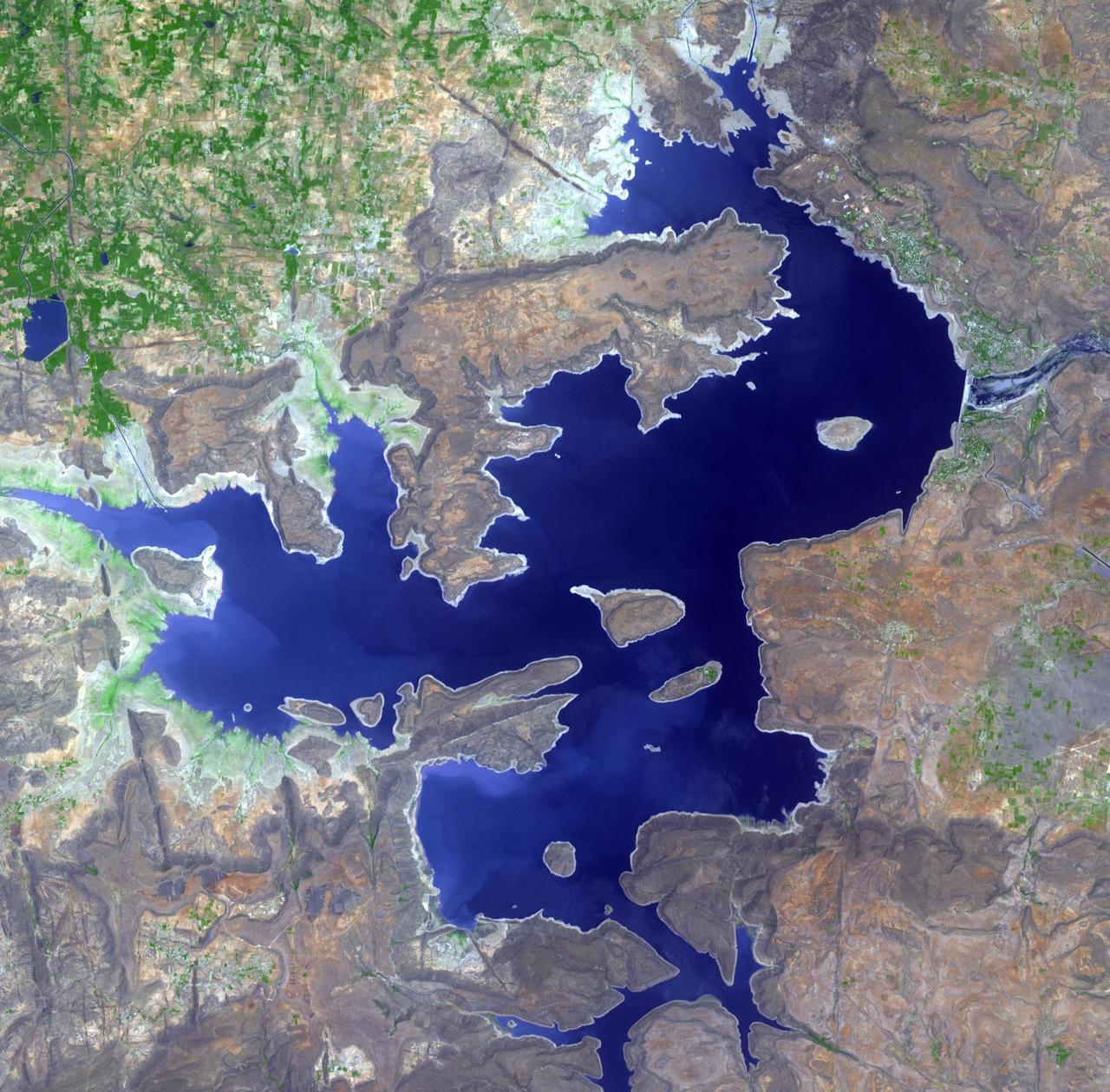
The Nagarunja Sagar Dam on India Krishna River is the largest masonry dam in operation in the world. This image is from NASA Terra spacecraft.
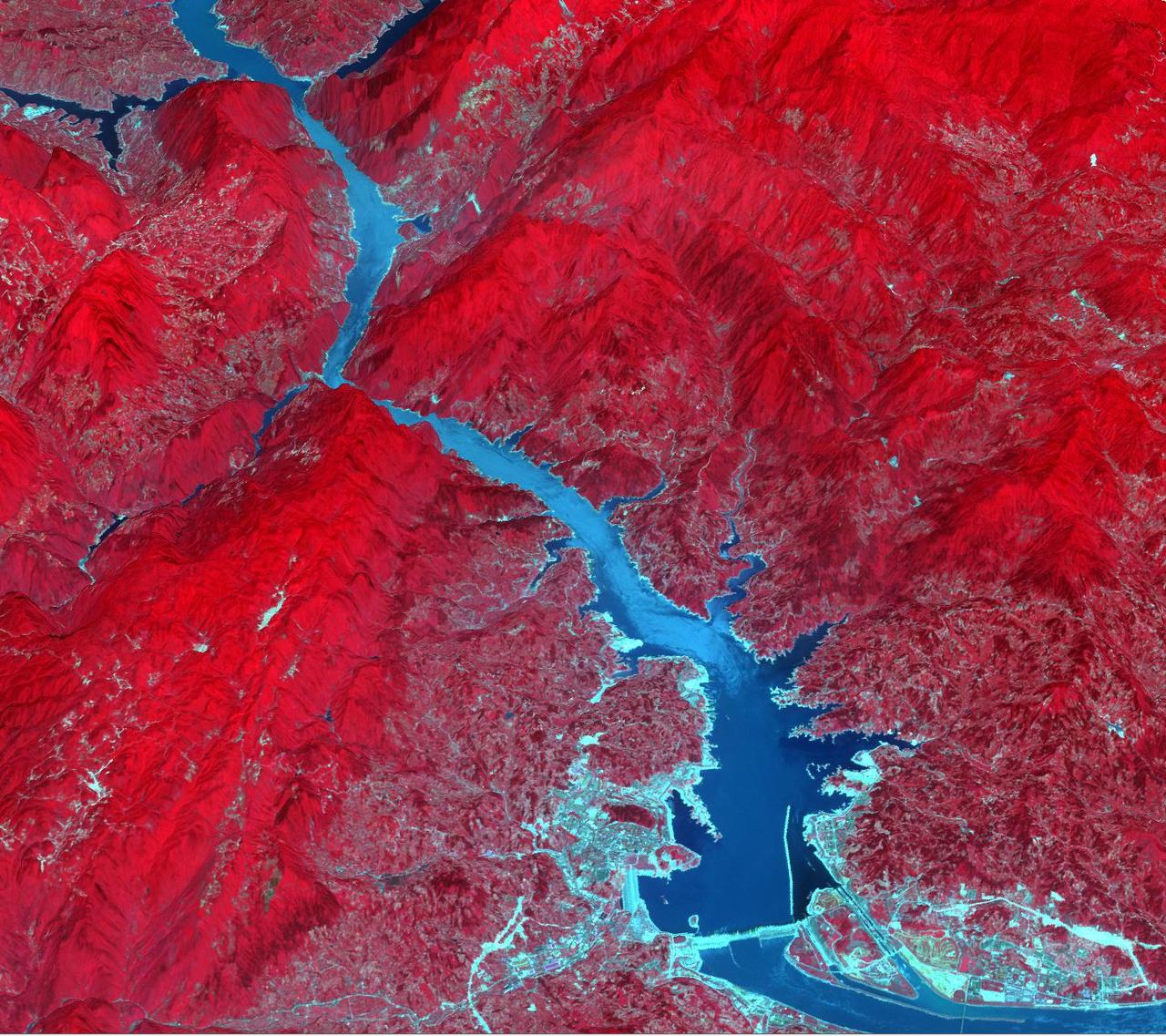

Acquired by NASA Terra spacecraft, this image shows the Three Gorges Dam which spans the Yangtze River in east-central China, and is the world largest power station in terms of installed capacity.
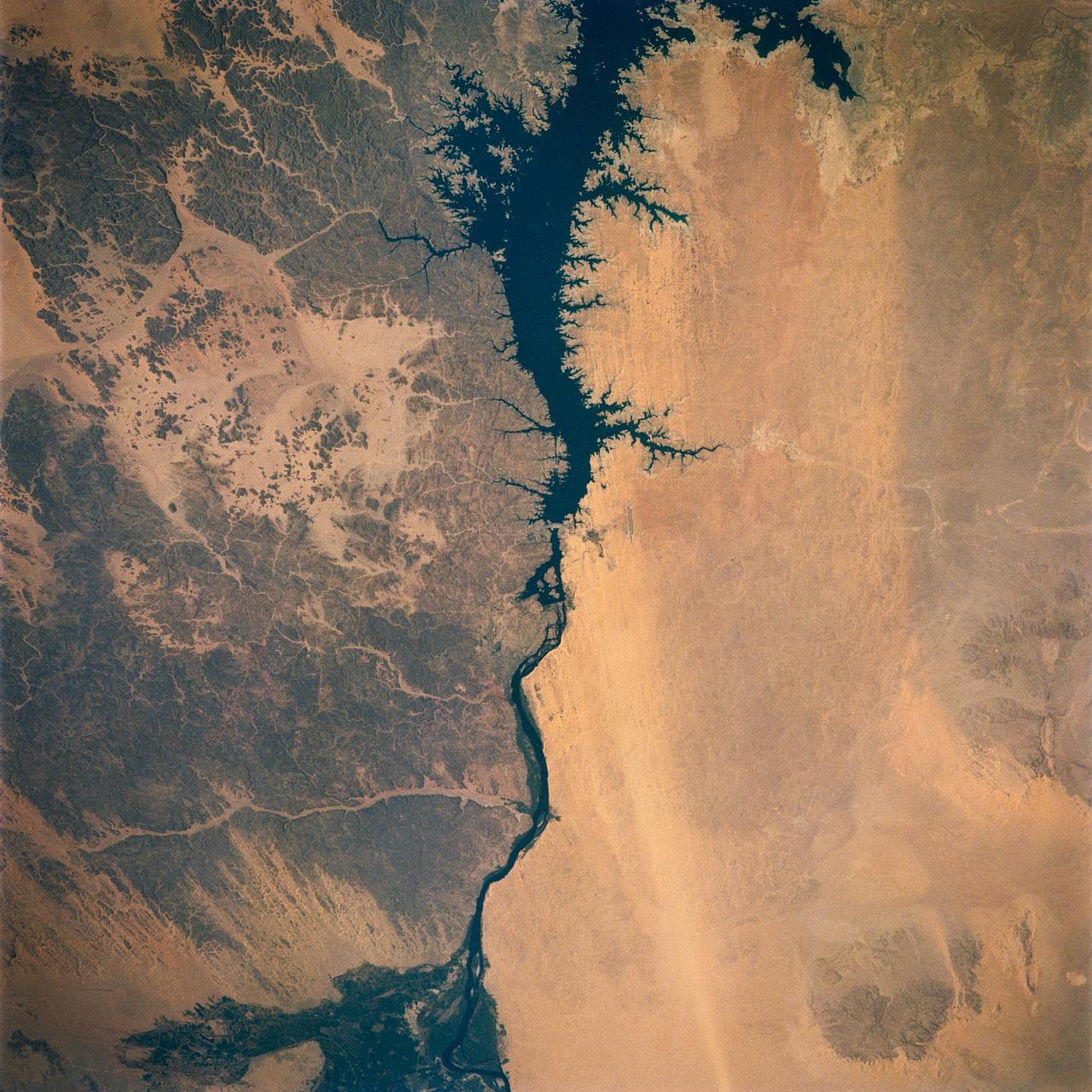

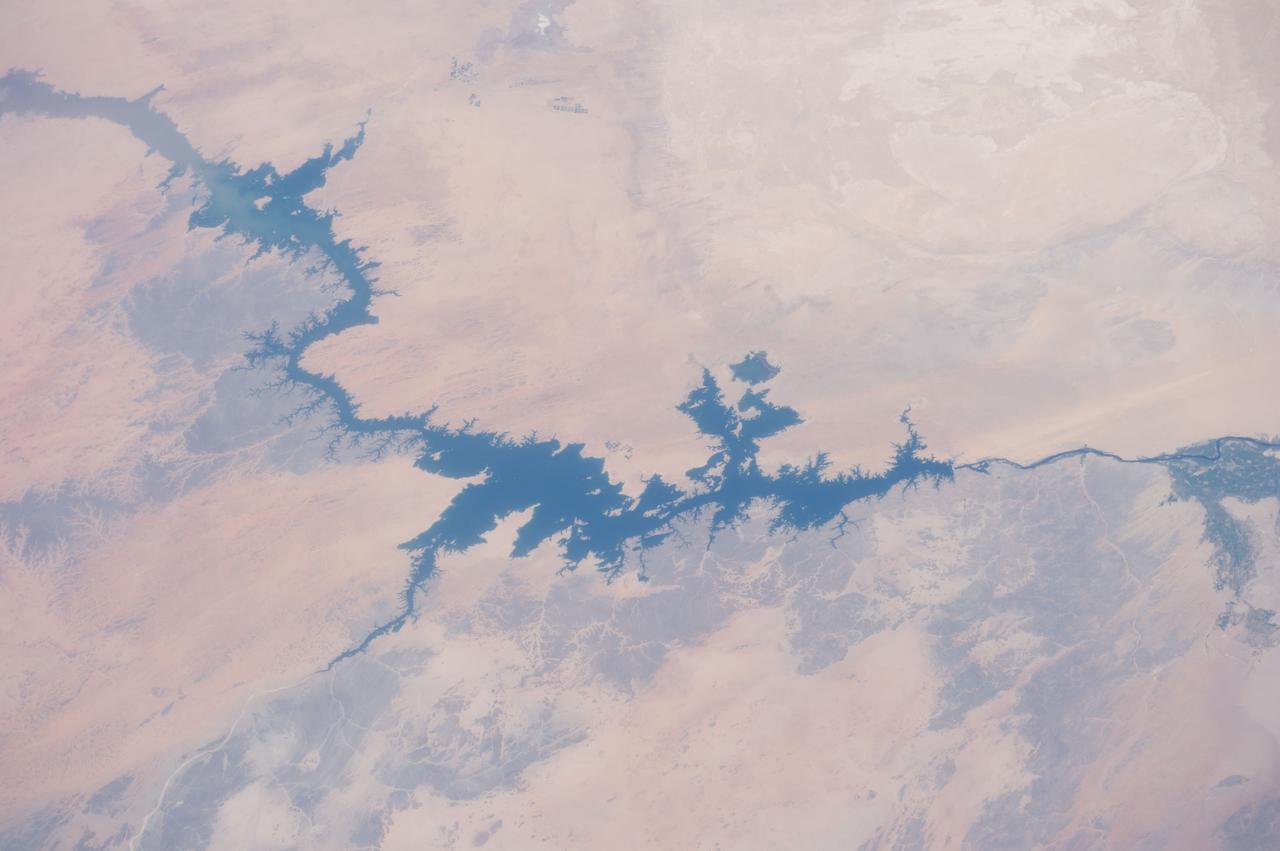
Egypt's High Aswan Dam on the Nile River at the first cataracts, Nile River, (24.0N, 33.0E) was completed in 1971 to provide cheap hydroelectric power and to regulate the historically uneven flow of the Nile River. The contrast between the largely base rock desert east of the Nile versus the sand covered desert west of the river and the ancient irrigated floodplain downstream from the damsite is clearly shown.
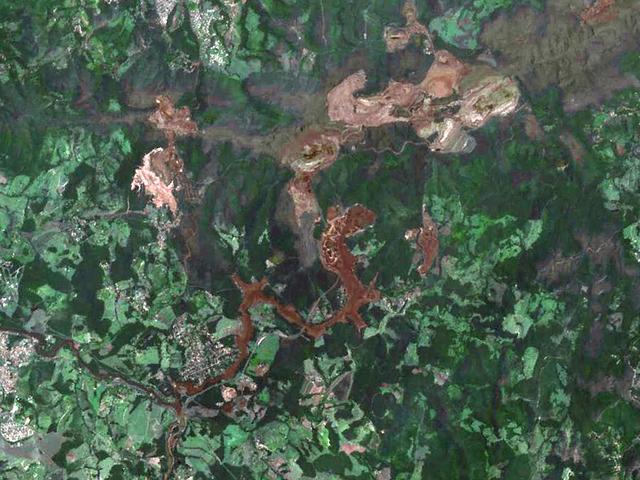

On January 25, 2019, a dam burst at a Brazilian iron ore mine. The dam's breach unleashed a torrent of mud and mine debris, covering the city of Brumadinho. The image was acquired by ASTER on February 1, 2019, covers an area of 10.8 by 14.8 kilometers, and is located at 20.1 degrees south, 44.1 degrees west. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22824
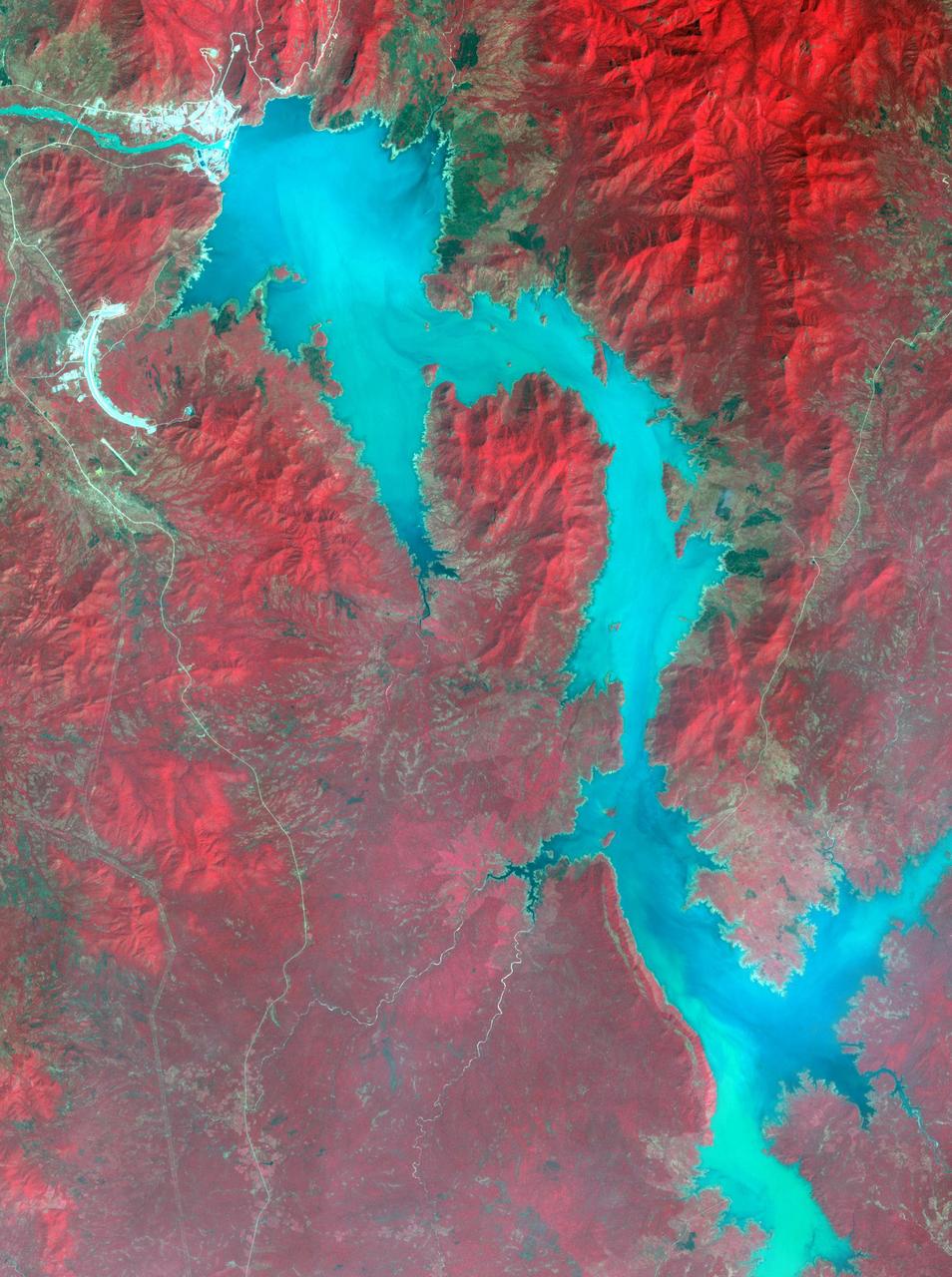

Filling of the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (GERD) along the Blue Nile River is well under way near the Ethiopia-Sudan border. For a decade, Egypt and Ethiopia have been at a diplomatic stalemate over the Nile's management. Egypt proposes that Ethiopia should be able to generate hydropower from the GERD while minimizing the harm on downstream communities in Egypt and Sudan. Ethiopia's objective is to assert control over the Blue Nile, the largest tributary of the Nile River. The image was acquired November 6, 2020, covers an area of 32 by 42.9 kilometers, and is located near 11.1 degrees north, 35.2 degrees east. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24150
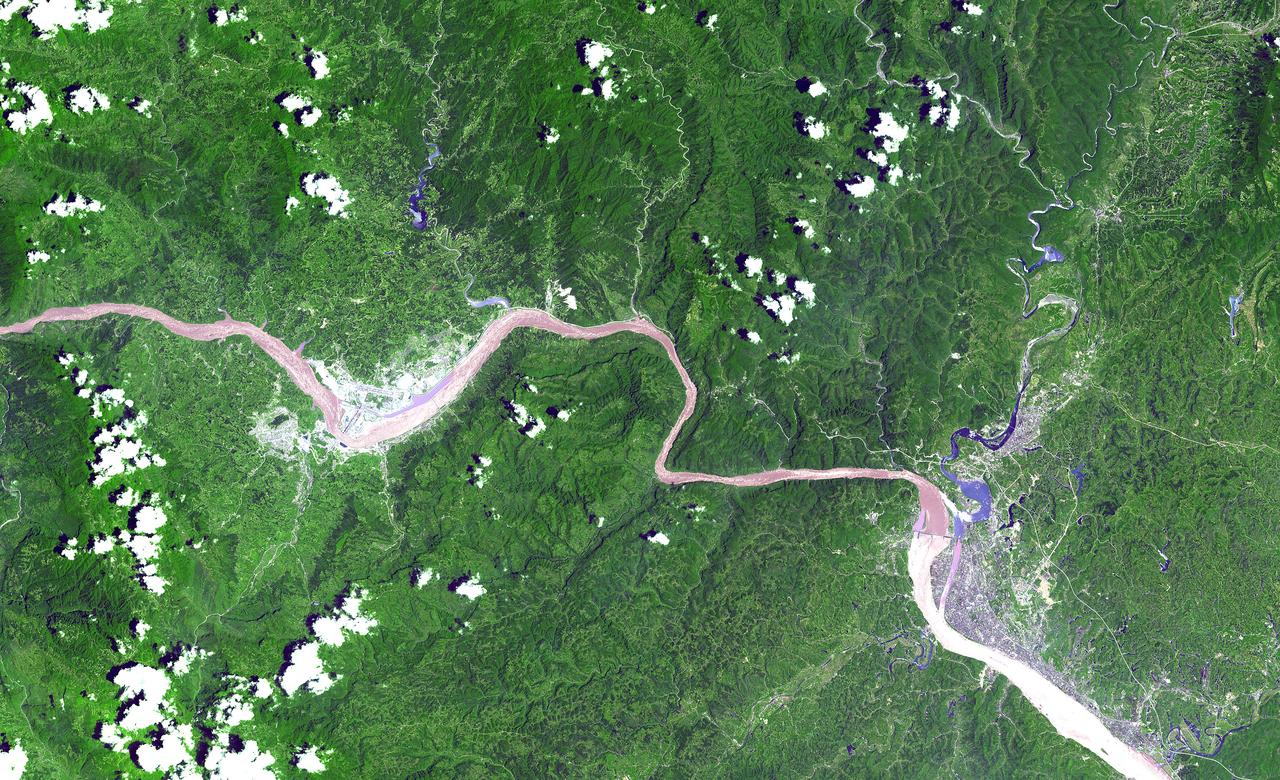

This ASTER image shows a 60 km stretch of the Yangtze River in China, including the Xiling Gorge, the eastern of the three gorges. In the left part of the image is the construction site of the Three Gorges Dam, the world's largest. This image was acquired on July 20, 2000 by the Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) on NASA's Terra satellite. With its 14 spectral bands from the visible to the thermal infrared wavelength region, and its high spatial resolution of 15 to 90 meters (about 50 to 300 feet), ASTER will image Earth for the next 6 years to map and monitor the changing surface of our planet. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA03852

iss072e069220 (Oct. 16, 2024) --- The Jebba Dam (lower left) impounds the Niger River creating a reservoir in Nigeria in this photograph from the International Space Station as it orbited 259 miles above the African nation.
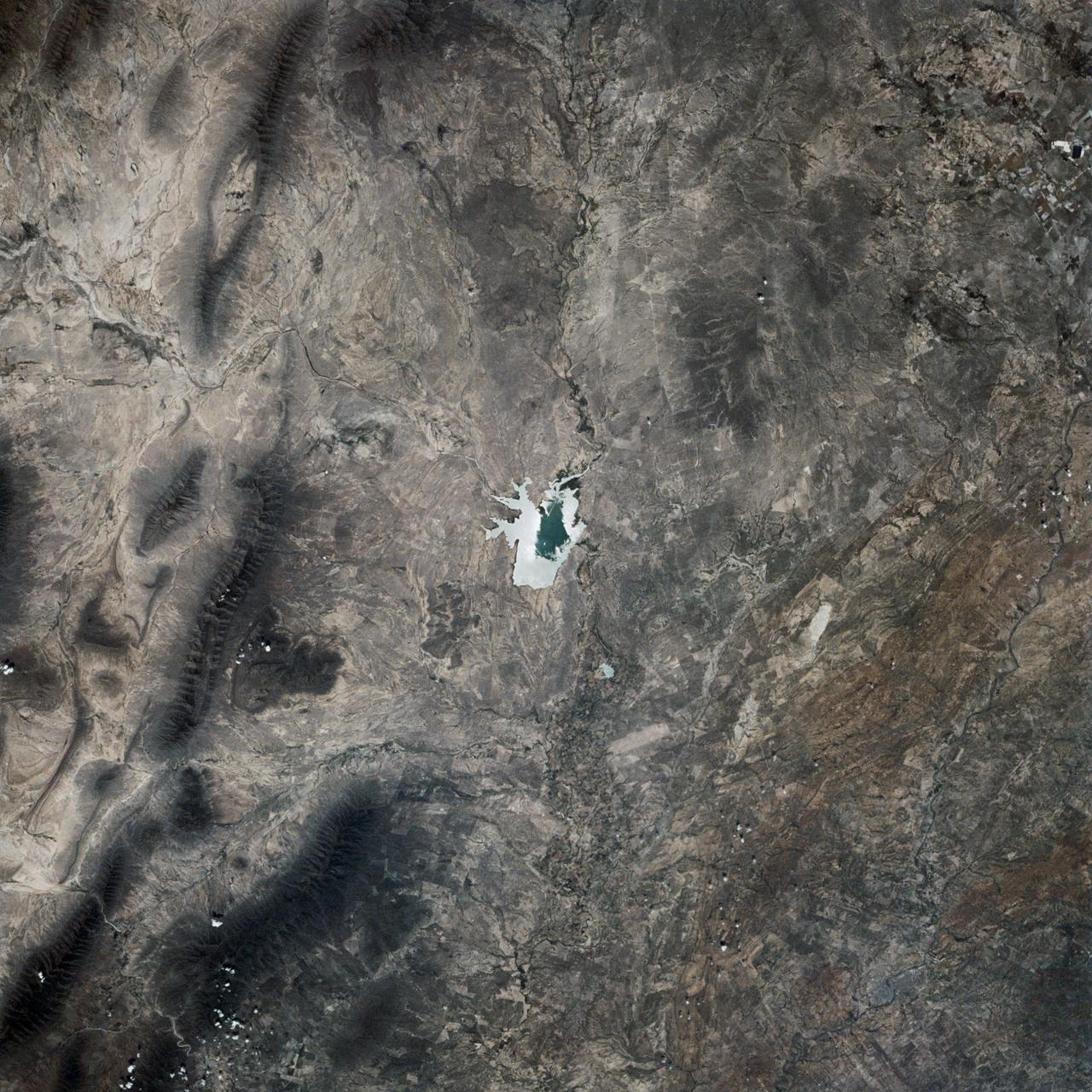

This is a single scene from a pair (frames 021 & 024) to study the effects of polarized light in Earth Observations. One scene was exposed with vertically polarized light, the other, horizontally. The subject in this study, is a lake behind Presa (dam) Don Martin (27.5N, 100.5W) on the edge of the Rio Grande Plain near it's boundry with the Sierra Madre Orientral in Coahuila, Mexico.
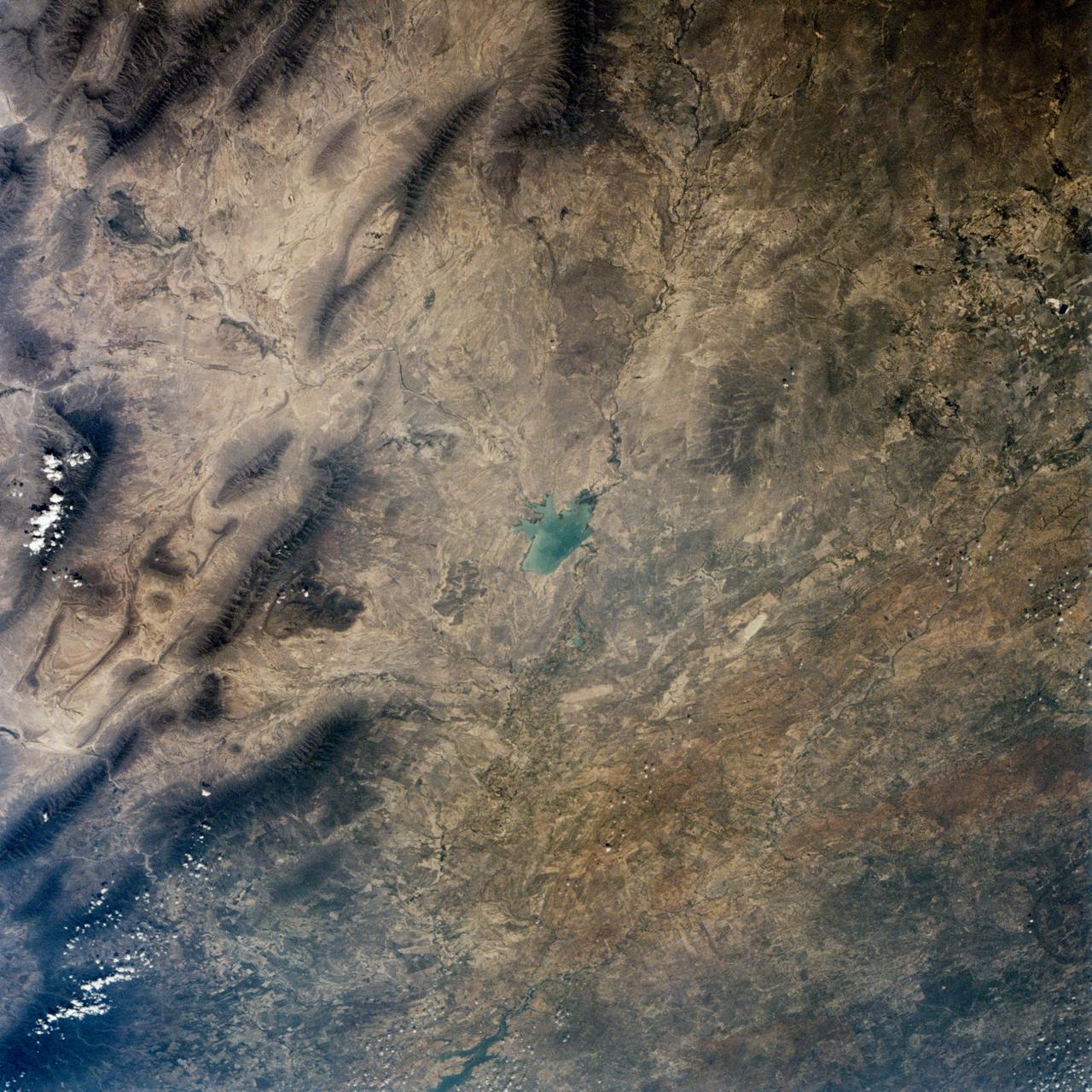

This is a single scene from a pair (frames 021 & 024) to study the effects of polarized light in Earth Observations. One scene was exposed with vertically polarized light, the other, horizontally. The subject in this study, is a lake behind Presa (dam) Don Martin (27.5N, 100.5W) on thge edge of the Rio Grande Plain near it's boundry with the Sierra Madre Oriental in Coahuila, Mexico.

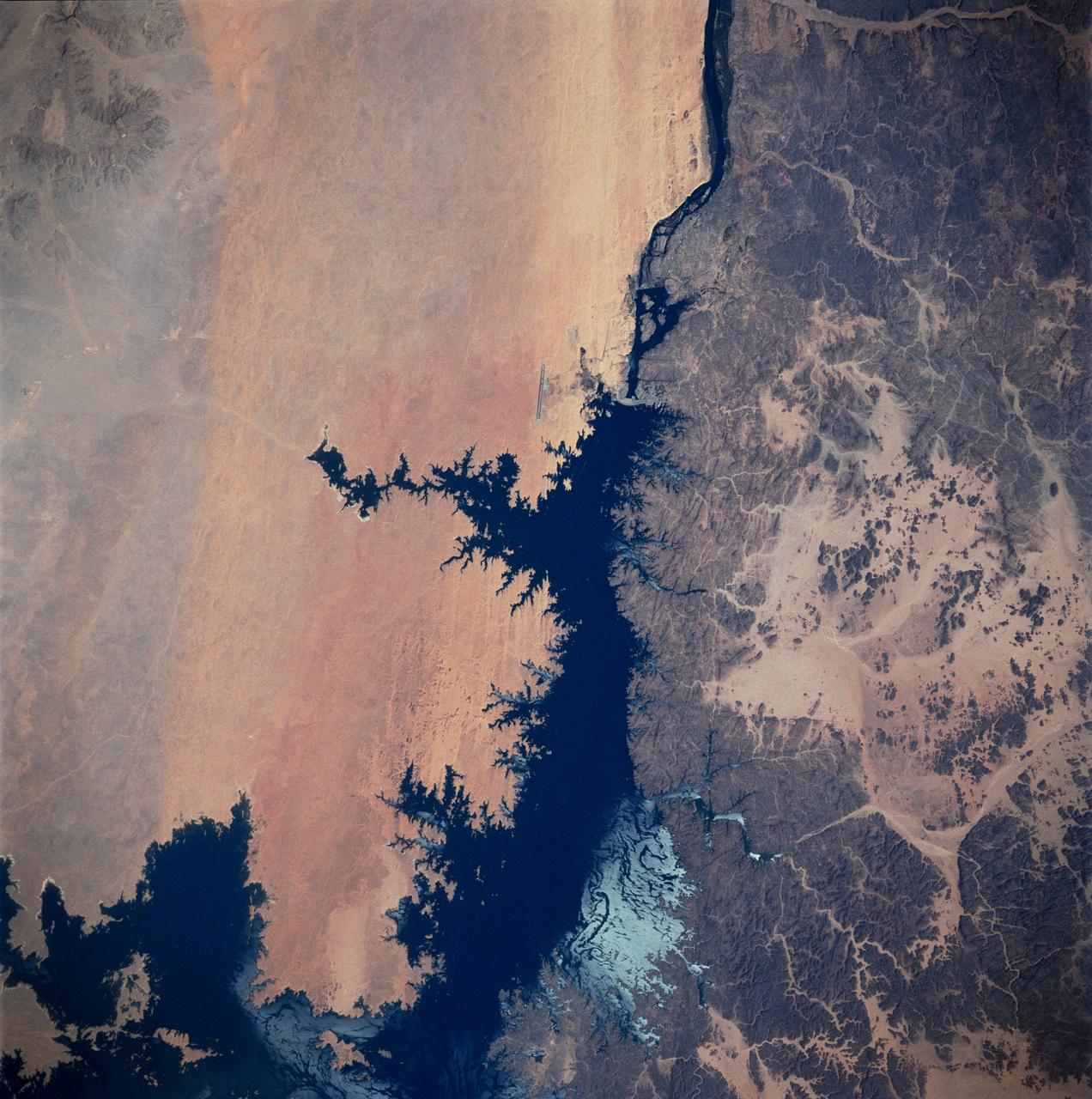
iss073e0879542 (Oct. 13, 2025) --- Lake Nasser, created by the Aswan High Dam in southern Egypt, is one of the world’s largest man-made reservoirs. Extending into northern Sudan, it stores water from the Upper Nile and regulates its flow into the Lower Nile. This photograph was taken from the International Space Station while orbiting 260 miles above the eastern Sahara.
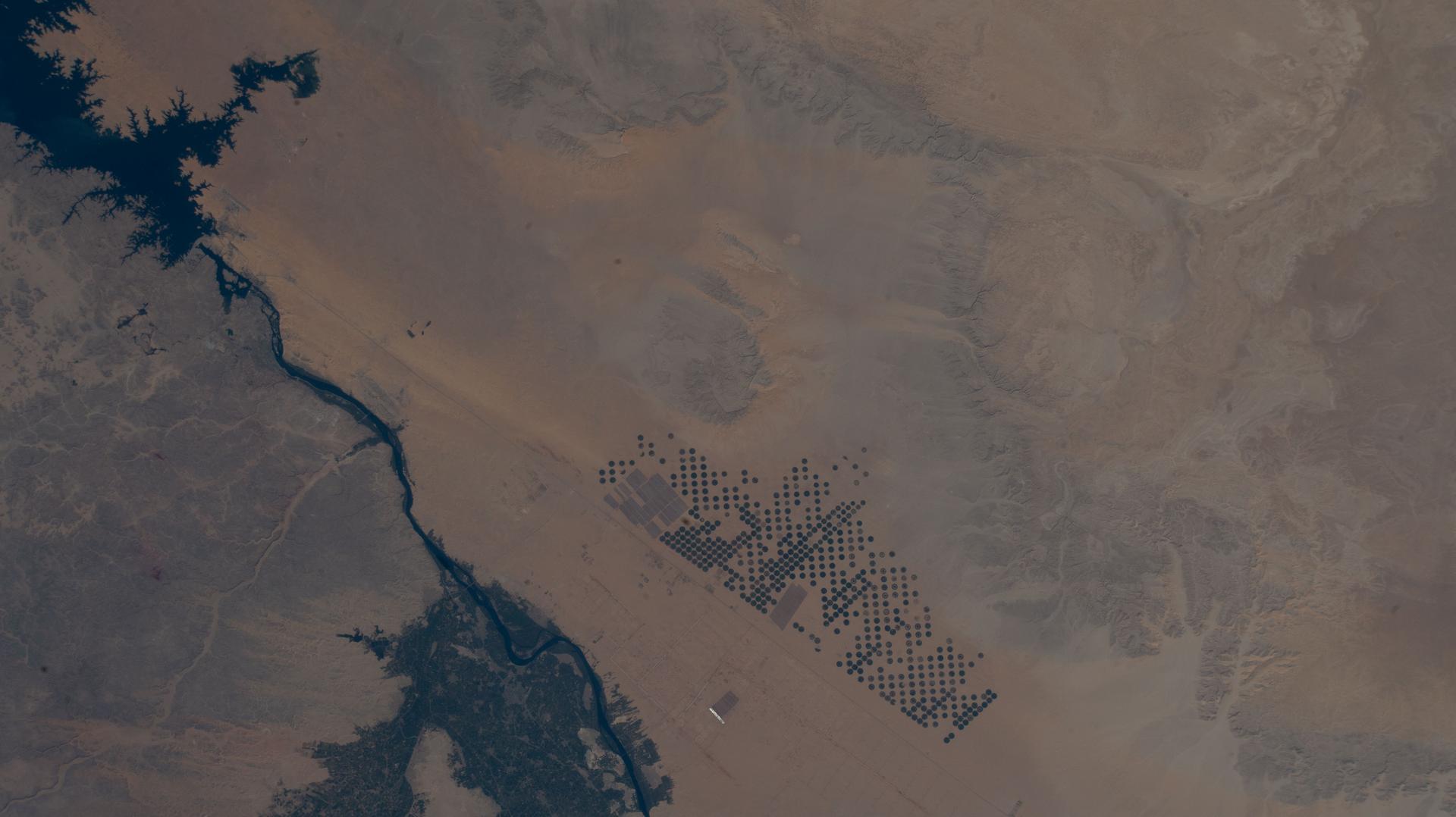

iss074e0315952 (Feb. 16, 2026) --- Egypt’s Nile River turns into Lake Nasser (upper left) at the Aswan High Dam, where the water spreads into a vast artificial reservoir that controls the river’s flow, prevents flooding, and generates hydroelectric power. Center‑pivot irrigation systems appear near the center bottom, forming perfect circles of crops such as potatoes and wheat. The International Space Station was orbiting 258 miles above the African nation at the time of this photograph. Credit: NASA

The Lake Palanskoye in northern Kamchatka was formed when a large landslide disrupted the drainage pattern, forming a natural dam.

ISS019-E-007720 (15 April 2009) --- Three Gorges Dam in China is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 19 crew member on the International Space Station. A new reservoir is filling in central China. The Three Gorges Dam on the Yangtze River - the world?s largest dam ? was completed in 2006, and the river is filling up its valley behind the dam to form a narrow reservoir extending more than 600 kilometers. This image is one of the first images documenting the flooding behind the dam. The main objective for the dam is to supply water for the largest hydroelectric plant in the world and help control the devastating floods that plague the lowlands downstream from the dam.

Oroville Dam in Northern California is an earth fill embankment dam, and is the tallest dam in the U.S. Lake Oroville is the second largest man-made lake in the state of California. The lake's capacity reflects the large swings in California's annual rainfall accumulation. With the reality of a very dry 2020-21 rain year, the 2014 data may anticipate this year's water shortage. On May 7, 2012, the lake held 3.5 million acre-feet of water, and was at maximum capacity. Two years later, on August 1, 2014, the lake held 1.2 million acre-feet of water, threatening the water supply to users of its water. The images cover an area of 22.5 by 23.4 km, and are located at 39.6 degrees north, 121.5 degrees west. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24555

Oblique Earth Observation taken by the Apollo 9 crew. View is the United Arab Republic,the Nile River,The Red Sea and the Aswan Dam. Film magazine was E,film type was SO-368 Ektachrome with 0.460 - 0.710 micrometers film / filter transmittance response and haze filter,80mm lens. Latitude was 19.38 N by Longitude 30.24 E, Overlap was 50%, Altitude was 97 nautical miles and cloud cover was 5%.
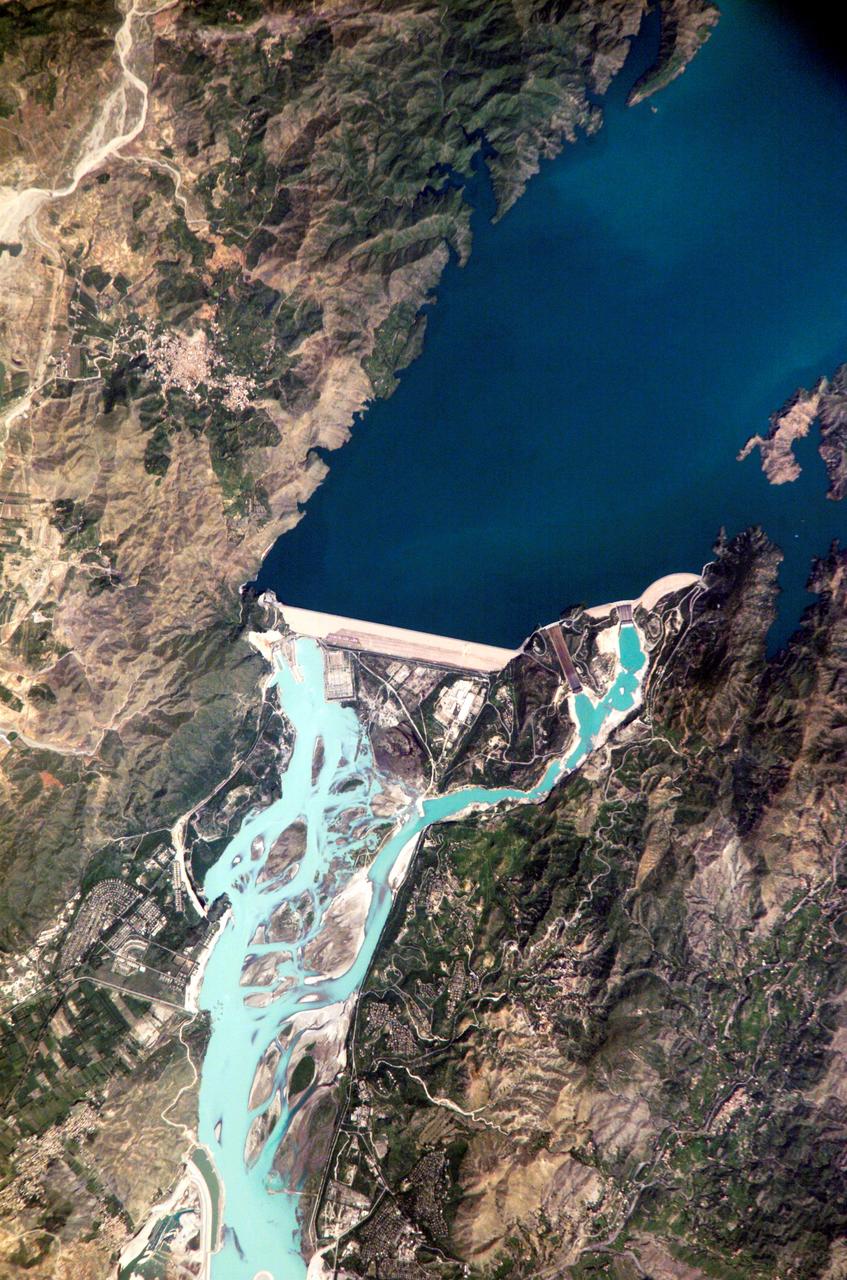

ISS005-E-12804 (6 September 2002) --- Tarbela Dam, Pakistan is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 5 crewmember on the International Space Station (ISS). The Indus River basin extends from the Himalaya mountain ranges forming the northeastern boundary of Pakistan, to the alluvial plains of Sindh near the Arabian Sea coastline. Tarbela Dam is part of the Indus Basin Project that resulted from a water treaty signed in 1960 between India and Pakistan. This treaty guaranteed Pakistan water supplies independent of upstream control by India. Designed primarily for water storage rather than power generation, the dam was completed in 1977. Turquoise waters of the Indus River (to the south of the dam) reflect the high proportion of silt and clay suspended in waters released by the spillways (chutes on either of side of the main dam). With a volume of 142,000,000 cubic meters, the Tarbela Dam is the largest earth and rockfill dam in the world and stands 147 meters above the Indus riverbed. Its reservoir occupies an area of 37 square kilometers. While the dam has fulfilled its purpose in storing water for agricultural use in Pakistan, there have been environmental consequences to the Indus river delta, according to NASA scientists who are studying the Space Station photography. Reduction of seasonal flooding and reduced water flows to the delta have resulted in decrease of mangrove stands and abundance of some fish species.
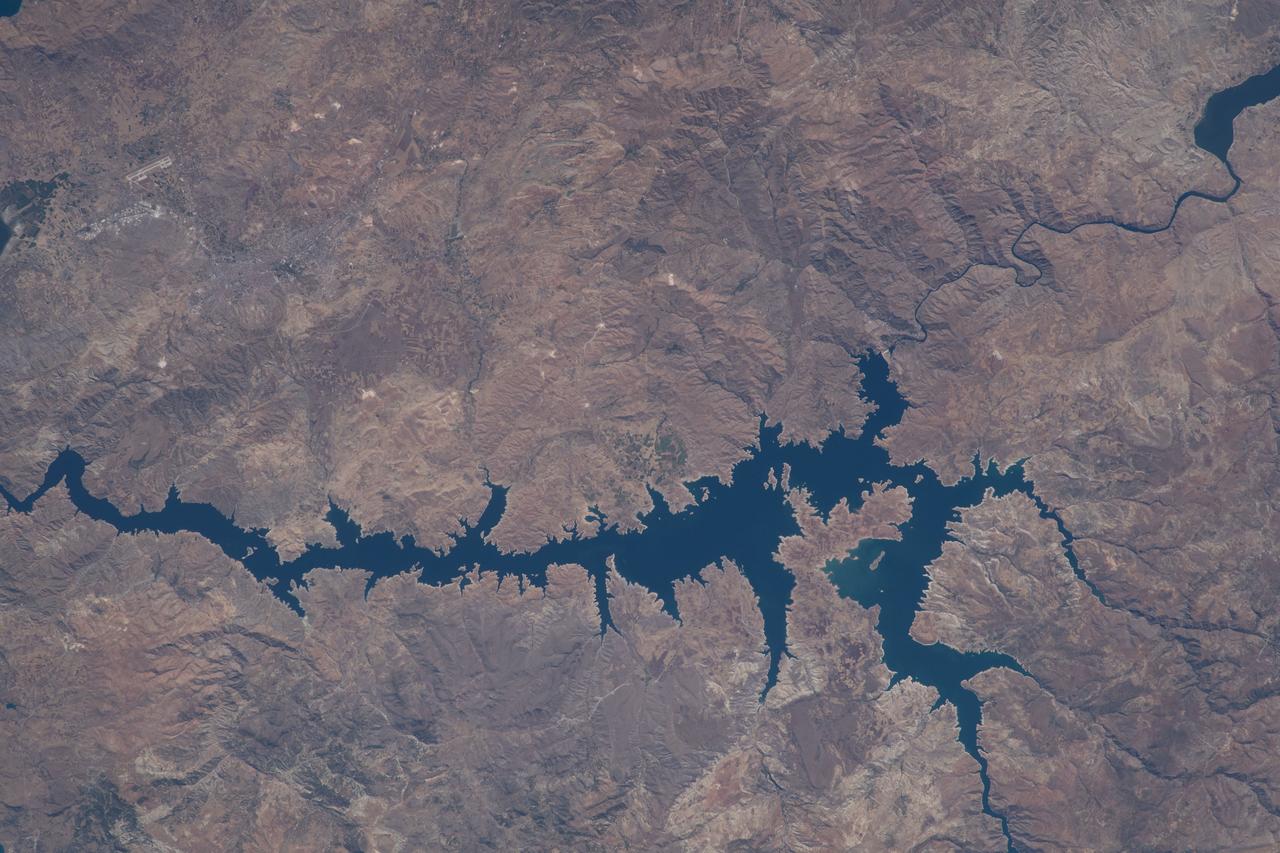

iss068e006715 (Oct. 1, 2022) --- This portion of the Euphrates River, containing the Keban Dam Reservoir created by the Keban Dam, is pictured in eastern Turkey from the International Space Station as it orbited 260 miles above.
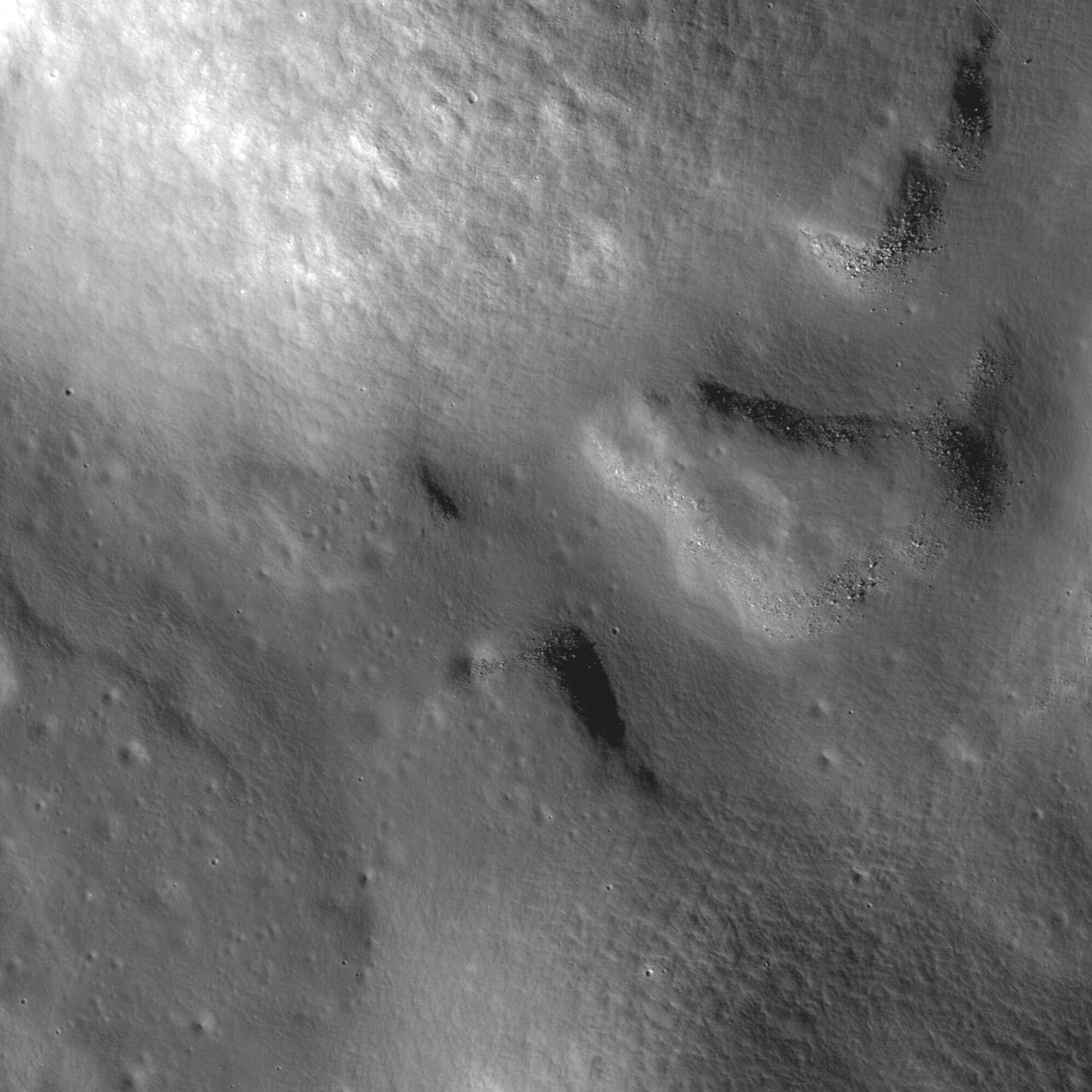

A bottleneck at the start of the lunar sinuous rille within Vallis Alpes formed several morphologic features including a lava pond, a breached dam, and an island in the rille in this image captured by NASA Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter.
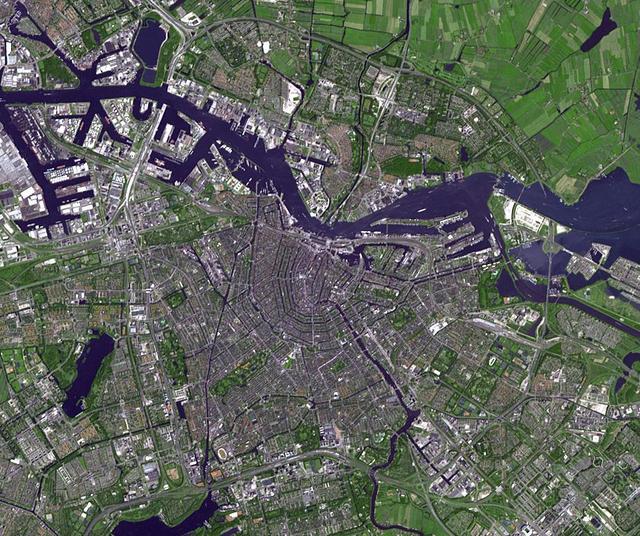

Amsterdam is the largest city and the capital of the Netherlands. Its name derives from a dam in the river Amstel. Founded in the 12th century as a fishing village, Amsterdam was one of the most important ports in the world in the 17th century.

This image from NASA Terra satellite shows the Kachchh region in the Gujarat province of western India. On January 26, 2001, a magnitude 7.7 earthquake devastated this area, killing 20,000 people and destroying buildings, dams, and port facilities.

iss071e523521 (Aug. 21, 2024) --- Brazil's Single Island Dam (top) leads into the Paranaiba River which splits into the Rio Grande that leads into the Red Water Dam. The International Space Station was orbiting 260 miles above the South American nation at the time of this photograph.

STS083-747-026 (4-8 April 1997) --- Aswan Dam and Lake Nasser along the Nile River, Egypt. The Aswan Dam controls the flow of the Nile River forming Lake Nasser. Lake Nasser is reaching relatively high water levels due to the plentiful rains since December 1996 in Kenya, near the headwaters of the Nile river. The light colored areas in the Lake are where the sun is reflecting off the surface of the water. These areas are fairly calm and not disturbed by wind gusts enabling the sunglint to show water current patterns on the surface. The Aswan runway is seen as a dark set of lines west of the Aswan Dam.

iss071e462180 (Aug. 9, 2024) --- Lake Assad in Syria (upper right) and lakes created by hydroelectric dams in Turkiye, all along the Euphrates River, are pictured from the International Space Station as it orbited 263 miles above the Turkish nation that connects Europe with Asia.

iss063e002302 (April 22, 2020) --- The Idriss I Dam in Morocco is pictured from the International Space Station as it orbited off the Atlantic coast of the North African nation.
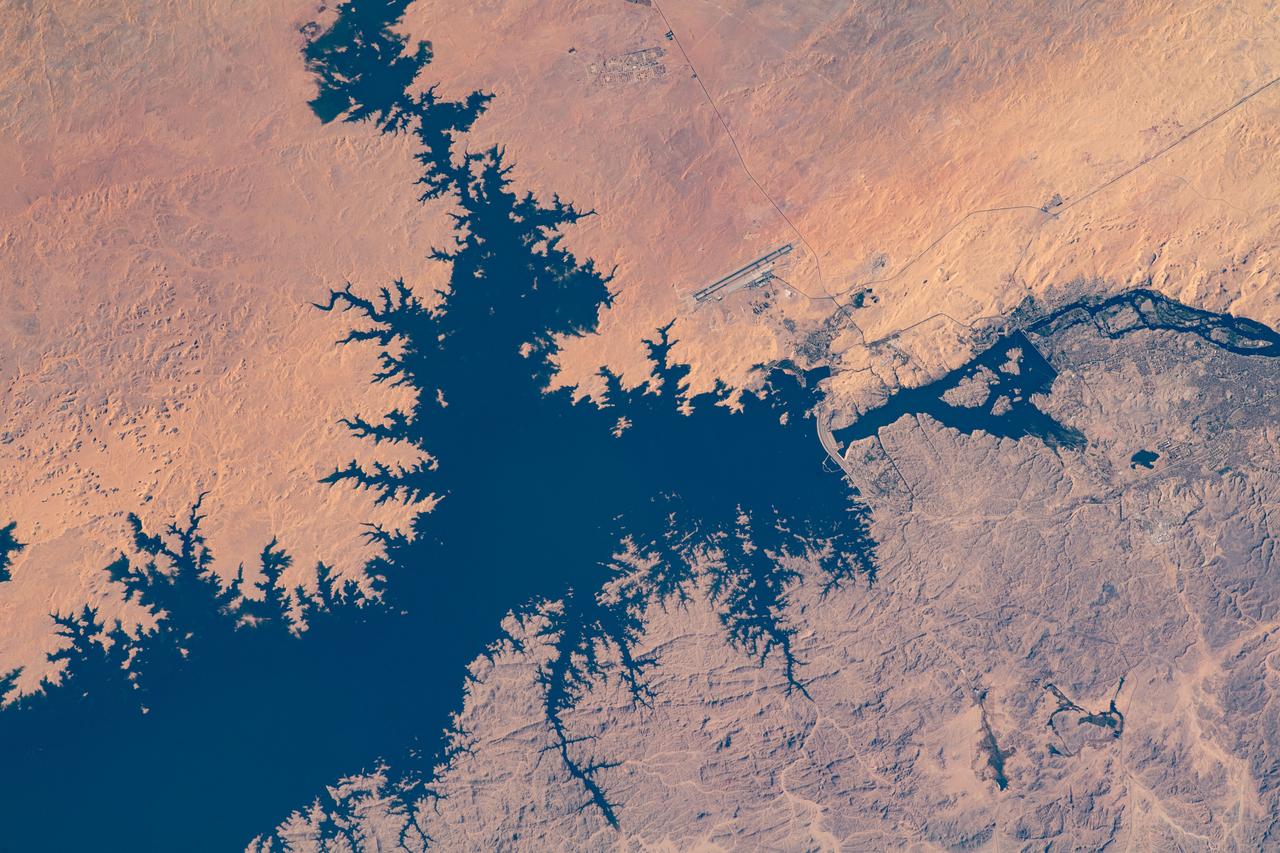

iss064e006268 (Nov. 26, 2020) --- Pictured from the International Space Station, the Aswan Dam in Egypt separates Lake Nasser from the Nile River.
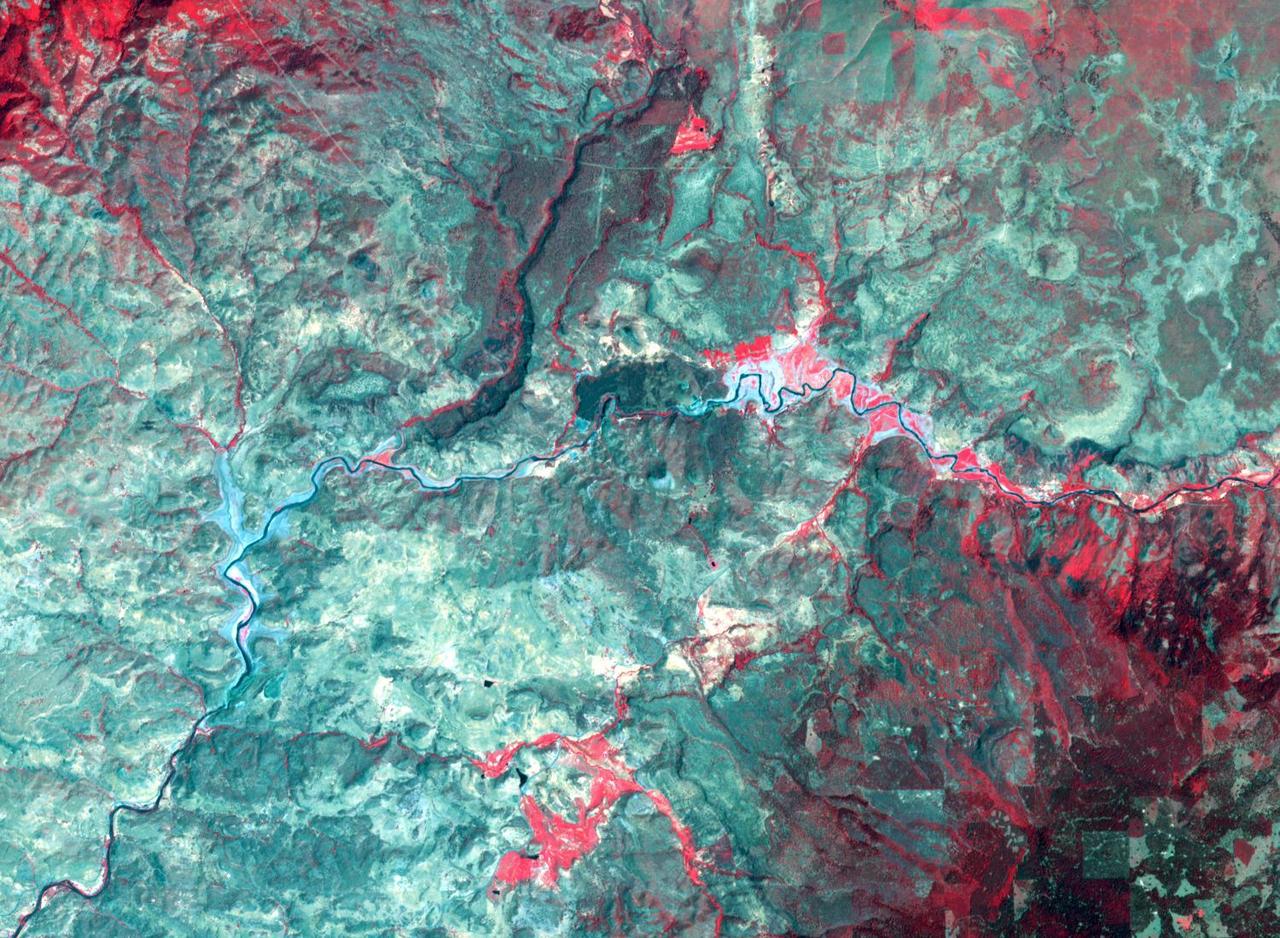

By August, 2024, the four dams blocking the flow of the Klamath River in California and Oregon were removed. After more than 100 years, nearly 640 km of salmon habitat were restored. Two of the dams and their reservoirs, Copco 1 and Copco 2 in northern California, are shown before and after removal. The images were acquired July 18, 2024 and August 15, 2020, cover an area of 16.5 by 22.5 km, and are located at 42.1 degrees north, 122.2 degrees west. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26448

ISS008-E-12372 (10 January 2004) --- The Biobio River in Chile was featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 8 crewmember onboard the International Space Station (ISS). The river flows northwestward from the high Cordillera of the Andes to the Pacific Ocean near Concepcion, about 450 kilometers south of Santiago. This image shows a section of the river that skirts around Antuco volcano in the Andes, and features the Pangue dam and reservoir filling a narrow, meandering segment of the Biobio River valley. Upstream from the Pangue Reservoir (right frame), the cleared areas associated with earth moving and construction of the Ralco Dam are visible. The straight white lines in cleared forest between the two dams probably represent power transmission lines.
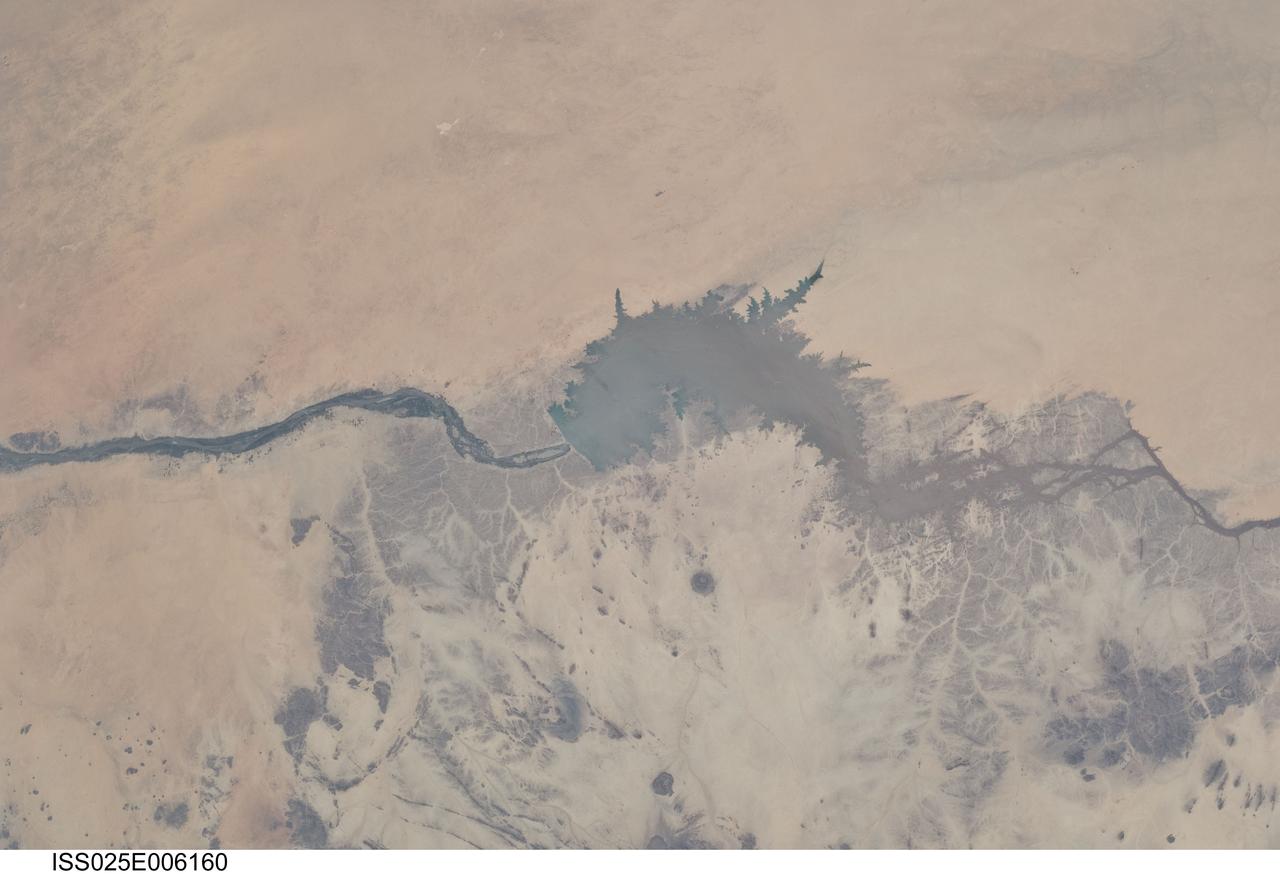

ISS025-E-006160 (5 Oct. 2010) --- Merowe Dam, Nile River and the Republic of the Sudan are featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 25 crew member on the International Space Station. The Merowe Dam is located near the 4th cataract of the Nile River, in the Nubian Desert of the northeastern Republic of the Sudan (also known as Sudan). The dam was built to generate hydroelectric power—electricity intended to further industrial and agricultural development of the country. This photograph illustrates the current extent of the reservoir filling behind the dam; the final spill gate was closed in 2008. The Merowe Dam is located approximately 350 kilometers (215 miles) to the northwest of Sudan’s capital, Khartoum. The nearest settlement downstream of the dam is Karima. Following Sudan’s independence from Egypt and the United Kingdom in 1956, allocation and control of Nile River water was divided between Egypt and Sudan by the Nile Waters Treaty signed in 1959. Today, other countries within the Nile basin—including Ethiopia, Kenya, Rwanda, Tanzania, and Uganda—are seeking more equitable allocation and utilization of the water and recently (2010) signed a new water use pact challenging the 1959 treaty. Beyond the issues of water rights, several local tribes will be displaced by the planned 170 kilometer-long reservoir, and the flooded region contains significant but little-studied archeological sites. The Sudanese government has a resettlement program in place for the tribes. A variety of international institutions have been conducting “salvage” or “rescue” archeological surveys since 1999. Such rescue surveys seek to preserve as much information as possible from sites that will be destroyed or otherwise made inaccessible (in this case by flooding).
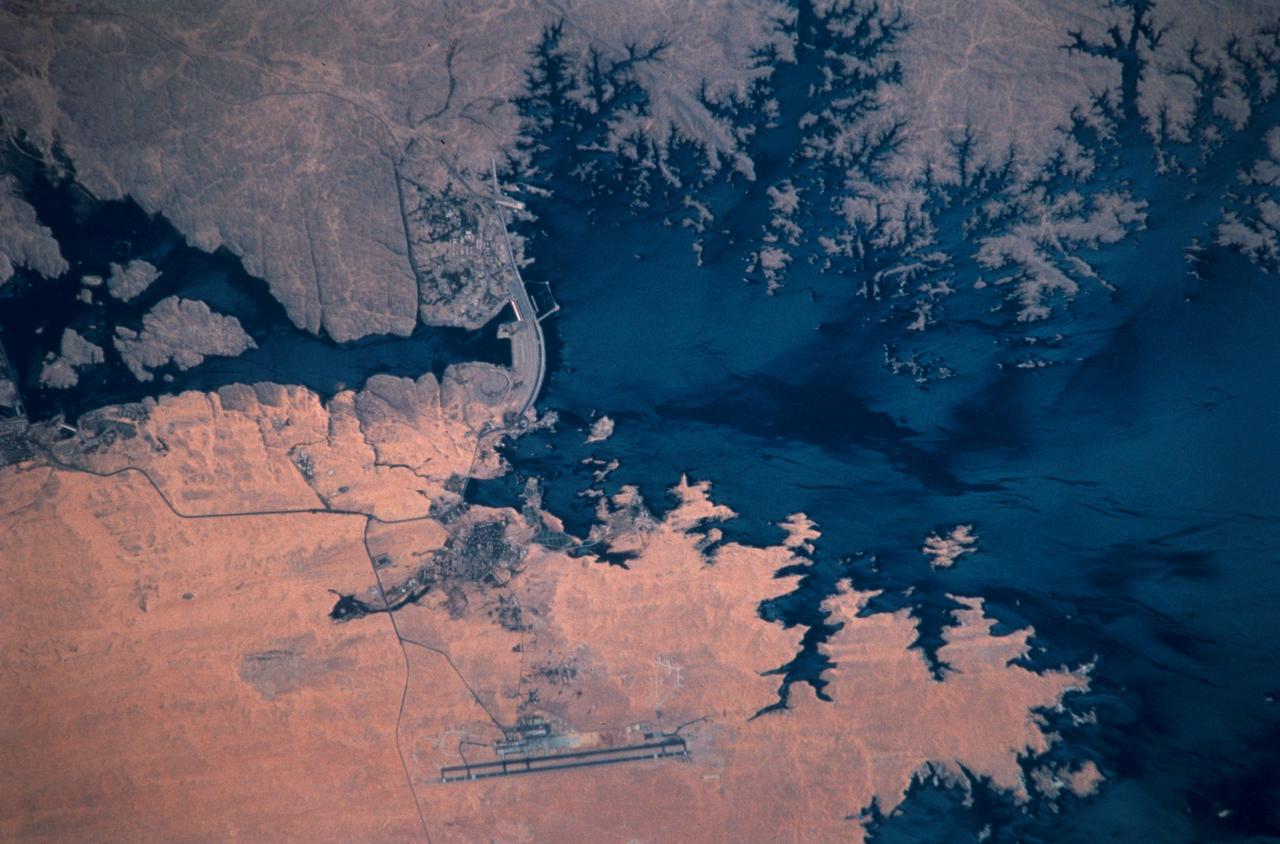

STS102-303-017 (8-21 March 2001)--- The STS-102 crew members used a 35mm camera on the flight deck of the Space Shuttle Discovery to record this image of the Aswan High Dam. The structure was completed in 1970 and is one of the largest earthen embankment dams in the world. It is 364 feet (111 meters) tall, 12,565 feet (3,830 meters) long and nearly 3,281 feet (1,000 meters) wide. When it was built the new reservoir required relocation of nearly 100,000 residents and some archaeological sites. Although the reservoir has benefited Egypt by providing power and controlling floods, according to NASA scientists, it has also had detrimental effects on the Nile system. Before the dam, an estimated 110 million tons of silt was deposited by the annual flood of the Nile, enriching agricultural lands and maintaining the land of the Nile delta. Now this sediment is trapped behind the dam, requiring artificial fertilization of agricultural lands and leading to erosion and saltwater intrusion where the Nile river meets the Mediterranean Sea.
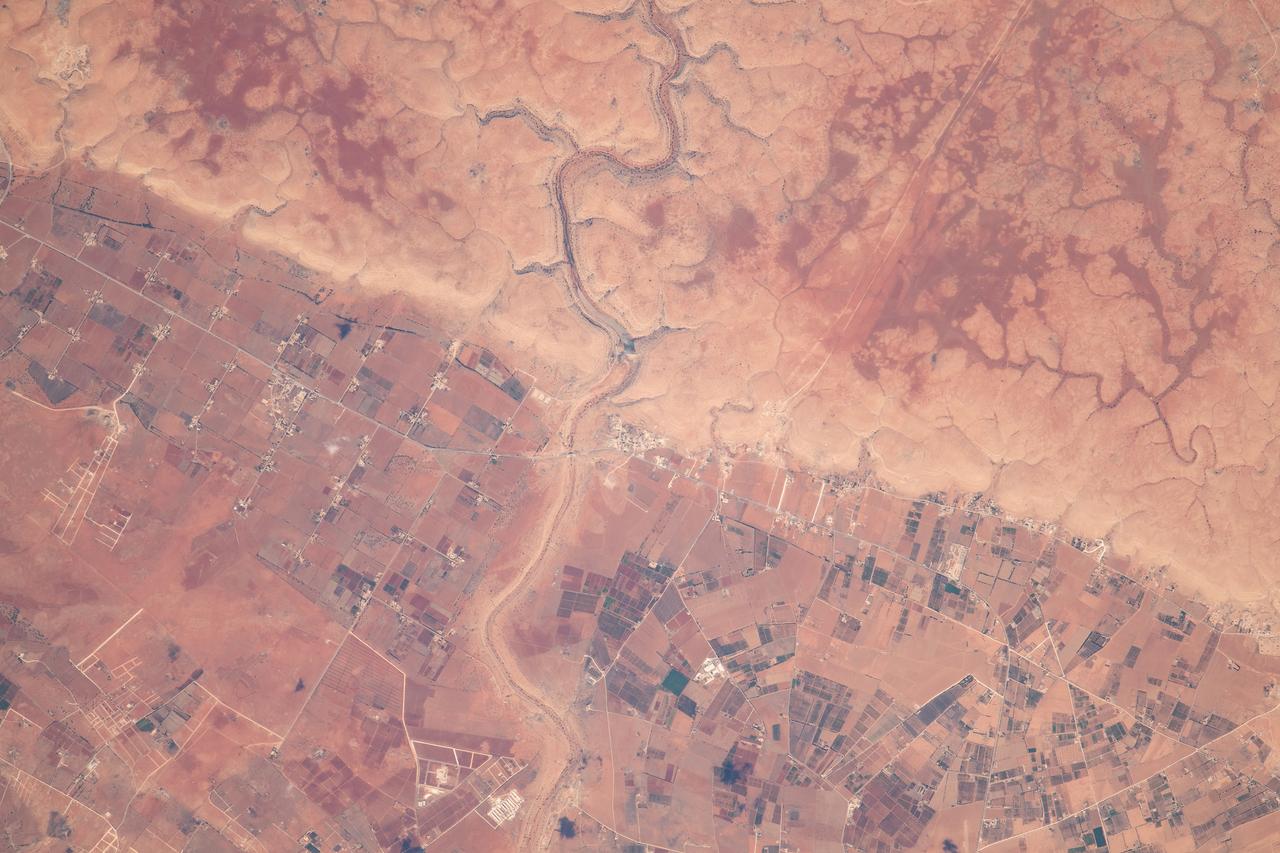

iss069e061443 (Aug. 17, 2023) --- Wadi al Qattarah, containing an agricultural zone, grazing land, and a dam, is located southeast of Benghazi, Libya, in this photograph from the International Space Station as it orbited 263 miles above the Mediterranean Sea.
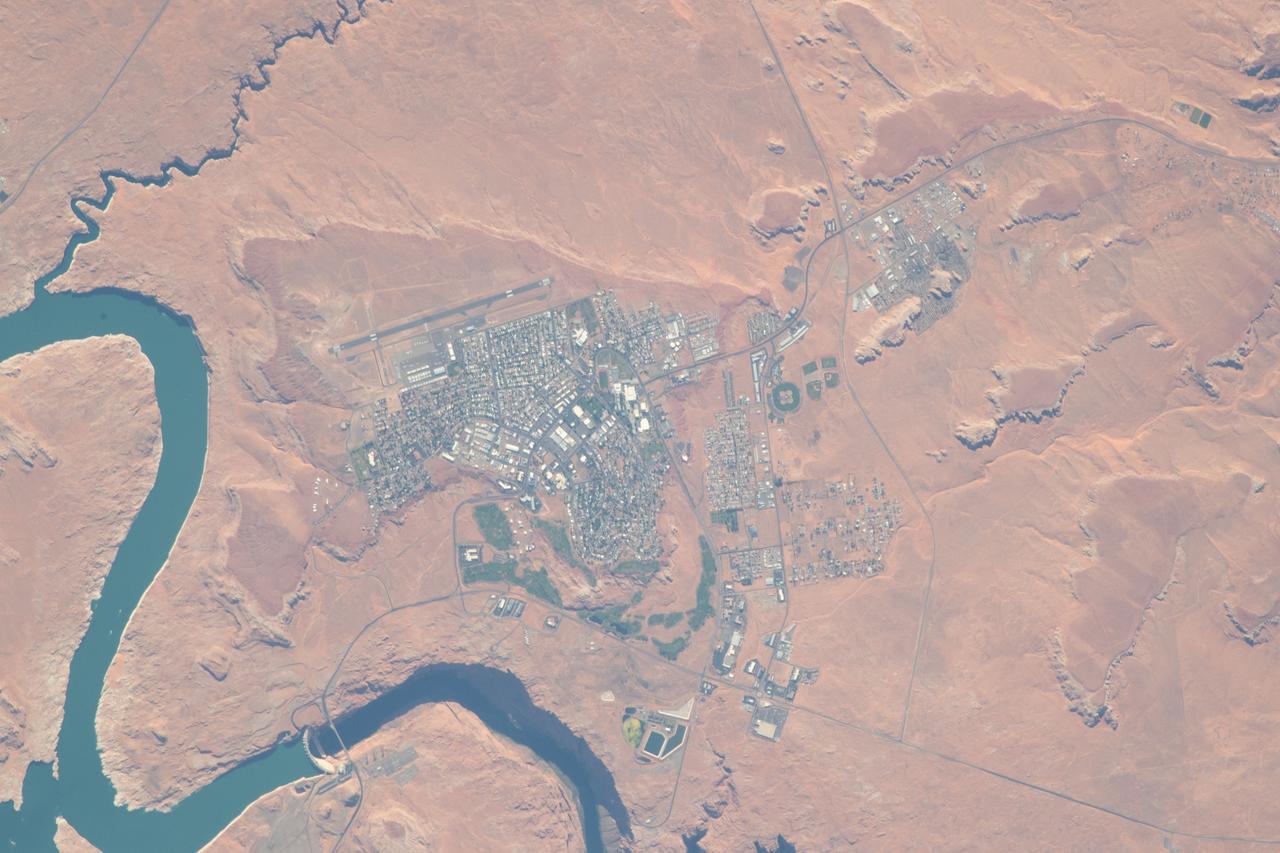

iss056e094592 (July 10, 2018) --- The city of Page, Ariz., the Colorado River and Glen Canyon Dam which forms Lake Powell are pictured as the International Space Station's orbital trek took it over the southwestern United States.

iss060e004214 (July 4, 2019) --- Lake Isabella in California, pictured as the International Space Station orbited 256 miles above the Golden State, is a reservoir formed in 1953 when the Kern River was dammed by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers.
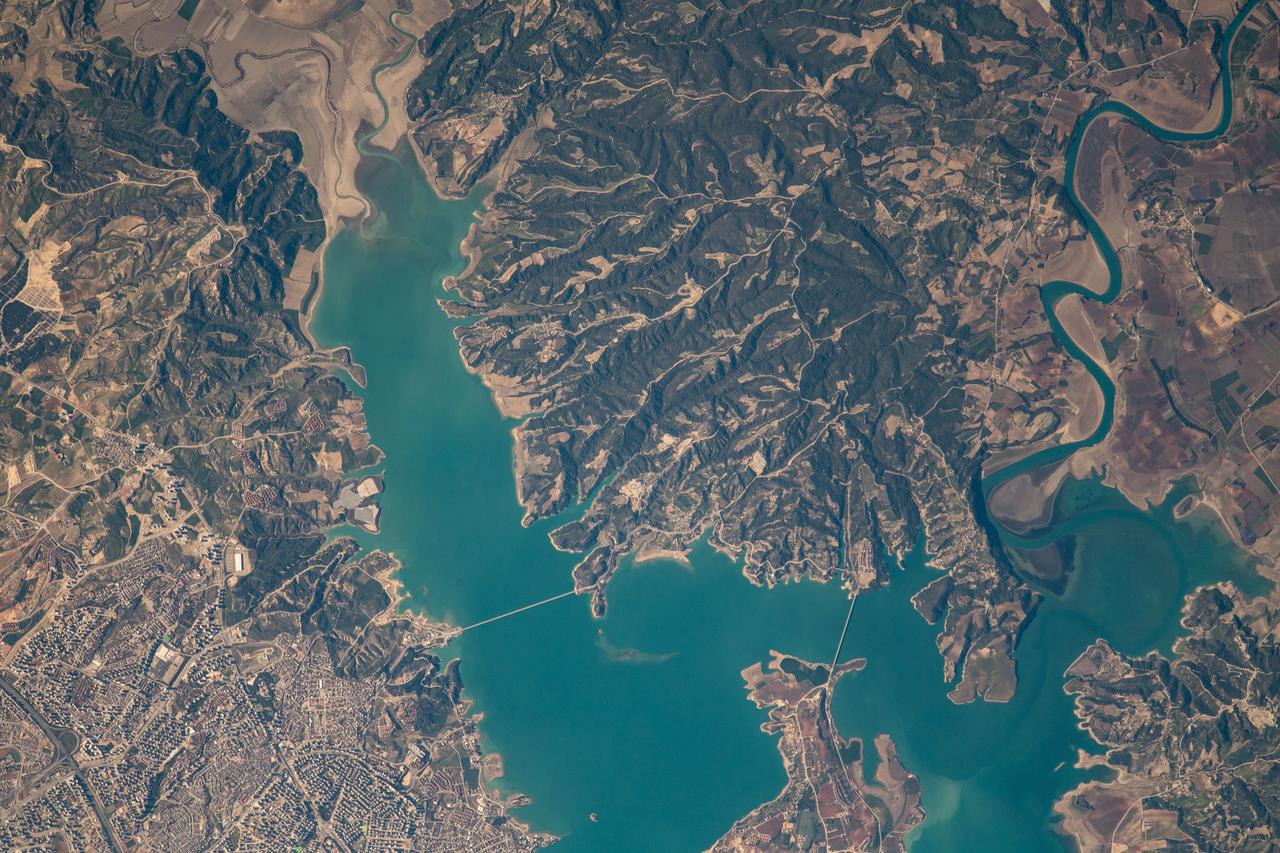

iss068e053748 (Feb. 14, 2023) --- At lower left, the city of Adana, Turkey, rests on the banks of the Seyhan Dam Lake in this photograph from the International Space Station as it orbited 264 miles above. Prominent at lower center, is the Çatalan Bridge.

iss071e064589 (May 8, 2024) --- An artifical lake created by the Florentino Ameghino Dam on the Chubut River is pictured from the International Space Station as it orbited 266 miles above the Patagonia region of Argentina.

iss071e130671 (May 26, 2024) --- Ute Reservoir in Utah, created by Ute Dam in New Mexico and filled by the Canadian River, is pictured frm the International Space Station as it orbited 262 miles above the southwestern United States.
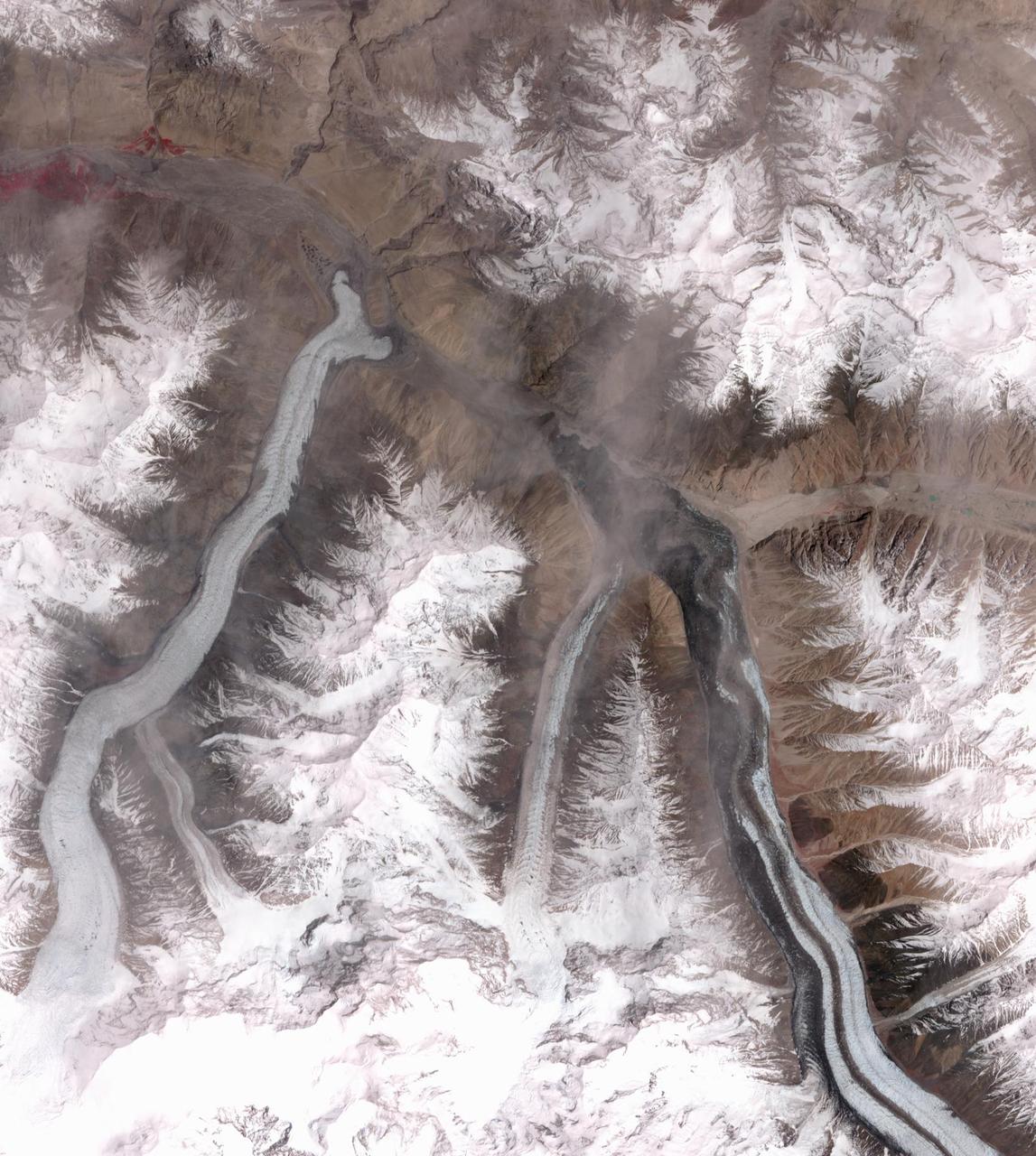

In October 2016, the Khurdopin Glacier in Pakistan began a rapid surge after 20 years of little movement. By March, 2017, a large lake had formed in the Shimshal River, where the glacier had formed a dam. Fortunately, the river carved an outlet through the glacier before the lake could empty catastrophically. In this pair of ASTER images, acquired August 20, 2015 and May 21, 2017, the advance of the Khurdopin Glacier (dark gray and white "river" in lower right quarter of image) is obvious by comparing the before and after images. The images cover an area of 25 by 27.8 km, and are located at 36.3 degrees north, 75.5 degrees east. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22304
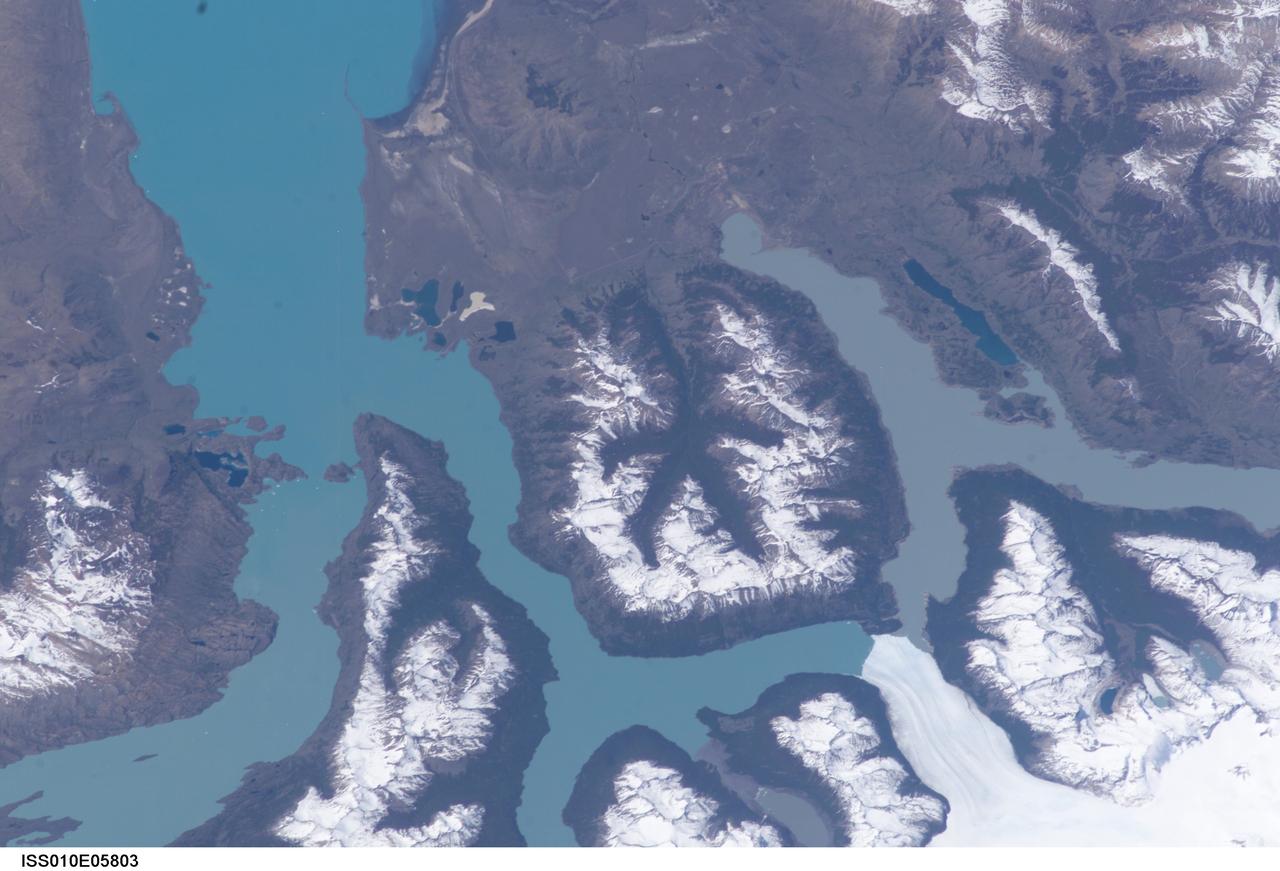

ISS010-E-05803 (4 November 2004) --- Moreno Glacier, Argentina is featured in this digital image photographed by an Expedition 10 crewmember on the International Space Station (ISS). Perito Moreno (or Moreno Glacier) is located in the ice fields of southern Patagonia and is the centerpiece of the Parque Nacional Los Glaciares. The glacier is also noteworthy as a tourist attraction, due to periodic formation of an ice dam between the main portion of Lago (Lake) Argentino to the northeast and a southern extension of the lake (Brazo Rico). NASA scientists studying the Space Station imagery made the following observations about the photo: Meltwater runoff from the surrounding mountains fills Brazo Rico to a higher elevation than nearby Lago Argentino and exerts hydrostatic pressure on the ice dam. This pressure leads to formation of drainage tunnels and fractures in the ice dam, which eventually fails. Earlier this year (March 2004) the ice dam collapsed in a spectacular show. A new ice dam across the Brazo Rico arm of Lago Argentino is visible in this image. The past extent of glaciations in the region is marked by several valleys formerly filled by flowing ice. A particularly striking example of this landscape feature is in the center of the image, where five glacial valleys converge to a central star-shaped outflow valley. Widespread recession of the glaciers in southern Patagonia has occurred over the last 30 years possibly due to warming of the regional climate. Contrary to this trend, Perito Moreno seems to be maintaining equilibrium between ice formation in the mountains and ice loss due to melting and calving into Lago Argentino.

The Channeled Scablands in Washington were formed about 19,000 years ago when glacial Lake Missoula in Montana burst through its ice dam, and a 320 m deep lake emptied in a catastrophic flood that reached the Pacific Ocean. The basaltic terrain of Washington was deeply carved into channels, mesas, and giant dunes as the water scoured the landscape. The image was acquired August 4, 2021, covers an area of 40.2 by 48.8 km, and is located at 47.5 degrees north, 119.2 degrees west. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26008

On Nov. 5, 2015, a dam at an iron-ore mine in southeastern Brazil burst, sending a wall of water, clay-red mud and debris downstream, overwhelming several villages in the path as seen by NASA Terra spacecraft. The Germano mine is near the town of Mariana in Minas Gerais state. The region is seen in this image from the Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) instrument aboard NASA's Terra spacecraft was acquired Nov. 12, 2015, covers an area of 6.8 by 14.3 miles (11 by 23 kilometers), and is located at 20.2 degrees south, 43.5 degrees west. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20156

iss067e170414 (July 1, 2022) --- The Colorado River leads to Lake Buchanan (lower right) formed by the Buchanan Dam that provides water supply and hydroelectric power in Texas. The International Space Station was orbiting 262 miles above the Lone Star state at the time of this photograph.
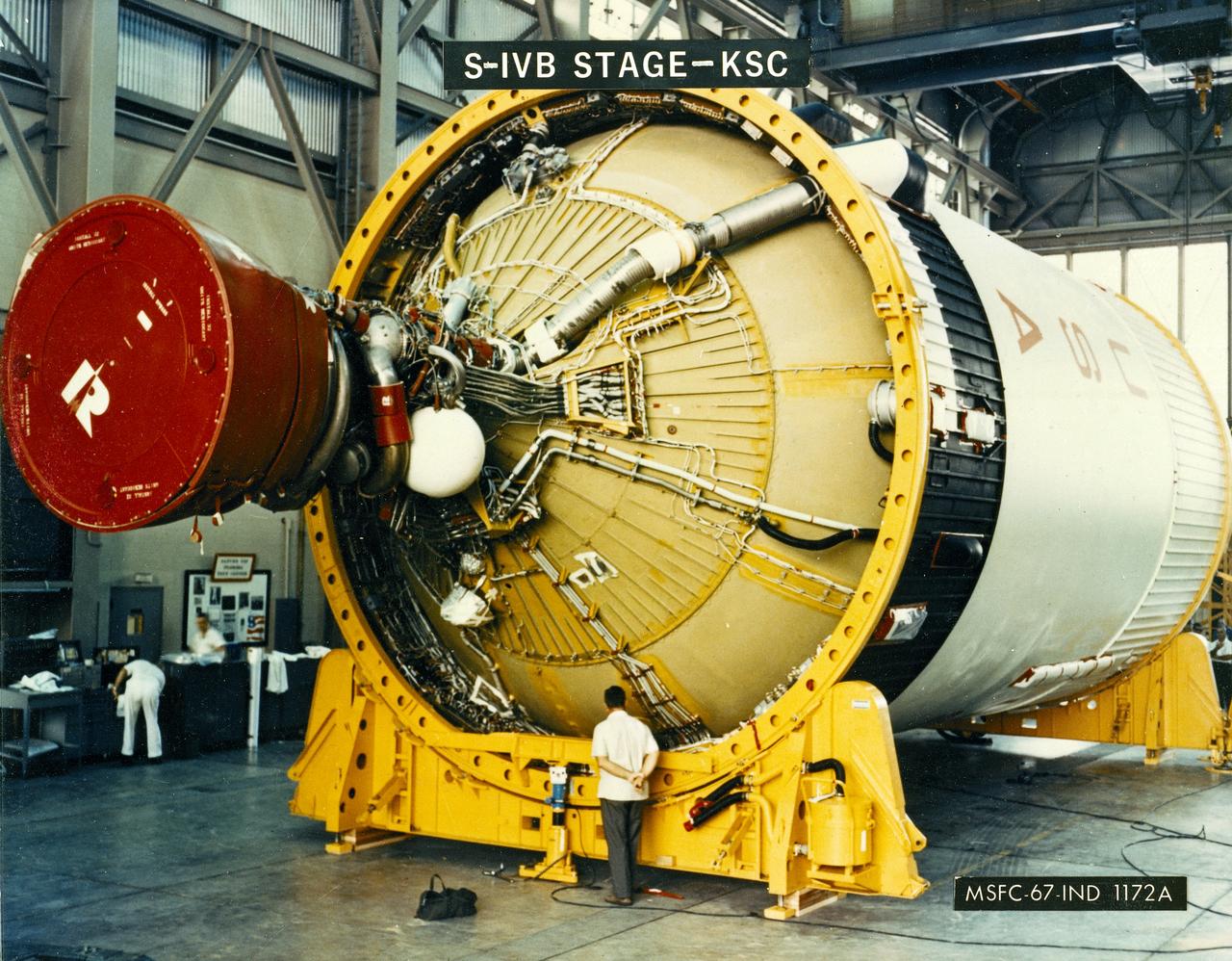
A NASA technician is dwarfed by the gigantic Third Stage (S-IVB) as it rests on supports in a facility at KSC. The towering 363-foot Saturn V was a multi-stage, multi-engine launch vehicle standing taller than the Statue of Liberty. Altogether, the Saturn V engines produced as much power as 85 Hoover Dams.
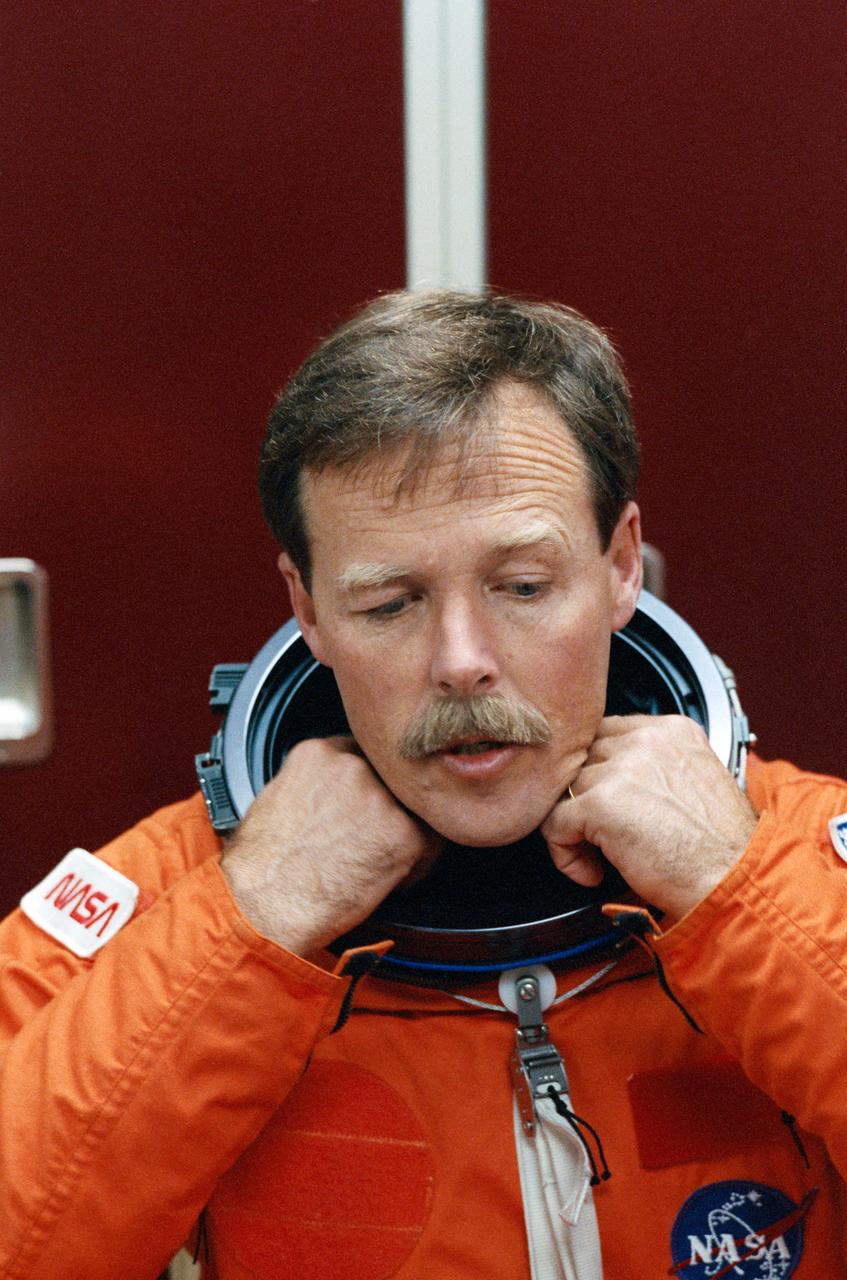

STS-47 Endeavour, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 105, Commander Robert L. Gibson adjusts the launch and entry suit (LES) neck dam during suit donning in JSC's Mockup and Integration Laboratory (MAIL) Bldg 9A. Gibson is preparing for launch emergency egress (bailout) exercises in the Crew Compartment Trainer (CCT).
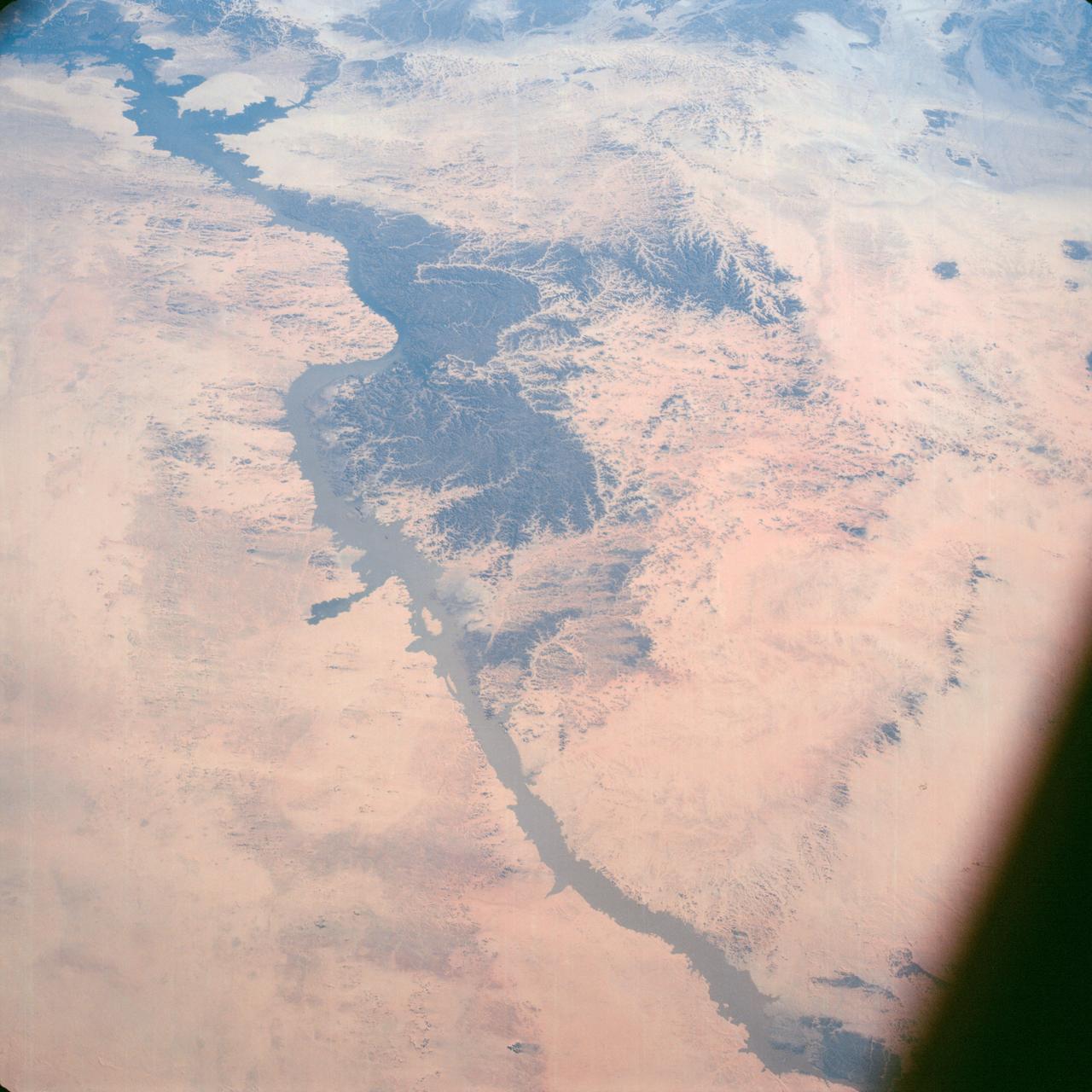

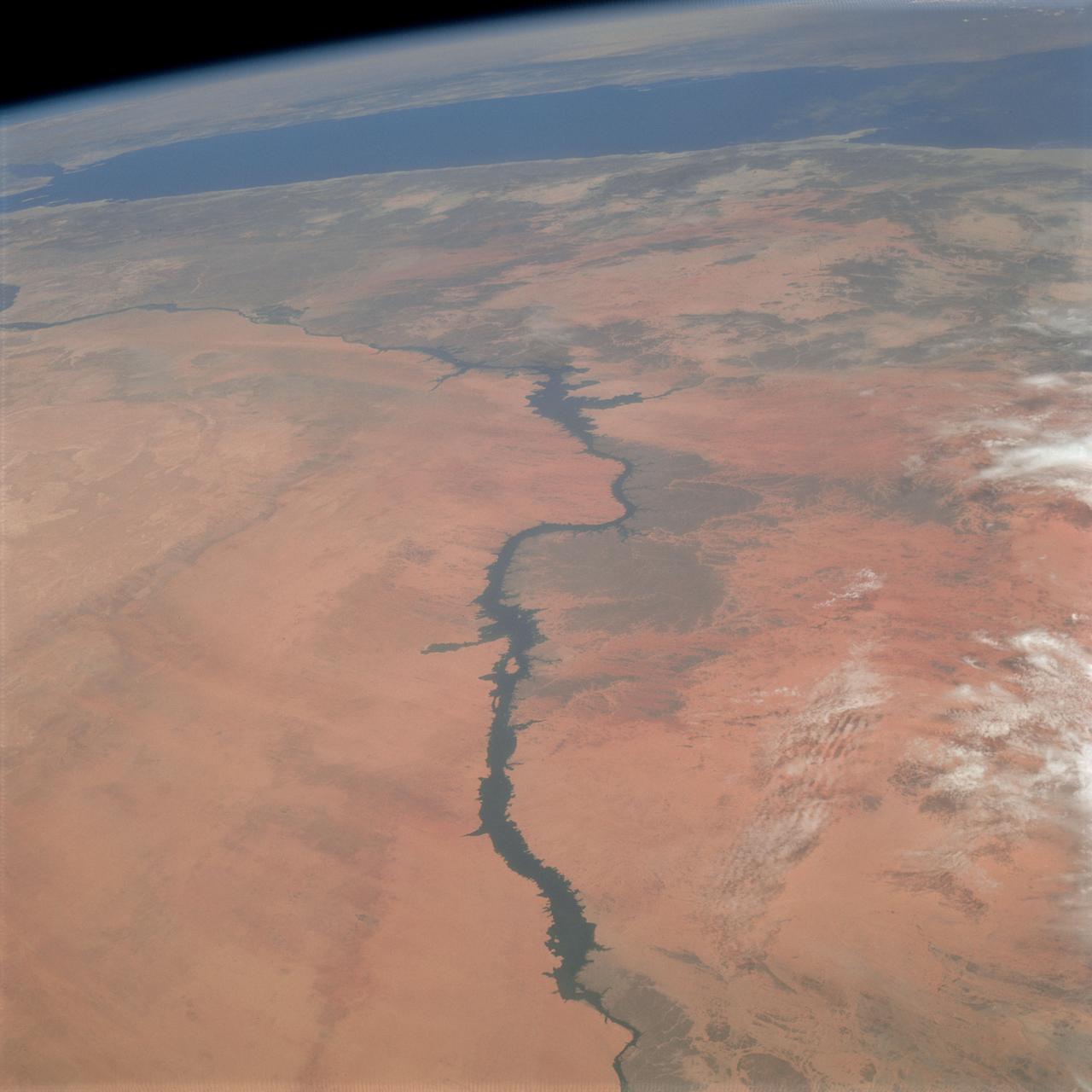
Lake Nasser on the Nile River in southeastern United Arab Republic (Egypt) as seen from the Apollo 7 spacecraft during its 10th revolution of the earth. Photographed from an altitude of 130 nautical miles, at ground elapsed time of 14 hours and 56 minutes. Lake Nasser was created by the contruction of the Aswan Dam on the Nile.
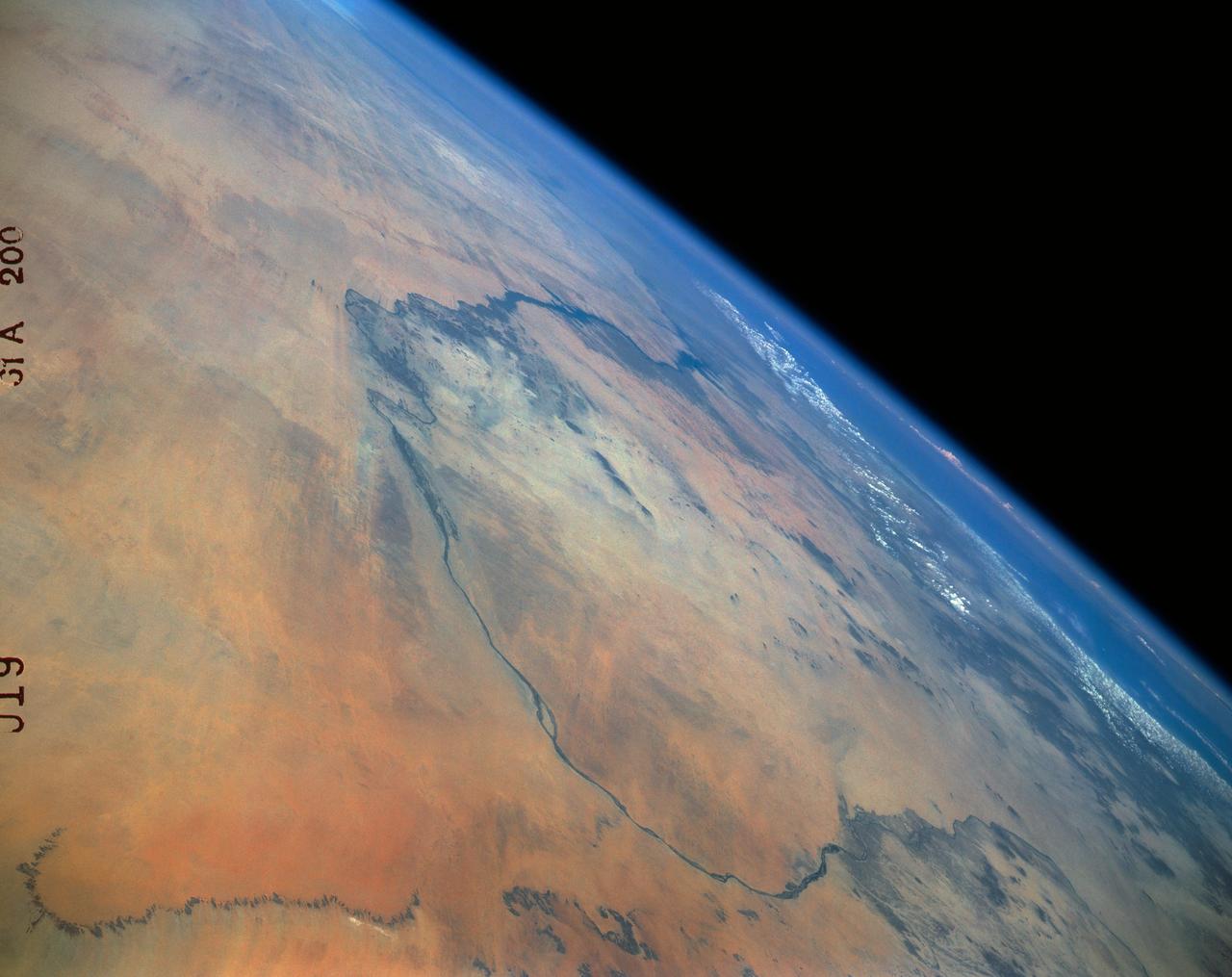

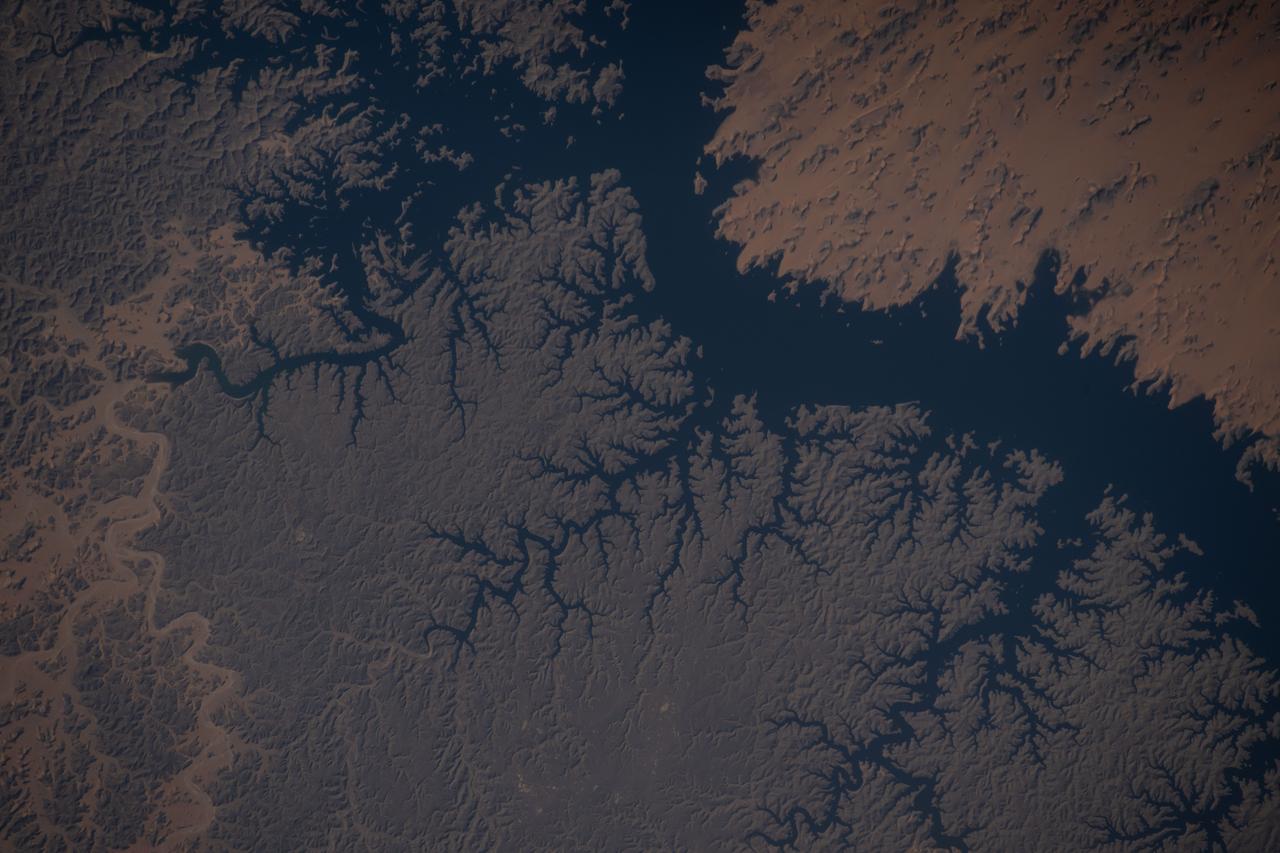
61A-200-019 (30 Oct-6 Nov 1985) --- The Nubian Desert of northern Sudan and southern Egypt. This view to the northeast, taken from a point 200 miles west of Khartoum, shows the Nile from Abu-Hamed downstream beyond Lake Nasser and the Aswan High Dam to the bend at Luxor.
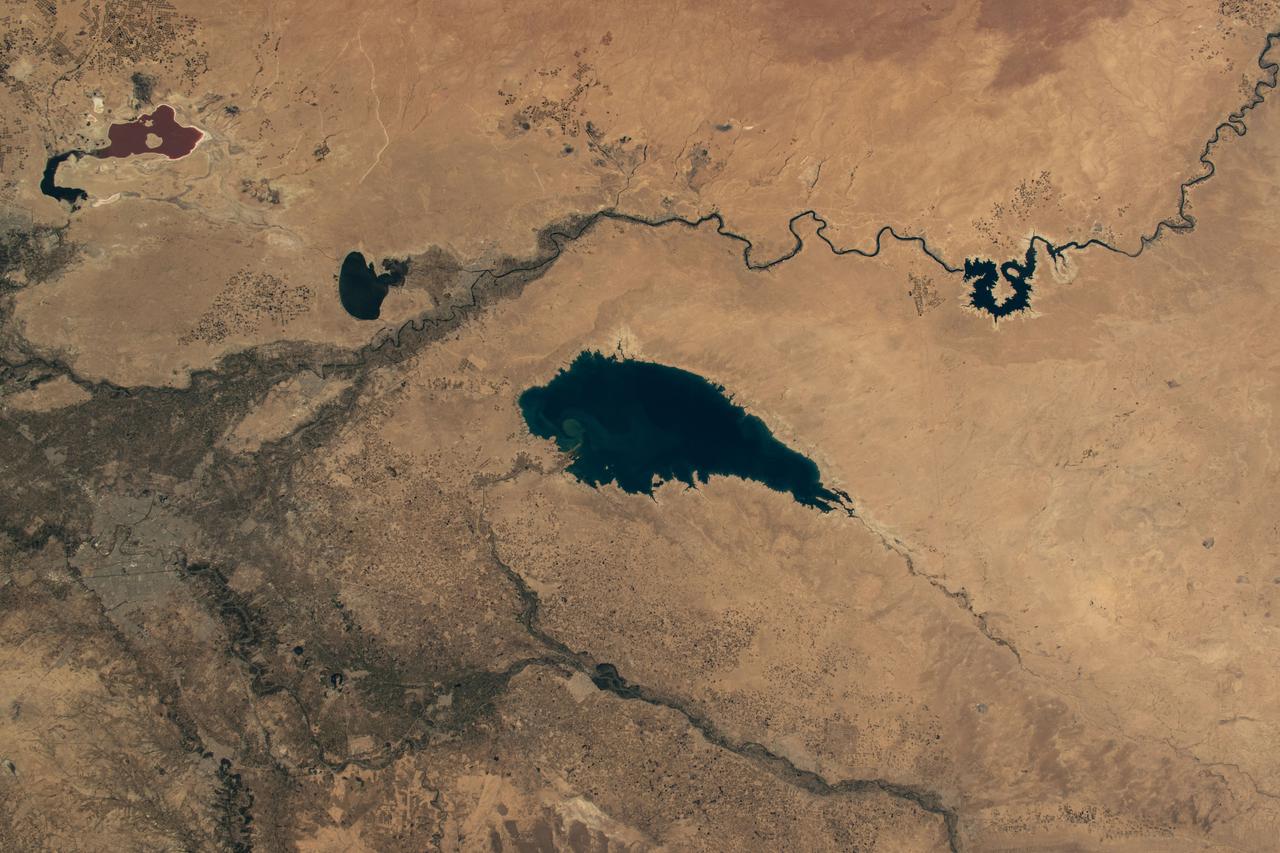

iss071e163367 (June 4, 2024) --- Baghdad, Iraq (lower left), is pictured near several bodies of water including (from left) Razazza Lake, Habbaniyah Lake, Therthar Lake, the Euphrates River, and Lake Qadisiyah created by the damming of the Euphrates. The International Space Station was orbiting 260 miles above the Middle East at the time of this photograph.
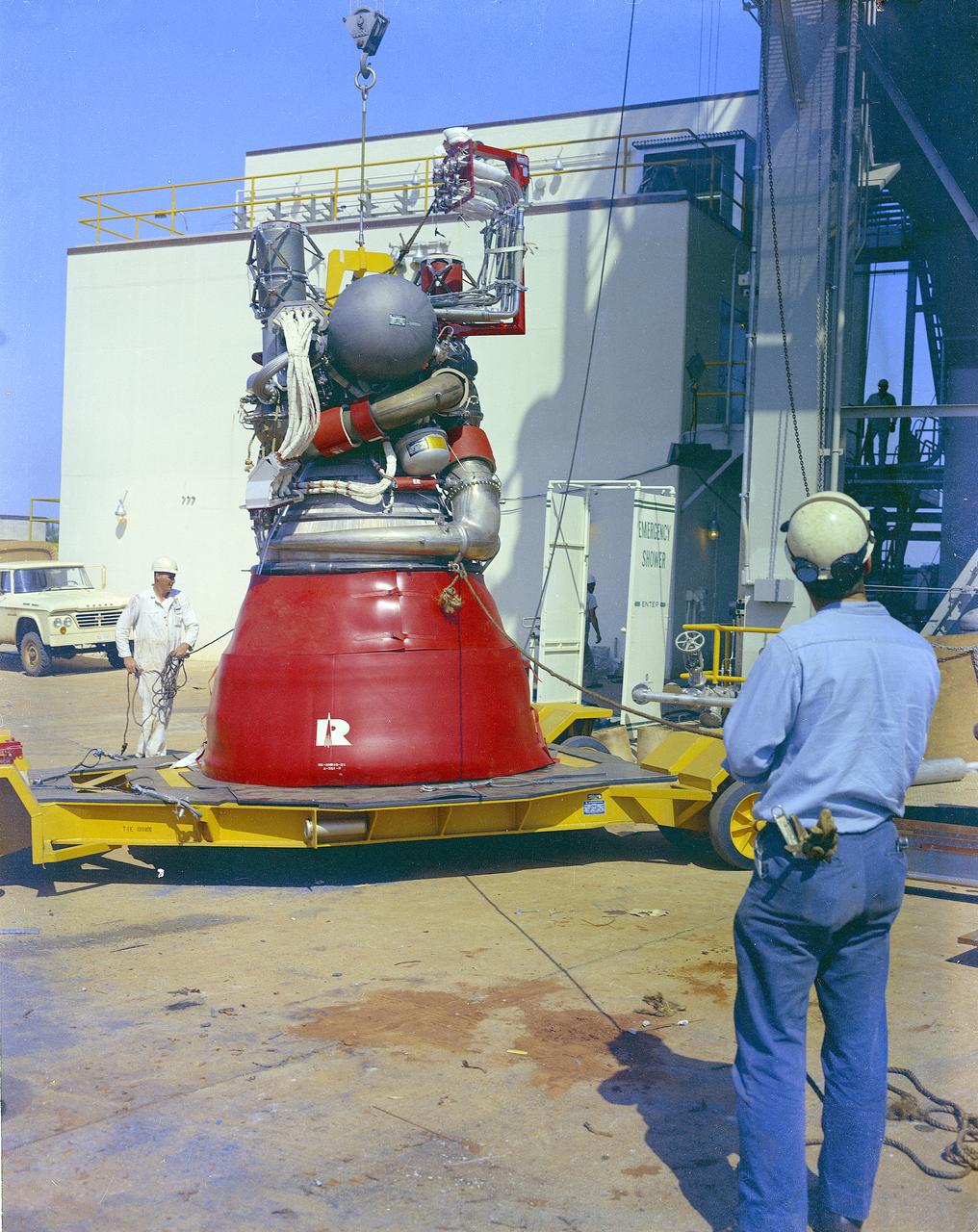

Two technicians watch carefully as cables prepare to lift a J-2 engine into a test stand. The J-2 powered the second stage and the third stage of the Saturn V moon rocket. The towering 363-foot Saturn V was a multi-stage, multi-engine launch vehicle standing taller than the Statue of Liberty. Altogether, the Saturn V engines produced as much power as 85 Hoover Dams.
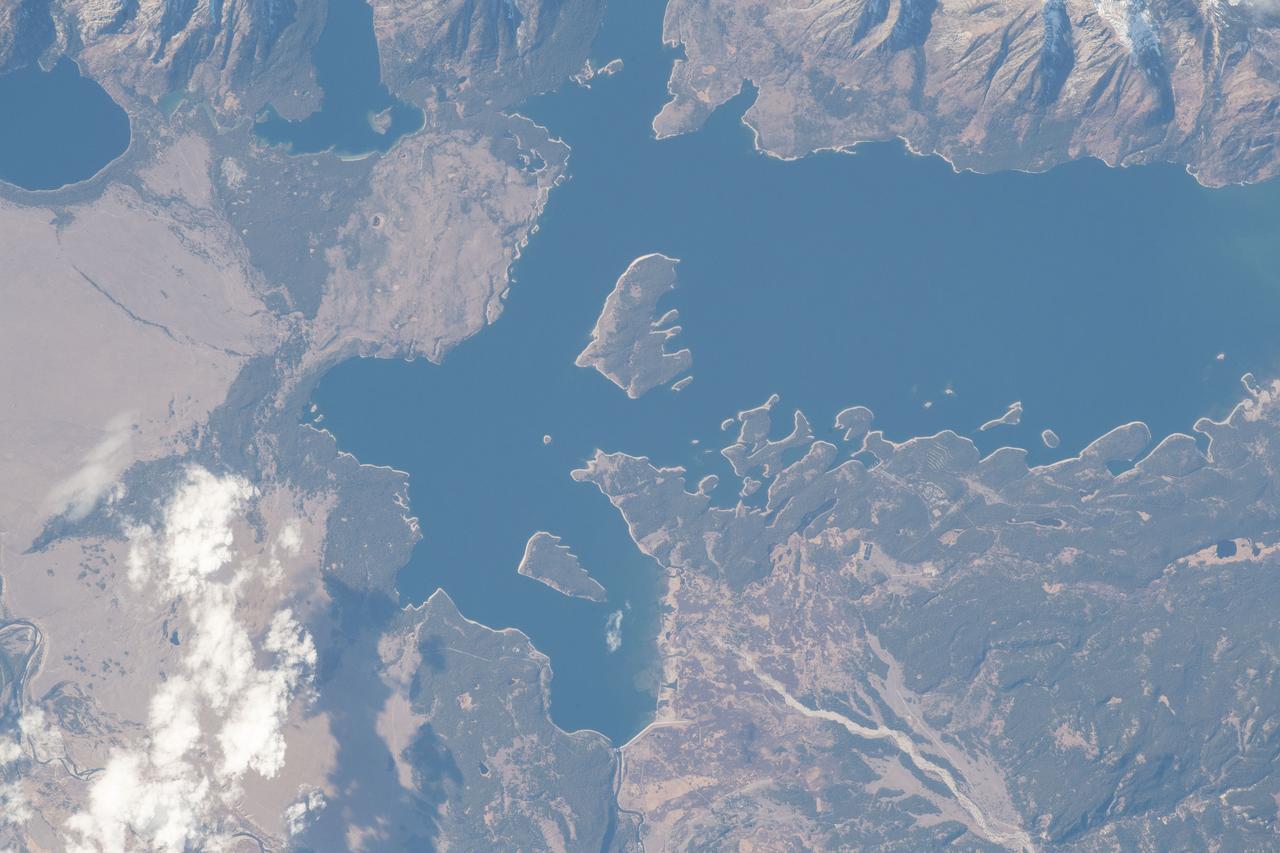

iss057e055571 (Oct. 22, 2018) --- Jackson Lake, in the state of Wyoming's Grand Teton National Park, is a natural remnant of glacial gouging and was enlarged by the construction of the Jackson Lake Dam in the early 20th century. The International Space Station was orbiting nearly 256 miles above North America when this photograph was taken by an Expedition 57 crew member.
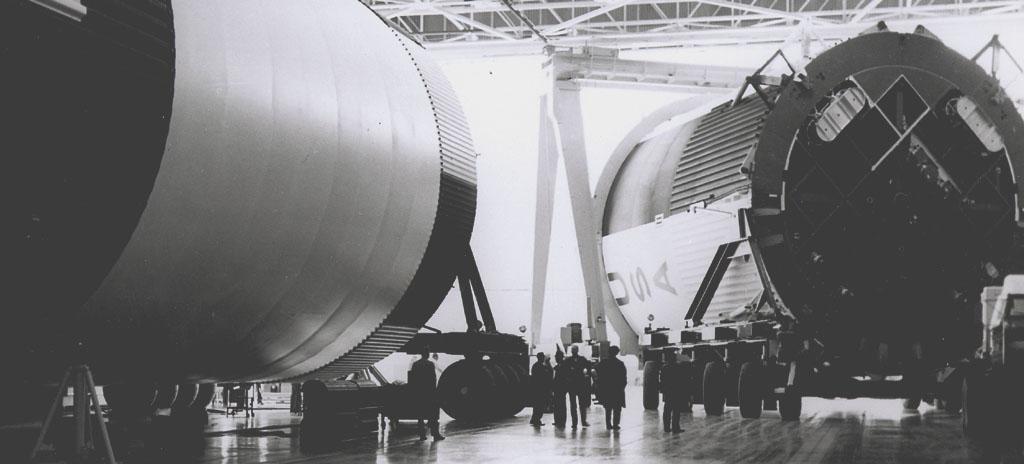

This photograph shows the Saturn V assembled LOX (Liquid Oxygen) and fuel tanks ready for transport from the Manufacturing Engineering Laboratory at Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The tanks were then shipped to the launch site at Kennedy Space Center for a flight. The towering 363-foot Saturn V was a multi-stage, multi-engine launch vehicle standing taller than the Statue of Liberty. Altogether, the Saturn V engines produced as much power as 85 Hoover Dams.
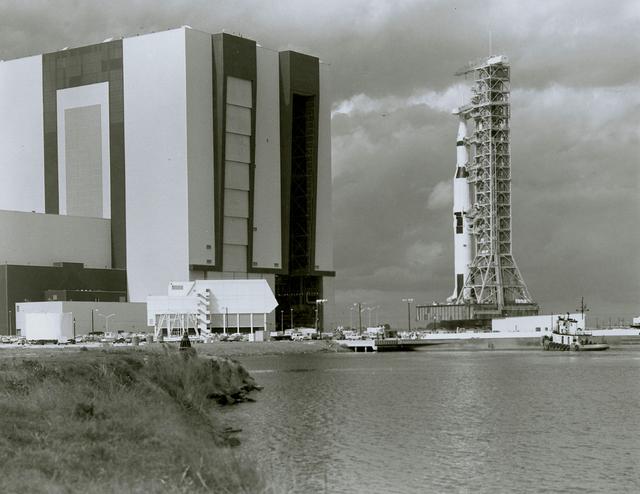
Apollo 6, the second and last of the unmarned Saturn V test flights, is slowly transported past the Vehicle Assembly Building on the way to launch pad 39-A. The towering 363-foot Saturn V was a multi-stage, multi-engine launch vehicle standing taller than the Statue of Liberty. Altogether, the Saturn V engines produced as much power as 85 Hoover Dams.

A bird's-eye view of Apollo 6 and its gantry leaving the Vehicle Assembly Building on the transporter heading to the launch site on Pad 39-A at Kennedy Space Center. The towering 363-foot Saturn V was a multi-stage, multi-engine launch vehicle standing taller than the Statue of Liberty. Altogether, the Saturn V engines produced as much power as 85 Hoover Dams.
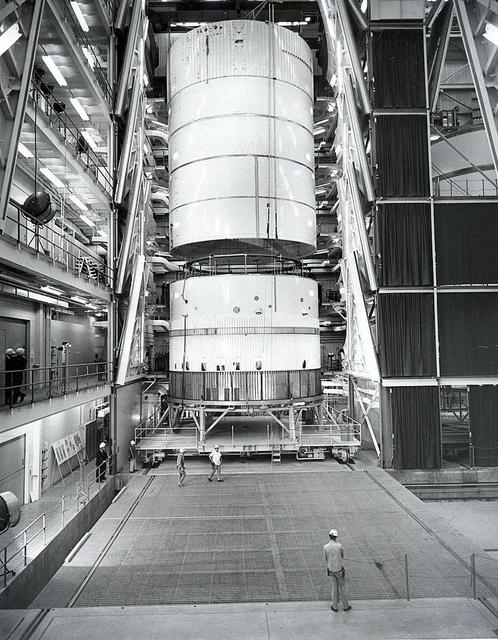
The hydrogen-powered second stage is being lowered into place during the final phase of fabrication of the Saturn V moon rocket at North American's Seal Beach, California facility. The towering 363-foot Saturn V was a multi-stage, multi-engine launch vehicle standing taller than the Statue of Liberty. Altogether, the Saturn V engines produced as much power as 85 Hoover Dams.

Astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., Gemini 5 Pilot, sits in the Gemini Static Article 5 Spacecraft and prepares to be lowered from the deck of the NASA Motor Vessel Retriever for Water Egress Training. The rubber "hat" on Astronaut Conrad's head is a neck dam and pulls down and fits tightly around the collar of his suit to prevent water from entering the suit.

ISS040-E-105768 (23 Aug. 2014) --- One of the Expedition 40 crew members aboard the International Space Station, flying at an altitude of 221 nautical miles, captured this image of Egypt's Nile River and Lake Nasser on Aug. 23, 2014. The Aswan High Dam is to the right of center in the 70mm focal-length image, as the Nile flows southward (to the right in this image) toward Cairo and it?s Mediterranean delta (both out of frame at right). The Red Sea, which runs more or less parallel to the Nile, is out of frame at bottom.
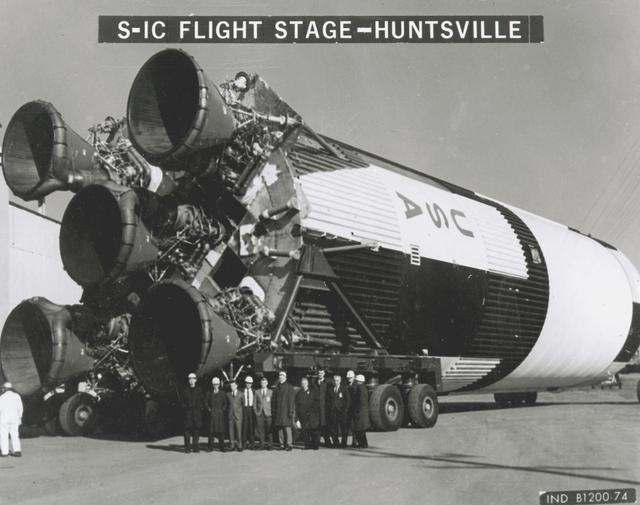

This small group of unidentified officials is dwarfed by the gigantic size of the Saturn V first stage (S-1C) at the shipping area of the Manufacturing Engineering Laboratory at Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The towering 363-foot Saturn V was a multi-stage, multi-engine launch vehicle standing taller than the Statue of Liberty. Altogether, the Saturn V engines produced as much power as 85 Hoover Dams.
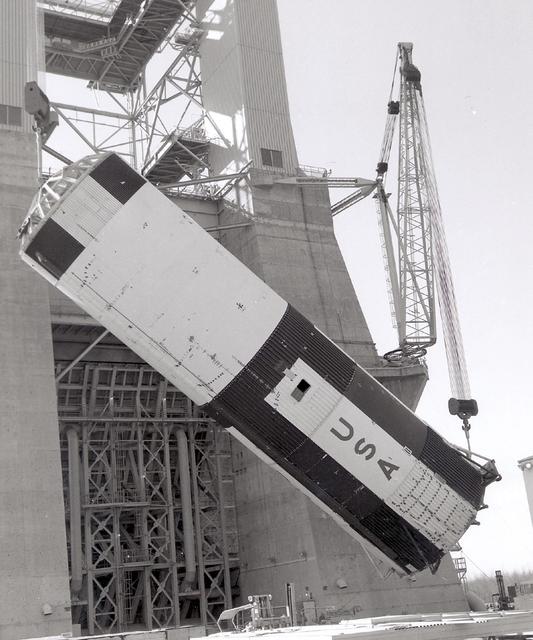

This vintage photograph shows the 138-foot long first stage of the Saturn V being lowered to the ground following a successful static test firing at Marshall Space flight Center's S-1C test stand. The firing provided NASA engineers information on the booster's systems. The towering 363-foot Saturn V was a multi-stage, multi-engine launch vehicle standing taller than the Statue of Liberty. Altogether, the Saturn V engines produced as much power as 85 Hoover Dams.
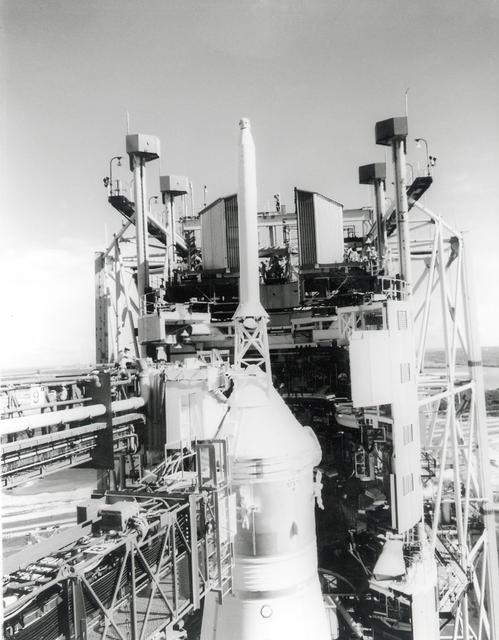
A technician can be seen working atop the white room across from the escape tower of the Apollo 11 spacecraft a few days prior to the launch of the Saturn V moon rocket. The towering 363-foot Saturn V was a multi-stage, multi-engine launch vehicle standing taller than the Statue of Liberty. Altogether, the Saturn V engines produced as much power as 85 Hoover Dams

STS009-48-3139 (6 Dec 1983) --- A vertical view of the Manicouagan Impact Crater, some 300 miles (480 kilometers) north-northwest of Quebec City. The 50-mile (80 kilometers) diameter structure was left by a massive meteorite collision in the distant past. Untrue to the winter season, this picture is missing the conspicuous presence of ice on the Manicouagan Reservoir, which is created by the Daniel Johnson Dam.

ISS028-E-018657 (23 July 2011) --? One of the Expedition 28 crew members aboard the International Space Station photographed this northward looking view featuring the reservoir of Cahora Bassa in extreme western Mozambique, formed by damming the Zambezi River. Also visible are numerous plumes from fires in the wooded plateau region north of the lake on the Mozambique-Zambia frontier.
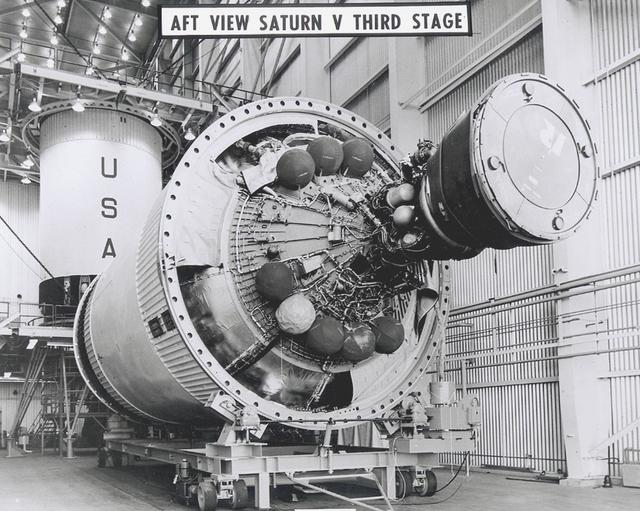
The powerful J-2 engine is prominent in this photograph of a Saturn V Third Stage (S-IVB) resting on a transporter in the Manufacturing Facility at Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The towering 363-foot Saturn V was a multi-stage, multi-engine launch vehicle standing taller than the Statue of Liberty. Altogether, the Saturn V engines produced as much power as 85 Hoover Dams.
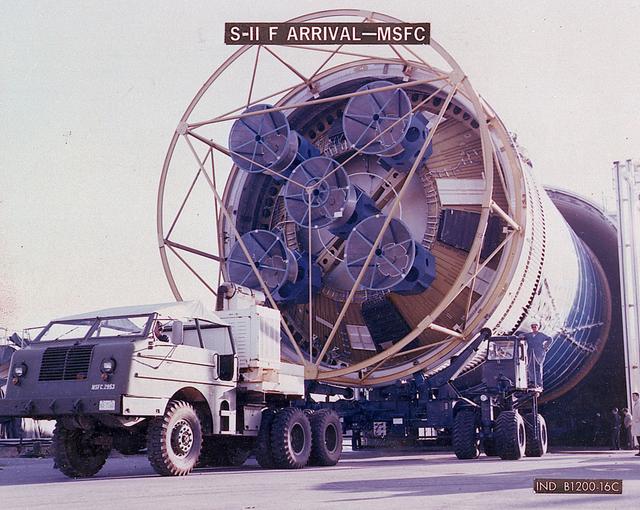

The business end of a Second Stage (S-II) slowly emerges from the shipping container as workers prepare to transport the Saturn V component to the testing facility at MSFC. The Second Stage (S-II) underwent vibration and engine firing tests. The towering 363-foot Saturn V was a multi-stage, multi-engine launch vehicle standing taller than the Statue of Liberty. Altogether, the Saturn V engines produced as much power as 85 Hoover Dams.
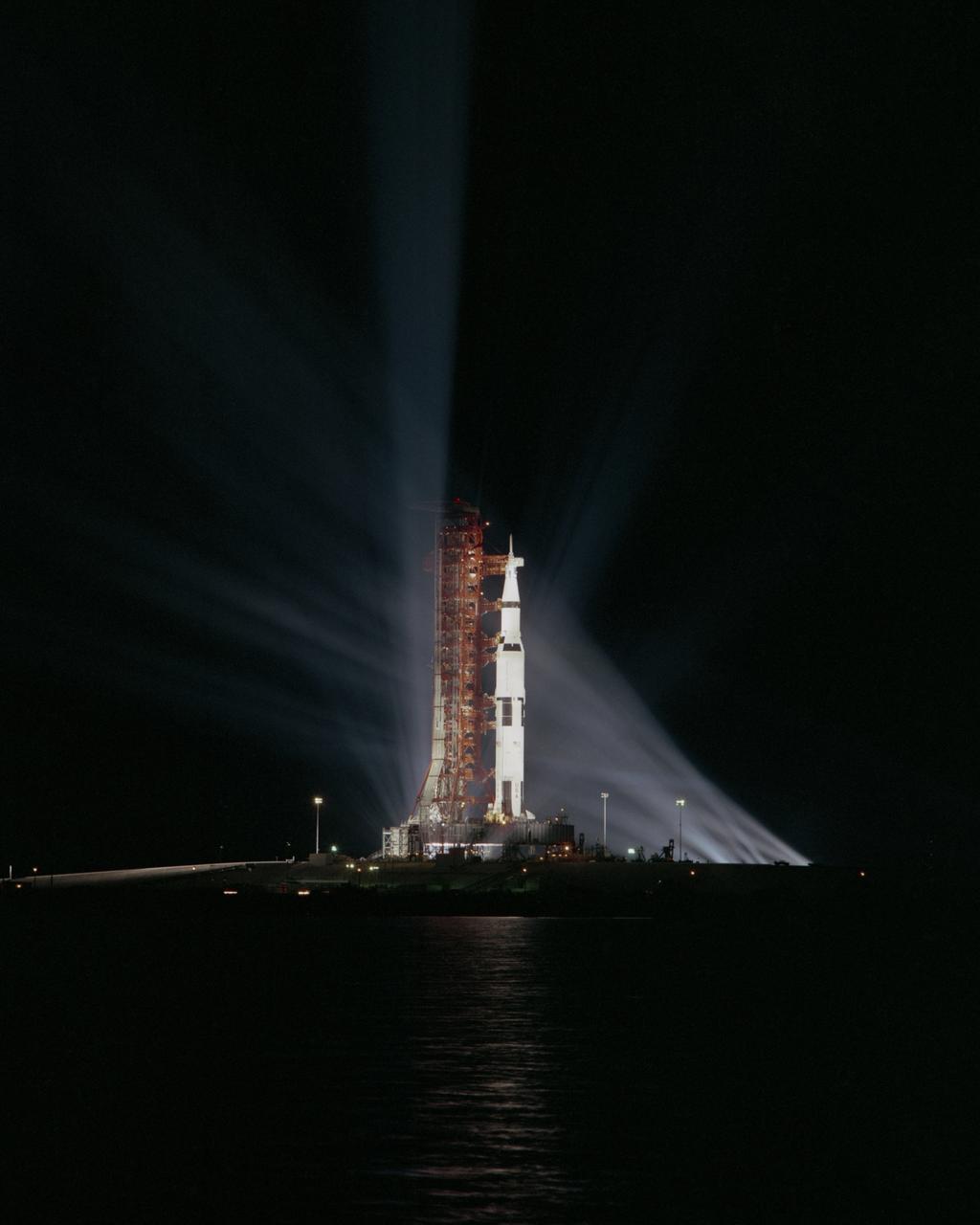

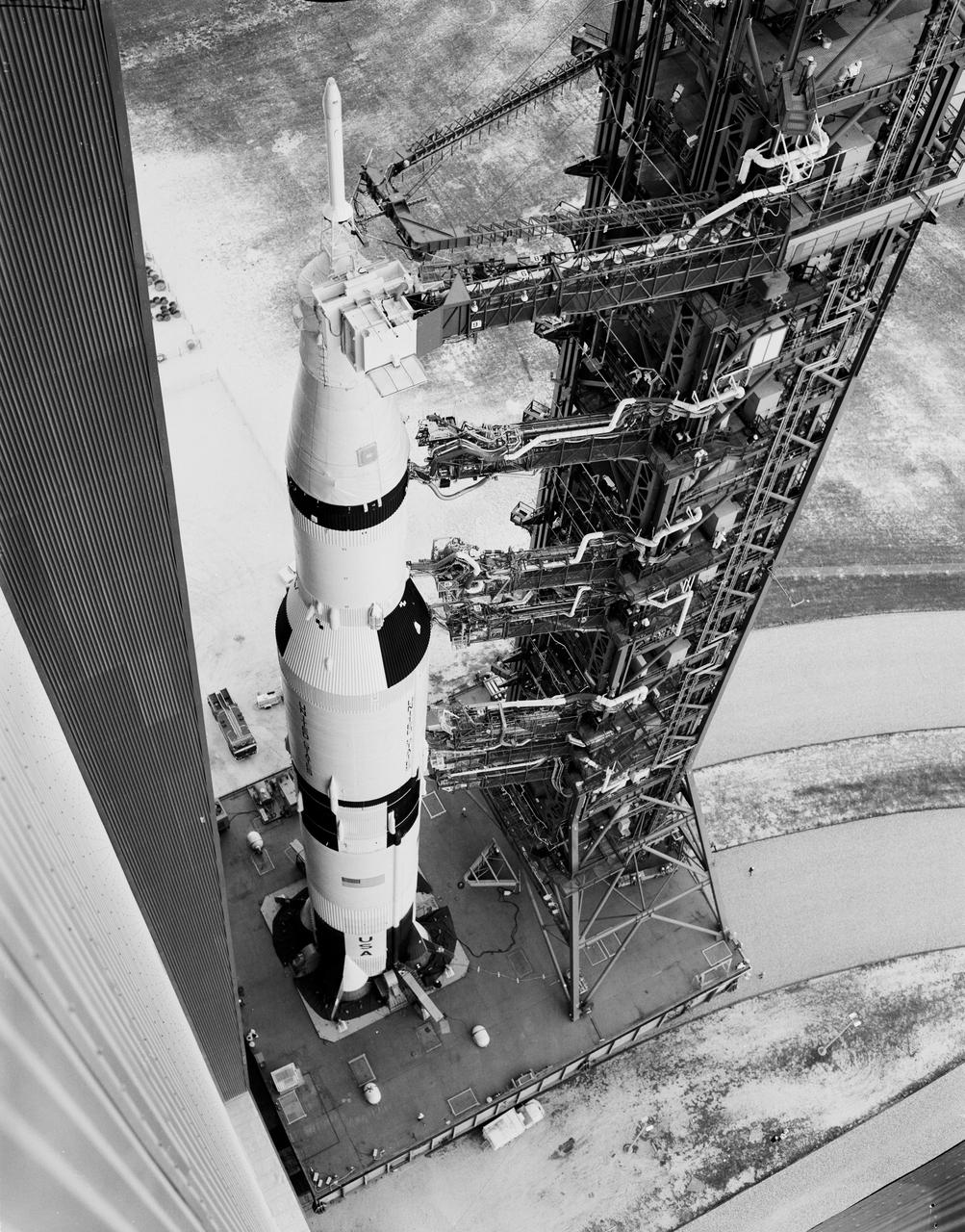
Searchlights penetrate the darkness surrounding Apollo 8 on Pad 39-A at Kennedy Space Center. This mission was the first manned flight using the Saturn V. The towering 363-foot Saturn V was a multi-stage, multi-engine launch vehicle standing taller than the Statue of Liberty. Altogether, the Saturn V engines produced as much power as 85 Hoover Dams.
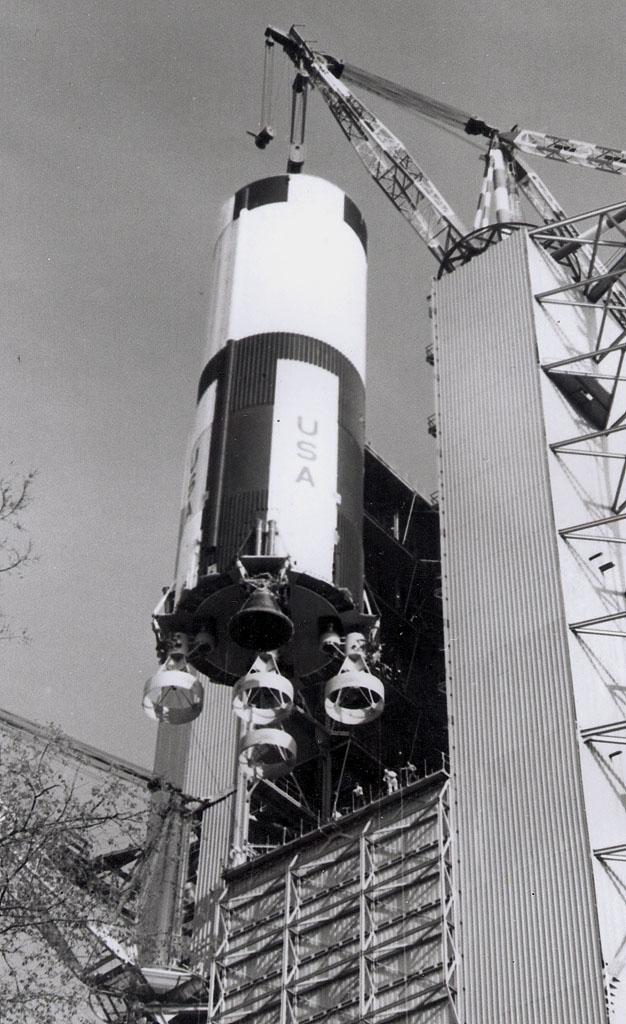
This photo shows the Saturn V first stage being lowered to the ground following a successful test to determine the effects of continual vibrations simulating the effects of an actual launch. The towering 363-foot Saturn V was a multi-stage, multi-engine launch vehicle standing taller than the Statue of Liberty. Altogether, the Saturn V engines produced as much power as 85 Hoover Dams.
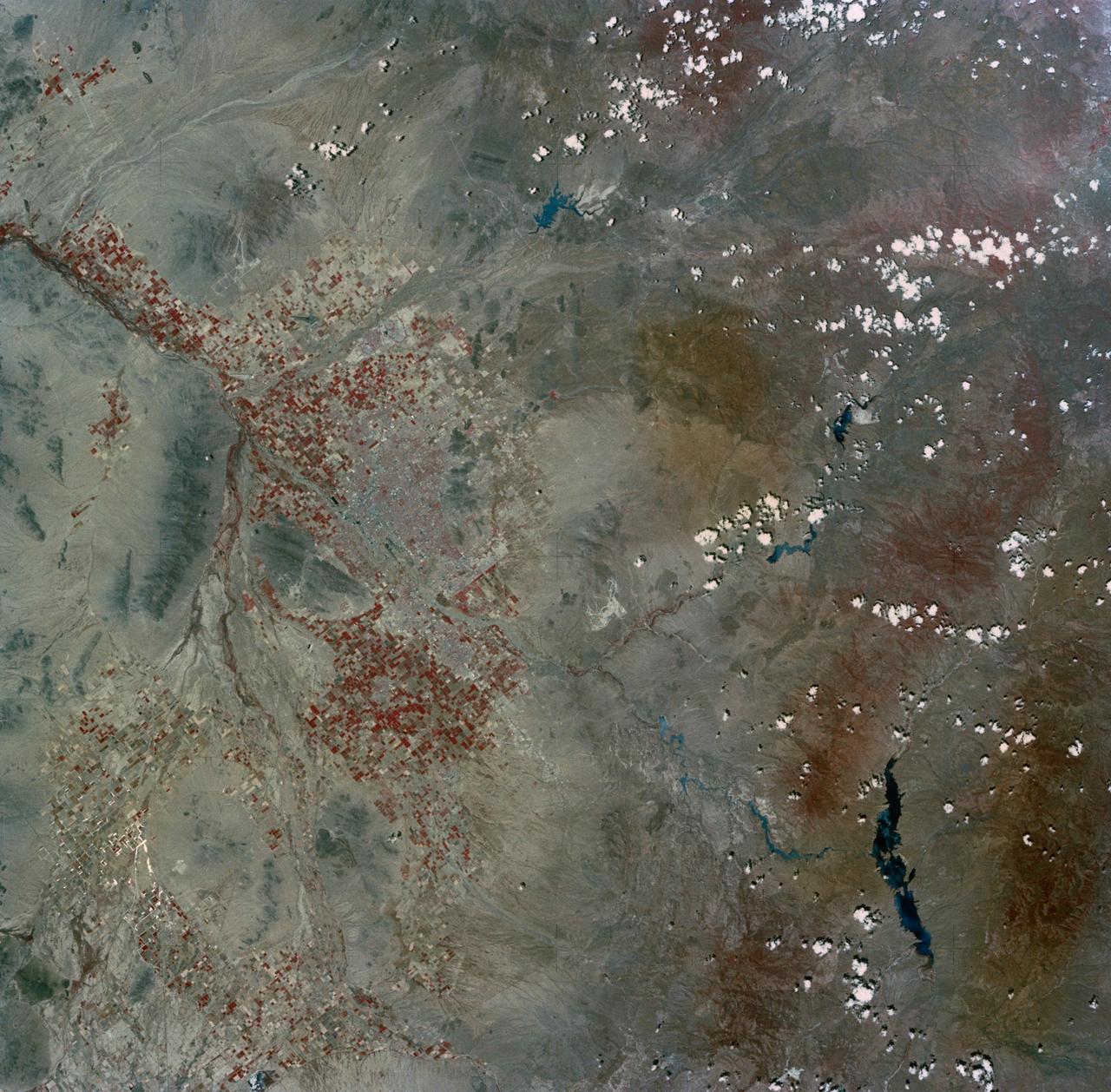

SL2-03-200 (22 June 1973) --- The city of Phoenix, AZ (33.5N, 112.0W) can be seen in good detail in this color infrared scene. Situated among truck crop agriculture fields, the color infrared photo depicts the vegetated fields as shades of red making the agriculture stand out in this desert environment. To the east, Lake Theodore Roosevelt and dam can be easily seen. Photo credit: NASA
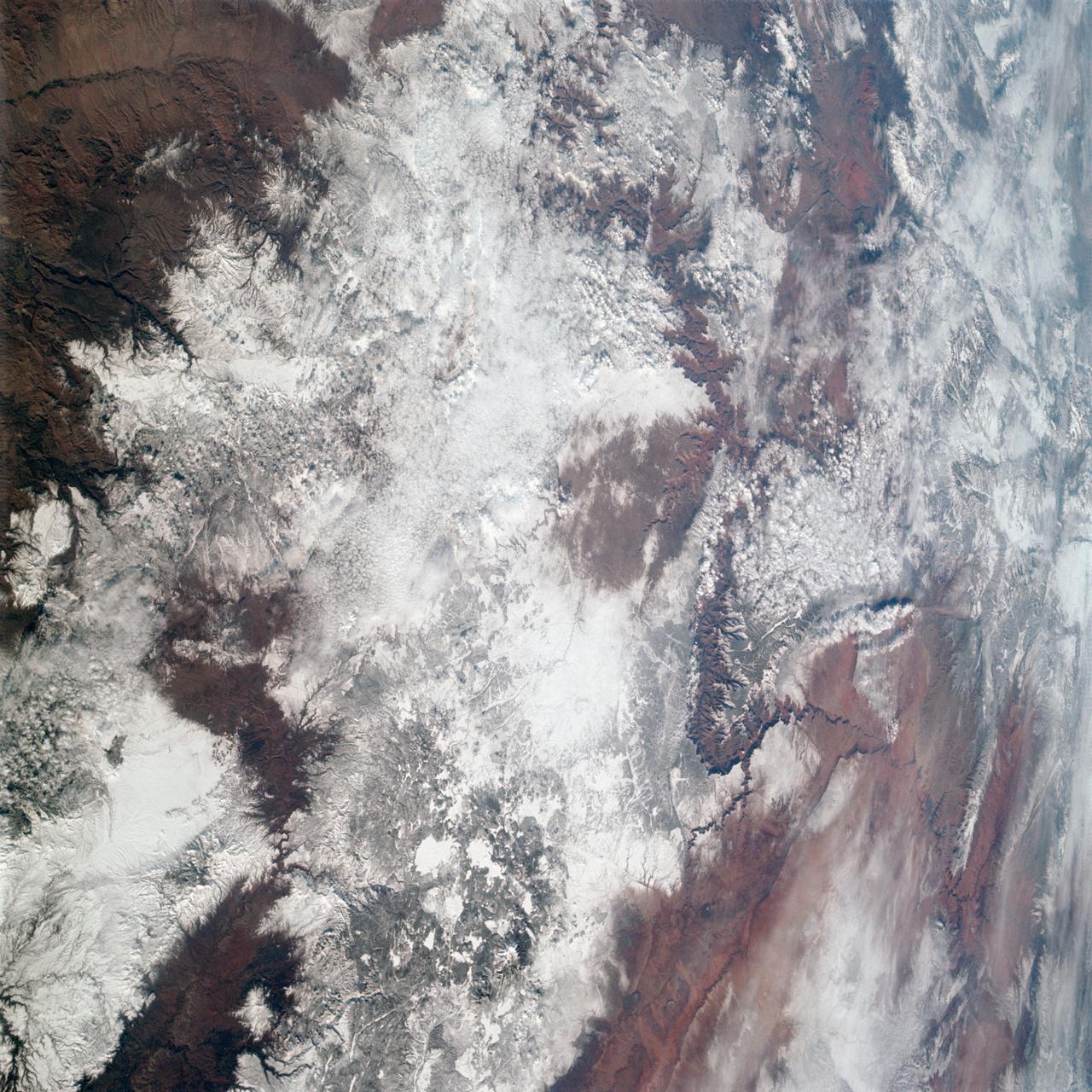

AS09-20-3137 (3-13 March 1969) --- The Grand Canyon is sharply etched on the snow-covered Colorado Plateau in Arizona in this photograph from the Apollo 9 spacecraft during its Earth-orbital mission. Lake Powell behind Glen Canyon Dam is in the upper right corner. Humphreys Peak and the many volcanic craters around the San Francisco Mountains near Flagstaff, Arizona, are right of center. Prescott is under clouds at lower center.
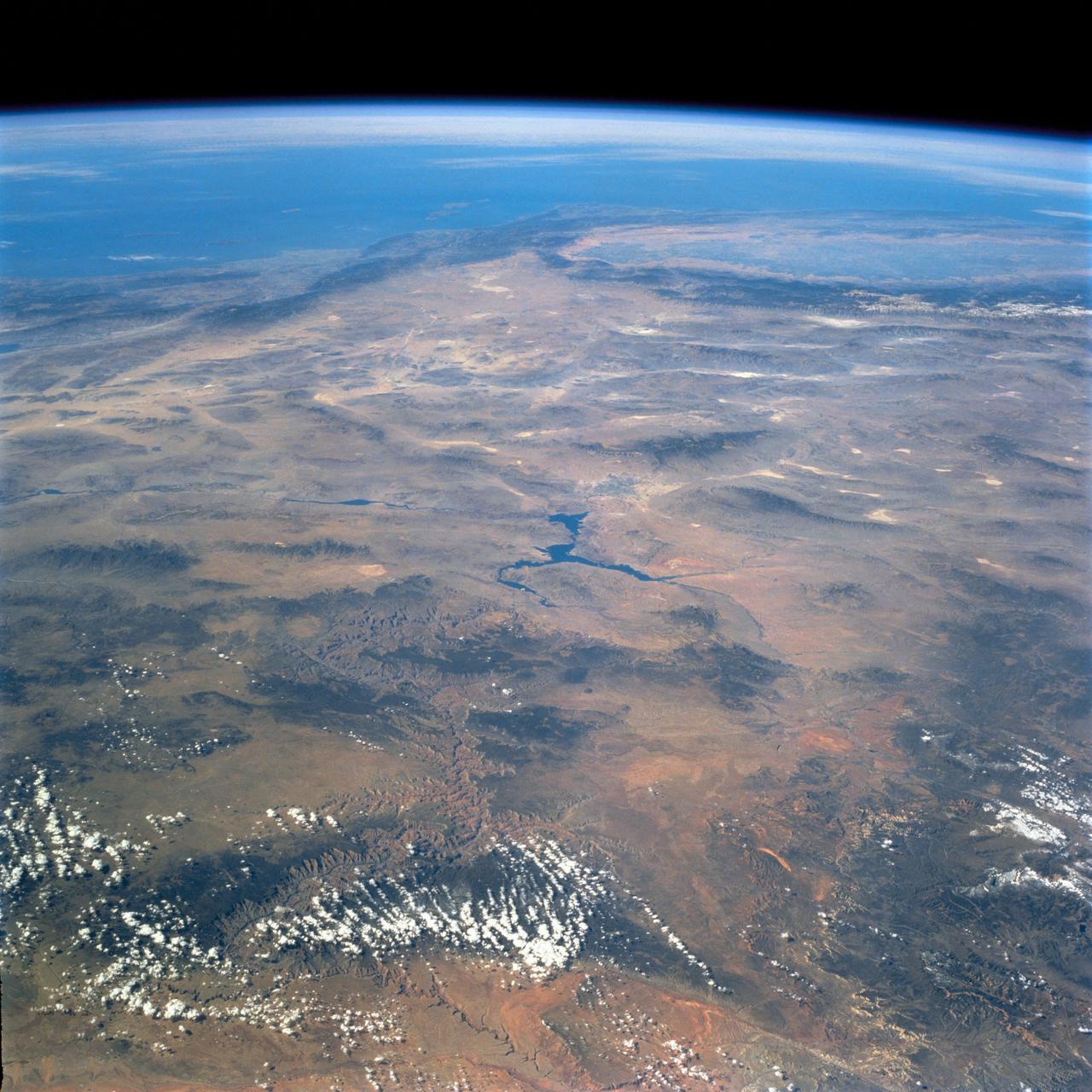

STS058-74-000R (18 Oct-1 Nov 1993) --- A broad view westward along the Colorado River from just below Glen Canyon Dam (out of picture), through the entire Grand Canyon to Lake Mead and Las Vegas, and westward to include southern Nevada and much of California. The Salton Sea, Los Angeles Basin, and Great Valley rim the Pacific Coast in the distance. Photo credit: NASA

Two technicians apply insulation to the outer surface of the S-II second stage booster for the Saturn V moon rocket. The towering 363-foot Saturn V was a multi-stage, multi-engine launch vehicle standing taller than the Statue of Liberty. Altogether, the Saturn V engines produced as much power as 85 Hoover Dams.
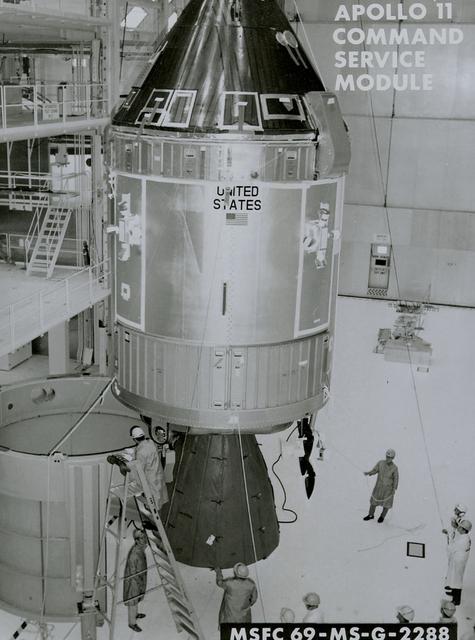

A close-up view of the Apollo 11 command service module ready to be mated with the spacecraft LEM adapter of the third stage. The towering 363-foot Saturn V was a multi-stage, multi-engine launch vehicle standing taller than the Statue of Liberty. Altogether, the Saturn V engines produced as much power as 85 Hoover Dams.

iss050e052024 (02/22/2017) --- International Space Station crewmember Sergey Ryzhikov captured this image of Lake Oroville and the Oroville Dam. To decrease reservoir levels and prevent a collapse of the emergency spillway following high amounts of precipitation earlier in February, water continues to be released from the main spillway. A state of emergency was declared on February 13th after the spillway was discovered to be damaged and the threat of its collapse caused the evacuation of more than 100,000 people downstream of Lake Oroville.
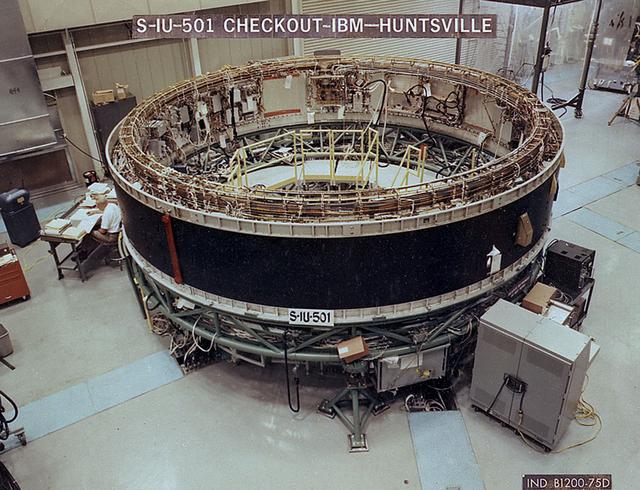
A technician checks the systems of the Saturn V instrument unit in a test facility in Huntsville. This instrument unit was flown aboard Apollo 4 on November 7, 1967, which was the first test flight of the Saturn V. The towering 363-foot Saturn V was a multi-stage, multi-engine launch vehicle standing taller than the Statue of Liberty. Altogether, the Saturn V engines produced as much power as 85 Hoover Dams.
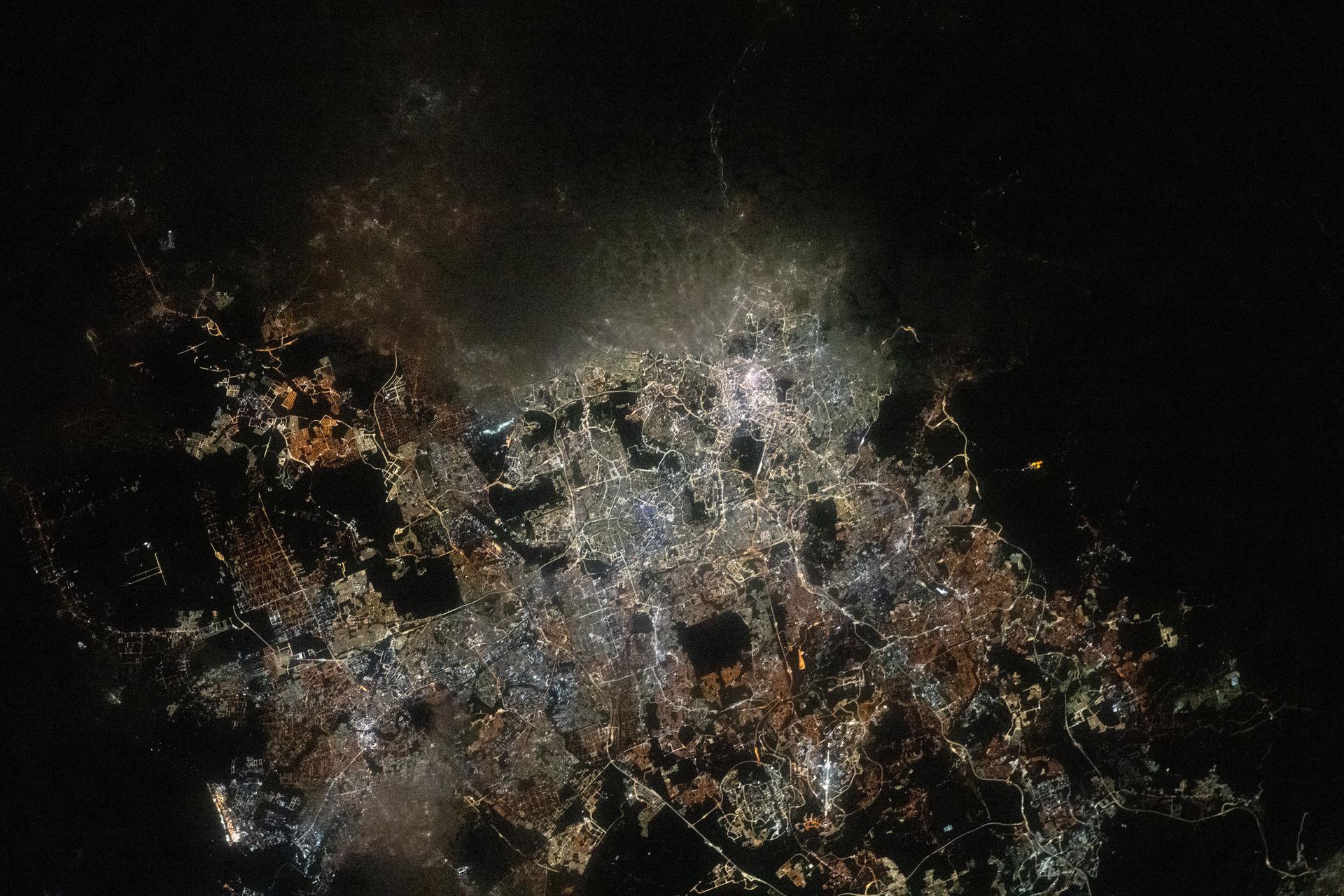

iss073e0763824 (Sept. 21, 2025) --- The Greater Kuala Lumpur area of Malaysia, home to approximately 9.1 million people, is pictured from the International Space Station as it orbited 260 miles above Earth at approximately 3:33 a.m. local time. Dark patches scattered throughout the urban landscape mark nature preserves and parks, many of which feature dams, waterfalls, and hiking trails.
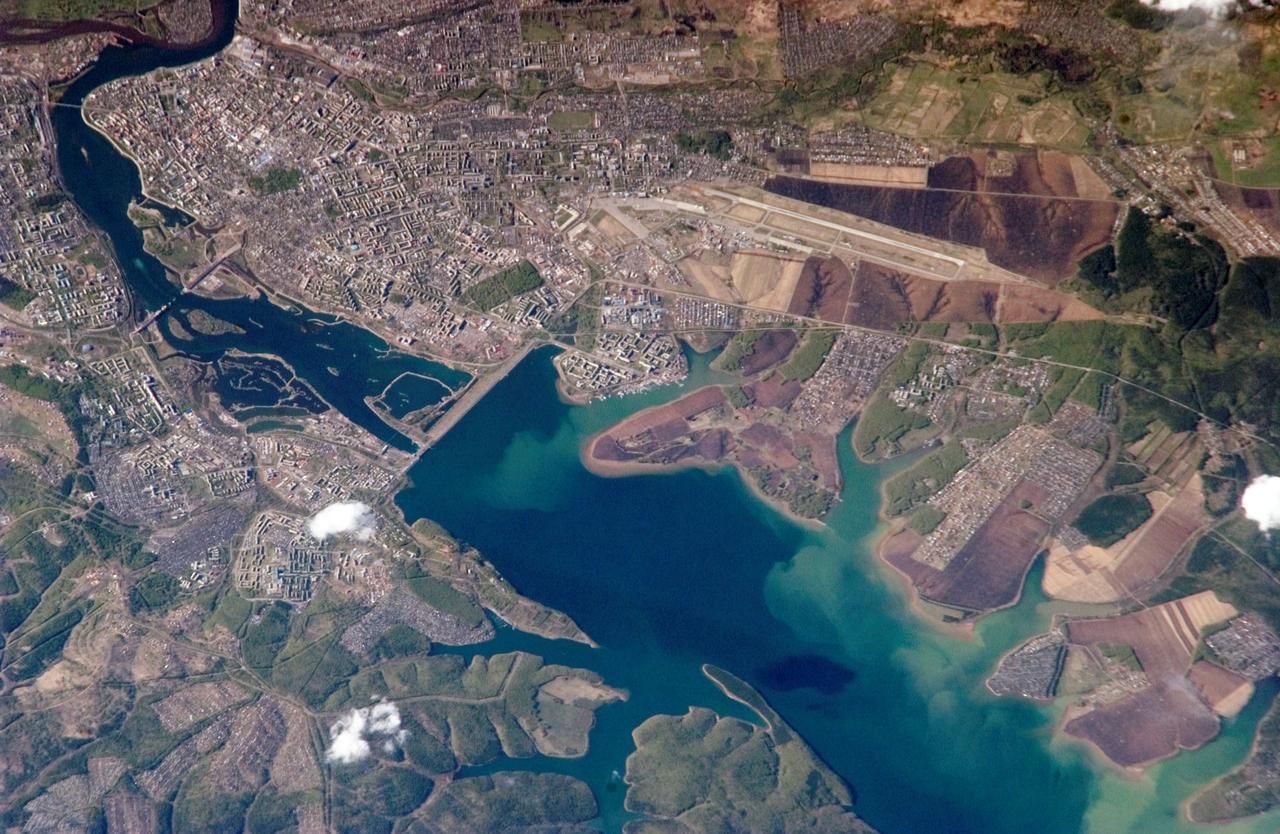

ISS011-E-09913 (24 May 2005) --- Irkutsk, Siberia, Russian Federation is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 11 crewmember on the International Space Station. Located approximately 55 kilometers (34 miles) to the northwest of Lake Baikal, Irkutsk is also the chief city of Irkutsk Oblast (equating to a province) in Siberia. The city is located on the Angara River. The central downtown area of the city is depicted in this photograph, as well as the Akademgorodok district around the State University (left of image along the southern bank of the Angara River). The oblique (non-vertical) look angle of this image imparts a three dimension perspective to the scene that accentuates the blockiness of Soviet-era building projects to the east of the downtown area. The Irkutsk Dam (center), built for the generation of hydroelectric power, dramatically widened the river and drowned several stream outlet channels along the north and south banks. The Angara River is the only outlet from Lake Baikal to the southeast, and impoundment of water behind the dam has raised the lake level by 6 meters (20 ft).
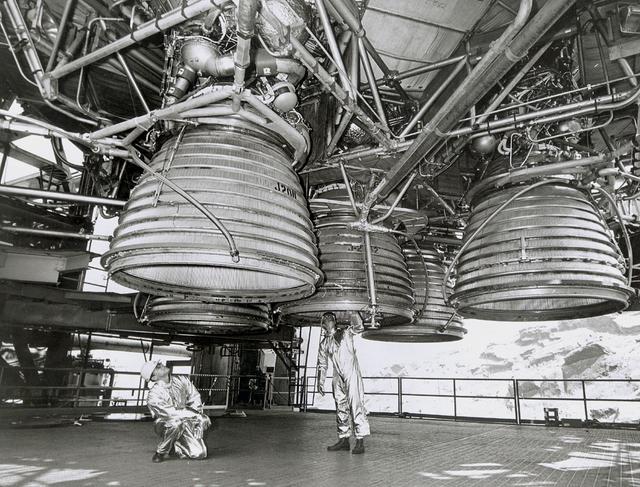

Two workers are dwarfed by the five J-2 engines of the Saturn V second stage (S-II) as they make final inspections prior to a static test firing by North American Space Division. These five hydrogen -fueled engines produced one million pounds of thrust, and placed the Apollo spacecraft into earth orbit before departing for the moon. The towering 363-foot Saturn V was a multi-stage, multi-engine launch vehicle standing taller than the Statue of Liberty. Altogether, the Saturn V engines produced as much power as 85 Hoover Dams.
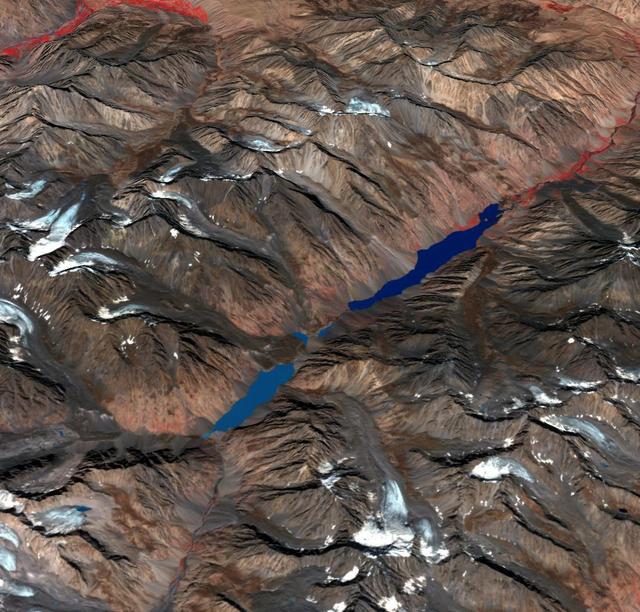

In the Hindu Kush Mtns. in northern Pakistan, landslides from the steep, glaciated terrain are common. When the landslides block rivers, they form temporary lakes or cause small lakes to grow larger. If the landslide dams fail catastrophically, an instantaneous flood surges down the narrow valley, endangering downstream villages. A good example is Lake Shuwarang Chhat, that is upstream of villages of Barsat, Tery, Bahach, and Hundarap. The perspective view data were acquired September23, 2019, and are located at 36 degrees north, 72.6 degrees east. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25355
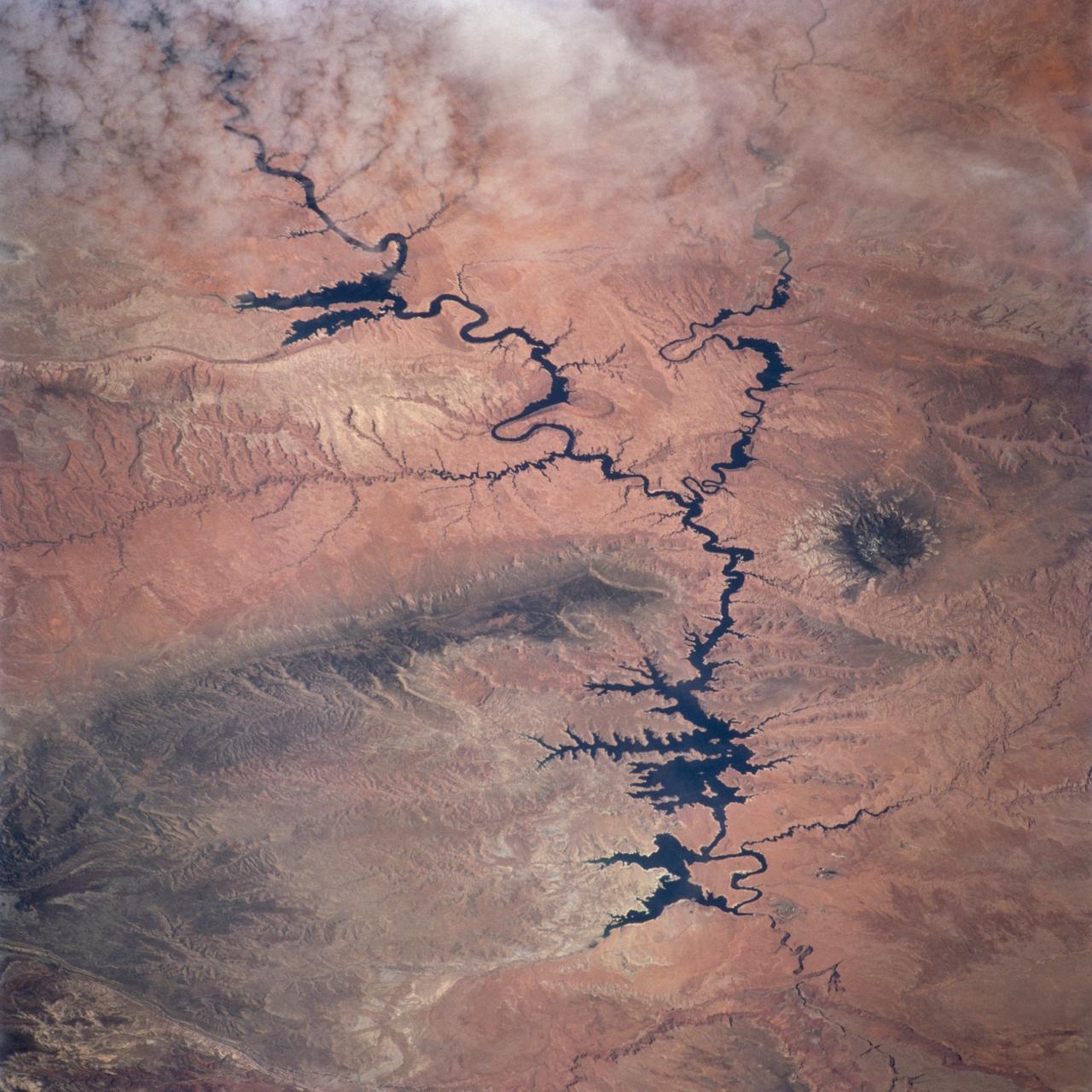

STS100-716-176 (19 April-1 May 2001) --- The deeply entrenched, meandering Colorado River is distinctively dark as the river winds its way across the arid terrain of southeast Utah in this 70mm frame photographed from the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Endeavour. While Glen Canyon Dam (bottom of image) is located in northern Arizona, the reservoir of Lake Powell is in Utah. The Escalante and San Juan Rivers, two major tributaries that flow into Lake Powell (from the northwest and east respectively) are also discernable. The darker-looking, elongated and elevated feature north of Lake Powell is the Kaiparowits Plateau. Navajo Mountain is the darker circular feature to the south (to the right) of the lake.
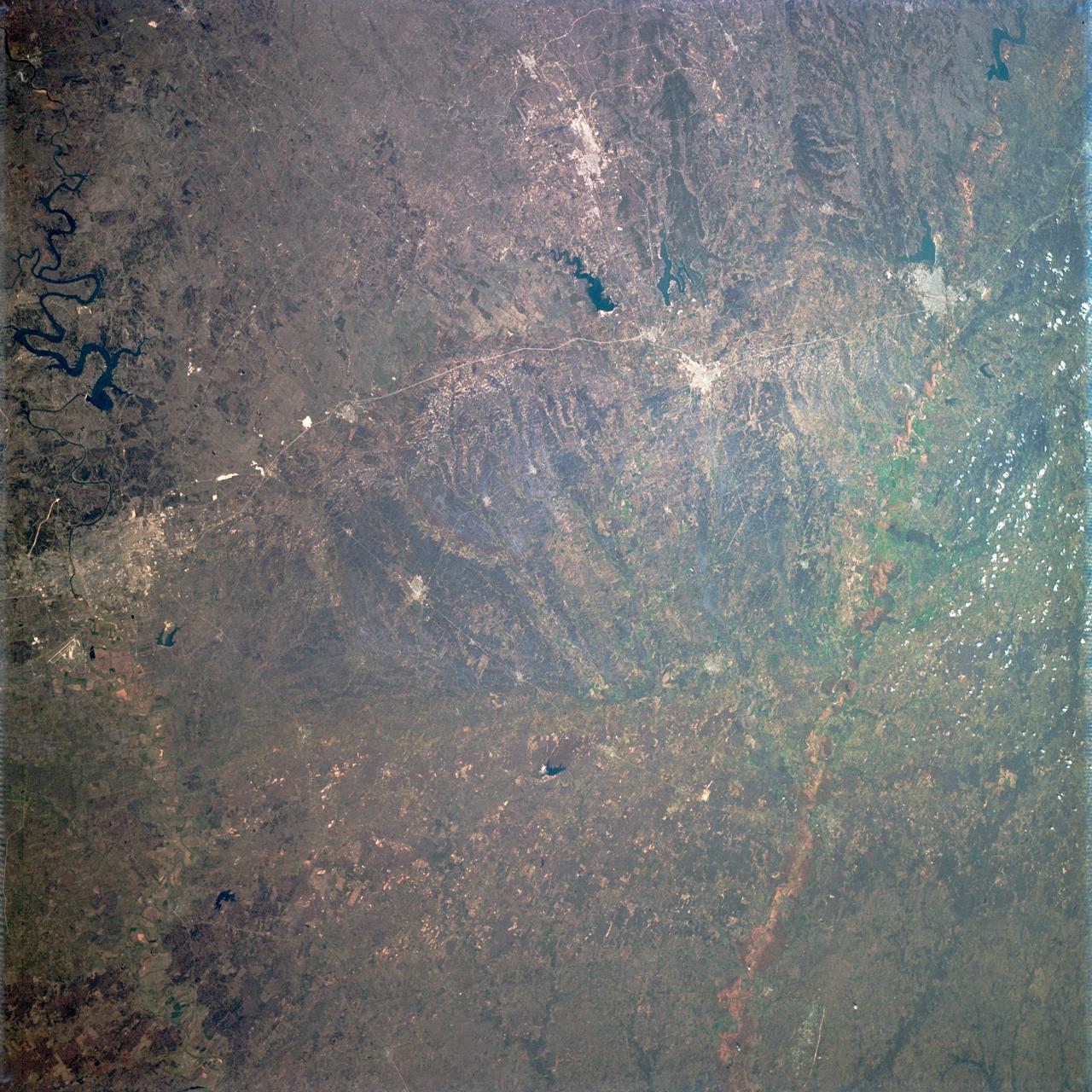

AS09-22-3341 (3-13 March 1969) --- Central Texas area as photographed from the Apollo 9 spacecraft during its Earth-orbital mission. Interstate 35 runs from Austin (right center edge of picture) to Waco (near bottom left corner). Also visible are the cities of Georgetown, Taylor, Temple and Killeen. The Colorado River runs through Austin. The Brazos River flows through Waco. Lake Travis is upstream from Austin. Lake Whitney is at bottom left corner of picture. The Belton Reservoir is near bottom center. The lake formed by the dam on the Lampasas River near Belton is also clearly visible.

The Falcon International Reservoir is on the Rio Grande, 65 km southeast of Laredo, Texas, USA and Nuevo Laredo, Tamaulipas, Mexico. The Falcon Dam was constructed in 1953 to provide water conservation, irrigation, and hydroelectricity. Its maximum surface area, seen in the 2010 image, was 34,000 hectares. As a result of the 2010s-20s drought, the reservoir holds only a small fraction of its capacity. In 2010, vegetation in the area was healthy (dark red); in 2022, the area is parched. The images were acquired 14 July 2010 and 31 July 2022, cover an area of 29.8 by 46.9 km, and are located at 26.6 degrees north, 99.2 degrees west. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25446
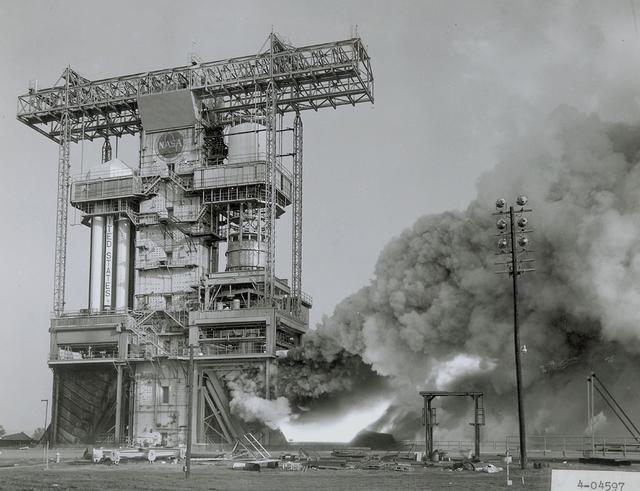
The flame and exhaust from the test firing of an F-1 engine blast out from the Saturn S-IB Static Test Stand in the east test area of the Marshall Space Flight Center. A Cluster of five F-1 engines, located in the S-IC (first) stage of the Saturn V vehicle, provided over 7,500,000 pounds of thrust to launch the giant rocket. The towering 363-foot Saturn V was a multistage, multiengine launch vehicle standing taller than the Statue of Liberty. Altogether, the Saturn V engines produced as much power as 85 Hoover Dams.
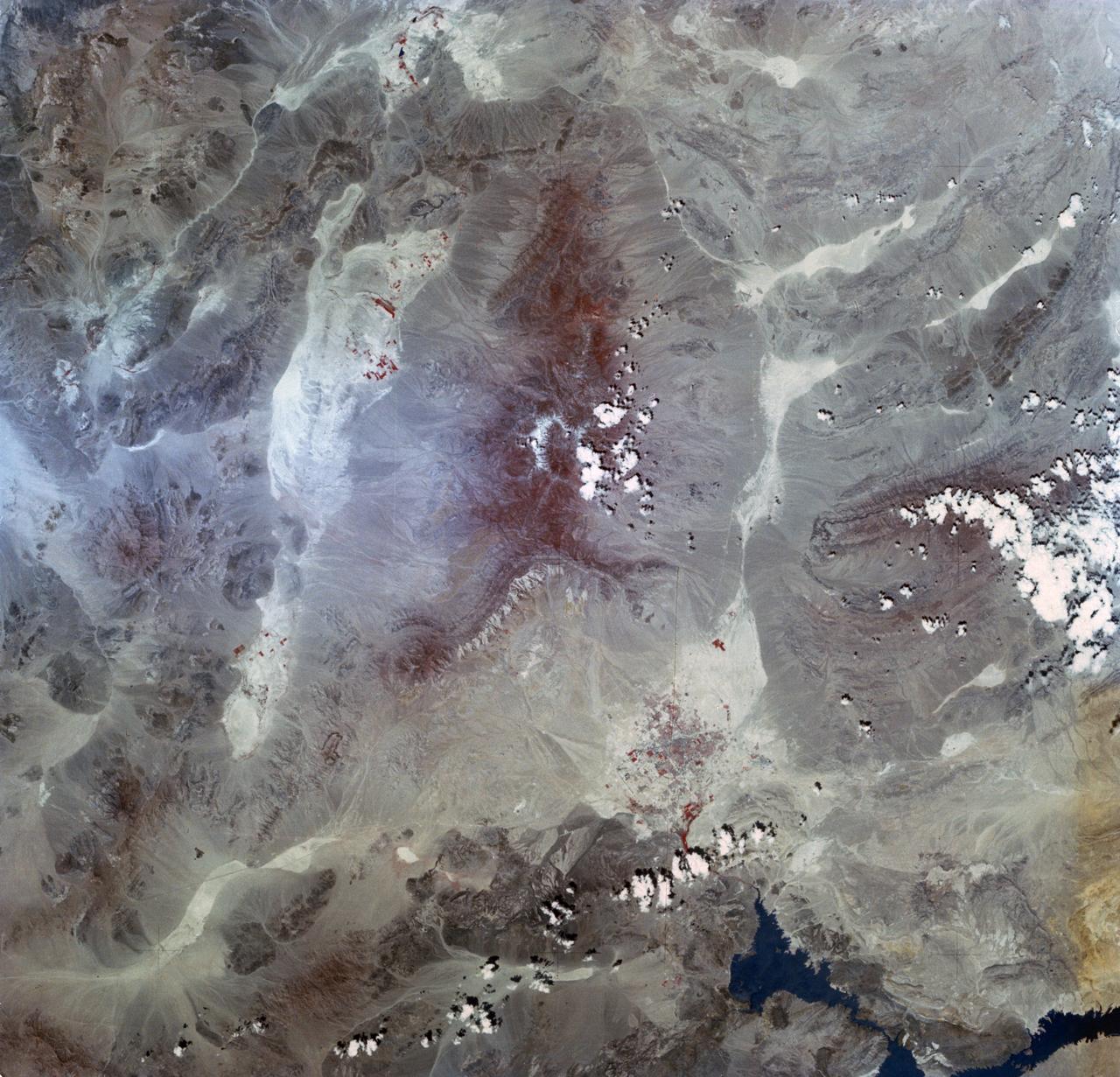

SL2-03-192 (22 June 1973) --- Lake Mead, Nevada, (36.0N, 114.5E) where the water from the Colorado River empties after it's 273 mile journey through the Grand Canyon of Arizona is the subject of this photo. Other features of interest are Hoover Dam on the south shore of Lake Mead where cheap hydroelectric power is secondary to the water resources made available in this northern desert region and the resort city of Las Vegas, just to the west of Lake Mead. In this harsh desert environment, color infrared photography readily penetrates haze, detects and portrays vegetation as shades of red. Photo credit: NASA
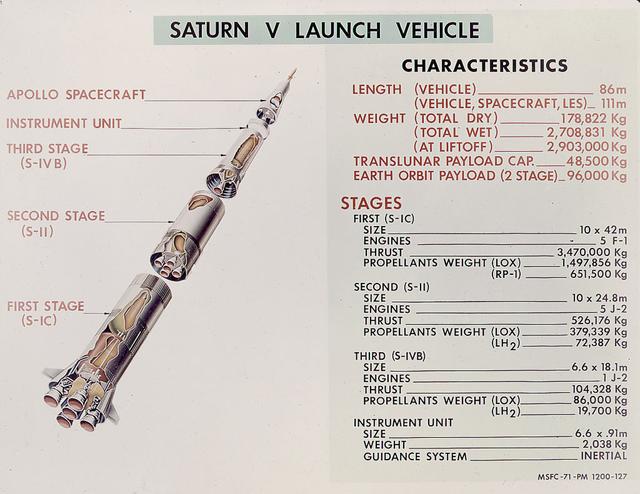
This is a good cutaway diagram of the Saturn V launch vehicle showing the three stages, the instrument unit, and the Apollo spacecraft. The chart on the right presents the basic technical data in clear metric detail. The Saturn V is the largest and most powerful launch vehicle in the United States. The towering, 111 meter, Saturn V was a multistage, multiengine launch vehicle standing taller than the Statue of Liberty. Altogether, the Saturn V engines produced as much power as 85 Hoover Dams. Development of the Saturn V was the responsibility of the Marshall Space Flight Center at Huntsville, Alabama, directed by Dr. Wernher von Braun.
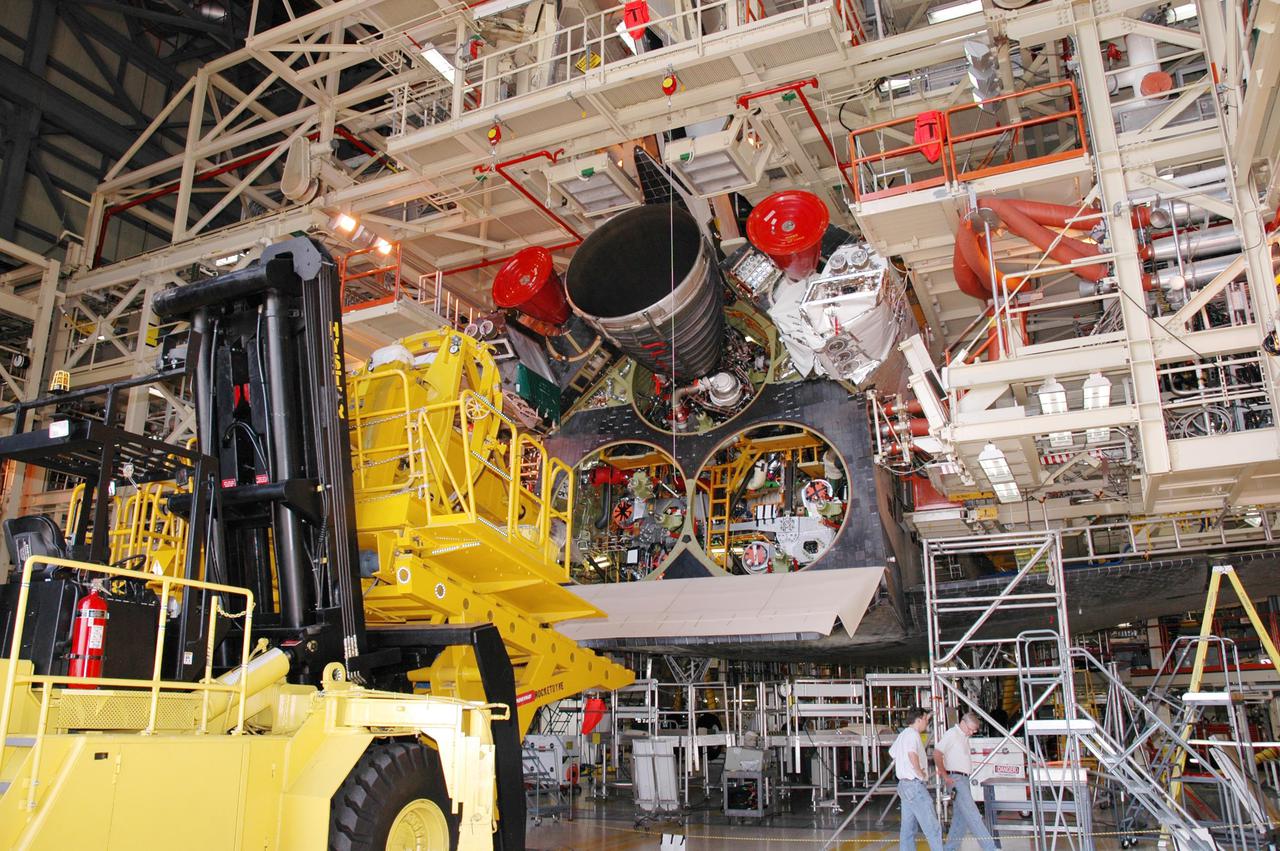

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility, the Hyster lift backs away from the orbiter Discovery after placing a Space Shuttle Main Engine (SSME) into position for installation. Discovery is the vehicle designated for the Return to Flight mission STS-114. Overall, an SSME weighs approximately 7,000 pounds. An SSME operates at greater temperature extremes than any mechanical system in common use today. The liquid hydrogen fuel is -423 degrees Fahrenheit, the second coldest liquid on Earth. When the hydrogen is burned with liquid oxygen, the temperature in the engine's combustion chamber reaches +6000 degrees Fahrenheit -- that's higher than the boiling point of Iron. The maximum equivalent horsepower developed by the three SSMEs is just over 37 million horsepower. The energy released by the three SSMEs is equivalent to the output of 23 Hoover Dams.
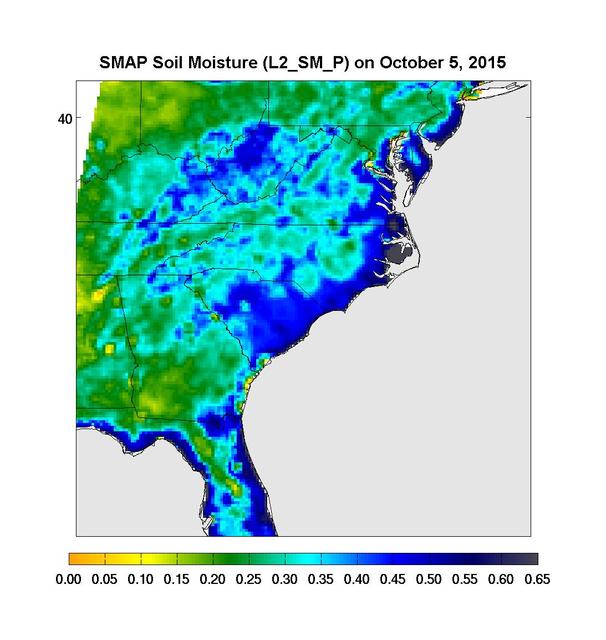
Surface soil moisture in the Southeastern United States as retrieved from NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) satellite observatory at around 6 a.m. on Oct. 5, 2015. Large parts of South Carolina appear blue, representing the impact of heavy localized rains and flooding. Regions in blue indicate areas with saturated soil conditions and possible standing water. Large-scale flooding was experienced all over South Carolina on Oct. 5-6, 2015. As of Oct. 7, 17 deaths had been attributed to these floods, with heavy economic losses. In some regions, the intensity of these floods was described as a 1,000-year storm (1-in-1,000 chance of happening in any given year). At least 14 dams have already failed as a result of these floods. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20001
STS073-727-045 (21 October 1995) --- Photographed by the astronauts aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia is this scene over Lake Powell. The lake was formed by the Glen Canyon Dam on the Colorado River. The vertical stabilizer of Columbia points northeastward. Navaho Mountain, northwest of the tail, according to NASA geologists, was formed by an intrusion of molten rock that uplifted older, layered rocks, then cooled, and has been exposed by erosion. The rest of the landscape is dominated by faulted layers of sandstone, shale, and limestone that were formed in shallow seas and great deserts 80 to 250 million years ago. These rocks of the Colorado Plateau were uplifted a few million years ago to be dissected by the meandering Colorado River, San Juan River, and their tributaries.
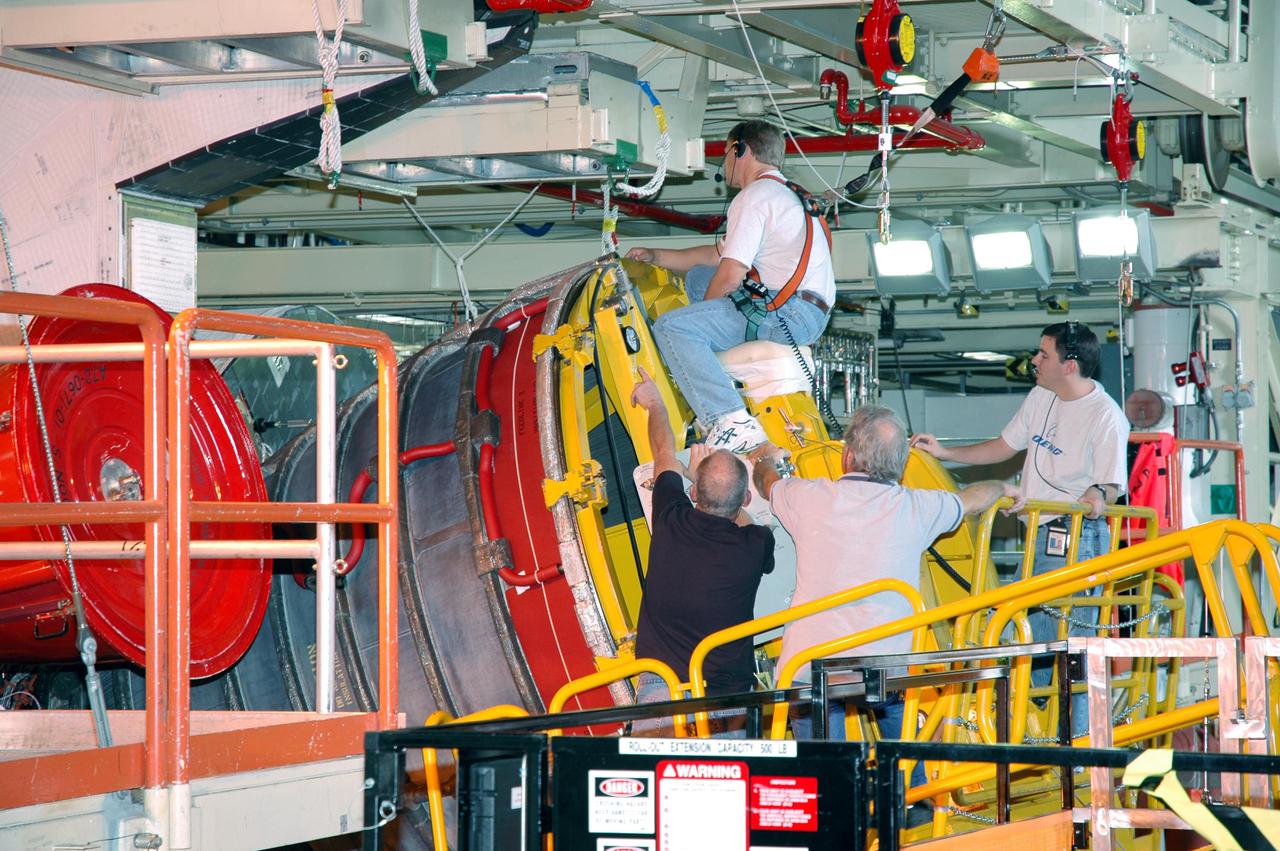

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility, a technician appears to ride the Space Shuttle Main Engine (SSME) as he maneuvers the SSME on the Hyster lift into position for installation on Discovery, the vehicle designated for the Return to Flight mission STS-114. Overall, an SSME weighs approximately 7,000 pounds. An SSME operates at greater temperature extremes than any mechanical system in common use today. The liquid hydrogen fuel is -423 degrees Fahrenheit, the second coldest liquid on Earth. When the hydrogen is burned with liquid oxygen, the temperature in the engine's combustion chamber reaches +6000 degrees Fahrenheit -- that's higher than the boiling point of Iron. The maximum equivalent horsepower developed by the three SSMEs is just over 37 million horsepower. The energy released by the three SSMEs is equivalent to the output of 23 Hoover Dams.
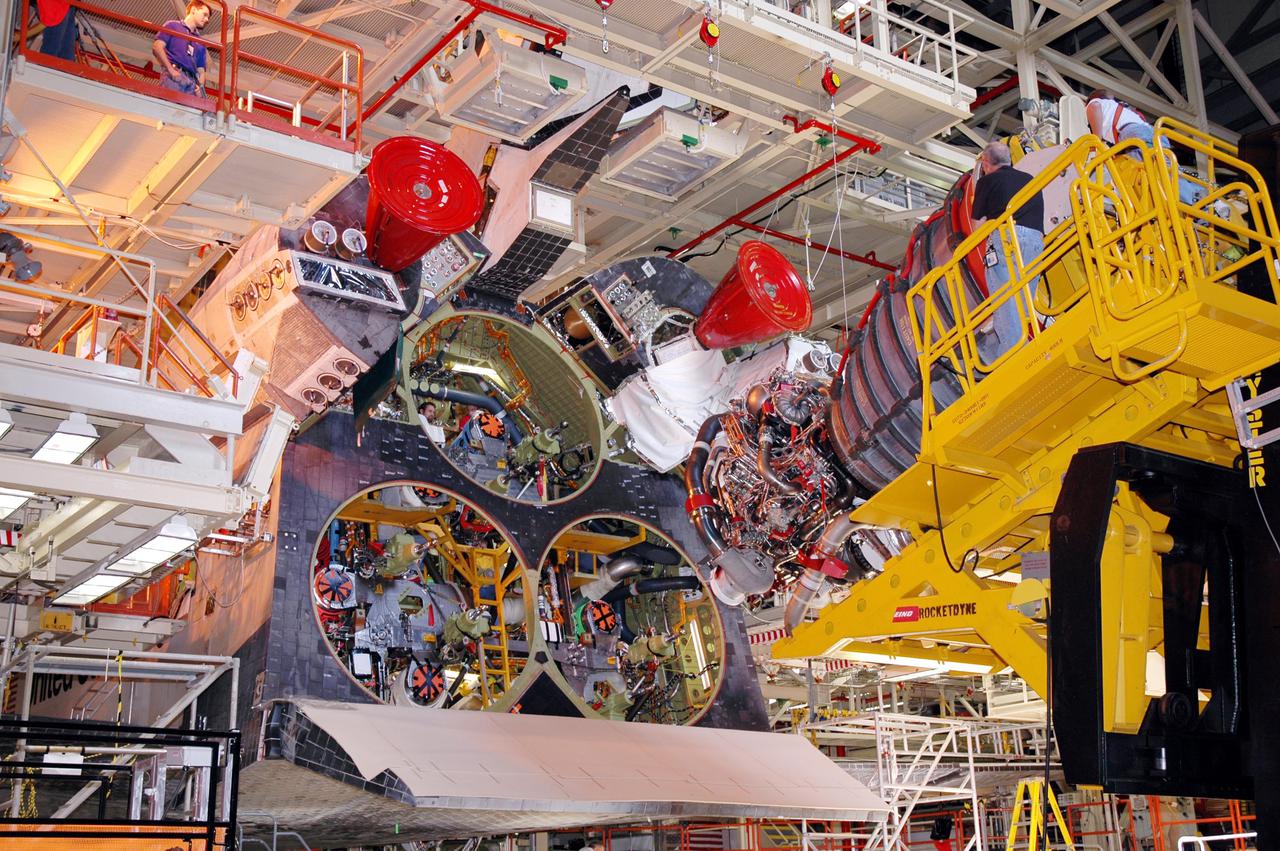

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility, Discovery waits as the first of three Space Shuttle Main Engines (SSME) moves into position for installation on Discovery, the vehicle designated for the Return to Flight mission STS-114. Overall, an SSME weighs approximately 7,000 pounds. An SSME operates at greater temperature extremes than any mechanical system in common use today. The liquid hydrogen fuel is -423 degrees Fahrenheit, the second coldest liquid on Earth. When the hydrogen is burned with liquid oxygen, the temperature in the engine's combustion chamber reaches +6000 degrees Fahrenheit -- that's higher than the boiling point of Iron. The maximum equivalent horsepower developed by the three SSMEs is just over 37 million horsepower. The energy released by the three SSMEs is equivalent to the output of 23 Hoover Dams.
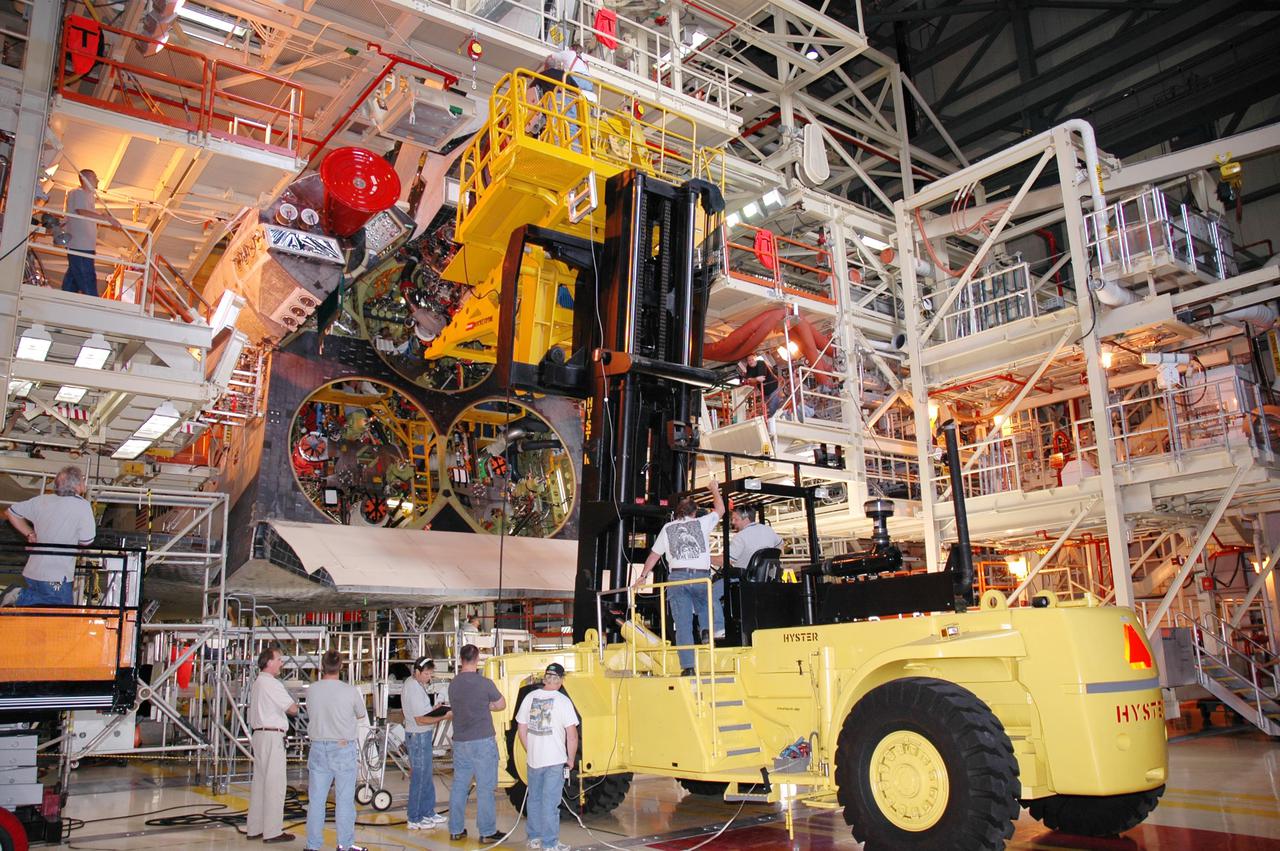

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility, technicians wait below while a Hyster lift moves the first of three Space Shuttle Main Engines (SSME) into position above for installation on Discovery, the vehicle designated for the Return to Flight mission STS-114. Overall, an SSME weighs approximately 7,000 pounds. An SSME operates at greater temperature extremes than any mechanical system in common use today. The liquid hydrogen fuel is -423 degrees Fahrenheit, the second coldest liquid on Earth. When the hydrogen is burned with liquid oxygen, the temperature in the engine's combustion chamber reaches +6000 degrees Fahrenheit -- that's higher than the boiling point of Iron. The maximum equivalent horsepower developed by the three SSMEs is just over 37 million horsepower. The energy released by the three SSMEs is equivalent to the output of 23 Hoover Dams.
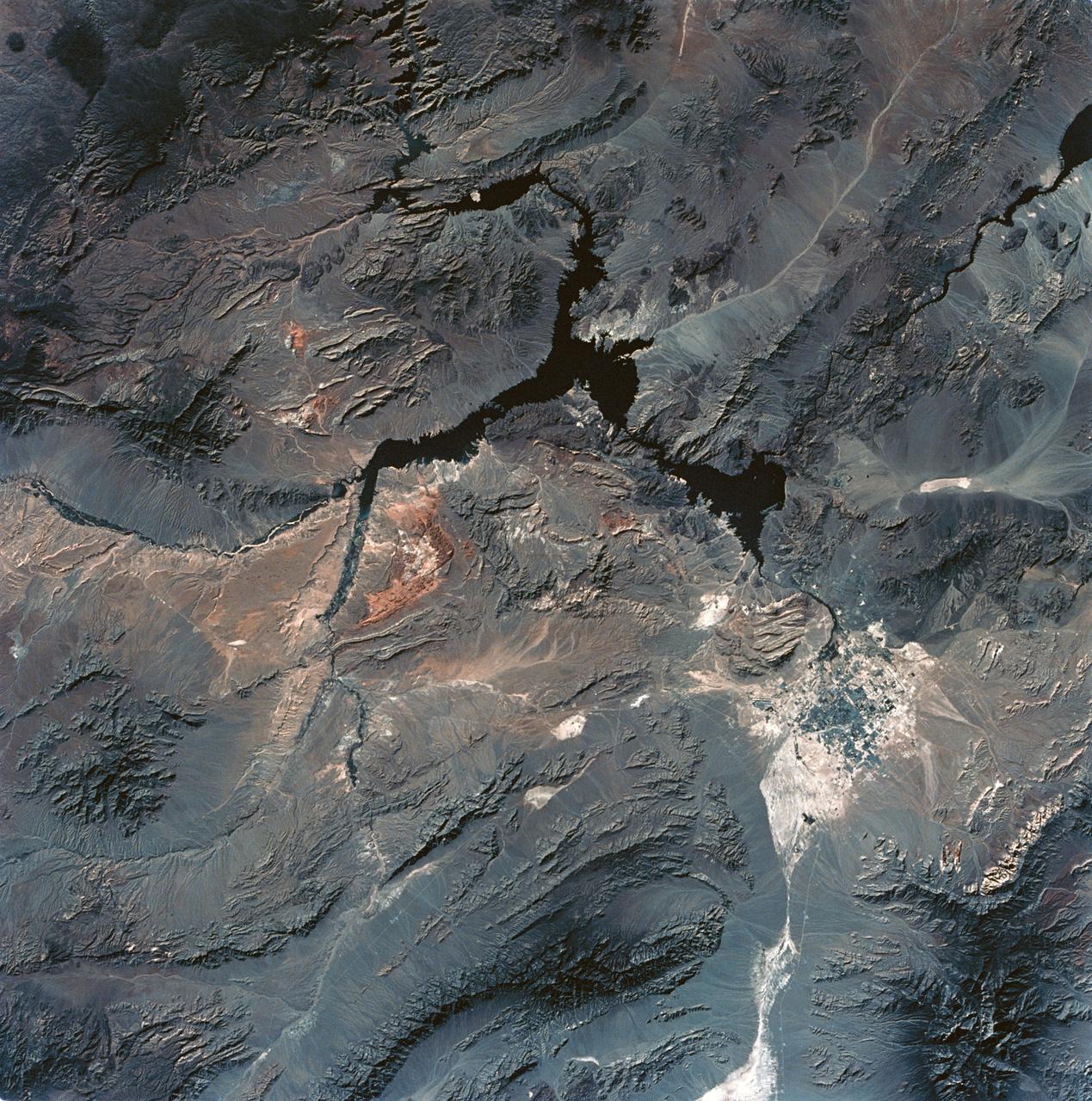

SL3-28-059 (July-September 1973) --- A vertical view of the Lake Mead and Las Vegas, Nevada area as photographed from Earth orbit by one of the six lenses of the Itek-furnished S190-A Multispectral Photographic Facility Experiment aboard the Skylab space station. Lake Mead is water of the Colorado River impounded by Hoover Dam. Most of the land in the picture is Nevada. However, a part of the northwest corner of Arizona can be seen. Federal agencies participating with NASA on the EREP project are the Departments of Agriculture, Commerce, Interior, the Environmental Protection Agency and the Corps of Engineers. All EREP photography is available to the public through the Department of Interior?s Earth Resources Observations Systems Data Center, Sioux Falls, South Dakota, 57198. Photo credit: NASA
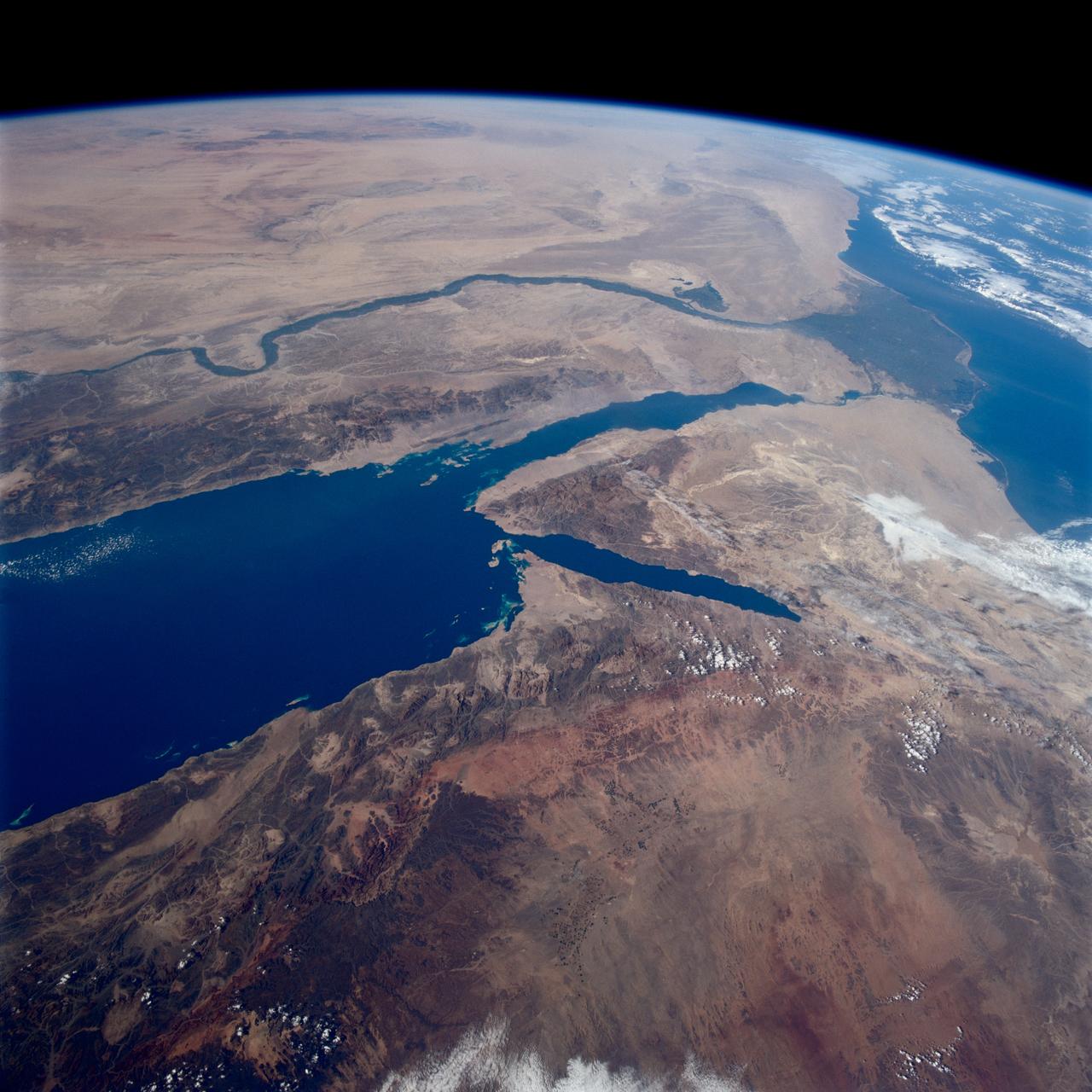

STS080-745-004 (19 Nov.-7 Dec. 1996) --- A view to the west showing Asia in the foreground and Africa in the background, as photographed by the space shuttle Columbia crewmembers. The Mediterranean Sea is to the upper right and the Red Sea to the lower left (holding photograph with NASA numbers on left). Sinai Peninsula is between the two with the Gulf of Suez above and the Gulf of Aqaba below. The Suez Canal connects the Gulf of Suez with the Mediterranean Sea. The triangular shaped dark area beyond is the Nile River Delta. The thin green fertile valley of the Nile crosses the photograph from a point at Cairo (near dark triangle area) past the great bend at Luxor with Thebes and the Valley of the Kings, and on the left into the Nubian Desert with the Aswan High Dam at the very left edge of the photograph. To the horizon is the Western Desert of Egypt and Libya. The foreground is the northwest portion of Saudi Arabia, an area known as the Hejaz with the southern portions of Israel and Jordan to the lower right.
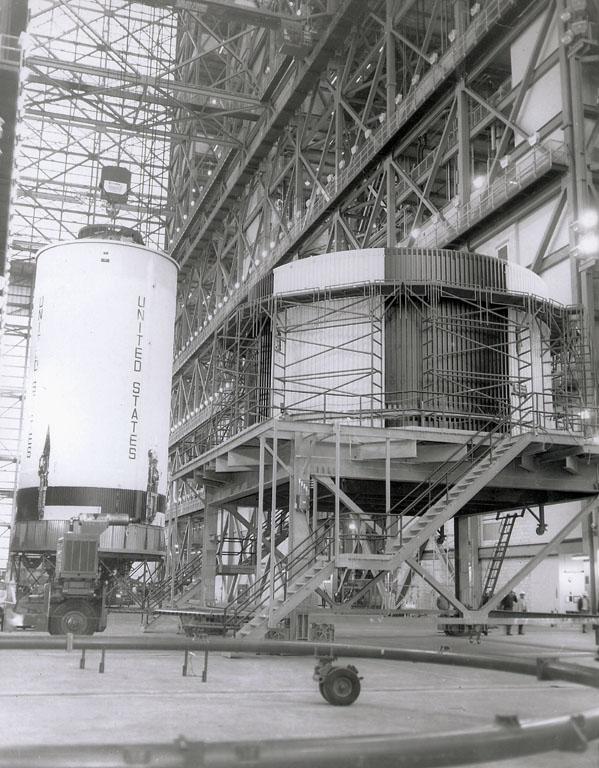
This Saturn V S-II (second) stage is being lifted into position for a test at the Vehicle Assembly Building at the Kennedy Space Center. When the Saturn V booster stage (S-IC) burned out and dropped away, power for the Saturn was provided by the 82-foot-long and 33-foot-diameter S-II stage. Developed by the Space Division of North American Aviation under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center, the stage utilized five J-2 engines, each producing 200,000 pounds of thrust. The engines used liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen as propellants. The towering 363-foot Saturn V was a multi-stage, multi-engine launch vehicle standing taller than the Statue of Liberty. Altogether, the Saturn V engines produced as much power as 85 Hoover Dams.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility, a technician (lower right) watches from inside as a Space Shuttle Main Engine (SSME) on the Hyster lift is maneuvered into position on Discovery, the vehicle designated for the Return to Flight mission STS-114. Overall, an SSME weighs approximately 7,000 pounds. An SSME operates at greater temperature extremes than any mechanical system in common use today. The liquid hydrogen fuel is -423 degrees Fahrenheit, the second coldest liquid on Earth. When the hydrogen is burned with liquid oxygen, the temperature in the engine's combustion chamber reaches +6000 degrees Fahrenheit -- that's higher than the boiling point of Iron. The maximum equivalent horsepower developed by the three SSMEs is just over 37 million horsepower. The energy released by the three SSMEs is equivalent to the output of 23 Hoover Dams.
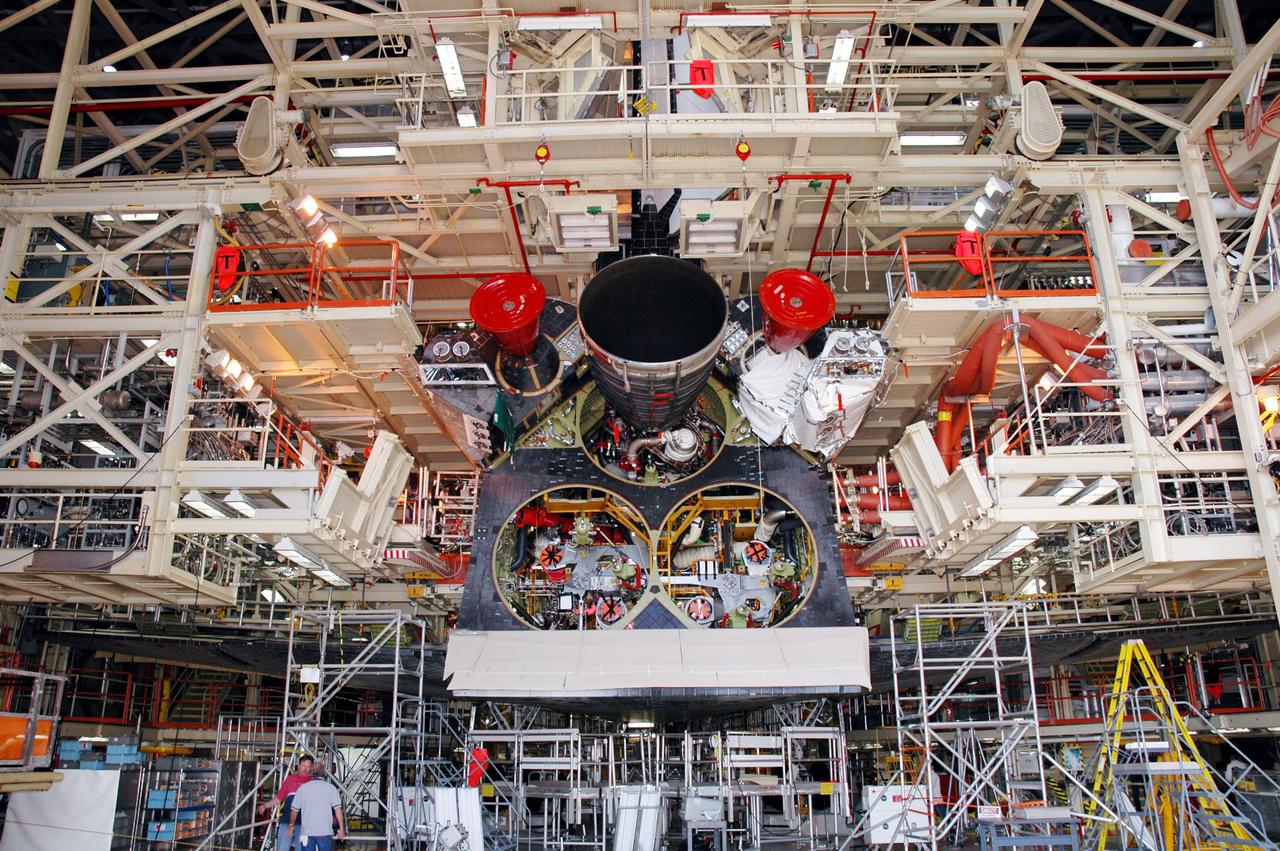
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In this view from the floor of the Orbiter Processing Facility, the first of three Space Shuttle Main Engines (SSME) is seen after installation. Discovery is the vehicle designated for the Return to Flight mission STS-114. Overall, an SSME weighs approximately 7,000 pounds. An SSME operates at greater temperature extremes than any mechanical system in common use today. The liquid hydrogen fuel is -423 degrees Fahrenheit, the second coldest liquid on Earth. When the hydrogen is burned with liquid oxygen, the temperature in the engine's combustion chamber reaches +6000 degrees Fahrenheit -- that's higher than the boiling point of Iron. The maximum equivalent horsepower developed by the three SSMEs is just over 37 million horsepower. The energy released by the three SSMEs is equivalent to the output of 23 Hoover Dams.
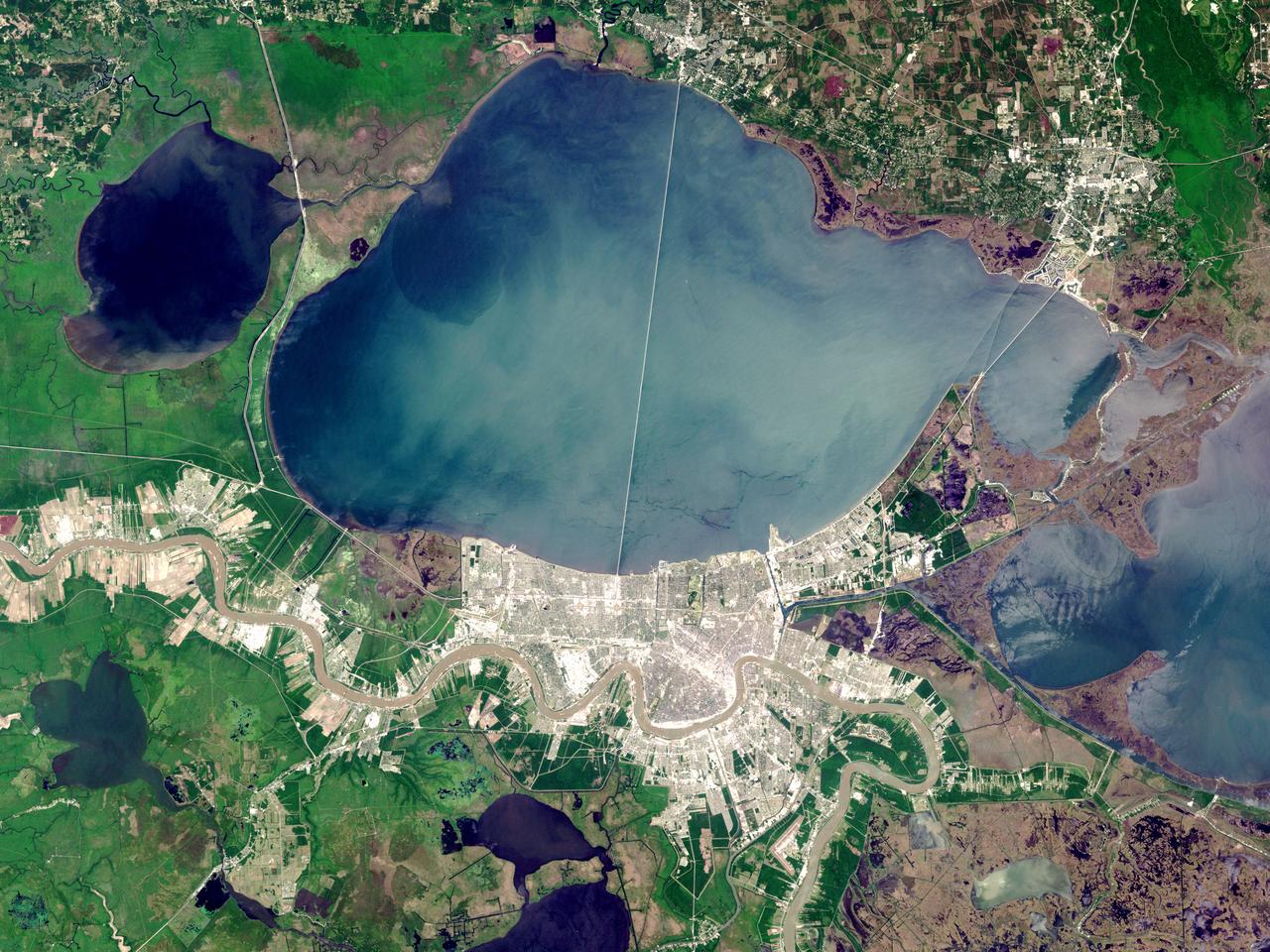

On Sunday, February 3, roughly 800 million eyes from all over the world focused on the Louisiana Superdome in New Orleans as the New England Patriots battled the St. Louis Rams for the NFL Championship in Super Bowl XXXVI. This true color image of New Orleans was acquired on April 26, 2000, by the Enhanced Thematic Mapper plus (ETM+), flying aboard the Landsat 7 satellite. Lake Pontchartrain borders the city to the north. The big river winding its way east to west through the image is the Mississippi. The Louisiana Superdome, built in 1975, sits just inside the rightmost portion of the big river bend that cradles downtown New Orleans. The city, however, may not be around to hold a Super Bowl in 2102. New Orleans is slowly sinking into the Gulf of Mexico. The construction of flood walls and dams north of New Orleans over the past century have prevented sediments carried by the Mississippi River from reaching New Orleans and the Mississippi River Delta. Before the dams were built, river sediments would empty out onto the delta adding layer upon layer of new soil each year. The additional soil prevented the Gulf from subsuming the delta. Unless drastic measures are taken, the city and the delta could be awash in seawater by the end of this century. Image by Robert Simmon, based on data provided by the Landsat 7 Science Team Credit: NASA/GSFC/Landsat <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>

ISS038-E-023651 (26 Dec. 2013) --- Lake Sharpe near Lower Brule, South Dakota is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 38 crew member on the International Space Station. The Missouri River rises in the Rocky Mountains of western Montana, and flows generally to the southeast for approximately 3,767 kilometers (2,341 miles) to its confluence with the Mississippi River north of St. Louis, Missouri -- making it the longest river in North America. The river does not follow a straight southeasterly course along this distance, but includes may meander bends such as illustrated in this photograph. This particular bend is occupied by Lake Sharpe, an approximately 130-kilometer (80 miles) long reservoir formed behind the Big Bend Dam on the Missouri River. The lake surface is frozen and covered with snow, presenting a uniform white appearance in the image. As meander bends develop, they tend to assume a distinctive U-shape when viewed from above. Over time, the river channel can continue to cut into the ends of the "U", eventually bringing them so close together that the river then cuts across the gap to achieve a shorter flow path, essentially short-circuiting or cutting off the meander bend. When this happens and the meander ceases to be part of the active river channel, it may become an oxbow lake. The distance across the narrow neck of land (lower right) associated with this meander near Lower Brule, South Dakota is approximately one kilometer (0.62 miles); however, as the river flow is controlled by the Big Bend Dam downstream, the natural process of meander cutoff has been significantly slowed. The snow cover also highlights circular agricultural fields on the small peninsula within the meander bend. This type of field indicates center-pivot irrigation, where water is distributed from a central point radially outwards using sprinklers to cover the field area. Crops grown here include corn and soybeans according to data from the US Department of Agriculture's CropScape database.
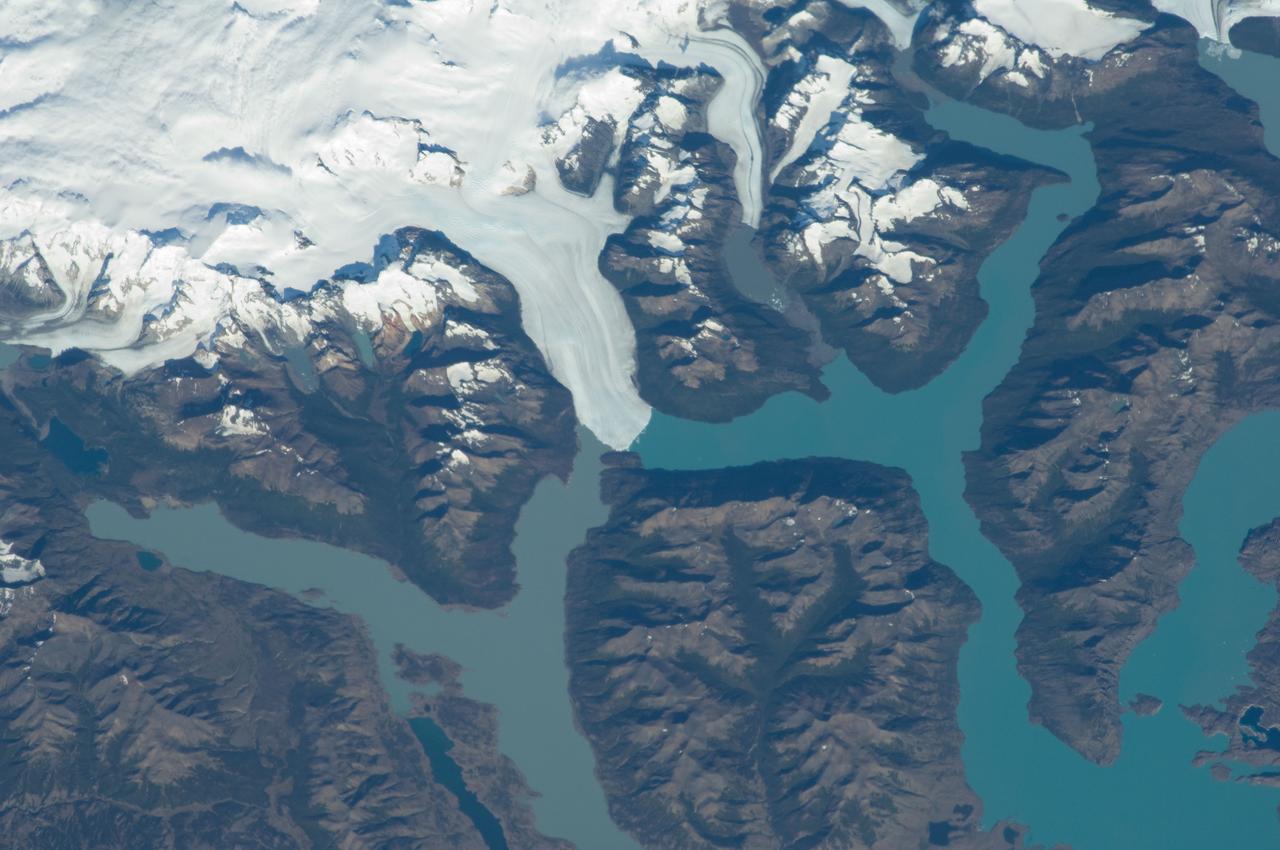

ISS030-E-091253 (21 Feb. 2012) --- Perito Moreno Glacier near Lake Argentino, Argentina is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 30 crew member on the International Space Station. The largest glacier tongue in this image is known as the Perito Moreno Glacier (center). It descends from the Southern Patagonian Icefield (top) at great altitudes (greater than 2,100 meters, 6,825 feet) in the southern Andes Mountains, down into the water and warmer altitudes of Lake Argentino at approximately 180 meters above sea level. The glacier is 30 kilometers long (image width represents approximately 60 kilometers on the ground). Perito Moreno is one of the largest glaciers in Patagonia, and is perhaps the most famous for the fact that it periodically cuts off the major southern arm (known as Brazo Rico) of Lake Argentino completely from the rest of the lake. This is because the glacier advances right across the lake until it meets the opposite shoreline. The ice tongue is “grounded” (meaning that it is not floating, as occurs at the termini of glaciers and ice shelves where they enter the sea), thus forming a natural dam which prevents the lake water on either side from circulating, which in turn causes muddier, “milkier” water to concentrate in Brazo Rico. Sub-ice water, flows under the ice, not only carrying the mud into the lake but also helping lubricate the glacier’s downhill movement. Because of its effect as a dam, meltwater from the south raises water levels in Brazo Rico by as much as 30 meters above the level of the water in Lago Argentino. The great pressure of this higher water ultimately causes the ice tongue to rupture catastrophically, in a great natural spectacle. The last rupture took place in March 2012. The process then repeats, on average every four to five years, as the glacier starts to grow back towards the opposite shoreline. The repeatability of the rupture has contributed to the event becoming a major tourist attraction in the region.

SL4-93-153 (February 1974) --- A vertical view of the Birmingham and central Alabama area is seen in this Skylab 4 Earth Resources Experiments Package S190-B (five-inch earth terrain camera) infrared photographed taken from the Skylab space station in Earth orbit. Illustrated here is the utility of color infrared film in depicting distribution of living vegetation in the 3,600 square mile Birmingham region. The Birmingham industrial complex, with a population of nearly 850,000, is the light gray area nestled in the valley between the northeast-trending ridges that are prominent topographic features in the southern Appalachian Mountains. The narrow ridges and adjacent valleys reflect folded and faulted sedimentary rocks, indicating the complex geological history of the region. Two major rivers and several reservoirs are easily distinguished in this photograph. Bankhand Lake, formed by a dam on the Black Warrior River, appears as bright blue west of Birmingham. Two lakes are formed by dams on the Goosa River east of Birmingham. Federal and state highways appear as thin white lines and are easily identified. Interstate 65 to Montgomery is the prominent white line extending southward from Birmingham. Power line clearings are visible in the center of the picture along the Goosa River, and can be traced northwestward to northern parts of Birmingham. The predominant deep red color of the picture is due to the reflections from living vegetation. In contrast are the light tan areas that commonly occur as rectangular patterns in the east part of the photograph and represent mature agricultural crops or grazing lands. Analysis of the photographic data from the earth terrain camera will be conducted by Dr. H. Jayroe of the Marshall Space Flight Center in developing analytical techniques. All EREP photography is available to the public through the Department of Interior's Earth Resources Observations Systems Data Center, Sioux Falls, South Dakota, 57198. Photo credit: NASA

ISS017-E-013856 (19 Aug. 2008) --- Amazon River, Brazil is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 17 crewmember on the International Space Station. This image shows the huge sunglint zone, common to oblique views from space, of the setting sun shining off the Amazon River and numerous lakes on its floodplain. About 150 kilometers of the sinuous Amazon course is shown here, as it appears about 1,000 kilometers from the Atlantic Ocean. The Uatuma River enters on the north side of the Amazon (top). A small side channel of the very large Madeira River enters the view from the left. Tupinambarama Island occupies the swampy wetlands between the Amazon and Madeira rivers. Sunglint images reveal great detail in waterbodies -- in this case the marked difference between the smooth outline of the Amazon and the jagged shoreline of the Uatuma River. The jagged shoreline results from valley sides being eroded in relatively hard rocks. The Uatuma River has since been dammed up by the sediment mass of the Amazon floodplain. Because the Amazon flows in its own soft sediment, its huge water discharge smooths the banks. Another dammed valley (known as a ria) is visible beneath the cirrus cloud of a storm (bottom). Although no smoke plumes from forest fires are visible in the view, two kinds of evidence show that there is smoke in the atmosphere. The coppery color of the sunglint is typically produced by smoke particles and other aerosols scattering yellow and red light. Second, a small patch of cloud (top right) casts a distinct shadow. The shadow, say scientists, is visible because so many particles in the surrounding sunlit parts of the atmosphere reflect light to the camera.
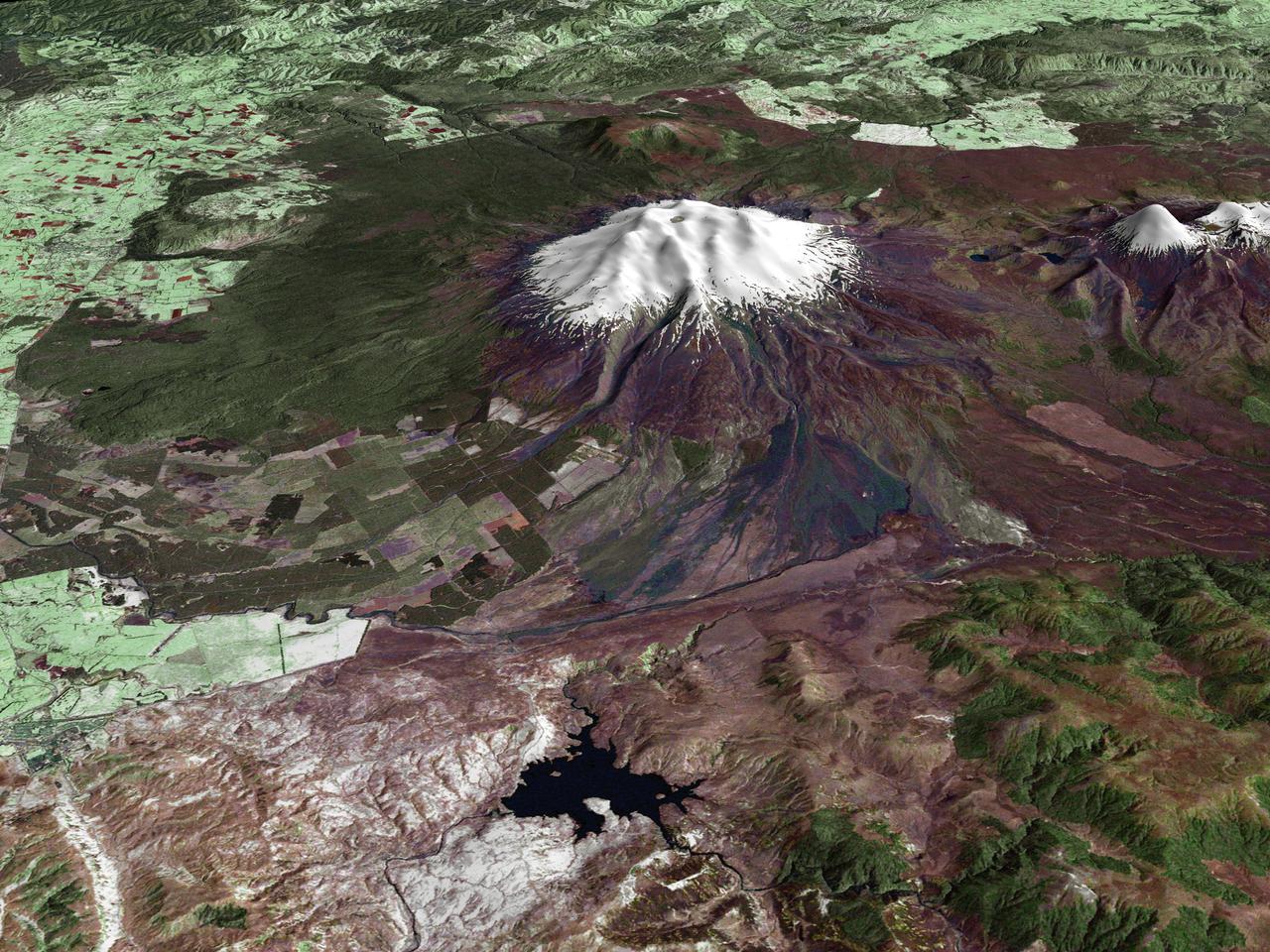
All around the world, people live in places where the threat of natural disaster is high. On the North Island of New Zealand, the Mount Ruapehu volcano is just such a threat. A towering, active stratovolcano (the classic cone-shaped volcano), snow-capped Ruapehu Volcano is pictured in this enhanced-color image. The image is made from topography data collected by the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour, launched on February 11, 2000, and imagery collected by the Landsat satellite on October 23, 2002. Ruapehu is one of New Zealand’s most active volcanoes, with ten eruptions since 1861. The eruptions aren’t the only threat from the volcano, however. Among the most serious threats is a volcanic mudflow called a lahar. In between eruptions, a lake forms in the volcano’s caldera from melting snow. If a previous eruption has deposited a dam of ash, rocks and mud in the lake’s natural overflow point, then the lake becomes dangerously full, held back only by the temporary dam. In this scene, the lake is nestled among the ridges at the top of the volcano. Eventually, the dam gives way and a massive flow of mud and debris churns down the mountain toward farmland and towns below. Scientists estimate that Ruapehu has experienced 60 lahars in the last 150 years. A devastating lahar in 1953 killed more than 150 people, who died when a passenger train plunged into a ravine when a railroad bridge was taken out by the lahar. The flank of the volcano below the lake is deeply carved by the path of previous lahars; the gouge can be seen just left of image center. Currently scientists in the region are predicting that the lake will overflow in a lahar sometime in the next year. There is great controversy about how to deal with the threat. News reports from the region indicate that the government is planning to invest in a high-tech warning system that will alert those who might be affected well in advance of any catastrophic release. Others feel that the government should combat the threat through engineering at the top of the mountain, for example, by undertaking a controlled release of the lake. Credit Landsat data provided courtesy of the University of Maryland Global Land Cover Facility Landsat processing by Laura Rocchio, Landsat Project Science Office SRTM 3-arcsecond elevation data courtesy of SRTM Team NASA/JPL/NIMA Visualization created by Earth Observatory staff. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
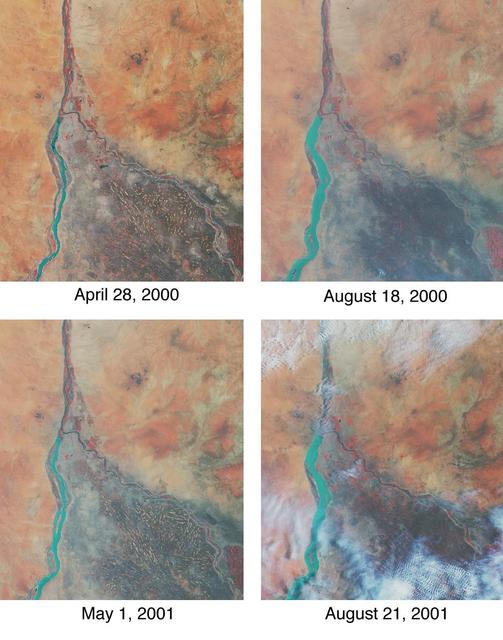
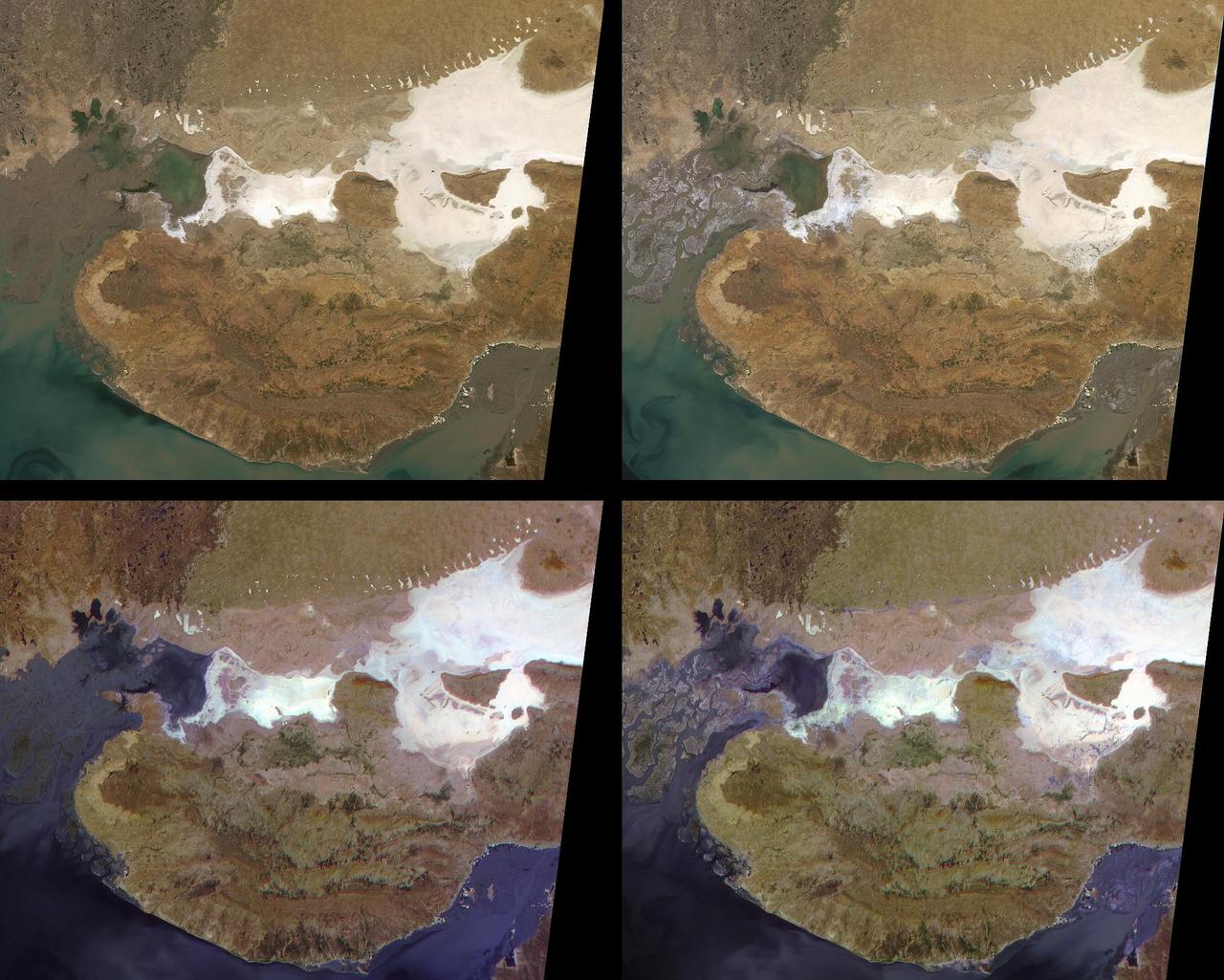
Throughout history, the rising and falling waters of the mighty Nile River have directly impacted the lives of the people who live along its banks. These images of the area around Sudan's capital city of Khartoum capture the river's dynamic nature. Acquired by the Multi-angle Imaging SpectroRadiometer's nadir (vertical-viewing) camera, they display the extent of the Nile waters before and after the onset of the rainy seasons of 2000 (top pair) and 2001 (bottom pair). The images are displayed in "false color," using the camera's near-infrared, green, and blue bands. With this particular spectral combination, water appears in shades of blue and turquoise, and highly vegetated areas show up as bright red. Originating in Uganda and Ethiopia, respectively, the waters of the White Nile (western branch) and Blue Nile (eastern branch) converge at Khartoum (about half-way between image center and the left-hand side), and continue to flow northward as the Great Nile. Although the most obvious feature in these images is the increased width of the White Nile between spring and summer, careful inspection shows that the Great Nile is at its widest in August 2001 (note in particular the area between the clouds near the top of this panel). Heavy rains in the Blue Nile catchment area of the Ethiopian highlands led to a rapid overflow of the river's floodwaters into the main stream of the Great Nile, leading to extensive flooding, the worst effects of which occurred north of Khartoum. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, tens of thousands of people have fled their homes, and the number of people in need of urgent food assistance in Sudan, estimated at three million earlier in the year, was likely to increase with the onset of these floods. South of the confluence of the White Nile and the Blue Nile, the area of a cross-hatched appearance is the irrigated plain of El Gezira. The Gezira irrigation scheme uses water from the Makwar Dam (now called the Sennar Dam), located across the Blue Nile south of Khartoum. Among the main agricultural products of this region are cotton, millet, peanuts and fodder crops. Overall prospects for Sudan's 2001 grain crop were already poor prior to the flooding due to a late start of the rainy season in parts of the country. Following two consecutive years of serious drought, precipitation arrived too late to save the grain harvest that normally begins in late August. Lower harvests for the past two years coupled with depletion of stocks have led to a rise in cereal prices, reducing access to food for the Sudan's poorer citizens, already suffering from the effects of Africa's longest running civil war. Each of these images represents an area of about 130 kilometers x 150 kilometers. The data were obtained during Terra orbits 1922, 3553, 7281, and 8912. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA03420
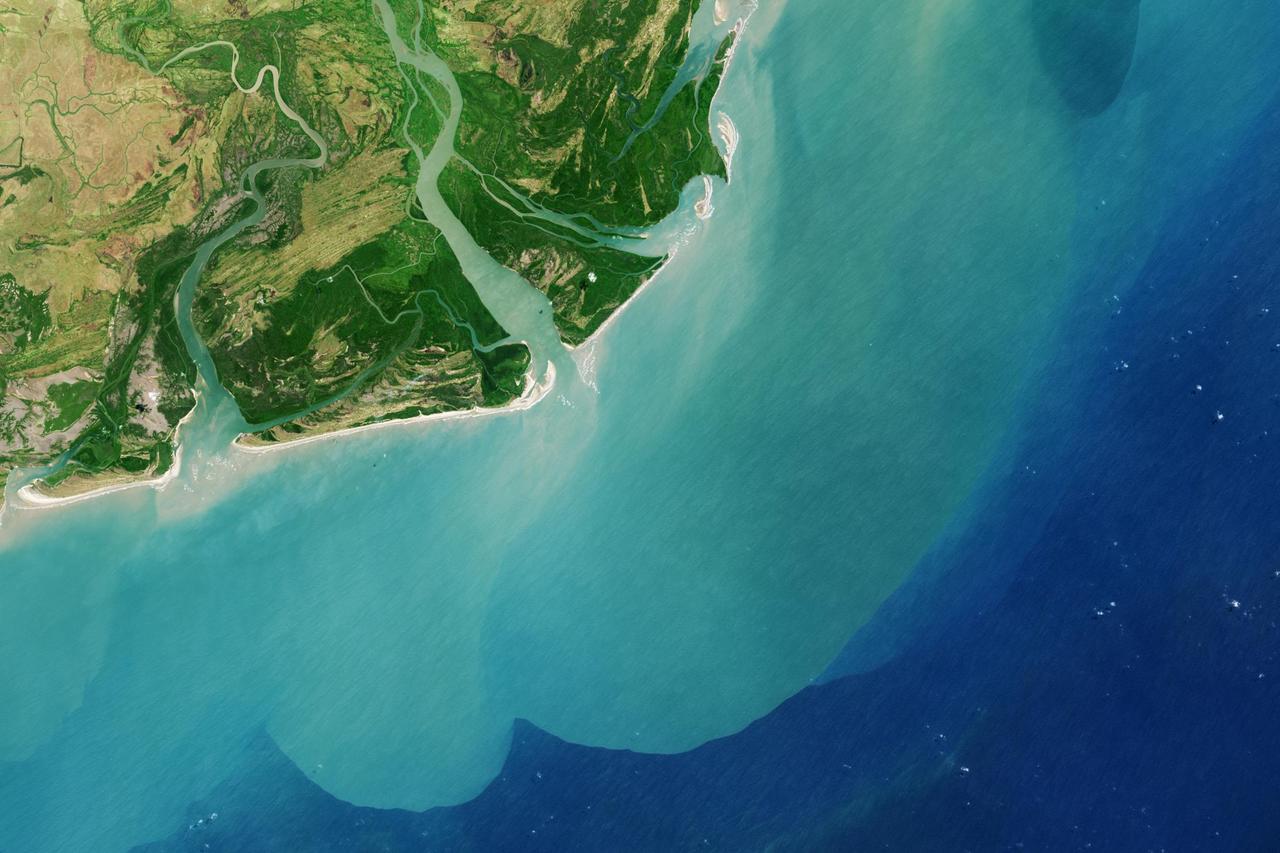

It drains a watershed that spans eight countries and nearly 1.6 million square kilometers 600,000 square miles. The Zambezi also Zambeze is the fourth largest river in Africa, and the largest east-flowing waterway. The Operational Land Imager on the Landsat 8 satellite acquired this natural-color image of the Zambezi Delta on August 29, 2013. Sandbars and barrier spits stretch across the mouths of the delta, and suspended sediment extends tens of kilometers out into the sea. The sandy outflow turns the coastal waters to a milky blue-green compared to the deep blue of open water in the Indian Ocean. The Zambezi Delta includes 230 kilometers of coastline fronting 18,000 square kilometers (7,00 square miles) of swamps, floodplains, and even savannahs (inland). The area has long been prized by subsistence fishermen and farmers, who find fertile ground for crops like sugar and fertile waters for prawns and fish. Two species of endangered cranes and one of the largest concentration of buffalo in Africa -- among many other species of wildlife -- have found a haven in this internationally recognized wetland. However, the past six decades have brought great changes to the Zambezi Delta, which used to pour more water and sediment off of the continent. Hydropower dams upstream-most prominently, the Kariba and the Cahora Bassa-greatly reduce river flows during the wet season; they also trap sediments that would otherwise flow downstream. The result has been less water reaching the delta and the floodplains, which rely on pulses of nutrients and sediments from annual (and mostly benign) natural flooding. The change in the flow of the river affects freshwater availability and quality in the delta. Strong flows push fresh water further out into the sea and naturally keep most of a delta full of fresh (or mostly fresh) water. When that fresh flow eases, the wetlands become drier and more prone to fire. Salt water from the Indian Ocean also can penetrate further into the marsh, upsetting the ecological balance for aquatic plant and animal species. Researchers have found that the freshwater table in the delta has dropped as much as five meters in the 50 years since dams were placed on the river. Less river flow also affects the shape and extent of the delta. Today there is less sediment replenishing the marshes and beaches as they are scoured by ocean waves and tides. "What strikes me in this image is the suspended sediment offshore," said Liviu Giosan, a delta geologist at the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution. "Sediment appears to be transferred from the delta offshore in plumes that not only originate in active river mouths but also from deactivated former mouths, now tidal channels. This shows the power of tidal scouring contributing to the slow but relentless erosion of the delta." http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA18155
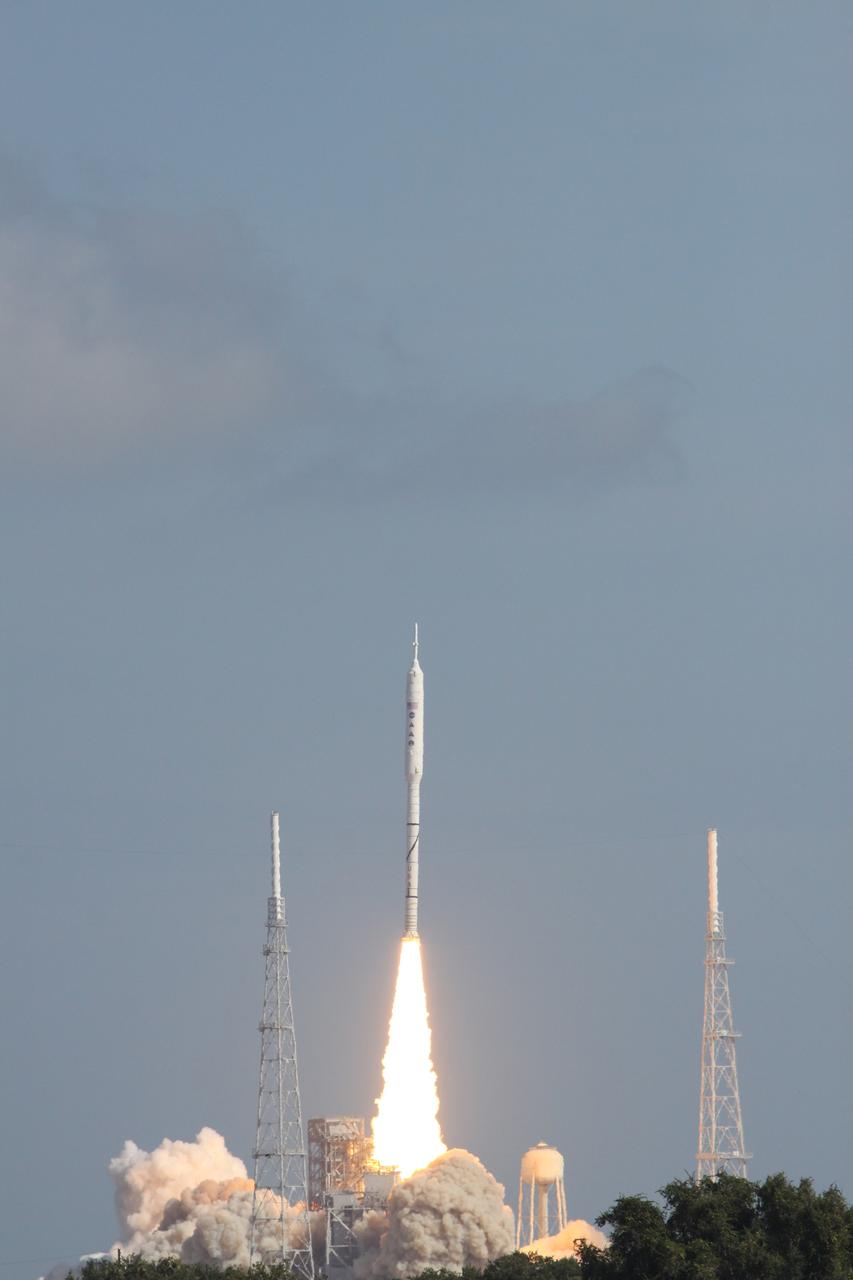

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - With more than 23 times the power output of the Hoover Dam, the Constellation Program's Ares I-X test rocket zooms off Launch Complex 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The rocket produces 2.96 million pounds of thrust at liftoff and reaches a speed of 100 mph in eight seconds. Liftoff of the 6-minute flight test was at 11:30 a.m. EDT Oct. 28. This was the first launch from Kennedy's pads of a vehicle other than the space shuttle since the Apollo Program's Saturn rockets were retired. The parts used to make the Ares I-X booster flew on 30 different shuttle missions ranging from STS-29 in 1989 to STS-106 in 2000. The data returned from more than 700 sensors throughout the rocket will be used to refine the design of future launch vehicles and bring NASA one step closer to reaching its exploration goals. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
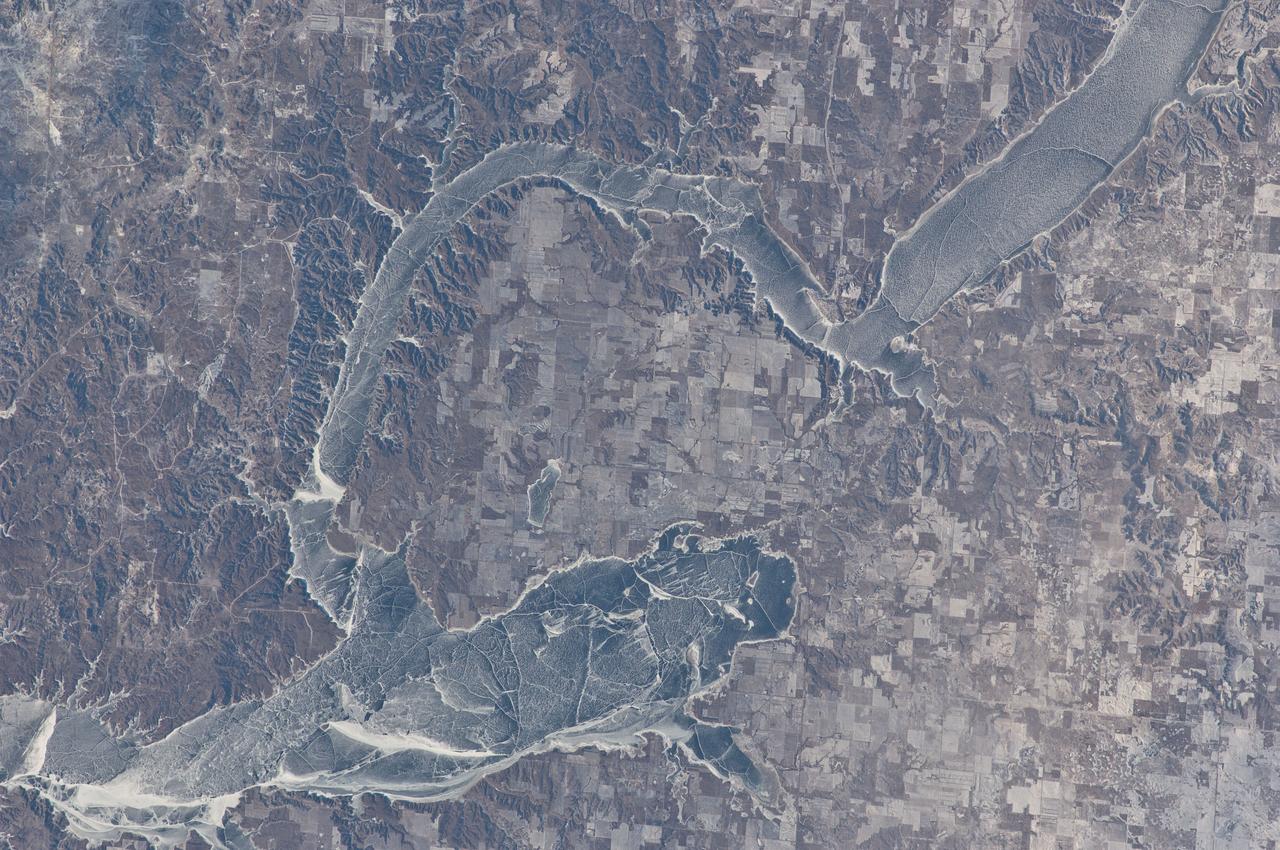

ISS030-E-059433 (19 Jan. 2012) --- Ice cover on Lake Sakakawea in North Dakota is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 30 crew member on the International Space Station. This striking photograph illustrates the harsh winter conditions frequently experienced in North Dakota. Ice covers the surface of northwestern Lake Sakakawea, a reservoir on the Missouri River in west-central North Dakota. A local weather station near New Town, ND reported an air temperature of approximately -24 °C (-11 °F), with a wind chill of approximately -32 °C (-25 °F) at 10:36 local time – six minutes before the image was taken. In addition to the grey ice on the lake, a dusting of white snow highlights agricultural fields to the north and northeast, as well as fissures and irregularities in the ice surfaces. For a sense of scale, the arms of the lake to either side of New Town are approximately 10 kilometers (6 miles) apart. Lake Sakakawea is named—in the Hidatsa language—for the Shoshone woman generally known as Sacagawea, or “Bird Woman”. She accompanied the Lewis and Clark Expedition in 1805–1806 as an interpreter and guide. The lake was created following the completion of Garrison Dam (not shown) on the Missouri River in 1954. With a surface area of approximately 148,924 hectares (368,000 acres) and length of 286 kilometers (178 miles), Lake Sakakawea is one of the largest artificial reservoirs in the USA.