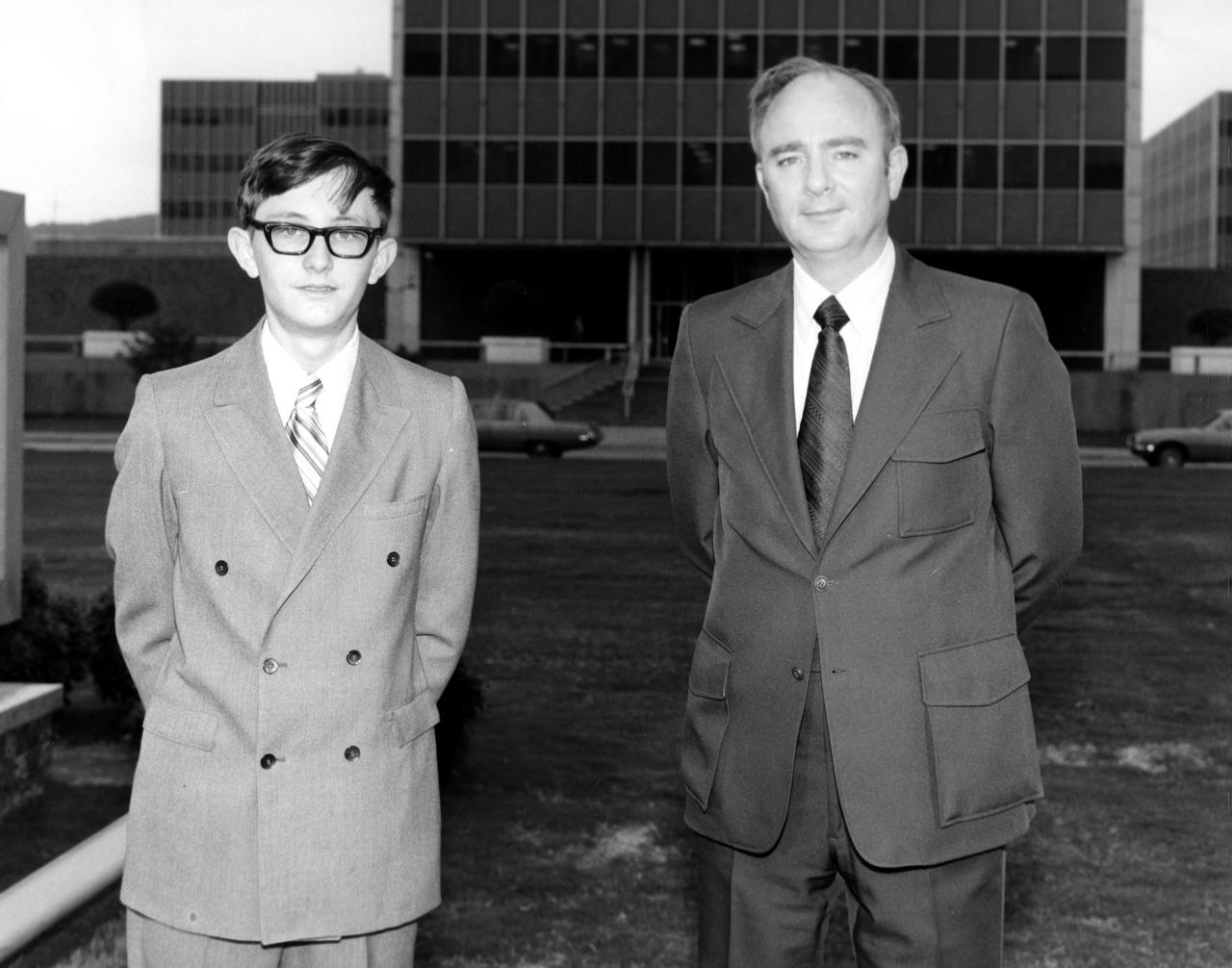

W. Brain Dunlap (left), high school student from Youngstown, Ohio, is pictured here with Harry Coons of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) during a visit to the center. Dunlap was among 25 winners of a contest in which some 3,500 high school students proposed experiments for the following year’s Skylab mission. The nationwide scientific competition was sponsored by the National Science Teachers Association and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). The winning students, along with their parents and sponsor teachers, visited MSFC where they met with scientists and engineers, participated in design reviews for their experiments, and toured MSFC facilities. Of the 25 students, 6 did not see their experiments conducted on Skylab because the experiments were not compatible with Skylab hardware and timelines. Of the 19 remaining, 11 experiments required the manufacture of additional equipment.
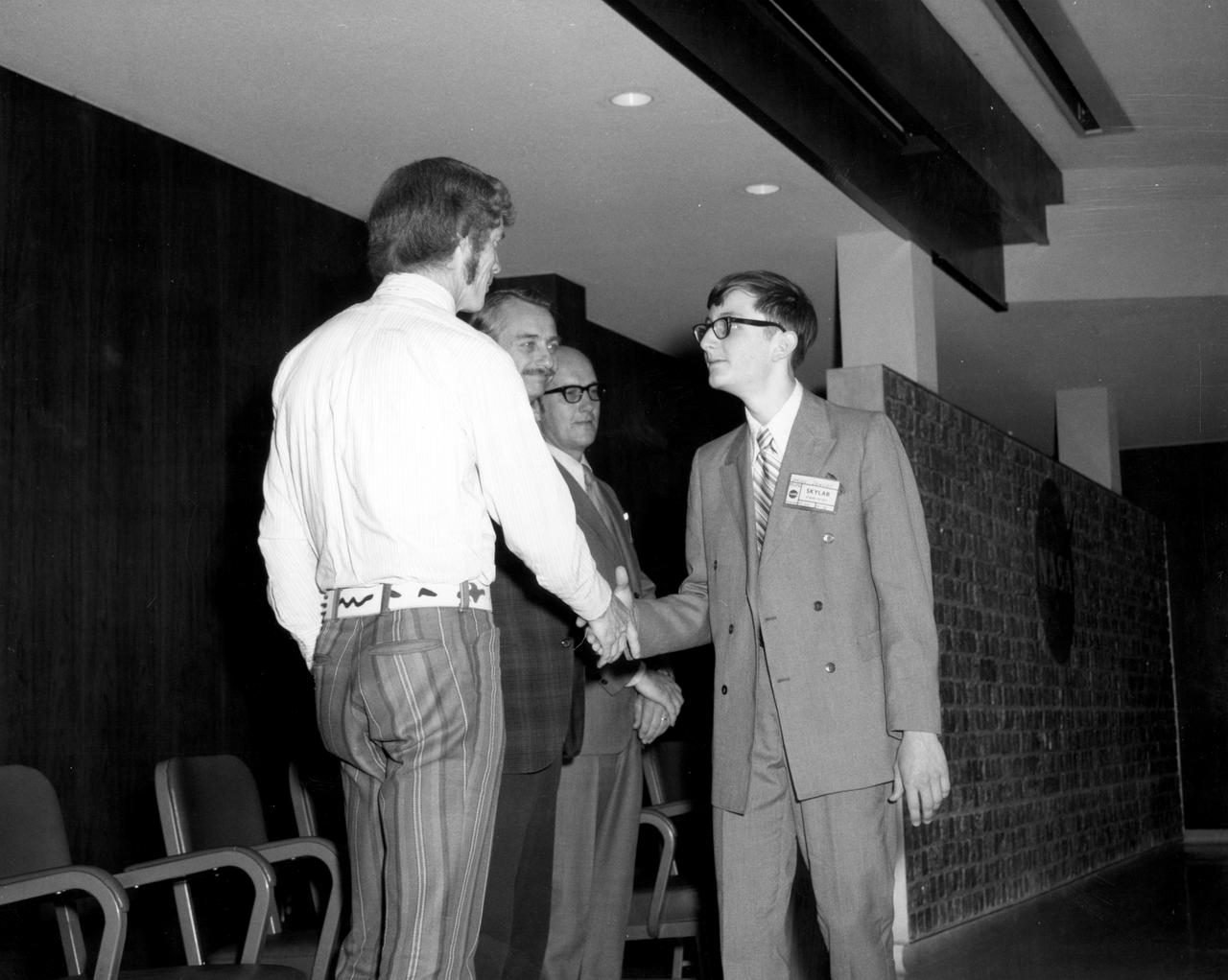

Youngstown, Ohio high school student, W. Brian Dunlap, is greeted by (left to right): Astronauts Russell L. Schweickart, and Owen K. Garriott; Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Skylab Program Manager, Leland Belew; and MSFC Director of Administration and Technical Services, David Newby, during a tour of MSFC. Dunlap was among 25 winners of a contest in which some 3,500 high school students proposed experiments for the following year’s Skylab mission. The nationwide scientific competition was sponsored by the National Science Teachers Association and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). The winning students, along with their parents and sponsor teachers, visited MSFC where they met with scientists and engineers, participated in design reviews for their experiments, and toured MSFC facilities. Of the 25 students, 6 did not see their experiments conducted on Skylab because the experiments were not compatible with Skylab hardware and timelines. Of the 19 remaining, 11 experiments required the manufacture of additional equipment.
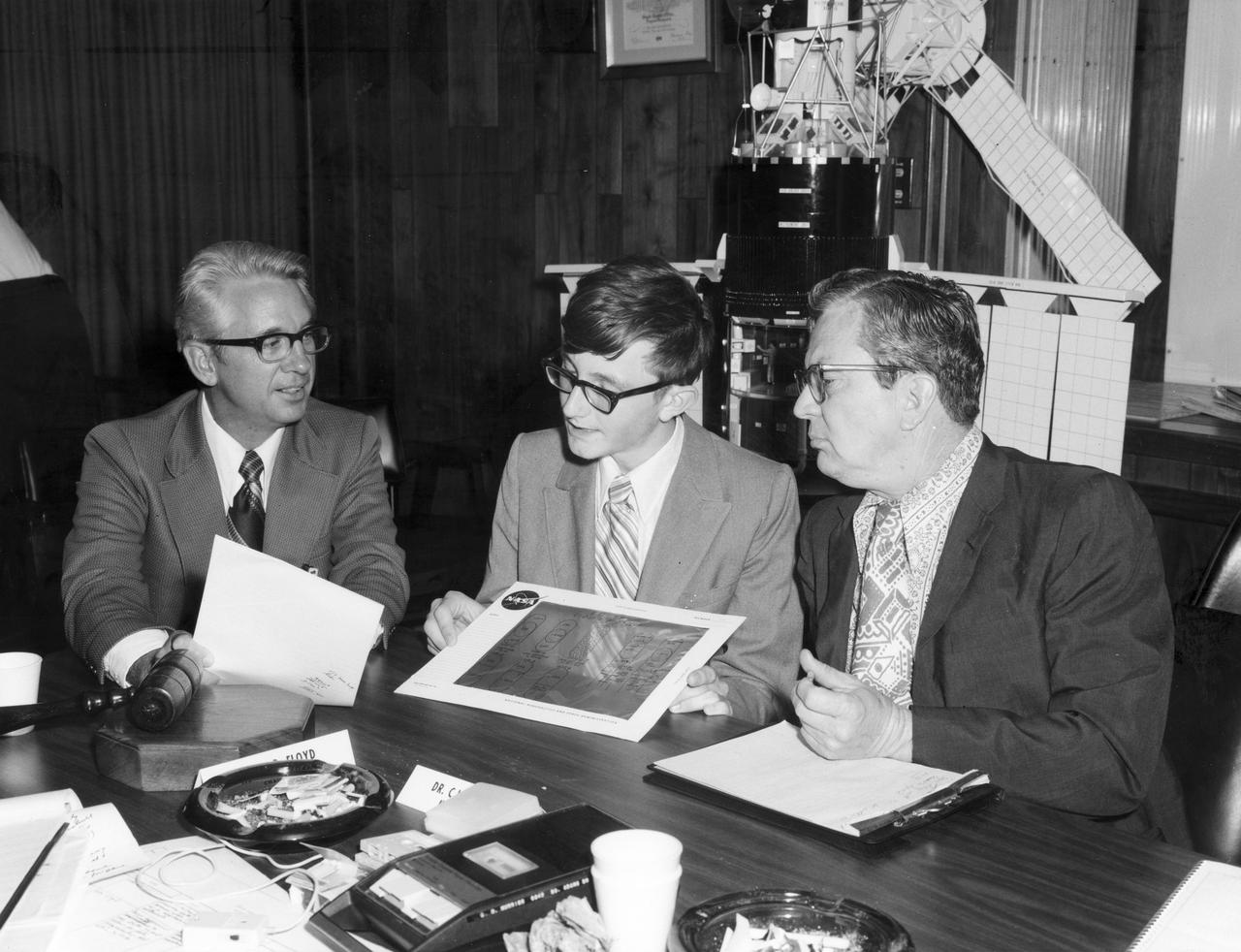

Youngstown, Ohio high school student, W. Brian Dunlap (center), discusses with Dr. Robert Head (right), and Henry Floyd, both of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), his experiment to be performed aboard the Skylab the following year. His experiment, “Wave Motion Trough A Liquid in Zero Gravity” used a container attached to the end of a leaf spring which was oscillated at specific rates using two thickness differentiated types of liquids. Dunlap was among 25 winners of a contest in which some 3,500 high school students proposed experiments for the following year’s Skylab mission. The nationwide scientific competition was sponsored by the National Science Teachers Association and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). The winning students, along with their parents and sponsor teachers, visited MSFC where they met with scientists and engineers, participated in design reviews for their experiments, and toured MSFC facilities. Of the 25 students, 6 did not see their experiments conducted on Skylab because the experiments were not compatible with Skylab hardware and timelines. Of the 19 remaining, 11 experiments required the manufacture of additional equipment. The equipment for the experiments was manufactured at MSFC.

W. Brian Dunlap of Youngstown, Ohio, proposed Skylab student experiment ED-78, Liquid Motion in Zero-G, a study of wave motion in a liquid. He was particularly interested in comparing surface waves over a liquid in zero-gravity with those occurring on Earth. In space, with the absence of gravity, a liquid does not necessarily take the shape of its container as it does on Earth. Adhesion forces may hold the liquid in contact with its container, but the liquid can also assume a free-floating condition. It was in this latter state that Dunlap wished to examine the behavior of surface waves. Data were recorded on videotape and subsequently converted to 16-mm film. Dunlap analyzed these data to determine periods of oscillation of free-floating globules and found agreement with the theory to be much better than expected. In March 1972, NASA and the National Science Teachers Association selected 25 experiment proposals for flight on Skylab. Science advisors from the Marshall Space Flight Center aided and assisted the students in developing the proposals for flight on Skylab.

Caitlin Dunlap, with the Engineering Directorate, speaks to participants during an internal knowledge sharing program hosted by Launching Leaders at the Kennedy Learning Institute on May 3, 2023. Launching leaders is an employee resource group that works to identify opportunities to engage emerging professionals at Kennedy Space Center to stimulate the growth of leadership skills, increase overall employee satisfaction, and enhance retention.
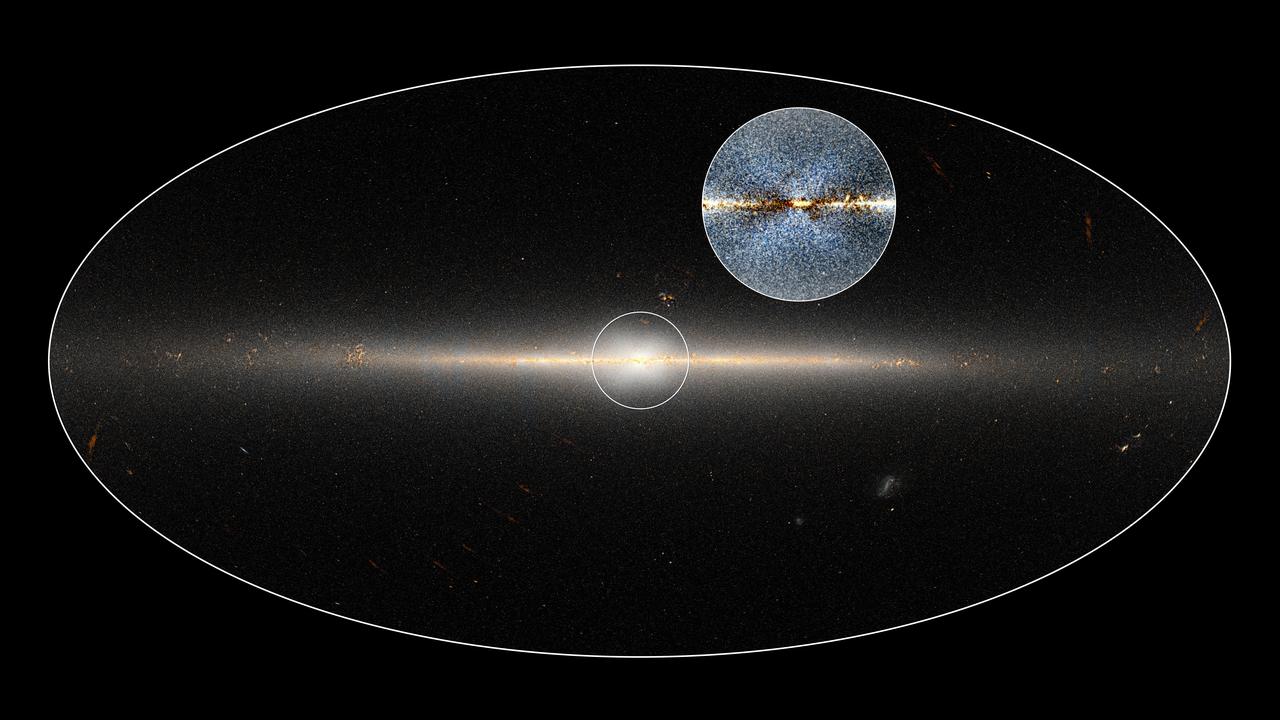
In 2010, NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE) mission observed the entire sky twice. Astronomers used these data to point out the X-shaped structure in the bulge of the Milky Way, contained in the small circle at center, as well as the inset image. The circled central portion covers roughly the area of sky that would be blocked by a basketball when held out at arm's length. Dustin Lang, an astronomer at the Dunlap Institute of the University of Toronto, used these data to make this map, which shows the full 360-degree panorama of the sky as seen by WISE. Lang collaborated with Melissa Ness, postdoctoral researcher at the Max Planck Institute for Astronomy in Germany, http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20699
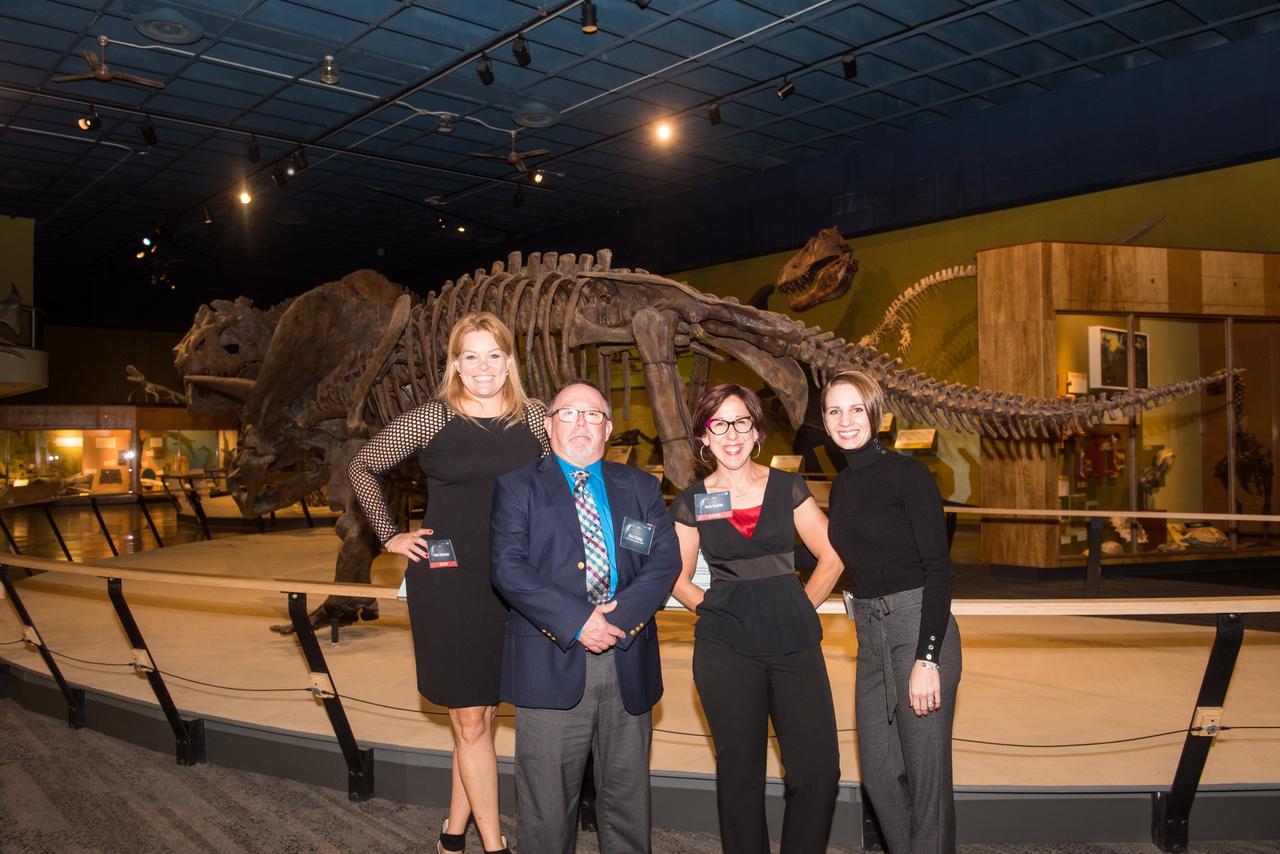

Evening With The Stars - 2019
Evening With The Stars - 2019
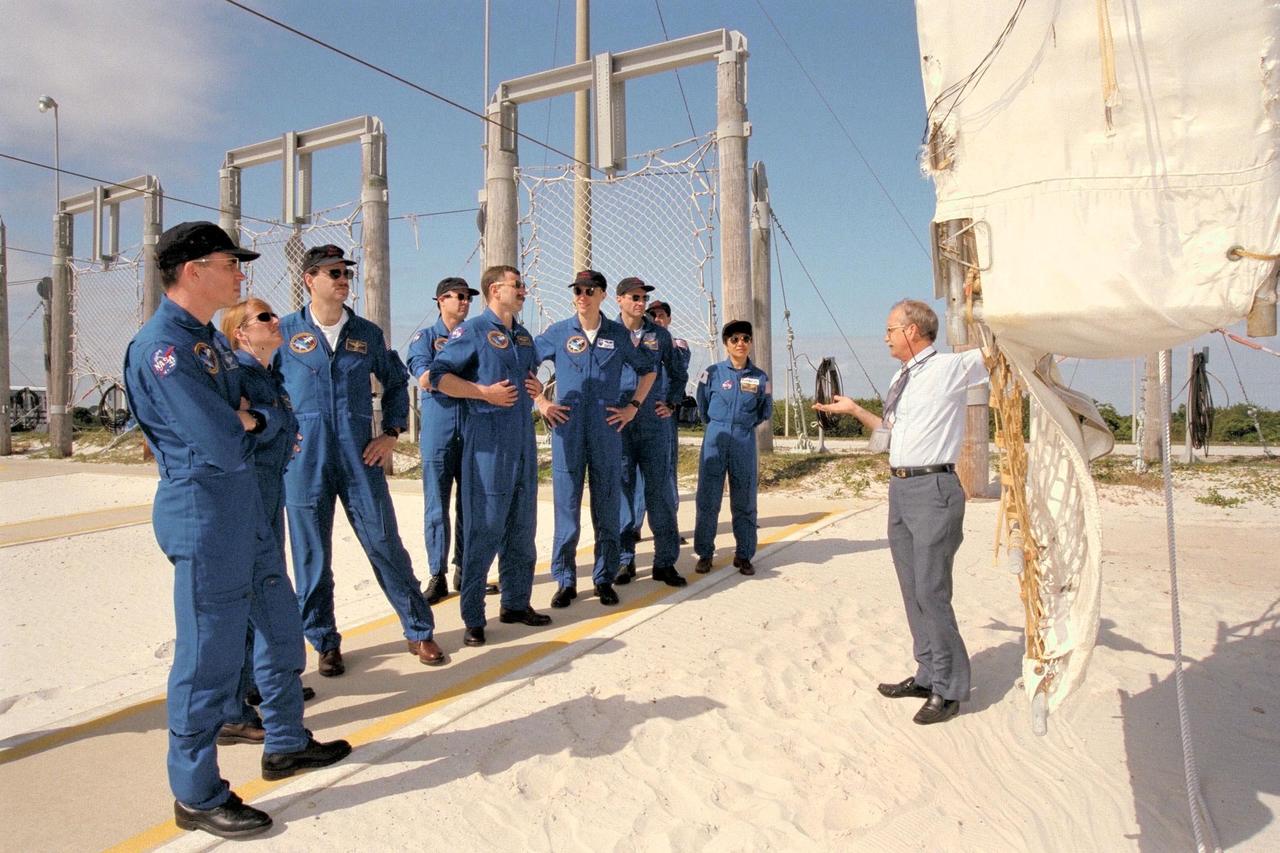

Members of the STS-90 flight crew train in the braking pit area for the emergency egress system slidewire baskets for Launch Pad 39B during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities for that mission. The TCDT is held at KSC prior to each Space Shuttle flight to provide crews with the opportunity to participate in simulated countdown activities. From left to right are Commander Richard Searfoss, Mission Specialist Kathryn (Kay) Hire, Pilot Scott Altman, Payload Specialist Jay Buckey, M.D. (behind), Mission Specialist Dafydd (Dave) Williams, M.D., with the Canadian Space Agency, Payload Specialist James Pawelczyk, Ph.D., and Mission Specialist Richard Linnehan, D.V.M. Backup Payload Specialists Alexander Dunlap (holding camera), D.V.M., M.D., and Chiaki Mukai, M.D., Ph.D., with the National Space Development Agency of Japan are also listening to USA technical trainer Bob Parks' instruction. Columbia is targeted for launch of STS-90 on April 16 at 2:19 p.m. EDT and will be the second mission of 1998. The mission is scheduled to last nearly 17 days
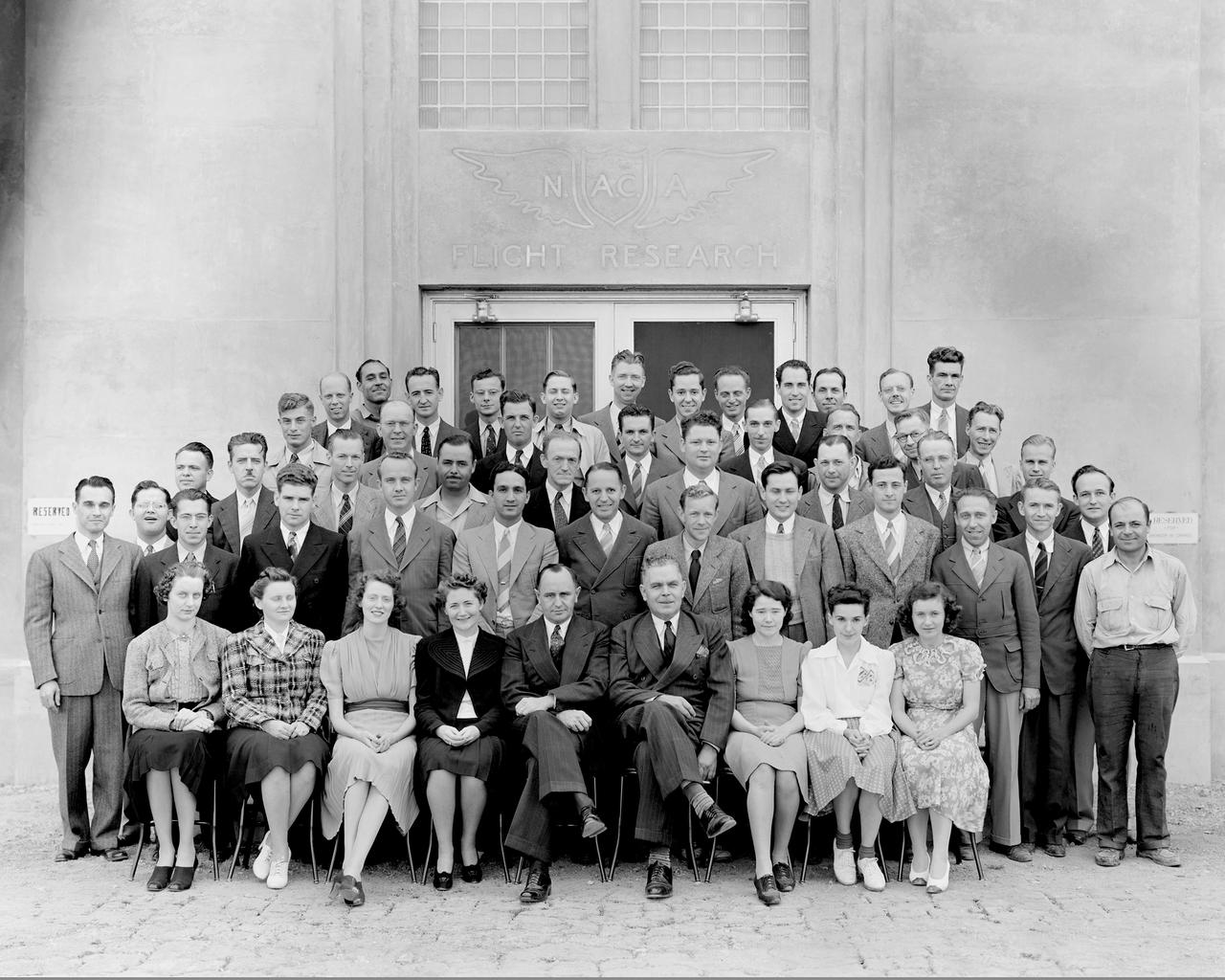

AMES STAFF STANDING IN FRONT OF THE NEW FLIGHT RESEARCH BUILDING. FROM LEFT TO RIGHT: FIRST ROW: M.U. NETTLE, M.A. WILLEY, M.H. DAVIES, M.W. ST. JOHN, S.J. DEFRANCE, E.R. SHARP, M.G. POOLE, V. BURGESS, R.A. PIPKIN. SECOND ROW: A.B. FREEMAN, T.W. O'BRIANT, L.T. VIDELL, C. F. WILSON, R.M. FOSTER, M.C. MASSA, M.J. HOOD, C. BIOLETTI, C.W. FRICK, W.G. VINCENTI, H.W. KIRSCHBAUM, L. A. RODERT, E.C. BRAIG, C. GERBO. THIRD ROW: R.E. BROWNING, E.H. WOOD, R HUGHES, G BULIFANT, J.V. KELLEY, H.J. ALLEN, J. P. HOUSTON, K.S. BURCHARD, M. A. GREENE, FOURTH ROW: A. G. BUCK, E.W. BETTS, R.E. BRAIG, H.J. GOETT, J.F. PARSONS, H.S. DUNLAP, L.E. MINDEN, R.J. CLARKE. FIFTH ROW: W.O. PETERSON, W. WALKER, C.H. HARVEY, J.C. DELANEY, T.W. MACOMBER, A.L. BLOCKER, N.K. DELANY, A.S. HERTZOG, R.R. NICKLE, P.T. PRIZLER, R.R. BENN, E.H.A. SCHNITKER.

The STS-90 crew patch reflects the dedication of the mission to neuroscience in celebration of the decade of the brain. Earth is revealed through a neuron-shaped window, which symbolizes new perspectives in the understanding of nervous system development, structure and function, both here on Earth and in the microgravity environment of space. The Space Shuttle Columbia is depicted with its open payload bay doors revealing the Spacelab within. An integral component of the mission, the laboratory/science module provided by the European Space Agency (ESA), signifies the strong international involvement in the mission. The seven crew members and two alternate payload specialists, Chiaki Naito-Mukai and Alexander W. Dunlap, are represented by the nine major stars of the constellation Cetus (the whale) in recognition of the International Year of the Ocean. The distant stars illustrate the far reaching implications of the mission science to the many sponsoring agencies, helping prepare for long-duration space flight aboard the International Space Station (ISS). The moon and Mars are depicted to reflect the crew's recognition that those two celestial bodies will be the next great challenges in human exploration of space and represent the key role that life science research will play in supporting such missions.

Evening With The Stars - 2019

Evening With The Stars - 2019

NASA internship and Fellowship Participants, Spring, 2020