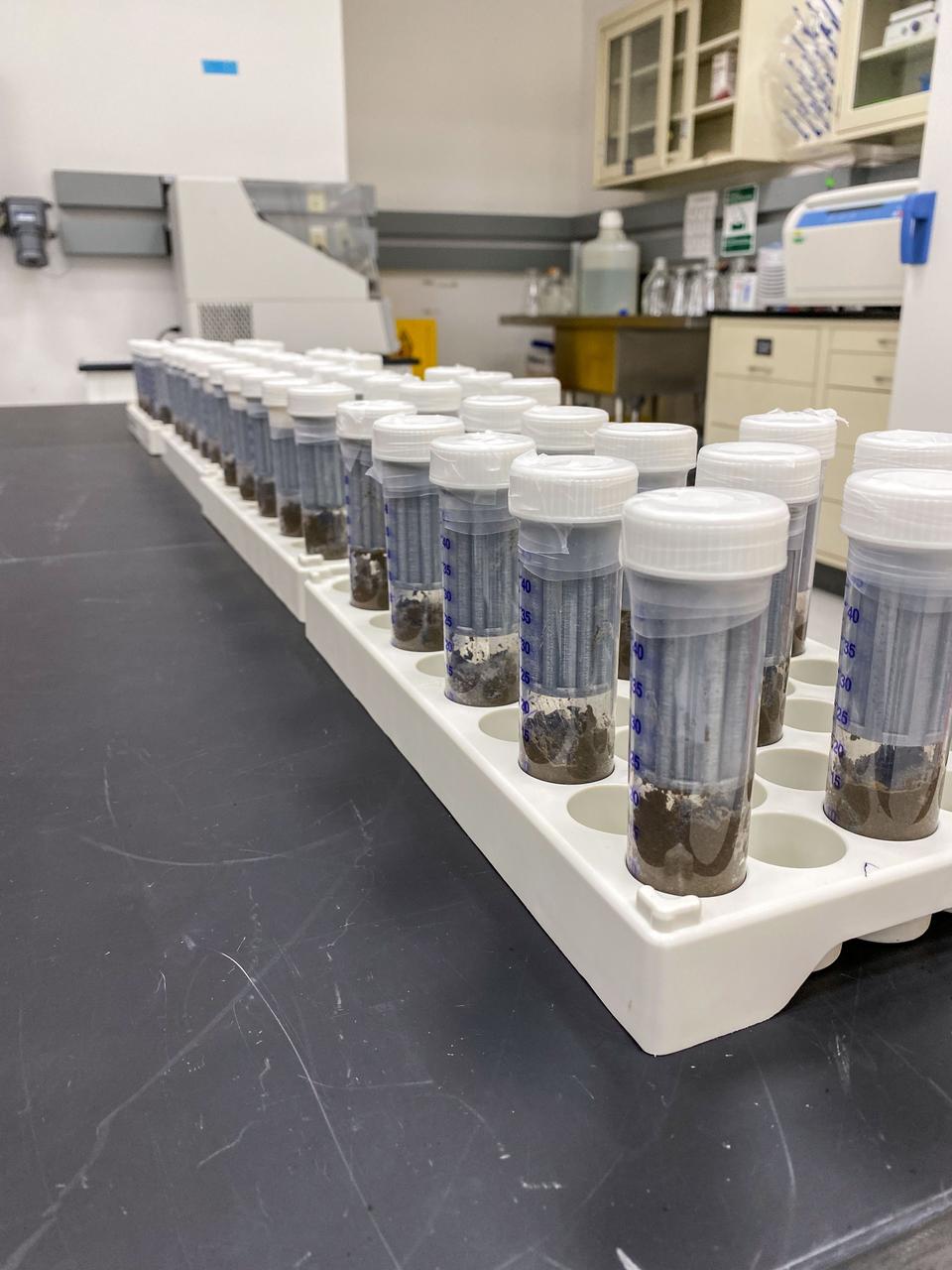

jsc2022e042490 (9/24/2021) --- Preflight image of a rack of tubes containing different cultures of bacteria to be added to sterile soil. The Dynamics of the Microbiome in Space (DynaMoS) investigation. Image courtesy of the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory.

Seen here are science tubes containing soil and soil microbes for the Dynamics of Microbiomes in Space (DynaMoS) experiment after they’ve been prepared for flight to the International Space Station inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 11, 2022. The DynaMoS experiment will launch on SpaceX’s 25th cargo resupply services mission to examine how microgravity affects metabolic interactions in communities of soil microbes. This will help NASA understand the function of soil microorganisms in space versus on Earth and how they can be used to enhance plant growth for crew consumption during long-duration missions to the Moon and Mars. SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon spacecraft are scheduled to lift off from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A at 8:44 p.m. EDT on Thursday, July 14.
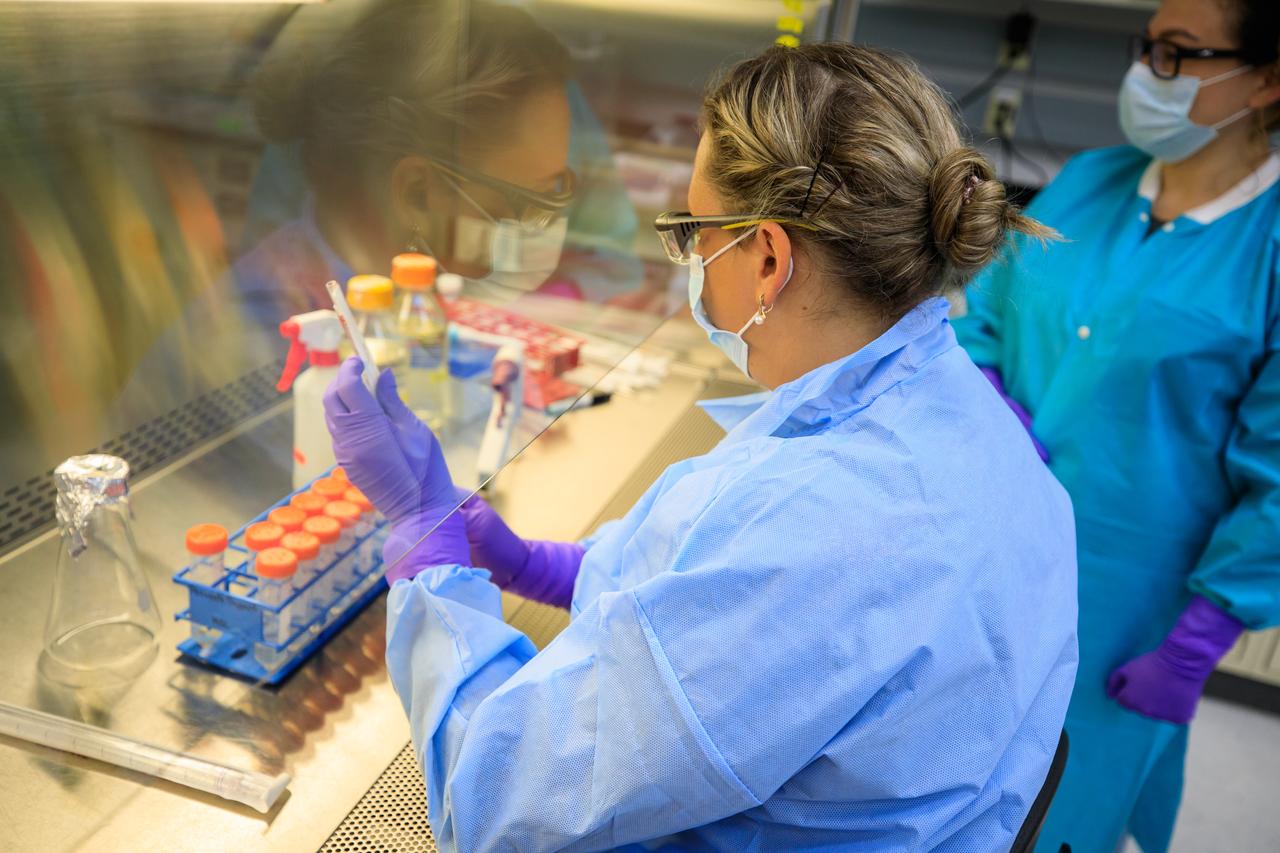

Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL) Scientist Yuliya Farris (left) prepares the Dynamics of Microbiomes in Space (DynaMoS) experiment inside a laboratory at the Florida spaceport’s Space Station Processing Facility on July 11, 2022. The DynaMoS experiment will launch on SpaceX’s 25th cargo resupply services mission to examine how microgravity affects metabolic interactions in communities of soil microbes. This will help NASA understand the function of soil microorganisms in space versus on Earth and how they can be used to enhance plant growth for crew consumption during long-duration missions to the Moon and Mars. SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon spacecraft are scheduled to lift off from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A at 8:44 p.m. EDT on Thursday, July 14.
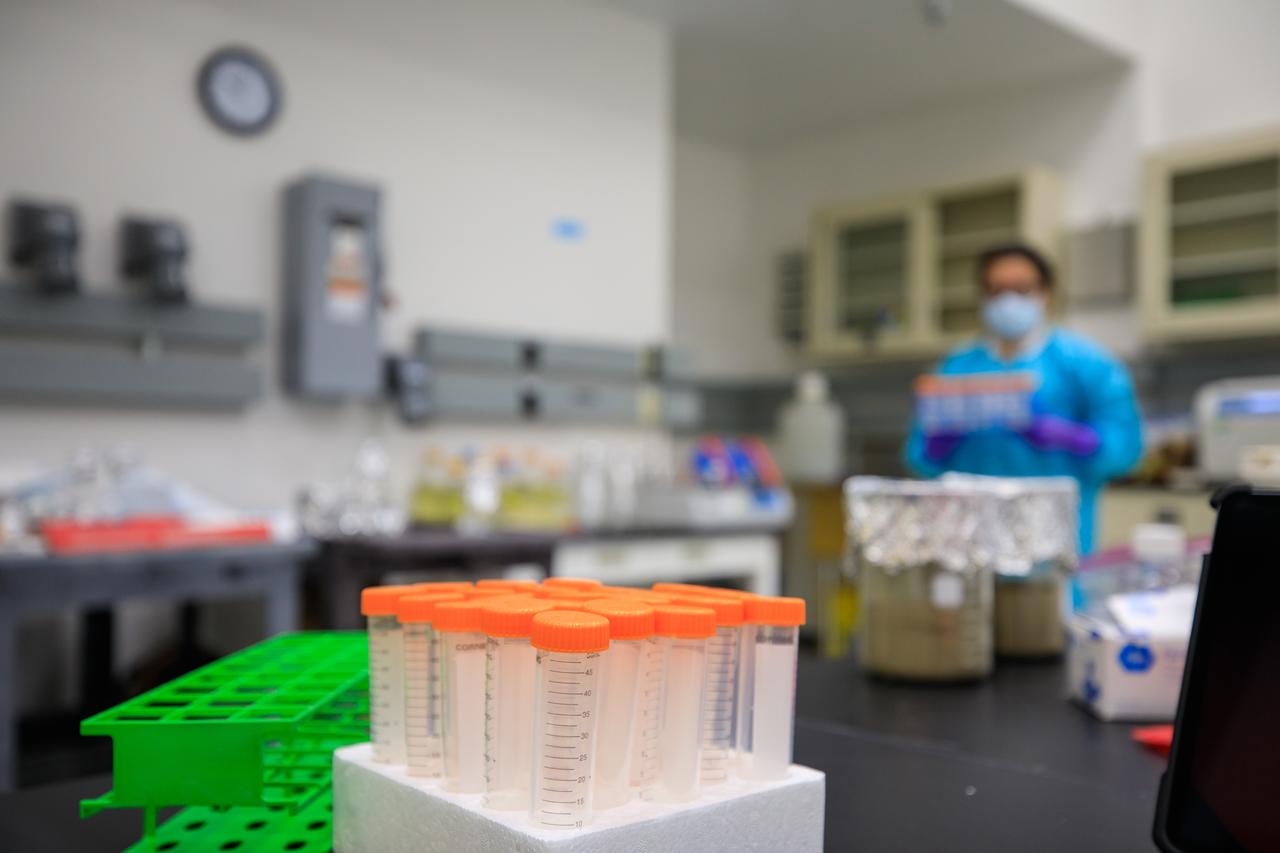

In this photo, science tubes containing bacterial cells are being prepped for cleaning as part of the Dynamics of Microbiomes in Space (DynaMoS) experiment inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 11, 2022. Once clean, the cells will be moved to a larger space for continued growth in order to generate enough biomass to inoculate the soil that will be used in the experiment. The DynaMoS experiment will launch on SpaceX’s 25th cargo resupply services mission to examine how microgravity affects metabolic interactions in communities of soil microbes. This will help NASA understand the function of soil microorganisms in space versus on Earth and how they can be used to enhance plant growth for crew consumption during long-duration missions to the Moon and Mars. SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon spacecraft are scheduled to lift off from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A at 8:44 p.m. EDT on Thursday, July 14.
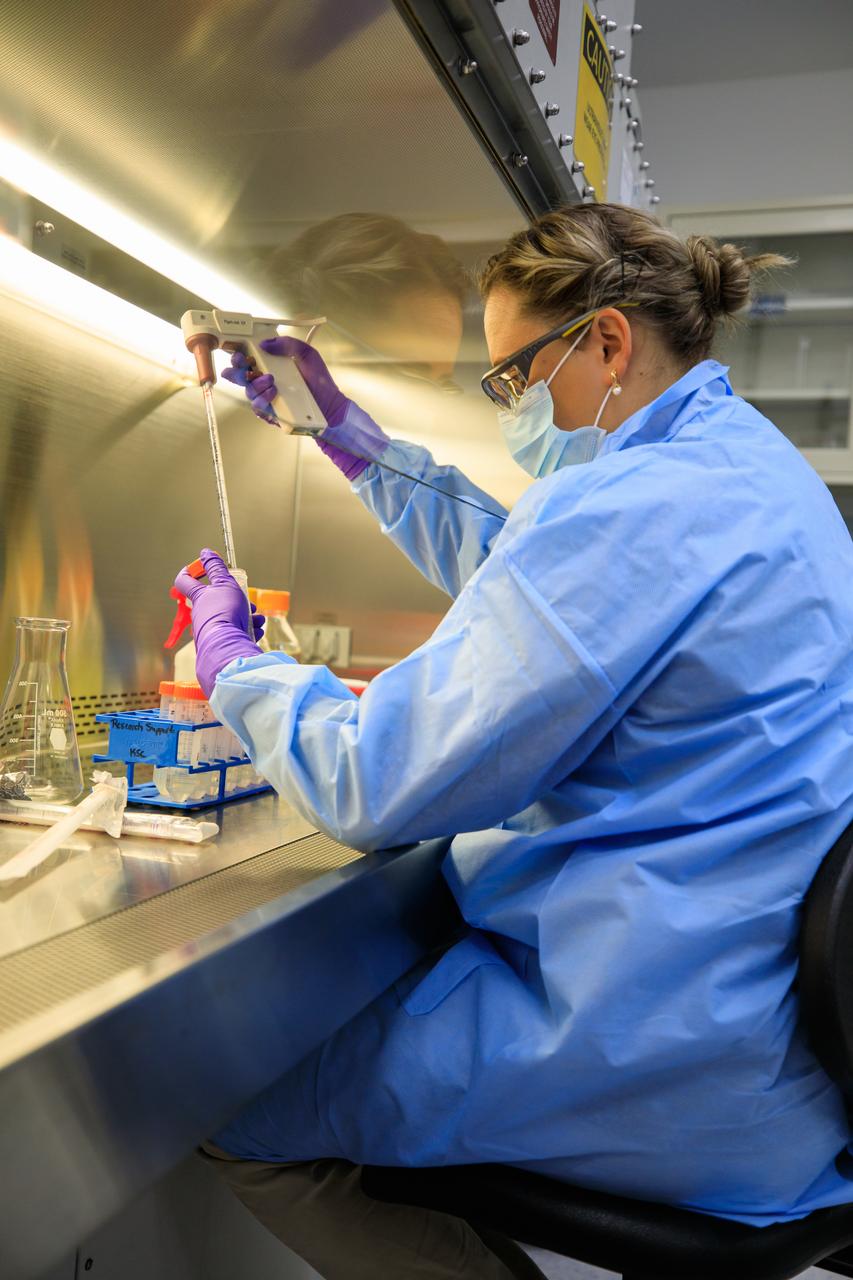

Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL) Scientist Yuliya Farris prepares the Dynamics of Microbiomes in Space (DynaMoS) experiment inside a laboratory at the Florida spaceport’s Space Station Processing Facility on July 11, 2022. The DynaMoS experiment will launch on SpaceX’s 25th cargo resupply services mission to examine how microgravity affects metabolic interactions in communities of soil microbes. This will help NASA understand the function of soil microorganisms in space versus on Earth and how they can be used to enhance plant growth for crew consumption during long-duration missions to the Moon and Mars. SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon spacecraft are scheduled to lift off from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A at 8:44 p.m. EDT on Thursday, July 14.
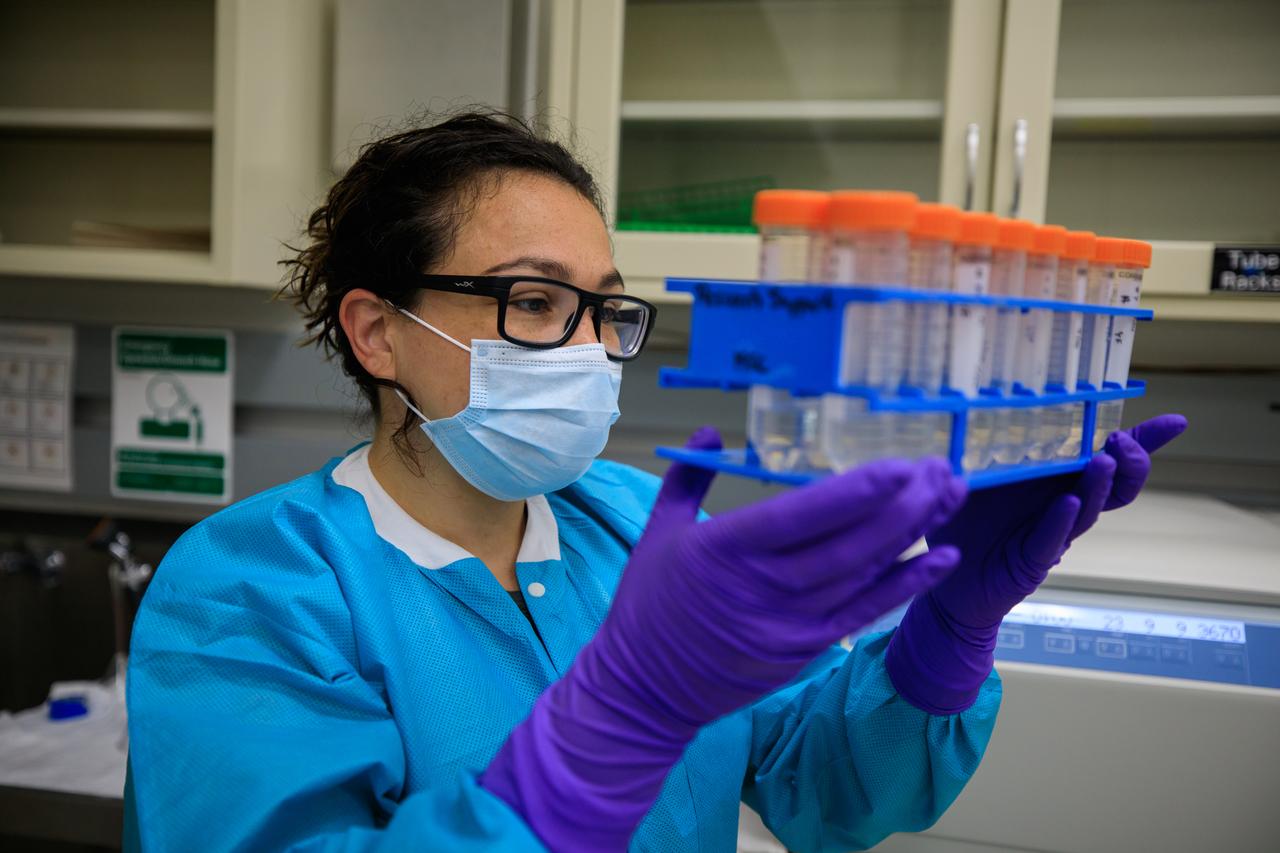

Marci Garcia, a research associate at Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL), examines some of the science tubes that make up the Dynamics of Microbiomes in Space (DynaMoS) experiment inside a laboratory at the Space Station Processing Facility on July 11, 2022. The DynaMoS experiment will launch on SpaceX’s 25th cargo resupply services mission to examine how microgravity affects metabolic interactions in communities of soil microbes. This will help NASA understand the function of soil microorganisms in space versus on Earth and how they can be used to enhance plant growth for crew consumption during long-duration missions to the Moon and Mars. SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon spacecraft are scheduled to lift off from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A at 8:44 p.m. EDT on Thursday, July 14.
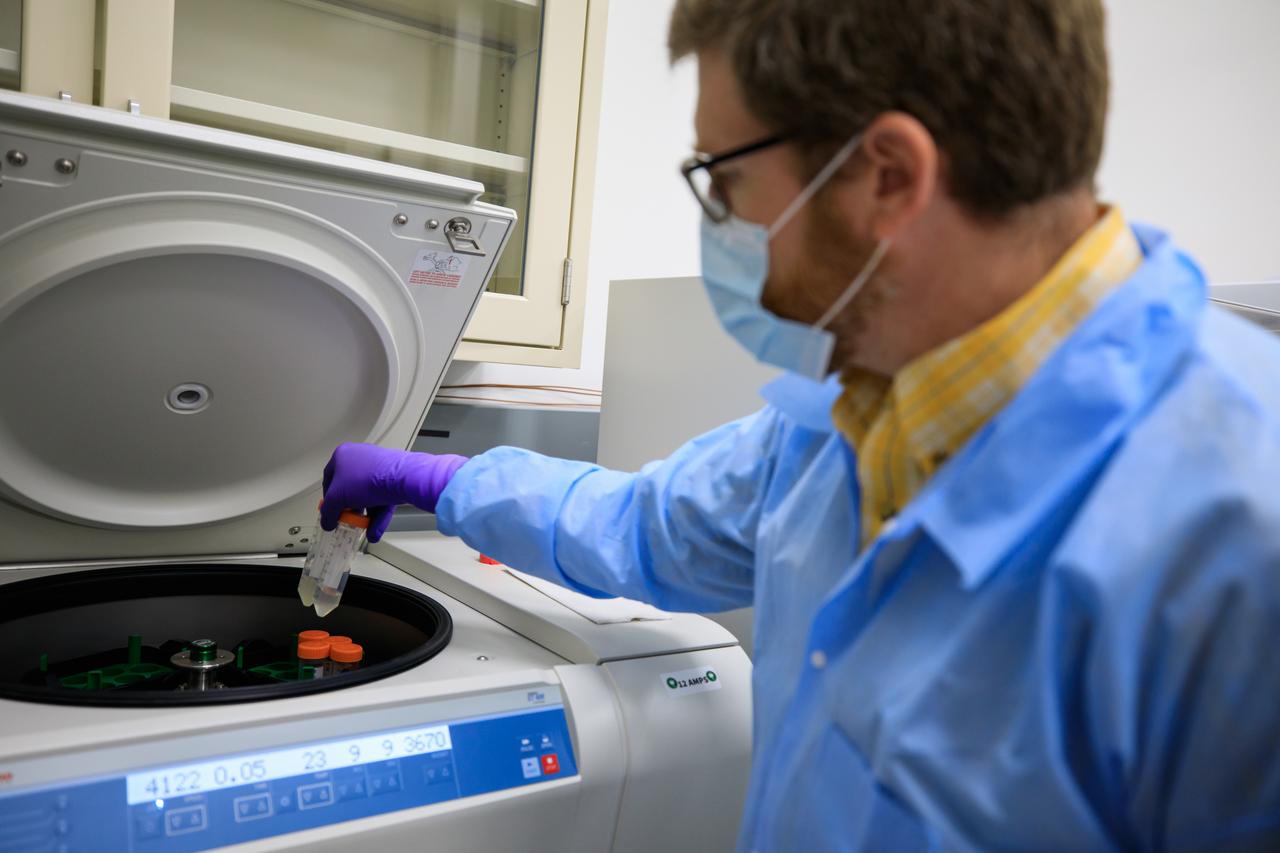

Ryan McClure, scientist with Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL) prepare the Dynamics of Microbiomes in Space (DynaMoS) experiment inside a laboratory at the Space Station Processing Facility on July 11, 2022. The DynaMoS experiment will launch on SpaceX’s 25th cargo resupply services mission to examine how microgravity affects metabolic interactions in communities of soil microbes. This will help NASA understand the function of soil microorganisms in space versus on Earth and how they can be used to enhance plant growth for crew consumption during long-duration missions to the Moon and Mars. SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon spacecraft are scheduled to lift off from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A at 8:44 p.m. EDT on Thursday, July 14.
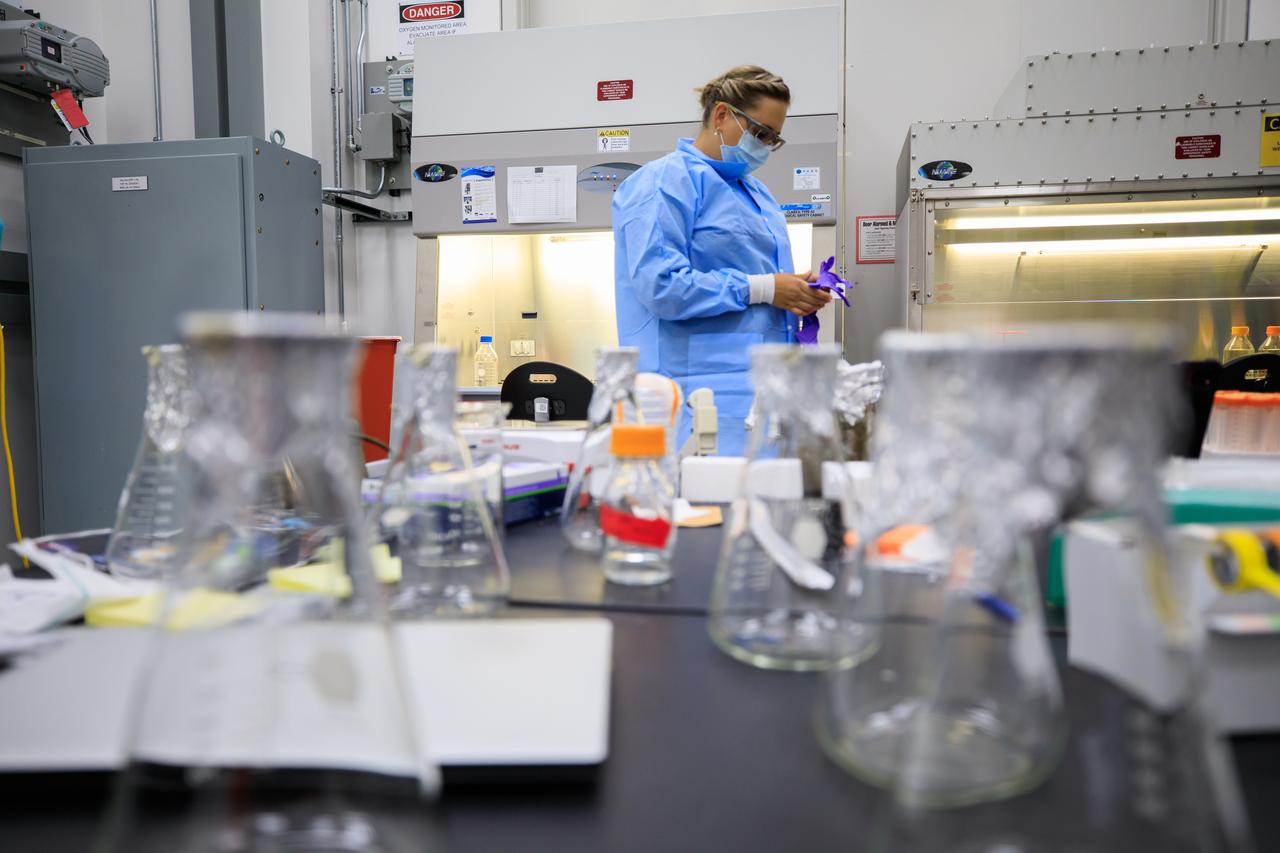

Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL) Scientist Yuliya Farris prepares the Dynamics of Microbiomes in Space (DynaMoS) experiment inside a laboratory at the Florida spaceport’s Space Station Processing Facility on July 11, 2022. The DynaMoS experiment will launch on SpaceX’s 25th cargo resupply services mission to examine how microgravity affects metabolic interactions in communities of soil microbes. This will help NASA understand the function of soil microorganisms in space versus on Earth and how they can be used to enhance plant growth for crew consumption during long-duration missions to the Moon and Mars. SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon spacecraft are scheduled to lift off from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A at 8:44 p.m. EDT on Thursday, July 14.
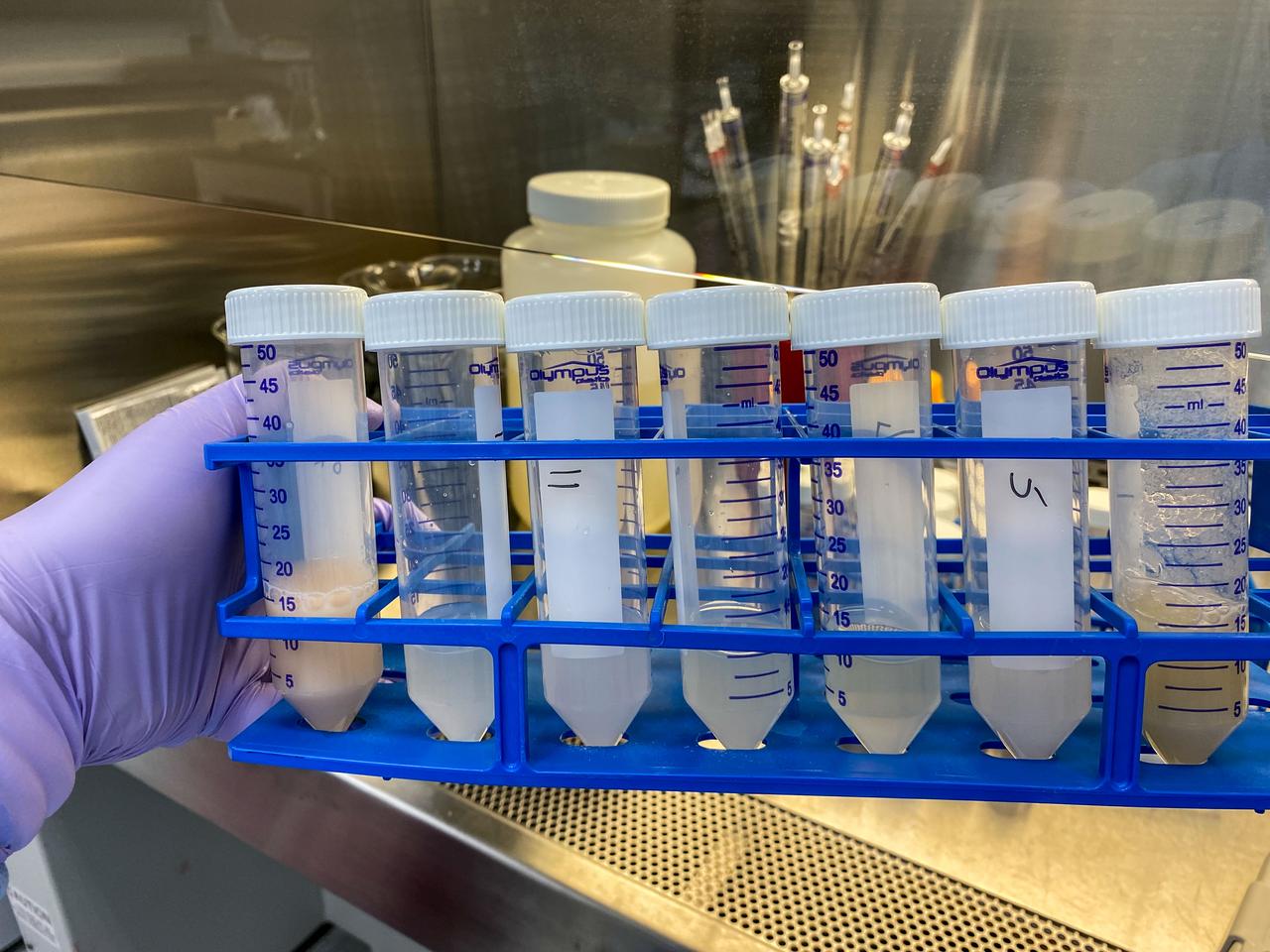
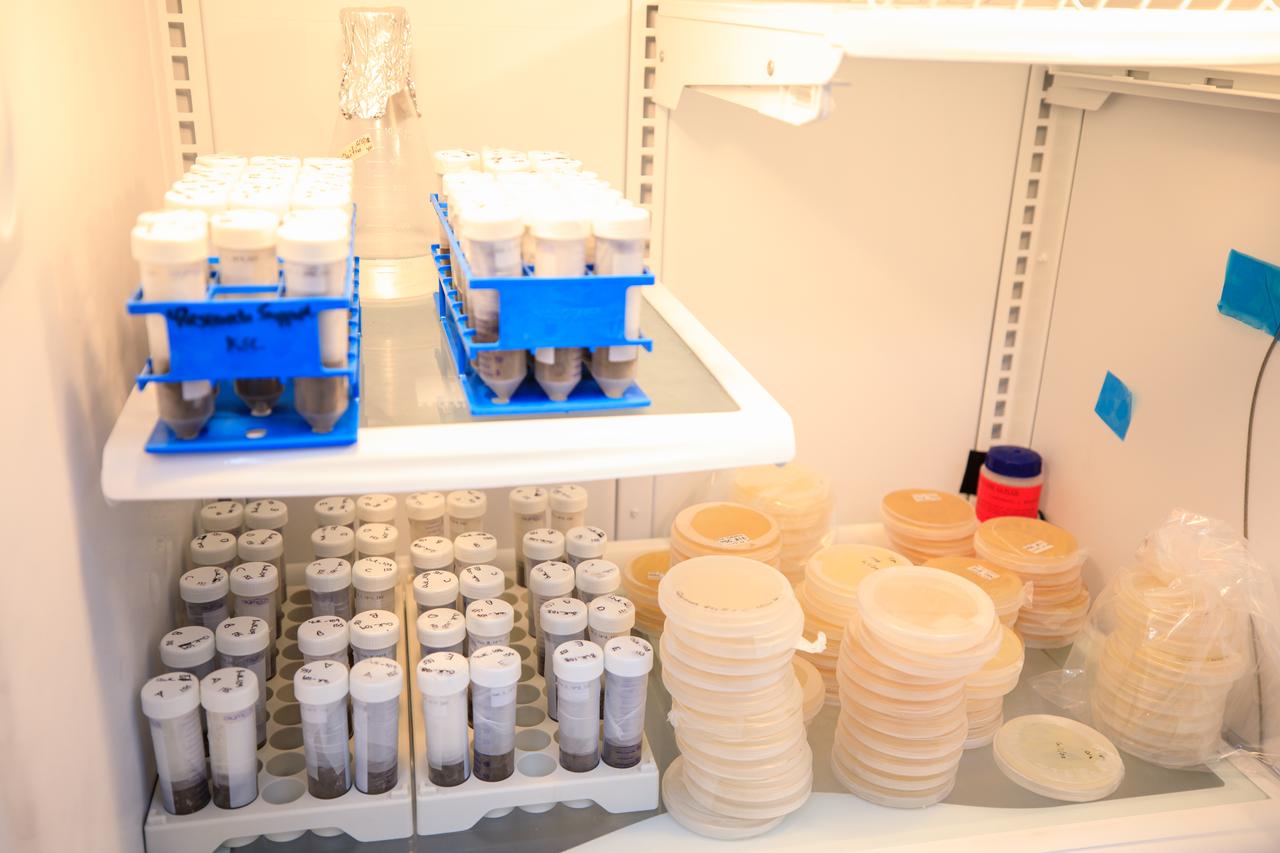
jsc2022e042489 (9/23/2021) --- Preflight image of a rack of tubes containing soil samples that have been inoculated with a model soil consortium for the Dynamics of the Microbiome in Space (DynaMoS) investigation, examines how microgravity affects metabolic interactions in communities of soil microbes. Image courtesy of the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory.
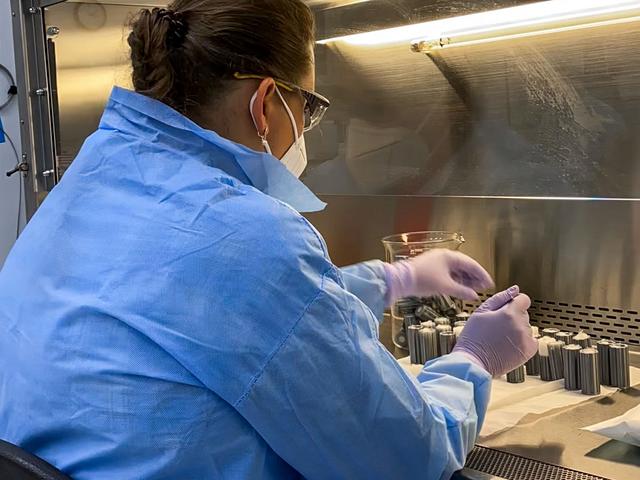

jsc2022e042488 (4/20/2022) --- A closeup of Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL) staff technician Yuliya Farris preparing sterile spaces used to hold soil in place during Dynamics of the Microbiome in Space (DynaMoS). Image courtesy of the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory.

This is an artist concept comparing the present day magnetic fields on Earth and Mars. Earth magnetic field is generated by an active dynamo -- a hot core of molten metal.
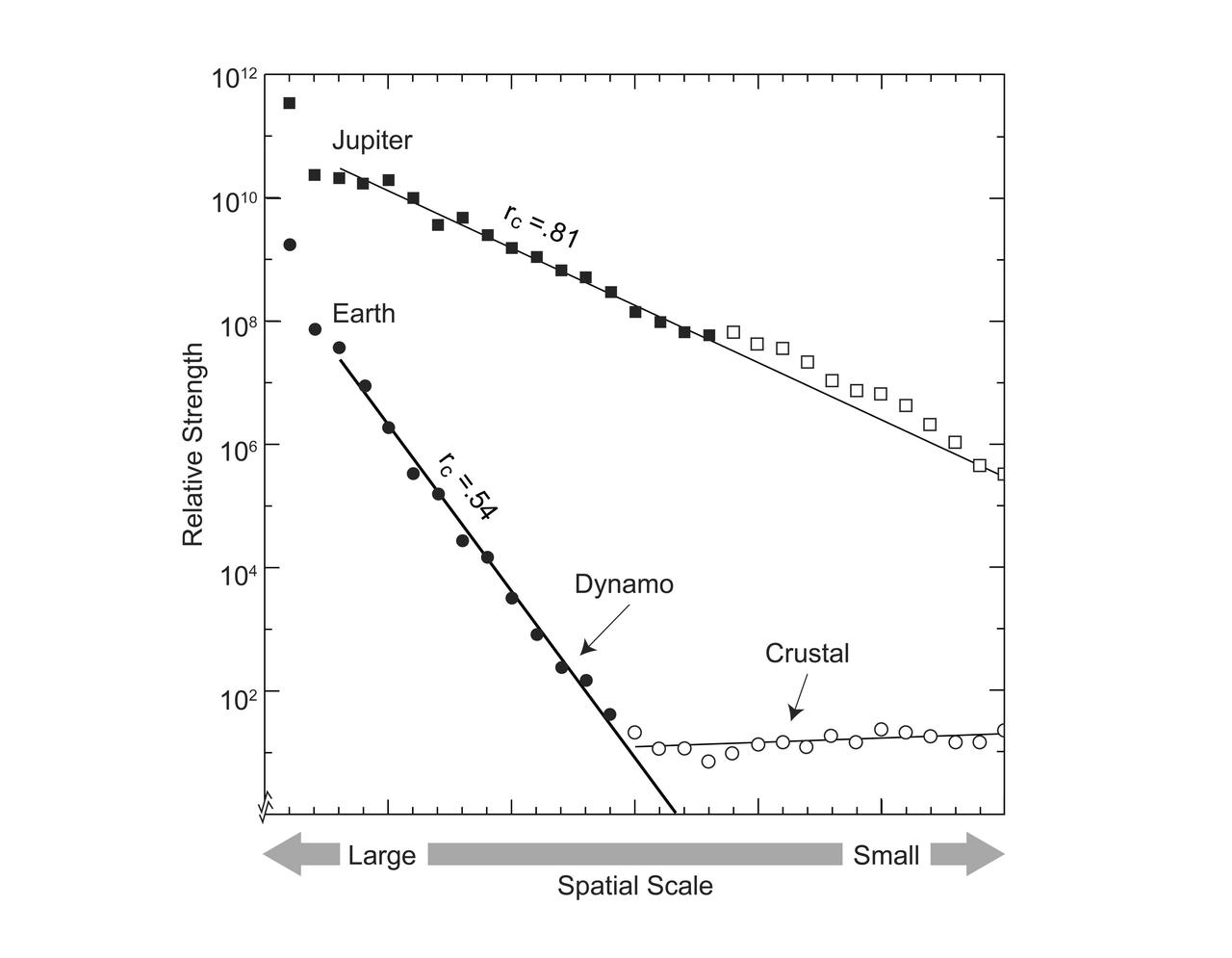
This graphic compares the magnetic fields of Earth and Jupiter, characterizing the field on the surface of each planet in terms of spatial scale, with large scale to the left, and small scale to the right. The linear progression of terms characterizing Earth's field identifies a dynamo core radius at 0.54 planet radius and crustal magnetization at smaller scales. By analogy, the new Jupiter model identifies a dynamo core radius at 0.81 planet radius, in the convective metallic hydrogen just beneath a zone stabilized by helium rain. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25064

In the summer of the year 1054 AD, Chinese astronomers saw a new "guest star," that appeared six times brighter than Venus. So bright in fact, it could be seen during the daytime for several months. This "guest star" was forgotten about until 700 years later with the advent of telescopes. Astronomers saw a tentacle-like nebula in the place of the vanished star and called it the Crab Nebula. Today we know it as the expanding gaseous remnant from a star that self-detonated as a supernova, briefly shining as brightly as 400 million suns. The explosion took place 6,500 light-years away. If the blast had instead happened 50 light-years away it would have irradiated Earth, wiping out most life forms. In the late 1960s astronomers discovered the crushed heart of the doomed star, an ultra-dense neutron star that is a dynamo of intense magnetic field and radiation energizing the nebula. Astronomers therefore need to study the Crab Nebula across a broad range of electromagnetic radiation, from X-rays to radio waves. This image combines data from five different telescopes: the VLA (radio) in red; Spitzer Space Telescope (infrared) in yellow; Hubble Space Telescope (visible) in green; XMM-Newton (ultraviolet) in blue; and Chandra X-ray Observatory (X-ray) in purple. More images and an animation are available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21474