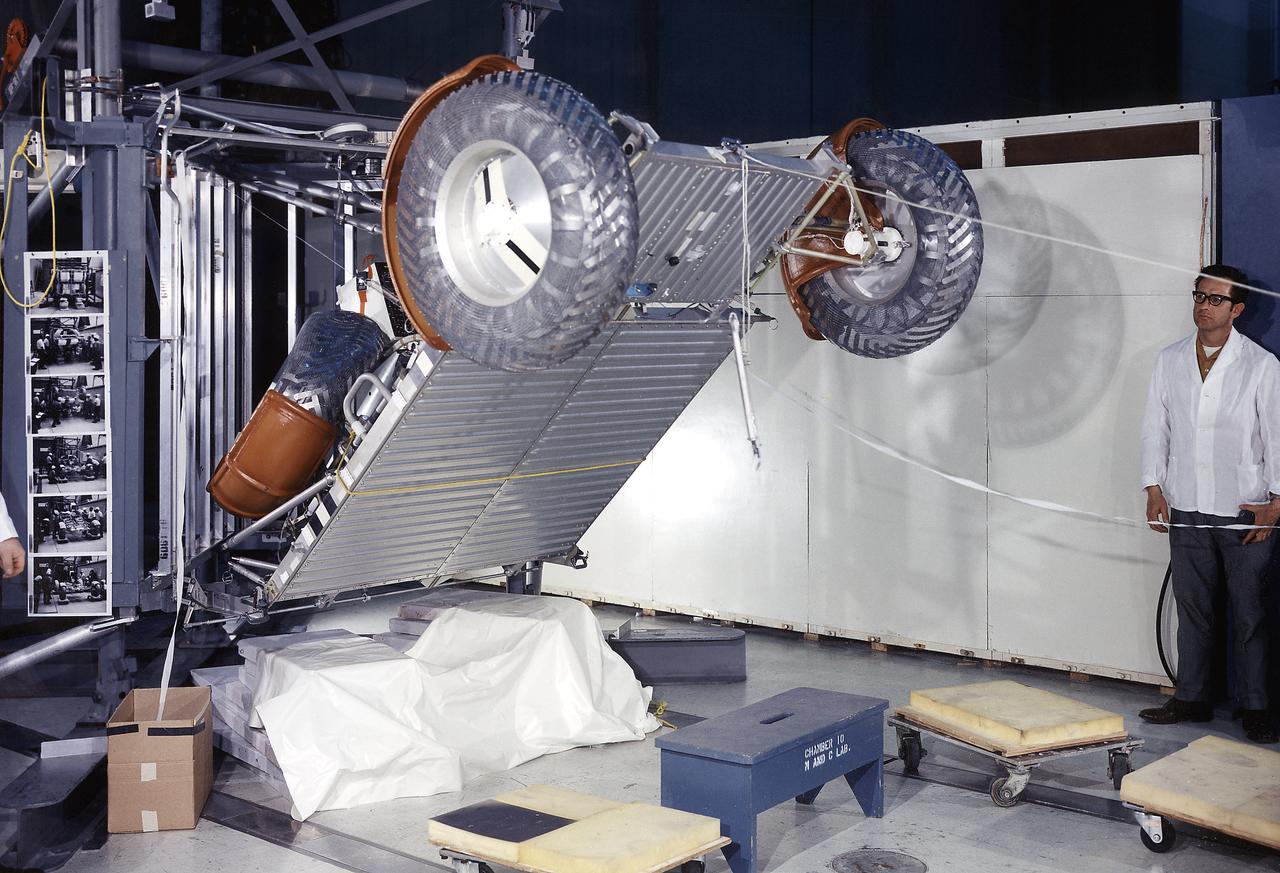
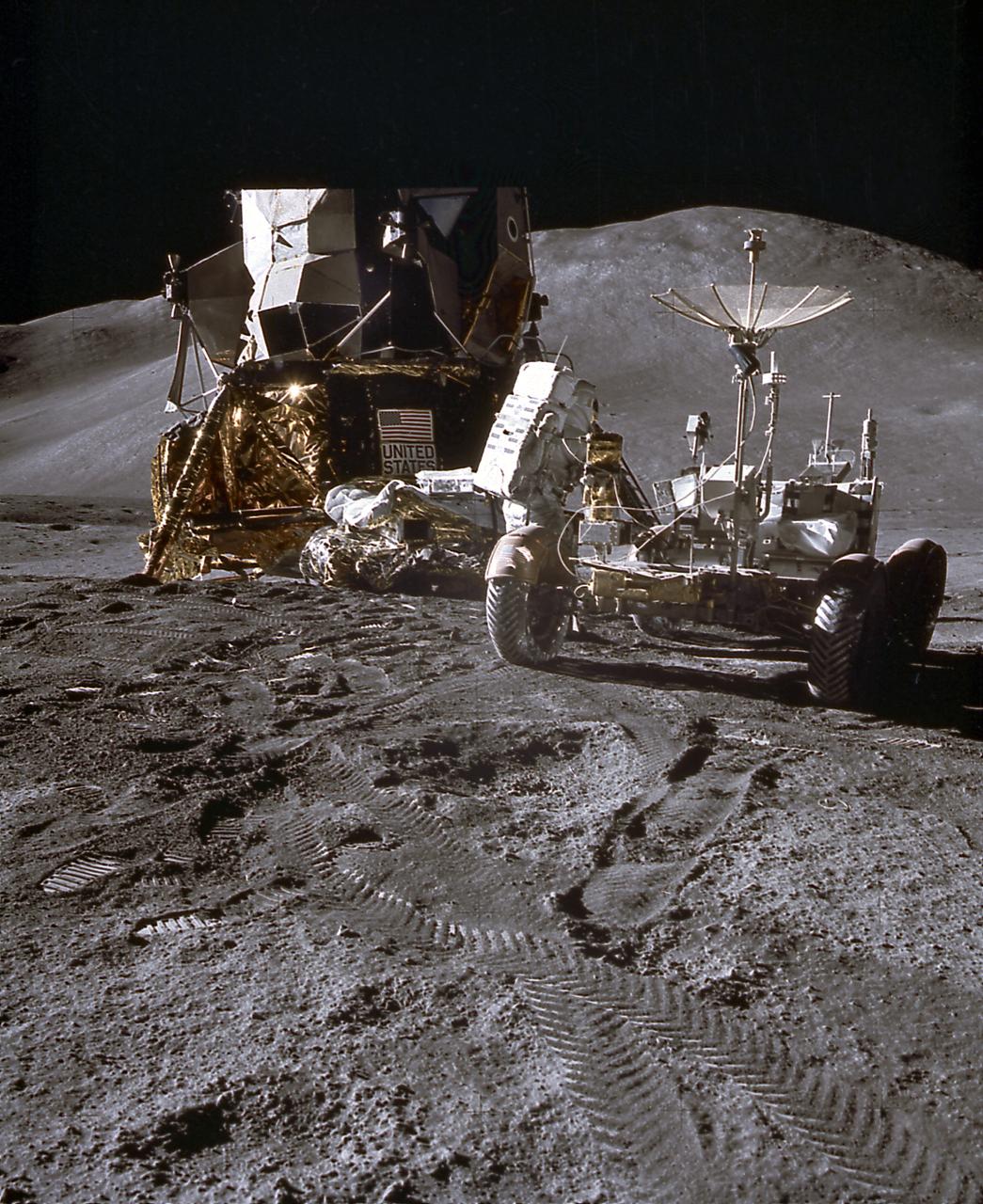
This photograph was taken during a deployment simulation of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). The LRV was built to give Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during the last three lunar exploration missions; Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17. It was designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and built by the Boeing Company.
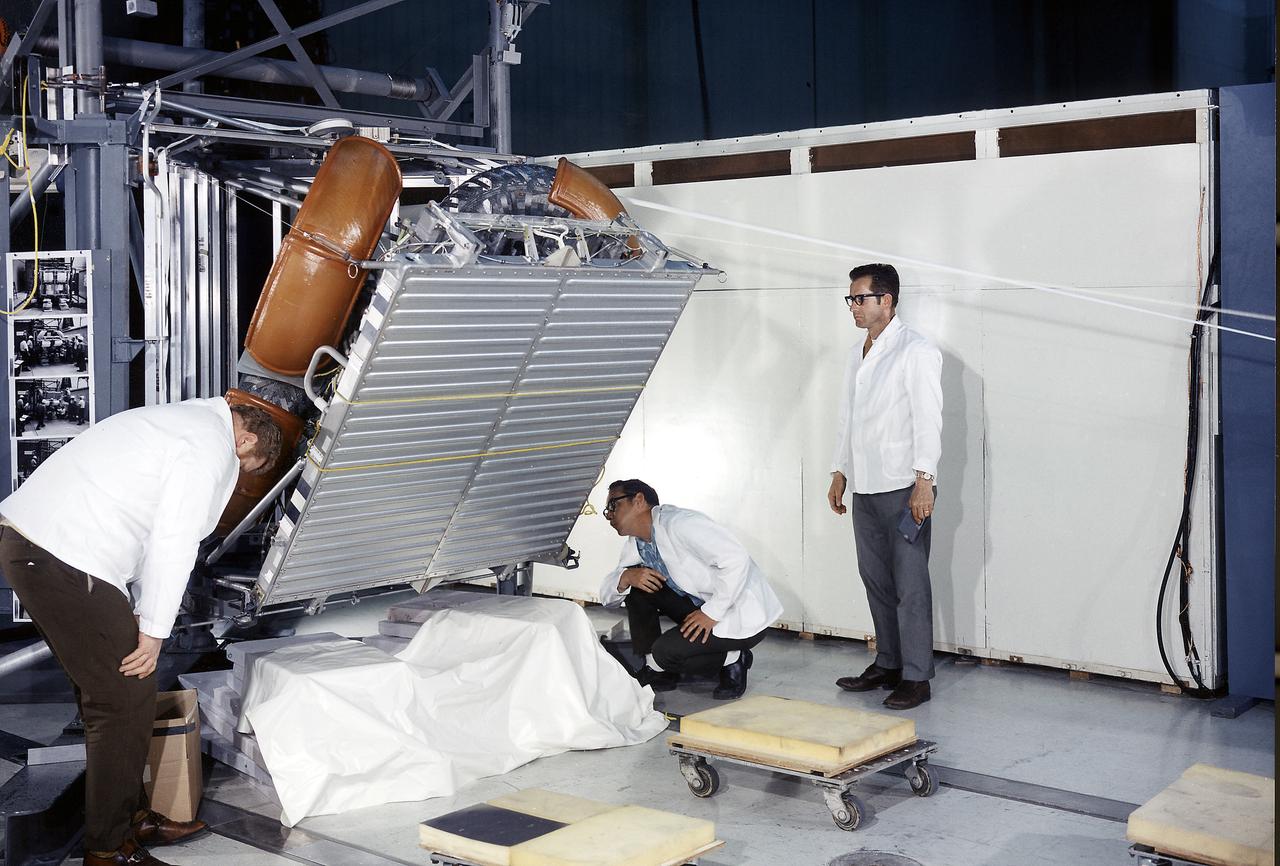

This photograph was taken during a deployment simulation of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). The LRV was built to give Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during the last three lunar exploration missions; Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17. It was designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and built by the Boeing Company.
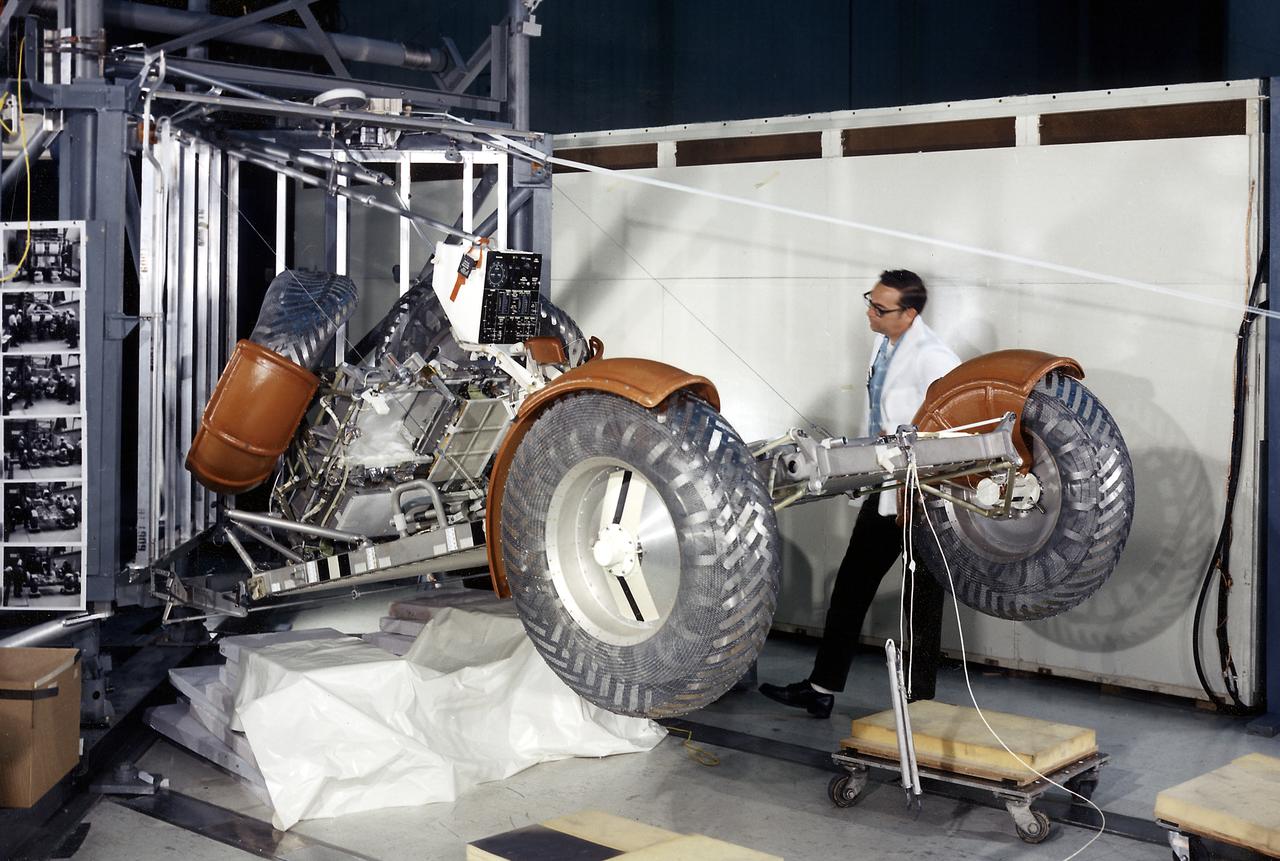

This photograph was taken during a deployment simulation of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). The LRV was built to give Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during the last three lunar exploration missions; Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17. It was designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and built by the Boeing Company.
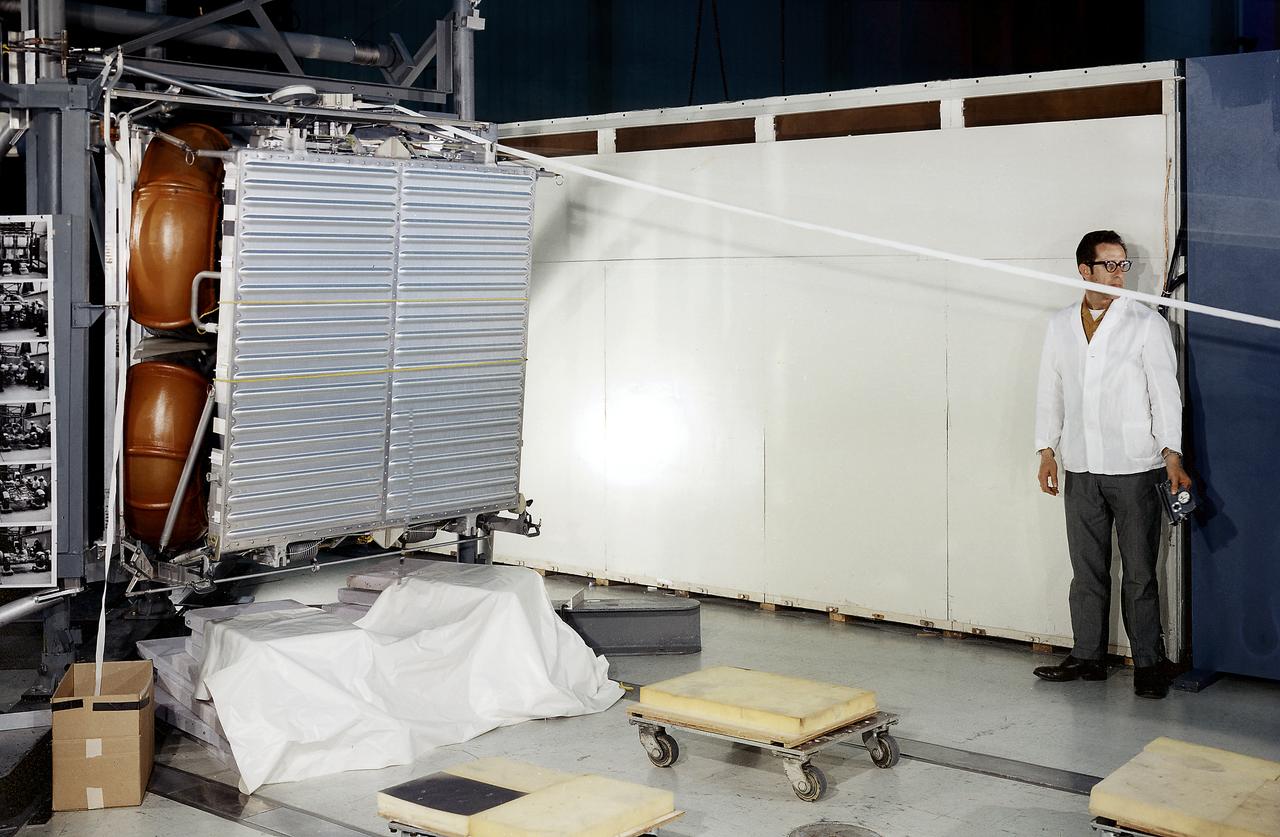

This photograph was taken during a deployment simulation of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). The LRV was built to give Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during the last three lunar exploration missions; Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17. It was designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and built by the Boeing Company.

This animated GIF shows the deployment of the Perseverance rover's remote sensing mast during a cold test in a space simulation chamber at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory. The test took place in October 2019. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23889

This photograph of an astronaut getting the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) ready for exploration of the lunar surface was taken during activities of the Apollo 15 mission. Designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center and built by the Boeing Company, the LRV was first used on the Apollo 15 mission and increased the range of astronauts' mobility and productivity on the lunar surface.
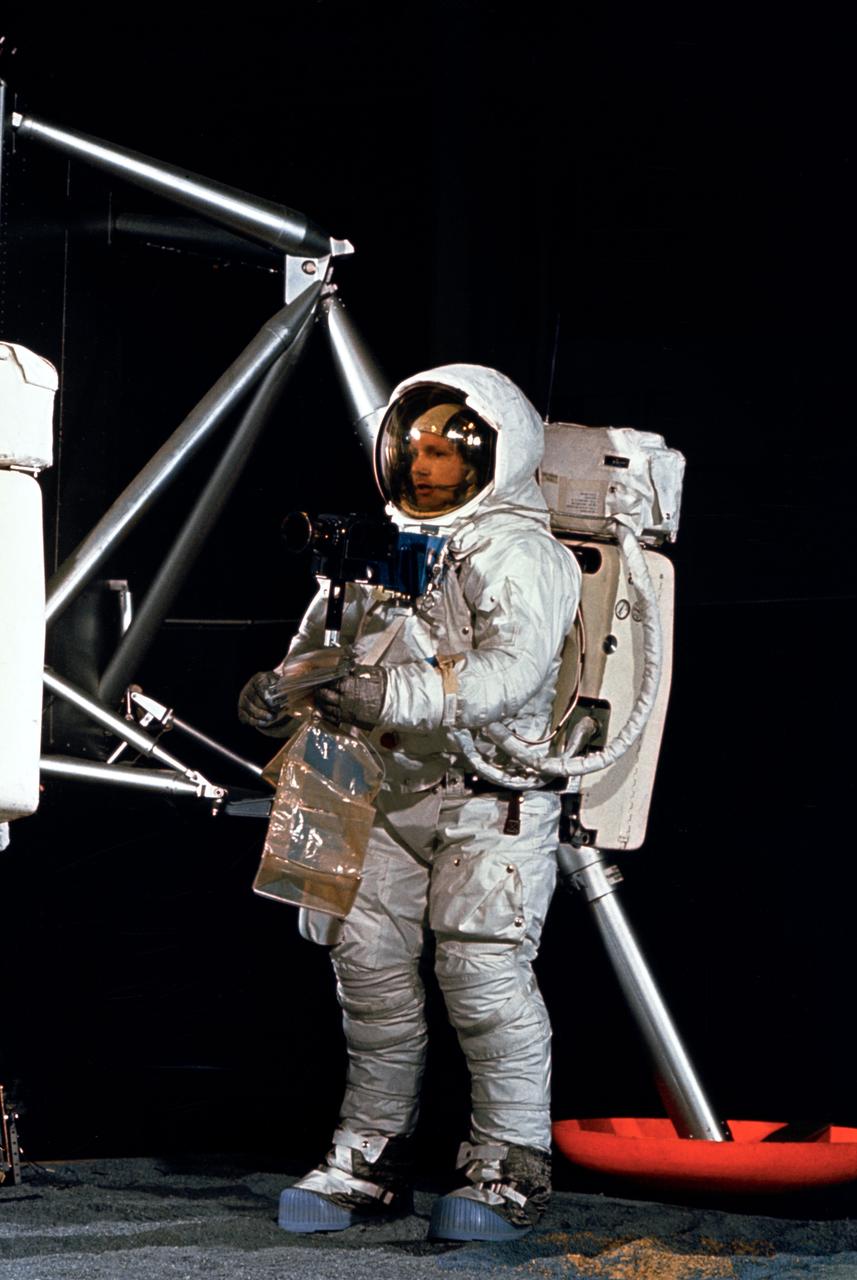

S69-32242 (22 April 1969) --- Astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, wearing an Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU), participates in a simulation of deploying and using lunar tools, on the surface of the moon, during a training exercise in Building 9 on April 22, 1969. Armstrong, commander of the Apollo 11 lunar landing mission, is holding sample bags. On the left is the Lunar Module (LM) mock-up.
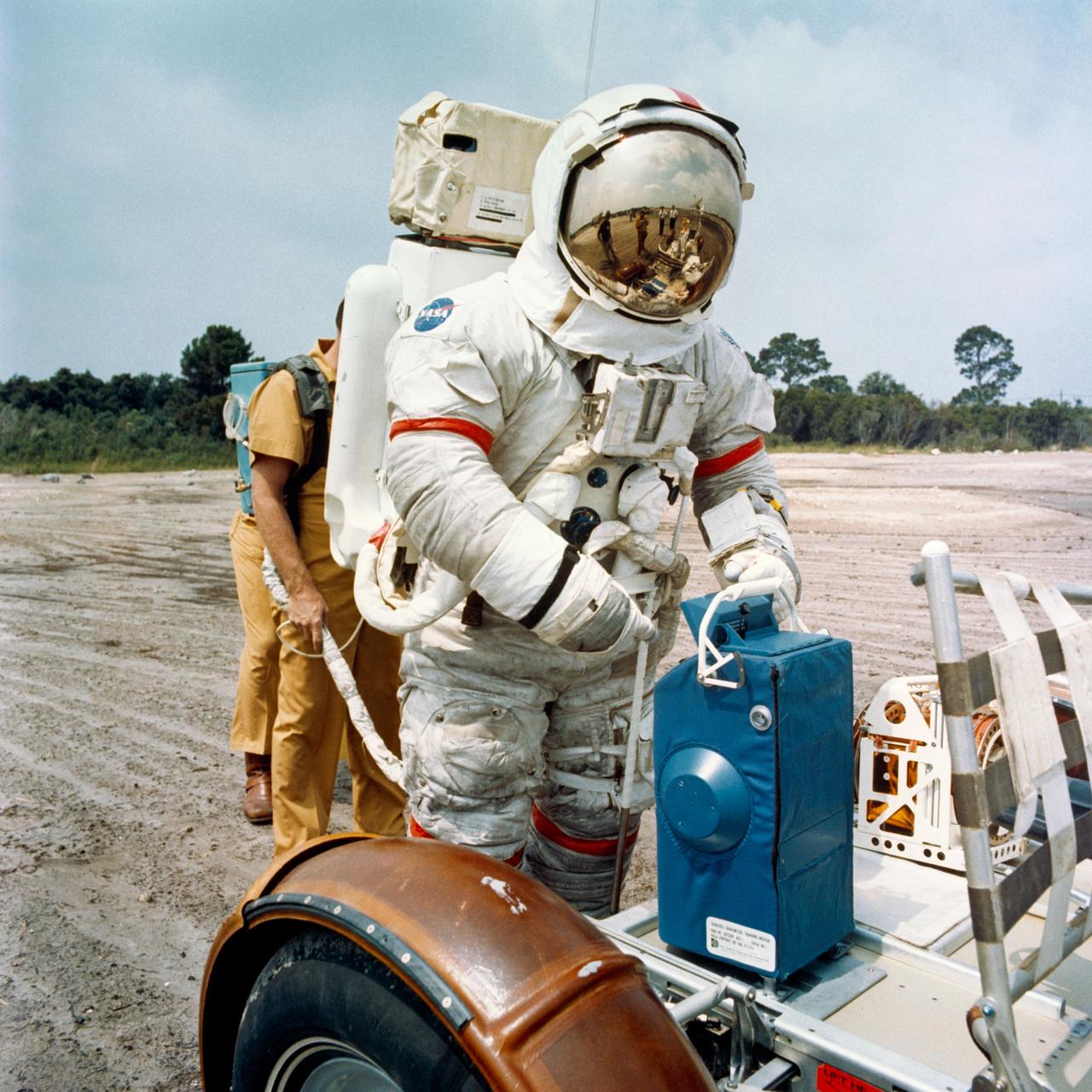

S72-44420 (8 June 1972) --- Astronaut Eugene A. Cernan, commander of the Apollo 17 lunar landing mission, prepares to remove a traverse gravimeter training mock-up from a Lunar Roving Vehicle for deployment during lunar surface extravehicular activity simulations at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC), Florida.
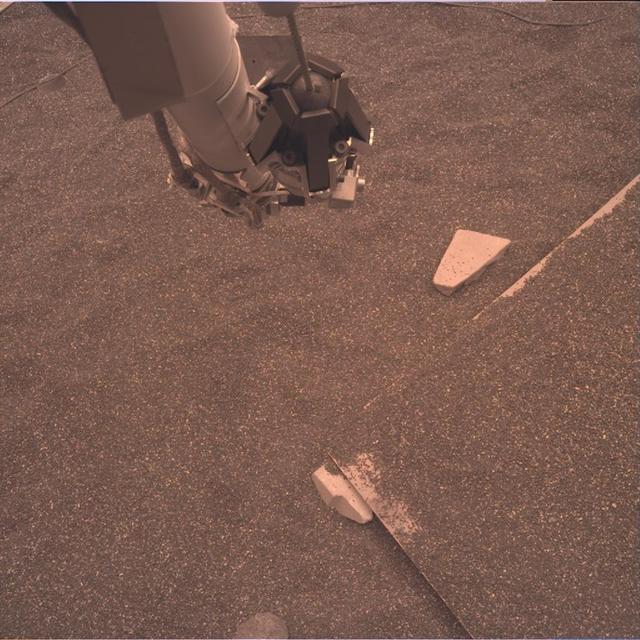

This test image from an engineering model of NASA's InSight lander shows part of the lander's robotic arm and the simulated Martian ground at a testbed at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. The testbed aims to mimic the environment InSight will encounter at Mars so engineers can prepare for the spacecraft operations to come. This image is expected to be similar to the raw or unprocessed images that InSight will send back to Earth. It was taken by the instrument deployment camera attached to InSight's robotic arm. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22827
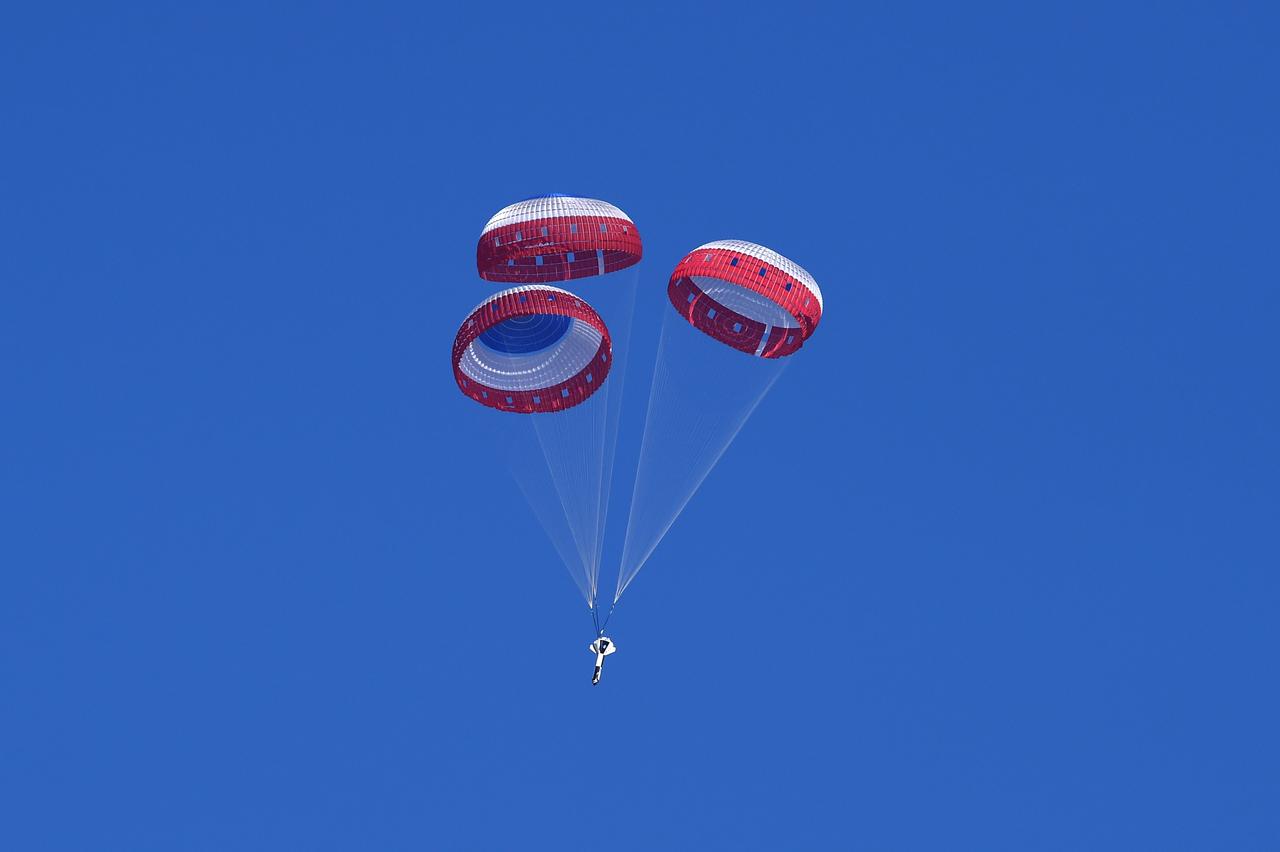

Boeing conducted the first in a series of reliability tests of its CST-100 Starliner flight drogue and main parachute system by releasing a long, dart-shaped test vehicle from a C-17 aircraft over Yuma, Arizona. Two more tests are planned using the dart module, as well as three similar reliability tests using a high fidelity capsule simulator designed to simulate the CST-100 Starliner capsule’s exact shape and mass. In both the dart and capsule simulator tests, the test spacecraft are released at various altitudes to test the parachute system at different deployment speeds, aerodynamic loads, and or weight demands. Data collected from each test is fed into computer models to more accurately predict parachute performance and to verify consistency from test to test.
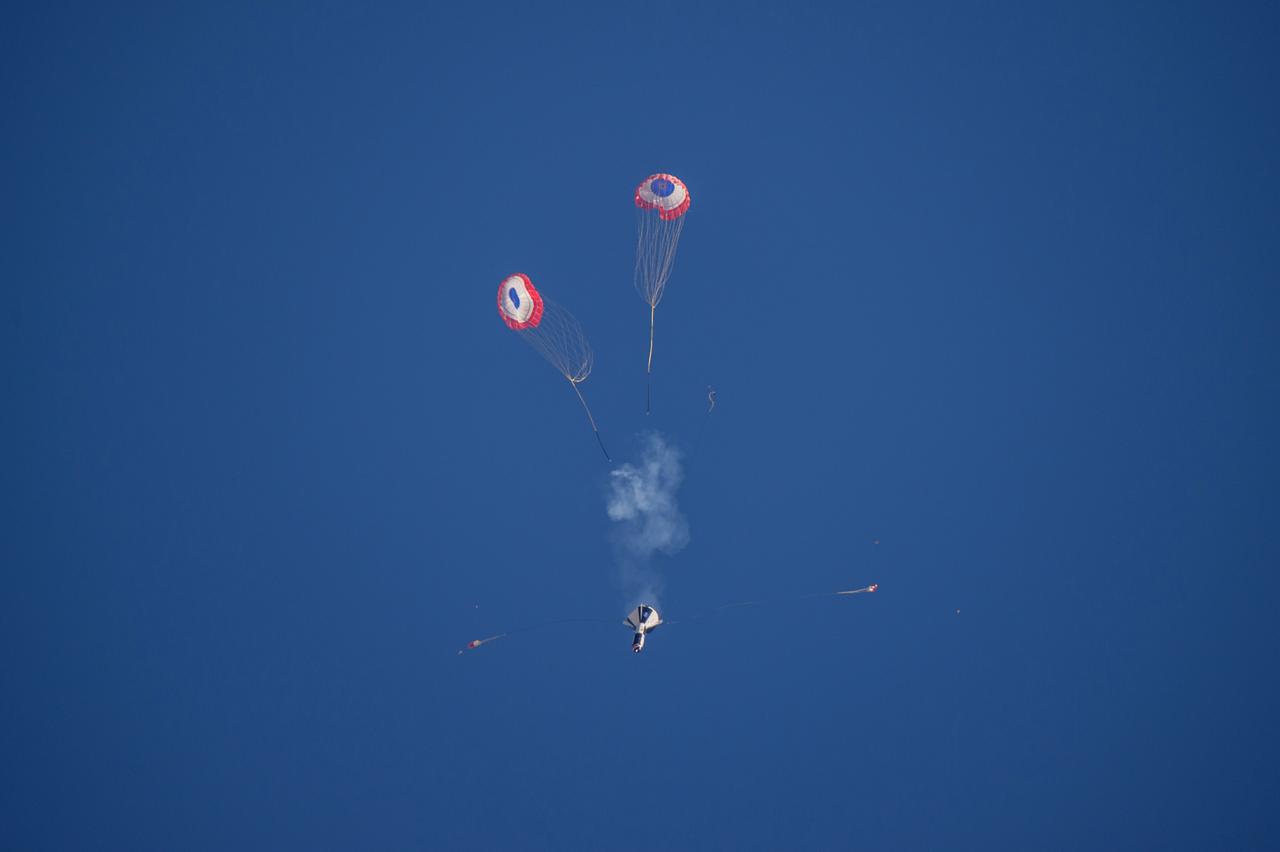

Boeing conducted the first in a series of reliability tests of its CST-100 Starliner flight drogue and main parachute system by releasing a long, dart-shaped test vehicle from a C-17 aircraft over Yuma, Arizona. Two more tests are planned using the dart module, as well as three similar reliability tests using a high fidelity capsule simulator designed to simulate the CST-100 Starliner capsule’s exact shape and mass. In both the dart and capsule simulator tests, the test spacecraft are released at various altitudes to test the parachute system at different deployment speeds, aerodynamic loads, and or weight demands. Data collected from each test is fed into computer models to more accurately predict parachute performance and to verify consistency from test to test.
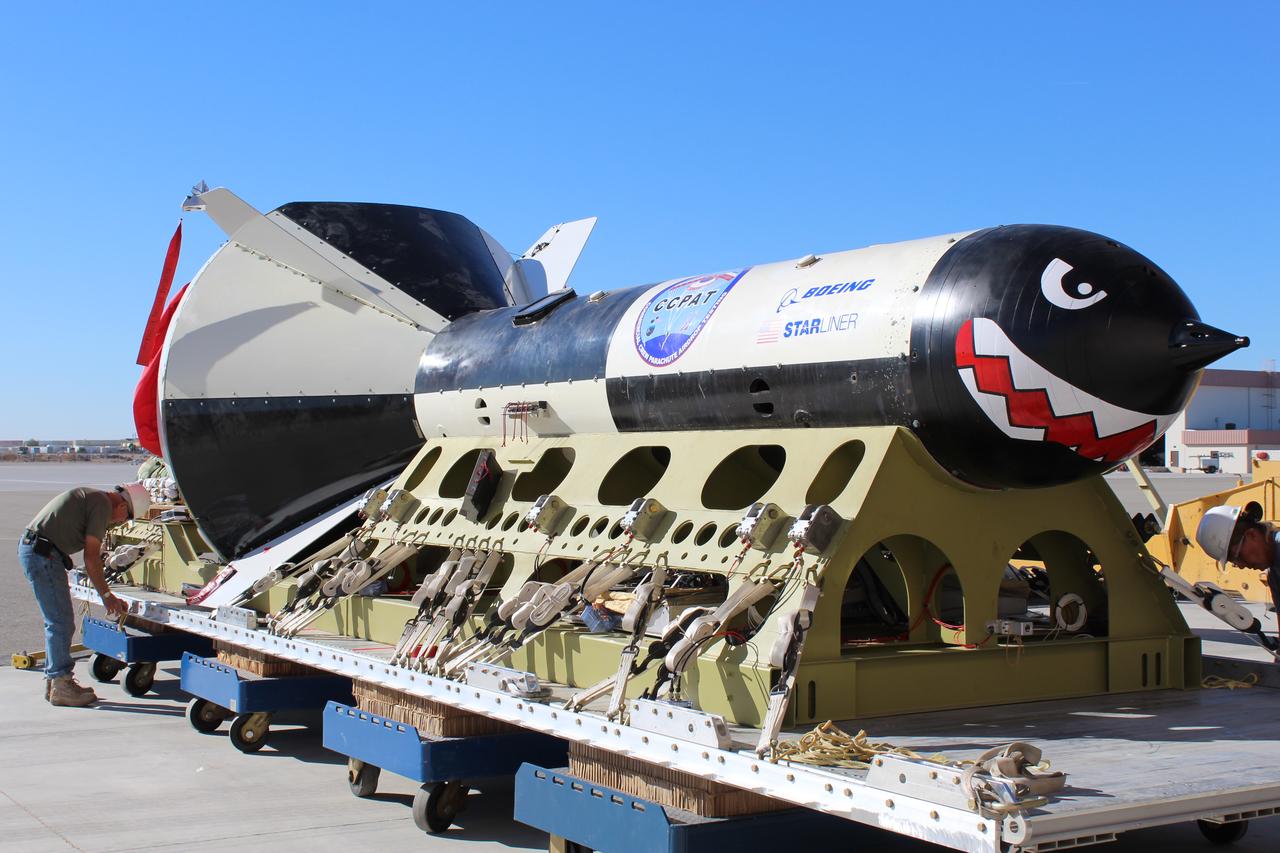

Boeing conducted the first in a series of reliability tests of its CST-100 Starliner flight drogue and main parachute system by releasing a long, dart-shaped test vehicle from a C-17 aircraft over Yuma, Arizona. Two more tests are planned using the dart module, as well as three similar reliability tests using a high fidelity capsule simulator designed to simulate the CST-100 Starliner capsule’s exact shape and mass. In both the dart and capsule simulator tests, the test spacecraft are released at various altitudes to test the parachute system at different deployment speeds, aerodynamic loads, and or weight demands. Data collected from each test is fed into computer models to more accurately predict parachute performance and to verify consistency from test to test.

Boeing conducted the first in a series of reliability tests of its CST-100 Starliner flight drogue and main parachute system by releasing a long, dart-shaped test vehicle from a C-17 aircraft over Yuma, Arizona. Two more tests are planned using the dart module, as well as three similar reliability tests using a high fidelity capsule simulator designed to simulate the CST-100 Starliner capsule’s exact shape and mass. In both the dart and capsule simulator tests, the test spacecraft are released at various altitudes to test the parachute system at different deployment speeds, aerodynamic loads, and or weight demands. Data collected from each test is fed into computer models to more accurately predict parachute performance and to verify consistency from test to test.
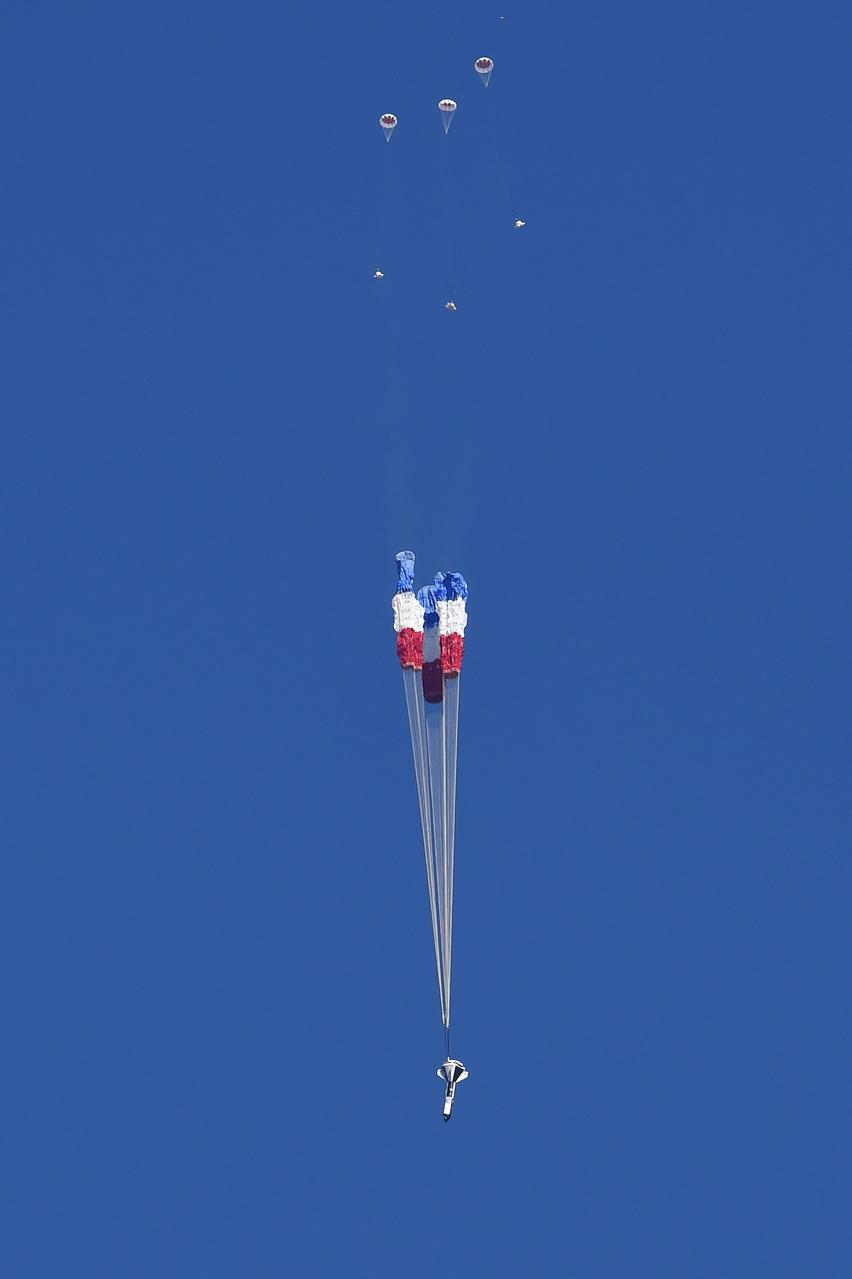

Boeing conducted the first in a series of reliability tests of its CST-100 Starliner flight drogue and main parachute system by releasing a long, dart-shaped test vehicle from a C-17 aircraft over Yuma, Arizona. Two more tests are planned using the dart module, as well as three similar reliability tests using a high fidelity capsule simulator designed to simulate the CST-100 Starliner capsule’s exact shape and mass. In both the dart and capsule simulator tests, the test spacecraft are released at various altitudes to test the parachute system at different deployment speeds, aerodynamic loads, and or weight demands. Data collected from each test is fed into computer models to more accurately predict parachute performance and to verify consistency from test to test.
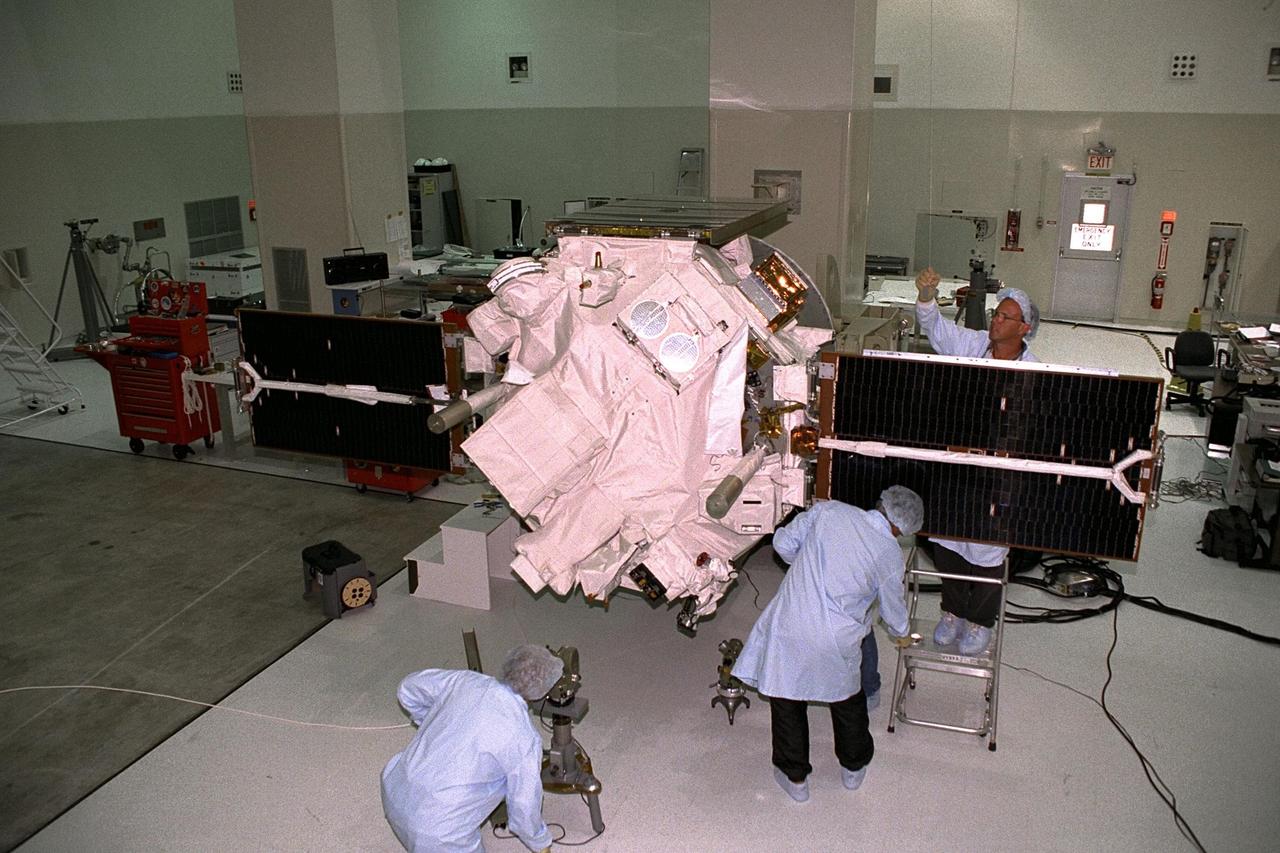

Applied Physics Laboratory engineers and technicians from Johns Hopkins University test solar array deployment of the Advanced Composition Explorer (ACE) in KSC’s Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility-II (SAEF-II). The wire hanging from the ceiling above the black solar array panel is used for "g-negation," which takes the weight off of the panel’s hinges to simulate zero gravity, mimicking deployment in space. Scheduled for launch on a Delta II rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Station on Aug. 25, ACE will study low-energy particles of solar origin and high-energy galactic particles for a better understanding of the formation and evolution of the solar system as well as the astrophysical processes involved. The collecting power of instrumentation aboard ACE is at least 100 times more sensitive than anything previously flown to collect similar data by NASA
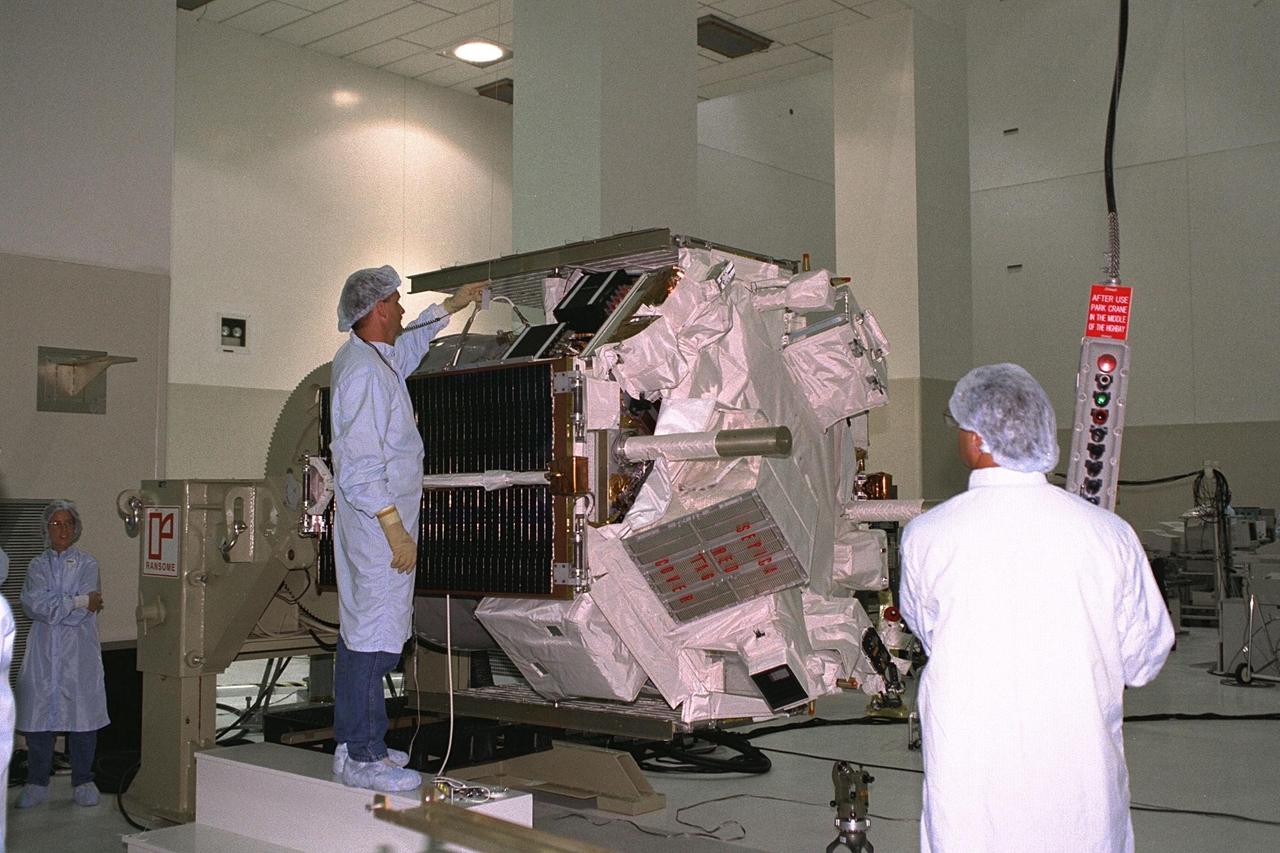

Applied Physics Laboratory engineers and technicians from Johns Hopkins University test solar array deployment of the Advanced Composition Explorer (ACE) in KSC’s Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility-II (SAEF-II). The wire hanging from the ceiling above the black solar array panel is used for "g-negation," which takes the weight off of the panel’s hinges to simulate zero gravity, mimicking deployment in space. Scheduled for launch on a Delta II rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Station on Aug. 25, ACE will study low-energy particles of solar origin and high-energy galactic particles. The collecting power of instruments aboard ACE is 10 to 1,000 times greater than anything previously flown to collect similar data by NASA
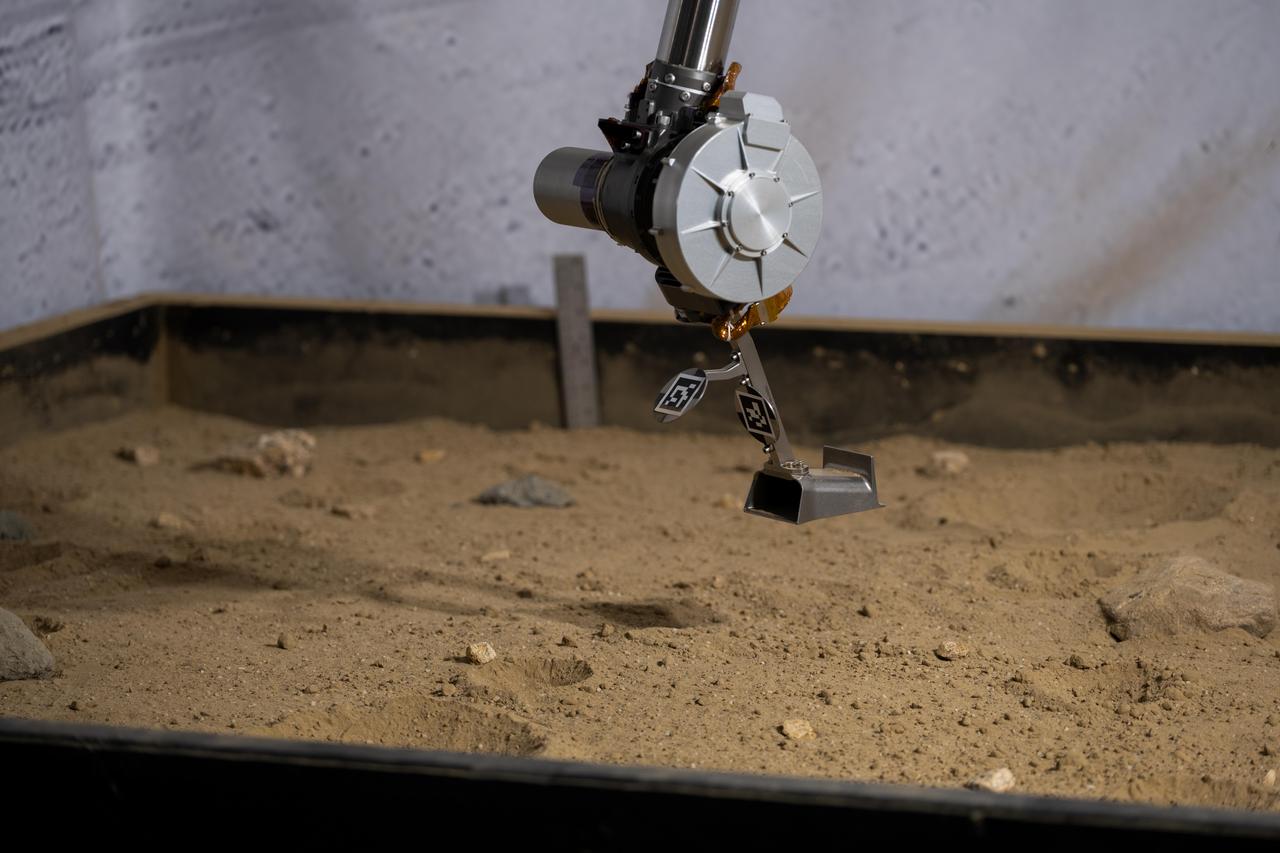

The 3D-printed titanium scoop of the Cold Operable Lunar Deployable Arm (COLDArm) robotic arm system is poised above a test bed filled with material to simulate lunar regolith (broken rocks and dust) at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. COLDArm can function in temperatures as cold as minus 280 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 173 degrees Celsius). COLDArm is designed to go on a Moon lander and operate during lunar night, a period that lasts about 14 Earth days. Frigid temperatures during lunar night would stymie current spacecraft, which must rely on energy-consuming heaters to stay warm. To operate in the cold, the 6-foot-6-inch (2-meter) arm combines several key new technologies: gears made of bulk metallic glass that require no lubrication or heating, cold motor controllers that don't need to be kept warm in an electronics box near the core of the spacecraft, and a cryogenic six-axis force torque sensor that lets the arm "feel" what it's doing and make adjustments. A variety of attachments and small instruments could go on the end of the arm, including the scoop, which could be used for collecting samples from a planet's surface. Like the arm on NASA's InSight Mars lander, COLDArm could deploy science instruments to the surface. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25318
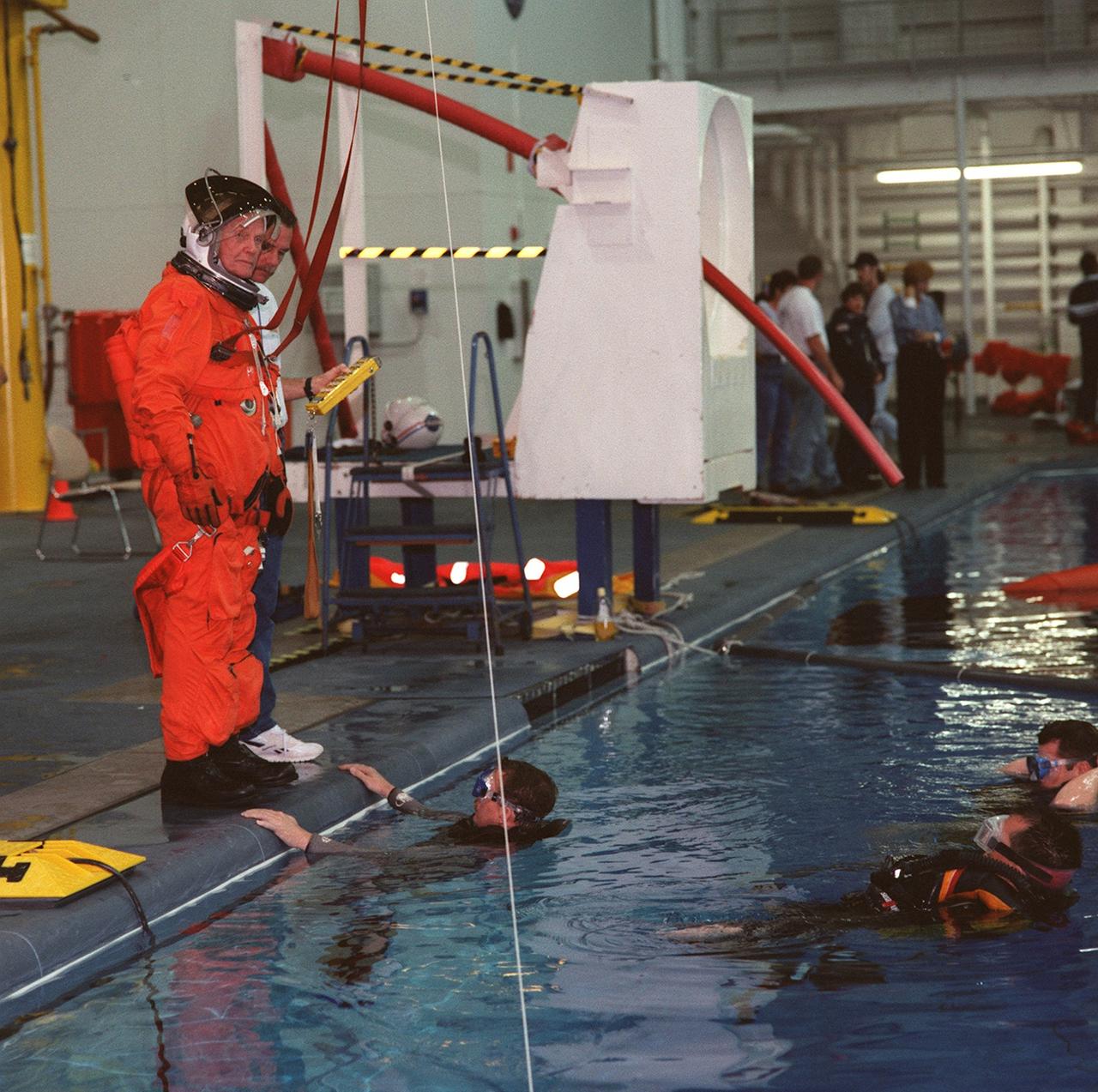

S98-04610 (6 April 1998) --- U.S. Sen. John H. Glenn Jr. (D.-Ohio), attired in a training version of the Space Shuttle partial pressure launch and entry suit, surveys the scene of a bailout training exercise. The giant pool in the Neutral Buoyancy Laboratory (NBL)at the Sonny Carter Training Facility allows the STS-95 crewmembers the opportunity to simulate ejection from an aircraft over water. A number of SCUBA-equipped divers assist in the training exercises. The nearby structure contains a simulated version of the escape pole which is located in the middeck on each of four NASA Space Shuttle vehicles. Parachute drops, raft deployment, water bailing, flare signaling and other survival techniques are also covered in the session.
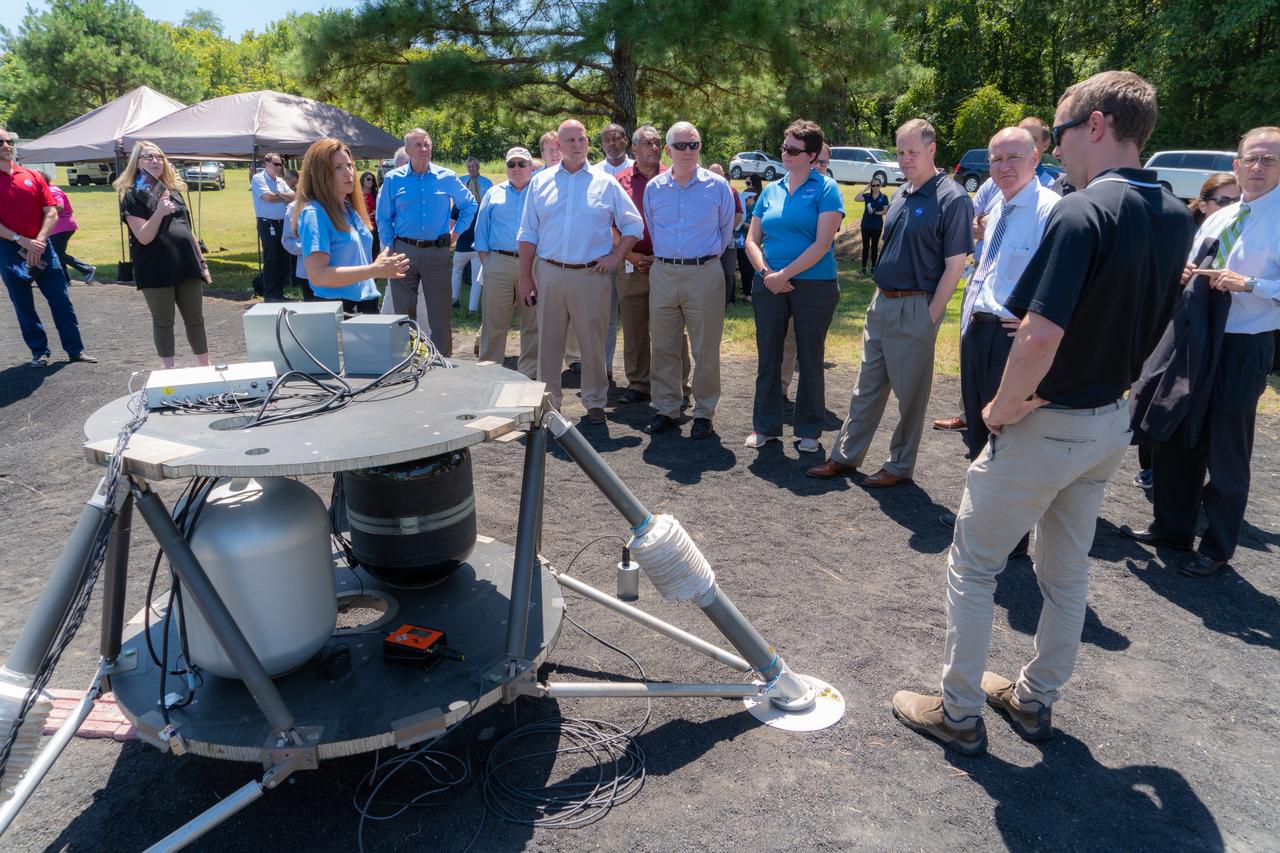

Lisa Watson-Morgan, center left, program manager of NASA’s Human Landing System Program at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, shows NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine equipment used to test seismic sensors on a lunar lander platform on a simulated lunar surface at the center Aug. 16, 2019. Bridenstine was joined by Representatives Mo Brooks and Robert Aderholt of Alabama and Representative Scott DesJarlais of Tennessee. Planetary scientists performed the experiment to learn how these waves travel through simulated regolith, which is material similar to the Moon’s surface. The experiment will help guide instrument deployment scenarios for NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Service (CLPS) Program, delivering small science and technology payloads for Artemis. That same day, Bridenstine announced Marshall will lead the agency’s Human Landing System Program. (NASA/Fred Deaton) For more information: https://www.nasa.gov/artemis-1
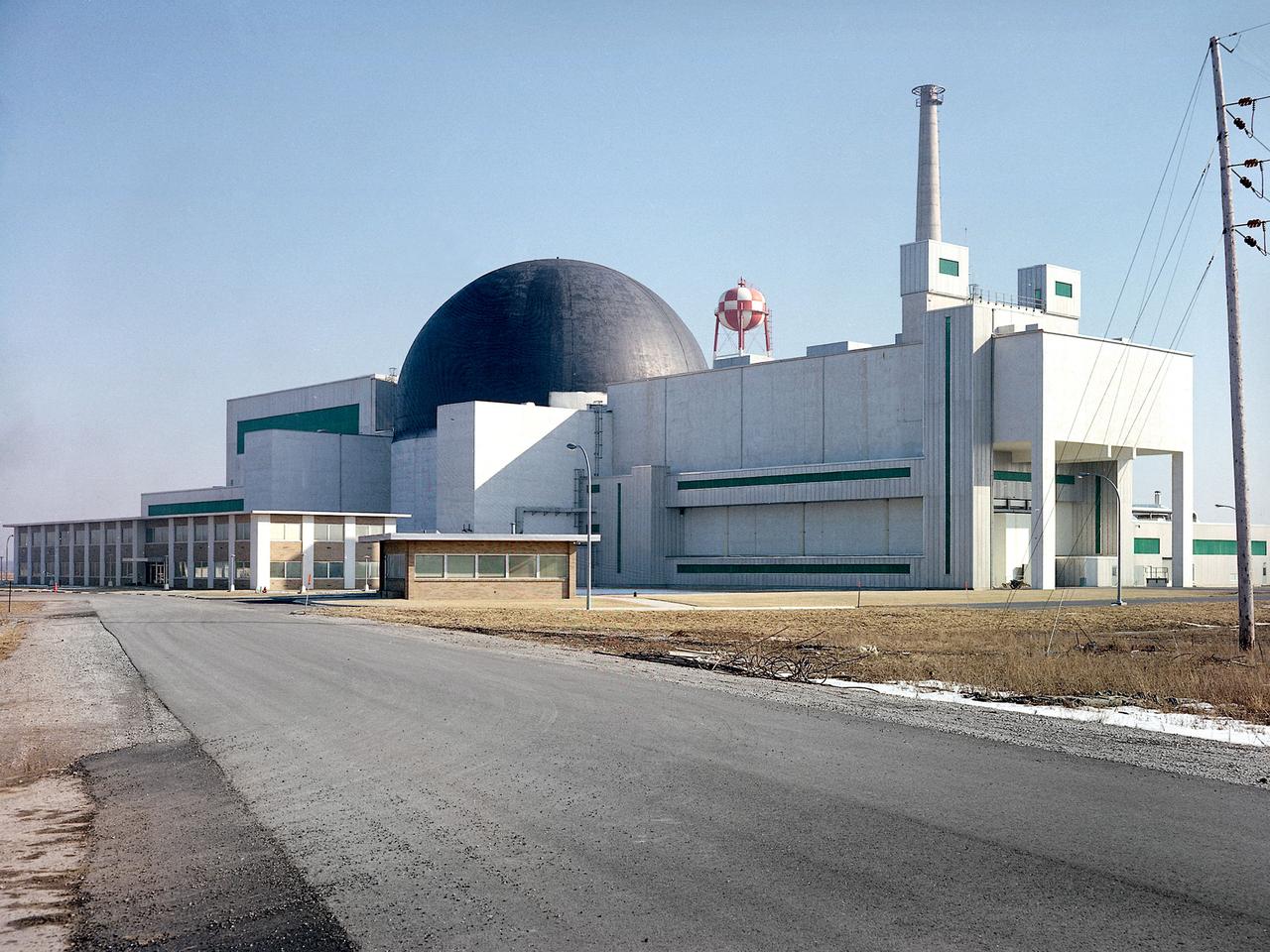

Exterior view of the Space Power Facility at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration’s (NASA) Plum Brook Station in Sandusky, Ohio. The $28.4-million facility, which began operations in 1969, is the largest high vacuum chamber ever built. The chamber is 100 feet in diameter and 120 feet high. It produces a vacuum deep enough to simulate the conditions at 300 miles altitude. The facility can sustain a high vacuum; simulate solar radiation via a 4-megawatt quartz heat lamp array, solar spectrum by a 400-kilowatt arc lamp, and cold environments. The Space Power Facility was originally designed to test nuclear power sources for spacecraft during long durations in a space atmosphere, but it was never used for that purpose. The facility’s first test in 1970 involved a 15 to 20-kilowatt Brayton Cycle Power System for space applications. Three different methods of simulating solar heat were employed during the Brayton tests. The facility was also used for jettison tests of the Centaur Standard Shroud. The shroud was designed for the new Titan-Centaur rocket that was scheduled to launch the Viking spacecraft to Mars. The new shroud was tested under conditions that simulated the time from launch to the separation of the stages. Test programs at the facility include high-energy experiments, shroud separation tests, Mars Lander system tests, deployable Solar Sail tests and International Space Station hardware tests.
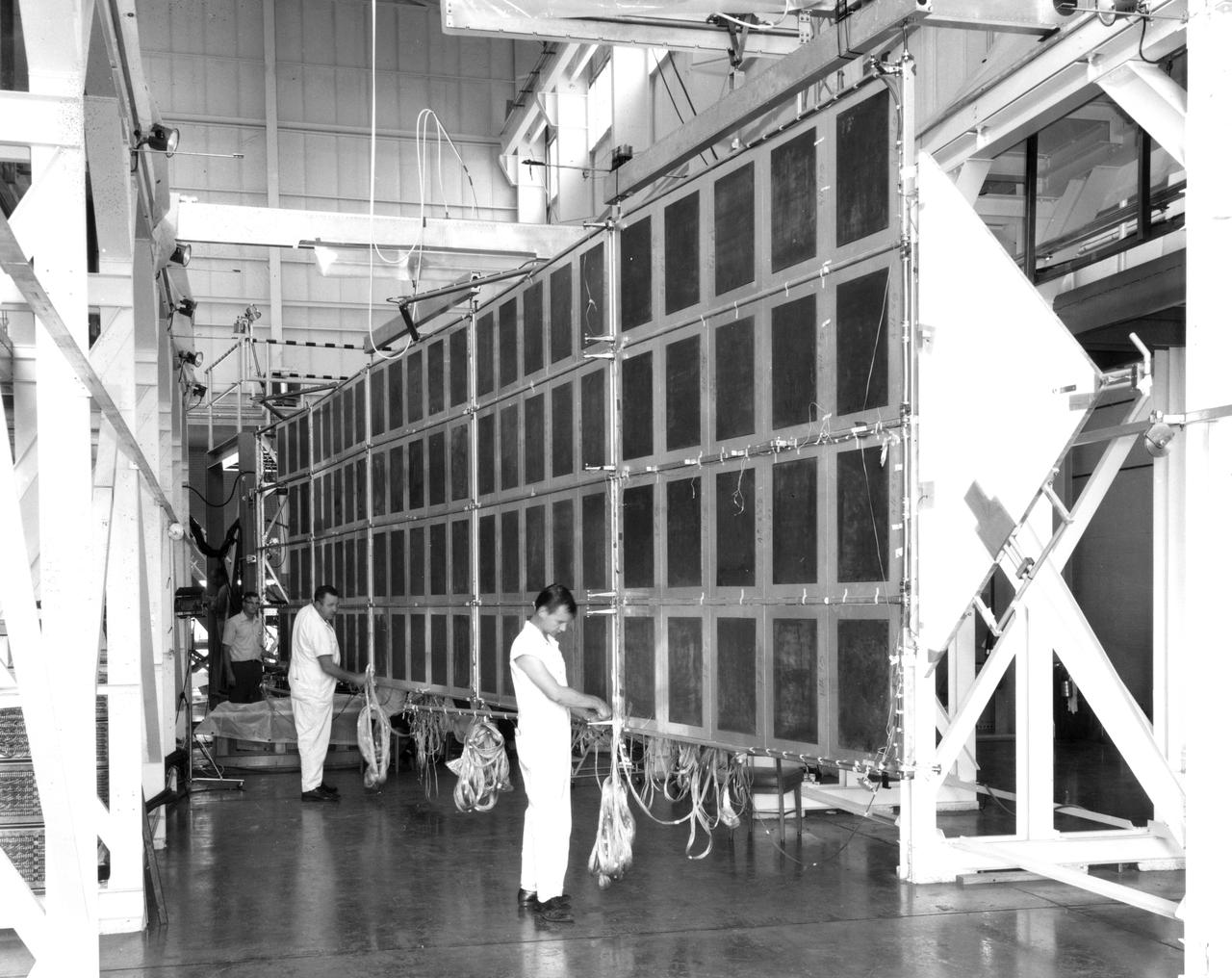

Technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center check the wiring on a mechanical test article of the Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) solar array. Four such arrays were joined in a cross to provide electric power for the ATM in Earth orbit. The deployment mechanism for extending the wing to the fully open position had just been tested when this photograph was taken. The array was suspended from beams riding on air bearings to closely simulate the weightless conditions under which it would be deployed in space. The wings are folded against the sides of the ATM for launch and are deployed by a scissors mechanism in Earth’s orbit.
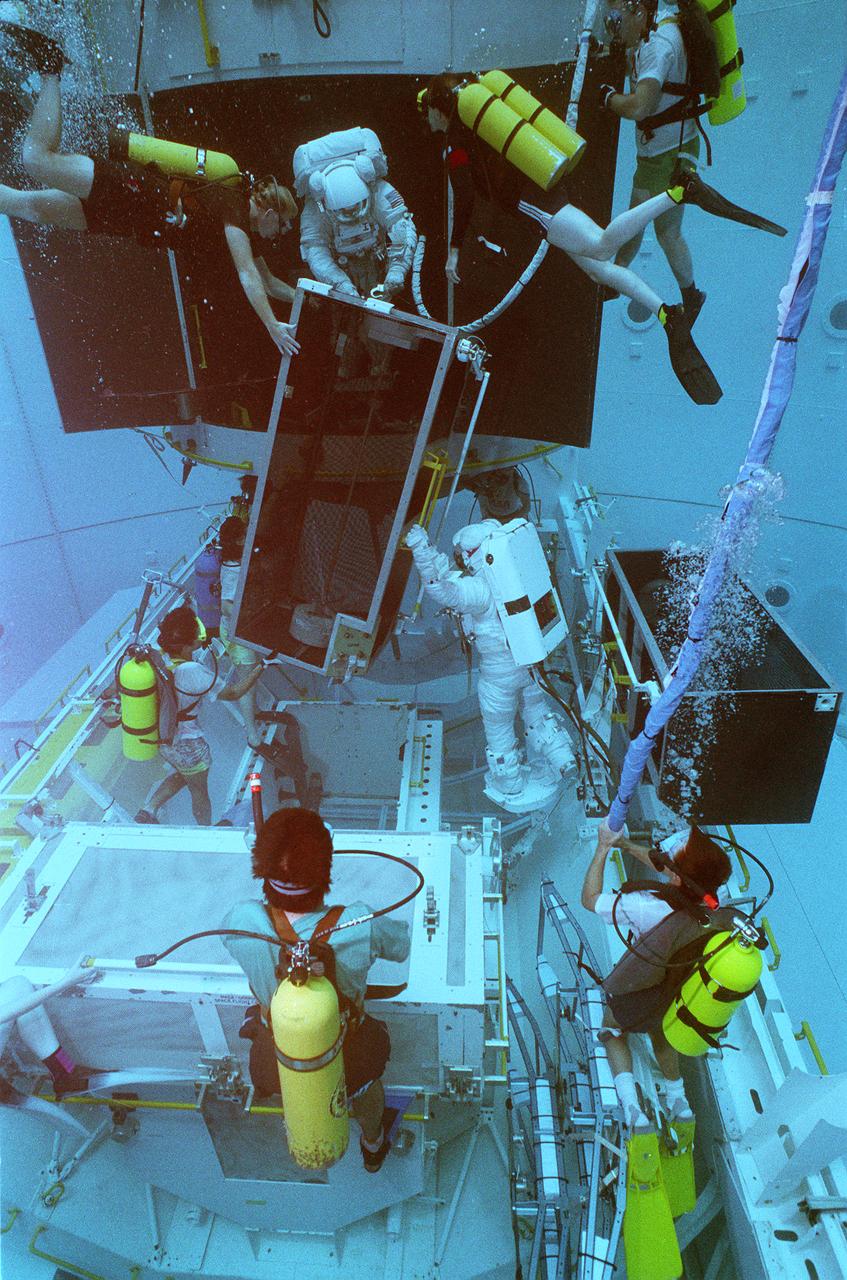

This photograph shows STS-61 crewmemmbers training for the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) servicing mission in the Marshall Space Flight Center's (MSFC's) Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS). Two months after its deployment in space, scientists detected a 2-micron spherical aberration in the primary mirror of the HST that affected the telescope's ability to focus faint light sources into a precise point. This imperfection was very slight, one-fiftieth of the width of a human hair. A scheduled Space Service servicing mission (STS-61) in 1993 permitted scientists to correct the problem. The MSFC NBS provided an excellent environment for testing hardware to examine how it would operate in space and for evaluating techniques for space construction and spacecraft servicing.
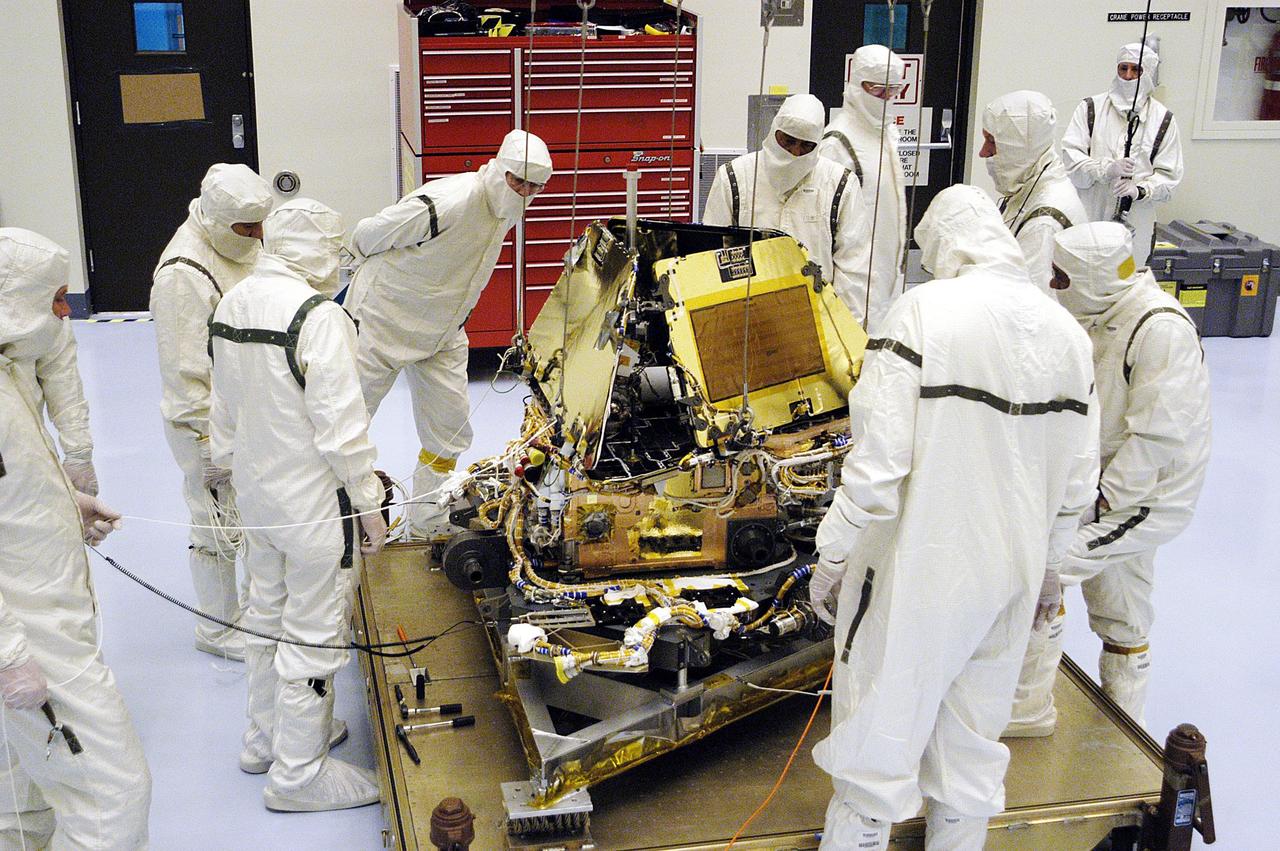

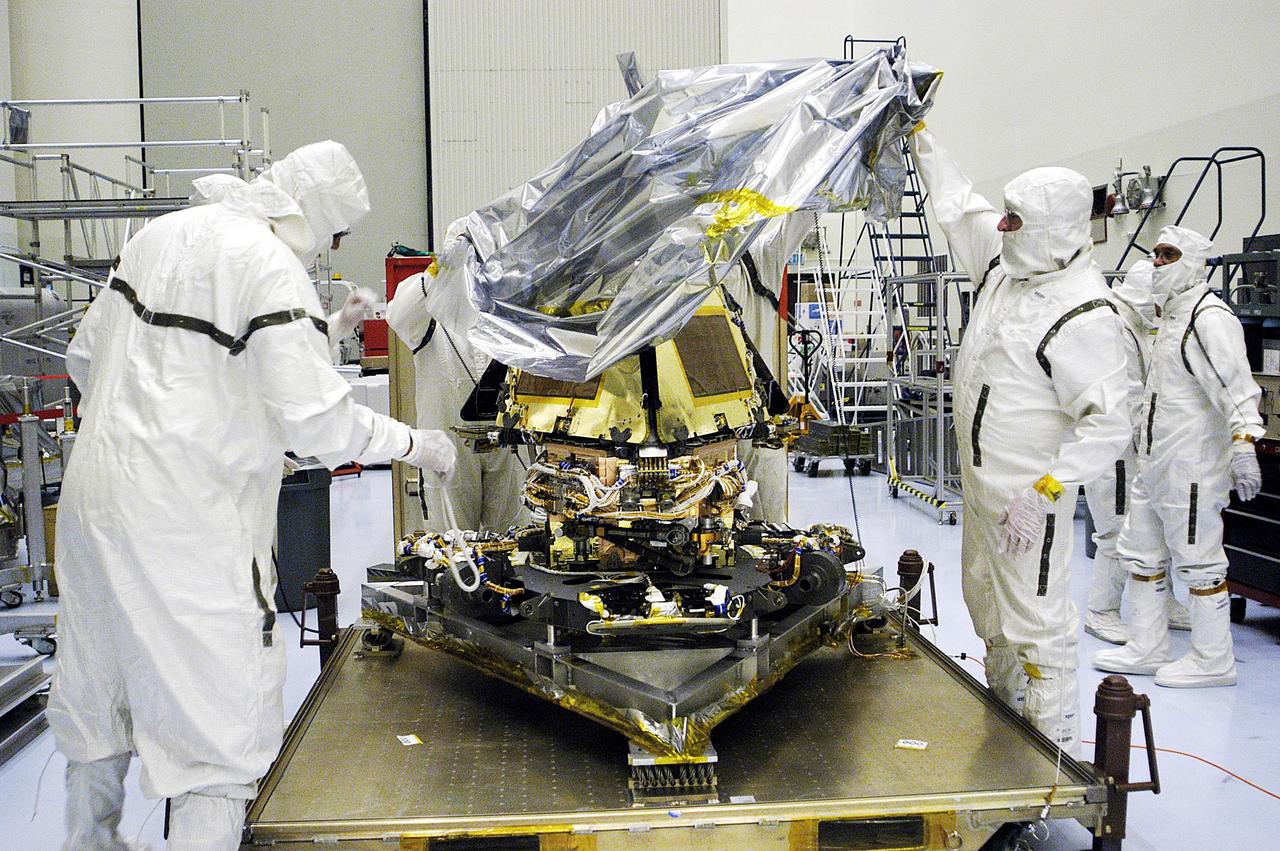
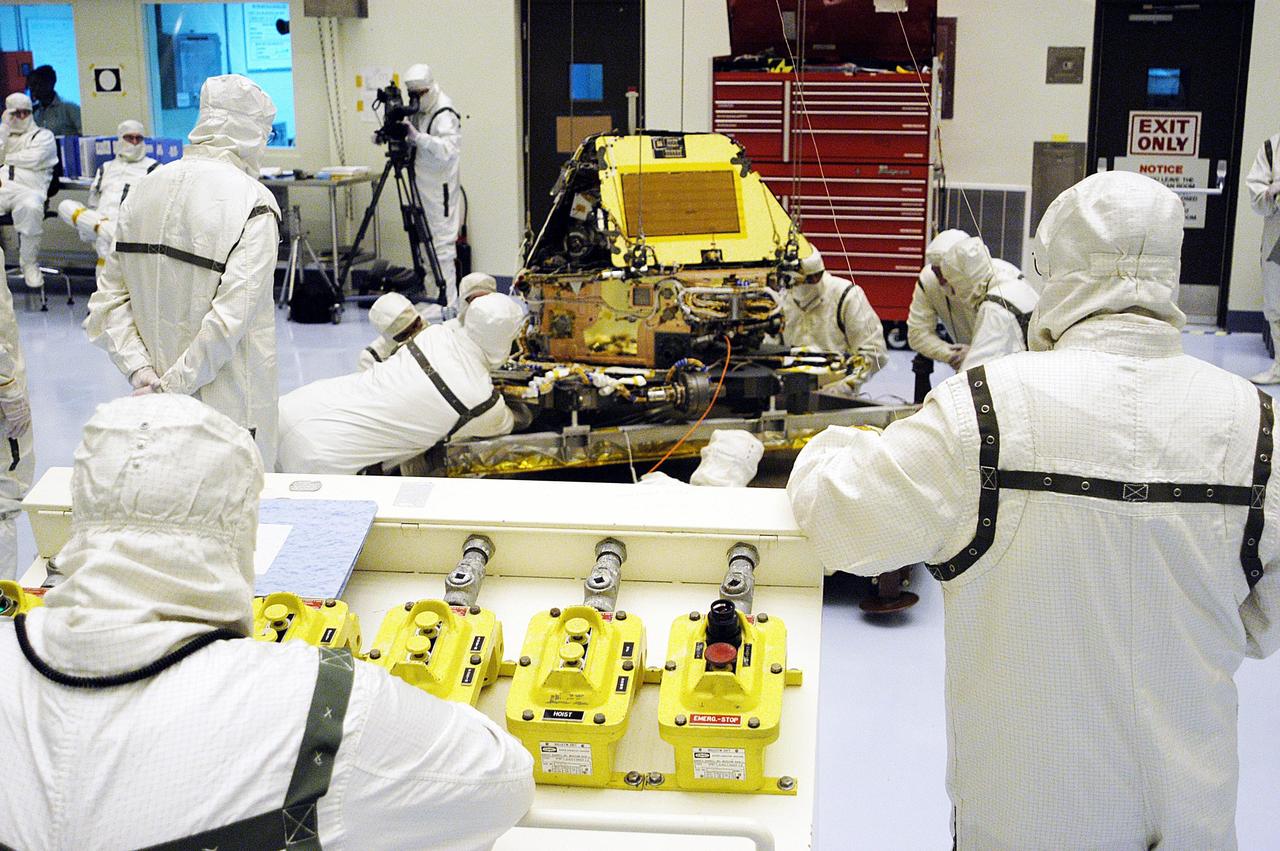
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. - Mars Exploration Rover-1 is ready for prelaunch testing including deployment of the lander petals, the rover's solar arrays, camera mast and camera. While at KSC, each of the rovers, their aeroshells and landers will undergo a full mission simulation. After spin balance testing, each spacecraft will be mated to a solid propellant upper stage booster that will propel the spacecraft out of Earth orbit. Approximately 10 days before launch they will be transported to the launch pad for mating with their respective Boeing Delta II rockets. The rovers will serve as robotic geologists to seek answers about the evolution of Mars, particularly for a history of water. The rovers are identical to each other, and will land at different regions of Mars. Launch of the MER-1 is scheduled for May 30. MER-2 will follow June 25.
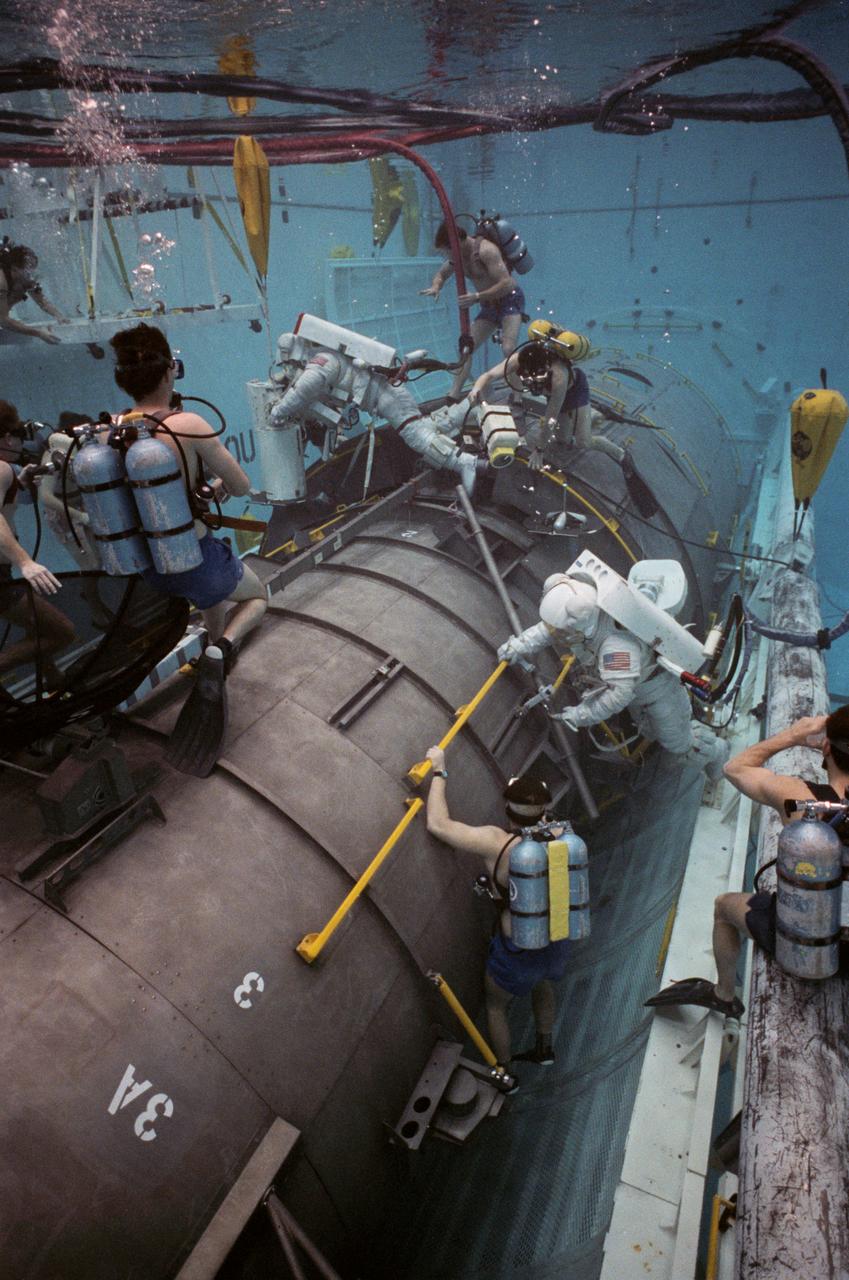

This overall view shows STS-31 Mission Specialist (MS) Bruce McCandless II (left) and MS Kathryn D. Sullivan making a practice space walk in JSC's Weightless Environment Training Facility (WETF) Bldg 29 pool. McCandless works with a mockup of the remote manipulator system (RMS) end effector which is attached to a grapple fixture on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) mockup. Sullivan manipulates HST hardware on the Support System Module (SSM) forward shell. SCUBA-equipped divers monitor the extravehicular mobility unit (EMU) suited crewmembers during this simulated extravehicular activity (EVA). No EVA is planned for the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) deployment, but the duo has trained for contingencies which might arise during the STS-31 mission aboard Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103. Photo taken by NASA JSC photographer Sheri Dunnette.
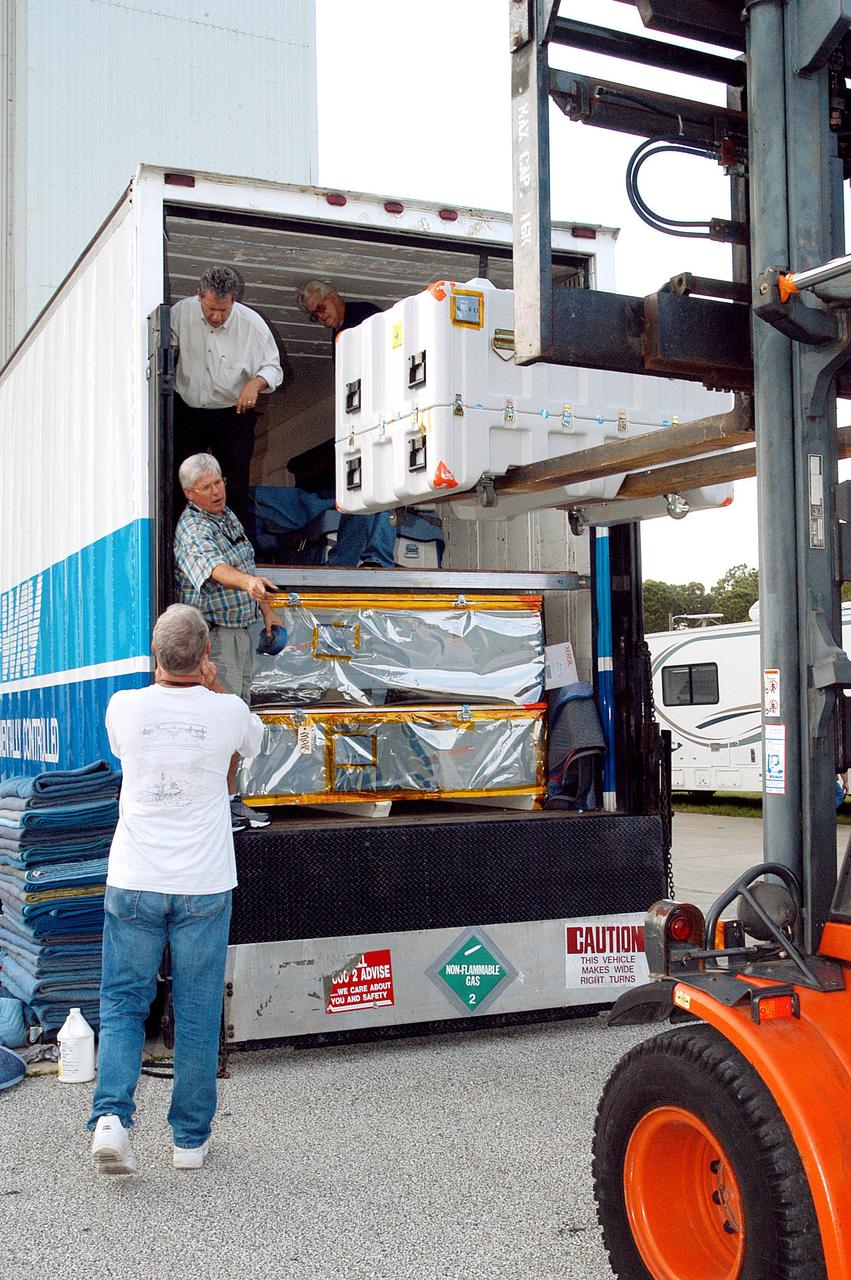

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. - Outside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility hardware related to the Mars Exploration Rovers (MER) is offloaded from a transport vehicle. MER-1 will undergo prelaunch testing, including deployment of the lander petals, the rover's solar arrays, camera mast and camera. While at KSC, MER-1 and MER-2, their aeroshells and landers will undergo a full mission simulation. After spin balance testing, each spacecraft will be mated to a solid propellant upper stage booster that will propel the spacecraft out of Earth orbit. Approximately 10 days before launch they will be transported to the launch pad for mating with their respective Boeing Delta II rockets. The rovers will serve as robotic geologists to seek answers about the evolution of Mars, particularly for a history of water. The rovers are identical to each other, and will land at different regions of Mars. Launch of the MER-1 is scheduled for May 30. MER-2 will follow June 25.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. - Workers in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility check over the newly arrived second Mars Exploration Rover, MER-1. It will undergo prelaunch testing, including deployment of the lander petals, the rover's solar arrays, camera mast and camera. While at KSC, each of the rovers, their aeroshells and landers will undergo a full mission simulation. After spin balance testing, each spacecraft will be mated to a solid propellant upper stage booster that will propel the spacecraft out of Earth orbit. Approximately 10 days before launch they will be transported to the launch pad for mating with their respective Boeing Delta II rockets. The rovers will serve as robotic geologists to seek answers about the evolution of Mars, particularly for a history of water. The rovers are identical to each other, and will land at different regions of Mars. Launch of the MER-1 is scheduled for May 30. MER-2 will follow June 25.
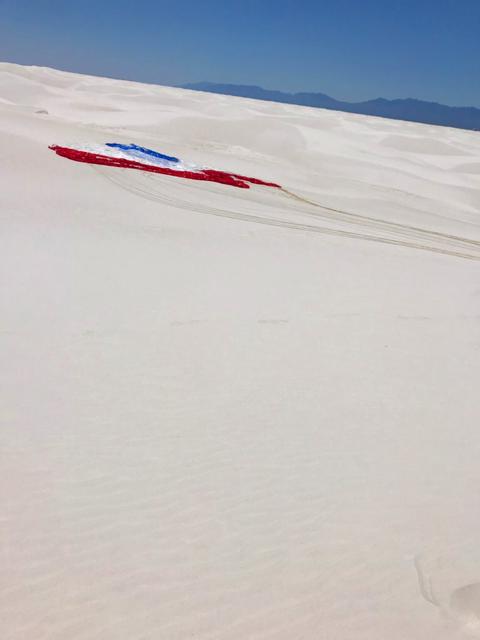

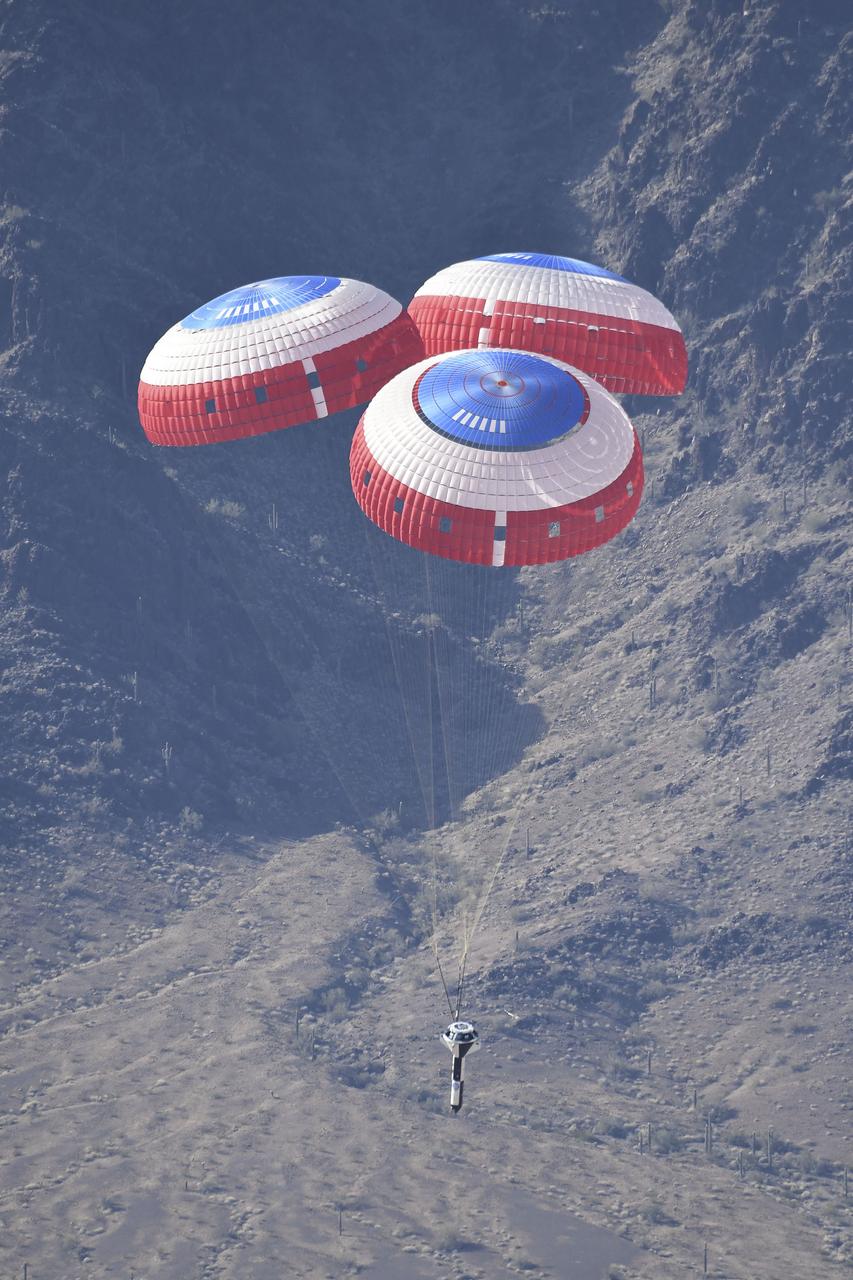
Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner’s parachute systems are successfully tested at the U.S. Army’s White Sands Missile Range in New Mexico on June 24, 2019. Boeing conducted the test using a full-scale Starliner test article, known as a boiler plate, designed to simulate the actual spacecraft. The test involved intentionally disabling one of the parachute system’s two drogue parachutes and one of the three main parachutes to evaluate how the remaining parachutes handled the additional loads during deployment and descent. This was one of a series of important parachute tests to validate the system is safe to carry astronauts to and from the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Boeing is targeting an uncrewed Orbital Flight Test to the space station this summer, followed by its Crew Flight Test. Starliner will launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. - A worker in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility checks the newly arrived second Mars Exploration Rover, MER-1. It will undergo prelaunch testing, including deployment of the lander petals, the rover's solar arrays, camera mast and camera. While at KSC, each of the rovers, their aeroshells and landers will undergo a full mission simulation. After spin balance testing, each spacecraft will be mated to a solid propellant upper stage booster that will propel the spacecraft out of Earth orbit. Approximately 10 days before launch they will be transported to the launch pad for mating with their respective Boeing Delta II rockets. The rovers will serve as robotic geologists to seek answers about the evolution of Mars, particularly for a history of water. The rovers are identical to each other, and will land at different regions of Mars. Launch of the MER-1 is scheduled for May 30. MER-2 will follow June 25.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. - Workers in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility unwrap the second Mars Exploration Rover, MER-1. MER-2 and other hardware have already arrived at KSC for processing. MER-1 will undergo prelaunch testing, including deployment of the lander petals, the rover's solar arrays, camera mast and camera. While at KSC, each of the rovers, their aeroshells and landers will undergo a full mission simulation. After spin balance testing, each spacecraft will be mated to a solid propellant upper stage booster that will propel the spacecraft out of Earth orbit. Approximately 10 days before launch they will be transported to the launch pad for mating with their respective Boeing Delta II rockets. The rovers will serve as robotic geologists to seek answers about the evolution of Mars, particularly for a history of water. The rovers are identical to each other, and will land at different regions of Mars. Launch of the MER-1 is scheduled for May 30. MER-2 will follow June 25.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. - Workers in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility look over Mars Exploration Rover-1, which is ready for prelaunch testing including deployment of the lander petals, the rover's solar arrays, camera mast and camera. While at KSC, each of the two rovers, their aeroshells and landers will undergo a full mission simulation. After spin balance testing, each spacecraft will be mated to a solid propellant upper stage booster that will propel the spacecraft out of Earth orbit. Approximately 10 days before launch they will be transported to the launch pad for mating with their respective Boeing Delta II rockets. The rovers will serve as robotic geologists to seek answers about the evolution of Mars, particularly for a history of water. The rovers are identical to each other, and will land at different regions of Mars. Launch of the MER-1 is scheduled for May 30. MER-2 will follow June 25.
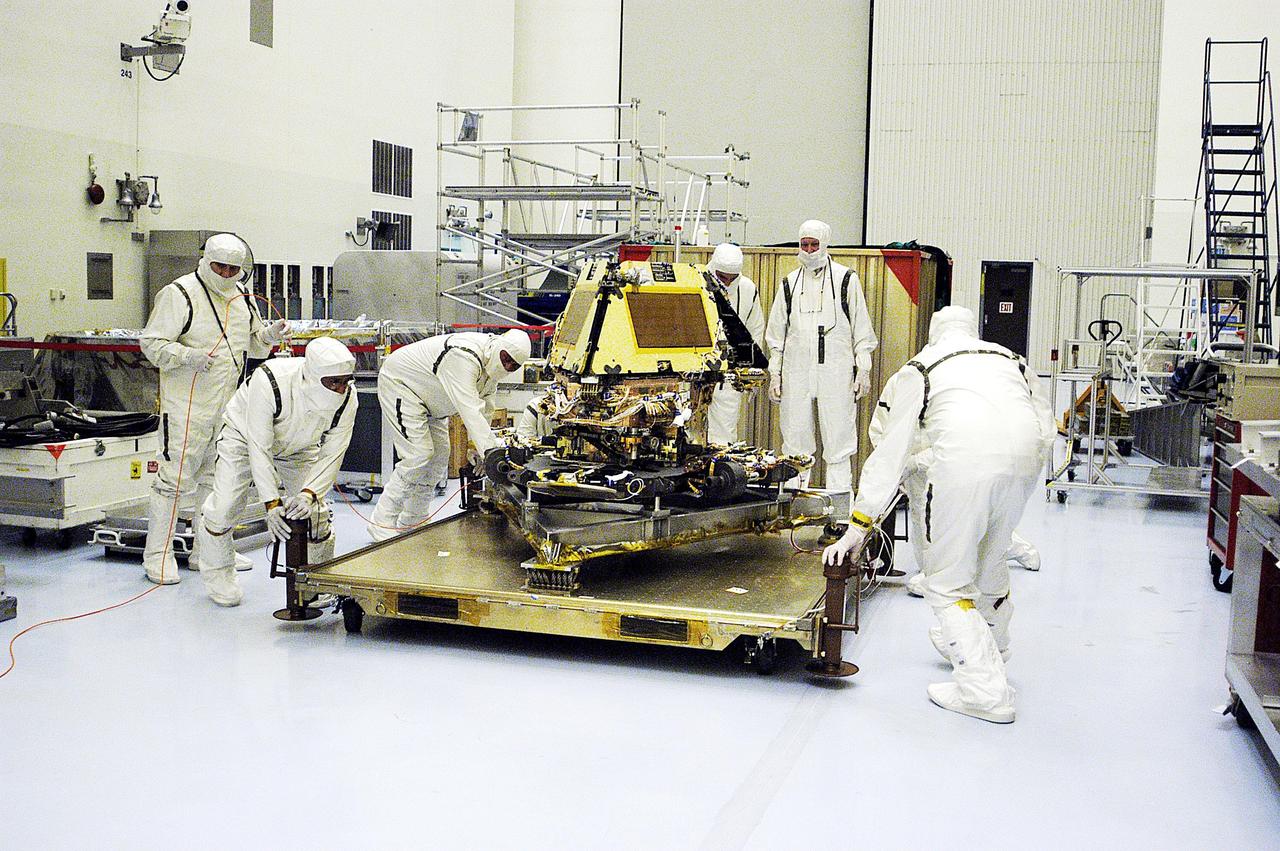
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. - In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility, workers appear to adjust the platform holding the second Mars Exploration Rover, MER-1. It will undergo prelaunch testing, including deployment of the lander petals, the rover's solar arrays, camera mast and camera. While at KSC, each of the rovers, their aeroshells and landers will undergo a full mission simulation. After spin balance testing, each spacecraft will be mated to a solid propellant upper stage booster that will propel the spacecraft out of Earth orbit. Approximately 10 days before launch they will be transported to the launch pad for mating with their respective Boeing Delta II rockets. The rovers will serve as robotic geologists to seek answers about the evolution of Mars, particularly for a history of water. The rovers are identical to each other, and will land at different regions of Mars. Launch of the MER-1 is scheduled for May 30. MER-2 will follow June 25.
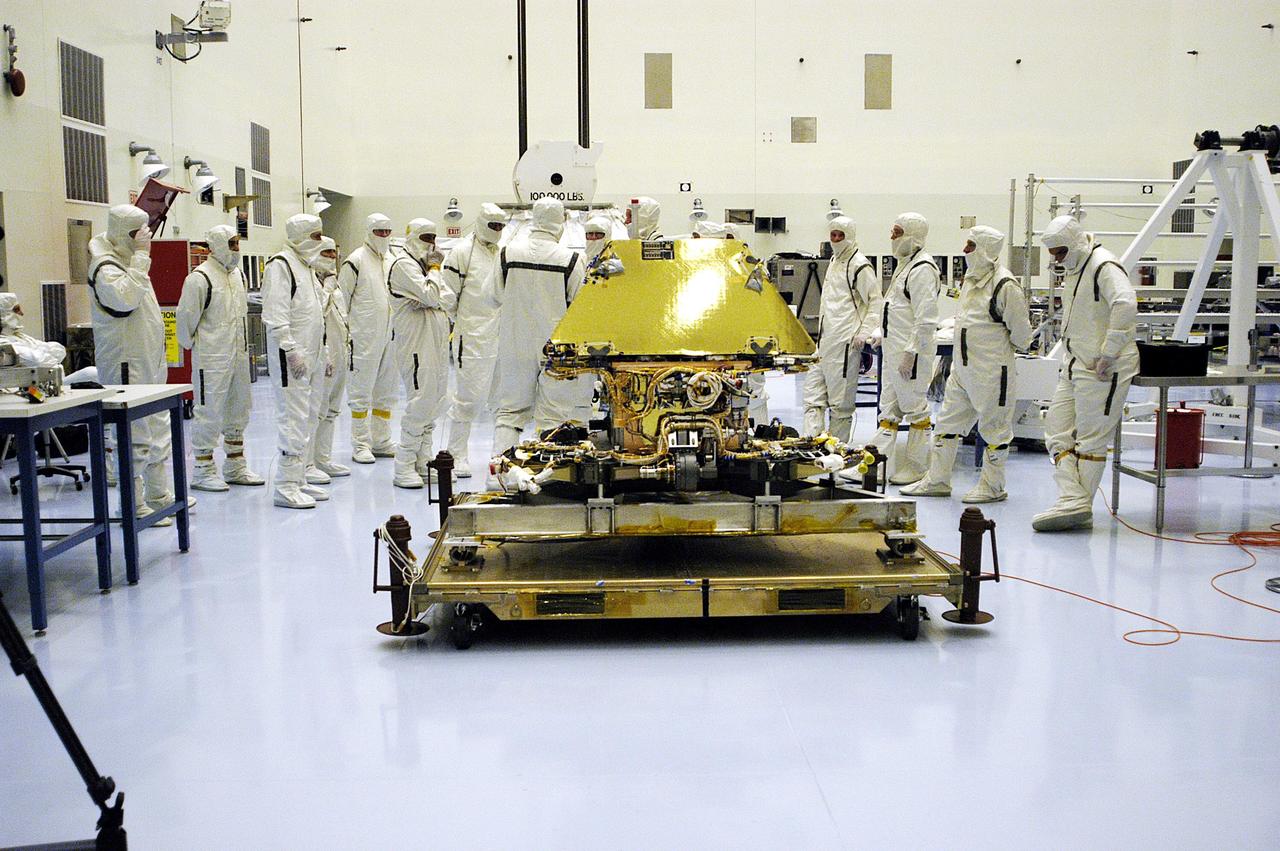

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. - In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility, the second Mars Exploration Rover, MER-1, is displayed. It will undergo prelaunch testing, including deployment of the lander petals, the rover's solar arrays, camera mast and camera. While at KSC, each of the rovers, their aeroshells and landers will undergo a full mission simulation. After spin balance testing, each spacecraft will be mated to a solid propellant upper stage booster that will propel the spacecraft out of Earth orbit. Approximately 10 days before launch they will be transported to the launch pad for mating with their respective Boeing Delta II rockets. The rovers will serve as robotic geologists to seek answers about the evolution of Mars, particularly for a history of water. The rovers are identical to each other, and will land at different regions of Mars. Launch of the MER-1 is scheduled for May 30. MER-2 will follow June 25.
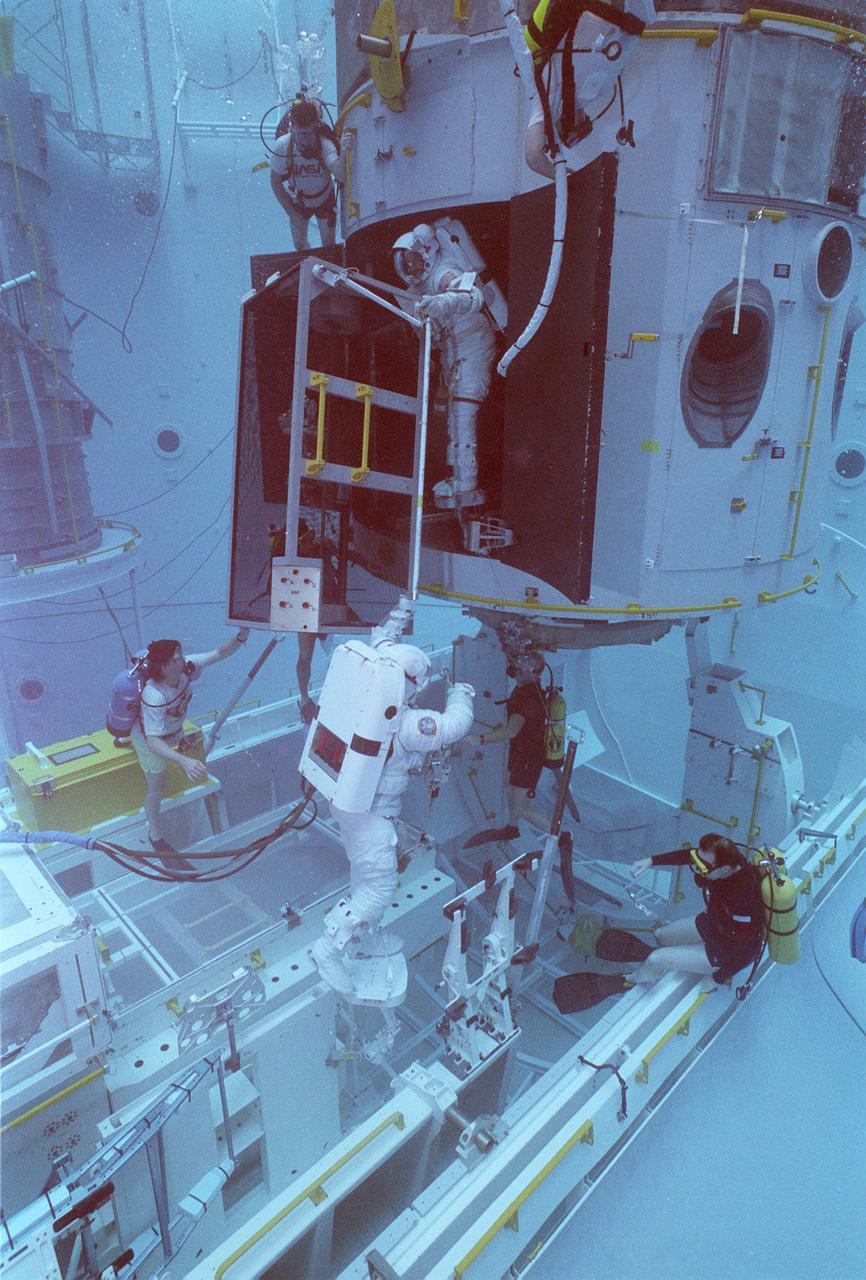

This photograph shows an STS-61 astronaut training for the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) servicing mission (STS-61) in the Marshall Space Flight Center's (MSFC's) Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS). Two months after its deployment in space, scientists detected a 2-micron spherical aberration in the primary mirror of the HST that affected the telescope's ability to focus faint light sources into a precise point. This imperfection was very slight, one-fiftieth of the width of a human hair. A scheduled Space Service servicing mission (STS-61) in 1993 permitted scientists to correct the problem. The MSFC NBS provided an excellent environment for testing hardware to examine how it would operate in space and for evaluating techniques for space construction and spacecraft servicing.
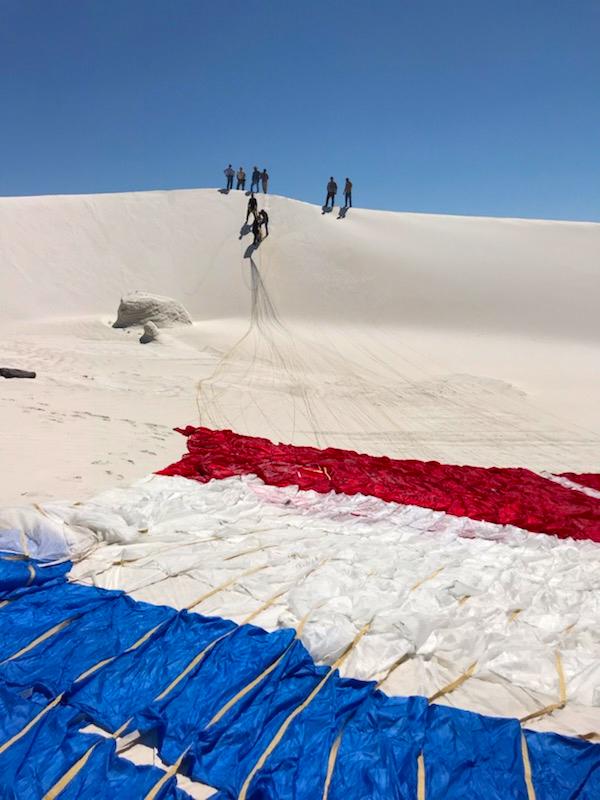

Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner’s parachute systems are successfully tested at the U.S. Army’s White Sands Missile Range in New Mexico on June 24, 2019. Boeing conducted the test using a full-scale Starliner test article, known as a boiler plate, designed to simulate the actual spacecraft. The test involved intentionally disabling one of the parachute system’s two drogue parachutes and one of the three main parachutes to evaluate how the remaining parachutes handled the additional loads during deployment and descent. This was one of a series of important parachute tests to validate the system is safe to carry astronauts to and from the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Boeing is targeting an uncrewed Orbital Flight Test to the space station this summer, followed by its Crew Flight Test. Starliner will launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
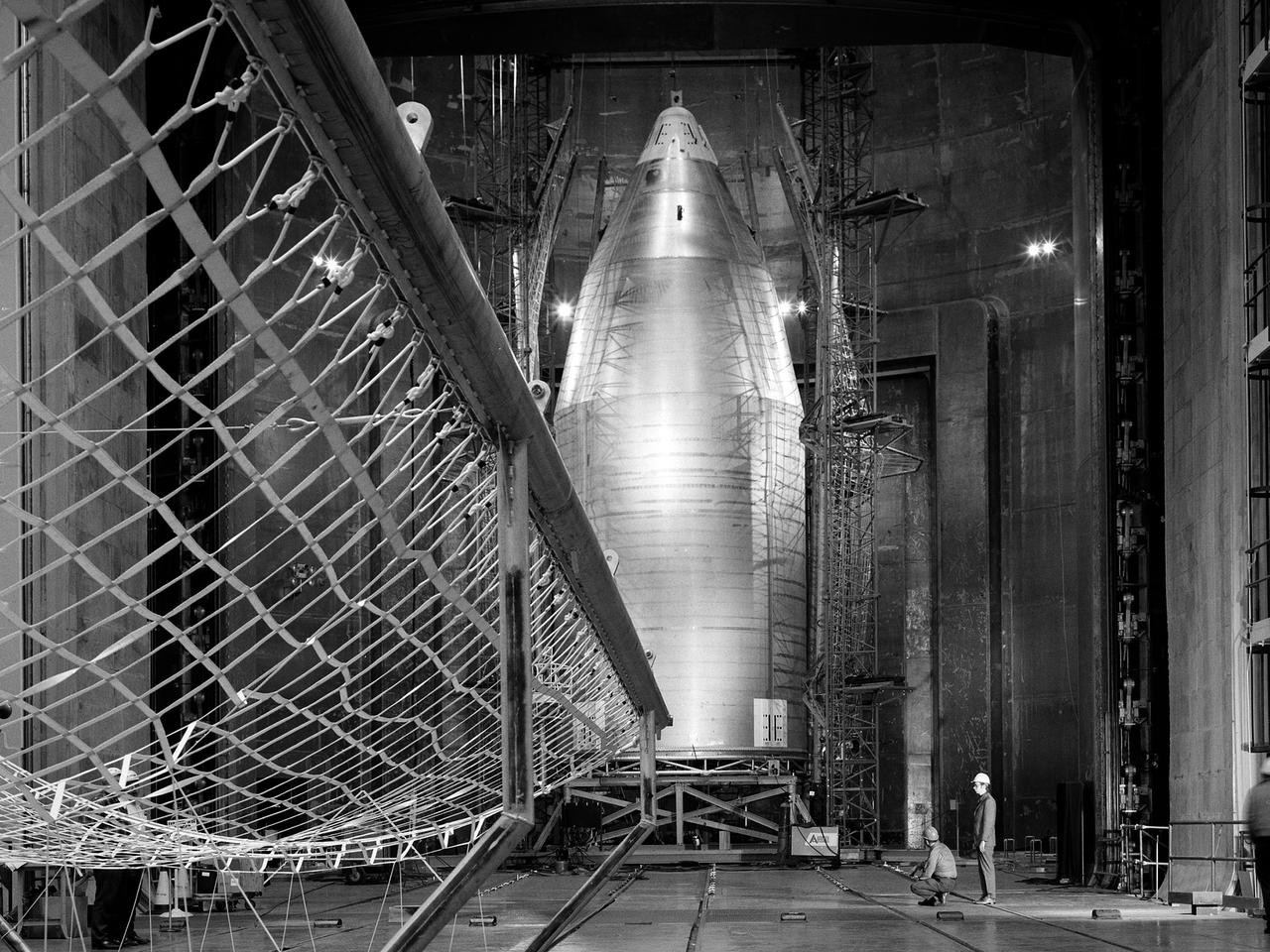

The 56-foot tall, 24,400-pound Skylab shroud installed in the Space Power Facility’s vacuum chamber at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration’s (NASA) Plum Brook Station. The Space Power Facility, which began operations in 1969, is the largest high vacuum chamber ever built. The chamber is 100 feet in diameter and 120 feet high. It can produce a vacuum deep enough to simulate the conditions at 300 miles altitude. The Space Power Facility was originally designed to test nuclear-power sources for spacecraft during long durations in a space atmosphere, but it was never used for that purpose. Payload shrouds are aerodynamic fairings to protect the payload during launch and ascent to orbit. The Skylab mission utilized the largest shroud ever attempted. Unlike previous launches, the shroud would not be jettisoned until the spacecraft reached orbit. NASA engineers designed these tests to verify the dynamics of the jettison motion in a simulated space environment. Fifty-four runs and three full-scale jettison tests were conducted from mid-September 1970 to June 1971. The shroud behaved as its designers intended, the detonators all fired, and early design issues were remedied by the final test. The Space Power Facility continues to operate today. The facility can sustain a high vacuum; simulate solar radiation via a 4-megawatt quartz heat lamp array, solar spectrum by a 400-kilowatt arc lamp, and cold environments. Test programs at the facility include high-energy experiments, shroud separation tests, Mars Lander system tests, deployable Solar Sail tests and International Space Station hardware tests.
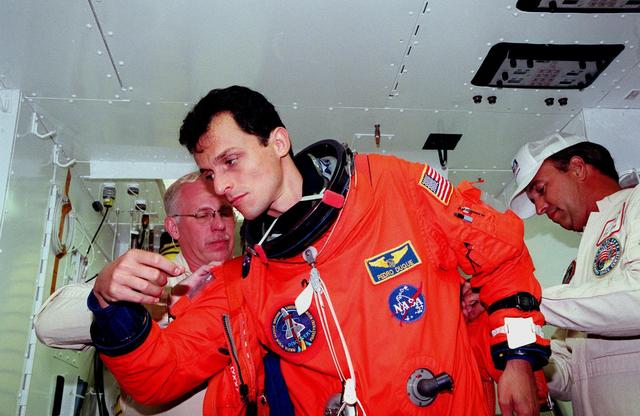

STS-95 Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency (ESA) is checked by Danny Wyatt (left), with KSC, and Dave Martin (right), with United Space Alliance, in the white room before entry into Space Shuttle Discovery for a pre-launch countdown exercise. Duque and other crew members are at KSC to participate in the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) which includes mission familiarization activities, emergency egress training, and a simulated main engine cutoff. The other crew members are Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai (M.D., Ph.D.), representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA), Pilot Steven W. Lindsey, Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski, Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson, Payload Specialist John H. Glenn Jr., senator from Ohio, and Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown. The STS-95 mission, targeted for liftoff on Oct. 29, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process. Following the TCDT, the crew will be returning to Houston for final flight preparations
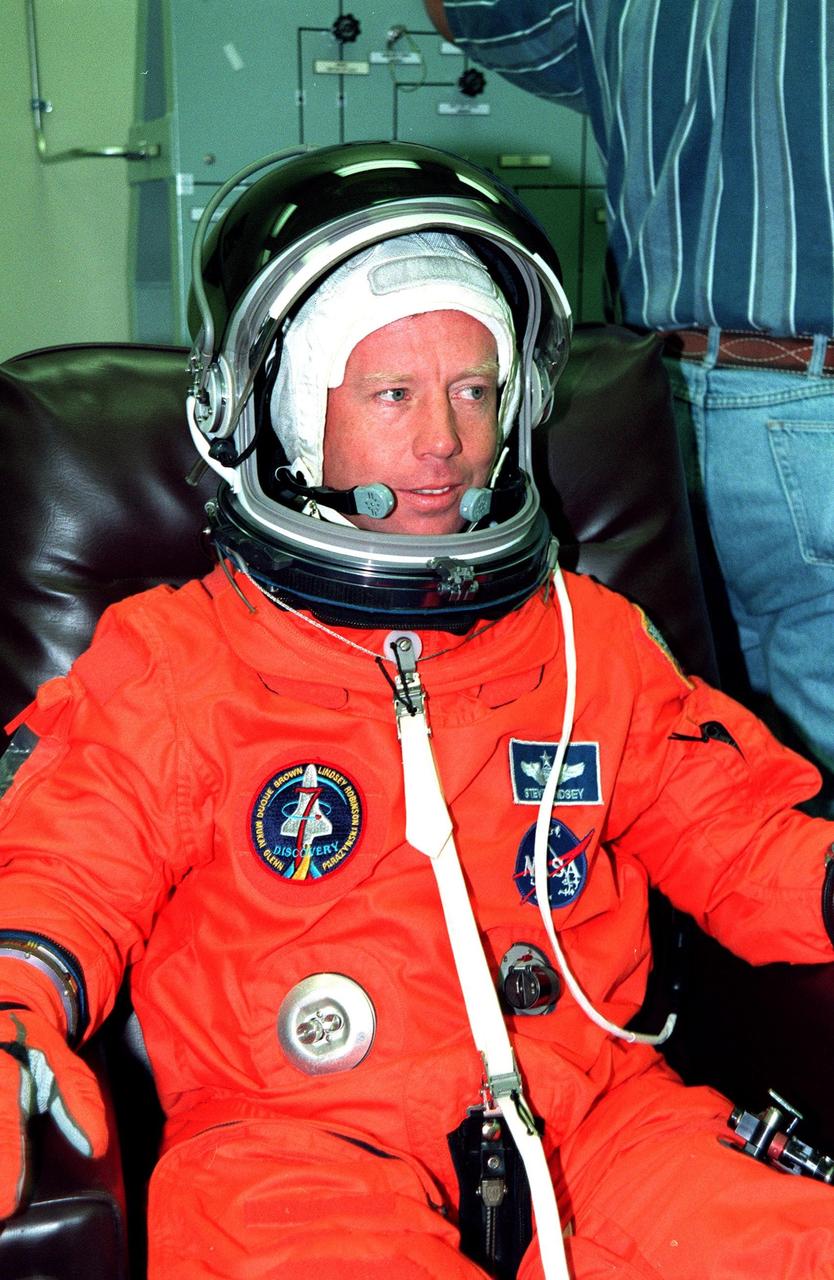

STS-95 Pilot Steven W. Lindsey suits up in the Operations and Checkout Building prior to his trip to Launch Pad 39-B. Lindsey and the rest of the STS-95 crew are at KSC to participate in the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) which includes mission familiarization activities, emergency egress training, and a simulated main engine cutoff. The other crew members are Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai (M.D., Ph.D.), representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA), Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski, Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson, Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency (ESA), Payload Specialist John H. Glenn Jr., senator from Ohio, and Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown. The STS-95 mission, targeted for liftoff on Oct. 29, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process. Following the TCDT, the crew will be returning to Houston for final flight preparations
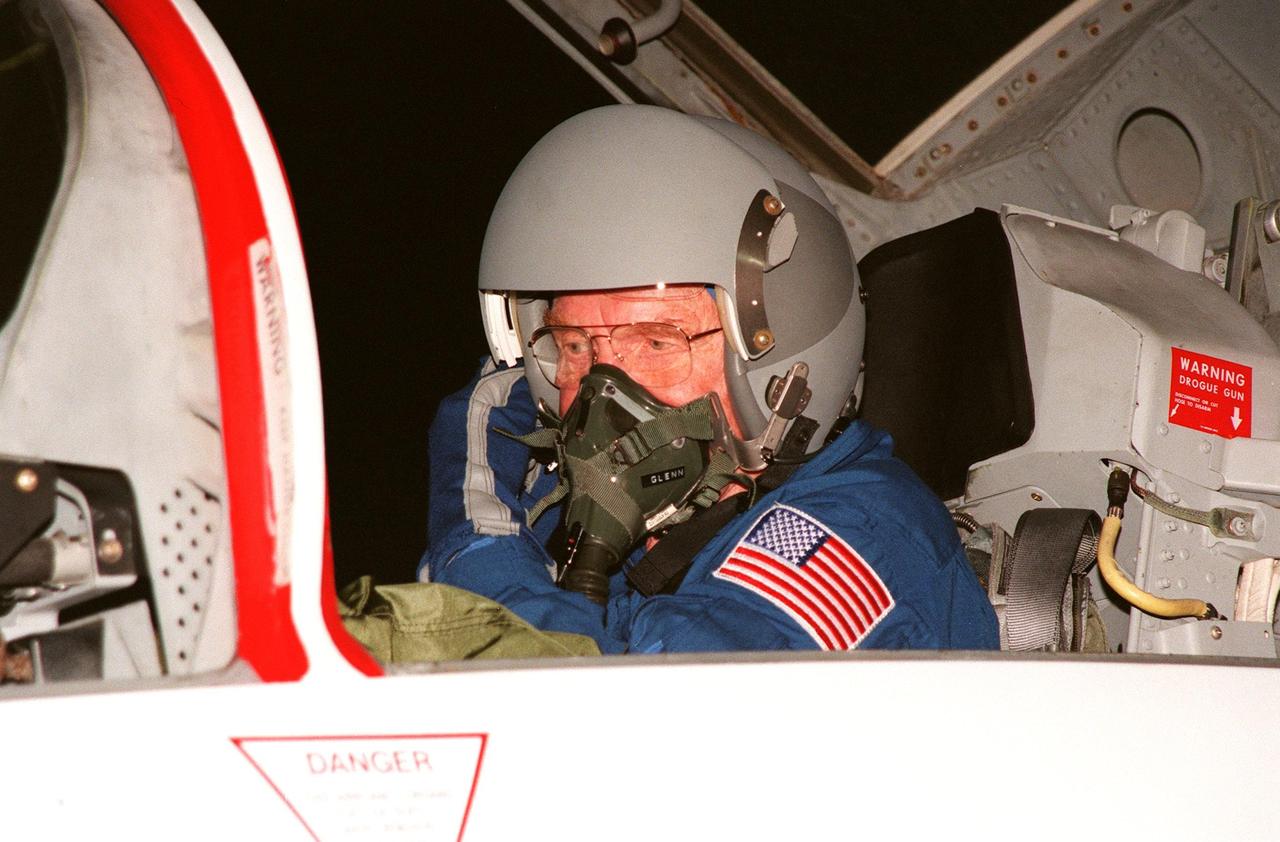

STS-95 Payload Specialist John H. Glenn Jr. arrives aboard a T-38 jet aircraft at the Shuttle Landing Facility at KSC to participate in a Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) for the launch scheduled for liftoff on Oct. 29, 1998. The TCDT includes activities to familiarize them with the mission, training in emergency exit from the orbiter and launch pad, and a simulated main engine cut-off exercise. Other crew members on the mission are Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown , Pilot Steven W. Lindsey; Mission Specialists Scott E. Parazynski, Stephen K. Robinson, and Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency (ESA); and Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai, representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). The STS-95 mission includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process

STS-95 Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency, suits up in the Operations and Checkout Building prior to his trip to Launch Pad 39-B. Duque and the rest of the STS-95 crew are at KSC to participate in the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) which includes mission familiarization activities, emergency egress training, and a simulated main engine cutoff. The other crew members are Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai (M.D., Ph.D.), representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA), Pilot Steven W. Lindsey, Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski, Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson, Payload Specialist John H. Glenn Jr., senator from Ohio, and Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown. The STS-95 mission, targeted for liftoff on Oct. 29, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process. Following the TCDT, the crew will be returning to Houston for final flight preparations
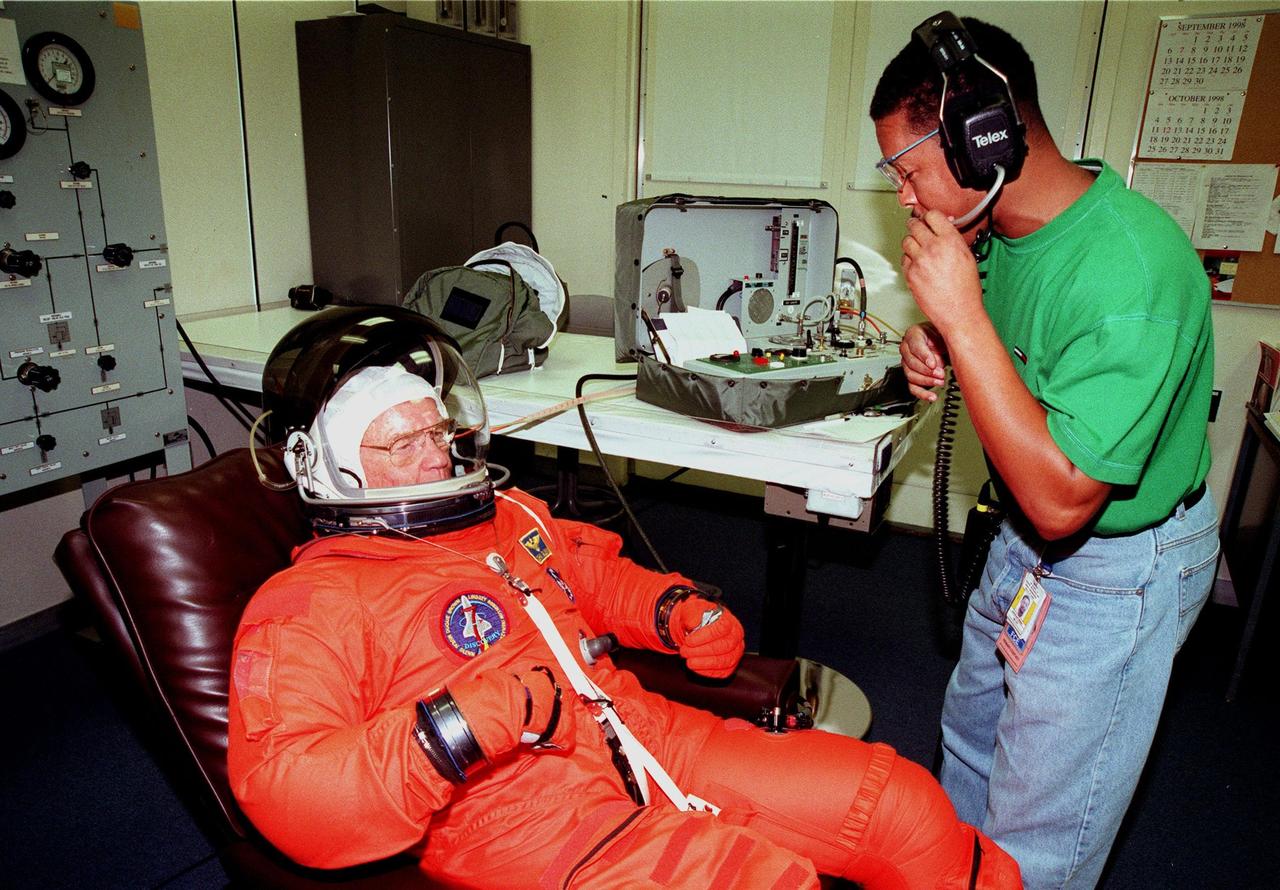

STS-95 Payload Specialist John H. Glenn Jr., a senator from Ohio and one of the original seven Project Mercury astronauts, suits up with the help of George Brittingham, of United Space Alliance, in the Operations and Checkout (O&C)Building prior to his trip to Launch Pad 39-B. Glenn and the rest of the STS-95 crew are at KSC to participate in the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) which includes mission familiarization activities, emergency egress training, and a simulated main engine cutoff. The other crew members are Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai (M.D., Ph.D.), representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA), Pilot Steven W. Lindsey, Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski, Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson, Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency (ESA), and Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown. The STS-95 mission, targeted for liftoff on Oct. 29, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process. Following the TCDT, the crew will be returning to Houston for final flight preparations
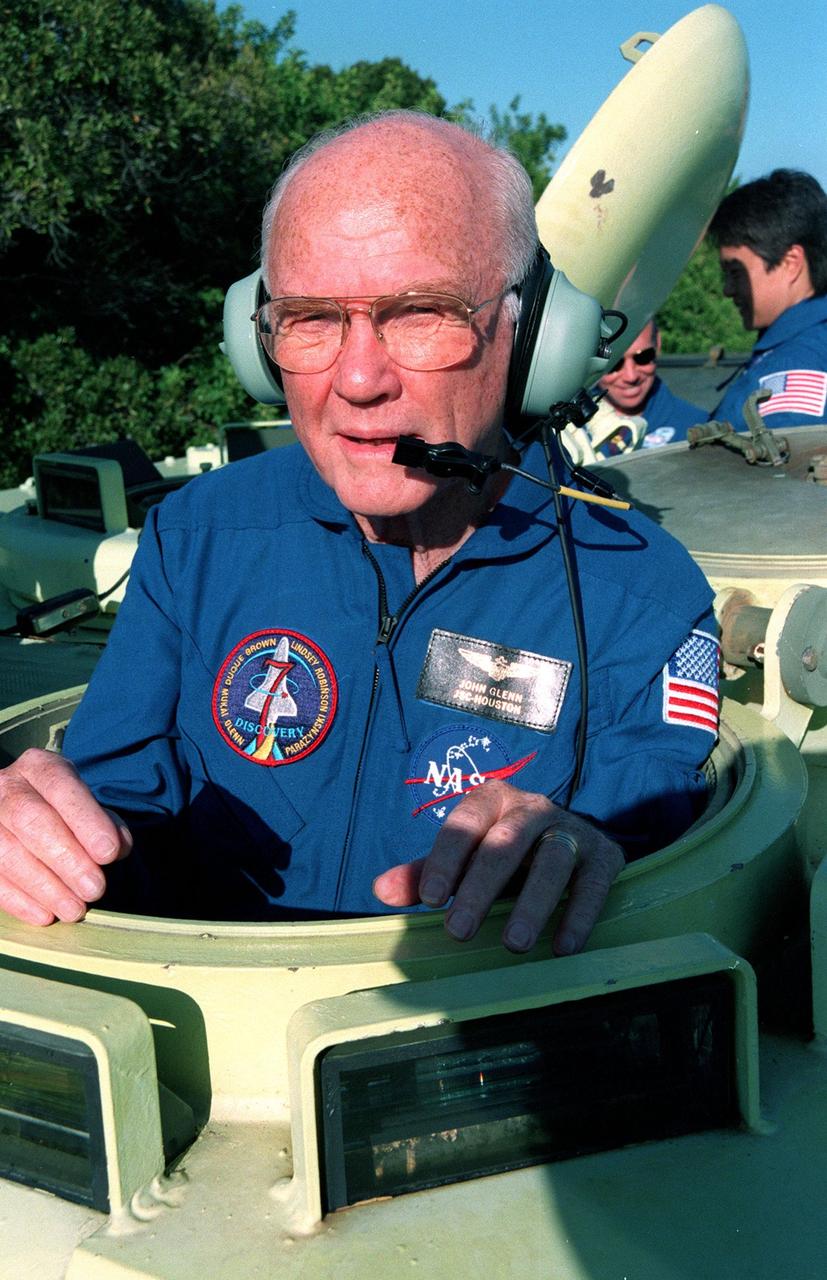

Near Launch Pad 39-B, STS-95 Payload Specialist John H. Glenn Jr. climbs into an M-113, a small armored personnel carrier, that is part of emergency egress training. The tracked vehicle could be used by the crew in the event of an emergency at the pad during which the crew must make a quick exit from the area. The STS-95 crew is at KSC to participate in a Test Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) which also includes mission familiarization activities and a simulated main engine cut-off exercise. The other members on the mission are Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown, Pilot Steven W. Lindsey, Mission Specialists Scott E. Parazynski, Stephen K. Robinson, and Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency (ESA); and Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai, representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). The STS-95 mission, targeted for liftoff on Oct. 29, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process
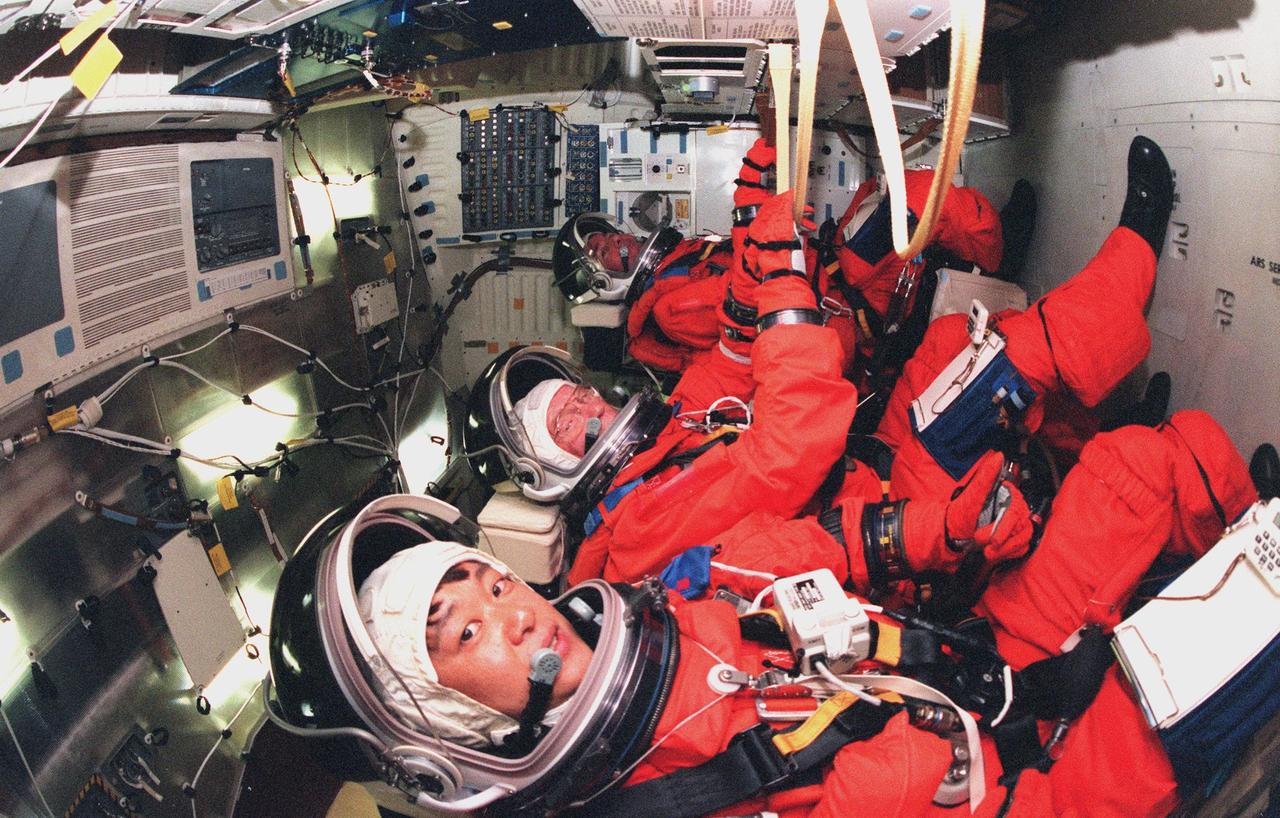

In their flight seats aboard Space Shuttle Discovery are (front to back) STS-95 Payload Specialists Chiaki Mukai (M.D., Ph.D.), representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA), and John H. Glenn Jr., senator from Ohio, and Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson. Mukai, Glenn and Robinson, along with other crew members are at KSC to participate in the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) which includes mission familiarization activities, emergency egress training, and a simulated main engine cutoff. Not shown are Pilot Steven W. Lindsey, Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski, Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency (ESA), and Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown. The STS-95 mission, targeted for liftoff on Oct. 29, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process. Following the TCDT, the crew will be returning to Houston for final flight preparations
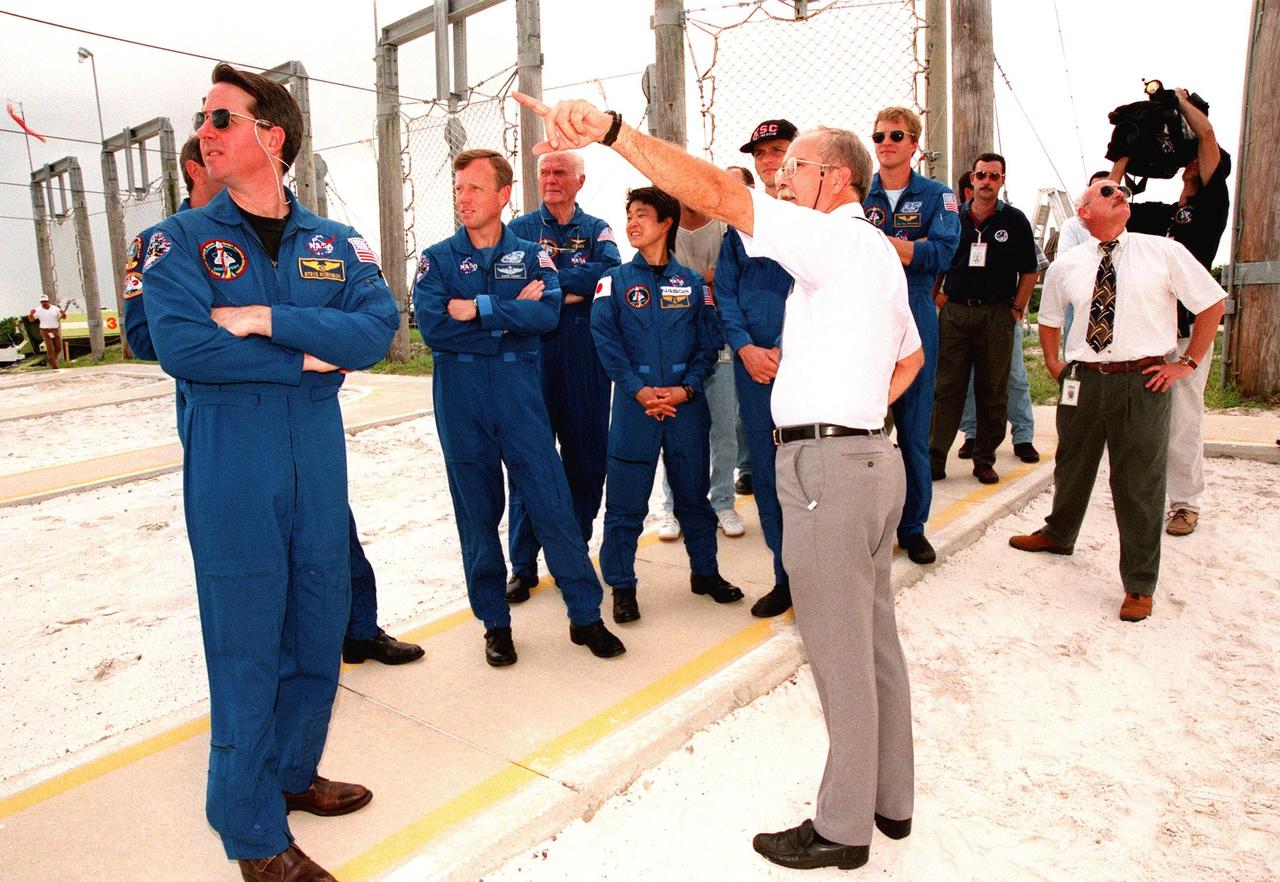

On Launch Pad 39-B, a Safety Egress trainer points out to the STS-95 crew the path the slidewire baskets, emergency egress vehicles, will take if the crew needs to use them before launch. Watching are (left to right) Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson, Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown (partially hidden behind Robinson), Pilot Steven W. Lindsey, Payload Specialists John H. Glenn Jr., senator from Ohio, and Chiaki Mukai, representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA), Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency (ESA), and Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski. The STS-95 crew are at KSC to participate in a Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) which includes mission familiarization activities, emergency egress training, and a simulated main engine cut-off exercise. The STS-95 mission, targeted for liftoff on Oct. 29, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process. Following the TCDT, the crew will be returning to Houston for final flight preparations
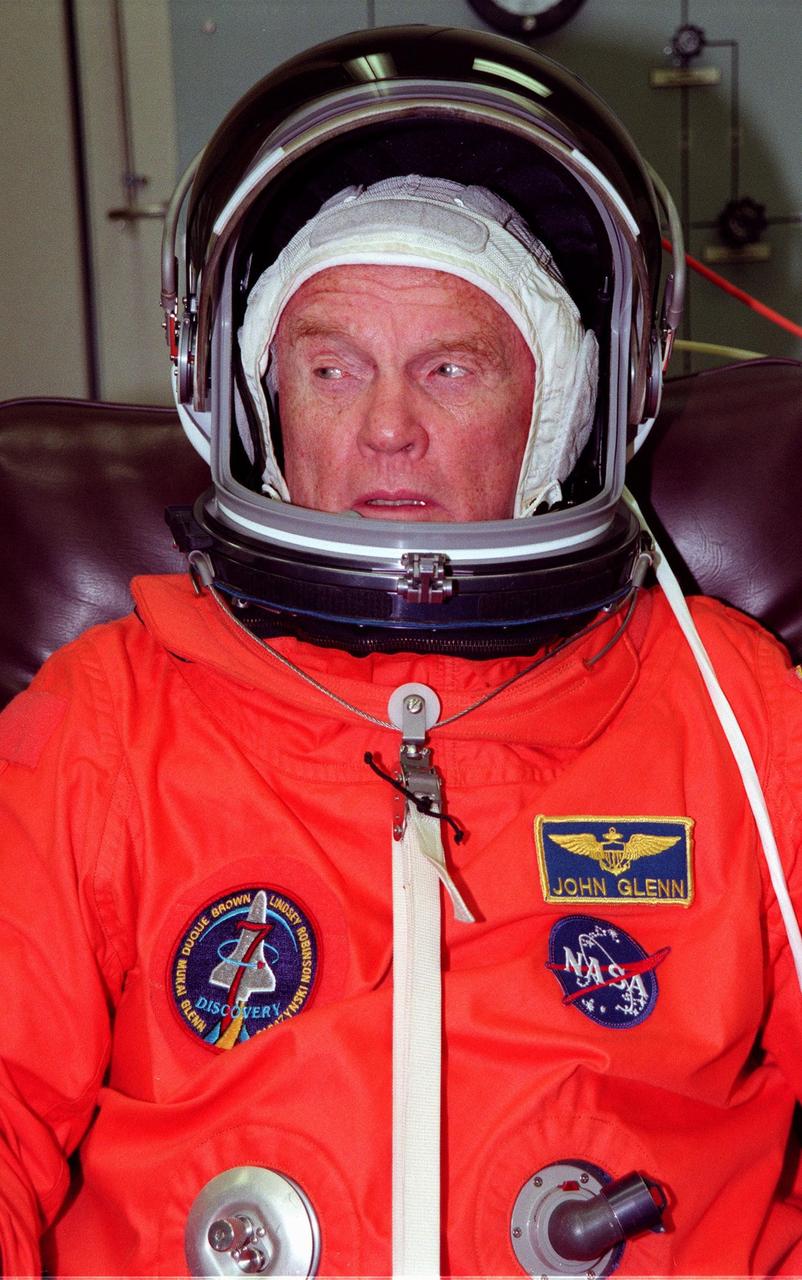

STS-95 Payload Specialist John H. Glenn Jr., a senator from Ohio and one of the original seven Project Mercury astronauts, suits up in the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building prior to his trip to Launch Pad 39-B. Glenn and the rest of the STS-95 crew are at KSC to participate in the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) which includes mission familiarization activities, emergency egress training, and a simulated main engine cutoff. The other crew members are Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai (M.D., Ph.D.), representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA), Pilot Steven W. Lindsey, Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski, Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson, Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency (ESA), and Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown. The STS-95 mission, targeted for liftoff on Oct. 29, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process. Following the TCDT, the crew will be returning to Houston for final flight preparations
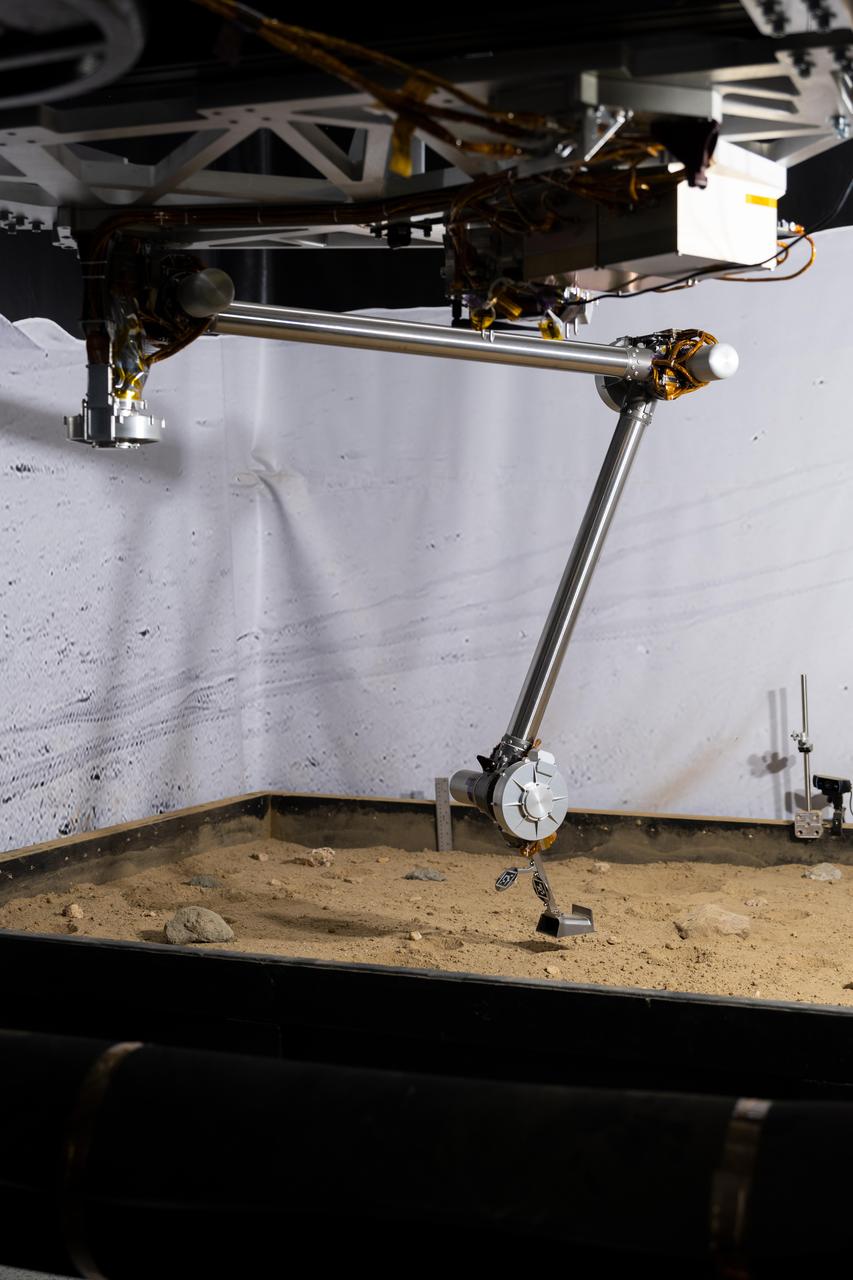
The 3D-printed titanium scoop of the Cold Operable Lunar Deployable Arm (COLDArm) robotic arm system is poised above a test bed filled with material to simulate lunar regolith (broken rocks and dust) at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. COLDArm can function in temperatures as cold as minus 280 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 173 degrees Celsius). COLDArm is designed to go on a Moon lander and operate during lunar night, a period that lasts about 14 Earth days. Frigid temperatures during lunar night would stymie current spacecraft, which must rely on energy-consuming heaters to stay warm. To operate in the cold, the 6-foot-6-inch (2-meter) arm combines several key new technologies: gears made of bulk metallic glass that require no lubrication or heating, cold motor controllers that don't need to be kept warm in an electronics box near the core of the spacecraft, and a cryogenic six-axis force torque sensor that lets the arm "feel" what it's doing and make adjustments. A variety of attachments and small instruments could go on the end of the arm, including the scoop, which could be used for collecting samples from a planet's surface. Like the arm on NASA's InSight Mars lander, COLDArm could deploy science instruments to the surface. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25317
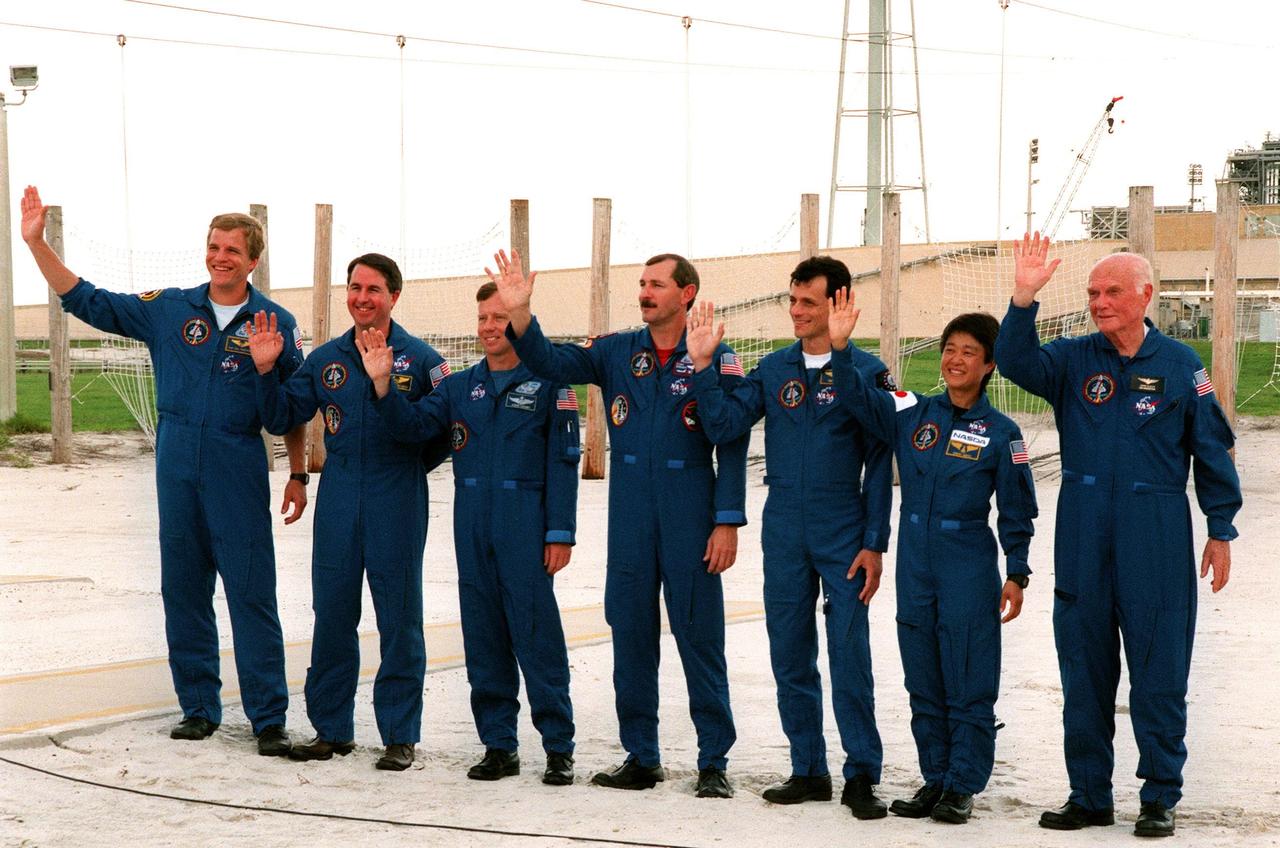

Near the slide wire basket drop point on Launch Pad 39-B, the STS-95 crew wave at 106 reporters and photographers during a brief break from the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) to answer questions about the mission and training. The crew were at the pad for emergency egress training after the break. Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown (center) introduced the rest of the crew: (left to right) Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski, Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson, who also serves as Payload Commander, Pilot Steven W. Lindsey, (Brown), Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency (ESA), Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai, representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA), and Payload Specialist John H. Glenn Jr., senator from Ohio. The TCDT also involves mission familiarization activities and a simulated main engine cut-off exercise. The STS-95 mission, targeted for liftoff on Oct. 29, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process. Following the TCDT, the crew will be returning to Houston for final flight preparations
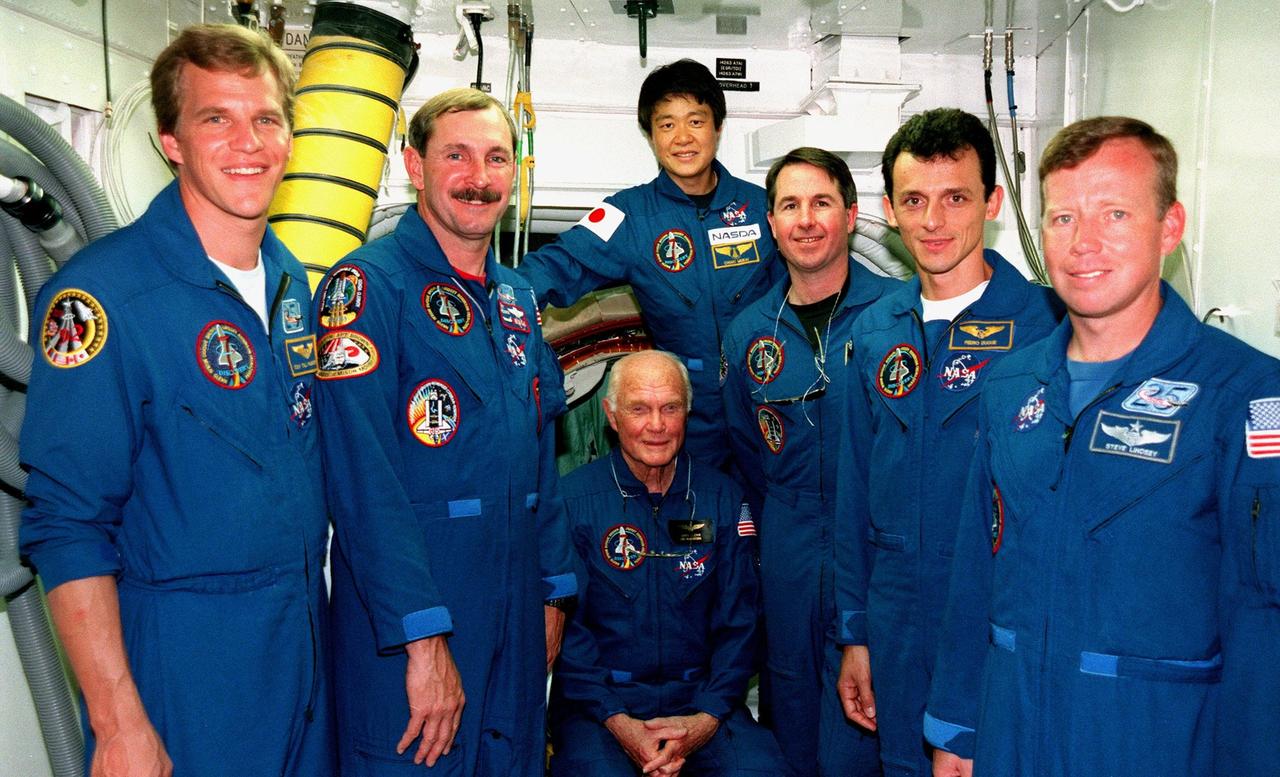

At Launch Pad 39-B, the STS-95 crew pose for a closeup photo while in the white room, an environmental chamber that mates with the orbiter and can provide emergency egress for the flight crew before launch. The white room is the outer end of the orbiter access arm, which is part of the fixed service structure on the pad. Pictured are (left to right) Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski, Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown, Payload Specialist John H. Glenn Jr. (seated), senator from Ohio, Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai (behind Glenn), representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA), Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson, Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency (ESA), and Pilot Steven W. Lindsey. The STS-95 crew are at KSC to participate in a Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) which includes mission familiarization activities, emergency egress training, and a simulated main engine cut-off exercise. The STS-95 mission, targeted for liftoff on Oct. 29, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process. Following the TCDT, the crew will be returning to Houston for final flight preparations
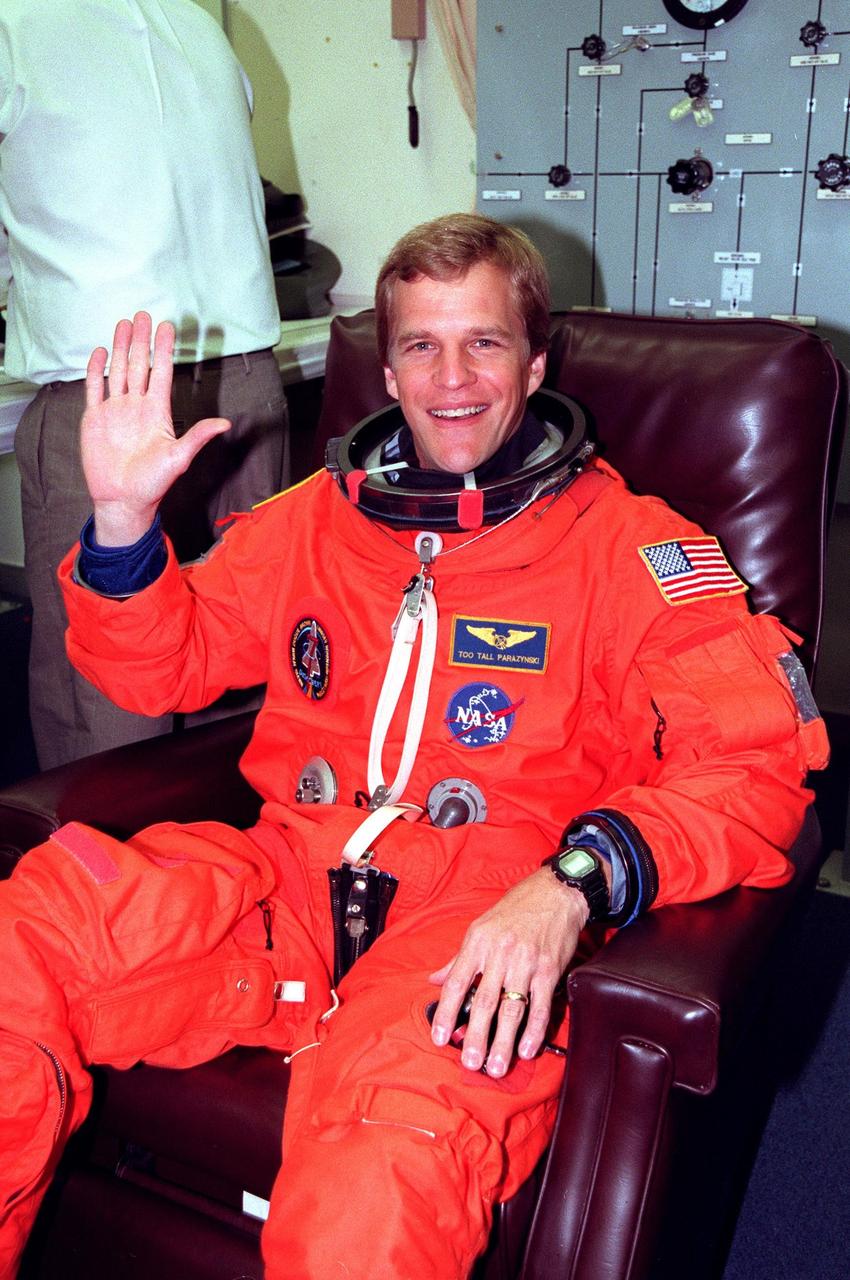

STS-95 Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski suits up in the Operations and Checkout Building prior to his trip to Launch Pad 39-B. Parazynski and the rest of the STS-95 crew are at KSC to participate in the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) which includes mission familiarization activities, emergency egress training, and a simulated main engine cutoff. The other crew members are Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai (M.D., Ph.D.), representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA), Pilot Steven W. Lindsey, Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson, Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency (ESA), Payload Specialist John H. Glenn Jr., senator from Ohio, and Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown. The STS-95 mission, targeted for liftoff on Oct. 29, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process. Following the TCDT, the crew will be returning to Houston for final flight preparations

At Launch Pad 39-B, (far right) STS-95 Payload Specialist John H. Glenn Jr., senator from Ohio, responds to one of the many questions he was asked about the mission and training by reporters during a brief break from the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT). Amused with his answer are other crew members (from left) Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski, Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson, who also serves as Payload Commander, Pilot Steven W. Lindsey, Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown, Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency (ESA), and Chiaki Mukai, representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). The crew were at the pad for emergency egress training after the break. The TCDT also involves mission familiarization activities and a simulated main engine cut-off exercise. The STS-95 mission, targeted for liftoff on Oct. 29, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process. Following the TCDT, the crew will be returning to Houston for final flight preparations
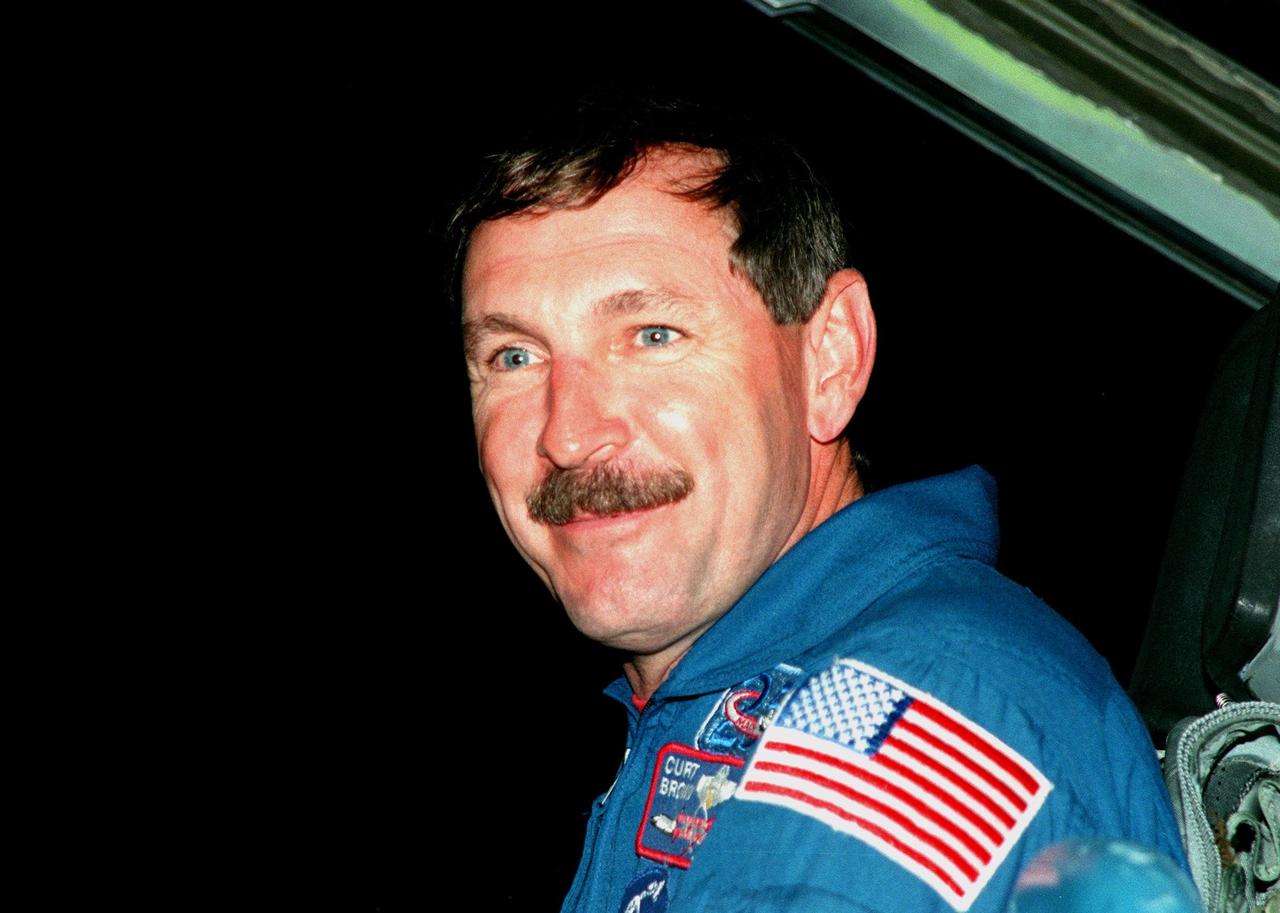

STS-95 Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown arrives aboard a T-38 jet aircraft at the Shuttle Landing Facility at KSC to participate in a Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT). Mission launch is scheduled for liftoff on Oct. 29, 1998. The TCDT includes mission familiarization activities, training in emergency exit from the orbiter and launch pad, and a simulated main engine cut-off exercise. Other crew members on the mission are Pilot Steven W. Lindsey; Mission Specialists Scott E. Parazynski, Stephen K. Robinson, and Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency (ESA); and Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai, representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). The STS-95 mission includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process
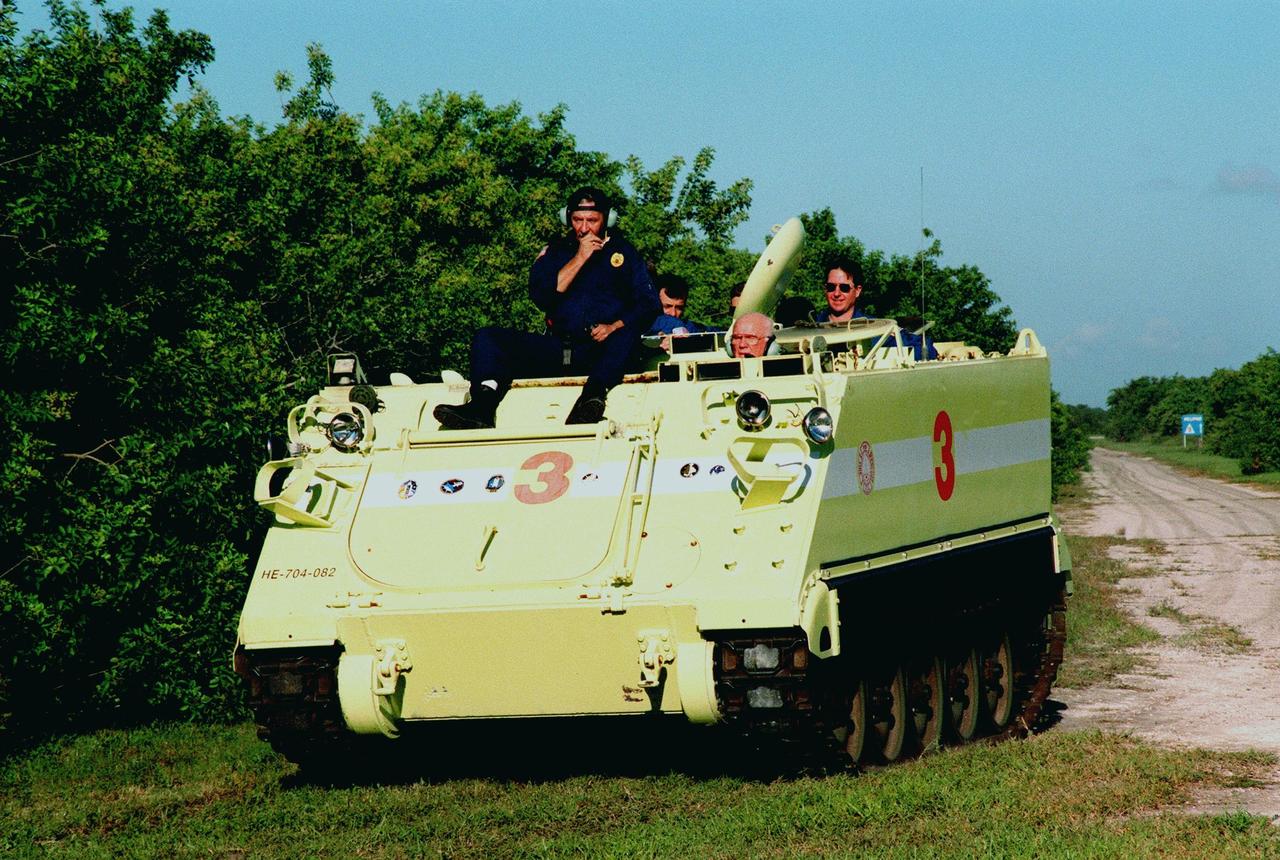

Under the watchful eye of Capt. George Hoggard, trainer with the KSC Fire Department, STS-95 crew members participate in training on the M-113, a small armored personnel carrier, that is part of emergency egress training. Payload Specialist John H. Glenn Jr. (front right) drives, with Mission Specialists Pedro Duque of Spain (left) and Stephen K. Robinson (right) as passengers. Duque represents the European Space Agency (ESA). The tracked vehicle could be used by the crew in the event of an emergency at the pad during which the crew must make a quick exit from the area. The STS-95 crew is at KSC to participate in a Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) which also includes mission familiarization activities and a simulated main engine cut-off exercise. The other members on the mission are Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown, Pilot Steven W. Lindsey, Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski; and Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai, representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). STS-95, which is targeted for launch on Oct. 29, 1998, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process
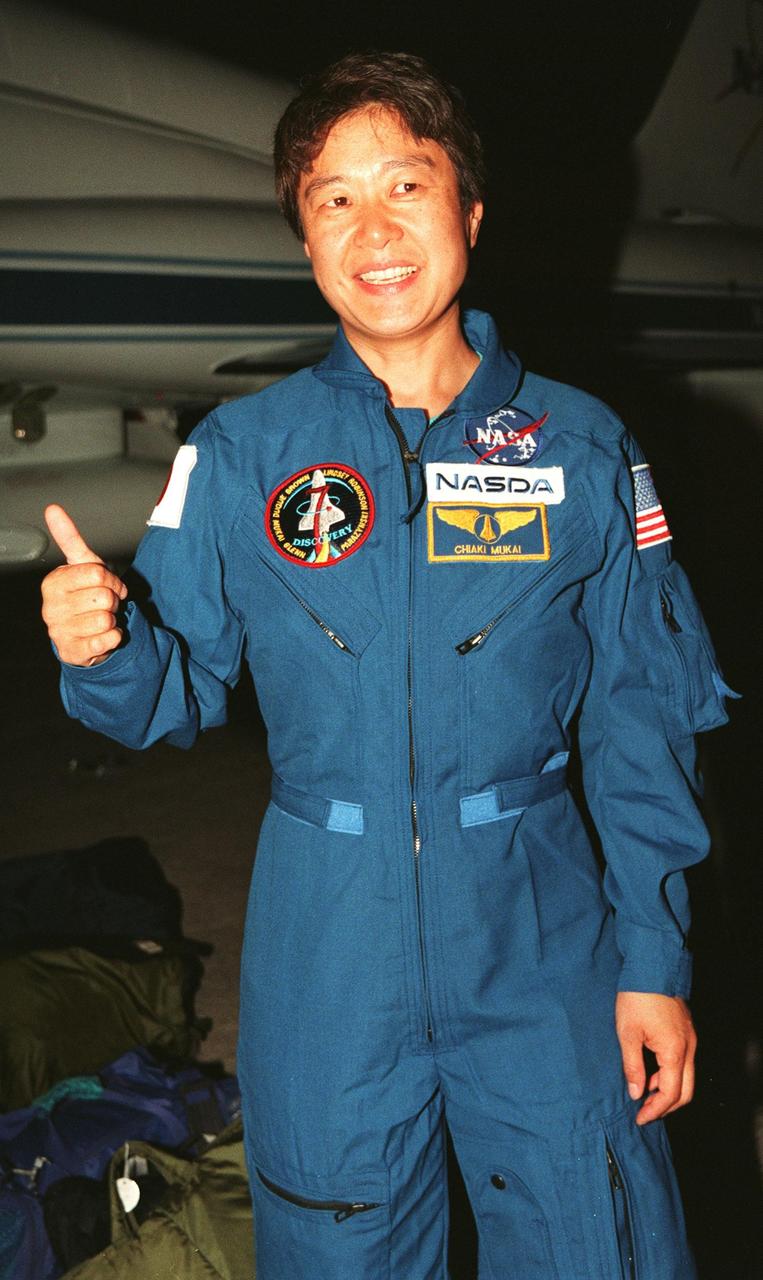

STS-95 Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai, representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA), gives a thumbs up after her arrival aboard a T-38 jet aircraft at the Shuttle Landing Facility at KSC. Mukai and the rest of the crew are at KSC to participate in a Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT). The TCDT includes mission familiarization activities, training in emergency exit from the orbiter and launch pad, and a simulated main engine cut-off exercise. The other members on the mission are Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown, Pilot Steven W. Lindsey; Mission Specialists Scott E. Parazynski, Stephen K. Robinson, and Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency (ESA); and Payload Specialist John H. Glenn Jr., senator from Ohio. The STS-95 mission, scheduled for liftoff on Oct. 29, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process
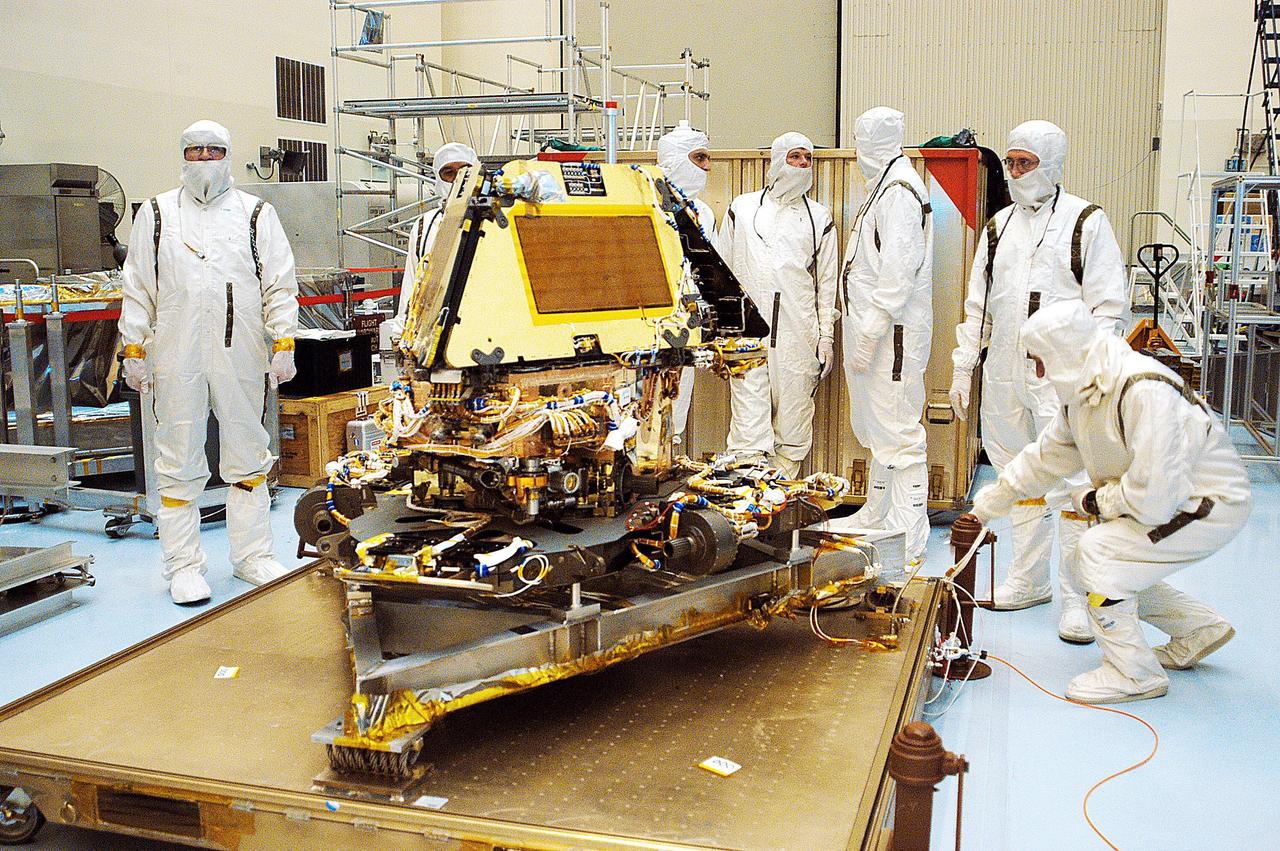

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. - The second Mars Exploration Rover, MER-1, sits revealed on a platform in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility after being unwrapped . MER-2 and other hardware have already arrived at KSC for processing. MER-1 will undergo prelaunch testing, including deployment of the lander petals, the rover's solar arrays, camera mast and camera. While at KSC, each of the rovers, their aeroshells and landers will undergo a full mission simulation. After spin balance testing, each spacecraft will be mated to a solid propellant upper stage booster that will propel the spacecraft out of Earth orbit. Approximately 10 days before launch they will be transported to the launch pad for mating with their respective Boeing Delta II rockets. The rovers will serve as robotic geologists to seek answers about the evolution of Mars, particularly for a history of water. The rovers are identical to each other, and will land at different regions of Mars. Launch of the MER-1 is scheduled for May 30. MER-2 will follow June 25.

In this view looking up, Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner’s parachutes deploy above the U.S. Army’s White Sands Missile Range in New Mexico during parachute system testing on June 24, 2019. Boeing conducted the test using a full-scale Starliner test article, known as a boiler plate, designed to simulate the actual spacecraft. The test involved intentionally disabling one of the parachute system’s two drogue parachutes and one of the three main parachutes to evaluate how the remaining parachutes handled the additional loads during deployment and descent. This was one of a series of important parachute tests to validate the system is safe to carry astronauts to and from the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Boeing is targeting an uncrewed Orbital Flight Test to the space station this summer, followed by its Crew Flight Test. Starliner will launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
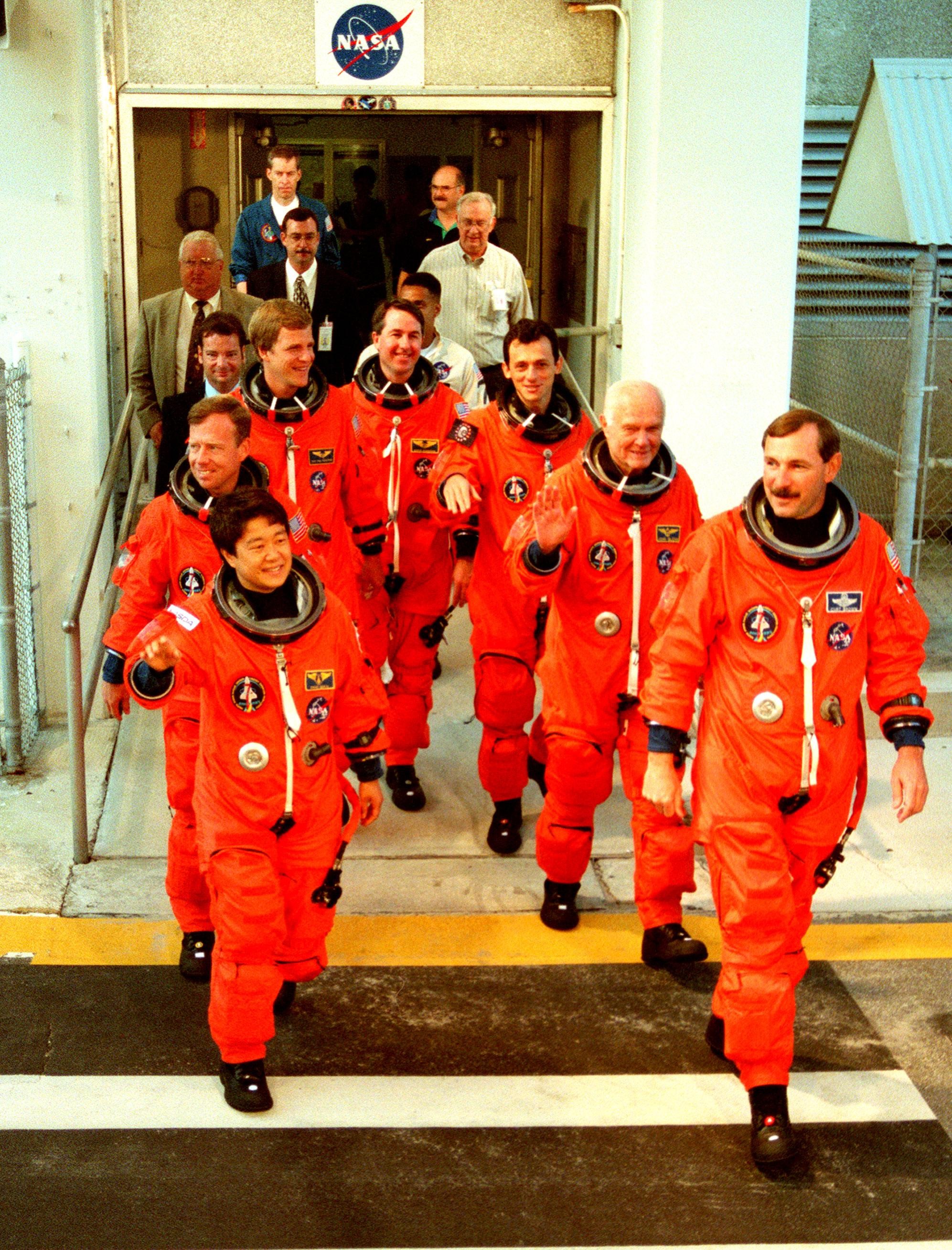

STS-95 crew members exit the Operations and Checkout Building where they suited up before leaving for Launch Pad 39-B. Pictured are (clockwise from lower left) Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai (M.D., Ph.D.), representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA), Pilot Steven W. Lindsey, Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski, Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson, Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency (ESA), Payload Specialist John H. Glenn Jr., senator from Ohio, and Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown. The STS-95 crew are at KSC to participate in a Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) which includes mission familiarization activities, emergency egress training, and the simulated main engine cut-off exercise. The STS-95 mission, targeted for liftoff on Oct. 29, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process. Following the TCDT, the crew will be returning to Houston for final flight preparations
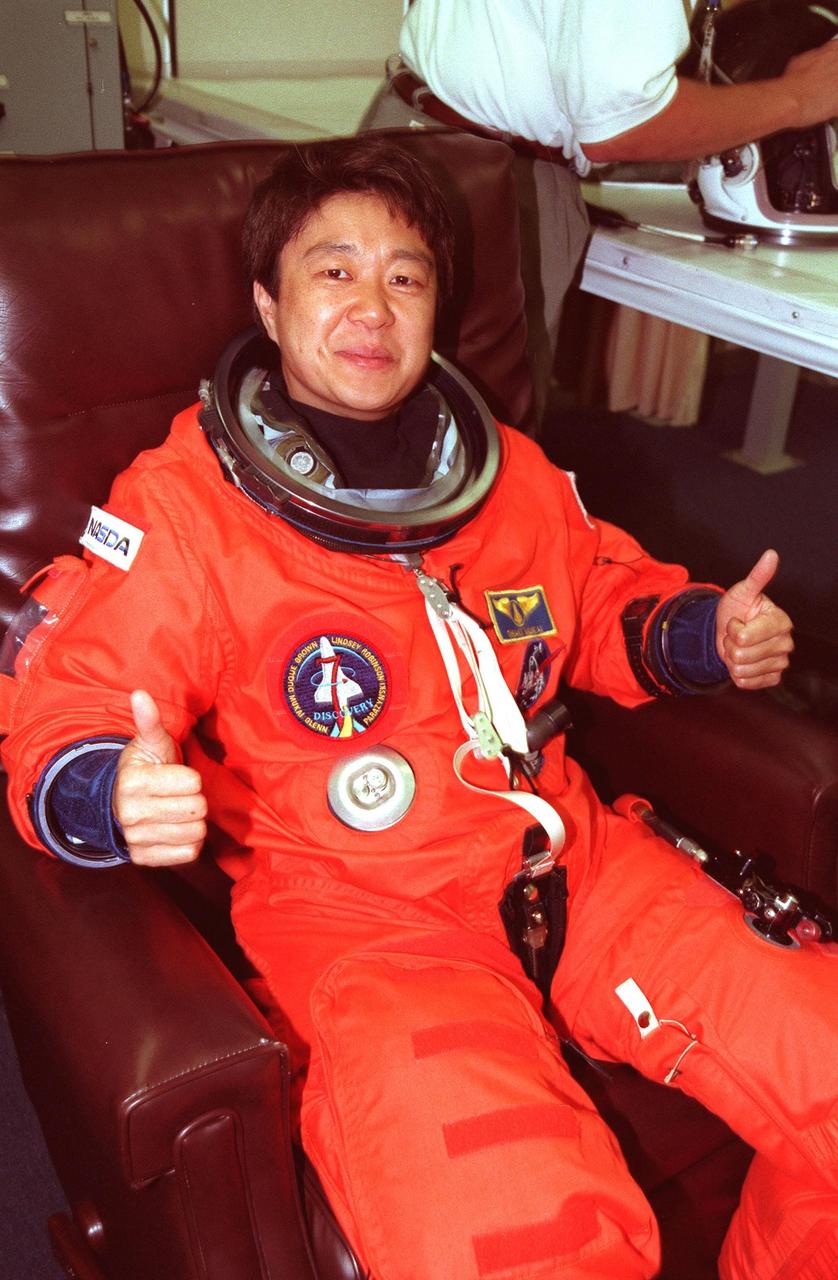

STS-95 Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai (M.D., Ph.D.), representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA), gives a two-thumbs up salute while suiting up in the Operations and Checkout Building prior to her trip to Launch Pad 39-B. Mukai and the rest of the STS-95 crew are at KSC to participate in the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) which includes mission familiarization activities, emergency egress training, and a simulated main engine cutoff. The other crew members are Pilot Steven W. Lindsey, Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski, Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson, Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency (ESA), Payload Specialist John H. Glenn Jr., senator from Ohio, and Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown. The STS-95 mission, targeted for liftoff on Oct. 29, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process. Following the TCDT, the crew will be returning to Houston for final flight preparations
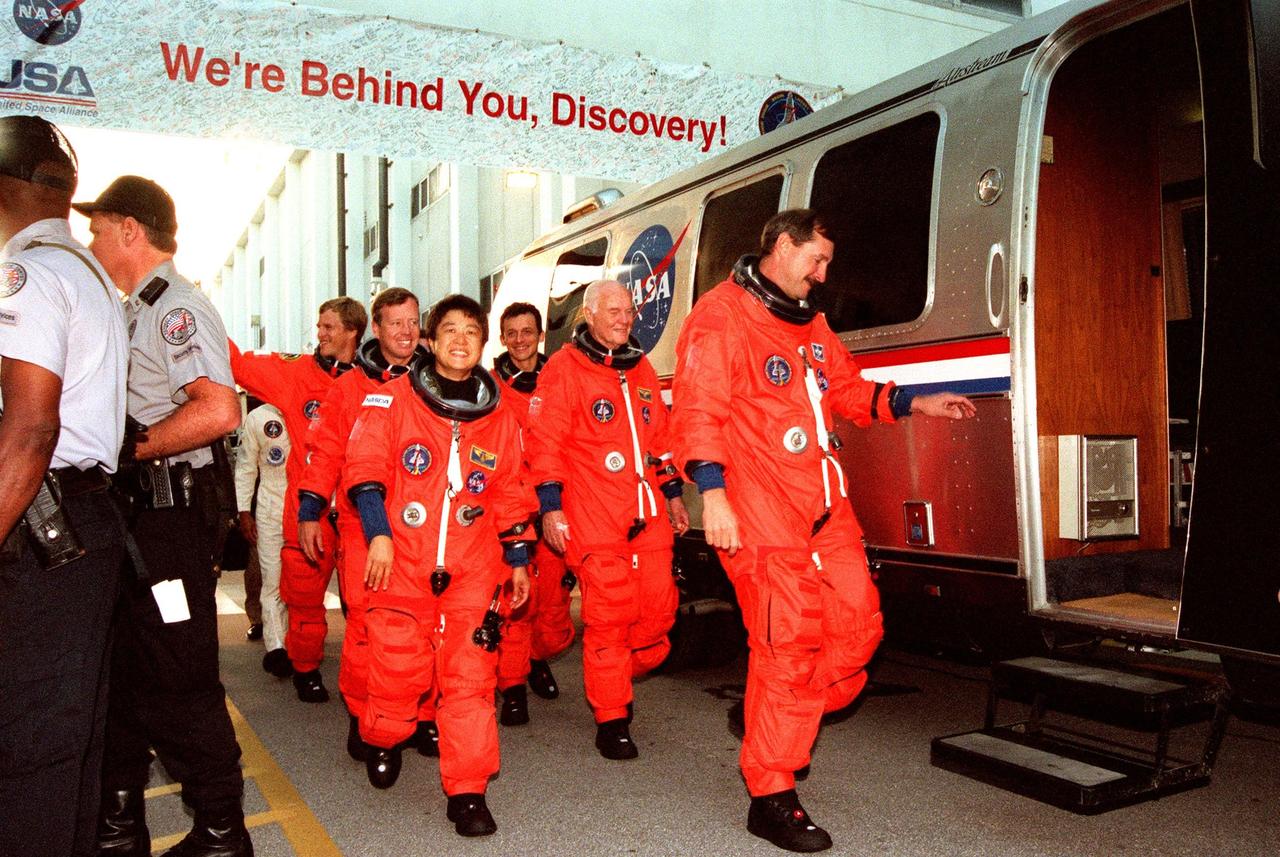

After suiting up for their practice countdown exercise, STS-95 crew members head for the bus outside the Operations and Checkout Building for the trip to Launch Pad 39-B. Pictured are (left to right) Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski, Pilot Steven W. Lindsey, Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai (M.D., Ph.D.), representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA), Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency (ESA), Payload Specialist John H. Glenn Jr., senator from Ohio, and Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown. Not seen is Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson. The STS-95 crew are at KSC to participate in a Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) which includes mission familiarization activities, emergency egress training, and the simulated main engine cut-off exercise. The STS-95 mission, targeted for liftoff on Oct. 29, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process. Following the TCDT, the crew will be returning to Houston for final flight preparations
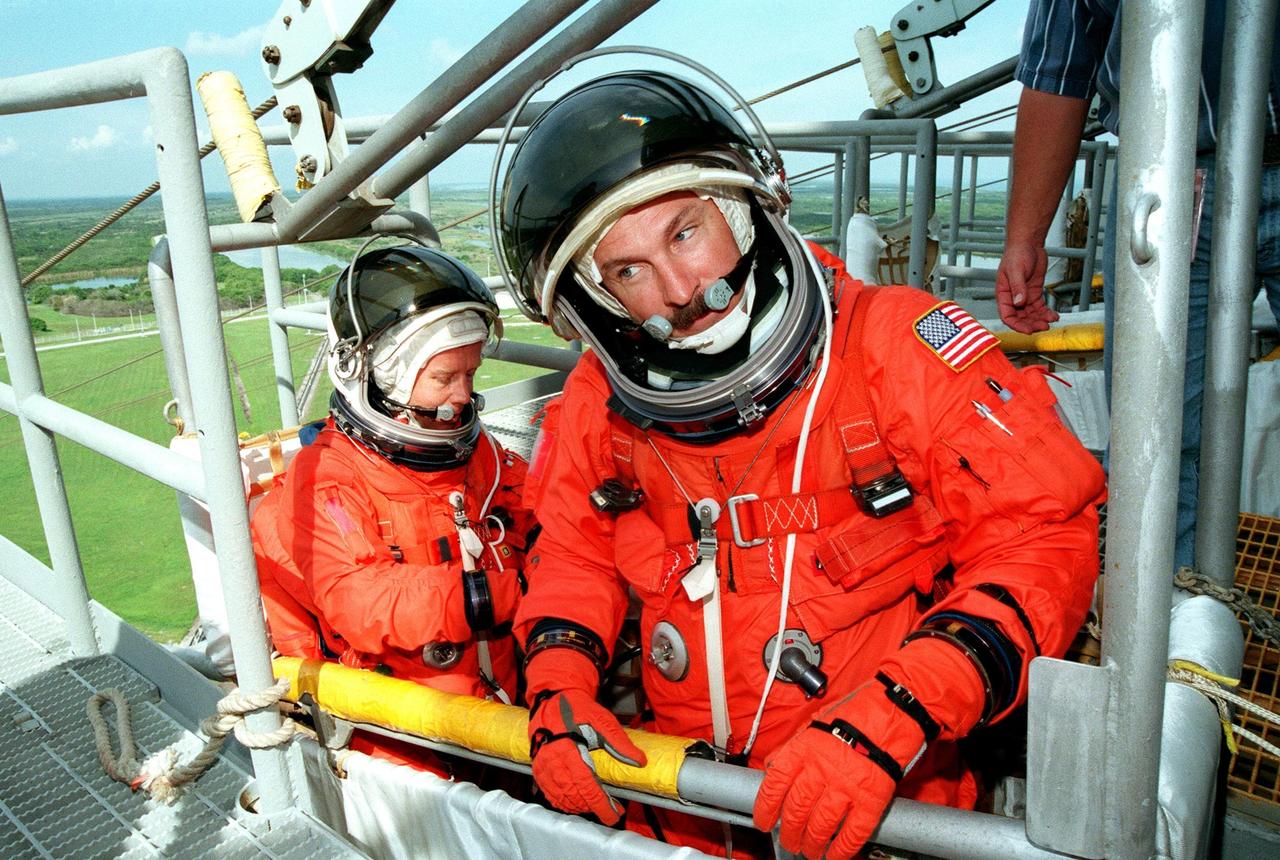

STS-95 Pilot Steven W. Lindsey (left) and Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown are ready to leave Launch Pad 39B in the slidewire basket during an emergency egress exercise. Lindsey and Brown, along with other crew members, are at KSC to participate in the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) which includes mission familiarization activities, emergency egress training, and a simulated main engine cutoff. Not shown are Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency (ESA), Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski, Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson, Payload Specialists John H. Glenn Jr., senator from Ohio, and Chiaki Mukai (M.D., Ph.D.), representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). The STS-95 mission, targeted for liftoff on Oct. 29, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process. Following the TCDT, the crew will be returning to Houston for final flight preparations

Near Launch Pad 39-B, the STS-95 crew members respond to questions about the mission and training from reporters during a brief break from the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT). From left they are Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski, Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson, who also serves as Payload Commander, Pilot Steven W. Lindsey, Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown, Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency (ESA), Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai, representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA), and Payload Specialist John H. Glenn Jr., senator from Ohio, holding a microphone. The crew were at the pad for emergency egress training after the break. Behind them are the catch nets for the slidewire baskets that are used in emergency egress. The TCDT also involves mission familiarization activities and a simulated main engine cut-off exercise. The STS-95 mission, targeted for liftoff on Oct. 29, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process. Following the TCDT, the crew will be returning to Houston for final flight preparations
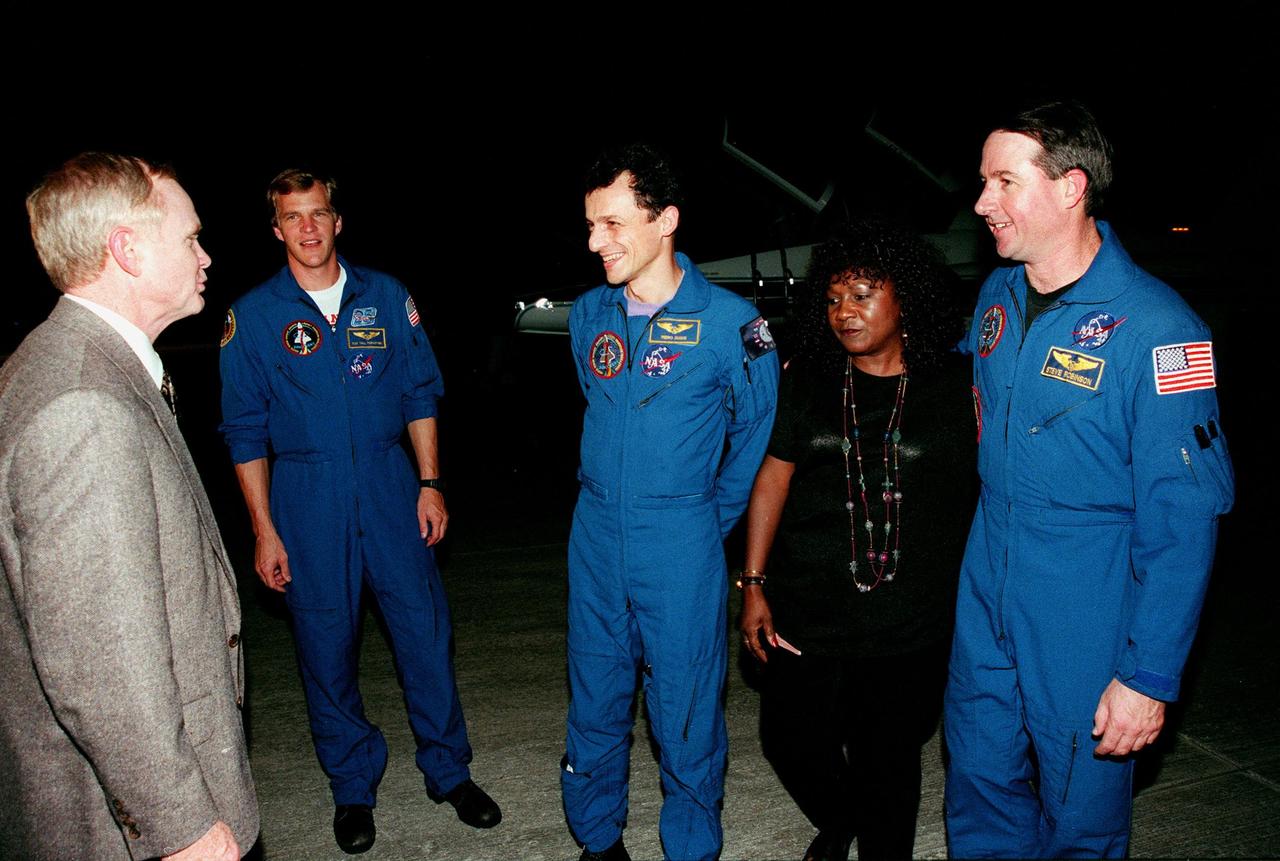

(Left to right) Center Director Roy Bridges welcomes STS-95 Mission Specialists Scott E. Parazynski, Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency (ESA), and Stephen K. Robinson (far right) after their arrival aboard T-38 jet aircraft at the Shuttle Landing Facility at KSC. Standing between Duque and Robinson is Dolores Green, NASA. The STS-95 crew are at KSC to participate in a Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT). The TCDT includes mission familiarization activities, training in emergency exit from the orbiter and launch pad, and a simulated main engine cut-off exercise. The other members on the mission are Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown, Pilot Steven W. Lindsey; and Payload Specialists Chiaki Mukai, representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA), and John H. Glenn Jr., senator from Ohio. The STS-95 mission, scheduled for liftoff on Oct. 29, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process
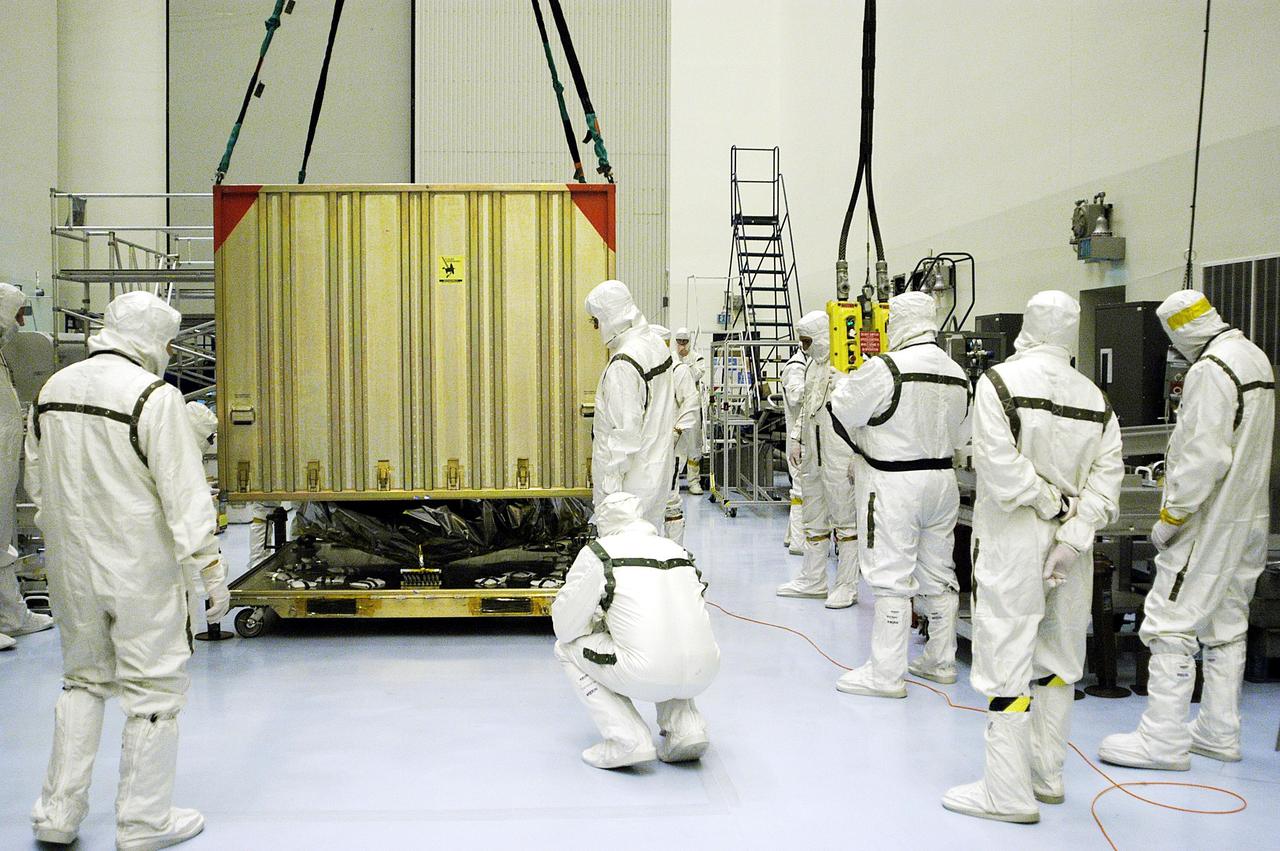

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. - Workers in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility watch as the cover is lifted off the second Mars Exploration Rover, MER-1. MER-2 and other hardware have already arrived at KSC for processing. MER-1 will undergo prelaunch testing, including deployment of the lander petals, the rover's solar arrays, camera mast and camera. While at KSC, each of the rovers, their aeroshells and landers will undergo a full mission simulation. After spin balance testing, each spacecraft will be mated to a solid propellant upper stage booster that will propel the spacecraft out of Earth orbit. Approximately 10 days before launch they will be transported to the launch pad for mating with their respective Boeing Delta II rockets. The rovers will serve as robotic geologists to seek answers about the evolution of Mars, particularly for a history of water. The rovers are identical to each other, and will land at different regions of Mars. Launch of the MER-1 is scheduled for May 30. MER-2 will follow June 25.
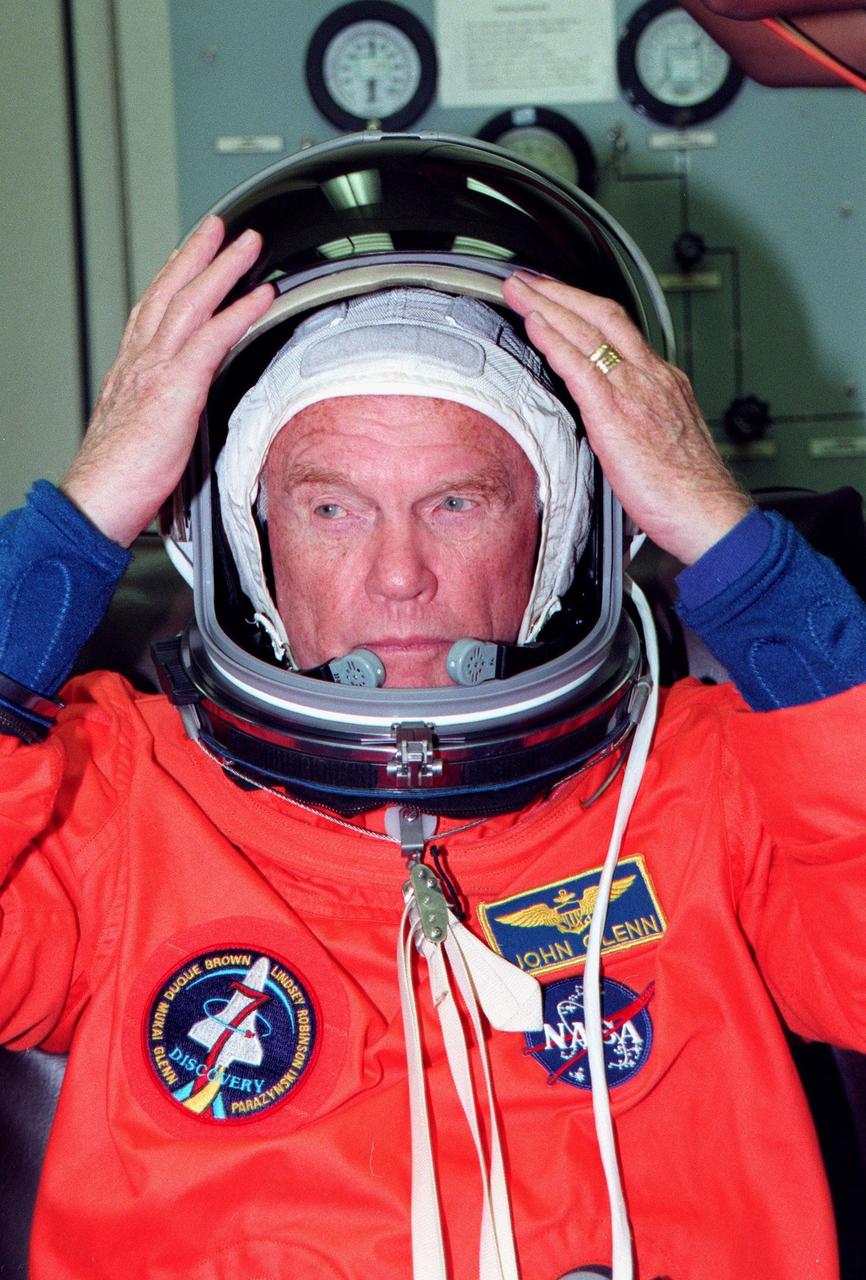

STS-95 Payload Specialist John H. Glenn Jr., a senator from Ohio and one of the original seven Project Mercury astronauts, adjusts his helmet during suitup in the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building prior to his trip to Launch Pad 39-B. Glenn and the rest of the STS-95 crew are at KSC to participate in the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) which includes mission familiarization activities, emergency egress training, and a simulated main engine cutoff. The other crew members are Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai (M.D., Ph.D.), representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA), Pilot Steven W. Lindsey, Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski, Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson, Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency (ESA), and Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown. The STS-95 mission, targeted for liftoff on Oct. 29, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process. Following the TCDT, the crew will be returning to Houston for final flight preparations
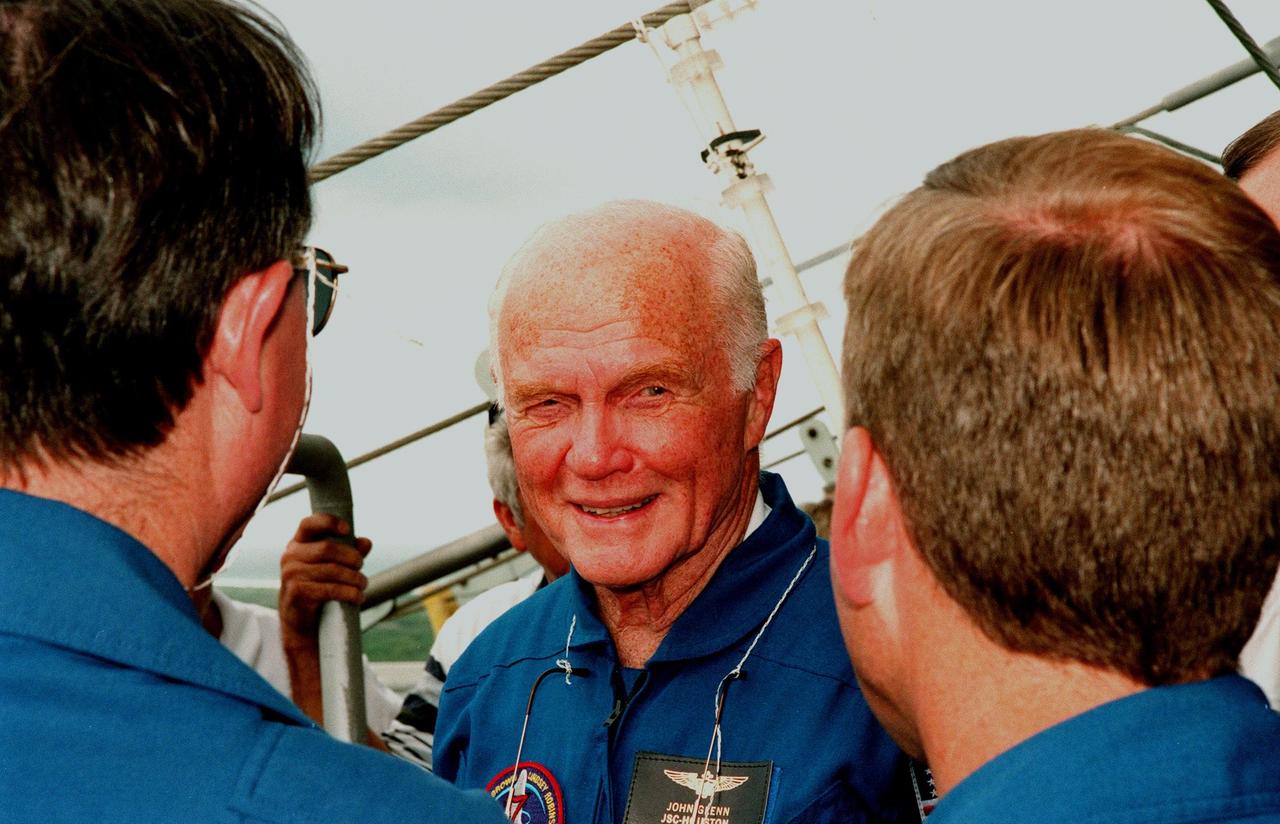

At Launch Pad 39-B, at the 195-foot level, STS-95 Payload Specialist John H. Glenn Jr., senator from Ohio, takes a moment from emergency egress training to talk to (left) Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson and Pilot Steven W. Lindsey (right). The STS-95 crew are at KSC to participate in a Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) which includes mission familiarization activities, emergency egress training, and a simulated main engine cut-off exercise. Other crew members are Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski, Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency (ESA), Mission Specialist Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai, representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA), and Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown. The STS-95 mission, targeted for liftoff on Oct. 29, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process. Following the TCDT, the crew will be returning to Houston for final flight preparations
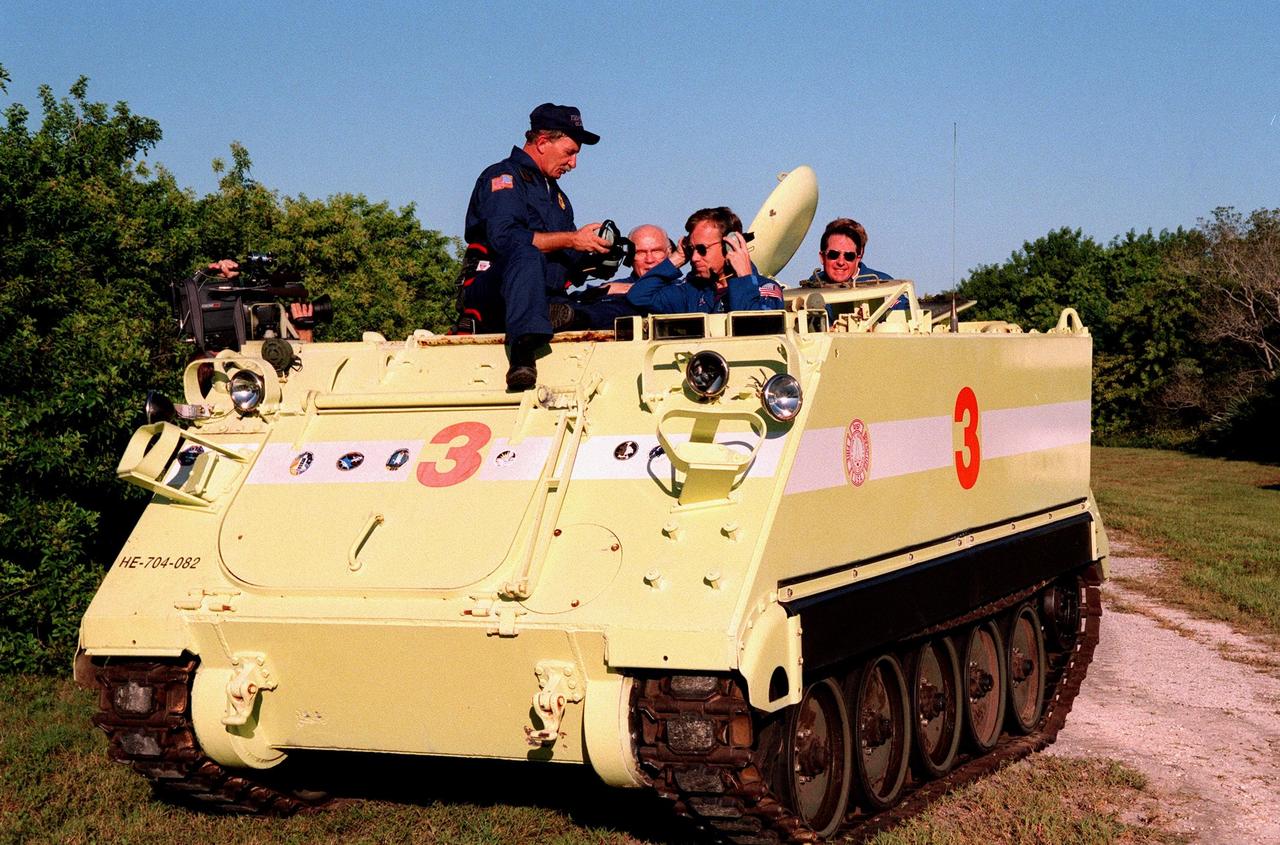

Capt. George Hoggard (left), trainer with the KSC Fire Department, reviews procedures with STS-95 crew members before beginning training on the M-113, a small armored personnel carrier, that is part of emergency egress training. Pilot Steven W. Lindsey (front right) prepares to take his turn in the driver seat, with Payload Specialists John H. Glenn Jr. (rear left) and Stephen K. Robinson (right) as passengers. The tracked vehicle could be used by the crew in the event of an emergency at the pad during which the crew must make a quick exit from the area. The STS-95 crew is at KSC to participate in a Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) which also includes mission familiarization activities and a simulated main engine cut-off exercise. The other members on the mission are Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown, Mission Specialists Scott E. Parazynski and Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency (ESA); and Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai, representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). STS-95, which is targeted for launch on Oct. 29, 1998, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process
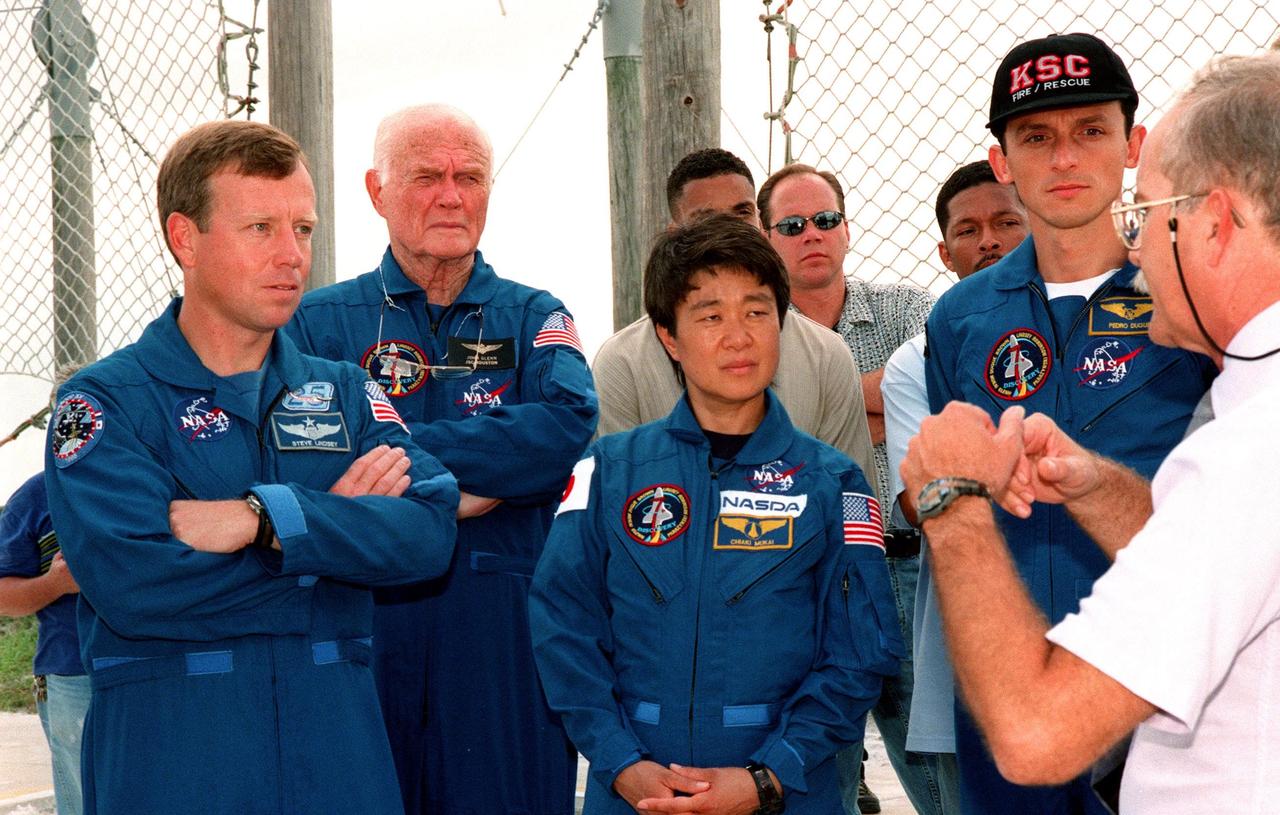

At Launch Pad 39-B, a Safety Egress trainer explains the use of the slidewire basket system for emergency egress before launch to STS-95 crew members (left to right) Pilot Steven W. Lindsey, Payload Specialists John H. Glenn Jr., senator from Ohio, and Chiaki Mukai, representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA), and Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency. The STS-95 crew are at KSC to participate in a Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) which includes mission familiarization activities, emergency egress training, and a simulated main engine cut-off exercise. Other members of the crew not shown are Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski, Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown, and Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson. The STS-95 mission, targeted for liftoff on Oct. 29, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process. Following the TCDT, the crew will be returning to Houston for final flight preparations

STS-95 Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson, with the help of Carlos Gillis, of Lockheed Martin, suits up in the Operations and Checkout Building prior to his trip to Launch Pad 39-B. Robinson and the rest of the STS-95 crew are at KSC to participate in the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) which includes mission familiarization activities, emergency egress training, and a simulated main engine cutoff. The other crew members are Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai (M.D., Ph.D.), representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA), Pilot Steven W. Lindsey, Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski, Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency (ESA), Payload Specialist John H. Glenn Jr., senator from Ohio, and Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown. The STS-95 mission, targeted for liftoff on Oct. 29, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process. Following the TCDT, the crew will be returning to Houston for final flight preparations
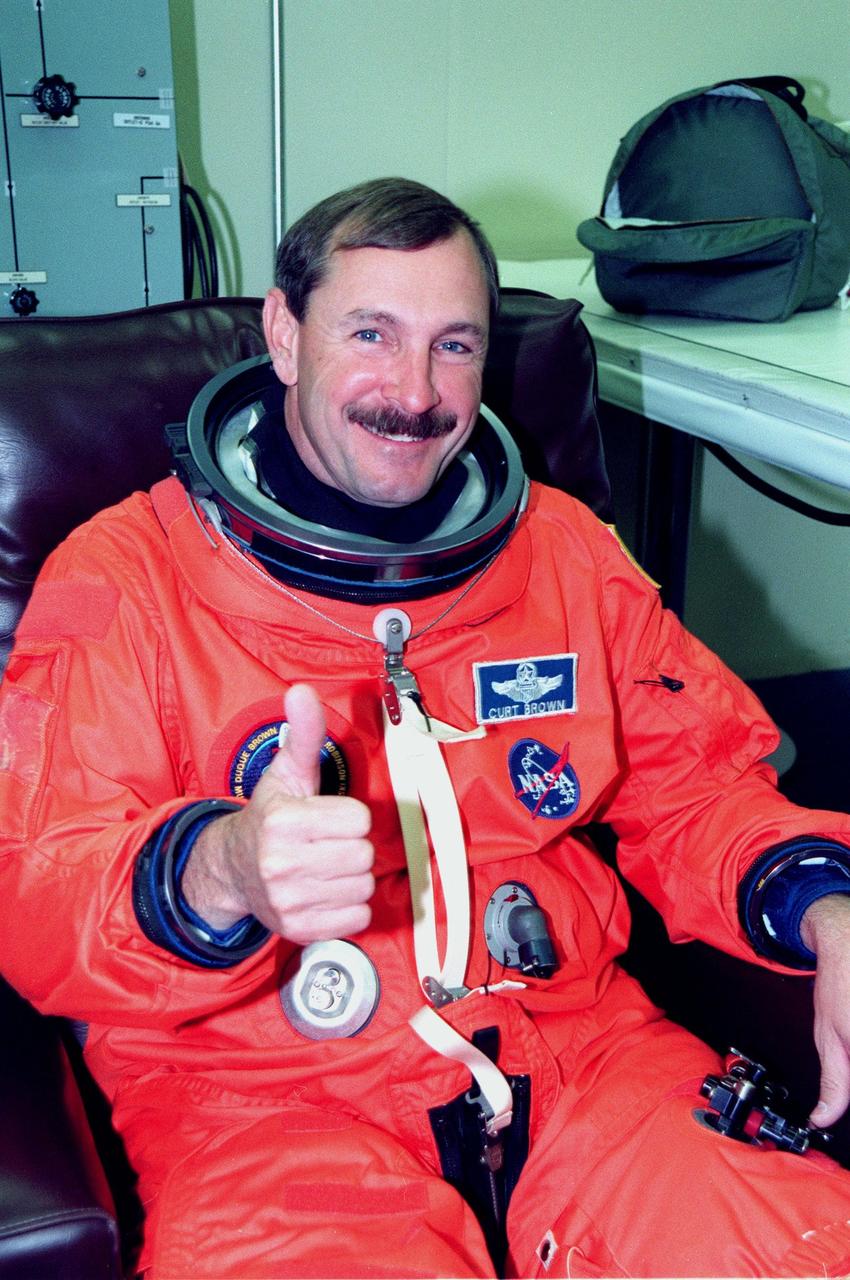

STS-95 Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown suits up in the Operations and Checkout Building prior to his trip to Launch Pad 39-B. Brown and the rest of the STS-95 crew are at KSC to participate in the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) which includes mission familiarization activities, emergency egress training, and a simulated main engine cutoff. The other crew members are Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai (M.D., Ph.D.), representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA), Pilot Steven W. Lindsey, Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski, Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson, Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency (ESA), and Payload Specialist John H. Glenn Jr., senator from Ohio. The STS-95 mission, targeted for liftoff on Oct. 29, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process. Following the TCDT, the crew will be returning to Houston for final flight preparations
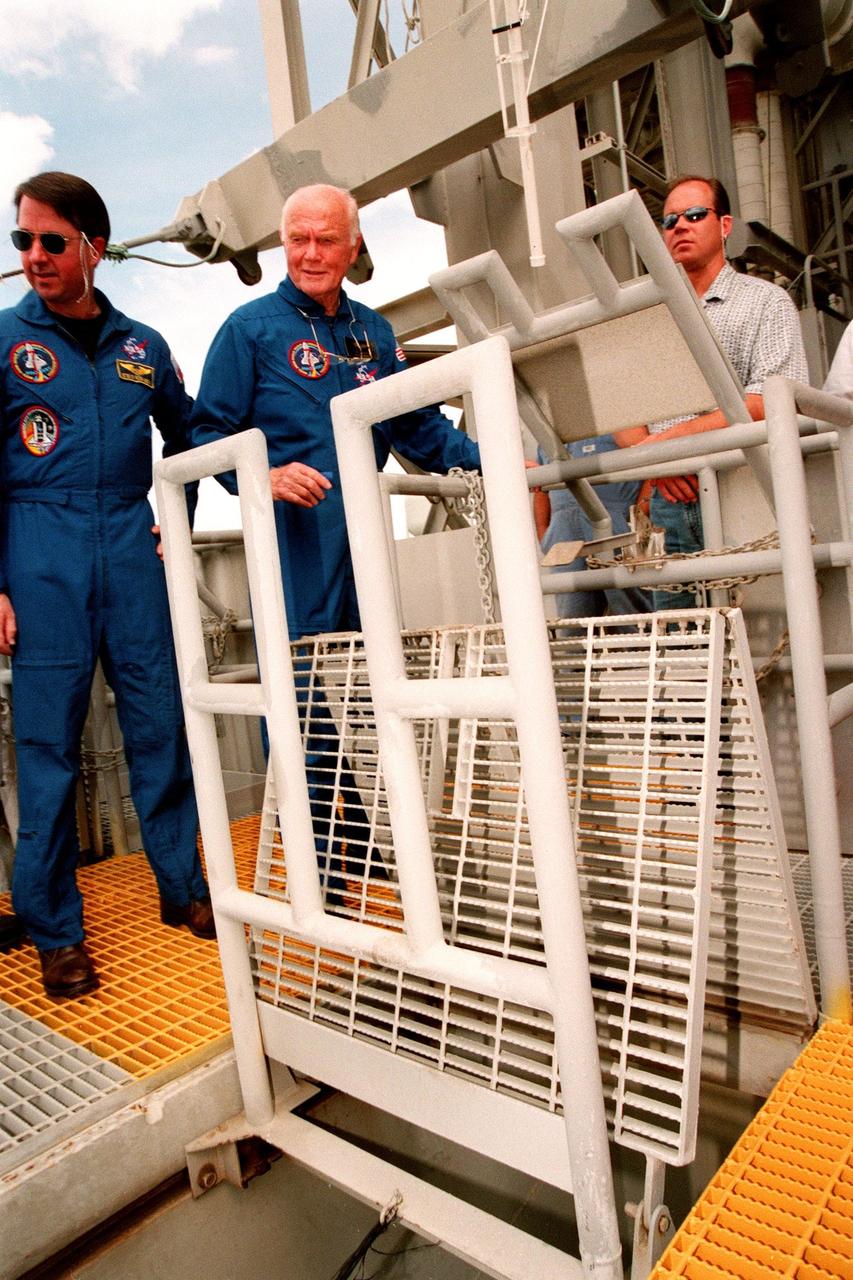

STS-95 Payload Specialist John H. Glenn Jr. (right) releases the slidewire basket, an emergency egress vehicle, at the 195-foot level of Launch Pad 39-B, while Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson (left) watches. The STS-95 crew are at KSC to participate in a Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) which includes mission familiarization activities, emergency egress training, and a simulated main engine cut-off exercise. Other crew members are Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski, Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency (ESA), Pilot Steven W. Lindsey, Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai, representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA), and Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown. The STS-95 mission, targeted for liftoff on Oct. 29, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process. Following the TCDT, the crew will be returning to Houston for final flight preparations
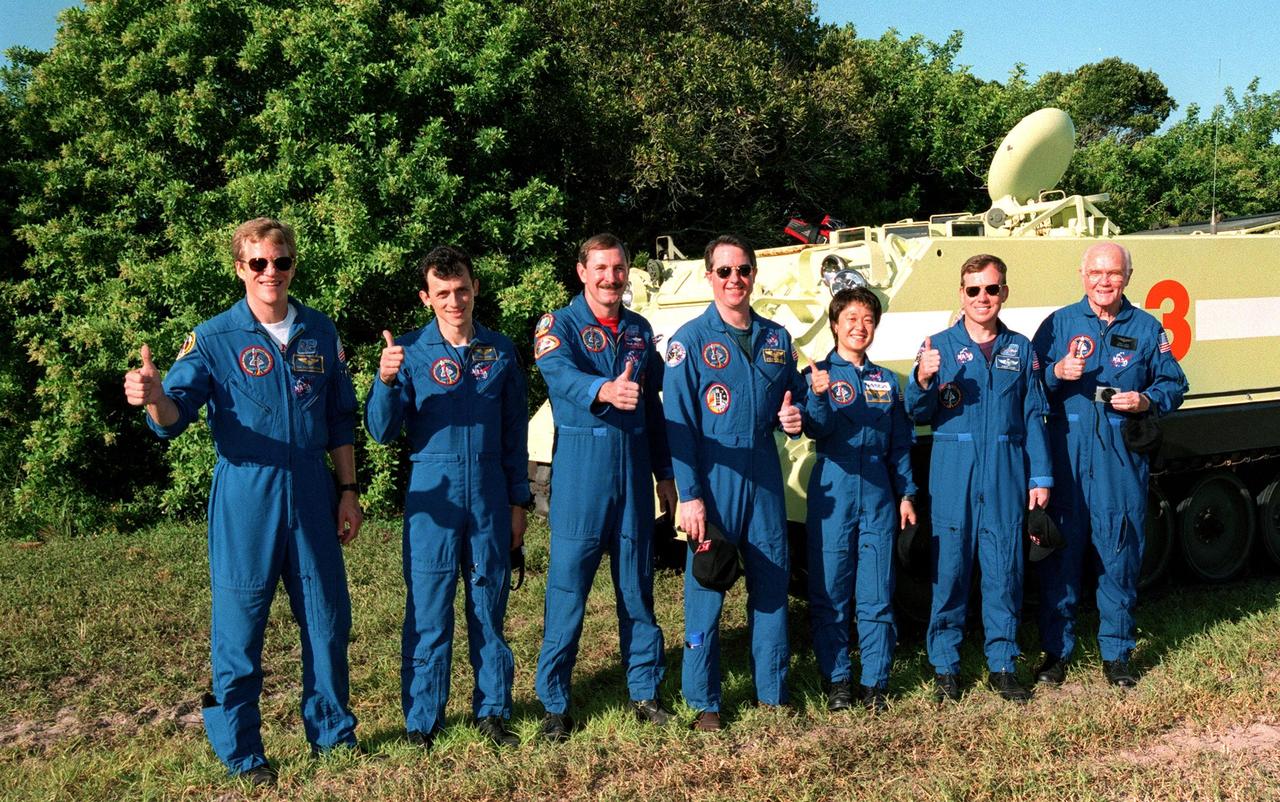

Giving a thumbs up after training on the M-113, a small armored personnel carrier, are STS-95 crew members (left to right) Mission Specialists Scott E. Parazynski and Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency, Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown, Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson, Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai, representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA), Pilot Steven W. Lindsey and Payload Specialist John H. Glenn, senator from Ohio. The M-113 is a tracked vehicle that could be used by the crew in the event of an emergency at the pad during which they must make a quick exit from the area. The STS-95 crew is at KSC to participate in a Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) which also includes mission familiarization activities and a simulated main engine cut-off exercise. STS-95, which is targeted for launch on Oct. 29, 1998, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process
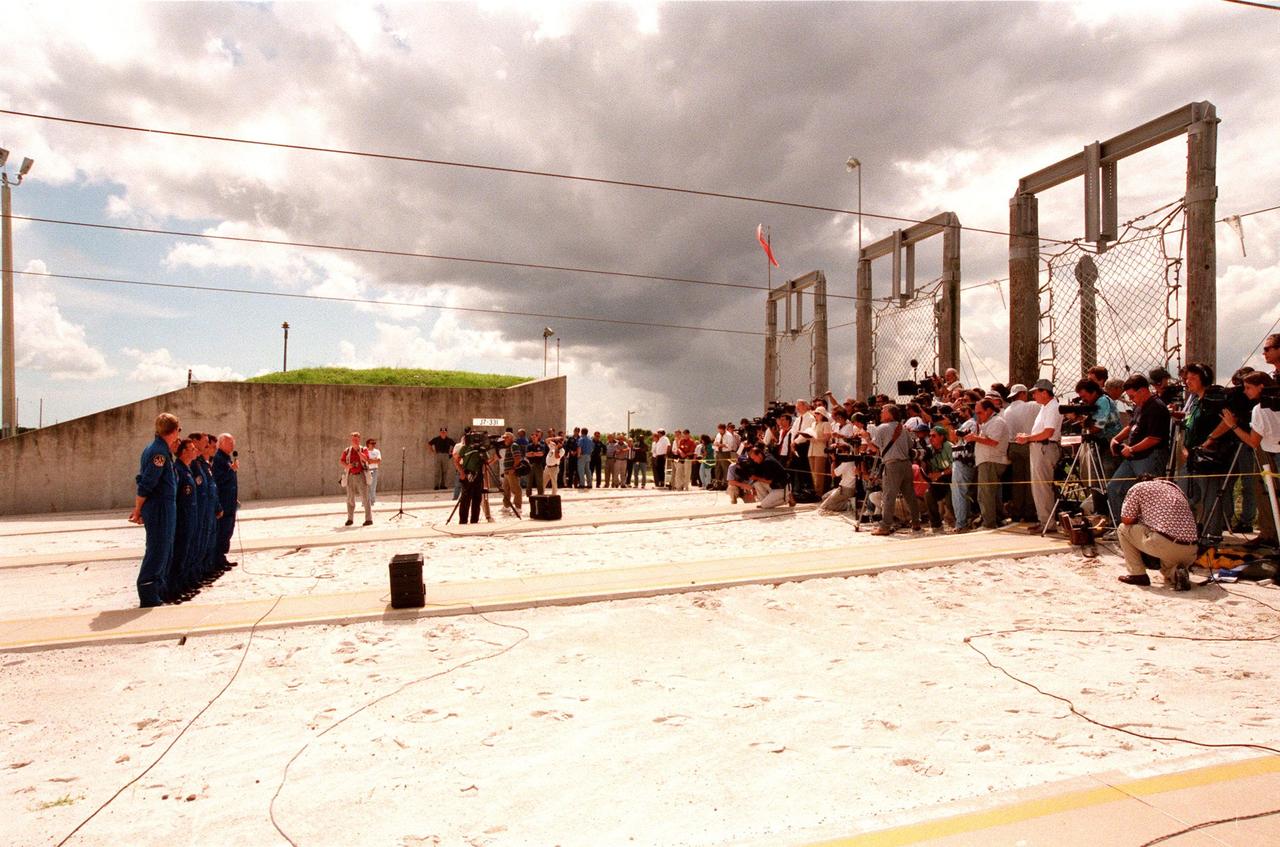

In front of the bunker near Launch Pad 39-B, the STS-95 crew members (at left) respond to questions about the mission and training from 106 reporters and photographers during a brief break from the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT). From left they are Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski, Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson, who also serves as Payload Commander, Pilot Steven W. Lindsey, Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown, Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency (ESA), Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai, representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA), and Payload Specialist John H. Glenn Jr., senator from Ohio, holding a microphone. The crew were at the pad for emergency egress training after the break. Above them are the slidewires leading to the catch nets for the baskets that are used in emergency egress. The TCDT also involves mission familiarization activities and a simulated main engine cut-off exercise. The STS-95 mission, targeted for liftoff on Oct. 29, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process. Following the TCDT, the crew will be returning to Houston for final flight preparations
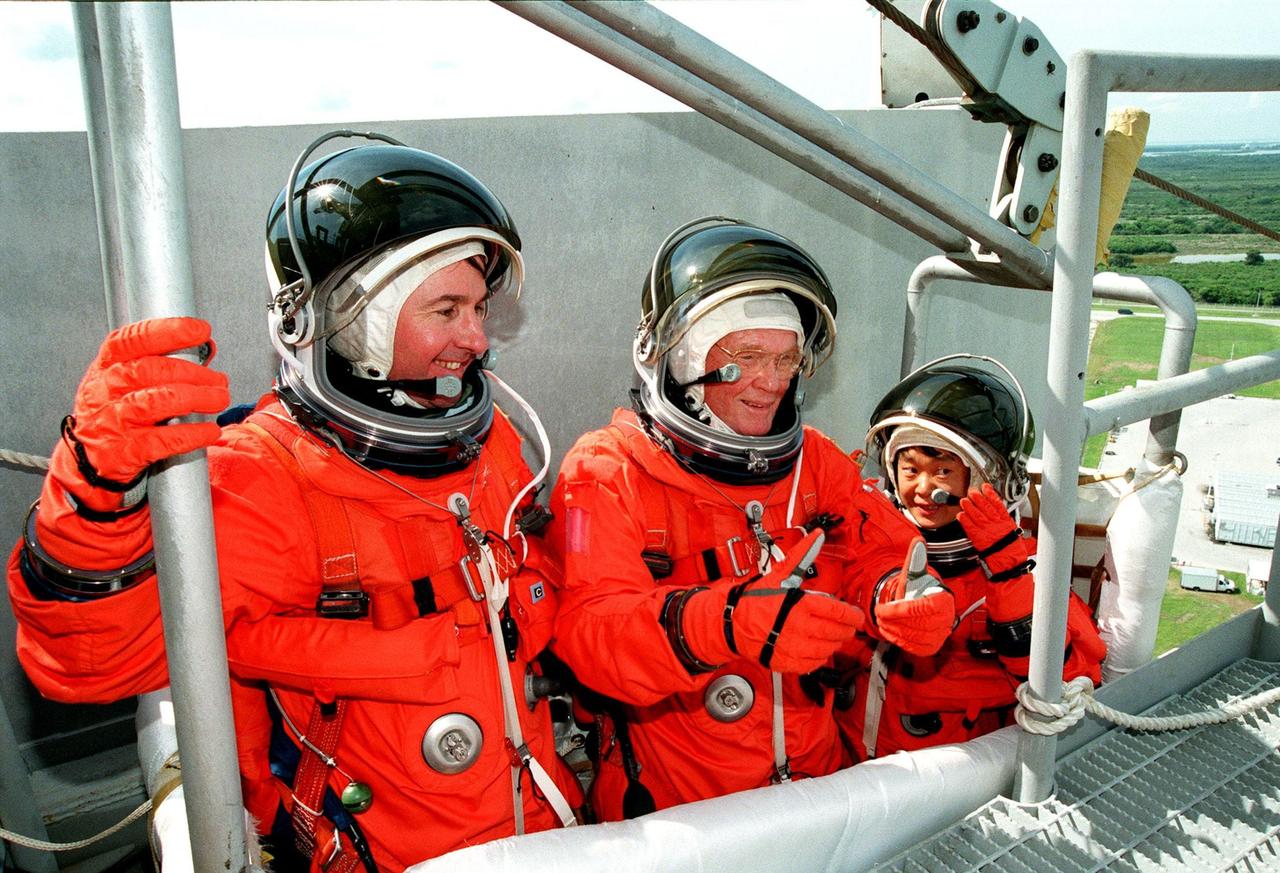

(Left to right) STS-95 Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson, Payload Specialist John H. Glenn Jr., senator from Ohio, and Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai (M.D., Ph.D.), representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA), are ready to leave Launch Pad 39B in the slidewire basket during an emergency egress exercise. Robinson, Glenn and Mukai, along with other crew members, are at KSC to participate in the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) which includes mission familiarization activities, emergency egress training, and a simulated main engine cutoff. Not shown are Pilot Steven W. Lindsey, Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski, Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency (ESA), and Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown. The STS-95 mission, targeted for liftoff on Oct. 29, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process. Following the TCDT, the crew will be returning to Houston for final flight preparations
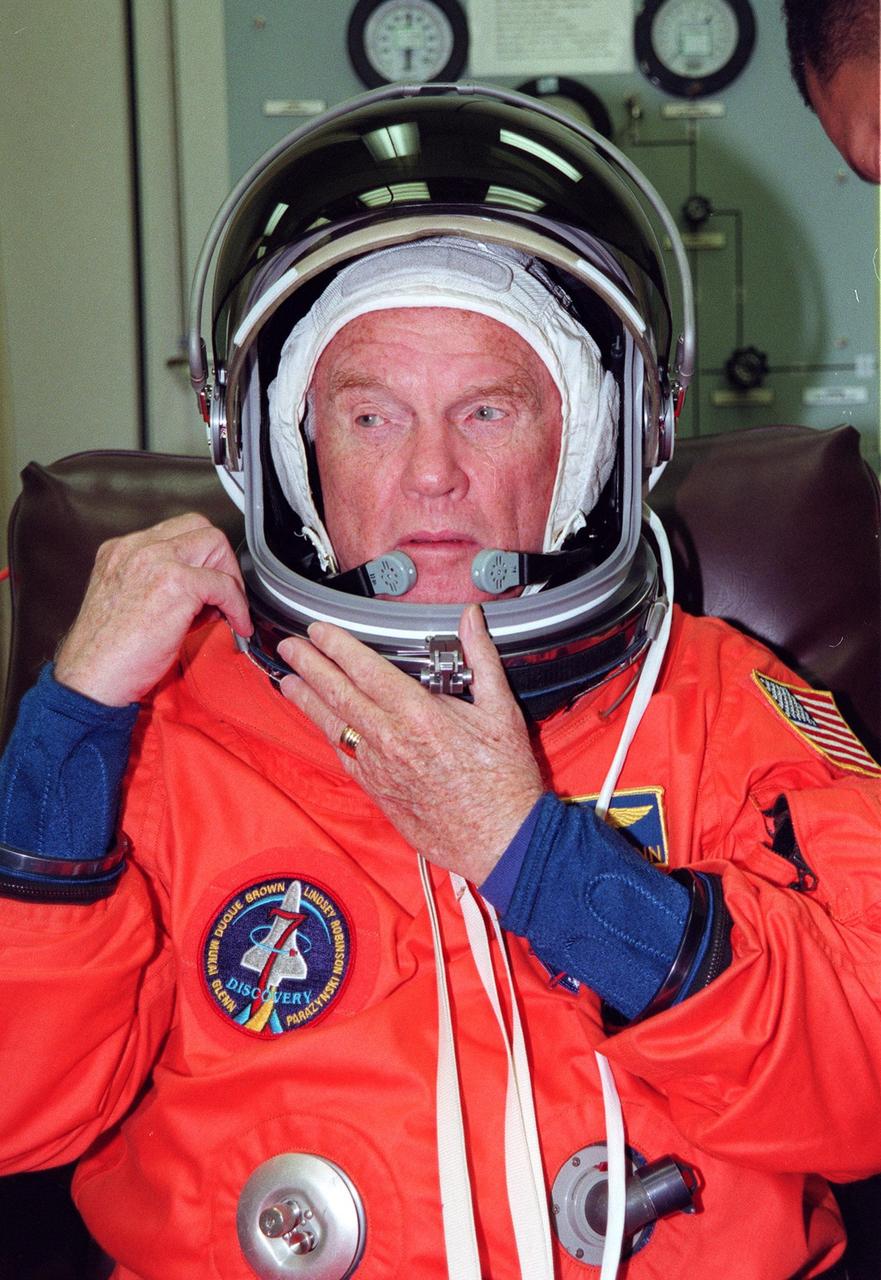

STS-95 Payload Specialist John H. Glenn Jr., a senator from Ohio and one of the original seven Project Mercury astronauts, suits up in the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building prior to his trip to Launch Pad 39-B. Glenn and the rest of the STS-95 crew are at KSC to participate in the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) which includes mission familiarization activities, emergency egress training, and a simulated main engine cutoff. The other crew members are Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai (M.D., Ph.D.), representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA), Pilot Steven W. Lindsey, Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski, Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson, Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency (ESA), and Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown. The STS-95 mission, targeted for liftoff on Oct. 29, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process. Following the TCDT, the crew will be returning to Houston for final flight preparations
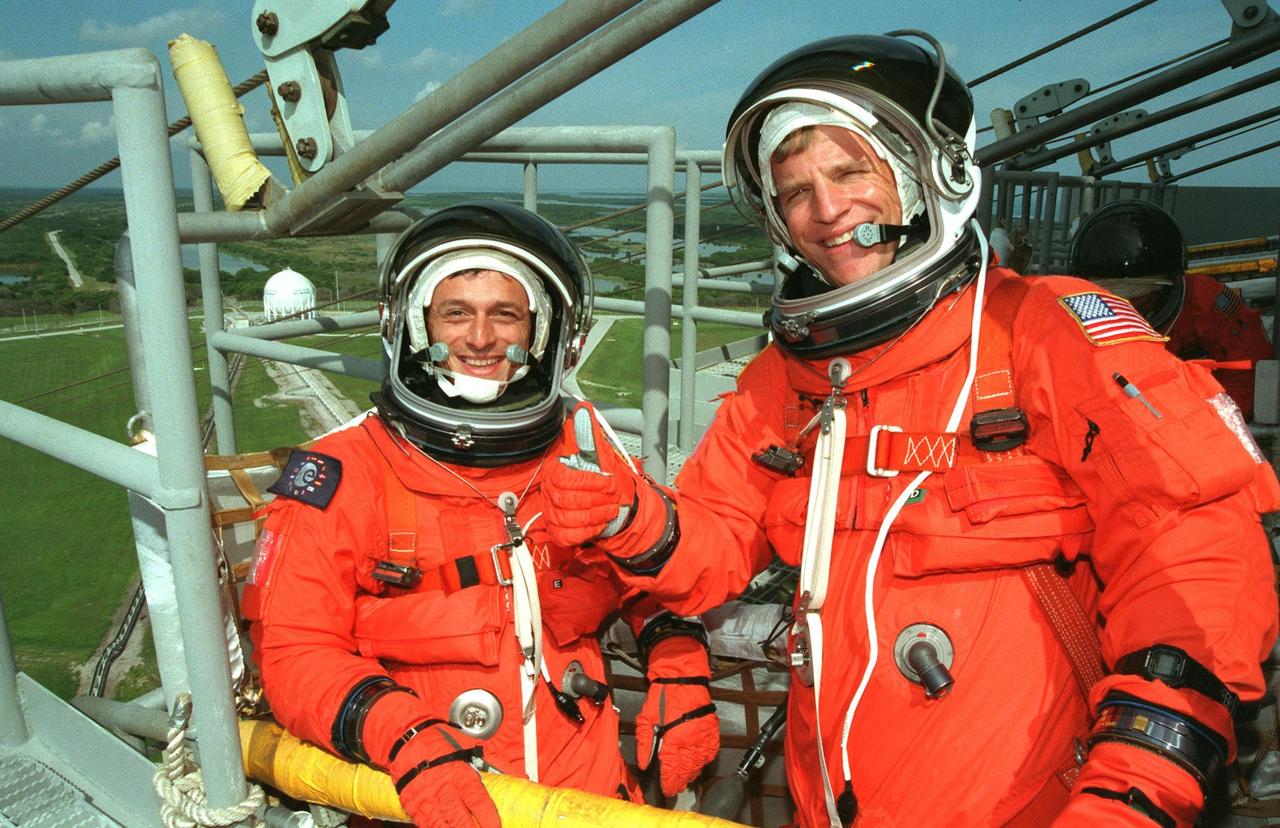

STS-95 Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain (left), representing the European Space Agency (ESA), and Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski (right) signal they are ready to leave Launch Pad 39B in the slidewire basket during an emergency egress exercise. Duque and Parazynski, along with other crew members, are at KSC to participate in the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) which includes mission familiarization activities, emergency egress training, and a simulated main engine cutoff. Not shown are Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown, Pilot Steven W. Lindsey, Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson, Payload Specialists John H. Glenn Jr., senator from Ohio, and Chiaki Mukai (M.D., Ph.D.), representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). The STS-95 mission, targeted for liftoff on Oct. 29, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process. Following the TCDT, the crew will be returning to Houston for final flight preparations

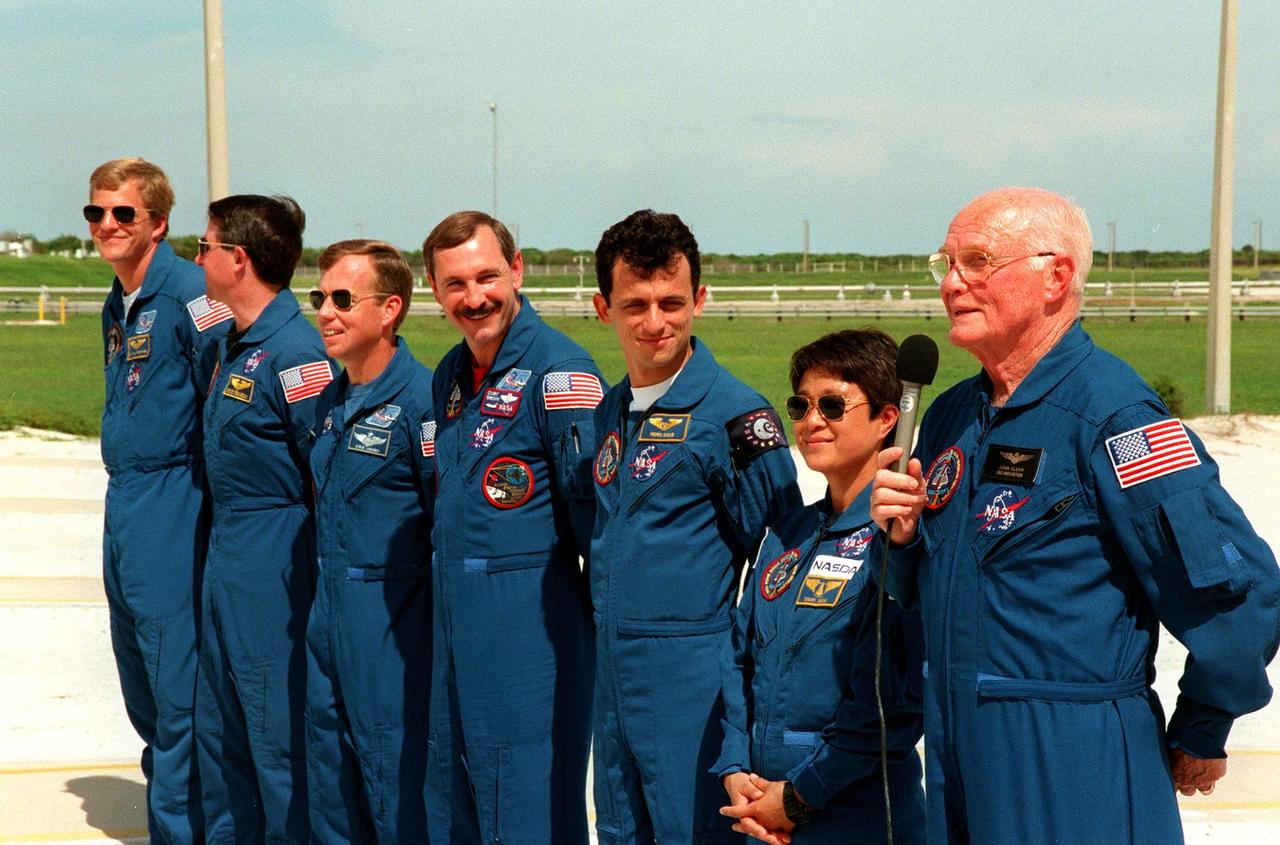
At Launch Pad 39-B, STS-95 Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown (center, with microphone) responds to questions about the mission and training from reporters during a brief break from the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT). Amused with his answer are other crew members (from left) Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski, Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson, who also serves as Payload Commander, Pilot Steven W. Lindsey, (Brown), Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency (ESA), Chiaki Mukai, representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA), and Payload Specialist John H. Glenn Jr., senator from Ohio. The crew were at the pad for emergency egress training after the break. The TCDT also involves mission familiarization activities and a simulated main engine cut-off exercise. The STS-95 mission, targeted for liftoff on Oct. 29, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process. Following the TCDT, the crew will be returning to Houston for final flight preparations
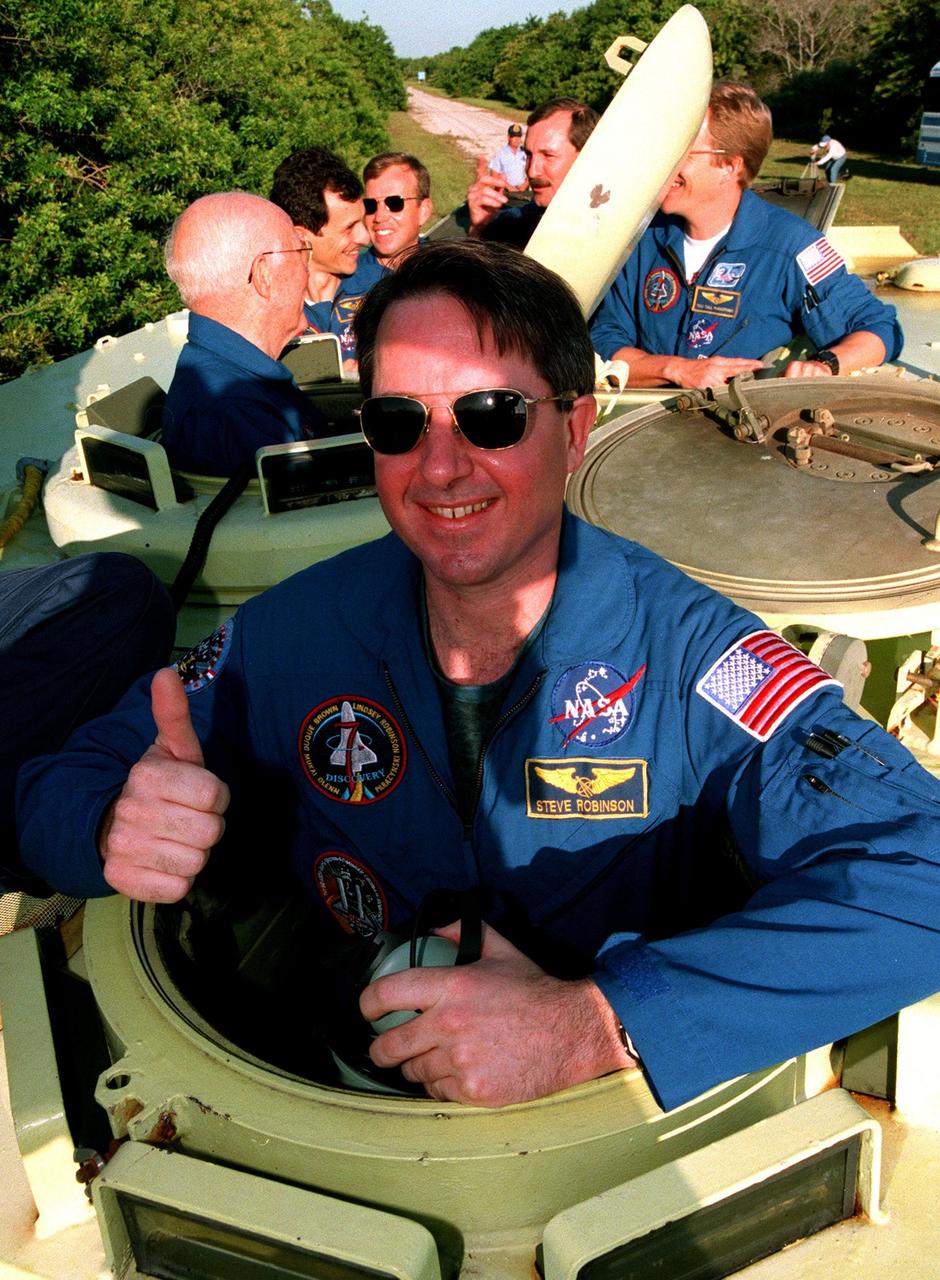

Near Launch Pad 39-B, STS-95 Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson climbs out of the M-113, a small armored personnel carrier, that is part of emergency egress training. The tracked vehicle could be used by the crew in the event of an emergency at the pad during which the crew must make a quick exit from the area. The STS-95 crew is at KSC to participate in a Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) which also includes mission familiarization activities and a simulated main engine cut-off exercise. Behind Robinson on the M-113 are other members of the mission: (left to right) Payload Specialist John H. Glenn Jr., senator from Ohio, Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency (ESA), Pilot Steven W. Lindsey, Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown and Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski. Not shown is Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai, representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). The STS-95 mission, targeted for liftoff on Oct. 29, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process
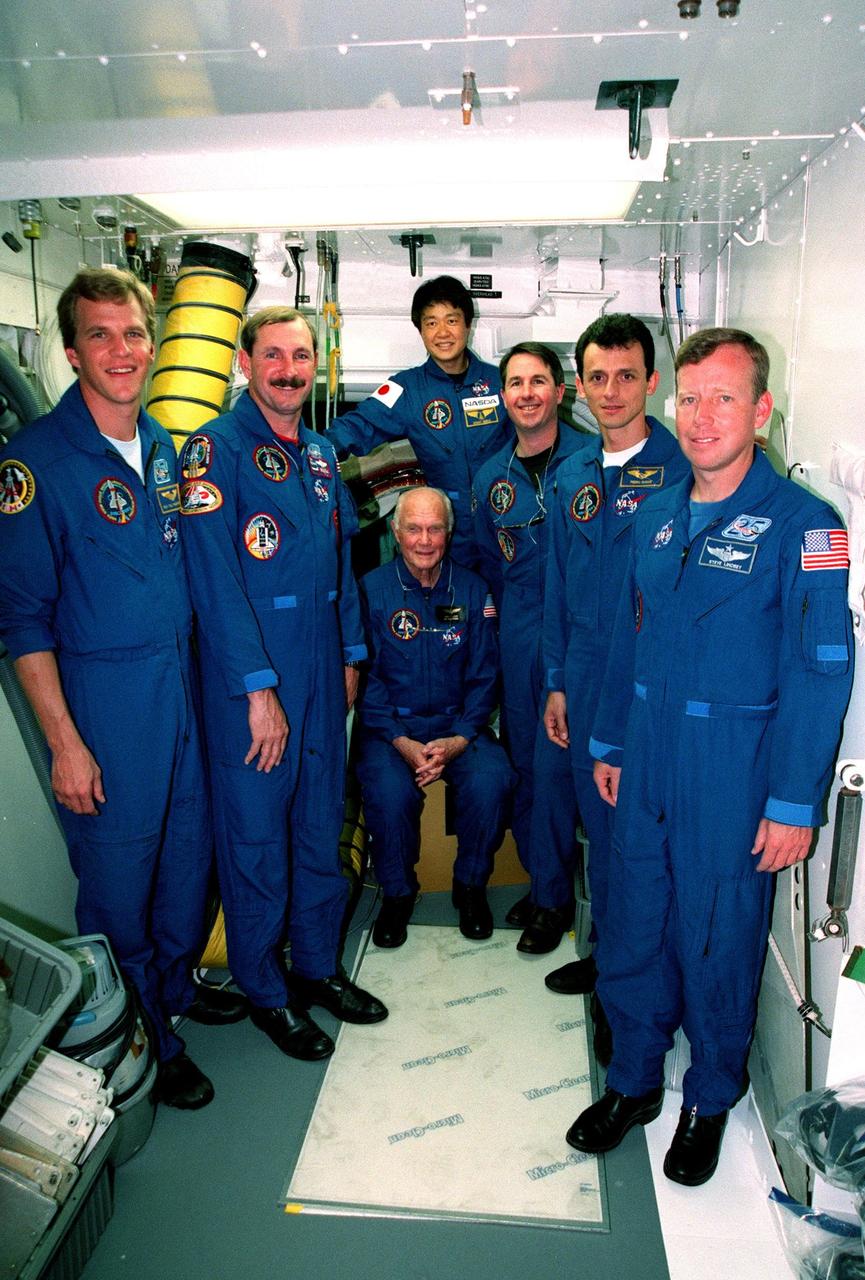

At Launch Pad 39-B, the STS-95 crew gather in the white room, an environmental chamber that mates with the orbiter and can provide emergency egress for the flight crew before launch. The white room is the outer end of the orbiter access arm, which is part of the fixed service structure on the pad. Pictured are (left to right) Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski, Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown, Payload Specialist John H. Glenn Jr. (seated), senator from Ohio, Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai (behind Glenn), representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA), Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson, Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency (ESA), and Pilot Steven W. Lindsey. The STS-95 crew are at KSC to participate in a Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) which includes mission familiarization activities, emergency egress training, and a simulated main engine cut-off exercise. The STS-95 mission, targeted for liftoff on Oct. 29, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process. Following the TCDT, the crew will be returning to Houston for final flight preparations
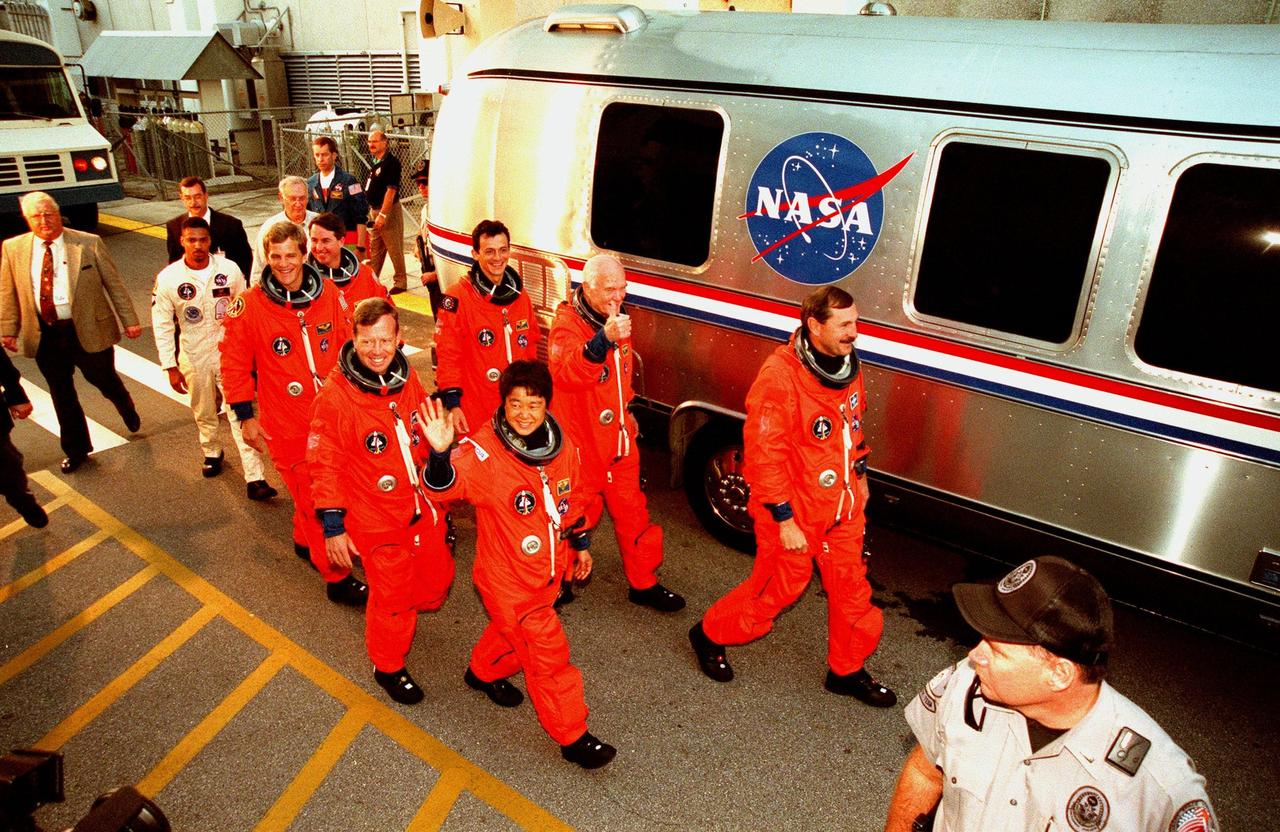

STS-95 crew members exit the Operations & Checkout Building after suiting up for their practice countdown at Launch Pad 39-B. Pictured are (front) Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski, Pilot Steven W. Lindsey, Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai (M.D., Ph.D.), representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA); (back) Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson, Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency (ESA), Payload Specialist John H. Glenn Jr., senator from Ohio, and Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown. The STS-95 crew are at KSC to participate in a Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) which includes mission familiarization activities, emergency egress training, and the simulated main engine cut-off exercise. The STS-95 mission, targeted for liftoff on Oct. 29, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process. Following the TCDT, the crew will be returning to Houston for final flight preparations

STS-95 Pilot Steven W. Lindsey, Payload Specialist John H. Glenn Jr., senator from Ohio, and Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai, representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA), listen to the Safety Egress trainer talk about the emergency egress system from the pad. The STS-95 crew are at KSC to participate in a Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) which includes mission familiarization activities, emergency egress training, and a simulated main engine cut-off exercise. Other crew members are Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski, Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency (ESA), Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown, and Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson. The STS-95 mission, targeted for liftoff on Oct. 29, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process. Following the TCDT, the crew will be returning to Houston for final flight preparations
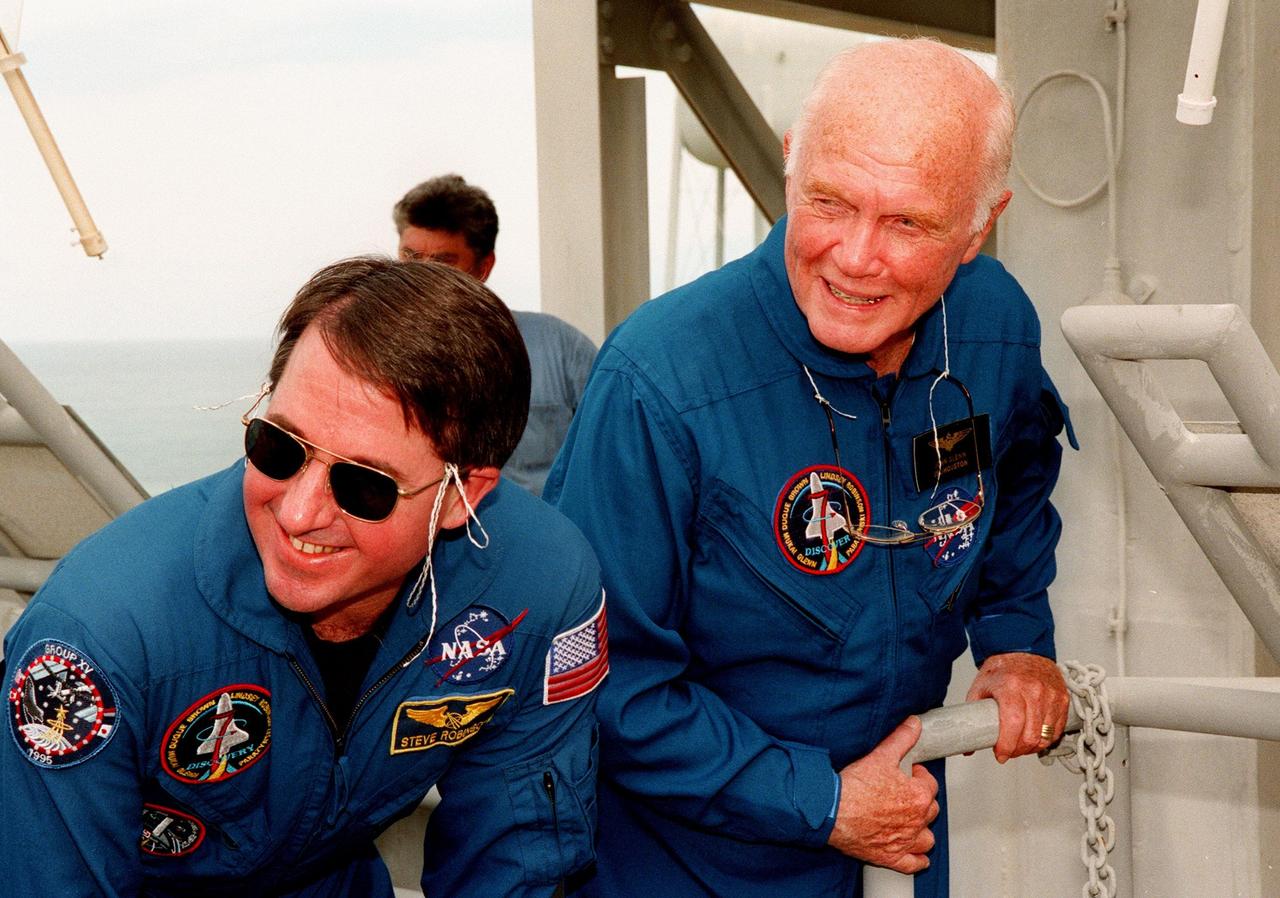

STS-95 Payload Specialist John H. Glenn Jr. and Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson watch the progress of the slidewire basket, an emergency egress vehicle, Glenn released at the 195-foot level of Launch Pad 39-B. The STS-95 crew are at KSC to participate in a Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) which includes mission familiarization activities, emergency egress training, and a simulated main engine cut-off exercise. Other crew members are Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski, Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency (ESA), Pilot Steven W. Lindsey, Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai, representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA), and Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown. The STS-95 mission, targeted for liftoff on Oct. 29, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process. Following the TCDT, the crew will be returning to Houston for final flight preparations
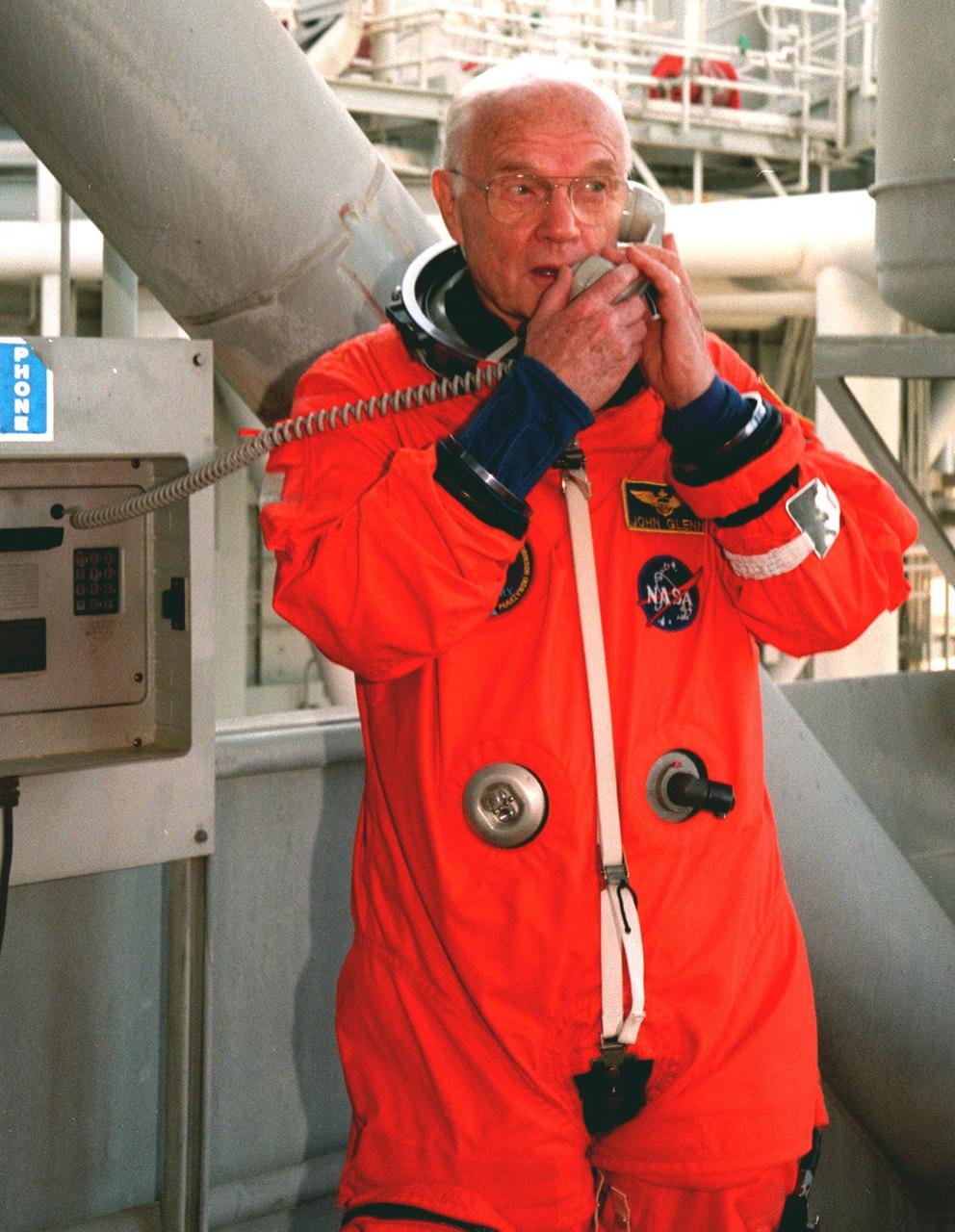

STS-95 Payload Specialist John H. Glenn Jr., senator from Ohio, takes a break to make a phone call on the 195-foot level of Launch Pad 39B before a pre-launch countdown exercise. Glenn and other crew members are at KSC to participate in the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) which includes mission familiarization activities, emergency egress training, and a simulated main engine cutoff. The other crew members are Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai (M.D., Ph.D.), representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA), Pilot Steven W. Lindsey, Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski, Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson, Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency (ESA), and Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown. The STS-95 mission, targeted for liftoff on Oct. 29, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process. Following the TCDT, the crew will be returning to Houston for final flight preparations

On Launch Pad 39B, the STS-95 crew pose after successfully completing a pre-launch countdown exercise on Space Shuttle Discovery. Standing from left to right are Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski, Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson, Payload Specialist John H. Glenn Jr., senator from Ohio, Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai (M.D., Ph.D.), representing the National Space Development Agency in Japan (NASDA), Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown, Pilot Steven W. Lindsey, and Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency (ESA). In the background (left) can be seen one of the solid rocket boosters and the external tank. The STS-95 crew are at KSC to participate in the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) which includes mission familiarization activities, emergency egress training, and a simulated main engine cutoff. The STS-95 mission, targeted for liftoff on Oct. 29, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process. Following the TCDT, the crew will be returning to Houston for final flight preparations

In this view looking up, Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner’s parachutes deploy above the U.S. Army’s White Sands Missile Range in New Mexico during parachute system testing on June 24, 2019. Boeing conducted the test using a full-scale Starliner test article, known as a boiler plate, designed to simulate the actual spacecraft. The test involved intentionally disabling one of the parachute system’s two drogue parachutes and one of the three main parachutes to evaluate how the remaining parachutes handled the additional loads during deployment and descent. This was one of a series of important parachute tests to validate the system is safe to carry astronauts to and from the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Boeing is targeting an uncrewed Orbital Flight Test to the space station this summer, followed by its Crew Flight Test. Starliner will launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
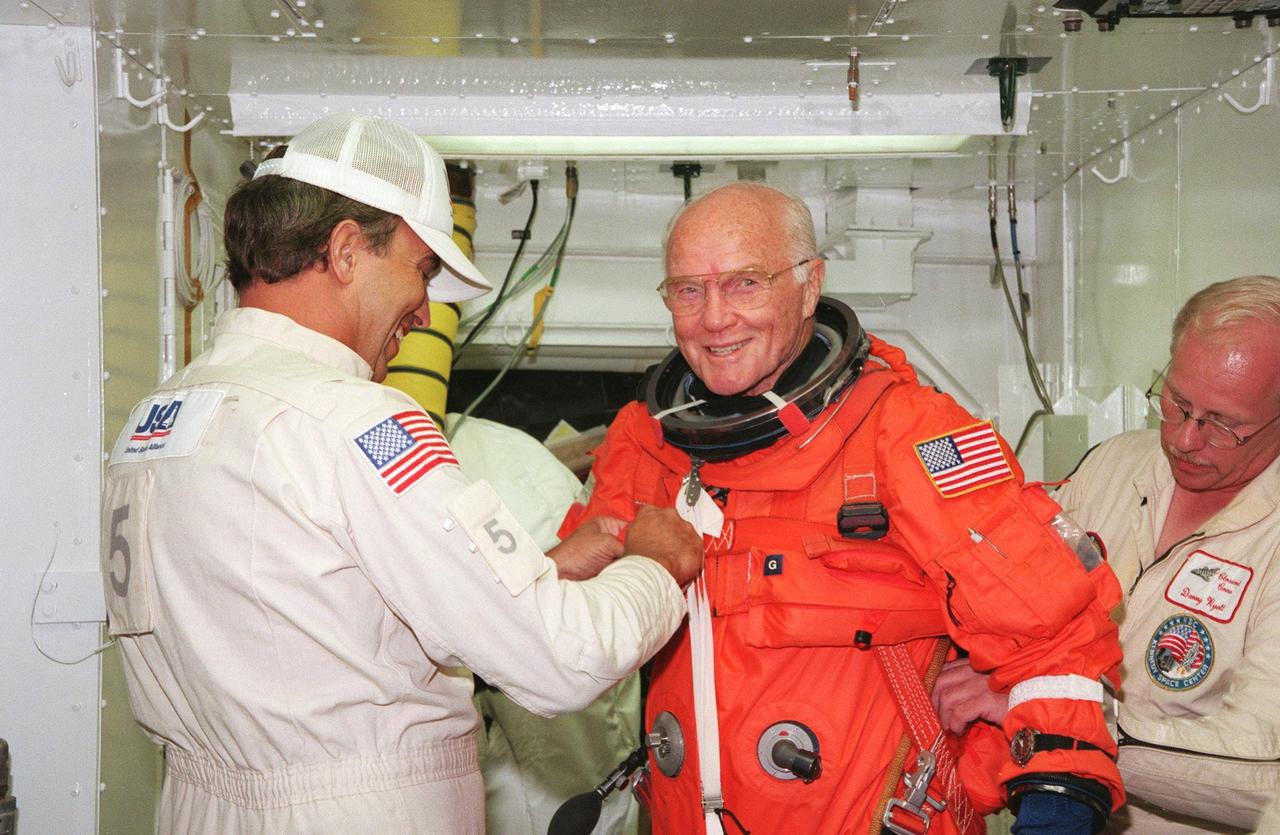

STS-95 Payload Specialist John H. Glenn Jr., senator from Ohio, is checked by Dave Martin(left), with United Space Alliance, and Danny Wyatt (right), of KSC, before entry into Space Shuttle Discovery for a pre-launch countdown exercise. Glenn and other crew members are at KSC to participate in the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) which includes mission familiarization activities, emergency egress training, and a simulated main engine cutoff. The other crew members are Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai (M.D., Ph.D.), representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA), Pilot Steven W. Lindsey, Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski, Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson, Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency (ESA), and Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown. The STS-95 mission, targeted for liftoff on Oct. 29, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process. Following the TCDT, the crew will be returning to Houston for final flight preparations
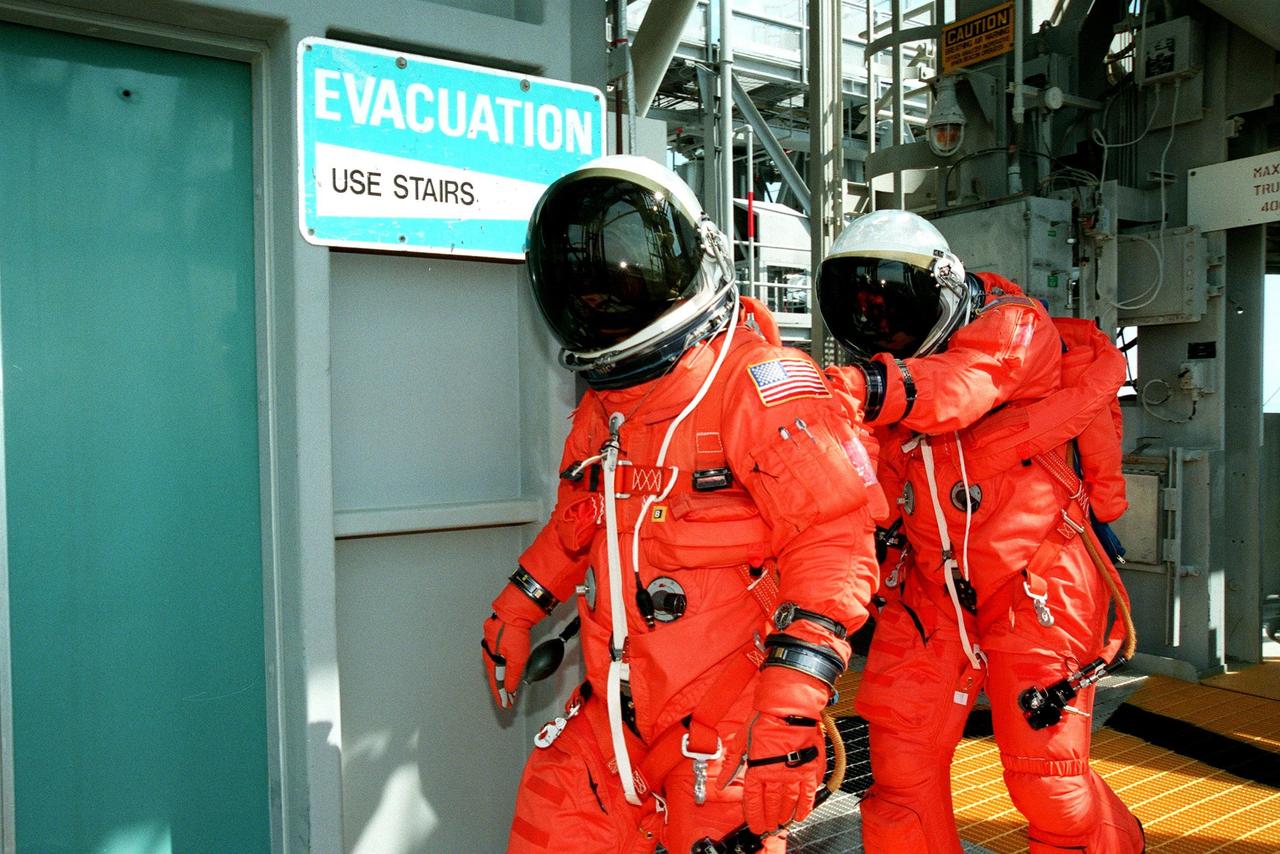

Behind the dark visors of their helmets are STS-95 Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown (left) and Pilot Steven W. Lindsey (right), practicing emergency egress from the Space Shuttle Discovery. Brown and Lindsey, along with the rest of the STS-95 crew, are at KSC to participate in the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) which includes mission familiarization activities, emergency egress training, and a simulated main engine cutoff. The other crew members are Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski, Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency (ESA), Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson, Payload Specialists John H. Glenn Jr., senator from Ohio, and Chiaki Mukai (M.D., Ph.D.), representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). The STS-95 mission, targeted for liftoff on Oct. 29, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process. Following the TCDT, the crew will be returning to Houston for final flight preparations

At Launch Pad 39-B, at the 195-foot level, STS-95 crew members learn about the slidewire basket, lower right, that is part of the emergency egress system from the orbiter before launch. Shown are (left to right) Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski, Pilot Steven W. Lindsey, Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency (ESA), Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson, Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai, representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA), Payload Specialist John H. Glenn Jr., senator from Ohio, and Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown. The STS-95 crew are at KSC to participate in a Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) which includes mission familiarization activities, emergency egress training, and a simulated main engine cut-off exercise. The STS-95 mission, targeted for liftoff on Oct. 29, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process. Following the TCDT, the crew will be returning to Houston for final flight preparations
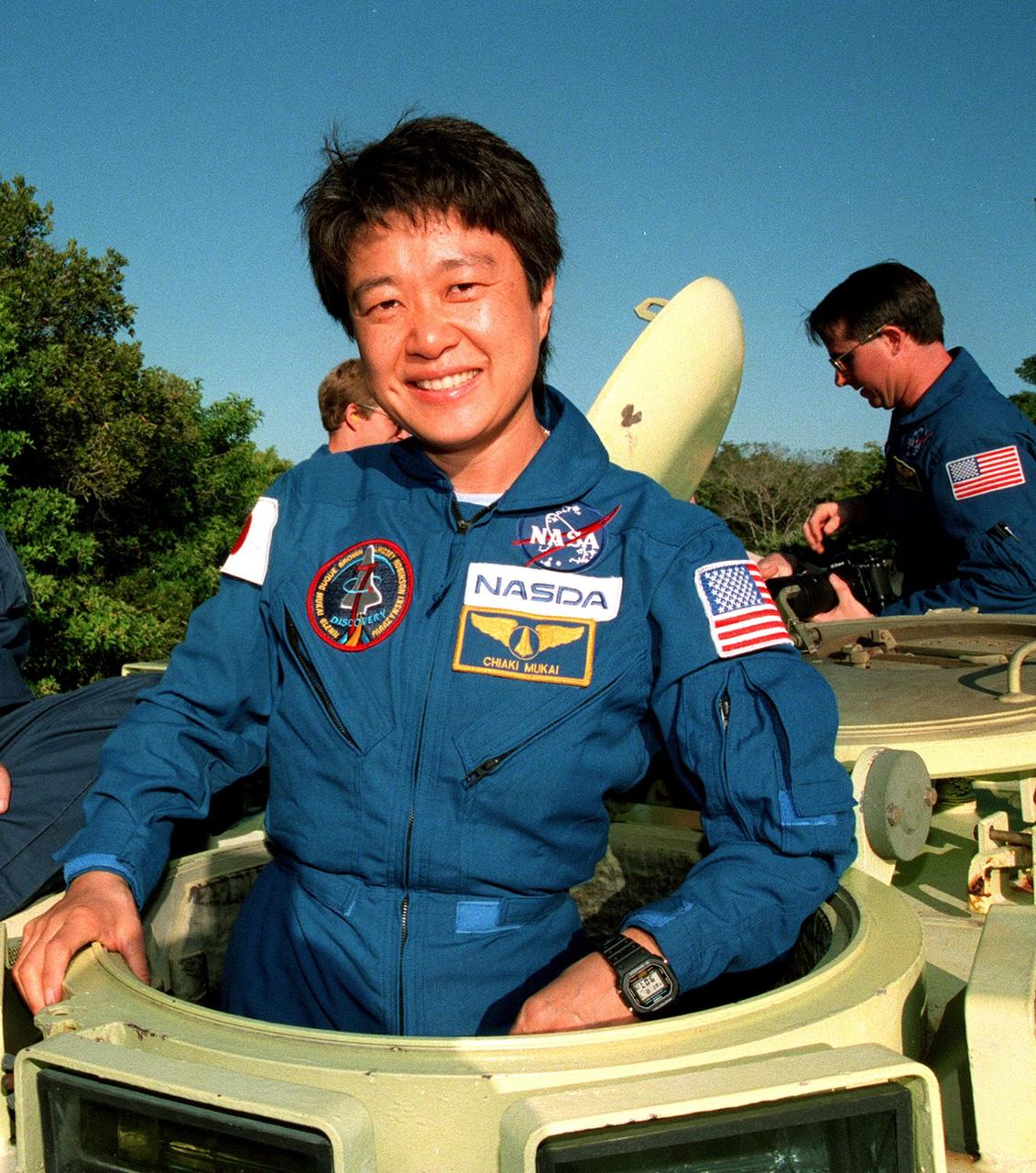
Near Launch Pad 39-B, STS-95 Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai, representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA), climbs into an M-113, a small armored personnel carrier, that is part of emergency egress training. The tracked vehicle could be used by the crew in the event of an emergency at the pad during which the crew must make a quick exit from the area. The STS-95 crew is at KSC to participate in a Test Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) which also includes mission familiarization activities and a simulated main engine cut-off exercise. The other members on the mission are Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown, Pilot Steven W. Lindsey, Mission Specialists Scott E. Parazynski, Stephen K. Robinson, and Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency (ESA); and Payload Specialist John H. Glenn Jr., senator from Ohio. The STS-95 mission, targeted for liftoff on Oct. 29, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. - Outside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility, the second Mars Exploration Rover (MER-1), in its shipping container, is moved inside. MER-2 and other hardware have already arrived at KSC for processing. MER-1 will begin prelaunch testing, including deployment of the lander petals, the rover's solar arrays, camera mast and camera. While at KSC, each of the rovers, their aeroshells and landers will undergo a full mission simulation. After spin balance testing, each spacecraft will be mated to a solid propellant upper stage booster that will propel the spacecraft out of Earth orbit. Approximately 10 days before launch they will be transported to the launch pad for mating with their respective Boeing Delta II rockets. The rovers will serve as robotic geologists to seek answers about the evolution of Mars, particularly for a history of water. The rovers are identical to each other, and will land at different regions of Mars. Launch of the MER-1 is scheduled for May 30. MER-2 will follow June 25.
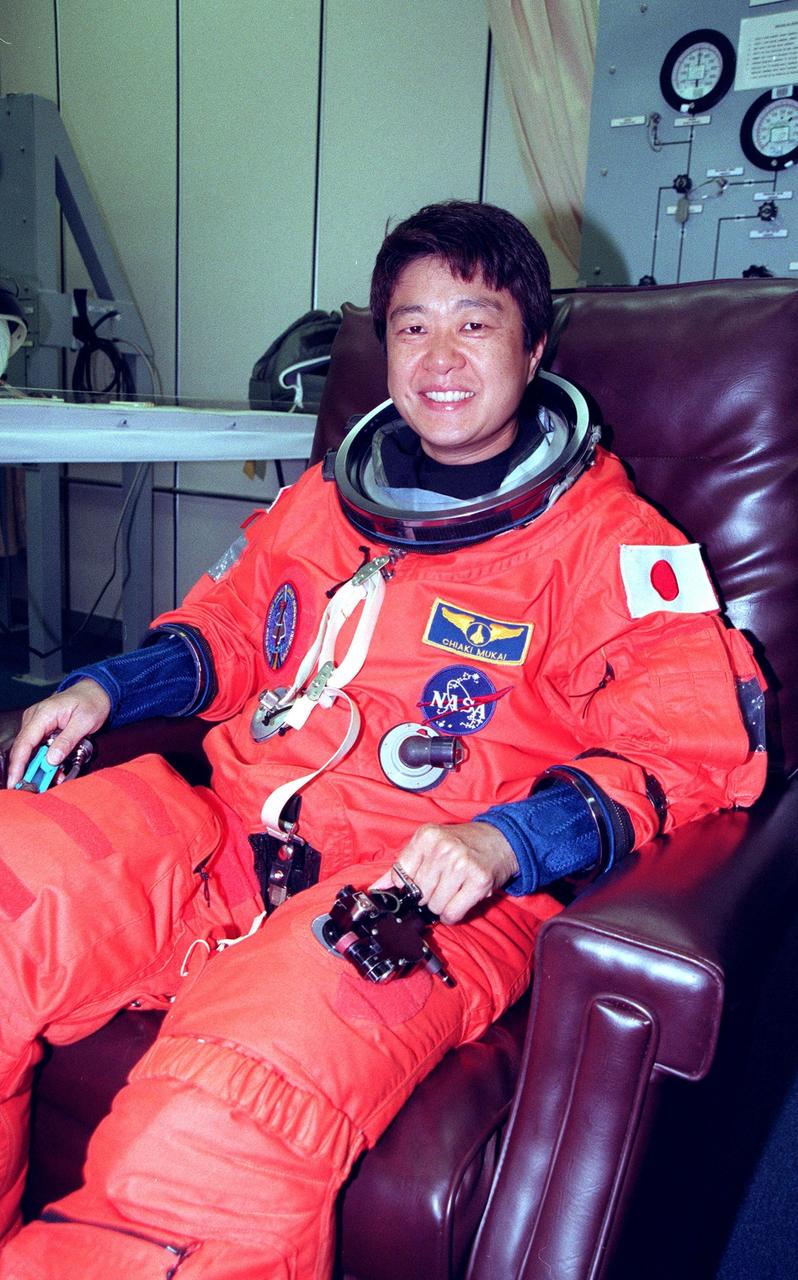

STS-95 Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai (M.D., Ph.D.), representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA), suits up in the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building prior to her trip to Launch Pad 39-B. Mukai and the rest of the STS-95 crew are at KSC to participate in the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) which includes mission familiarization activities, emergency egress training, and a simulated main engine cutoff. The other crew members are Pilot Steven W. Lindsey, Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski, Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson, Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency (ESA), Payload Specialist John H. Glenn Jr., senator from Ohio, and Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown. The STS-95 mission, targeted for liftoff on Oct. 29, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process. Following the TCDT, the crew will be returning to Houston for final flight preparations
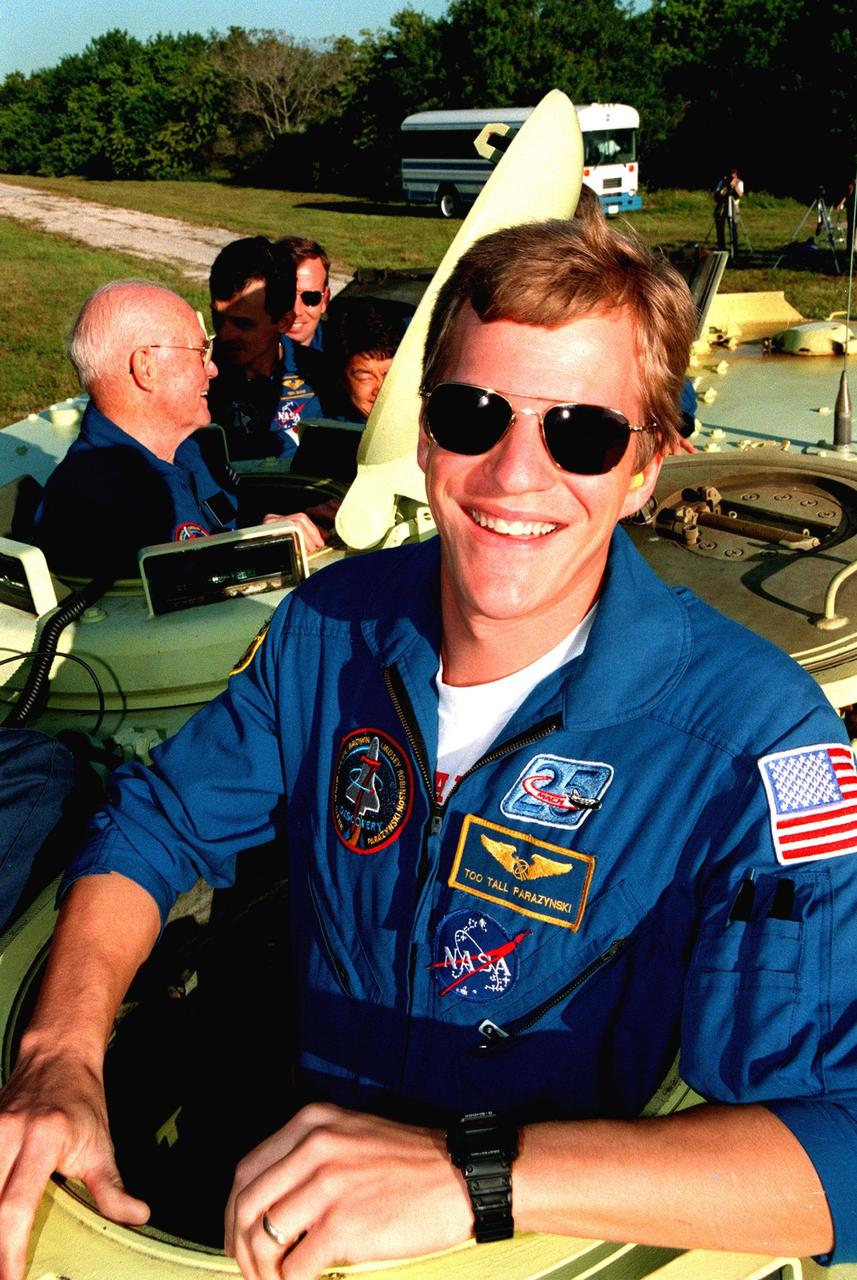

Near Launch Pad 39-B, STS-95 Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski climbs out of the M-113, a small armored personnel carrier, that is part of emergency egress training. To his left is Payload Specialist John H. Glenn Jr., and behind Glenn are (left to right) Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency (ESA), Pilot Steven W. Lindsey, and Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai, representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). The tracked vehicle could be used by the crew in the event of an emergency at the pad during which the crew must make a quick exit from the area. The STS-95 crew is at KSC to participate in a Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) which also includes mission familiarization activities and a simulated main engine cut-off exercise. The other members on the mission are Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown and Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson. The STS-95 mission, targeted for liftoff on Oct. 29, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process

At Launch Pad 39-B, a Safety Egress trainer explains the use of the slidewire basket system for emergency egress before launch to STS-95 crew members (left to right) Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson, , Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown (behind Robinson), Pilot Steven W. Lindsey, Payload Specialists John H. Glenn Jr., senator from Ohio, Chiaki Mukai (in front of Glenn), representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA), Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency, and Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski . The STS-95 crew are at KSC to participate in a Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) which includes mission familiarization activities, emergency egress training, and a simulated main engine cut-off exercise. The STS-95 mission, targeted for liftoff on Oct. 29, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process. Following the TCDT, the crew will be returning to Houston for final flight preparations
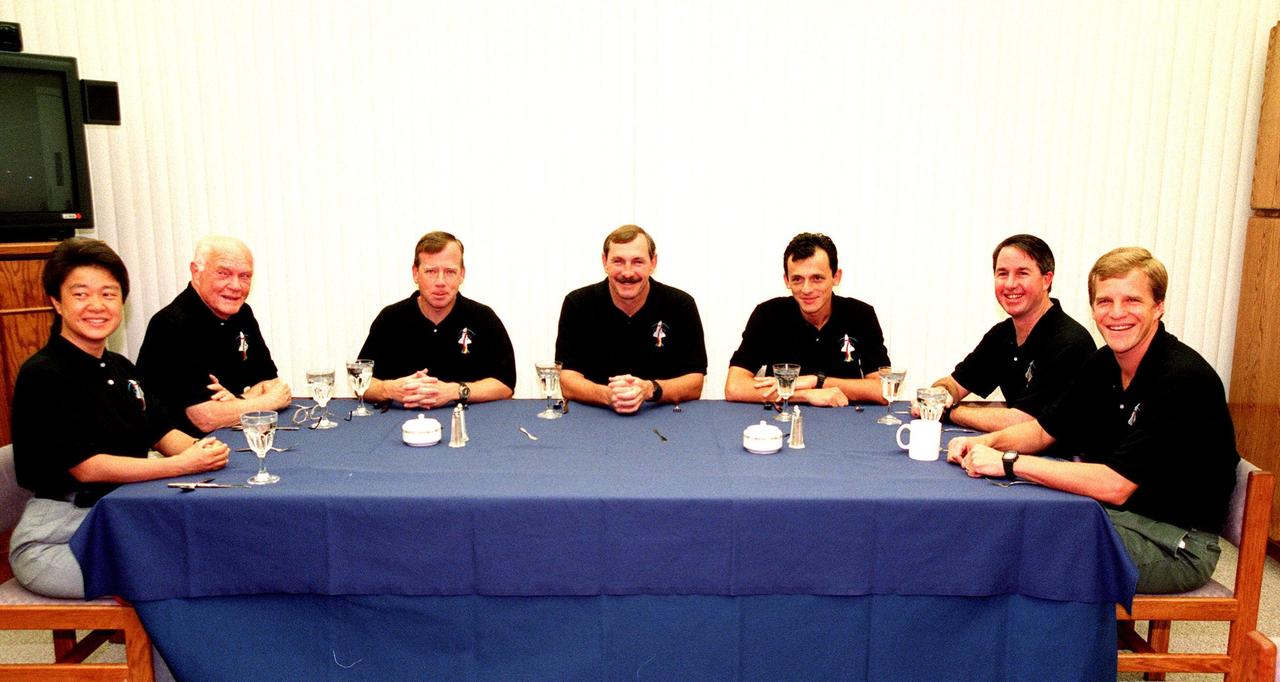

The STS-95 crew partakes in the traditional breakfast in the crew quarters at the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building prior to their suitup for their trip to Launch Pad 39-B. Seated (left to right) are Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai (M.D., Ph.D.), representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA), Payload Specialist John H. Glenn Jr., senator from Ohio, Pilot Steven W. Lindsey, Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown, Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency (ESA), Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson, and Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski. The STS-95 crew are at KSC to participate in the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) which includes mission familiarization activities, emergency egress training, and a simulated main engine cutoff. The STS-95 mission, targeted for liftoff on Oct. 29, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process. Following the TCDT, the crew will be returning to Houston for final flight preparations
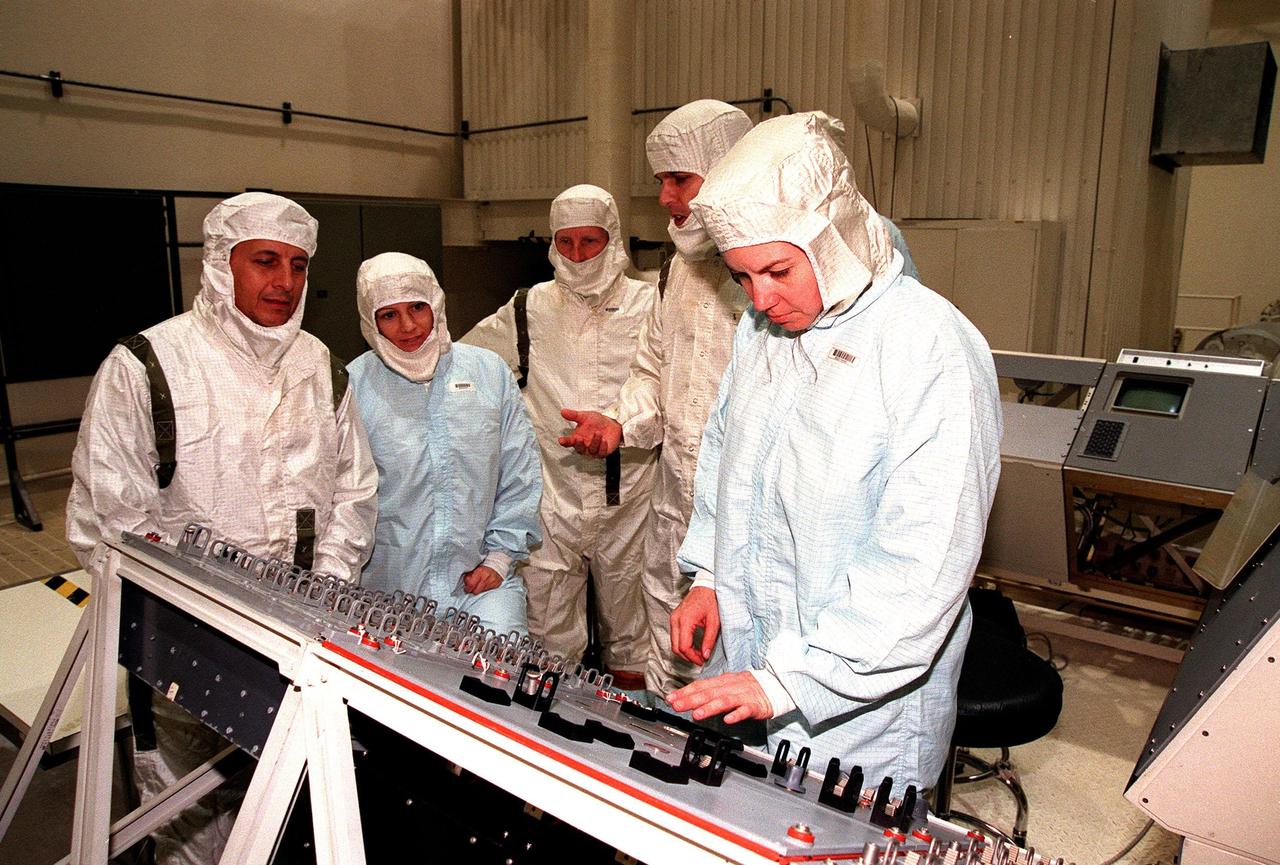

In the Vertical Processing Facility (VPF), the STS-93 crew stands in front of the VPF Aft Flight Deck simulator, which is part of KSC's Cargo Integration Test Equipment. From left, they are Mission Specialist Michel Tognini of France, Commander Eileen M. Collins, Mission Specialist Steven A. Hawley, Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby and Mission Specialist Catherine G. Coleman. Tognini represents France's space agency, the Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales (CNES). STS-93, scheduled to launch July 9 aboard Space Shuttle Columbia, has the primary mission of the deployment of the Chandra X-ray Observatory, which is undergoing testing in the VPF. Formerly called the Advanced X-ray Astrophysics Facility, Chandra comprises three major elements: the spacecraft, the science instrument module (SIM), and the world's most powerful X-ray telescope. Chandra will allow scientists from around the world to see previously invisible black holes and high-temperature gas clouds, giving the observatory the potential to rewrite the books on the structure and evolution of our universe
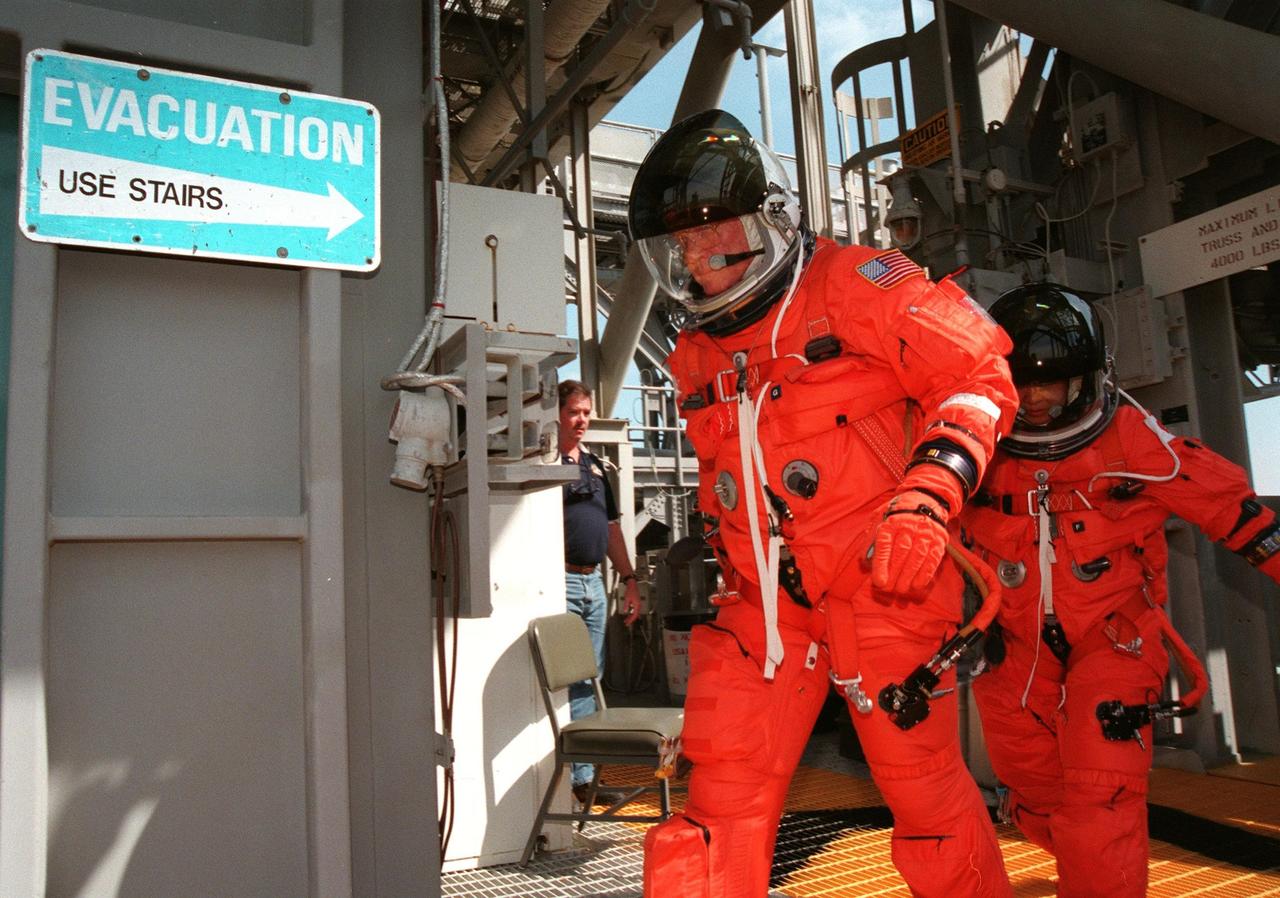

STS-95 Payload Specialists John H. Glenn Jr. (left), senator from Ohio, and Chiaki Mukai (M.D., Ph.D.) (right), representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA), hurry toward the basket at the 195-foot level of Launch Pad 39B during an emergency egress exercise. Glenn and Mukai, along with other crew members, are at KSC to participate in the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) which includes mission familiarization activities, emergency egress training, and a simulated main engine cutoff. The other crew members are Pilot Steven W. Lindsey, Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski, Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency (ESA), Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson, and Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown. The STS-95 mission, targeted for liftoff on Oct. 29, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process. Following the TCDT, the crew will be returning to Houston for final flight preparations
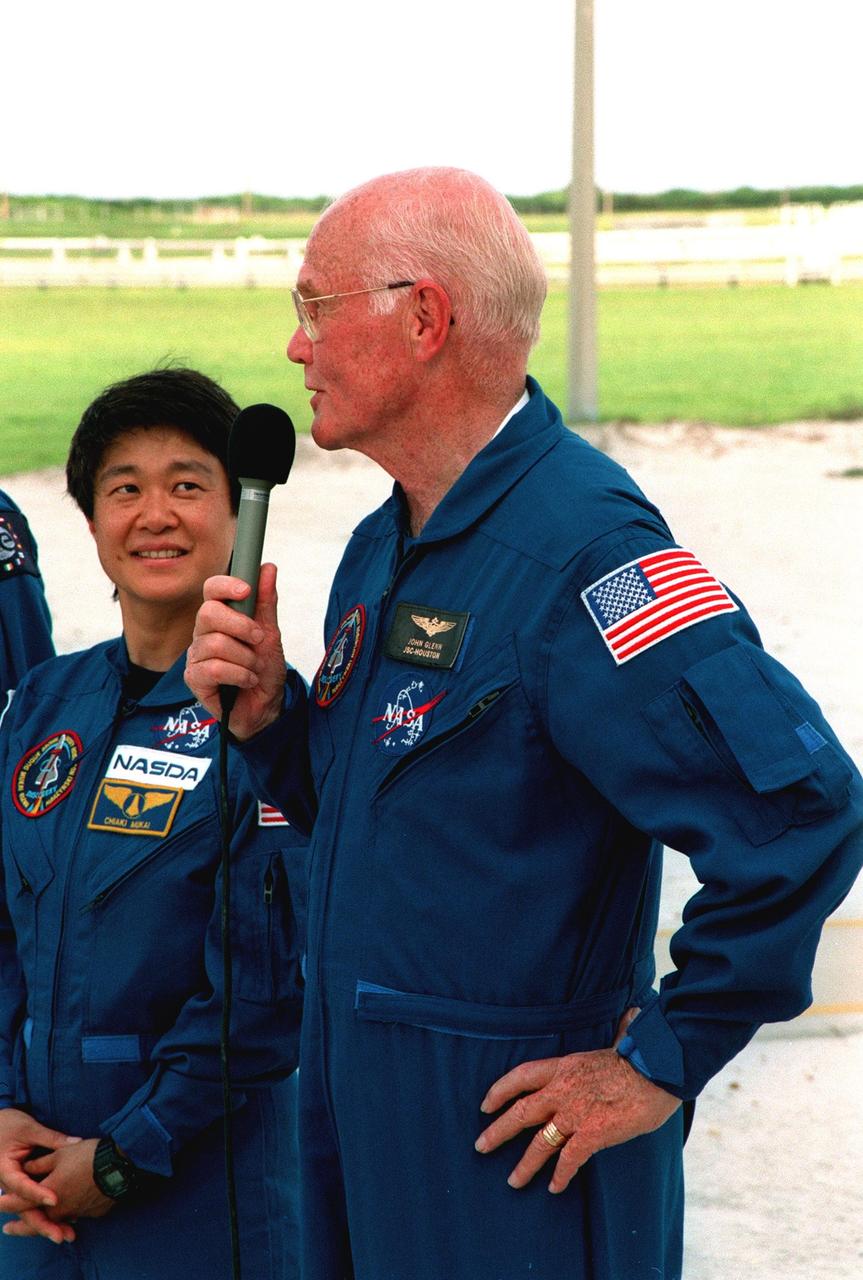

At Launch Pad 39-B, STS-95 Payload Specialist John H. Glenn Jr., senator from Ohio, (right) responds to one of many questions he was asked about the mission and training by reporters during a brief break from the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT). Amused with his answer is Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai, representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). Other crew members (not shown) are Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski, Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson, who also serves as Payload Commander, Pilot Steven W. Lindsey, Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown, and Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency (ESA). The crew were at the pad for emergency egress training after the break. The TCDT also involves mission familiarization activities and a simulated main engine cut-off exercise. The STS-95 mission, targeted for liftoff on Oct. 29, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process. Following the TCDT, the crew will be returning to Houston for final flight preparations

Center Director Roy Bridges (left) greets STS-95 Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown after his arrival on a T-38 jet aircraft at the Shuttle Landing Facility at KSC. Payload Specialist John H. Glenn Jr., a senator from Ohio, is at the right. Glenn arrived with Brown. They and the rest of the crew are at KSC to participate in a Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT). The TCDT includes mission familiarization activities, training in emergency exit from the orbiter and launch pad, and a simulated main engine cut-off exercise. Other crew members on the mission are Pilot Steven W. Lindsey; Mission Specialists Scott E. Parazynski, Stephen K. Robinson, and Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency (ESA); and Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai, representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). The STS-95 mission includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process
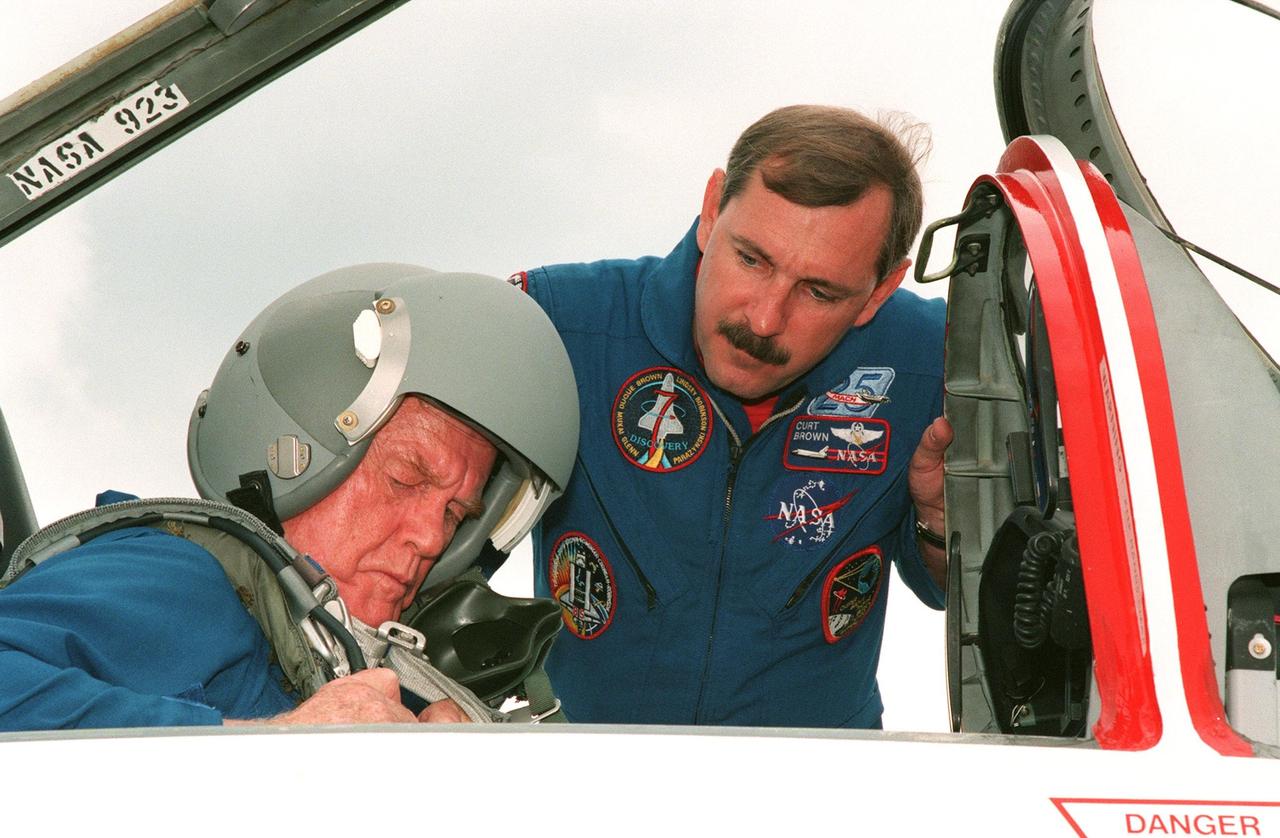

STS-95 Payload Specialist John H. Glenn Jr., senator from Ohio, straps into the seat of the T-38 jet aircraft that will carry him back to Houston. Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown, his pilot on the jet, looks on. The STS-95 successfully completed their Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) which included mission familiarization activities, emergency egress training, and a simulated main engine cutoff. Other crew members participating were Pilot Steven W. Lindsey, Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson, Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai (M.D., Ph.D.), representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA), Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency (ESA), and Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski. The STS-95 mission, targeted for liftoff on Oct. 29, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process. Following the TCDT, the entire crew returned to Houston for final flight preparations
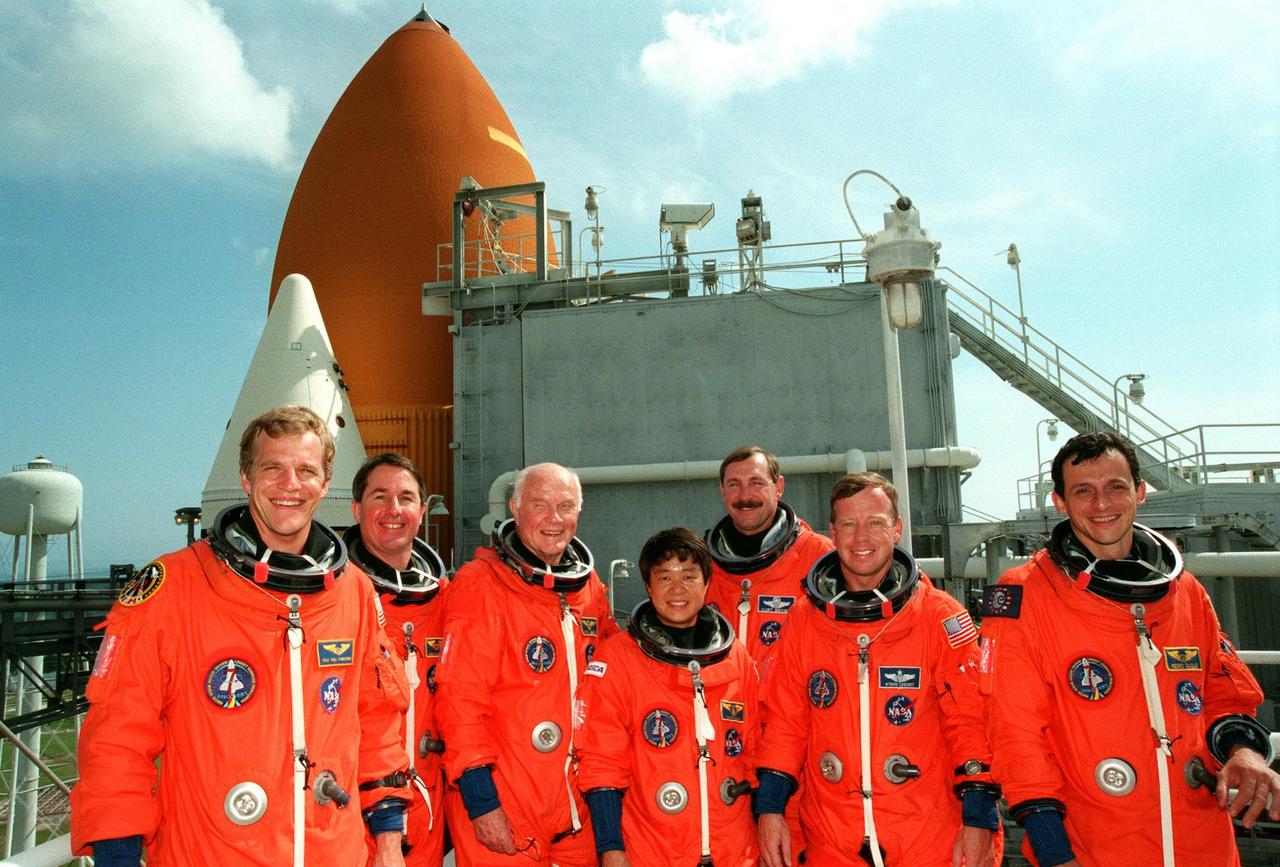

On Launch Pad 39B, the STS-95 crew pose after successfully completing a pre-launch countdown exercise on Space Shuttle Discovery. Standing from left to right are Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski, Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson, Payload Specialist John H. Glenn Jr., senator from Ohio, Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai (M.D., Ph.D.), representing the National Space Development Agency in Japan (NASDA), Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown, Pilot Steven W. Lindsey, and Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency (ESA). In the background can be seen one of the solid rocket boosters and the external tank. The STS-95 crew are at KSC to participate in the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) which includes mission familiarization activities, emergency egress training, and a simulated main engine cutoff. The STS-95 mission, targeted for liftoff on Oct. 29, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process. Following the TCDT, the crew will be returning to Houston for final flight preparations
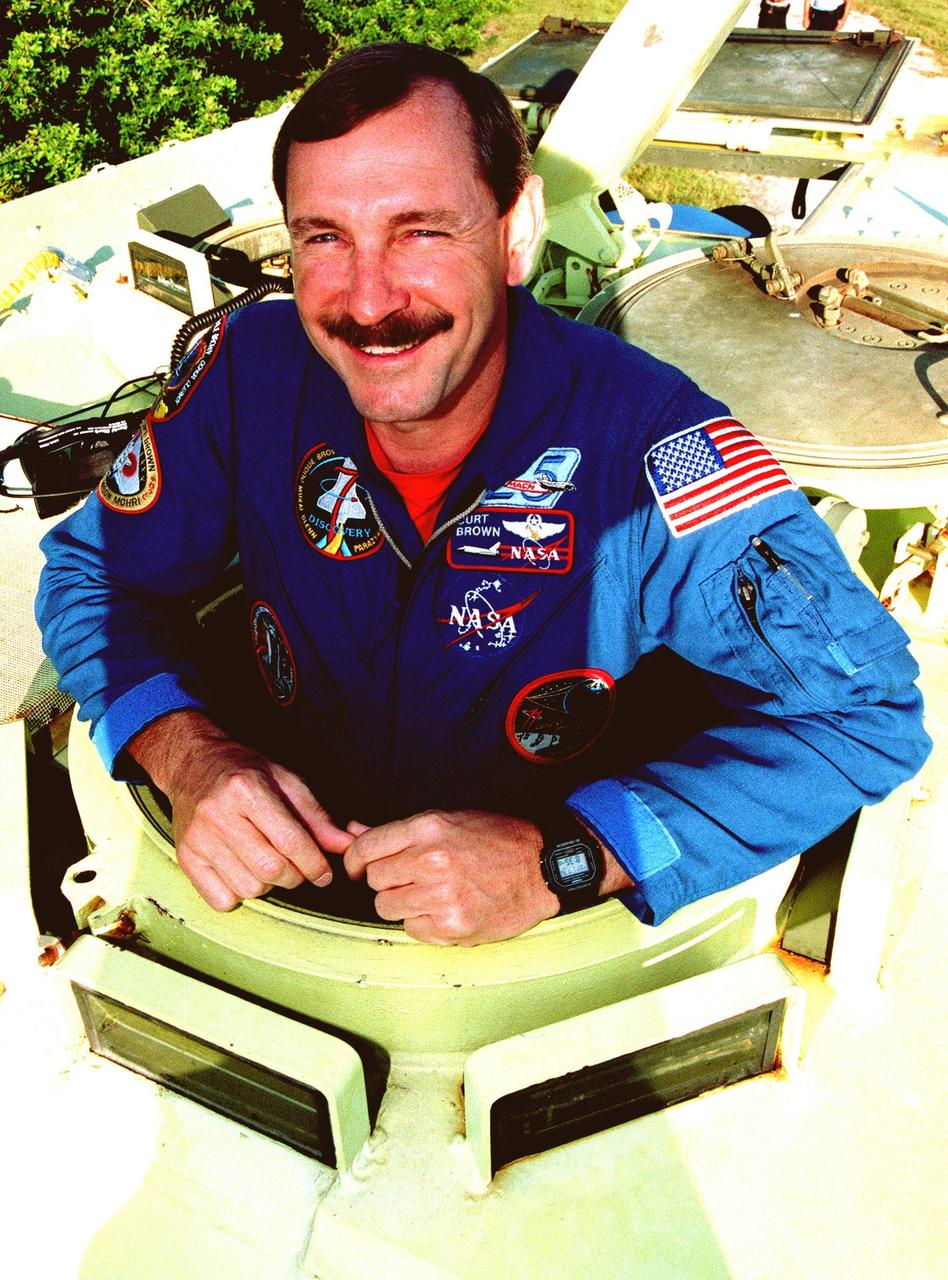

Near Launch Pad 39-B, STS-95 Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown climbs into the M-113, a small armored personnel carrier, that is part of emergency egress training. The tracked vehicle could be used by the crew in the event of an emergency at the pad during which the crew must make a quick exit from the area. The STS-95 crew is at KSC to participate in a Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) which also includes mission familiarization activities and a simulated main engine cut-off exercise. The other members on the mission are Pilot Steven W. Lindsey, Mission Specialists Scott E. Parazynski, Stephen K. Robinson and Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency (ESA), and Payload Specialists John H. Glenn Jr., senator from Ohio, and Chiaki Mukai, representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). The STS-95 mission, targeted for liftoff on Oct. 29, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process
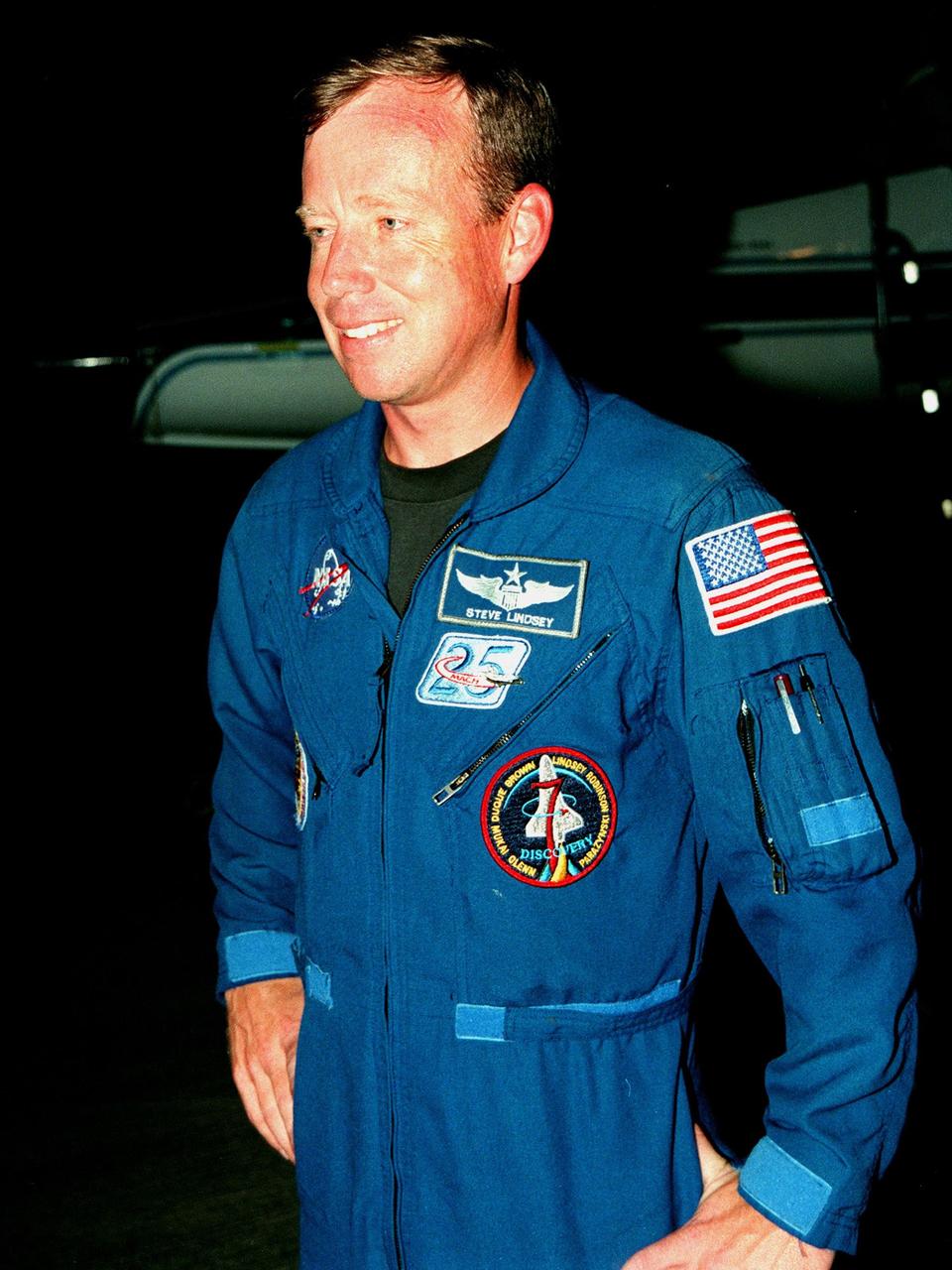

STS-95 Pilot Steven W. Lindsey smiles after his arrival aboard a T-38 jet aircraft at the Shuttle Landing Facility at KSC. The STS-95 crew are at KSC to participate in a Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT). The TCDT includes mission familiarization activities, training in emergency exit from the orbiter and launch pad, and a simulated main engine cut-off exercise. The other members on the mission are Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown, Mission Specialists Scott E. Parazynski, Stephen K. Robinson, and Pedro Duque of Spain, representing the European Space Agency (ESA); and Payload Specialists John H. Glenn Jr., senator from Ohio, and Chiaki Mukai, representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). The STS-95 mission, scheduled for liftoff on Oct. 29, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process
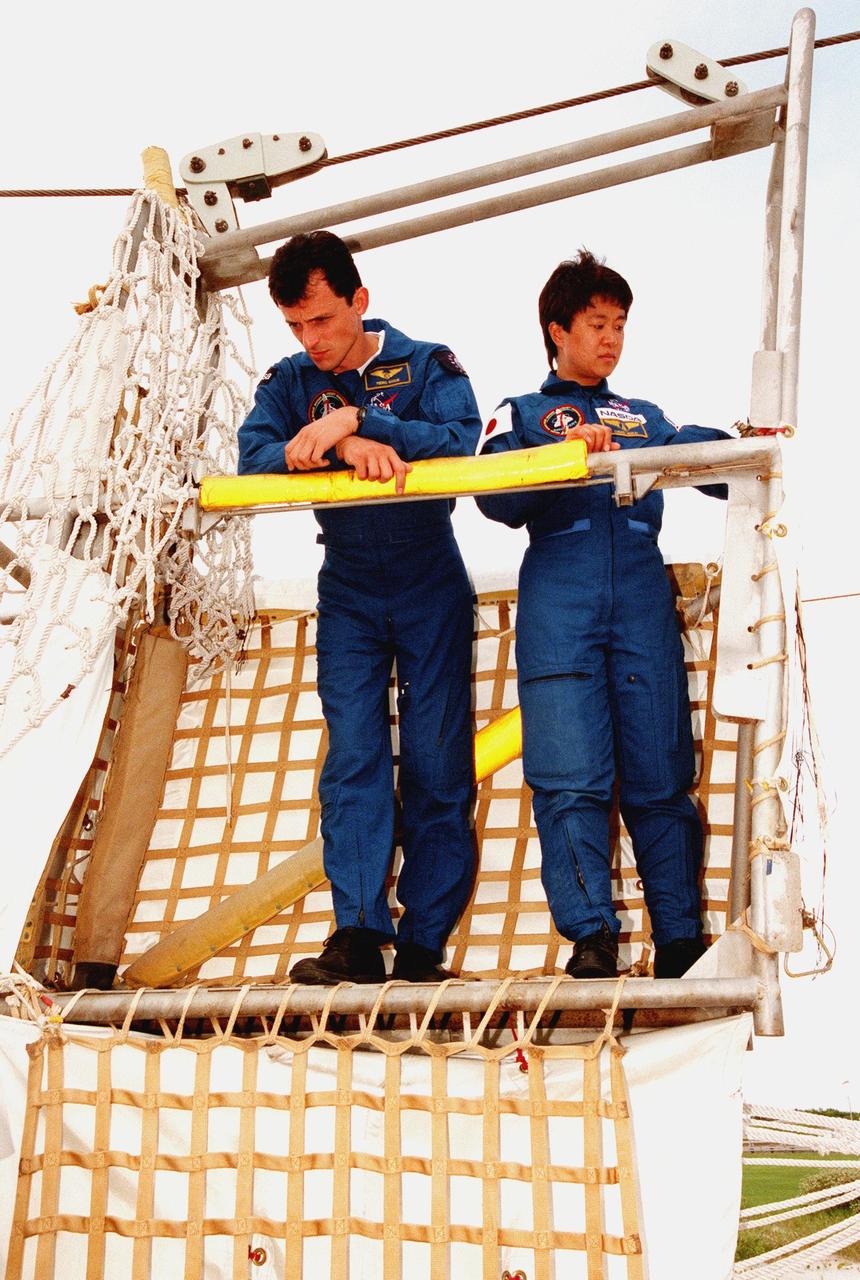

At Launch Pad 39-B, STS-95 Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain (left) and Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai look over the gate for the slidewire basket, part of the emergency egress system on the pad. Mukai represents the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA), and Duque the European Space Agency (ESA). The STS-95 crew are at KSC to participate in a Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) which includes mission familiarization activities, emergency egress training, and a simulated main engine cut-off exercise. Other STS-95 crew members are Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson, Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown, Pilot Steven W. Lindsey, Payload Specialists John H. Glenn Jr., senator from Ohio, and Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski. The STS-95 mission, targeted for liftoff on Oct. 29, includes research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process. Following the TCDT, the crew will be returning to Houston for final flight preparations