
The Saturn V vehicle, carrying the unmarned orbital workshop for the Skylab-1 mission, lifted off successfully and all systems performed normally. Sixty-three seconds into the flight, engineers in the operation support and control center saw an unexpected telemetry indication that signalled that damages occurred on one solar array and the micrometeoroid shield during the launch. The micrometeoroid shield, a thin protective cylinder surrounding the workshop protecting it from tiny space particles and the sun's scorching heat, ripped loose from its position around the workshop. This caused the loss of one solar wing and jammed the other. Still unoccupied, the Skylab was stricken with the loss of the heat shield and sunlight beat mercilessly on the lab's sensitive skin. Internal temperatures soared, rendering the station uninhabitable, threatening foods, medicines, films, and experiments. This image, taken during a fly-around inspection by the Skylab-2 crew, shows the station's remaining solar panel jammed against its side. The Marshall Space Flight Center had a major role in developing the procedures to repair the damaged Skylab.
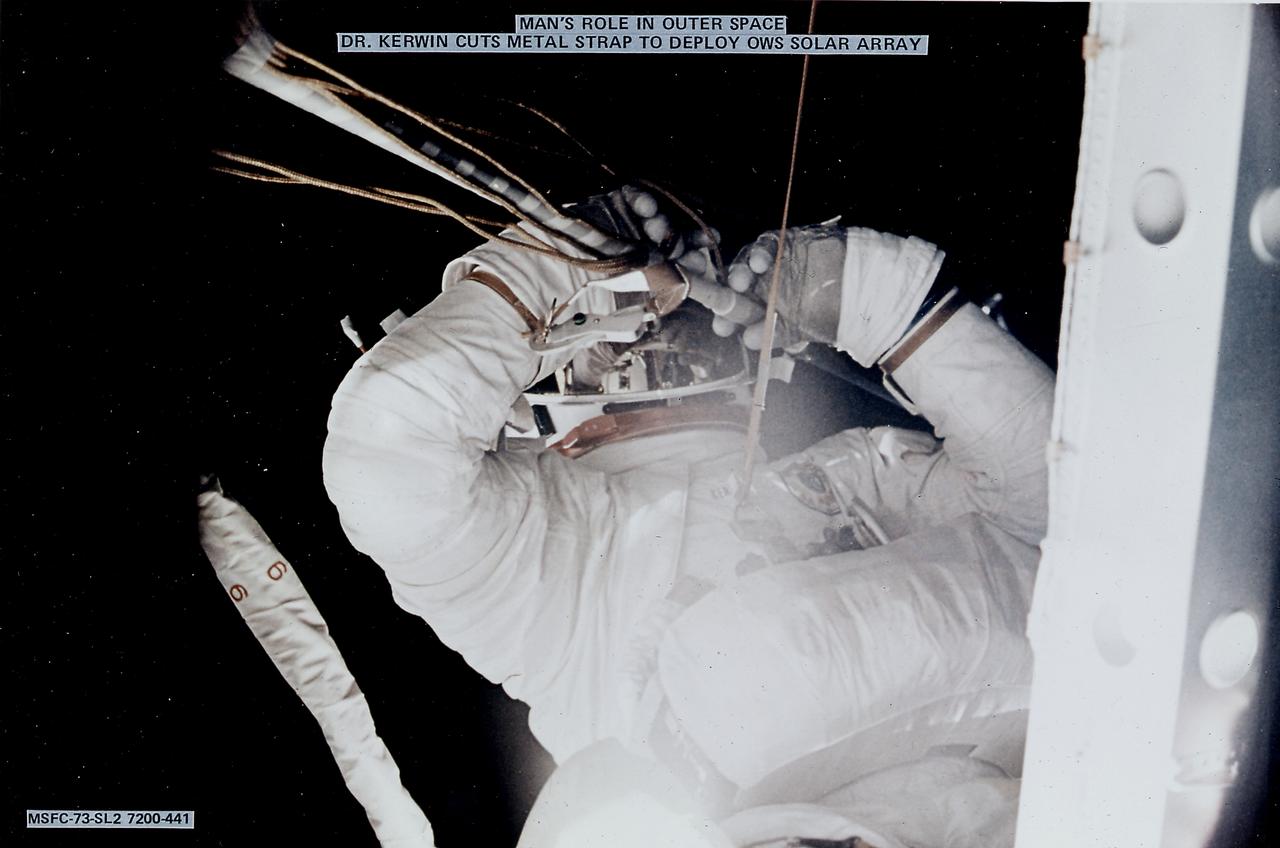

The Saturn V vehicle, carrying the unmarned orbital workshop for the Skylab-1 mission, lifted off successfully and all systems performed normally. Sixty-three seconds into the flight, engineers in the operation support and control center saw an unexpected telemetry indication that signalled that damages occurred on one solar array and the micrometeoroid shield during the launch. The micrometeoroid shield, a thin protective cylinder surrounding the workshop protecting it from tiny space particles and the sun's scorching heat, ripped loose from its position around the workshop. This caused the loss of one solar wing and jammed the other. Still unoccupied, the Skylab was stricken with the loss of the heat shield and sunlight beat mercilessly on the lab's sensitive skin. Intrnal temperatures soared, rendering the station uninhabitable, threatening foods, medicines, films, and experiments. This image shows astronaut Kerwin cutting the metal strap to free and deploy the Orbital Workshop solar array. Kerwin used special cutting tools developed by engineers at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The MSFC had a major role in developing the procedures to repair the damaged Skylab.
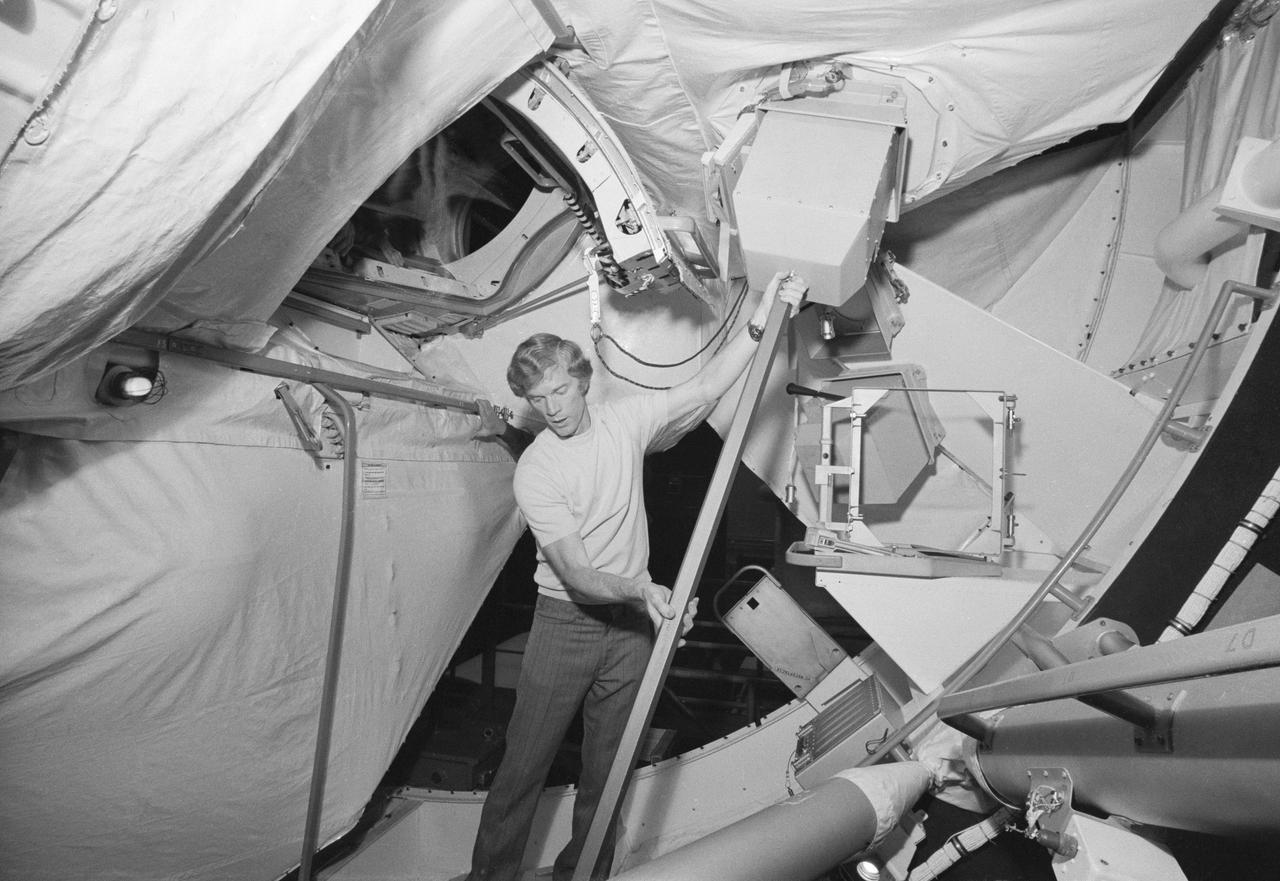

S73-25884 (1973) --- Astronaut Russell Schweickart in Orbital Workshop Simulator (OWS) working out procedure to be used for repair of damaged thermal protection cover on Skylab 2 spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA
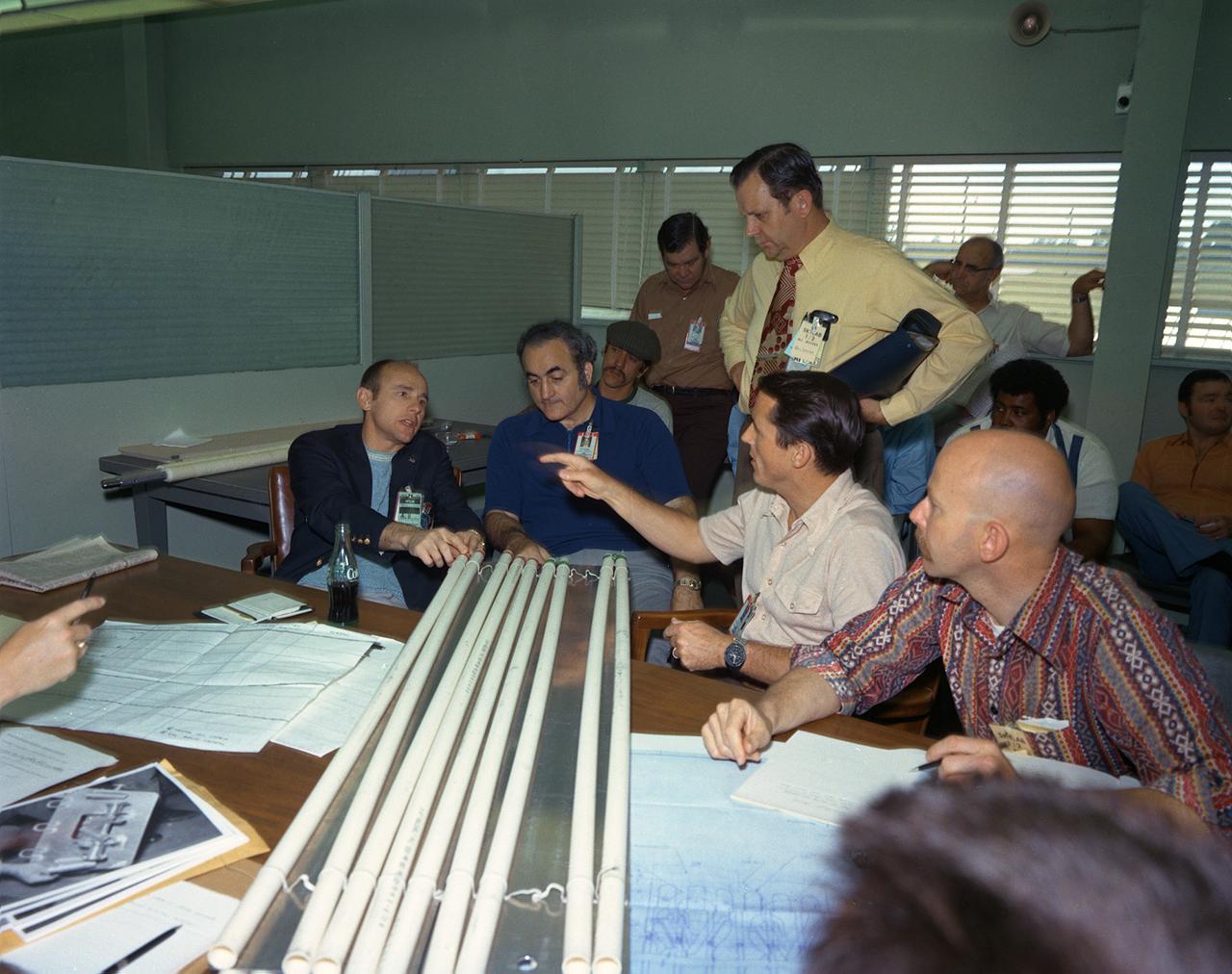

Sixty-three seconds after the launch of the modified Saturn V vehicle carrying the Skylab cluster, engineers in the operation support and control center saw an unexpected telemetry indication that signalled that damages occurred on one solar array and the micrometeoroid shield during the launch. Still unoccupied, the Skylab was stricken with the loss of the heat shield and sunlight beat mercilessly on the lab's sensitive skin. Internal temperatures soared, rendering the the station uninhabitable, threatening foods, medicines, films, and experiments. The launch of the first marned Skylab (Skylab-2) mission was delayed until methods were devised to repair and salvage the workshop. Personnel from other NASA Centers and industries quickly joined the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in efforts to save the damaged Skylab. They worked day and night for the next several days. Eventually the MSFC developed, tested, rehearsed, and approved three repair options. These options included a parasol sunshade and a twin-pole sunshade to restore the temperature inside the workshop, and a set of metal cutting tools to free the jammed solar panel. This photograph was taken during a discussion of the methods of the twin-pole Sun shield by (left to right) Astronaut Alan Bean, MSFC Director Dr. Rocco Petrone, Astronaut Edward Gibson, and MSFC engineer Richard Heckman. Dr. William Lucas, who became MSFC Director after Dr. Petrone left MSFC in March of 1974, is standing.
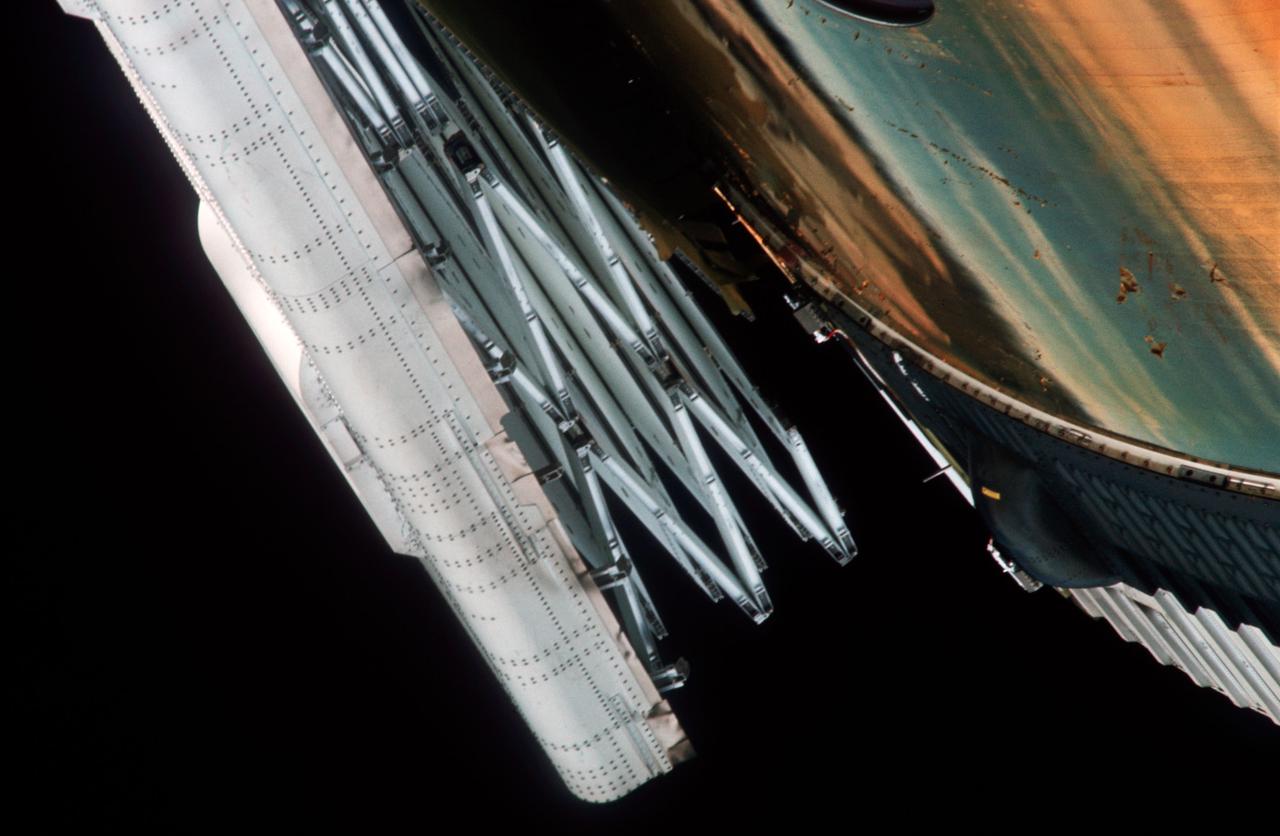

Close-up view of partially deployed, damaged solar array before astronauts performed extravehicular activity (EVA) to completey deploy it.
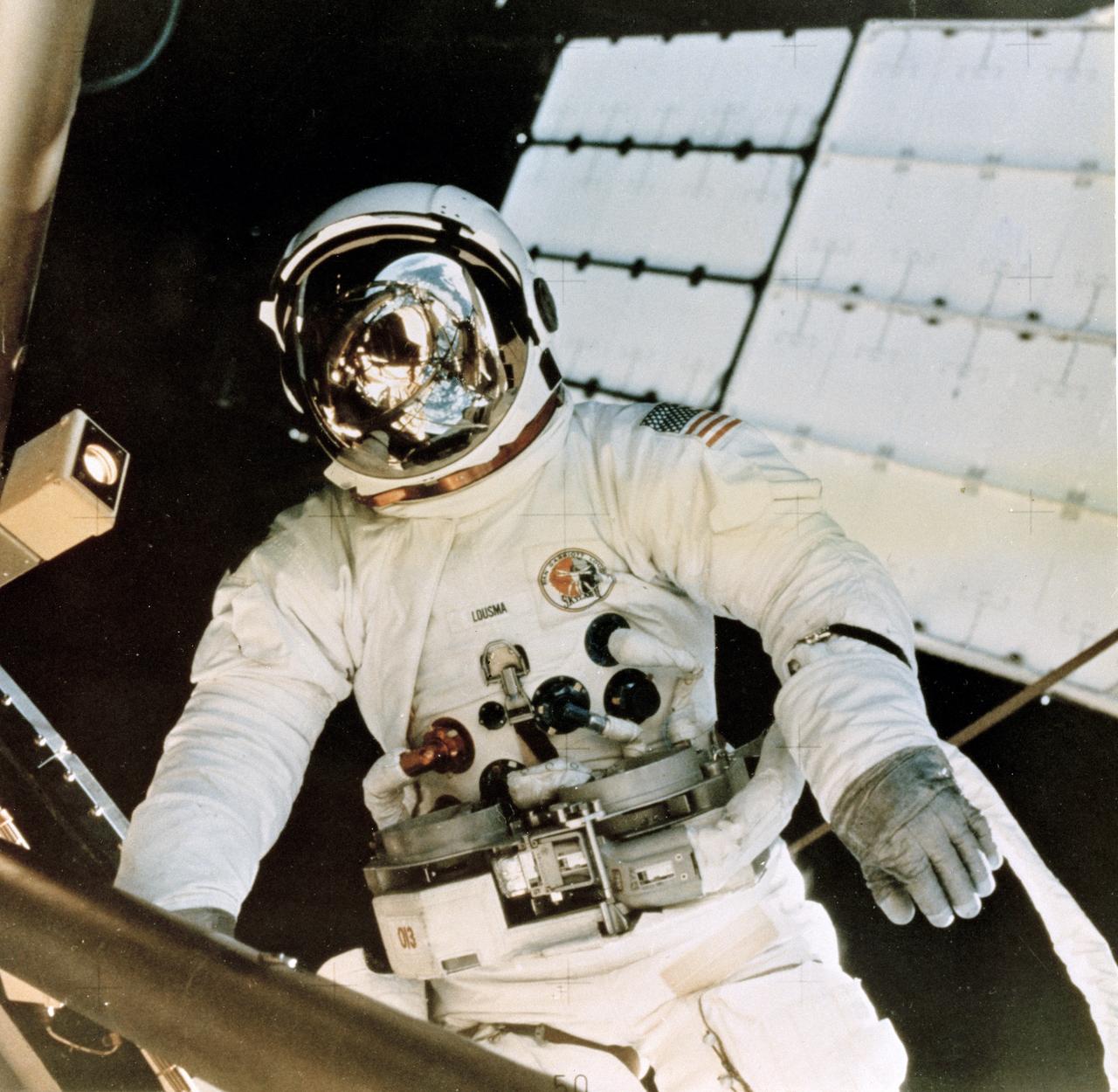

Skylab-3 was the second marned mission in the skylab project. The crew spent 59 days in orbit. In this photo, Astronaut Jack Lousma deploys the Twin Pole Sun Shield created by Marshall Space Flight Center team members to replace the micrometeoroid shield, a thin protective cylinder surrounding the workshop protecting it from tiny space particles and the sun's scorching heat. The shield was damaged during the Skylab-2 mission.
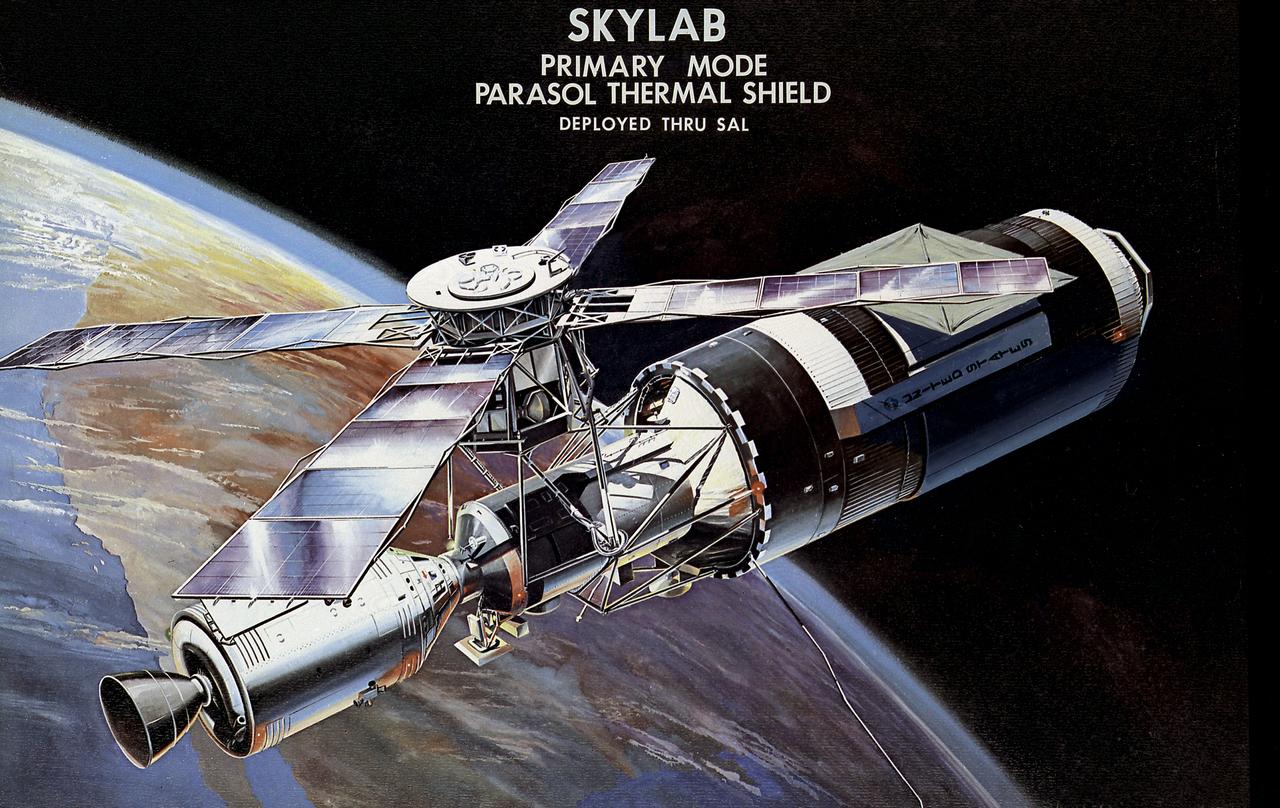

This image illustrates the deployment of the Skylab parasol thermal shield. Skylab lost its thermal protection shield during its launch on May 14, 1973. The Skylab-2 crew deployed a parasol thermal shield to protect the workshop from overheating. The crew attached the canister containing the parasol to the scientific airlock and extended the folded shield through the opening and into space. Slowly, the struts extended, the sunshade took shape, and was in place over the workshop's outer surface. This illustration shows the parasol being fully deployed and retracted for service. Emergency procedures to repair and salvage the damaged Skylab were a joint effort of the Marshall Space Flight Center, other NASA centers, and contractors.

This image illustrates the deployment of the Skylab parasol thermal shield. Skylab lost its thermal protection shield during its launch on May 14, 1973. The Skylab-2 crew deployed a parasol thermal shield to protect the workshop from overheating. The crew attached the canister containing the parasol to the scientific airlock and extended the folded shield through the opening and into space. Slowly, the struts extended and the sunshade took shape and was in place over the workshop's outer surface. This illustration shows the parasol at partial extension. Emergency procedures to repair and salvage the damaged Skylab were a joint effort of the Marshall Space Flight Center, other NASA centers, and contractors.
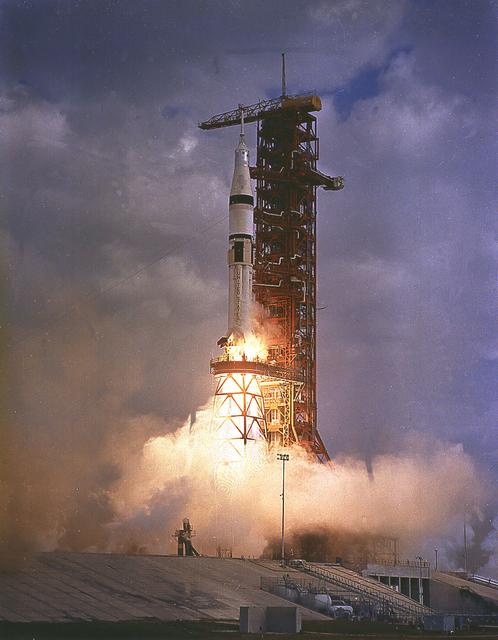
This is an image of the Saturn IB vehicle that lifted off on May 25, 1973, carrying the crew of the Skylab-2 (SL-2) mission. The Saturn IV launch vehicle was used to carry a crew of three astronauts to the Skylab. The SL-2 mission launched the first crew to the Skylab; astronauts Charles "Pete" Conrad, Joseph Kerwin and Paul Weitz. This crew made urgent repair work on the damaged Skylab to make it operational and habitable. The goals of the Skylab were to enrich our scientific knowledge of the Earth, the Sun, the stars, and cosmic space; to study the effects of weightlessness on living organisms, including man; to study the effects of the processing and manufacturing of materials utilizing the absence of gravity; and to conduct Earth resource observations. The duration of this mission was 28 days.
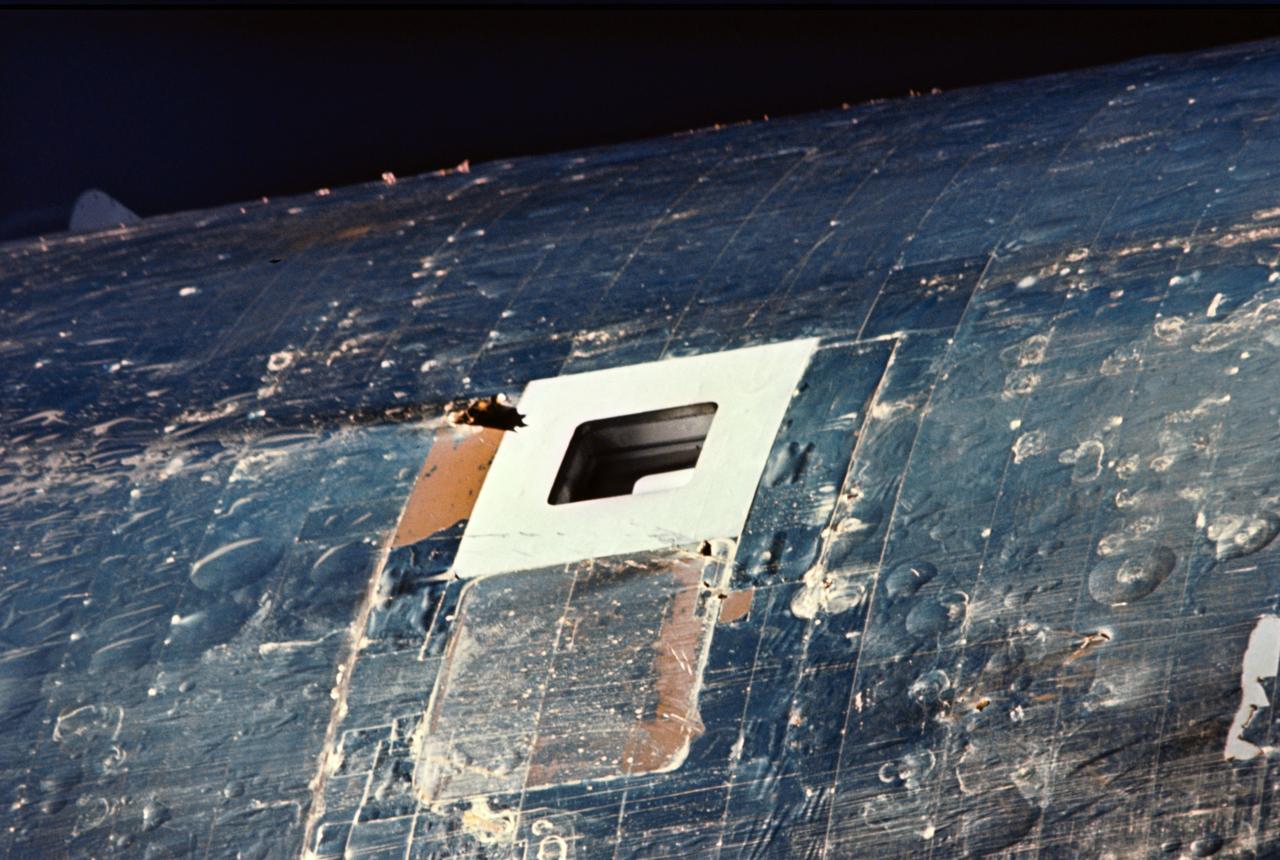

This close up view of one of the two scientific airlocks on the Skylab Orbital Workshop Section was taken from the Skylab 2 Command/Service Module during its initial fly around inspection. The micrometeoroid shield can be seen to be missing from this section of the orbital workshop. A parasol solar shield was later devised and put in place over this damaged area through this very same airlock opening.
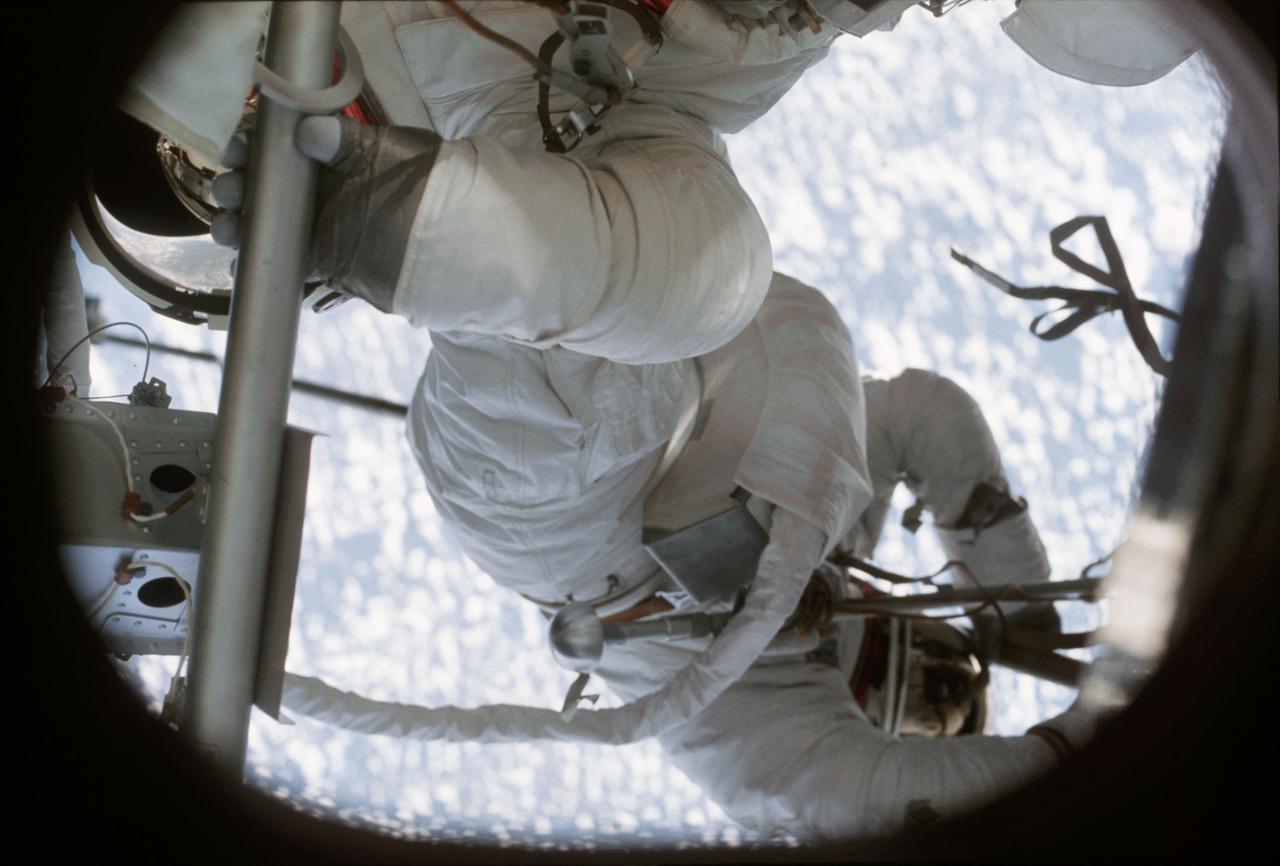

SL2-100-799 (7 June 1973) --- This medium close-up view shows astronauts Charles Conrad, commander for Skylab 2, and Science Pilot Joseph P. Kerwin performing an extravehicular activity (EVA) to repair the damaged and partially deployed solar array system on the Skylab complex. The photo was taken from inside the Orbital Workshop (OWS) by astronaut Paul J. Weitz, pilot. Photo credit: NASA
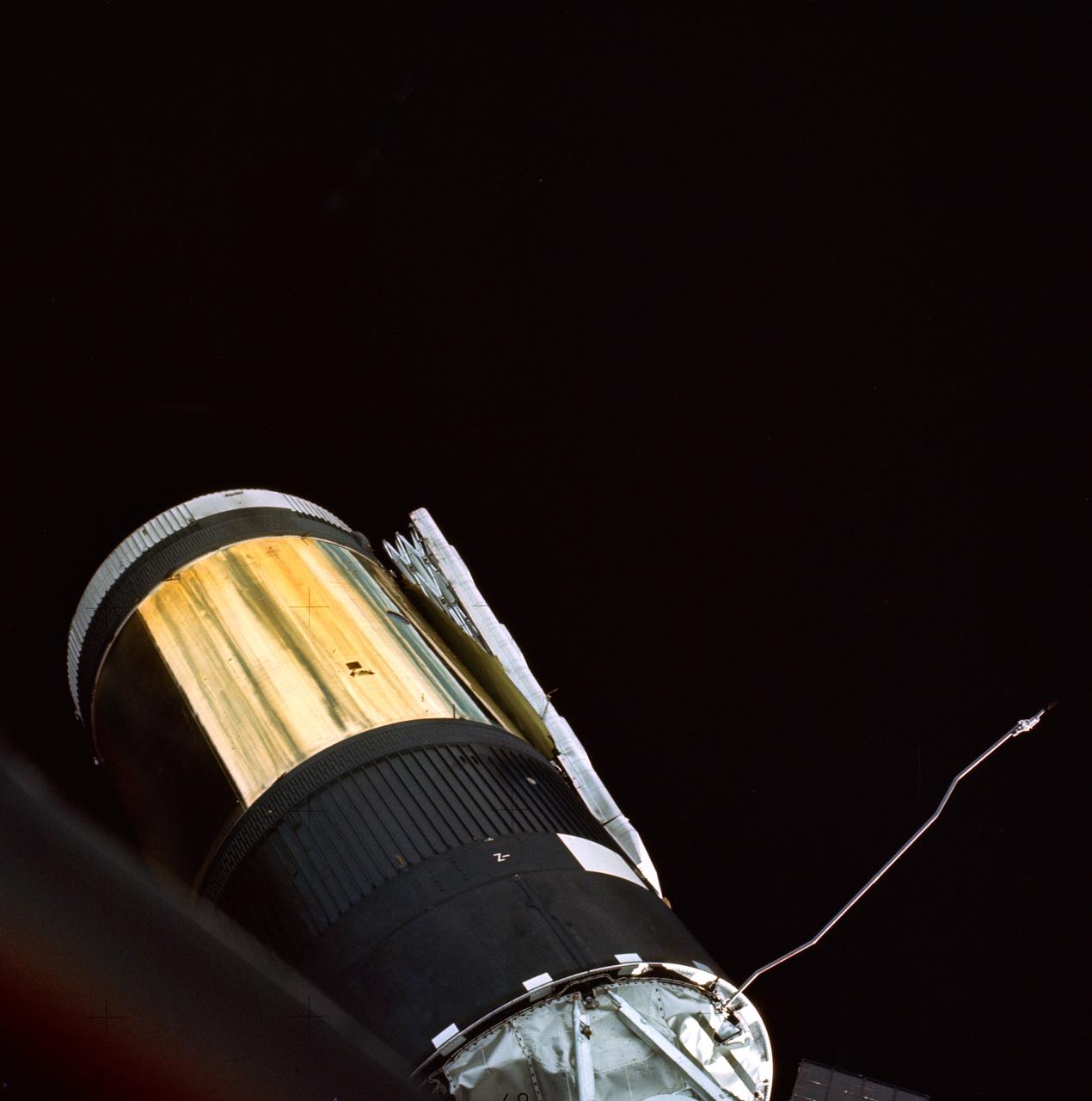

This view of the Skylab Orbital Space Station was taken from the Skylab 2 Command/Service Module during it's initial fly around inspection. The micrometeoroid shield can be seen to be missing and a parasol solar shield was later fitted in its place. The damaged and partially deployed solar array, in the center of the scene, can be seen to be restrained by a strap that was later cut during an early EVA, allowing the panel to fully deploy.

The Saturn V vehicle, carrying the unmarned orbital workshop for the Skylab-1 mission, lifted off successfully and all systems performed normally. Sixty-three seconds into flight, engineers in the operation support and control center saw an unexpected telemetry indication that signalled that damages occurred on one solar array and the micrometeoroid shield during the launch. The micrometeoroid shield, a thin protective cylinder surrounding the workshop protecting it from tiny space particles and the sun's scorching heat, ripped loose from its position around the workshop. This caused the loss of one solar wing and jammed the other. Still unoccupied, the Skylab was stricken with the loss of the heat shield and sunlight beat mercilessly on the lab's sensitive skin. Internal temperatures soared, rendering the the station uninhabitable, threatening foods, medicines, films, and experiments. This image shows the sun-ravaged skin of the Orbital Workshop, bared by the missing heat shield, with blister scars and tarnish from temperatures that reached 300 degrees F. The rectangular opening at the upper center is the scientific airlock through which the parasol to protect the workshop from sun's rays was later deployed. This view was taken during a fly-around inspection by the Skylab-2 crew. The Marshall Space Flight Center had a major role in developing the procedures to repair the damaged Skylab.
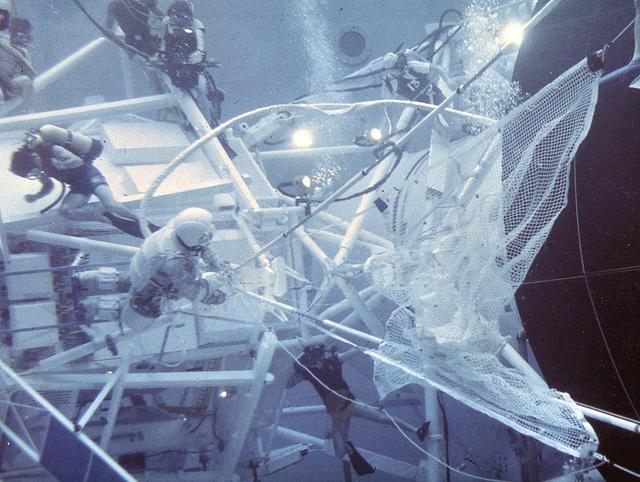

After its launch on May 14, 1973, it was immediately known that there were some major problems with Skylab. The large, delicate, meteoroid shield on the outside of the workshop was ripped off by the vibration of the launch. Its tearing off caused serious damage to the two wings of solar cells that were to supply most of the electric power to the workshop. Once in orbit, the news worsened. The loss of the big shade exposed the metal skin of the workshop to the sun. Internal temperatures soared to 126 degrees F. This heat not only threatened its habitation by astronauts, but if prolonged, would cause serious damage to instruments and film. After twice delaying the launch of the first astronaut crew, engineers worked frantically to develop solutions to these problems and salvage the Skylab. After designing a protective solar sail to cover the workshop, crews needed to practice using the specially designed tools and materials to facilitate the repair procedure. Marshall Space Flight Center's Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS), was used to practice these maneuvers. Pictured here are the astronauts in the NBS deploying the protecticve solar sail. On may 25, 1973, an Apollo command and service module was launched and later docked with Skylab. The next day, astronauts Conrad and Kerwin were able to complete the needed repairs to Skylab, salvaging the entire program.
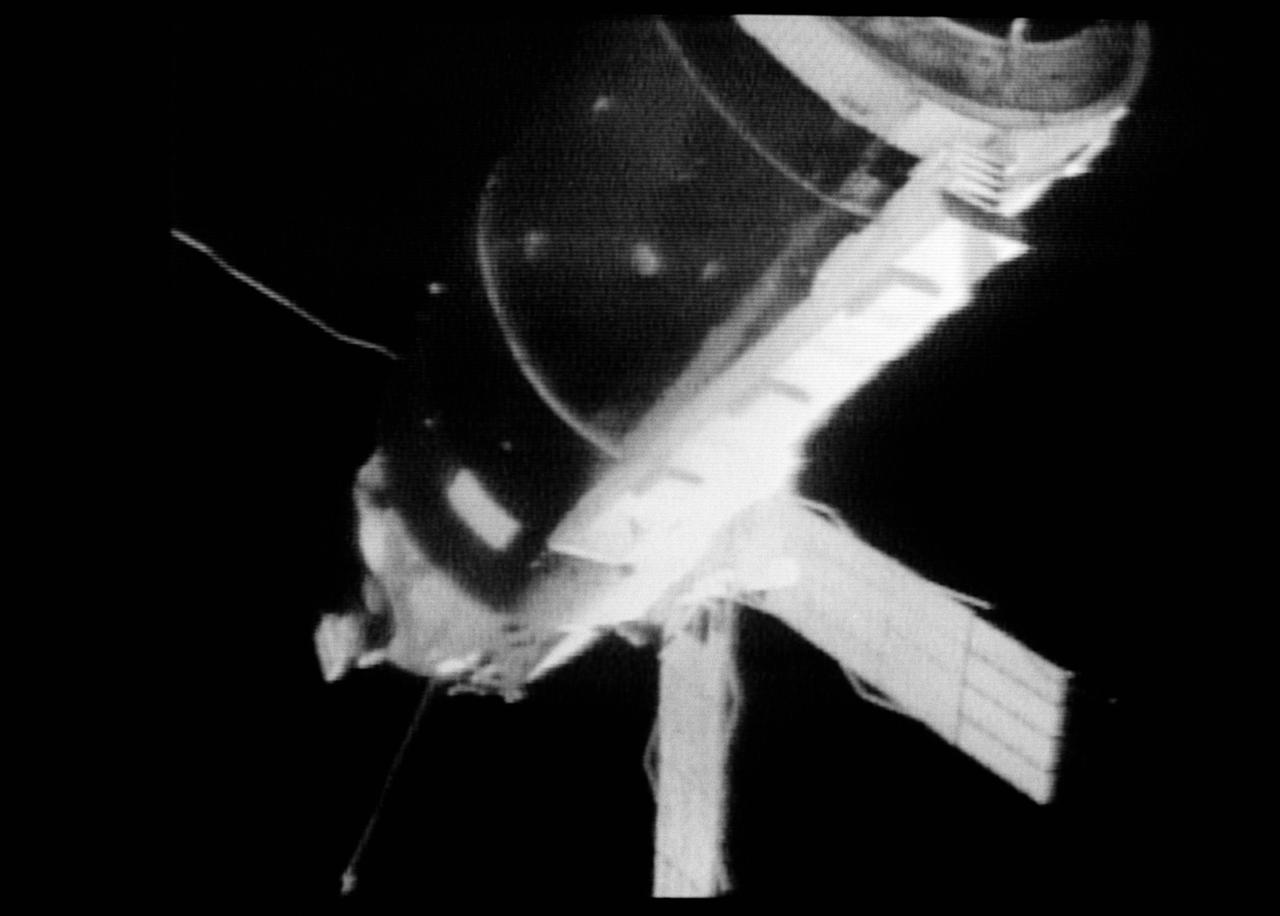
S73-27182 (25 May 1973) --- A close-up view of the Skylab 1 space station cluster can be seen in this reproduction taken from a color television transmission made by a TV camera aboard the Skylab 2 Command Module during its "fly around" inspection of the cluster. This view has been enhanced. At left center the damaged solar array system wing on the Orbital Workshop (OWS) appears to be partly folded. In their preliminary inspection the crewmen noted that portions of the micrometeoroid shield had slid back underneath the OWS solar wing. Solar panels on the Apollo Telescope Mount extend out at the top center. Photo credit: NASA

The Saturn V vehicle, carrying the unmarned orbital workshop for the Skylab-1 mission, lifted off successfully and all systems performed normally. Sixty-three seconds into flight, engineers in the operation support and control center saw an unexpected telemetry indication that signalled that damages occurred on one solar array and the micrometeoroid shield during the launch. The micrometeoroid shield, a thin protective cylinder surrounding the workshop protecting it from tiny space particles and the sun's scorching heat, ripped loose from its position around the workshop. This caused the loss of one solar wing and jammed the other. Still unoccupied, the Skylab was stricken with the loss of the heat shield and sunlight beat mercilessly on the lab's sensitive skin. Internal temperatures soared, rendering the station uninhabitable, threatening foods, medicines, films, and experiments. This image, taken during a fly-around inspection by the Skylab-2 crew, shows the damaged meteoroid shield being held by a thin aluminum strap entangled with green-hued remnants of the lost heat shield. The Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) developed, tested, rehearsed, and approved three repair options. These options included a parasol sunshade and a twin-pole sunshade to restore the temperature inside the workshop, and a set of metal cutting tools to free the jammed solar panel.

The rate of neutron flow is commonly referred to as a flux. The measurement of neutron fluxes in Skylab was the subject of a proposal by Terry Quist of San Antonio, Texas. This chart describes Quist's experiment, Neutron Analysis, Skylab student experiment ED-76. These measurements were considered important not only by NASA but also by the scientific community for four reasons. High energy neutrons can be harmful to human tissue if they are present in significant quantities. Fluxes of neutrons can damage film and other sensitive experimental equipment in a marner similar to those produced by x-rays or other radiation. Furthermore, neutron fluxes can be used as a calibration source for other space-oriented particle physics experiments. Finally, neutron fluxes can affect sensitive x-ray and gamma-ray astronomy observations. Quist's objectives were to measure the neutron fluxes present in Skylab and, with the assistance of NASA and other physicists, to attempt determination of their origin as well as their energy range or spectrum. This experiment had stimulated interest in further studies of neutron phenomena in space. In March 1972, NASA and the National Science Teachers Association selected 25 experiment proposals for flight on Skylab. Science advisors from the Marshall Space Flight Center aided and assisted the students in developing the proposals for flight on Skylab.

S73-26738 (25 May 1973) --- A close-up view of the Skylab 1 space station cluster can be seen in this reproduction taken from a color television transmission made by a TV camera aboard the Skylab 2 Command Module during its ?fly-around? inspection of the cluster. The numbers across the top of the picture indicate the Skylab 1 ground lapse time. Note the missing portion of the micrometeoroid shield on the Orbital Workshop. The shield area was reported to be solid gold by the Skylab 2 crewmen. A cable appears to be wrapped around the damaged OWS solar array system wing. The crewmen reported that the other OWS solar panel was completely gone, with only tubes and wiring sticking out. One of the discone antennas extends out form the Airlock Module. The Multiple Docking Adapter is in the lower left corner of the picture. A portion of a solar panel on the Apollo Telescope Mount is visible at the bottom and at the left edge. In their ?fly around? inspection the crewmen noted that portions of the micrometeoroid shield had slid back underneath the OWS solar wing. Photo credit: NASA
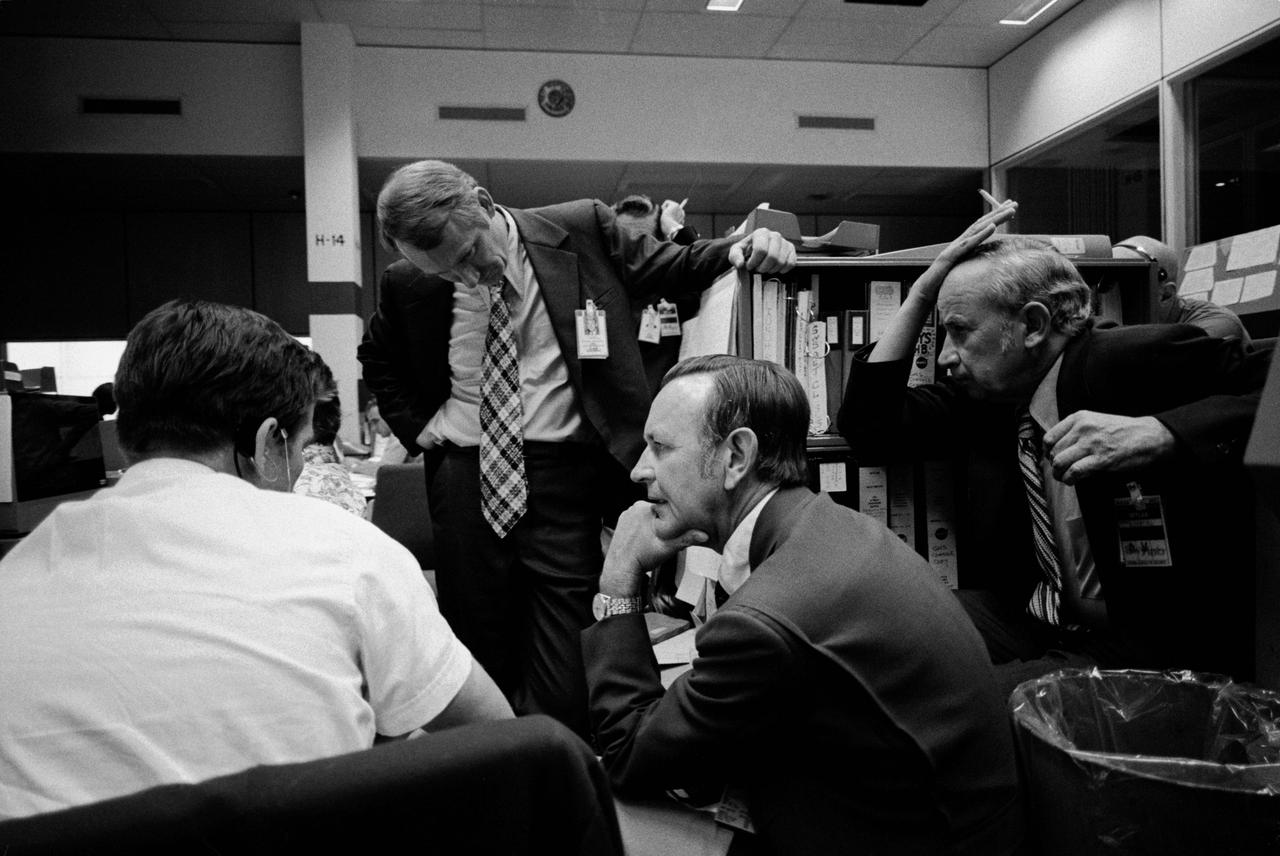

S73-31875 (2 Aug. 1973) --- After learning of a problem in the Command/Service Module which was used to transport the Skylab 3 crew to the orbiting Skylab space station cluster, NASA officials held various meetings to discuss the problem. Here, four men monitor the current status of the problem in the Mission Operations Control Room (MOCR) of the Mission Control Center (MCC) at the Johnson Space Center (JSC). From the left are Gary E. Coen, Guidance and Navigation System flight controller; Howard W. Tindall Jr., Director of Flight Operations at JSC; Dr. Christopher C. Kraft Jr., JSC Director; and Sigurd A. Sjoberg, JSC Deputy Director. Photo credit: NASA
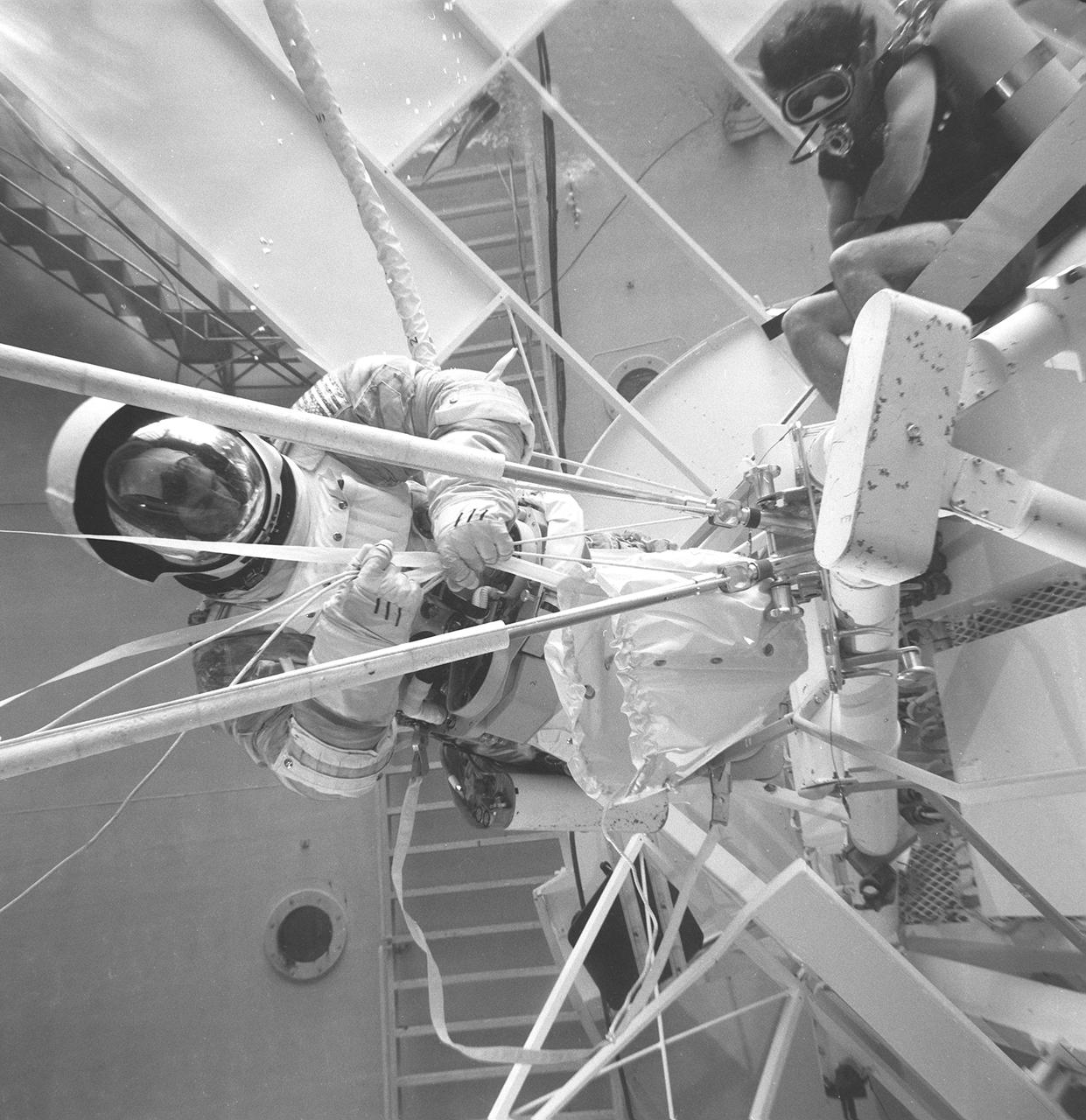

This photograph was taken in the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) during the testing of an emergency procedure to deploy a twin-pole sunshade to protect the orbiting workshop from overheating due to the loss of its thermal shield. The spacecraft suffered damage to its sunshield during its launch on May 14, 1973. This photograph shows the base plate used to hold the twin-pole in place, the bag to hold the fabric sail, and the lines that were used to draw the sail into place. Extensive testing and many hours of practice in simulators, such as the NBS, helped prepare the Skylab crewmen for extravehicular performance in the weightless environment. This huge water tank simulated the weightless environment that the astronauts would encounter in space.