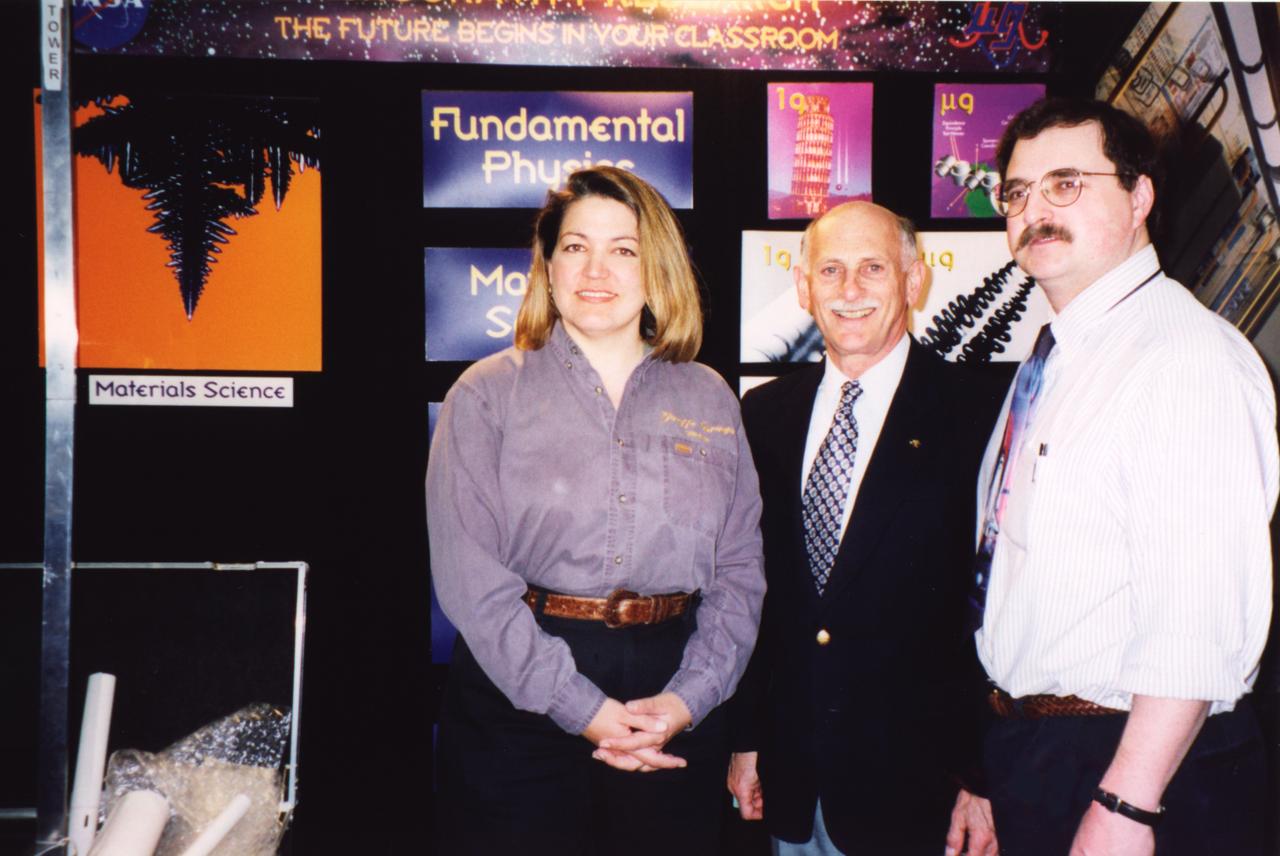

Representatives of NASA materials science experiments supported the NASA exhibit at the Rernselaer Polytechnic Institute's Space Week activities, April 5 through 11, 1999. From left to right are: Angie Jackman, project manager at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center for dendritic growth experiments; Dr. Martin Glicksman of Rennselaer Polytechnic Instutute, Troy, NY, principal investigator on the Isothermal Dendritic Growth Experiment (IDGE) that flew three times on the Space Shuttle; and Dr. Matthew Koss of College of the Holy Cross in Worcester, MA, a co-investigator on the IDGE and now principal investigator on the Transient Dendritic Solidification Experiment being developed for the International Space Station (ISS). The image at far left is a dendrite grown in Glicksman's IDGE tests aboard the Shuttle. Glicksman is also principal investigator for the Evolution of Local Microstructures: Spatial Instabilities of Coarsening Clusters.
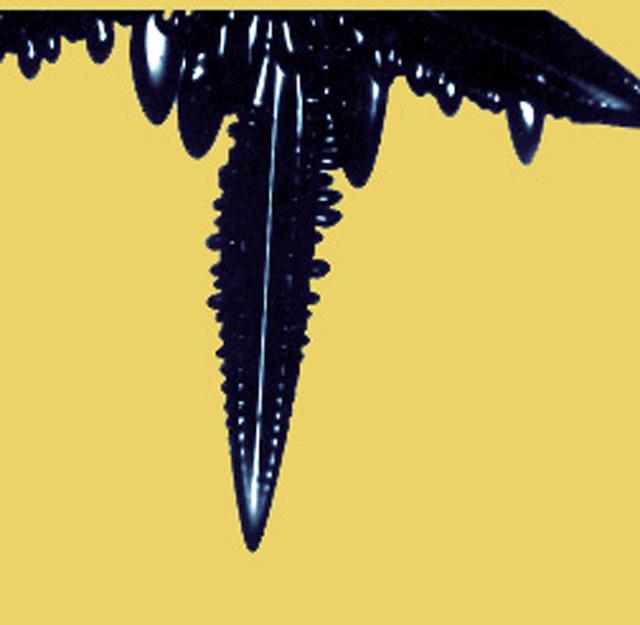

Researchers have found that as melted metals and alloys (combinations of metals) solidify, they can form with different arrangements of atoms, called microstructures. These microstructures depend on the shape of the interface (boundary) between the melted metal and the solid crystal it is forming. There are generally three shapes that the interface can take: planar, or flat; cellular, which looks like the cells of a beehive; and dendritic, which resembles tiny fir trees. Convection at this interface can affect the interface shape and hide the other phenomena (physical events). To reduce the effects of convection, researchers conduct experiments that examine and control conditions at the interface in microgravity. Microgravity also helps in the study of alloys composed of two metals that do not mix. On Earth, the liquid mixtures of these alloys settle into different layers due to gravity. In microgravity, the liquid metals do not settle, and a solid more uniform mixture of both metals can be formed.

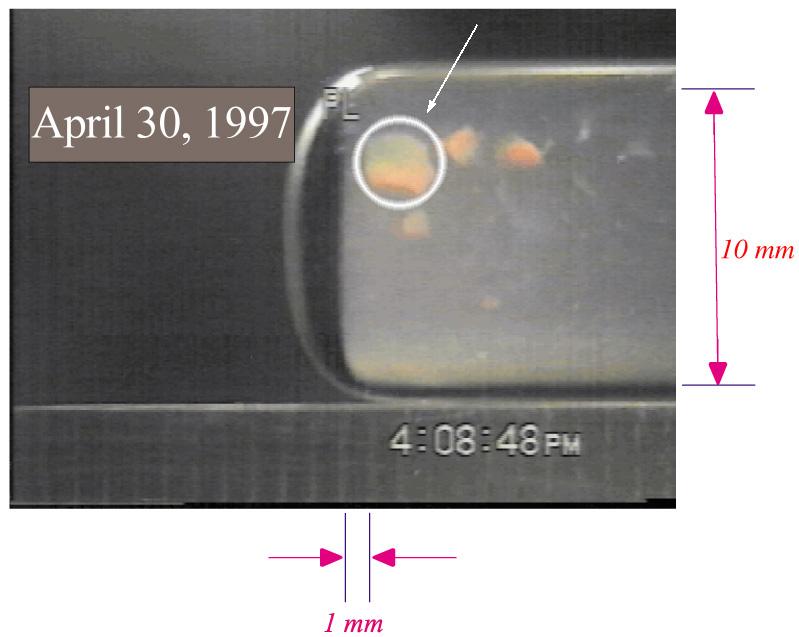
This series of images, captured during the mission, shows the growth of a dendrite in the IDGE. Flown on STS-84 USMP-4.

Typical picture of a dendrite: Notice how the branch on the left has no arms coming off the top. This is because of the convective forces (hot liquid rises) that the top of the branch is not solidifying (growing arms) like the bottom, cooler area. The is a gravitational effect. This does not happen in space.
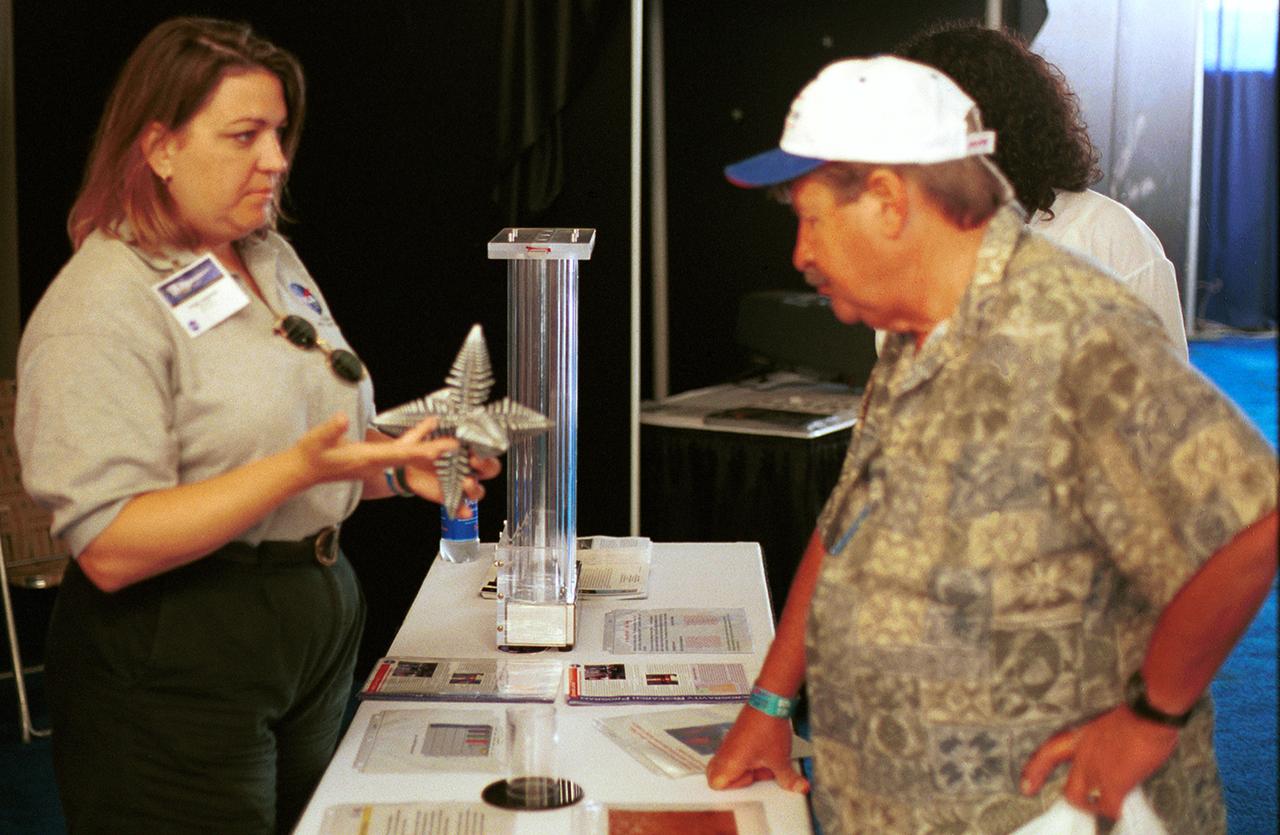

Angie Jackman, a NASA project manager in microgravity research, explains a model of a dendrite to a visitor to the NASA exhibit at AirVenture 2000 sponsored by the Experimental Aircraft Association in Oshkosh, WI. The model depicts microscopic dendrites that grow as molten metals solidify. NASA sponsored three experiments aboard the Space Shuttle that used the microgravity environment to study the formation of large (1 to 4 mm) dendrites without Earth's gravity disrupting their growth. Three advanced follow-on experiments, managed by Jackman, are being developed for the International Space Station (ISS).
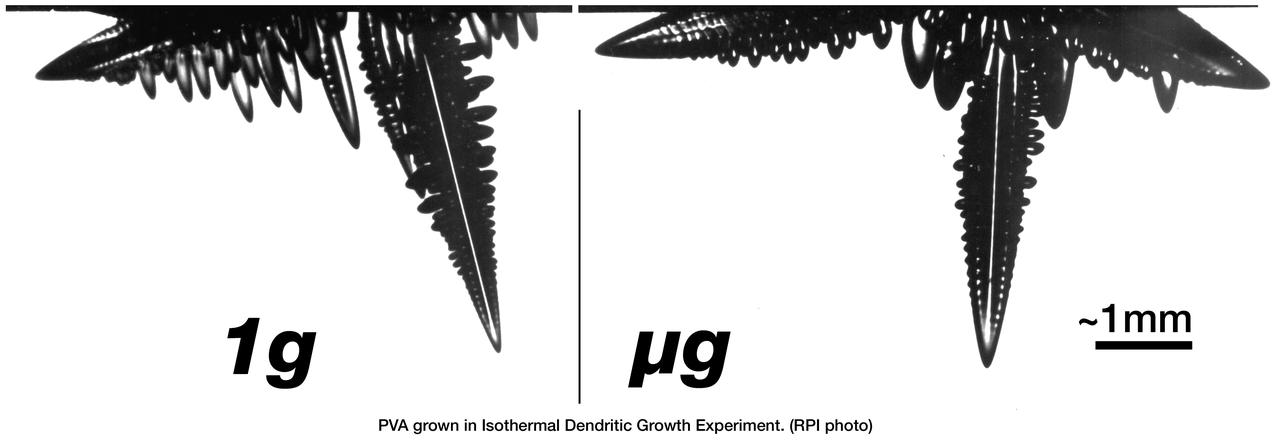

The Isothermal Dendritic Growth Experiment (IDGE), flown on three Space Shuttle missions, is yielding new insights into virtually all industrially relevant metal and alloy forming operations. IDGE used transparent organic liquids that form dendrites (treelike structures) similar to those inside metal alloys. Comparing Earth-based and space-based dendrite growth velocity, tip size and shape provides a better understanding of the fundamentals of dentritic growth, including gravity's effects. Shalowgraphic images of pivalic acid (PVA) dendrites forming from the melt show the subtle but distinct effects of gravity-driven heat convection on dentritic growth. In orbit, the dendrite grows as its latent heat is liberated by heat conduction. This yields a blunt dendrite tip. On Earth, heat is carried away by both conduction and gravity-driven convection. This yields a sharper dendrite tip. In addition, under terrestrial conditions, the sidebranches growing in the direction of gravity are augmented as gravity helps carry heat out of the way of the growing sidebranches as opposed to microgravity conditions where no augmentation takes place. IDGE was developed by Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute and NASA/Glenn Research Center. Advanced follow-on experiments are being developed for flight on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: NASA/Glenn Research Center

The Equiaxed Dendritic Solidification Experiment (EDSE) is a material sciences investigation under the Formation of Microstructures/pattern formation discipline. The objective is to study the microstructural evolution of and thermal interactions between several equiaxed crystals growing dendritically in a supercooled melt of a pure and transparent substance under diffusion controlled conditions. Dendrites growing at .4 supercooling from a 2 stinger growth chamber for the EDSE in the Microgravity Development Lab (MDL).

The Equiaxed Dendritic Solidification Experiment (EDSE) is a material sciences investigation under the Formation of Microstructures/pattern formation discipline. The objective is to study the microstructural evolution of and thermal interactions between several equiaxed crystals growing dendritically in a supercooled melt of a pure and transparent substance under diffusion controlled conditions. Dendrite irritator control for the EDSE in the Microgravity Development Lab (MDL).
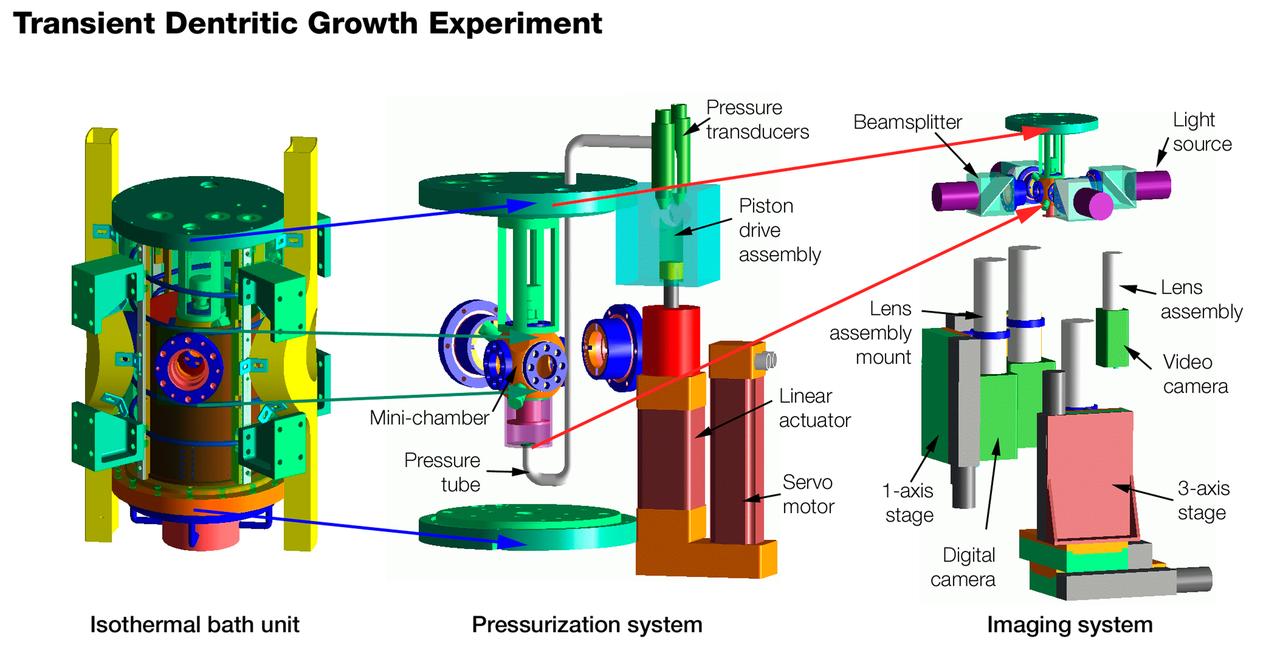
The Transient Dendritic Solidification Experiment (TDSE) is being developed as a candidate for flight aboard the International Space Station. TDSE will study the growth of dendrites (treelike crystalline structures) in a transparent material (succinonitrile or SCN) that mimics the behavior or widely used iron-based metals. Basic work by three Space Shuttle missions of the Isothermal Dendritic Growth Experiment (IDGE) is yielding new insights into virtually all industrially relevant metal and alloy forming operations. The TDSE is similar to IDGE, but will maintain a constant temperature while varying pressure on the dendrites. Shown here is an exploded view of major elements of the TDSE. A similar view is availble without labels. The principal investigator is Matthew Koss of College of the Holy Cross in Worcester, MA. Photo credit: NASA/Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC)
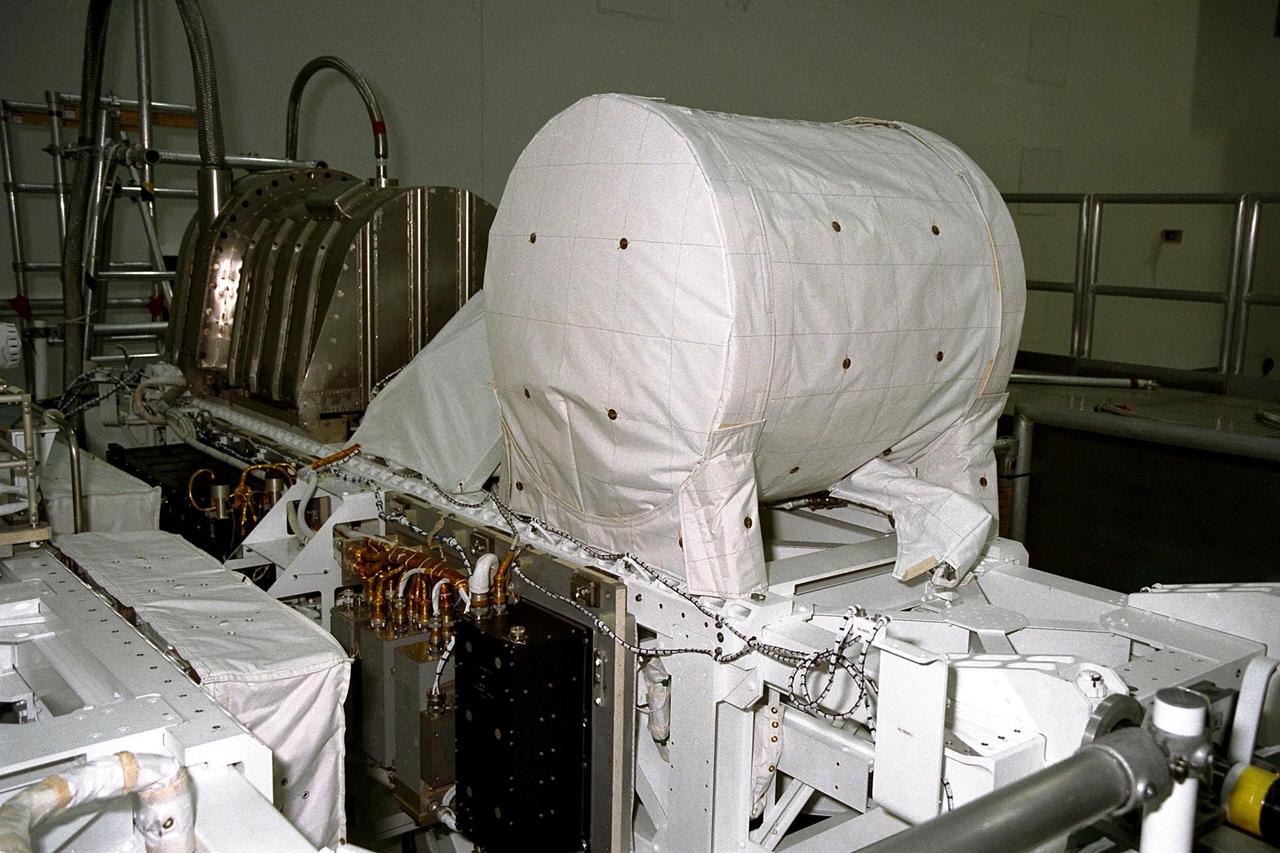

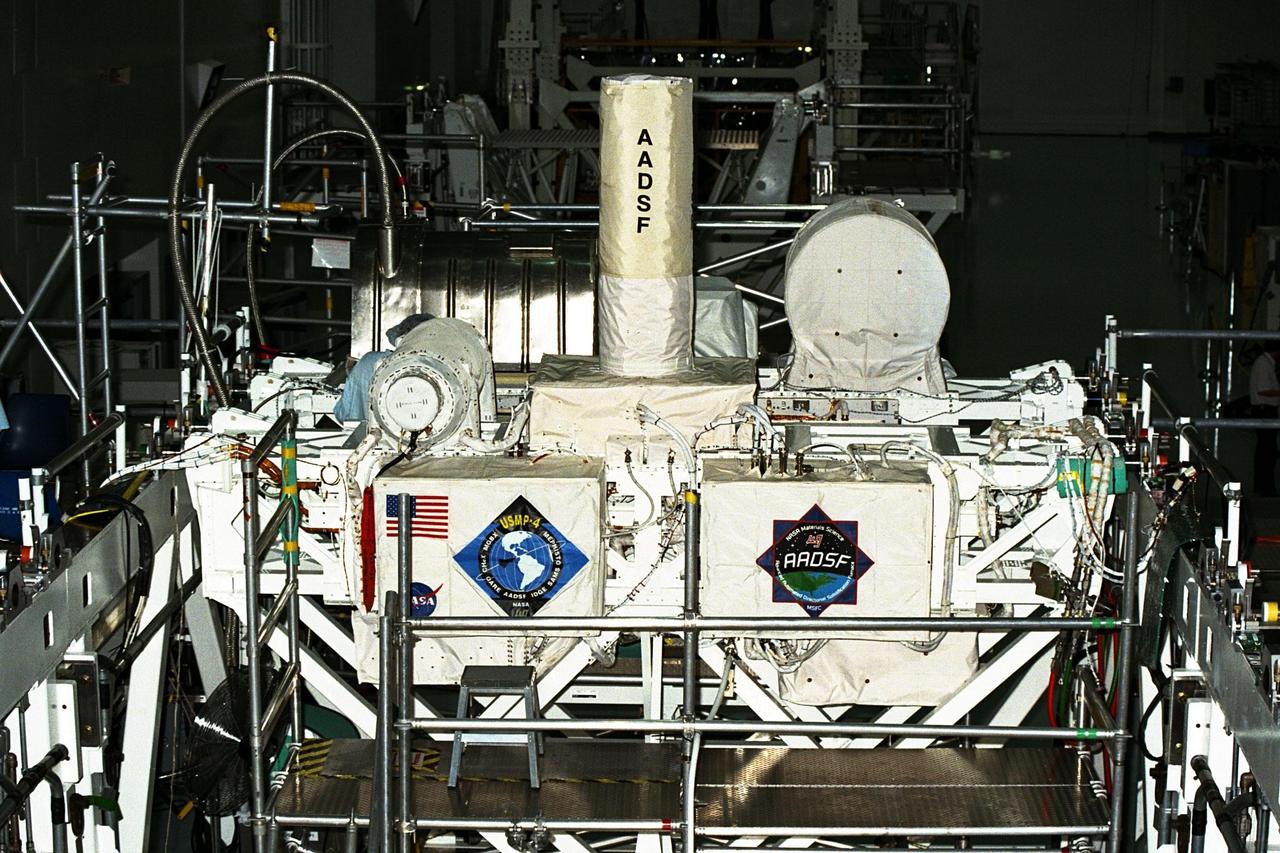
United States Microgravity Payload-4 (USMP-4) experiments are prepared to be flown on Space Shuttle mission STS-87 in the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center (KSC). Seen in the foreground at right is the Isothermal Dendritic Growth Experiment (IDGE), which will be used to study the dendritic solidification of molten materials in the microgravity environment. The metallic breadbox-like structure behind the IDGE is the Confined Helium Experiment (CHeX) that will study one of the basic influences on the behavior and properties of materials by using liquid helium confined between solid surface, and microgravity. These experiments are scheduled for launch aboard STS-87 on Nov. 19 from KSC
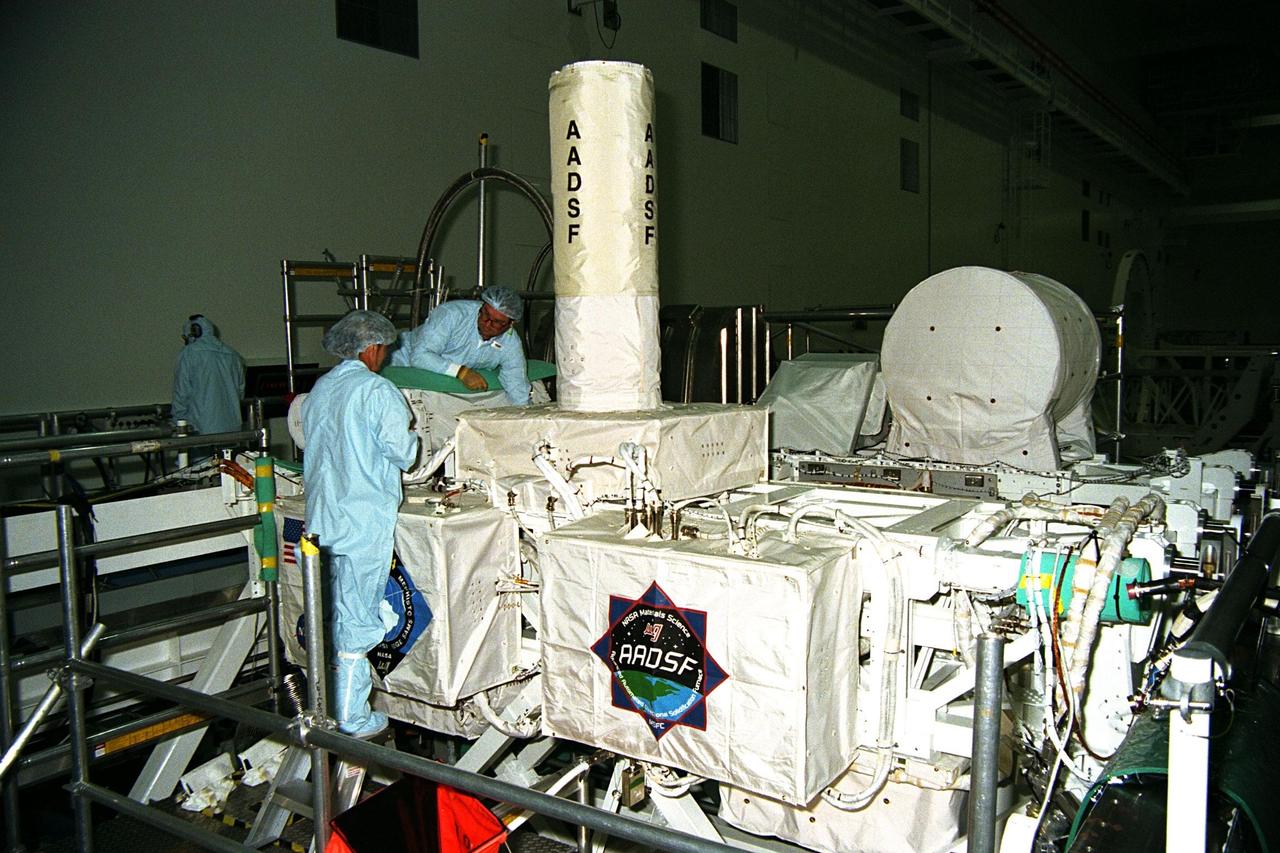

Technicians are monitoring experiments on the United States Microgravity Payload-4 (USMP-4) in preparation for its scheduled launch aboard STS-87 on Nov. 19 from Kennedy Space Center (KSC). USMP-4 experiments are prepared in the Space Station Processing Facility at KSC. The large white vertical cylinder in the center of the photo is the Advanced Automated Directional Solidification Furnace (AADSF), which is a sophisticated materials science facility used for studying a common method of processing semiconductor crystals called directional solidification. The white horizontal tube to the right is the Isothermal Dendritic Growth Experiment (IDGE), which will be used to study the dendritic solidification of molten materials in the microgravity environment
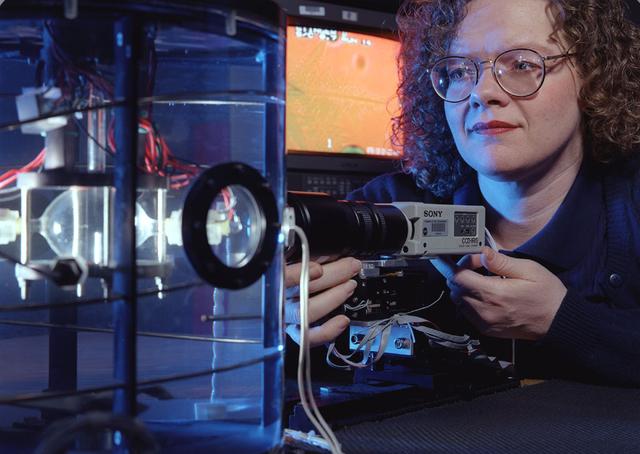

Jeri Briscoe of the video team inspects the optical system for proper alignment during a test run of the Equiaxed Dendritic Solidification Experiment (EDSE) located in the Microgravity Development Laboratory (MDL).
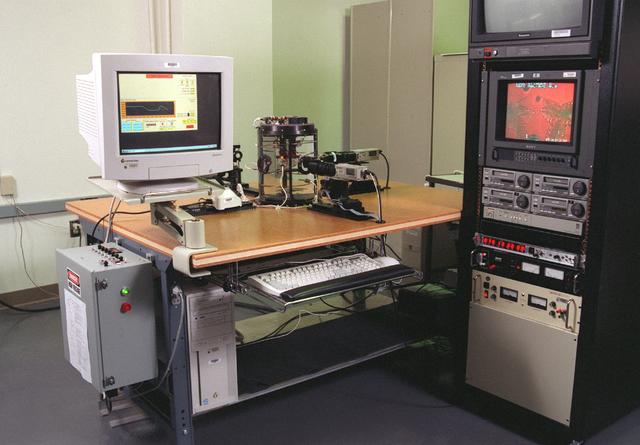

The Equiaxed Dendritic Solidification Experiment (EDSE) is a material sciences investigation under the Formation of Microstructures/pattern formation discipline. The objective is to study the microstructural evolution of and thermal interactions between several equiaxed crystals growing dendritically in a supercooled melt of a pure and transparent substance under diffusion controlled conditions. This image shows the overview for the EDSE in the Microgravity Development Lab (MDL).
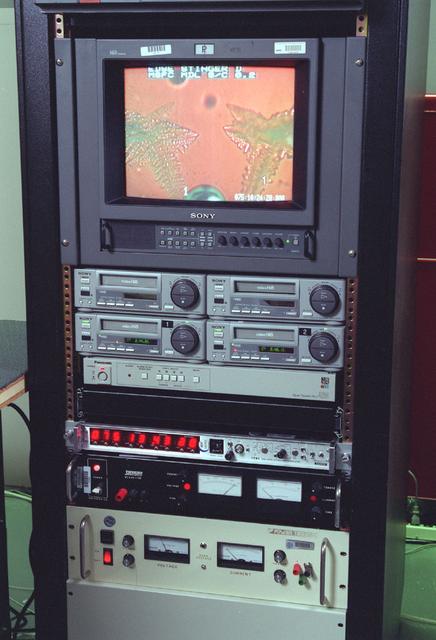

The Equiaxed Dendritic Solidification Experiment (EDSE) is a material sciences investigation under the Formation of Microstructures/pattern formation discipline. The objective is to study the microstructural evolution of and thermal interactions between several equiaxed crystals growing dendritically in a supercooled melt of a pure and transparent substance under diffusion controlled conditions. Video and power rack for the EDSE in the Microgravity Development Lab (MDL).
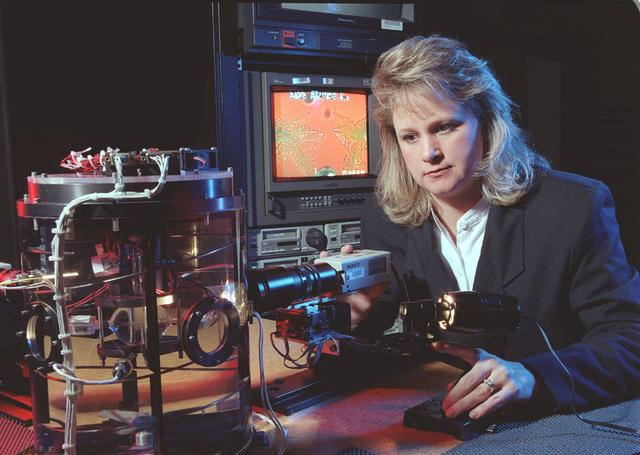

The Equiaxed Dendritic Solidification Experiment (EDSE) is a material sciences investigation under the Formation of Microstructures/pattern formation discipline. The objective is to study the microstructural evolution of and thermal interactions between several equiaxed crystals growing dendritically in a supercooled melt of a pure and transparent substance under diffusion controlled conditions. EDSE/TDSE project engineer, Zena Hester, monitors a test run of the EDSE located in the Microgravity Development Laboratory (MDL).
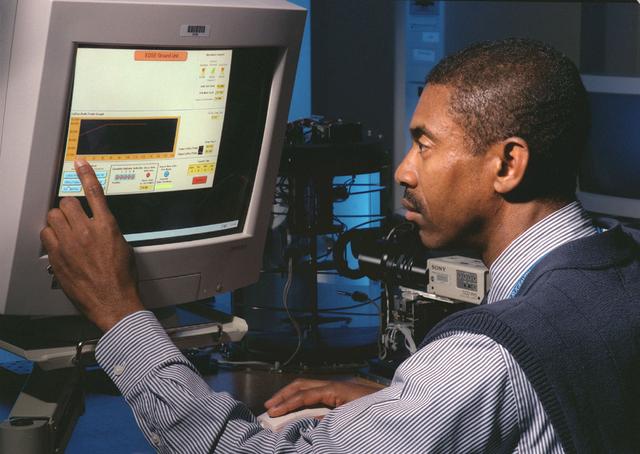

The Equiaxed Dendritic Solidification Experiment (EDSE) is a material sciences investigation under the Formation of Microstructures/pattern formation discipline. The objective is to study the microstructural evolution of and thermal interactions between several quiaxed crystals growing dendritically in a supercooled melt of a pure and transparent substance under diffusion controlled conditions. George Myers, controls engineer, monitors the thermal environment of a ground test for the EDSE located in the Microgravity Development Laboratory (MDL).
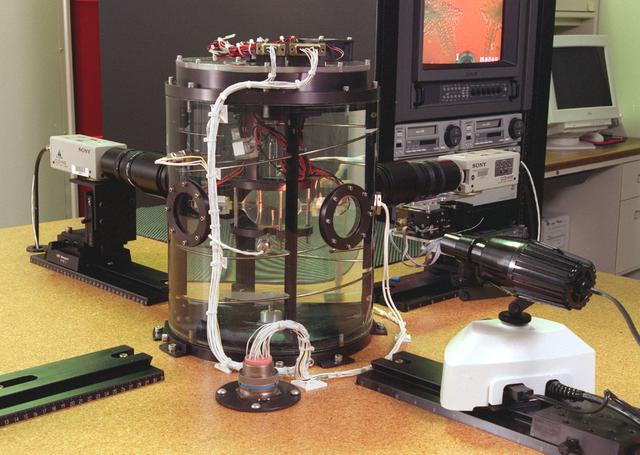

The Equiaxed Dendritic Solidification Experiment (EDSE) is a material sciences investigation under the Formation of Microstructures/pattern formation discipline. The objective is to study the microstructural evolution of and thermal interactions between several equiaxed crystals growing dendritically in a supercooled melt of a pure and transparent substance under diffusion controlled conditions. This image shows the isothermal bath and video system for the EDSE in the Microgravity Development Lab (MDL).
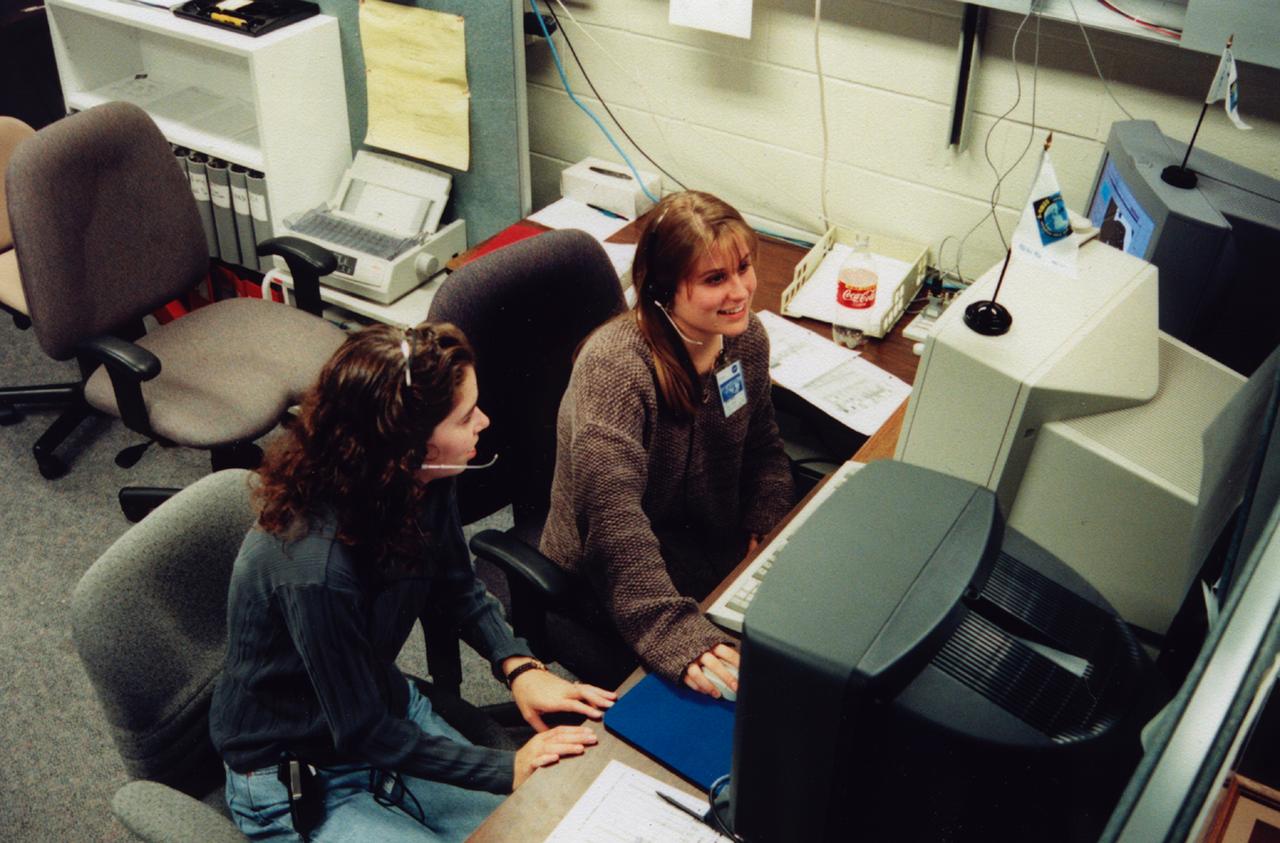

Undergraduate students Kristina Wines and Dena Renzo at Rensselaer Poloytech Institute (RPI) in Troy, NY, monitor the progress of the Isothermal Dendritic Growth Experiment (IDGE) during the U.S. Microgravity Payload-4 (USMP-4) mission (STS-87), Nov. 19 - Dec.5, 1997). Remote Operations Control Center (ROCC) like this one will become more common during operations with the International Space Station. The Isothermal Dendritic Growth Experiment (IDGE), flown on three Space Shuttle missions, is yielding new insights into virtually all industrially relevant metal and alloy forming operations. Photo credit: Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute (RPI)
United States Microgravity Payload-4 (USMP-4) experiments are prepared to be flown on Space Shuttle mission STS-87 in the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center (KSC). Seen in the foreground at left is the USMP-4 logo with the acronyms of its experiments. Above the American flag at left is the MEPHISTO experiment, a cooperative American and French investigation of the fundamentals of crystal growth. The large white vertical cylinder in the center of the photo is the Advanced Automated Directional Solidification Furnace (AADSF), which is a sophisticated materials science facility used for studying a common method of processing semiconductor crystals called directional solidification. The white horizontal tube to the right is the Isothermal Dendritic Growth Experiment (IDGE), which will be used to study the dendritic solidification of molten materials in the microgravity environment. All USMP-4 experiments are scheduled for launch aboard STS-87 on Nov. 19 from KSC
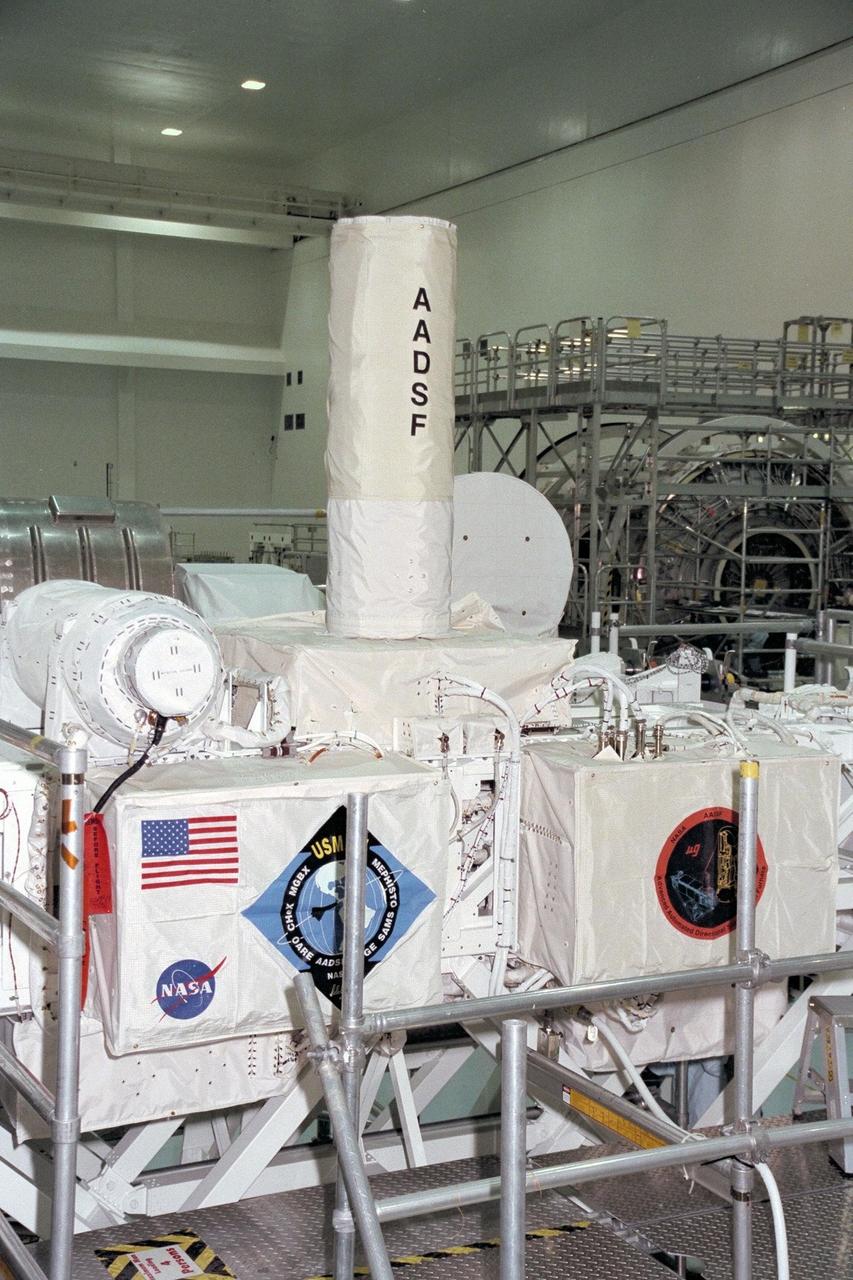
United States Microgravity Payload-4 (USMP-4) experiments are prepared to be flown on Space Shuttle mission STS-87 in the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center (KSC). The large white vertical cylinder in the center of the photo is the Advanced Automated Directional Solidification Furnace (AADSF) and the horizontal tube to the left of it is MEPHISTO, a French acronym for a cooperative American-French investigation of the fundamentals of crystal growth. Seen at right behind the AADSF in the circular white cover is the Isothermal Dendritic Growth Experiment (IDGE), which will be used to study the dendritic solidification of molten materials in the microgravity environment. Under the multi-layer insulation with the American flag and mission logo is the Space Acceleration Measurement System, or SAMS, which measures the microgravity conditions in which the experiments are conducted. All of these experiments are scheduled for launch aboard STS-87 on Nov. 19 from KSC
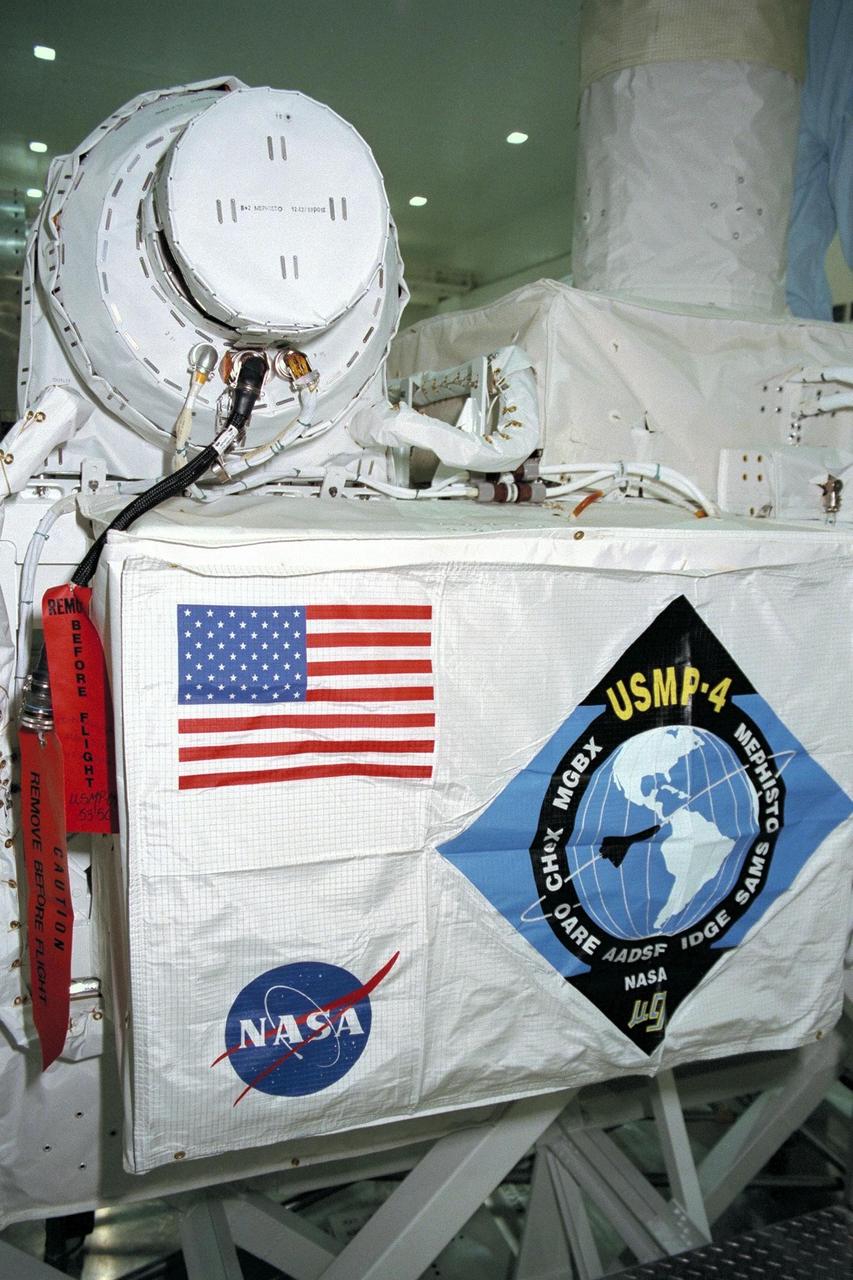

United States Microgravity Payload-4 (USMP-4) experiments are prepared to be flown on Space Shuttle mission STS-87 in the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center (KSC). The large white vertical cylinder in the middle of the photo is the Advanced Automated Directional Solidification Furnace (AADSF) and the horizontal tube to its left is MEPHISTO, the French acronym for a cooperative American-French investigation of the fundamentals of crystal growth. Seen to the right of the AADSF is the Isothermal Dendritic Growth Experiment (IDGE), which will be used to study the dendritic solidification of molten materials in the microgravity environment. Under the multi-layer insulation with the American flag and mission logo is the Space Acceleration Measurement System, or SAMS, which measures the microgravity conditions in which the experiments are conducted. All of these experiments are scheduled for launch aboard STS-87 on Nov. 19 from KSC
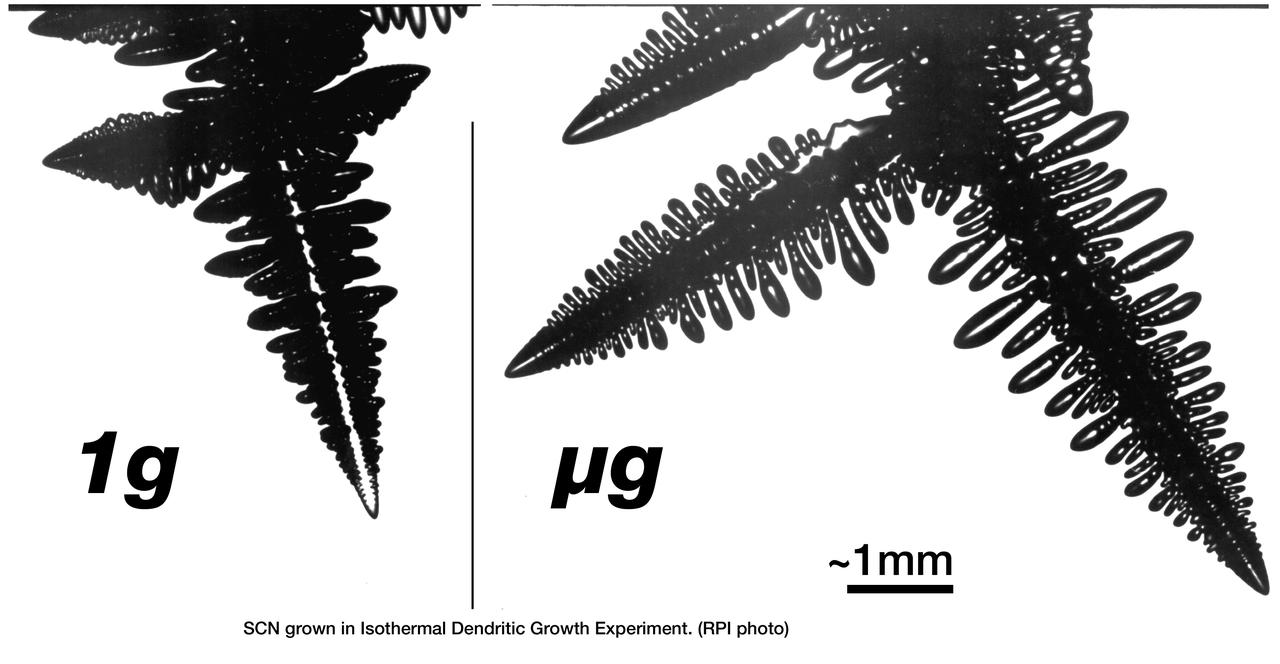
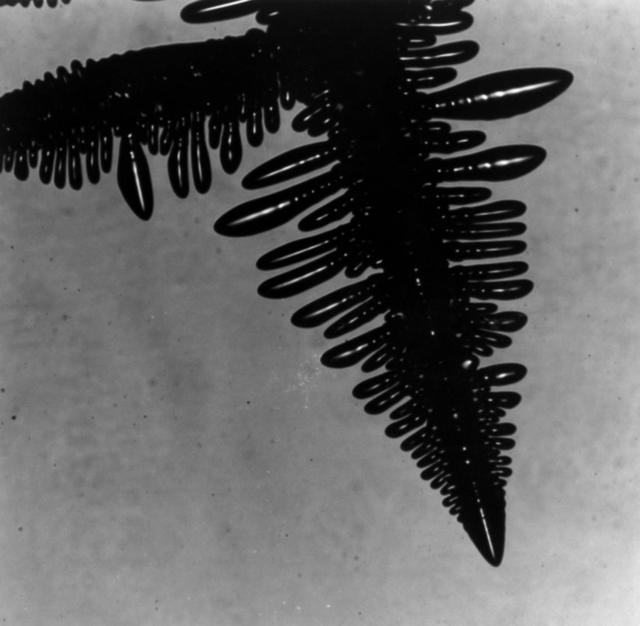
The Isothermal Dendritic Growth Experiment (IDGE), flown on three Space Shuttle missions, is yielding new insights into virtually all industrially relevant metal and alloy forming operations. IDGE used transparent organic liquids that form dendrites (treelike structures) similar to the crystals that form inside metal alloys. Comparing Earth-based and space-based dentrite growth velocity, tip size and shape provid a better understanding of the fundamentals of dentritic growth, including gravity's effects. These shadowgraphic images show succinonitrile (SCN) dentrites growing in a melt (liquid). The space-grown crystals also have cleaner, better defined sidebranches. IDGE was developed by Rensselaer Polytechnic Institude (RPI) and NASA/ Glenn Research Center(GRC). Advanced follow-on experiments are being developed for flight on the International Space Station. Photo gredit: NASA/Glenn Research Center
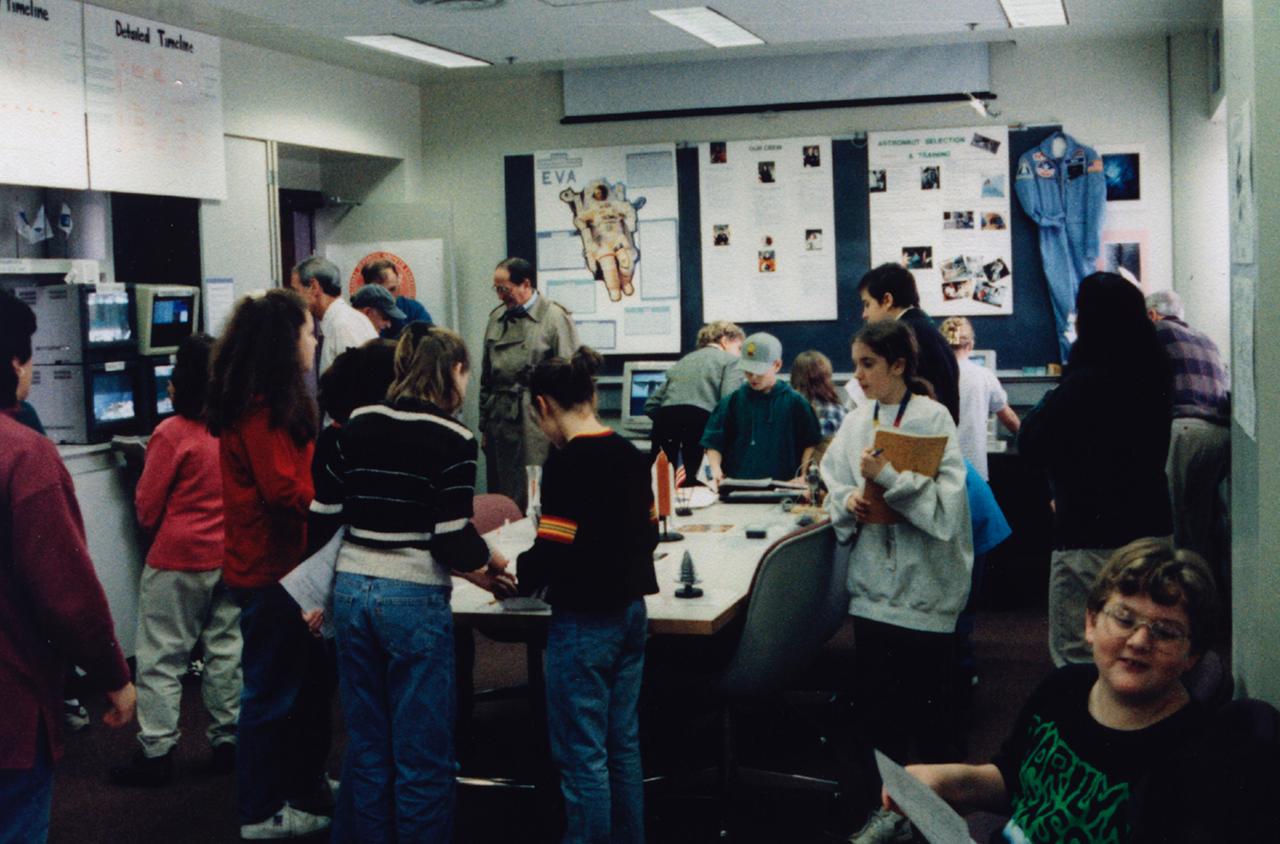

High school students observe the progress of the Isothermal Dendritic Growth Experiment (IDGE) during the U.S. Microgravity Payload-4 mission (STS-87, Nov. 19 - Dec. 5, 1997) at the IDGE Remote Operations Control Center (ROCC) at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute (RPI) in Troy, NY. As part of the its outreach activity, the experiment team set up the center so students and the public could observe IDGE in progress and learn more about space and microgravity research. Photo credit: RPI
Experiments with colloidal solutions of plastic microspheres suspended in a liquid serve as models of how molecules interact and form crystals. For the Dynamics of Colloidal Disorder-Order Transition (CDOT) experiment, Paul Chaikin of Princeton University has identified effects that are attributable to Earth's gravity and demonstrated that experiments are needed in the microgravity of orbit. Space experiments have produced unexpected dendritic (snowflake-like) structures. To date, the largest hard sphere crystal grown is a 3 mm single crystal grown at the cool end of a ground sample. At least two more additional flight experiments are plarned aboard the International Space Station. This image is from a video downlink.
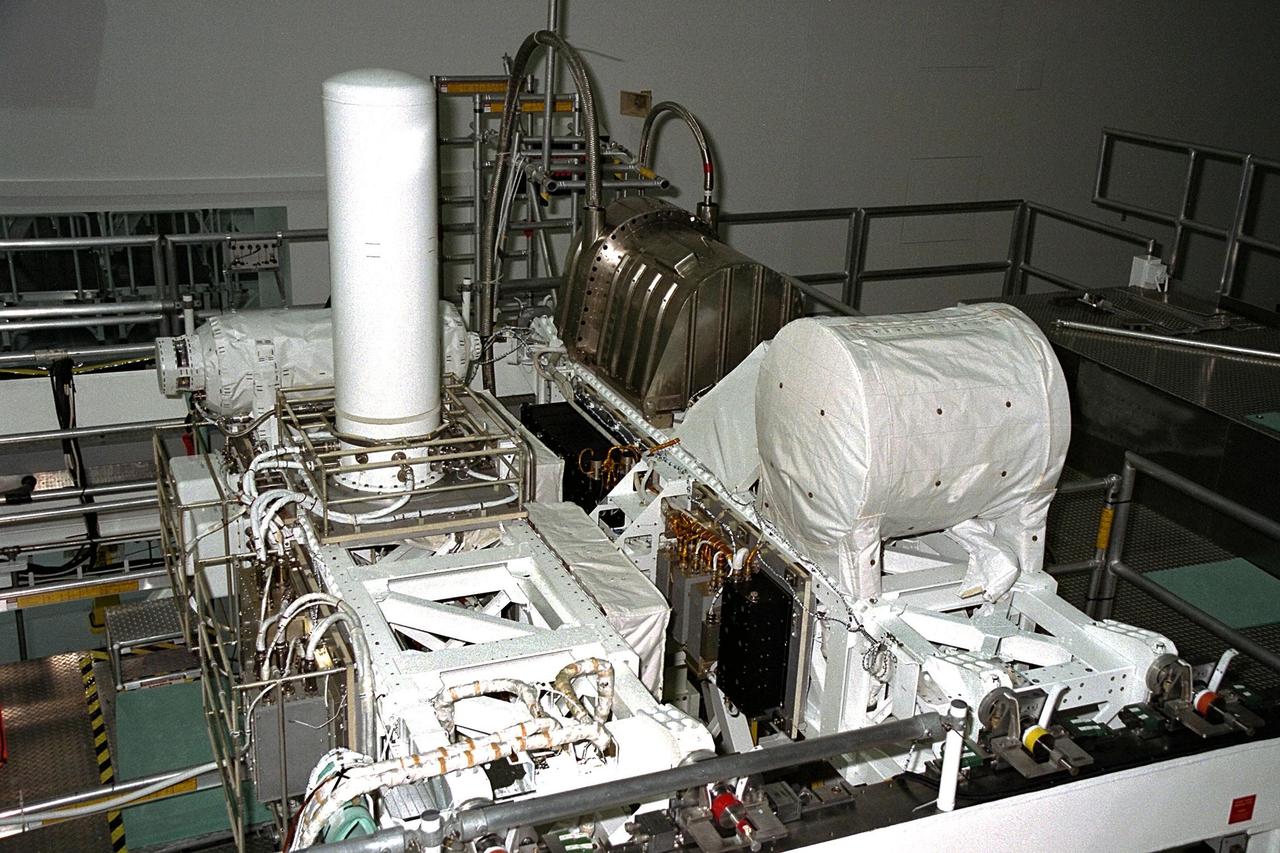

United States Microgravity Payload-4 (USMP-4) experiments are prepared to be flown on Space Shuttle mission STS-87 in the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center (KSC). Seen in the foreground at right is the Isothermal Dendritic Growth Experiment (IDGE), which will be used to study the dendritic solidification of molten materials in the microgravity environment. The metallic breadbox-like structure behind the IDGE is the Confined Helium Experiment (CHeX) that will study one of the basic influences on the behavior and properties of materials by using liquid helium confined between solid surfaces and microgravity. The large white vertical cylinder at left is the Advanced Automated Directional Solidification Furnace (AADSF) and the horizontal tube behind it is MEPHISTO, the French acronym for a cooperative American-French investigation of the fundamentals of crystal growth. Just below the left end of MEPHISTO is the Space Acceleration Measurement System, or SAMS, which measures the microgravity conditions in which the experiments are conducted. All of these experiments are scheduled for launch aboard STS-87 on Nov. 19 from KSC
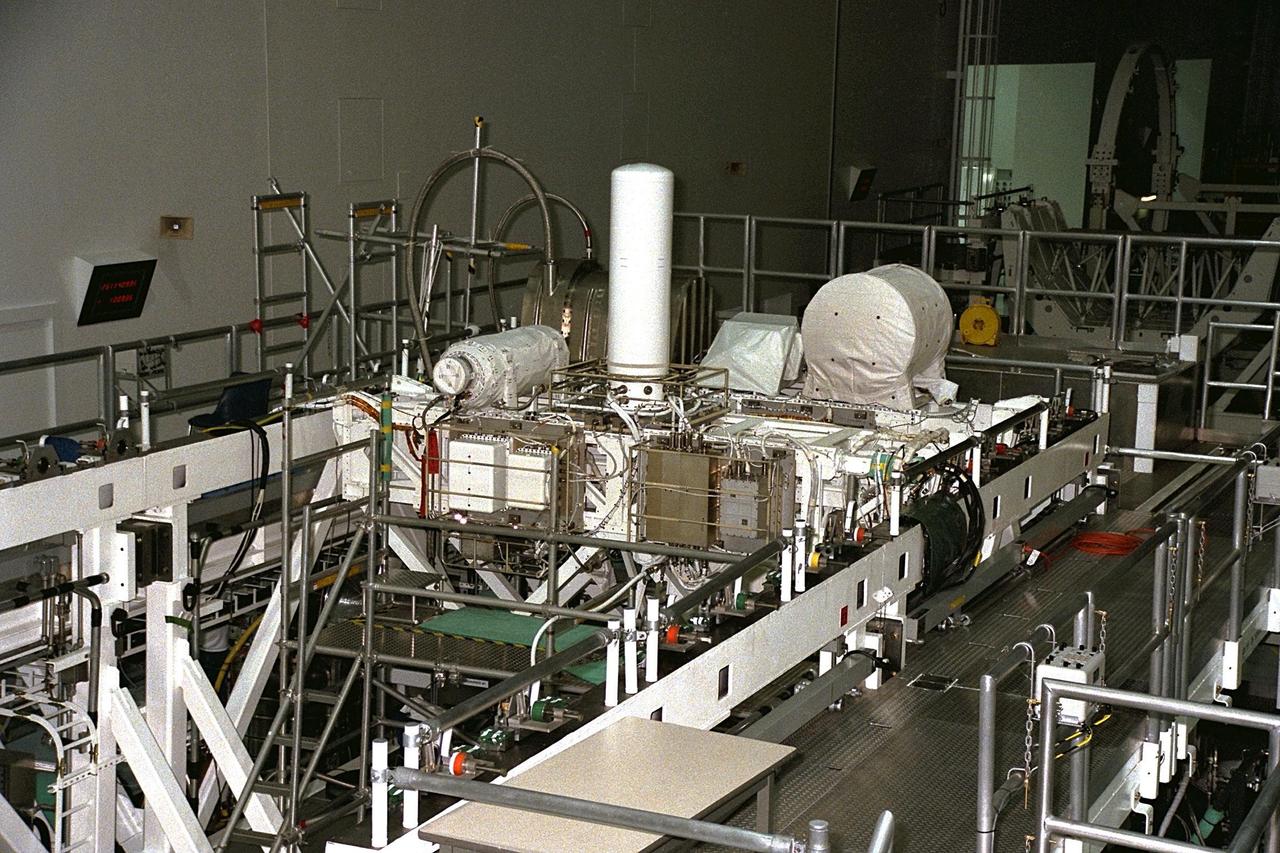
United States Microgravity Payload-4 (USMP-4) experiments are prepared to be flown on Space Shuttle mission STS-87 in the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center (KSC). Seen at right in the circular white cover is the Isothermal Dendritic Growth Experiment (IDGE), which will be used to study the dendritic solidification of molten materials in the microgravity environment. The large white vertical cylinder in the center of the photo is the Advanced Automated Directional Solidification Furnace (AADSF) and the horizontal tube to the left of it is MEPHISTO, a French acronym for a cooperative American-French investigation of the fundamentals of crystal growth. Just below MEPHISTO is the Space Acceleration Measurement System, or SAMS, which measures the microgravity conditions in which the experiments are conducted. The The metallic breadbox-like structure behind the AADSF is the Confined Helium Experiment (CHeX) that will study one of the basic influences on the behavior and properties of materials by using liquid helium confined between solid surfaces and microgravity. All of these experiments are scheduled for launch aboard STS-87 on Nov. 19 from KSC
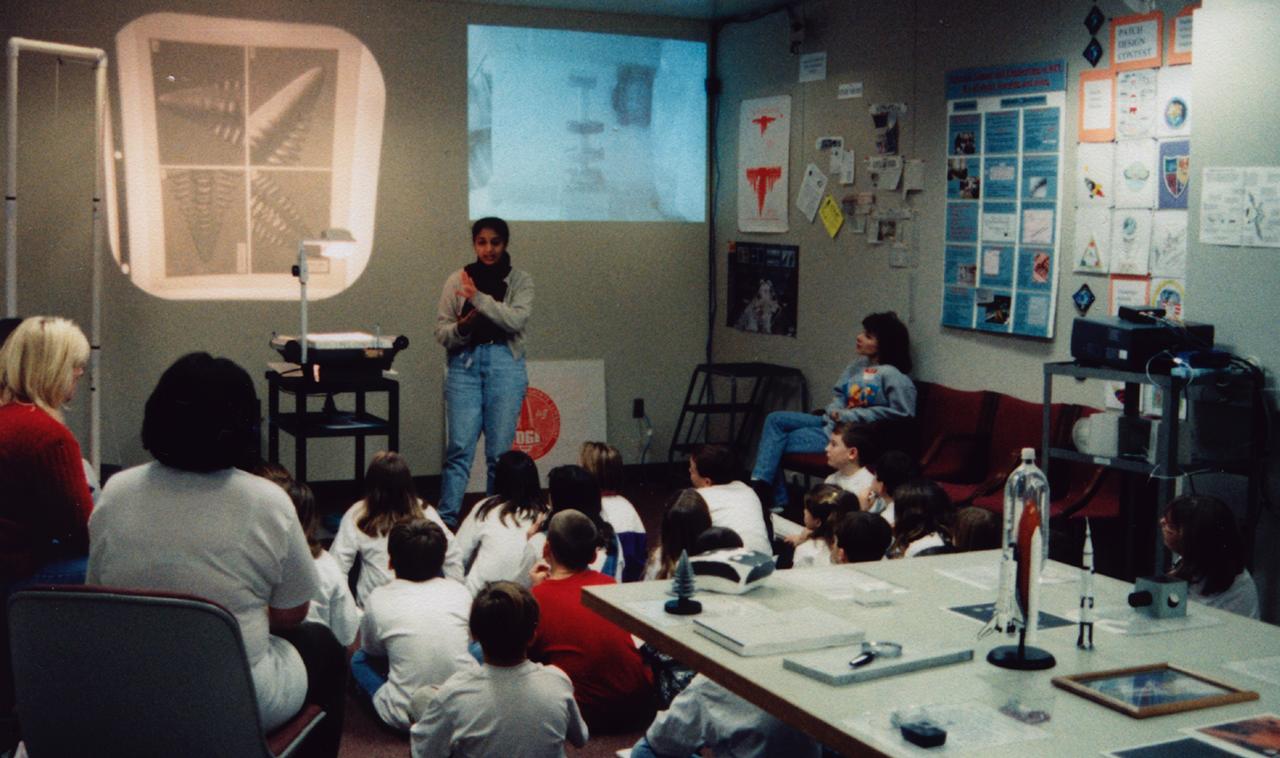

Pratima Rao lectures students about materials science research in space during the U.S. Microgravity Payload-4 (USMP-4) mission (STS-87, Nov. 19 - Dec. 5, 1997) in the visitor's center set up by the Isothermal Dendritic Growth Experiment (IDGE) team at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute (RPI) in Troy, NY. IDGE, flown on three Space Shuttle missions, is yielding new insights into virtually all industrially relevant metal and alloy forming operations. Photo credit: RPI
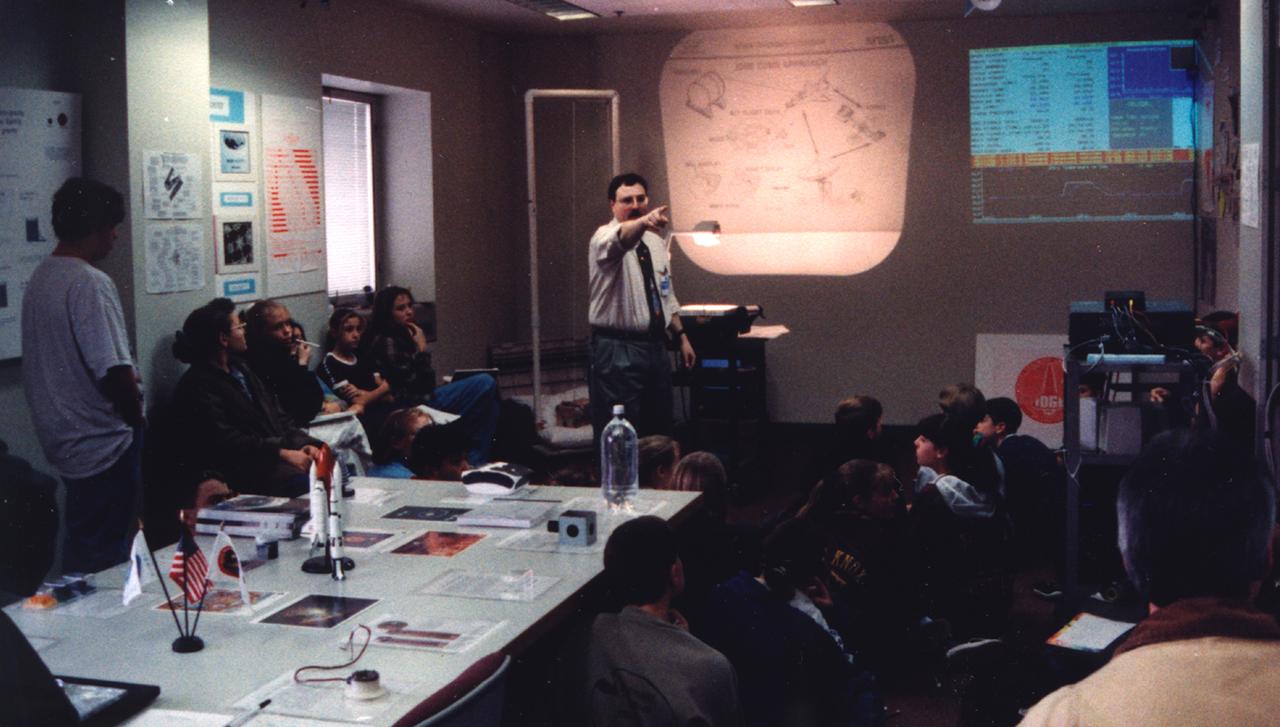

Matthew Koss lectures middle-school students about materials science research in space during the U.S. Microgravity Payload-4 (USMP-4) mission (STS-87, Nov. 19 - Dec. 5, 1997) in the visitor's center set up by the Isothermal Dendritic Growth Experiment (IDGE) team at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute (RPI)in Troy, NY. IDGE, flown on three Space Shuttle missions, is yielding new insights into virtually all industrially relevant metal and alloy forming operations. Photo credit: RPI
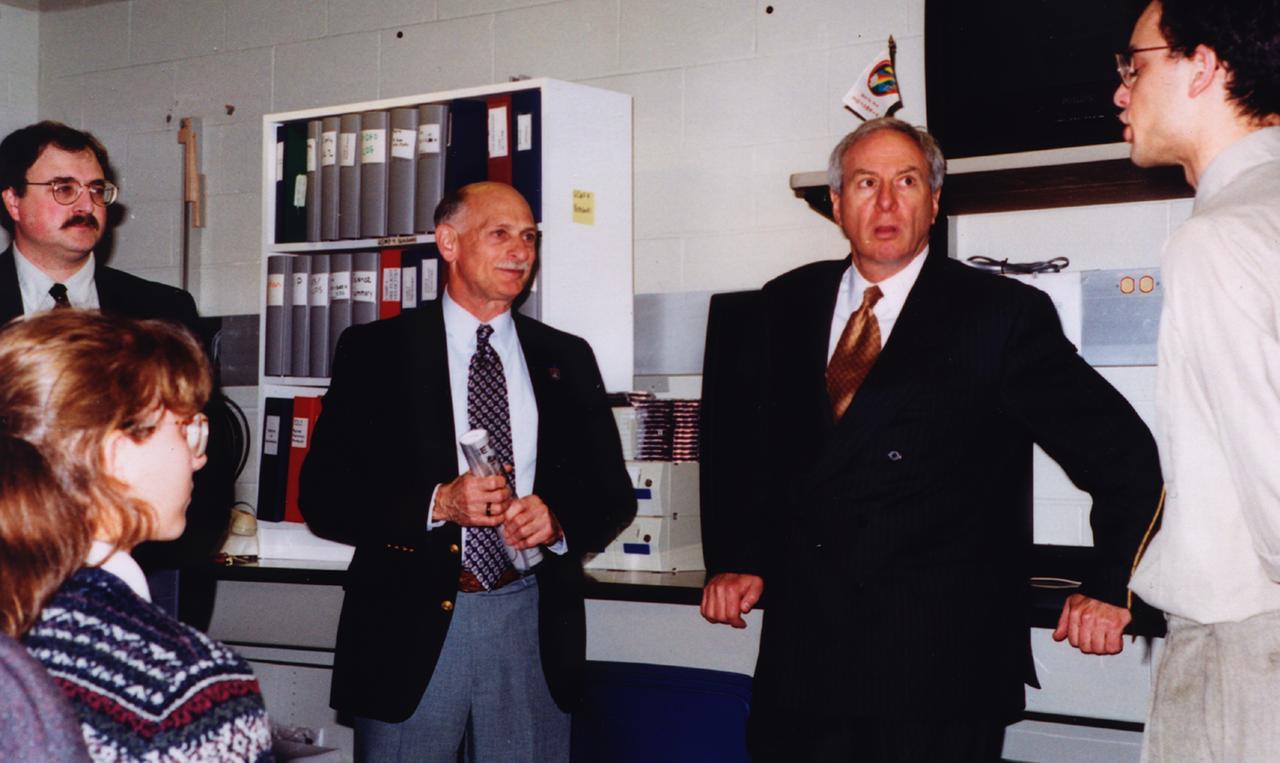

NASA Administrator Daniel Goldin (second from right) visits the control room of the Isothermal Dendritic Growth Experiment (IDGE) in Remote Operations Control Center (ROCC) at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute (RPI)in Troy, NY, during RPI's 175th arniversary. IDGE, flown on three Space Shuttle missions, is yielding new insights into virtually all industrially relevant metal and alloy forming operations. Photo credit: RPI
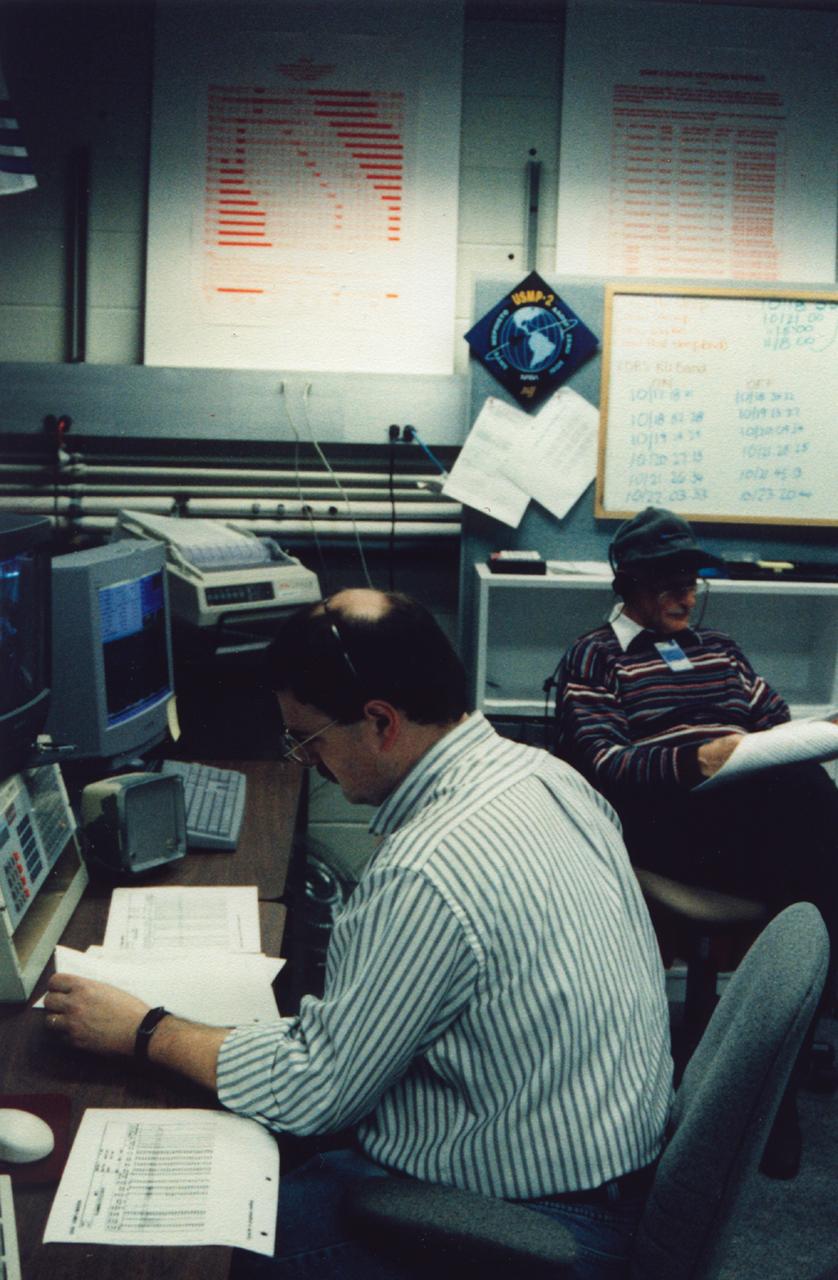

Matthew Koss (forground) and Martin Glicksman (rear), principal investigator and lead scientist (respectively), review plans for the next step in the Isothermal Dendritic Growth Experiment (IDGE) during the U.S. Microgravity Payload-4 (USMP-4) mission (STS-87, Nov. 19 - Dec. 5, 1997). Remote Operations Control Center (ROCC) like this one, at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute (RPI) in Troy, NY, will become more common during operations with the International Space Station. IDGE, flown on three Space Shuttle missions, is yielding new insights into virtually all industrially relavent metal and alloy forming operations. Photo credit: Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute (RPI)
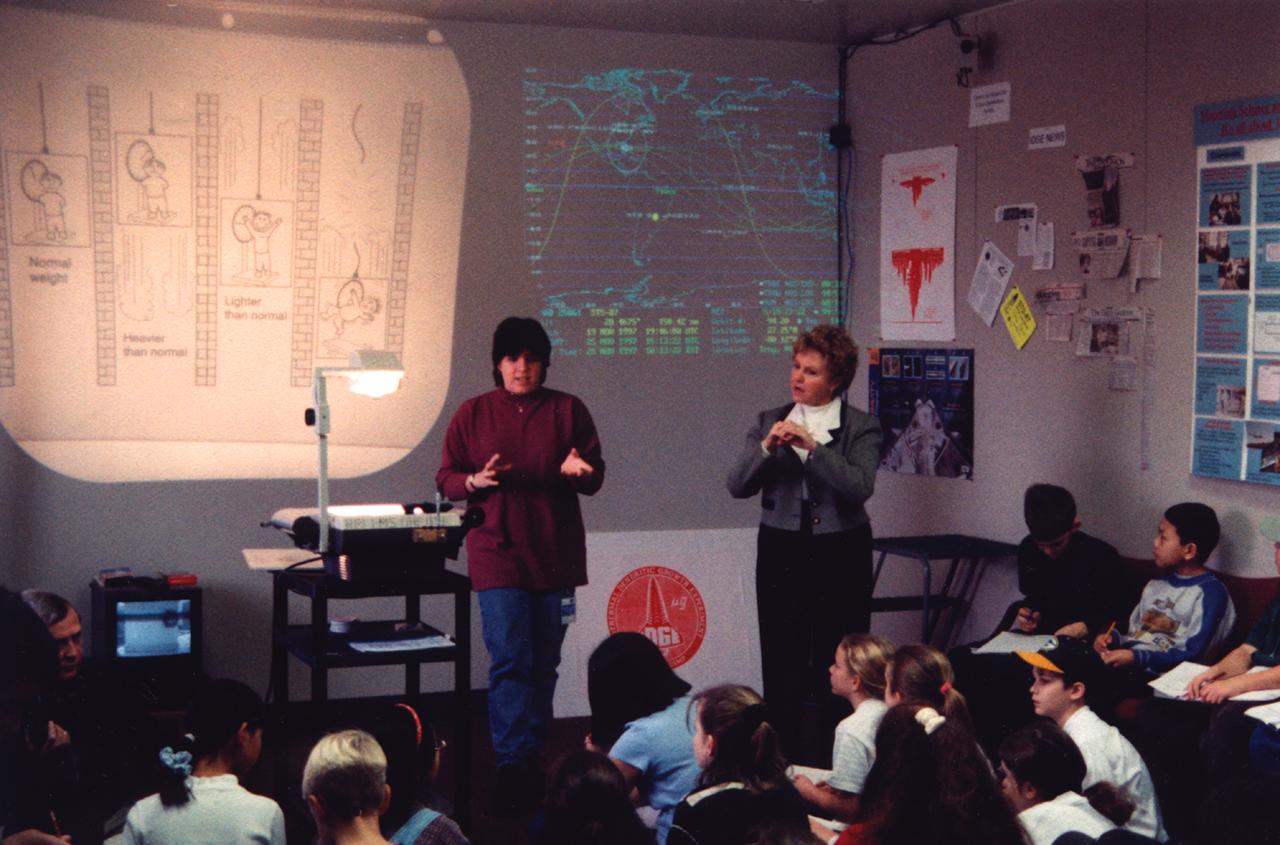

Paula Crawford (assisted by an American Sign Language interpreter) lectures students about materials science research in space during the U.S. Microgravity Payload-4 mission (STS-87, Nov. 19 - Dec. 5, 1997) in the visitor's center set up by the Isothermal Dendritic Growth Experiment (IDGE) team at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute (RPI) in Troy, NY. IDGE, flown on three Space Shuttle mission, is yielding new insights into virtually all industrially relevant metal and alloy forming operation. Photo credit: Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute (RPI)
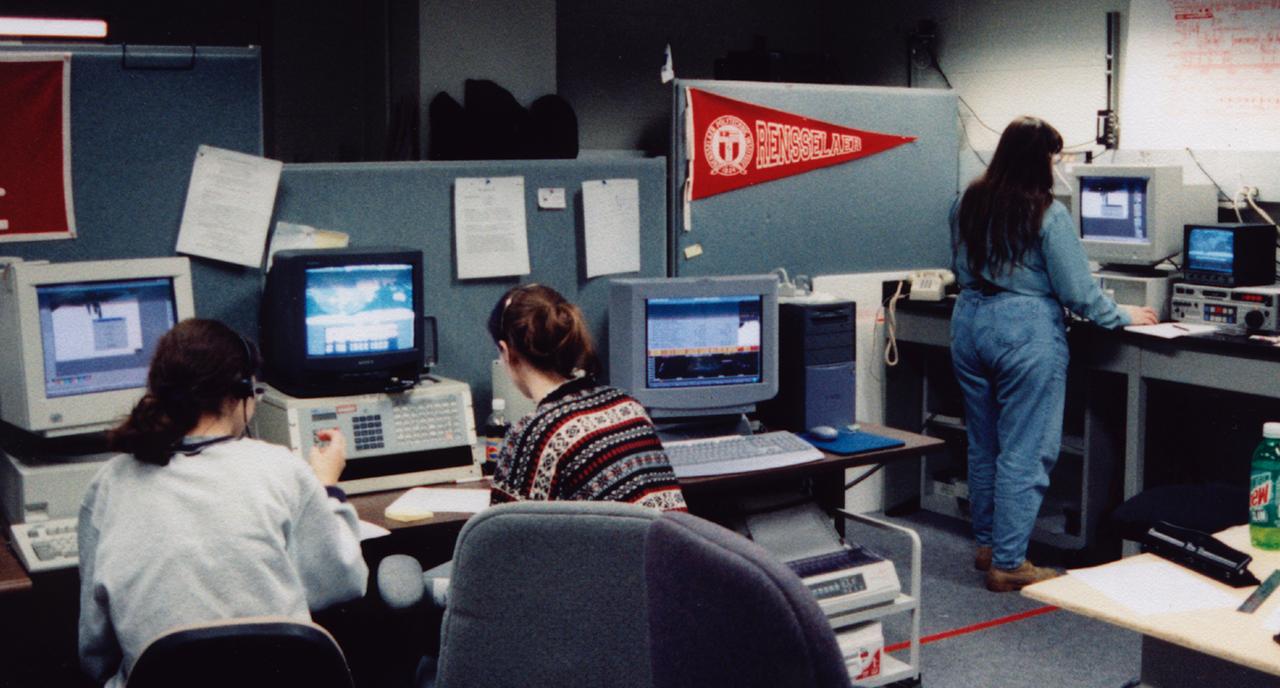

Students at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute (RPI) in Troy, NY, monitor the progress of the Isothermal Dendritic Growth Experiment (IDGE) during the U.S. Microgravity Payload-4 (USMP-4) mission (STS-87, Nov. 19 - Dec. 5, 1997). Remote Operation Control Center (ROCC) like this one will become more common during operations with International Space Station. IDGE, flown on three Space Shuttle missions, is yielding new insights into virtually all industrially relevant metal and alloy forming operations. Photo credit: Renssenlaer Polythnic Institute (RPI)
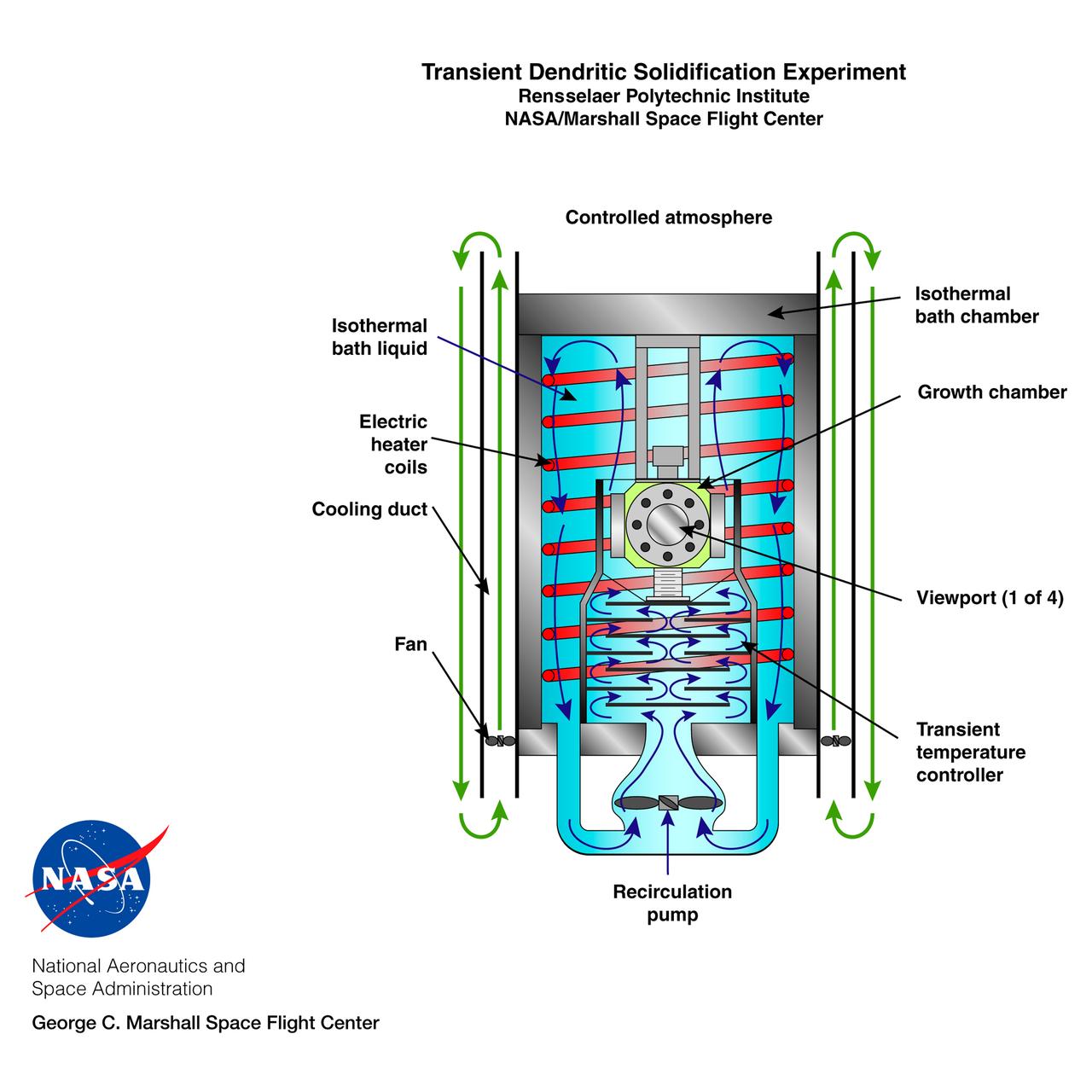
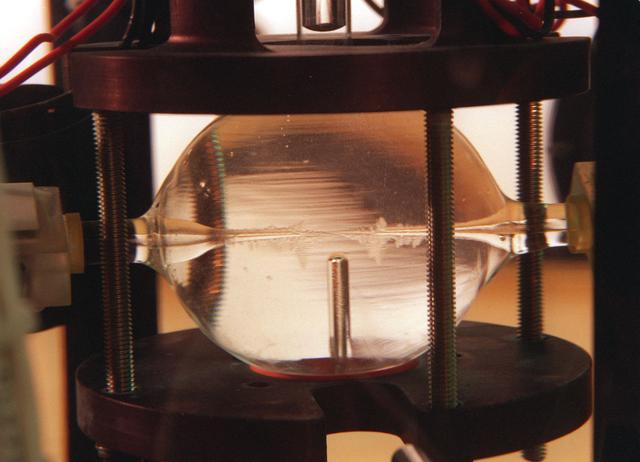
The Transient Dentritic Solidification Experiment (TDSE) is being developed as a candidate for flight aboard the International Space Station. TDSE will study the growth of dentrites (treelike crystalline structures) in a transparent material (succinonitrile or SCN) that mimics the behavior of widely used iron-based metals. Basic work by three Space Shuttle flights (STS-62, STS-75, and STS-87) of the Isothermal Dendritic Growth Experiment (IDGE) is yielding new insights into virtually all industrially relevant metal and alloy forming operations. The TDSE is similar to IDGE, but will maintain a constant temperature while varying pressure on the dentrites. Shown here is a cutaway of the isothermal bath containing its growth cell at the heart of the TDSE. The principal investigator is Matthew Koss of College of the Holy Cross in Worcester, MA. Note: an Acrobat PDF version is available from http://microgravity.nasa.gov/gallery
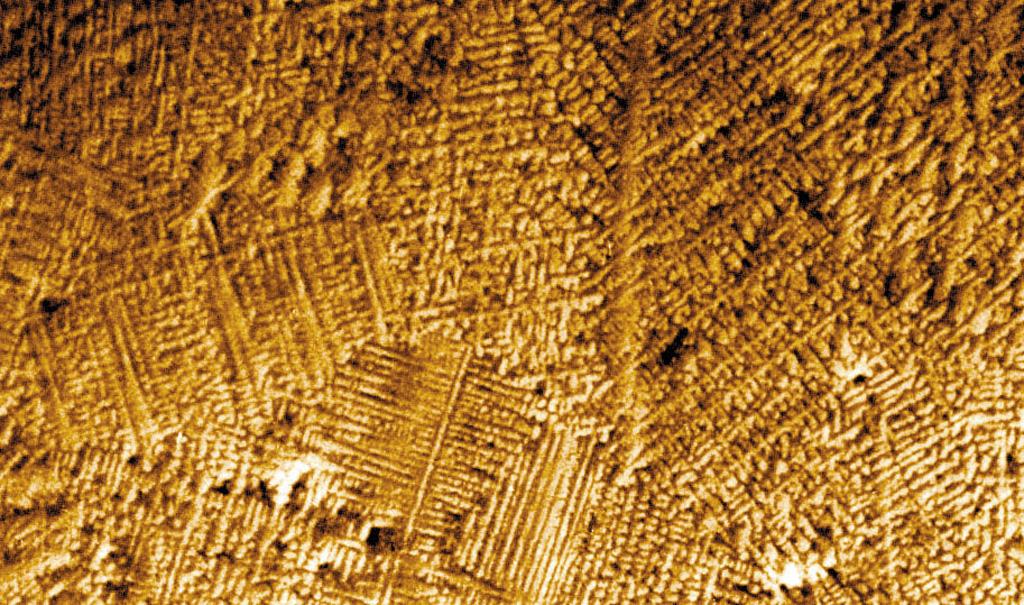
Researchers have found that as melted metals and alloys (combinations of metals) solidify, they can form with different arrangements of atoms, called microstructures. These microstructures depend on the shape of the interface (boundary) between the melted metal and the solid crystal it is forming. There are generally three shapes that the interface can take: planar, or flat; cellular, which looks like the cells of a beehive; and dendritic, which resembles tiny fir trees. Convection at this interface can affect the interface shape and hide the other phenomena (physical events). To reduce the effects of convection, researchers conduct experiments that examine and control conditions at the interface in microgravity. Microgravity also helps in the study of alloys composed of two metals that do not mix. On Earth, the liquid mixtures of these alloys settle into different layers due to gravity. In microgravity, the liquid metals do not settle, and a solid more uniform mixture of both metals can be formed.