
SNC delivers Dream Chaser to NASA Armstrong posing it with the HL-10 lifting body flown the 1960s.

NASA's Langley Research Center in Hampton, Va., recently conducted hypersonic testing of Dream Chaser models for SNC as part of the agency's Commercial Crew Program in order to obtain necessary data for the material selection and design of the TPS
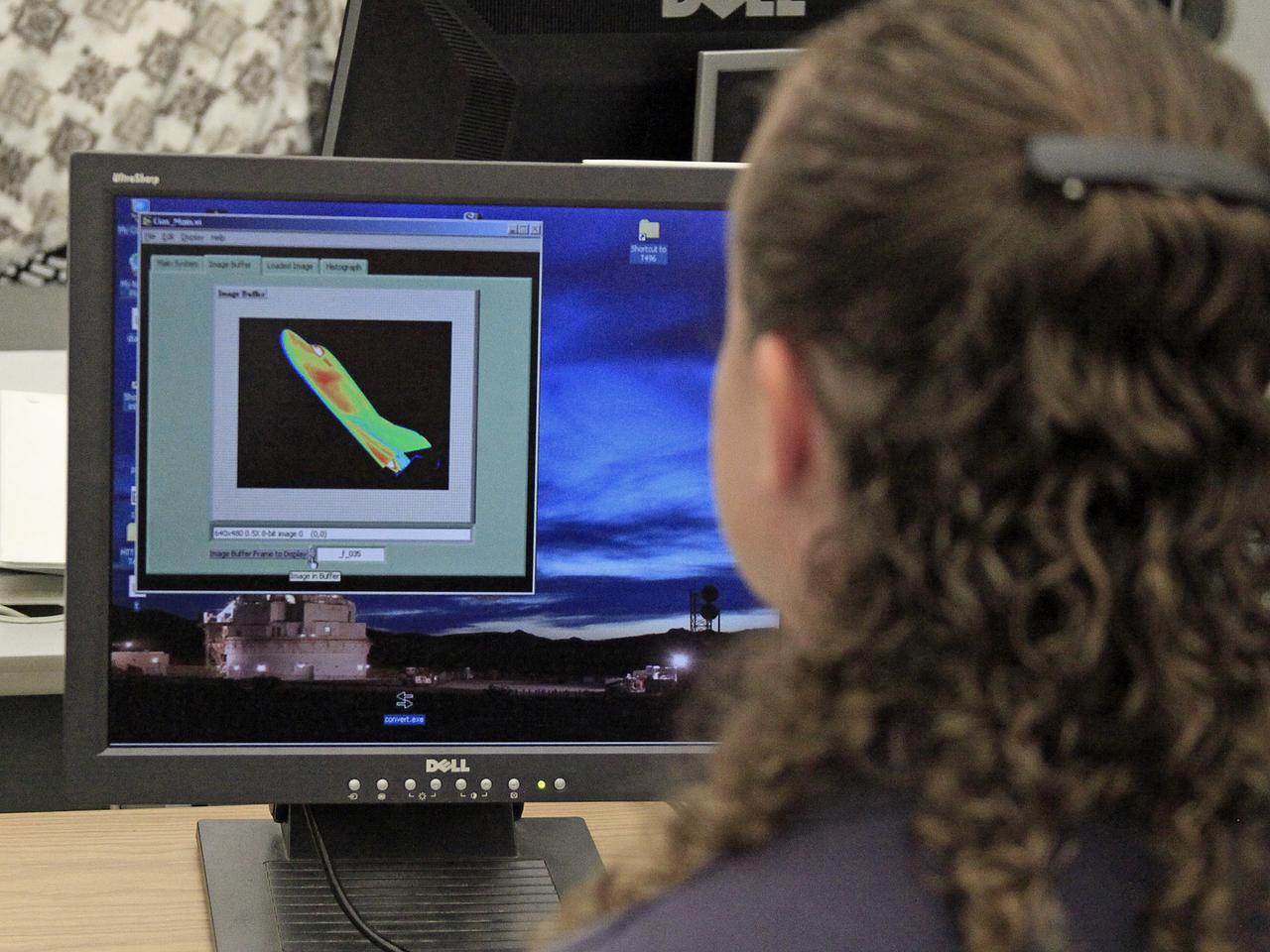

NASA's Langley Research Center in Hampton, Va., recently conducted hypersonic testing of Dream Chaser models for SNC as part of the agency's Commercial Crew Program in order to obtain necessary data for the material selection and design of the TPS
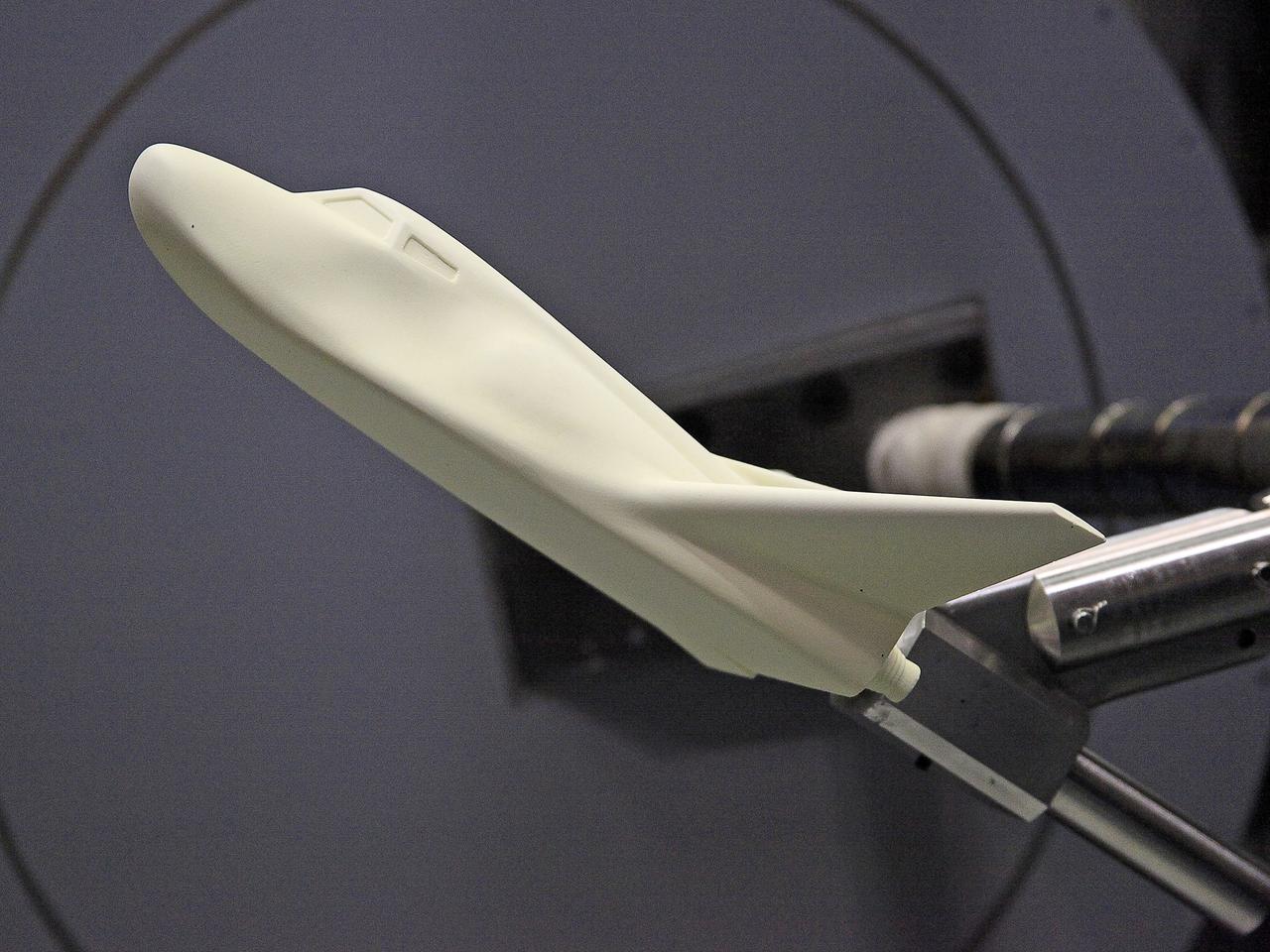

NASA's Langley Research Center in Hampton, Va., recently conducted hypersonic testing of Dream Chaser models for SNC as part of the agency's Commercial Crew Program in order to obtain necessary data for the material selection and design of the TPS
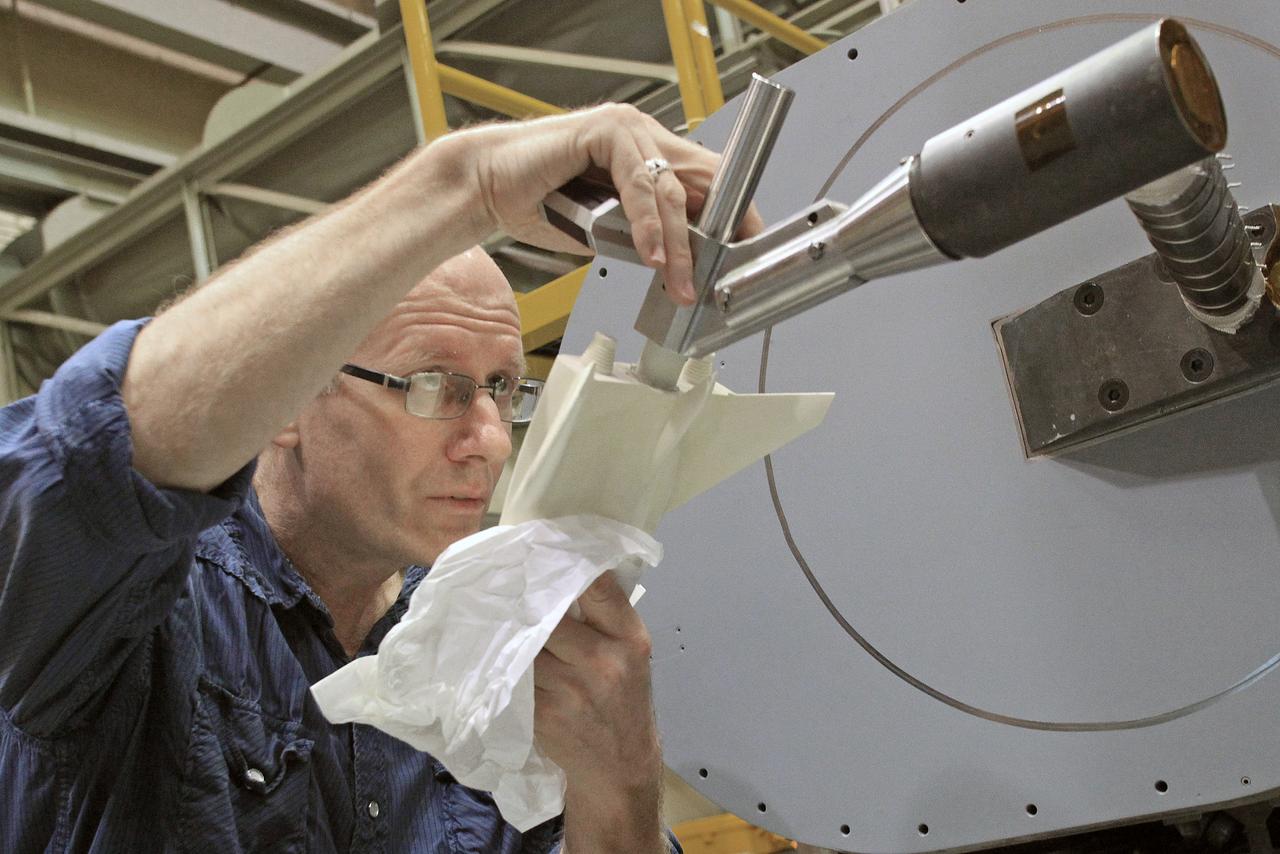

NASA's Langley Research Center in Hampton, Va., recently conducted hypersonic testing of Dream Chaser models for SNC as part of the agency's Commercial Crew Program in order to obtain necessary data for the material selection and design of the TPS
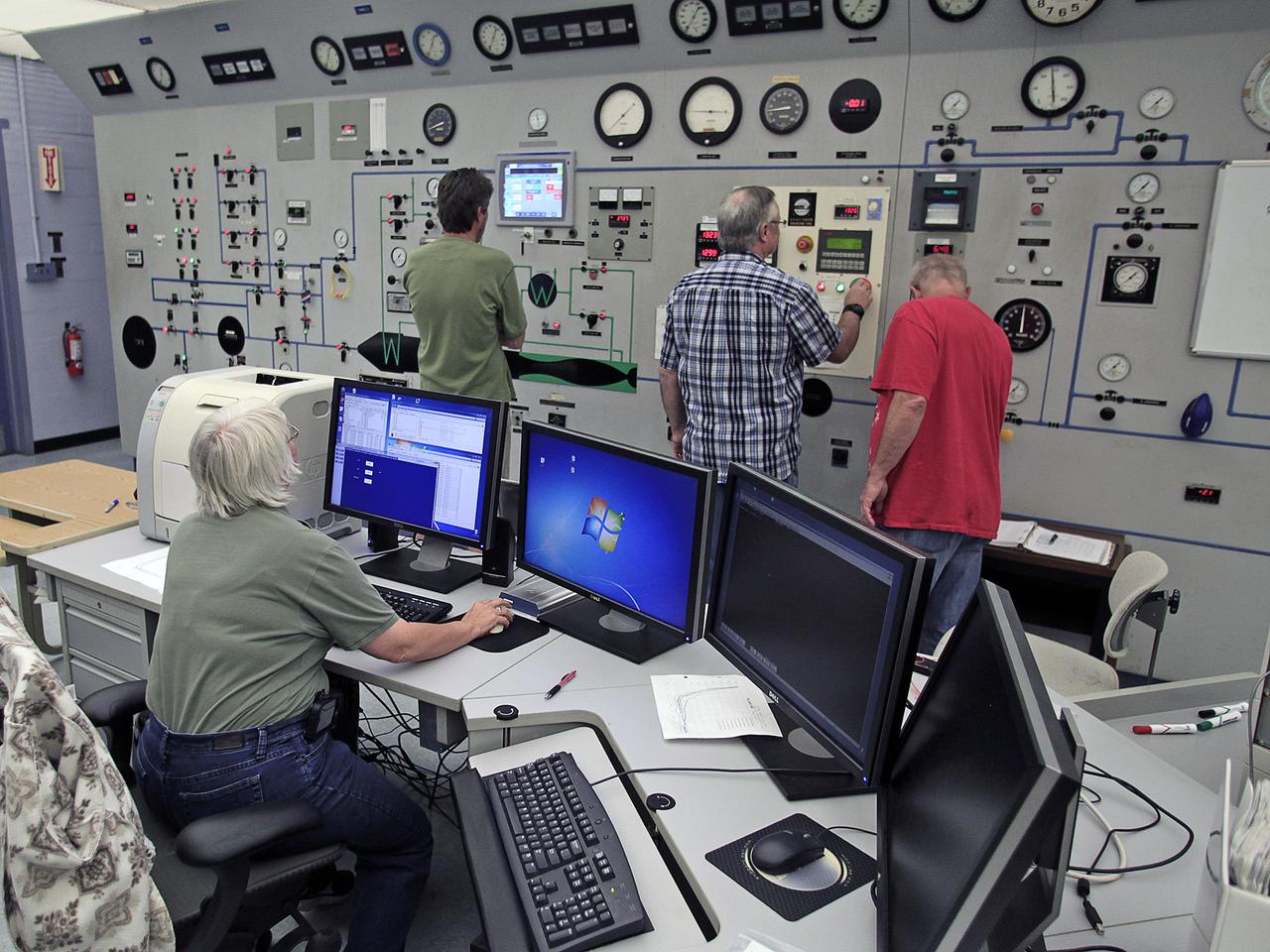

NASA's Langley Research Center in Hampton, Va., recently conducted hypersonic testing of Dream Chaser models for SNC as part of the agency's Commercial Crew Program in order to obtain necessary data for the material selection and design of the TPS
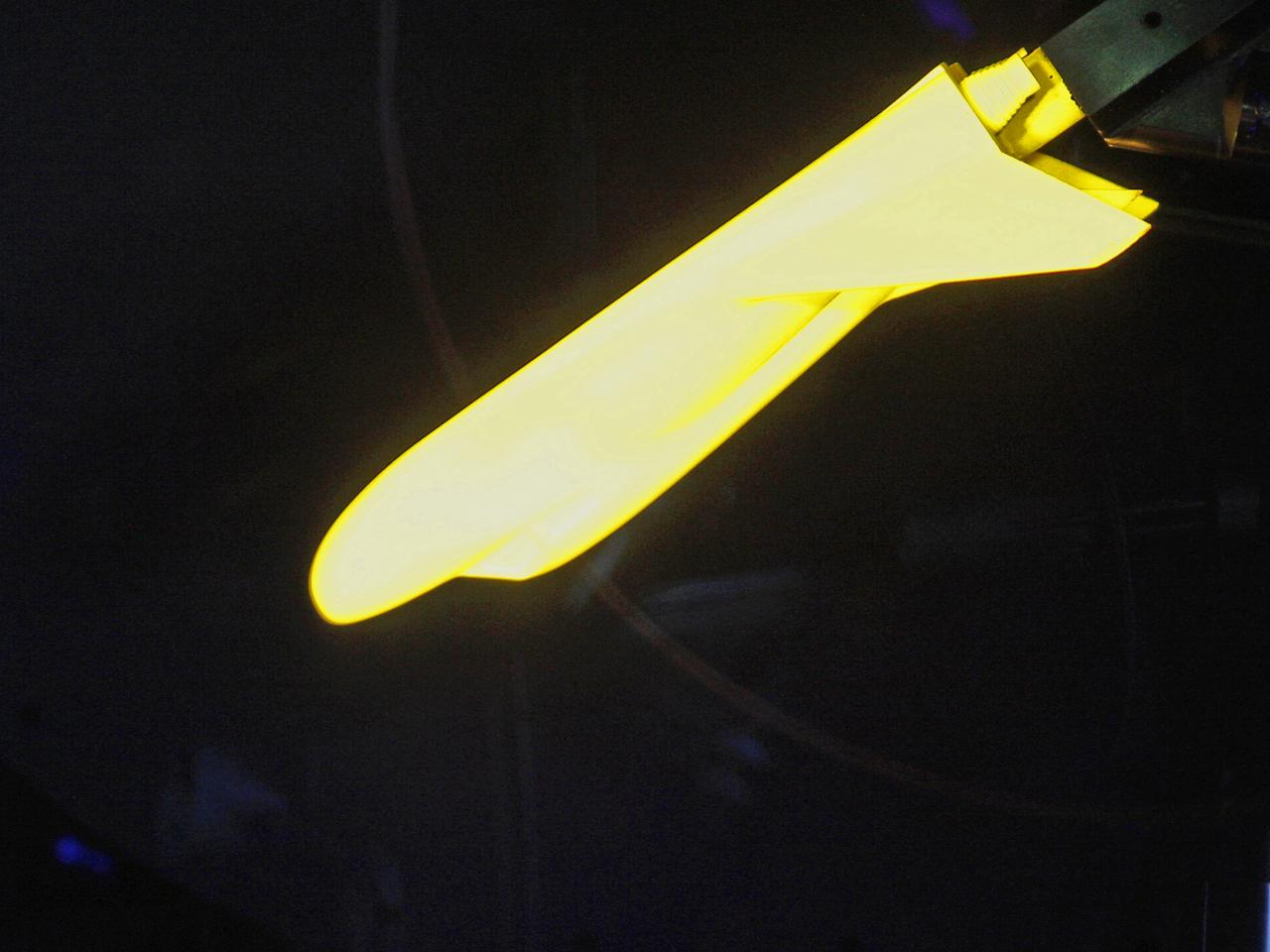

NASA's Langley Research Center in Hampton, Va., recently conducted hypersonic testing of Dream Chaser models for SNC as part of the agency's Commercial Crew Program in order to obtain necessary data for the material selection and design of the TPS
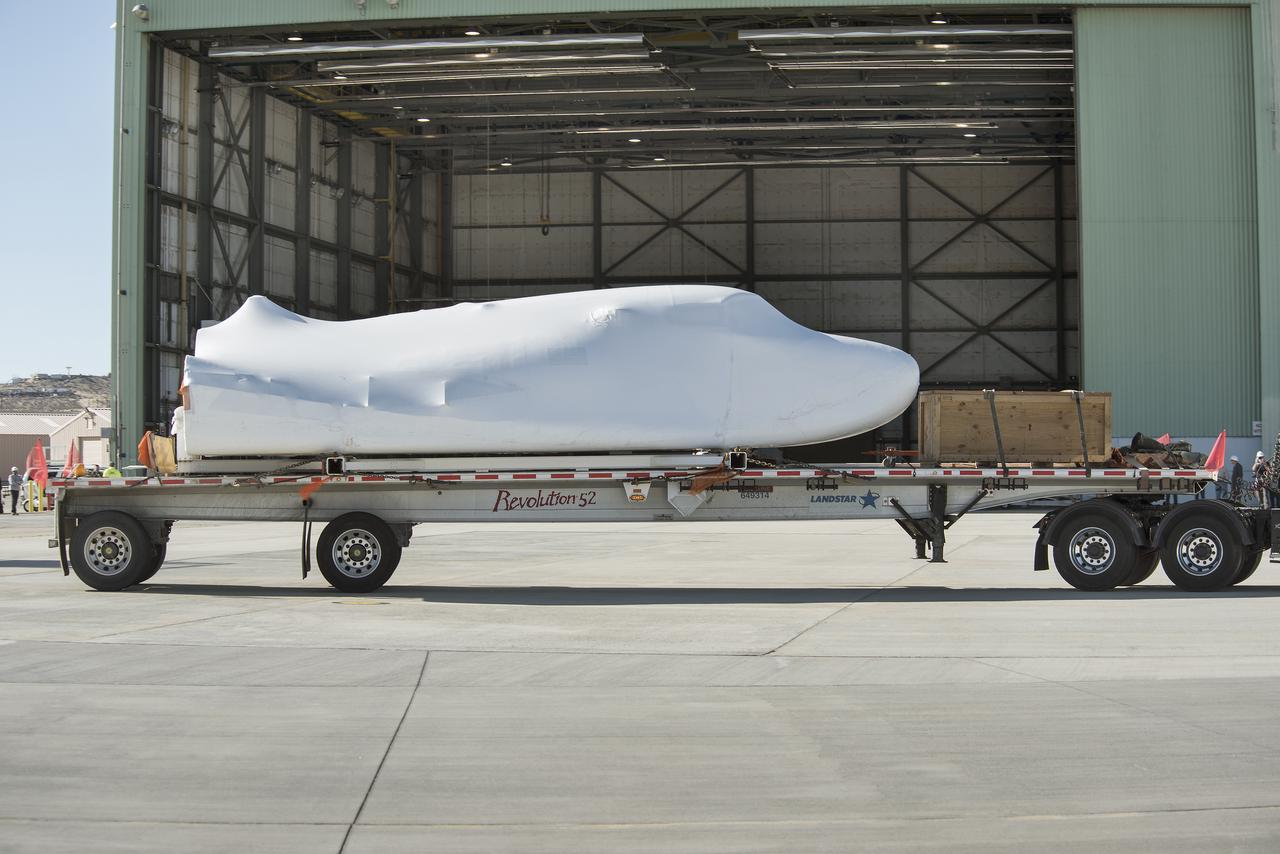

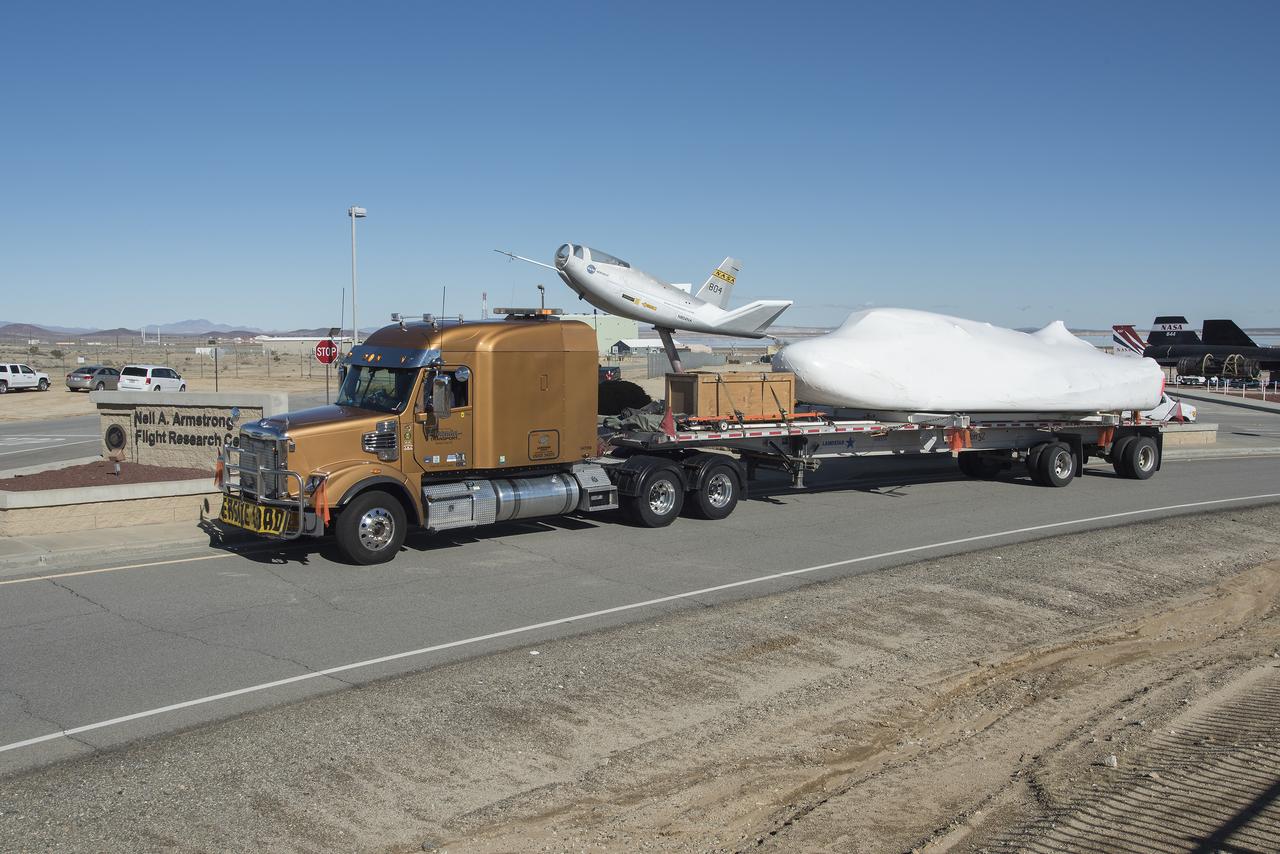
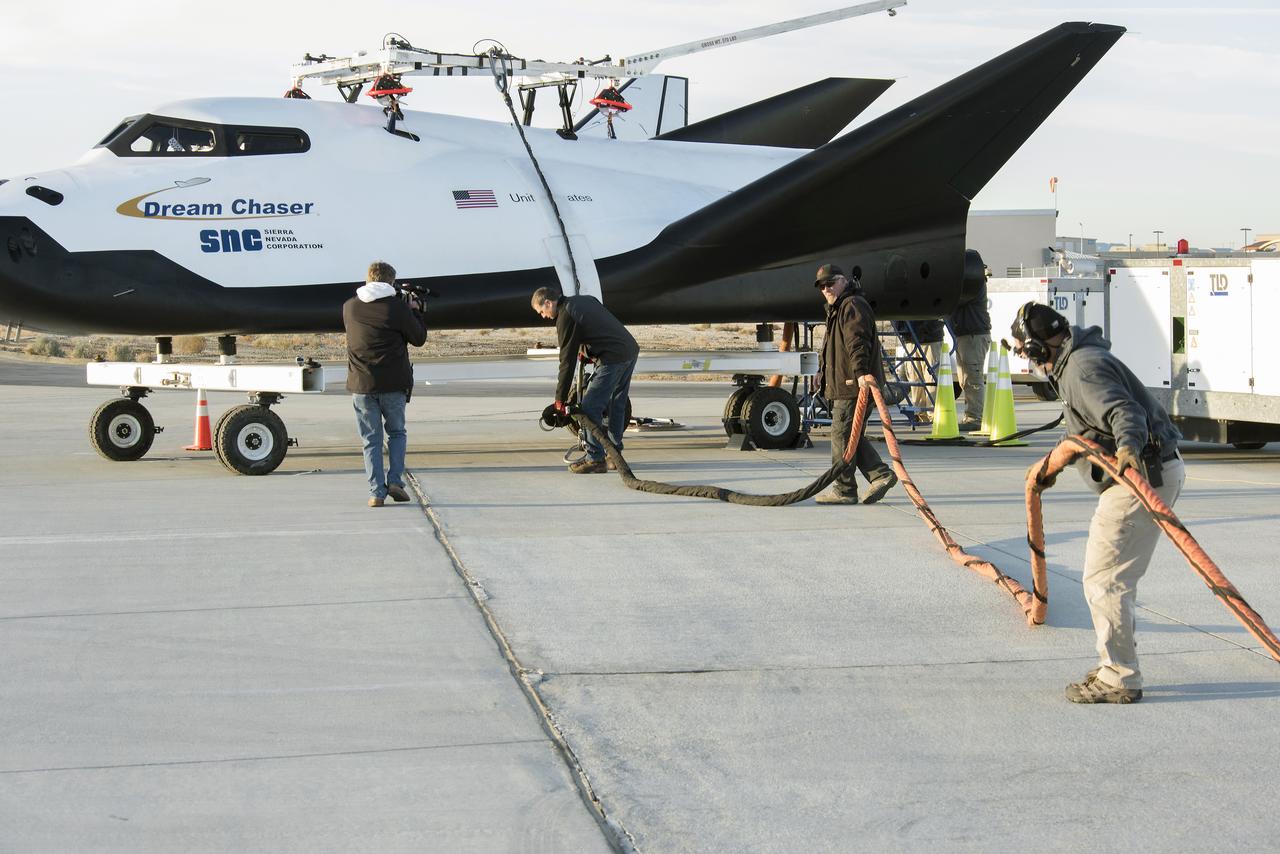
Sierra Nevada Corporation’s Dream Chaser spacecraft arrives by truck at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, located on Edwards Air Force Base. The spacecraft will undergo several months of testing in preparation for its approach and landing flight on the base’s 22L runway. The test series is part of a developmental space act agreement SNC has with NASA’s Commercial Crew Program and will help SNC validate aerodynamic properties, flight software and control system performance. The Dream Chaser is also being prepared to deliver cargo to the International Space Station under NASA’s Commercial Resupply Services 2 contract beginning in 2019. The cargo Dream Chaser will fly at least six delivery missions to and from the space station by 2024.
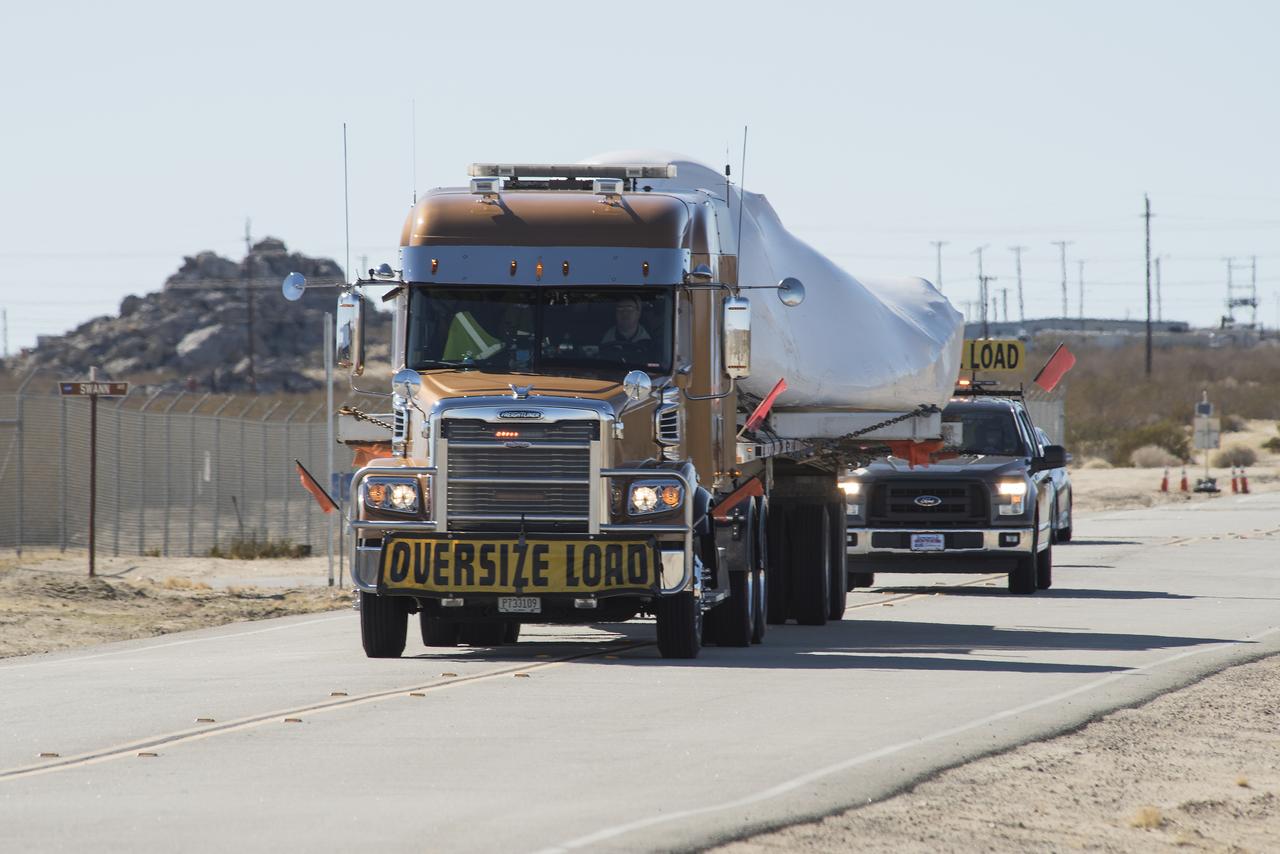

Sierra Nevada Corporation’s Dream Chaser spacecraft arrives by truck at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, located on Edwards Air Force Base. The spacecraft will undergo several months of testing in preparation for its approach and landing flight on the base’s 22L runway. The test series is part of a developmental space act agreement SNC has with NASA’s Commercial Crew Program and will help SNC validate aerodynamic properties, flight software and control system performance. The Dream Chaser is also being prepared to deliver cargo to the International Space Station under NASA’s Commercial Resupply Services 2 contract beginning in 2019. The cargo Dream Chaser will fly at least six delivery missions to and from the space station by 2024.
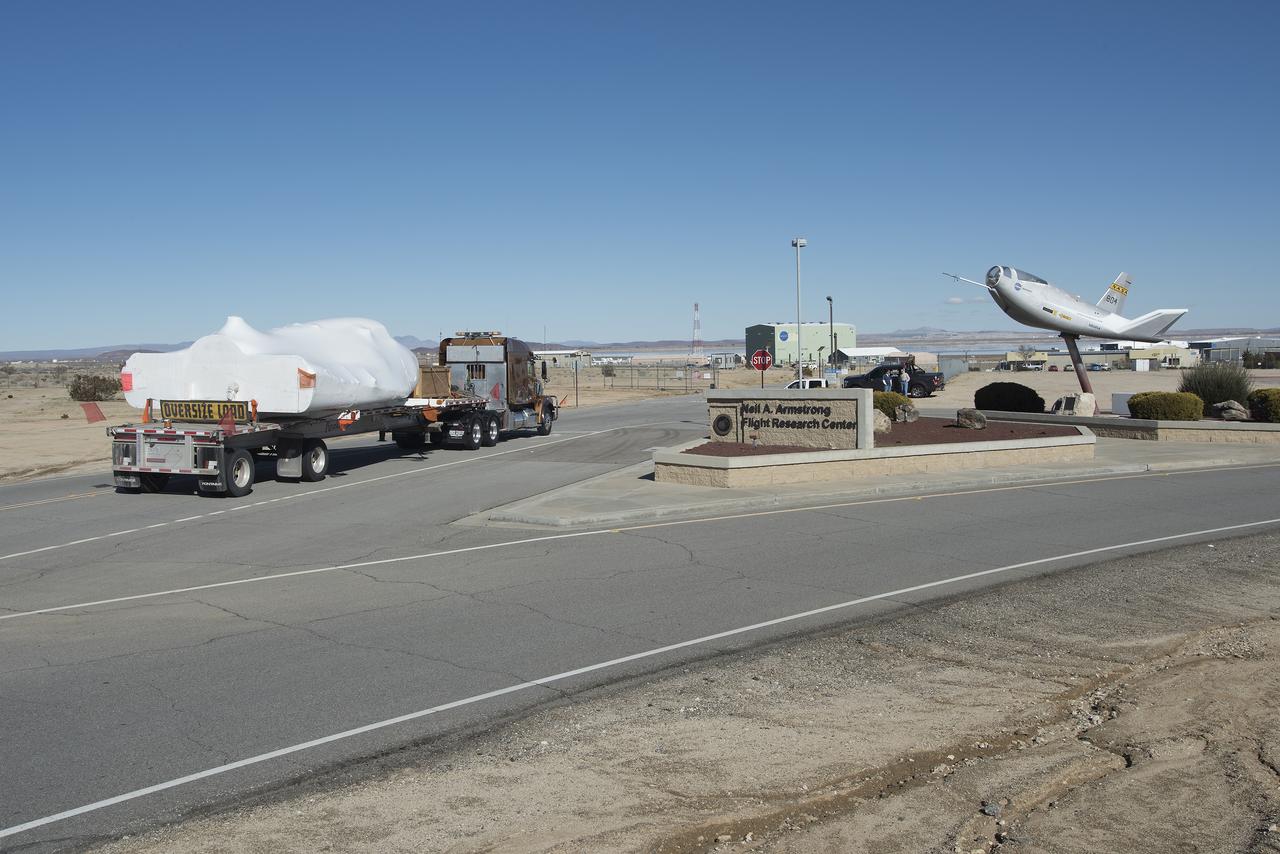

Sierra Nevada Corporation’s Dream Chaser spacecraft arrives by truck at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, located on Edwards Air Force Base. The spacecraft will undergo several months of testing in preparation for its approach and landing flight on the base’s 22L runway. The test series is part of a developmental space act agreement SNC has with NASA’s Commercial Crew Program and will help SNC validate aerodynamic properties, flight software and control system performance. The Dream Chaser is also being prepared to deliver cargo to the International Space Station under NASA’s Commercial Resupply Services 2 contract beginning in 2019. The cargo Dream Chaser will fly at least six delivery missions to and from the space station by 2024.
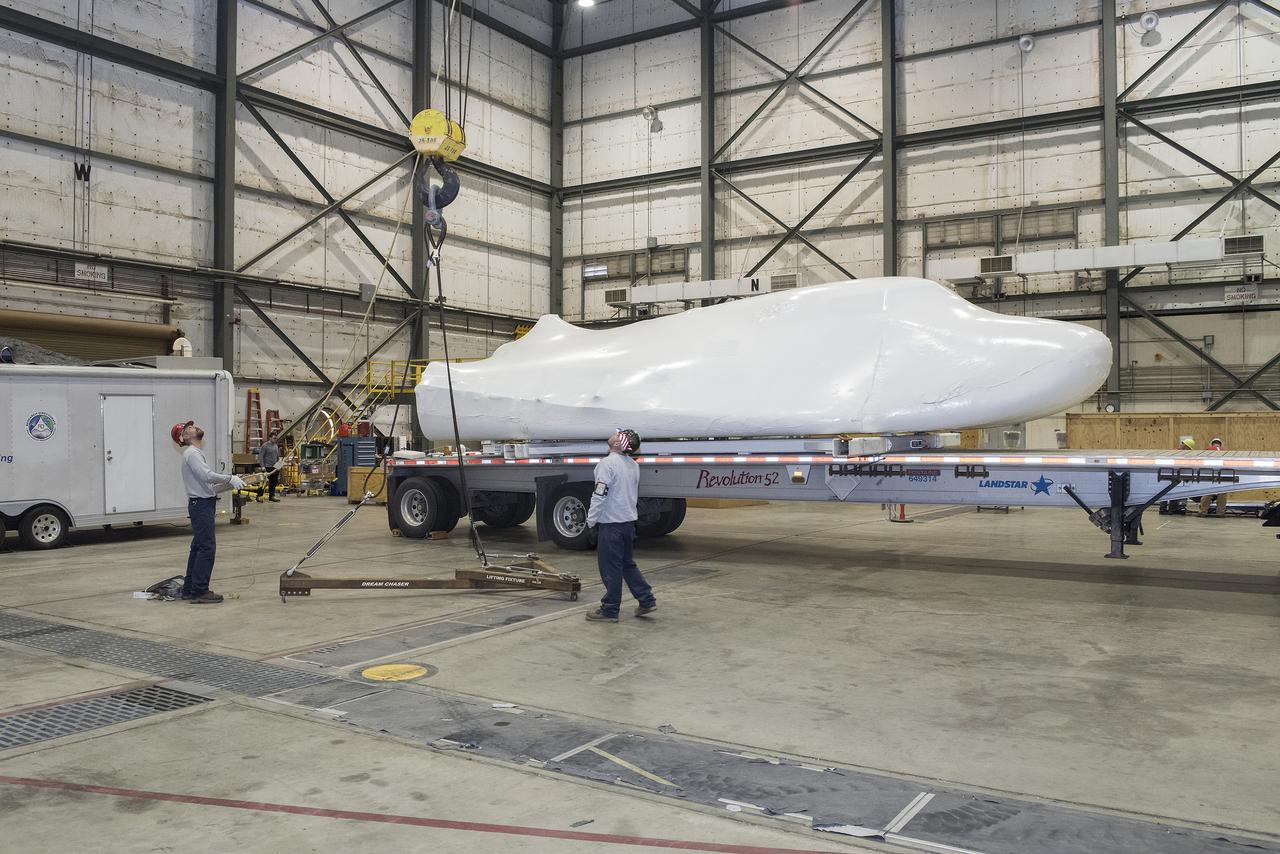

Sierra Nevada Corporation’s Dream Chaser spacecraft arrives by truck at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, located on Edwards Air Force Base. The spacecraft will undergo several months of testing in preparation for its approach and landing flight on the base’s 22L runway. The test series is part of a developmental space act agreement SNC has with NASA’s Commercial Crew Program and will help SNC validate aerodynamic properties, flight software and control system performance. The Dream Chaser is also being prepared to deliver cargo to the International Space Station under NASA’s Commercial Resupply Services 2 contract beginning in 2019. The cargo Dream Chaser will fly at least six delivery missions to and from the space station by 2024.
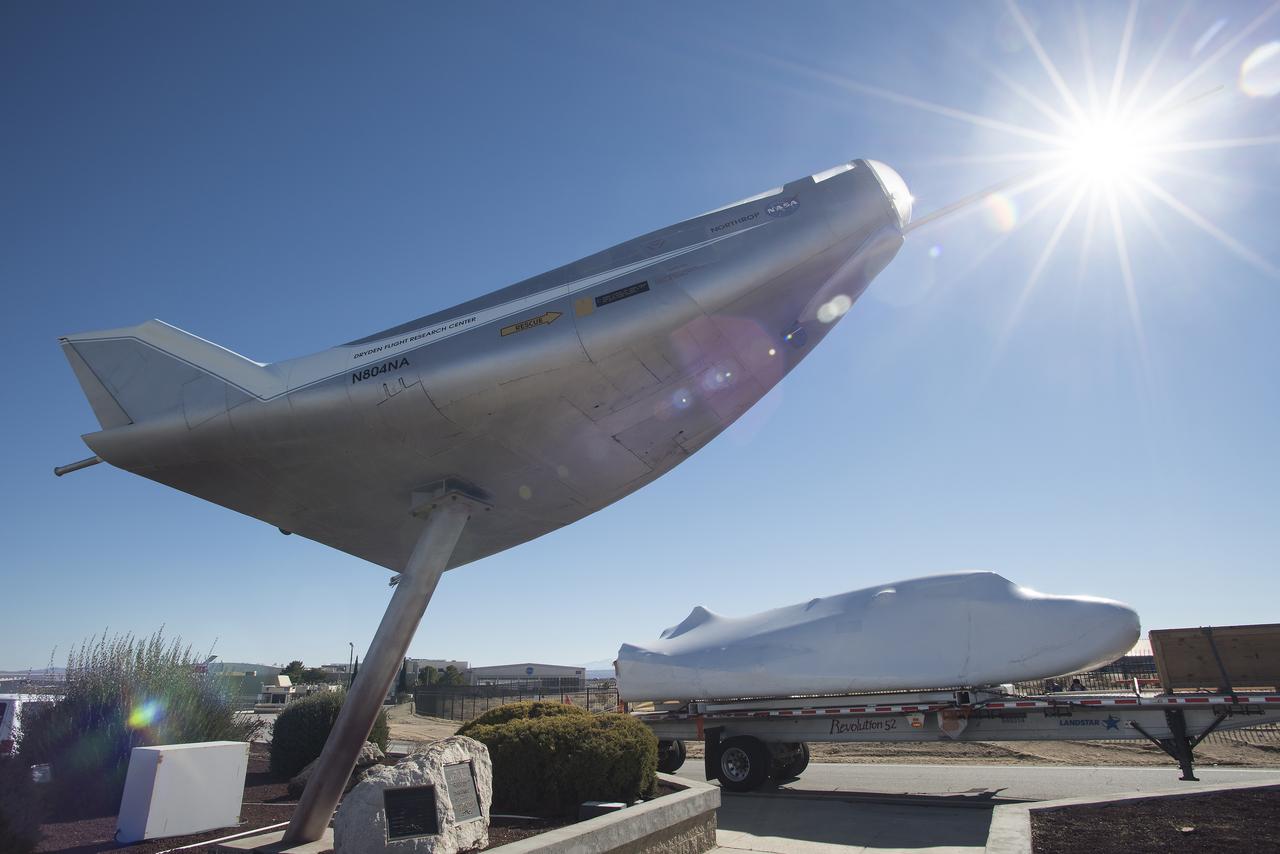

Sierra Nevada Corporation’s Dream Chaser spacecraft arrives by truck at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, located on Edwards Air Force Base. The spacecraft will undergo several months of testing in preparation for its approach and landing flight on the base’s 22L runway. The test series is part of a developmental space act agreement SNC has with NASA’s Commercial Crew Program and will help SNC validate aerodynamic properties, flight software and control system performance. The Dream Chaser is also being prepared to deliver cargo to the International Space Station under NASA’s Commercial Resupply Services 2 contract beginning in 2019. The cargo Dream Chaser will fly at least six delivery missions to and from the space station by 2024.
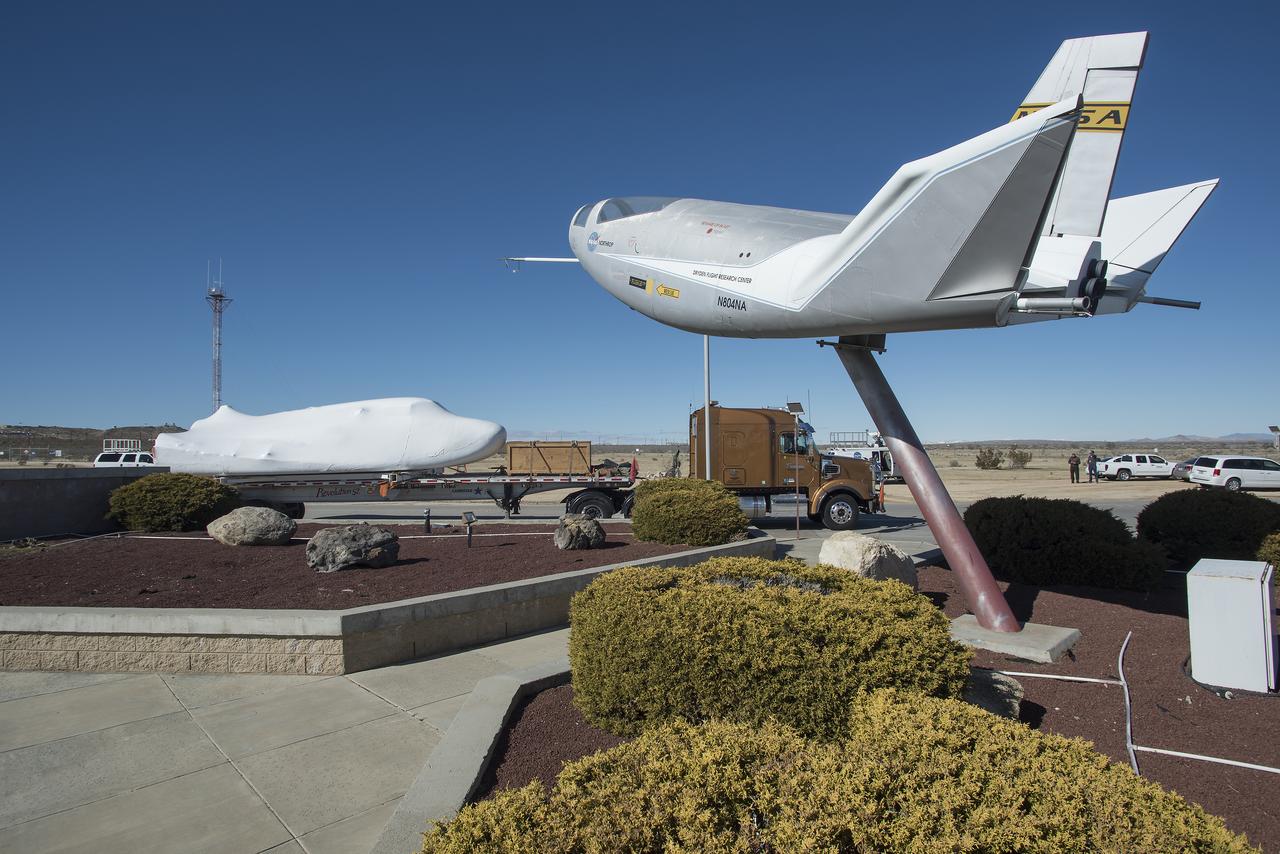

Sierra Nevada Corporation’s Dream Chaser spacecraft arrives by truck at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, located on Edwards Air Force Base. The spacecraft will undergo several months of testing in preparation for its approach and landing flight on the base’s 22L runway. The test series is part of a developmental space act agreement SNC has with NASA’s Commercial Crew Program and will help SNC validate aerodynamic properties, flight software and control system performance. The Dream Chaser is also being prepared to deliver cargo to the International Space Station under NASA’s Commercial Resupply Services 2 contract beginning in 2019. The cargo Dream Chaser will fly at least six delivery missions to and from the space station by 2024.
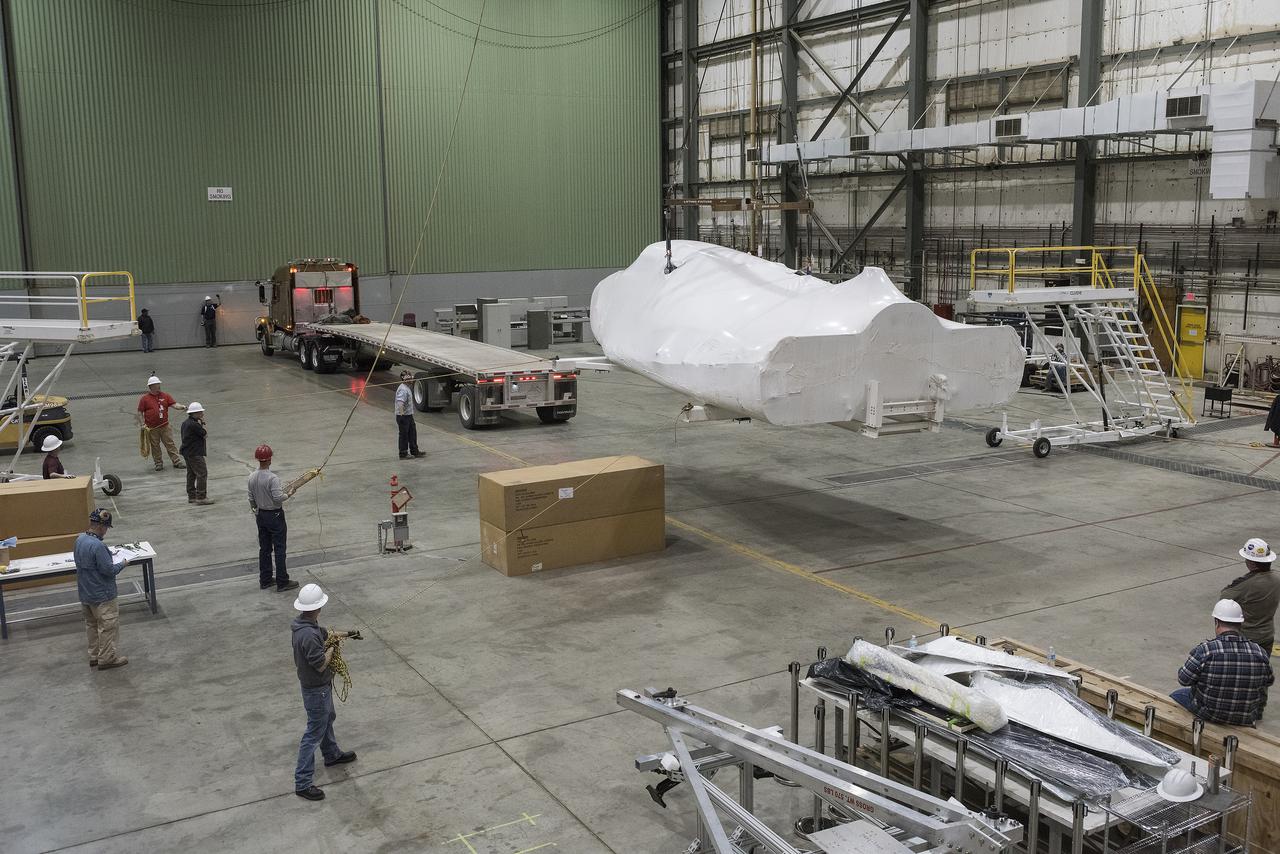

Sierra Nevada Corporation’s Dream Chaser spacecraft is removed from its delivery truck after arriving at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, located on Edwards Air Force Base. The spacecraft will undergo several months of testing in preparation for its approach and landing flight on the base’s 22L runway. The test series is part of a developmental space act agreement SNC has with NASA’s Commercial Crew Program and will help SNC validate aerodynamic properties, flight software and control system performance. The Dream Chaser is also being prepared to deliver cargo to the International Space Station under NASA’s Commercial Resupply Services 2 contract beginning in 2019. The cargo Dream Chaser will fly at least six delivery missions to and from the space station by 2024.
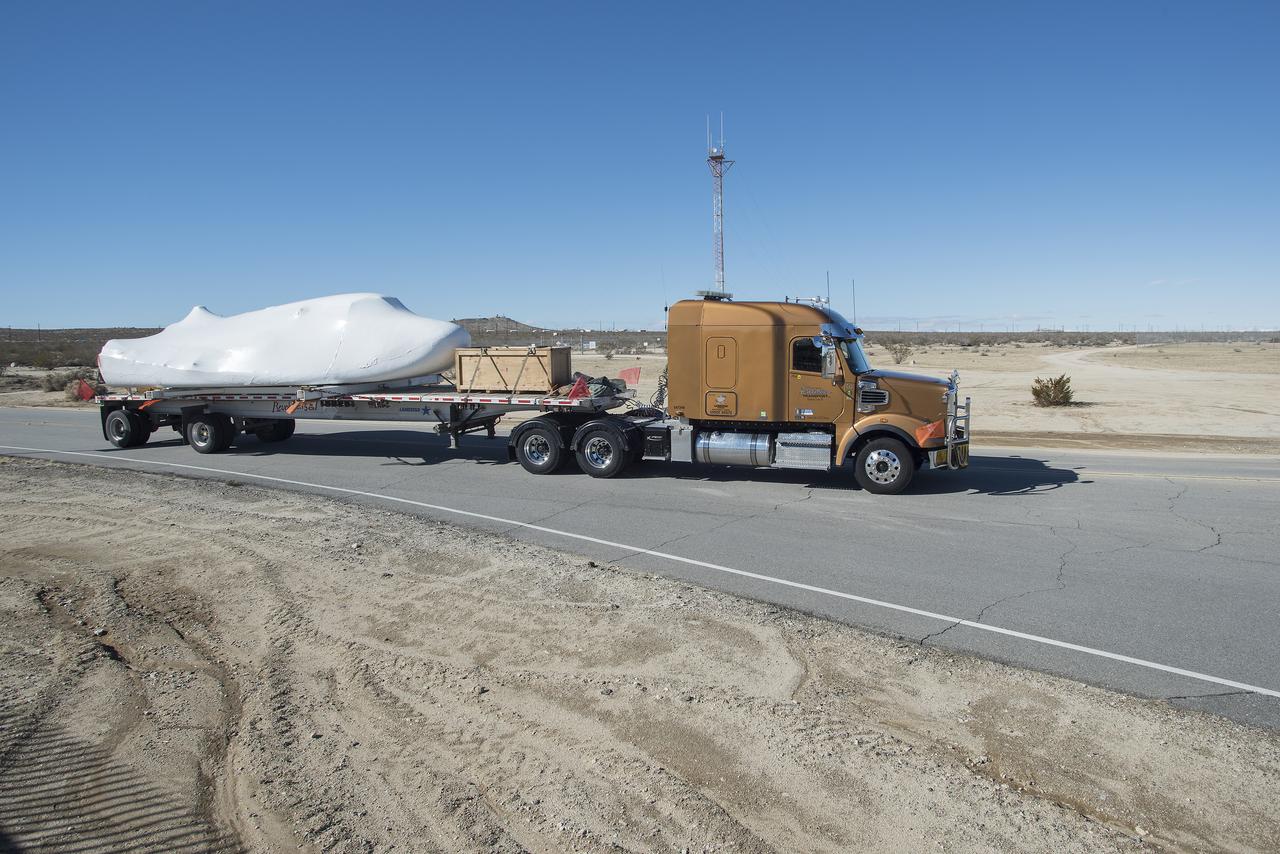

Sierra Nevada Corporation’s Dream Chaser spacecraft arrives by truck at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, located on Edwards Air Force Base. The spacecraft will undergo several months of testing in preparation for its approach and landing flight on the base’s 22L runway. The test series is part of a developmental space act agreement SNC has with NASA’s Commercial Crew Program and will help SNC validate aerodynamic properties, flight software and control system performance. The Dream Chaser is also being prepared to deliver cargo to the International Space Station under NASA’s Commercial Resupply Services 2 contract beginning in 2019. The cargo Dream Chaser will fly at least six delivery missions to and from the space station by 2024.

Sierra Nevada Corporation’s Dream Chaser spacecraft arrives by truck at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, located on Edwards Air Force Base. The spacecraft will undergo several months of testing in preparation for its approach and landing flight on the base’s 22L runway. The test series is part of a developmental space act agreement SNC has with NASA’s Commercial Crew Program and will help SNC validate aerodynamic properties, flight software and control system performance. The Dream Chaser is also being prepared to deliver cargo to the International Space Station under NASA’s Commercial Resupply Services 2 contract beginning in 2019. The cargo Dream Chaser will fly at least six delivery missions to and from the space station by 2024.

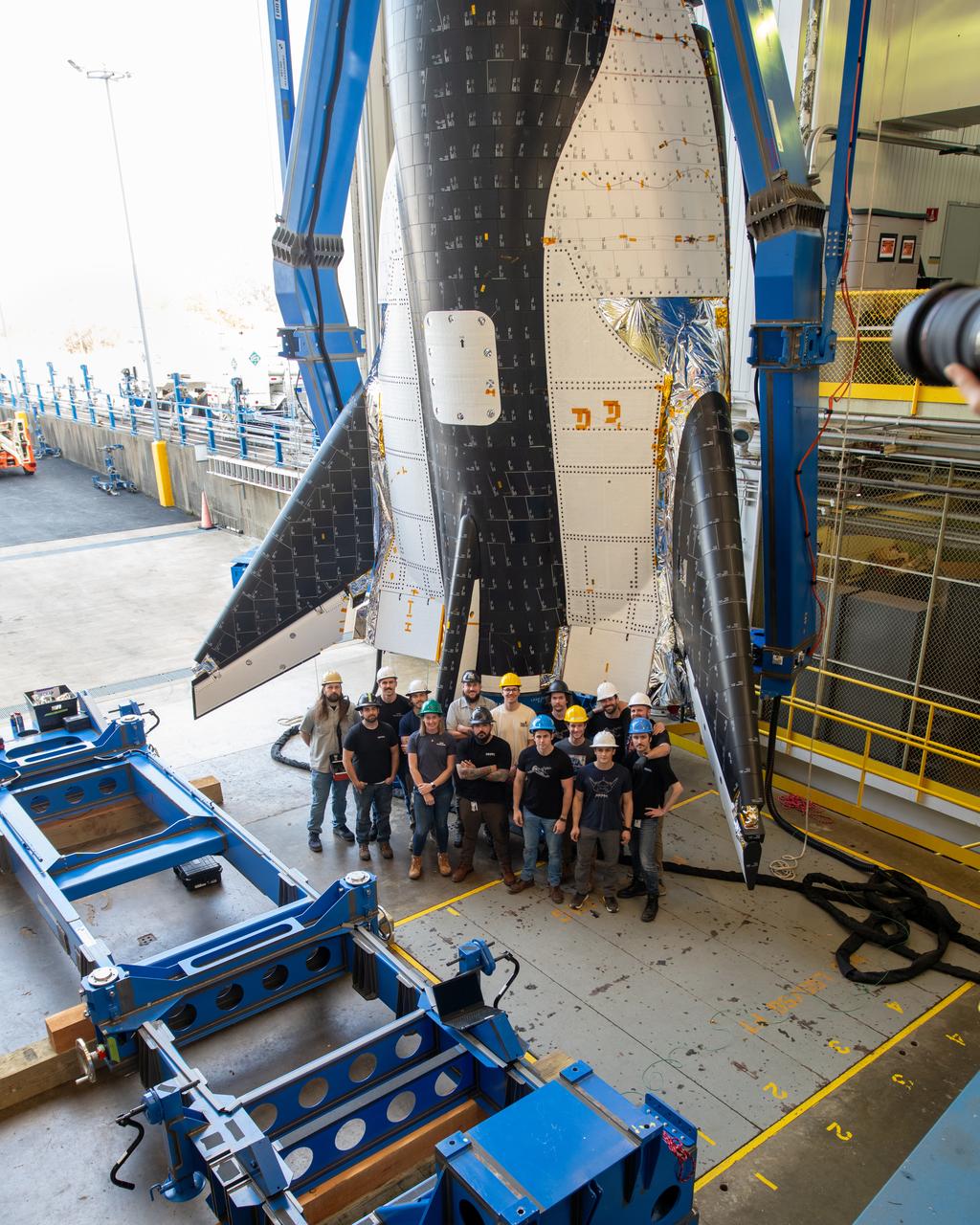
Sierra Space Dream Chaser Spaceplane Documentation Photographs
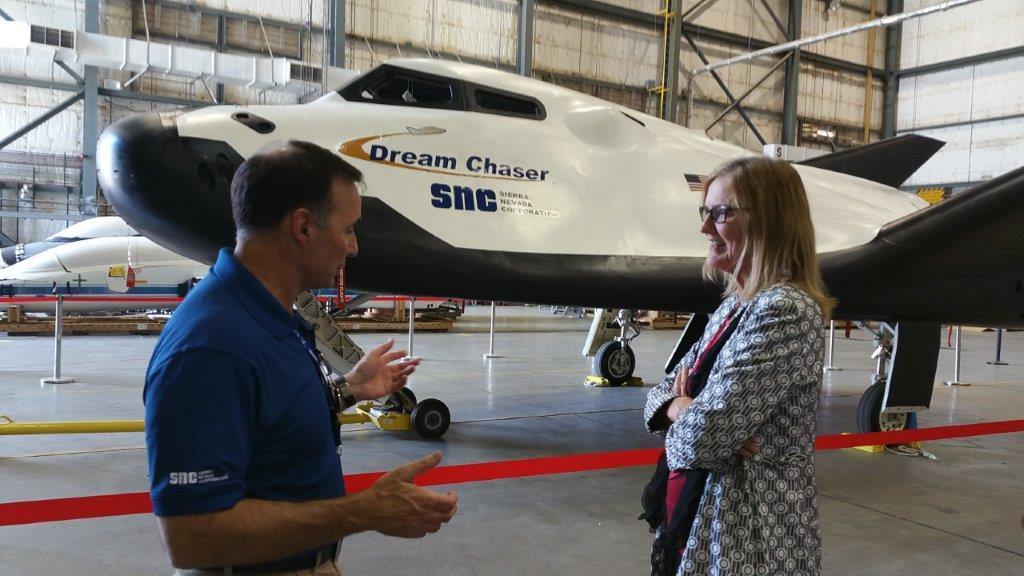

NASA Acting Deputy Chief Technologist Vicki Crisp discusses Sierra Nevada Corporation’s Dream Chaser captive carry flight and future tests with former Astronaut Lee "Bru" Archambault, who is now a test pilot for the American company. The Dream Chaser completed a successful captive carry flight at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center at Edwards, California, on Aug. 30, 2017.
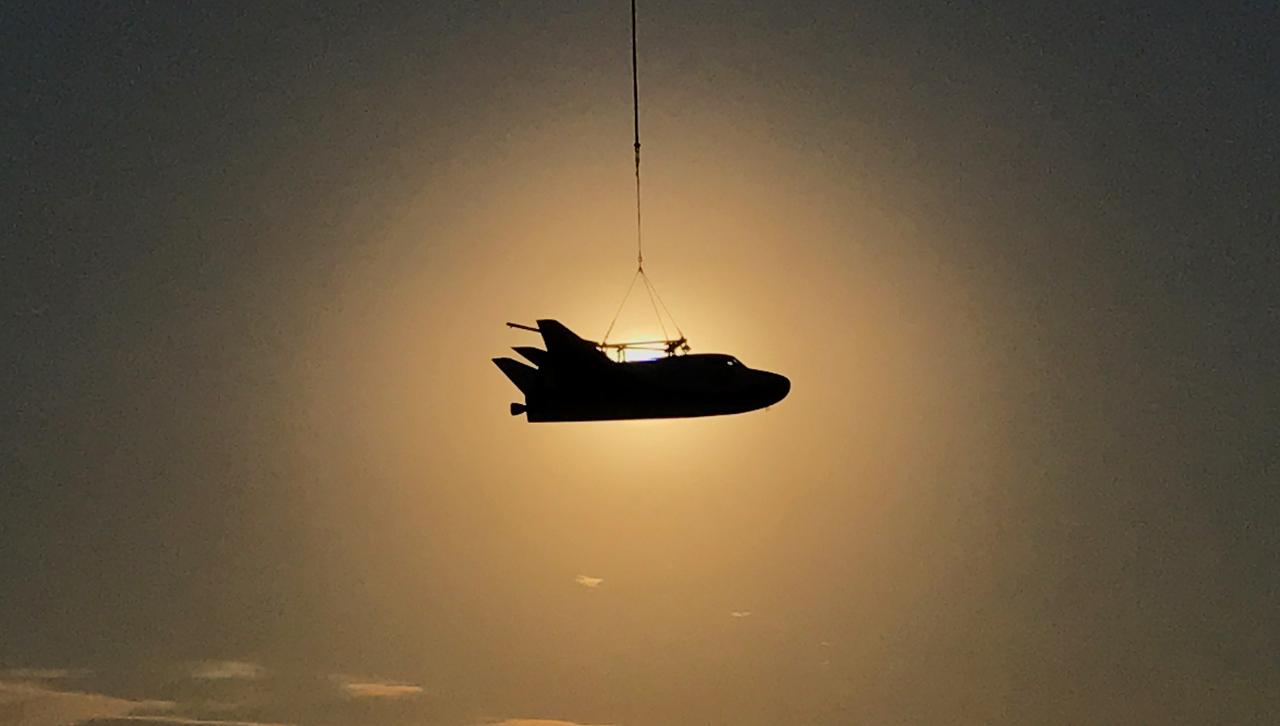

Sierra Nevada Corporation’s Dream Chaser completed an important step toward orbital flight with a successful captive carry test at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, located on Edwards Air Force Base. A helicopter successfully carried a Dream Chaser test article, which has the same specifications as a flight-ready spacecraft, to the same altitude and flight conditions of an upcoming free flight test. The Dream Chaser is a lifting-body, winged spacecraft that will fly back to Earth in a manner similar to NASA’s space shuttles. The successful captive carry test clears the way for a free flight test of the spacecraft later this year in which the uncrewed Dream Chaser will be released to glide on its own and land.

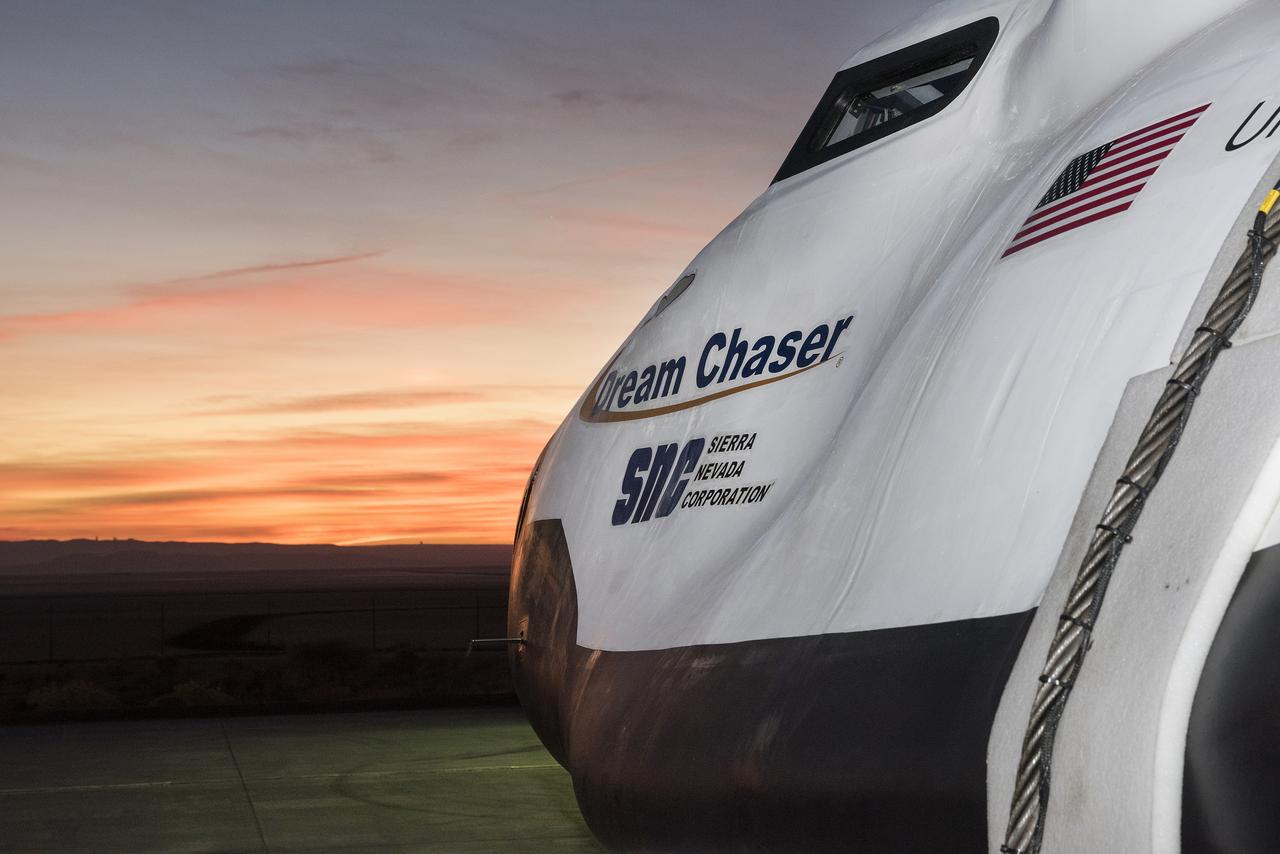
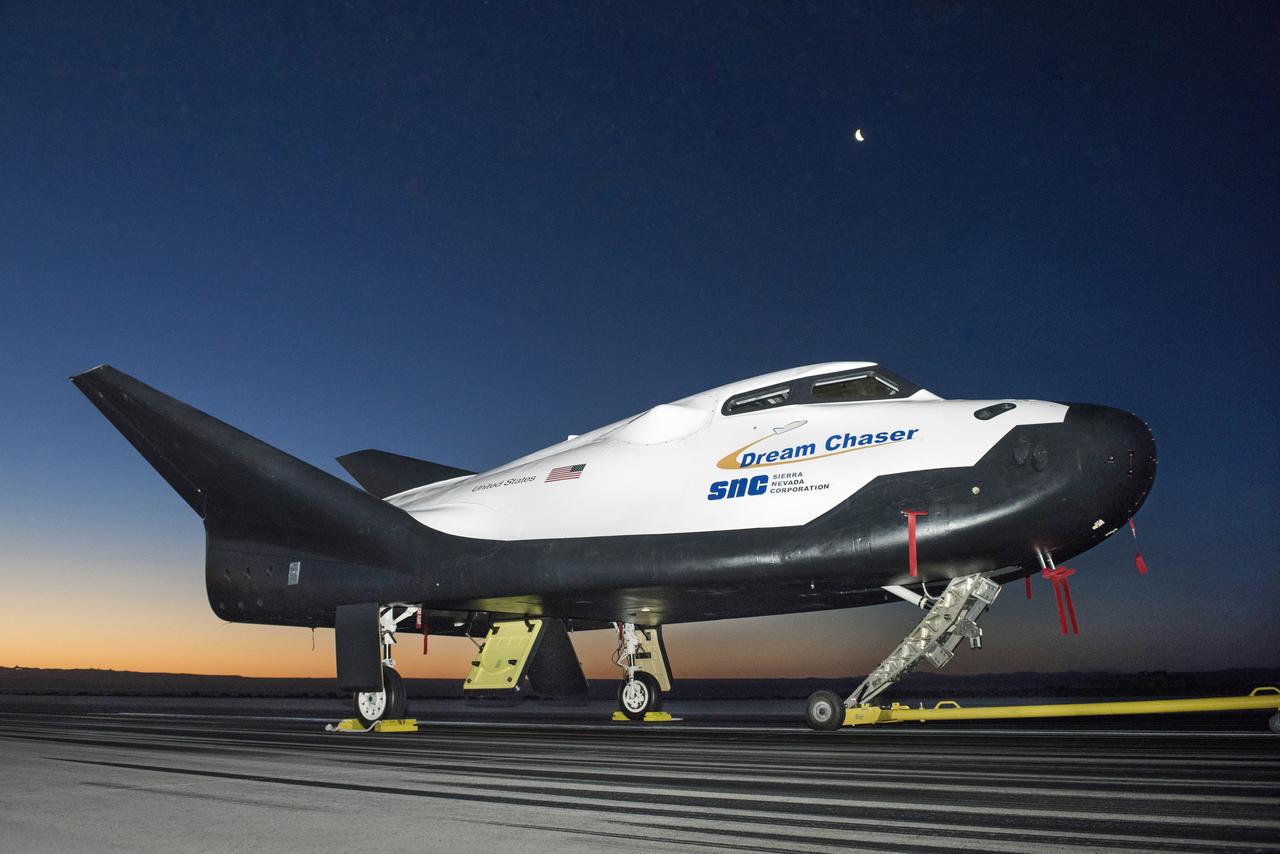
Sierra Nevada Corp’s Dream Chaser posed on ramp at sunrise at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center in California where the aircraft has gone through a series of tests in preparation for flight.
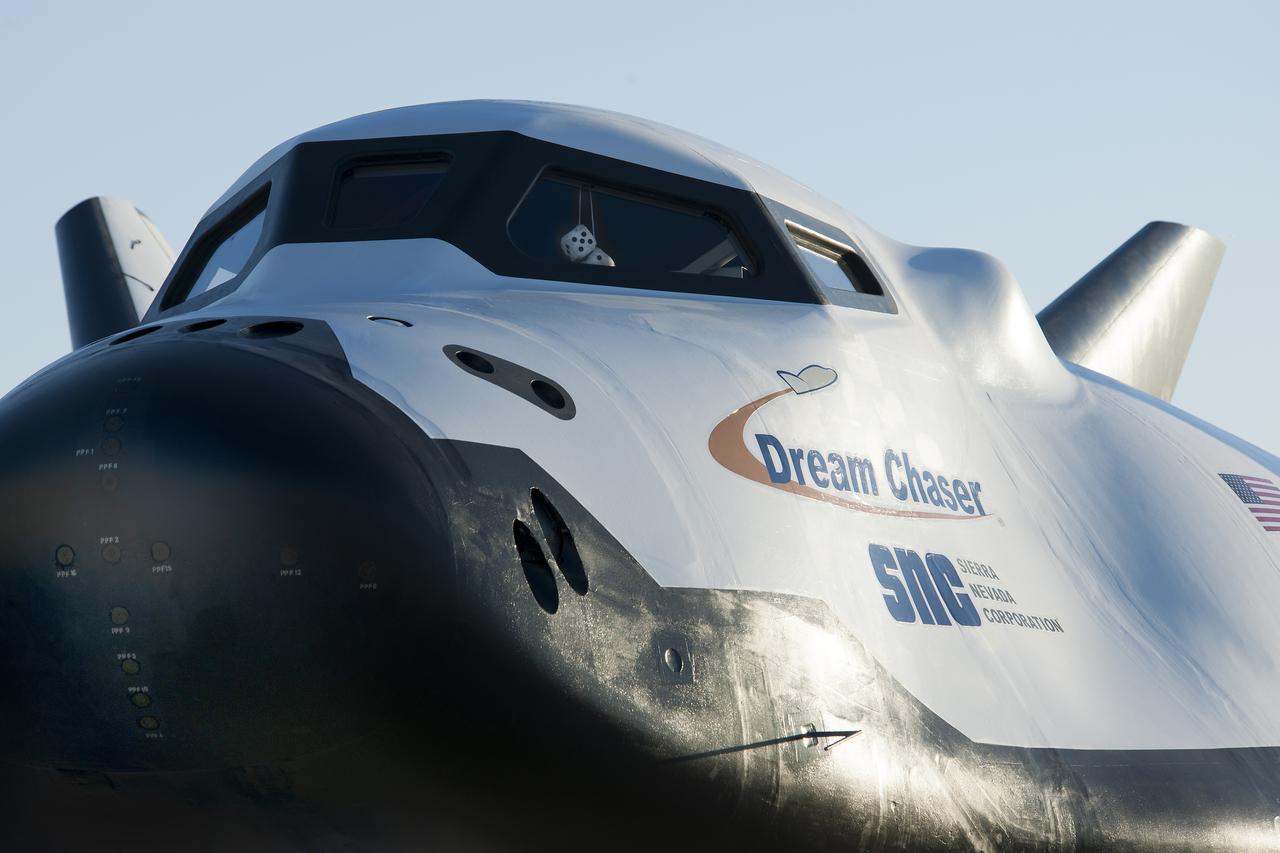

Sierra Nevada Corp’s Dream Chaser posed on ramp at sunrise at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center in California where the aircraft has gone through a series of tests in preparation for flight.
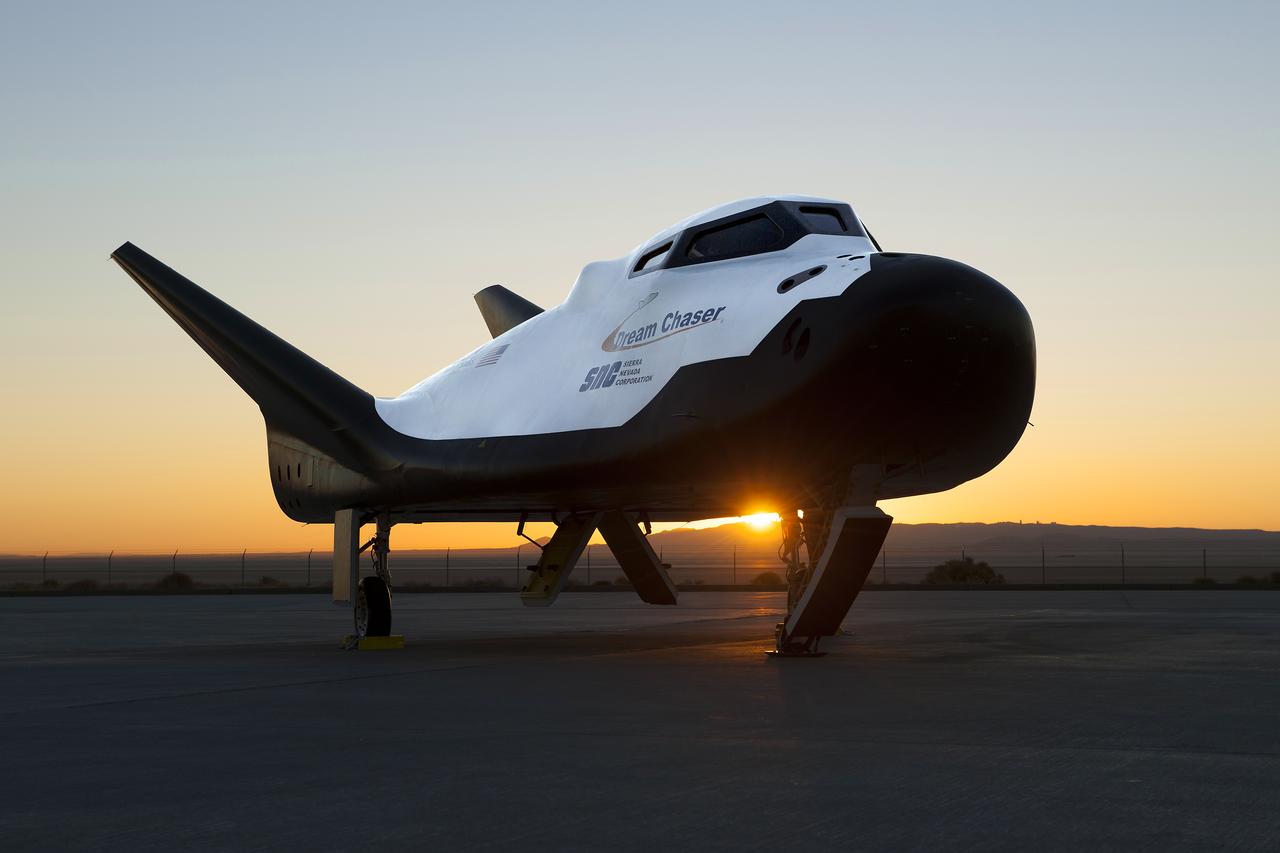

Sierra Nevada Corp’s Dream Chaser posed on ramp at sunrise at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center in California where the aircraft has gone through a series of tests in preparation for flight.
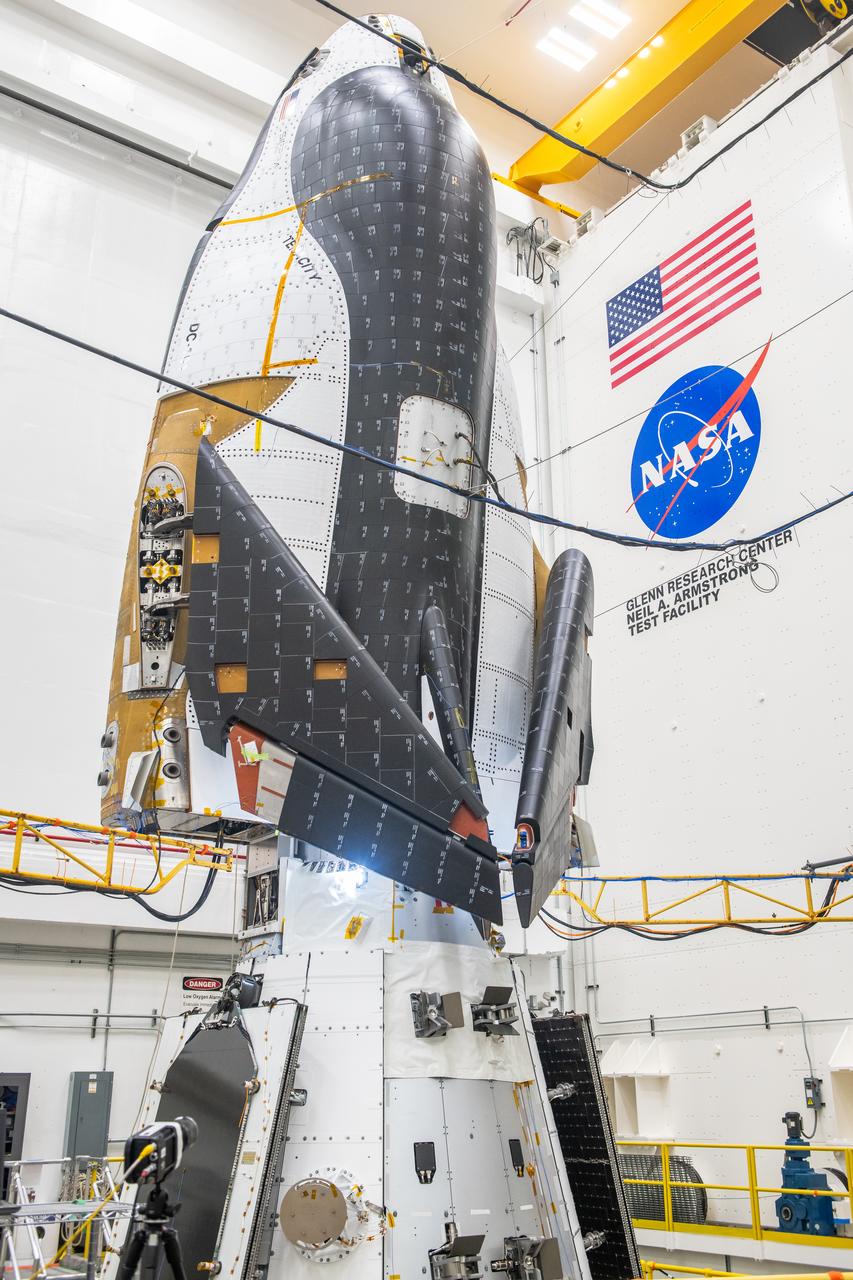

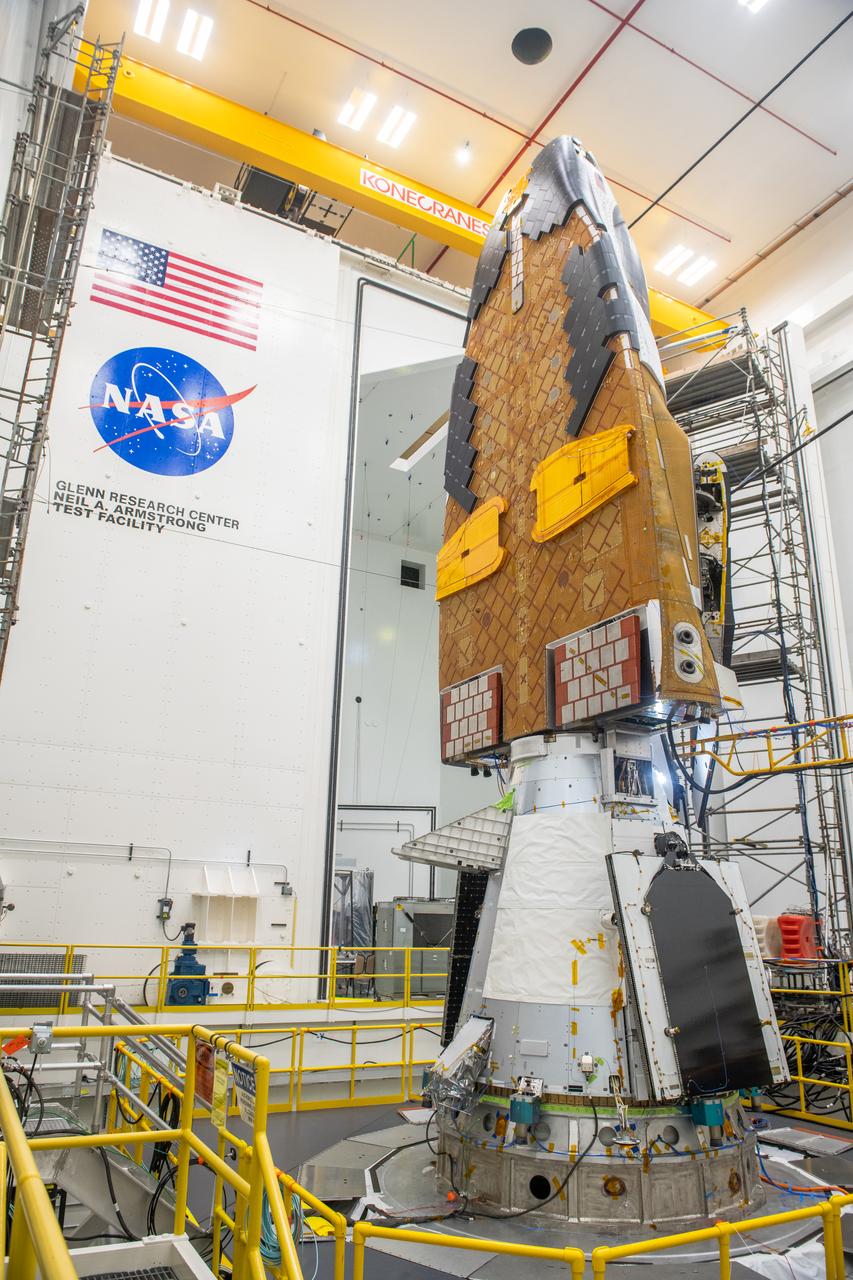
The Neil Armstrong Test Facility, part of NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland, is home to multiple test facilities, including the Space Environments Complex and the In-Space Propulsion Facility, both stops for Dream Chaser. The complex is home to the Mechanical Vibration Facility, which subjects test articles to the rigorous conditions of launch. While at Armstrong, the Dream Chaser winged spacecraft was stacked atop its Shooting Star cargo module on the vibration table to experience vibrations like those during launch and re-entry to the Earth’s atmosphere.
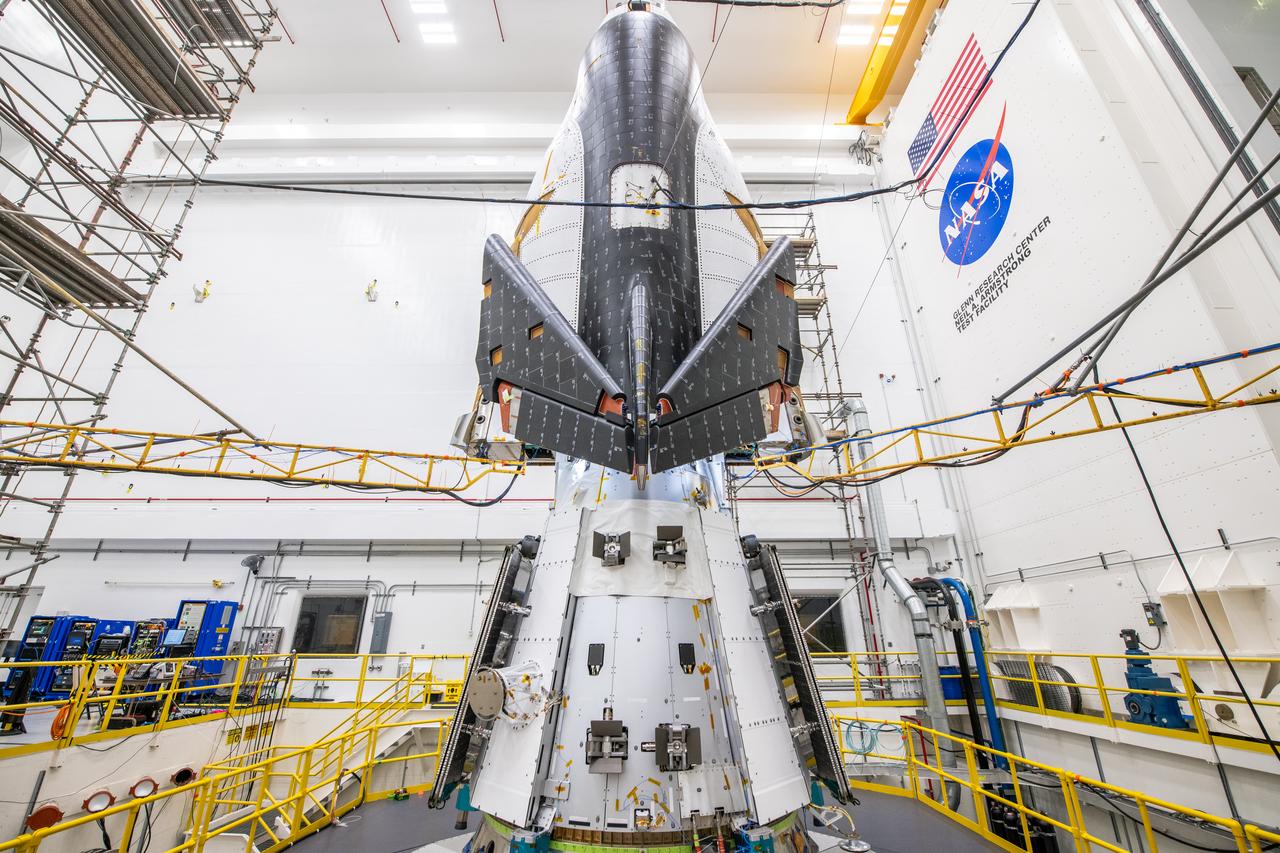

The Neil Armstrong Test Facility, part of NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland, is home to multiple test facilities, including the Space Environments Complex and the In-Space Propulsion Facility, both stops for Dream Chaser. The complex is home to the Mechanical Vibration Facility, which subjects test articles to the rigorous conditions of launch. While at Armstrong, the Dream Chaser winged spacecraft was stacked atop its Shooting Star cargo module on the vibration table to experience vibrations like those during launch and re-entry to the Earth’s atmosphere.
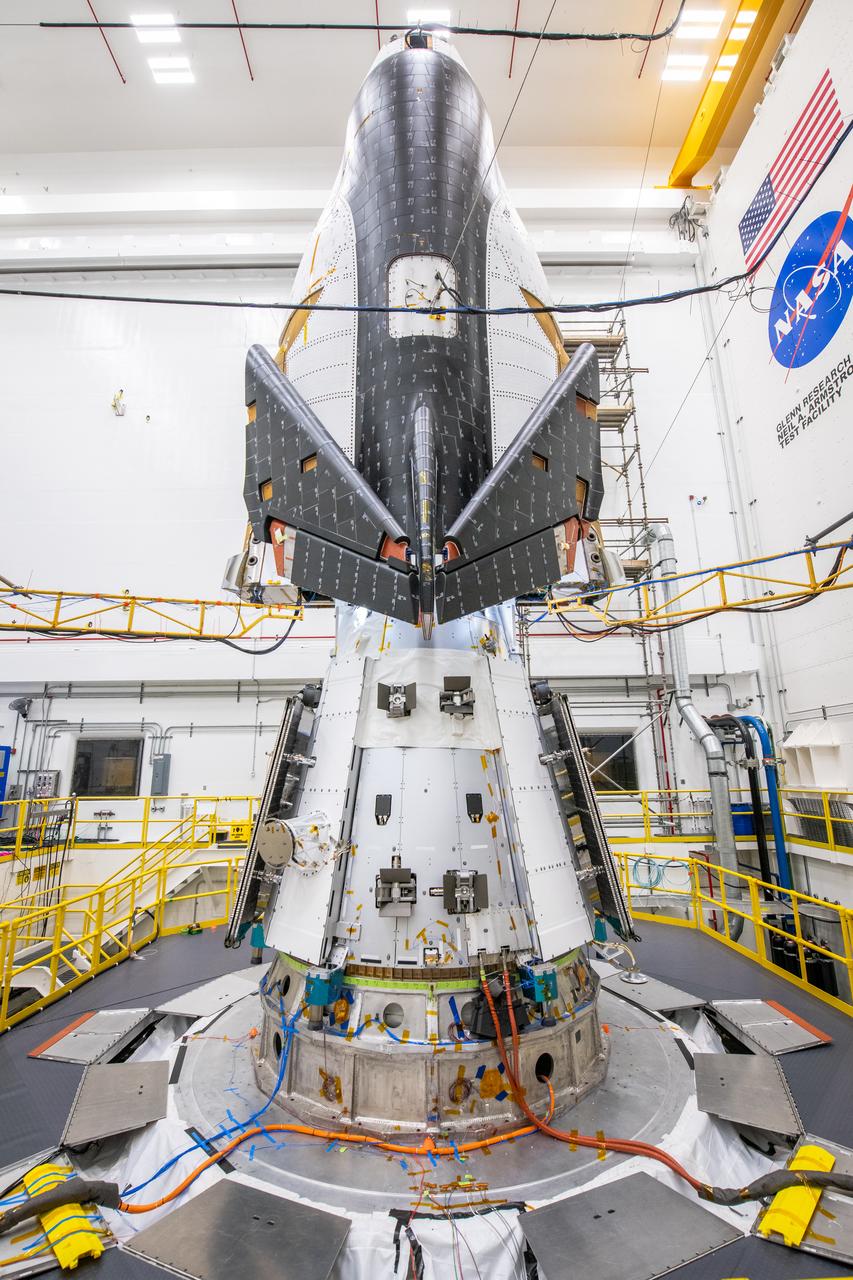

The Neil Armstrong Test Facility, part of NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland, is home to multiple test facilities, including the Space Environments Complex and the In-Space Propulsion Facility, both stops for Dream Chaser. The complex is home to the Mechanical Vibration Facility, which subjects test articles to the rigorous conditions of launch. While at Armstrong, the Dream Chaser winged spacecraft was stacked atop its Shooting Star cargo module on the vibration table to experience vibrations like those during launch and re-entry to the Earth’s atmosphere.
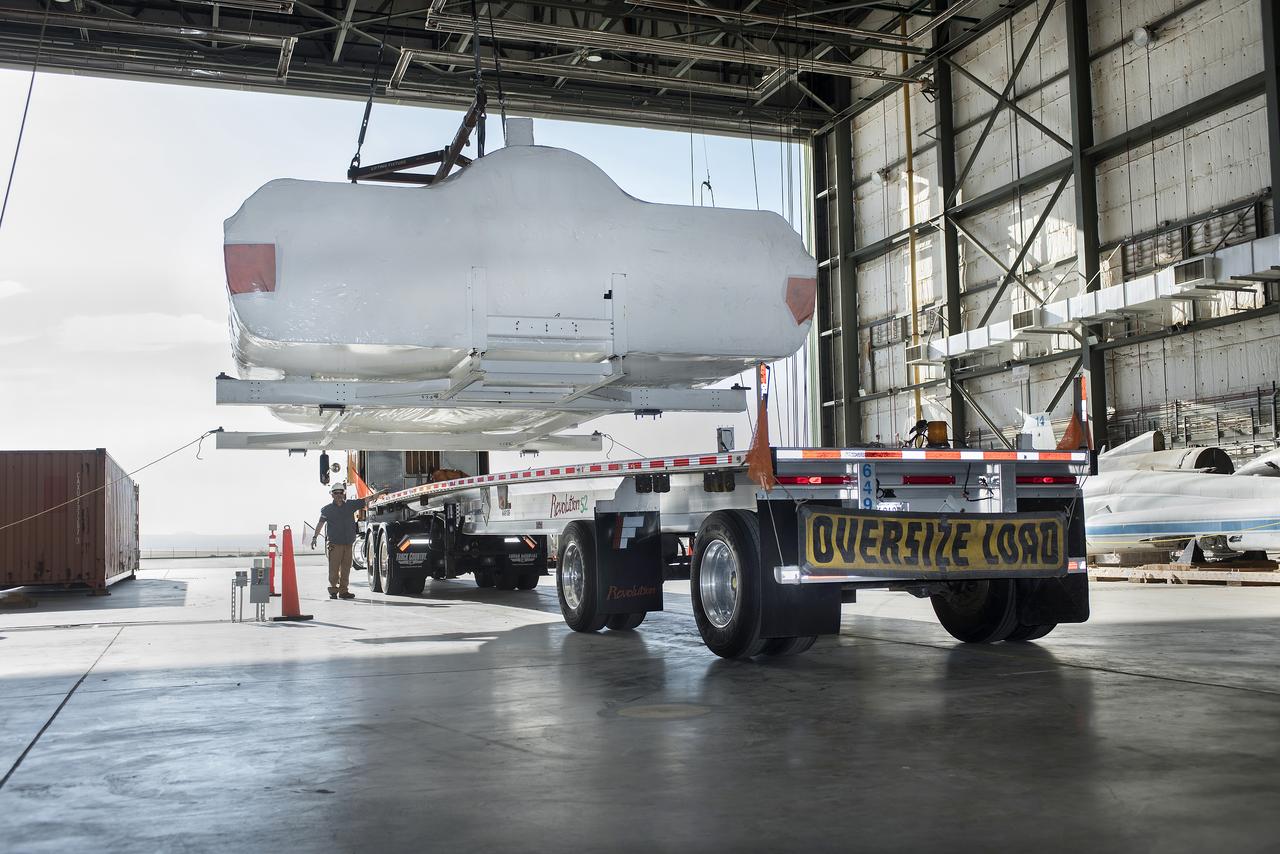

SNC Dream Chaser is lifted on to a truck in NASA Armstrong’s historic space shuttle hangar where the spacecraft stayed as it was being prepared for testing and flights. Dream Chaser is in Colorado at a SNC facility.

A technician in shown inside Sierra Space’s Dream Chaser spaceplane preparing for vibration testing at the Neil Armstrong Test Facility’s Mechanical Vibration Facility. Using the world’s most powerful spacecraft shaker system in February 2024, NASA exposed Dream Chaser and its Shooting Star cargo module to vibrations like those it will experience during launch and re-entry into the atmosphere. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)
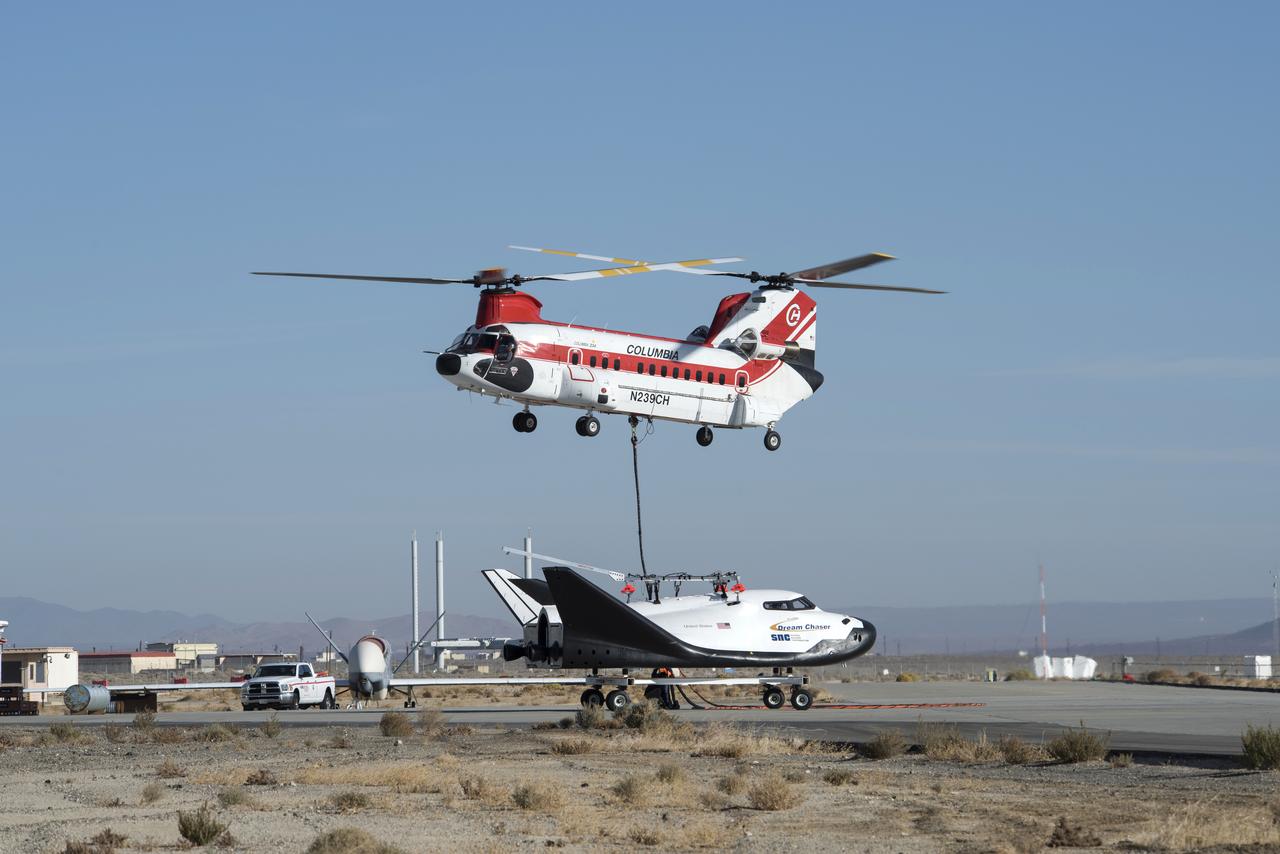

Sierra Nevada Corp’s Dream Chaser was lifted by helicopter from the ramp at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, before its successful approach and landing flight test on Nov. 11, 2017.
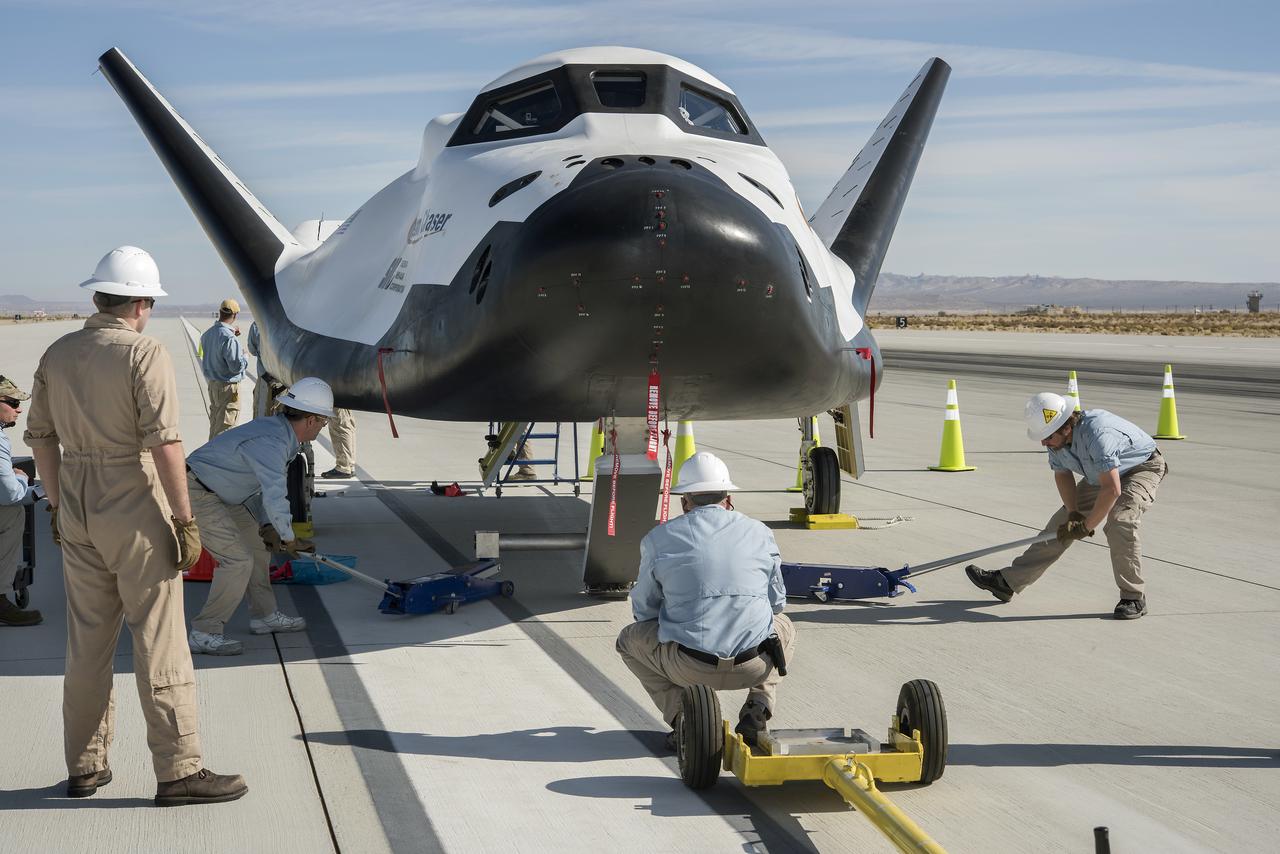

After successfully landing on an Edwards Air Force Base runway on Nov. 11, 2017, Sierra Nevada Corp’s Dream Chaser was prepared for its tow back to NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center in California.
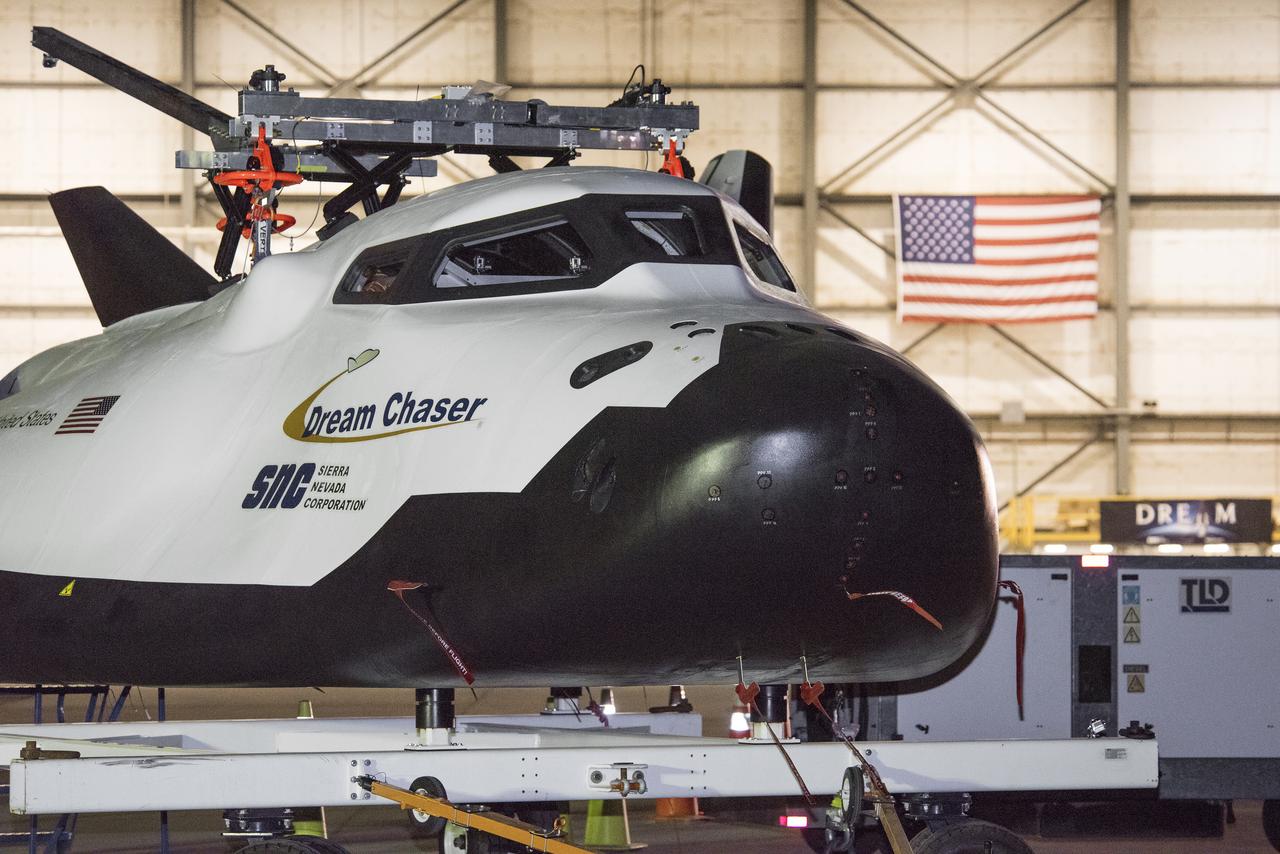

A lift device was attached to Sierra Nevada Corp’s Dream Chaser for a helicopter to pick it up to drop for its successful approach and landing test at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California on Nov. 11, 2017.
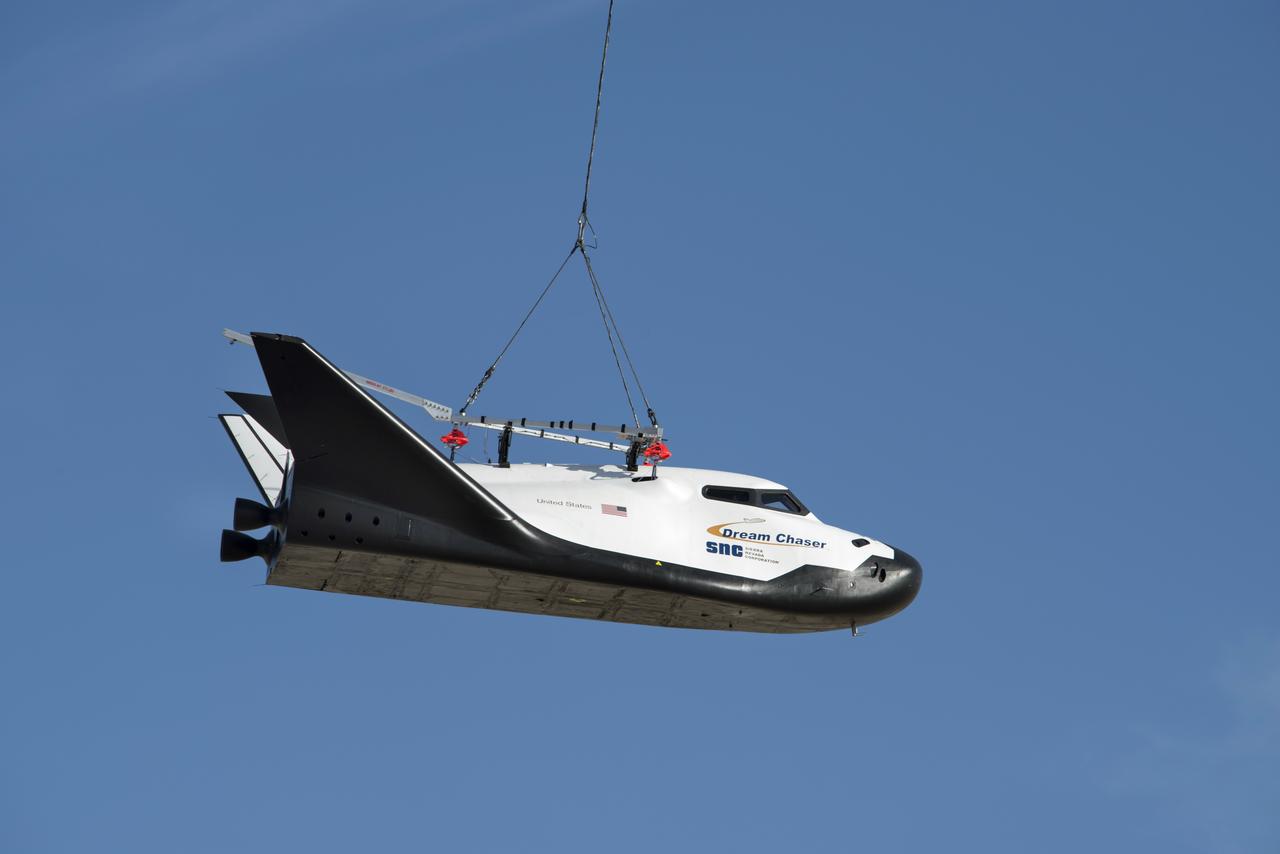

Sierra Nevada Corp’s Dream Chaser was lifted by helicopter from the ramp at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, before its successful approach and landing flight test on Nov. 11, 2017.

Sierra Nevada Corp’s Dream Chaser was lifted by helicopter from the ramp at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, before its successful approach and landing flight test on Nov. 11, 2017.

Sierra Nevada Corp’s Dream Chaser crew prepared for helicopter lift off ramp at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, for its successful approach and landing flight test on Nov. 11, 2017.
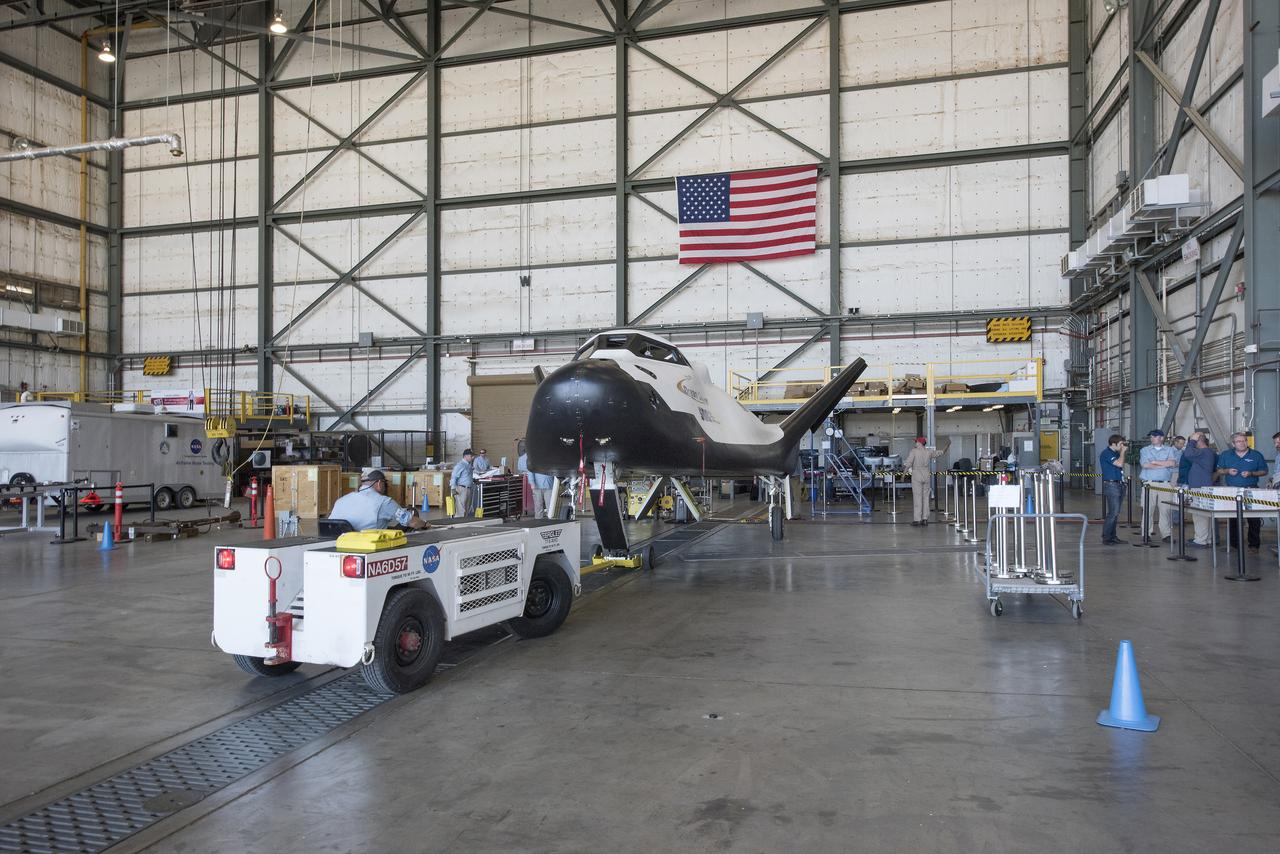

After a successful approach and landing flight test on Nov. 11, 2017, Sierra Nevada Corp’s Dream Chaser was towed back to NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, and placed in the former space shuttle hangar.
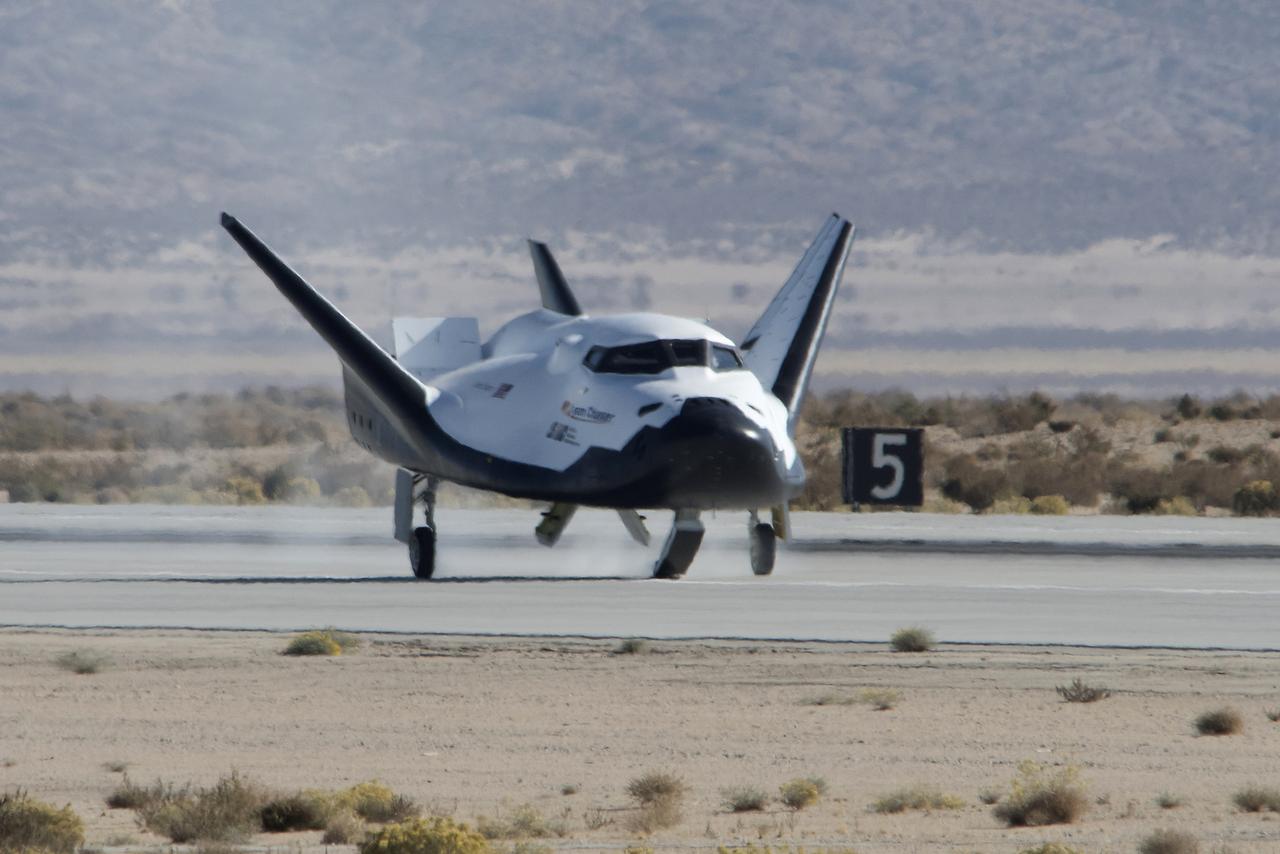

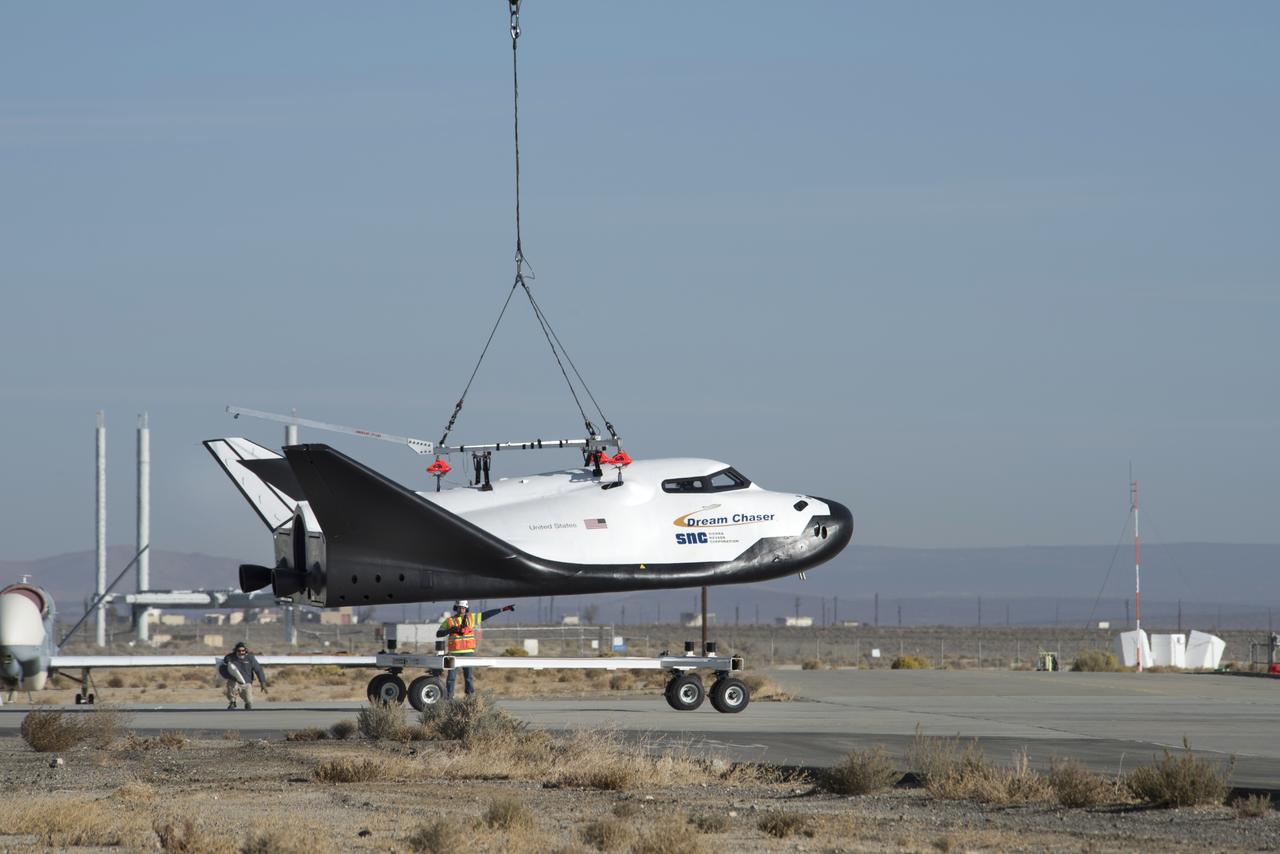
Sierra Nevada Corp’s Dream Chaser successfully landed on an Edwards Air Force Base runway on Nov. 11, 2017, after being lifted from the ramp at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center in California.
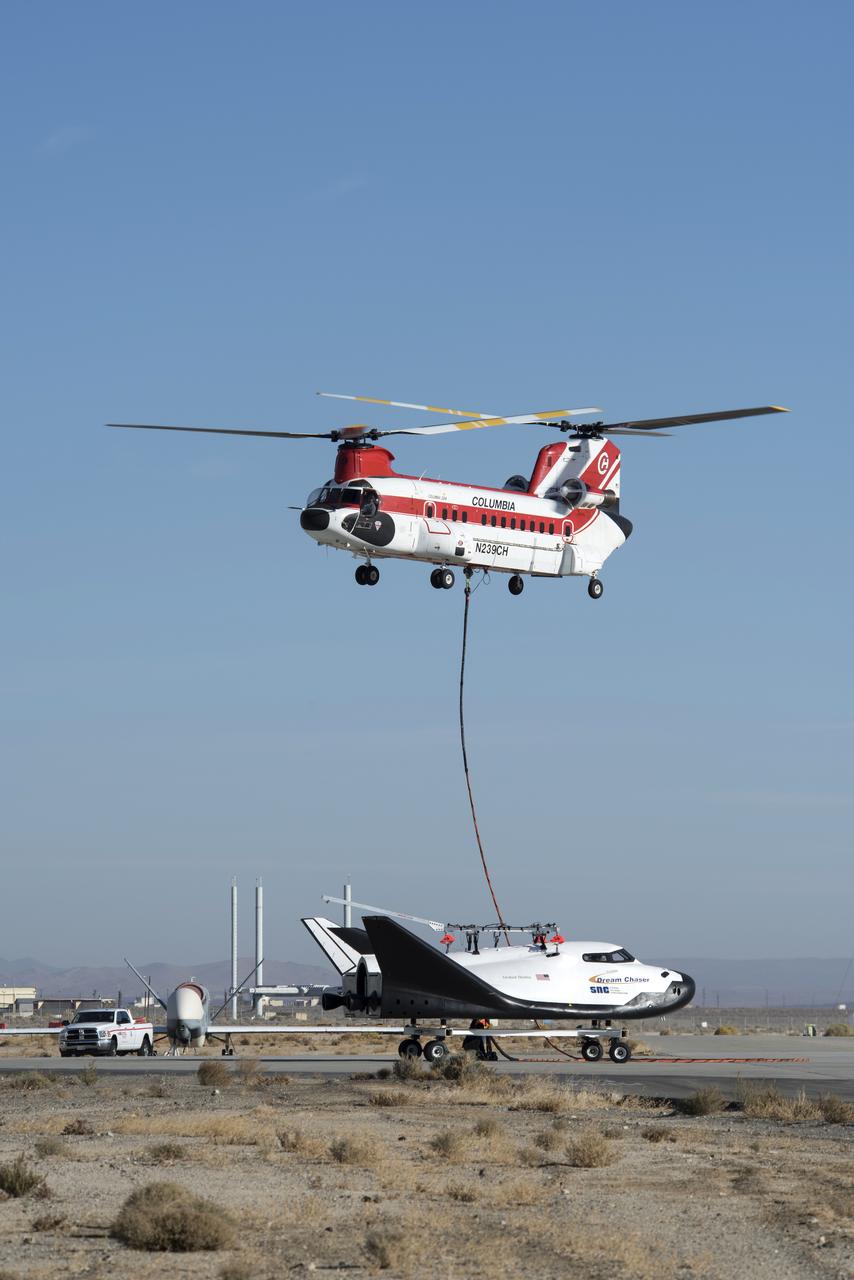

Sierra Nevada Corp’s Dream Chaser was lifted by helicopter from the ramp at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, before its successful approach and landing flight test on Nov. 11, 2017.

Sierra Nevada Corp’s Dream Chaser facing sunrise over Rogers Dry Lake by NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center in California where it was being prepared for a successful approach and landing test Nov. 11, 2017.

SNC Dream Chaser is in NASA Armstrong, previously known as space shuttle, hangar being loaded on truck for its departure from the center heading to SNC in Colorado.
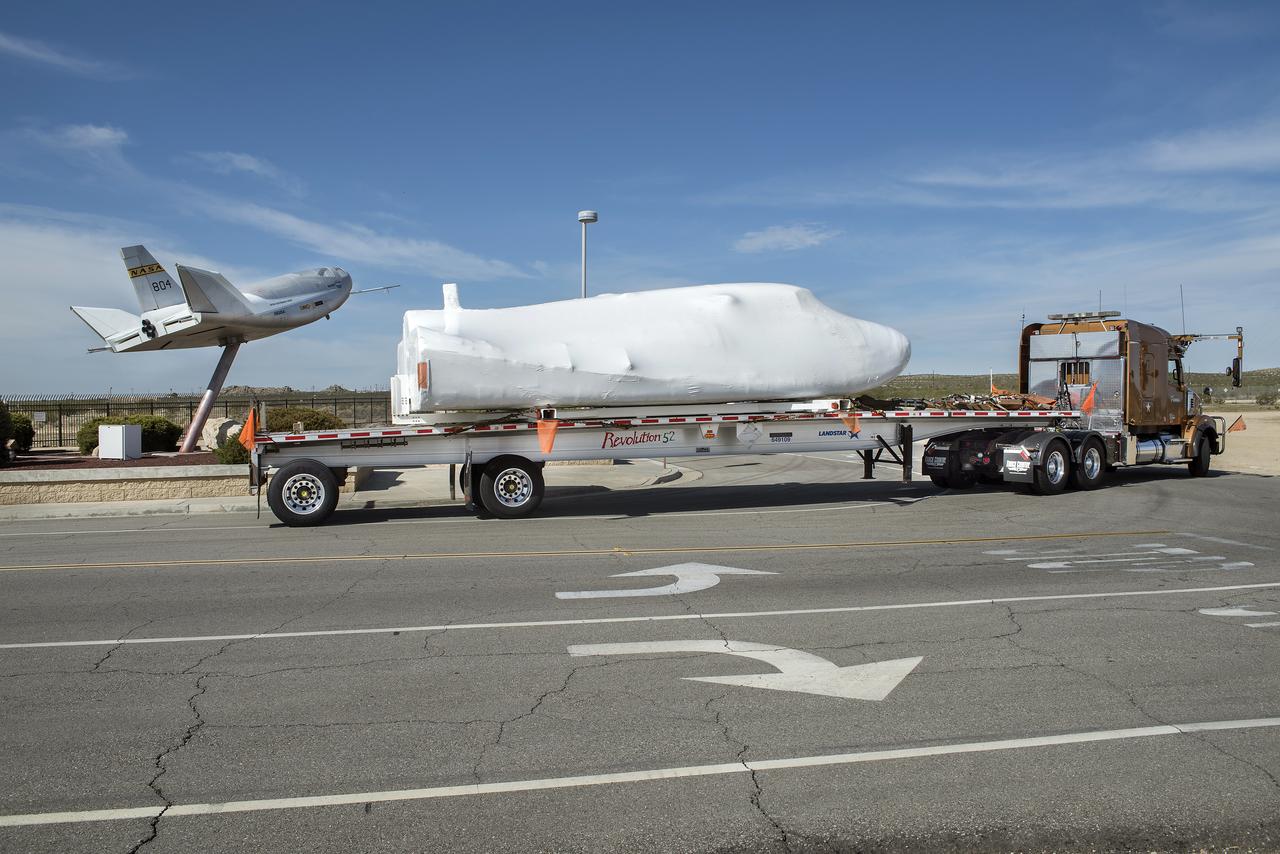

Dream Chaser departs in front of HL-10 at NASA Armstrong where it underwent testing and preparation for successful approach and landing flight. The spacecraft returned to SNC facility in Colorado.

Group photo of the crew just before the critical lift of Dream Chaser into the chamber at ISP (In Space Propulsion) NASA GRC-ATF. Once lifted and lowered into the test chamber, it will be exposed to the harsh cold conditions of space for extended periods of time. Sierra Space Dream Chaser space plane will be lifted into the chamber at ISP (In Space Propulsion) facility, building 3211 at ATF (Armstrong Test Facility) for environmental testing

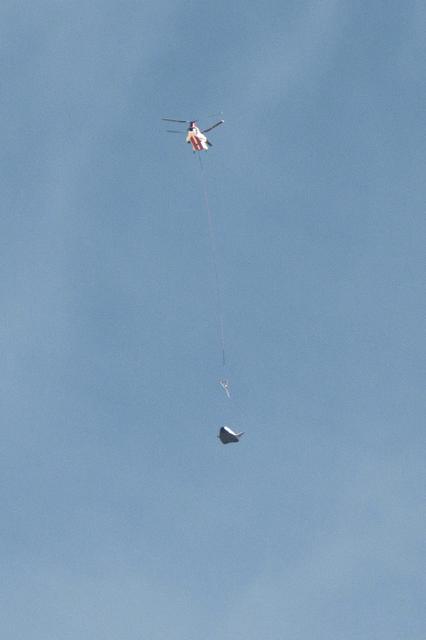
Sierra Nevada Corp’s Dream Chaser was released from a helicopter for a landing on an Edwards Air Force Base runway after it was lifted from the ramp at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, for its successful approach and landing flight test on Nov. 11, 2017.

The Sierra Space Plane, Dream Chaser, suspended by a crane sits just inside the overhead door of the ISP (In Space Propulsion) test facility at NASA GRC-ATF. Once lifted and lowered into the test chamber, it will be exposed to the harsh cold conditions of space for testing in extended periods of time.

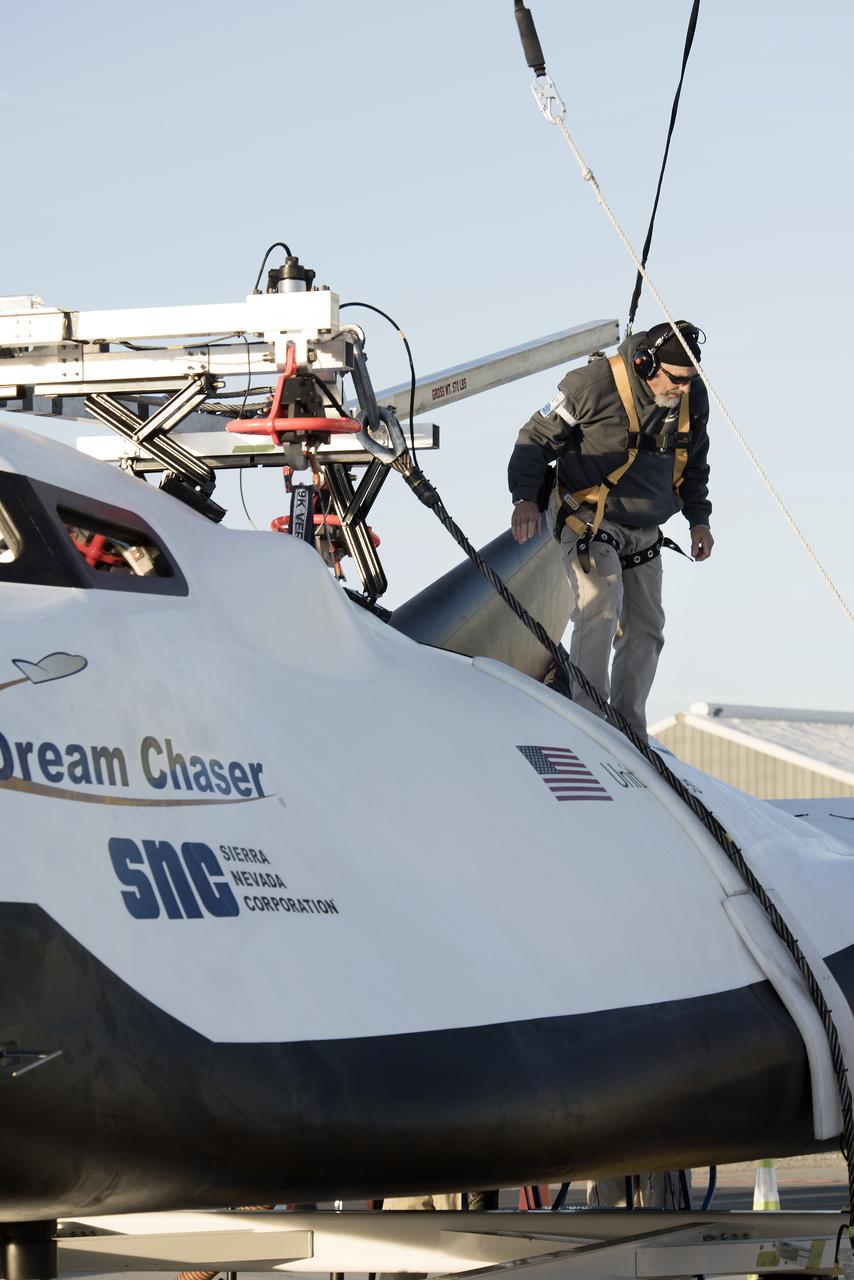
Sierra Nevada Corp’s Dream Chaser crew attached the wires that the helicopter would use to pick it up from NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California in preparation for its successful approach and landing test Nov. 11, 2017.
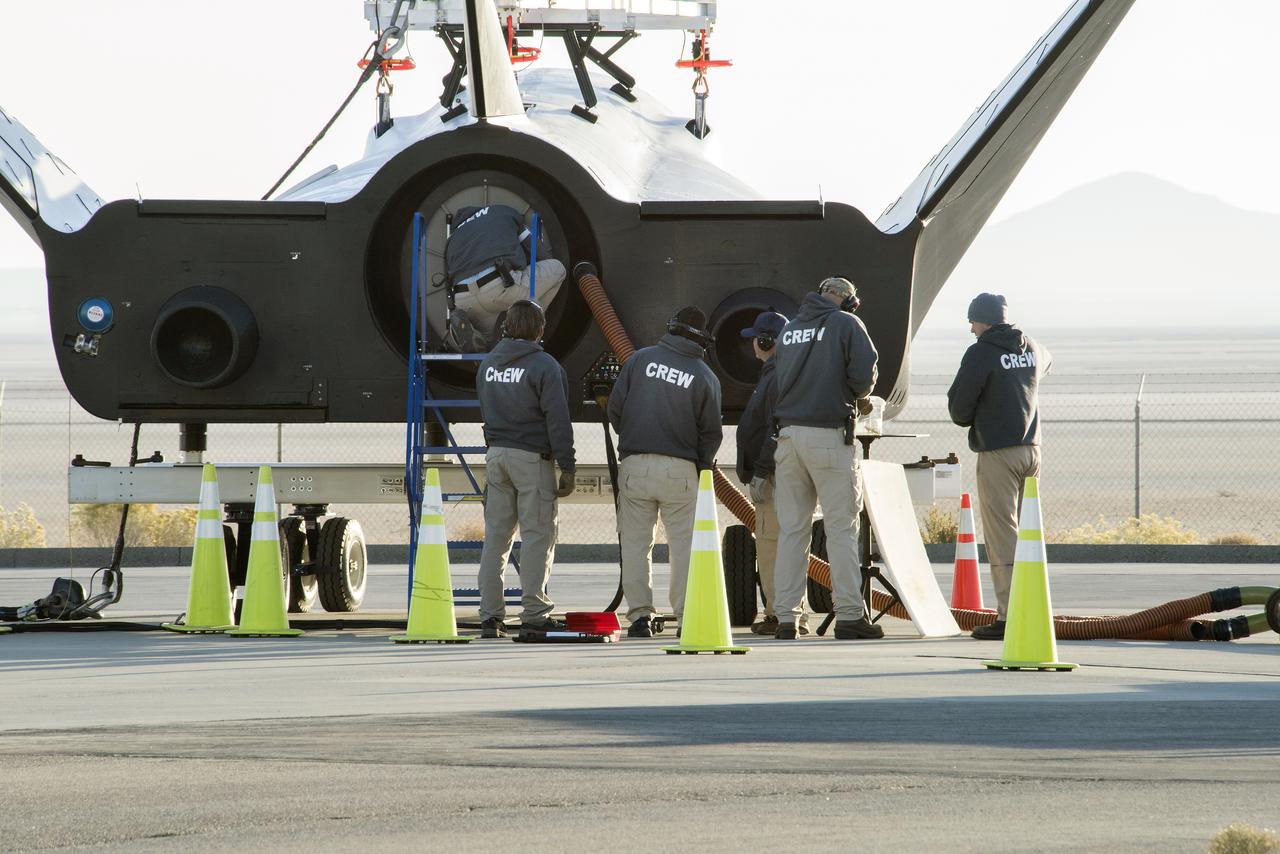

Sierra Nevada Corp’s Dream Chaser crew attached the wires that the helicopter would use to pick it up from NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California in preparation for its successful approach and landing test Nov. 11, 2017.

Sierra Nevada Corp’s Dream Chaser being towed from the former space shuttle hangar at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center in California where it was housed and prepared for its successful Nov. 11, 2017 approach and landing test.

Sierra Nevada Corp’s Dream Chaser crew attached the wires that the helicopter would use to pick it up from NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California in preparation for its successful approach and landing test Nov. 11, 2017.

Sierra Nevada Corp’s Dream Chaser is released for a landing on Edwards Air Force Base runway after departing a ramp at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, for its successful approach and landing flight test on Nov. 11, 2017.
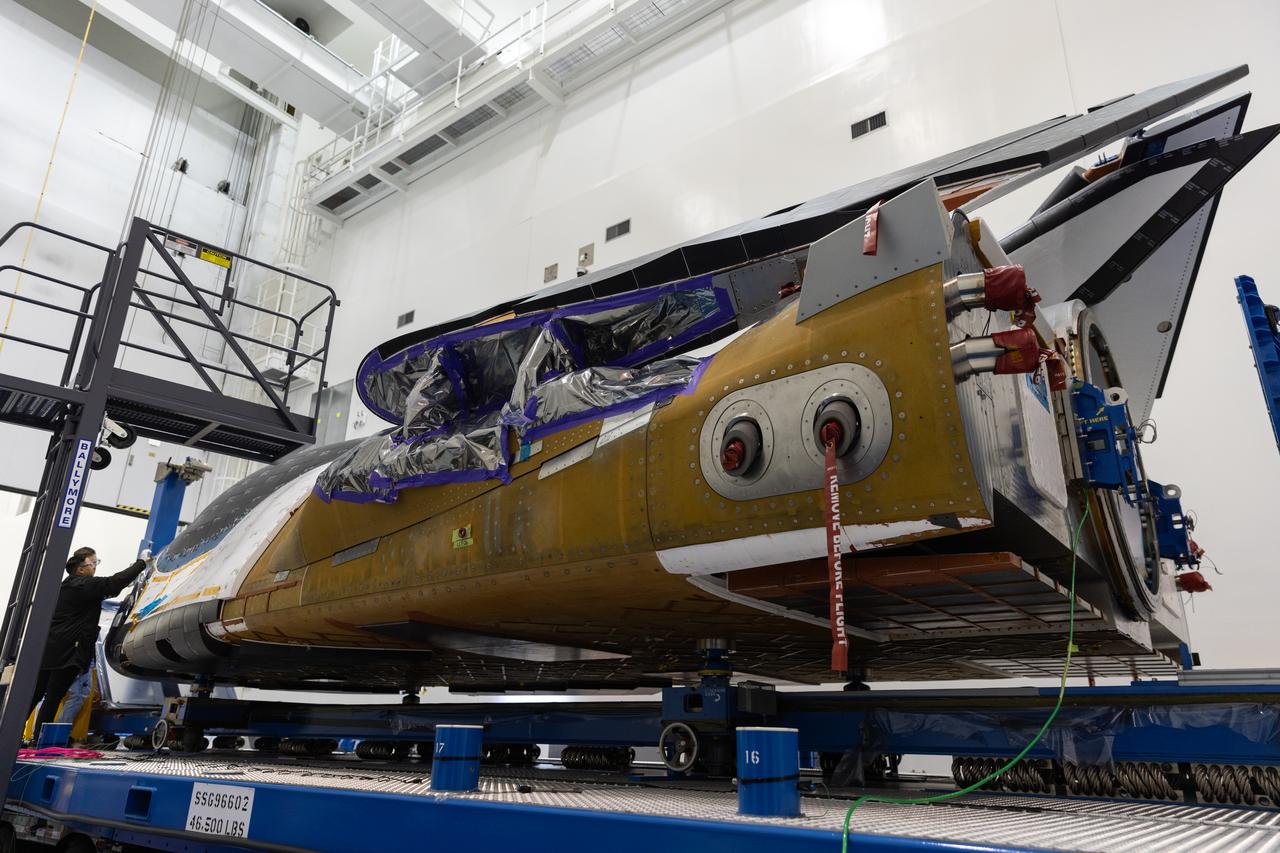

Teams process Dream Chaser Tenacity, Sierra Space's uncrewed cargo spaceplane, inside the Space Systems Processing Facility (SSPF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, May 20, 2024, following its arrival from the agency's Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Ohio. Dream Chaser Tenacity will undergo final testing and prelaunch processing inside the high bay of the SSPF ahead of its inaugural launch atop a ULA (United Launch Alliance) Vulcan rocket from nearby Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. The reusable transportation system is contracted to perform a minimum of seven cargo missions to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s efforts to expand commercial resupply services to low Earth orbit.
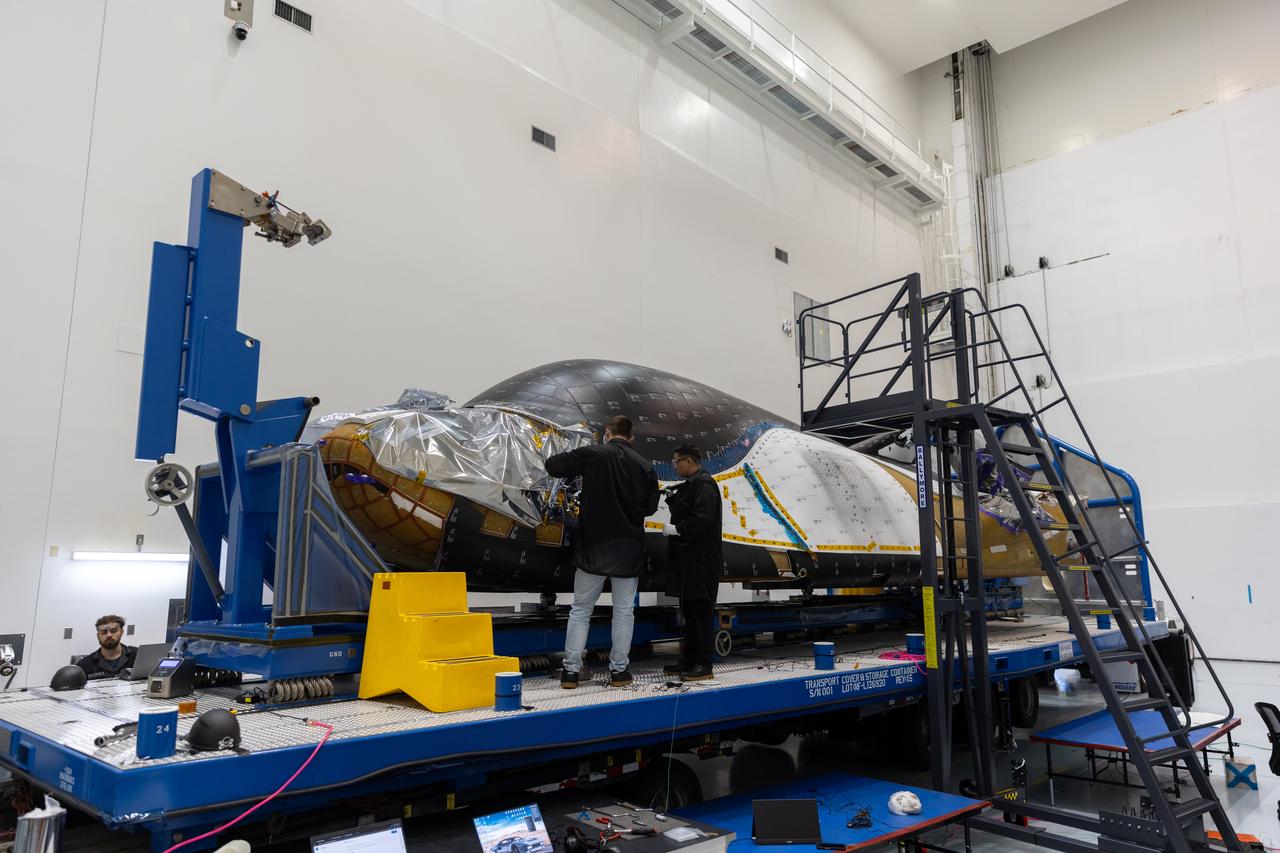

Teams process Dream Chaser Tenacity, Sierra Space's uncrewed cargo spaceplane, inside the Space Systems Processing Facility (SSPF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, May 20, 2024, following its arrival from the agency's Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Ohio. Dream Chaser Tenacity will undergo final testing and prelaunch processing inside the high bay of the SSPF ahead of its inaugural launch atop a ULA (United Launch Alliance) Vulcan rocket from nearby Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. The reusable transportation system is contracted to perform a minimum of seven cargo missions to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s efforts to expand commercial resupply services to low Earth orbit.
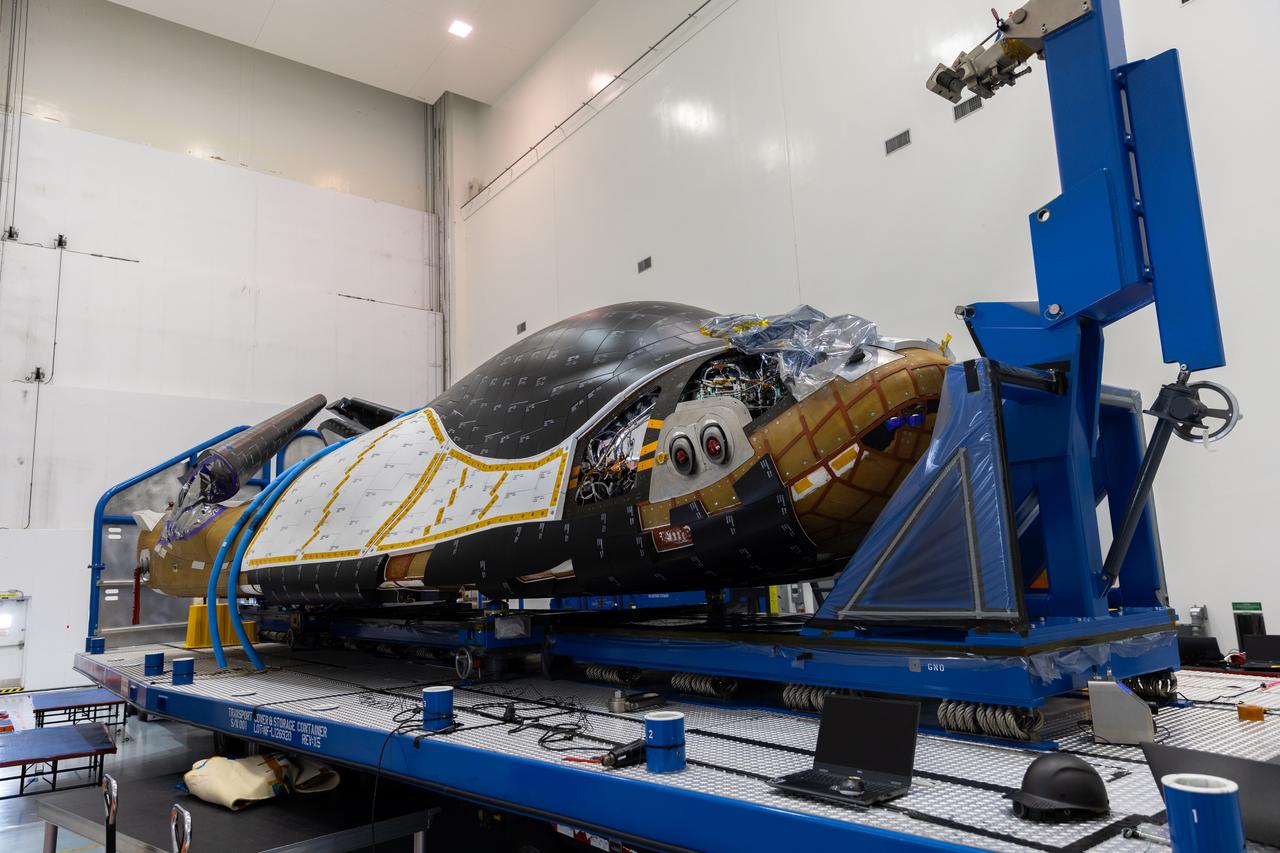

Dream Chaser Tenacity, Sierra Space's uncrewed cargo spaceplane is processed inside the Space Systems Processing Facility (SSPF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, May 20, 2024, after arriving by truck inside a climate-controlled transportation container, completing the journey from the agency's Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Ohio. Dream Chaser Tenacity will undergo final testing and prelaunch processing inside the high bay of the SSPF ahead of its inaugural launch atop a ULA (United Launch Alliance) Vulcan rocket from nearby Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. The reusable transportation system is contracted to perform a minimum of seven cargo missions to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s efforts to expand commercial resupply services to low Earth orbit.
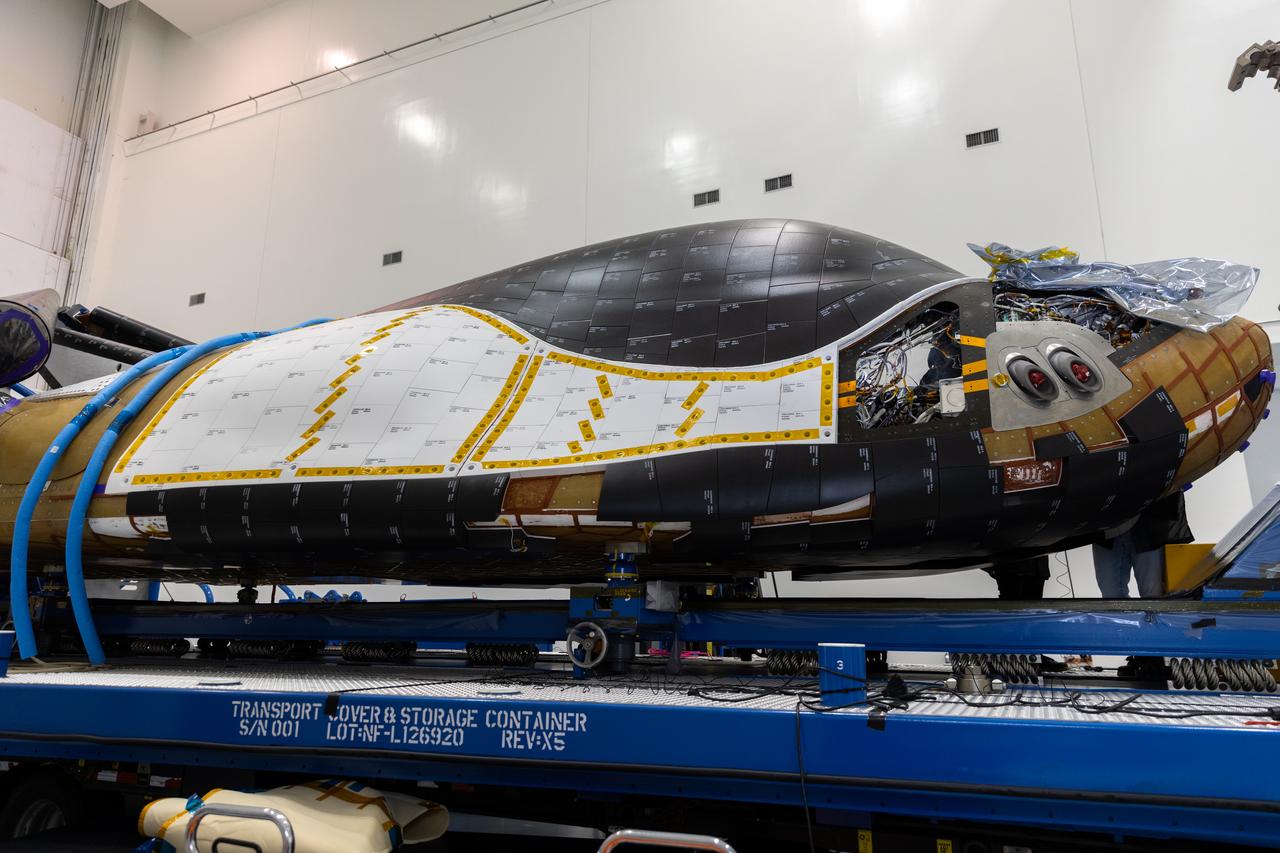

Dream Chaser Tenacity, Sierra Space's uncrewed cargo spaceplane is processed inside the Space Systems Processing Facility (SSPF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, May 20, 2024, after arriving by truck inside a climate-controlled transportation container, completing the journey from the agency's Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Ohio. Dream Chaser Tenacity will undergo final testing and prelaunch processing inside the high bay of the SSPF ahead of its inaugural launch atop a ULA (United Launch Alliance) Vulcan rocket from nearby Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. The reusable transportation system is contracted to perform a minimum of seven cargo missions to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s efforts to expand commercial resupply services to low Earth orbit.
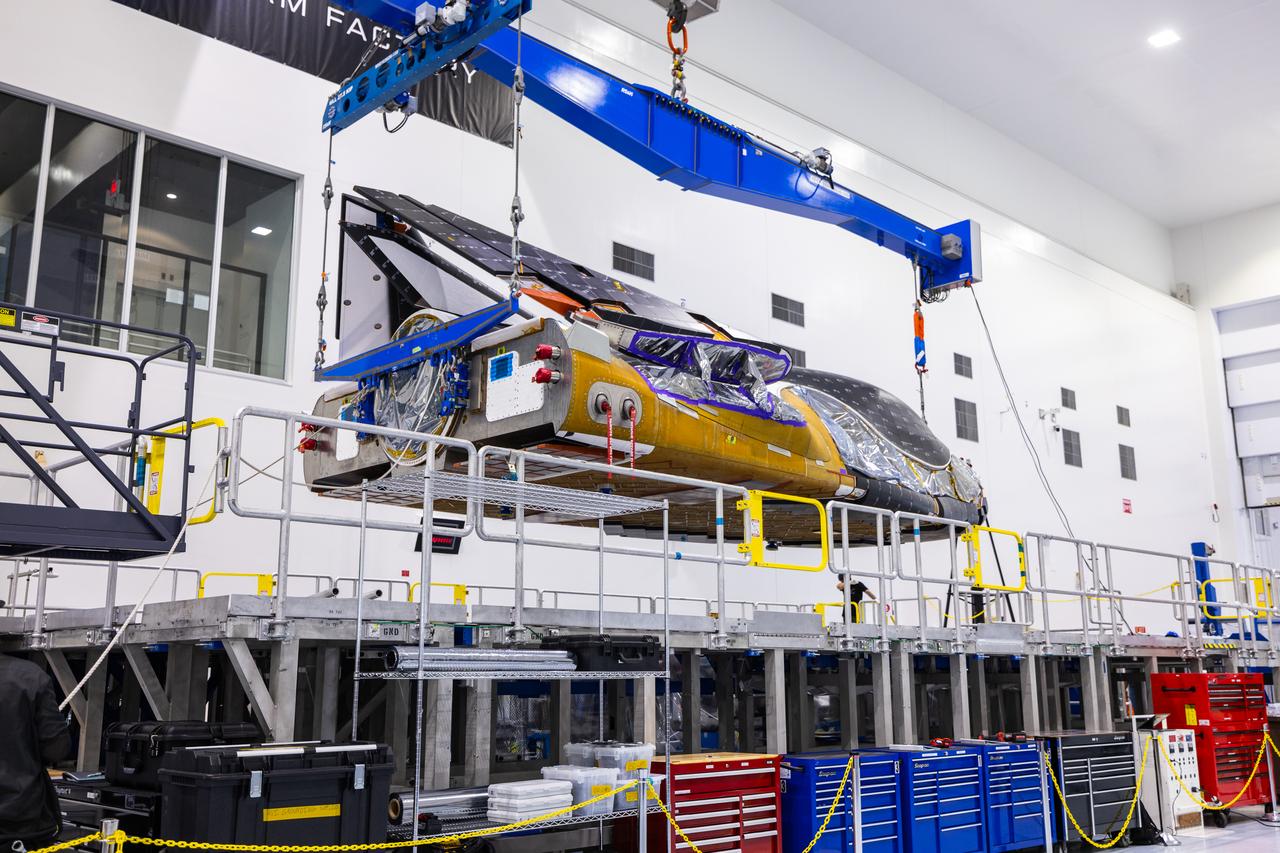

Dream Chaser Tenacity, Sierra Space's uncrewed cargo spaceplane is lifted and moved by crane inside the Space Systems Processing Facility (SSPF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, May 20, 2024. Dream Chaser Tenacity will undergo final testing and prelaunch processing inside the high bay of the SSPF ahead of its inaugural launch atop a ULA (United Launch Alliance) Vulcan rocket from nearby Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. The reusable transportation system is contracted to perform a minimum of seven cargo missions to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s efforts to expand commercial resupply services to low Earth orbit.
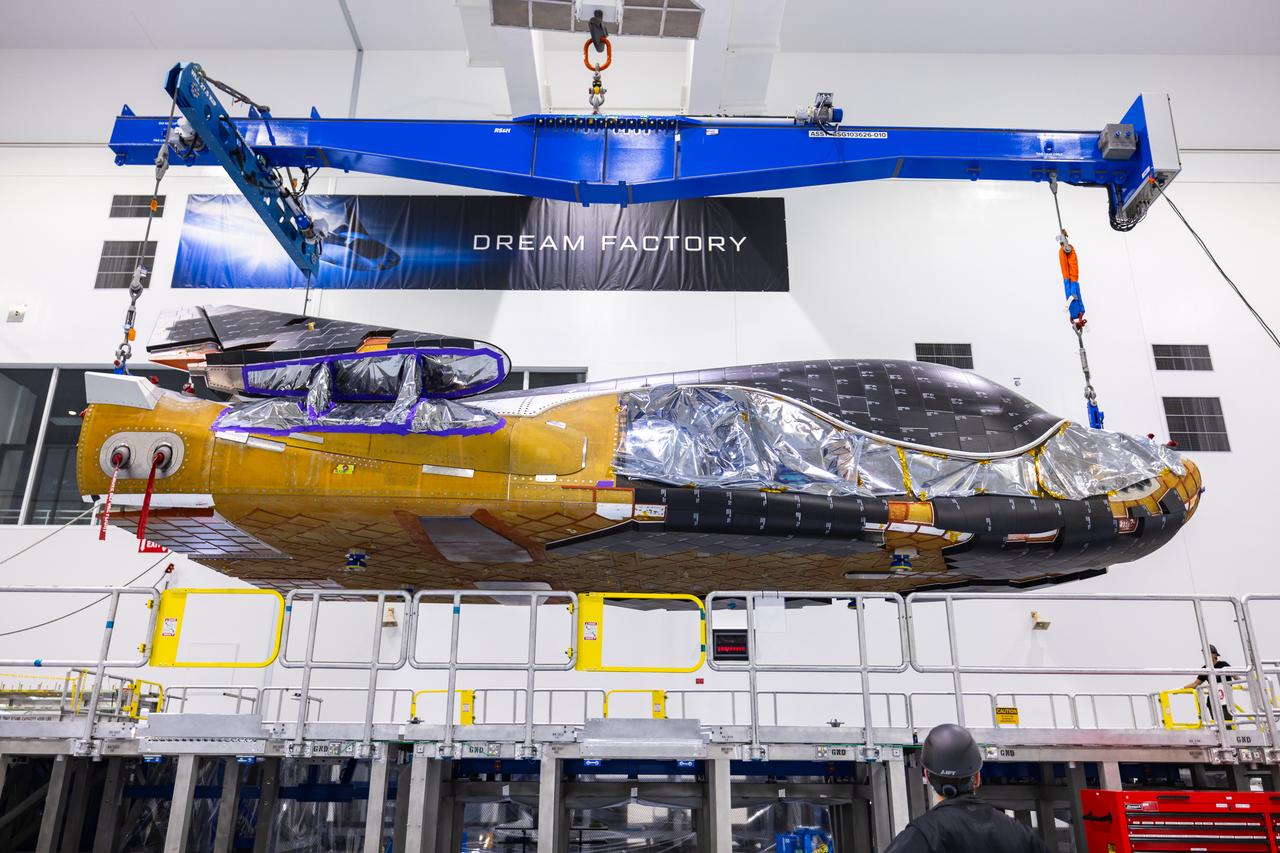

Dream Chaser Tenacity, Sierra Space's uncrewed cargo spaceplane is lifted and moved by crane inside the Space Systems Processing Facility (SSPF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, May 20, 2024. Dream Chaser Tenacity will undergo final testing and prelaunch processing inside the high bay of the SSPF ahead of its inaugural launch atop a ULA (United Launch Alliance) Vulcan rocket from nearby Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. The reusable transportation system is contracted to perform a minimum of seven cargo missions to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s efforts to expand commercial resupply services to low Earth orbit.

Sierra Nevada Corporation's (SNC) Dream Chaser® spacecraft shown on the runway at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center on May 20 preparing for a tow-test. The spacecraft is undergoing ground tests leading up to a free flight test later this year.
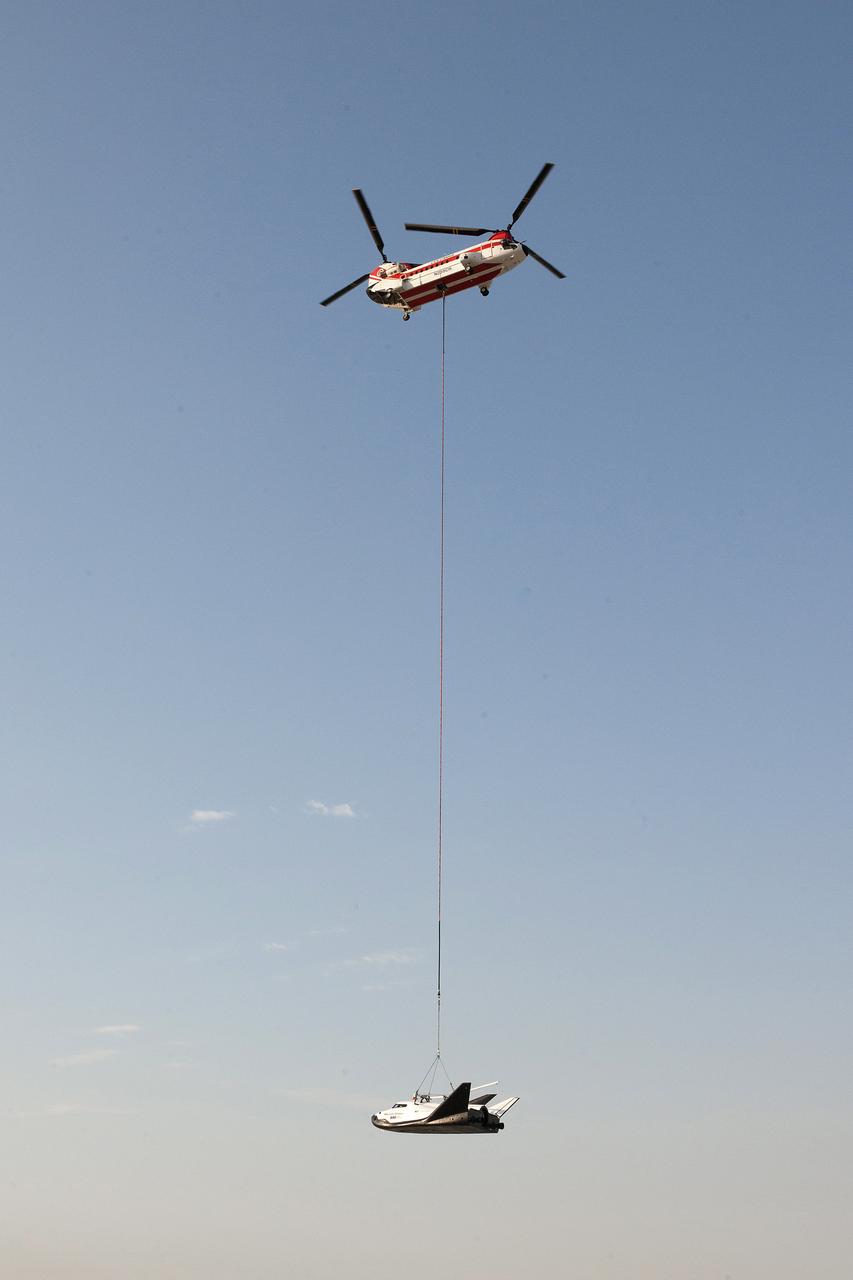

Sierra Nevada's Dream Chaser lifted off ramp on Wednesday, Aug. 30 at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center by Columbia 234 UT helicopter for captive carry flight.
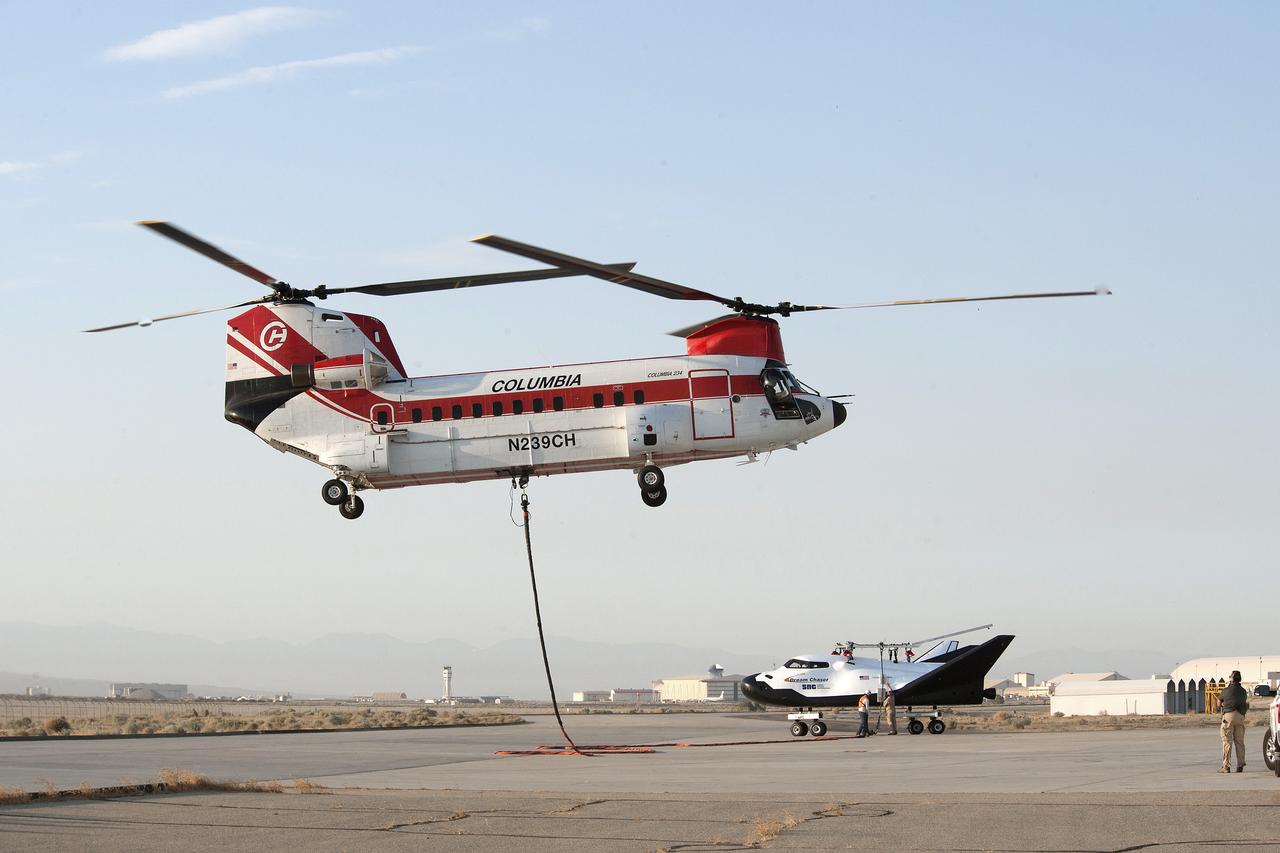

Sierra Nevada Corporation's (SNC) Dream Chaser® being lifted by Columbia 234 UT helicopter for a captive carry flight test on Wednesday, Aug. 30 at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center.
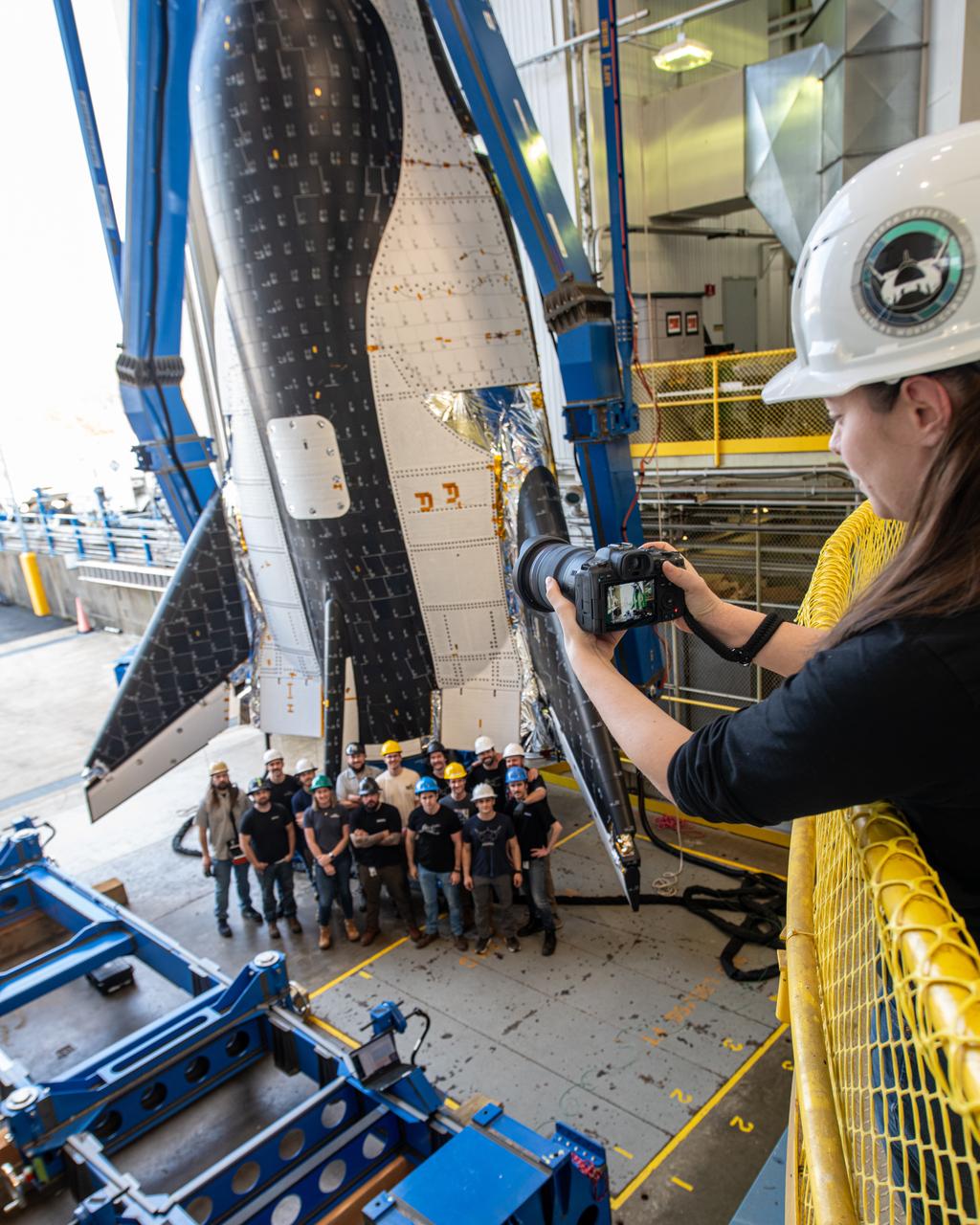

Sierra Space photographer, Shay Saldana is photographed taking a group photo of the crew just before the critical lift of Dream Chaser into the chamber at ISP (In Space Propulsion) NASA GRC-ATF. Once lifted and lowered into the test chamber, it will be exposed to the harsh cold conditions of space for extended periods of time
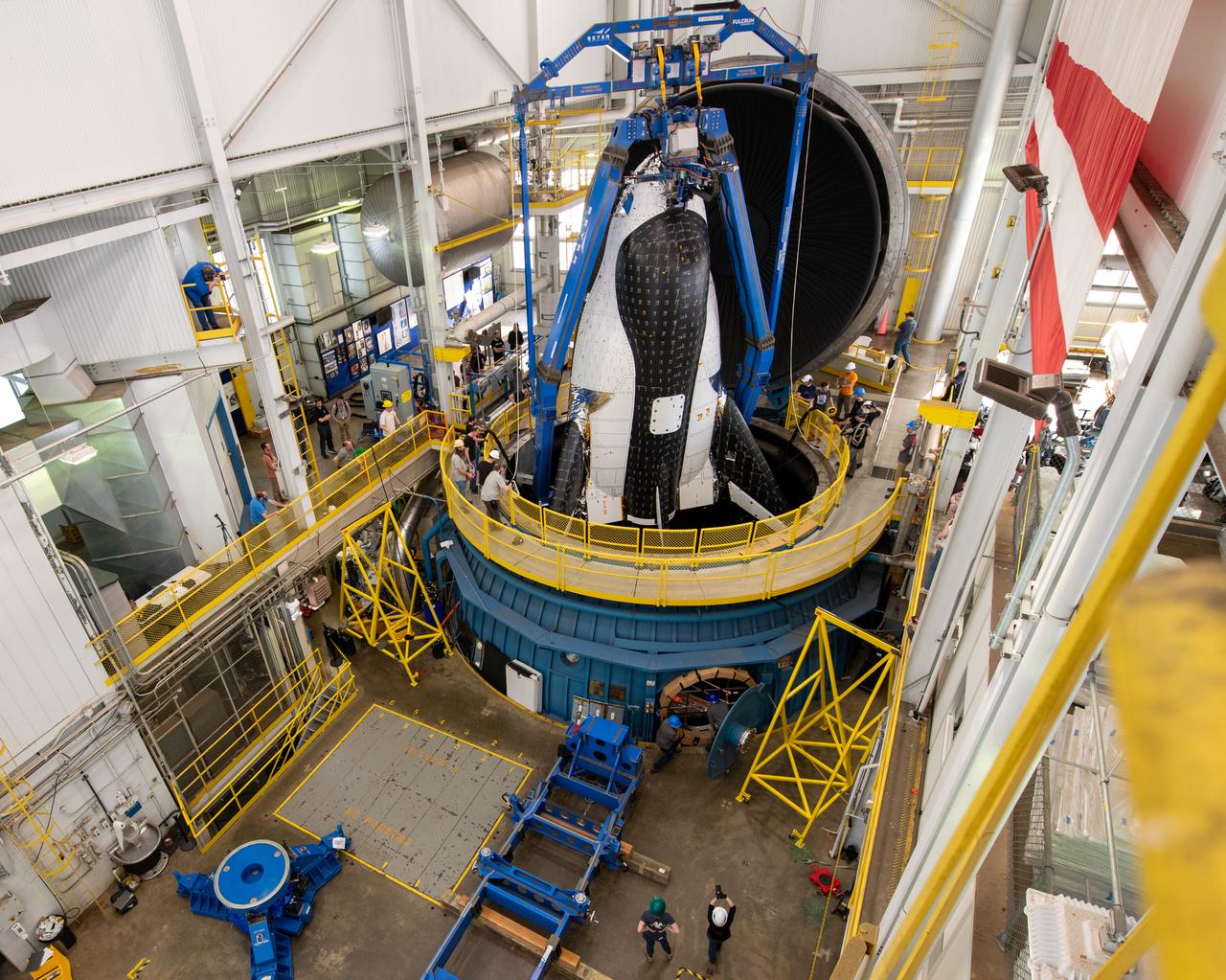

Sierra Space Dream Chaser space plane is lifted into the chamber at ISP (In Space Propulsion) facility, building 3211 at ATF (Armstrong Test Facility) for environmental testing. Once lowered into the test chamber, it will be exposed to the harsh cold conditions of space for extended periods of time.
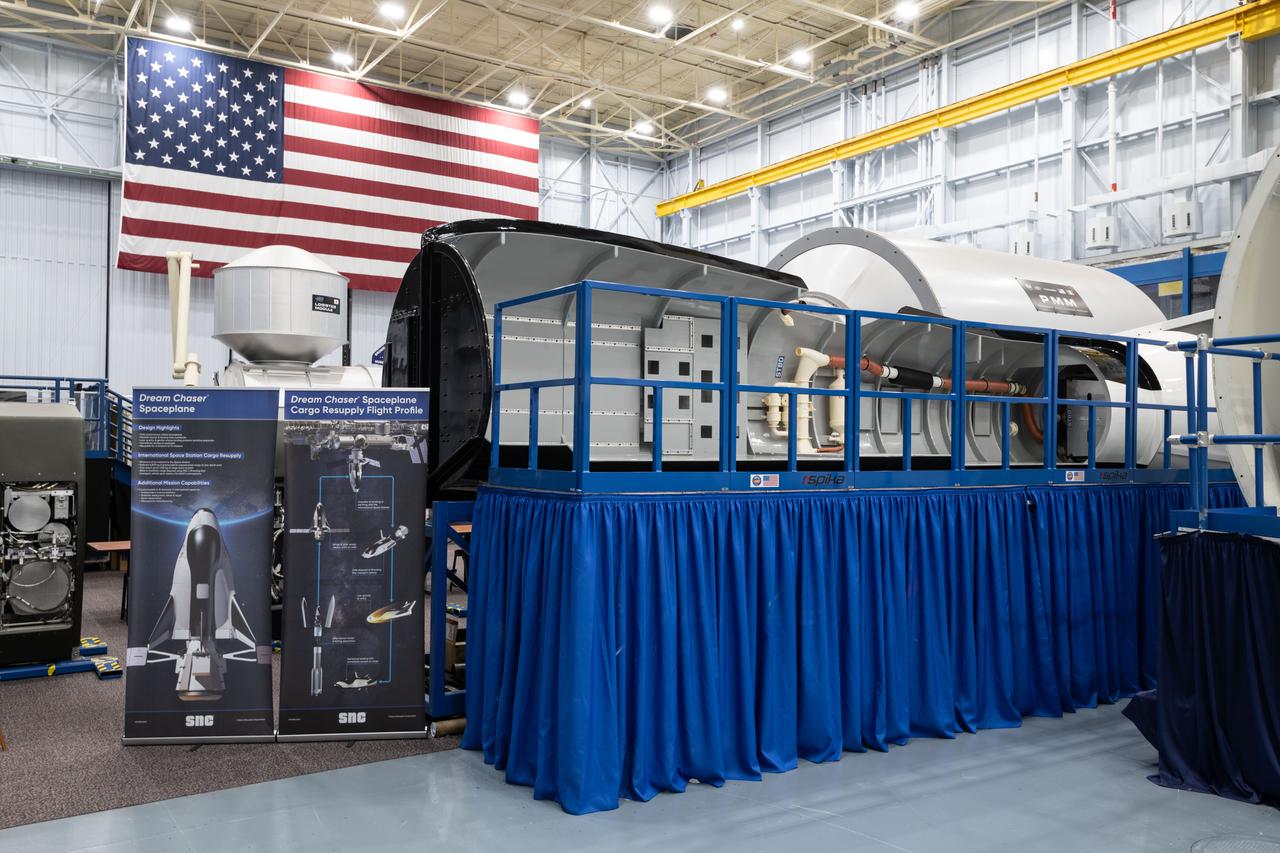

jsc2021e004389 (Jan. 21, 2021) --- External view of the Sierra Nevada Dream Chaser mockup located in Building 9N, Space Vehicle Mockup Facility (SVMF) at the NASA Johnson Space Center.

jsc2021e004388 (Jan. 21, 2021) --- External view of the Sierra Nevada Dream Chaser mockup located in Building 9N, Space Vehicle Mockup Facility (SVMF) at the NASA Johnson Space Center.
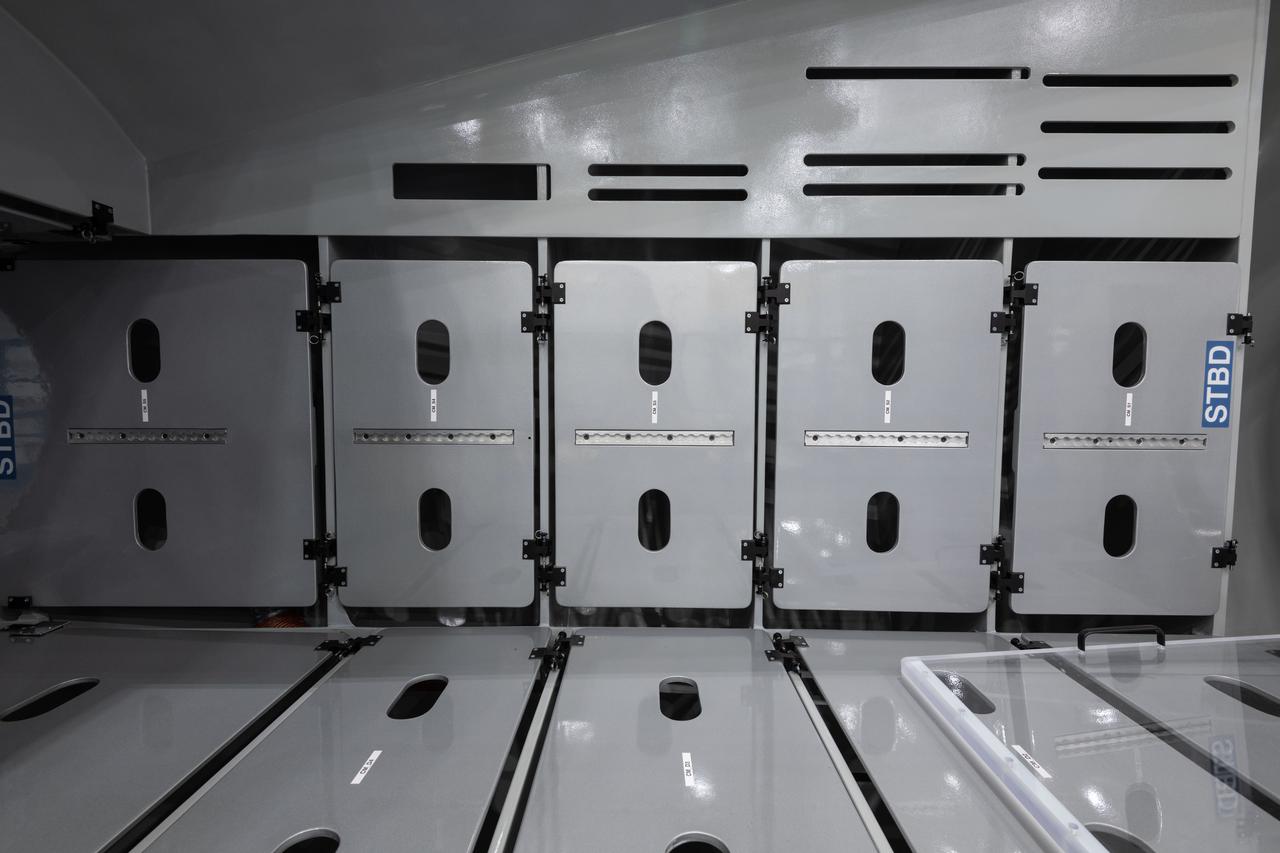

jsc2021e004396 (Jan. 21, 2021) --- Internal view of the Sierra Nevada Dream Chaser mockup located in Building 9N, Space Vehicle Mockup Facility (SVMF) at the NASA Johnson Space Center.
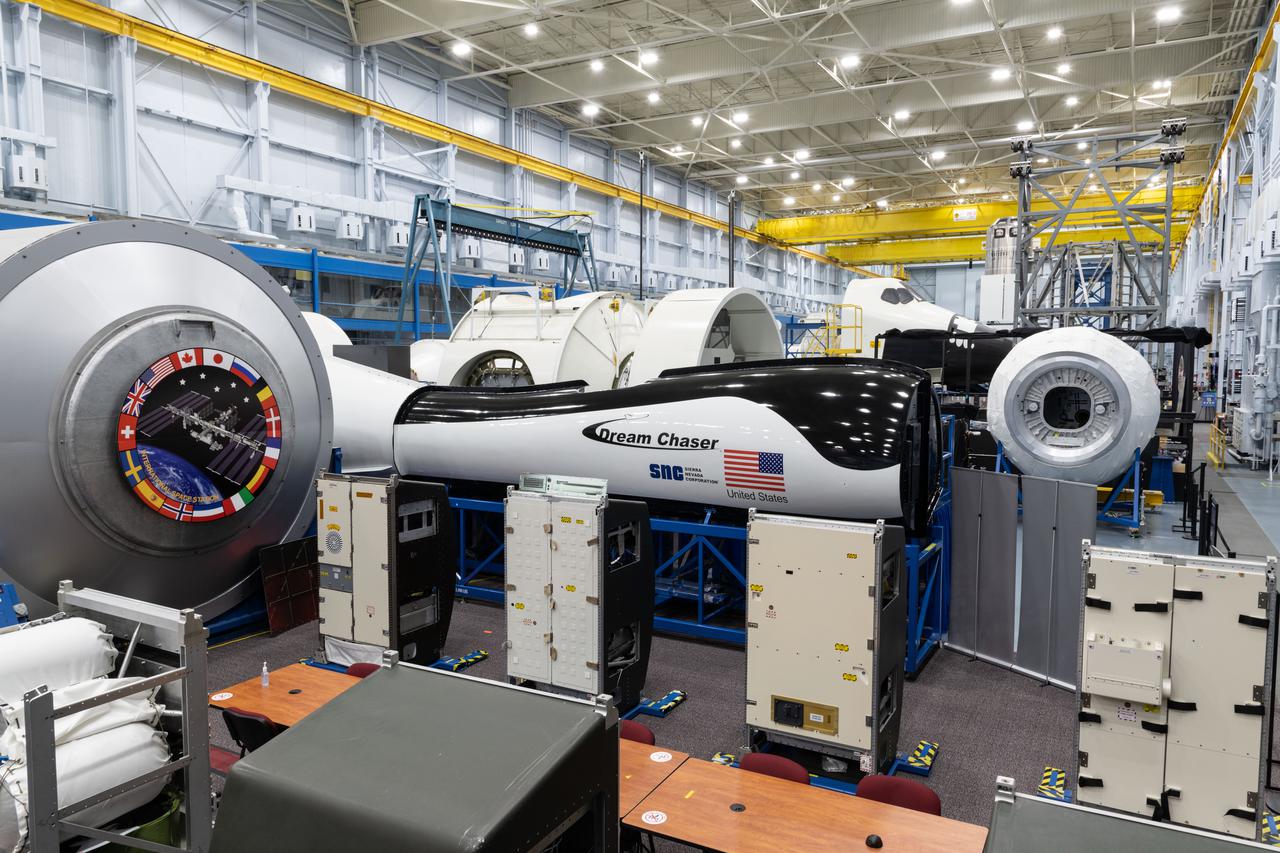

jsc2021e004391 (Jan. 21, 2021) --- External view of the Sierra Nevada Dream Chaser mockup located in Building 9N, Space Vehicle Mockup Facility (SVMF) at the NASA Johnson Space Center.
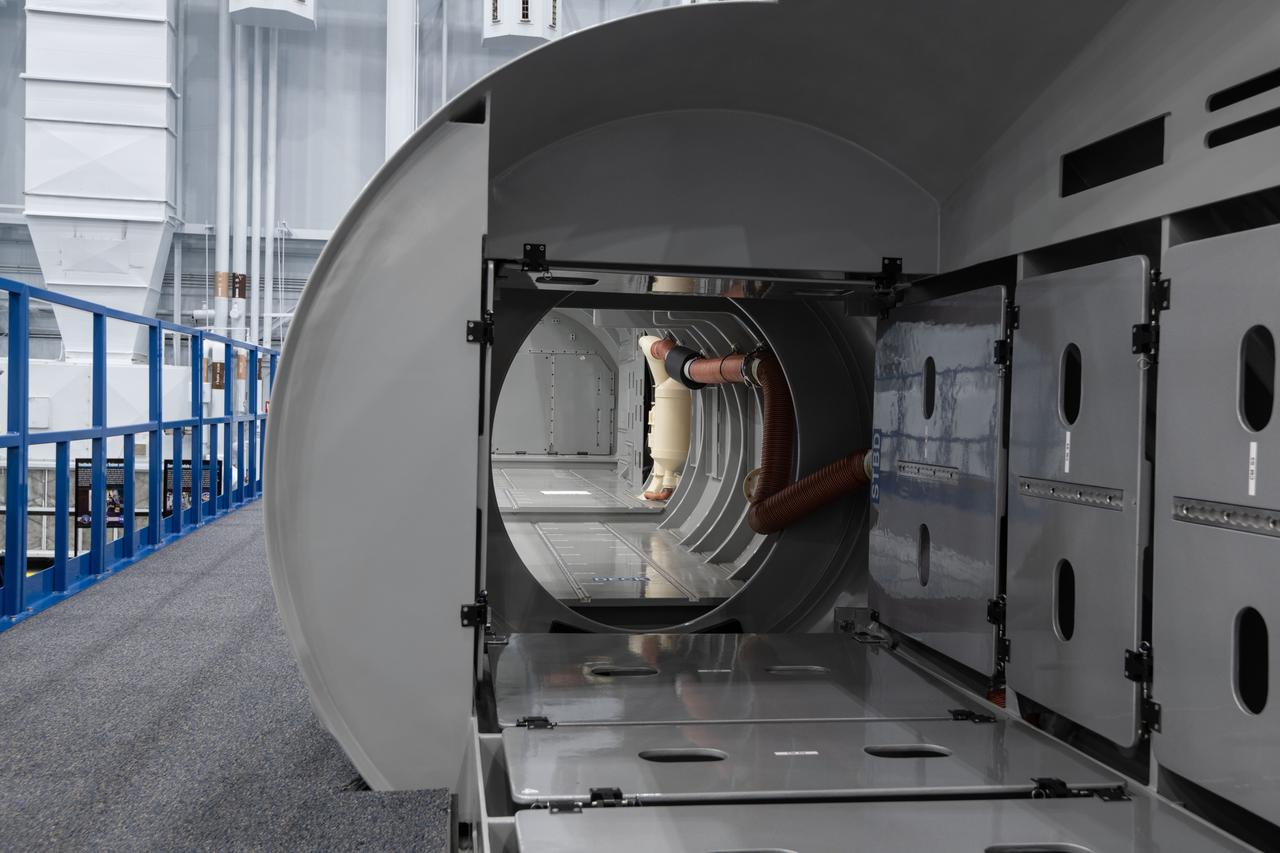

jsc2021e004397 (Jan. 21, 2021) --- Internal view of the Sierra Nevada Dream Chaser mockup located in Building 9N, Space Vehicle Mockup Facility (SVMF) at the NASA Johnson Space Center.

jsc2021e004394 (Jan. 21, 2021) --- Internal view of the Sierra Nevada Dream Chaser mockup located in Building 9N, Space Vehicle Mockup Facility (SVMF) at the NASA Johnson Space Center.
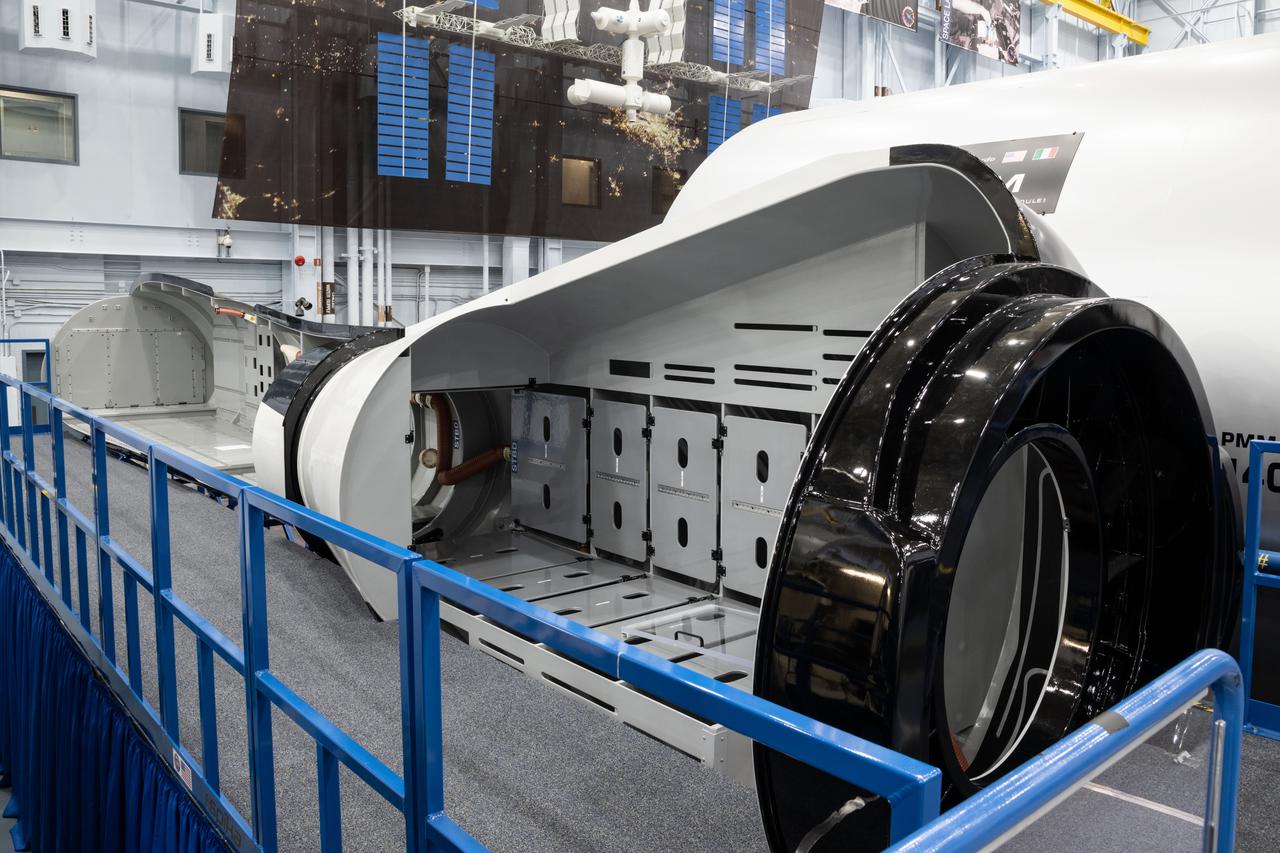

jsc2021e004392 (Jan. 21, 2021) --- Internal view of the Sierra Nevada Dream Chaser mockup located in Building 9N, Space Vehicle Mockup Facility (SVMF) at the NASA Johnson Space Center.
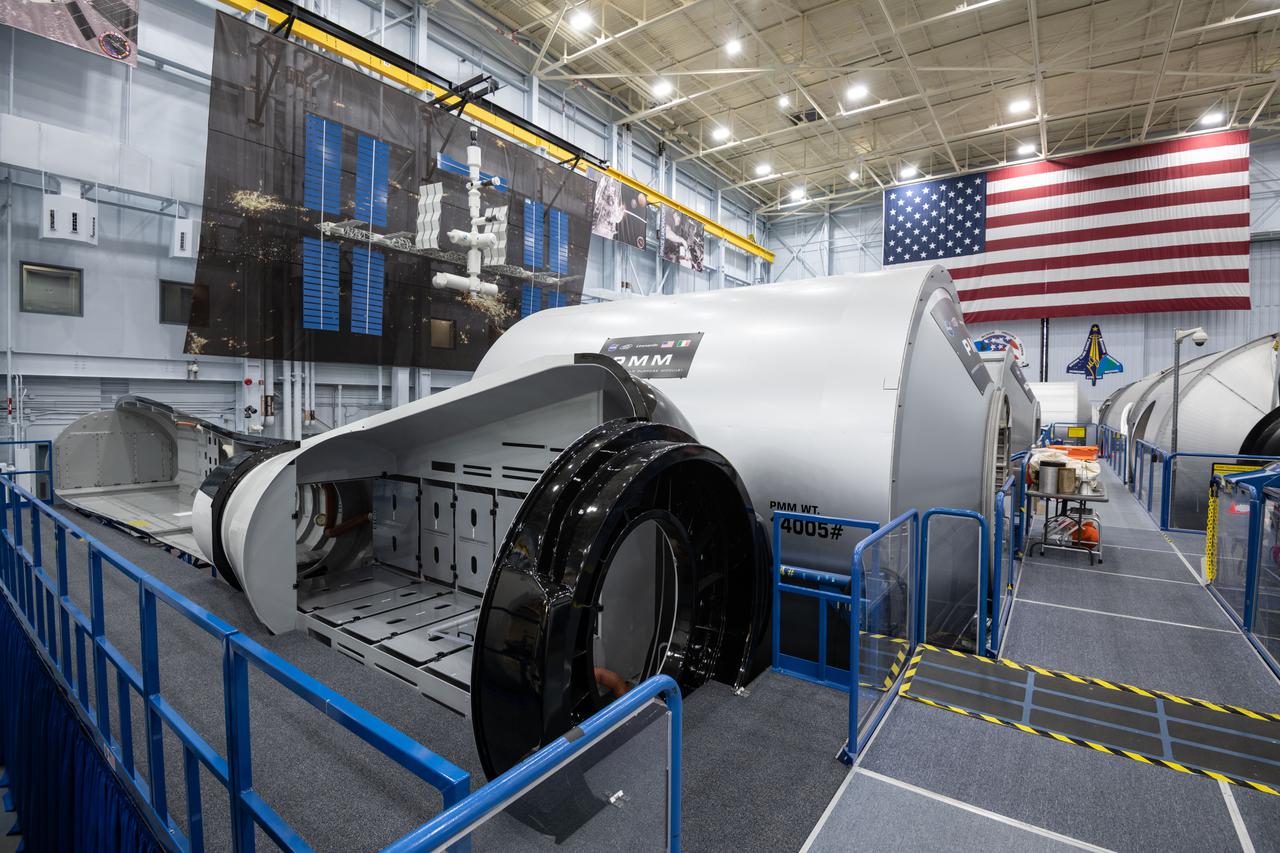

jsc2021e004393 (Jan. 21, 2021) --- Internal view of the Sierra Nevada Dream Chaser mockup located in Building 9N, Space Vehicle Mockup Facility (SVMF) at the NASA Johnson Space Center.
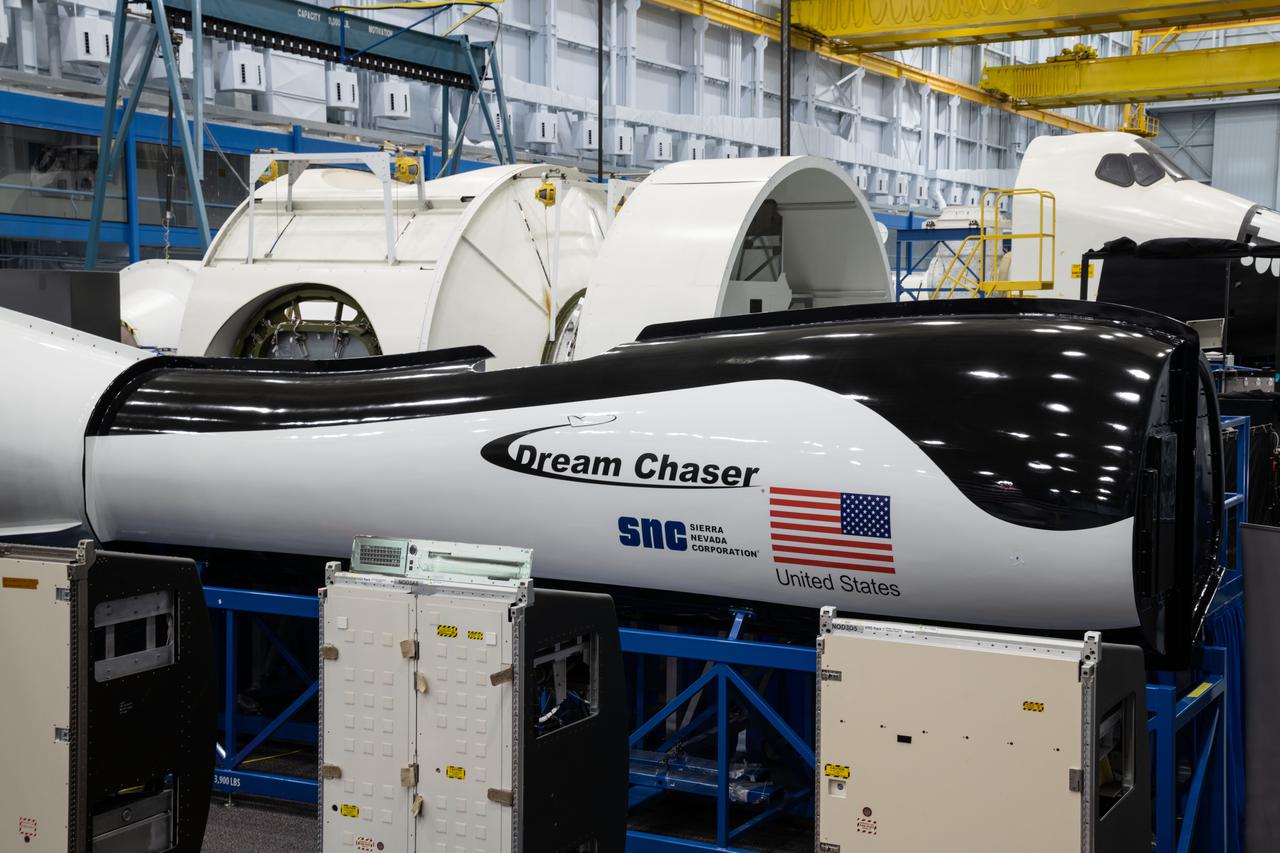

jsc2021e004390 (Jan. 21, 2021) --- External view of the Sierra Nevada Dream Chaser mockup located in Building 9N, Space Vehicle Mockup Facility (SVMF) at the NASA Johnson Space Center.
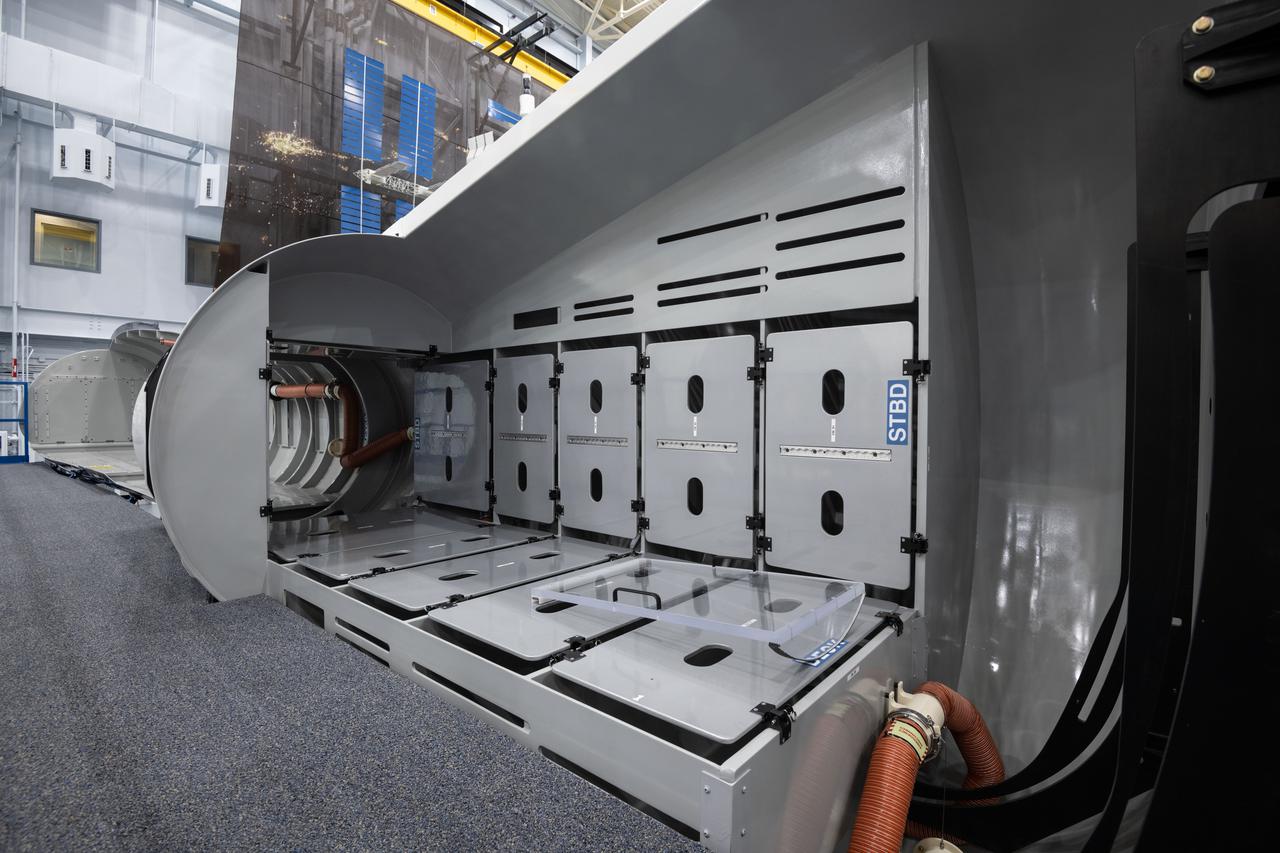

jsc2021e004395 (Jan. 21, 2021) --- Internal view of the Sierra Nevada Dream Chaser mockup located in Building 9N, Space Vehicle Mockup Facility (SVMF) at the NASA Johnson Space Center.
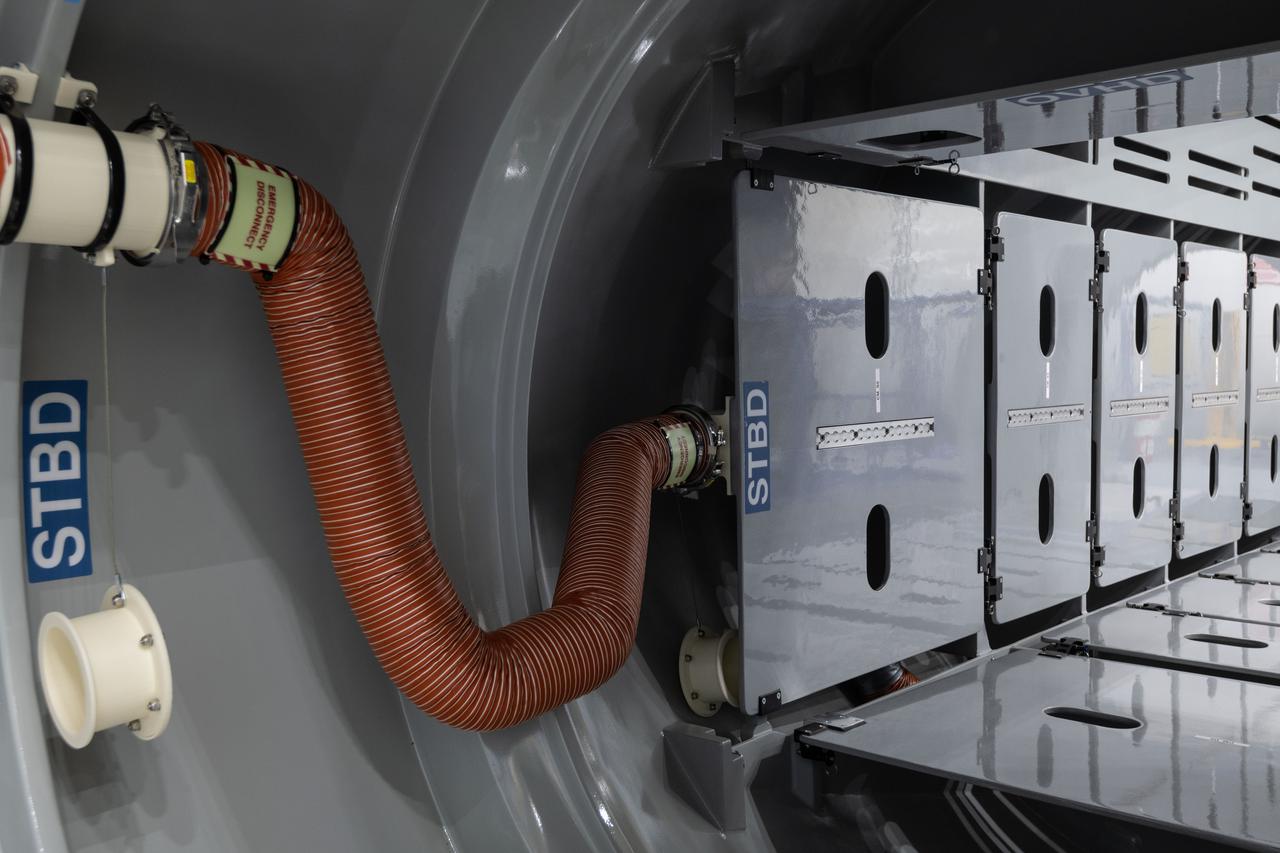

jsc2021e00439 (Jan. 21, 2021) --- Internal view of the Sierra Nevada Dream Chaser mockup located in Building 9N, Space Vehicle Mockup Facility (SVMF) at the NASA Johnson Space Center.
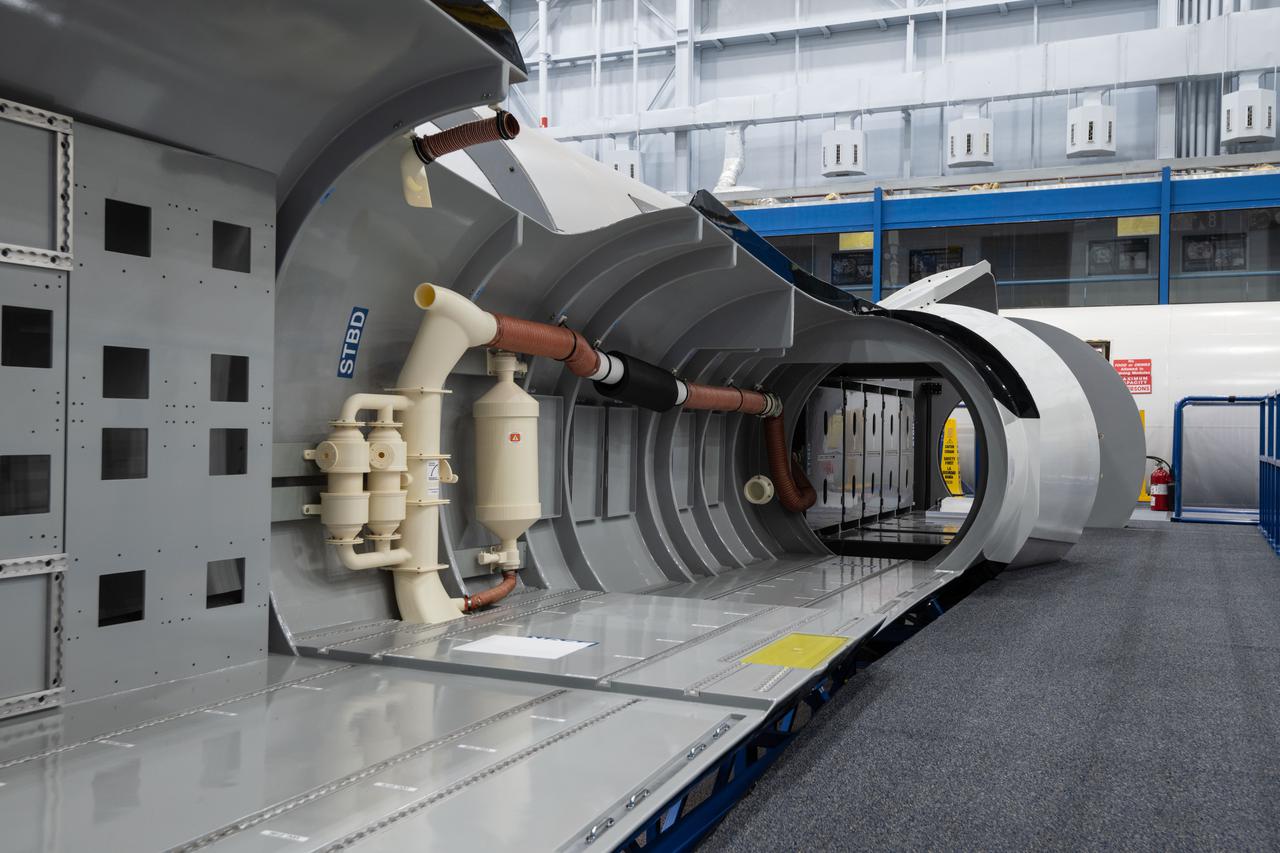

jsc2021e004398 (Jan. 21, 2021) --- Internal view of the Sierra Nevada Dream Chaser mockup located in Building 9N, Space Vehicle Mockup Facility (SVMF) at the NASA Johnson Space Center.
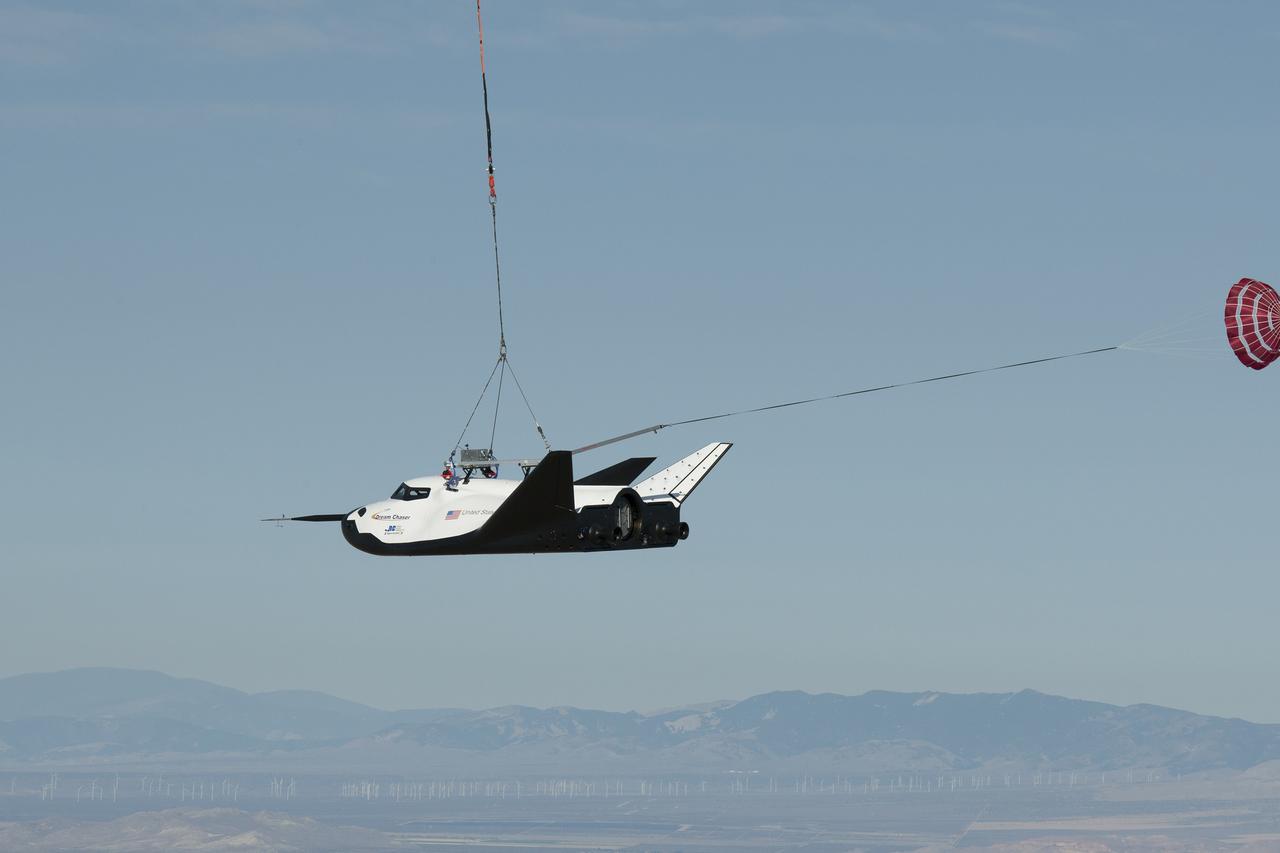

EDWARDS AFB, Calif. - ED13-0300-002 – An Erickson Air-Crane helicopter lifts Sierra Nevada Corporation's Dream Chaser flight vehicle during a captive-carry flight test. The test was a rehearsal for free flights at Edwards later this year. The spacecraft is under development in partnership with NASA's Commercial Crew Program. Although the spacecraft is designed for crew members, the vehicle will not have anyone onboard during the free flights. Photo credit: NASA/Carla Thomas

EDWARDS AFB, Calif. - ED13-0300-003 – An Erickson Air-Crane helicopter lifts Sierra Nevada Corporation's Dream Chaser flight vehicle during a captive-carry flight test. The test was a rehearsal for free flights at Edwards later this year. The spacecraft is under development in partnership with NASA's Commercial Crew Program. Although the spacecraft is designed for crew members, the vehicle will not have anyone onboard during the free flights. Photo credit: NASA/Carla Thomas
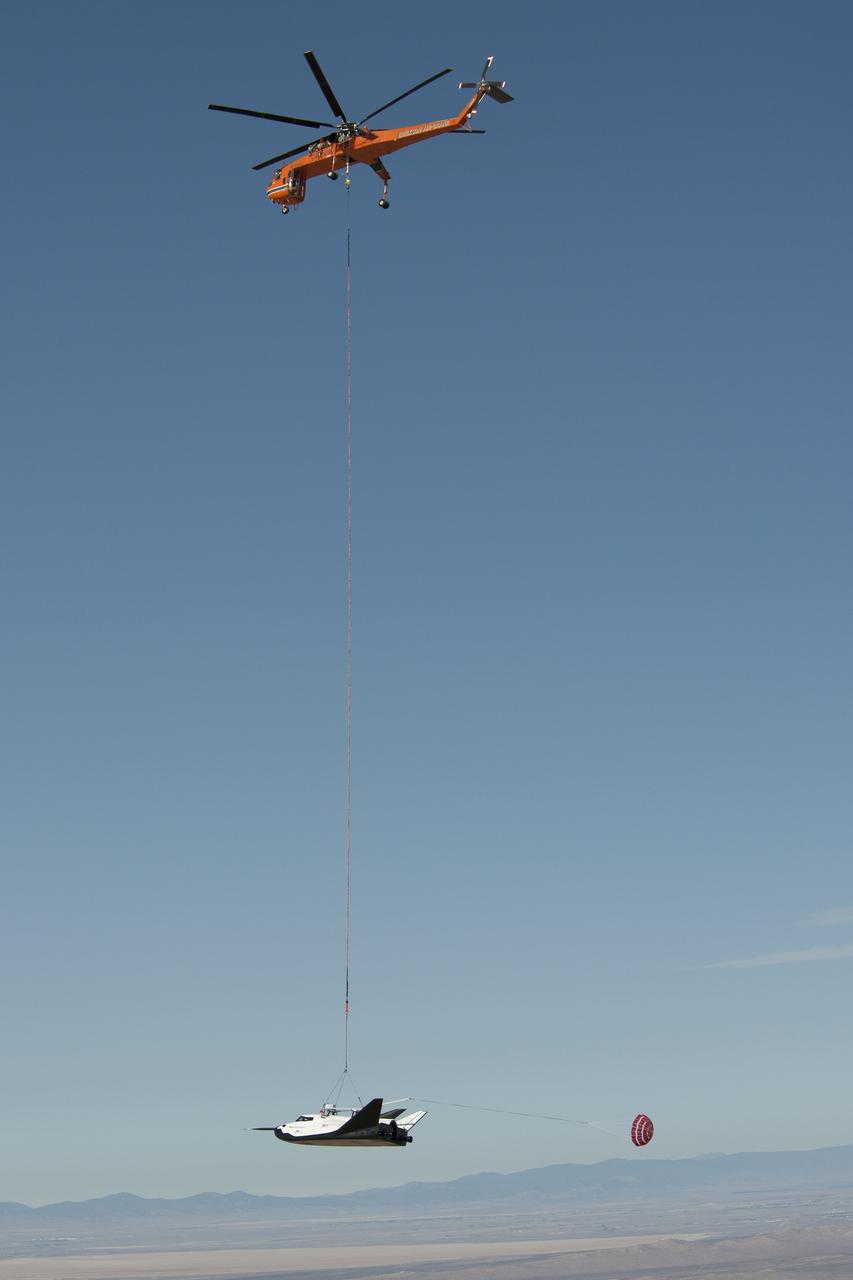

EDWARDS AFB, Calif. - ED13-0300-001 – An Erickson Air-Crane helicopter lifts Sierra Nevada Corporation's Dream Chaser flight vehicle during a captive-carry flight test. The test was a rehearsal for free flights at Edwards later this year. The spacecraft is under development in partnership with NASA's Commercial Crew Program. Although the spacecraft is designed for crew members, the vehicle will not have anyone onboard during the free flights. Photo credit: NASA/Carla Thomas
Sierra Space Dream Chaser space plane is lifted into the chamber at ISP (In Space Propulsion) facility, building 3211 at ATF (Armstrong Test Facility) for environmental testing. Once lowered into the test chamber, it will be exposed to the harsh cold conditions of space for extended periods of time.
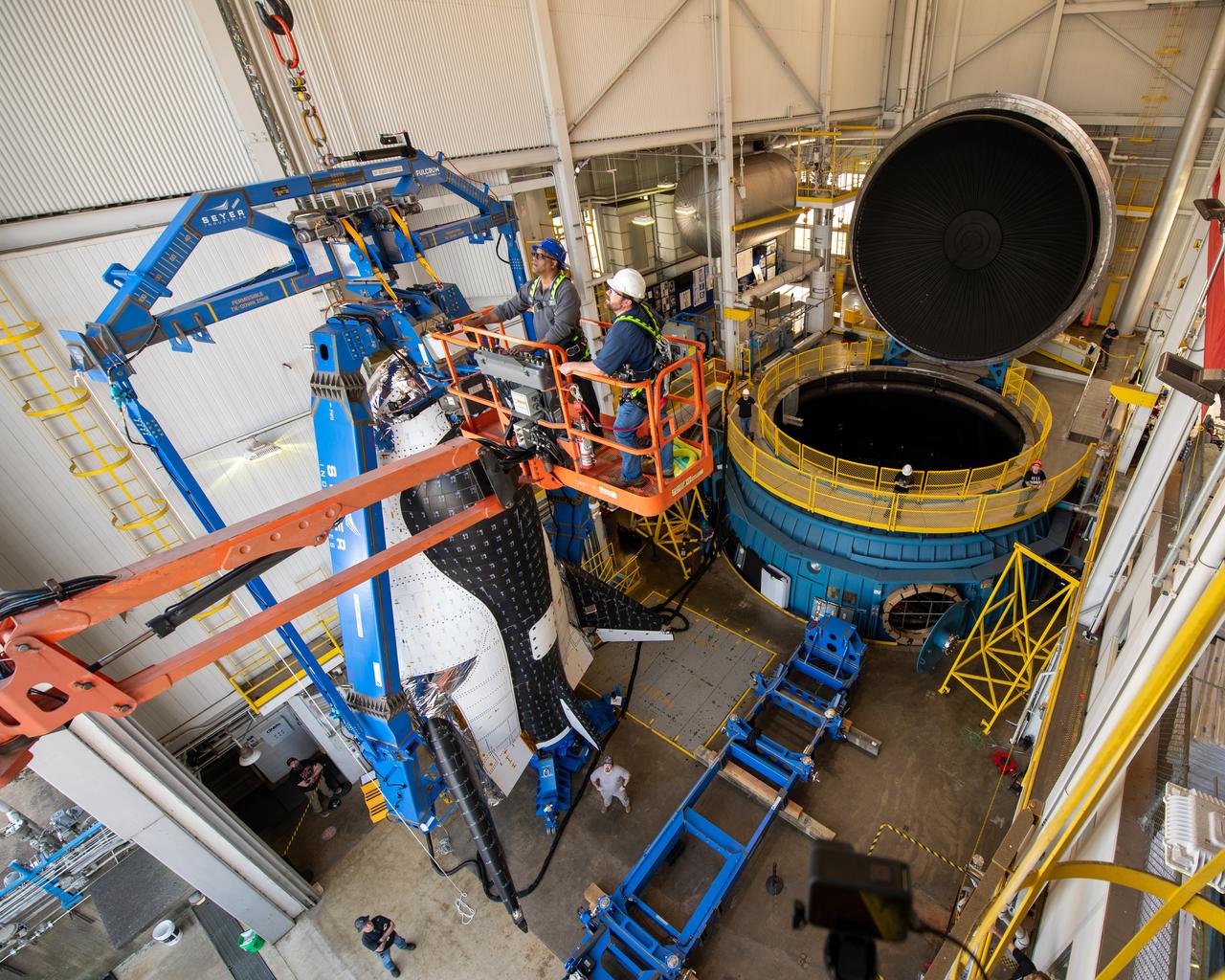

Final inspection of the crane operation just before the critical lift of the Sierra Space Plane, Dream Chaser. It will go into the chamber at ISP (In Space Propulsion) NASA GRC-ATF. Once lowered into the test chamber, it will be exposed to the harsh cold conditions of space for extended periods of time at building 3211 at ATF (Armstrong Test Facility) for environmental testing.
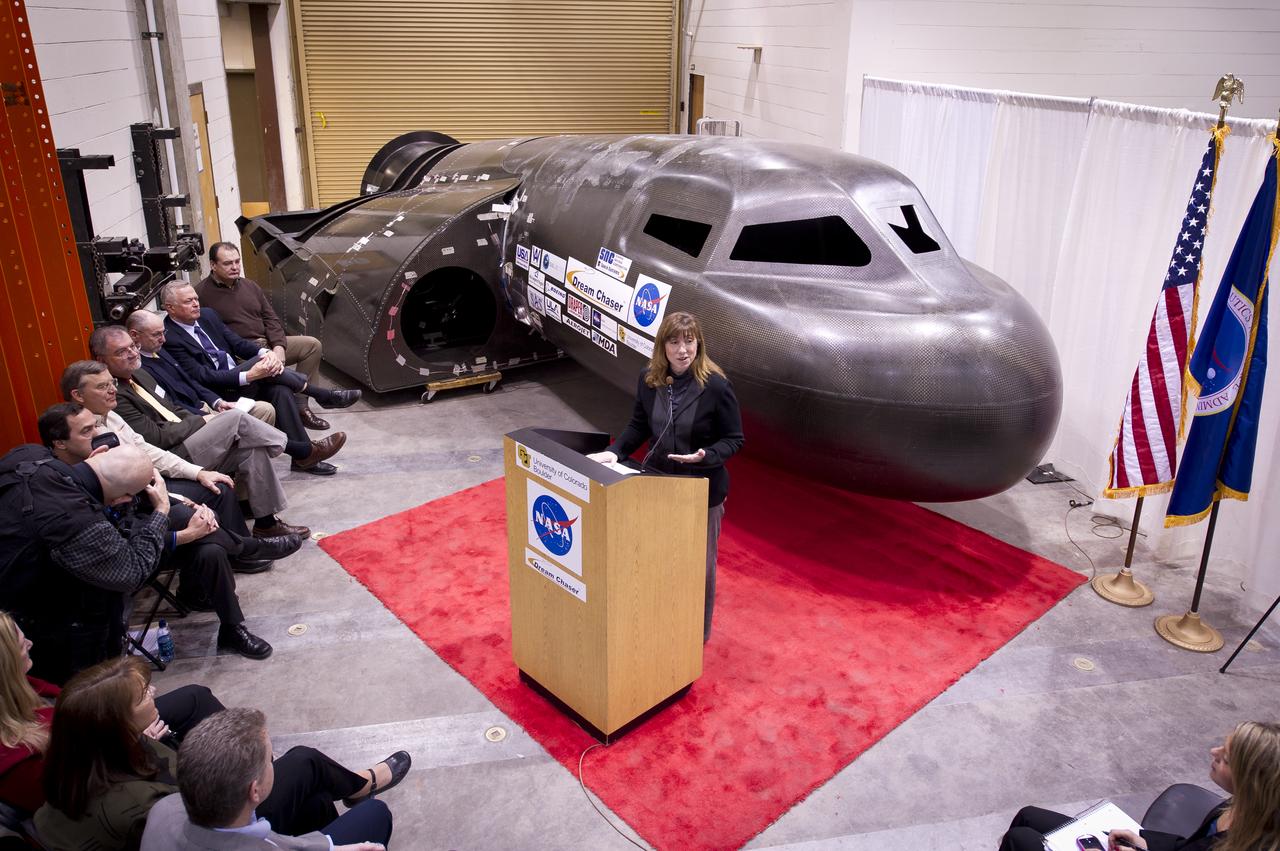

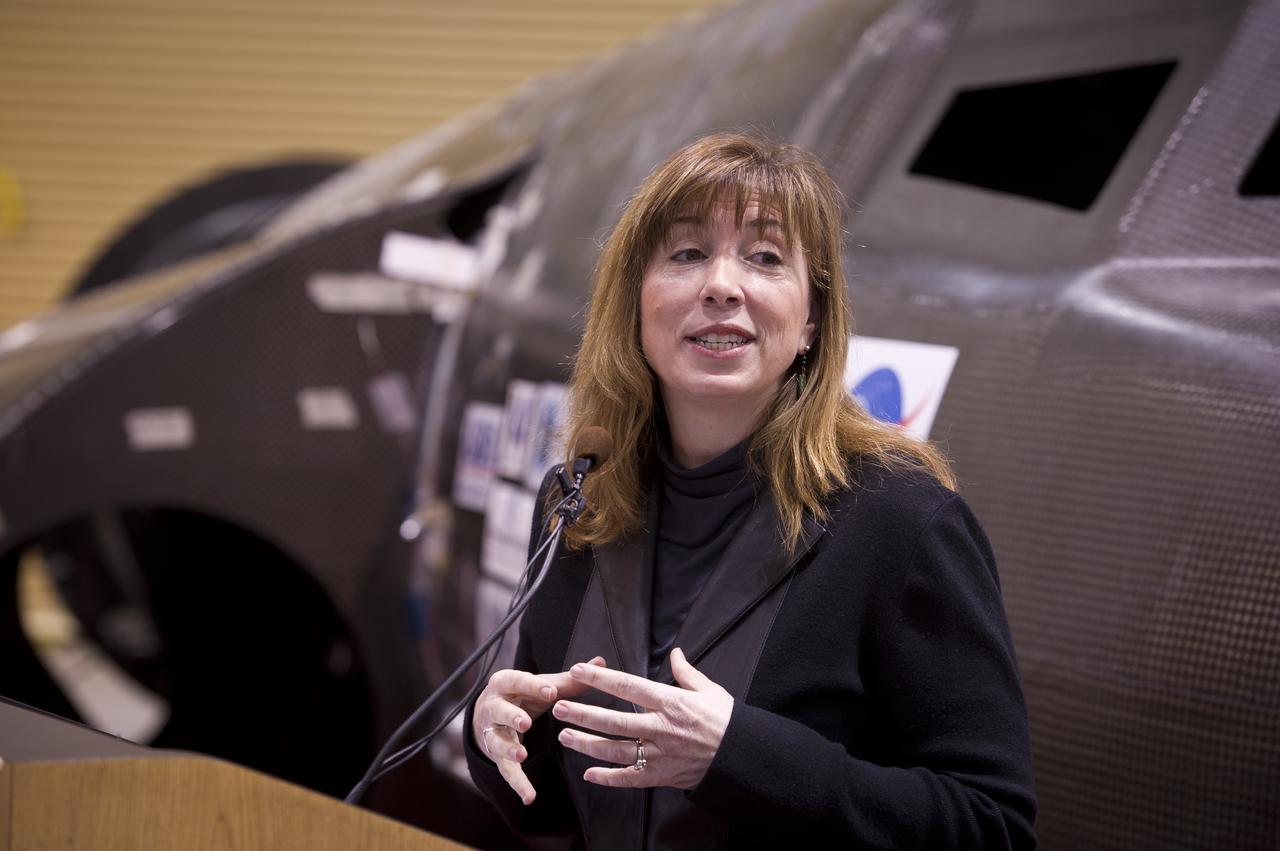
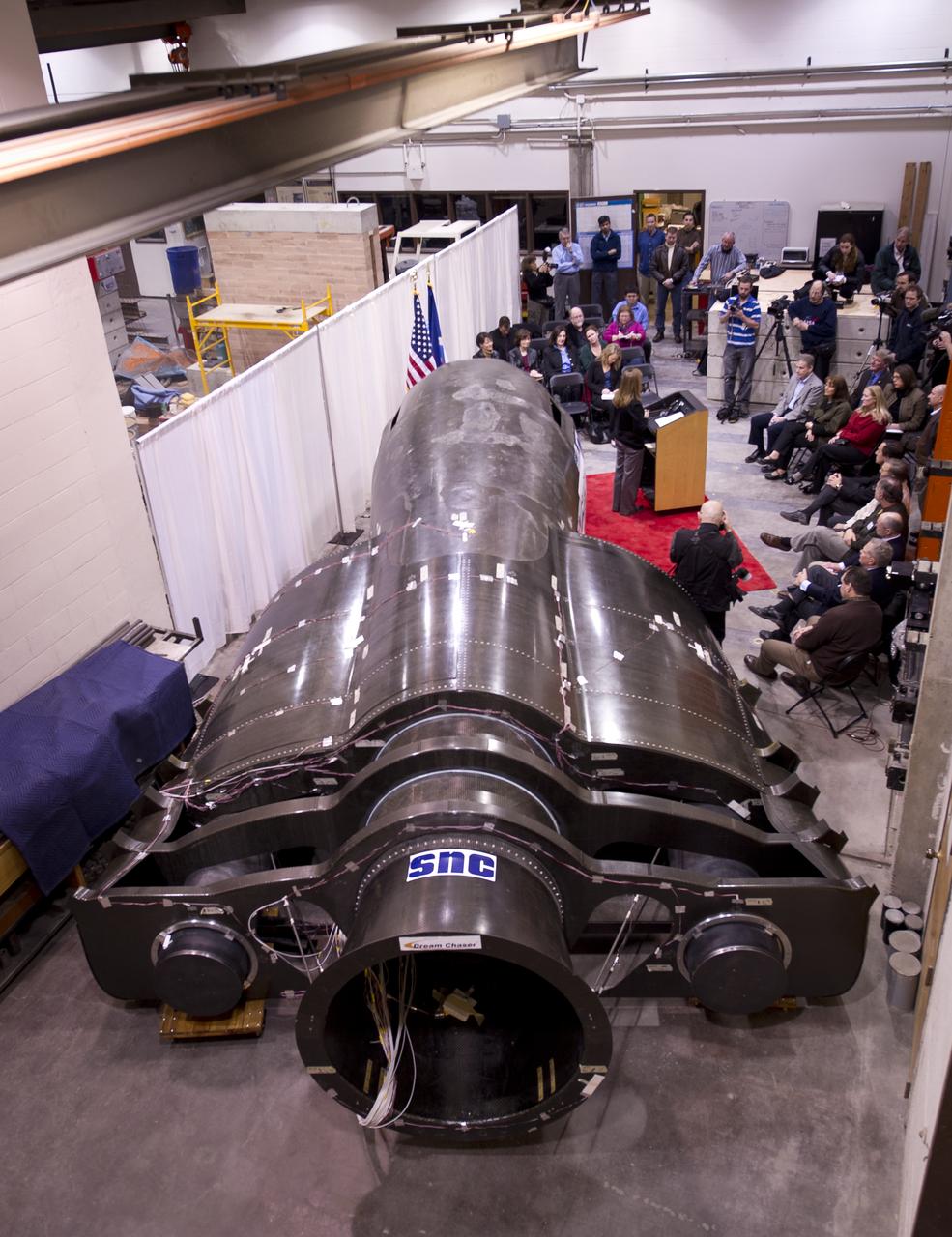
NASA Deputy Administrator Lori Garver talks during a press conference with Sierra Nevada's Dream Chaser spacecraft in the background on Saturday, Feb. 5, 2011, at the University of Colorado at Boulder. Sierra Nevada's Dream Chaser spacecraft is under development with support from NASA's Commercial Crew Development Program to provide crew transportation to and from low Earth orbit. NASA is helping private companies develop innovative technologies to ensure that the U.S. remains competitive in future space endeavors. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Deputy Administrator Lori Garver talks during a press conference with Sierra Nevada's Dream Chaser spacecraft in the background on Saturday, Feb. 5, 2011, at the University of Colorado at Boulder. Sierra Nevada's Dream Chaser spacecraft is under development with support from NASA's Commercial Crew Development Program to provide crew transportation to and from low Earth orbit. NASA is helping private companies develop innovative technologies to ensure that the U.S. remains competitive in future space endeavors. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
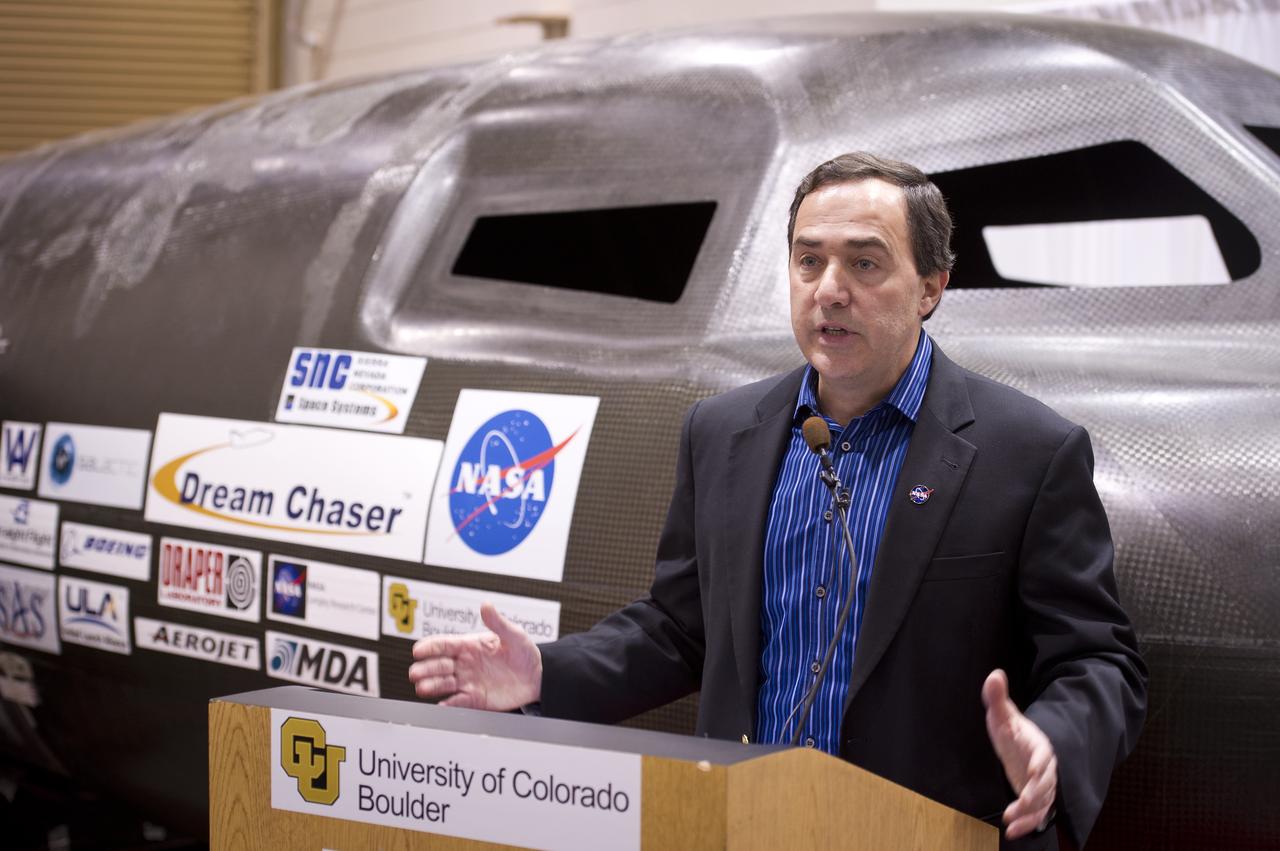

Sierra Nevada Space Systems chairman Mark Sirangello talks during a press conference with Sierra Nevada's Dream Chaser spacecraft in the background on Saturday, Feb. 5, 2011, at the University of Colorado at Boulder. Sierra Nevada's Dream Chaser spacecraft is under development with support from NASA's Commercial Crew Development Program to provide crew transportation to and from low Earth orbit. NASA is helping private companies develop innovative technologies to ensure that the U.S. remains competitive in future space endeavors. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Sierra Nevada's Dream Chaser spacecraft is seen as NASA Deputy Administrator Lori Garver talks during a press conference on Saturday, Feb. 5, 2011, at the University of Colorado at Boulder. Sierra Nevada's Dream Chaser spacecraft is under development with support from NASA's Commercial Crew Development Program to provide crew transportation to and from low Earth orbit. NASA is helping private companies develop innovative technologies to ensure that the U.S. remains competitive in future space endeavors. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
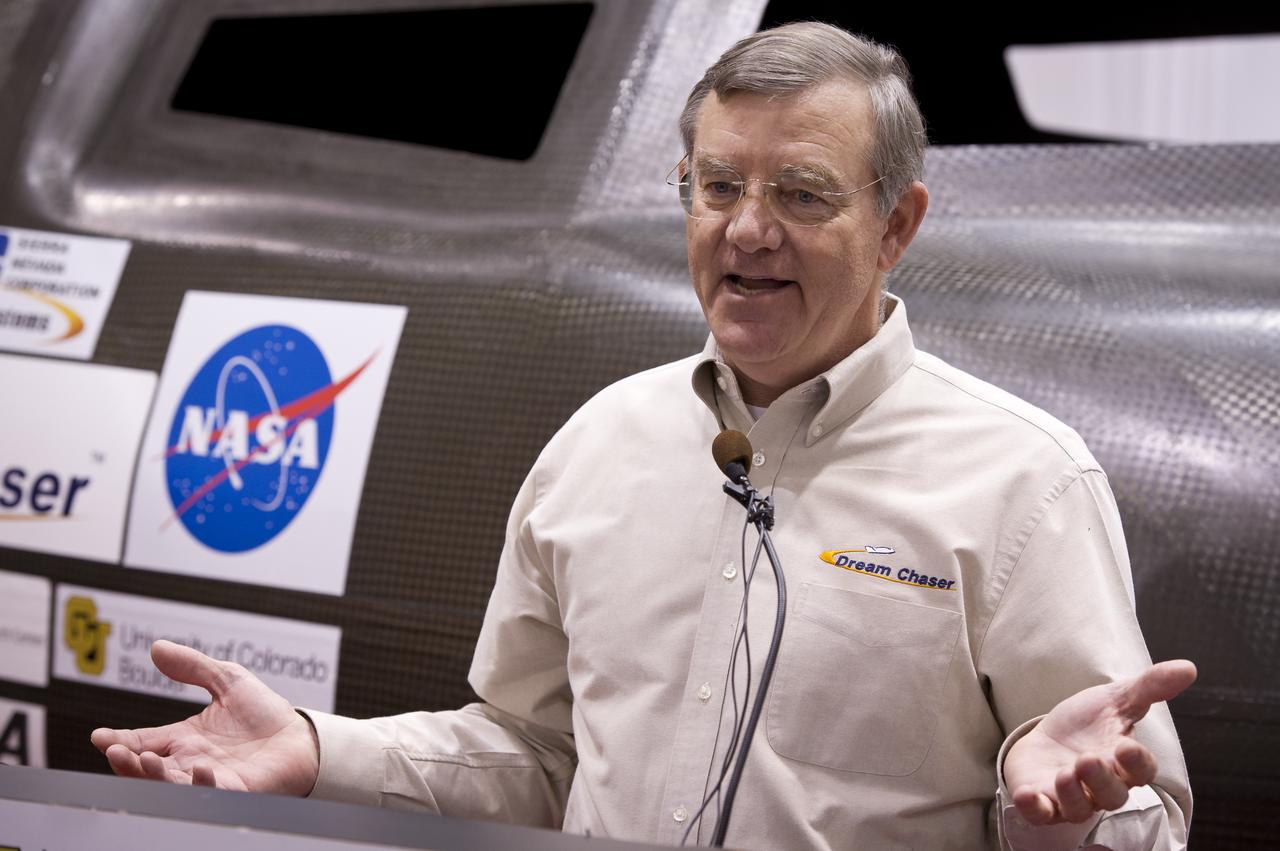

Director of Advanced Programs, Sierra Nevada Corporation, Jim Voss talks during a press conference with Sierra Nevada's Dream Chaser spacecraft in the background on Saturday, Feb. 5, 2011, at the University of Colorado at Boulder. Sierra Nevada's Dream Chaser spacecraft is under development with support from NASA's Commercial Crew Development Program to provide crew transportation to and from low Earth orbit. NASA is helping private companies develop innovative technologies to ensure that the U.S. remains competitive in future space endeavors. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
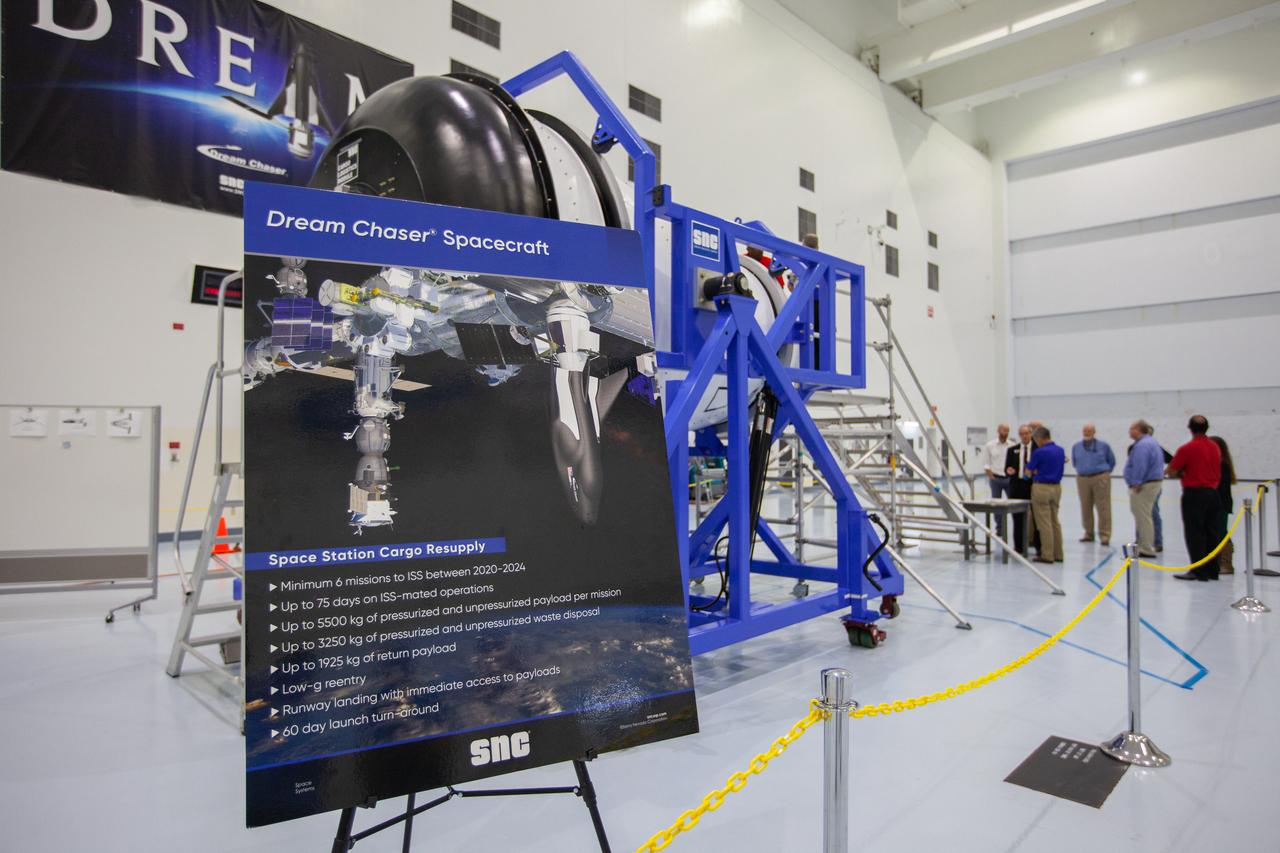

A mockup of the cargo logistics module for Sierra Nevada Corporation’s Dream Chaser, the company’s reusable spaceplane, arrived at the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in August. On Sept. 20, 2019, senior leadership had the opportunity to view the cargo module in the SSPF high bay. The SSPF is providing support for current and future NASA and commercial provider programs, including Commercial Resupply Services, Artemis 1, sending the first woman and next man to the Moon, and deep space destinations including Mars.
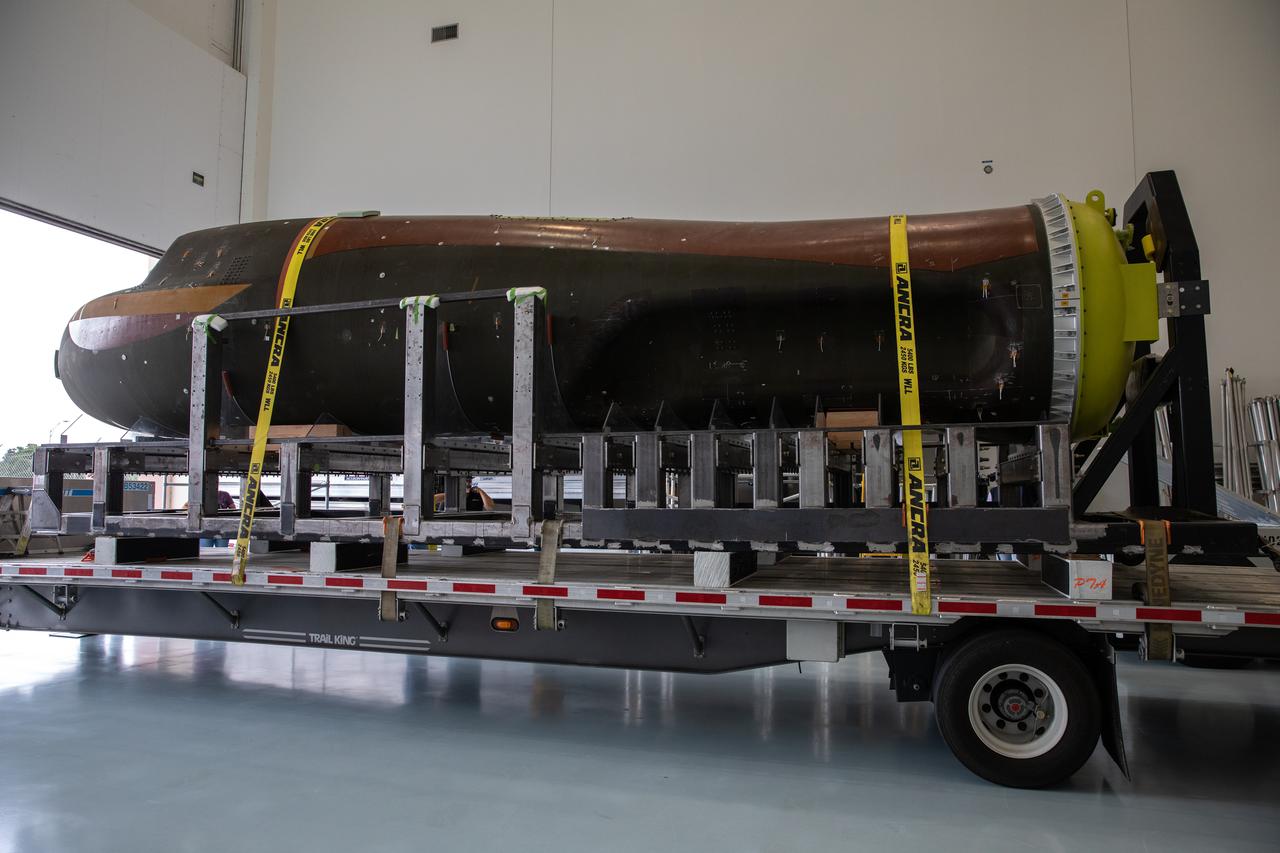

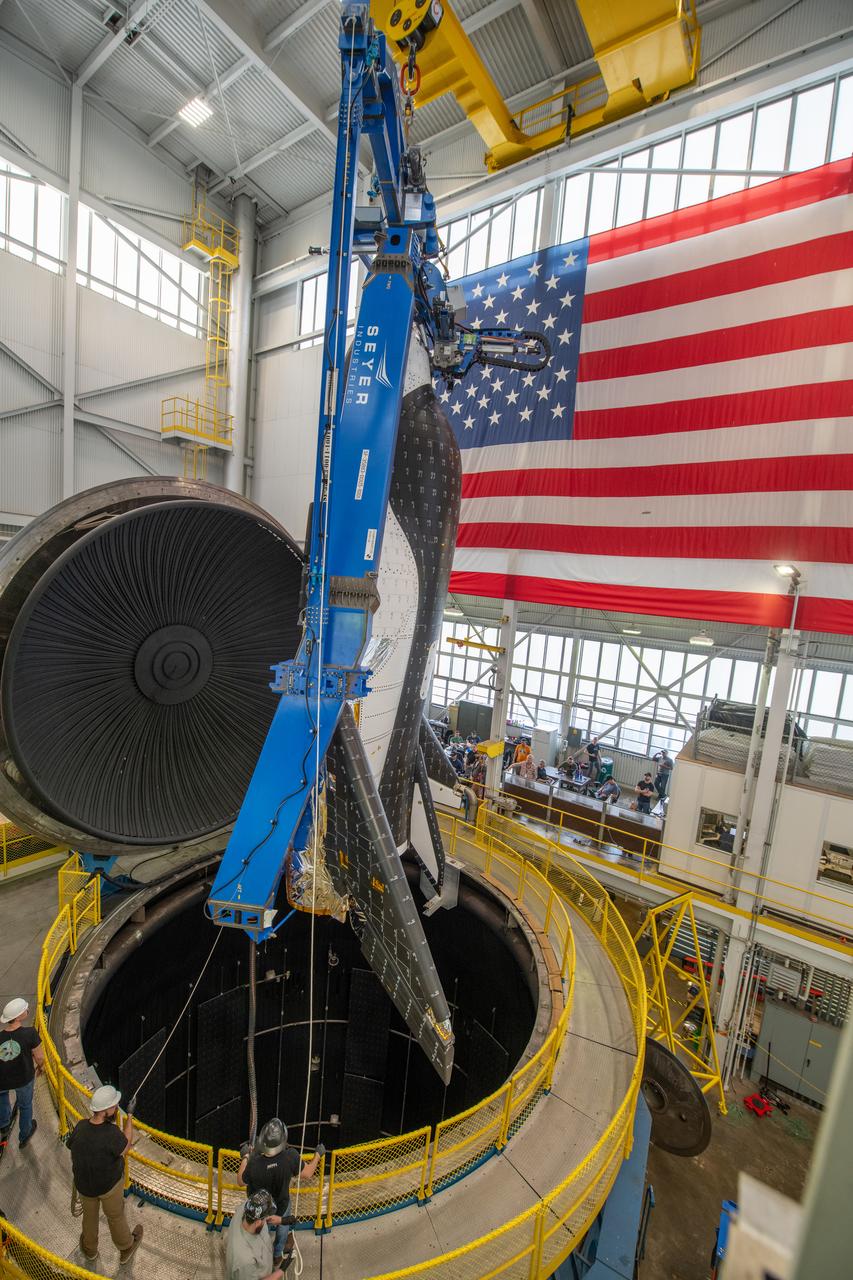
Sierra Nevada Corporation’s (SNC) Dream Chaser pressure test article is moved into the low bay of the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 3, 2020. The test article was shipped from Louisville, Colorado. It is similar to the actual pressurized cabin being used in the Dream Chaser spaceplane for Commercial Resupply Services-2 (CRS-2) missions. NASA selected Dream Chaser to provide cargo delivery, return and disposal service for the International Space Station under the CRS-2 contract. The test article will remain at Kennedy while SNC engineers use it to develop and verify refurbishment operations that will be used on Dream Chaser between flights.
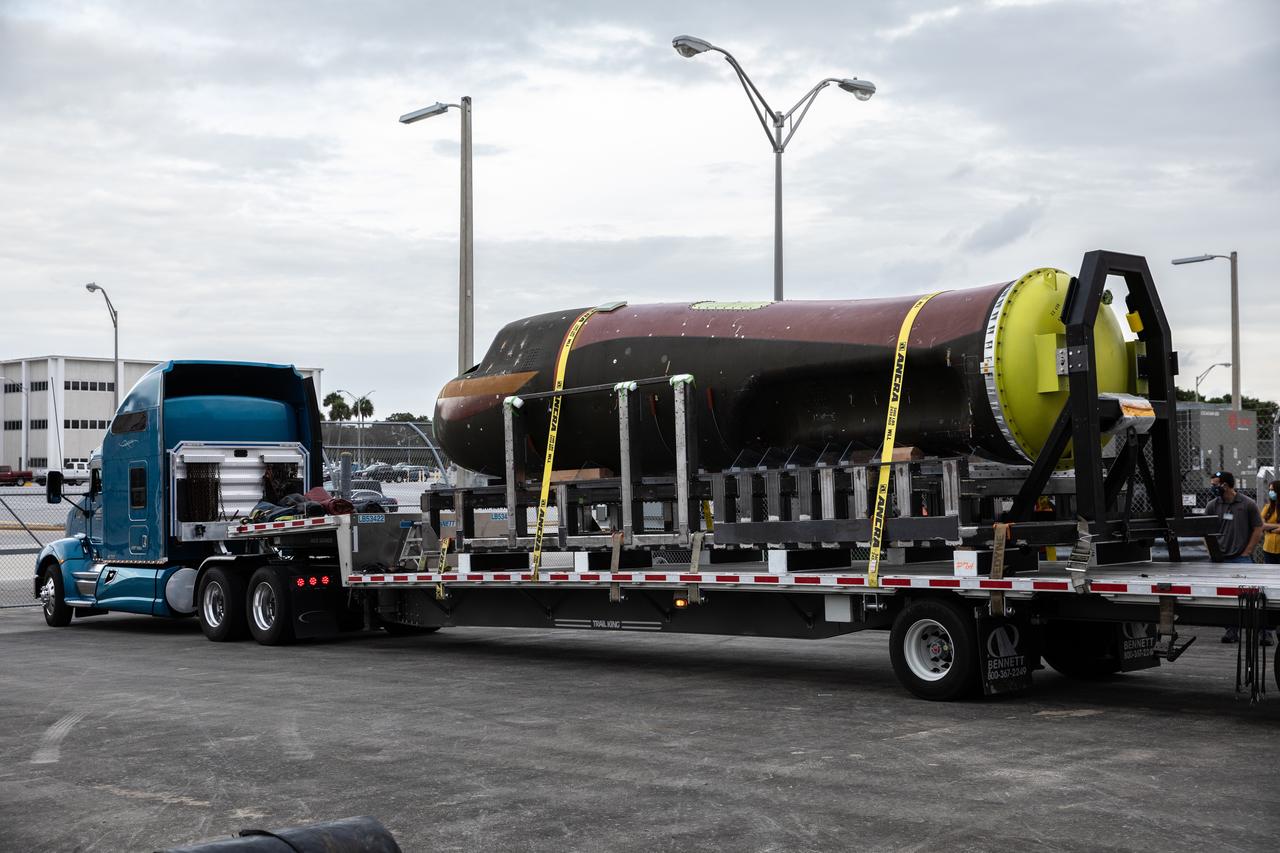

Sierra Nevada Corporation’s (SNC) Dream Chaser pressure test article arrives by flatbed truck at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 3, 2020, from Louisville, Colorado. It will be transported to the high bay in the Space Station Processing Facility. The test article is similar to the actual pressurized cabin being used in the Dream Chaser spaceplane for Commercial Resupply Services-2 (CRS-2) missions. NASA selected Dream Chaser to provide cargo delivery, return and disposal service for the International Space Station under the CRS-2 contract. The test article will remain at Kennedy while SNC engineers use it to develop and verify refurbishment operations that will be used on Dream Chaser between flights.
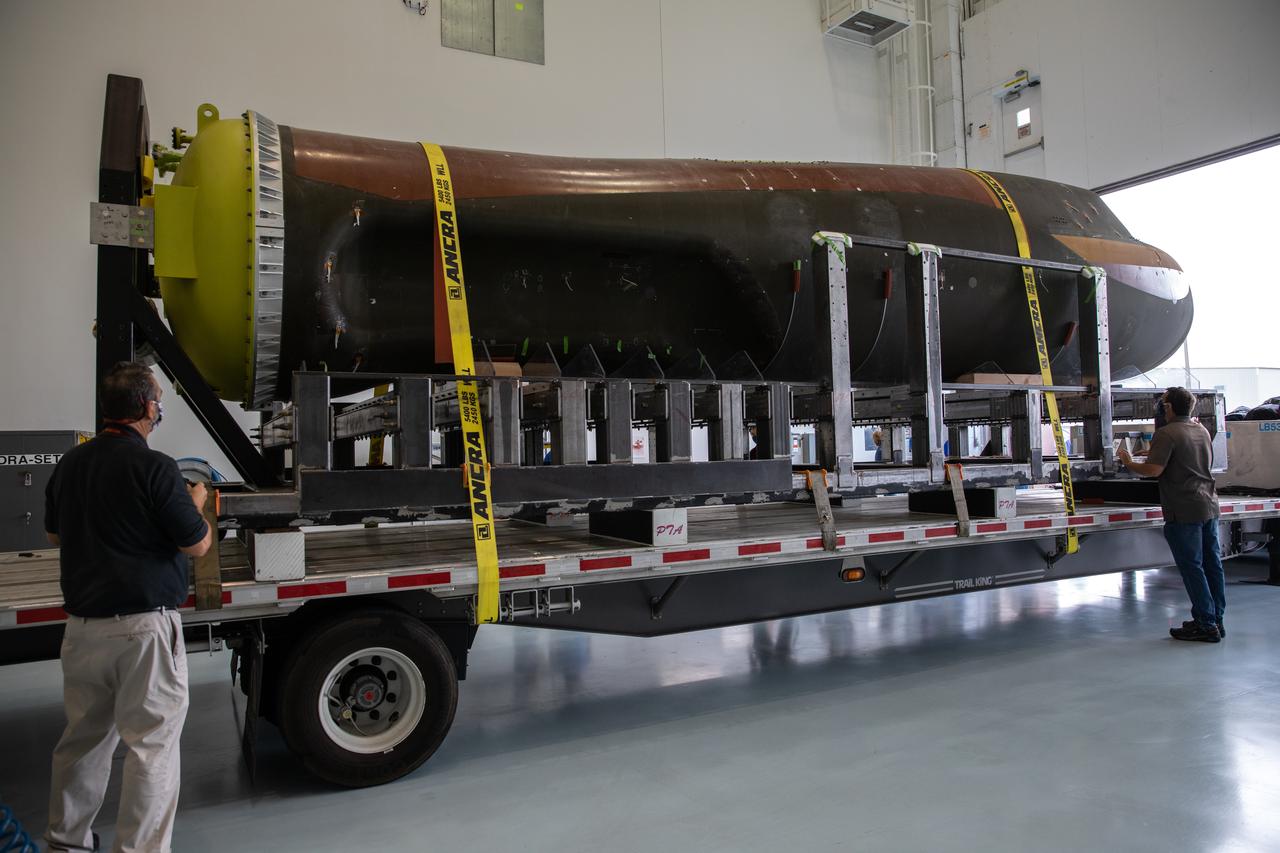

Sierra Nevada Corporation’s (SNC) Dream Chaser pressure test article is moved into the low bay of the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 3, 2020. The test article was shipped from Louisville, Colorado. It is similar to the actual pressurized cabin being used in the Dream Chaser spaceplane for Commercial Resupply Services-2 (CRS-2) missions. NASA selected Dream Chaser to provide cargo delivery, return and disposal service for the International Space Station under the CRS-2 contract. The test article will remain at Kennedy while SNC engineers use it to develop and verify refurbishment operations that will be used on Dream Chaser between flights.
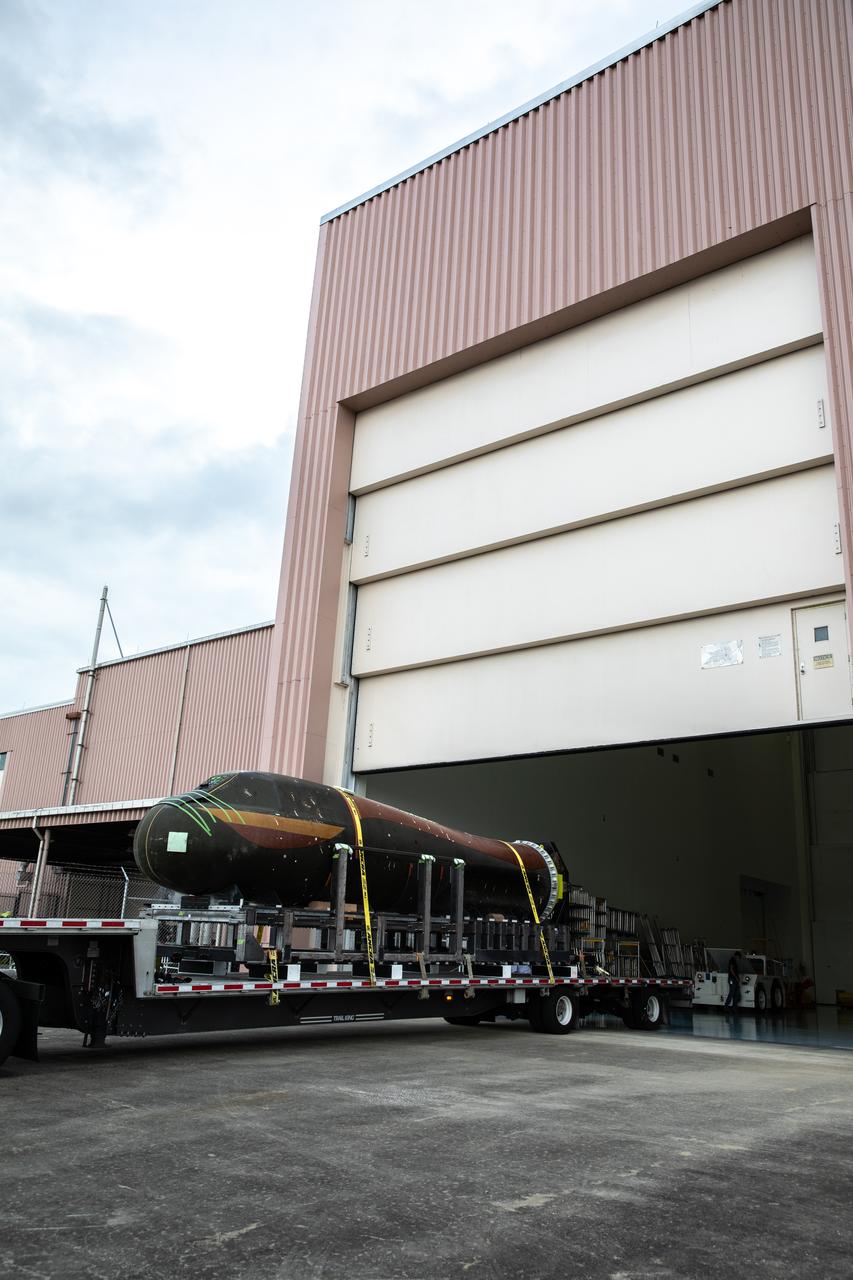

Sierra Nevada Corporation’s (SNC) Dream Chaser pressure test article arrives by flatbed truck at the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 3, 2020, from Louisville, Colorado. The test article is similar to the actual pressurized cabin being used in the Dream Chaser spaceplane for Commercial Resupply Services-2 (CRS-2) missions. NASA selected Dream Chaser to provide cargo delivery, return and disposal service for the International Space Station under the CRS-2 contract. The test article will remain at Kennedy while SNC engineers use it to develop and verify refurbishment operations that will be used on Dream Chaser between flights.
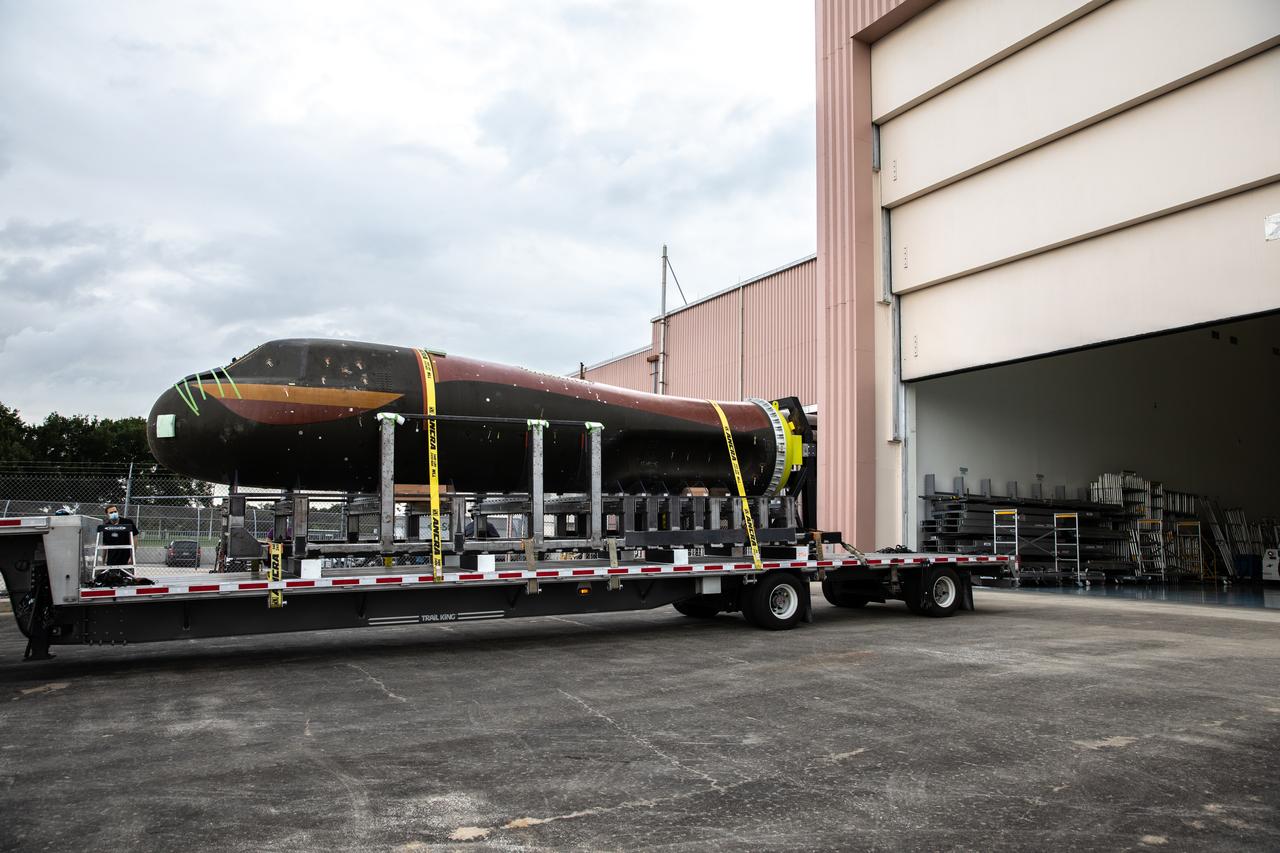

Sierra Nevada Corporation’s (SNC) Dream Chaser pressure test article arrives by flatbed truck at the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 3, 2020, from Louisville, Colorado. The test article is similar to the actual pressurized cabin being used in the Dream Chaser spaceplane for Commercial Resupply Services-2 (CRS-2) missions. NASA selected Dream Chaser to provide cargo delivery, return and disposal service for the International Space Station under the CRS-2 contract. The test article will remain at Kennedy while SNC engineers use it to develop and verify refurbishment operations that will be used on Dream Chaser between flights.
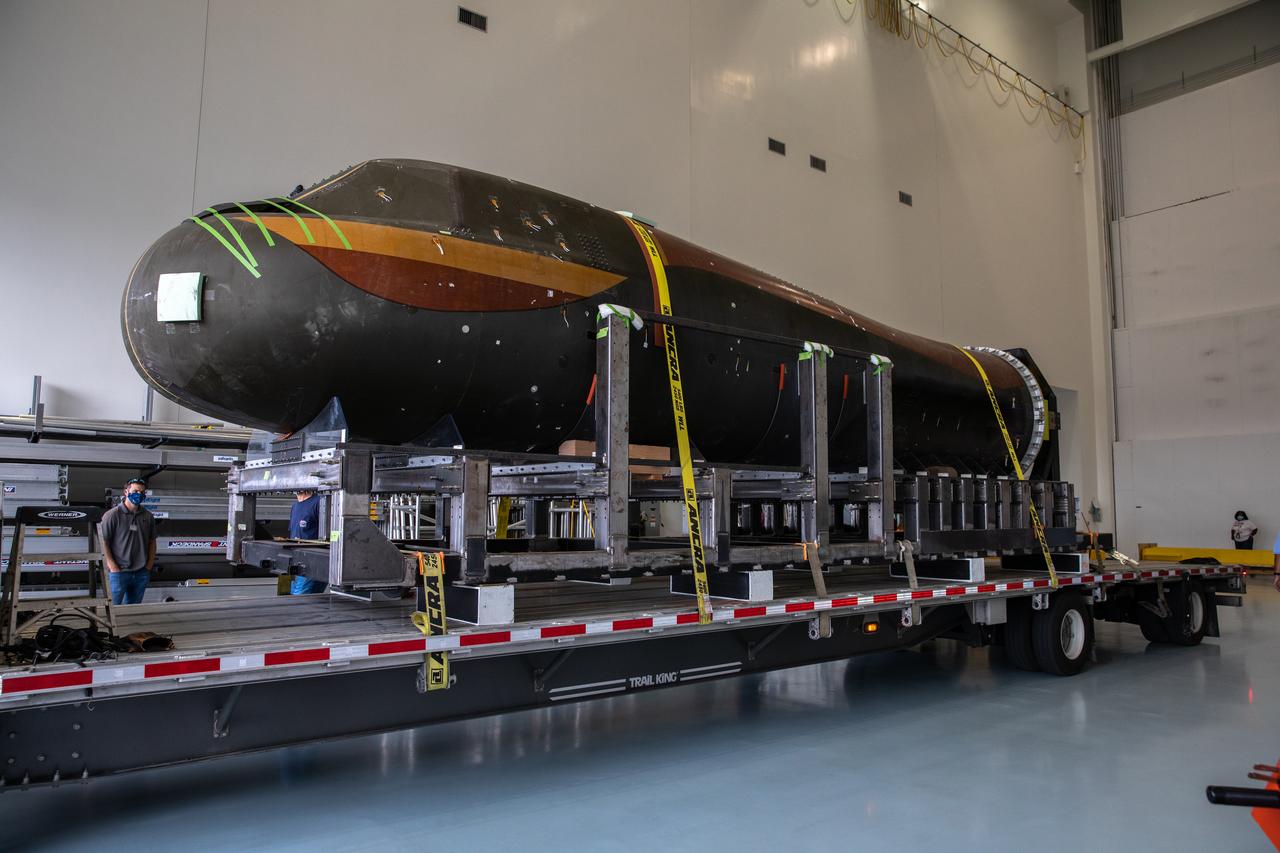

Sierra Nevada Corporation’s (SNC) Dream Chaser pressure test article is moved into the low bay of the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 3, 2020. The test article was shipped from Louisville, Colorado. It is similar to the actual pressurized cabin being used in the Dream Chaser spaceplane for Commercial Resupply Services-2 (CRS-2) missions. NASA selected Dream Chaser to provide cargo delivery, return and disposal service for the International Space Station under the CRS-2 contract. The test article will remain at Kennedy while SNC engineers use it to develop and verify refurbishment operations that will be used on Dream Chaser between flights.
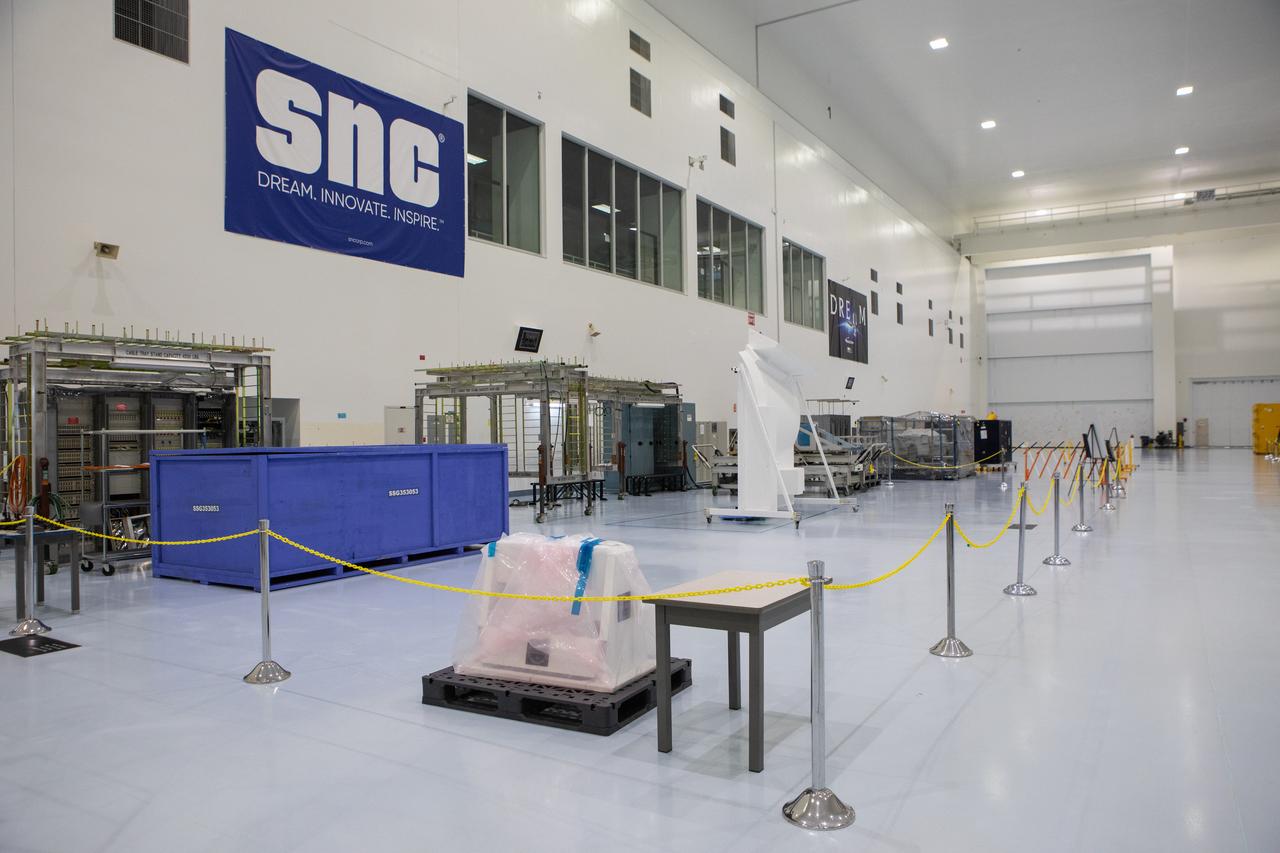

In view in this photograph, taken on May 16, 2019, is the area where the Sierra Nevada Corporation will process its Dream Chaser spacecraft in the high bay of the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center is celebrating the SSPF’s 25th anniversary. The facility was built to process elements for the International Space Station. Now it is providing support for current and future NASA and commercial provider programs, including Commercial Resupply Services, Artemis 1, sending the first woman and next man to the Moon, and deep space destinations including Mars.
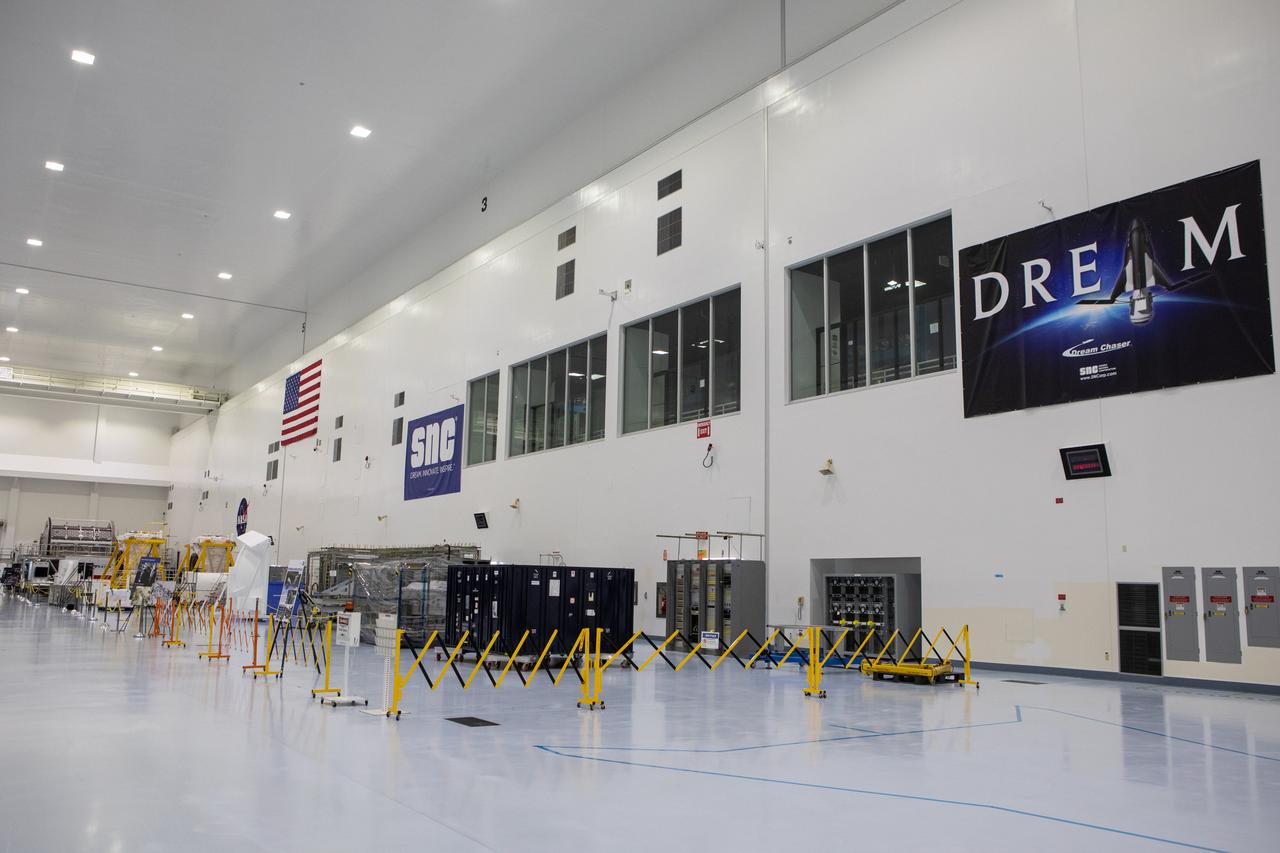

In view in this photograph, taken on May 16, 2019, is the area where the Sierra Nevada Corporation will process its Dream Chaser spacecraft in the high bay of the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center is celebrating the SSPF’s 25th anniversary. The facility was built to process elements for the International Space Station. Now it is providing support for current and future NASA and commercial provider programs, including Commercial Resupply Services, Artemis 1, sending the first woman and next man to the Moon, and deep space destinations including Mars.
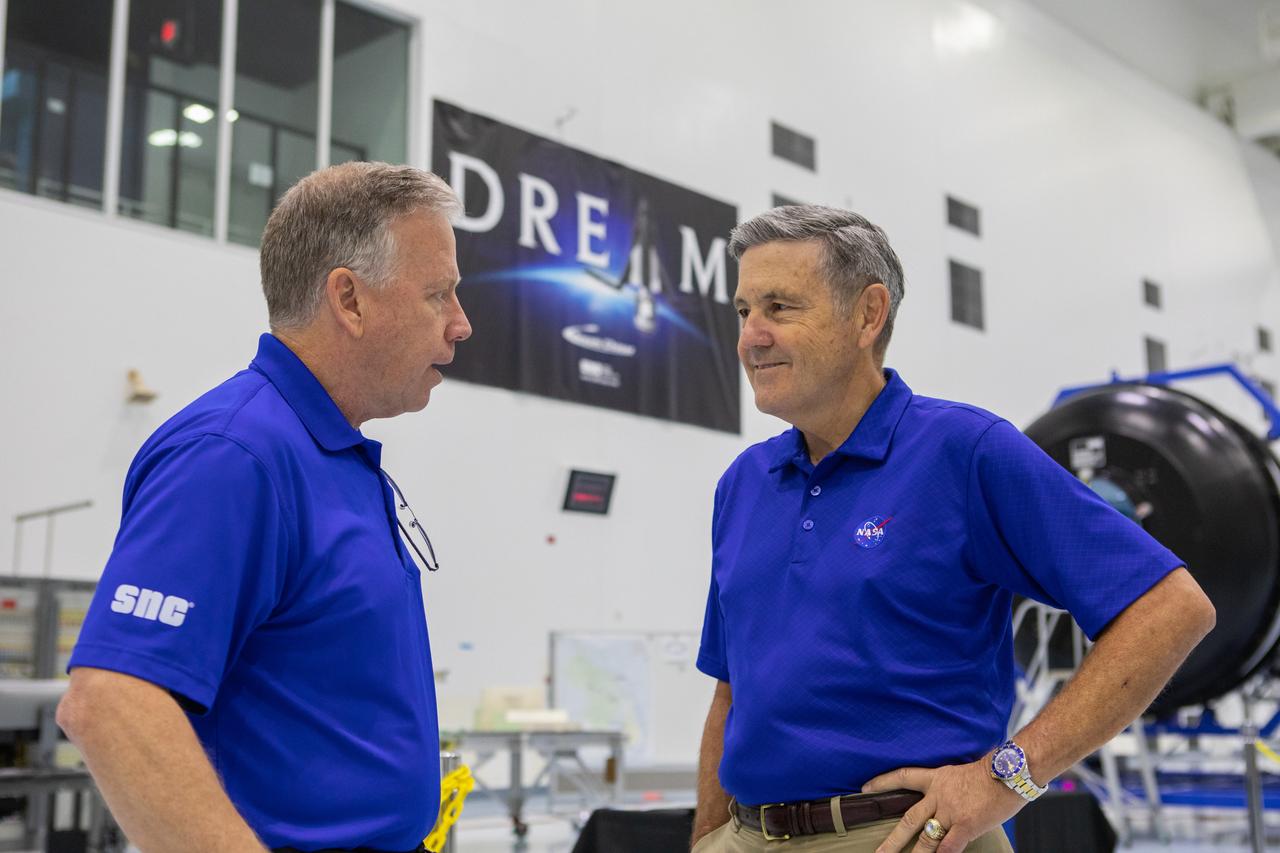

A mockup of the cargo logistics module for Sierra Nevada Corporation’s Dream Chaser, the company’s reusable spaceplane, arrived at the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in August. On Sept. 20, 2019, senior leadership had the opportunity to view the cargo module in the SSPF high bay. Kennedy Center Director Bob Cabana, at right, speaks with Steve Lindsey, vice president, Space Exploration Systems, Sierra Nevada Corporation. The SSPF is providing support for current and future NASA and commercial provider programs, including Commercial Resupply Services, Artemis 1, sending the first woman and next man to the Moon, and deep space destinations including Mars.
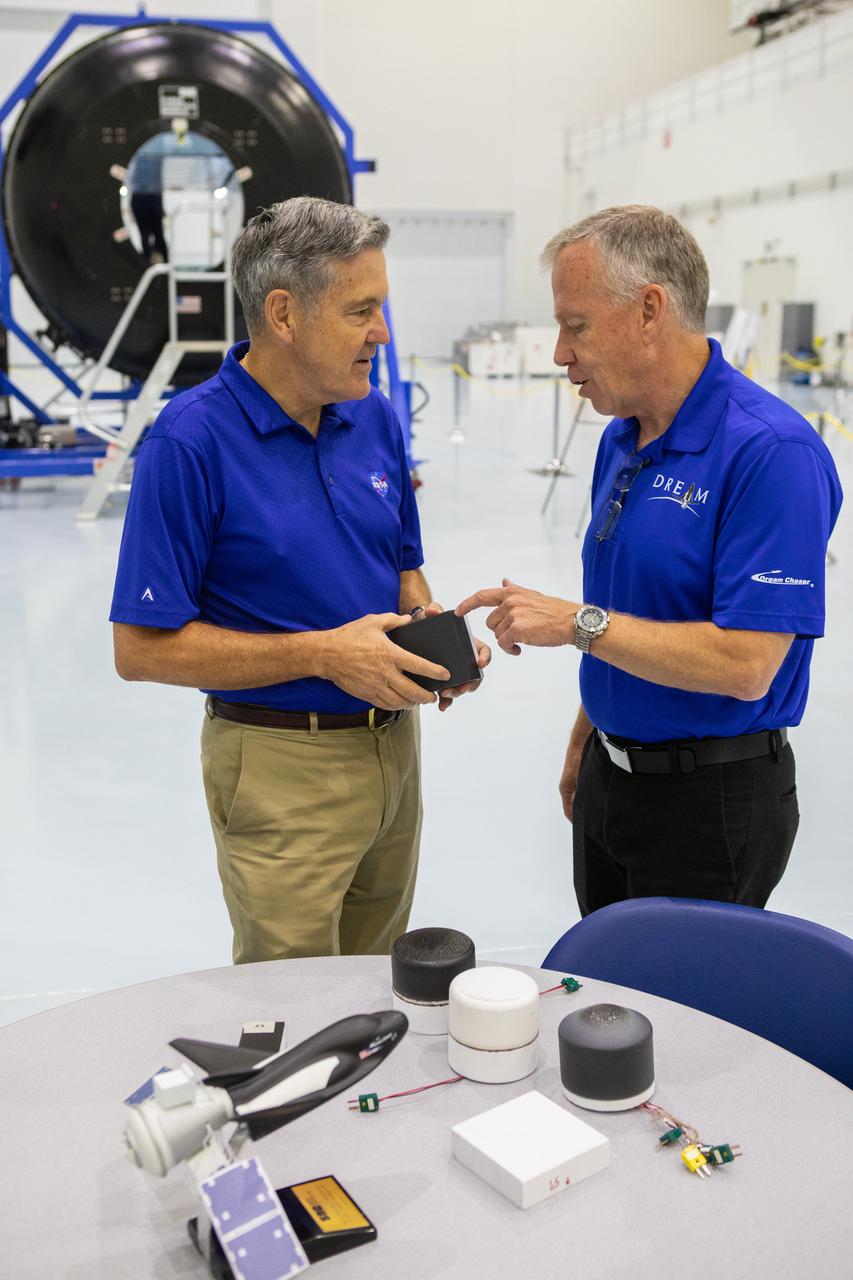

A mockup of the cargo logistics module for Sierra Nevada Corporation’s Dream Chaser, the company’s reusable spaceplane, arrived at the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in August. On Sept. 20, 2019, senior leadership had the opportunity to view the cargo module in the SSPF high bay. Kennedy Center Director Bob Cabana, left, speaks to Steve Lindsey, vice president, Space Exploration Systems, Sierra Nevada Corporation. The SSPF is providing support for current and future NASA and commercial provider programs, including Commercial Resupply Services, Artemis 1, sending the first woman and next man to the Moon, and deep space destinations including Mars.
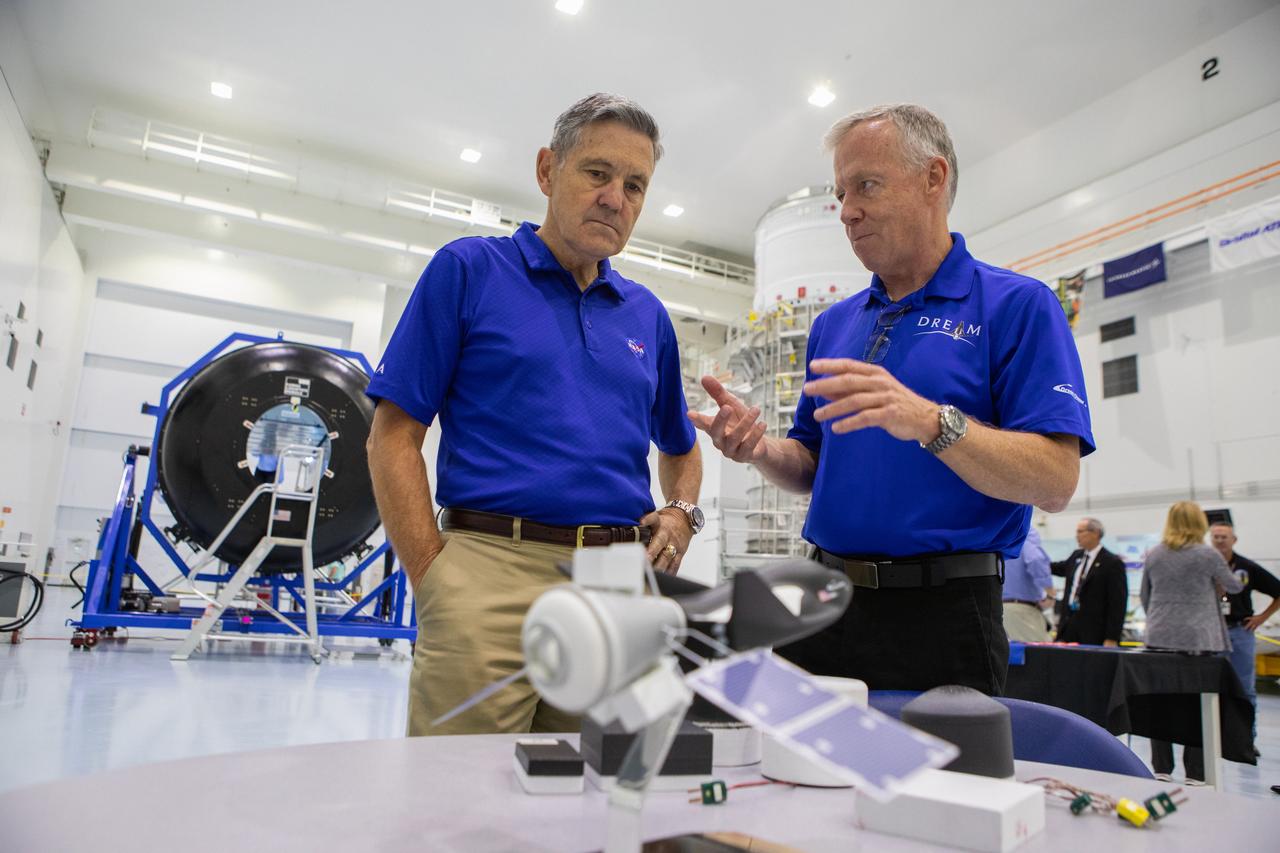

A mockup of the cargo logistics module for Sierra Nevada Corporation’s Dream Chaser, the company’s reusable spaceplane, arrived at the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in August. On Sept. 20, 2019, senior leadership had the opportunity to view the cargo module in the SSPF high bay. Kennedy Center Director Bob Cabana, left, speaks to Steve Lindsey, vice president, Space Exploration Systems, Sierra Nevada Corporation. The SSPF is providing support for current and future NASA and commercial provider programs, including Commercial Resupply Services, Artemis 1, sending the first woman and next man to the Moon, and deep space destinations including Mars.

In view in this photograph, taken on May 16, 2019, is the area where the Sierra Nevada Corporation will process its Dream Chaser spacecraft in the high bay of the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center is celebrating the SSPF’s 25th anniversary. The facility was built to process elements for the International Space Station. Now it is providing support for current and future NASA and commercial provider programs, including Commercial Resupply Services, Artemis 1, sending the first woman and next man to the Moon, and deep space destinations including Mars.
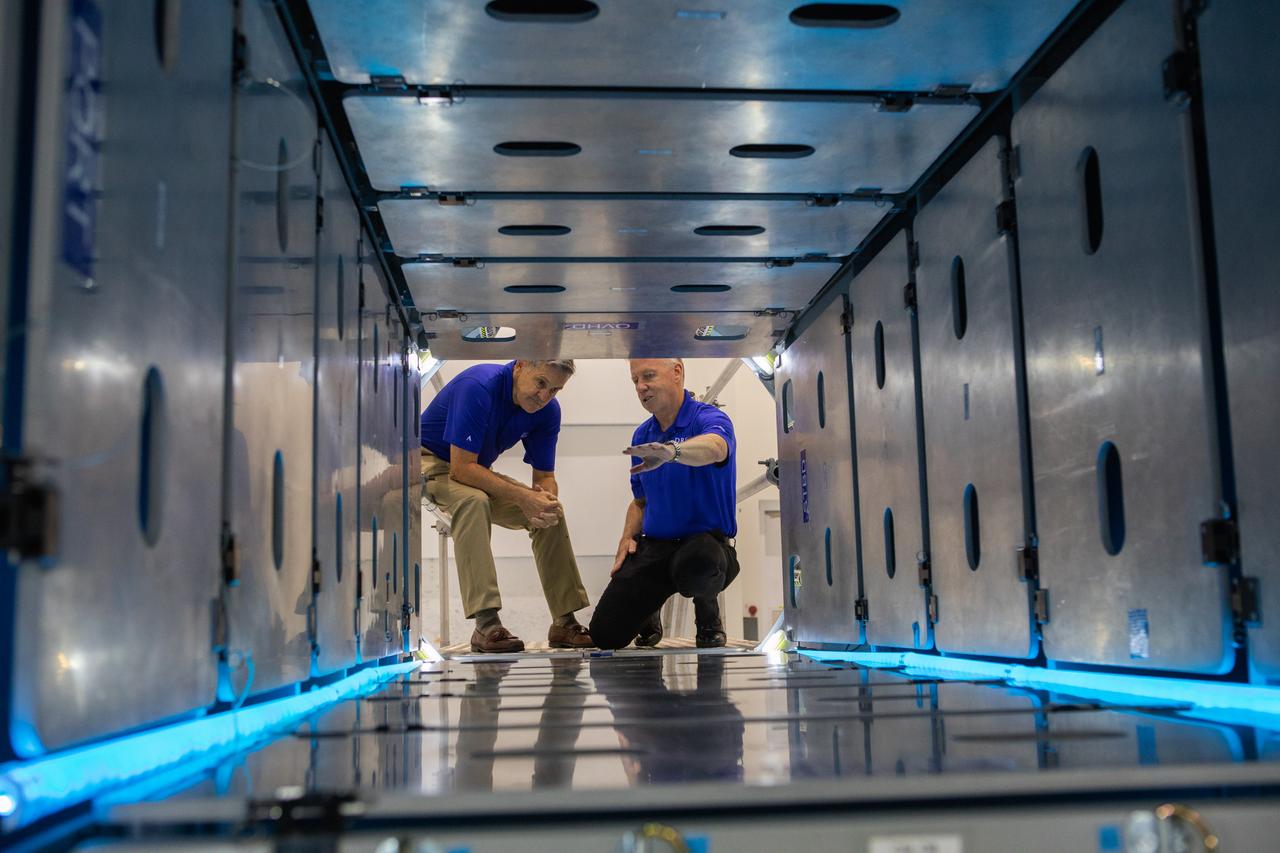

A mockup of the cargo logistics module for Sierra Nevada Corporation’s Dream Chaser, the company’s reusable spaceplane, arrived at the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in August. On Sept. 20, 2019, senior leadership had the opportunity to view the cargo module in the SSPF high bay. Kennedy Center Director Bob Cabana, views the interior of the cargo module with Steve Lindsey, vice president, Space Exploration Systems, Sierra Nevada Corporation. The SSPF is providing support for current and future NASA and commercial provider programs, including Commercial Resupply Services, Artemis 1, sending the first woman and next man to the Moon, and deep space destinations including Mars.
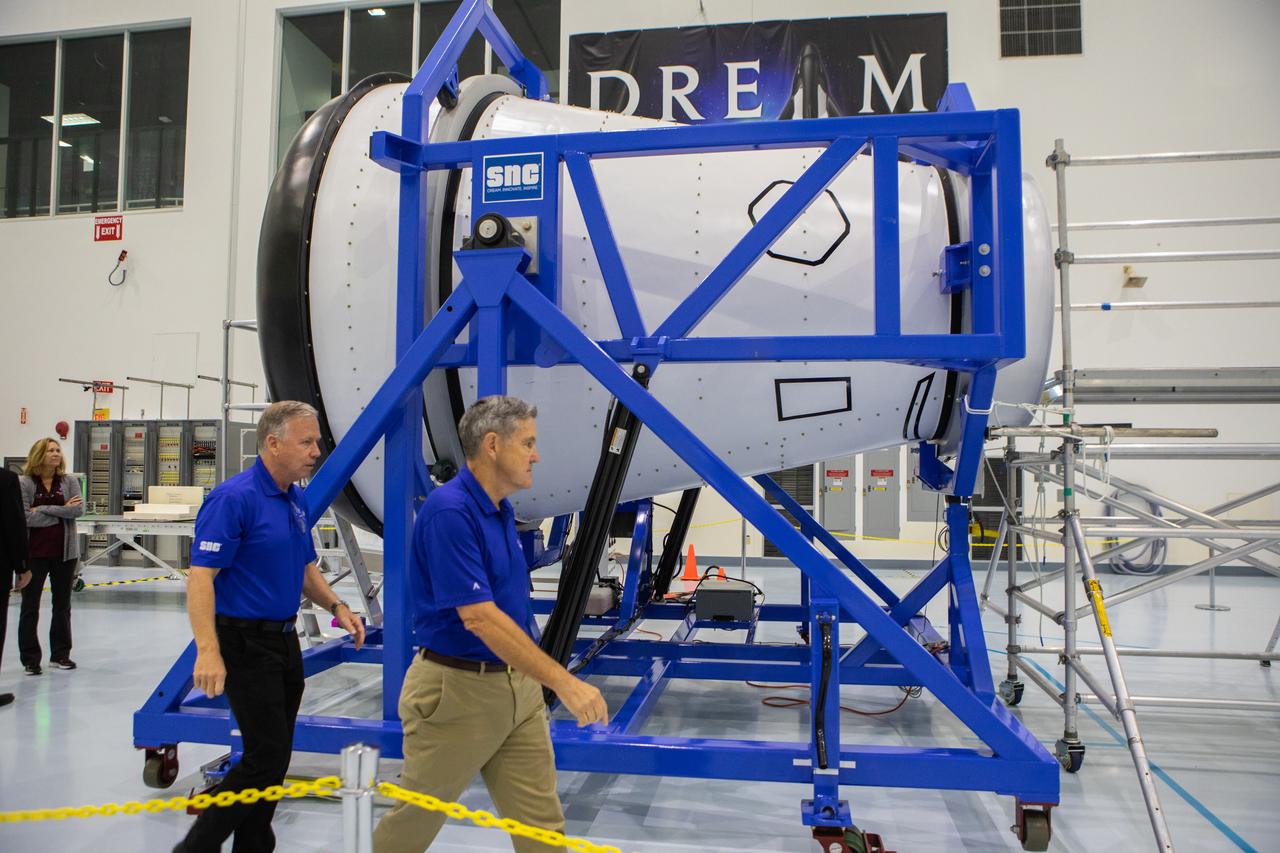

A mockup of the cargo logistics module for Sierra Nevada Corporation’s Dream Chaser, the company’s reusable spaceplane, arrived at the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in August. On Sept. 20, 2019, senior leadership had the opportunity to view the cargo module in the SSPF high bay. Kennedy Center Director Bob Cabana, at right, views the cargo module with Steve Lindsey, vice president, Space Exploration Systems, Sierra Nevada Corporation. The SSPF is providing support for current and future NASA and commercial provider programs, including Commercial Resupply Services, Artemis 1, sending the first woman and next man to the Moon, and deep space destinations including Mars.
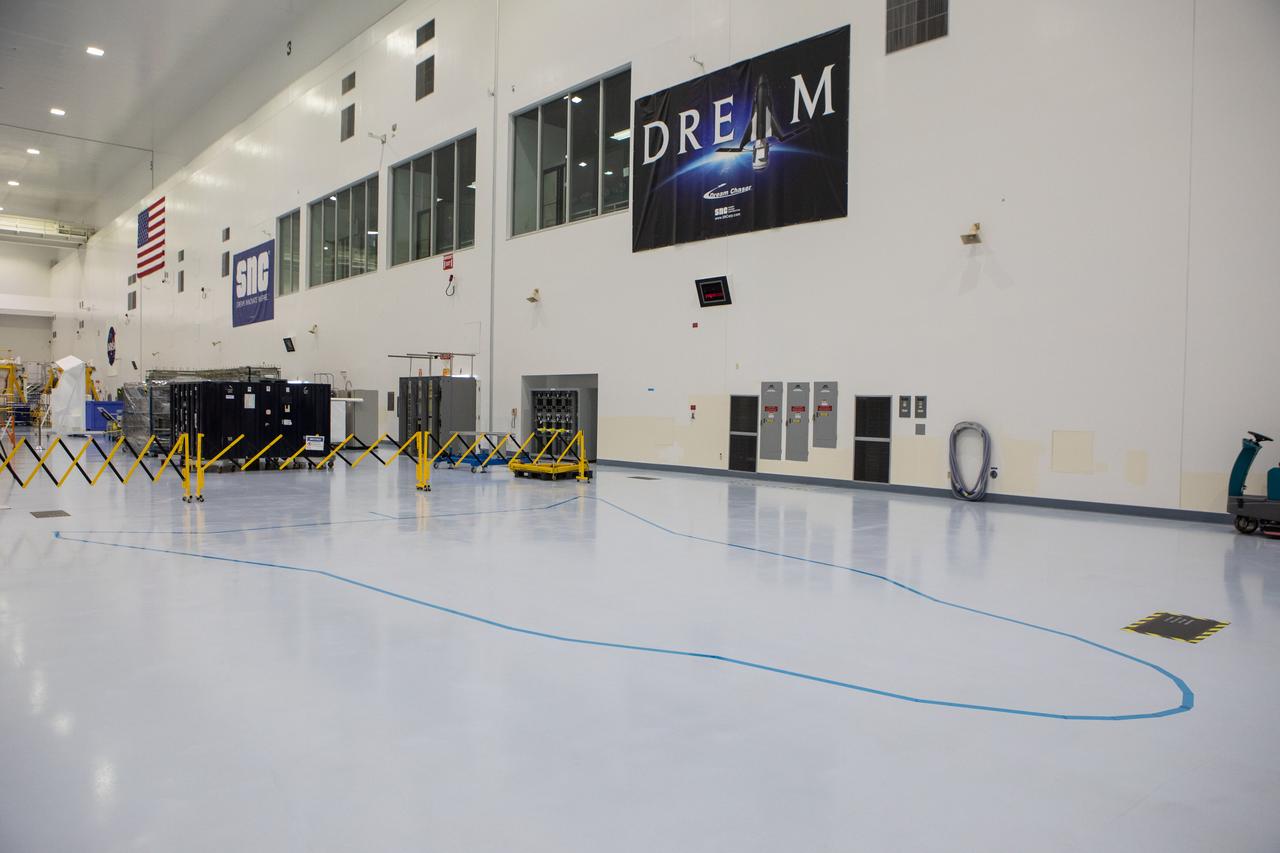

In view in this photograph, taken on May 16, 2019, is the area where the Sierra Nevada Corporation will process its Dream Chaser spacecraft in the high bay of the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center is celebrating the SSPF’s 25th anniversary. The facility was built to process elements for the International Space Station. Now it is providing support for current and future NASA and commercial provider programs, including Commercial Resupply Services, Artemis 1, sending the first woman and next man to the Moon, and deep space destinations including Mars.
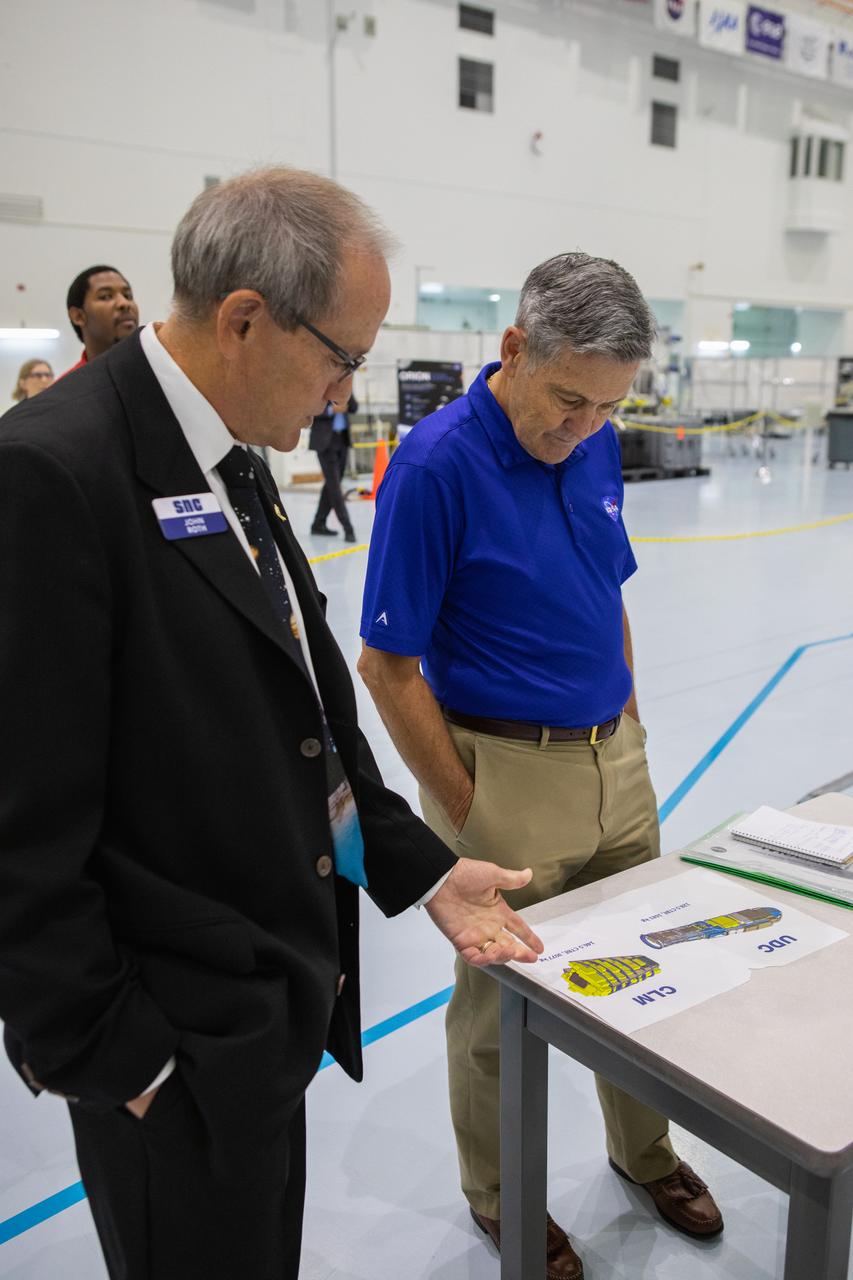

A mockup of the cargo logistics module for Sierra Nevada Corporation’s Dream Chaser, the company’s reusable spaceplane, arrived at the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in August. On Sept. 20, 2019, senior leadership had the opportunity to view the cargo module in the SSPF high bay. Kennedy Center Director Bob Cabana, at right, listens to John Roth, vice president, Business Development Space Systems, Sierra Nevada Corporation. The SSPF is providing support for current and future NASA and commercial provider programs, including Commercial Resupply Services, Artemis 1, sending the first woman and next man to the Moon, and deep space destinations including Mars.

A mockup of the cargo logistics module for Sierra Nevada Corporation’s Dream Chaser, the company’s reusable spaceplane, arrived at the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in August. On Sept. 20, 2019, senior leadership had the opportunity to view the cargo module in the SSPF high bay. From left, are Josie Burnett, director of Exploration Research and Technology Programs; Kelvin Manning, Kennedy associate director, technical; Kennedy Deputy Director Janet Petro; Kennedy Center Director Bob Cabana; Burt Summerfield, Kennedy associate director, management; and Ronnie Lawson, deputy director of Exploration Research and Technology Programs. The SSPF is providing support for current and future NASA and commercial provider programs, including Commercial Resupply Services, Artemis 1, sending the first woman and next man to the Moon, and deep space destinations including Mars.

A mockup of the cargo logistics module for Sierra Nevada Corporation’s Dream Chaser, the company’s reusable spaceplane, arrived at the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in August. On Sept. 20, 2019, senior leadership had the opportunity to view the cargo module in the SSPF high bay. From left, are Kelvin Manning, Kennedy associate director, technical; Kennedy Deputy Director Janet Petro; Kennedy Center Director Bob Cabana; and Burt Summerfield, Kennedy associate director, management. The SSPF is providing support for current and future NASA and commercial provider programs, including Commercial Resupply Services, Artemis 1, sending the first woman and next man to the Moon, and deep space destinations including Mars.
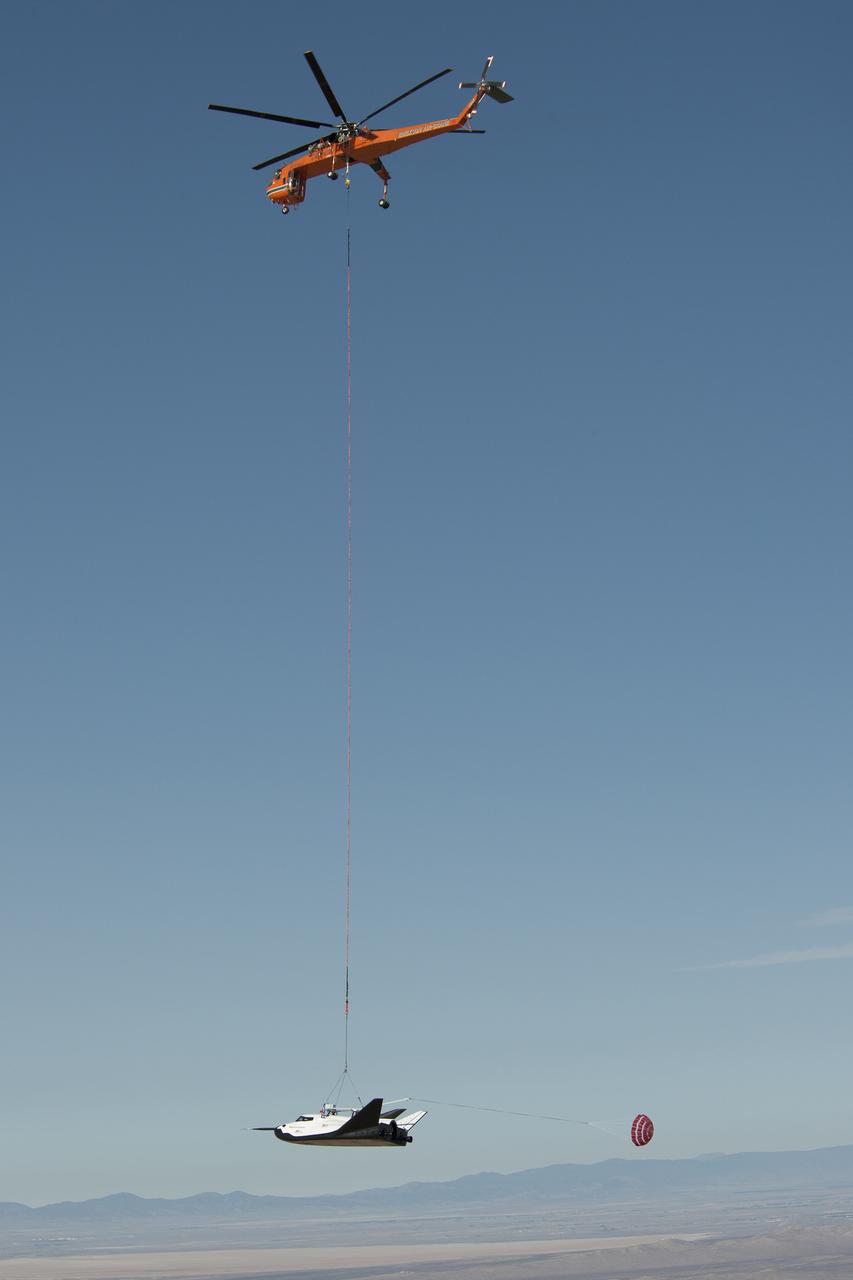

Dream Chaser Captive Carry Flight #1