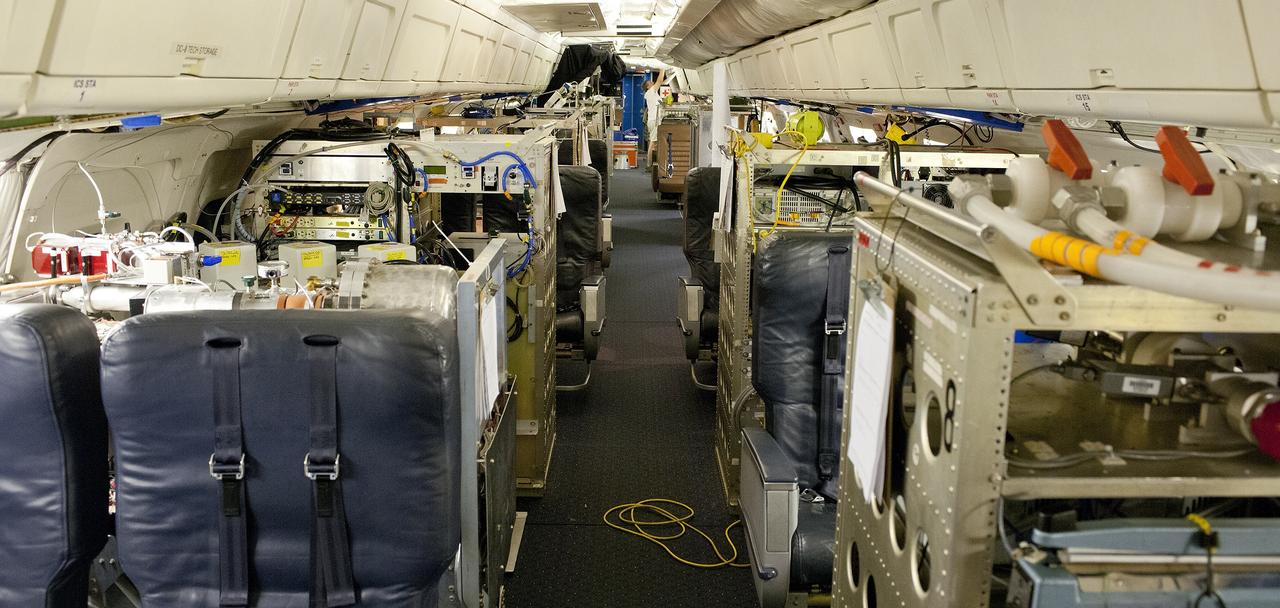

NASA's DC-8 flying laboratory is fully loaded with seats and instrument racks in preparation for NASA's 2013 SEAC4RS climate science mission.
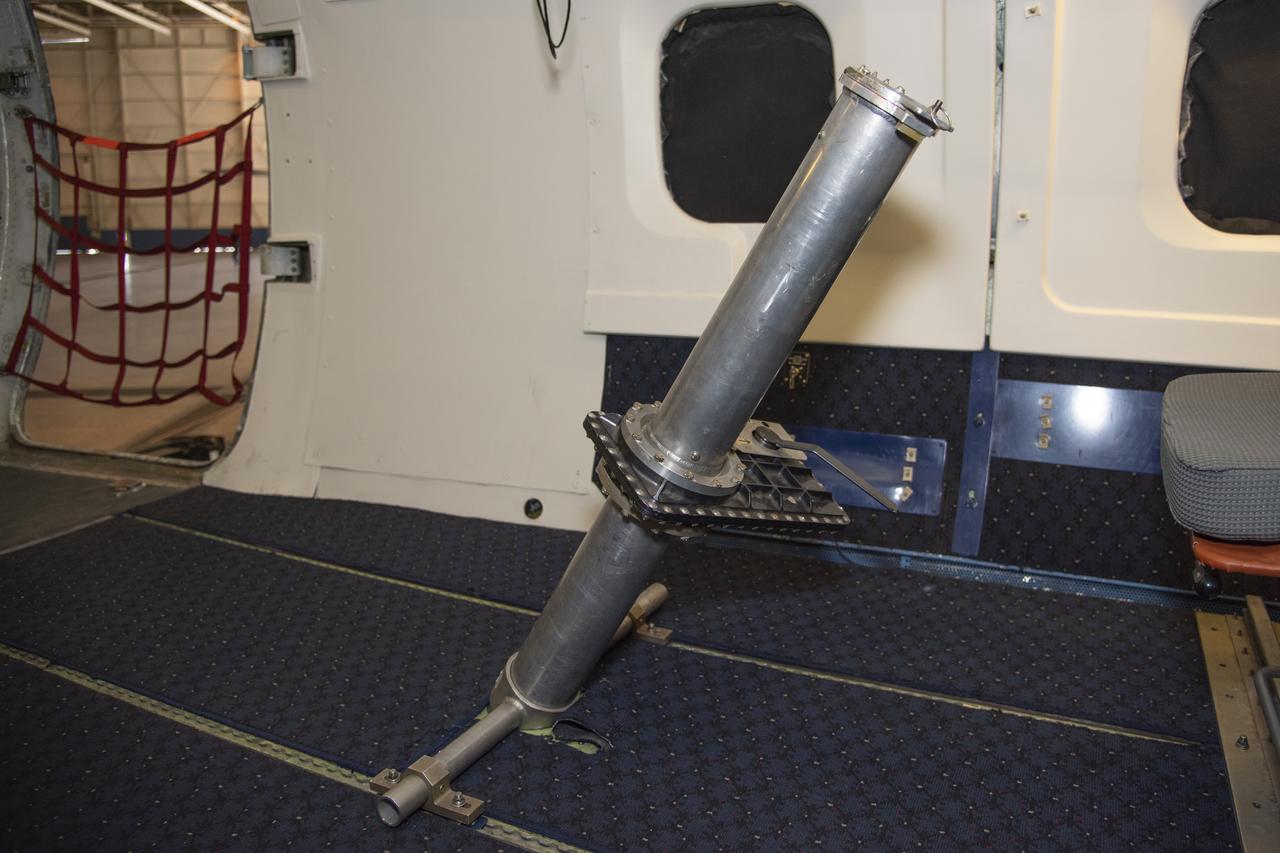

To verify the lidar data they're collecting on the DC-8 airborne science laboratory, Aeolus mission scientists will use dropsondes, which are devices they'll drop from this tube in the aircraft to collect wind and water vapor data.
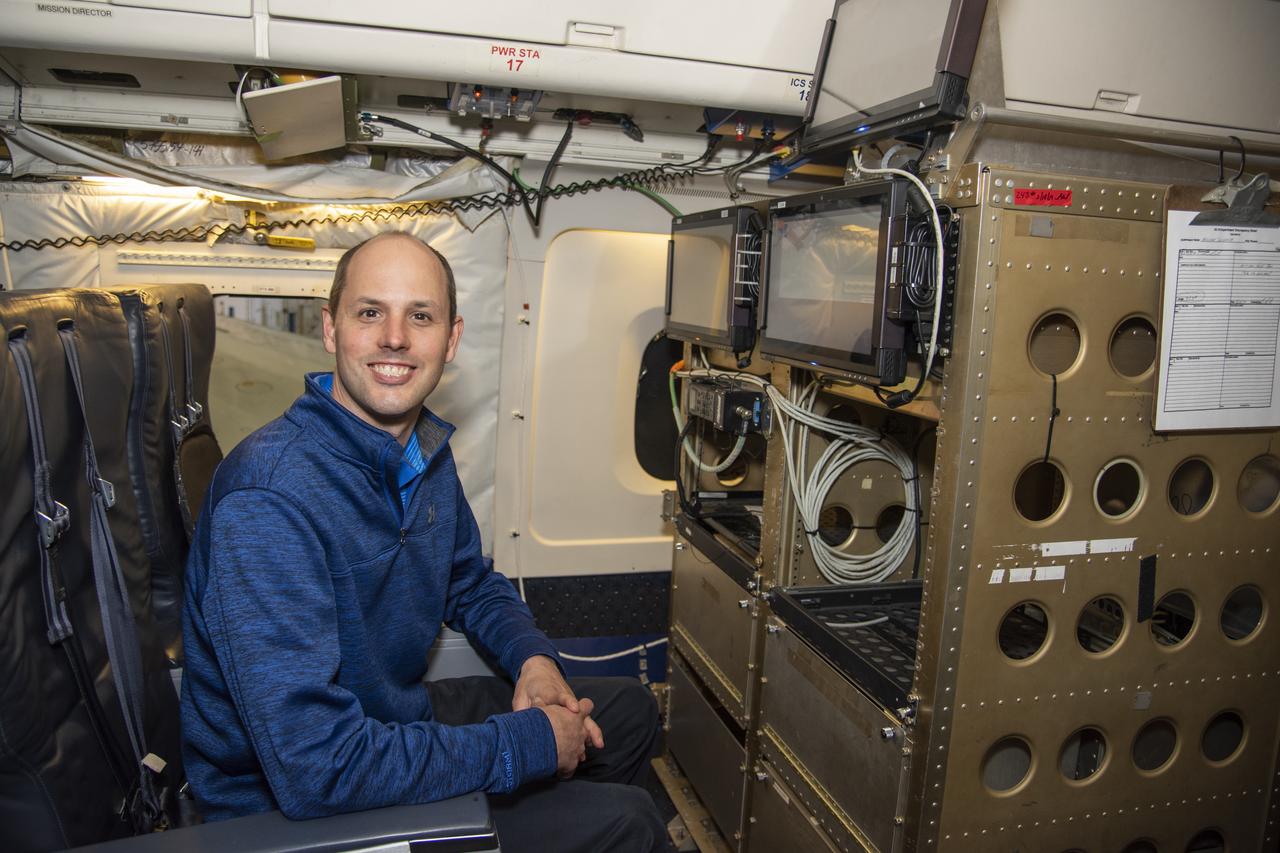

NASA Langley Research Center's Kris Bedka, pictured here on the DC-8 flying laboratory, is the lead for an airborne mission called Aeoulus that is advancing laser-based technologies for measuring winds in the lower atmosphere.
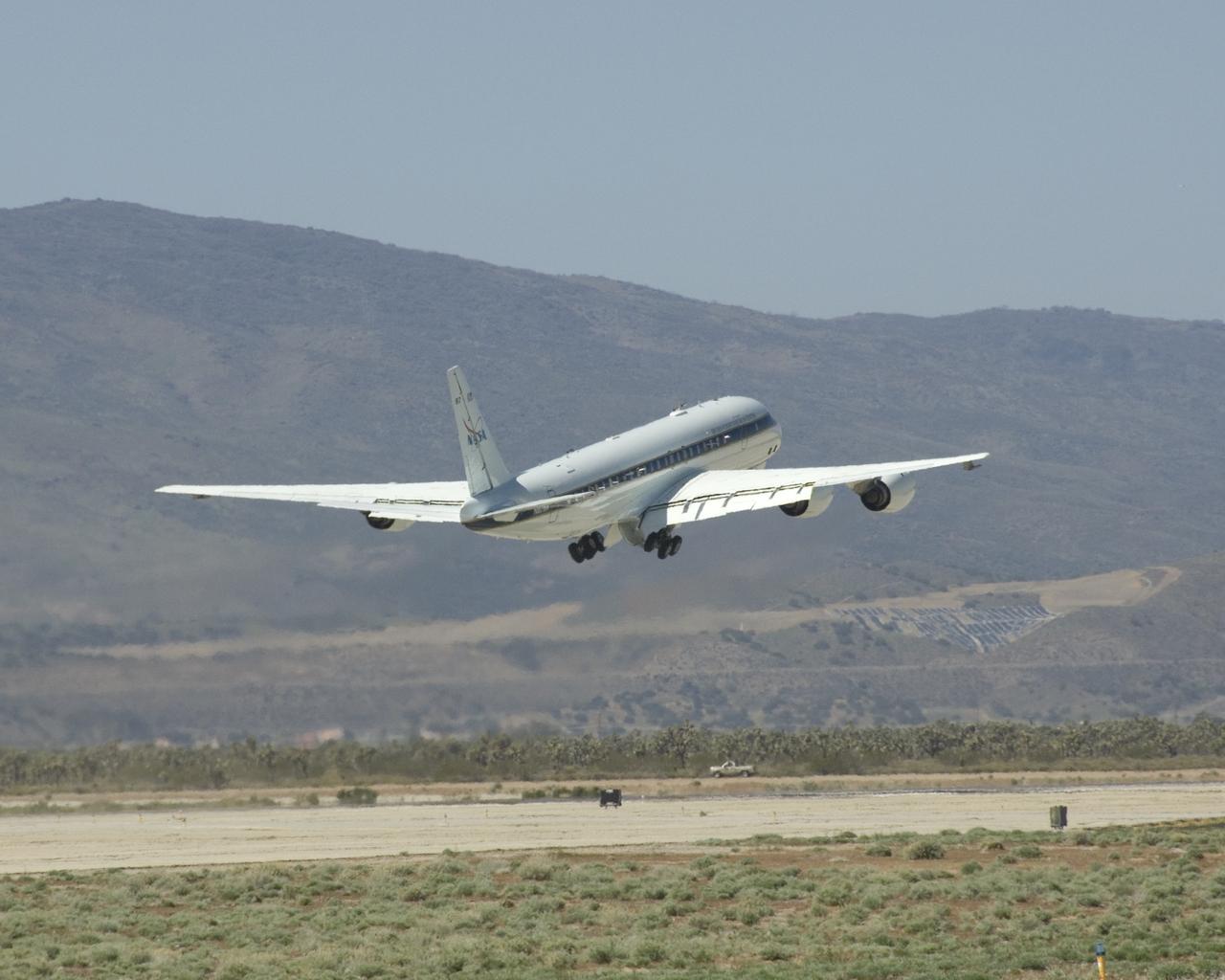

NASA's DC-8 flying laboratory lifts off the runway at Air Force Plant 42 in Palmdale, Calif., on its first flight in the ARCTAS atmospheric science mission.
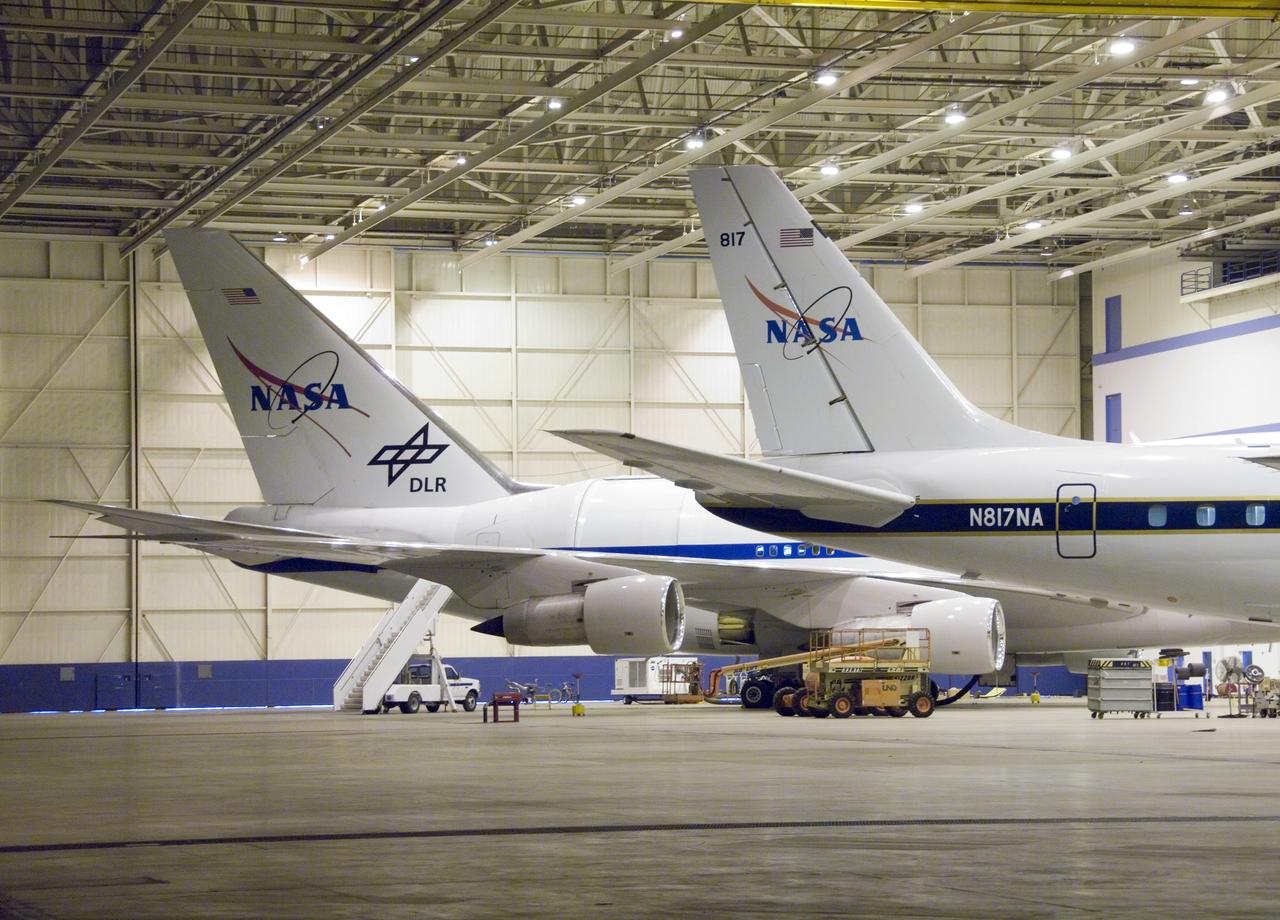

Two large science aircraft, a DC-8 flying laboratory and the SOFIA 747SP, are based at NASA's Dryden Aircraft Operations Facility in Palmdale, Calif.
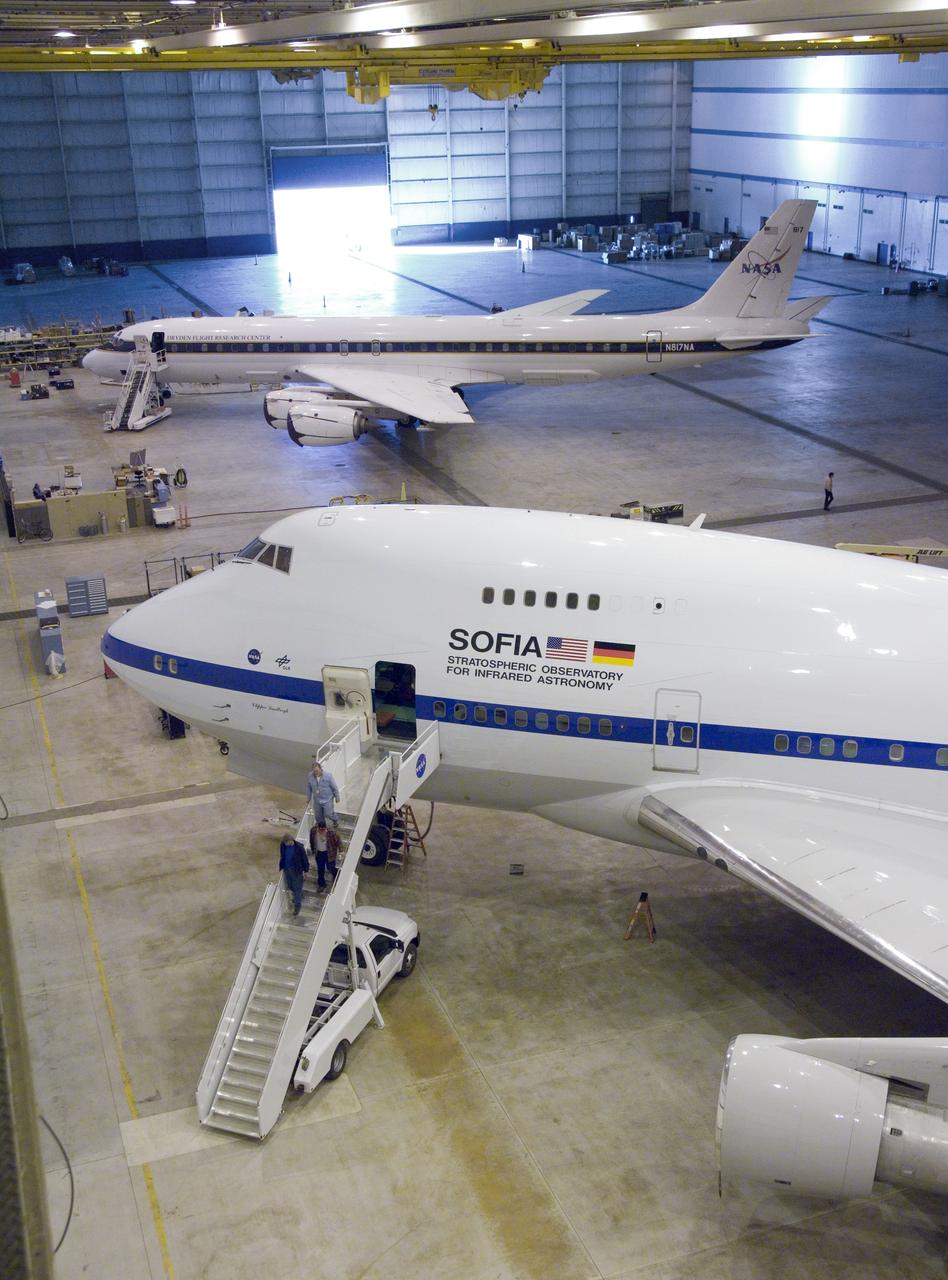

NASA'S SOFIA infrared observatory 747SP (front) and DC-8 flying laboratory (rear) are now housed at the Dryden Aircraft Operations Facility in Palmdale, Calif.
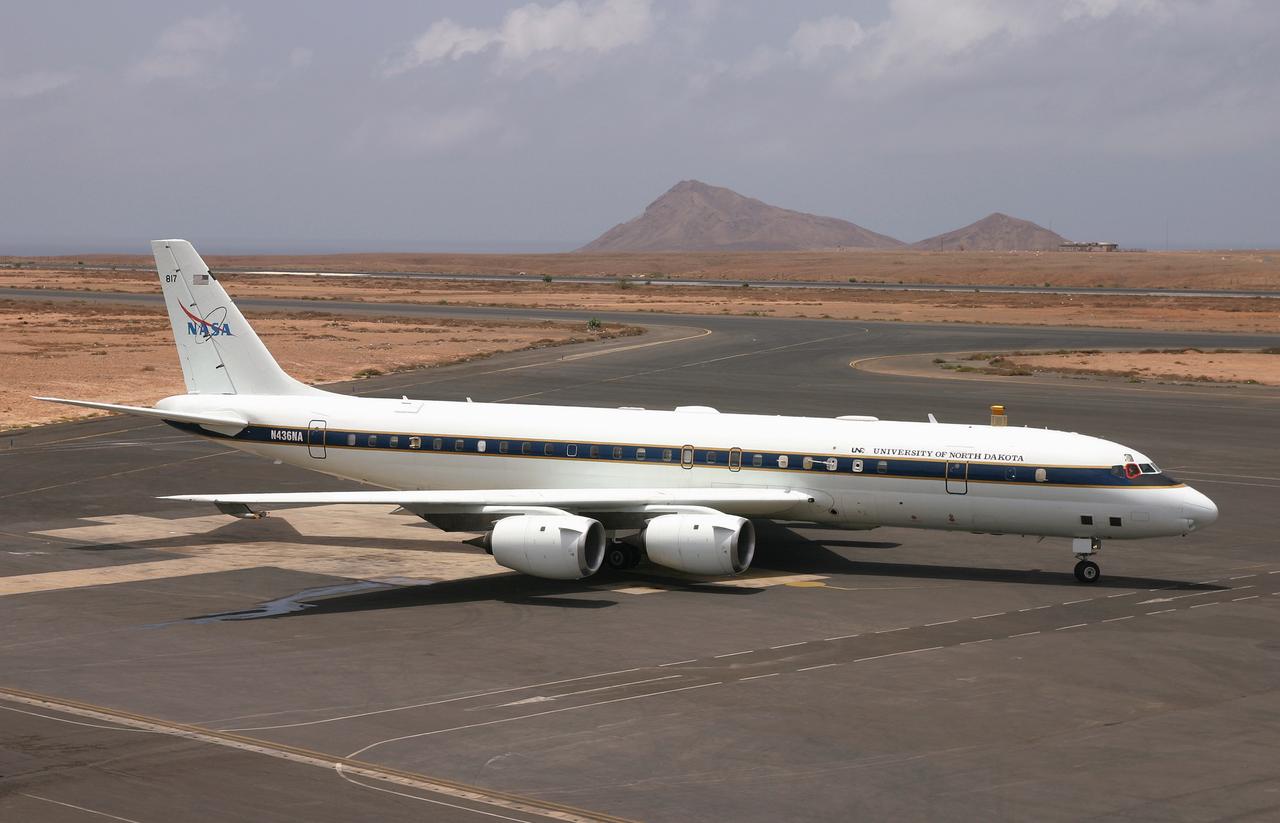

NASA's DC-8 Flying Laboratory taxis up to the ramp at Sal Island's Amilcar Cabral International Airport after a science flight for the NAMMA mission. (Ames photo # ACD06-0135-035)
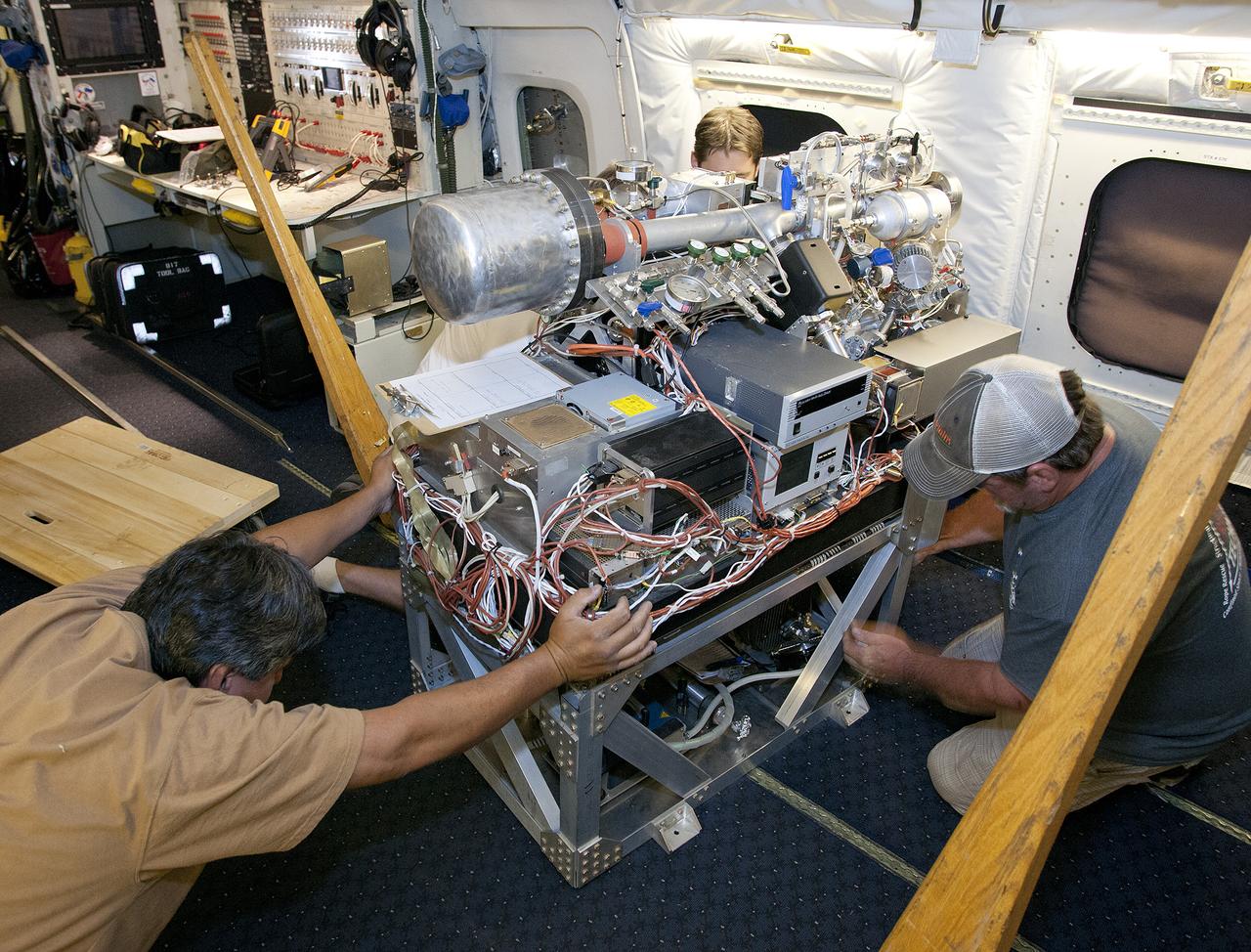

Scientists and technicians ready an instrument rack for mounting in NASA's DC-8 flying laboratory in preparation for a complex mission to study how air pollution and natural emissions affect climate change
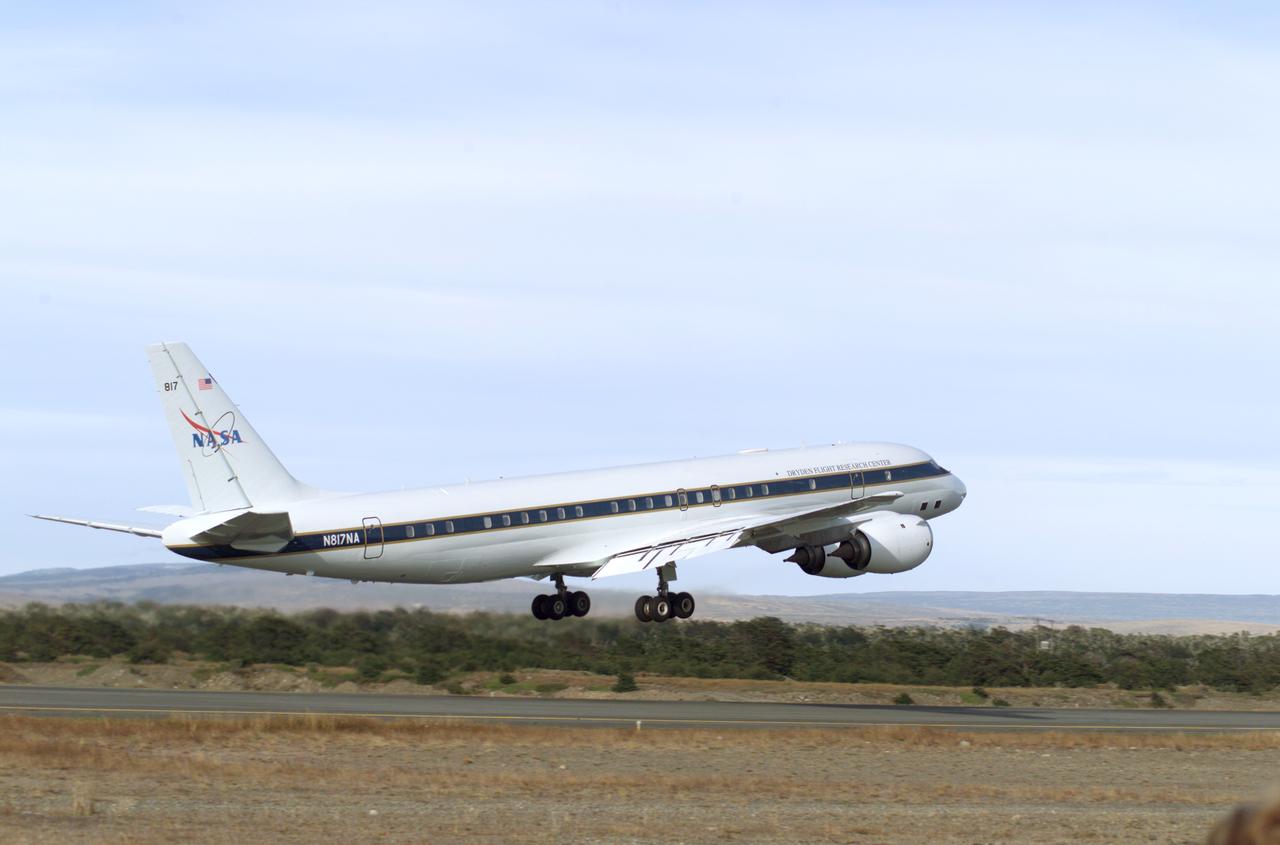

NASA's DC-8 flying laboratory takes off from Carlos Ibanez International Airport in Punta Arenas, Chile, during NASA's AirSAR 2004 campaign. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition in Central and South America by an international team of scientists that is using an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR), located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world are combining ground research with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct.
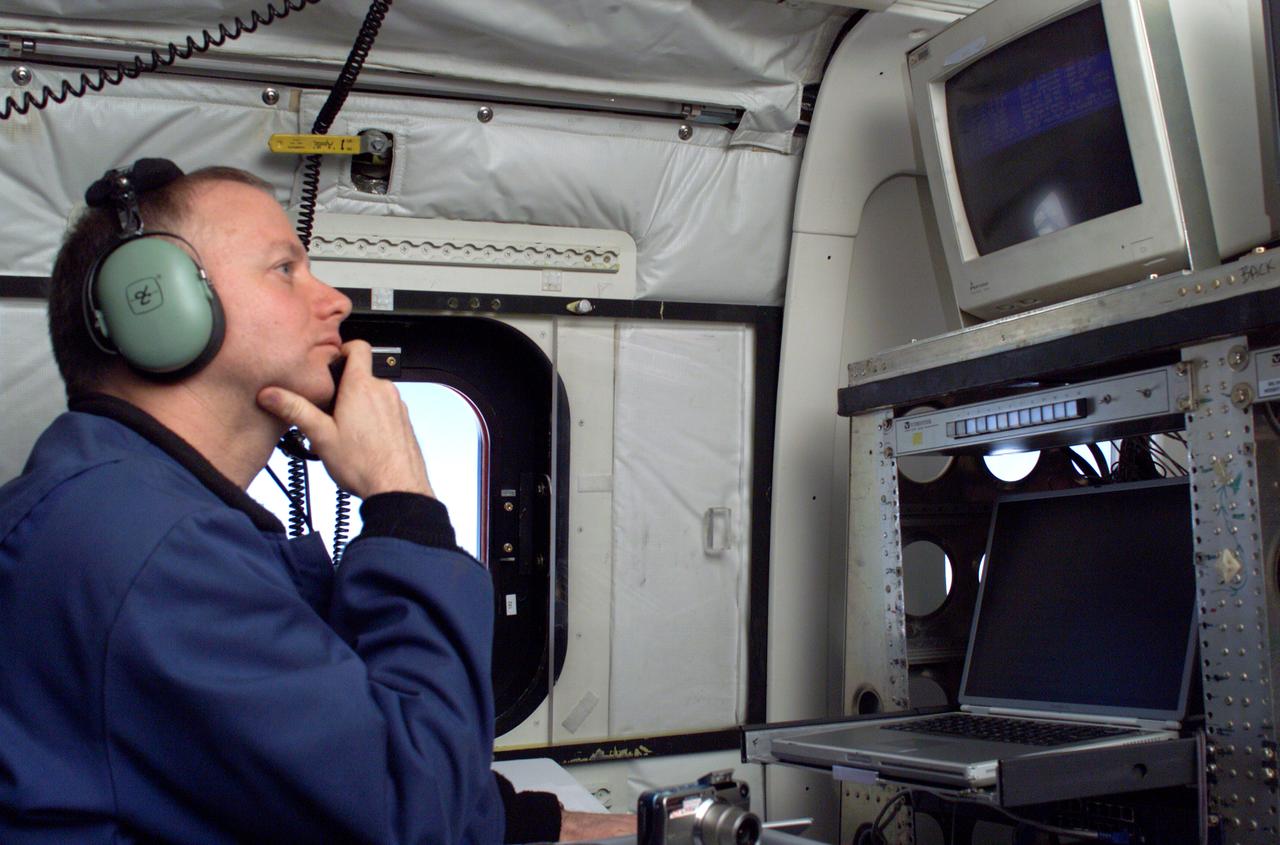

JPL Researcher Bruce Chapman at an AirSAR station aboard NASA's DC-8 flying laboratory during the AirSAR 2004 campaign. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition by an international team of scientists that will use an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR), in a mission ranging from the tropical rain forests of Central America to frigid Antarctica.
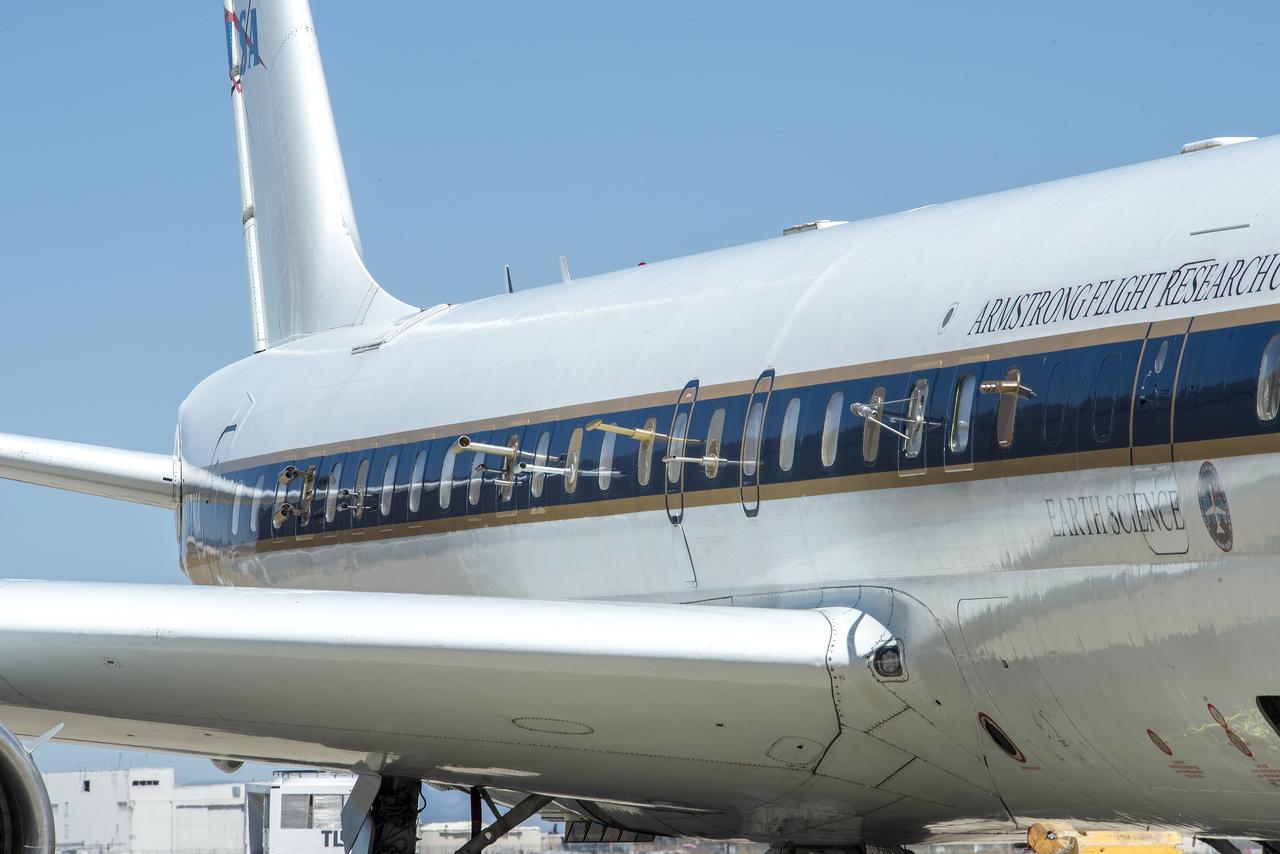

NASA’s DC-8 flying laboratory carried the Fire Influence on Regional to Global Environments and Air Quality, or FIREX-AQ, science team and a suite of state-of-the-art instrumentation to observe different components of fire smoke in varying altitudes and weather. The aircraft is based at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California.
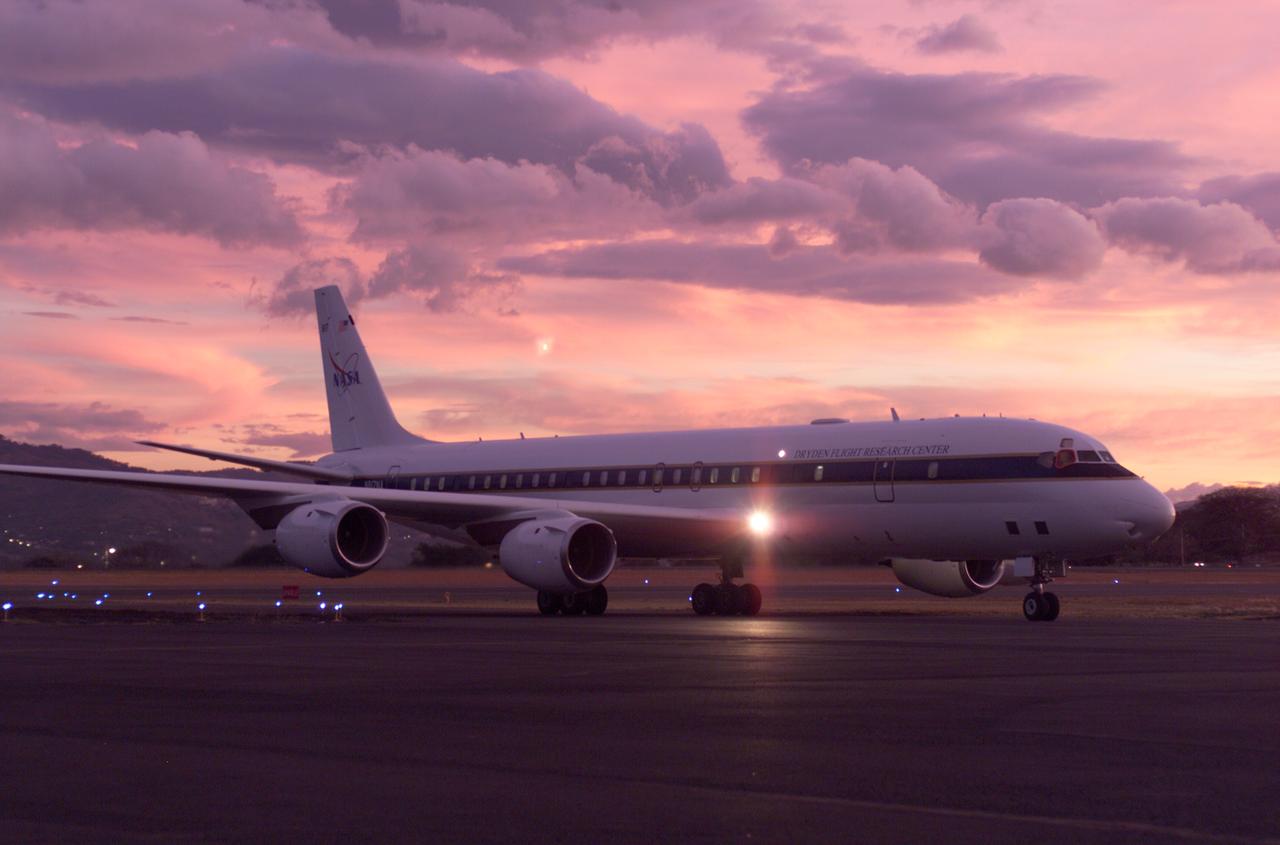

NASA's DC-8 flying laboratory seen at sunset after a flight supporting the AirSAR 2004 Mesoamerica campaign. AirSAR 2004 Mesoamerica is a three-week expedition by an international team of scientists that uses an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR) which is located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world including NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory are combining ground research done in several areas in Central America with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. The radar, developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, can penetrate clouds and also collect data at night. Its high-resolution sensors operate at multiple wavelengths and modes, allowing AirSAR to see beneath treetops, through thin sand, and dry snow pack. AirSAR's 2004 campaign is a collaboration of many U.S. and Central American institutions and scientists, including NASA; the National Science Foundation; the Smithsonian Institution; National Geographic; Conservation International; the Organization of Tropical Studies; the Central American Commission for Environment and Development; and the Inter-American Development Bank.
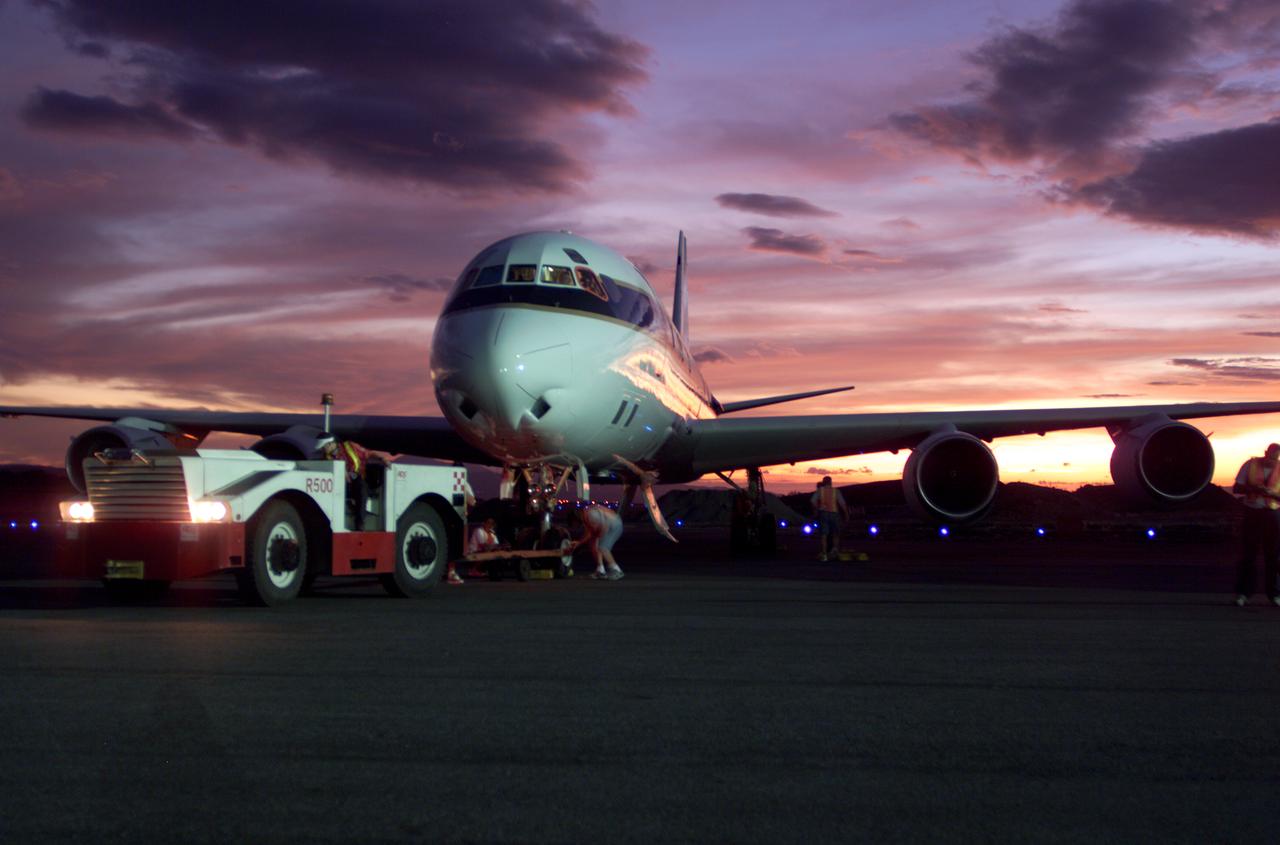

NASA's DC-8 flying laboratory seen at sunset after a flight supporting the AirSAR 2004 Mesoamerica campaign. AirSAR 2004 Mesoamerica is a three-week expedition by an international team of scientists that uses an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR) which is located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world including NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory are combining ground research done in several areas in Central America with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. The radar, developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, can penetrate clouds and also collect data at night. Its high-resolution sensors operate at multiple wavelengths and modes, allowing AirSAR to see beneath treetops, through thin sand, and dry snow pack. AirSAR's 2004 campaign is a collaboration of many U.S. and Central American institutions and scientists, including NASA; the National Science Foundation; the Smithsonian Institution; National Geographic; Conservation International; the Organization of Tropical Studies; the Central American Commission for Environment and Development; and the Inter-American Development Bank.
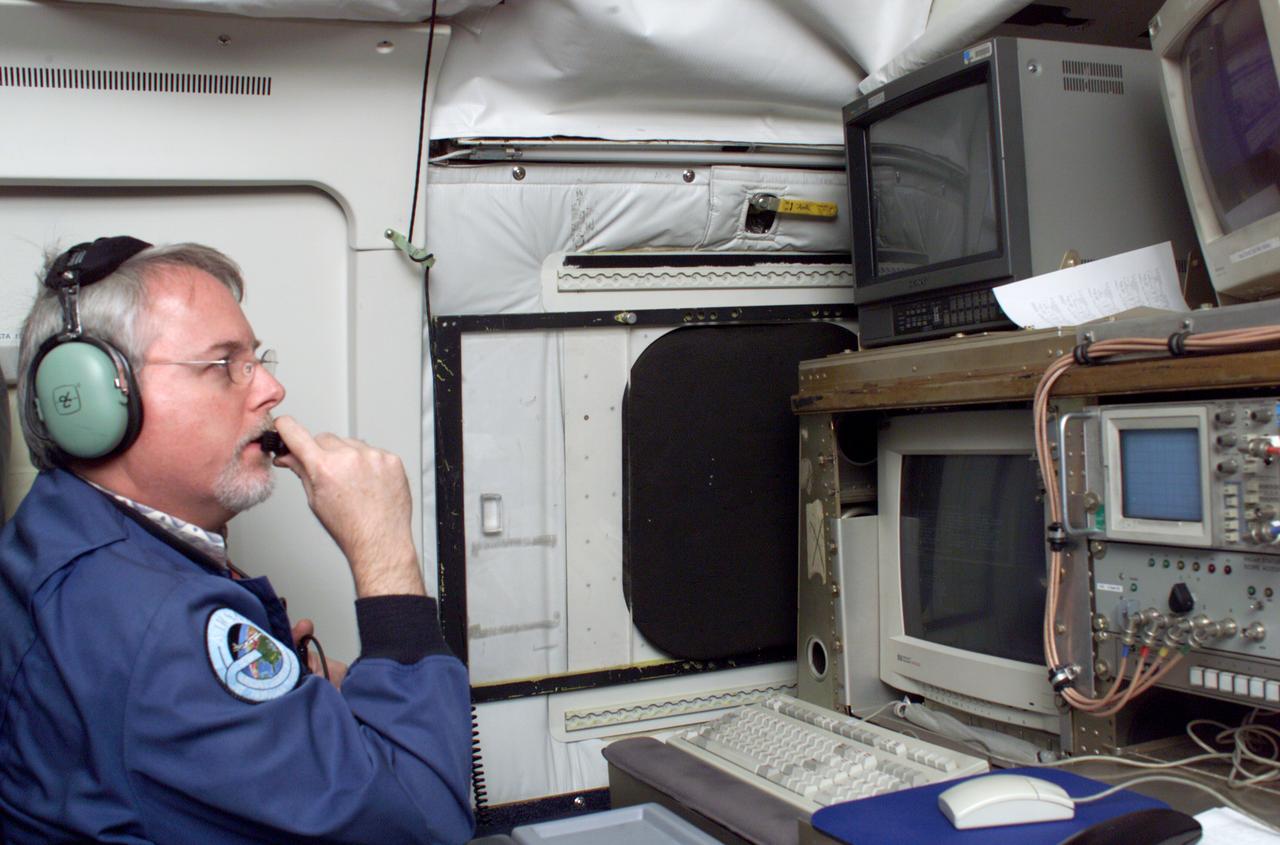

JPL Researcher Tim Miller at the primary AirSAR station aboard NASA's DC-8 flying laboratory during the AirSAR 2004 campaign. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition by an international team of scientists that will use an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR), in a mission ranging from the tropical rain forests of Central America to frigid Antarctica.
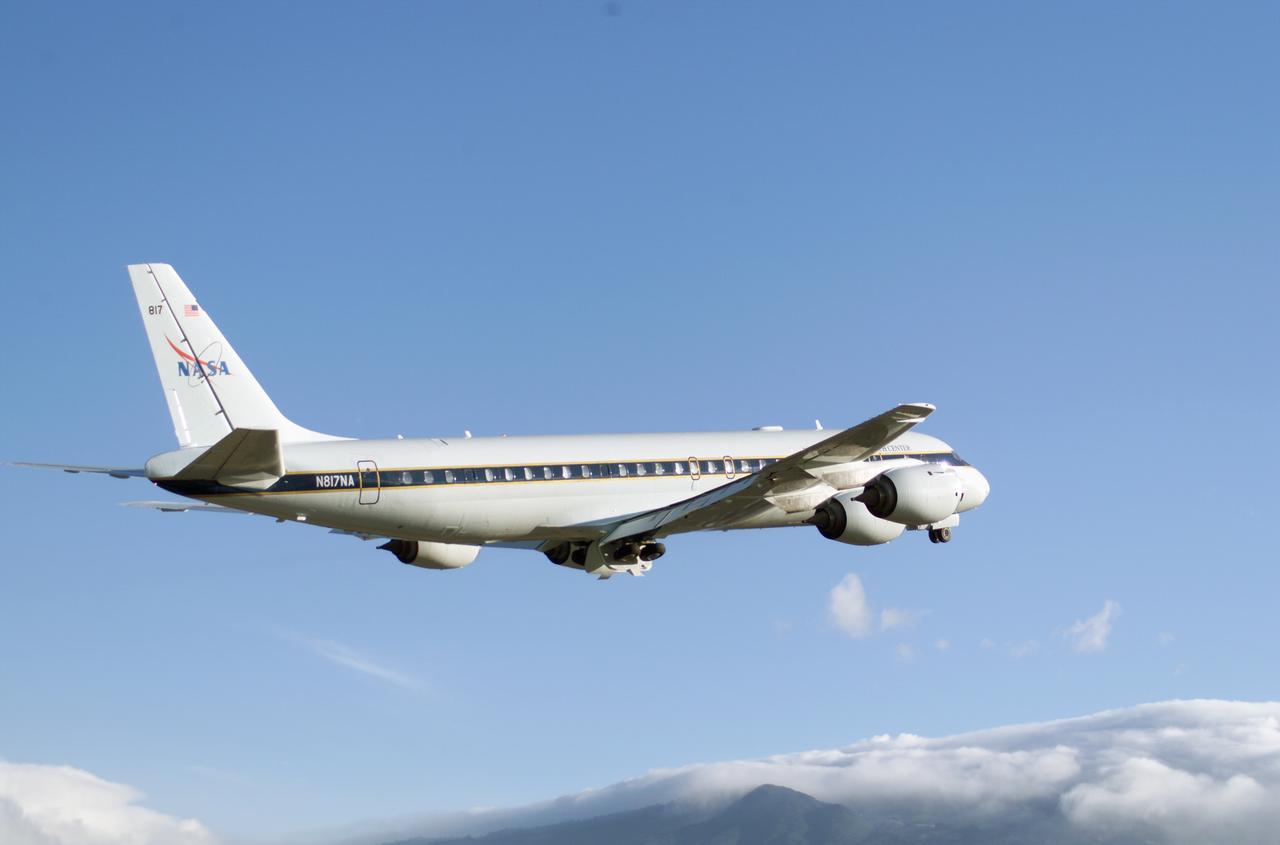

NASA's DC-8 flying laboratory takes off from Juan Santamaria International Airport in San Jose, Costa Rica, on NASA's AirSAR 2004 campaign. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition by an international team of scientists that will use an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR), in a mission ranging from the tropical rain forests of Central America to frigid Antarctica.

NASA's DC-8 flying laboratory takes off from Juan Santamaria International Airport in San Jose, Costa Rica, on NASA's AirSAR 2004 campaign. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition by an international team of scientists that will use an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR), in a mission ranging from the tropical rain forests of Central America to frigid Antarctica.
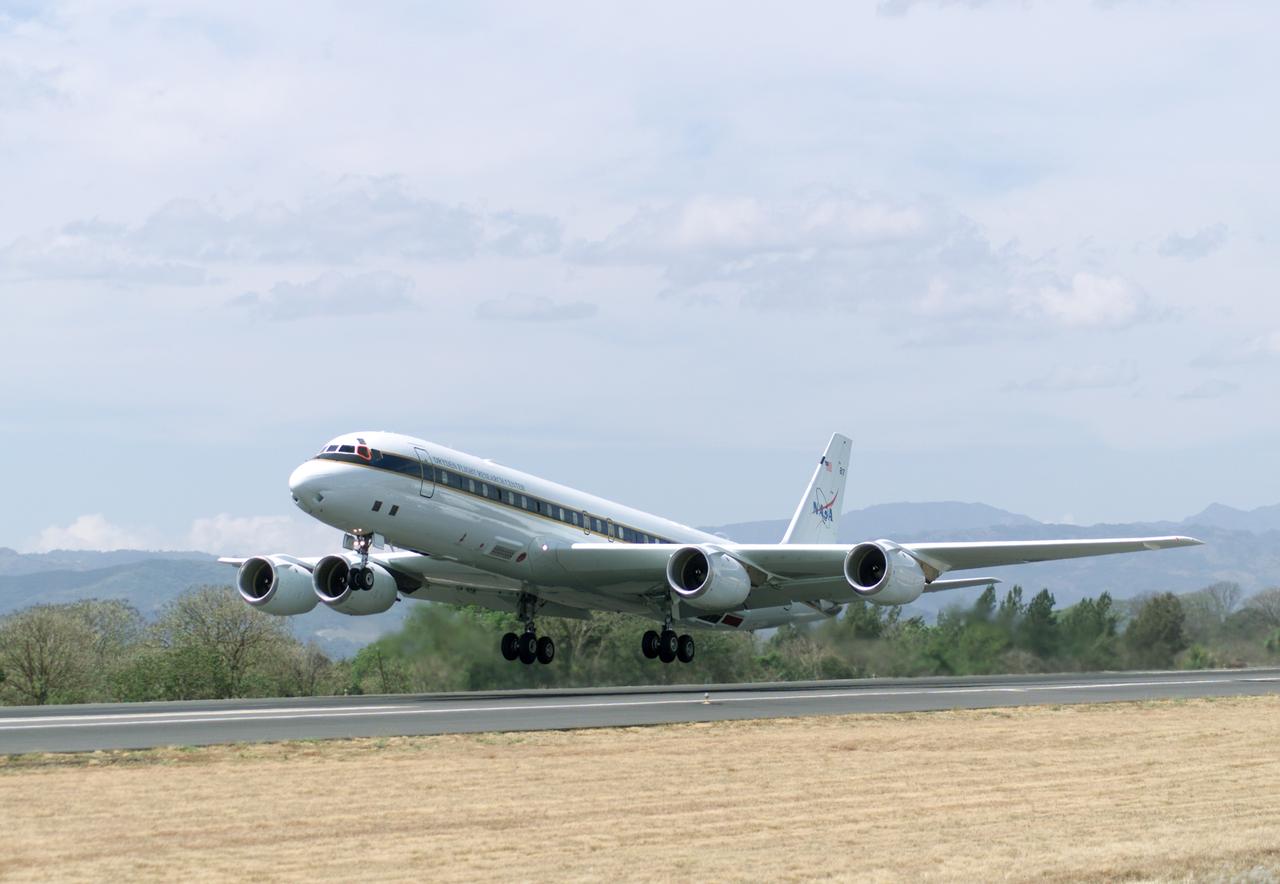

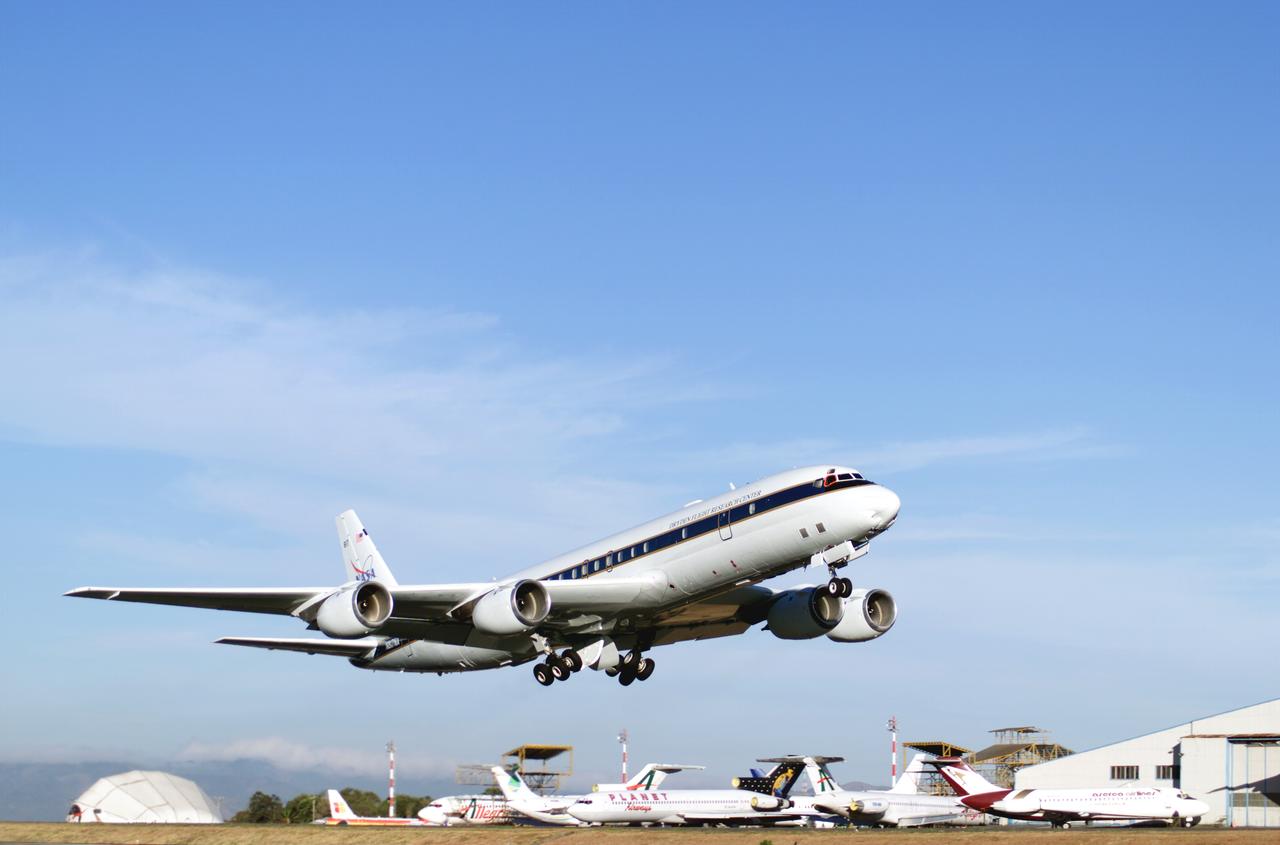
NASA's DC-8 flying laboratory takes off from Juan Santamaria International Airport in San Jose, Costa Rica, on NASA's AirSAR 2004 campaign. AirSAR 2004 Mesoamerica is a three-week expedition by an international team of scientists that uses an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR) which is located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world including NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory are combining ground research done in several areas in Central America with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. The radar, developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, can penetrate clouds and also collect data at night. Its high-resolution sensors operate at multiple wavelengths and modes, allowing AirSAR to see beneath treetops, through thin sand, and dry snow pack. AirSAR's 2004 campaign is a collaboration of many U.S. and Central American institutions and scientists, including NASA; the National Science Foundation; the Smithsonian Institution; National Geographic; Conservation International; the Organization of Tropical Studies; the Central American Commission for Environment and Development; and the Inter-American Development Bank.
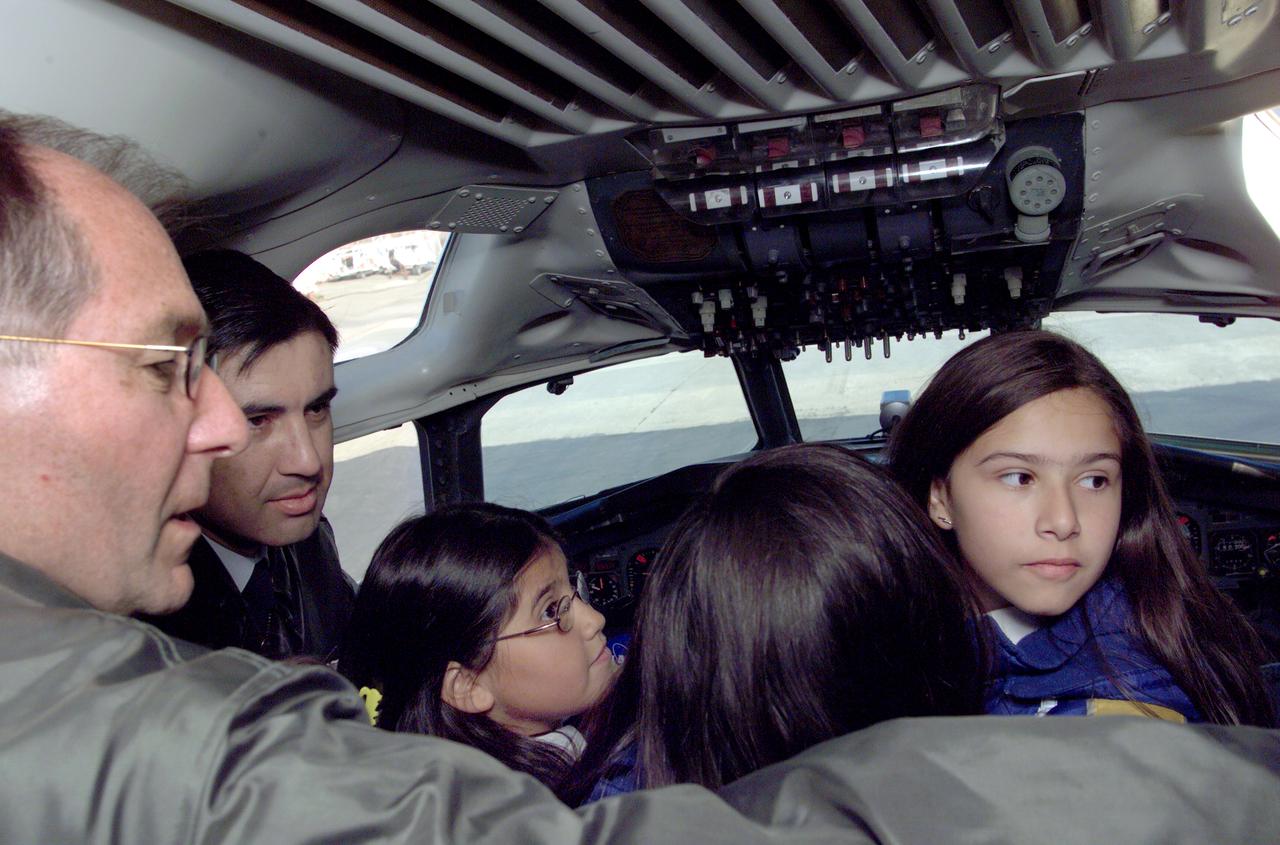

Pilot Bill Brockett (left) and Chilean Air Force Captain Saez with school children in the cockpit of NASA Dryden's DC-8 flying laboratory. Brockett explained NASA's AirSAR 2004 mission in Chile. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition by an international team of scientists that uses an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR) which is located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world including NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory are combining ground research done in several areas in Central and South America with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. In South America and Antarctica, AirSAR collected imagery and data to help determine the contribution of Southern Hemisphere glaciers to sea level rise due to climate change. In Patagonia, researchers found this contribution had more than doubled from 1995 to 2000, compared to the previous 25 years. AirSAR data will make it possible to determine whether that trend is continuing or accelerating. AirSAR will also provide reliable information on ice shelf thickness to measure the contribution of the glaciers to sea level.

NASA DC-8 airborne laboratory flying over Mint Canyon near the snow-covered San Gabriel Mountains of California. The mostly white aircraft is silhouetted against the darker mountains in the background.
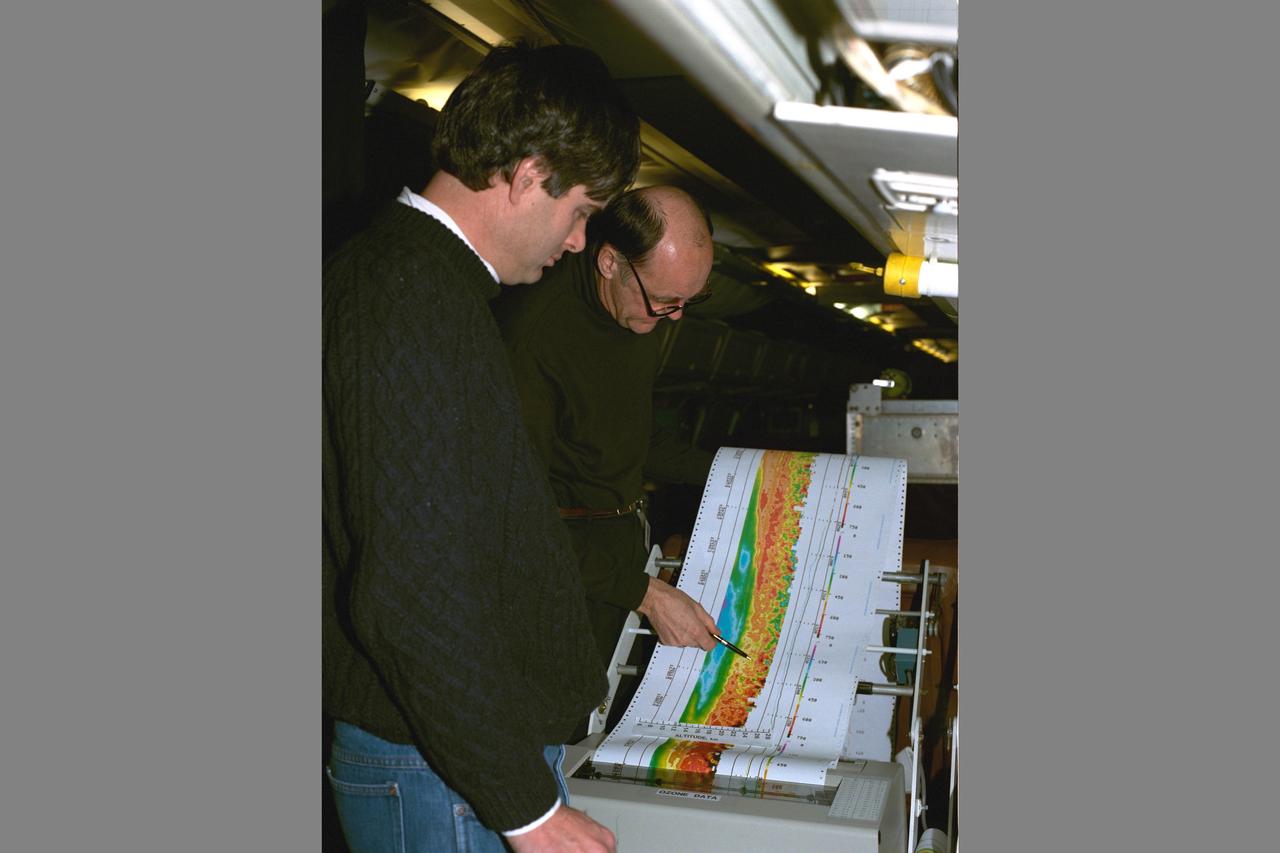

Arctic Ozone Expedition Stavanger Norway: Arlin Carter, NASA Langley Research Center, is shown here with colleague during flight collecting data on the laser ozone mapping experiment. This experiment uses laser beams to determine the extent of column ozone above the DC-8 flying laboratory on which the laser experiment flys.

Climate researchers from the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) and several universities install and perform functional checkouts of a variety of sensitive atmospheric instruments on NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory prior to beginning the ARCTAS mission.
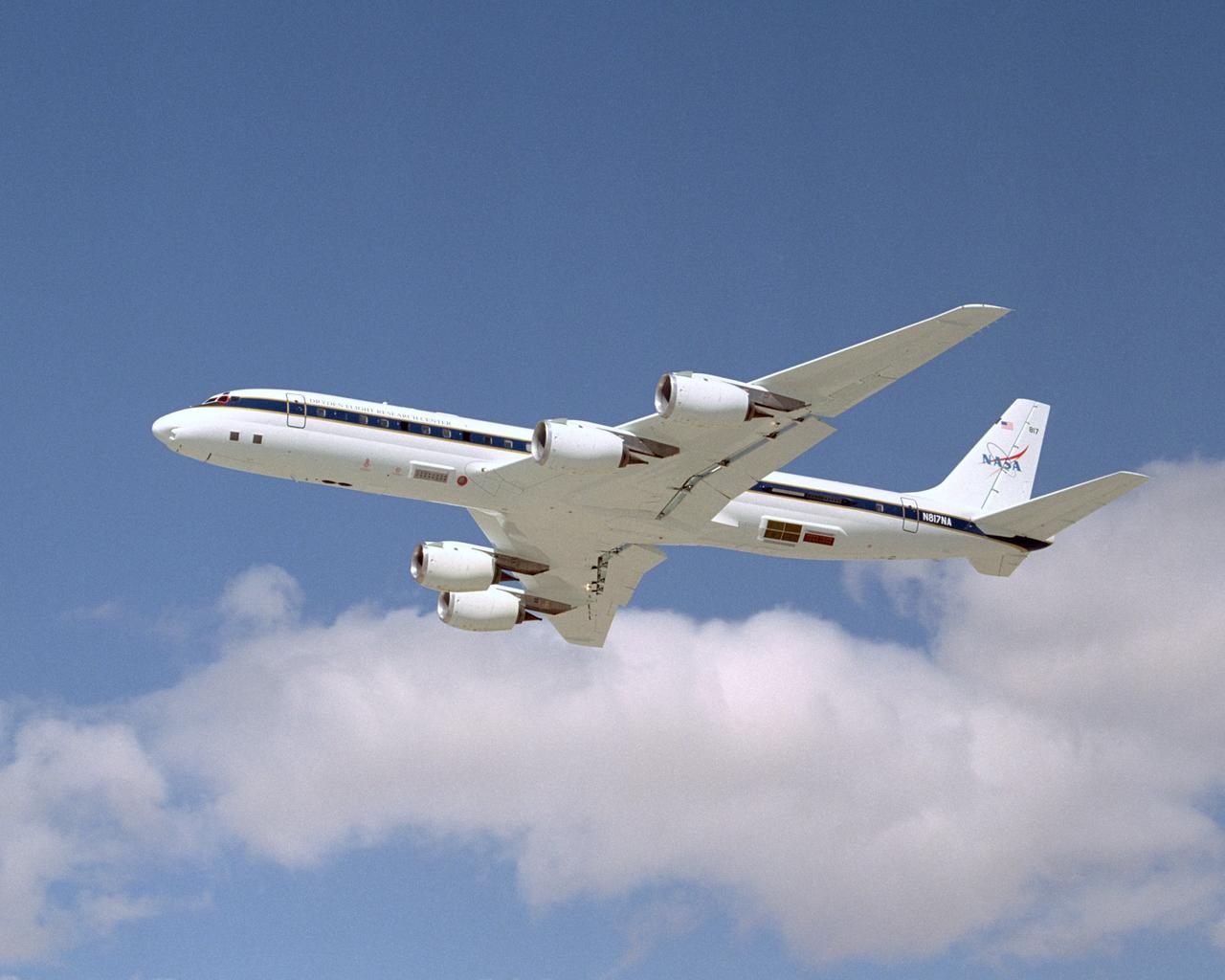

NASA's DC-8 Airborne Science research aircraft, in new colors and markings, takes off Feb. 24, 2004. Dark panels on lower fuselage are synthetic aperture radar antennas enabling sophisticated studies of Earth features.
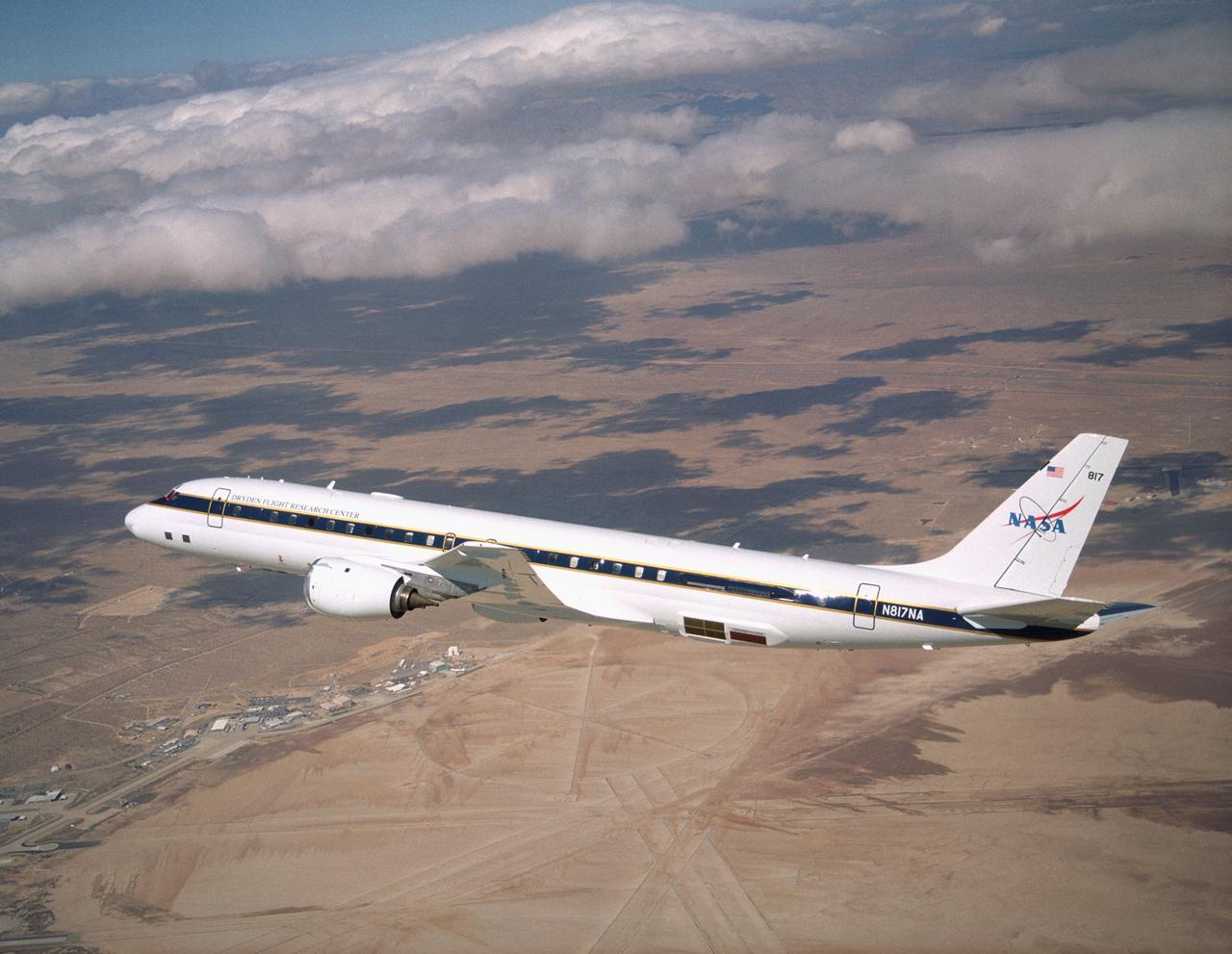

NASA's large Airborne Science research aircraft, a modified DC-8 airliner, displayed new colors in a check flight Feb. 24, 2004, over its home base, the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards AFB, California.
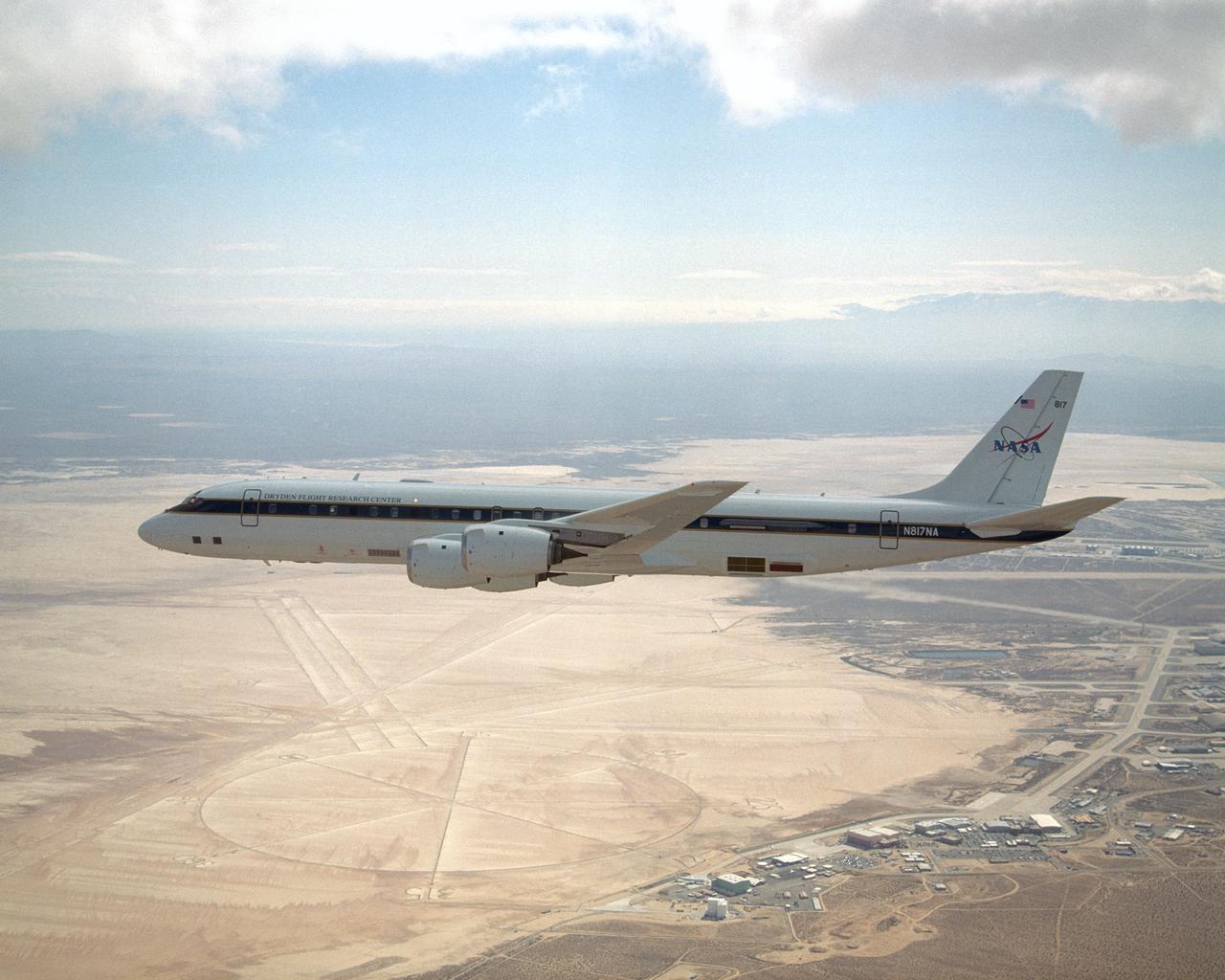

NASA's large Airborne Science research aircraft, a modified DC-8 airliner, displayed new colors in a check flight Feb. 24, 2004, over its home base, the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards AFB, California.
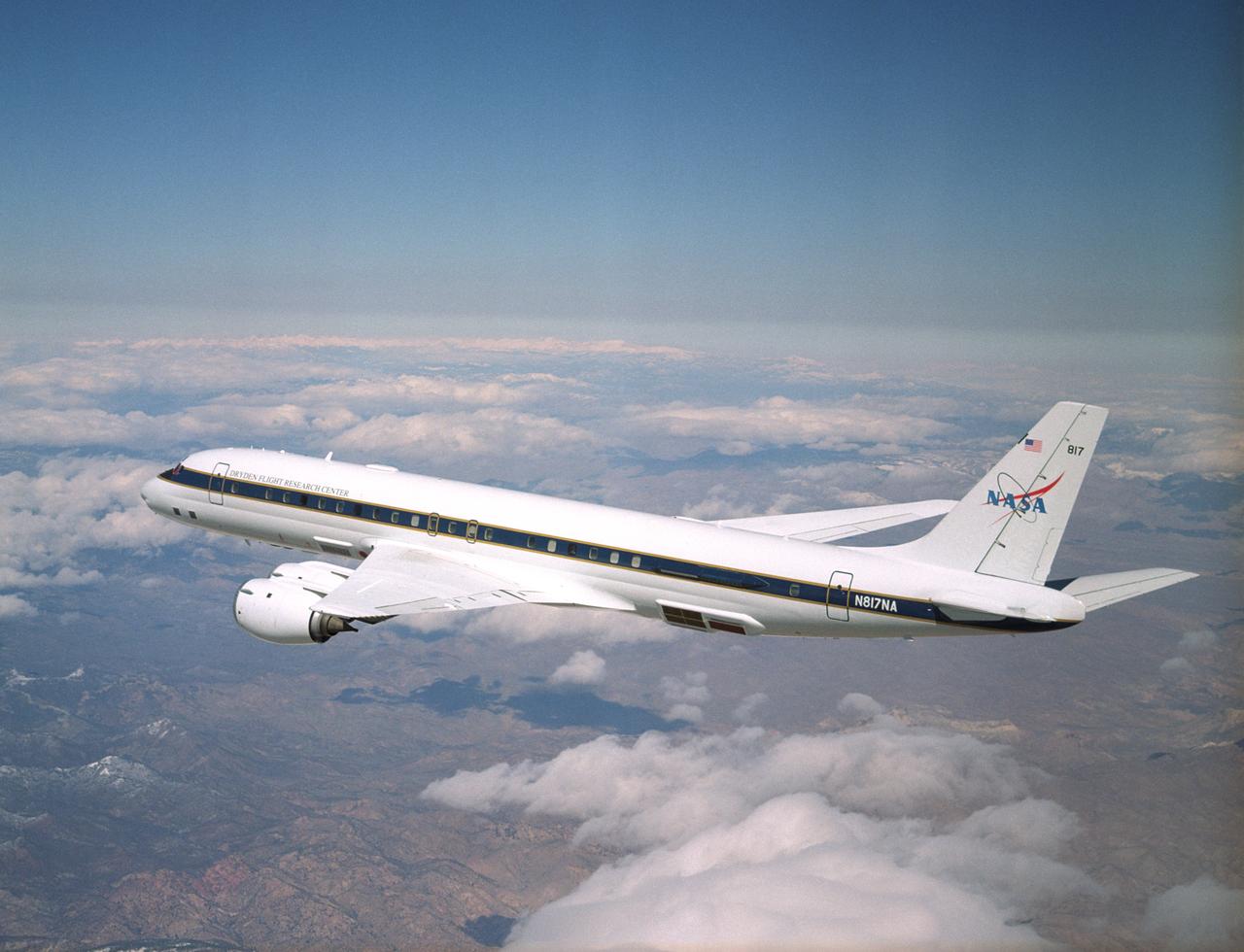

NASA's DC-8 Airborne Science research aircraft, in new colors and markings, in flight Feb. 24, 2004. Dark panels on lower fuselage are synthetic aperture radar antennas enabling sophisticated studies of Earth features.
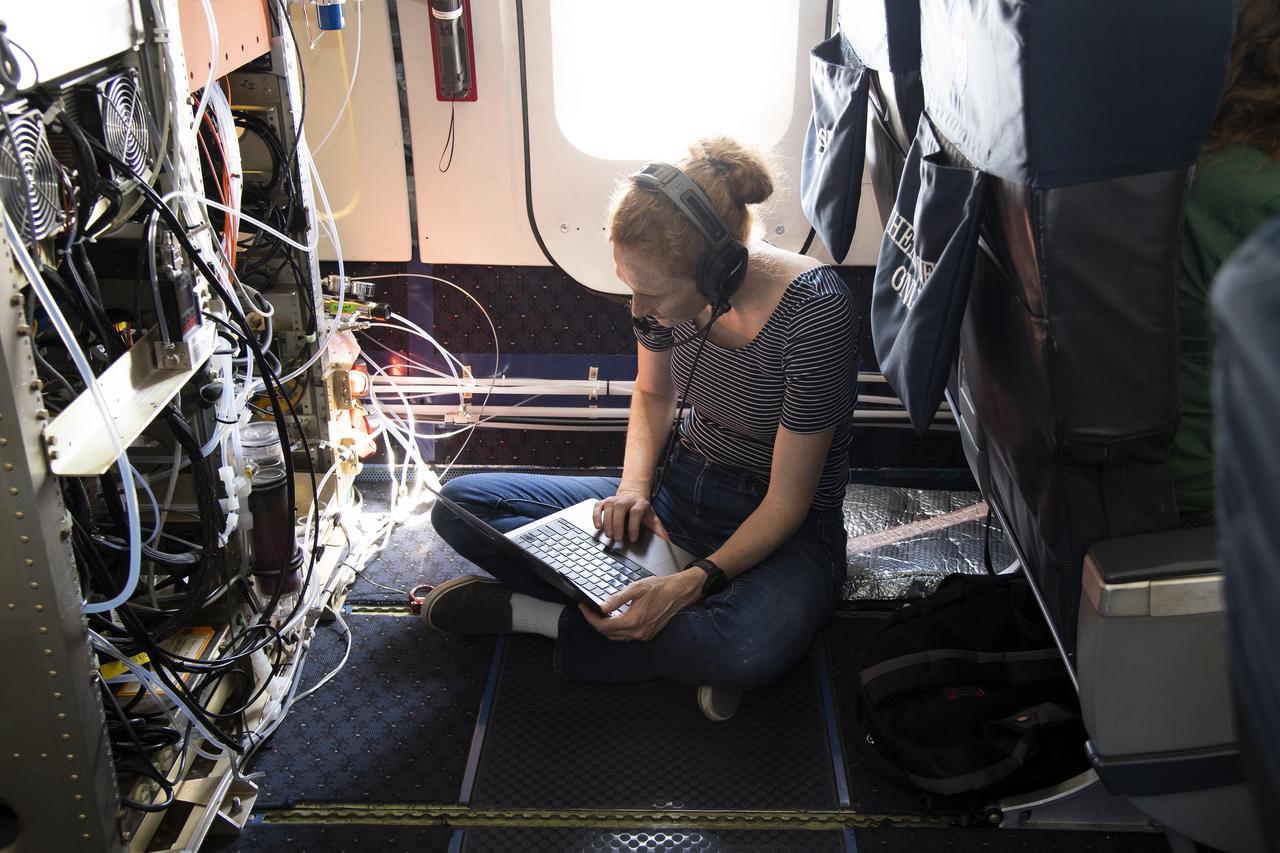

NASA Armstrong’s Student Airborne Research Program celebrates 15 years of success in 2023. An eight-week summer internship program, SARP offers upper-level undergraduate students the opportunity to acquire hands-on research experience as part of a scientific campaign using NASA Airborne Science Program flying science laboratories—aircraft outfitted specifically for research projects. Students onboard NASA’s DC-8 aircraft, the largest flying science laboratory in the world, help scientists from NOAA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration with a science project investigating air quality and non-vehicular pollution sources called AEROMMA, which measures Atmospheric Emissions and Reactions Observed from Megacities to Marine Areas. In 2023, NASA also introduced a sister program, SARP East to complement the West Coast program.
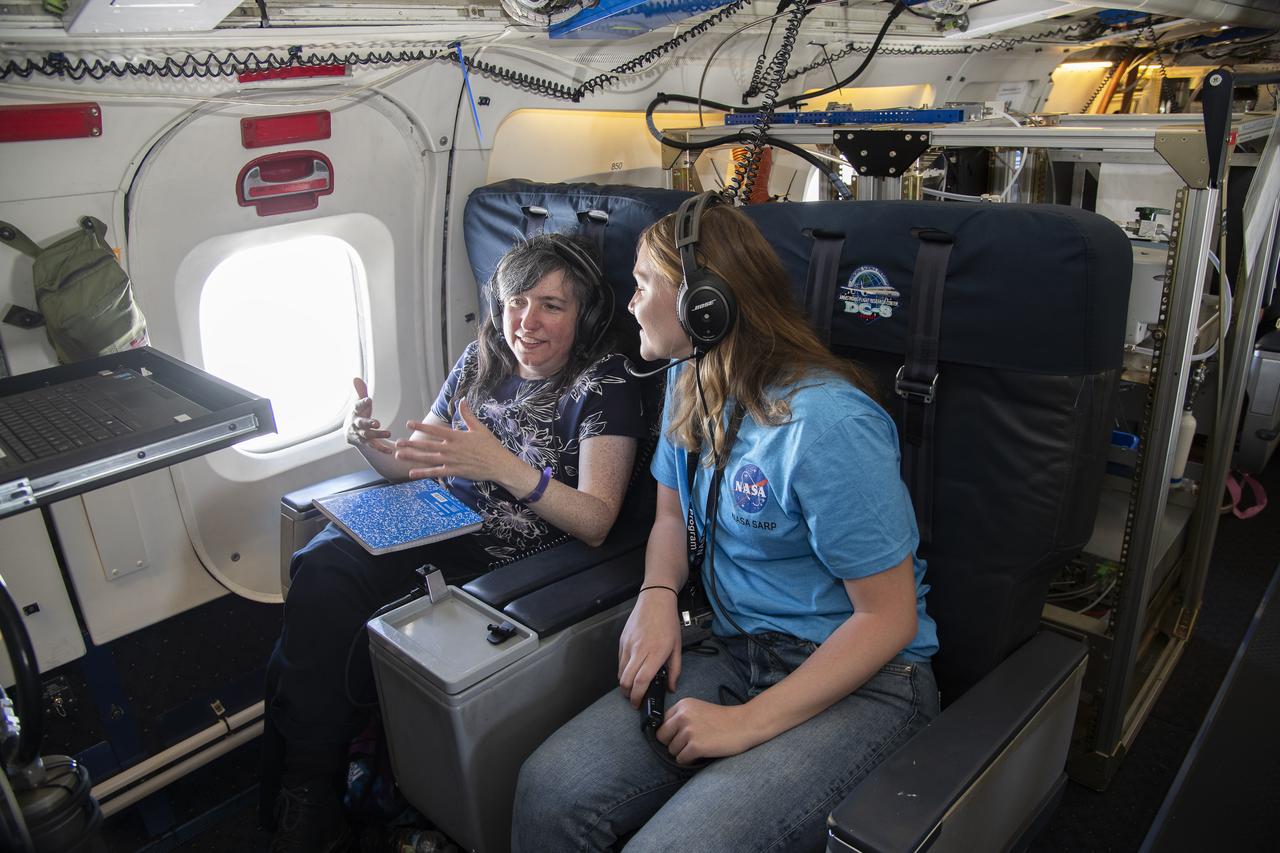

NASA Armstrong’s Student Airborne Research Program celebrates 15 years of success in 2023. An eight-week summer internship program, SARP offers upper-level undergraduate students the opportunity to acquire hands-on research experience as part of a scientific campaign using NASA Airborne Science Program flying science laboratories—aircraft outfitted specifically for research projects. Students onboard NASA’s DC-8 aircraft, the largest flying science laboratory in the world, help scientists from NOAA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration with a science project investigating air quality and non-vehicular pollution sources called AEROMMA, which measures Atmospheric Emissions and Reactions Observed from Megacities to Marine Areas. In 2023, NASA also introduced a sister program, SARP East to complement the West Coast program.
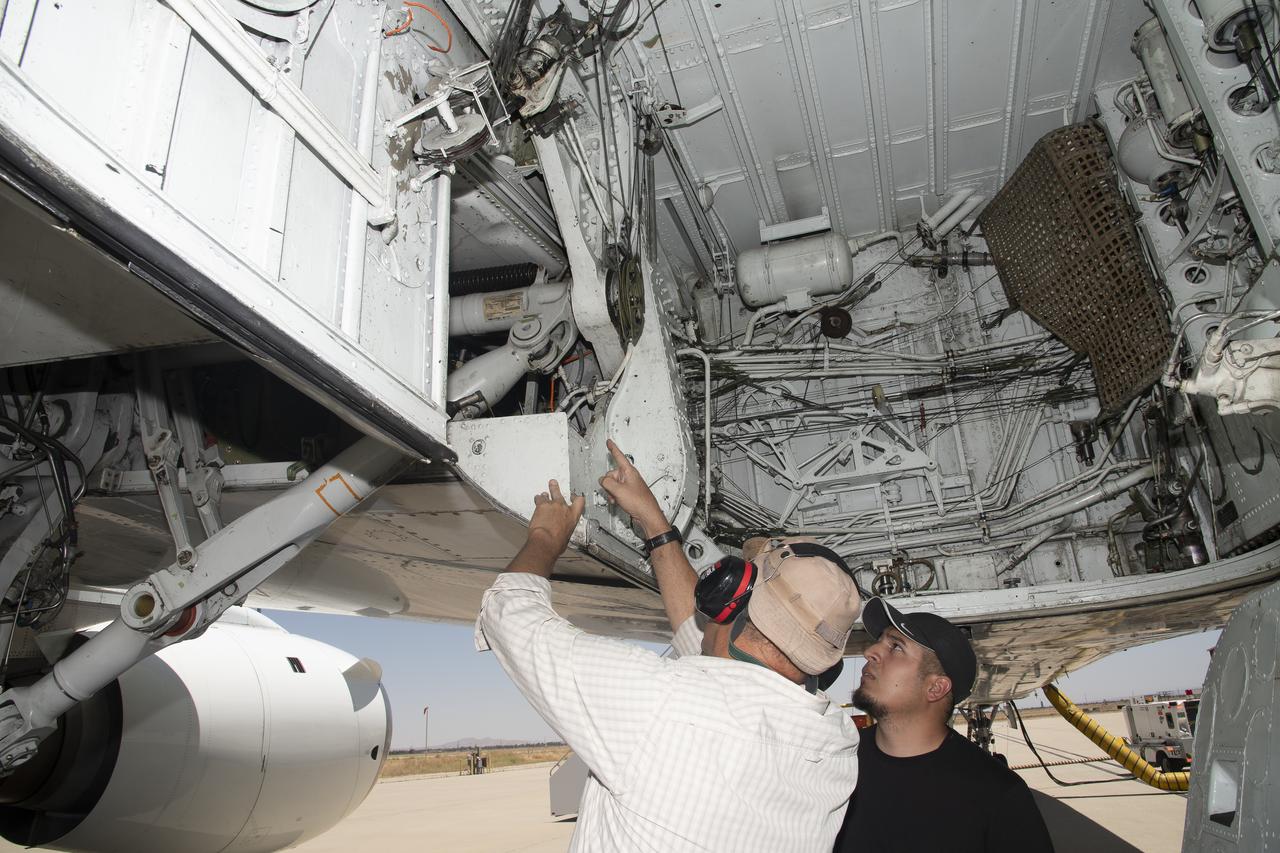

NASA Armstrong’s Student Airborne Research Program celebrates 15 years of success in 2023. An eight-week summer internship program, SARP offers upper-level undergraduate students the opportunity to acquire hands-on research experience as part of a scientific campaign using NASA Airborne Science Program flying science laboratories—aircraft outfitted specifically for research projects. Students onboard NASA’s DC-8 aircraft, the largest flying science laboratory in the world, help scientists from NOAA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration with a science project investigating air quality and non-vehicular pollution sources called AEROMMA, which measures Atmospheric Emissions and Reactions Observed from Megacities to Marine Areas. In 2023, NASA also introduced a sister program, SARP East to complement the West Coast program.
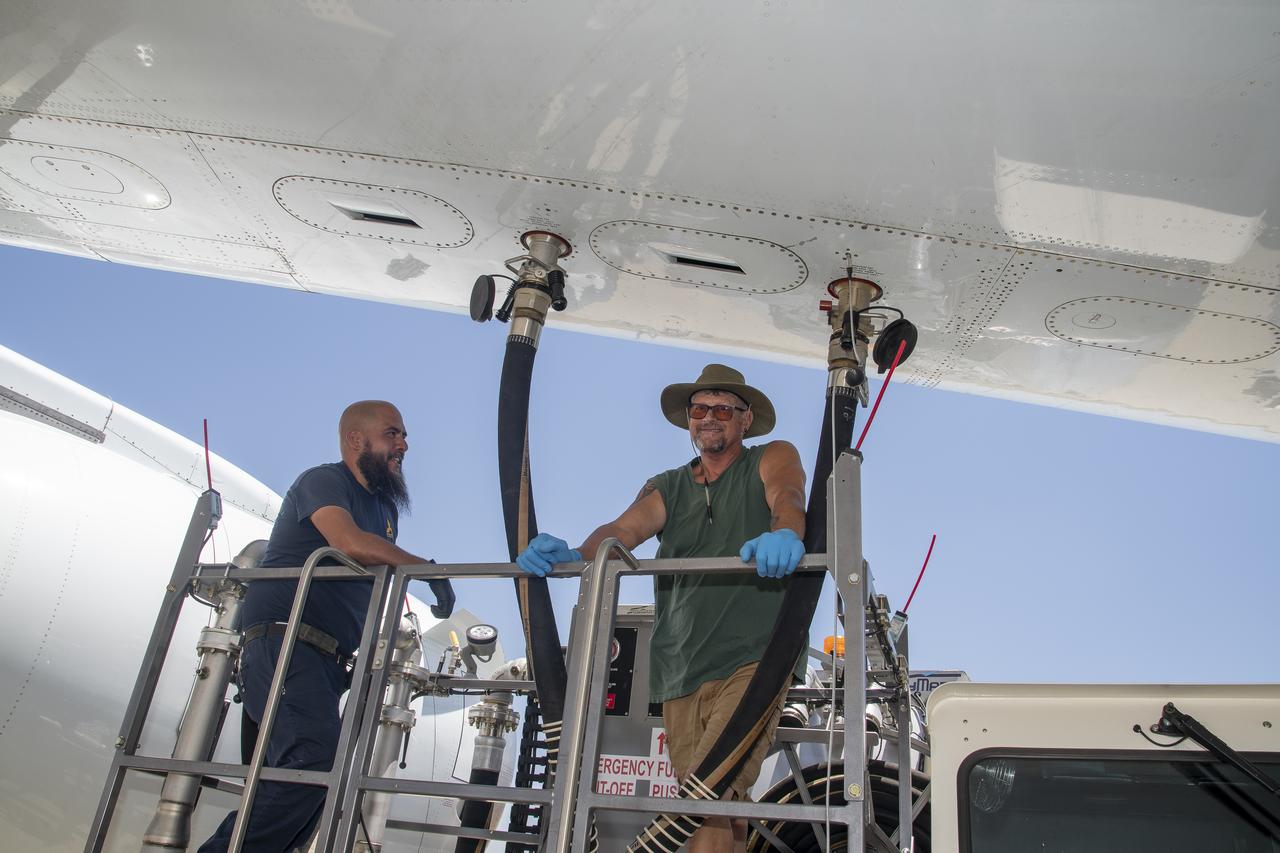

NASA Armstrong’s Student Airborne Research Program celebrates 15 years of success in 2023. An eight-week summer internship program, SARP offers upper-level undergraduate students the opportunity to acquire hands-on research experience as part of a scientific campaign using NASA Airborne Science Program flying science laboratories—aircraft outfitted specifically for research projects. Students onboard NASA’s DC-8 aircraft, the largest flying science laboratory in the world, help scientists from NOAA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration with a science project investigating air quality and non-vehicular pollution sources called AEROMMA, which measures Atmospheric Emissions and Reactions Observed from Megacities to Marine Areas. In 2023, NASA also introduced a sister program, SARP East to complement the West Coast program.
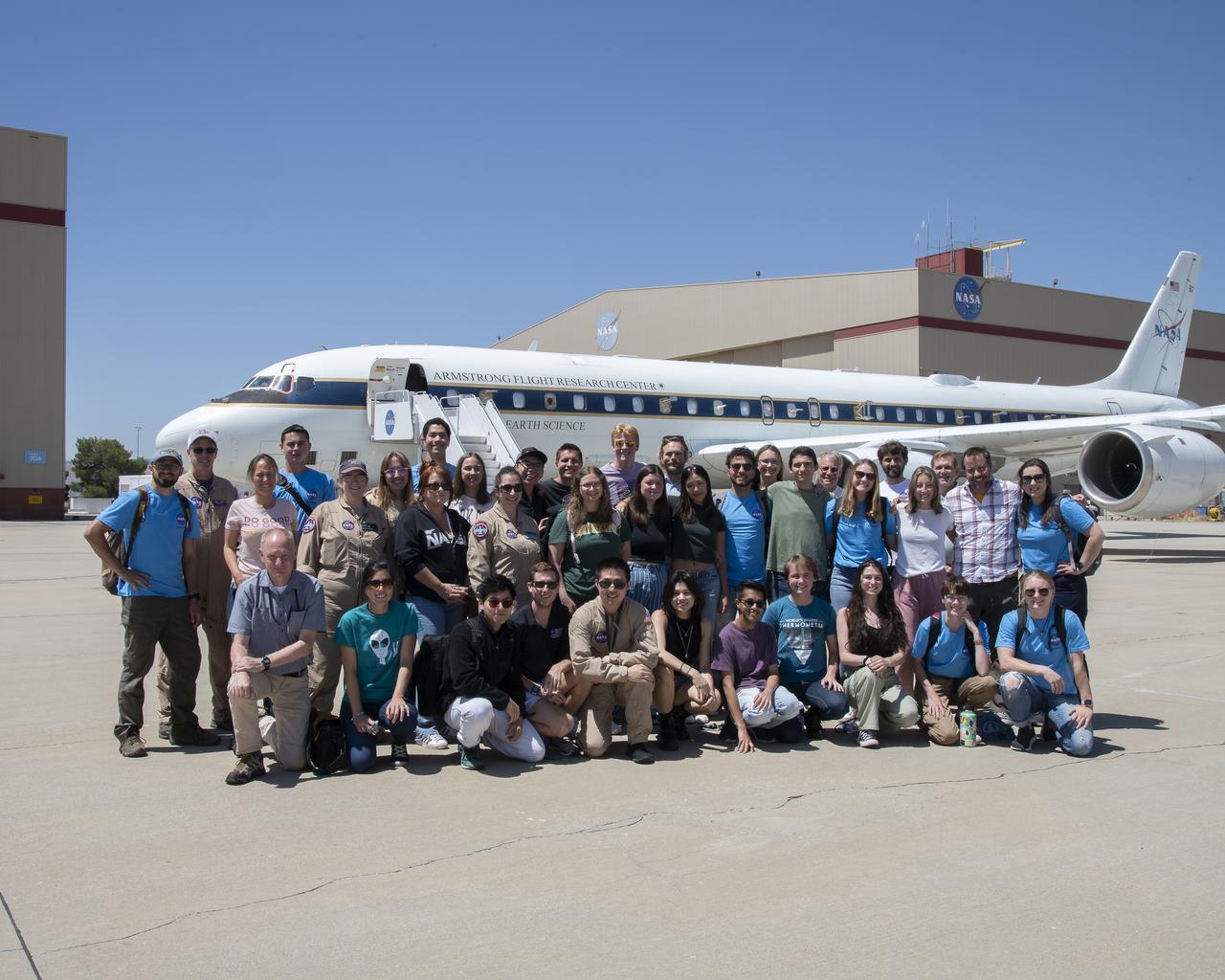

NASA Armstrong’s Student Airborne Research Program celebrates 15 years of success in 2023. An eight-week summer internship program, SARP offers upper-level undergraduate students the opportunity to acquire hands-on research experience as part of a scientific campaign using NASA Airborne Science Program flying science laboratories—aircraft outfitted specifically for research projects. Students onboard NASA’s DC-8 aircraft, the largest flying science laboratory in the world, help scientists from NOAA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration with a science project investigating air quality and non-vehicular pollution sources called AEROMMA, which measures Atmospheric Emissions and Reactions Observed from Megacities to Marine Areas. In 2023, NASA also introduced a sister program, SARP East to complement the West Coast program.
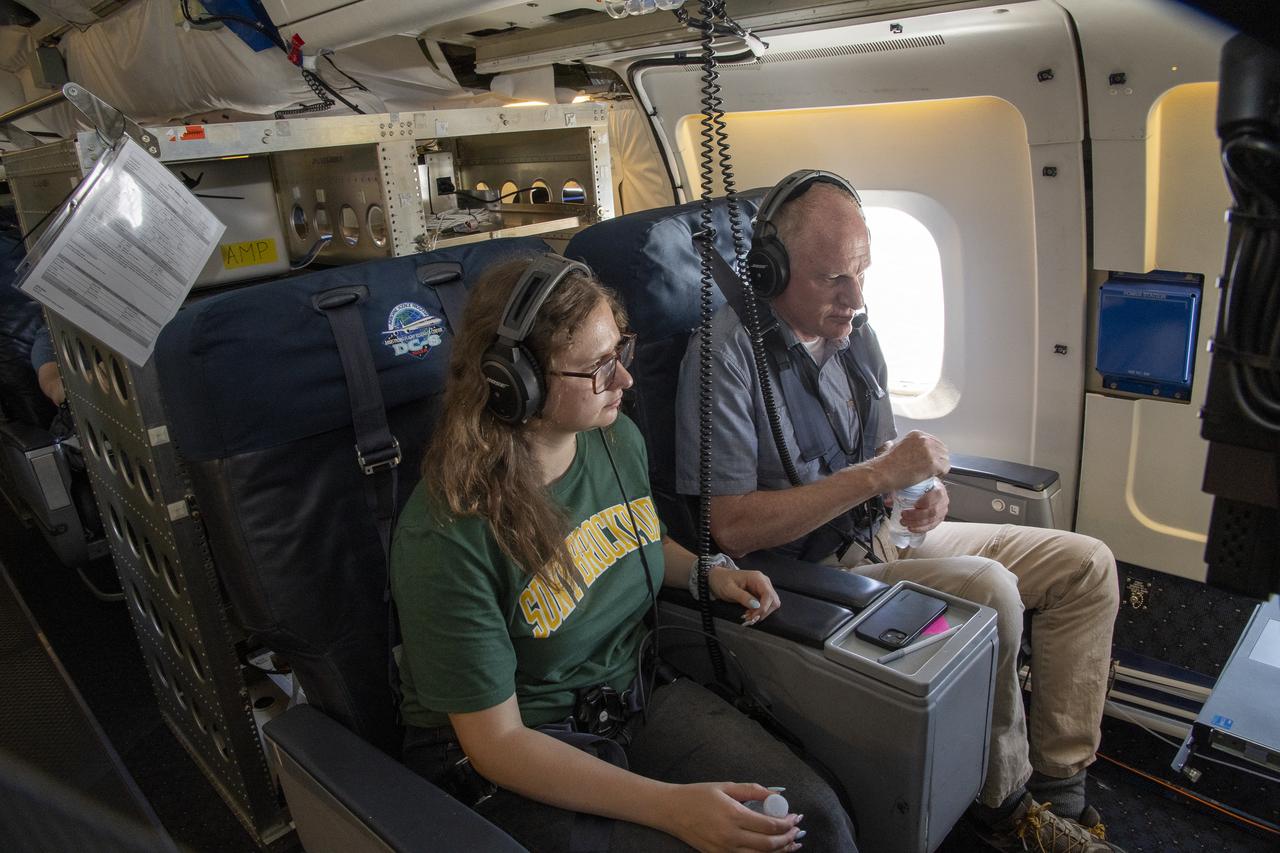

NASA Armstrong’s Student Airborne Research Program celebrates 15 years of success in 2023. An eight-week summer internship program, SARP offers upper-level undergraduate students the opportunity to acquire hands-on research experience as part of a scientific campaign using NASA Airborne Science Program flying science laboratories—aircraft outfitted specifically for research projects. Students onboard NASA’s DC-8 aircraft, the largest flying science laboratory in the world, help scientists from NOAA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration with a science project investigating air quality and non-vehicular pollution sources called AEROMMA, which measures Atmospheric Emissions and Reactions Observed from Megacities to Marine Areas. In 2023, NASA also introduced a sister program, SARP East to complement the West Coast program.

NASA Armstrong’s Student Airborne Research Program celebrates 15 years of success in 2023. An eight-week summer internship program, SARP offers upper-level undergraduate students the opportunity to acquire hands-on research experience as part of a scientific campaign using NASA Airborne Science Program flying science laboratories—aircraft outfitted specifically for research projects. Students onboard NASA’s DC-8 aircraft, the largest flying science laboratory in the world, help scientists from NOAA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration with a science project investigating air quality and non-vehicular pollution sources called AEROMMA, which measures Atmospheric Emissions and Reactions Observed from Megacities to Marine Areas. In 2023, NASA also introduced a sister program, SARP East to complement the West Coast program.
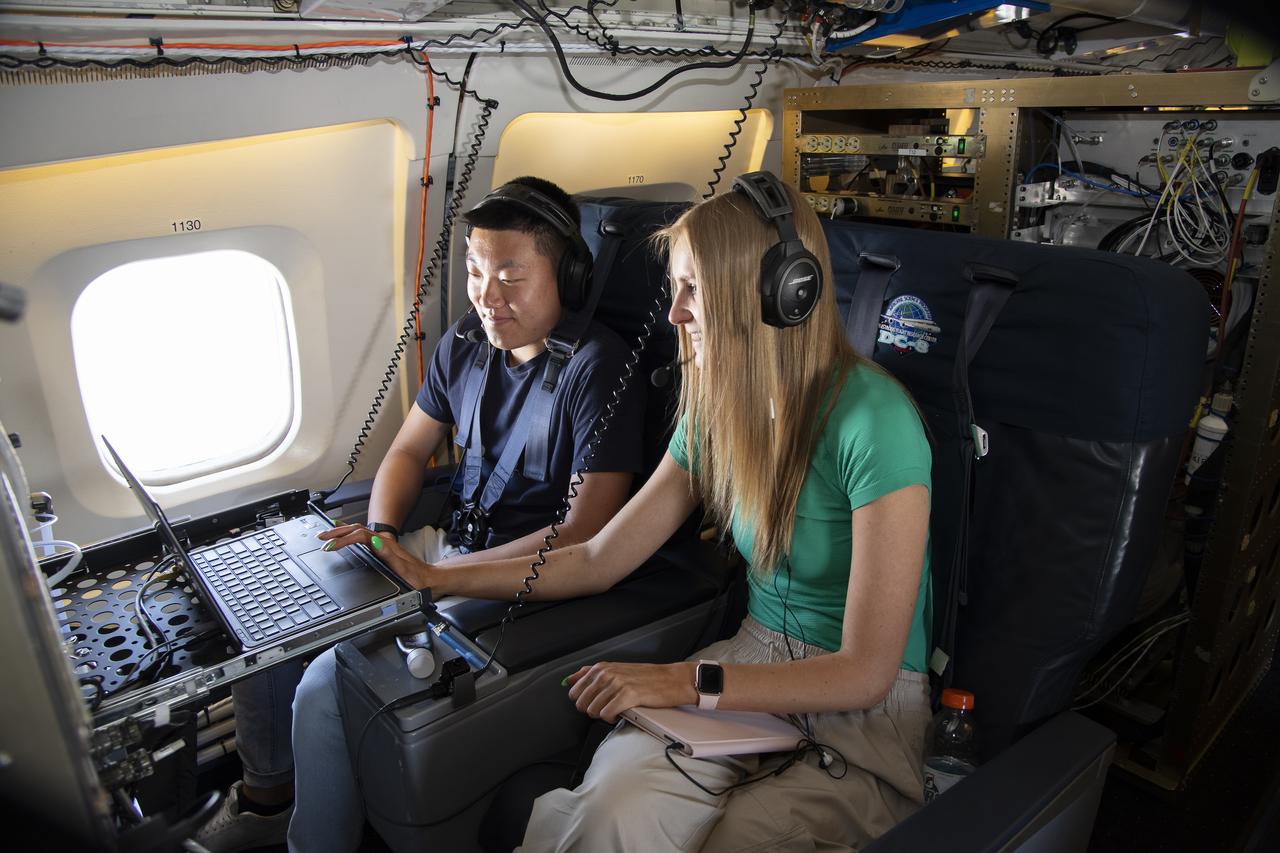

NASA Armstrong’s Student Airborne Research Program celebrates 15 years of success in 2023. An eight-week summer internship program, SARP offers upper-level undergraduate students the opportunity to acquire hands-on research experience as part of a scientific campaign using NASA Airborne Science Program flying science laboratories—aircraft outfitted specifically for research projects. Students onboard NASA’s DC-8 aircraft, the largest flying science laboratory in the world, help scientists from NOAA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration with a science project investigating air quality and non-vehicular pollution sources called AEROMMA, which measures Atmospheric Emissions and Reactions Observed from Megacities to Marine Areas. In 2023, NASA also introduced a sister program, SARP East to complement the West Coast program.
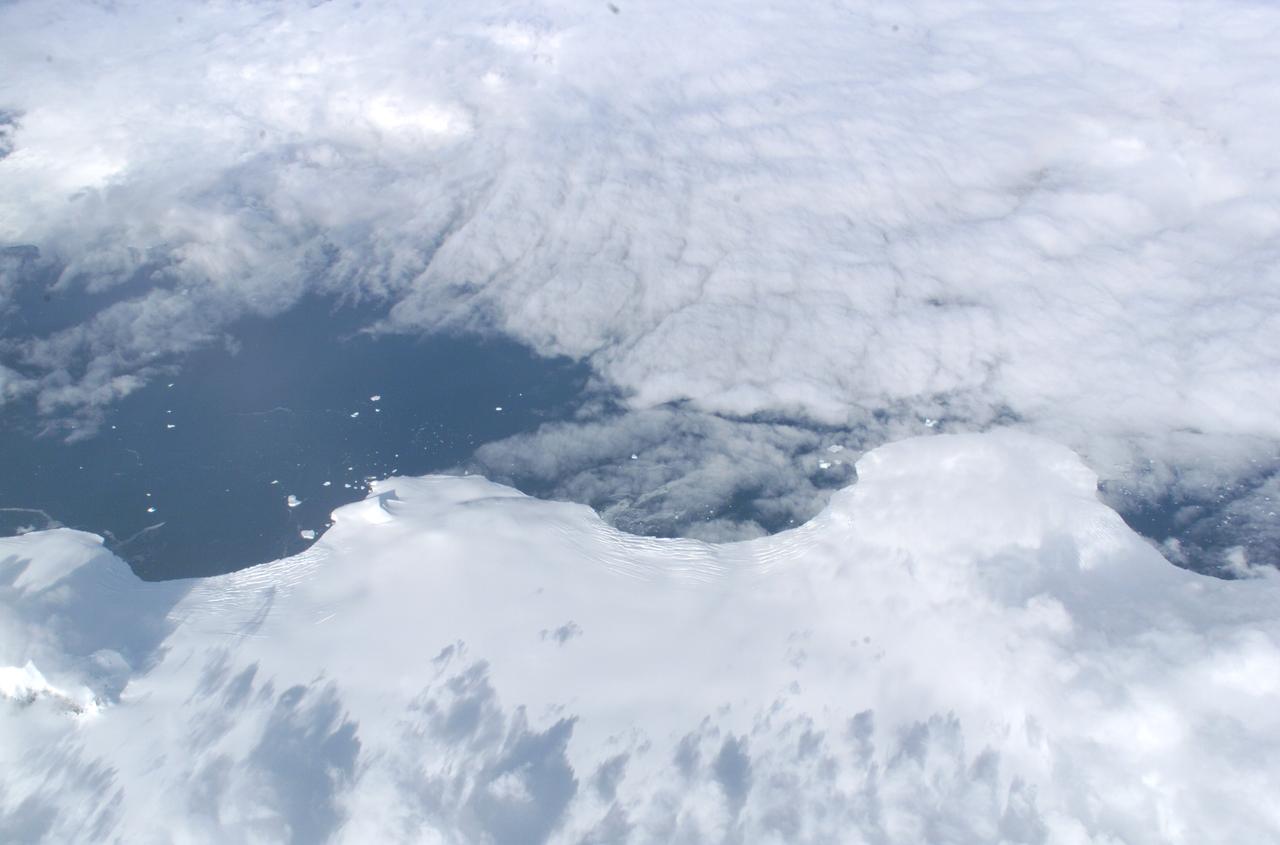

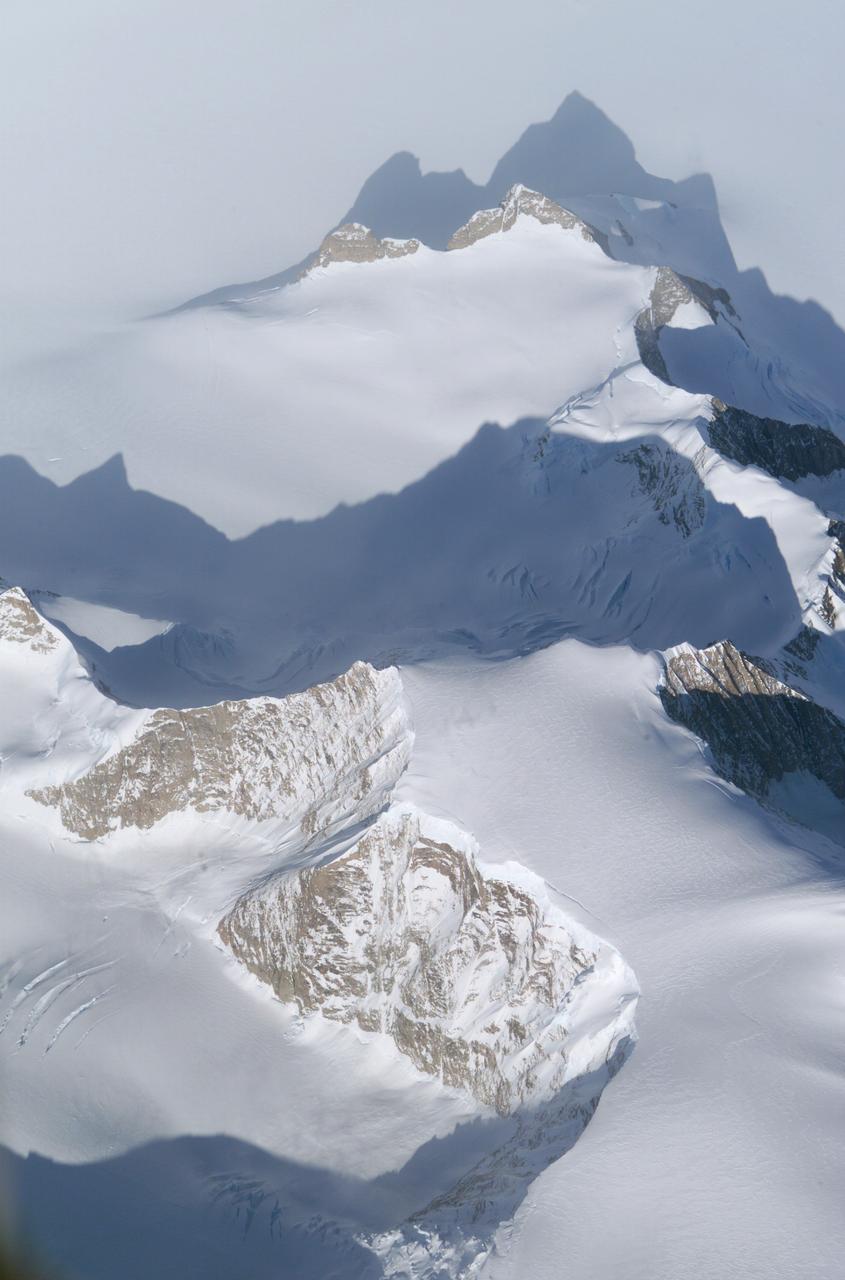
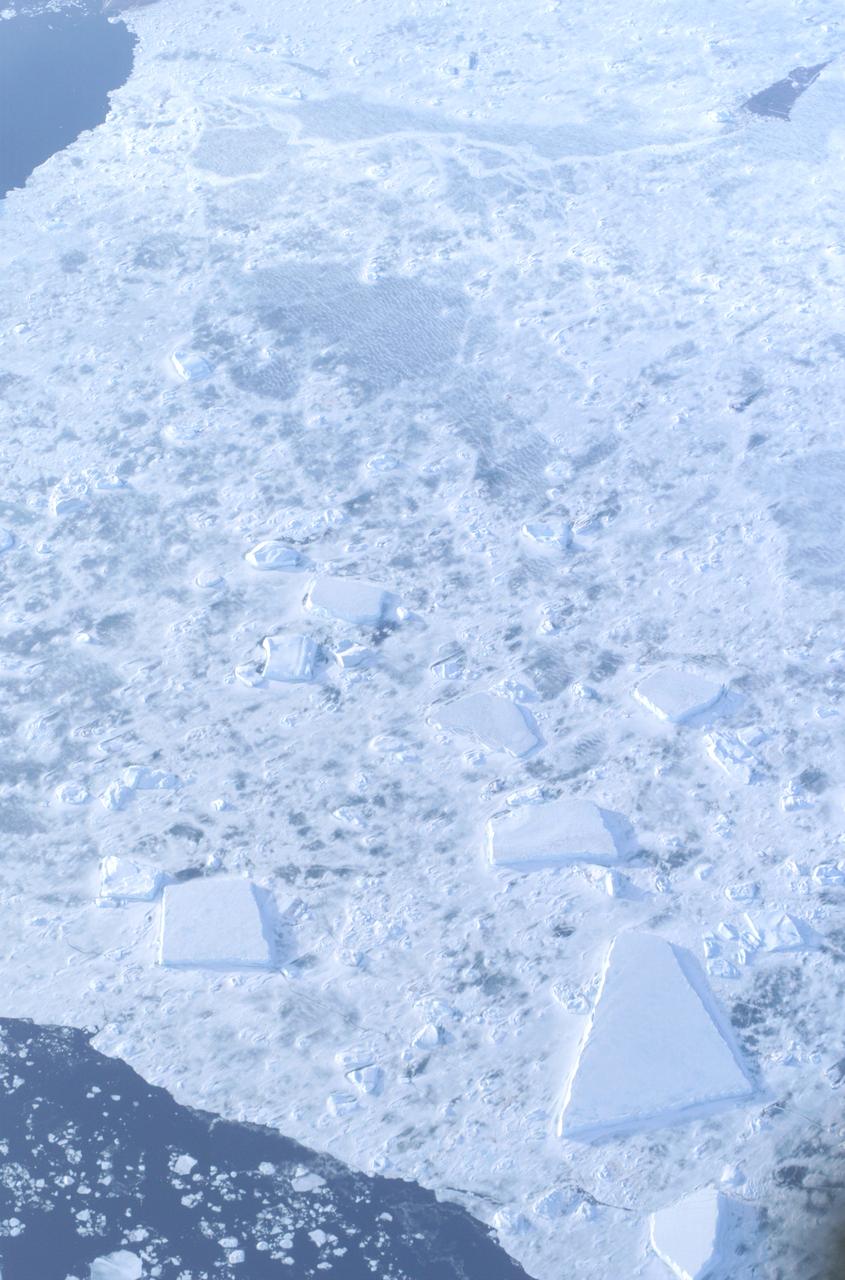
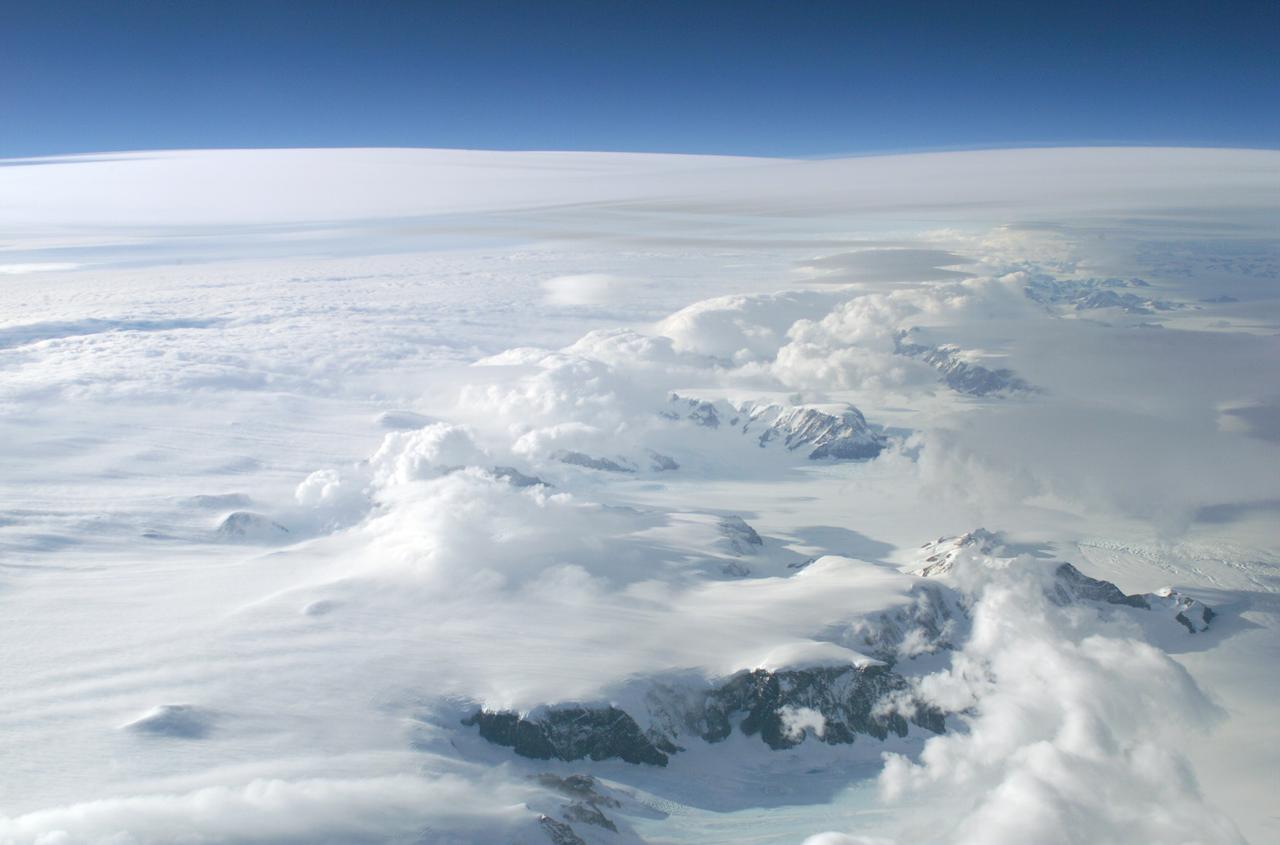
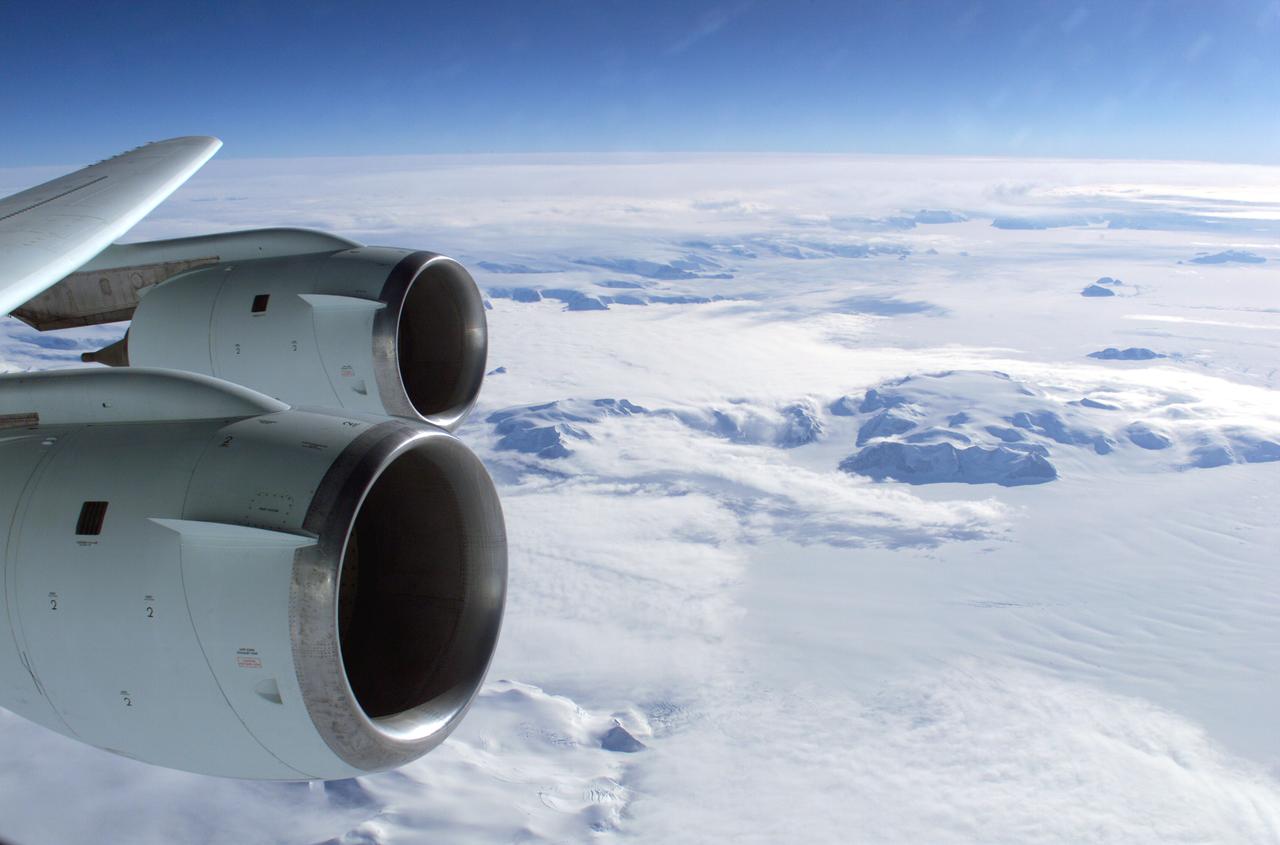
The Larsen Ice Shelf in Antarctica viewed from NASA's DC-8 aircraft during the AirSAR 2004 campaign. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition in Central and South America by an international team of scientists that is using an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR), located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world are combining ground research with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. These photos are from the DC-8 aircraft while flying an AirSAR mission over Antarctica. The Antarctic Peninsula is more similar to Alaska and Patagonia than to the rest of the Antarctic continent. It is drained by fast glaciers, receives abundant precipitation, and melts significantly in the summer months. In recent decades, the Peninsula has experienced significant atmospheric warming (about 2 degrees C since 1950), which has triggered a vast and spectacular retreat of its floating ice shelves, glacier reduction, a decrease in permanent snow cover and a lengthening of the melt season. As a result, the contribution to sea level from this region could be rapid and substantial. With an area of 120,000 km, or ten times the Patagonia ice fields, the Peninsula could contribute as much as 0.4mm/yr sea level rise, which would be the largest single contribution to sea level from anywhere in the world. This region is being studied by NASA using a DC-8 equipped with the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar developed by scientists from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. AirSAR will provide a baseline model and unprecedented mapping of the region. This data will make it possible to determine whether the warming trend is slowing, continuing or accelerating. AirSAR will also provide reliable information on ice shelf thickness to measure the contribution of the glaciers to sea level.

The Larsen Ice Shelf in Antarctica viewed from NASA's DC-8 aircraft during the AirSAR 2004 campaign. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition in Central and South America by an international team of scientists that is using an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR), located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world are combining ground research with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. These photos are from the DC-8 aircraft while flying an AirSAR mission over Antarctica. The Antarctic Peninsula is more similar to Alaska and Patagonia than to the rest of the Antarctic continent. It is drained by fast glaciers, receives abundant precipitation, and melts significantly in the summer months. In recent decades, the Peninsula has experienced significant atmospheric warming (about 2 degrees C since 1950), which has triggered a vast and spectacular retreat of its floating ice shelves, glacier reduction, a decrease in permanent snow cover and a lengthening of the melt season. As a result, the contribution to sea level from this region could be rapid and substantial. With an area of 120,000 km, or ten times the Patagonia ice fields, the Peninsula could contribute as much as 0.4mm/yr sea level rise, which would be the largest single contribution to sea level from anywhere in the world. This region is being studied by NASA using a DC-8 equipped with the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar developed by scientists from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. AirSAR will provide a baseline model and unprecedented mapping of the region. This data will make it possible to determine whether the warming trend is slowing, continuing or accelerating. AirSAR will also provide reliable information on ice shelf thickness to measure the contribution of the glaciers to sea level.
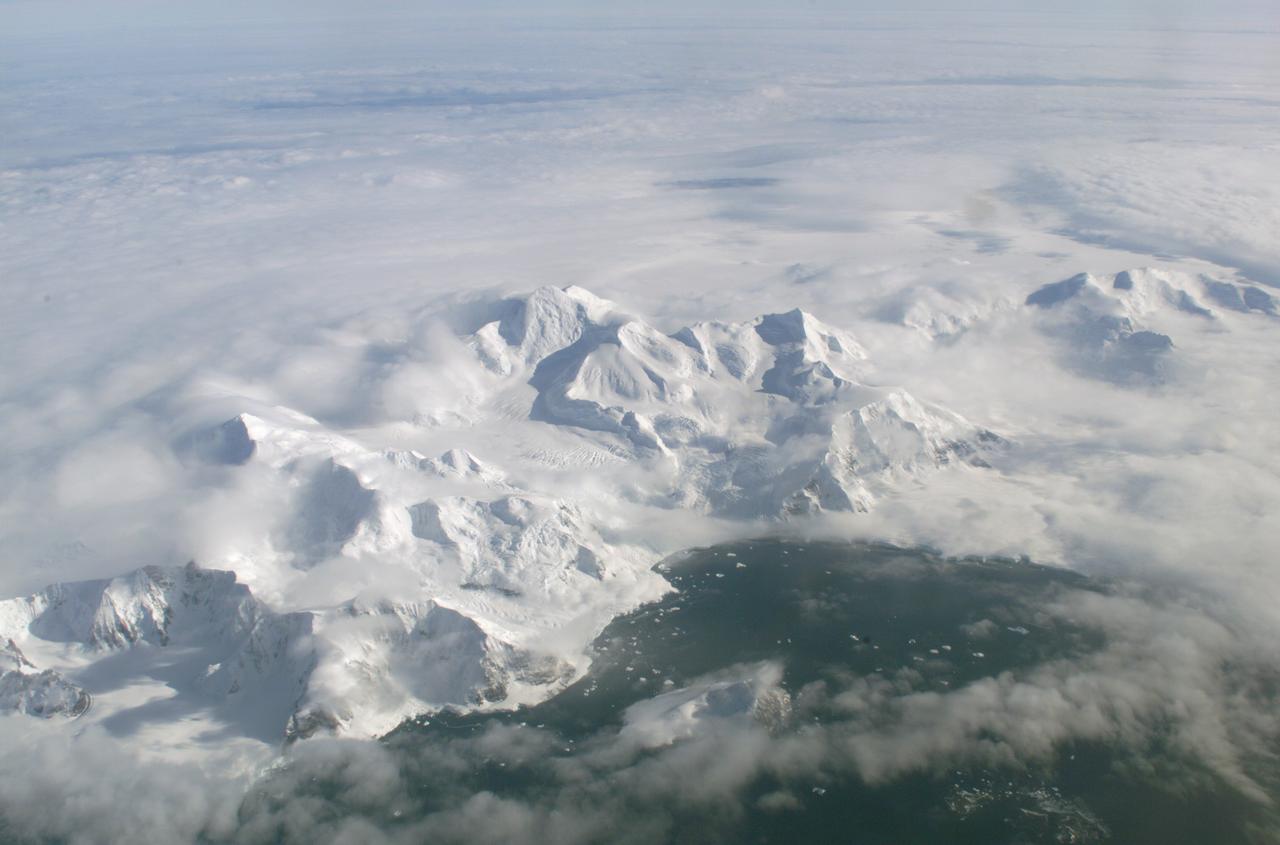

An AirSAR 2004 view from the DC-8 as it approaches the Larsen Ice Shelf, which is part of the Antarctic Peninsula. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition in Central and South America by an international team of scientists that is using an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR), located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world are combining ground research with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. These photos are from the DC-8 aircraft while flying an AirSAR mission over Antarctica. The Antarctic Peninsula is more similar to Alaska and Patagonia than to the rest of the Antarctic continent. It is drained by fast glaciers, receives abundant precipitation, and melts significantly in the summer months. In recent decades, the Peninsula has experienced significant atmospheric warming (about 2 degrees C since 1950), which has triggered a vast and spectacular retreat of its floating ice shelves, glacier reduction, a decrease in permanent snow cover and a lengthening of the melt season. As a result, the contribution to sea level from this region could be rapid and substantial. With an area of 120,000 km, or ten times the Patagonia ice fields, the Peninsula could contribute as much as 0.4mm/yr sea level rise, which would be the largest single contribution to sea level from anywhere in the world. This region is being studied by NASA using a DC-8 equipped with the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar developed by scientists from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. AirSAR will provide a baseline model and unprecedented mapping of the region. This data will make it possible to determine whether the warming trend is slowing, continuing or accelerating. AirSAR will also provide reliable information on ice shelf thickness to measure the contribution of the glaciers to sea level.

The Larsen Ice Shelf in Antarctica viewed from NASA's DC-8 aircraft during the AirSAR 2004 campaign. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition in Central and South America by an international team of scientists that is using an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR), located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world are combining ground research with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. These photos are from the DC-8 aircraft while flying an AirSAR mission over Antarctica. The Antarctic Peninsula is more similar to Alaska and Patagonia than to the rest of the Antarctic continent. It is drained by fast glaciers, receives abundant precipitation, and melts significantly in the summer months. In recent decades, the Peninsula has experienced significant atmospheric warming (about 2 degrees C since 1950), which has triggered a vast and spectacular retreat of its floating ice shelves, glacier reduction, a decrease in permanent snow cover and a lengthening of the melt season. As a result, the contribution to sea level from this region could be rapid and substantial. With an area of 120,000 km, or ten times the Patagonia ice fields, the Peninsula could contribute as much as 0.4mm/yr sea level rise, which would be the largest single contribution to sea level from anywhere in the world. This region is being studied by NASA using a DC-8 equipped with the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar developed by scientists from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. AirSAR will provide a baseline model and unprecedented mapping of the region. This data will make it possible to determine whether the warming trend is slowing, continuing or accelerating. AirSAR will also provide reliable information on ice shelf thickness to measure the contribution of the glaciers to sea level.

The Larsen Ice Shelf in Antarctica viewed from NASA's DC-8 aircraft during the AirSAR 2004 campaign. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition in Central and South America by an international team of scientists that is using an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR), located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world are combining ground research with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. These photos are from the DC-8 aircraft while flying an AirSAR mission over Antarctica. The Antarctic Peninsula is more similar to Alaska and Patagonia than to the rest of the Antarctic continent. It is drained by fast glaciers, receives abundant precipitation, and melts significantly in the summer months. In recent decades, the Peninsula has experienced significant atmospheric warming (about 2 degrees C since 1950), which has triggered a vast and spectacular retreat of its floating ice shelves, glacier reduction, a decrease in permanent snow cover and a lengthening of the melt season. As a result, the contribution to sea level from this region could be rapid and substantial. With an area of 120,000 km, or ten times the Patagonia ice fields, the Peninsula could contribute as much as 0.4mm/yr sea level rise, which would be the largest single contribution to sea level from anywhere in the world. This region is being studied by NASA using a DC-8 equipped with the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar developed by scientists from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. AirSAR will provide a baseline model and unprecedented mapping of the region. This data will make it possible to determine whether the warming trend is slowing, continuing or accelerating. AirSAR will also provide reliable information on ice shelf thickness to measure the contribution of the glaciers to sea level.

The Larsen Ice Shelf in Antarctica viewed from NASA's DC-8 aircraft during the AirSAR 2004 campaign. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition in Central and South America by an international team of scientists that is using an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR), located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world are combining ground research with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. These photos are from the DC-8 aircraft while flying an AirSAR mission over Antarctica. The Antarctic Peninsula is more similar to Alaska and Patagonia than to the rest of the Antarctic continent. It is drained by fast glaciers, receives abundant precipitation, and melts significantly in the summer months. In recent decades, the Peninsula has experienced significant atmospheric warming (about 2 degrees C since 1950), which has triggered a vast and spectacular retreat of its floating ice shelves, glacier reduction, a decrease in permanent snow cover and a lengthening of the melt season. As a result, the contribution to sea level from this region could be rapid and substantial. With an area of 120,000 km, or ten times the Patagonia ice fields, the Peninsula could contribute as much as 0.4mm/yr sea level rise, which would be the largest single contribution to sea level from anywhere in the world. This region is being studied by NASA using a DC-8 equipped with the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar developed by scientists from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. AirSAR will provide a baseline model and unprecedented mapping of the region. This data will make it possible to determine whether the warming trend is slowing, continuing or accelerating. AirSAR will also provide reliable information on ice shelf thickness to measure the contribution of the glaciers to sea level.

The Larsen Ice Shelf in Antarctica viewed from NASA's DC-8 aircraft during the AirSAR 2004 campaign. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition in Central and South America by an international team of scientists that is using an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR), located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world are combining ground research with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. These photos are from the DC-8 aircraft while flying an AirSAR mission over Antarctica. The Antarctic Peninsula is more similar to Alaska and Patagonia than to the rest of the Antarctic continent. It is drained by fast glaciers, receives abundant precipitation, and melts significantly in the summer months. In recent decades, the Peninsula has experienced significant atmospheric warming (about 2 degrees C since 1950), which has triggered a vast and spectacular retreat of its floating ice shelves, glacier reduction, a decrease in permanent snow cover and a lengthening of the melt season. As a result, the contribution to sea level from this region could be rapid and substantial. With an area of 120,000 km, or ten times the Patagonia ice fields, the Peninsula could contribute as much as 0.4mm/yr sea level rise, which would be the largest single contribution to sea level from anywhere in the world. This region is being studied by NASA using a DC-8 equipped with the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar developed by scientists from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. AirSAR will provide a baseline model and unprecedented mapping of the region. This data will make it possible to determine whether the warming trend is slowing, continuing or accelerating. AirSAR will also provide reliable information on ice shelf thickness to measure the contribution of the glaciers to sea level.
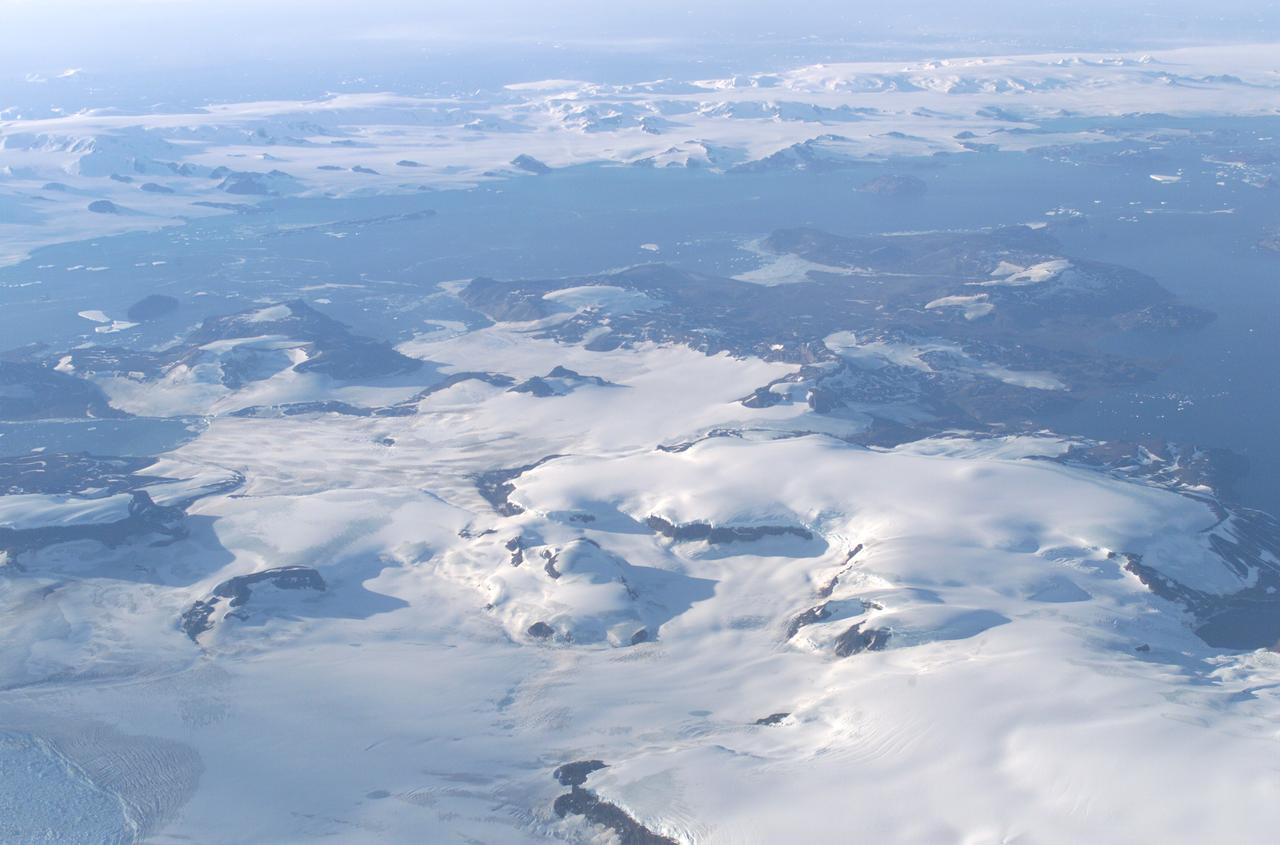

James Ross Island captured by NASA photographer James Ross(no relation), from NASA's DC-8 aircraft during an AirSAR 2004 mission over the Antarctic Peninsula. James Ross Island, named for 19th century British polar explorer Sir James Clark Ross, is located at the northern tip of the Antarctic Peninsula. The island is about 1500 m high and 40-60 km wide. In recent decades, the area has experienced significant atmospheric warming (about 2 degrees C since 1950), which has triggered a vast and spectacular retreat of its floating ice shelves, glacier reduction, a decrease in permanent snow cover and a lengthening of the melt season. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition in Central and South America by an international team of scientists that is using an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR), located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world are combining ground research with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. These photos are from the DC-8 aircraft while flying an AirSAR mission over Antarctica. The Antarctic Peninsula is more similar to Alaska and Patagonia than to the rest of the Antarctic continent. It is drained by fast glaciers, receives abundant precipitation, and melts significantly in the summer months. This region is being studied by NASA using a DC-8 equipped with the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar developed by scientists from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. AirSAR will provide a baseline model and unprecedented mapping of the region. This data will make it possible to determine whether the warming trend is slowing, continuing or accelerating. AirSAR will also provide reliable information on ice shelf thickness to measure the contribution of the glaciers to sea level.
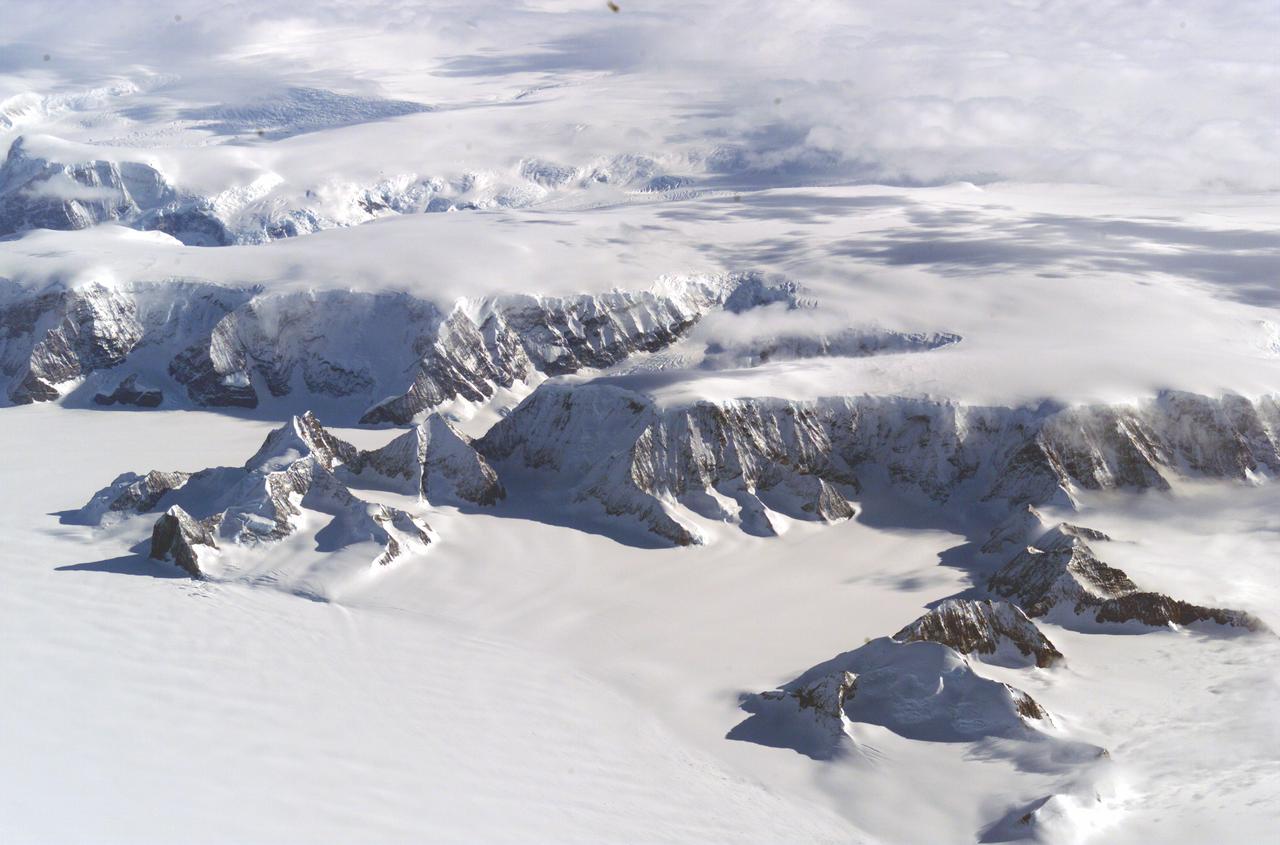

The Larsen Ice Shelf in Antarctica viewed from NASA's DC-8 aircraft during the AirSAR 2004 campaign. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition in Central and South America by an international team of scientists that is using an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR), located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world are combining ground research with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. These photos are from the DC-8 aircraft while flying an AirSAR mission over Antarctica. The Antarctic Peninsula is more similar to Alaska and Patagonia than to the rest of the Antarctic continent. It is drained by fast glaciers, receives abundant precipitation, and melts significantly in the summer months. In recent decades, the Peninsula has experienced significant atmospheric warming (about 2 degrees C since 1950), which has triggered a vast and spectacular retreat of its floating ice shelves, glacier reduction, a decrease in permanent snow cover and a lengthening of the melt season. As a result, the contribution to sea level from this region could be rapid and substantial. With an area of 120,000 km, or ten times the Patagonia ice fields, the Peninsula could contribute as much as 0.4mm/yr sea level rise, which would be the largest single contribution to sea level from anywhere in the world. This region is being studied by NASA using a DC-8 equipped with the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar developed by scientists from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. AirSAR will provide a baseline model and unprecedented mapping of the region. This data will make it possible to determine whether the warming trend is slowing, continuing or accelerating. AirSAR will also provide reliable information on ice shelf thickness to measure the contribution of the glaciers to sea level.

The Larsen Ice Shelf in Antarctica viewed from NASA's DC-8 aircraft during the AirSAR 2004 campaign. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition in Central and South America by an international team of scientists that is using an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR), located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world are combining ground research with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. These photos are from the DC-8 aircraft while flying an AirSAR mission over Antarctica. The Antarctic Peninsula is more similar to Alaska and Patagonia than to the rest of the Antarctic continent. It is drained by fast glaciers, receives abundant precipitation, and melts significantly in the summer months. In recent decades, the Peninsula has experienced significant atmospheric warming (about 2 degrees C since 1950), which has triggered a vast and spectacular retreat of its floating ice shelves, glacier reduction, a decrease in permanent snow cover and a lengthening of the melt season. As a result, the contribution to sea level from this region could be rapid and substantial. With an area of 120,000 km, or ten times the Patagonia ice fields, the Peninsula could contribute as much as 0.4mm/yr sea level rise, which would be the largest single contribution to sea level from anywhere in the world. This region is being studied by NASA using a DC-8 equipped with an Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR) developed by scientists from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. AirSAR will provide a baseline model and unprecedented mapping of the region. This data will make it possible to determine whether the warming trend is slowing, continuing or accelerating. AirSAR will also provide reliable information on ice shelf thickness to measure the contribution of the glaciers to sea level.
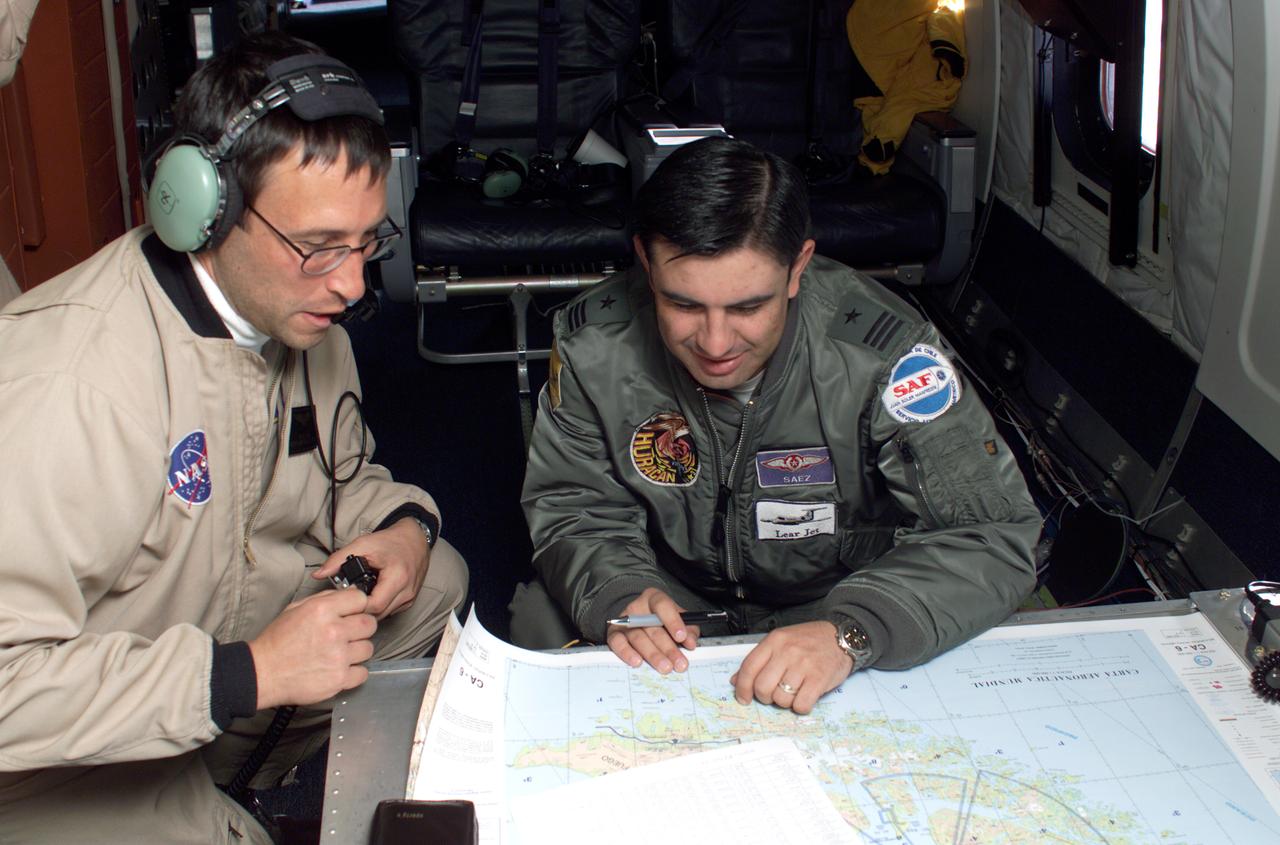

NASA DC-8 Mission Manager Walter Klein and Chilean Air Force Advisor Captain Saez review maps of the Antarctic Peninsula during an AirSAR 2004 mission. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition in Central and South America by an international team of scientists that is using an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR), located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world are combining ground research with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. These photos are from the DC-8 aircraft while flying an AirSAR mission over Antarctica. The Antarctic Peninsula is more similar to Alaska and Patagonia than to the rest of the Antarctic continent. It is drained by fast glaciers, receives abundant precipitation, and melts significantly in the summer months. In recent decades, the Peninsula has experienced significant atmospheric warming (about 2 degrees C since 1950), which has triggered a vast and spectacular retreat of its floating ice shelves, glacier reduction, a decrease in permanent snow cover and a lengthening of the melt season. As a result, the contribution to sea level from this region could be rapid and substantial. With an area of 120,000 km, or ten times the Patagonia ice fields, the Peninsula could contribute as much as 0.4mm/yr sea level rise, which would be the largest single contribution to sea level from anywhere in the world. This region is being studied by NASA using a DC-8 equipped with the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar developed by scientists from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. AirSAR will provide a baseline model and unprecedented mapping of the region. This data will make it possible to determine whether the warming trend is slowing, continuing or accelerating. AirSAR will also provide reliable information on ice shelf thickness to measure the contribution of the glaciers to sea level.
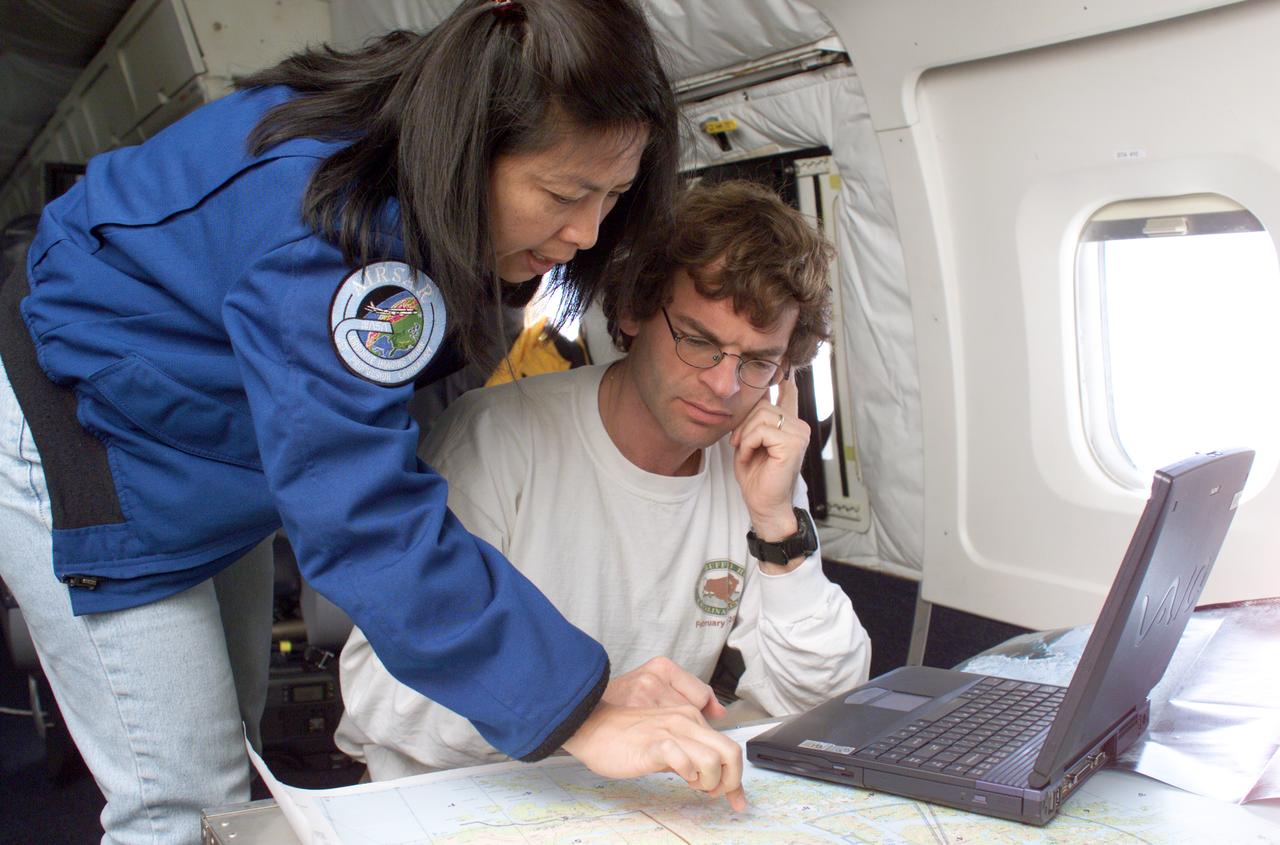

NASA JPL scientists Yunling Lou and Dr. Eric Rignot work on line selection while flying AirSAR missions over the Antarctic Peninsula. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition in Central and South America by an international team of scientists that is using an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR), located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world are combining ground research with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. These photos are from the DC-8 aircraft while flying an AirSAR mission over Antarctica. The Antarctic Peninsula is more similar to Alaska and Patagonia than to the rest of the Antarctic continent. It is drained by fast glaciers, receives abundant precipitation, and melts significantly in the summer months. In recent decades, the Peninsula has experienced significant atmospheric warming (about 2 degrees C since 1950), which has triggered a vast and spectacular retreat of its floating ice shelves, glacier reduction, a decrease in permanent snow cover and a lengthening of the melt season. As a result, the contribution to sea level from this region could be rapid and substantial. With an area of 120,000 km, or ten times the Patagonia ice fields, the Peninsula could contribute as much as 0.4mm/yr sea level rise, which would be the largest single contribution to sea level from anywhere in the world. This region is being studied by NASA using a DC-8 equipped with the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar developed by scientists from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. AirSAR will provide a baseline model and unprecedented mapping of the region. This data will make it possible to determine whether the warming trend is slowing, continuing or accelerating. AirSAR will also provide reliable information on ice shelf thickness to measure the contribution of the glaciers to sea level.
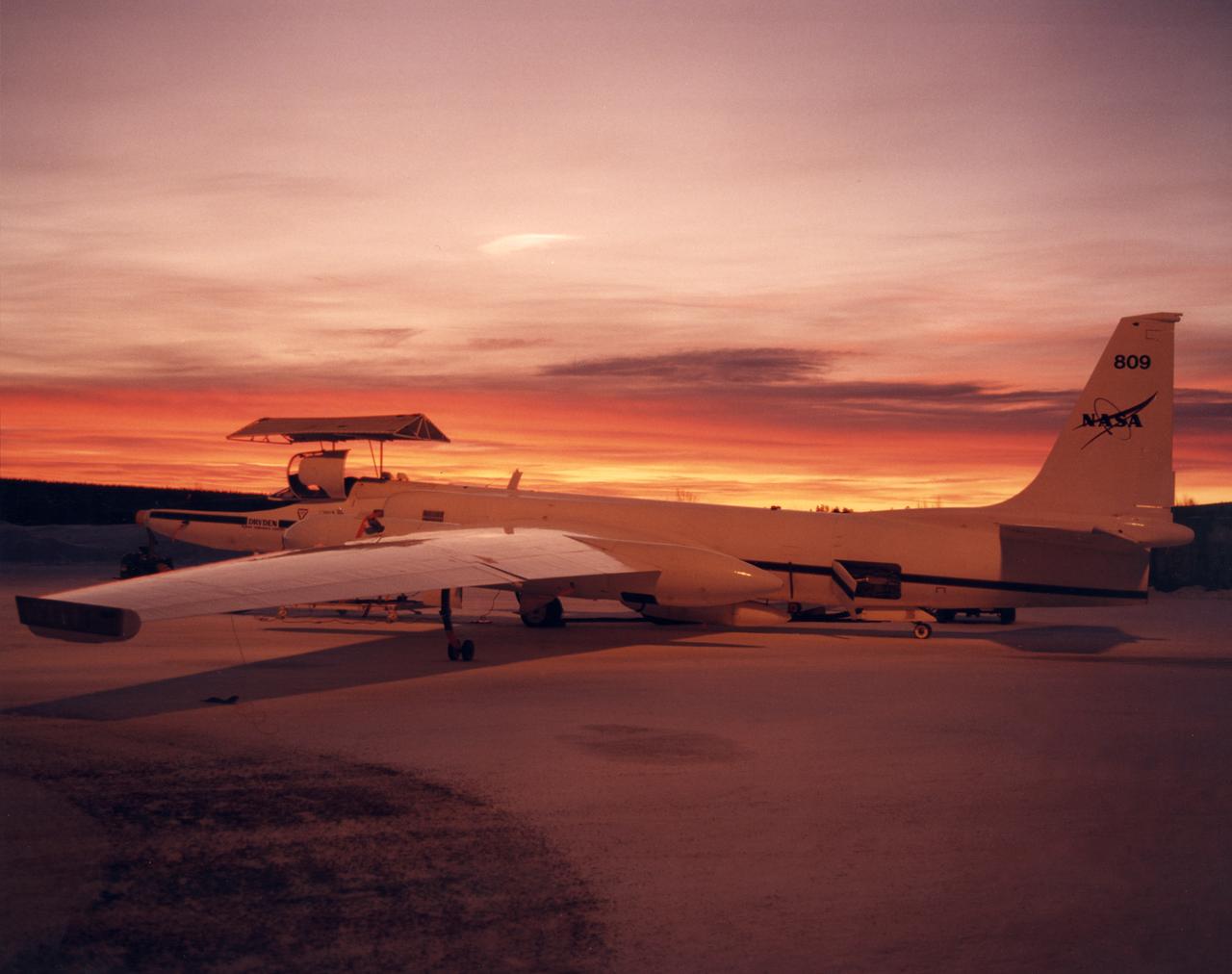

ER-2 #809 awaiting pilot entry for the third flight of the SAGE III Ozone Loss and Validation Experiment (SOLVE). The ER-2, a civilian variant of Lockheed's U-2, and another NASA flying laboratory, Dryden's DC-8, were based north of the Arctic Circle in Kiruna, Sweden during the winter of 2000 to study ozone depletion as part of SOLVE. A large hangar built especially for research, "Arena Arctica" housed the instrumented aircraft and the scientists. Scientists have observed unusually low levels of ozone over the Arctic during recent winters, raising concerns that ozone depletion there could become more widespread as in the Antarctic ozone hole. The NASA-sponsored international mission took place between November 1999 and March 2000 and was divided into three phases. The DC-8 was involved in all three phases returning to Dryden between each phase. The ER-2 flew sample collection flights between January and March, remaining in Sweden from Jan. 9 through March 16. "The collaborative campaign will provide an immense new body of information about the Arctic stratosphere," said program scientist Dr. Michael Kurylo, NASA Headquarters. "Our understanding of the Earth's ozone will be greatly enhanced by this research."

There’s more than one way to study the impact of biofuels. For NASA scientists, it means trailing an aircraft from as little as 300 feet behind while flying 34,000 feet in the air. Earlier this year, a NASA-led team conducted a series of carefully choreographed flights over California in order to sniff out how aircraft emissions differ when using petroleum fuels or biofuels. Early results from the Alternative Fuel Effects on Contrails and Cruise Emissions (ACCESS II) experiment confirm that blended biofuel is the cleaner-burning fuel. "Our findings show we definitely see a 50 percent reduction in soot emissions from the DC-8 when it burns the blended fuel as opposed to jet fuel alone," said Bruce Anderson, ACCESS principal investigator from NASA's Langley Research Center. The DC-8 is a NASA science workhorse: a flying laboratory equipped to collect—or, in this case, produce—data for basic Earth science research. During the ACESS experiment, scientists took advantage of the aircraft's segregated fuel tank. On the fly, the pilot switched the fuel type sent to each of the four engines. The engines burned either jet fuel, or a 50-50 blend of jet fuel and a renewable alternative produced from camelina plant oil. With each change of fuel, three other instrumented aircraft took turns lining up in the DC-8's wake and flying anywhere from 90 meters (300 feet) to more than 30 kilometers (20 miles) behind to catch a sniff. Richard Moore, a post-doctoral fellow at NASA Langley, took this photograph with a DSLR camera on May 7, 2014, during an ACCESS II test flight over Edwards Air Force Base in California. The photo was taken from Langley's HU-25C Guardian jet as it descended toward NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center after a successful three-hour sampling flight behind the DC-8. The aircraft trailing the DC-8 in the photo was a Falcon 20-E5 jet owned by the German Aerospace Center. The flight on May 7 was just the first in a series of flights that lasted throughout the month. After the campaign, researchers continued to examine the data to determine whether a reduction in soot emissions translates to a reduction in contrail formation, and how that might affect climate. Read more: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/1wBfaKq" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/1wBfaKq</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Mark Pestana is a research pilot and project manager at the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, Calif. He is a pilot for the Beech B200 King Air, the T-34C and the Predator B. He flies the F-18 Hornet as a co-pilot and flight test engineer. Pestana has accumulated more than 4,000 hours of military and civilian flight experience. He was also a flight engineer on the NASA DC-8 flying laboratory. Pestana was the project manager and pilot for the Hi–rate Wireless Airborne Network Demonstration flown on the NASA B200 research aircraft. He flew B200 research missions for the X-38 Space Integrated Inertial Navigation Global Positioning System experiment. Pestana also participated in several deployments of the DC-8, including Earth science expeditions ranging from hurricane research over the Caribbean Sea to ozone studies over the North Pole, atmospheric chemistry over the South Pacific, rain forest health in Central America, Rocky Mountain ice pack assessment, and volcanic and tectonic activity around the Pacific Rim. He came to Dryden as a DC-8 mission manager in June 1998 from NASA Johnson Space Center, Houston, where he served as the Earth and Space Science discipline manager for the International Space Station Program at Johnson. Pestana also served as a flight crew operations engineer in the Astronaut Office, developing the controls, displays, tools, crew accommodations and procedures for on-orbit assembly, test, and checkout of the International Space Station. He led the analysis and technical negotiations for modification of the Russian Soyuz spacecraft as an emergency crew return vehicle for space station crews. He joined the U.S. Air Force Reserve in 1991 and held various positions as a research and development engineer, intelligence analyst, and Delta II launch vehicle systems engineer. He retired from the U.S. Air Force Reserve with the rank of colonel in 2005. Prior to 1990, Pestana was on active duty with the U.S. Air Force as the director of mi
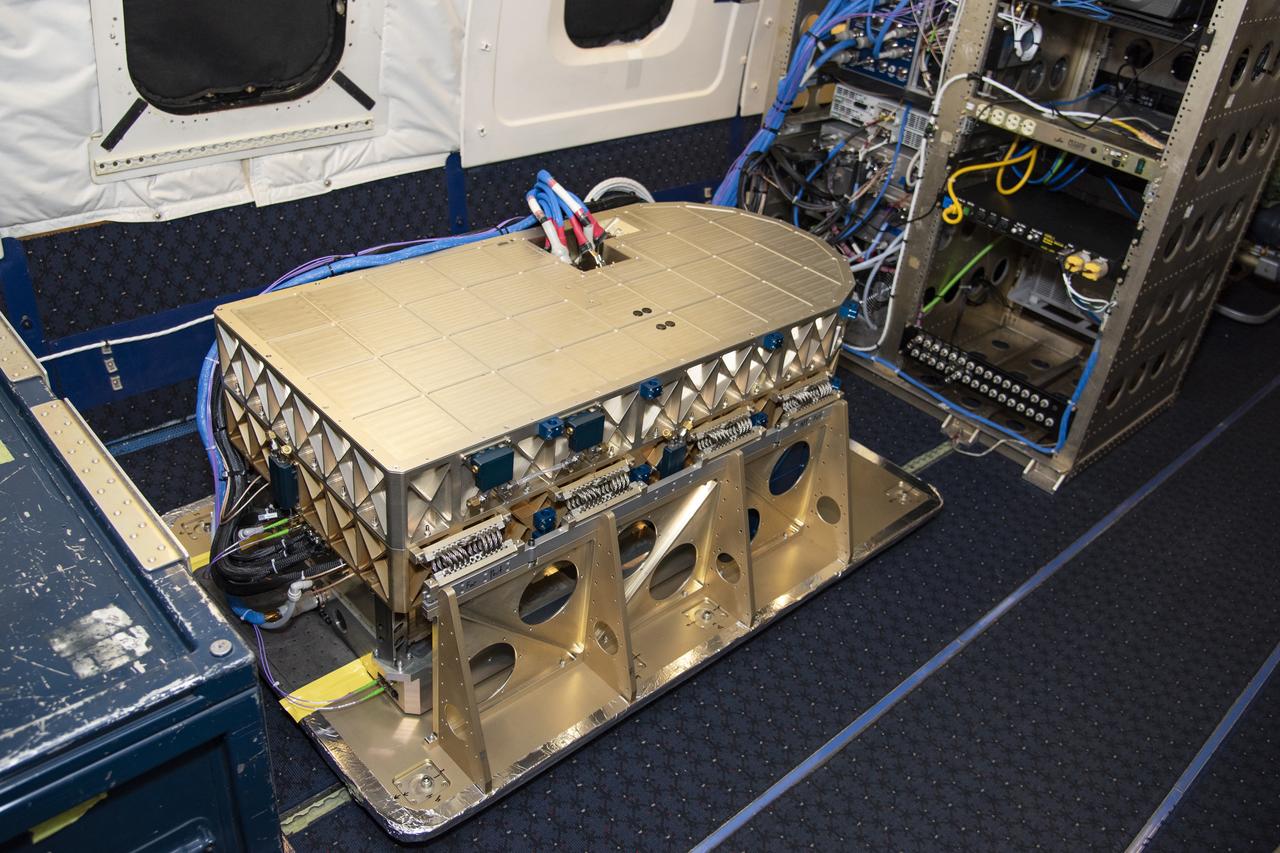

Aerosol data from the High Altitude Lidar Observatory (HALO), pictured here, will give mission scientists a better sense how Doppler Aerosol Wind Lidar (DAWN) is working and what its strengths and weaknesses are.
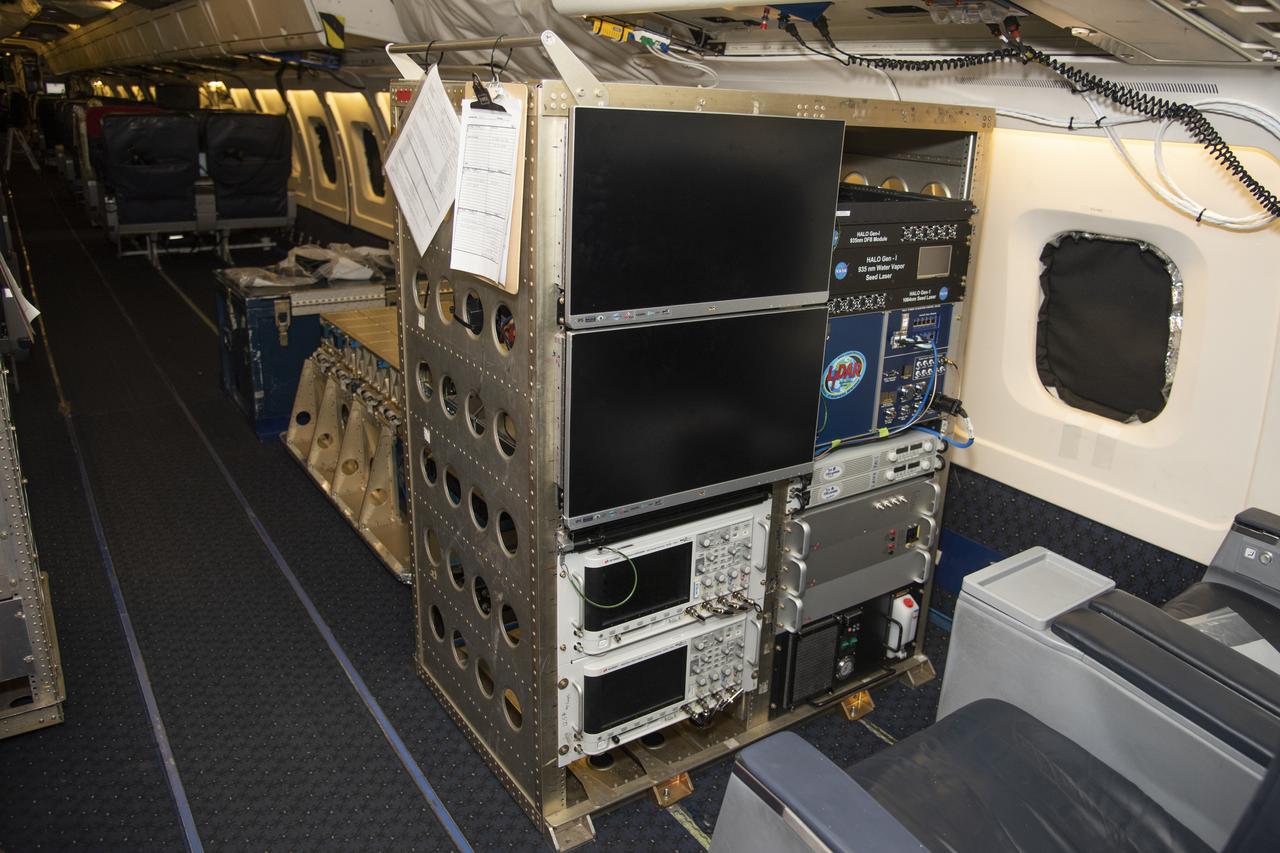

The High Altitude Lidar Observatory (HALO) system electronics and diagnostic tools are integrated onto the DC-8 airborne science laboratory at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. The lidar system control electronics are on the right hand side of the rack. The large monitors on the left are used to display real-time images of water vapor and aerosol profiles, which are used by the science team to guide in-flight decisions and navigation. The compact HALO instrument head can be seen directly behind the electronics rack.

The High Altitude Lidar Observatory (HALO) instrument head, which houses the lidar instrument, is installed onto the DC-8 airborne science laboratory at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. The gold and blue casing holds the laser, optics, detectors, and electronics, which are at the heart of the lidar.
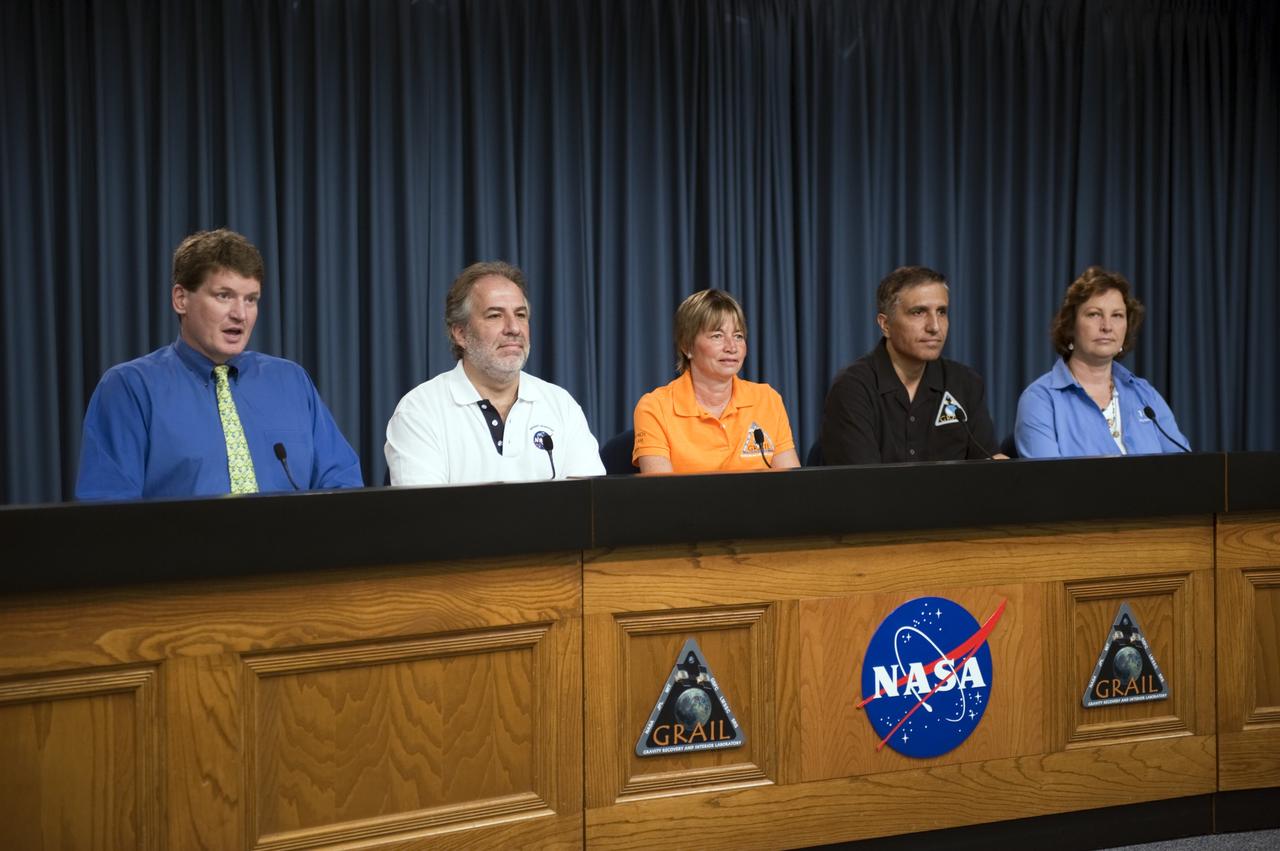

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – – A Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory (GRAIL) mission science briefing is held in the NASA Press Site auditorium at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. From left are DC Agle, NASA Public Affairs; Robert Fogel, NASA’s GRAIL program scientist; Maria Zuber, GRAIL principal investigator with the Massachusetts Institute of Technology; Sami Asmar, GRAIL deputy project scientist, NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory; and Leesa Hubbard, teacher in residence, Sally Ride Science, San Diego. GRAIL is scheduled to launch Sept. 8 aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. GRAIL will fly twin spacecraft in tandem around the moon to precisely measure and map variations in the moon's gravitational field. The mission will provide the most accurate global gravity field to date for any planet, including Earth. This detailed information will reveal differences in the density of the moon's crust and mantle and will help answer fundamental questions about the moon's internal structure, thermal evolution, and history of collisions with asteroids. The aim is to map the moon's gravity field so completely that future moon vehicles can safely navigate anywhere on the moon’s surface. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/grail. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
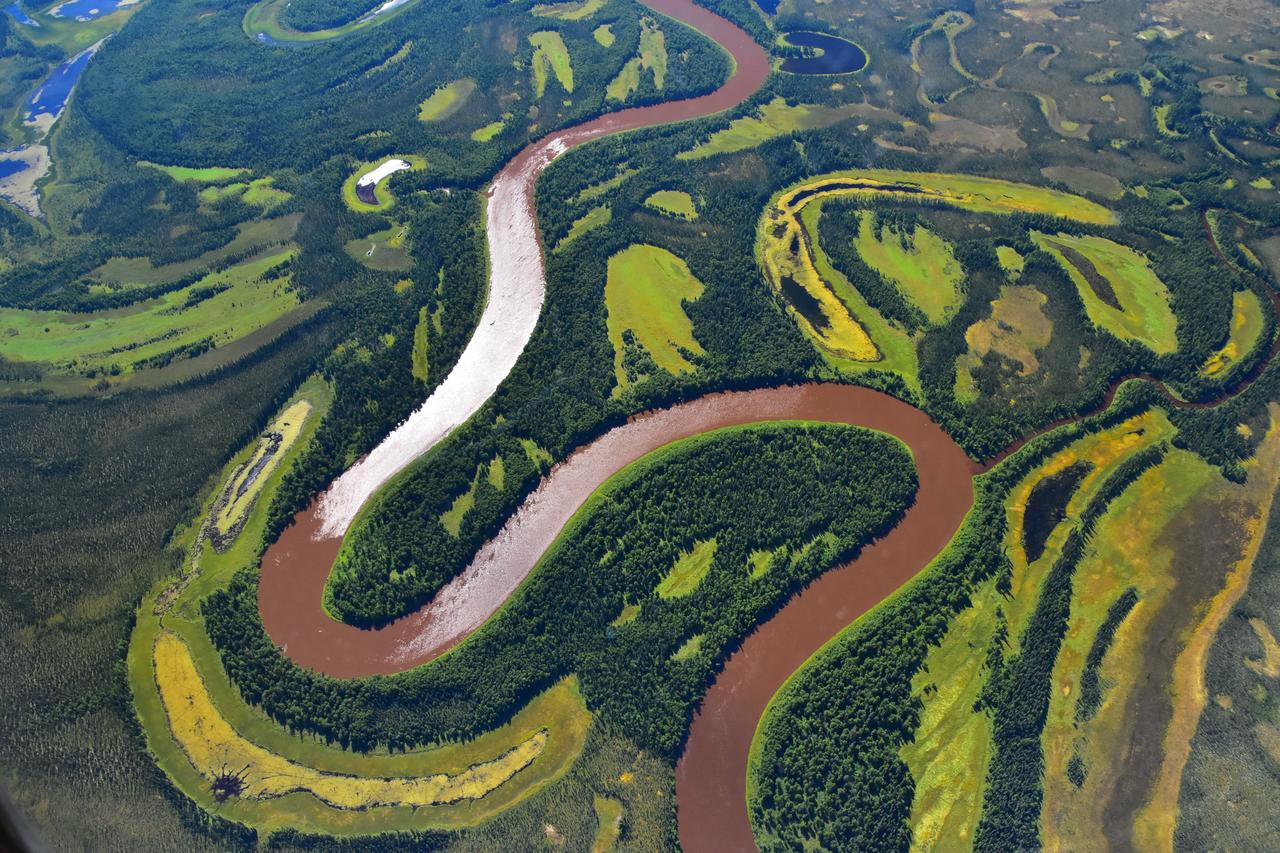

As part of the Arctic Boreal Vulnerability Experiment (ABoVE), NASA scientists are flying over Alaska and Canada, measuring the elevation of rivers and lakes to study how thawing permafrost affects hydrology in the landscape. This view of was taken from NASA’s DC-8 “flying laboratory” as part of the Active Sensing of CO2 Emissions over Nights, Days and Seasons (ASCENDS) experiment. Scientists on NASA’s Air Surface, Water and Ocean Topography (AirSWOT) mission have been flying over the same location, investigating how water levels in the Arctic landscape change as permafrost thaws. Under typical conditions, the frozen layer of soil keeps water from sinking into the ground and percolating away. As permafrost thaws, the water has new ways to move between rivers and lakes, which can raise or lower the elevation of the bodies of water. These changes in water levels will have effects on Arctic life— plants, animals, and humans—in the near future. Credit: NASA/Peter Griffith <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
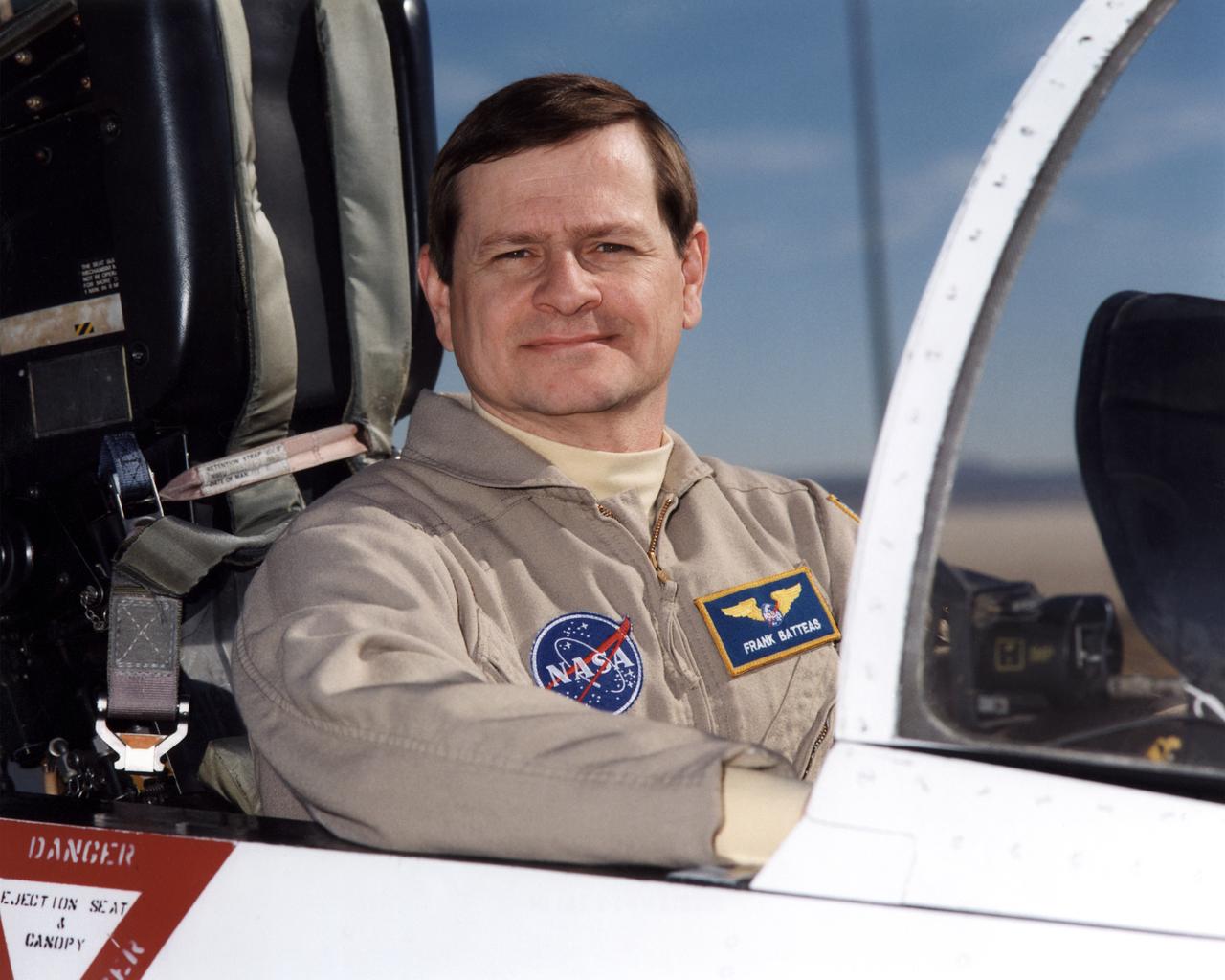

Frank Batteas is a research test pilot in the Flight Crew Branch of NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. He is currently a project pilot for the F/A-18 and C-17 flight research projects. In addition, his flying duties include operation of the DC-8 Flying Laboratory in the Airborne Science program, and piloting the B-52B launch aircraft, the King Air, and the T-34C support aircraft. Batteas has accumulated more than 4,700 hours of military and civilian flight experience in more than 40 different aircraft types. Batteas came to NASA Dryden in April 1998, following a career in the U.S. Air Force. His last assignment was at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, Dayton, Ohio, where Lieutenant Colonel Batteas led the B-2 Systems Test and Evaluation efforts for a two-year period. Batteas graduated from Class 88A of the Air Force Test Pilot School, Edwards Air Force Base, California, in December 1988. He served more than five years as a test pilot for the Air Force's newest airlifter, the C-17, involved in nearly every phase of testing from flutter and high angle-of-attack tests to airdrop and air refueling envelope expansion. In the process, he achieved several C-17 firsts including the first day and night aerial refuelings, the first flight over the North Pole, and a payload-to-altitude world aviation record. As a KC-135 test pilot, he also was involved in aerial refueling certification tests on a number of other Air Force aircraft. Batteas received his commission as a second lieutenant in the U. S. Air Force through the Reserve Officer Training Corps and served initially as an engineer working on the Peacekeeper and Minuteman missile programs at the Ballistic Missile Office, Norton Air Force Base, Calif. After attending pilot training at Williams Air Force Base, Phoenix, Ariz., he flew operational flights in the KC-135 tanker aircraft and then was assigned to research flying at the 4950th Test Wing, Wright-Patterson. He flew extensively modified C-135

Researchers Anna Noe and Eric Altman check out the Doppler Aerosol Wind Lidar (DAWN), an airborne instrument that uses pulsed lasers to detect the movement of atmospheric aerosols such as dust or sea salt. In detecting those movements, it can profile wind vector — both speed and direction. Researchers are testing DAWNs capabilities during flights over the eastern Pacific.
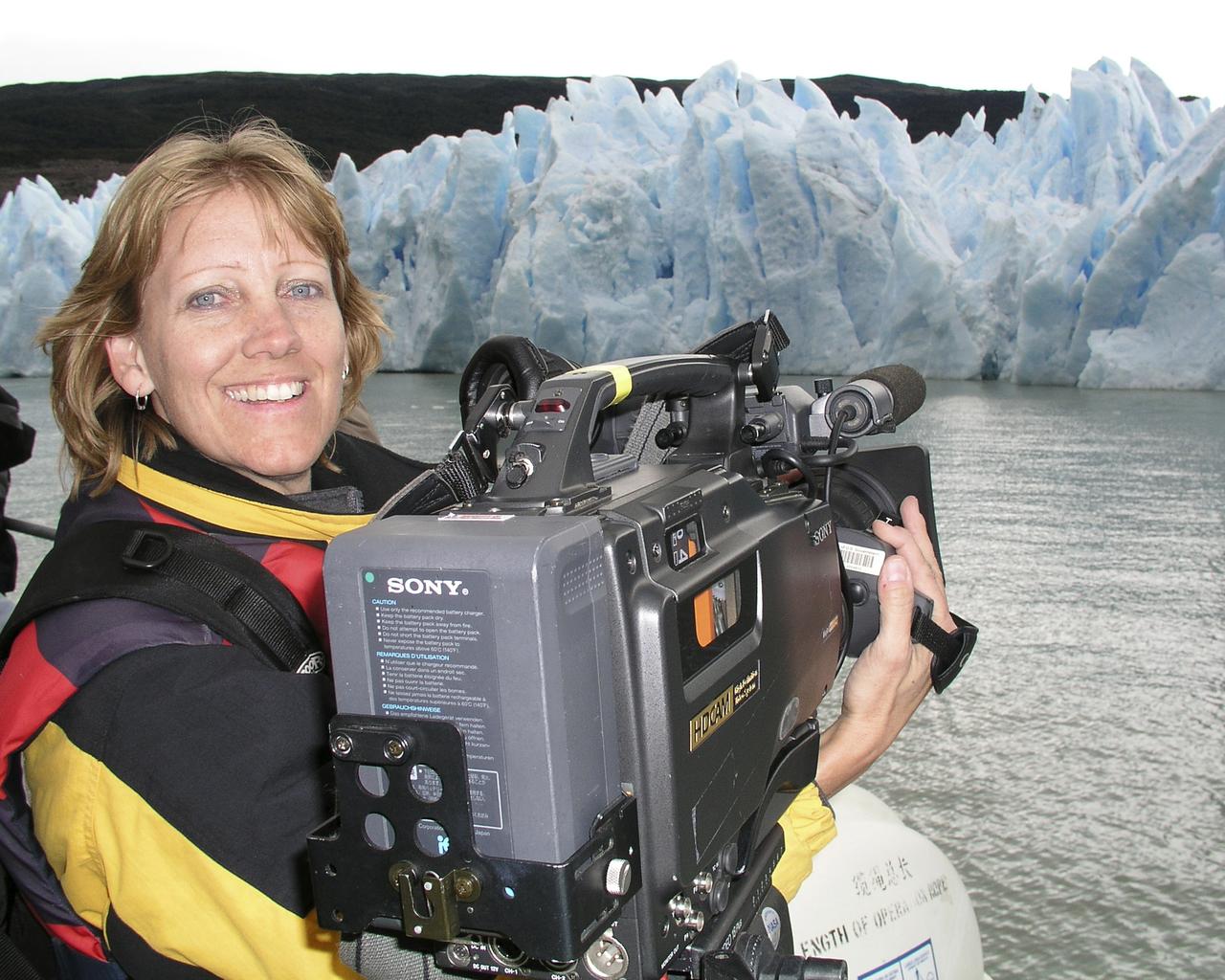

Lori Losey, an employee of Arcata Associates at Dryden, was honored with NASA's 2004 Videographer of the Year award for her work in two of the three categories in the NASA video competition, public affairs and documentation. In the public affairs category, Losey received a first-place citation for her footage of an Earth Science mission that was flown aboard NASA's DC-8 Flying Laboratory in South America last year. Her footage not only depicted the work of the scientists aboard the aircraft and on the ground, but she also obtained spectacular footage of flora and fauna in the mission's target area that helped communicate the environmental research goals of the project. Losey also took first place in the documentation category for her acquisition of technical videography of the X-45A Unmanned Combat Air Vehicle flight tests. The video, shot with a hand-held camera from the rear seat of a NASA F/A-18 mission support aircraft, demonstrated her capabilities in recording precise technical visual data in a very challenging airborne environment. The award was presented to Losey during a NASA reception at the National Association of Broadcasters convention in Las Vegas April 19. A three-judge panel evaluated entries for public affairs, documentation and production videography on professional excellence, technical quality, originality, creativity within restrictions of the project, and applicability to NASA and its mission. Entries consisted of a continuous video sequence or three views of the same subject for a maximum of three minutes duration. Linda Peters, Arcata Associates' Video Systems Supervisor at NASA Dryden, noted, "Lori is a talented videographer who has demonstrated extraordinary abilities with the many opportunities she has received in her career at NASA." Losey's award was the second major NASA video award won by members of the Dryden video team in two years. Steve Parcel took first place in the documentation category last year for his camera and editing

Climate researchers from the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) and several universities install and perform functional checkouts of a variety of sensitive atmospheric instruments on NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory prior to beginning the ARCTAS mission.
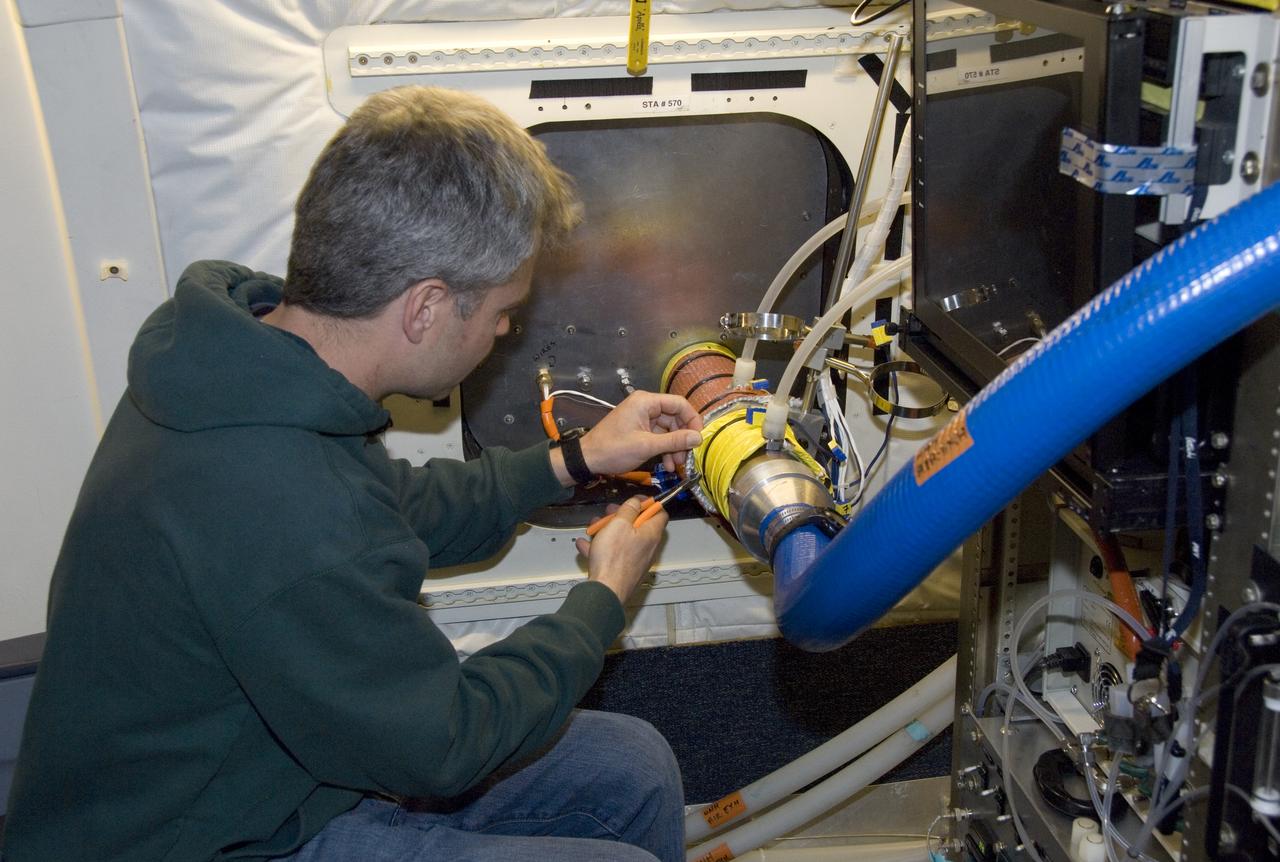

Climate researchers from the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) and several universities install and perform functional checkouts of a variety of sensitive atmospheric instruments on NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory prior to beginning the ARCTAS mission.
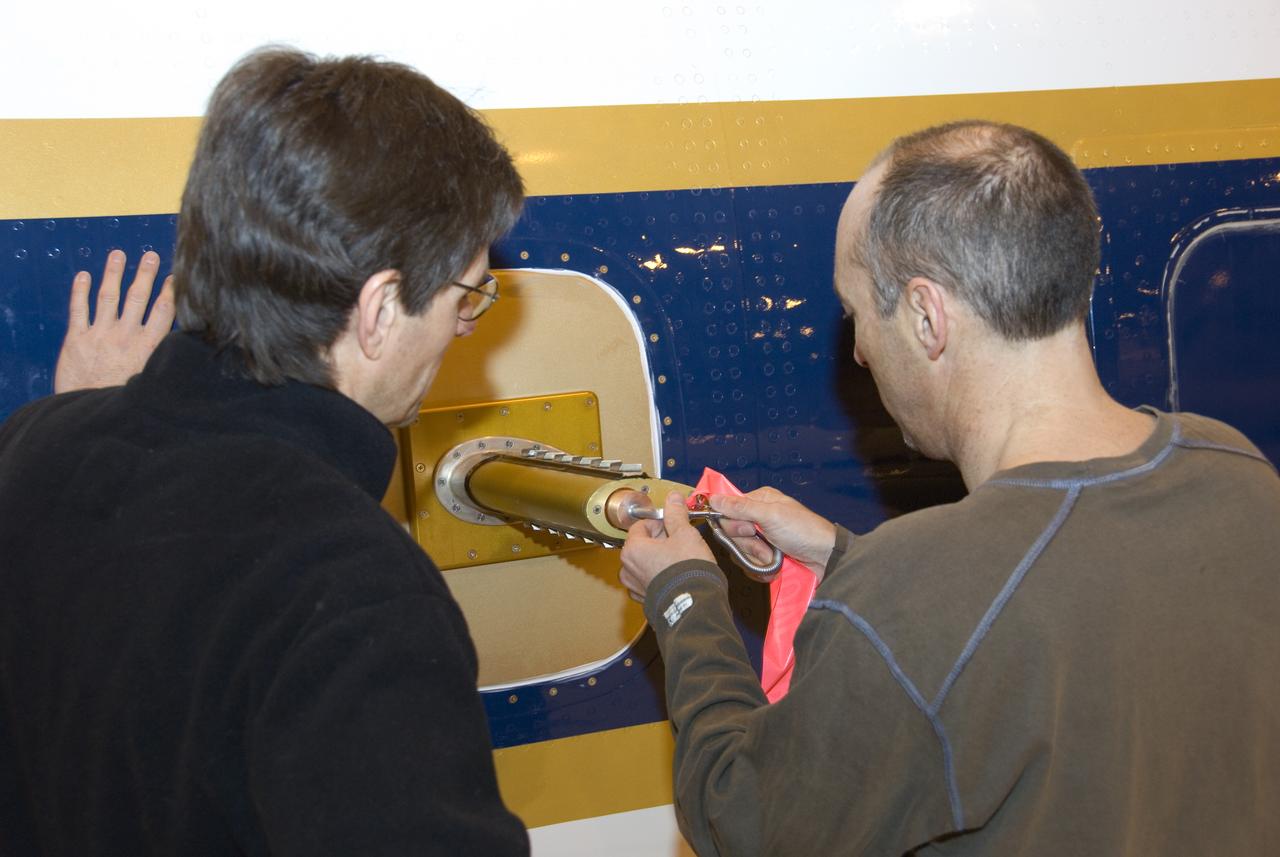

Climate researchers from the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) and several universities install and perform functional checkouts of a variety of sensitive atmospheric instruments on NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory prior to beginning the ARCTAS mission.
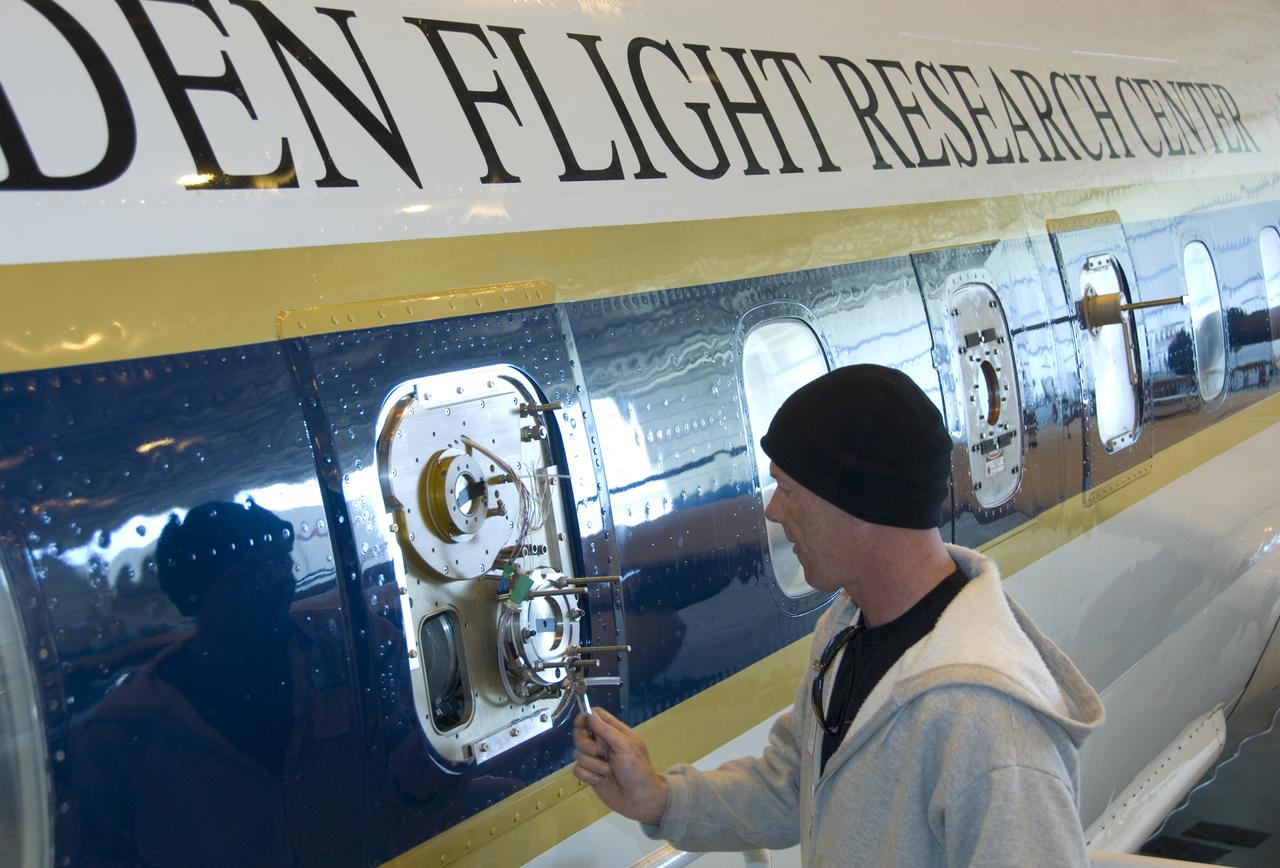

Climate researchers from the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) and several universities install and perform functional checkouts of a variety of sensitive atmospheric instruments on NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory prior to beginning the ARCTAS mission.
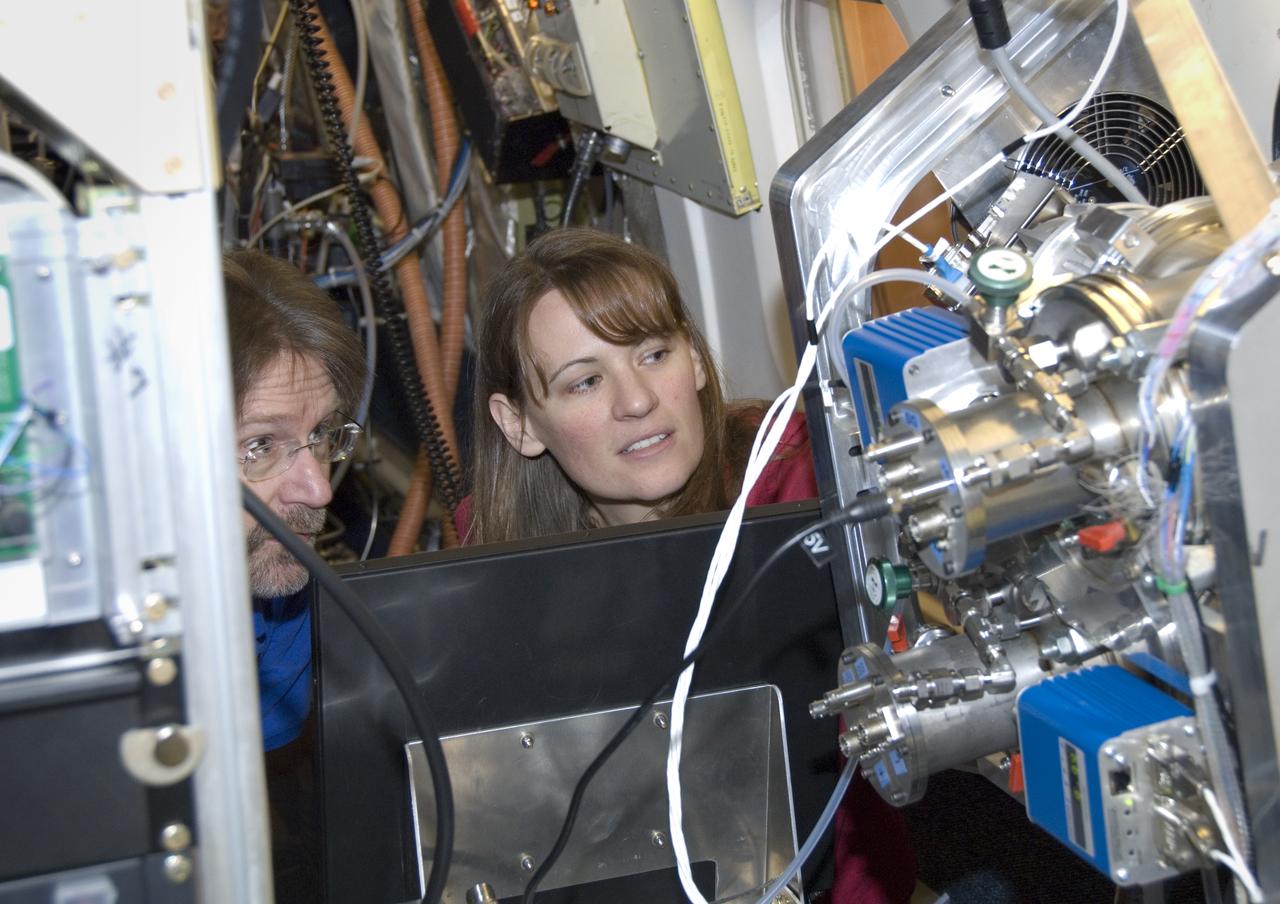
Climate researchers from the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) and several universities install and perform functional checkouts of a variety of sensitive atmospheric instruments on NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory prior to beginning the ARCTAS mission.