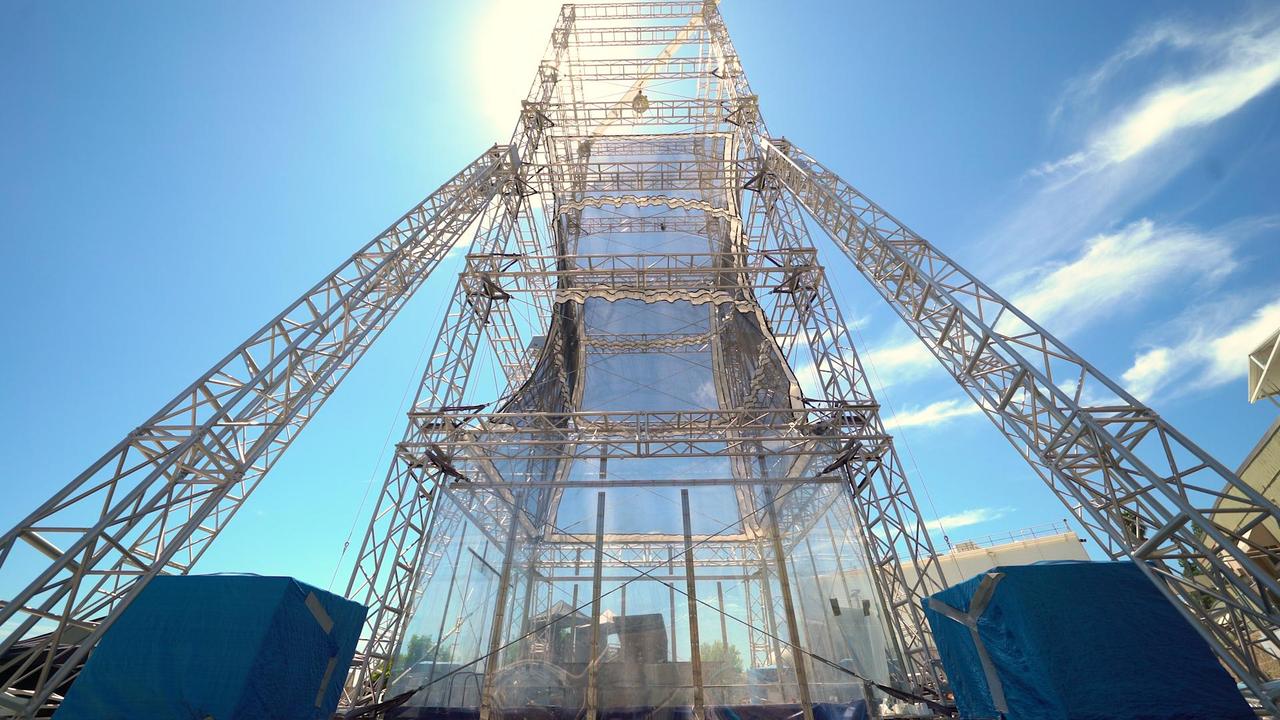

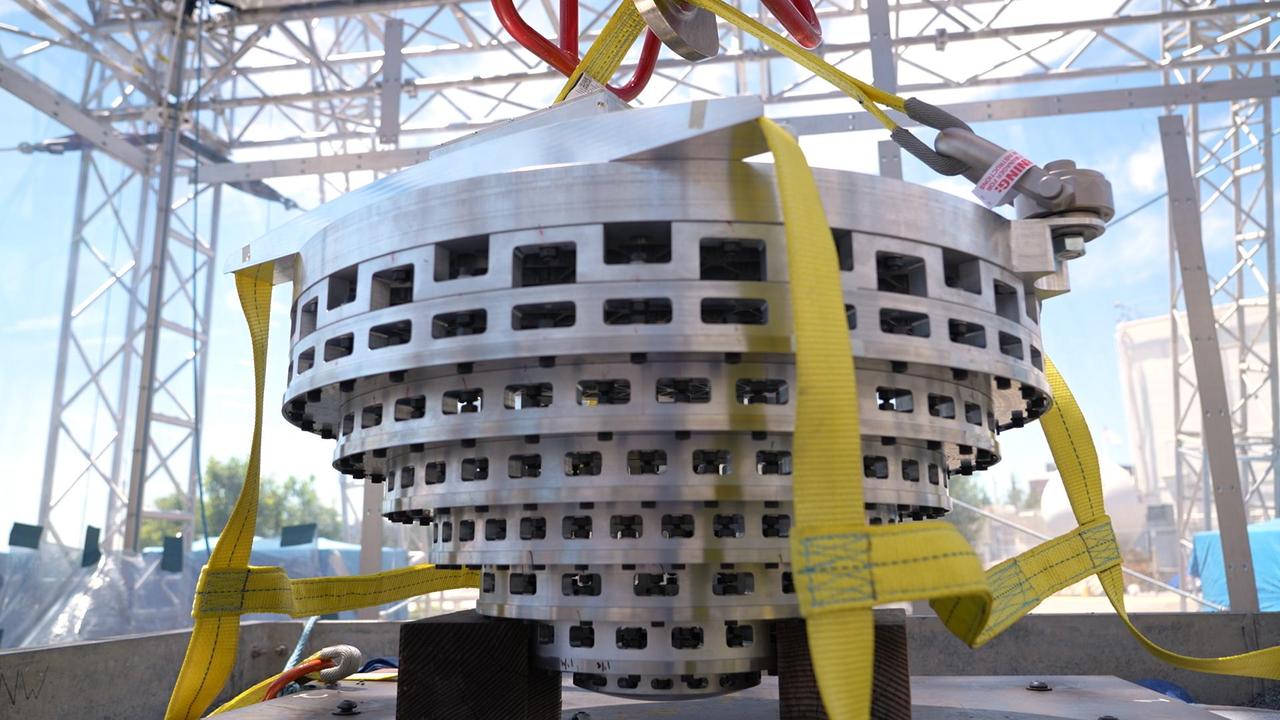
This drop tower at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California includes a bow launch system, which can hurl test articles 110 mph into the ground, re-creating the forces they would experience during a Mars landing. The drop tower was used for testing the collapsible-base of a prototype Mars lander design called SHIELD (Simplified High Impact Energy Landing Device) on Aug. 12, 2022. The SHIELD concept could one day allow lower-cost missions to reach the Martian surface. In this image, the SHIELD base prototype can be seen being lifted up to the top of the tower. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25581
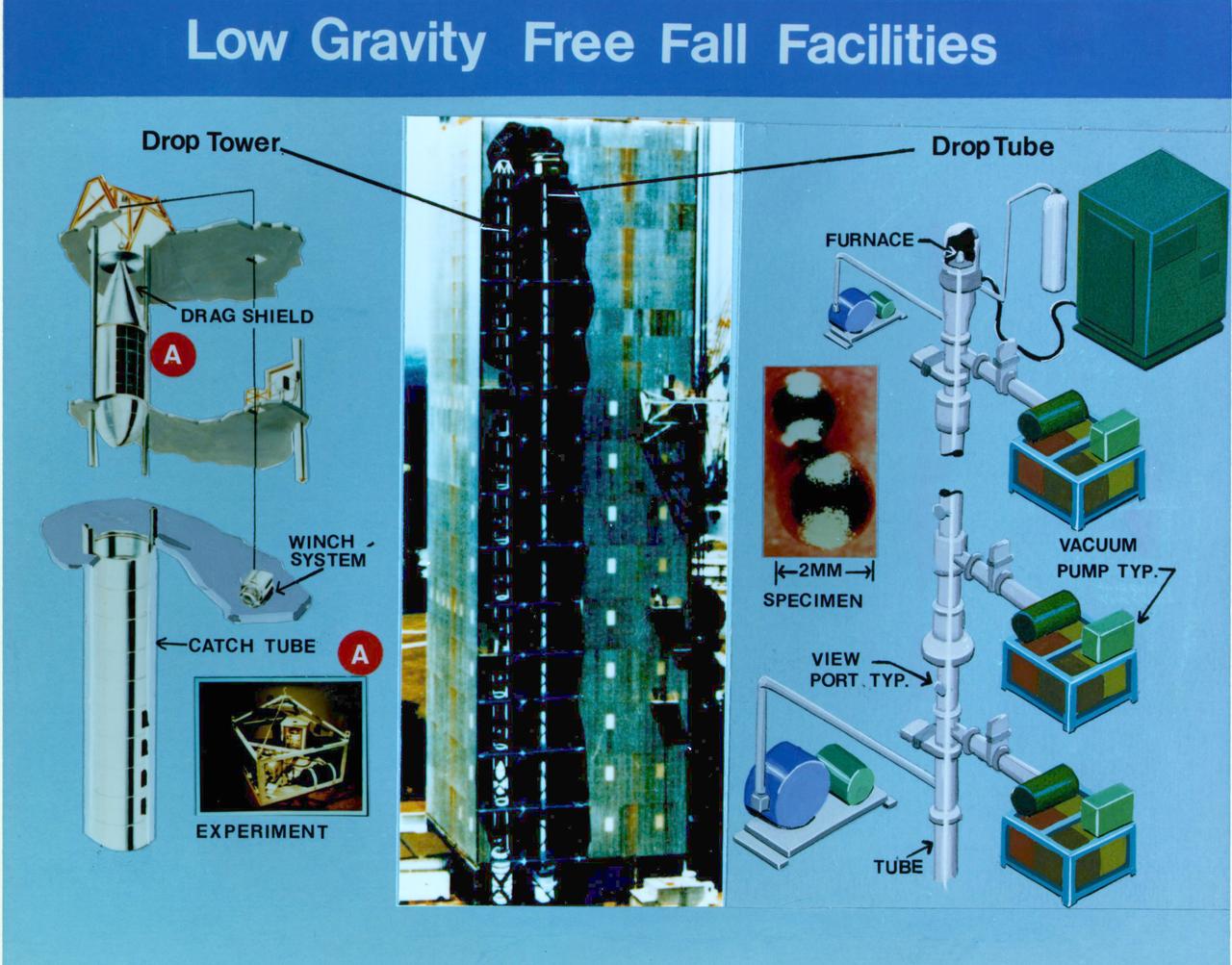
Composite of Marshall Space Flight Center's Low-Gravity Free Fall Facilities.These facilities include a 100-meter drop tower and a 100-meter drop tube. The drop tower simulates in-flight microgravity conditions for up to 4.2 seconds for containerless processing experiments, immiscible fluids and materials research, pre-flight hardware design test and flight experiment simulation. The drop tube simulates in-flight microgravity conditions for up to 4.6 seconds and is used extensively for ground-based microgravity convection research in which extremely small samples are studied. The facility can provide deep undercooling for containerless processing experiments that require materials to remain in a liquid phase when cooled below the normal solidification temperature.

Students pause while waiting their turn at the 2.2-second Drop Tower during the second Dropping in a Microgravity Environment (DIME) competition held April 23-25, 2002, at NASA's Glenn Research Center. Competitors included two teams from Sycamore High School, Cincinnati, OH, and one each from Bay High School, Bay Village, OH, and COSI Academy, Columbus, OH. DIME is part of NASA's education and outreach activities. Details are on line at http://microgravity.grc.nasa.gov/DIME_2002.html.

A NASA test conductor at the top of the 2.2-second Drop Tower monitors a student lecture at a lower level. This was part of the Microgravity Environment (DIME) competition held April 23-25, 2002, at NASA's Glenn Research Center. Competitors included two teams from Sycamore High School, Cincinnati, OH, and one each from Bay High School, Bay Village, OH, and COSI Academy, Columbus, OH. DIME is part of NASA's education and outreach activities. Details are on line at http://microgravity.grc.nasa.gov/DIME_2002.html.

Jimmy Grisham of the Microgravity Program Plarning Integration Office at NASA/Marshall Space Flight Center, demonstrates the classroom-size Microgravity Drop Tower Demonstrator. The apparatus provides 1/6 second of microgravity for small experiments. A video camera helps teachers observe what happens inside the package. This demonstration was at the April 2000 conference of the National Council of Teachers of Mathematics (NCTM) in Chicago. Photo credit: NASA/Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC)

Don Gillies, a materials scientist at NASA/Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), demonstrates the classroom-size Microgravity Drop Tower Demonstrator. The apparatus provides 1/6 second of microgravity for small experiments. A video camera helps teachers observe what happens inside the package. This demonstration was at the April 2000 conference of the National Council of Teachers of Mathematics (NCTM) in Chicago. Photo credit: NASA/Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC)

A researcher fills a small container used to represent a liquid hydrogen tank in preparation for a microgravity test in the 2.2-Second Drop Tower at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. For over a decade, NASA Lewis endeavored to make liquid hydrogen a viable propellant. Hydrogen’s light weight and high energy made it very appealing for rocket propulsion. One of the unknowns at the time was the behavior of fluids in the microgravity of space. Rocket designers needed to know where the propellant would be inside the fuel tank in order to pump it to the engine. NASA Lewis utilized sounding rockets, research aircraft, and the 2.2 Second Drop Tower to study liquids in microgravity. The drop tower, originally built as a fuel distillation tower in 1948, descended into a steep ravine. By early 1961 the facility was converted into an eight-floor, 100-foot tower connected to a shop and laboratory space. Small glass tanks, like this one, were installed in experiment carts with cameras to film the liquid’s behavior during freefall. Thousands of drop tower tests in the early 1960s provided an increased understanding of low-gravity processes and phenomena. The tower only afforded a relatively short experiment time but was sufficient enough that the research could be expanded upon using longer duration freefalls on sounding rockets or aircraft. The results of the early experimental fluid studies verified predictions made by Lewis researchers that the total surface energy would be minimized in microgravity.
Interior of a combustion experiment apparatus used in the 2.2-second drop tower at NASA's Glenn Research Center. This was shown to students participating in the second Dropping in a Microgravity Environment (DIME) competition held April 23-25, 2002, at NASA's Glenn Research Center. Competitors included two teams from Sycamore High School, Cincinnati, OH, and one each from Bay High School, Bay Village, OH, and COSI Academy, Columbus, OH. DIME is part of NASA's education and outreach activities. Details are on line at http://microgravity.grc.nasa.gov/DIME_2002.html.
This prototype of a collapsible Mars lander base is part of SHIELD (Simplified High Impact Energy Landing Device), a project aimed at developing spacecraft that would intentionally crash land on the Red Planet, using an accordion-like, collapsible base that acts like the crumple zone of a car to absorb the energy of a hard impact. The design could drastically reduce the cost of landing on Mars by simplifying the harrowing entry, descent, and landing process and expanding options for possible landing sites. Developed at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California, the prototype was attached to a drop tower on Aug. 12, 2022, at JPL. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25420
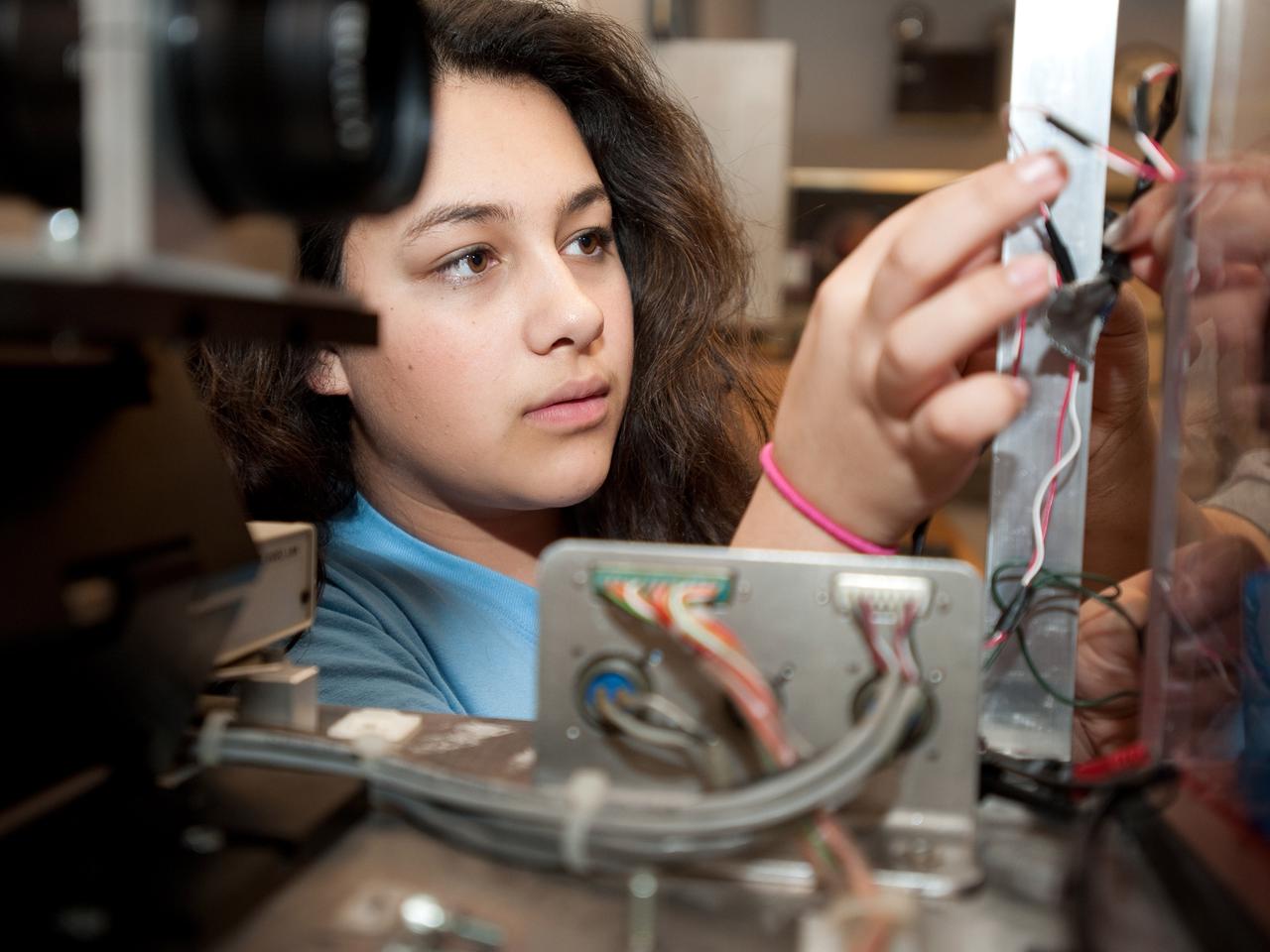

Neera Martin, a NASA Glenn student intern, works on a drop package for the 'Dropping in Microgravity Environment (DIME)' event held in NASA Glenn's 2.2 Second Drop Tower.

The first NASA Dropping In a Microgravity Environment (DIME) student competition pilot project came to a conclusion at the Glenn Research Center in April 2001. The competition involved high-school student teams who developed the concept for a microgravity experiment and prepared an experiment proposal. The two student teams - COSI Academy, sponsored by the Columbus Center of Science and Industry, and another team from Cincinnati, Ohio's Sycamore High School, designed a microgravity experiment, fabricated the experimental apparatus, and visited NASA Glenn to operate their experiment in the 2.2 Second Drop Tower. Here, students are briefed by NASA engineer Daniel Dietrich at the top of the drop tower. This image is from a digital still camera; higher resolution is not available.

Marshall Space Flight Center employees visited DuPont Manual High School in Louisville, Kentucky. NASA's Mini Drop Tower was used to demonstrate free fall and a presentation was given on microgravity and the science performed in a microgravity environment. The visit coincided with the Pan-Pacific Basin Workshop on Microgravity Sciences held in Pasadena, California. Materials engineer Chris Cochrane explains the operation of the mini-drop tower. This image is from a digital still camera; higher resolution is not available.

Marshall Space Flight Center employees visited DuPont Manual High School in Louisville, Kentucky. NASA's Mini Drop Tower was used to demonstrate free fall and a presentation was given on microgravity and the science performed in a microgravity environment. The visit coincided with the Pan-Pacific Basin Workshop on Microgravity Sciences held in Pasadena, California. Students watch the playback of video from the mini-drop tower. This image is from a digital still camera; higher resolution is not available.

Marshall Space Flight Center employees visited DuPont Manual High School in Louisville, Kentucky. NASA's Mini Drop Tower was used to demonstrate free fall and a presentation was given on microgravity and the science performed in a microgravity environment. The visit coincided with the Pan-Pacific Basin Workshop on Microgravity Sciences held in Pasadena, California. Materials engineer Chris Cochrane explains the operation of the mini-drop tower. This image is from a digital still camera; higher resolution is not available.

Marshall Space Flight Center employees visited DuPont Manual High School in Louisville, Kentucky. NASA's Mini Drop Tower was used to demonstrate free fall and a presentation was given on microgravity and the science performed in a microgravity environment. The visit coincided with the Pan-Pacific Basin Workshop on Microgravity Sciences held in Pasadena, California. Students experiment with the mini-drop tower. This image is from a digital still camera; higher resolution is not available.

The first NASA Dropping In a Microgravity Environment (DIME) student competition pilot project came to a conclusion at the Glenn Research Center in April 2001. The competition involved high-school student teams who developed the concept for a microgravity experiment and prepared an experiment proposal. The two student teams - COSI Academy, sponsored by the Columbus Center of Science and Industry, and another team from Cincinnati, Ohio's Sycamore High School, designed a microgravity experiment, fabricated the experimental apparatus, and visited NASA Glenn to operate their experiment in the 2.2 Second Drop Tower. Here students from Sycamore High School in Cincinnati, Ohio, talk with Dr. Dennis Stocker, one of Glenn's lead microgravity scientists, about the uses of the drop tower. This image is from a digital still camera; higher resolution is not available.

The first NASA Dropping In a Microgravity Environment (DIME) student competition pilot project came to a conclusion at the Glenn Research Center in April 2001. The competition involved high-school student teams who developed the concept for a microgravity experiment and prepared an experiment proposal. The two student teams - COSI Academy, sponsored by the Columbus Center of Science and Industry, and another team from Cincinnati, Ohio's Sycamore High School, designed a microgravity experiment, fabricated the experimental apparatus, and visited NASA Glenn to operate their experiment in the 2.2 Second Drop Tower. Here Jose Carrion, a lab mechanic with AKAC, starts the orange-colored drag shield, and the experiment apparatus inside, on the hoist upward to the control station at the top of the drop tower. This image is from a digital still camera; higher resolution is not available.

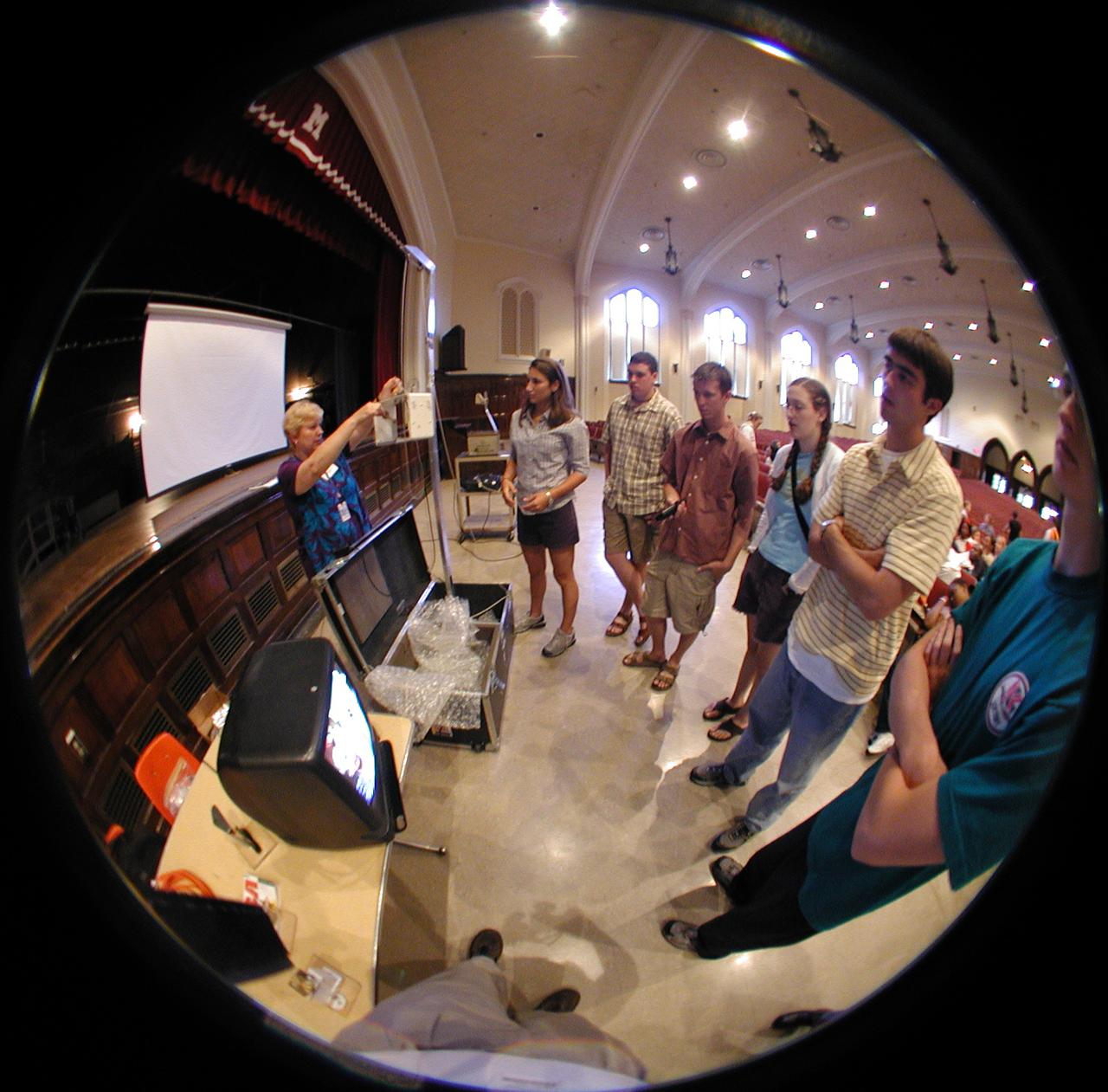
Students discuss fine points of their final design for the Drop Tower experiment during the second Dropping in a Microgravity Environment (DIME) competition held April 23-25, 2002, at NASA's Glenn Research Center. Competitors included two teams from Sycamore High School, Cincinnati, OH, and one each from Bay High School, Bay Village, OH, and COSI Academy, Columbus, OH. DIME is part of NASA's education and outreach activities. Details are on line at http://microgravity.grc.nasa.gov/DIME_2002.html.
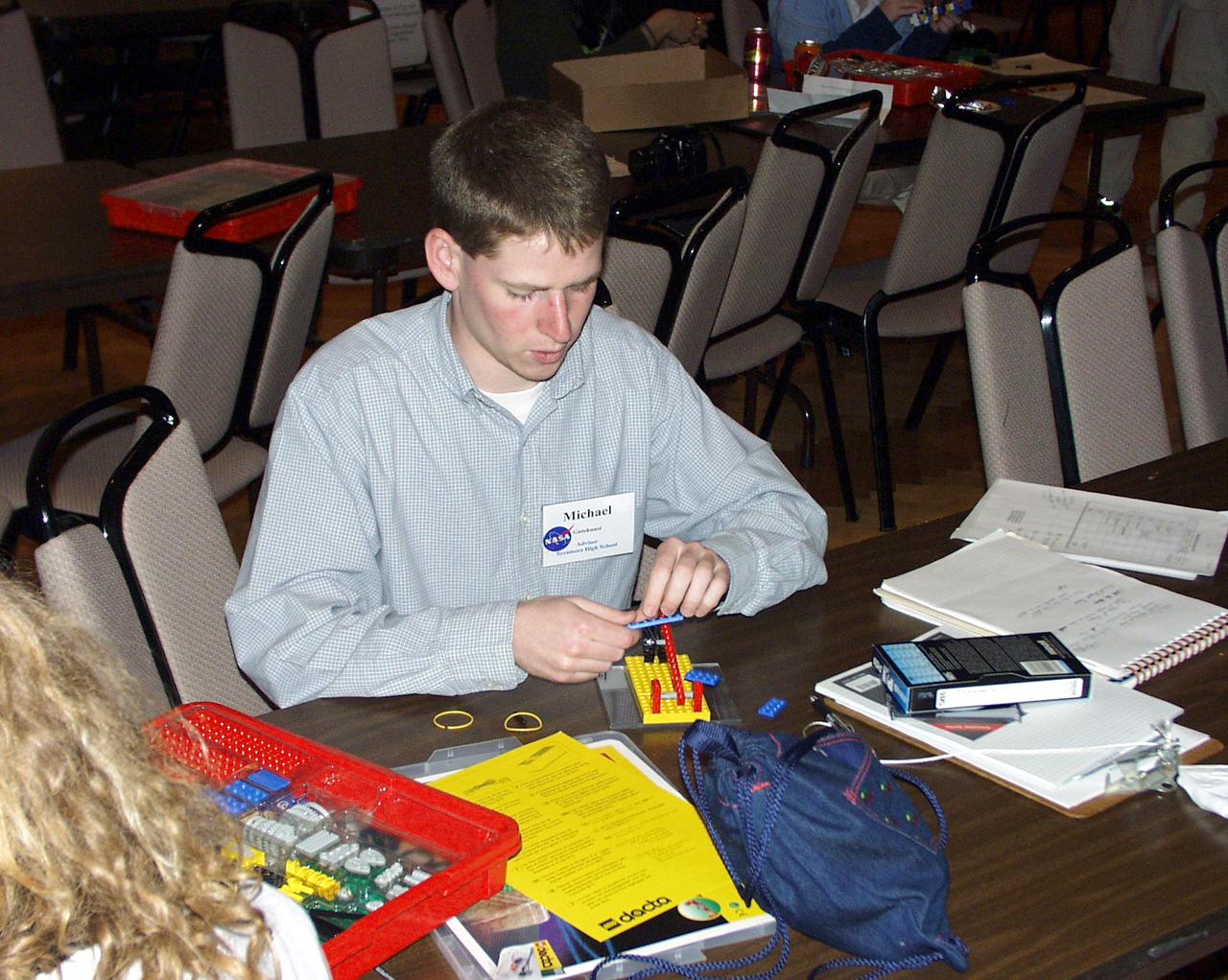

A student assembles a Lego (TM) Challenge device designed to operate in the portable drop tower demonstrator as part of the second Dropping in a Microgravity Environment (DIME) competition held April 23-25, 2002, at NASA's Glenn Research Center. Competitors included two teams from Sycamore High School, Cincinnati, OH, and one each from Bay High School, Bay Village, OH, and COSI Academy, Columbus, OH. DIME is part of NASA's education and outreach activities. Details are on line at http://microgravity.grc.nasa.gov/DIME_2002.html.
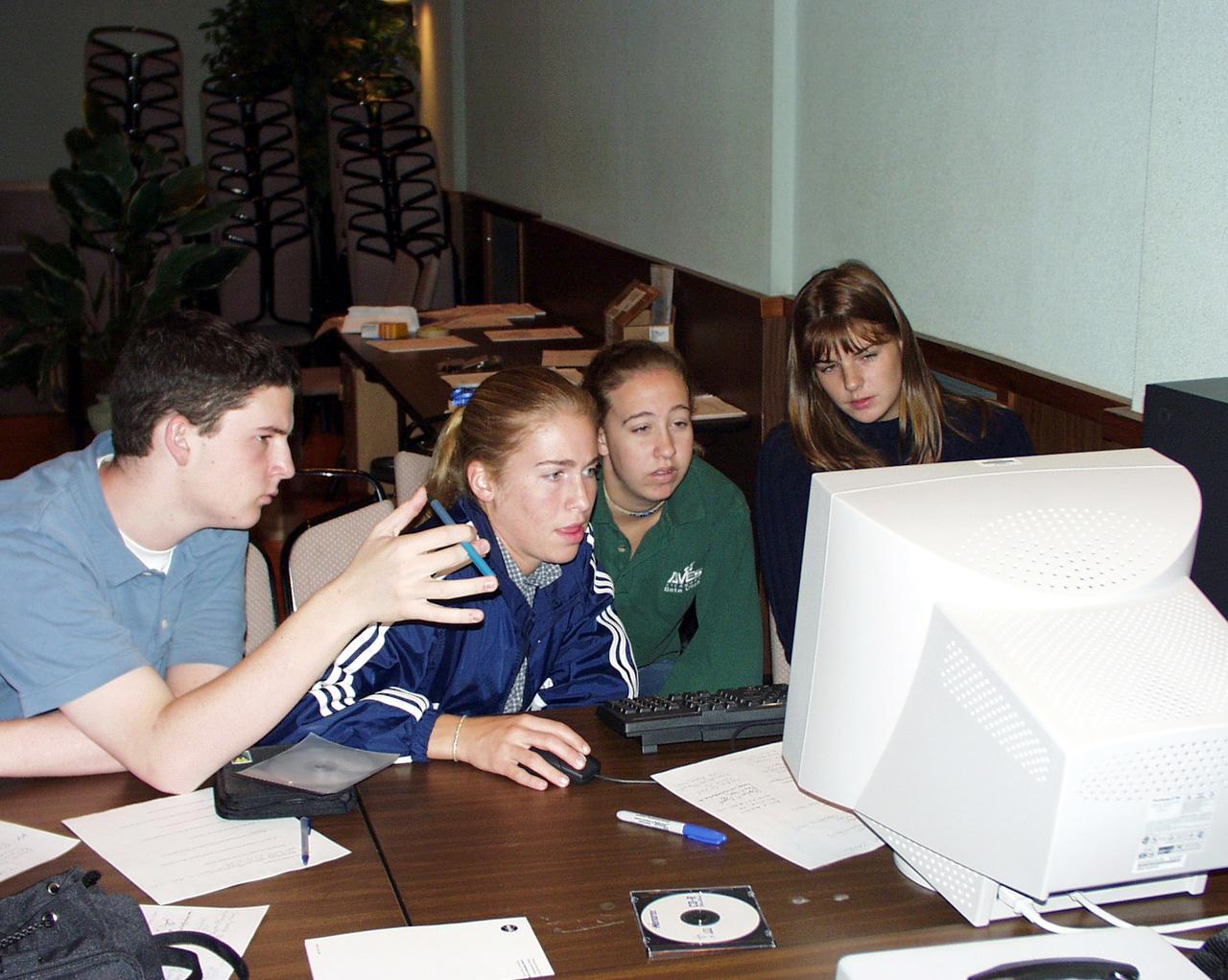

Students discuss fine points of their final design for the drop tower experiment during the second Dropping in a Microgravity Environment (DIME) competition held April 23-25, 2002, at NASA's Glenn Research Center. Competitors included two teams from Sycamore High School, Cincinnati, OH, and one each from Bay High School, Bay Village, OH, and COSI Academy, Columbus, OH. DIME is part of NASA's education and outreach activities. Details are on line at http://microgravity.grc.nasa.gov/DIME_2002.html.
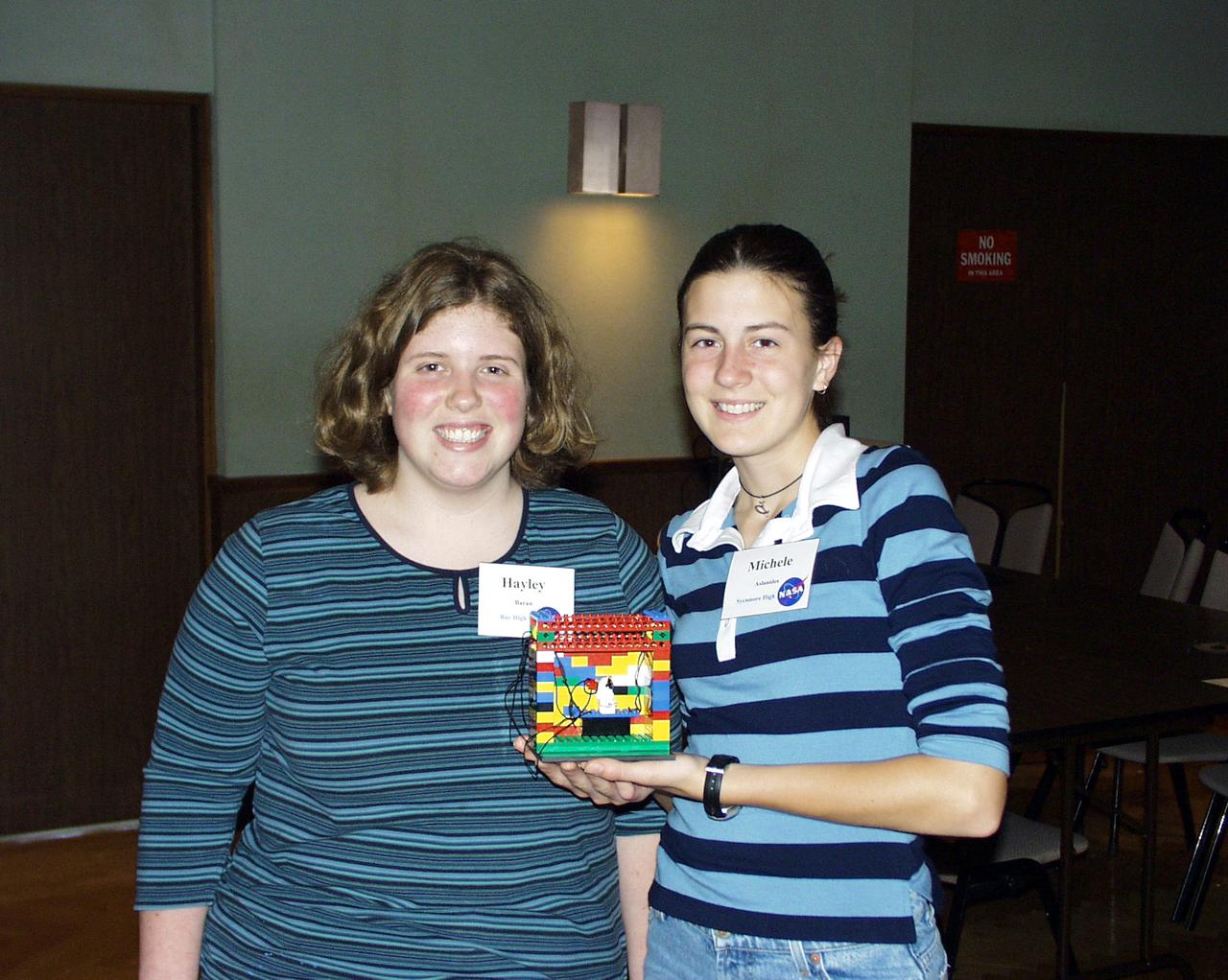

Two students show the Lego (TM) Challenge device they designed and built to operate in the portable drop tower demonstrator as part of the second Dropping in a Microgravity Environment (DIME) competition held April 23-25, 2002, at NASA's Glenn Research Center. Competitors included two teams from Sycamore High School, Cincinnati, OH, and one each from Bay High School, Bay Village, OH, and COSI Academy, Columbus, OH. DIME is part of NASA's education and outreach activities. Details are on line at http://microgravity.grc.nasa.gov/DIME_2002.html.
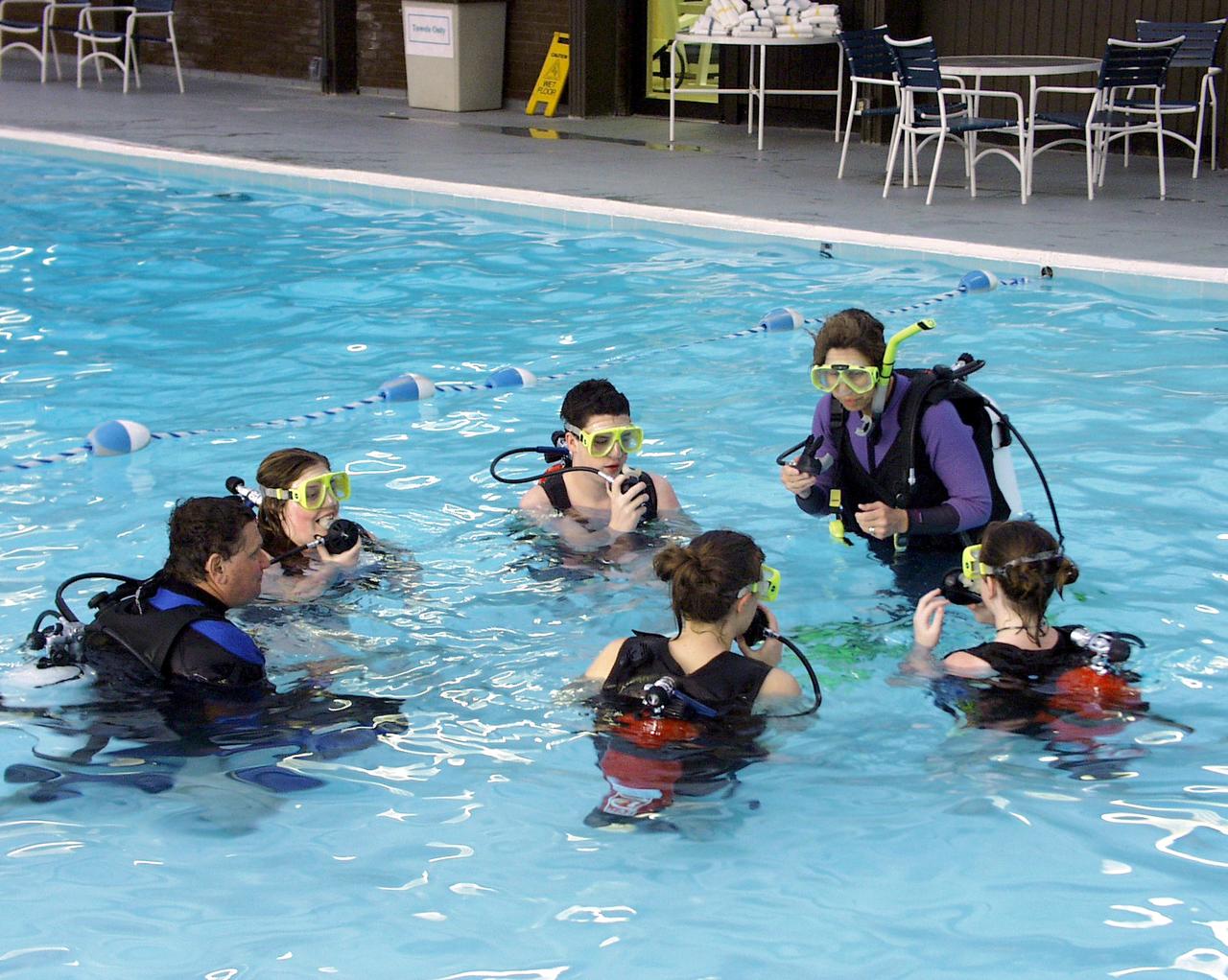

In addition to drop tower activities, students assembled a plastic pipe structure underwater in a SCUBA exercise similar to training astronauts receive at NASA Johnson Space Center. This was part of the second Dropping in a Microgravity Environment (DIME) competition held April 23-25, 2002, at NASA's Glenn Research Center. Competitors included two teams from Sycamore High School, Cincinnati, OH, and one each from Bay High School, Bay Village, OH, and COSI Academy, Columbus, OH. DIME is part of NASA's education and outreach activities. Details are on line at http://microgravity.grc.nasa.gov/DIME_2002.html.
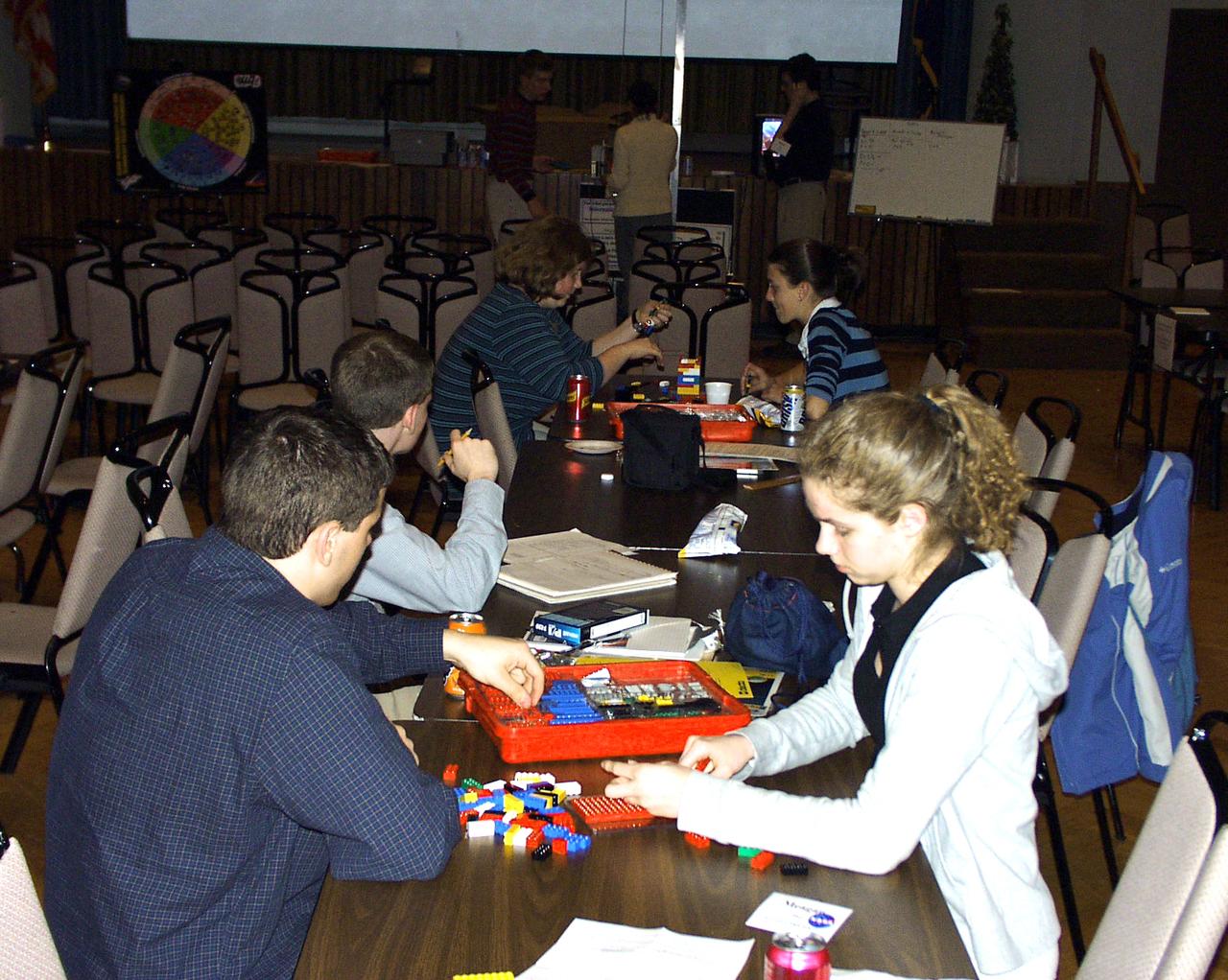

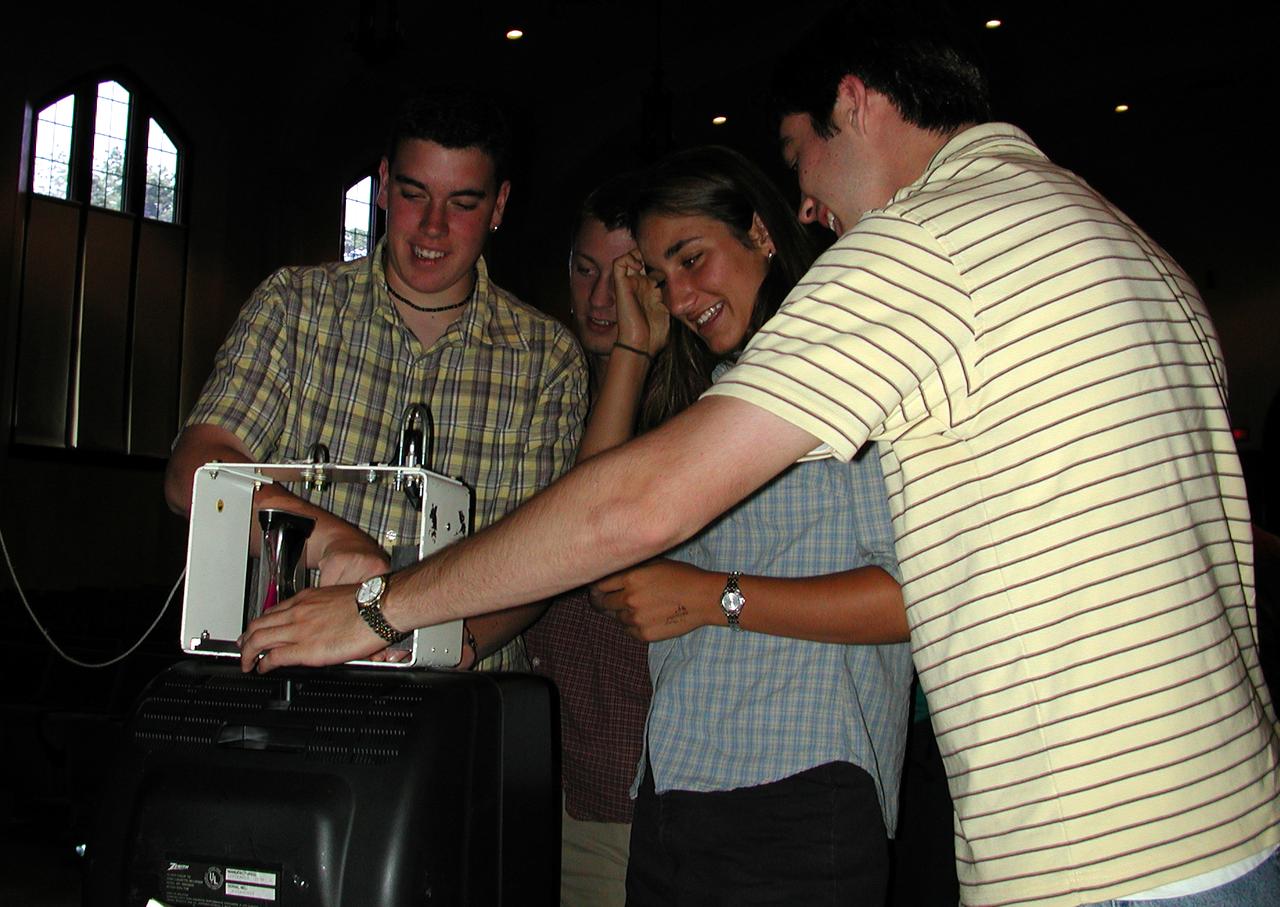
Members from all four teams were mixed into pairs to work on a Lego (TM) Challenge device to operate in the portable drop tower demonstrator (background). These two team members are about to try out their LEGO (TM) creation. This was part of the second Dropping in a Microgravity Environment (DIME) competition held April 23-25, 2002, at NASA's Glenn Research Center. Competitors included two teams from Sycamore High School, Cincinnati, OH, and one each from Bay High School, Bay Village, OH, and COSI Academy, Columbus, OH. DIME is part of NASA's education and outreach activities. Details are on line at http://microgravity.grc.nasa.gov/DIME_2002.html.

The first NASA Dropping In a Microgravity Environment (DIME) student competition pilot project came to a conclusion at the Glenn Research Center in April 2001. The competition involved high-school student teams who developed the concept for a microgravity experiment and prepared an experiment proposal. The two student teams - COSI Academy, sponsored by the Columbus Center of Science and Industry, and another team from Cincinnati, Ohio's Sycamore High School, designed a microgravity experiment, fabricated the experimental apparatus, and visited NASA Glenn to operate their experiment in the 2.2 Second Drop Tower. Meredith Mendenhall of Sycamore High School, Cincinnati, Ohio, flips on a tape recorder in preparation for a drop. This image is from a digital still camera; higher resolution is not available.

The first NASA Dropping In a Microgravity Environment (DIME) student competition pilot project came to a conclusion at the Glenn Research Center in April 2001. The competition involved high-school student teams who developed the concept for a microgravity experiment and prepared an experiment proposal. The two student teams - COSI Academy, sponsored by the Columbus Center of Science and Industry, and another team from Cincinnati, Ohio's Sycamore High School, designed a microgravity experiment, fabricated the experimental apparatus, and visited NASA Glenn to operate their experiment in the 2.2 Second Drop Tower. Sandi Thompson of the National Center for Microgravity Research GRC makes a final adjustment to the drop package. This image is from a digital still camera; higher resolution is not available.
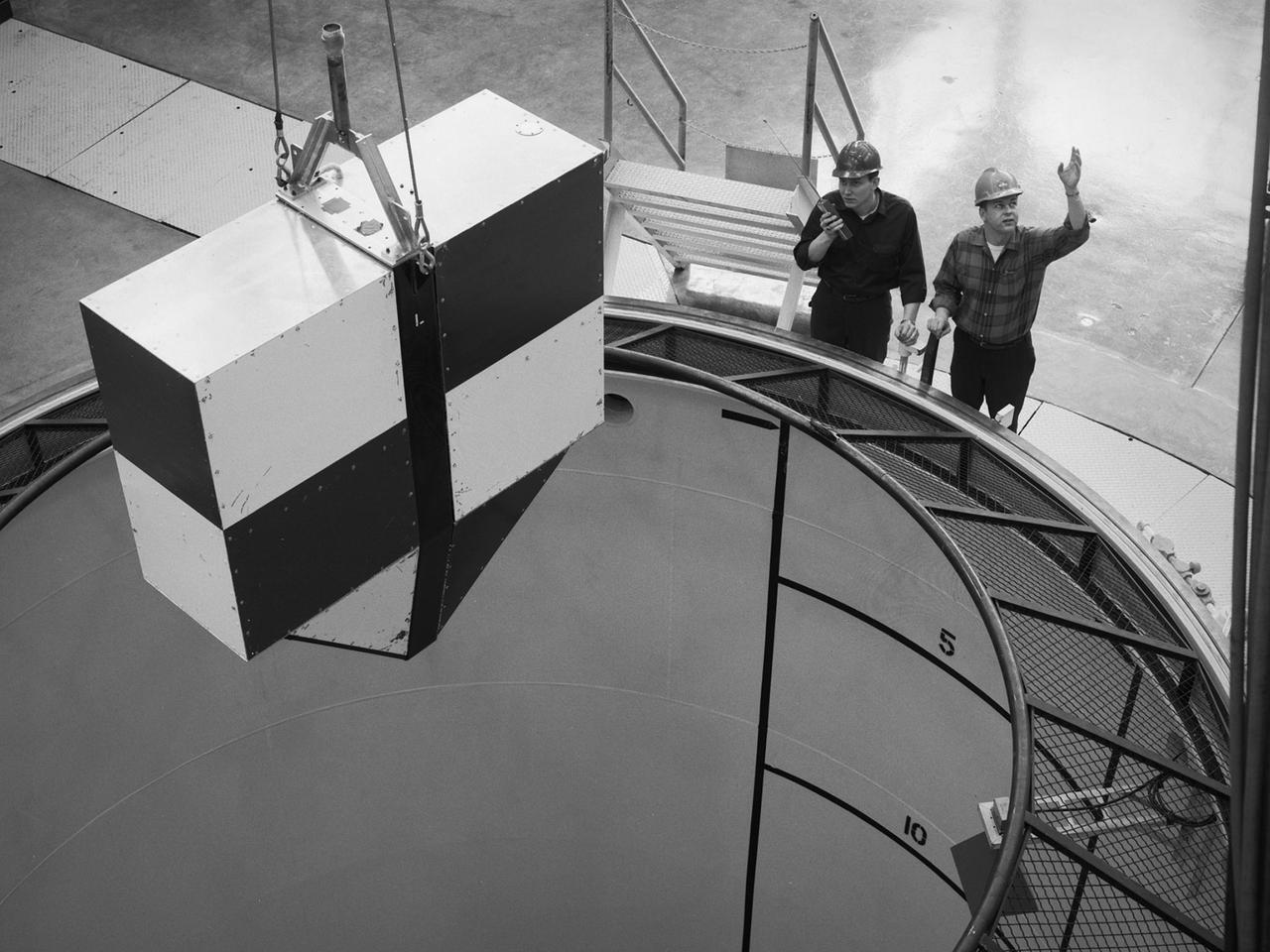
A rectangular drop test vehicle perched above 450-foot shaft at the Zero Gravity Research Facility at NASA Lewis Research Center. The drop tower was designed to provide five seconds of microgravity during a normal drop, but had a pneumatic gun that could quickly propel the vehicle to the top of the shaft prior to its drop, thus providing ten seconds of microgravity. The shaft contained a steel-lined vacuum chamber 20 feet in diameter and 469 feet deep. The package was stopped at the bottom of the pit by a 15-foot deep deceleration cart filled with polystyrene pellets. During normal operations, a cylindrical 3-foot diameter and 11-foot long vehicle was used to house the experiments, instrumentation, and high speed cameras. The 4.5-foot long and 1.5-foot wide rectangular vehicle, seen in this photograph, was used less frequently. A 3-foot diameter orb was used for the ten second drops. After the test vehicle was prepared it was suspended above the shaft from the top of the chamber. A lid was used to seal the top of the chamber. The vacuum system reduced the pressure levels inside the chamber. The bolt holding the vehicle was then sheared and the vehicle plummeted into the deceleration cart.

The first NASA Dropping In a Microgravity Environment (DIME) student competition pilot project came to a conclusion at the Glenn Research Center in April 2001. The competition involved high-school student teams who developed the concept for a microgravity experiment and prepared an experiment proposal. The two student teams - COSI Academy, sponsored by the Columbus Center of Science and Industry, and another team from Cincinnati, Ohio's Sycamore High School, designed a microgravity experiment, fabricated the experimental apparatus, and visited NASA Glenn to operate their experiment in the 2.2 Second Drop Tower. NASA and contractor personnel who conducted the DIME activity with the students. Shown (L-R) are: Daniel Dietrich (NASA) mentor for Sycamore High School team), Carol Hodanbosi (National Center for Microgravity Research; DIME staff), Jose Carrion (GRC Akima, drop tower technician), Dennis Stocker (NASA; DIME staff), Richard DeLombard (NASA; DIME staff), Sandi Thompson (NSMR sabbatical teacher; DIME staff), Peter Sunderland (NCMR, mentor for COSI Academy student team), Adam Malcolm (NASA co-op student; DIME staff). This image is from a digital still camera; higher resolution is not available.
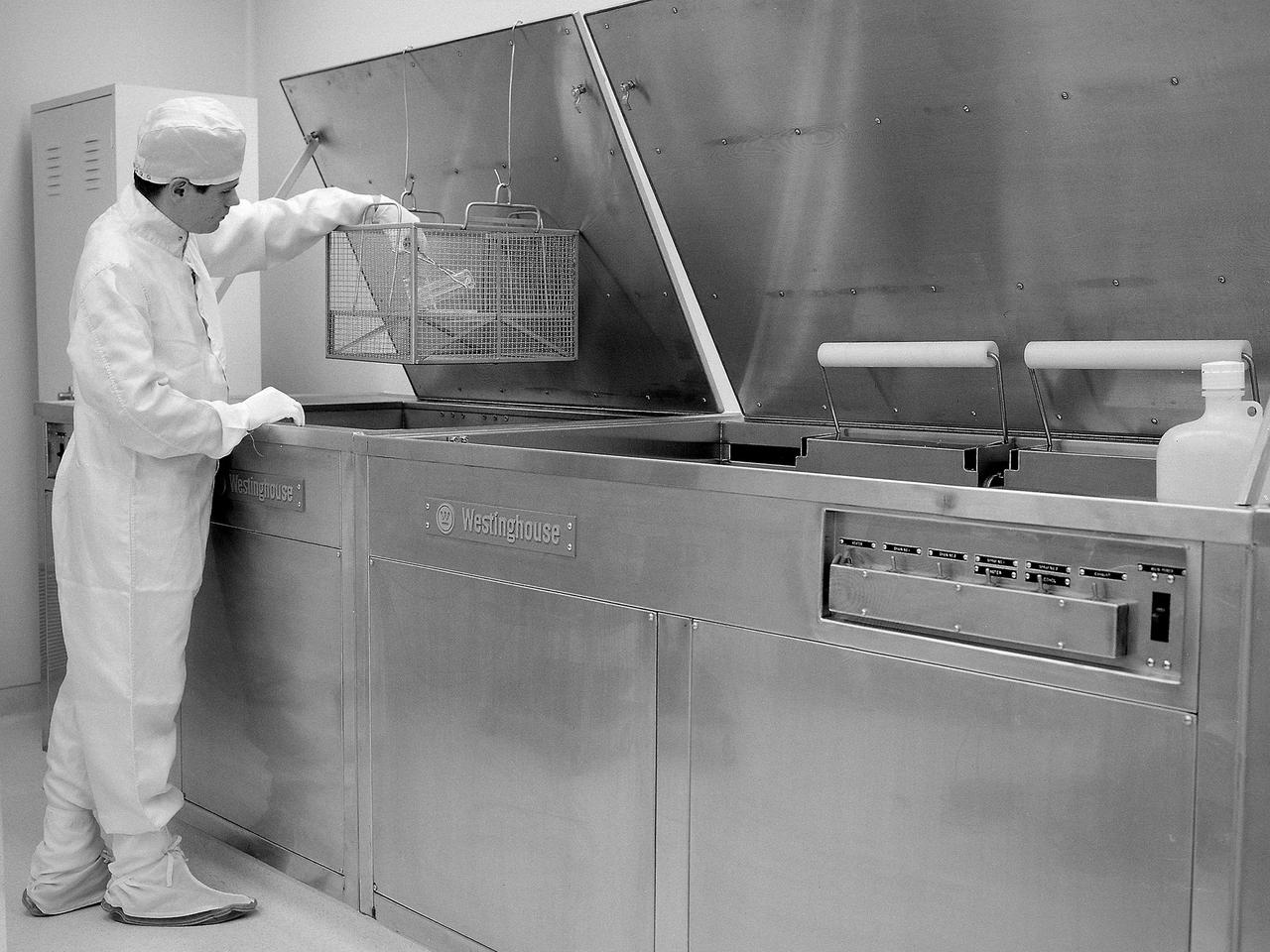

A technician prepares a test sample in the Zero Gravity Research Facility clean room at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. The Zero Gravity Research Facility contained a drop tower which provided five seconds of microgravity during freefall in its 450-foot deep vacuum chamber. The facility has been used for a variety of studies relating to the behavior of fluids and flames in microgravity. During normal operations, a cylindrical 3-foot diameter and 11-foot long vehicle was used to house the experiments, instrumentation, and high speed cameras. The 4.5-foot long and 1.5-foot wide rectangular vehicle, seen in this photograph, was used less frequently. A 3-foot diameter orb was used for the special ten-second drops in which the package was pneumatically shot to the top of the tower then dropped. The facility also contained a control room, shop offices, tool and equipment rooms, and this clean room. The 242.5-foot long and 19.5-foot wide clean room was equipped with specialized cleaning equipment. In the 1960s the room was rated as a class 10,000 clean room, but I was capable of meeting the class 100 requirements. The room included a fume hood, ultrasonic cleaner, and a laminar flow station which operated as a class 100 environment. The environment in the clean room was maintained at 71° F and a relative humidity of 45- percent.

The first NASA Dropping In a Microgravity Environment (DIME) student competition pilot project came to a conclusion at the Glenn Research Center in April 2001. The competition involved high-school student teams who developed the concept for a microgravity experiment and prepared an experiment proposal. The two student teams - COSI Academy, sponsored by the Columbus Center of Science and Industry, and another team from Cincinnati, Ohio's Sycamore High School, designed a microgravity experiment, fabricated the experimental apparatus, and visited NASA Glenn to operate their experiment in the 2.2 Second Drop Tower. NASA and contractor personnel who conducted the DIME activity with the students. Shown (L-R) are: Eric Baumann (NASA, 2.2-second Drop Tower Facility manager), Daniel Dietrich (NASA) mentor for Sycamore High School team), Carol Hodanbosi (National Center for Microgravity Research; DIME staff), Richard DeLombard (NASA; DIME staff), Jose Carrion (GRC Akima, drop tower technician), Dennis Stocker (NASA; DIME staff), Peter Sunderland (NCMR, mentor for COSI Academy student team), Sandi Thompson (NSMR sabbatical teacher; DIME staff), Dan Woodard (MASA Microgravity Outreach Program Manager), Adam Malcolm (NASA co-op student; DIME staff), Carla Rosenberg (NCMR; DIME staff), and Twila Schneider (Infinity Technology; NASA Microgravity Research program contractor). This image is from a digital still camera; higher resolution is not available.

The arnual conference for the Educator Resource Center Network (ERCN) Coordinators was held at Glenn Research Center at Lewis Field in Cleveland, Ohio. The conference included participants from NASA's Educator Resource Centers located throughout the country. The Microgravity Science Division at Glenn sponsored a Microgravity Day for all the conference participants. Dr. Wil Roberson and Marge Lehky prepare a demonstration with the mini-drop tower. This image is from a digital still camera; higher resolution is not available.

The arnual conference for the Educator Resource Center Network (ERCN) Coordinators was held at Glenn Research Center at Lewis Field in Cleveland, Ohio. The conference included participants from NASA's Educator Resource Centers located throughout the country. The Microgravity Science Division at Glenn sponsored a Microgravity Day for all the conference participants. Dr. Wil Roberson and Marge Lehky prepare a demonstration with the mini-drop tower. This image is from a digital still camera; higher resolution is not available.

Marshall Space Flight Center employees visited DuPont Manual High School in Louisville, Kentucky. NASA's Mini Drop Tower was used to demonstrate free fall and a presentation was given on microgravity and the science performed in a microgravity environment. The visit coincided with the Pan-Pacific Basin Workshop on Microgravity Sciences held in Pasadena, California. Materials engineer Chris Cochrane explains the basics of microgravity research. This image is from a digital still camera; higher resolution is not available.
The first NASA Dropping In a Microgravity Environment (DIME) student competition pilot project came to a conclusion at the Glenn Research Center in April 2001. The competition involved high-school student teams who developed the concept for a microgravity experiment and prepared an experiment proposal. The two student teams - COSI Academy, sponsored by the Columbus Center of Science and Industry, and another team from Cincinnati, Ohio's Sycamore High School, designed a microgravity experiment, fabricated the experimental apparatus, and visited NASA Glenn to operate their experiment in the 2.2 Second Drop Tower. This is the interior of the Sycamore High School (Cincinnati, Ohio) students' experiment to observe the flame spreading on a 100 percent cotton T-shirt under low-g. This image is from a digital still camera; higher resolution is not available.

The first NASA Dropping In a Microgravity Environment (DIME) student competition pilot project came to a conclusion at the Glenn Research Center in April 2001. The competition involved high-school student teams who developed the concept for a microgravity experiment and prepared an experiment proposal. The two student teams - COSI Academy, sponsored by the Columbus Center of Science and Industry, and another team from Cincinnati, Ohio's Sycamore High School, designed a microgravity experiment, fabricated the experimental apparatus, and visited NASA Glenn to operate their experiment in the 2.2 Second Drop Tower. Here, students from Sycamore High School in Cincinnati, Ohio, help a NASA technician prepare their experiment. This image is from a digital still camera; higher resolution is not available.
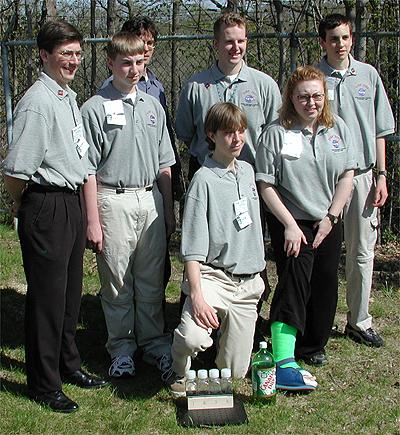

The first NASA Dropping In a Microgravity Environment (DIME) student competition pilot project came to a conclusion at the Glenn Research Center in April 2001. The competition involved high-school student teams who developed the concept for a microgravity experiment and prepared an experiment proposal. The two student teams - COSI Academy, sponsored by the Columbus Center of Science and Industry, and another team from Cincinnati, Ohio's Sycamore High School, designed a microgravity experiment, fabricated the experimental apparatus, and visited NASA Glenn to operate their experiment in the 2.2 Second Drop Tower. Pictured are students from COSI Academy, Columbus, Ohio and their teacher. The other team was from Sycamore High School in Cincinnati, Ohio. This image is from a digital still camera; higher resolution is not available.

The first NASA Dropping In a Microgravity Environment (DIME) student competition pilot project came to a conclusion at the Glenn Research Center in April 2001. The competition involved high-school student teams who developed the concept for a microgravity experiment and prepared an experiment proposal. The two student teams - COSI Academy, sponsored by the Columbus Center of Science and Industry, and another team from Cincinnati, Ohio's Sycamore High School, designed a microgravity experiment, fabricated the experimental apparatus, and visited NASA Glenn to operate their experiment in the 2.2 Second Drop Tower. Here Carol Hodanbosi of the National Center for Microgravity Research and Jose Carrion, a lab mechanic with AKAC, prepare a student experiment package (inside the silver-colored frame) inside the orange-colored drag shield that encloses all experiment hardware. This image is from a digital still camera; higher resolution is not available.

The first NASA Dropping In a Microgravity Environment (DIME) student competition pilot project came to a conclusion at the Glenn Research Center in April 2001. The competition involved high-school student teams who developed the concept for a microgravity experiment and prepared an experiment proposal. The two student teams - COSI Academy, sponsored by the Columbus Center of Science and Industry, and another team from Cincinnati, Ohio's Sycamore High School, designed a microgravity experiment, fabricated the experimental apparatus, and visited NASA Glenn to operate their experiment in the 2.2 Second Drop Tower. Students from Sycamore High School in Cincinnati, Ohio (girls), and the COSI Academy, Columbus, Ohio (boys), participated. This image is from a digital still camera; higher resolution is not available.
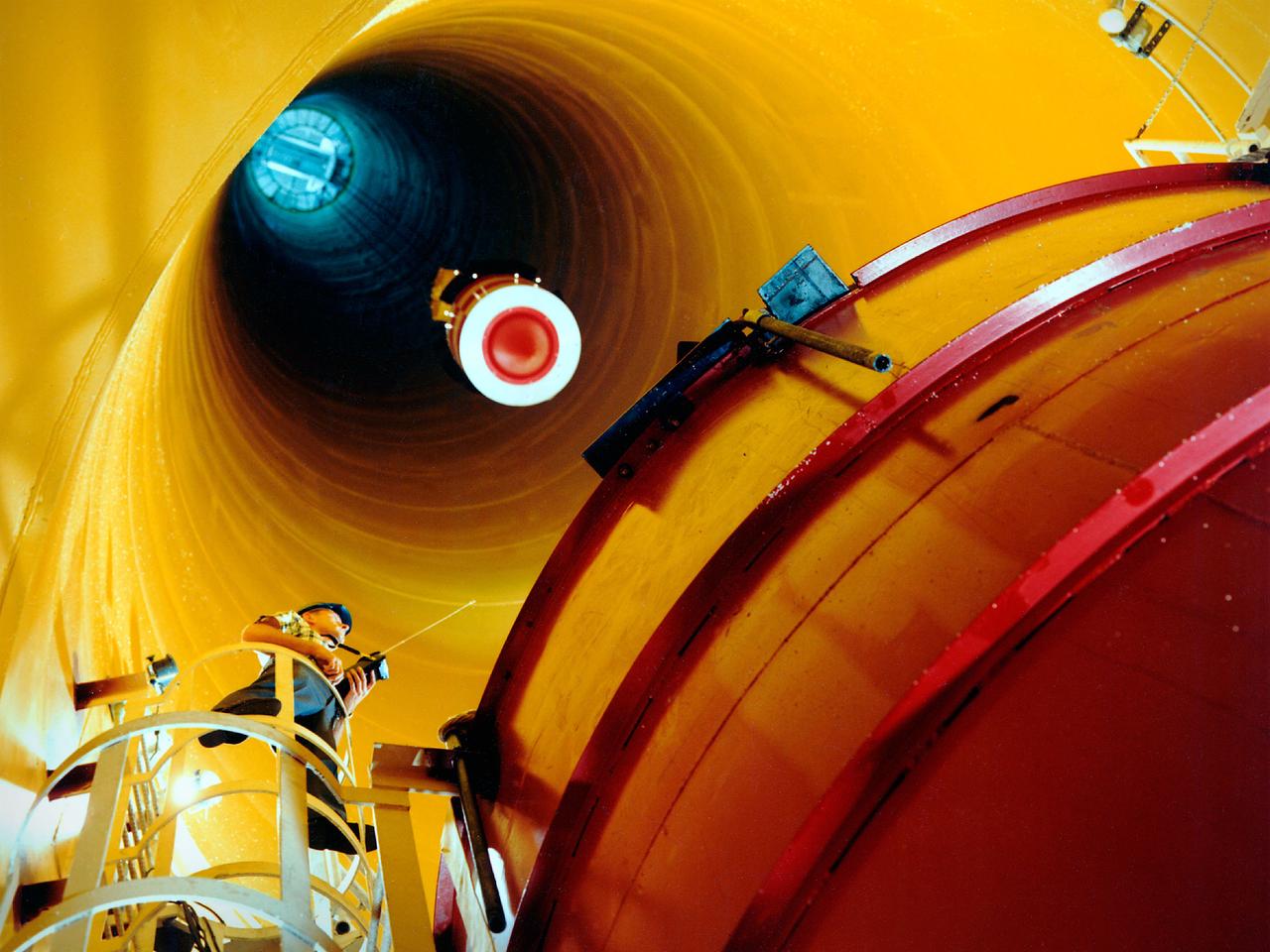

National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. Lewis researchers had been studying the behavior of liquid in microgravity for several years using ballistic rocket flights, aircraft flying series of parabolas, and in the 2.2-Second Drop Tower. It was easier to control experiments and repeat tests based on almost instantaneous test results in the Zero Gravity Research Facility than missiles or aircraft. It also more than doubled the microgravity time of the original drop tower. The experiments were enclosed in a large experiment package that was suspended inside the chamber. A vacuum was introduced to the chamber before the package was released. The test equipment allowed researchers to film and take measurements of the experiment as it was falling. The 2500‐pound package was slowed by special Styrofoam‐like pellets in a decelerator cart. An experiment, traveling 176 feet per second, was stopped in about 15 feet of deceleration material. The facility’s designers struggled to determine the correct type of deceleration pellets to use. For several years Lewis engineers tested various samples from manufacturers. The final selection was not made until the facility’s completion in May 1966, just before the facility made its public debut at the 1966 Inspection of the Center.
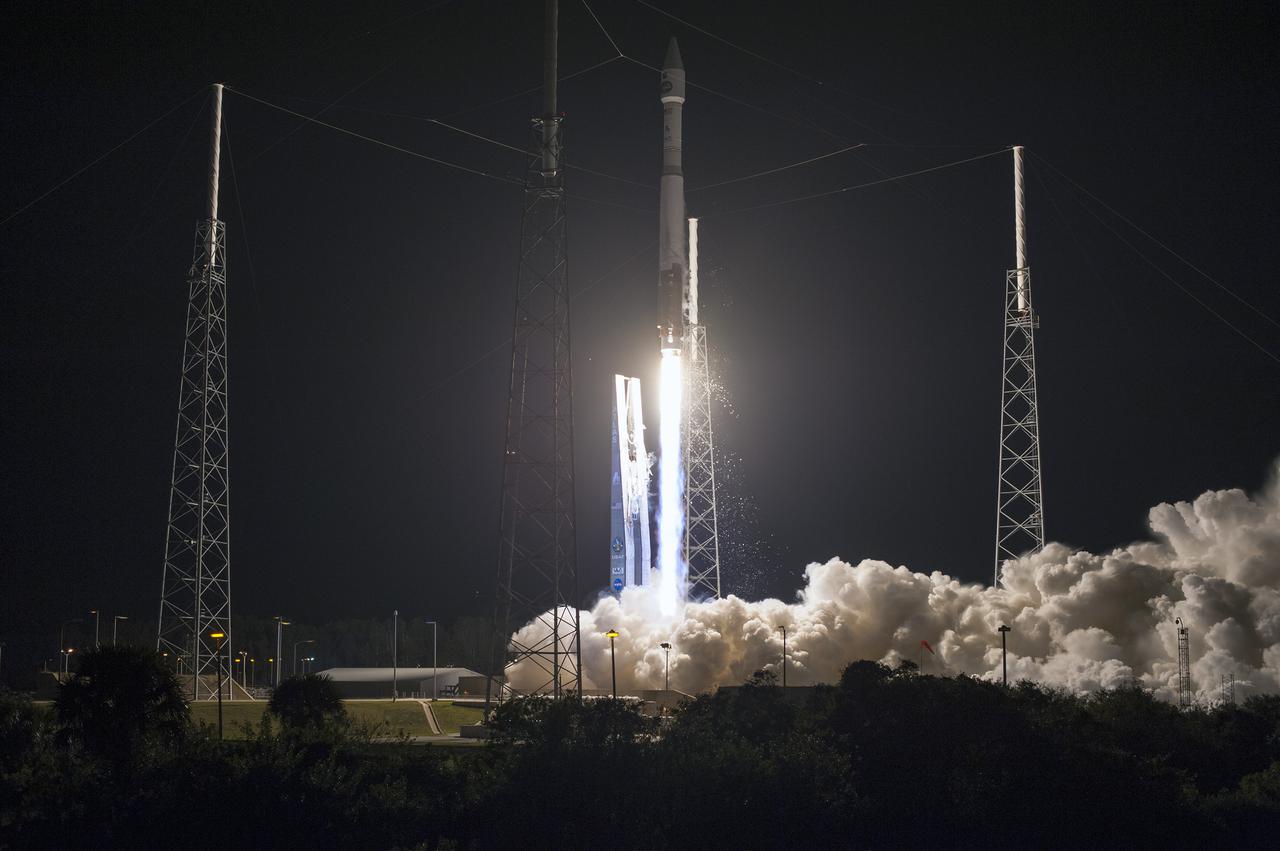

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The umbilical tower drops back from a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 401 rocket as it lifts off Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Launch, with NASA's Tracking and Data Relay Satellite-K or TDRS-K aboard, was at 8:48 p.m. EST. he TDRS-K spacecraft is part of the next-generation series in the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System, a constellation of space-based communication satellites providing tracking, telemetry, command and high-bandwidth data return services. For more information, visit http:__www.nasa.gov_mission_pages_tdrs_index.html. Photo credit: NASA_Tony Gray and Rick Wetherington
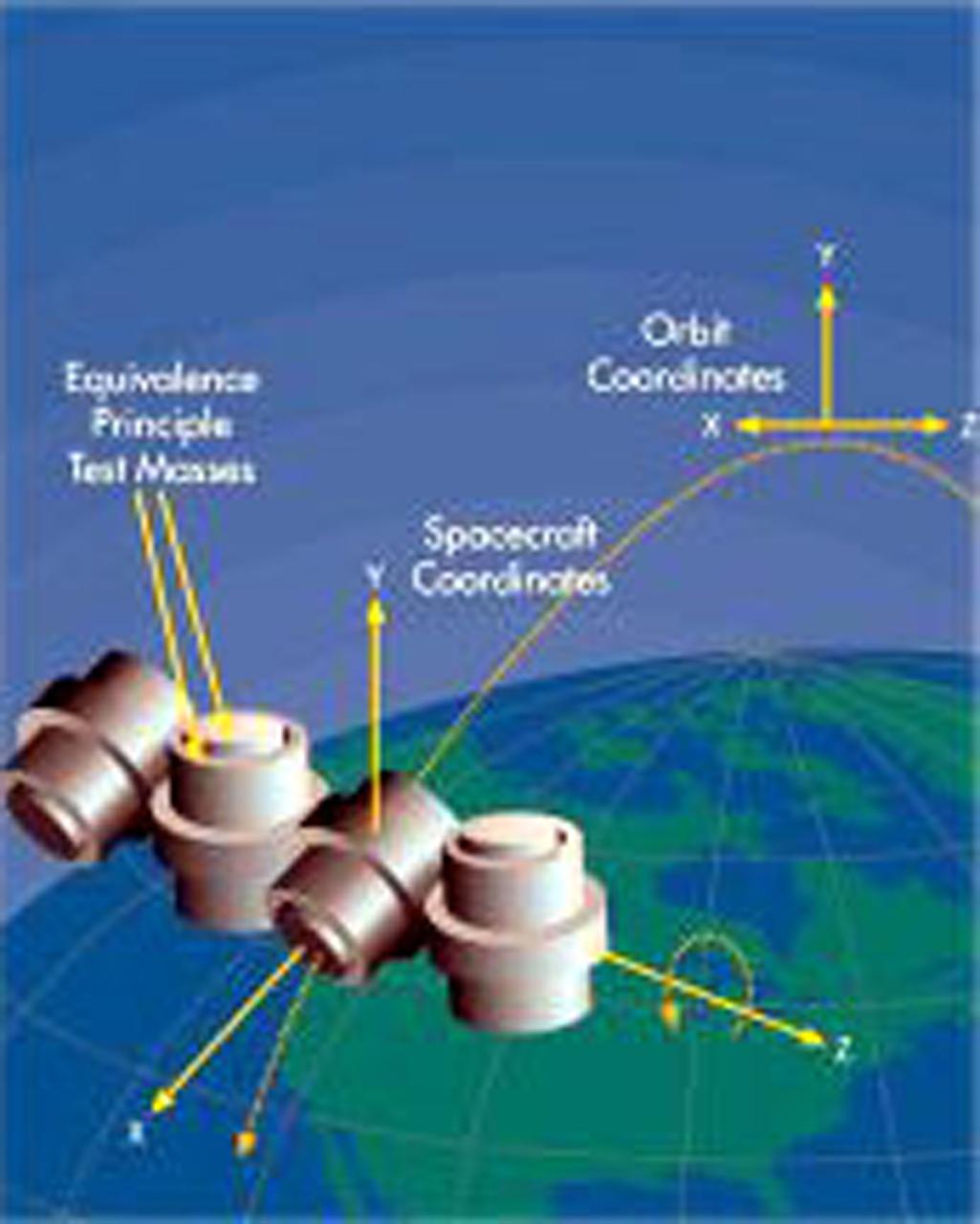
STEP will carry concentric test masses to Earth orbit to test a fundamental assumption underlying Einstein's theory of general relativity: that gravitational mass is equivalent to inertial mass. STEP is a 21st-century version of the test that Galileo is said to have performed by dropping a carnon ball and a musket ball simultaneously from the top of the Leaning Tower of Pisa to compare their accelerations. During the STEP experiment, four pairs of test masses will be falling around the Earth, and their accelerations will be measured by superconducting quantum interference devices (SQUIDS). The extended time sensitivity of the instruments will allow the measurements to be a million times more accurate than those made in modern ground-based tests.
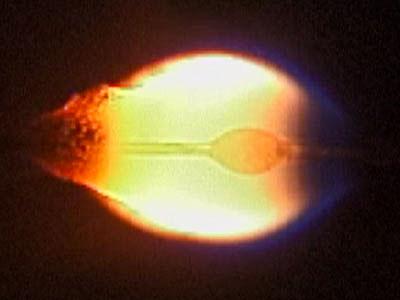
jsc2024e016238 (2/14/2024) --- Flame spreading over wire insulation in microgravity obtained by 10 s drop tower of the Japan Microgravity Center. Uniform low speed air flow is suppled from right to left. Molten PE ball is observed in the flame. Soot particles are continuously emitted at the rear of the flame. Fundamental Research on International Standard of Fire Safety in Space – Base for Safety of Future Manned Missions (FLARE), a Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) investigation, explores the flammability of materials in microgravity. Image courtesy of Hokkaido University.
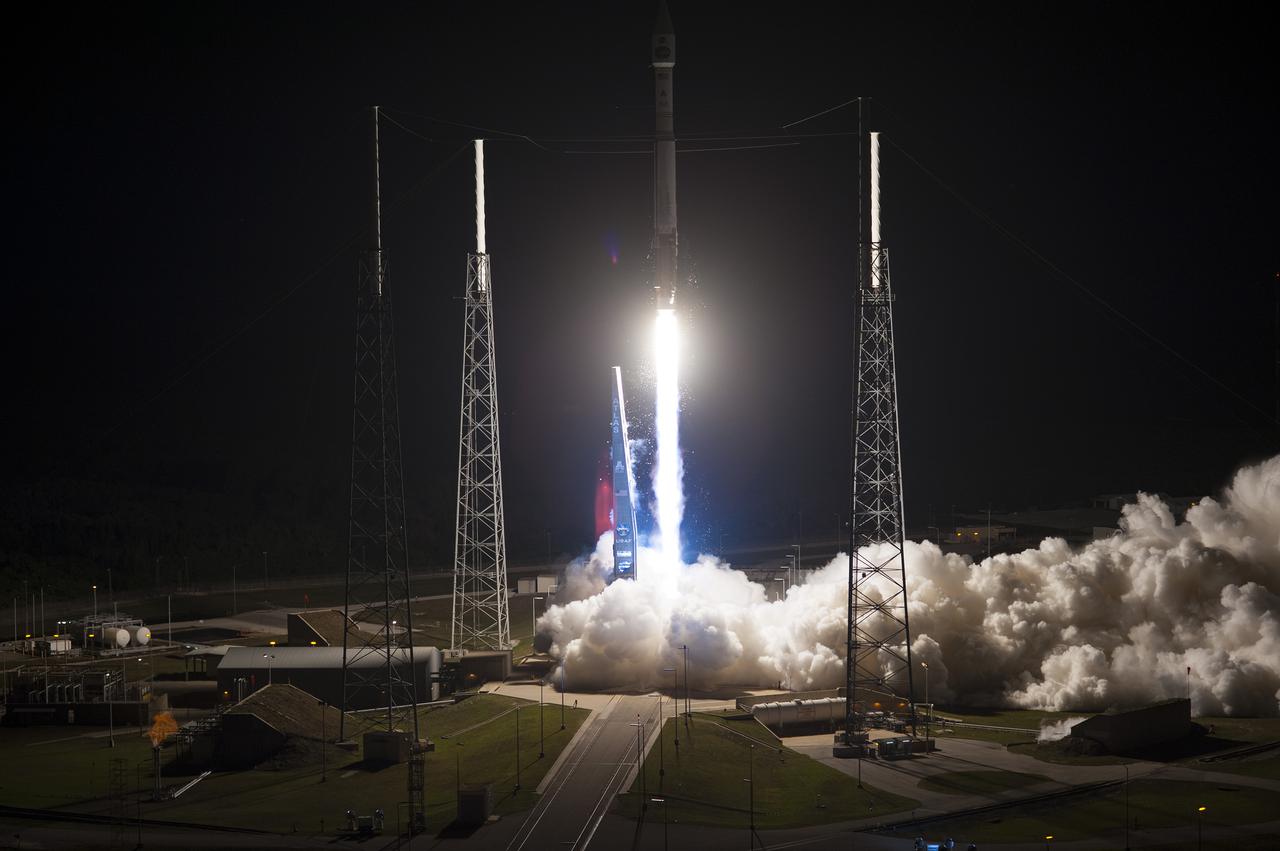

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The umbilical tower drops back from a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 401 rocket as it lifts off Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Launch, with NASA's Tracking and Data Relay Satellite-K or TDRS-K aboard, was at 8:48 p.m. EST. he TDRS-K spacecraft is part of the next-generation series in the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System, a constellation of space-based communication satellites providing tracking, telemetry, command and high-bandwidth data return services. For more information, visit http:__www.nasa.gov_mission_pages_tdrs_index.html. Photo credit: NASA_Tony Gray and Robert Murray
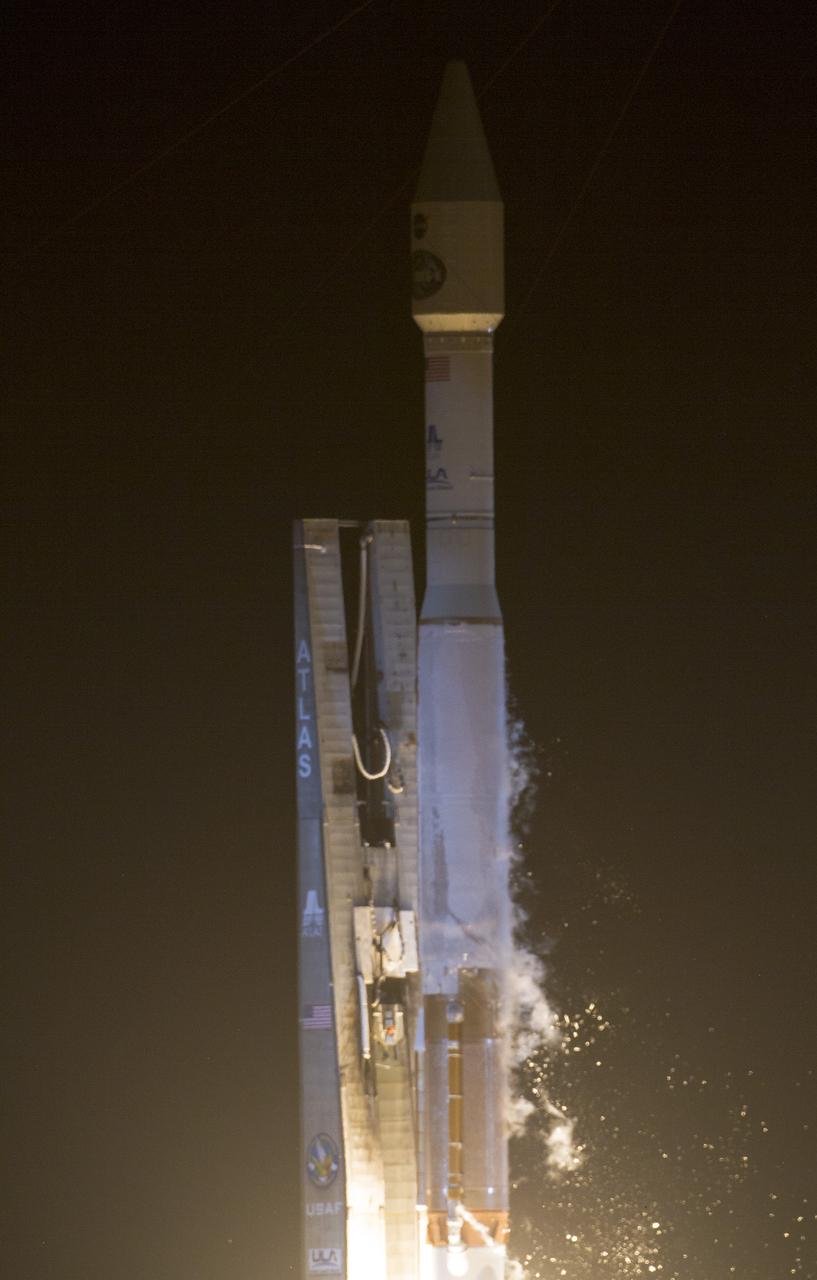

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The umbilical tower drops away from a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 401 rocket as it lifts off Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Launch, with NASA's Tracking and Data Relay Satellite-K or TDRS-K aboard, was at 8:48 p.m. EST. The TDRS-K spacecraft is part of the next-generation series in the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System, a constellation of space-based communication satellites providing tracking, telemetry, command and high-bandwidth data return services. For more information, visit http:__www.nasa.gov_mission_pages_tdrs_index.html. Photo credit: NASA_George Roberts
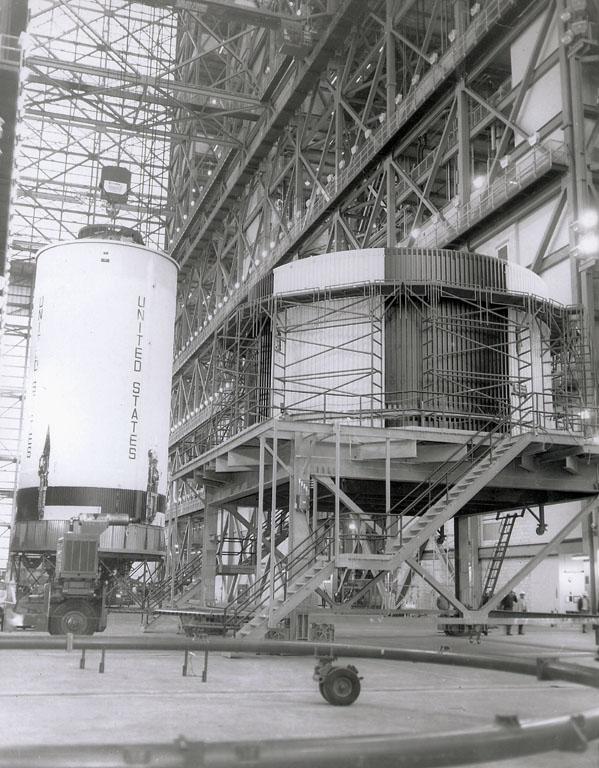
This Saturn V S-II (second) stage is being lifted into position for a test at the Vehicle Assembly Building at the Kennedy Space Center. When the Saturn V booster stage (S-IC) burned out and dropped away, power for the Saturn was provided by the 82-foot-long and 33-foot-diameter S-II stage. Developed by the Space Division of North American Aviation under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center, the stage utilized five J-2 engines, each producing 200,000 pounds of thrust. The engines used liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen as propellants. The towering 363-foot Saturn V was a multi-stage, multi-engine launch vehicle standing taller than the Statue of Liberty. Altogether, the Saturn V engines produced as much power as 85 Hoover Dams.

Office of the Chief Technologist, OCT Innovation Workshop, and Facility Tours
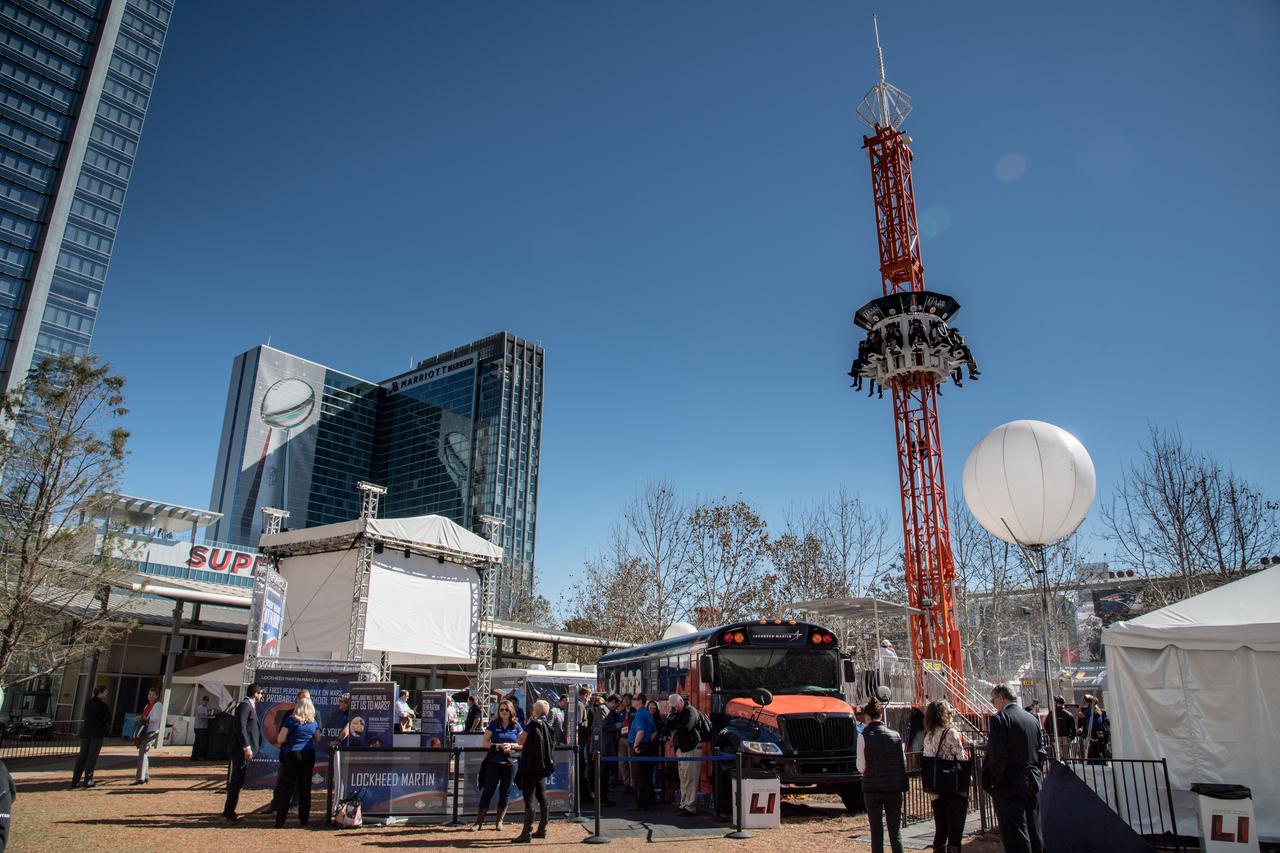

jsc2017e011393 (01/30/2017) --- Space exploration will feature prominently at Super Bowl LIVE, a nine-day fan festival running Jan. 28 through Feb. 5 on Discovery Green, Houston Texas where 100,000 visitors are expected each day. NASA is collaborating with the Houston Super Bowl Host Committee, which is the fan festival organizer, to share NASA’s contributions with the Houston community and to the nation. At NASA's Future Flight, the primary attraction at the free fan festival, riders will take a trip to Mars and back using virtual reality goggles on a 90-foot drop tower ride. Visitors also will get a chance to see several NASA assets that have been transported to downtown Houston for the activities. These assets include: the Orion mockup used for water recovery testing, Space Exploration Vehicle (SEV /Rover), the Driven to Explore mobile exhibit, Mars Science Laboratory – Curiosity Rover - replica, Robonaut 1 (Centaur configuration), EMU space suit presentation unit, Arctic meteorite and astromaterials display, and the Mark III advanced space suit photo-op. Several of NASA’s industry partners sponsoring Future Flight will also have assets on display, and a replica of the James Webb Space Telescope will be located near but not inside the activities on Discovery Green. NASA and industry partner volunteers will be staffing the Future Flight area. NASA PHOTOGRAPHER: Bill Stafford
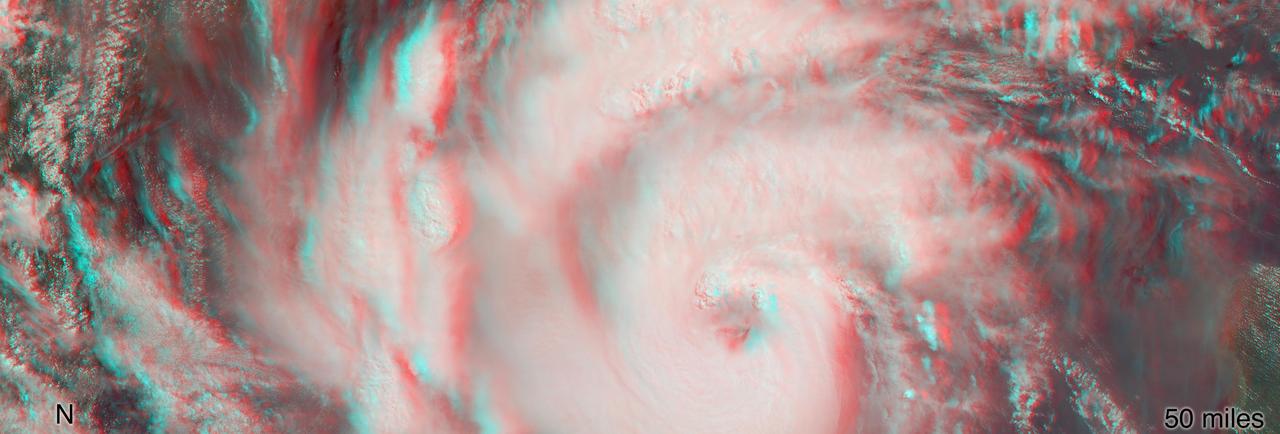
MISR's stereo anaglyph shows a three-dimensional view of Michael and combines two of MISR's nine camera angles. Using 3D red-blue glasses, you can see the 3D effect. Apparent in the 3D stereo anaglyph as well as the height field are a number of bright "clumps." These are groups of strong thunderstorms embedded within the larger circulation of the hurricane. Known as "vortical hot towers" the presence of these features indicates rapid transport of heat energy from the ocean surface into the storm, typically indicative of rapid intensification of the hurricane. In fact, between 11 a.m. and 2 p.m. EDT, while MISR imaged the hurricane, the estimated central pressure dropped 8 hPa and the maximum sustained winds increased about 12 mph (19 kph) and over the next 24 hours Hurricane Michael intensified from a Category 2 to a Category 4 storm. The National Hurricane Center clocked Michael's sustained wind speed at 150 mph (240 kph) just before noon local time on Wednesday. It is expected to bring strong winds, storm surge and heavy rain to much of the southeast. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22748
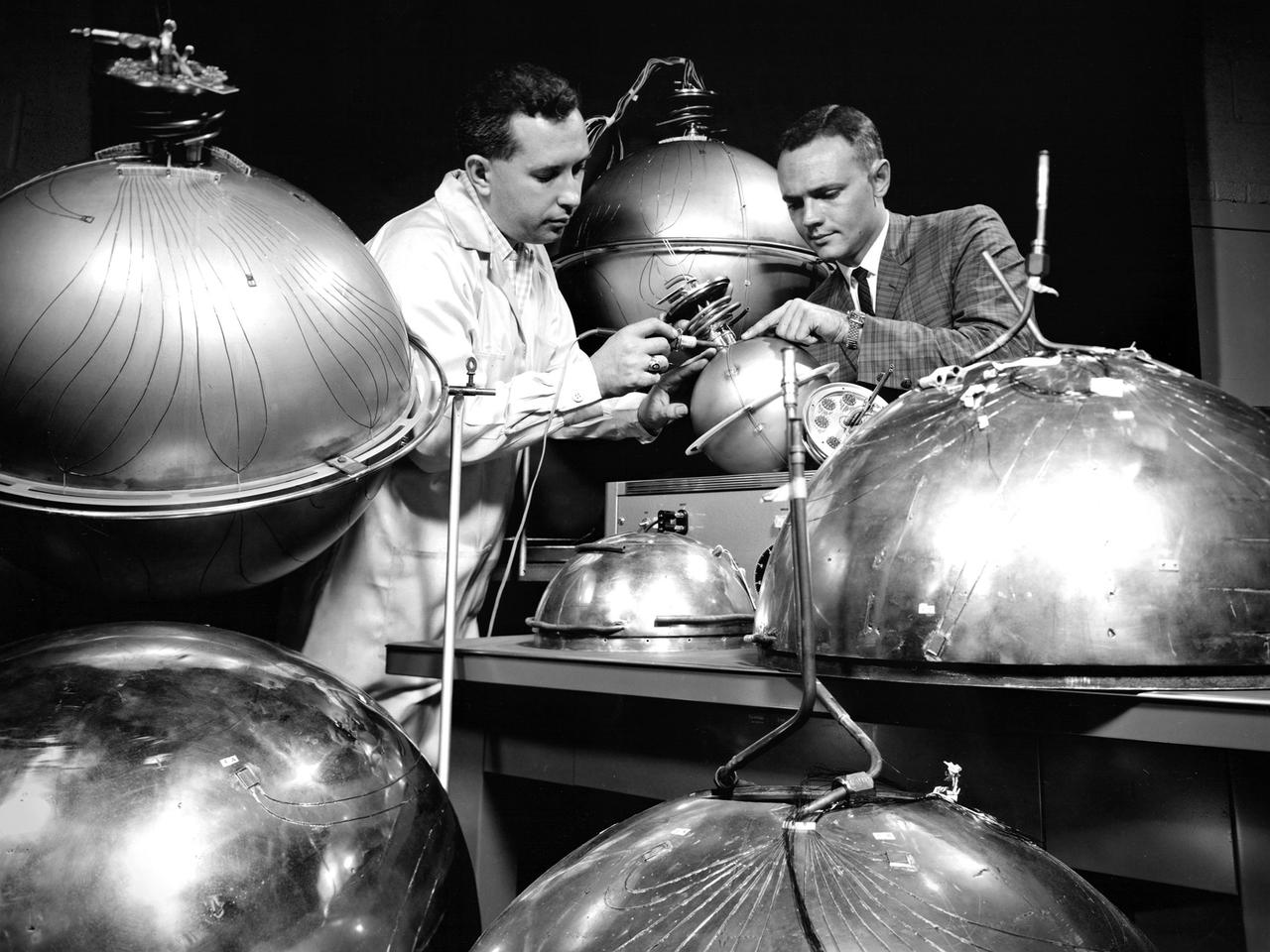

An engineer and technician at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center install the instrumentation on spherical fuel tanks for an investigation of the behavior of liquids in microgravity. Lewis researchers were undertaking a broad effort to study the heat transfer properties of high energy propellants such as liquid hydrogen in microgravity. In the center’s 2.2-Second Drop Tower they investigated the wetting characteristics of liquid and the liquid-vapor configurations, and predicted the equilibrium state in microgravity conditions. Lewis was also conducting a series microgravity investigations which launched 9-inch diameter spherical dewars, seen here, on an Aerobee sounding rocket. A camera inside the rocket filmed the liquid hydrogen’s behavior during its 4 to 7 minutes of freefall. The researchers concluded, however, that they needed to extend the weightlessness period to obtain better results. So they designed an experiment to be launched on an Atlas missile that would provide 21 minutes of weightlessness. The experiment was flight qualified at Lewis. The 36-percent full liquid hydrogen stainless steel dewar was launched on the Atlas on February 25, 1964. The instrumentation measured temperature, pressure, vacuum, and liquid level. Temperature instrumentation indicated wall drying during the freefall. The resultant pressure-rise characteristics were similar to those used for the normal-gravity test.

ISS025-E-005259 (28 Sept. 2010) --- Pyramid Lake in Nevada is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 25 crew member on the International Space Station (ISS). Pyramid Lake, located in western Nevada near the California border, is a remnant of the ancient and much larger Lake Lahontan. According to scientists, Lake Lahontan formed during the last Ice Age when the regional climate of Nevada was significantly cooler and wetter than today—abundant precipitation and low rates of evaporation led to the formation of numerous lakes that began to coalesce as they overfilled their original basins. Pyramid Lake and the nearby now-dry Lake Winnemucca are two of seven lakes that formed Lake Lahontan. At its highest water level, during the late Pleistocene Epoch (approximately 15,000 years ago), Lake Lahontan covered much of western Nevada and extended into California, according to scientists. The deepest part of Lake Lahontan survives today as the perennial Pyramid Lake. Pyramid Lake is well known to geologists because of the spectacular tufa—calcium carbonate—deposits found here; the lake takes its name from one such pyramid-shaped deposit. Tufa is a rock formed by precipitation of calcium carbonate from spring water, lake water, or a combination of the two. Over time, these deposits can develop a wide variety of forms including mounds, towers, sheets, reefs and coatings on other rocks. These may then be exposed when the water level drops due to changes in regional climate, diversion of water for human use, or both (Mono Lake in California for example). This photograph also captures sunglint—light reflected off of a water surface back towards the observer on the space station—on the northern and southeastern ends of the lake. Two large spiral whorls are visible in sunglint at the northern end of the lake; these likely trace surface wind patterns disturbing the water surface that cause localized variations in the amount of light reflected back to the ISS.

Office of the Chief Technologist, OCT Innovation Workshop, and Facility Tours

Office of the Chief Technologist, OCT Innovation Workshop, and Facility Tours

Office of the Chief Technologist, OCT Innovation Workshop, and Facility Tours