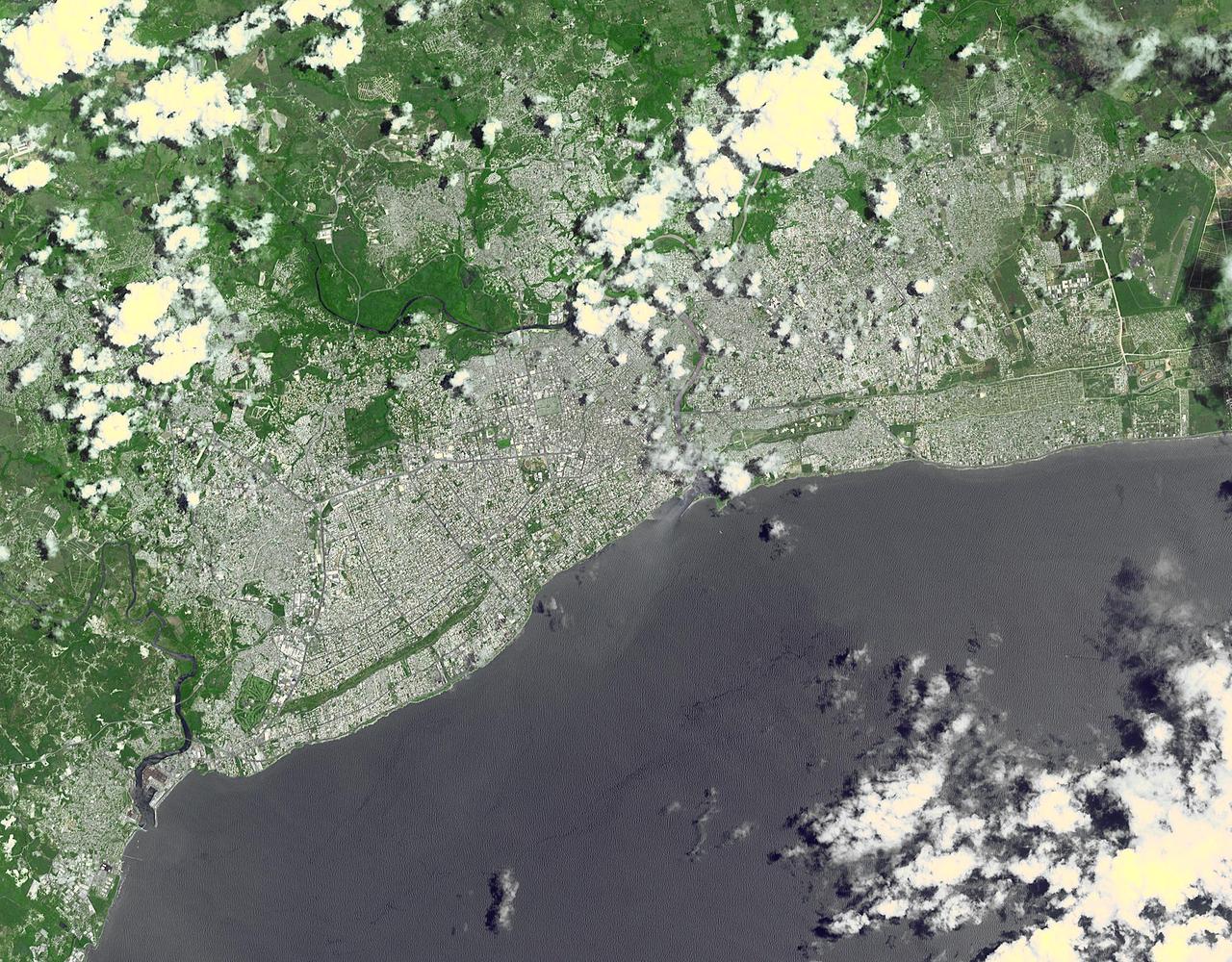

This image, acquired by NASA Terra spacecraft, shows Santo Domingo, the capital of the Dominican Republic, founded in 1496 Christopher Columbus, it is the oldest continuously inhabited European settlement in the Americas.
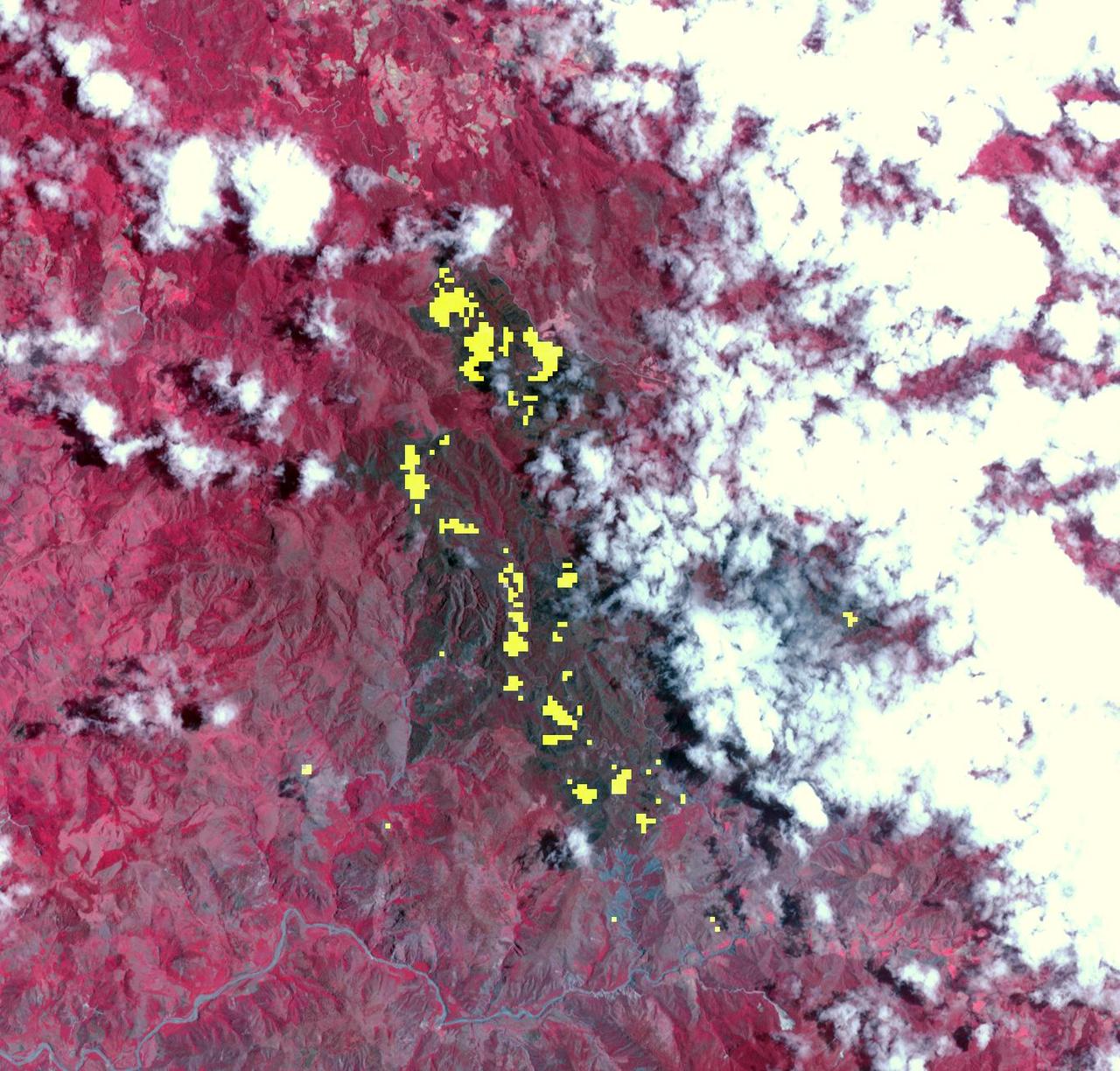

NASA Terra spacecraft captured this thermal infrared view of the spread of the forest fire in Valle Nuevo National Park near Costanza, Dominican Republic.
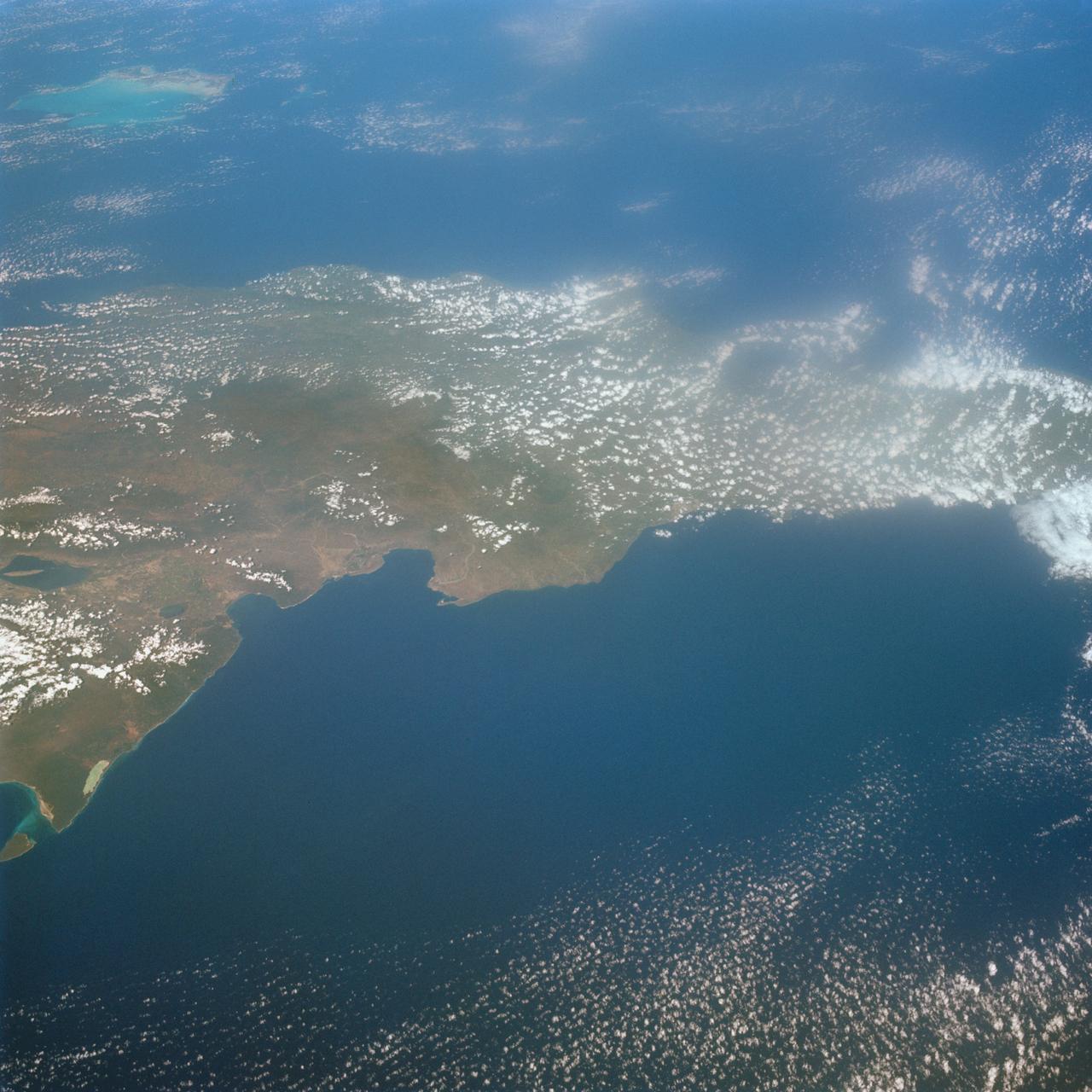

S65-63926 (16 Dec. 1965) --- Island of Hispaniola, Dominican Republic end, as seen from the National Aeronautics and Space Administration's Gemini-7 spacecraft during its 179th revolution of Earth. North is toward the left of the picture. This photograph was taken with a modified 70mm Hasselblad camera, using Eastman Kodak, Ektachrome MS (S.O. 217) color film. Photo credit: NASA
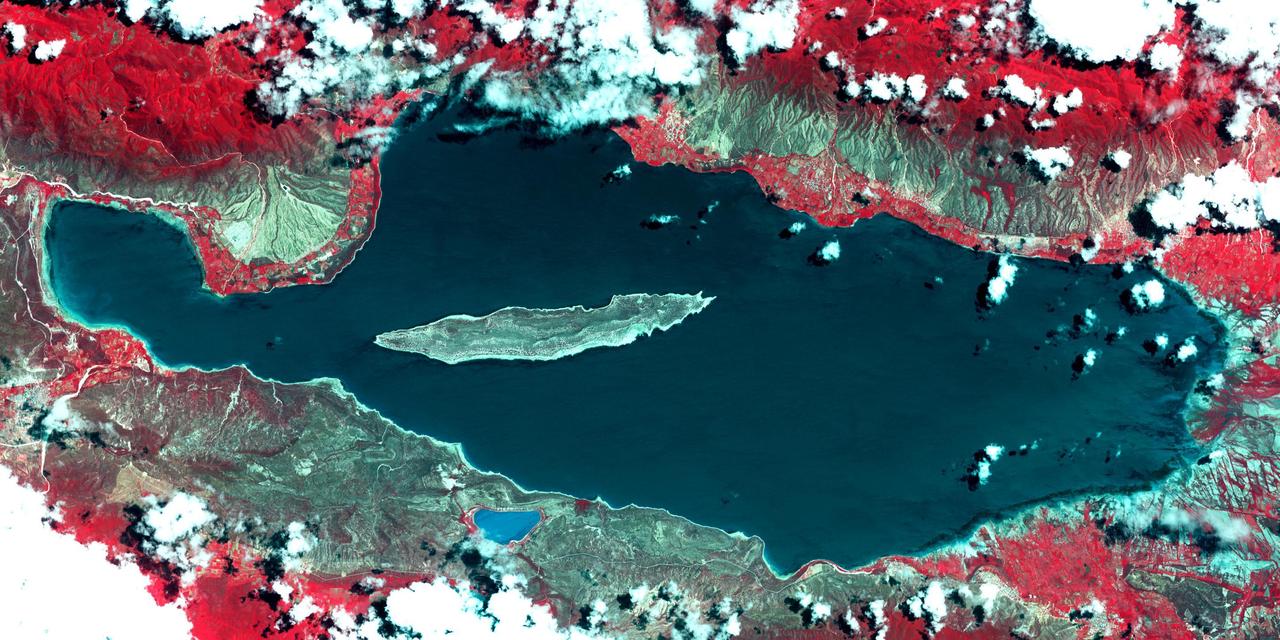

Lake Enriquillo is a hypersaline lake in the Dominican Republic. In 2004, the lake covered an area of 164 square kilometers; by 2011, it had doubled in size and grown to 350 km2, inundating farmland and homes. Various reasons for the flooding include increases in rainfall; increase of sediments going into the lake, raising the lakebed; and milder temperatures, reducing surface evaporation. The lake is home to the largest population of American crocodiles in the Caribbean. The images were acquired October 26, 2003 and June 10, 2017, cover an area of 22.7 by 45.4 km, and are located at 18.5 degrees north, 71.6 degrees west. An image of Lake Enriquillo taken in 2003 is available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21815
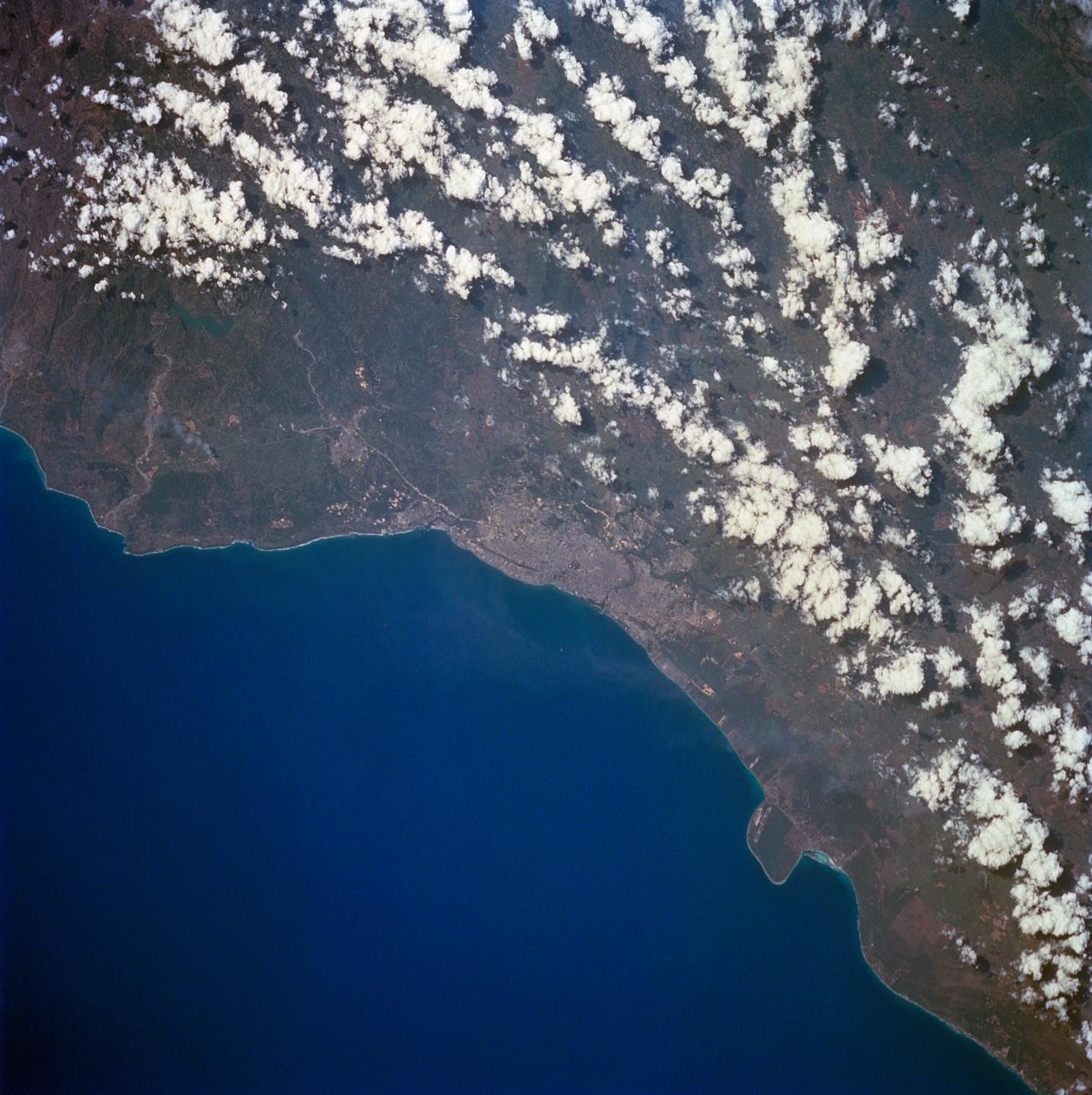

STS060-84-063 (3-11 Feb 1994) --- This is an excellent photograph of the coastal city of Santo Domingo on the Caribbean Sea. The airports including De las Americas International Airport are clearly seen. This photo illustrates the resolving power of the films. For example, two isolated smoke plumes are clearly seen each side of the city.
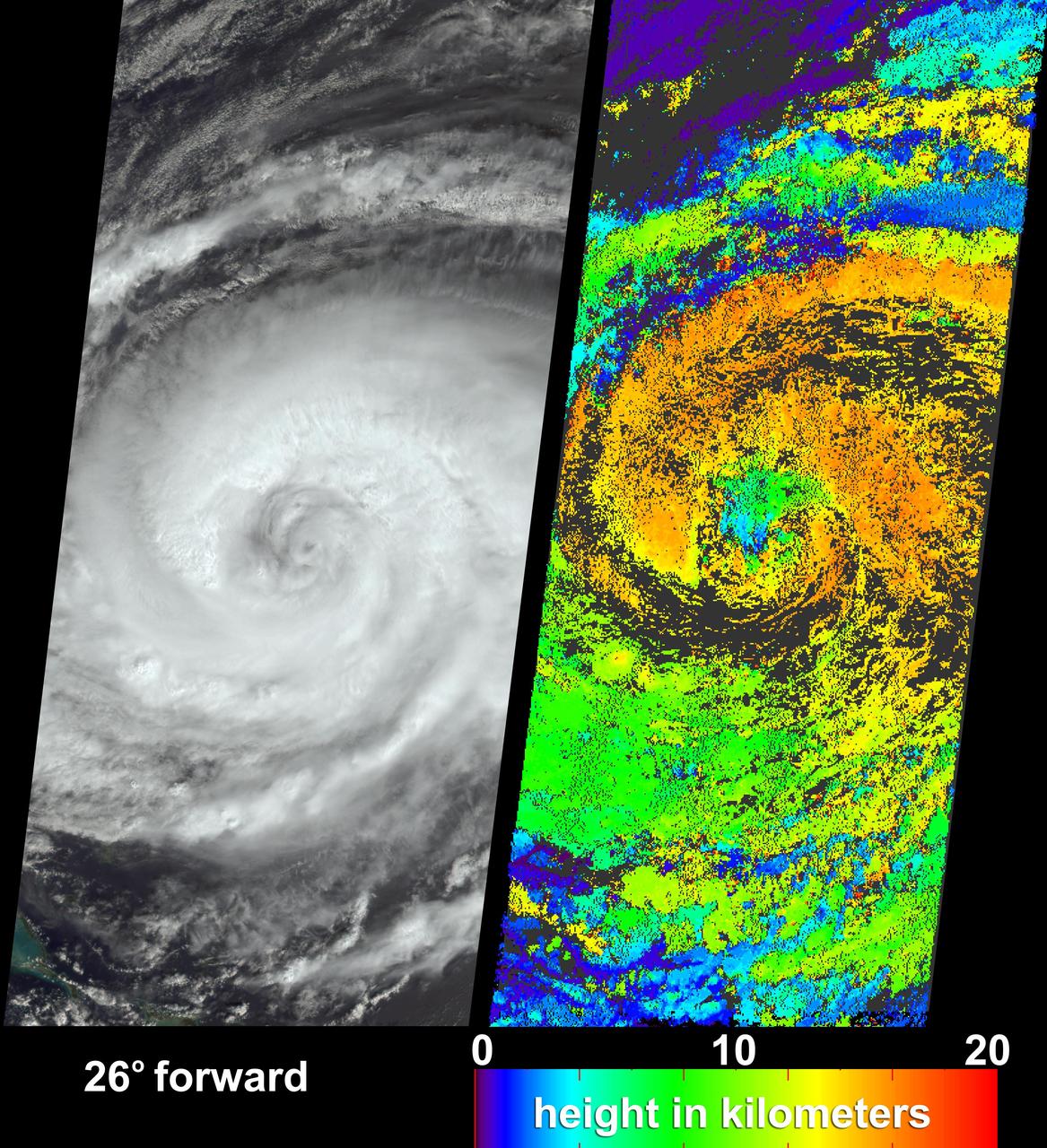
These visualizations of Hurricane Jeanne on September 24, 2004 were captured by NASA Terra spacecraft after the hurricane caused widespread destruction on Puerto Rico, Haiti and the Dominican Republic.
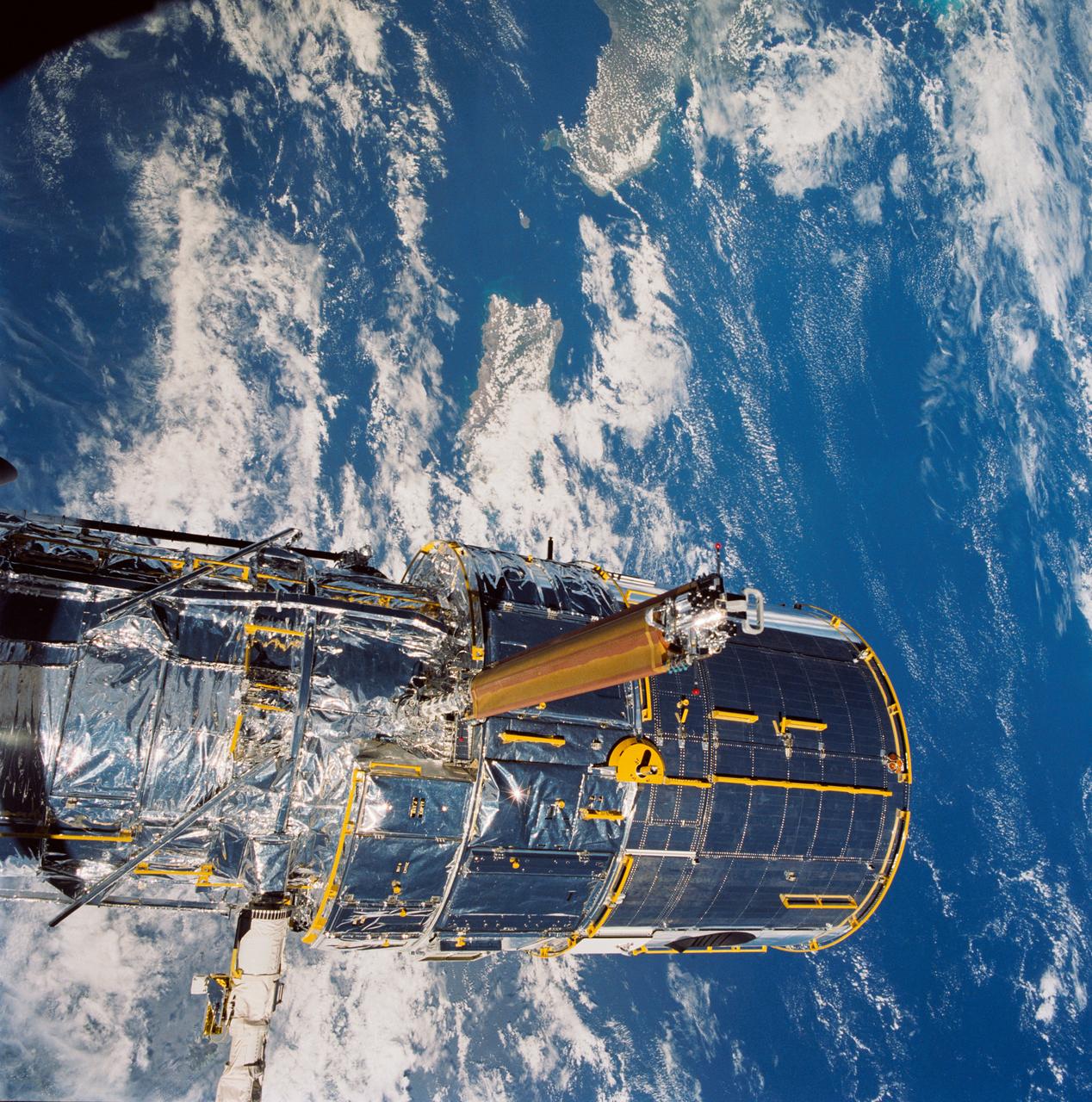

During STS-31, the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) grappled by the remote manipulator system (RMS) end effector is held in appendage deploy position above Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103. The solar array (SA) bistem cassette has been released from its latch fittings. The bistem spreader bars begin to unfurl the SA wing. The secondary deployment mechanism (SDM) handle is visible at the SA end. Stowed against either side of the HST System Support Module (SSM) forward shell are the high-gain antennae (HGA). Puerto Rico and the Dominican Republic are recognizable at the left of the frame.
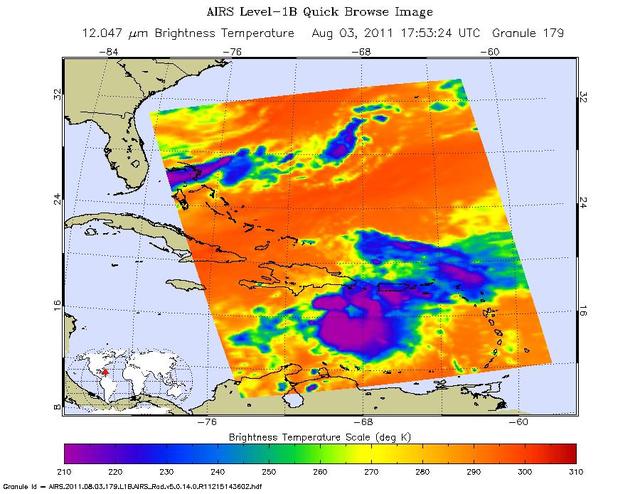
Tropical Storm Emily continues its march toward Hispaniola, which it is expected to reach later on Aug. 3. NASA Aqua spacecraft captured this infrared image 1:53 p.m. EDT on Aug. 3, with the storm located south of Santo Domingo, Dominican Republic.
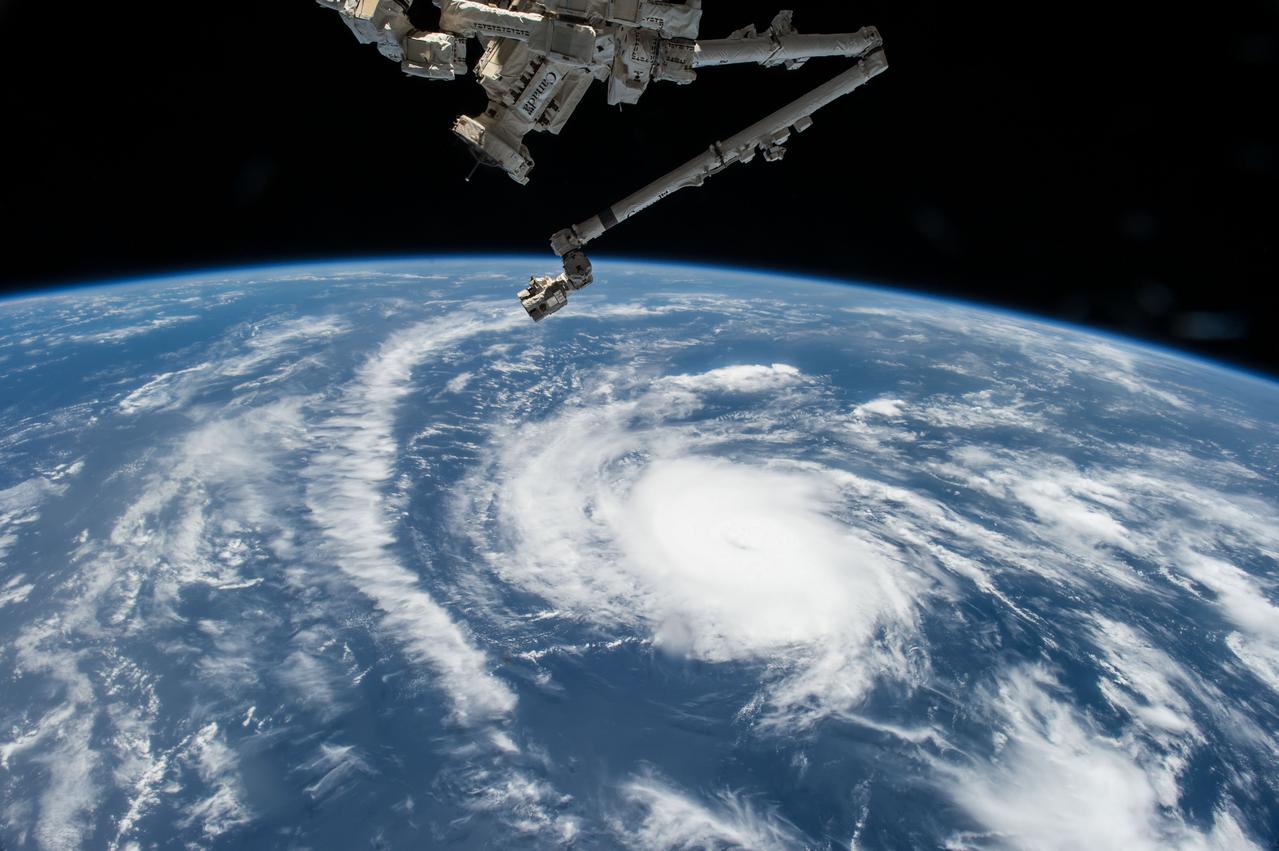

ISS044E059041 (08/21/2015) --- Hurricane Danny as seen from the International Space Station as it traversed the Caribbean Sea headed for Puerto Rico, the Dominican Republic and Cuba.
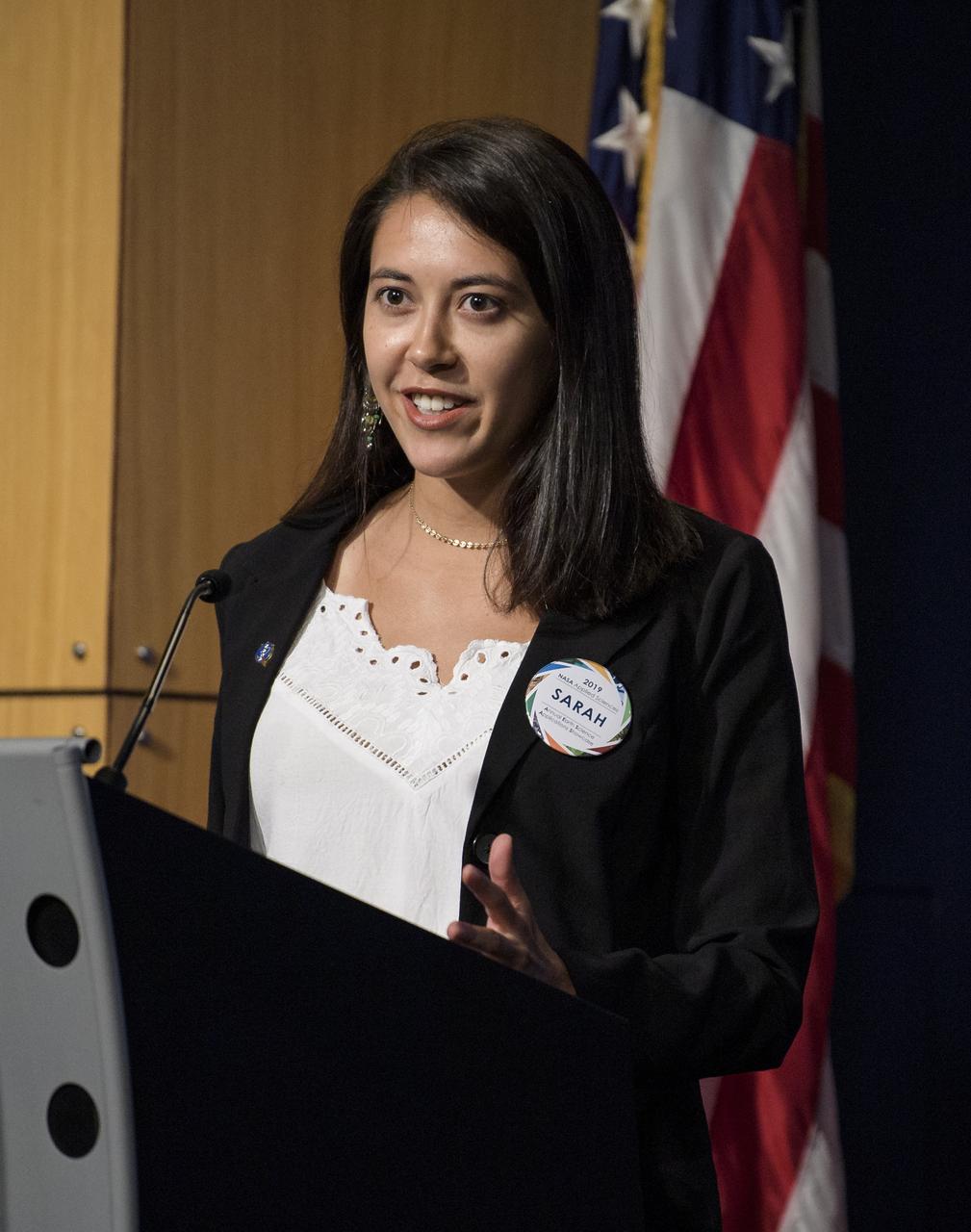

Sarah Aldama, project lead for DEVELOP Dominican Republic Disasters, speaks about mapping landslide susceptibility and exposure in the Dominican Republic using NASA's earth observation data during the 2019 Annual Earth Science Applications Showcase, Thursday, Aug. 1, 2019 at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC. Every summer students and young professionals from NASA’s Applied Sciences’ DEVELOP National Program come to NASA Headquarters and present their research projects. DEVELOP is a training and development program where students work on Earth science research projects, mentored by science advisers from NASA and partner agencies, and extend research results to local communities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

iss054e012391 (Jan. 1, 2018) --- Despite the cloudiness during this nighttime photograph taken by Expedition 54 crew members aboard the International Space Station, the Caribbean islands of (from top left to bottom right) Puerto Rico, Cuba, Haiti and the Dominican Republic are seen from an altitude of 250 miles.
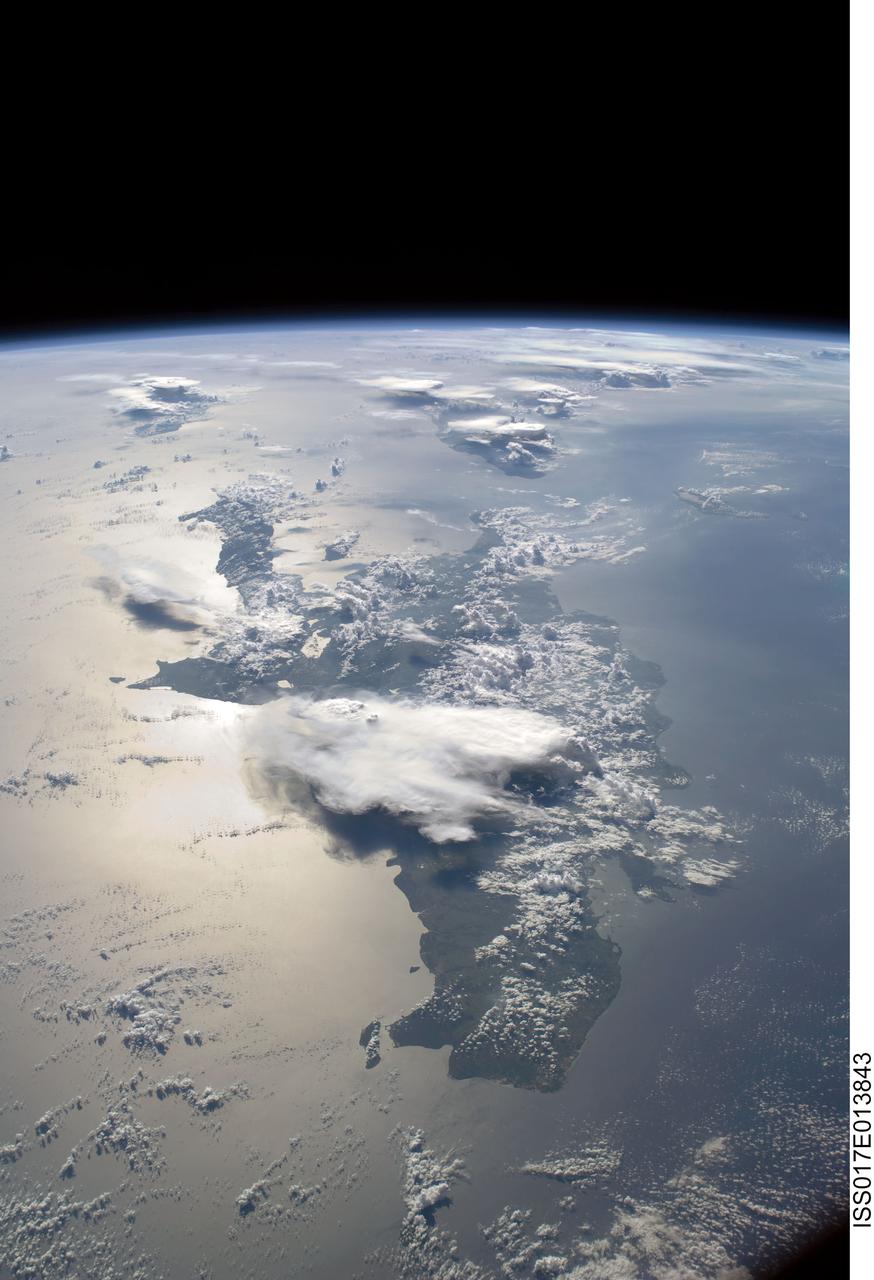

ISS017-E-013843 (19 Aug. 2008) --- A panoramic view of the island of Hispaniola in the foreground and Cuba extending to over the horizon. The sunglint is illuminating Haiti and the Dominican Republic while the thunderstorms persist in the late afternoon of the summertime day. Taken by the Expedition 17 crew onboard the ISS on Aug 19, 2008 with a 28 mm lens.

iss073e0838653 (Sept. 14, 2025) --- The Soyuz MS-27 crew spacecraft is pictured docked to the International Space Station's Prichal module as the orbital outpost soared 257 miles above a gleaming blue Atlantic Ocean, north of the Dominican Republic.
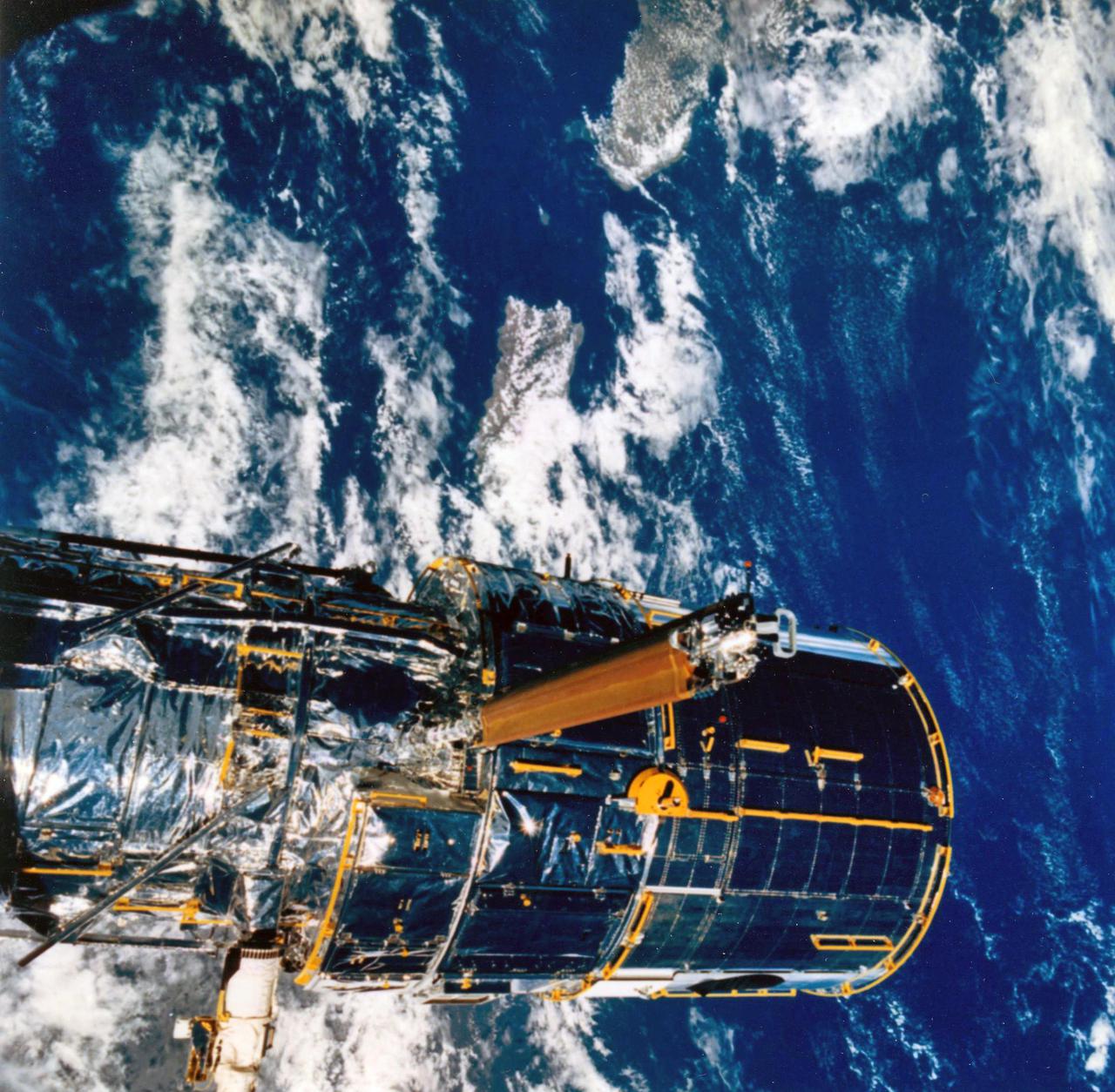

JOHNSON SPACE CENTER, HOUSTON, TEXAS-- STS-31 ONBOARD SCENE -- The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is suspended in space by Discovery's remote manipulator system prior to deployment of its solar array panels and antennae and its ultimate release. Puerto Rico and the Dominican Republic are recognizable at left of the frame. The photo was taken with a handheld Hasselblad camera. This was among the first photos NASA released on April 30 from the five-day mission.
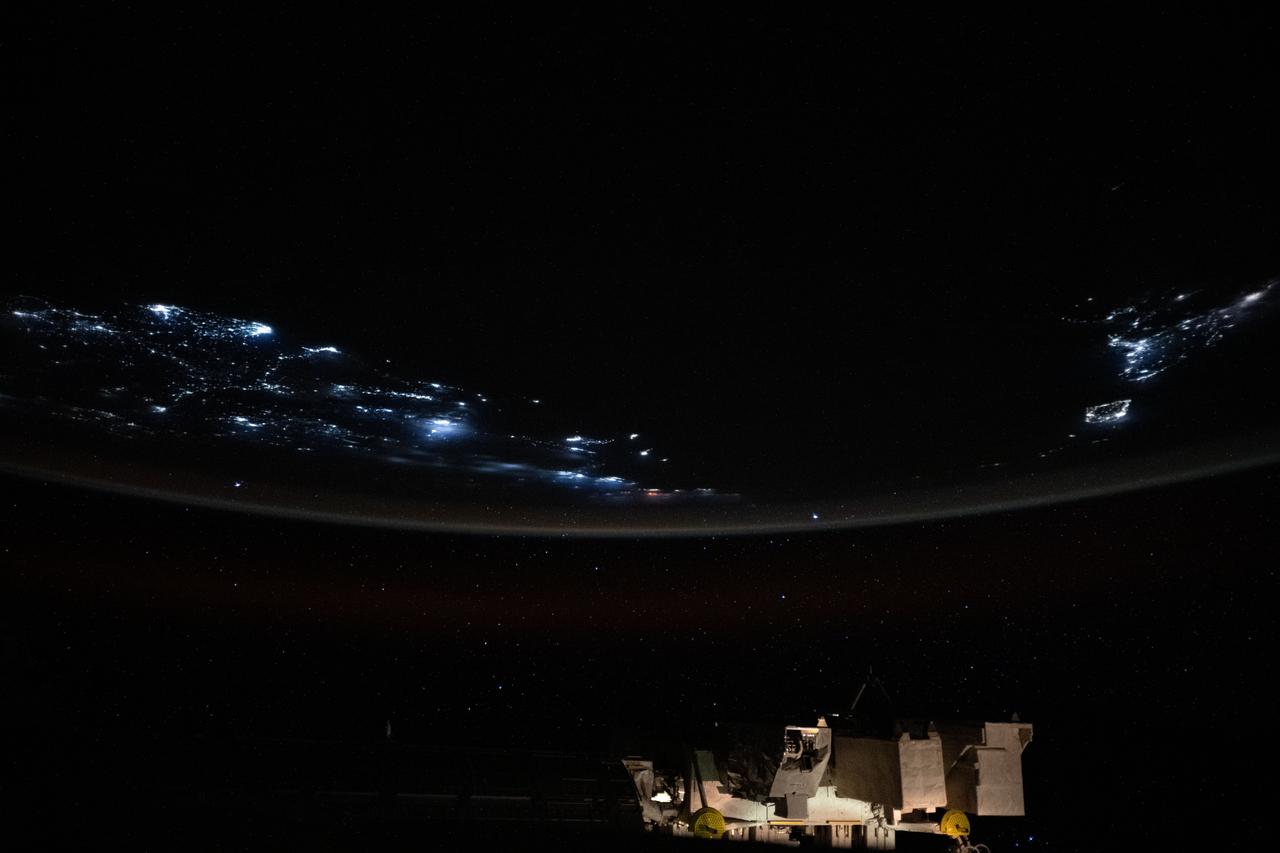

iss073e0854494 (Sept. 21, 2025) --- The coastlines of Colombia and Venezuela (left), illuminated by city lights, are separated from the island nations of the Dominican Republic and Puerto Rico (far right) by the dark expanse of the Caribbean Sea. The International Space Station was orbiting approximately 260 miles above Earth when this photograph was taken at around 1:06 a.m. local time.
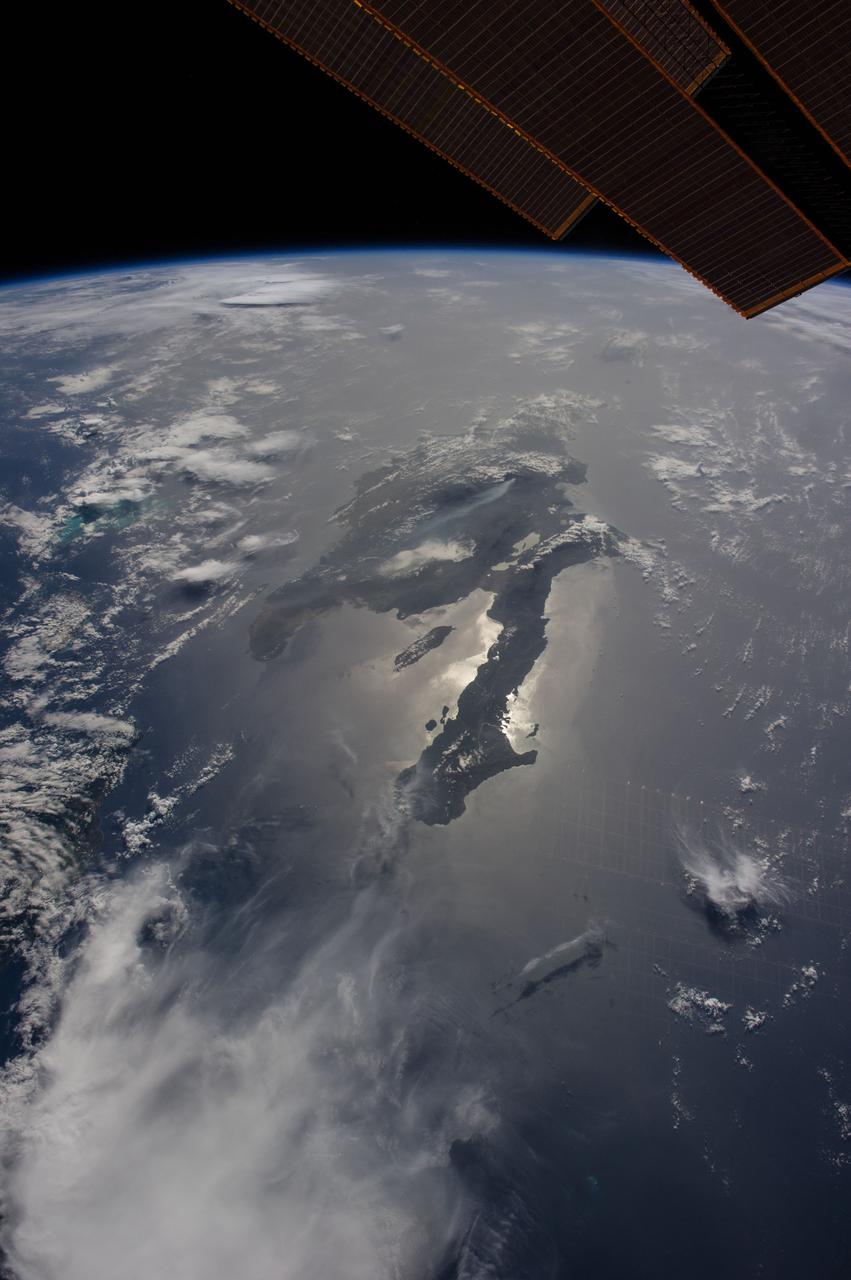

ISS040-E-080921 (26 June 2014) --- Dominican Republic and Haiti, Hispaniola, Caribbean are featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 40 crew member on the International Space Station. Looking east into a rising sun, the crew took this panorama of Hispaniola with the sun’s glint point illuminating the long western peninsula of Haiti. Several thunderheads throw shadows towards the camera (left). The plume from a very large wildfire stretches west (center). The Constanza Fire started in a national forest on the Dominican Republic growing to the extent that it threatened surrounding towns and prompting an International Disaster Charter activation, whereby requests for imagery were uplinked to the station crew as possible assistance to help firefighters on the ground. Hurricane Bertha tracked over the island a week later helping to douse the flames. The view looks hazy probably because of dust in the atmosphere. Dust blows across the Atlantic Ocean from Africa reaching the western hemisphere every month of the year. Despite the austere tone of the image, touches of color are blue waters of the Turks and Caicos Islands extending from under a large thundercloud (left) and the edge of a space station solar panel (top right).
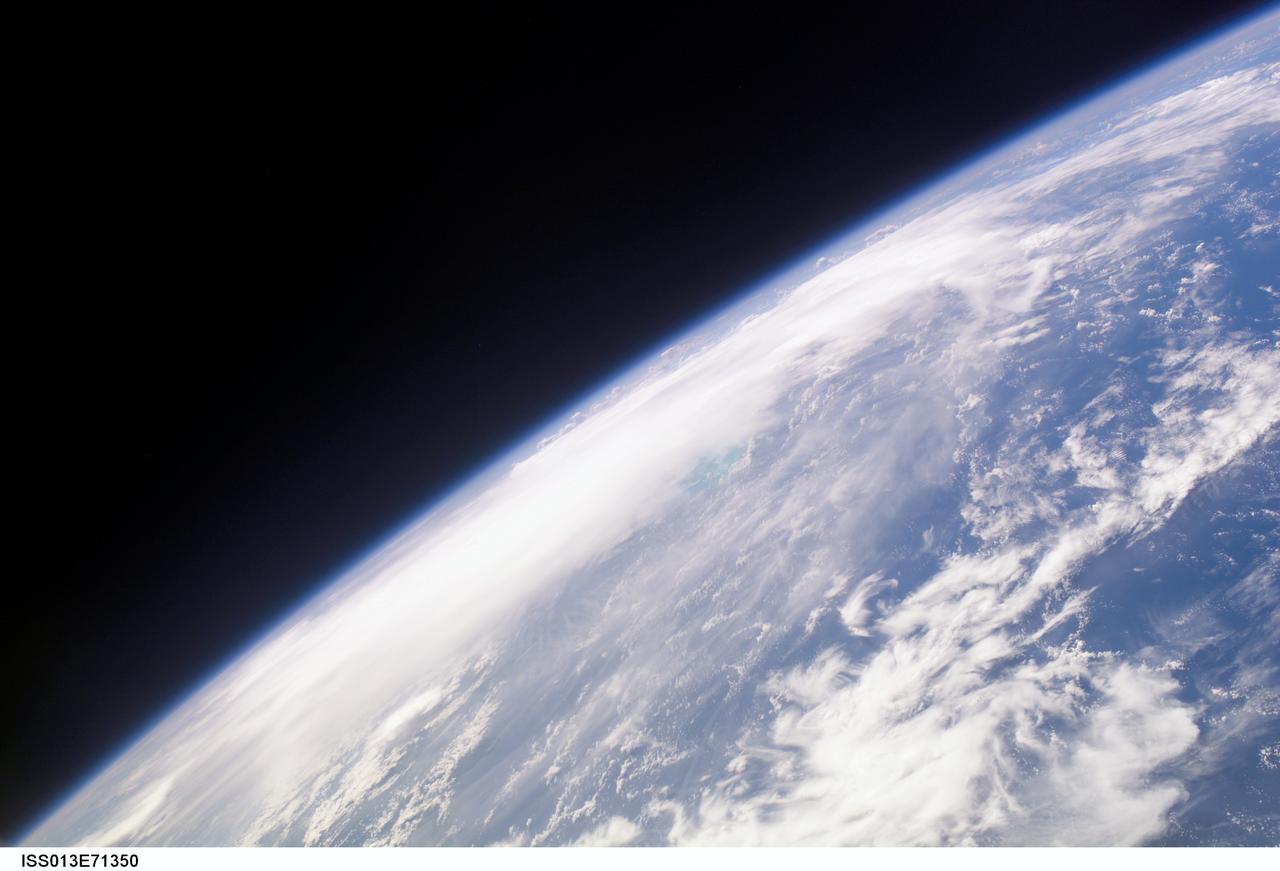

ISS013-E-71350 (28 August 2006) --- The crewmembers aboard the International Space Station took this oblique picture of Ernesto on Earth's horizon early afternoon on August 28, 2006. The tropical storm's center was located near 20.3 degrees north latitude and 75.7 degrees west longitude when the photo was taken. Movement was toward the northwest at 9 nautical miles per hour. Maximum sustained winds were at 35 nautical miles with gusts to 45 nautical miles. Ernesto had earlier passed between the east side of the Dominican Republic and Grand Turk Island (the light blue area near frame center).
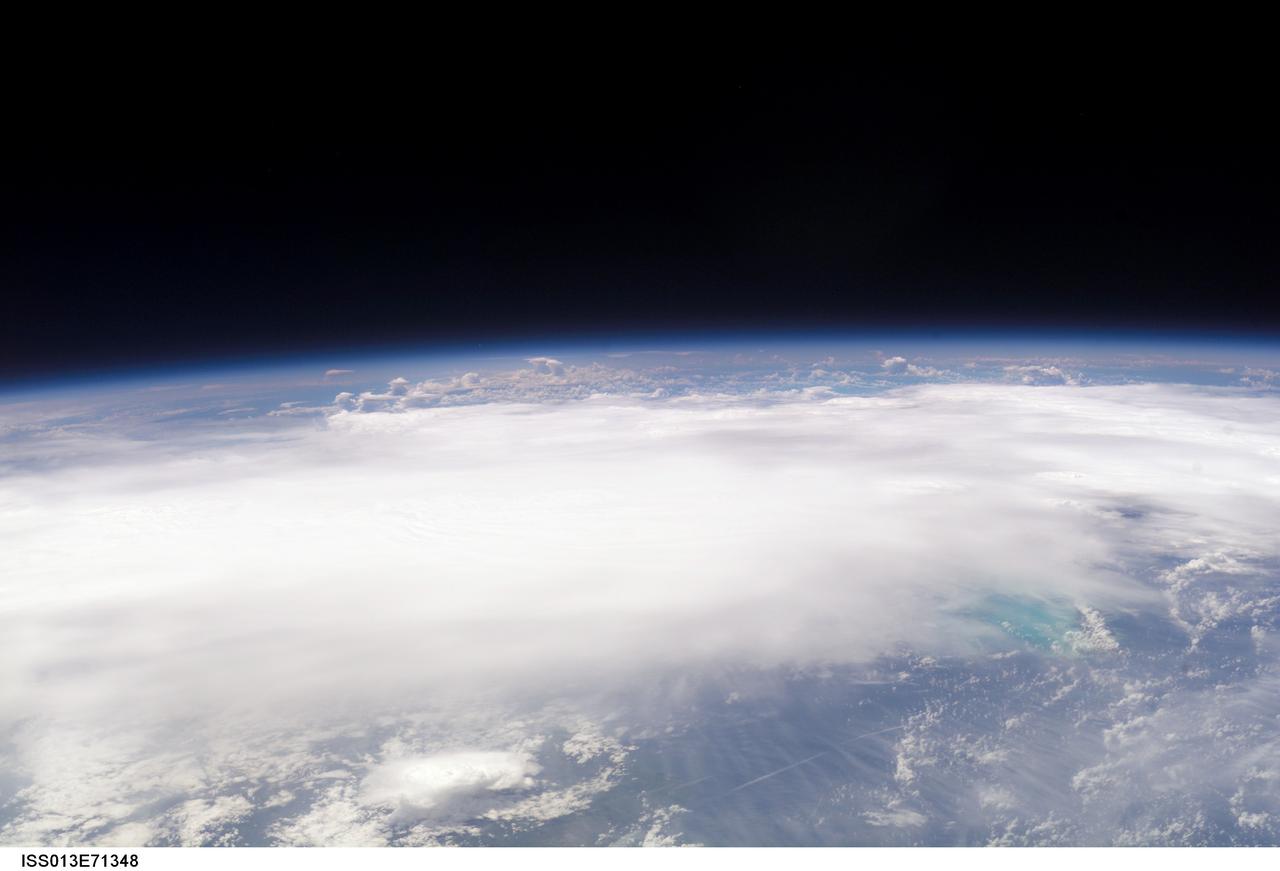

ISS013-E-71348 (28 August 2006) --- The crewmembers aboard the International Space Station took this picture of Ernesto early afternoon on August 28, 2006. The tropical storm's center was located near 20.3 degrees north latitude and 75.7 degrees west longitude when the photo was taken. Movement was toward the northwest at 9 nautical miles per hour. Maximum sustained winds were at 35 nautical miles with gusts to 45 nautical miles. Ernesto had earlier passed between the east side of the Dominican Republic and Grand Turk Island (the blue area in lower right corner).
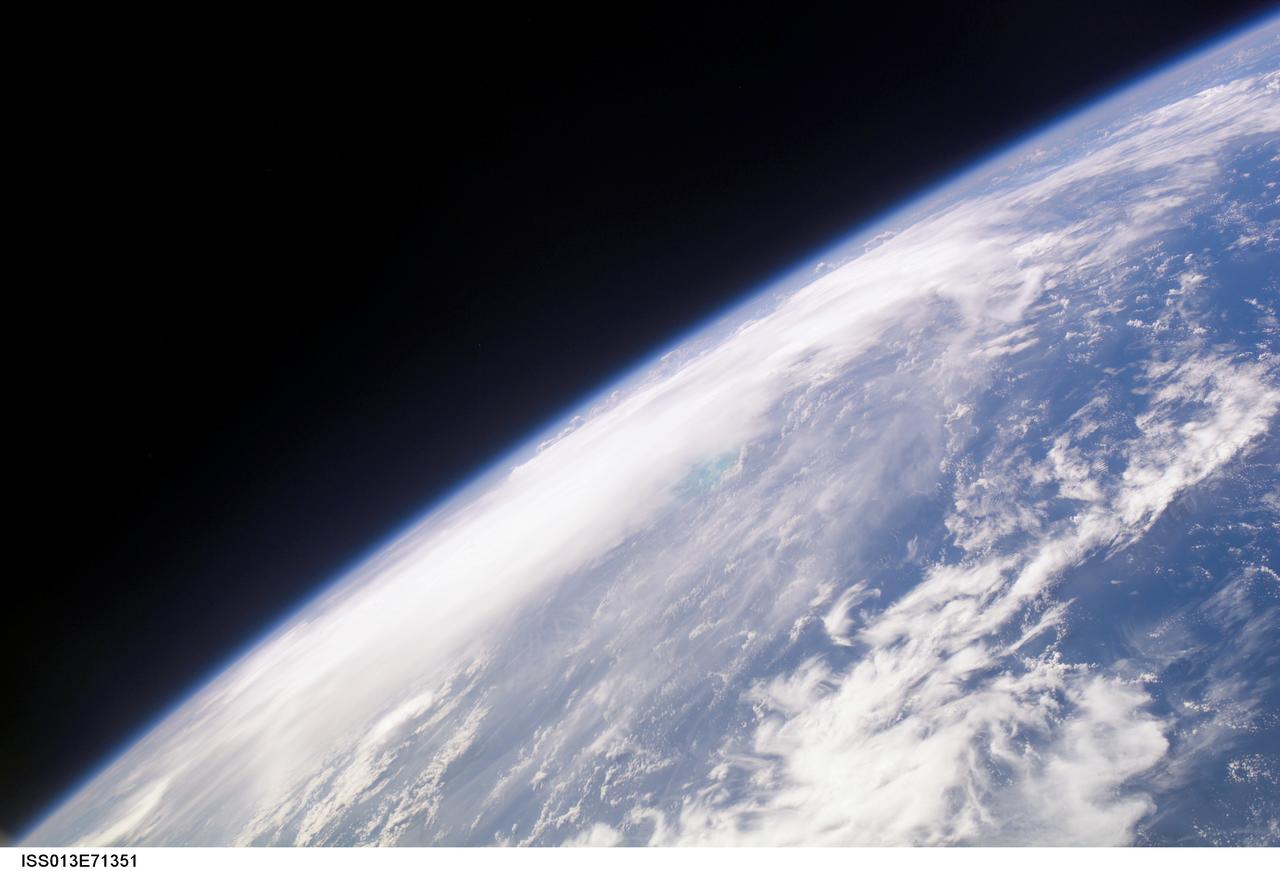

ISS013-E-71351 (28 August 2006) --- The crewmembers aboard the International Space Station took this oblique picture of Ernesto on Earth's horizon early afternoon on August 28, 2006. The tropical storm's center was located near 20.3 degrees north latitude and 75.7 degrees west longitude when the photo was taken. Movement was toward the northwest at 9 nautical miles per hour. Maximum sustained winds were at 35 nautical miles with gusts to 45 nautical miles. Ernesto had earlier passed between the east side of the Dominican Republic and Grand Turk Island (the light blue area near frame center).
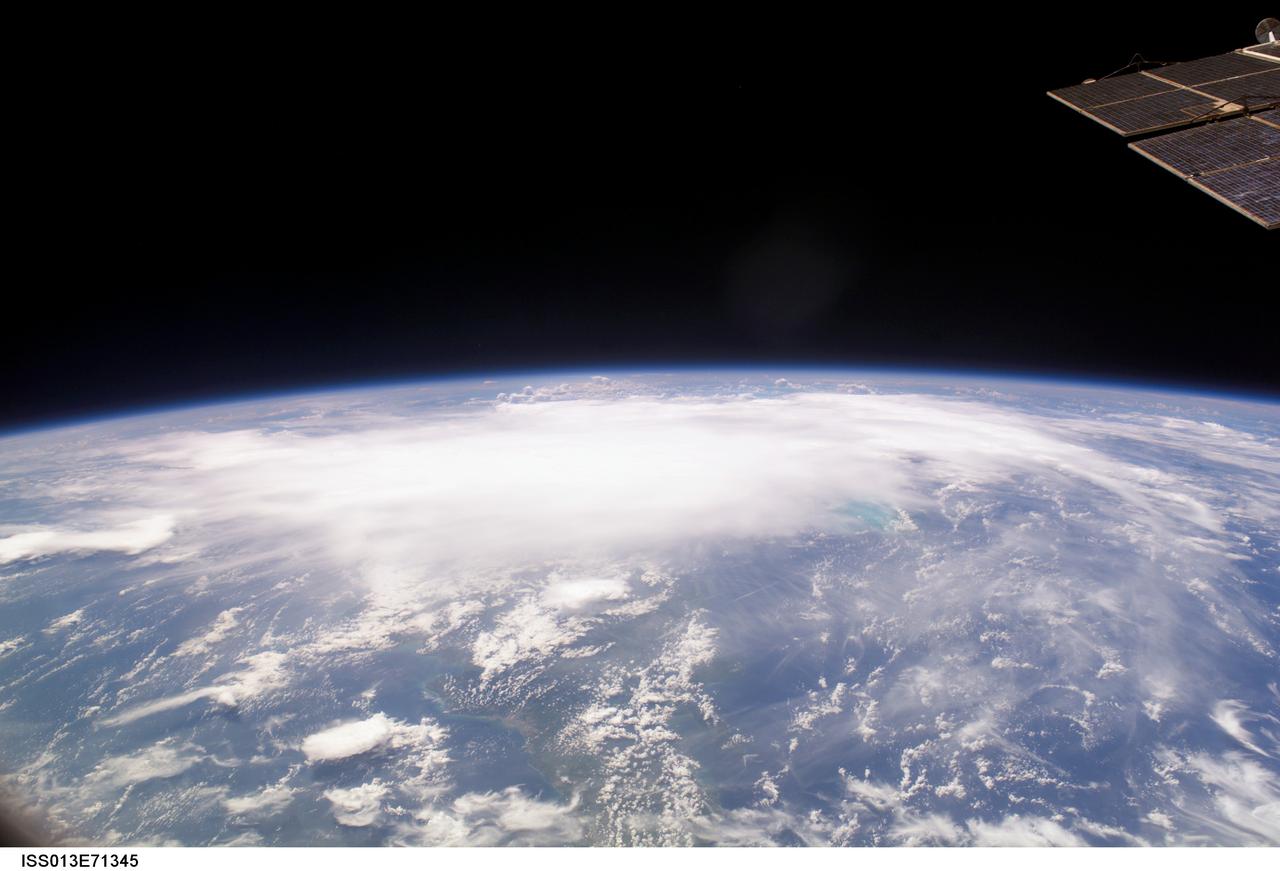

ISS013-E-71345 (28 August 2006) --- The crewmembers aboard the International Space Station took this oblique picture of Ernesto on Earth's horizon early afternoon on August 28, 2006. The tropical storm's center was located near 20.3 degrees north latitude and 75.7 degrees west longitude when the photo was taken. Movement was toward the northwest at 9 nautical miles per hour. Maximum sustained winds were at 35 nautical miles with gusts to 45 nautical miles. Ernesto had earlier passed between the east side of the Dominican Republic and Grand Turk Island (the light blue area to the right of center frame).
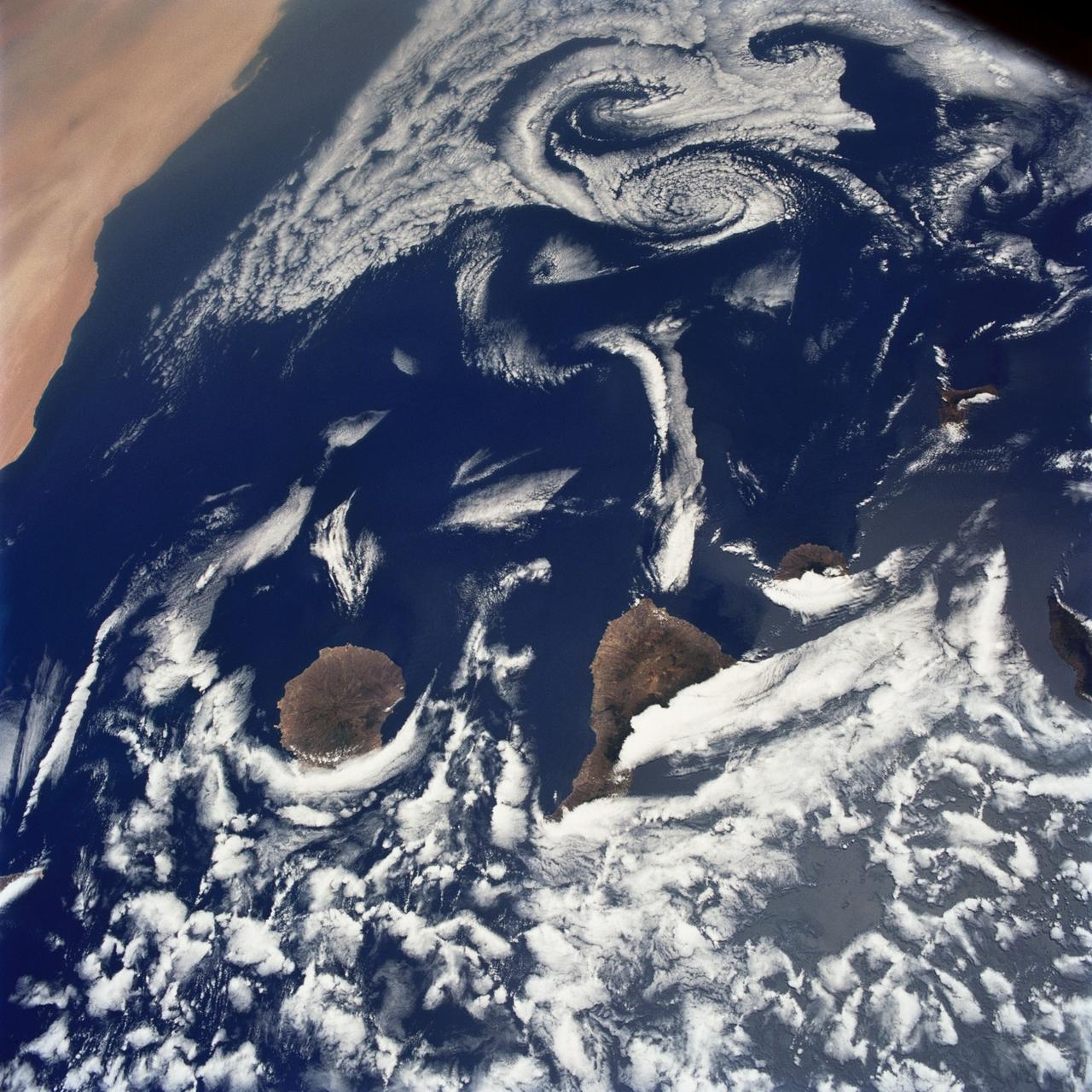

STS040-75-003 (5-14 June 1991) --- This image shows several of the Canary Islands, located in the North Atlantic Ocean just west of Africa. Low level stratus clouds often form here (and along the west coast of continents at these latitudes) are trapped in vertical movement due to an overlying atmospheric temperature inversion. The islands are generating disturbances in the low-level wind flow which is generally from the north-northeast or from top to bottom in the image. These disturbances travel downstream from the islands and manifest themselves as cloud swirls which are called von Karman vortices. The northern extent of a large dust storm moving off the coast of Africa is apparent at the lower right of the image. The dust, extended across the Atlantic Ocean as far west as the Dominican Republic later in the mission.
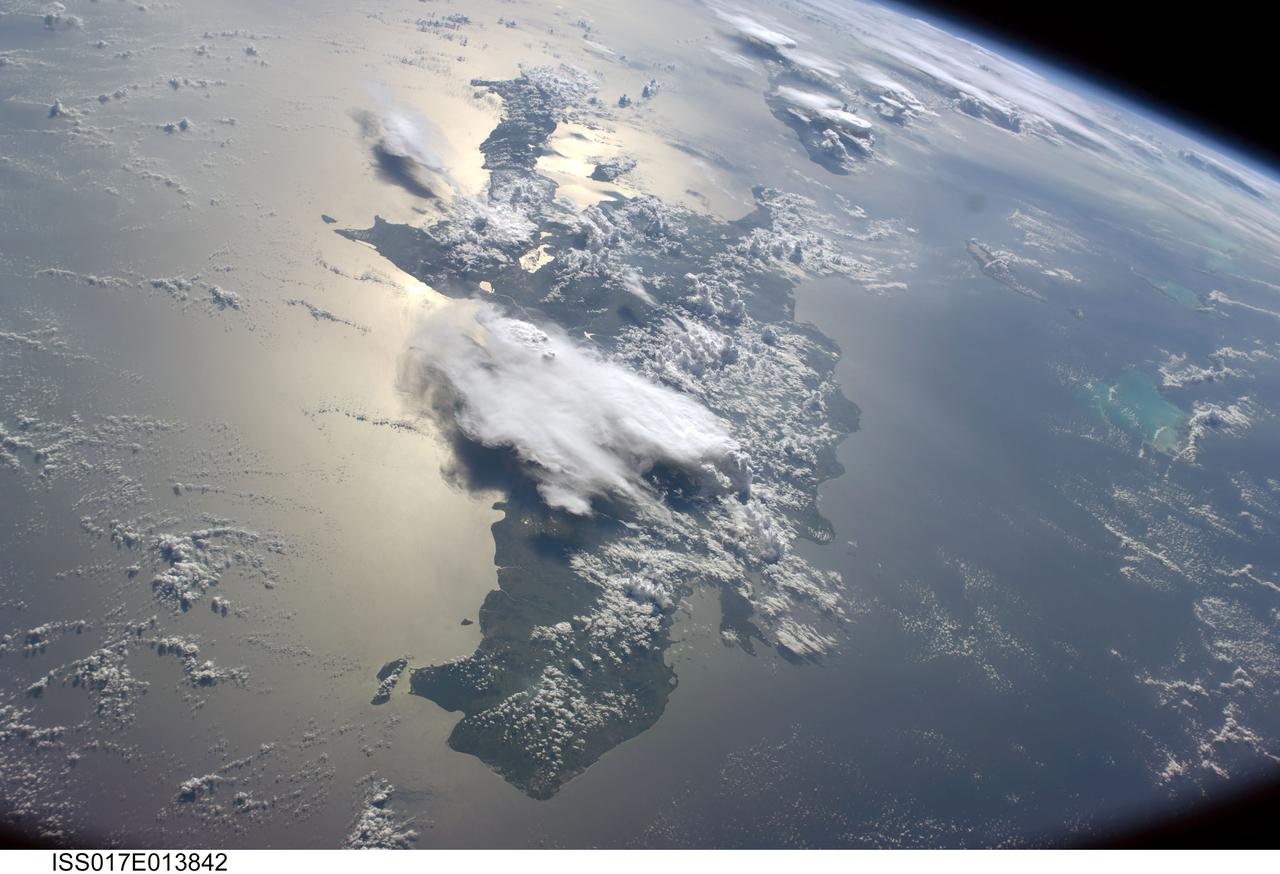

ISS017-E-013842 (19 Aug. 2008) --- A serene view of a portion of the Greater Antilles islands in the Caribbean Sea. The island of Hispaniola is in the foreground, comprised of the Dominican Republic and Haiti (in the sunglint). Looking toward the horizon, the eastern tip of Cuba is seen through the clouds and thunderstorms that are scattered over the islands. The light blue shallower areas, to the right or north of Hispaniola and extending toward the Earths limb, are the Turks and Caicos islands and the Acklins Islands. The Great Inagua island is off the coast of Haiti. These islands are located along the geological border of the North American Plate (to the right) and the Caribbean Plate (to the left). The photo was taken by the Expedition 17 crew onboard the International Space Station on Aug 19, 2008 with a 28 mm lens.
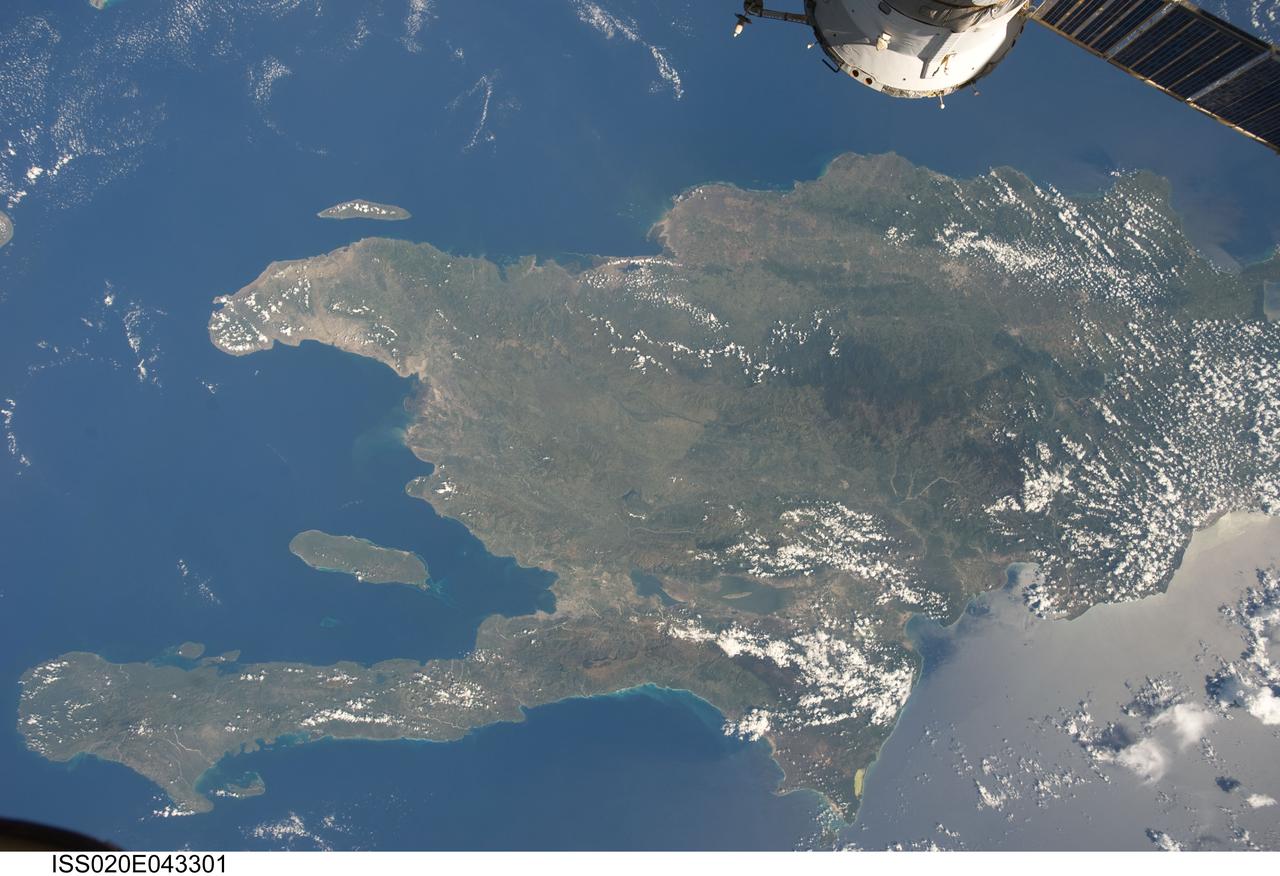

ISS020-E-043301 (28 Sept. 2009) ?-- A view of the Caribbean island of Hispaniola from the International Space Station. This island is comprised of Haiti (in the center left of the image) and the Dominican Republic and is part of the Greater Antilles island chain which lies along the geological boarder of the North America Plate and the Caribbean Plate. A major fault line in the region, Enriquillo-Plantain Garden Fault, runs along the longer peninsula, in the foreground, and just south of Port-Au-Prince. Part of a docked Russian spacecraft can be seen in the foreground. The epicenter of the recent disastrous earthquake occurred near this fault. This image was taken by the Expedition 20 crew on the International Space Station on Sept. 28, 2009 using a 25 mm lens setting.

Chantal's satellite presentation has deteriorated markedly this morning and is barely classifiable by the Dvorak Technique. Forecasted strong westerly shear and interactions with land over the next couple of days should cause further weakening of the storm as it transitions back into a tropical wave. Tropical Storm Warnings remain in effect for the entire coast of the Dominican Republic, the entire coast of Haiti, Turks and Caicos and the southeastern Bahamas. This image was taken by GOES West at 1200Z on July 10, 2013. Copy credit: NOAA Photo credit: <b><a href="http://goes.gsfc.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow">Credit: NOAA/NASA GOES Project</a></b> More info about the storm: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/12mvQcC" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/12mvQcC</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
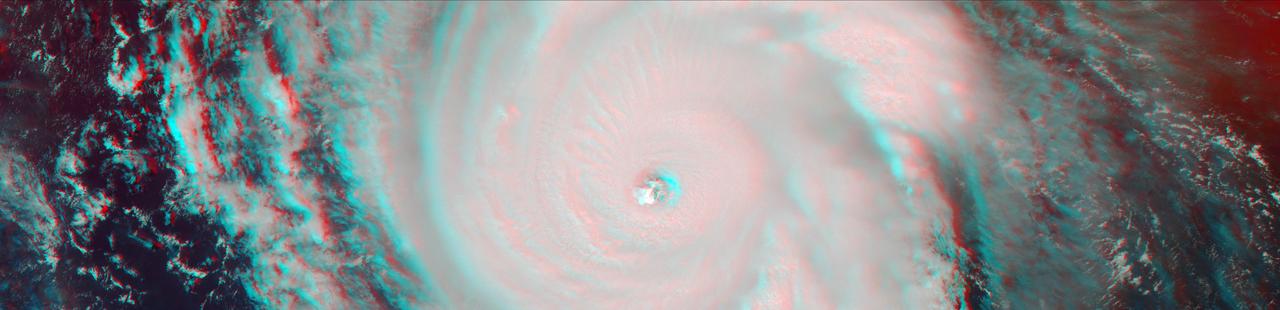
On Sept. 7, the Multi-angle Imaging SpectroRadiometer (MISR) instrument on NASA's Terra satellite passed over Hurricane Irma at approximately 11:20 am local time. The MISR instrument comprises nine cameras that view the Earth at different angles, and since it takes roughly seven minutes for all nine cameras to capture the same location, the motion of the clouds between images allows scientists to calculate the wind speed at the cloud tops. This stereo anaglyph combines two of the MISR angles to show a three-dimensional view of Irma. You will need red-blue glasses to view the anaglyph; place the red lens over your left eye. At this time, Irma's eye was located approximately 60 miles (100 kilometers) north of the Dominican Republic and 140 miles (230 kilometers) north of its capital, Santo Domingo. Irma was a powerful Category 5 hurricane, with wind speeds at the ocean surface up to 185 miles (300 kilometers) per hour. The MISR data show that at cloud top, winds near the eye wall (the most destructive part of the storm) were approximately 90 miles per hour (145 kilometers per hour), and the maximum cloud-top wind speed throughout the storm calculated by MISR was 135 miles per hour (220 kilometers per hour). While the hurricane's dominant rotation direction is counter-clockwise, winds near the eye wall are consistently pointing outward from it. This is an indication of outflow, the process by which a hurricane draws in warm, moist air at the surface and ejects cool, dry air at its cloud tops. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21945
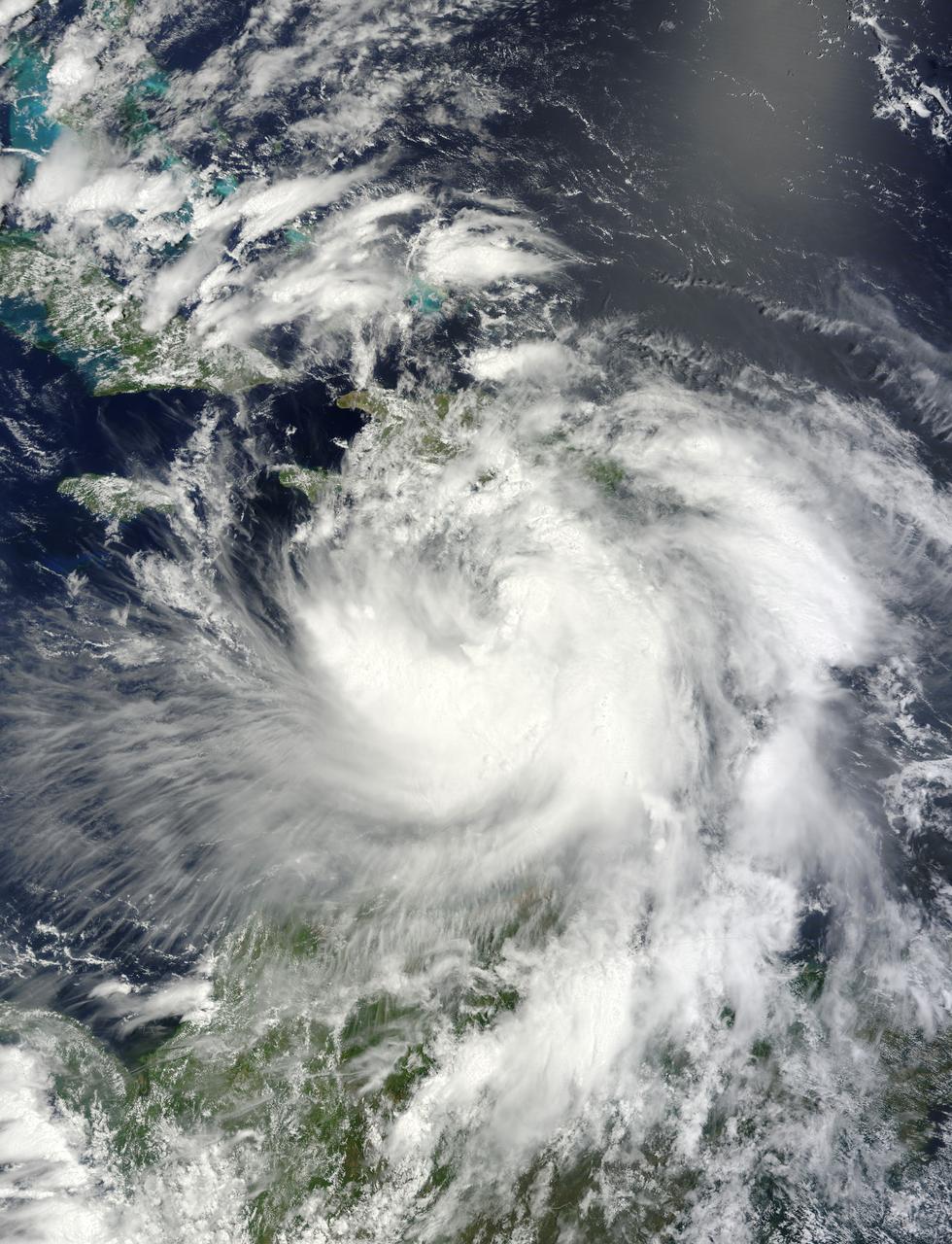

NASA's Terra satellite passed over Tropical Storm Isaac on Aug. 24 at 15:20 UTC (11:20 a.m. EDT) as it continued moving through the eastern Caribbean Sea. The MODIS instrument onboard Aqua captured this visible image. At 2 p.m. EDT on Aug. 24, Isaac's maximum sustained winds were near 60 mph (95 kmh). The National Hurricane Center noted that Isaac could strengthen later before reaching the coast of Hispaniola tonight, Aug. 24. Hispaniola is an island that contains the Dominican Republic and Haiti. Isaac is located about 135 miles (215 km) south-southeast of Port au Prince, Haiti, near latitude 16.8 north and longitude 71.4 west. Isaac is now moving toward the northwest near 14 mph (22 kmh). Isaac is expected to reach hurricane status over the weekend of Aug. 25-26 and NASA satellites will continue providing valuable temperature, rainfall, visible and infrared data. Text Credit: Rob Gutro NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md. <b>To read more go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hurricanes/archives/2012/h2012_Isaac.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hurricanes/archives/2012/h2012...</a></b> Credit: NASA Goddard MODIS Rapid Response Team <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Read more from: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/2duxEeZ" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/2duxEeZ</a> On October 4, 2016, Hurricane Matthew made landfall on southwestern Haiti as a category-4 storm—the strongest storm to hit the Caribbean nation in more than 50 years. Just hours after landfall, the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on NASA’s Terra satellite acquired this natural-color image. At the time, Matthew had top sustained winds of about 230 kilometers (145 miles) per hour. Earlier on October 4, temperature data collected by MODIS on NASA’s Aqua satellite revealed that the cloud tops around Matthew were very cold (at least -57° Celsius, or -70° Fahrenheit). Cold cloud tops are known to produce heavy rainfall. The National Hurricane Center called for 380 to 500 millimeters (15 to 20 inches) of rain in Southern Haiti and in the southwestern Dominican Republic. The northward movement of the storm should bring the center of Matthew over eastern Cuba late on October 4. Dangerous conditions can extend far beyond a storm’s center. According to National Hurricane Center forecasters, Matthew is “likely to produce devastating impacts from storm surge, extreme winds, heavy rains, flash floods, and/or mudslides in portions of the watch and warning areas in Haiti, Cuba, and the Bahamas.” NASA Earth Observatory image by Joshua Stevens, using MODIS data from the Land Atmosphere Near real-time Capability for EOS (LANCE). Caption by Kathryn Hansen.
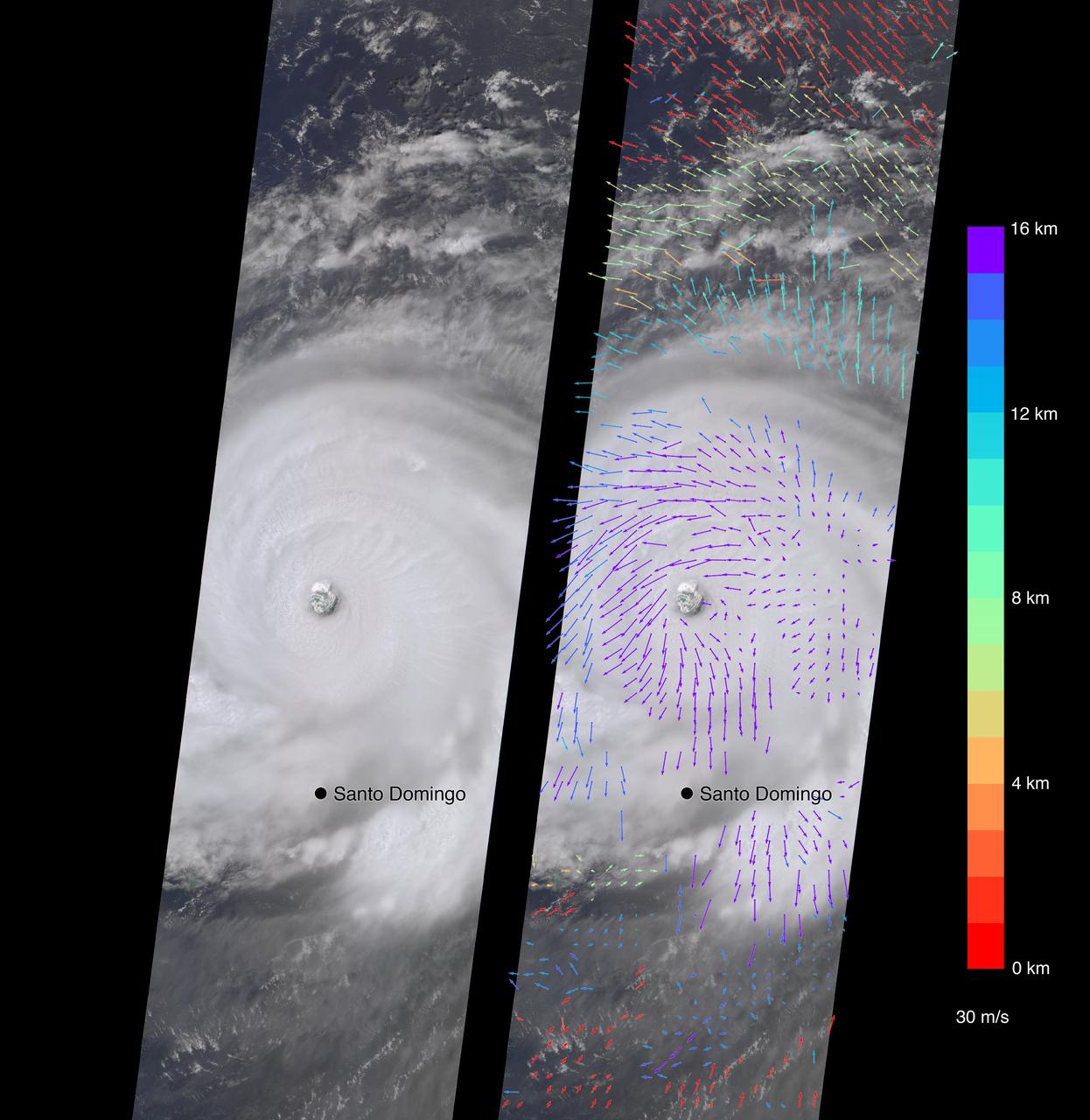
On Sept. 7, the Multi-angle Imaging SpectroRadiometer (MISR) instrument on NASA's Terra satellite passed over Hurricane Irma at approximately 11:20 a.m. local time. The MISR instrument comprises nine cameras that view the Earth at different angles, and since it takes roughly seven minutes for all nine cameras to capture the same location, the motion of the clouds between images allows scientists to calculate the wind speed at the cloud tops. The animated GIF shows Irma's motion over the seven minutes of the MISR imagery. North is toward the top of the image. This composite image shows Hurricane Irma as viewed by the central, downward-looking camera (left), as well as the wind speeds (right) superimposed on the image. The length of the arrows is proportional to the wind speed, while their color shows the altitude at which the winds were calculated. At the time the image was acquired, Irma's eye was located approximately 60 miles (100 kilometers) north of the Dominican Republic and 140 miles (230 kilometers) north of its capital, Santo Domingo. Irma was a powerful Category 5 hurricane, with wind speeds at the ocean surface up to 185 miles (300 kilometers) per hour, according to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. The MISR data show that at cloud top, winds near the eye wall (the most destructive part of the storm) were approximately 90 miles per hour (145 kilometers per hour), and the maximum cloud-top wind speed throughout the storm calculated by MISR was 135 miles per hour (220 kilometers per hour). While the hurricane's dominant rotation direction is counter-clockwise, winds near the eye wall are consistently pointing outward from it. This is an indication of outflow, the process by which a hurricane draws in warm, moist air at the surface and ejects cool, dry air at its cloud tops. These data were captured during Terra orbit 94267. An animation is available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21946
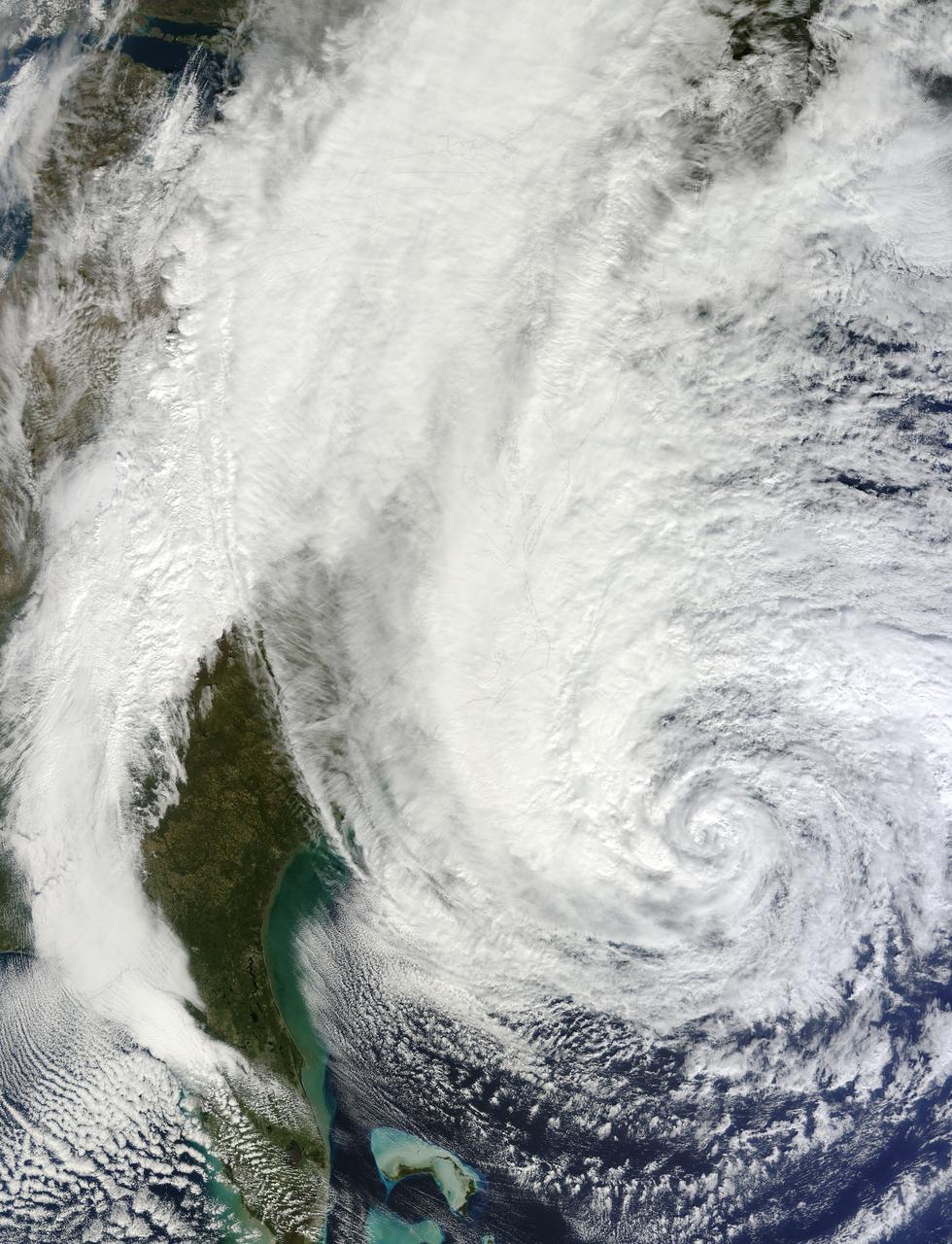

NASA image acquired acquired October 28, 2012 <b>For the latest info from NASA on Hurricane Sandy go to: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/Ti5SgS" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/Ti5SgS</a></b> At noon Eastern Daylight Time (16:00 Universal Time) on October 28, 2012, the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on NASA’s Terra satellite acquired this image of Hurricane Sandy off the southeastern United States. At 11 a.m. local time (one hour before the image was captured), the U.S. National Hurricane Center reported that the storm was located at 32.5° North and 72.6° West, about 250 miles (400 kilometers) southeast of Cape Hatteras, North Carolina, and 575 miles (930 kilometers) south of New York City. Maximum sustained winds were 75 miles (120 kilometers) per hour, and the central pressure was 951 millibars (28.08 inches). Forecasters predicted that the storm would continue heading north-northeast until the morning of October and then take a hard turn to the northwest into the coastaline of Delaware, New Jersey, or New York. The wind field from the storm was said to stretch 500 to 700 miles and was likely to affect an area from South Carolina to Maine, and as far inland as the Great Lakes. The storm has already caused significant damage in the Bahamas, Cuba, Jamaica, Puerto Rico, the Dominican Republic, and Haiti; at least 65 lives have been lost to the storm. NASA image courtesy LANCE MODIS Rapid Response Team at NASA GSFC. Caption by Michael Carlowicz. Instrument: Terra - MODIS Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
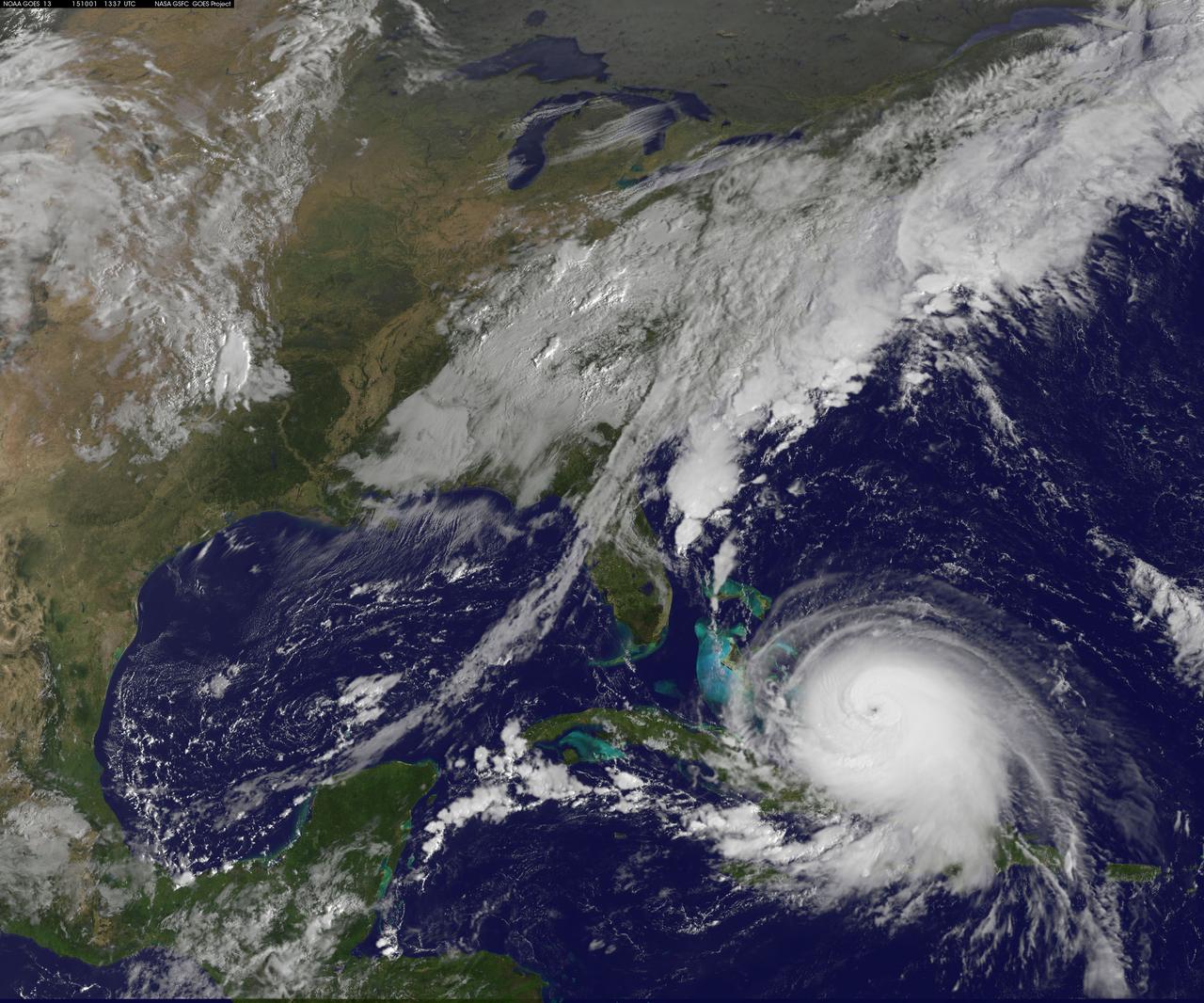
Hurricane Joaquin continued to intensify in the Bahamas on October 1 and NASA and NOAA satellites have been providing valuable data on the storm. NASA's GPM and Terra satellites and NOAA's GOES-East satellite provided rainfall, cloud extent, cloud height and other data to forecasters. Joaquin became a major hurricane today, October 1, reaching Category 3 status on the Saffir-Simpson Wind Scale. On October 1 at 1330 UTC (9:30 a.m. EDT) NOAA's GOES-East satellite captured this visible image of Hurricane Joaquin covering the southern Bahamas and extending over southeastern Cuba, and the island of Hispaniola (which includes Haiti and the Dominican Republic). Joaquin's eye had become completely visible now that the storm had reached Category 3 status. On October 1, a Hurricane Warning was in effect for the Central Bahamas, Northwestern Bahamas including the Abacos, Berry Islands, Eleuthera, Grand Bahama Island, and New Providence, The Acklins, Crooked Island, and Mayaguana in the southeastern Bahamas. A Hurricane Watch was in effect for Bimini and Andros Island, and a Tropical Storm Warning was in effect for the remainder of the southeastern Bahamas excluding the Turks and Caicos Islands and Andros Island. According to NHC, at 8 a.m. EDT (1200 UTC), the center of Hurricane Joaquin was located near latitude 23.2 North, longitude 73.7 West. That's just 10 miles (15 km) north of Samana Cays, Bahamas and about 75 miles (120 km) southeast of San Salvador, Bahamas. Joaquin was moving toward the west-southwest near 5 mph (7 kph), and this motion is expected to continue today. NHC noted that a turn toward the west- northwest is forecast tonight (Oct. 1), followed by a turn toward the north and an increase in forward speed on Friday, Oct. 2. On the forecast track, the center of Joaquin will move near or over portions of the central Bahamas today and tonight and pass near or over portions of the northwestern Bahamas on Friday. Maximum sustained winds are near 120 mph (195 km/h) with higher gusts. Joaquin is a category 3 hurricane on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale. Some strengthening is forecast in the next day or so, with some fluctuations in intensity possible on Friday. Hurricane force winds extend outward up to 35 miles (55 km) from the center and tropical storm force winds extend outward up to 140 miles (220 km). The minimum central pressure just extrapolated by an Air Force Reserve Hurricane Hunter aircraft is 942 millibars. For updated forecasts, watches and warnings visit the National Hurricane Center (NHC) website: <a href="http://www.nhc.noaa.gov" rel="nofollow">www.nhc.noaa.gov</a>. Credit: NASA/NOAA GOES Project <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
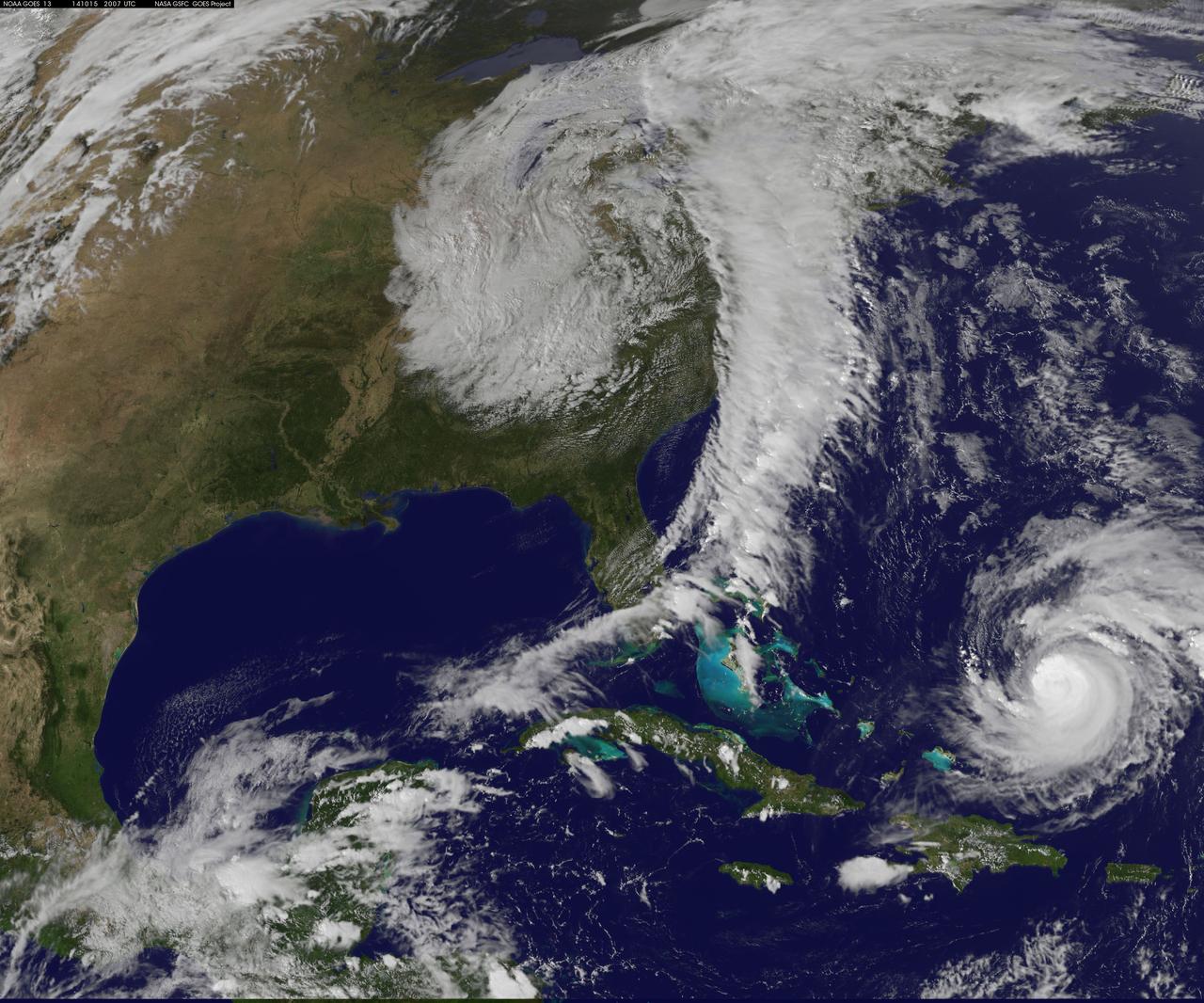
Hurricane Gonzalo has made the jump to major hurricane status and on Oct. 15 was a Category 4 storm on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale. NOAA's GOES-East satellite provided imagery of the storm. According to the National Hurricane Center, Gonzalo is the first category 4 hurricane in the Atlantic basin since Ophelia in 2011. NOAA's GOES-East satellite provides visible and infrared images of weather from its orbit in a fixed position over the Earth. On Oct. 15 at 15:15 UTC (11:15 a.m. EDT) GOES saw Gonzalo had tightly wrapped bands of thunderstorms spiraling into the center of its circulation. The eye of the storm was obscured by high clouds in the image. NOAA aircraft data and microwave images clearly show concentric eyewalls, with the inner radius of maximum winds now only about 4-5 nautical miles from the center. NOAA manages the GOES satellites, while NASA/NOAA's GOES Project at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland created the image. The NASA/NOAA GOES Project creates images and animations from GOES data. At 11 a.m. EDT on Oct. 15, Gonzalo's maximum sustained winds increased to near 130 mph (215 kph) and the National Hurricane Center (NHC) noted that fluctuations in intensity are expected over the next couple of days. Gonzalo's cloud-covered eye was located near latitude 23.5 north and longitude 68.0 west, about 640 miles (1,025 km) south-southwest of Bermuda. Gonzalo is moving toward the northwest near 12 mph (19 kph). The minimum central pressure recently reported by an air force reconnaissance aircraft was 949 millibars. Tropical storm conditions are possible in Bermuda by late Thursday night, Oct. 16, and hurricane conditions are possible over Bermuda on Friday Oct. 16. Ocean swells however, will be felt over a much larger area, reached the U.S. east coast on Oct. 16. Large swells generated by Gonzalo are affecting portions of the Virgin Islands, the northern coasts of Puerto Rico and the Dominican Republic and portions of the Bahamas. Swells will reach much of the east coast of the United States and Bermuda on Thursday. By late Oct. 16, Gonzalo is expected to turn to the northeast and the center is expected to approach Bermuda sometime on Oct. 17. Credit: NASA/GSFC/Jeff Schmaltz/MODIS Land Rapid Response Team <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>