
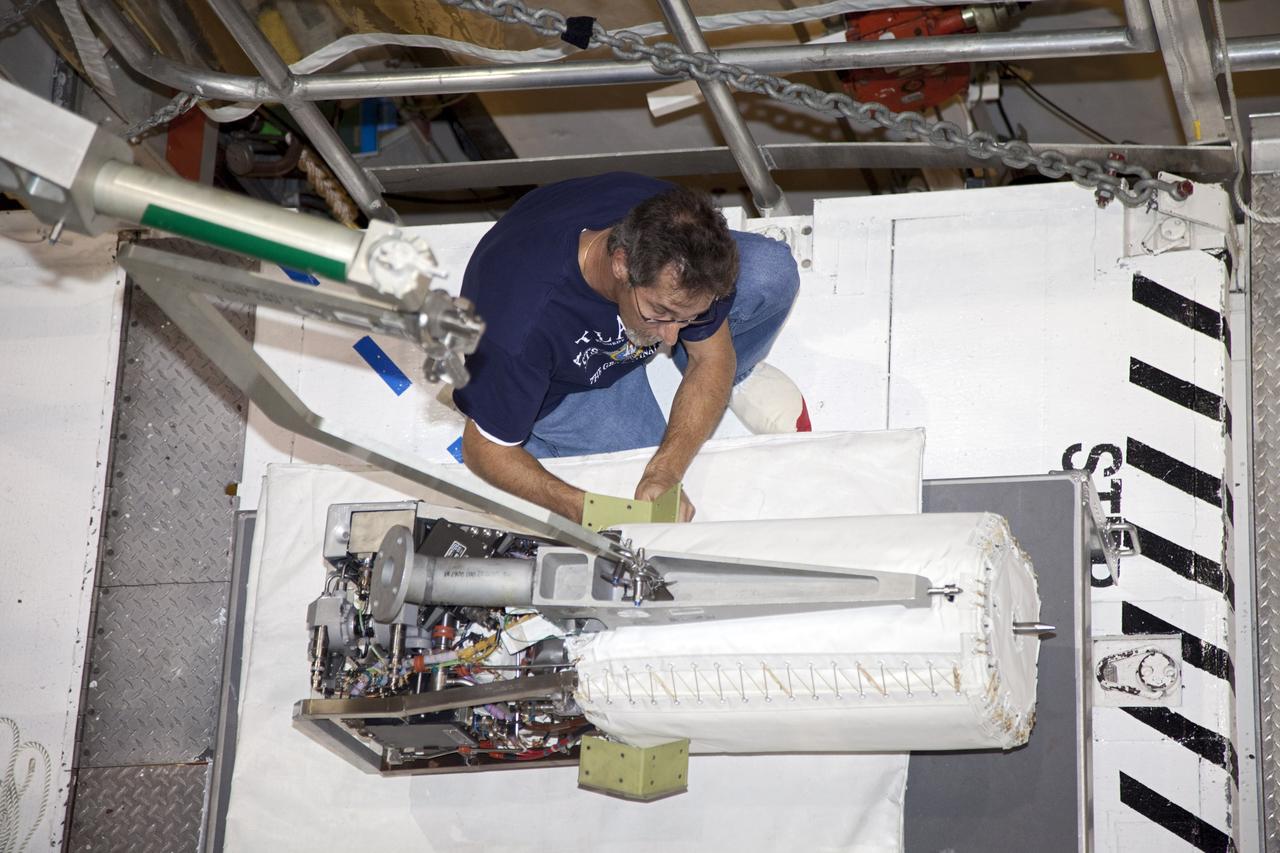
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Orbiter Processing Facility bay 3, technicians remove a piece of hardware from the side of a fuel cell removed from the orbiter Discovery. Fuel cells are located under the forward portion of the payload bay. They make power for the orbiter by mixing hydrogen and oxygen to produce electricity. Fuel cells also create potable water that is pumped into storage tanks for the crew to use in orbit. Discovery is the designated orbiter for the second return-to-flight mission, STS-121, scheduled for launch in May. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
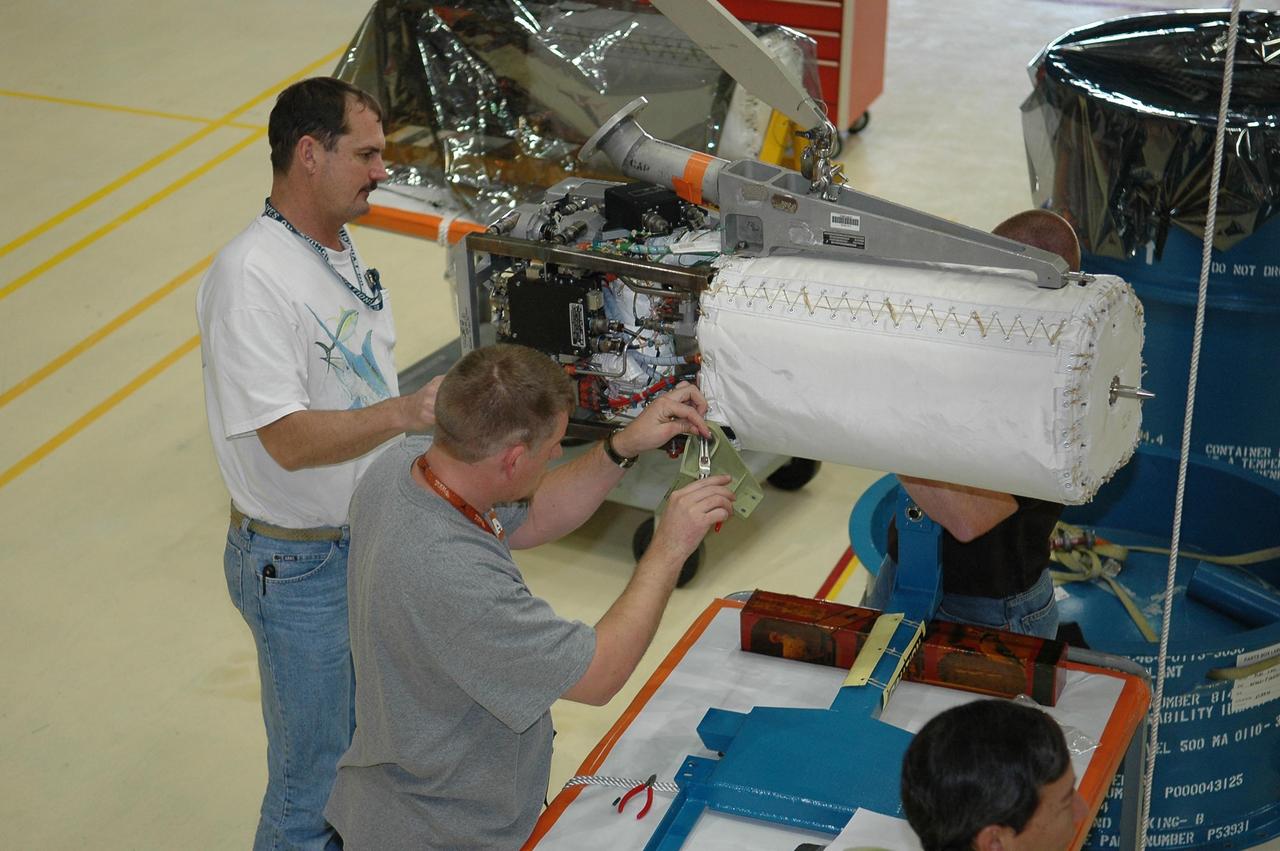

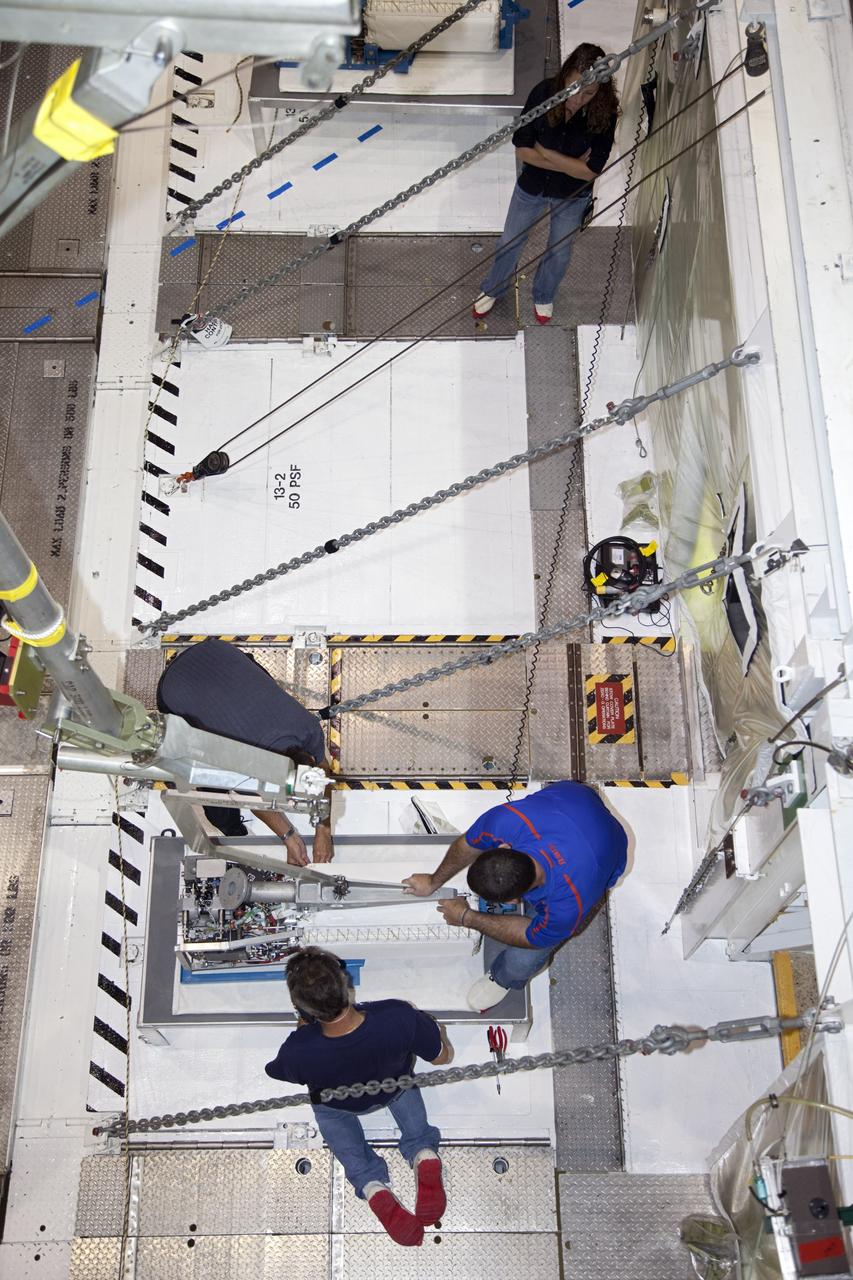
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Orbiter Processing Facility bay 3, technicians begin removing a piece of hardware from the side of a fuel cell removed from the orbiter Discovery. Fuel cells are located under the forward portion of the payload bay. They make power for the orbiter by mixing hydrogen and oxygen to produce electricity. Fuel cells also create potable water that is pumped into storage tanks for the crew to use in orbit. Discovery is the designated orbiter for the second return-to-flight mission, STS-121, scheduled for launch in May. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

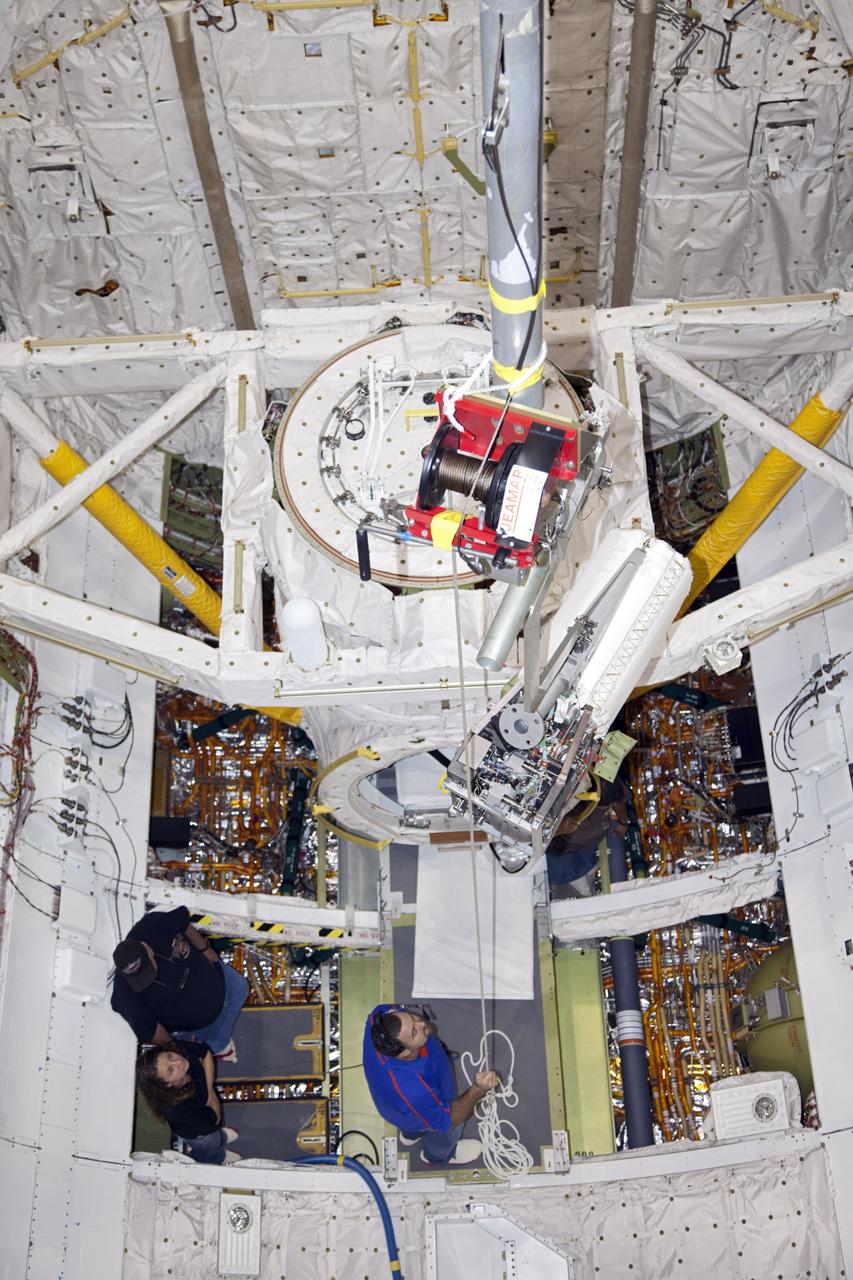
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Orbiter Processing Facility bay 3, a fuel cell removed from the orbiter Discovery is lowered toward the floor. Fuel cells are located under the forward portion of the payload bay. They make power for the orbiter by mixing hydrogen and oxygen to produce electricity. Fuel cells also create potable water that is pumped into storage tanks for the crew to use in orbit. Discovery is the designated orbiter for the second return-to-flight mission, STS-121, scheduled for launch in May. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
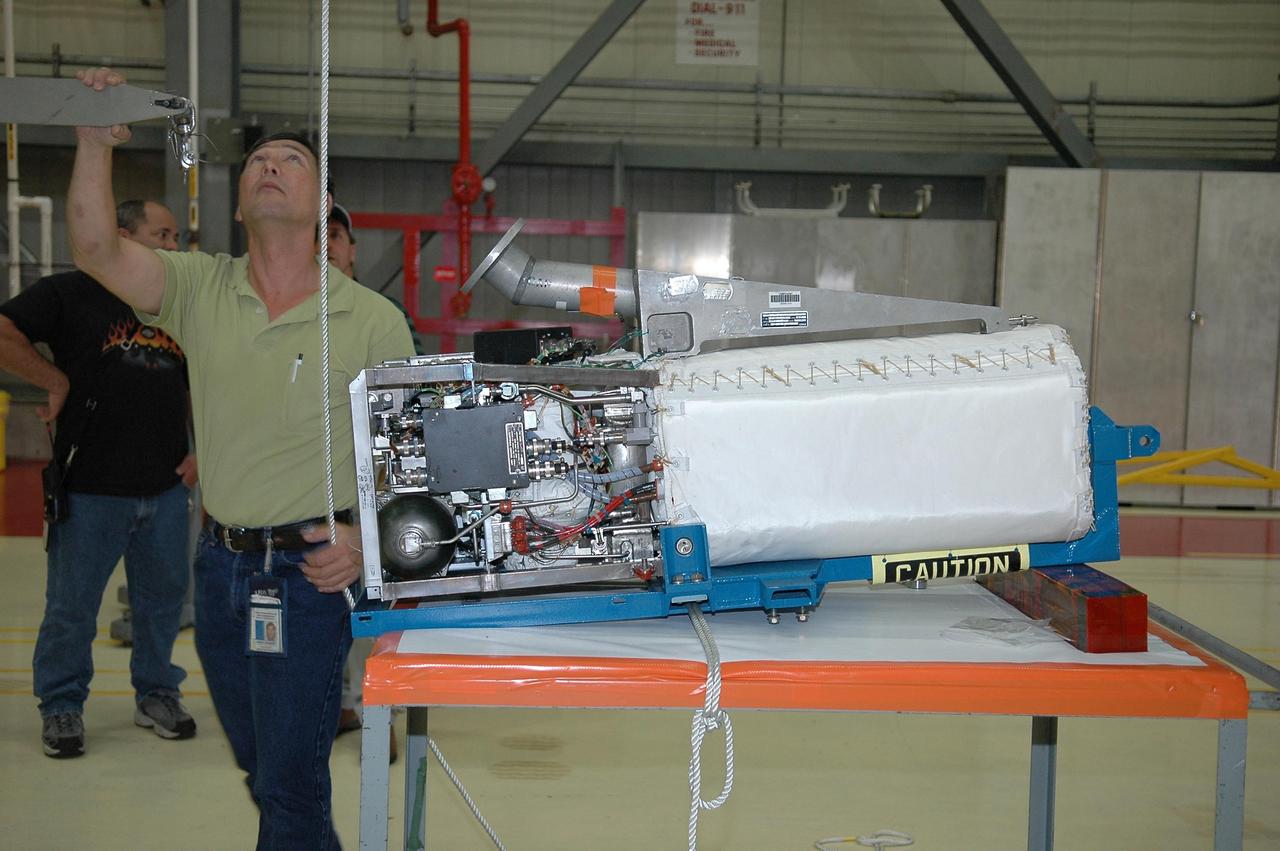

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Orbiter Processing Facility bay 3, the fuel cell removed from the orbiter Discovery is lowered onto a bracket on the work stand. Fuel cells are located under the forward portion of the payload bay. They make power for the orbiter by mixing hydrogen and oxygen to produce electricity. Fuel cells also create potable water that is pumped into storage tanks for the crew to use in orbit. Discovery is the designated orbiter for the second return-to-flight mission, STS-121, scheduled for launch in May. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
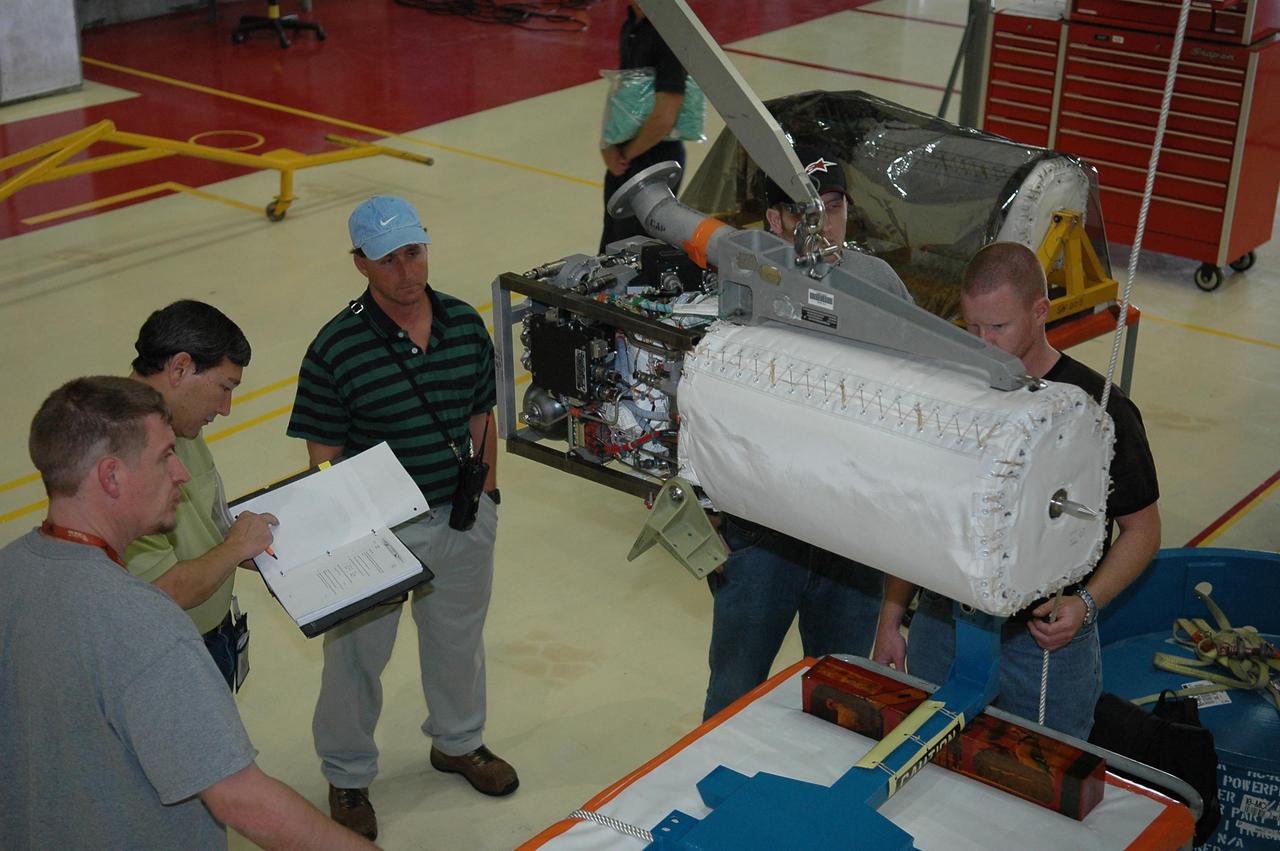

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Orbiter Processing Facility bay 3, a fuel cell removed from the orbiter Discovery is lowered toward a work stand. Fuel cells are located under the forward portion of the payload bay. They make power for the orbiter by mixing hydrogen and oxygen to produce electricity. Fuel cells also create potable water that is pumped into storage tanks for the crew to use in orbit. Discovery is the designated orbiter for the second return-to-flight mission, STS-121, scheduled for launch in May. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
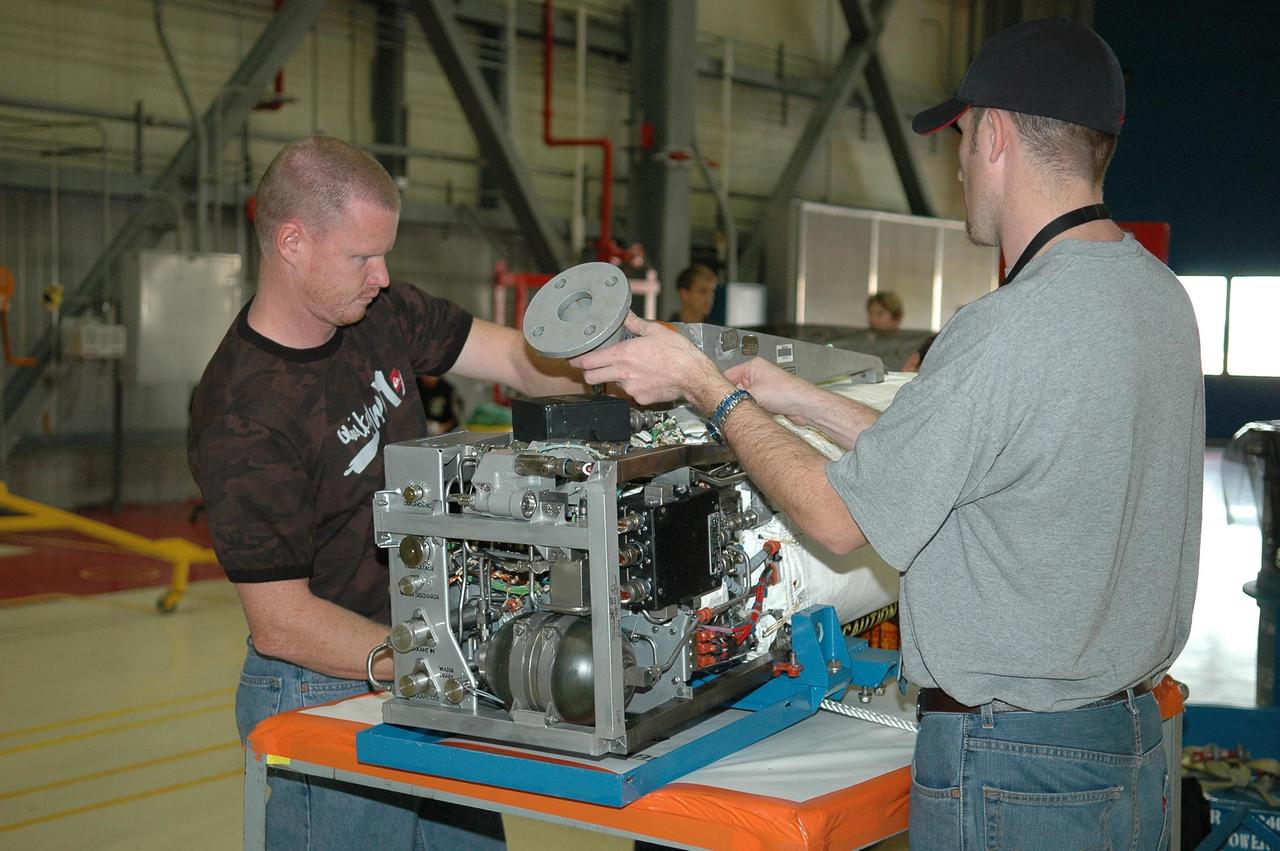

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Orbiter Processing Facility bay 3, technicians begin dismantling the fuel cell removed from the orbiter Discovery. Fuel cells are located under the forward portion of the payload bay. They make power for the orbiter by mixing hydrogen and oxygen to produce electricity. Fuel cells also create potable water that is pumped into storage tanks for the crew to use in orbit. Discovery is the designated orbiter for the second return-to-flight mission, STS-121, scheduled for launch in May. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians monitor the progress as space shuttle Discovery’s fuel cells are drained of all fluids. After all of the coolant is removed, the fuel cells will be returned to their previous location within Discovery’s mid-body. The hydrogen and oxygen dewars which feed reactants to the fuel cells remain in Discovery’s mid-body and have been purged with inert gases and vented down. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of shuttle Discovery. Discovery is being prepared for display at the Smithsonian’s National Air and Space Museum, Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians prepare space shuttle Discovery’s three fuel cells to be drained of all fluids. After all of the coolant is removed, the fuel cells will be returned to their previous location within Discovery’s mid-body. The hydrogen and oxygen dewars which feed reactants to the fuel cells remain in Discovery’s mid-body and have been purged with inert gases and vented down. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of shuttle Discovery. Discovery is being prepared for display at the Smithsonian’s National Air and Space Museum, Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians monitor the progress as space shuttle Discovery’s fuel cells are drained of all fluids. After all of the coolant is removed, the fuel cells will be returned to their previous location within Discovery’s mid-body. The hydrogen and oxygen dewars which feed reactants to the fuel cells remain in Discovery’s mid-body and have been purged with inert gases and vented down. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of shuttle Discovery. Discovery is being prepared for display at the Smithsonian’s National Air and Space Museum, Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a technician prepares one of space shuttle Discovery’s three fuel cells to be drained of all fluids. After all of the coolant is removed, the fuel cells will be returned to their previous location within Discovery’s mid-body. The hydrogen and oxygen dewars which feed reactants to the fuel cells remain in Discovery’s mid-body and have been purged with inert gases and vented down. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of shuttle Discovery. Discovery is being prepared for display at the Smithsonian’s National Air and Space Museum, Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
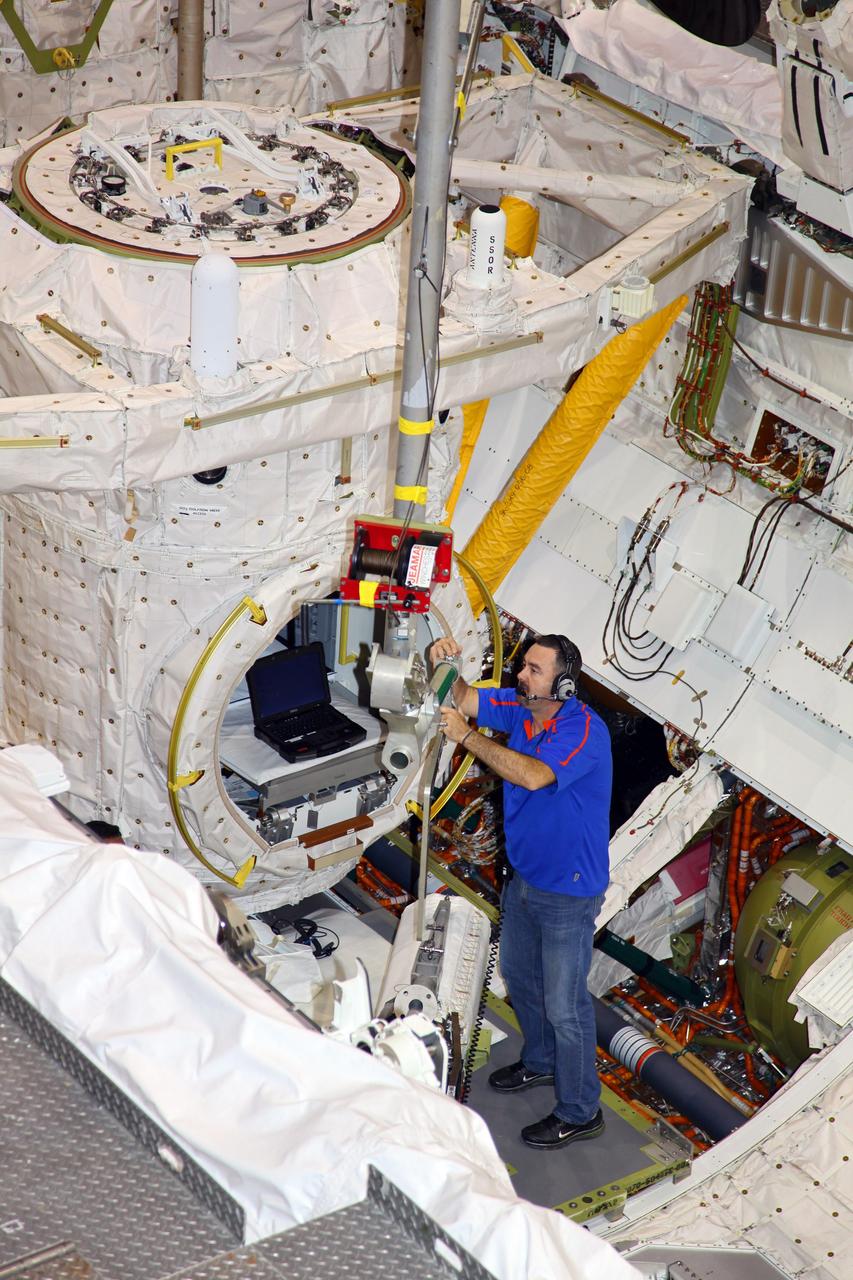

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians prepare space shuttle Discovery’s three fuel cells to be drained of all fluids. After all of the coolant is removed, the fuel cells will be returned to their previous location within Discovery’s mid-body. The hydrogen and oxygen dewars which feed reactants to the fuel cells remain in Discovery’s mid-body and have been purged with inert gases and vented down. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of shuttle Discovery. Discovery is being prepared for display at the Smithsonian’s National Air and Space Museum, Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
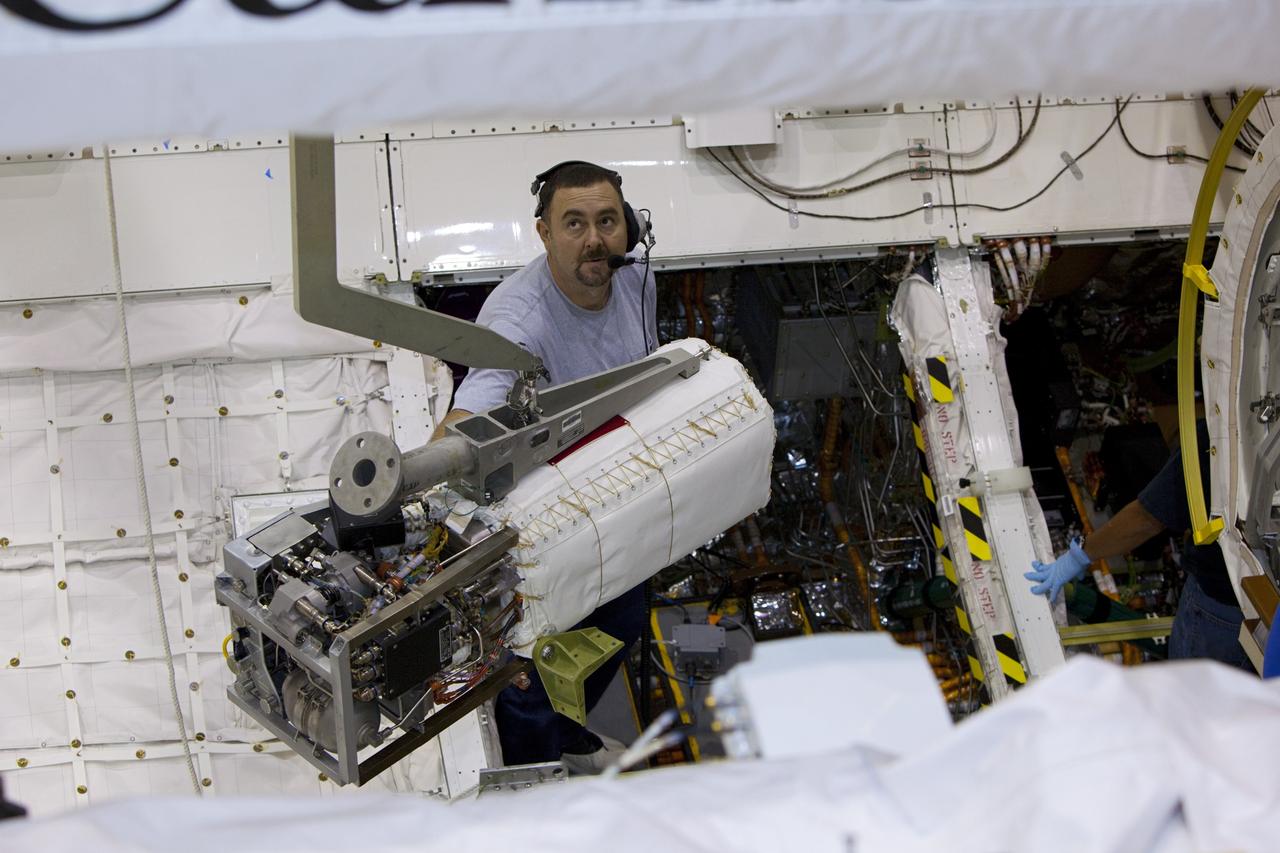

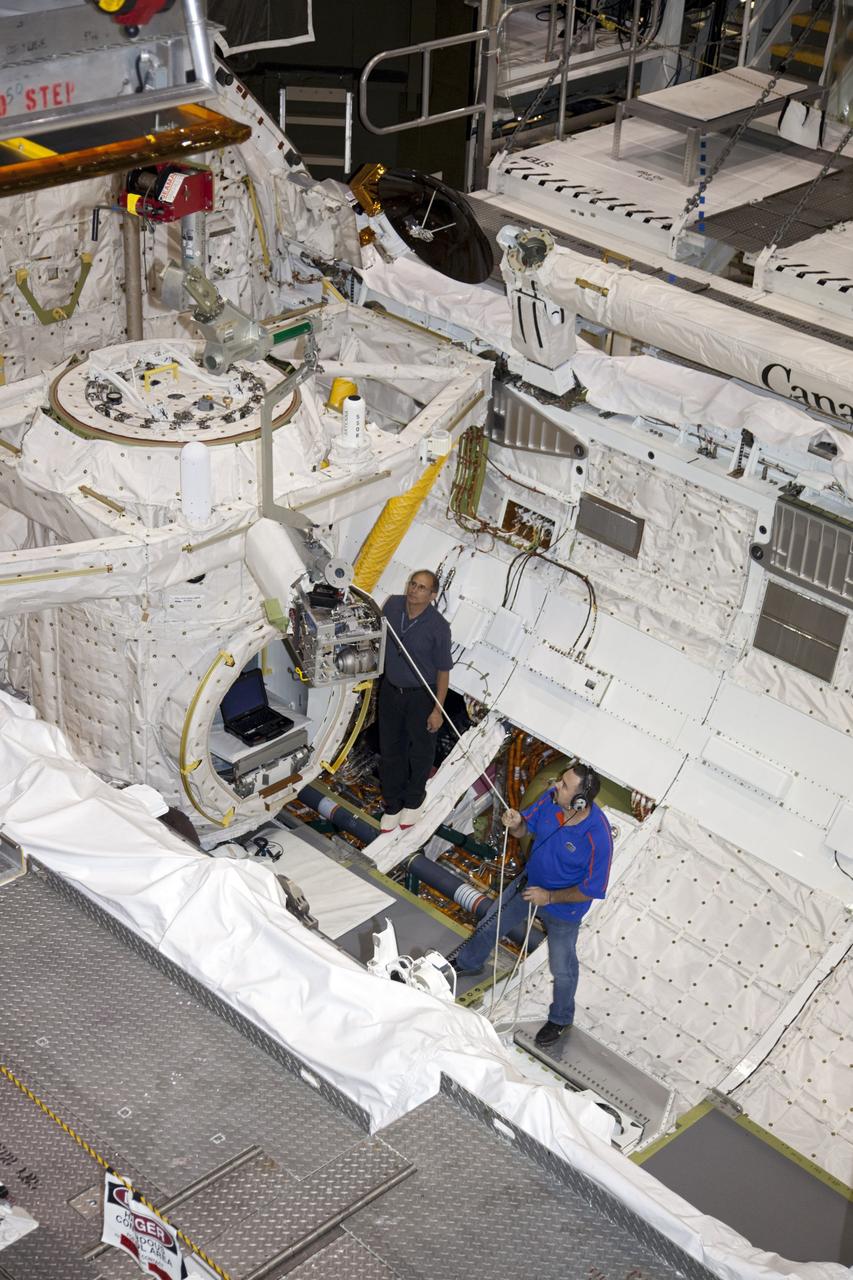
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians prepare to re-install the three fuel cells in space shuttle Discovery’s mid-body. The fuel cells were removed and drained of all fluids. The hydrogen and oxygen dewars which feed reactants to the fuel cells remain in Discovery’s mid-body and have been purged with inert gases and vented down. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of shuttle Discovery. Discovery is being prepared for display at the Smithsonian’s National Air and Space Museum, Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
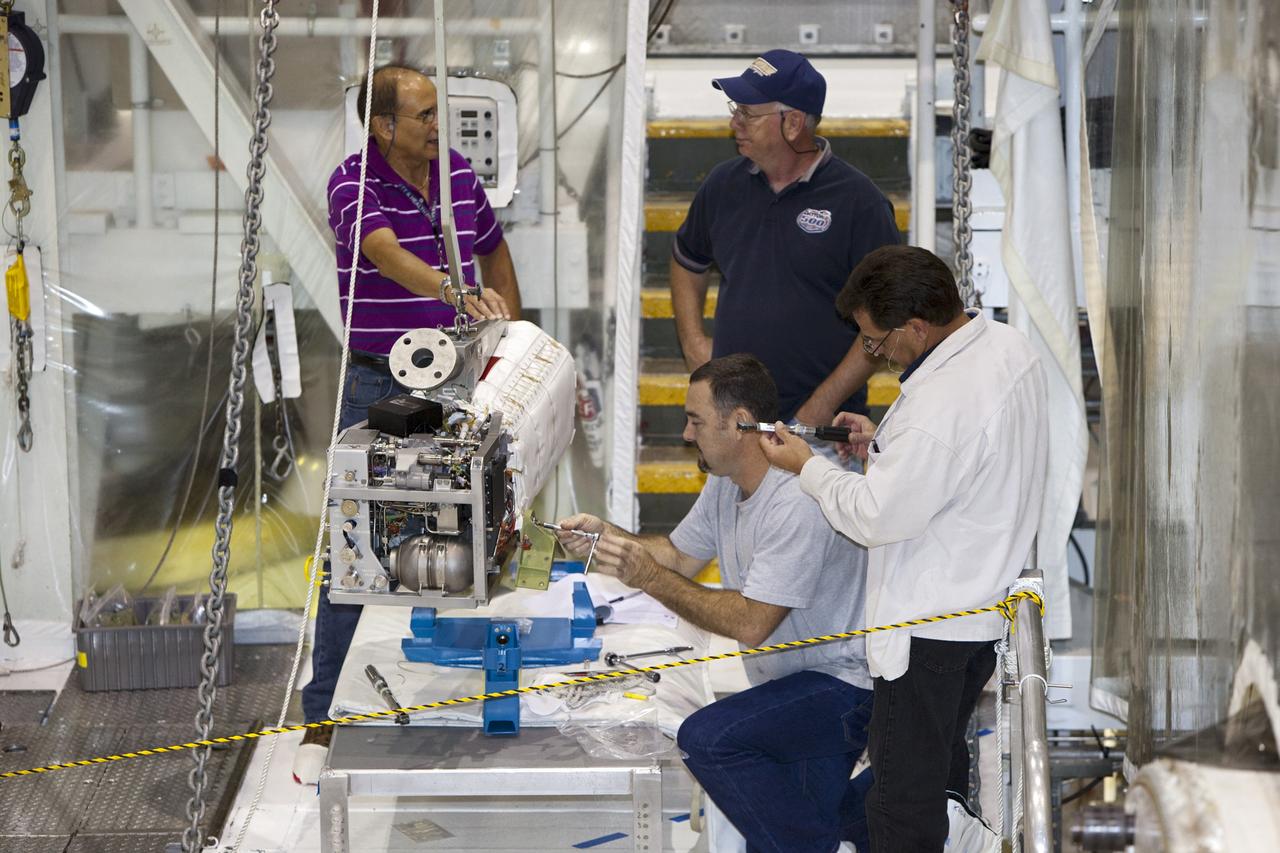

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians prepare to re-install the three fuel cells in space shuttle Discovery’s mid-body. The fuel cells were removed and drained of all fluids. The hydrogen and oxygen dewars which feed reactants to the fuel cells remain in Discovery’s mid-body and have been purged with inert gases and vented down. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of shuttle Discovery. Discovery is being prepared for display at the Smithsonian’s National Air and Space Museum, Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
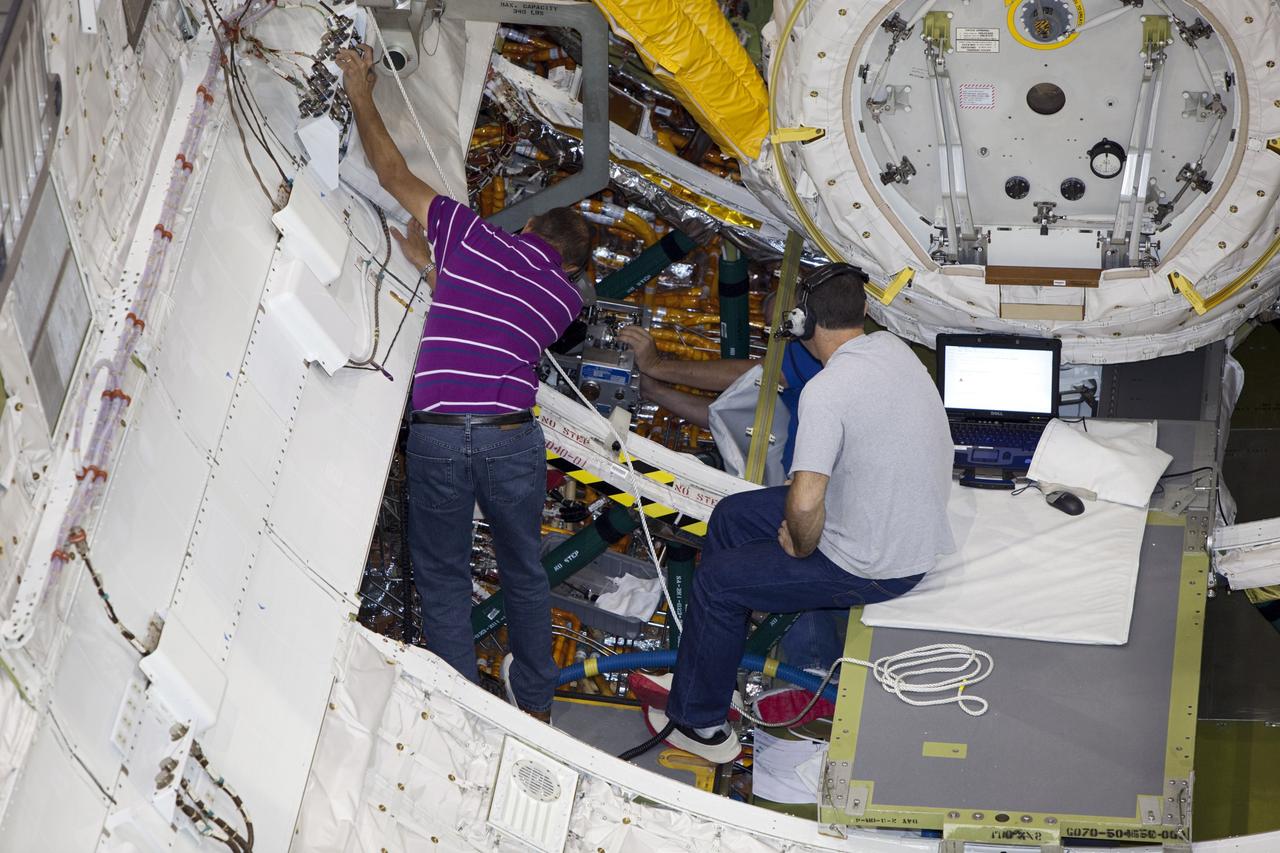

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians re-install the three fuel cells in space shuttle Discovery’s mid-body. The fuel cells were removed and drained of all fluids. The hydrogen and oxygen dewars which feed reactants to the fuel cells remain in Discovery’s mid-body and have been purged with inert gases and vented down. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of shuttle Discovery. Discovery is being prepared for display at the Smithsonian’s National Air and Space Museum, Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians prepare to re-install the three fuel cells in space shuttle Discovery’s mid-body. The fuel cells were removed and drained of all fluids. The hydrogen and oxygen dewars which feed reactants to the fuel cells remain in Discovery’s mid-body and have been purged with inert gases and vented down. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of shuttle Discovery. Discovery is being prepared for display at the Smithsonian’s National Air and Space Museum, Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
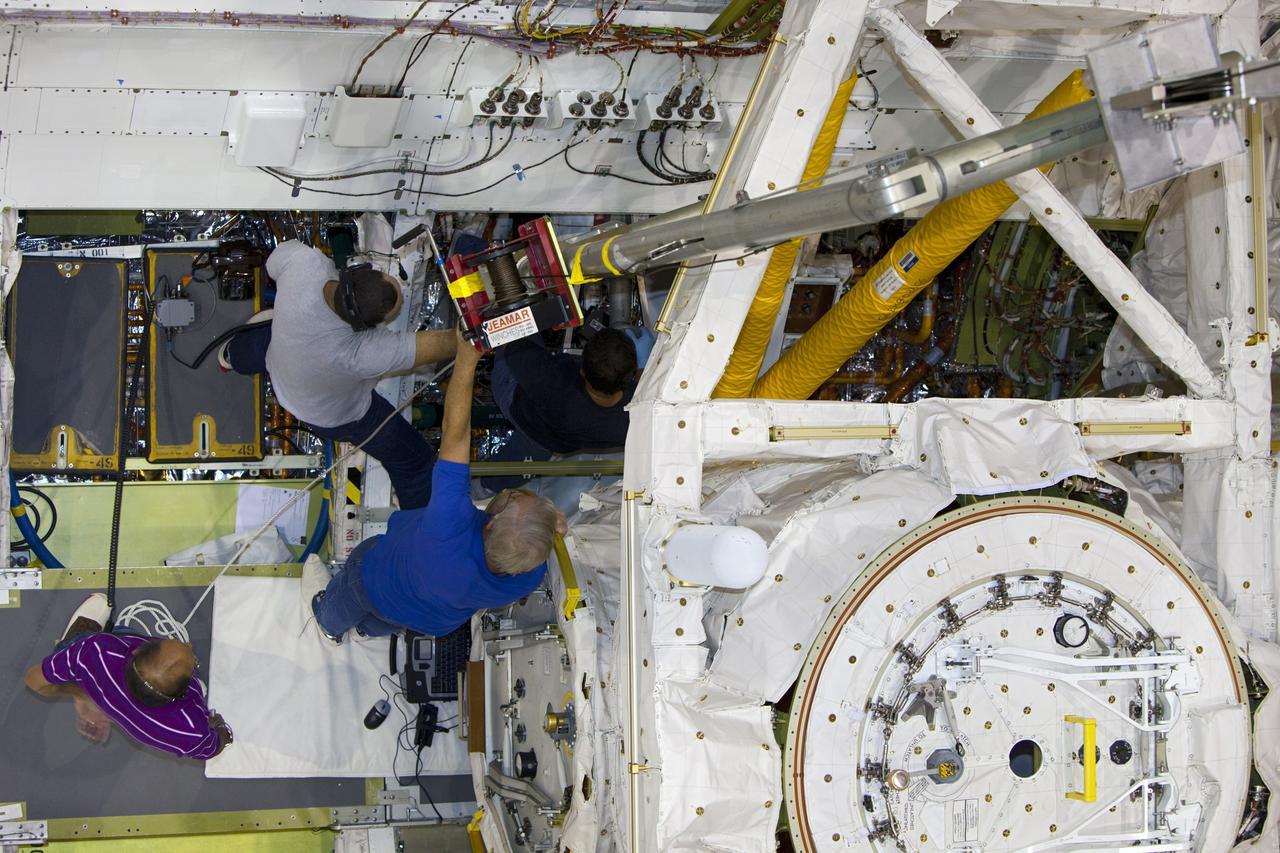
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians re-install the three fuel cells in space shuttle Discovery’s mid-body. The fuel cells were removed and drained of all fluids. The hydrogen and oxygen dewars which feed reactants to the fuel cells remain in Discovery’s mid-body and have been purged with inert gases and vented down. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of shuttle Discovery. Discovery is being prepared for display at the Smithsonian’s National Air and Space Museum, Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
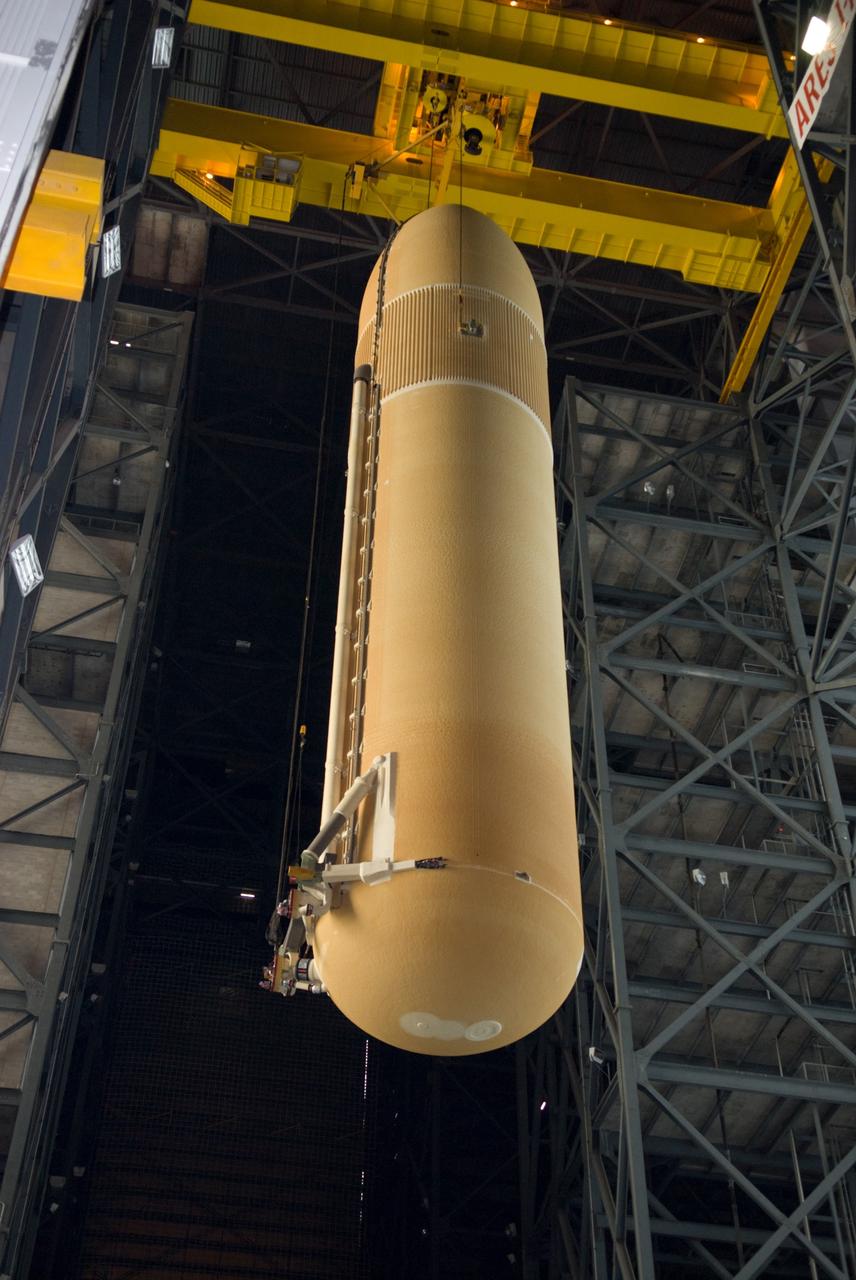

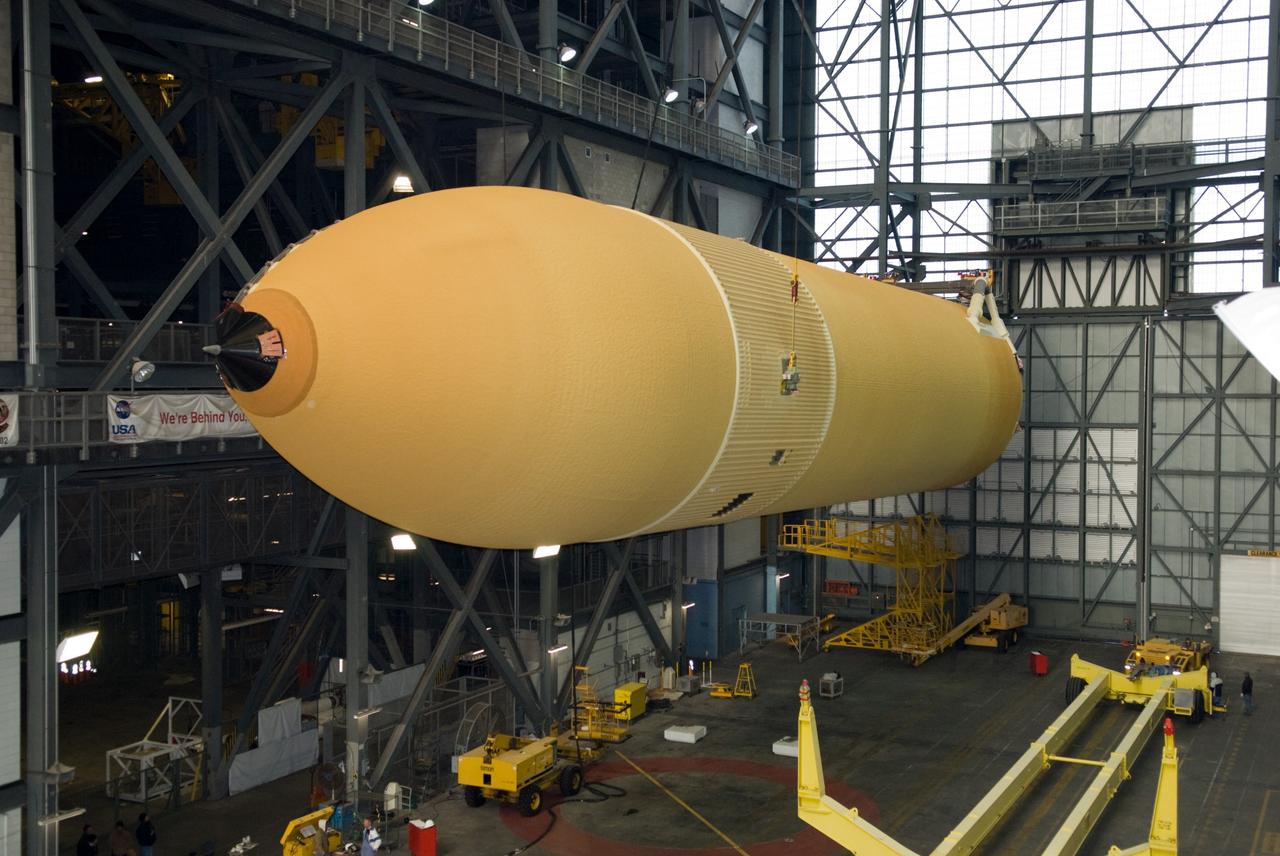
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane is enlisted to lift the external fuel tank for space shuttle Discovery's STS-131 mission, ET-135, into a test cell. The tank was delivered to Kennedy aboard the Pegasus barge from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility on Dec. 26. The tank will remain in the test cell until it is transferred into a high bay for mating with the twin solid rocket boosters that will be used on the mission. Launch of the STS-131 mission to the International Space Station is targeted for March 18. For information on the STS-131 mission and crew, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts131/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Glenn Benson
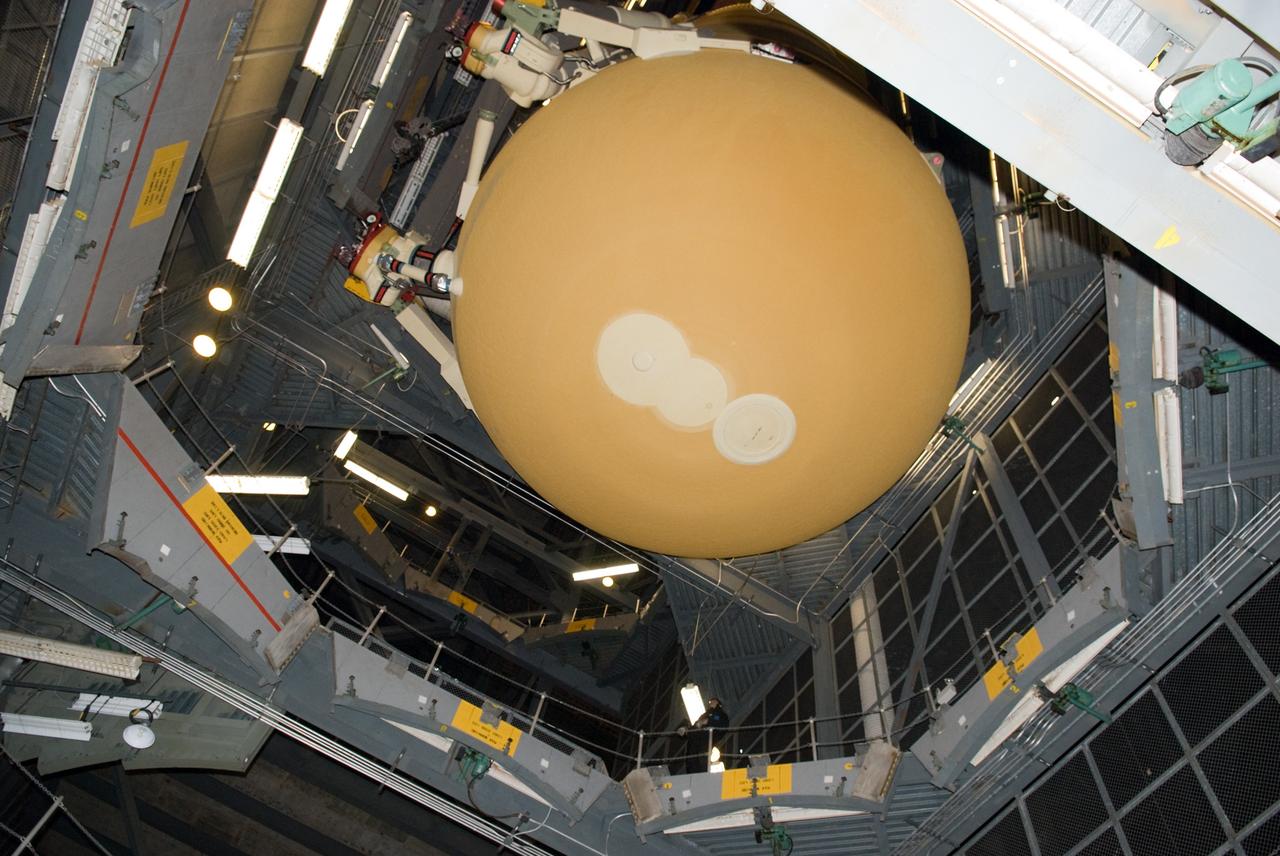

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the external fuel tank for space shuttle Discovery's STS-131 mission, ET-135, is lowered into a test cell. The tank was delivered to Kennedy aboard the Pegasus barge from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility on Dec. 26. The tank will remain in the test cell until it is transferred into a high bay for mating with the twin solid rocket boosters that will be used on the mission. Launch of the STS-131 mission to the International Space Station is targeted for March 18. For information on the STS-131 mission and crew, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts131/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Glenn Benson

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the external fuel tank for space shuttle Discovery's STS-131 mission, ET-135, has arrived in its test cell. The tank was delivered to Kennedy aboard the Pegasus barge from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility on Dec. 26. The tank will remain in the test cell until it is transferred into a high bay for mating with the twin solid rocket boosters that will be used on the mission. Launch of the STS-131 mission to the International Space Station is targeted for March 18. For information on the STS-131 mission and crew, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts131/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Glenn Benson
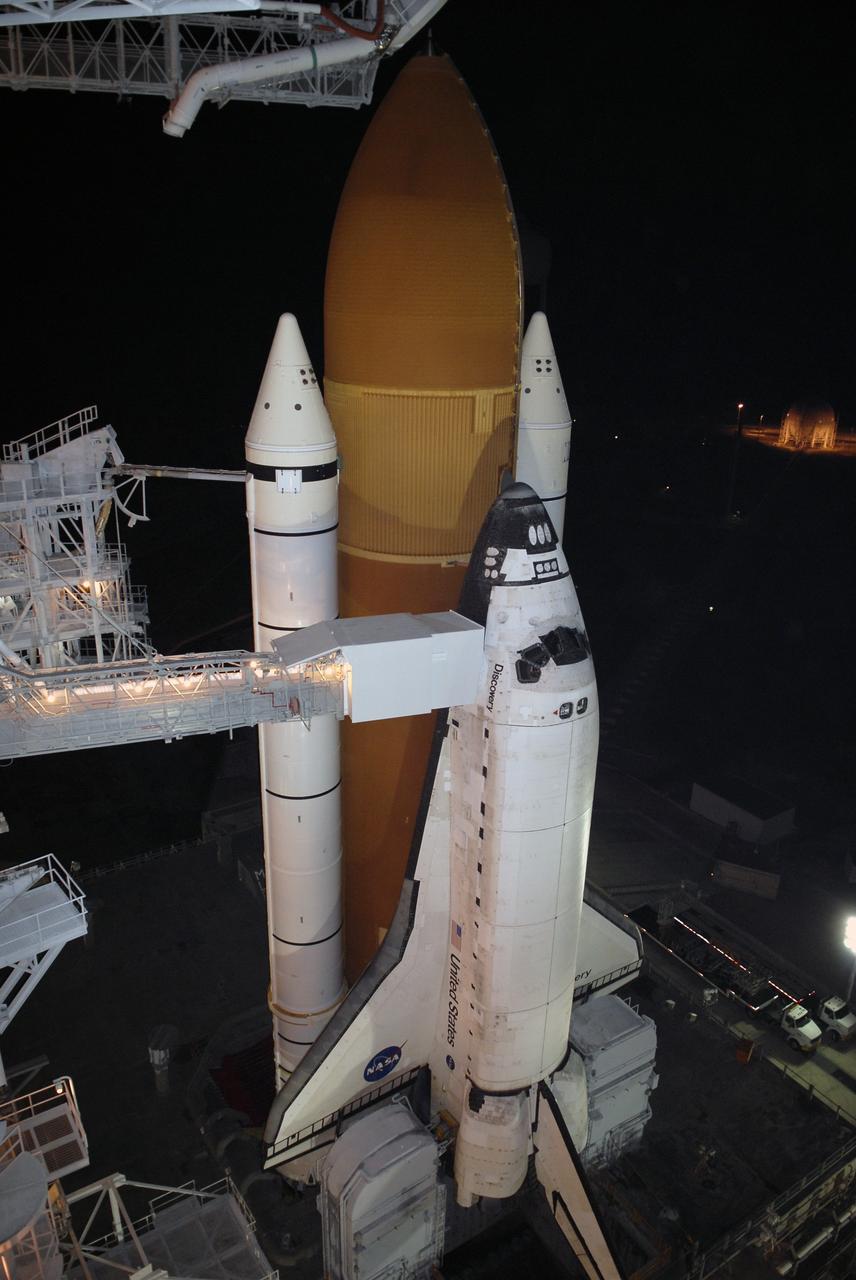

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the orbiter access arm and White Room are extended toward space shuttle Discovery after rollback of the rotating service structure. The White Room provides crew access into the shuttle. The rollback is in preparation for Discovery's liftoff on the STS-119 mission with a crew of seven. The rotating structure provides protected access to the shuttle for changeout and servicing of payloads at the pad. After the RSS is rolled back, the orbiter is ready for fuel cell activation and external tank cryogenic propellant loading operations. The mission is the 28th to the International Space Station and the 125th space shuttle flight. Discovery will deliver the final pair of power-generating solar array wings and the S6 truss segment. Installation of S6 will signal the station's readiness to house a six-member crew for conducting increased science. Liftoff of Discovery is scheduled for 9:20 p.m. EDT on March 11. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, space shuttle Discovery is revealed after the rotating service structure has been rolled back. The rollback is in preparation for Discovery's liftoff on the STS-119 mission with a crew of seven. The rotating structure provides protected access to the shuttle for changeout and servicing of payloads at the pad. After the RSS is rolled back, the orbiter is ready for fuel cell activation and external tank cryogenic propellant loading operations. The mission is the 28th to the International Space Station and the 125th space shuttle flight. Discovery will deliver the final pair of power-generating solar array wings and the S6 truss segment. Installation of S6 will signal the station's readiness to house a six-member crew for conducting increased science. Liftoff of Discovery is scheduled for 9:20 p.m. EDT on March 11. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the external fuel tank for space shuttle Discovery's STS-131 mission, ET-135, is lifted from its transporter toward a test cell. The tank was delivered to Kennedy aboard the Pegasus barge from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility on Dec. 26. The tank will remain in the test cell until it is transferred into a high bay for mating with the twin solid rocket boosters that will be used on the mission. Launch of the STS-131 mission to the International Space Station is targeted for March 18. For information on the STS-131 mission and crew, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts131/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Glenn Benson
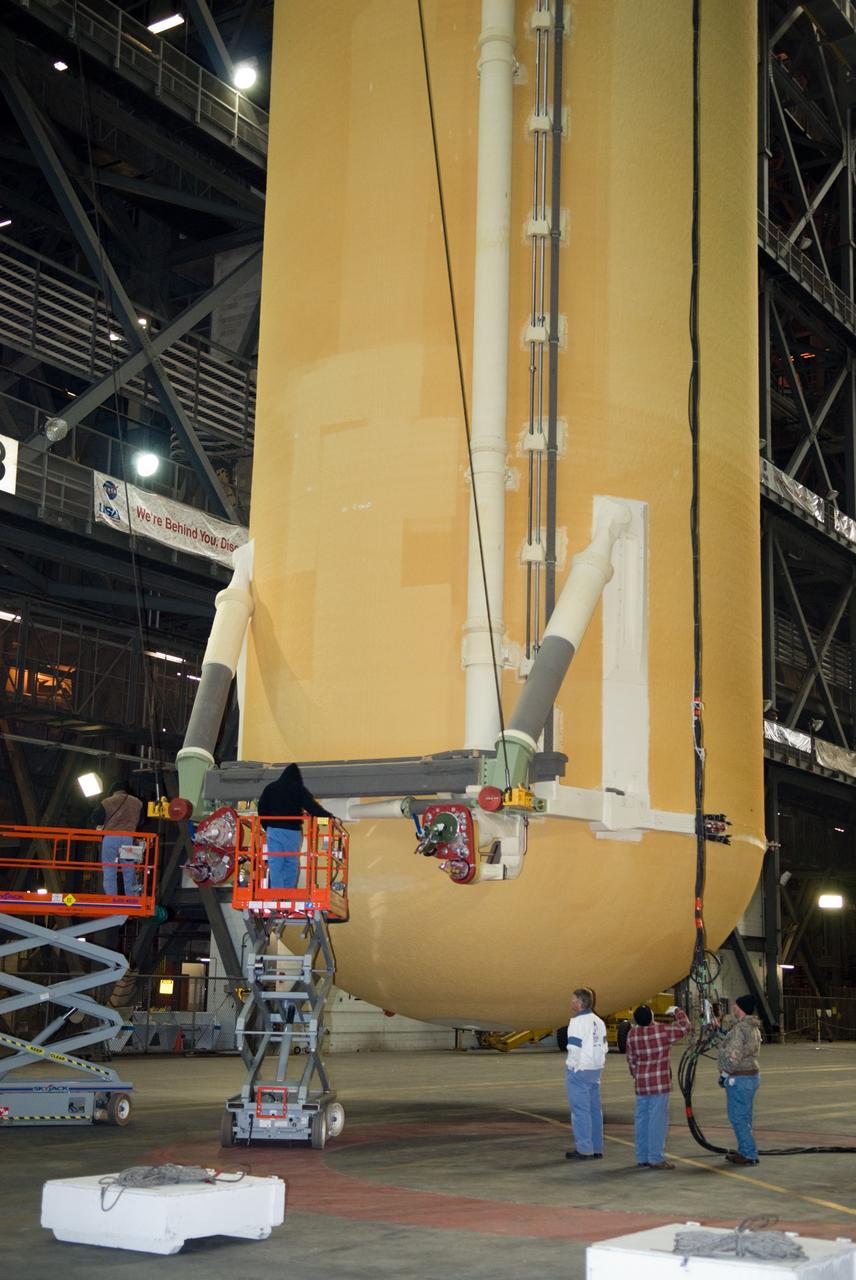

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers prepare the external fuel tank for space shuttle Discovery's STS-131 mission, ET-135, hanging vertically in the transfer aisle, for its lift into a test cell. The tank was delivered to Kennedy aboard the Pegasus barge from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility on Dec. 26. The tank will remain in the test cell until it is transferred into a high bay for mating with the twin solid rocket boosters that will be used on the mission. Launch of the STS-131 mission to the International Space Station is targeted for March 18. For information on the STS-131 mission and crew, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts131/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Glenn Benson

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane lifts the external fuel tank for space shuttle Discovery's STS-131 mission, ET-135, from its transporter toward a test cell. The tank was delivered to Kennedy aboard the Pegasus barge from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility on Dec. 26. The tank will remain in the test cell until it is transferred into a high bay for mating with the twin solid rocket boosters that will be used on the mission. Launch of the STS-131 mission to the International Space Station is targeted for March 18. For information on the STS-131 mission and crew, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts131/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Glenn Benson
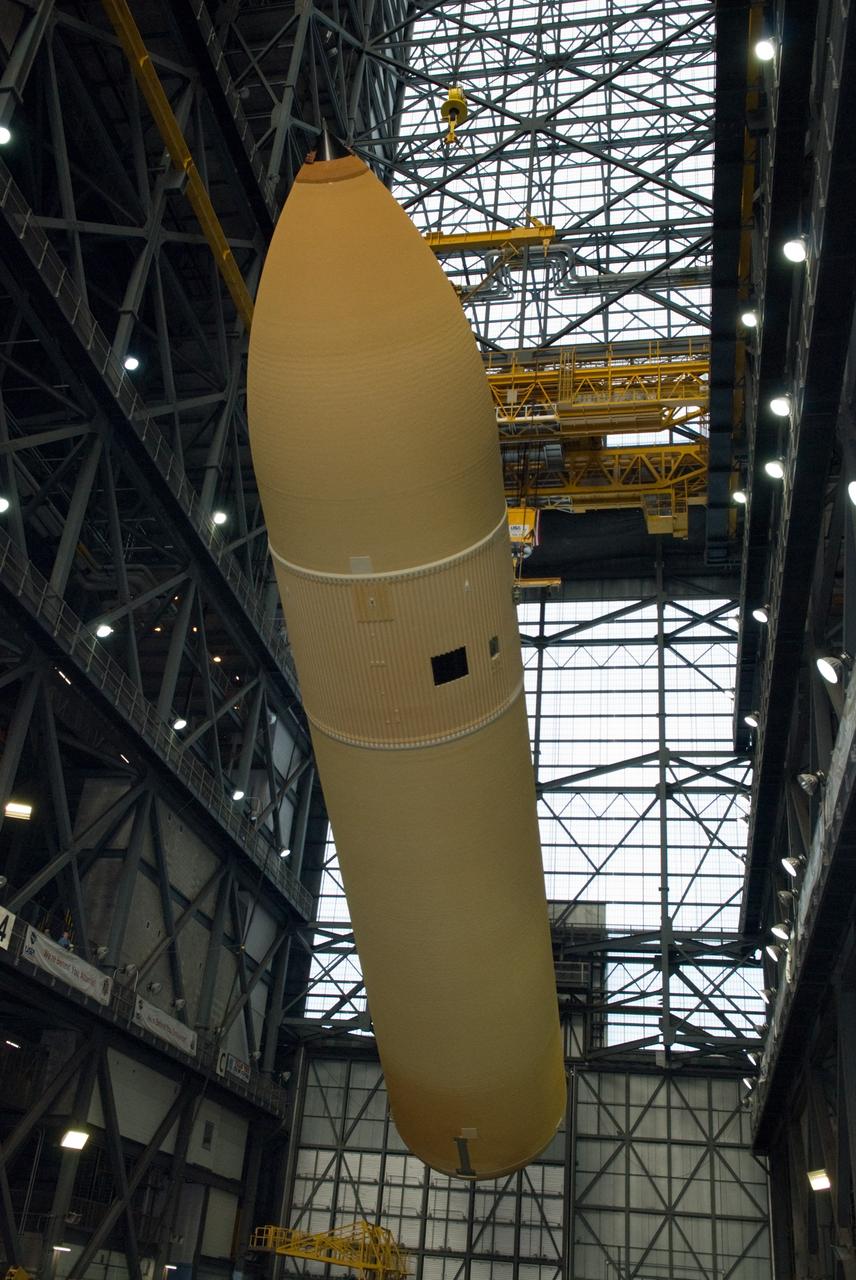

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the external fuel tank for space shuttle Discovery's STS-131 mission, ET-135, is rotated into a vertical position as it is lifted toward a test cell. The tank was delivered to Kennedy aboard the Pegasus barge from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility on Dec. 26. The tank will remain in the test cell until it is transferred into a high bay for mating with the twin solid rocket boosters that will be used on the mission. Launch of the STS-131 mission to the International Space Station is targeted for March 18. For information on the STS-131 mission and crew, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts131/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Glenn Benson
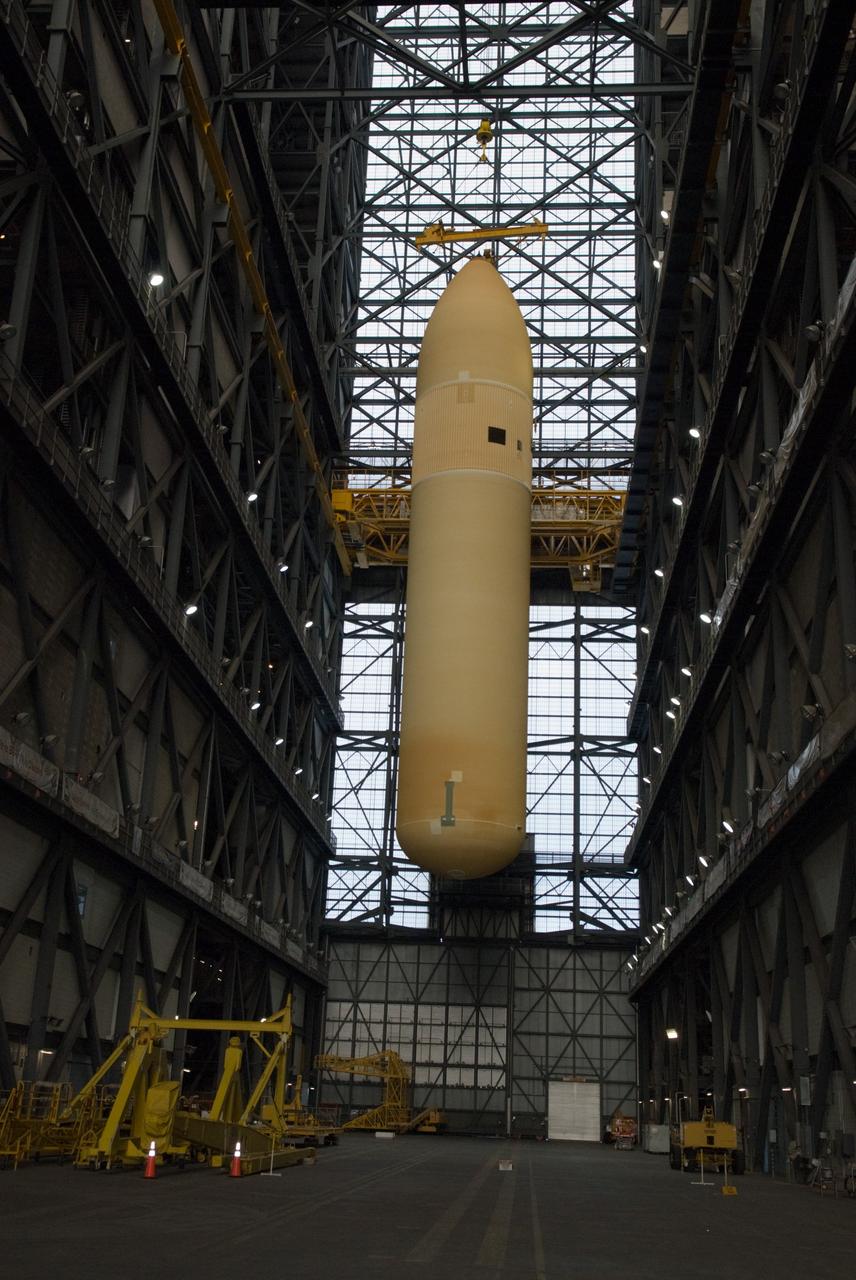

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the external fuel tank for space shuttle Discovery's STS-131 mission, ET-135, is lifted above the transfer aisle for transfer into a test cell. The tank was delivered to Kennedy aboard the Pegasus barge from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility on Dec. 26. The tank will remain in the test cell until it is transferred into a high bay for mating with the twin solid rocket boosters that will be used on the mission. Launch of the STS-131 mission to the International Space Station is targeted for March 18. For information on the STS-131 mission and crew, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts131/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Glenn Benson
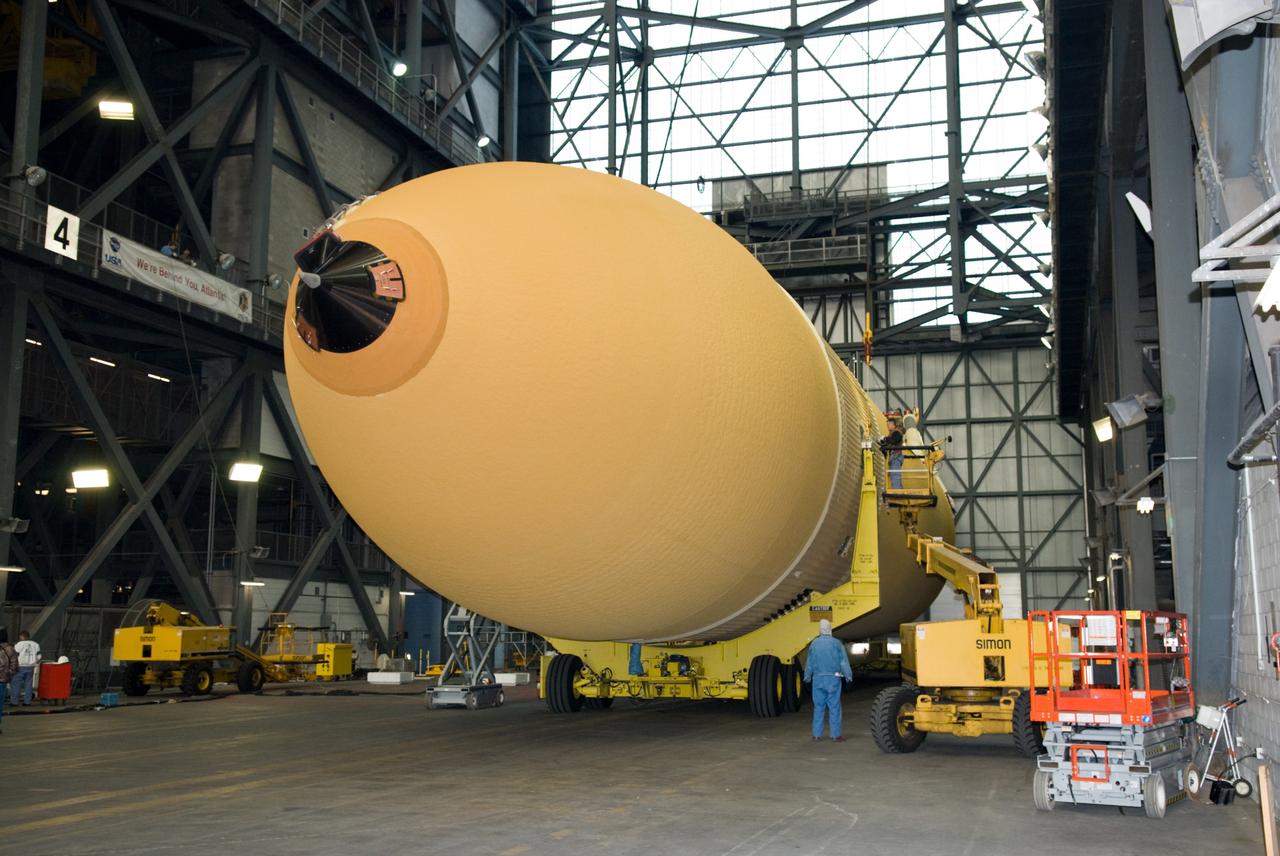

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers prepare to lift the external fuel tank for space shuttle Discovery's STS-131 mission, ET-135, from the transfer aisle into a test cell. The tank was delivered to Kennedy aboard the Pegasus barge from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility on Dec. 26. The tank will remain in the test cell until it is transferred into a high bay for mating with the twin solid rocket boosters that will be used on the mission. Launch of the STS-131 mission to the International Space Station is targeted for March 18. For information on the STS-131 mission and crew, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts131/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Glenn Benson
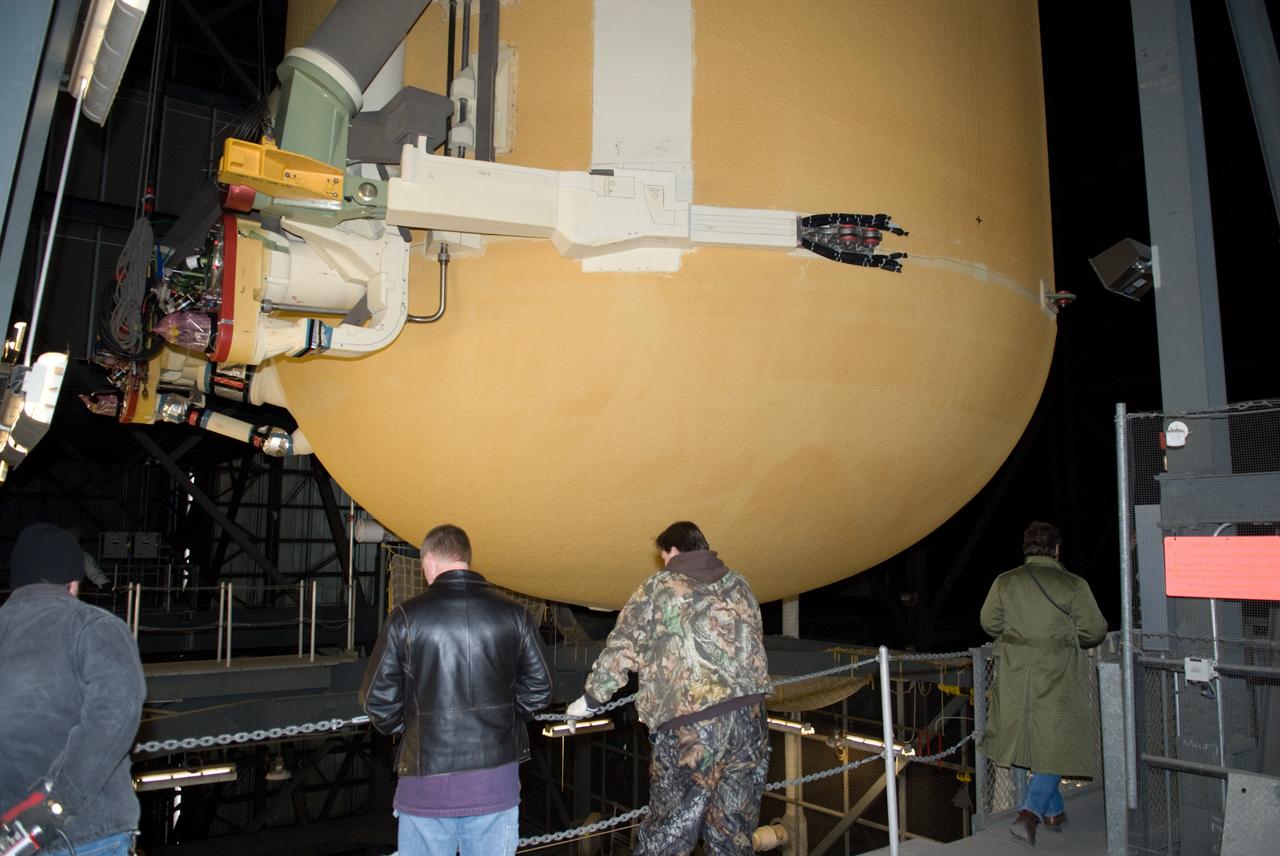

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers are on hand to monitor the external fuel tank for space shuttle Discovery's STS-131 mission, ET-135, as it is positioned into a test cell. The tank was delivered to Kennedy aboard the Pegasus barge from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility on Dec. 26. The tank will remain in the test cell until it is transferred into a high bay for mating with the twin solid rocket boosters that will be used on the mission. Launch of the STS-131 mission to the International Space Station is targeted for March 18. For information on the STS-131 mission and crew, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts131/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Glenn Benson
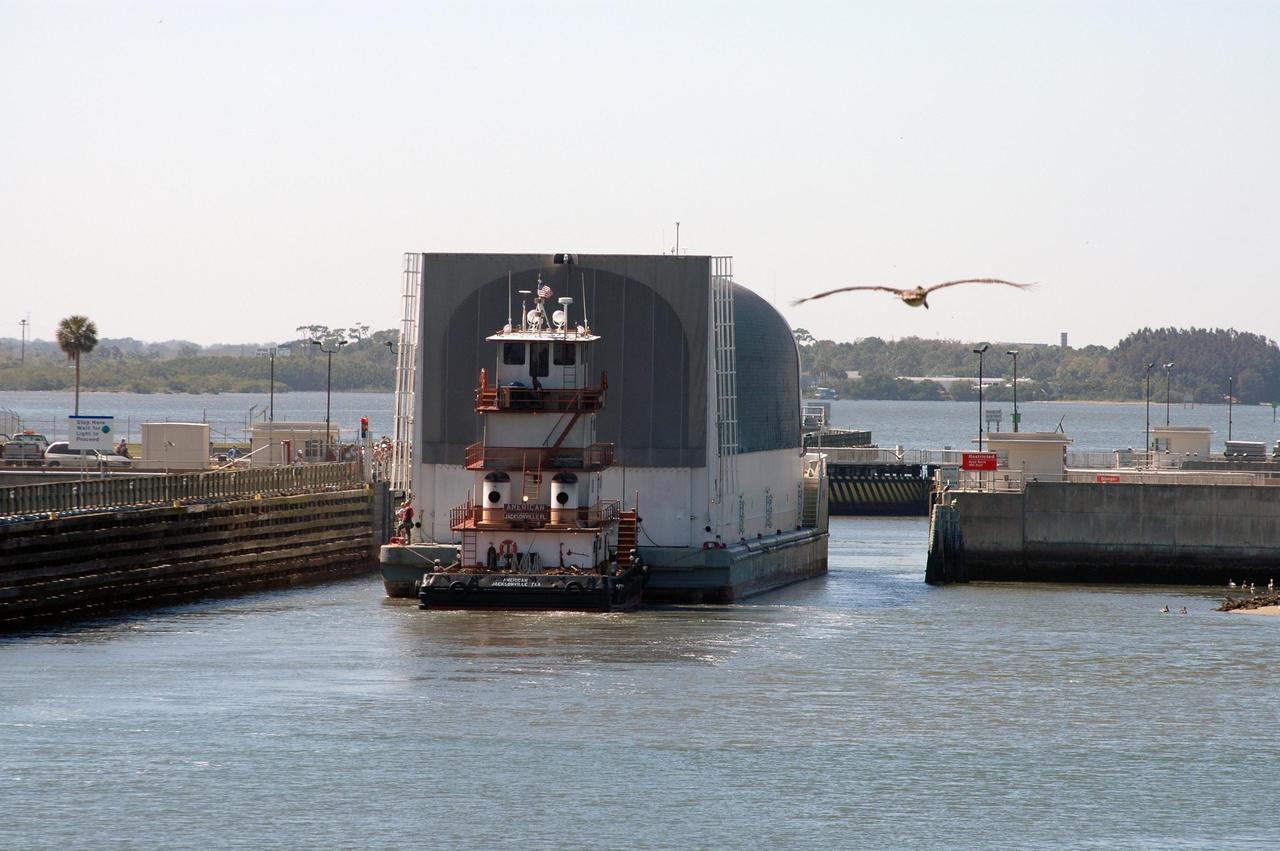

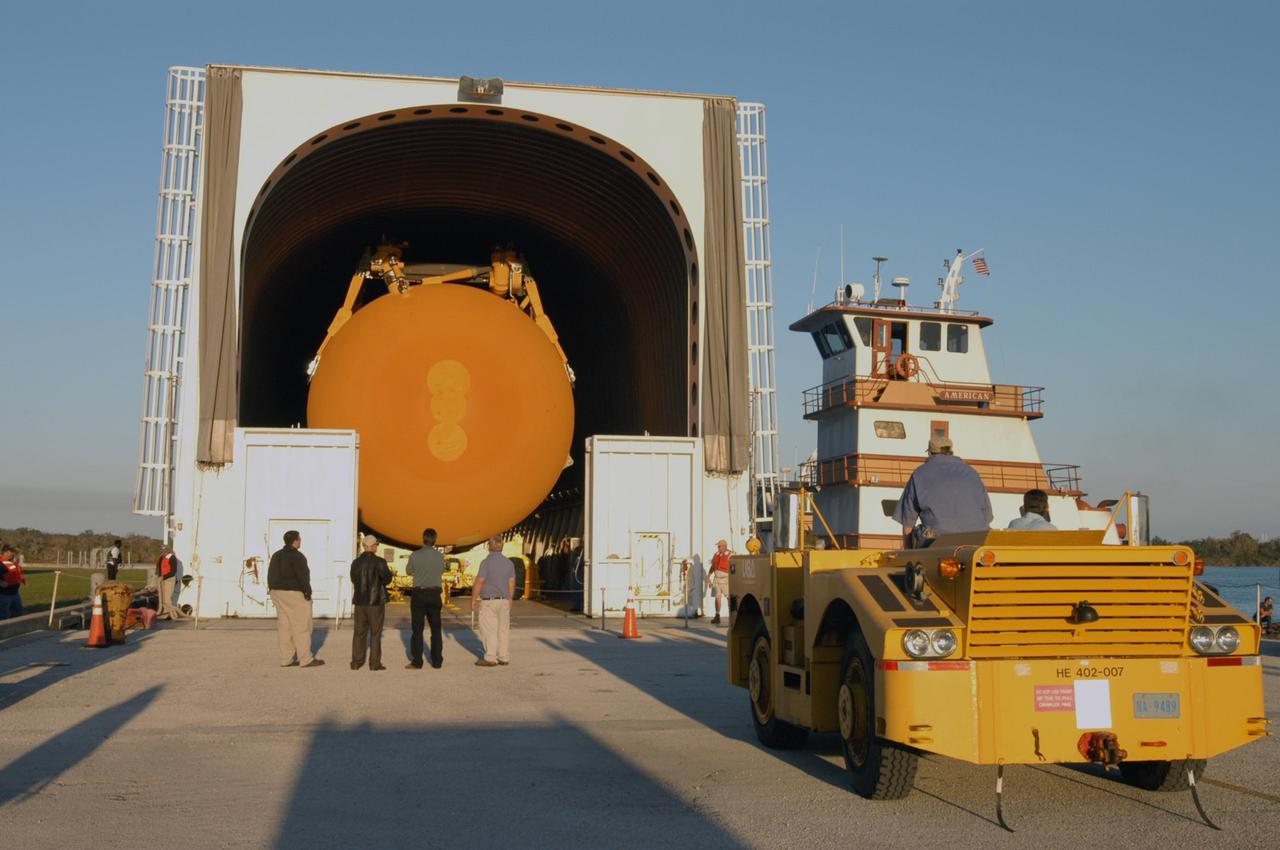
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Pegasus barge traverses the locks at Port Canaveral, as it nears the end of its journey from the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans to Kennedy Space Center. The barge carries the redesigned external fuel tank that will launch Space Shuttle Discovery on the next shuttle mission, STS-121. After off-loading, the tank will be moved into the Vehicle Assembly Building and lifted into a checkout cell for further work. The tank, designated ET-119, will fly with many major safety changes, including the removal of the protuberance air load ramps. A large piece of foam from a ramp came off during the last shuttle launch in July 2005. The ramps were removed to eliminate a potential source of damaging debris to the space shuttle. The next launch of Discovery is scheduled for May 2006.
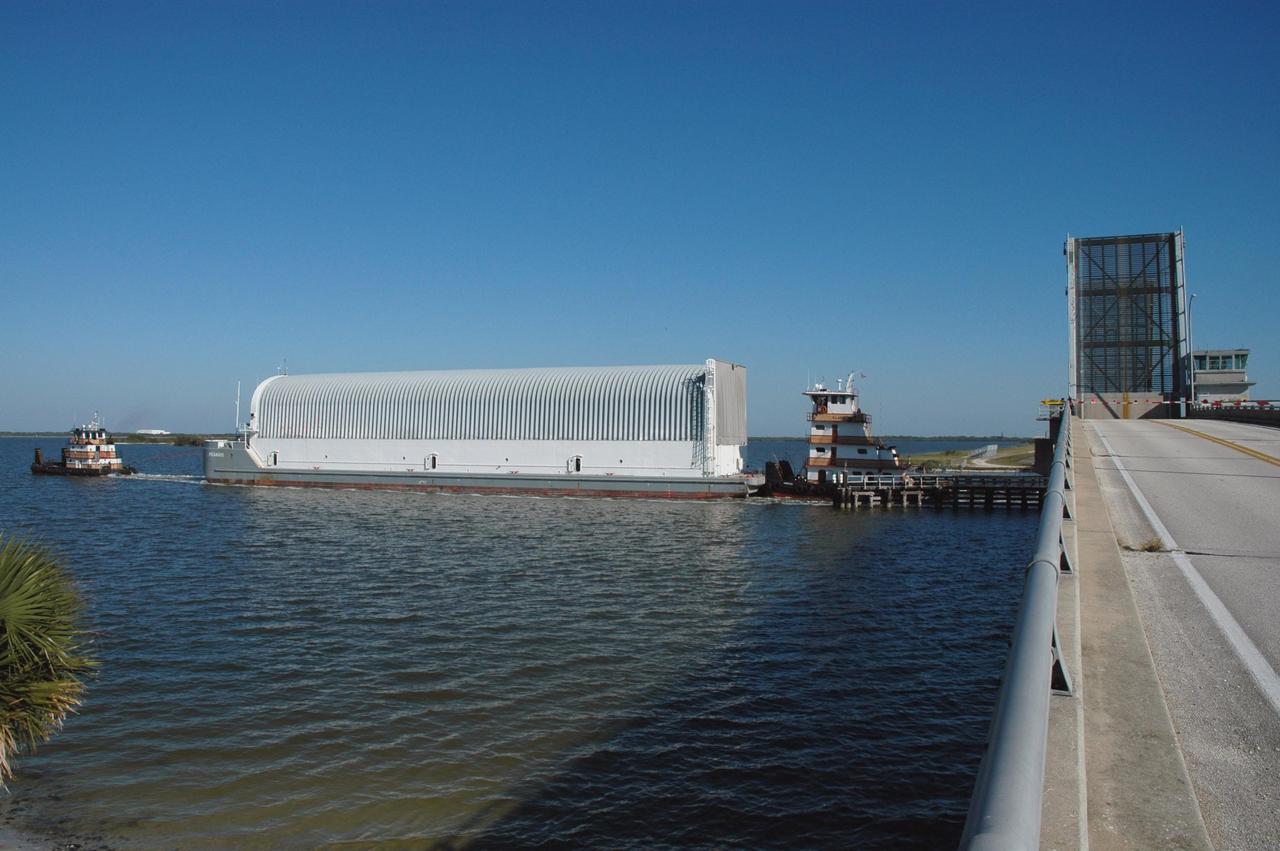

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Pegasus barge passes under the Roy D. Bridges Bridge in the Banana River, as it nears the end of its journey from the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans to Kennedy Space Center. The barge carries the redesigned external fuel tank that will launch Space Shuttle Discovery on the next shuttle mission, STS-121. After off-loading, the tank will be moved into the Vehicle Assembly Building and lifted into a checkout cell for further work. The tank, designated ET-119, will fly with many major safety changes, including the removal of the protuberance air load ramps. A large piece of foam from a ramp came off during the last shuttle launch in July 2005. The ramps were removed to eliminate a potential source of damaging debris to the space shuttle. The next launch of Discovery is scheduled for May 2006.

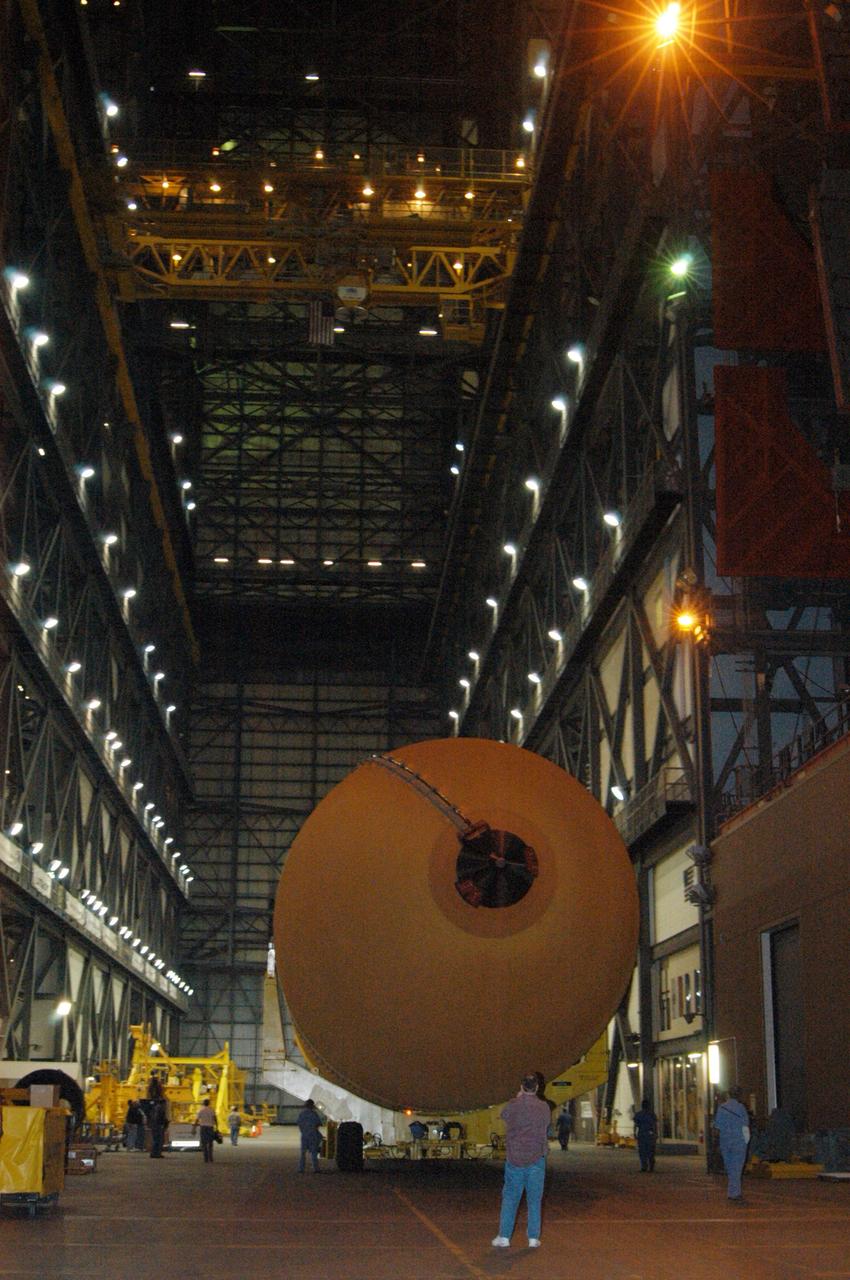
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Technicians monitor the redesigned external fuel tank that will launch Space Shuttle Discovery on the next shuttle mission, STS-121, as it is moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building in the background. The Pegasus barge delivered the tank from the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans to NASA's Kennedy Space Center. Once in the VAB, the tank will be lifted into a checkout cell for further work. The tank, designated ET-119, will fly with many major safety changes, including the removal of the protuberance air load ramps. A large piece of foam from a ramp came off during the last shuttle launch in July 2005. The ramps were removed to eliminate a potential source of damaging debris to the space shuttle. The next launch of Discovery is scheduled for May 2006.
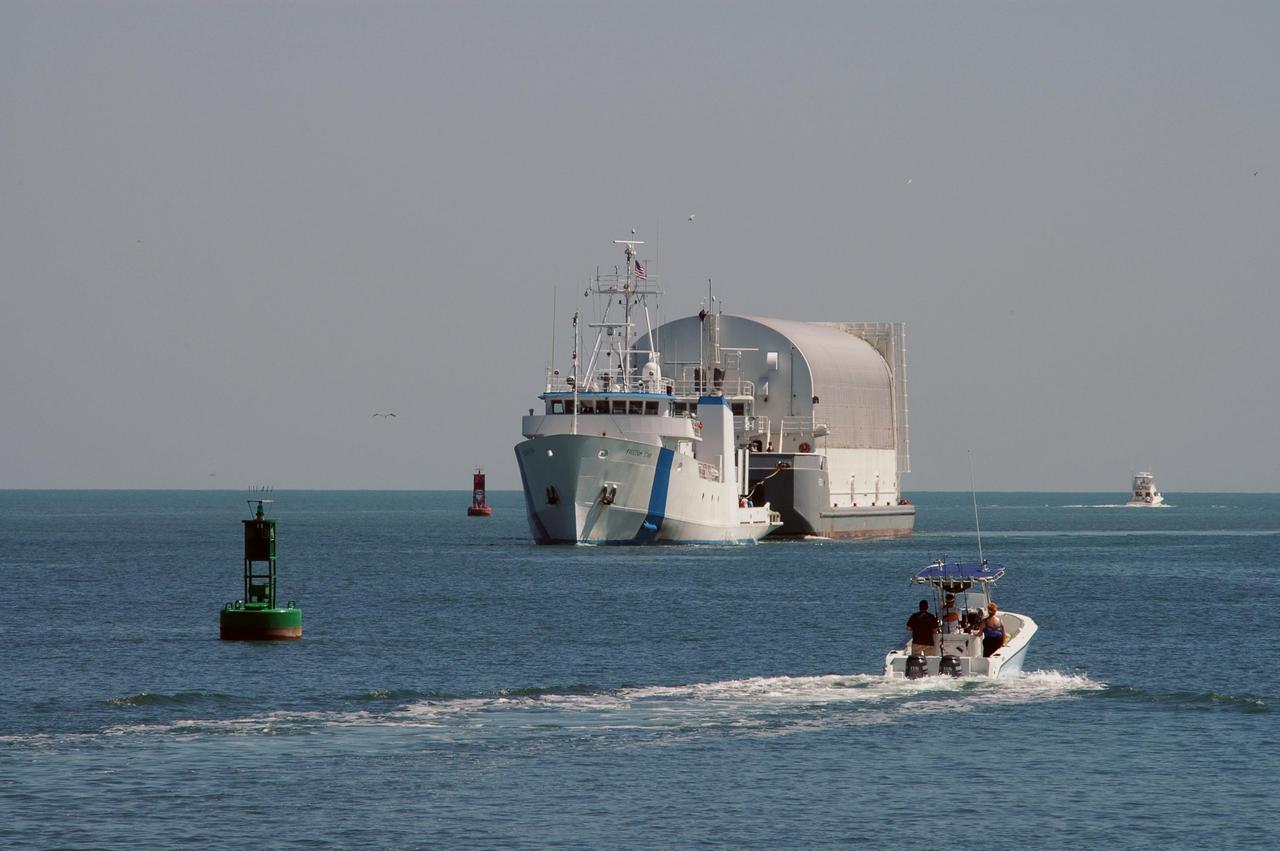

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Towed by the Freedom Star, the Pegasus barge enters Port Canaveral, the last leg of its journey from the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans to Kennedy Space Center. The barge carries the redesigned external fuel tank that will launch Space Shuttle Discovery on the next shuttle mission, STS-121. After off-loading, the tank will be moved into the Vehicle Assembly Building and lifted into a checkout cell for further work. The tank, designated ET-119, will fly with many major safety changes, including the removal of the protuberance air load ramps. A large piece of foam from a ramp came off during the last shuttle launch in July 2005. The ramps were removed to eliminate a potential source of damaging debris to the space shuttle. The next launch of Discovery is scheduled for May 2006.

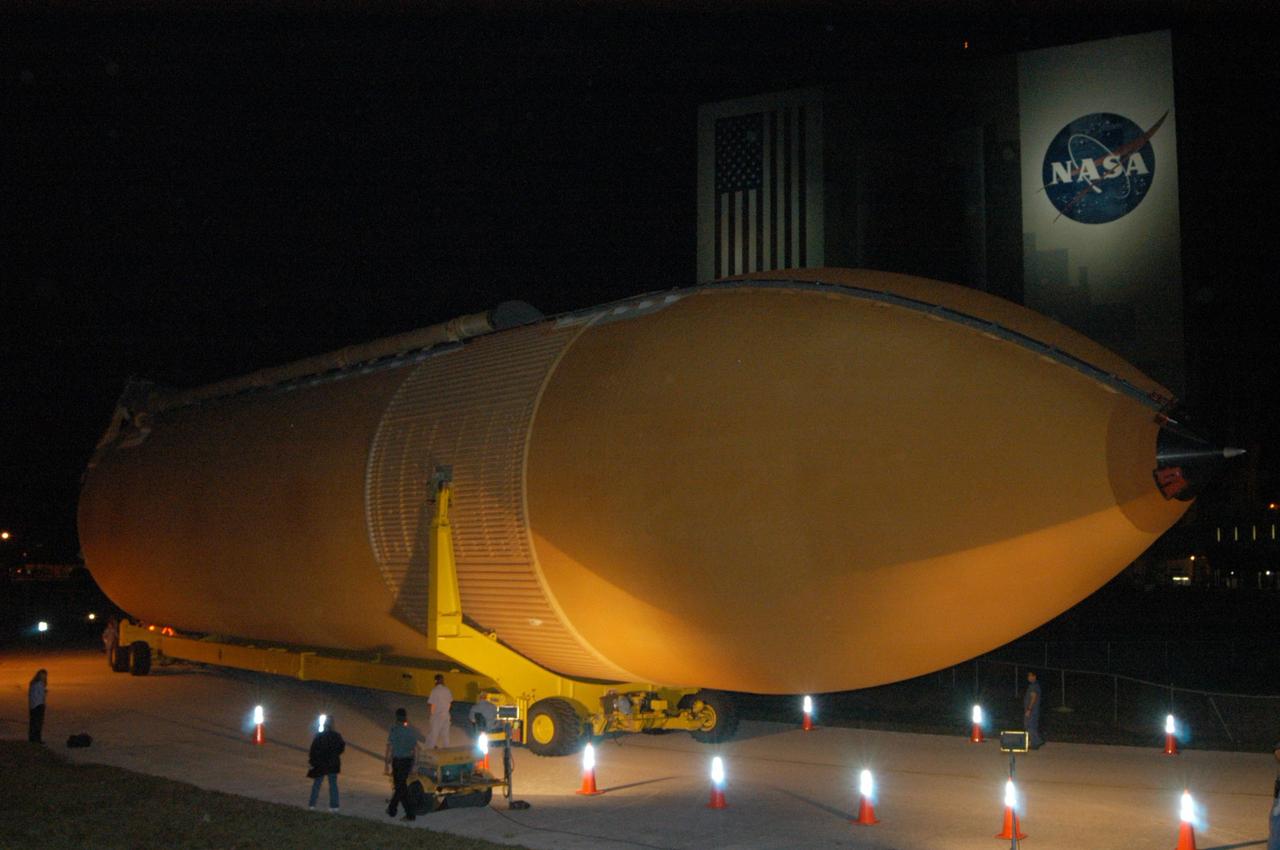
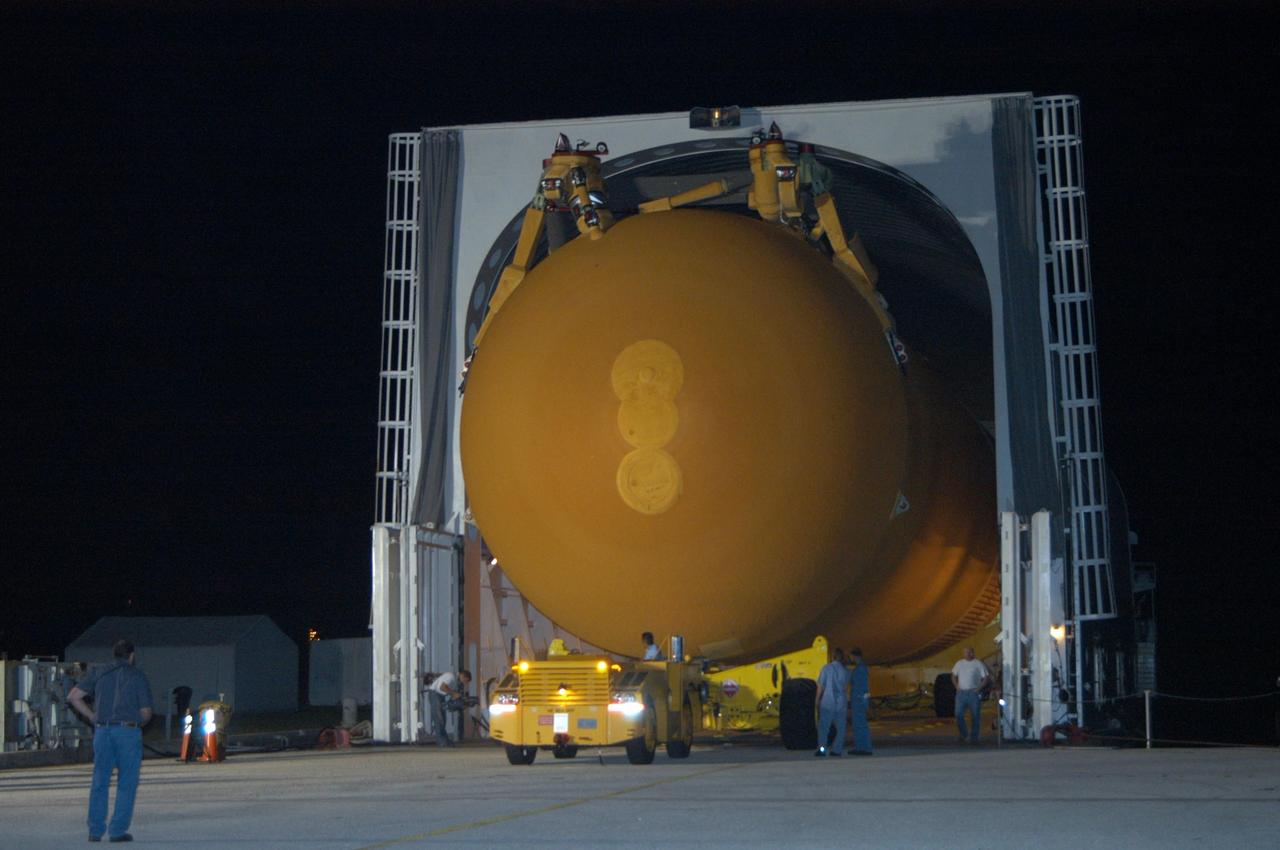
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The redesigned external fuel tank that will launch Space Shuttle Discovery on the next shuttle mission, STS-121, arrives safely in the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building. The Pegasus barge delivered the tank from the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans to NASA's Kennedy Space Center. Next, the tank will be lifted into a checkout cell for further work. The tank, designated ET-119, will fly with many major safety changes, including the removal of the protuberance air load ramps. A large piece of foam from a ramp came off during the last shuttle launch in July 2005. The ramps were removed to eliminate a potential source of damaging debris to the space shuttle. The next launch of Discovery is scheduled for May 2006.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Freedom Star tows the Pegasus barge to the entrance of Port Canaveral, the last leg of its journey from the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans to Kennedy Space Center. The barge carries the redesigned external fuel tank that will launch Space Shuttle Discovery on the next shuttle mission, STS-121. After off-loading, the tank will be moved into the Vehicle Assembly Building and lifted into a checkout cell for further work. The tank, designated ET-119, will fly with many major safety changes, including the removal of the protuberance air load ramps. A large piece of foam from a ramp came off during the last shuttle launch in July 2005. The ramps were removed to eliminate a potential source of damaging debris to the space shuttle. The next launch of Discovery is scheduled for May 2006.

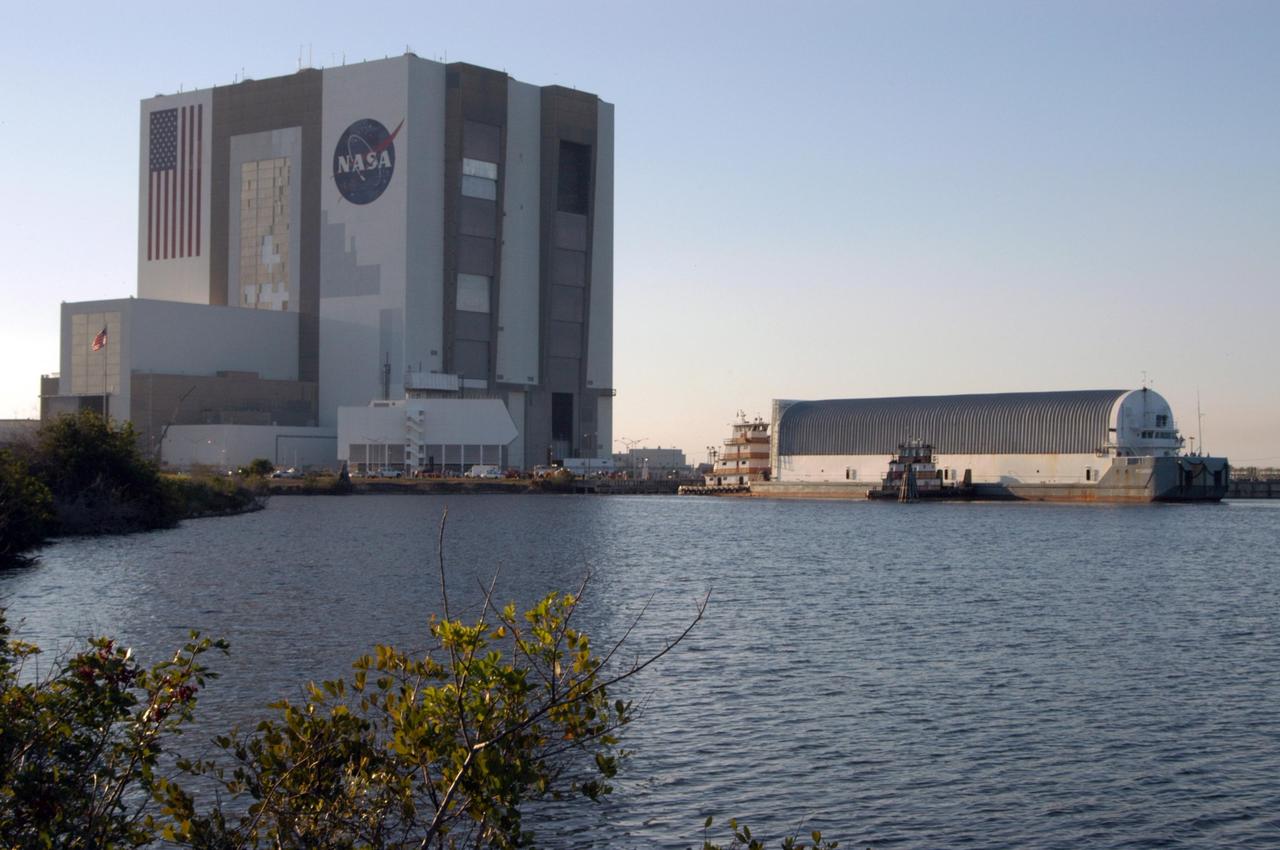
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Off-loading of the redesigned external fuel tank that will launch Space Shuttle Discovery on the next shuttle mission, STS-121, begins in the Launch Complex 39 turn basin. The Pegasus barge delivered the tank from the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans to NASA's Kennedy Space Center. After off-loading, the tank will be moved into the Vehicle Assembly Building and lifted into a checkout cell for further work. The tank, designated ET-119, will fly with many major safety changes, including the removal of the protuberance air load ramps. A large piece of foam from a ramp came off during the last shuttle launch in July 2005. The ramps were removed to eliminate a potential source of damaging debris to the space shuttle. The next launch of Discovery is scheduled for May 2006.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The redesigned external fuel tank that will launch Space Shuttle Discovery on the next shuttle mission, STS-121, is towed from the Launch Complex 39 turn basin to the Vehicle Assembly Building. The Pegasus barge delivered the tank from the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans to NASA's Kennedy Space Center. After the tank is moved into the VAB, it will be lifted into a checkout cell for further work. The tank, designated ET-119, will fly with many major safety changes, including the removal of the protuberance air load ramps. A large piece of foam from a ramp came off during the last shuttle launch in July 2005. The ramps were removed to eliminate a potential source of damaging debris to the space shuttle. The next launch of Discovery is scheduled for May 2006.

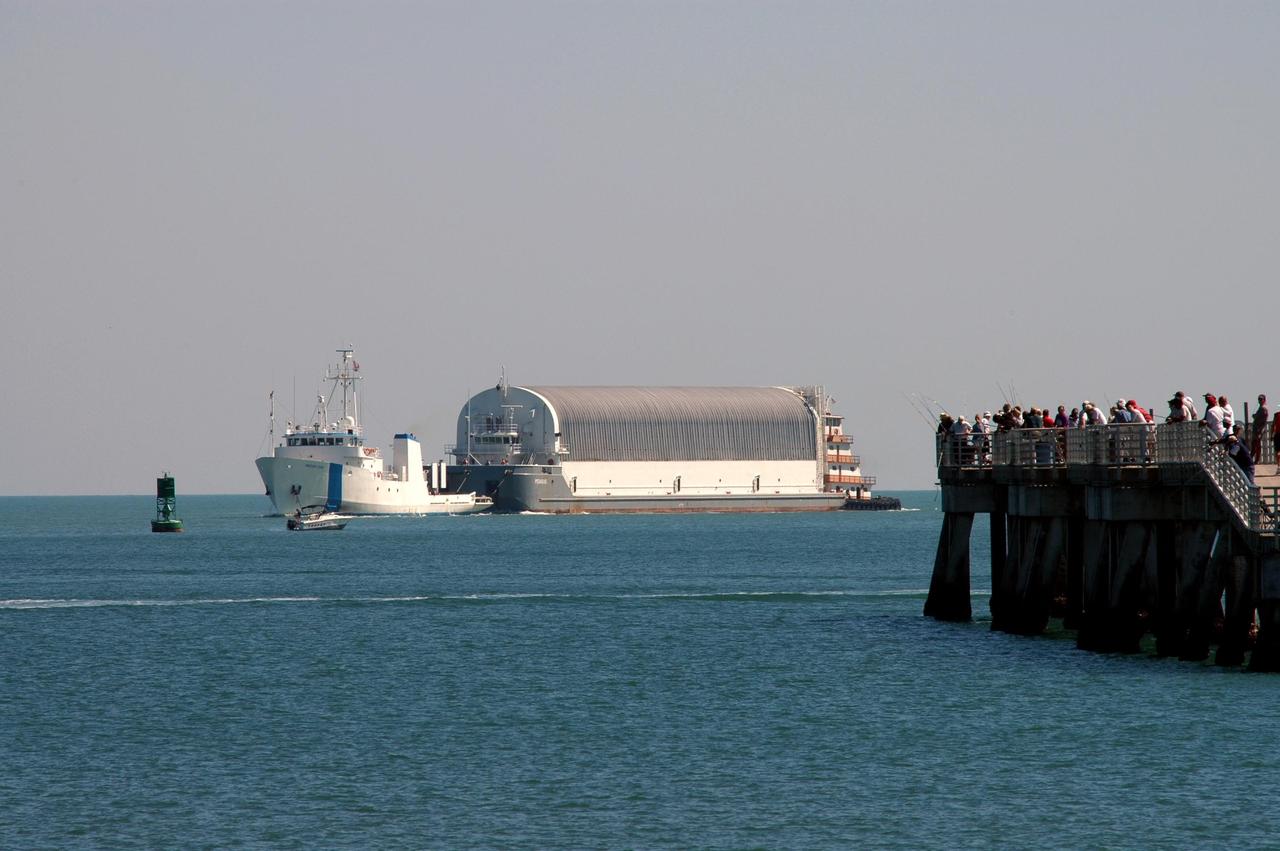
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Towed by the solid rocket booster retrieval ship Freedom Star, the Pegasus barge approaches the dock in the turn basin near the Vehicle Assembly Building. The barge is on the last leg of its journey from the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans to NASA's Kennedy Space Center. The barge carries the redesigned external fuel tank that will launch Space Shuttle Discovery on the next shuttle mission, STS-121. After off-loading, the tank will be moved into the Vehicle Assembly Building and lifted into a checkout cell for further work. The tank, designated ET-119, will fly with many major safety changes, including the removal of the protuberance air load ramps. A large piece of foam from a ramp came off during the last shuttle launch in July 2005. The ramps were removed to eliminate a potential source of damaging debris to the space shuttle. The next launch of Discovery is scheduled for May 2006.
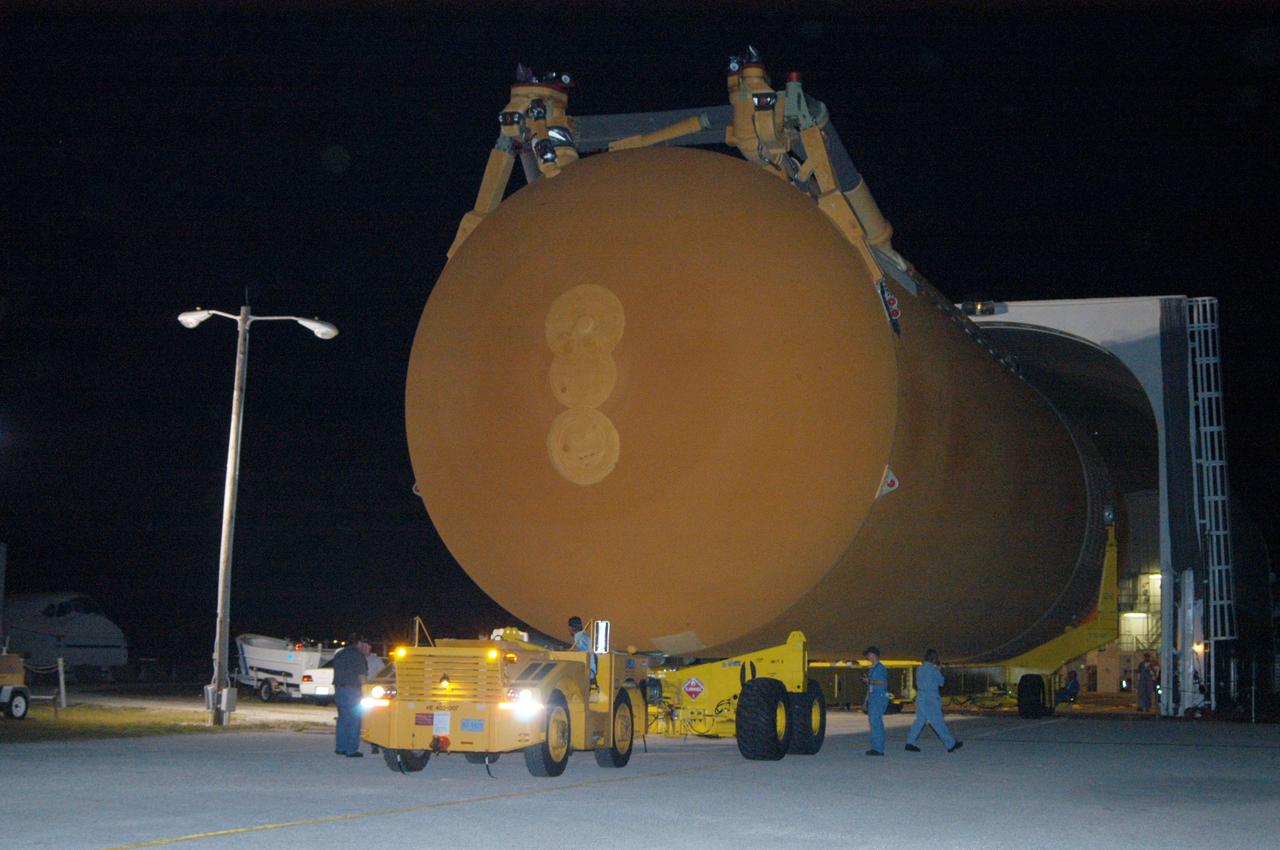

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A tow vehicle is connected to the transporter supporting the redesigned external fuel tank that will launch Space Shuttle Discovery on the next shuttle mission, STS-121. The Pegasus barge delivered the tank from the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans to NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Complex 39 turn basin. After off-loading, the tank will be moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building and lifted into a checkout cell for further work. The tank, designated ET-119, will fly with many major safety changes, including the removal of the protuberance air load ramps. A large piece of foam from a ramp came off during the last shuttle launch in July 2005. The ramps were removed to eliminate a potential source of damaging debris to the space shuttle. The next launch of Discovery is scheduled for May 2006.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Pegasus barge makes its way through Port Canaveral, the last leg of its journey from the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans to Kennedy Space Center. The barge carries the redesigned external fuel tank that will launch Space Shuttle Discovery on the next shuttle mission, STS-121. After off-loading, the tank will be moved into the Vehicle Assembly Building and lifted into a checkout cell for further work. The tank, designated ET-119, will fly with many major safety changes, including the removal of the protuberance air load ramps. A large piece of foam from a ramp came off during the last shuttle launch in July 2005. The ramps were removed to eliminate a potential source of damaging debris to the space shuttle. The next launch of Discovery is scheduled for May 2006.
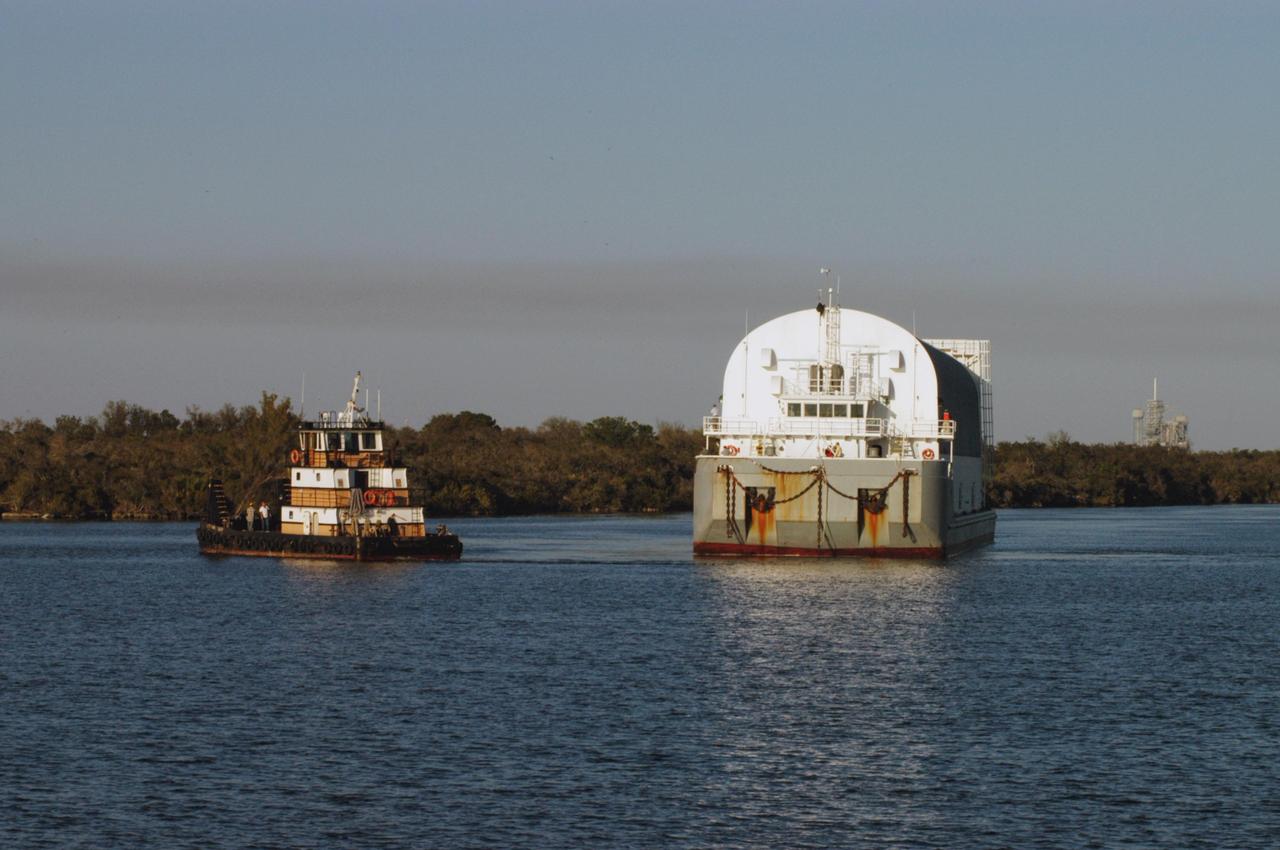

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - One of the two space shuttle launch pads in Launch Complex 39 is visible behind the Pegasus barge as it traverses the turn basin near the Vehicle Assembly Building. The barge is on the last leg of its journey from the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans to NASA's Kennedy Space Center. The barge carries the redesigned external fuel tank that will launch Space Shuttle Discovery on the next shuttle mission, STS-121. After off-loading, the tank will be moved into the Vehicle Assembly Building and lifted into a checkout cell for further work. The tank, designated ET-119, will fly with many major safety changes, including the removal of the protuberance air load ramps. A large piece of foam from a ramp came off during the last shuttle launch in July 2005. The ramps were removed to eliminate a potential source of damaging debris to the space shuttle. The next launch of Discovery is scheduled for May 2006.

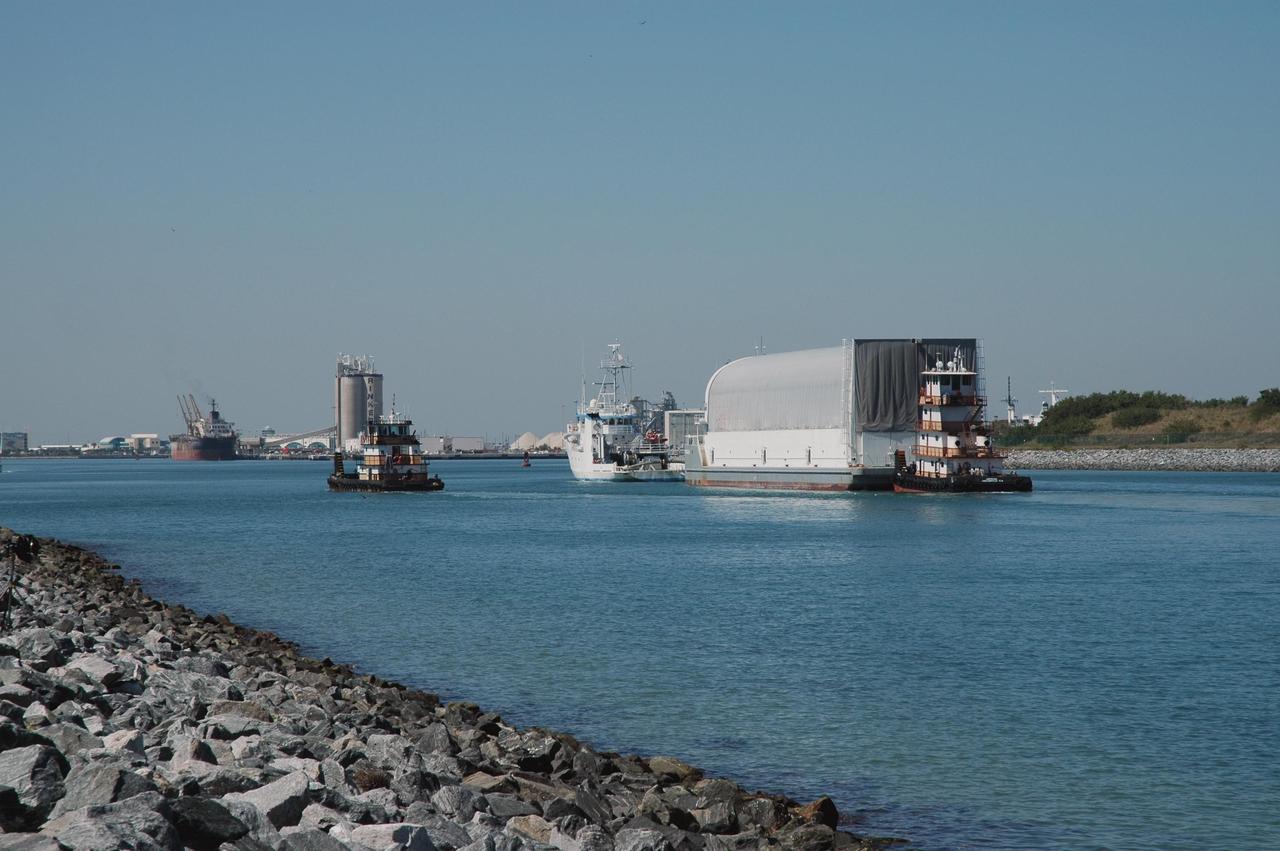
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Pegasus barge is docked in the turn basin close by the Vehicle Assembly Building. The barge delivered the redesigned external fuel tank that will launch Space Shuttle Discovery on the next shuttle mission, STS-121, from the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans to NASA's Kennedy Space Center. After off-loading, the tank will be moved into the Vehicle Assembly Building and lifted into a checkout cell for further work. The tank, designated ET-119, will fly with many major safety changes, including the removal of the protuberance air load ramps. A large piece of foam from a ramp came off during the last shuttle launch in July 2005. The ramps were removed to eliminate a potential source of damaging debris to the space shuttle. The next launch of Discovery is scheduled for May 2006.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Freedom Star tows the Pegasus barge through Port Canaveral, the last leg of its journey from the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans to Kennedy Space Center. The barge carries the redesigned external fuel tank that will launch Space Shuttle Discovery on the next shuttle mission, STS-121. After off-loading, the tank will be moved into the Vehicle Assembly Building and lifted into a checkout cell for further work. The tank, designated ET-119, will fly with many major safety changes, including the removal of the protuberance air load ramps. A large piece of foam from a ramp came off during the last shuttle launch in July 2005. The ramps were removed to eliminate a potential source of damaging debris to the space shuttle. The next launch of Discovery is scheduled for May 2006.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Lights around Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida bathe space shuttle Discovery on Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida after rollback of the rotating service structure. The orbiter access arm and White Room are extended toward Discovery. The White Room provides crew access into the shuttle. Above the external tank is the oxygen vent hood, called the "beanie cap." The rollback is in preparation for Discovery's liftoff on the STS-119 mission with a crew of seven. The rotating structure provides protected access to the shuttle for changeout and servicing of payloads at the pad. After the RSS is rolled back, the orbiter is ready for fuel cell activation and external tank cryogenic propellant loading operations. The mission is the 28th to the International Space Station and the 125th space shuttle flight. Discovery will deliver the final pair of power-generating solar array wings and the S6 truss segment. Installation of S6 will signal the station's readiness to house a six-member crew for conducting increased science. Liftoff of Discovery is scheduled for 9:20 p.m. EDT on March 11. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
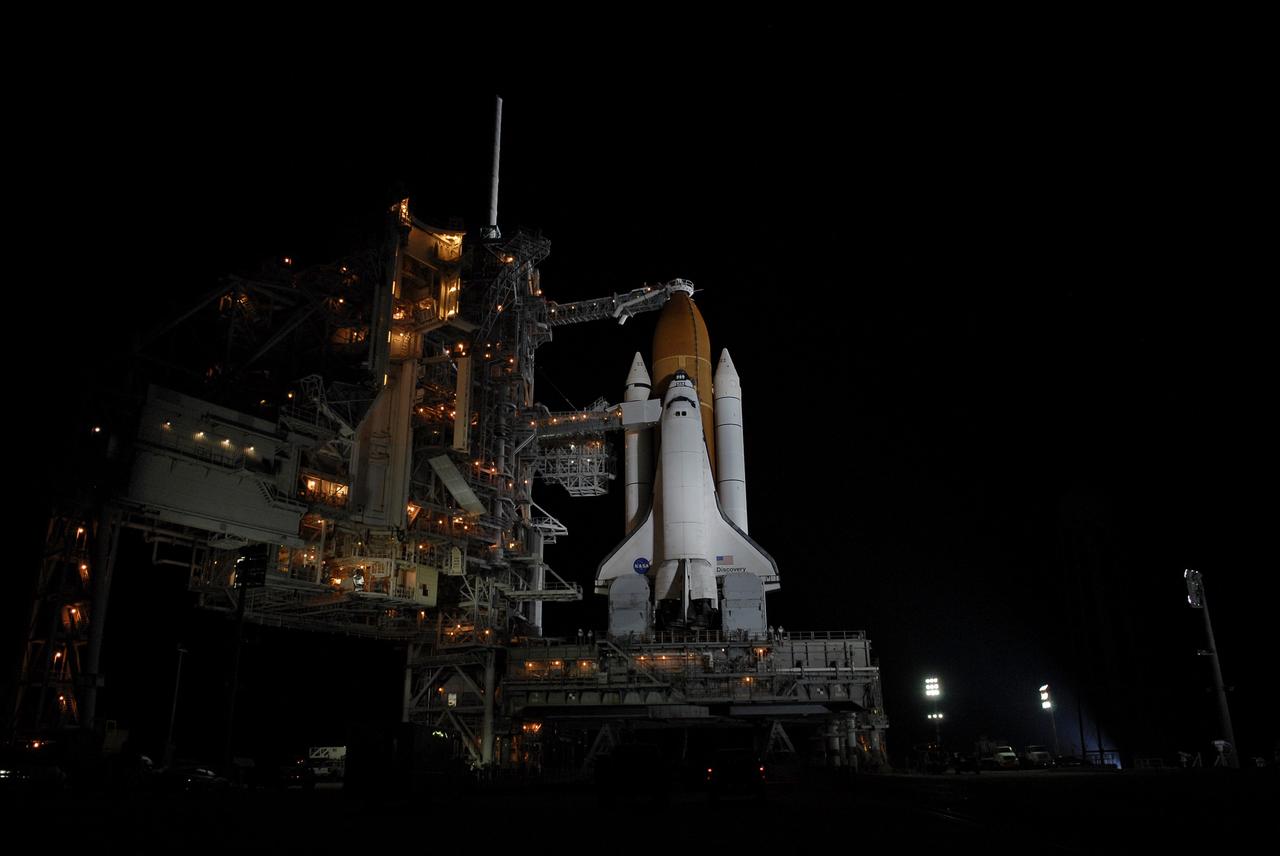

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Lights bathe space shuttle Discovery on Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida after rollback of the rotating service structure. The orbiter access arm and White Room are extended toward Discovery. The White Room provides crew access into the shuttle. Above the external tank is the oxygen vent hood, called the "beanie cap." The rollback is in preparation for Discovery's liftoff on the STS-119 mission with a crew of seven. The rotating structure provides protected access to the shuttle for changeout and servicing of payloads at the pad. After the RSS is rolled back, the orbiter is ready for fuel cell activation and external tank cryogenic propellant loading operations. The mission is the 28th to the International Space Station and the 125th space shuttle flight. Discovery will deliver the final pair of power-generating solar array wings and the S6 truss segment. Installation of S6 will signal the station's readiness to house a six-member crew for conducting increased science. Liftoff of Discovery is scheduled for 9:20 p.m. EDT on March 11. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
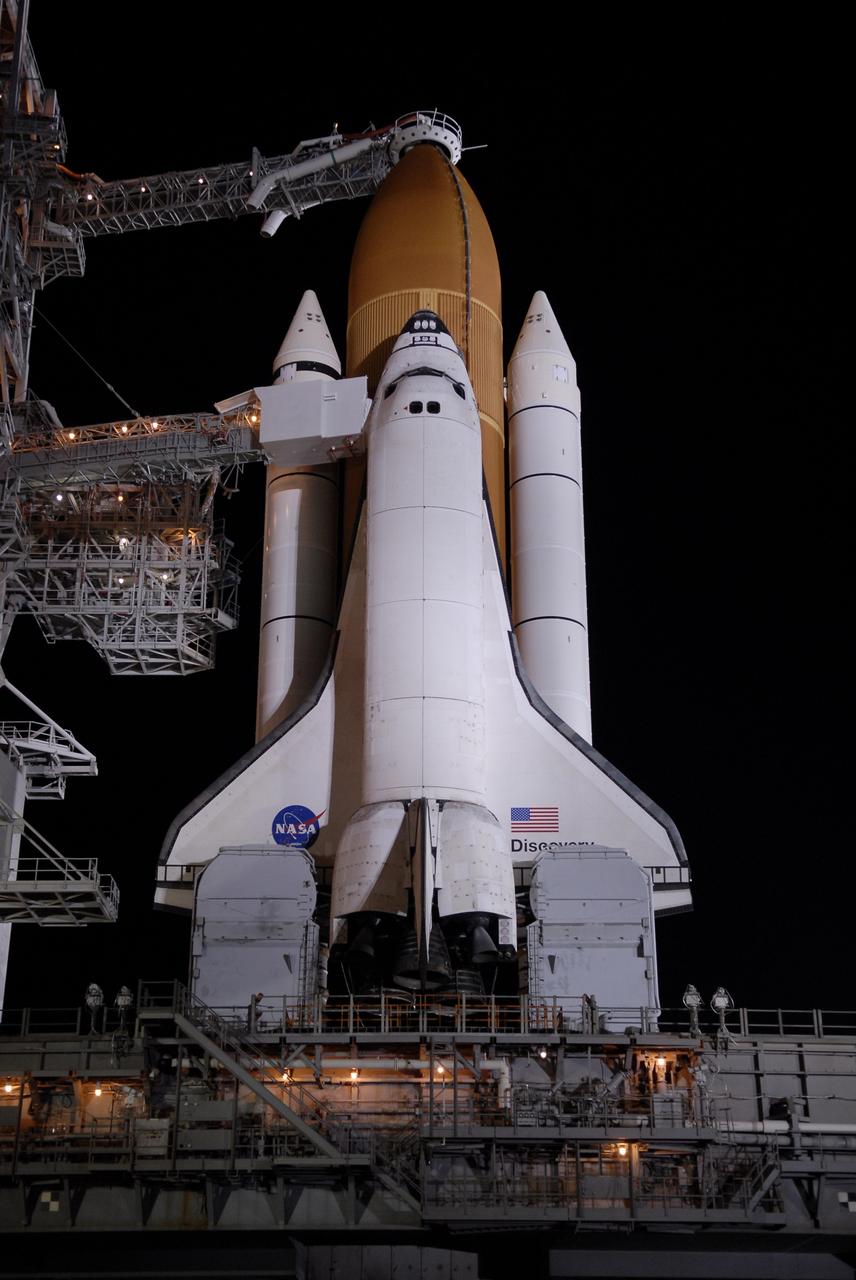

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the orbiter access arm and White Room are extended toward space shuttle Discovery after rollback of the rotating service structure. The White Room provides crew access into the shuttle. Above the external tank is the oxygen vent hood, called the "beanie cap." The rollback is in preparation for Discovery's liftoff on the STS-119 mission with a crew of seven. The rotating structure provides protected access to the shuttle for changeout and servicing of payloads at the pad. After the RSS is rolled back, the orbiter is ready for fuel cell activation and external tank cryogenic propellant loading operations. The mission is the 28th to the International Space Station and the 125th space shuttle flight. Discovery will deliver the final pair of power-generating solar array wings and the S6 truss segment. Installation of S6 will signal the station's readiness to house a six-member crew for conducting increased science. Liftoff of Discovery is scheduled for 9:20 p.m. EDT on March 11. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
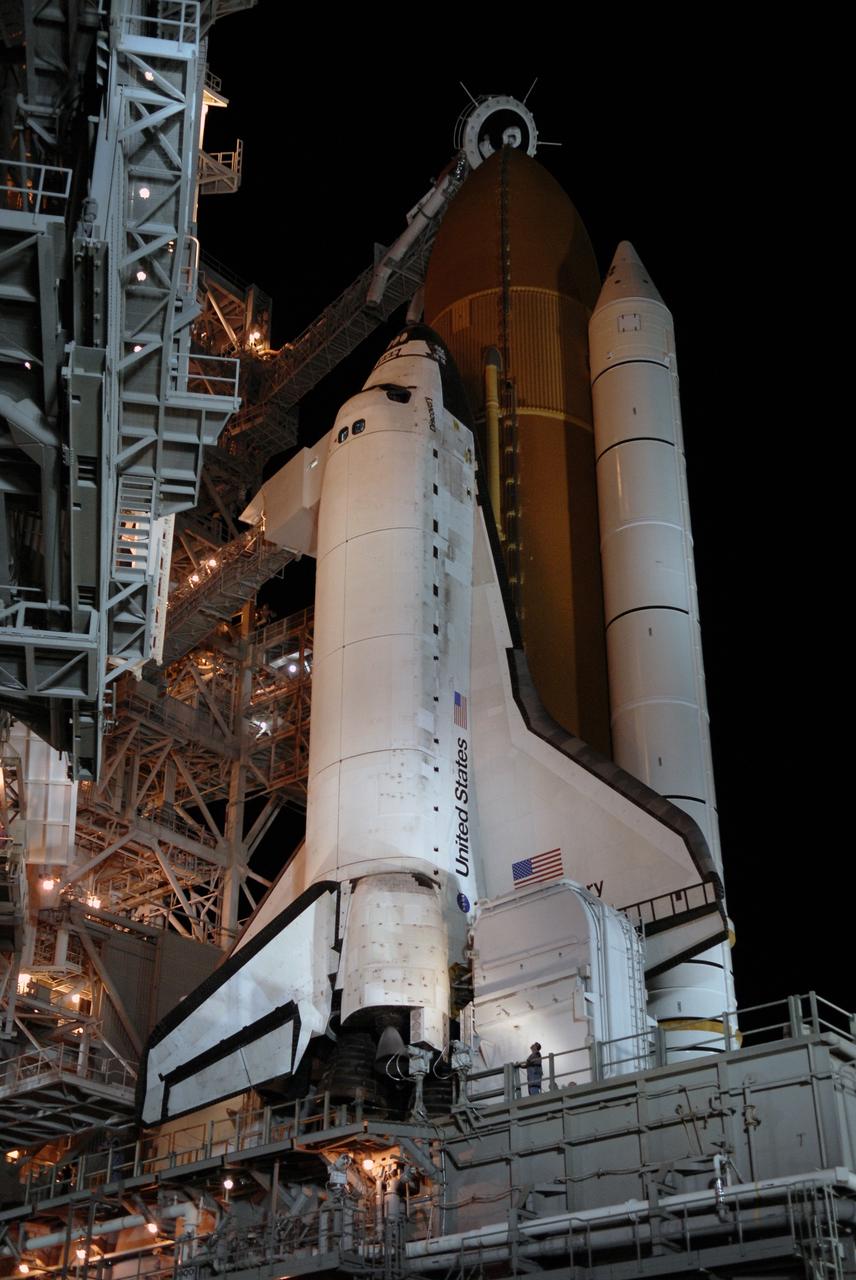

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the orbiter access arm and White Room are extended toward space shuttle Discovery after rollback of the rotating service structure. Above the external tank is the oxygen vent hood, called the "beanie cap." The rollback is in preparation for Discovery's liftoff on the STS-119 mission with a crew of seven. The rotating structure provides protected access to the shuttle for changeout and servicing of payloads at the pad. After the RSS is rolled back, the orbiter is ready for fuel cell activation and external tank cryogenic propellant loading operations. The mission is the 28th to the International Space Station and the 125th space shuttle flight. Discovery will deliver the final pair of power-generating solar array wings and the S6 truss segment. Installation of S6 will signal the station's readiness to house a six-member crew for conducting increased science. Liftoff of Discovery is scheduled for 9:20 p.m. EDT on March 11. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
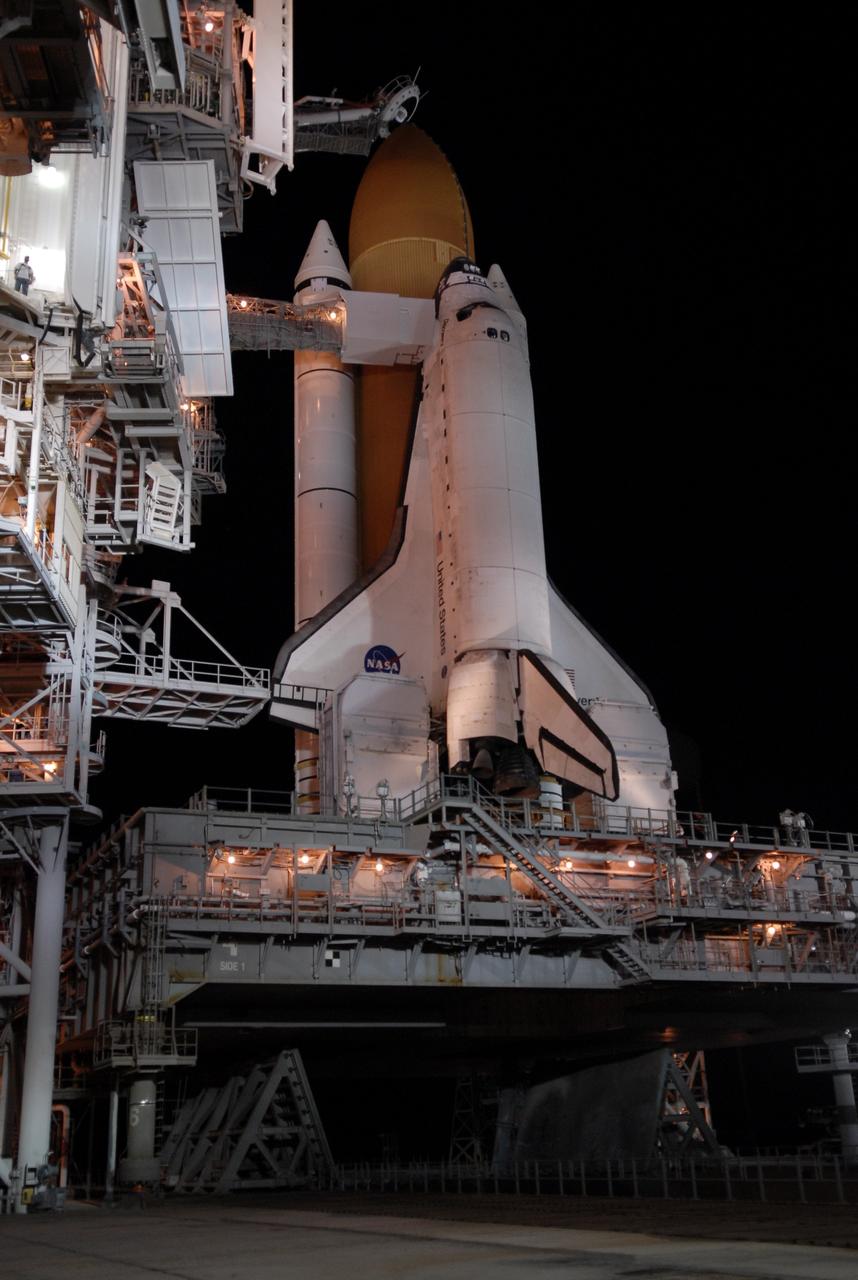

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the orbiter access arm and White Room are extended toward space shuttle Discovery after rollback of the rotating service structure. The White Room provides crew access into the shuttle. Above the external tank is the oxygen vent hood, called the "beanie cap." The rollback is in preparation for Discovery's liftoff on the STS-119 mission with a crew of seven. The rotating structure provides protected access to the shuttle for changeout and servicing of payloads at the pad. After the RSS is rolled back, the orbiter is ready for fuel cell activation and external tank cryogenic propellant loading operations. The mission is the 28th to the International Space Station and the 125th space shuttle flight. Discovery will deliver the final pair of power-generating solar array wings and the S6 truss segment. Installation of S6 will signal the station's readiness to house a six-member crew for conducting increased science. Liftoff of Discovery is scheduled for 9:20 p.m. EDT on March 11. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
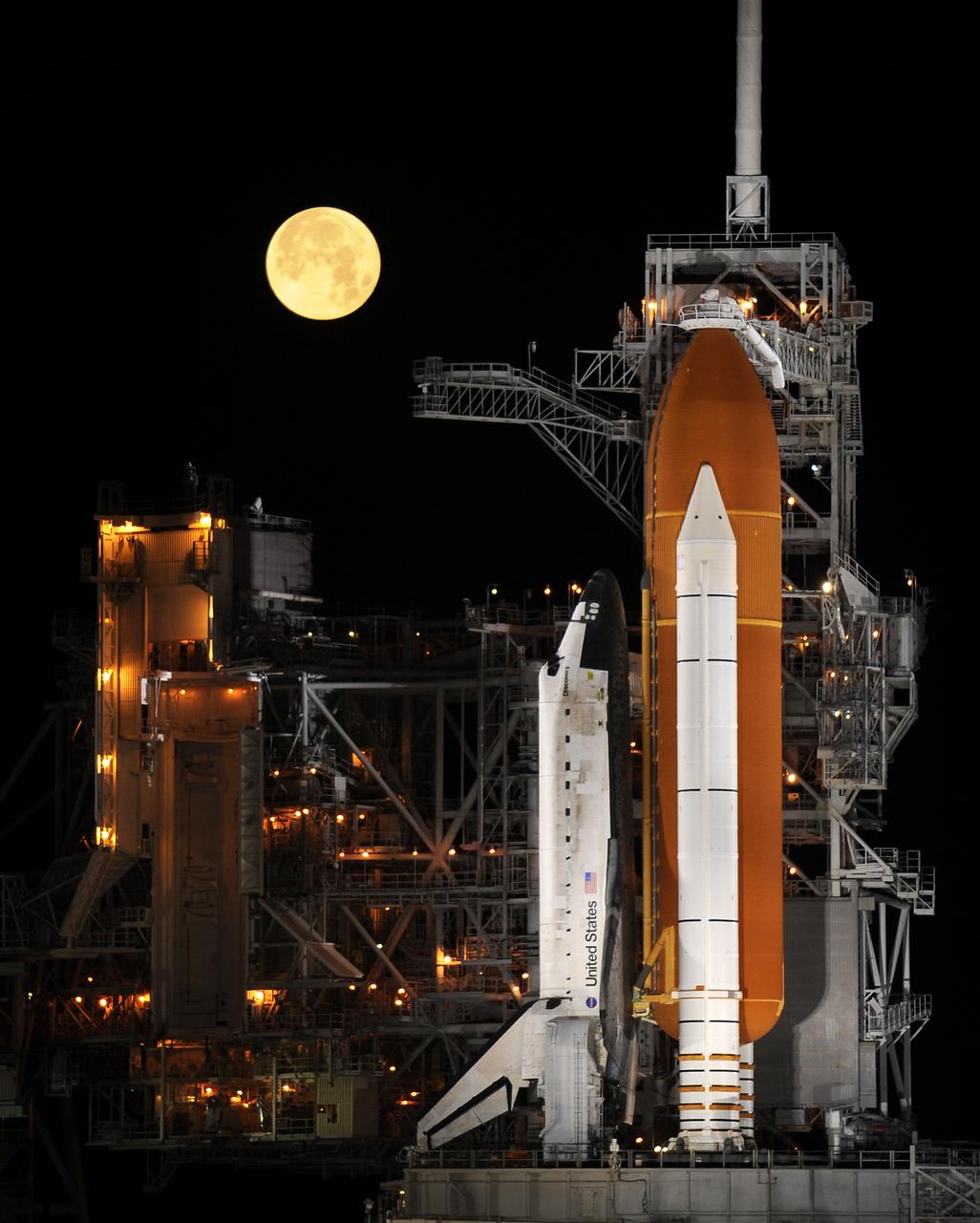

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Under a full moon on Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, space shuttle Discovery is revealed after the rotating service structure has been rolled back. The rollback is in preparation for Discovery's liftoff on the STS-119 mission with a crew of seven. The rotating structure provides protected access to the shuttle for changeout and servicing of payloads at the pad. It is supported by a rotating bridge that pivots on a vertical axis on the west side of the pad's flame trench. After the RSS is rolled back, the orbiter is ready for fuel cell activation and external tank cryogenic propellant loading operations. The mission is the 28th to the International Space Station and the 125th space shuttle flight. Discovery will deliver the final pair of power-generating solar array wings and the S6 truss segment. Installation of S6 will signal the station's readiness to house a six-member crew for conducting increased science. Liftoff of Discovery is scheduled for 9:20 p.m. EDT on March 11. Photo courtesy of NASA/Bill Ingalls
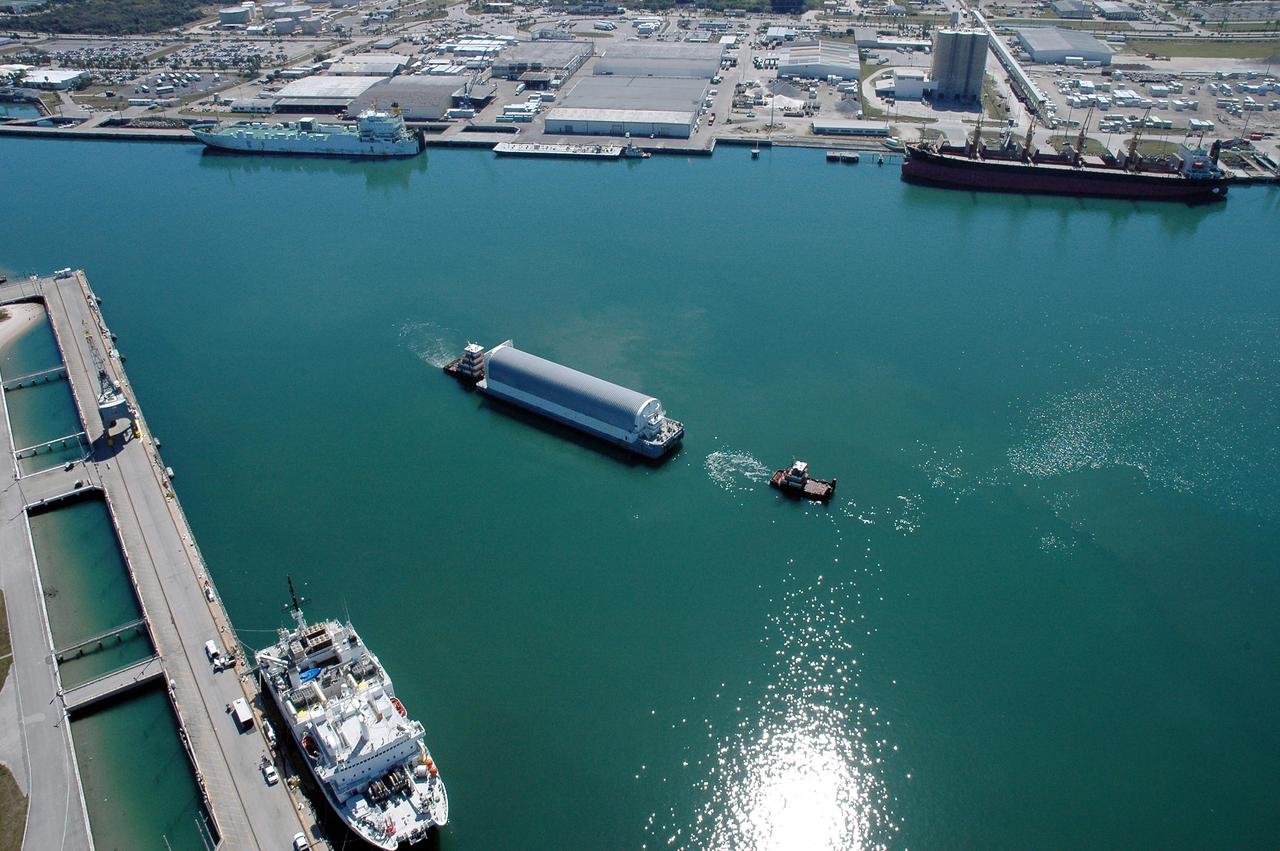

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Pegasus barge, towed by the solid rocket booster retrieval ship Freedom Star to Port Canaveral from the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, waits for a tug boat to finish the trip to the turn basin near NASA Kennedy Space Center's Vehicle Assembly Building. The barge carries the redesigned external fuel tank that will launch the Space Shuttle Discovery on the next shuttle mission, STS-121. After off-loading, the tank will be moved into the Vehicle Assembly Building and lifted into a checkout cell for further work. The tank, designated ET-119, will fly with many major safety changes, including the removal of the protuberance air load ramps. A large piece of foam from one of the ramps came off during the July 2005 launch of the last shuttle mission. The ramps were removed to help eliminate a potential source of damaging debris to the space shuttle. Launch of Discovery is scheduled for May 2006. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
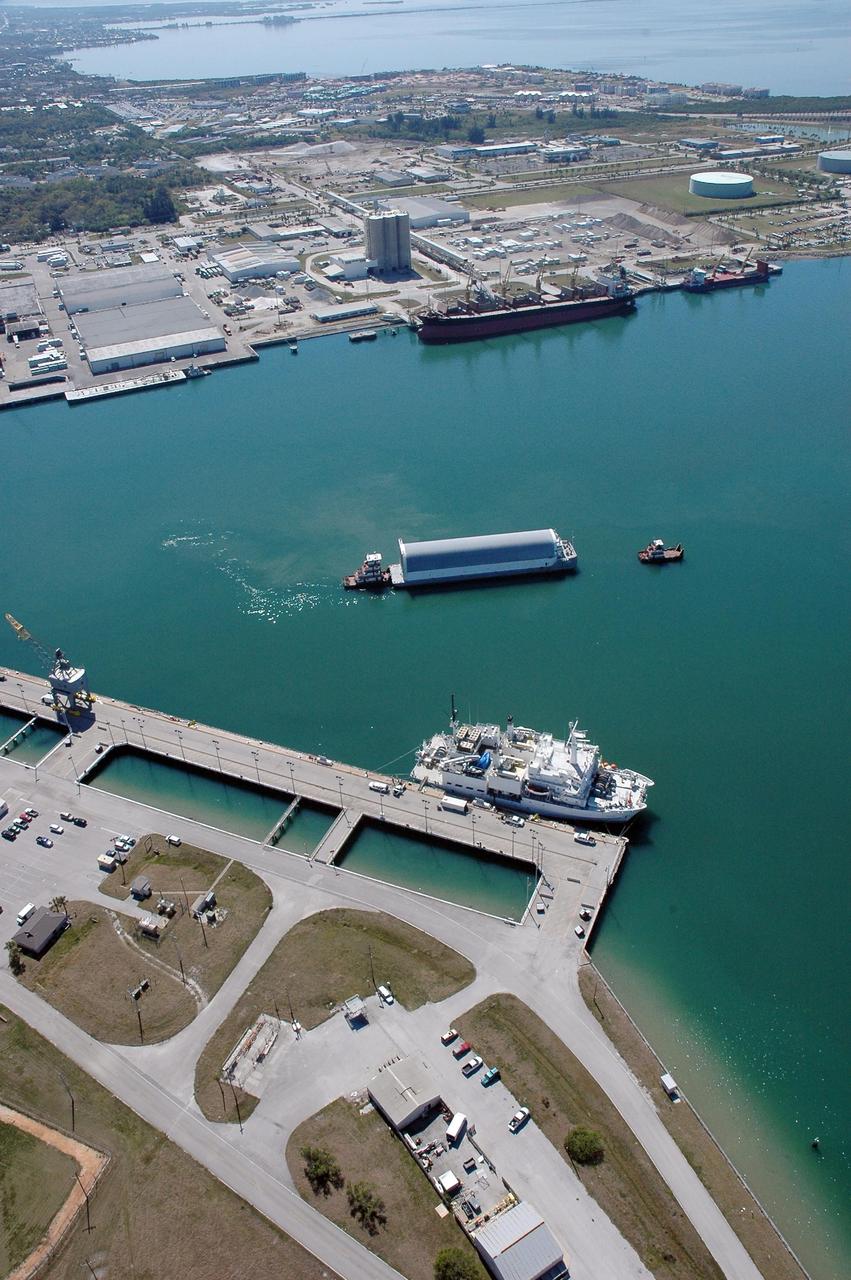

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Pegasus barge, towed by the solid rocket booster retrieval ship Freedom Star to Port Canaveral from the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, waits for a tug boat to finish the trip to the turn basin near NASA Kennedy Space Center's Vehicle Assembly Building. The barge carries the redesigned external fuel tank that will launch the Space Shuttle Discovery on the next shuttle mission, STS-121. After off-loading, the tank will be moved into the Vehicle Assembly Building and lifted into a checkout cell for further work. The tank, designated ET-119, will fly with many major safety changes, including the removal of the protuberance air load ramps. A large piece of foam from one of the ramps came off during the July 2005 launch of the last shuttle mission. The ramps were removed to help eliminate a potential source of damaging debris to the space shuttle. Launch of Discovery is scheduled for May 2006. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
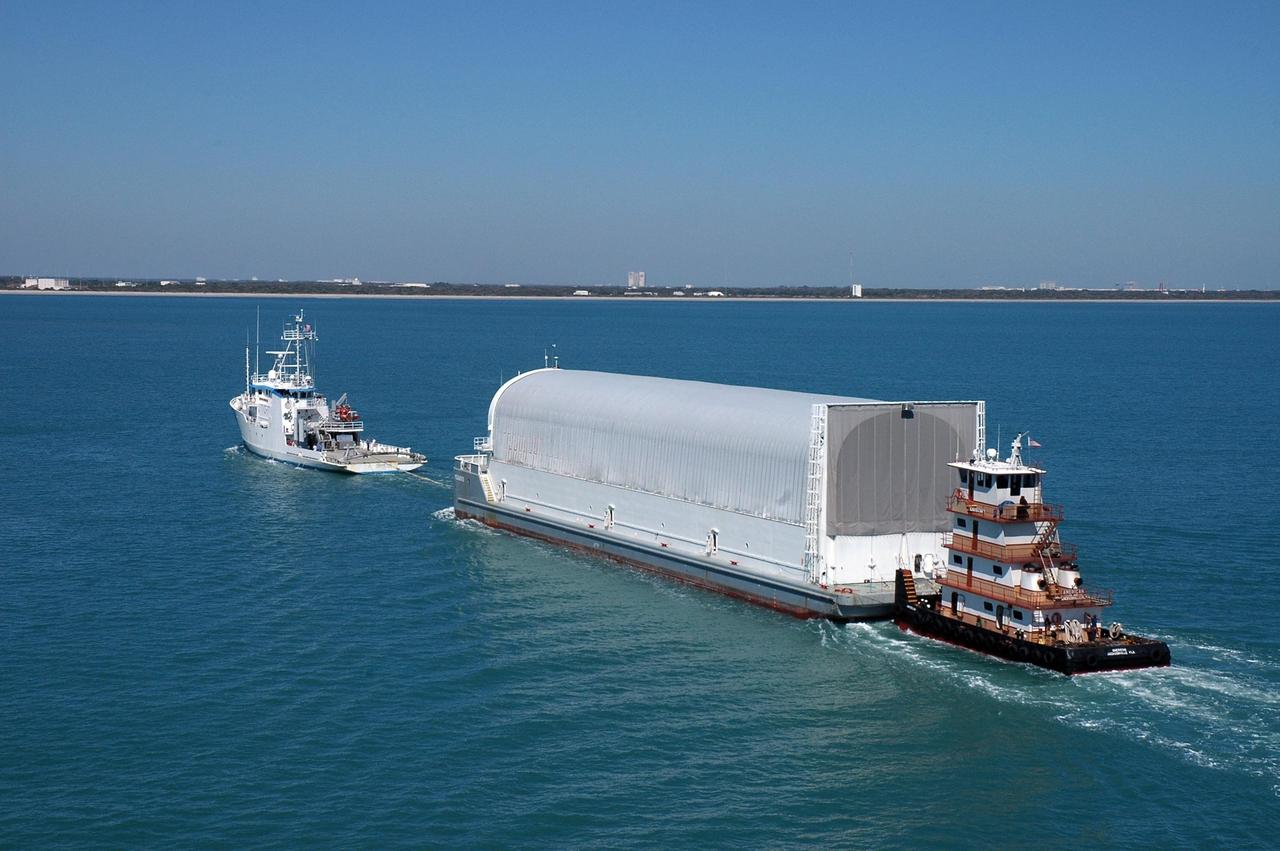

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Pegasus barge, towed by the solid rocket booster retrieval ship Freedom Star, approaches Port Canaveral. The barge carries the redesigned external fuel tank that will launch the Space Shuttle Discovery on the next shuttle mission, STS-121. It left the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans Feb. 25, making the voyage around the Florida Peninsula in five days. Next stop for the barge is the turn basin near NASA Kennedy Space Center's Vehicle Assembly Building. After off-loading, the tank will be moved into the Vehicle Assembly Building and lifted into a checkout cell for further work. The tank, designated ET-119, will fly with many major safety changes, including the removal of the protuberance air load ramps. A large piece of foam from one of the ramps came off during the July 2005 launch of the last shuttle mission. The ramps were removed to help eliminate a potential source of damaging debris to the space shuttle. Launch of Discovery is scheduled for May 2006. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
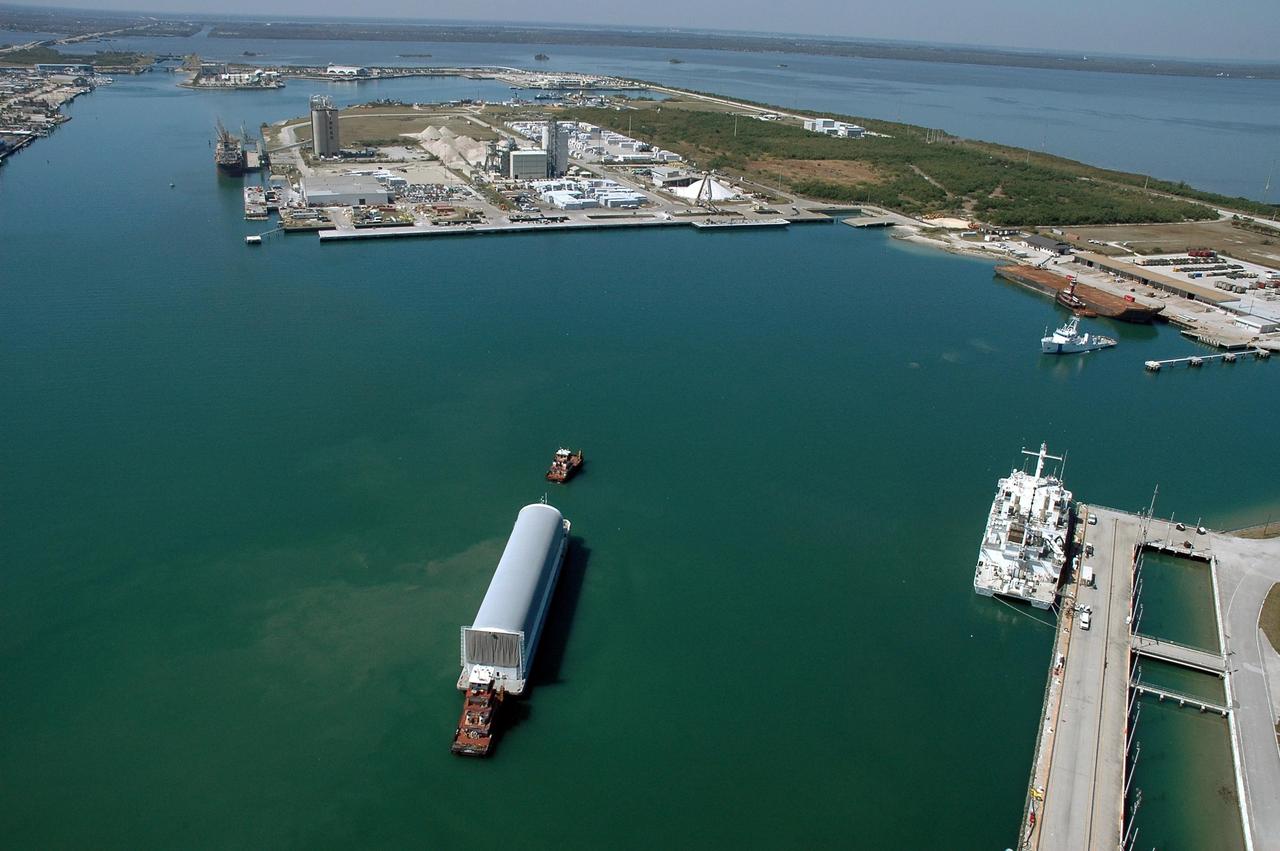

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Pegasus barge, towed by the solid rocket booster retrieval ship Freedom Star to Port Canaveral from the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, waits for a tug boat to finish the trip to the turn basin near NASA Kennedy Space Center's Vehicle Assembly Building. The barge carries the redesigned external fuel tank that will launch the Space Shuttle Discovery on the next shuttle mission, STS-121. After off-loading, the tank will be moved into the Vehicle Assembly Building and lifted into a checkout cell for further work. The tank, designated ET-119, will fly with many major safety changes, including the removal of the protuberance air load ramps. A large piece of foam from one of the ramps came off during the July 2005 launch of the last shuttle mission. The ramps were removed to help eliminate a potential source of damaging debris to the space shuttle. Launch of Discovery is scheduled for May 2006. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
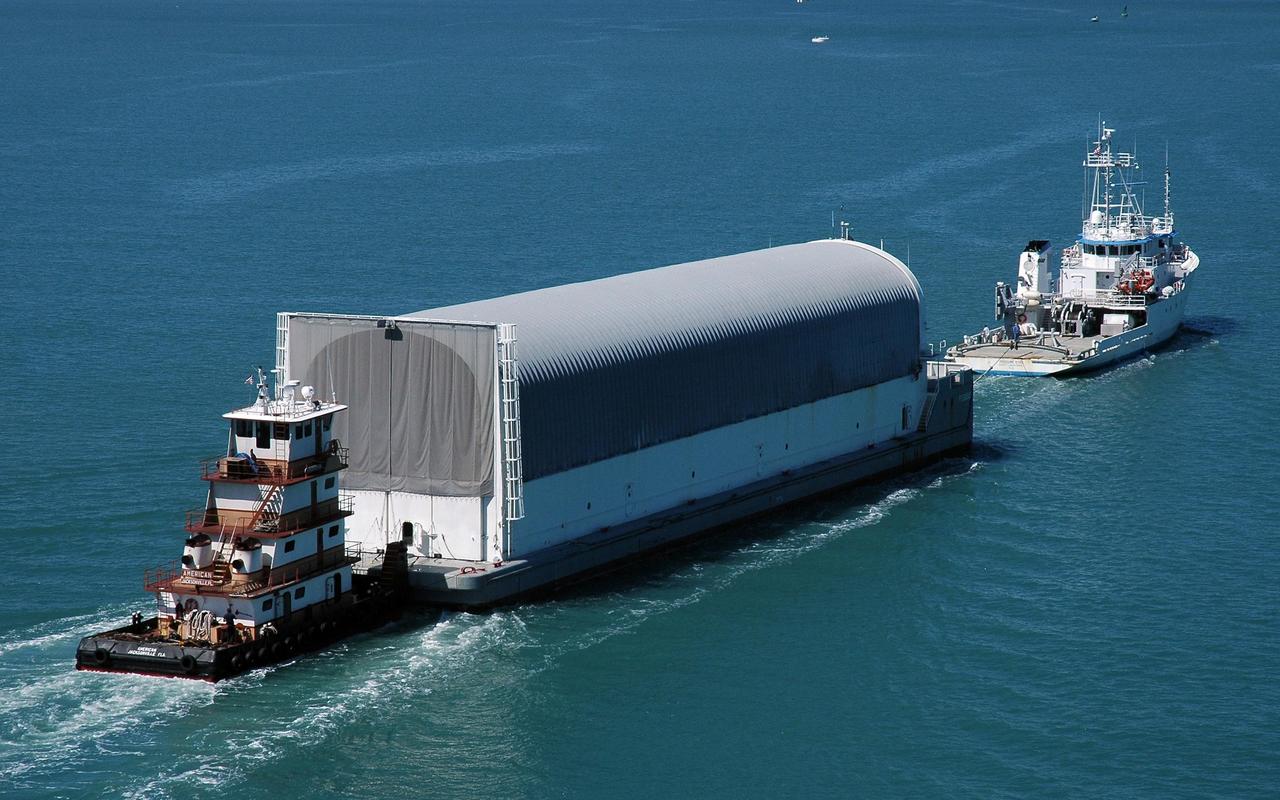

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Pegasus barge, towed by the solid rocket booster retrieval ship Freedom Star, approaches Port Canaveral. The barge carries the redesigned external fuel tank that will launch the Space Shuttle Discovery on the next shuttle mission, STS-121. It left the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans Feb. 25, making the voyage around the Florida Peninsula in five days. Next stop for the barge is the turn basin near NASA Kennedy Space Center's Vehicle Assembly Building. After off-loading, the tank will be moved into the Vehicle Assembly Building and lifted into a checkout cell for further work. The tank, designated ET-119, will fly with many major safety changes, including the removal of the protuberance air load ramps. A large piece of foam from one of the ramps came off during the July 2005 launch of the last shuttle mission. The ramps were removed to help eliminate a potential source of damaging debris to the space shuttle. Launch of Discovery is scheduled for May 2006. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
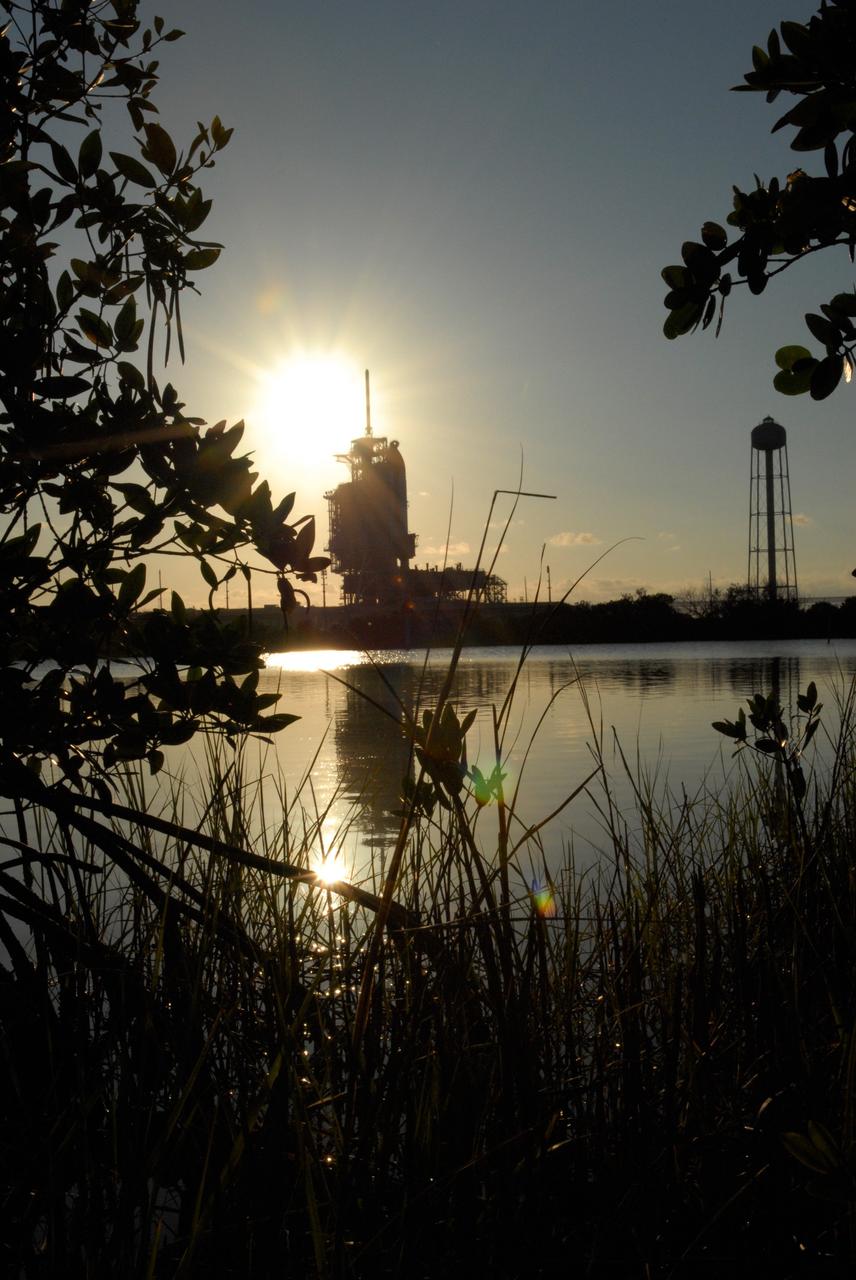

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The setting sun backlights space shuttle Discovery on Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center just before rollback of the rotating service structure in preparation for launch on the STS-124 mission. The structure provides protected access to the shuttle for changeout and servicing of payloads at the pad. It is supported by a rotating bridge that pivots on a vertical axis on the west side of the pad's flame trench. After the RSS is rolled back, the orbiter is ready for fuel cell activation and external tank cryogenic propellant loading operations. The pad is cleared to the perimeter gate for operations to fill the external tank with about 500,000 gallons of cryogenic propellants used by the shuttle’s main engines. This is done at the pad approximately eight hours before the scheduled launch. The STS-124 mission is the second of three flights launching components to complete the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Kibo laboratory. The shuttle crew will install Kibo's large Japanese Pressurized Module and its remote manipulator system, or RMS. The 14-day flight includes three spacewalks. Launch is scheduled for 5:02 p.m. May 31. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
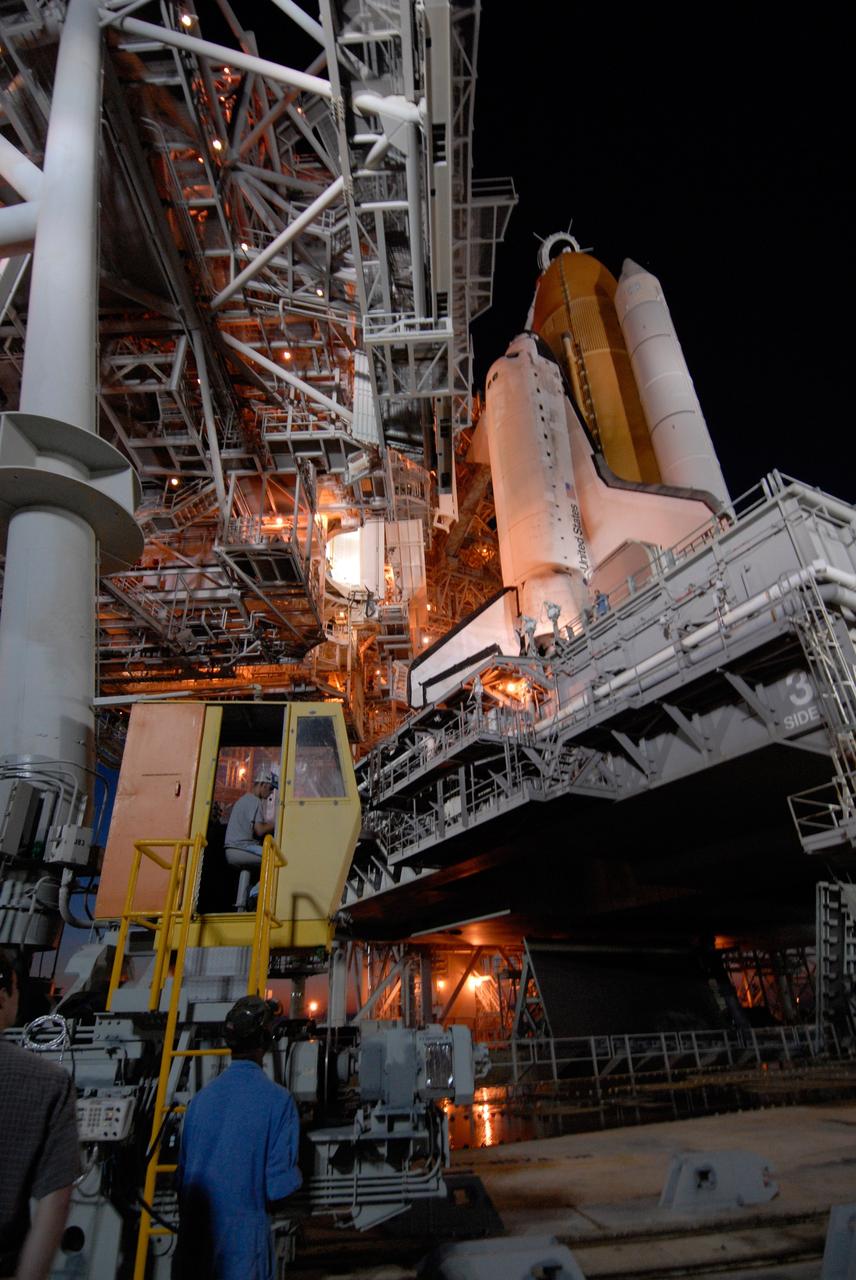

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- On Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the rotating service structure begins rolling on its axis to uncover space shuttle Discovery in preparation for launch on the STS-124 mission. Support for the outer end of the bridge is provided by two eight-wheel, motor-driven trucks (one is seen at bottom left) that move along circular twin rails installed flush with the pad surface. First motion was at 8:33 p.m. and rollback was complete at 9:07 p.m. The structure provides protected access to the shuttle for changeout and servicing of payloads at the pad. It is supported by a rotating bridge that pivots on a vertical axis on the west side of the pad's flame trench. After the RSS is rolled back, the orbiter is ready for fuel cell activation and external tank cryogenic propellant loading operations. The pad is cleared to the perimeter gate for operations to fill the external tank with about 500,000 gallons of cryogenic propellants used by the shuttle’s main engines. This is done at the pad approximately eight hours before the scheduled launch. The STS-124 mission is the second of three flights launching components to complete the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Kibo laboratory. The shuttle crew will install Kibo's large Japanese Pressurized Module and its remote manipulator system, or RMS. The 14-day flight includes three spacewalks. Launch is scheduled for 5:02 p.m. May 31. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
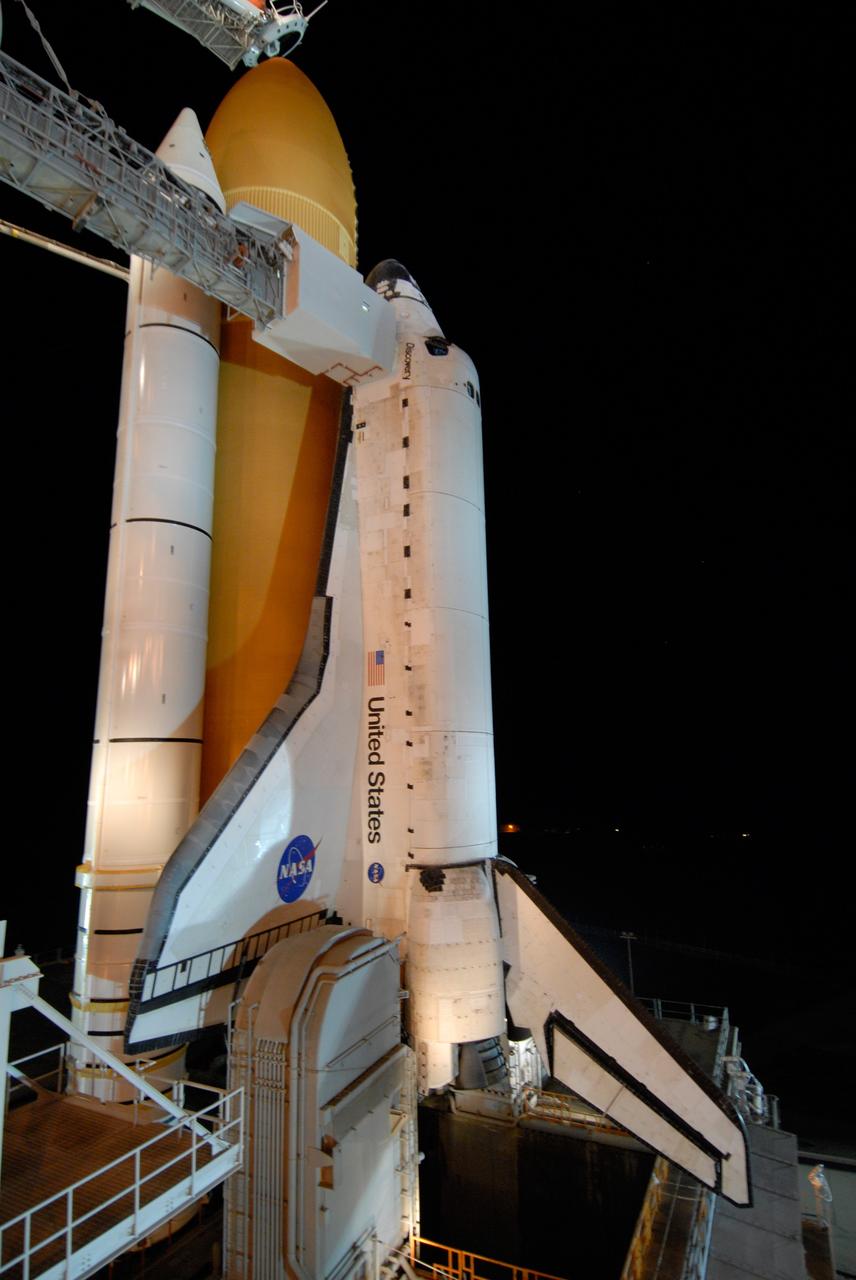

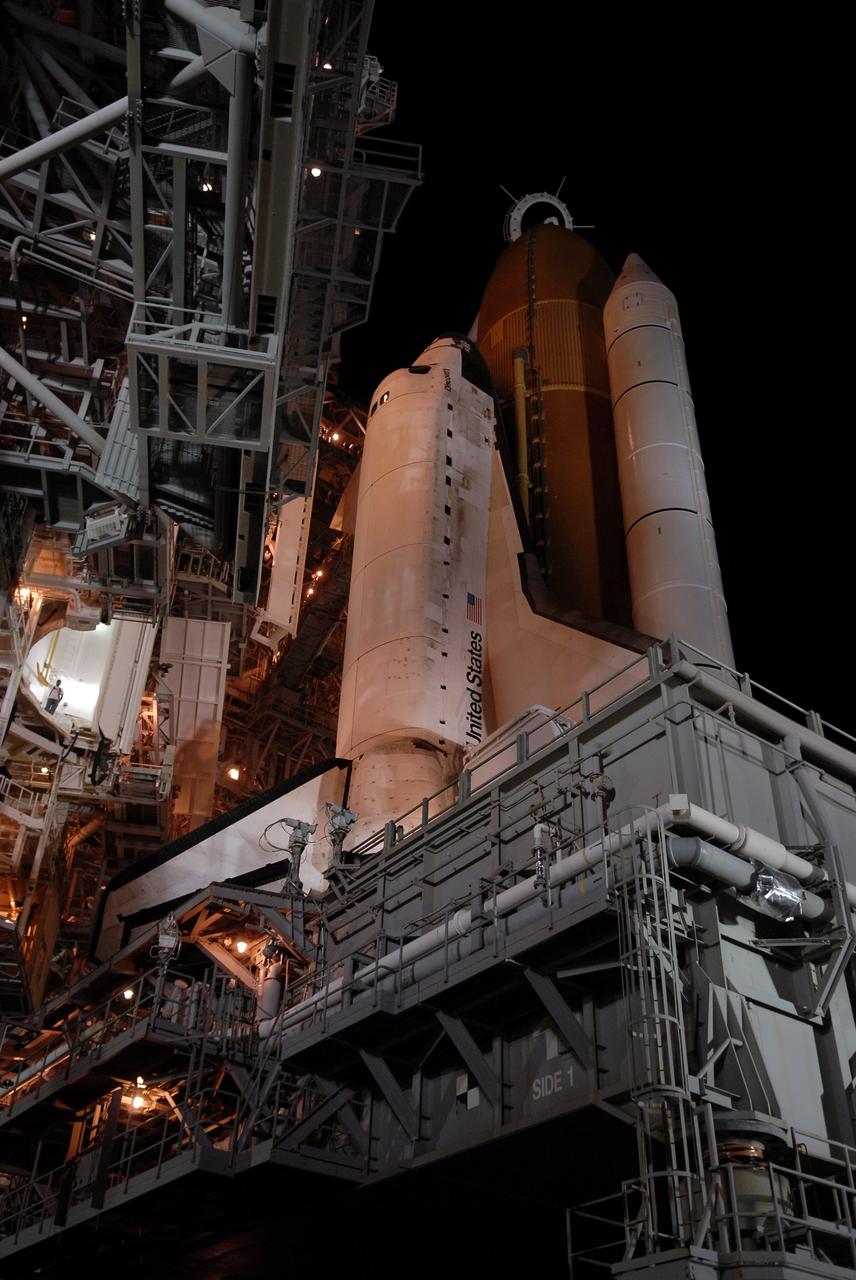
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Bathed in lights surrounding Launch Pad 39A and its structures at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, space shuttle Discovery is poised for launch on the STS-124 mission after rollback of the rotating service structure. First motion was at 8:33 p.m. and rollback was complete at 9:07 p.m. The structure provides protected access to the shuttle for changeout and servicing of payloads at the pad. It is supported by a rotating bridge that pivots on a vertical axis on the west side of the pad's flame trench. After the RSS is rolled back, the orbiter is ready for fuel cell activation and external tank cryogenic propellant loading operations. The pad is cleared to the perimeter gate for operations to fill the external tank with about 500,000 gallons of cryogenic propellants used by the shuttle’s main engines. This is done at the pad approximately eight hours before the scheduled launch. Behind the shuttle is the orange external tank and the two solid rocket boosters (only one seen here). Beneath the shuttle's starboard wing is one of two tail service masts, which provide several umbilical connections to the orbiter, including a liquid-oxygen line through one and a liquid-hydrogen line through another. The STS-124 mission is the second of three flights launching components to complete the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Kibo laboratory. The shuttle crew will install Kibo's large Japanese Pressurized Module and its remote manipulator system, or RMS. The 14-day flight includes three spacewalks. Launch is scheduled for 5:02 p.m. May 31. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
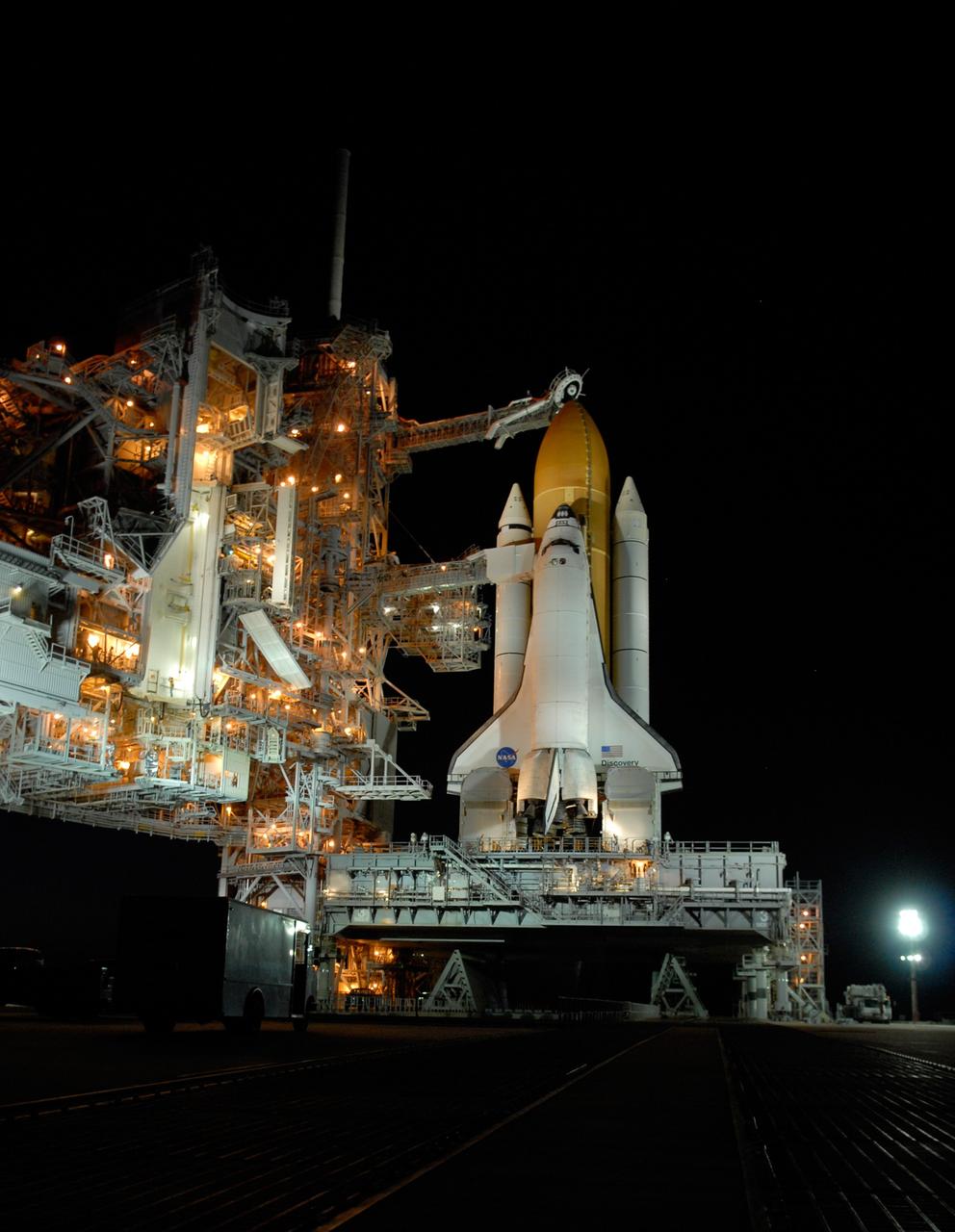

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Against the dark sky, lights bathe space shuttle Discovery, revealed after rollback of the rotating service structure in preparation for launch on the STS-124 mission. First motion was at 8:33 p.m. and rollback was complete at 9:07 p.m. The rotating structure provides protected access to the shuttle for changeout and servicing of payloads at the pad. It is supported by a rotating bridge that pivots on a vertical axis on the west side of the pad's flame trench. After the RSS is rolled back, the orbiter is ready for fuel cell activation and external tank cryogenic propellant loading operations. The pad is cleared to the perimeter gate for operations to fill the external tank with about 500,000 gallons of cryogenic propellants used by the shuttle’s main engines. This is done at the pad approximately eight hours before the scheduled launch. Above the orange external tank is the oxygen vent hood, called the "beanie cap," at the end of the gaseous oxygen vent arm extending from the fixed service structure. Vapors are created as the liquid oxygen in the external tank boil off. The hood vents the gaseous oxygen vapors away from the space shuttle vehicle. Below is the orbiter access arm with the White Room at the end, flush against the shuttle. The White Room provides access into the shuttle. The STS-124 mission is the second of three flights launching components to complete the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Kibo laboratory. The shuttle crew will install Kibo's large Japanese Pressurized Module and its remote manipulator system, or RMS. The 14-day flight includes three spacewalks. Launch is scheduled for 5:02 p.m. May 31. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
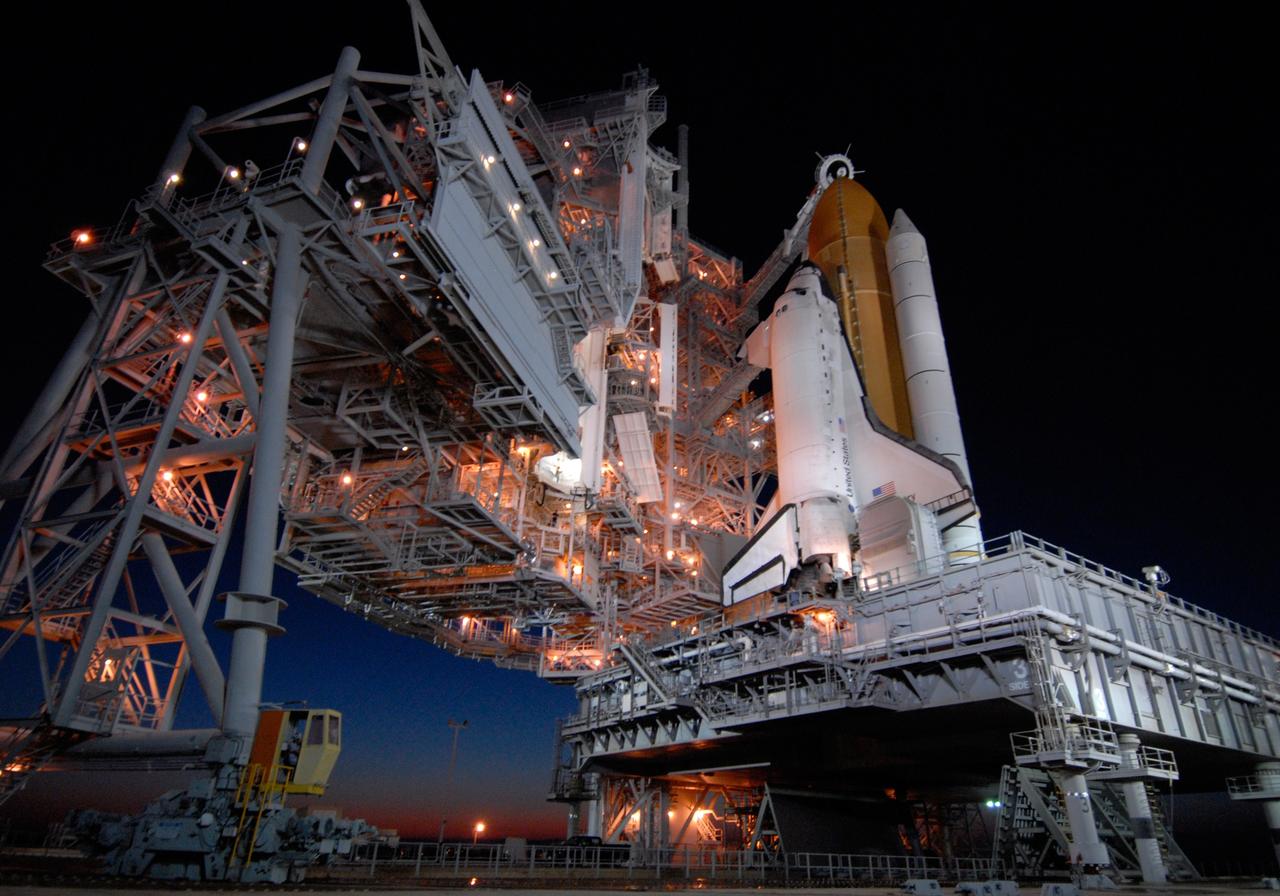

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- On Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the rotating service structure, or RSS, is rolling on its axis to uncover space shuttle Discovery in preparation for launch on the STS-124 mission. Support for the outer end of the bridge is provided by two eight-wheel, motor-driven trucks (one is seen at bottom left) that move along circular twin rails installed flush with the pad surface. First motion was at 8:33 p.m. and rollback was complete at 9:07 p.m. The structure provides protected access to the shuttle for changeout and servicing of payloads at the pad. It is supported by a rotating bridge that pivots on a vertical axis on the west side of the pad's flame trench. After the RSS is rolled back, the orbiter is ready for fuel cell activation and external tank cryogenic propellant loading operations. The pad is cleared to the perimeter gate for operations to fill the external tank with about 500,000 gallons of cryogenic propellants used by the shuttle’s main engines. This is done at the pad approximately eight hours before the scheduled launch. The STS-124 mission is the second of three flights launching components to complete the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Kibo laboratory. The shuttle crew will install Kibo's large Japanese Pressurized Module and its remote manipulator system, or RMS. The 14-day flight includes three spacewalks. Launch is scheduled for 5:02 p.m. May 31. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
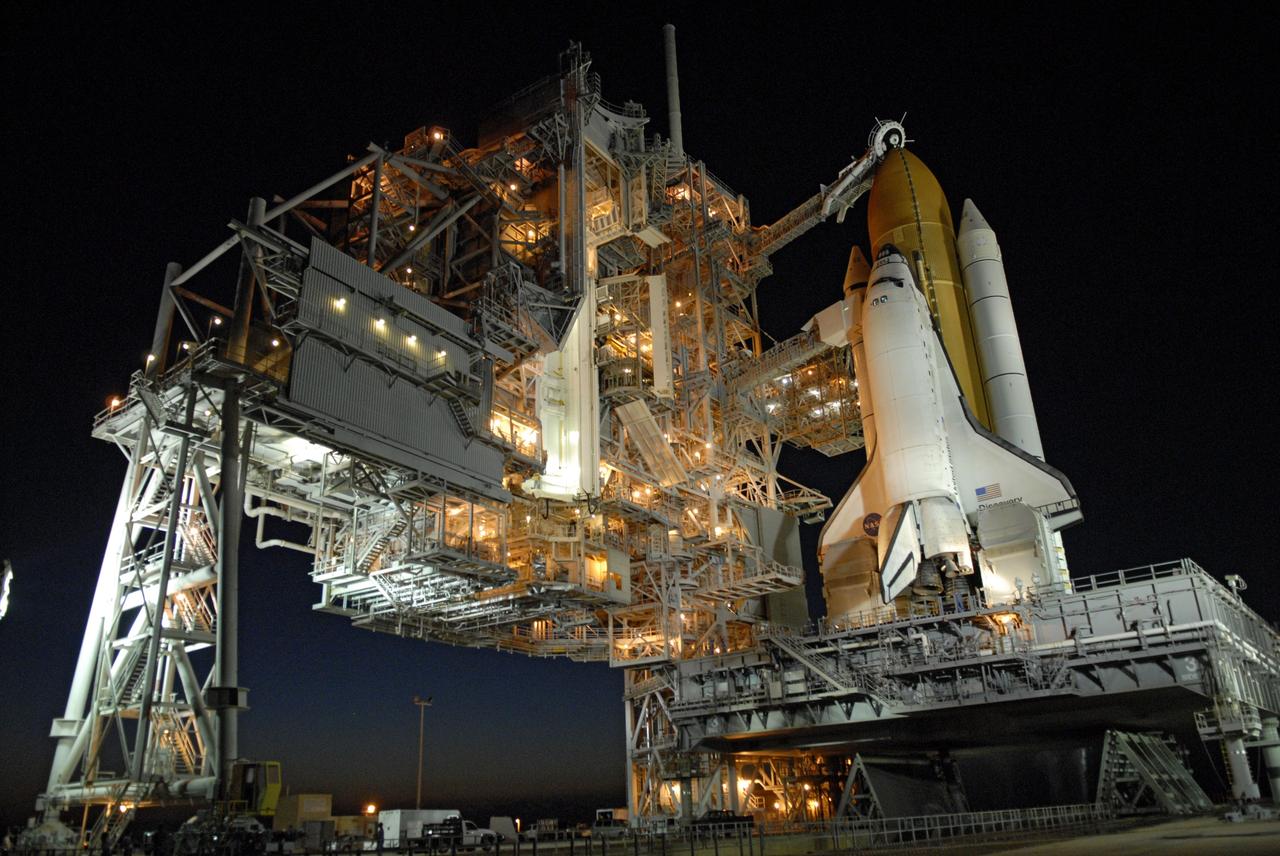

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- On Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the rotating service structure, or RSS, has rolled back on its axis to uncover space shuttle Discovery, lighted against the night sky, in preparation for launch on the STS-124 mission. Support for the outer end of the bridge is provided by two eight-wheel, motor-driven trucks (one is seen at bottom left) that move along circular twin rails installed flush with the pad surface. First motion was at 8:33 p.m. and rollback was complete at 9:07 p.m. The structure provides protected access to the shuttle for changeout and servicing of payloads at the pad. It is supported by a rotating bridge that pivots on a vertical axis on the west side of the pad's flame trench. After the RSS is rolled back, the orbiter is ready for fuel cell activation and external tank cryogenic propellant loading operations. The pad is cleared to the perimeter gate for operations to fill the external tank with about 500,000 gallons of cryogenic propellants used by the shuttle’s main engines. This is done at the pad approximately eight hours before the scheduled launch. Above the orange external tank is the oxygen vent hood, called the "beanie cap," at the end of the gaseous oxygen vent arm extending from the fixed service structure. Vapors are created as the liquid oxygen in the external tank boil off. The hood vents the gaseous oxygen vapors away from the space shuttle vehicle. Below is the orbiter access arm with the White Room at the end, flush against the shuttle. The White Room provides access into the shuttle. The STS-124 mission is the second of three flights launching components to complete the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Kibo laboratory. The shuttle crew will install Kibo's large Japanese Pressurized Module and its remote manipulator system, or RMS. The 14-day flight includes three spacewalks. Launch is scheduled for 5:02 p.m. May 31. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
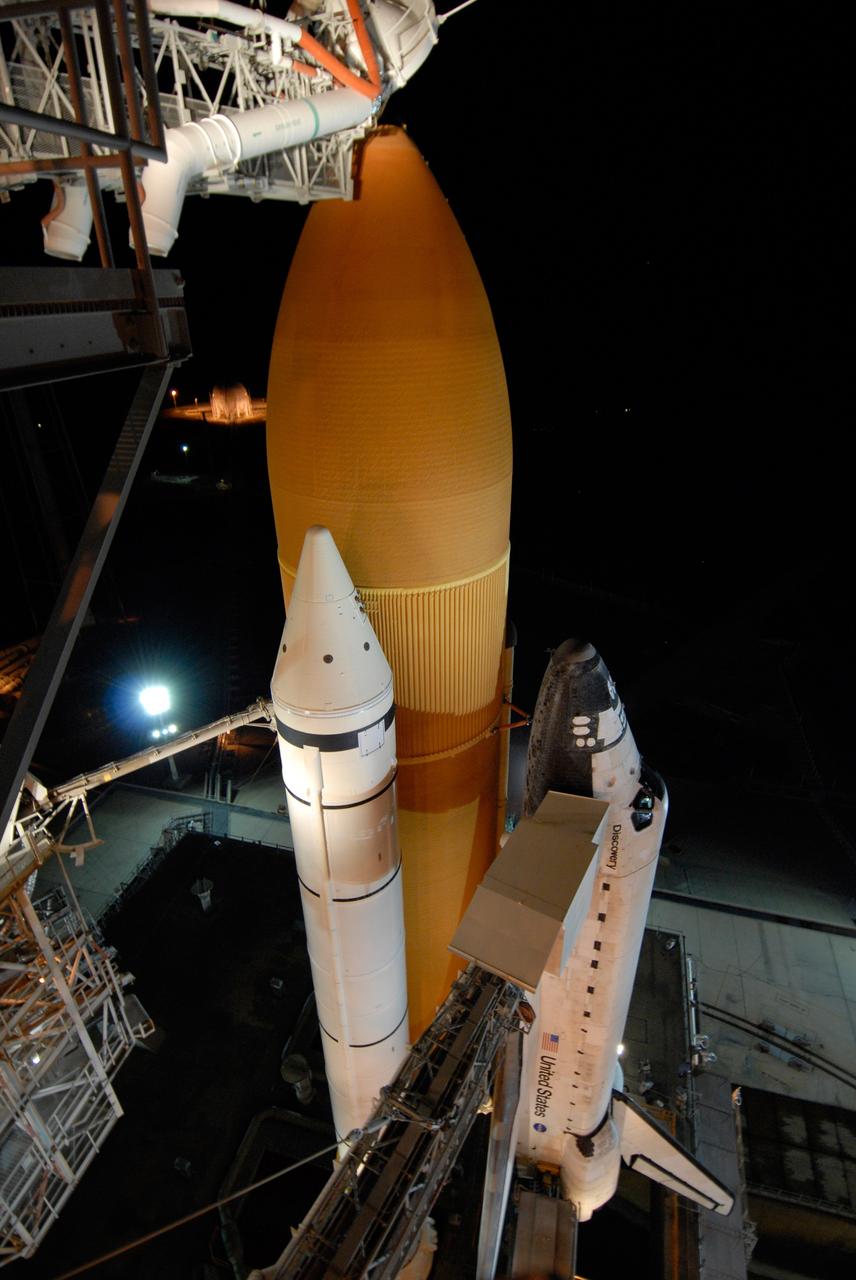

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Bathed in lights surrounding Launch Pad 39A and its structures at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, space shuttle Discovery looks polished and ready for launch on the STS-124 mission after rollback of the rotating service structure. First motion was at 8:33 p.m. and rollback was complete at 9:07 p.m. The rotating structure provides protected access to the shuttle for changeout and servicing of payloads at the pad. It is supported by a rotating bridge that pivots on a vertical axis on the west side of the pad's flame trench. After the RSS is rolled back, the orbiter is ready for fuel cell activation and external tank cryogenic propellant loading operations. The pad is cleared to the perimeter gate for operations to fill the external tank with about 500,000 gallons of cryogenic propellants used by the shuttle’s main engines. This is done at the pad approximately eight hours before the scheduled launch. Along with the orange external tank and one of the two solid rocket boosters, the orbiter access arm is seen extended to the side of the shuttle. At the end is the White Room, which provides access into the shuttle. The STS-124 mission is the second of three flights launching components to complete the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Kibo laboratory. The shuttle crew will install Kibo's large Japanese Pressurized Module and its remote manipulator system, or RMS. The 14-day flight includes three spacewalks. Launch is scheduled for 5:02 p.m. May 31. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder