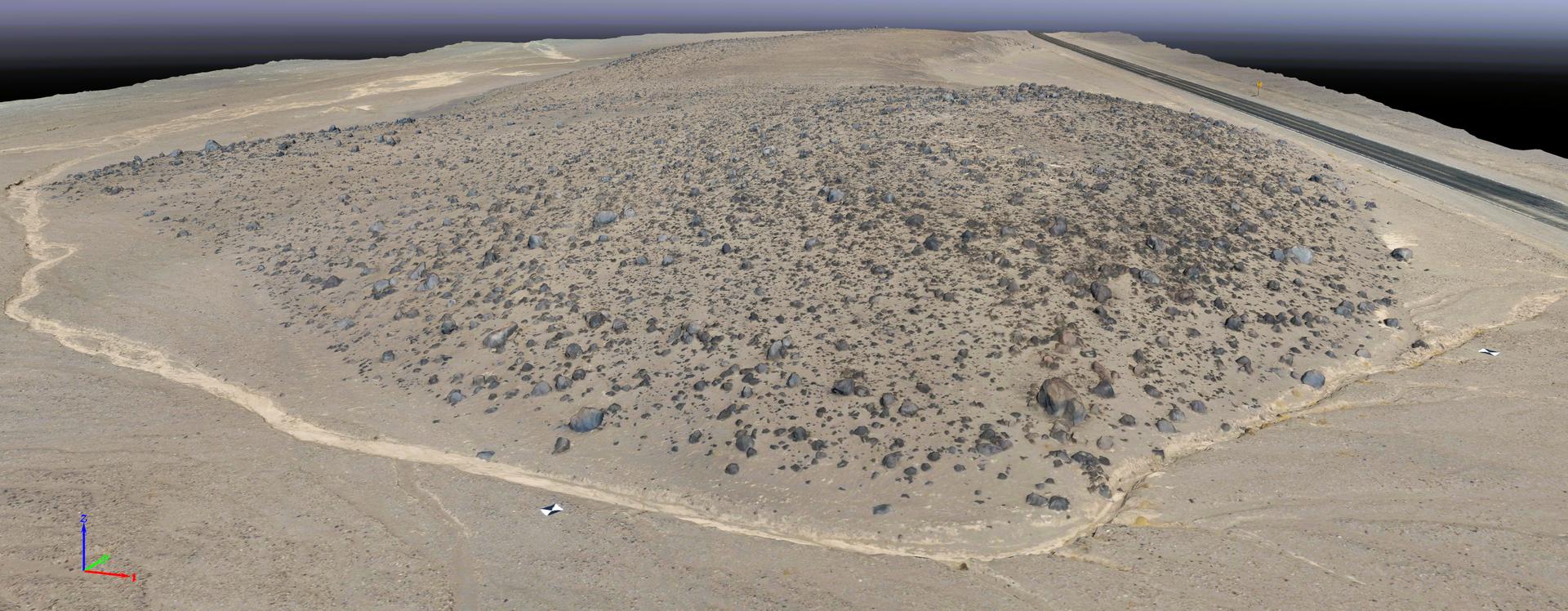

This rendering was created by research drones flying over Mars Hill, a region of Death Valley National Park that has been used by NASA’s Mars researchers since the 1970s, when the agency was preparing to land the twin Viking spacecraft. The hill’s rubbly, volcanic rock resembles the kind of inhospitable terrain that Mars rovers must navigate around and which posed a landing hazard for the Ingenuity Mars Helicopter. In September 2025, researchers from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California flew research drones over Mars Hill as part of a test campaign to develop navigation software for future Mars rotorcraft. Being able to precisely land between rocks like those seen here is a critical capability to access similar Martian terrain in the future.
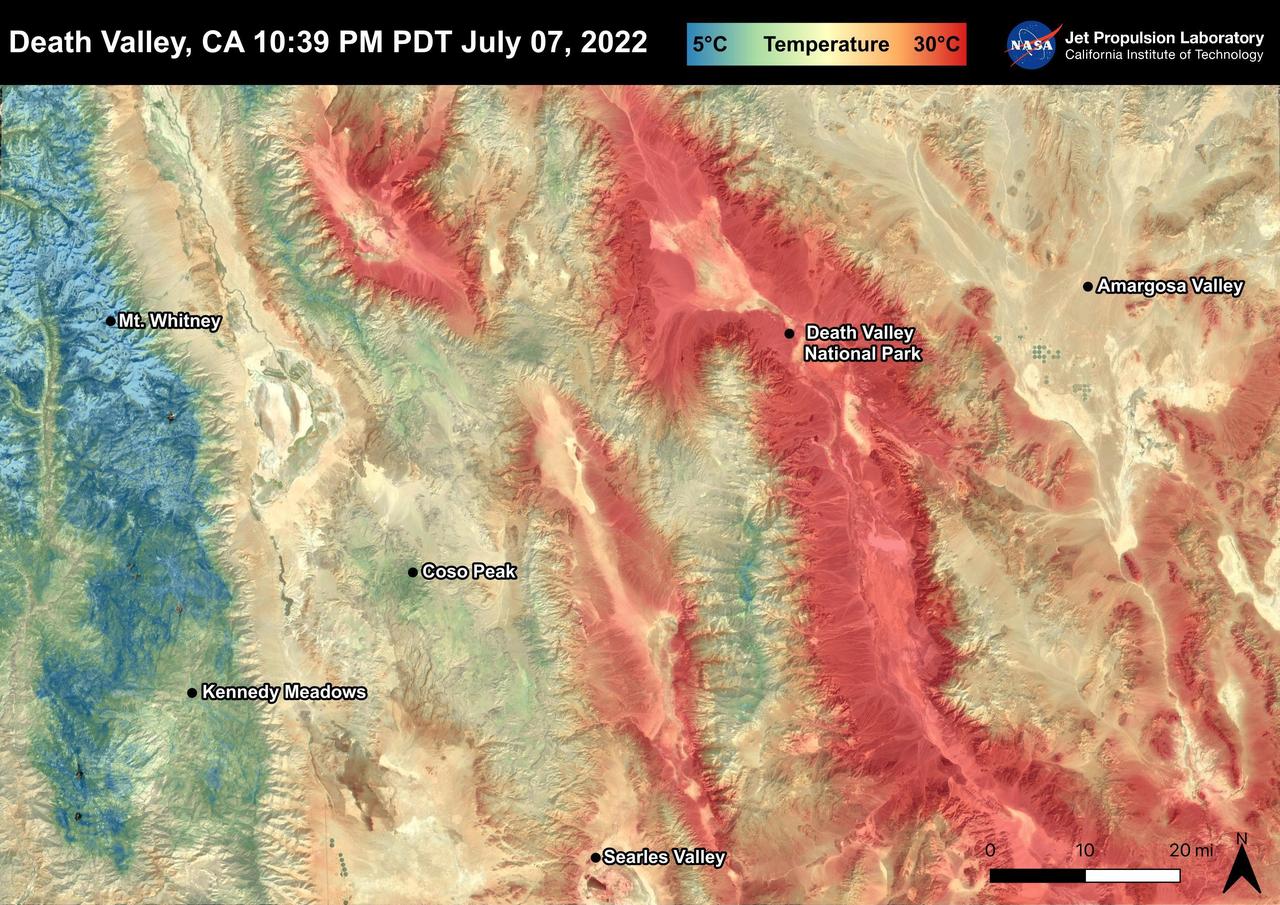
Death Valley, California is a desert valley in the Northern Mojave Desert. During the summer months, Death Valley can become one of the hottest places on Earth. Death Valley is about 85 miles from Mt. Whitney, the highest point in the contiguous United States with an elevation of 14,505 ft. This Land Surface Temperature image captured by ECOSTRESS on July 07, 2022 shows temperatures exceeding 90 degrees Fahrenheit in Death Valley and temperatures below 40 degrees Fahrenheit in the Sierra Nevada Mountain Range. ECOSTRESS is a thermal instrument on the International Space Station that measures the temperature of the ground, which is hotter than the air temperature during the day. It was launched to the space station in 2018. Its primary mission is to identify critical thresholds of water use and water stress in plants and to detect the timing, location, and predictive factors leading to plant water uptake decline and/or cessation. The nature of the high-resolution data provided by ECOSTRESS allows it to record heat related phenomena such as heat waves and wildfires. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25482
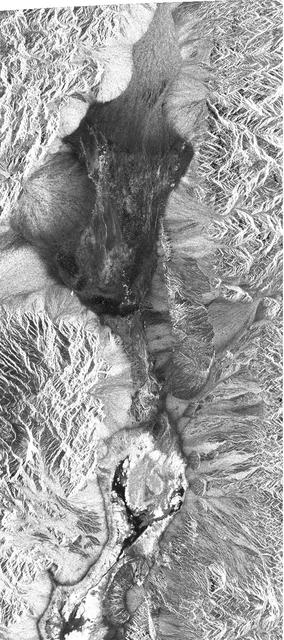
This image shows Death Valley, California, centered at 36.629 degrees north latitude, 117.069 degrees west longitude.
Death Valley, Calif., has the lowest point in North America, Badwater at 85.5 meters 282 feet below sea level. It is also the driest and hottest location in North America. This image is from NASA Terra spacecraft.
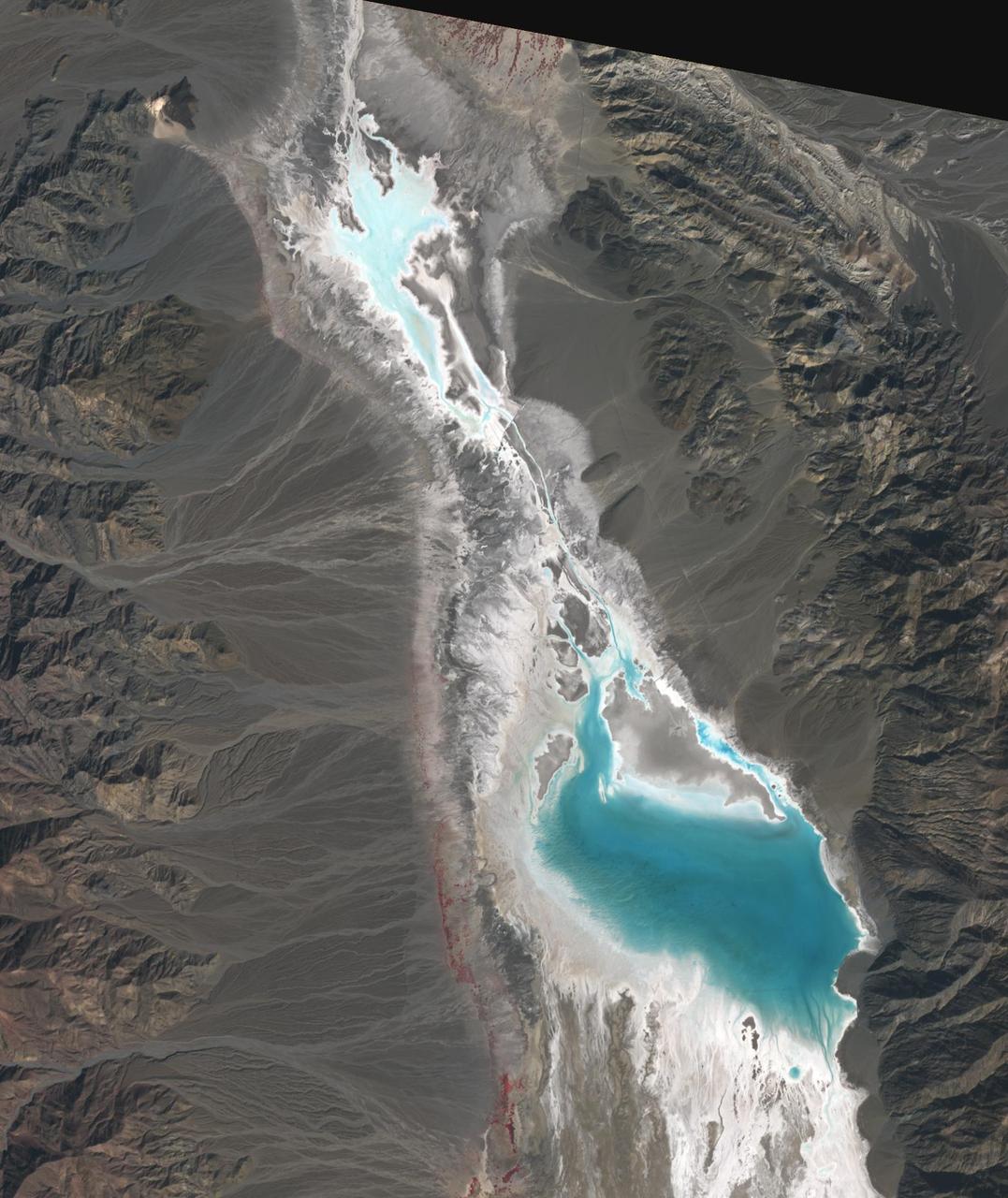

Badwater Basin in Death Valley, California, is one of the driest places on Earth. In August, Hurricane Hilary dropped a year's worth of rain in a single day. Floodwaters have filled the ephemeral lake to a depth of about 60 cm. But the lake may evaporate in the next weeks. The scenes were acquired October 25, 2023 and November 10, 2012; cover an area of 24 by 28.5 km, and are located at 36.3 degrees north, 116.8 degrees west. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26197
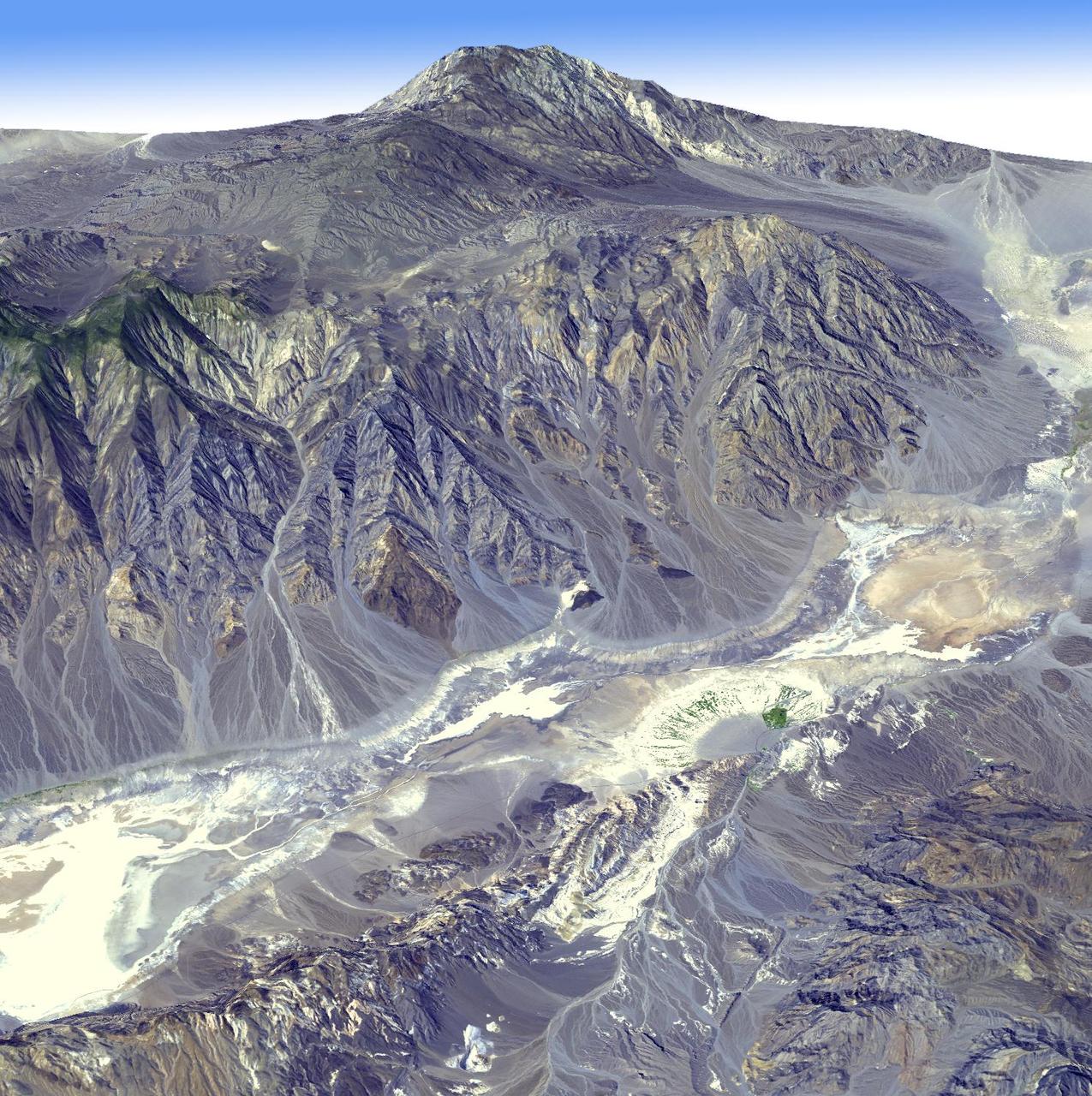
This picture is a three-dimensional perspective view of Death Valley, California. This view was constructed by overlaying a NASA SIR-C radar image on a U.S. Geological Survey digital elevation map.

The work was among 25 projects funded by NASA’s Mars Exploration Program this past year to push the limits of future technologies. Sand dunes confused the navigation algorithm of the Ingenuity Mars helicopter during several of its last flights, including its 72nd and final flight on the Red Planet in January 2024. The navigation software in development would help future rotorcraft track the surface of especially bland, featureless terrain similar to the barren sand dunes seen in Death Valley’s Mesquite Flats Sand Dunes as well as in Dumont Dunes in the Mojave Desert, where testing was also conducted. Tests included flights over a region in Death Valley called Mars Hill, which is littered with rubbly volcanic rocks and has been used by NASA’s Mars researchers since the 1970s, during preparations for the Viking lander missions.
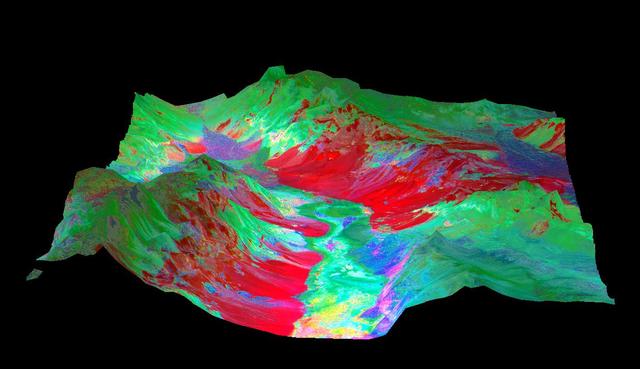
This 3-D perspective view looking north over Death Valley, California, was produced by draping ASTER nighttime thermal infrared data over topographic data from the US Geological Survey. The ASTER data were acquired April 7, 2000 with the multi-spectral thermal infrared channels, and cover an area of 60 by 80 km (37 by 50 miles). Bands 13, 12, and 10 are displayed in red, green and blue respectively. The data have been computer enhanced to exaggerate the color variations that highlight differences in types of surface materials. Salt deposits on the floor of Death Valley appear in shades of yellow, green, purple, and pink, indicating presence of carbonate, sulfate, and chloride minerals. The Panamint Mtns. to the west, and the Black Mtns. to the east, are made up of sedimentary limestones, sandstones, shales, and metamorphic rocks. The bright red areas are dominated by the mineral quartz, such as is found in sandstones; green areas are limestones. In the lower center part of the image is Badwater, the lowest point in North America. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA02663

This radar image shows the area of Death Valley, California and the different surface types in the area. Radar is sensitive to surface roughness with rough areas showing up brighter than smooth areas, which appear dark.
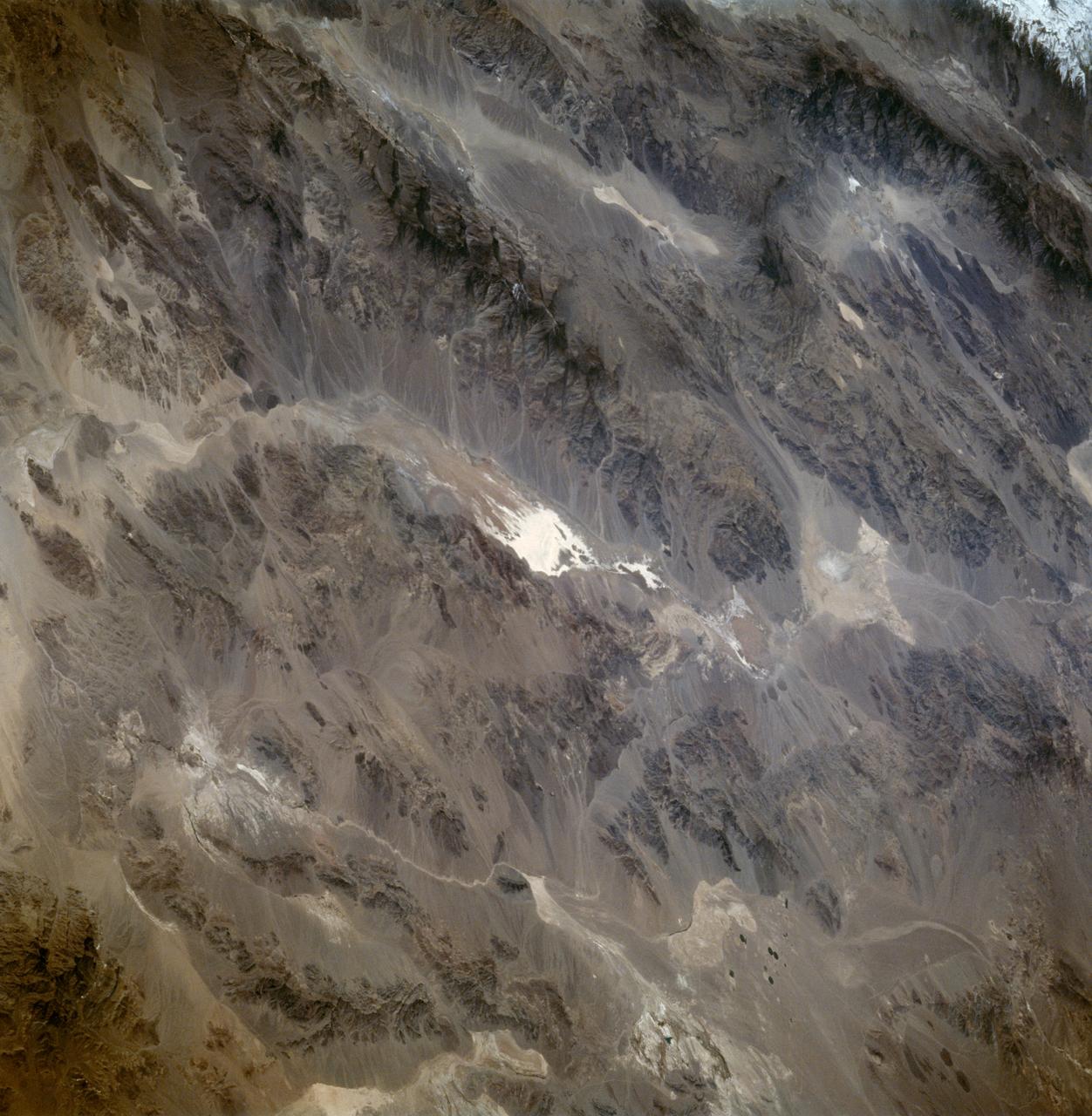

STS059-86-059 (9-20 April 1994) --- This oblique handheld Hasselblad 70mm photo shows Death Valley, near California's border with Nevada. The valley -- the central feature of Death Valley National Monument -- extends north to south for some 140 miles (225 kilometers). Hemmed in to the east by the Amargosa Range and to the west by the Panamints, its width varies from 5 to 15 miles (8 to 24 kilometers). Using Spaceborne Imaging Radar (SIR-C) and X-band Synthetic Aperture Radar (X-SAR) onboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour, the crew was able to record a great deal of data on this and other sites, as part of NASA's Mission to Planet Earth.
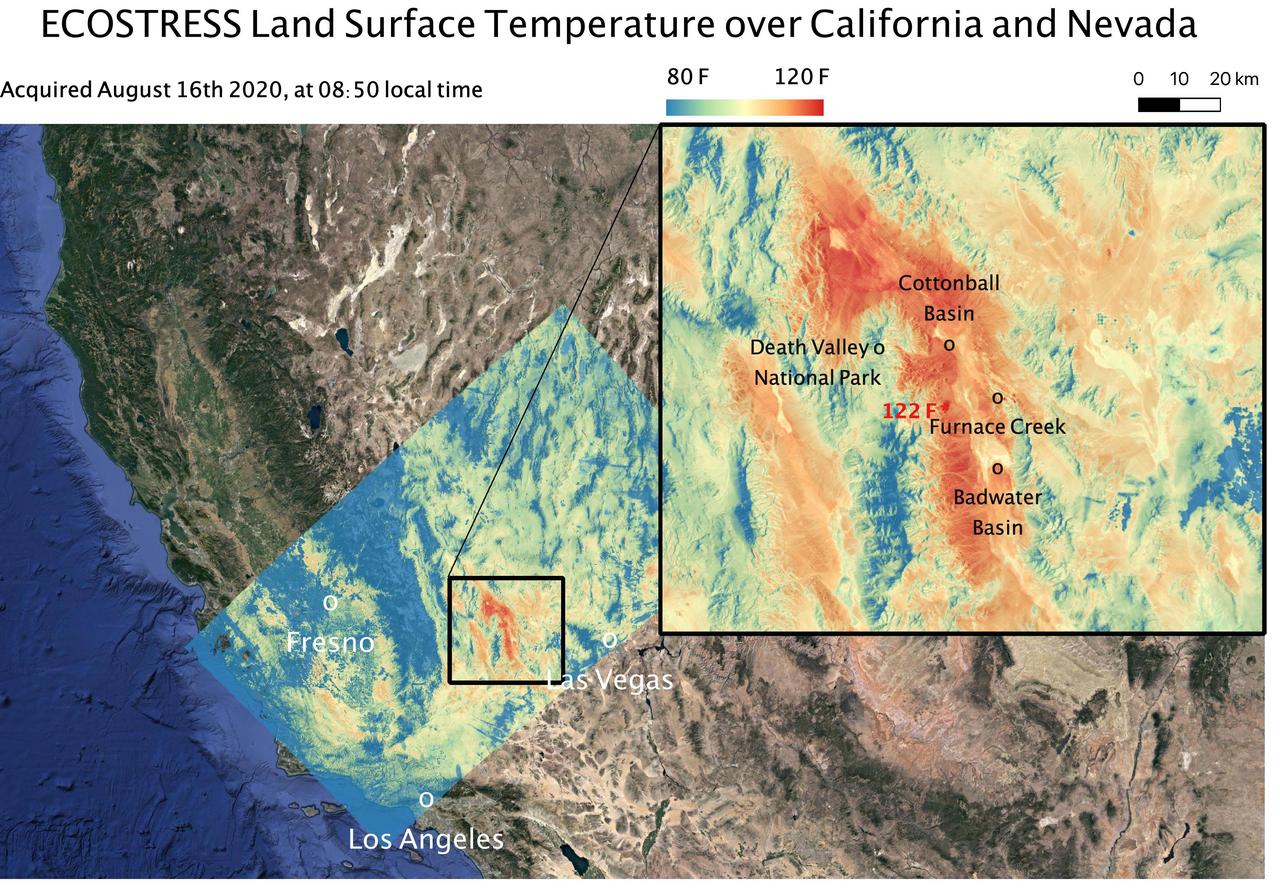
This temperature map shows the land surface temperatures around Death Valley in California's Mojave Desert on Aug. 16, 2020. The observation was made possible by NASA's Ecosystem Spaceborne Thermal Radiometer Experiment on Space Station (ECOSTRESS), which measured a peak land surface temperature of 122.52 degrees Fahrenheit (50.29 degrees Celsius) near Furnace Creek. ECOSTRESS collected this data when the space station passed over California at about 8:50 a.m. PDT (11:50 a.m. EDT) during a record-breaking heat wave that gripped the region. With a resolution of about 77 by 77 yards (70 by 70 meters), the image enables the study of surface-temperature conditions down to the size of a football field. The hottest temperatures are shown in dark red, with the coolest temperatures in blue. ECOSTRESS measures the temperature of plants as they heat up when they run out of water. But it can also measure and track heat-related phenomena like heat waves, fires, and volcanoes. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23787
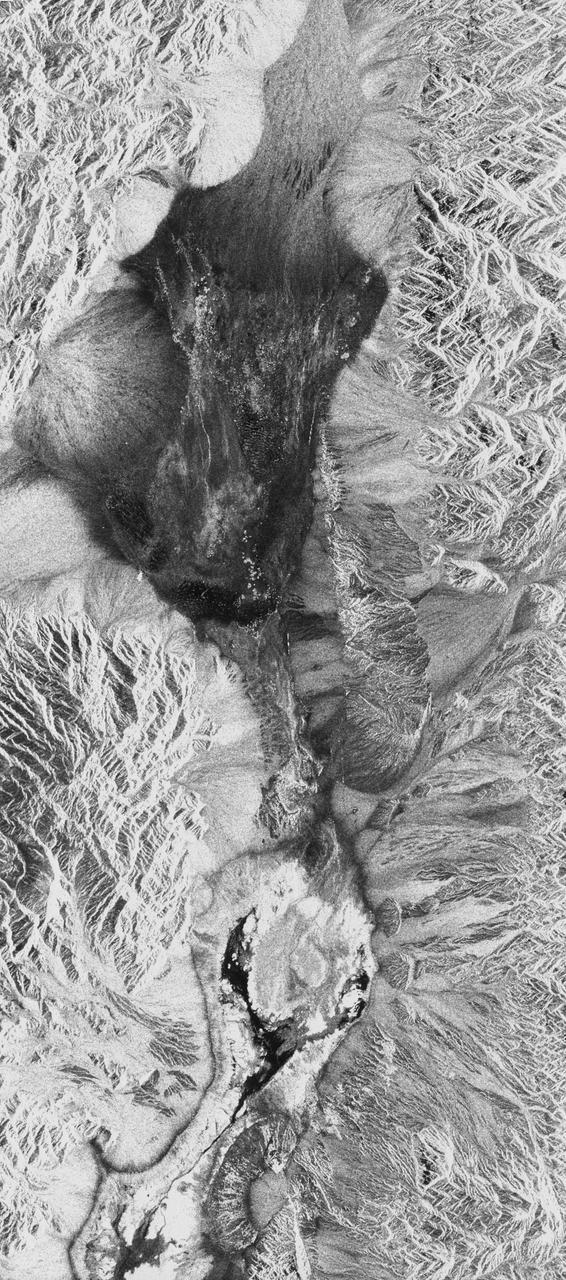
STS059-S-026 (11 April 1994) --- This is an image of Death Valley, California, centered at 36.629 degrees north latitude, 117.069 degrees west longitude. The image shows Furnace Creek alluvial fan and Furnace Creek Ranch at the far right, and the sand dunes near Stove Pipe Wells at the center. The dark fork-shaped feature between Furnace Creek fan and the dunes is a smooth flood-plain which encloses Cottonball Basin. The SIR-C/X-SAR supersite is an area of extensive field investigations and has been visited by both Space Radar Lab astronaut crews. Elevations in the Valley range from 70 meters below sea level, the lowest in the United States, to more than 3300 meters above sea level. Scientists are using SIR-C/X-SAR data from Death Valley to help answer a number of different questions about the Earth's geology. One question concerns how alluvial fans are formed and change through time under the influence of climatic changes and earthquakes. Alluvial fans are gravel deposits that wash down from the mountains over time. They are visible in the image as circular, fan-shaped bright areas extending into the darker valley floor from the mountains. Information about the alluvial fans help scientists study Earth's ancient climate. Scientists know the fans are bulit up through climatic and tectonic processes and they will use the SIR-C/X-SAR data to understand the nature and rates of weathering processes on the fans, soil formation, and the transport of sand and dust by the wind. SIR-C/X-SAR's sensitivity to centimeter-scale (or inch-scale) roughness provides detailed maps of surface texture. Such information can be used to study the occurrence and movement of dust storms and sand dunes. the goal of these studies is to gain a better understanding of the record of past climatic changes and the effects of those changes on a sensitive environment. This may lead to a better ability to predict future response of the land to different potential global cimate-change scenarios. Death Valley is also one of the primary calibration sites for SIR-C/X-SAR. The bright dots near the center of the image are corner reflectors that have been set-up to calibrate the radar as the Shuttle passes overhead. Thirty triangular-shaped reflectors (they look like aluminum pyramids) have been deployed by the calibration team from JPL over a 40 kilometer by 40 kilometer area in and around Death Valley. The calibration team will also deploy transponders (electronic reflectors) and recievers to measure the radar signals from SIR-C/X-SAR on the ground. Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C and X-Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR) is part of NASA's Mission to Planet Earth (MTPE). The radars illuminate Earth with microwaves allowing detailed observations at any time, regardless of weather or sunlight conditions. SIR-C/X-SAR uses three microwave wavelengths: L-Band (24 cm), C-Band (6 cm), and X-Band (3 cm). The multi-frequency data will be used by the international scientific community to better understand the global environment and how it is changing. The SIR-C/X-SAR data, complemented by aircraft and ground studies, will give scientists clearer insights into those environmental changes which are caused by nature and those changes which are induced by human activity. SIR-C was develpoed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL). X-SAR was developed by the Dornire and Alenia Spazio Companies for the German Space Agency, Deutsche Agentur fuer Raumfahrtangelegenheiten (DARA), and the Italian Space Agency, Agenzia Spaziale Italiana (ASI). JPL Photo ID: P-43883

The work was among 25 projects funded by NASA’s Mars Exploration Program this past year to push the limits of future technologies. Sand dunes confused the navigation algorithm of the Ingenuity Mars helicopter during several of its last flights, including its 72nd and final flight on the Red Planet in January 2024. The navigation software in development would help future rotorcraft track the surface of especially bland, featureless terrain similar to the barren Dumont Dunes. Tests also included flights over a region in Death Valley called Mars Hill, which is littered with rubbly volcanic rocks and has been used by NASA’s Mars researchers since the 1970s, during preparations for the Viking lander missions.
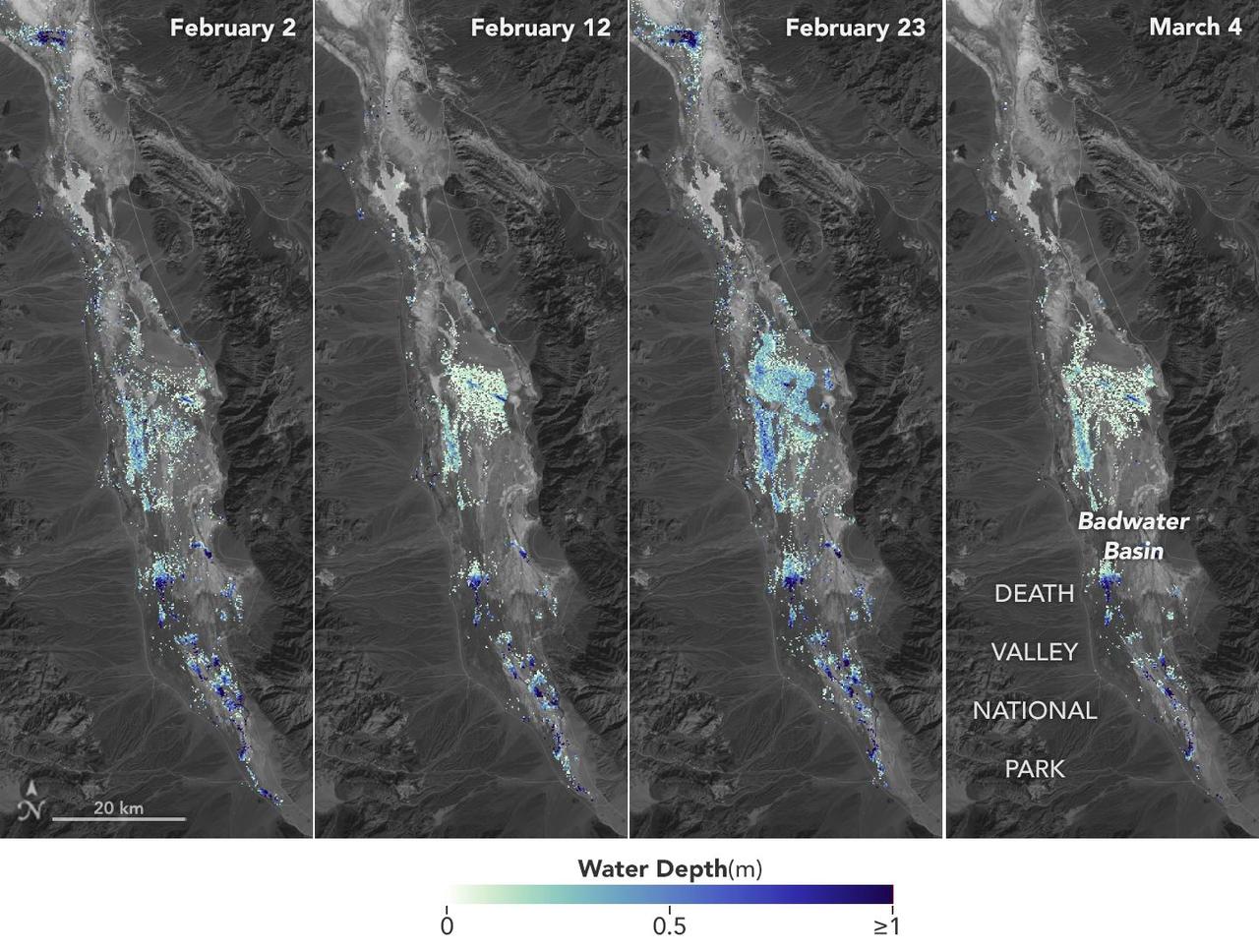
California's Death Valley, the driest place in North America, has hosted an ephemeral lake since late 2023. In March 2024, a NASA-led analysis calculated water depths in the temporary lake over several weeks in February and March 2024, demonstrating the possibilities of the latest water-observing mission, the U.S.-French Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) satellite. The analysis found that water depths in the lake ranged between about 3 feet (1 meter) to less than 1.5 feet (0.5 meters) over the course of several weeks. This period included a series of storms that swept across California, bringing record amounts of rainfall. To estimate the depth of the lake, known informally as Lake Manly, researchers used water level data collected by SWOT and subtracted corresponding U.S. Geological Survey land elevation information for Badwater Basin. The researchers found that the water levels varied across space and time in the roughly 10-day period between SWOT observations. In the visualization above, water depths of about 3 feet (1 meter) appear dark blue; those of less than 1.5 feet (0.5 meters) appear light yellow. Right after a series of storms in early February, the temporary lake was about 6 miles (10 kilometers) long and 3 miles (5 kilometers) wide. Each pixel in the image represents an area that is about 330 feet by 330 feet (100 meters by 100 meters). Unlike many lakes around the world, Death Valley's lake is temporary, relatively shallow, and strong winds are enough to move the freshwater body a couple of miles, as happened from Feb. 29 to March 2. Since there isn't typically water in Badwater Basin, researchers don't have permanent instruments in place for studying water in this area. SWOT can fill the data gap for when places like this, and others around the world, become inundated. Since shortly after launch in December 2022, SWOT has been measuring the height of nearly all water on Earth's surface, developing one of the most detailed and comprehensive views of the planet's oceans and freshwater lakes and rivers. Not only can the satellite detect the extent of water, as other satellites can, but SWOT can also measure water surface levels. Combined with other types of information, SWOT measurements can yield water depth data for inland features like lakes and rivers. The SWOT science team makes its measurements using the Ka-band Radar Interferometer (KaRIn) instrument. With two antennas spread 33 feet (10 meters) apart on a boom, KaRIn produces a pair of data swaths as it circles the globe, bouncing radar pulses off water surfaces to collect surface-height information. Launched from Vandenberg Space Force Base in central California, SWOT is now in its operations phase, collecting data that will be used for research and other purposes. Animation available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26184
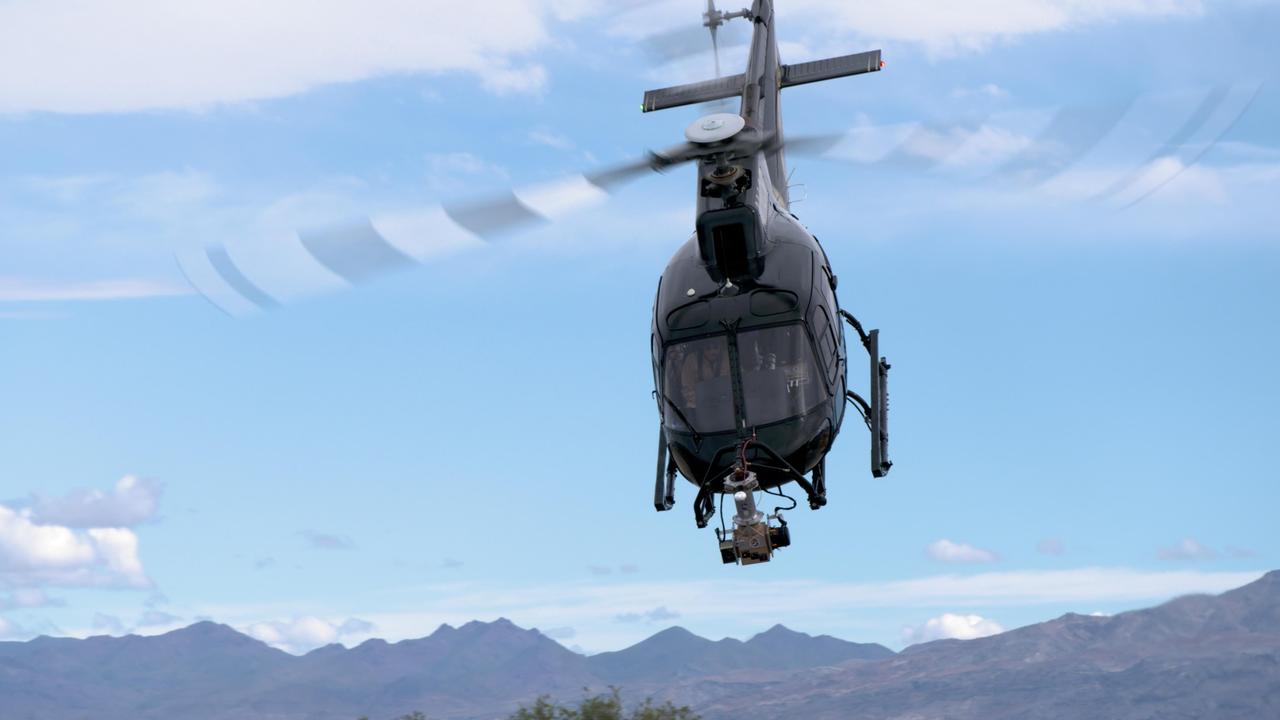

On a test flight in Death Valley, California, an Airbus helicopter carried an engineering model of the Lander Vision System (LVS) that will help guide NASA's next Mars mission to a safe touchdown on the Red Planet. During the flight — one in a series — the helicopter (which is not part of the mission and was used just for testing) and its two-person crew flew a pre-planned sequence of maneuvers while LVS collected and analyzed imagery of the barren, mountainous terrain below. LVS is an integral part of a guidance system called Terrain-Relative Navigation (TRN) that will steer NASA's Mars 2020 rover away from hazardous areas during its final descent to Jezero Crater on Feb. 18, 2021. Mars 2020 will be the first spacecraft in the history of planetary exploration with the ability to accurately retarget its point of touchdown during the landing sequence. Also among the firsts of the mission, the 2020 rover carries a sample-caching system that will collect samples of Martian rock and soil and store them on the surface of the planet for retrieval and return to Earth by subsequent missions. Mars 2020 will launch from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida in July of 2020. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23265
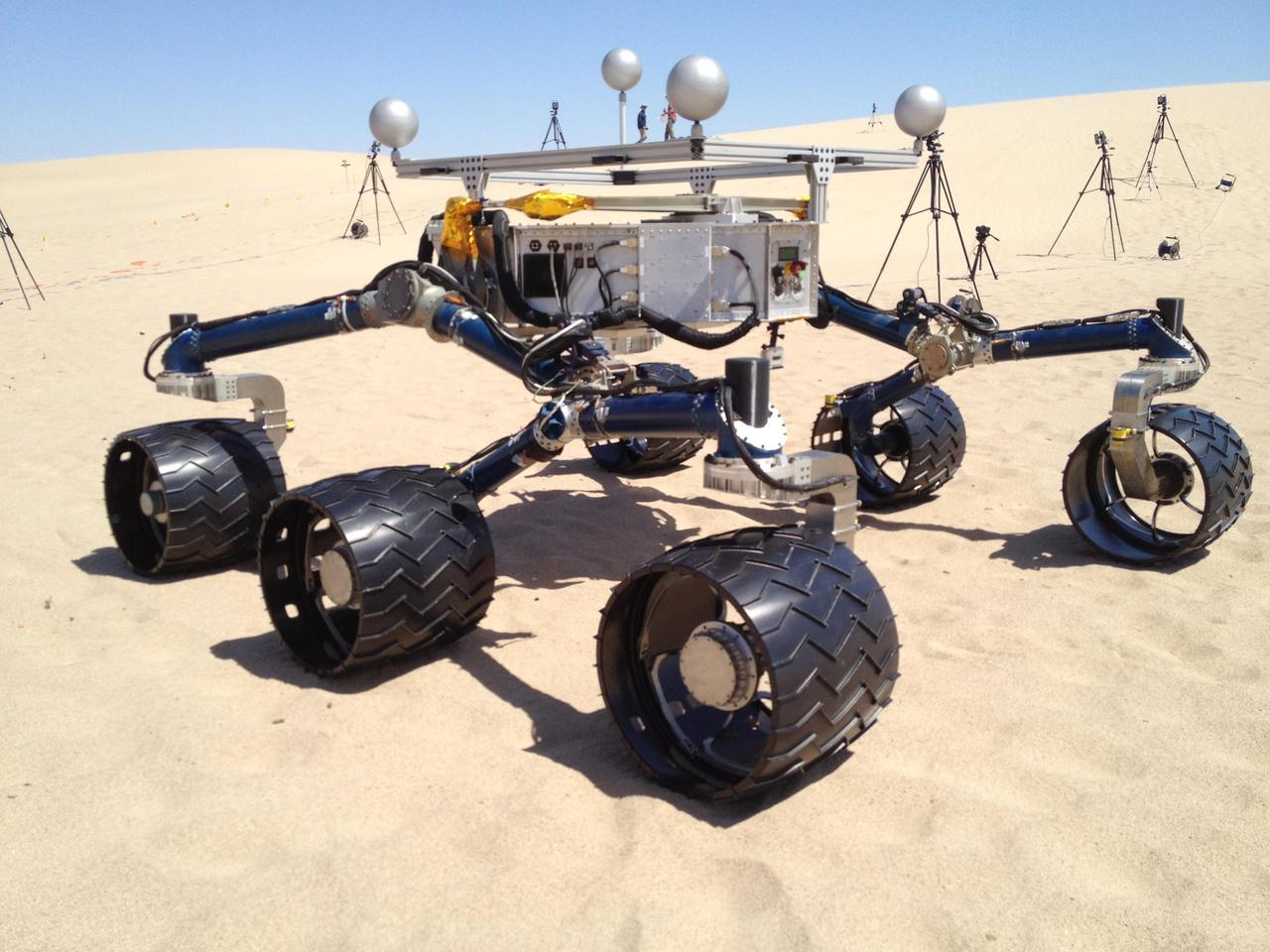

NASA Mars Science Laboratory mission team members ran mobility tests on the test rover called Scarecrow on sand dunes near Death Valley, Ca. in early May 2012 in preparation for operating the Curiosity rover, currently en route to Mars.
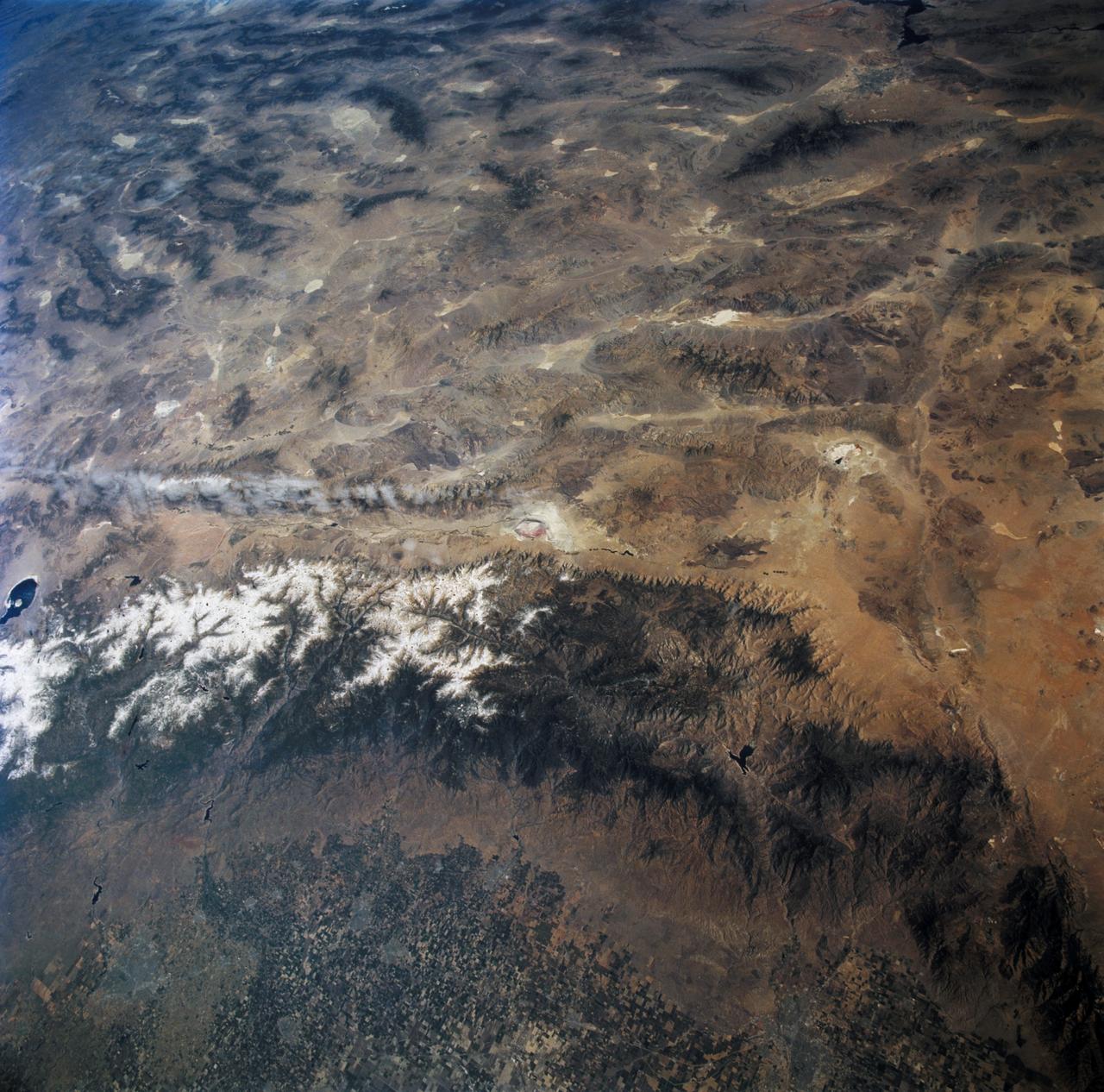

STS068-267-097 (30 September-11 October 1994) --- An extensive view eastward from the irrigated San Joaquin Valley in the foreground, across the Sierra Nevada (living up to its name in early October), into the desert of eastern California and Nevada (which has no snow, despite the name). Mono Lake is just visible at the left edge of the frame; Owens Valley extends southward to Owens Lake, the next valley is Panamint Valley, and then Death Valley. Las Vegas and Lake Mead are visible at the upper right of the frame. The Space Radar Laboratory 2 (SRL-2) obtained extensive, multiple-pass data from many test sites within the region displayed, including Mammoth Mountain ski area south of Mono Lake, and in Death Valley.
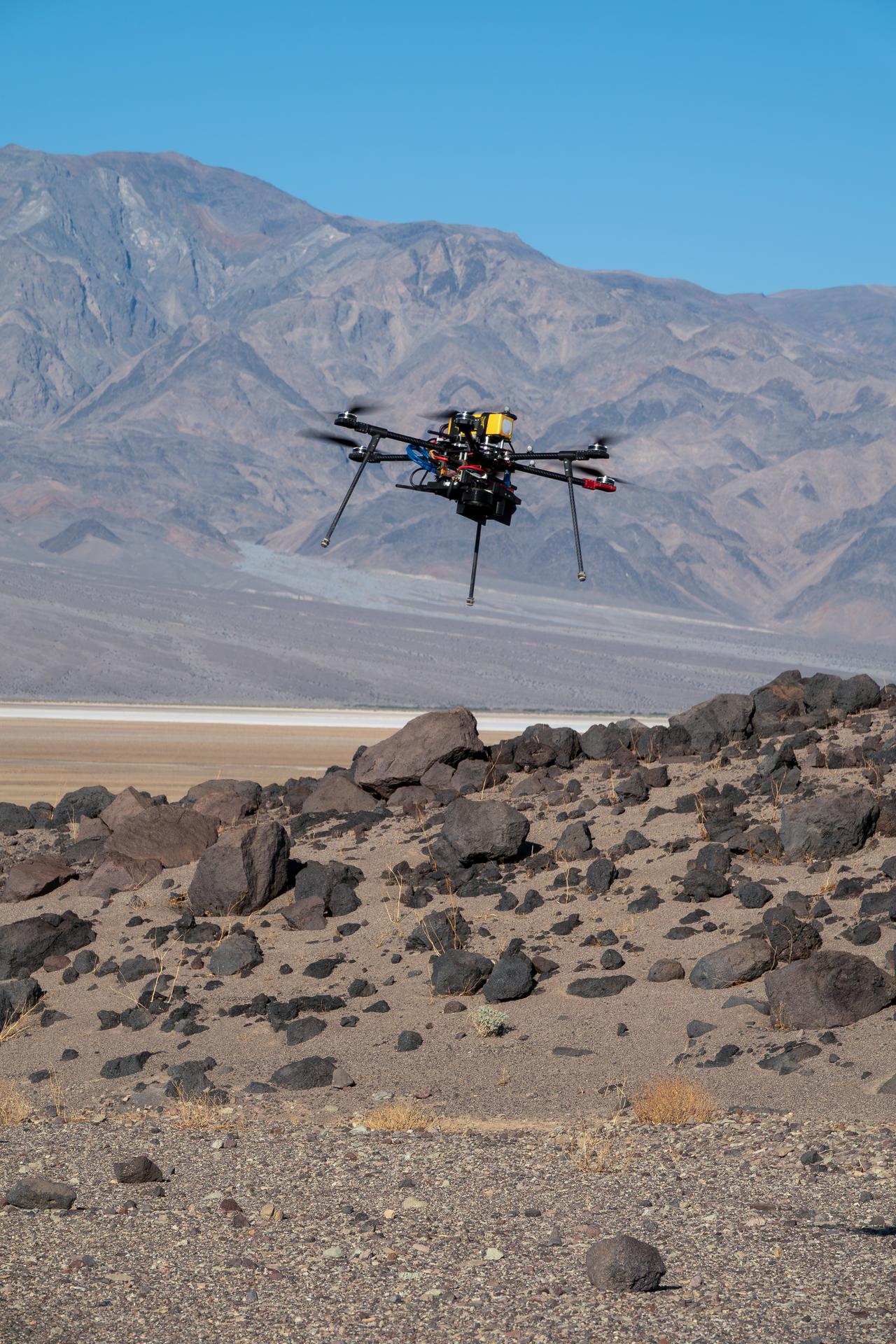

One of three drones used in recent tests by NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California flies over Mars Hill, a region of Death Valley National Park, in September 2025. The region’s rubbly, volcanic rocks have served as a Mars-like testing area and analog site for scientists since the 1970s, when NASA was preparing to land the twin Viking spacecraft on the Red Planet. The drone research — tests of navigation software for the Martian surface — was one of 25 projects funded by NASA’s Mars Exploration Program this past year to push the limits of future technologies. Sand dunes confused the navigation algorithm of the Ingenuity Mars helicopter during several of its last flights, including its 72nd and final flight on the Red Planet in January 2024. The navigation software in development would help future rotorcraft to track the surface of especially bland, featureless terrain similar to the barren sand dunes seen in parts of Death Valley and in the Mojave Desert and to land safely in cluttered environments like Mars Hill.
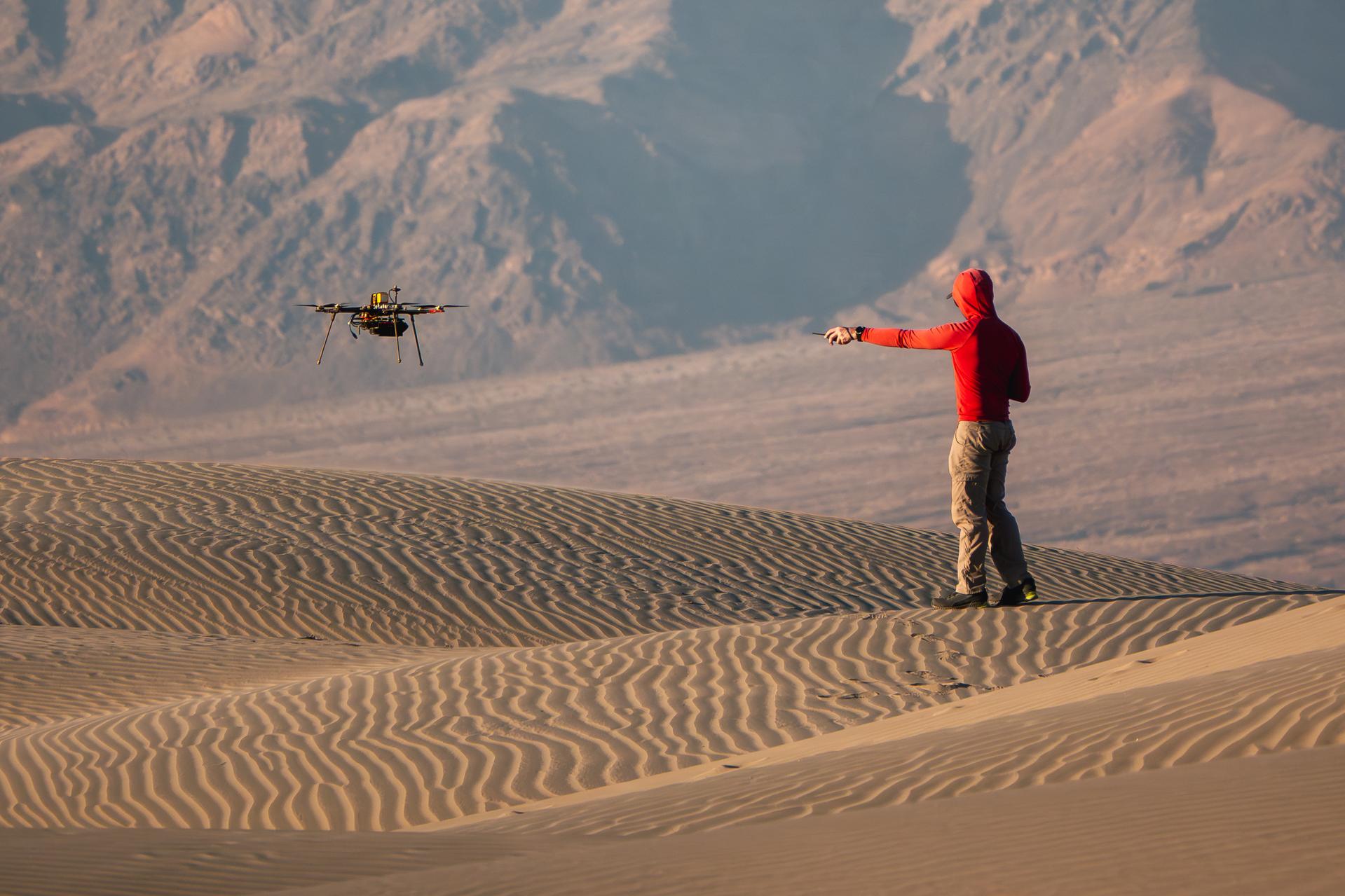

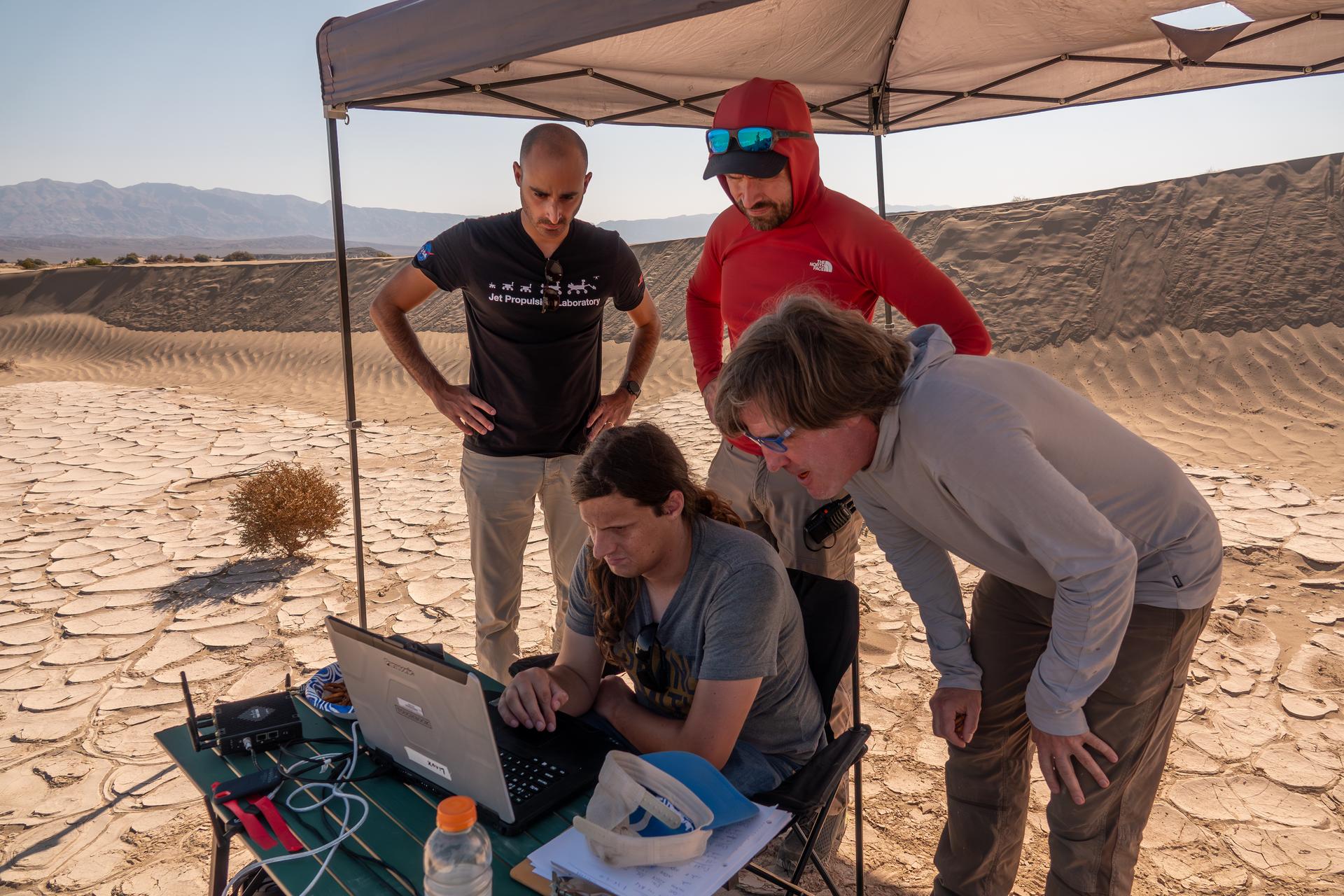
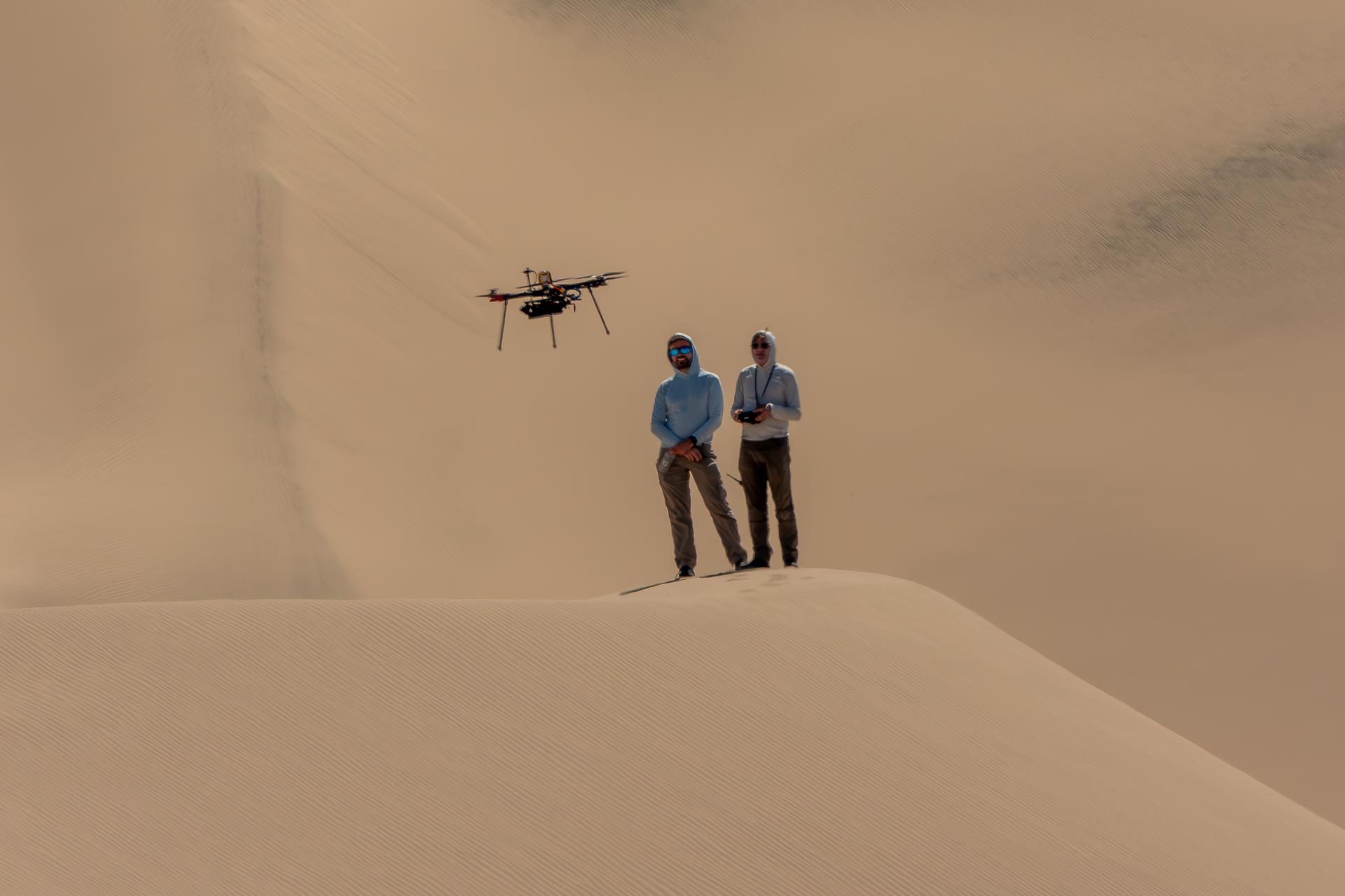
A researcher from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California monitors a drone as it flies over sand dunes in September 2025. This image was captured in Death Valley National Park during a larger test campaign to develop navigation software that would guide future rotorcraft on Mars. The work was among 25 projects funded by NASA’s Mars Exploration Program this past year to push the limits of future technologies. Sand dunes confused the navigation algorithm of the Ingenuity Mars helicopter during several of its last flights, including its 72nd and final flight on the Red Planet in January 2024. The navigation software in development would help future rotorcraft track the surface of especially bland, featureless terrain similar to the barren sand dunes seen in parts of Death Valley. Tests also included flights over a region of the park called Mars Hill, which is littered with rubbly volcanic rocks and has been used by NASA’s Mars researchers since the 1970s, during preparations for the Viking lander missions.
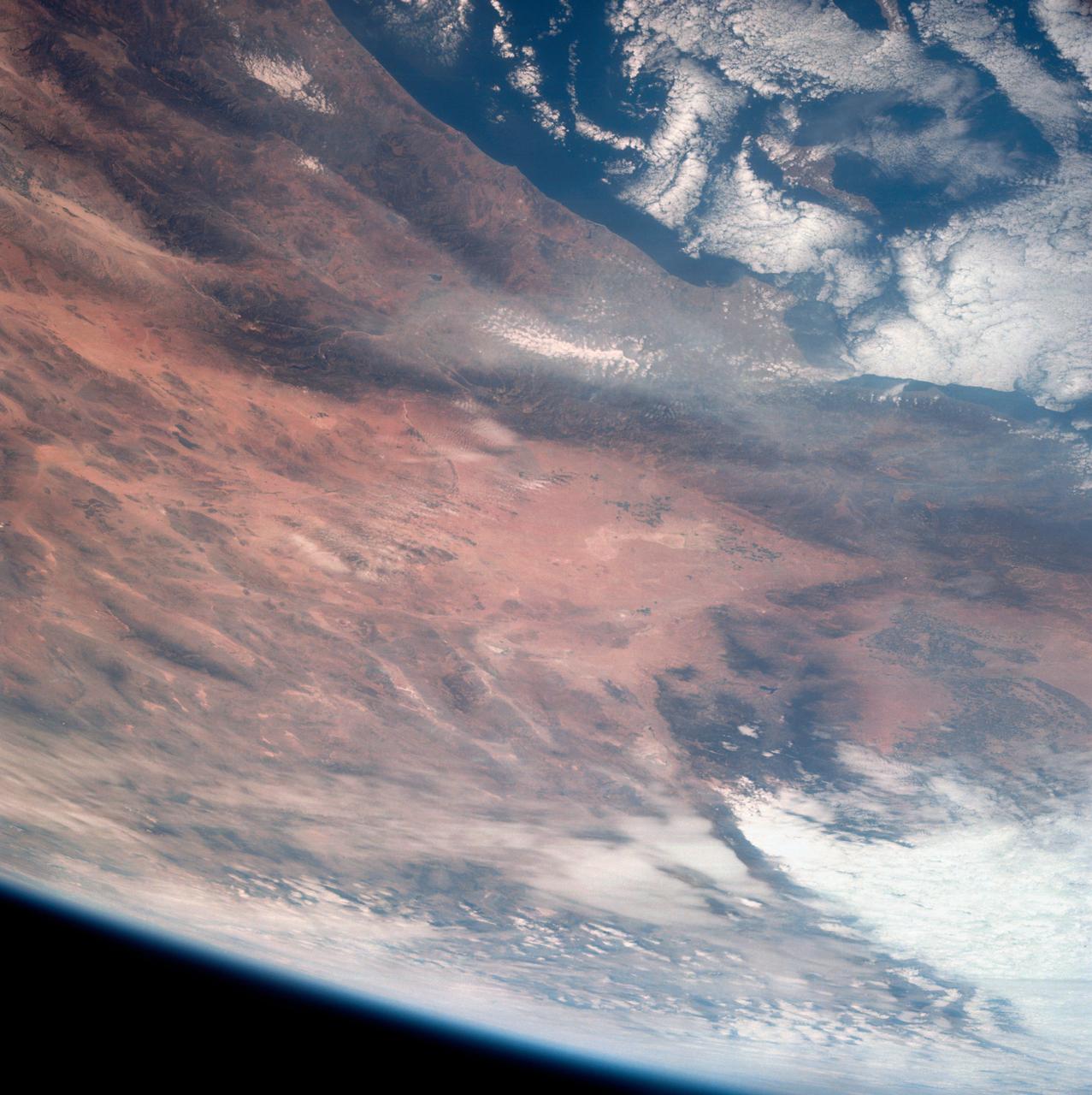

This view of southern California as seen from the Apollo 7 spacecraft during its 18th revolution of the earth. Photographed from an altitude of 124 nautical miles. The coast of California can be seen from Point Mugu southward to Oceanside. Santa Catalina can be seen below the off shore clouds. Details of the Los Angeles area are obscured by pollution which extends from Banning westard for 100 miles to beyond Malibu. In the upper portion of the photograph can be seen (left to right) the San Joaquin Valley beyond Bakersfield, the Techachapi Mountains, the Sierra Nevada, Owens Valley, Death Valley and the Mojave Desert.
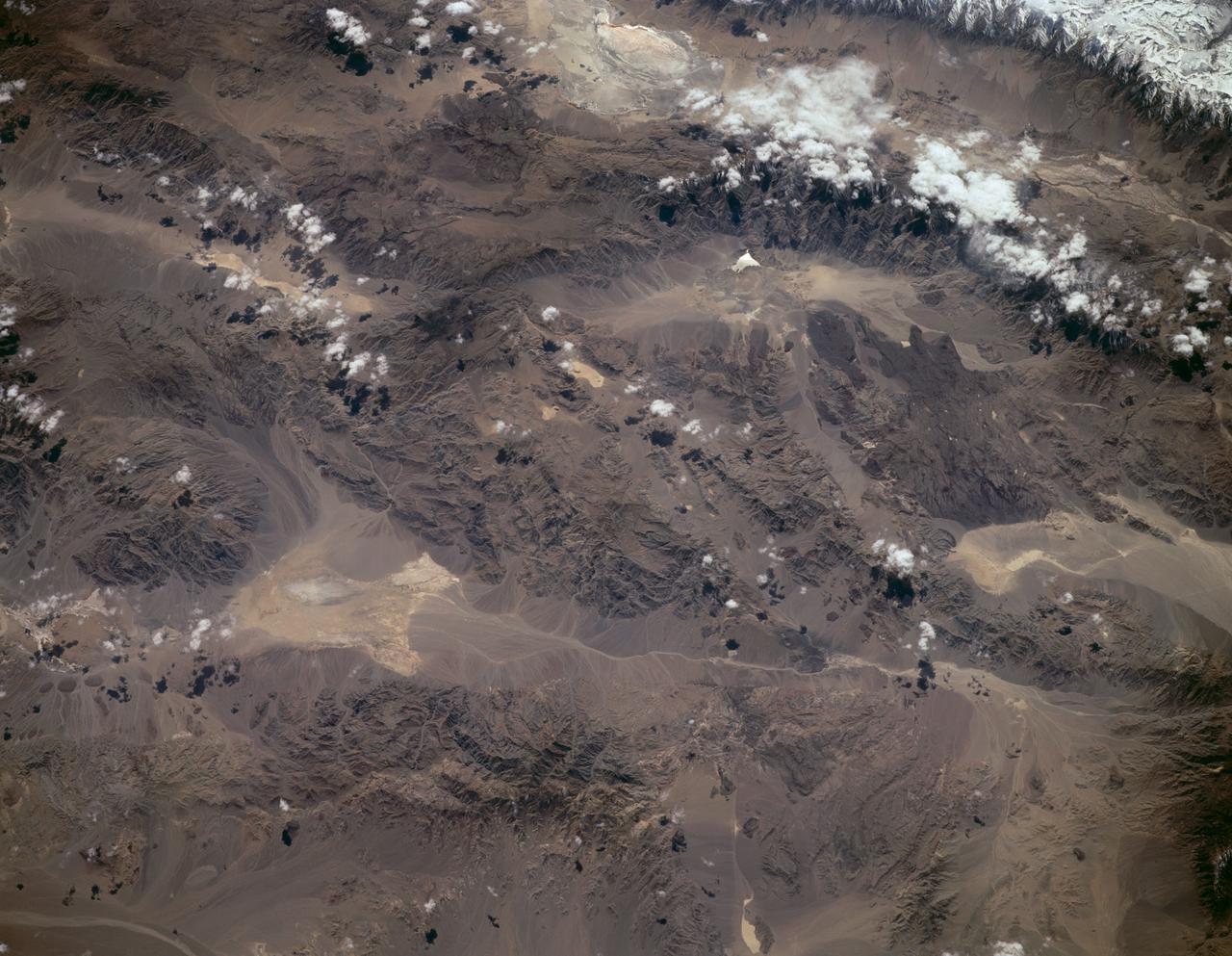

STS059-L09-162 (9-20 April 1994) --- Orient with the snow-covered mountains (Sierra Nevada of California) in the upper right corner. Then Owens Valley runs along the top of the photograph to Owens Lake playa at top center. The upper end of Death Valley extends from right to left in the foreground, with the drainage running down to a playa at Stovepipe Wells in the left foreground. Geologists are studying microwave signatures of the different playa surfaces, and the coatings on alluvial fans that extend from mountain masses, to try to sort out the history of different climates in this formerly wet but now hyperarid region.
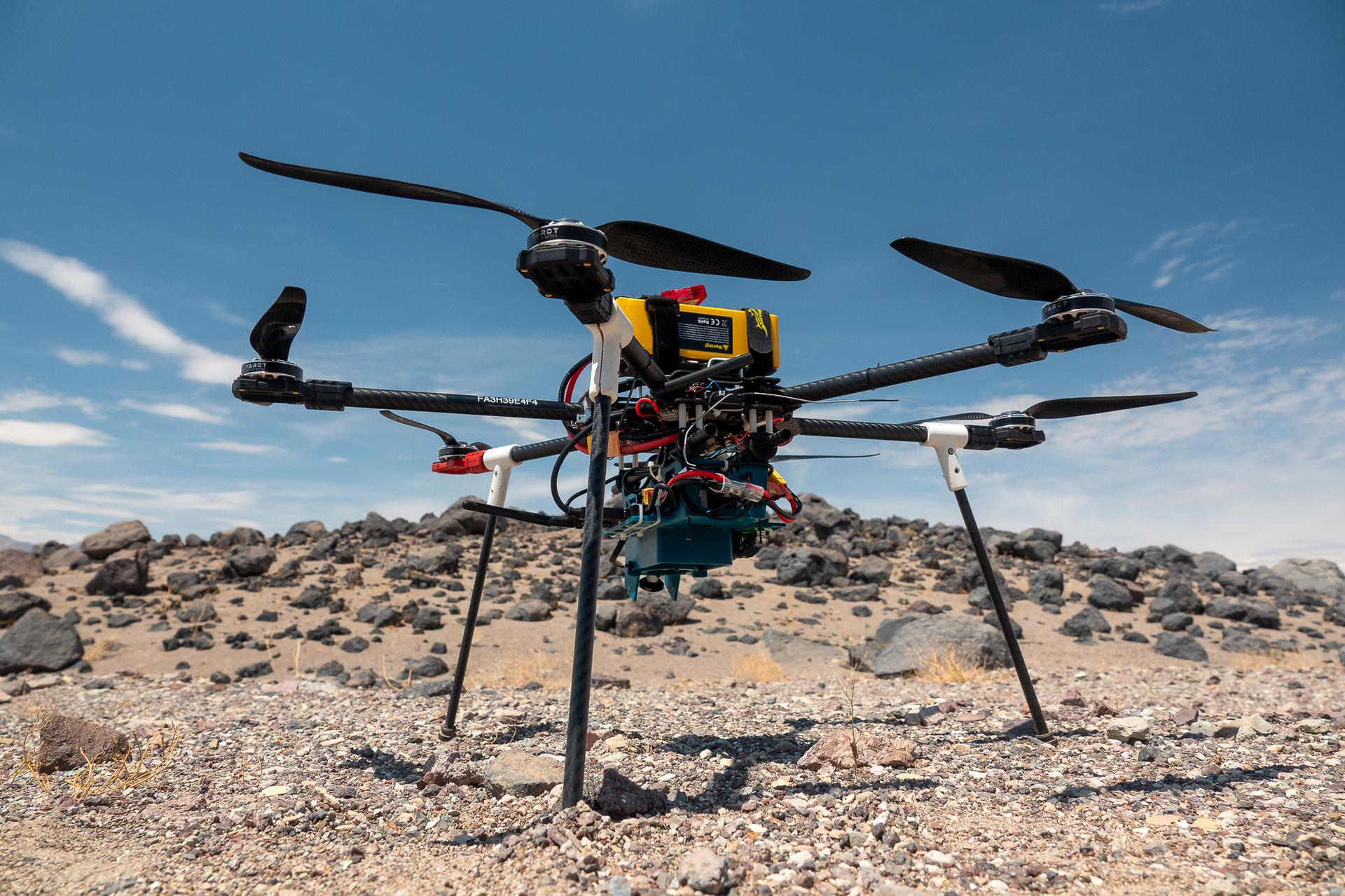

This is one of three research drones that NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California used in September 2025 to test navigation software that could be used by future rotorcraft on Mars. The drone is sitting in front of a location within Death Valley National Park called Mars Hill, which is littered with rubbly volcanic rocks and has been used by NASA’s Mars researchers since the 1970s, during preparations for the Viking lander missions. The work was among 25 projects funded by NASA’s Mars Exploration Program this past year to push the limits of future technologies. Sand dunes confused the navigation algorithm of the Ingenuity Mars helicopter during several of its last flights, including its 72nd and final flight on the Red Planet in January 2024. The navigation software in development would help future rotorcraft to track the surface of especially bland, featureless terrain similar to the barren sand dunes seen in parts of Death Valley and to land safely in cluttered environments like Mars Hill.

The rocks at Racetrack Playa in Death Valley, Calif., are famous. Photo credit: NASA/GSFC/Maggie McAdam To read a feature story on the Racetrack Playa go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/topics/earth/features/roving-rocks.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/topics/earth/features/roving-rocks.html</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> is home to the nation's largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a><b></b></b>

ISS013-E-81687 (17 Sept. 2006) --- A forest fire in southern California is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 13 crewmember on the International Space Station. The day fire started in Los Padres National Forest north of Los Angeles on Sept. 4, 2006. Easterly winds on Sept. 17 blew the smoke west out to sea, and this wind shift was observed by station crewmembers. The forested mountains north of Los Angeles appear dark green, the smoke a dusky gray. Dense farmland at the south end of California's central valley is framed by the forested Sierra Nevada mountain range. White patches near the center of the view are dry lakes of the Mojave Desert, one of which acts as a landing site for the space shuttle. The dark irregular shape at image right is part of the space station. Death Valley and Las Vegas are visible at image right. The extent of the day fire smoke plume can be gauged from the gray urban region of greater Los Angeles (center) which stretches along 50 miles of coastline. The plume obscures the northern Channel Islands, but the southern Channel Islands are silhouetted against the ocean.
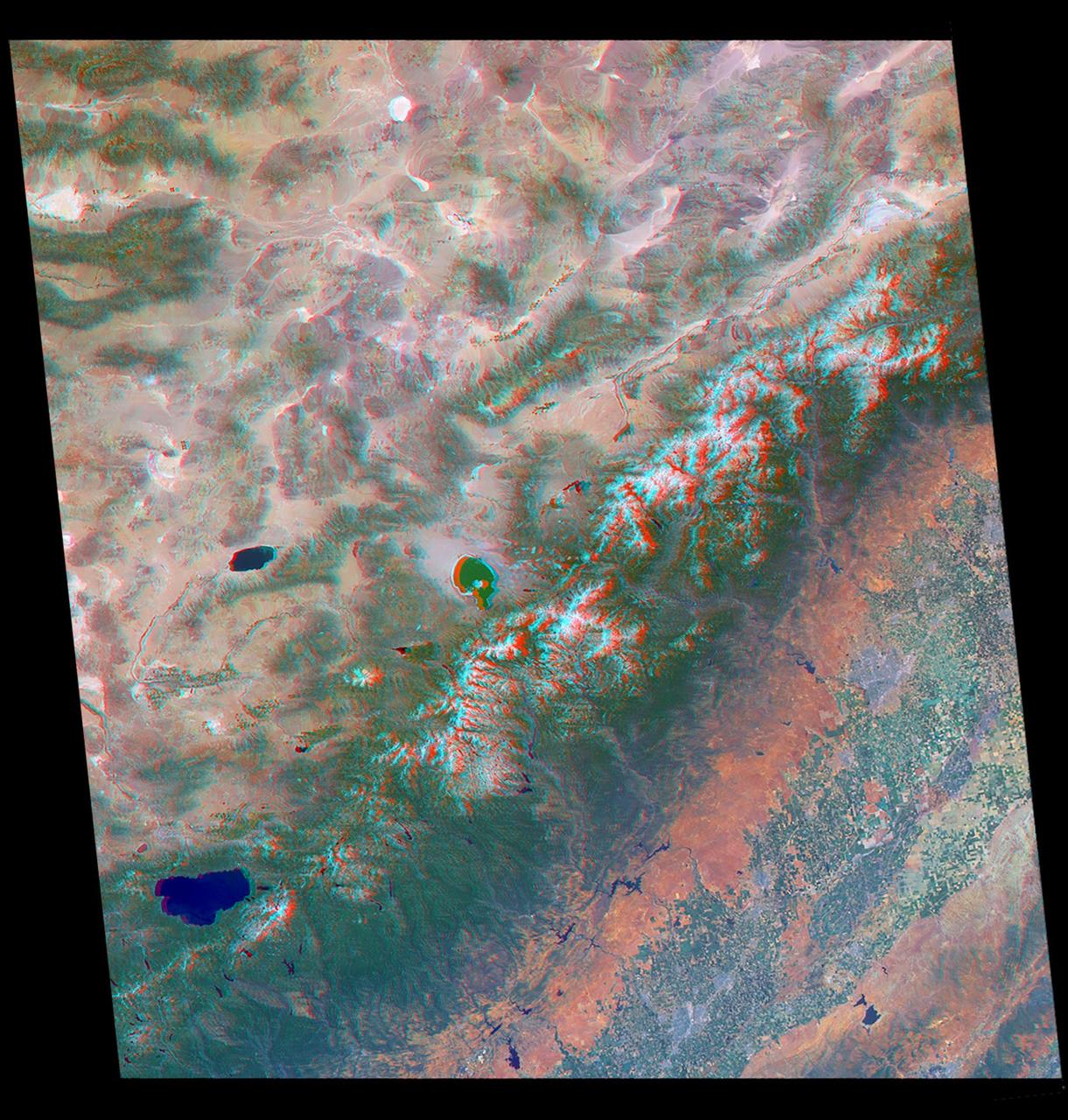
Just in time for the U.S. National Park Service's Centennial celebration on Aug. 25, NASA's Multiangle Imaging SpectroRadiometer (MISR) instrument aboard NASA's Terra satellite is releasing four new anaglyphs that showcase 33 of our nation's national parks, monuments, historical sites and recreation areas in glorious 3D. Shown in the annotated image are Sequoia National Park, Kings Canyon National Park, Manzanar National Historic Site, Devils Postpile National Monument, Yosemite National Park, and parts of Death Valley National Park. MISR views Earth with nine cameras pointed at different angles, giving it the unique capability to produce anaglyphs, stereoscopic images that allow the viewer to experience the landscape in three dimensions. The anaglyphs were made by combining data from MISR's vertical-viewing and 46-degree forward-pointing camera. You will need red-blue glasses in order to experience the 3D effect; ensure you place the red lens over your left eye. The images have been rotated so that north is to the left in order to enable 3D viewing because the Terra satellite flies from north to south. All of the images are 235 miles (378 kilometers) from west to east. These data were acquired July 7, 2016, Orbit 88051. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20892
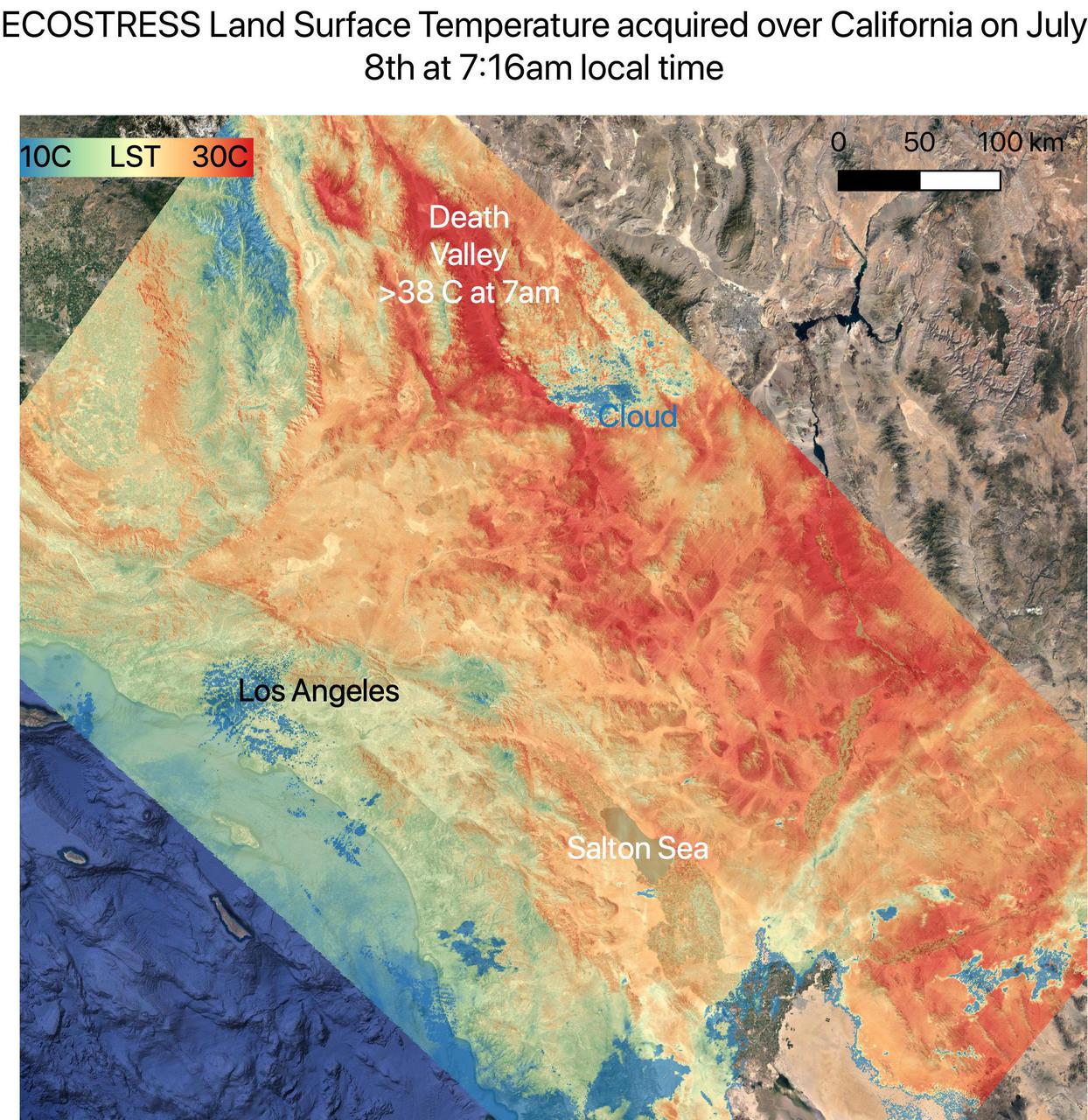
On July 8, NASA's ECOsystem Spaceborne Thermal Radiometer Experiment on Space Station (ECOSTRESS) instrument captured ground surface temperature data over California. In the image, areas in red – including Death Valley – had surpassed 86 degrees Fahrenheit (30 degrees Celsius) by 7:16 a.m. local time, well above average ground surface temperatures for the area. Tasked with detecting plant water use and stress, ECOSTRESS's primary mission is to measure the temperature of plants heating up as they run out of water. But it can also measure and track heat-related phenomena like heat waves, wildfires, and volcanoes. ECOSTRESS observations have a spatial resolution of about 77 by 77 yards (70 by 70 meters), which enables researchers to study surface-temperature conditions down to the size of a football field. Due to the space station's unique orbit, the mission can acquire images of the same regions at different times of the day, as opposed to crossing over each area at the same time of day like satellites in other orbits do. This is advantageous when monitoring plant stress in the same area throughout the day, for example. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23694
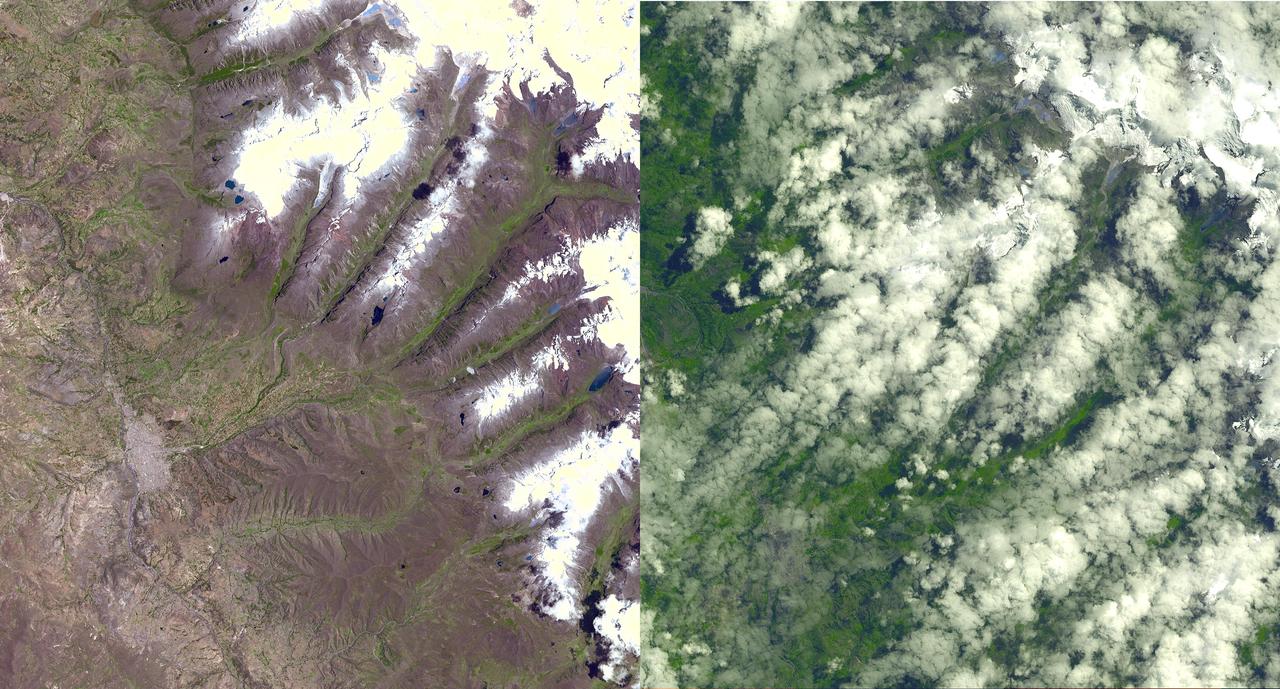
An Earth-monitoring instrument aboard NASA's Terra satellite is keeping a close eye on a potential glacial disaster in the making in Peru's spectacular, snow-capped Cordillera Blanca (White Mountains), the highest range of the Peruvian Andes. Data from NASA's Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (Aster) is assisting Peruvian government officials and geologists in monitoring a glacier that feeds Lake Palcacocha, located high above the city of Huaraz, 270 kilometers (168 miles) north of Lima. An ominous crack has developed in the glacier. Should the large glacier chunk break off and fall into the lake, the ensuing flood could hurtle down the Cojup Valley into the Rio Santa Valley below, reaching Huaraz, population 60,000, in less than 15 minutes. "Glacial natural hazards like the one in Huaraz are an increasing threat to people in many parts of the world," said Dr. Michael Abrams, associate Aster team leader at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif. "Remote sensing instruments like Aster can serve a vital role in mountain hazard management and disaster mapping by providing rapid access to data, even in regions not easily accessible by humans. Aster's unique vantage point from space gives scientists another tool with which to see early signs of potential glacial flood-burst events and to monitor changes in glacial behavior over time. In Huaraz, Peruvian authorities and scientists will incorporate Aster data along with data from ground-based monitoring techniques to better assess current conditions and take steps necessary to reduce risks to human lives and property." Comparison images of the area are available at: http://asterweb.jpl.nasa.gov . Huaraz can be seen in the images' left-center, with Lake Palcacocha in the images' upper right corners at the head of a valley, below the snow and glacier cap. The left image was acquired on November 5, 2001; the right on April 8, 2003. Glacial flood-bursts, known by Peruvians as "aluviones," occur periodically when water is released abruptly from a previously ice-dammed lake alongside, within, or above a glacier. The release can be caused by various triggering events. These flood-bursts typically arrive with little or no warning, carrying liquid mud, large rock boulders and blocks of ice. The Rio Santa Valley is no stranger to such disasters. Since 1702, floods caused by glaciological conditions have repeatedly caused death and destruction in the region. One particularly devastating event in 1941 destroyed approximately one-third of Huaraz, killing an estimated 5,000 to 7,000 people. Since then, the Peruvian government has emphasized control of the water level in Lake Palcacocha and other lakes in the region that pose similar threats. The efforts appear to have worked; since 1972, no destructive floods resulting from the breakout of glacial lakes have occurred. Nevertheless, officials are still monitoring the current situation closely. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA03899
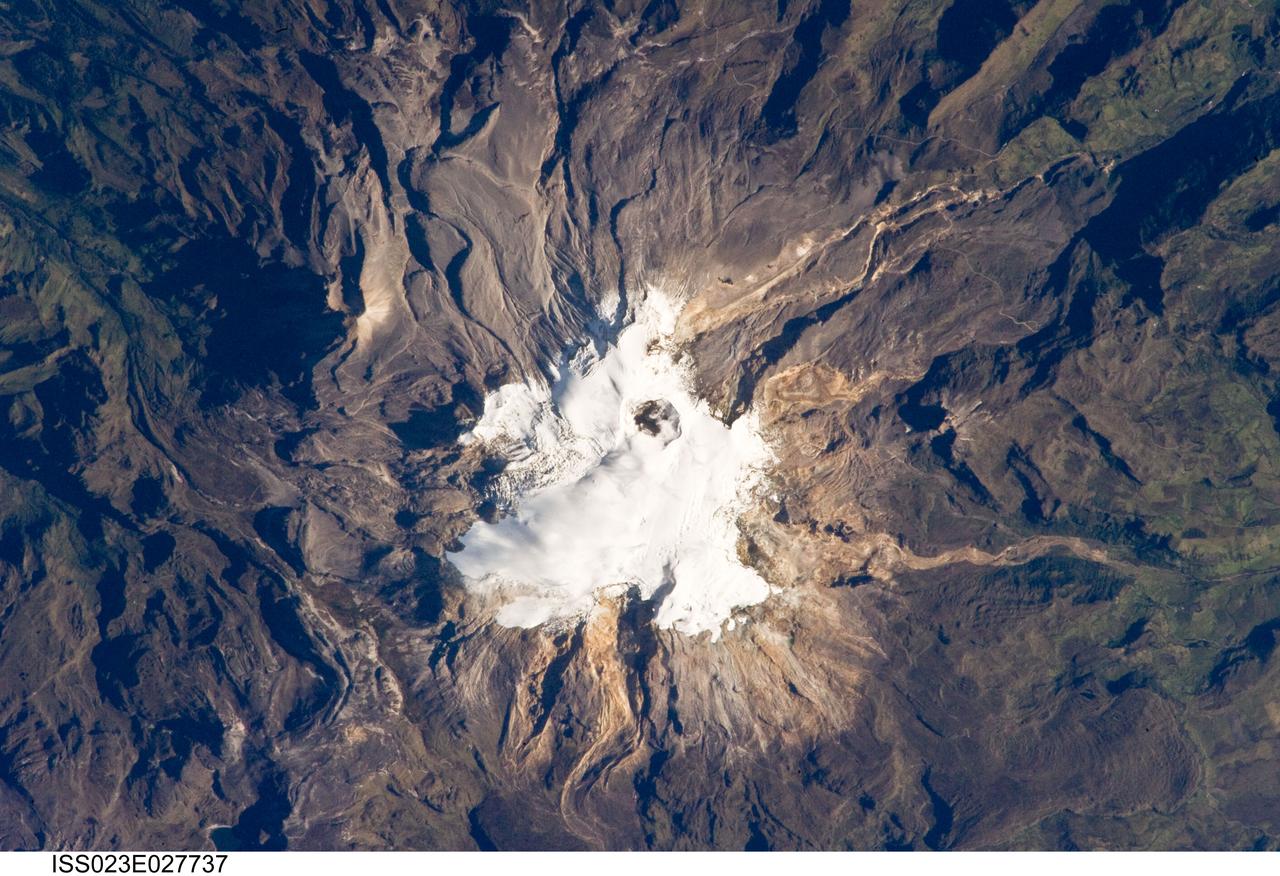
ISS023-E-027737 (23 April 2010) --- Nevado del Ruiz volcano in Colombia is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 23 crew member on the International Space Station. The large Nevado del Ruiz volcano (center) is located approximately 140 kilometers to the northwest of the capital city of Bogota and covers an area of over 200 square kilometers. Nevado del Ruiz is a stratovolcano – a type of volcano built from successive layers of lava, ash, and pyroclastic flow deposits – formed by magma generated above the boundary between the subducting Nazca and overriding South American tectonic plates. The historical record of eruptions extends back to 1570, but the most damaging eruption in recent times took place in 1985. On Nov. 13, 1985, an explosive eruption at the Arenas Crater (center) melted ice and snow at the summit of the volcano. This lead to the formation of mudflows (or lahars) that swept tens of kilometers down river valleys along the volcano’s flanks, resulting in the deaths of at least 23,000 people. Most of the fatalities occurred in the town of Armero which was completely inundated by lahars. Eruptive activity at Nevado del Ruiz may have occurred in 1994, but this is not confirmed. The volcano’s summit and upper flanks are covered by several glaciers that appear as a white mass surrounding the one-kilometer-wide Arenas Crater; meltwater from these glaciers has incised the gray to tan ash and pyroclastic flow deposits mantling the lower slopes. A well-defined lava flow is visible at lower right. This photograph was taken at approximately 7:45 a.m. local time when the sun was still fairly low above the horizon, leading to shadowing to the west of topographic high points.

NASA's Curiosity Mars rover found preserved, ancient mud cracks that scientists believe were formed after long cycles of wet and dry conditions over many years. The discovery marks the first evidence of these wet-dry cycles on Mars. The cracks were found while the rover explored a transitional region between an area enriched with clay minerals and one enriched with sulfate minerals. The mud cracks were captured in this mosaic by Curiosity's Mastcam on June 20, 2021, the 3,154th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. The mosaic is made up of 143 images that were stitched together after being sent back to Earth. The hexagonal shapes are similar to those found at locations on Earth such as Death Valley National Park's Racetrack playa. They form only after many years of alternating wet and dry conditions. When the mud cracks initially form, they have sharp, T-shaped angles within their "pits." After being gently rehydrated many times, those sharp angles soften into Y-shapes that become ridges as the rock is eroded. Evidence pointing to wet-dry cycles is exciting to Curiosity's scientists because while no one is exactly sure how life first forms, one prevailing theory suggests that these wet-dry cycles are supportive, perhaps even required. The conditions that sustain microbial life – a long-lasting lake, for example – differ from those that scientists think kickstart the chemical reactions that might lead to life. Driving those chemical reactions are long chains of carbon-based molecules called polymers, which require just the right conditions. Water is needed to mix chemicals into a soup, where they can react with one another. Too much water will dilute the soup, making it difficult for polymer-forming chemical reactions to occur; too little water, and the chemicals can't adequately mix and react. Wet-dry cycling can strike a balance between the two. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25915

This group photo of the LPSA interns and trip leaders was taken at Tea Kettle Junction in Death Valley, Calif. (Standing on left side, left to right): Kristopher Schwebler, Valerie Fox, Emily Kopp, Kyle Yawn, Dan Burger, Ian Schoch, Devon Miller; (left to right, sitting) Justin Wilde, Jessica Marbourg, Maggie McAdam (a trip leader), Leva McIntire, Ann Parsons (a trip leader), Mindy Krzykowski, Emma McKinney, Cynthia Cheung (LPSA principal investigator and a trip leader), George Fercana; (standing on right side): Kynan Rilee, Gregory Romine, Clint Naquin, Gunther Kletetschka (a trip leader), Andrew Ryan, and in the very back, Brian Jackson (a trip leader). Photo credit: NASA/GSFC/ Leva McIntire/LPSA intern To read a feature story on the Racetrack Playa go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/topics/earth/features/roving-rocks.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/topics/earth/features/roving-rocks.html</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> is home to the nation's largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a><b></b></b>