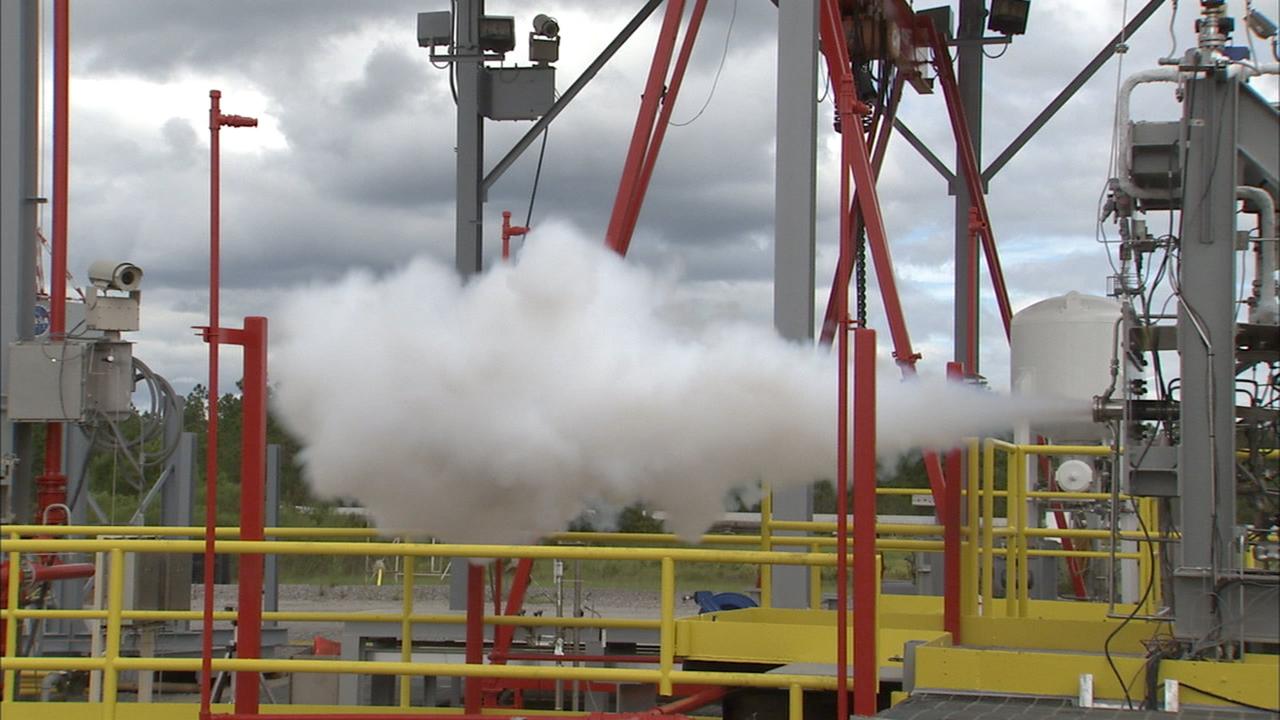

Tests begun at Stennis Space Center's E Complex Sept. 13 evaluated a liquid oxygen lead for engine start performance, part of the A-3 Test Facility Subscale Diffuser Risk Mitigation Project at SSC's E-3 Test Facility. Phase 1 of the subscale diffuser project, completed Sept. 24, was a series of 18 hot-fire tests using a 1,000-pound liquid oxygen and gaseous hydrogen thruster to verify maximum duration and repeatability for steam generation supporting the A-3 Test Stand project. The thruster is a stand-in for NASA's developing J-2X engine, to validate a 6 percent scale version of A-3's exhaust diffuser. Testing the J-2X at altitude conditions requires an enormous diffuser. Engineers will generate nearly 4,600 pounds per second of steam to reduce pressure inside A-3's test cell to simulate altitude conditions. A-3's exhaust diffuser has to be able to withstand regulated pressure, temperatures and the safe discharge of the steam produced during those tests. Before the real thing is built, engineers hope to work out any issues on the miniature version. Phase 2 testing is scheduled to begin this month.
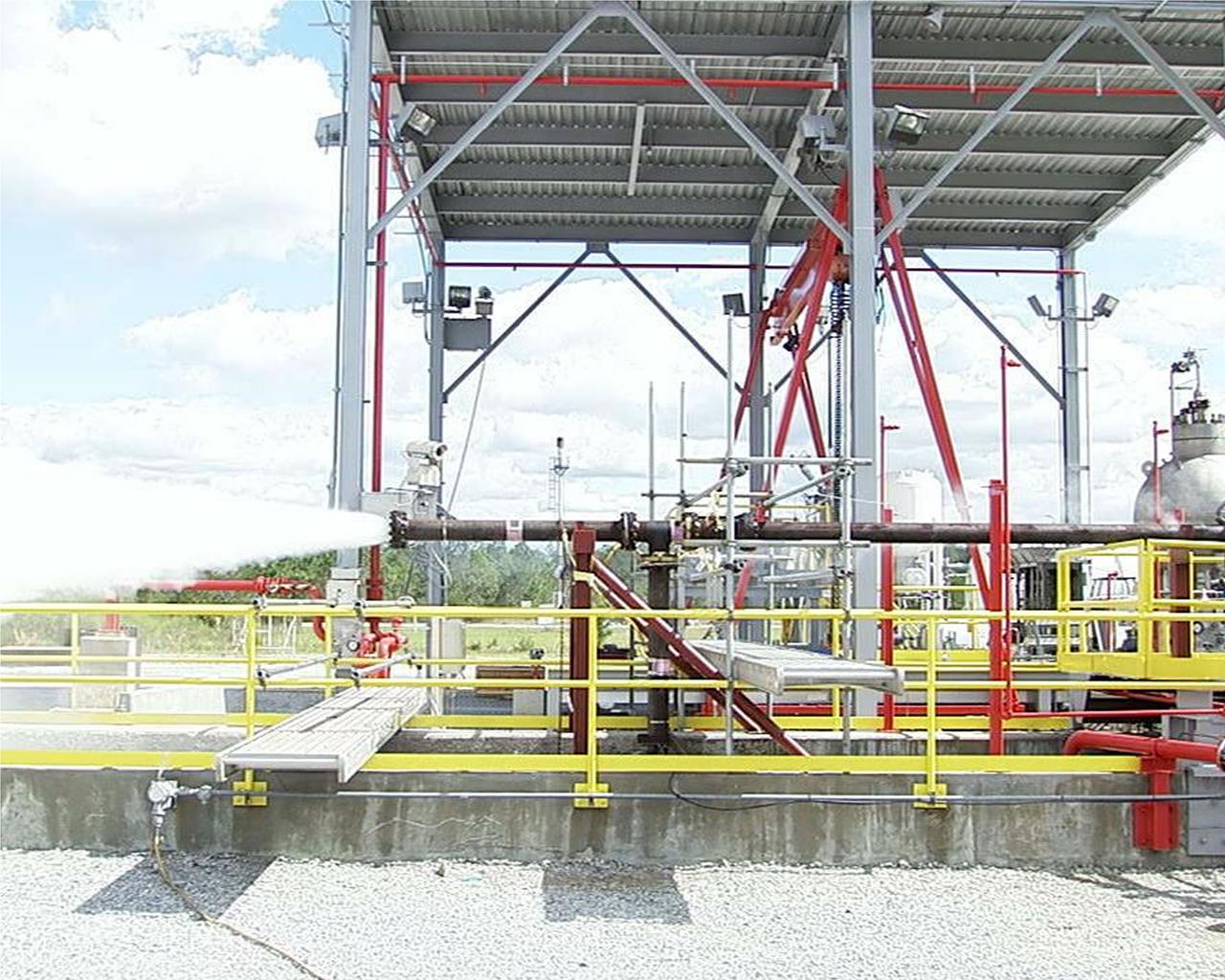

Phase 2 of the A-3 Test Facility Subscale Diffuser Risk Mitigation Project at Stennis Space Center reached a milestone Oct. 25 when the E-3 Test Facility produced superheated (500+ degrees) steam for approximately 3 seconds at more than 400 psi. The test team, led by Barry Robinson of NASA's Test Projects Office, followed that success with further tests to lengthen the duration of steam production. On Nov. 1, they were able to maintain a consistent pressure and temperature of steam for 60 seconds. In December, the team began Phase 3 of the testing, providing data for the design and procurement to build the full-scale version of the steam diffuser for SSC's A-3 Test Stand.
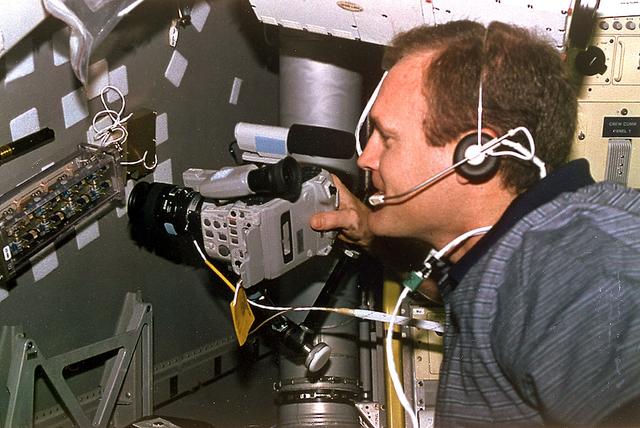

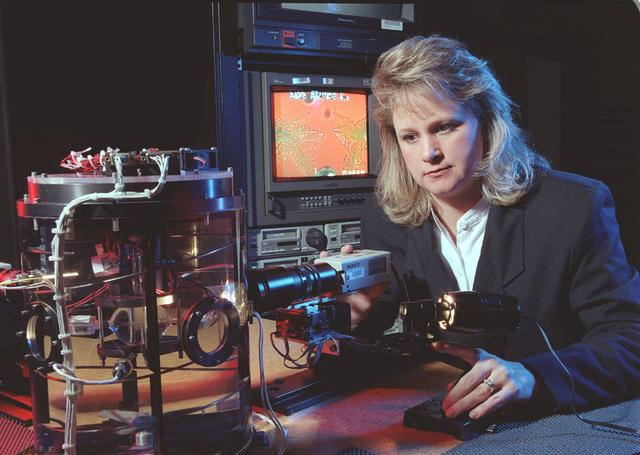
Astronaut James D. Halsell, Jr., mission commander, uses a Hi-8mm camcorder to videotape the Hand Held Diffusion Test Cells (HHDTC), in the Spacelab Science Module aboard the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-94). Each test cell has three chambers containing a protein solution, a buffer solution and a precipitant solution chamber. Using the liquid-liquid diffusion method, the different fluids are brought into contact but not mixed. Over a period of time, the fluids will diffuse into each other through the random motion of molecules. The gradual increase in concentration of the precipitant within the protein solution causes the proteins to crystallize.
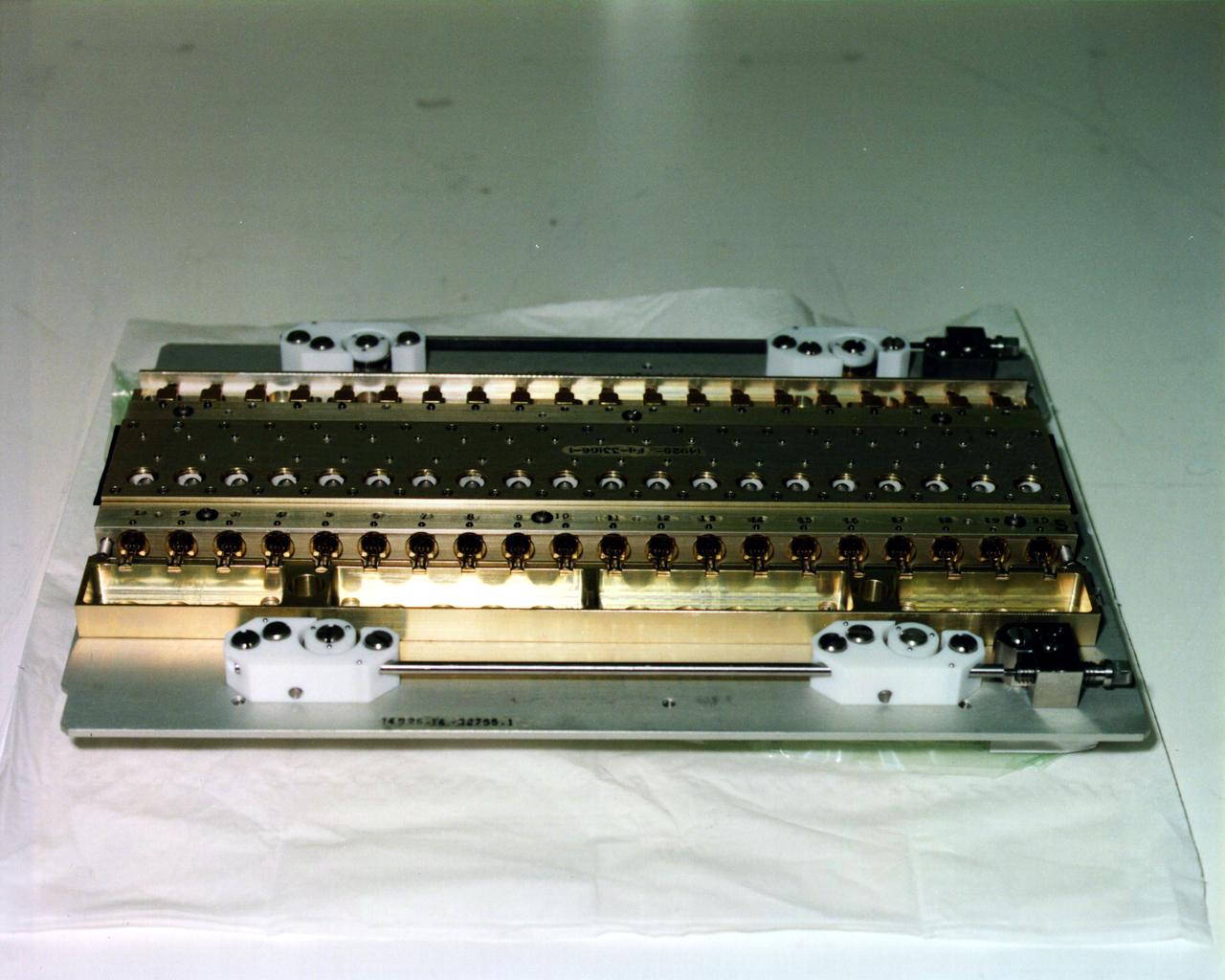
These Vapor Diffusion Apparatus (VDA) trays were first flown in the Thermal Enclosure System (TES) during the USMP-2 (STS-62) mission. Each tray can hold 20 protein crystal growth chambers. Each chamber contains a double-barrel syringe; one barrel holds protein crystal solution and the other holds precipitant agent solution. During the microgravity mission, a torque device is used to simultaneously retract the plugs in all 20 syringes. The two solutions in each chamber are then mixed. After mixing, droplets of the combined solutions are moved onto the syringe tips so vapor diffusion can begin. During the length of the mission, protein crystals are grown in the droplets. Shortly before the Shuttle's return to Earth, the experiment is deactivated by retracting the droplets containing protein crystals, back into the syringes.
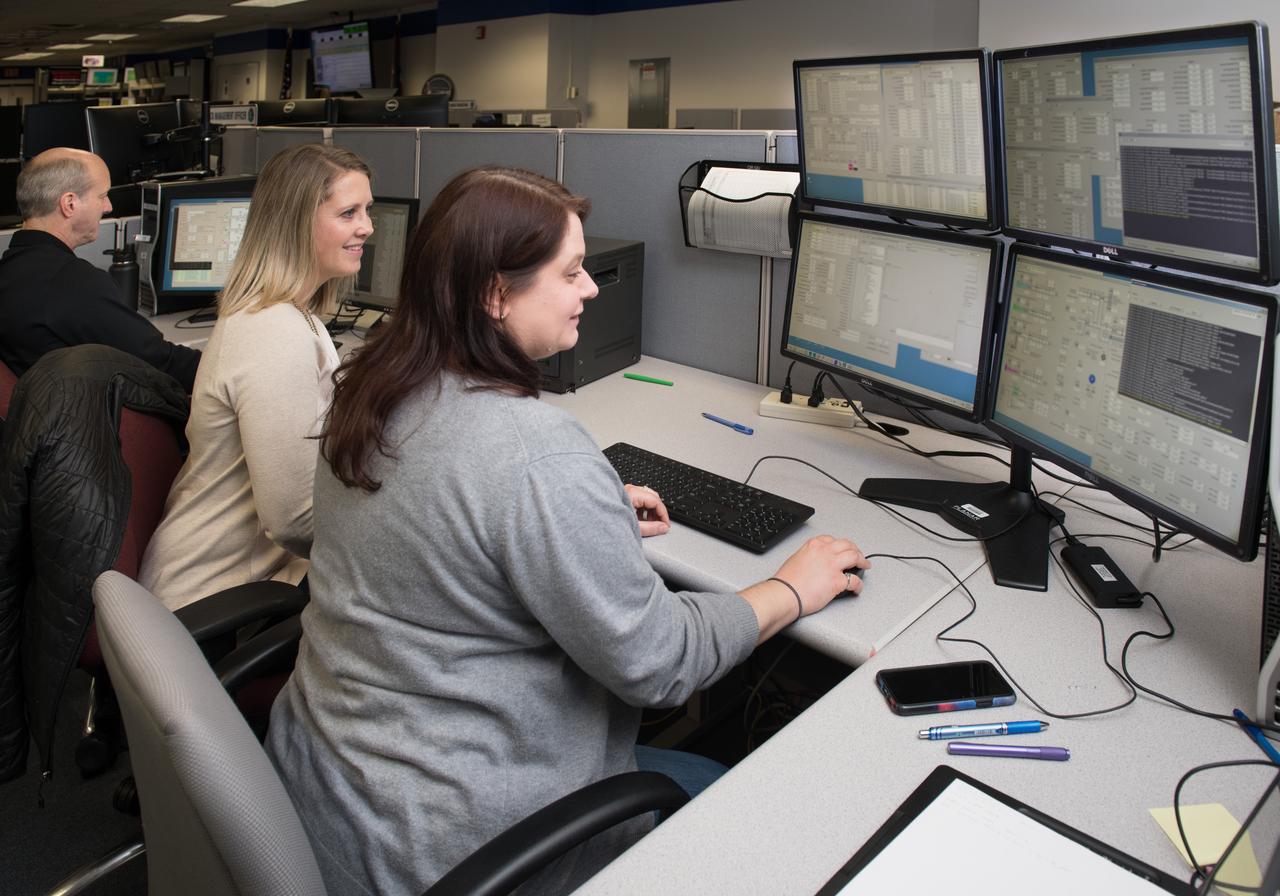

Testing of software with ground hardware for the Structue and Response of Spherical Diffusion Flames, s-Flame, experiment - of the Advanced Combustion via Microgravity Experiments, ACME, project conducted in the ISS Combustion Integrated Rack, CIR - by ACME Software Engineer Jeffrey Eggers, Operations Lead Angela Adams, and Planning Lead Melani Smajdek in the Telescience Support Center, TSC, also known as the Glenn ISS Payload Operations Center, GIPOC
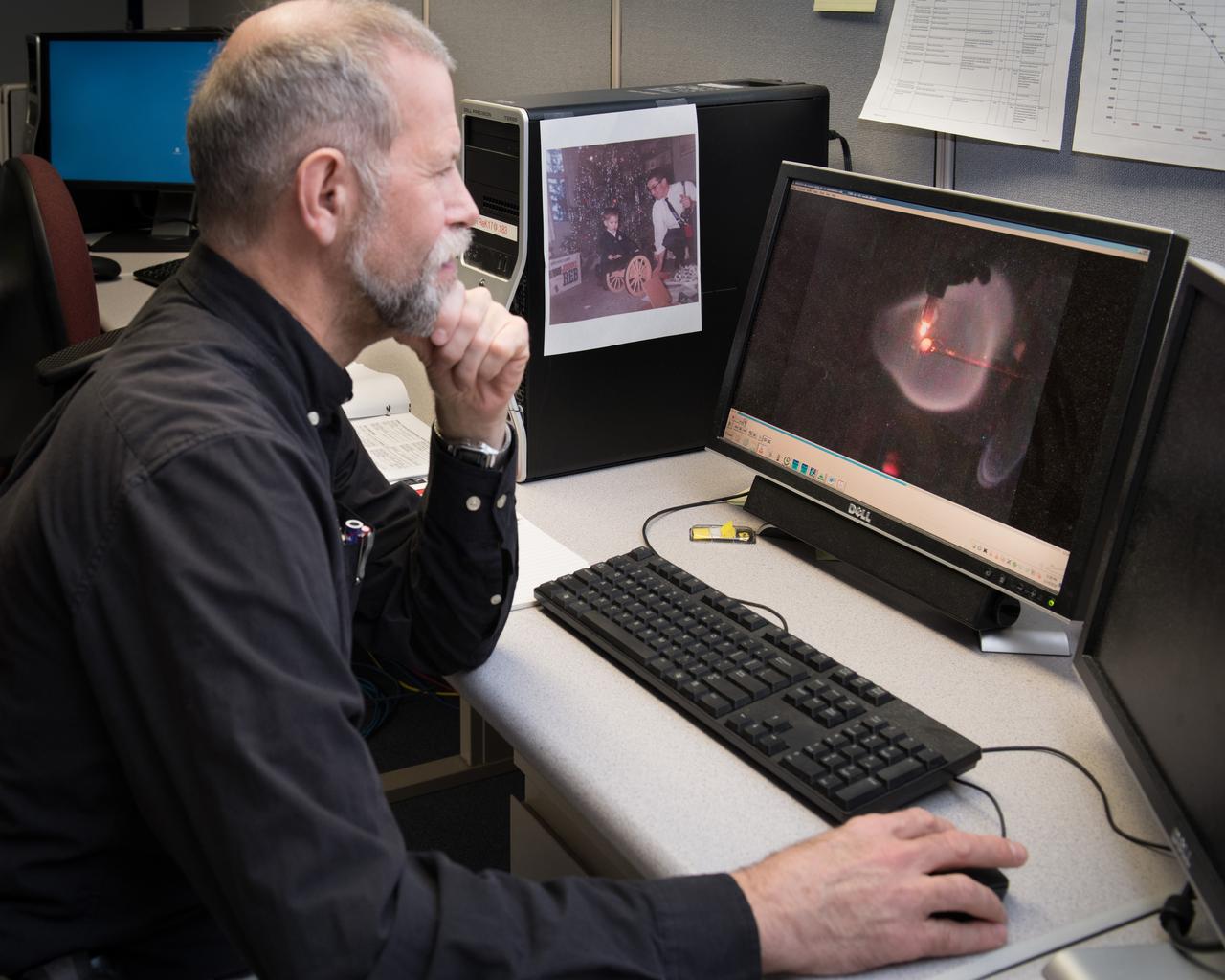
Review of ISS data from the Structure and Response of Spherical Diffusion Flames (s-Flame) experiment - of the Advanced Combustion via Microgravity Experiments. ACME project conducted in the Combustion Integrated Rack, CIR - by ACME Project Scientist Dennis Stocker in the Telescience Support Center,TSC, also known as the Glenn ISS Payload Operations Center, GIPOC
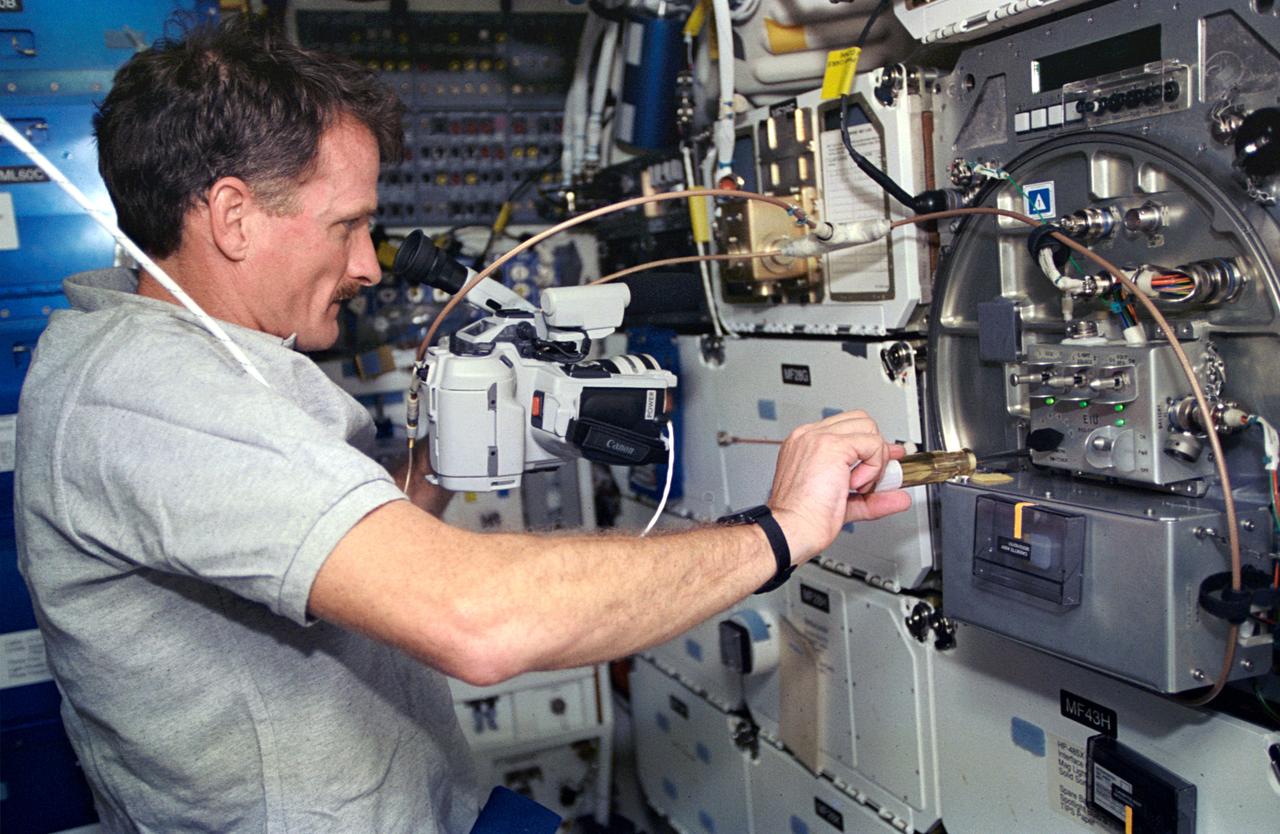

On the Space Shuttle Atlantis' mid-deck, astronaut Joseph R. Tanner, mission specialist, works at area amidst several lockers onboard the Shuttle which support the Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) experiment. This particular section is called the Crystal Observation System, housed in the Thermal Enclosure System (COS/TES). Together with the Vapor Diffusion Apparatus (VDA), housed in a Single Locker Thermal Enclosure (SLTES) which is out of frame, the Cos/TES represents the continuing research into the structures of proteins and other macromolecules such as viruses.
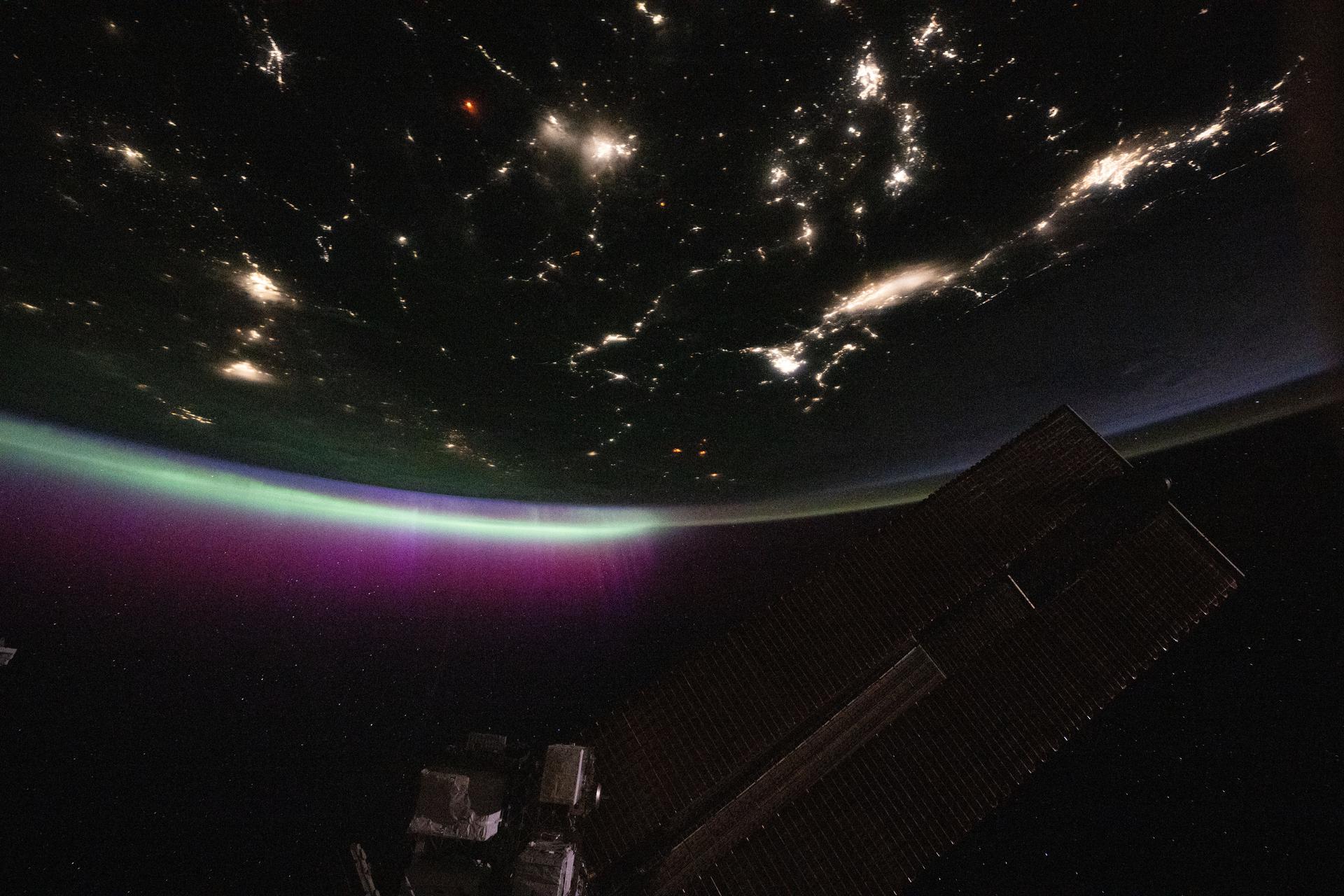

iss073e0780439 (Sept. 2, 2025) --- A diffuse aurora glows above Earth's horizon over Canada as its red and green hues shimmer like neon lights—an effect created by excited oxygen atoms high in the atmosphere. The city lights of the U.S.-Canadian Pacific Northwest (toward upper right) trace the continent eastward. The red aurora is produced by high-altitude oxygen atoms (~300 km), while the green glow comes from lower-altitude oxygen (~100 km), both excited by energetic electrons guided into the atmosphere by Earth's magnetic field during solar activity.
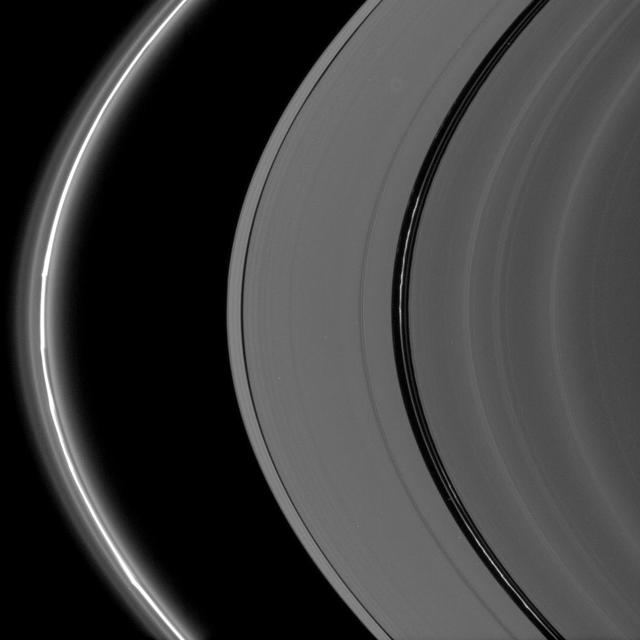
Bright, kinked ringlets fill the Encke Gap, while the F ring glows brilliantly and displays its signature knots and flanking, diffuse ringlets
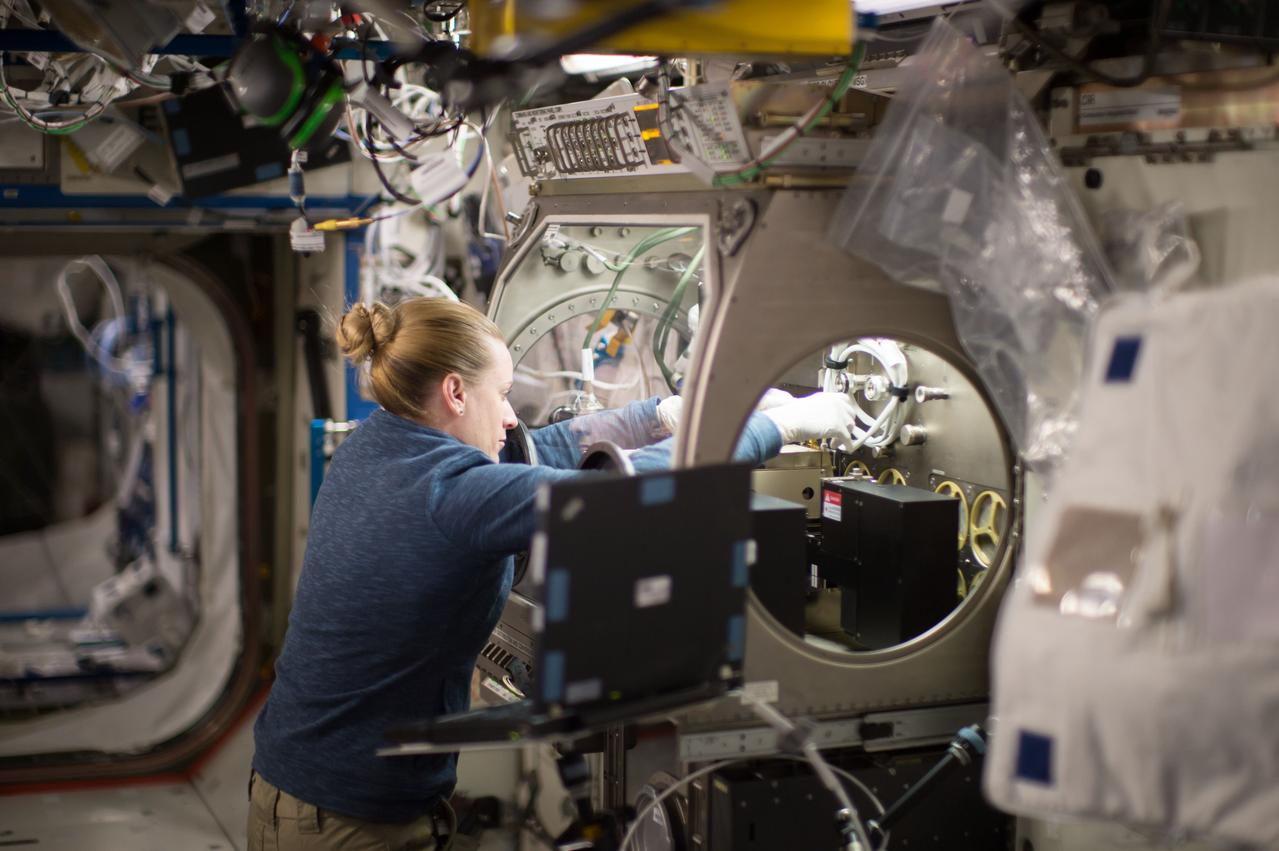

NASA astronaut Kate Rubins works on Selectable Optical Diagnostics Instrument Experiment Diffusion Coefficient Mixture-3 (SODI) DCMix-3 Installation inside the station’s Microgravity Science Glovebox. The glovebox is one of the major dedicated science facilities inside the Destiny laboratory and provides a sealed environment for conducting science and technology experiments. The glovebox is particularly suited for handling hazardous materials when the crew is present.
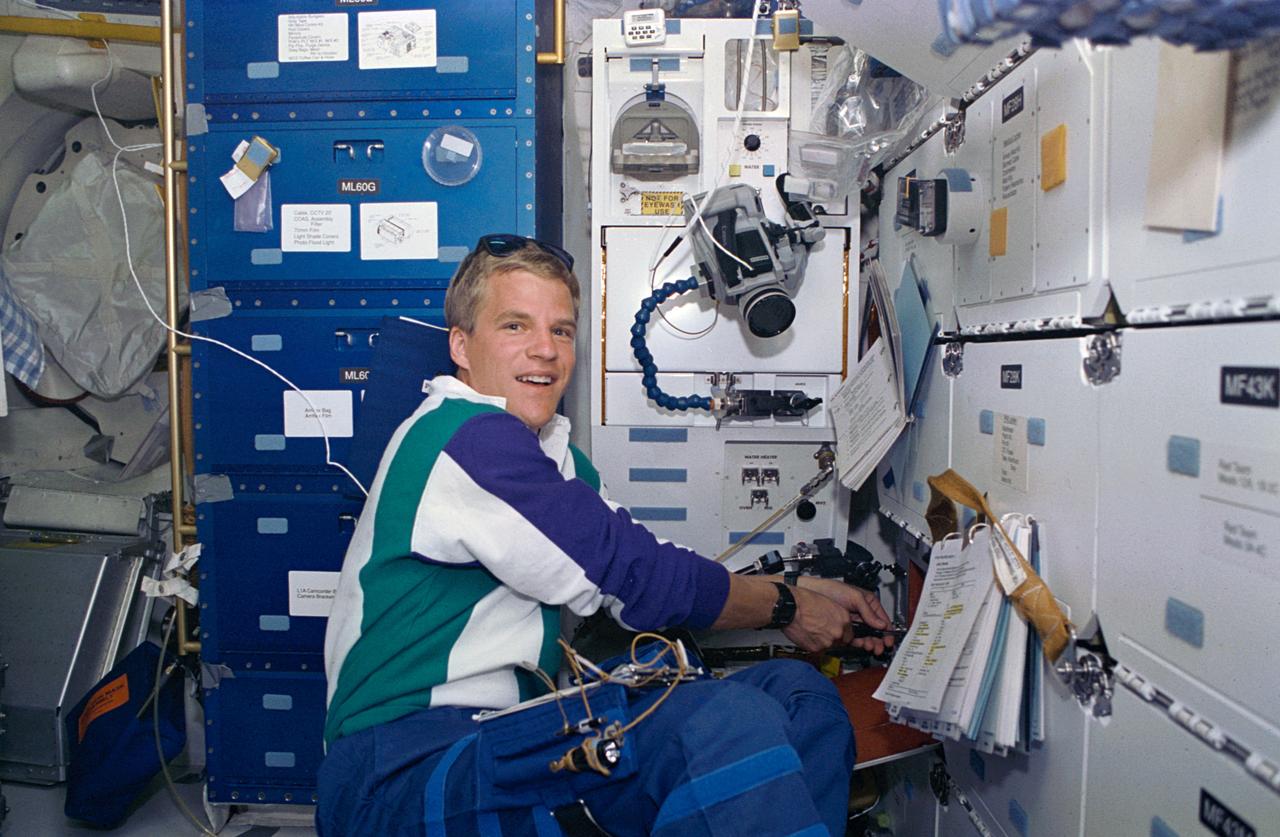

STS066-13-029 (3-14 Nov 1994) --- On the Space Shuttle Atlantis' mid-deck, astronaut Scott E. Parazynski, mission specialist, works at one of two areas onboard the Shuttle which support the Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) experiment. This particular section is called the Vapor Diffusion Apparatus (VDA), housed in a Single Locker Thermal Enclosure (STES). Together with the Crystal Observation System, housed in the Thermal Enclosure System (COS/TES) the VDA represents the continuing research into the structures of proteins and other macromolecules such as viruses. In addition to using the microgravity of space to grow high-quality protein crystals for structural analyses, the experiments are expected to help develop technologies and methods to improve the protein crystallization process on Earth as well as in space.
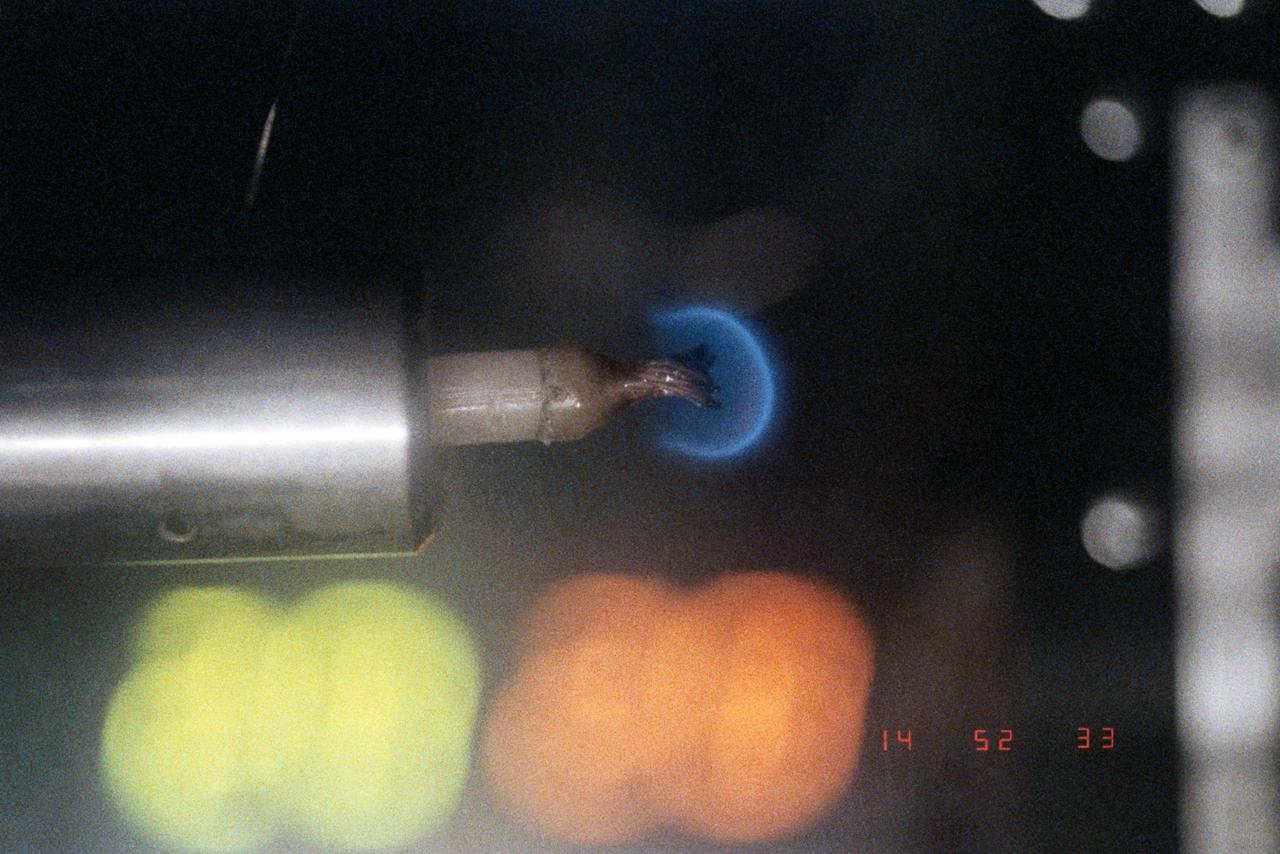
Closeup view inside glovebox showing a candle flame. The Candle Flames in Microgravity experiment is carried onboard Columbia to examine whether candle flames can be sustained in space; to study the interaction and physical properties of diffusion flames. In space, where buoyancy-driven convection is reduced, the role diffusion plays in sustaining candle flames can be isolated. Results have implications for other diffusion flame studies. Diffusion flames are the most common type of flame on Earth.
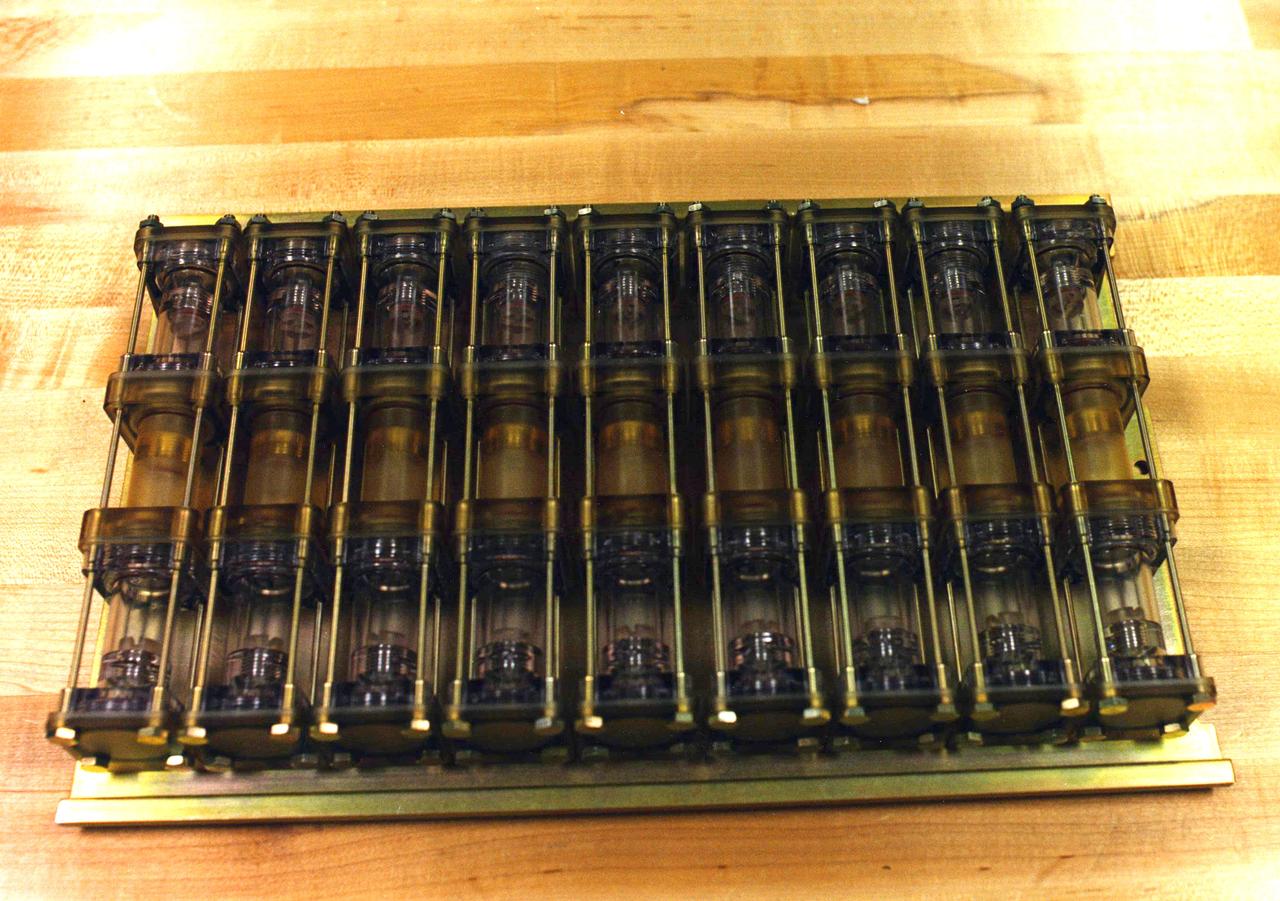

DCAM, developed by MSFC, grows crystals by the dialysis and liquid-liquid diffusion methods. In both methods, protein crystal growth is induced by changing conditions in the protein. In dialysis, a semipermeable membrane retains the protein solution in one compartment, while allowing molecules of precipitant to pass freely through the membrane from an adjacent compartment. As the precipitant concentration increases within the protein compartment, crystallization begins. In liquid-liquid diffusion, a protein solution and a precipitant solution are layered in a container and allowed to diffuse into each other. This leads to conditions which may induce crystallization of the protein. Liquid-liquid diffusion is difficult on Earth because density and temperature differences cause the solutions to mix rapidly.
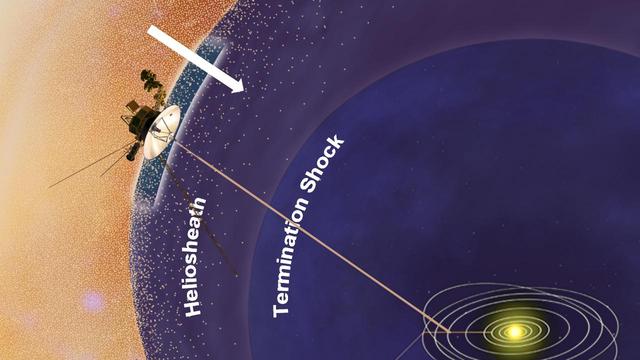
This artist concept shows NASA Voyager 1 spacecraft in a new region at the edge of our solar system where the amount of high-energy particles diffusing into our solar system from outside has increased.
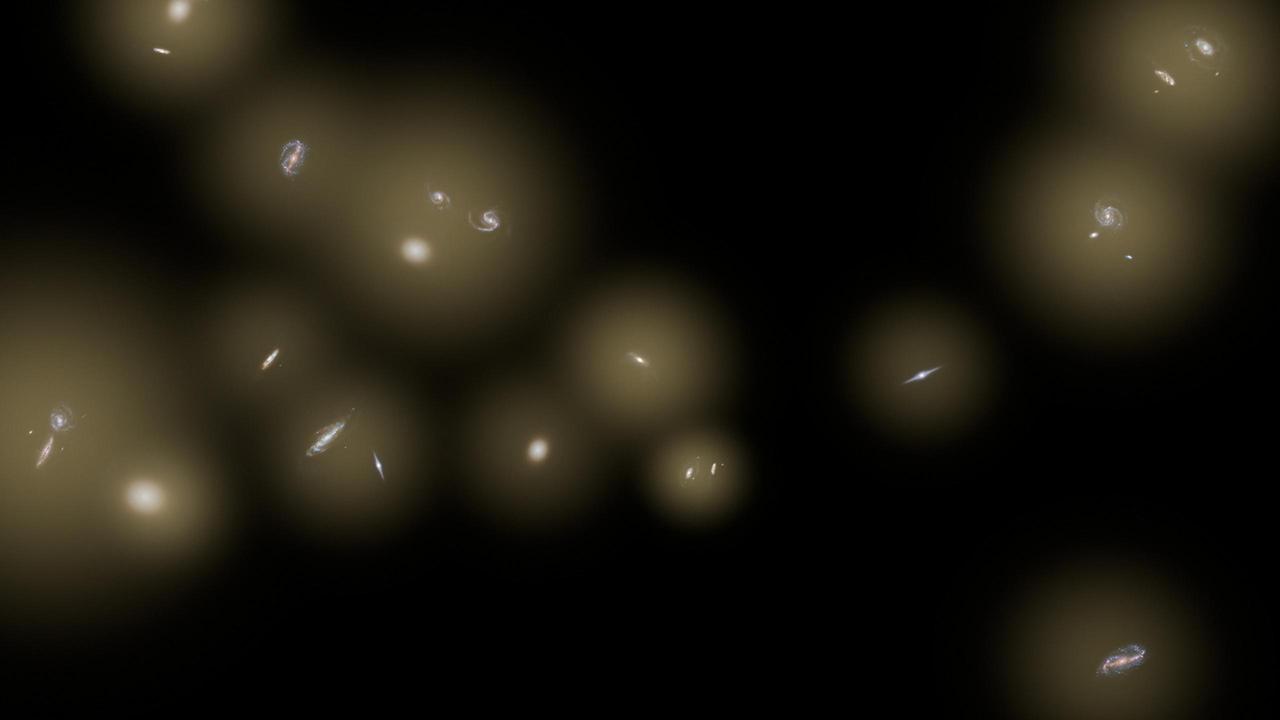

This artist concept shows a view of a number of galaxies sitting in huge halos of stars. The stars are too distant to be seen individually and instead are seen as a diffuse glow, colored yellow in this illustration.

Our sky is filled with a diffuse background glow, known as the cosmic infrared background. Much of the light is from galaxies we know about, but previous Spitzer measurements have shown an extra component of unknown origin.

This plot shows data from the Cosmic Infrared Background Experiment, or CIBER, rockets launched in 2010 and 2012. The experiment measures a diffuse glow of infrared light in the sky, known as the cosmic infrared background.

NASA NuSTAR will be able to identify individual black holes making up the diffuse X-ray glow, also called the X-ray background. At bottom right is a simulated view of what NuSTAR will see.
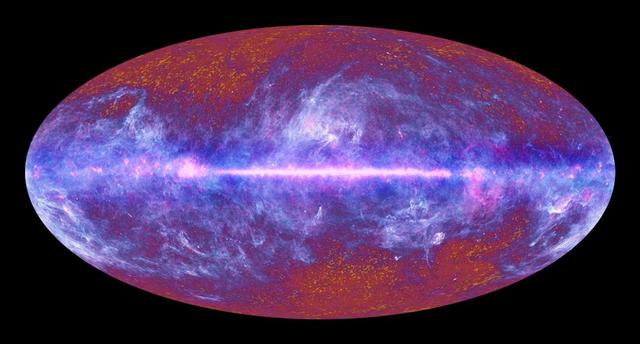
This image of the microwave sky was synthesized using data spanning the range of light frequencies detected by ESA Planck. A vast portion of the sky is dominated by the diffuse emission from gas and dust in our Milky Way galaxy.
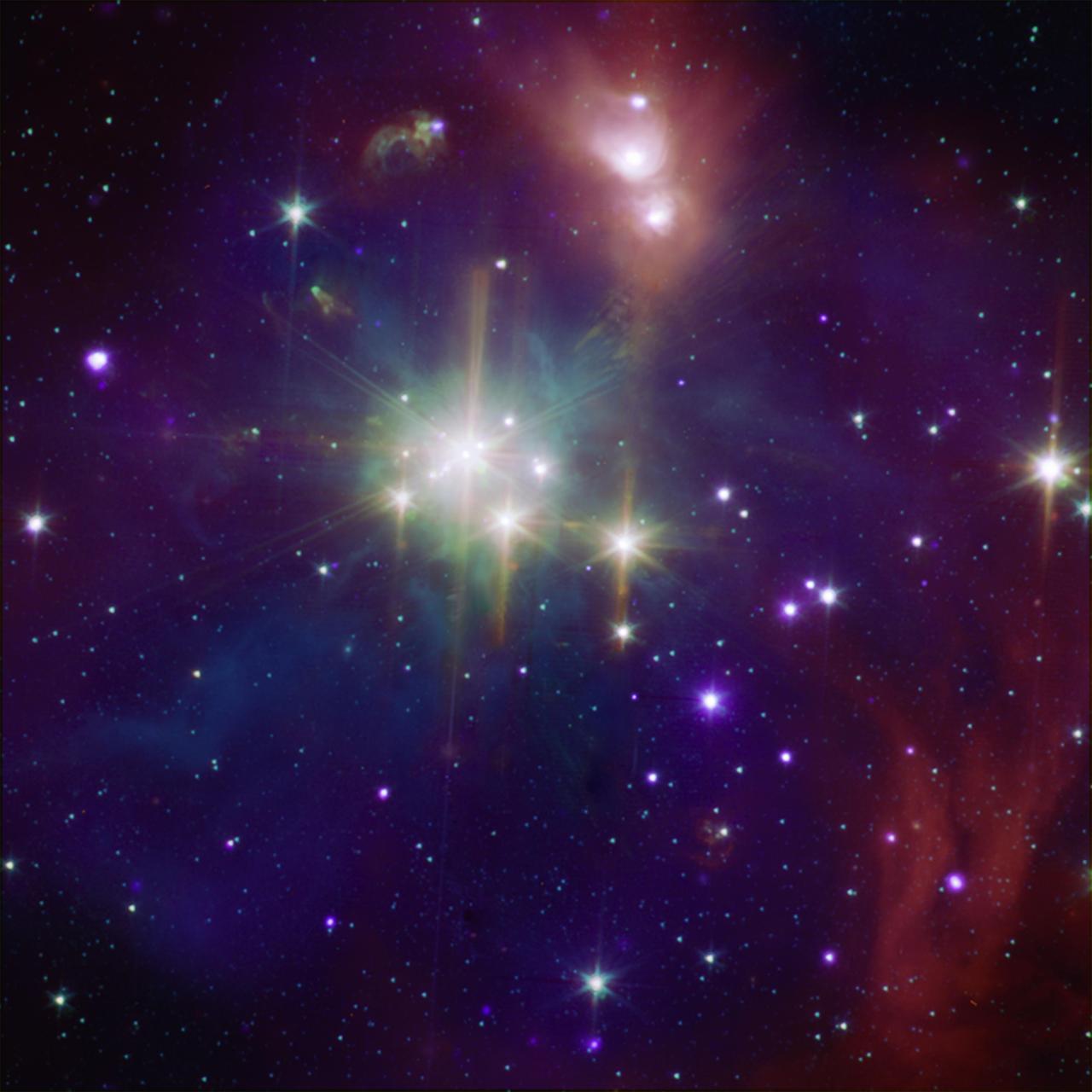

This composite image shows the Coronet in X-rays from Chandra and infrared from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope orange, green, and cyan. The Spitzer data show young stars plus diffuse emission from dust.
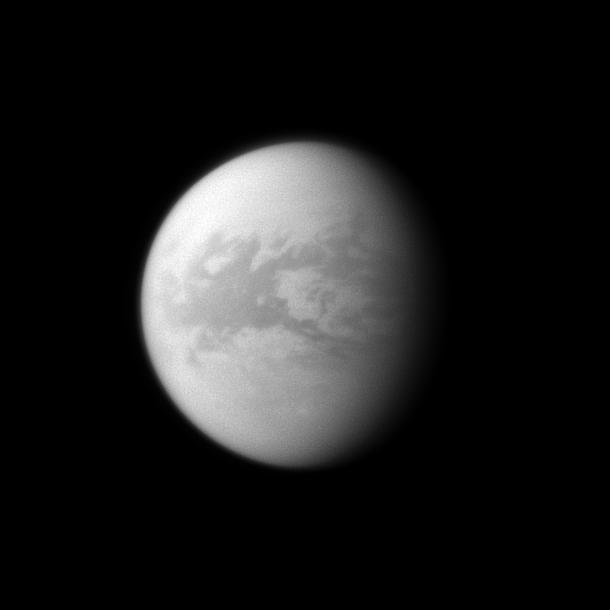
NASA Cassini spacecraft looks toward the dark region of Belet on Saturn largest moon, Titan. This large region on the moon has a low albedo, meaning it diffusely reflects little light.

This graphic illustrates how the Cosmic Infrared Background Experiment, or CIBER, team measures a diffuse glow of infrared light filling the spaces between galaxies. The glow does not come from any known stars and galaxies.

This image from NASA Herschel, in the constellation of Vulpecula, shows an entire assembly line of newborn stars. The diffuse glow reveals the widespread cold reservoir of raw material that our Milky Way galaxy has in stock for building stars.
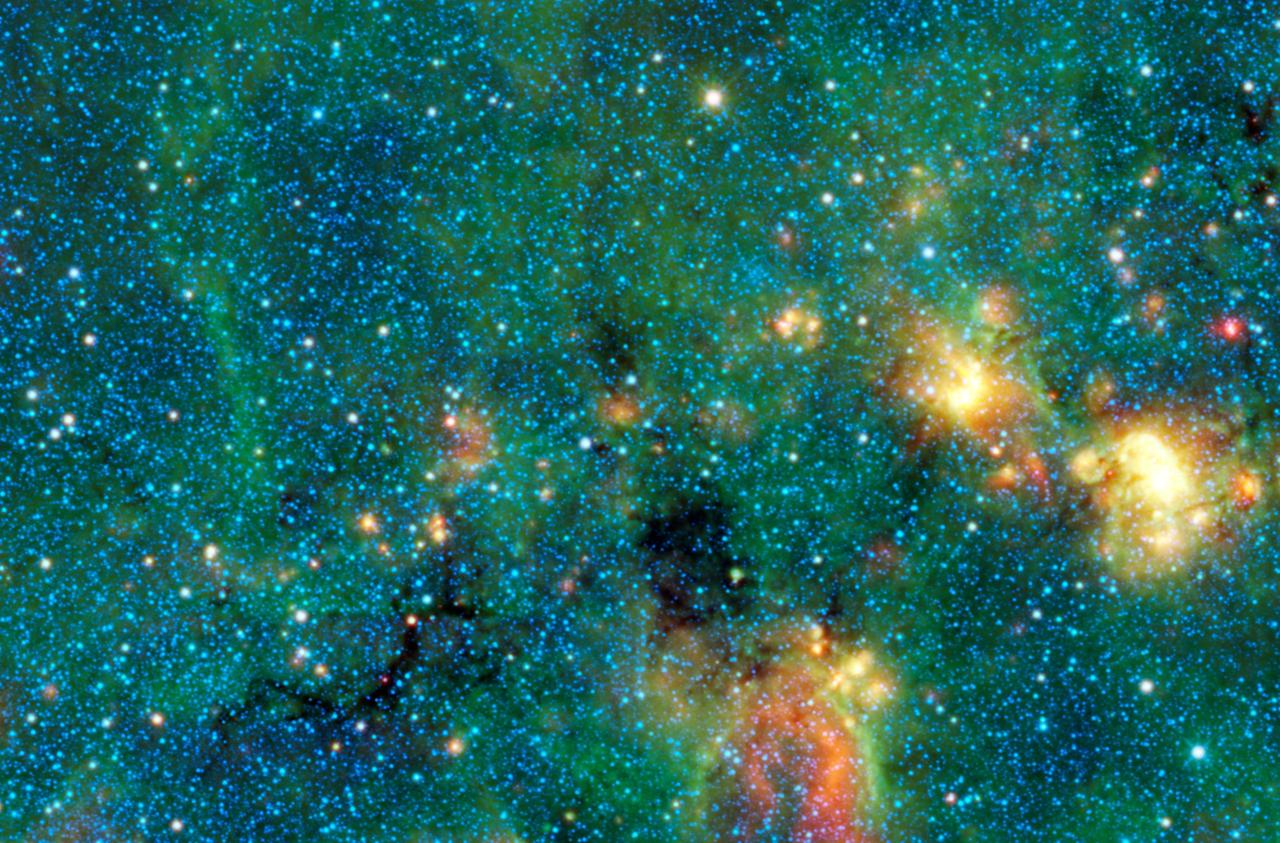

This infrared image from NASA Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer shows exceptionally cold, dense cloud cores seen in silhouette against the bright diffuse infrared glow of the plane of the Milky Way galaxy.
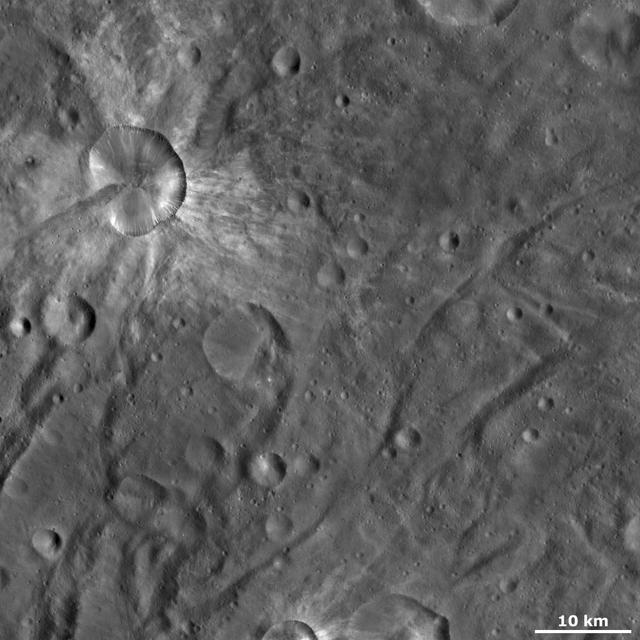

This image from NASA Dawn spacecraft of asteroid Vesta shows Canuleia crater, a large, irregularly shaped crater. Other interesting features of Canuleia include the diffuse bright material that is both inside and outside of its rim.
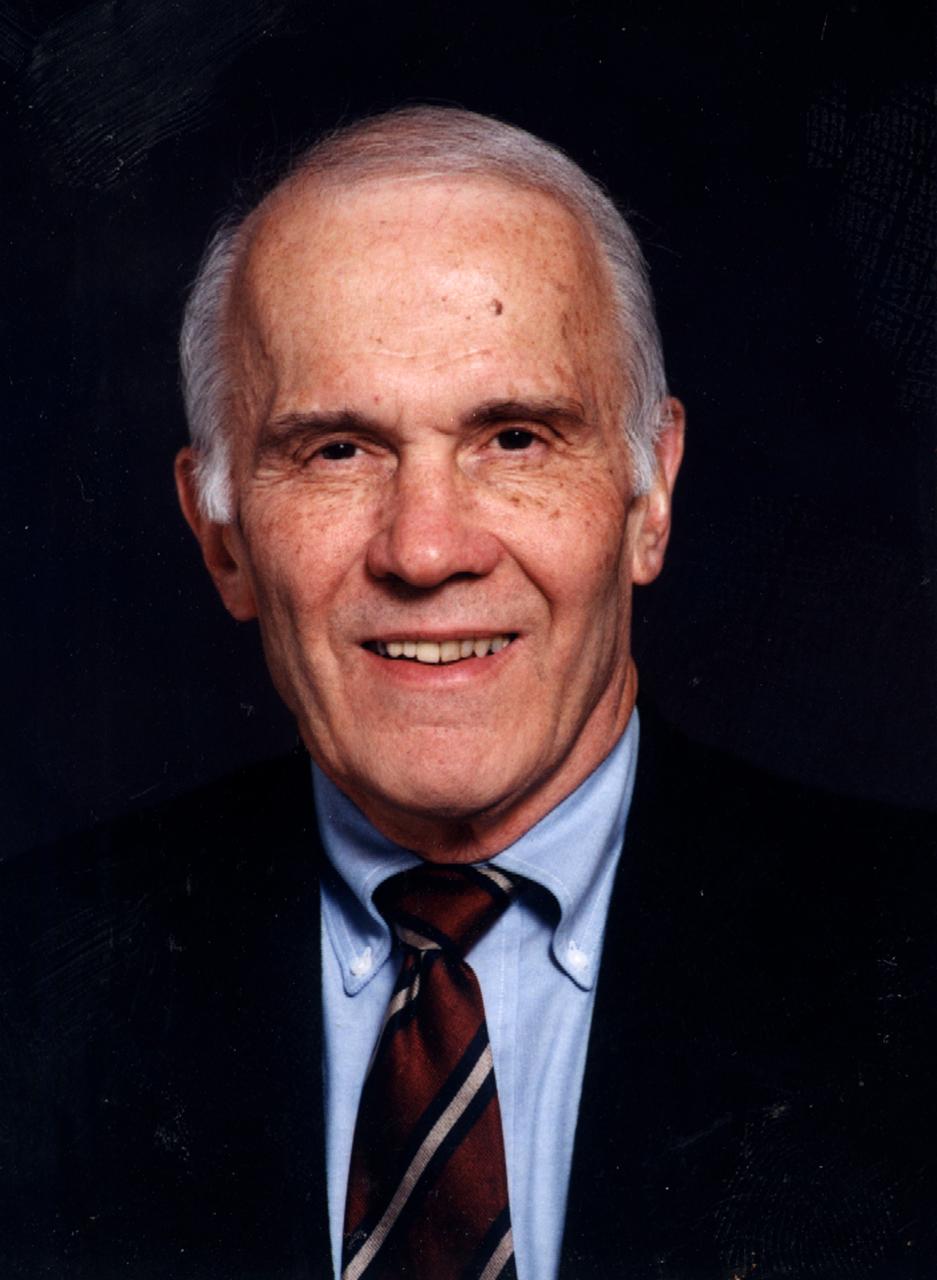

Gerard M. Faeth, University of Michigan, principal investigator in combustion science experiments, including Flow/Soot-Formation in Nonbuoyant Laminar Diffusion Flames, investigation of Laminar Jet Diffusion Flames in Microgravity: A Paradigm for Soot Processes in Turbulent Flames, and Soot Processes in Freely-Propagating Laminar Premixed Flames.

CLOSE UP SHOTS OF HARDWARE OF TRANSITION GAS DIFFUSION FLAME

Marshall researcher studies hydrogen diffusion and corrosion effects on metals.

N-227 Unitary 11ft w.t. safety screen in diffuser
Final (VDA) Vapor Diffusion Apparatus Tray adjustments before loading into shuttle.
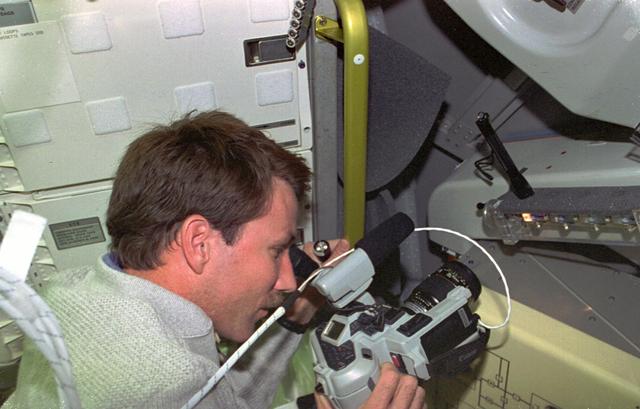
STS073-131-014 (20 October-5 November 1995) --- Astronaut Kent V. Rominger, STS-73 pilot, uses a camcorder to record progress in the Hand-Held Diffusion Test Cell (HHDTC) experiment. This test dealt with crystal growth by liquid-to-liquid diffusion. Four HHDTC units containing four test cells each produced protein crystals by diffusing one liquid to another. Rominger joined four other NASA astronauts and two guest researchers for 16 days of in-space United States Microgravity Laboratory 2 (USML-2) research aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia.
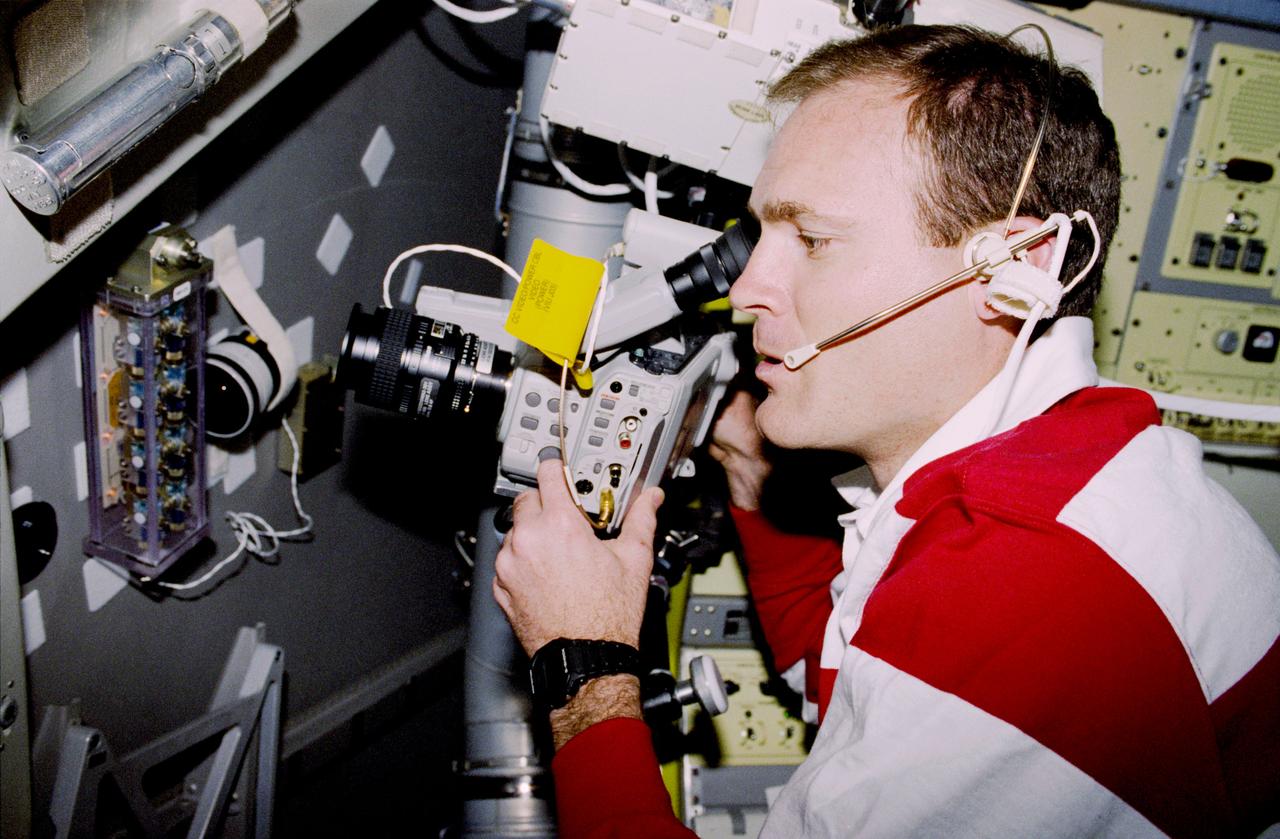

STS083-313-012 (4-8 April 1997) --- Astronaut James D. Halsell, Jr., mission commander, uses a Hi-8mm camcorder to videotape the Hand Held Diffusion Test Cells (HHDTC), in the Spacelab Module aboard the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Columbia. Each test cell has three chambers containing a protein solution, a buffer solution and a precipitant solution chamber. Using the liquid-liquid diffusion method, the different fluids are brought into contact but not mixed. Over a period of time, the fluids will diffuse into each other through the random motion of molecules. The gradual increase in concentration of the precipitant within the protein solution causes the proteins to crystallize.
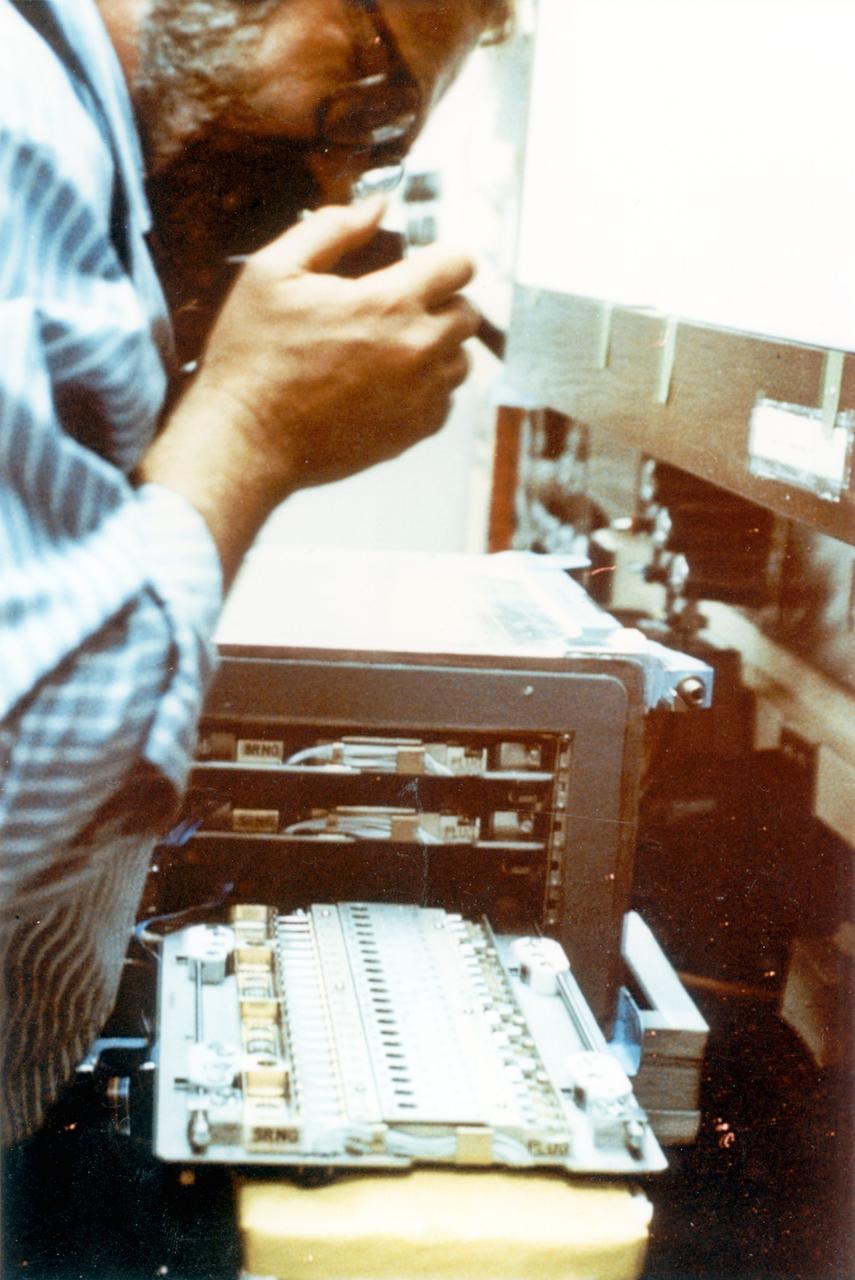

Scientist photographs STS- 26 Post-flight (VDA) Vapor Diffusion Apparatus Tray with (PCG) Protein Crystal Growth Samples.
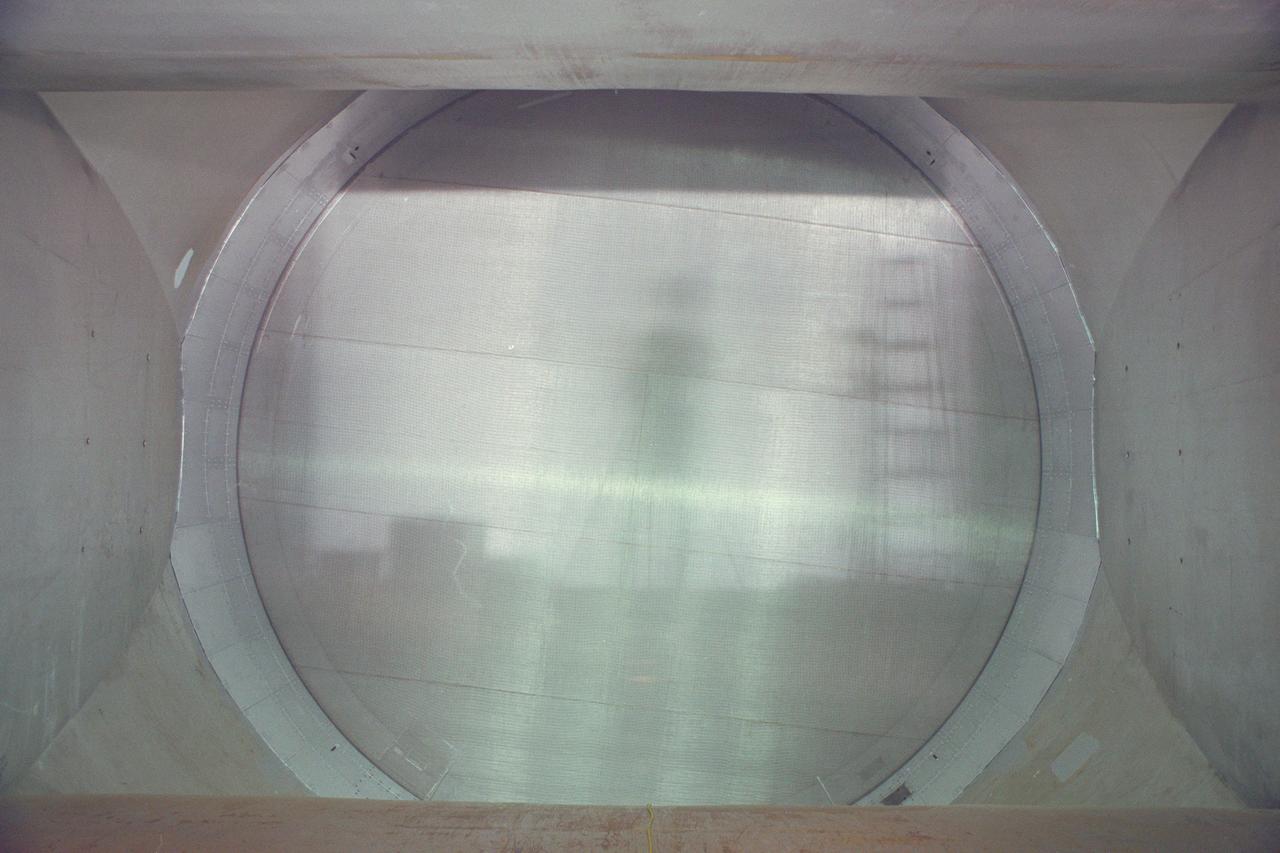

N-227 Unitary Plan Wind Tunnel Modification Project - diffuser & contraction vanes (image show reflection of photographer on vane)
N-227 Unitary Plan Wind Tunnel Modification Project - diffuser & contraction vanes
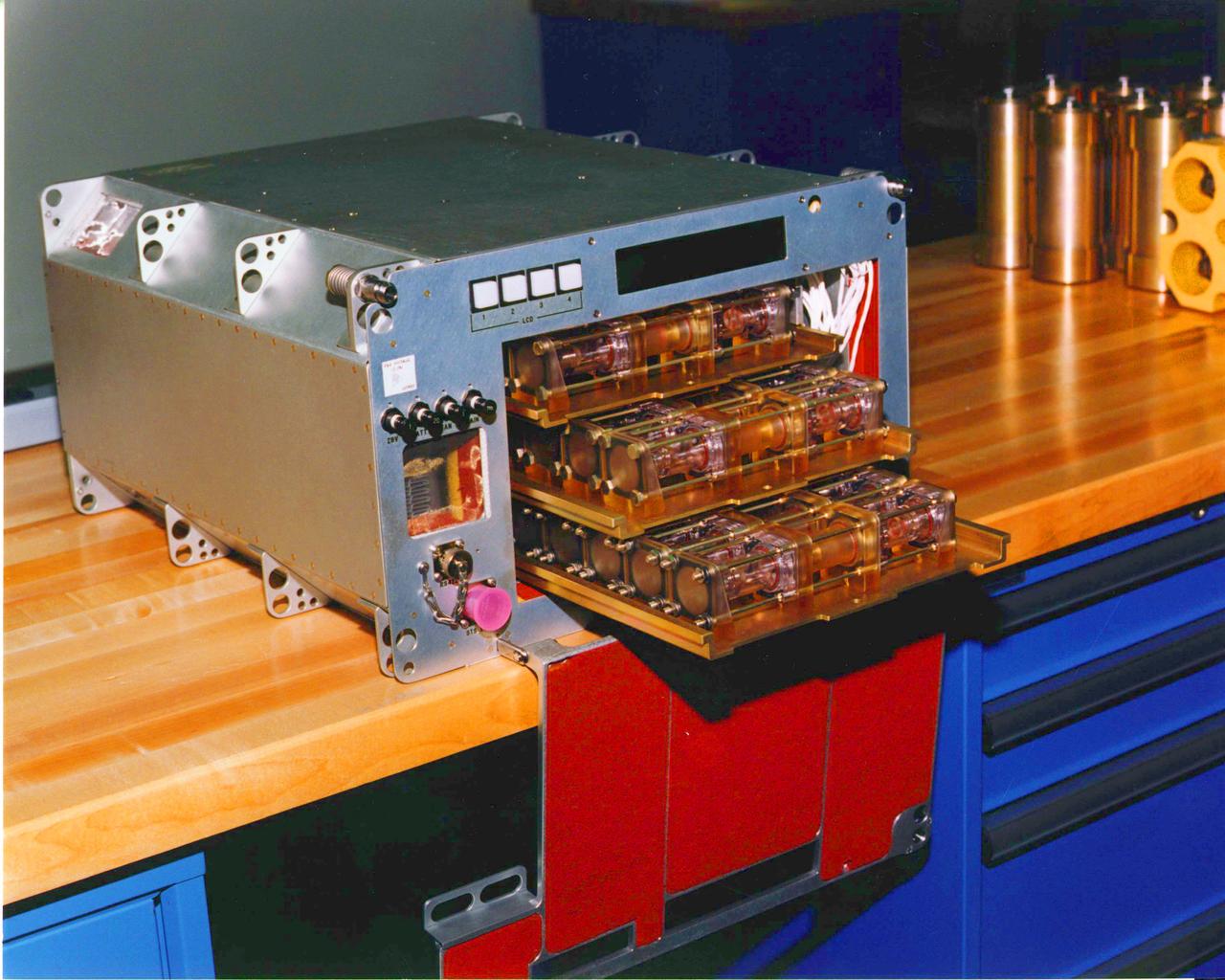

(DCAM) Diffusion Controlled Crystallization Apparatus for Microgravity Trays mounted in (STES) Single Locker Thermal Enclosure System.
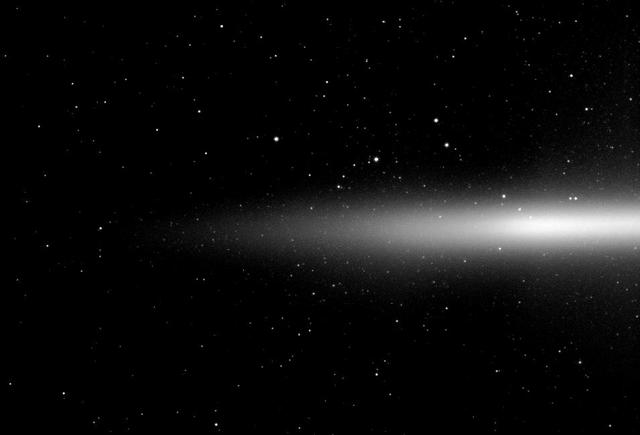

NASA Cassini spacecraft takes a look at Saturn diffuse E ring which is formed from icy material spewing out of the south pole of the moon Enceladus. The E ring is seen nearly edge-on from slightly above the northern side of Saturn ring plane.
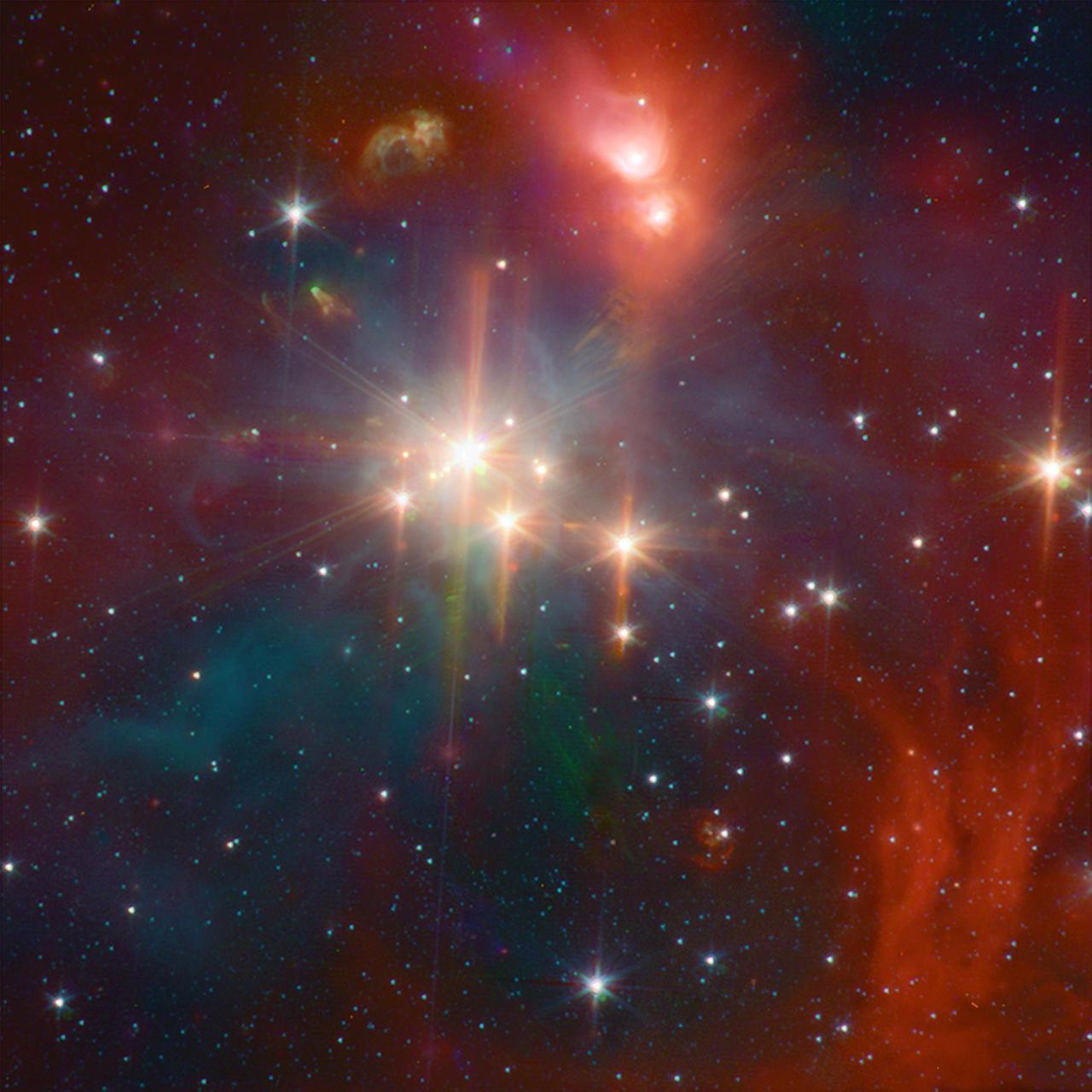

This image from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope shows young stars plus diffuse emission from dust. The Corona Australis region containing, at its heart, the Coronet cluster is one of the nearest and most active regions of ongoing star formation.
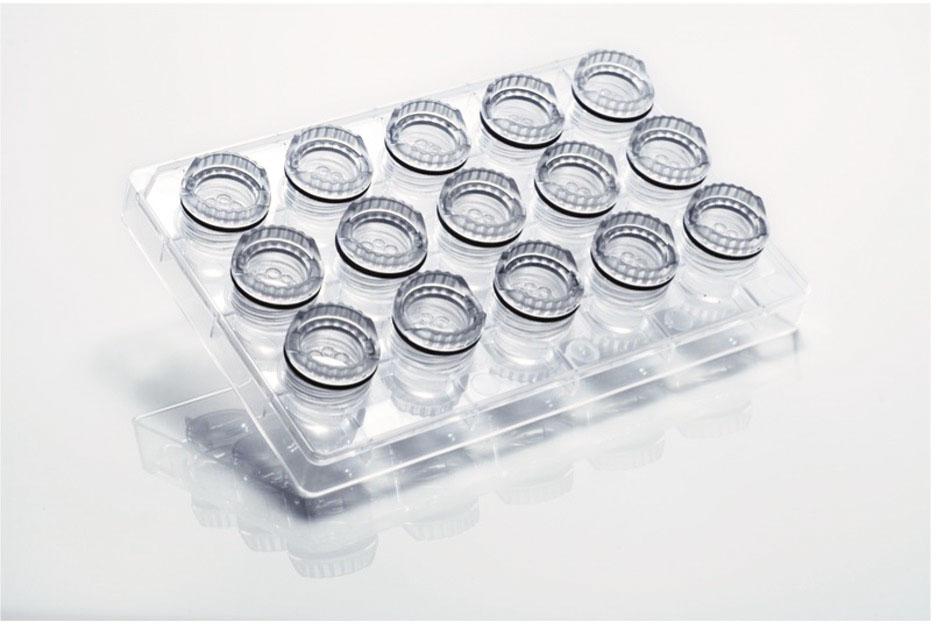

jsc2021e010281 (3/10/2021) --- A preflight view of the EasyXtal hanging-drop vapor diffusion crystal plates. Photo courtesy of Timothy Mueser.
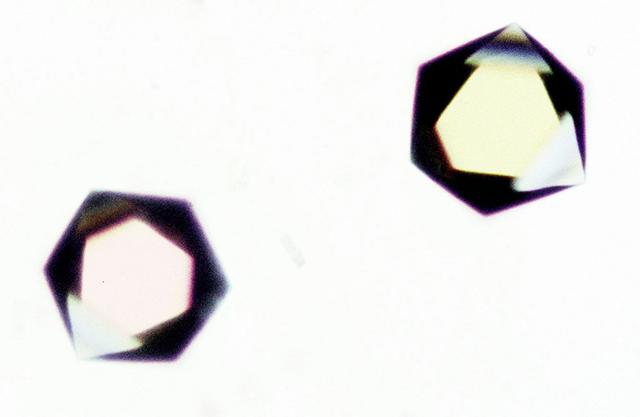
Crystals of Proteinase K complex grown in the VDA-2 (Vapor Diffusion Apparatus) hardware aboard MSL-1. Principal Investigator: Larry DeLucas
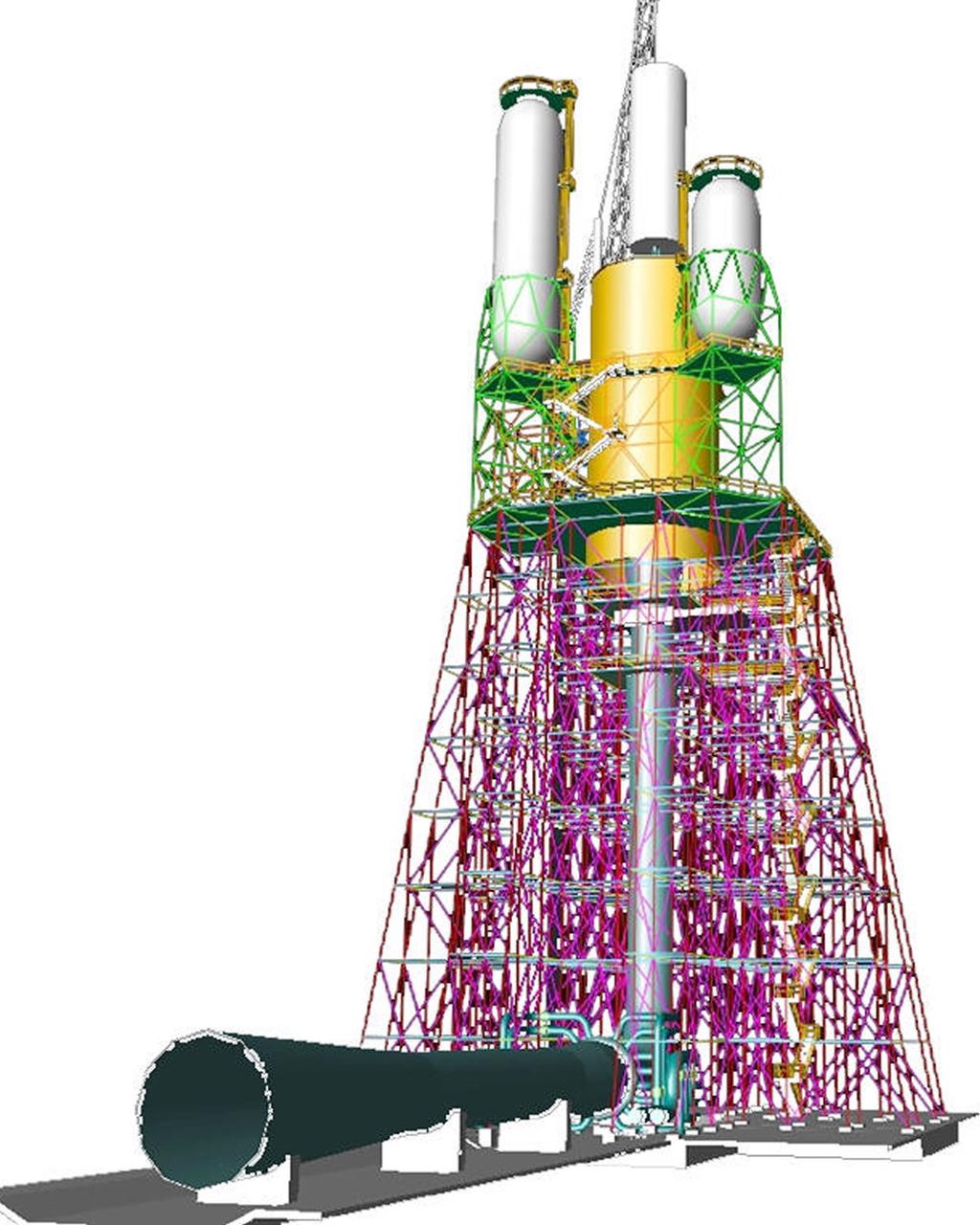

This engineer's concept drawing of the A-3 Test Stand shows the 300-foot-tall structure's open steel frame and large exhaust diffuser.
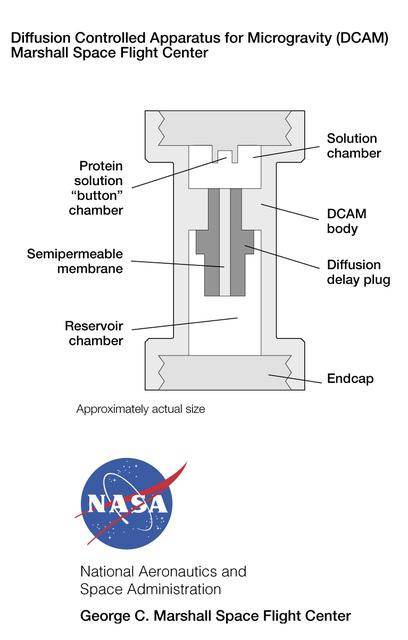
The Diffusion-Controlled Apparatus for Microgravity (DCAM) was developed at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center. A semi-permeable plug or fuse at the center controls the rate at which a precipitant diffuses from the reservoir chamber into the solution chamber , thus prompting protein molecules in the solution to form crystals. The principal investigator is Dr. Dan Carter of New Century Pharmaceuticals in Huntsville, AL.
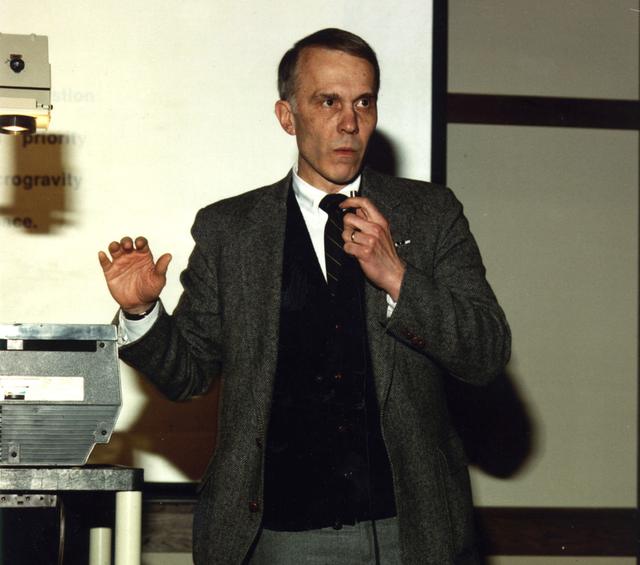

Professor Gerard M. Faeth, Department of Aerospace Engineering, University of Michigan, Arn Arbor, MI, is a principal investigator in NASA combustion science directed by Glenn Research Center. His projects include: Soot Processes in Freely-Propagating Laminar Premixed Flames; Investigation of Laminar Jet Diffusion Flames in Microgravity: A Paradigm for Soot Processes in Turbulent Flames (scheduled to fly on the STS-107 mission); and Flow/Soot- Formation in Nonbuoyant Laminar Diffusion Flames.
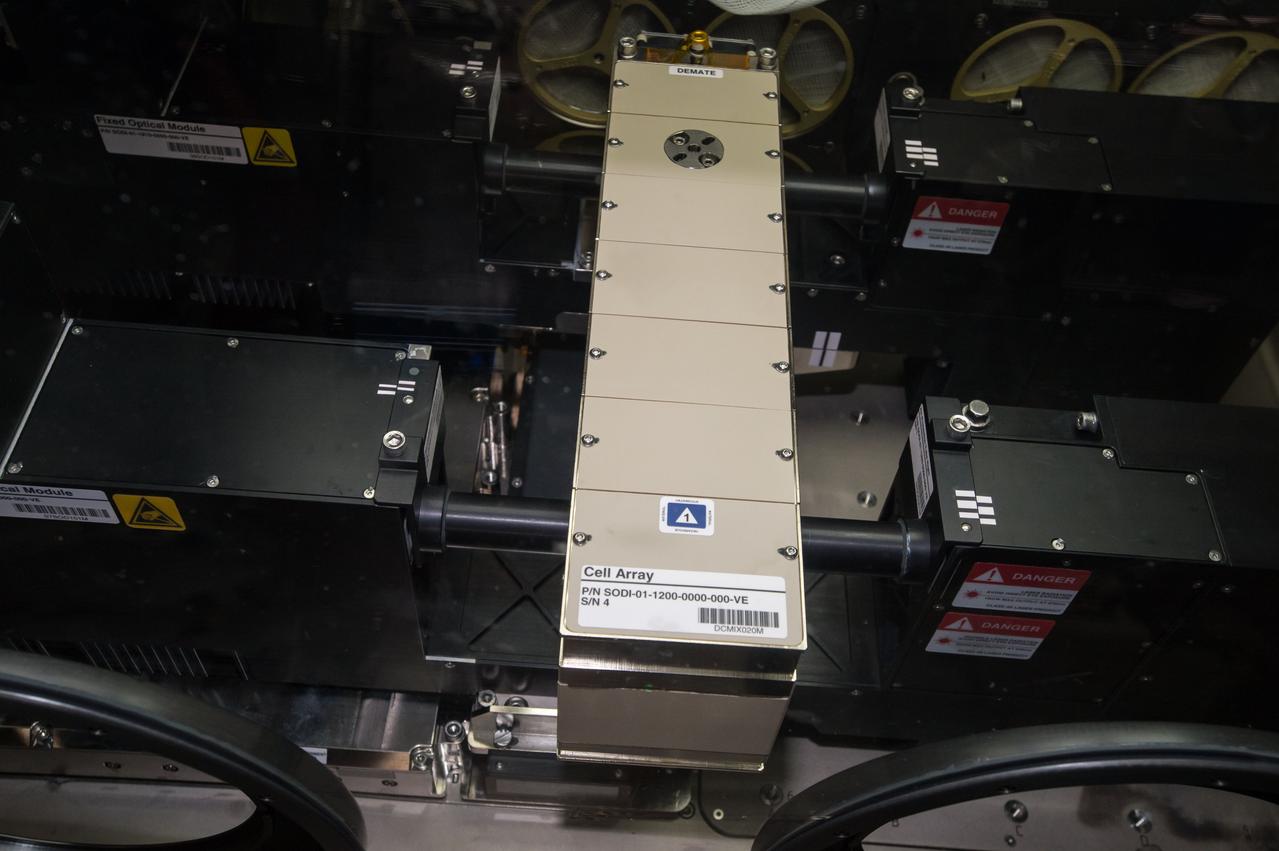

iss049e002308 (9/13/2016) --- A view taken during Selectable Optics Diagnostic Instrument (SODI) DSC Hardware Setup the MSG Work Volume. The Selectable Optical Diagnostics Instrument - Diffusion and Soret Coefficient (SODI-DSC) experiment will study diffusion in six different liquids over time in the absence of convection induced by the gravity field. The SODI-DSC investigation will provide information to scientist which can be used to more efficiently extract oil resources.
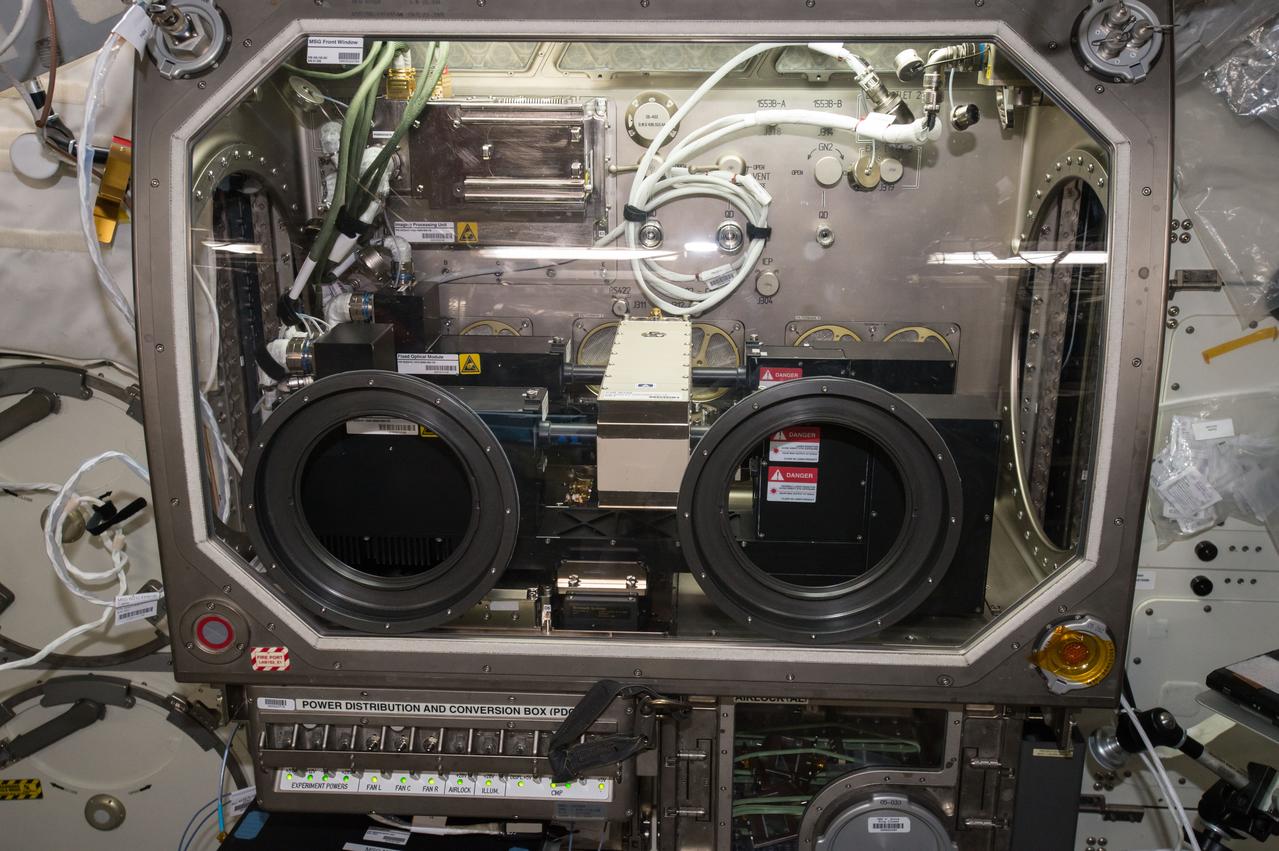
iss049e002305 (9/13/2016) --- A view taken during Selectable Optics Diagnostic Instrument (SODI) DSC Hardware Setup the MSG Work Volume. The Selectable Optical Diagnostics Instrument - Diffusion and Soret Coefficient (SODI-DSC) experiment will study diffusion in six different liquids over time in the absence of convection induced by the gravity field. The SODI-DSC investigation will provide information to scientist which can be used to more efficiently extract oil resources.
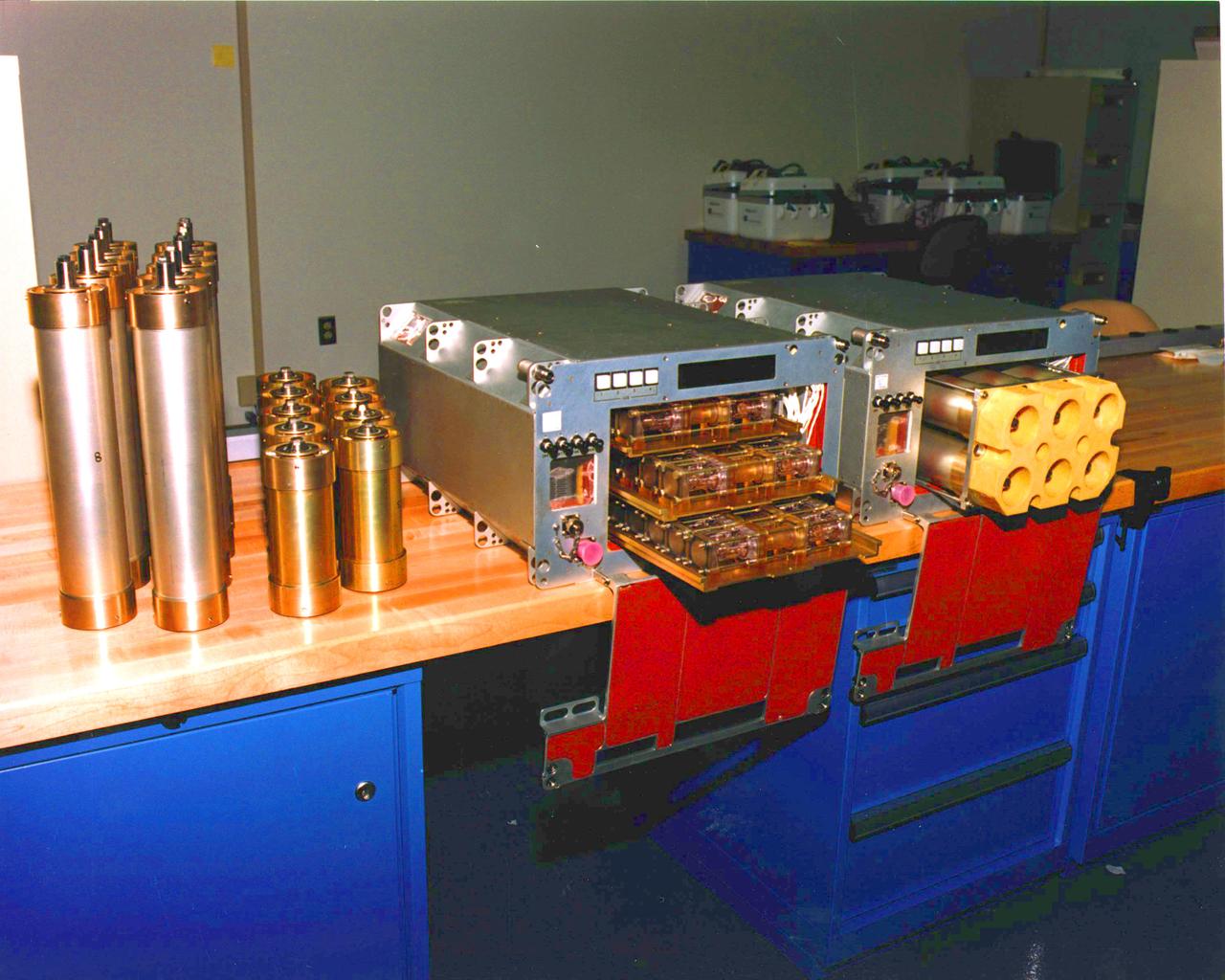

Two versions of (PCAM) Protein Crystallization Apparatus for Microgravity, (DCAM) Diffusion Controled Crystallization Apparatus is in the (STES) Single Locker Thermal Enclosure System. Principal Investigator was Dan Carter.
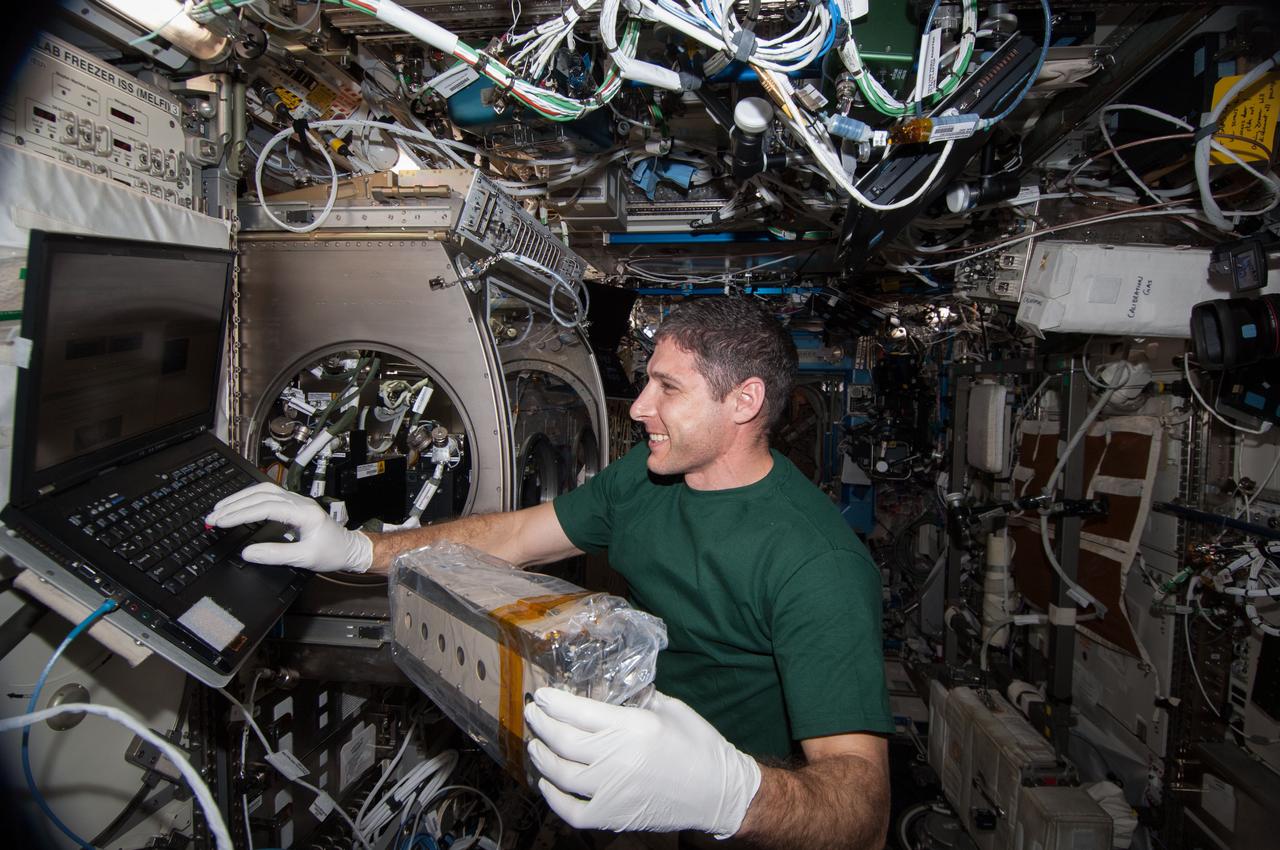

ISS038-E-009255 (26 Nov. 2013) --- In the International Space Station?s Destiny laboratory, NASA astronaut Michael Hopkins, Expedition 38 flight engineer, prepares to install and activate the Selectable Optics Diagnostic Instrument (SODI) cell array two in the Microgravity Science Glovebox (MSG) for the Selectable Optics Diagnostic Instrument-Diffusion Coefficient in Mixtures 2 (SODI-DCMIX 2) experiment. SODI-DCMIX 2 is supporting research to determine diffusion coefficients in different petroleum field samples and refine petroleum reservoir models to help lead to more efficient extraction of oil resources.
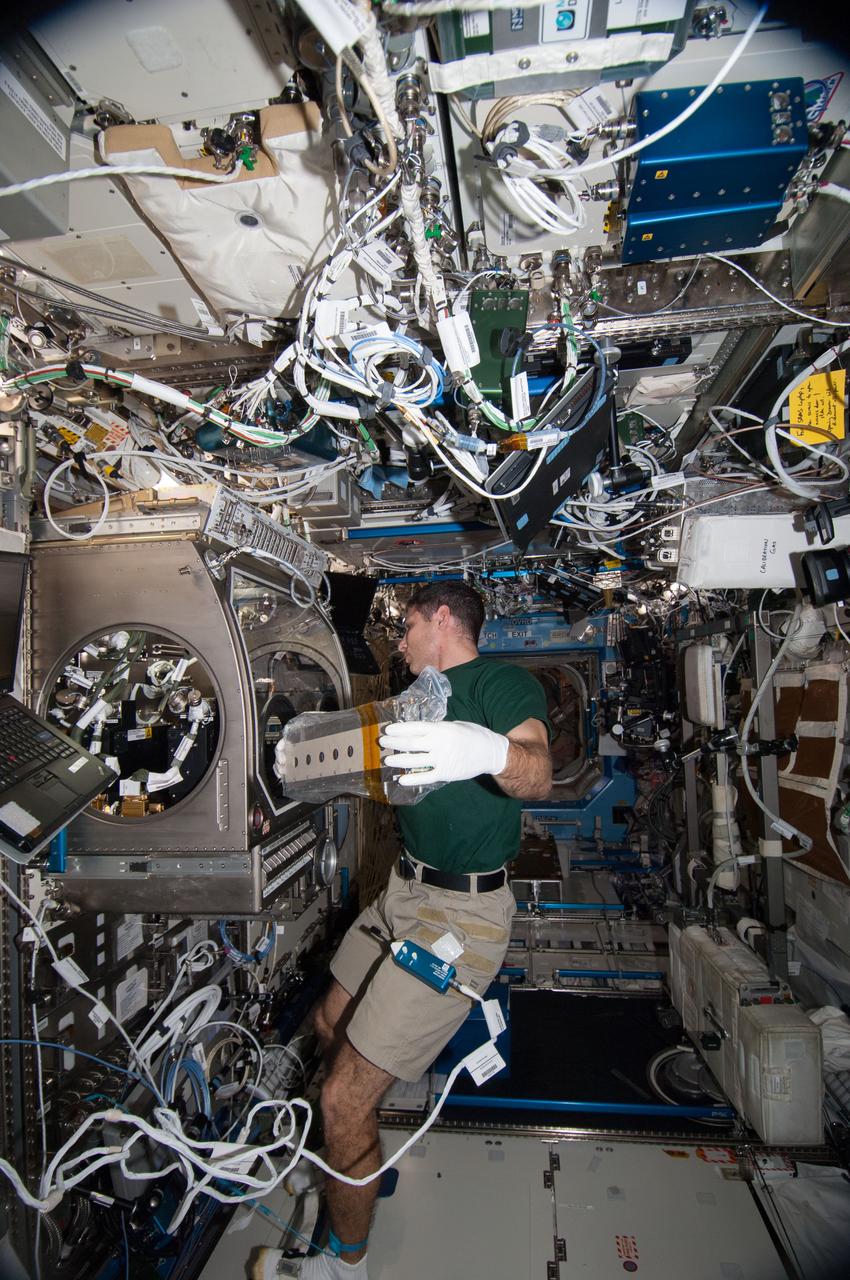

ISS038-E-009253 (26 Nov. 2013) --- In the International Space Station’s Destiny laboratory, NASA astronaut Michael Hopkins, Expedition 38 flight engineer, prepares to install and activate the Selectable Optics Diagnostic Instrument (SODI) cell array two in the Microgravity Science Glovebox (MSG) for the Selectable Optics Diagnostic Instrument-Diffusion Coefficient in Mixtures 2 (SODI-DCMIX 2) experiment. SODI-DCMIX 2 is supporting research to determine diffusion coefficients in different petroleum field samples and refine petroleum reservoir models to help lead to more efficient extraction of oil resources.
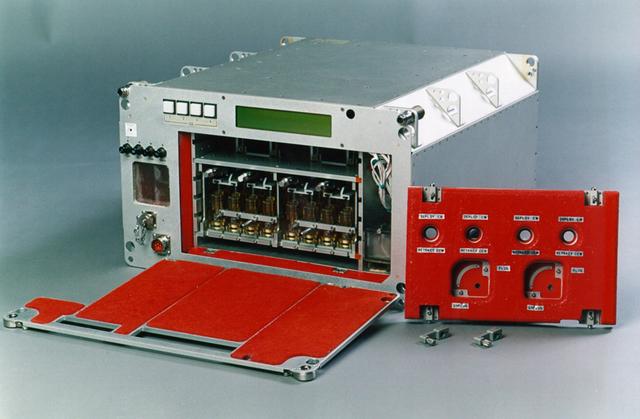
The Commercial Vapor Diffusion Apparatus will be used to perform 128 individual crystal growth investigations for commercial and science research. These experiments will grow crystals of several different proteins, including HIV-1 Protease Inhibitor, Glycogen Phosphorylase A, and NAD Synthetase. The Commercial Vapor Diffusion Apparatus supports multiple commercial investigations within a controlled environment. The goal of the Commercial Protein Crystal Growth payload on STS-95 is to grow large, high-quality crystals of several different proteins of interest to industry, and to continue to refine the technology and procedures used in microgravity for this important commercial research.

Smokeless flame juts from the diffuser of a unique vacuum chamber in which the upper stage rocket engine, the hydrogen fueled J-2, was tested at a simulated space altitude in excess of 60,000 feet. The smoke you see is actually steam. In operation, vacuum is established by injecting steam into the chamber and is maintained by the thrust of the engine firing through the diffuser. The engine was tested in this environment for start, stop, coast, restart, and full-duration operations. The chamber was located at Rocketdyne's Propulsion Field Laboratory, in the Santa Susana Mountains, near Canoga Park, California. The J-2 engine was developed by Rocketdyne for the Marshall Space Flight Center.

The Andromeda Galaxy, also known as M31 since it is the 31st object on Messier's list of diffuse sky objects, is the nearest large galaxy to our own Milky Way galaxy. Our galaxy is thought to look much like Andromeda, but it is about four times as massive as the Milky Way. Together these two galaxies dominate the Local Group of galaxies. The diffused light from Andromeda is caused by hundreds of billions of stars that compose it. The several distinct stars that surround Andromeda's image are actually stars in our galaxy that are well in front of the background object. Andromeda is so distant that it takes approximately two millions years for light to reach us from there.
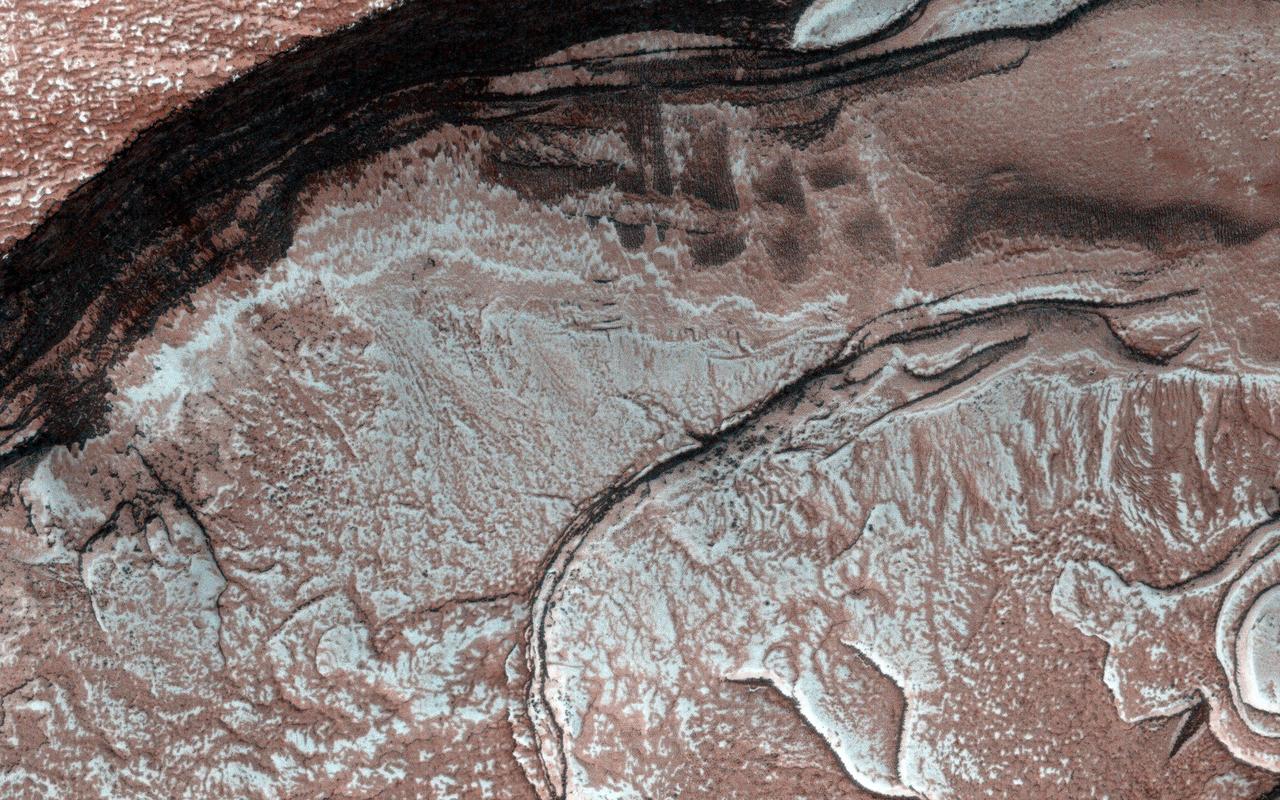
Sunlight was just starting to reach the high Northern latitudes in late winter when NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter HiRISE camera captured this image of part of the steep scarps around portions of the North Polar layered deposits.
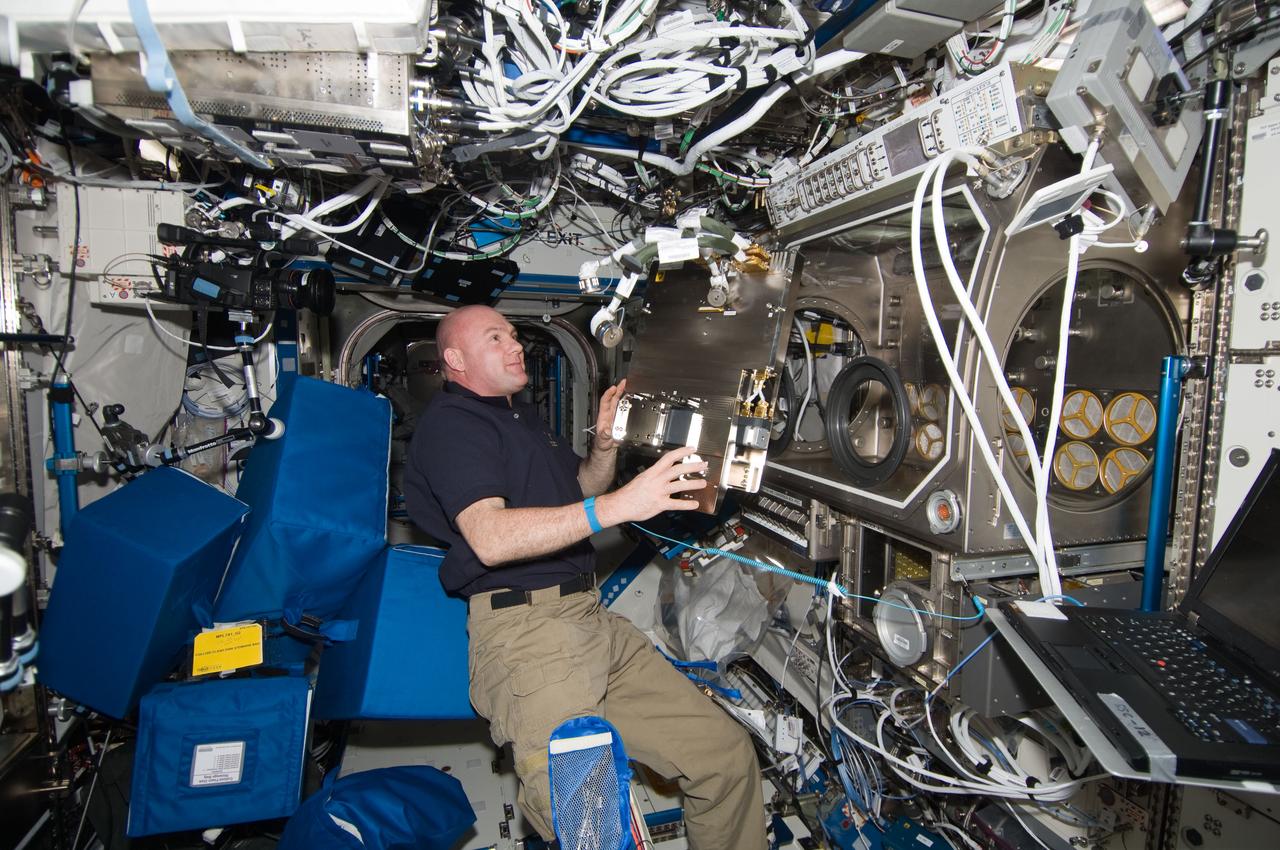

ISS030-E-155917 (16 Jan. 2012) --- European Space Agency astronaut Andre Kuipers, Expedition 30 flight engineer, prepares to place Diffusion Soret Coefficient (DSC) hardware in stowage containers in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station.
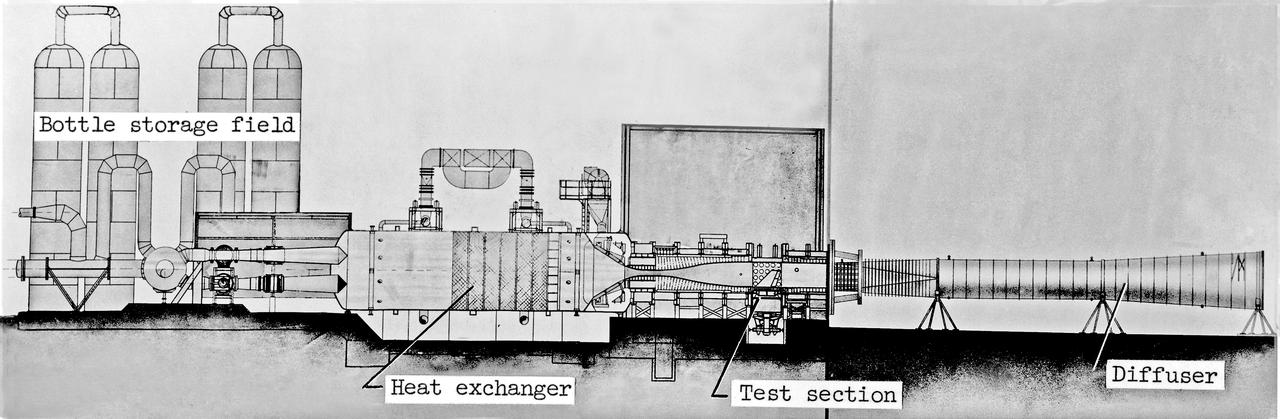
Scale Model of 9x6 Thermal Structures Tunnel: Image L-7256.01 is a Drawing Figure 12 in NASA Document L-1265. The Major components of the 9-by6-Foot Thermal Structures Tunnel. The 97 foot-long diffuser was added in 1960 to reduce noise.
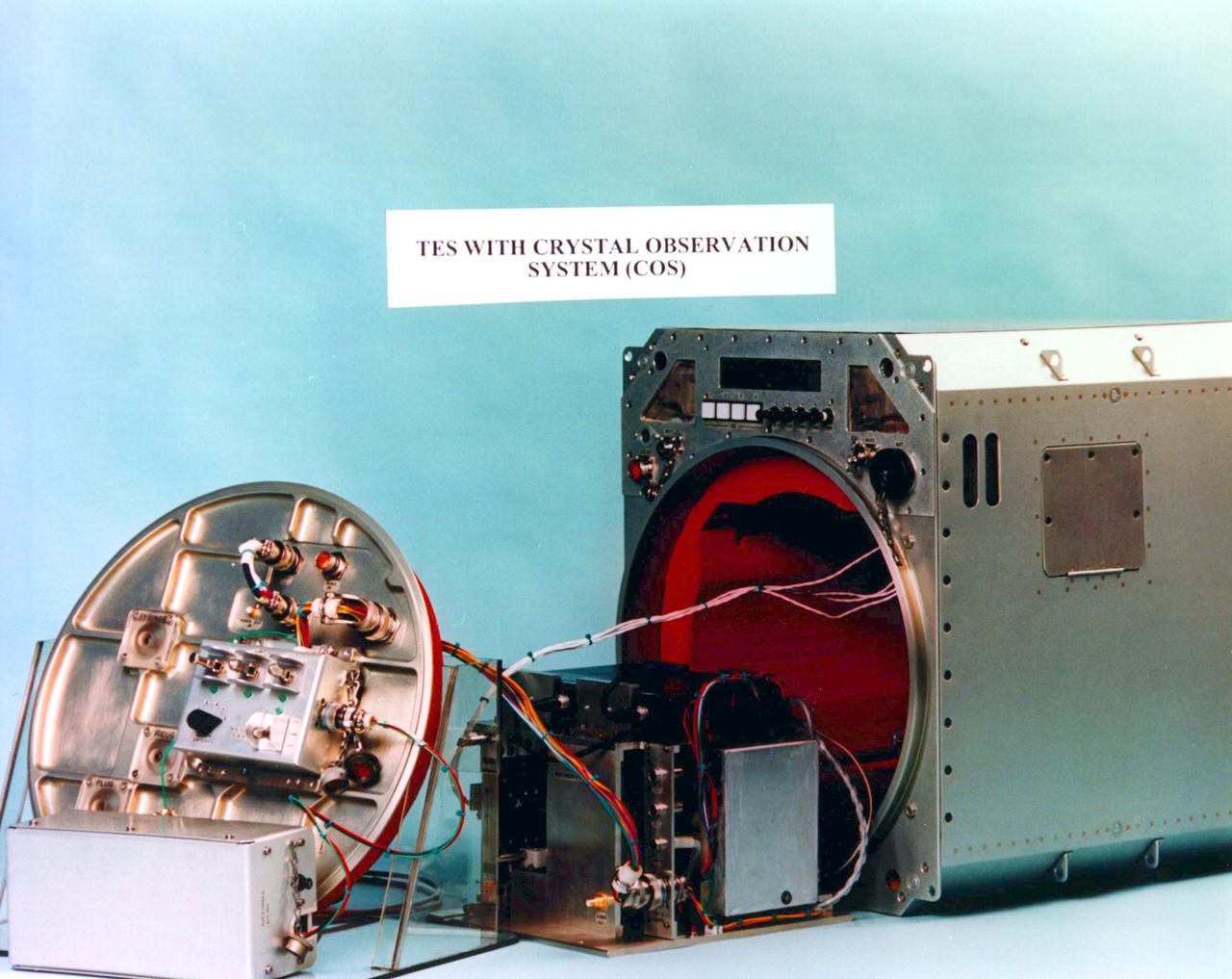
The COS consists of a specially designed (VDA) Vapor Diffusion Apparatus tray with 6 chambers, a video camera for each chamber, a lighting system, and associated hardware. By observing the crystal growth in each chamber, researchers can identify which conditions and concentrations of proteins and precipitants are best for promoting the crystal growth to a particular protein.
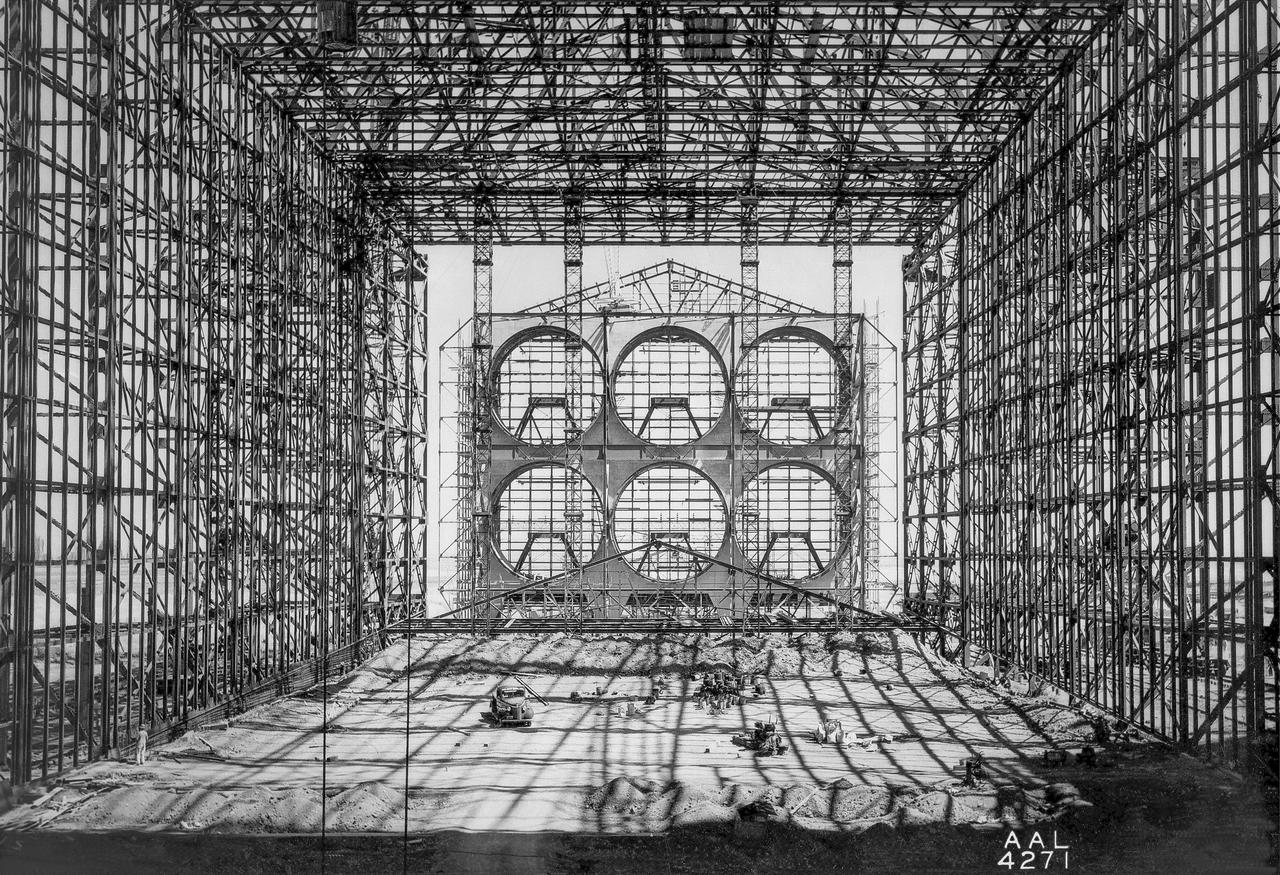
Looking South from inside the diffuser of the 40x80 foot wind tunnel at NACA's Ames Research Center. Construction began in late 1941, the mammoth construction task sorely taxing the resources of the new center. Two and a half years later, in dune 1944, the 40 x 80-foot full-scale tunnel went into operation.
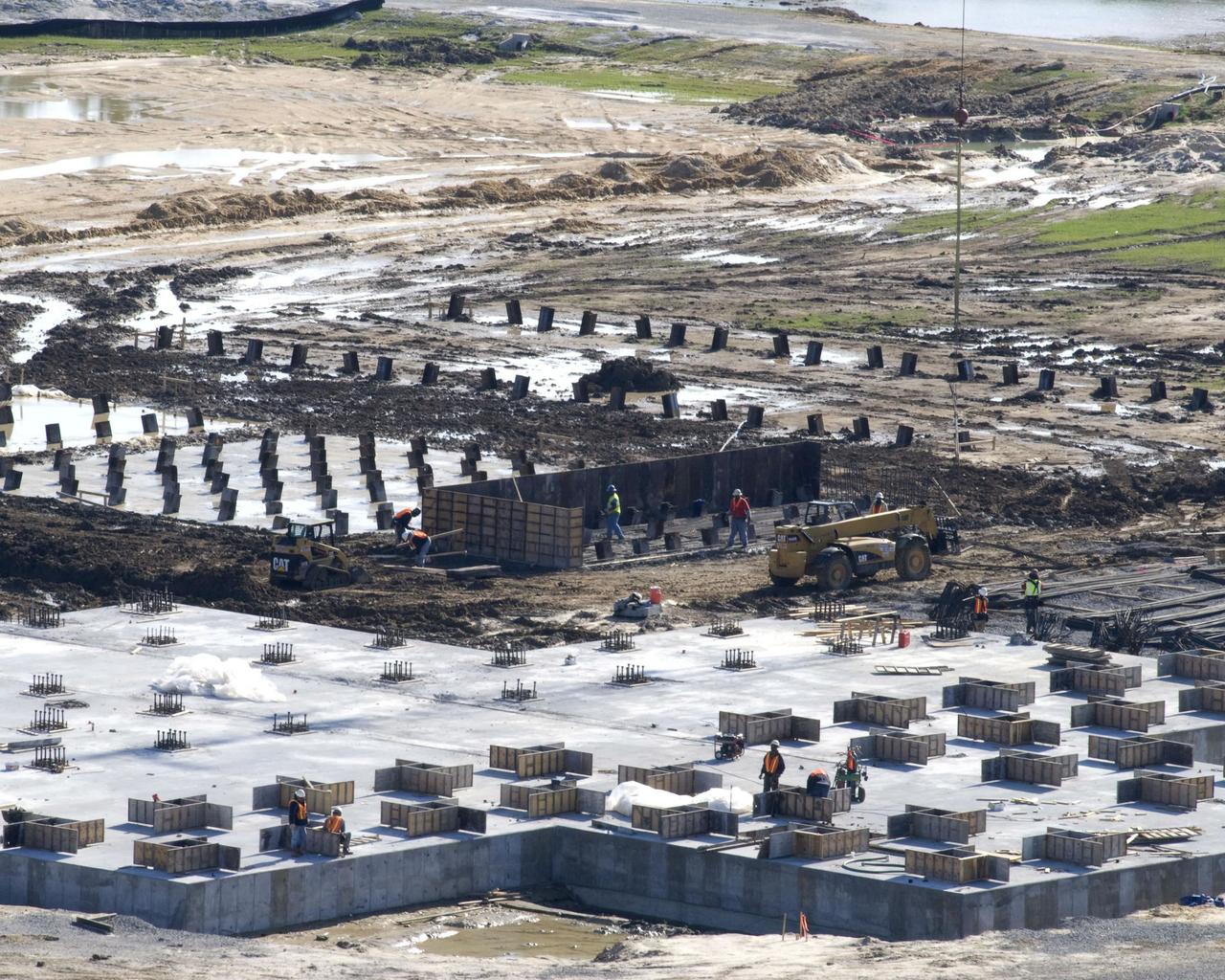

The concrete foundation placed Dec. 18 (foreground) for Stennis Space Center's future A-3 Test Stand has almost completely cured by early January, according to Bo Clarke, NASA's contracting officer technical representative for the foundation contract. By late December, construction on foundations for many of the test stand's support structures - diffuser, liquid oxygen, isopropyl alcohol and water tanks and gaseous nitrogen bottle battery - had begun with the installation of (background) `mud slabs.' The slabs provide a working surface for the reinforcing steel and foundation forms.
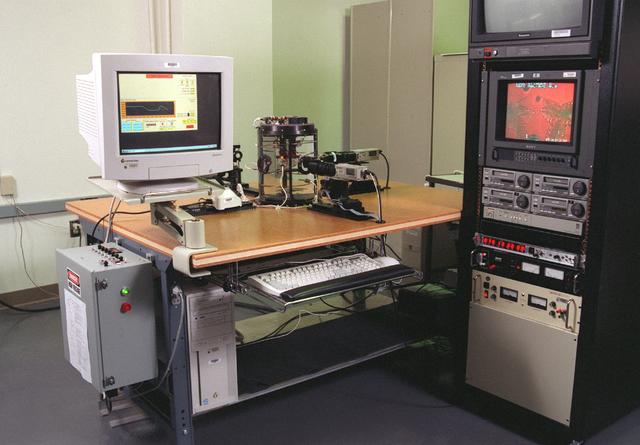

The Equiaxed Dendritic Solidification Experiment (EDSE) is a material sciences investigation under the Formation of Microstructures/pattern formation discipline. The objective is to study the microstructural evolution of and thermal interactions between several equiaxed crystals growing dendritically in a supercooled melt of a pure and transparent substance under diffusion controlled conditions. This image shows the overview for the EDSE in the Microgravity Development Lab (MDL).
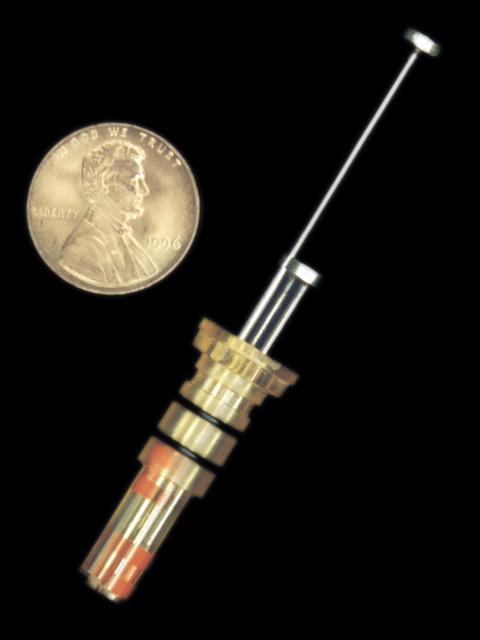
Vapor Diffusion Apparatus (VDA-2) was developed by the University of Alabama in Birmingham for NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center. In the original VDA, a protein solution and a precipitant are extruded by two plungers onto the tip of a small syringe and allowed to evaporate, raising the concentration and prompting protein molecules to crystallize. In the VDA-2 version, a third plunger was added to mix the two solutions before returning the mix to the syringe tip. The principal investigator is Dr. Larry Delucas of the University of Alabama in Birmingham.
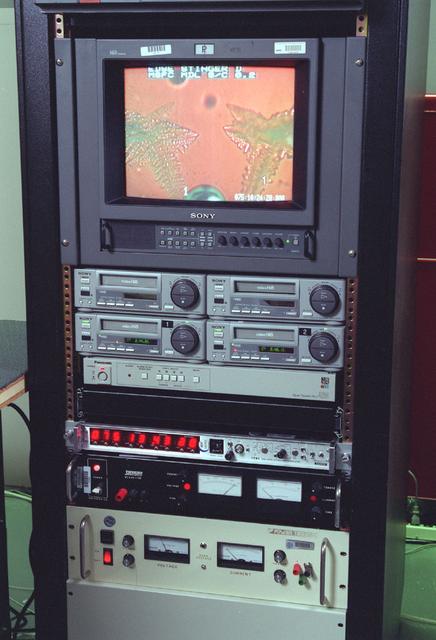

The Equiaxed Dendritic Solidification Experiment (EDSE) is a material sciences investigation under the Formation of Microstructures/pattern formation discipline. The objective is to study the microstructural evolution of and thermal interactions between several equiaxed crystals growing dendritically in a supercooled melt of a pure and transparent substance under diffusion controlled conditions. Video and power rack for the EDSE in the Microgravity Development Lab (MDL).
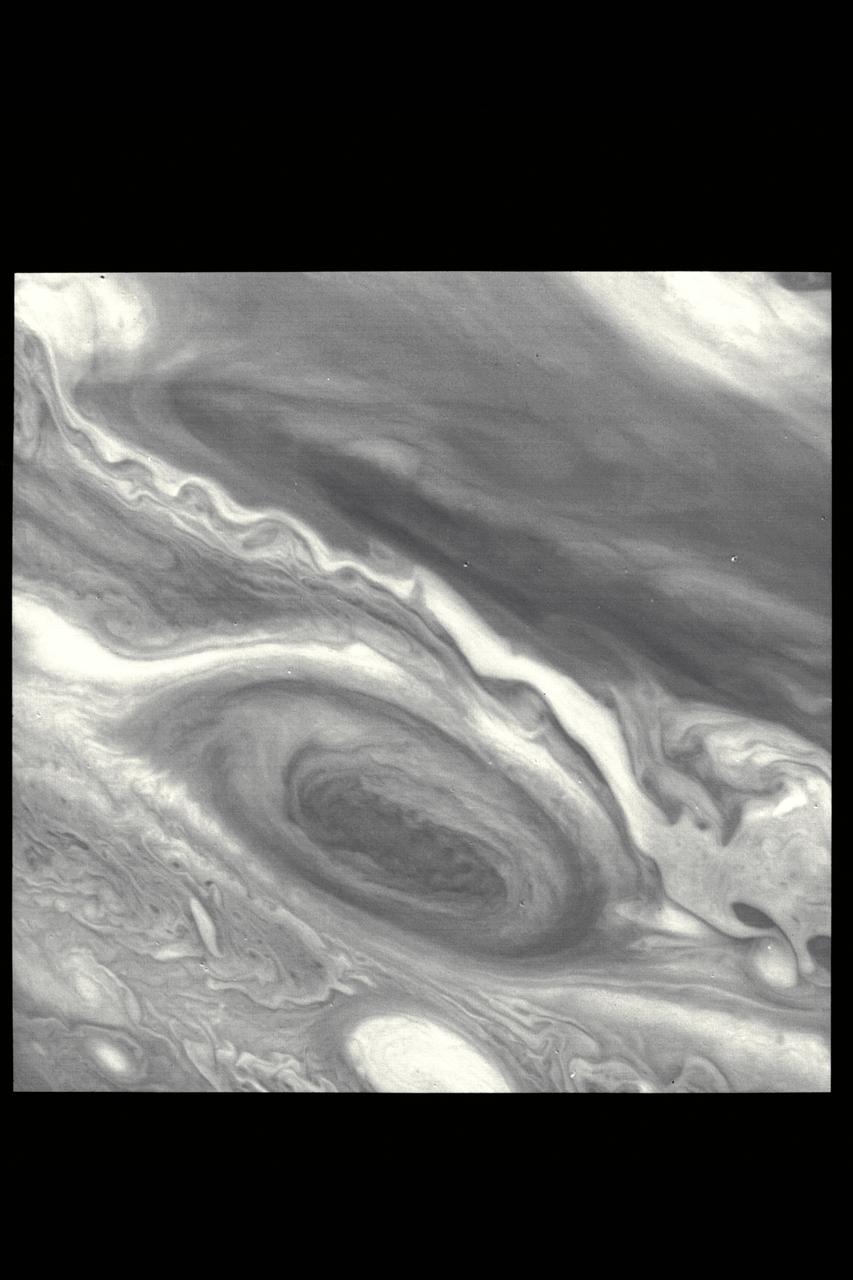
P-21736 BW This Voyager 2 pictures shows the Great Red Spot and the south equatorial belt extending into the equatorial region. At right is an interchange of material between the south equatorial belt and the equatorial zone. The clouds in this zone are more diffuse and do not display the structures seen in other locations. Considerable structure is evident within the Great Red Spot.
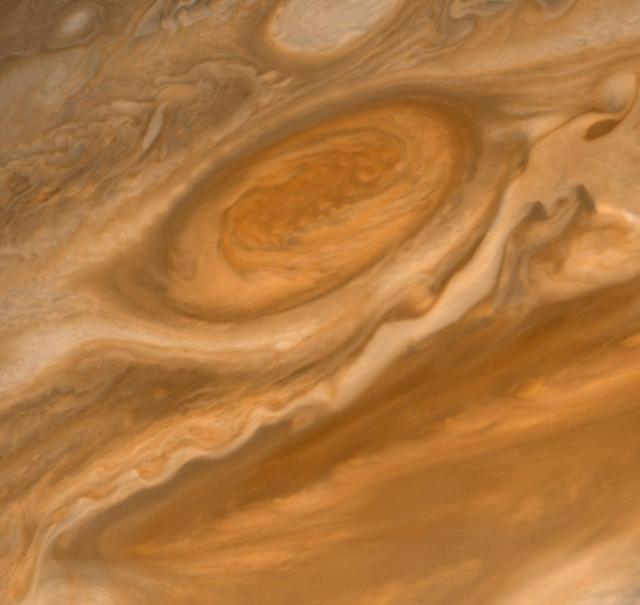

NASA Voyager 2 shows the Great Red Spot and the south equatorial belt extending into the equatorial region. At right is an interchange of material between the south equatorial belt and the equatorial zone. The clouds in the equatorial zone are more diffuse and do not display the structures seen in other locations. Considerable structure is evident within the Great Red Spot. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00456
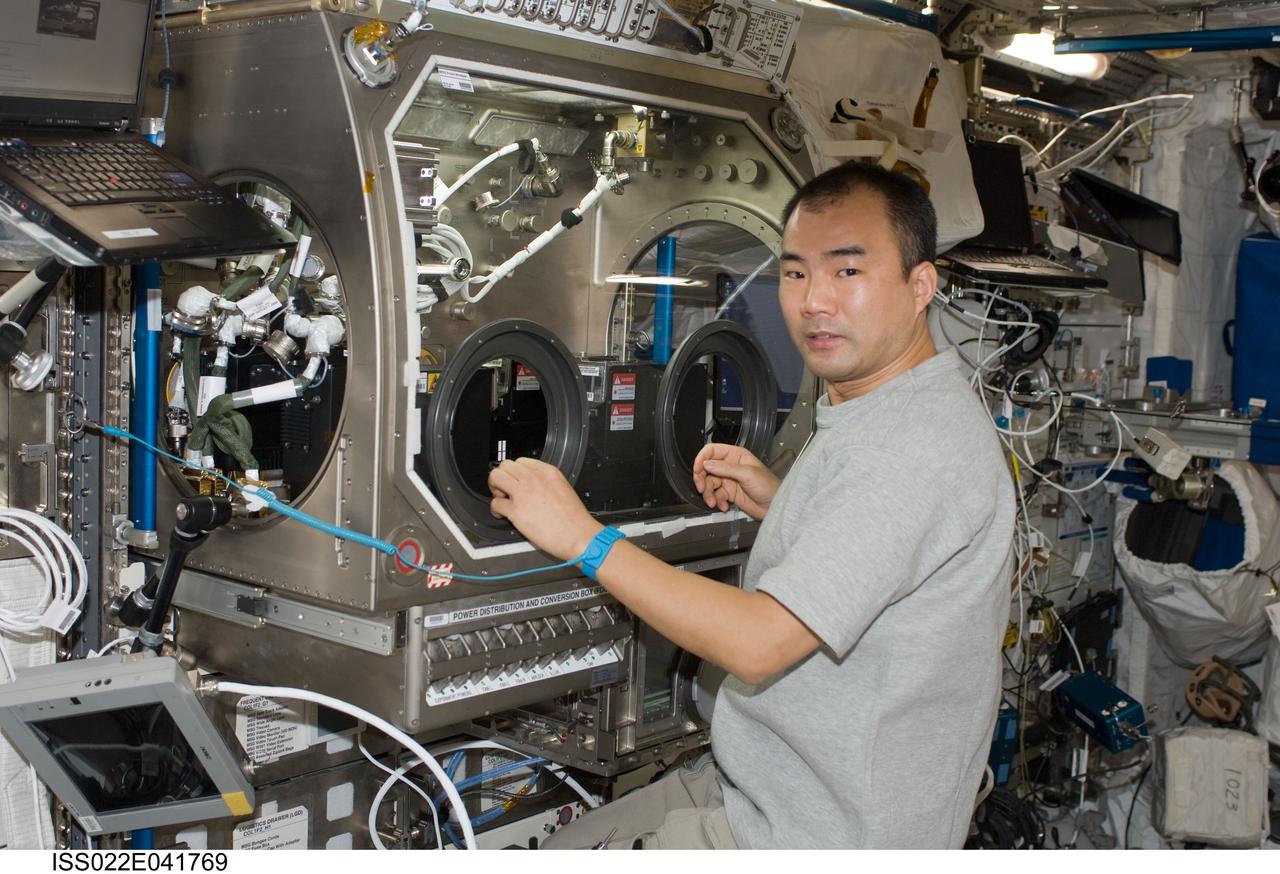
ISS022-E-041769 (28 Jan. 2010) --- Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Soichi Noguchi, Expedition 22 flight engineer, works with the European Space Agency (ESA) science payload Selectable Optical Diagnostics Instrument / Influence of Vibration on Diffusion in Liquids (SODI/IVIDIL) hardware in the Microgravity Science Glovebox (MSG) facility located in the Columbus laboratory of the International Space Station.
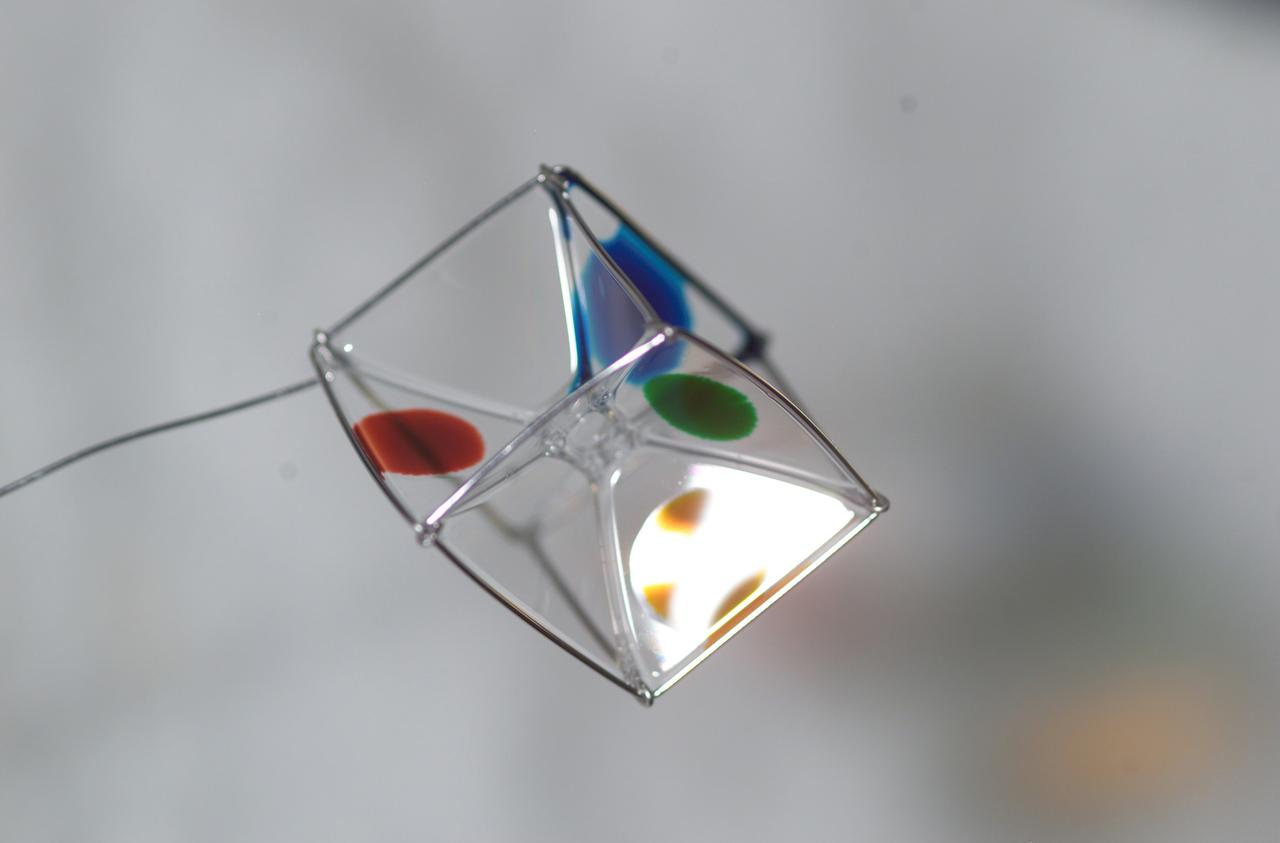
Expedition 6 astronaut Dr. Don Pettit photographed a cube shaped wire frame supporting a thin film made from a water-soap solution during his Saturday Morning Science aboard the International Space Station’s (ISS) Destiny Laboratory. Food coloring was added to several faces to observe the effects of diffusion within the film.
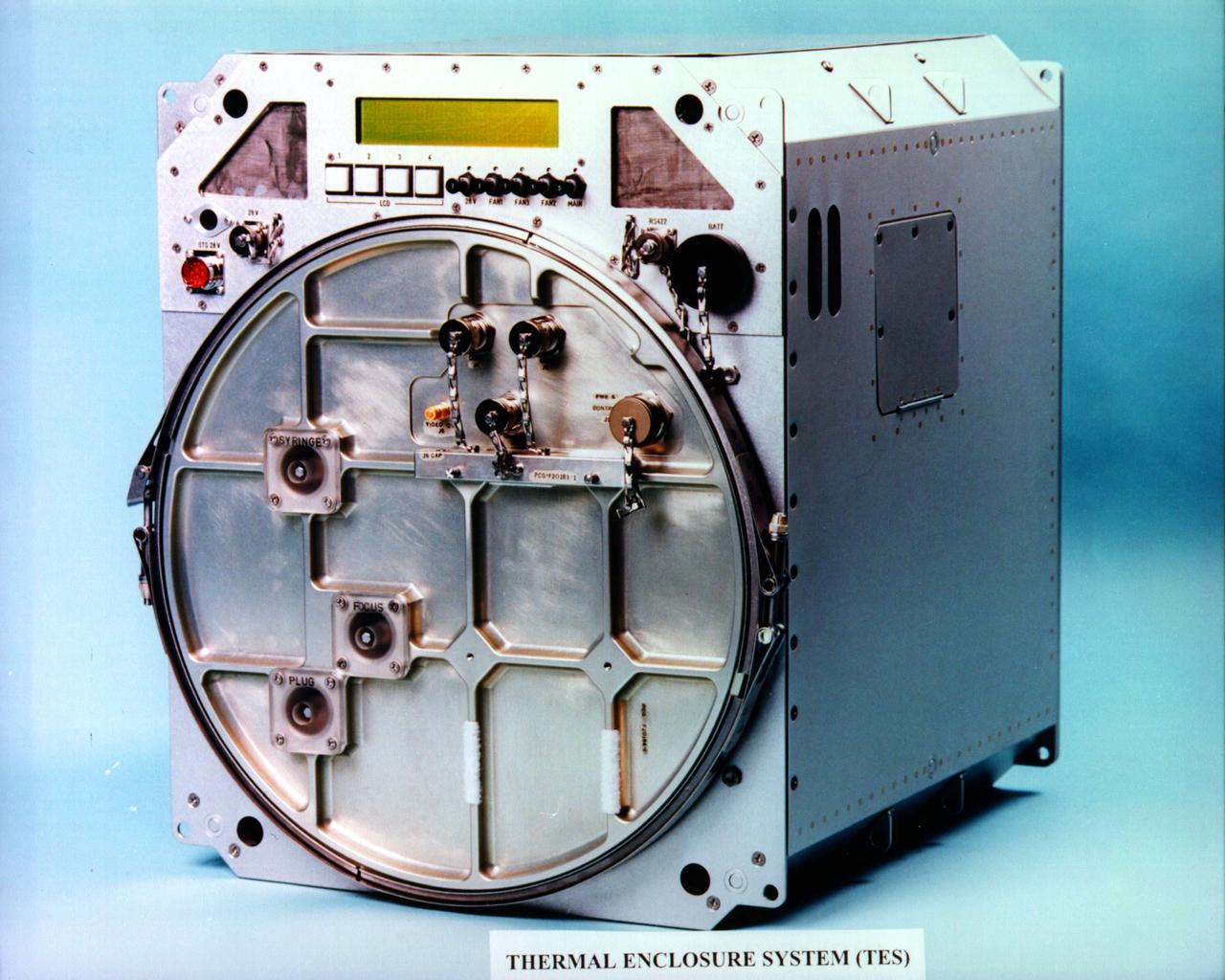
The Thermal Enclosure System (TES) provides thermal control for protein crystal growth experiments. The TES, housed in two middeck lockers on board the Space Shuttle, contains four Vapor Diffusion Apparatus (VDA) trays. Each can act as either a refrigerator or an incubator and its temperature can be controlled to within one-tenth degree C. The first flight of the TES was during USMP-2 (STS-62).
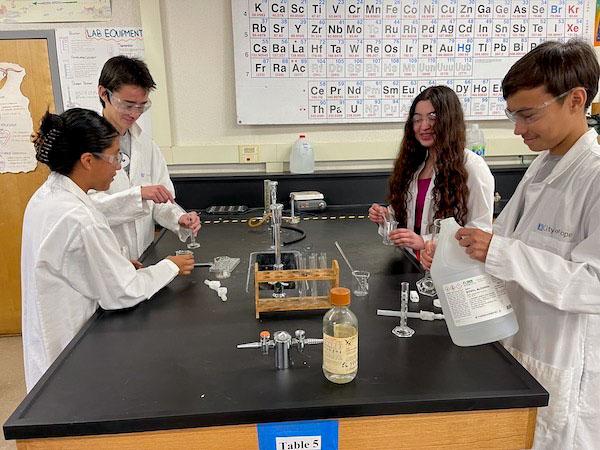

jsc2024e066520 (1/31/2024) --- Glendora High School students test ethanol concentrations to minimize diffusion loss. Their experiment, Cyanobacteria (Trichormus variabilis) Growth in Extreme Conditions of Microgravity, is part of the Nanoracks-National Center for Earth and Space Science Education-Surveyor-Student Spaceflight Experiments Program Mission 18 to ISS (Nanoracks-NCESSE-Surveyor-SSEP).
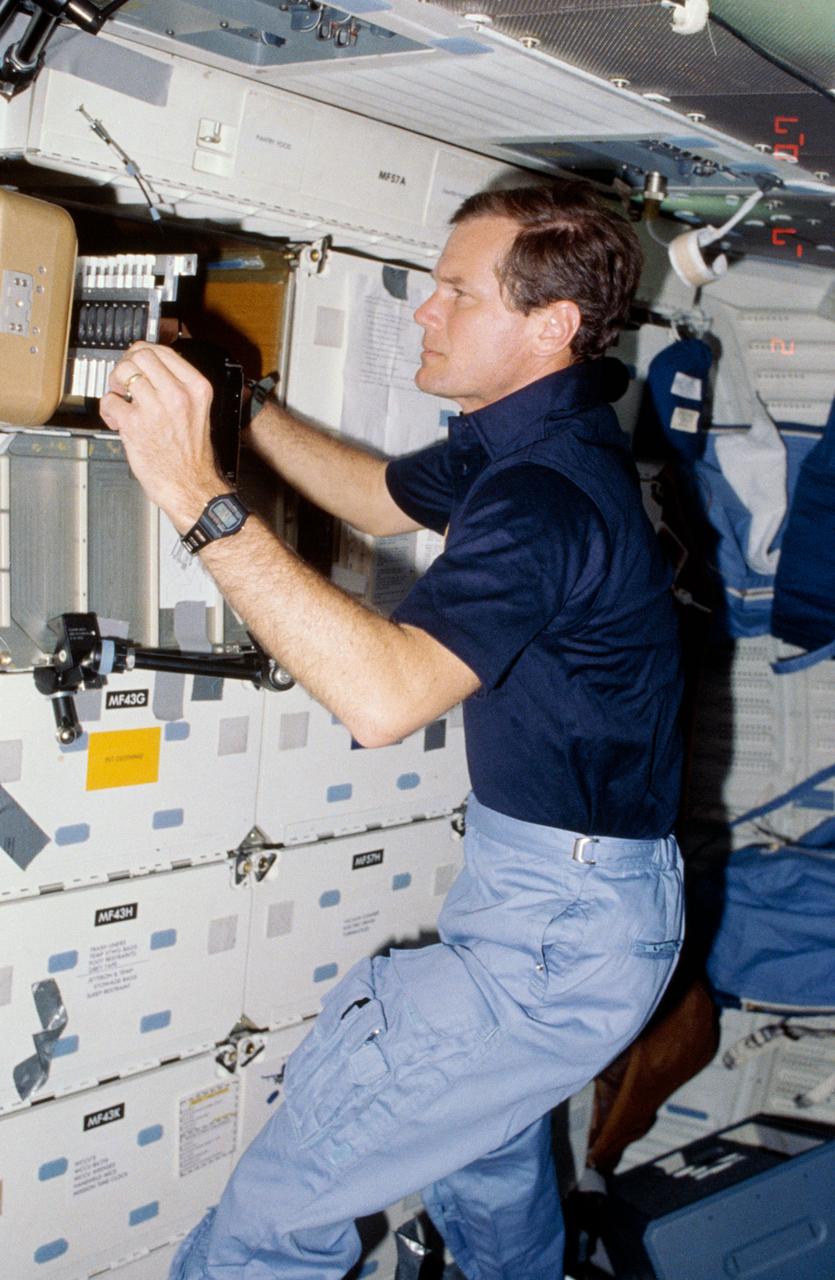

61C-05-036 (12-18 Jan. 1986) --- U.S. Representative Bill Nelson (Democrat - Florida), STS-61C payload specialist, prepares to photograph individual samples in the Handheld Protein Crystal Growth Experiment (HPCG) on Columbia's middeck. The operations involve the use of four pieces of equipment to attempt the growth of 60 different types of crystals -- 12 by means of dialysis and 48 via the vapor diffusion method. The photo was used by members of the STS-61C crew at their Jan. 23, 1986, Post-Flight Press Conference.
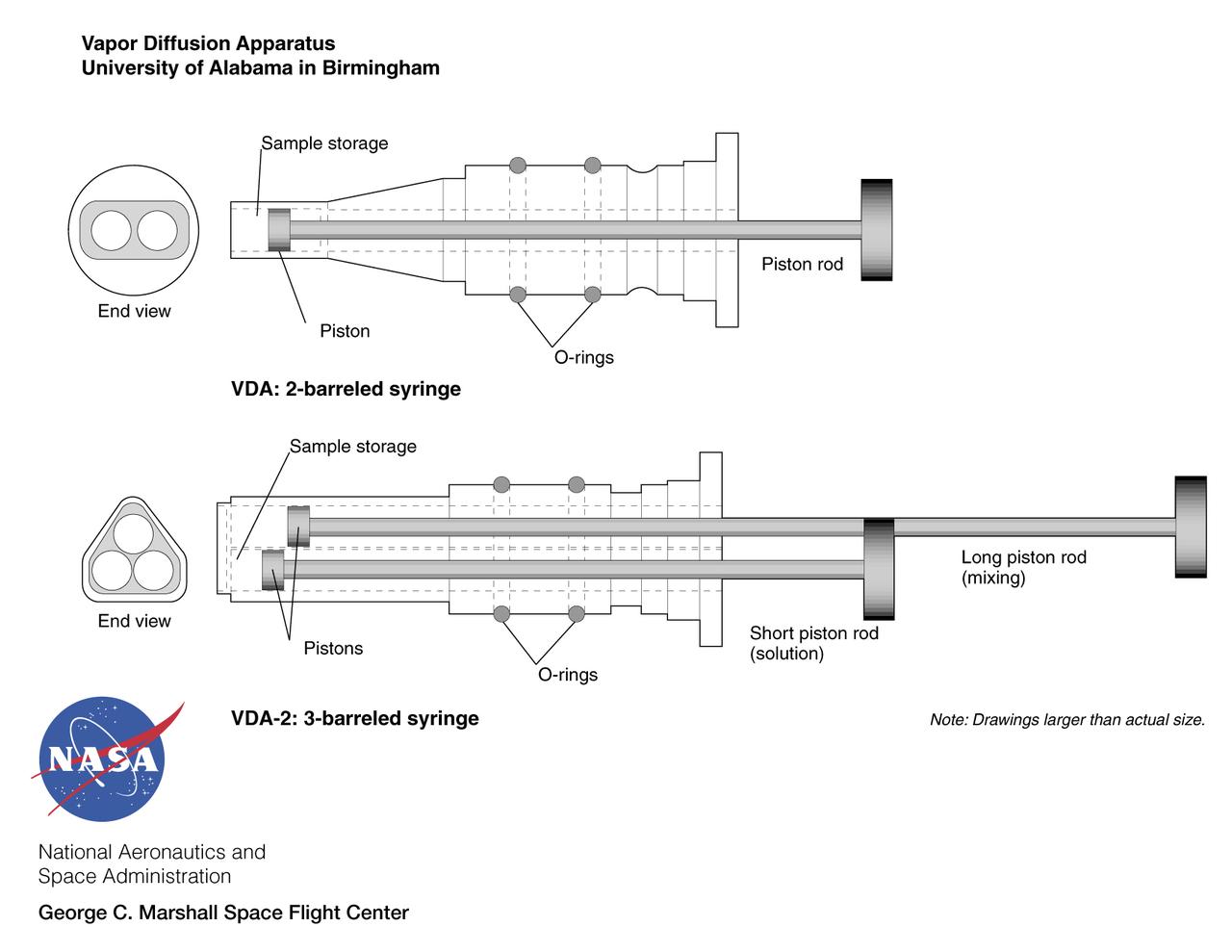
Vapor Diffusion Apparatus (VDA and VDA-2) was developed by the University of Alabama in Birmingham for NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center. In the original VDA, a protein solution and a precipitant are extruded by two plungers onto the tip of a small syringe and allowed to evaporate, raising the concentration and prompting protein molecules to crystallize. In the VDA-2 version, a third plunger was added to mix the two solutions before returning the mix to the syringe tip. The principal investigator is Dr. Larry Delucas of the University of Alabama in Birmingham

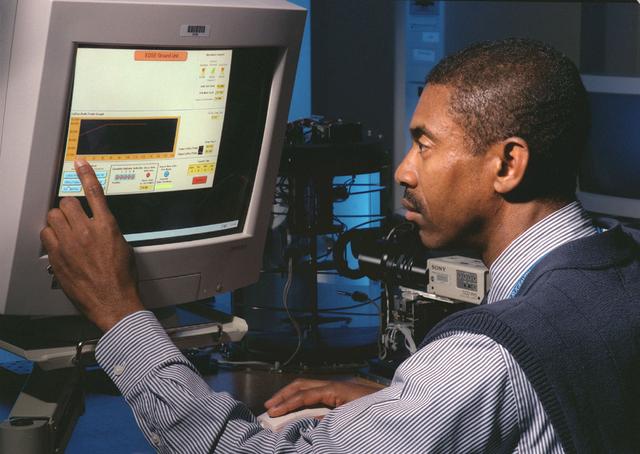
The Equiaxed Dendritic Solidification Experiment (EDSE) is a material sciences investigation under the Formation of Microstructures/pattern formation discipline. The objective is to study the microstructural evolution of and thermal interactions between several equiaxed crystals growing dendritically in a supercooled melt of a pure and transparent substance under diffusion controlled conditions. EDSE/TDSE project engineer, Zena Hester, monitors a test run of the EDSE located in the Microgravity Development Laboratory (MDL).

The Equiaxed Dendritic Solidification Experiment (EDSE) is a material sciences investigation under the Formation of Microstructures/pattern formation discipline. The objective is to study the microstructural evolution of and thermal interactions between several quiaxed crystals growing dendritically in a supercooled melt of a pure and transparent substance under diffusion controlled conditions. George Myers, controls engineer, monitors the thermal environment of a ground test for the EDSE located in the Microgravity Development Laboratory (MDL).
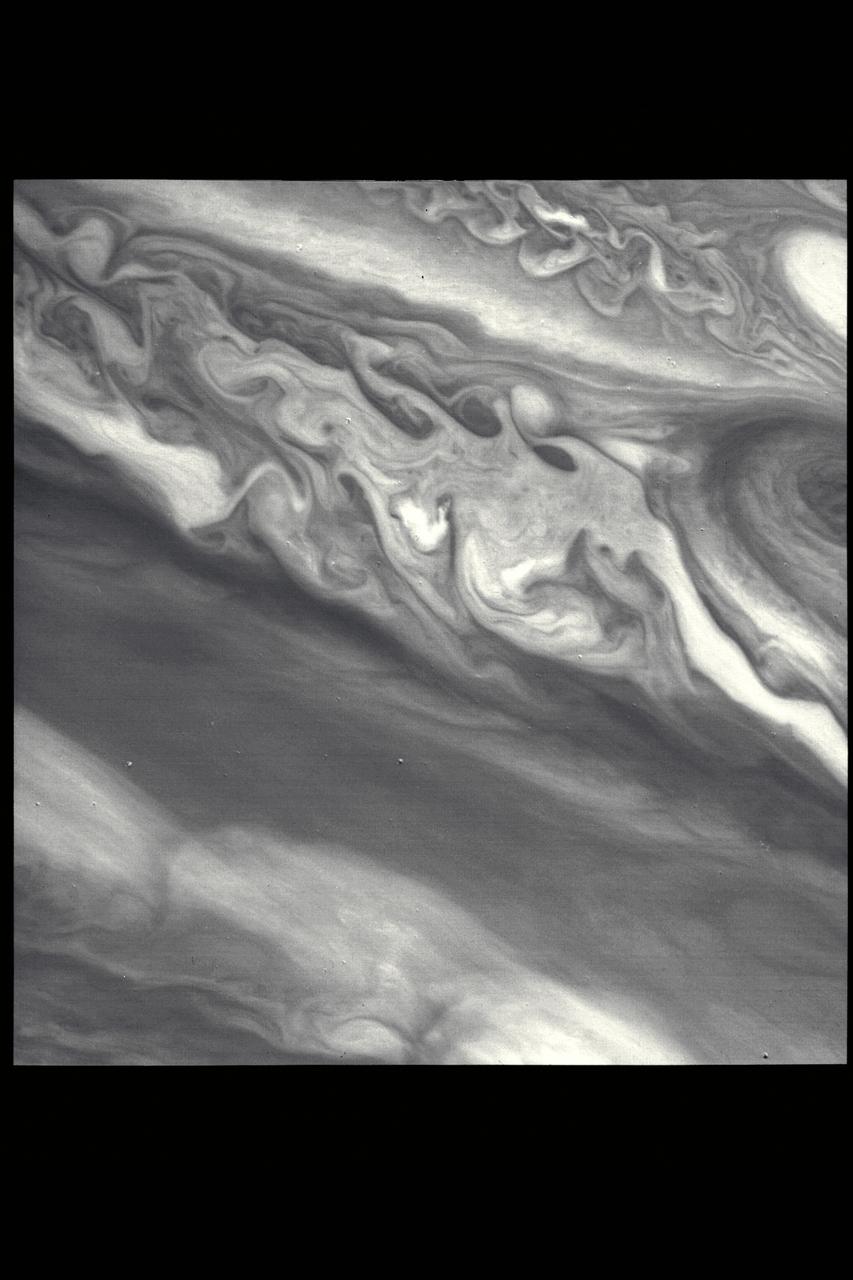
P-21735 BW This Jupiter image taken by Voyager 2 shows an area from 10° N. Lat. to 34° S. Lat. in a region west of the Great Red Spot. At the top of the picture, equatorial plumes are seen. These features move along the edge of the equatorial zone. The remainder of the equatorial region is characterized by diffuse clouds. The region west of the Great Red Spot is seen as a disturbed wave-like pattern. Similiar flows are seen to the west of the white oval at bottom.
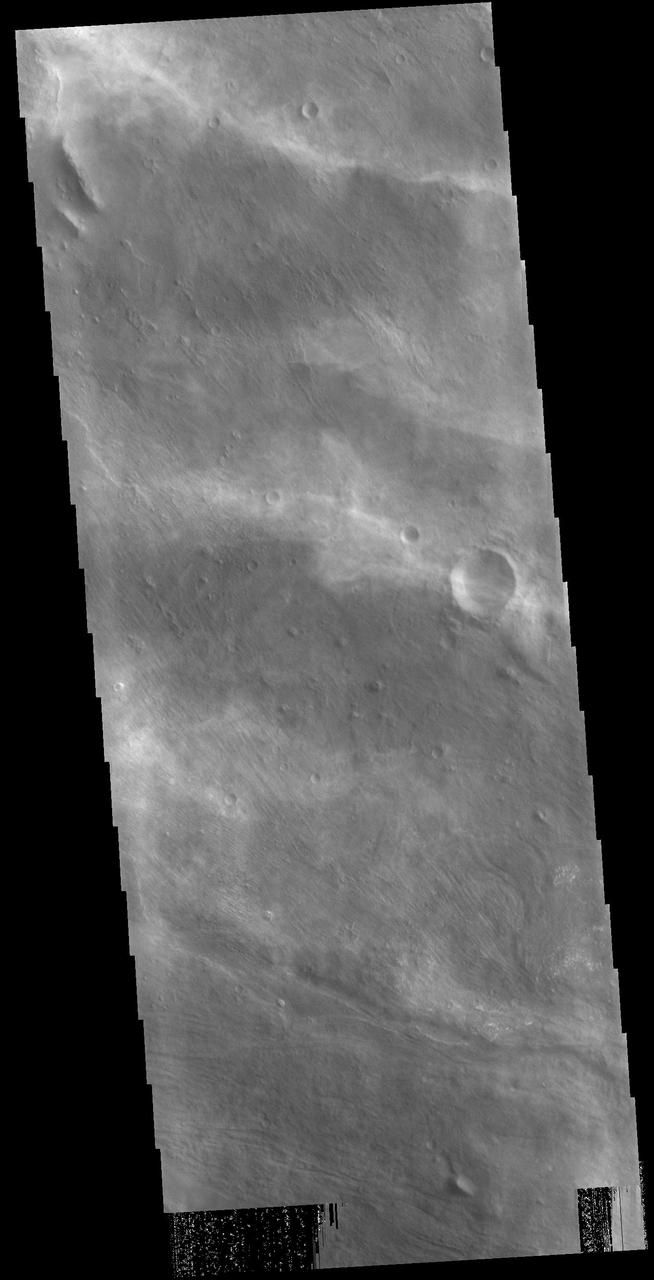

The diffuse streaks of white in this VIS image are clouds. These are high altitude winter clouds over Melas Chasma. Streamers of clouds like this are moving very quickly in high altitude winds. Orbit Number: 88213 Latitude: -11.5665 Longitude: 290.207 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2021-11-02 18:14 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25195
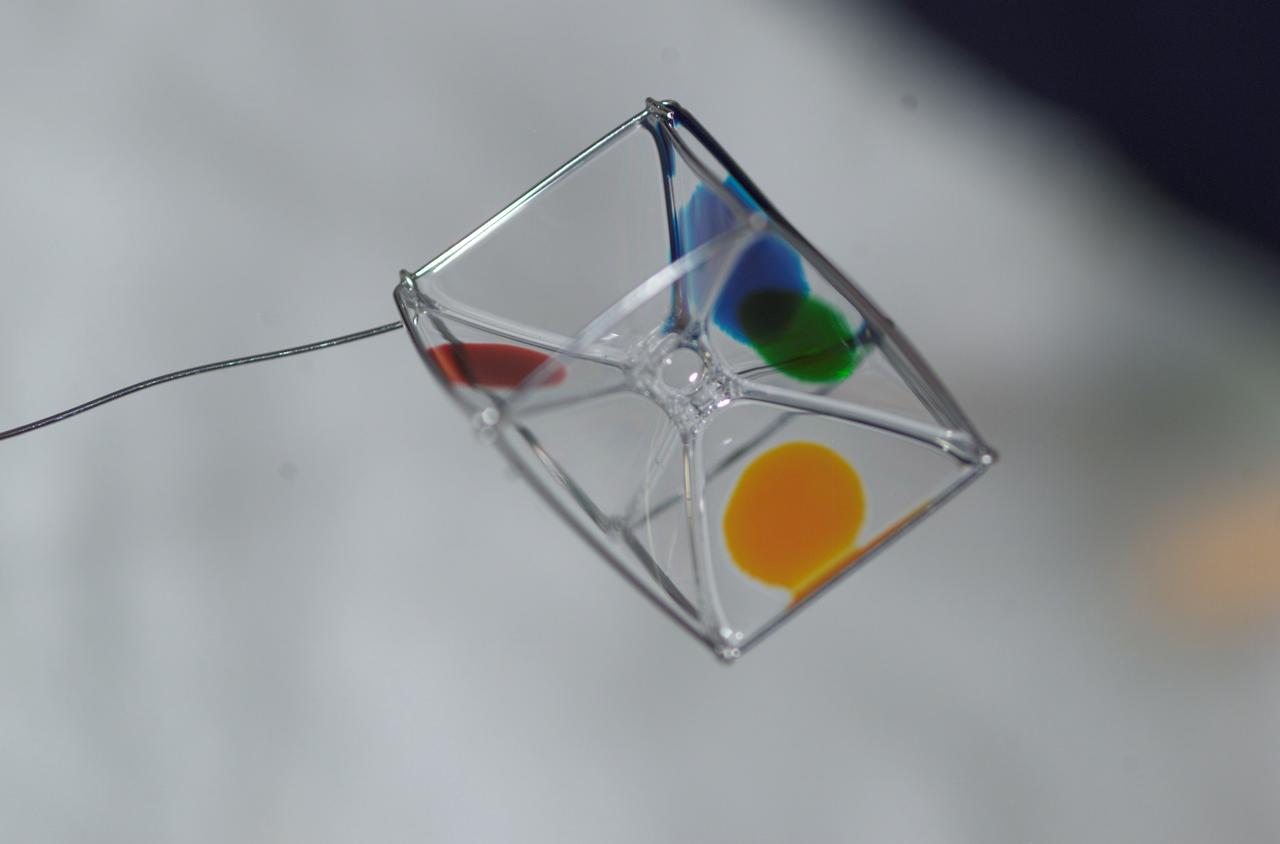

Expedition 6 astronaut Dr. Don Pettit photographed a cube shaped wire frame supporting a thin film made from a water-soap solution during his Saturday Morning Science aboard the International Space Station’s (ISS) Destiny Laboratory. Food coloring was added to several faces to observe the effects of diffusion within the film.
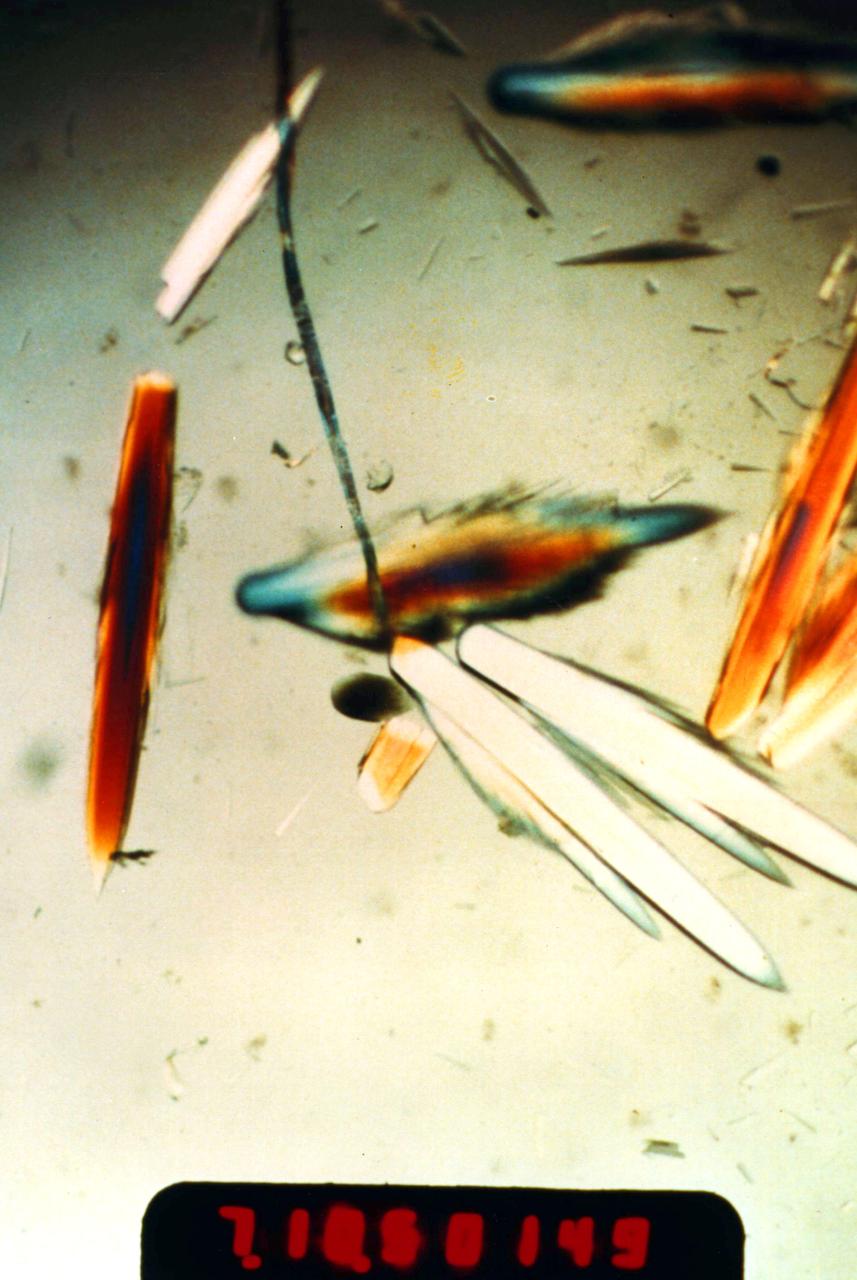
Horse Serum Albumin crystals grown during the USML-1 (STS-50) mission's Protein Crystal Growth Glovebox Experiment. These crystals were grown using a vapor diffusion technique at 22 degrees C. The crystals were allowed to grow for nine days while in orbit. Crystals of 1.0 mm in length were produced. The most abundant blood serum protein, regulates blood pressure and transports ions, metabolites, and therapeutic drugs. Principal Investigator was Edward Meehan.
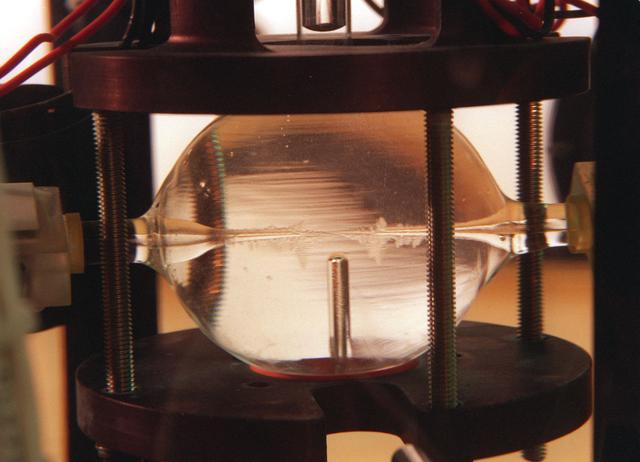

The Equiaxed Dendritic Solidification Experiment (EDSE) is a material sciences investigation under the Formation of Microstructures/pattern formation discipline. The objective is to study the microstructural evolution of and thermal interactions between several equiaxed crystals growing dendritically in a supercooled melt of a pure and transparent substance under diffusion controlled conditions. Dendrites growing at .4 supercooling from a 2 stinger growth chamber for the EDSE in the Microgravity Development Lab (MDL).
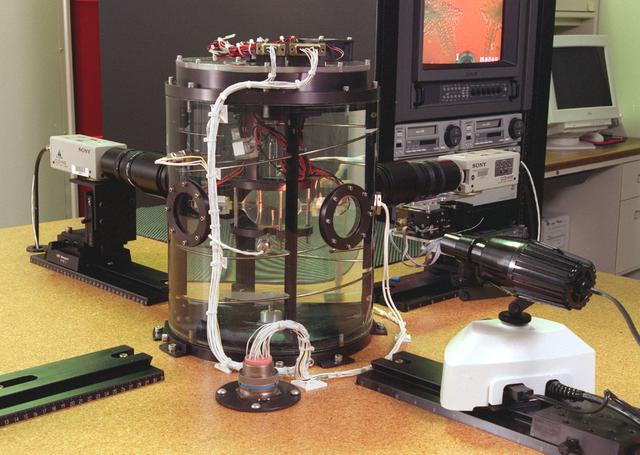

The Equiaxed Dendritic Solidification Experiment (EDSE) is a material sciences investigation under the Formation of Microstructures/pattern formation discipline. The objective is to study the microstructural evolution of and thermal interactions between several equiaxed crystals growing dendritically in a supercooled melt of a pure and transparent substance under diffusion controlled conditions. This image shows the isothermal bath and video system for the EDSE in the Microgravity Development Lab (MDL).
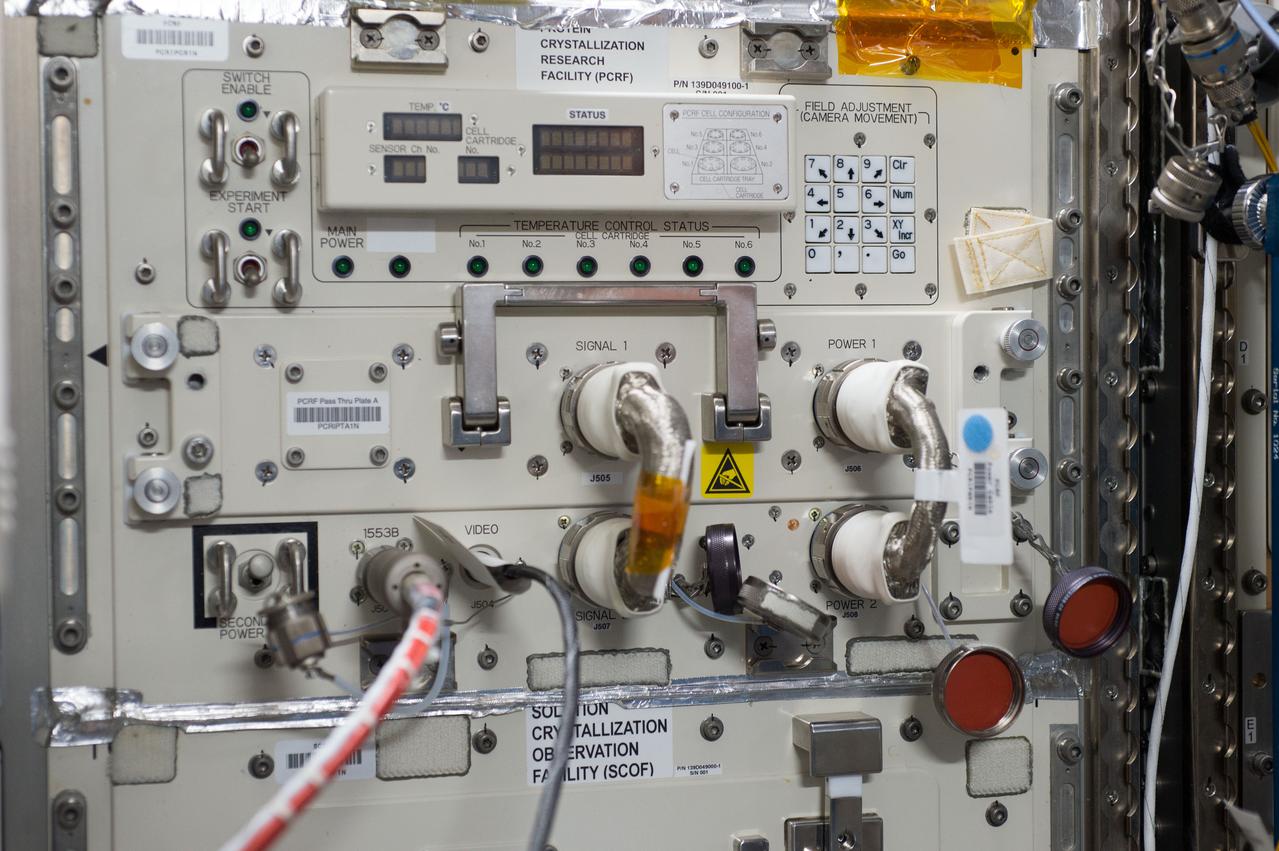

iss047e105727 (5/10/2016) --- Photographic documentation of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) High Quality Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) Removal. The PCG-Canister Bags were removed from the Cell Biology Experiment Facility (CBEF) and the Protein Crystallization Research Facility (PCRF) before being stowed for return on SpX-8. The JAXA PCG-Demo investigation crystallizes proteins using the counter-diffusion technique and permeation method that minimizes impurities, forming high-quality crystals for use in medical studies and ecological applications.
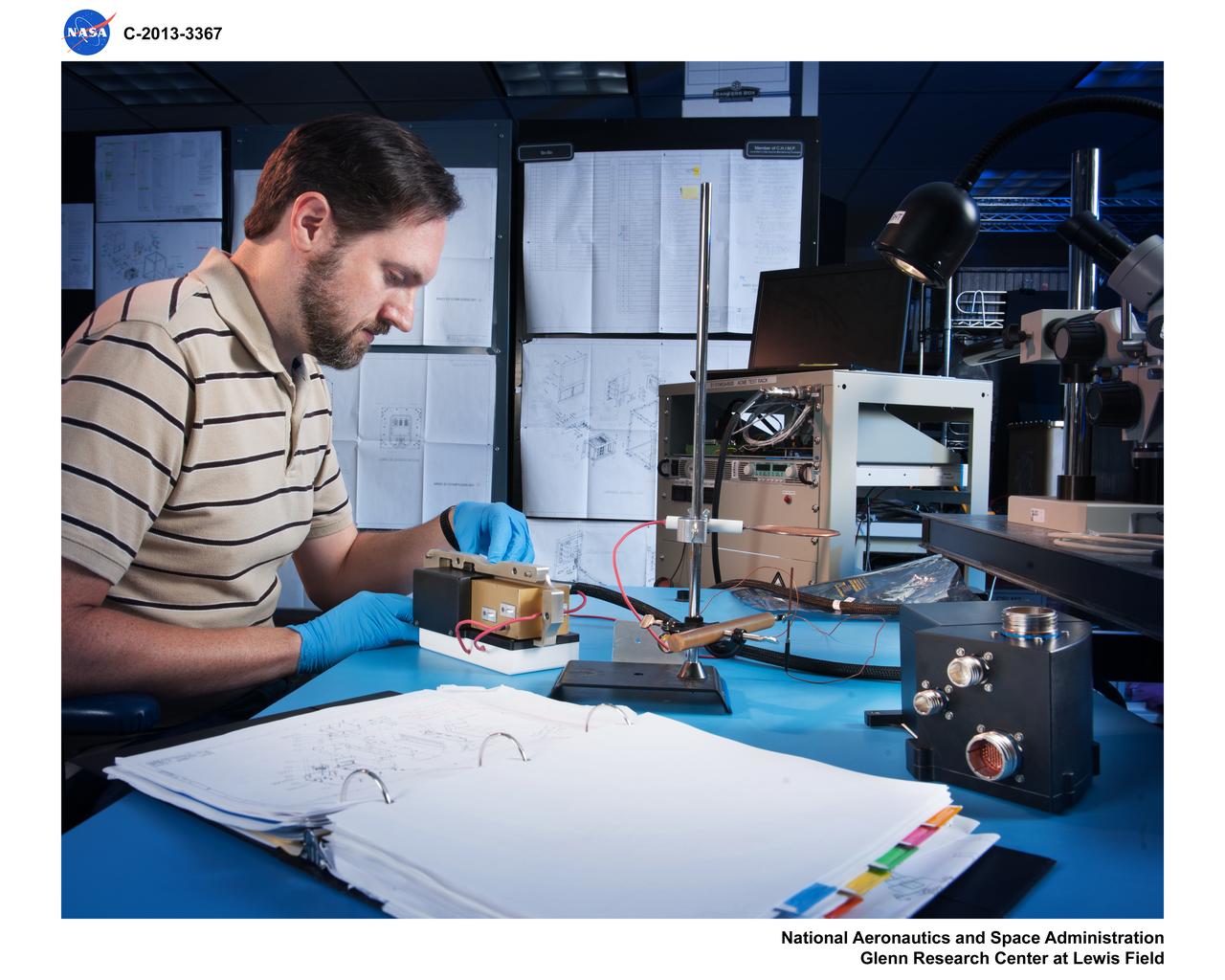

Mechanical Engineer Adrian Drake inspects engineering model hardware built to generate a high-voltage electric field for the Electric-Field Effects on Laminar Diffusion Flames (E-FIELD Flames) experiment of the Advanced Combustion via Microgravity Experiments (ACME) project. ACME’s small computer (i.e., the Cube) for data acquisition and control within the CIR combustion chamber is seen in the right foreground. The E-FIELD Flames tests were conducted in the Combustion Integrated Rack (CIR) on the International Space Station (ISS) in 2018.
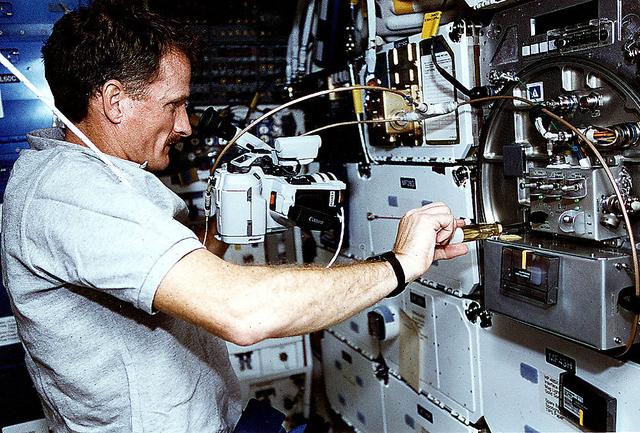

On the Space Shuttle Orbiter Atlantis' middeck, Astronaut Joseph R. Tarner, mission specialist, works at an area amidst several lockers which support the Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) experiment during the STS-66 mission. This particular section is called the Crystal Observation System, housed in the Thermal Enclosure System (COS/TES). Together with the Vapor Diffusion Apparatus (VDA), housed in Single Locker Thermal Enclosure (SLTES), the COS/TES represents the continuing research into the structure of proteins and other macromolecules such as viruses.
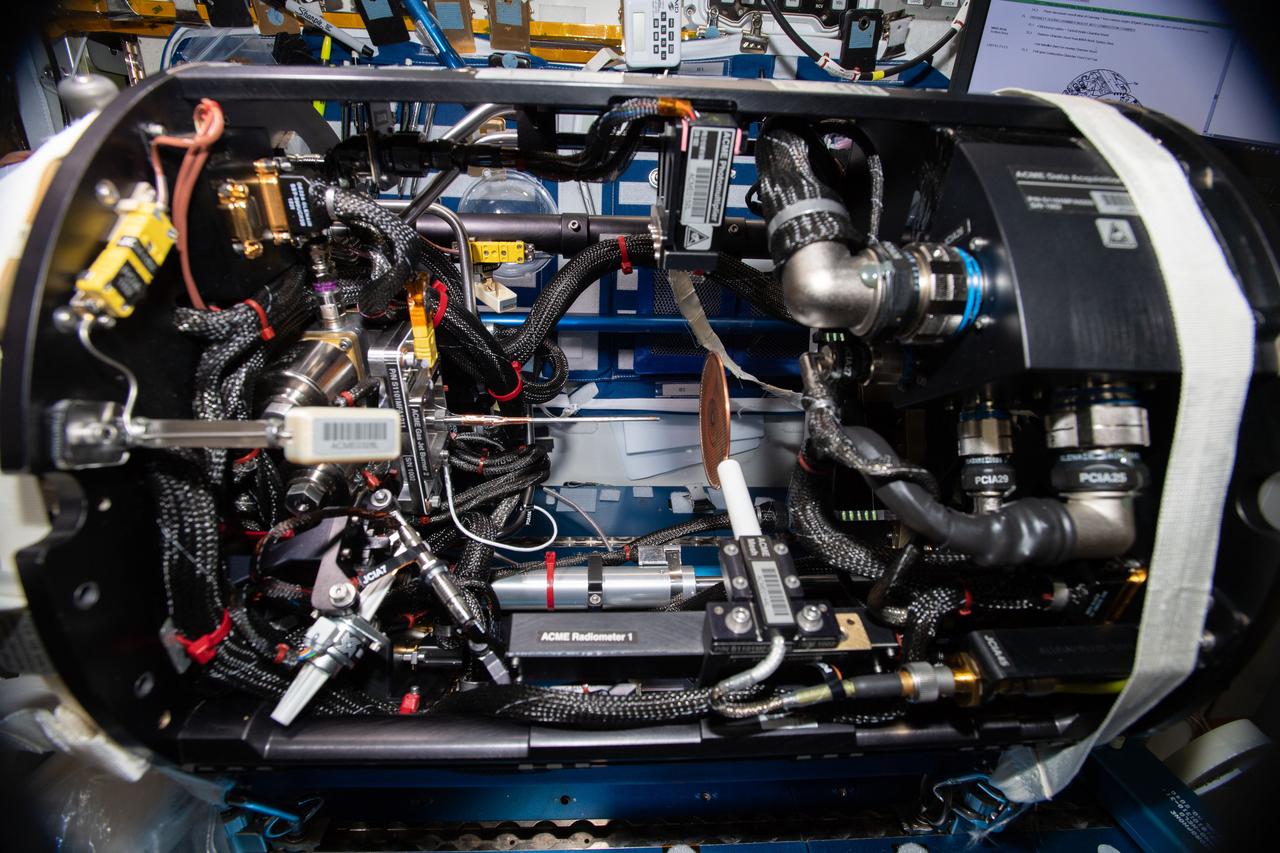
iss057e055269 (10/22/2018) --- Photo documentation of the Combustion Integrated Rack (CIR) Combustion Chamber, with Advanced Combustion via Microgravity Experiments (ACME) Mesh installed, during operations (OPS) to reconfigure CIR ACME hardware for the Electric-Field Effects on Laminar Diffusion Flames (E-FIELD Flames) experiment aboard the International Space Station (ISS).
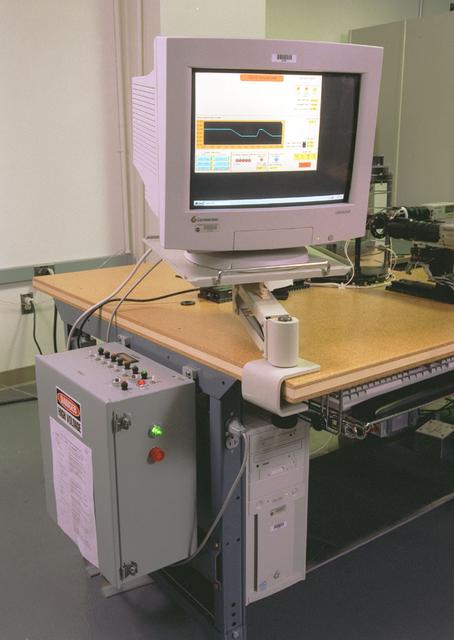

The Equiaxed Dendritic Solidification Experiment (EDSE) is a material sciences investigation under the Formation of Microstructures/pattern formation discipline. The objective is to study the microstructural evolution of and thermal interactions between several equiaxed crystals growing dendritically in a supercooled melt of a pure and transparent substance under diffusion controlled conditions. Dendrite irritator control for the EDSE in the Microgravity Development Lab (MDL).
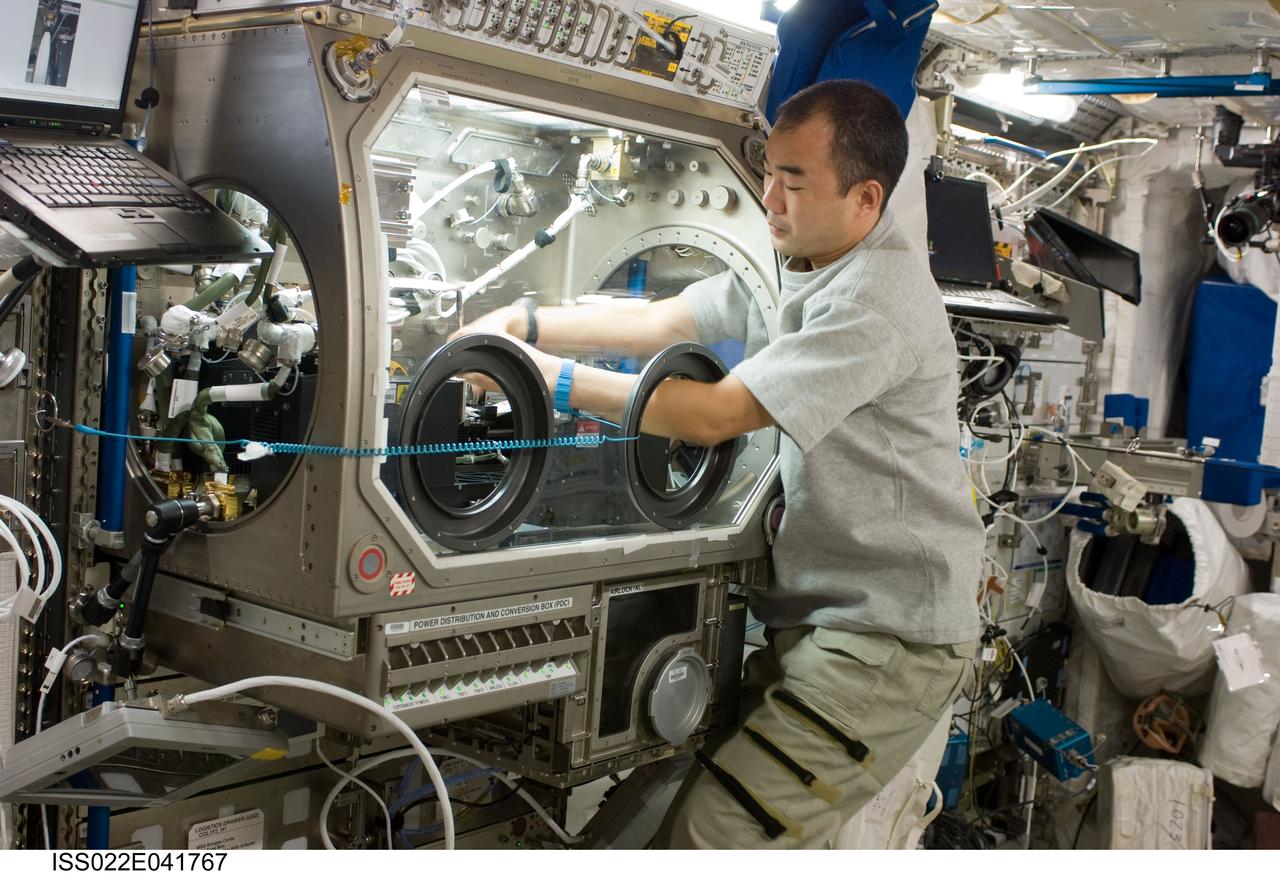

ISS022-E-041767 (28 Jan. 2010) --- Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Soichi Noguchi, Expedition 22 flight engineer, works with the European Space Agency (ESA) science payload Selectable Optical Diagnostics Instrument / Influence of Vibration on Diffusion in Liquids (SODI/IVIDIL) hardware in the Microgravity Science Glovebox (MSG) facility located in the Columbus laboratory of the International Space Station.
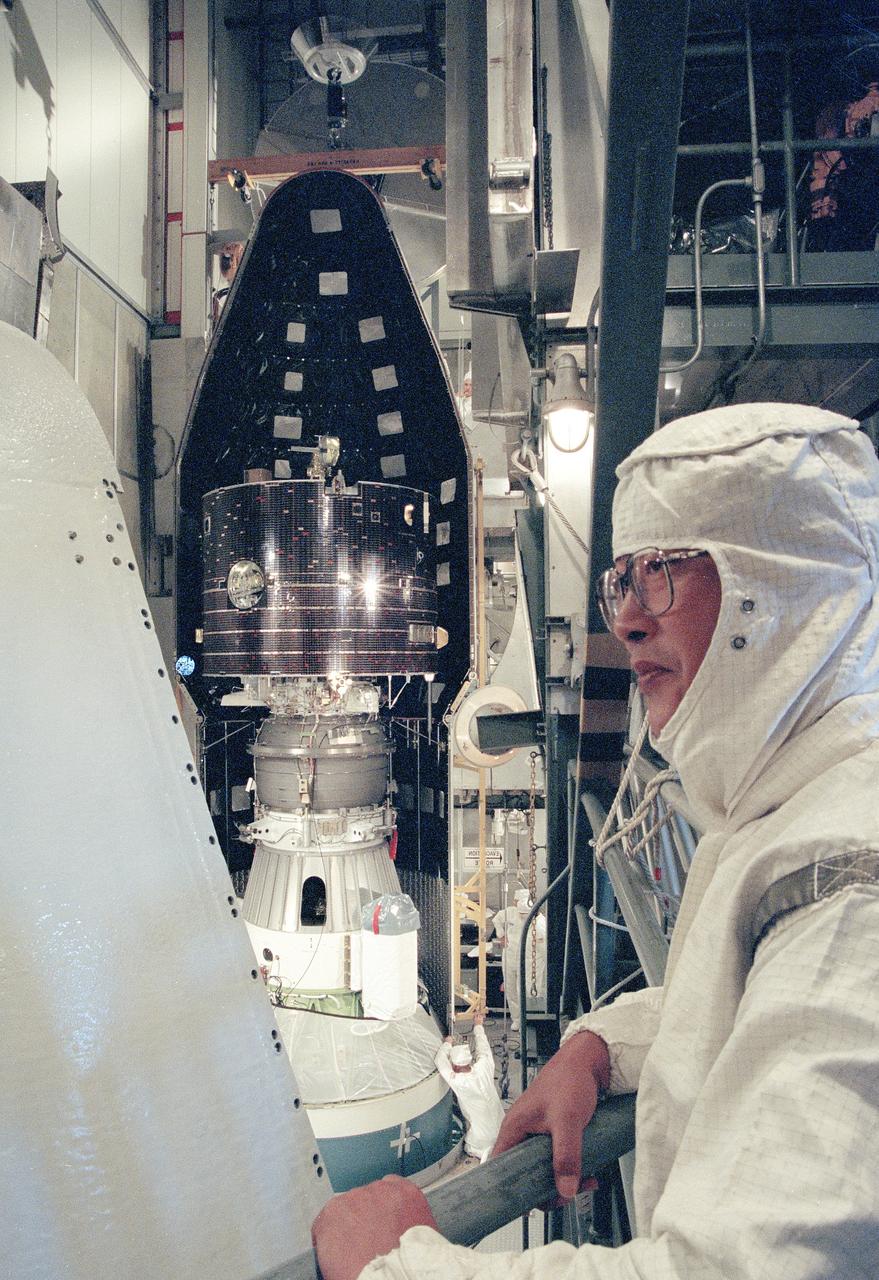
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Complex 17, Pad A, technicians encapsulate the Geotail spacecraft upper and attached Payload Assist Module-D upper stage lower in the protective payload fairing. Geotail and secondary payload Diffuse Ultraviolet Experiment DUVE are scheduled for launch about the Delta II rocket on July 24. The GEOTAIL mission is a collaborative project undertaken by the Institute of Space and Astronautical Science ISAS, Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency JAXA and NASA. Photo Credit: NASA

ISS022-E-041766 (28 Jan. 2010) --- Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Soichi Noguchi, Expedition 22 flight engineer, works with the European Space Agency (ESA) science payload Selectable Optical Diagnostics Instrument / Influence of Vibration on Diffusion in Liquids (SODI/IVIDIL) hardware in the Microgravity Science Glovebox (MSG) facility located in the Columbus laboratory of the International Space Station.
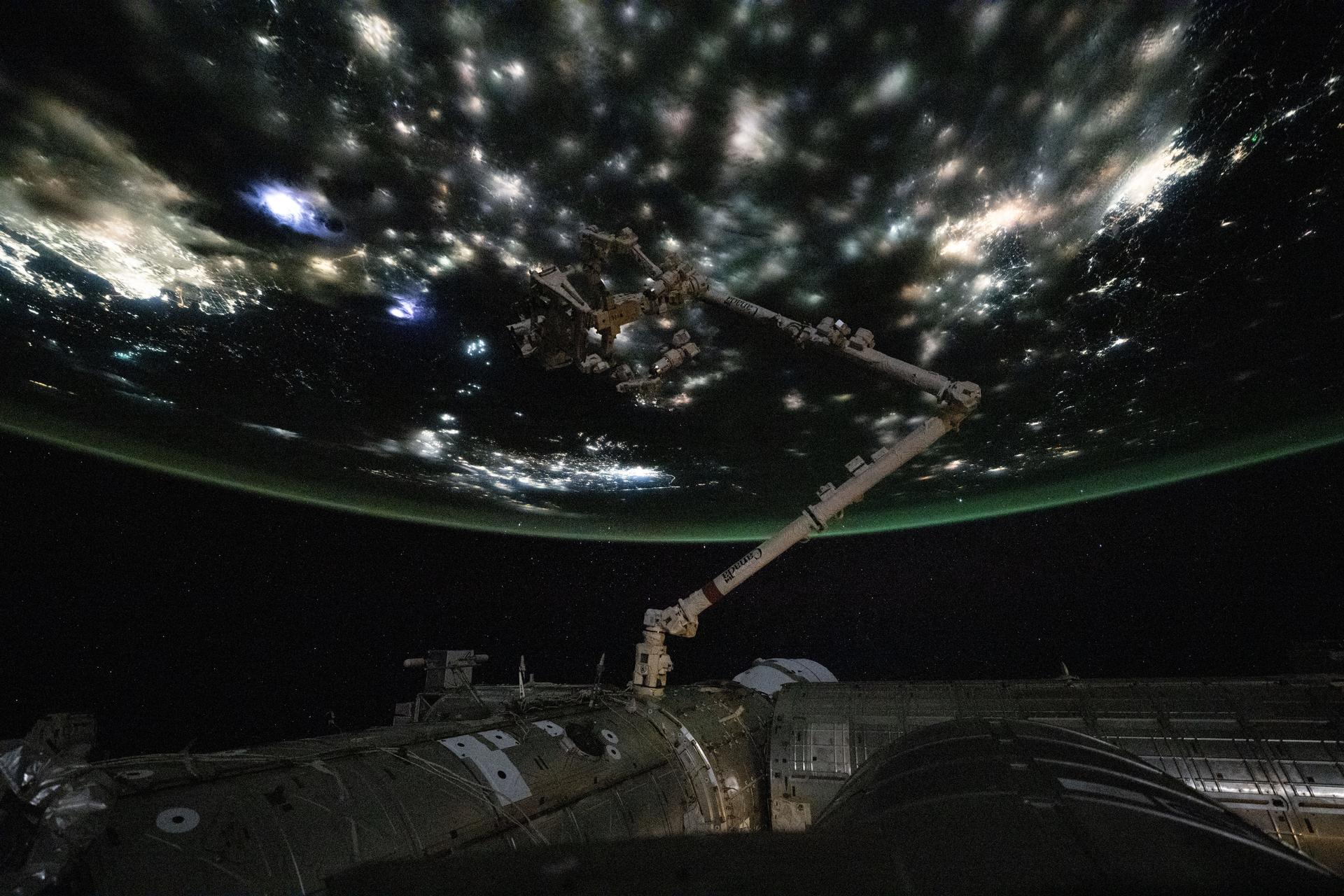

iss073e0742298 (Aug. 30, 2025) --- City lights beneath the clouds highlight the North China Plain near the Yellow Sea, where concentrated points of light mark fishing boats using illumination to attract anchovies, squid, sardines, and other species. Across the Yellow Sea, urban areas in South Korea are visible beneath a diffuse atmospheric glow near the horizon. In the foreground, the Canadarm2 robotic arm extends from a grapple fixture on the International Space Station's Harmony module.
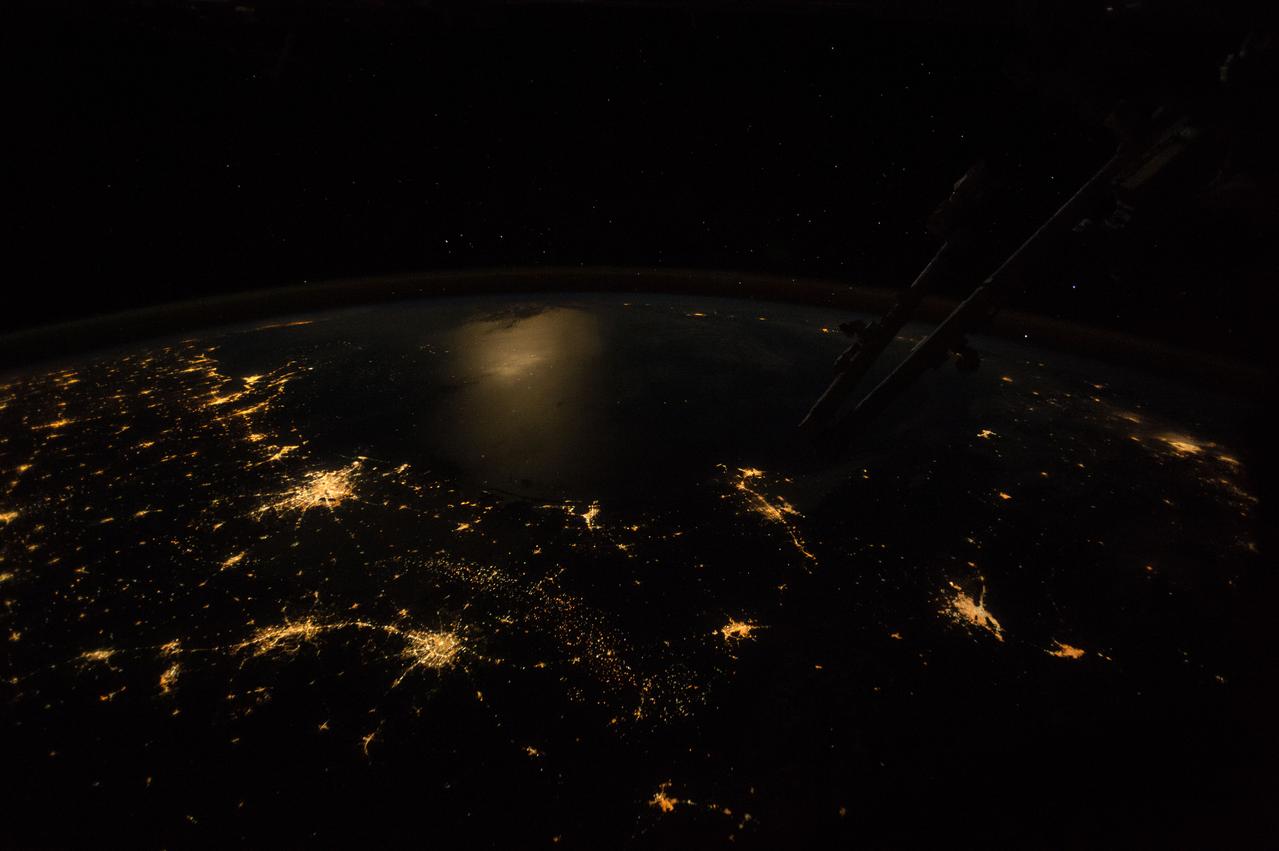

ISS042E241898 (02/11/2015) --- Texas and the Gulf Coast at night as seen by the International Space Stations Earth observation cameras. This wide-angle, nighttime image was taken by astronauts looking out southeastward over the Gulf of Mexico. Lower center left shows the twin lights of San Antonio Texas with a short string of lights to Austin (further left). Houston, the home of the Johnson Space Center is the brightest directly above (Center left). Moonlight reflects diffusely off the waters of the gulf (image center left) making the largest but diffused illuminated area in the image. The sharp edge of light patterns of coastal cities trace out the long curve of the gulf shoreline—from New Orleans at the mouth of the Mississippi River, to Houston (both image left), to Brownsville (image center) in the westernmost gulf. City lights at great distances in Florida (image top left) and on Mexico’s Yucatán peninsula (image center right) suggest the full extent of the gulf basin, more than 930 miles, from Brownsville to Florida.
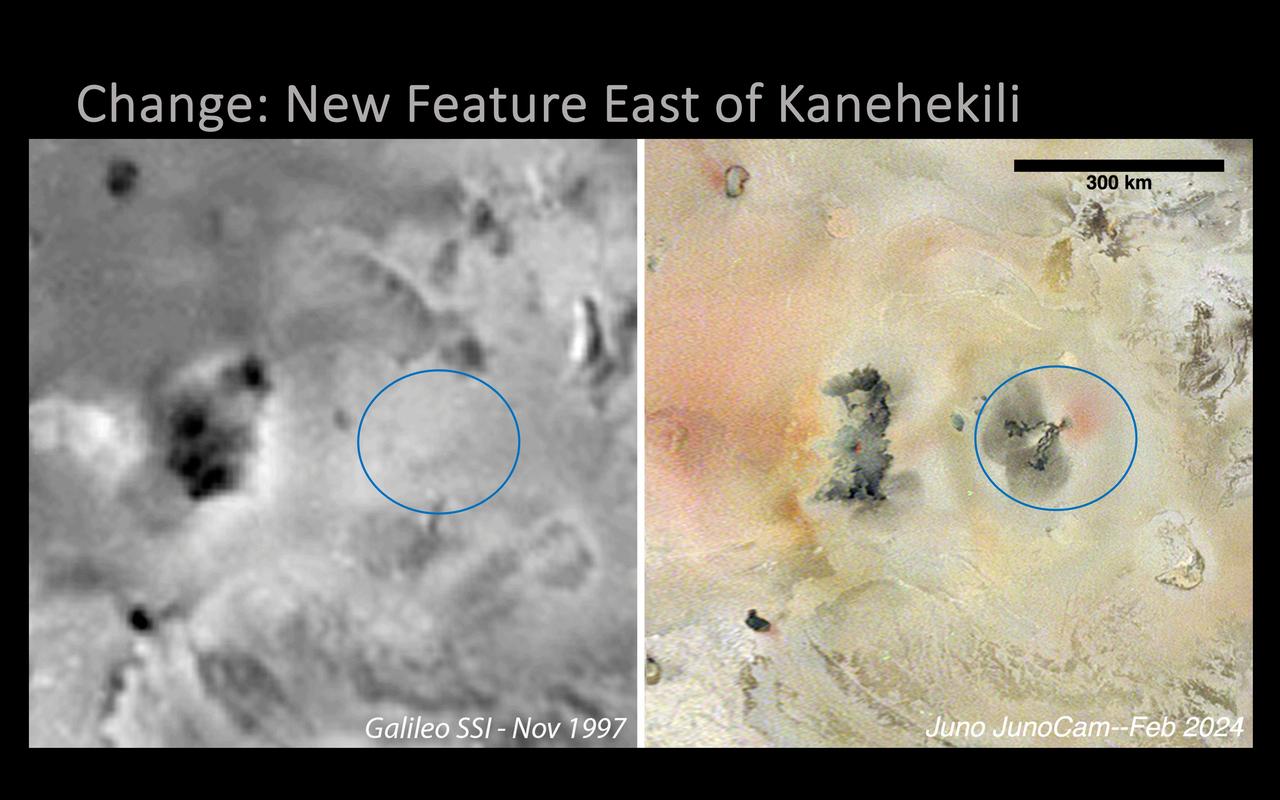

A new volcanic feature east of Kanehekili on Jupiter's moon Io was imaged by NASA's Juno mission during its 58th close flyby of the gas giant on Feb. 3, 2024. The image was captured in Jupiter-shine at 1.1 miles (1.8 kilometers) per pixel by the mission's JunoCam instrument. The feature is new since NASA's Galileo captured the area in 1997 (image at left), and consists of two thin, digitate flows, running roughly to the west and southwest from a common point at 17 degrees 2 minutes south latitude and 21 degrees 9 minutes west longitude. Dark gray diffuse deposits surround the ends of each flow, extending 25 to 34 miles (40 to 55 kilometers) out from the flow termini, perhaps from lava fragmentation during interaction with volatile frosts. A diffuse red deposit is seen wrapping from the eastern to the southern side of the flow field's source in the northeast, similar in appearance to features attributed to elemental sulfur deposits being actively ejected from a vent. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26487
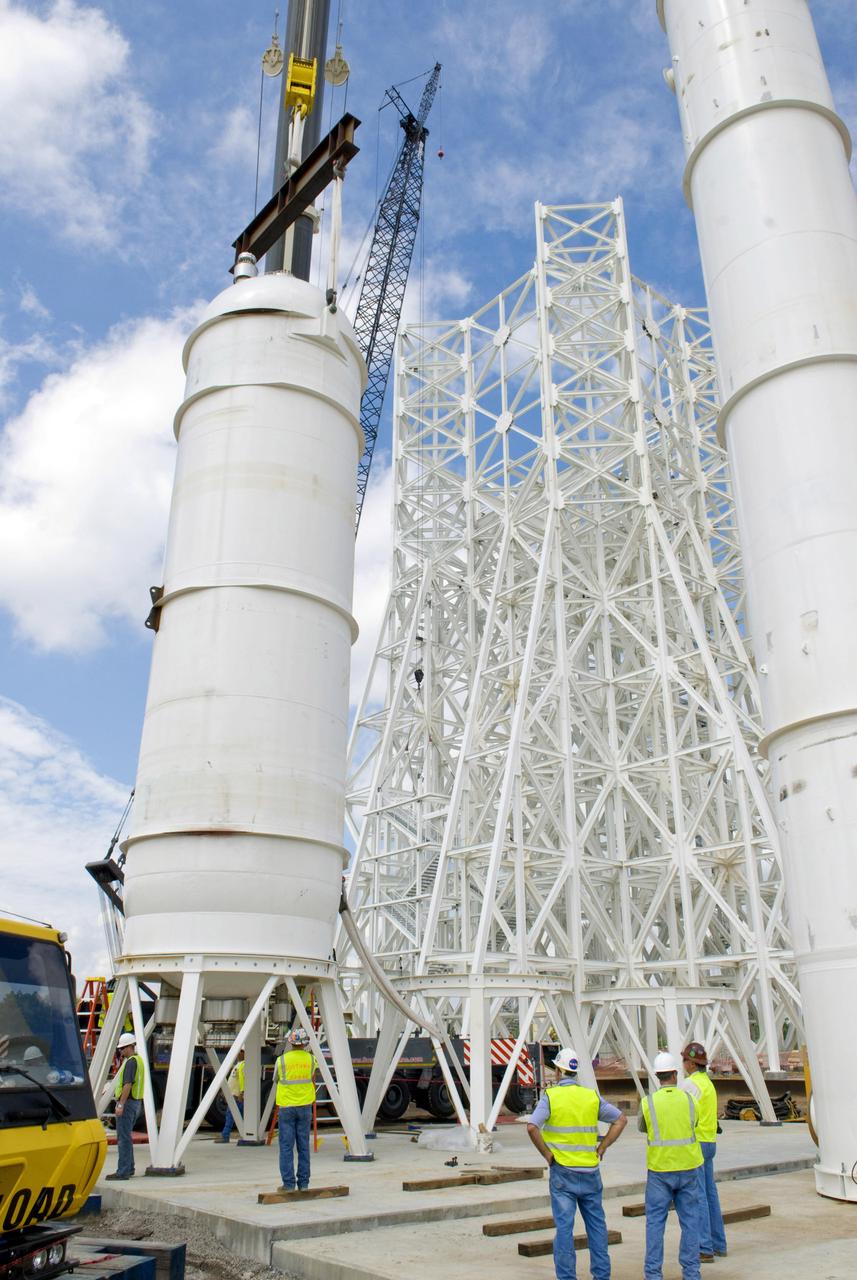

A liquid oxygen (LOX) tank is lifted into place at the A-3 Test Stand being built at NASA's John C. Stennis Space Center. Fourteen LOX, isopropyl alcohol (IPA) and water tanks are being installed to support the chemical steam generators to be used on the A-3 Test Stand. The IPA and LOX tanks will provide fuel for the generators. The water will allow the generators to produce steam that will be used to reduce pressure inside the stand's test cell diffuser, enabling operators to simulate altitudes up to 100,000 feet. In that way, operators can perform the tests needed on rocket engines being built to carry humans back to the moon and possibly beyond. The A-3 Test Stand is set for completion and activation in 2011.
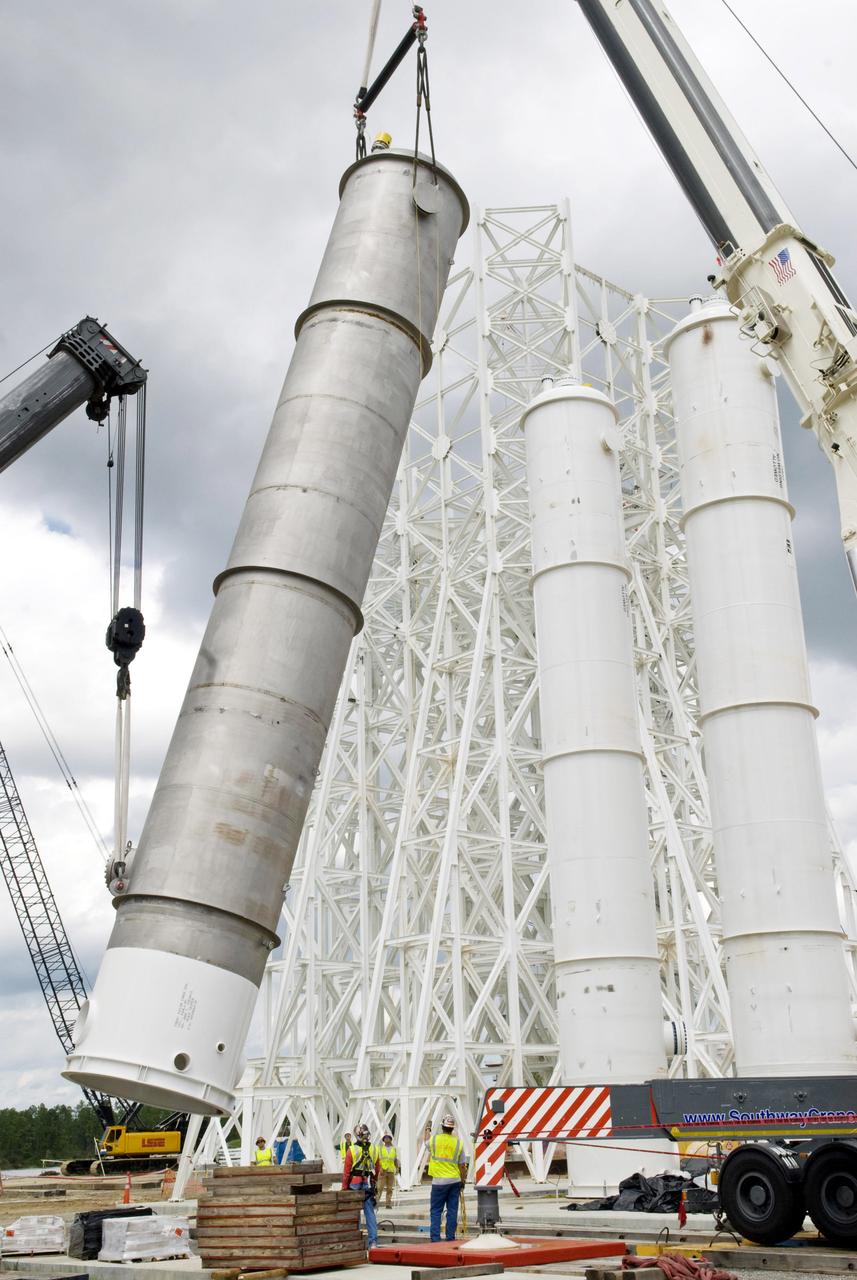

An isopropyl alcohol (IPA) tank is lifted into place at the A-3 Test Stand being built at NASA's John C. Stennis Space Center. Fourteen IPA, water and liquid oxygen (LOX) tanks are being installed to support the chemical steam generators to be used on the A-3 Test Stand. The IPA and LOX tanks will provide fuel for the generators. The water will allow the generators to produce steam that will be used to reduce pressure inside the stand's test cell diffuser, enabling operators to simulate altitudes up to 100,000 feet. In that way, operators can perform the tests needed on rocket engines being built to carry humans back to the moon and possibly beyond. The A-3 Test Stand is set for completion and activation in 2011.
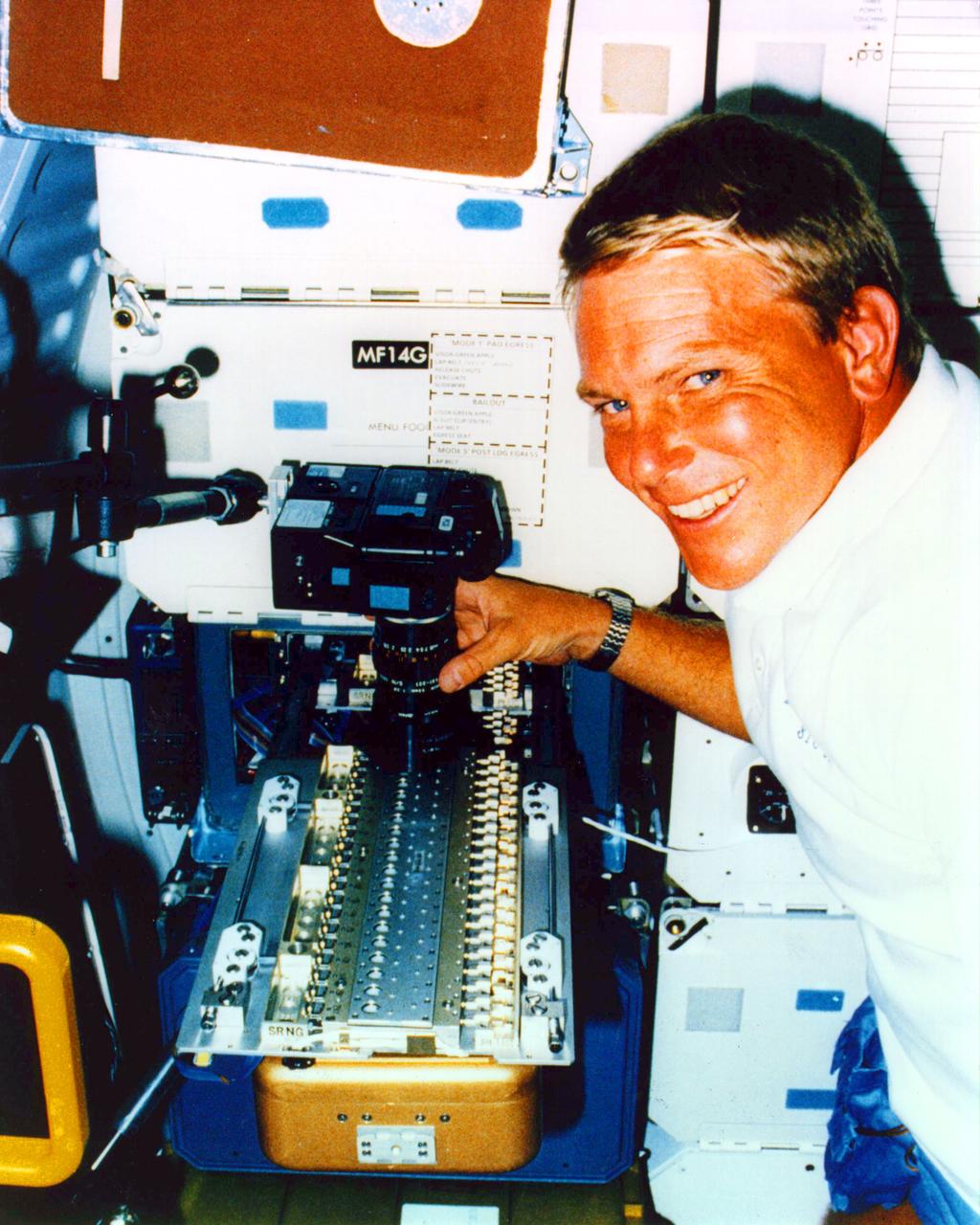
Mission Specialist George (Pinky) D. Nelson uses a 35 mm camera to photograph a protein crystal grown during the STS-26 Protein Crystal Growth (PCG-II-01) experiment. The protein crystal growth (PCG) carrier is shown deployed from the PCG Refrigerator/Incubator Mocule (R/IM) located in the middeck forward locker. The R/IM contained three Vapor Diffusion Apparatus (VDS) trays (one of which is shown). A total of sixty protein crystal samples were processed during the STS-26 mission.
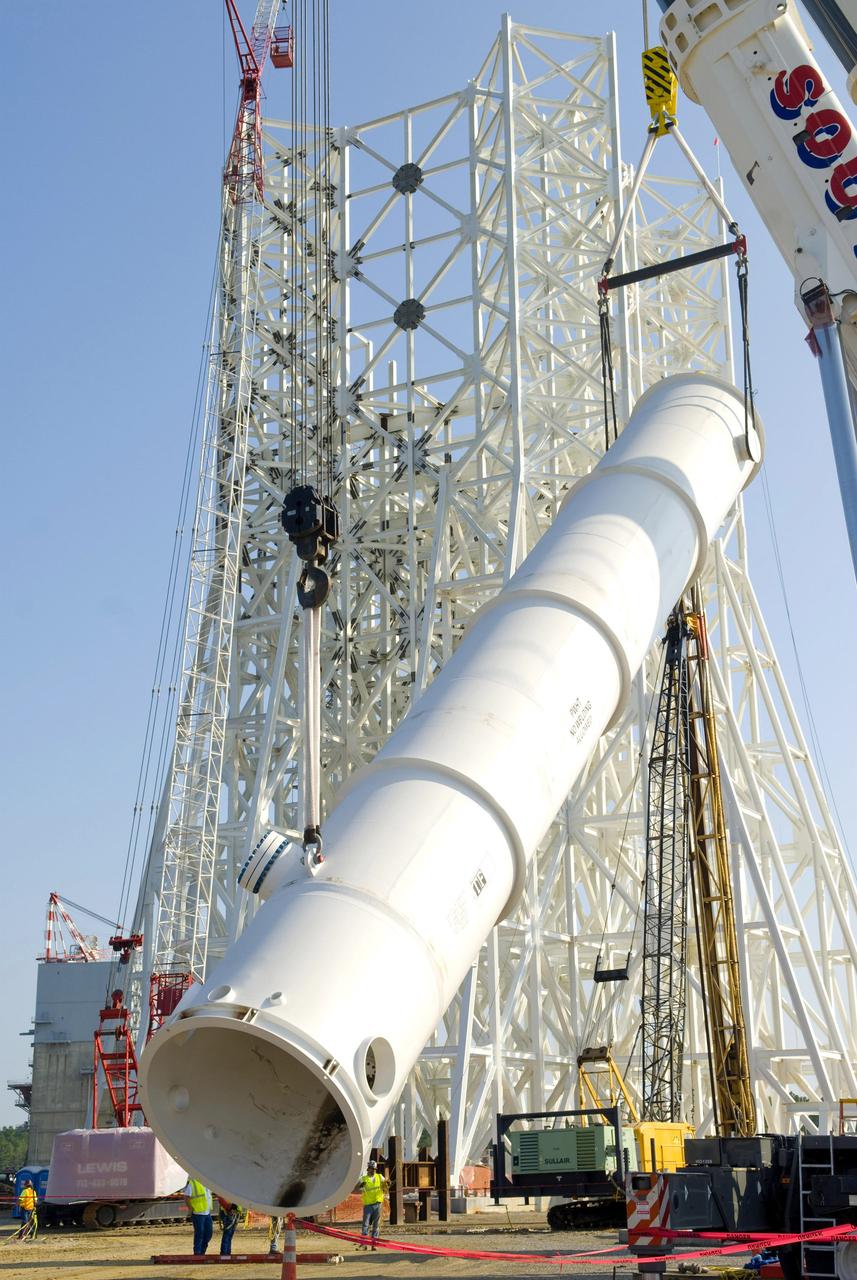

A water tank is lifted into place at the A-3 Test Stand being built at NASA's John C. Stennis Space Center. Fourteen water, liquid oxygen (LOX) and isopropyl alcohol (IPA) tanks are being installed to support the chemical steam generators to be used on the A-3 Test Stand. The IPA and LOX tanks will provide fuel for the generators. The water will allow the generators to produce steam that will be used to reduce pressure inside the stand's test cell diffuser, enabling operators to simulate altitudes up to 100,000 feet. In that way, operators can perform the tests needed on rocket engines being built to carry humans back to the moon and possibly beyond. The A-3 Test Stand is set for completion and activation in 2011.
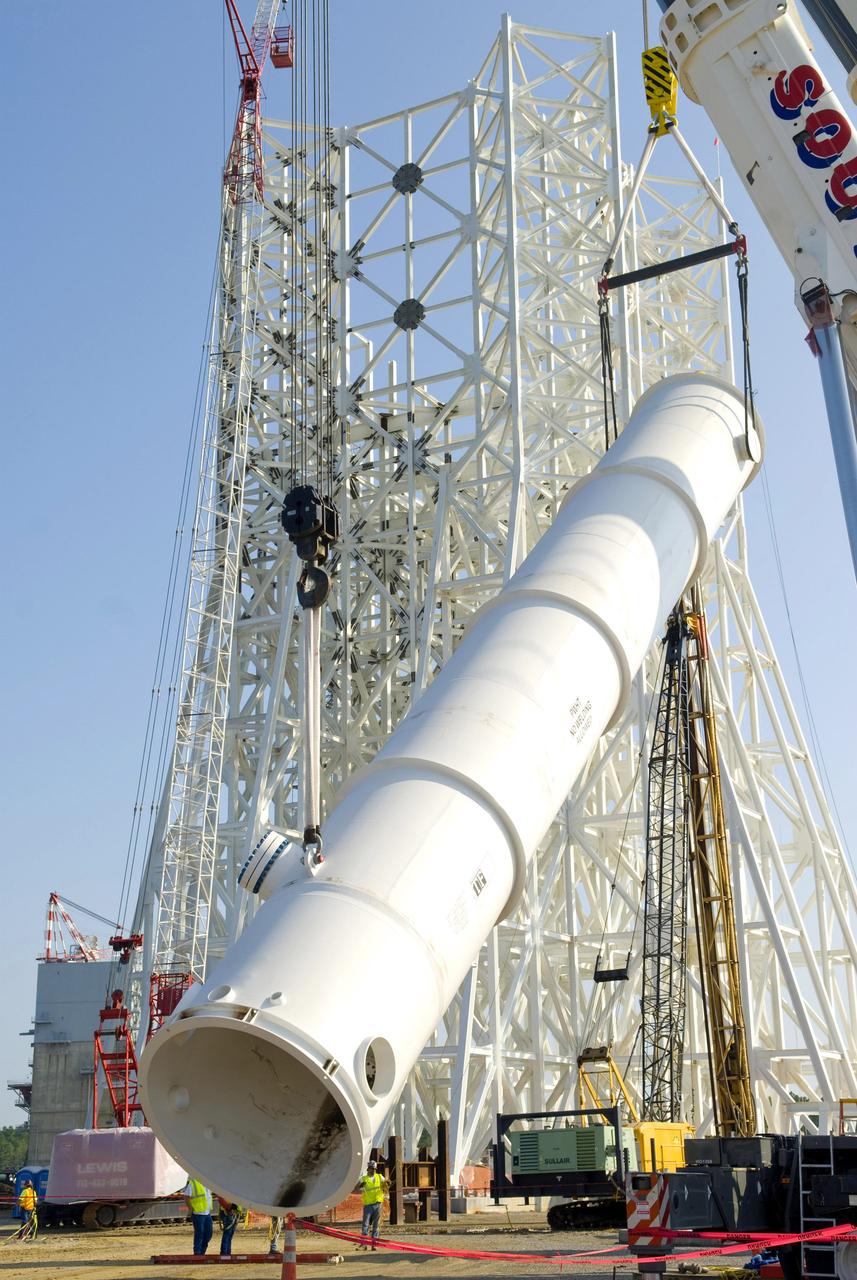

A water tank is lifted into place at the A-3 Test Stand being built at NASA's John C. Stennis Space Center. Fourteen water, liquid oxygen (LOX) and isopropyl alcohol (IPA) tanks are being installed to support the chemical steam generators to be used on the A-3 Test Stand. The IPA and LOX tanks will provide fuel for the generators. The water will allow the generators to produce steam that will be used to reduce pressure inside the stand's test cell diffuser, enabling operators to simulate altitudes up to 100,000 feet. In that way, operators can perform the tests needed on rocket engines being built to carry humans back to the moon and possibly beyond. The A-3 Test Stand is set for completion and activation in 2011.
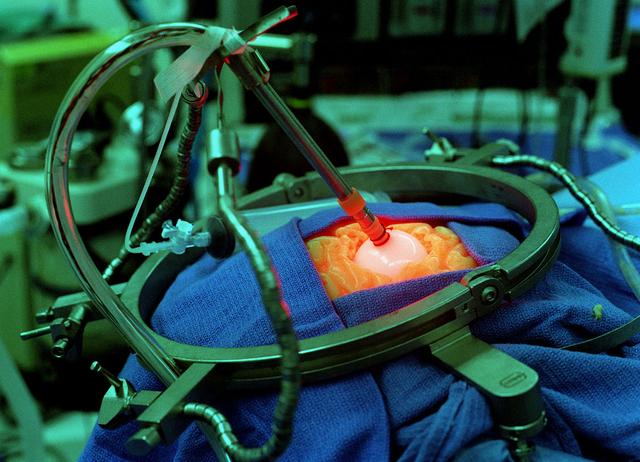
What started out as an attempt to develop a light which would allow for the growth of plants in space led to a remarkable discovery: The Light Emitting Diode (LED). This device through extensive study and experimentation has developed into a tool used by surgeons in the fight against brain cancer in children. Pictured is a mock-up of brain surgery being performed. By encapsulating the end of the LED with a balloon, light is diffused over a larger area of the brain allowing the surgeon a better view. This is one of many programs that begin as research for the space program, and through extensive study end up benefitting all of mankind.
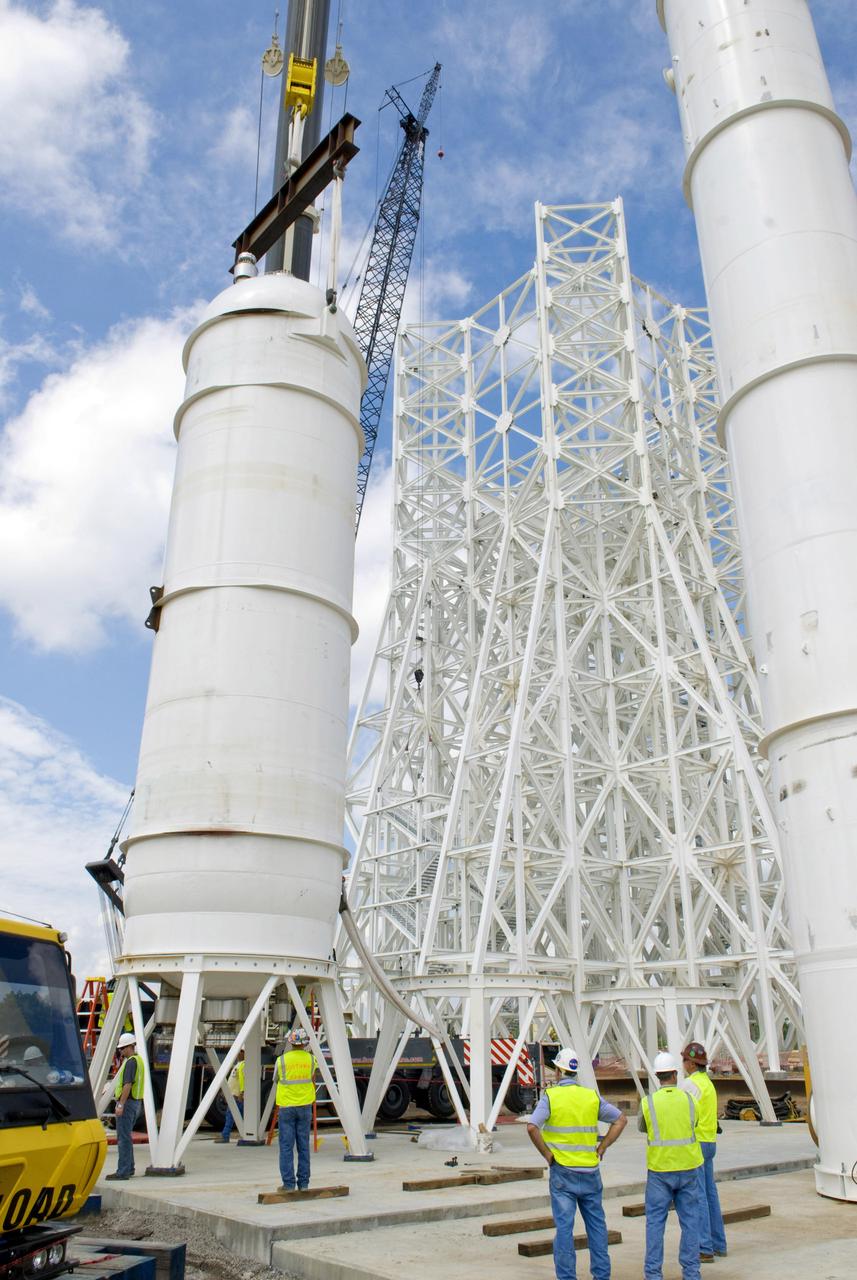

A liquid oxygen (LOX) tank is lifted into place at the A-3 Test Stand being built at NASA's John C. Stennis Space Center. Fourteen LOX, isopropyl alcohol (IPA) and water tanks are being installed to support the chemical steam generators to be used on the A-3 Test Stand. The IPA and LOX tanks will provide fuel for the generators. The water will allow the generators to produce steam that will be used to reduce pressure inside the stand's test cell diffuser, enabling operators to simulate altitudes up to 100,000 feet. In that way, operators can perform the tests needed on rocket engines being built to carry humans back to the moon and possibly beyond. The A-3 Test Stand is set for completion and activation in 2011.
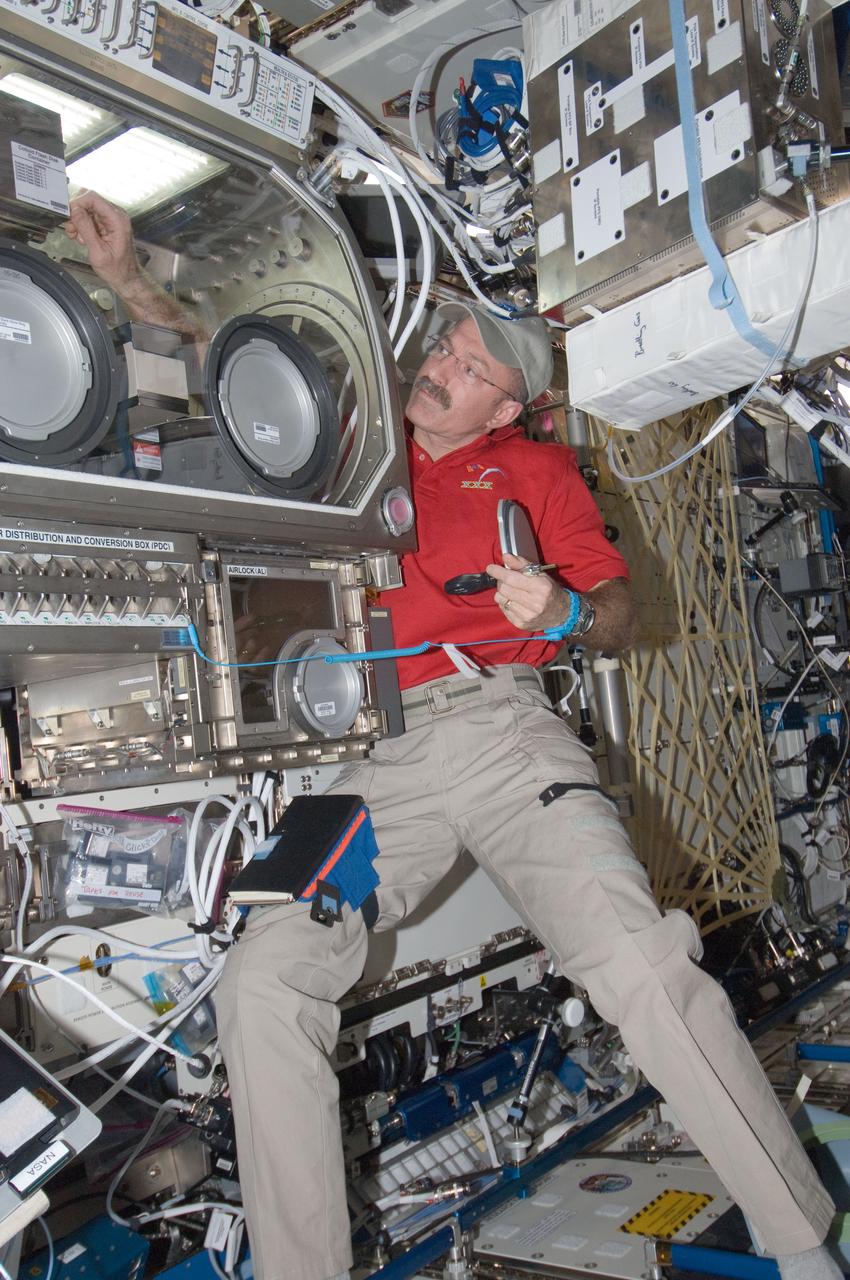

ISS030-E-030125 (10 Jan. 2012) --- NASA astronaut Dan Burbank, Expedition 30 commander, works on the Selectable Optical Diagnostics Instrument C Colloid (SODI-COLLOID) hardware in the Microgravity Science Glovebox in the International Space Station?s Destiny laboratory. Burbank is supporting ground-commanded operations by exchanging out some disks. COLLOID is part of ESA?s triple experiment series for advancement in liquids, diffusion measurements in petroleum reservoirs and the study on growth and properties of advanced photonic materials within colloidal solutions. The commander is currently joined by five other Expedition 30 astronauts and cosmonauts, all flight engineers, aboard the orbital outpost.
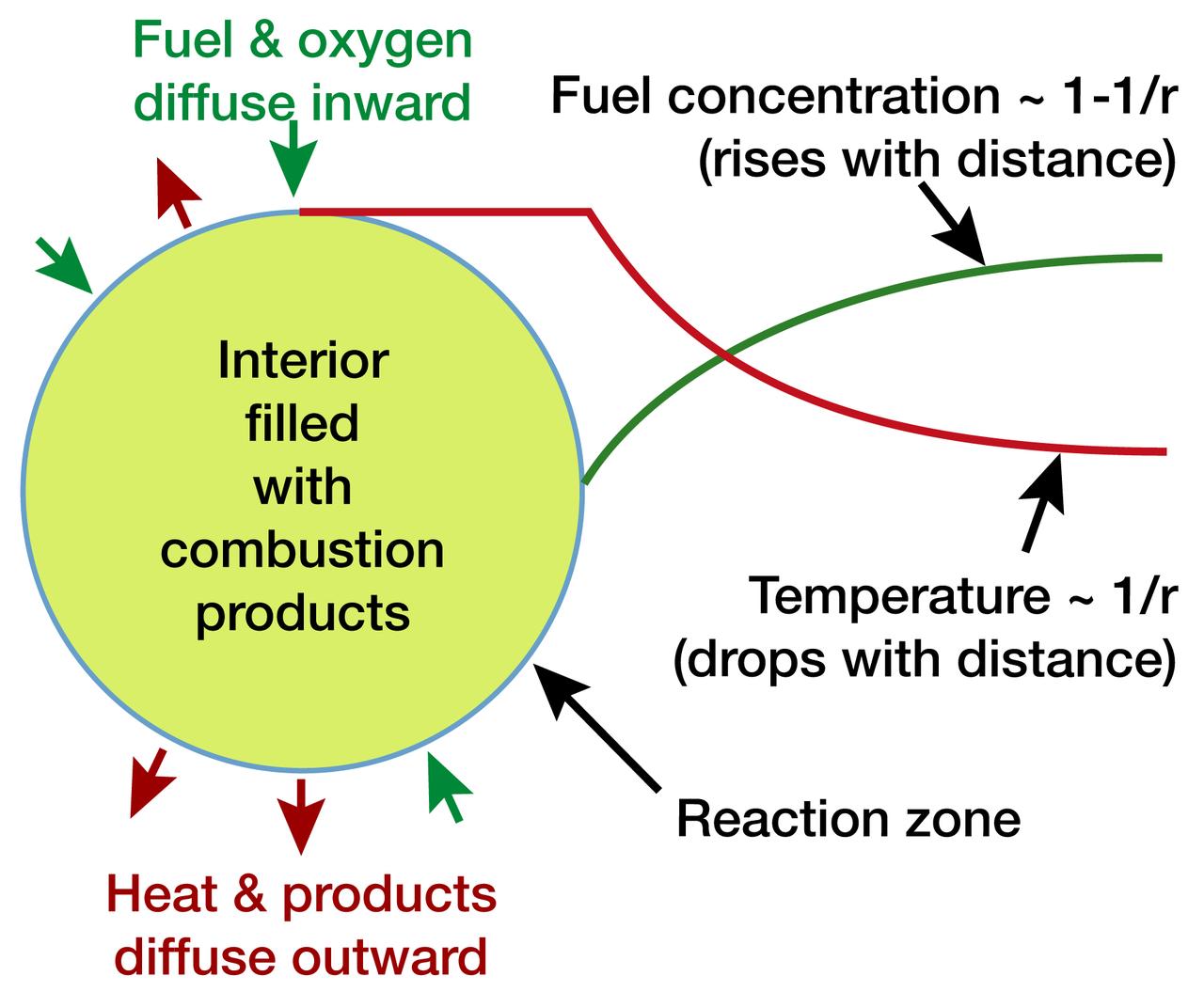
The potential for investigating combustion at the limits of flammability, and the implications for spacecraft fire safety, led to the Structures Of Flame Balls At Low Lewis-number (SOFBALL) experiment flown twice aboard the Space Shuttle in 1997. The success there led to reflight on STS-107 Research 1 mission plarned for 2002. All the combustion in a flame ball takes place in a razor-thin reaction zone that depends on diffusion to keep the ball alive. Such a fragile balance is impossible on Earth. The principal investigator is Dr. Paul Ronney of the University of Southern California, Los Angeles. Glenn Research in Cleveland, OH, manages the project.
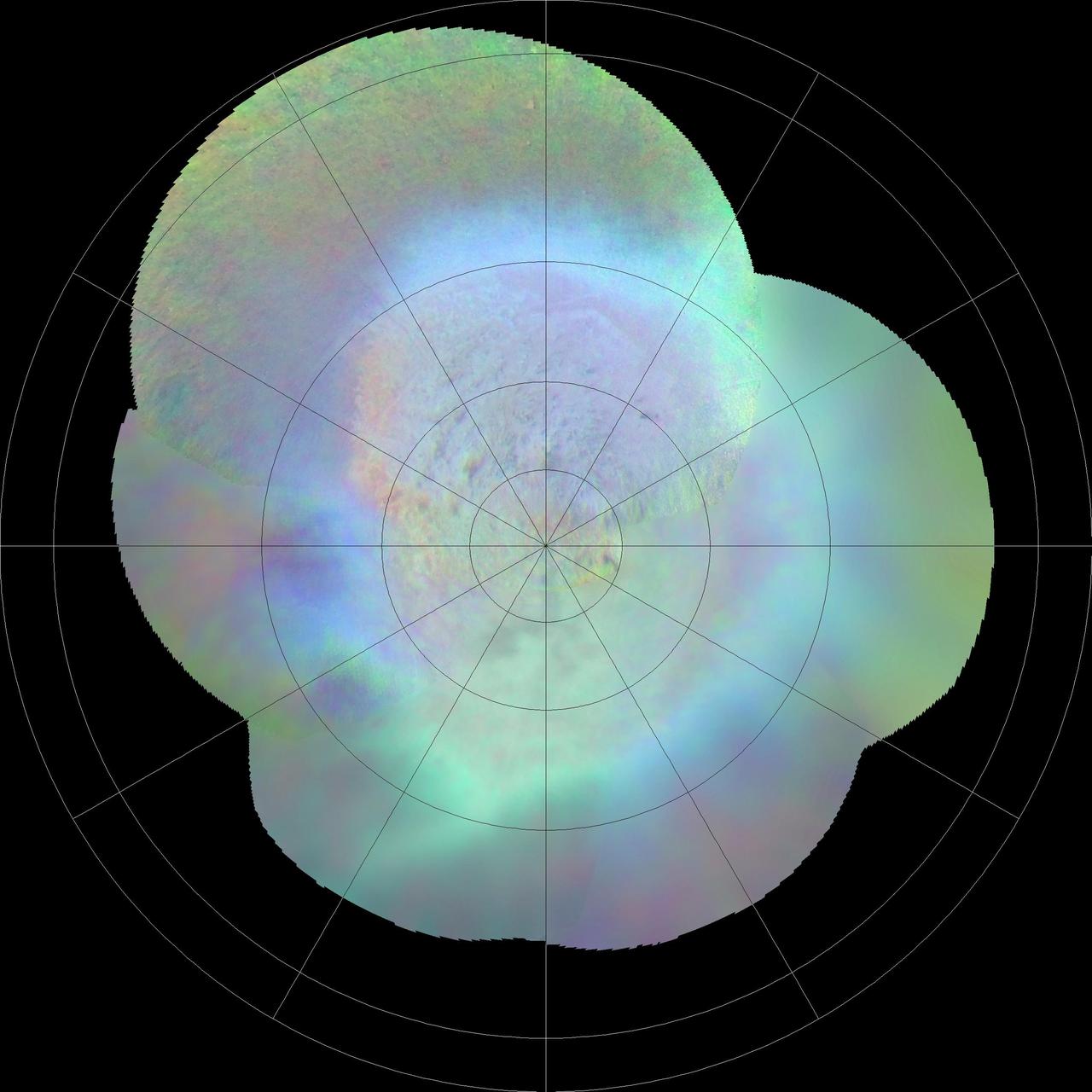
This polar projection from NASA Voyager 2 of Triton southern hemisphere provides a view of the southern polar cap and bright equatorial fringe. The margin of the cap is scalloped and ranges in latitude from +10 degrees to -30 degrees. The bright fringe is closely associated with the cap's margin; from it, diffuse bright rays extend north-northeast for hundreds of kilometers. The bright fringe probably consists of very fresh nitrogen frost or snow, and the rays consist of bright-fringe materials that were redistributed by north-moving Coriolis-deflected winds. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00423
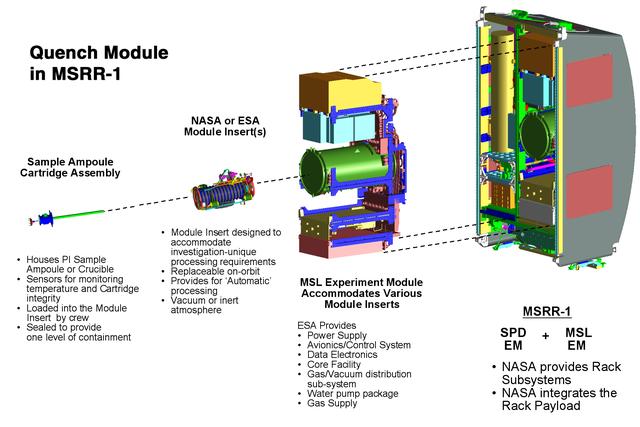
This computer-generated image depicts the Materials Science Research Rack-1 (MSRR-1) being developed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center and the European Space Agency (ESA) for placement in the Destiny laboratory module aboard the International Space Station. The rack is part of the plarned Materials Science Research Facility (MSRF) and is expected to include two furnace module inserts, a Quench Module Insert (being developed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center) to study directional solidification in rapidly cooled alloys and a Diffusion Module Insert (being developed by the European Space Agency) to study crystal growth, and a transparent furnace (being developed by NASA's Space Product Development program). Multi-user equipment in the rack is being developed under the auspices of NASA's Office of Biological and Physical Research (OBPR) and ESA. Key elements are labeled in other images (0101754, 0101829, 0101830).
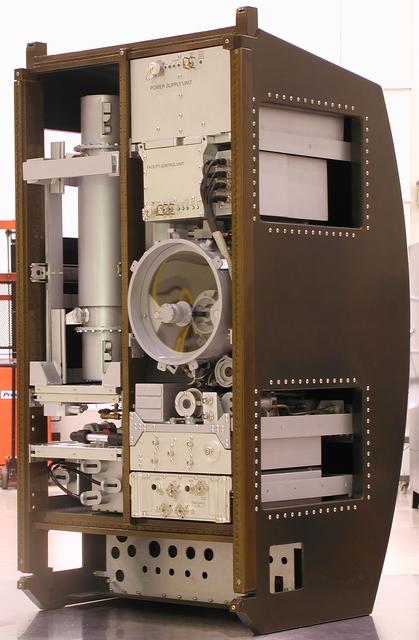
This scale model depicts the Materials Science Research Rack-1 (MSRR-1) being developed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center and the European Space Agency (ESA) for placement in the Destiny laboratory module aboard the International Space Station. The rack is part of the plarned Materials Science Research Facility (MSRF) and is expected to include two furnace module inserts, a Quench Module Insert (being developed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center) to study directional solidification in rapidly cooled alloys and a Diffusion Module Insert (being developed by the European Space Agency) to study crystal growth, and a transparent furnace (being developed by NASA's Space Product Development program). Multi-user equipment in the rack is being developed under the auspices of NASA's Office of Biological and Physical Research (OBPR) and ESA. Key elements are labeled in other images (0101754, 0101829, 0101830, and TBD). This image is from a digital still camera; higher resolution is not available.

This scale model depicts the Materials Science Research Rack-1 (MSRR-1) being developed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center and the European Space Agency (ESA) for placement in the Destiny laboratory module aboard the International Space Station. The rack is part of the plarned Materials Science Research Facility (MSRF) and is expected to include two furnace module inserts, a Quench Module Insert (being developed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center) to study directional solidification in rapidly cooled alloys and a Diffusion Module Insert (being developed by the European Space Agency) to study crystal growth, and a transparent furnace (being developed by NASA's Space Product Development program). Multi-user equipment in the rack is being developed under the auspices of NASA's Office of Biological and Physical Research (OBPR) and ESA. Key elements are labeled in other images (0101754, 0101829, 0101830, and TBD).