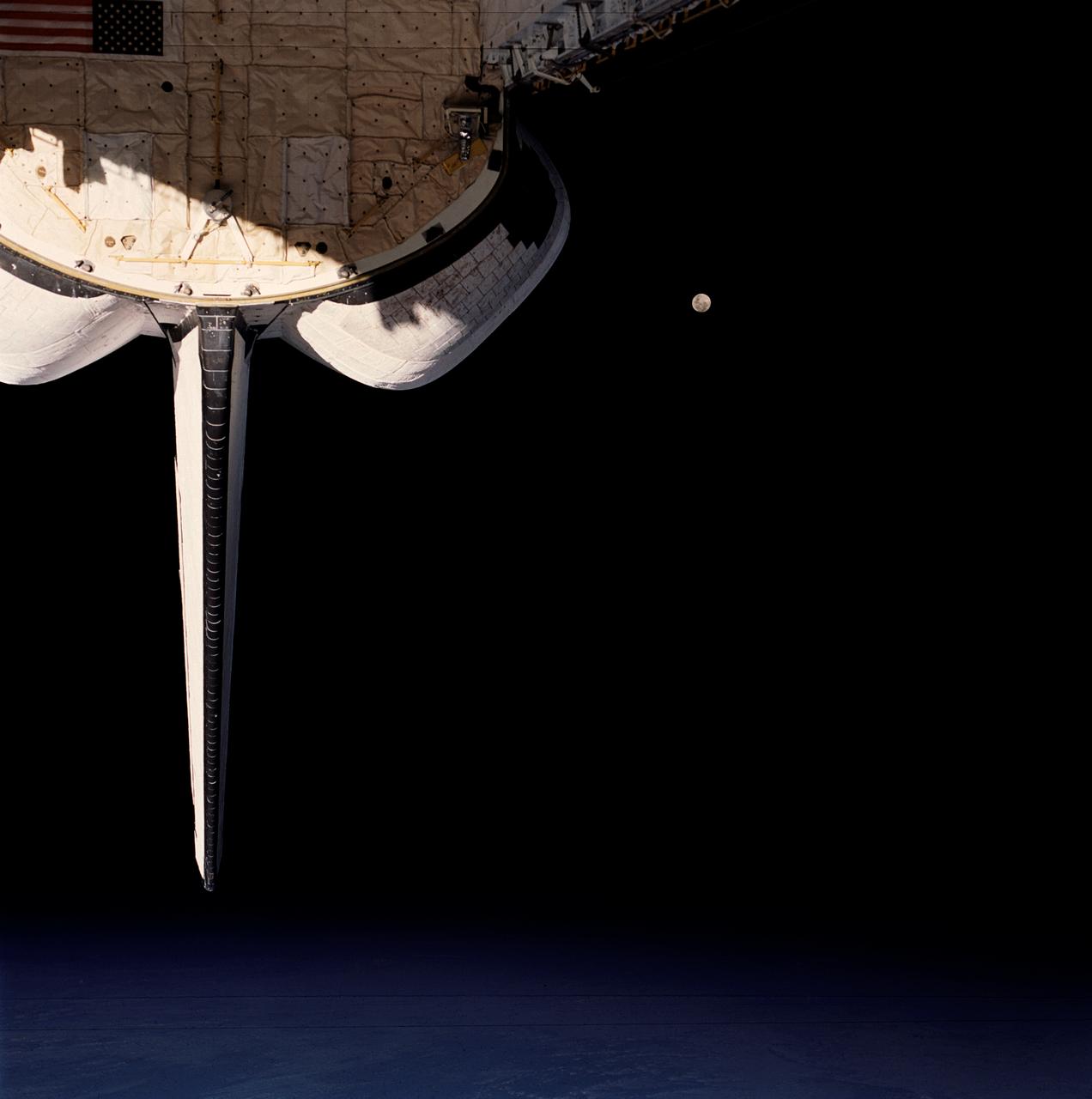

STS053-105-002 (2-9 Dec. 1992) --- A crew member onboard the space shuttle Discovery used a 70mm camera to capture this scene of a full Moon backdropped against the blackness of space. Part of Discovery's aft cargo bay and clouds over an ocean complete the scene.
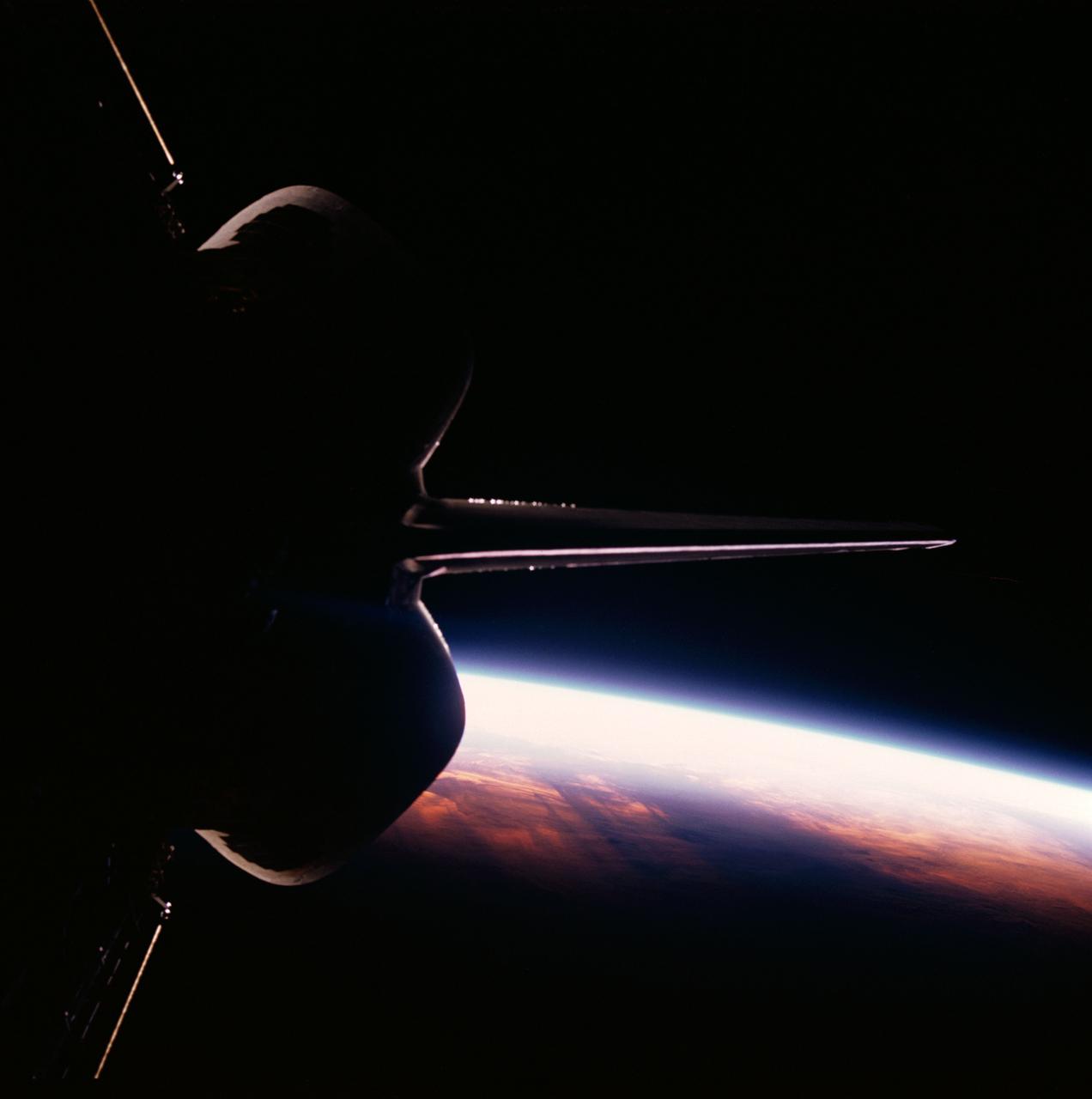

Discovery's, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103's, vertical stabilizer and orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pods are backdropped against the contrasted blackness of space illuminated by a colorful Earth / sunrise panorama. View was taken through the aft flight deck viewing windows during STS-26.

STS060-84-021 (3-11 Feb 1994) --- The Kennedy Space Center (KSC) and its partially cloud-covered environs were captured on 70mm by one of the STS-60 crew members during the eight-day mission. The Shuttle landing facility, on which Discovery landed February 11, 1994, visible at left center.
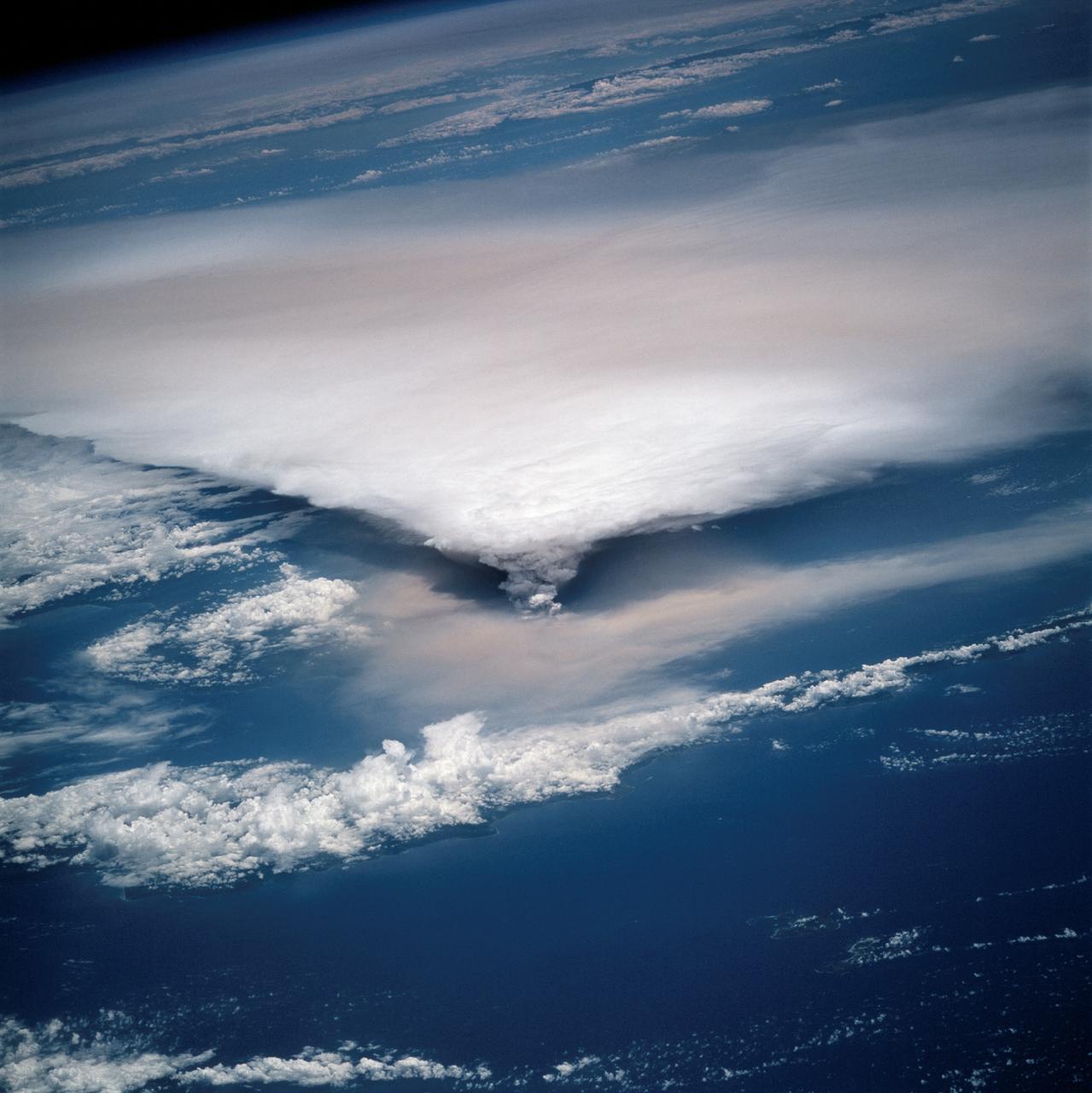

STS064-116-064 (20 Sept. 1994) --- Near the end of the mission, the crew aboard space shuttle Discovery was able to document the beginning of the second day of activity of the Rabaul volcano, on the east end of New Britain. On the morning of Sept. 19, 1994, two volcanic cones on the opposite sides of the 6-kilometer sea crater had begun to erupt with very little warning. Discovery flew just east of the eruption roughly 24 hours after it started and near the peak of its activity. New Ireland, the cloud-covered area in the foreground, lies just east of Rabaul harbor. The eruption, which sent a plume up to over 60,000 feet into the atmosphere, caused over 50,000 people to evacuate the area. Because winds were light at the time of the eruption, most of the ash was deposited in a region within 20 kilometers of the eruption zone. This photo shows the large white billowing eruption plume is carried in a westerly direction by the weak prevailing winds. At the base of the eruption column is a layer of yellow-brown ash being distributed by lower level winds. A sharp boundary moving outward from the center of the eruption in the lower cloud is a pulse of laterally-moving ash which results from a volcanic explosion. Geologists theorize that the large white column and the lower gray cloud are likely from the two main vents on each side of the harbor. The bay and harbor of Rabaul are covered with a layer of ash, possibly partly infilled with volcanic material. Matupit Island and the airport runway have disappeared into the bay. More than a meter of ash has fallen upon the city of Rabaul. Up to five vents were reported to have erupted at once, including the two cones Vulcan and Tavurvur, which are opposites of the harbor as well as new vents below the bay. Half of the Vulcan cone has collapsed into the sea. The extra day in space due to bad weather at the landing site afforded the crew the opportunity for both still and video coverage of the event. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
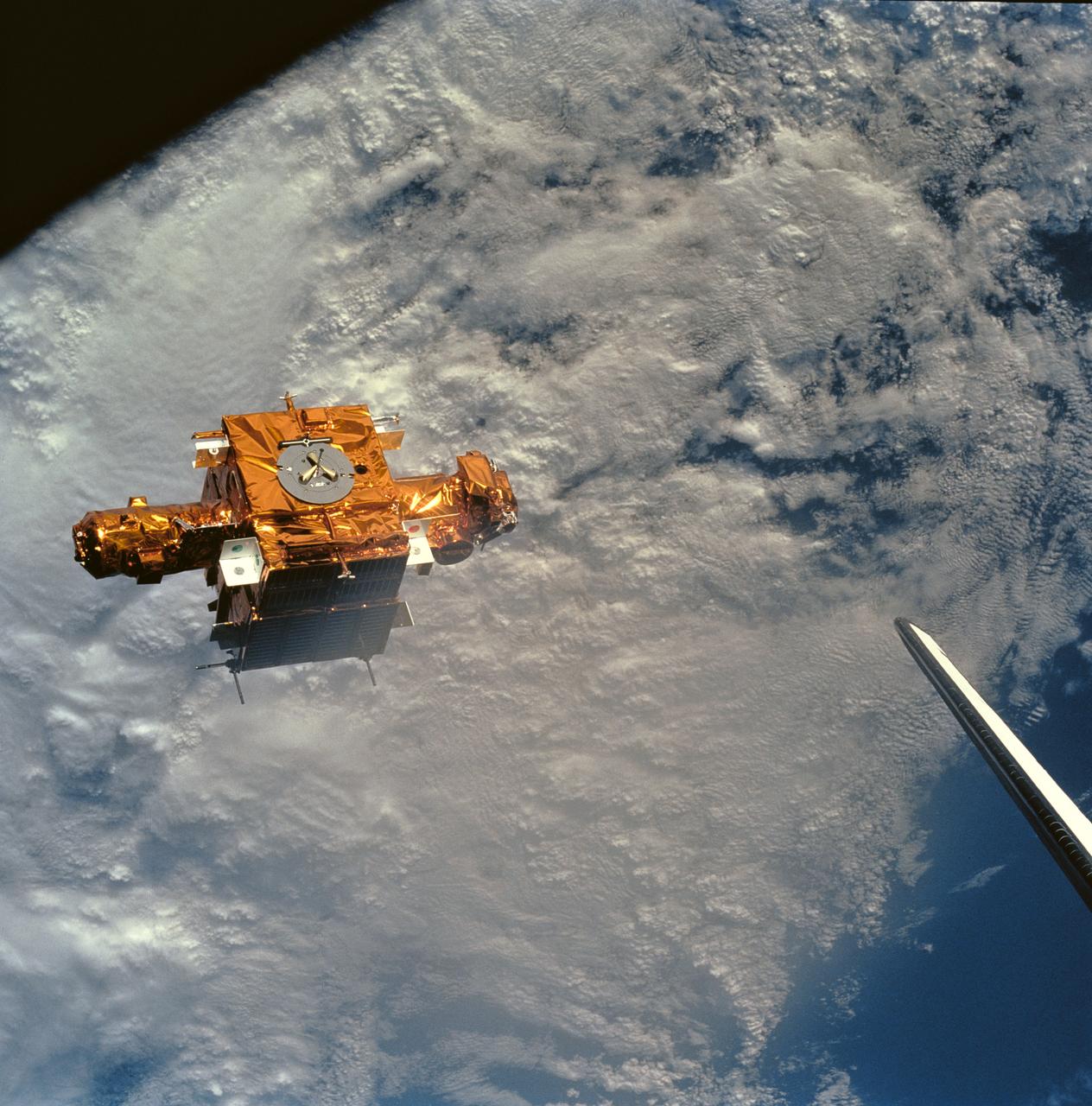

STS056-90-034 (8-17 April 1993) --- Backdropped against heavy cloud cover over the Mediterranean Sea, the SPARTAN-201 satellite was captured on 70mm by crewmembers aboard the Space Shuttle Discovery. SPARTAN is a free-flying payload designed to study the solar wind and part of the sun's corona. The project was conceived in the late 1970s to take advantage of the opportunity offered by the Space Shuttle to provide more observation time for the increasingly more sophisticated experiments than the five to ten minutes provided by sounding rocket flights. On the mission's third day, Astronaut Ellen Ochoa, Mission Specialist, used the remote manipulator system (RMS) to lift the satellite from its support structure on Discovery and release it in space. The reusable craft was later recaptured and returned to Earth with the crew. Note the tip of Discovery's vertical stabilizer at frame's edge.
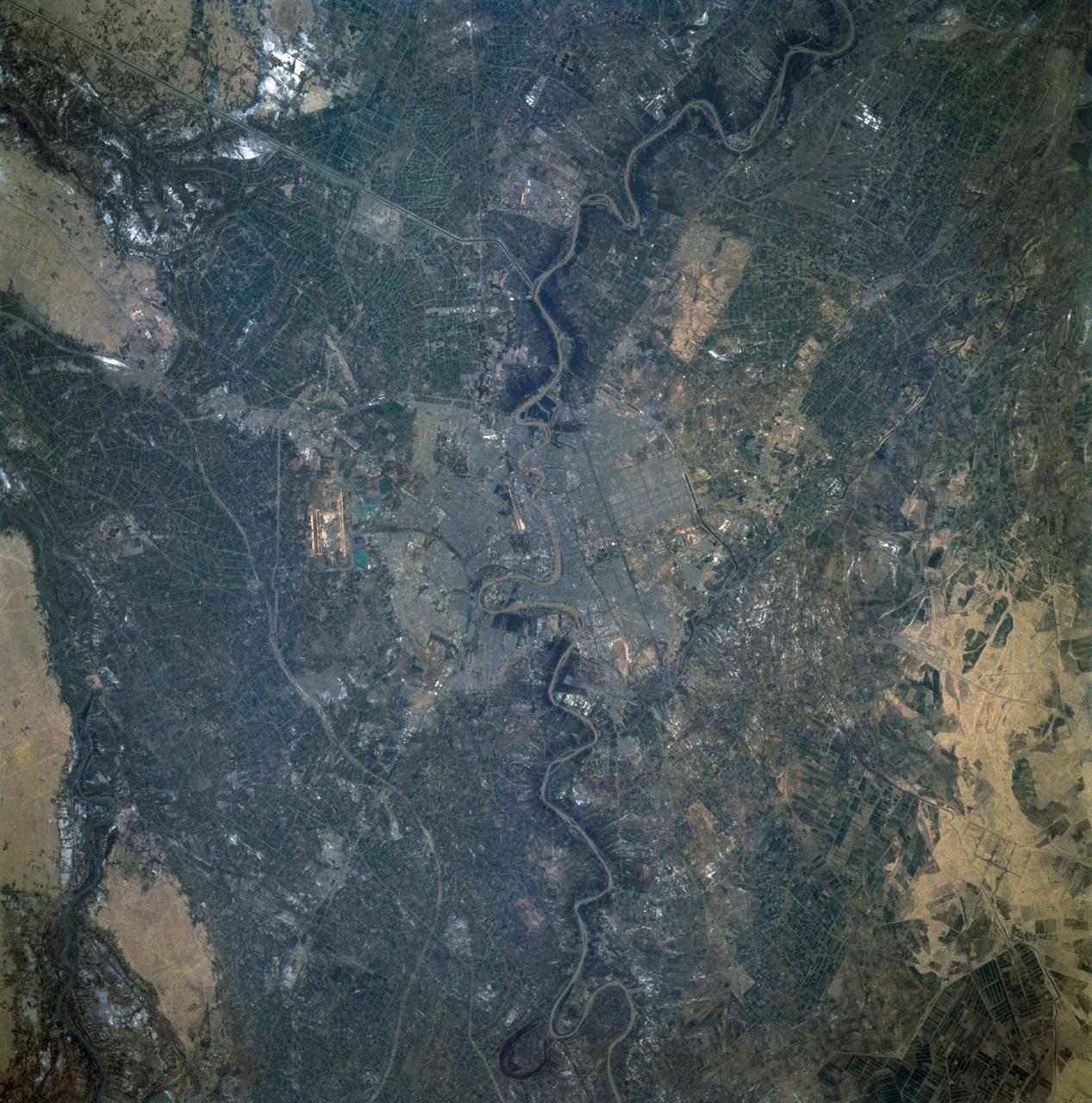

STS060-92-082 (3-11 Feb 1994) --- This cloud-free view is centered on the city of Baghdad, Iraq. Baghdad has had a reputation for scholarship and learning from ancient times in the Islamic world. Modern Baghdad is a city with a typical urban land use patterns. The color of Tigris river flowing through the city indicates the heavily sediment laden waters of the river. Agricultural land uses are evident in the surrounding areas of the city.
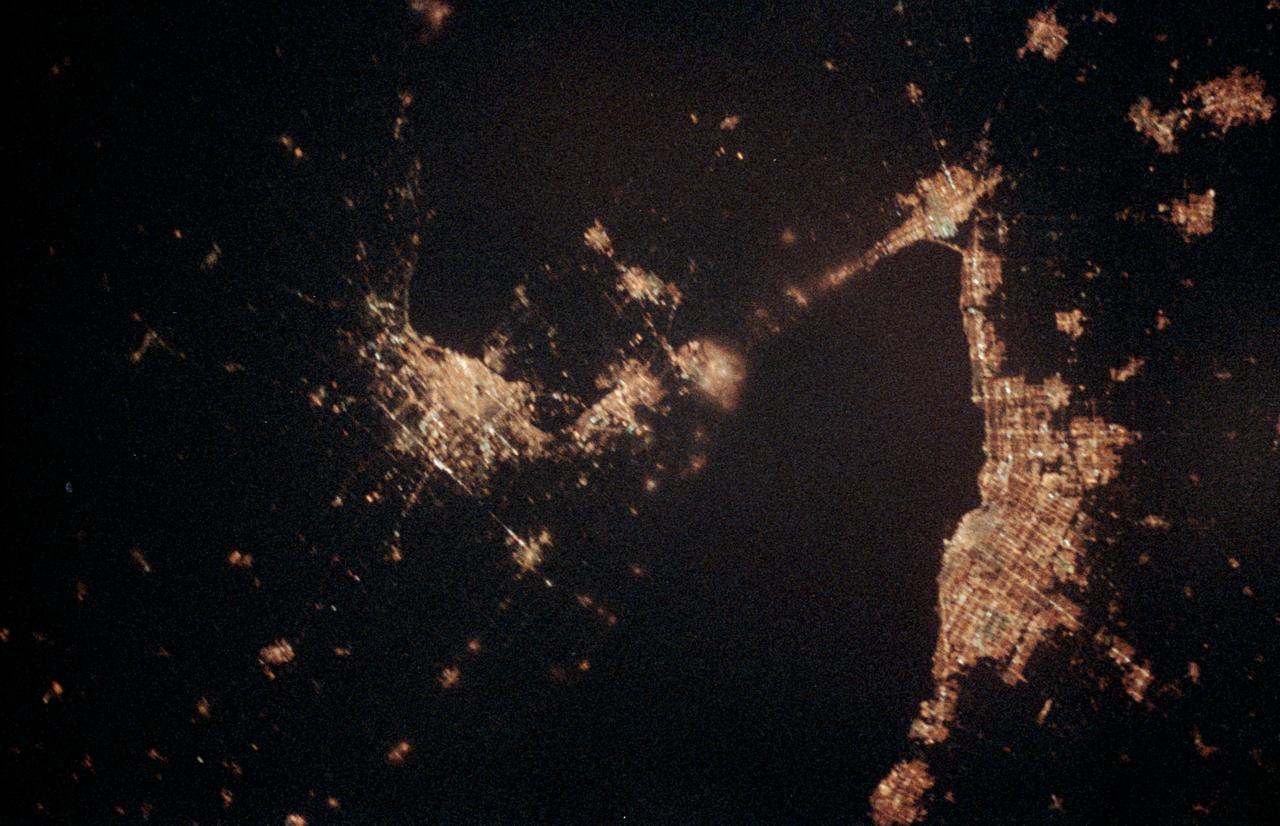

STS060-06-037 (3-11 Feb 1994) --- The city lights of Buffalo and Toronto outline the shores of the east end of Lake Erie and the west end of Lake Ontario in this night scene of western New York and southern Ontario. Between the two major cities are the cities of Niagara Falls, New York and Niagara Falls, Canada, which straddle the Niagara River just north of the actual falls. This photograph was taken with a special ASA-1600 film that is normally used for night-time photography of aurora, noctilucent clouds, biomass burning, and city lights.
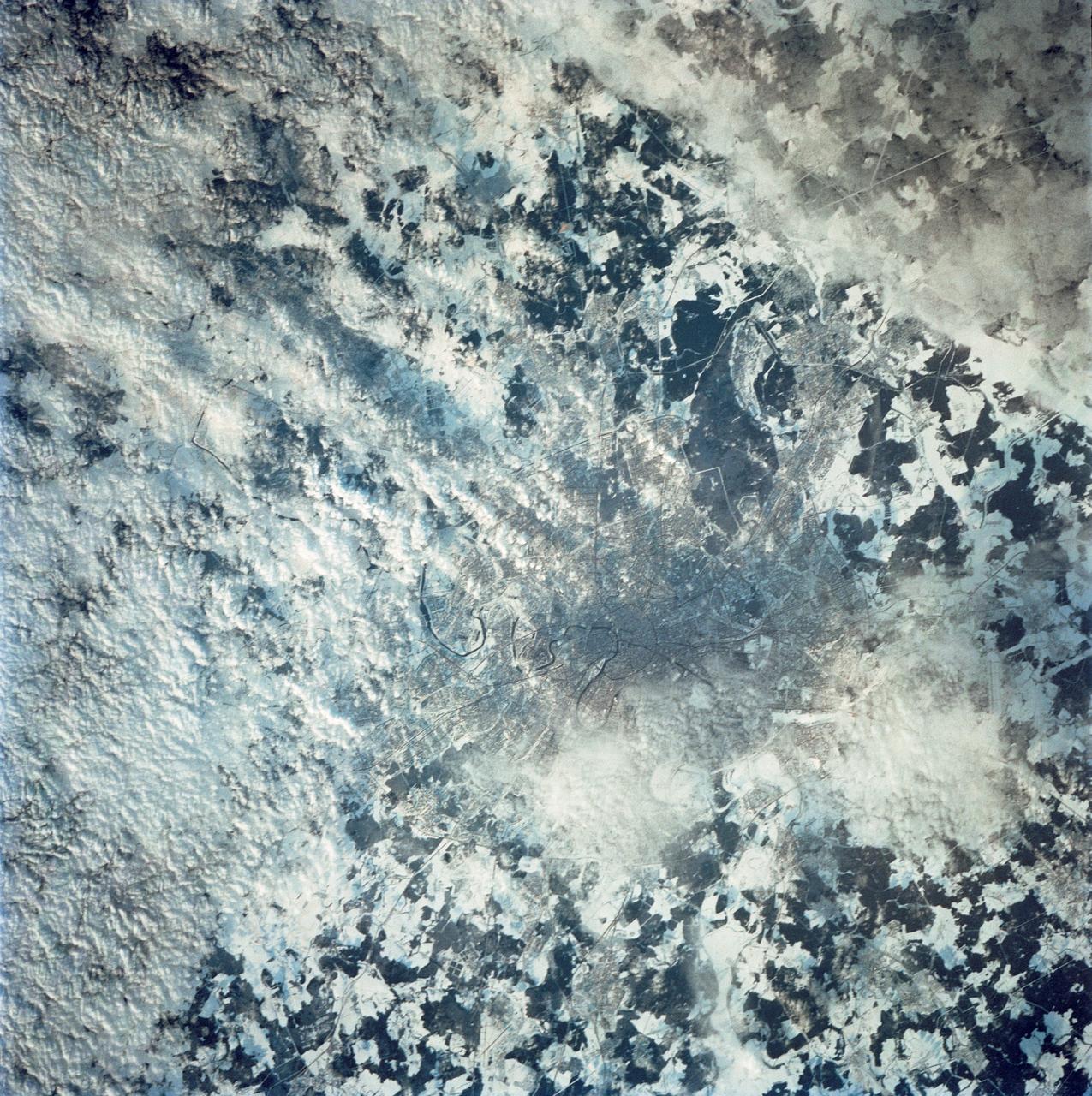

STS042-80-000AV (22-30 Jan. 1992) --- Moscow is arranged as a series of concentric transportation routes crossed by straight spokes which lead away from the Kremlin at the city center. One of the inner rings, the Garden Ring, follows the line of the Sixteenth Century city wall and moat. Both this and the outer ring of the Moscow Circular Motorway can be seen. The Kremlin, established in the Twelfth Century, lies on the north bank of the winding Moskva River. Very large high-rise buildings were erected after World War II. Clusters of these produce a coarser pattern and can be detected at two points within the outer ring road. Of the five airports surrounding the city, Vnukovo Airport to the south is easily distinguished, and Sheremetyevo to the west can also be delineated. The once-secret Ramenskoye Airport, with the longest runways in the world, lies under clouds to the northeast.
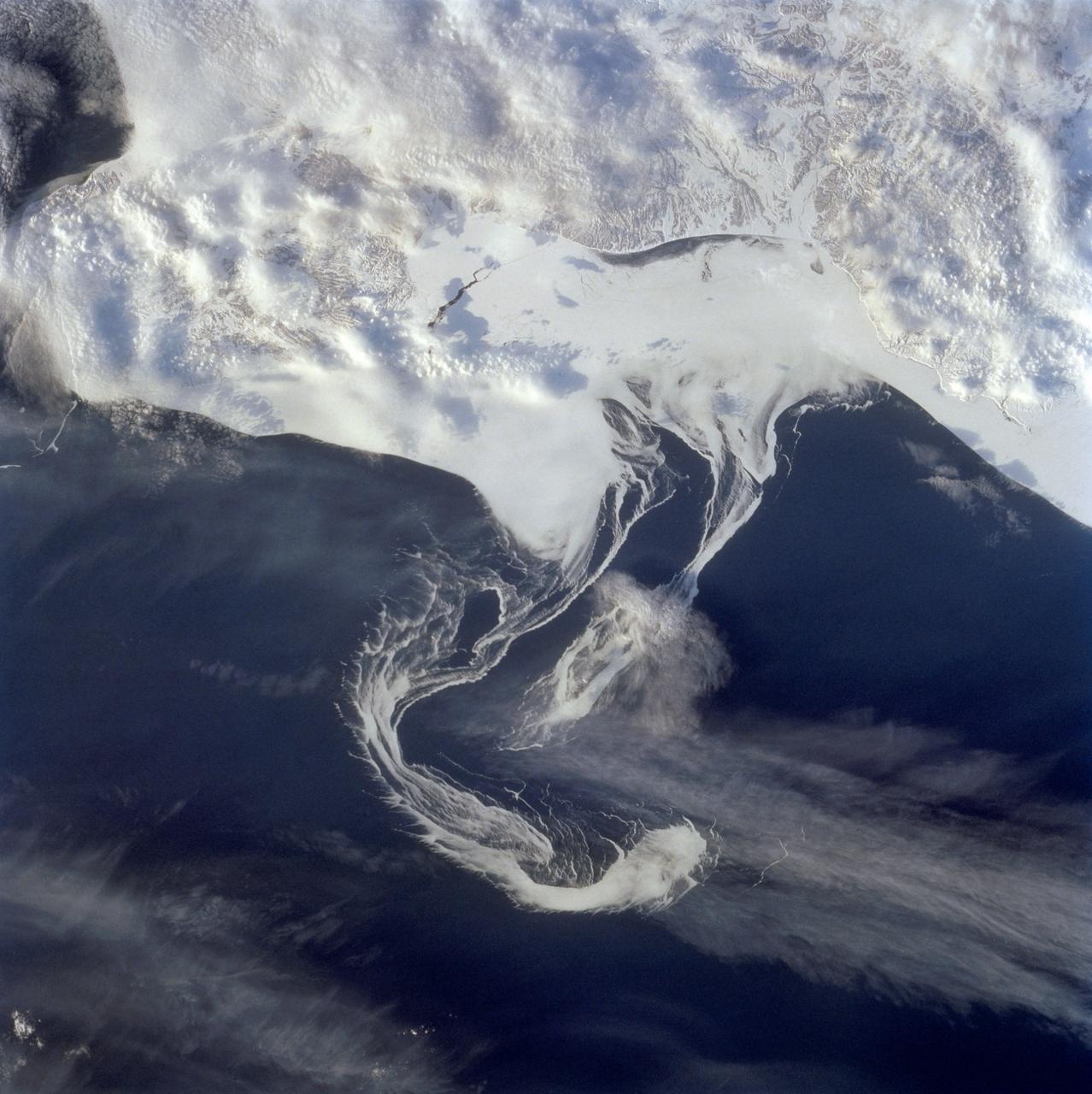

STS060-73-038 (3-11 Feb 1994) --- Pack ice is documented in this photograph along the coast of the Kamchatka Peninsula of Russia in Zaliv Ozernoj. Newly formed ice continually breaks away from the land and takes the form imposed by coastal currents. Detailed photographs of the ice provide information to scientists in both Russia and the united States about the location and fluctuation of ice edges, and how this new sea ice interacts with ocean and littoral currents. This information results in better ice warnings to shipping traffic and provides data points for long-range climate change research for both the Mission-To-Planet Earth and the Russian Priroda ("Nature") monitoring and assessment programs that are respectively coordinated by NASA and the Russian Academy of Sciences. This photography of ice development in the North Pacific, North Atlantic, the Southern Ocean, the Baltic and North Seas, and the Great Lakes is of great interest to the international scientific community. NASA scientists feel high-resolution analog and digital photography from the Space Shuttle and future craft can be a particularly important component in satisfying their data needs on both an operational and a long-term research basis.

STS060-87-087 (3-11 Feb 1994) --- Lake Baikal, in southeastern Siberia, is the largest freshwater lake in the world by volume, holding nearly 20 per cent of the world's fresh water. Lake Baikal is a biospheric reserve of high international interest to the global scientific community. It is home to some 600 endemic species, many found in no other location. This view shows the northern end of the lake, and was taken in the early morning with low sun highlighting the mountain ranges rimming the lake basin. Pristine forests surround the lake, although heavy logging is evident in other photography of the central and southern portions of the lake. Another unique aspect of Lake Baikal is the existence of the world's only known freshwater hydrothermal springs. The fault system which bounds the lake allows fluids to circulate deep into the Earth and resurface as hot springs around and in the lake. Russian and American scientists are using the Shuttle photography to examine the relationship of the lake's ice cover to areas of known hydrothermal activity. Thus Lake Baikal has been and continues to be a high-priority site for photography from space from both the Space Shuttle and the Russian Space Station MIR.
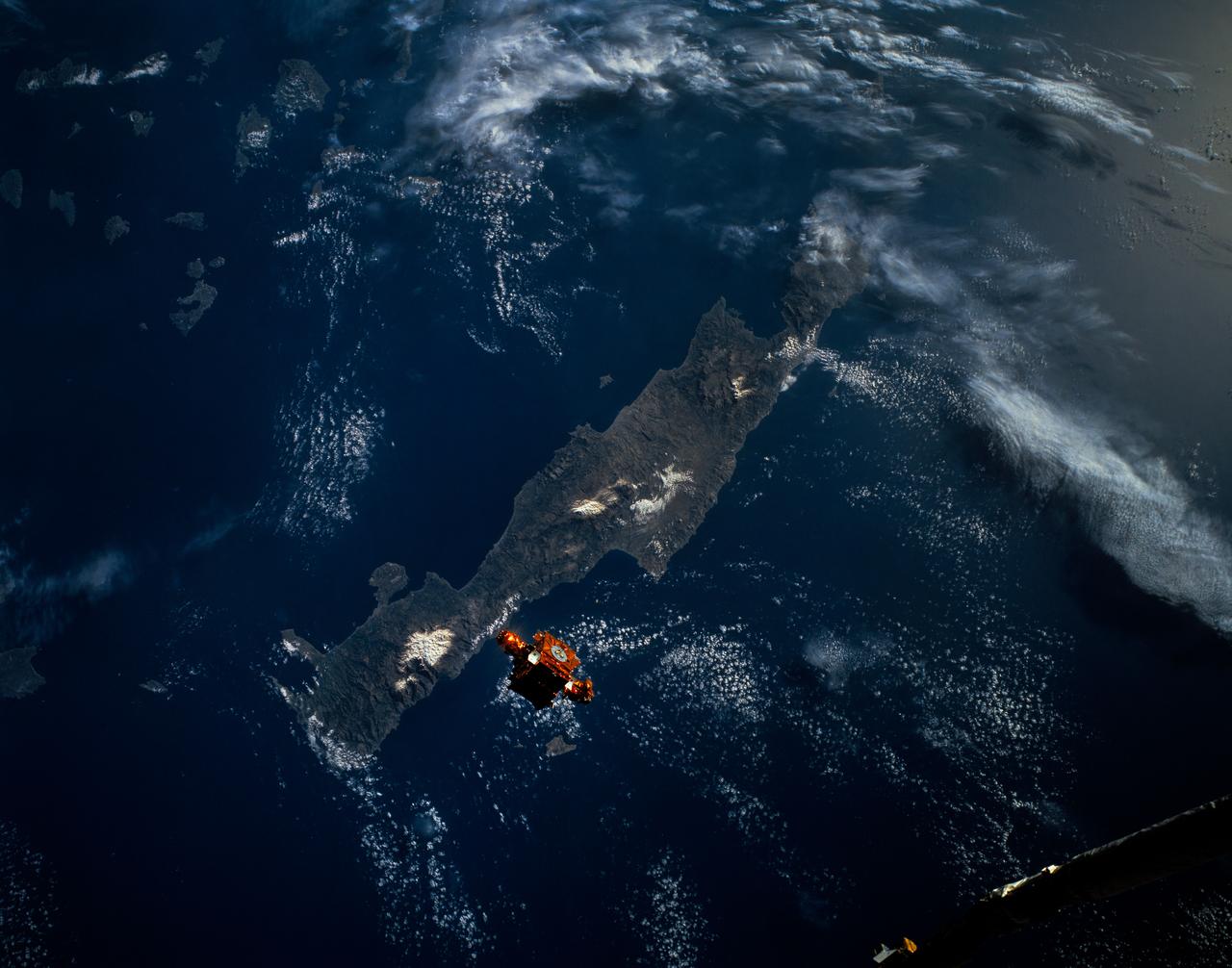

During STS-56, the Shuttle Pointed Autonomous Research Tool for Astronomy 201 (SPARTAN-201), a freeflying payload, was photographed by Discovery's, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103's, crewmembers as it drifted above the Mediterranean Sea near the island of Crete. On the mission's third day, the remote manipulator system (RMS) arm was used to lift SPARTAN-201 from its support structure in OV-103's payload bay and release it in space. SPARTAN-201 was later recaptured by OV-103's RMS and returned to Earth with the astronaut crew.
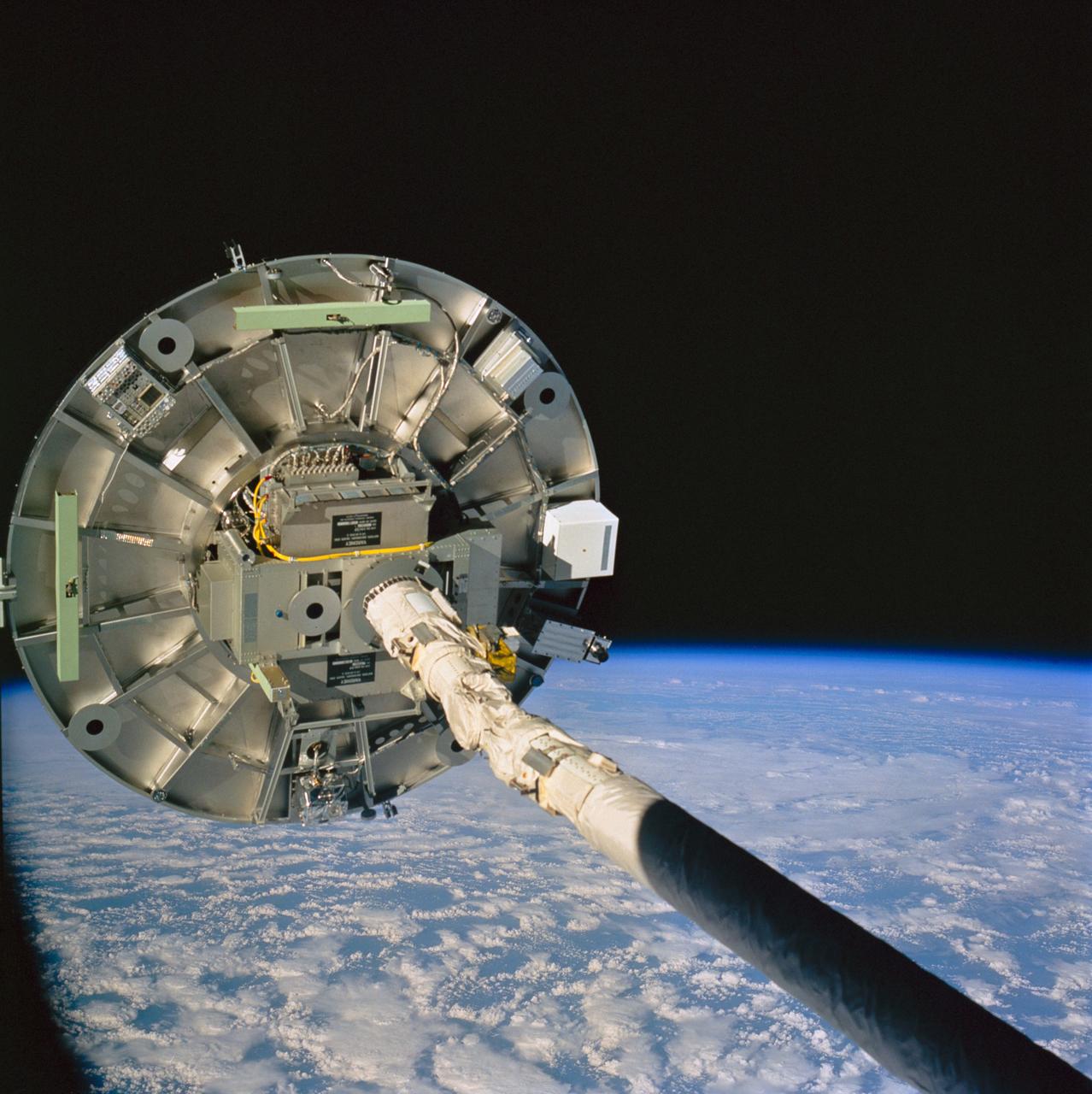

STS060-76-095 (3-11 Feb 1994) --- The ram side of the Wake Shield Facility (WSF) in the grasp of the Space Shuttle Discovery's Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm is featured in this 70mm frame. Clouds over the Atlantic Ocean and the blackness of space share the backdrop for the picture. Five NASA astronauts and a Russian cosmonaut spent eight days in Earth orbit in support of the STS-60 mission.
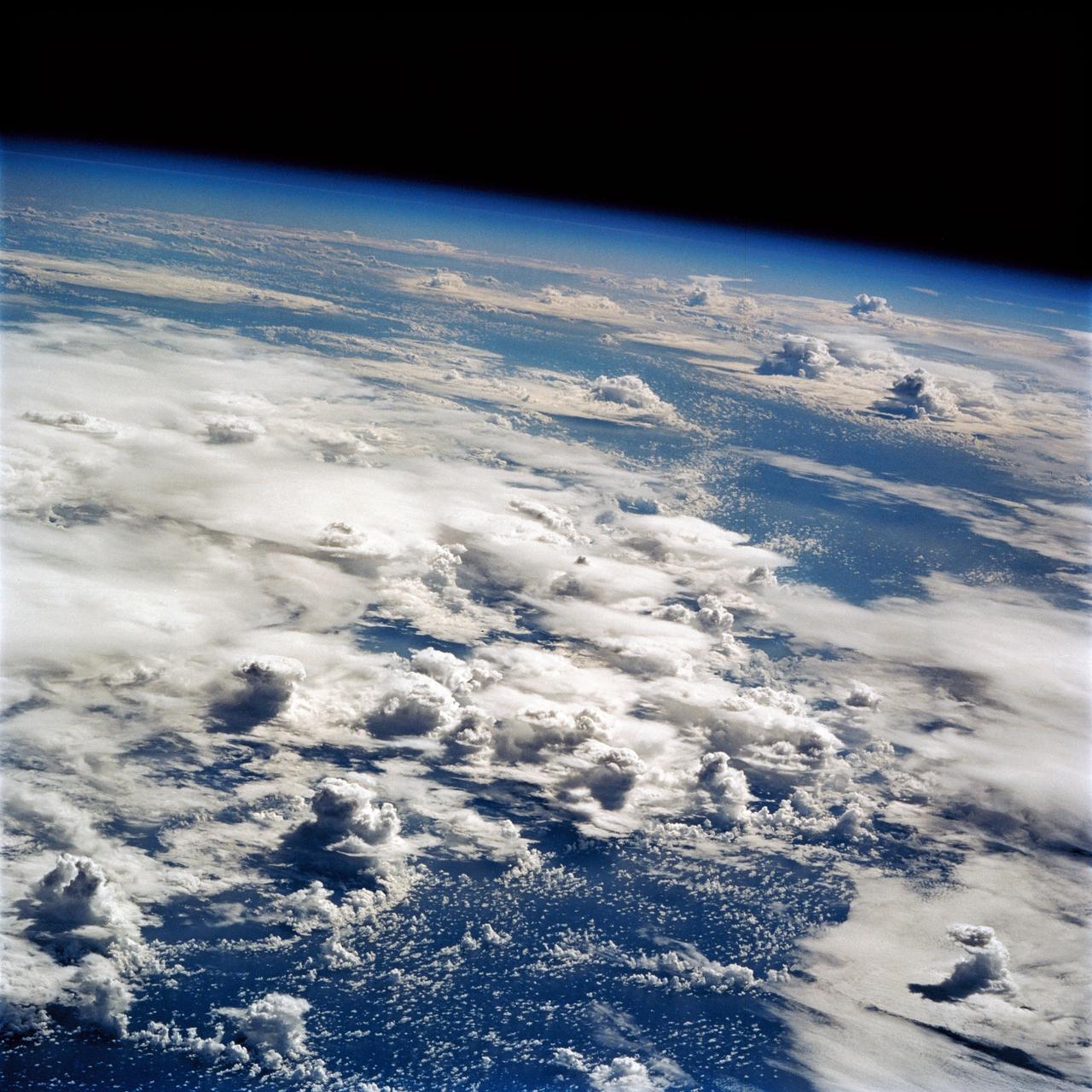

STS064-83-099 (9-20 Sept. 1994) --- Multiple thunderstorm cells leading to Earth's atmosphere were photographed on 70mm by the astronauts, orbiting aboard the space shuttle Discovery 130 nautical miles away. These thunderstorms are located about 16 degrees southeast of Hawaii in the Pacific Ocean. Every stage of a developing thunderstorm is documented in this photo; from the building cauliflower tops to the mature anvil phase. The anvil or the tops of the clouds being blown off are at about 50,000 feet. The light line in the blue atmosphere is either clouds in the distance or an atmospheric layer which is defined but different particle sizes. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
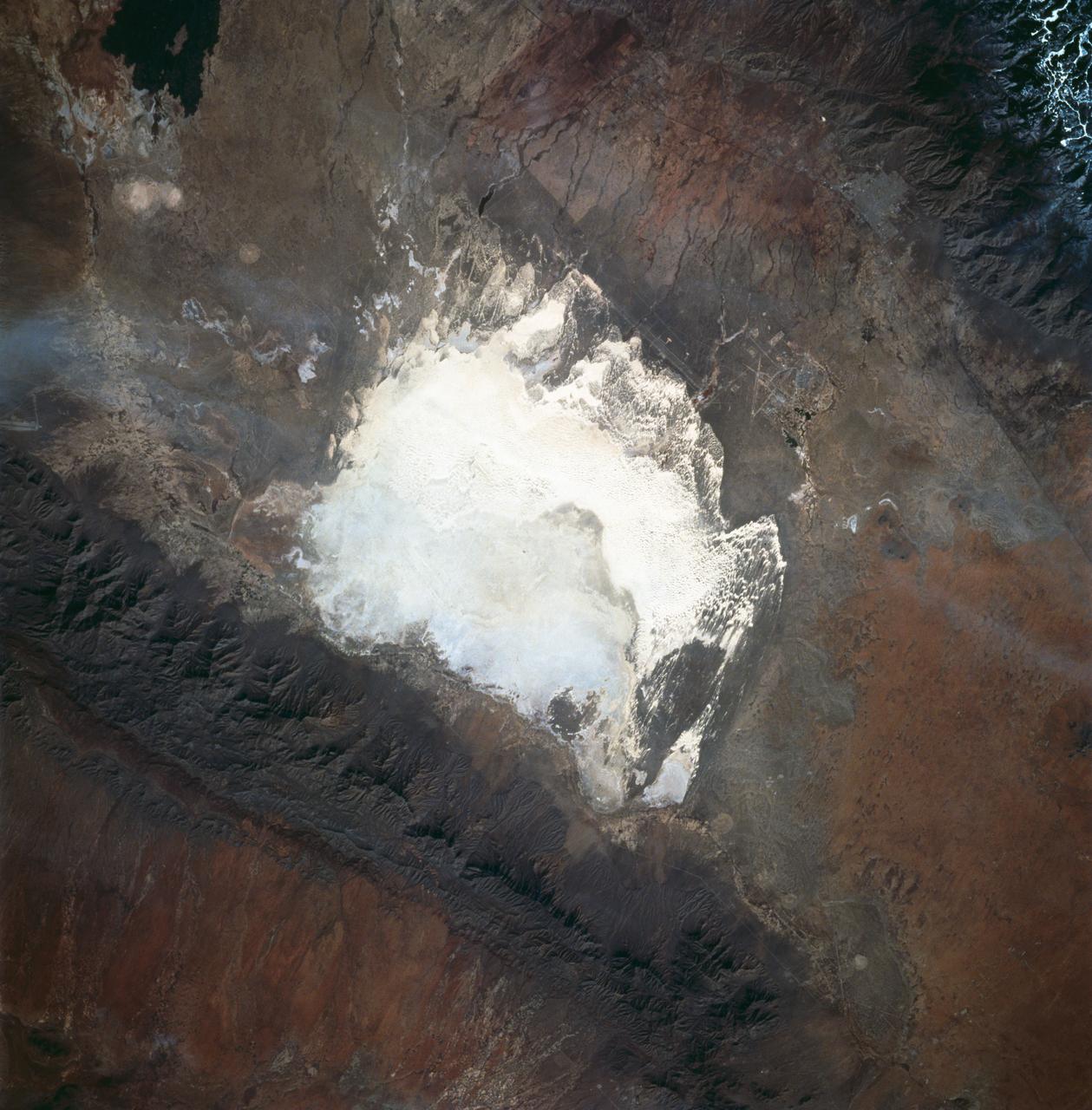

STS060-83-016 (3-11 Feb 1994) --- White Sands National Monument (Park) is easily recognized in the center of this near-vertical color photograph. White Sands is the world's largest gypsum dune field. It represents an alabaster sea that covers nearly 300 square miles. The National Park Service has the responsibility to preserve this unique feature, allowing the dune world to unfold in its natural environment, but without interference from humans. White Sands lies within a spectacular, oblong geological depression called the Tularosa Basin bounded by the Sacramento Mountains on the east and the San Andres Mountains on the west. Climatically the basin is a true desert, averaging less than 10 inches of rainfall per year. In terms of topographic relief the Sacramento Mountains attain elevations greater than 9,000 feet above sea level, while the San Andres Mountains on the west exceed altitudes of 8,000 feet. At the southwest corner of the White Sands is dry lake, Lucero. This lake is the lowest point in the Tularosa Basin at 3,900 feet. In terms of cultural features the city of Alamogordo (over 20,000 population) and Holloman Air Force Base can be seen with great clarity on this photograph. The area is accessible by highways U.S.70 & 82 from Las Cruces, New Mexico, and U.S.54 from El Paso, Texas.
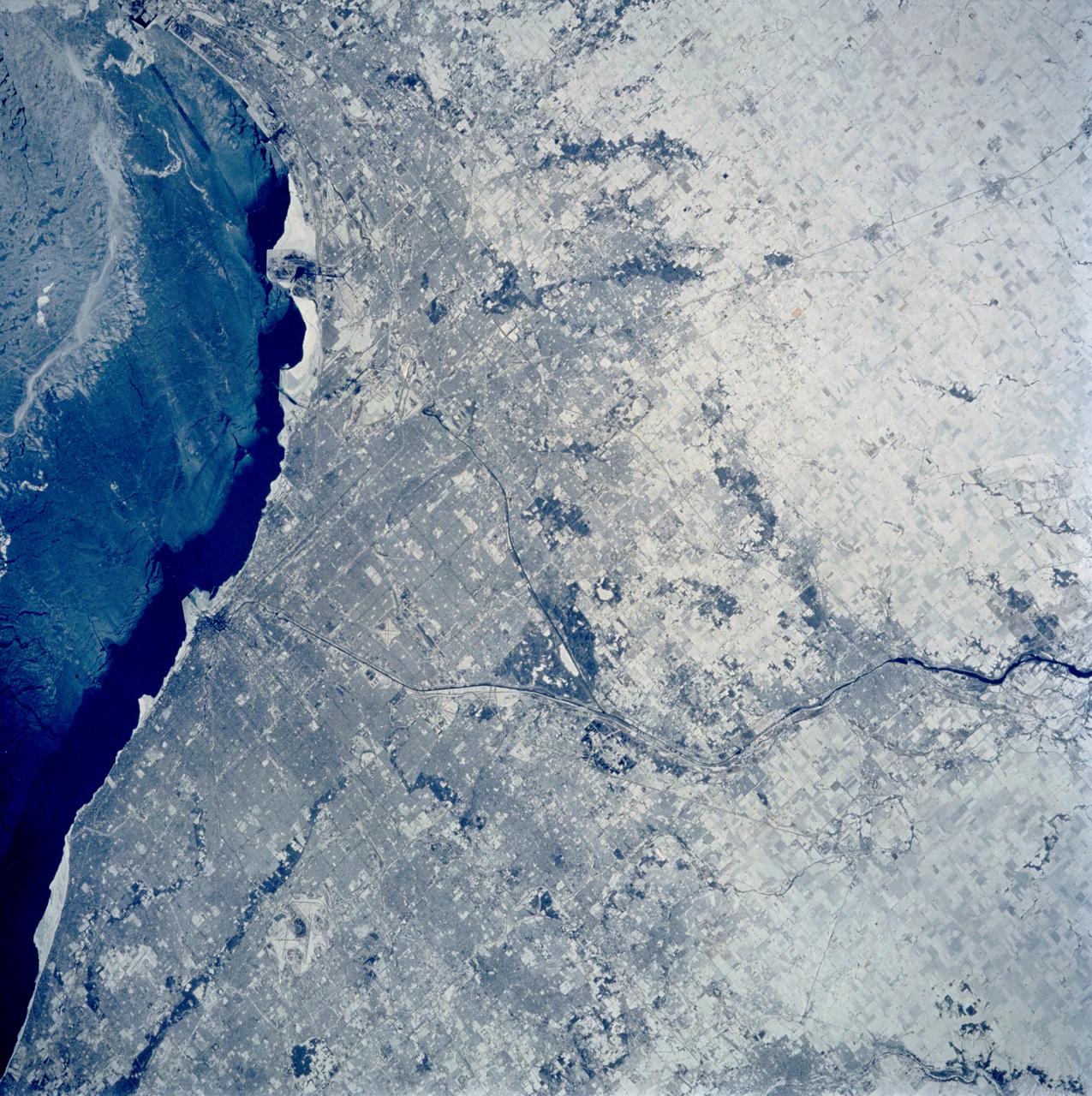

STS060-103-089 (3-11 Feb. 1994) --- The Chicago, Illinois area is in this northeast looking low oblique view obtained in February, 1994. Lake Michigan, a good portion covered with ice due to the very cold winter weather that has plagued this region since early December, 1993, can be seen to the east of the city. The Des Plaines river is visible traversing northeast to southwest through the center of the city. O'Hare International Airport and the Glenview Naval Air Station can be seen to the north of the Des Plaines River. Midway Airport is visible just to the south of the river. Chicago is a port of entry; a major Great Lakes port located at the junction of the St. Lawrence Seaway with the Mississippi River system; the busiest air center in the United States; and an important rail and highway transportation hub. Chicago is known for large grain mills and elevators, iron and steel works, steel fabrication plants, stockyards, meat-packing establishments, and printing and publishing houses. In the early days of settlement, the narrow watershed between Lake Michigan and the Des Plaines River (draining the Mississippi River through the Illinois River), offered an easy portage that led explorers like Father Marquette and Louis Joliet and others to the Great Central Plains. Fort Dearborn, a military post was established in 1803. By 1860, the railroad connected Chicago to the rest of the country and the city became a great mid-continent shipping and receiving center. In 1871, the city built of wood, was almost entirely destroyed by a great fire. After the fire, Chicago was built as a city of steel and stone. During the World's Colombian Exposition held in Chicago in 1893, the city became a leading architectural center. It was here during the Exposition that the skyscraper came into being. Chicago continues to lead the way in this type of architectural structure as is evidenced with the completion of the Sears Tower in 1974.
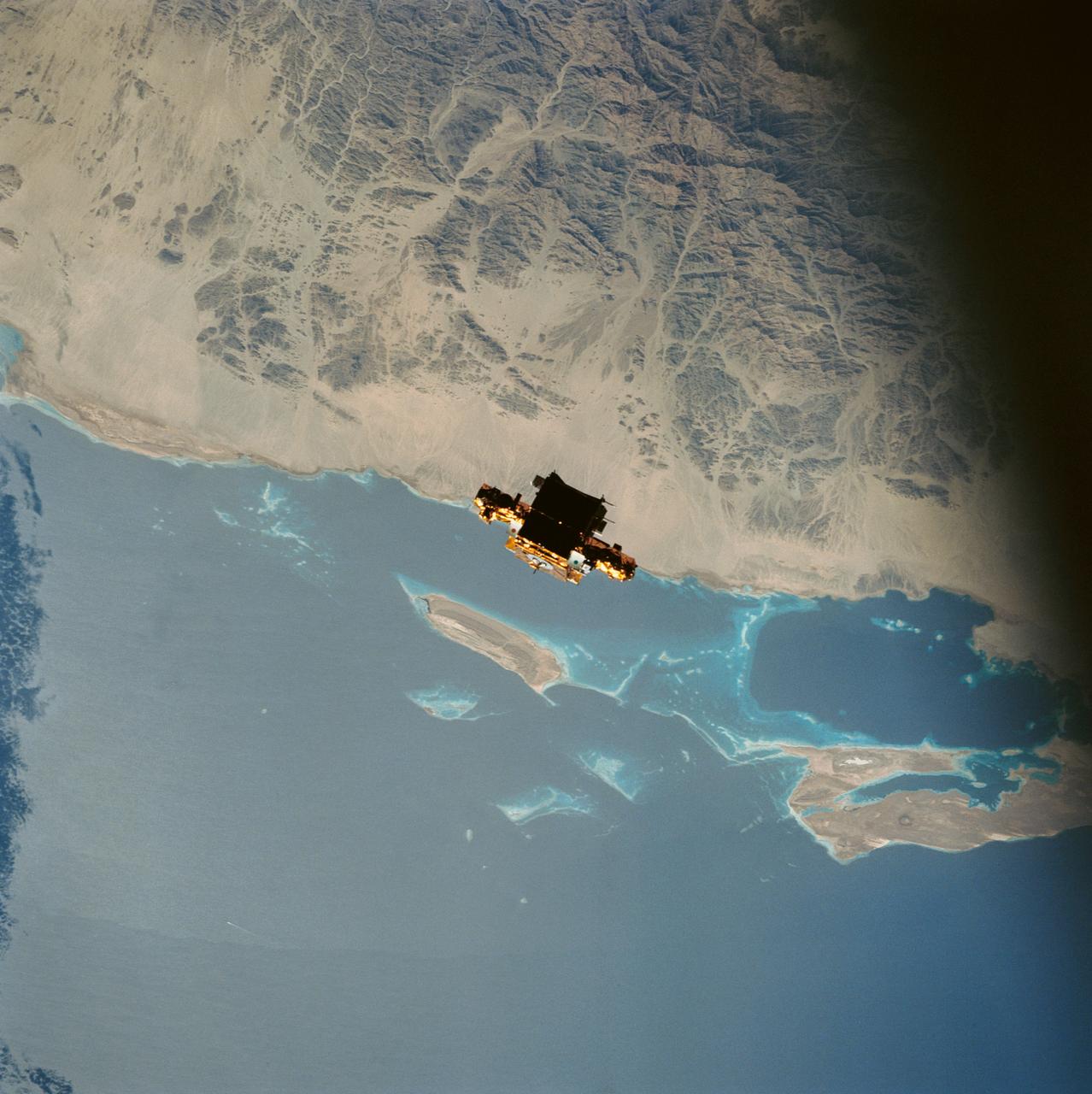

During STS-56, the Shuttle Pointed Autonomous Research Tool for Astronomy 201 (SPARTAN-201), a freeflying payload, was captured on 70mm film as it drifts over the Red Sea coast of Sudan. SPARTAN-201 was photographed by the crewmembers aboard Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103. On the mission's third day, crewmembers used the remote manipulator system (RMS) to lift the satellite from its support structure in OV-103's payload bay (PLB) and release it into space. SPARTAN-201 was later recaptured by OV-103's RMS and returned to Earth with the astronaut crew. The cape structure in the background is Ras abu Shagara, north of Port Sudan.
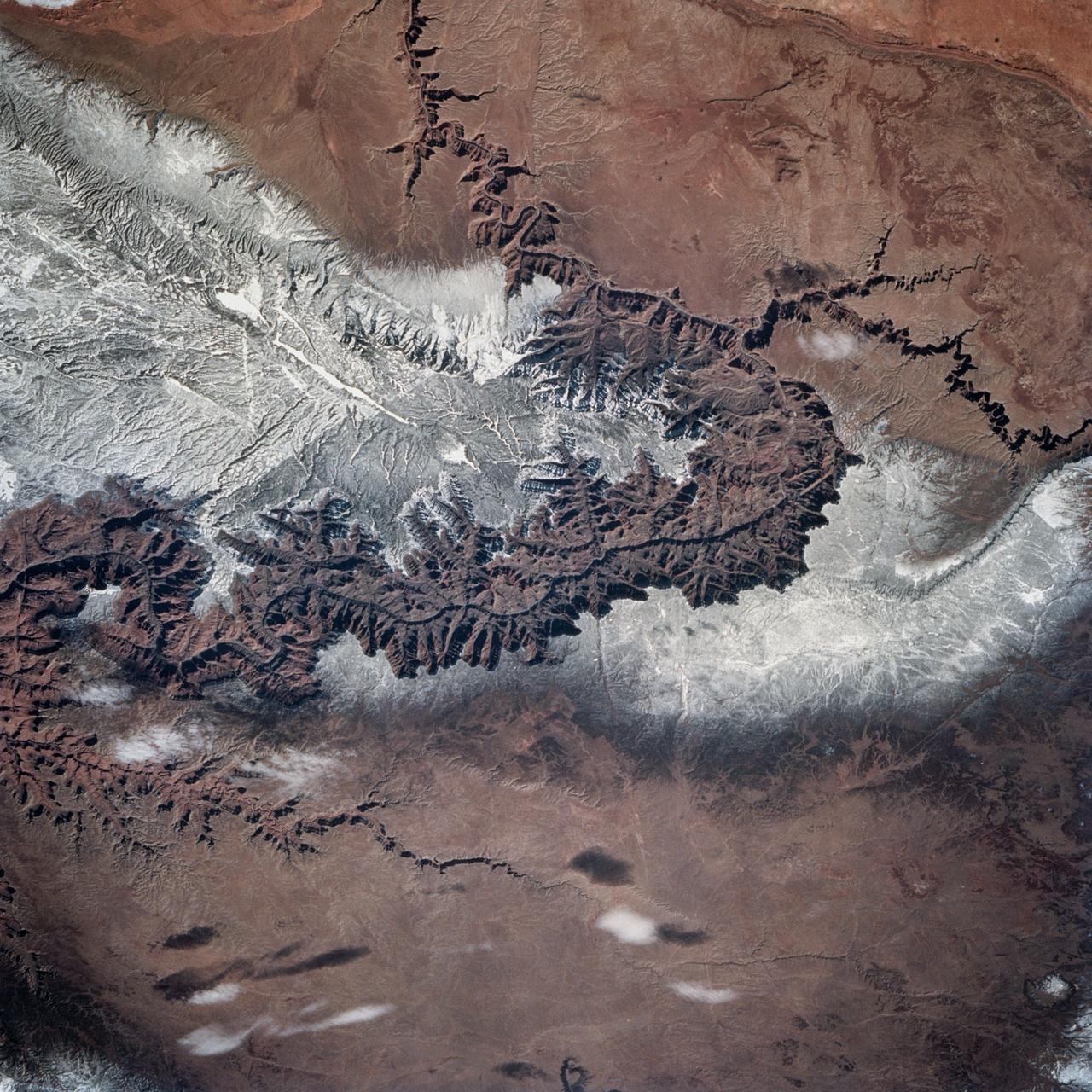

STS060-83-004 (3-11 Feb 1994) --- In this winter scene of the Grand Canyon of Arizona, the canyon is particularly well revealed because snow lies on the rims of the canyon, and exits mid-right; the Little Colorado River enters from the left, joining the Colorado just upstream of its big bend. Visitors to the South Rim can view the canyon in both the east-west and north-south reaches. The South Rim is closer to centers of transportation so that tourists mostly see the canyon from this area, that is from about 7,000 feet. The canyon floor lies at 2,000 feet in this sector. The most heavily snow covered area is the highest, reaching more than 9,000 feet (bottom right). Visitors see this protected area by hiking and mule and helicopter rides. The ecology of this part of the Colorado has been changed since the building of a lake upstream: river water is now derived from snow melt water from the bottom of the lake. This water is much colder than the water which used to flow through the canyon. According to NASA scientists, the view is unusual because the snow also reveals so well the higher country around the canyon, a swath stretching from bottom right to middle left of the view. This higher swath is an arch of uplifted rocks known as the Kaibab Plateau, raised vertically by tectonic forces in the recent geologic past. Despite this up parching, the Colorado River managed to maintain its course to the sea by cutting an ever deeper canyon into the Plateau. The white snow cover hides the fact that the Kaibab Plateau is thickly forested and thus appears dark green in summer, except in areas of clear-cutting. Since the Plateau reaches altitudes of 6 to 9,000 feet, it is both cooler and moister than the surrounding lower desert floor (top and bottom in this view) - where sparse vegetation and rocky country appear as brown colors. The zone of dark color running parallel to the snow line is all that can be seen of the pine forest on the south flanks of the Plateau.

STS060-88-070 (3-11 Feb 1994) --- This view shows sunglint in the Strait of Gibralter. In this photograph a high pressure atmospheric system over the Iberian Peninsula has set the conditions for seeing a plankton bloom along the Moroccan coast in the Alboran Sea (Western Mediterranean) coastal counter current as well as illumining the influence of winds in the sunglint pattern near the Strait of Gibraltar. Where the water is ruffled from a wind gust, such as off Cadiz, Spain, the surface is less reflective and thus appears dark. A combination of the effects of the tide and the surface winds through the Strait of Gibraltar have created a unique sunglint pattern at the entrance of the Mediterranean. The Atlantic Ocean waters are flowing with the tide through the Strait of Gibraltar into the Mediterranean Sea and are probably smoothing out some of the smaller waves at the surface. The incoming tide generates internal waves as can be faintly seen in this photograph. The incoming relatively cooler, less dense Atlantic water flows over the warm, more saline Mediterranean water. As the tide moves into the Strait of Gibraltar it encounters the Camarinal Sill, which is like a cliff under the water, south of Camarinal Point, Spain. Internal waves are generated at this sill and they travel along the density boundary between the Atlantic water and the Mediterranean water masses. There is little evidence of the internal waves at the surface of the ocean. We can see them in spacecraft photography because of the sunglint which reflects off the different water layers in differential patterns. The internal waves also smooth out some of the bands of capillary waves at the surface. That is, the sun reflects more brightly from these smooth areas, showing the pattern of the underwater waves more prominently than do the surface waves. The Bay of Cadiz on the southwest coast of Spain, the Rock of Gibraltar, and the Moroccan coast are also beautifully illustrated in this photography. The focus for scientists, however, remains the high clarity and spatial resolution given by sunglint studies to physical phenomena in the ocean.
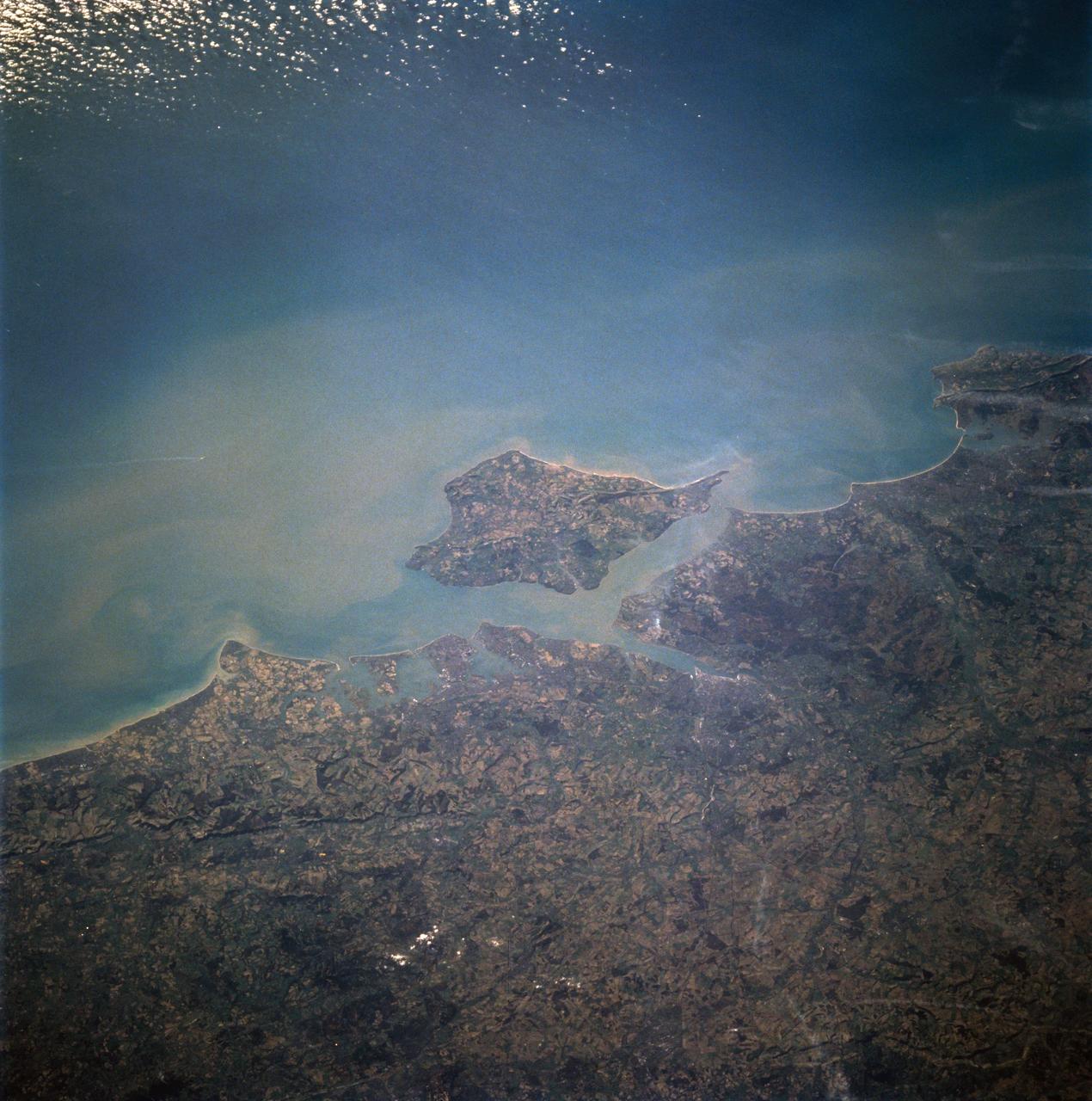

STS060-94-007 (3-11 Feb 1994) --- The Isle of Wight, over 380 square kilometers, is a diamond-shaped island located off the south coast of England. Separated from the mainland by The Solent, a narrow channel of water, the island is a popular resort area due to its scenery and mild climate. Sediment from English Lowland drainage systems, most notably the River Test, is visible entering The Solent and spilling into the English Channel. At the tip of the linear, northwestward inlet is the mouth of the Test and the city of Southampton, discernible as a small patch of lighter gray. Further east is a series of protected bays which are, from west to east: Portsmouth Harbour, Langstone Harbour, and Chichester Harbour. The city of Portsmouth is the location of Great Britain's chief naval station and arsenal. Portsmouth houses numerous ships of past and present glory. Two of the most notable vessels in Portsmouth are the 104-gun Victory, and the remains of the Mary Rose. The renowned HMS Victory, still carried on active duty rolls of the Royal Navy, and the acting Post Ship of the Royal Navy Base Commander, was built in 1765. The HMS Victory was severely damaged and dismasted in battle. A careful inspection of the original film will show the 175-foot long HMS Victory in this frame. According to NASA geologists it is extremely unusual for Portsmouth to be this cloud-free. It has been a site of some interest for many Space Shuttle missions during the past 10 years.
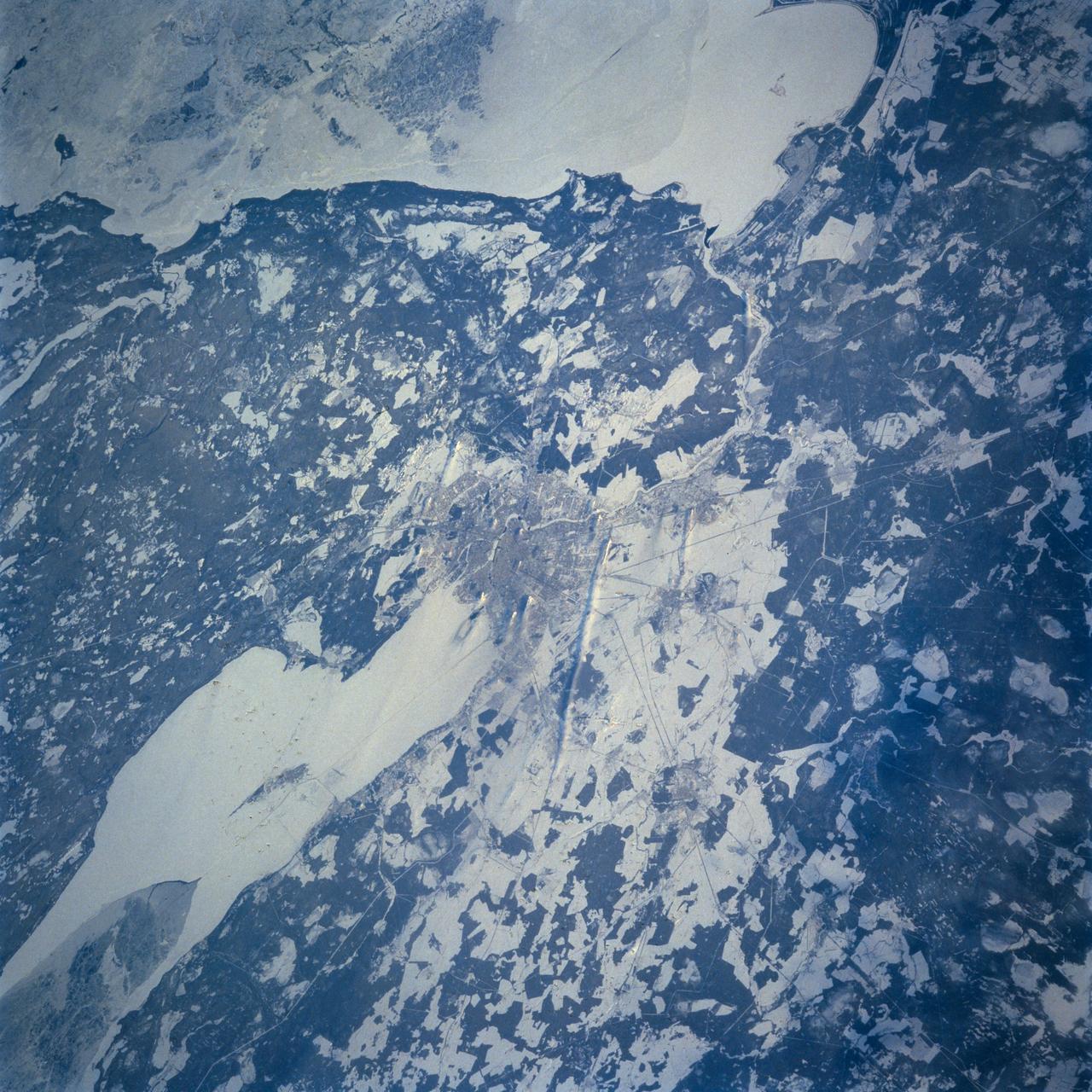

STS060-103-055 (3-11 Feb 1994) --- This wintertime photograph shows the large city of St. Petersburg Russia at the head of the Gulf of Finland. The city, built by Peter the Great, is situated in the former swampy delta of the Neva River which connects the large Lake Ladoga (the frozen white surface on the edge of the photograph) to the Gulf of Finland. An interesting feature of St. Petersburg which can be discerned in this photograph is the new storm surge barrier built from both sides of the Gulf of Finland out to the island of Kronstadt in the middle. This barrier, similar to that which was built on the Thames River south of London to protect it from storm surges out of the North Sea, was constructed to protect St. Petersburg from storm surges coming out of the Baltic Sea and being magnified by the topography and hydrography of the Gulf of Finland. Also visible as a thin line between Kronstadt and St. Petersburg is the ice-free shipping channel kept open much of the winter. Power plant plumes are also visible on the frame. St. Petersburg is the home of the Russian cosmonaut, Sergei Krikalev, who flew aboard the Space Shuttle Discovery during STS-60.
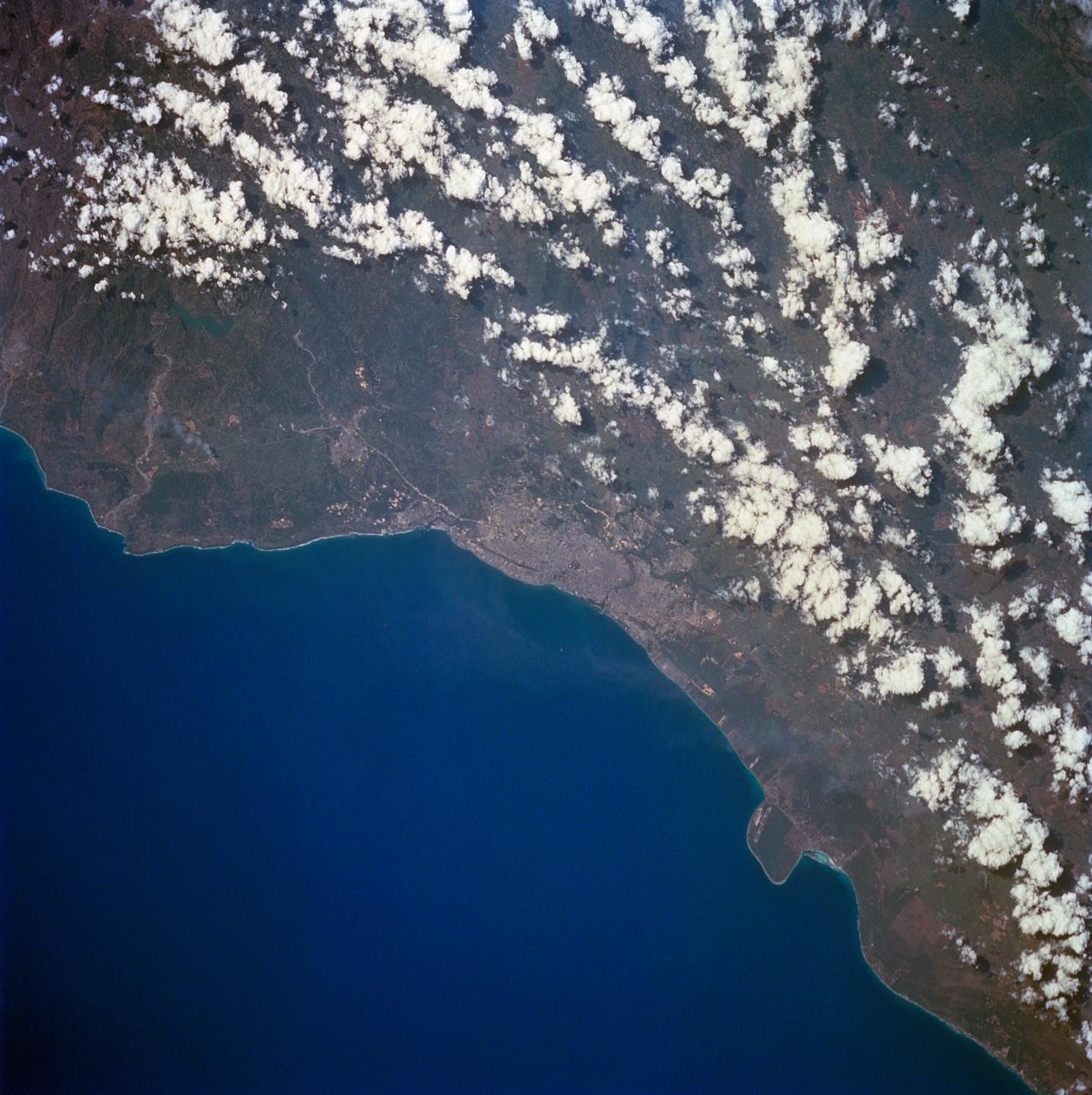

STS060-84-063 (3-11 Feb 1994) --- This is an excellent photograph of the coastal city of Santo Domingo on the Caribbean Sea. The airports including De las Americas International Airport are clearly seen. This photo illustrates the resolving power of the films. For example, two isolated smoke plumes are clearly seen each side of the city.
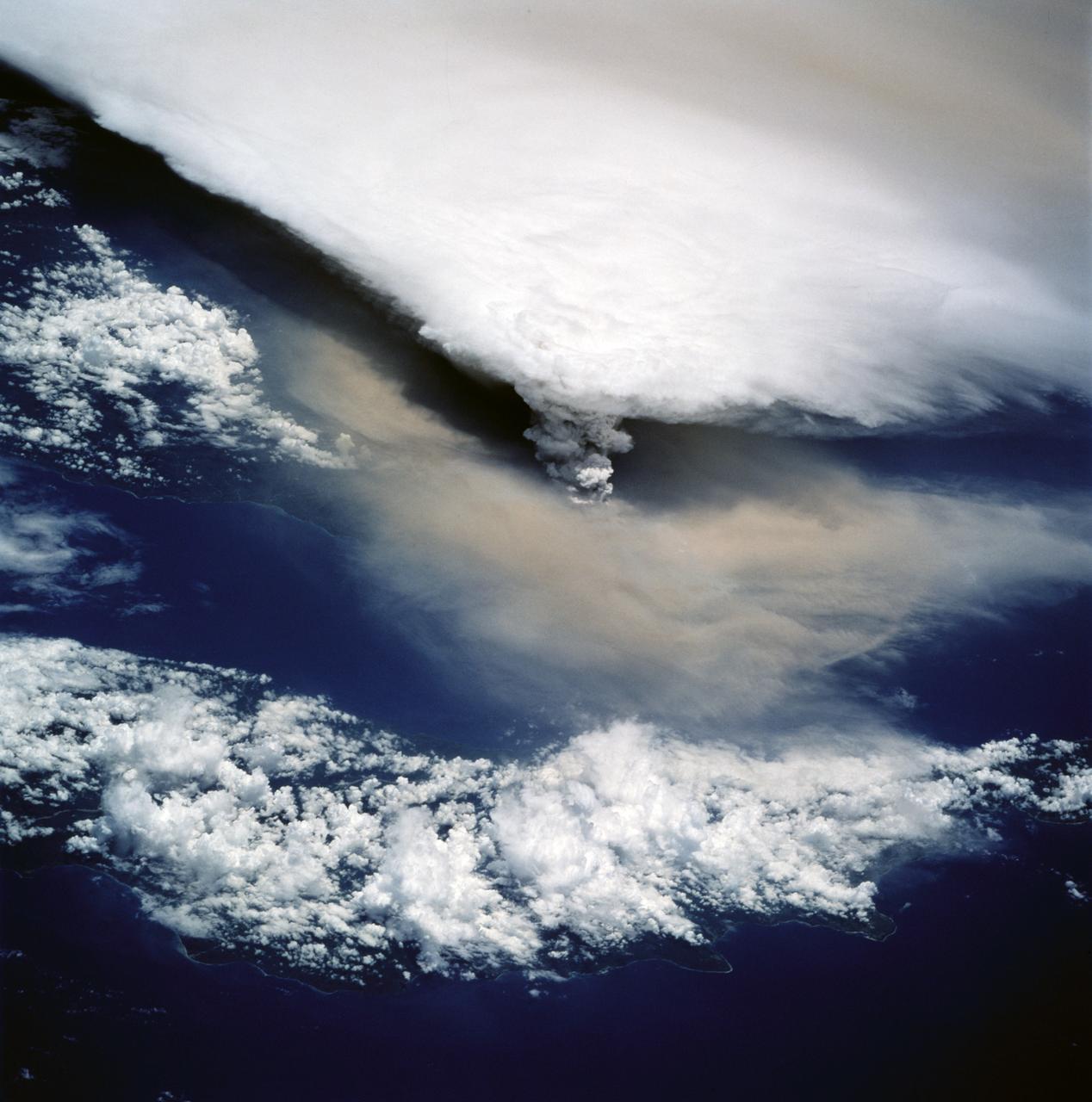

STS064-116-055 (20 Sept. 1994) --- Near the end of its mission, the crew aboard space shuttle Discovery was able to document the beginning of the second day of activity of the Rabaul volcano, on the east end of New Britain. On the morning of Sept. 19, 1994, two volcanic cones on the opposite sides of the 6-kilometer sea crater had begun to erupt with very little warning. Discovery flew just east of the eruption roughly 24 hours after it started and near the peak of its activity. The eruption, which sent a plume up to over 60,000 feet into the atmosphere, caused over 50,000 people to evacuate the area. Because winds were light at the time of the eruption, most of the ash was deposited in a region within 20 kilometers of the eruption zone. This photo shows the large white billowing eruption plume is carried in a westerly direction by the weak prevailing winds. At the base of the eruption column is a layer of yellow-brown ash being distributed by lower level winds. A sharp boundary moving outward from the center of the eruption in the lower cloud is a pulse of laterally-moving ash which results from a volcanic explosion. Geologists theorize that the large white column and the lower gray cloud are likely from the two main vents on each side of the harbor. The cloud-covered island in the foreground is New Ireland. The bay and harbor of Rabaul are covered with a layer of ash, possibly partly infilled with volcanic material. Matupit Island and the airport runway have disappeared into the bay. More than a meter of ash has fallen upon the city of Rabaul. Up to five vents were reported to have erupted at once, including the cones Vulcan and Tavurvur, which are opposites of the harbor as well as new vents below the bay. Half of the Vulcan cone has collapsed into the sea. The extra day in space due to bad weather at the landing site afforded the crew the opportunity for both still and video coverage of the event. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
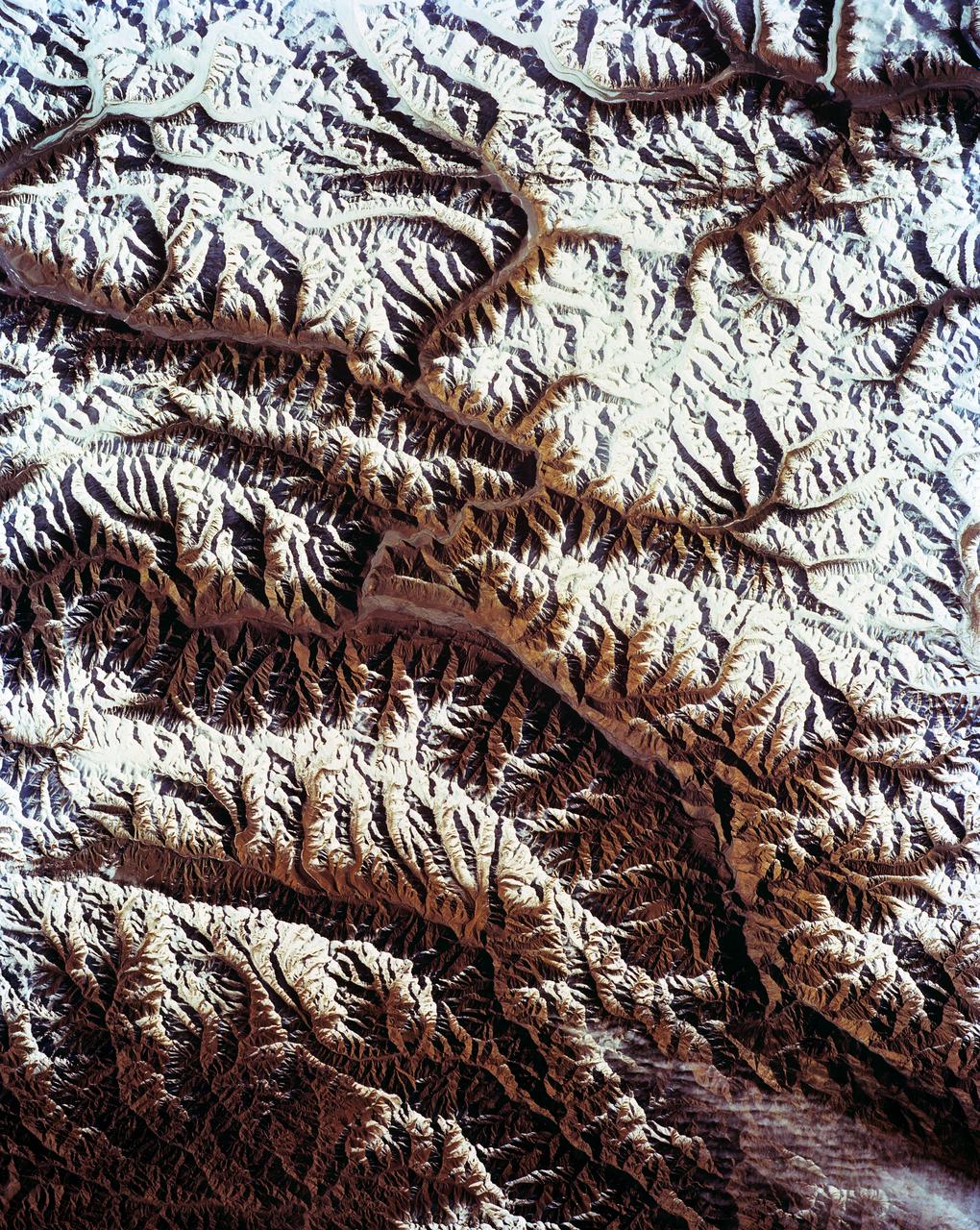

STS-56 Earth observation shows of some of the highest mountain peaks in the world taken from Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, as it passed over India and China. The top of the view shows one of the snow and ice-covered massifs in the great Karakorum Range of north India. A star-shaped peak at top left reaches 23,850 feet. Glaciers can be seen in valleys at these high elevations. The international border between India to the south (top) and China (bottom) snakes left to right along a river near the top of the scene, then veers into the muntains at top left. Larger valleys, despite their elevation (all in excess of 14,000 feet), are occupied by transport routes joining points in India, China and the southern republics of the CIS. The ancient Silk Route between China and the Middle East lies not far to the north (outside the bottom of the frame).
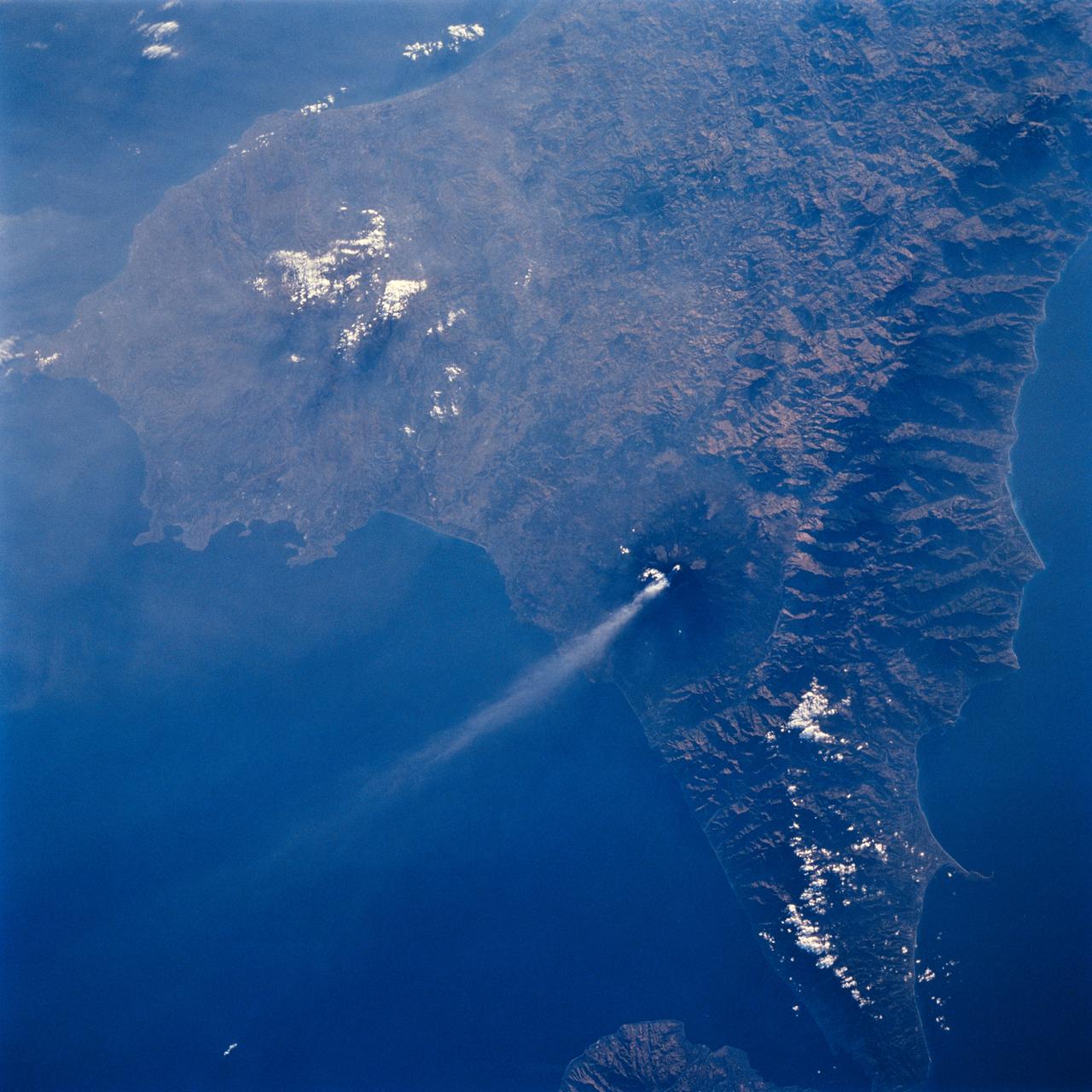

STS064-71-037 (9-20 Sept. 1994) --- Mt. Etna on Sicily displays a steam plume from its summit. Geologists attribute the volcano's existence to the collision of tectonic plates. Unlike the sudden, explosive eruption at Rabaul, Mt. Etna's activity is ongoing and is generally not explosive - Etna's slopes have been settled with villages and cultivated land for centuries. Other Mediterranean volcanoes (like Santorini) have experienced large catastrophic eruptions. Etna recently finished a two-year eruption (ending in 1993), marked by relatively gentle lava flows down the eastern flank. It has been continually degassing since then, according to the geologists, producing an omnipresent steam plume, as seen here. The 1993 flow is difficult to identify in this image because it lies within shadows on the eastern flank, but small cinder cones on the western flank mark earlier episodes of volcanic activity. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
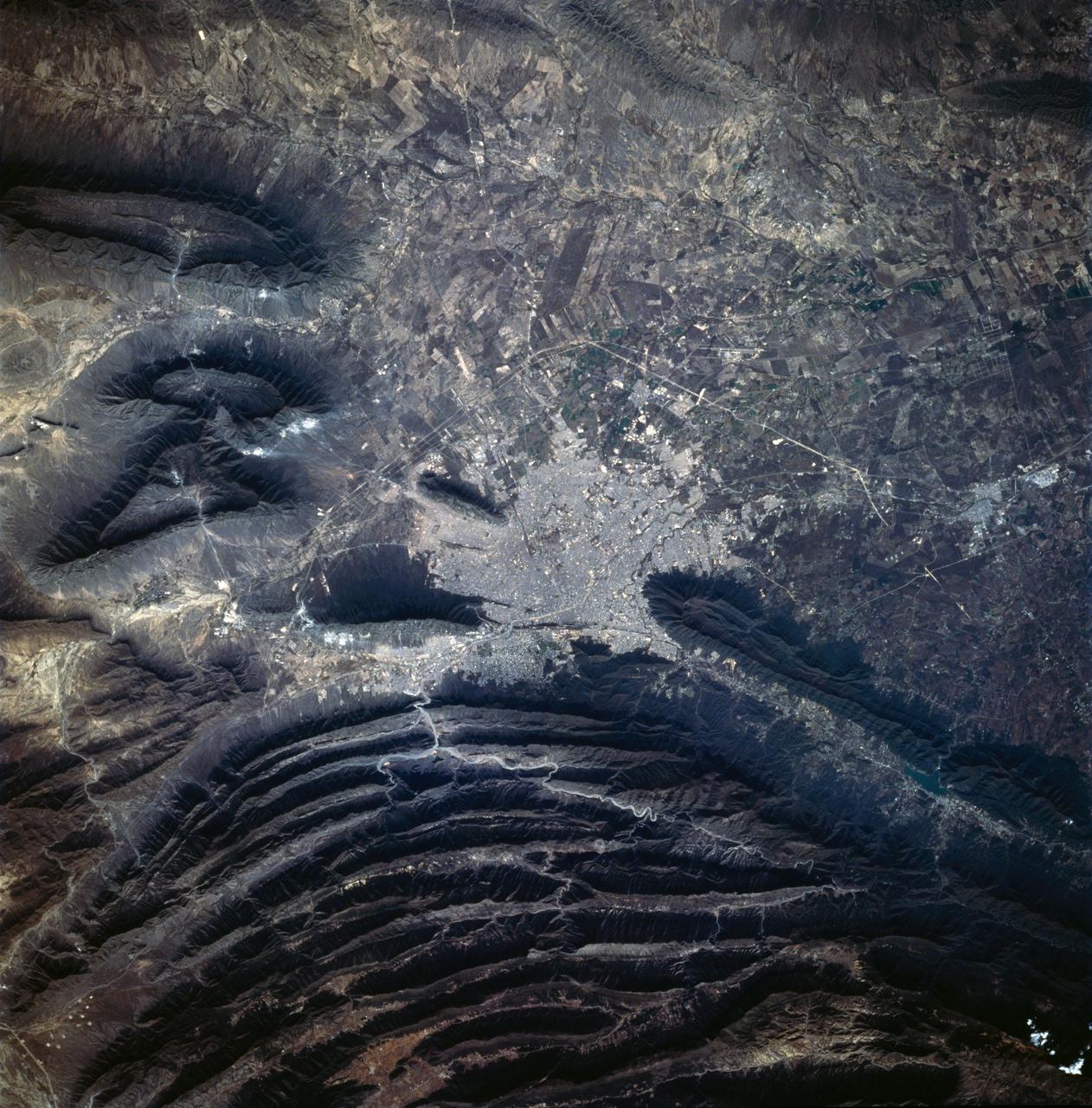

STS060-83-041 (3-11 Feb 1994) --- The large city of Monterrey, in northeastern Mexico, was founded at the edge between the Sierra Madre Oriental and the Rio Grande Embayment portion of the Gulf Coastal Plain. This location is analogous to the Fall Line along the United States eastern seaboard, but instead of lying along a stream at the head of navigation, Monterrey lies at the boundary between a well-watered mountain range and a semi-arid plain where irrigation is often necessary for successful agriculture. The mountains themselves are formed from folded limestone and shale beds; to the south of the city, beds are crumpled into tight folds. Around and north of the city, more open folds gradually give way to nearly flat-lying beds of the coastal plain. Because of the water and other resources such as shale and limestone to quarry and burn for cement, Monterrey early became a thriving industrial center. It is now one of Mexico's largest cities with a population of approximately 5 million. According to NASA geologists, the STS-60 photography of this area is the best that has been acquired during the past 32 years of space photography by the United States. Monterrey remains an area of high interest for future photography in order to assess the impact of urbanization in this area.
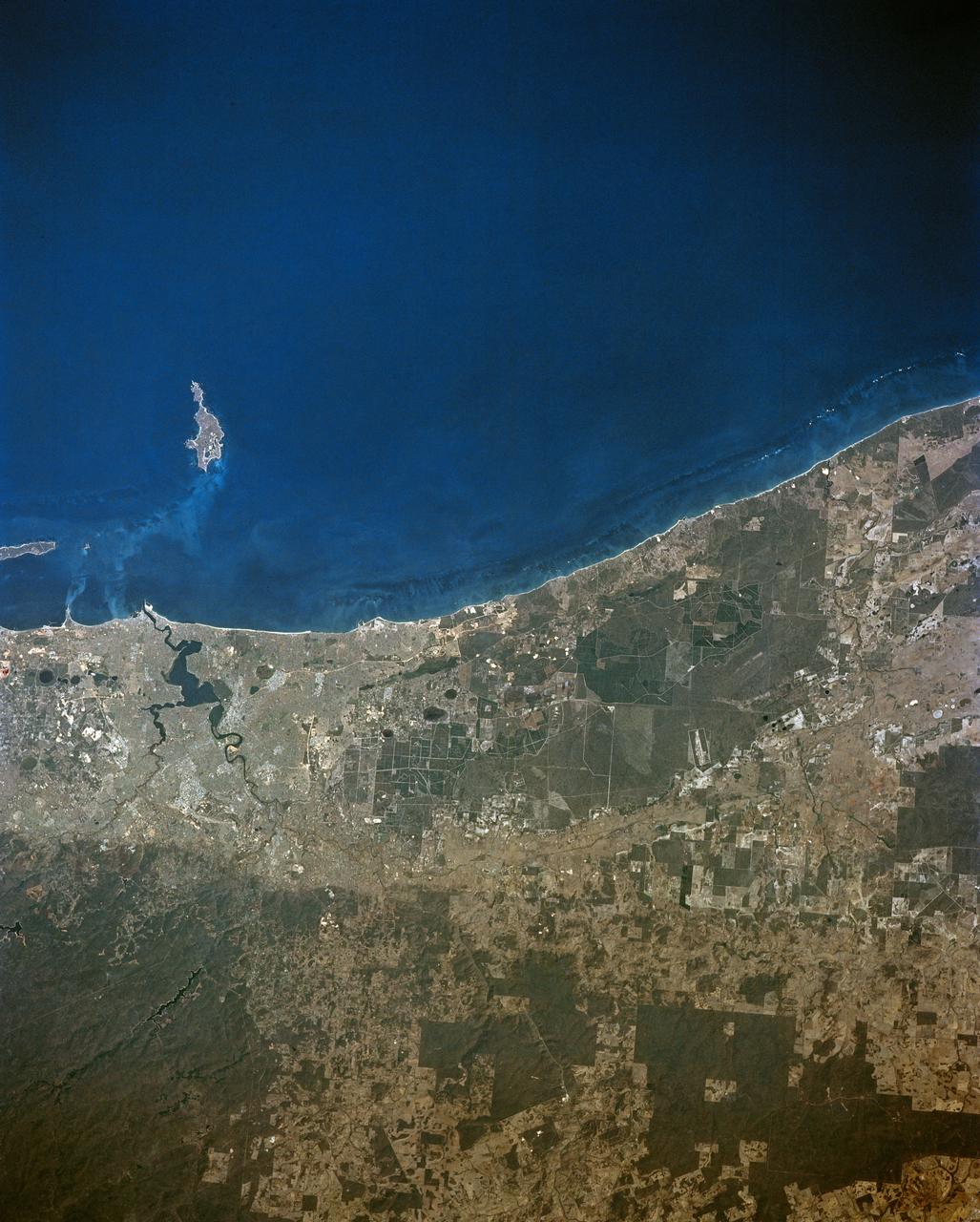

STS-56 Earth observation taken aboard Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, is probably the best view of Perth in Western Australia. (For orientation purposes, note that the coastline runs north and south). The major feature on the coast is the large estuary of the Swan River. The large port city of Perth is situated on the north bank and the smaller city of Freemantle on the south bank by the sea. Smaller seaside towns trail off north and south of this center of urban life. Inland lies a prominent escarpment, more than 600 feet high, seen running down the middle of the view and dividing the lighter-colored coastal lowlands from the highlands where dark-colored tree savanna and desert scrub dominates the land. The Moore River can be seen entering the sea at the top of the frame. Rottnest Island is visible in the sea and Garden Island near bottom edge of the frame. Perth is the largest economic center in Western Australia. It receives natural gas from an offshore field hundreds of miles to the north. It lies 3,400 kilometers west of Sydney on the opposite side of this island continent.
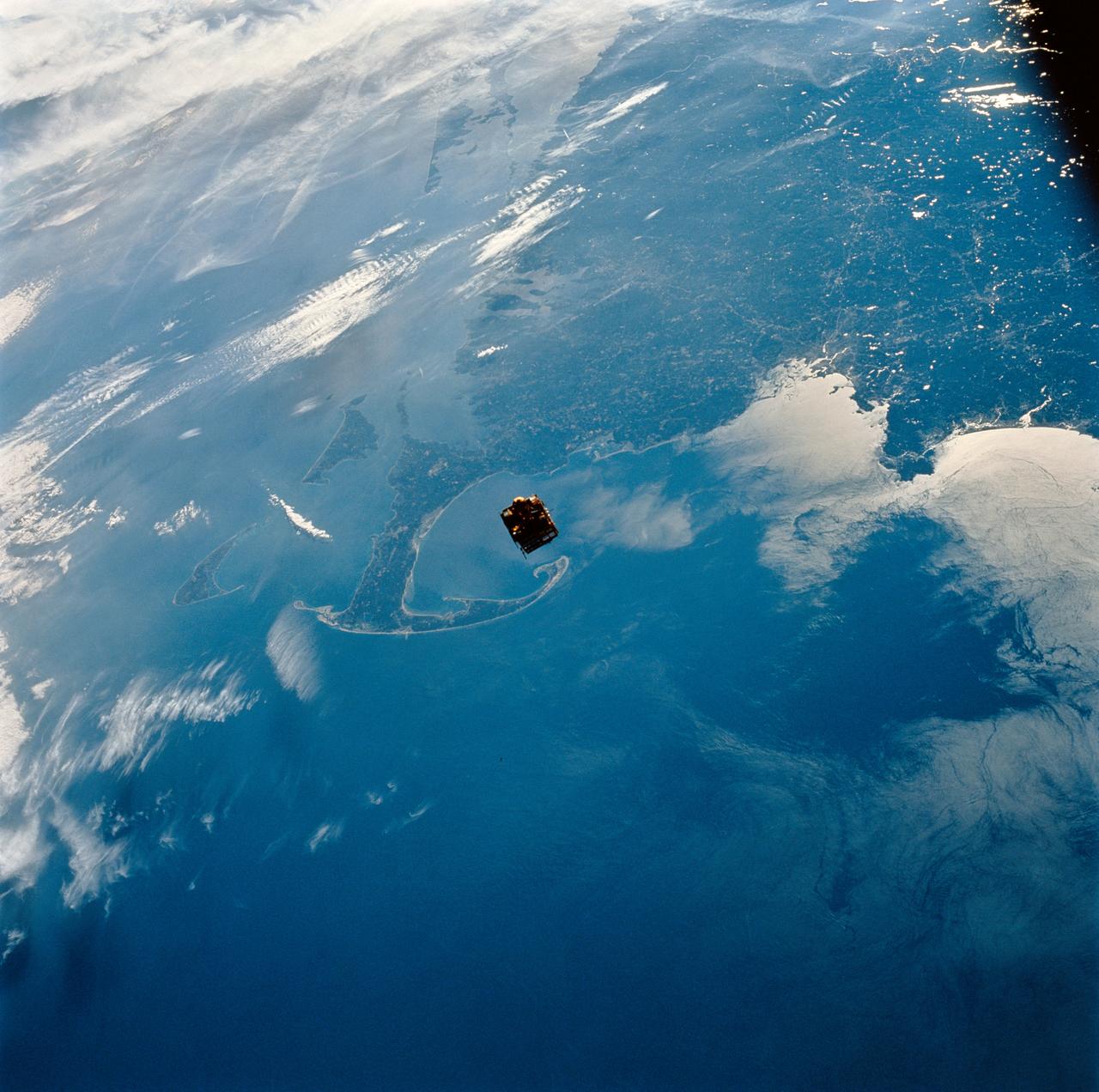

STS064-111-041 (12 Sept. 1994) ---- Backdropped against New England's coast, the Shuttle Pointed Autonomous Research Tool for Astronomy (SPARTAN-201) satellite begins its separation from the space shuttle Discovery. The free-flying spacecraft, 130 nautical miles above Cape Cod at frame center, remained some 40 miles away from Discovery until the crew retrieved it two days later. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
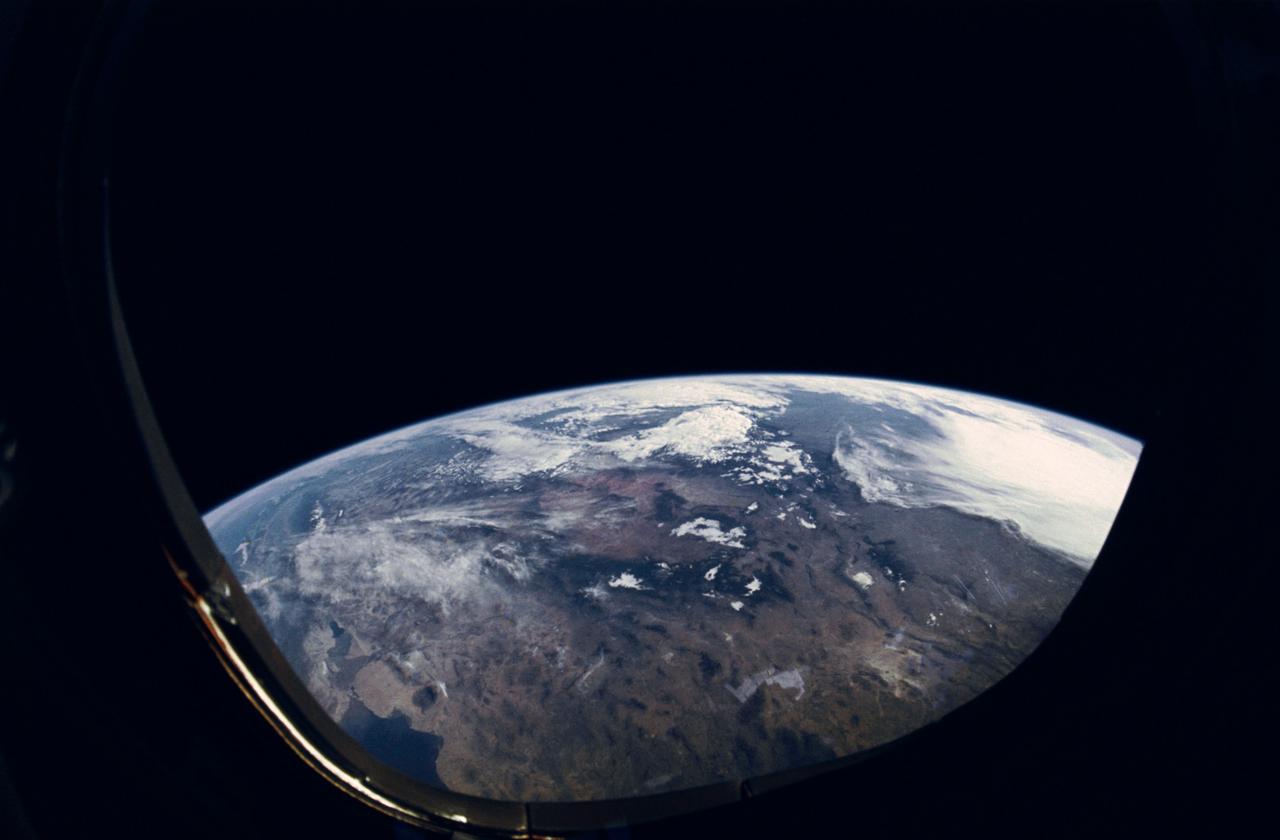

STS-31 Earth observation taken aboard Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, is of the western United States with the Salton Sea and Imperial Valley area recognizable at the lower left. The view is framed in a flight deck window and was photographed using a fish-eye lens.
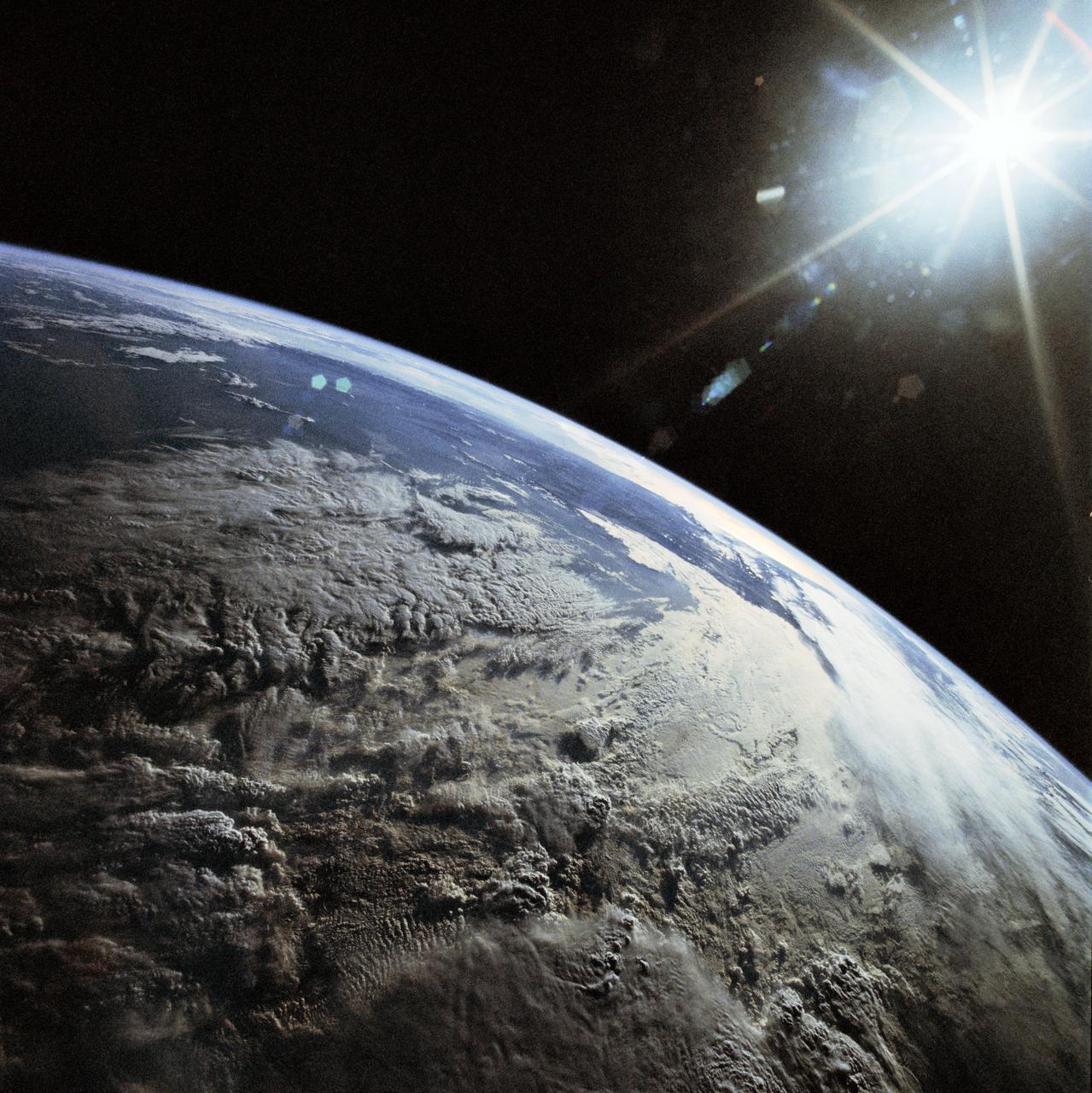

STS031-83-090 (24-29 April 1990) --- This late afternoon scene over the Andes Mountains features sun glare, heavy cloud illumination and sunglint against the Pacific Ocean. This photo was among those selected by the crew members for showing at their May 9, 1990, Post-Flight Press Conference (PFPC) at the Johnson Space Center (JSC) Public Affairs Office (PAO) Facility briefing room. Onboard the Space Shuttle Discovery for the flight, which lifted off on April 24, 1990, and landed on April 29, 1990, were astronauts Loren J. Shriver, Charles F. Bolden, Jr., Bruce McCandless II, Kathryn D. Sullivan and Steven A. Hawley. Some of the slides were not actually shown due to a shortage of time.
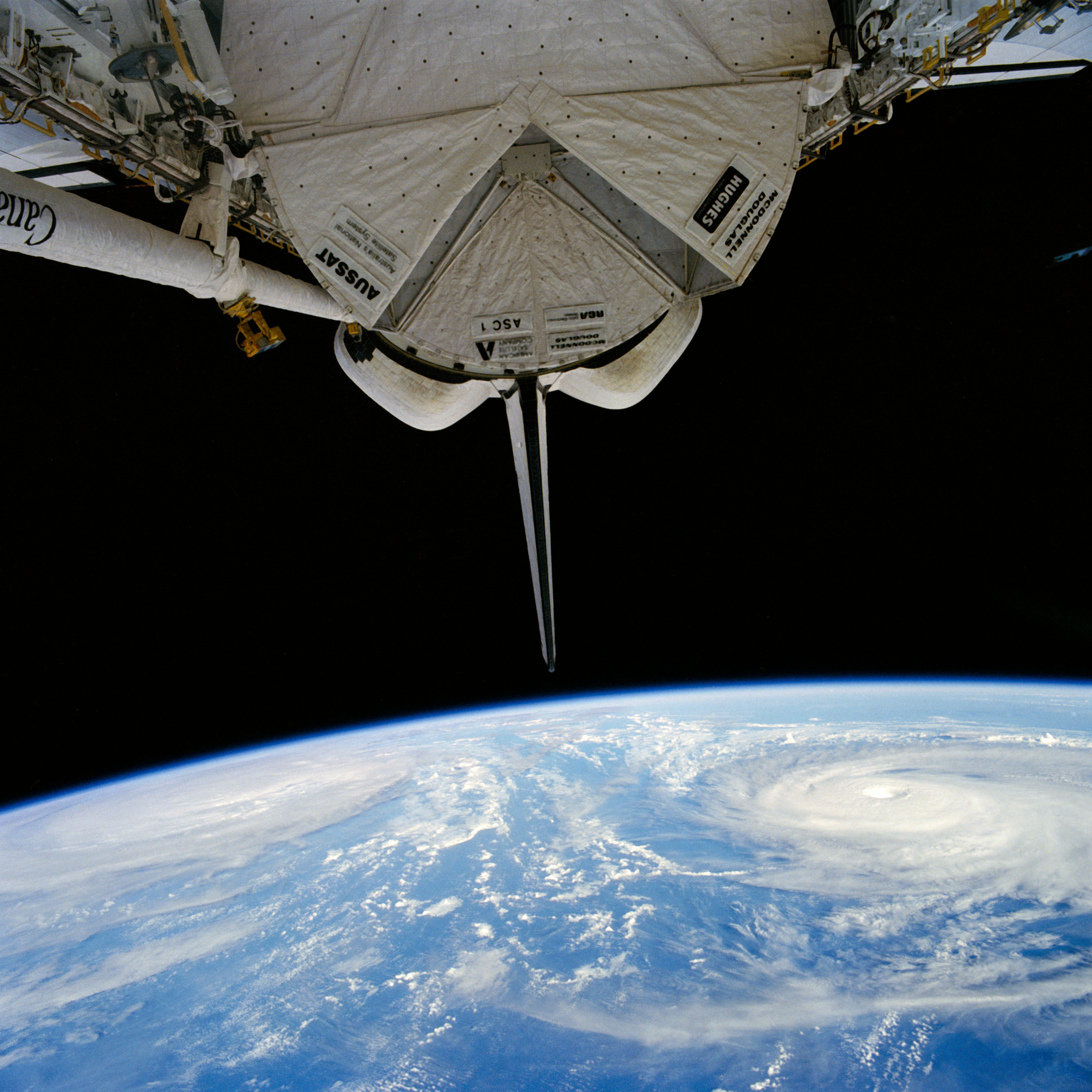

51I-35-078 (30 Aug 1985) --- Typhoons Pat (left) and Odessa in the western Pacific. Of the many tropical cyclones photographed by the STS 51-I crew, the dual typhoons of Pat and Odessa were the most unusual. The twin typhoons constitute a Fujiwara system of connected cyclones first described by the Japanese meteorologist after whom the phenomena has been named. Never before have such paired typhoons been photographed from orbit.
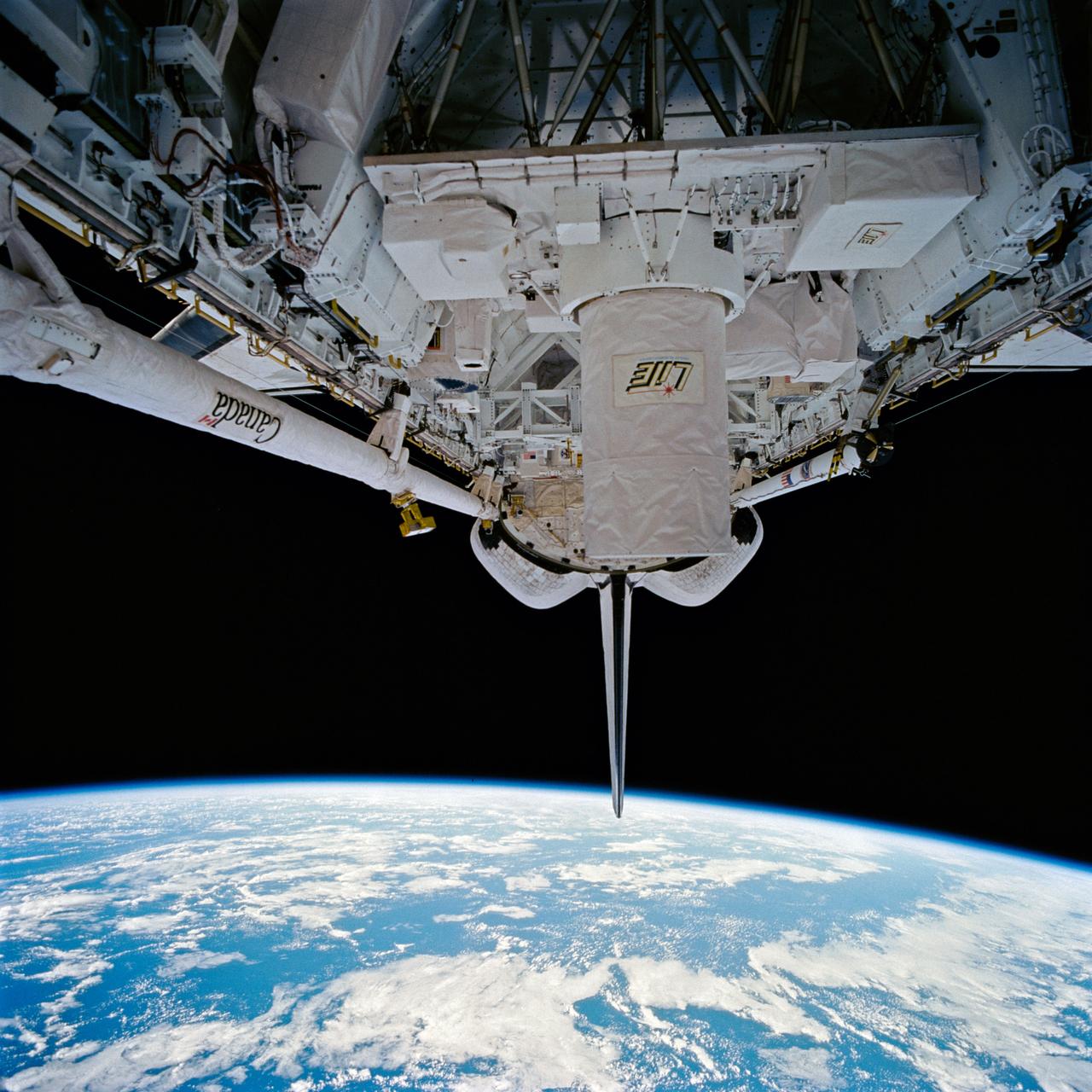

STS064-90-031 (9-20 Sept. 1994) --- Backdropped against the darkness of space beneath Earth's horizon 130 nautical miles away, the cargo bay of the space shuttle Discovery and its related payloads were captured on 70mm film by one of the six cabin-bound astronauts. In the foreground is the Lidar In-space Technology Experiment (LITE). The robot arm portion of the Remote Manipulator System (RMS), busy throughout much of the almost 11-day mission, is in a stowed position on Discovery's port side. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
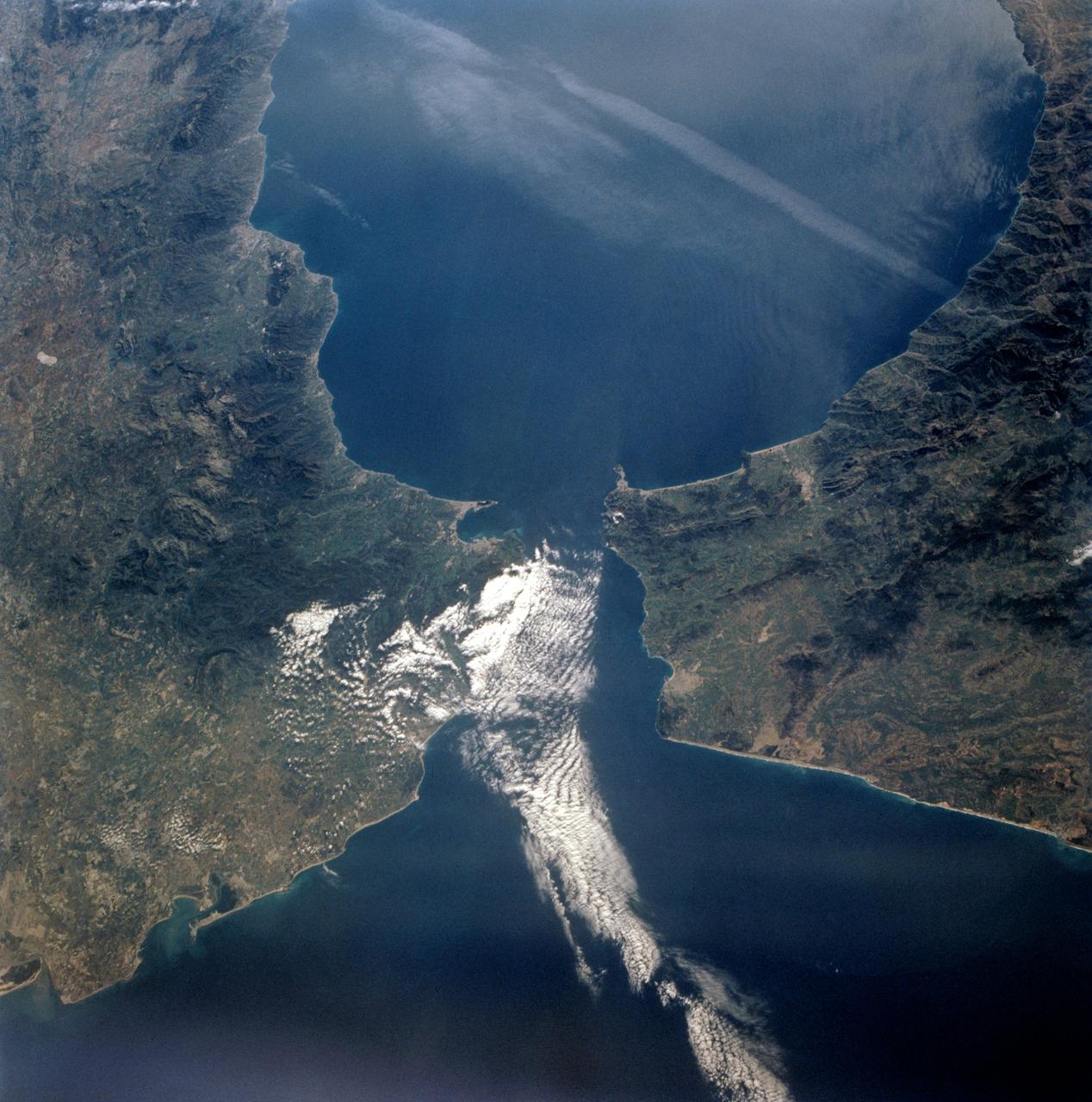

STS-56 Earth observation taken aboard Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, is of the Strait of Gibraltar. A small bank of clouds marks the passage between Spain and Morocco at the western edge of the Mediterranean Sea. This passage, one of the two Pilars of Hercules of the Ancient Greeks, is now known as the Strait of Gibraltar. The cities of Cadiz on the Atlantic Coast of Spain and Malaga on the Mediterranean coast, as well as Tangier, Morocco (facing the strait), can be seen. According to NASA scientists studying the STS-56 photos, a subtle difference in the water color on the Atlantic side suggests that a pulse of surface water had recently flowed out of the Mediterranean into the Atlantic.

STS064-72-093 (10 Sept. 1994) --- With the blue and white Earth as a backdrop 130 miles below, the Shuttle Plume Impingement Flight Experiment (SPIFEX) is at work on the end of the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm. The 50-feet-long arm is extended to 80 feet with the temporary addition of the SPIFEX hardware. The image was exposed with a 70mm handheld Hasselblad camera from inside the space shuttle Discovery's crew cabin. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
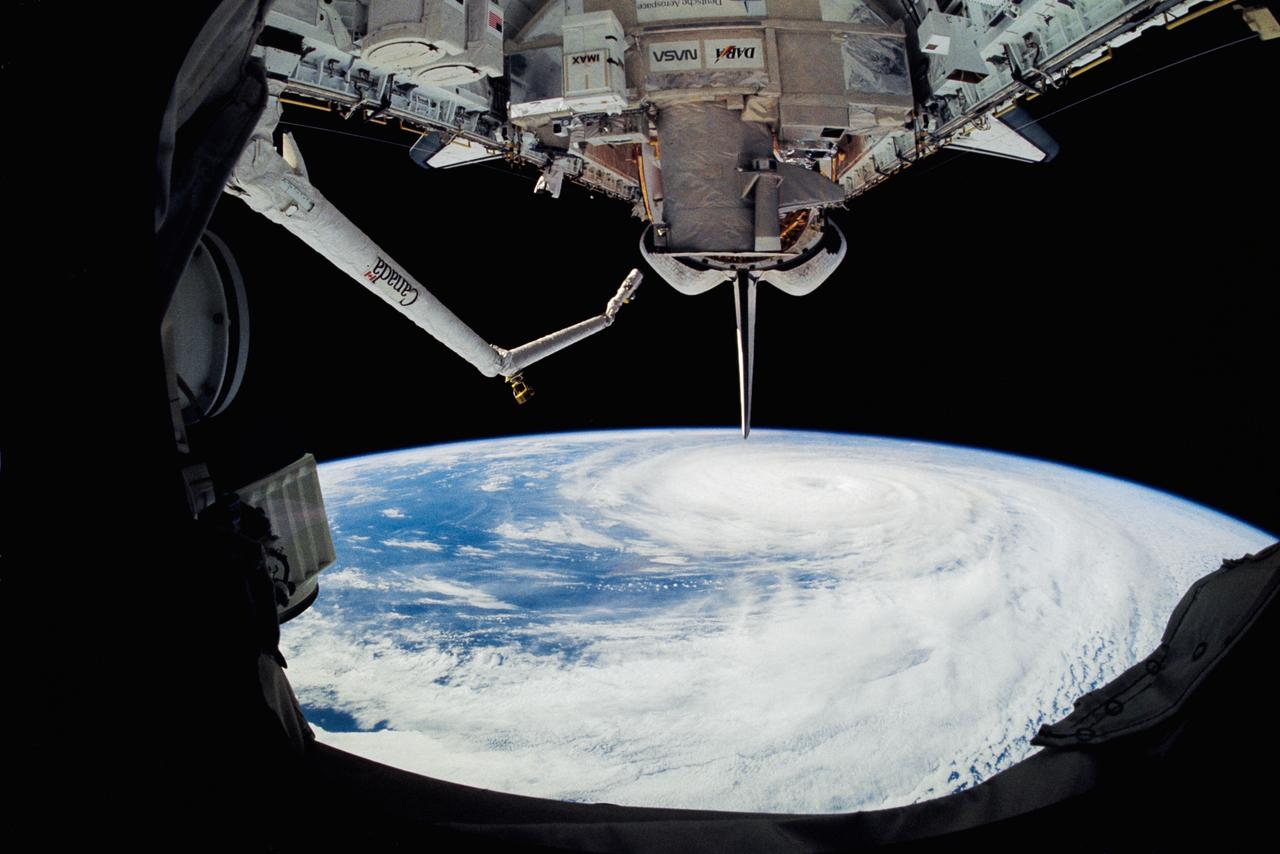

One of the STS-51 astronauts used a "fish-eye" lens on a 35mm cmaera to photograph this view of Hurricane Kenneth in the Pacific Ocean. The Orbiting Retrievable Far and Extreme Ultraviolet Spectrometer/Shuttle Pallet Satellite (ORFEUS/SPAS) is still in the cargo bay. The Remote Manipulator System (RMS) is extended towards the open payload bay.
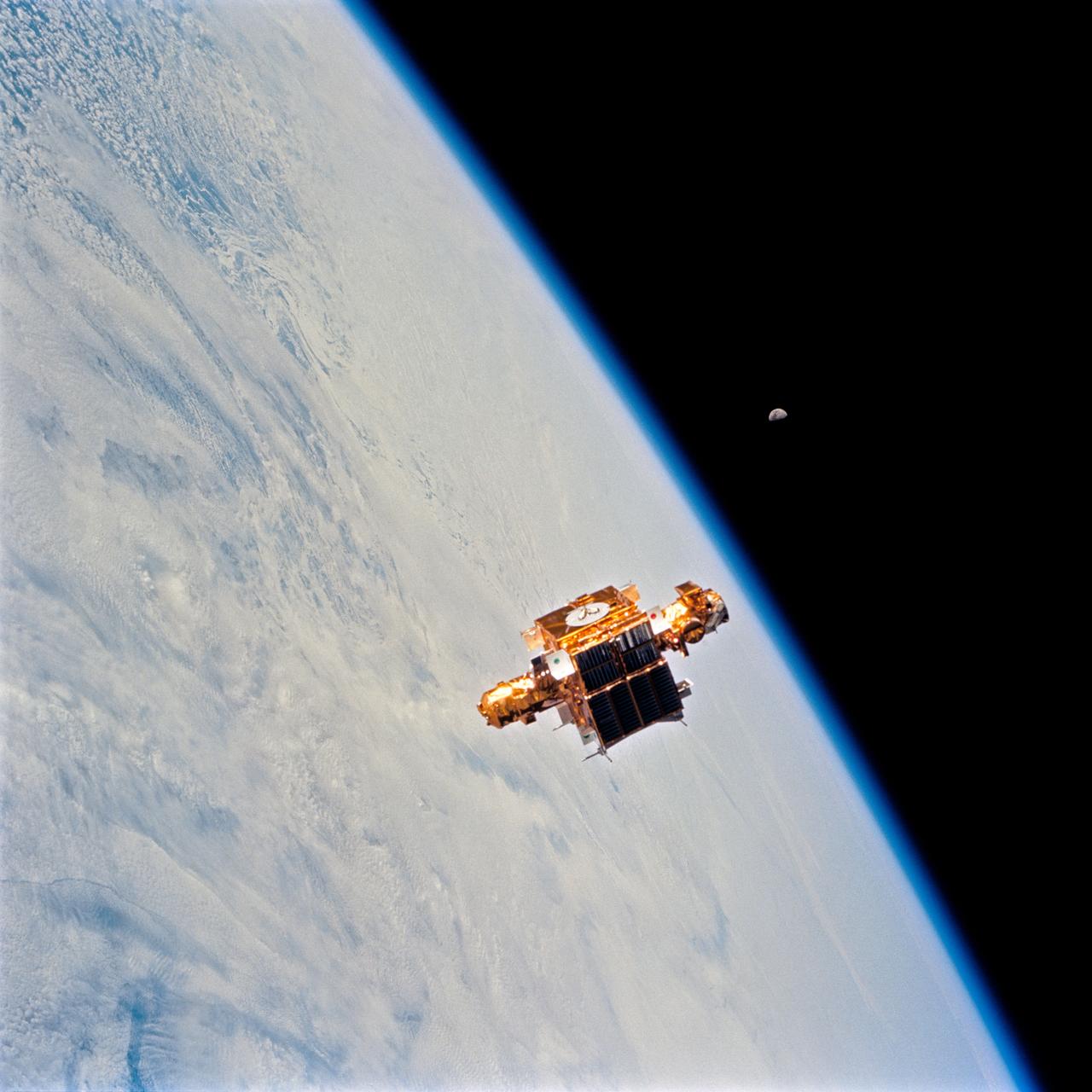

STS064-74-052 (9-20 Sept. 1994) --- Astronauts onboard the space shuttle Discovery used a 70mm camera to capture this photograph of the retrieval operations with the Shuttle Pointed Autonomous Research Tool for Astronomy 201 (SPARTAN 201). A gibbous moon can be seen in the background. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
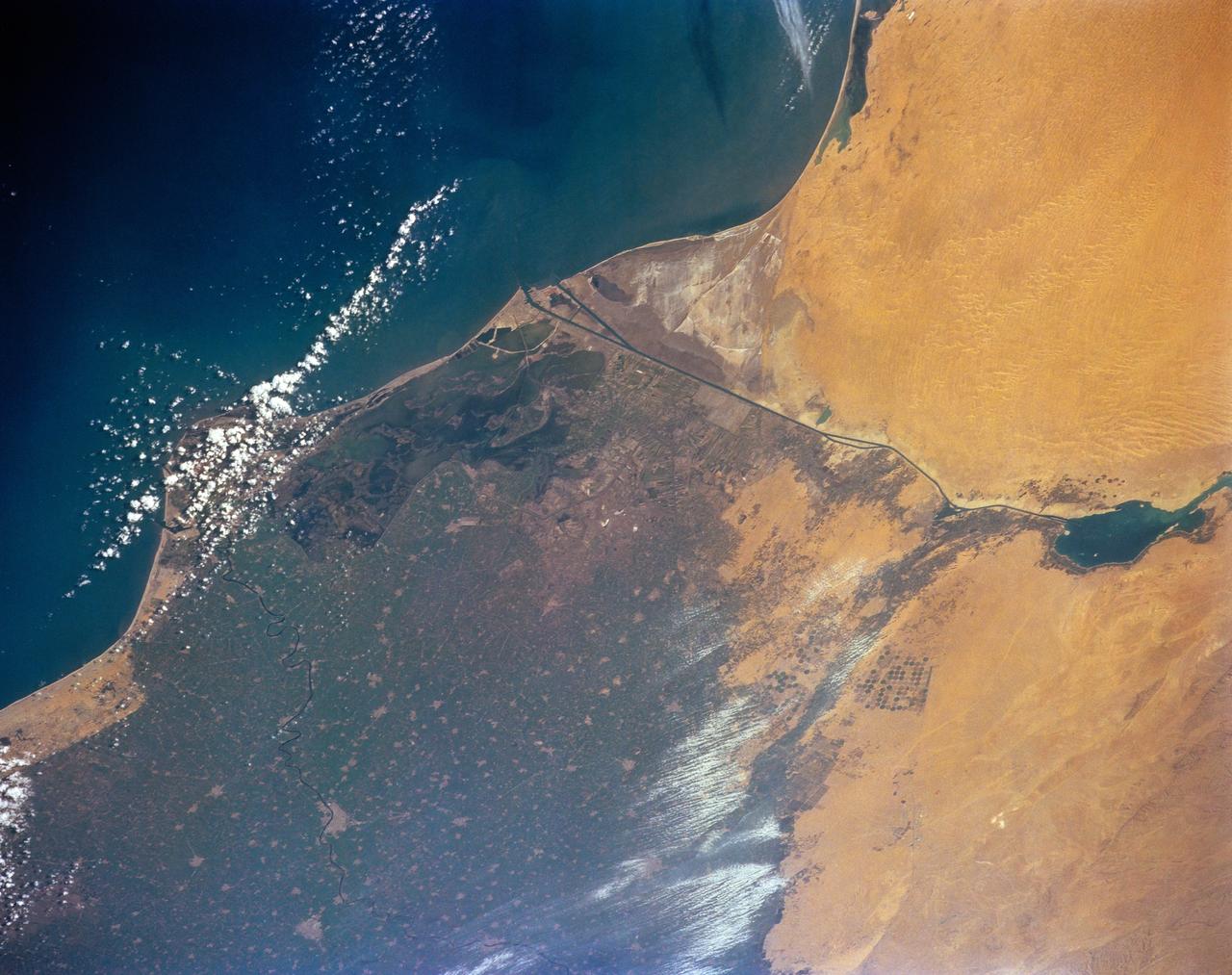

STS-56 Earth observation of the northeastern Nile Delta was photographed from the Earth-orbiting Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103. The branch of the Nile featured in the frame is Daimietta. The Suez Canal marks the boundary of the Nile Delta agriculture and the Sinai Desert to the right. Lake Masada, the dark waterlogged area to the west (left) of Port Said is becoming more saline as the Aswan Dam has reduced sediment downstream. This sediment reduction, according to NASA scientists studying the STS-56 photography, has resulted in increased coastal erosion and the intrusion of a salt-water lens to the ground water, particularly in the northeastern portions of the delta. Center pivot irrigation fields are located along either side of the Ramses Canal, which connects the Daimietta Nile with Great Bitter Lake. This canal has been re-dug three or four times in the past 3,000 years. Historians note that the canal's most famous use was as the departure point of the fleet of Pharaoh Necho. The fleet circumnavigated Africa clockwise from the head of the Red Sea to the Mediterranean coast of the Nile (probably the Rosetta Nile) in a three-year voyage circa 660 BC.
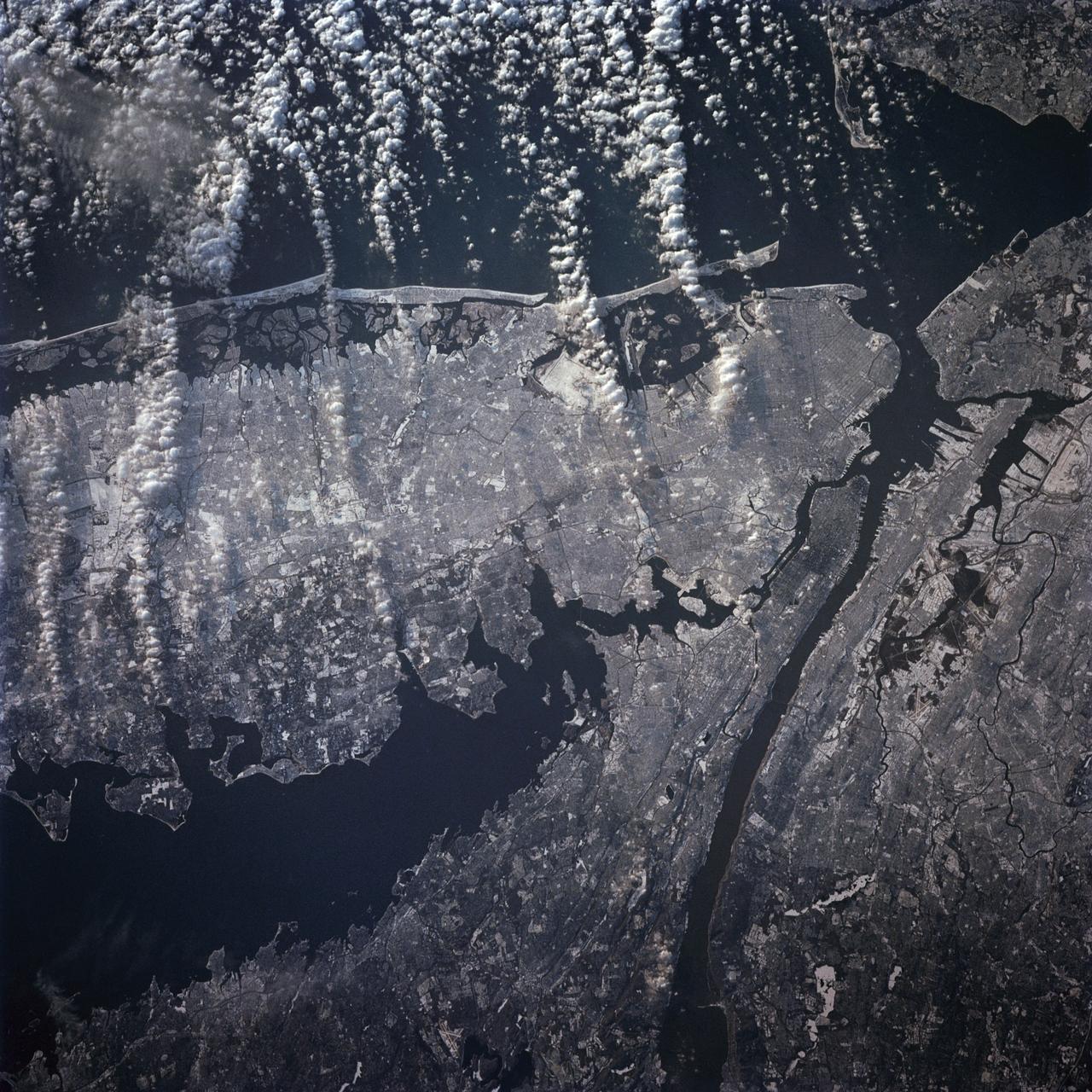

STS-42 Earth observation taken aboard Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, is of New York City (NYC), New York (41.0N, 74.0W). Snow cover highlights the large areas of development and the many reservoirs in this wintertime scene of the metropolitan NYC area. Features such as Central Park in Manhattan, the George Washington Bridge connecting Manhattan with New Jersey, street patterns in most of the boroughs, La Guardia and JFK airports in Queens, and the extensive harbor system are easily identified.
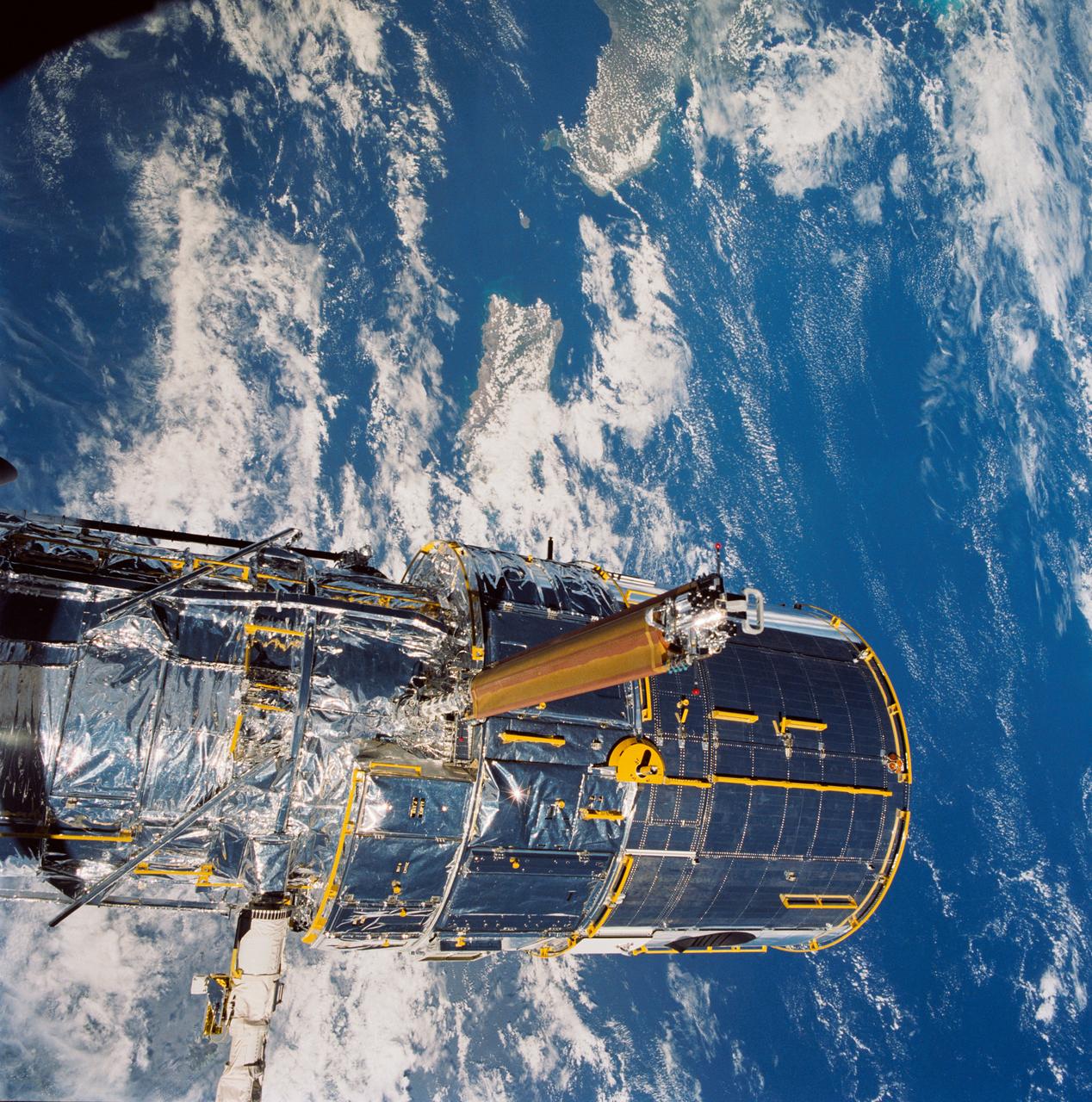

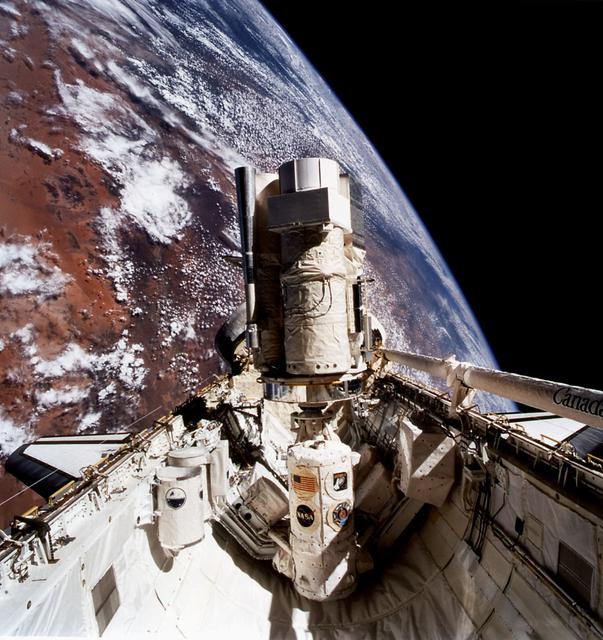
During STS-31, the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) grappled by the remote manipulator system (RMS) end effector is held in appendage deploy position above Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103. The solar array (SA) bistem cassette has been released from its latch fittings. The bistem spreader bars begin to unfurl the SA wing. The secondary deployment mechanism (SDM) handle is visible at the SA end. Stowed against either side of the HST System Support Module (SSM) forward shell are the high-gain antennae (HGA). Puerto Rico and the Dominican Republic are recognizable at the left of the frame.
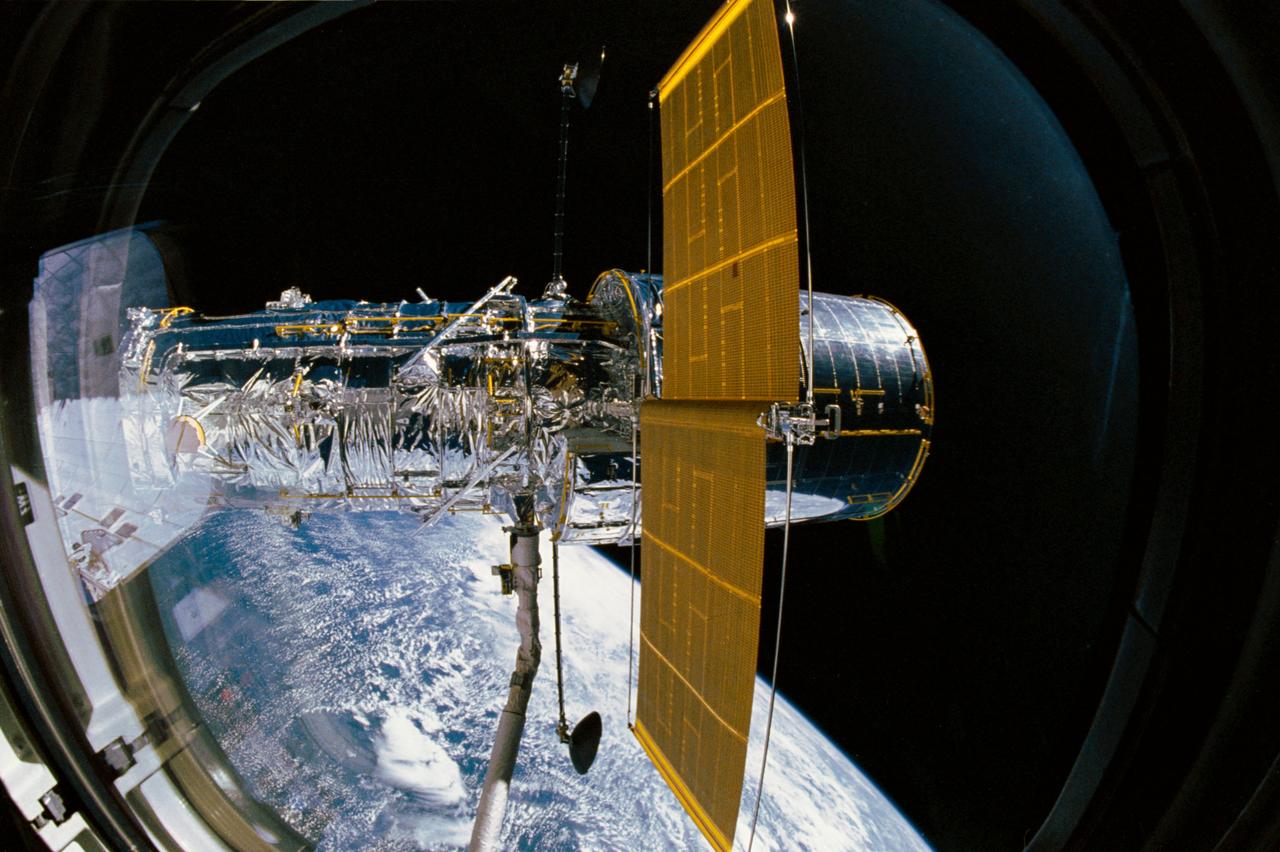

STS031-03-009 (25 April 1990) --- The Hubble Space Telescope (HST), still in the grasp of Discovery's remote manipulator system (RMS), is backdropped over Earth some 332 nautical miles below. In this scene, HST has deployed one of its solar array panels but is yet to have extended the second. This scene was captured with a 35mm camera aimed through an overhead window on the aft flight deck.
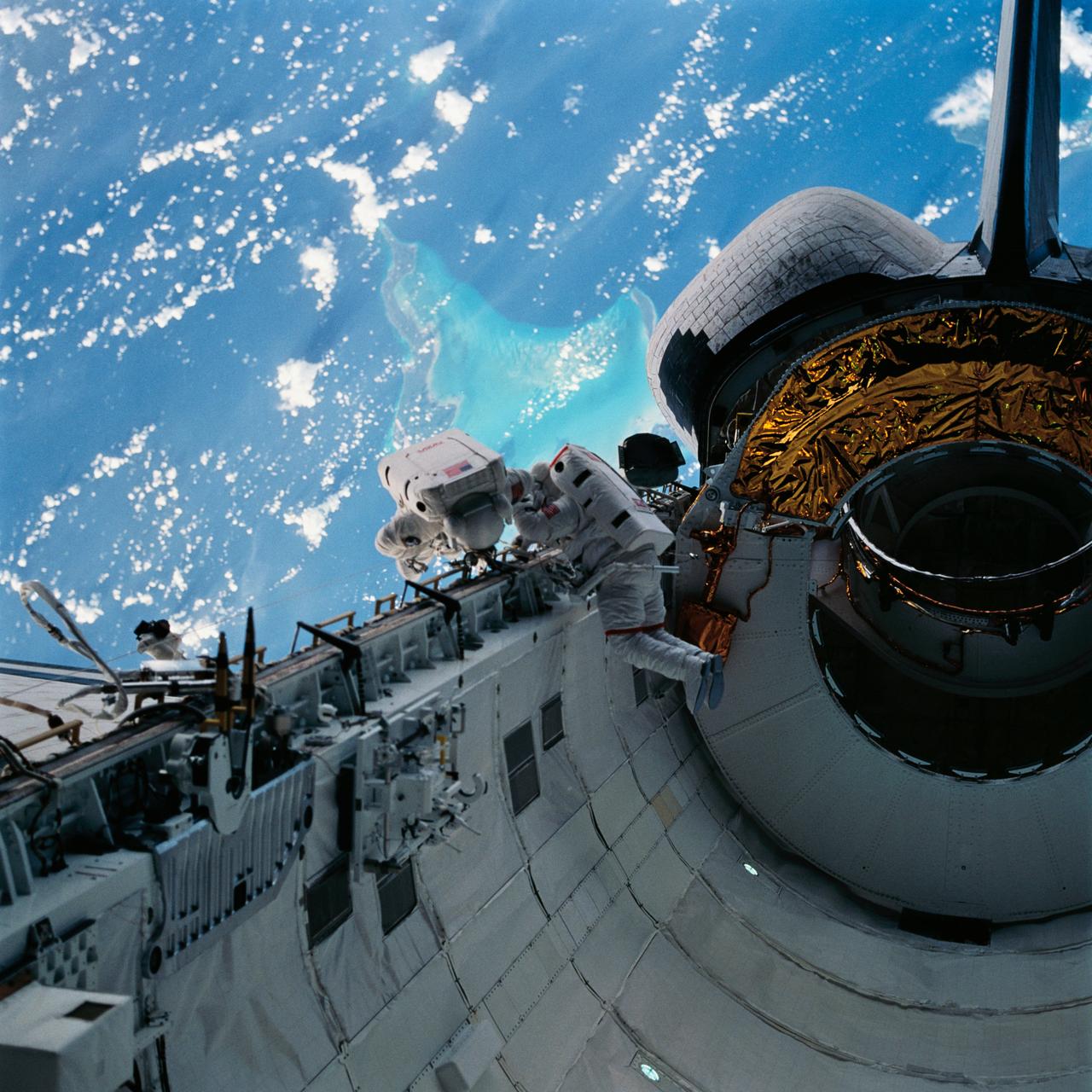

With the Caribbean Sea and part of the Bahama Islands chain as a backdrop, two STS-51 crewmembers evaluate procedures and gear to be used on the upcoming Hubble Space Telescope (HST)-servicing mission. Sharing the lengthy extravehicular activity in and around Discovery's cargo bay were astronauts James H. Newman (left), and Carl E. Walz, mission specialists.
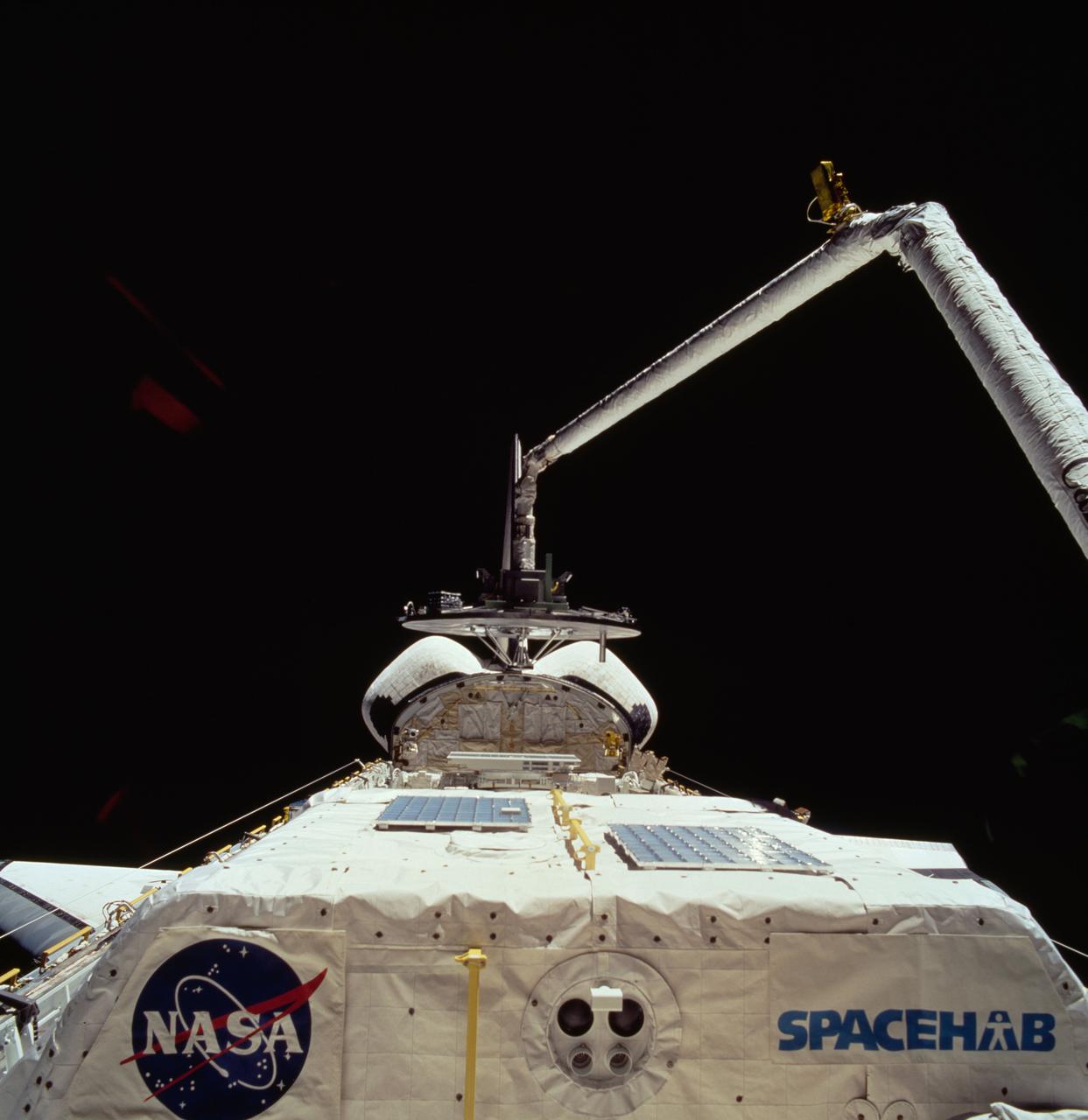

STS060-74-054 (3-11 Feb 1994) --- The Wake Shield Facility (WSF) is held in the grasp of Discovery's Remote Manipulator System (RMS). The 70mm image, backdropped against the blackness of space, also shows the SPACEHAB module in the forward cargo area.
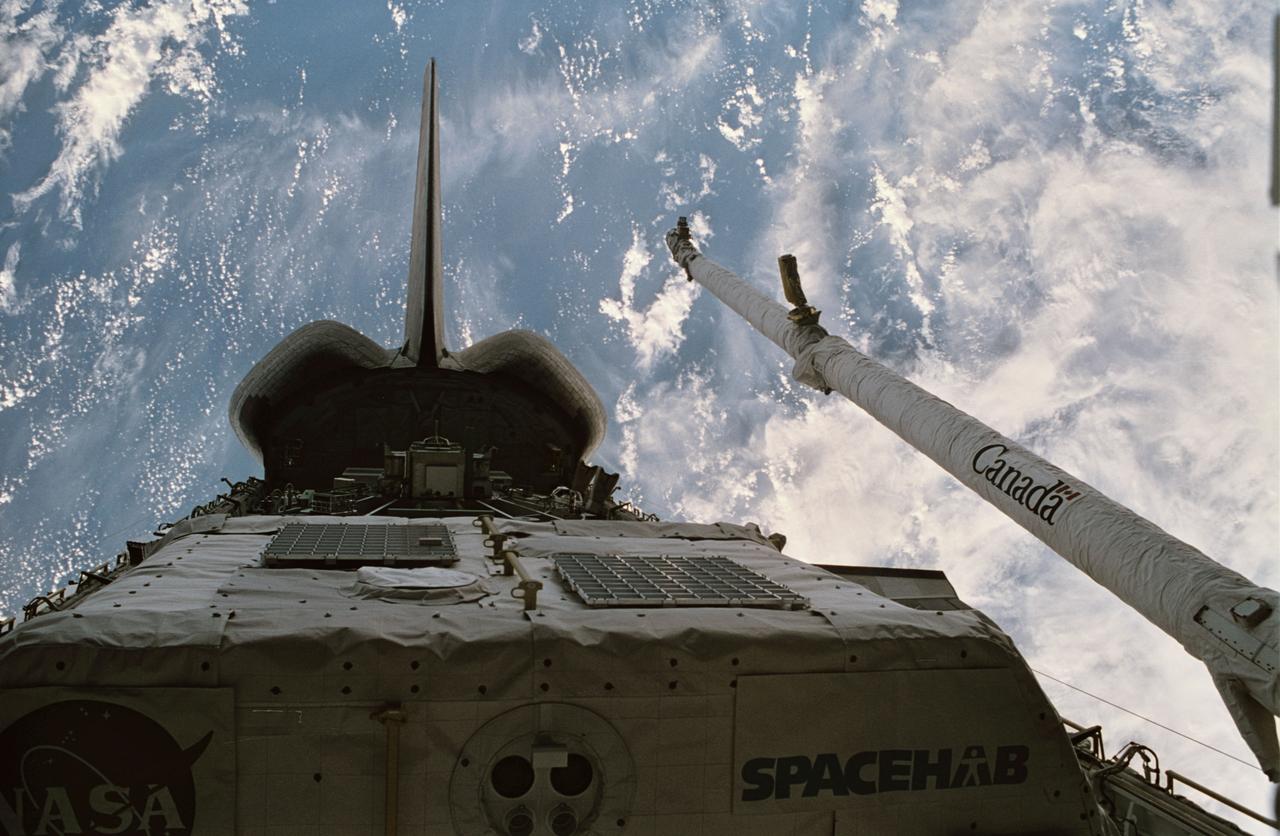

STS060-15-003 (3-11 Feb 1994) --- This 35mm frame shows the major payloads of the Space Shuttle Discovery's STS-60 mission, backdropped against clouds over the Atlantic Ocean. In the foreground is the SPACEHAB module, with the Wake Shield Facility (WSF) partially visible in its berthed position near the Orbital Maneuvering System (OMS) pods and the vertical stabilizer. Television cameras on the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) were being used for a survey of the cargo. Five NASA astronauts and a Russian cosmonaut went on to spend eight days in Earth orbit in support of the mission.
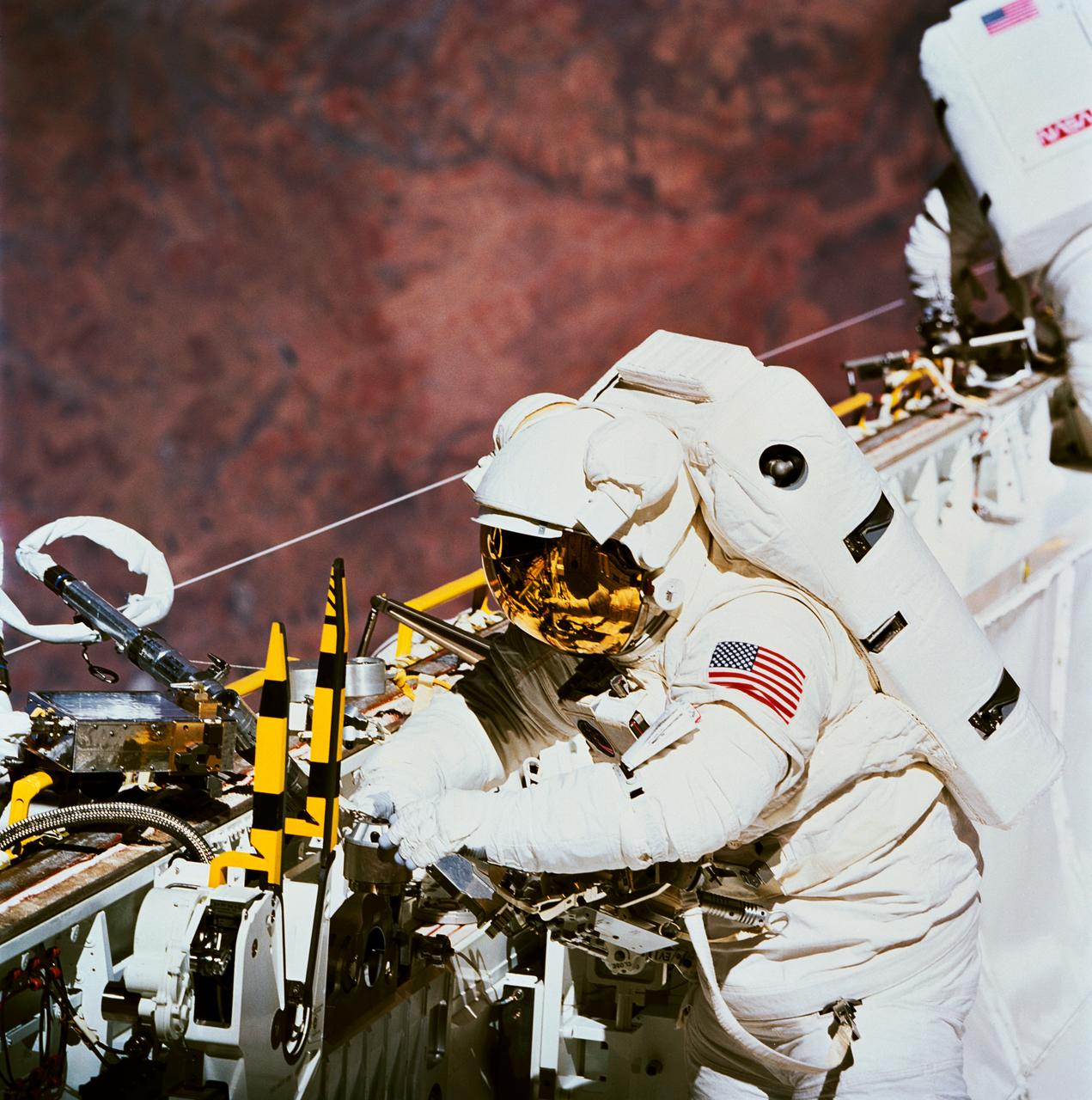

In Discovery's cargo bay, astronaut James H. Newman works with the power ratchet tool (PRT). Astronaut Carl E. Walz, who joined Newman for the lengthy period of extravehicular activity (EVA), is partially visible in the background. The two mission specialists devoted part of their EVA to evaluating tools and equipment expected to be used in the Hubble Space Telescope servicing. A desert area in Africa forms the backdrop for the 70mm scene.
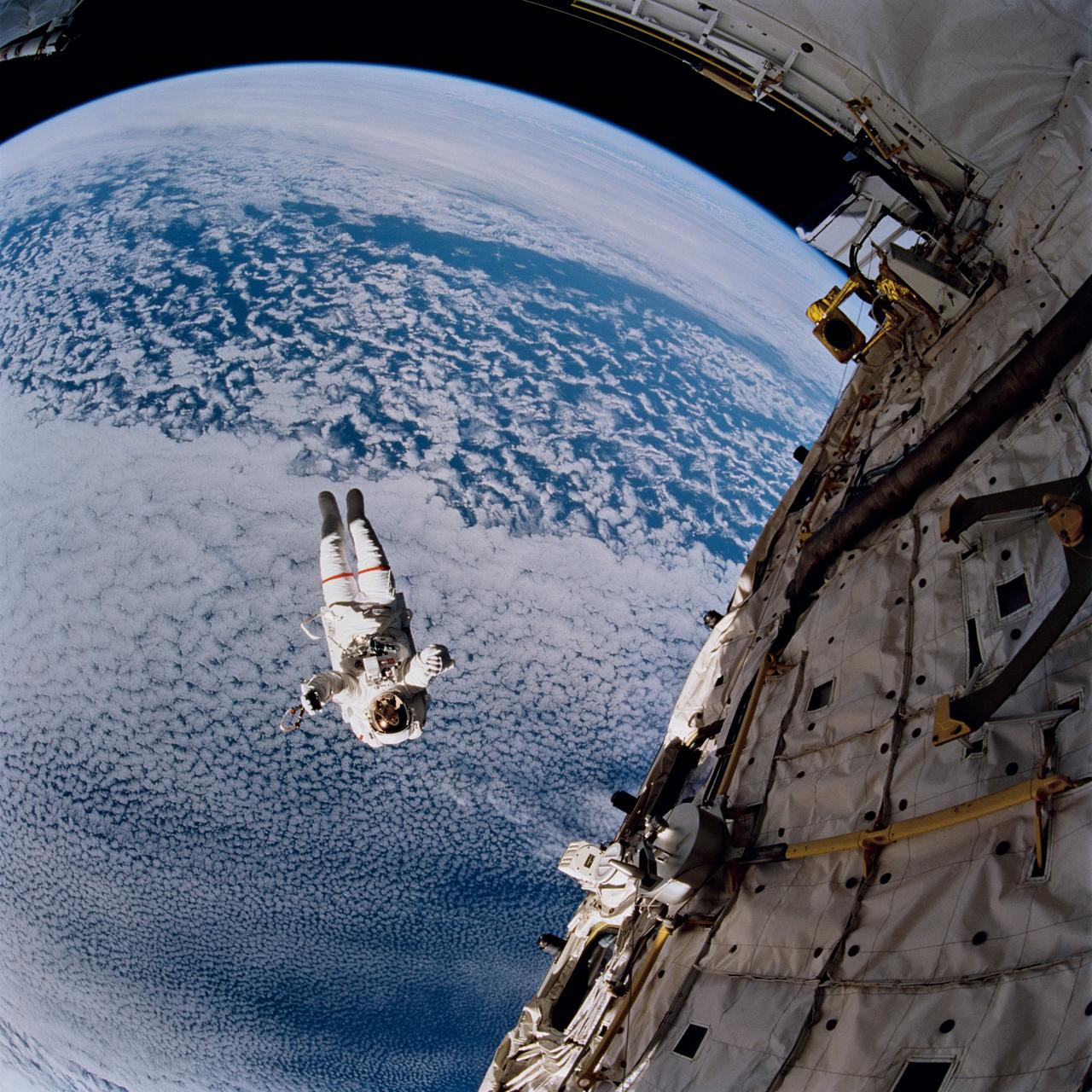

STS064-217-008 (16 Sept. 1994) --- Backdropped against the blue and white Earth, 130 nautical miles below, astronaut Mark C. Lee tests the new Simplified Aid for EVA Rescue (SAFER) system. The scene was captured with a 70mm handheld Hasselblad camera with a 30mm lens attached. Astronauts Lee and Carl J. Meade took turns using the SAFER hardware during their shared Extravehicular Activity (EVA) of Sept. 16, 1994. The test of SAFER is the first phase of a larger SAFER program whose objectives are to establish a common set of requirements for both space shuttle and space station program needs, develop a flight demonstration of SAFER, validate system performance and, finally, develop a production version of SAFER for the shuttle and station programs. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration

STS051-34-028 (16 Sept. 1993) --- This unusual scene of Extravehicular Activity (EVA) was captured on 35mm film by one of the supportive in-cabin crew members. Astronaut James H. Newman, working on the Space Shuttle Discovery's starboard side, is nearer the camera, with astronaut Carl E. Walz traversing near the aft firewall and the Airborne Support Equipment (ASE).
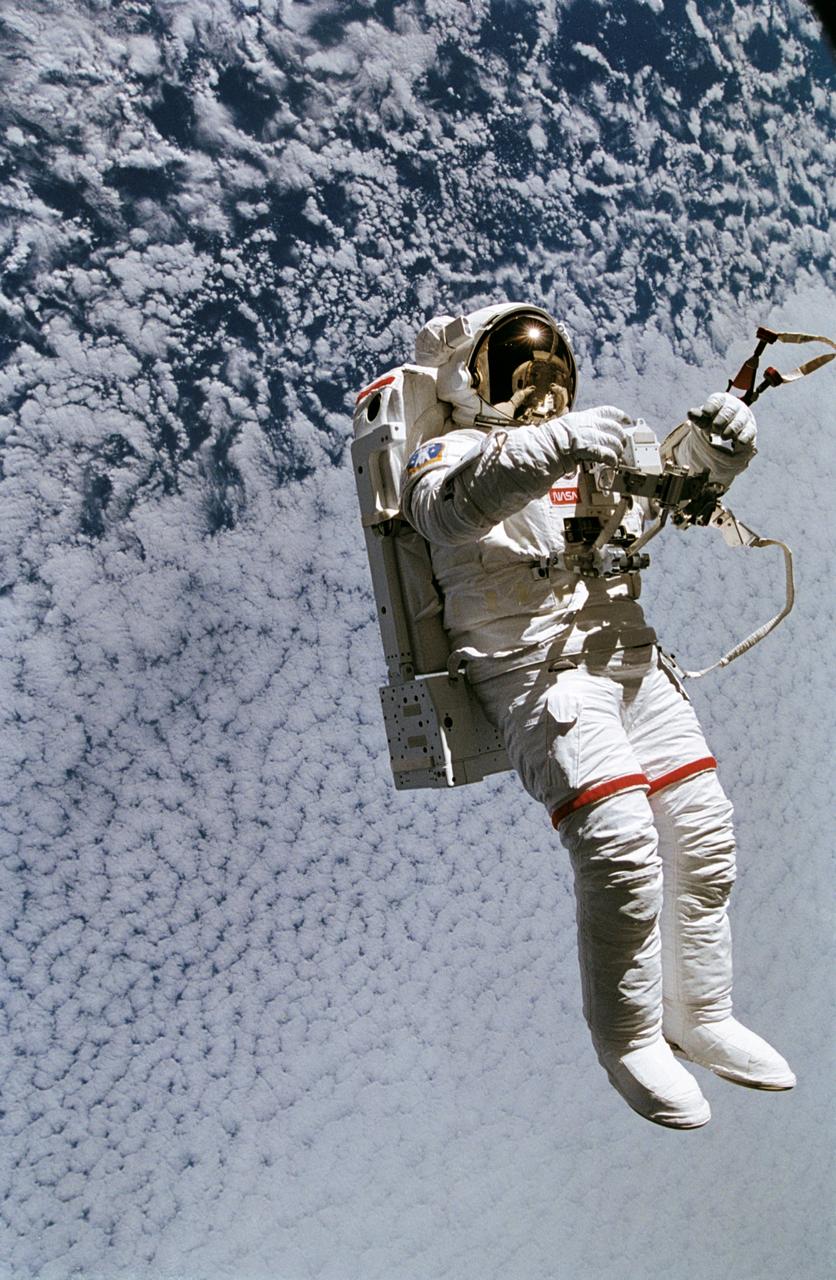

STS064-45-014 (16 Sept. 1994) --- Backdropped against a massive wall of white clouds 130 nautical miles below, astronaut Mark C. Lee floats freely as he tests the new Simplified Aid for EVA Rescue (SAFER) system. The image was exposed with a 35mm camera from the shirt-sleeve environment of the space shuttle Discovery. Astronauts Lee and Carl J. Meade took turns using the SAFER hardware during their shared Extravehicular Activity (EVA) on Sept. 16, 1994. The test of SAFER is the first phase of a larger SAFER program whose objectives are to establish a common set of requirements for both space shuttle and space station program needs, develop a flight demonstration of SAFER, validate system performance and, finally, develop a production version of SAFER for the shuttle and station programs. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
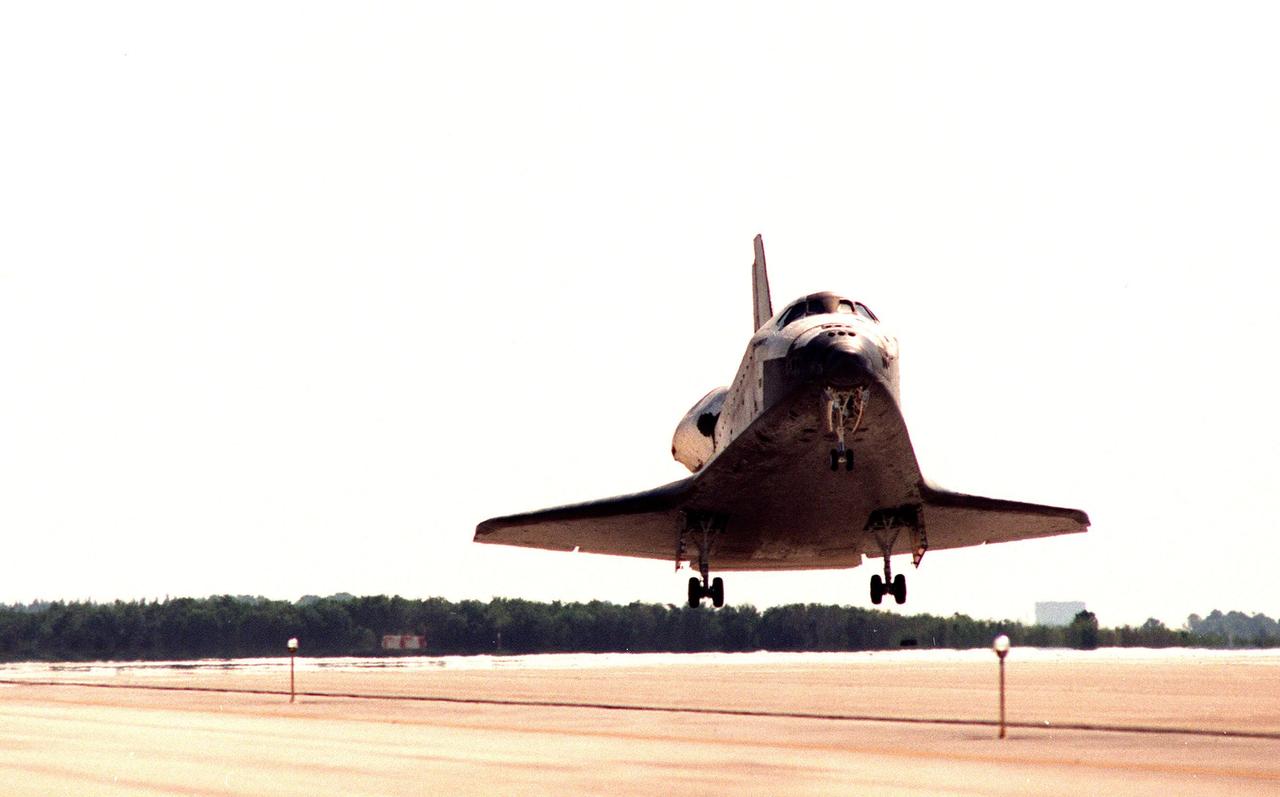

After nine days and 3.6 million miles in space, orbiter Discovery prepares to land on runway 33 at the Shuttle Landing Facility. Discovery returns to Earth with its crew of seven after successfully completing mission STS-95. The STS-95 crew members are Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr.; Pilot Steven W. Lindsey; Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski; Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson; Payload Specialist John H. Glenn Jr., a senator from Ohio; Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain, with the European Space Agency (ESA); and Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai, with the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). The mission included research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process

iss071-s-001 (Aug. 31, 2023) --- For nearly a quarter of a century the International Space Station (ISS) has hosted crews and accommodated science experiments even as it has continued to evolve into the highly capable orbiting laboratory of today. With its unique vantage point, the ISS serves as an intersection for discoveries ranging from the vast, such as the search for dark matter and cosmological origins, to the near, such as detailed observation of our home planet and its atmosphere, to the microscopic, including behavior of microbial life, DNA sequencing, and molecular biology in the microgravity environment. The Expedition 71 patch celebrates this science as well as the thousands of multinational scientists and technicians that have contributed to numerous groundbreaking experiments. The ISS is the ultimate destination for the scientifically curious. The symbology represents onboard research into quantum behavior of novel states of matter, antibodies and immune function, the search for dark matter, flame and combustion physics, DNA expression, plant growth and root behavior, and direct earth observation. The human eye and microscope objectives at upper left form the apex of a cone of vision culminating in the Expedition number 71, and represents the deliberate and disciplined practice of scientific observation. Earth’s moon and Mars are also depicted as next steps for exploration, with an anticipation of further rich scientific discovery using many techniques and skills honed aboard the ISS.
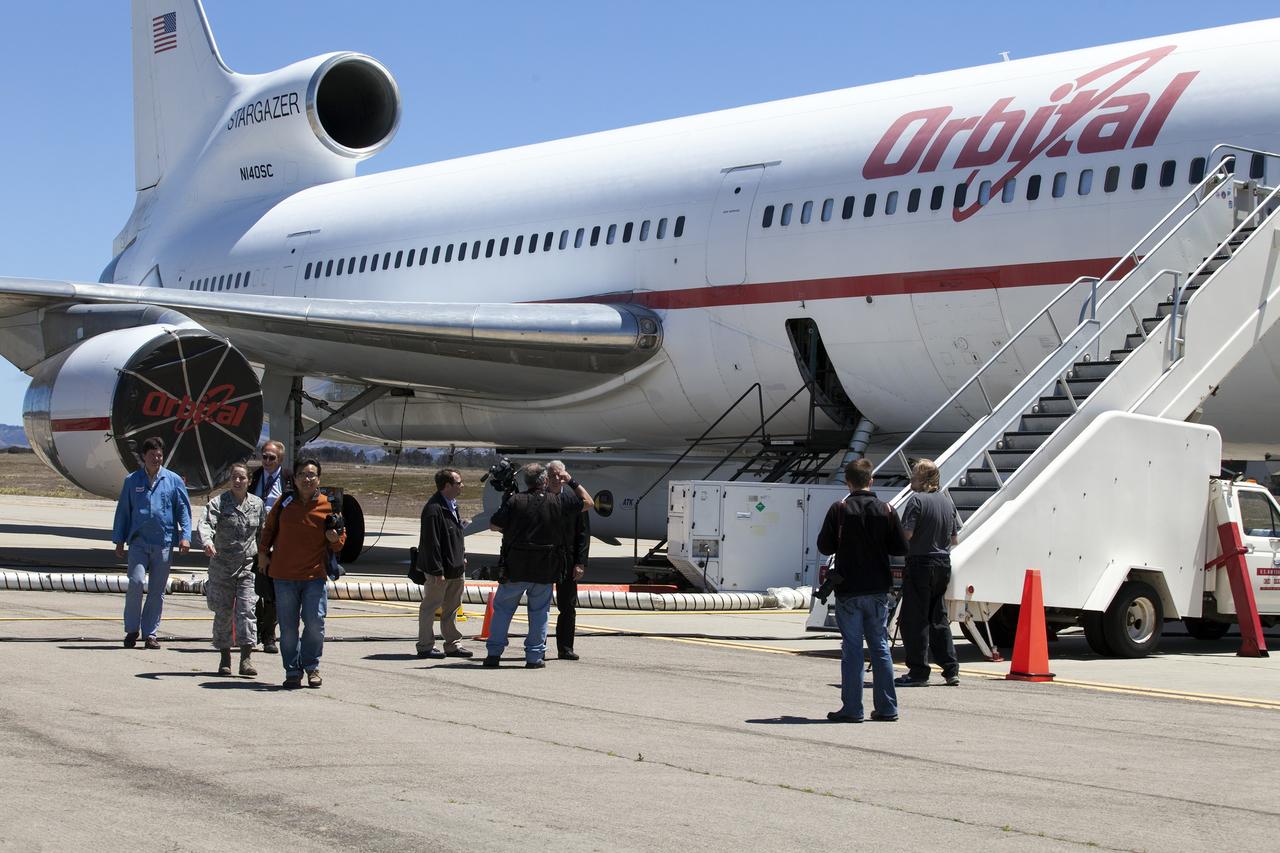

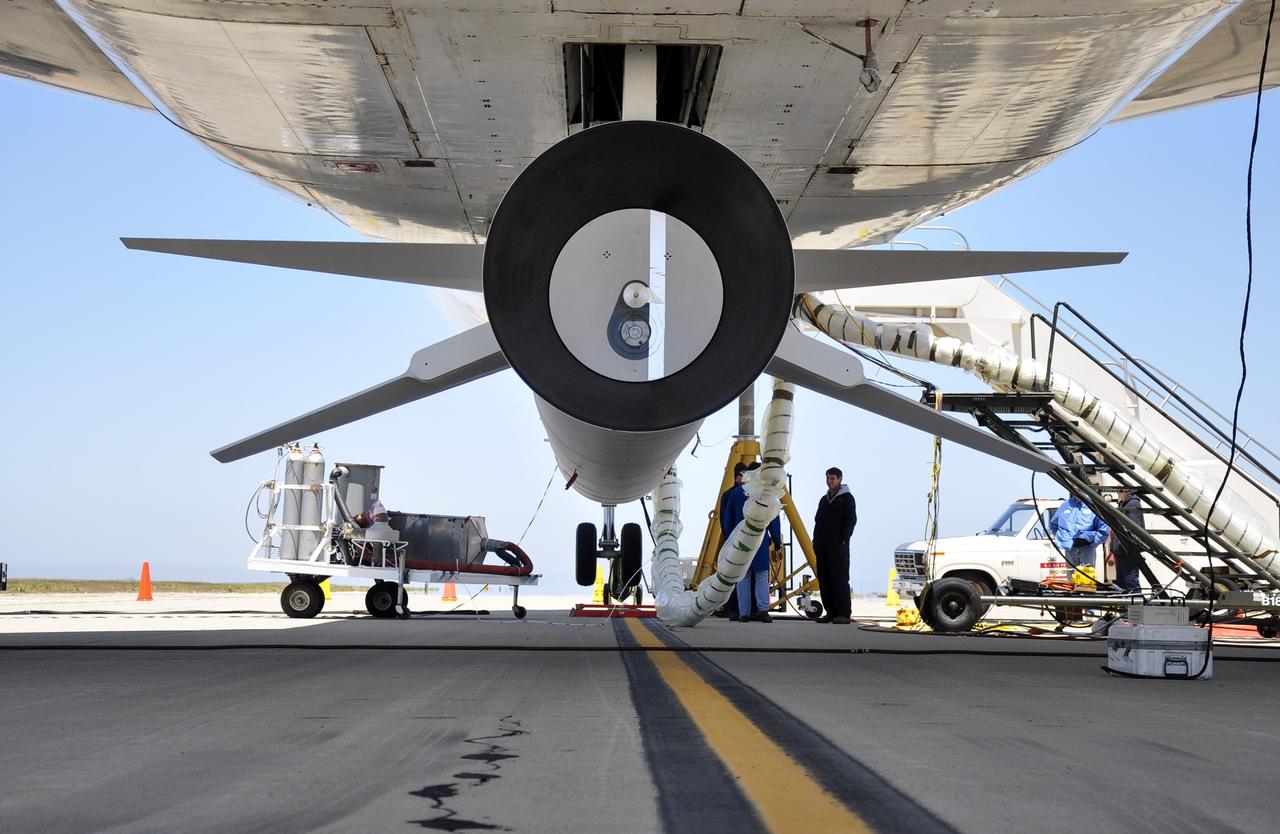
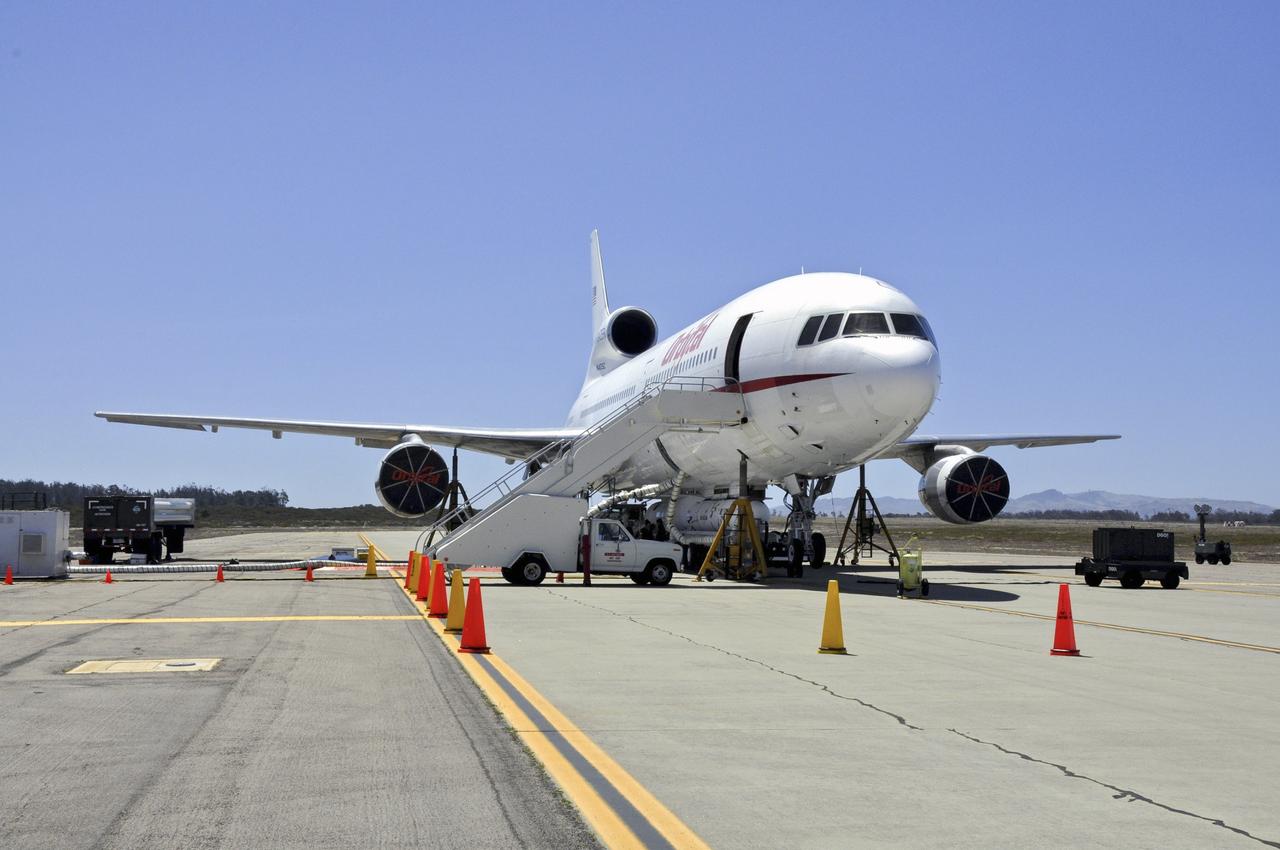
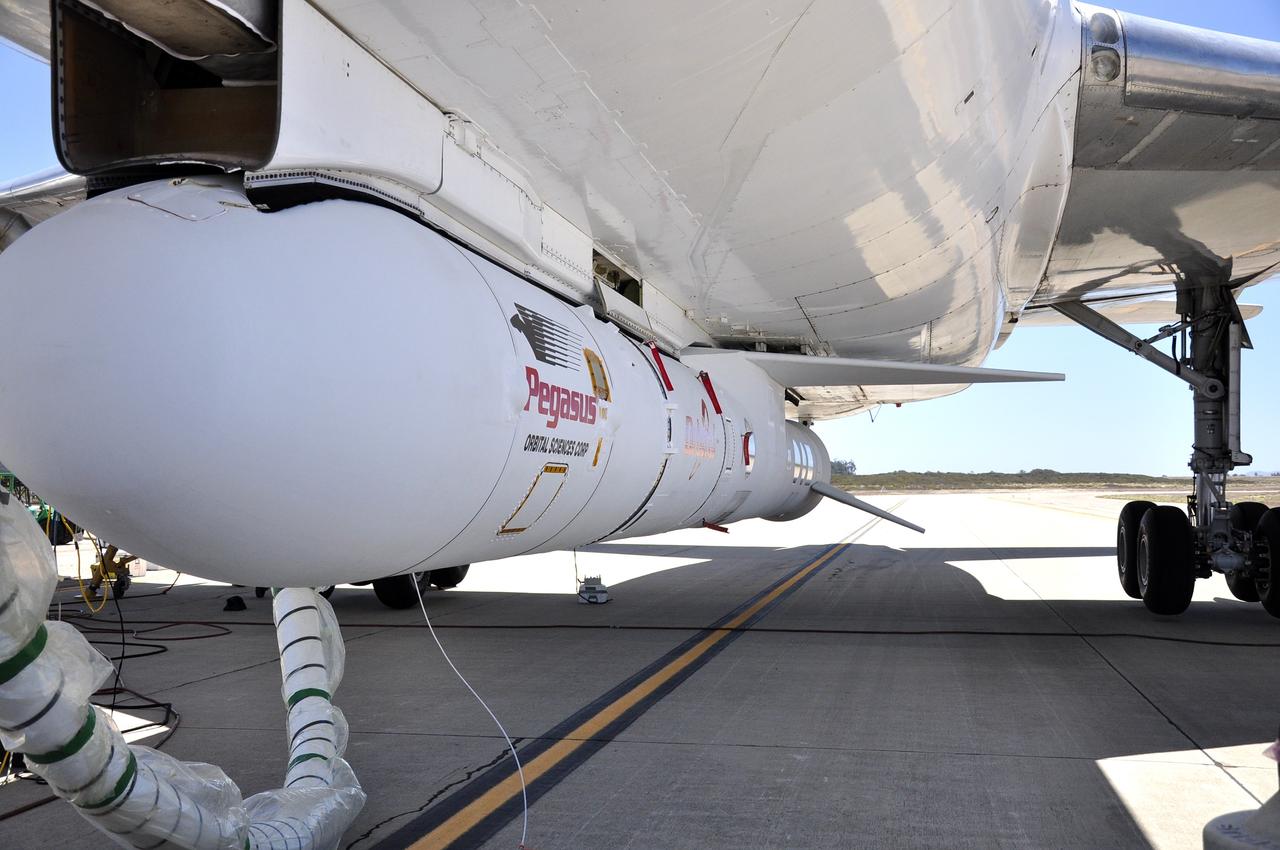
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Final checkouts are being completed at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California as preparations continue for the launch from the L-1011 carrier aircraft of the Orbital Sciences Corp. Pegasus XL rocket with the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, solar observatory. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg on June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. The IRIS mission will observe how solar material moves, gathers energy and heats up as it travels through a largely unexplored region of the solar atmosphere. The interface region, located between the sun's visible surface and upper atmosphere, is where most of the sun's ultraviolet emission is generated. These emissions impact the near-Earth space environment and Earth's climate. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/iris Photo credit: NASA/ Daniel Casper

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Final checkouts are being completed at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California as preparations continue for the launch from the L-1011 carrier aircraft of the Orbital Sciences Corp. Pegasus XL rocket with the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, solar observatory. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg on June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. The IRIS mission will observe how solar material moves, gathers energy and heats up as it travels through a largely unexplored region of the solar atmosphere. The interface region, located between the sun's visible surface and upper atmosphere, is where most of the sun's ultraviolet emission is generated. These emissions impact the near-Earth space environment and Earth's climate. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/iris Photo credit: NASA/ Daniel Casper
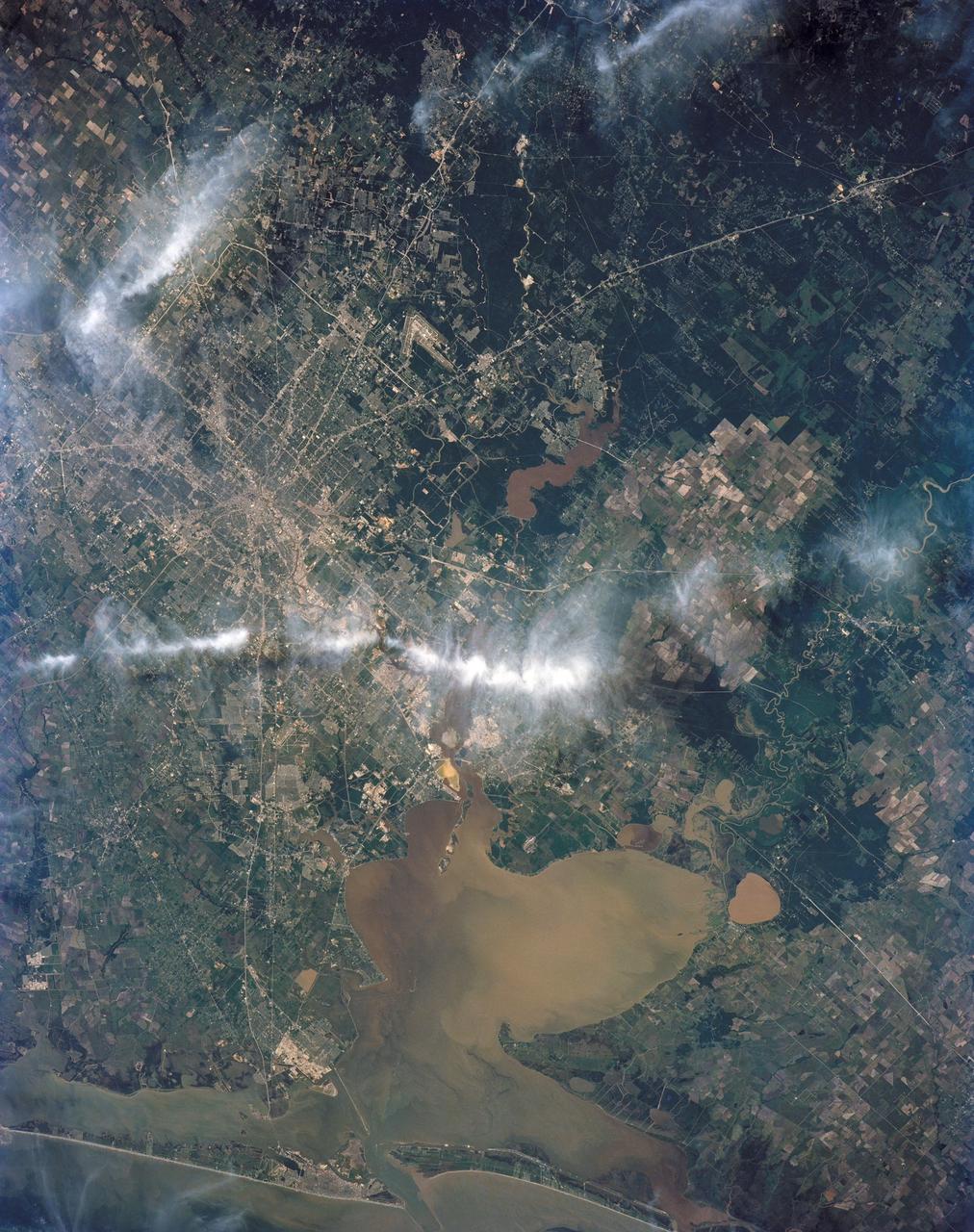

STS039-151-175 (28 April-6 May 1991) --- Large format (five-inch) frame of part of the greater Houston metropolitan area photographed from the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Discovery. (Hold photo vertically with Galveston at bottom so that north will be at top.) Heavier than normal spring rains emphasize the several bodies of water in the area. Thanks to Sun angle, the interstate highways, Houston's belt and loop systems and even city streets, farm-to-market roads and airport runways are easily observed in the frame. NASA and Clear Lake City, work and home areas of the seven Discovery astronaut crew members, are easily spotted near upper Galveston Bay in bottom (south portion) of the frame. Houston's central business district and the Harris County Domed Stadium are seen in the upper left quadrant.
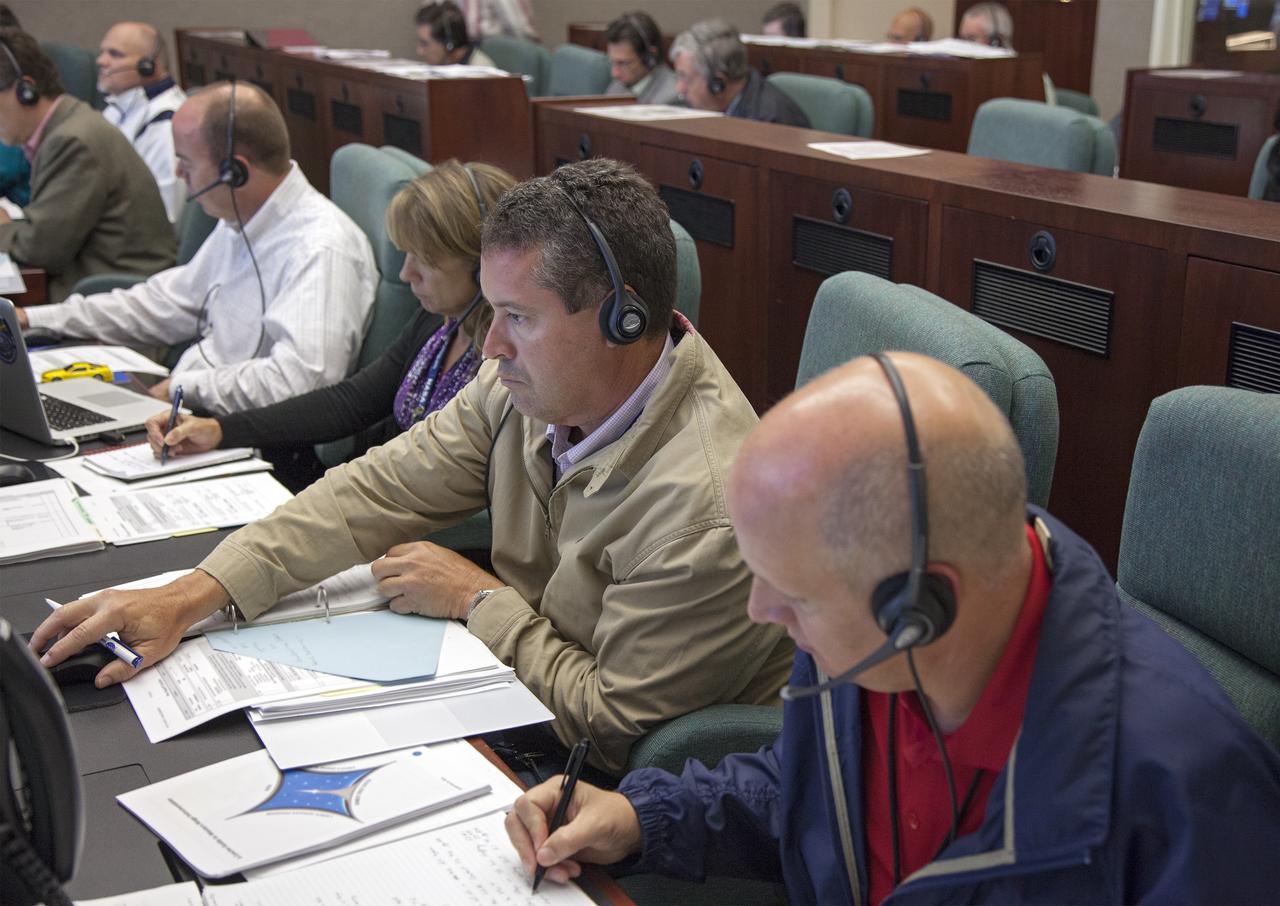

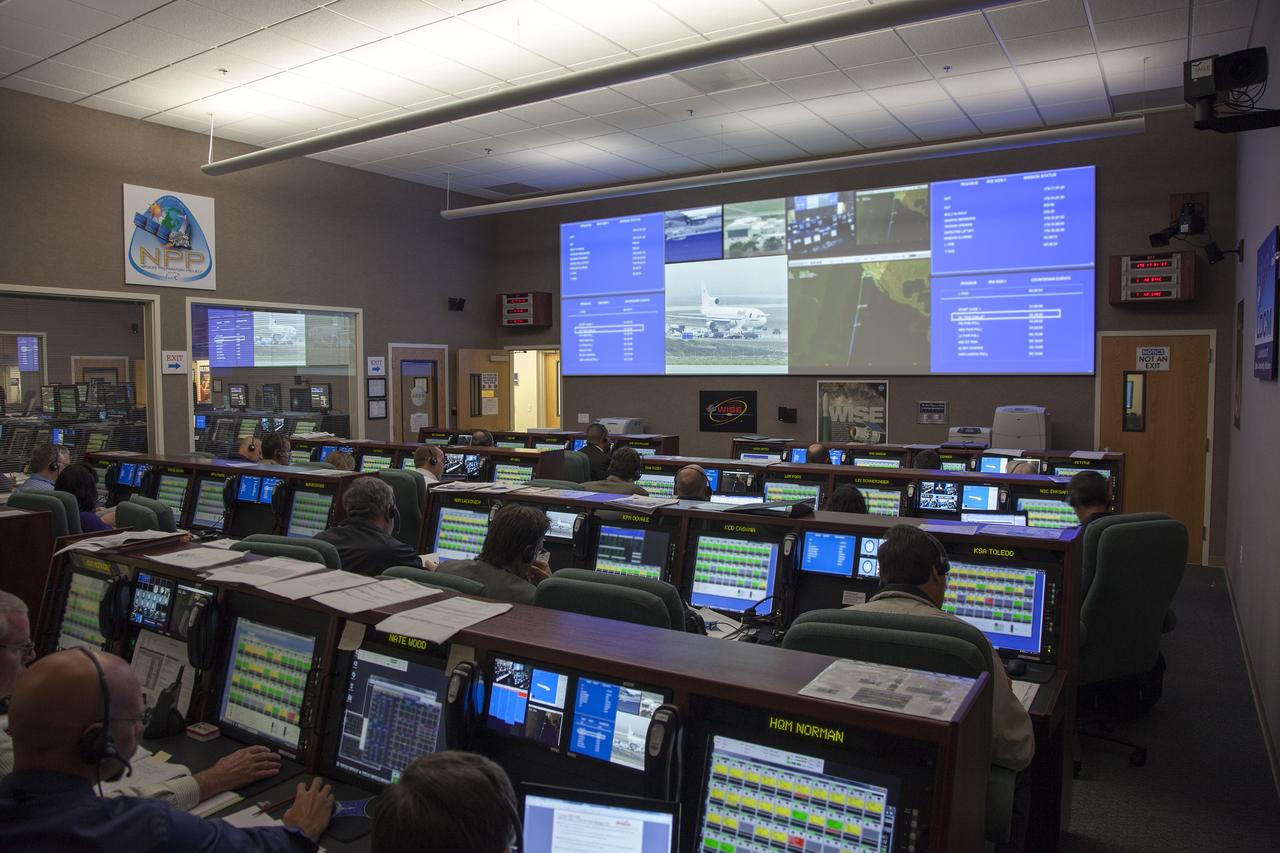
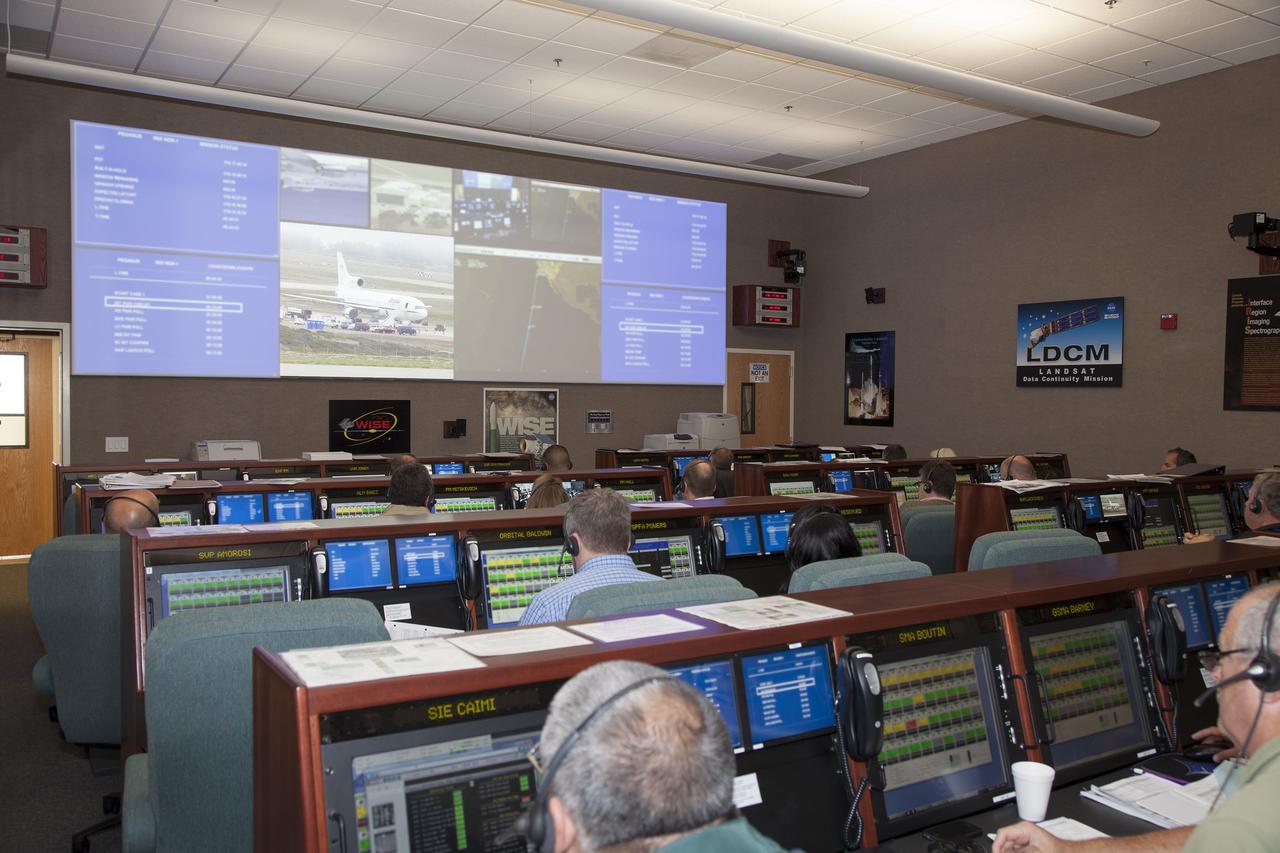
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, mission managers participate in a pre-launch dress rehearsal in the Launch Vehicle Data Center for NASA’s Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, solar observatory. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg on June 26 aboard an Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region in to the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. The IRIS mission will observe how solar material moves, gathers energy and heats up as it travels through a largely unexplored region of the solar atmosphere. The interface region, located between the sun’s visible surface and upper atmosphere, is where most of the sun’s ultraviolet emission is generated. These emissions impact the near-Earth space environment and Earth’s climate. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/iris. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper

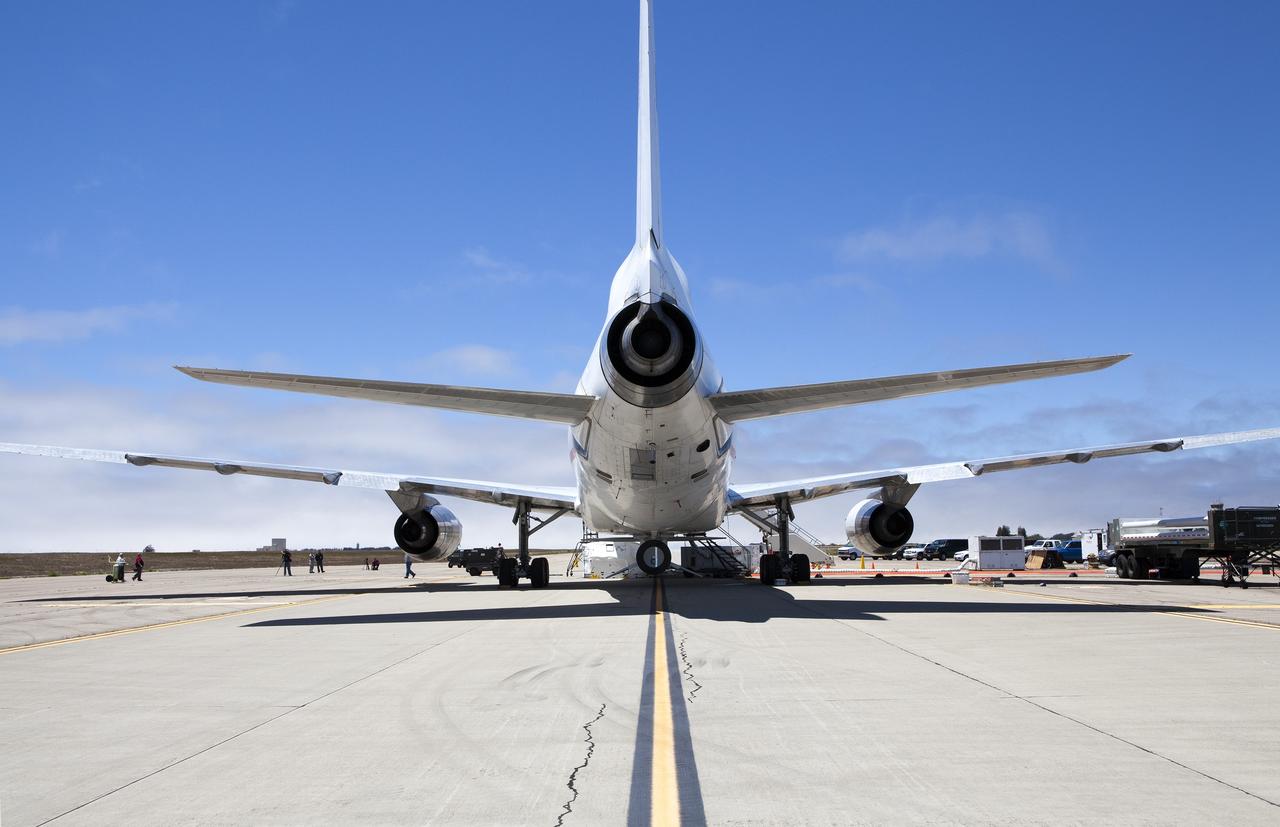
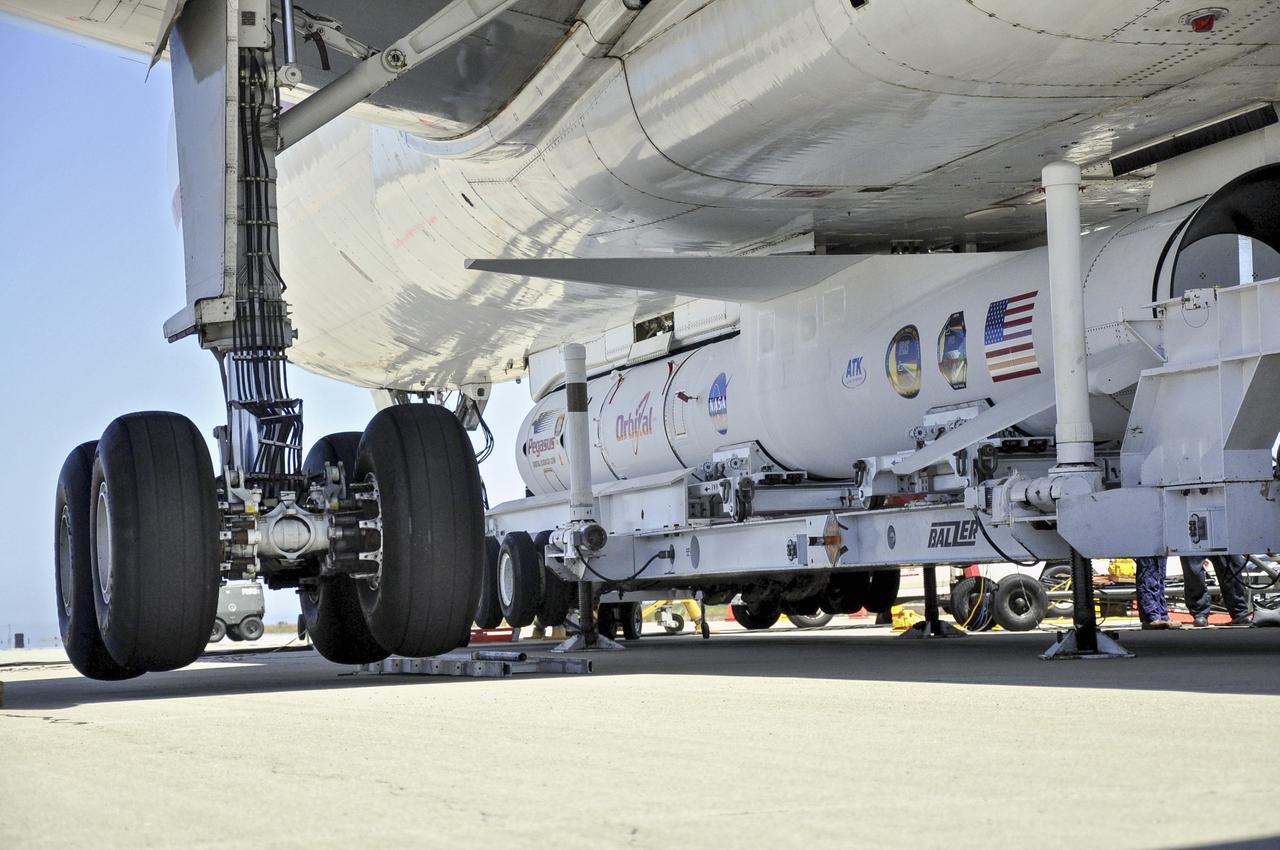
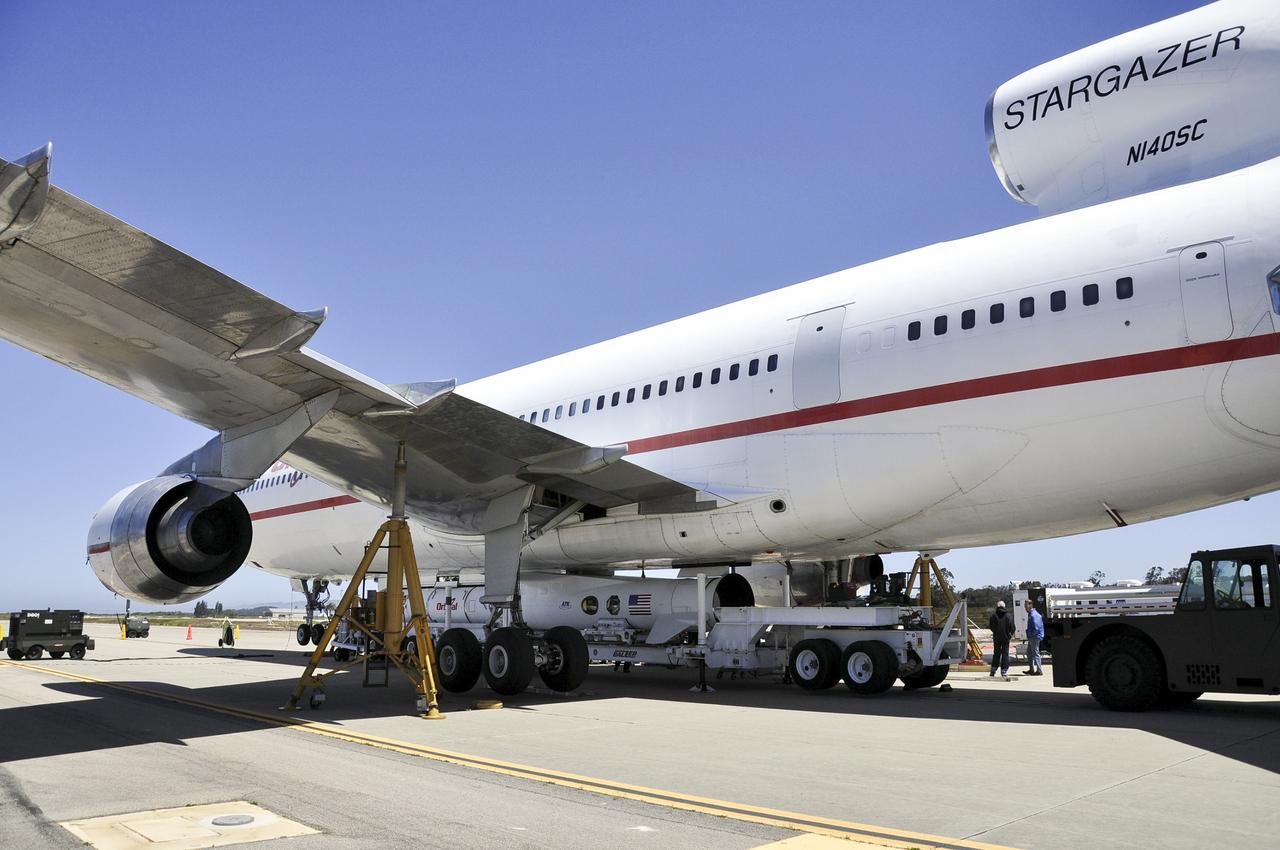
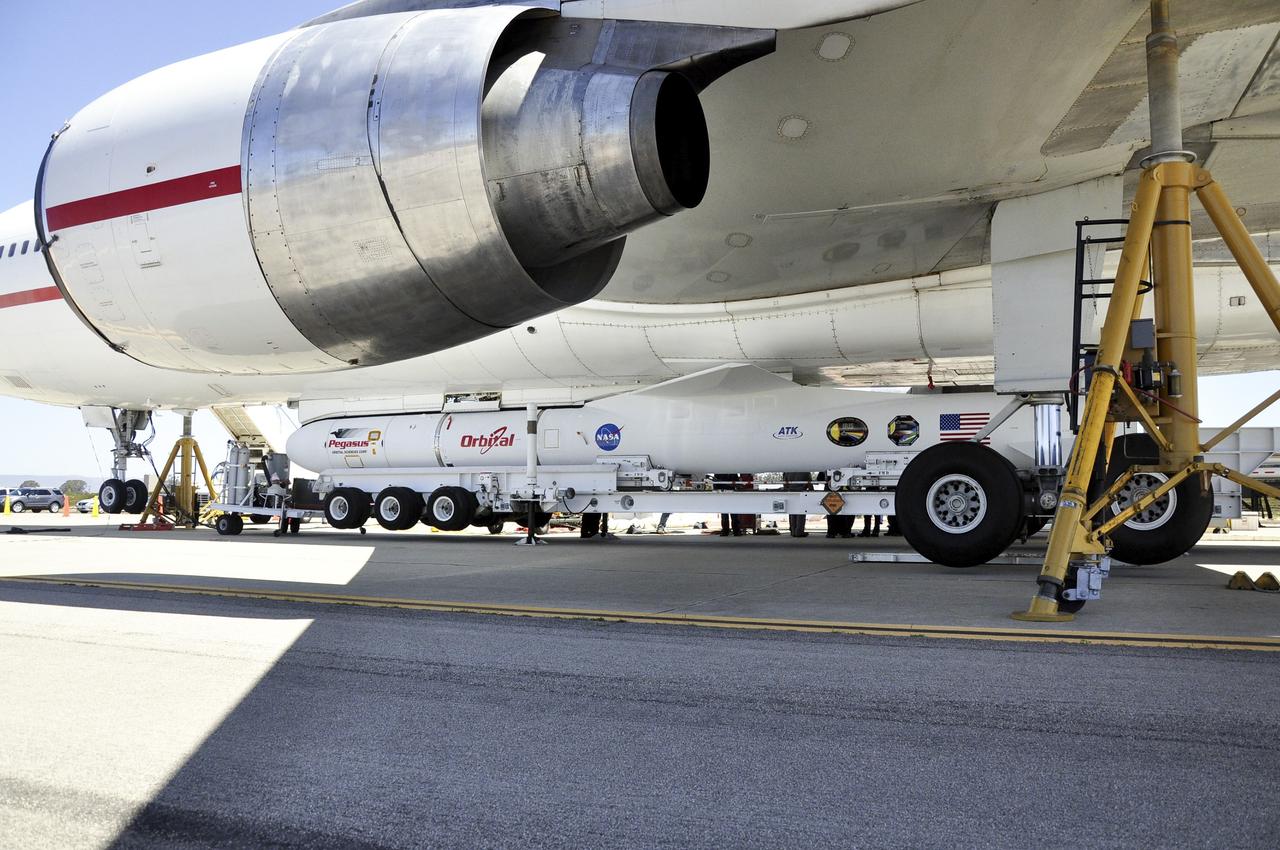
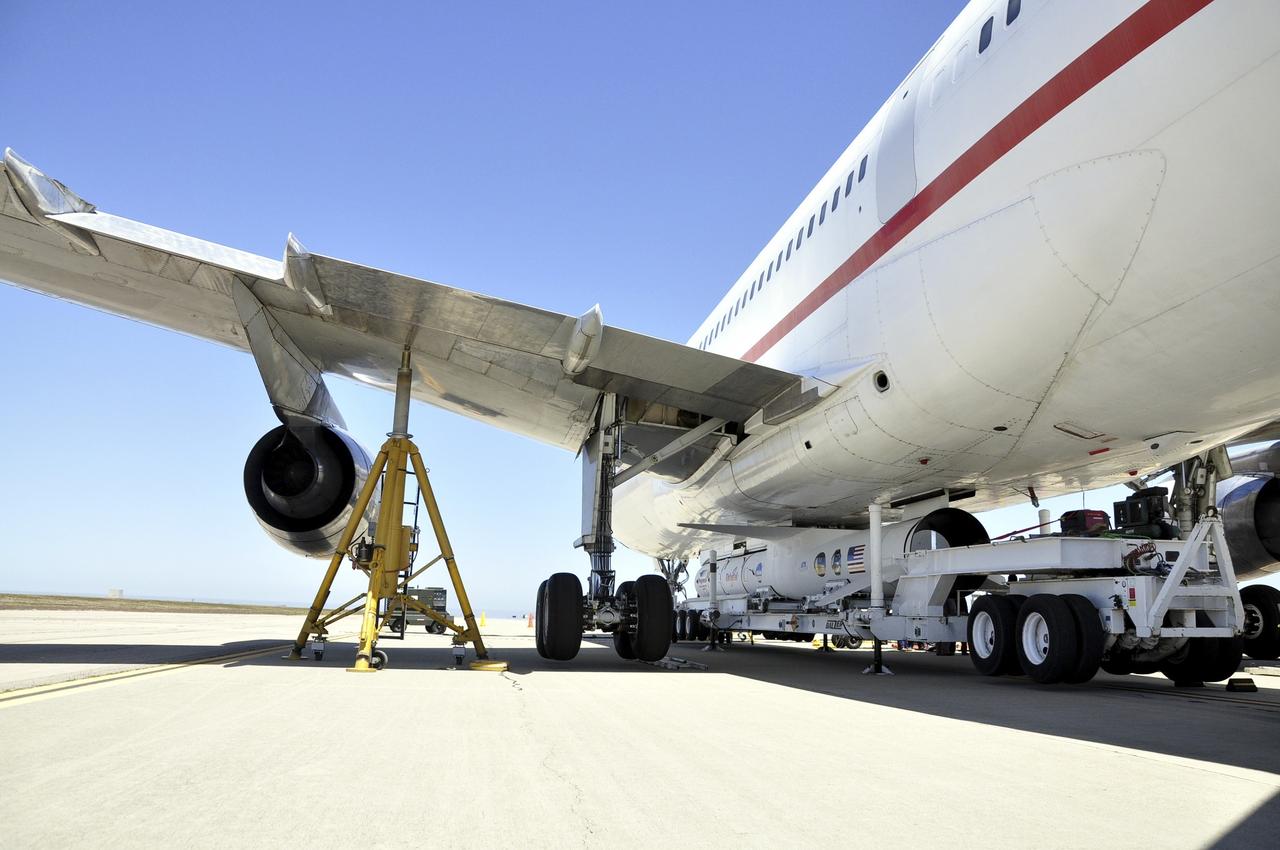
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Technicians and engineers at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California mate the Pegasus XL rocket with the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, solar observatory to the Orbital Sciences L-1011 carrier aircraft. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg on June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. The IRIS mission will observe how solar material moves, gathers energy and heats up as it travels through a largely unexplored region of the solar atmosphere. The interface region, located between the sun's visible surface and upper atmosphere, is where most of the sun's ultraviolet emission is generated. These emissions impact the near-Earth space environment and Earth's climate. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/iris Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
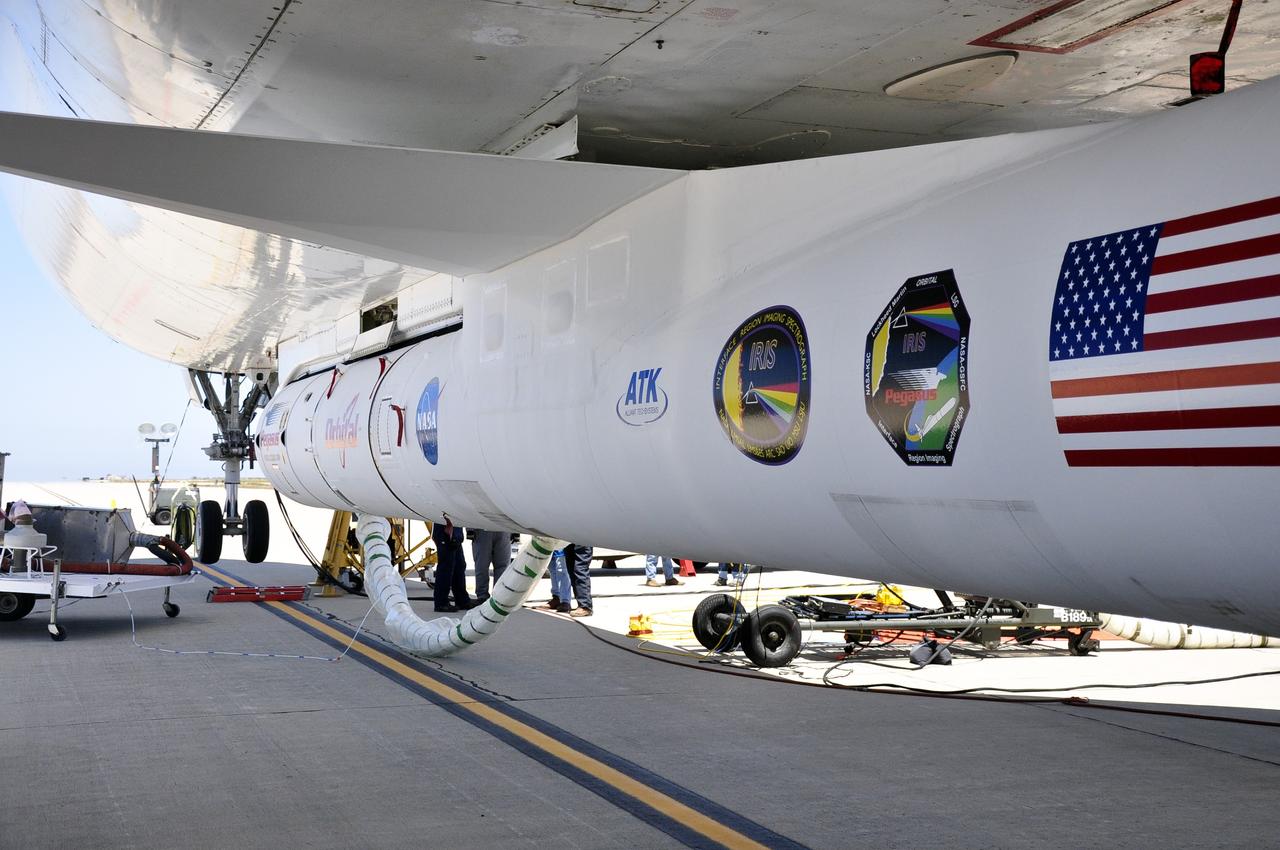

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Technicians and engineers at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California mate the Pegasus XL rocket with the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, solar observatory to the Orbital Sciences L-1011 carrier aircraft. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg on June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. The IRIS mission will observe how solar material moves, gathers energy and heats up as it travels through a largely unexplored region of the solar atmosphere. The interface region, located between the sun's visible surface and upper atmosphere, is where most of the sun's ultraviolet emission is generated. These emissions impact the near-Earth space environment and Earth's climate. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/iris Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Technicians and engineers at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California mate the Pegasus XL rocket with the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, solar observatory to the Orbital Sciences L-1011 carrier aircraft. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg on June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. The IRIS mission will observe how solar material moves, gathers energy and heats up as it travels through a largely unexplored region of the solar atmosphere. The interface region, located between the sun's visible surface and upper atmosphere, is where most of the sun's ultraviolet emission is generated. These emissions impact the near-Earth space environment and Earth's climate. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/iris Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Technicians and engineers at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California mate the Pegasus XL rocket with the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, solar observatory to the Orbital Sciences L-1011 carrier aircraft. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg on June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. The IRIS mission will observe how solar material moves, gathers energy and heats up as it travels through a largely unexplored region of the solar atmosphere. The interface region, located between the sun's visible surface and upper atmosphere, is where most of the sun's ultraviolet emission is generated. These emissions impact the near-Earth space environment and Earth's climate. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/iris Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Technicians and engineers at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California mate the Pegasus XL rocket with the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, solar observatory to the Orbital Sciences L-1011 carrier aircraft. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg on June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. The IRIS mission will observe how solar material moves, gathers energy and heats up as it travels through a largely unexplored region of the solar atmosphere. The interface region, located between the sun's visible surface and upper atmosphere, is where most of the sun's ultraviolet emission is generated. These emissions impact the near-Earth space environment and Earth's climate. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/iris Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
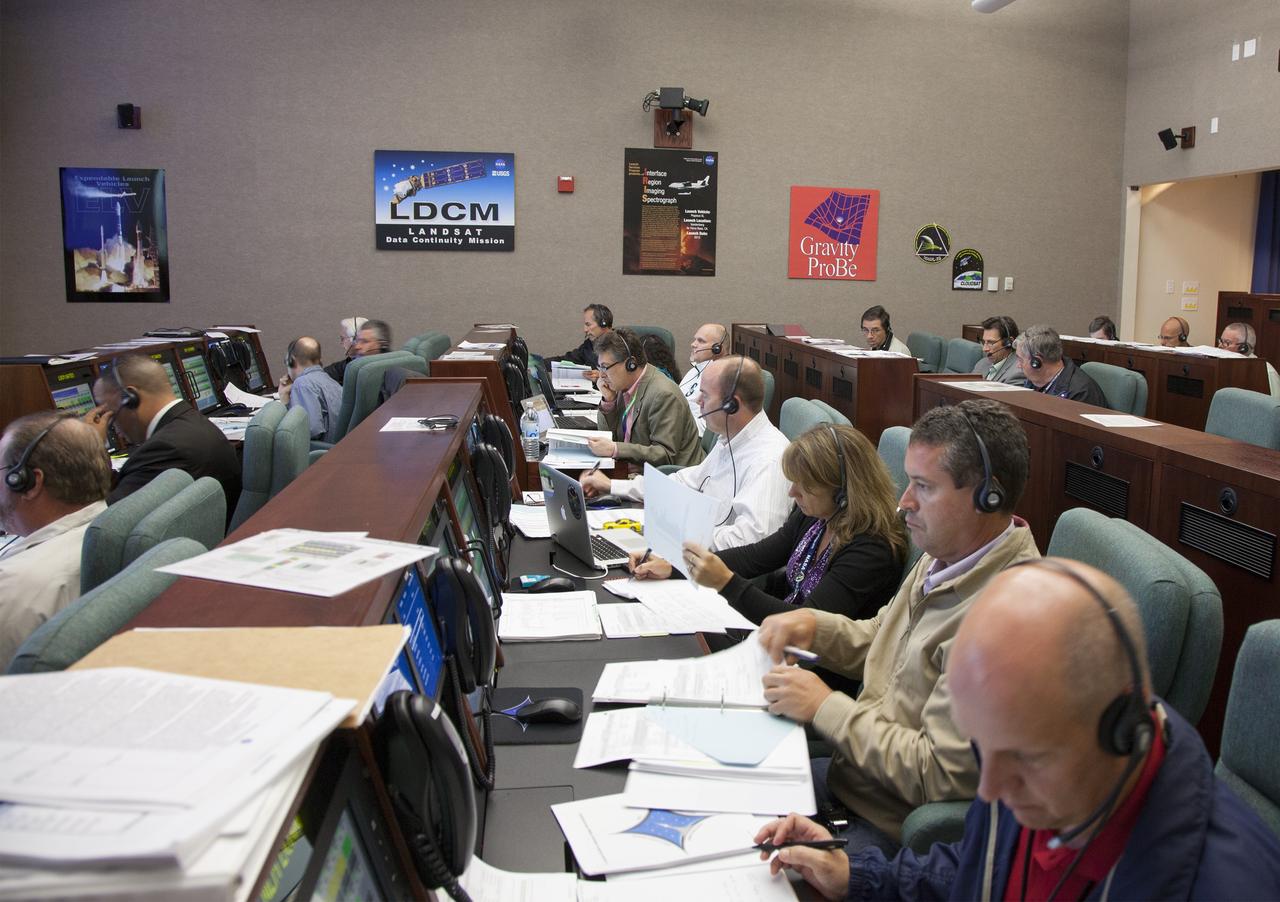

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, mission managers participate in a pre-launch dress rehearsal in the Launch Vehicle Data Center for NASA’s Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, solar observatory. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg on June 26 aboard an Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region in to the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. The IRIS mission will observe how solar material moves, gathers energy and heats up as it travels through a largely unexplored region of the solar atmosphere. The interface region, located between the sun’s visible surface and upper atmosphere, is where most of the sun’s ultraviolet emission is generated. These emissions impact the near-Earth space environment and Earth’s climate. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/iris. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Technicians and engineers at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California mate the Pegasus XL rocket with the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, solar observatory to the Orbital Sciences L-1011 carrier aircraft. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg on June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. The IRIS mission will observe how solar material moves, gathers energy and heats up as it travels through a largely unexplored region of the solar atmosphere. The interface region, located between the sun's visible surface and upper atmosphere, is where most of the sun's ultraviolet emission is generated. These emissions impact the near-Earth space environment and Earth's climate. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/iris Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, mission managers participate in a pre-launch dress rehearsal in the Launch Vehicle Data Center for NASA’s Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, solar observatory. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg on June 26 aboard an Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region in to the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. The IRIS mission will observe how solar material moves, gathers energy and heats up as it travels through a largely unexplored region of the solar atmosphere. The interface region, located between the sun’s visible surface and upper atmosphere, is where most of the sun’s ultraviolet emission is generated. These emissions impact the near-Earth space environment and Earth’s climate. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/iris. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Technicians and engineers at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California mate the Pegasus XL rocket with the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, solar observatory to the Orbital Sciences L-1011 carrier aircraft. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg on June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. The IRIS mission will observe how solar material moves, gathers energy and heats up as it travels through a largely unexplored region of the solar atmosphere. The interface region, located between the sun's visible surface and upper atmosphere, is where most of the sun's ultraviolet emission is generated. These emissions impact the near-Earth space environment and Earth's climate. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/iris Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Technicians and engineers at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California mate the Pegasus XL rocket with the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, solar observatory to the Orbital Sciences L-1011 carrier aircraft. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg on June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. The IRIS mission will observe how solar material moves, gathers energy and heats up as it travels through a largely unexplored region of the solar atmosphere. The interface region, located between the sun's visible surface and upper atmosphere, is where most of the sun's ultraviolet emission is generated. These emissions impact the near-Earth space environment and Earth's climate. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/iris Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Technicians and engineers at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California mate the Pegasus XL rocket with the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, solar observatory to the Orbital Sciences L-1011 carrier aircraft. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg on June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. The IRIS mission will observe how solar material moves, gathers energy and heats up as it travels through a largely unexplored region of the solar atmosphere. The interface region, located between the sun's visible surface and upper atmosphere, is where most of the sun's ultraviolet emission is generated. These emissions impact the near-Earth space environment and Earth's climate. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/iris Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, mission managers participate in a pre-launch dress rehearsal in the Launch Vehicle Data Center for NASA’s Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, solar observatory. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg on June 26 aboard an Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region in to the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. The IRIS mission will observe how solar material moves, gathers energy and heats up as it travels through a largely unexplored region of the solar atmosphere. The interface region, located between the sun’s visible surface and upper atmosphere, is where most of the sun’s ultraviolet emission is generated. These emissions impact the near-Earth space environment and Earth’s climate. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/iris. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Technicians and engineers at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California mate the Pegasus XL rocket with the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, solar observatory to the Orbital Sciences L-1011 carrier aircraft. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg on June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. The IRIS mission will observe how solar material moves, gathers energy and heats up as it travels through a largely unexplored region of the solar atmosphere. The interface region, located between the sun's visible surface and upper atmosphere, is where most of the sun's ultraviolet emission is generated. These emissions impact the near-Earth space environment and Earth's climate. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/iris Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Technicians and engineers at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California mate the Pegasus XL rocket with the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, solar observatory to the Orbital Sciences L-1011 carrier aircraft. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg on June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. The IRIS mission will observe how solar material moves, gathers energy and heats up as it travels through a largely unexplored region of the solar atmosphere. The interface region, located between the sun's visible surface and upper atmosphere, is where most of the sun's ultraviolet emission is generated. These emissions impact the near-Earth space environment and Earth's climate. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/iris Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

Hubble Space Telescope (HST), with its solar array (SA) wings and high gain antennae (HGA) fully extended,is released from Discovery's, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103's, remote manipulator system (RMS) end effector and is set free into Earth orbit by the STS-31 crew. HST drifts away from the end effector over the Andes Mountains.Parts of Bolivia, Peru, Chile, and Argentina are visible. The view covers a huge area of the western half of South America stretching from 14 degrees south latitude to 23 degrees, about 1,000 kilometers.

Orbiter Discovery lowers its nose wheel after touching down on runway 33 at the Shuttle Landing Facility. Main gear touchdown was at 12:04 p.m. EST, landing on orbit 135. Discovery returns to Earth with its crew of seven after successfully completing mission STS-95, lasting nearly nine days and 3.6 million miles. The STS-95 crew consists of Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr.; Pilot Steven W. Lindsey; Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski; Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson; Payload Specialist John H. Glenn Jr., a senator from Ohio; Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain, with the European Space Agency (ESA); and Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai, M.D., with the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). The mission included research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process
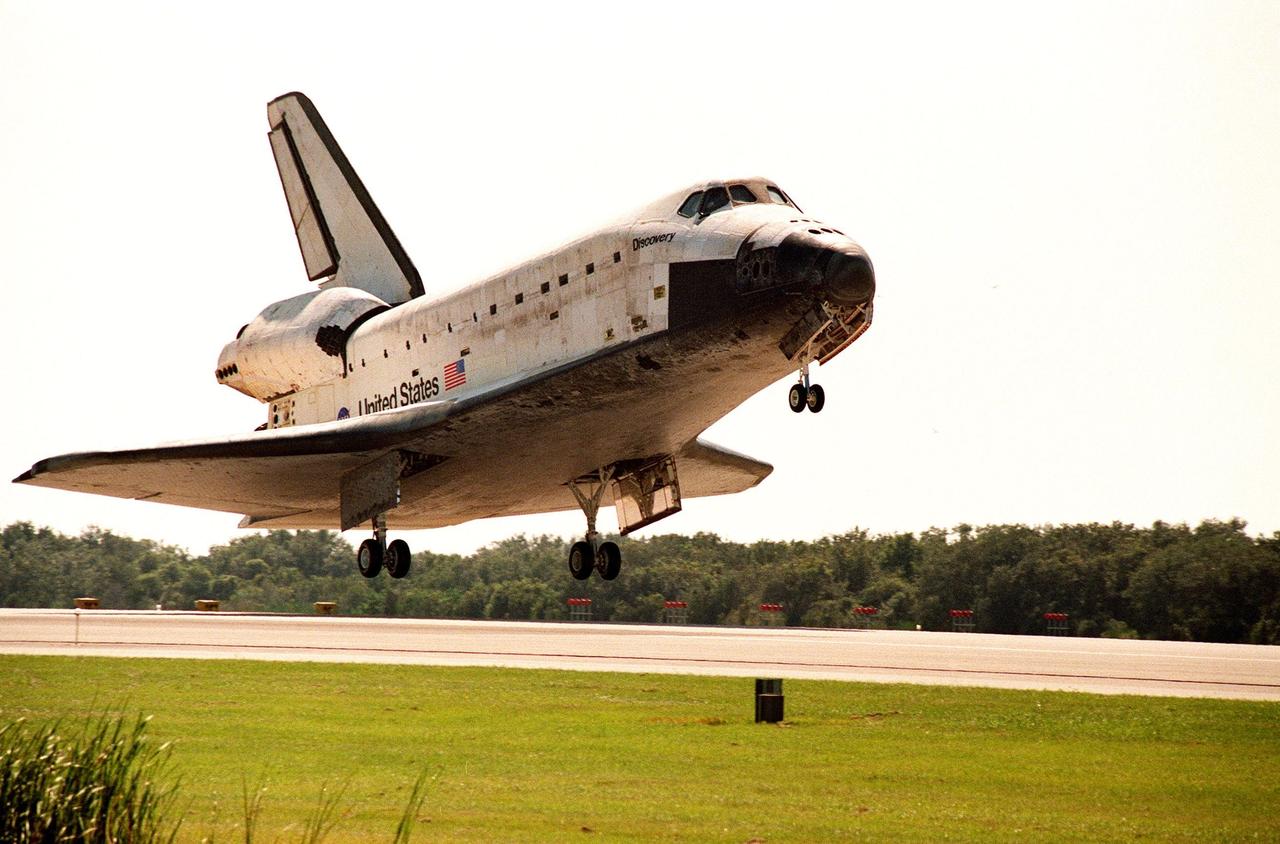

Orbiter Discovery prepares to land on runway 33 at the Shuttle Landing Facility. Main gear touchdown was at 12:04 p.m. EST, landing on orbit 135. Discovery returns to Earth with its crew of seven after successfully completing mission STS-95, lasting nearly nine days and 3.6 million miles. The crew members are Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr.; Pilot Steven W. Lindsey; Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski; Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson; Payload Specialist John H. Glenn Jr., a senator from Ohio; Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain, with the European Space Agency (ESA); and Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai, M.D., with the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). The mission included research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process
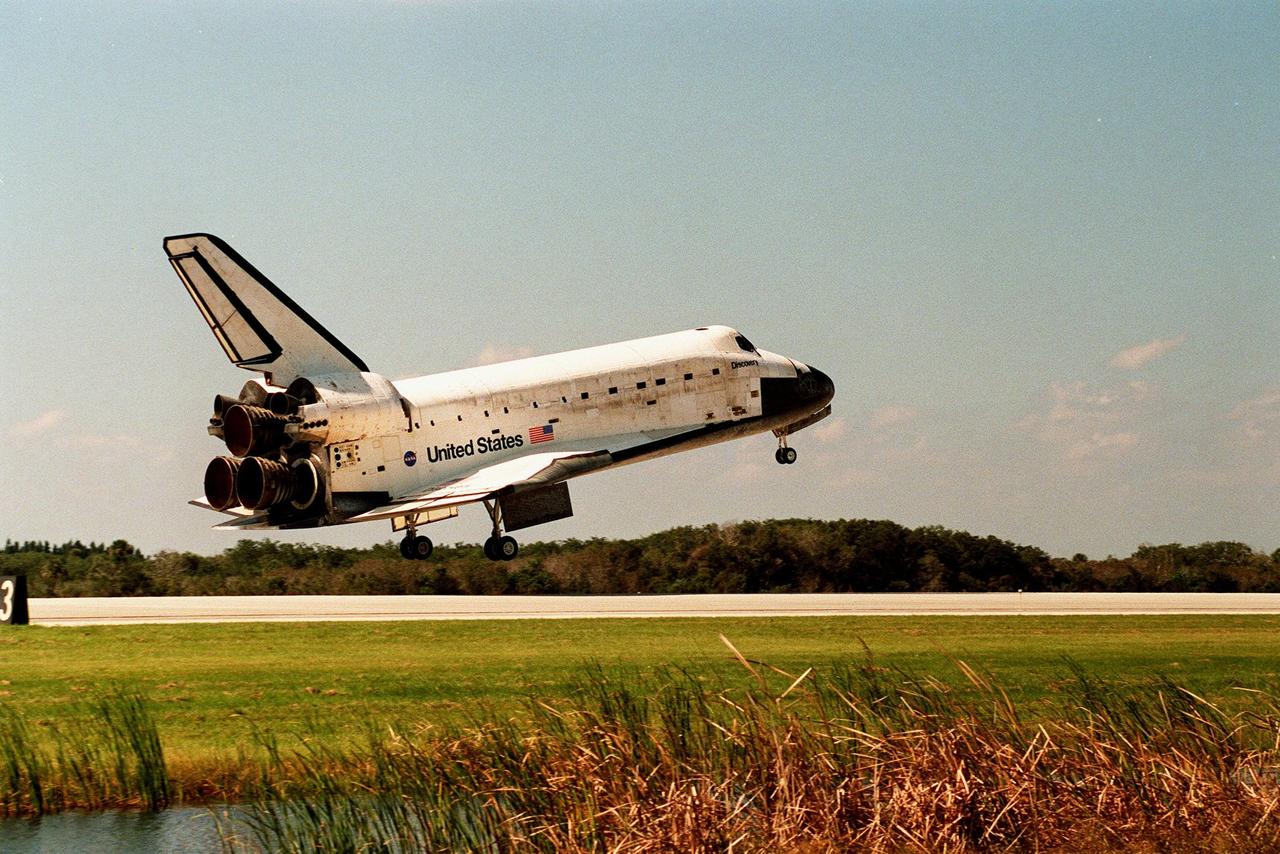

Orbiter Discovery prepares to land on runway 33 at the Shuttle Landing Facility. Main gear touchdown was at 12:04 p.m. EST, landing on orbit 135. Discovery returns to Earth with its crew of seven after successfully completing mission STS-95, lasting nearly nine days and 3.6 million miles. The crew members are Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr.; Pilot Steven W. Lindsey; Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski; Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson; Payload Specialist John H. Glenn Jr., a senator from Ohio; Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain, with the European Space Agency (ESA); and Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai, M.D., with the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). The mission included research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process
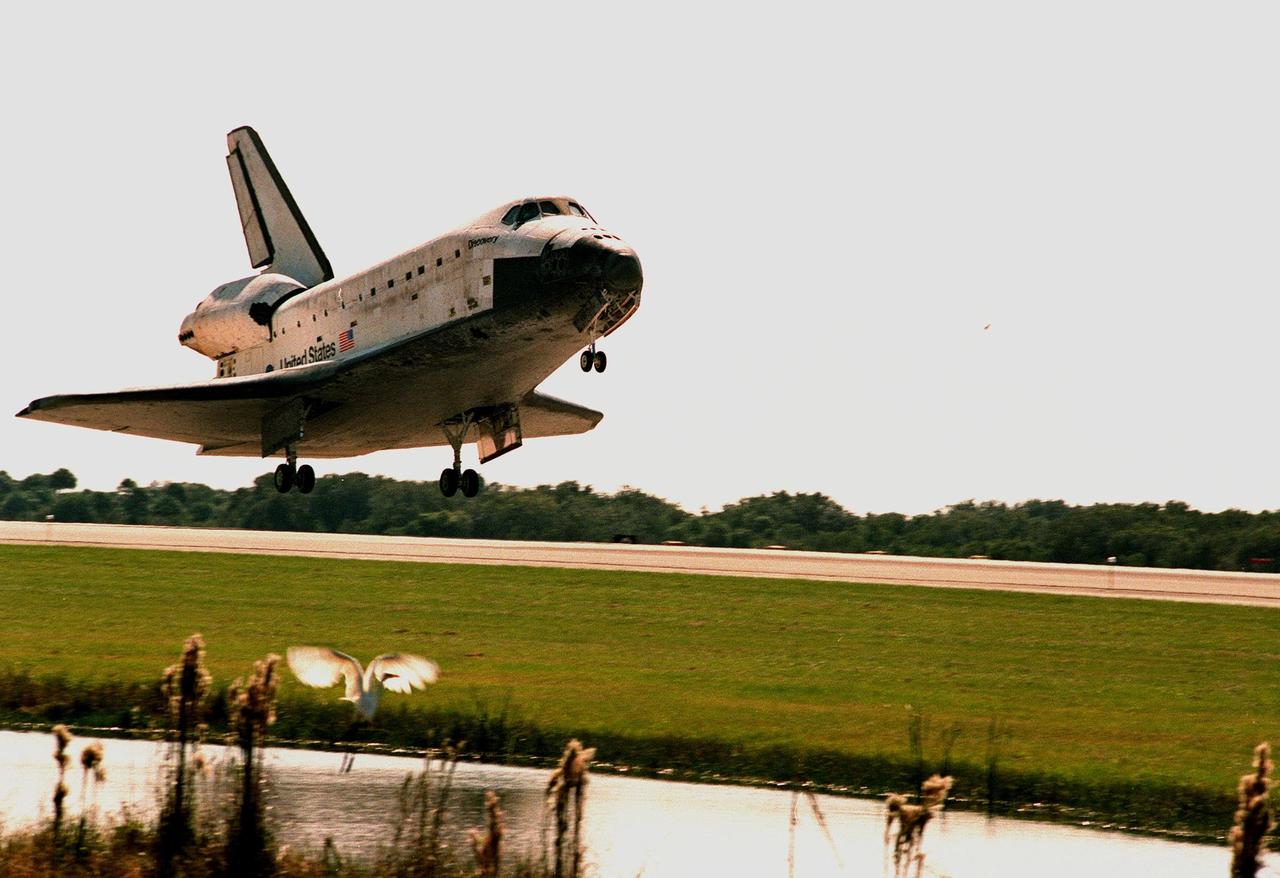

Orbiter Discovery startles a great white egret (below) next to runway 33 as it touches down at the Shuttle Landing Facility. Main gear touchdown was at 12:04 p.m. EST, landing on orbit 135. Discovery returns to Earth with its crew of seven after successfully completing mission STS-95, lasting nearly nine days and 3.6 million miles. The crew consists of Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr.; Pilot Steven W. Lindsey; Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski; Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson; Payload Specialist John H. Glenn Jr., a senator from Ohio; Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain, with the European Space Agency (ESA); and Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai, M.D., with the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). The mission included research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process
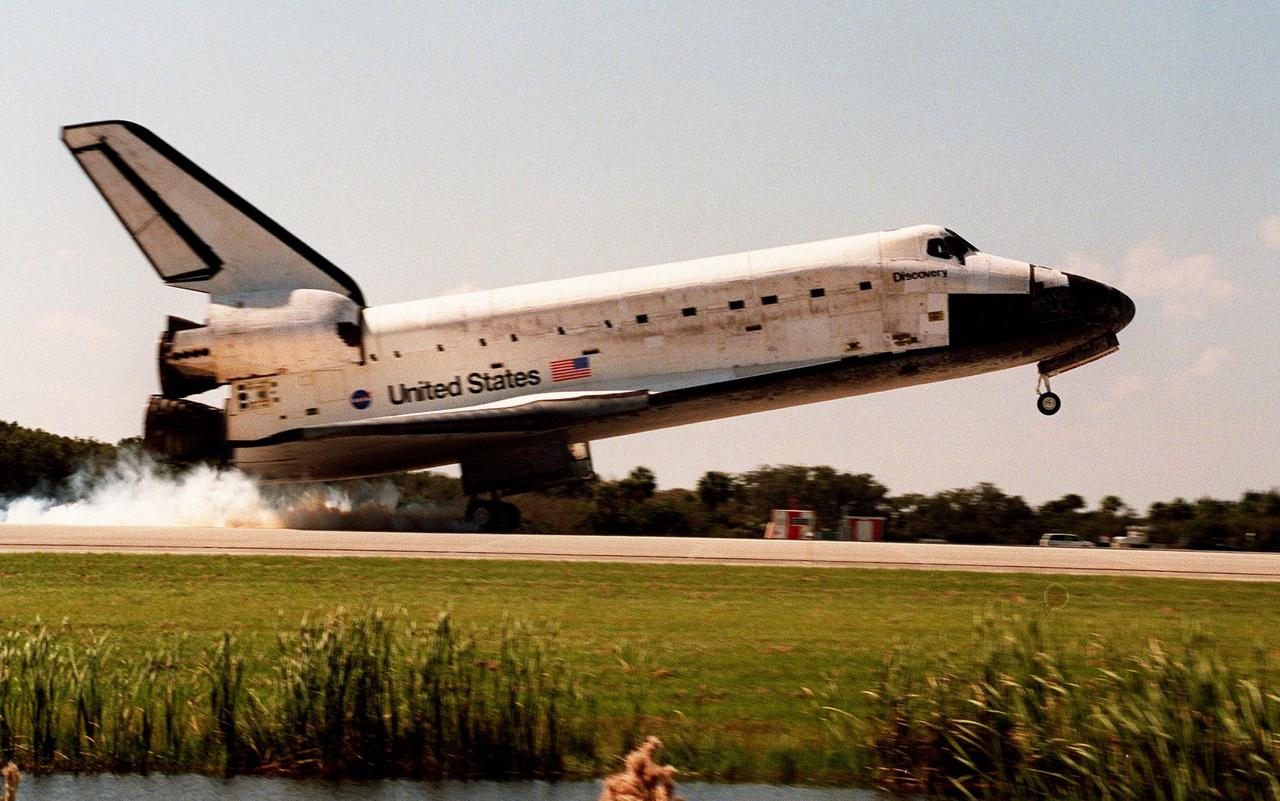

Orbiter Discovery smokes its tires as it touches down on runway 33 at the Shuttle Landing Facility. Main gear touchdown was at 12:04 p.m. EST, landing on orbit 135. Discovery returns to Earth with its crew of seven after successfully completing mission STS-95, lasting nearly nine days and 3.6 million miles. The crew consists of Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr.; Pilot Steven W. Lindsey; Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski; Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson; Payload Specialist John H. Glenn Jr., senator from Ohio; Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain, with the European Space Agency (ESA); and Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai,M.D., with the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). The mission included research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process
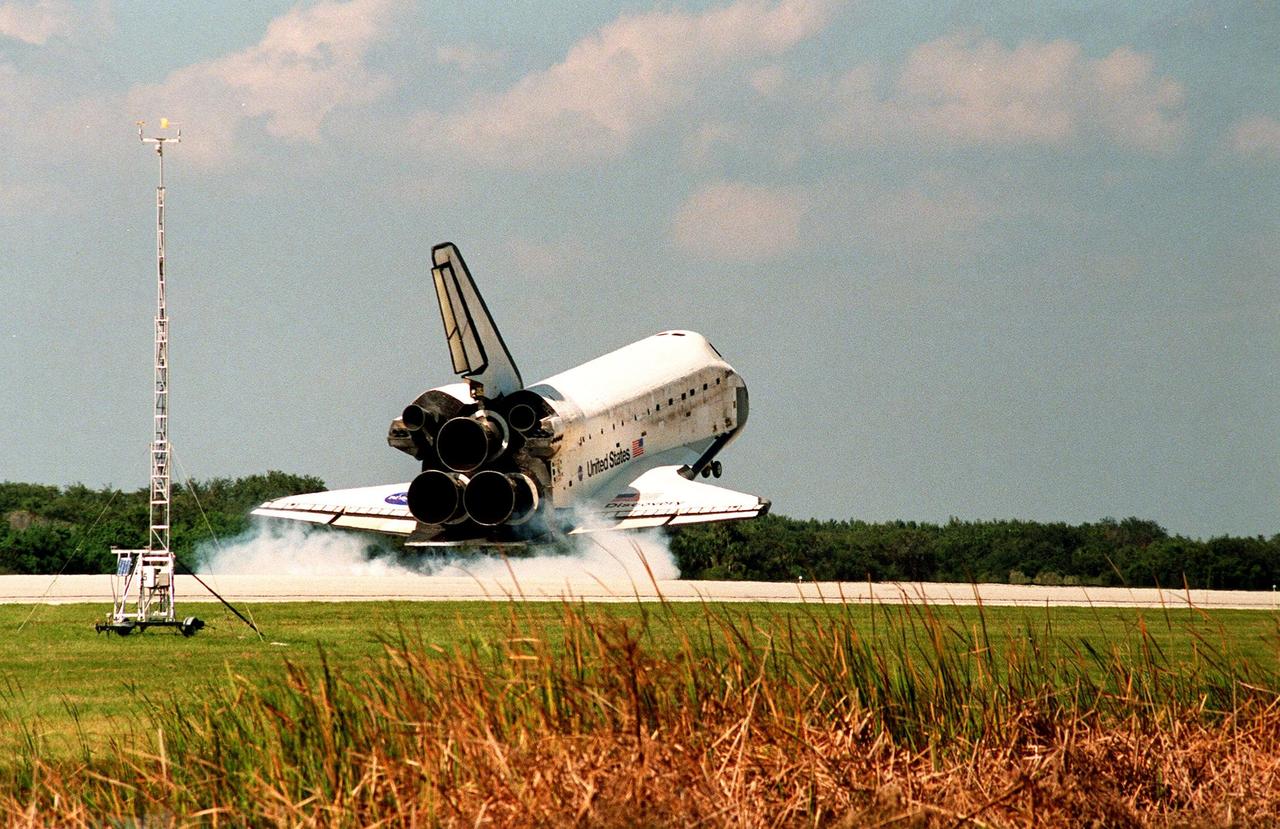

Orbiter Discovery touches down in a cloud of smoke on runway 33 at the Shuttle Landing Facility. Main gear touchdown was at 12:04 p.m. EST, landing on orbit 135. Discovery returns to Earth with its crew of seven after successfully completing mission STS-95, lasting nearly nine days and 3.6 million miles. The crew members are Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr.; Pilot Steven W. Lindsey; Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski; Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson; Payload Specialist John H. Glenn Jr., a senator from Ohio; Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain, with the European Space Agency (ESA); and Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai, M.D., with the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). The mission included research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process
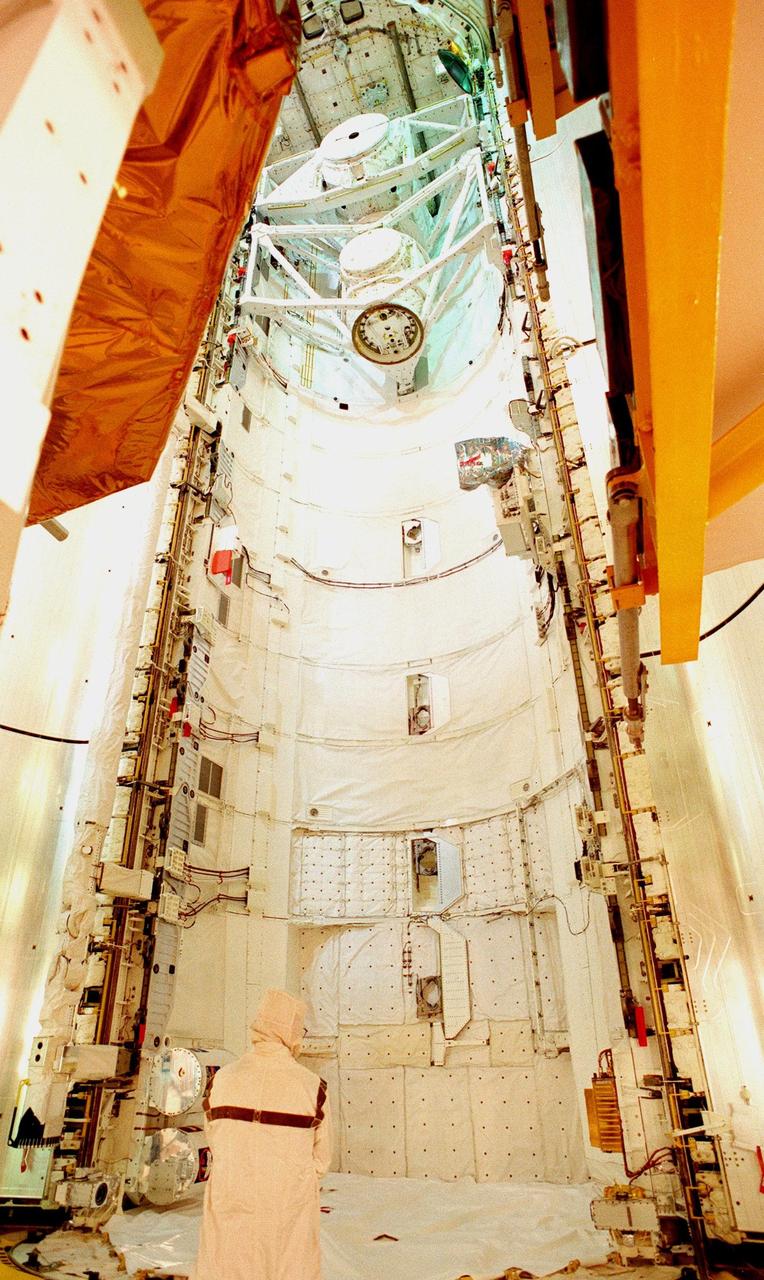
The open doors of the payload bay on Space Shuttle Discovery await the transfer of four of the payloads on mission STS-95: the SPACEHAB single module, Spartan, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbiting Systems Test Platform (HOST), and the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker (IEH-3). At the top of bay are the airlock (used for depressurization and repressurization during extravehicular activity and transfer to Mir) and the tunnel adapter (enables the flight crew members to transfer from the pressurized middeck crew compartment to Spacelab's pressurized shirt-sleeve environment). SPACEHAB involves experiments on space flight and the aging process. Spartan is a solar physics spacecraft designed to perform remote sensing of the hot outer layers of the sun's atmosphere or corona. HOST carries four experiments to validate components planned for installation during the third Hubble Space Telescope servicing mission and to evaluate new technologies in an Earth-orbiting environment. IEH-3 comprises several experiments that will study the Jovian planetary system, hot stars, planetary and reflection nebulae, other stellar objects and their environments through remote observation of EUV/FUV emissions; study spacecraft interactions, Shuttle glow, thruster firings, and contamination; and measure the solar constant and identify variations in the value during a solar cycle. Discovery is scheduled to launch on Oct. 29, 1998

ASTRO-2 was the second dedicated Spacelab mission to conduct astronomical observations in the ultraviolet spectral regions. It consisted of three unique instruments: the Hopkins Ultraviolet Telescope (HUT), the Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (UIT) and the Wisconsin Ultraviolet Photo-Polorimeter Experiment ((WUPPE). These experiments selected targets from a list of over 600 and observed objects ranging from some inside the solar system to individual stars, nebulae, supernova remnants, galaxies, and active extra galactic objects. This data supplemented data collected on the ASTRO-1 mission flown on the STS-35 mission in December 1990. Because most ultraviolet radiation is absorbed by Earth's atmosphere, it carnot be studied from the ground. The far and extreme ultraviolet regions of the spectrum were largely unexplored before ASTRO-1, but knowledge of all wavelengths is essential to obtain an accurate picture of the universe. ASTRO-2 had almost twice the duration of its predecessor, and a launch at a different time of year allows the telescopes to view different portions of the sky. The mission served to fill in large gaps in astronomers' understanding of the universe and laid the foundations for more discovery in the future. ASTRO-2, a primary payload of STS-67 flight, was launched on March 2, 1995 aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour.
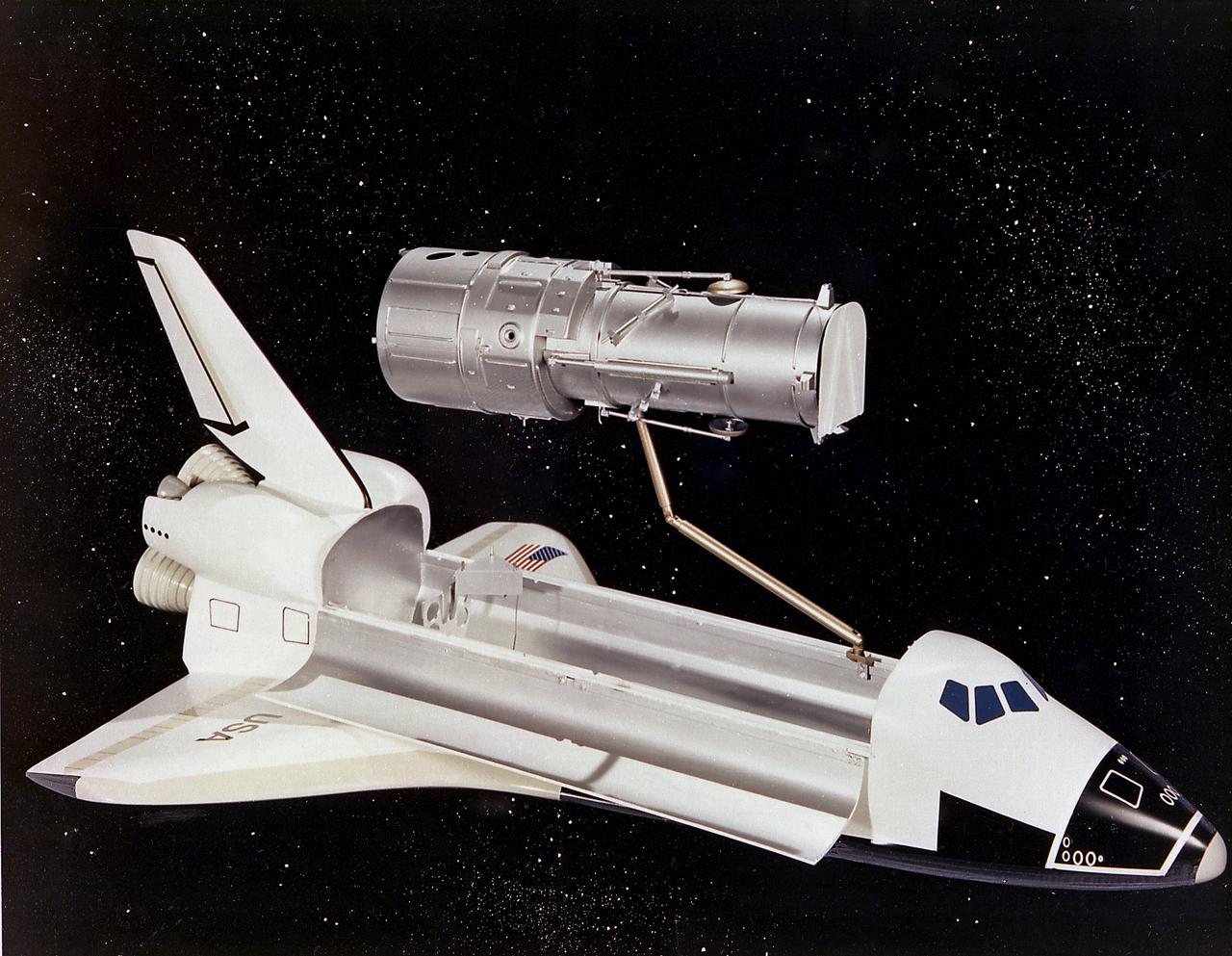
This artist's concept depicts the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) being positioned for release from the Space Shuttle orbiter by the Remote Manipulator System (RMS). The HST is the product of a partnership between NASA, European Space Agency Contractors, and the international community of astronomers. It is named after Edwin P. Hubble, an American Astronomer who discovered the expanding nature of the universe and was the first to realize the true nature of galaxies. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The major elements of the HST are the Optical Telescope Assembly (OTA), the Support System Module (SSM), and the Scientific Instruments (SI). The HST is 42.5-feet (13- meters) long and weighs about 25,000 pounds (11,600 kilograms). The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Cornecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. The Lockheed Missile and Space Company of Sunnyvale, California produced the protective outer shroud and spacecraft systems, and assembled and tested the finished telescope.
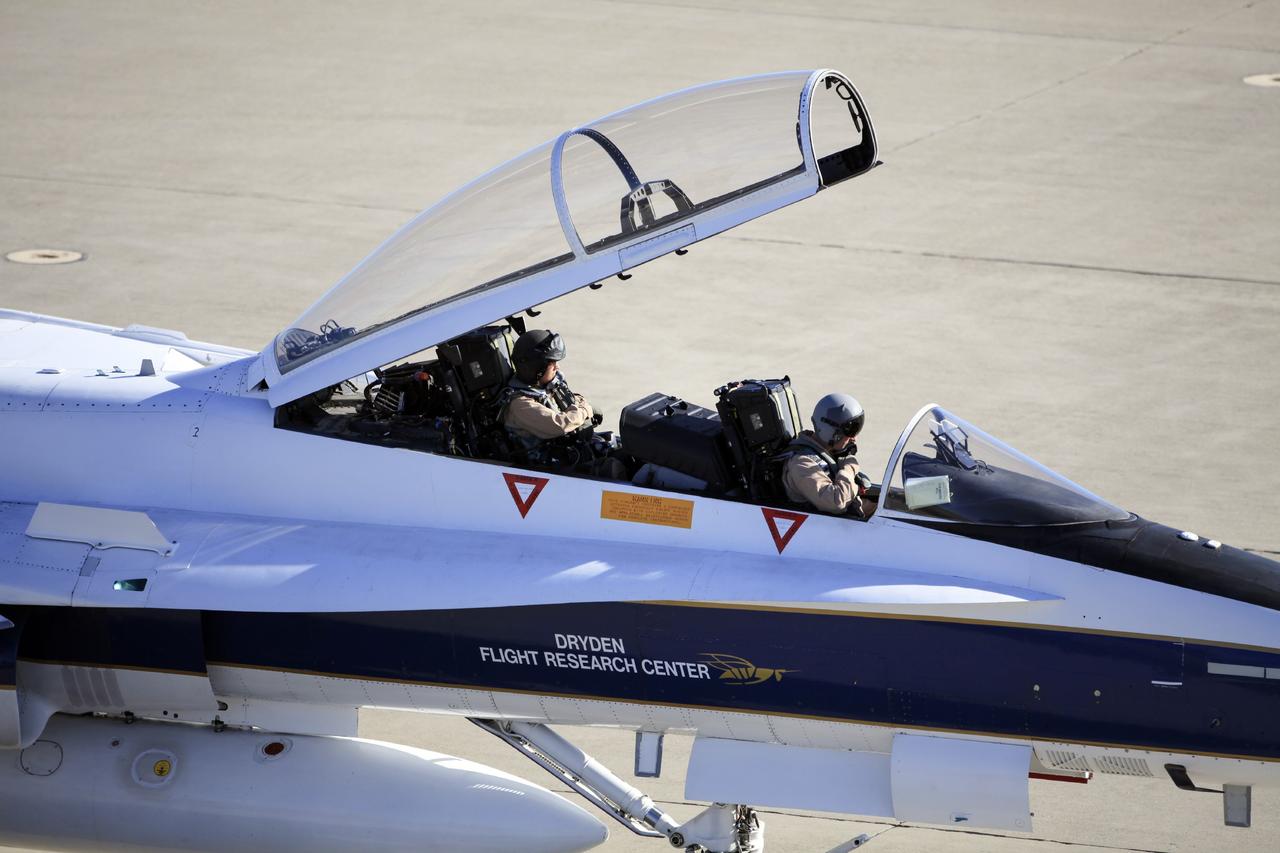

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Videographer Lori Losey, back seat, and pilot Jim Less board an F-18 aircraft at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The F-18 will be the "chase plane" for the Orbital Sciences L-1011 aircraft transporting the Pegasus XL rocket that will launch NASA's Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, solar observatory to orbit. Release of the rocket from under the wing of the L-1011 is scheduled for 10:27 p.m. EDT. IRIS will open a new window of discovery using spectrometry and imaging to trace the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona. The spacecraft will observe how solar material moves, gathers energy and heats up as it travels through a largely unexplored region of the solar atmosphere. This interface region, located between the sun's visible surface and its upper atmosphere, is where most of its ultraviolet emission is generated. These emissions impact the near-Earth space environment and Earth's climate. NASA's Launch Services Program at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida is managing the countdown and launch. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/iris. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
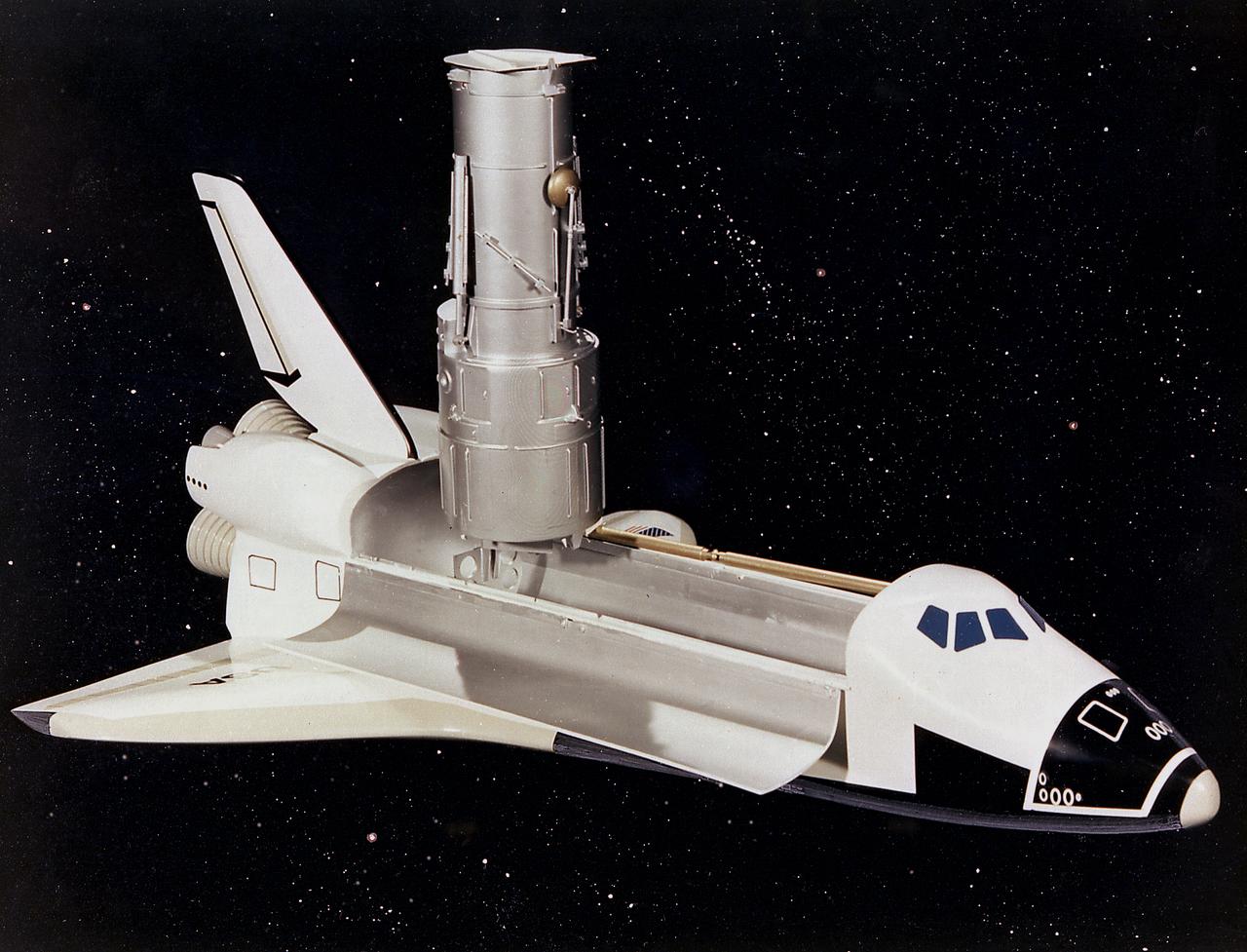
This artist's concept depicts the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) being raised to a vertical position in the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle orbiter. The HST is the product of a partnership between NASA, European Space Agency Contractors, and the international community of astronomers. It is named after Edwin P. Hubble, an American Astronomer who discovered the expanding nature of the universe and was the first to realize the true nature of galaxies. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The major elements of the HST are the Optical Telescope Assembly (OTA), the Support System Module (SSM), and the Scientific Instruments (SI). The HST is 42.5-feet (13-meters) long and weighs about 25,000 pounds (11,600 kilograms). The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Cornecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. The Lockheed Missile and Space Company of Sunnyvale, California produced the protective outer shroud and spacecraft systems, and assembled and tested the finished telescope.

The day after their return to Earth on board the orbiter Discovery, members of the STS-95 crew participate in a media briefing at the Kennedy Space Center Press Site Auditorium before returning to the Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas. From left to right are Lisa Malone, moderator and chief of NASA Public Affairs' Media Services at Kennedy Space Center; Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr.; Pilot Steven W. Lindsey; Mission Specialist and Payload Commander Stephen K. Robinson; Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski; Mission Specialist Pedro Duque, with the European Space Agency (ESA); Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai, with the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA); and Payload Specialist John H. Glenn Jr., a senator from Ohio and one of the original seven Project Mercury astronauts. The STS-95 mission ended with landing at Kennedy Space Center's Shuttle Landing Facility at 12:04 p.m. EST on Nov. 7. The mission included research payloads such as the Spartan-201 solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as a SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process
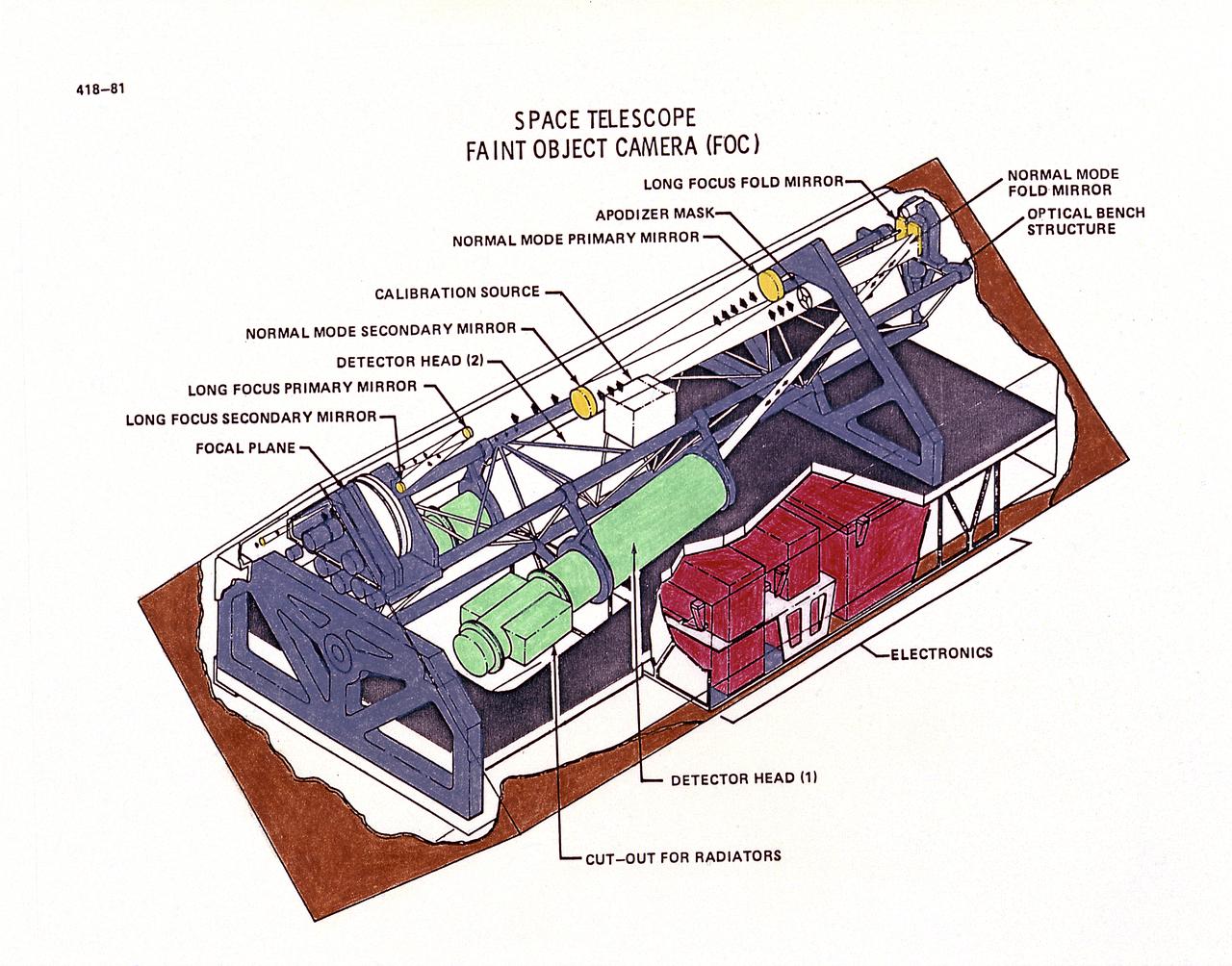
This drawing illustrates Hubble Space Telescope's (HST's), Faint Object Camera (FOC). The FOC reflects light down one of two optical pathways. The light enters a detector after passing through filters or through devices that can block out light from bright objects. Light from bright objects is blocked out to enable the FOC to see background images. The detector intensifies the image, then records it much like a television camera. For faint objects, images can be built up over long exposure times. The total image is translated into digital data, transmitted to Earth, and then reconstructed. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Cornecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors.
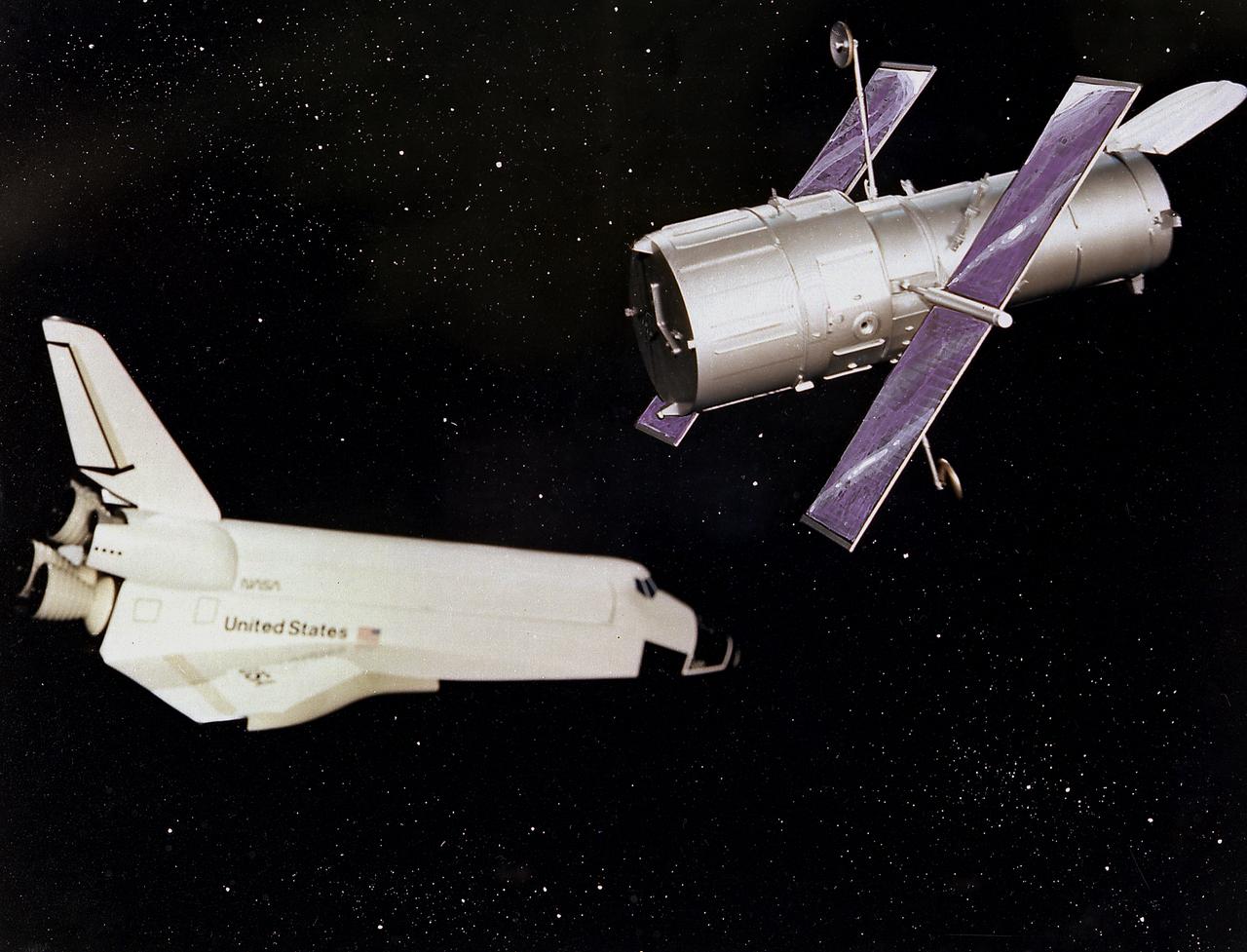
This artist's concept depicts the Hubble Space Telescope after being released into orbit, with the high gain anternas and solar arrays deployed and the aperture doors opened. The HST is the product of a partnership between NASA, European Space Agency Contractors, and the international community of astronomers. It is named after Edwin P. Hubble, an American Astronomer who discovered the expanding nature of the universe and was the first to realize the true nature of galaxies. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The major elements of the HST are the Optical Telescope Assembly (OTA), the Support System Module (SSM), and the Scientific Instruments (SI). The HST is 42.5-feet (13-meters) long and weighs about 25,000 pounds (11,600 kilograms). The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Connecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. The Lockheed Missile and Space Company of Sunnyvale, California produced the protective outer shroud and spacecraft systems, and assembled and tested the finished telescope.
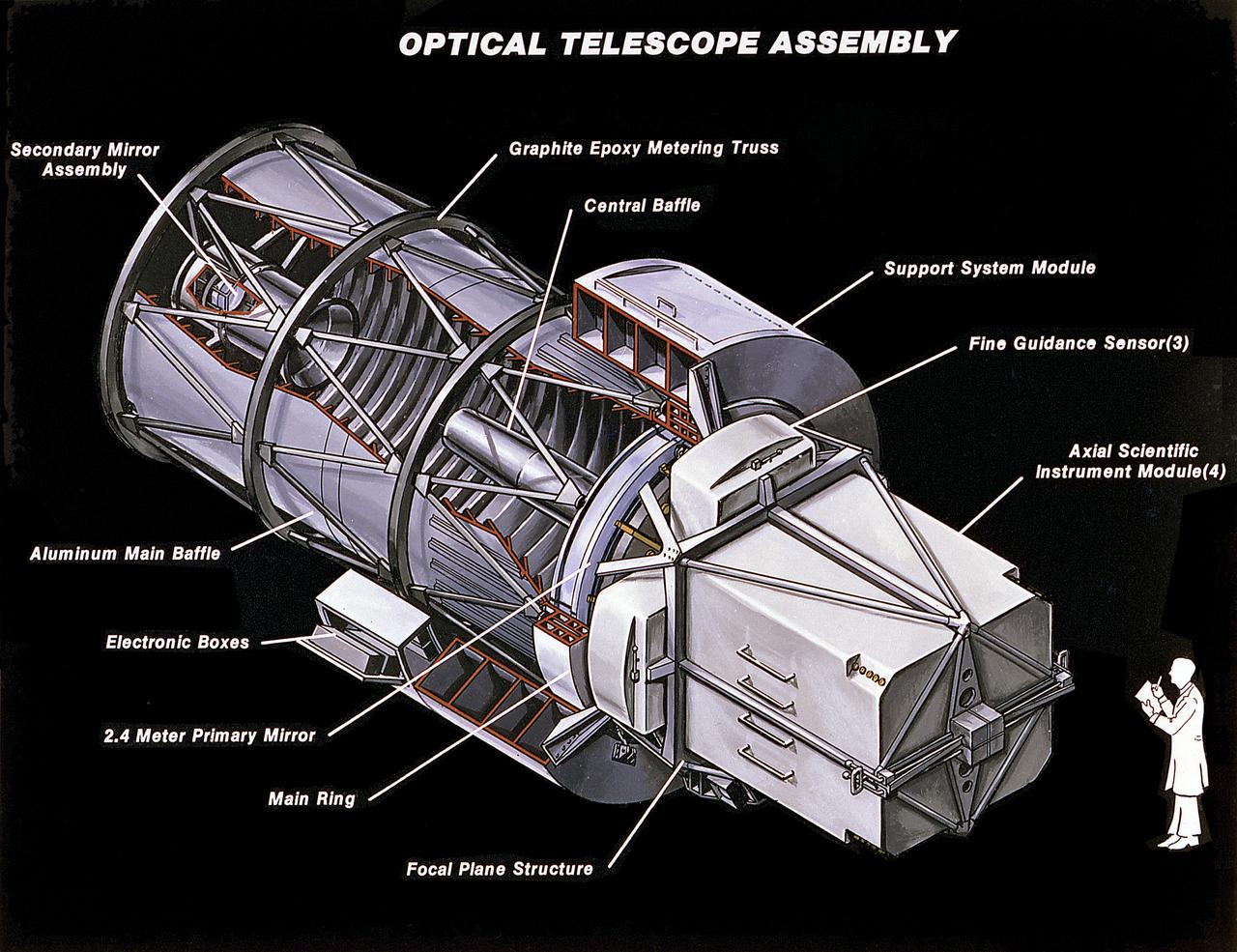
This image illustrates the Hubble Space Telescope's (HST's) Optical Telescope Assembly (OTA). One of the three major elements of the HST, the OTA consists of two mirrors (a primary mirror and a secondary mirror), support trusses, and the focal plane structure. The mirrors collect and focus light from selected celestial objects and are housed near the center of the telescope. The primary mirror captures light from objects in space and focuses it toward the secondary mirror. The secondary mirror redirects the light to a focal plane where the Scientific Instruments are located. The primary mirror is 94.5 inches (2.4 meters) in diameter and the secondary mirror is 12.2 inches (0.3 meters) in diameter. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth Orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from the Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The spacecraft is 42.5 feet (13 meters) long and weighs 25,000 pounds (11,600 kilograms). The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Cornecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. The Lockheed Missile and Space Company of Sunnyvale, California produced the protective outer shroud and spacecraft systems, and assembled and tested the finished telescope.

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – An Orbital Sciences L-1011 aircraft departs from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California at 9:30 p.m. EDT, headed over the Pacific Ocean to release the Pegasus XL rocket carrying NASA's Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, solar observatory. Release of the rocket from under the wing of the aircraft is scheduled for 10:27 p.m. EDT. IRIS will open a new window of discovery using spectrometry and imaging to trace the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona. The spacecraft will observe how solar material moves, gathers energy and heats up as it travels through a largely unexplored region of the solar atmosphere. This interface region, located between the sun's visible surface and its upper atmosphere, is where most of its ultraviolet emission is generated. These emissions impact the near-Earth space environment and Earth's climate. NASA's Launch Services Program at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida is managing the countdown and launch. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/iris. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – An F-18 aircraft flies by a launch pad as it departs from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The plane will serve as the "chase plane" accompanying the Orbital Sciences L-1011 aircraft as it transports the Pegasus XL rocket carrying NASA's Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, solar observatory over the Pacific Ocean. Release of the rocket from under the wing of the L-1011 is scheduled for 10:27 p.m. EDT. IRIS will open a new window of discovery using spectrometry and imaging to trace the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona. The spacecraft will observe how solar material moves, gathers energy and heats up as it travels through a largely unexplored region of the solar atmosphere. This interface region, located between the sun's visible surface and its upper atmosphere, is where most of its ultraviolet emission is generated. These emissions impact the near-Earth space environment and Earth's climate. NASA's Launch Services Program at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida is managing the countdown and launch. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/iris. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
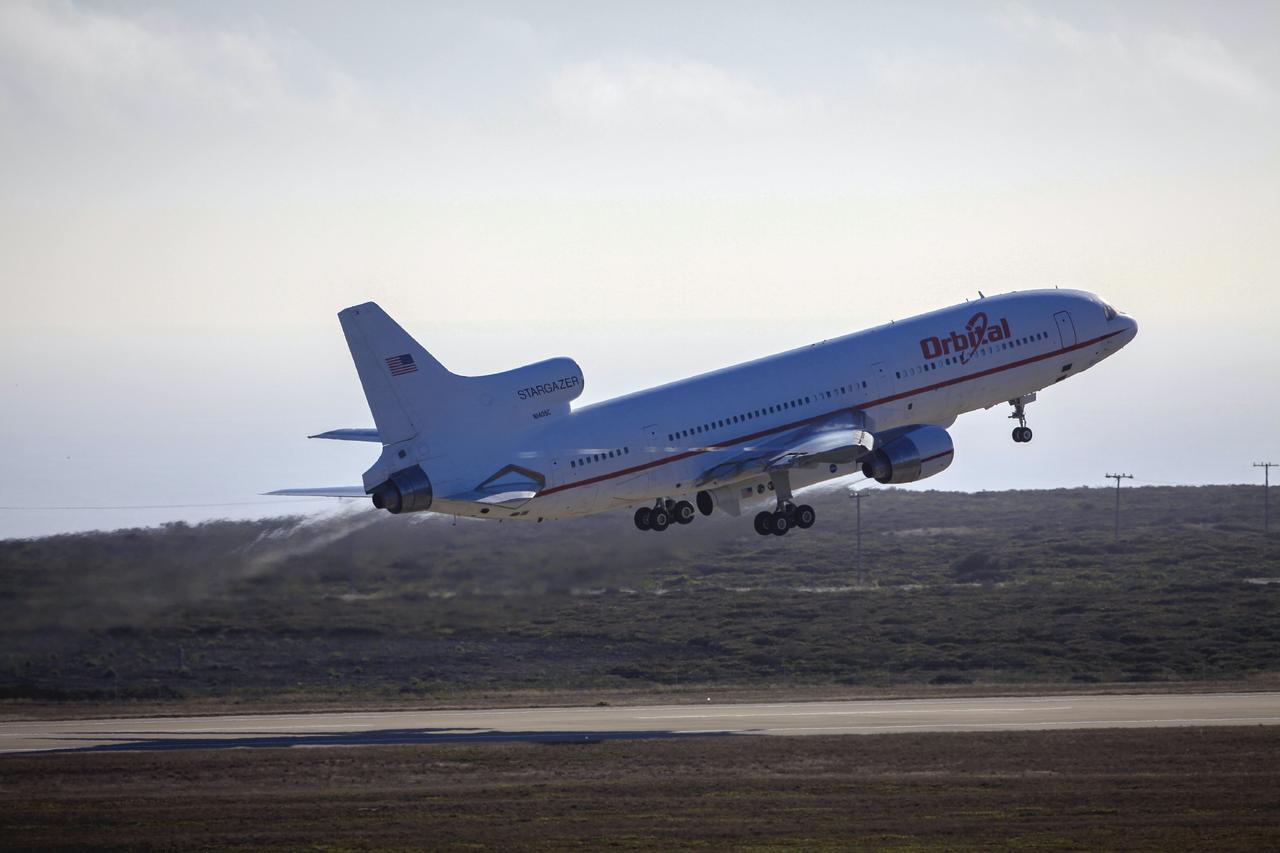

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The Orbital Sciences L-1011 aircraft takes off from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California at 9:30 p.m. EDT, headed over the Pacific Ocean to release the Pegasus XL rocket carrying NASA's Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, solar observatory. Release of the rocket from under the wing of the aircraft is scheduled for 10:27 p.m. EDT. IRIS will open a new window of discovery using spectrometry and imaging to trace the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona. The spacecraft will observe how solar material moves, gathers energy and heats up as it travels through a largely unexplored region of the solar atmosphere. This interface region, located between the sun's visible surface and its upper atmosphere, is where most of its ultraviolet emission is generated. These emissions impact the near-Earth space environment and Earth's climate. NASA's Launch Services Program at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida is managing the countdown and launch. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/iris. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
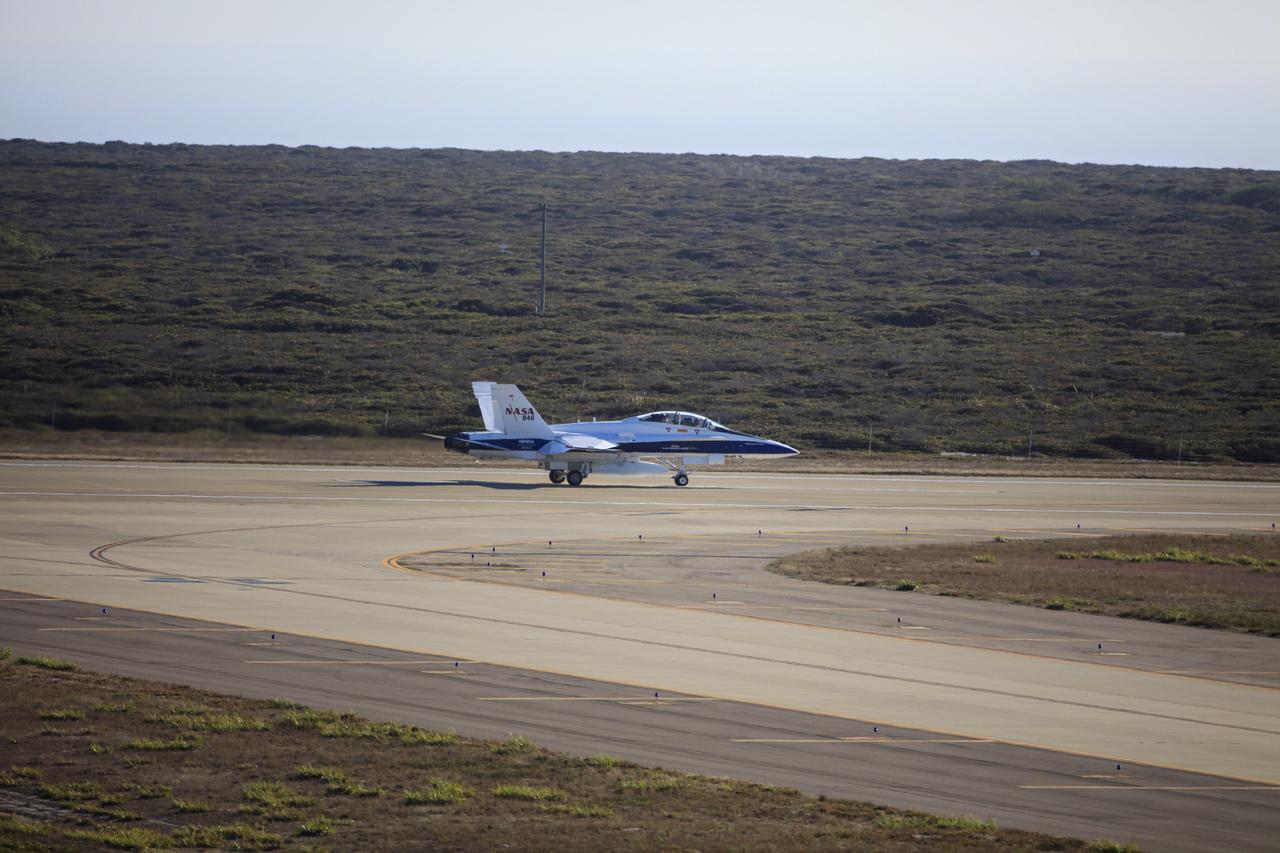

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – An F-18 aircraft departs from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The plane will serve as the "chase plane" accompanying the Orbital Sciences L-1011 aircraft as it transports the Pegasus XL rocket carrying NASA's Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, solar observatory over the Pacific Ocean. Release of the rocket from under the wing of the L-1011 is scheduled for 10:27 p.m. EDT. IRIS will open a new window of discovery using spectrometry and imaging to trace the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona. The spacecraft will observe how solar material moves, gathers energy and heats up as it travels through a largely unexplored region of the solar atmosphere. This interface region, located between the sun's visible surface and its upper atmosphere, is where most of its ultraviolet emission is generated. These emissions impact the near-Earth space environment and Earth's climate. NASA's Launch Services Program at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida is managing the countdown and launch. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/iris. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – An Orbital Sciences L-1011 aircraft departs from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California at 9:30 p.m. EDT, headed over the Pacific Ocean to release the Pegasus XL rocket carrying NASA's Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, solar observatory. Release of the rocket from under the wing of the aircraft is scheduled for 10:27 p.m. EDT. IRIS will open a new window of discovery using spectrometry and imaging to trace the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona. The spacecraft will observe how solar material moves, gathers energy and heats up as it travels through a largely unexplored region of the solar atmosphere. This interface region, located between the sun's visible surface and its upper atmosphere, is where most of its ultraviolet emission is generated. These emissions impact the near-Earth space environment and Earth's climate. NASA's Launch Services Program at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida is managing the countdown and launch. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/iris. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
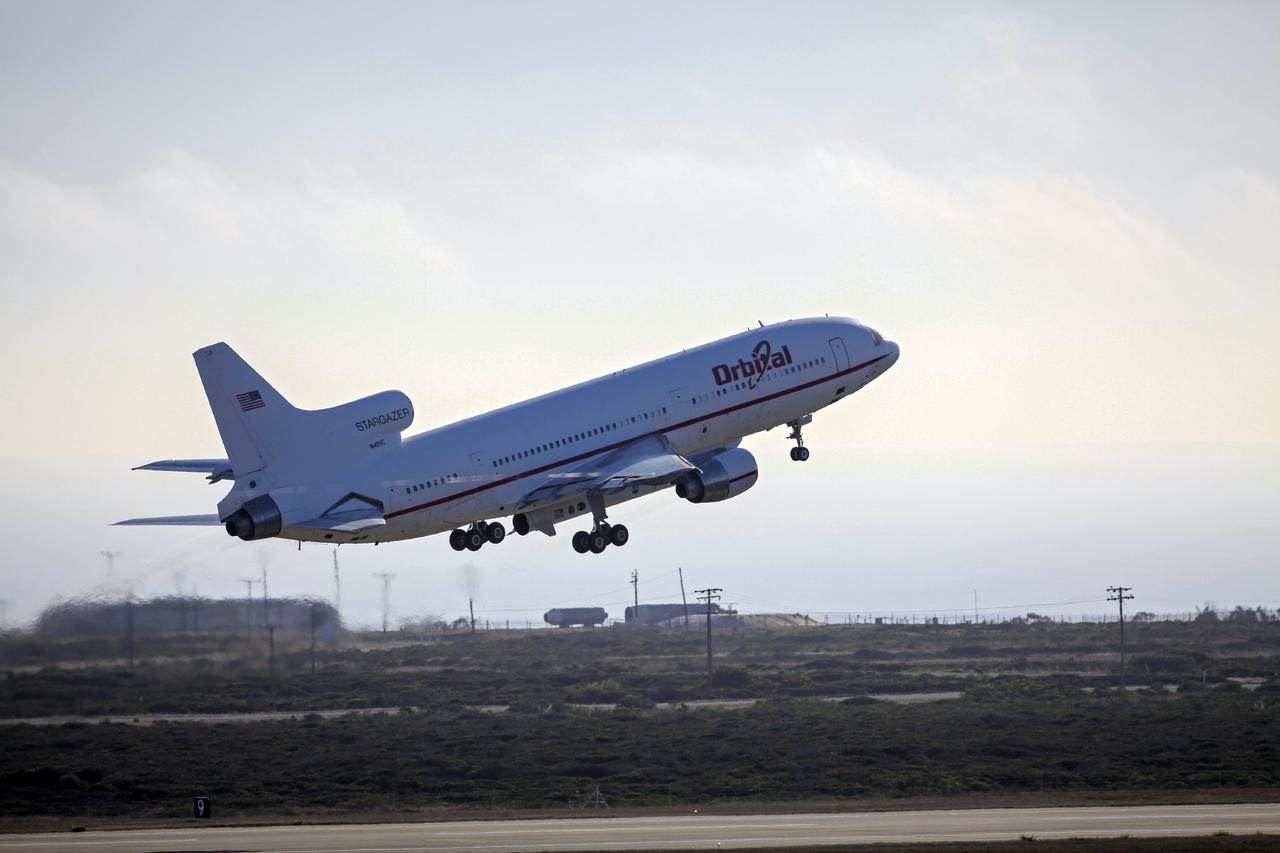

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – An Orbital Sciences L-1011 aircraft takes off from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California at 9:30 p.m. EDT, headed over the Pacific Ocean to release the Pegasus XL rocket carrying NASA's Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, solar observatory. Release of the rocket from under the wing of the aircraft is scheduled for 10:27 p.m. EDT. IRIS will open a new window of discovery using spectrometry and imaging to trace the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona. The spacecraft will observe how solar material moves, gathers energy and heats up as it travels through a largely unexplored region of the solar atmosphere. This interface region, located between the sun's visible surface and its upper atmosphere, is where most of its ultraviolet emission is generated. These emissions impact the near-Earth space environment and Earth's climate. NASA's Launch Services Program at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida is managing the countdown and launch. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/iris. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper

This is an artist's concept of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The HST is the product of a partnership between NASA, European Space Agency Contractors, and the international community of astronomers. It is named after Edwin P. Hubble, an American Astronomer who discovered the expanding nature of the universe and was the first to realize the true nature of galaxies. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than is visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The major elements of the HST are the Optical Telescope Assembly (OTA), the Support System Module (SSM), and the Scientific Instruments (SI). The HST is approximately the size of a railroad car, with two cylinders joined together and wrapped in a silvery reflective heat shield blanket. Wing-like solar arrays extend horizontally from each side of these cylinders, and dish-shaped anternas extend above and below the body of the telescope. The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Connecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. The Lockheed Missile and Space Company of Sunnyvale, California produced the protective outer shroud and spacecraft systems, and assembled and tested the finished telescope.
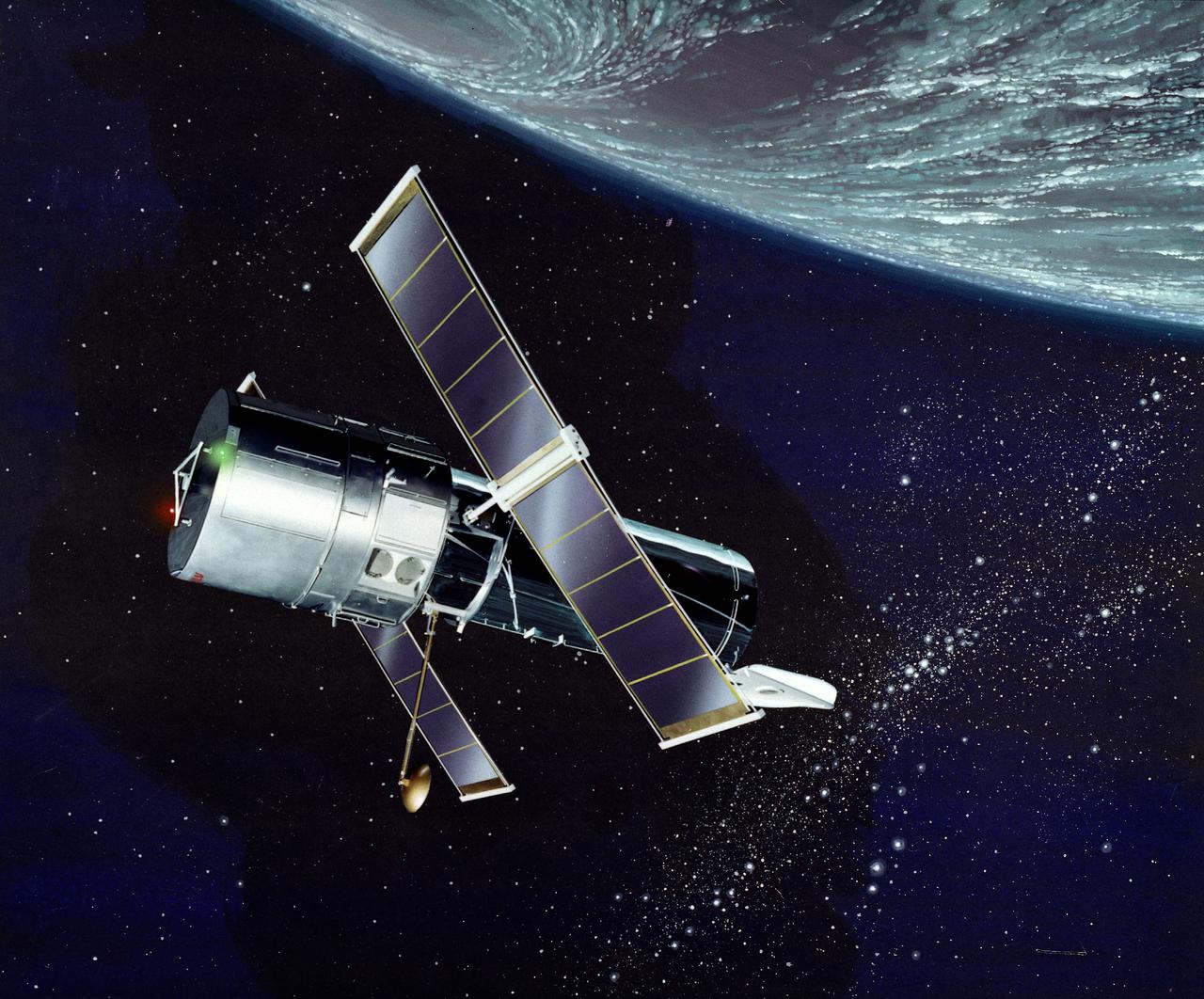

This illustration depicts a side view of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The HST is the product of a partnership between NASA, European Space Agency Contractors, and the international community of astronomers. It is named after Edwin P. Hubble, an American Astronomer who discovered the expanding nature of the universe and was the first to realize the true nature of galaxies. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The major elements of the HST are the Optical Telescope Assembly (OTA), the Support System Module (SSM), and the Scientific Instruments (SI). The HST is approximately the size of a railroad car, with two cylinders joined together and wrapped in a silvery reflective heat shield blanket. Wing-like solar arrays extend horizontally from each side of these cylinders, and dish-shaped anternas extend above and below the body of the telescope. The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Connecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. The Lockheed Missile and Space Company of Sunnyvale, California produced the protective outer shroud and spacecraft systems, and assembled and tested the finished telescope.
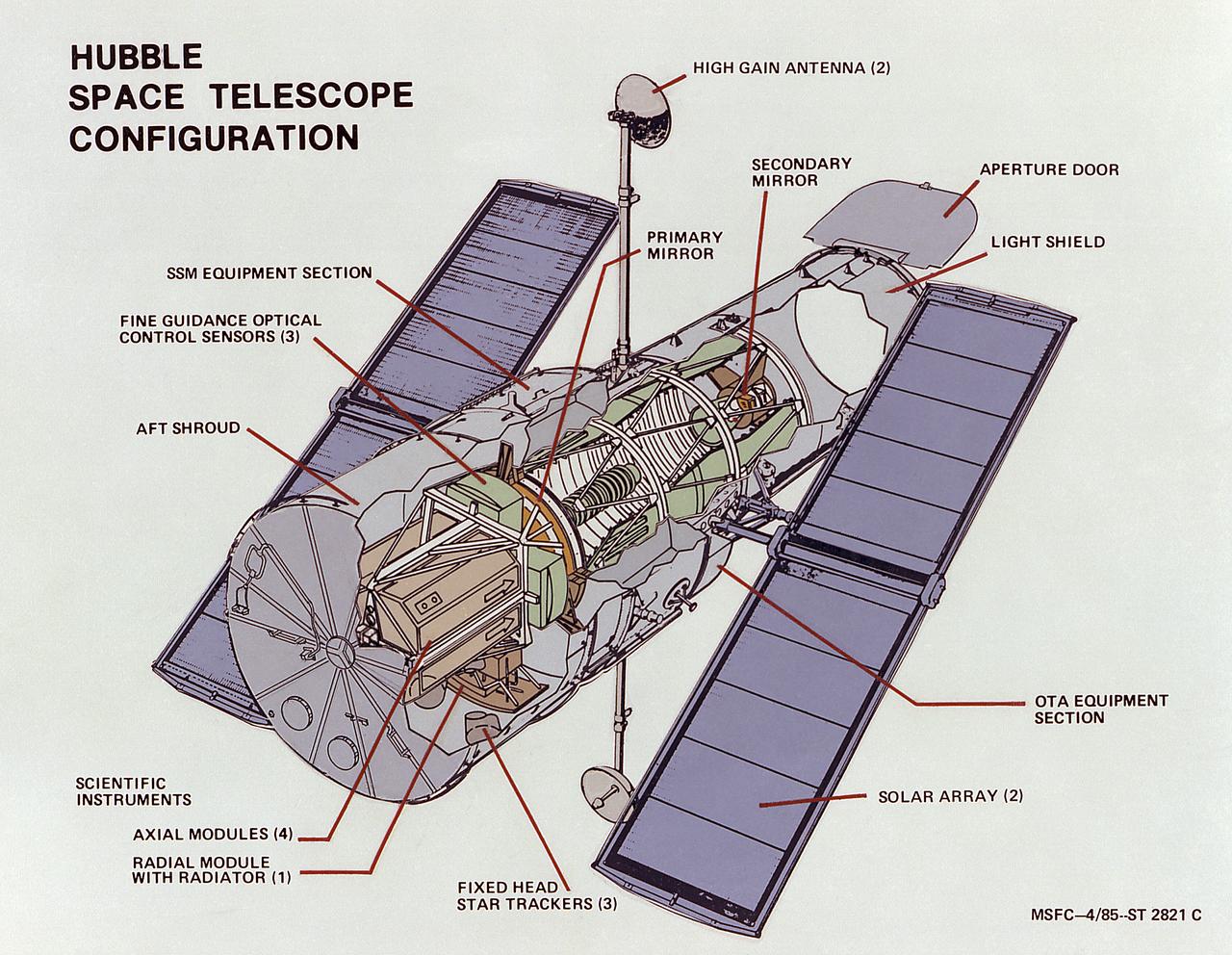
This image illustrates the overall Hubble Space Telescope (HST) configuration. The HST is the product of a partnership between NASA, European Space Agency Contractors, and the international community of astronomers. It is named after Edwin P. Hubble, an American Astronomer who discovered the expanding nature of the universe and was the first to realize the true nature of galaxies. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The major elements of the HST are the Optical Telescope Assembly (OTA), the Support System Module (SSM), and the Scientific Instruments (SI). The HST is approximately the size of a railroad car, with two cylinders joined together and wrapped in a silvery reflective heat shield blanket. Wing-like solar arrays extend horizontally from each side of these cylinders, and dish-shaped anternas extend above and below the body of the telescope. The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Connecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. The Lockheed Missile and Space Company of Sunnyvale, California produced the protective outer shroud and spacecraft systems, and assembled and tested the finished telescope.
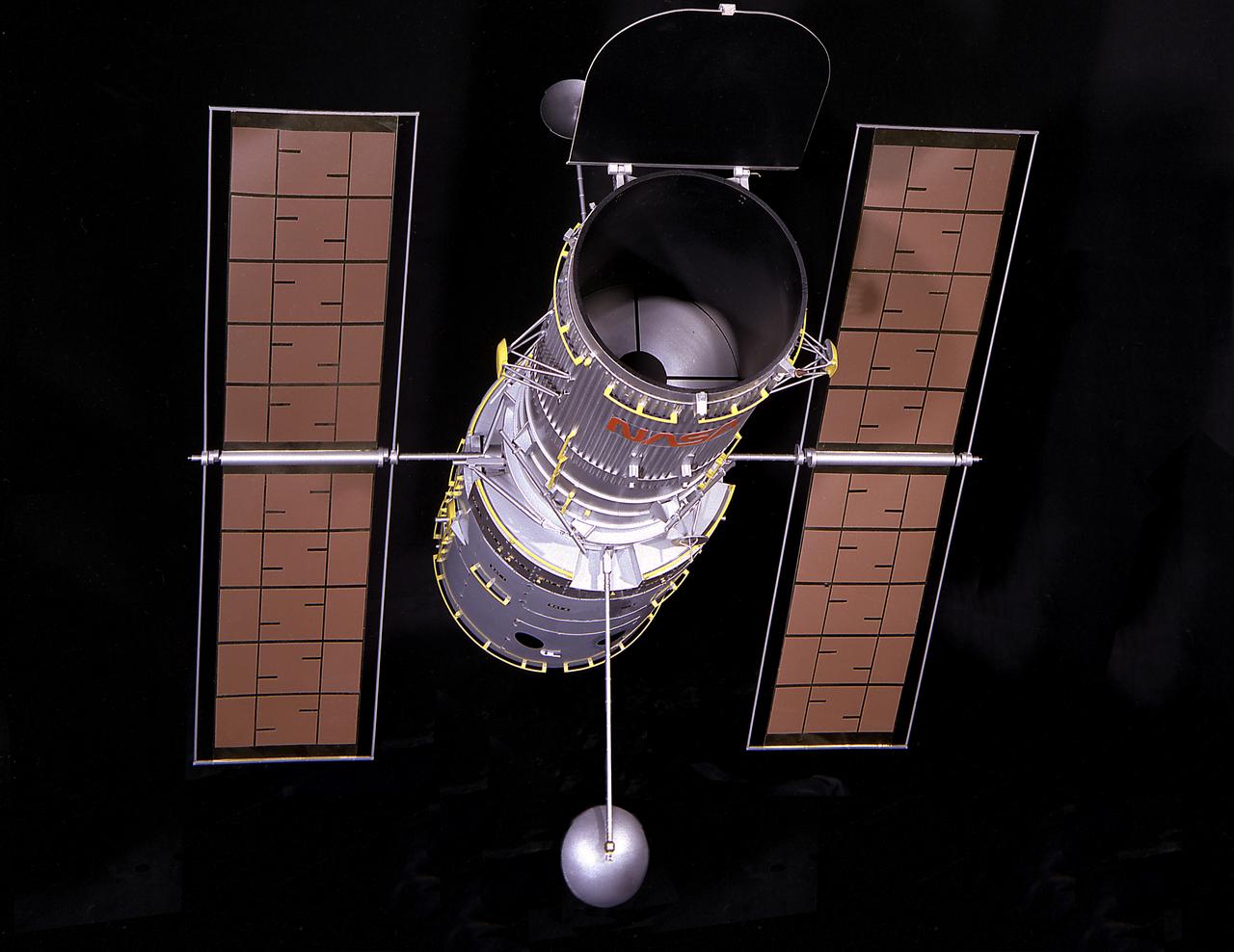
This is a photograph of a 1/15 scale model of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The HST is the product of a partnership between NASA, European Space Agency Contractors, and the international community of astronomers. It is named after Edwin P. Hubble, an American Astronomer who discovered the expanding nature of the universe and was the first to realize the true nature of galaxies. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The major elements of the HST are the Optical Telescope Assembly (OTA), the Support System Module (SSM), and the Scientific Instruments (SI). The HST is 42.5-feet (13- meters) long and weighs about 25,000 pounds (11,600 kilograms). The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Cornecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. The Lockheed Missile and Space Company of Sunnyvale, California produced the protective outer shroud and spacecraft systems, and assembled and tested the finished telescope.
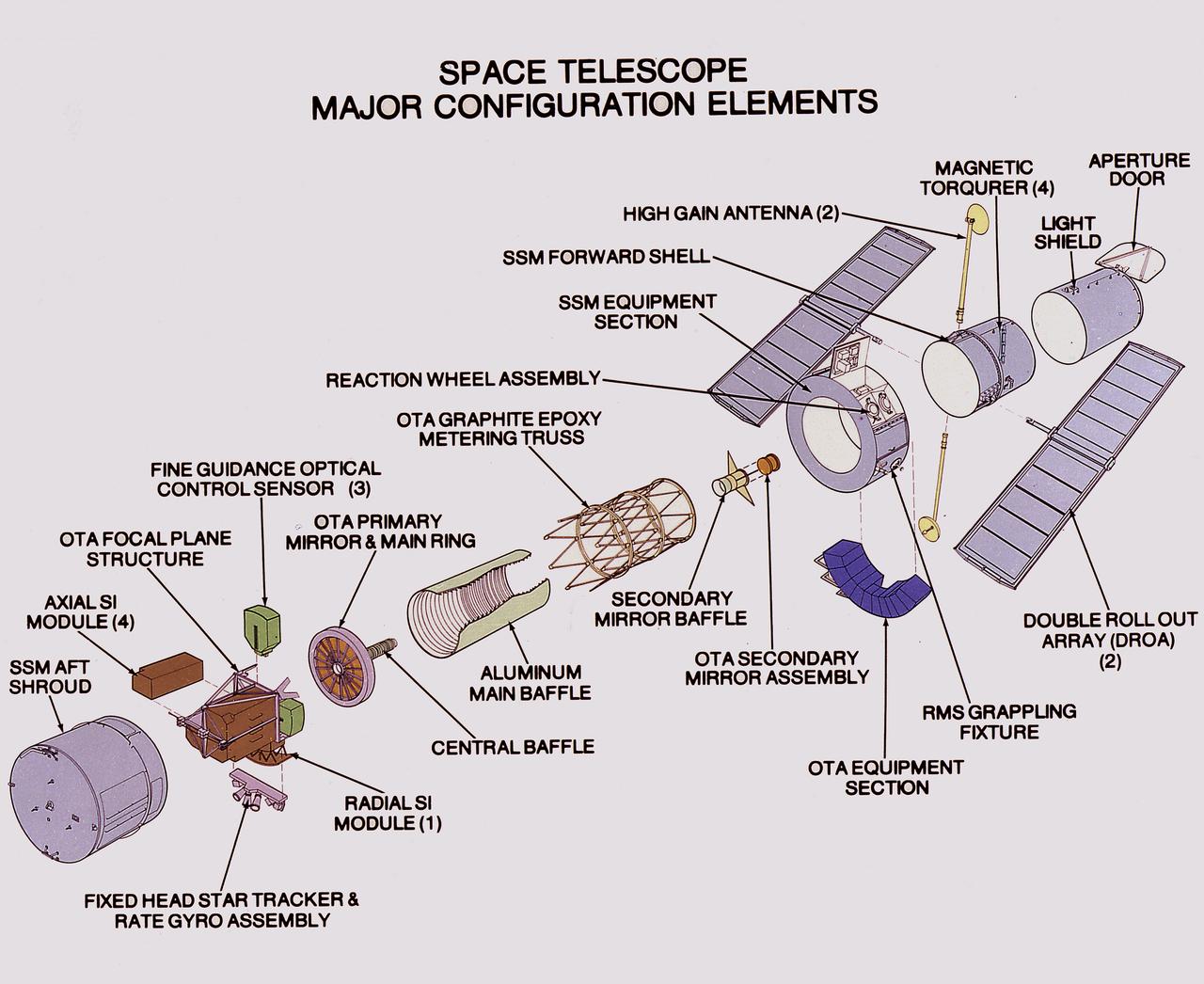
This illustration shows the Hubble Space Telescope's (HST's) major configuration elements. The spacecraft has three interacting systems: The Support System Module (SSM), an outer structure that houses the other systems and provides services such as power, communication, and control; The Optical Telescope Assembly (OTA), which collects and concentrates the incoming light in the focal plane for use by the Scientific Instruments (SI); and five SIs. The SI Control and Data Handling (CDH) unit controls the five SI's, four that are housed in an aft section focal plane structure and one that is placed along the circumference of the spacecraft. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Cornecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. The Lockheed Missile and Space Company of Sunnyvale, California produced the protective outer shroud and spacecraft systems, and assembled and tested the finished telescope.

This illustration depicts the design features of the Hubble Space Telescope's (HST's) Support Systems Module (SSM). The SSM is one of the three major elements of the HST and encloses the other two elements, the Optical Telescope Assembly (OTA) and the Scientific Instruments (SI's). The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The spacecraft is 42.5-feet (13-meters) long and weighs 25,000 pounds (11,600 kilograms). Two communication anternas, two solar array panels that collect energy for the HST, and storage bays for electronic gear are on the outside. The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Connecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. The Lockheed Missile and Space Company of Sunnyvale, California produced the protective outer shroud and spacecraft systems, and assembled and tested the finished telescope.
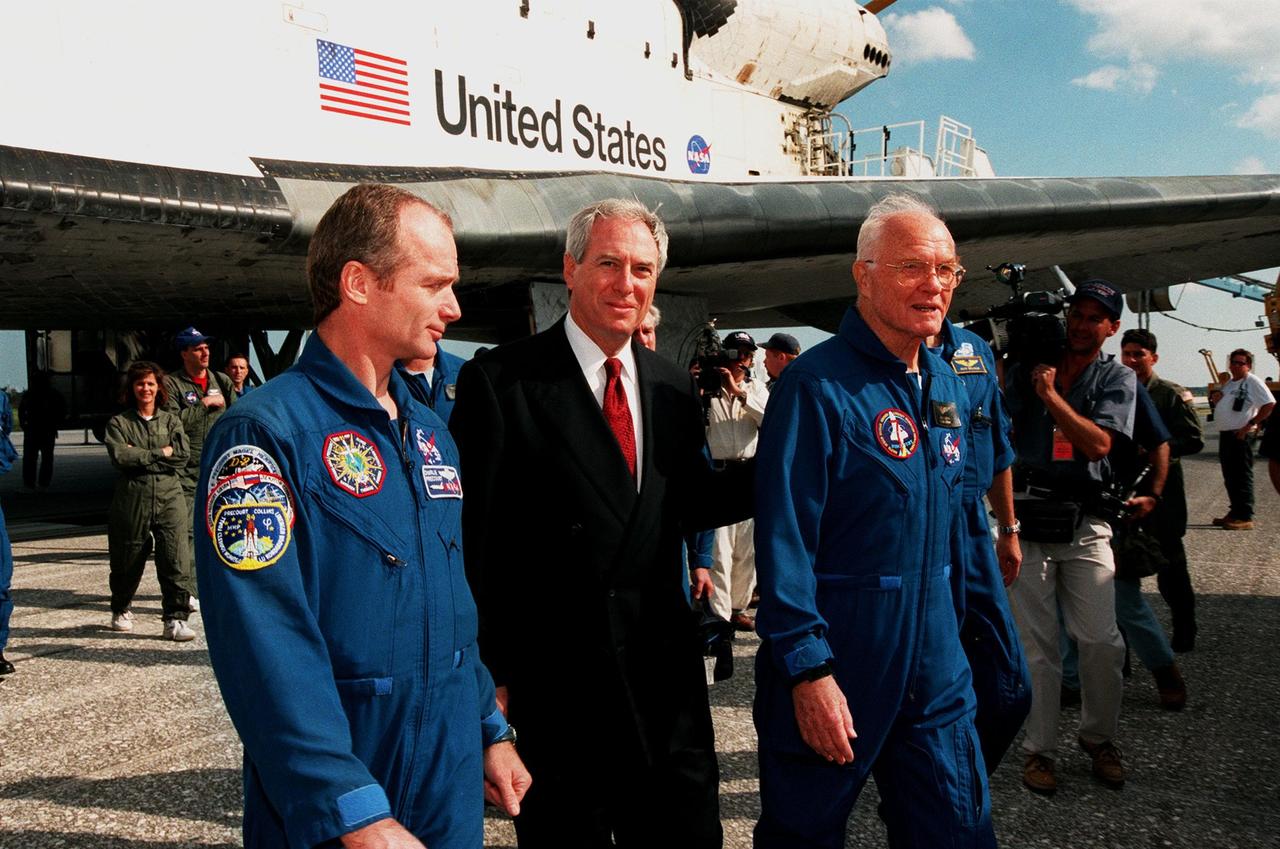

Charles Precourt, chief of the Astronaut office in Houston, and Daniel Goldin, NASA administrator, welcome back to Earth Senator John H. Glenn Jr., from a successful mission STS-95 aboard orbiter Discovery. Glenn served as payload specialist, one of a crew of seven that included Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr.; Pilot Steven W. Lindsey; Mission Specialists Stephen K. Robinson, Scott E. Parazynski and Pedro Duque of Spain, with the European Space Agency; and Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai, M.D., with the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). They landed at the Shuttle Landing Facility at 12:04 p.m. EST, after 9 days in space, traveling 3.6 million miles. The mission included research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process
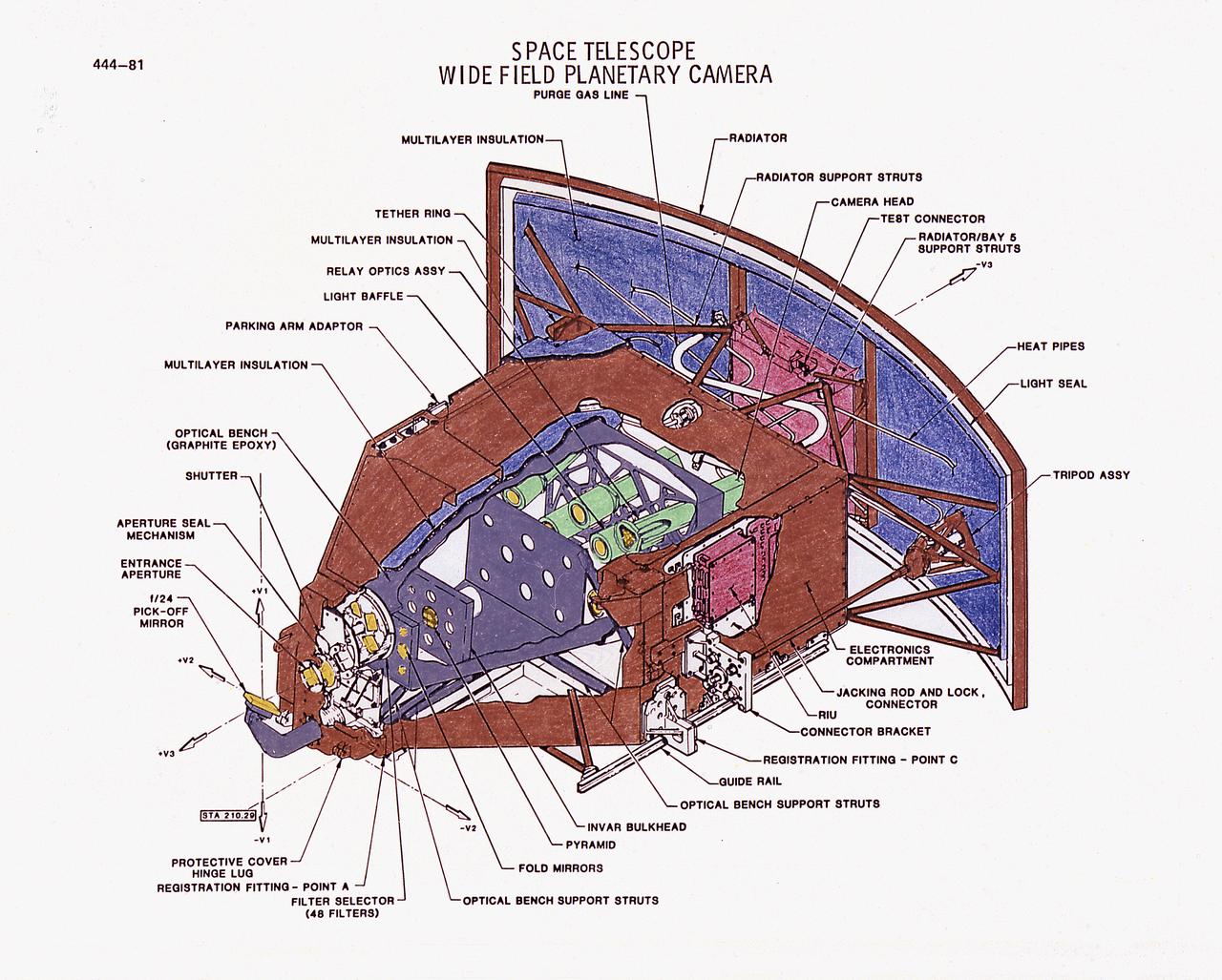
This illustration is a diagram of the Hubble Space Telescope's (HST's), Wide Field Planetary Camera (WF/PC), one of the five Scientific Instruments. The WF/PC uses a four-sided pyramid mirror to split a light image into quarters. It then focuses each quadrant onto one of two sets of four sensors. The sensors are charge-coupled detectors and function as the electronic equivalent of extremely sensitive photographic plates. The WF/PC operates in two modes. The Wide-Field mode that will view 7.2-arcmin sections of the sky, and the Planetary mode that will look at narrower fields of view, such as planets or areas within other galaxies. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Cornecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors.
STS070-386-027 (13-22 JULY 1995) --- High-speed film provided this close-up view of the Space Shuttle Discovery’s aft, featuring the ignition of one of the primary thrusters. Note the impact of the firing on the starboard side of the vertical stabilizer. Crew members told a August 11, 1995, gathering of Johnson Space Center (JSC) employees that the Window Experiment (WINDEX) paid close attention to surface glow, jet plumes, water dumps, aurora and airglow. The data collection is part of an effort to avoid misinterpretation of measurements of Earth, the solar system and starts taken from satellites in low Earth-orbits and prevent damage to sensitive systems and solar arrays during rendezvous and docking. Such firings of the thrusters increase local densities of gases in the atmosphere dramatically and introduce non-natural elements that react with the atmosphere dramatically and spacecraft systems enveloped by the thruster plume. WINDEX recorded phenomena associated with thruster start-up and shut-down transients and observed the effect of the transients on Shuttle glow phenomenon.
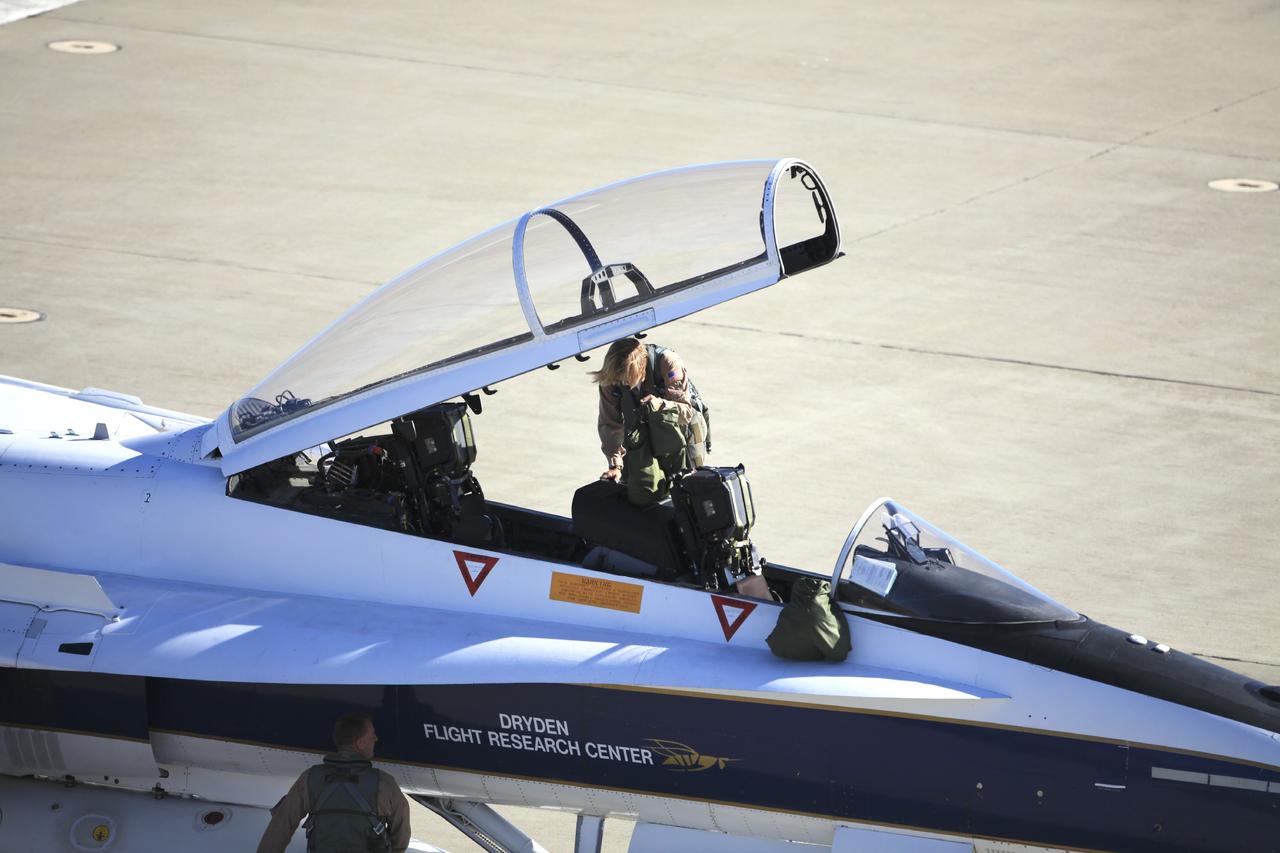

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Videographer Lori Losey boards an F-18 aircraft at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The F-18 "chase plane" will accompany the Orbital Sciences L-1011 aircraft as it transports the Pegasus XL rocket carrying NASA's Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, solar observatory over the Pacific Ocean. Release of the rocket from under the wing of the L-1011 is scheduled for 10:27 p.m. EDT. IRIS will open a new window of discovery using spectrometry and imaging to trace the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona. The spacecraft will observe how solar material moves, gathers energy and heats up as it travels through a largely unexplored region of the solar atmosphere. This interface region, located between the sun's visible surface and its upper atmosphere, is where most of its ultraviolet emission is generated. These emissions impact the near-Earth space environment and Earth's climate. NASA's Launch Services Program at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida is managing the countdown and launch. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/iris. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
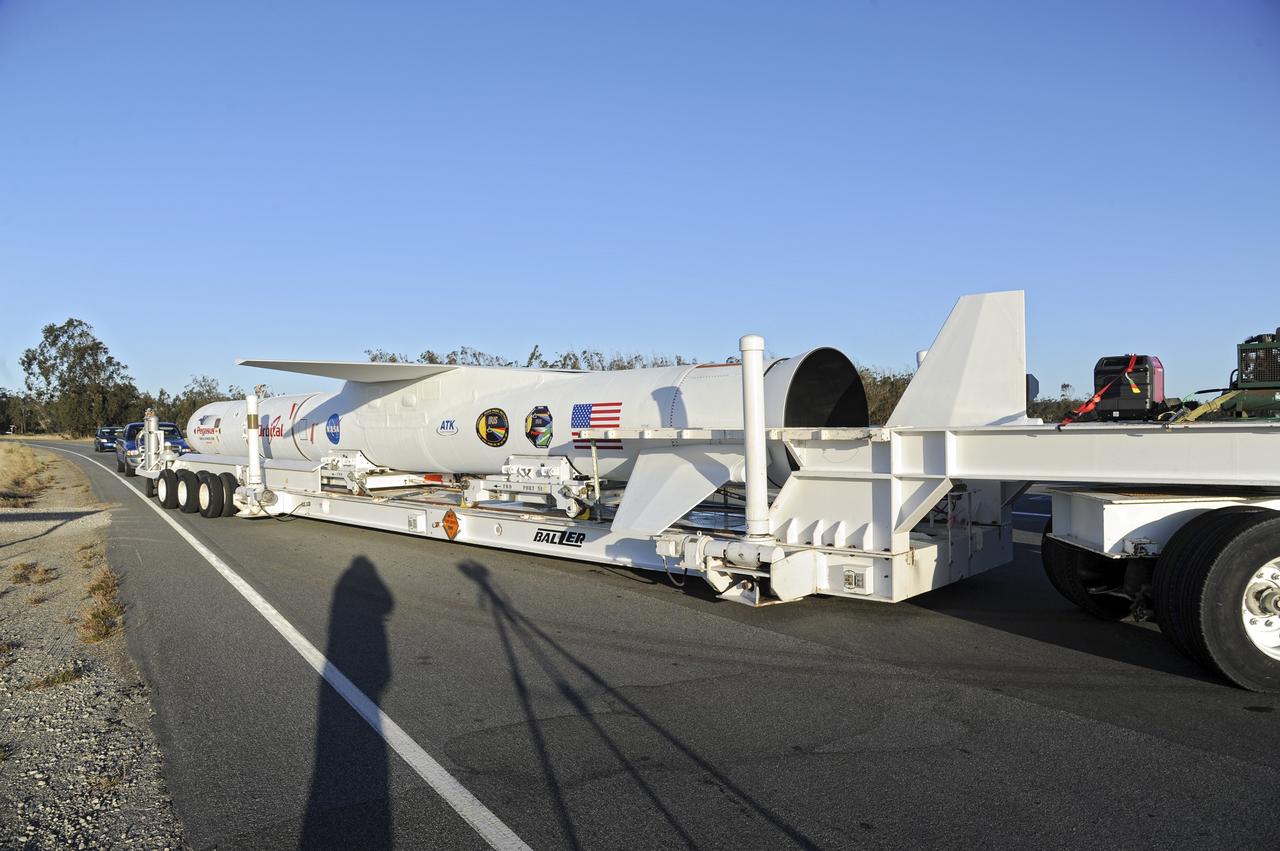

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Pegasus XL rocket with the attached Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph IRIS solar observatory rolled out of the hangar on its transporter to the runway at Vandenberg. There, the rocket and spacecraft were mated with the Orbital Sciences L-1011 carrier aircraft. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg on June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. The IRIS mission will observe how solar material moves, gathers energy and heats up as it travels through a largely unexplored region of the solar atmosphere. The interface region, located between the sun's visible surface and upper atmosphere, is where most of the sun's ultraviolet emission is generated. These emissions impact the near-Earth space environment and Earth's climate. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/iris Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
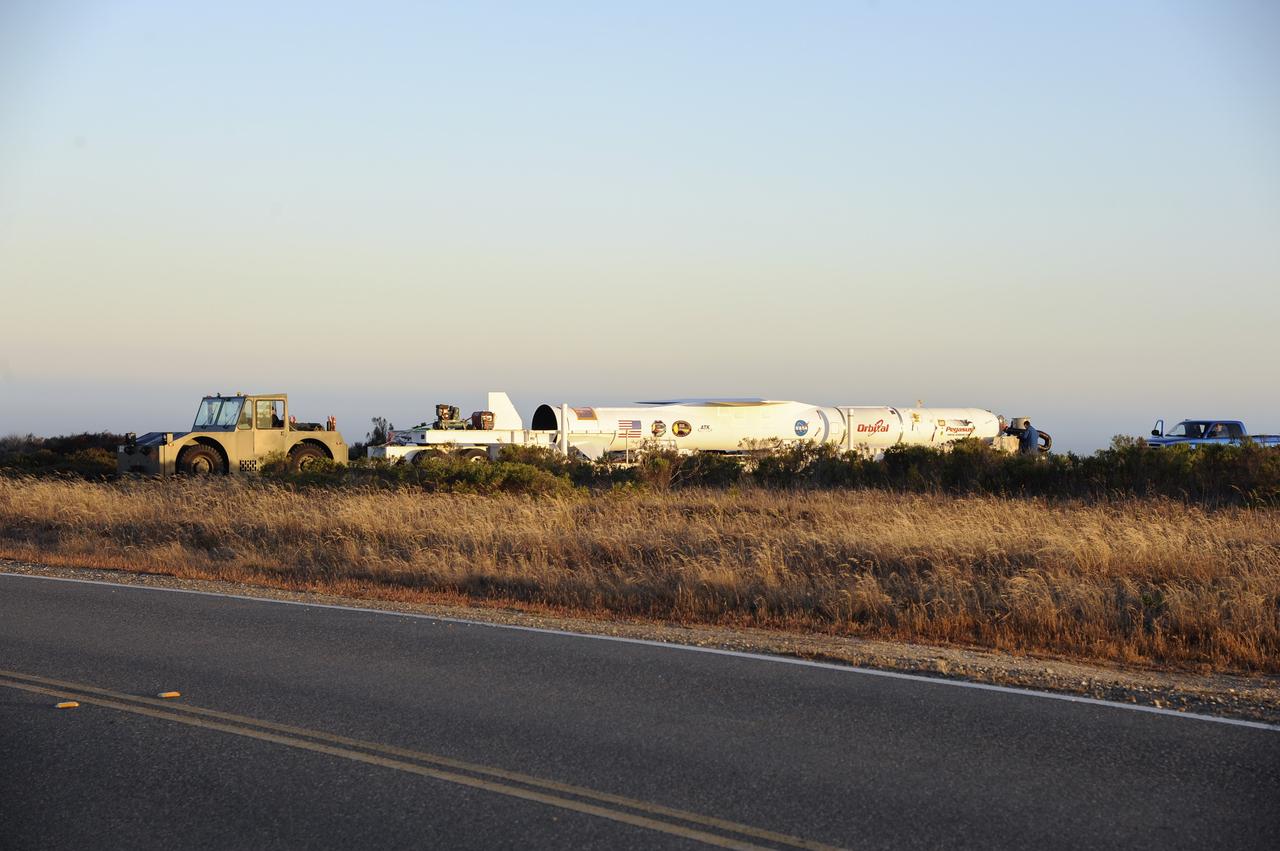

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Pegasus XL rocket with the attached Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph IRIS solar observatory rolled out of the hangar on its transporter to the runway at Vandenberg. There, the rocket and spacecraft were mated with the Orbital Sciences L-1011 carrier aircraft. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg on June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. The IRIS mission will observe how solar material moves, gathers energy and heats up as it travels through a largely unexplored region of the solar atmosphere. The interface region, located between the sun's visible surface and upper atmosphere, is where most of the sun's ultraviolet emission is generated. These emissions impact the near-Earth space environment and Earth's climate. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/iris Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin