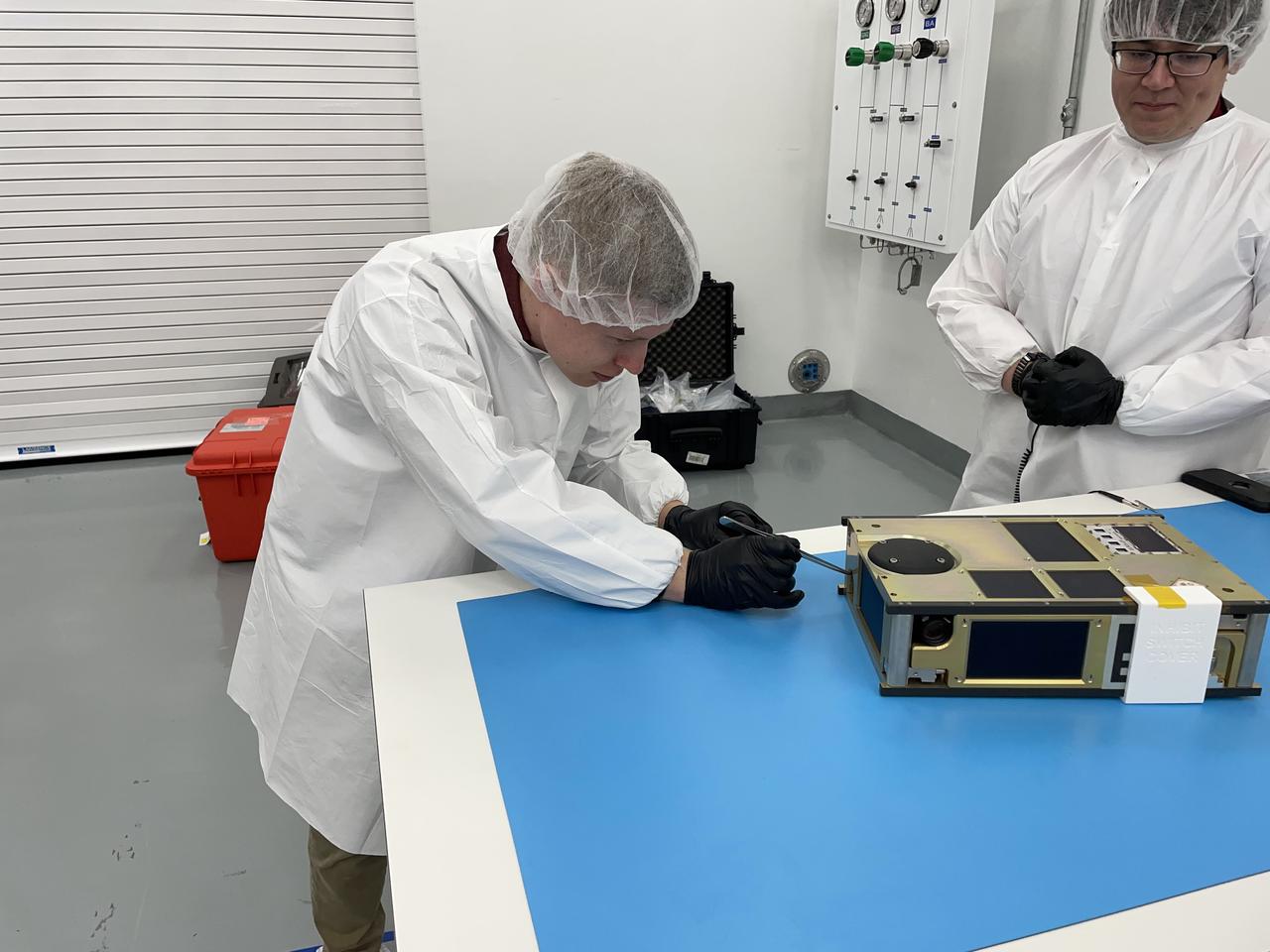

From left, NASA engineer James Berck removes the foreign object debris (FOD) cover from the relative navigation camera on the agency’s CubeSat R5 Spacecraft 4 (R5-S4) while NASA engineer Jacob Nunez-Kearny observes, at Firefly Aerospace’s Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base, California on Wednesday, April 24, 2024. The spacecraft will soon be integrated for launch aboard the company’s Alpha rocket, as part of launch services provided for NASA's CubeSat Launch Initiative and Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 43 mission in support of the agency ’s Venture-Class Launch Services Demonstration 2 contract.
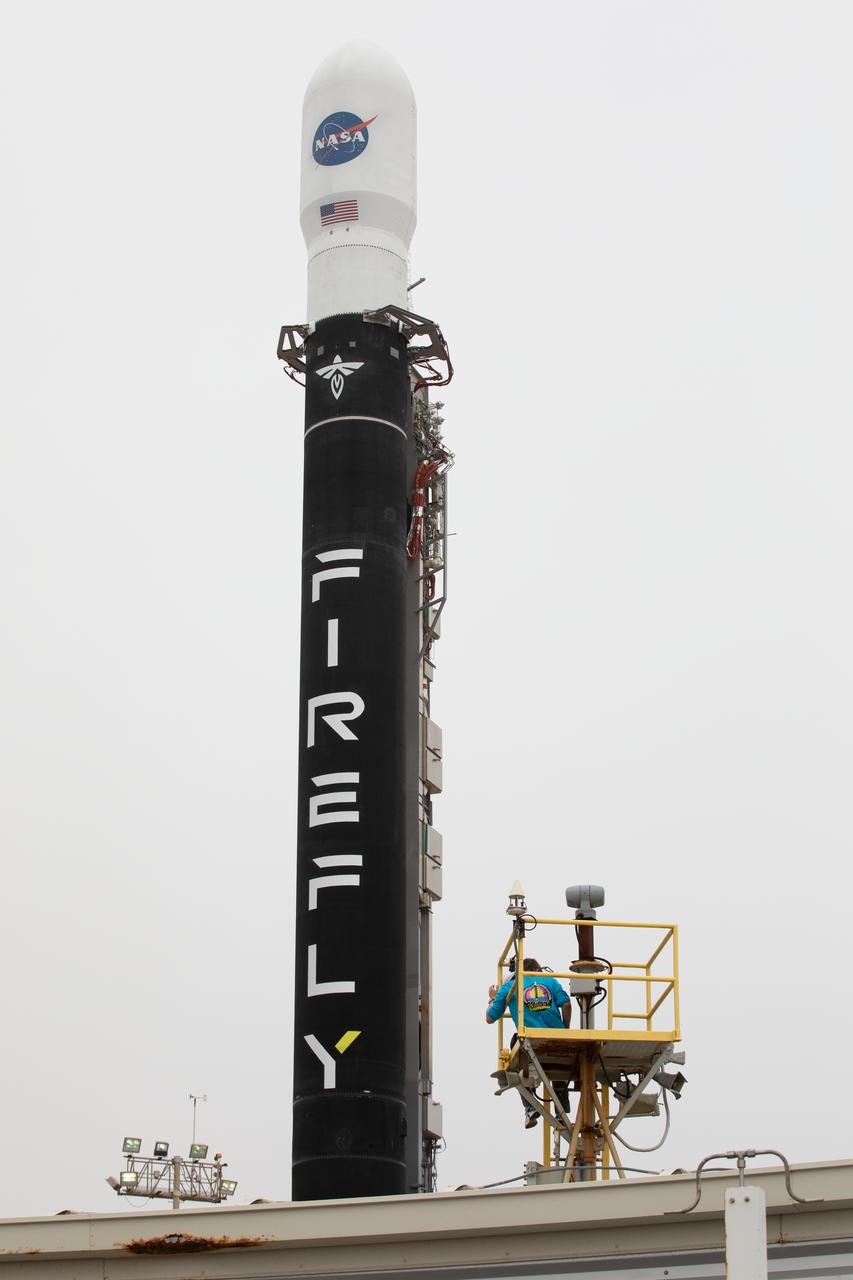

Firefly Aerospace’s Alpha rocket carrying eight CubeSats as part of NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative’s (CSLI) ELaNa 43 (Educational Launch of Nanosatellites) mission stands vertical at Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Space Force Base, California, on Monday, July 1, 2024. Firefly Aerospace is one of three companies selected to fly small satellites to space under NASA’s Launch Services Program Venture-Class Launch Services Demonstration 2 (VCLS Demo 2) contract awarded in December 2020.
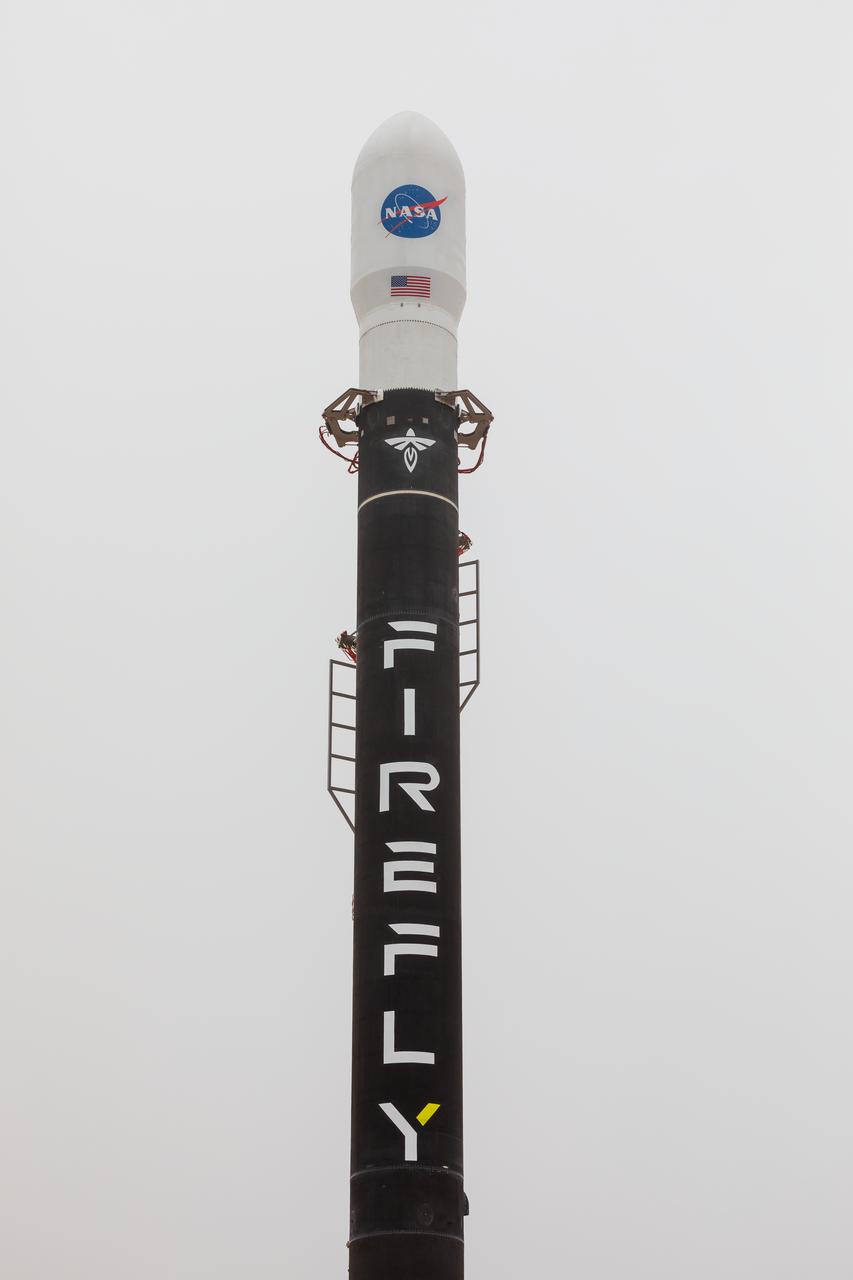

Firefly Aerospace’s Alpha rocket carrying eight CubeSats as part of NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative’s (CSLI) ELaNa 43 (Educational Launch of Nanosatellites) mission stands vertical at Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Space Force Base, California, on Monday, July 1, 2024. Firefly Aerospace is one of three companies selected to fly small satellites to space under NASA’s Launch Services Program Venture-Class Launch Services Demonstration 2 (VCLS Demo 2) contract awarded in December 2020.

Firefly Aerospace’s Alpha rocket carrying eight CubeSats as part of NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative’s (CSLI) ELaNa 43 (Educational Launch of Nanosatellites) mission stands vertical at Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Space Force Base, California, on Monday, July 1, 2024. Firefly Aerospace is one of three companies selected to fly small satellites to space under NASA’s Launch Services Program Venture-Class Launch Services Demonstration 2 (VCLS Demo 2) contract awarded in December 2020.
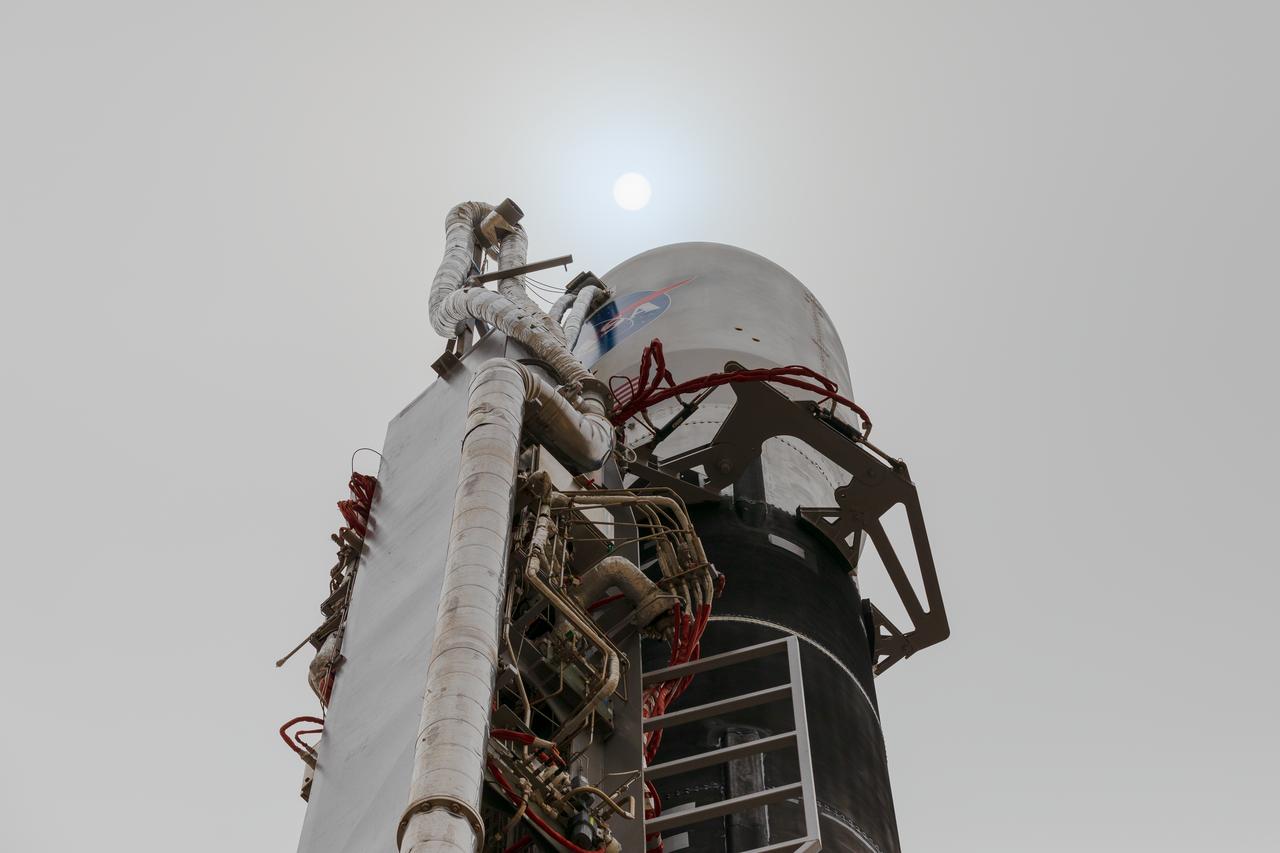

Firefly Aerospace’s Alpha rocket carrying eight CubeSats as part of NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative’s (CSLI) ELaNa 43 (Educational Launch of Nanosatellites) mission stands vertical at Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Space Force Base, California, on Monday, July 1, 2024. Firefly Aerospace is one of three companies selected to fly small satellites to space under NASA’s Launch Services Program Venture-Class Launch Services Demonstration 2 (VCLS Demo 2) contract awarded in December 2020.
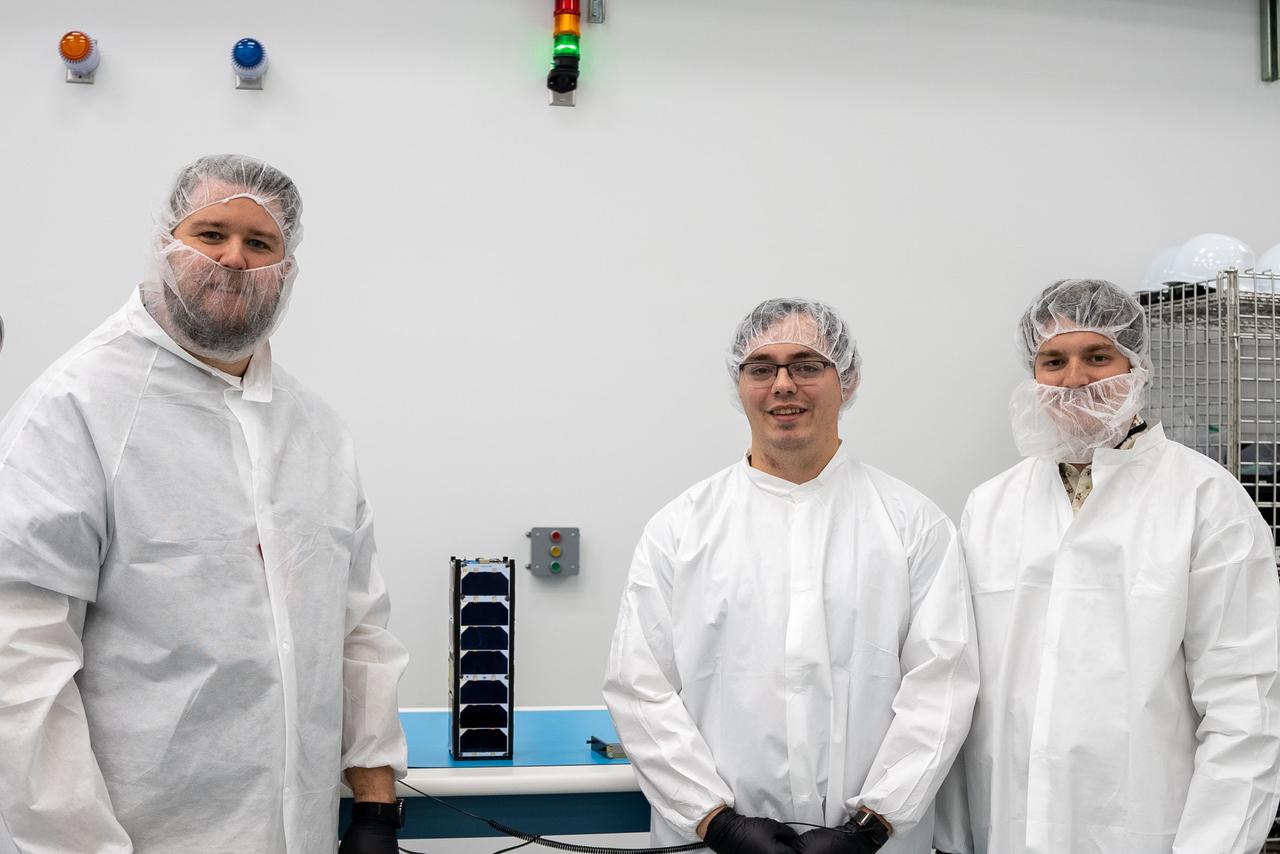

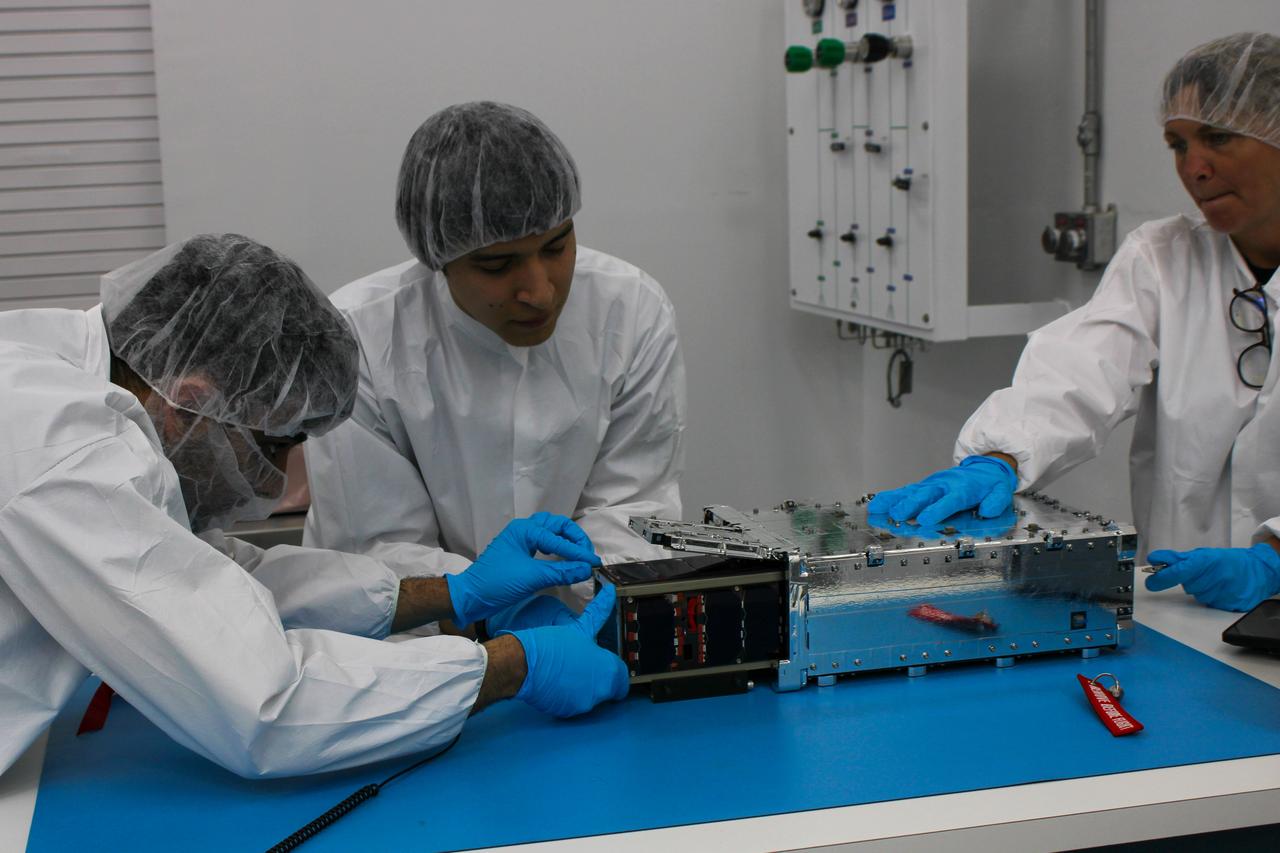
Technicians with the University of Kansas prepare their KUbeSat-1 for integration at Firefly’s Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base, California on Thursday, April 25, 2024. KUbeSat-1, along with several other CubeSats, will launch to space on an Alpha rocket during NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellites (ELaNa) 43 mission as part of the agency’s CubeSat Launch Initiative and Firefly’s Venture-Class Launch Services Demonstration 2 contract.

Technicians with the University of Kansas prepare their KUbeSat-1 for integration at Firefly’s Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base, California on Thursday, April 25, 2024. KUbeSat-1, along with several other CubeSats, will launch to space on an Alpha rocket during NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellites (ELaNa) 43 mission as part of the agency’s CubeSat Launch Initiative and Firefly’s Venture-Class Launch Services Demonstration 2 contract.

Technicians with the University of Kansas prepare their KUbeSat-1 for integration at Firefly’s Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base, California on Thursday, April 25, 2024. KUbeSat-1, along with several other CubeSats, will launch to space on an Alpha rocket during NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellites (ELaNa) 43 mission as part of the agency’s CubeSat Launch Initiative and Firefly’s Venture-Class Launch Services Demonstration 2 contract.
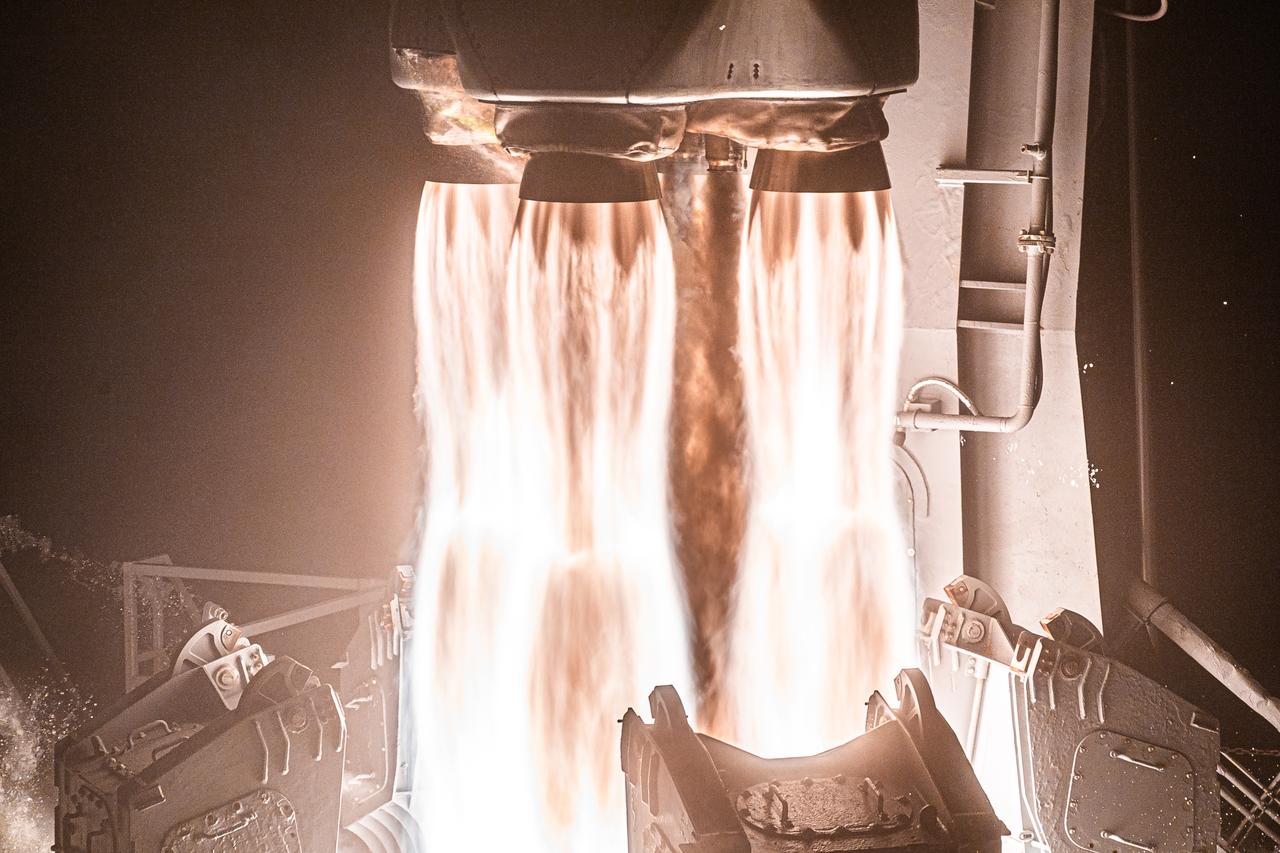

Firefly Aerospace’s Alpha rocket carrying eight CubeSats as part of NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative (CSLI) lifts off from Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California at 9:04 p.m. PDT Wednesday, July 3, 2024. The successful launch of the rocket, named “Noise of Summer,” completed the company’s Venture-Class Launch Services Demonstration 2 (VCLS Demo 2) contract with the agency. The CubeSat missions were designed by universities and NASA centers to conduct climate studies, satellite technology development, and educational outreach to students.
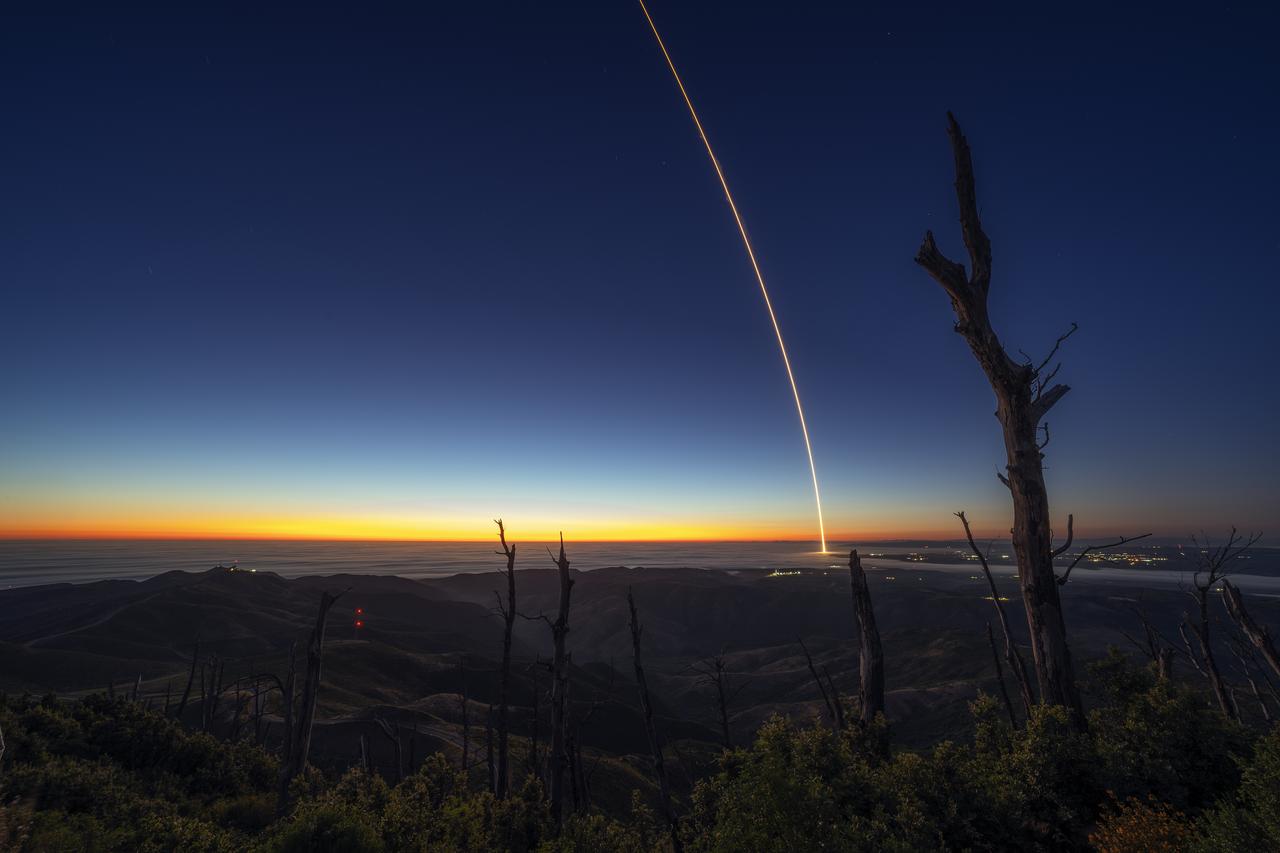

Firefly Aerospace’s Alpha rocket carrying eight CubeSats as part of NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative (CSLI) lifts off from Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California at 9:04 p.m. PDT Wednesday, July 3, 2024. The successful launch of the rocket, named “Noise of Summer,” completed the company’s Venture-Class Launch Services Demonstration 2 (VCLS Demo 2) contract with the agency. The CubeSat missions were designed by universities and NASA centers to conduct climate studies, satellite technology development, and educational outreach to students.
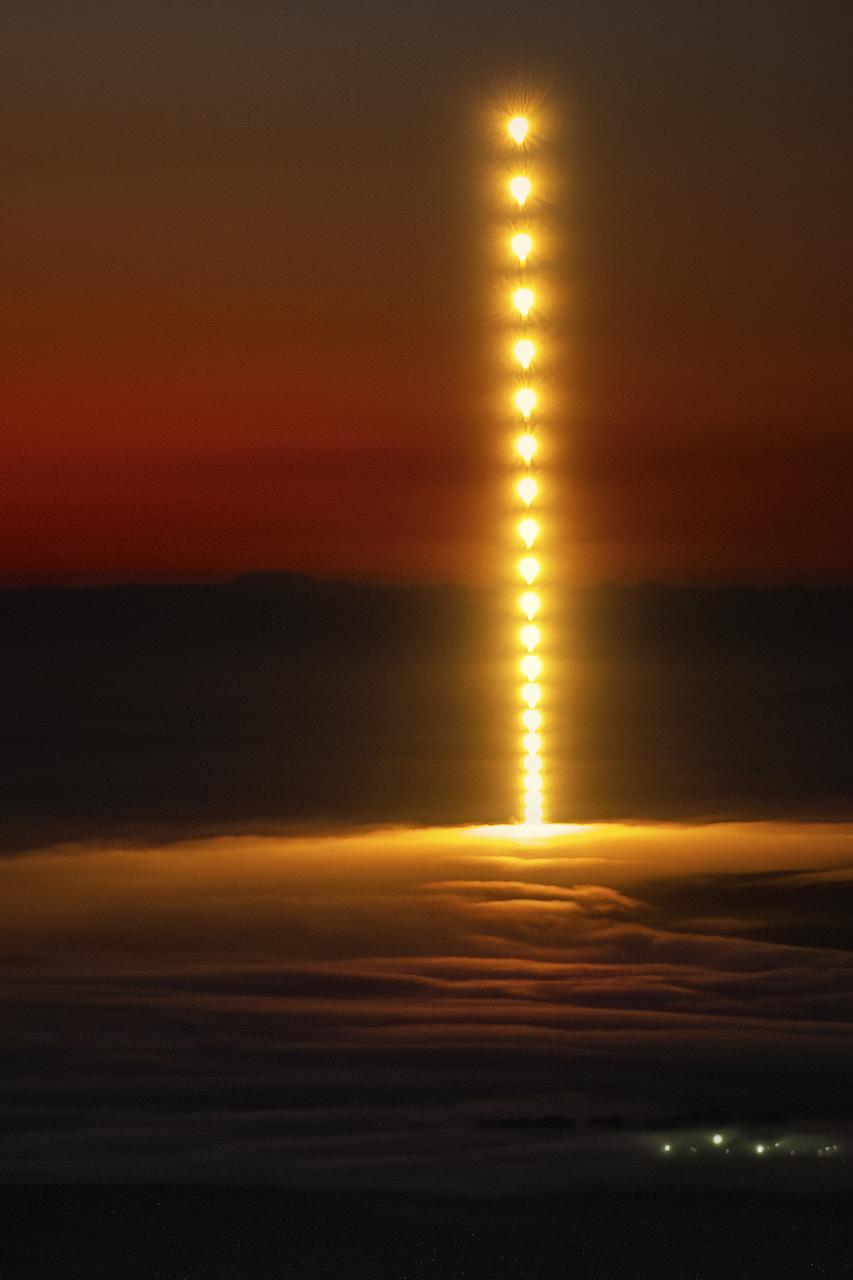

Firefly Aerospace’s Alpha rocket carrying eight CubeSats as part of NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative (CSLI) lifts off from Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California at 9:04 p.m. PDT Wednesday, July 3, 2024. The successful launch of the rocket, named “Noise of Summer,” completed the company’s Venture-Class Launch Services Demonstration 2 (VCLS Demo 2) contract with the agency. The CubeSat missions were designed by universities and NASA centers to conduct climate studies, satellite technology development, and educational outreach to students.

Firefly Aerospace’s Alpha rocket carrying eight CubeSats as part of NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative (CSLI) lifts off from Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California at 9:04 p.m. PDT Wednesday, July 3, 2024. The successful launch of the rocket, named “Noise of Summer,” completed the company’s Venture-Class Launch Services Demonstration 2 (VCLS Demo 2) contract with the agency. The CubeSat missions were designed by universities and NASA centers to conduct climate studies, satellite technology development, and educational outreach to students.
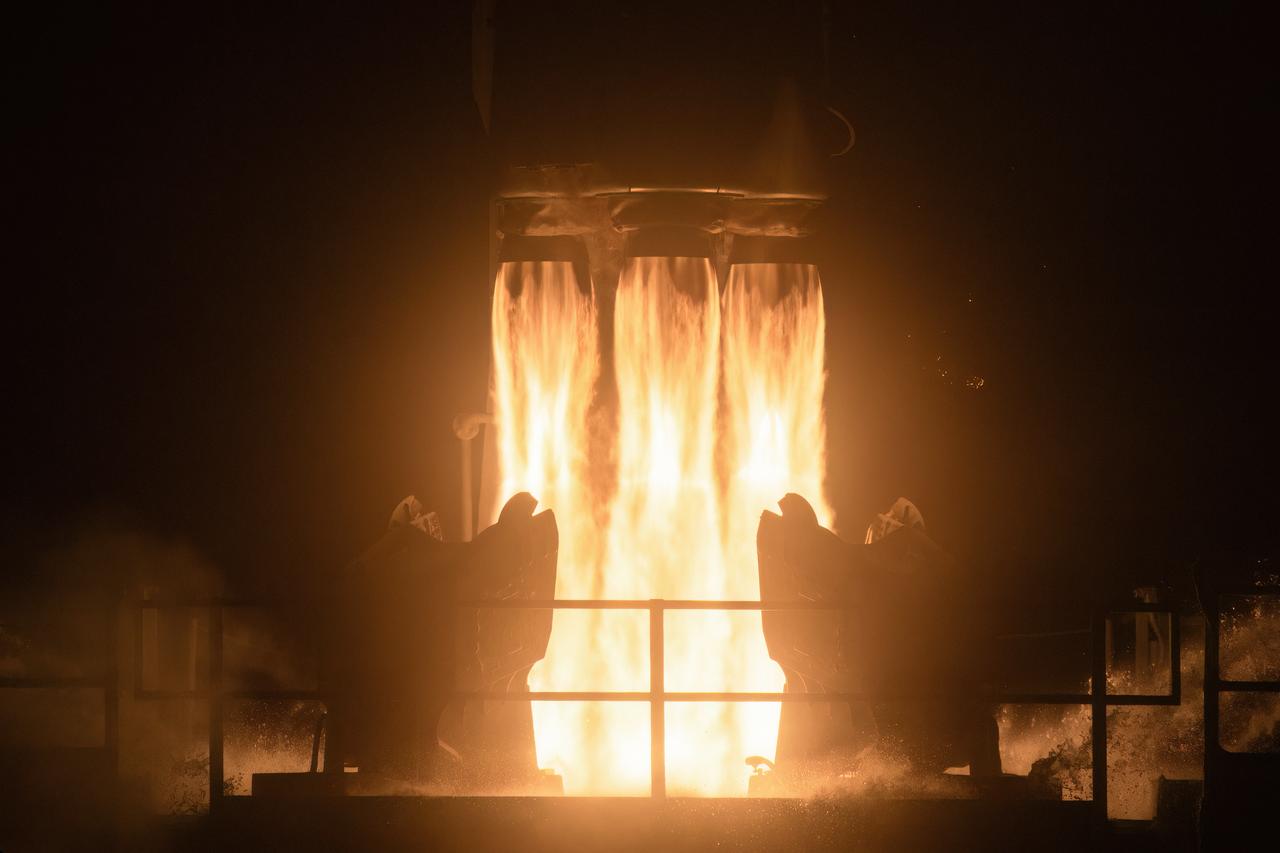

Firefly Aerospace’s Alpha rocket carrying eight CubeSats as part of NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative (CSLI) lifts off from Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California at 9:04 p.m. PDT Wednesday, July 3, 2024. The successful launch of the rocket, named “Noise of Summer,” completed the company’s Venture-Class Launch Services Demonstration 2 (VCLS Demo 2) contract with the agency. The CubeSat missions were designed by universities and NASA centers to conduct climate studies, satellite technology development, and educational outreach to students.
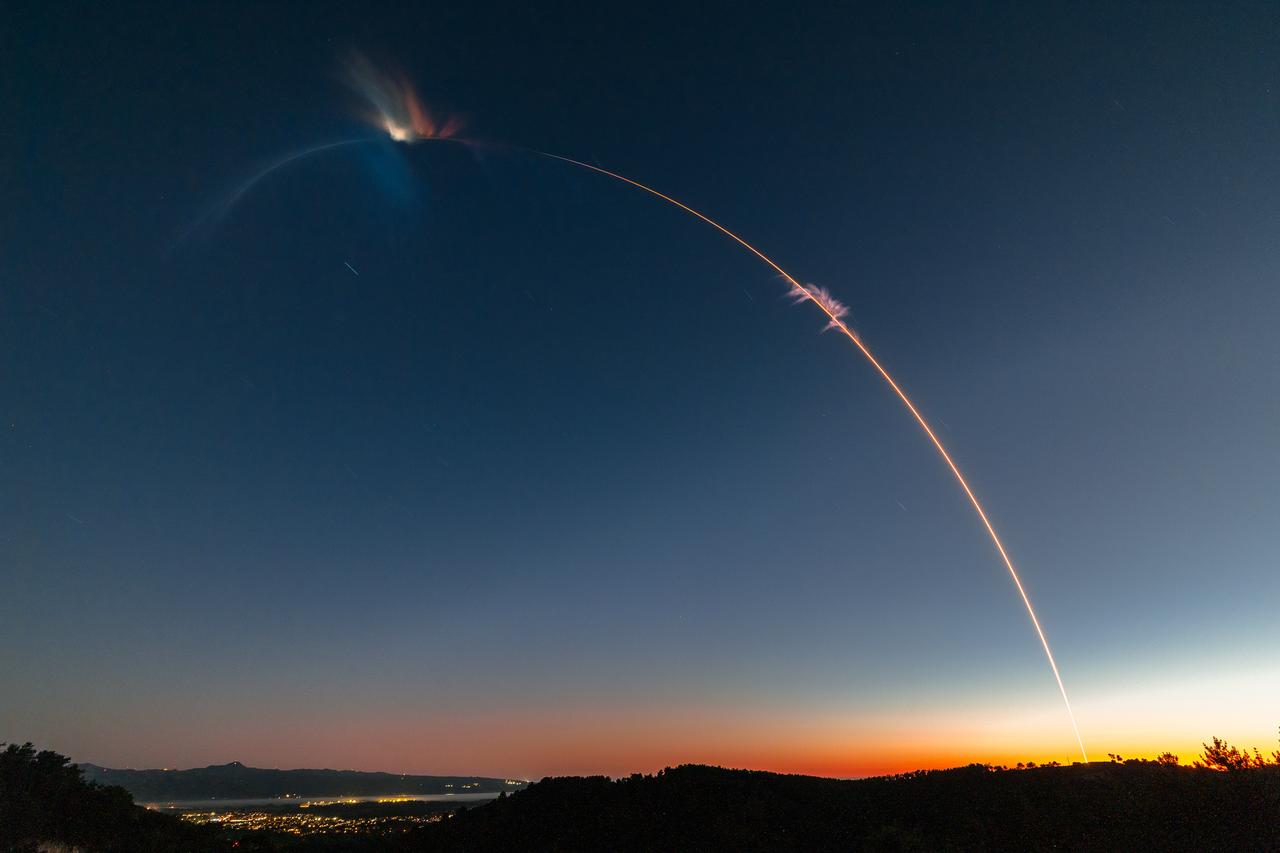

Firefly Aerospace’s Alpha rocket carrying eight CubeSats as part of NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative (CSLI) lifts off from Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California at 9:04 p.m. PDT Wednesday, July 3, 2024. The successful launch of the rocket, named “Noise of Summer,” completed the company’s Venture-Class Launch Services Demonstration 2 (VCLS Demo 2) contract with the agency. The CubeSat missions were designed by universities and NASA centers to conduct climate studies, satellite technology development, and educational outreach to students.
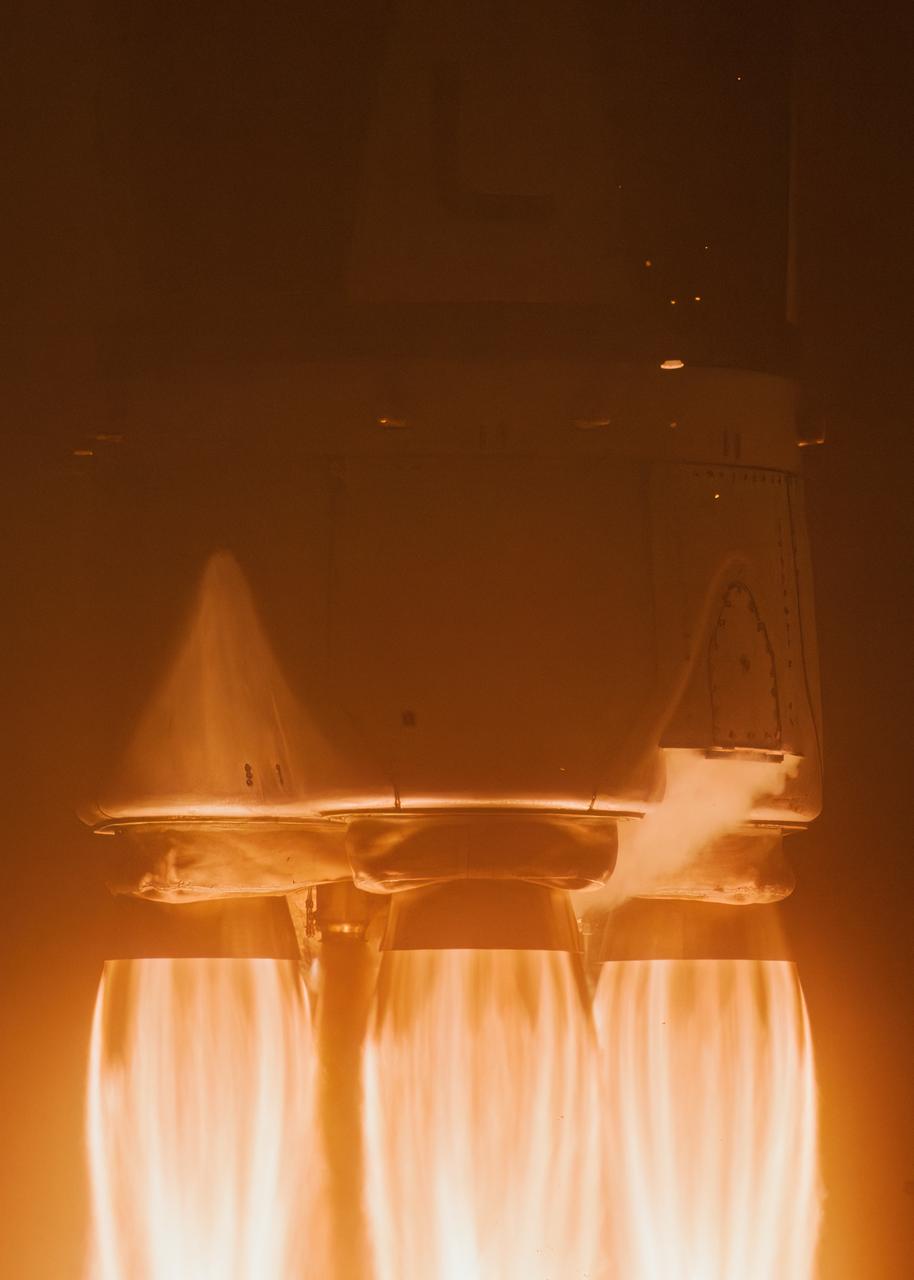

Firefly Aerospace’s Alpha rocket carrying eight CubeSats as part of NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative (CSLI) lifts off from Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California at 9:04 p.m. PDT Wednesday, July 3, 2024. The successful launch of the rocket, named “Noise of Summer,” completed the company’s Venture-Class Launch Services Demonstration 2 (VCLS Demo 2) contract with the agency. The CubeSat missions were designed by universities and NASA centers to conduct climate studies, satellite technology development, and educational outreach to students.
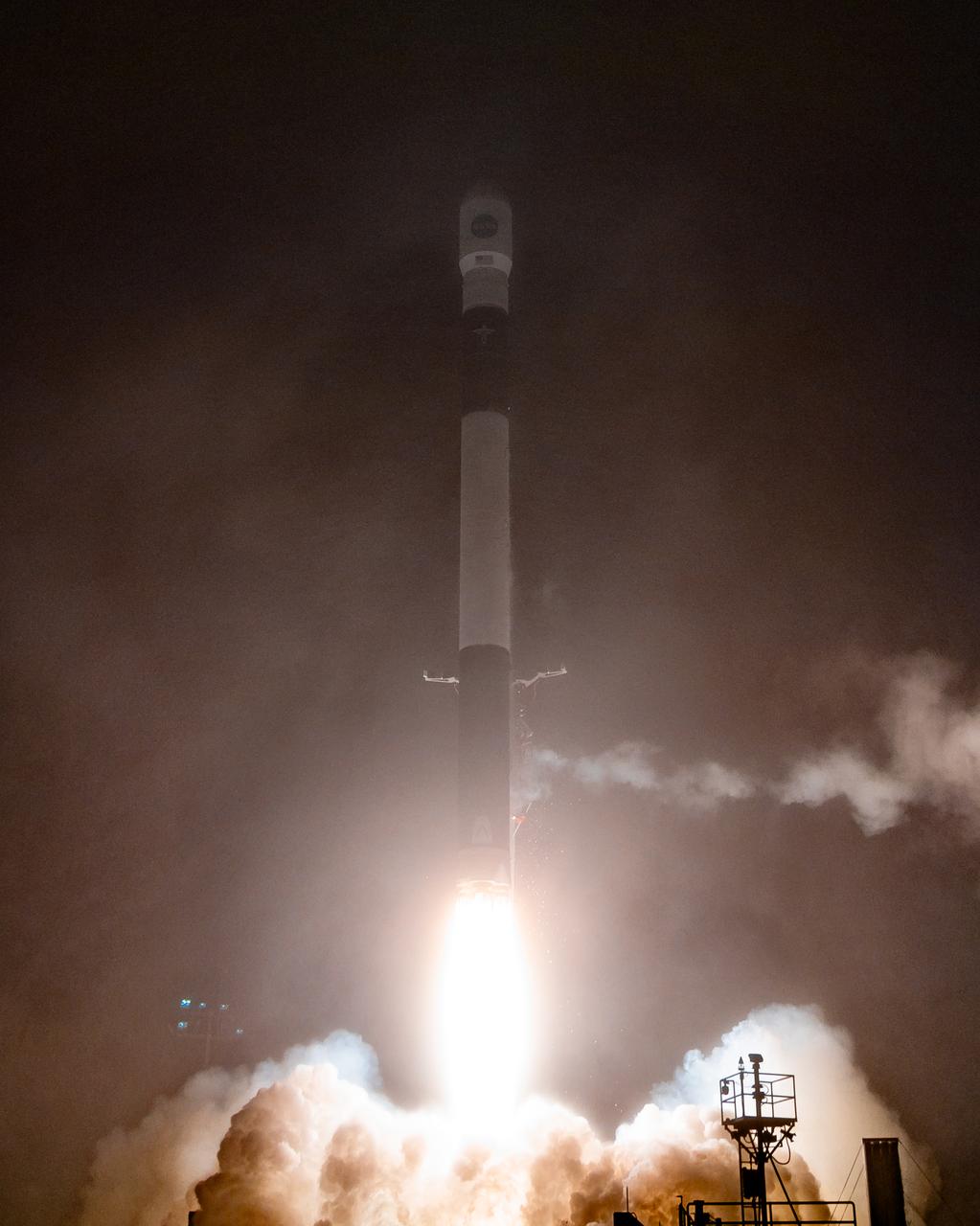

Firefly Aerospace’s Alpha rocket carrying eight CubeSats as part of NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative (CSLI) lifts off from Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California at 9:04 p.m. PDT Wednesday, July 3, 2024. The successful launch of the rocket, named “Noise of Summer,” completed the company’s Venture-Class Launch Services Demonstration 2 (VCLS Demo 2) contract with the agency. The CubeSat missions were designed by universities and NASA centers to conduct climate studies, satellite technology development, and educational outreach to students.
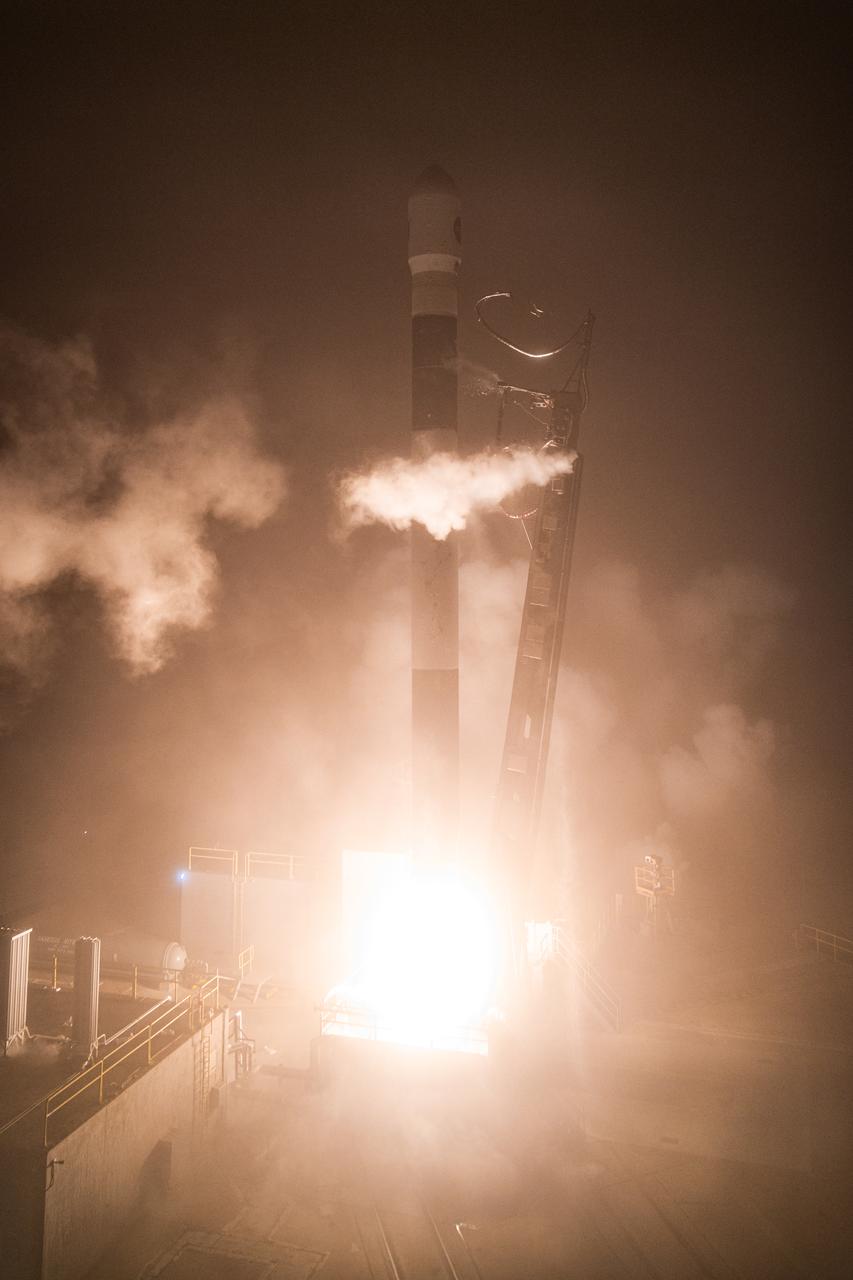

Firefly Aerospace’s Alpha rocket carrying eight CubeSats as part of NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative (CSLI) lifts off from Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California at 9:04 p.m. PDT Wednesday, July 3, 2024. The successful launch of the rocket, named “Noise of Summer,” completed the company’s Venture-Class Launch Services Demonstration 2 (VCLS Demo 2) contract with the agency. The CubeSat missions were designed by universities and NASA centers to conduct climate studies, satellite technology development, and educational outreach to students.
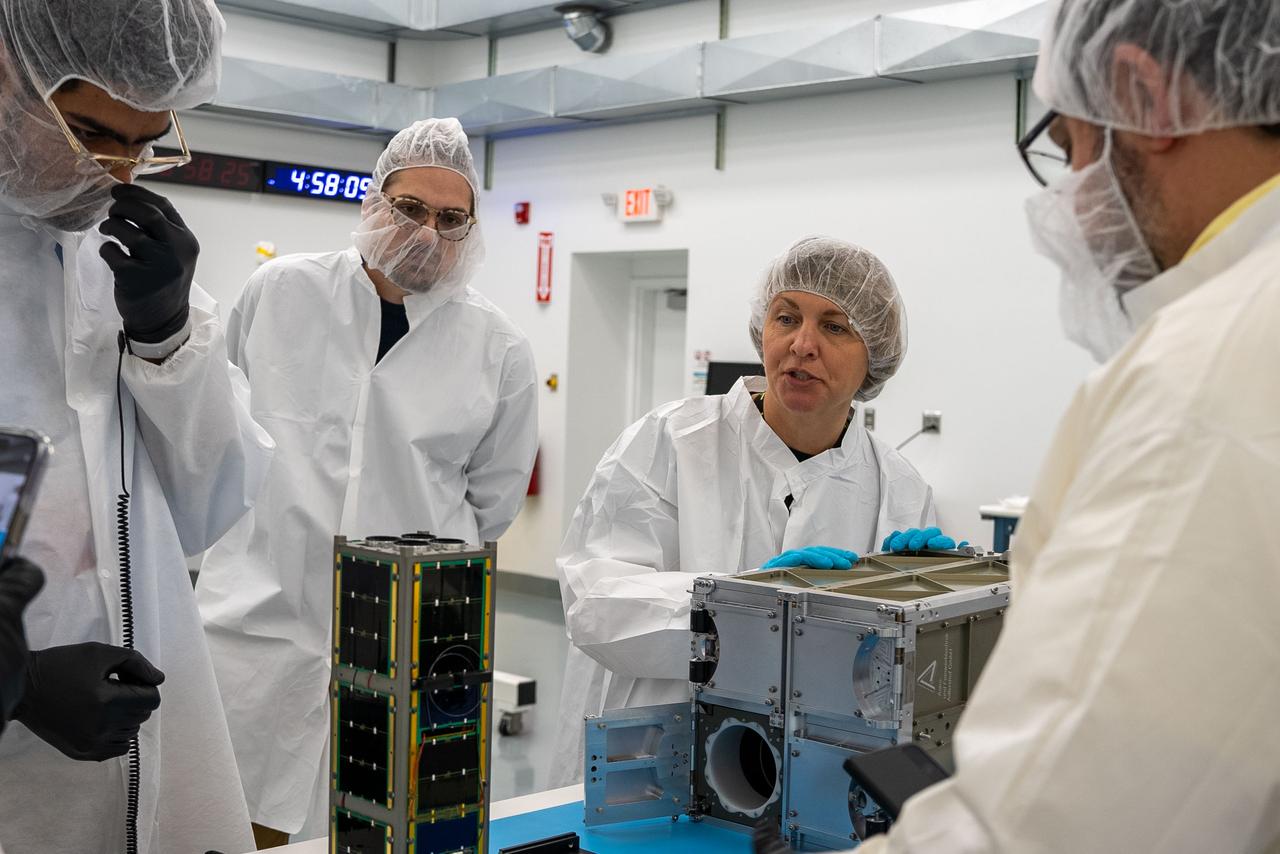

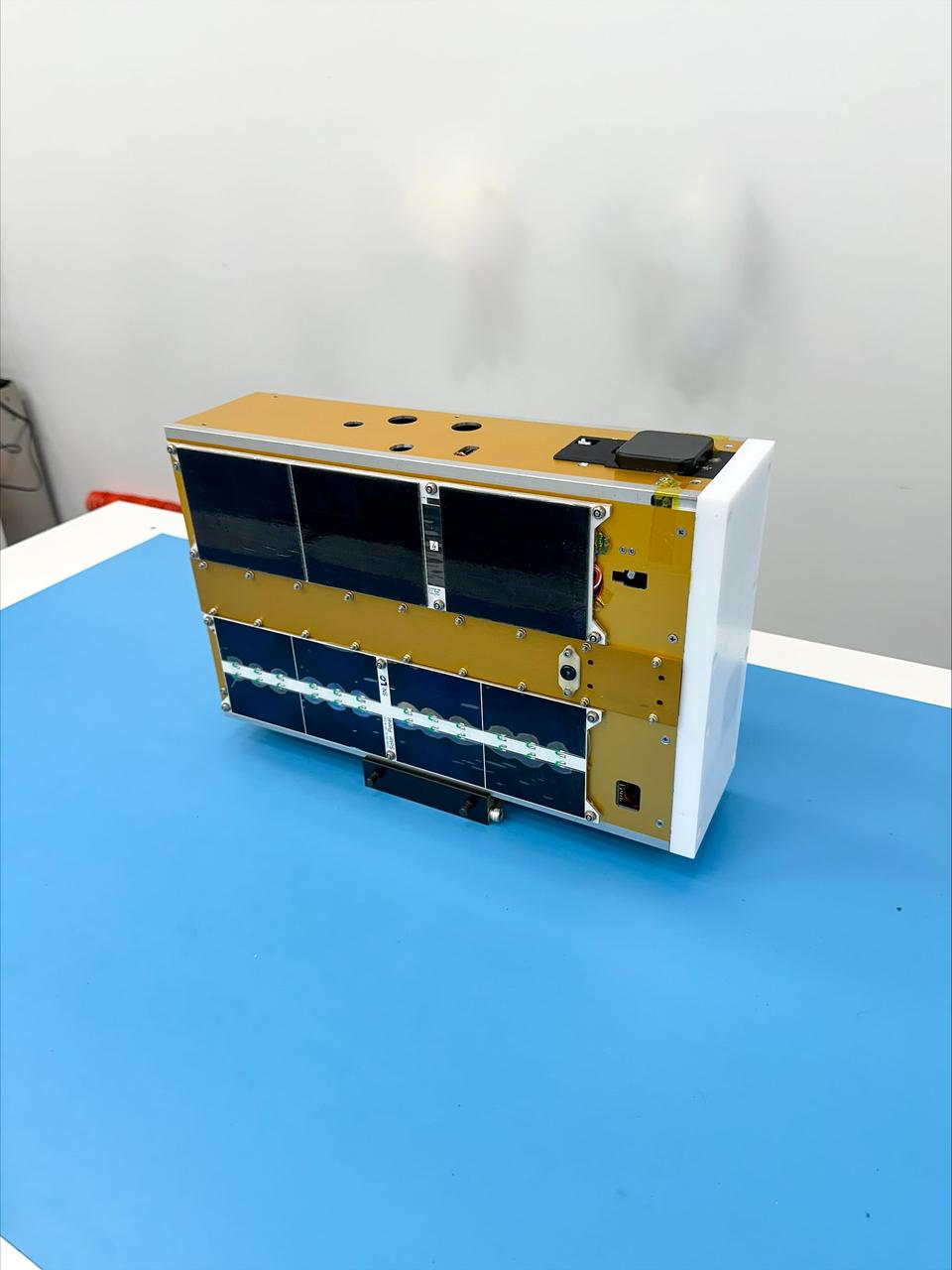
Technicians from the University of Maine prepare CubeSat MESAT-1 for integration at Firefly’s Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base, California on Monday, April 22, 2024. MESAT-1, along with seven other payloads, will be integrated into a Firefly Aerospace Alpha rocket for NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellites (ELaNa) 43 mission as part of the agency’s CubeSat Launch Initiative and Firefly’s Venture-Class Launch Services Demonstration 2 contract.
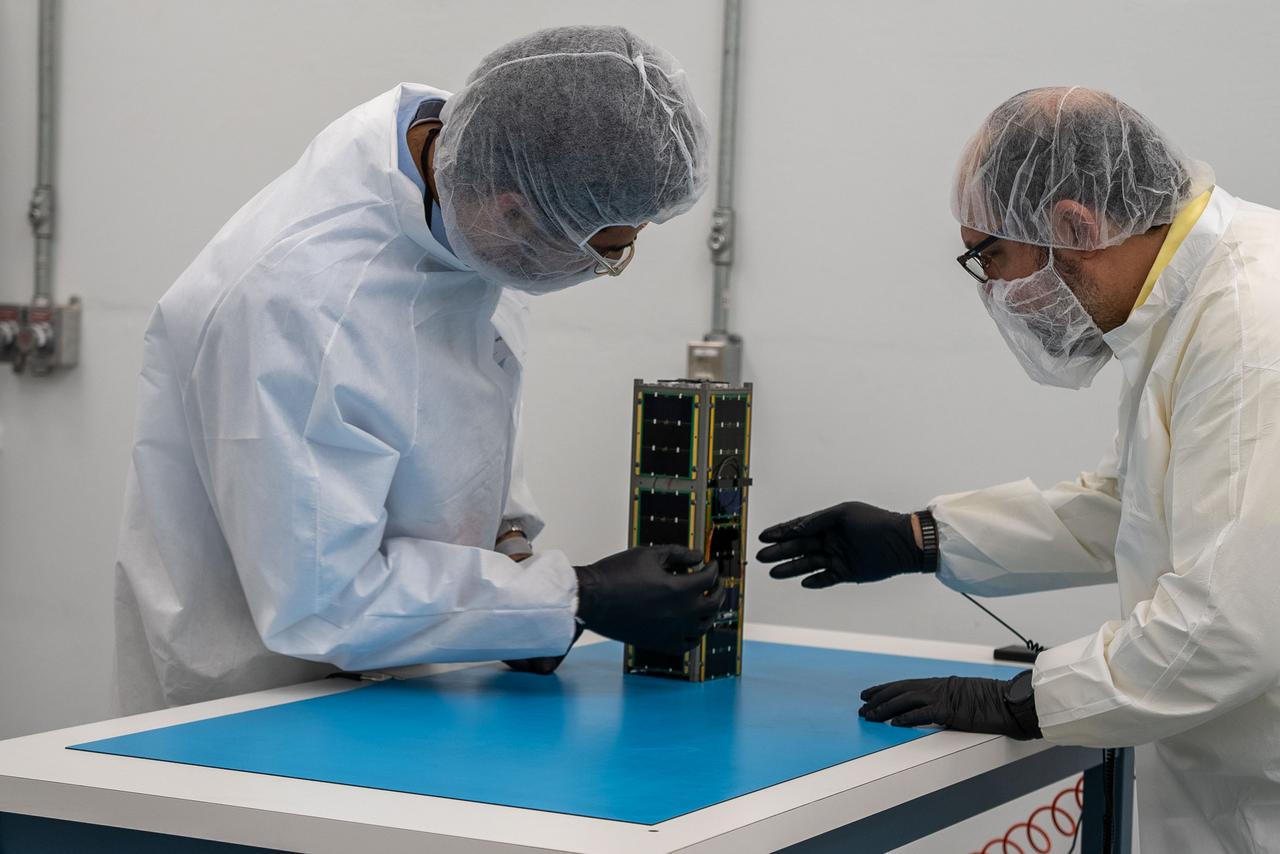

Technicians from the University of Maine prepare CubeSat MESAT-1 for integration at Firefly’s Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base, California on Monday, April 22, 2024. MESAT-1, along with seven other payloads, will be integrated into a Firefly Aerospace Alpha rocket for NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellites (ELaNa) 43 mission as part of the agency’s CubeSat Launch Initiative and Firefly’s Venture-Class Launch Services Demonstration 2 contract.
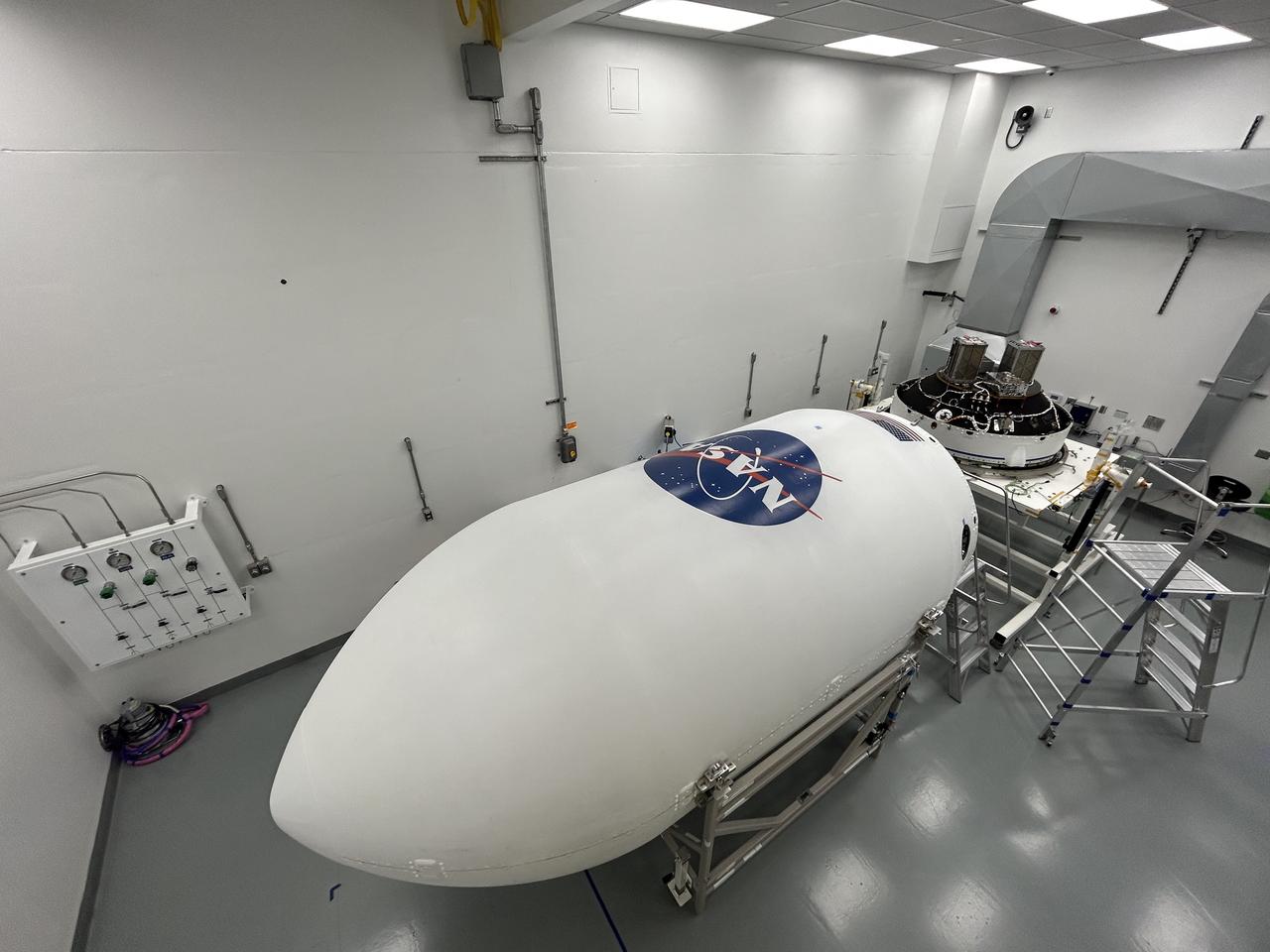

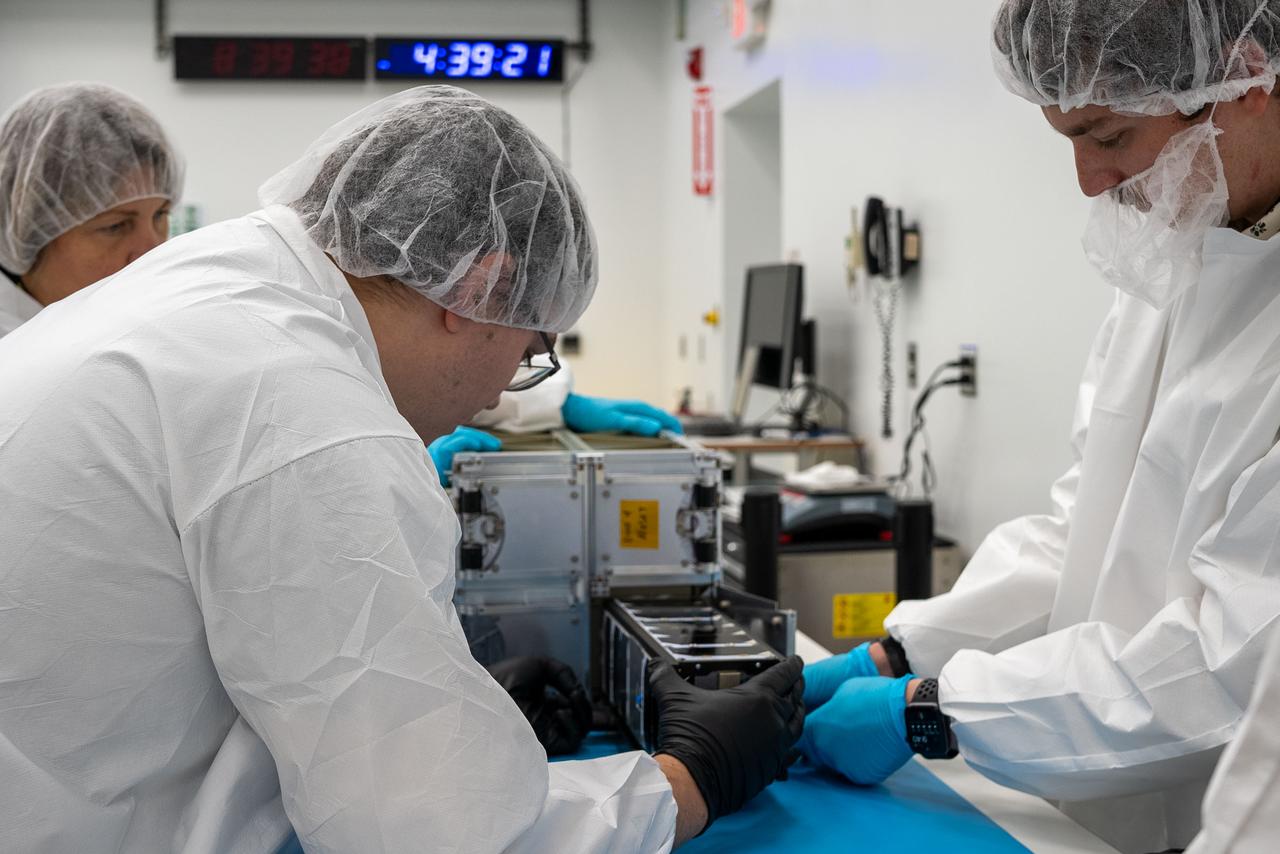
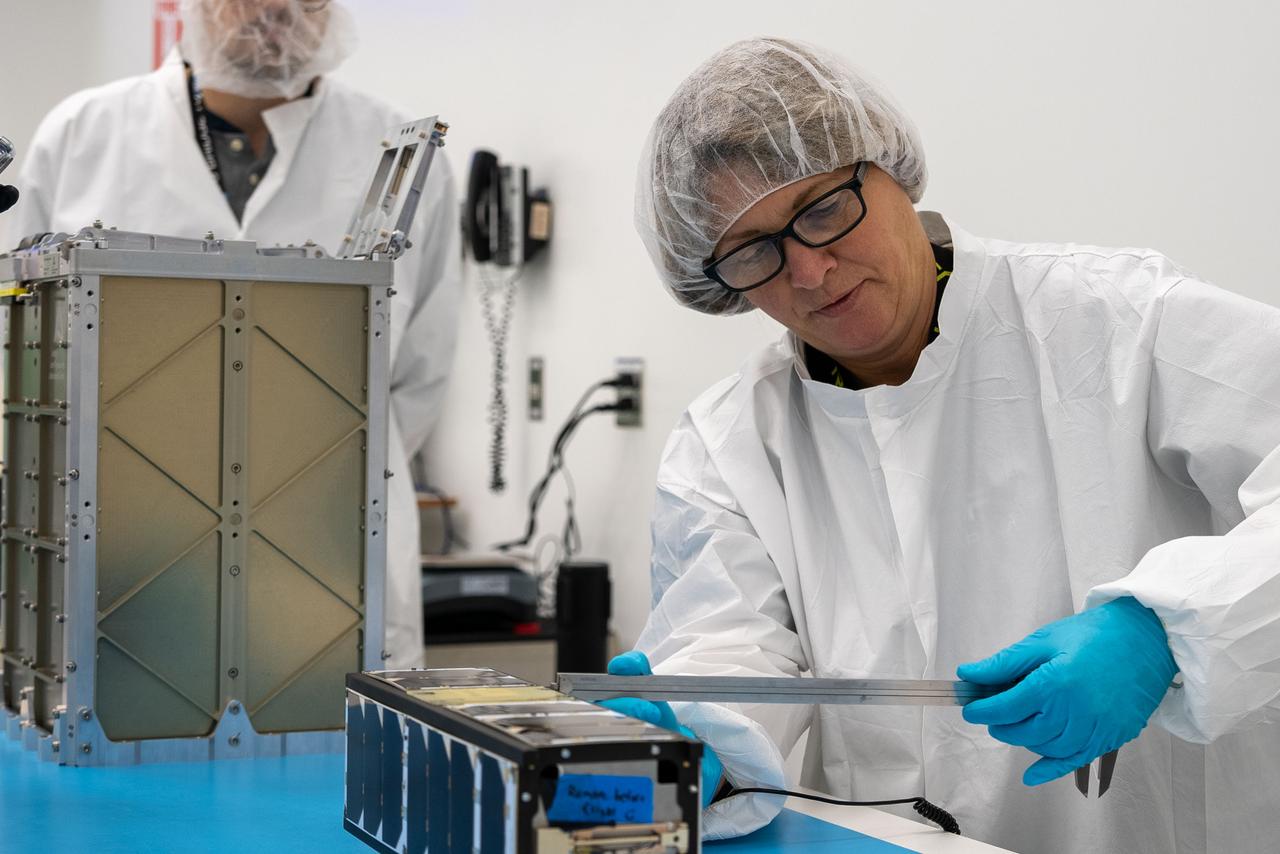
Technicians inside Firefly Aerospace’s Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base, California, integrate eight CubeSats as part of NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative’s (CSLI) ELaNa (Educational Launch of Nanosatellites) 43 mission into payload fairings on Sunday, June 30, 2024. The mission will launch on the company’s Alpha rocket from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Complex 2. Firefly Aerospace is one of three companies selected to fly small satellites to space under NASA’s Launch Services Program Venture-Class Launch Services Demonstration 2 (VCLS Demo 2) contract awarded in December 2020.
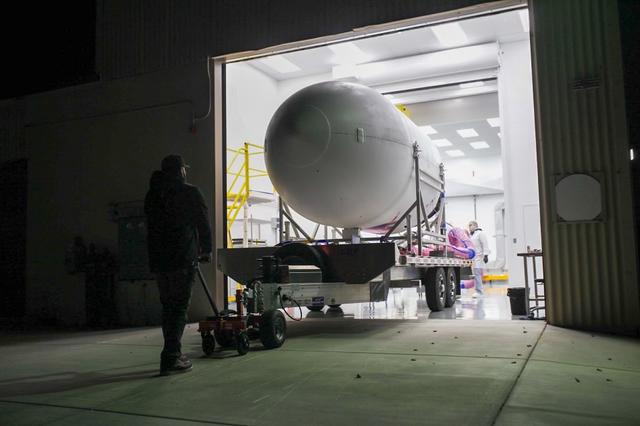

Firefly Aerospace’s Alpha rocket carrying eight CubeSats as part of NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative’s (CSLI) ELaNa (Educational Launch of Nanosatellites) 43 mission rolls out of the company’s Payload Processing Facility to Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Space Force Base, California, on Sunday, June 30, 2024. Firefly Aerospace is one of three companies selected to fly small satellites to space under NASA’s Launch Services Program Venture-Class Launch Services Demonstration 2 (VCLS Demo 2) contract awarded in December 2020.
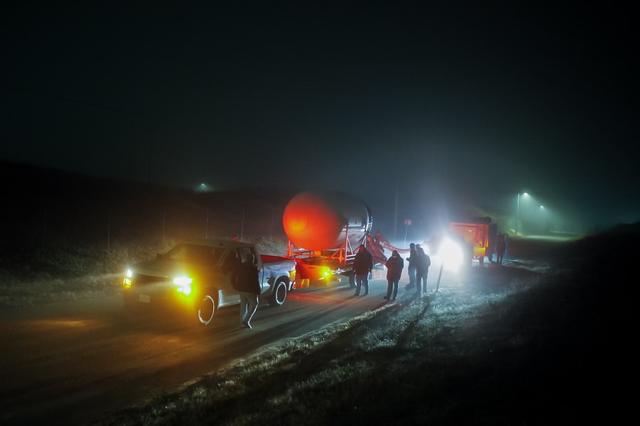

Firefly Aerospace’s Alpha rocket carrying eight CubeSats as part of NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative’s (CSLI) ELaNa (Educational Launch of Nanosatellites) 43 mission rolls out of the company’s Payload Processing Facility to Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Space Force Base, California, on Sunday, June 30, 2024. Firefly Aerospace is one of three companies selected to fly small satellites to space under NASA’s Launch Services Program Venture-Class Launch Services Demonstration 2 (VCLS Demo 2) contract awarded in December 2020.
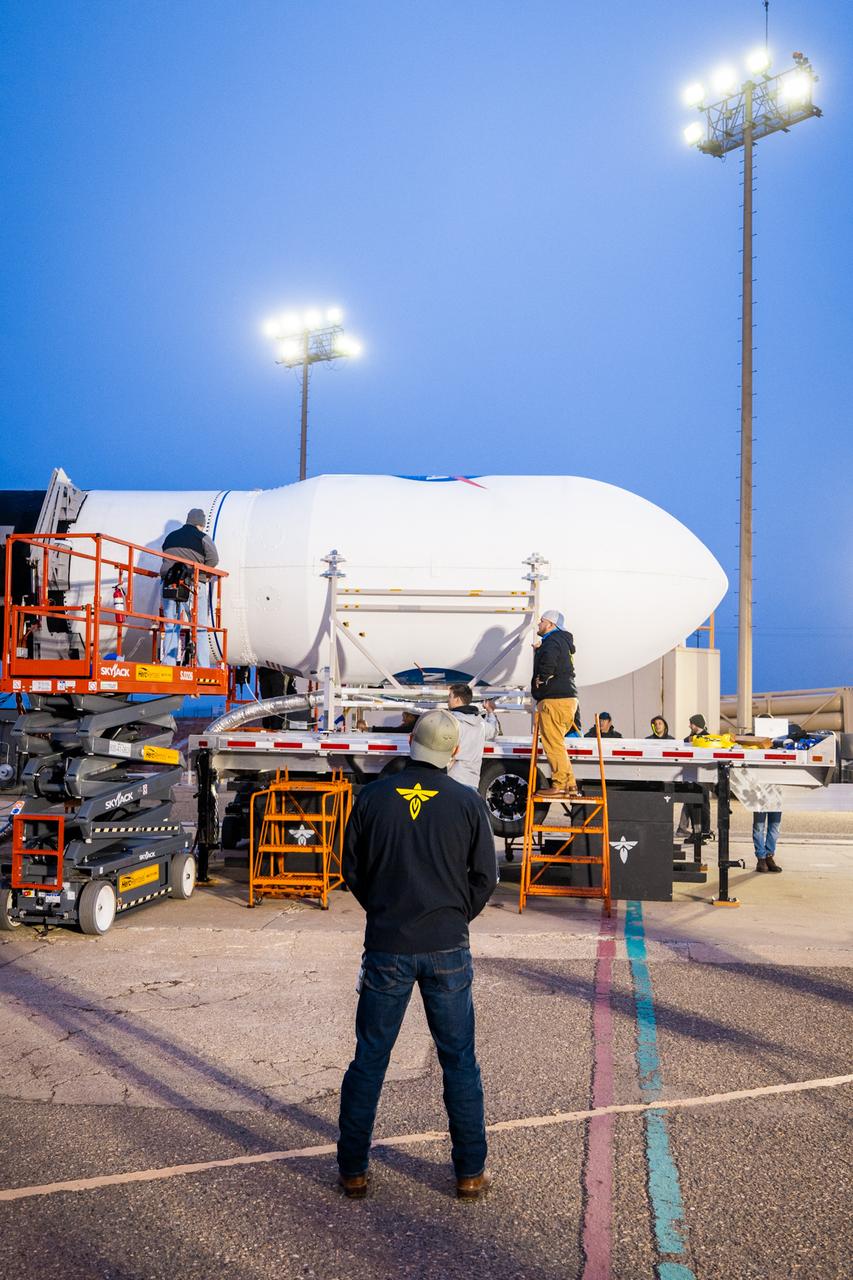

Firefly Aerospace’s Alpha rocket carrying eight CubeSats as part of NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative’s (CSLI) ELaNa (Educational Launch of Nanosatellites) 43 mission rolls out of the company’s Payload Processing Facility to Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Space Force Base, California, on Sunday, June 30, 2024. Firefly Aerospace is one of three companies selected to fly small satellites to space under NASA’s Launch Services Program Venture-Class Launch Services Demonstration 2 (VCLS Demo 2) contract awarded in December 2020.
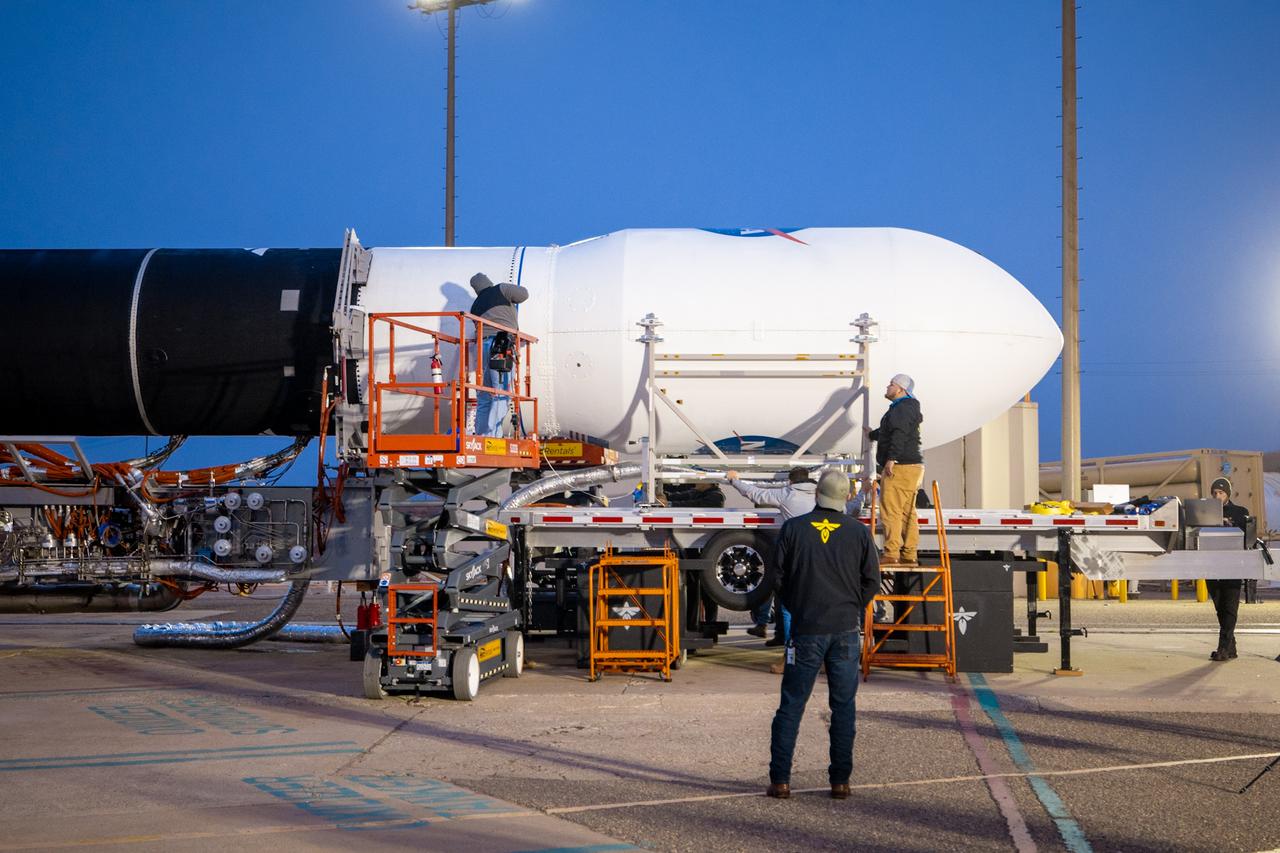

Firefly Aerospace’s Alpha rocket carrying eight CubeSats as part of NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative’s (CSLI) ELaNa (Educational Launch of Nanosatellites) 43 mission rolls out of the company’s Payload Processing Facility to Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Space Force Base, California, on Sunday, June 30, 2024. Firefly Aerospace is one of three companies selected to fly small satellites to space under NASA’s Launch Services Program Venture-Class Launch Services Demonstration 2 (VCLS Demo 2) contract awarded in December 2020.
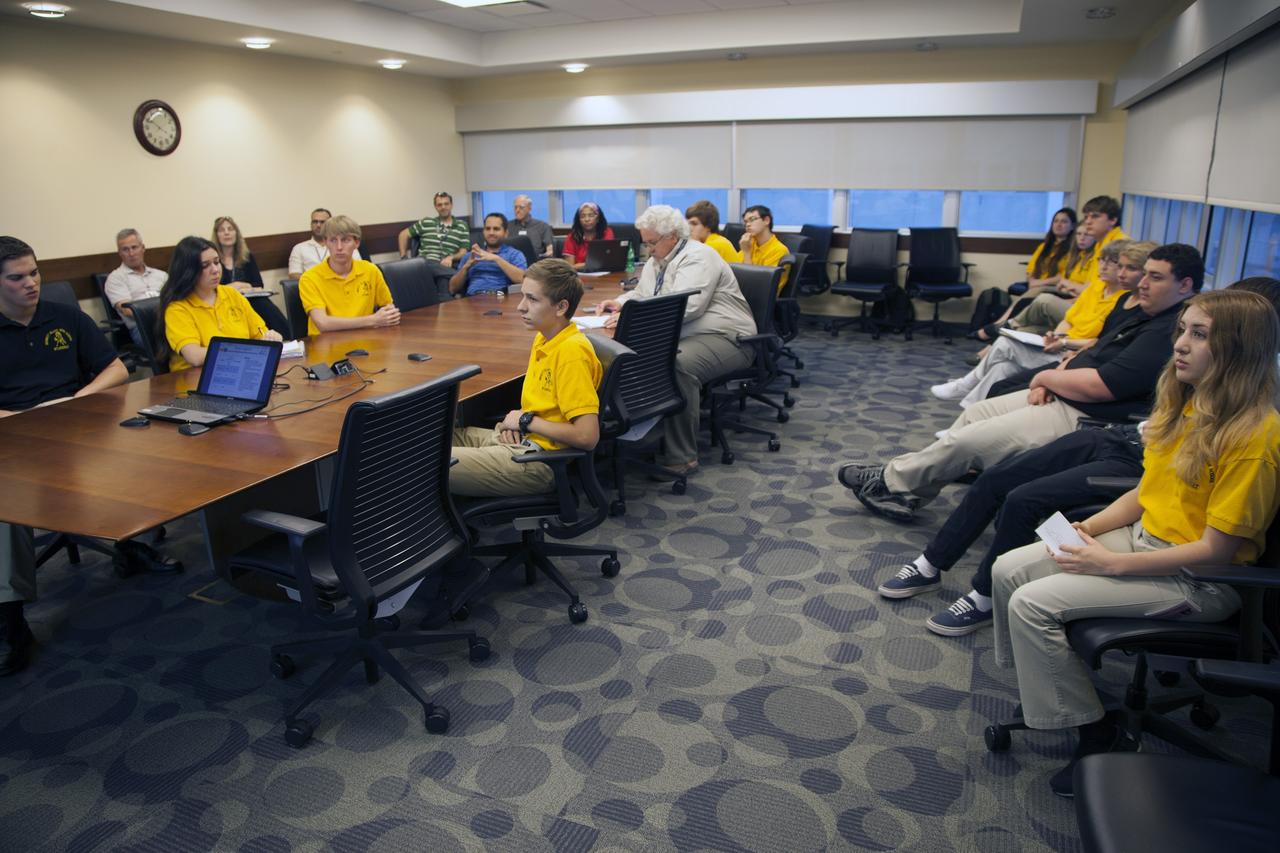

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Merritt Island High School students and their NASA mentors participate in a Critical Design Review of StangSat concepts in the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. StangSat is one of many CubeSats under development in a class of research spacecraft called nanosatellites. The cube-shaped satellites measure about 4 inches on each side, have a volume of about 1 quart and weigh less than 3 pounds. To date, 27 CubeSats have launched through the initiative as part of the agency's Launch Services Program's Educational Launch of Nanosatellite Program. This year, four separate launches will carry 17 CubeSats. To learn more about the CubeSat Launch Initiative, visit http://go.nasa.gov/CubeSat_initiative. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
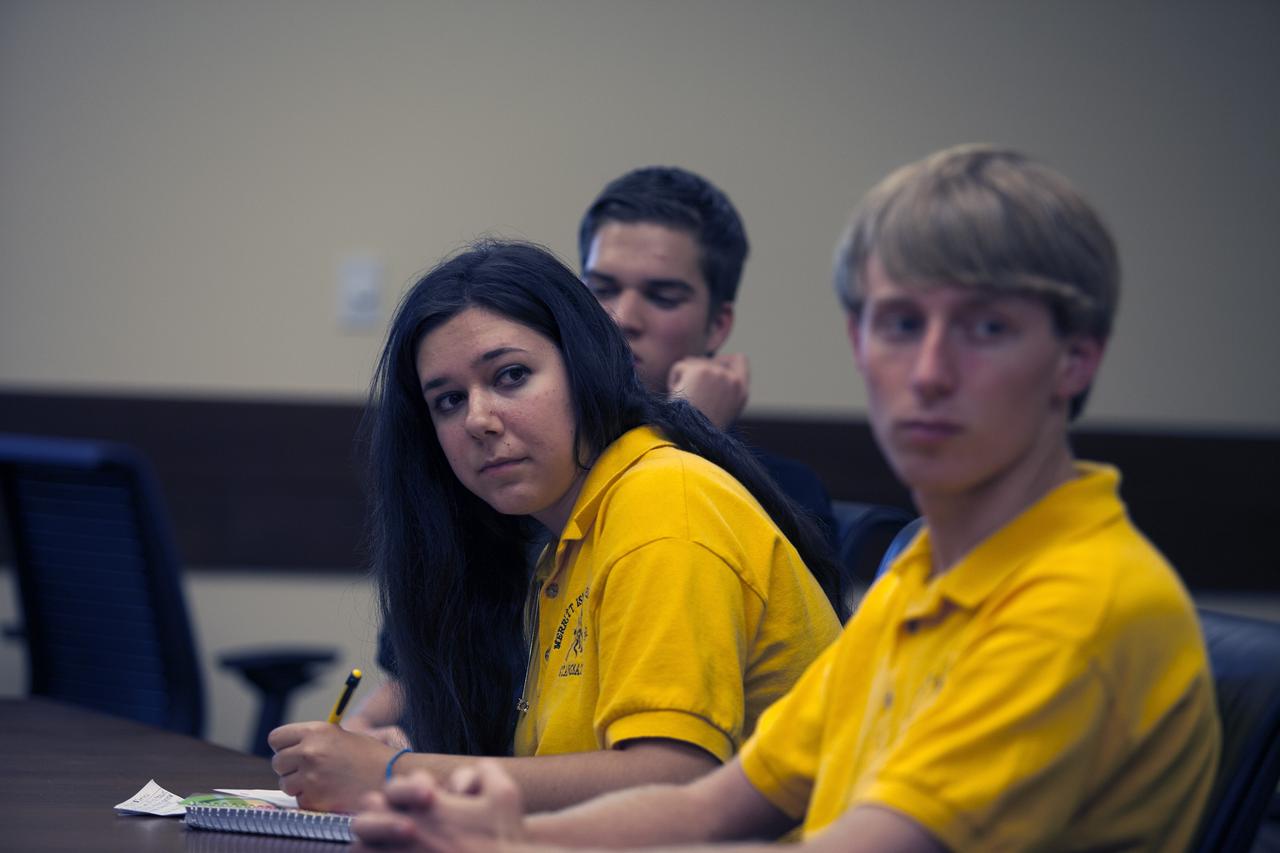

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Merritt Island High School students participate in a Critical Design Review of StangSat concepts with NASA engineers in the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. StangSat is one of many CubeSats under development in a class of research spacecraft called nanosatellites. The cube-shaped satellites measure about 4 inches on each side, have a volume of about 1 quart and weigh less than 3 pounds. To date, 27 CubeSats have launched through the initiative as part of the agency's Launch Services Program's Educational Launch of Nanosatellite Program. This year, four separate launches will carry 17 CubeSats. To learn more about the CubeSat Launch Initiative, visit http://go.nasa.gov/CubeSat_initiative. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A student representing a team from Merritt Island High School presents their StangSat concepts to NASA engineers at a Critical Design Review in the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. StangSat is one of many CubeSats under development in a class of research spacecraft called nanosatellites. The cube-shaped satellites measure about 4 inches on each side, have a volume of about 1 quart and weigh less than 3 pounds. To date, 27 CubeSats have launched through the initiative as part of the agency's Launch Services Program's Educational Launch of Nanosatellite Program. This year, four separate launches will carry 17 CubeSats. To learn more about the CubeSat Launch Initiative, visit http://go.nasa.gov/CubeSat_initiative. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
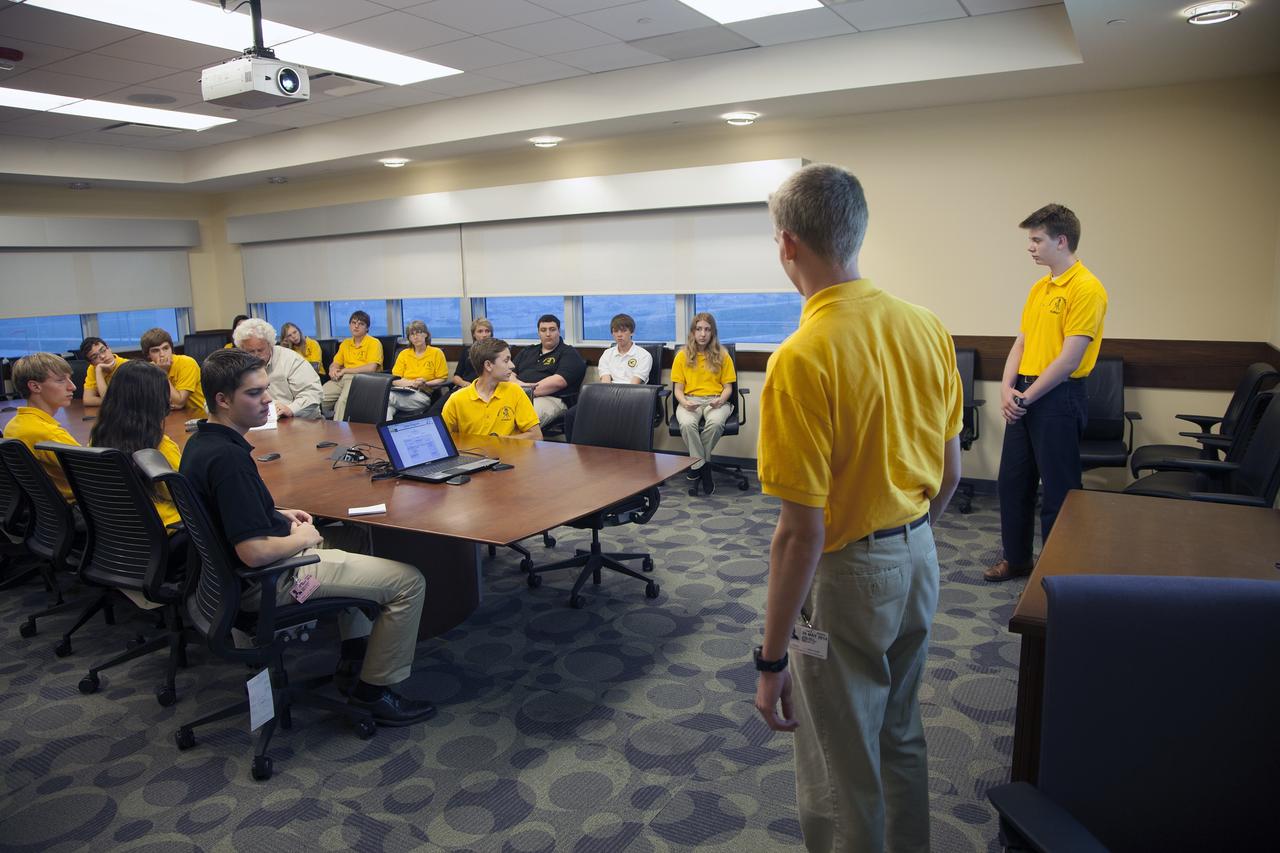

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Students representing a team from Merritt Island High School present their StangSat concepts to NASA engineers at a Critical Design Review in the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. StangSat is one of many CubeSats under development in a class of research spacecraft called nanosatellites. The cube-shaped satellites measure about 4 inches on each side, have a volume of about 1 quart and weigh less than 3 pounds. To date, 27 CubeSats have launched through the initiative as part of the agency's Launch Services Program's Educational Launch of Nanosatellite Program. This year, four separate launches will carry 17 CubeSats. To learn more about the CubeSat Launch Initiative, visit http://go.nasa.gov/CubeSat_initiative. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
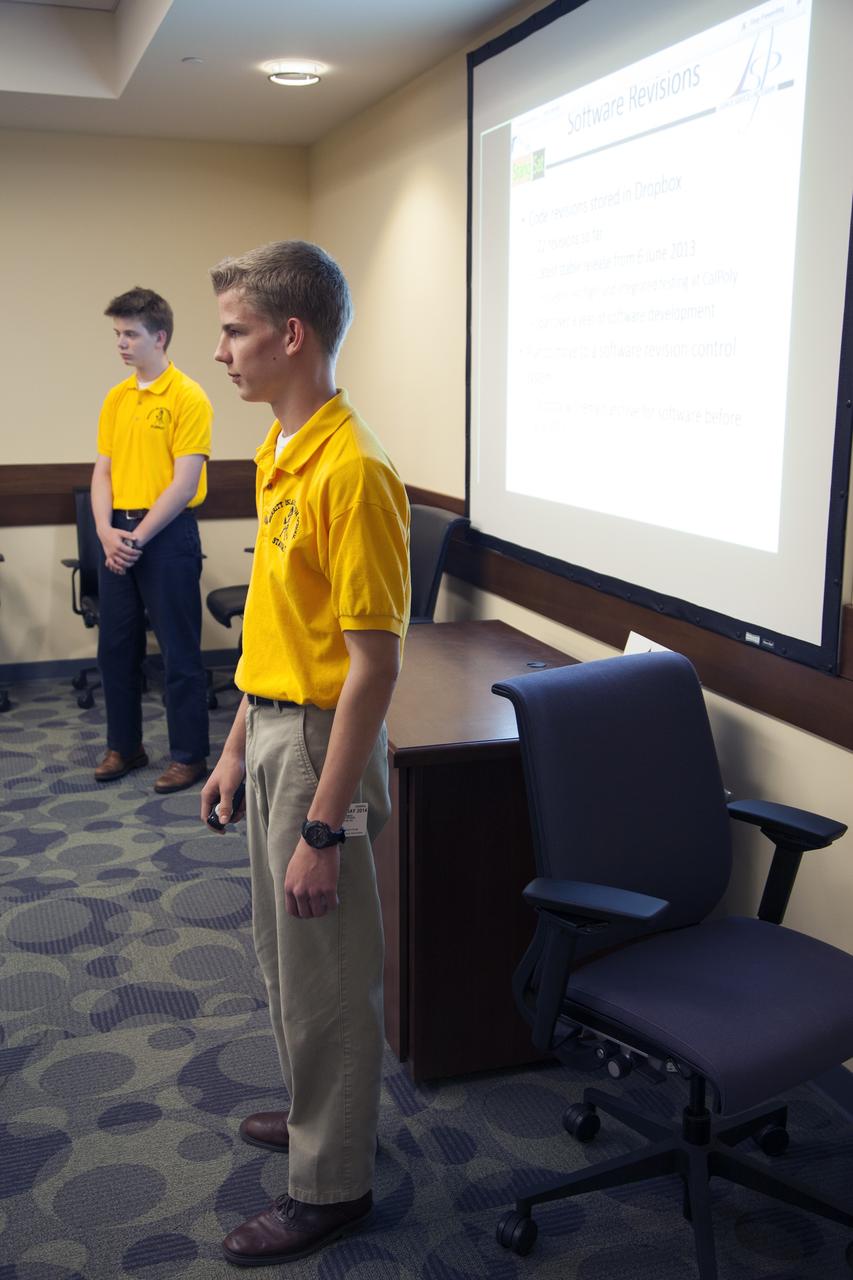

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Students representing a team from Merritt Island High School present their StangSat concepts to NASA engineers at a Critical Design Review in the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. StangSat is one of many CubeSats under development in a class of research spacecraft called nanosatellites. The cube-shaped satellites measure about 4 inches on each side, have a volume of about 1 quart and weigh less than 3 pounds. To date, 27 CubeSats have launched through the initiative as part of the agency's Launch Services Program's Educational Launch of Nanosatellite Program. This year, four separate launches will carry 17 CubeSats. To learn more about the CubeSat Launch Initiative, visit http://go.nasa.gov/CubeSat_initiative. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
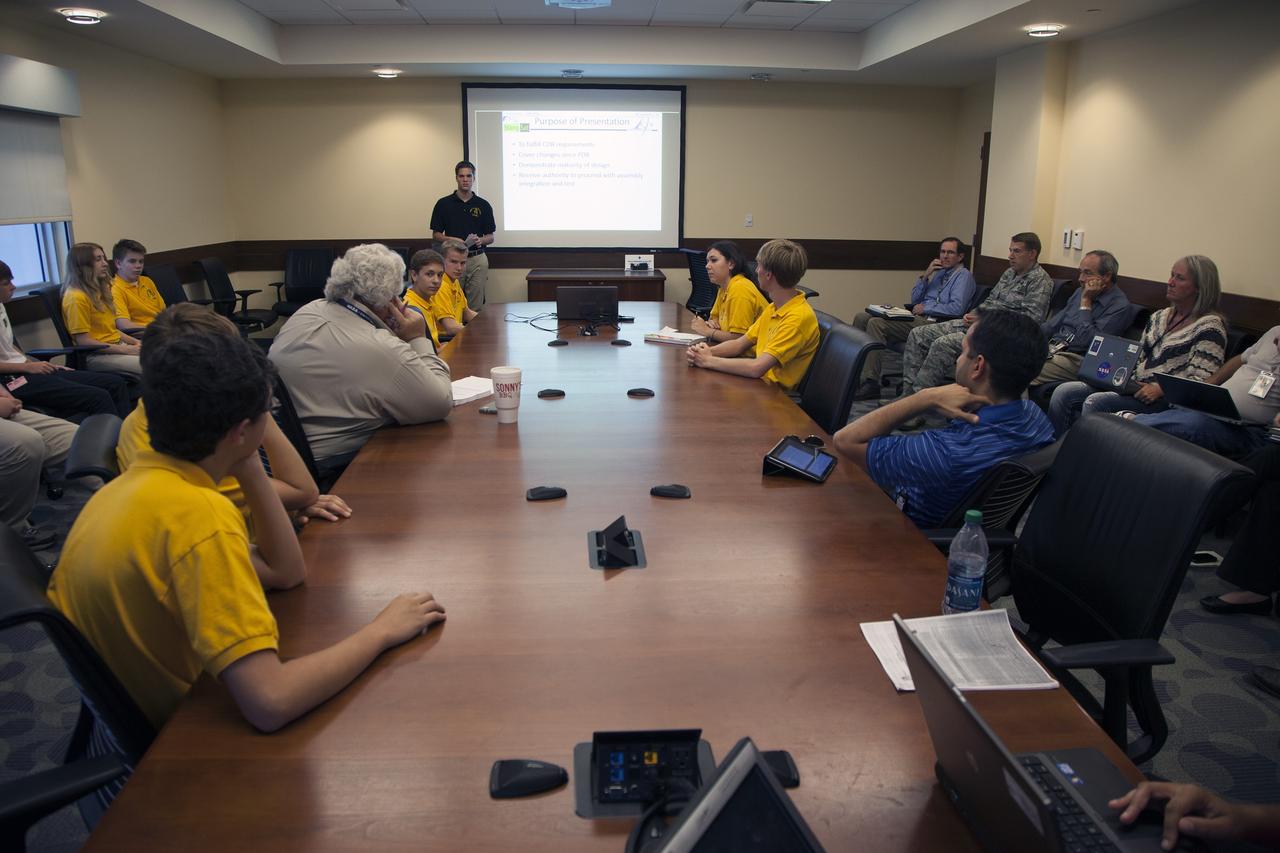

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A student representing a team from Merritt Island High School presents their StangSat concepts to NASA engineers at a Critical Design Review in the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. StangSat is one of many CubeSats under development in a class of research spacecraft called nanosatellites. The cube-shaped satellites measure about 4 inches on each side, have a volume of about 1 quart and weigh less than 3 pounds. To date, 27 CubeSats have launched through the initiative as part of the agency's Launch Services Program's Educational Launch of Nanosatellite Program. This year, four separate launches will carry 17 CubeSats. To learn more about the CubeSat Launch Initiative, visit http://go.nasa.gov/CubeSat_initiative. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
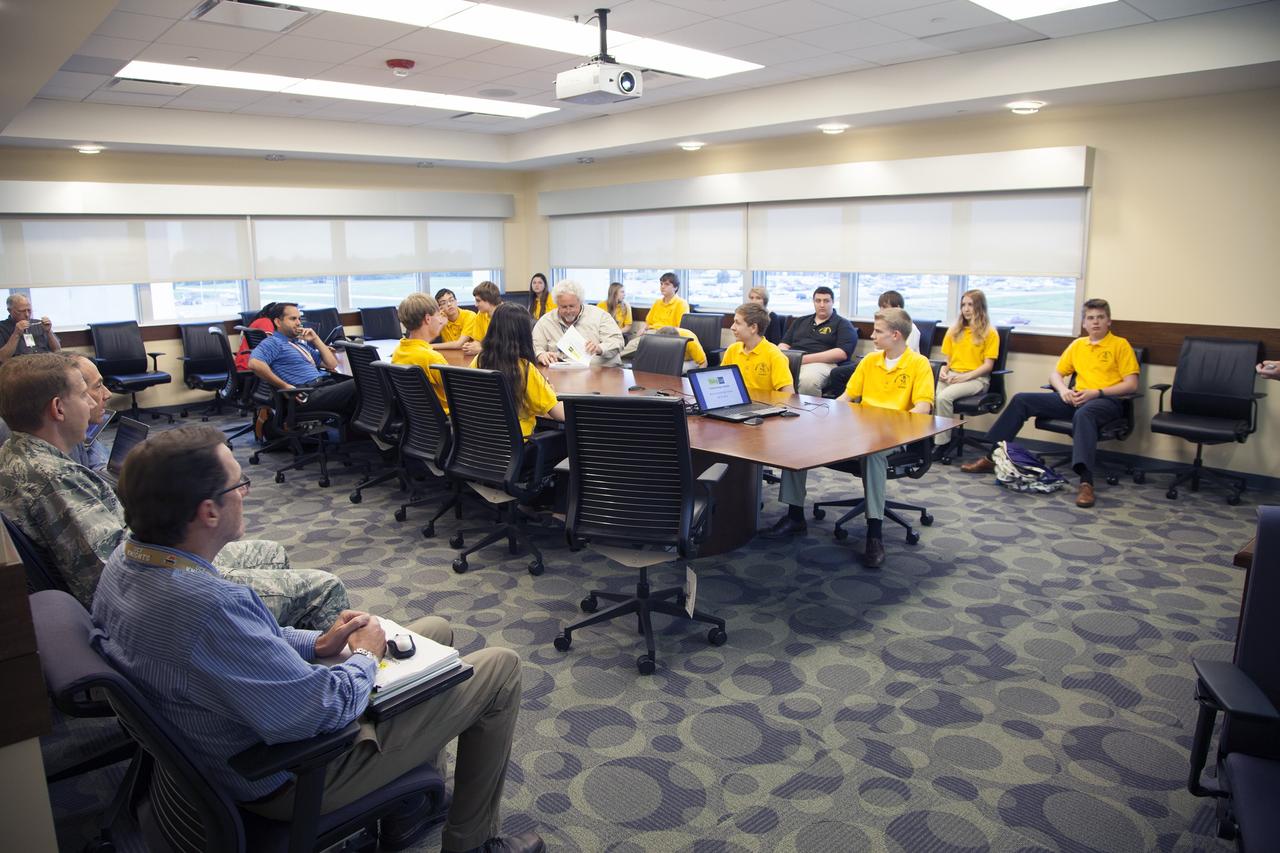

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Merritt Island High School students and their NASA mentors participate in a Critical Design Review of StangSat concepts in the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. StangSat is one of many CubeSats under development in a class of research spacecraft called nanosatellites. The cube-shaped satellites measure about 4 inches on each side, have a volume of about 1 quart and weigh less than 3 pounds. To date, 27 CubeSats have launched through the initiative as part of the agency's Launch Services Program's Educational Launch of Nanosatellite Program. This year, four separate launches will carry 17 CubeSats. To learn more about the CubeSat Launch Initiative, visit http://go.nasa.gov/CubeSat_initiative. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
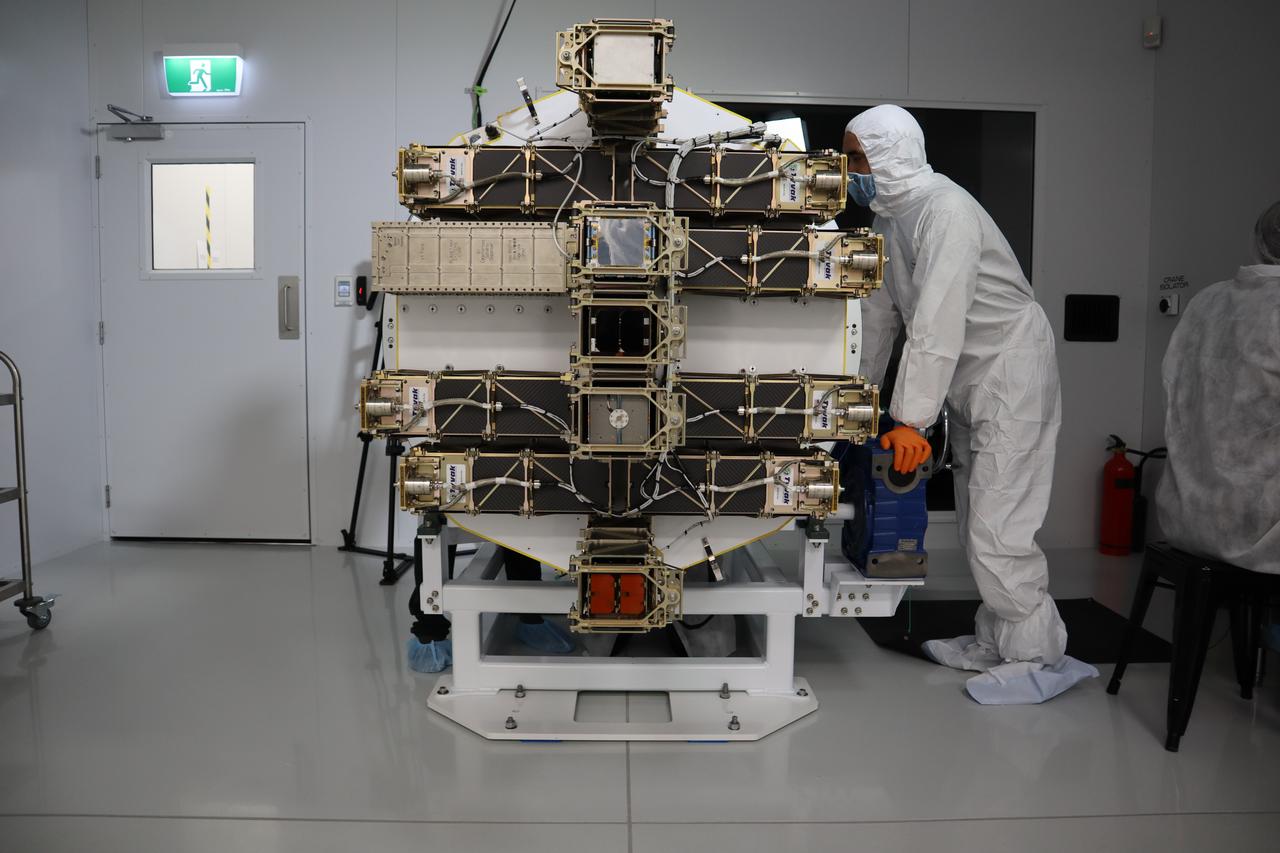

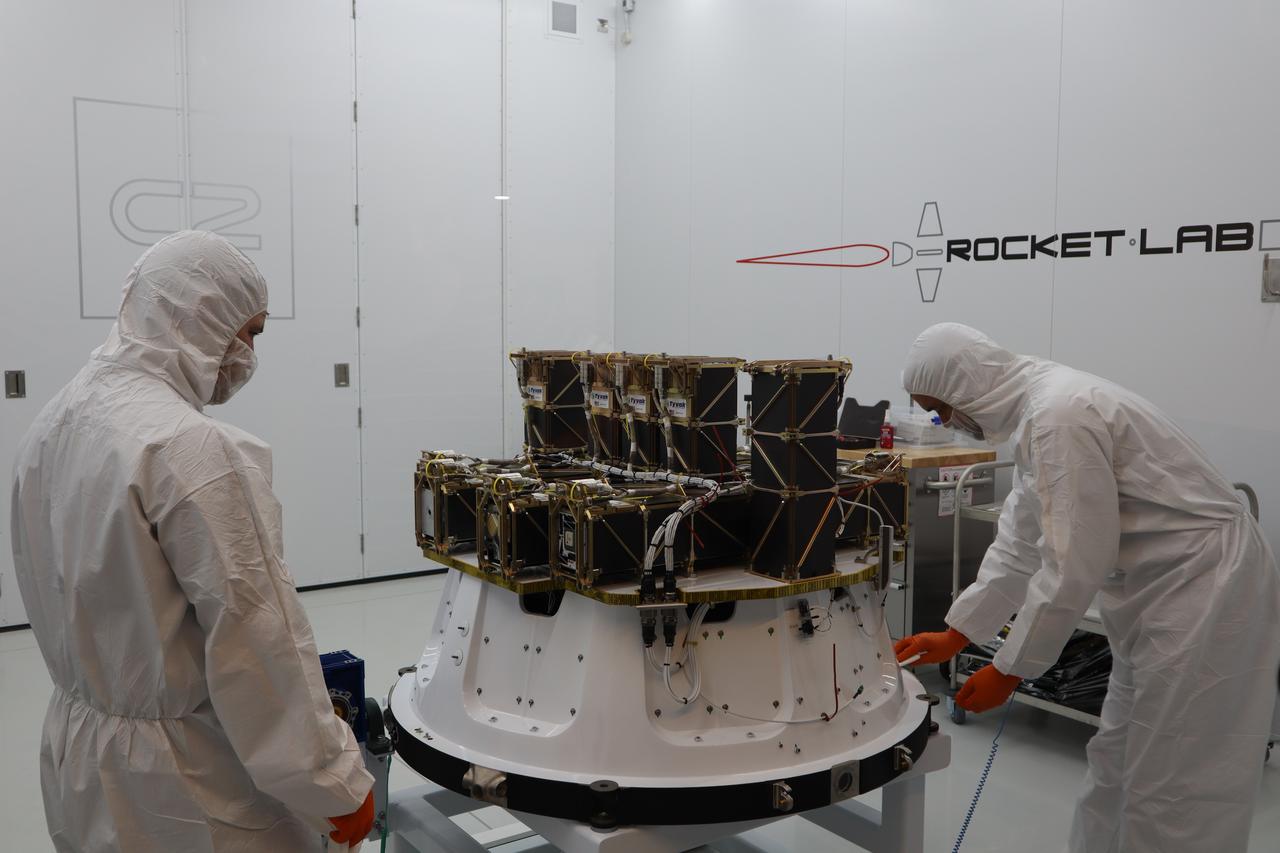
The Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 19 (ELaNa 19) payload has been encapsulated inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Dec. 1, 2018, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The ELaNa 19 payload comprises 10 CubeSats selected through NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative. The liftoff marks the debut of the agency’s innovative Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS) effort. Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to offer small payloads dedicated rides to space.
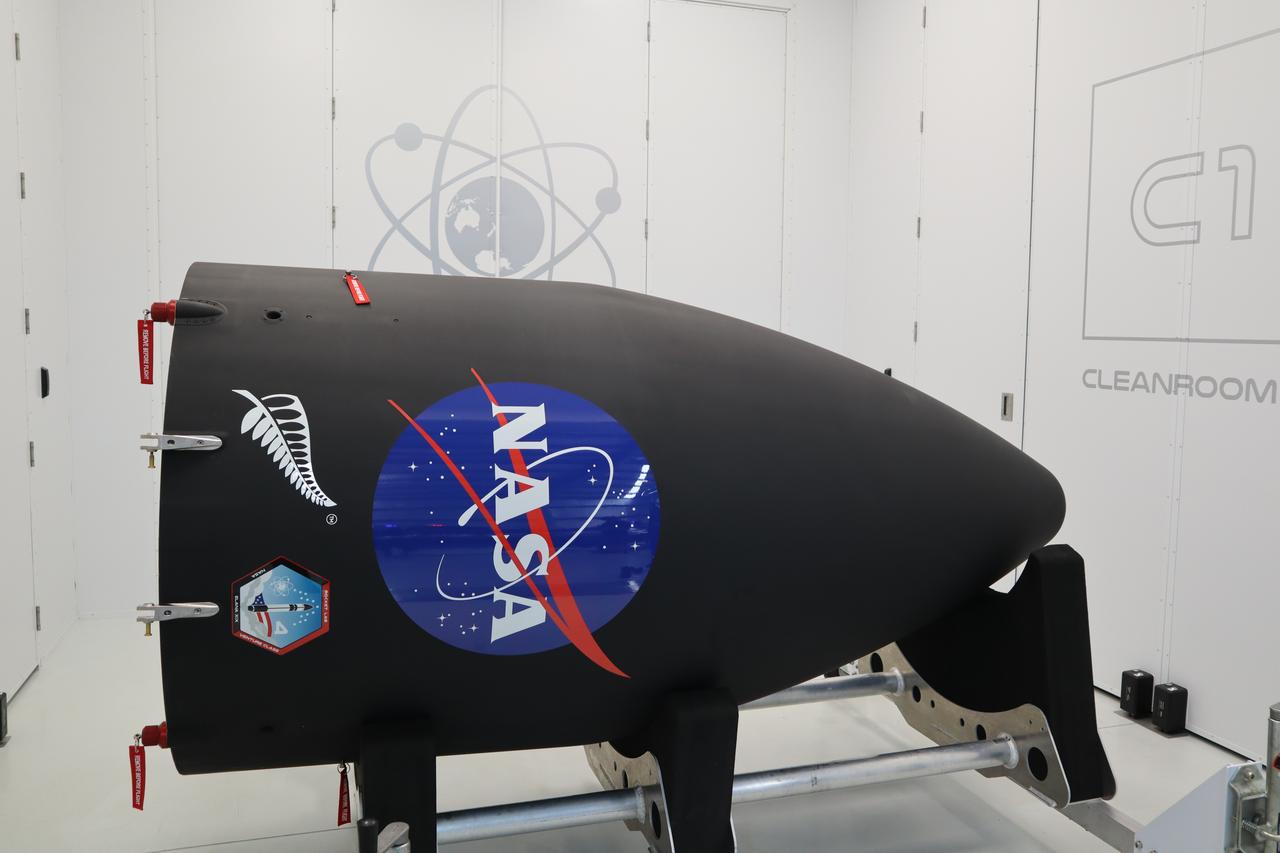
The Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 19 (ELaNa 19) payload has been encapsulated inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Dec. 1, 2018, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The ELaNa 19 payload comprises 10 CubeSats selected through NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative. The liftoff marks the debut of the agency’s innovative Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS) effort. Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to offer small payloads dedicated rides to space.

The Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 19 (ELaNa 19) payload is prepared to be encapsulated inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Dec. 1, 2018, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The ELaNa 19 payload comprises 10 CubeSats selected through NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative. The liftoff marks the debut of the agency’s innovative Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS) effort. Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to offer small payloads dedicated rides to space.

The Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 19 (ELaNa 19) payload is prepared to be encapsulated inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Dec. 1, 2018, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The ELaNa 19 payload comprises 10 CubeSats selected through NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative. The liftoff marks the debut of the agency’s innovative Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS) effort. Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to offer small payloads dedicated rides to space.
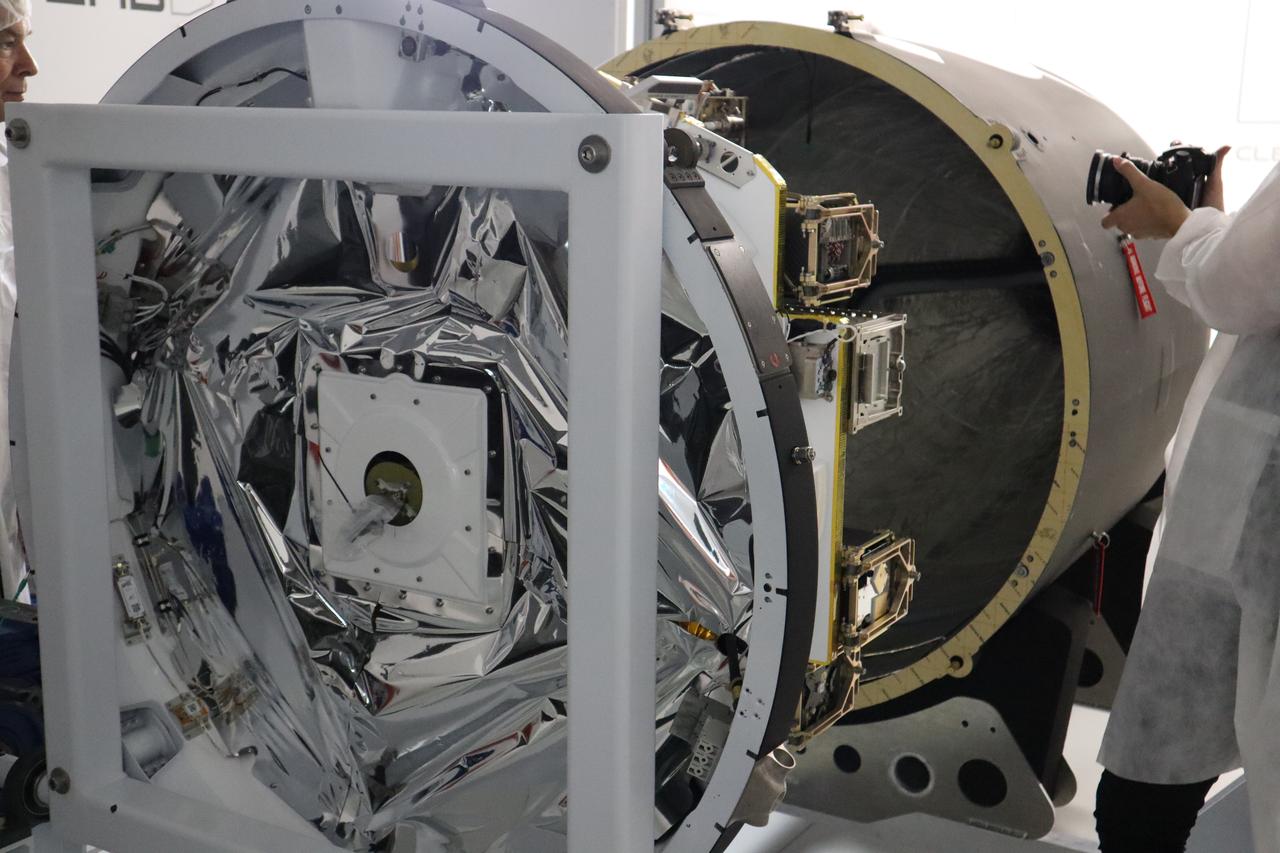
The Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 19 (ELaNa 19) payload is encapsulated inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Dec. 1, 2018, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The ELaNa 19 payload comprises 10 CubeSats selected through NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative. The liftoff marks the debut of the agency’s innovative Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS) effort. Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to offer small payloads dedicated rides to space.
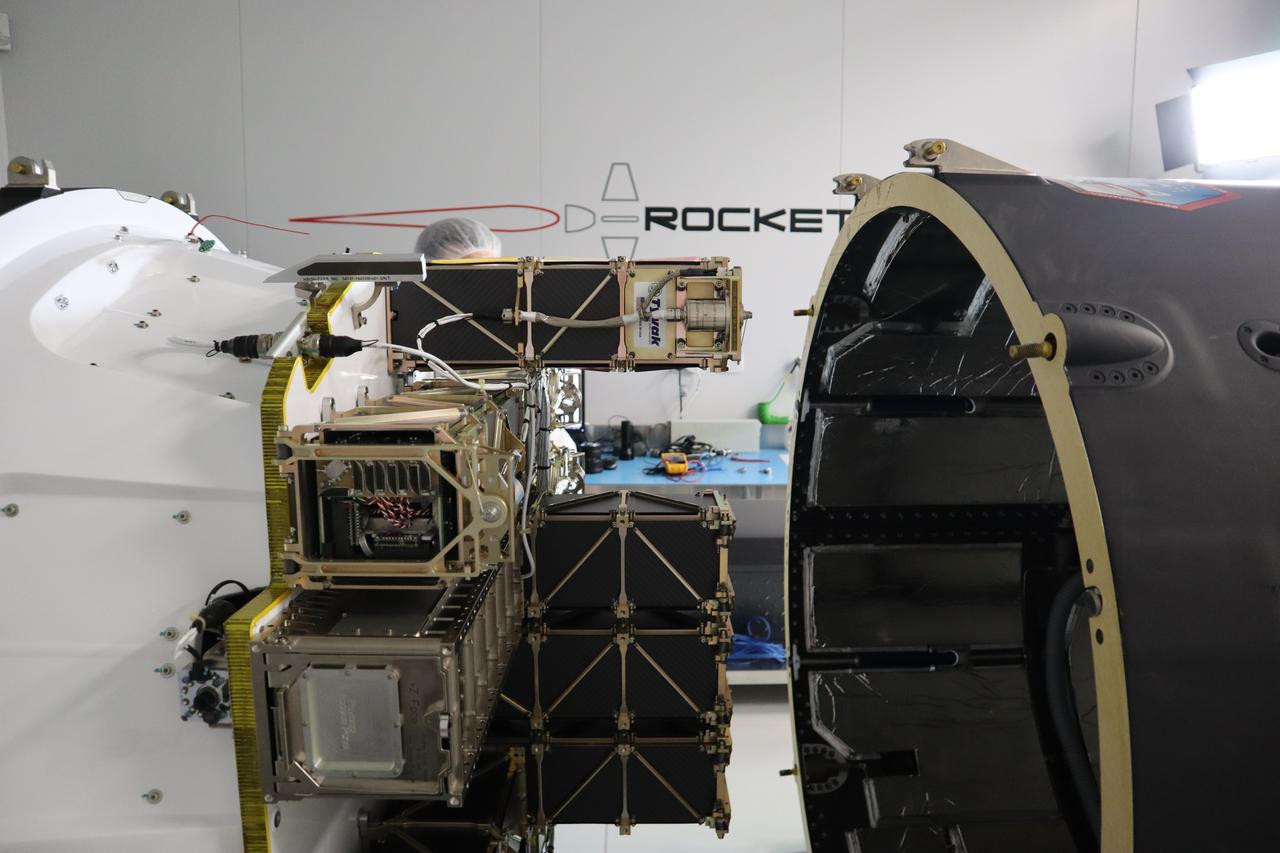

The Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 19 (ELaNa 19) payload is encapsulated inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Dec. 1, 2018, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The ELaNa 19 payload comprises 10 CubeSats selected through NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative. The liftoff marks the debut of the agency’s innovative Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS) effort. Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to offer small payloads dedicated rides to space.
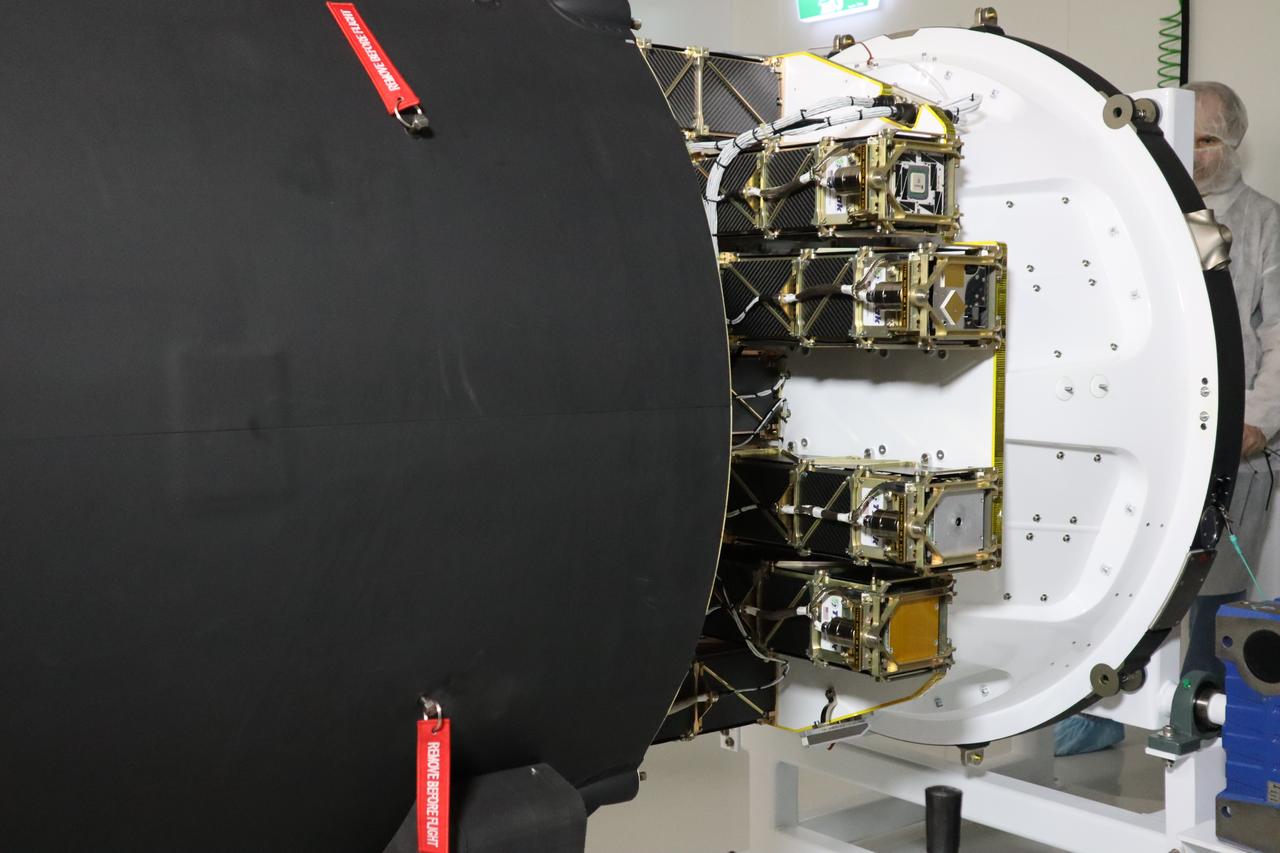

The Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 19 (ELaNa 19) payload is encapsulated inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Dec. 1, 2018, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The ELaNa 19 payload comprises 10 CubeSats selected through NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative. The liftoff marks the debut of the agency’s innovative Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS) effort. Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to offer small payloads dedicated rides to space.
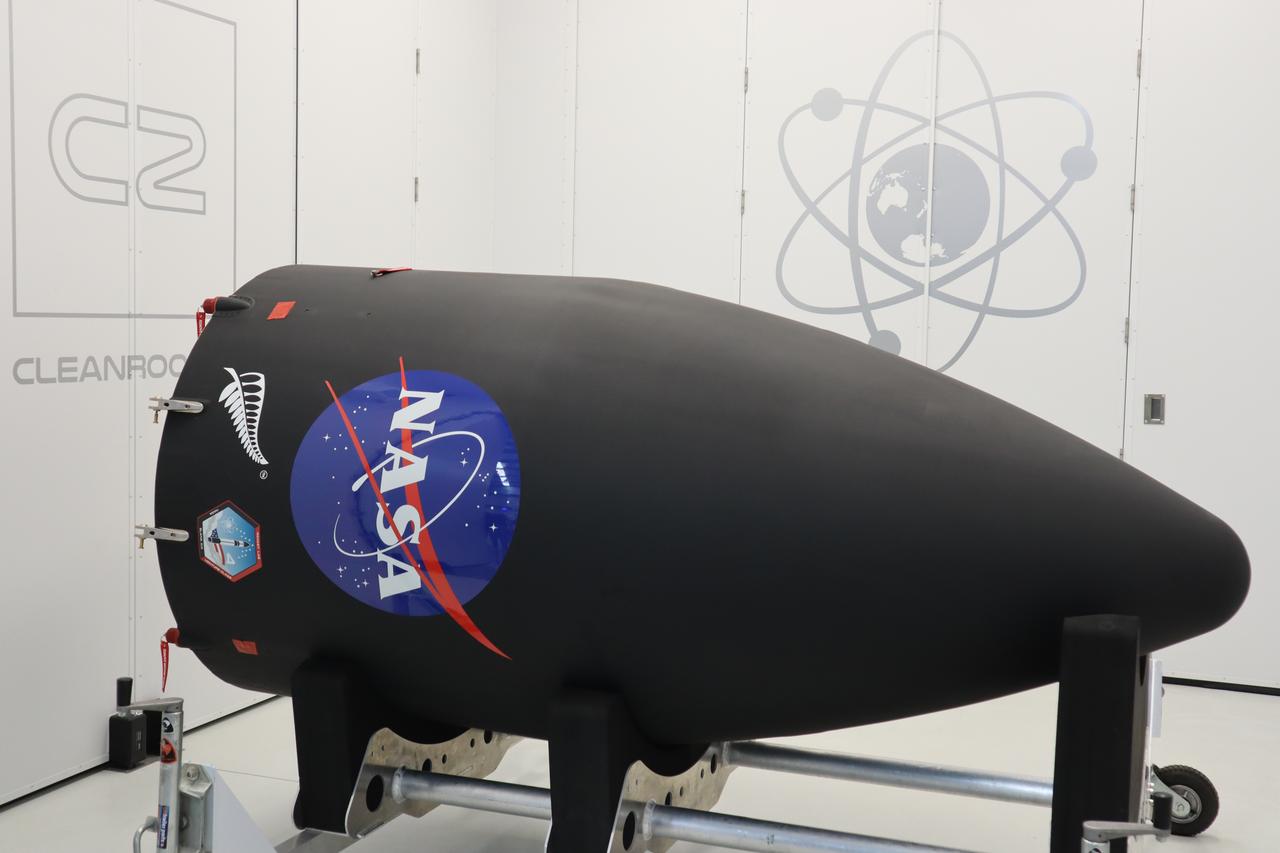
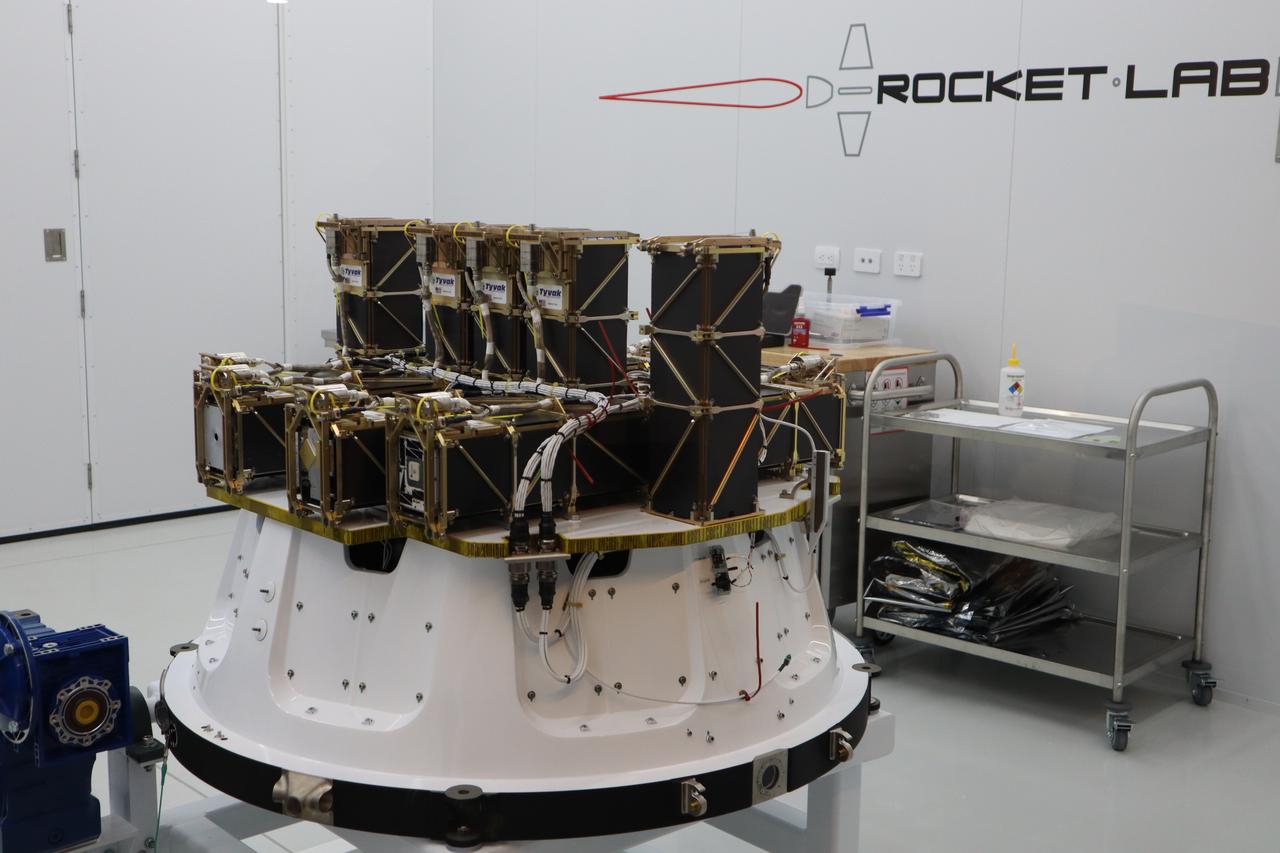
The Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing is prepared for the encapsulation of the Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 19 (ELaNa 19) payload on Dec. 1, 2018, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The ELaNa 19 payload comprises 10 CubeSats selected through NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative. The liftoff marks the debut of the agency’s innovative Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS) effort. Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to offer small payloads dedicated rides to space.
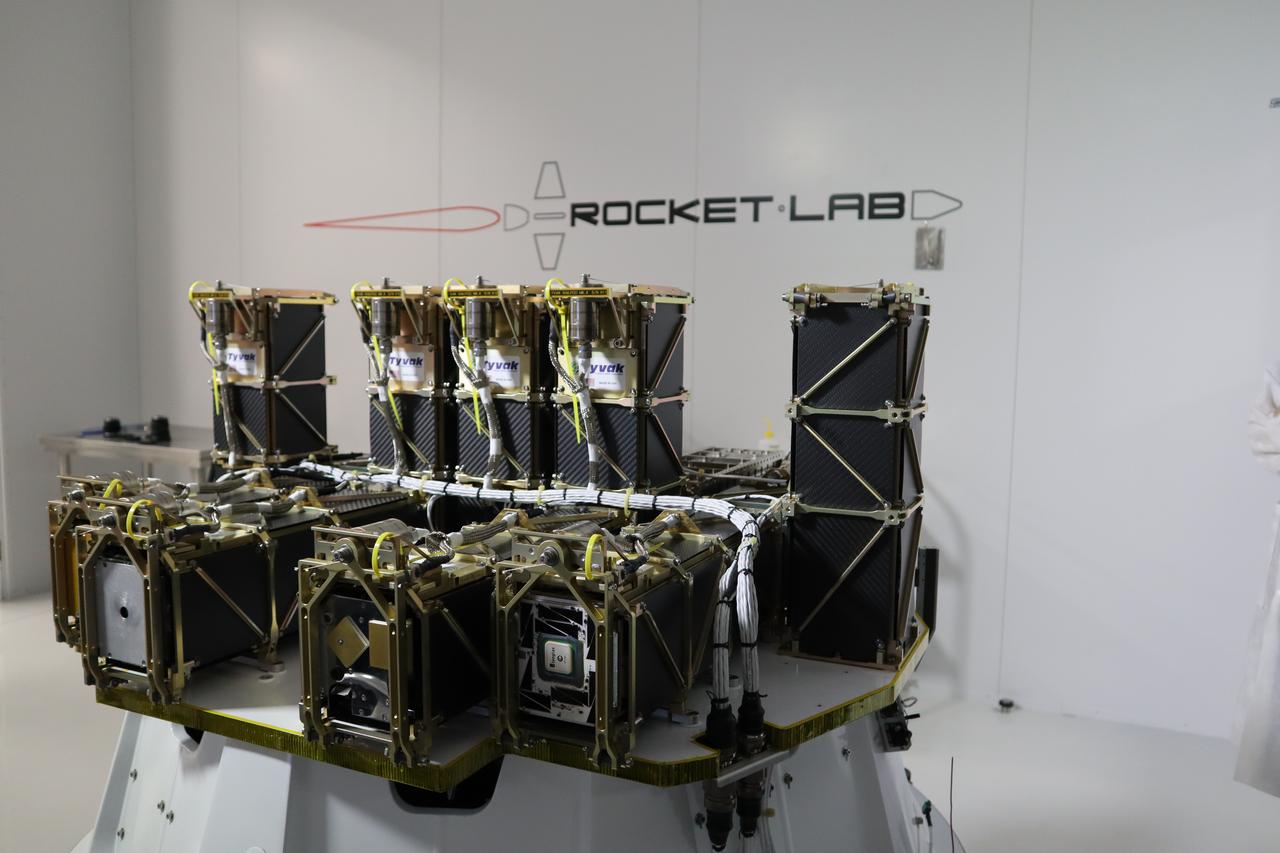

The Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 19 (ELaNa 19) payload has been encapsulated inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Dec. 1, 2018, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The ELaNa 19 payload comprises 10 CubeSats selected through NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative. The liftoff marks the debut of the agency’s innovative Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS) effort. Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to offer small payloads dedicated rides to space.
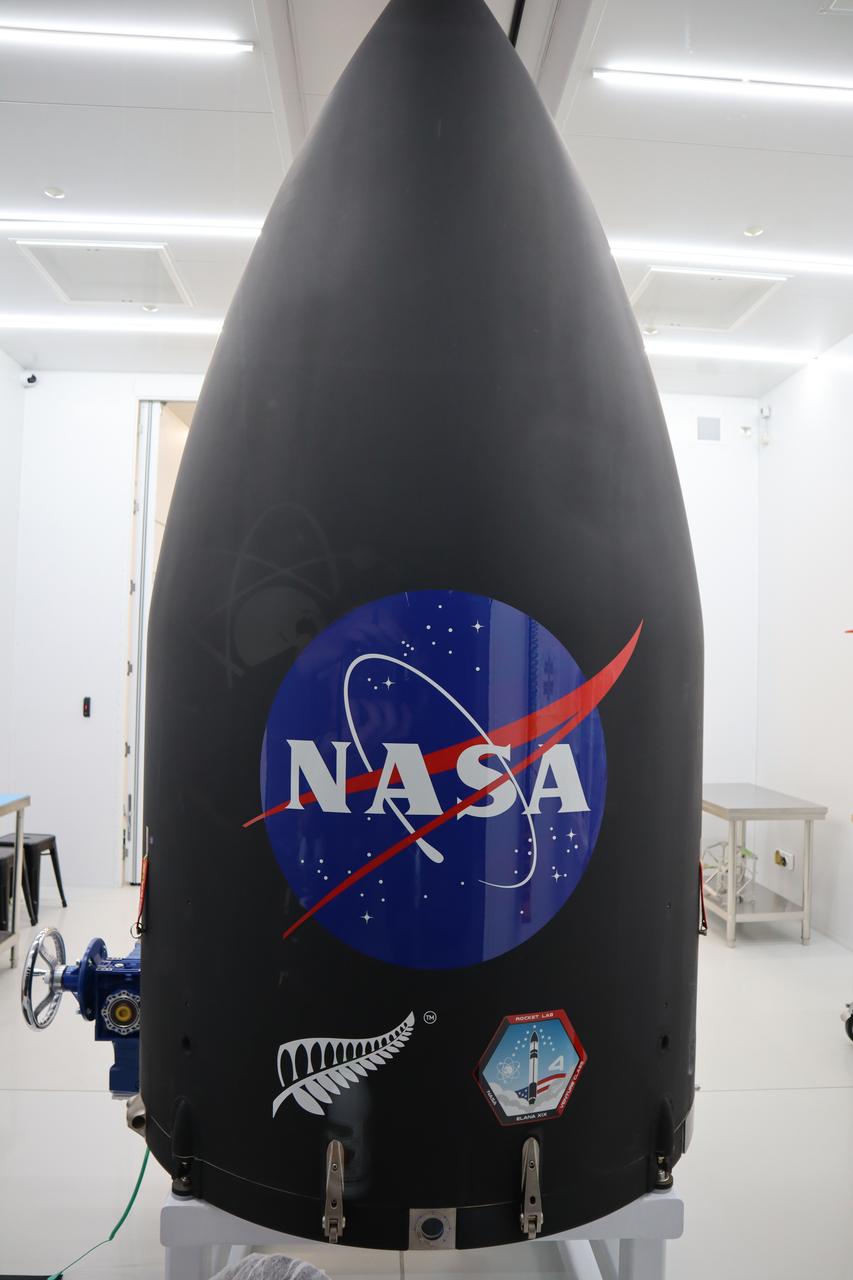

The Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 19 (ELaNa 19) payload has been encapsulated inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Dec. 1, 2018, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The ELaNa 19 payload comprises 10 CubeSats selected through NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative. The liftoff marks the debut of the agency’s innovative Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS) effort. Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to offer small payloads dedicated rides to space.

The Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 19 (ELaNa 19) payload is encapsulated inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Dec. 1, 2018, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The ELaNa 19 payload comprises 10 CubeSats selected through NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative. The liftoff marks the debut of the agency’s innovative Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS) effort. Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to offer small payloads dedicated rides to space.

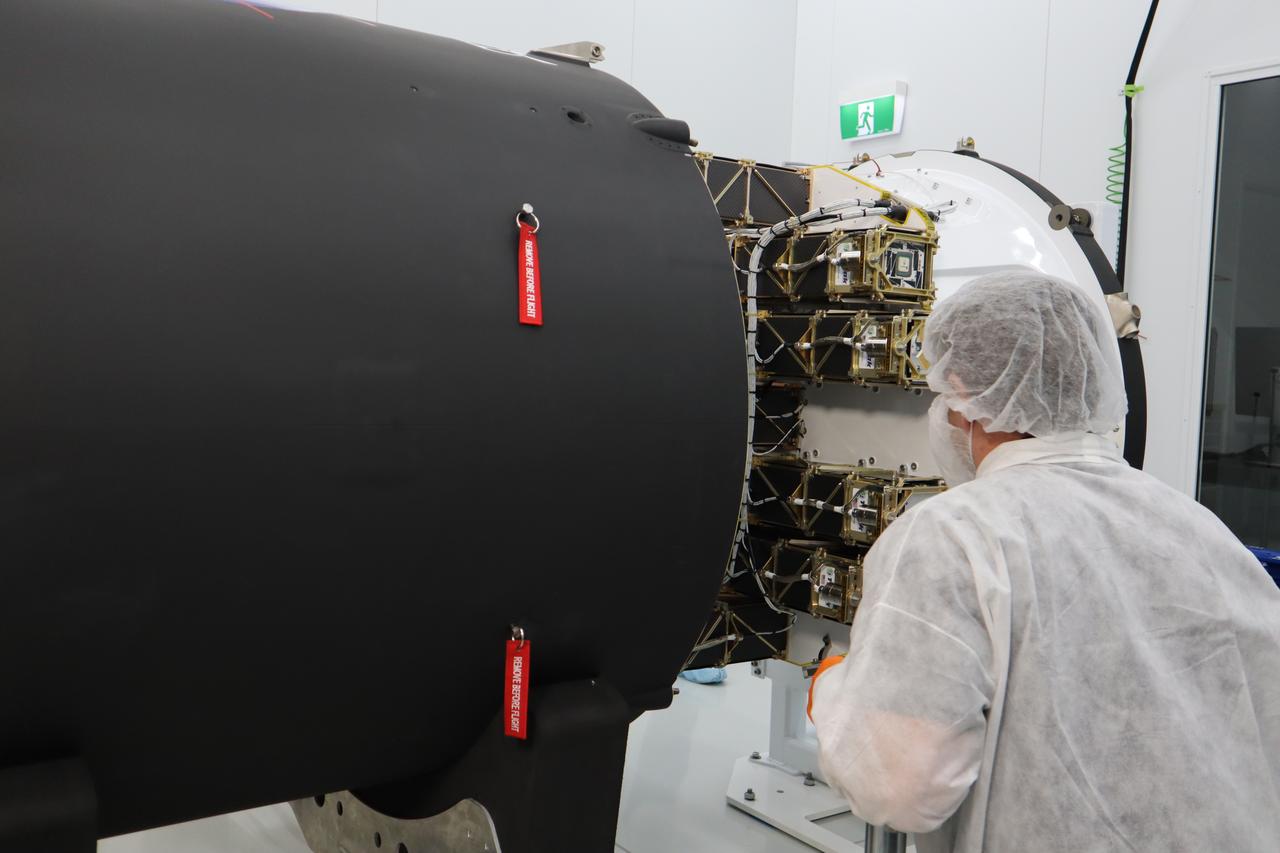
The Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 19 (ELaNa 19) payload is prepared to be encapsulated inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Dec. 1, 2018, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The ELaNa 19 payload comprises 10 CubeSats selected through NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative. The liftoff marks the debut of the agency’s innovative Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS) effort. Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to offer small payloads dedicated rides to space.

The Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 19 (ELaNa 19) payload is prepared to be encapsulated inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Dec. 1, 2018, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The ELaNa 19 payload comprises 10 CubeSats selected through NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative. The liftoff marks the debut of the agency’s innovative Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS) effort. Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to offer small payloads dedicated rides to space.

The Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 19 (ELaNa 19) payload is encapsulated inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Dec. 1, 2018, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The ELaNa 19 payload comprises 10 CubeSats selected through NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative. The liftoff marks the debut of the agency’s innovative Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS) effort. Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to offer small payloads dedicated rides to space.

The Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 19 (ELaNa 19) payload is prepared to be encapsulated inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Dec. 1, 2018, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The ELaNa 19 payload comprises 10 CubeSats selected through NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative. The liftoff marks the debut of the agency’s innovative Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS) effort. Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to offer small payloads dedicated rides to space.
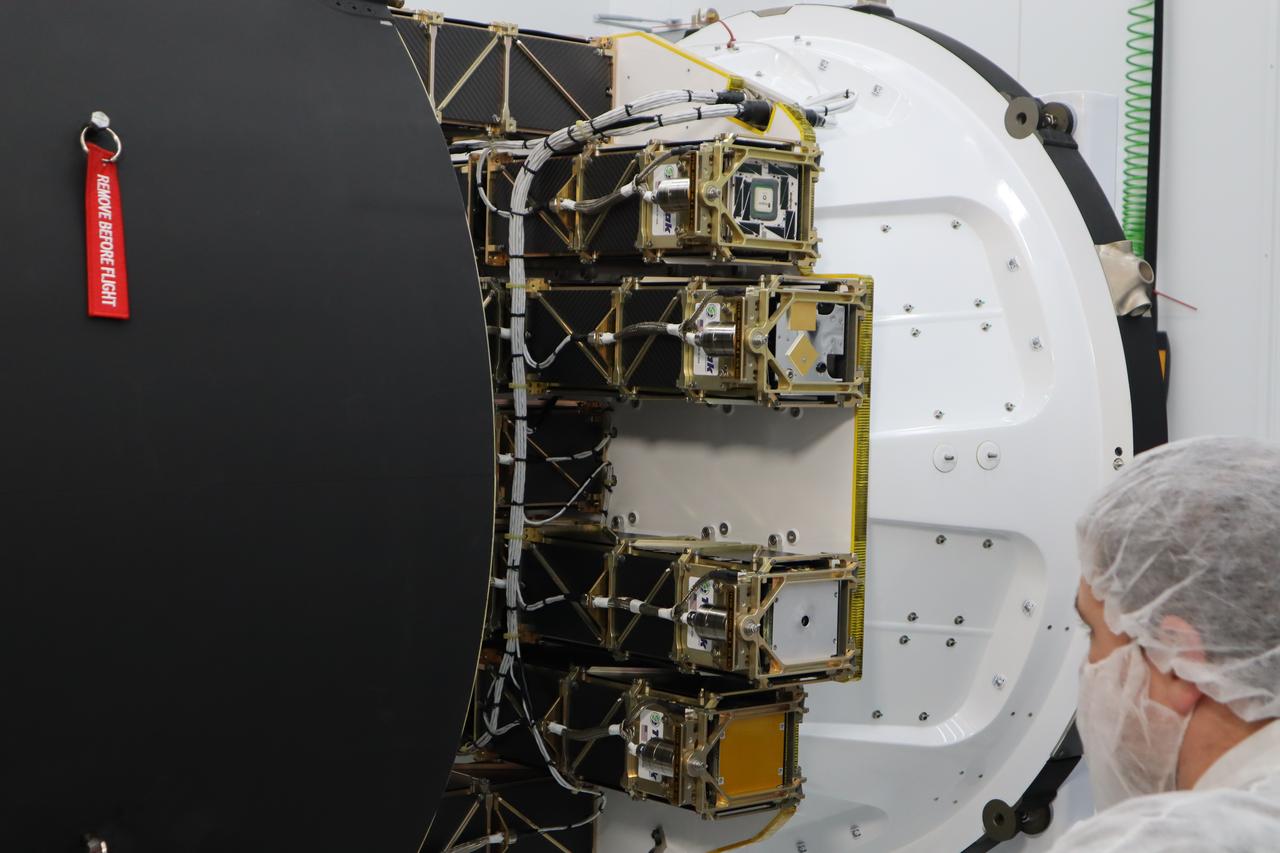
The Educational Launch of Nanosatellites 19 (ELaNa 19) payload is encapsulated inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Dec. 1, 2018, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The ELaNa 19 payload comprises 10 CubeSats selected through NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative. The liftoff marks the debut of the agency’s innovative Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS) effort. Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to offer small payloads dedicated rides to space.
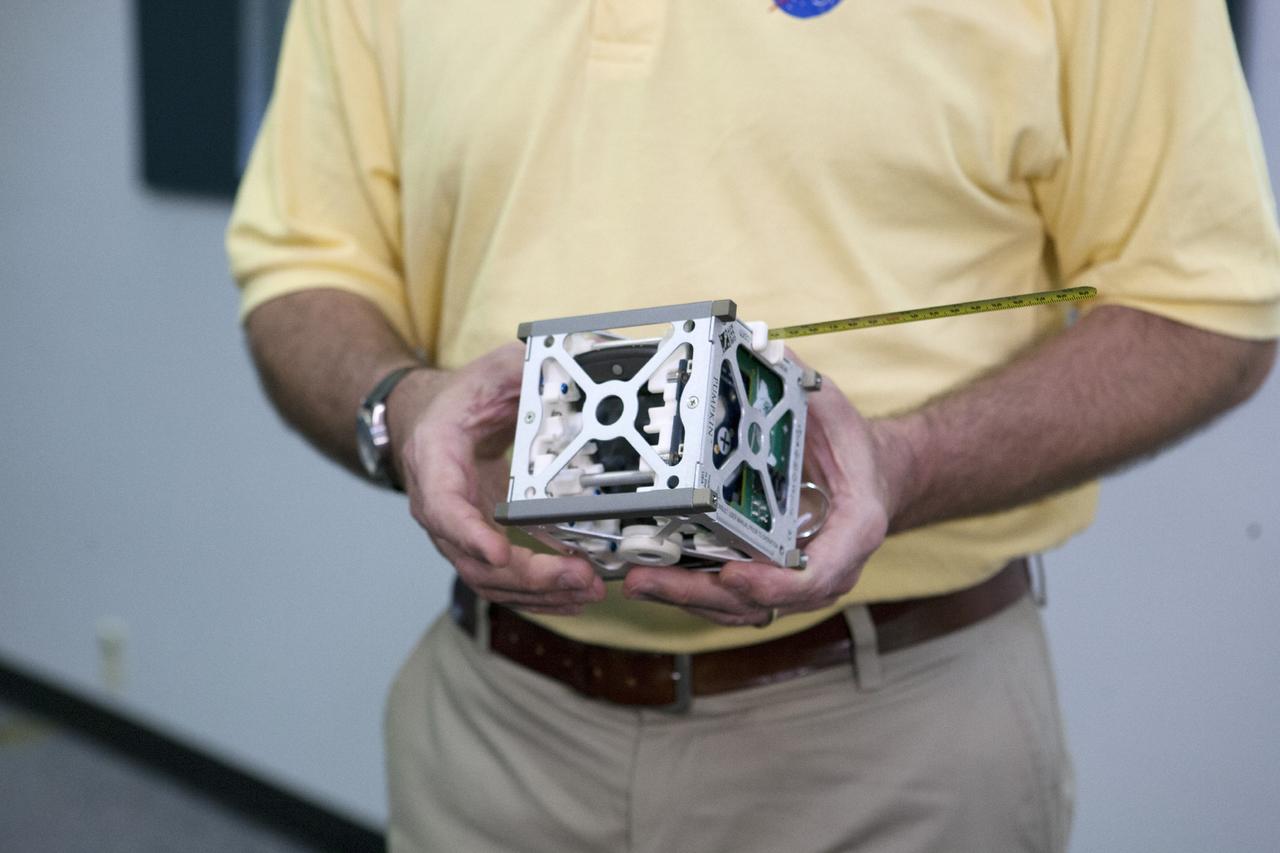
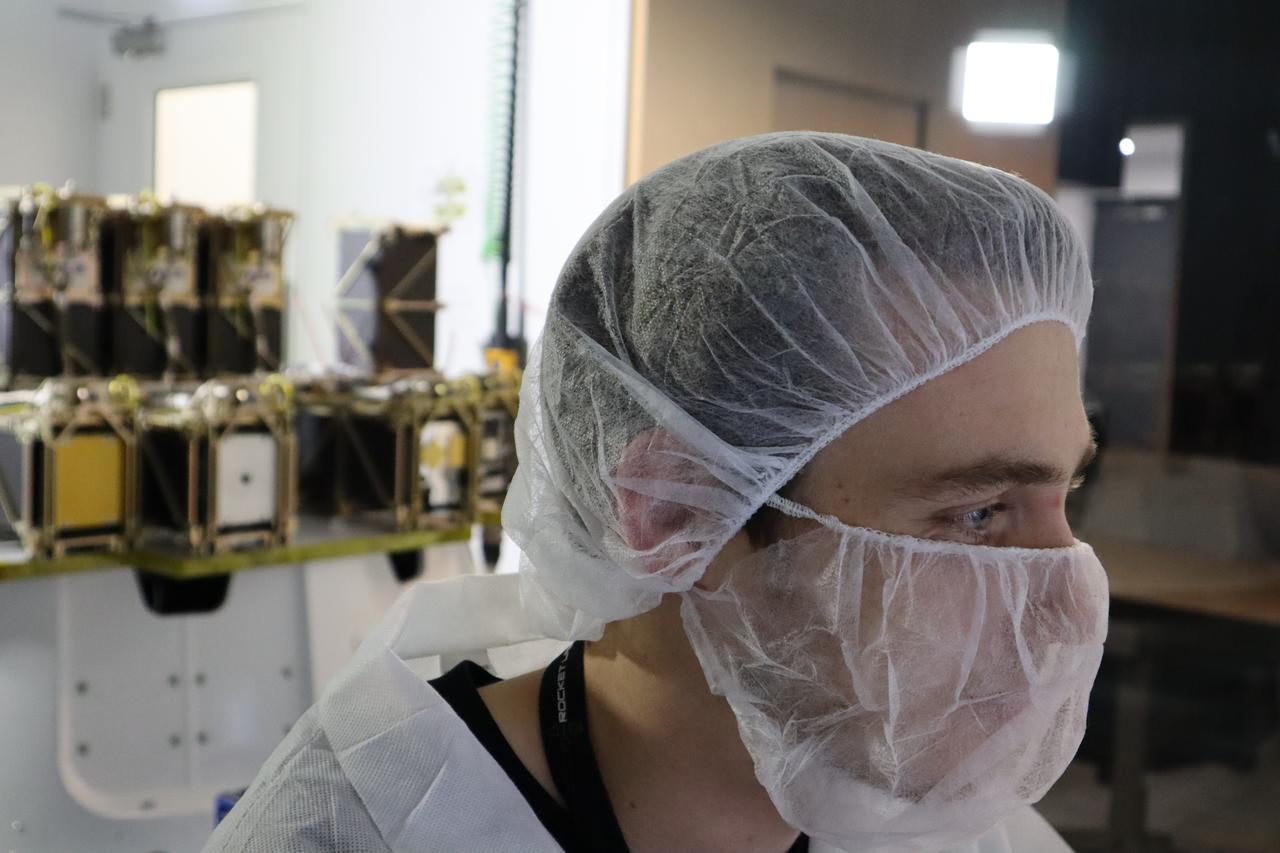
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the News Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Andrew Petro, the agency's acting director of the Early Stage Innovation Division of the Office of the Chief Technologist, discusses the agency’s CubeSat Launch initiative. CubeSats provide opportunities for small satellite payloads to fly on rockets planned for upcoming launches. CubeSats, a class of research spacecraft called nanosatellites, are flown as auxiliary payloads on previously planned missions. The cube-shaped satellites are approximately four inches long, have a volume of about one quart and weigh about three pounds. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/directorates/heo/home/CubeSats_initiative.html Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
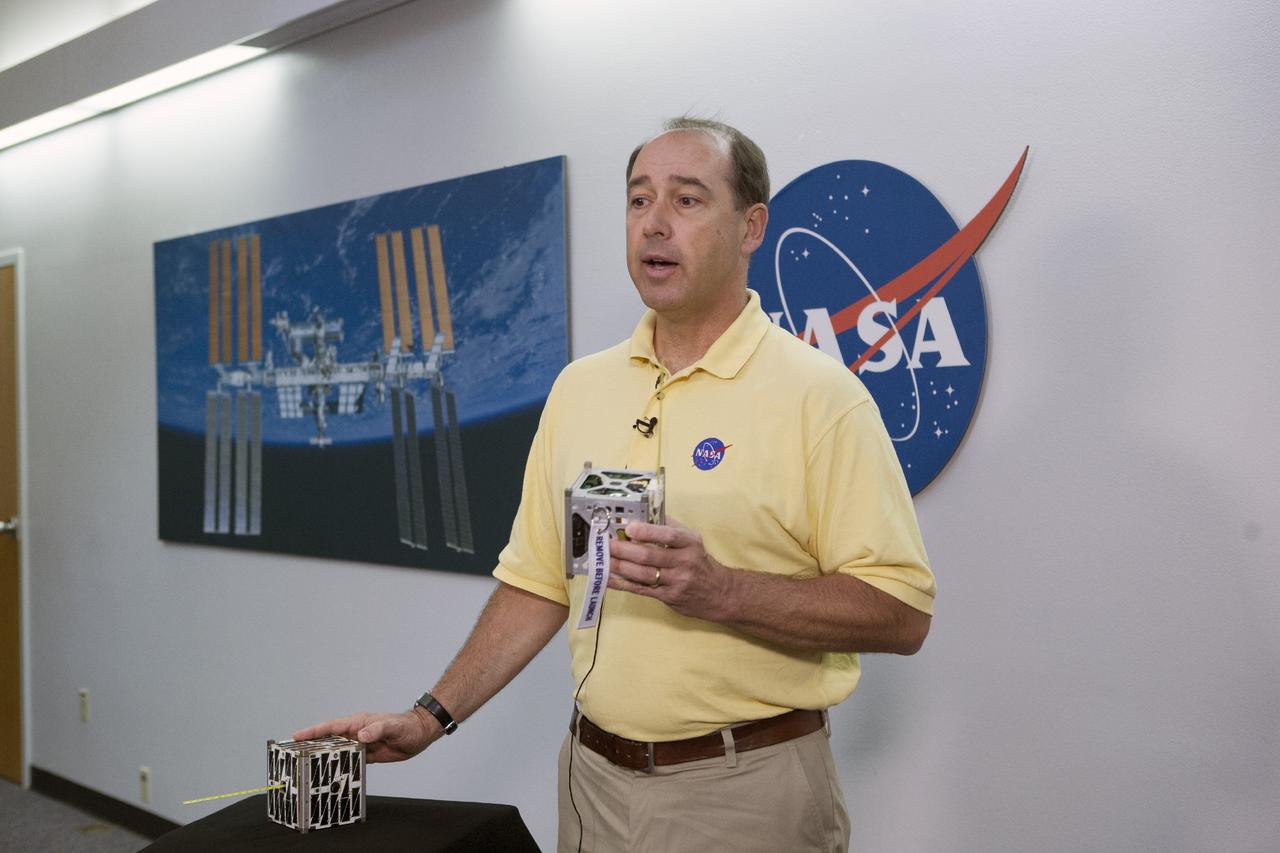

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the News Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Andrew Petro, the agency's acting director of the Early Stage Innovation Division of the Office of the Chief Technologist, discusses the agency’s CubeSat Launch initiative. CubeSats provide opportunities for small satellite payloads to fly on rockets planned for upcoming launches. CubeSats, a class of research spacecraft called nanosatellites, are flown as auxiliary payloads on previously planned missions. The cube-shaped satellites are approximately four inches long, have a volume of about one quart and weigh about three pounds. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/directorates/heo/home/CubeSats_initiative.html Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
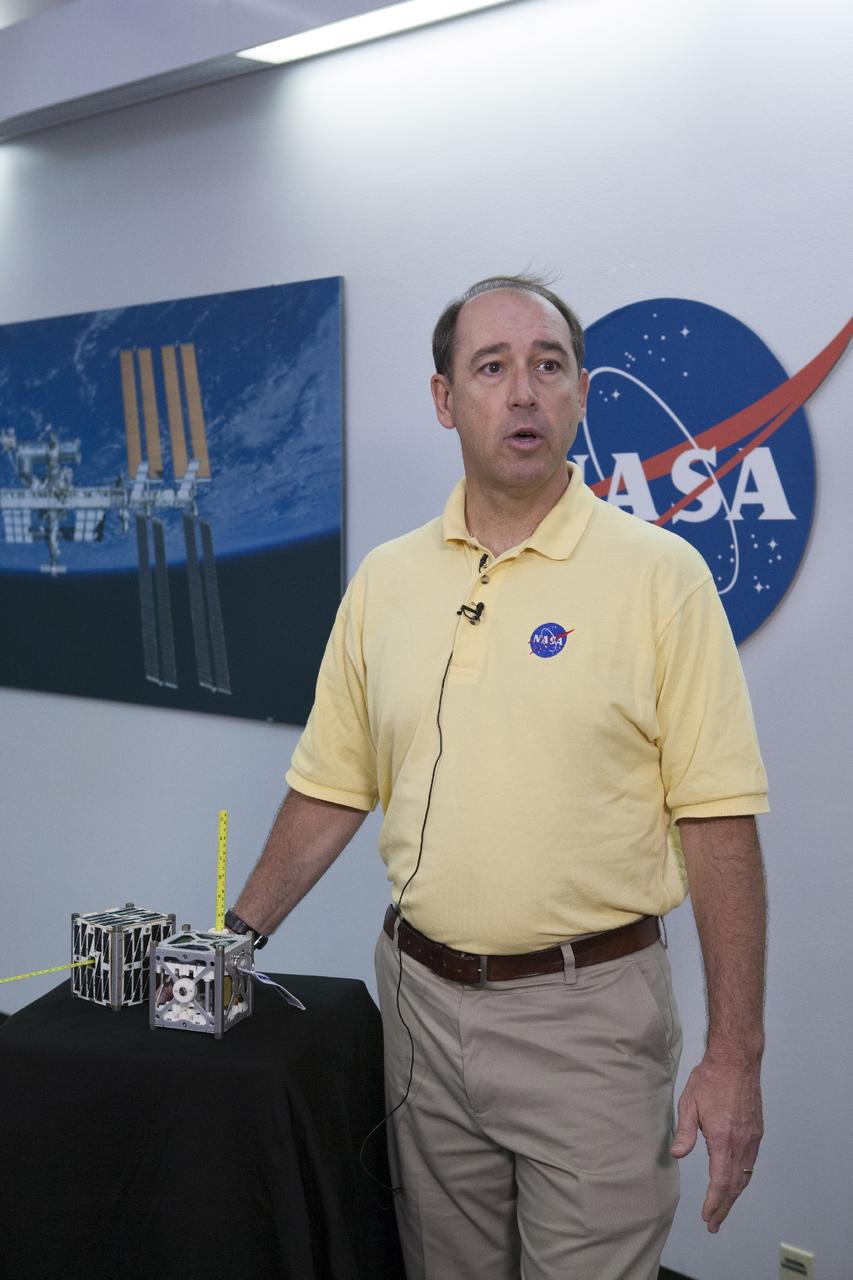

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the News Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Andrew Petro, the agency's acting director of the Early Stage Innovation Division of the Office of the Chief Technologist, discusses the agency’s CubeSat Launch initiative. CubeSats provide opportunities for small satellite payloads to fly on rockets planned for upcoming launches. CubeSats, a class of research spacecraft called nanosatellites, are flown as auxiliary payloads on previously planned missions. The cube-shaped satellites are approximately four inches long, have a volume of about one quart and weigh about three pounds. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/directorates/heo/home/CubeSats_initiative.html Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
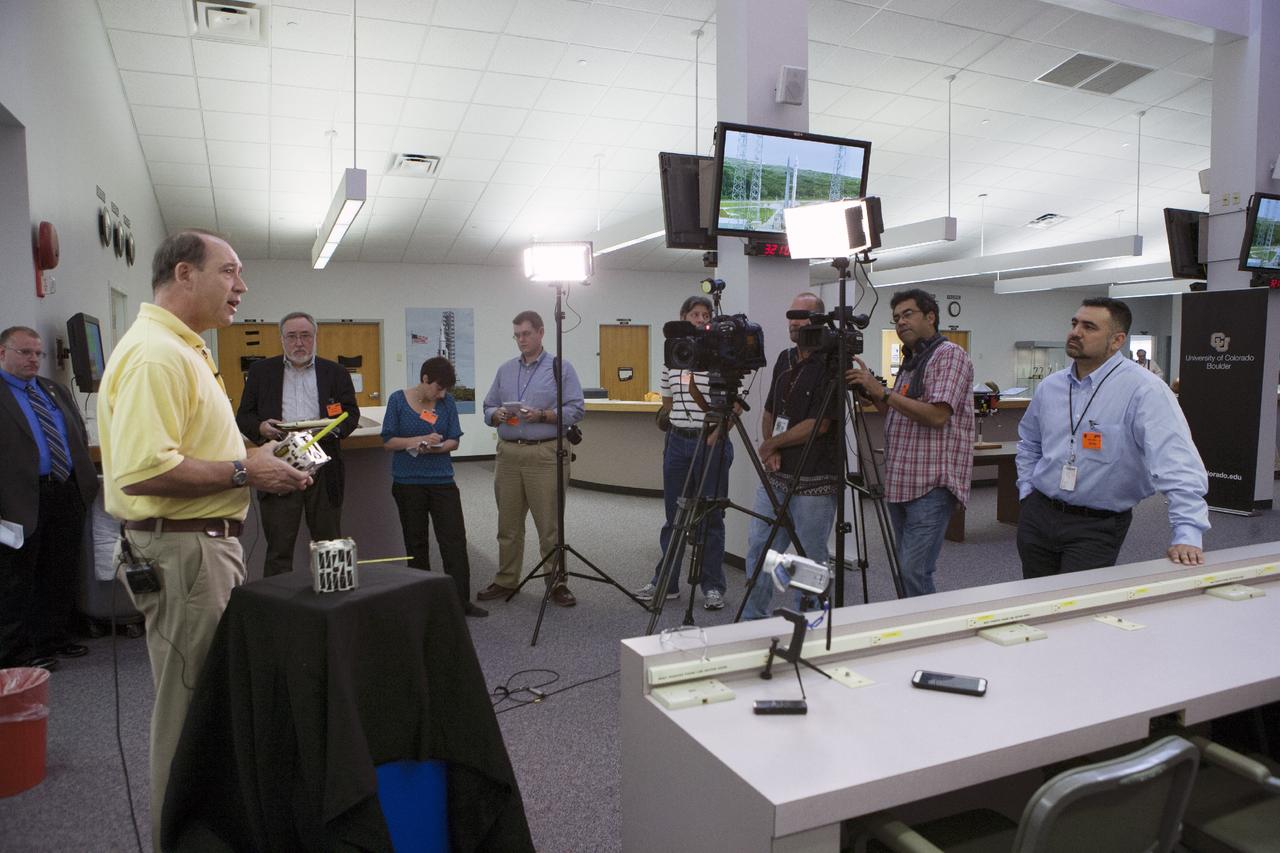

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the News Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Andrew Petro, the agency's acting director of the Early Stage Innovation Division of the Office of the Chief Technologist, discusses the agency’s CubeSat Launch initiative. CubeSats provide opportunities for small satellite payloads to fly on rockets planned for upcoming launches. CubeSats, a class of research spacecraft called nanosatellites, are flown as auxiliary payloads on previously planned missions. The cube-shaped satellites are approximately four inches long, have a volume of about one quart and weigh about three pounds. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/directorates/heo/home/CubeSats_initiative.html Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
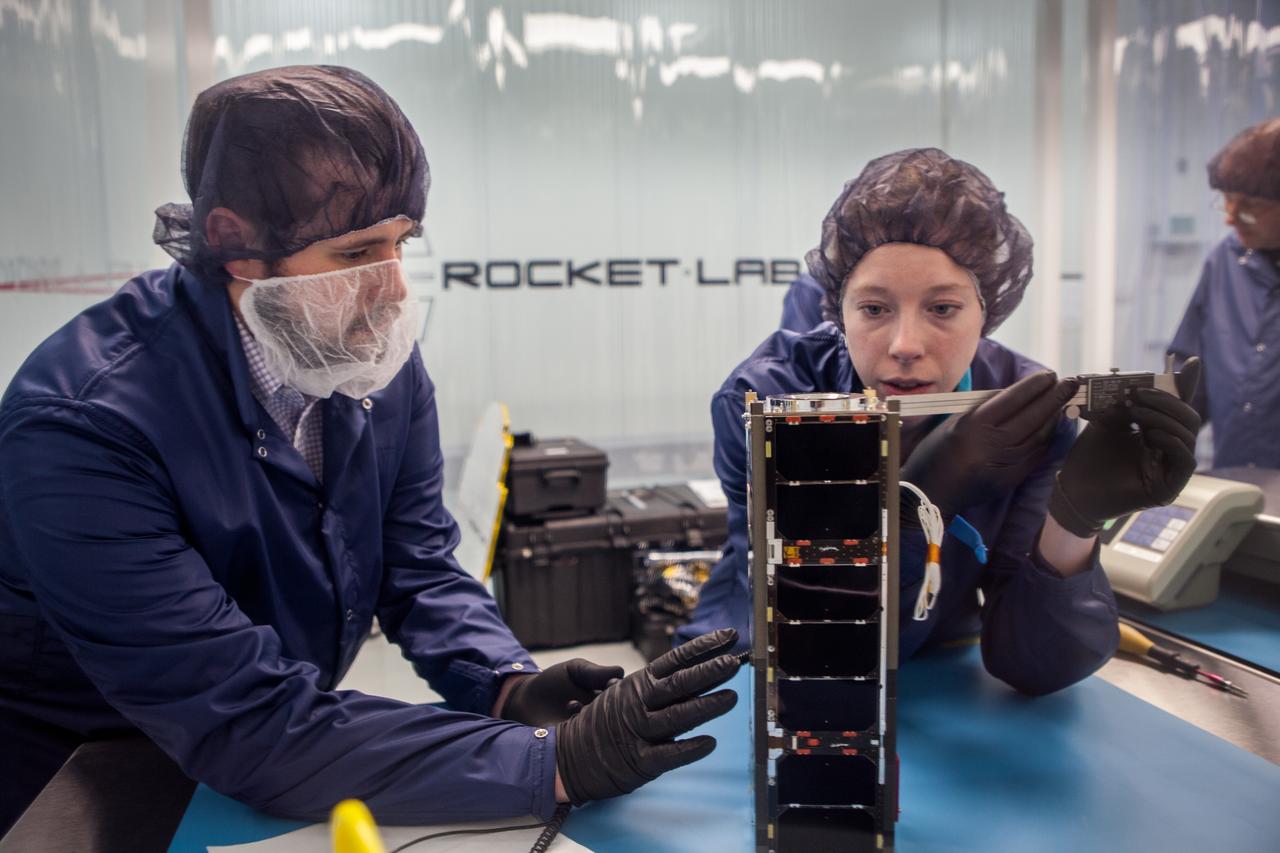

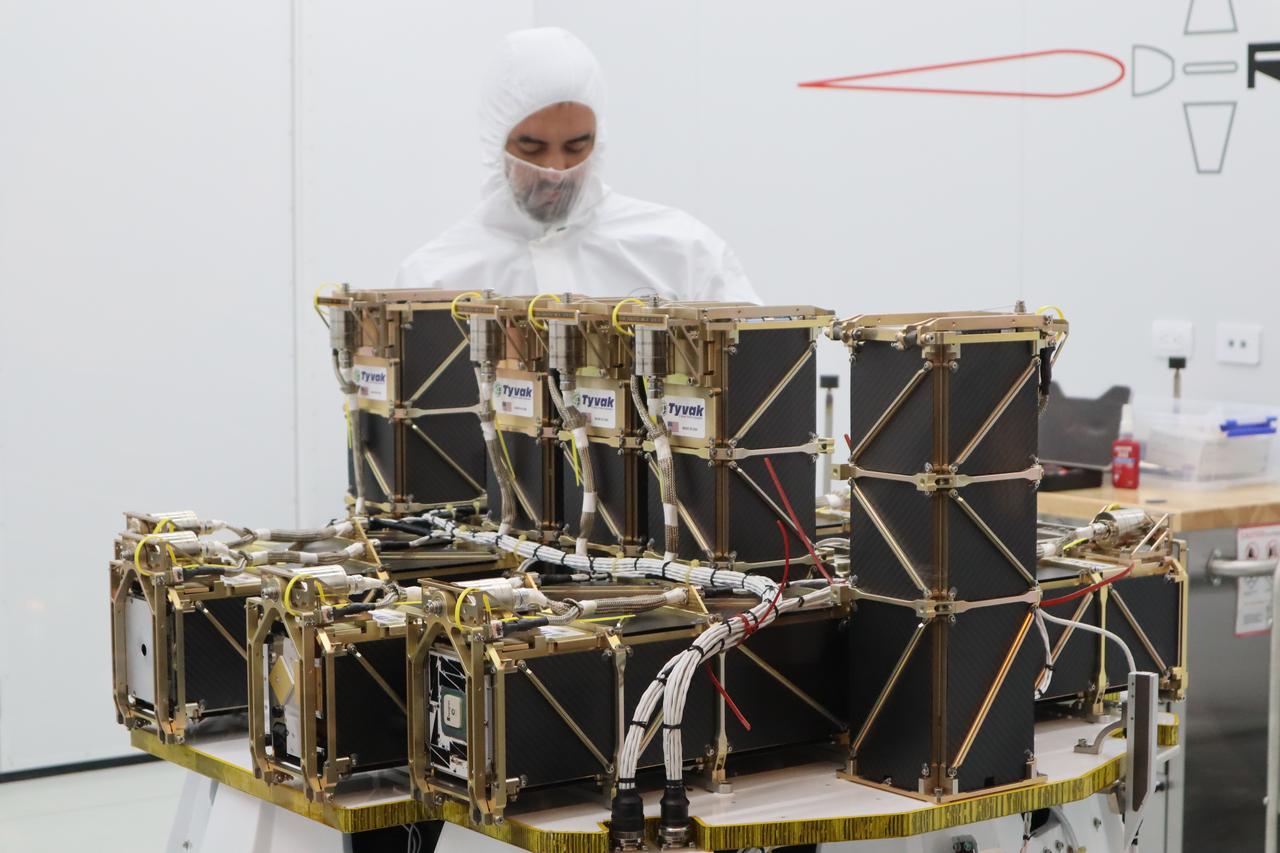
A host of CubeSats, or small satellites, are undergoing the final stages of processing at Rocket Lab USA’s facility in Huntington Beach, California, for NASA’s first mission dedicated solely to spacecraft of their size. This will be the first launch under the agency’s new Venture Class Launch Services. Scientists, including those from NASA and various universities, began arriving at the facility in early April with spacecraft small enough to be a carry-on to be prepared for launch. A team from NASA’s Goddard Spaceflight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, completed final checkouts of a CubeSat called the Compact Radiation Belt Explorer (CeREs), before placing the satellite into a dispenser to hold the spacecraft during launch inside the payload fairing. Among its missions, the satellite will examine the radiation belt and how electrons are energized and lost, particularly during events called microbursts — when sudden swarms of electrons stream into the atmosphere. This facility is the final stop for designers and builders of the CubeSats, but the journey will continue for the spacecraft. Rocket Lab will soon ship the satellites to New Zealand for launch aboard the company’s Electron orbital rocket on the Mahia Peninsula this summer. The CubeSats will be flown on an Educational Launch of Nanosatellites (ELaNa) mission to space through NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative. CeREs is one of the 10 ELaNa CubeSats scheduled to be a part of this mission.
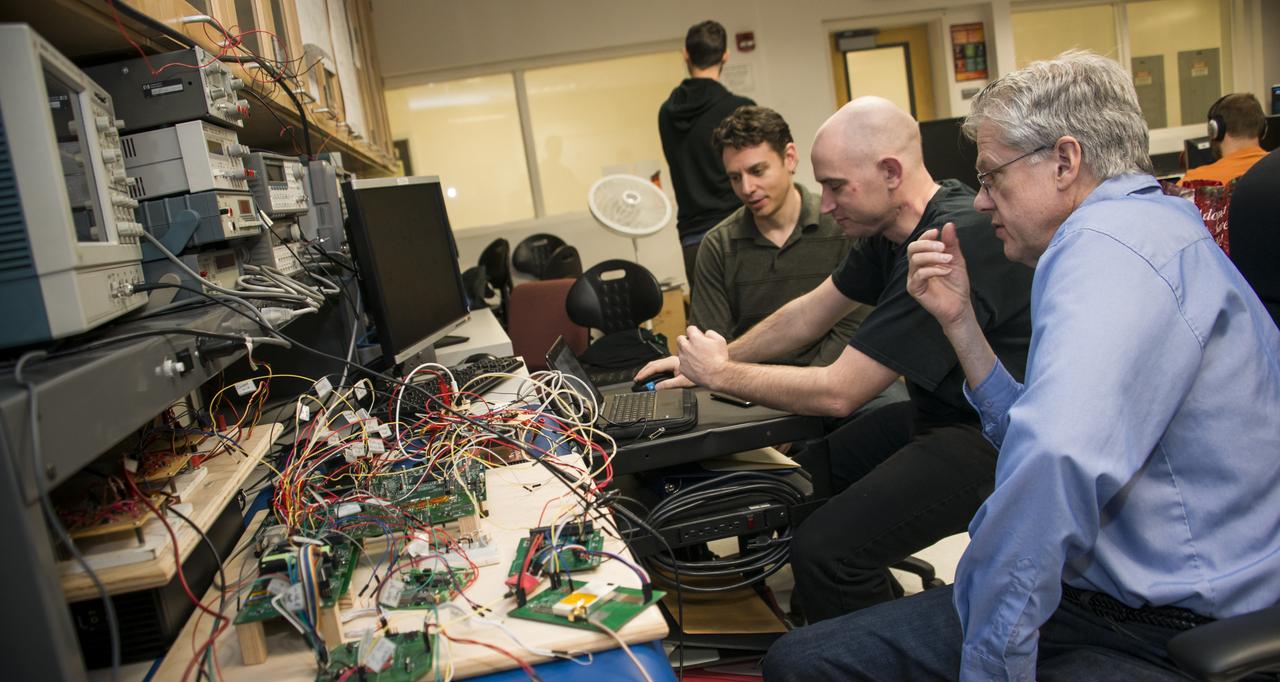

CSUNSat-1 Team (Adam Kaplan, James Flynn, Donald Eckels) working on their CubeSat at California State University Northridge. The primary mission of CSUNSat1 is to space test an innovative low temperature capable energy storage system developed by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, raising its TRL level to 7 from 4 to 5. The success of this energy storage system will enable future missions, especially those in deep space to do more science while requiring less energy, mass and volume. This CubeSat was designed, built, programmed, and tested by a team of over 70 engineering and computer science students at CSUN. The primary source of funding for CSUNSat1 comes from NASA’s Smallest Technology Partnership program. Launched by NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative NET April 18, 2017 ELaNa XVII mission on the seventh Orbital-ATK Cygnus Commercial Resupply Services (OA-7) to the International Space Station and deployed on tbd.
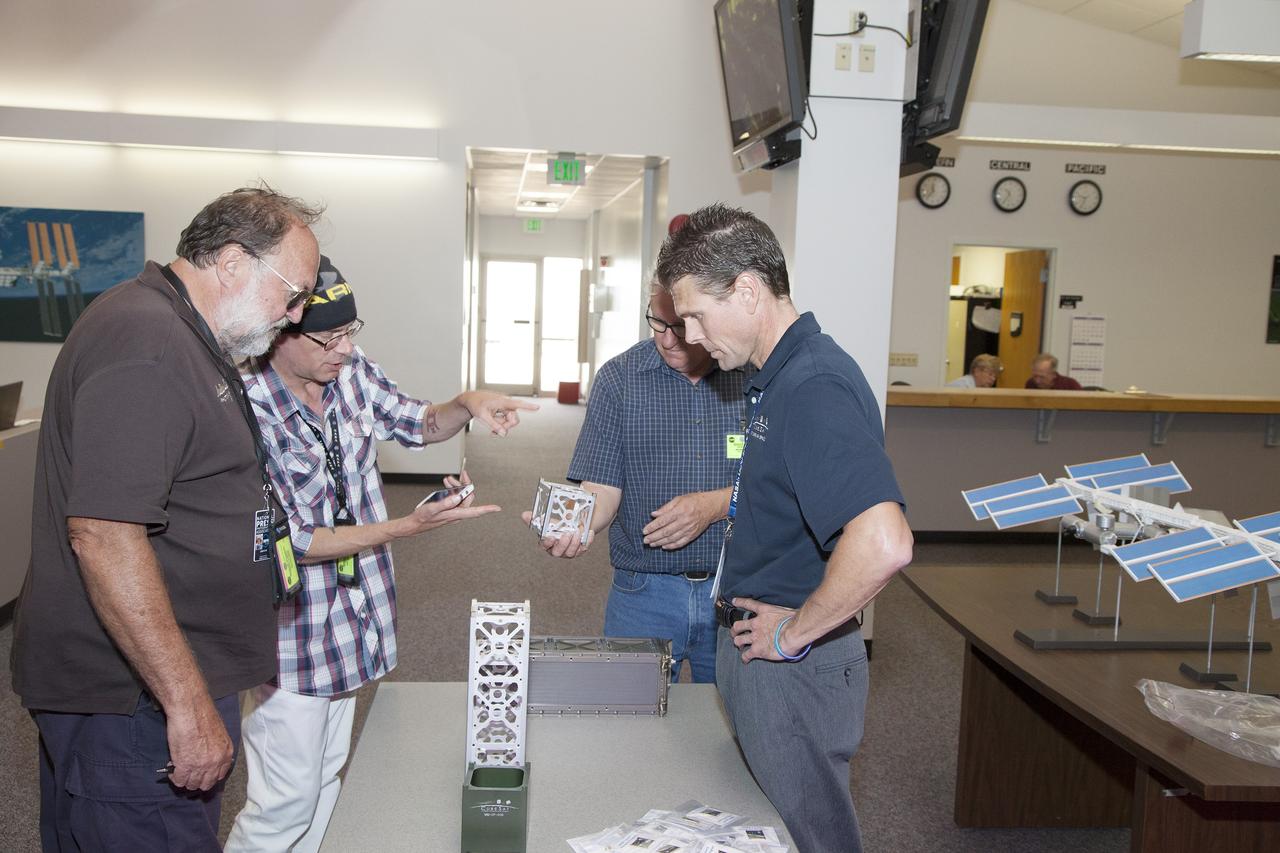

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Scott Higginbotham, right, mission manager for ELaNa V, discusses the concepts behind the design and deployment of the CubeSats flying on the ELaNa V mission with media representatives in the NASA Newsroom at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, using models of the Poly-Picosatellite Orbital Deployer, or P-POD, and various CubeSat canisters. NASA selected five small research satellites, or CubeSats, for the ELaNa V mission launching on SpaceX-3. Four P-PODs aboard the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket will ferry them to space. The CubeSats were designed by three universities and the agency's Ames Research Center in California. Launch is scheduled at about 4:58 p.m. EDT April 14. The SpaceX-3 mission, carrying almost 2.5 tons of supplies, technology and science experiments, is the third of 12 flights under NASA's Commercial Resupply Services contract to resupply the orbiting laboratory. For more information about NASA's CubeSat Launch Initiative, visit http://go.nasa.gov/CubeSat_initiative. Photo credit: NASA/Glenn Benson
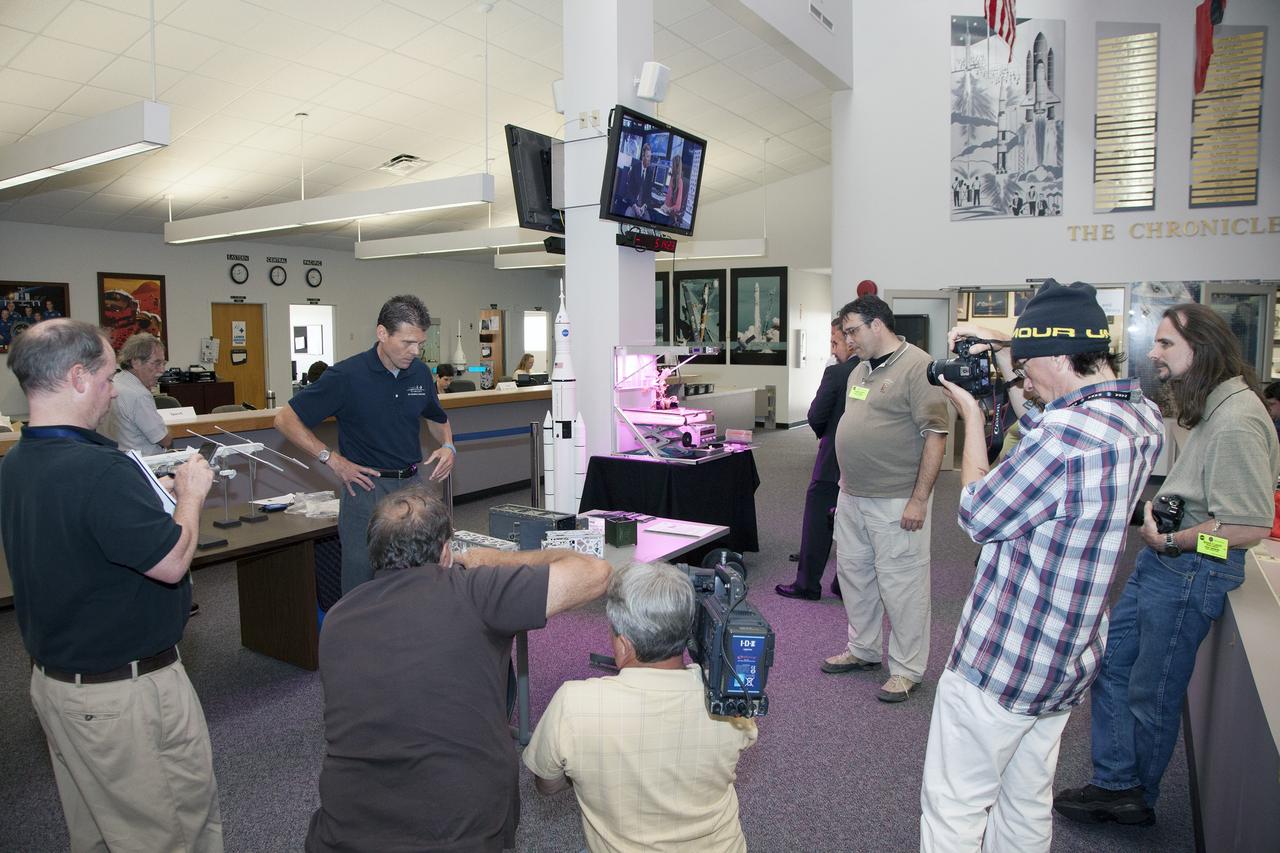

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Scott Higginbotham, center, mission manager for ELaNa V, discusses the concepts behind the design and deployment of the CubeSats flying on the ELaNa V mission with media representatives in the NASA Newsroom at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, using models of the Poly-Picosatellite Orbital Deployer, or P-POD, and various CubeSat canisters. NASA selected five small research satellites, or CubeSats, for the ELaNa V mission launching on SpaceX-3. Four P-PODs aboard the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket will ferry them to space. The CubeSats were designed by three universities and the agency's Ames Research Center in California. Launch is scheduled at about 4:58 p.m. EDT April 14. The SpaceX-3 mission, carrying almost 2.5 tons of supplies, technology and science experiments, is the third of 12 flights under NASA's Commercial Resupply Services contract to resupply the orbiting laboratory. For more information about NASA's CubeSat Launch Initiative, visit http://go.nasa.gov/CubeSat_initiative. Photo credit: NASA/Glenn Benson
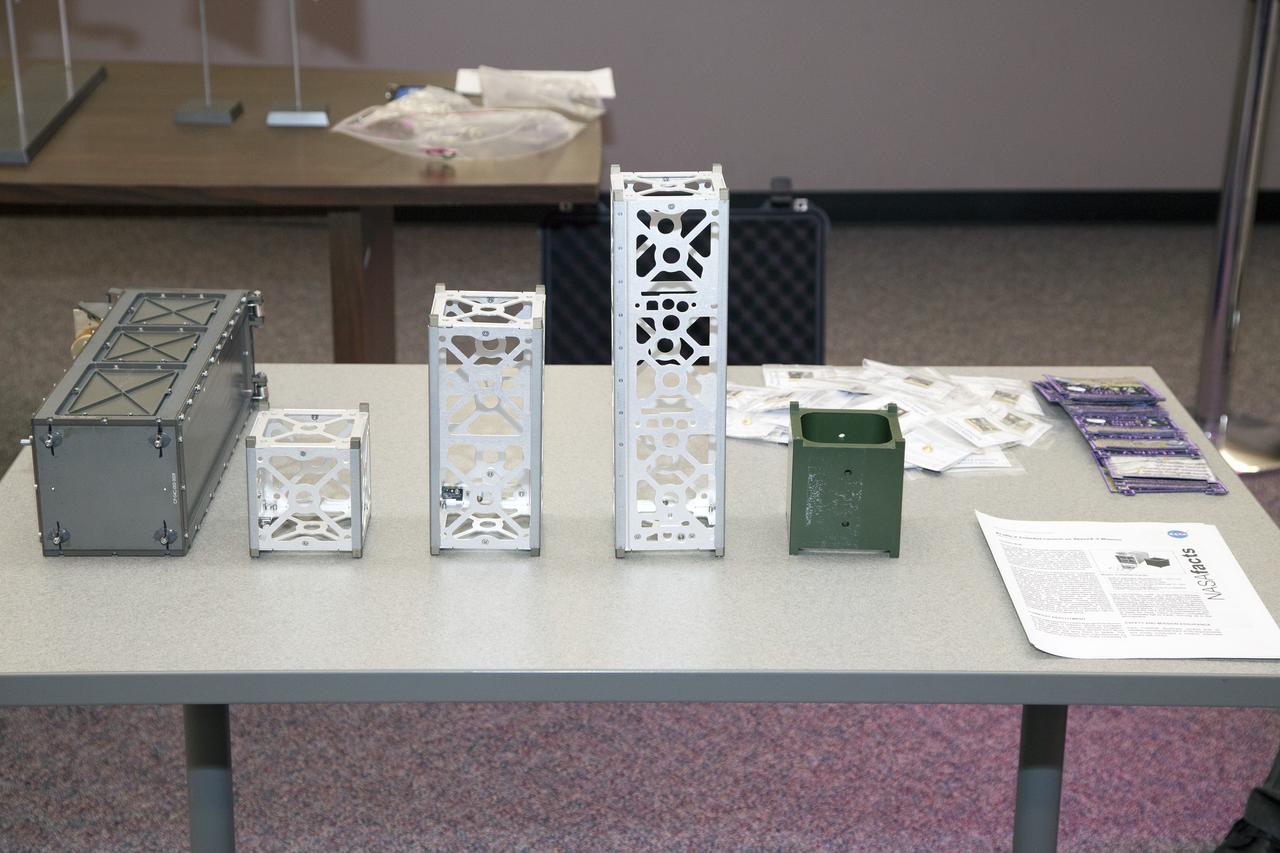

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Models of the hardware used to support the CubeSats flying on the ELaNa V mission are displayed in the NASA Newsroom at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. At left is a model of the Poly-Picosatellite Orbital Deployer, or P-POD, next to models of the various CubeSat canisters. NASA selected five small research satellites, or CubeSats, for the ELaNa V mission launching on SpaceX-3. Four P-PODs aboard the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket will ferry them to space. The CubeSats were designed by three universities and the agency's Ames Research Center in California. Launch is scheduled at about 4:58 p.m. EDT April 14. The SpaceX-3 mission, carrying almost 2.5 tons of supplies, technology and science experiments, is the third of 12 flights under NASA's Commercial Resupply Services contract to resupply the orbiting laboratory. For more information about NASA's CubeSat Launch Initiative, visit http://go.nasa.gov/CubeSat_initiative. Photo credit: NASA/Glenn Benson
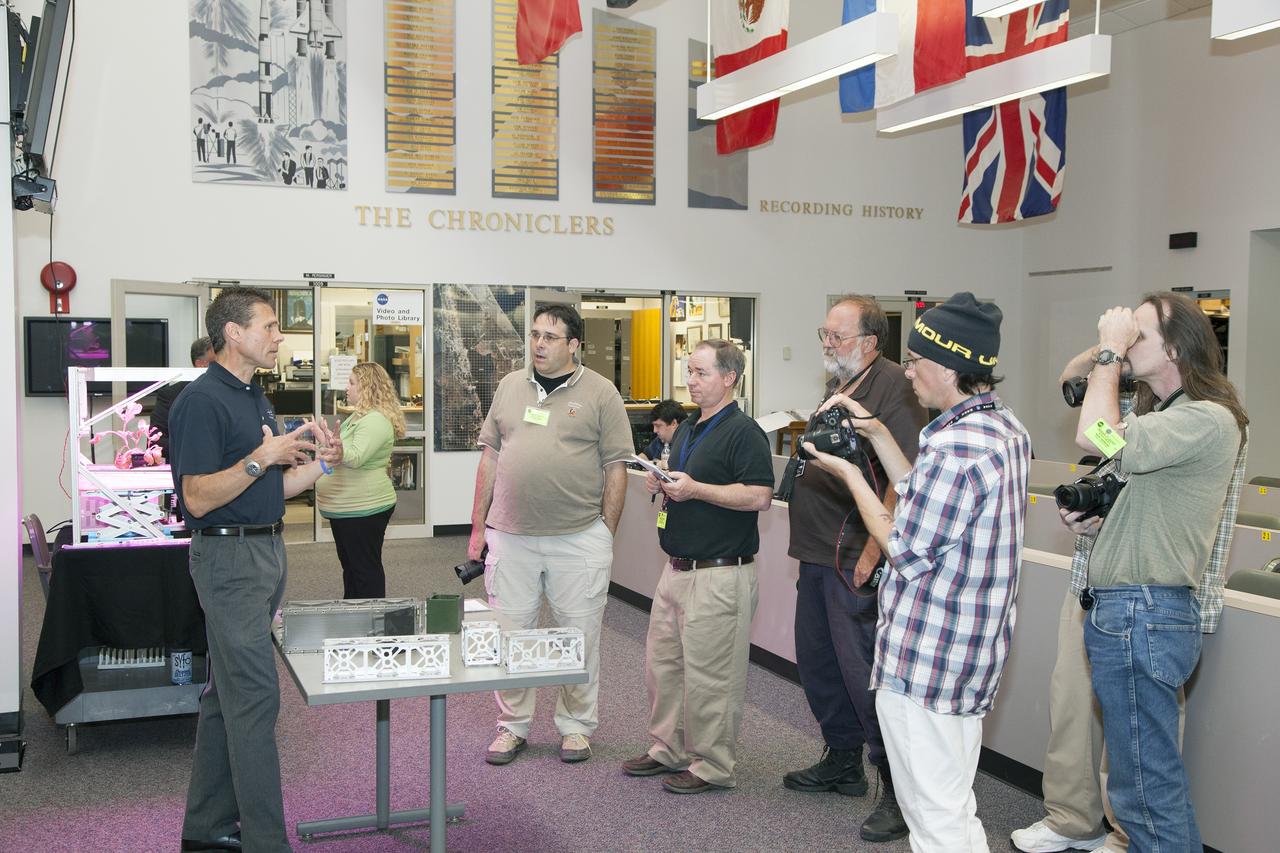

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Scott Higginbotham, left, mission manager for ELaNa V, discusses the concepts behind the design and deployment of the CubeSats flying on the ELaNa V mission with media representatives in the NASA Newsroom at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, using models of the Poly-Picosatellite Orbital Deployer, or P-POD, and various CubeSat canisters. NASA selected five small research satellites, or CubeSats, for the ELaNa V mission launching on SpaceX-3. Four P-PODs aboard the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket will ferry them to space. The CubeSats were designed by three universities and the agency's Ames Research Center in California. Launch is scheduled at about 4:58 p.m. EDT April 14. The SpaceX-3 mission, carrying almost 2.5 tons of supplies, technology and science experiments, is the third of 12 flights under NASA's Commercial Resupply Services contract to resupply the orbiting laboratory. For more information about NASA's CubeSat Launch Initiative, visit http://go.nasa.gov/CubeSat_initiative. Photo credit: NASA/Glenn Benson
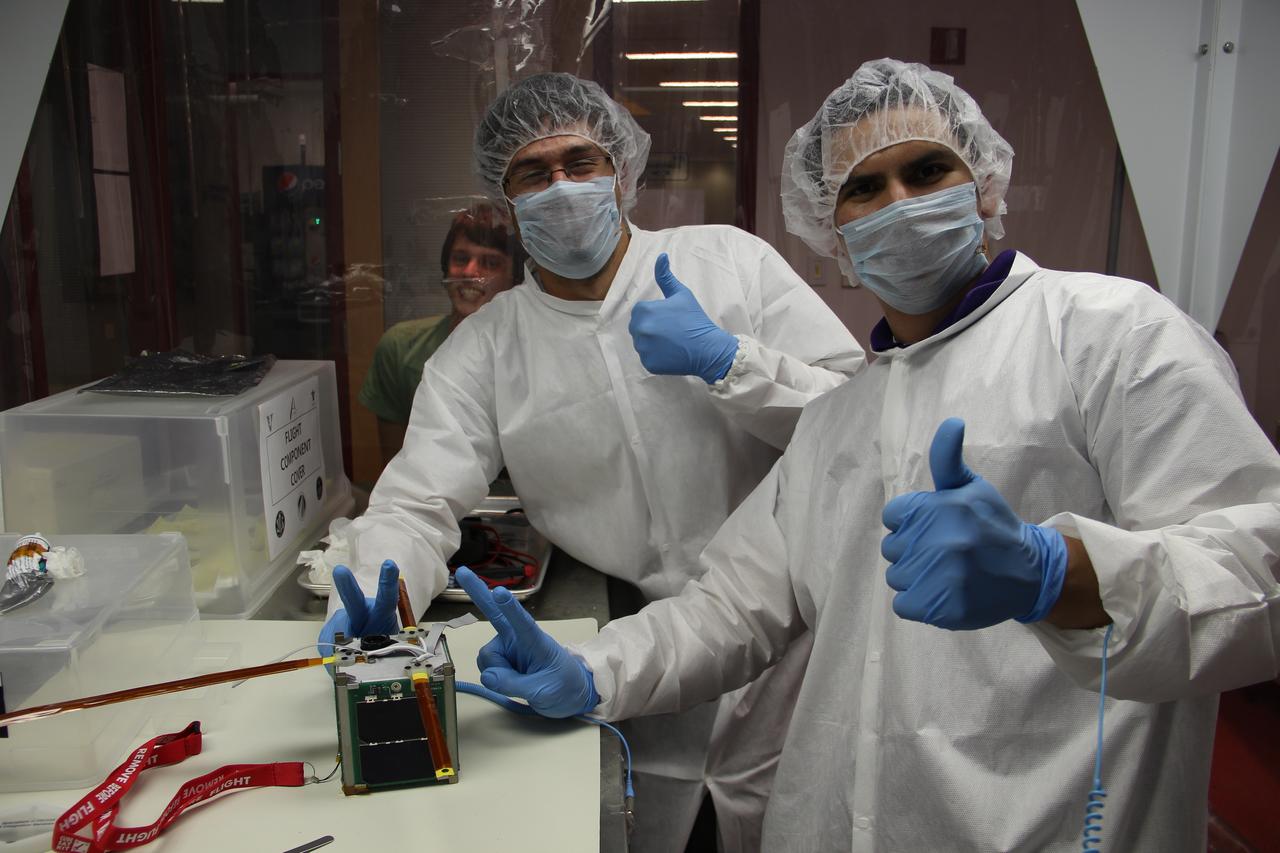

The Close Orbiting Propellant Plume Elemental Recognition (COPPER) was developed by students from St. Louis University as a technology demonstration mission whose objective is to test the suitability of a commercially-available compact uncooled microbolometer (tiny infrared camera) array for scientific imagery of Earth in the long-wave infrared range (LWIR, 7-13 microns). Launched by NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative on the ELaNa IV mission as an auxiliary payload aboard the U.S. Air Force-led Operationally Responsive Space (ORS-3) Mission on November 19, 2013.
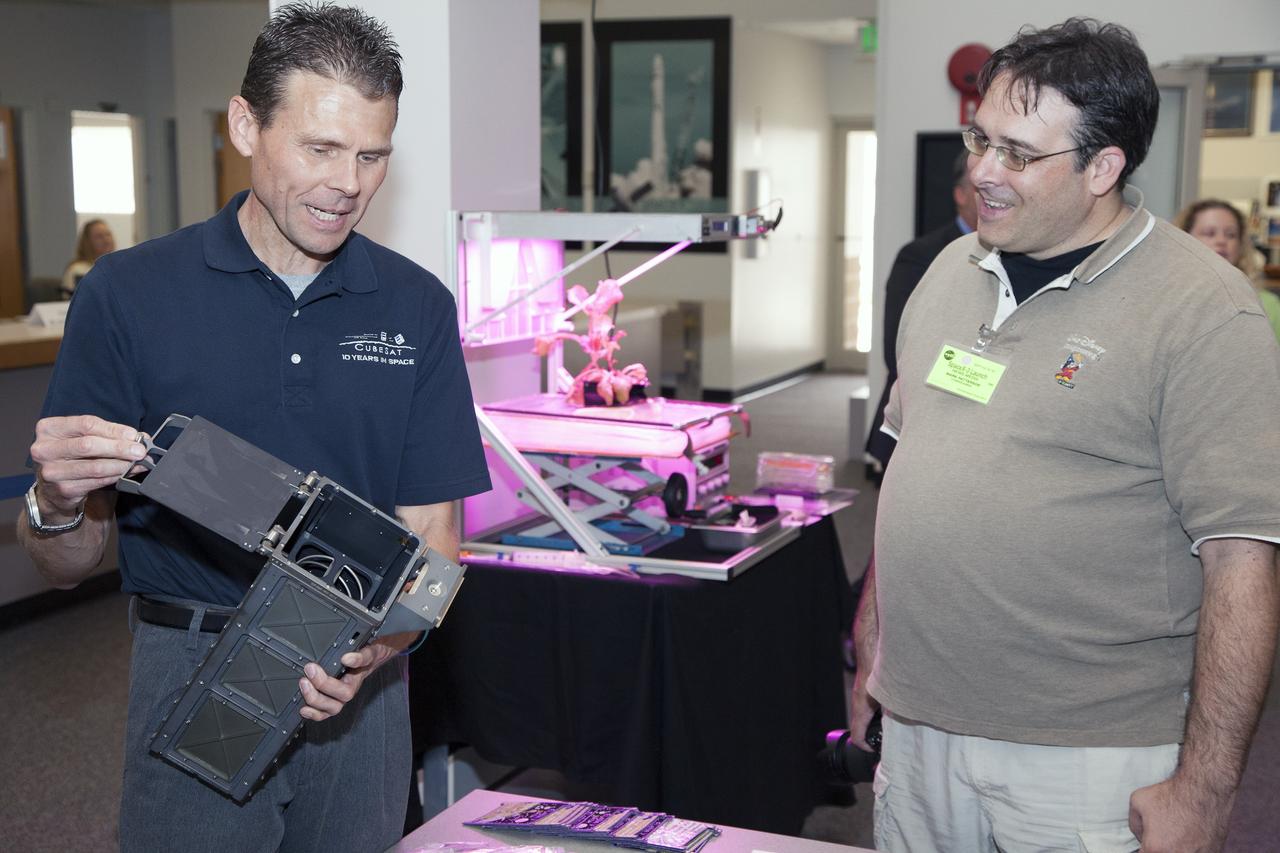

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Scott Higginbotham, left, mission manager for ELaNa V, demonstrates the concepts behind the design and deployment of the CubeSats flying on the ELaNa V mission with a media representative in the NASA Newsroom at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, using a model of the Poly-Picosatellite Orbital Deployer, or P-POD. NASA selected five small research satellites, or CubeSats, for the ELaNa V mission launching on SpaceX-3. Four P-PODs aboard the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket will ferry them to space. The CubeSats were designed by three universities and the agency's Ames Research Center in California. Launch is scheduled at about 4:58 p.m. EDT April 14. The SpaceX-3 mission, carrying almost 2.5 tons of supplies, technology and science experiments, is the third of 12 flights under NASA's Commercial Resupply Services contract to resupply the orbiting laboratory. For more information about NASA's CubeSat Launch Initiative, visit http://go.nasa.gov/CubeSat_initiative. Photo credit: NASA/Glenn Benson
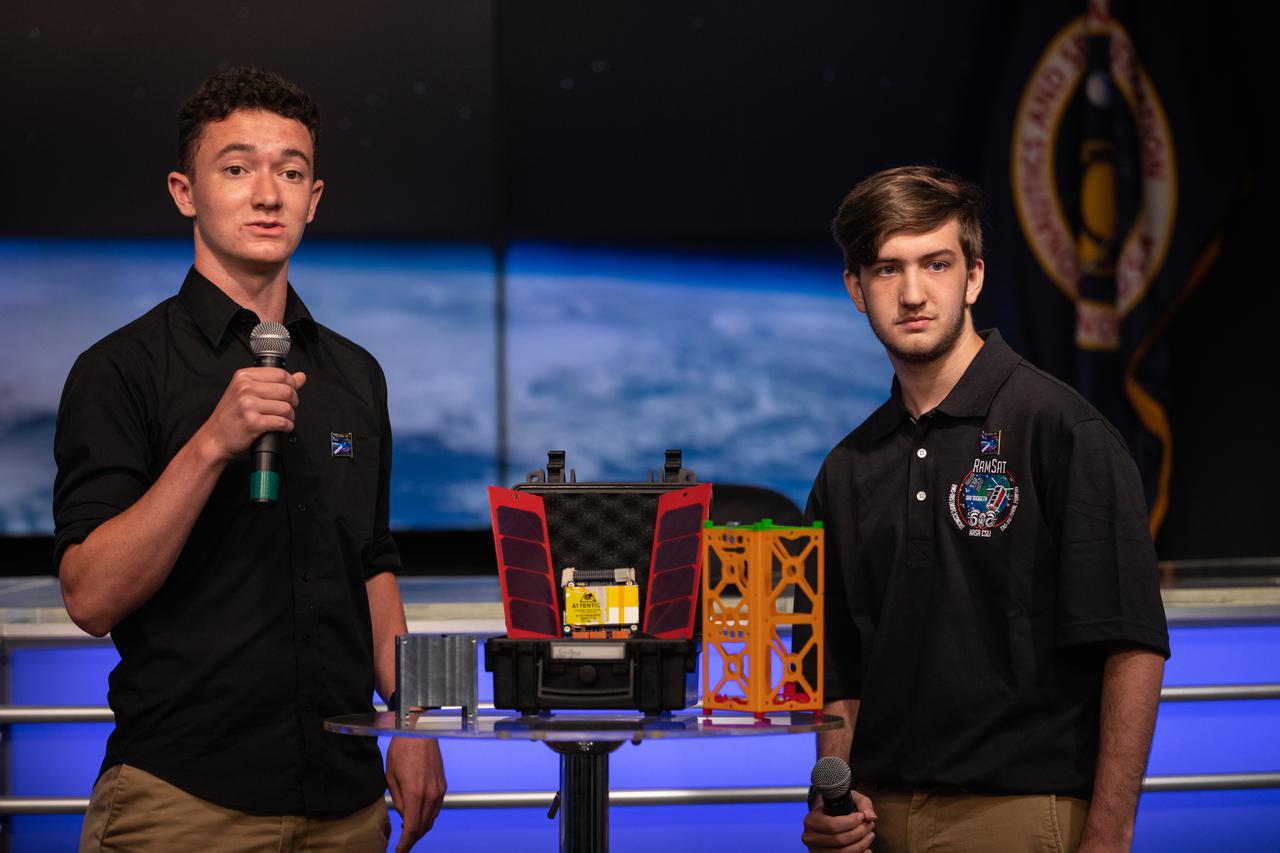

Students Joe Blair, at left, and Jonathon Bonamarte, describe a CubeSat, called RamSat, during a What’s On Board Science Briefing on June 2, 2021, at Kennedy Space Center in Florida for SpaceX’s 22nd Commercial Resupply Services Mission for NASA to the International Space Station. The small research satellite was developed by students and faculty at Robertsville Middle School in Oak Ridge, Tennessee. RamSat will observe forest regrowth in the Gatlinburg, Tennessee area which was devastated by wildfires in 2016. RamSat is the sole payload of the 36th Educational Launch of Nanosatellites (ELaNa) mission and was selected through NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative (CSLI). The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Dragon capsule atop is scheduled to launch at 1:29 p.m. EDT on Thursday, June 3, from the center’s Launch Complex 39A. Dragon will deliver more than 7,300 pounds of cargo and science experiments to the space station.
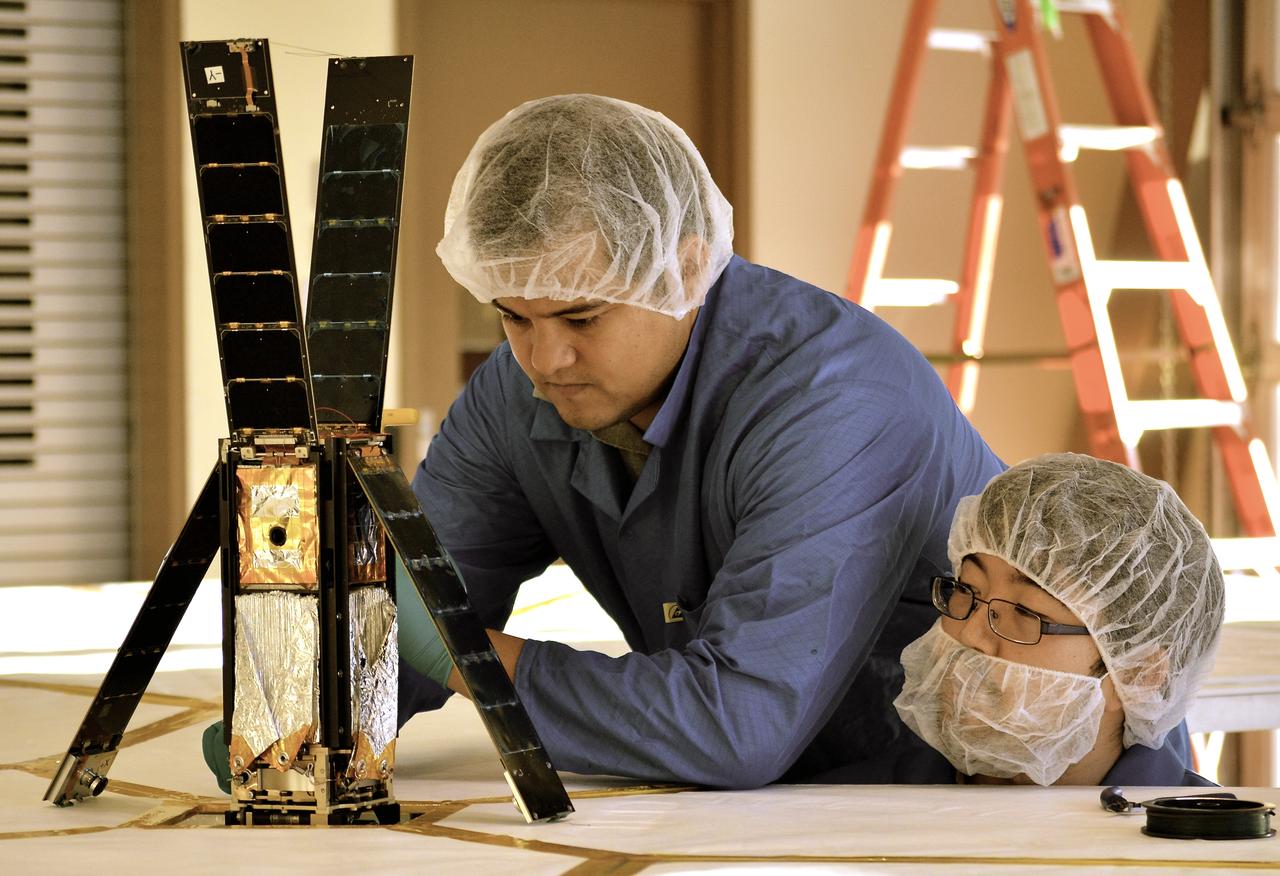

Students Alex Diaz and Riki Munakata of California Polytechnic State University testing the LightSail CubeSat. LightSail is a citizen-funded technology demonstration mission sponsored by the Planetary Society using solar propulsion for CubeSats. The spacecraft is designed to “sail” on the energy of solar photons striking the thin, reflective sail material. The first LightSail mission is designed to test the spacecraft’s critical systems, including the sequence to autonomously deploy a Mylar solar sail with an area of 32 square meters (344 square feet). The Planetary Society is planning a second, full solar sailing demonstration flight for 2016. Light is made of packets of energy called photons. While photons have no mass, they have energy and momentum. Solar sails use this momentum as a method of propulsion, creating flight by light. LightSail’s solar sail is packaged into a three-unit CubeSat about the size of a loaf of bread. Launched by NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative on the ELaNa XI mission as an auxiliary payload aboard the U.S. Air Force X-37B space plane mission on May 20, 2015.
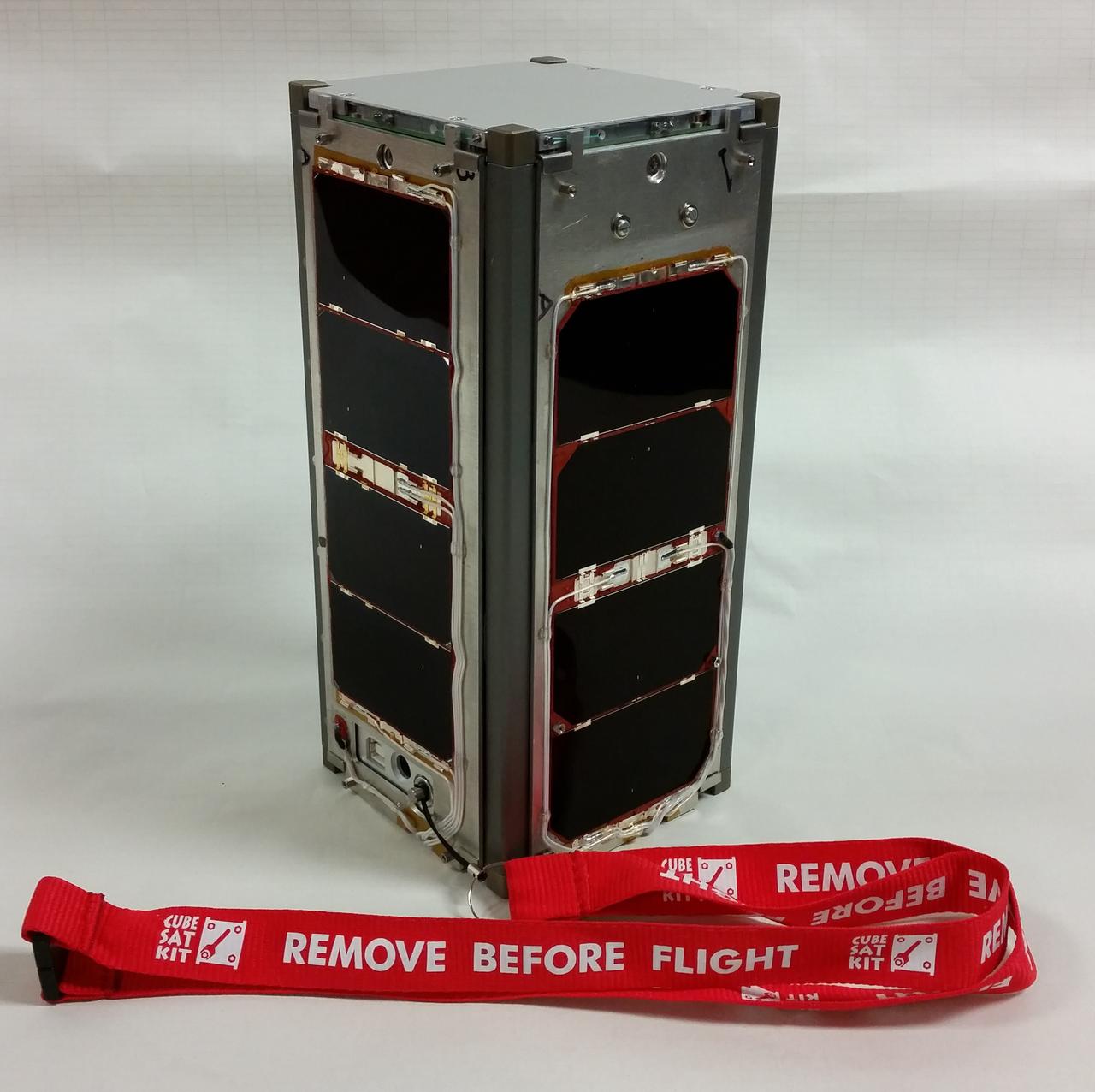

The primary mission of CSUNSat1 is to space test an innovative low temperature capable energy storage system developed by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, raising its TRL level to 7 from 4 to 5. The success of this energy storage system will enable future missions, especially those in deep space to do more science while requiring less energy, mass and volume. This CubeSat was designed, built, programmed, and tested by a team of over 70 engineering and computer science students at CSUN. The primary source of funding for CSUNSat1 comes from NASA’s Smallest Technology Partnership program. Launched by NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative on the NET April 18, 2017 ELaNa XVII mission on the seventh Orbital-ATK Cygnus Commercial Resupply Services (OA-7) to the International Space Station and deployed on tbd.
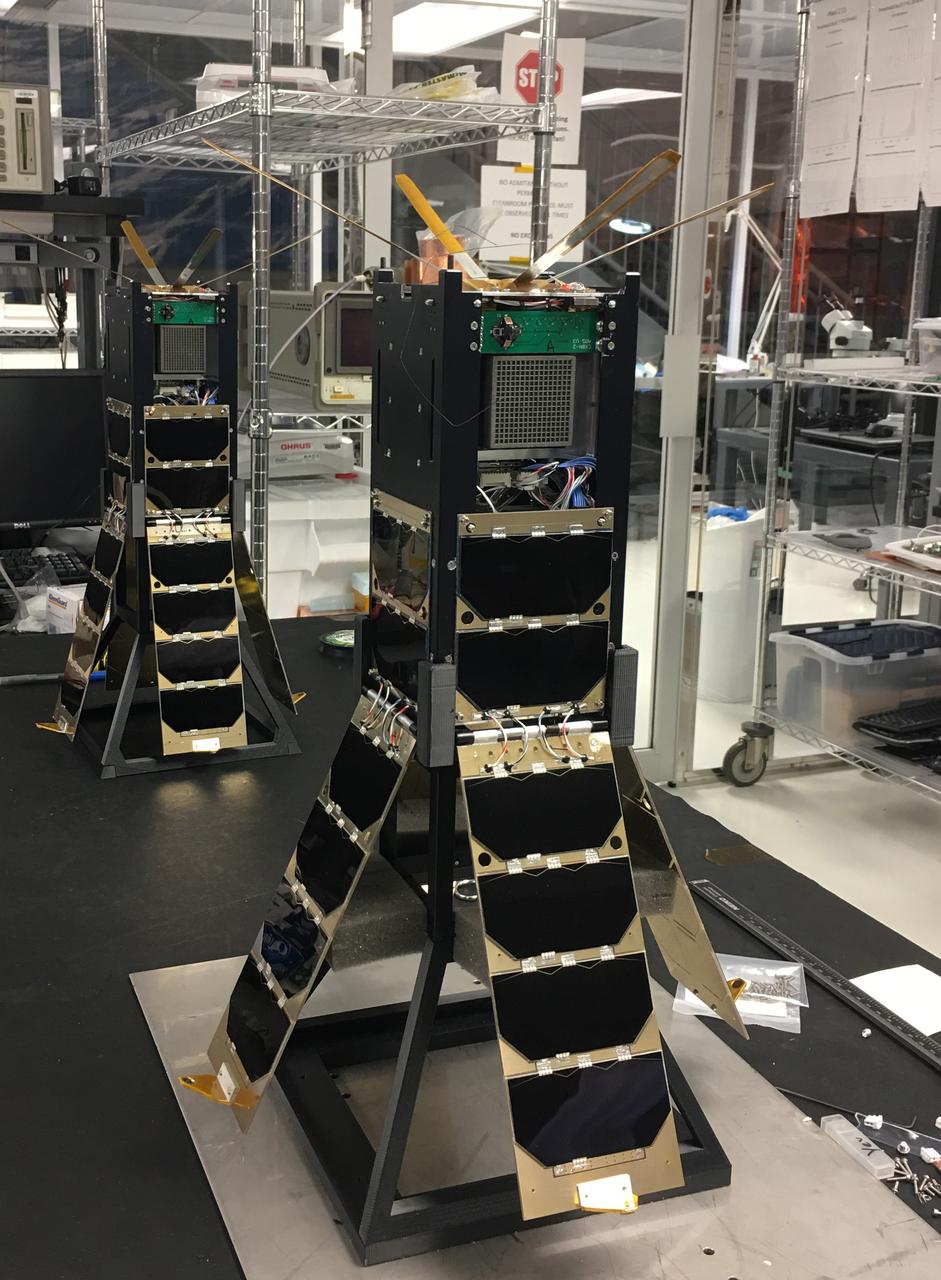

The Cosmic X-Ray Background NanoSat-2 (CXBN-2) CubeSat Mission developed by Morehead State University and its partners the Keldysh Institute (Moscow, Russia), the Maysville Community and Technical College (Morehead, KY) and KYSpace LLC (Lexington, KY) will increase the precision of measurements of the Cosmic X-Ray Background in the 30-50 keV range to a precision of <5%, thereby constraining models that attempt to explain the relative contribution of proposed sources lending insight into the underlying physics of the early universe. The mission addresses a fundamental science question that is central to our understanding of the structure, origin, and evolution of the universe by potentially lending insight into both the high-energy background radiation and into the evolution of primordial galaxies. Launched by NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative NET April 18, 2017 ELaNa XVII mission on the seventh Orbital-ATK Cygnus Commercial Resupply Services (OA-7) to the International Space Station and deployed on tbd.
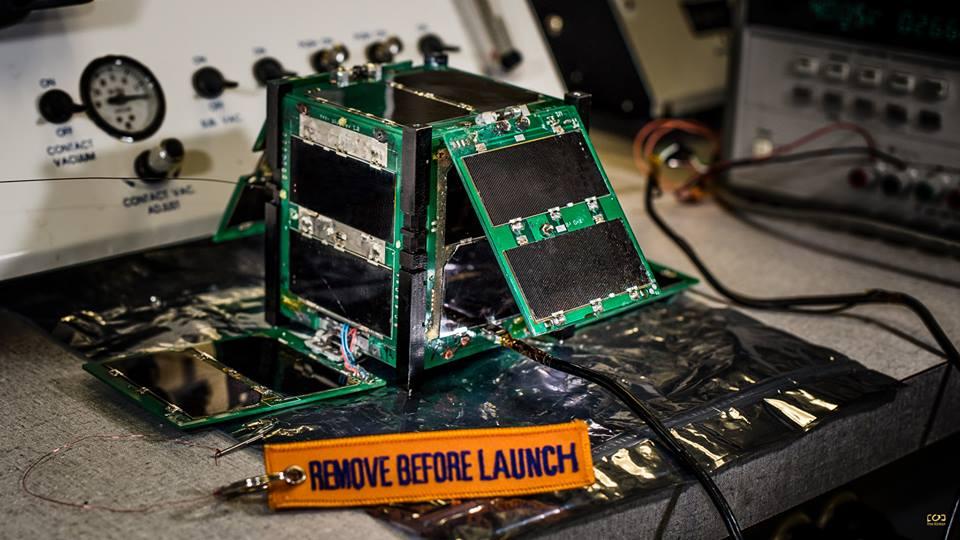

CAPE-2: Cajun Advanced Picosatellite Experiment – ELaNa IV CAPE-2 was developed by students from the University of Louisiana Lafayette to engage, inspire and educate K-12 students to encourage them to pursue STEM careers. The secondary focus is the technology demonstration of deployed solar panels to support the following payloads: text to speech, voice repeater, tweeting, email, file transfer and data collection from buoys. Launched by NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative on the ELaNa IV mission as an auxiliary payload aboard the U.S. Air Force-led Operationally Responsive Space (ORS-3) Mission on November 19, 2013.
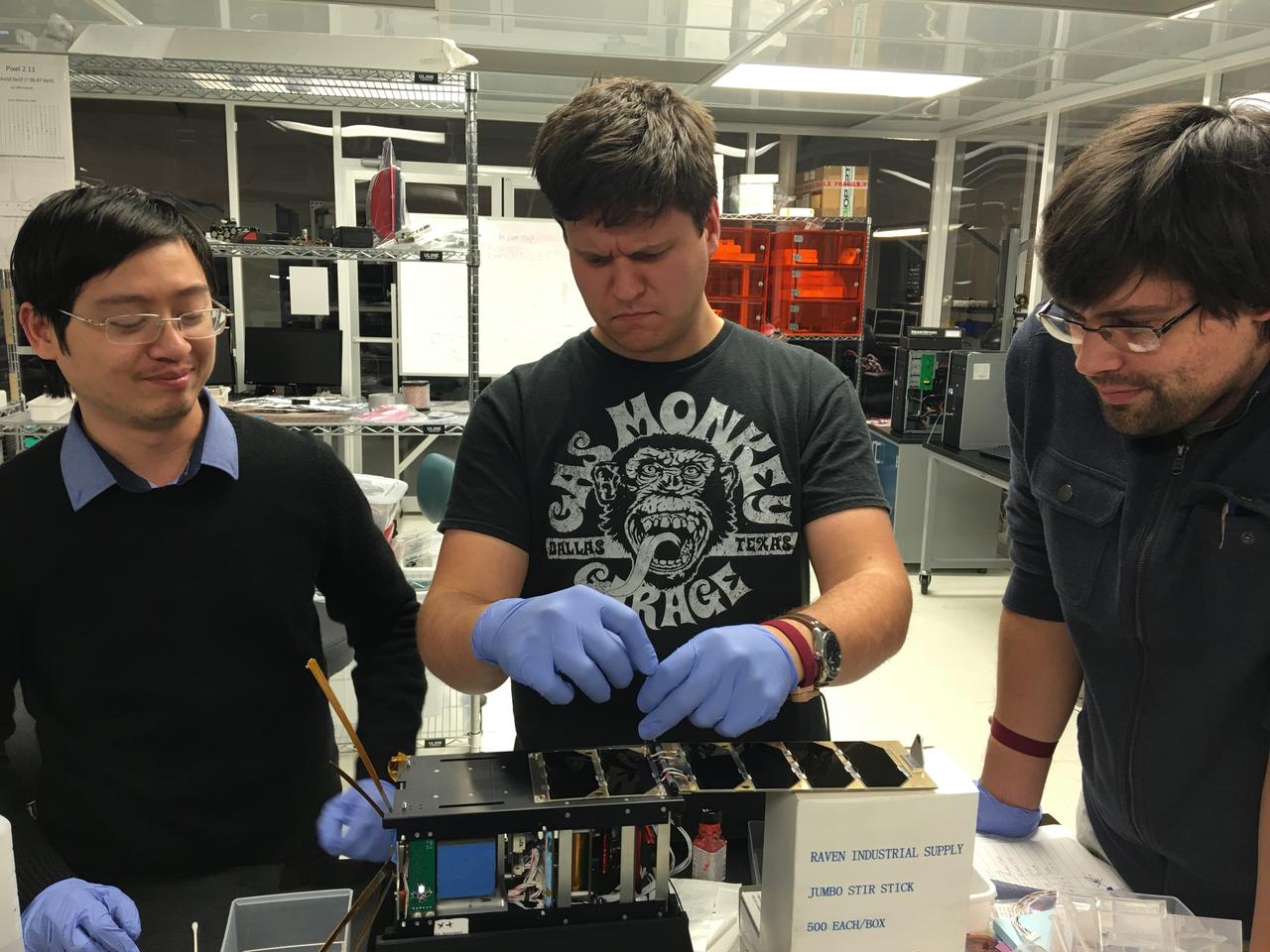
CXBN-2 Integration Team in the Morehead State University Spacecraft Integration and Assembly Facility. Left to right: Kein Dant, Yevgeniy Byleborodov, and Nate Richard. The Cosmic X-Ray Background NanoSat-2 (CXBN-2) CubeSat Mission developed by Morehead State University and its partners the Keldysh Institute (Moscow, Russia), the Maysville Community and Technical College (Morehead, KY) and KYSpace LLC (Lexington, KY) will increase the precision of measurements of the Cosmic X-Ray Background in the 30-50 keV range to a precision of <5%, thereby constraining models that attempt to explain the relative contribution of proposed sources lending insight into the underlying physics of the early universe. The mission addresses a fundamental science question that is central to our understanding of the structure, origin, and evolution of the universe by potentially lending insight into both the high-energy background radiation and into the evolution of primordial galaxies. Launched by NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative NET April 18, 2017 ELaNa XVII mission on the seventh Orbital-ATK Cygnus Commercial Resupply Services (OA-7) to the International Space Station and deployed on tbd.