
SpaceX’s Crew Dragon is at NASA’s Glenn Research Center, Plum Brook Station in Ohio, ready to undergo testing in the In-Space Propulsion Facility — the world’s only facility capable of testing full-scale upper-stage launch vehicles and rocket engines under simulated high-altitude conditions. The chamber will allow SpaceX and NASA to verify Crew Dragon’s ability to withstand the extreme temperatures and vacuum of space. This is the spacecraft that SpaceX will fly during its Demonstration Mission 1 flight test under NASA’s Commercial Crew Transportation Capability contract with the goal of returning human spaceflight launch capabilities to the U.S.
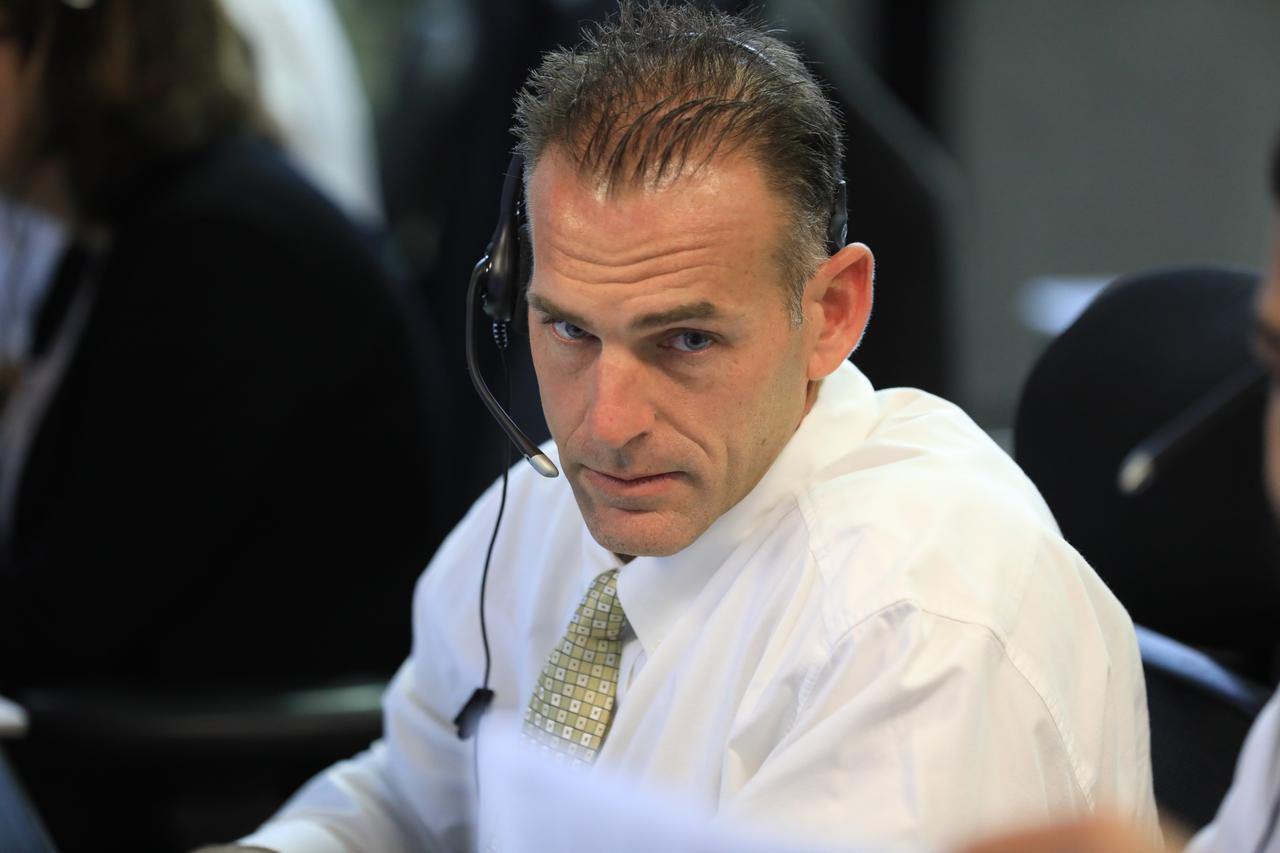

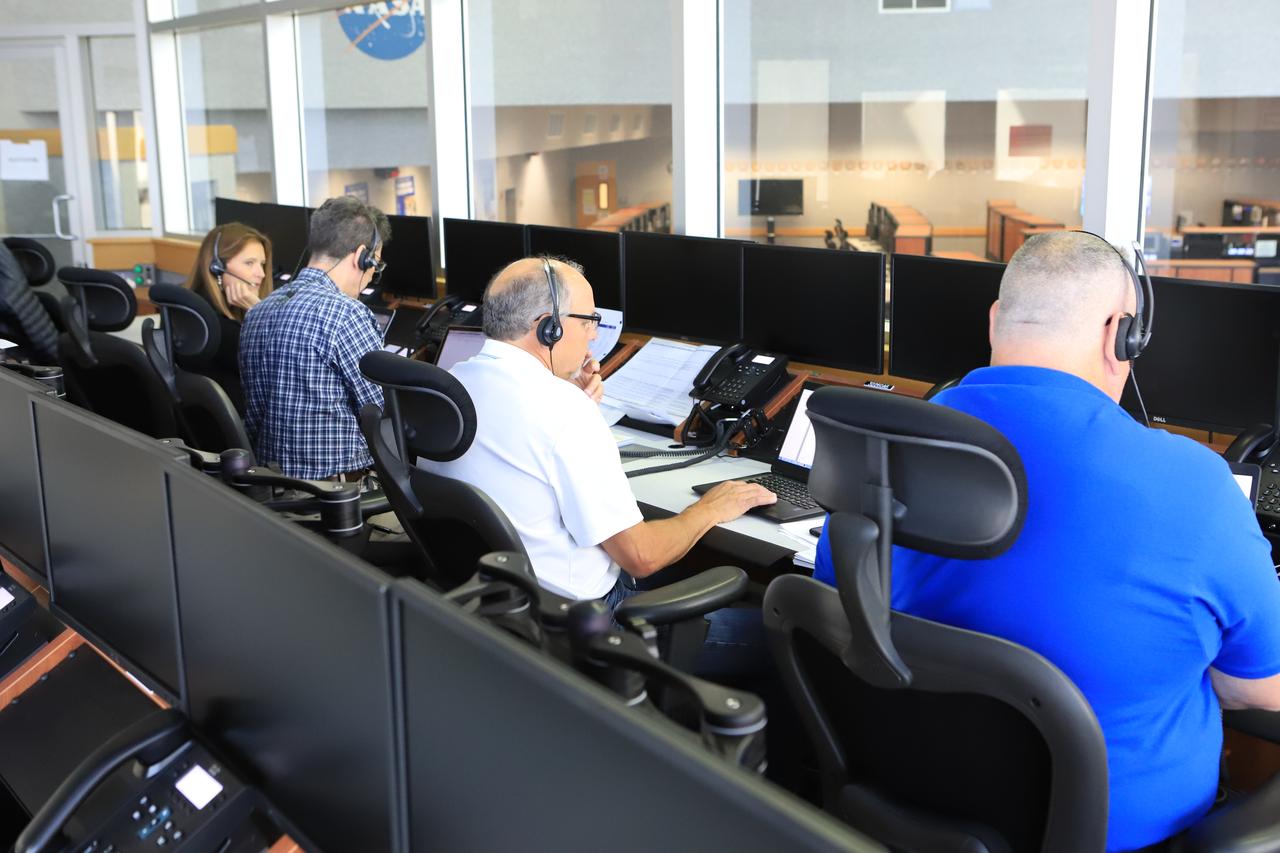
Mark Tripp, center, monitors his console in Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, during a terminal countdown demonstration for Exploration Mission 1, or EM-1, on Dec. 14, 2018. The launch will be the first integrated test of the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft that will eventually take astronauts beyond low-Earth orbit to destinations such as the Moon and Mars. The countdown demonstration was intended to validate the launch team's capability to perform an EM-1 countdown and respond to challenges put into the system for practice.
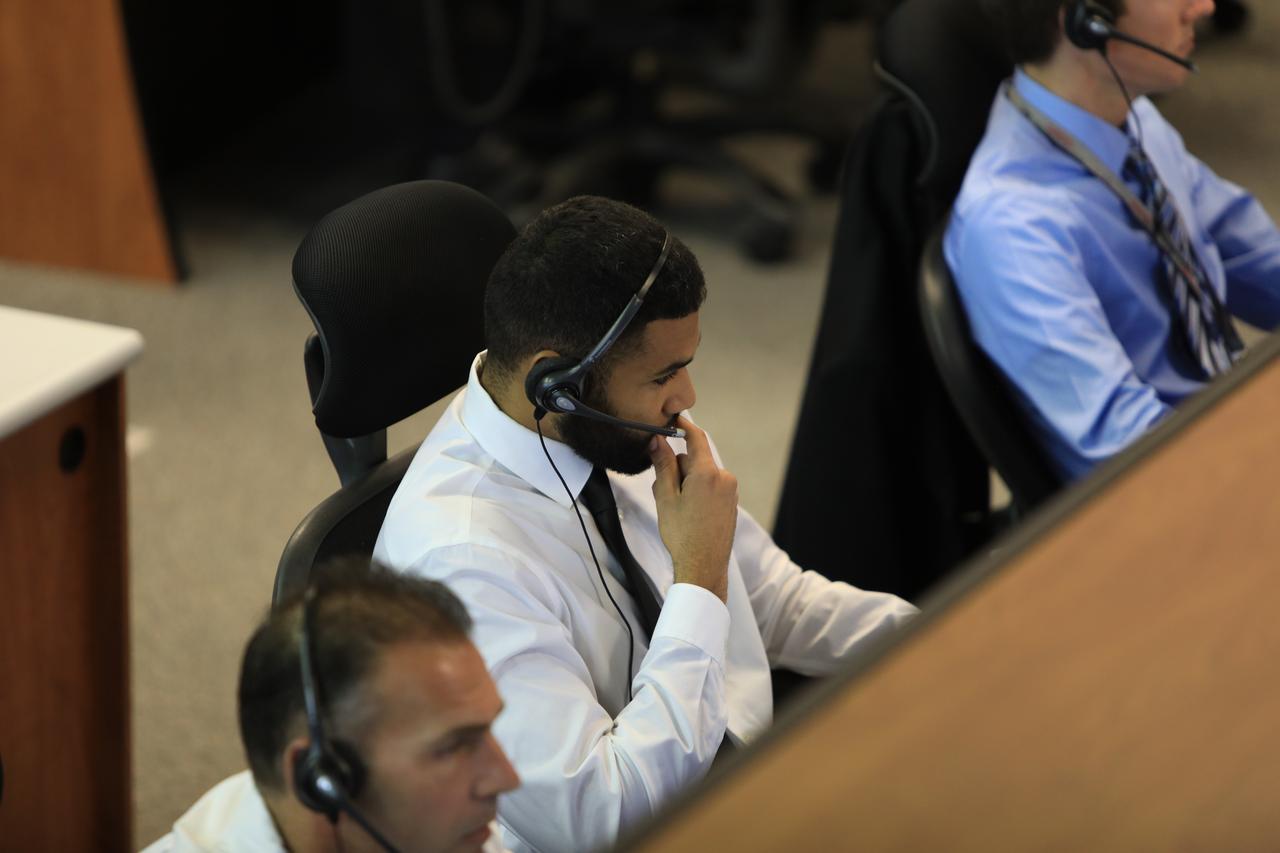

Michael Guzman, an umbilical engineer, monitors his console in Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, during a terminal countdown demonstration for Exploration Mission 1, or EM-1, on Dec. 14, 2018. The launch will be the first integrated test of the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft that will eventually take astronauts beyond low-Earth orbit to destinations such as the Moon and Mars. The countdown demonstration was intended to validate the launch team's capability to perform an EM-1 countdown and respond to challenges put into the system for practice.
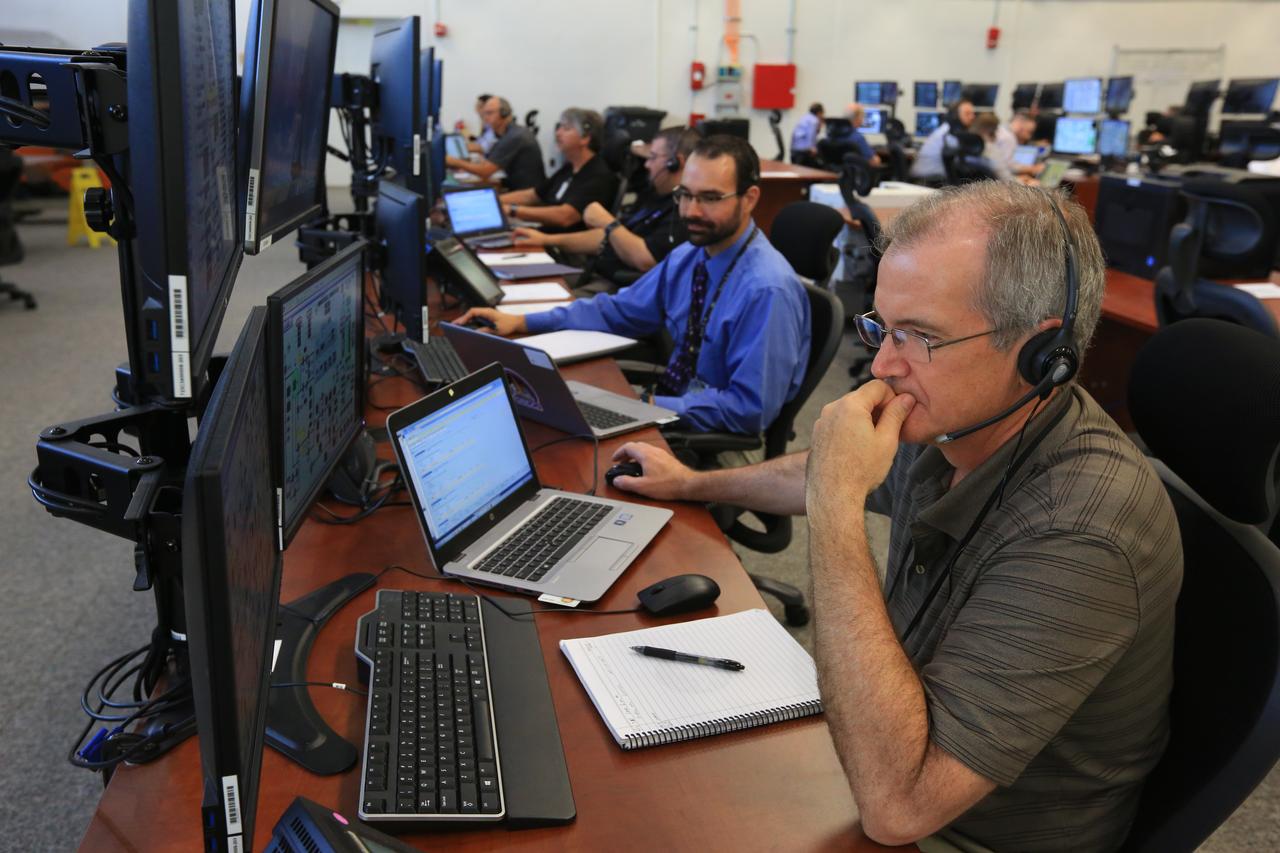

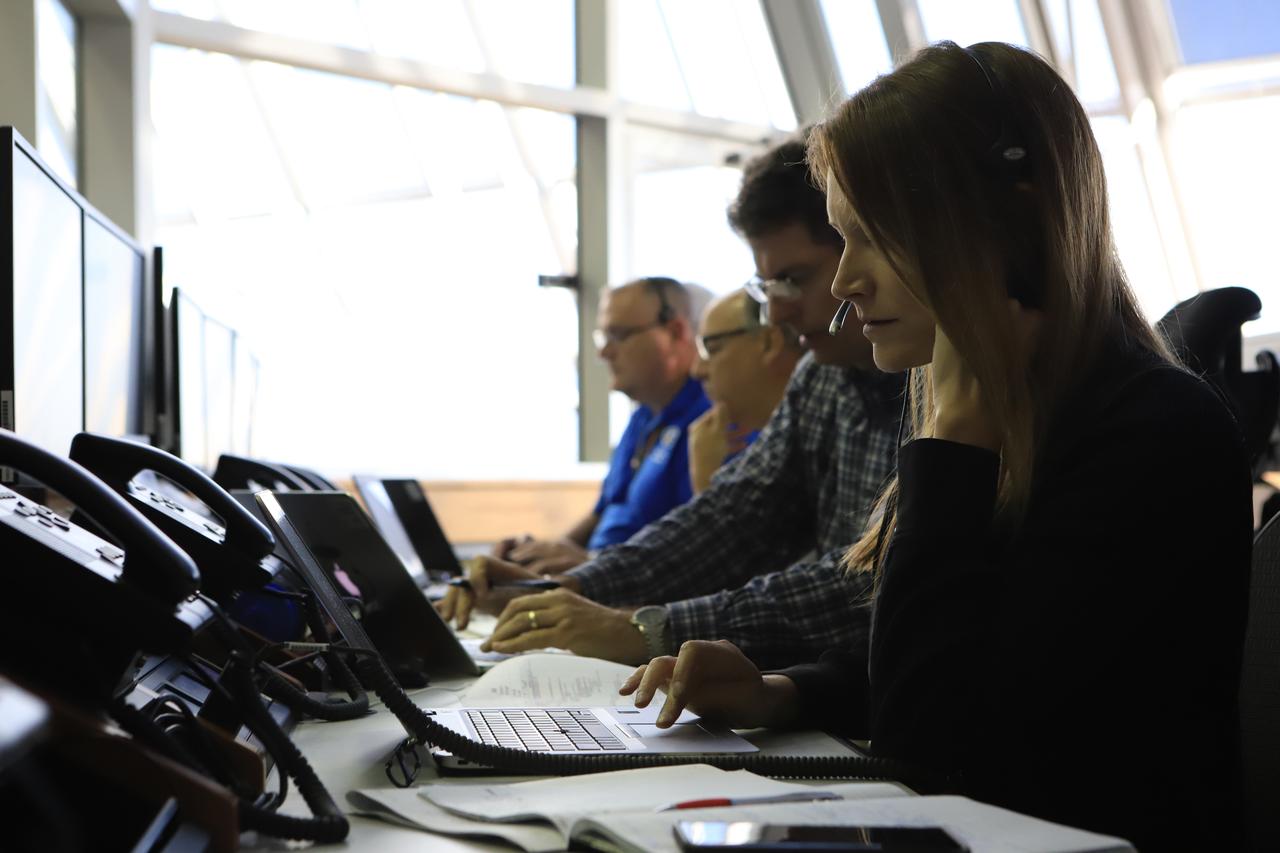
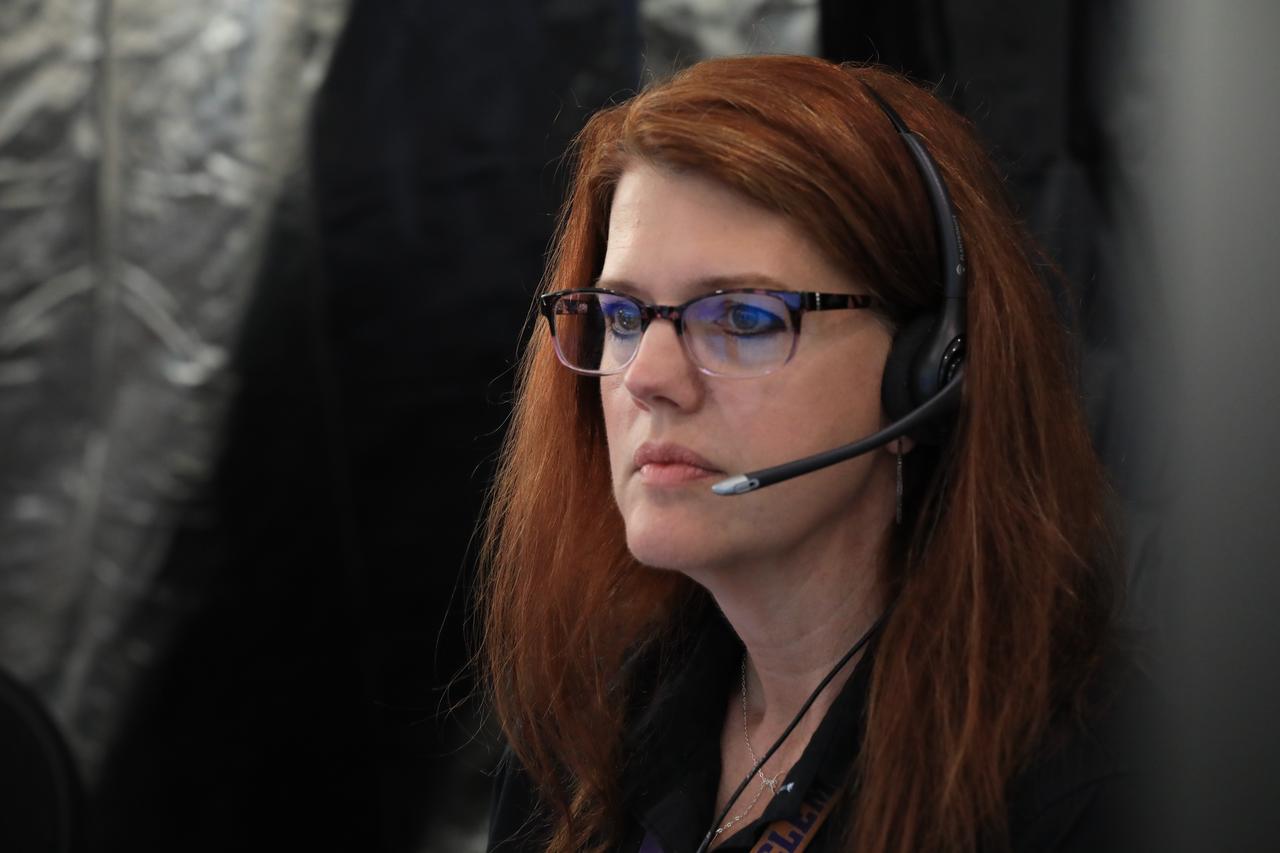
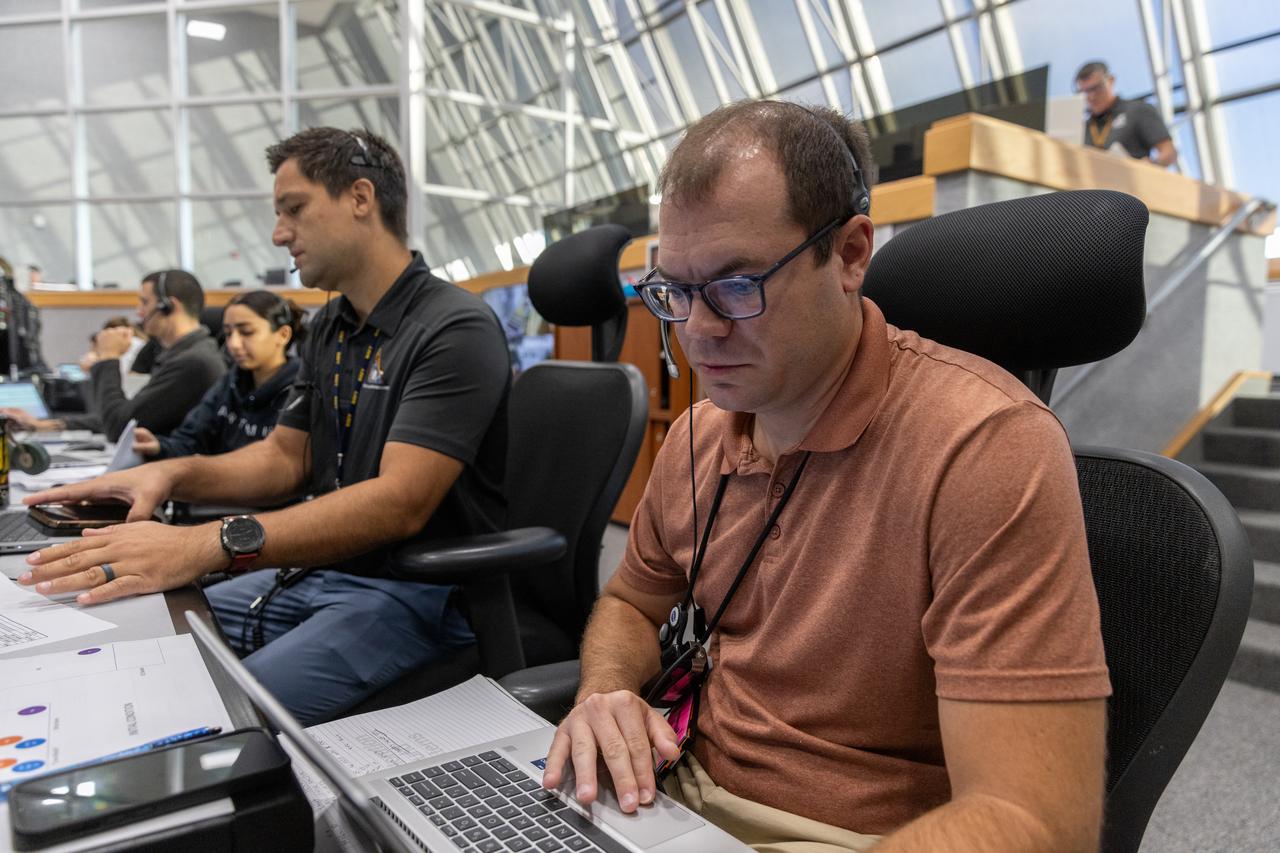
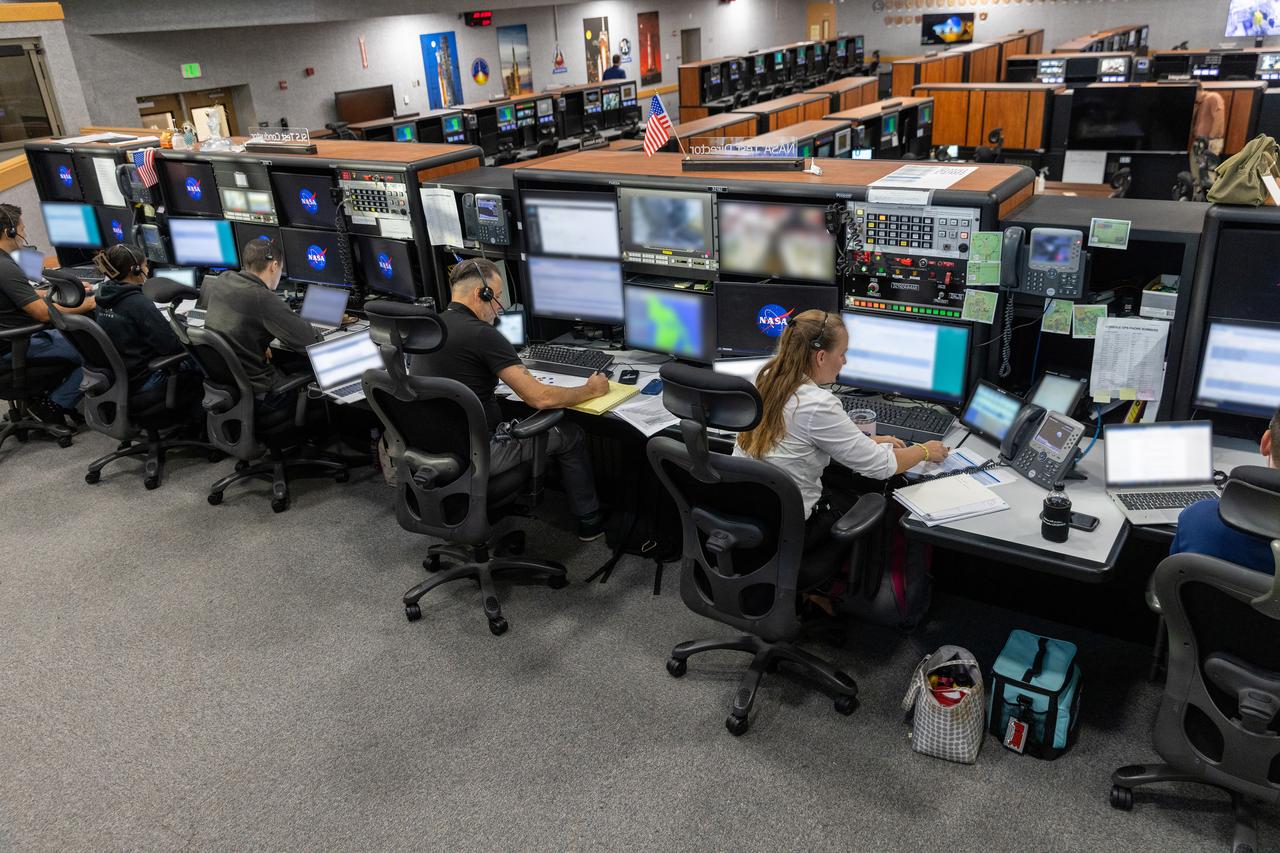
Engineers with NASA and contractor Jacobs monitor their consoles during a countdown demonstration event of cryogenic propellant loading April 12, 2019, inside Firing Room 2 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The practice simulation involved loading of liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen into the Space Launch System rocket’s core and upper stages to prepare for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). During the tanking exercise, the team worked through surprise issues in real-time. The practice countdown events are training opportunities coordinated by EM-1 Launch Director Charlie Blackwell-Thompson with Exploration Ground Systems.

Charlie Blackwell-Thompson, right, Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1) launch director, reviews procedures during a countdown demonstration event of cryogenic propellant loading April 12, 2019, inside Firing Room 2 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The practice simulation involved loading of liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen into the Space Launch System rocket’s core and upper stages to prepare for EM-1. During the tanking exercise, the team worked through surprise issues in real-time. The practice countdown events are training opportunities coordinated by Blackwell-Thompson with Exploration Ground Systems.

Engineers with NASA and contractor Jacobs monitor their consoles during a countdown demonstration event of cryogenic propellant loading April 12, 2019, inside Firing Room 2 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The practice simulation involved loading of liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen into the Space Launch System rocket’s core and upper stages to prepare for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). During the tanking exercise, the team worked through surprise issues in real-time. The practice countdown events are training opportunities coordinated by EM-1 Launch Director Charlie Blackwell-Thompson with Exploration Ground Systems.

Engineers with Exploration Ground Systems monitor their consoles during a countdown demonstration event of cryogenic propellant loading April 12, 2019, inside Firing Room 2 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The practice simulation involved loading of liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen into the Space Launch System rocket’s core and upper stages to prepare for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). During the tanking exercise, the team worked through surprise issues in real-time. The practice countdown events are training opportunities coordinated by EM-1 Launch Director Charlie Blackwell-Thompson with Exploration Ground Systems.

Charlie Blackwell-Thompson, standing, Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1) launch director, leads a countdown demonstration event of cryogenic propellant loading April 12, 2019, inside Firing Room 2 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Seated is Roberta Wyrick, spacecraft test conductor with contractor Jacobs. The practice simulation involved loading of liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen into the Space Launch System rocket’s core and upper stages to prepare for EM-1. During the tanking exercise, the team worked through surprise issues in real-time. The practice countdown events are training opportunities coordinated by Blackwell-Thompson with Exploration Ground Systems.

An engineer with NASA monitors his console during a countdown demonstration event of cryogenic propellant loading April 12, 2019, inside Firing Room 2 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The practice simulation involved loading of liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen into the Space Launch System rocket’s core and upper stages to prepare for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). During the tanking exercise, the team worked through surprise issues in real-time. The practice countdown events are training opportunities coordinated by EM-1 Launch Director Charlie Blackwell-Thompson with Exploration Ground Systems.
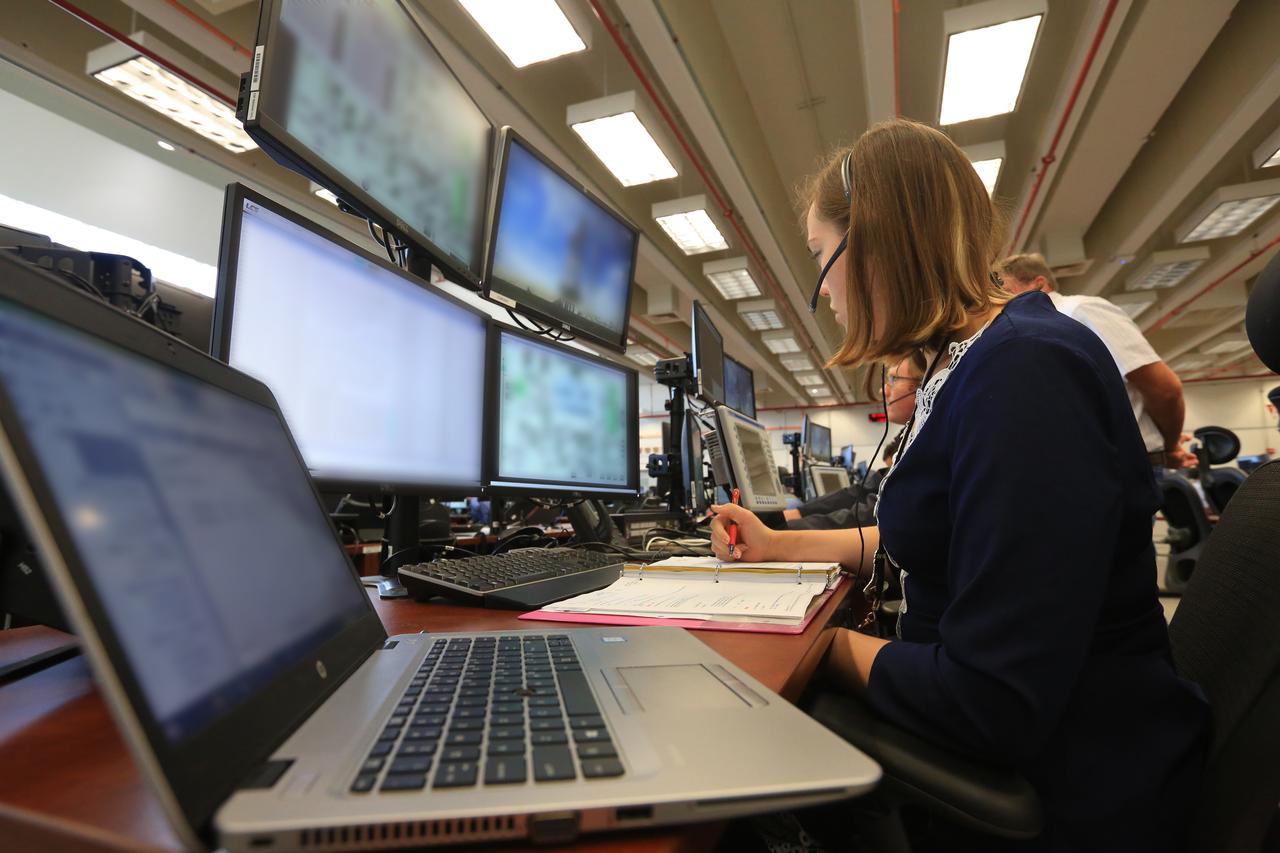

Engineers with NASA and contractor Jacobs monitor their consoles during a countdown demonstration event of cryogenic propellant loading April 12, 2019, inside Firing Room 2 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The practice simulation involved loading of liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen into the Space Launch System rocket’s core and upper stages to prepare for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). During the tanking exercise, the team worked through surprise issues in real-time. The practice countdown events are training opportunities coordinated by EM-1 Launch Director Charlie Blackwell-Thompson with Exploration Ground Systems.
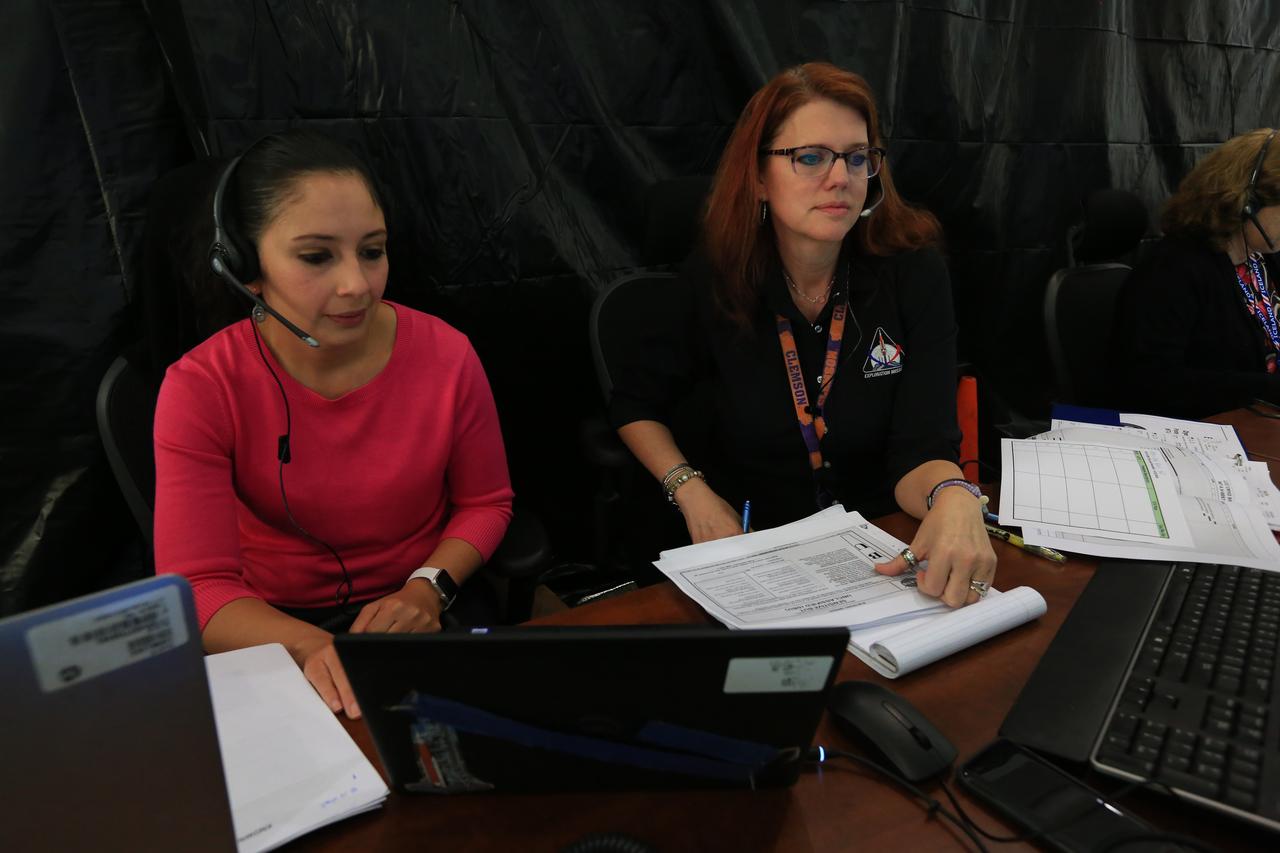

Charlie Blackwell-Thompson, at right, Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1) launch director, leads a countdown demonstration event of cryogenic propellant loading April 12, 2019, inside Firing Room 2 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Seated next to her is Jessica Parsons, technical assitant to the launch director. The practice simulation involved loading of liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen into the Space Launch System rocket’s core and upper stages to prepare for EM-1. During the tanking exercise, the team worked through surprise issues in real-time. The practice countdown events are training opportunities coordinated by Blackwell-Thompson with Exploration Ground Systems.

Engineers with NASA and contractor Jacobs monitor their consoles during a countdown demonstration event of cryogenic propellant loading April 12, 2019, inside Firing Room 2 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The practice simulation involved loading of liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen into the Space Launch System rocket’s core and upper stages to prepare for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). During the tanking exercise, the team worked through surprise issues in real-time. The practice countdown events are training opportunities coordinated by EM-1 Launch Director Charlie Blackwell-Thompson with Exploration Ground Systems.

Charlie Blackwell-Thompson, Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1) launch director, leads a countdown demonstration event of cryogenic propellant loading April 12, 2019, inside Firing Room 2 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The practice simulation involved loading of liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen into the Space Launch System rocket’s core and upper stages to prepare for EM-1. During the tanking exercise, the team worked through surprise issues in real-time. The practice countdown events are training opportunities coordinated by Blackwell-Thompson with Exploration Ground Systems.
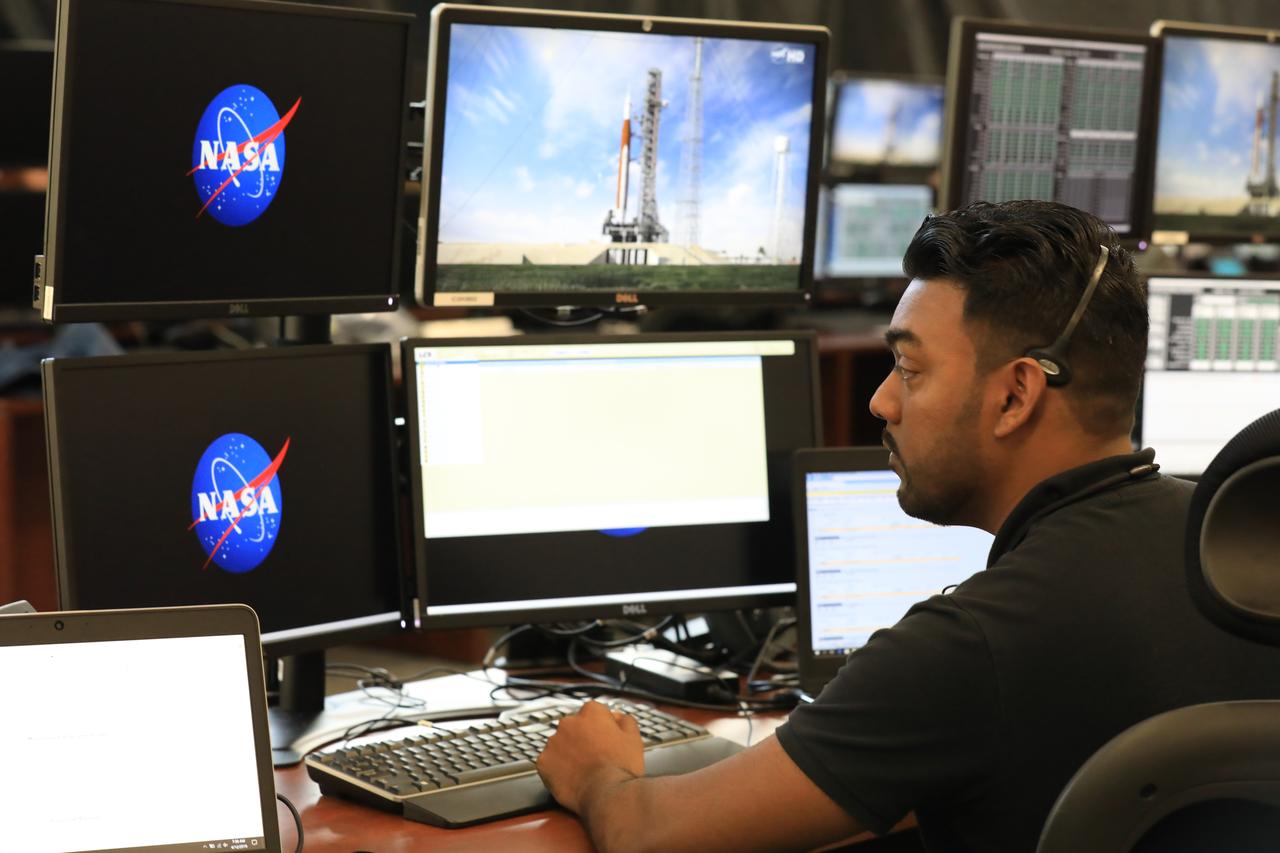

Anthony Bharrat, NASA engine avionics engineer, monitors his console during a countdown demonstration event of cryogenic propellant loading April 12, 2019, inside Firing Room 2 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The practice simulation involved loading of liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen into the Space Launch System rocket’s core and upper stages to prepare for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). During the tanking exercise, the team worked through surprise issues in real-time. The practice countdown events are training opportunities coordinated by EM-1 Launch Director Charlie Blackwell-Thompson with Exploration Ground Systems.
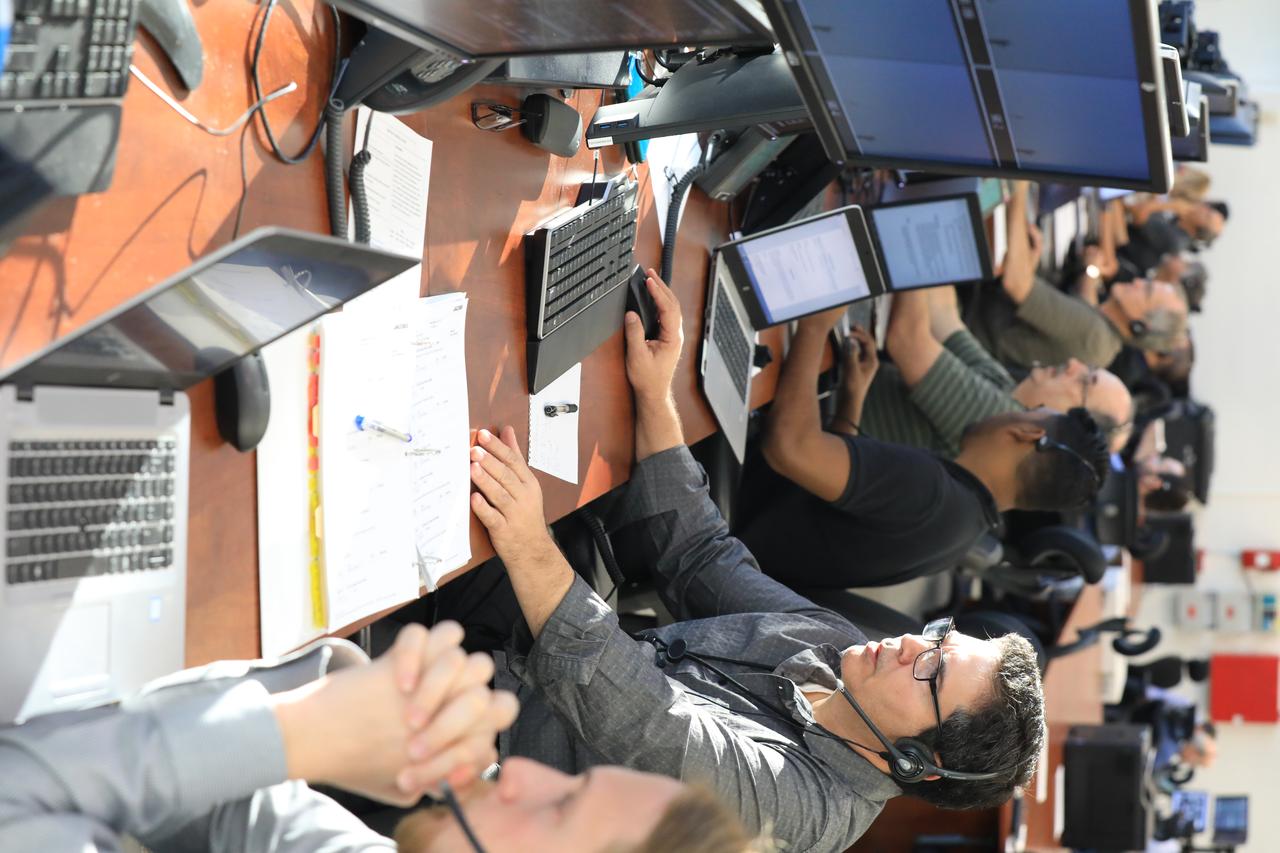

Engineers with NASA and contractor Jacobs monitor their consoles during a countdown demonstration event of cryogenic propellant loading April 12, 2019, inside Firing Room 2 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The practice simulation involved loading of liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen into the Space Launch System rocket’s core and upper stages to prepare for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). During the tanking exercise, the team worked through surprise issues in real-time. The practice countdown events are training opportunities coordinated by EM-1 Launch Director Charlie Blackwell-Thompson with Exploration Ground Systems.
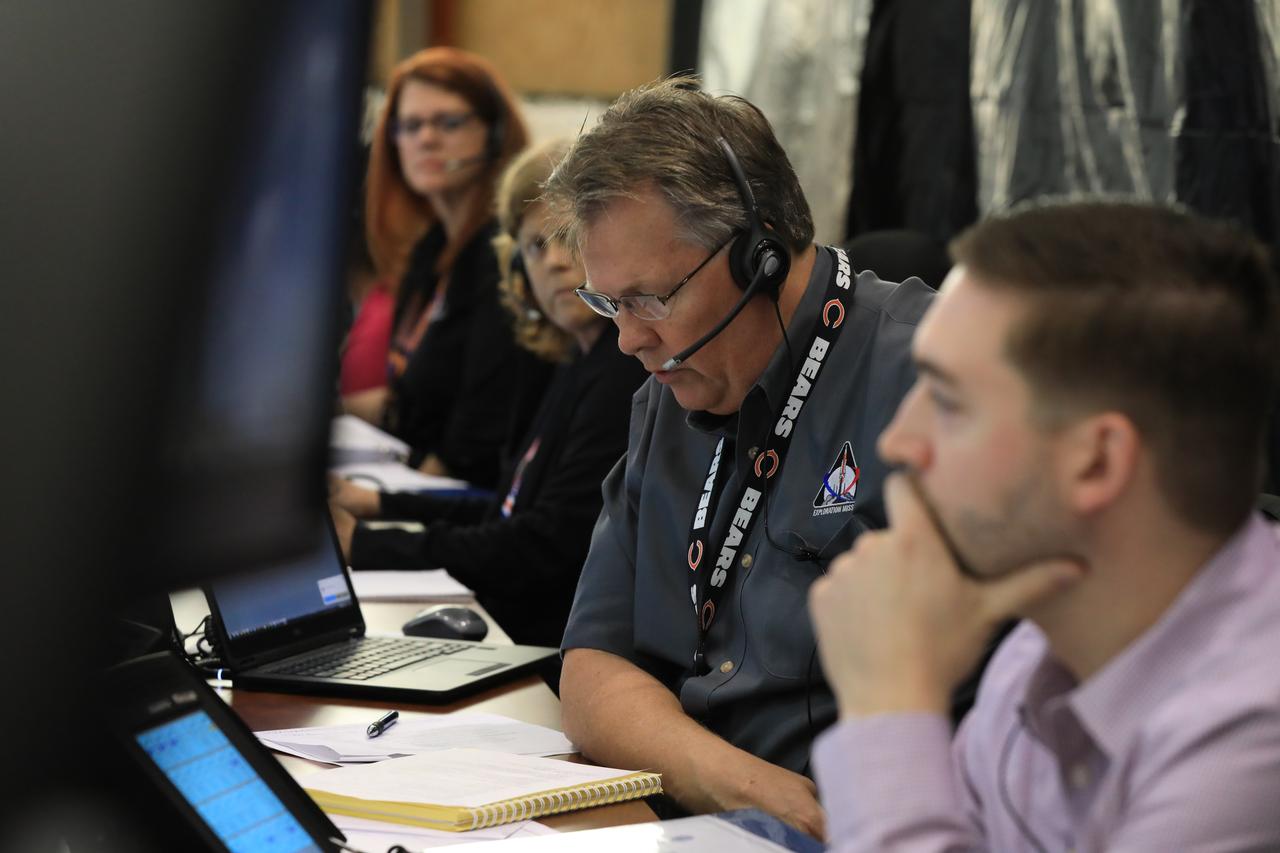

Charlie Blackwell-Thompson, far left, Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1) launch director, and engineers with NASA and Jacobs, participate in a countdown demonstration event of cryogenic propellant loading April 12, 2019, inside Firing Room 2 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The practice simulation involved loading of liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen into the Space Launch System rocket’s core and upper stages to prepare for EM-1. During the tanking exercise, the team worked through surprise issues in real-time. The practice countdown events are training opportunities coordinated by Blackwell-Thompson with Exploration Ground Systems.
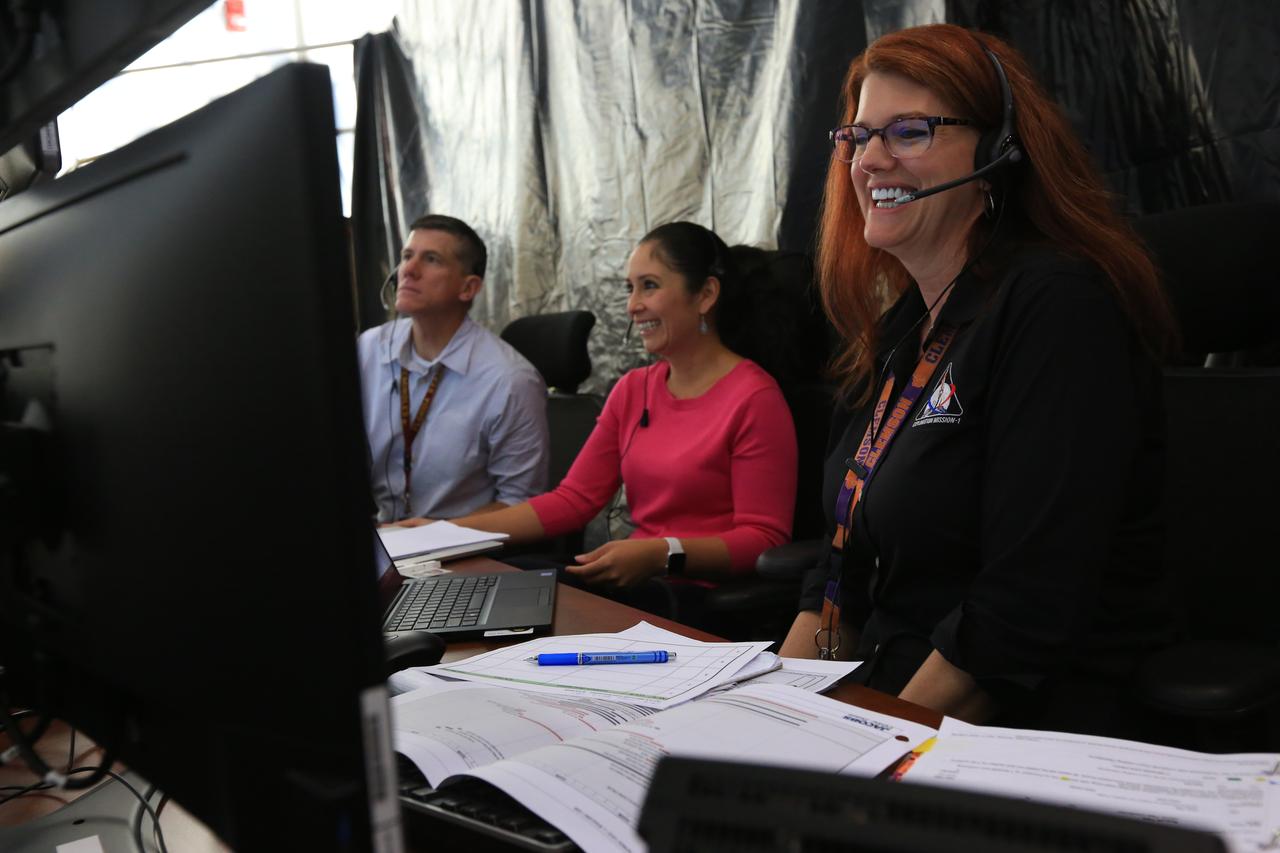

From left, Jeremy Graeber, chief NASA test director; Jessica Parsons, technical assistant to the launch director; and Charlie Blackwell-Thompson, Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1) launch director, participate in a countdown demonstration event of cryogenic propellant loading April 12, 2019, inside Firing Room 2 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The practice simulation involved loading of liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen into the Space Launch System rocket’s core and upper stages to prepare for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). During the tanking exercise, the team worked through surprise issues in real-time. The practice countdown events are training opportunities coordinated by Blackwell-Thompson with Exploration Ground Systems.
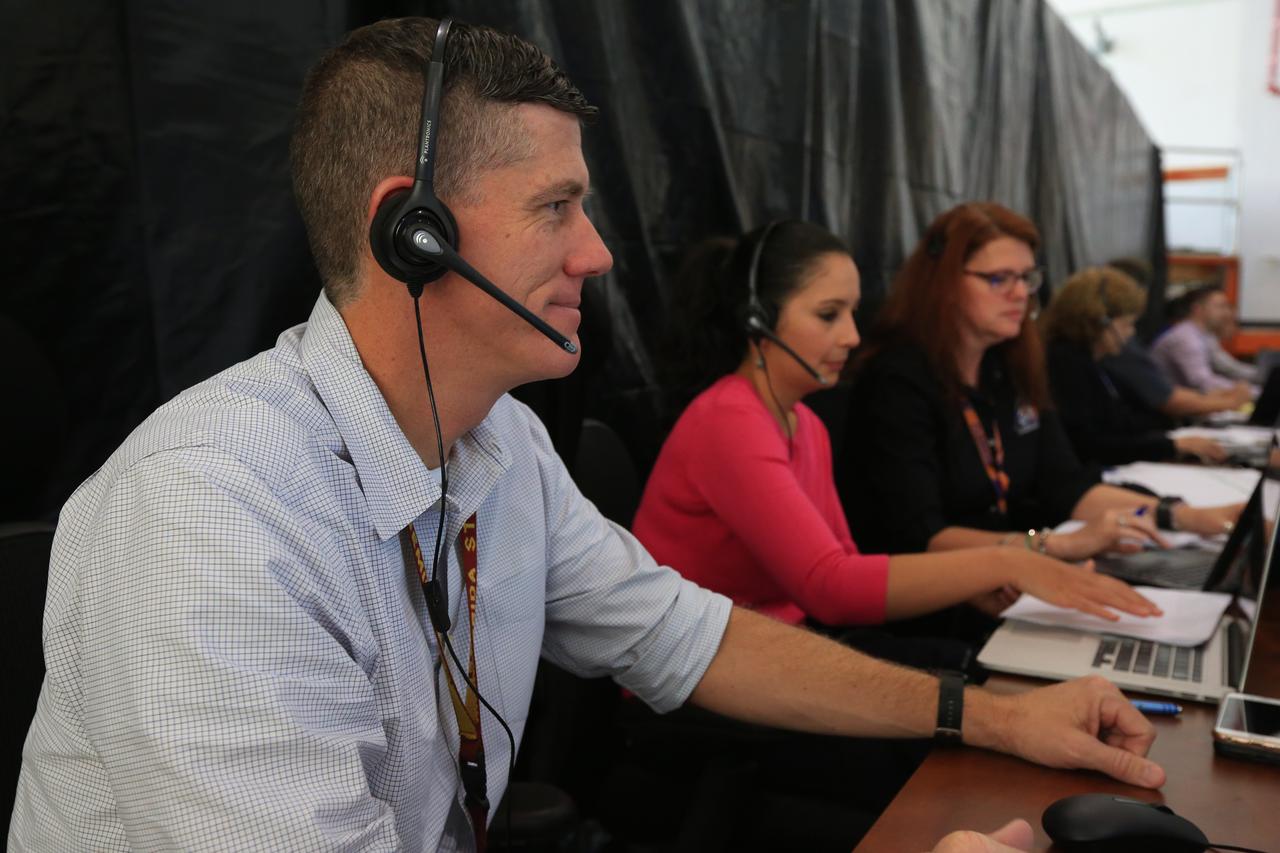

From left, Jeremy Graeber, chief NASA test director; Jessica Parsons, technical assistant to the launch director; and Charlie Blackwell-Thompson, Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1) launch director, participate in a countdown demonstration event of cryogenic propellant loading April 12, 2019, inside Firing Room 2 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The practice simulation involved loading of liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen into the Space Launch System rocket’s core and upper stages to prepare for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). During the tanking exercise, the team worked through surprise issues in real-time. The practice countdown events are training opportunities coordinated by Blackwell-Thompson with Exploration Ground Systems.
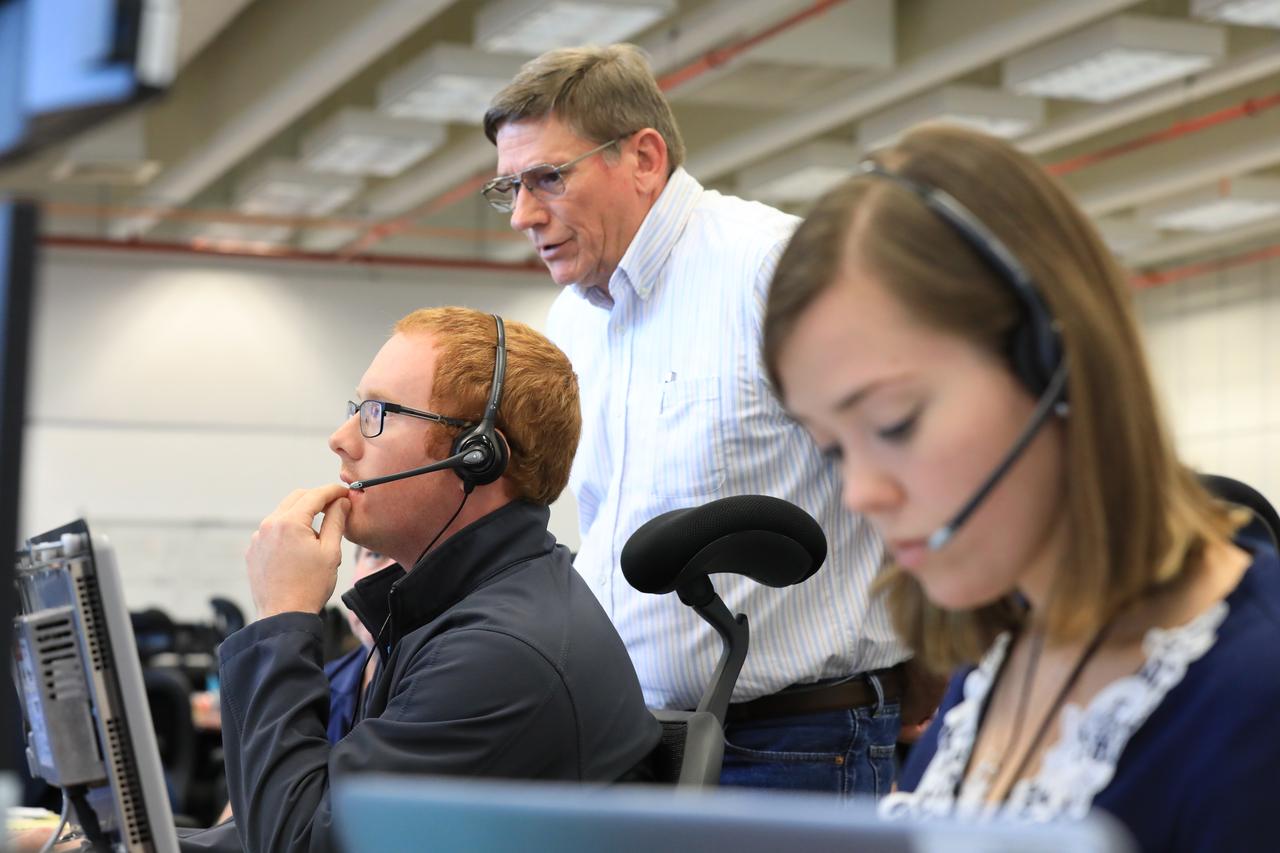

Tom Clark, standing, a manager with contractor ERC, works with Quentin Jones and Emily Hadley, both mechanical engineers for the liquid oxygen system, with ERC, during a countdown demonstration event of cryogenic propellant loading April 12, 2019, inside Firing Room 2 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The practice simulation involved loading of liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen into the Space Launch System rocket’s core and upper stages to prepare for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). During the tanking exercise, the team worked through surprise issues in real-time. The practice countdown events are training opportunities coordinated by EM-1 Launch Director Charlie Blackwell-Thompson with Exploration Ground Systems.
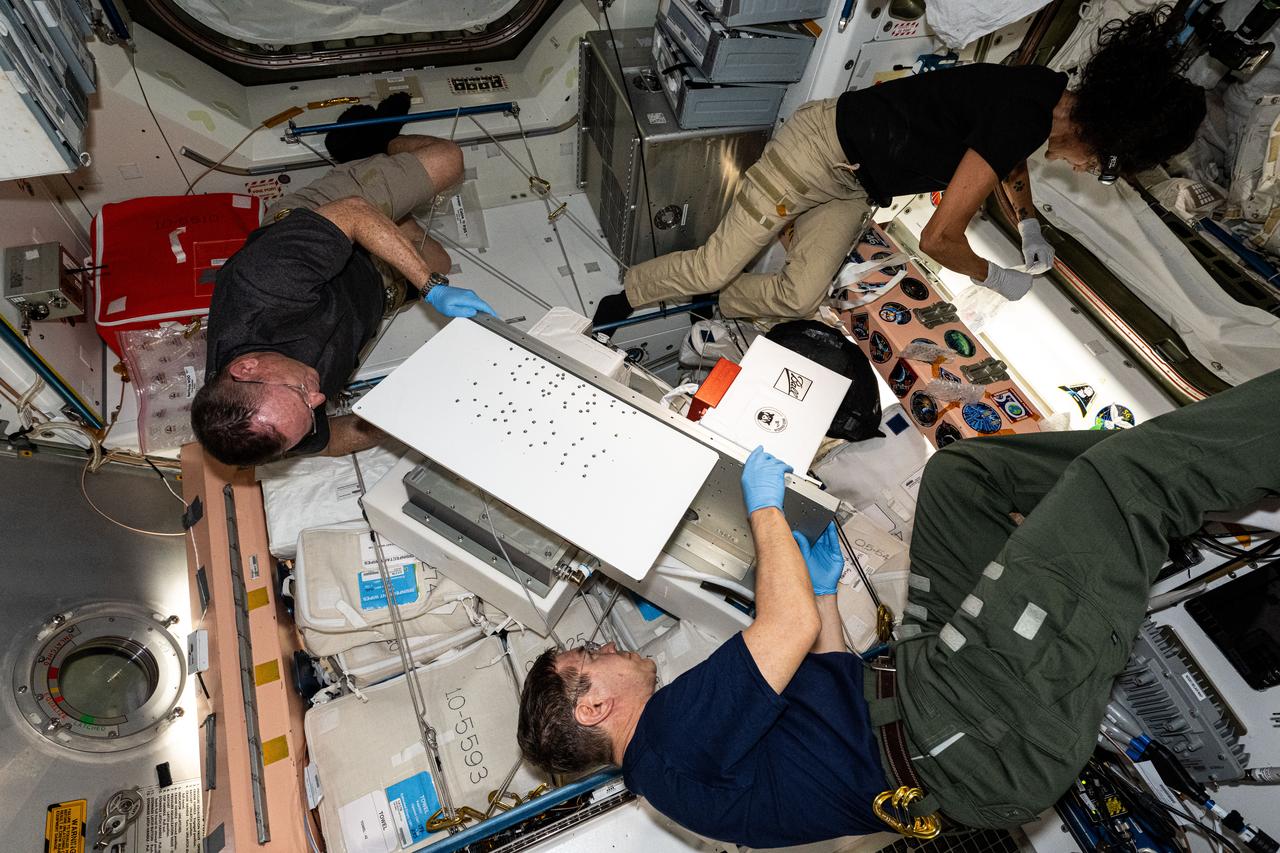

iss071e379489 (July 23, 2024) --- Clockwise from bottom, NASA astronauts Mike Barratt, Butch Wilmore, and Suni Williams are at work inside the International Space Station's Unity module. The trio was configuring the ArgUS Mission 1 technology demonstration hardware to test the external operations of communications, computer processing, and high-definition video gear in the vacuum of space.
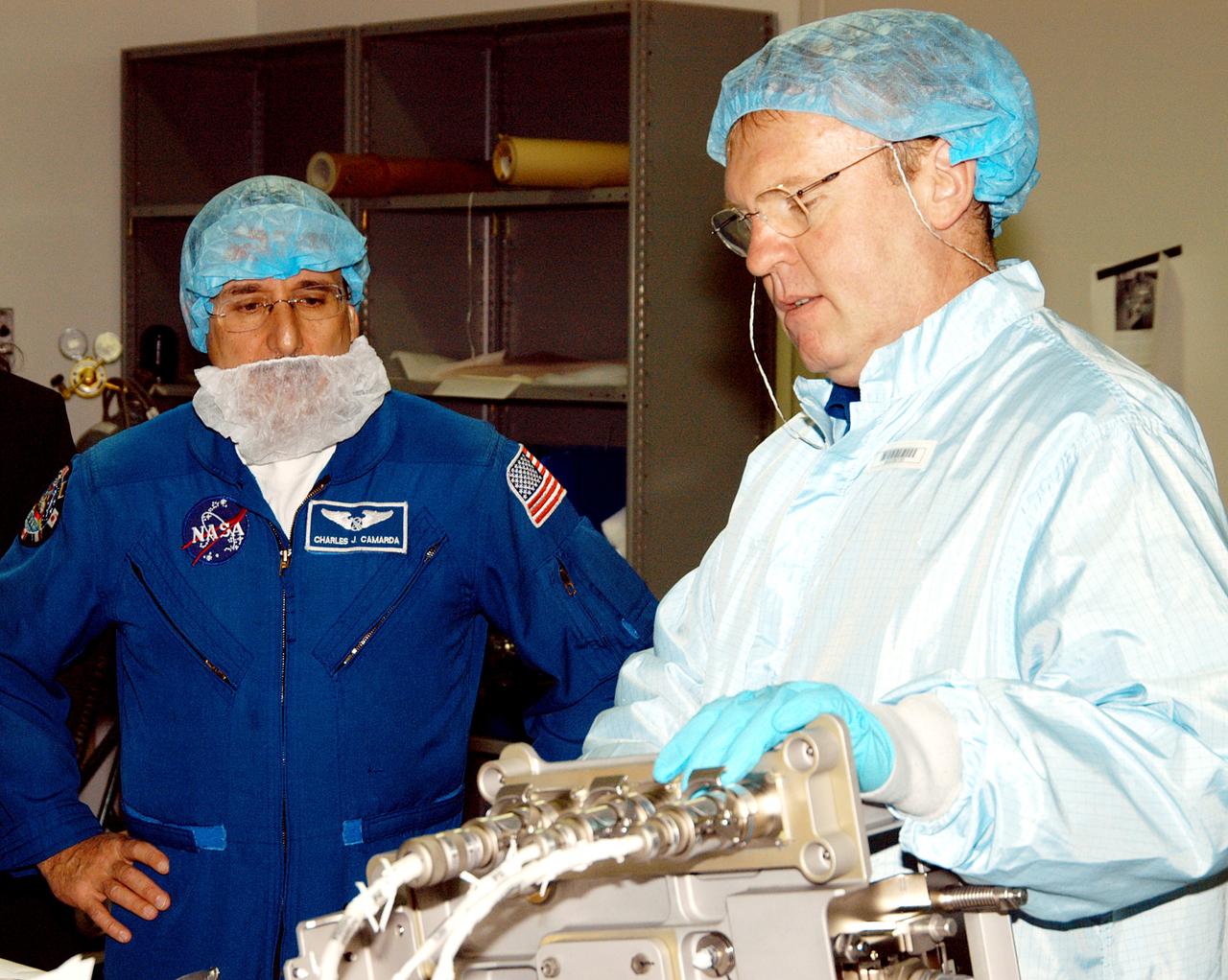

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - STS-114 Mission Specialist Charles Camarda (left) watches as Mission Specialist Andrew Thomas manipulates equipment that will be used on the mission. Crew members are at KSC for equipment familiarization. STS-114 is classified as Logistics Flight 1 to the International Space Station, delivering new supplies and replacing one of the orbital outpost’s Control Moment Gyroscopes (CMGs). STS-114 will also carry a Raffaello Multi-Purpose Logistics Module and the External Stowage Platform-2. The crew is slated to conduct at least three spacewalks: They will demonstrate repair techniques of the Shuttle’s Thermal Protection System, replace the failed CMG with one delivered by the Shuttle, and install the External Stowage Platform.
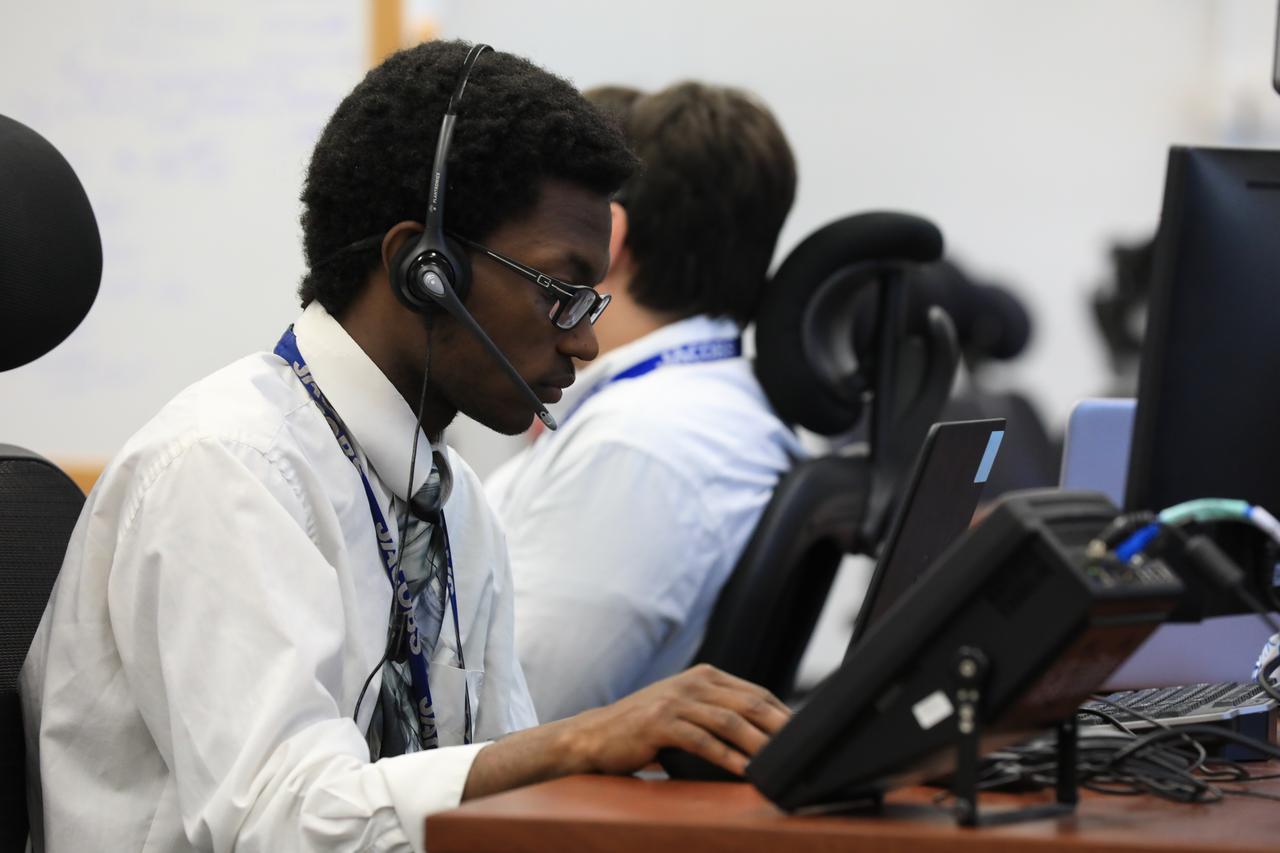

EM-1 Countdown Demonstration with Cryogenic Loading Simulation
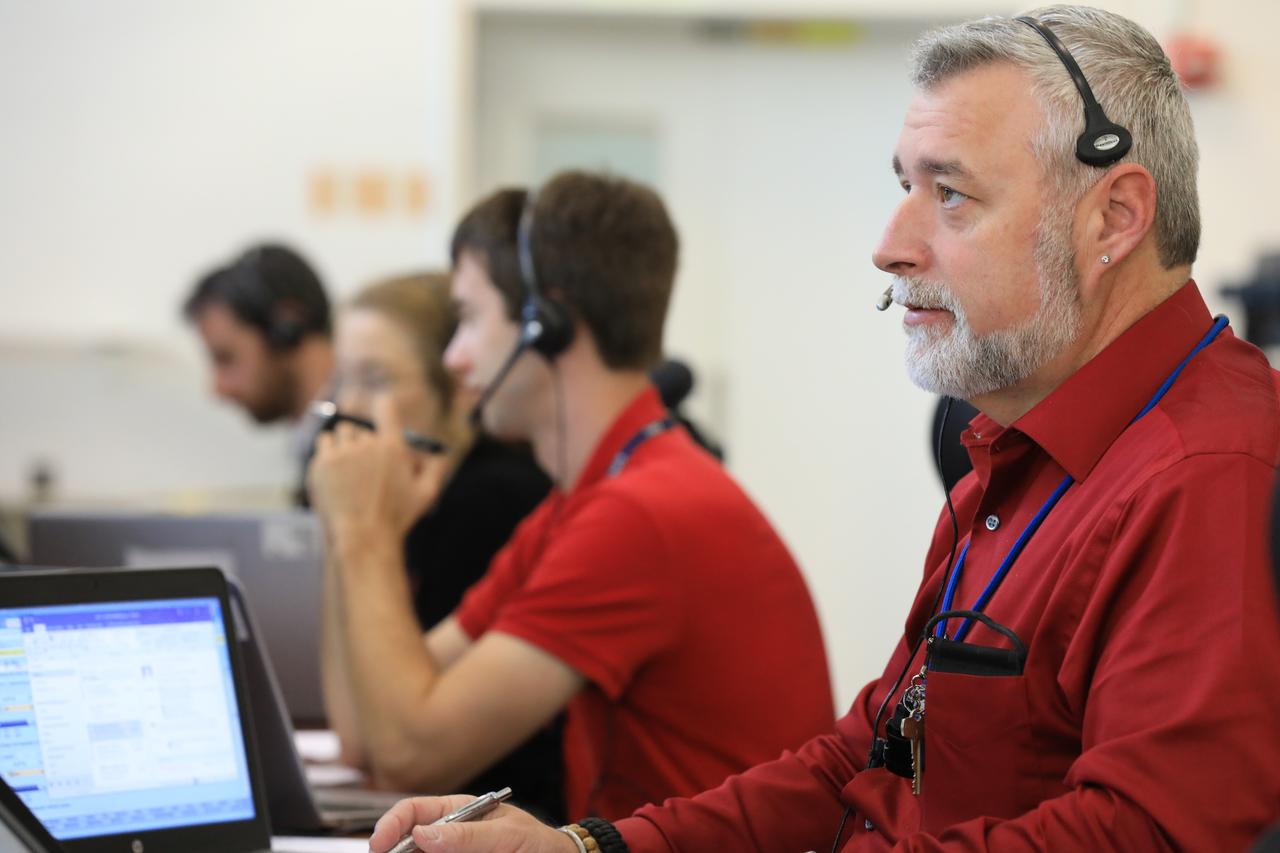

EM-1 Countdown Demonstration with Cryogenic Loading Simulation
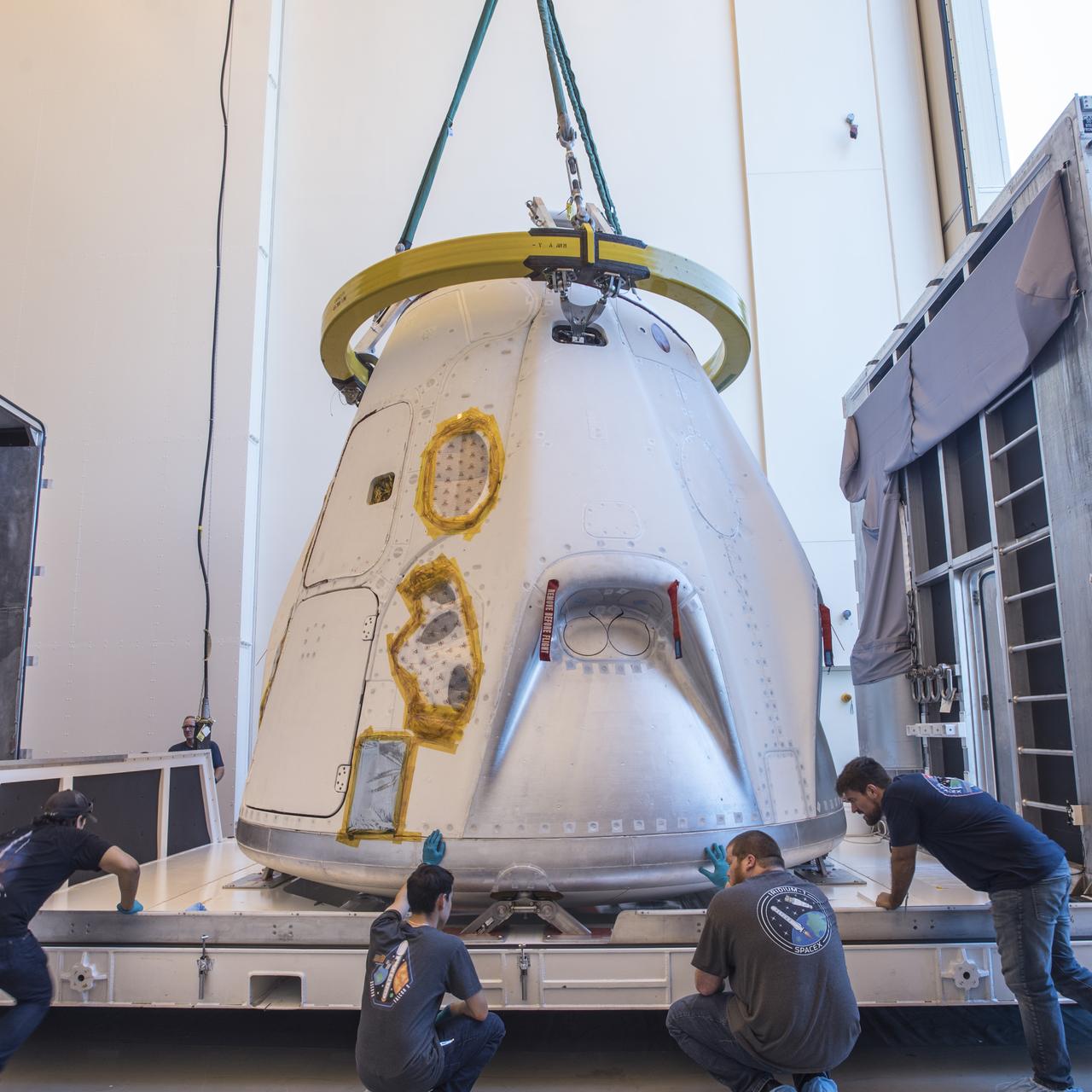

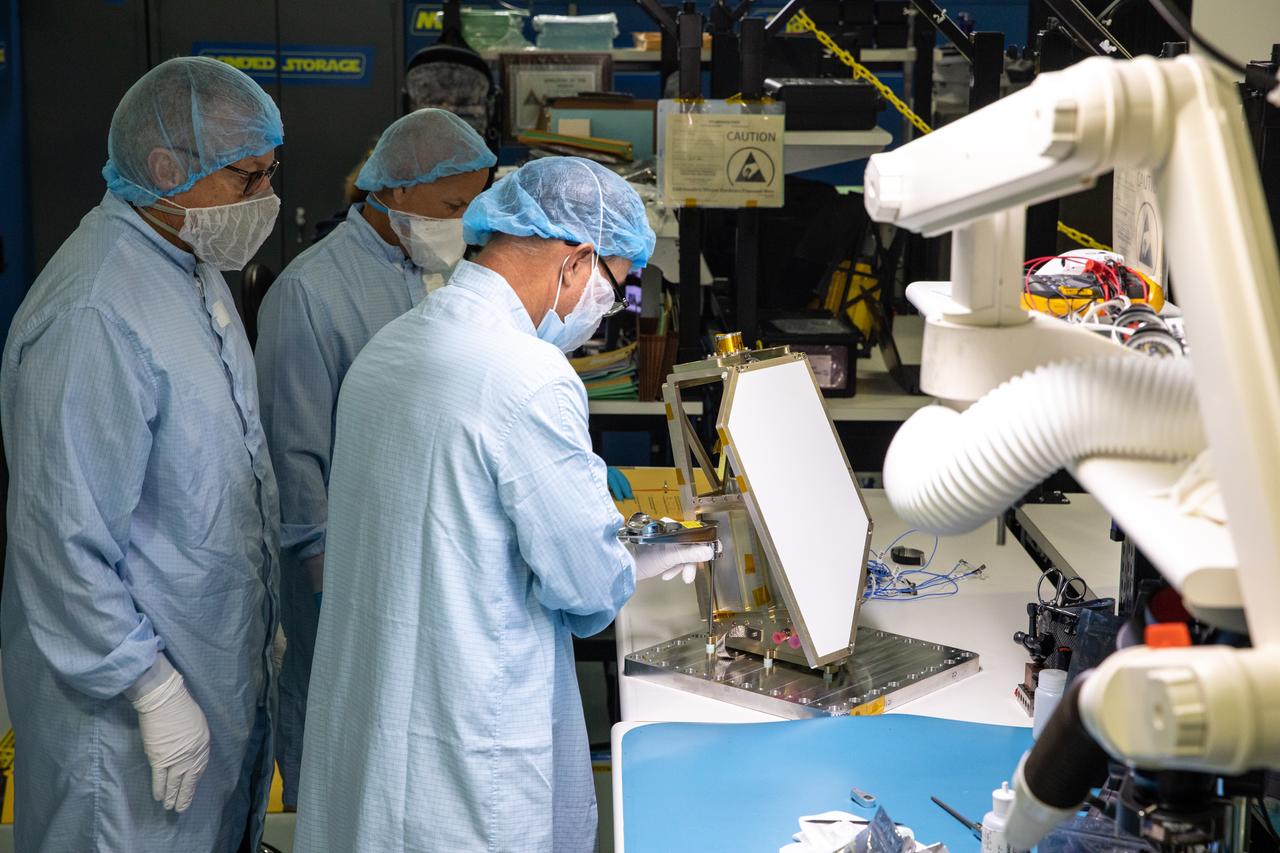
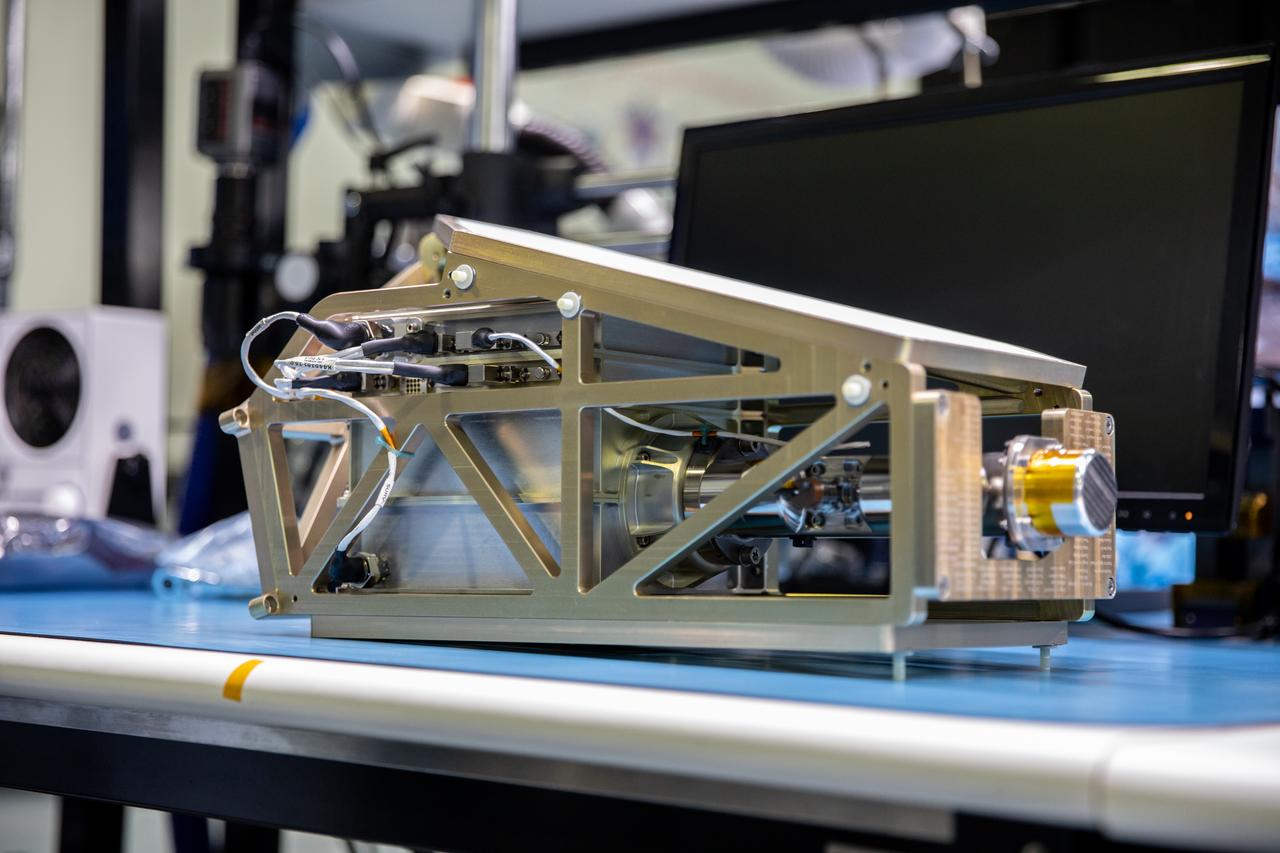
The SpaceX Crew Dragon spacecraft that will be used for the company’s uncrewed flight test, known as Demonstration Mission 1, arrived to Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Tuesday, July 10, 2018. The spacecraft recently underwent thermal vacuum and acoustic testing at NASA’s Plum Brook Station in Ohio. The Demonstration Mission 1 flight test is part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Transportation Capability contract with the goal of returning human spaceflight launch capabilities to the United States.
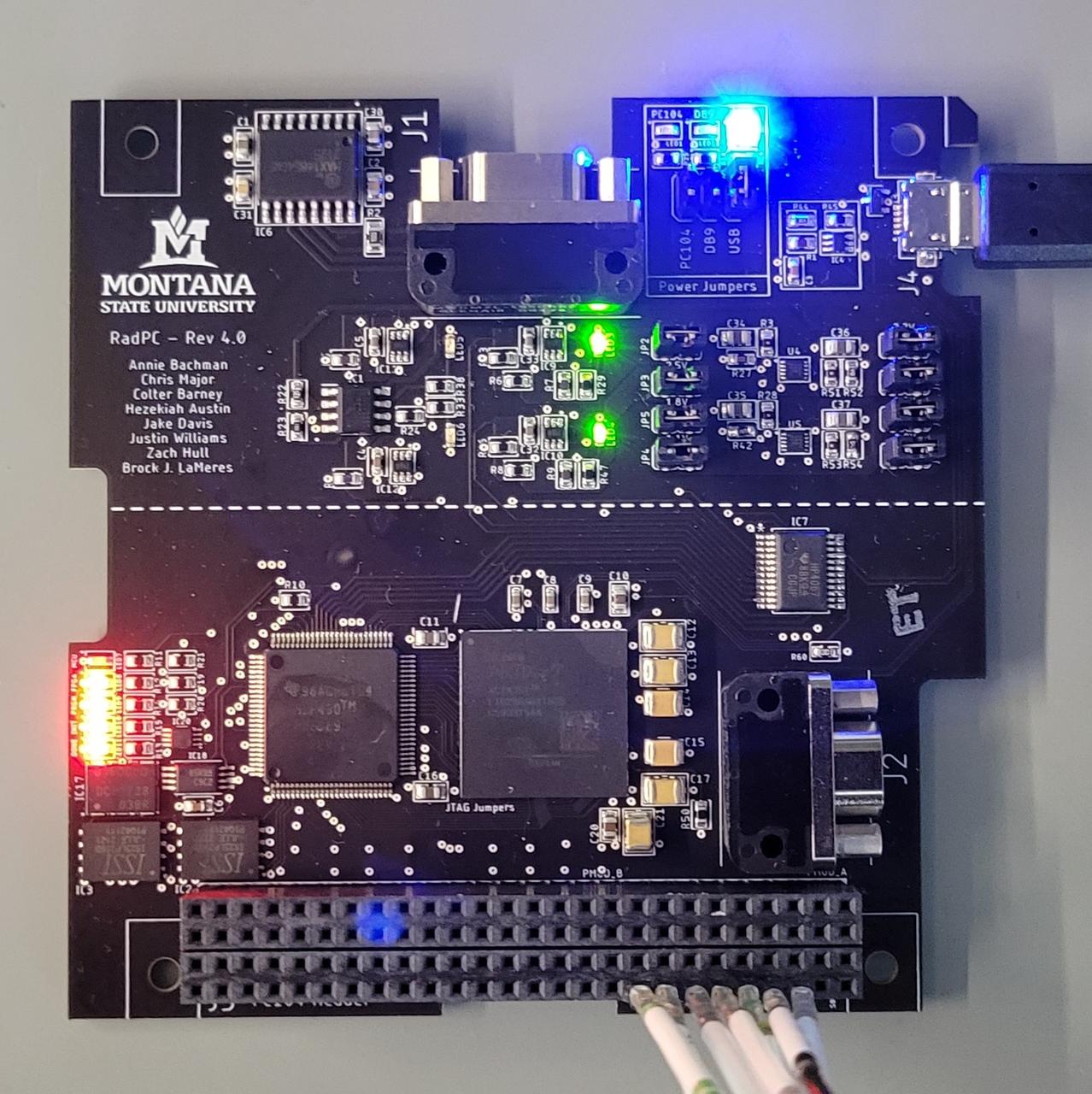
A technology demonstration flying aboard the next delivery for NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative could help mitigate radiation effects on computers in space. Radiation Tolerant Computer, or RadPC, is one of 10 payloads set to be carried to the Moon by the Blue Ghost 1 lunar lander in 2025. Developed by Montana State University in Bozeman, RadPC is designed designed to demonstrate computer recovery from faults caused by single-event effects of ionizing radiation. Investigations and demonstrations, such as RadPC, launched on CLPS flights will help NASA study Earth’s nearest neighbor under Artemis and pave the way for future crewed missions on the Moon. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the development for seven of the 10 CLPS payloads that will be carried on Firefly’s Blue Ghost lunar lander.
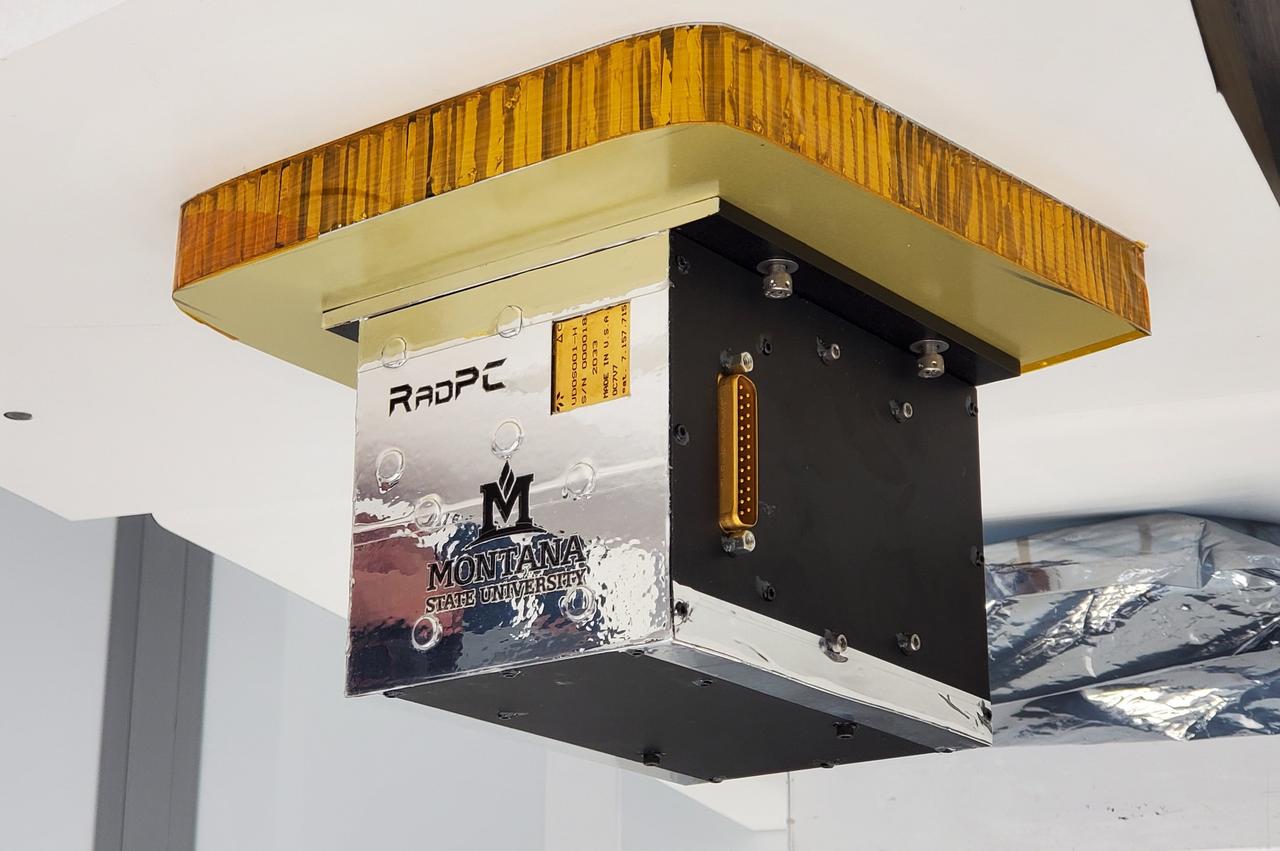

A technology demonstration flying aboard the next delivery for NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative could help mitigate radiation effects on computers in space. Radiation Tolerant Computer, or RadPC, is one of 10 payloads set to be carried to the Moon by the Blue Ghost 1 lunar lander in 2025. Developed by Montana State University in Bozeman, RadPC is designed designed to demonstrate computer recovery from faults caused by single-event effects of ionizing radiation. Investigations and demonstrations, such as RadPC, launched on CLPS flights will help NASA study Earth’s nearest neighbor under Artemis and pave the way for future crewed missions on the Moon. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the development for seven of the 10 CLPS payloads that will be carried on Firefly’s Blue Ghost lunar lander.
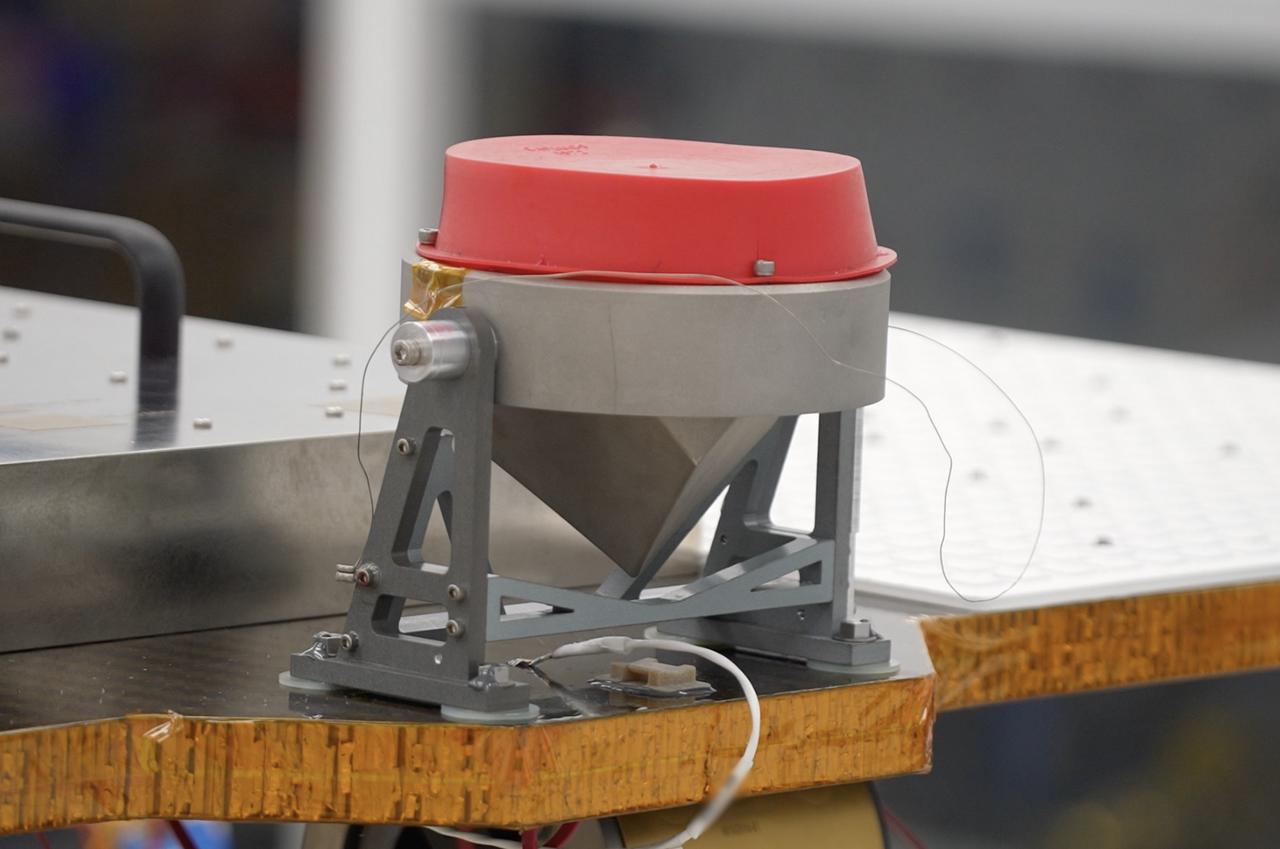

A science instrument flying aboard the next delivery for NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative is expected to significantly expand our knowledge of the Moon. Next Generation Lunar Retroreflector, or NGLR-1, is one of 10 payloads set to be carried to the Moon by the Blue Ghost 1 lunar lander in 2025. Developed by the University of Maryland in College Park, NGLR-1 is designed to reflect very short laser pulses from Earth-based lunar laser ranging observatories using a retroreflector, or a mirror designed to reflect the incoming light back in the same incoming direction. Investigations and demonstrations, such as NGLR-1, launched on CLPS flights will help NASA study Earth’s nearest neighbor under Artemis and pave the way for future crewed missions on the Moon. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the development for seven of the 10 CLPS payloads that will be carried on Firefly’s Blue Ghost lunar lander.

NASA Launch Director Charlie Blackwell-Thompson stands next to her console in Firing Room 1 at the Kennedy Space Center's Launch Control Center during a terminal countdown demonstration for Exploration Mission 1, or EM-1. The launch will be the first integrated test of the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft that will eventually take astronauts beyond low-Earth orbit to destinations such as the Moon and Mars. Taking place on Dec. 14, 2018, the countdown demonstration was intended to validate the launch team's capability to perform an EM-1 countdown and respond to challenges put into the system for practice.
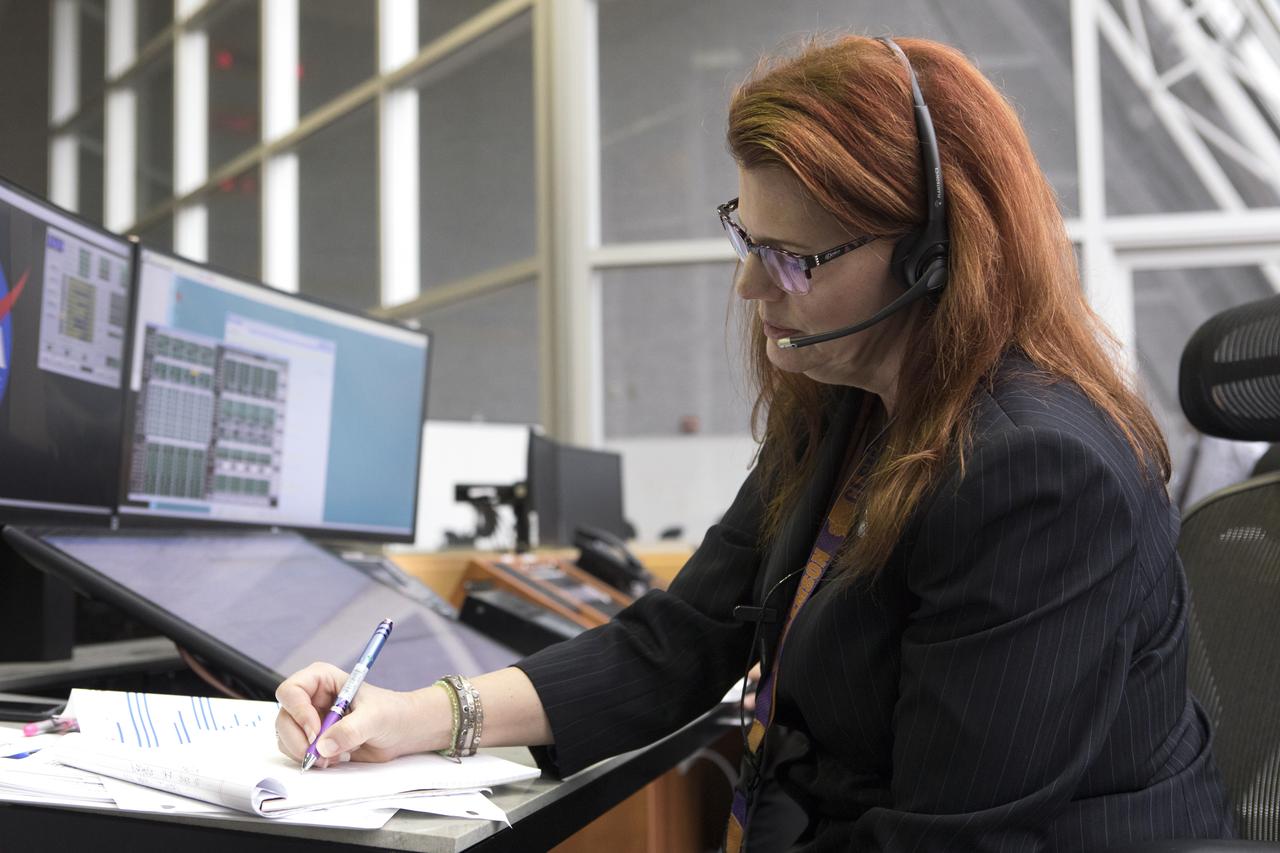

NASA Launch Director Charlie Blackwell-Thompson makes notes at her console in Firing Room 1 at the Kennedy Space Center's Launch Control Center during a terminal countdown demonstration for Exploration Mission 1, or EM-1. The launch will be the first integrated test of the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft that will eventually take astronauts beyond low-Earth orbit to destinations such as the Moon and Mars. Taking place on Dec. 14, 2018, the countdown demonstration was intended to validate the launch team's capability to perform an EM-1 countdown and respond to challenges put into the system for practice.
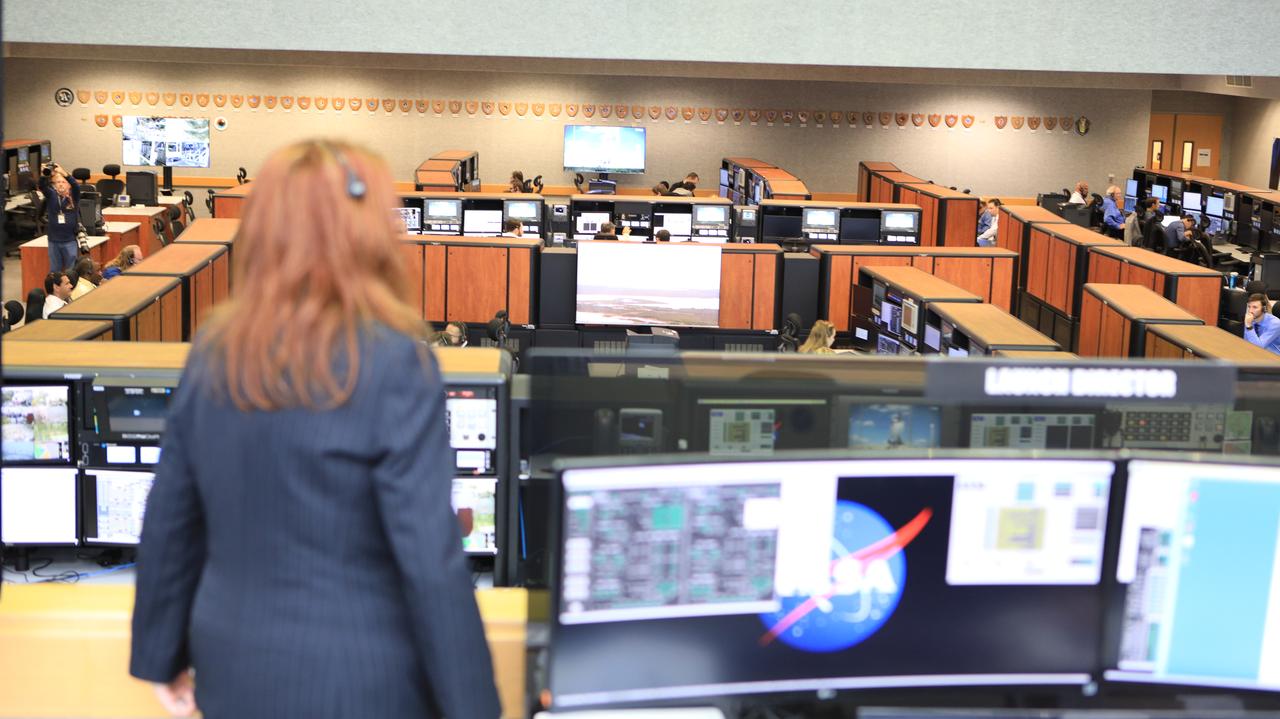

NASA Launch Director Charlie Blackwell-Thompson looks out over Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida during a terminal countdown demonstration for Exploration Mission 1, or EM-1, on Dec. 14, 2018. The launch will be the first integrated test of the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft that will eventually take astronauts beyond low-Earth orbit to destinations such as the Moon and Mars. The countdown demonstration was intended to validate the launch team's capability to perform an EM-1 countdown and respond to challenges put into the system for practice.

An overall view of Firing Room 1 at the Kennedy Space Center's Launch Control Center shows the launch team at work during a terminal countdown demonstration for Exploration Mission 1, or EM-1. The launch will be the first integrated test of the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft that will eventually take astronauts beyond low-Earth orbit to destinations such as the Moon and Mars. Taking place on Dec. 14, 2018, the countdown demonstration was intended to validate the launch team's capability to perform an EM-1 countdown and respond to challenges put into the system for practice.
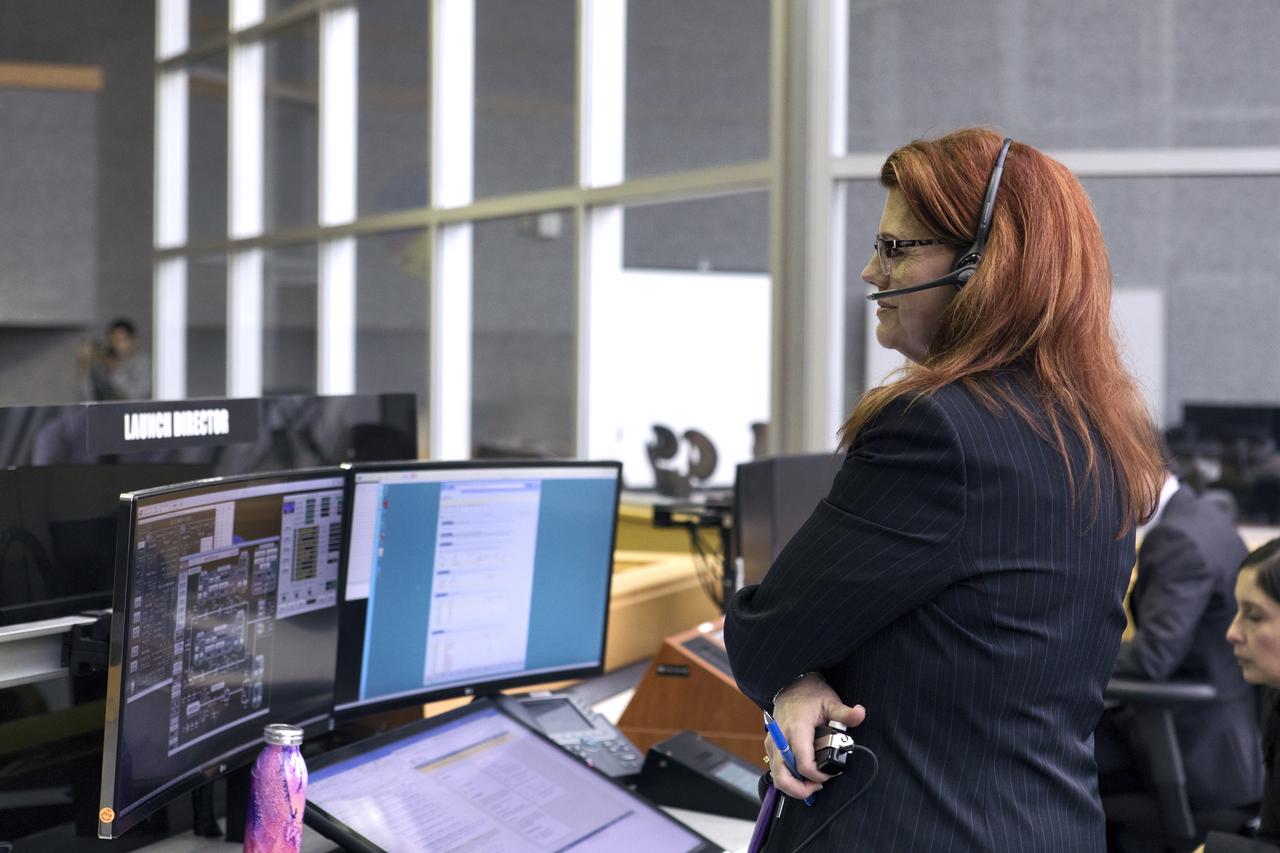

NASA Launch Director Charlie Blackwell-Thompson stands next to her console in Firing Room 1 at the Kennedy Space Center's Launch Control Center during a terminal countdown demonstration for Exploration Mission 1, or EM-1. The launch will be the first integrated test of the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft that will eventually take astronauts beyond low-Earth orbit to destinations such as the Moon and Mars. Taking place on Dec. 14, 2018, the countdown demonstration was intended to validate the launch team's capability to perform an EM-1 countdown and respond to challenges put into the system for practice.
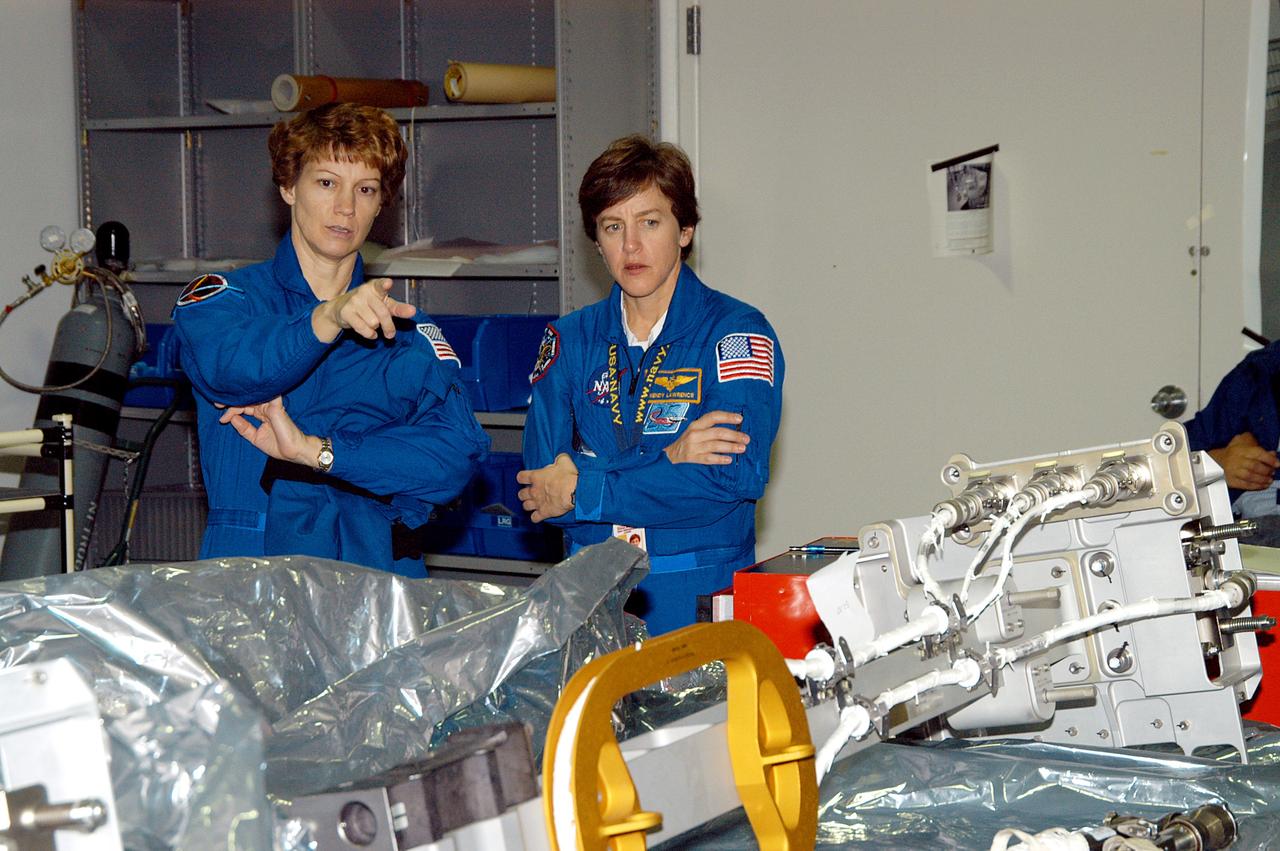

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - STS-114 Commander Eileen Collins and Mission Specialist Wendy Lawrence look over mission equipment in the Space Station Processing Facility. Crew members are at KSC for equipment familiarization. STS-114 is classified as Logistics Flight 1 to the International Space Station, delivering new supplies and replacing one of the orbital outpost’s Control Moment Gyroscopes (CMGs). STS-114 will also carry a Raffaello Multi-Purpose Logistics Module and the External Stowage Platform-2. The crew is slated to conduct at least three spacewalks: They will demonstrate repair techniques of the Shuttle’s Thermal Protection System, replace the failed CMG with one delivered by the Shuttle, and install the External Stowage Platform.
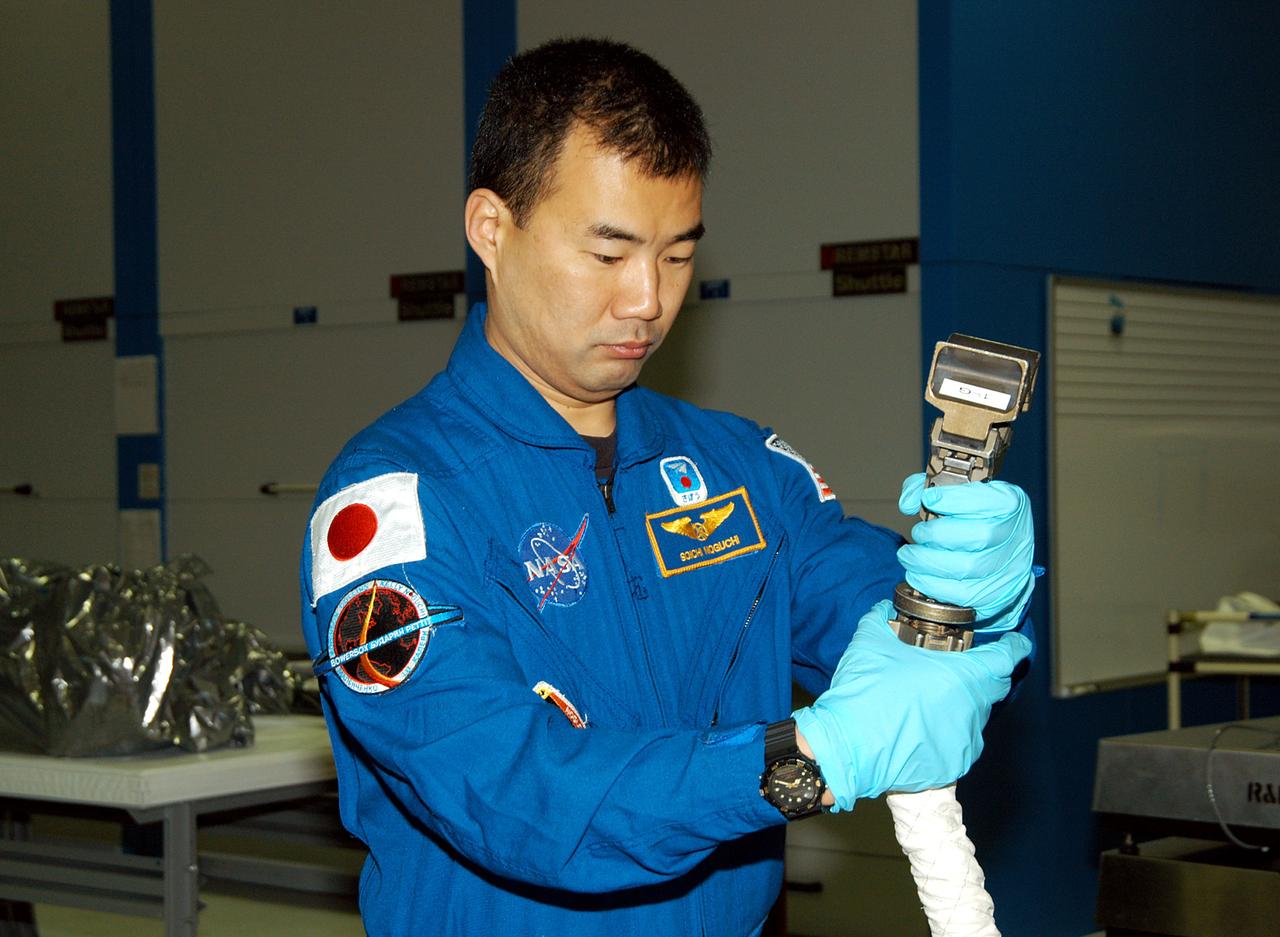

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - STS-114 Mission Specialist Soichi Noguchi, with the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), handles equipment that will be used on the mission. He and other crew members are at KSC for equipment familiarization. STS-114 is classified as Logistics Flight 1 to the International Space Station, delivering new supplies and replacing one of the orbital outpost’s Control Moment Gyroscopes (CMGs). STS-114 will also carry a Raffaello Multi-Purpose Logistics Module and the External Stowage Platform-2. The crew is slated to conduct at least three spacewalks: They will demonstrate repair techniques of the Shuttle’s Thermal Protection System, replace the failed CMG with one delivered by the Shuttle, and install the External Stowage Platform.
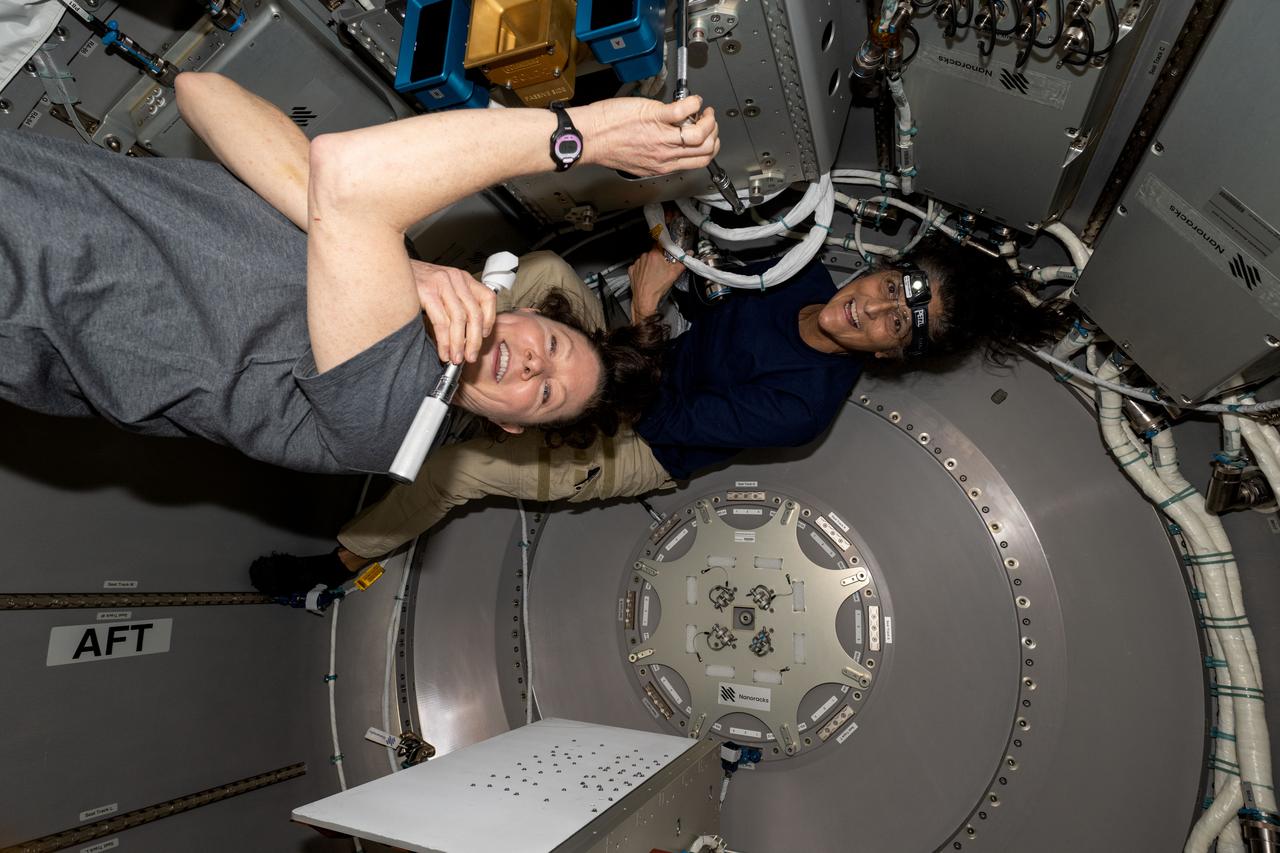

iss071e403704 (July 24, 2024) --- NASA astronauts (from left) Tracy C. Dyson, Expedition 71 Flight Engineer, and Suni Williams, Pilot for Boeing's Crew Flight Test, work inside the NanoRacks Bishop airlock located in the port side of the International Space Station's Tranquility module. The duo installed the the ArgUS Mission-1 technology demonstration hardware inside Bishop for placement outside in the vacuum of space to test the external operations of communications, computer processing, and high-definition video gear.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- STS-85 Payload Commander N. Jan Davis (left) and Mission Specialist Robert L. Curbeam, Jr., check out an emergency egress slidewire basket at the 195-foot level of Launch Pad 39A during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities for that mission. The primary payload aboard the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery is the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2). Other STS-85 payloads include the Manipulator Flight Demonstration (MFD), and Technology Applications and Science-1 (TAS-1) and International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker-2 (IEH-2)
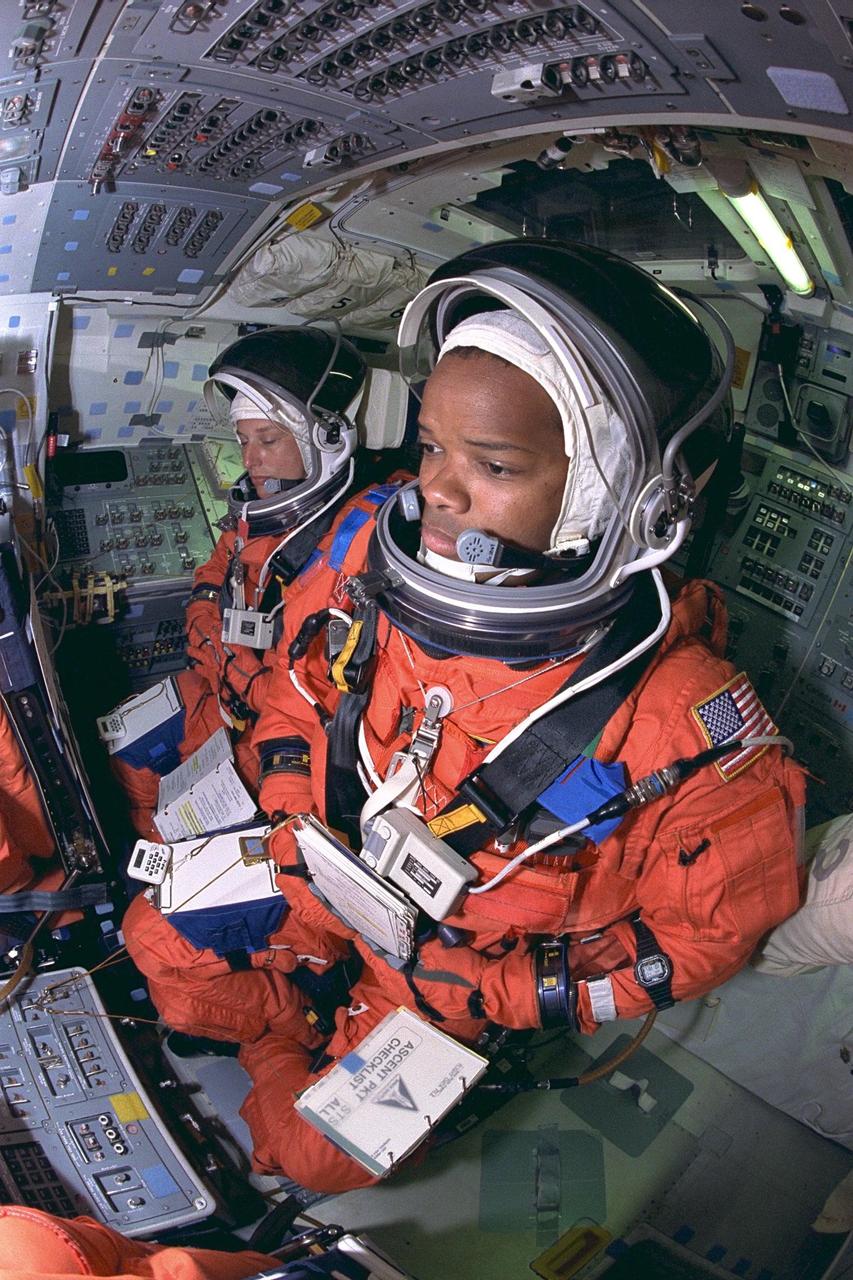

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-85 Payload Commander N. Jan Davis (left) and Mission Specialist Robert L. Curbeam, Jr., go through countdown procedures aboard the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities for that mission. The TCDT includes a simulation of the final launch countdown. The primary payload aboard the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery is the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2). Other STS-85 payloads include the Manipulator Flight Demonstration (MFD), and Technology Applications and Science-1 (TAS-1) and International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker-2 (IEH-2) experiments
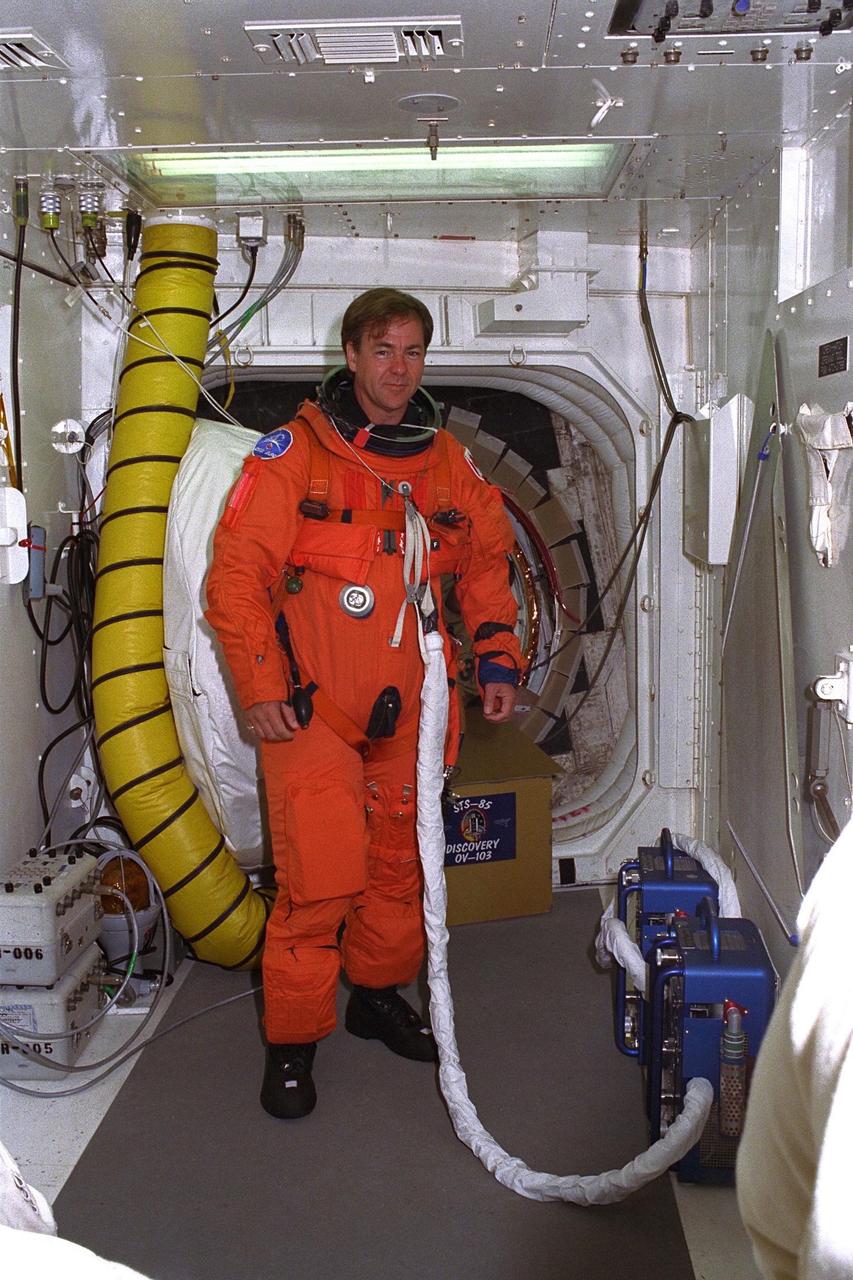

STS-85 Payload Specialist Bjarni V. Tryggvason poses in the white room at Launch Pad 39A with his ascent/reentry flight suit as he prepares to enter the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery at Launch Pad 39A during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities for that mission. The primary payload aboard the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery is the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2). Other payloads on the 11-day mission include the Manipulator Flight Demonstration (MFD), and Technology Applications and Science-1 (TAS-1) and International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker-2 (IEH-2) experiments

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- STS-85 Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson (left) and Payload Specialist Bjarni V. Tryggvason check out an emergency egress slidewire basket at the 195-foot level of Launch Pad 39A during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities for that mission. The primary payload aboard the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery is the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2). Other STS-85 payloads include the Manipulator Flight Demonstration (MFD), and Technology Applications and Science-1 (TAS-1) and International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker-2 (IEH-2)
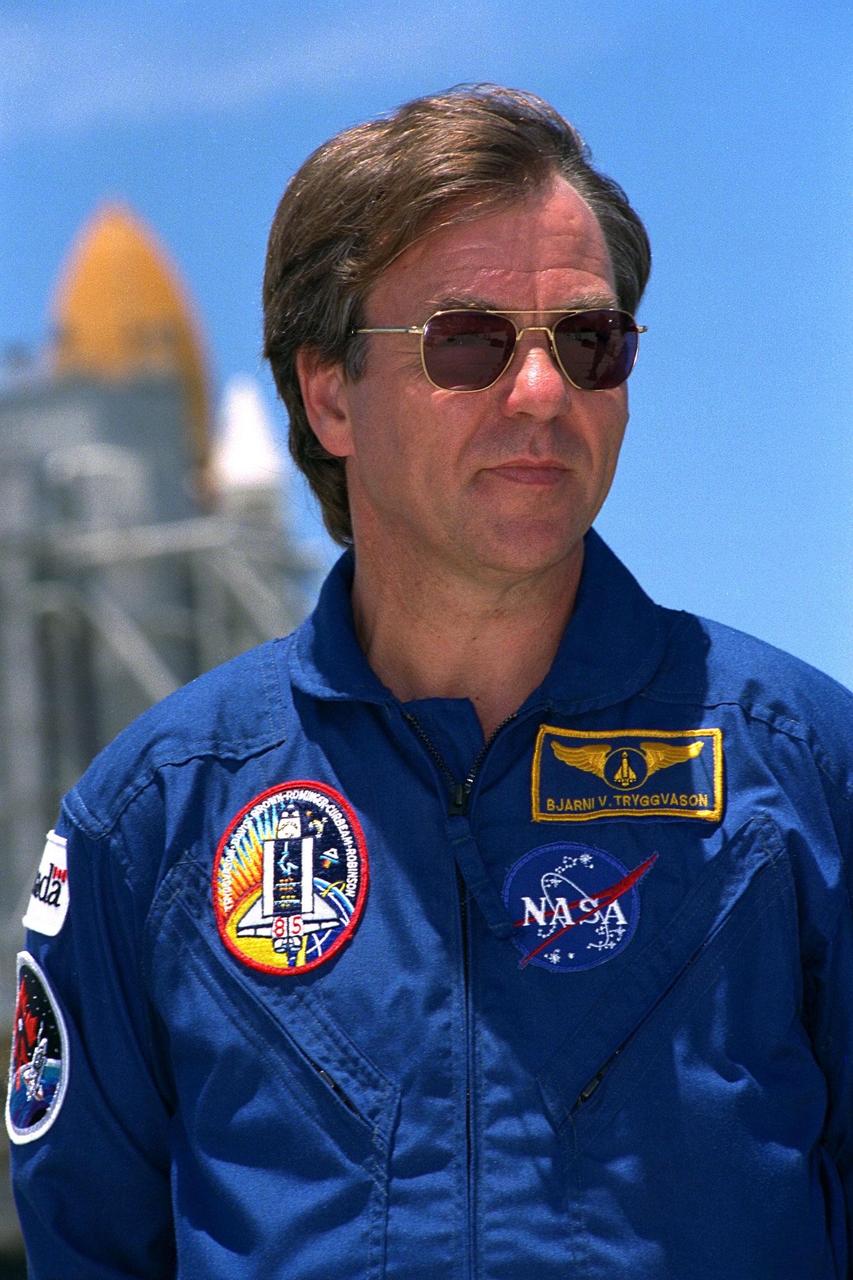

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- STS-85 Payload Specialist Bjarni V. Tryggvason stands ready for questions at a news briefing at Launch Pad 39A during a break in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities for that mission. The primary payload aboard the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery is the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2). Other payloads on the 11-day mission include the Manipulator Flight Demonstration (MFD), and Technology Applications and Science-1 (TAS-1) and International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker-2 (IEH-2) experiments

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-85 Payload Specialist Bjarni V. Tryggvason and Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson go through countdown procedures aboard the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities for that mission. The TCDT includes a simulation of the final launch countdown. The primary payload aboard the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery is the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-2 (CRISTA-SPAS- 2). Other STS-85 payloads include the Manipulator Flight Demonstration (MFD), and Technology Applications and Science-1 (TAS-1) and International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker-2 (IEH-2) experiments
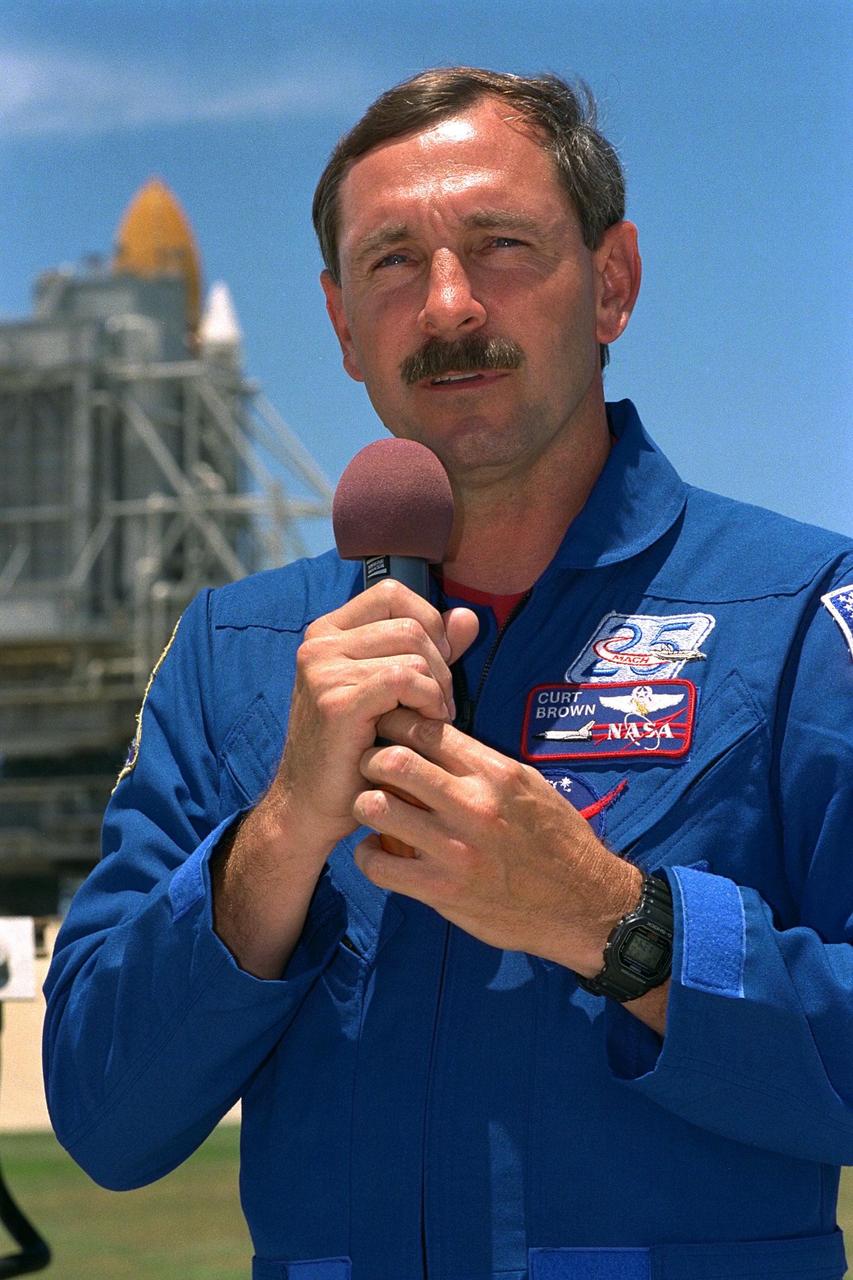

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- STS-85 Commander Curtis L. Brown, Jr., addresses the news media at a briefing at Launch Pad 39A during a break in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities for that mission. The primary payload aboard the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery is the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2). Other payloads on the 11-day mission include the Manipulator Flight Demonstration (MFD), and Technology Applications and Science-1 (TAS-1) and International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker-2 (IEH-2) experiments
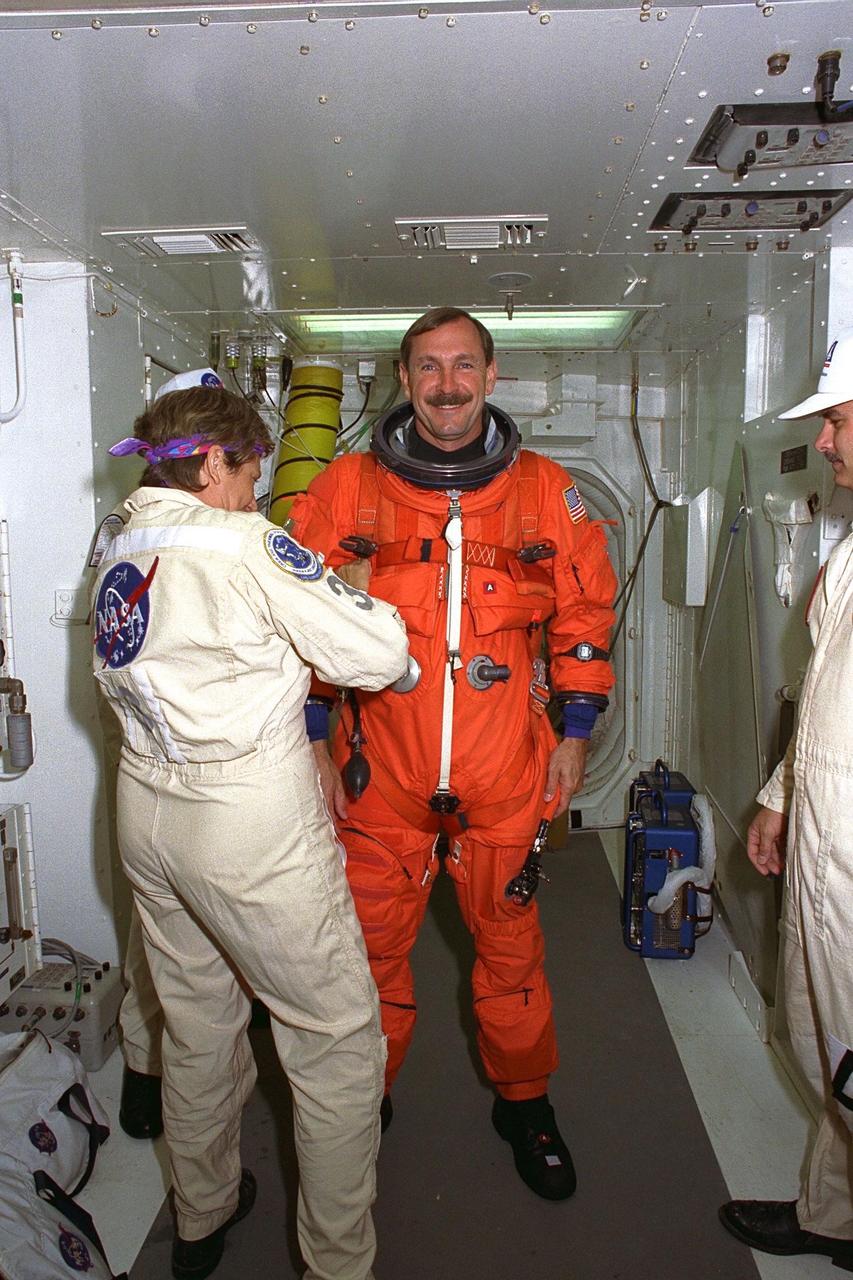

STS-85 Commander Curtis L. Brown, Jr., is assisted with his ascent/reentry flight suit by a white room crew member as he prepares to enter the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery at Launch Pad 39A during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities for that mission. The primary payload aboard the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery is the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2). Other payloads on the 11-day mission include the Manipulator Flight Demonstration (MFD), and Technology Applications and Science-1 (TAS-1) and International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker-2 (IEH-2) experiments
This is a photograph of the Spacelab module for the first United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML-1) mission, showing logos of the Spacelab mission on the left and the USML-1 mission on the right. The USML-1 was one part of a science and technology program that opened NASA's next great era of discovery and established the United States' leadership in space. From investigations designed to gather fundamental knowledge in a variety of areas to demonstrations of new equipment, USML-1 forged the way for future USML missions and helped prepare for advanced microgravity research and processing aboard the Space Station. Thirty-one investigations comprised the payload of the first USML-1 mission. The experiments aboard USML-1 covered five basic areas: fluid dynamics, the study of how liquids and gases respond to the application or absence of differing forces; crystal growth, the production of inorganic and organic crystals; combustion science, the study of the processes and phenomena of burning; biological science, the study of plant and animal life; and technology demonstrations. The USML-1 was managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia (STS-50) on June 25, 1992.
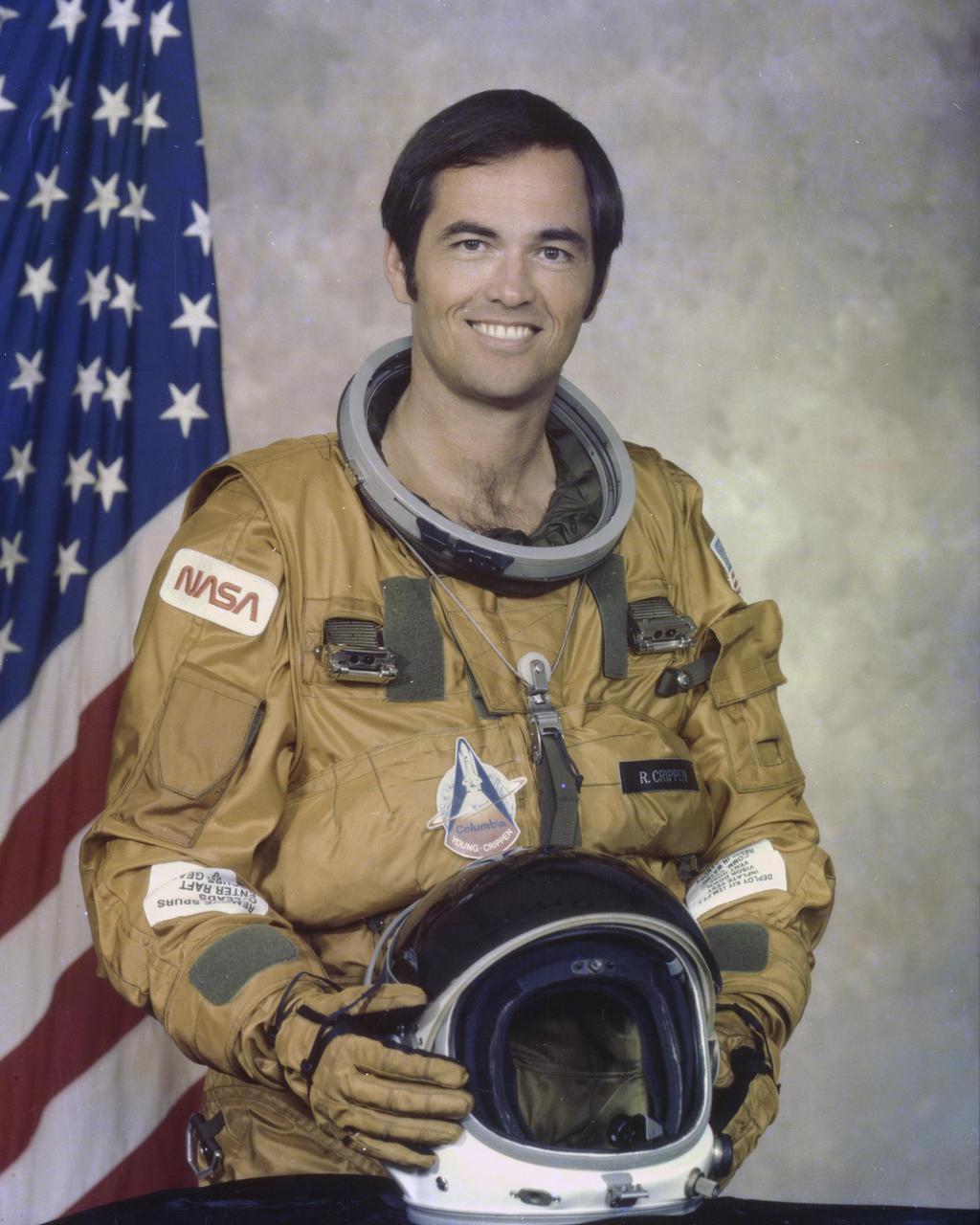

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Robert L. Crippen, Pilot for the STS-1 mission of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia. The STS-1 mission, known as a shuttle systems test flight, will seek to demonstrate safe launch into orbit and safe return of the orbiter and crew and verify the combined performance of the entire shuttle vehicle -- orbiter, solid rocket boosters and external tank. STS-1 will be launched from Pad A at the Kennedy Space Center's Launch Complex 39 no earlier than March 1981.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - John H. Young is the commander for the STS-1 mission of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia. The STS-1 mission, known as a shuttle systems test flight, will seek to demonstrate safe launch into orbit and safe return of the orbiter and crew and verify the combined performance of the entire shuttle vehicle -- orbiter, solid rocket boosters and external tank. STS-1 will be launched from Pad A at the Kennedy Space Center's Launch Complex 39 no earlier than March 1981.
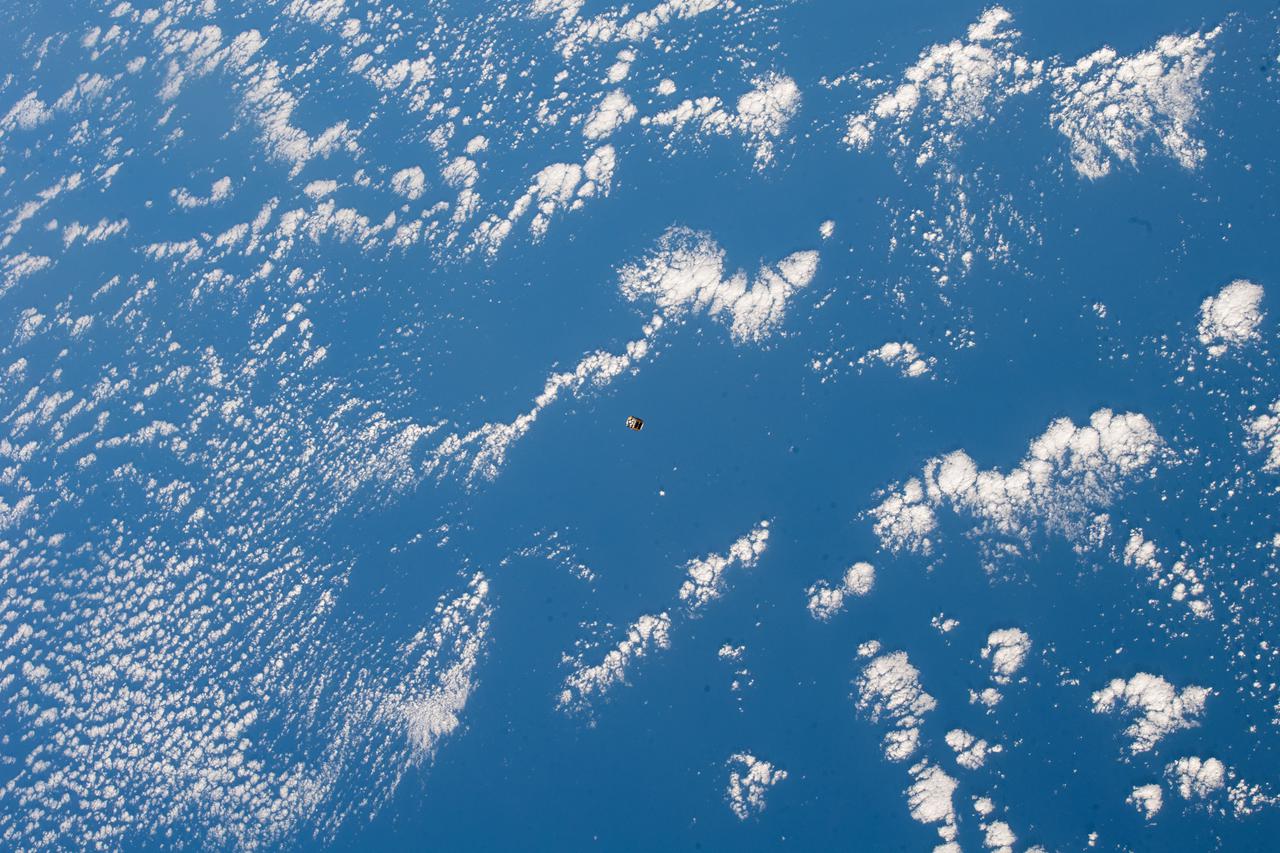

iss066e135744 (2/3/2022) --- A view of the deployed GT-1 CubeSat. The Georgia Institute of Technology-1 (GT-1) is a 1.14 kg 1-Unit (1U) CubeSat, developed by the Georgia Institute of Technology, with experimental deployable solar panels and a deployable UHF radio antenna. The GT-1 mission demonstrates a rapid “cradle-to-grave” development lifecycle of a university level CubeSat. GT-1 is deployed as a part of the JEM Small Satellite Orbital Deployer-20 (J-SSOD-20) CubeSat deployment mission, and is launched to the International Space Station (ISS) aboard the SpaceX-24 Dragon Cargo Vehicle.

iss066e135308 (2/3/2022) --- A view of the deployed GT-1 CubeSat. The Georgia Institute of Technology-1 (GT-1) is a 1.14 kg 1-Unit (1U) CubeSat, developed by the Georgia Institute of Technology, with experimental deployable solar panels and a deployable UHF radio antenna. The GT-1 mission demonstrates a rapid “cradle-to-grave” development lifecycle of a university level CubeSat. GT-1 is deployed as a part of the JEM Small Satellite Orbital Deployer-20 (J-SSOD-20) CubeSat deployment mission, and is launched to the International Space Station (ISS) aboard the SpaceX-24 Dragon Cargo Vehicle.
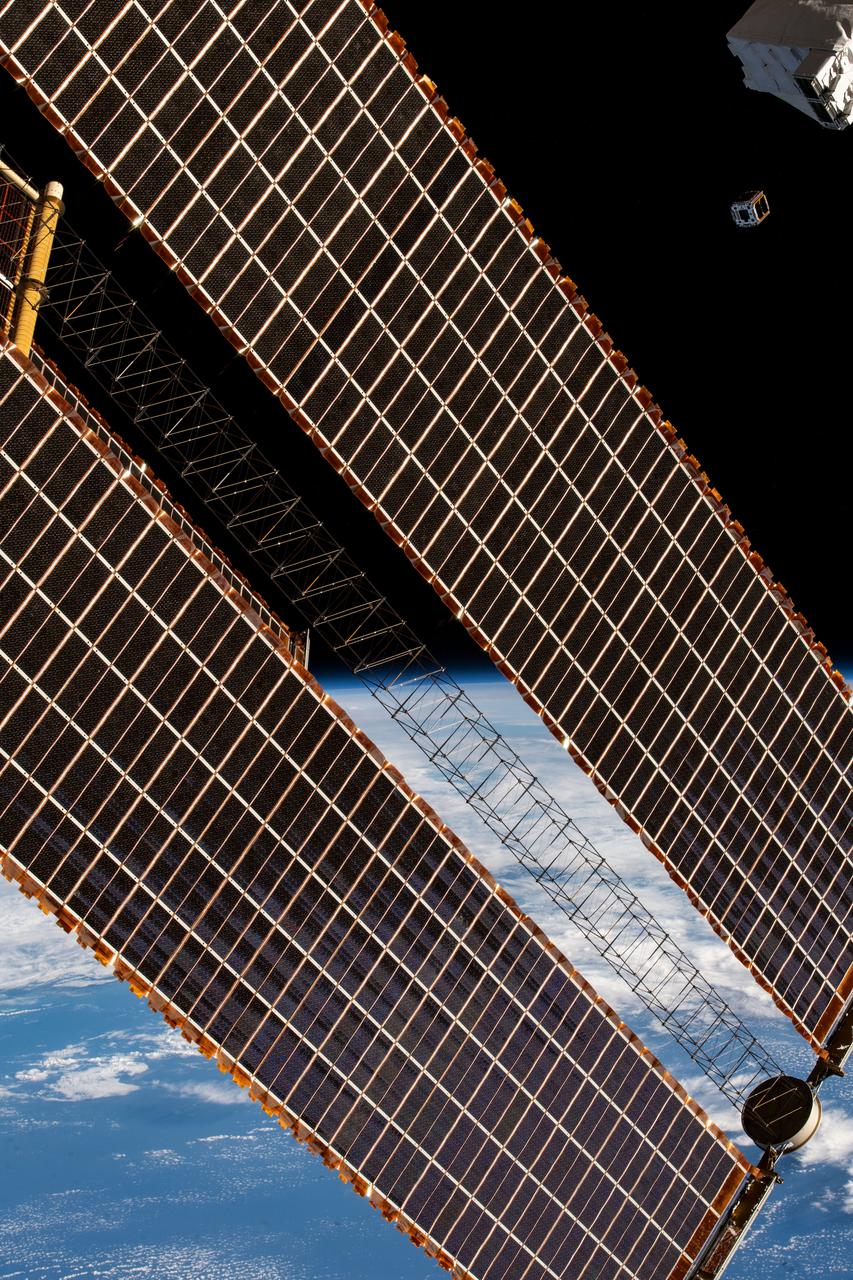

iss066e135704 (2/3/2022) --- A view of the deployed GT-1 CubeSat. The Georgia Institute of Technology-1 (GT-1) is a 1.14 kg 1-Unit (1U) CubeSat, developed by the Georgia Institute of Technology, with experimental deployable solar panels and a deployable UHF radio antenna. The GT-1 mission demonstrates a rapid “cradle-to-grave” development lifecycle of a university level CubeSat. GT-1 is deployed as a part of the JEM Small Satellite Orbital Deployer-20 (J-SSOD-20) CubeSat deployment mission, and is launched to the International Space Station (ISS) aboard the SpaceX-24 Dragon Cargo Vehicle.
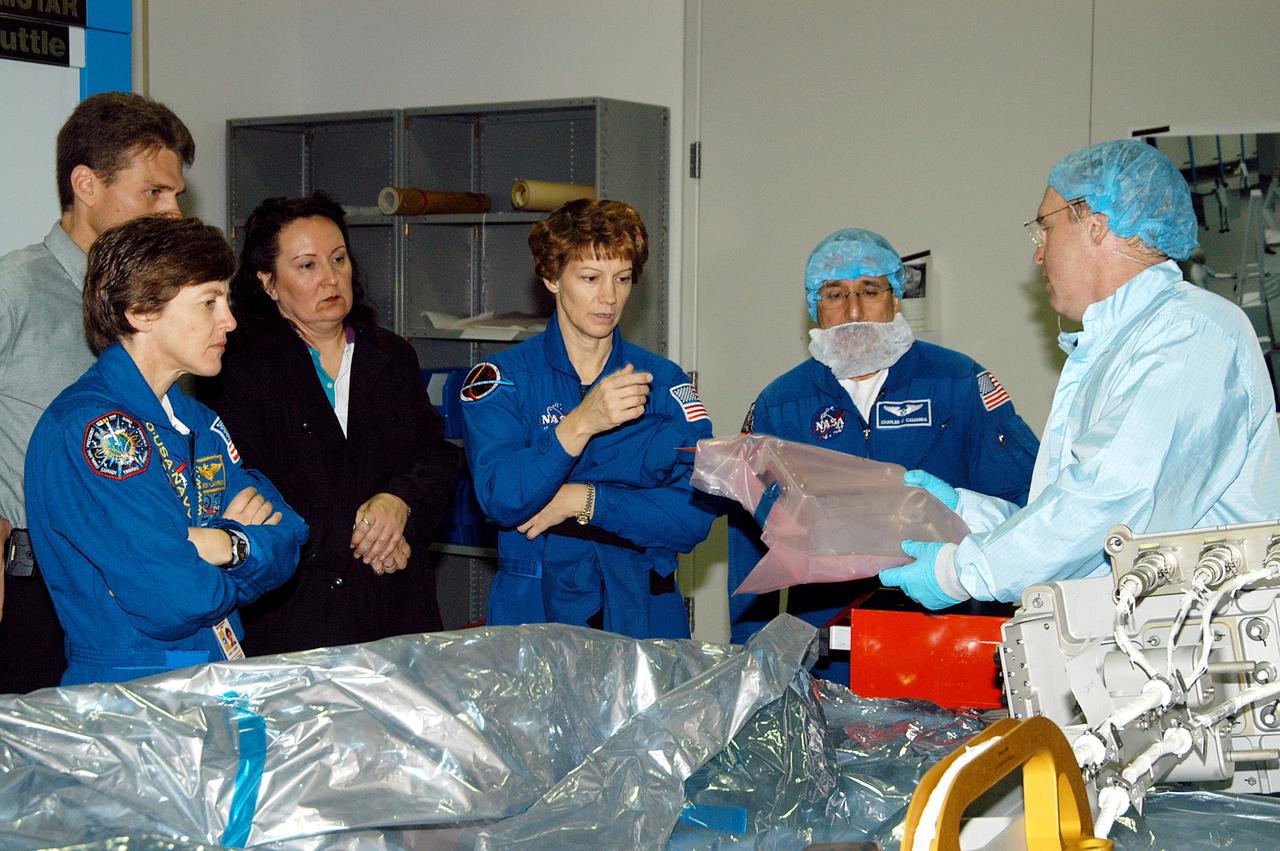

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - STS-114 Mission Specialist Andrew Thomas (right) shows some of the mission equipment to other crew members (from left) Wendy Lawrence, mission specialist; Eileen Collins, commander; and Charles Camarda, mission specialist. Crew members are at KSC for equipment familiarization. STS-114 is classified as Logistics Flight 1 to the International Space Station, delivering new supplies and replacing one of the orbital outpost’s Control Moment Gyroscopes (CMGs). STS-114 will also carry a Raffaello Multi-Purpose Logistics Module and the External Stowage Platform-2. The crew is slated to conduct at least three spacewalks: They will demonstrate repair techniques of the Shuttle’s Thermal Protection System, replace the failed CMG with one delivered by the Shuttle, and install the External Stowage Platform.
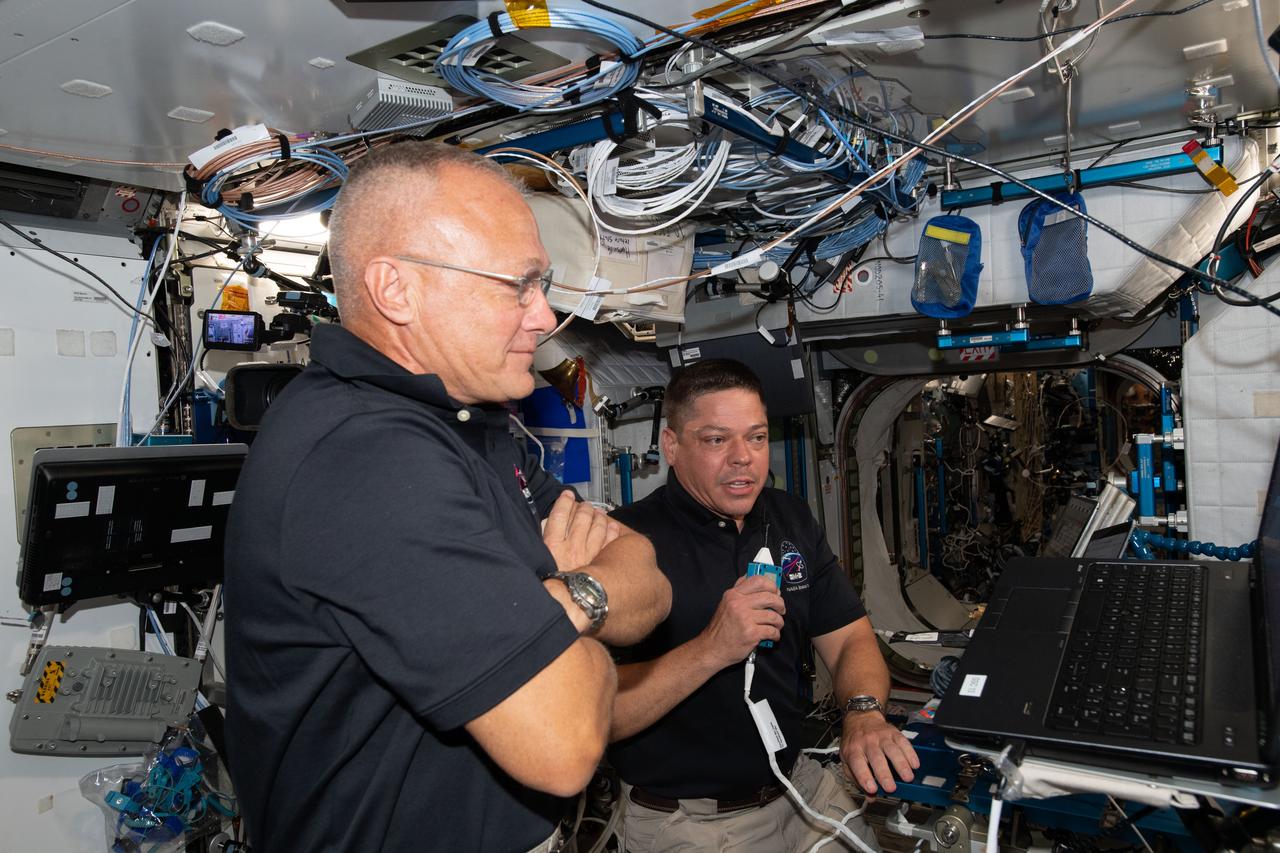

iss063e022398 (June 1, 2020) --- NASA astronauts Doug Hurley (foreground) and Bob Behnken, who flew the Crew Dragon spacecraft to the International Space Station during SpaceX Demonstration Mission-2, are pictured briefing mission controllers about their experience in the new vehicle.
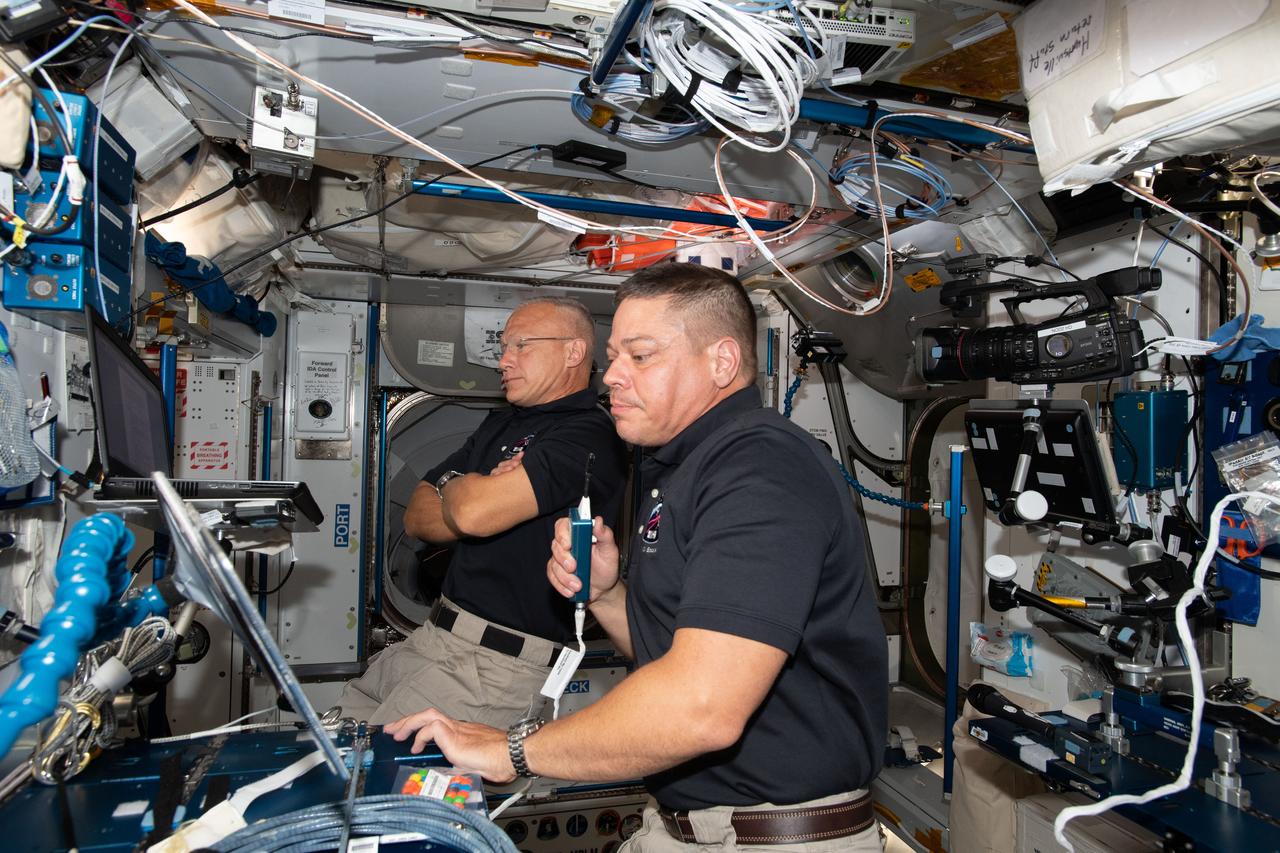

iss063e022389 (June 1, 2020) --- NASA astronauts Bob Behnken (foreground) and Doug Hurley, who flew the Crew Dragon spacecraft to the International Space Station during SpaceX Demonstration Mission-2, are pictured briefing mission controllers about their experience in the new vehicle.
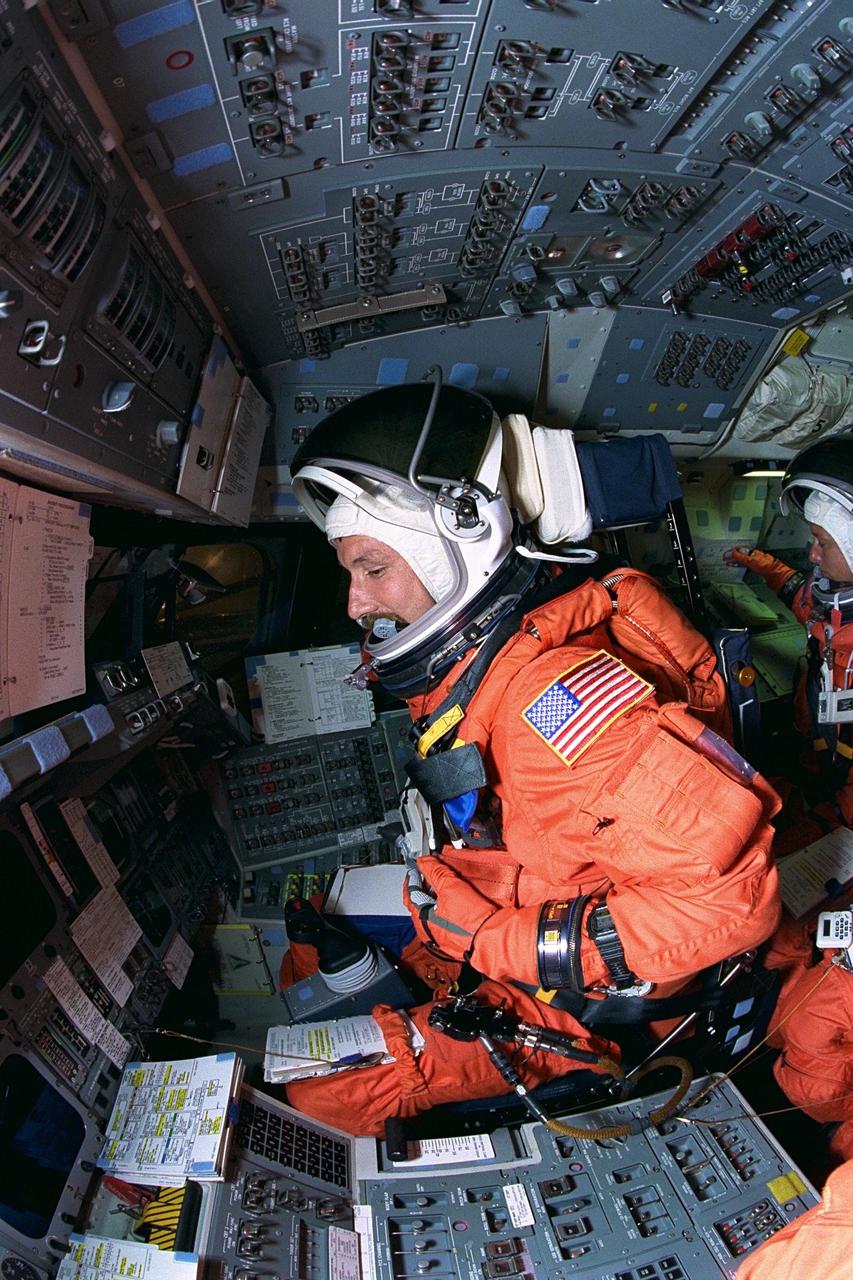

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-85 Pilot Kent V. Rominger goes through countdown procedures on the flight deck aboard the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities for that mission. The TCDT includes a simulation of the final launch countdown. The primary payload aboard the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery is the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2). Other STS-85 payloads include the Manipulator Flight Demonstration (MFD), and Technology Applications and Science-1 (TAS-1) and International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker-2 (IEH-2) experiments
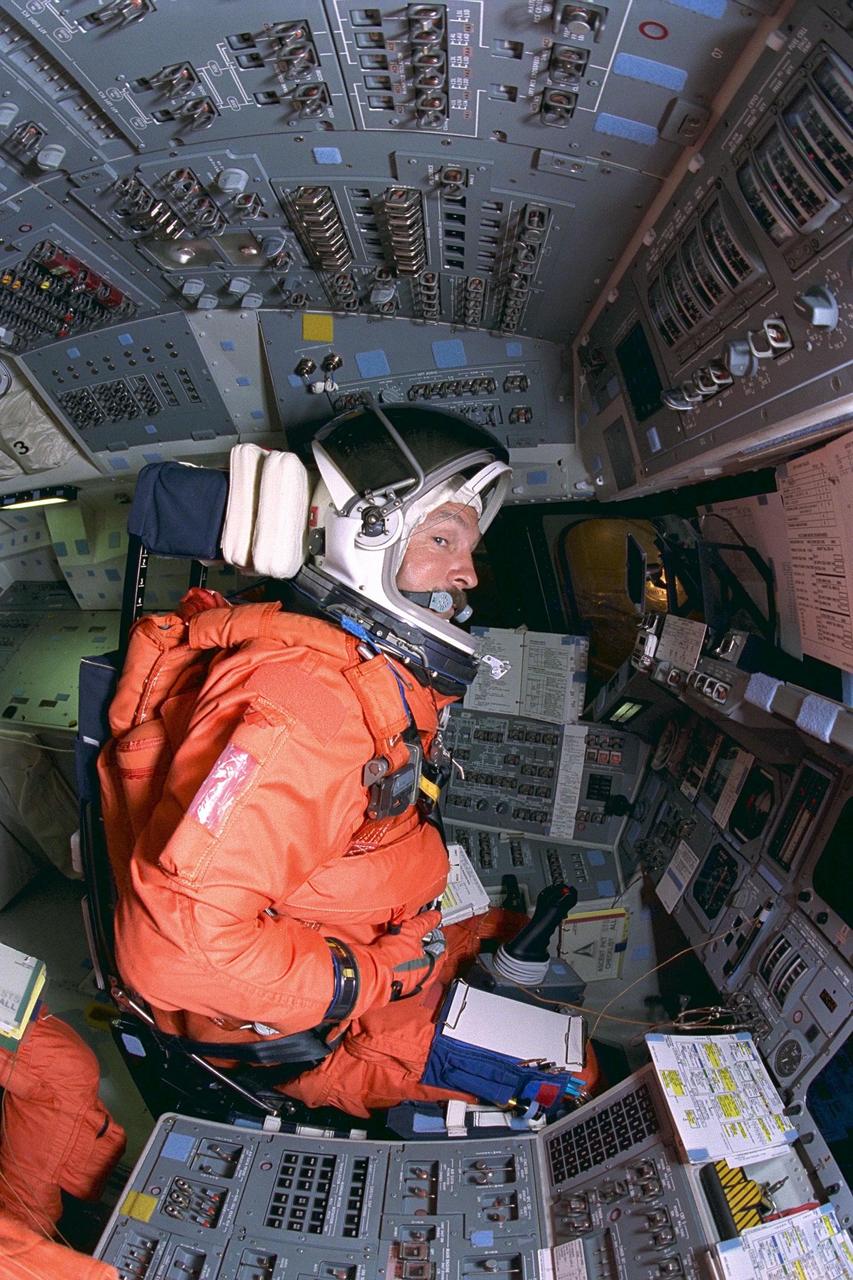

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-85 Commander Curtis L. Brown, Jr., goes through countdown procedures on the flight deck aboard the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities for that mission. The TCDT includes a simulation of the final launch countdown. The primary payload aboard the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery is the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2). Other STS-85 payloads include the Manipulator Flight Demonstration (MFD), and Technology Applications and Science-1 (TAS-1) and International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker-2 (IEH-2) experiments
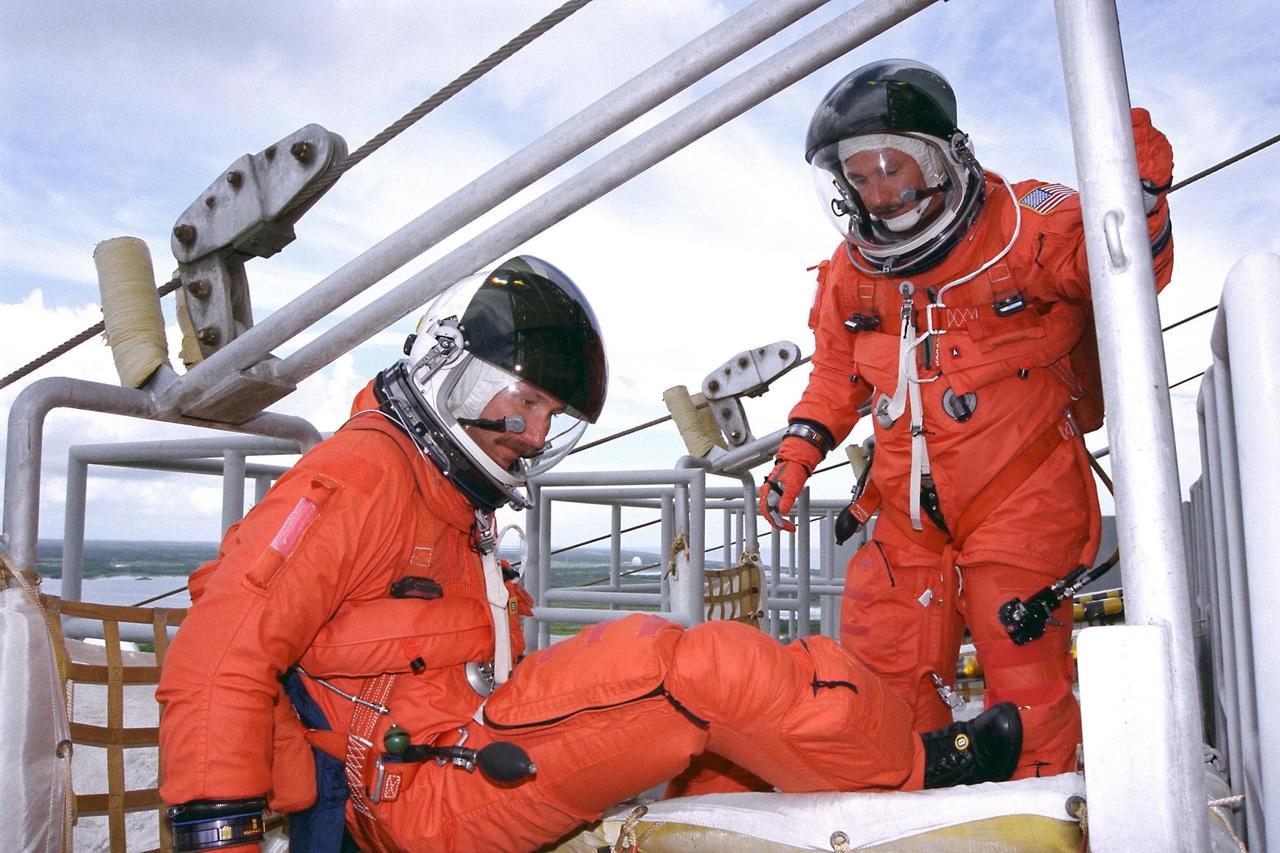

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- STS-85 Pilot Kent V. Rominger (left) and Commander Curtis L. Brown, Jr. exit an emergency egress slidewire basket at the 195-foot level of Launch Pad 39A during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities for that mission. The primary payload aboard the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery is the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2). Other STS-85 payloads include the Manipulator Flight Demonstration (MFD), and Technology Applications and Science-1 (TAS-1) and International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker-2 (IEH-2)
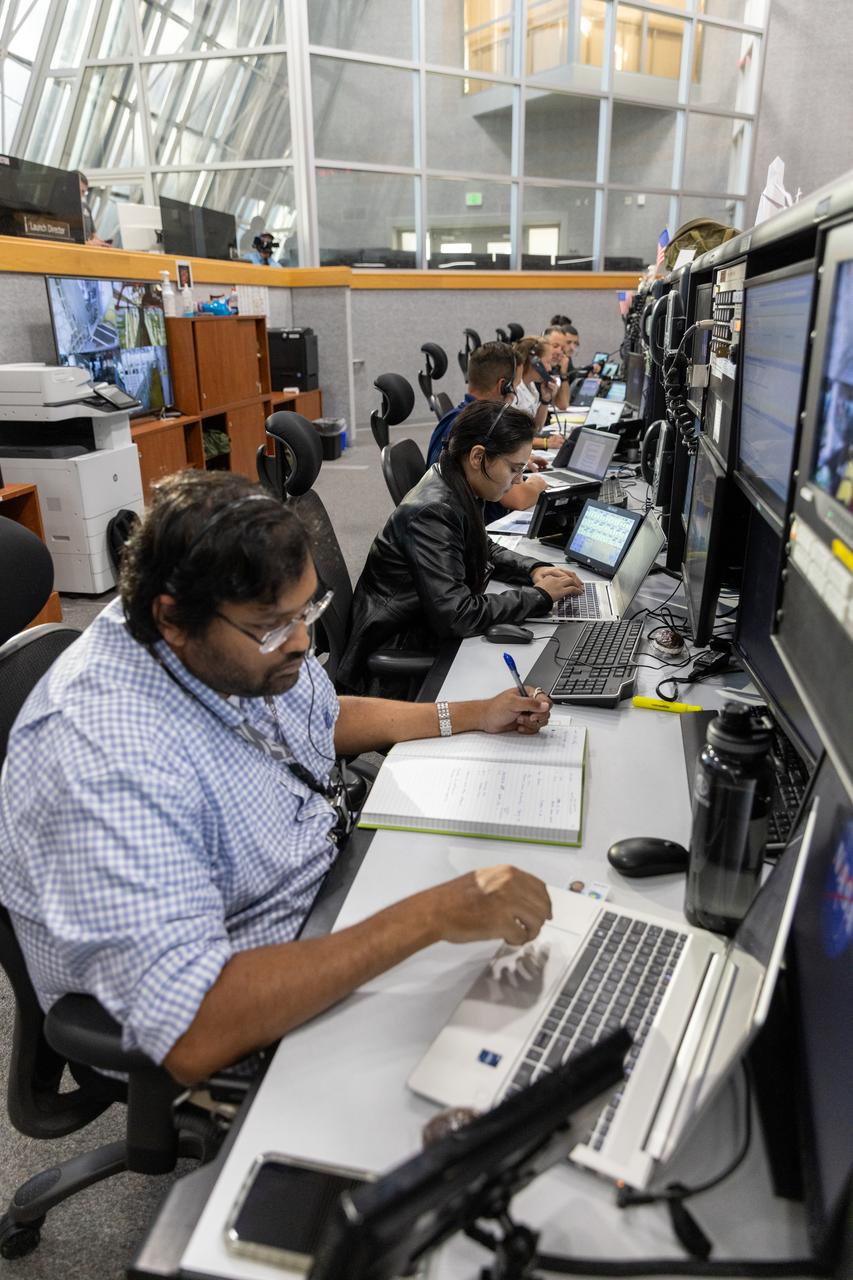

Members of the Artemis II launch team, including personnel with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems participate in an emergency escape or egress demonstration simulation for the Artemis II mission inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy on Monday, Aug. 12, 2024. Other members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program performed emergency egress demonstrations during a series of integrated system verification tests at Launch Pad 39B in preparation for the Artemis II launch.
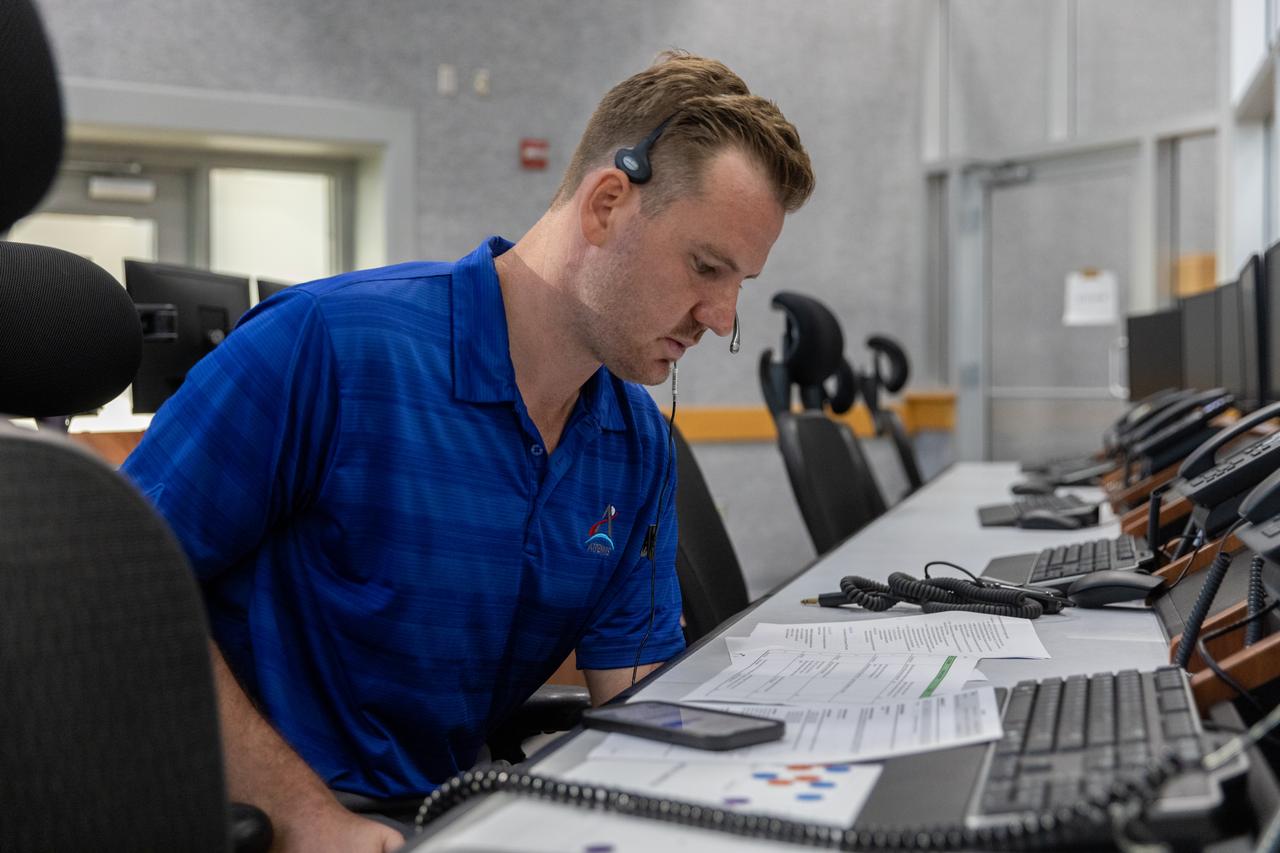

Joseph Pavicic, operations project engineer, Exploration Ground Systems at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, participates in an emergency escape or egress demonstration simulation for the Artemis II mission inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy on Monday, Aug. 12, 2024. Other members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program performed emergency egress demonstrations during a series of integrated system verification tests at Launch Pad 39B in preparation for the Artemis II launch.
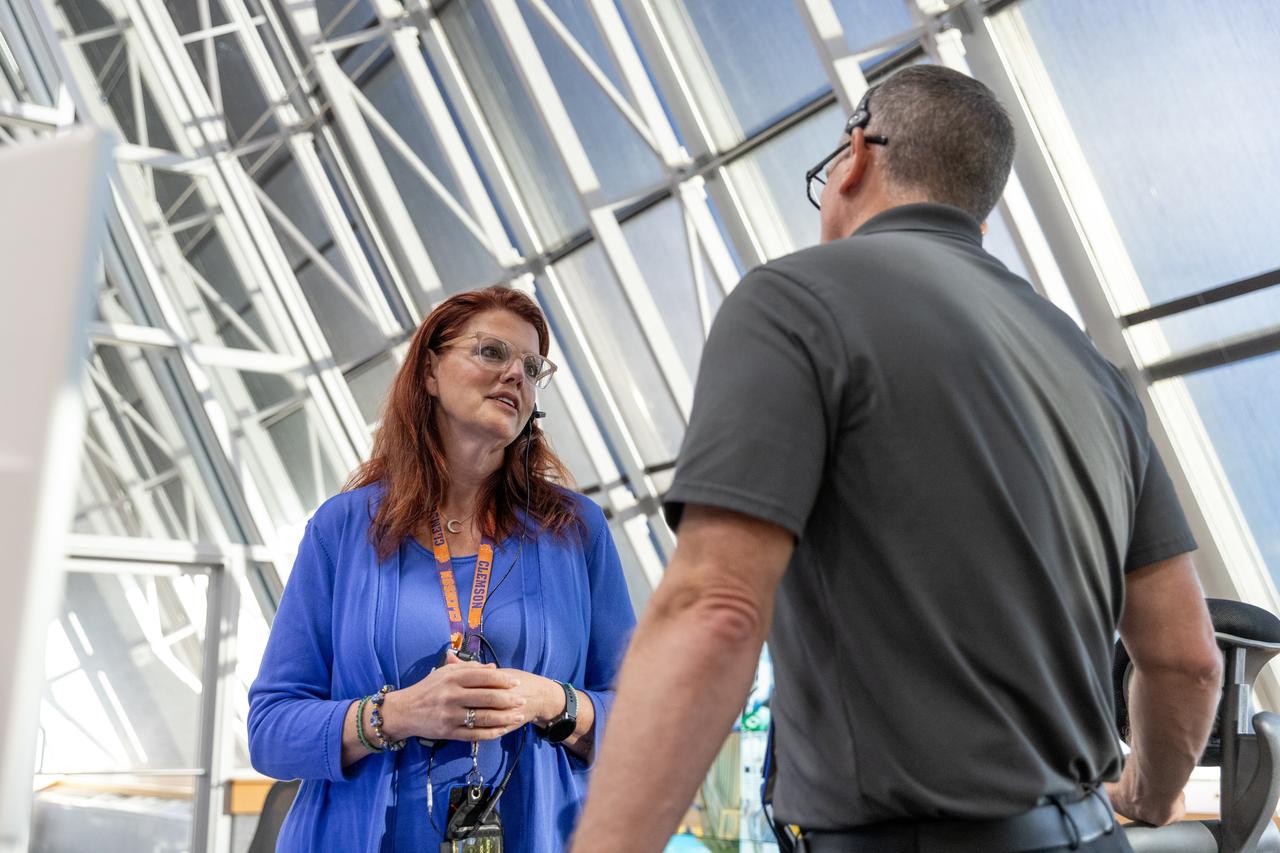

Charlie Blackwell-Thompson, Artemis launch director, Exploration Ground Systems at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, participates in an emergency escape or egress demonstration simulation for the Artemis II mission inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy on Monday, Aug. 12, 2024. Other members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program performed emergency egress demonstrations during a series of integrated system verification tests at Launch Pad 39B in preparation for the Artemis II launch.

Members of the Artemis II launch team, including personnel with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems participate in an emergency escape or egress demonstration simulation for the Artemis II mission inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy on Monday, Aug. 12, 2024. Other members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program performed emergency egress demonstrations during a series of integrated system verification tests at Launch Pad 39B in preparation for the Artemis II launch.

Jeremy Graeber, Artemis assistant launch director, Exploration Ground Systems at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, participates in an emergency escape or egress demonstration simulation for the Artemis II mission inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy on Monday, Aug. 12, 2024. Other members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program performed emergency egress demonstrations during a series of integrated system verification tests at Launch Pad 39B in preparation for the Artemis II launch.

Members of the Artemis II launch team, including personnel with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems participate in an emergency escape or egress demonstration simulation for the Artemis II mission inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy on Monday, Aug. 12, 2024. Other members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program performed emergency egress demonstrations during a series of integrated system verification tests at Launch Pad 39B in preparation for the Artemis II launch.
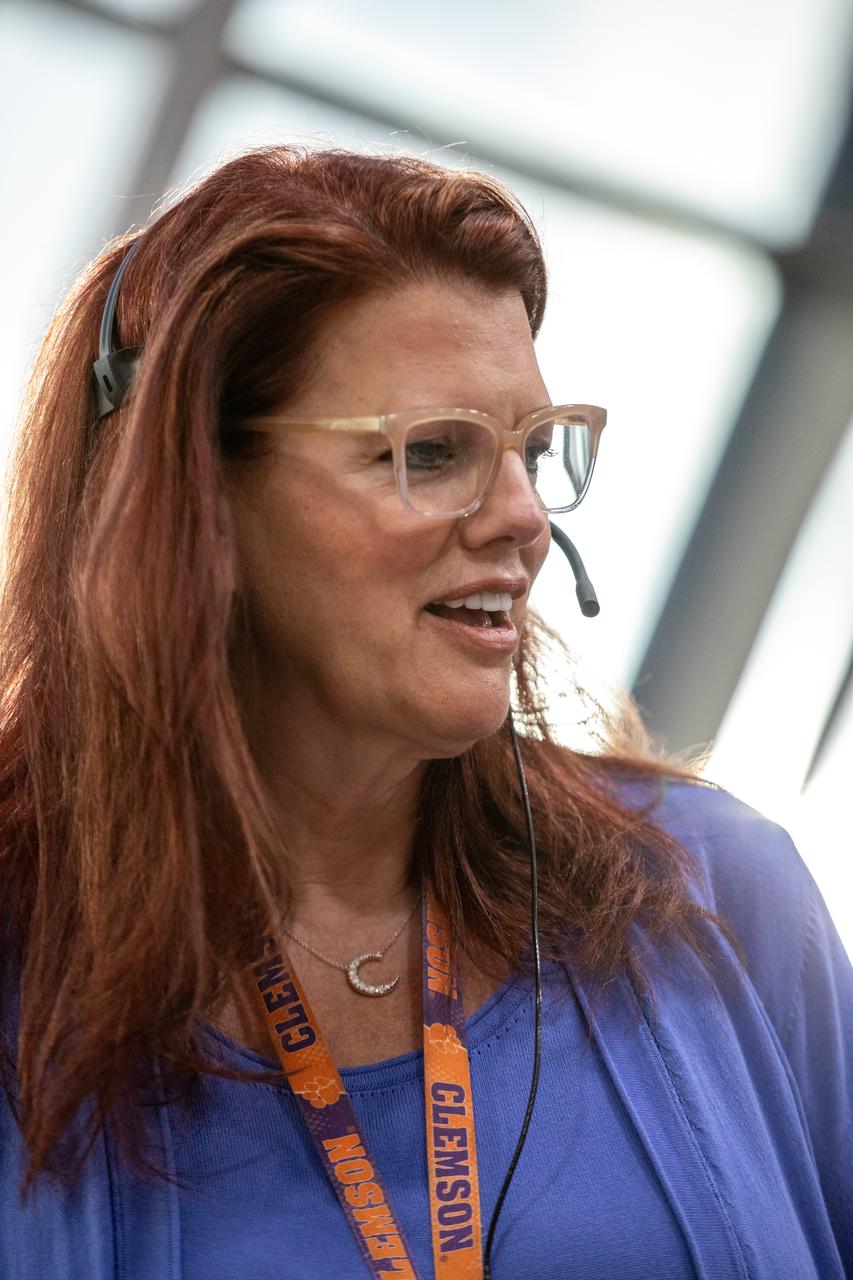

Charlie Blackwell-Thompson, Artemis launch director, Exploration Ground Systems at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, participates in an emergency escape or egress demonstration simulation for the Artemis II mission inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy on Monday, Aug. 12, 2024. Other members of the closeout crew, pad rescue team, and the Exploration Ground Systems Program performed emergency egress demonstrations during a series of integrated system verification tests at Launch Pad 39B in preparation for the Artemis II launch.
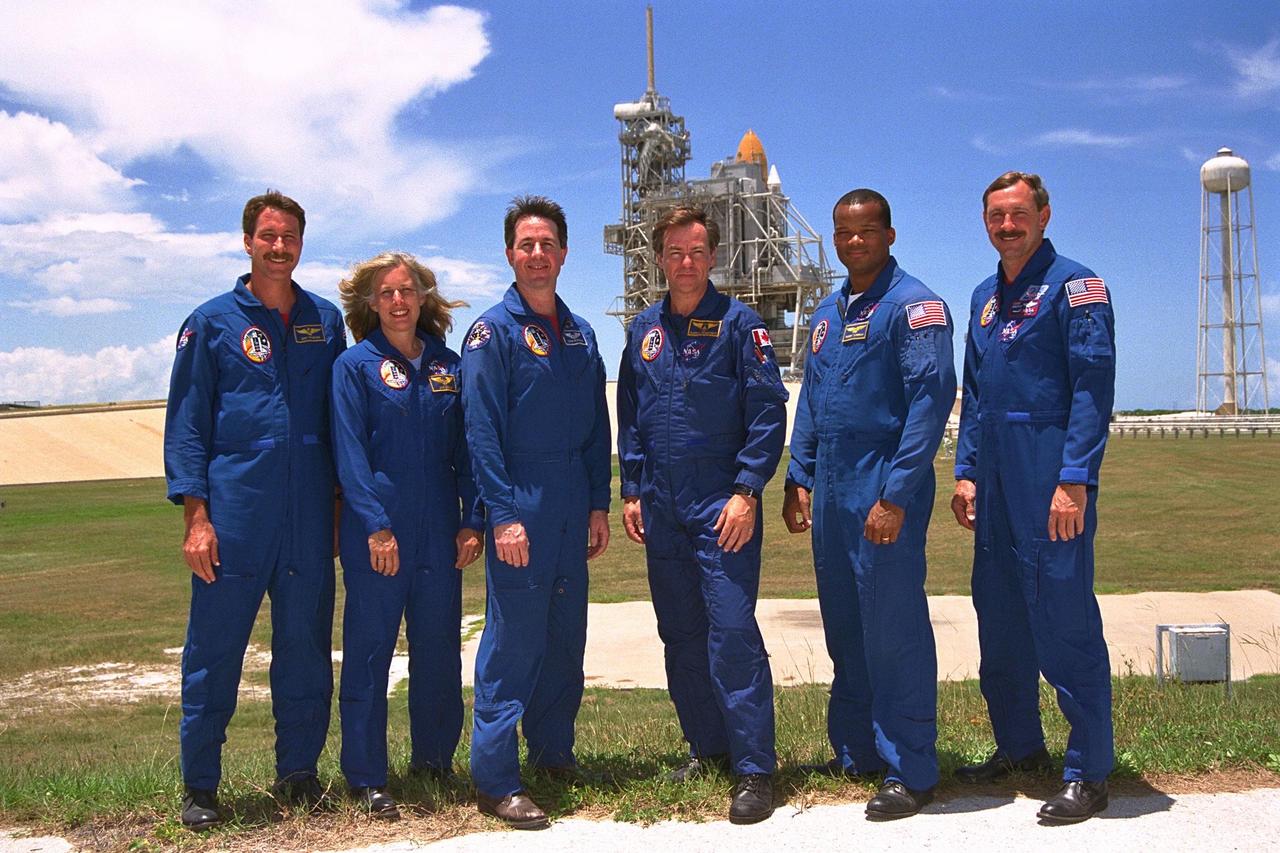

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The STS-85 flight crew poses at Launch Pad 39A during a break in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities for that mission. They are (back row, from left): Pilot Kent V. Rominger; Payload Commander N. Jan Davis; Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson; Payload Specialist Bjarni V. Tryggvason; Mission Specialist Robert L. Curbeam, Jr.; and Commander Curtis L. Brown, Jr. The primary payload aboard the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery is the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2). Other payloads on the 11-day mission include the Manipulator Flight Demonstration (MFD), and Technology Applications and Science-1 (TAS-1) and International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker-2 (IEH-2) experiments
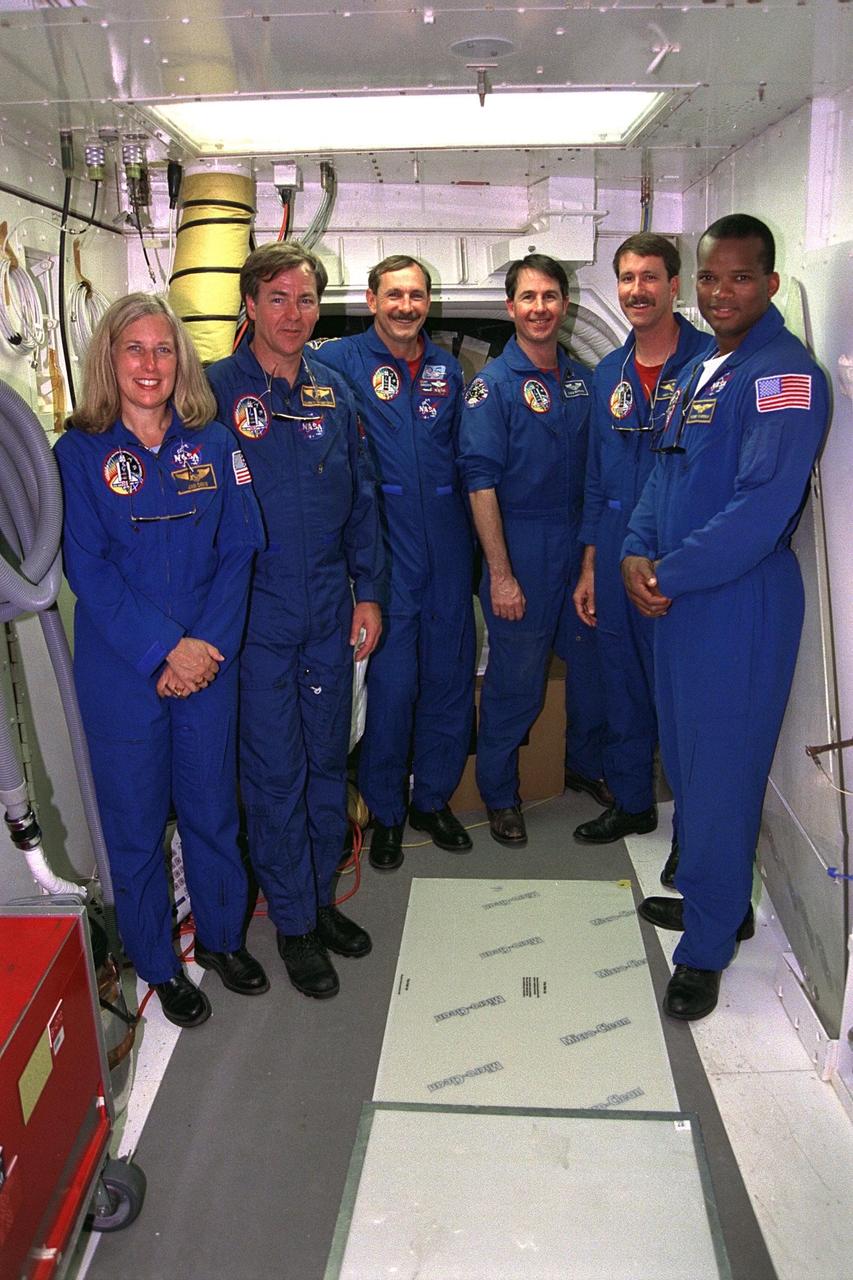

The STS-85 flight crew poses in the white room at Launch Pad 39A during a break in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities for that mission. They are (from left): Payload Commander N. Jan Davis; Payload Specialist Bjarni V. Tryggvason; Commander Curtis L. Brown, Jr.; Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson; Pilot Kent V. Rominger; and Mission Specialist Robert L. Curbeam, Jr. The primary payload aboard the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery is the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2). Other payloads on the 11-day mission include the Manipulator Flight Demonstration (MFD), and Technology Applications and Science-1 (TAS-1) and International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker-2 (IEH-2) experiments
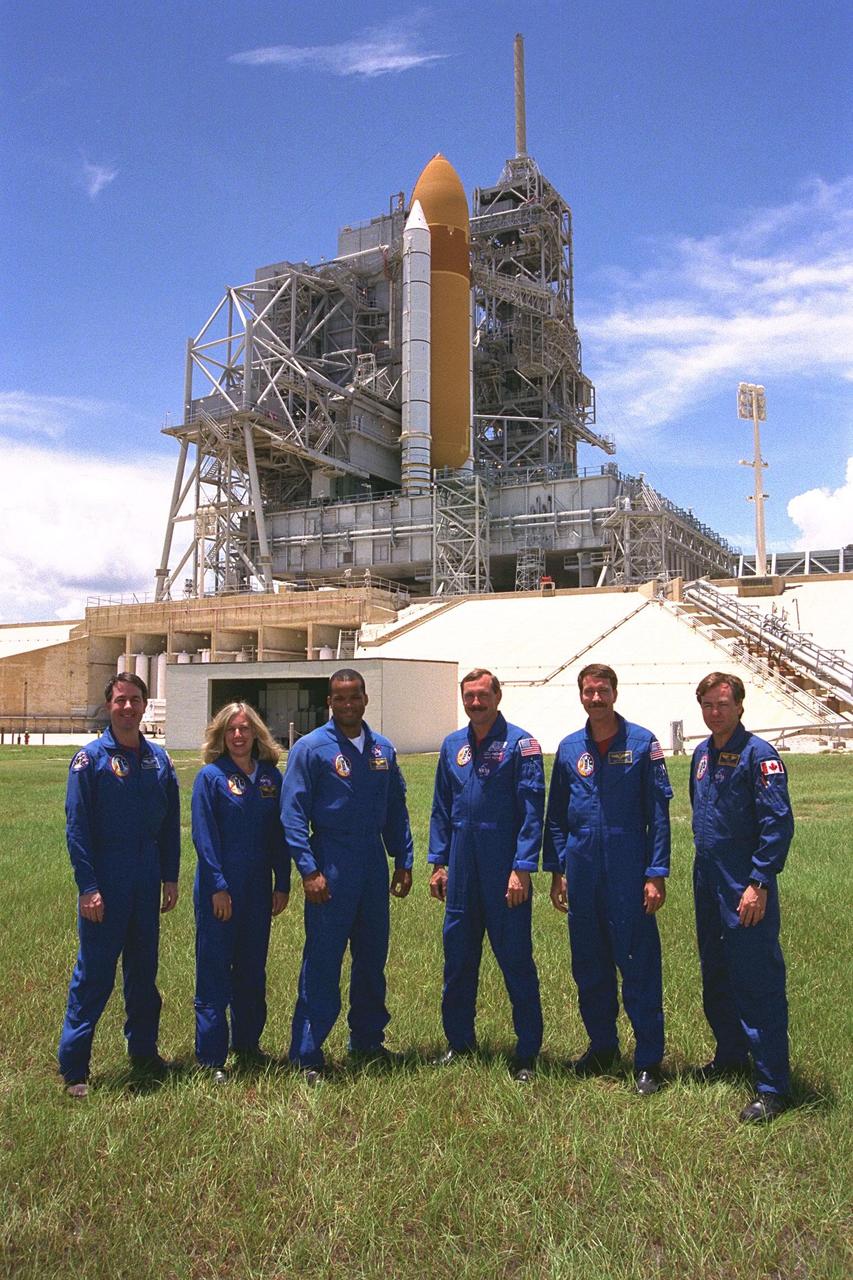

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The STS-85 flight crew poses in front of the Space Shuttle Discovery at Launch Pad 39A during a break in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities for that mission. They are (from left): Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson; Payload Commander N. Jan Davis; Mission Specialist Robert L. Curbeam, Jr.; Commander Curtis L. Brown, Jr.; Pilot Kent V. Rominger; and Payload Specialist Bjarni V. Tryggvason. The primary payload aboard the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery is the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2). Other payloads on the 11-day mission include the Manipulator Flight Demonstration (MFD), and Technology Applications and Science-1 (TAS-1) and International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker-2 (IEH-2) experiments
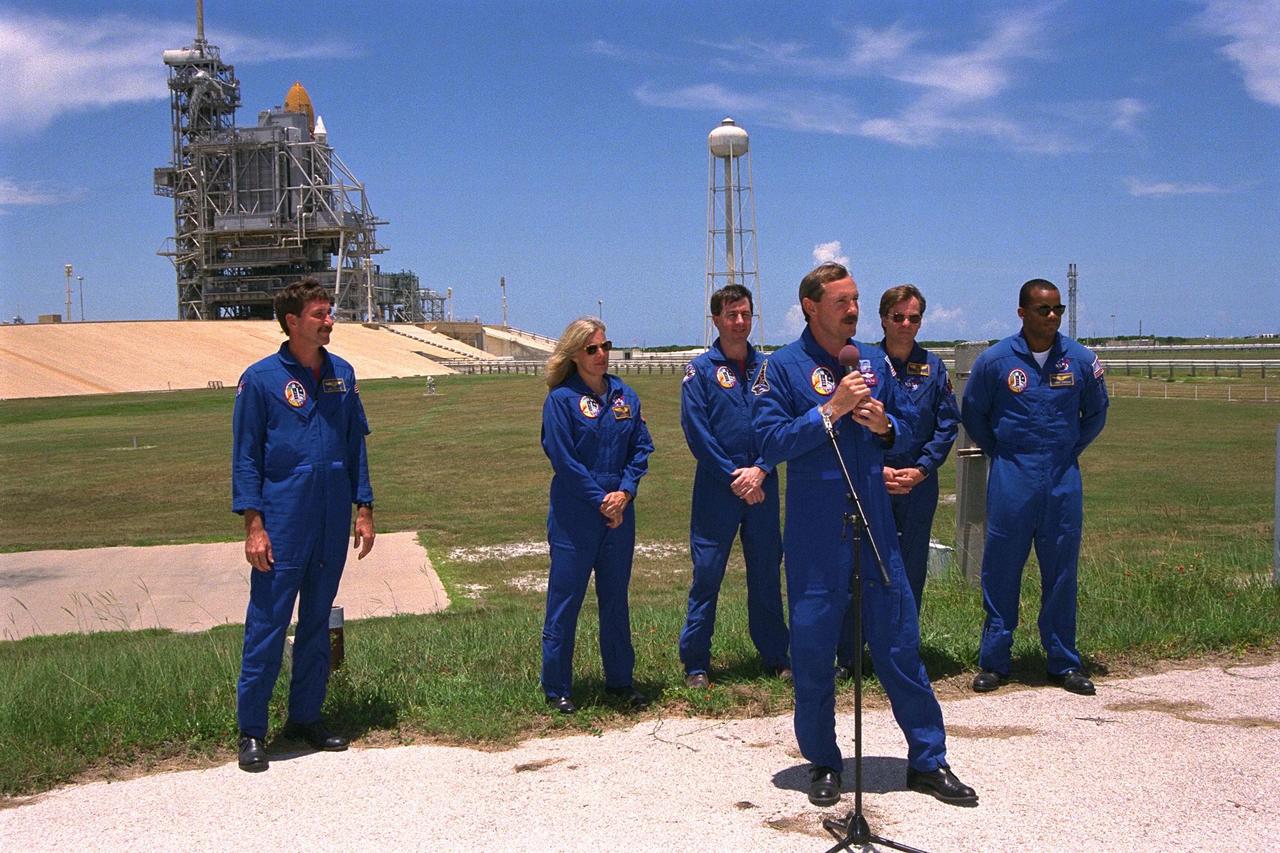

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- STS-85 Commander Curtis L. Brown, Jr., addresses the news media at a briefing at Launch Pad 39A while the other members of the flight crew in the background prepare to field questions during a break in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities for that mission. They are (back row, from left): Pilot Kent V. Rominger; Payload Commander N. Jan Davis; Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson; Payload Specialist Bjarni V. Tryggvason; and Mission Specialist Robert L. Curbeam, Jr. The primary payload aboard the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery is the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2). Other payloads on the 11-day mission include the Manipulator Flight Demonstration (MFD), and Technology Applications and Science-1 (TAS-1) and International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker-2 (IEH-2) experiments
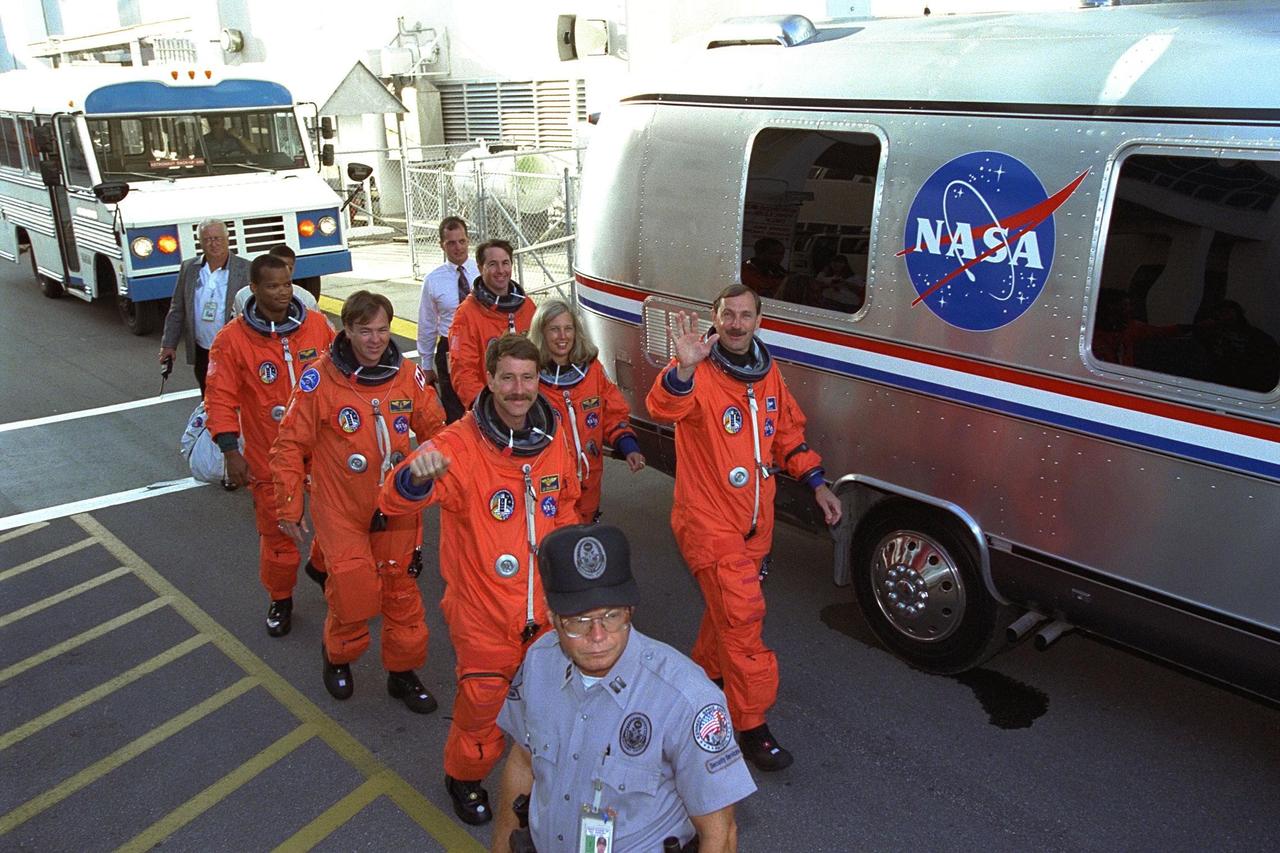

The STS-85 flight crew walks out of the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities for that mission to board the Astrovan for the ride to the Space Shuttle Discovery on Launch Pad 39A. Waving to the crowd is Commander Curtis L. Brown, Jr. (right). Directly behind him are Payload Commander N. Jan Davis and Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson. Pilot Kent V. Rominger (to Brown’s right) is leading the second row, followed by Payload Specialist Bjarni V. Tryggvason and Mission Specialist Robert L. Curbeam, Jr. The primary payload aboard the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery is the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2). Other payloads on the 11-day mission include the Manipulator Flight Demonstration (MFD), and Technology Applications and Science-1 (TAS-1) and International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker-2 (IEH-2) experiments
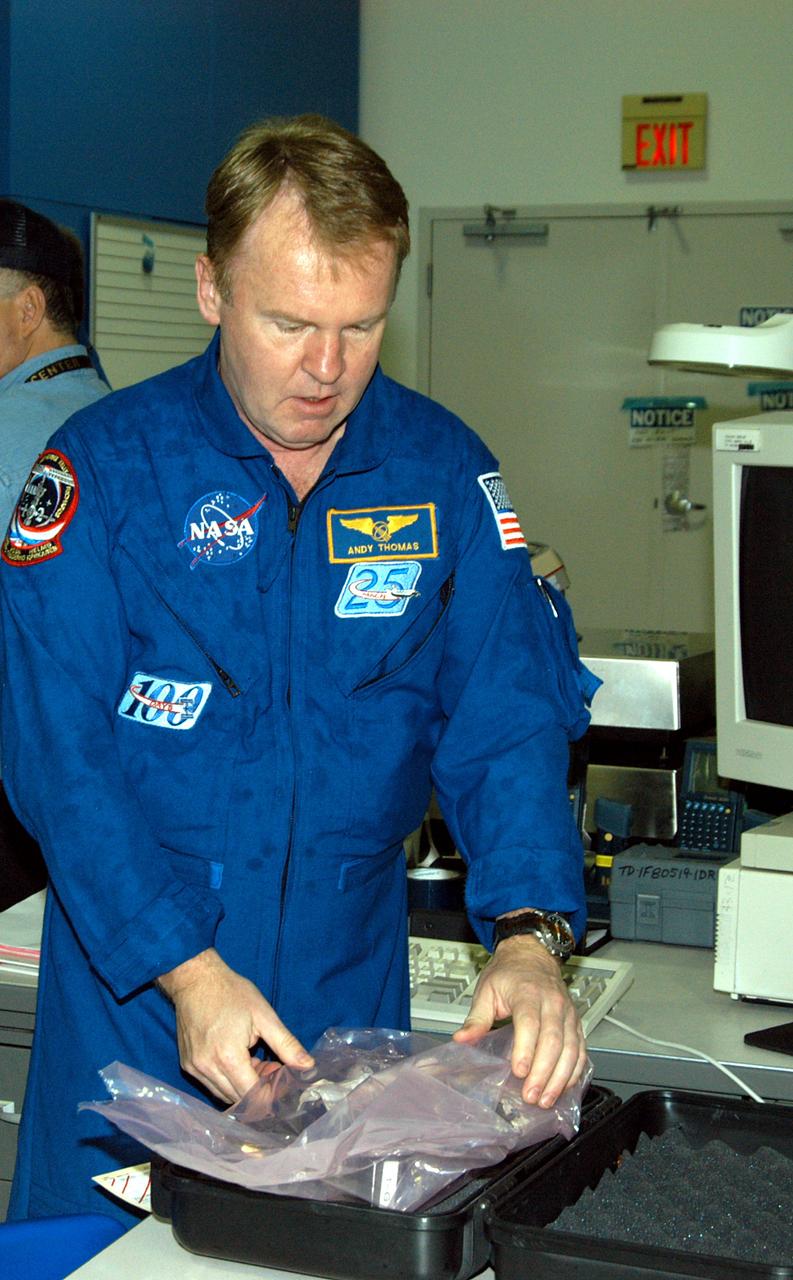

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - STS-114 Mission Specialist Andrew Thomas works on equipment in the Space Station Processing Facility. He and other crew members are at KSC for equipment familiarization. STS-114 is classified as Logistics Flight 1 to the International Space Station, delivering new supplies and replacing one of the orbital outpost’s Control Moment Gyroscopes (CMGs). STS-114 will also carry a Raffaello Multi-Purpose Logistics Module and the External Stowage Platform-2. The crew is slated to conduct at least three spacewalks: They will demonstrate repair techniques of the Shuttle’s Thermal Protection System, replace the failed CMG with one delivered by the Shuttle, and install the External Stowage Platform.
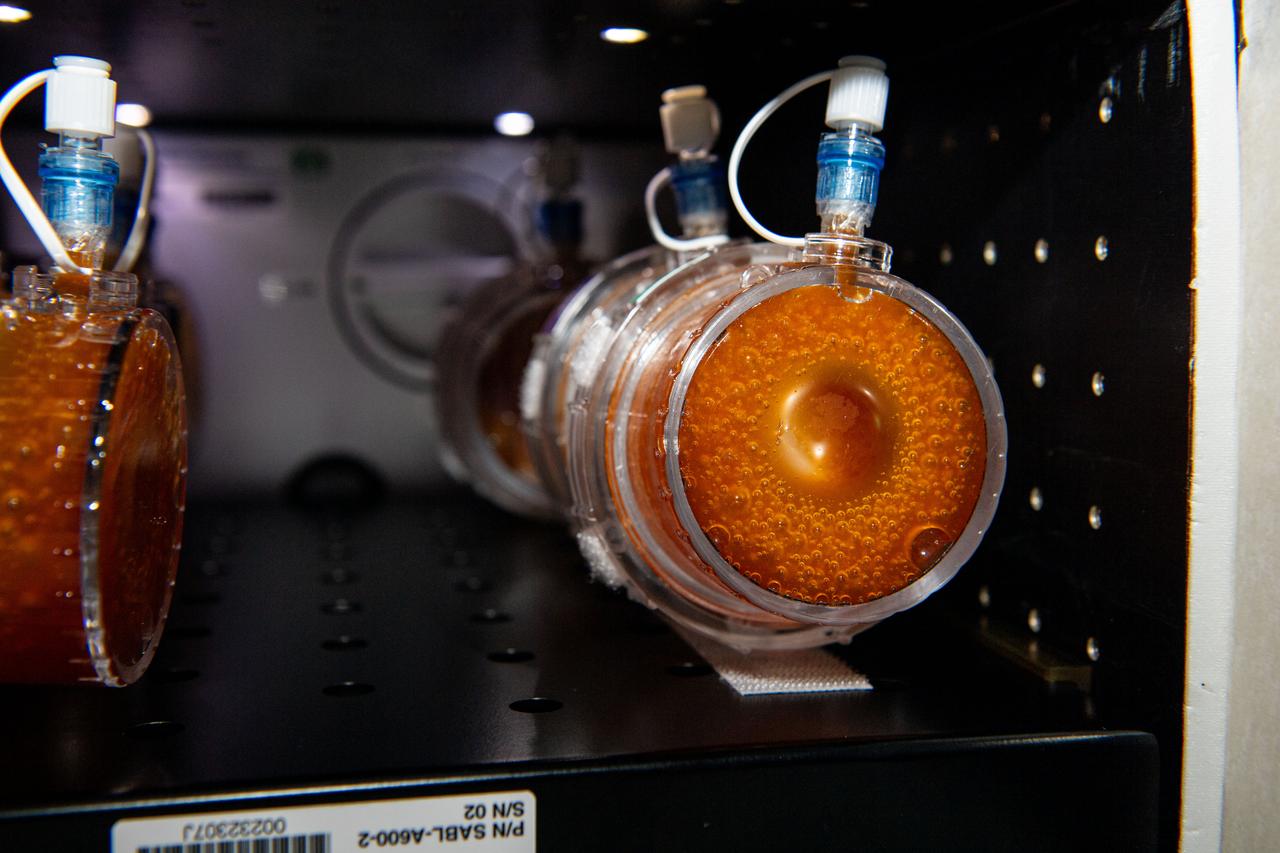

iss070e052298 (1/2/2024) --- BioNutrients completed five years of demonstrating technology to produce nutrients on demand aboard the space station. Since vitamins can degrade over time, the investigation used engineered microbes to test generating fresh nutrient supply for future long-duration missions.
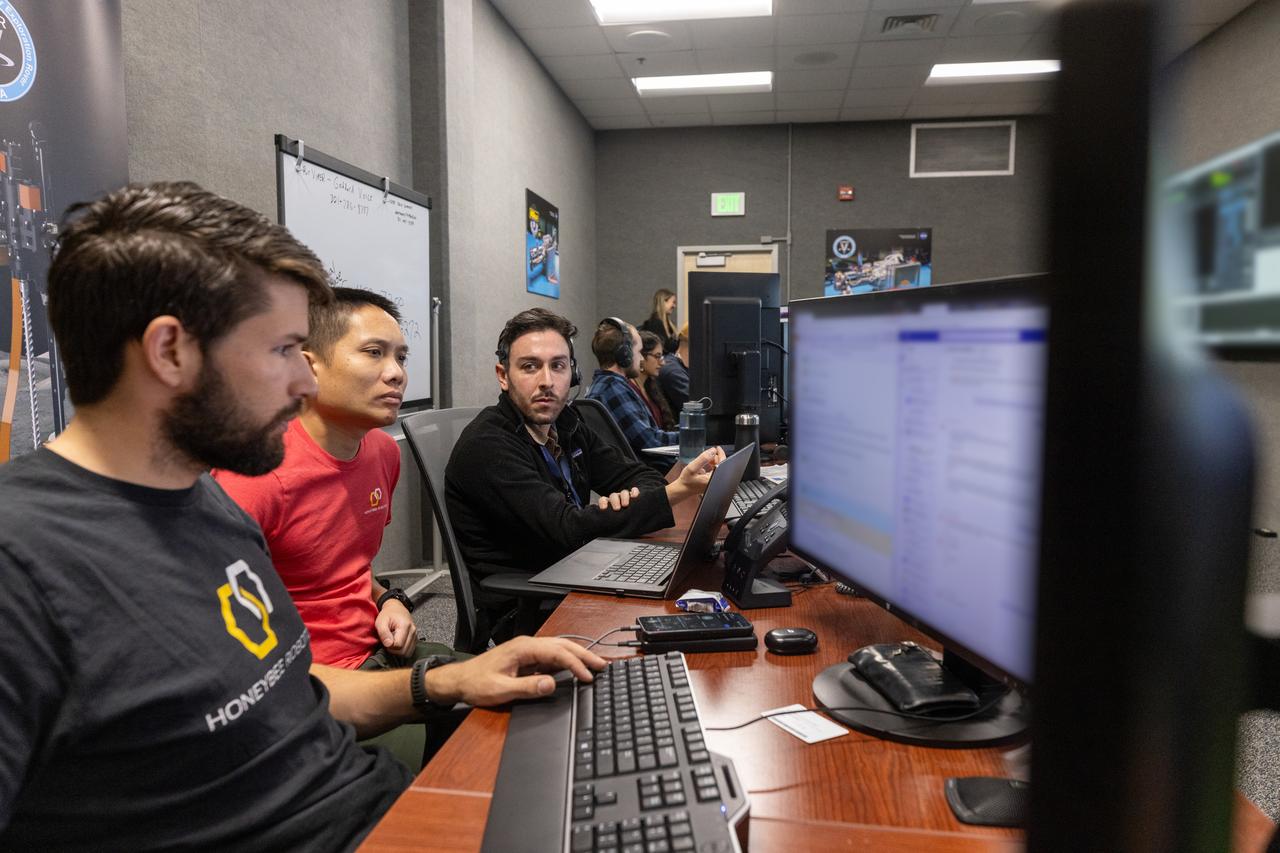

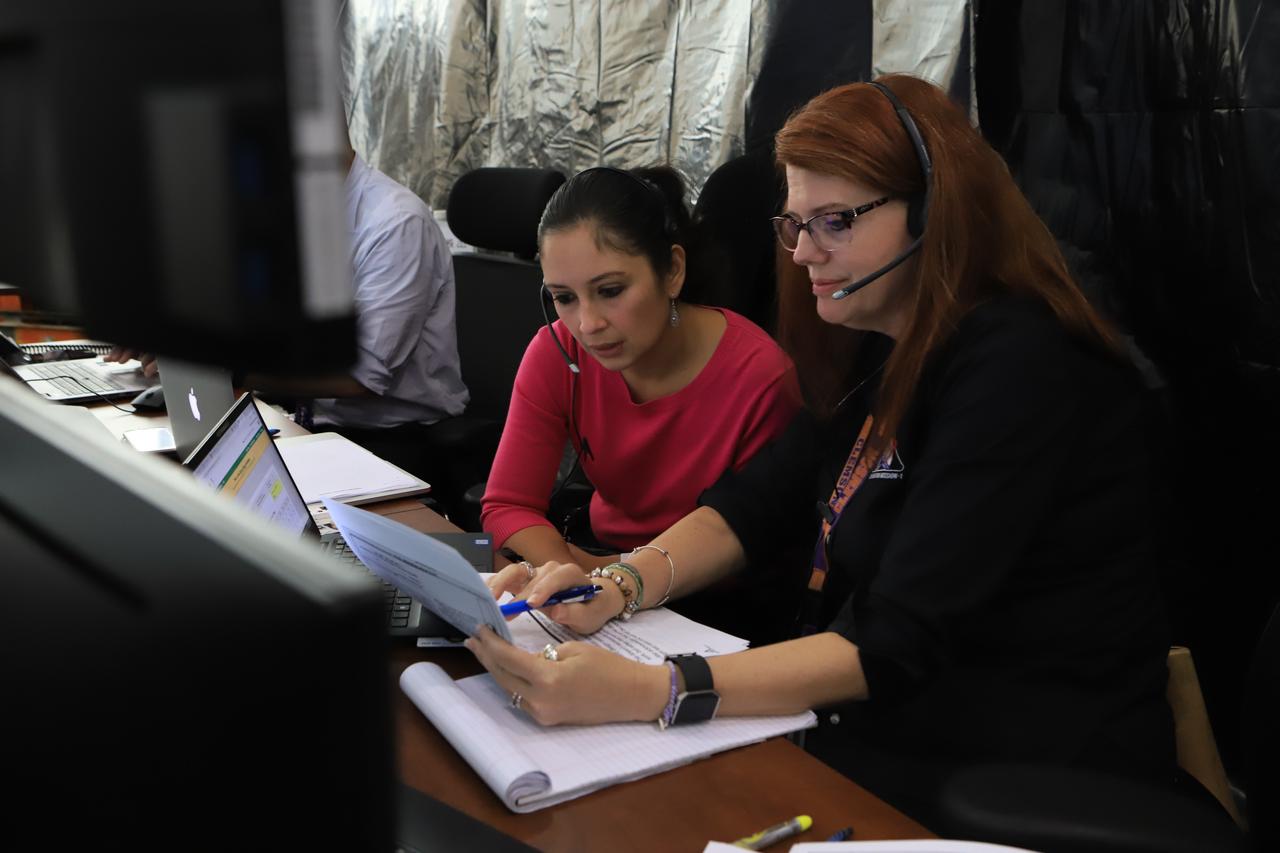
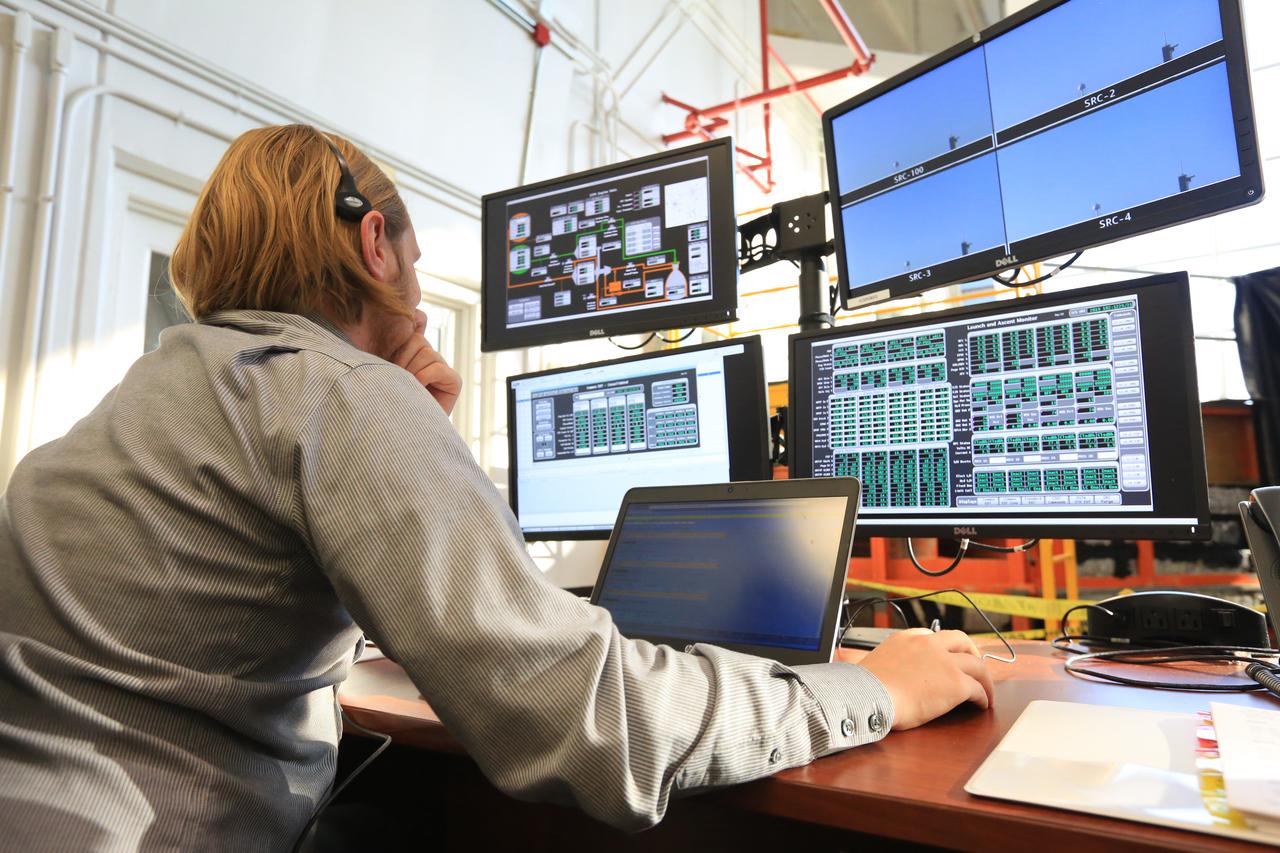
A team from Honeybee Robotics in Altadena, California participates in simulation training for the Polar Resources Ice Mining Experiment-1 (PRIME-1) on Thursday, Nov. 2, 2023, inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The purpose of the training is to get the integrated PRIME-1 team – engineers with PRIME-1’s MSOLO (Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations) and Honeybee Robotics’ TRIDENT (The Regolith and Ice Drill for Exploring New Terrain) drill – prepared to operate the instrument on the lunar surface. The team commanded the PRIME-1 hardware, located at Intuitive Machines in Houston, to operate MSOLO and TRIDENT. PRIME-1 is scheduled to launch through NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service) initiative and will be the first in-situ resource utilization demonstration on the Moon, with MSOLO and TRIDENT making up its two primary components. Through Artemis missions, CLPS deliveries will be used to perform science experiments, test technologies, and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human deep space exploration missions.
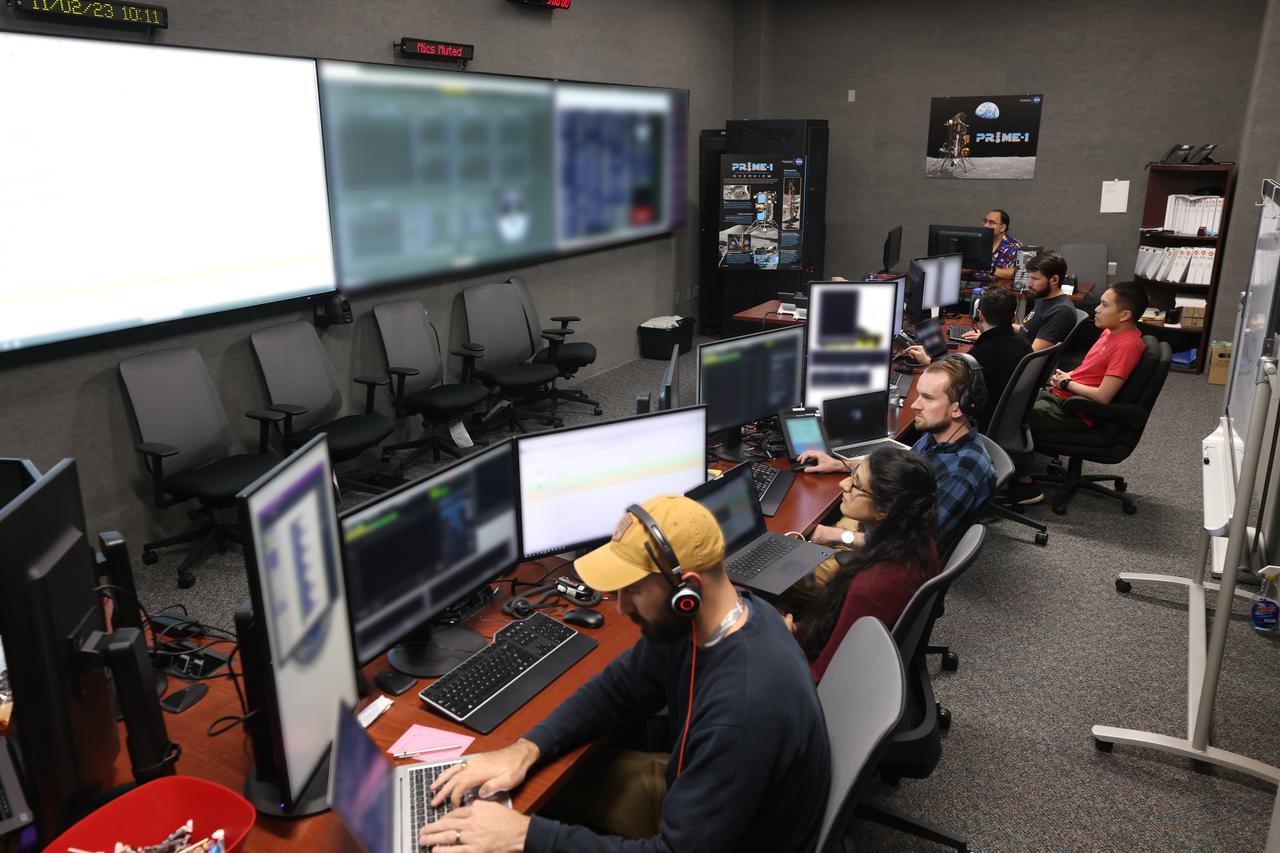

A team of engineers participates in simulation training for the Polar Resources Ice Mining Experiment-1 (PRIME-1) on Thursday, Nov. 2, 2023, inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The purpose of the training is to get the integrated PRIME-1 team – engineers with PRIME-1’s MSOLO (Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations) and Honeybee Robotics’ TRIDENT (The Regolith and Ice Drill for Exploring New Terrain) drill – prepared to operate the instrument on the lunar surface. The team commanded the PRIME-1 hardware, located at Intuitive Machines in Houston, to operate MSOLO and TRIDENT. PRIME-1 is scheduled to launch through NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service) initiative and will be the first in-situ resource utilization demonstration on the Moon, with MSOLO and TRIDENT making up its two primary components. Through Artemis missions, CLPS deliveries will be used to perform science experiments, test technologies, and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human deep space exploration missions.

A team of engineers participates in simulation training for the Polar Resources Ice Mining Experiment-1 (PRIME-1) on Thursday, Nov. 2, 2023, inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The purpose of the training is to get the integrated PRIME-1 team – engineers with PRIME-1’s MSOLO (Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations) and Honeybee Robotics’ TRIDENT (The Regolith and Ice Drill for Exploring New Terrain) drill – prepared to operate the instrument on the lunar surface. The team commanded the PRIME-1 hardware, located at Intuitive Machines in Houston, to operate MSOLO and TRIDENT. PRIME-1 is scheduled to launch through NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service) initiative and will be the first in-situ resource utilization demonstration on the Moon, with MSOLO and TRIDENT making up its two primary components. Through Artemis missions, CLPS deliveries will be used to perform science experiments, test technologies, and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human deep space exploration missions.

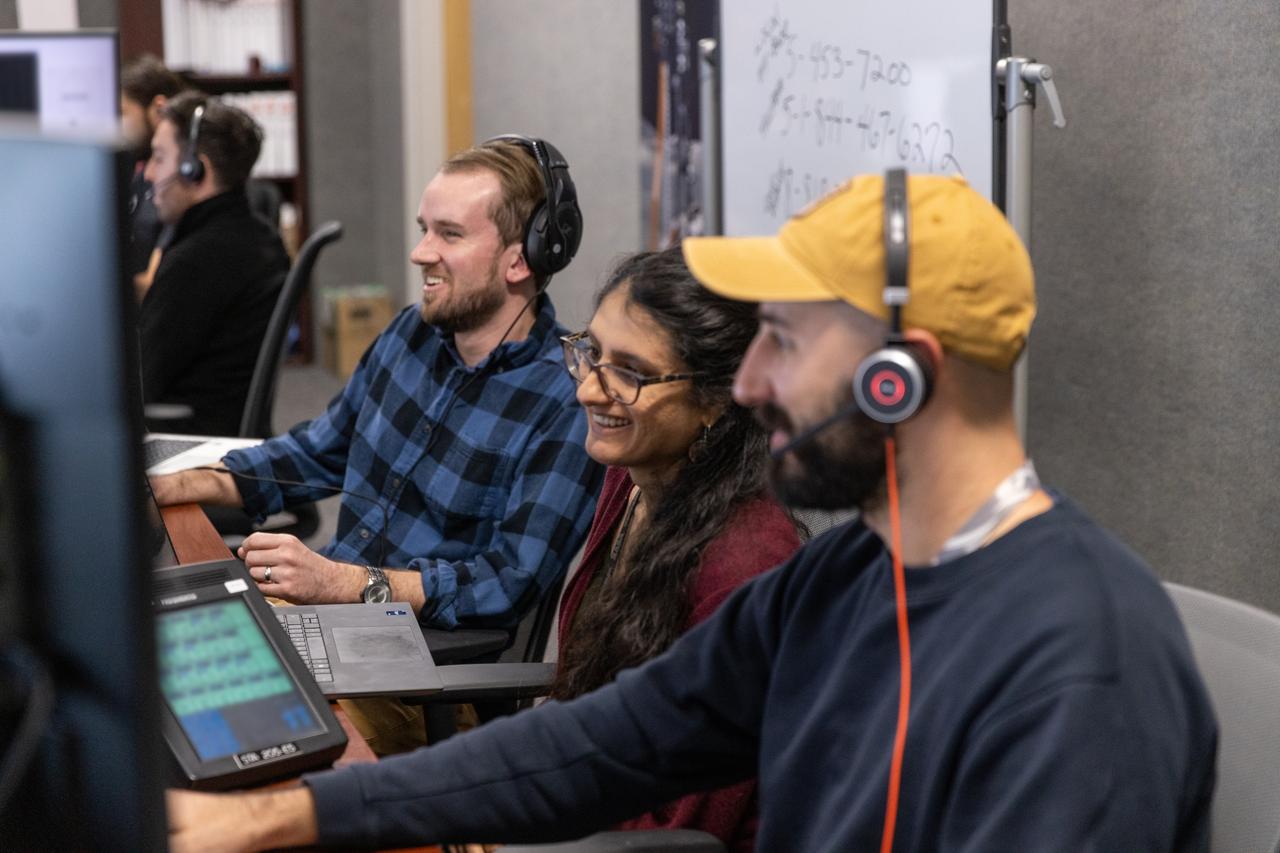
A team of engineers participates in simulation training for the Polar Resources Ice Mining Experiment-1 (PRIME-1) on Thursday, Nov. 2, 2023, inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The purpose of the training is to get the integrated PRIME-1 team – engineers with PRIME-1’s MSOLO (Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations) and Honeybee Robotics’ TRIDENT (The Regolith and Ice Drill for Exploring New Terrain) drill – prepared to operate the instrument on the lunar surface. The team commanded the PRIME-1 hardware, located at Intuitive Machines in Houston, to operate MSOLO and TRIDENT. PRIME-1 is scheduled to launch through NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service) initiative and will be the first in-situ resource utilization demonstration on the Moon, with MSOLO and TRIDENT making up its two primary components. Through Artemis missions, CLPS deliveries will be used to perform science experiments, test technologies, and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human deep space exploration missions.
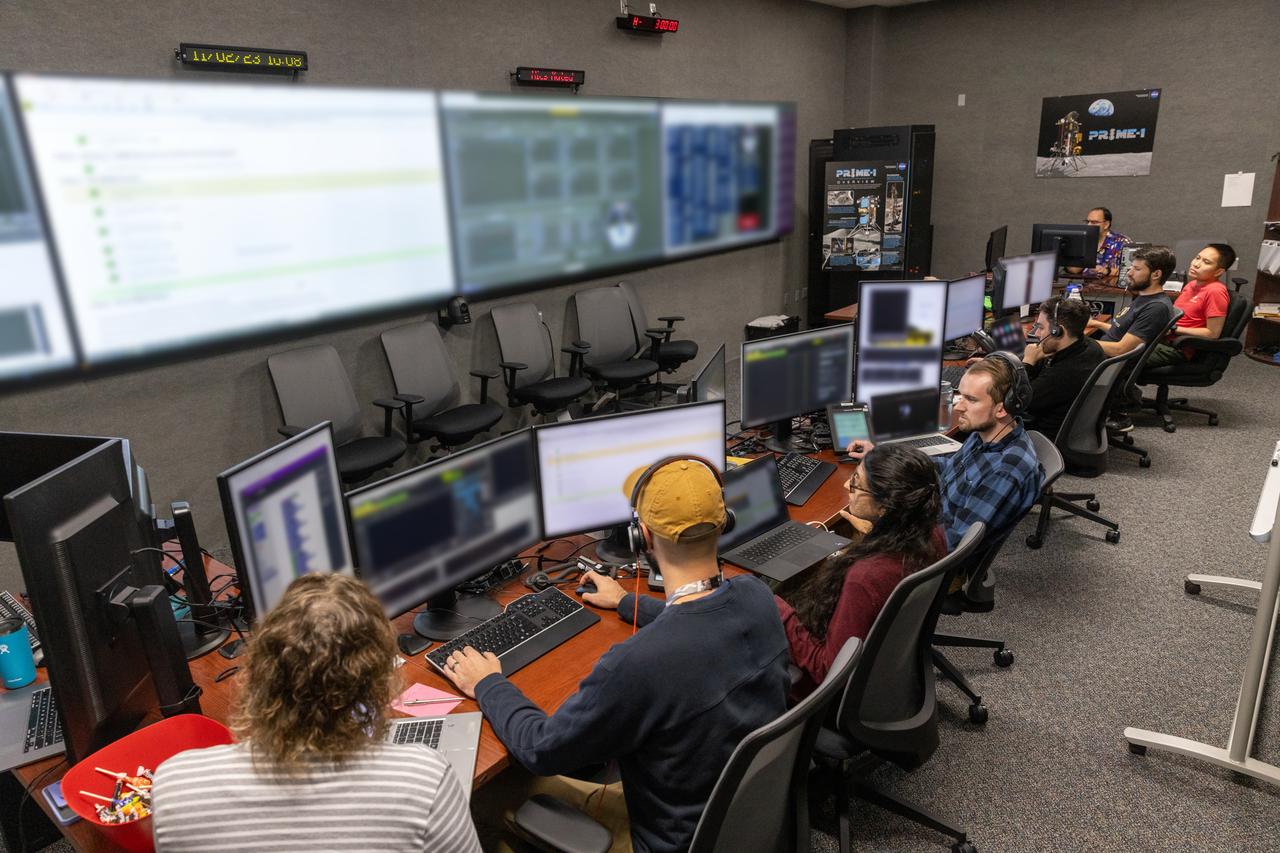

A team of engineers participates in simulation training for the Polar Resources Ice Mining Experiment-1 (PRIME-1) on Thursday, Nov. 2, 2023, inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The purpose of the training is to get the integrated PRIME-1 team – engineers with PRIME-1’s MSOLO (Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations) and Honeybee Robotics’ TRIDENT (The Regolith and Ice Drill for Exploring New Terrain) drill – prepared to operate the instrument on the lunar surface. The team commanded the PRIME-1 hardware, located at Intuitive Machines in Houston, to operate MSOLO and TRIDENT. PRIME-1 is scheduled to launch through NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service) initiative and will be the first in-situ resource utilization demonstration on the Moon, with MSOLO and TRIDENT making up its two primary components. Through Artemis missions, CLPS deliveries will be used to perform science experiments, test technologies, and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human deep space exploration missions.
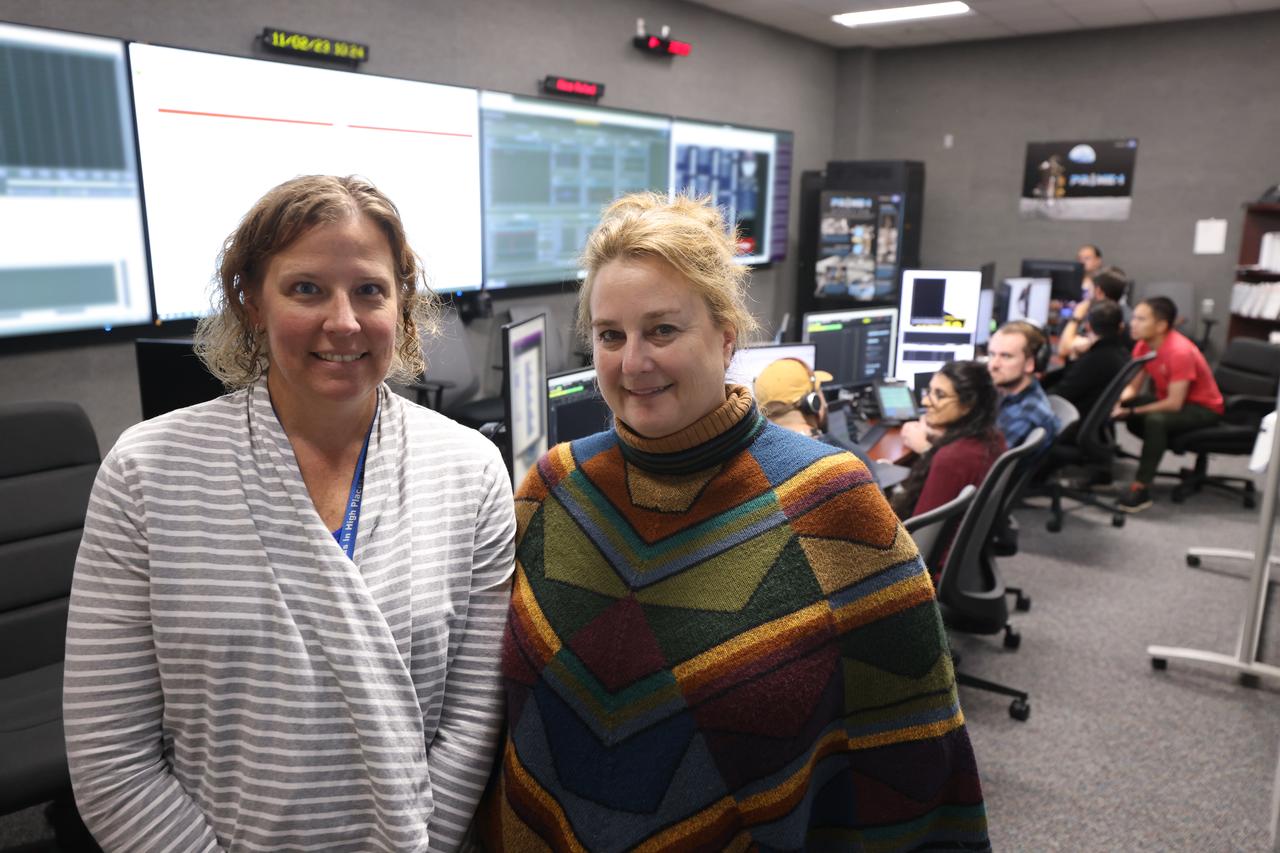

Janine Captain, left, and Jackie Quinn participate in simulation training for the Polar Resources Ice Mining Experiment-1 (PRIME-1) on Thursday, Nov. 2, 2023, inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The purpose of the training is to get the integrated PRIME-1 team – engineers with PRIME-1’s MSOLO (Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations) and Honeybee Robotics’ TRIDENT (Regolith and Ice Drill for Exploring New Terrain) drill – prepared to operate the instrument on the lunar surface. The team commanded the PRIME-1 hardware, located at Intuitive Machines in Houston, to operate MSOLO and TRIDENT. PRIME-1 is scheduled to launch through NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service) initiative and will be the first in-situ resource utilization demonstration on the Moon, with MSOLO and TRIDENT making up its two primary components. Through Artemis missions, CLPS deliveries will be used to perform science experiments, test technologies, and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human deep space exploration missions.
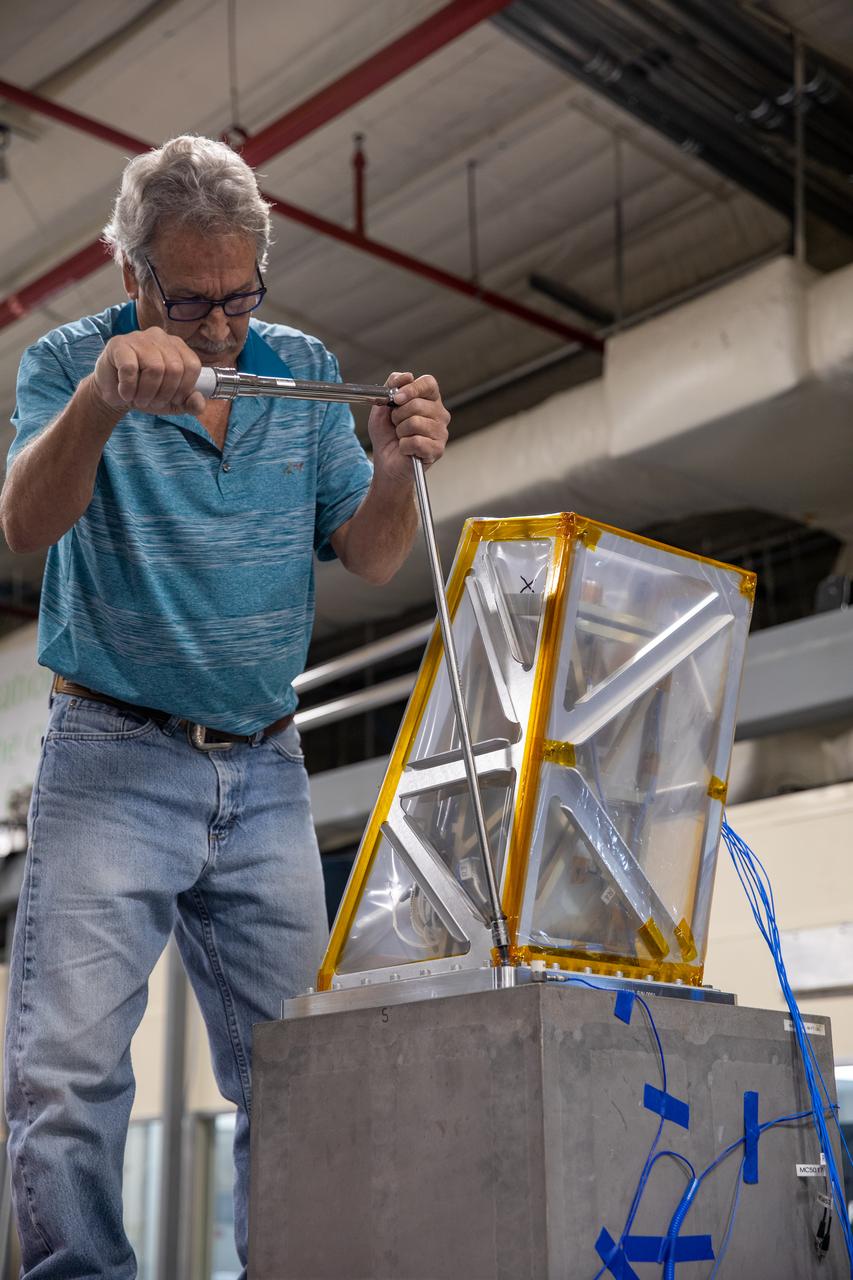

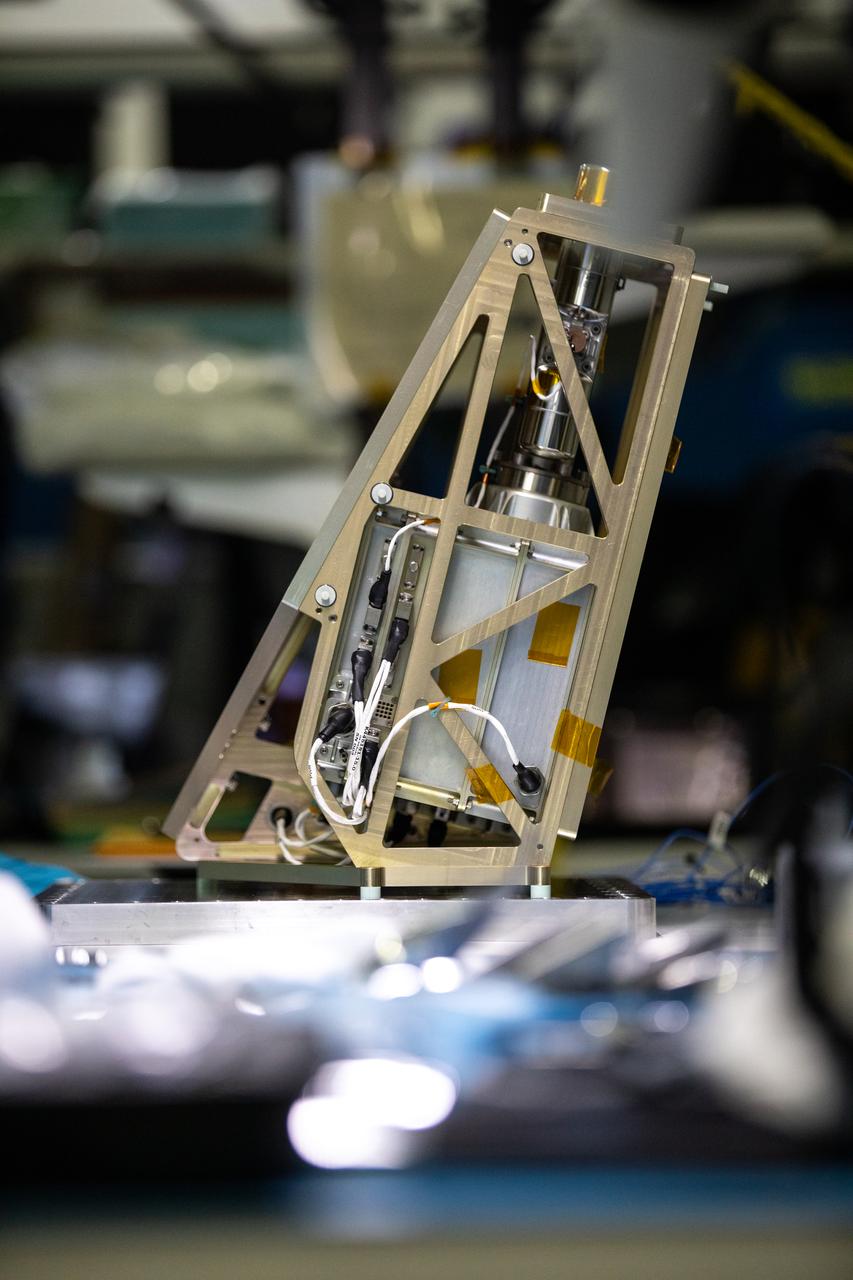
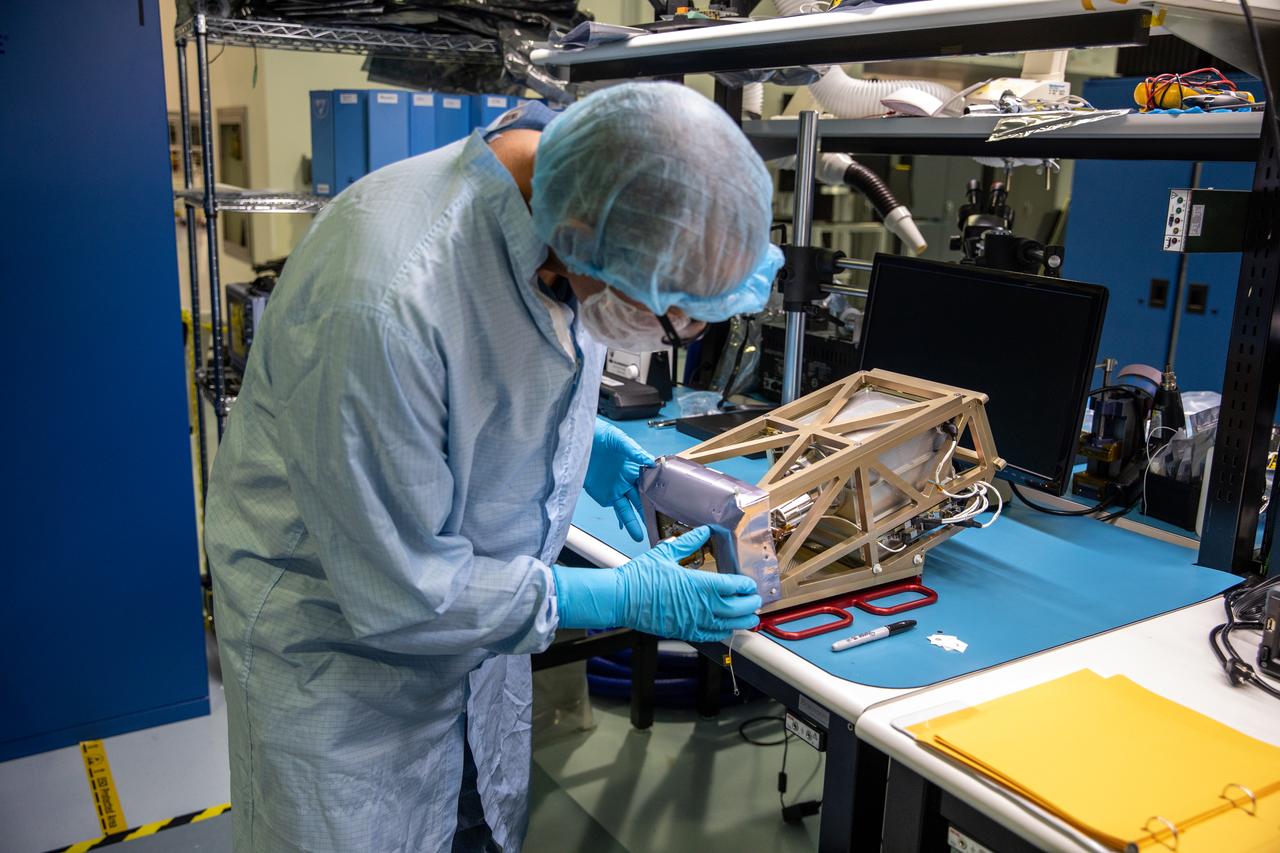
A Kennedy Space Center engineer prepares the Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) instrument for vibration testing inside the Florida spaceport’s Cryogenics Laboratory on Aug. 3, 2022. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. Researchers and engineers are preparing MSolo instruments to launch on four robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) – commercial deliveries that will perform science experiments, test technologies, and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for crewed missions to the lunar surface. This particular MSolo instrument is slated to fly on the agency’s Polar Resources Ice Mining Experiment-1 (PRIME-1) mission – the first in-situ resource utilization demonstration on the Moon – as part of the agency’s CLPS initiative.
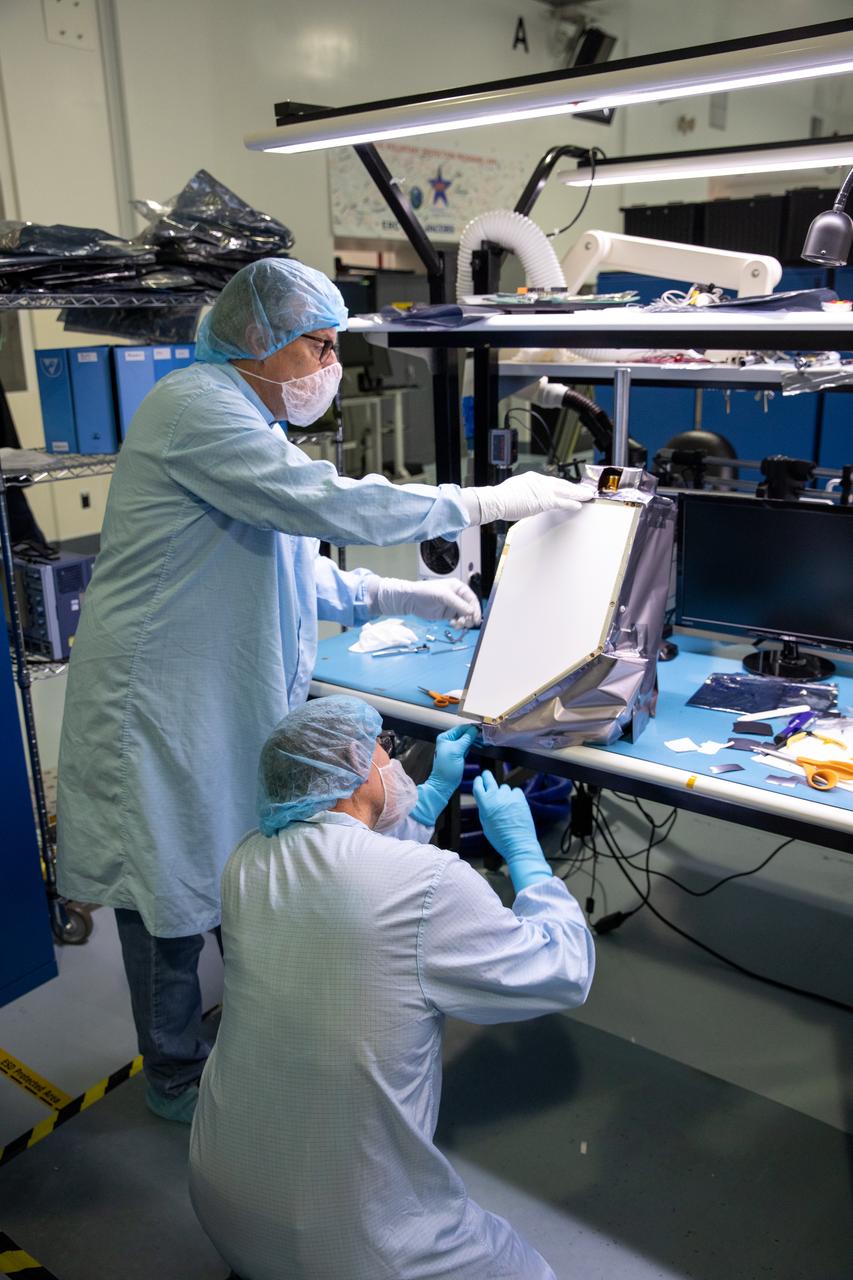

Engineers install multilayer insulation (MLI) on the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) instrument inside Kennedy Space Center’s Space Station Processing Facility on Oct. 20, 2022. The activity is in preparation for the Polar Resources Ice Mining Experiment-1 (PRIME-1) mission, which will be the first in-situ resource utilization demonstration on the Moon. MLI protects the instrument from thermal temperature extremes, helping to insulate at cold temperatures and to cool at higher temperatures when solar lighting conditions or lunar infrared reflects onto the instrument. Researchers and engineers are preparing MSolo instruments to launch on four robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services – commercial deliveries beginning in 2023 that will perform science experiments, test technologies, and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for crewed missions to the lunar surface.
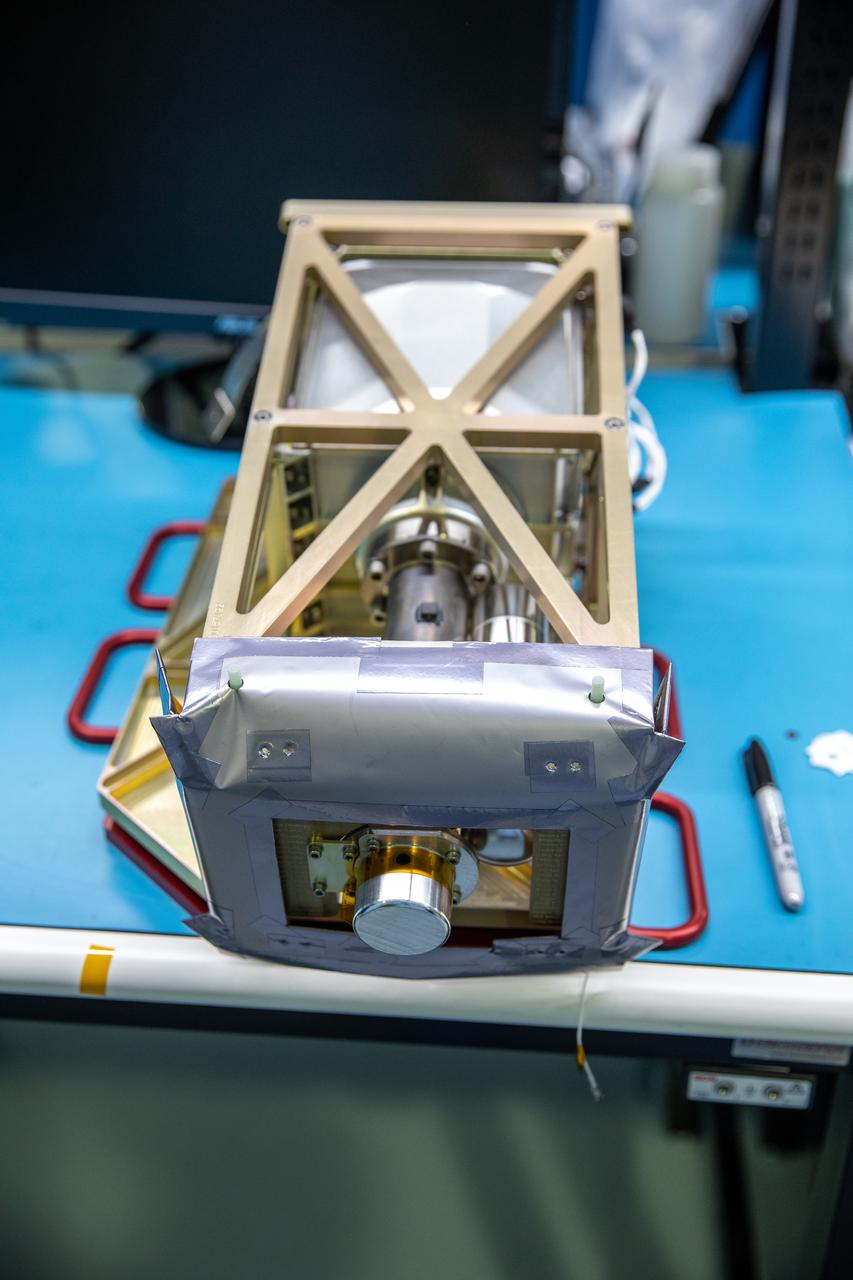

Engineers prepare the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) instrument for the multilayer insulation installation inside Kennedy Space Center’s Space Station Processing Facility on Oct. 19, 2022. The activity is in preparation for the Polar Resources Ice Mining Experiment-1 (PRIME-1) mission, which will be the first in-situ resource utilization demonstration on the Moon. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. Researchers and engineers are preparing MSolo instruments to launch on four robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services – commercial deliveries beginning in 2023 that will perform science experiments, test technologies, and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for crewed missions to the lunar surface.

Engineers install multilayer insulation (MLI) on the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) instrument inside Kennedy Space Center’s Space Station Processing Facility on Oct. 20, 2022. The activity is in preparation for the Polar Resources Ice Mining Experiment-1 (PRIME-1) mission, which will be the first in-situ resource utilization demonstration on the Moon. MLI protects the instrument from thermal temperature extremes, helping to insulate at cold temperatures and to cool at higher temperatures when solar lighting conditions or lunar infrared reflects onto the instrument. Researchers and engineers are preparing MSolo instruments to launch on four robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services – commercial deliveries beginning in 2023 that will perform science experiments, test technologies, and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for crewed missions to the lunar surface.
Engineers at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida remove the vibration fixture on the Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) instrument on Aug. 4, 2022. The activity followed a vibration test in preparation for the Polar Resources Ice Mining Experiment-1 (PRIME-1) mission, which will be the first in-situ resource utilization demonstration on the Moon. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. Researchers and engineers are preparing MSolo instruments to launch on four robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services – commercial deliveries beginning in 2023 that will perform science experiments, test technologies, and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for crewed missions to the lunar surface.
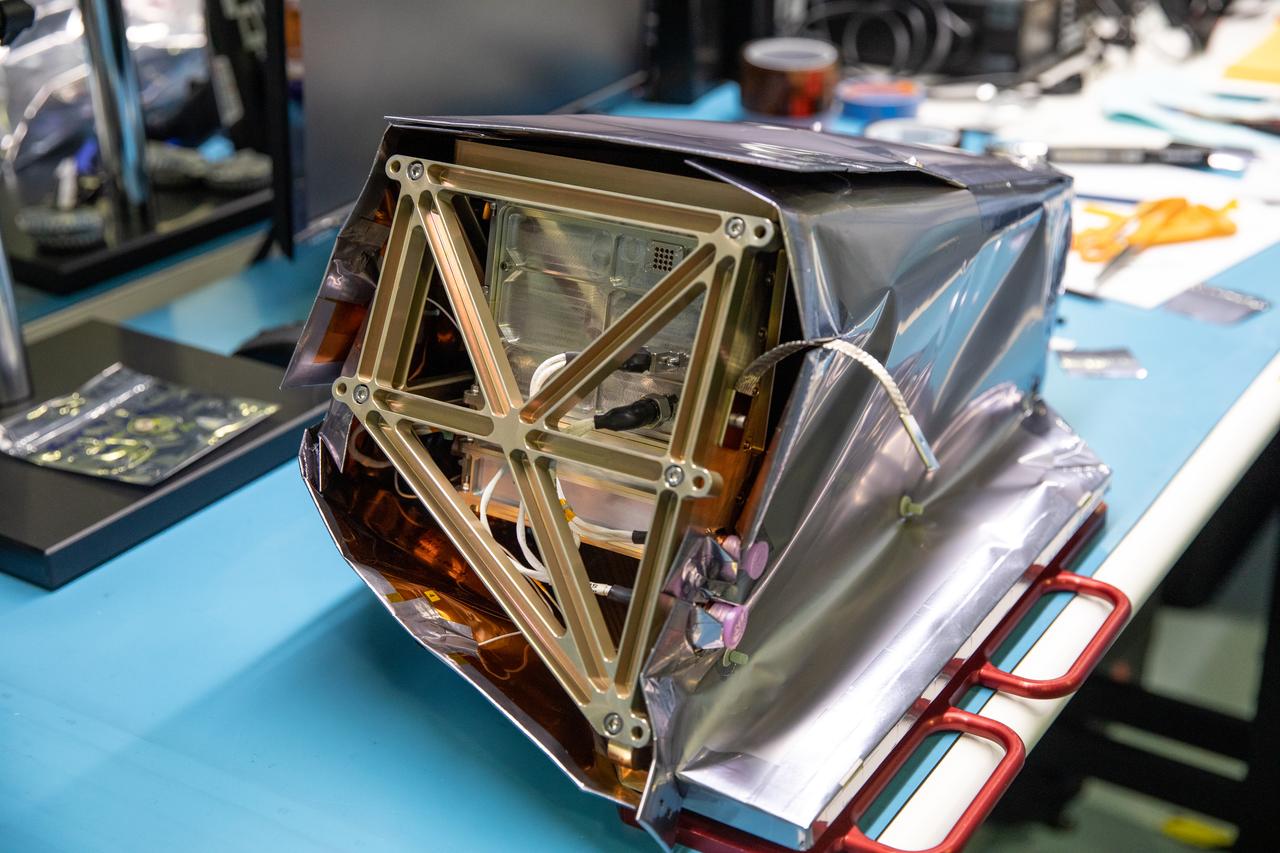
Engineers install multilayer insulation (MLI) on the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) instrument inside Kennedy Space Center’s Space Station Processing Facility on Oct. 20, 2022. The activity is in preparation for the Polar Resources Ice Mining Experiment-1 (PRIME-1) mission, which will be the first in-situ resource utilization demonstration on the Moon. MLI protects the instrument from thermal temperature extremes, helping to insulate at cold temperatures and to cool at higher temperatures when solar lighting conditions or lunar infrared reflects onto the instrument. Researchers and engineers are preparing MSolo instruments to launch on four robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services – commercial deliveries beginning in 2023 that will perform science experiments, test technologies, and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for crewed missions to the lunar surface.
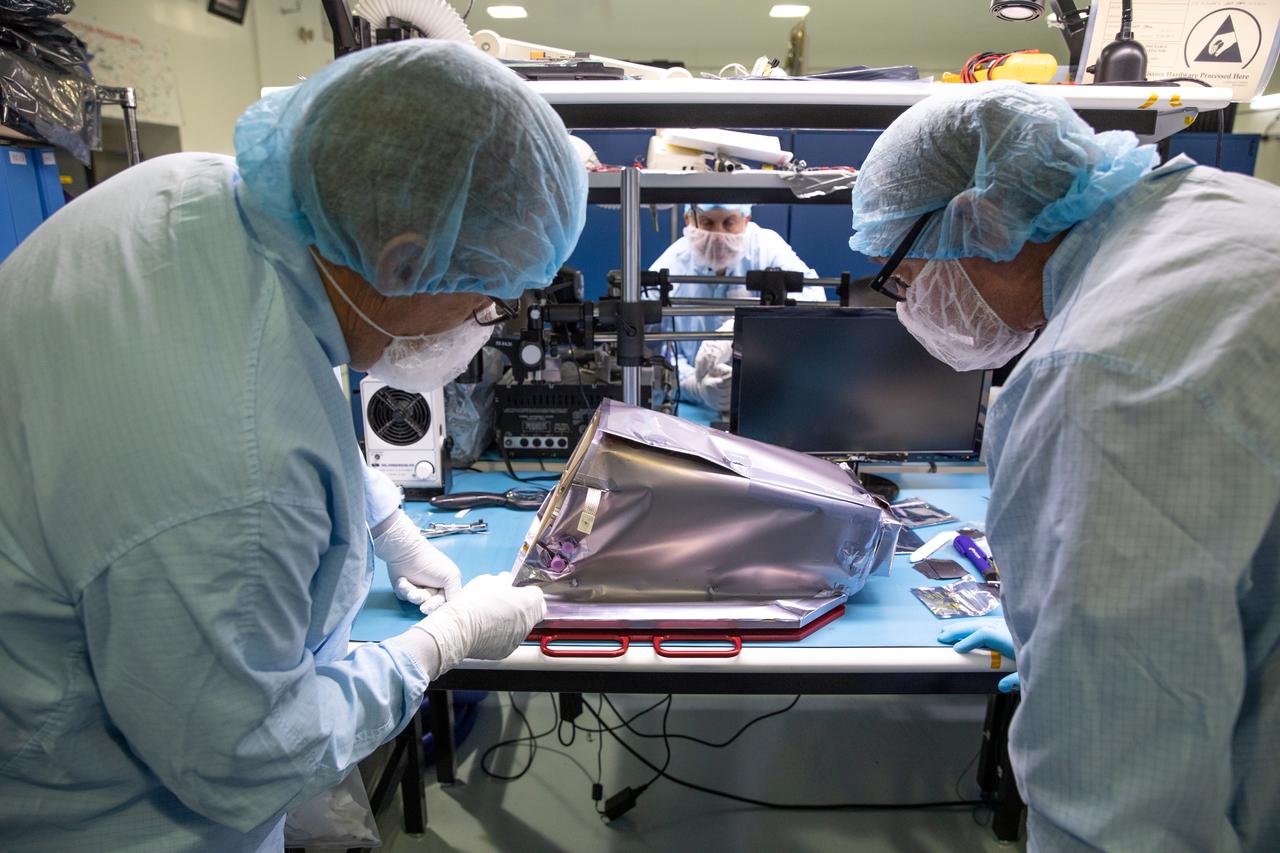

Engineers install multilayer insulation (MLI) on the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) instrument inside Kennedy Space Center’s Space Station Processing Facility on Oct. 20, 2022. The activity is in preparation for the Polar Resources Ice Mining Experiment-1 (PRIME-1) mission, which will be the first in-situ resource utilization demonstration on the Moon. MLI protects the instrument from thermal temperature extremes, helping to insulate at cold temperatures and to cool at higher temperatures when solar lighting conditions or lunar infrared reflects onto the instrument. Researchers and engineers are preparing MSolo instruments to launch on four robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services – commercial deliveries beginning in 2023 that will perform science experiments, test technologies, and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for crewed missions to the lunar surface.
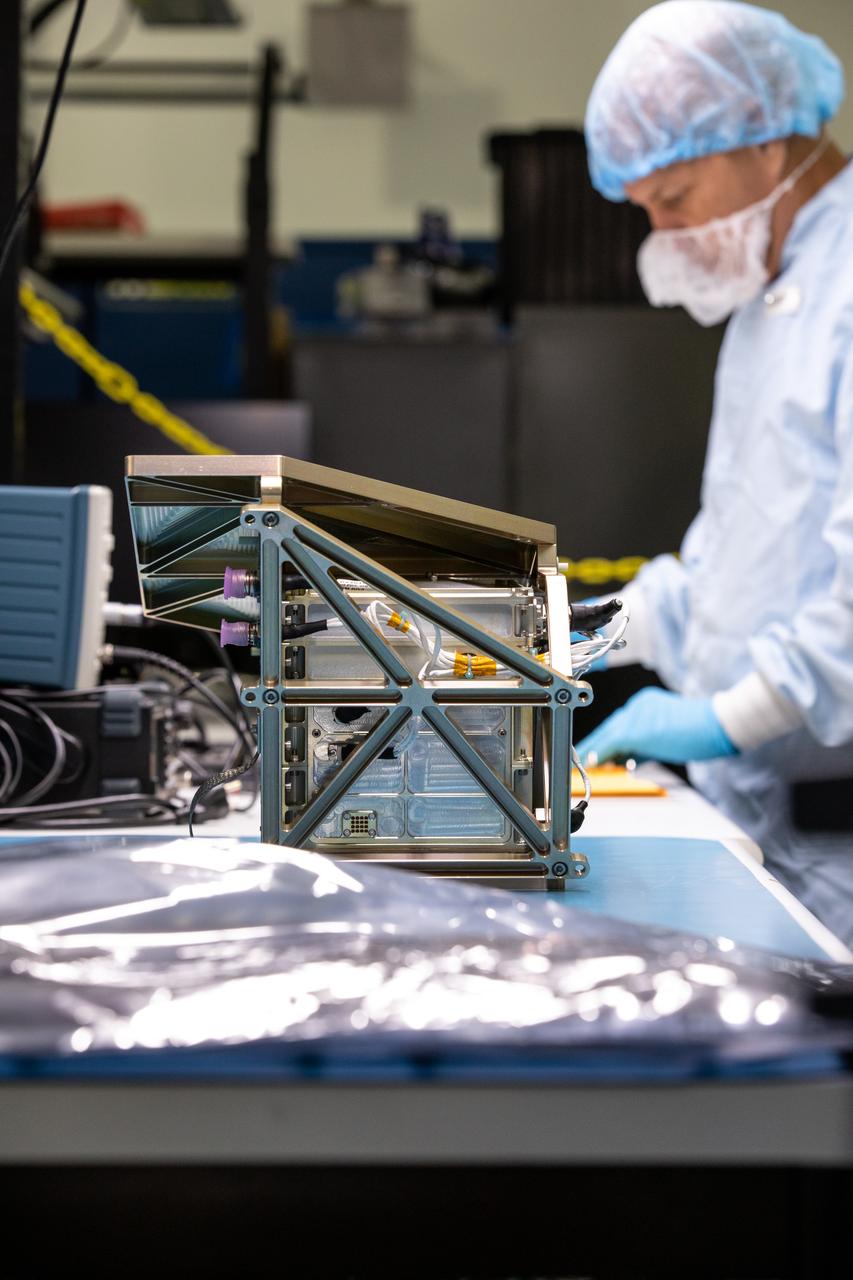

Engineers prepare the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) instrument for the multilayer insulation installation inside Kennedy Space Center’s Space Station Processing Facility on Oct. 19, 2022. The activity is in preparation for the Polar Resources Ice Mining Experiment-1 (PRIME-1) mission, which will be the first in-situ resource utilization demonstration on the Moon. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. Researchers and engineers are preparing MSolo instruments to launch on four robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services – commercial deliveries beginning in 2023 that will perform science experiments, test technologies, and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for crewed missions to the lunar surface.
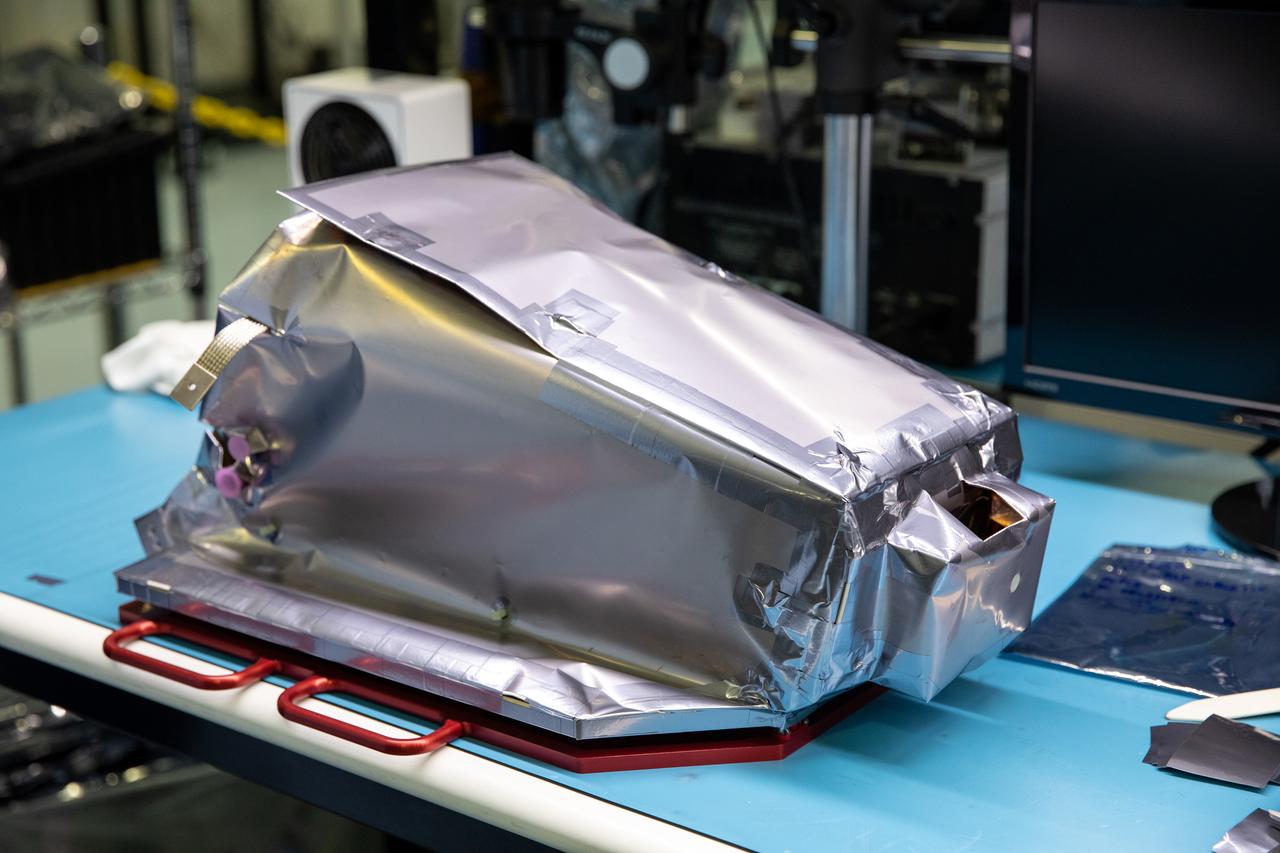

Engineers install multilayer insulation (MLI) on the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) instrument inside Kennedy Space Center’s Space Station Processing Facility on Oct. 20, 2022. The activity is in preparation for the Polar Resources Ice Mining Experiment-1 (PRIME-1) mission, which will be the first in-situ resource utilization demonstration on the Moon. MLI protects the instrument from thermal temperature extremes, helping to insulate at cold temperatures and to cool at higher temperatures when solar lighting conditions or lunar infrared reflects onto the instrument. Researchers and engineers are preparing MSolo instruments to launch on four robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services – commercial deliveries beginning in 2023 that will perform science experiments, test technologies, and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for crewed missions to the lunar surface.
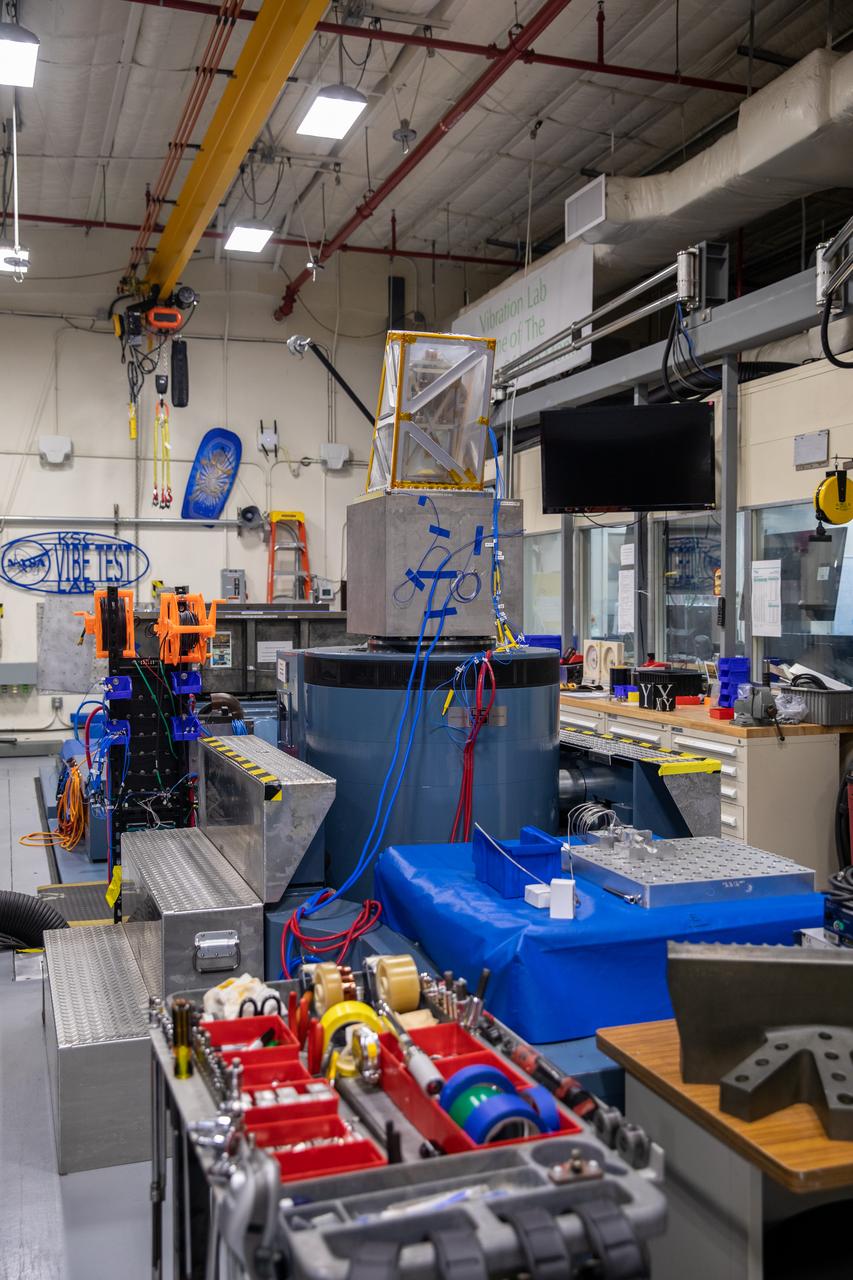

The Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) instrument undergoes vibration testing inside the Cryogenics Laboratory at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 3, 2022. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. Researchers and engineers are preparing MSolo instruments to launch on four robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) – commercial deliveries that will perform science experiments, test technologies, and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for crewed missions to the lunar surface. This particular MSolo instrument is slated to fly on the agency’s Polar Resources Ice Mining Experiment-1 (PRIME-1) mission – the first in-situ resource utilization demonstration on the Moon – as part of the agency’s CLPS initiative.
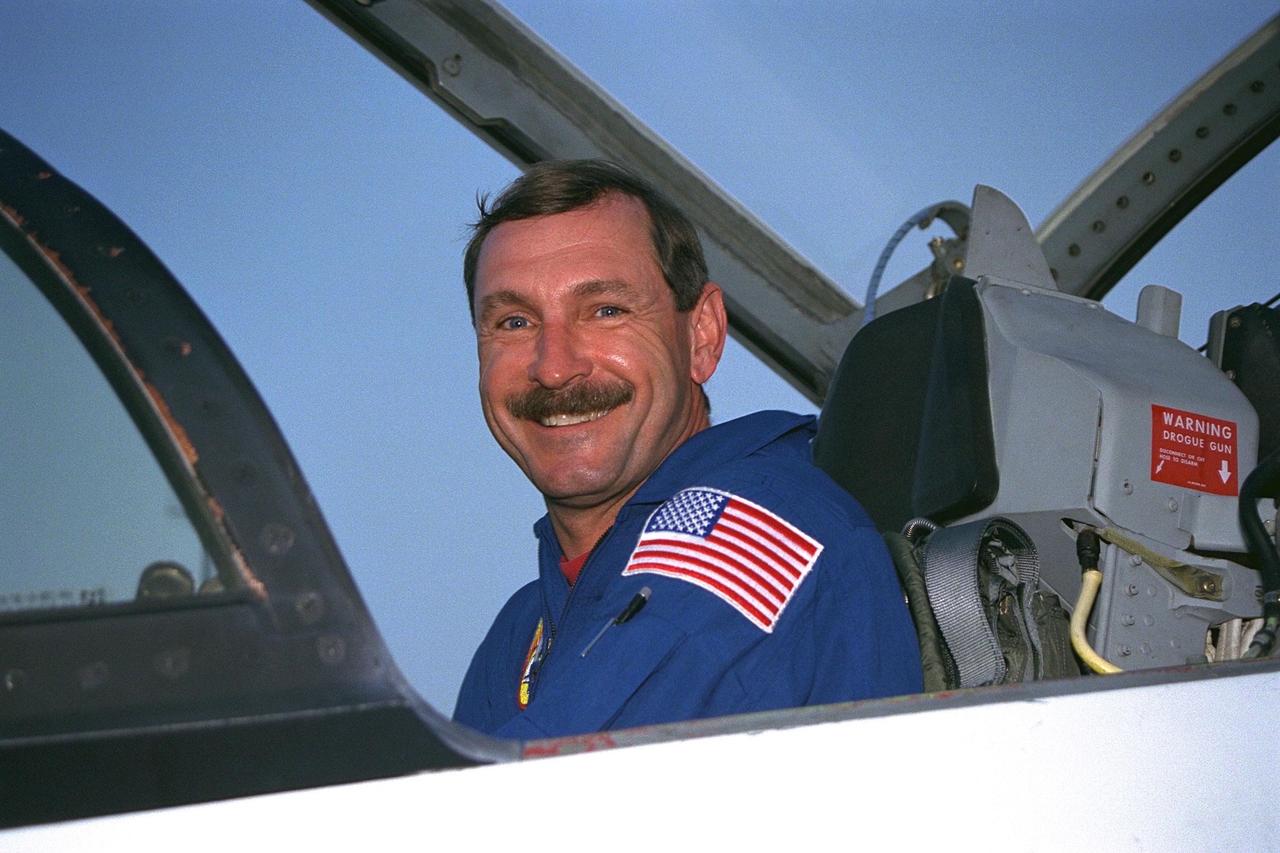

STS-85 Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown, Jr., poses in his T-38 jet trainer after landing with his crew at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility from NASA’s Johnson Space Center to begin Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities for that mission. The TCDT includes a dress rehearsal of the launch countdown. The STS-85 mission is now targeted for Aug. 7. The primary payload aboard the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery is the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2). Other STS-85 payloads include the Manipulator Flight Demonstration (MFD), and Technology Applications and Science-1 (TAS-1) and International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker-2 (IEH-2) experiments
Engineers at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida remove the vibration fixture on the Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) instrument on Aug. 4, 2022. The activity followed a vibration test in preparation for the Polar Resources Ice Mining Experiment-1 (PRIME-1) mission, which will be the first in-situ resource utilization demonstration on the Moon. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. Researchers and engineers are preparing MSolo instruments to launch on four robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services – commercial deliveries beginning in 2023 that will perform science experiments, test technologies, and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for crewed missions to the lunar surface.

Engineers at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center monitor the Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) instrument as it undergoes vibration testing inside the Florida spaceport’s Cryogenics Laboratory on Aug. 3, 2022. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. Researchers and engineers are preparing MSolo instruments to launch on four robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) – commercial deliveries that will perform science experiments, test technologies, and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for crewed missions to the lunar surface. This particular MSolo instrument is slated to fly on the agency’s Polar Resources Ice Mining Experiment-1 (PRIME-1) mission – the first in-situ resource utilization demonstration on the Moon – as part of the agency’s CLPS initiative.

Engineers at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida remove the vibration fixture on the Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) instrument on Aug. 4, 2022. The activity followed a vibration test in preparation for the Polar Resources Ice Mining Experiment-1 (PRIME-1) mission, which will be the first in-situ resource utilization demonstration on the Moon. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. Researchers and engineers are preparing MSolo instruments to launch on four robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services – commercial deliveries beginning in 2023 that will perform science experiments, test technologies, and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for crewed missions to the lunar surface.
Engineers prepare the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) instrument for the multilayer insulation installation inside Kennedy Space Center’s Space Station Processing Facility on Oct. 19, 2022. The activity is in preparation for the Polar Resources Ice Mining Experiment-1 (PRIME-1) mission, which will be the first in-situ resource utilization demonstration on the Moon. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. Researchers and engineers are preparing MSolo instruments to launch on four robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services – commercial deliveries beginning in 2023 that will perform science experiments, test technologies, and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for crewed missions to the lunar surface.
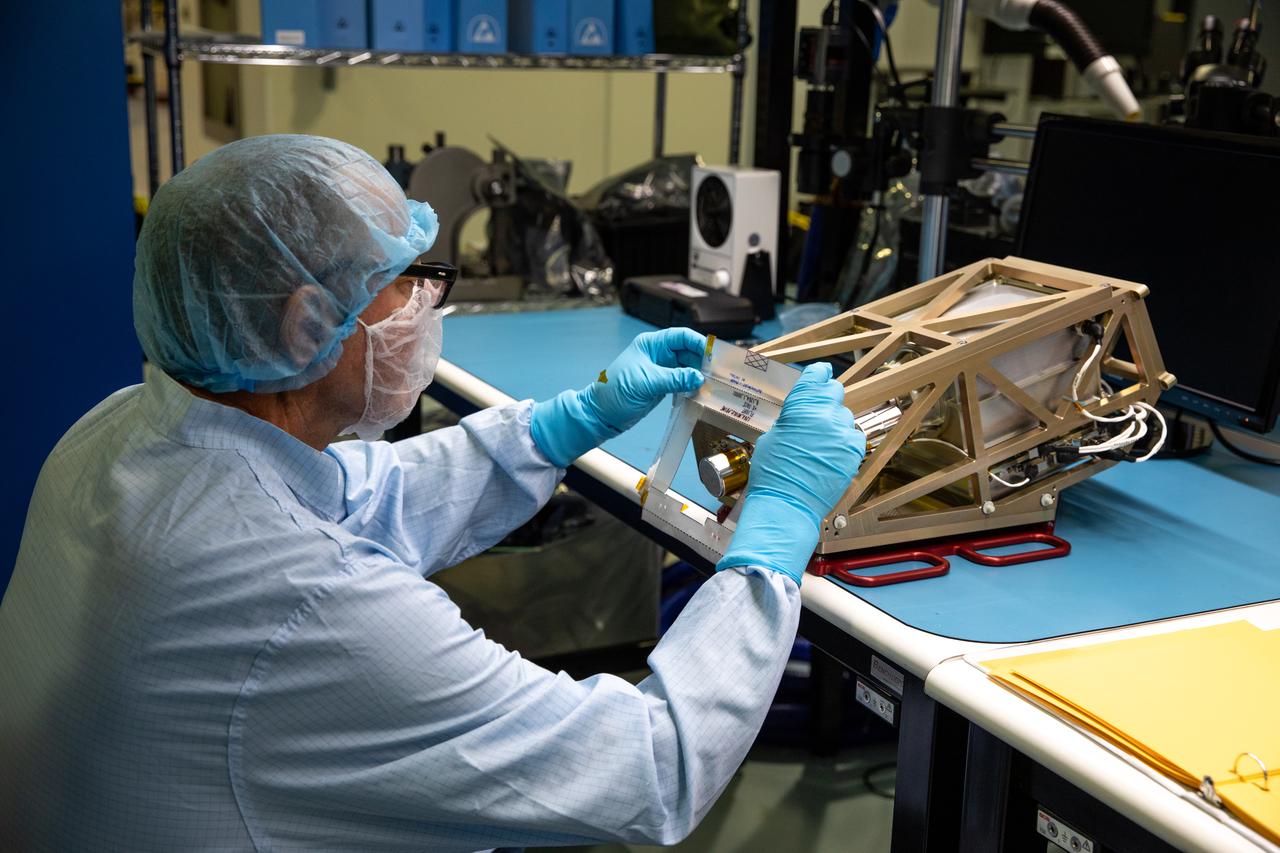

Engineers prepare the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) instrument for the multilayer insulation installation inside Kennedy Space Center’s Space Station Processing Facility on Oct. 19, 2022. The activity is in preparation for the Polar Resources Ice Mining Experiment-1 (PRIME-1) mission, which will be the first in-situ resource utilization demonstration on the Moon. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. Researchers and engineers are preparing MSolo instruments to launch on four robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services – commercial deliveries beginning in 2023 that will perform science experiments, test technologies, and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for crewed missions to the lunar surface.
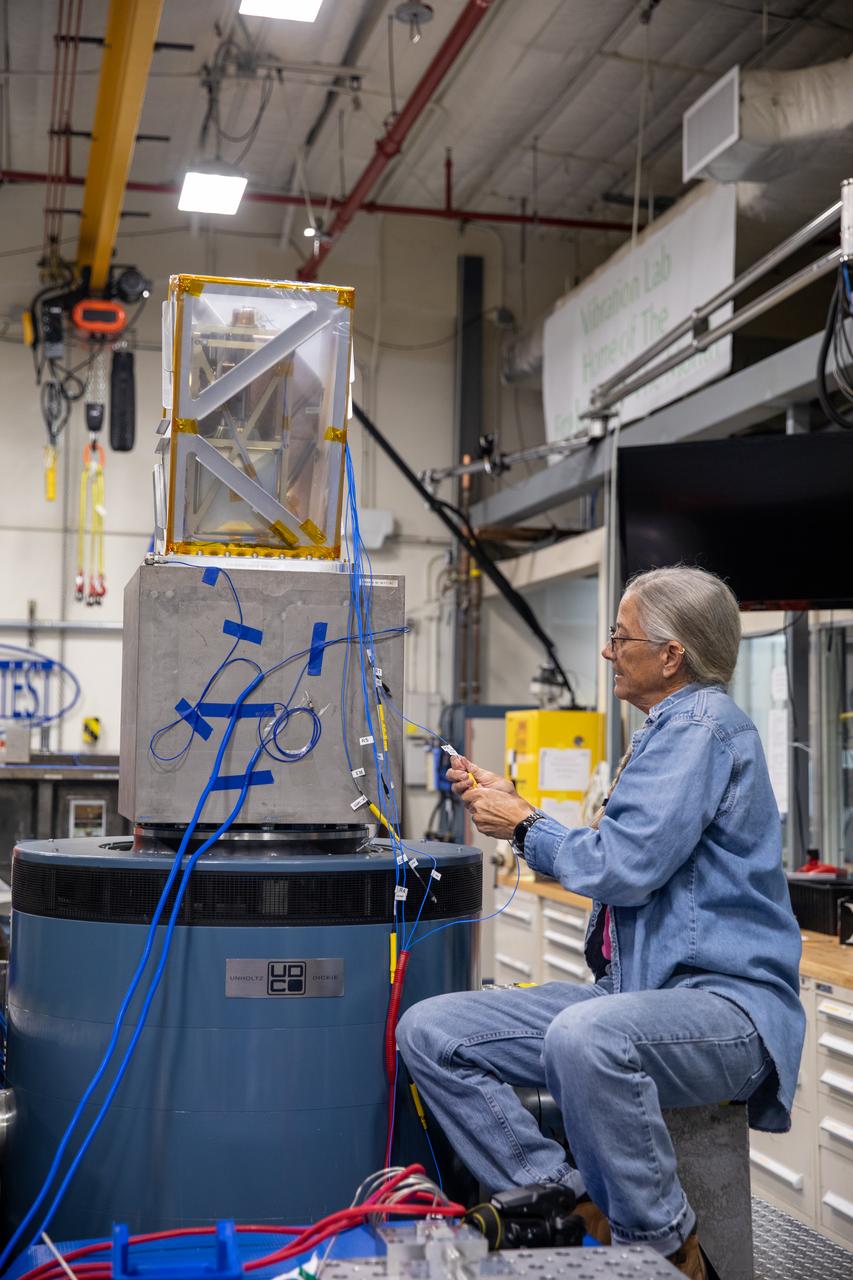

A Kennedy Space Center engineer prepares the Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) instrument for vibration testing inside the Florida spaceport’s Cryogenics Laboratory on Aug. 3, 2022. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. Researchers and engineers are preparing MSolo instruments to launch on four robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) – commercial deliveries that will perform science experiments, test technologies, and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for crewed missions to the lunar surface. This particular MSolo instrument is slated to fly on the agency’s Polar Resources Ice Mining Experiment-1 (PRIME-1) mission – the first in-situ resource utilization demonstration on the Moon – as part of the agency’s CLPS initiative.
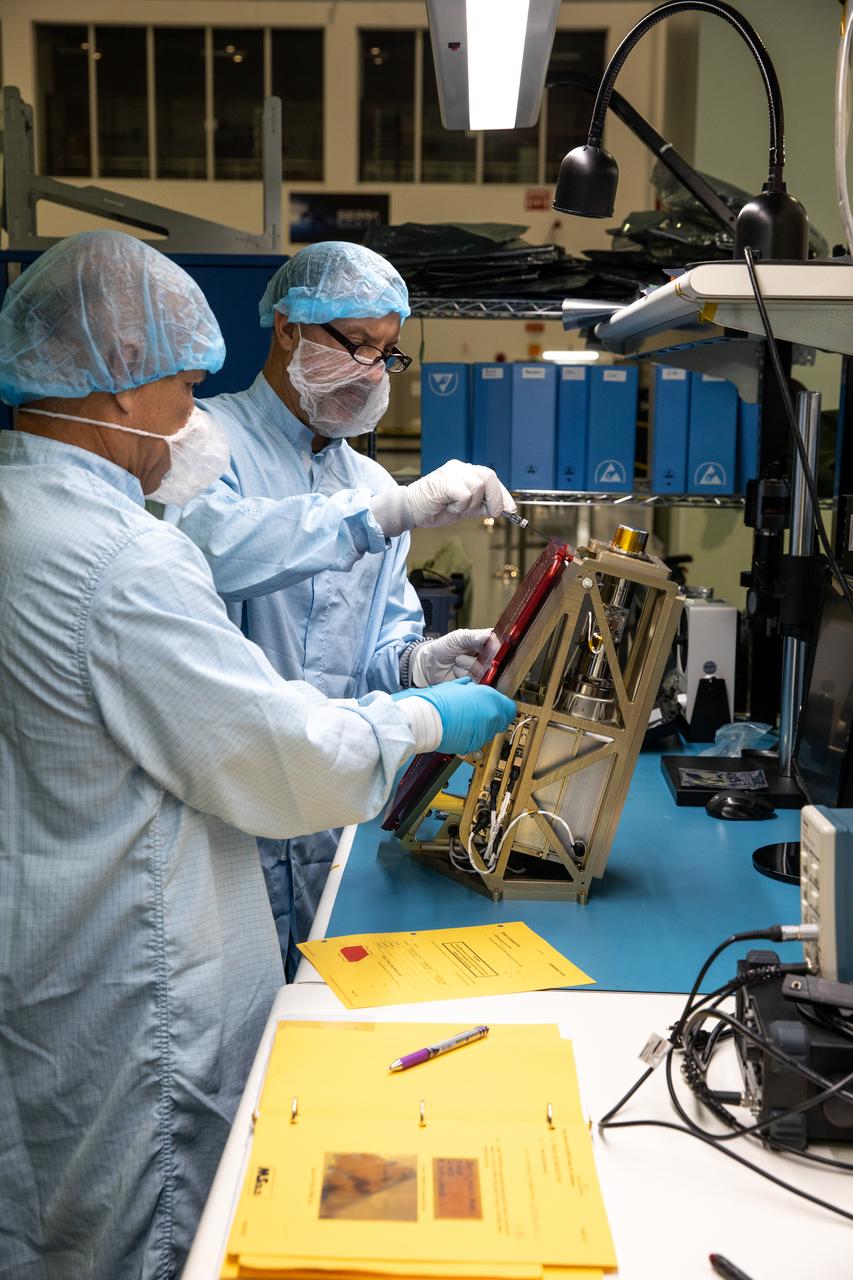

Engineers prepare the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) instrument for the multilayer insulation installation inside Kennedy Space Center’s Space Station Processing Facility on Oct. 19, 2022. The activity is in preparation for the Polar Resources Ice Mining Experiment-1 (PRIME-1) mission, which will be the first in-situ resource utilization demonstration on the Moon. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. Researchers and engineers are preparing MSolo instruments to launch on four robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services – commercial deliveries beginning in 2023 that will perform science experiments, test technologies, and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for crewed missions to the lunar surface.

Engineers at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida remove the vibration fixture on the Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) instrument on Aug. 4, 2022. The activity followed a vibration test in preparation for the Polar Resources Ice Mining Experiment-1 (PRIME-1) mission, which will be the first in-situ resource utilization demonstration on the Moon. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. Researchers and engineers are preparing MSolo instruments to launch on four robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services – commercial deliveries beginning in 2023 that will perform science experiments, test technologies, and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for crewed missions to the lunar surface.
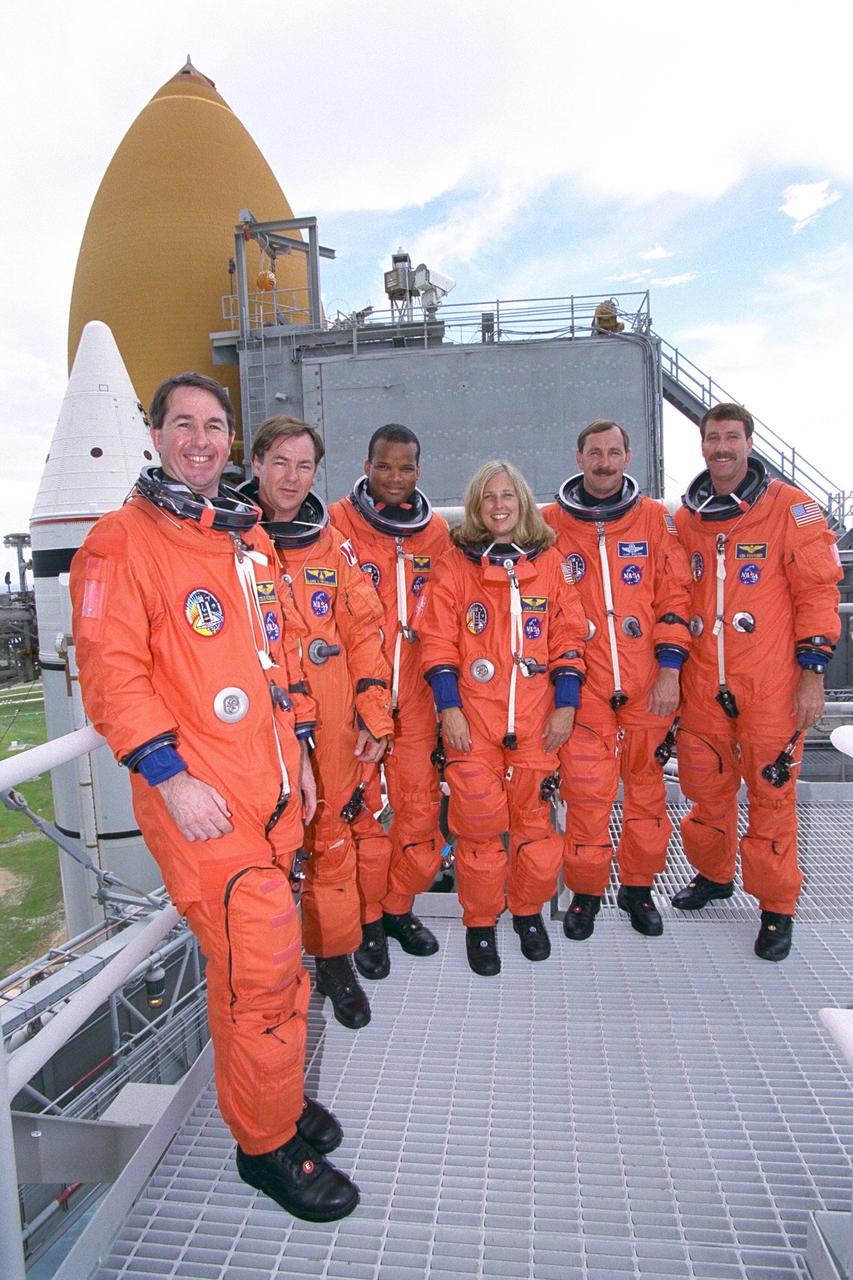

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The STS-85 flight crew members pose at the 195-foot level of Launch Pad 39A with the Space Shuttle Discovery in the background during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities for that mission. They are (from left): Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson; Payload Specialist Bjarni V. Tryggvason; Mission Specialist Robert L. Curbeam, Jr.; Payload Commander N. Jan Davis; Commander Curtis L. Brown, Jr.; and Pilot Kent V. Rominger. The primary payload aboard the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery is the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere-2 (CRISTA-SPAS-2). Other STS-85 payloads include the Manipulator Flight Demonstration (MFD), and Technology Applications and Science-1 (TAS-1) and International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker-2 (IEH-2) experiments

Engineers prepare the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) instrument for the multilayer insulation installation inside Kennedy Space Center’s Space Station Processing Facility on Oct. 19, 2022. The activity is in preparation for the Polar Resources Ice Mining Experiment-1 (PRIME-1) mission, which will be the first in-situ resource utilization demonstration on the Moon. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. Researchers and engineers are preparing MSolo instruments to launch on four robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services – commercial deliveries beginning in 2023 that will perform science experiments, test technologies, and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for crewed missions to the lunar surface.
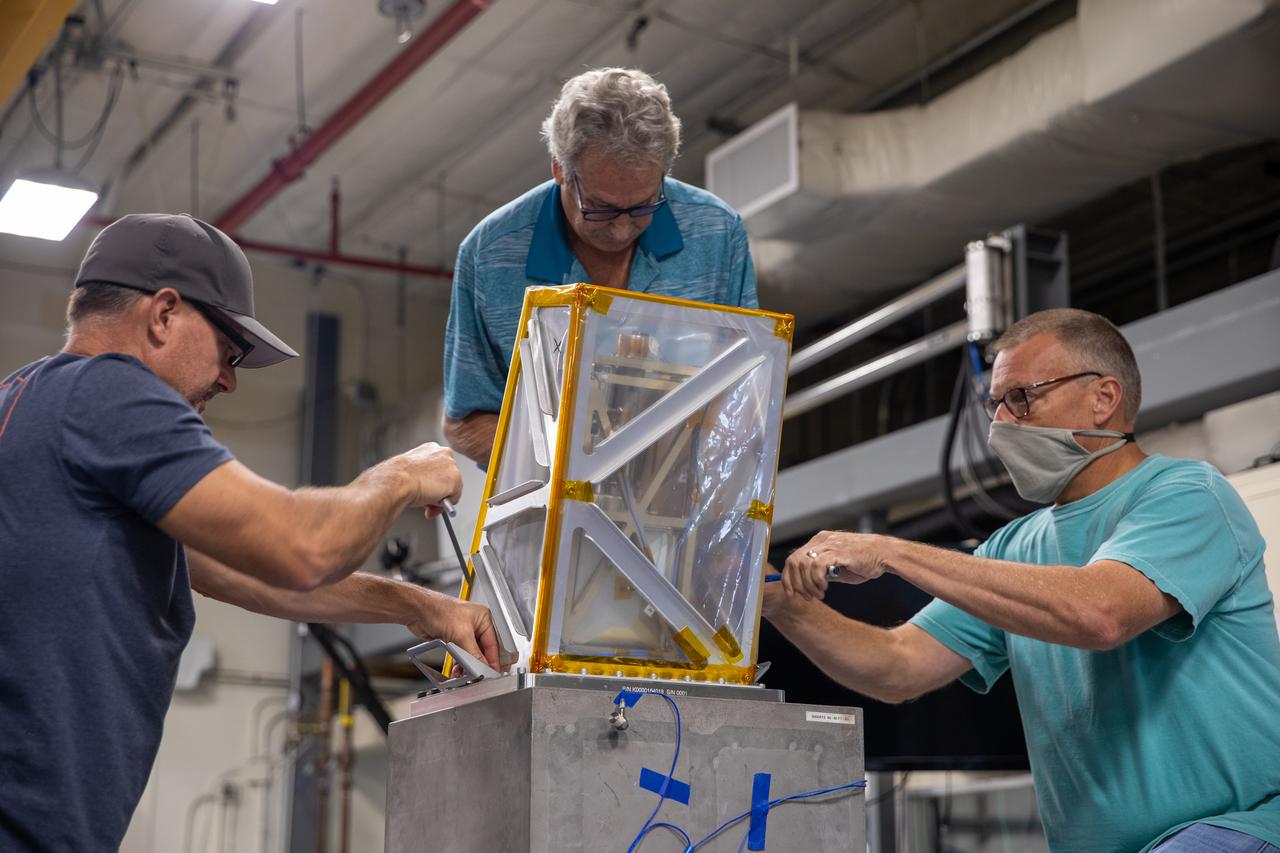

Engineers at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center prepare the Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) instrument for vibration testing inside the Florida spaceport’s Cryogenics Laboratory on Aug. 3, 2022. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. Researchers and engineers are preparing MSolo instruments to launch on four robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) – commercial deliveries that will perform science experiments, test technologies, and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for crewed missions to the lunar surface. This particular MSolo instrument is slated to fly on the agency’s Polar Resources Ice Mining Experiment-1 (PRIME-1) mission – the first in-situ resource utilization demonstration on the Moon – as part of the agency’s CLPS initiative.
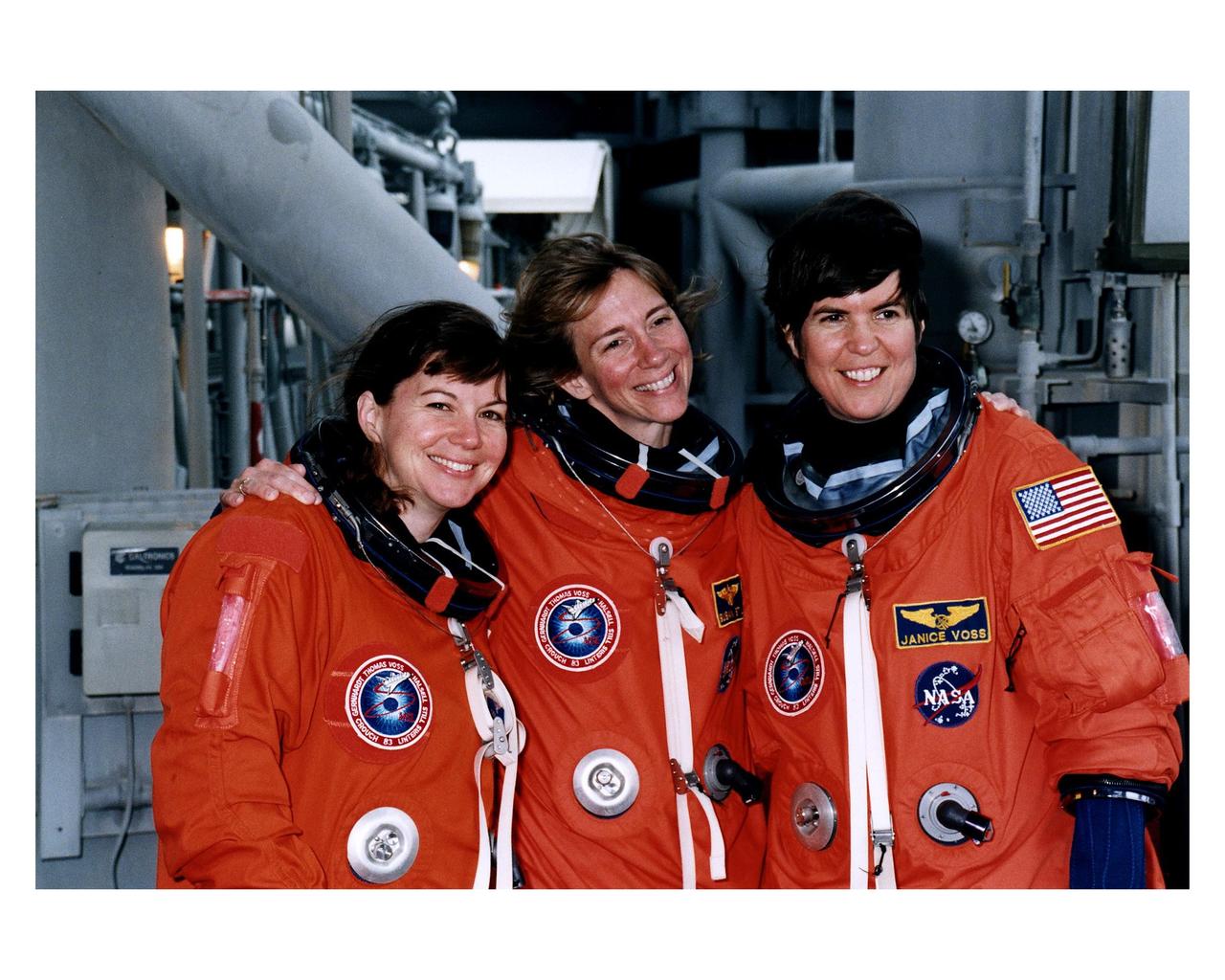

STS-83 Alternate Mission Specialist Catherine "Cady" Coleman, Pilot Susan L. Still and Payload Commander Janice Voss mug for the camera at the 195-foot level of Launch Pad 39A during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) exercises for that mission. The other crew members for the 16-day Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) mission are Mission Commander James D. Halsell, Jr.; Mission Specialist Donald A. Thomas; Payload Specialist Gregory T. Linteris; Mission Specialist Michael L. Gernhardt; and Payload Specialist Roger K. Crouch
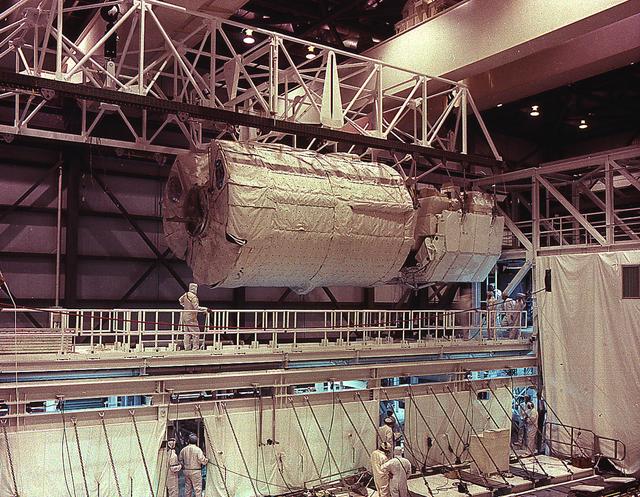

This photograph shows the Spacelab 1 module and pallet ready to be installed in the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia at the Kennedy Space Center. The overall goal of the first Spacelab mission was to verify its Space performance through a variety of scientific experiments. The investigation selected for this mission tested the Spacelab hardware, flight and ground systems, and crew to demonstrate their capabilities for advanced research in space. However, Spacelab 1 was not merely a checkout flight or a trial run. Important research problems that required a laboratory in space were scheduled for the mission. Spacelab 1 was a multidisciplinary mission; that is, investigations were performed in several different fields of scientific research. These fields were Astronomy and Solar Physics, Space Plasma Physics, Atmospheric Physics and Earth Observations, Life Sciences, and Materials Science. Spacelab 1 was launched aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-9 mission) on November 28, 1983.
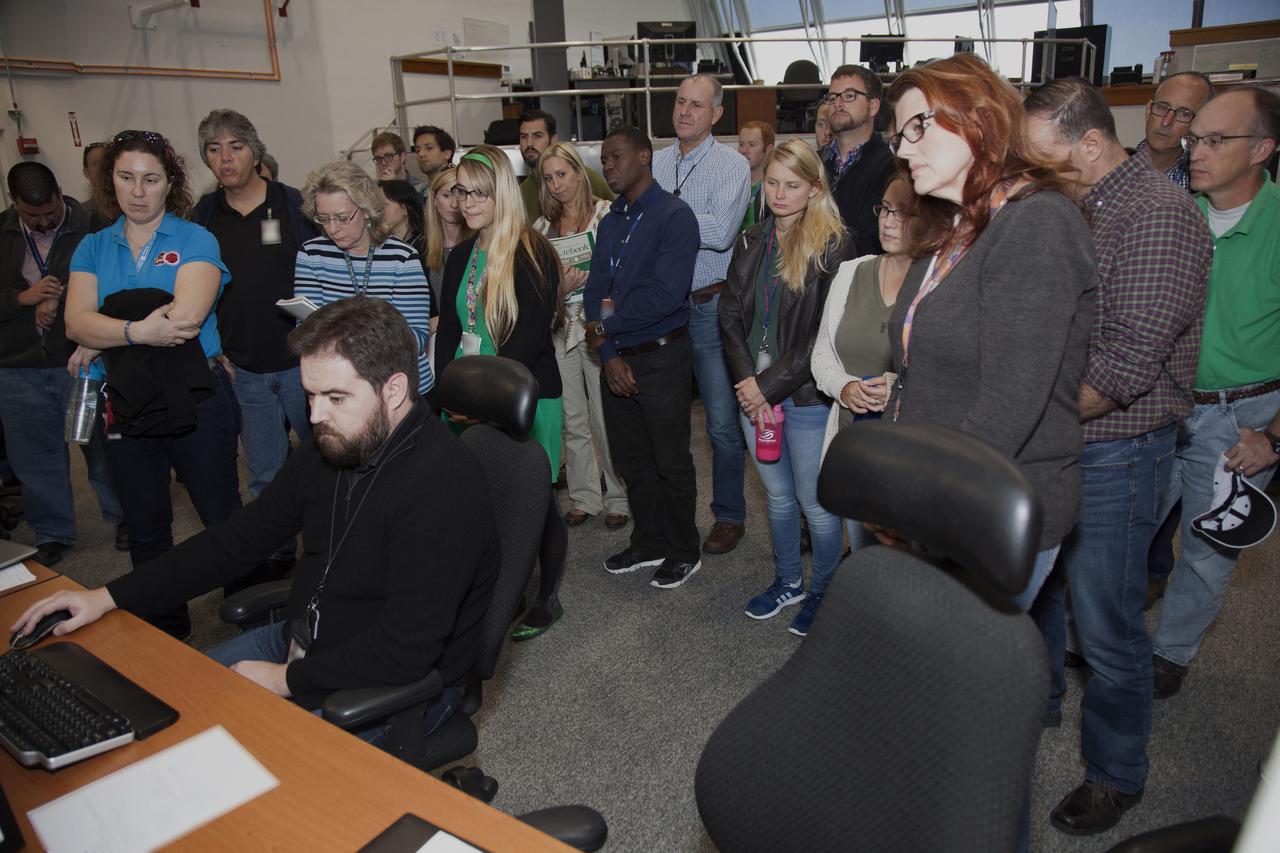

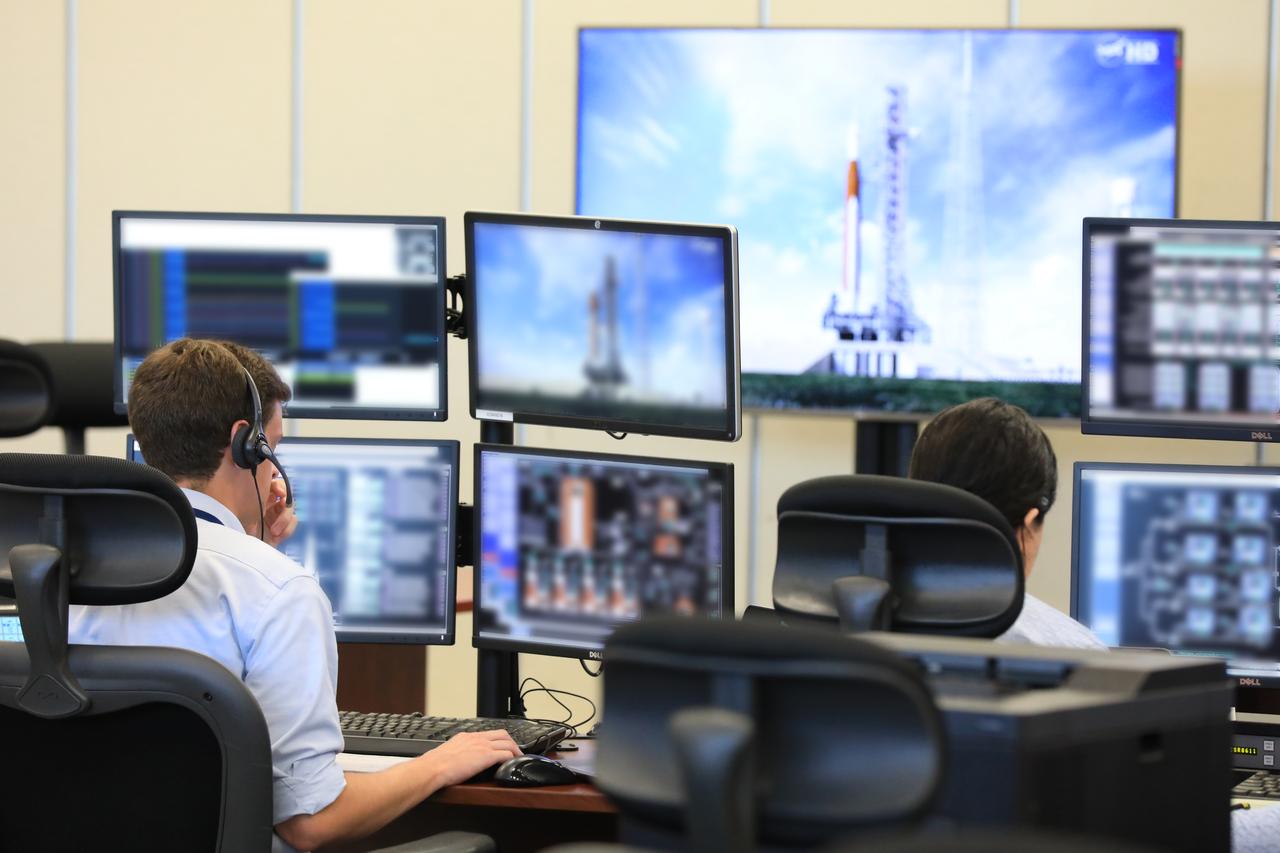
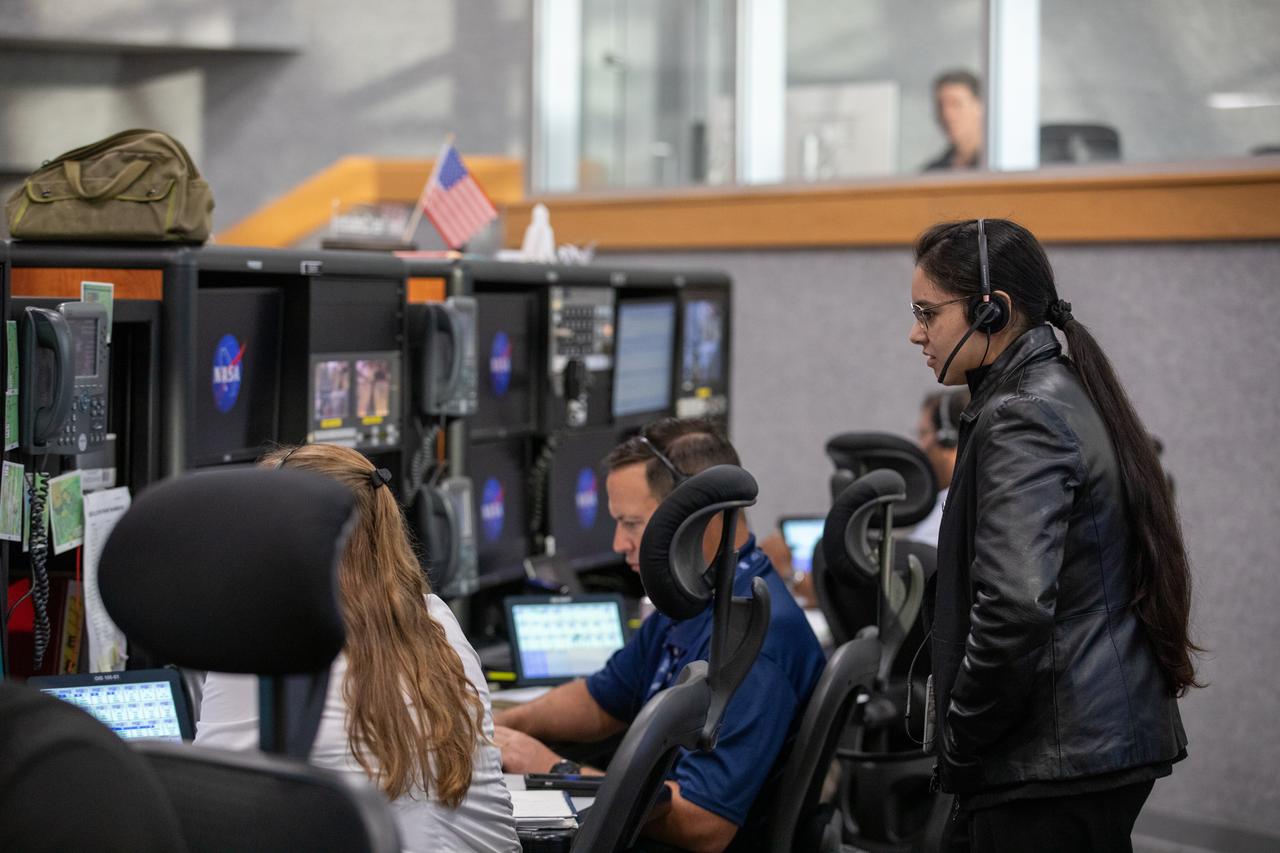
NASA engineers and test directors gather in Firing Room 3 in the Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, to watch a demonstration of the automated command and control software for the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion spacecraft. In front, far right, is Charlie Blackwell-Thompson, launch director for Exploration Mission 1 (EM-1). The software is called the Ground Launch Sequencer. It will be responsible for nearly all of the launch commit criteria during the final phases of launch countdowns. The Ground and Flight Application Software Team (GFAST) demonstrated the software. It was developed by the Command, Control and Communications team in the Ground Systems Development and Operations (GSDO) Program. GSDO is helping to prepare the center for the first test flight of Orion atop the SLS on EM-1.