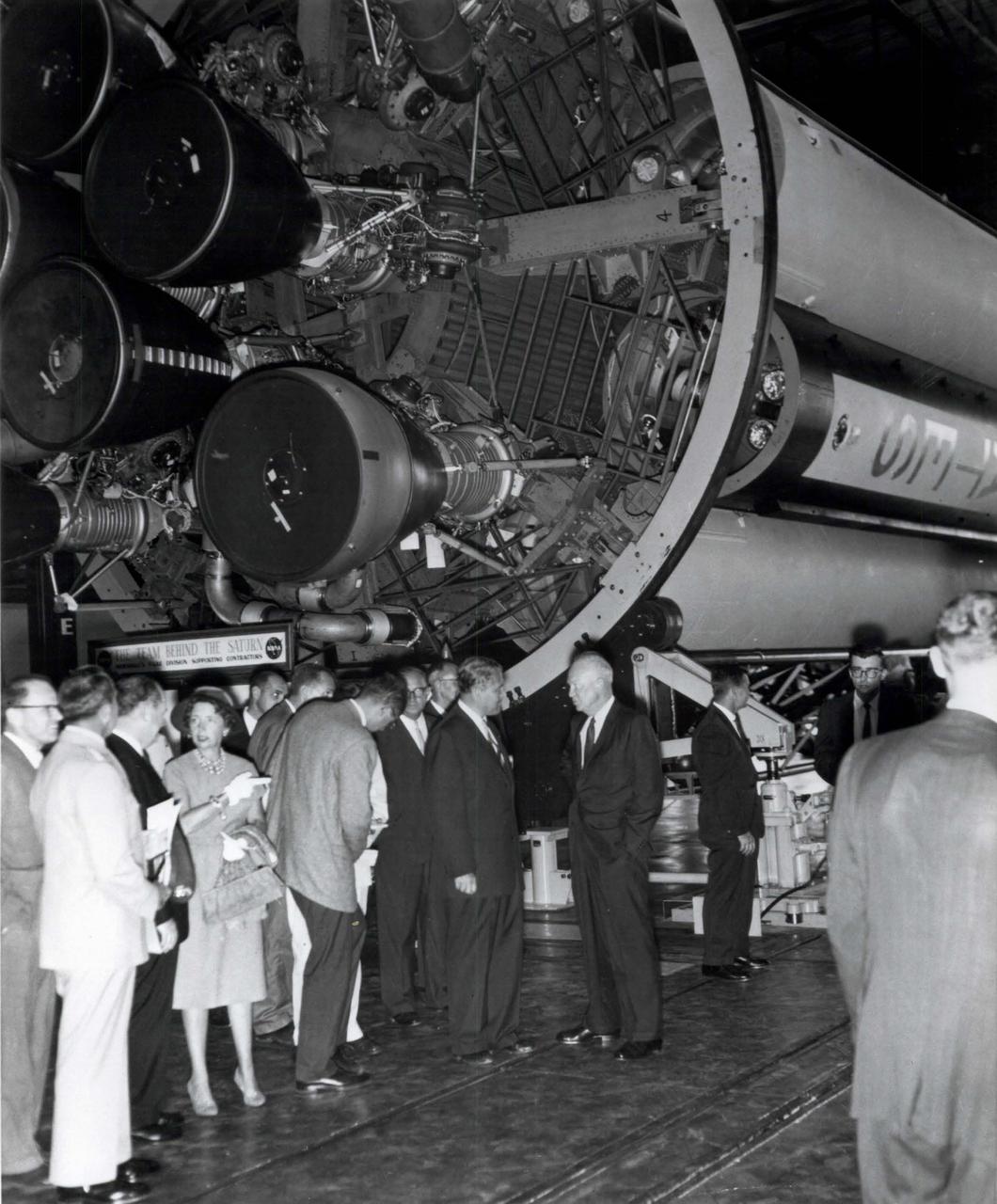
On September 8, 1960 President Dwight D. Eisenhower visited Huntsville, Alabama to dedicate a new NASA field center in honor of General George C. Marshall, Eisenhower's wartime colleague and the founder of the famous Marshall Plan for European recover after World War II. The new George C. Marshall Space Flight Center was placed under the control of Dr. Wernher Von Braun shown here talking with President Eisenhower. As parto f his remarks dedicating the center, President Eisenhowe refereed to General Marshall as a "man of yar, yet a builder of peace". the Marshall Center's first major assignment including building the huge Saturn V rocket that launched human beings on their first journey to the surface of the moon in 1969.
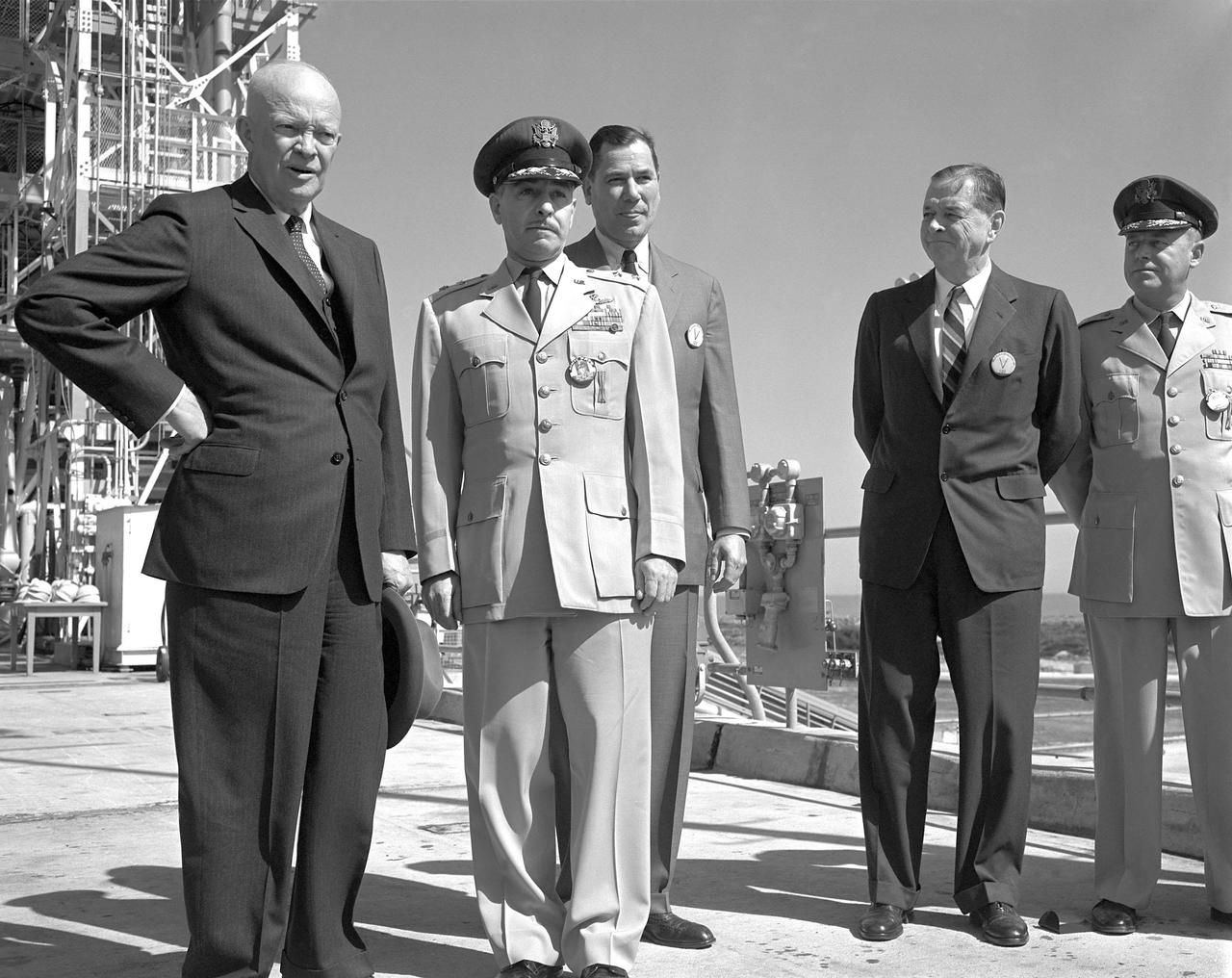

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- President Dwight D. Eisenhower visits Cape Kennedy.
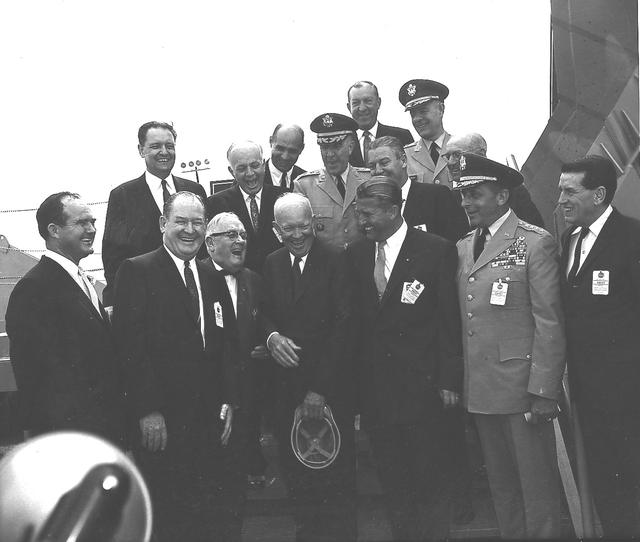

President Dwight D. Eisenhower and MSFC Director Dr. Wernher von Braun share a joke as other dignitaries look on. Eisenhower was visiting Marshall to participate in the September 8, 1960 dedication ceremony.
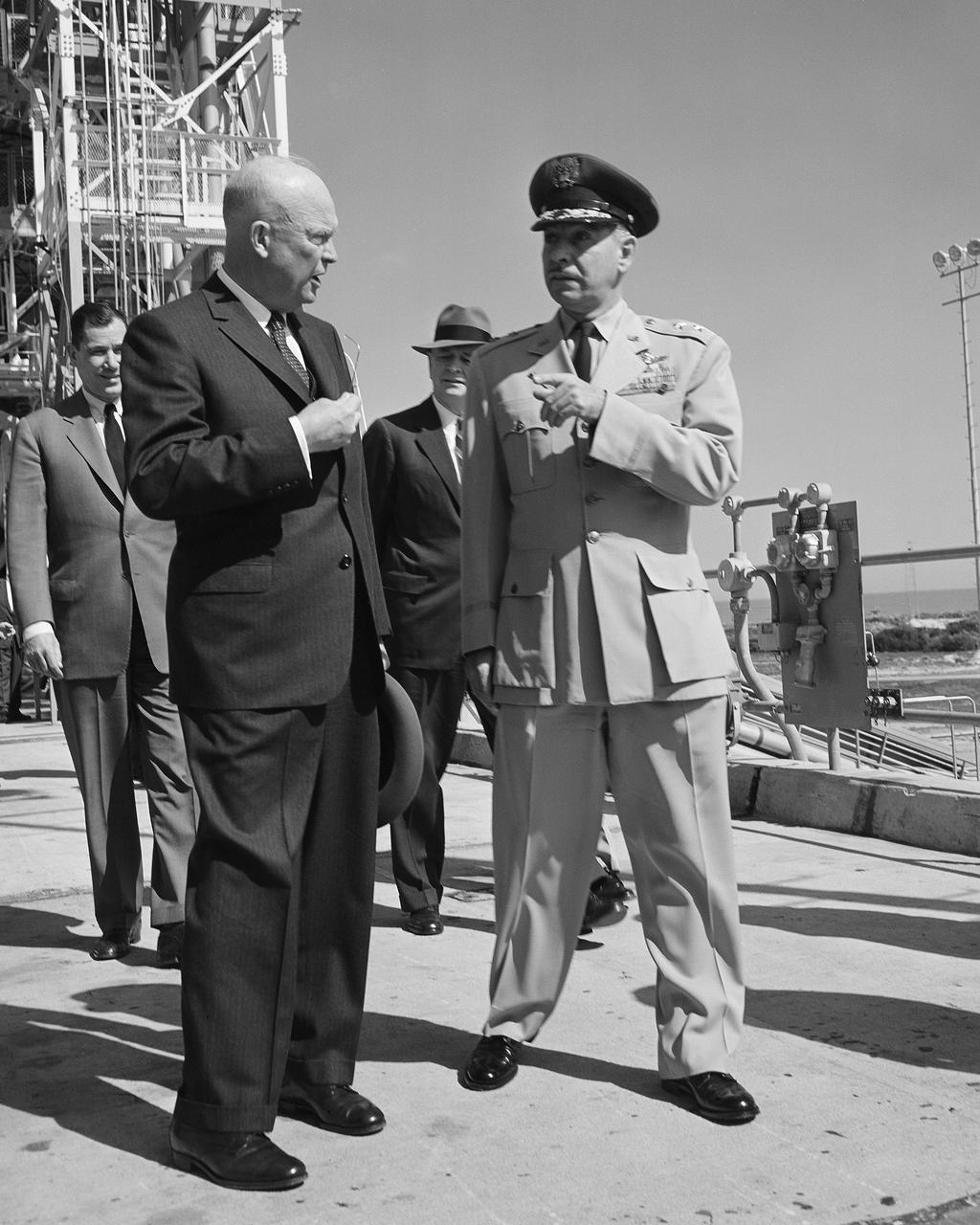

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- President Dwight D Eisenhower is briefed on operations at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Photo Credit: NASA
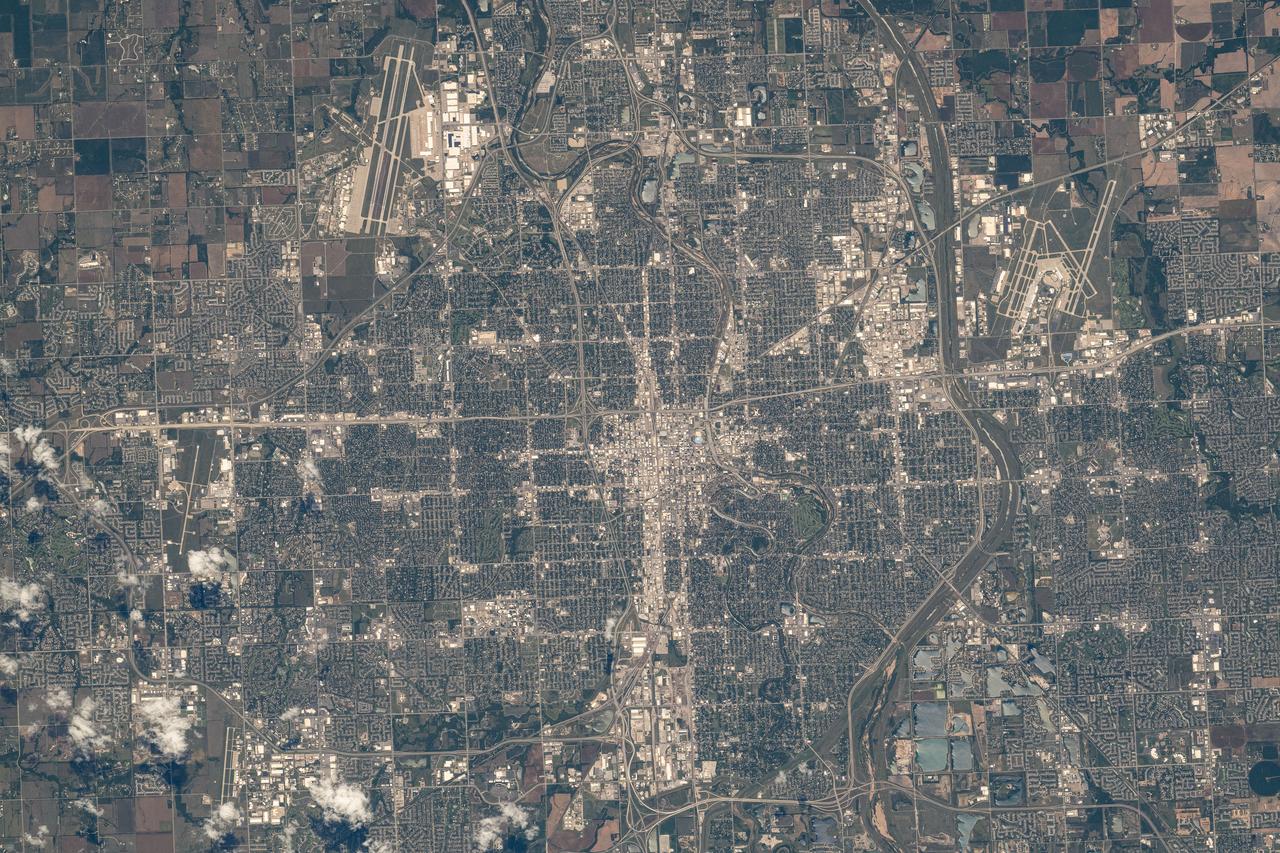

iss071e516926 (Aug. 18, 2024) --- Wichita, Kansas, a city with a population of nearly 400,000, with McConnell Air Force Base just outside the city limits (top left) and hosting the Dwight D. Eisenhower National Airport (upper right), is photographed from the International Space Station as it orbited 260 miles above.
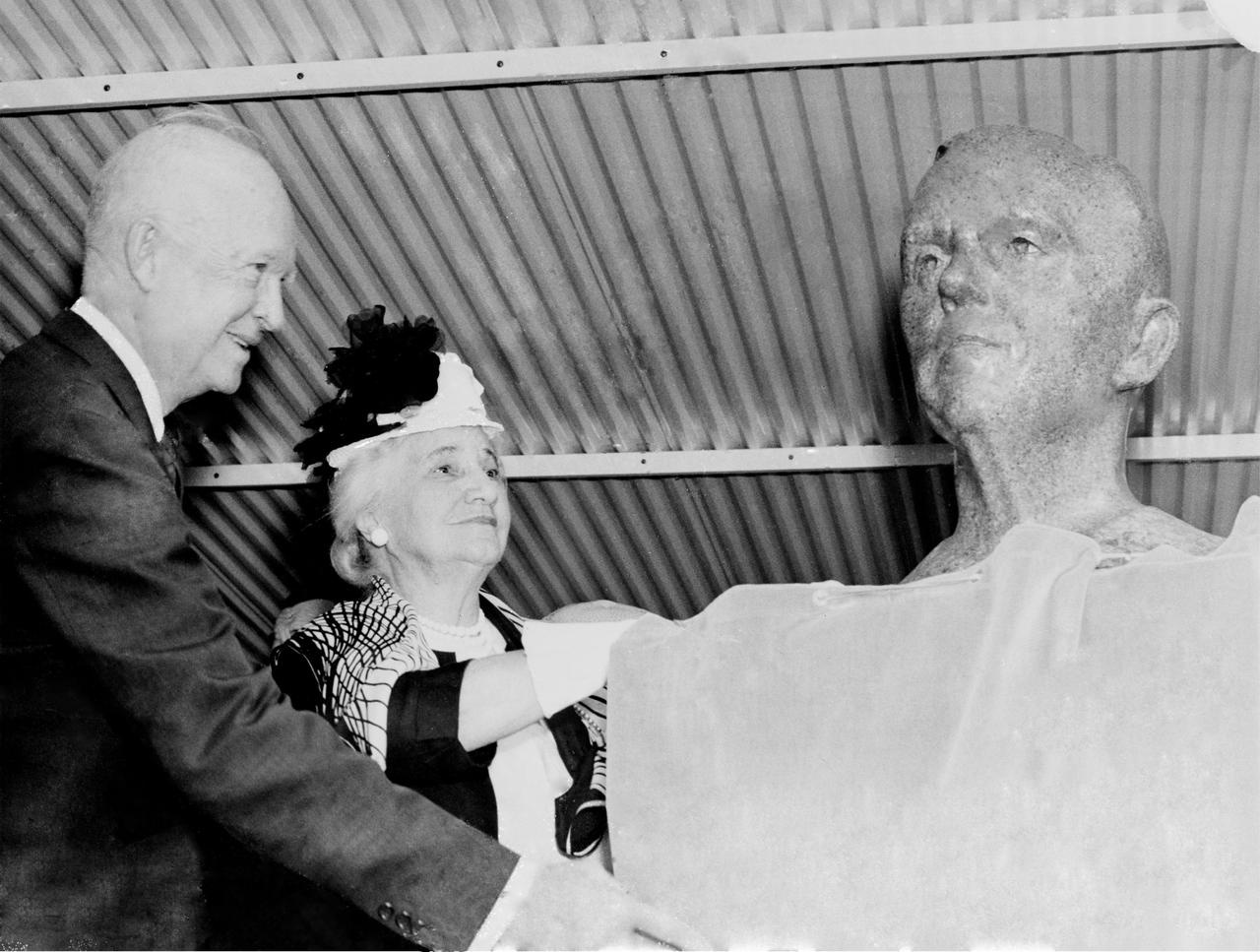

President Dwight D. Eisenhower and Mrs. George C. Marshall unveil the bronze bust of General George C. Marshall during the dedication of the Marshall Space Flight Center. Eisenhower signed an Executive Order on October 21, 1959 directing the transfer of persornel from the Redstone Arsenal's Army Ballistic Missile Agency Development Operations Division to NASA. On March 15, 1960, another Executive Order announced that the space complex formed within the boundaries of Redstone Arsenal would become the George C. Marshall Space Flight Center. The Center was activated on July 1, 1960, with dedication ceremonies taking place September 8, 1960.

Presidential Visits to Kennedy Space Center: All the U. S. presidents shown here were in office at the time they visited KSC. President Dwight D. Eisenhower, 02/10/1960 President Lyndon B. Johnson visited twice, 09/14/1964 and 09/27/1966 President Richard M. Nixon viewed the Apollo 12 launch on 11/14/1969 President Jimmy Carter came to KSC on 10/01/1978 President William J. Clinton viewed the STS-95 launch on 10/29/1998 and President Barack H. Obama visited KSC twice, 04/15/2010 and 04/29/2011. Poster designed by Kennedy Space Center Graphics Department/Greg Lee. Credit: NASA
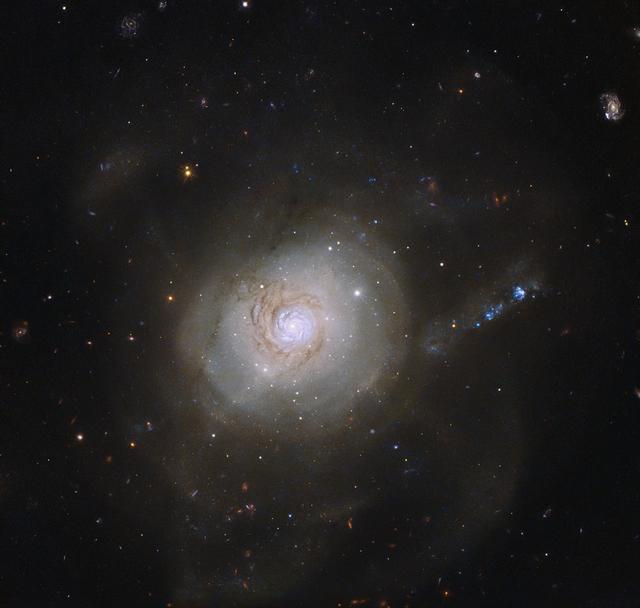

Only rarely does an astronomical object have a political association. However, the spiral galaxy NGC 7252 acquired exactly that when it was given an unusual nickname. In December 1953, the US President Dwight D. Eisenhower gave a speech advocating the use of nuclear power for peaceful purposes. This “Atoms for Peace” speech was significant for the scientific community, as it brought nuclear research into the public domain, and NGC 7252, which has a superficial resemblance to an atomic nucleus surrounded by the loops of electronic orbits, was dubbed the Atoms for Peace galaxy in honour of this. These loops are well visible in a wider field of view image. This nickname is quite ironic, as the galaxy’s past was anything but peaceful. Its peculiar appearance is the result of a collision between two galaxies that took place about a billion years ago, which ripped both galaxies apart. The loop-like outer structures, likely made up of dust and stars flung outwards by the crash, but recalling orbiting electrons in an atom, are partly responsible for the galaxy’s nickname. This NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope image shows the inner parts of the galaxy, revealing a pinwheel-shaped disc that is rotating in a direction opposite to the rest of the galaxy. This disc resembles a spiral galaxy like our own galaxy, the Milky Way, but is only about 10 000 light-years across — about a tenth of the size of the Milky Way. It is believed that this whirling structure is a remnant of the galactic collision. It will most likely have vanished in a few billion years’ time, when NGC 7252 will have completed its merging process.