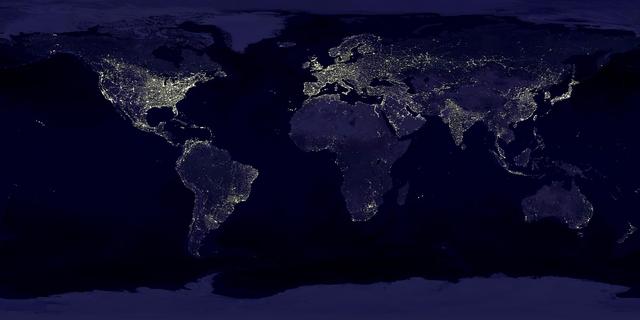
The Eastern U.S., Europe, and Japan are brightly lit by their cities, while interiors of Africa, Asia, Australia, and South America are dark and lightly populated in this image created in 2000 by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center.
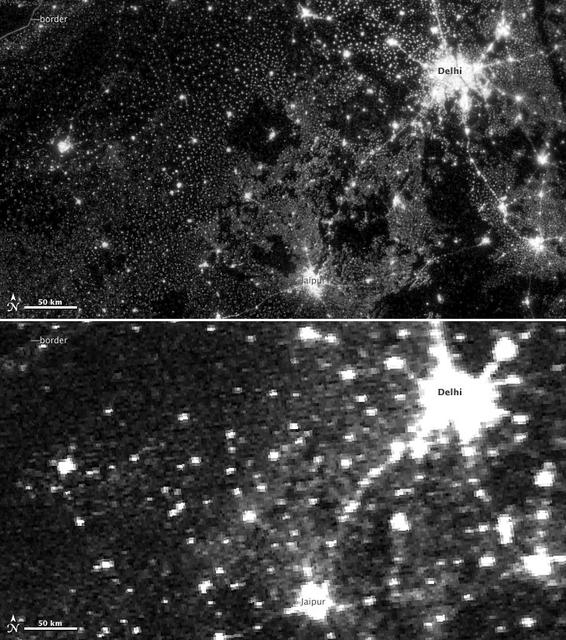

NASA image acquired November 11-12, 2012. On November 12, 2012, the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) on the Suomi NPP satellite captured the top nighttime image of city, village, and highway lights near Delhi, India. For comparison, the lower image shows the same area one night earlier, as observed by the Operational Line Scan (OLS) system on a Defense Meteorological Satellite Program (DMSP) spacecraft. Since the 1960s, the U.S. Air Force has operated DMSP in order to observe clouds and other weather variables in key wavelengths of infrared and visible light. Since 1972, the DMSP satellites have included the Operational Linescan System (OLS), which gives weather forecasters some ability to see in the dark. It has been a highly successful sensor, but it is dependent on older technology with lower resolution than most scientists would like. And for many years, DMSP data were classified. Through improved optics and “smart” sensing technology, the VIIRS “day-night band,” is ten to fifteen times better than the OLS system at resolving the relatively dim lights of human settlements and reflected moonlight. Each VIIRS pixel shows roughly 740 meters (0.46 miles) across, compared to the 3-kilometer footprint (1.86 miles) of DMSP. Beyond the resolution, the new sensor can detect dimmer light sources. And since the VIIRS measurements are fully calibrated (unlike DMSP), scientists now have the precision required to make quantitative measurements of clouds and other features. “In contrast to the Operational Line Scan system, the imagery from the new day-night band is almost like a nearsighted person putting on glasses for the first time and looking at the Earth anew,” says Steve Miller, an atmospheric scientist at Colorado State University. “VIIRS has allowed us to bring this coarse, blurry view of night lights into clearer focus. Now we can see things in such great detail and at such high precision that we’re really talking about a new kind of measurement.” Unlike a film camera that captures a photograph in one exposure, VIIRS produces an image by repeatedly scanning a scene and resolving it as millions of individual picture elements, or pixels. The day-night band goes a step further, determining on-the-fly whether to use its low, medium, or high-gain mode. If a pixel is very bright, a low-gain mode on the sensor prevents the pixel from over-saturating. If the pixel is dark, the signal will be amplified. “On a hand-held camera, there’s a nighttime setting where the shutter will stay open much longer than it would under daylight imaging conditions,” says Chris Elvidge, who leads the Earth Observation Group at NOAA’s National Geophysical Data Center. “The day-night band is similar. It increases the exposure time—the amount of time that it’s collecting photons for pixels.” NASA Earth Observatory image by Jesse Allen and Robert Simmon, using Suomi NPP VIIRS and DMSP OLS data provided courtesy of Chris Elvidge (NOAA National Geophysical Data Center). Suomi NPP is the result of a partnership between NASA, NOAA, and the Department of Defense. Caption by Mike Carlowicz. Instrument: Suomi NPP - VIIRS Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> <b>Click here to view all of the <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/Features/NightLights/" rel="nofollow"> Earth at Night 2012 images </a></b> <b>Click here to <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/NaturalHazards/view.php?id=79846" rel="nofollow"> read more </a> about this image </b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific
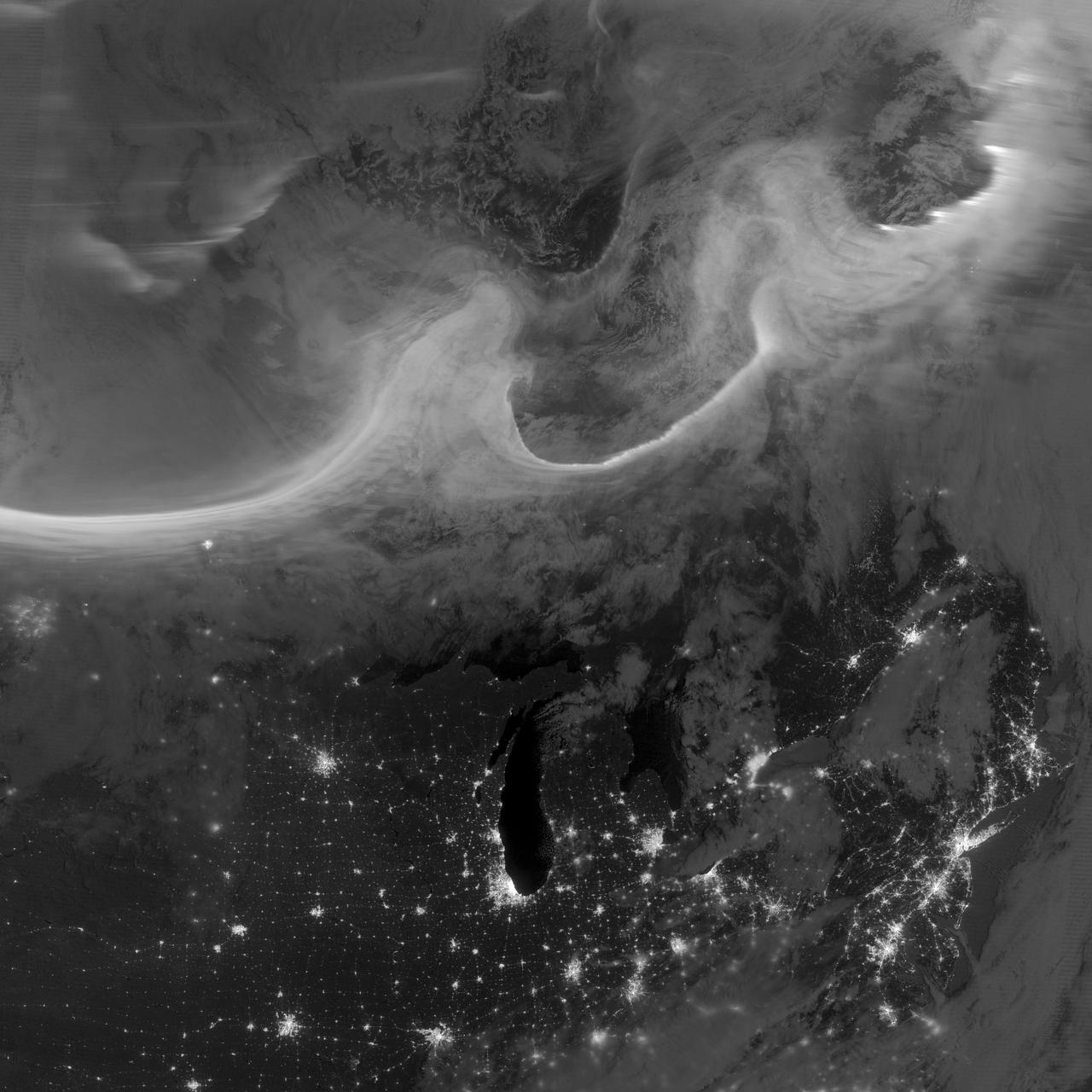

Overnight on October 4-5, 2012, a mass of energetic particles from the atmosphere of the Sun were flung out into space, a phenomenon known as a coronal mass ejection. Three days later, the storm from the Sun stirred up the magnetic field around Earth and produced gorgeous displays of northern lights. NASA satellites track such storms from their origin to their crossing of interplanetary space to their arrival in the atmosphere of Earth. Using the “day-night band” (DNB) of the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS), the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership (Suomi NPP) satellite acquired this view of the aurora borealis early on the morning of October 8, 2012. The northern lights stretch across Canada’s Quebec and Ontario provinces in the image, and are part of the auroral oval that expanded to middle latitudes because of a geomagnetic storm. The DNB sensor detects dim light signals such as auroras, airglow, gas flares, city lights, and reflected moonlight. In the case of the image above, the sensor detected the visible light emissions as energetic particles rained down from Earth’s magnetosphere and into the gases of the upper atmosphere. The images are similar to those collected by the Operational Linescan System flown on U.S. Defense Meteorological Satellite Program (DMSP) satellites for the past three decades. “When I first saw images like this as a graduate student, I was immediately struck by the fluid dynamic characteristics of the aurora,” said Tom Moore, a space physicist at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center. “Viewing the aurora in this way makes it immediately clear that space weather is an interaction of fluids from the Sun with those of the Earth's upper atmosphere. The electrodynamics make for important differences between plasmas and ordinary fluids, but familiar behaviors (for example, waves and vortices) are still very apparent. It makes me wonder at the ability of apparently empty space to behave like a fluid.” Auroras typically occur when solar flares and coronal mass ejections—or even an active solar wind stream—disturb and distort the magnetosphere, the cocoon of space protected by Earth’s magnetic field. The collision of solar particles and pressure into our planet’s magnetosphere accelerates particles trapped in the space around Earth (such as in the radiation belts). Those particles are sent crashing down into Earth’s upper atmosphere—at altitudes of 100 to 400 kilometers (60 to 250 miles)—where they excite oxygen and nitrogen molecules and release photons of light. The results are rays, sheets, and curtains of dancing light in the sky. Auroras are a beautiful expression of the connection between Sun and Earth, but not all of the connections are benign. Auroras are connected to geomagnetic storms, which can distort radio communications (particularly high frequencies), disrupt electric power systems on the ground, and give slight but detectable doses of radiation to flight crews and passengers on high-latitude airplane flights and on spacecraft. The advantage of images like those from VIIRS and DMSP is resolution, according to space physicist Patrick Newell of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory. “You can see very fine detail in the aurora because of the low altitude and the high resolution of the camera,” he said. Most aurora scientists prefer to use images from missions dedicated to aurora studies (such as Polar, IMAGE, and ground-based imagers), which can offer many more images of a storm (rather than one per orbit) and can allow researchers to calculate the energy moving through the atmosphere. There are no science satellites flying right now that provide such a view, though astronauts regularly photograph and film auroras from the International Space Station. NASA Earth Observatory image by Jesse Allen and Robert Simmon, using VIIRS Day-Night Band data from the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership (Suomi NPP) and the University of Wisconsin's Community Satellite Processing Package. Suomi NPP is the result of a partnership between NASA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, and the Department of Defense. Caption by Mike Carlowicz. Instrument: Suomi NPP - VIIRS Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

On August 29, 2012, the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) on the Suomi NPP satellite captured this nighttime view of wildfires burning in Idaho and Montana. The image was captured by the VIIRS “day-night band,” which detects light in a range of wavelengths from green to near-infrared and uses filtering techniques to observe signals such as gas flares, auroras, wildfires, city lights, and reflected moonlight. When the image was acquired, the moon was in its waxing gibbous phase, meaning it was more than half-lit, but less than full. Numerous hot spots from the Mustang Complex Fire are visible in northern Idaho. A plume of thick, billowing smoke streams west from the brightest fires near the Idaho-Montana border. The Halstead and Trinity Ridge fires are visible to the south. In addition to the fires, city lights from Boise and other smaller cities appear throughout the image. A bank of clouds is located west of the Mustang Complex, over southeastern Washington and northeastern Oregon. The Operational Line System (OLS)—an earlier generation of night-viewing sensors on the U.S. Defense Meteorological Satellite Program (DMSP) satellites—was also capable of detecting fires at night. But the VIIRS “day-night band” is far better than OLS at resolving them. Each pixel of an VIIRS image shows roughly 740 meters (0.46 miles), compared to the 3-kilometer footprint (1.86 miles) on the OLS system. NASA Earth Observatory image by Jesse Allen and Robert Simmon, using VIIRS Day-Night Band data from the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership. Suomi NPP is the result of a partnership between NASA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, and the Department of Defense. Caption by Adam Voiland. Instrument: Suomi NPP - VIIRS Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> <b>Click here to view all of the <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/Features/NightLights/" rel="nofollow"> Earth at Night 2012 images </a></b> <b>Click here to <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/NaturalHazards/view.php?id=79754" rel="nofollow"> read more </a> about this image </b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
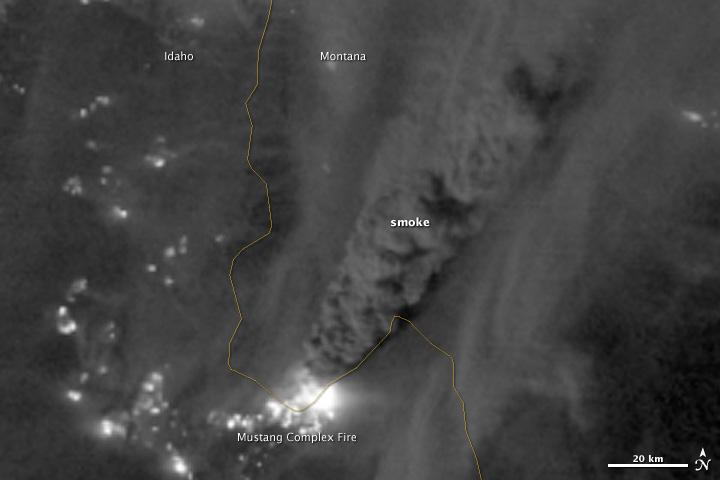

On August 29, 2012, the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) on the Suomi NPP satellite captured this nighttime view of wildfires burning in Idaho and Montana. The image was captured by the VIIRS “day-night band,” which detects light in a range of wavelengths from green to near-infrared and uses filtering techniques to observe signals such as gas flares, auroras, wildfires, city lights, and reflected moonlight. When the image was acquired, the moon was in its waxing gibbous phase, meaning it was more than half-lit, but less than full. Numerous hot spots from the Mustang Complex Fire are visible in northern Idaho. A plume of thick, billowing smoke streams west from the brightest fires near the Idaho-Montana border. The Halstead and Trinity Ridge fires are visible to the south. In addition to the fires, city lights from Boise and other smaller cities appear throughout the image. A bank of clouds is located west of the Mustang Complex, over southeastern Washington and northeastern Oregon. The Operational Line System (OLS)—an earlier generation of night-viewing sensors on the U.S. Defense Meteorological Satellite Program (DMSP) satellites—was also capable of detecting fires at night. But the VIIRS “day-night band” is far better than OLS at resolving them. Each pixel of an VIIRS image shows roughly 740 meters (0.46 miles), compared to the 3-kilometer footprint (1.86 miles) on the OLS system. NASA Earth Observatory image by Jesse Allen and Robert Simmon, using VIIRS Day-Night Band data from the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership. Suomi NPP is the result of a partnership between NASA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, and the Department of Defense. Caption by Adam Voiland. Instrument: Suomi NPP - VIIRS Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> <b>Click here to view all of the <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/Features/NightLights/" rel="nofollow"> Earth at Night 2012 images </a></b> <b>Click here to <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/NaturalHazards/view.php?id=79754" rel="nofollow"> read more </a> about this image </b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
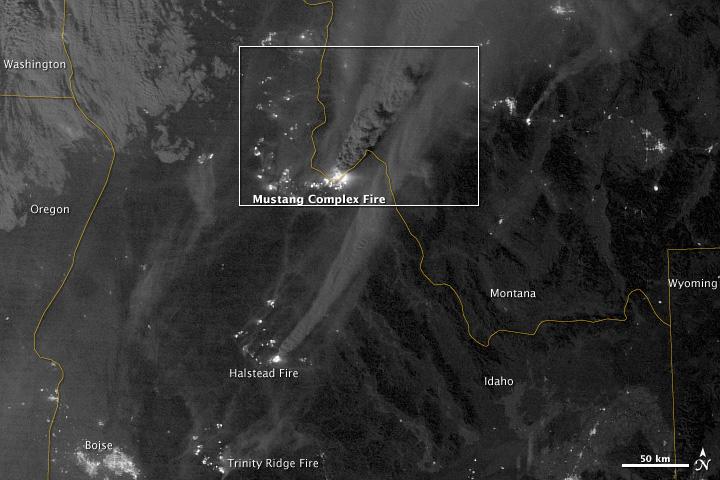
On August 29, 2012, the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) on the Suomi NPP satellite captured this nighttime view of wildfires burning in Idaho and Montana. The image was captured by the VIIRS “day-night band,” which detects light in a range of wavelengths from green to near-infrared and uses filtering techniques to observe signals such as gas flares, auroras, wildfires, city lights, and reflected moonlight. When the image was acquired, the moon was in its waxing gibbous phase, meaning it was more than half-lit, but less than full. Numerous hot spots from the Mustang Complex Fire are visible in northern Idaho. A plume of thick, billowing smoke streams west from the brightest fires near the Idaho-Montana border. The Halstead and Trinity Ridge fires are visible to the south. In addition to the fires, city lights from Boise and other smaller cities appear throughout the image. A bank of clouds is located west of the Mustang Complex, over southeastern Washington and northeastern Oregon. The Operational Line System (OLS)—an earlier generation of night-viewing sensors on the U.S. Defense Meteorological Satellite Program (DMSP) satellites—was also capable of detecting fires at night. But the VIIRS “day-night band” is far better than OLS at resolving them. Each pixel of an VIIRS image shows roughly 740 meters (0.46 miles), compared to the 3-kilometer footprint (1.86 miles) on the OLS system. NASA Earth Observatory image by Jesse Allen and Robert Simmon, using VIIRS Day-Night Band data from the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership. Suomi NPP is the result of a partnership between NASA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, and the Department of Defense. Caption by Adam Voiland. Instrument: Suomi NPP - VIIRS Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> <b>Click here to view all of the <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/Features/NightLights/" rel="nofollow"> Earth at Night 2012 images </a></b> <b>Click here to <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/NaturalHazards/view.php?id=79754" rel="nofollow"> read more </a> about this image </b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Using the “day-night band” (DNB) of the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS), the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership (Suomi NPP) satellite acquired this view of the aurora borealis on March 18, 2015. The northern lights stretch across Canada’s Quebec, Ontario, Manitoba, Nunavut, and Newfoundland provinces in the image, and are part of the auroral oval that expanded to middle latitudes because of a geomagnetic storm on March 17, 2015. The DNB sensor detects dim light signals such as auroras, airglow, gas flares, city lights, and reflected moonlight. In the case of the image above, the sensor detected the visible light emissions as energetic particles rained down from Earth’s magnetosphere and into the gases of the upper atmosphere. The images are similar to those collected by the Operational Linescan System flown on U.S. Defense Meteorological Satellite Program (DMSP) satellites for the past three decades. Auroras typically occur when solar flares and coronal mass ejections—or even an active solar wind stream—disturb and distort the magnetosphere, the cocoon of space protected by Earth’s magnetic field. The collision of solar particles and pressure into our planet’s magnetosphere accelerates particles trapped in the space around Earth (such as in the radiation belts). Those particles are sent crashing down into Earth’s upper atmosphere—at altitudes of 100 to 400 kilometers (60 to 250 miles)—where they excite oxygen and nitrogen molecules and release photons of light. The results are rays, sheets, and curtains of dancing light in the sky. Read more: <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/NaturalHazards/view.php?id=85556&eocn=home&eoci=nh" rel="nofollow">earthobservatory.nasa.gov/NaturalHazards/view.php?id=8555...</a> NASA Earth Observatory image by Jesse Allen, using VIIRS day-night band data from the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership. Suomi NPP is the result of a partnership between NASA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, and the Department of Defense. Caption by Mike Carlowicz and Adam Voiland. Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>